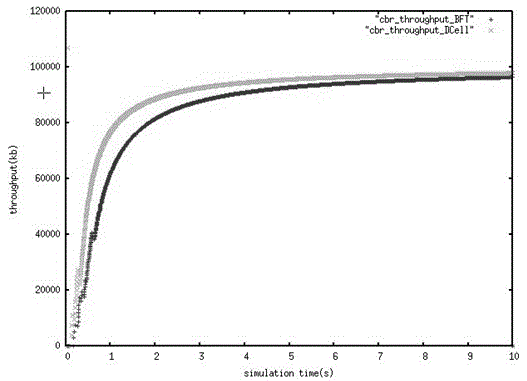
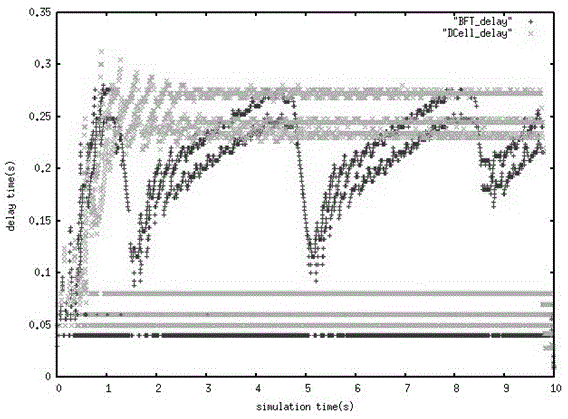
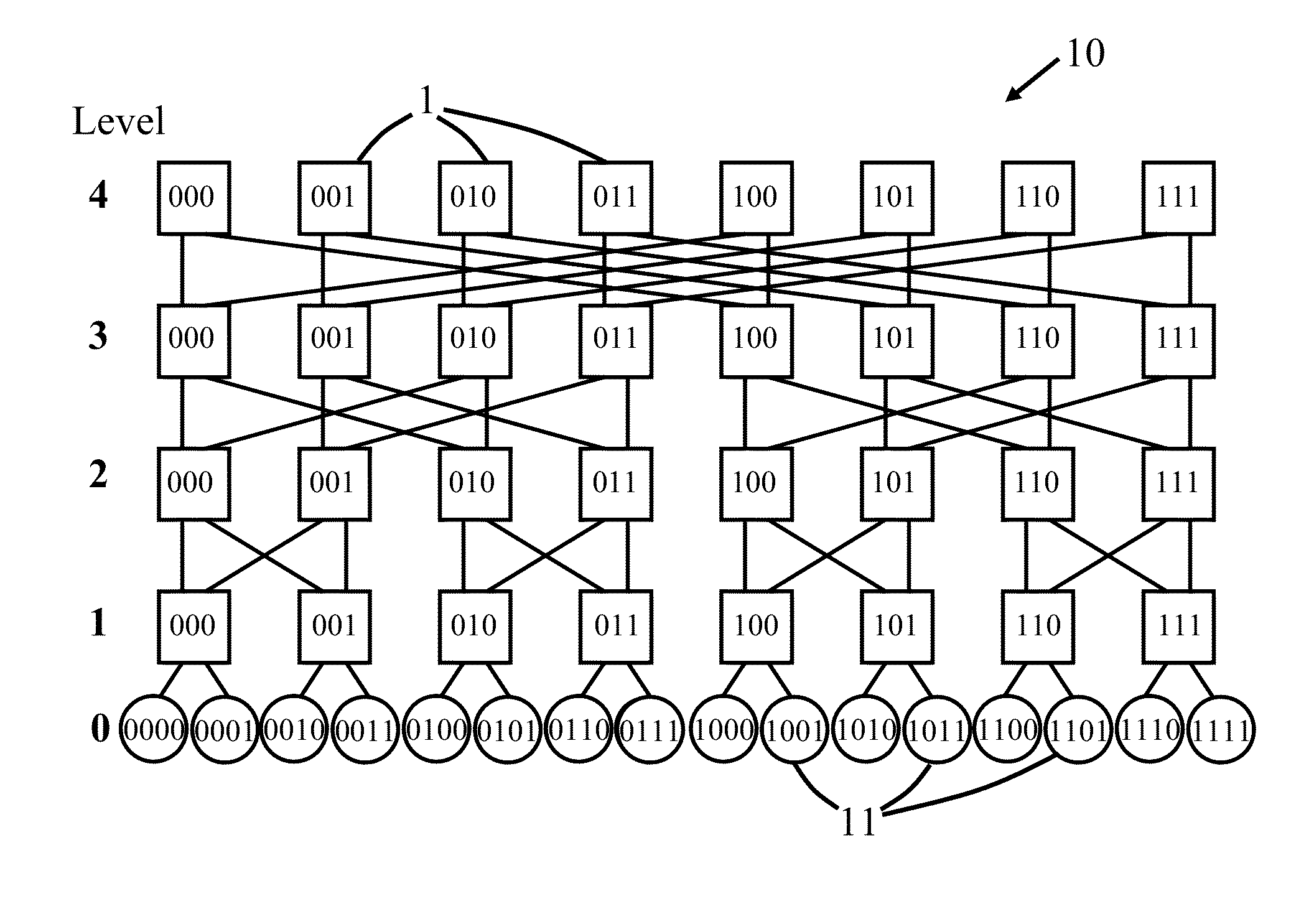
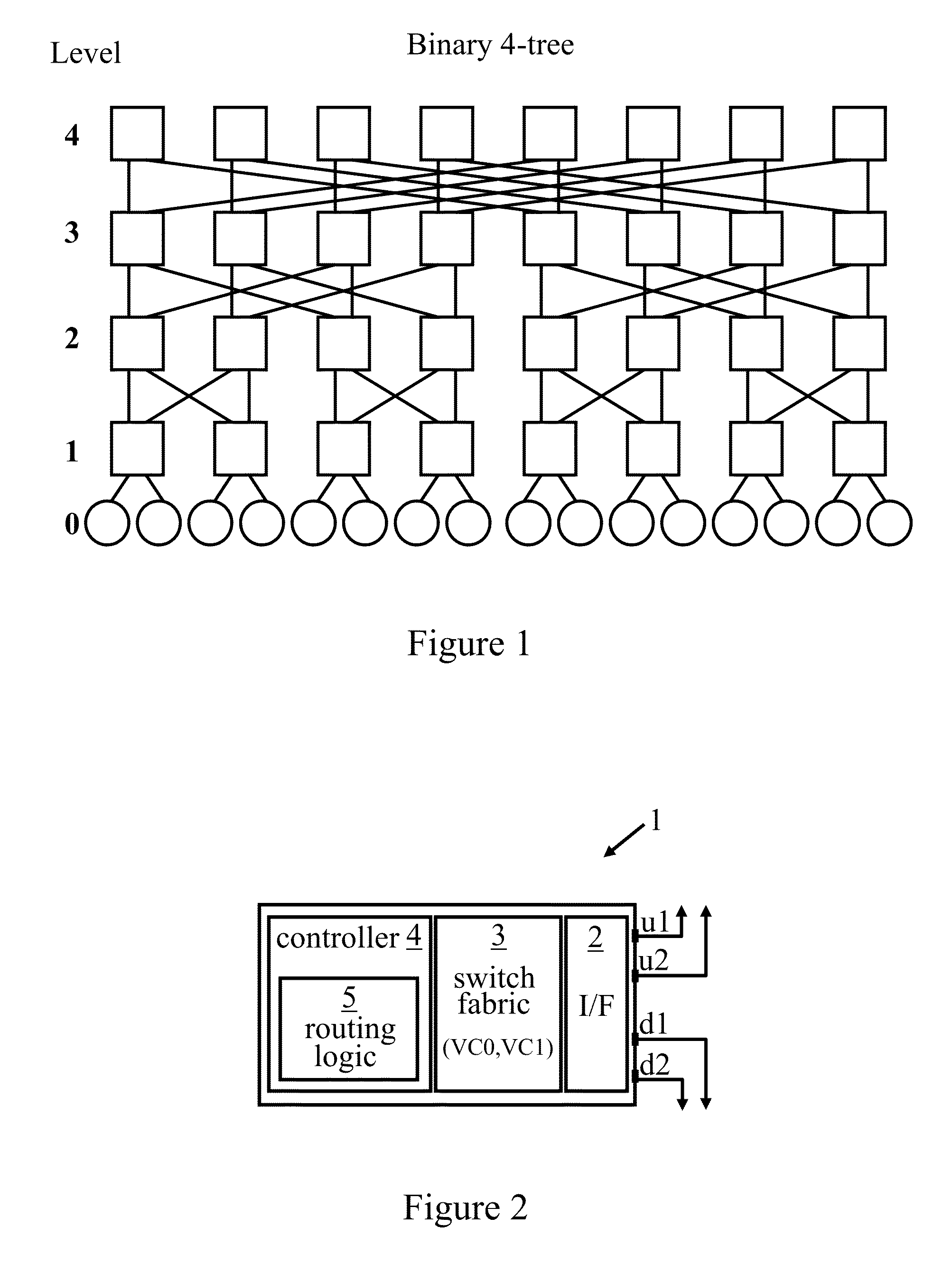
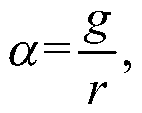Patents
Literature
87 results about "Fat tree" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
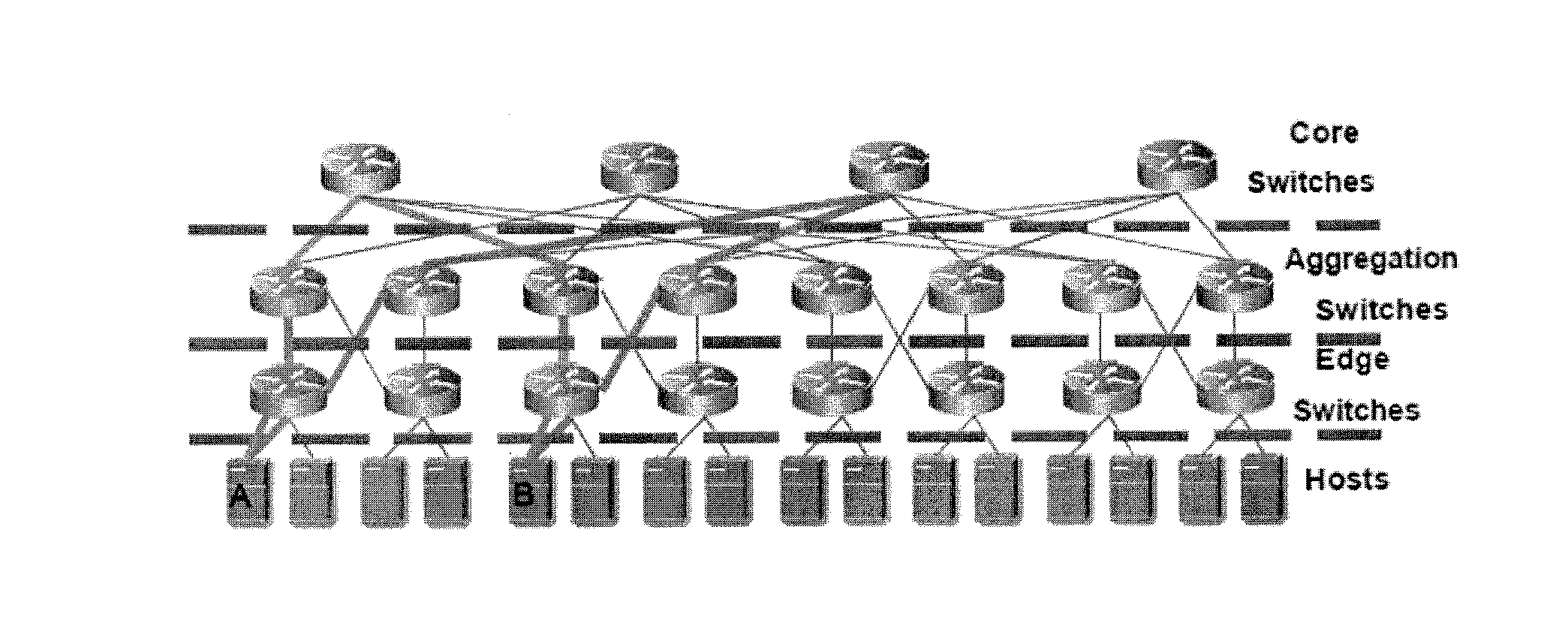
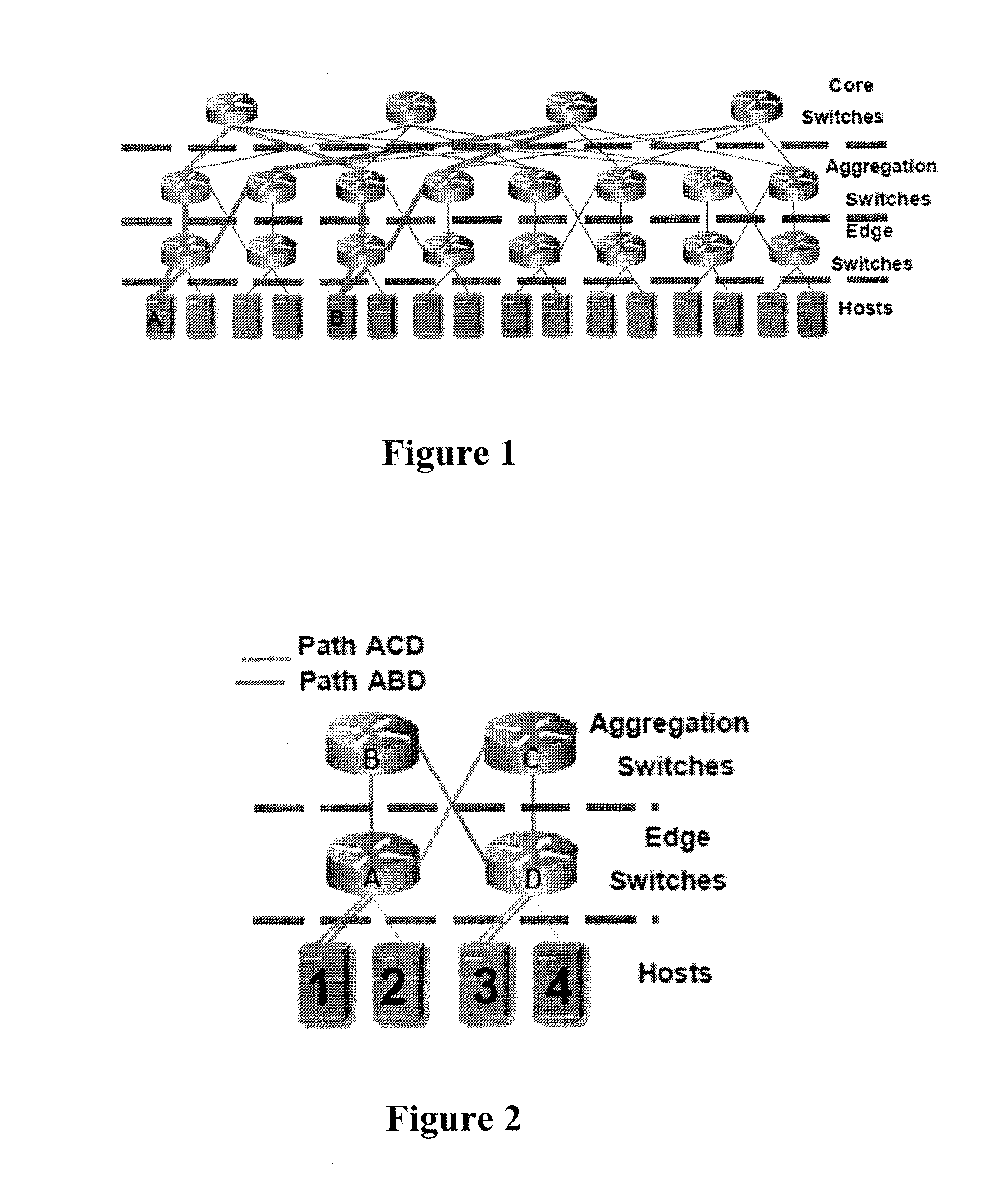
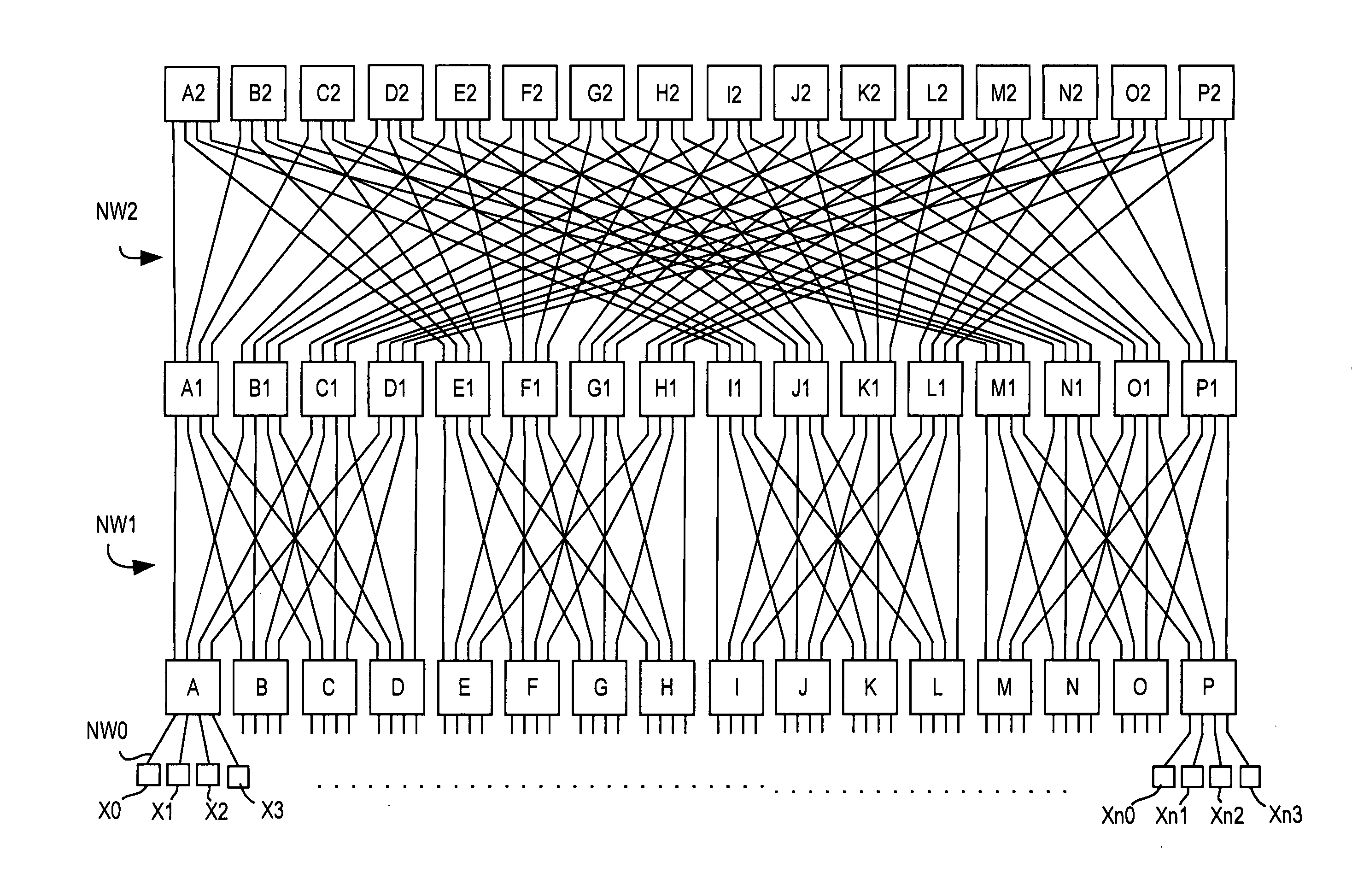
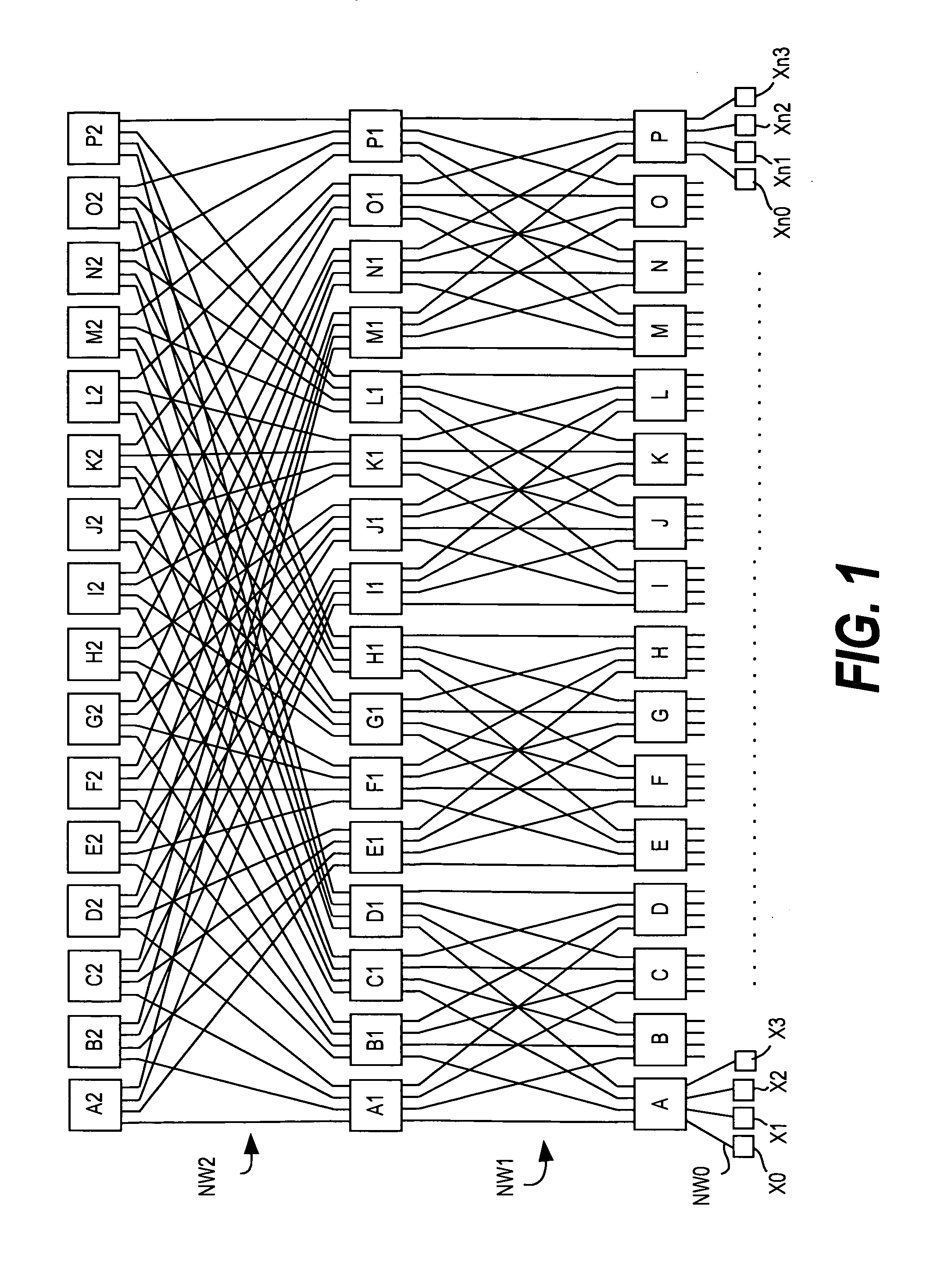
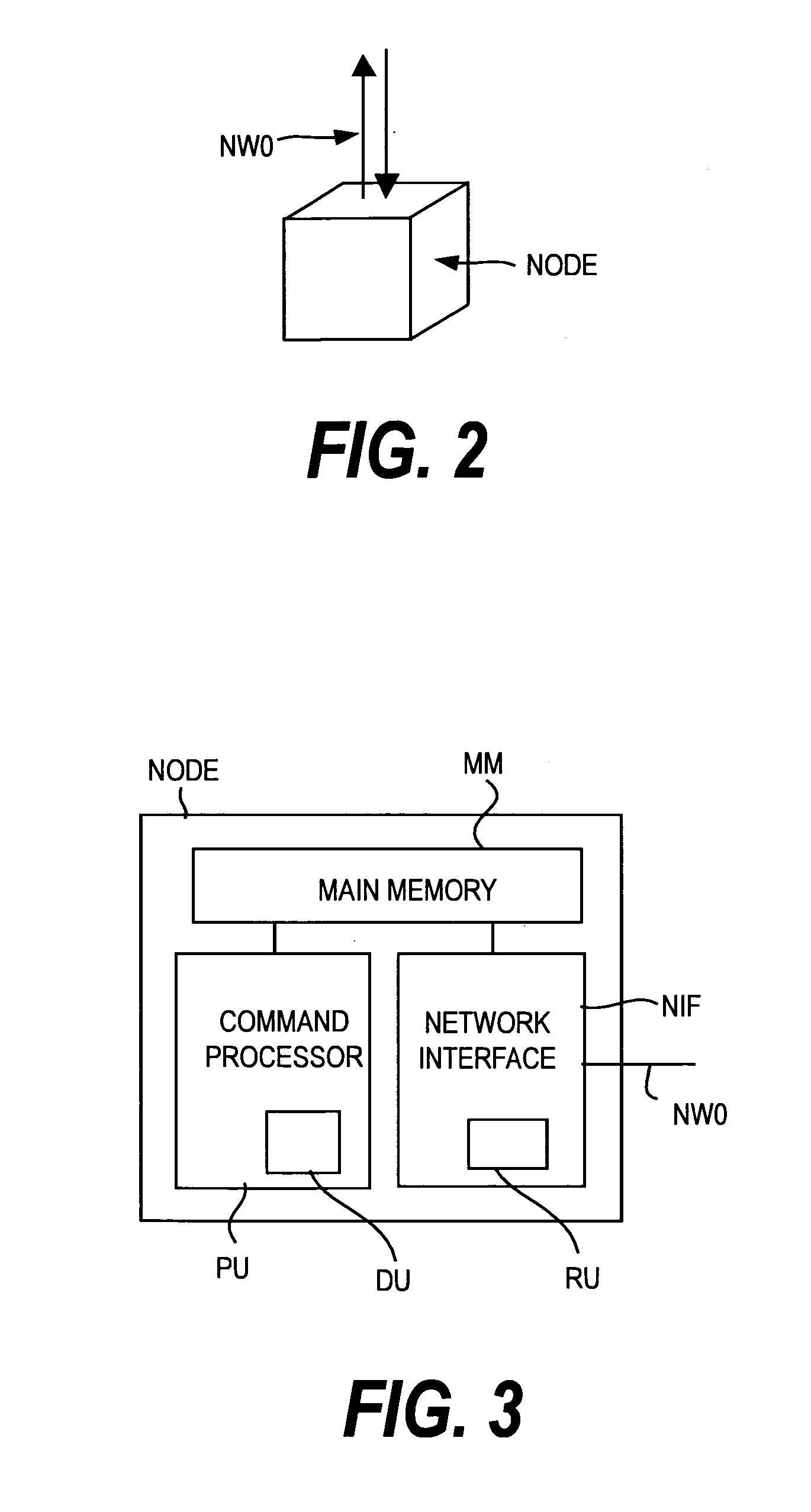
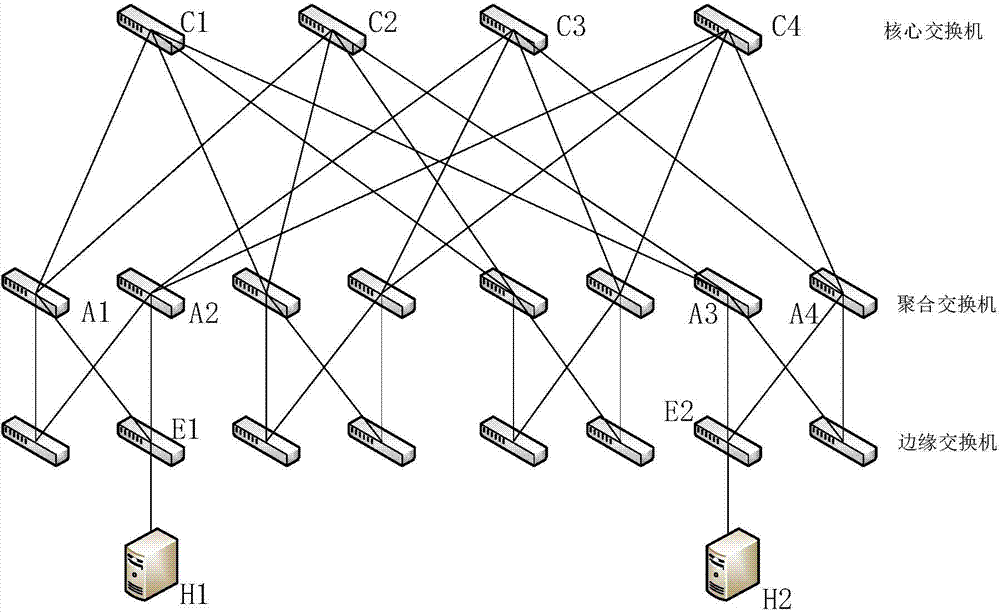
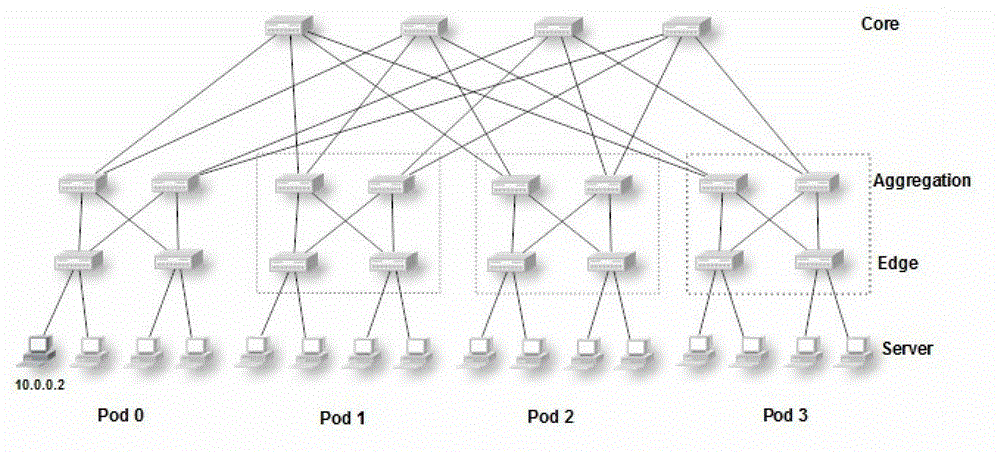
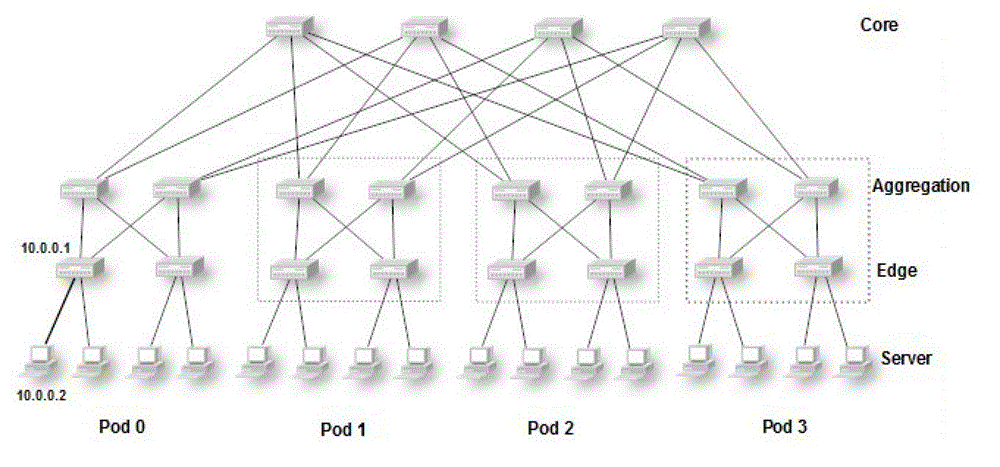
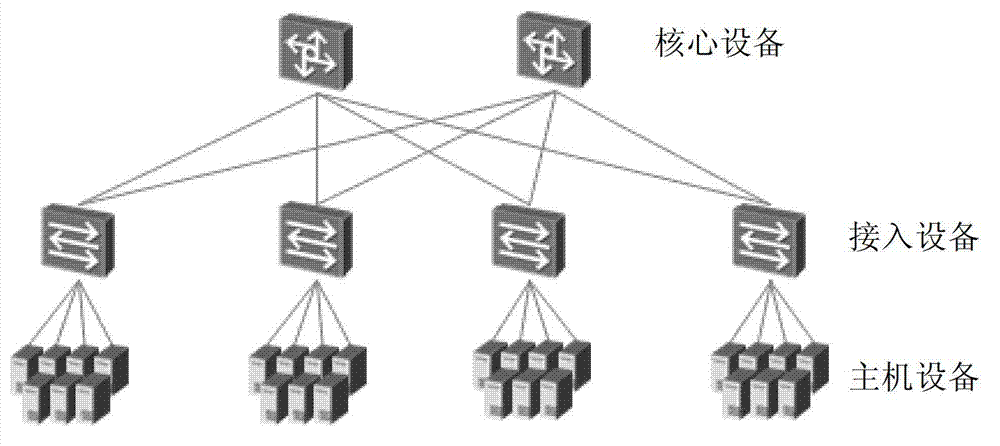
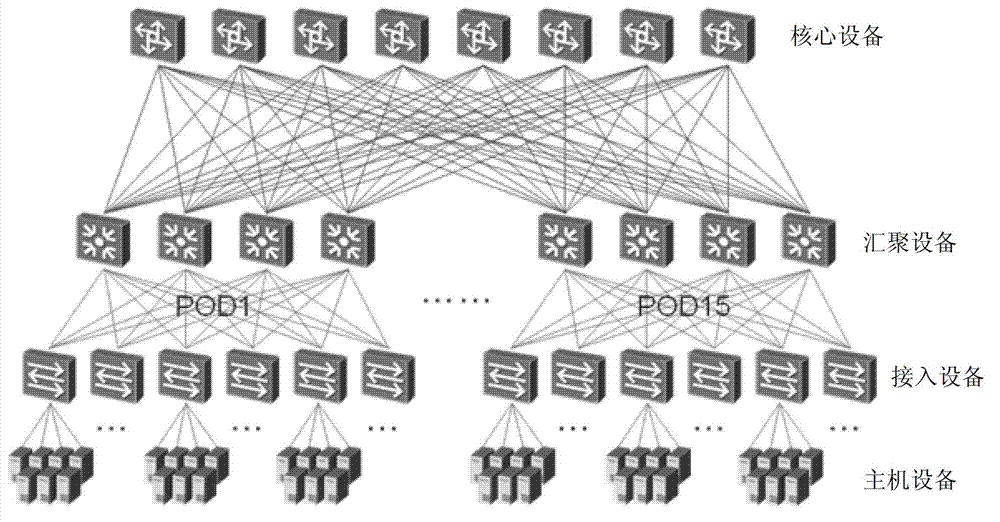
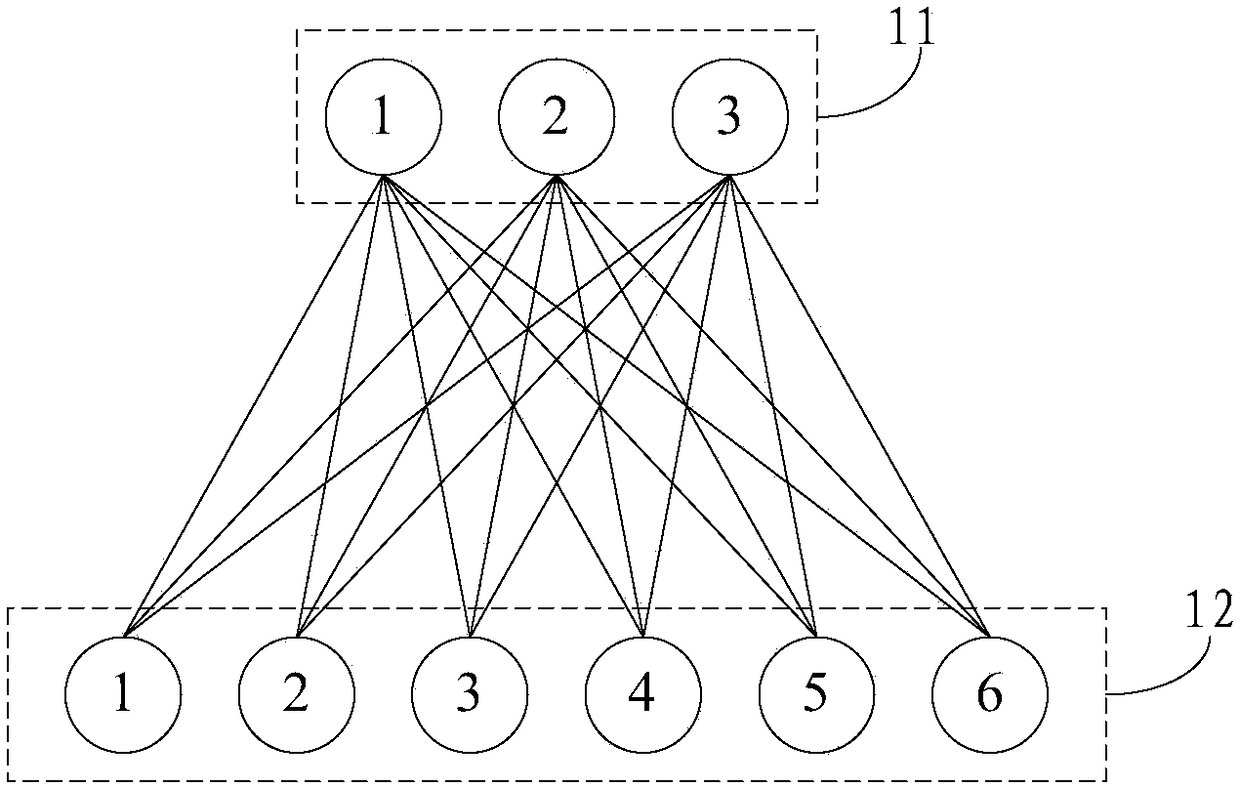
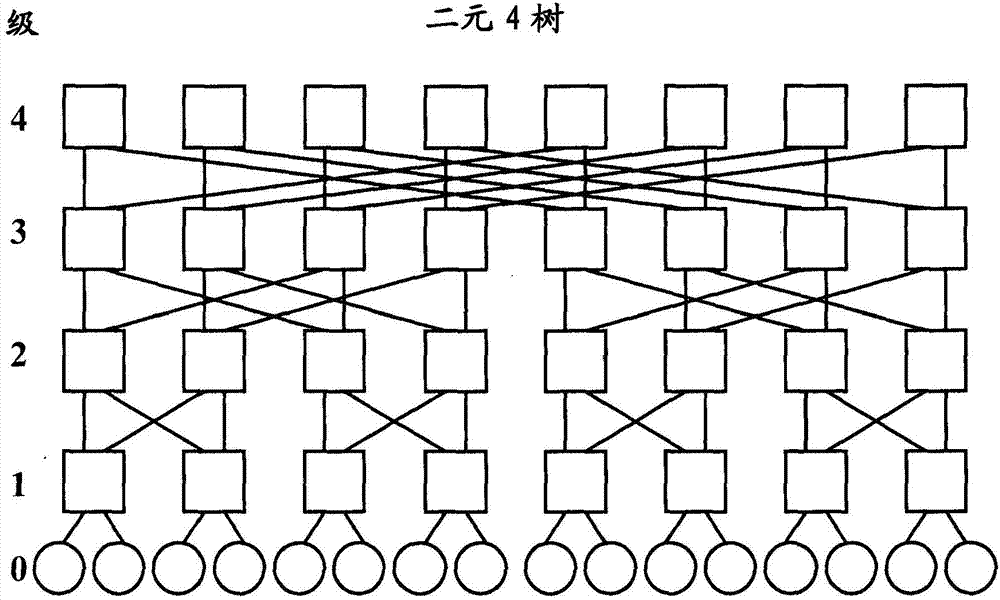
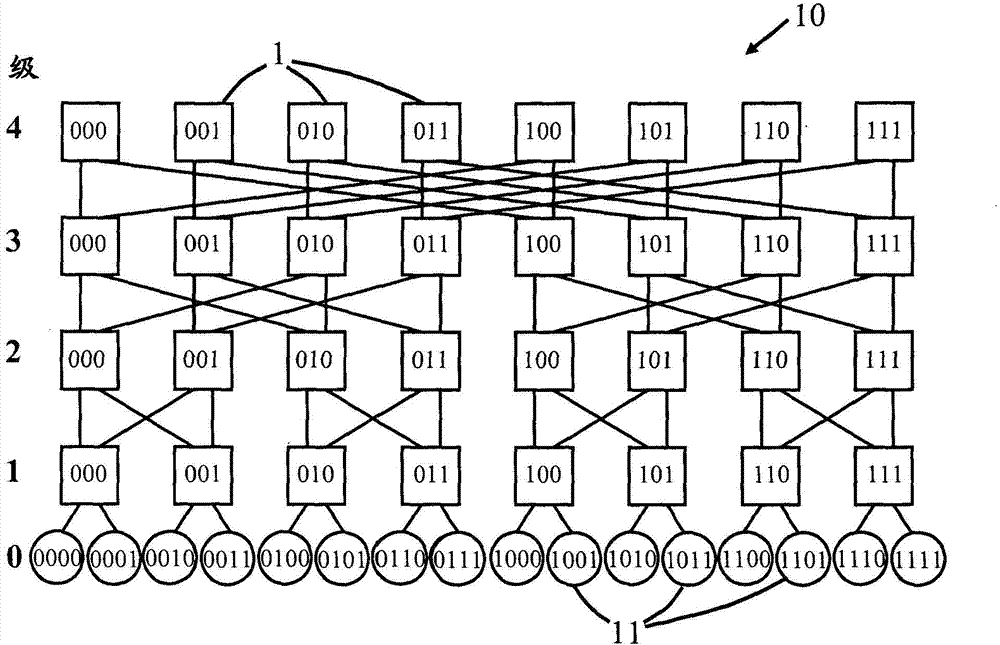
The fat tree network is a universal network for provably efficient communication. It was invented by Charles E. Leiserson of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology in 1985. In a tree data structure, every branch has the same thickness, regardless of their place in the hierarchy—they are all "skinny" (skinny in this context means low-bandwidth). In a fat tree, branches nearer the top of the hierarchy are "fatter" (thicker) than branches further down the hierarchy. In a telecommunications network, the branches are data links; the varied thickness (bandwidth) of the data links allows for more efficient and technology-specific use.
Molecular-wire crossbar interconnect (MWCI) for signal routing and communications
InactiveUS6314019B1Easy to manufactureSaving circuit areaNanoinformaticsDigital storageSignal routingActive switch
A molecular-wire crossbar interconnect for signal routing and communications between a first level and a second level in a molecular-wire crossbar is provided. The molecular wire crossbar comprises a two-dimensional array of a plurality of nanometer-scale switches. Each switch is reconfigurable and self-assembling and comprises a pair of crossed wires which form a junction where one wire crosses another and at least one connector species connecting the pair of crossed wires in the junction. The connector species comprises a bi-stable molecule. Each level comprises at least one group of switches and each group of switches comprises at least one switch, with each group in the first level connected to all other groups in the second level in an all-to-all configuration to provide a scalable, defect-tolerant, fat-tree networking scheme. The primary advantage is ease of fabrication, because an active switch is formed any time two wires cross. This saves tremendously on circuit area (a factor of a few times ten), since no other wires or ancillary devices are needed to operate the switch or store the required configuration. This reduction of the area of a configuration bit and its switch to just the area of two crossing wires is a major advantage in constructing a defect-tolerant interconnect network.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD CO +1
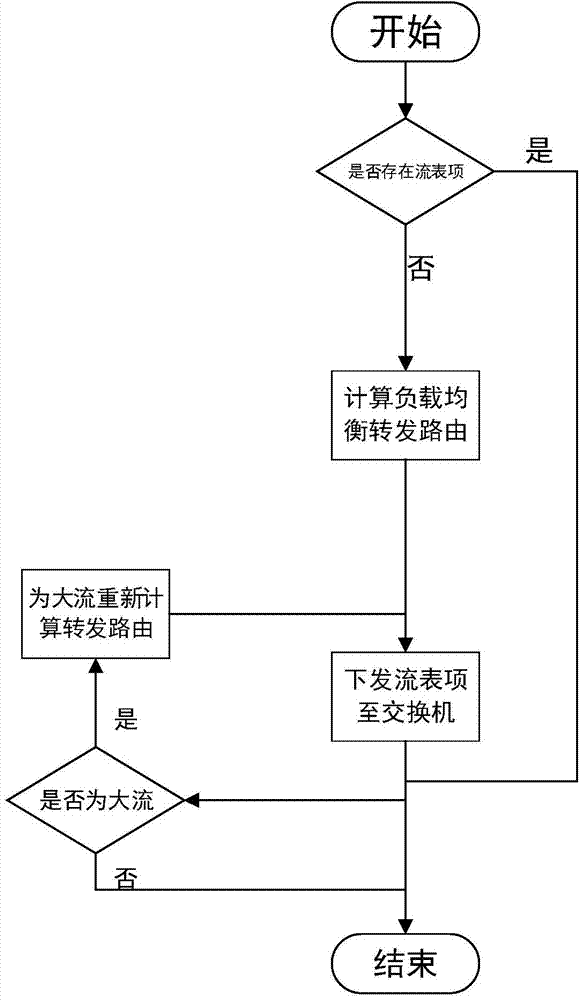
Load-balancing algorithms for data center networks
Multipath load-balancing algorithms, which can be used for data center networks (DCNs), are provided. A multipath load-balancing algorithm can be, for example, a distributed multipath load-balancing algorithm or a centralized multipath load-balancing algorithm. Algorithms of the subject invention can be used for, e.g., hierarchical DCNs and / or fat-tree DCNs. Algorithms of the subject invention are effective and scalable and significantly outperform existing solutions.
Owner:FLORIDA INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY
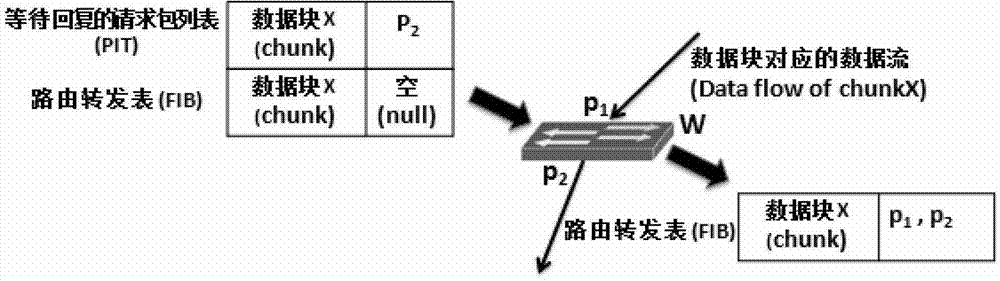
Data transmission method of content-centric datacenter network
InactiveCN103179037AMultiple available bandwidthImprove throughputData switching networksExtensibilityContent centric
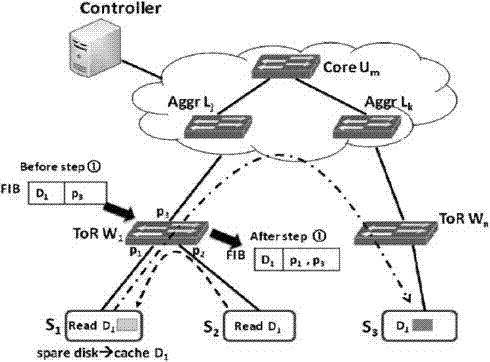
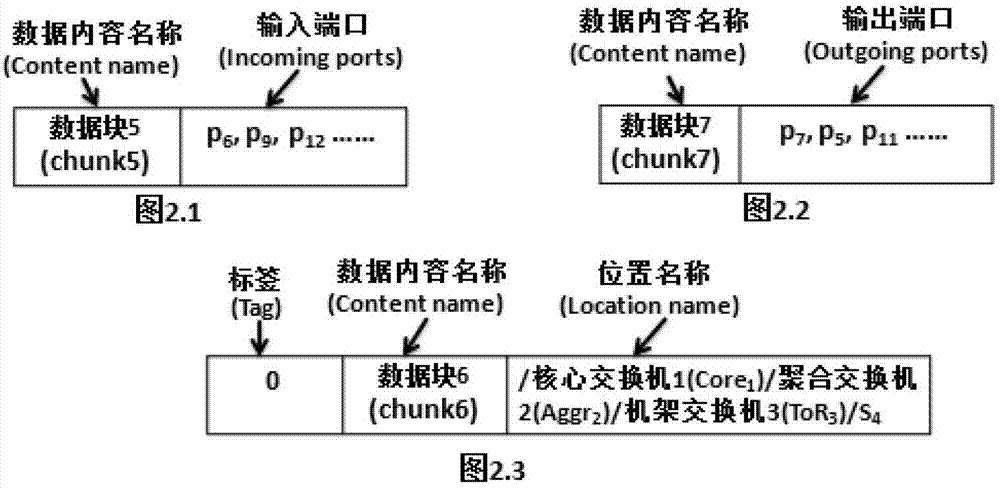
The invention belongs to a content data network technology, and discloses a data transmission method of a content-centric datacenter network. The method is characterized in that an NDN (Named Data Network) based content-centric routing and forwarding strategy is used; multicast characteristics and expandability of the CCDN (content-centric datacenter network) are guaranteed only by storing a complete PIT (Pending Interest Table) and part of an FIB (forwarding information base), by adopting a Hybrid Content and Location routing strategy and by taking limited storage resources and datacenter network topology of a datacenter switch into consideration; and different from an on-path caching strategy of the NDN, an off-path mechanism that a host provides data caching is adopted by taking large data volume characteristic of the datacenter network and host storage capacity of redundancy into consideration. According to multistage topological characteristics, of the datacenter network, such as Fat-Tree, the CCDN guarantees Distance-aware Content based Forwarding through FIB learning, average path length of data transmission is decreased, and network throughput is improved. By the aid of the adaptive forwarding strategy, the CCDN can still provide accurate and efficient data forwarding in network failure.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
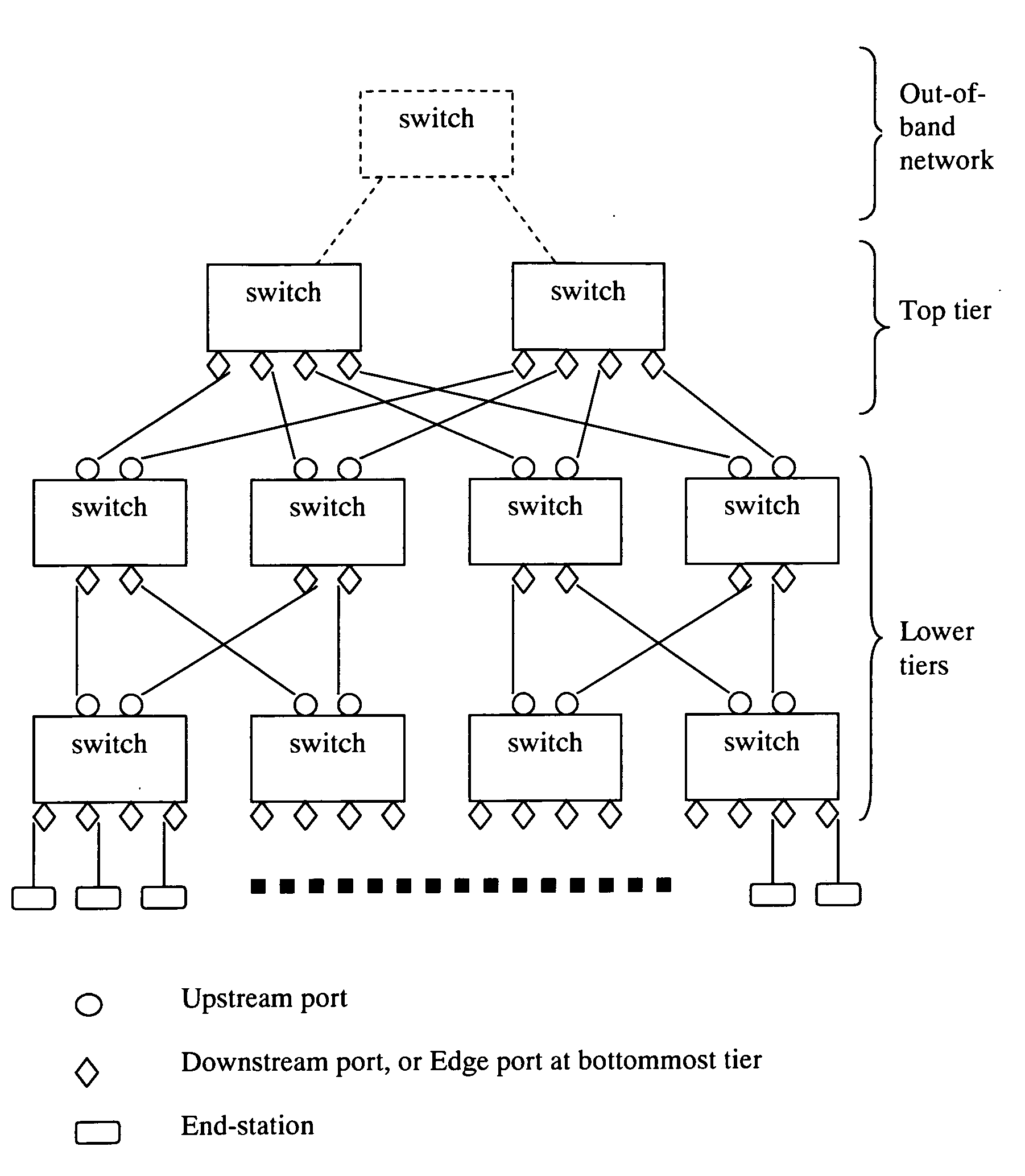
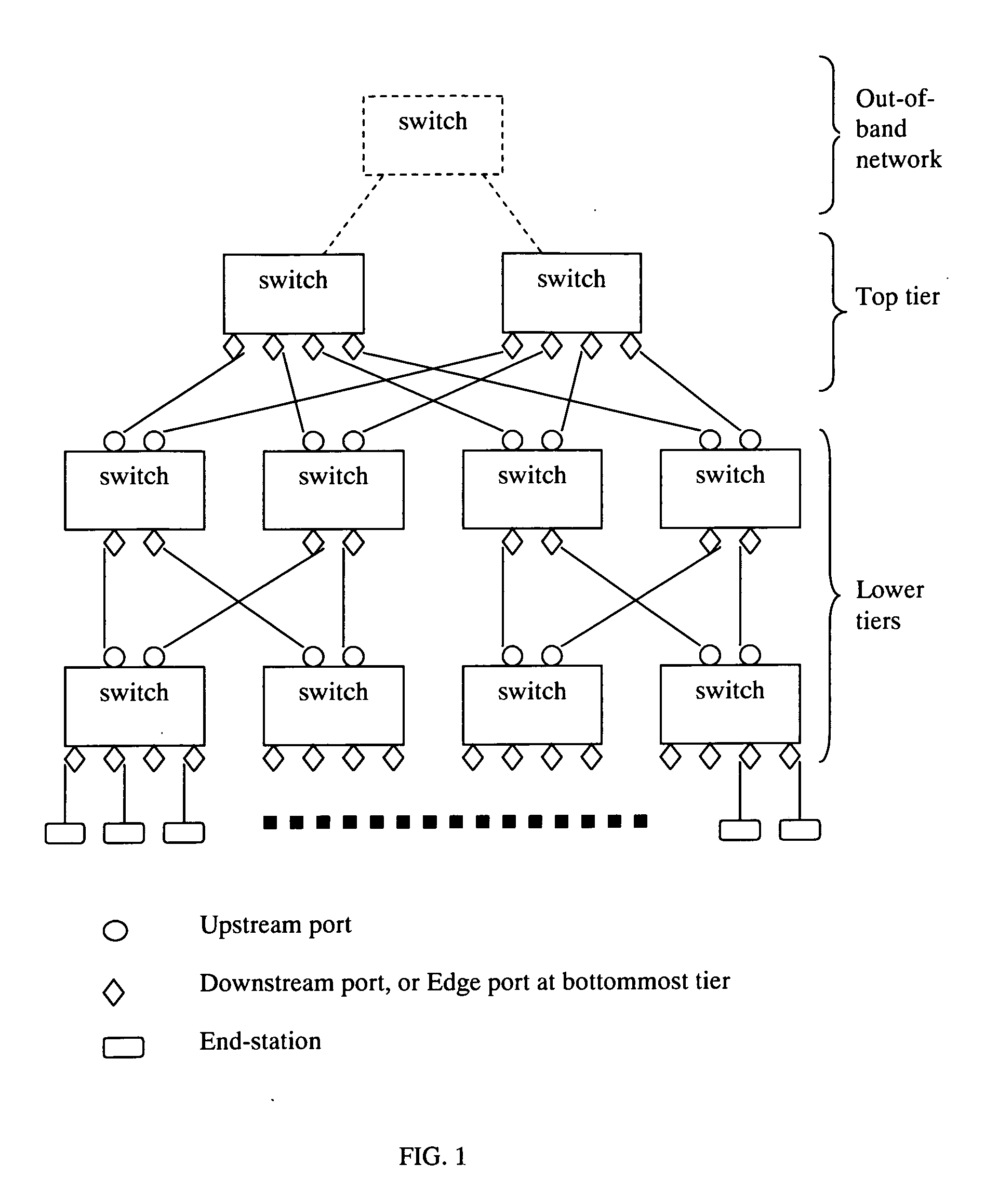
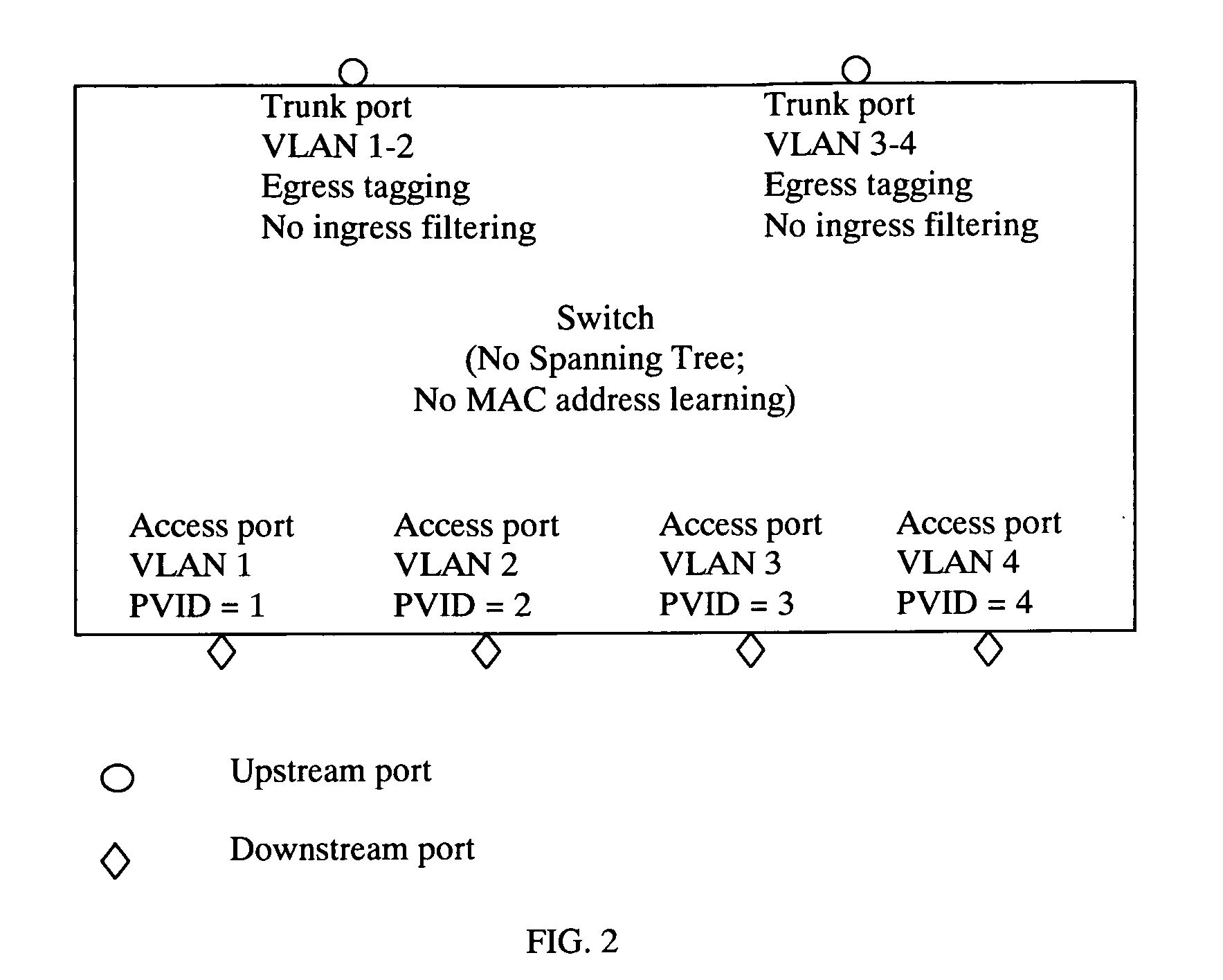
Method for Building Scalable Ethernet Switch Network and Huge Ethernet Switch
InactiveUS20110080855A1Reduce network congestionData switching by path configurationNetwork packetComputer terminal
A method for building scalable Ethernet switch network and huge Ethernet switch is provided. The switch network is composed of a plurality of tiers of Ethernet switches forming a fat-tree topology. The bottommost tier connects to the end-stations. All switches except those in the top tier are typical IEEE802.1Q switches configured purposefully such that all packets from the end-stations are forwarded upstream to the top tier and are tagged with ingress port information. The top-tier switches possess a novel learning and forwarding capability such that a received packet is forwarded downstream to the destination end-station through one of a plurality of possible paths selected by a load balancing algorithm. Said method can also be applied to build an Ethernet switch of a large number of ports.
Owner:FUNG HEI TAO
Parallel computer system
InactiveUS20090016332A1Increase speedLow costMultiplex system selection arrangementsDigital computer detailsCrossbar switchComputer network
To exchange data between adjacent nodes at high speed while using an existing network including a fat tree and a multistage crossbar switch. This invention provides a parallel computer system including: a plurality of nodes each of which includes a processor and a communication unit; a switch for connecting the plurality of nodes with each other; a first network for connecting each of the plurality of nodes and the switch; and a second network for partially connecting the plurality of nodes with each other. Further, the first network is comprised of one of a fat tree and a multistage crossbar network. Further, the second network partially connects predetermined nodes among the plurality of nodes directly with each other.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Data stream forwarding method facing Fat-Tree data center network architecture
ActiveCN104767694AReduce the chance of collisionIncrease usageData switching networksData center network architecturesData stream
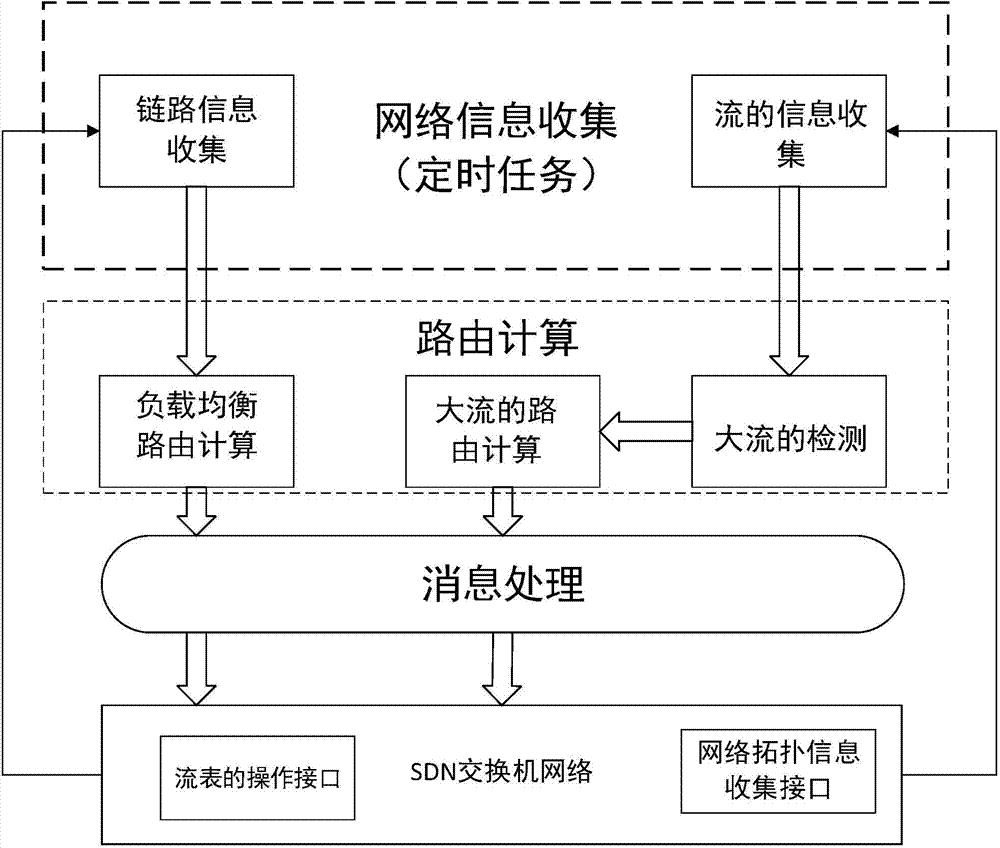
The invention discloses a data stream forwarding method facing Fat-Tree data center network architecture, and belongs to the technical field of data center networks. The data stream forwarding method facing the Fat-Tree data center network architecture is characterized in that forwarding of a stream in a network can be dynamically controlled and the route forwarding strategy of the stream can be dynamically adjusted according to the size of the stream in the network by combining a data center network and the SDN technology in the data center network regarding Fat-Tree as network topology. The method has the functions of a timing network link information acquisition module, a data stream information acquisition module, a large data stream detecting and processing module, a load balancing control forwarding module and a large data stream forwarding module. According to the data stream forwarding method facing the Fat-Tree data center network architecture, load balancing of a data stream in the data center network can be achieved, the forwarding strategy can be dynamically adjusted according to the different data stream sizes, the link utilization ratio of the data center network can be improved, the forwarding delay of the data stream can be shortened, and the probability of link jamming is reduced.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
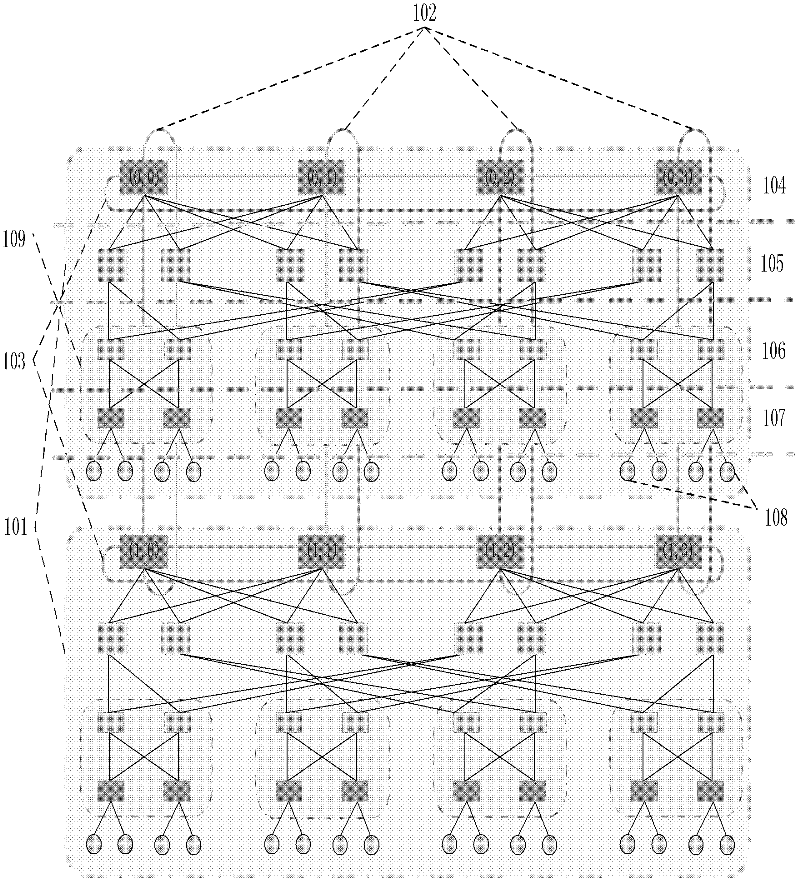
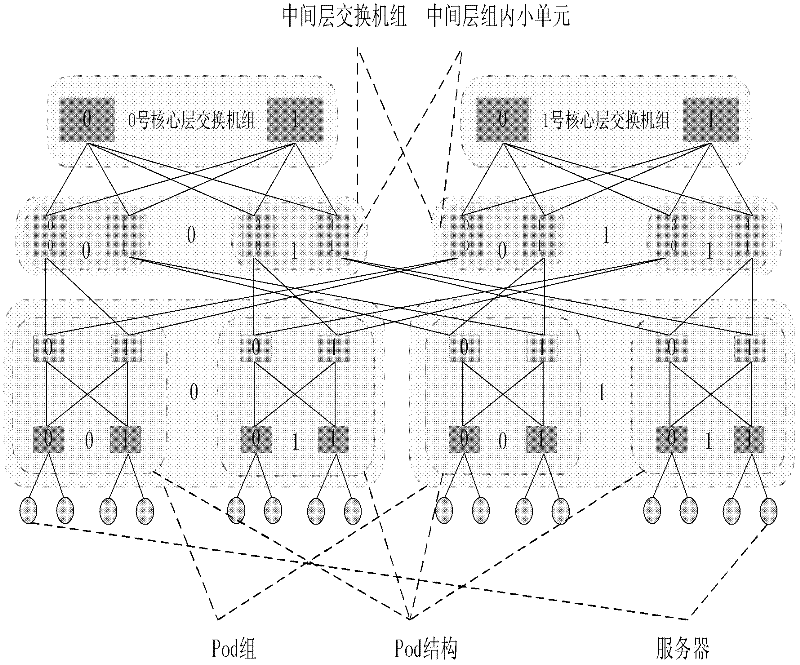
Data center network topology system based on module expansion
InactiveCN102394782AMeet application development needsAchieving dynamic selectivityData switching networksFault toleranceNetwork size
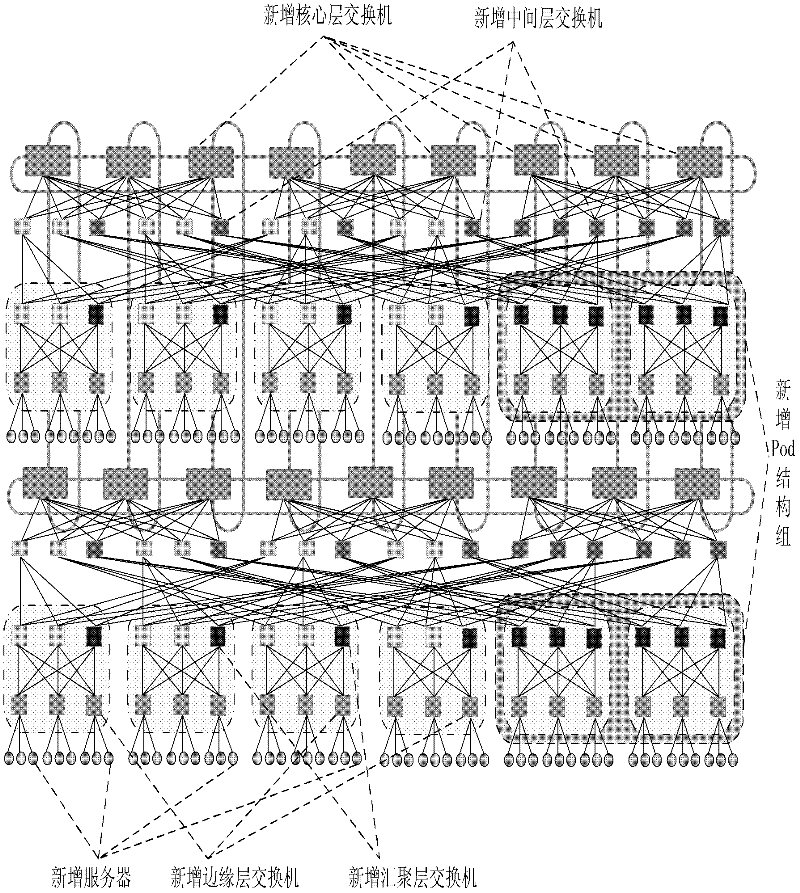
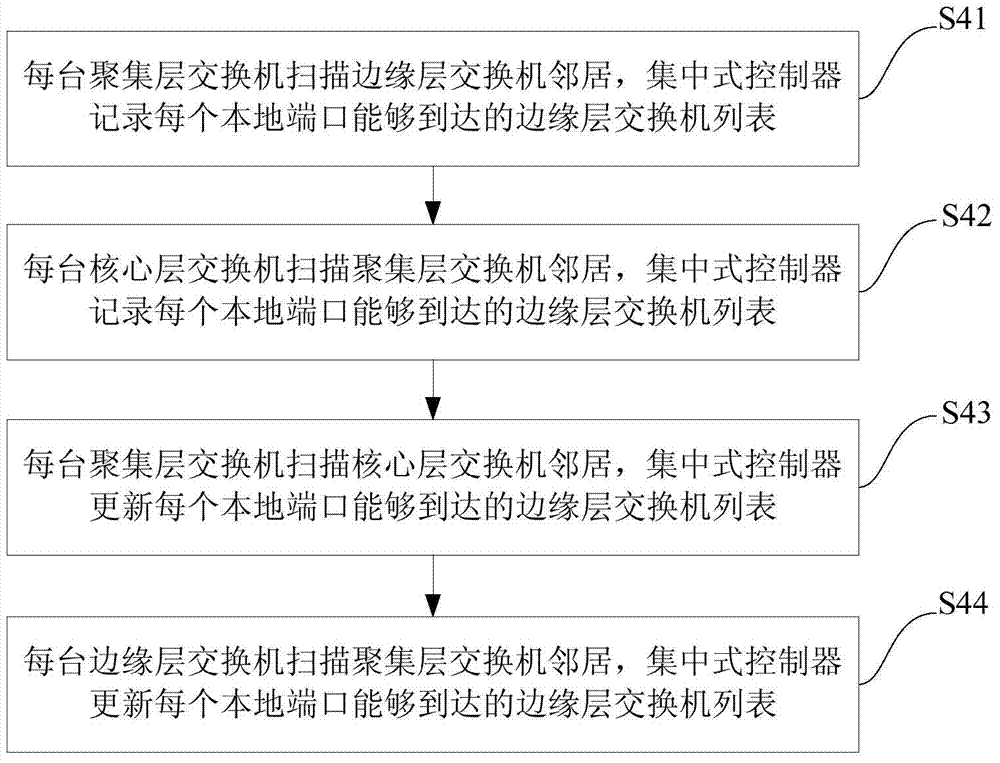
The invention discloses a data center network topology system based on module expansion. And therefore, a problem that an expansion capability of tree topology of a data center is limited to the number of ports of a switch device and insufficiency of dynamic selectivity of a downlink can be solved. The implementation steps of system are as follows: an intermediate layer is introduced between a core layer and a convergence layer of a fat tree structure; a small network that is formed by connection of switches and servers of each of the layer is recorded as a basic module, so that a plurality of basic modules are constructed; four additional ports of switches of the core layer are utilized to connect all the basic modules to form a large whole network, so that a demand of construction of a data center network can be met and dynamic selection of a down link can be satisfied as well as a high halving bandwidth is provided; and lateral expanding, vertical expanding or mixing expanding is carried out on the network topology system as well as expansion of the network scale is supported flexibly. According to the invention, the system has a high network fault tolerance performance; more server devices can be accommodated; and a demand of application expansion in the future can be met; therefore, the system can be applied to construction of a data center network and high bandwidth data transmission can be provided.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Three dimensional fat tree networks
InactiveUS20130010636A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsError preventionComputer scienceInter-domain
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
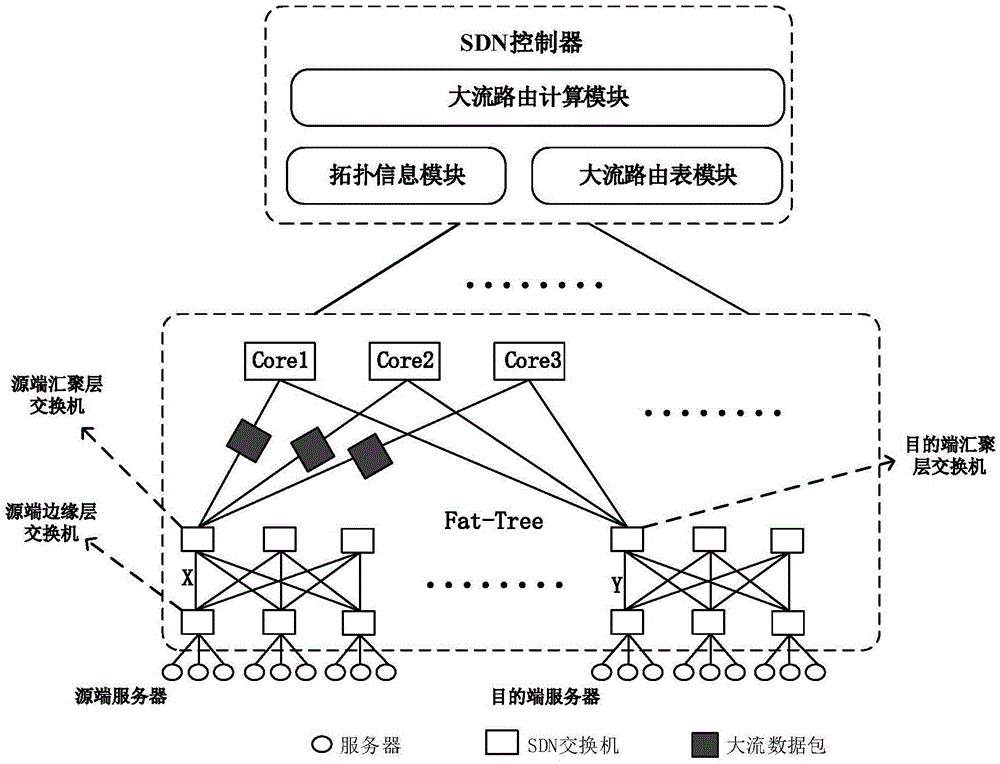
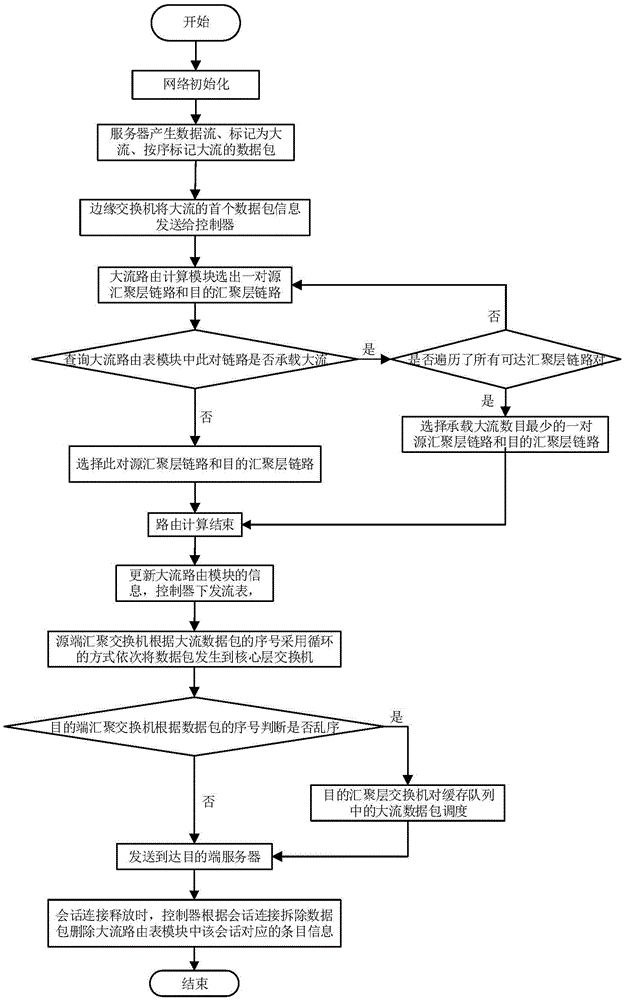
SDN-based high-volume data stream load balancing system and method
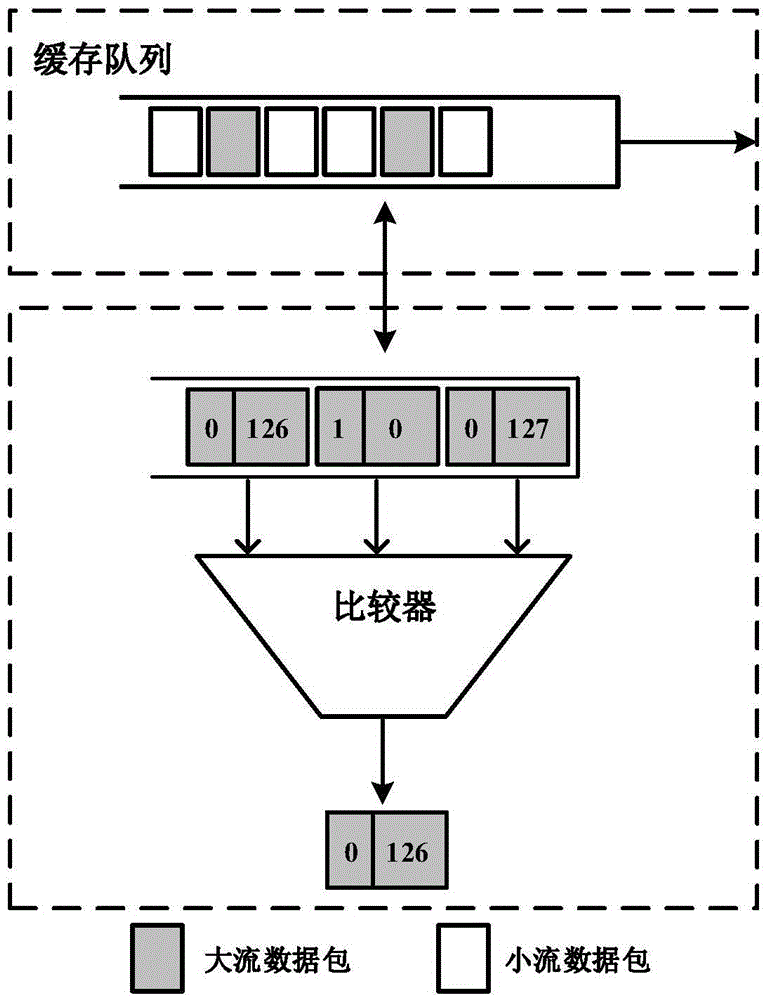
ActiveCN105610709AOvercoming the problem of out-of-order groupingData switching networksRouting tableData stream
The invention discloses an SDN-based high-volume data stream load balancing system and method, which mainly solve the problems of uneven loads and link congestion in a network core layer of the conventional data center. The system comprises a Fat-Tree underlying network and an SDN controller, wherein a topological information module, a high-volume data stream routing table module, and a high-volume data stream routing computation module are additionally arranged in the SDN controller; the high-volume data stream routing computation module computes paths for high-volume data streams according to information maintained by the topological information module and the high-volume data stream routing table module; a source aggregation layer switch adopts a packet-level multi-path routing strategy, and the scheduling processing of disordered packets is completed at a destination aggregation layer switch. The SDN-based high-volume data stream load balancing system and method provided by the invention have the advantages that a Fat-Tree network core layer adopts the multi-path routing strategy for the high-volume data streams, so as to solve the problems of uneven loads and link congestion in the network core layer of the data center; a scheduling mechanism for high-volume data stream data packets is introduced to overcome the problem of packet disordering. The SDN-based high-volume data stream load balancing system and method can be used for data forwarding.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV +1
Network topology structure based on fat tree high scalability hypercube
InactiveCN103957163AImprove scalabilityHigh bandwidth throughputData switching networksFault tolerancePath network
The invention is applied to the field of network communication, and provides a network topology structure based on a fat tree high scalability hypercube. The network topology structure comprises multiple switches and multiple servers. The switches employ a recursion unit hierarchical mode to form a topology network. A lowest recursion unit employs an m-port n- tree fat tree network structure, and the number of servers supported by the lower recursion unit is: g0=2*(m / 2)n, wherein m is the number of ports of the switches in a fat tree, and n is the number of layers of the fat tree structure. In a network topology, the k-th port of the i-th switch at a highest layer is interconnected with the k-th server of the i-th subunit for realizing a multipath network topology structure, wherein i and k belong to a set of {1,2, ..., gk-1}. Through fusing a fat tree network topology in hierarchical recursion, the high scalability of the network topology is realized, at the same time, the characteristics of equal bandwidth and multipath performance of a fat tree network are also inherited, the bandwidth throughput is quite large, the fault tolerance is quite good, and the average time delay is quite small.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
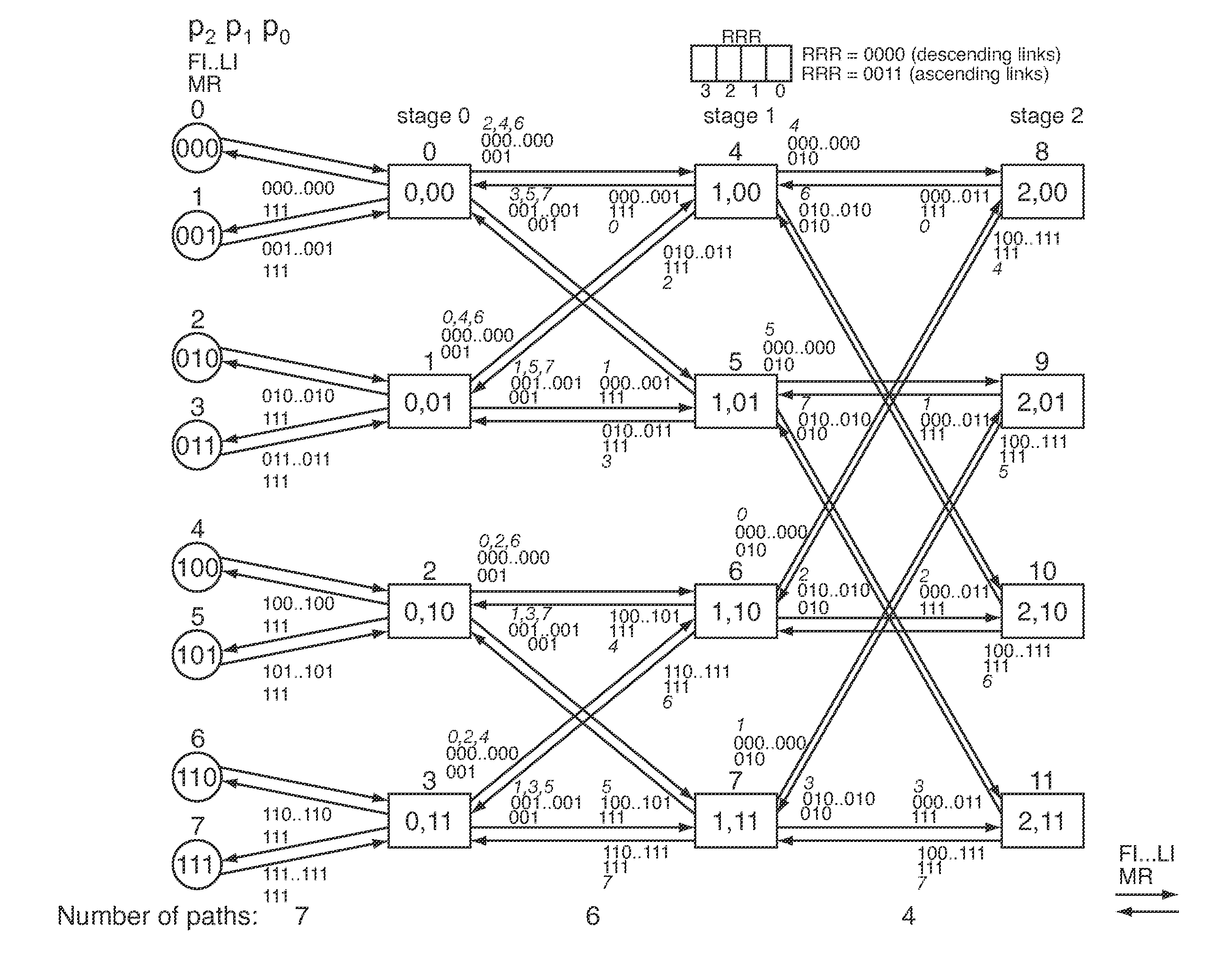
Deadlock-free routing in fat tree networks
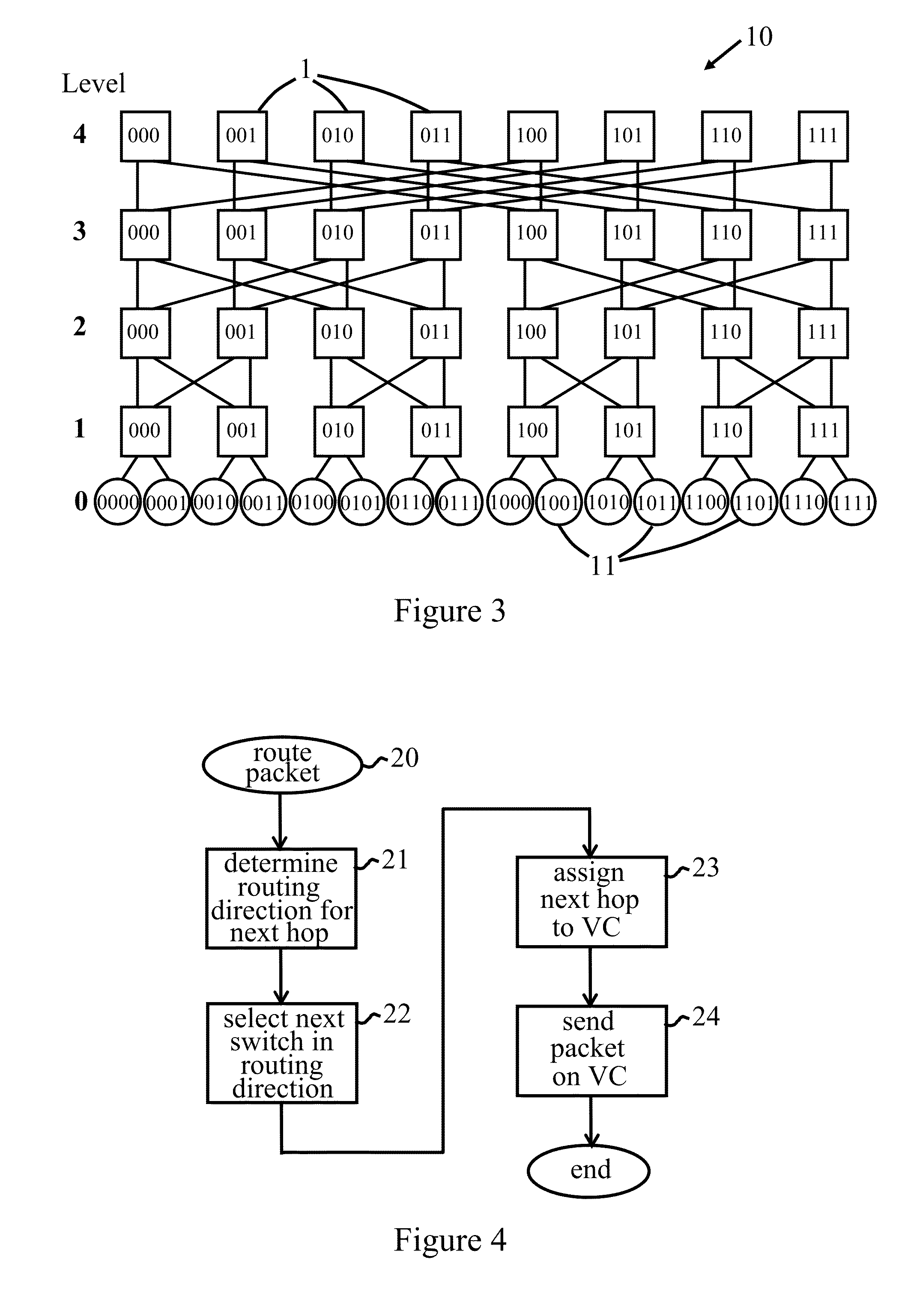
Methods and apparatus are provided for routing data packets between source and destination switches in a fat tree network. For each packet, a route is selected having three or less routing phases such that the route follows a shortest path across the network between the source and destination switches. The data packet is transmitted from the source switch to the destination switch, via the route, on one of first and second virtual channels unless the route includes a predetermined one of a down-up turn and an up-down turn. If the route includes the predetermined one of a down-up turn and an up-down turn, the data packet is transmitted, via the route, on the first virtual channel up to the switch 1 at which the turn occurs and on the second virtual channel from that switch. This provides full-connectivity in fat tree networks with deadlock free operation.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method and switch for routing data packets in interconnection networks
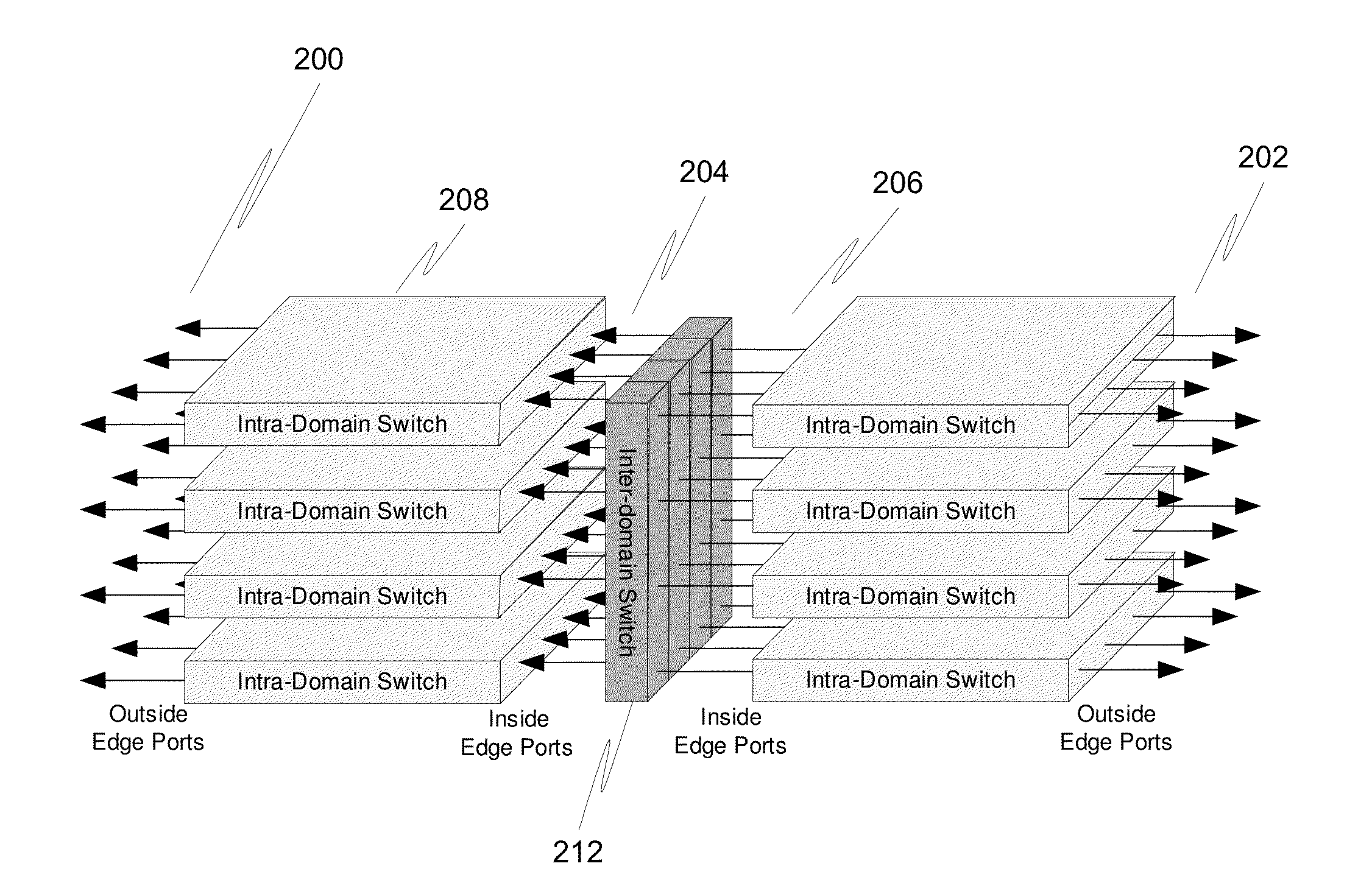
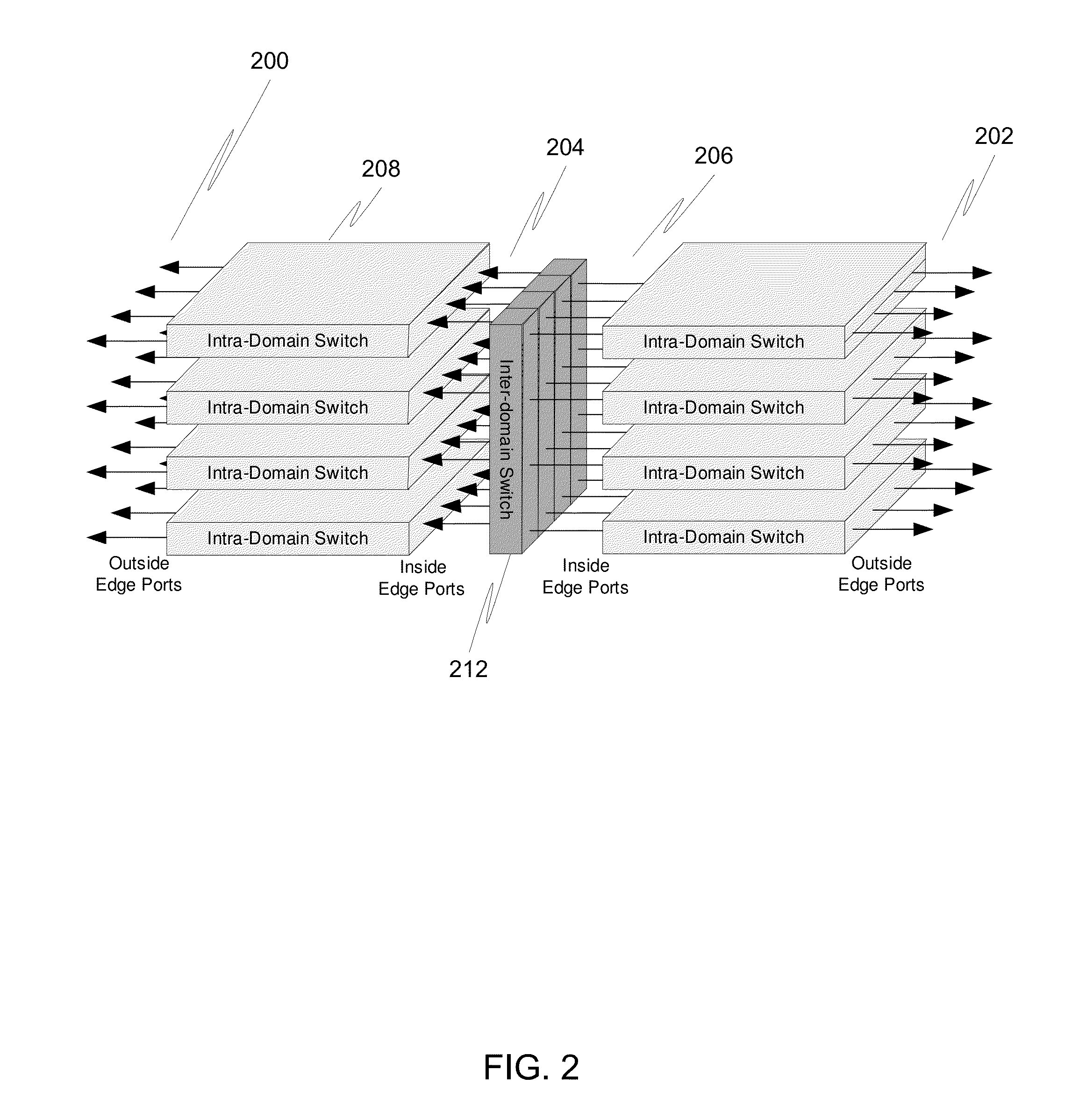
InactiveUS20090059913A1Easy to implementEfficient executionData switching by path configurationNetwork packetMultistage interconnection networks
The invention falls within the technology of multistage interconnection network such as fat-trees, comprising at least one switch located at a stage (s) and configured to send, through an output port from a number (k) of output ports forming an ordered list, at least a data packet containing a destination address identified by a n-tuple with a plurality (n) of components (pn−1, . . . , p1, p0), and sε{0 . . . (n−1)}. The invention has application for both source and distributed routing, as deterministic and as adaptive routing, selecting an output port to be the unique or the default option to forward the packets at the switch which is the output port that has a position in the ordered list of output ports corresponding to the component (ps) of the destination address at the position given by the stage (s) of the switch.
Owner:UNIV POLITECNICA DE VALENCIA
Data center network load balancing method based on SDN and employing fat-tree topological structure
InactiveCN105119840AReduce complexityGuaranteed communication qualityData switching networksLoss rateRound complexity
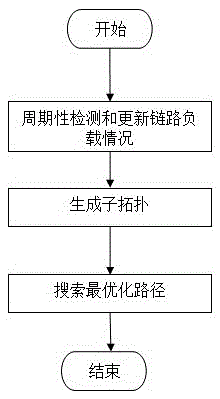
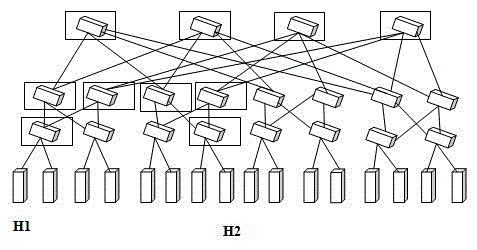
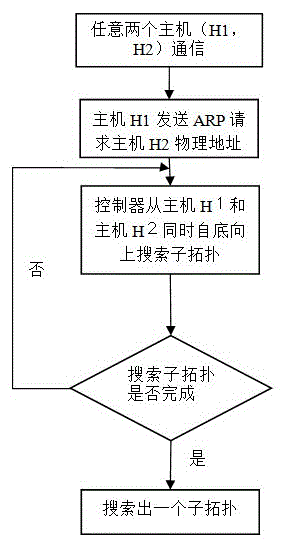
The invention discloses a data center network load balancing method based on an SDN and employing fat-tree topological structure. The data center network load balancing method comprises: a network link load can be updated in real time and dynamically, a sub-topology is found out between any two hosts in communication from the whole network topology, and a path lowest in link load is found out from the sub-topology. The route is the communication path of the two hosts. According to the data center network load balancing method, by taking the whole topological link load condition into account, the link load and the state information of a relevant switch are used as the Dijkstra algorithm of a search weight to search for the path lowest in link load. The data center network load balancing method has the advantages that the complexity of the algorithm is relative low, less information is stored at the controller end to ensure the network communication quality, reduce the loss rate of data packets and increase the network throughput, and therefore, the load balance of the network is guaranteed.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
Automatic allocation method of IP address of node inside fat tree structure networking data center
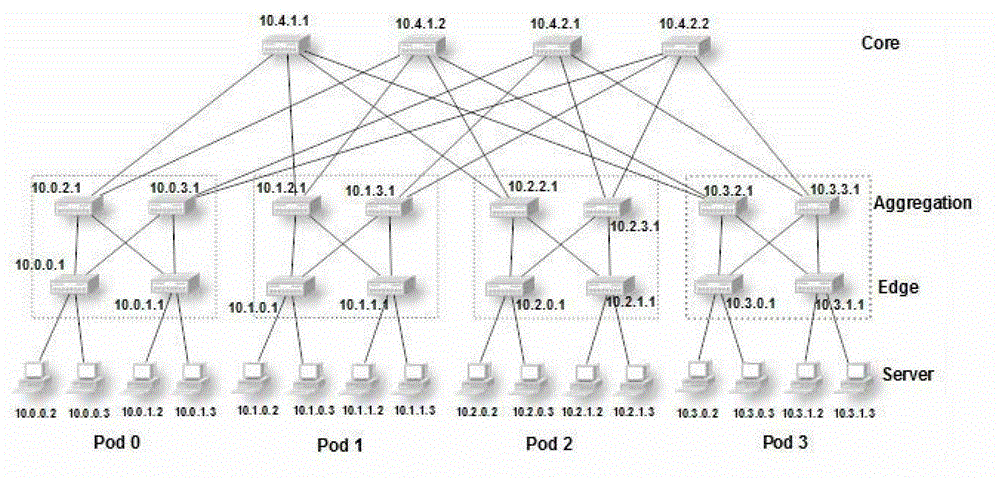
InactiveCN102917084AGuaranteed uptimeRealize automatic allocationTransmissionDistribution methodIp address
The invention provides an automatic allocation method of an IP address of a node inside a fat tree structure networking data center. The automatic allocation method comprises the following steps of: firstly, carrying out DHCP (dynamic host configuration protocol) server initial configuration, modifying and self-customizing a DHCP server end and a client end in a network for supporting rule-based IP address allocation; and secondly, carrying out specific IP address allocation, and carrying out IP address allocation by a DHCP server in a Pod by layers by the network node according to the count of hops away from the DHCP sever, wherein a DHCP relay function is started by a switchboard in the Pod after an address is obtained. According to the allocation method, a data center network of a fat tree structure is combined with a DHCP, thus the automatic allocation of all node addresses in the data center network of fat tree structure networking is realized, the network abnormity problem can be detected and solved, a large quantity of manpower and material resources are saved, and normal and stable operation of the data center network is ensured.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
Method and equipment for establishing route table
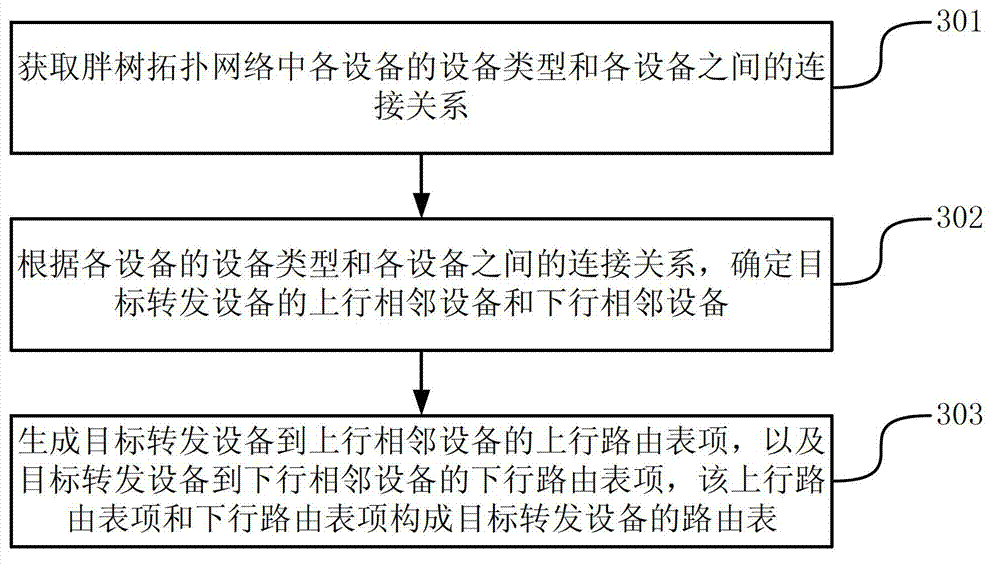
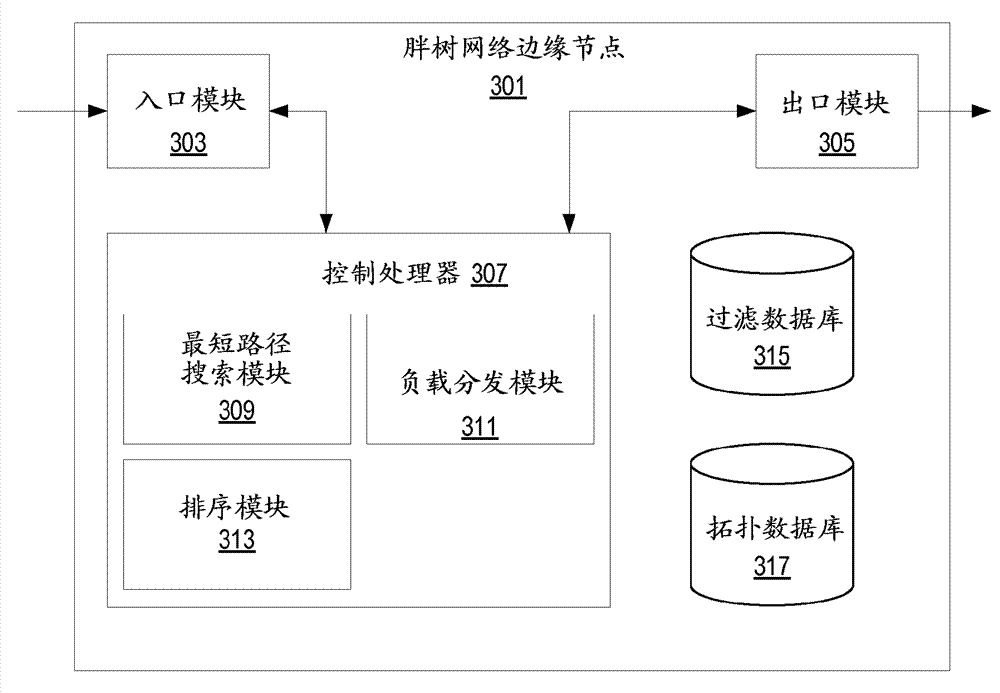
ActiveCN103078798AShorten convergence timeReduce the numberData switching networksDevice typeRouting table
The invention discloses a method and equipment for establishing a route table, belonging to the network communication field. The method is applied to a fat-tree topological network, and comprises the following steps: obtaining a connection relation between an equipment type of each equipment and each equipment in the fat-tree topological network; identifying uplink adjacent equipment and downlink adjacent equipment of target forwarding equipment according to the connection relation between the equipment type of each equipment and each equipment; generating an uplink route table item from the target forwarding equipment to the uplink adjacent equipment, and a downlink table route item from the target forwarding equipment to the downlink adjacent equipment; and constructing a route table of the target forwarding equipment formed by the uplink route table item and the downlink route table item. With the adoption of the method and the equipment, the number of the items of the equipment router table in the fat-tree topological network can be reduced, so that the convergence time is shortened.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
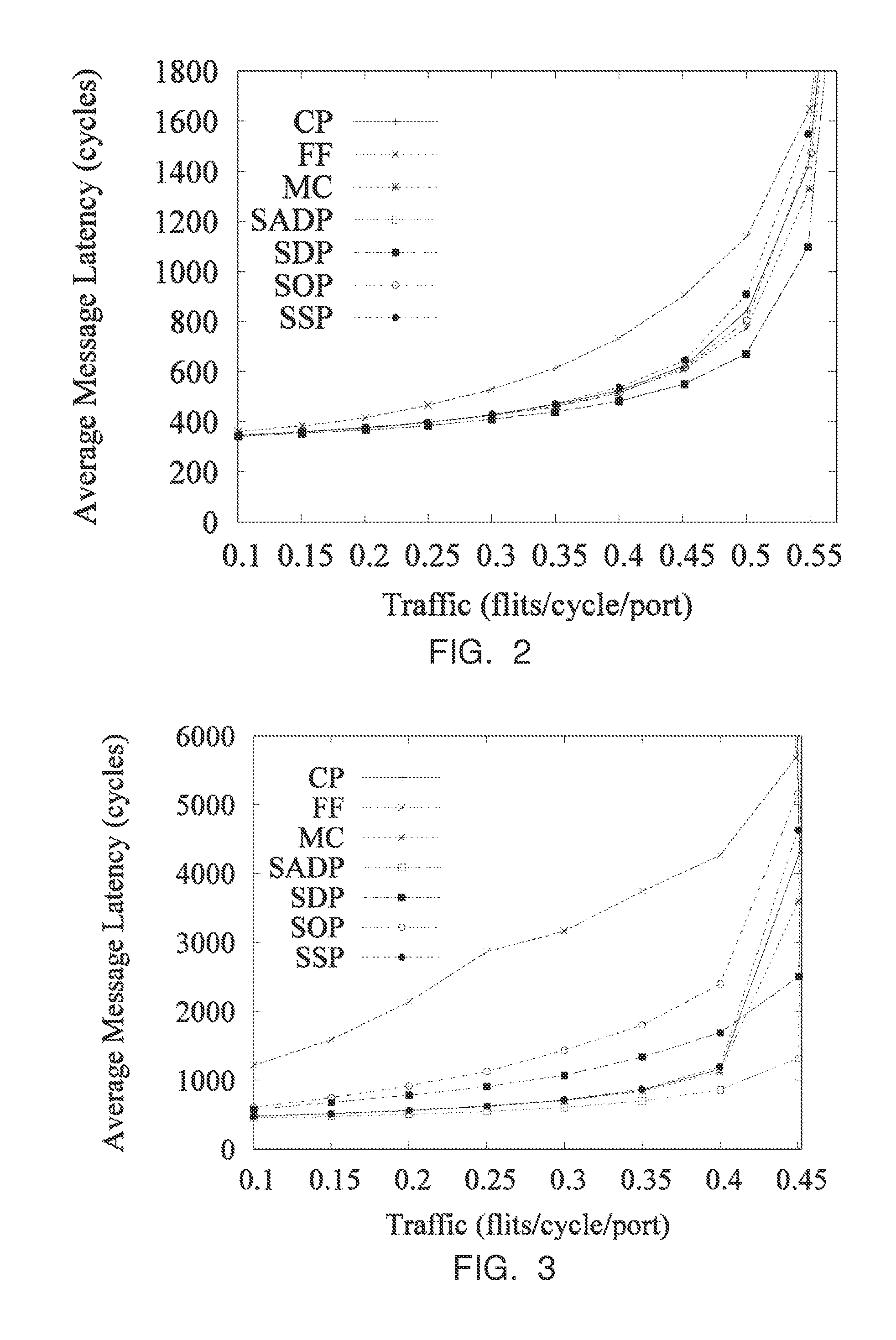
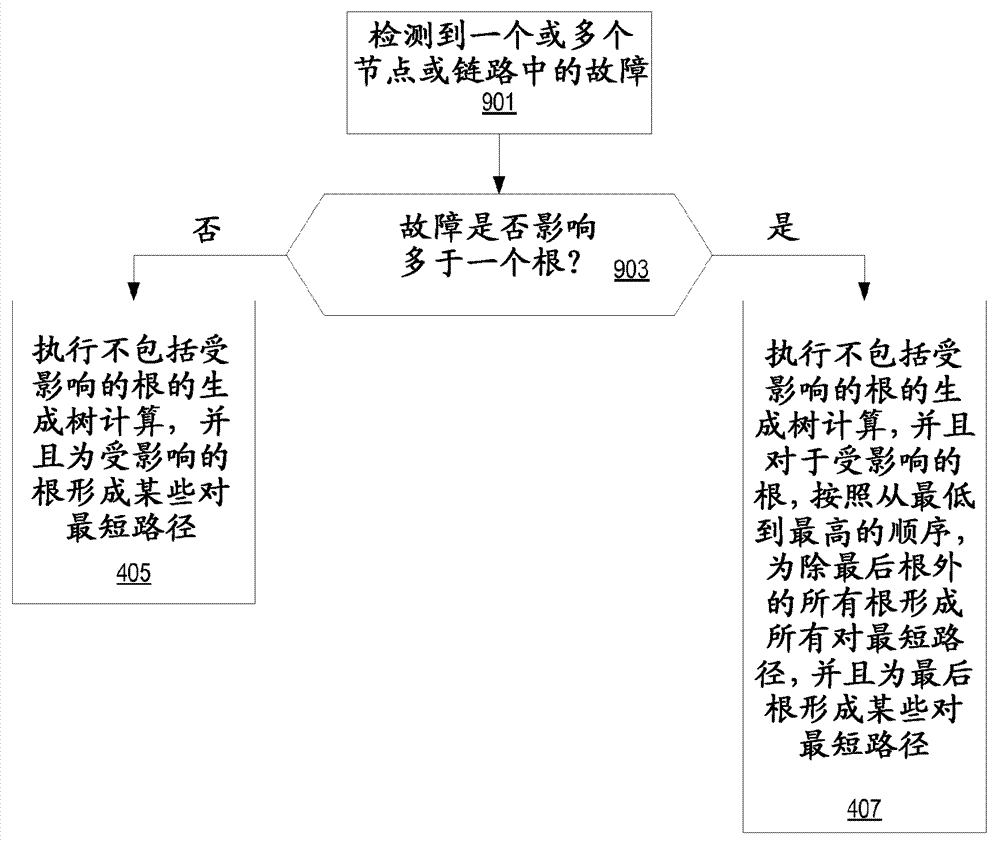
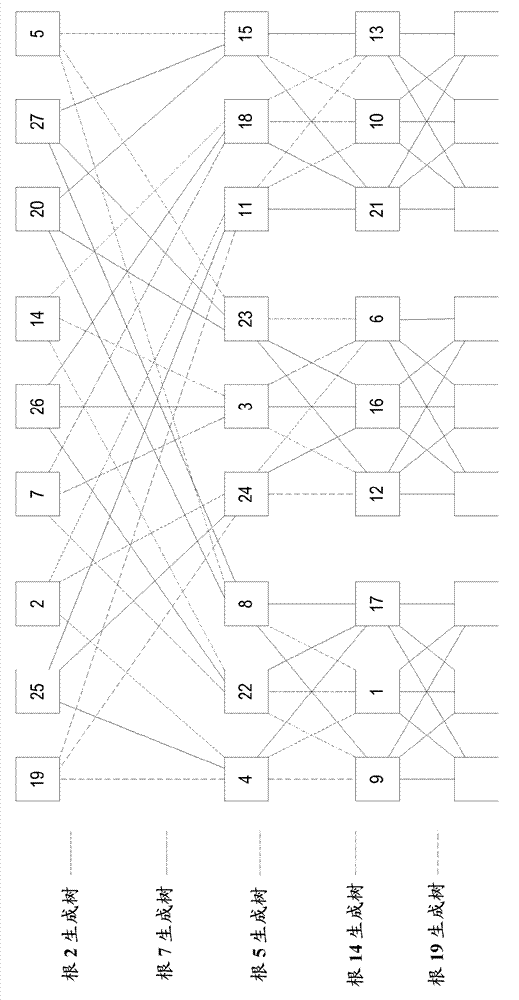
Automated traffic engineering for fat tree networks
ActiveCN103026668AReduce computational complexityDigital computer detailsData switching networksEngineeringMedia access control
Embodiments of a method implemented in at least one fat tree network node for improved load distribution, wherein the node is one of a plurality of fat tree network nodes in a fat tree network each of which implement a tie-breaking process to produce minimum cost trees, is described. In some embodiments, a spanning tree computation for each root node of the fat tree network in order from a lowest ranked root node to a highest ranked node is performed, a filtering database for each root node of the fat tree network, wherein the filtering database includes a set of media access control (MAC) addresses of the leaf nodes of the fat tree network generated, and link utilization for each computed tree to use as a prefix to link identifiers used for at least one tie-breaking algorithm added.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
High-performance load balancing system and method based on software defined network
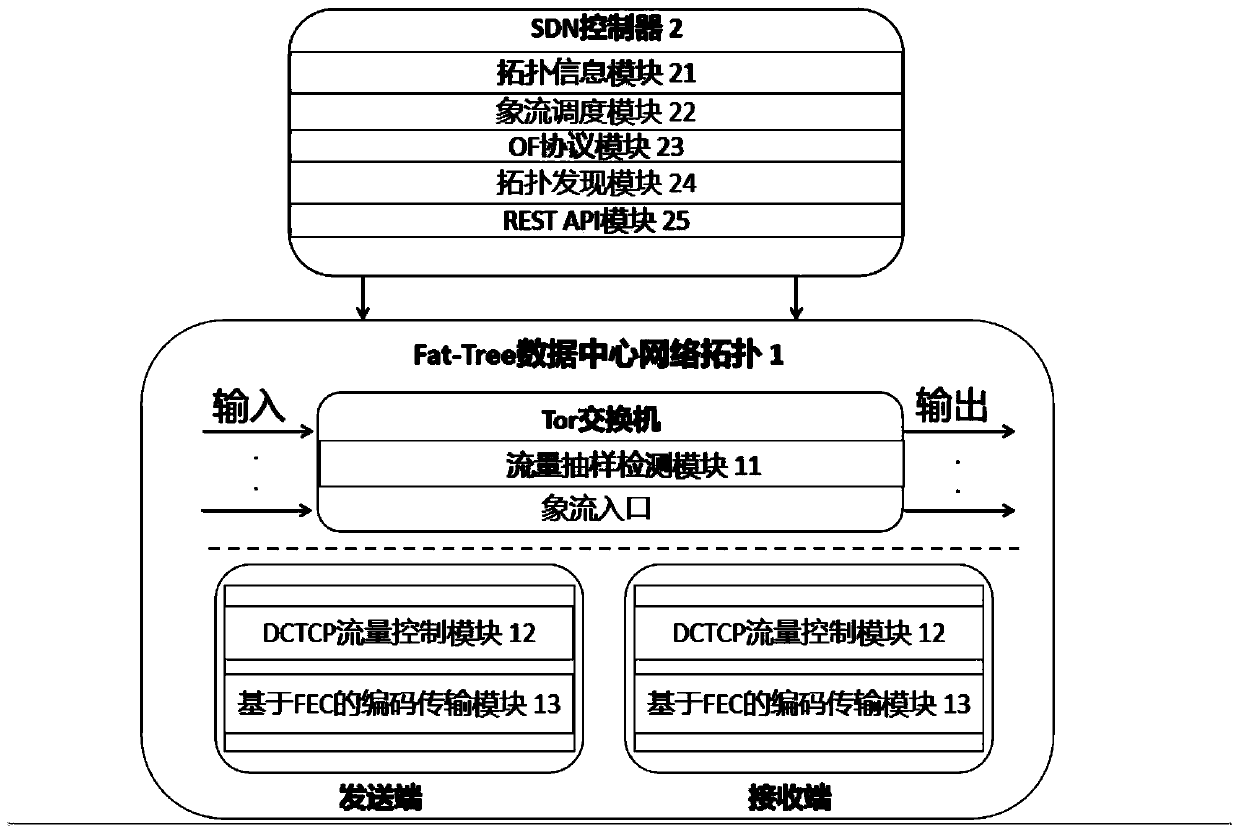
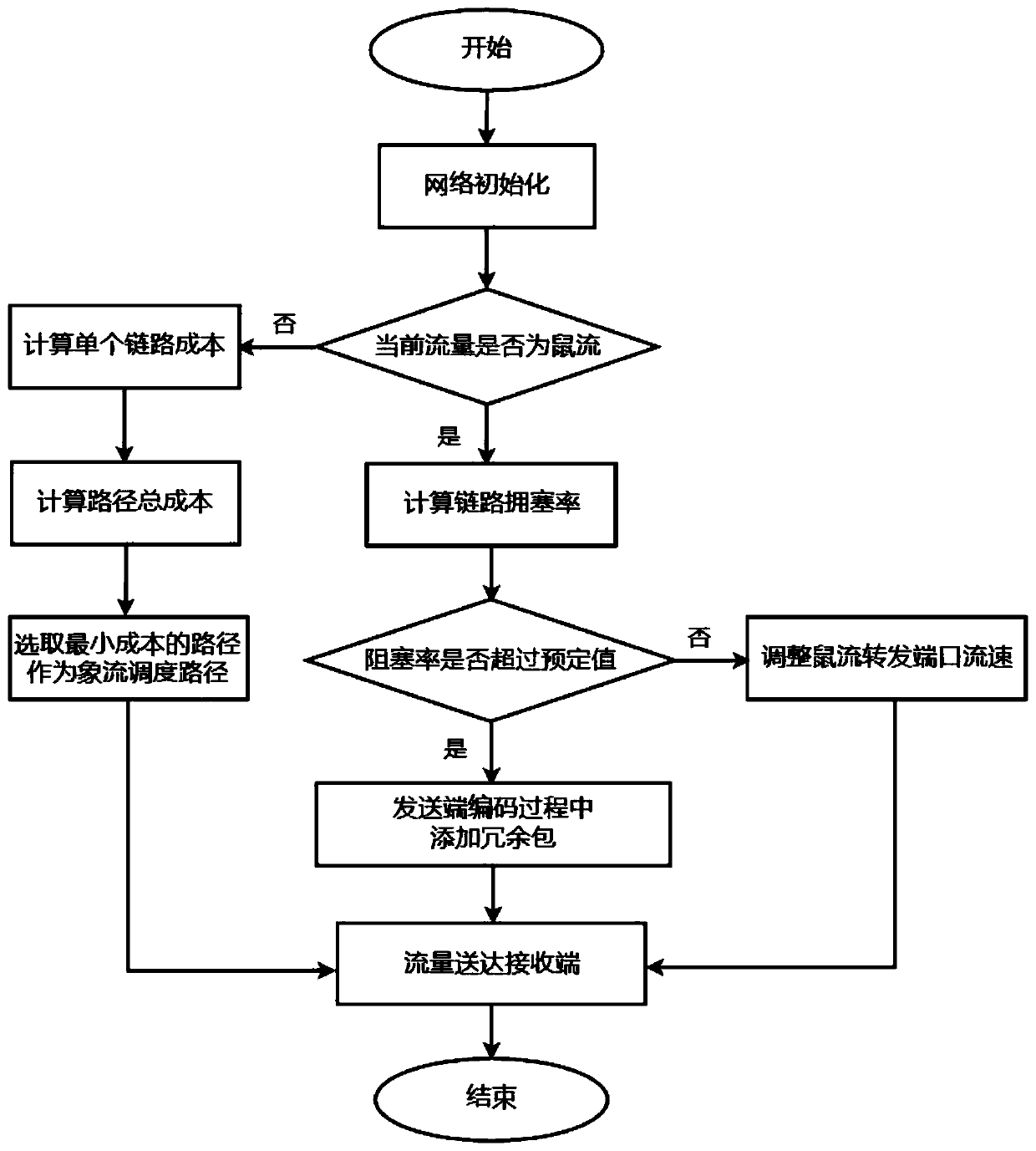
ActiveCN110191065AReal-time perception of traffic rateSolve the problem of the long-tail incubation period of rat flowChannel coding adaptationForward error control useTopology informationPacket loss
The invention discloses a high-performance load balancing system based on a software defined network. The high-performance load balancing system mainly solves the problems of uneven load and link congestion in a network core layer of an existing data center. The system comprises a Fat-Tree underlying network and an SDN controller, and Fat-Tree bottom layer network is provided with a flow samplingdetection module, a DCTCP flow control module and a coding transmission module based on FEC, and the functions of sensing flow in real time, distinguishing mouse flow image flow, adjusting the flow rate of a port according to link time delay and adding a redundant packet to reduce mouse flow time delay are completed respectively. The SDN controller is additionally provided with a topology information module and an image flow scheduling module which are used for storing topology information of an underlying network and scheduling an image flow to a path with the minimum path cost. According tothe invention, retransmission delay caused by packet loss is reduced, the problem of blocking of the head and the tail of a mouse stream is solved, the image stream throughput is improved, and the method can be used for Fat-Tree data center network topology.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
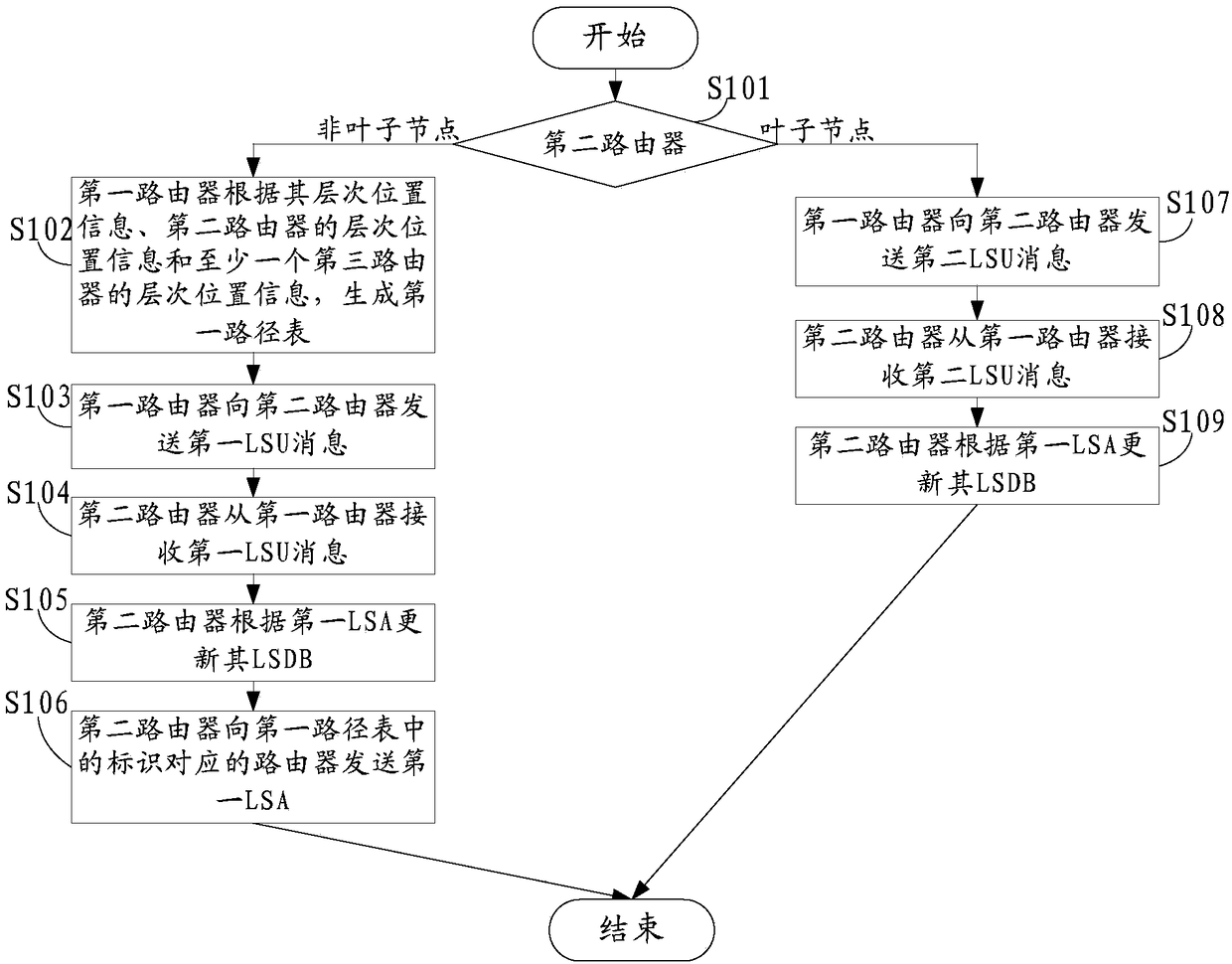
LSA sending method, apparatus and system
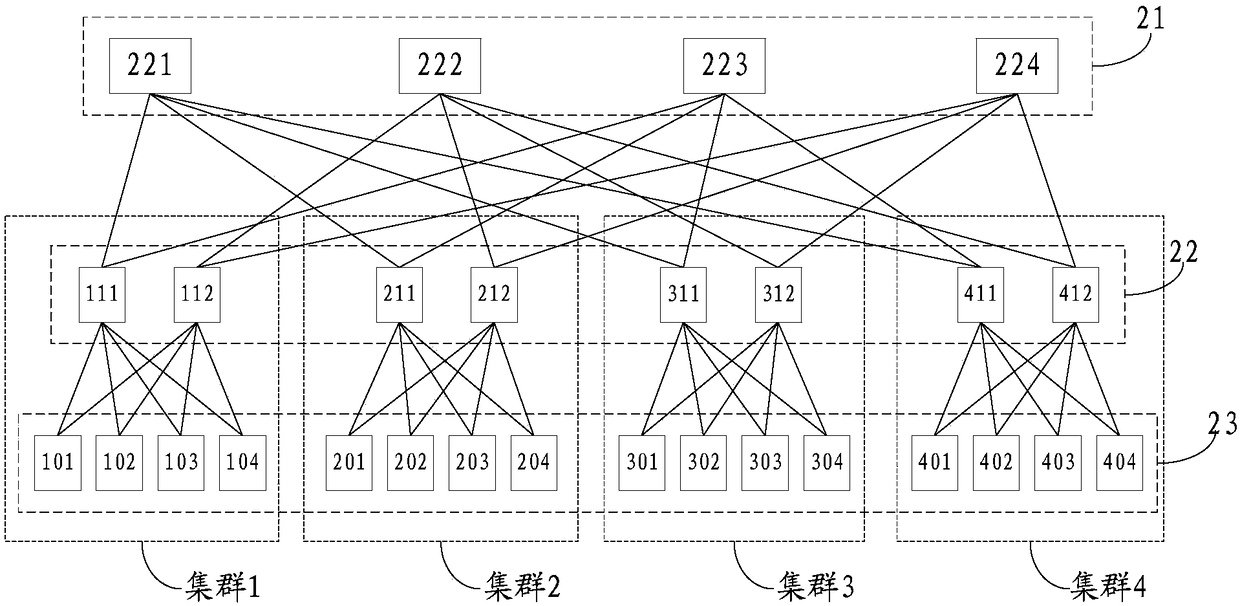
The invention discloses an LSA sending method, an apparatus and a system, related to the technical field of communication and used for reducing LSA sending times. The method comprises the following steps: a first router generates a first path table according to level position information thereof, the level position information of a second router and the level position information of at least one third router; the first router sends a first link sate updating LSU message to the second router; the second router receives the first link state updating LSU message from the first router; the secondrouter updates a link state database LSDB thereof according to the first LSA; and the second router sends the first LSA to the router corresponding to an identifier in the first path table. The method, the apparatus and the system provided by the embodiment of the invention are applied to sending of the LSA in leaf-spine topology or fat-tree topology.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
High speed, high character price ratio multi branch fat tree network topological structure
InactiveCN1514591AGuaranteed bandwidthCommunication without blockingData switching by path configurationSelection arrangementsHigh ratePrice ratio
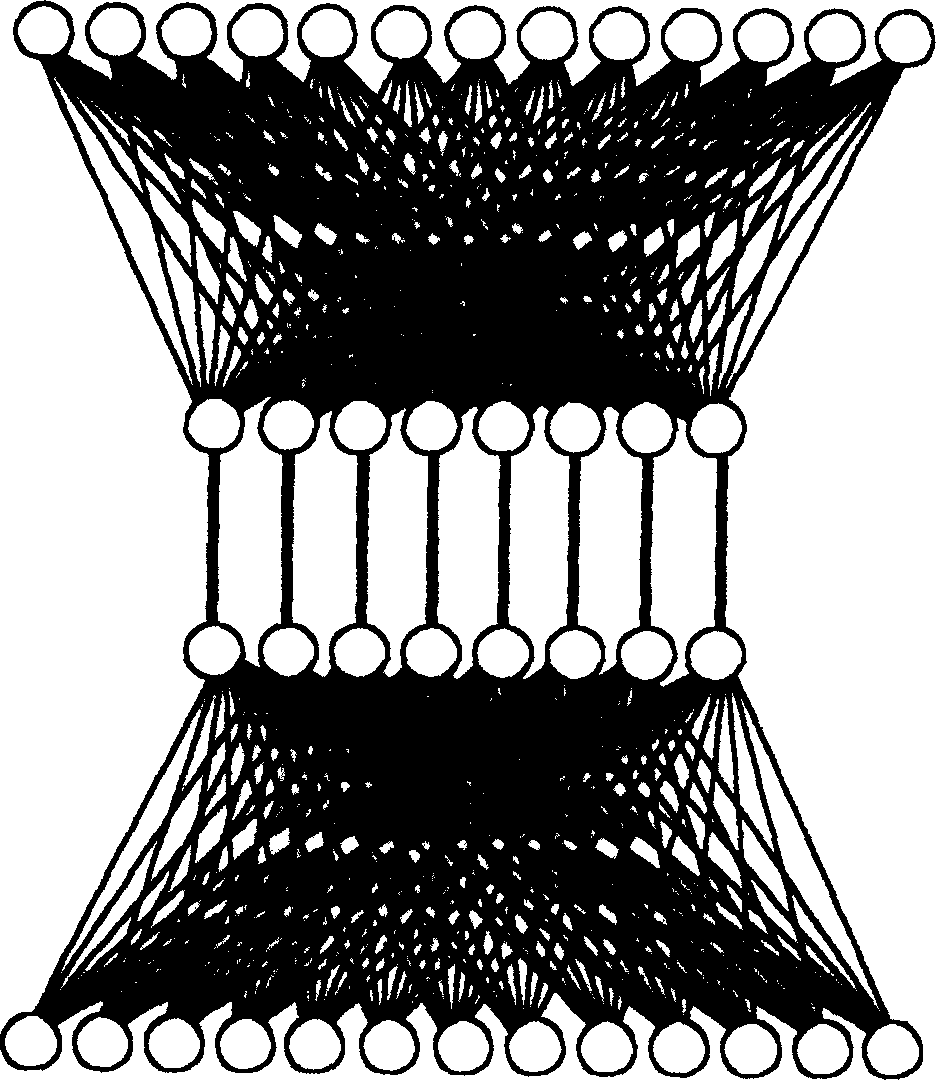
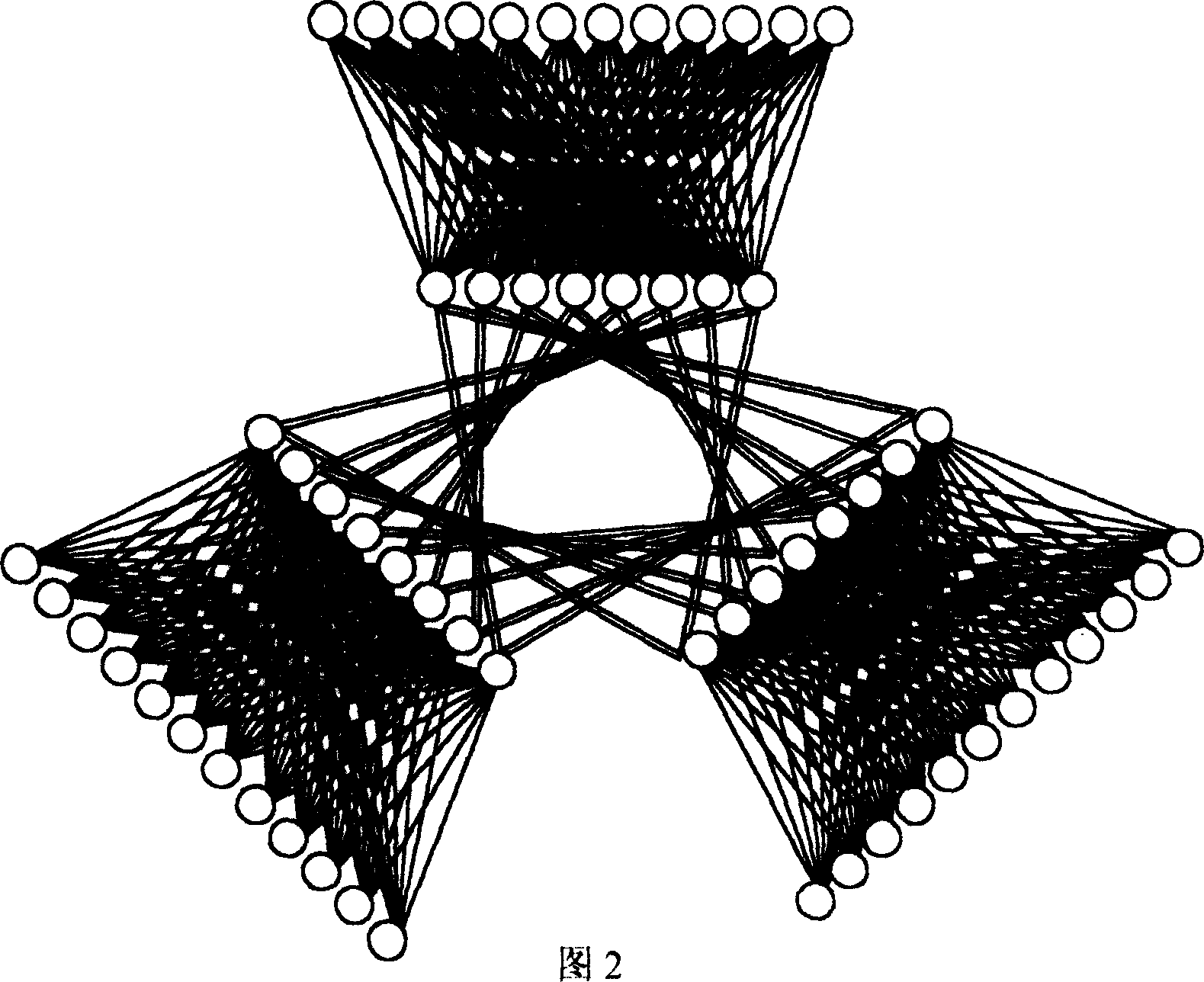
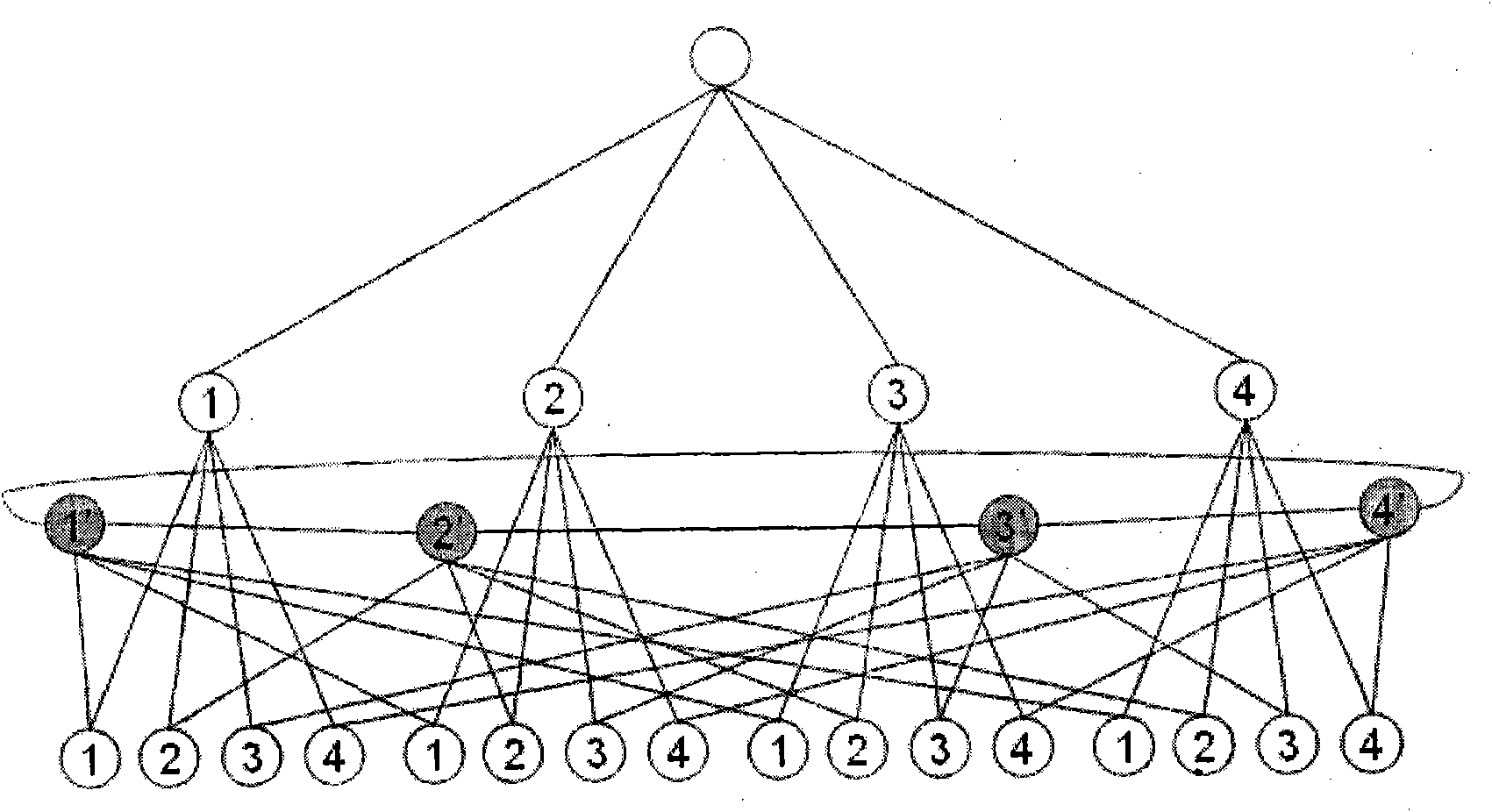
When numbers of node in network increases to a certain scale, network topology interconnection techniques between exchangers are produced. Synthesized interconnection mode of fat tree topology and full net topology is utilized in the invention, that is to say fat tree interconnection is utilized for each branch and full net interconnection mode is applied among branches. Based on number of branch, two branches fat trees, three branches fat trees and four branches fat trees are named. Comparing with network topology structure of nonblocking fat tree under condition of the same number of exchnger, the invented structure possesses advantages of available large scale of networked scale, lowered communication delay, and higher rate of performances / cost.
Owner:LANGCHAO ELECTRONIC INFORMATION IND CO LTD
Unified network architecture for scalable super-calculus systems
ActiveUS20130239121A1Reduce latencyReduce trafficInterprogram communicationDigital computer detailsSupercomputerSynchronization networks
A network architecture is used for the communication between elementary calculus units or nodes of a supercomputer to execute a super-calculus processing application, partitionable and scalable at the level of calculus power in the range of PetaFLOPS. The supercomputer comprises a plurality of modular structures, each of which comprises a plurality of elementary calculus units or nodes defined by node cards, a backplane, a root card, and a node communication network of the switched fabric fat tree type; ii) a synchronization architecture comprising a plurality of distinct node communication networks, configured for the communication of specific synchronization information different from network to network and with different characteristics; iii) a re-configurable Programmable Network Processor that implements the nodes both of the n-toroidal network and those of the synchronization networks.The node communication networks of the n-toroidal type and of the switched fabric fat tree type can be used alternately or simultaneously for the transmission between the calculus nodes of the same type of data and information also in a configuration of system partitions in order to achieve the desired interconnection topology of the nodes.
Owner:EUROTECH
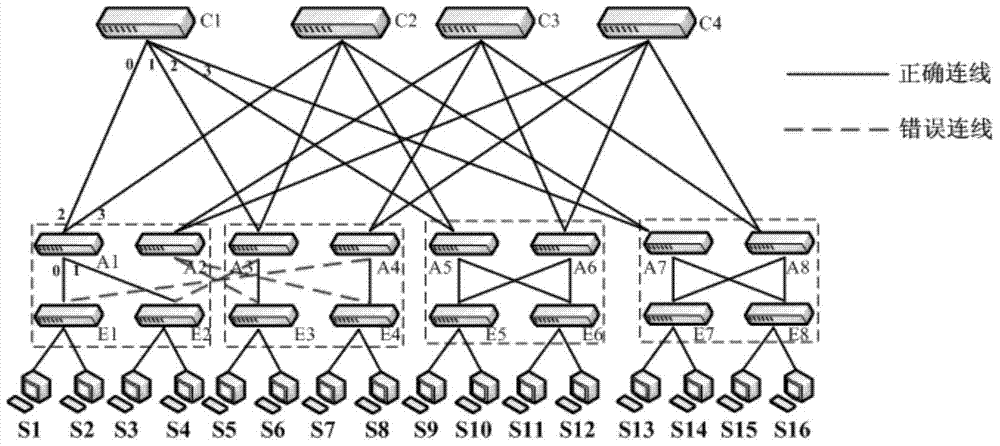
Detecting method and device of error connection in data center network
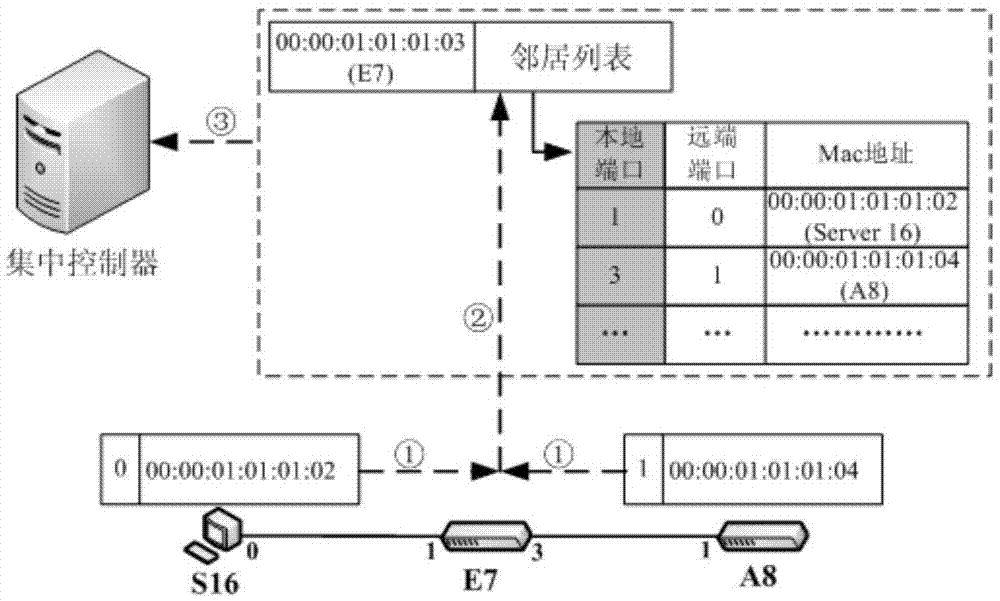
InactiveCN104518927ANo human judgment requiredImprove work efficiencyData switching networksTopology informationDistributed computing
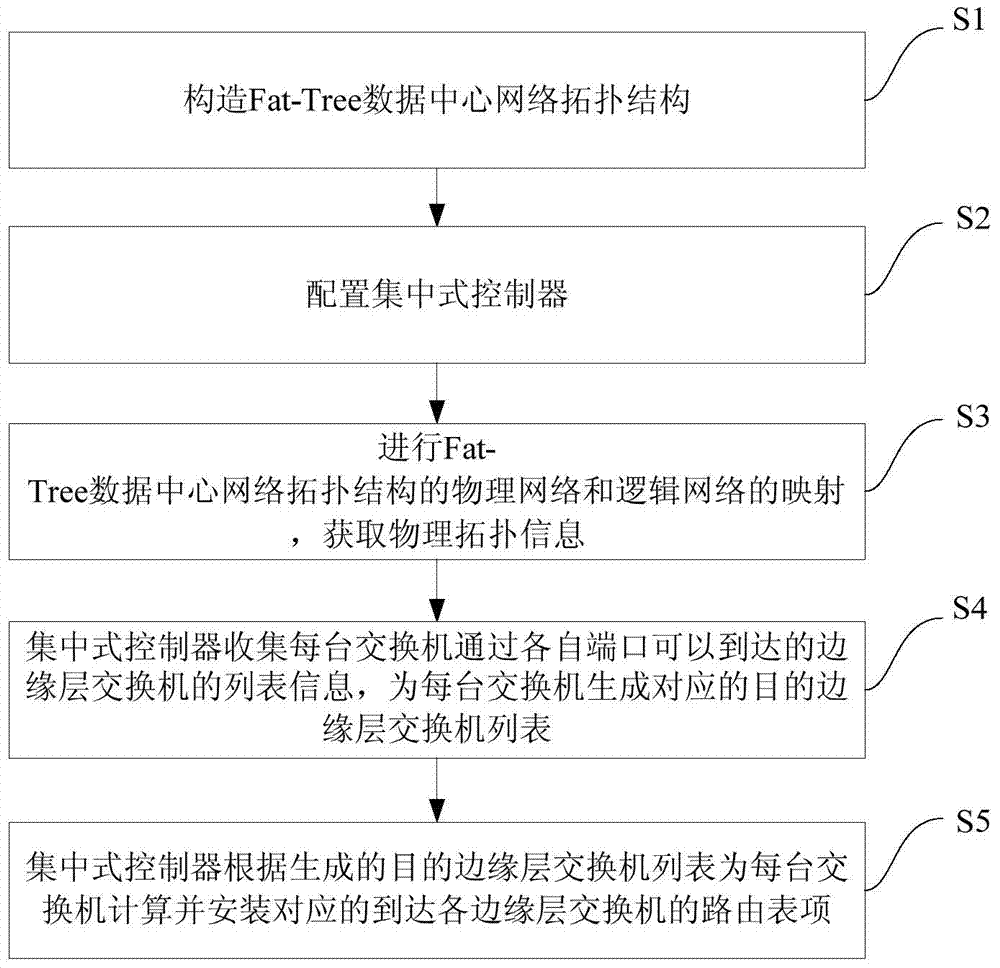
The invention discloses a detecting method and device of the error connection in a data center network. The method includes the steps of S1, constructing a data center network topology according to a Fat-Tree network; S2, configuring a centralized controller according to multiple servers and multiple switchers; S3, collecting Fat-Tree network topology information through the communication of the multiple servers and the multiple switchers with respective adjacent equipment; S4, transmitting the Fat-Tree network topology information to the centralized controller to generate whole-network Fat-Tree network topology information, and performing error connection detecting and restoring calculation according to the whole-network Fat-Tree network topology information. The method has the advantages that error connection detecting and restoring calculation are performed by constructing the data center network topology, simple and fast detecting is achieved, artificial judgment is not needed, automation is achieved, and work efficiency is increased.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
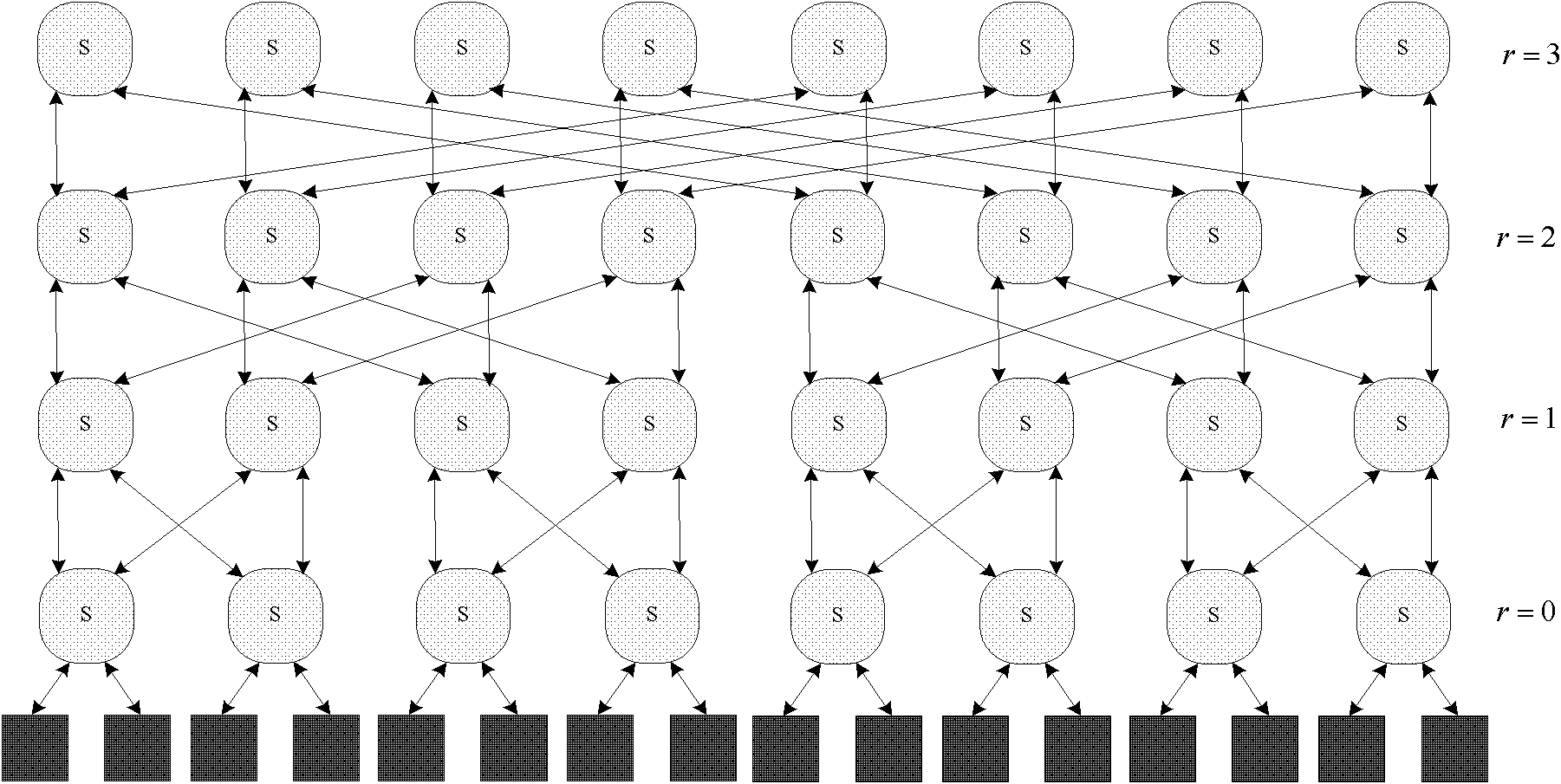
Fat tree type network-on-chip mapping method based on differential evolution and predatory search strategy
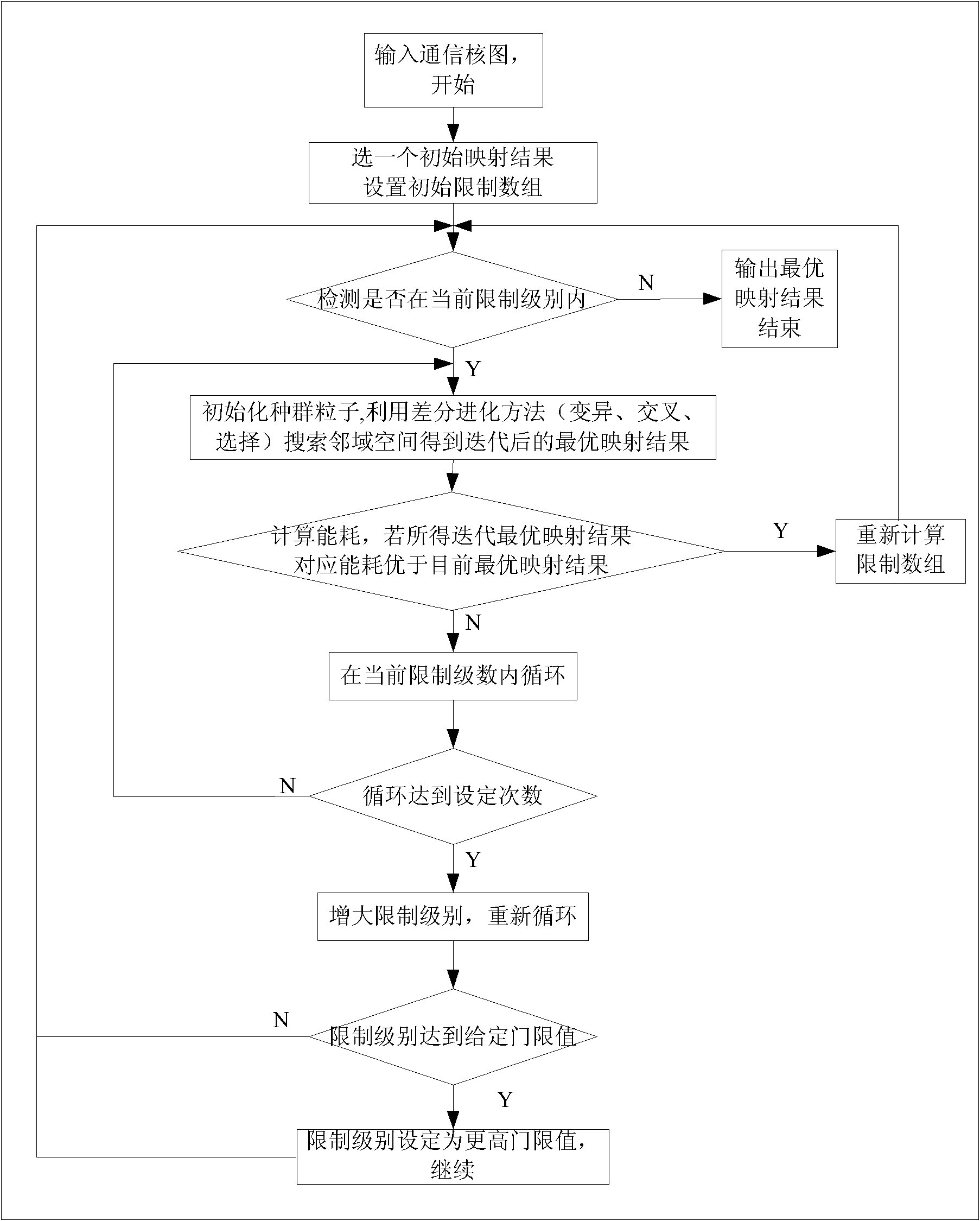
ActiveCN102325089AOvercoming the problem of being easily trapped in a local optimal solutionOptimum Energy Consumption ResultsData switching networksLocal optimumArray data structure
The invention discloses a fat tree type network-on-chip mapping method based on a differential evolution and predatory search strategy, which comprises the following steps of: (1) initializing the current optimal mapping result and defining a plurality of peripheral solutions which use any one solution as a center to form a limit array in the solution space; (2) setting limit arrays R[0], R[1],..., R[T-1] with the limit total amount of T at the periphery of the current optimal mapping result and defining the current limit variable to be R[i]; (3) searching the periphery of the current limit variable R[i] by adopting a differential evolution method; if a better solution is found out, updating the current optimal mapping result and turning back to the step (2); otherwise, turning to the step (4); (4) updating the current limit variable i which is equal to i plus 1; if i is smaller than T-1, turning back to the step (3); and otherwise, outputting the current optimal mapping result. By using the method, the problem of local optimum is solved through adjustment of limitation, the network energy consumption is greatly reduced, the mapping running time is reduced and the mapping of a low-energy consumption and rapid large-scale IP (Internet Protocol) core in the fat tree type network on a chip can be realized.
Owner:陕西光电子先导院科技有限公司
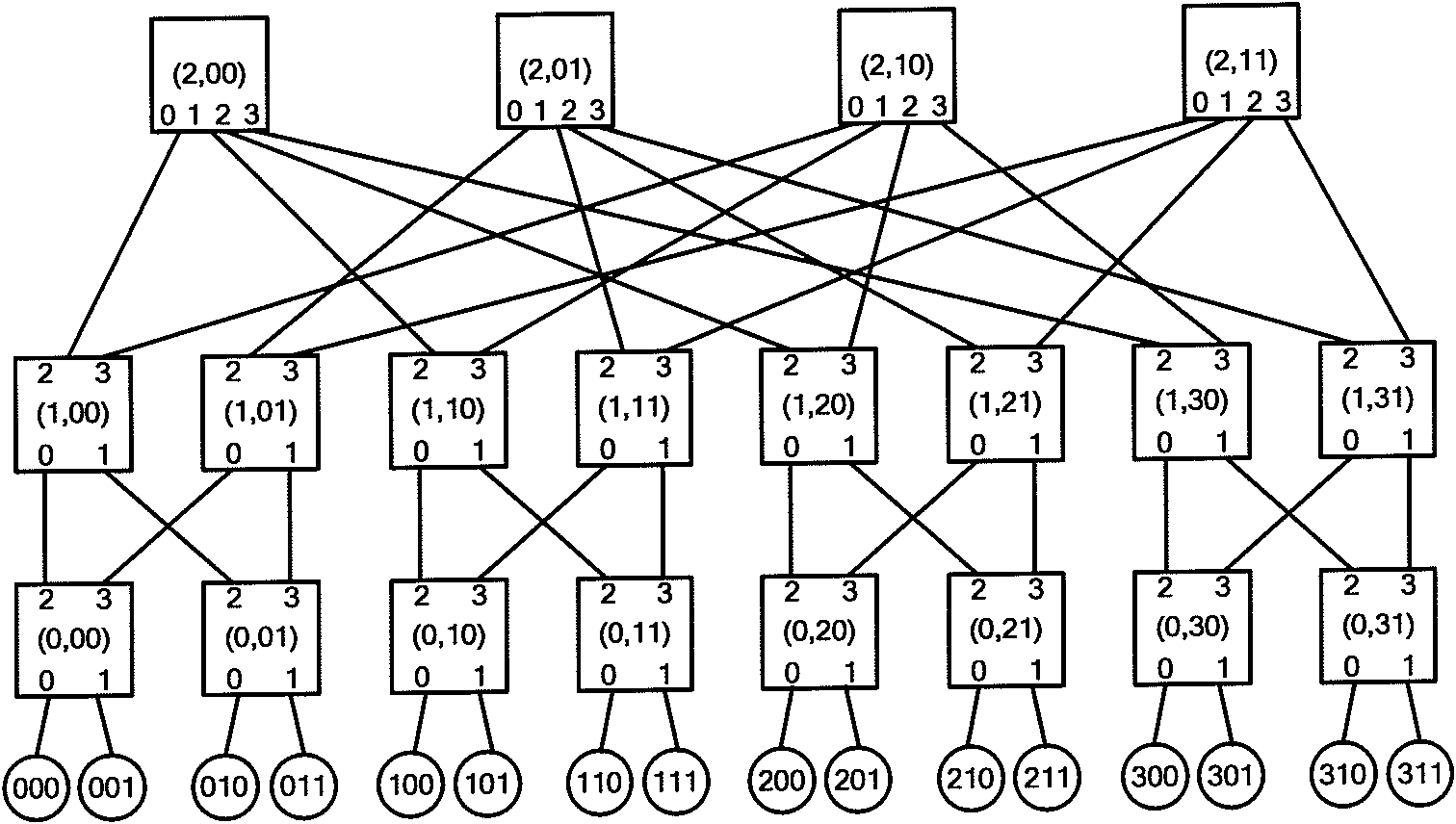
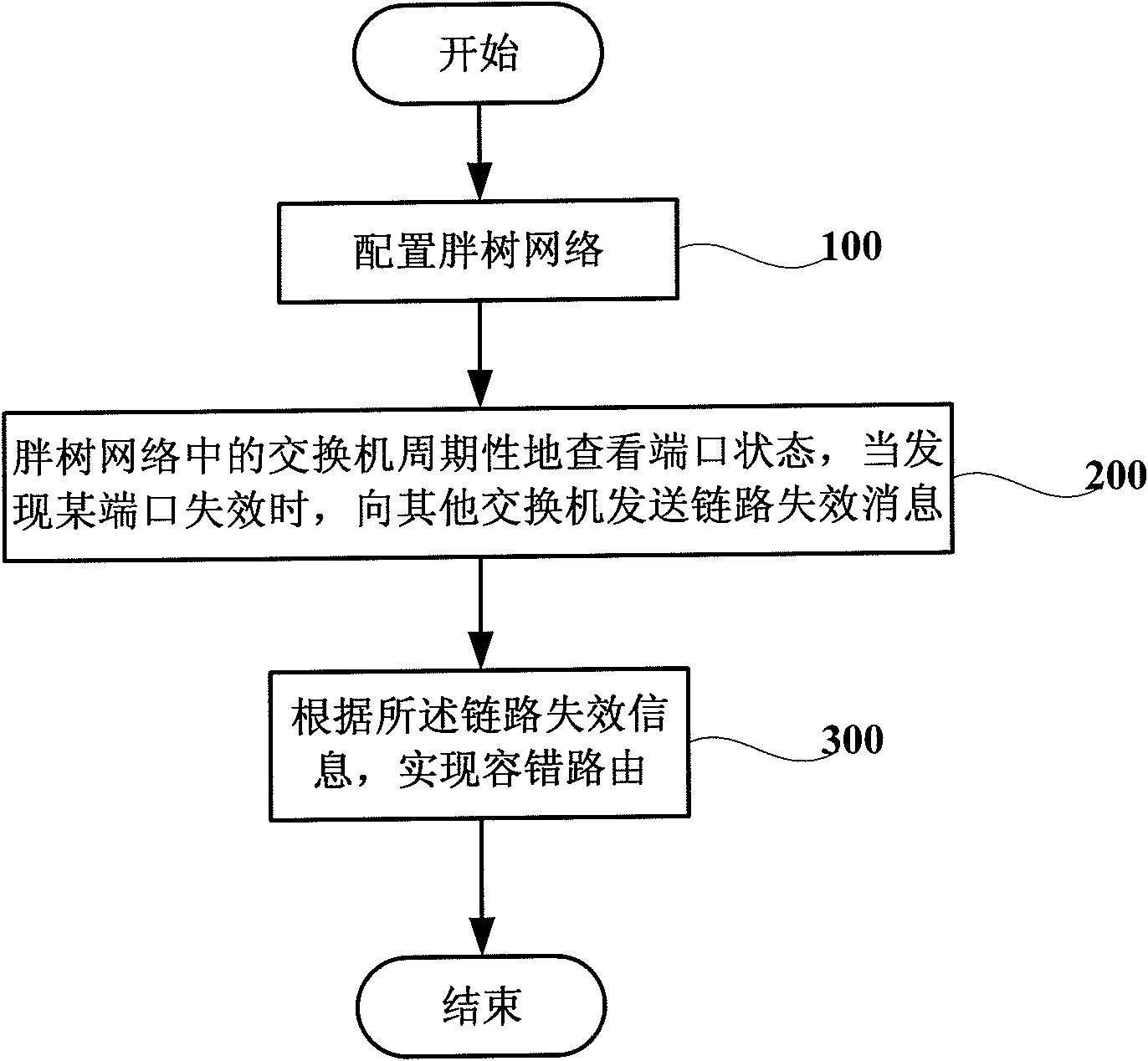
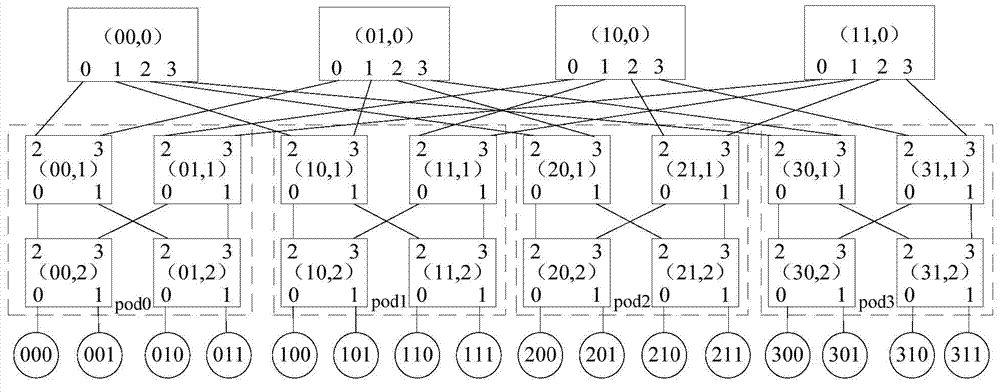
Dynamic fault tolerance method and system based on fat tree structure
ActiveCN101945050AReduce complexityImprove acceleration performanceData switching networksFault toleranceReal-time computing
The invention discloses a dynamic fault tolerance method and a system based on a fat tree structure. The method comprises the following steps: configuring a fat tree network; leading a switch in the fat tree network to periodically check the states of ports, and sending a link failure message to another switch when the certain port is found to fail; and realizing a dynamic fault tolerance routing according to the link failure information.
Owner:INST OF COMPUTING TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
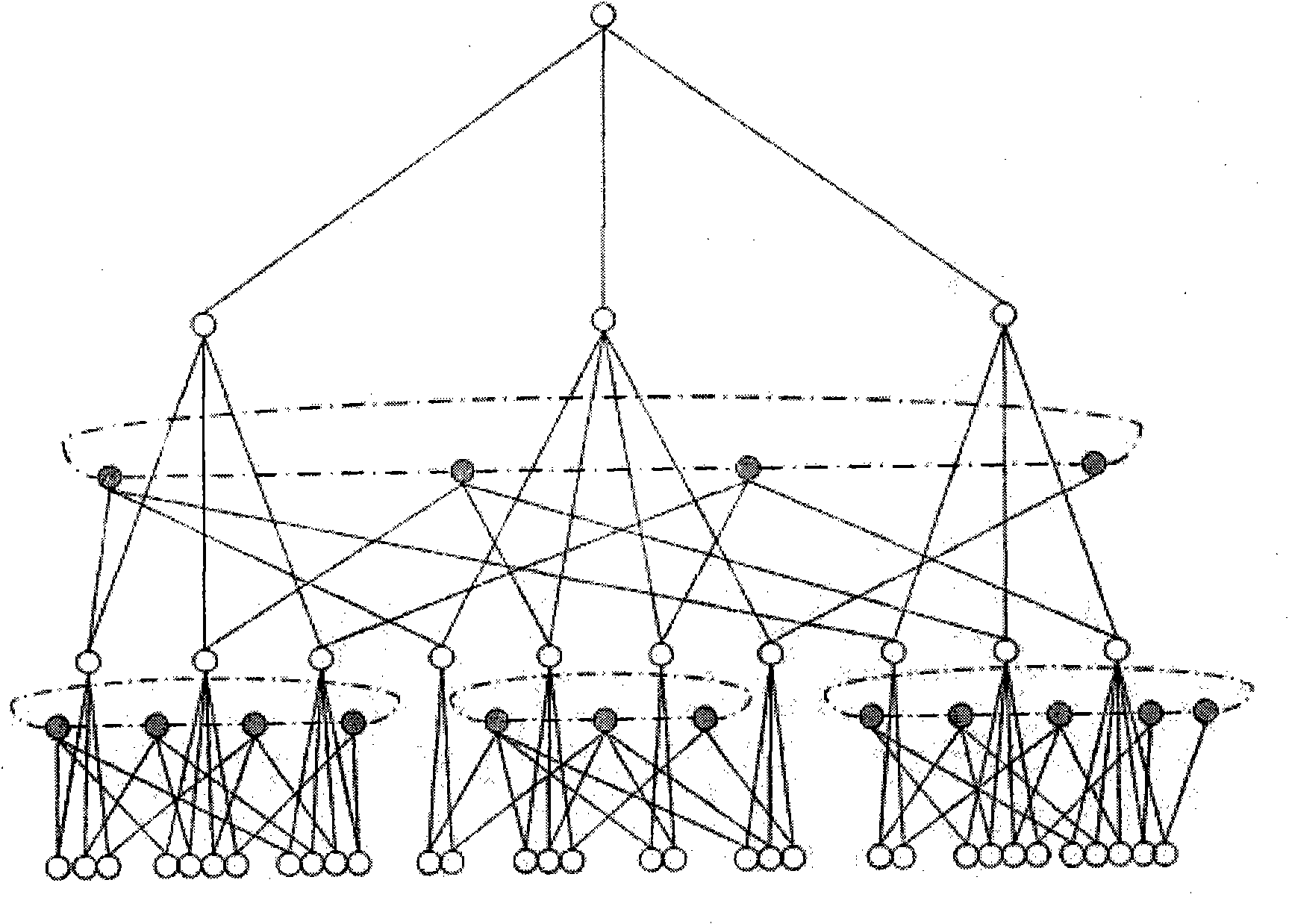
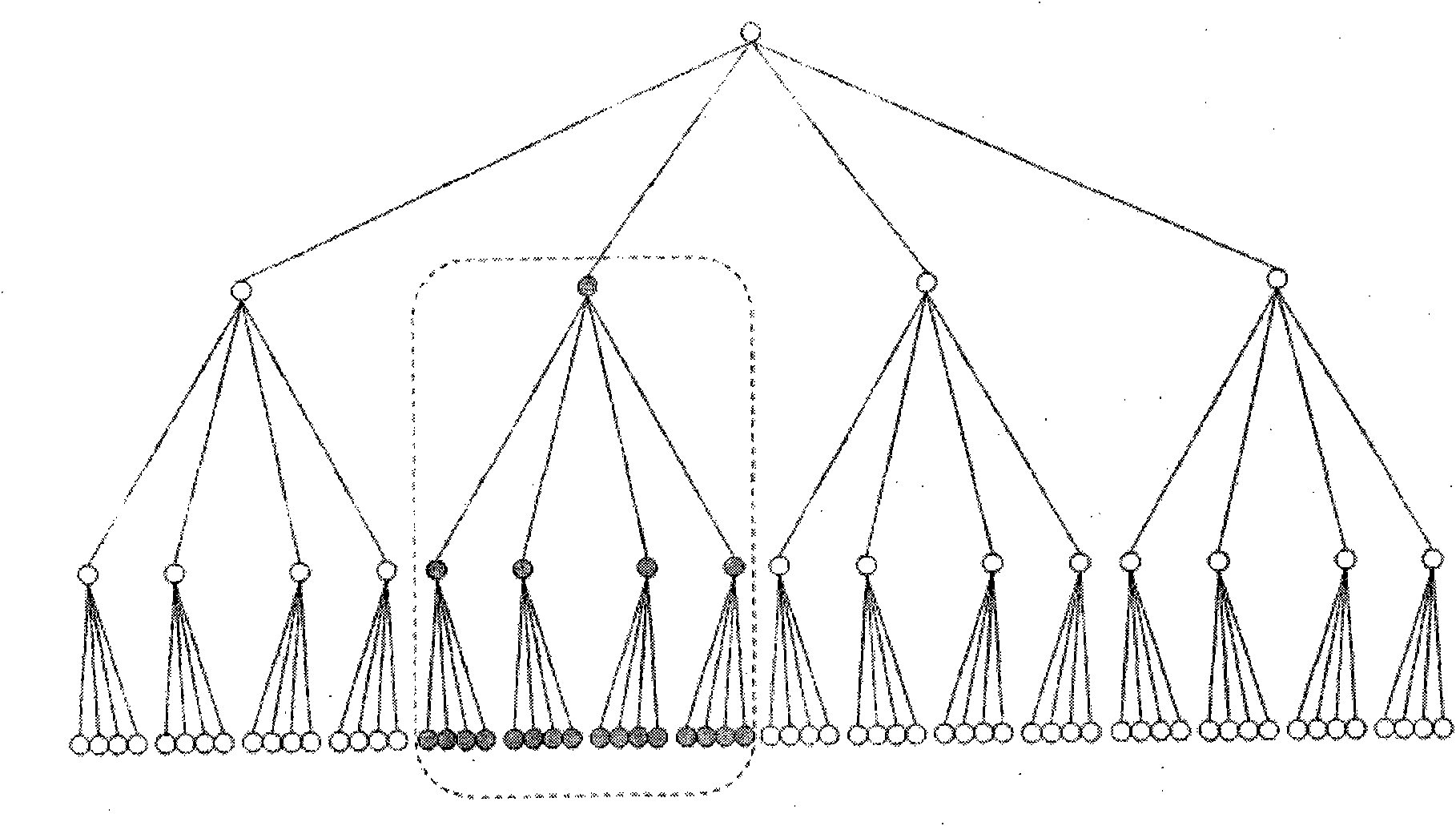
Method and device for creating multicast group in fat-tree network and fat-tree network
ActiveCN104518891AImprove multicast efficiencyRealize load sharingSpecial service provision for substationProgram/content distribution protectionSingle point of failureSingle point
The embodiment of the invention provides a method and device for creating a multicast group in a fat-tree network and the fat-tree network. The method comprises the following steps: sending a join request to a management exchange node of a target multicast group according to a target multicast group address by a network node, wherein the join request is used for requesting the joining of the network node in the target multicast group, and the management exchange node of the target multicast group is a core exchange node belonging to the target multicast group address. The fat-tree network comprises a plurality of exchange nodes, wherein each core exchange node is arranged at the top layer and used for managing a plurality of multicast group addresses. According to the method, the core exchange node only needs to manage multicast groups distributed to the core exchange node, and when joining in the multicast groups, the network equipment only needs to send the join request to the corresponding core exchange node, so that the load shunting is realized and the influence of a single-point fault on the whole network is avoided; moreover, the join request is self-routed from the bottom layer to the top layer, the complexity is low, and the multicast efficiency of the whole network is improved.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Method for realizing interconnection structure in same layer domain of tree topology
InactiveCN102130810AImprove fault toleranceStar/tree networksTheoretical computer scienceInterconnection
The invention discloses a method for realizing an interconnection structure in the same layer domain of a tree topology. The interconnection structure obtained by using the method is used for solving the defects of a tree structure, the average hop of the interconnection structure is smaller than that of the tree structure, the fault-tolerant capacity is stronger than that of the tree structure, and less extra switching nodes and links are utilized. Meanwhile, a fat tree structure can be regarded as the overlap of plurality of single tree structures. The method can also be applied to the fat tree structure, thus reducing the average hop of the fat tree structure and strengthening the fault-tolerant capacity of the fat tree structure.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
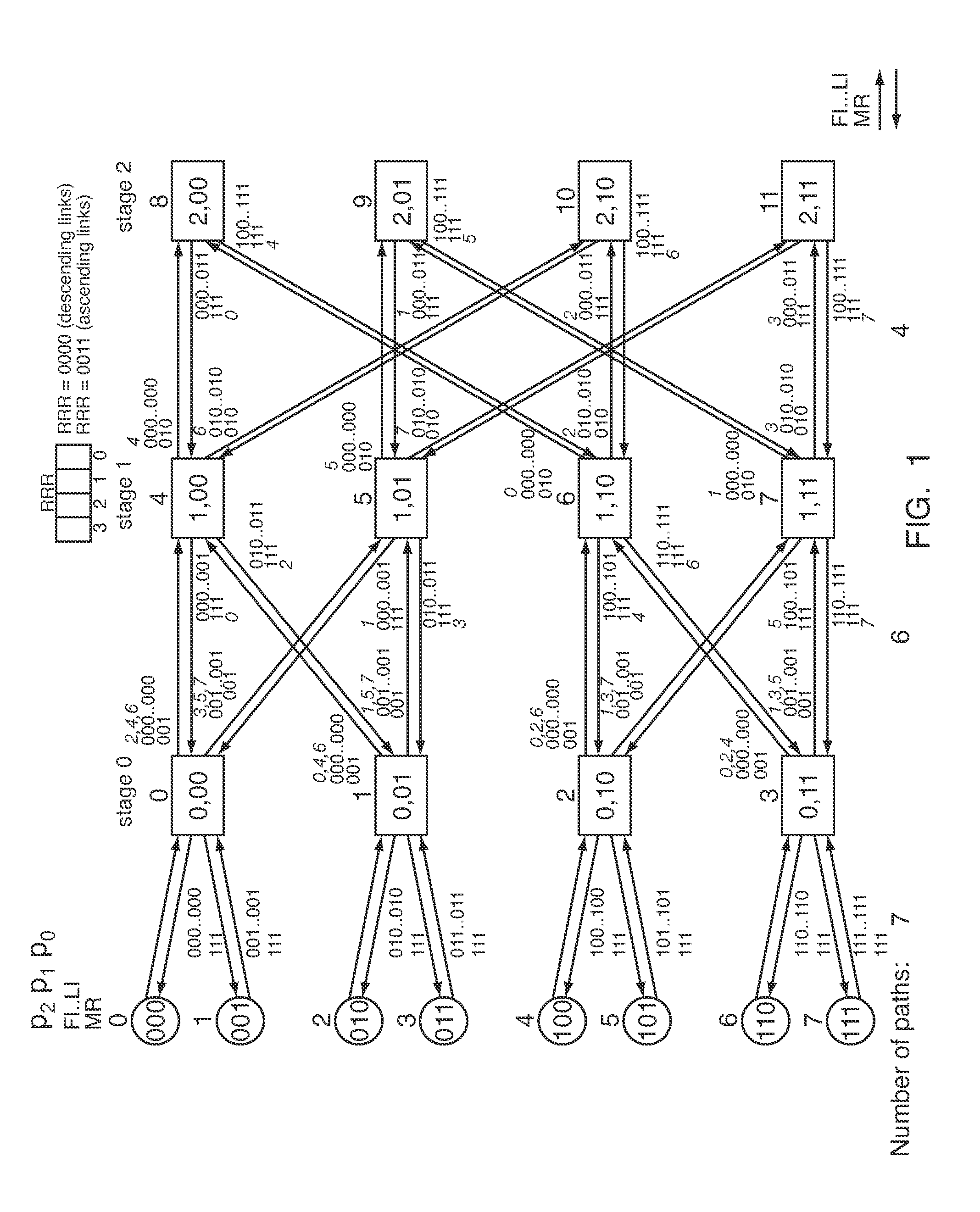
Deadlock-free routing of data packets in fat tree networks
ActiveCN103873367AAvoid deadlockLoad balancingData switching networksDeadlock freeReal-time computing
Deadlock-free routing of data packets between source and destination switches in a fat tree network is provided. For each packet, a route is selected having three or less routing phases such that the route follows a shortest path across the network between the source and destination switches. The data packet is transmitted from the source switch to the destination switch, via the route, on one of first and second virtual channels unless the route includes a predetermined one of a down-up turn and an up-down turn (see e.g. figures 7 and 8). If the route includes the predetermined turn, the data packet is transmitted, via the route, on the first virtual channel up to the switch at which the turn occurs and on the second virtual channel from that switch. Direct fat tree networks, in which end nodes are connected to switches in a plurality of levels of the fat tree topology, are also provided.
Owner:IBM CORP
8*8 optical switching array oriented to fat tree topological structure
InactiveCN103248578AReduce in quantityStar/tree networksElectromagnetic network arrangementsThree levelOptical router
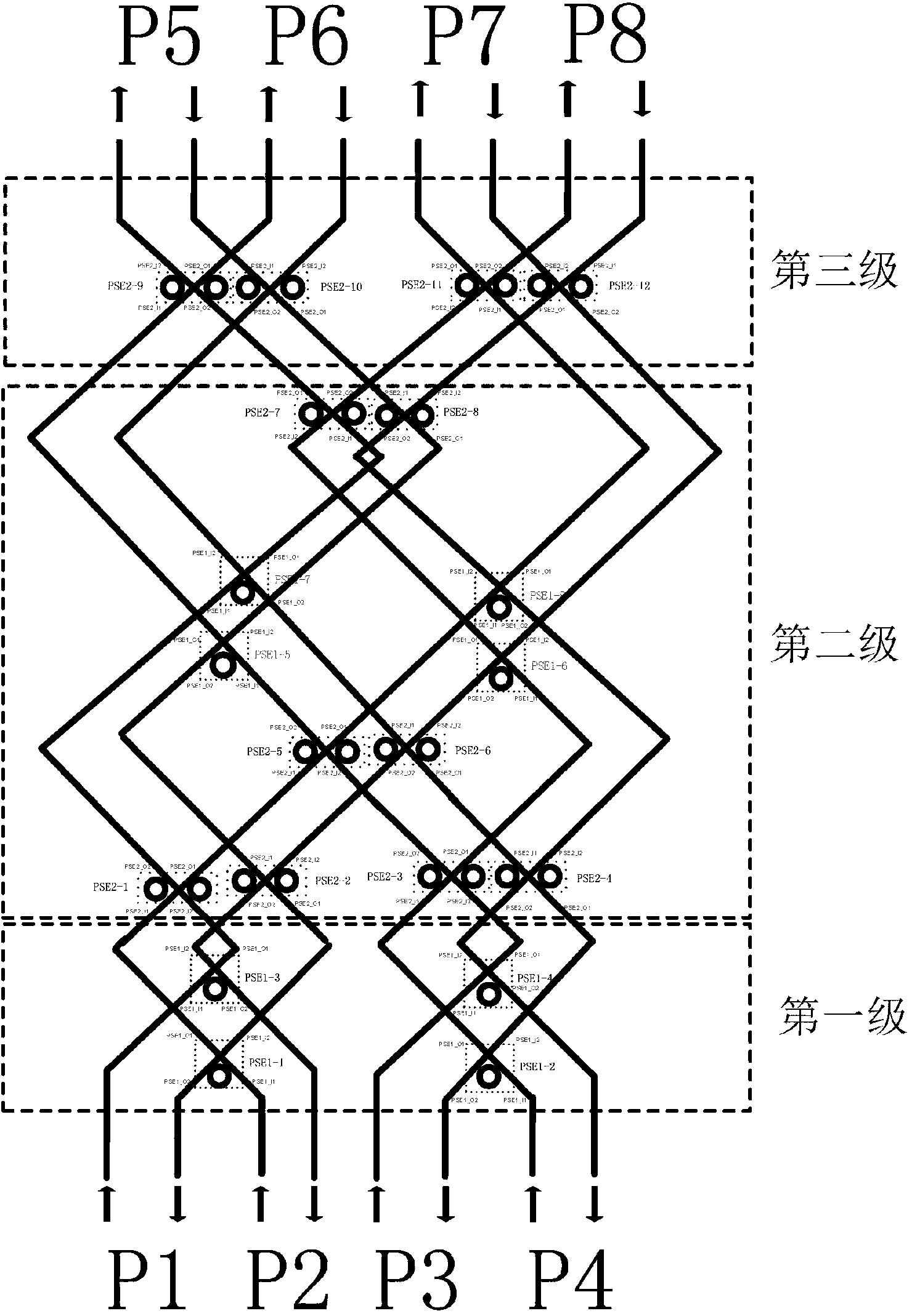
The invention discloses an 8*8 optical switching array oriented to a fat tree topological structure, aiming at providing the 8*8 optical switching array for on-chip optical router oriented to the fat tree topological structure to enable the quantity of used micro-rings to be smaller and optical loss to be smaller. The 8*8 optical switching array consists of switching sub-arrays at three levels. The switching sub-arrays are connected through optical waveguides. The switching sub-array at a first level consists of four PSE1. The switching sub-array at a second level consists of four PSE1 consists of four PSE1 and eight PSE2. The switching sub-array at a third level consists of four PSE2. The optical switching sub-array at the first level realizes optical switching between ports P1, P2, P3 and P4 and the optical switching sub-array at the second level. The optical switching sub-array at the third level realizes the optical switching between ports P5, P6, P7 and P8 and the optical switching sub-array at the second level. The optical switching sub-array at the second level realizes the optical switching sub-array at the first level and the optical switching sub-array at the third level. The 8*8 optical switching array oriented to the fat tree topological structure has the advantages that the quantity of the micro-rings is smaller and the optical loss is smaller.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Data center network routing method capable of tolerating error connection
ActiveCN104767681AImprove throughputTake advantage ofData switching networksTopology informationRouting table
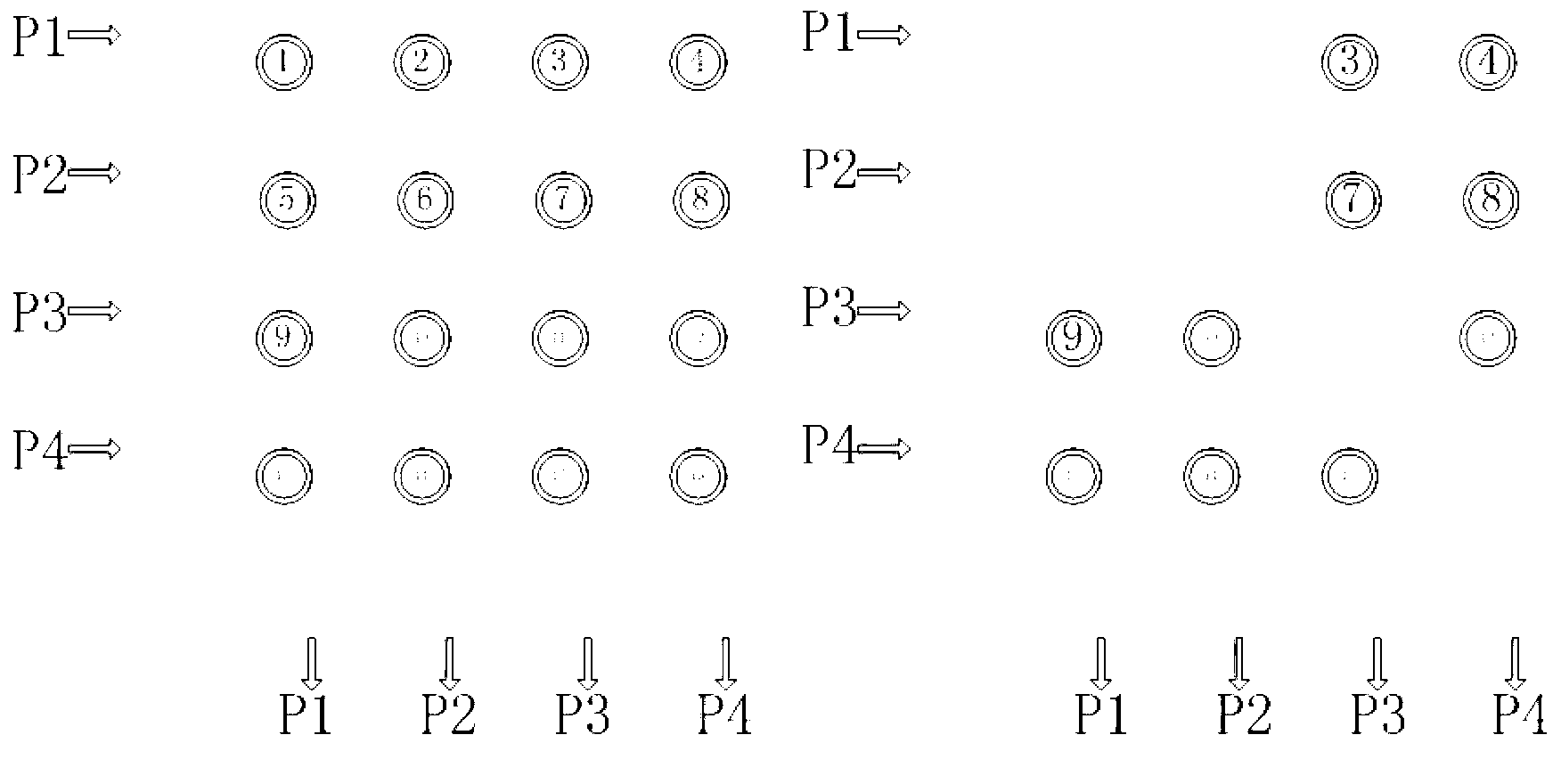
The invention provides a data center network routing method capable of tolerating error connection. The method comprises the following steps that a Fat-Tree data center network topology structure is constructed; a centralized controller is configured, and the centralized controller is communicated with each server or interchanger in the Fat-Tree data center network topology structure; physical network mapping and logical network mapping are performed on the Fat-Tree data center network topology structure, and physical topology information is obtained; the centralized controller collects the list information of edge layer interchangers at which each interchanger can arrive through respective ports, and a corresponding objective edge layer interchanger list is the generated for each interchanger; the centralized controller calculates and installs corresponding routing table entries for arriving at each edge layer interchanger for each interchanger according to the generated objective edge layer interchanger lists. The data center network routing method capable of tolerating the error connection has the double advantages of efficiently utilizing network resources and improving the network throughput.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Blended data center networking and routing method based on visible light communication
ActiveCN105634953AIncrease flexibilityClose-range type systemsData switching networksVisible light communicationWireless connectivity
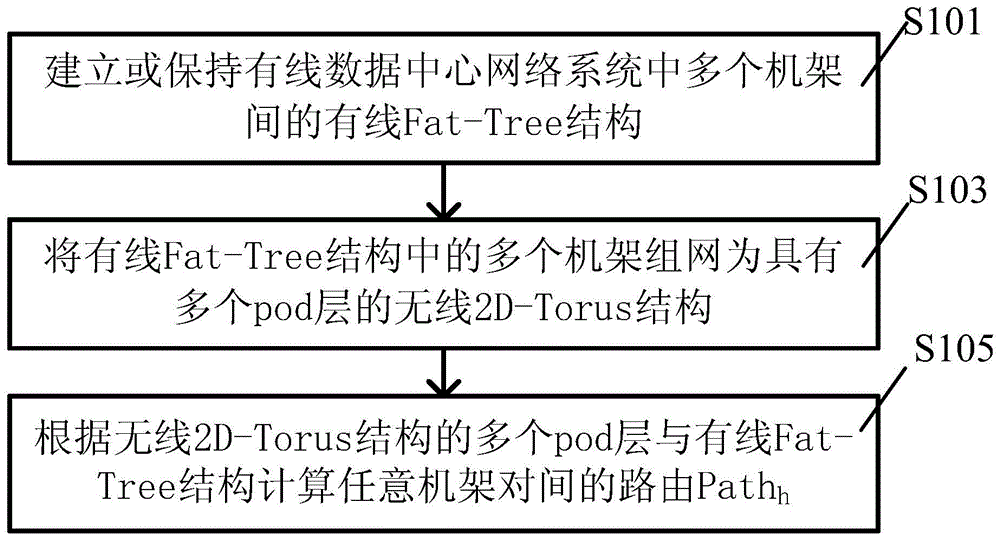
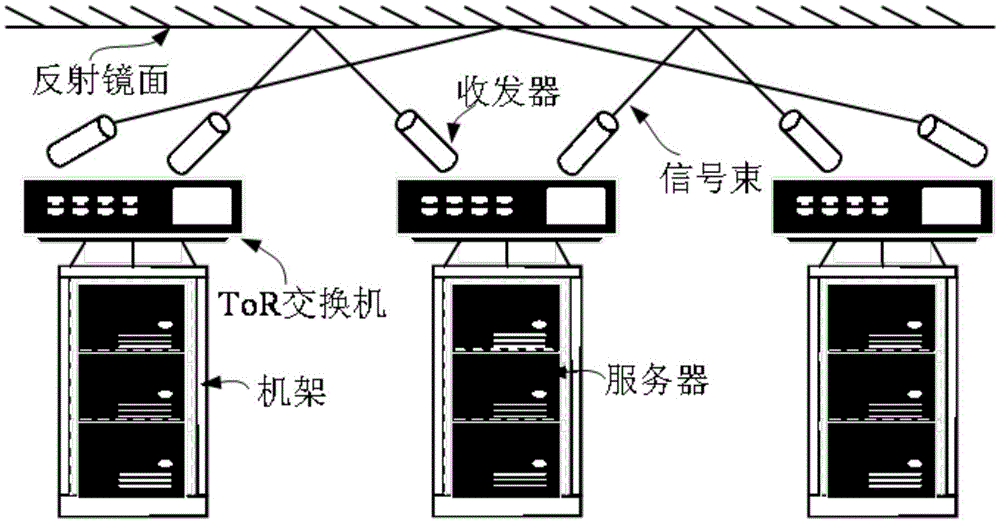
The invention discloses a blended data center networking and routing method based on visible light communication. The method comprises steps of establishing or keeping wired Fat-Tree structures among multiple racks in a wired data central network system; networking the racks in the Fat-Tree structures into wireless 2D-Torus structures with multiple pod layers; and calculating routing a Path h between any rack pairs according to the pod layers of the 2D-Torus structures and the wired Fat-Tree structures. According to the invention, by coupling networked wireless 2D-Torus structures with the wired Fat-Tree rack structures and using the mixed structure as a whole to work, on the premise that existing devices and layouts of a wired data center are not changed, a cross-rack wireless connection without any control is established, so a wired data center is greatly expanded in low cost and flexibility of the network is improved.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
System and method for providing deadlock free routing between switches in a fat-tree topology
A system and method can support routing packets between a plurality of switches in a middleware machine environment, thereby supporting Internet Protocol (IP) based management traffic via enabling IP over Infiniband (IPoIB) communication in the middleware machine environment. The plurality of switches can perform routing for inter-switch traffic in the middleware machine environment using a routing algorithm. Then, a switch in the middleware machine environment can be selected as a hub switch for inter-switch traffic that can not reach destination using the routing algorithm. Furthermore, a routing table associated with the hub switch can be updated when a path exists between a source switch and a destination switch via the hub switch.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com