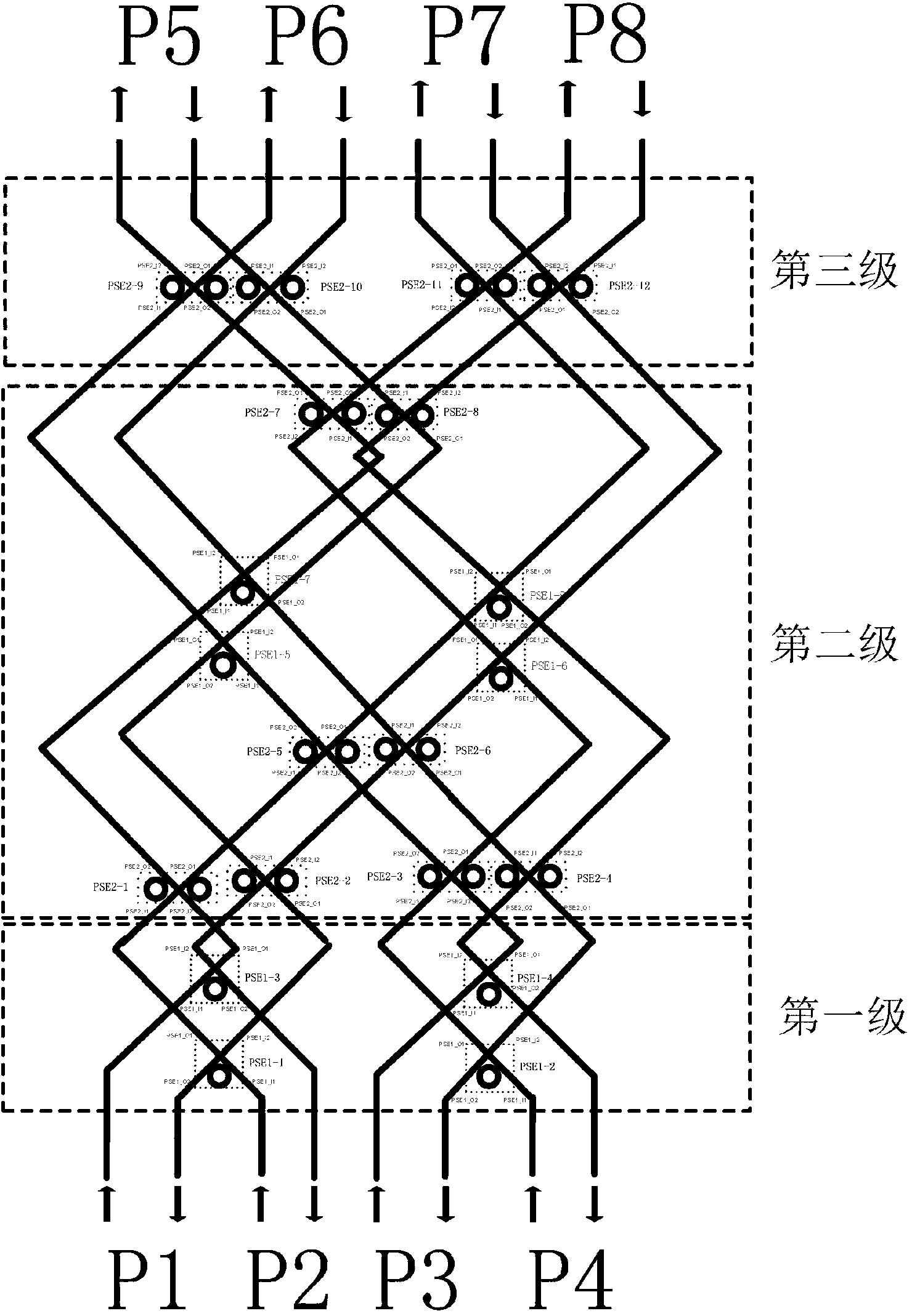
8*8 optical switching array oriented to fat tree topological structure
A topology, optical switching technology, applied in data switching networks, data switching through path configuration, star/tree networks, etc. The effect of reducing the number of rings
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
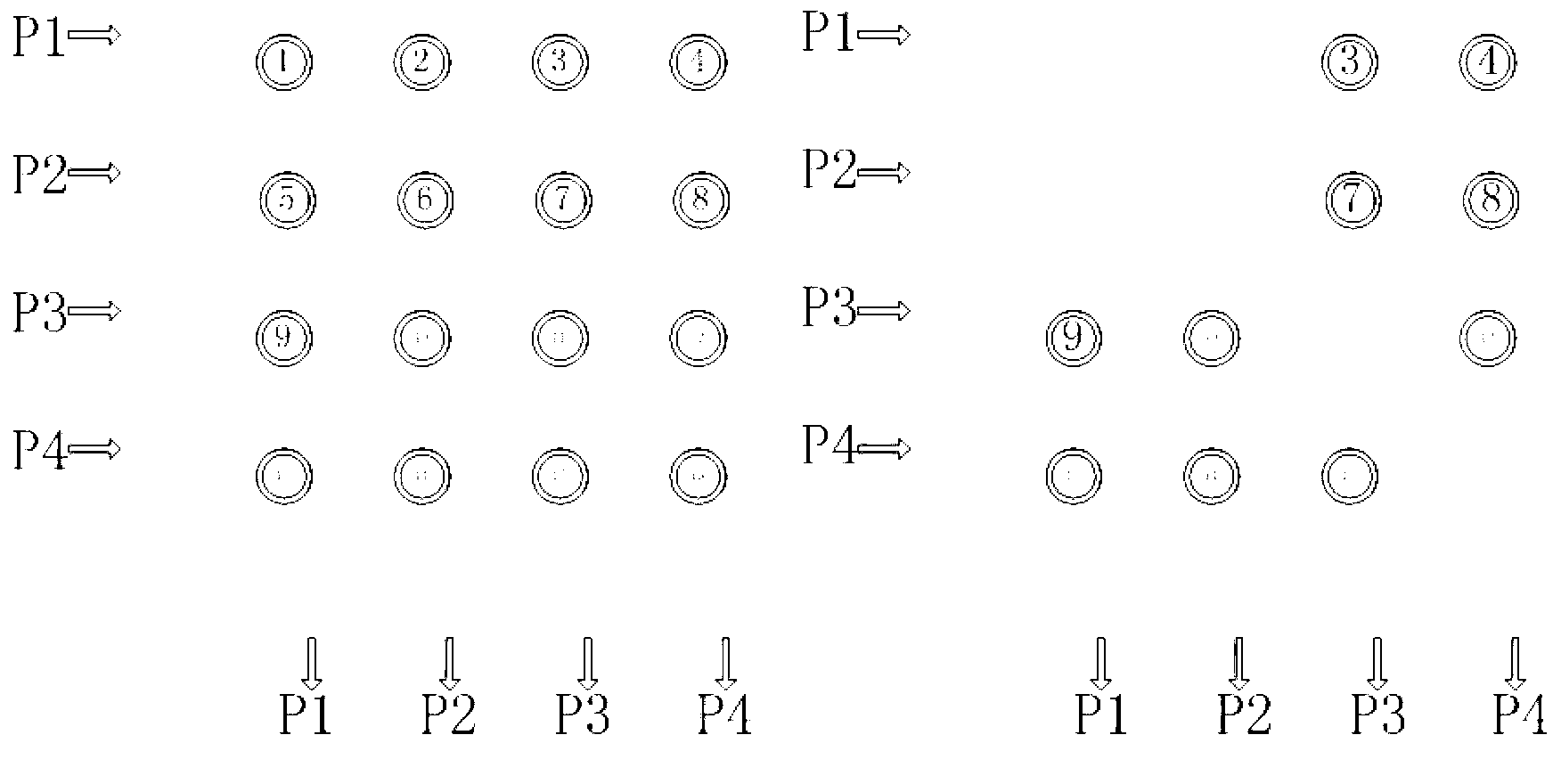
[0017] figure 1 (a) is a schematic diagram of a 4×4 optical crossbar, which consists of intersecting waveguides and microrings placed at the intersections. The optical Crossbar can provide multiple optical paths at the same time by configuring the working state of the intersection point between the input and output. The advantage of the Crossbar switching network is that there are independent switching channels between all inputs and outputs. The disadvantage is that the scalability is poor, and the number of microrings is proportional to the square of the number of ports. There are 16 microrings in this figure.
[0018] figure 1 (b) is a schematic diagram of a simplified 4×4 optical crossbar. In the figure, P1 and P3 are used as uplink ports of the fat tree, and P2 and P4 are used as downlink ports of the fat tree. The entire structure uses 10 microrings in total. Compared with the 4×4 optical Crossbar, a total of 6 micro-rings (10 more) were cut out, which are the 1st, 6th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com