Patents
Literature
172 results about "Synchronization networks" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
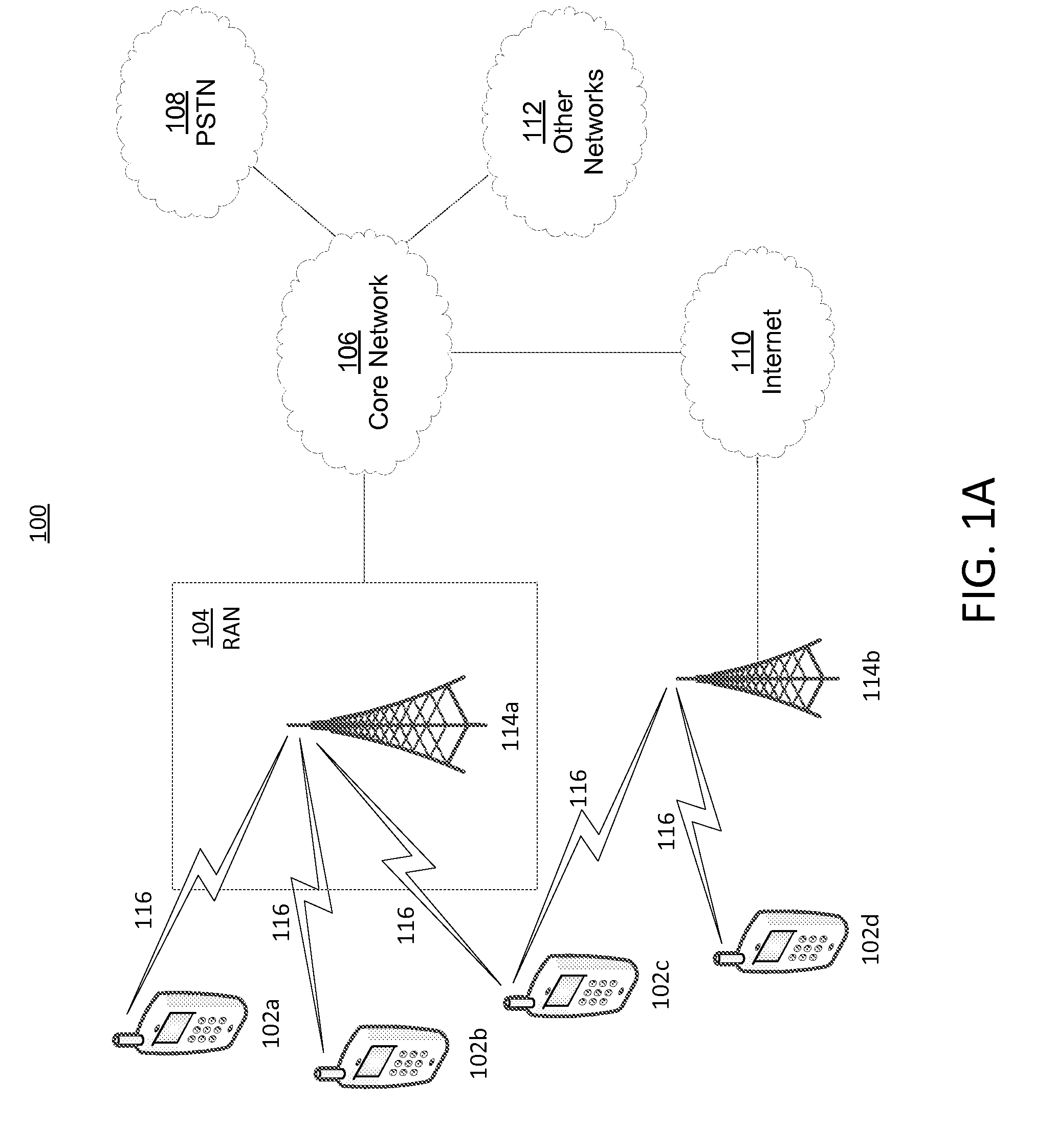
Synchronization networks are also often known as "networks of coupled dynamical systems". Both of these refer to networks connecting oscillators, where oscillators are nodes that emit a signal with somewhat regular (possibly variable) frequency, and are also capable of receiving a signal.
Communications system and method for synchronizing a communications cycle
ActiveUS20040249982A1Programme controlTime-division multiplexTelecommunications linkCommunications system
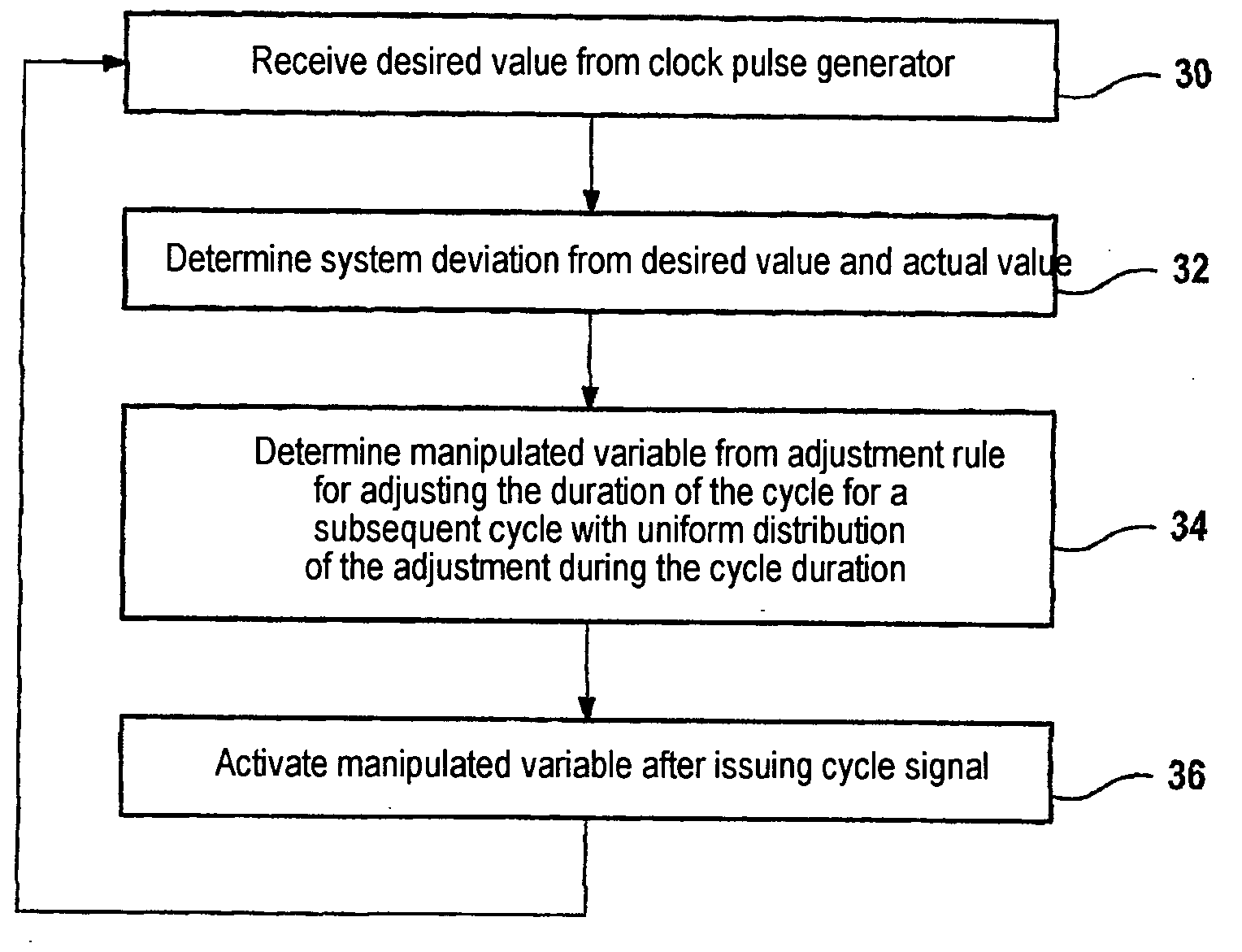
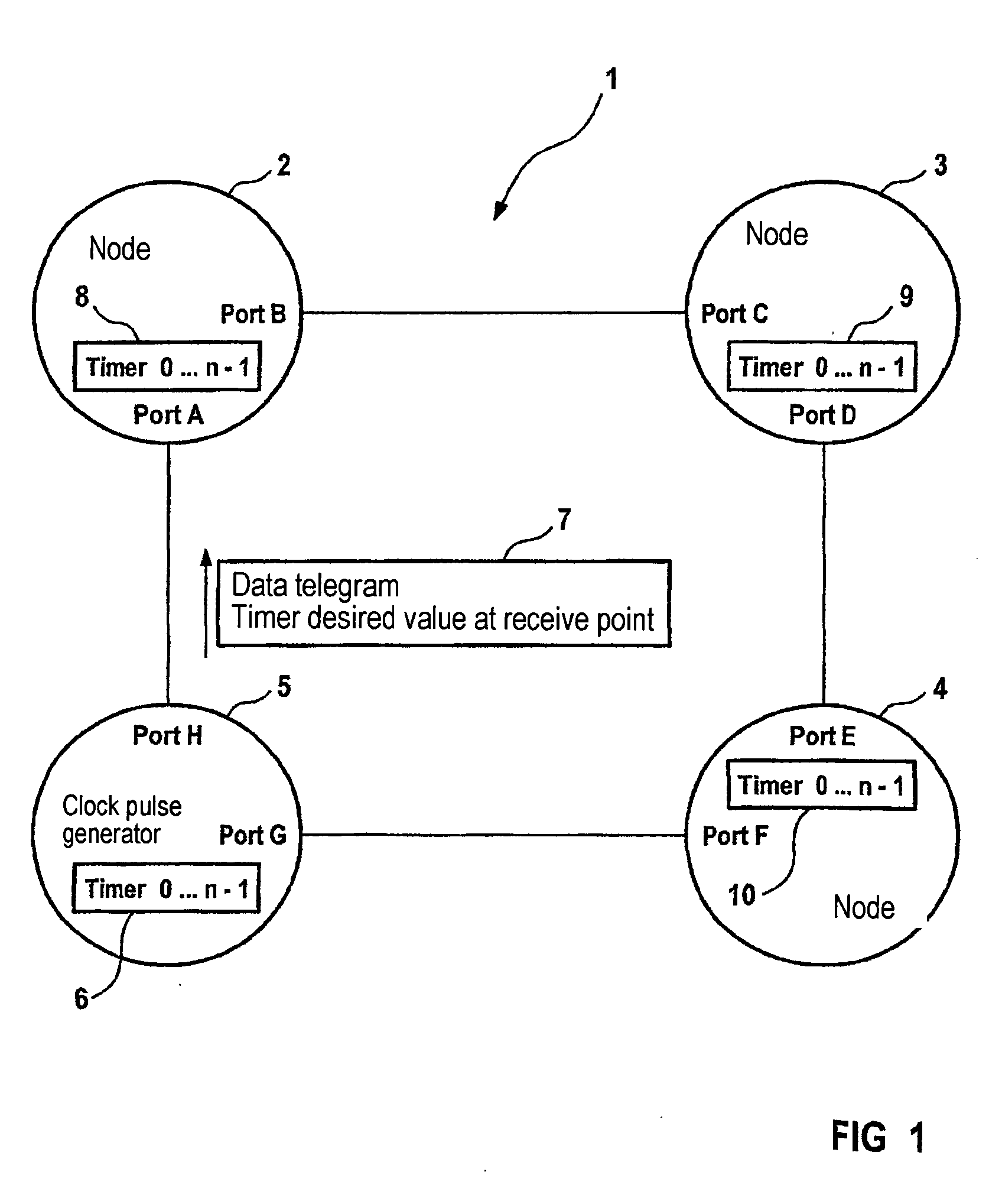
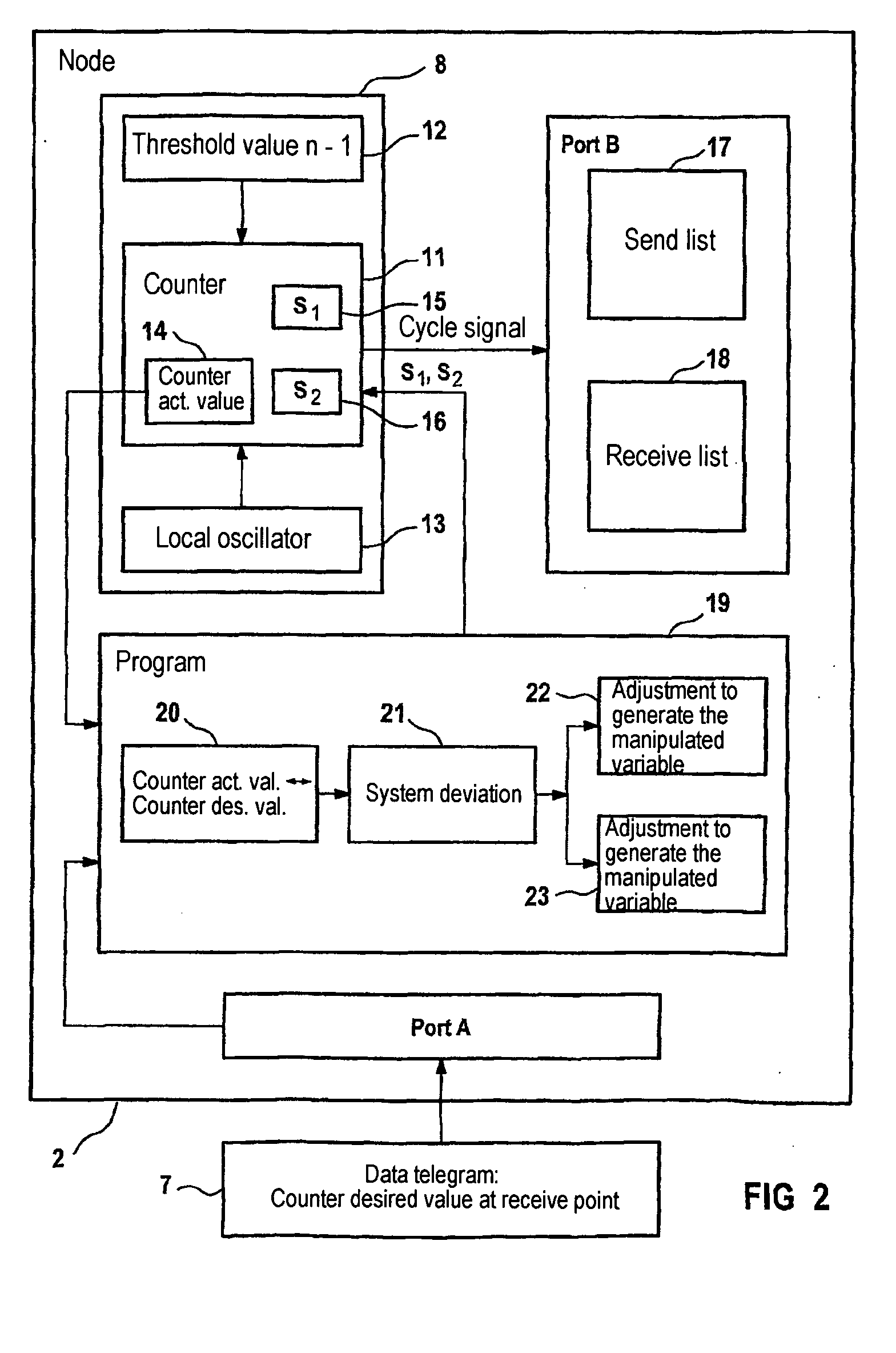
The invention relates to a method for synchronizing a communications cycle and a communications node in a network. Said node comprises: devices for receiving a desired value for a time base of a communications cycle of the communications node in a communications link to an additional communications node of the network; devices for determining a system deviation between the desired value and an actual value of the time base; and a device for generating a manipulated variable for correcting the time base in accordance with the system deviation.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Desynchronized network access in m2m networks
ActiveUS20120231828A1Power managementSynchronisation arrangementUplink transmissionSynchronous network
Systems, methods, and instrumentalities are disclosed to desynchronize transmissions in group-based operations. A group user equipment (UE), e.g., a UE that is a member of a group of UEs, may be in an inactive mode. The group UE may receive a multicast message indicating that the group UE may enter an active mode. For example, the group UE may use the active mode for periodic reporting of its monitoring activity to the network. The multicast message may indicate a mechanism for the group UE to use to send an uplink transmission to the network. The group UE may send the uplink transmission to the network at a transmission time indicated by the mechanism. The transmission time may be desynchronized from other UEs in the group.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL PATENT HLDG INC
Base station synchronization in a wireless network
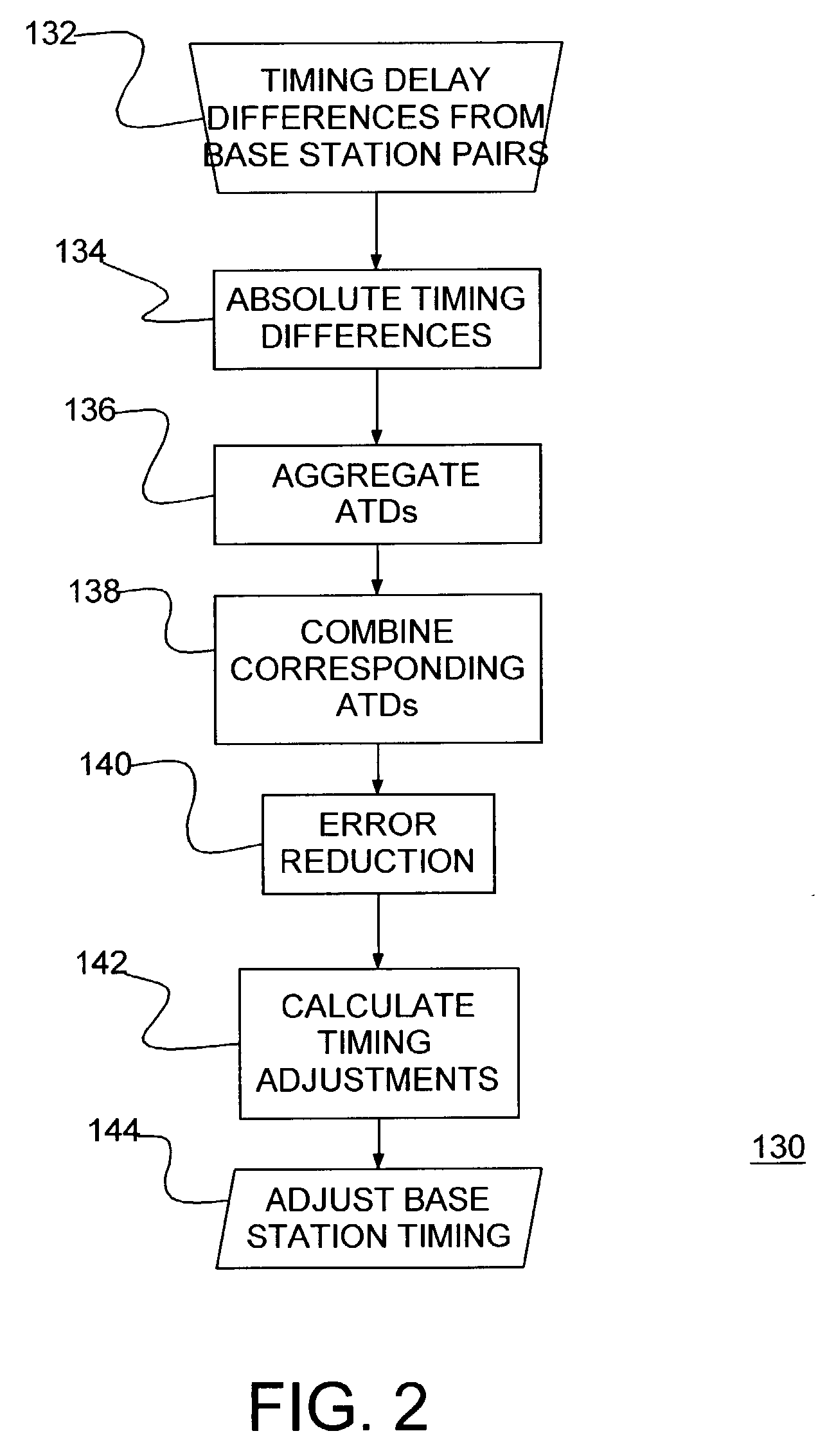
A wireless communications network and method of synchronizing network base stations. Wireless mobile units, e.g., cell phones, periodically measure transmission timing differences between pairs of adjacent base stations and each provide the measurements to a server base station. An absolute transmission timing difference (ATD) is determined for each difference measurement. ATDs are collected and combined for each pair of base stations. A timing relationship is developed for all base stations from the combined ATDs. A timing correction is extracted for each base station from the timing relationship. Application of the timing corrections synchronizes the base stations.
Owner:NOKIA SIEMENS NETWORKS GMBH & CO KG
Peer to peer syncronization system and method
InactiveUS20090172201A1Digital data processing detailsMultiple digital computer combinationsPathPingSynchronization networks
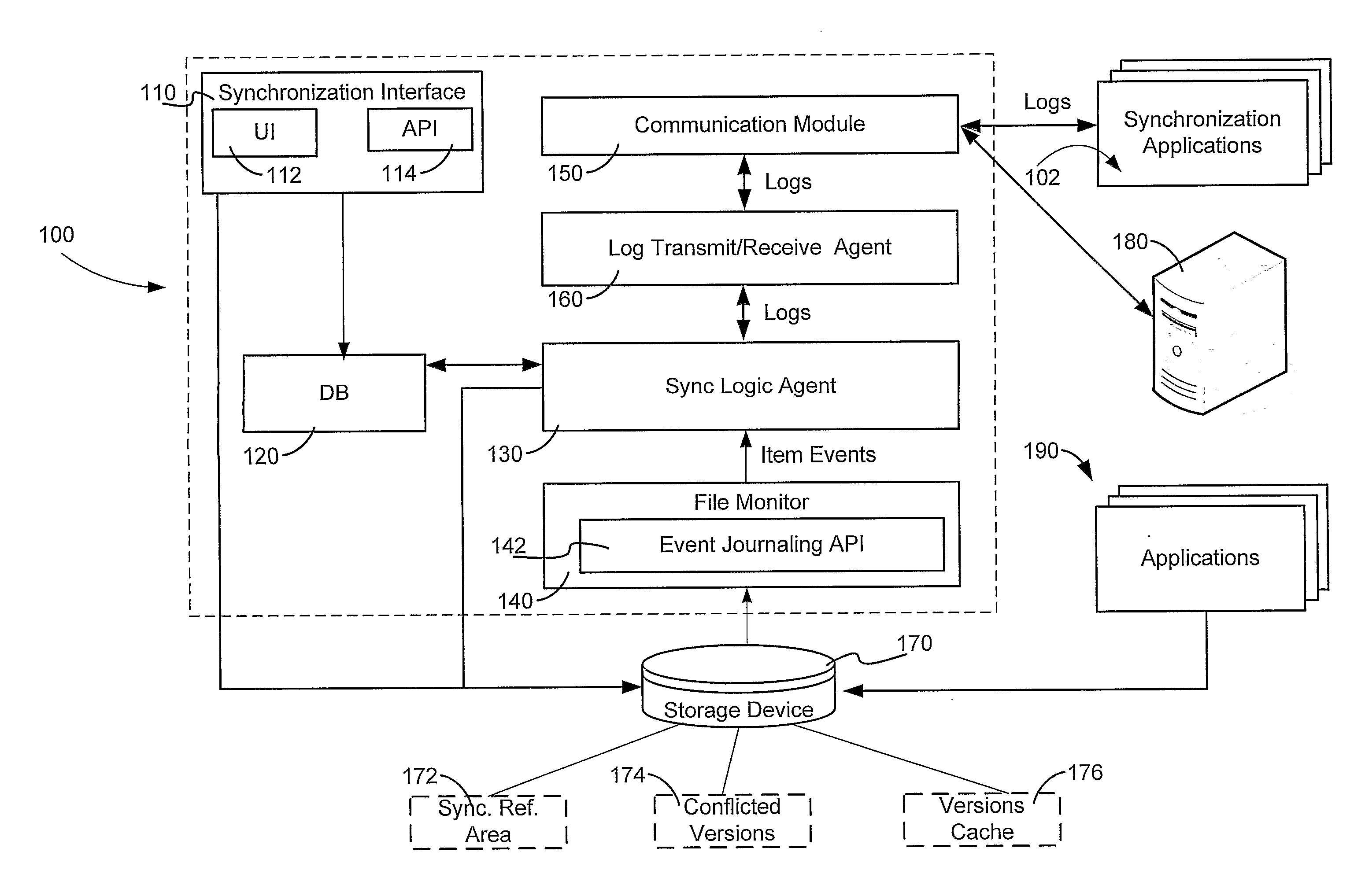
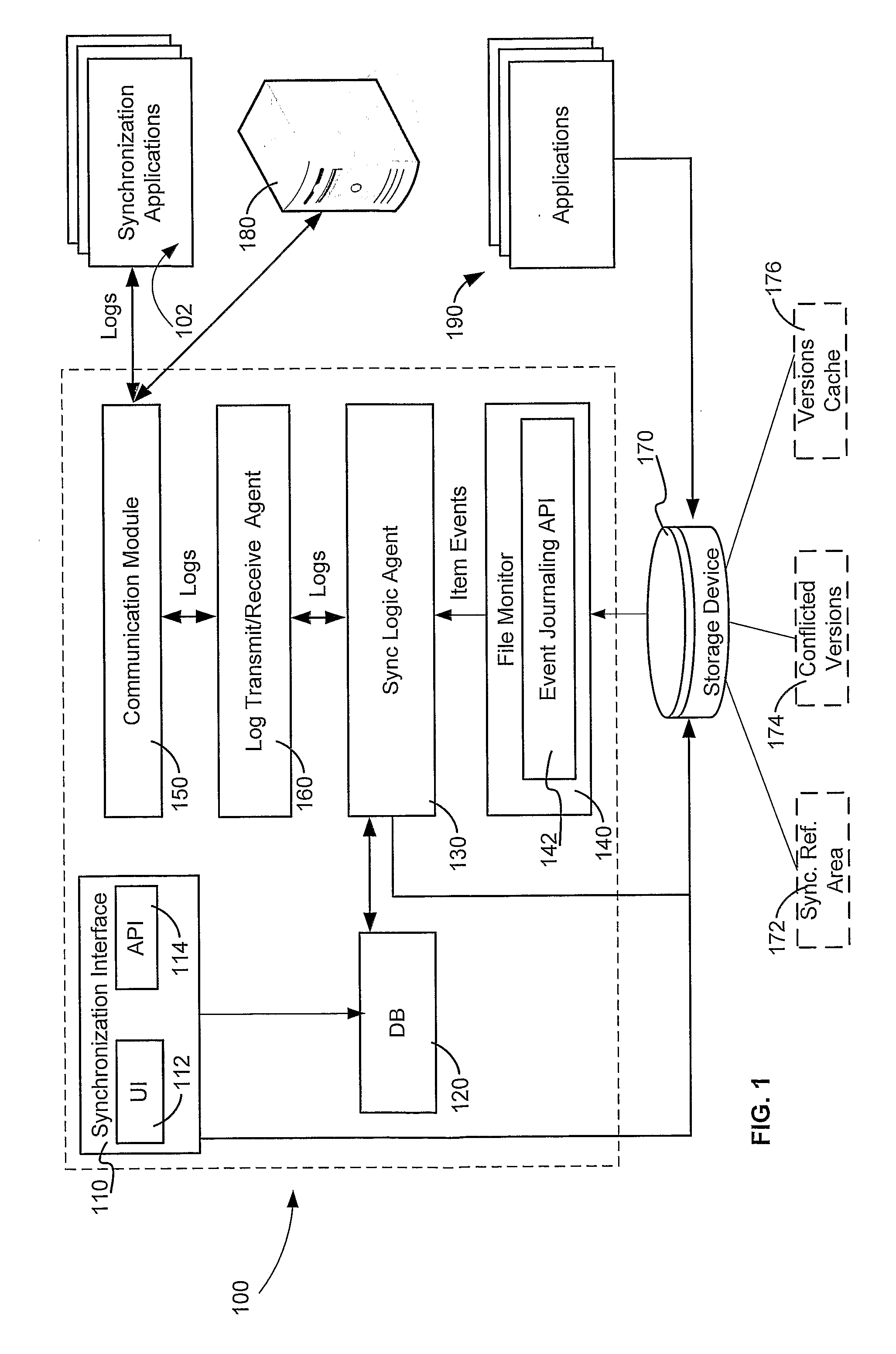
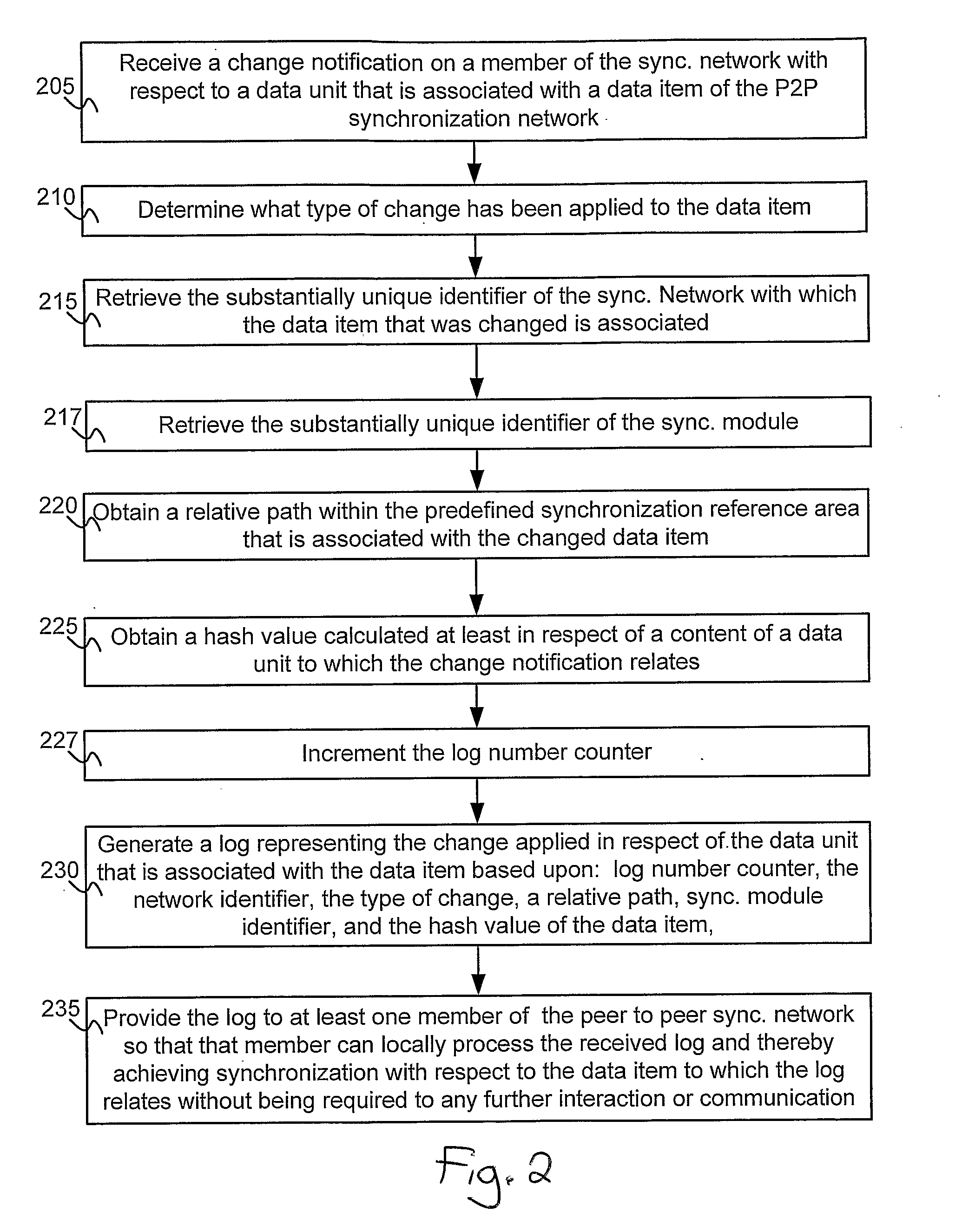
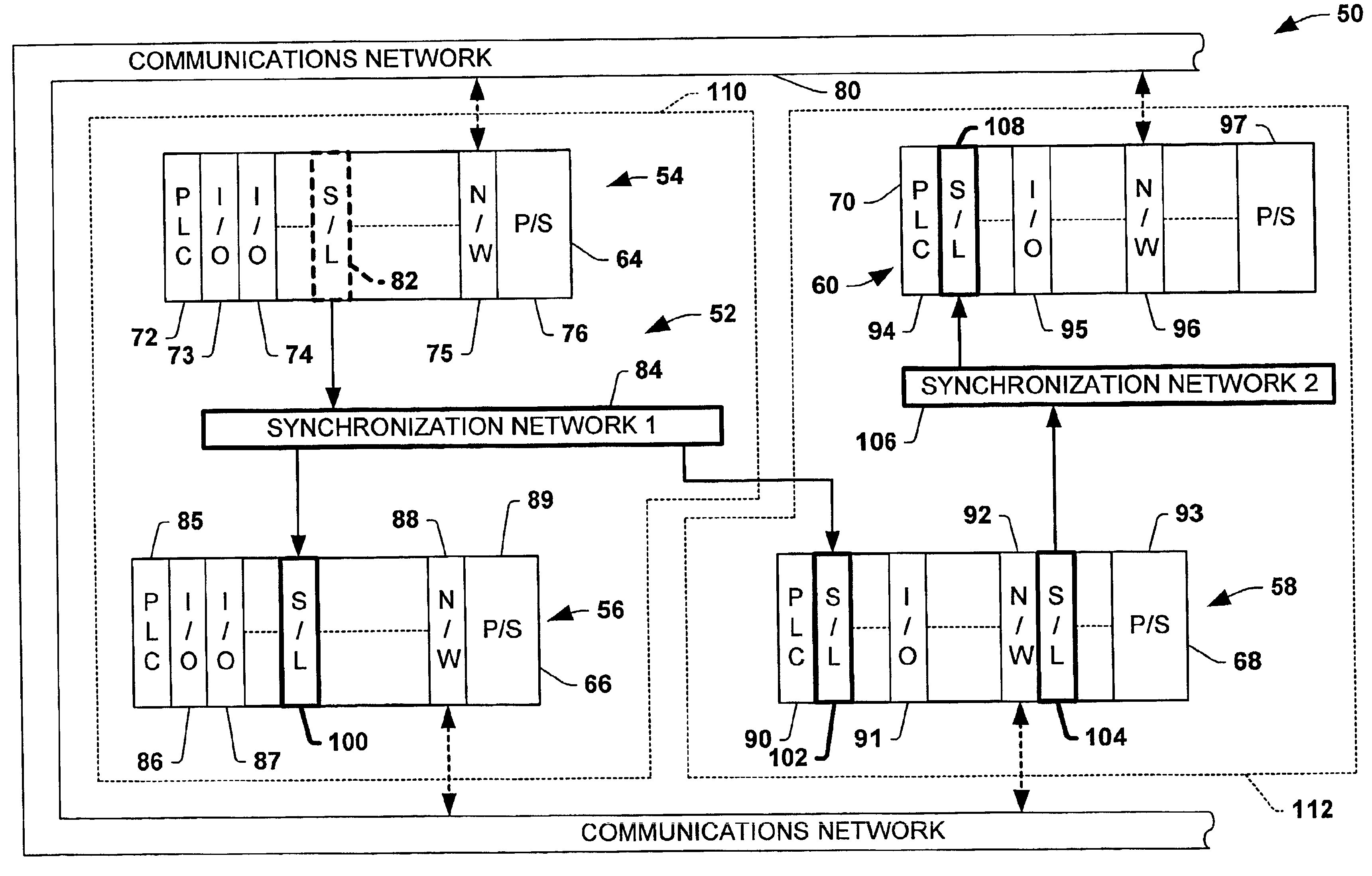
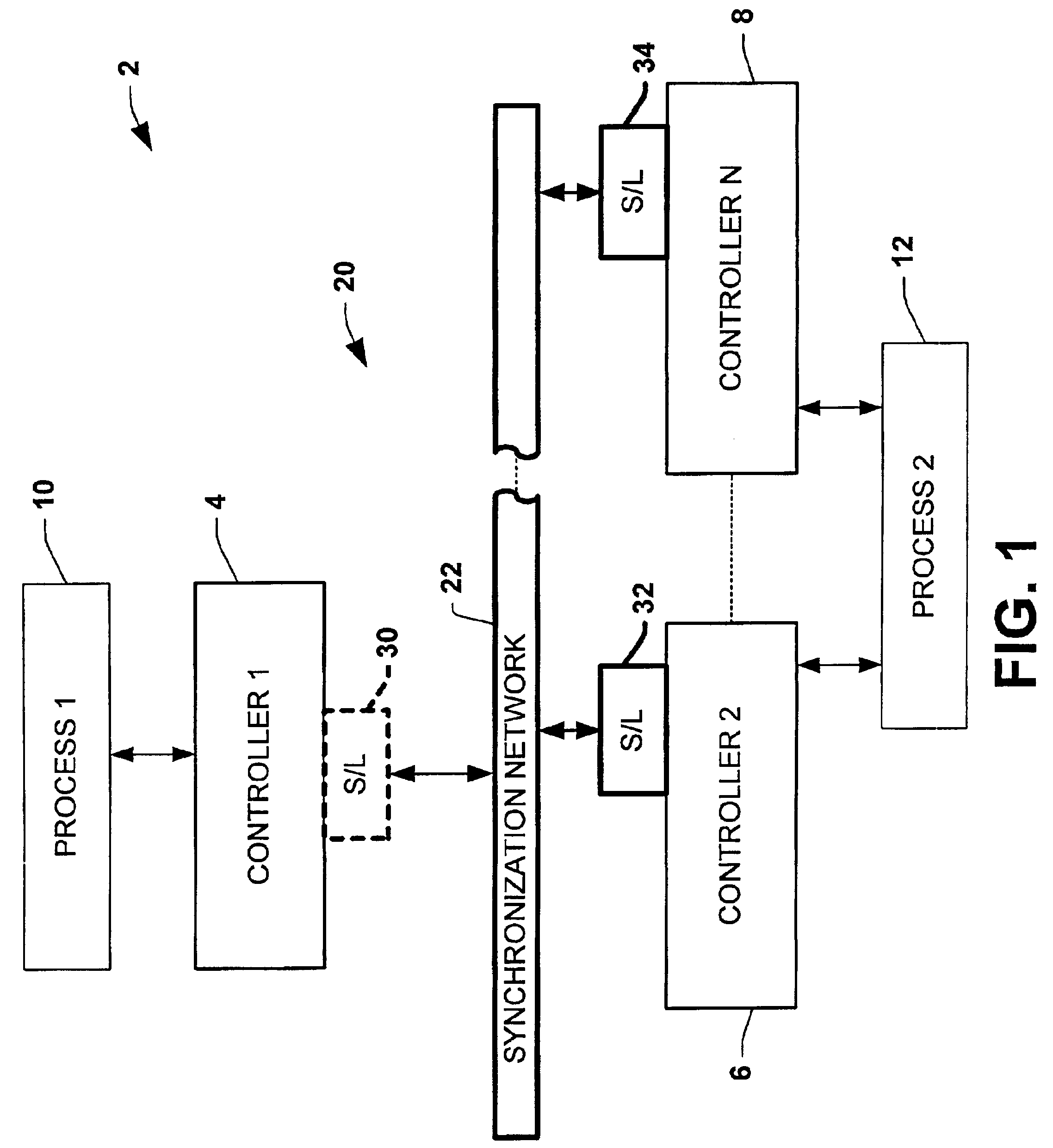
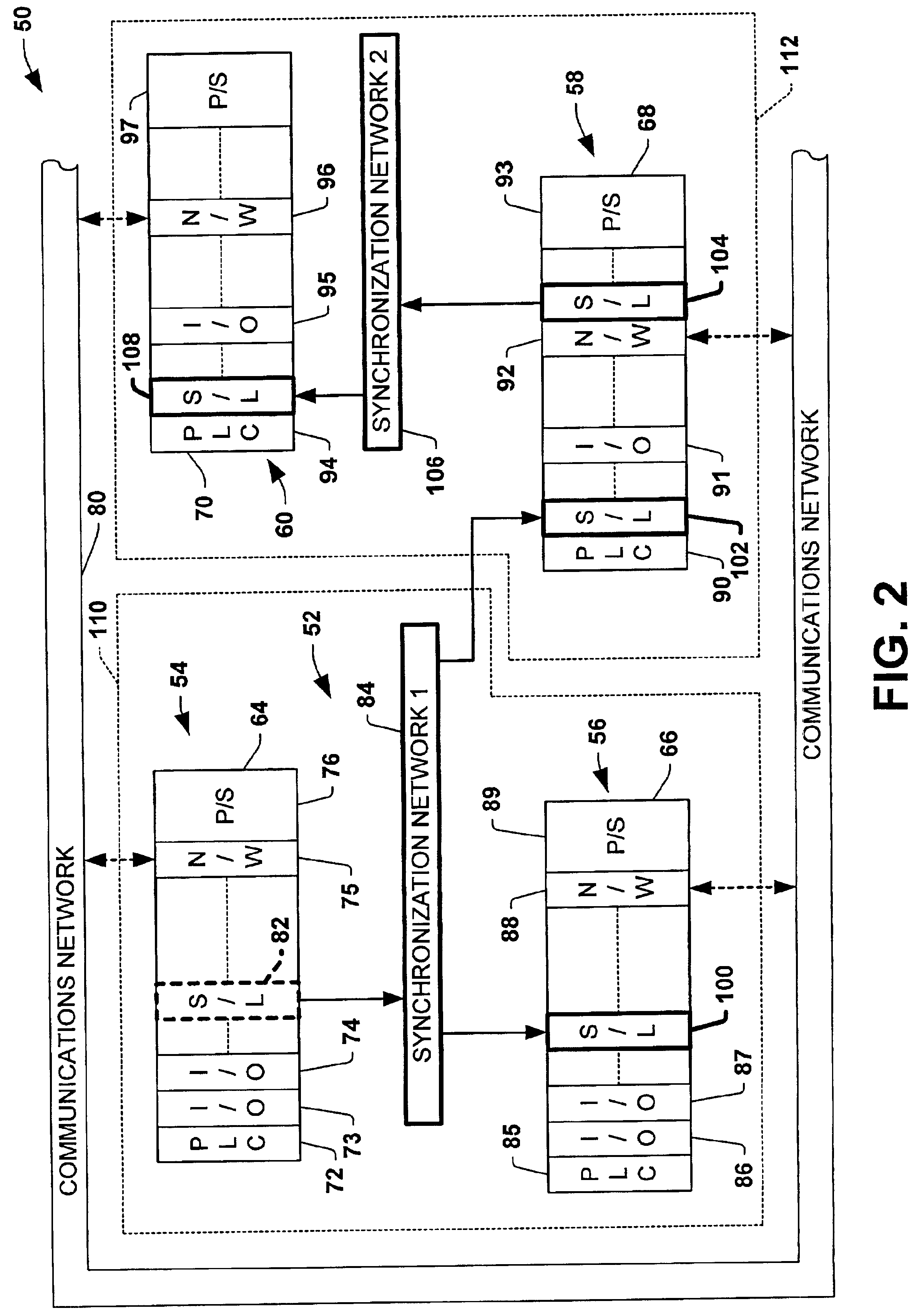
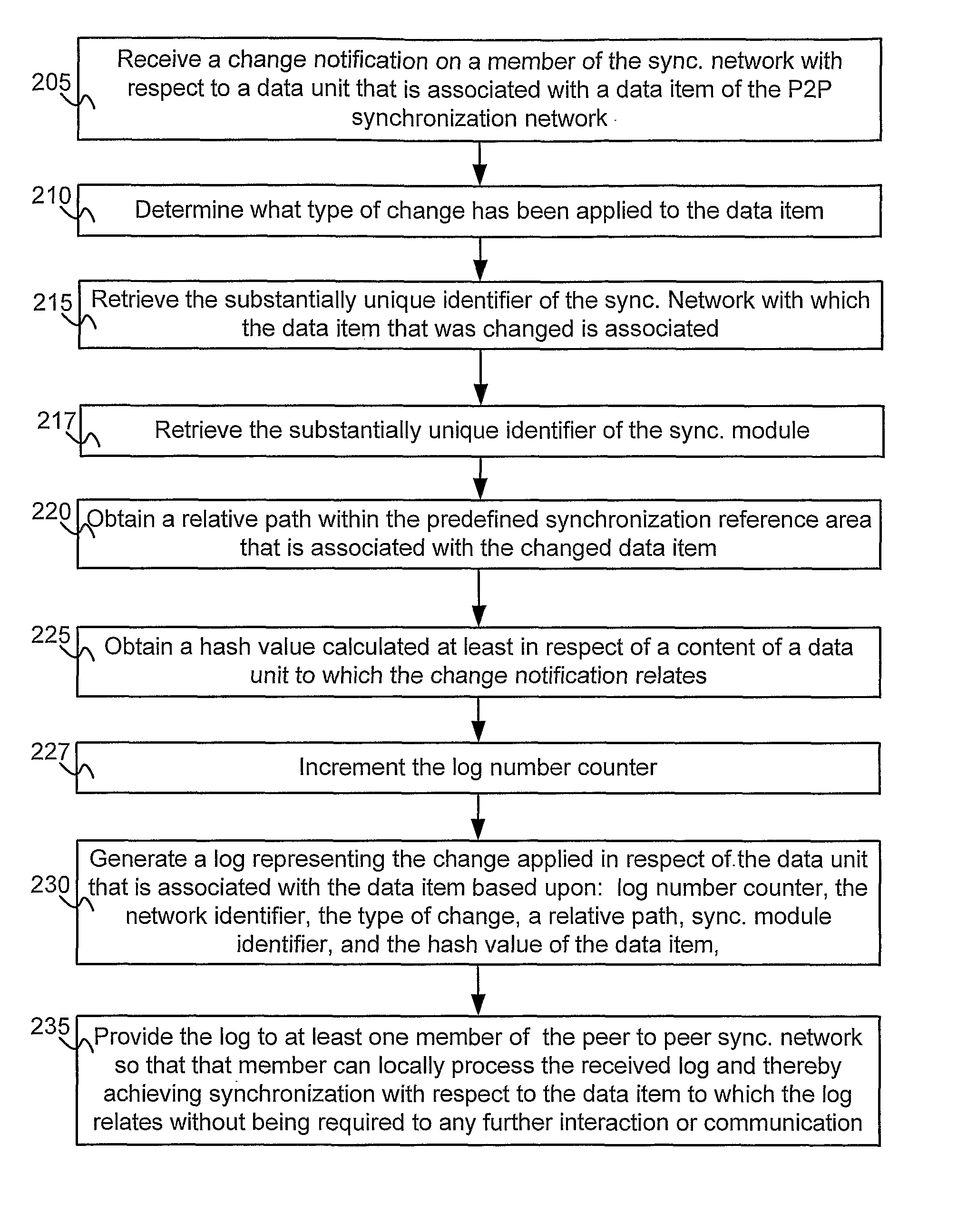
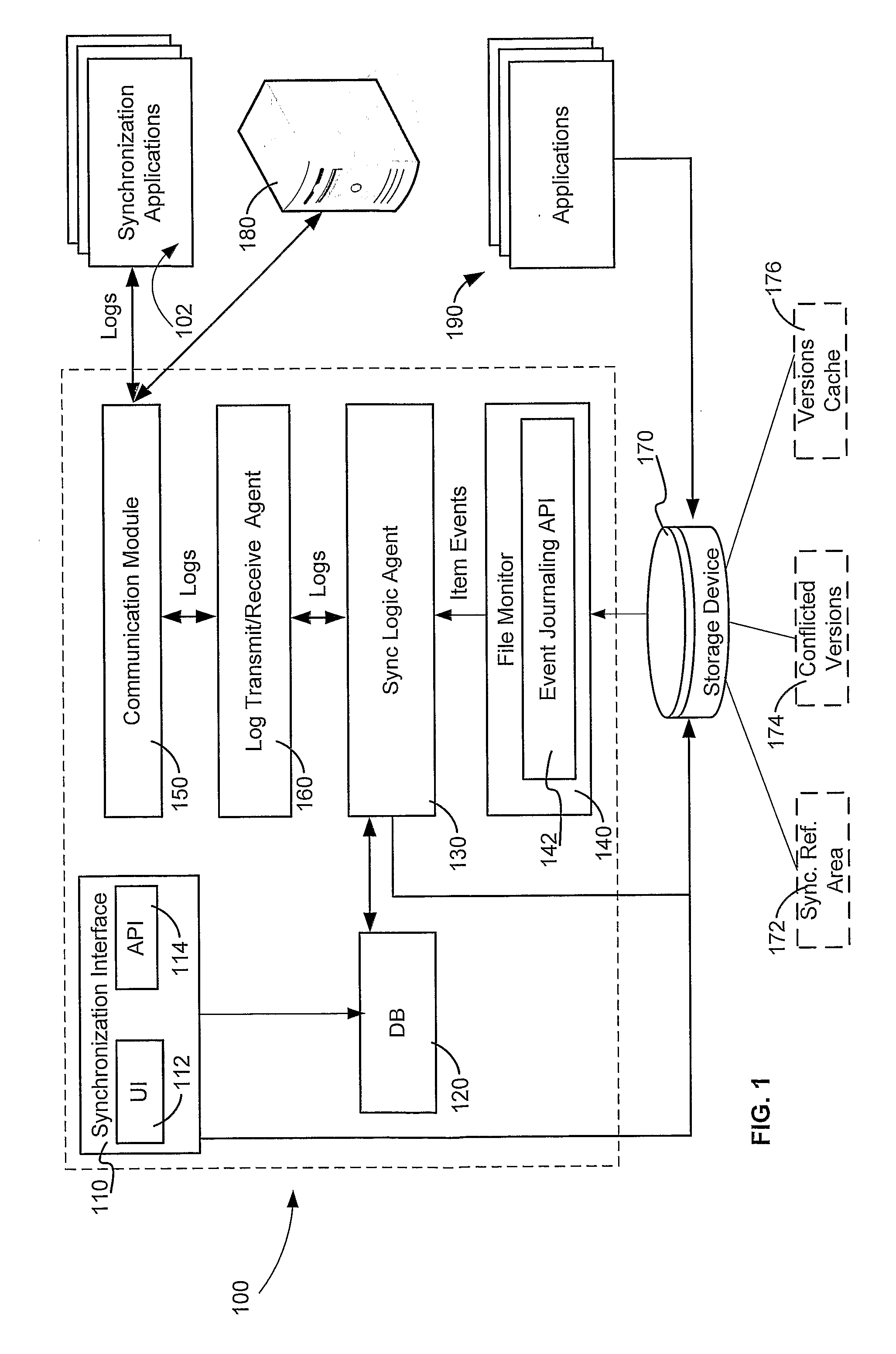
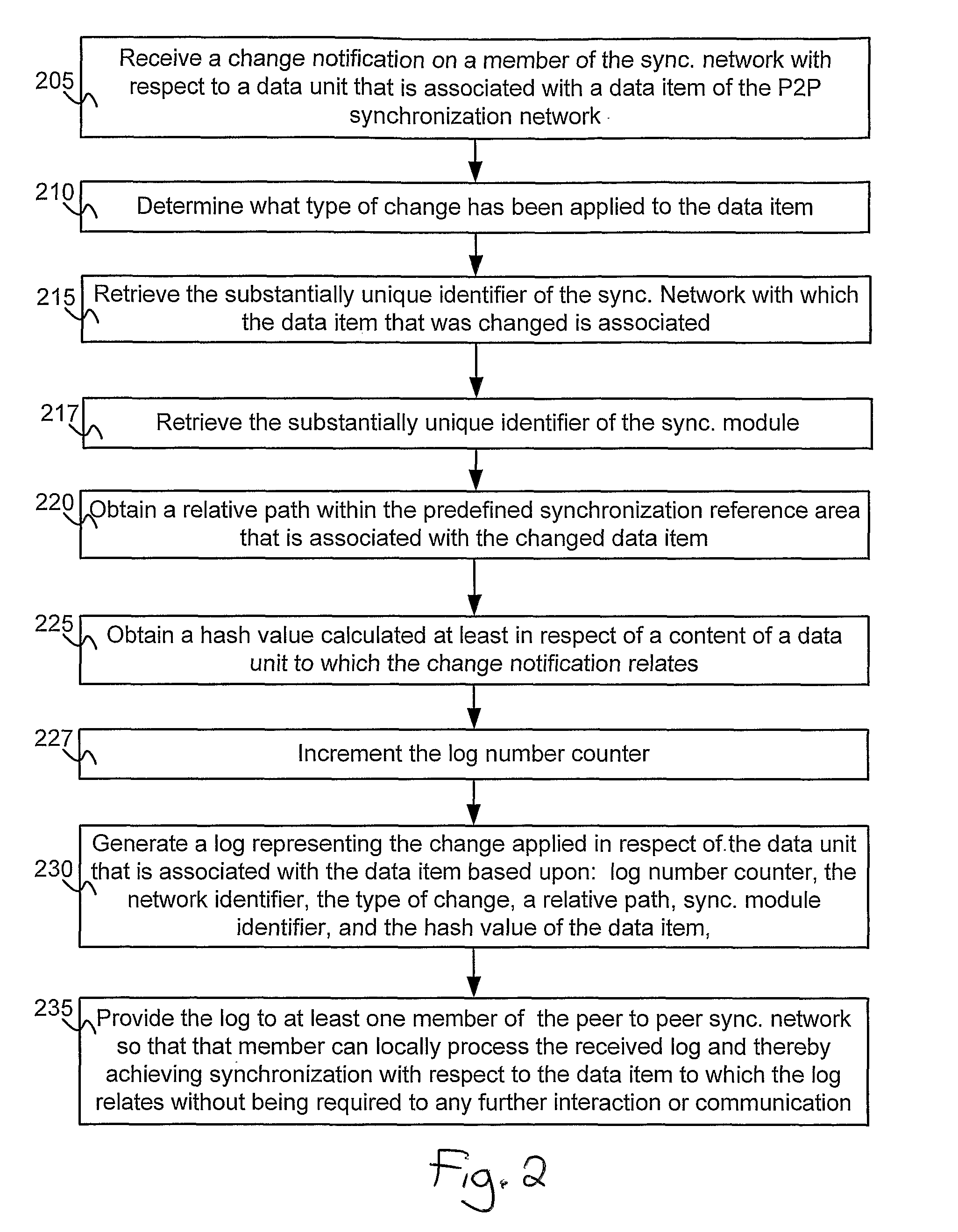
A method and system for enabling peer to peer synchronization between members of a synchronized network. A predefined synchronization reference area on each member of the network is provided. A common identifier associated with the synchronization network is provided to each member. Changes are detected on a member regarding a data item. A network identifier associated is obtained. A unique identifier of a synchronization module is obtained. A relative path to the data item within the predefined synchronization reference area is obtained. A unique value is calculated based upon a content of a version of the data item that is associated with the change. A log number counter is incremented. A log representing the data item and the chance is created. The log includes data regarding the type of change, the network identifier, the unique identifier of the synchronization module, the relative path, the unique value, and the log number.
Owner:KINGLITE HLDG INC
System and method for multi-chassis configurable time synchronization
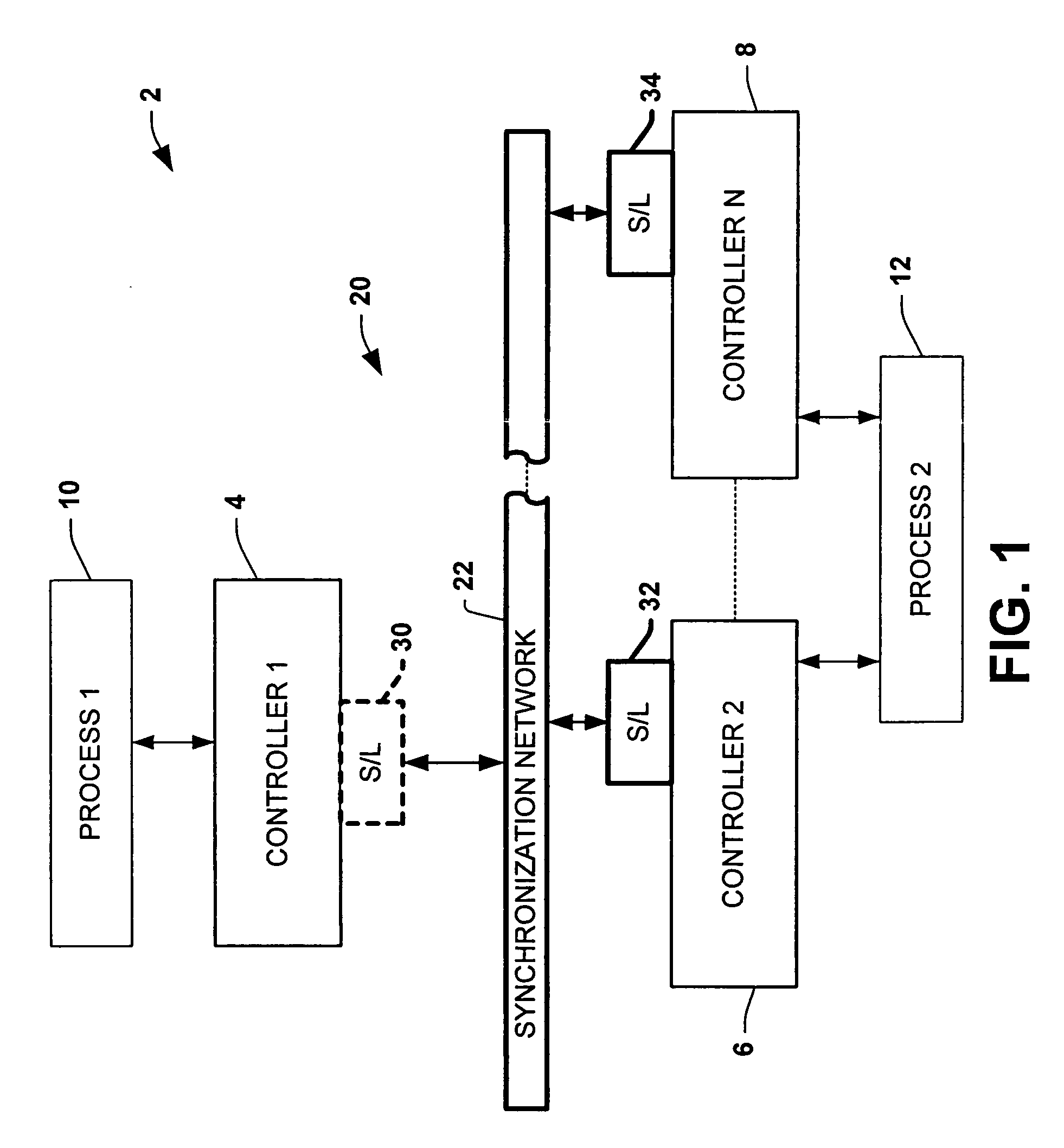
ActiveUS6914914B1Time-division multiplexProgramme control in sequence/logic controllersControl systemSynchronization networks
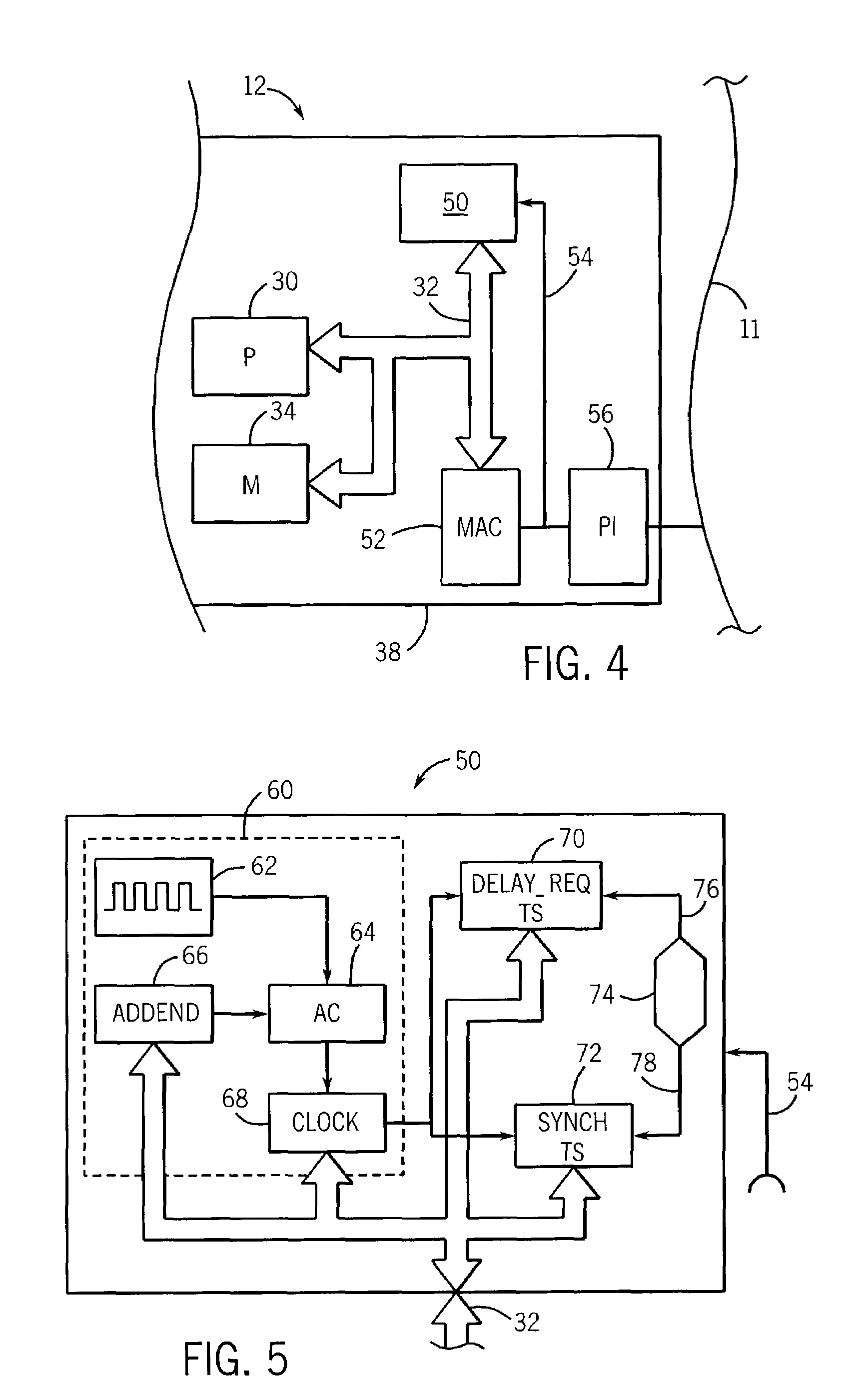
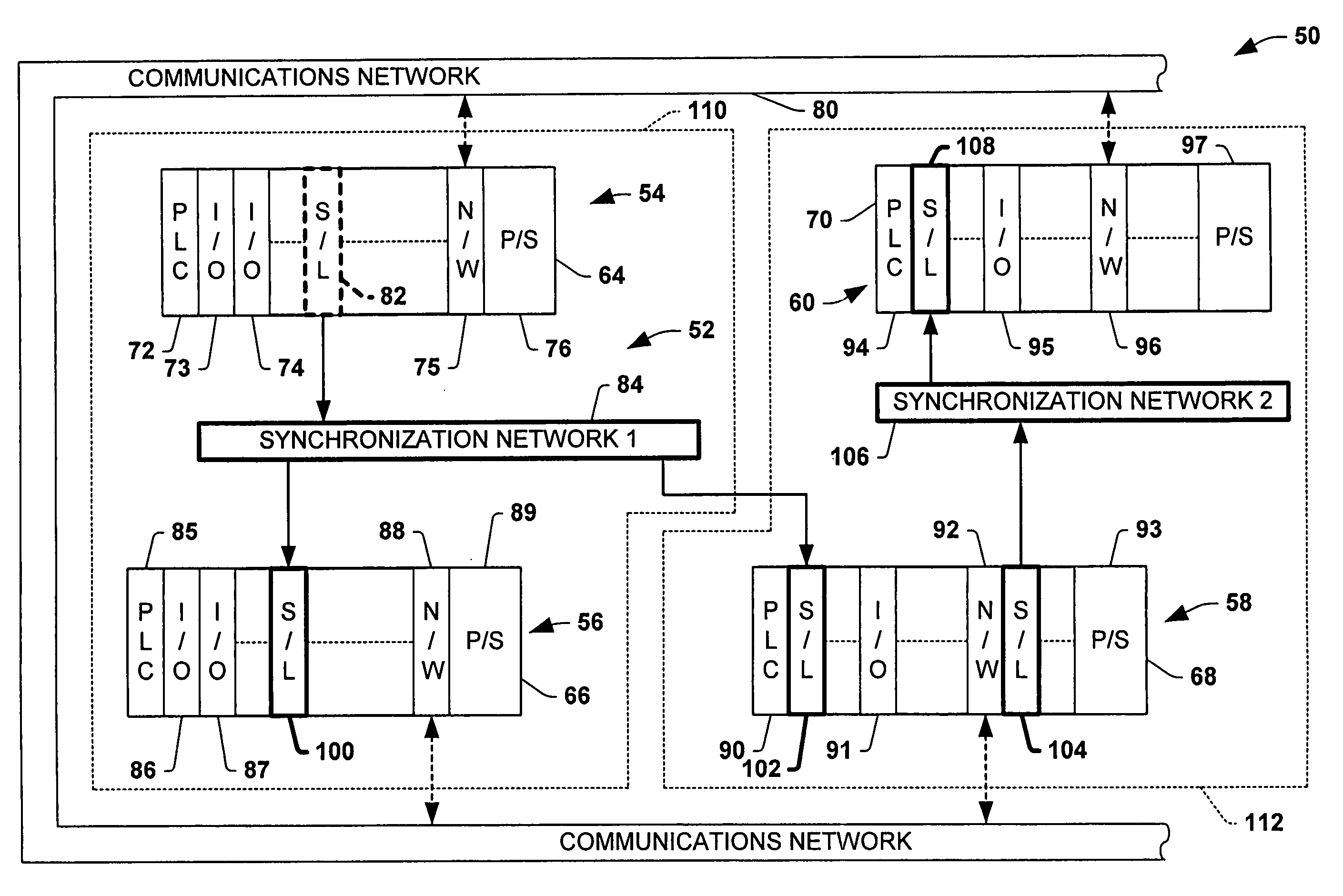
Systems and methods are disclosed for time synchronization of operations in a control system. Synchronization networks and devices are provided for transferring synchronization information between controllers in a distributed or localized control system, which is employed in order to allow operation of such controllers to be synchronized with respect to time. Also disclosed are synchronization protocols and hardware apparatus employed in synchronizing control operations in a control system.
Owner:ROCKWELL TECH
Peer to peer Synchronization system and method
InactiveUS8510404B2Digital data processing detailsMultiple digital computer combinationsData synchronizationSynchronization networks
A method and system for enabling peer to peer synchronization between members of a synchronized network. A predefined synchronization reference area on each member of the network is provided. A common identifier associated with the synchronization network is provided to each member. Changes are detected on a member regarding a data item. A network identifier associated is obtained. A unique identifier of a synchronization module is obtained. A relative path to the data item within the predefined synchronization reference area is obtained. A unique value is calculated based upon a content of a version of the data item that is associated with the change. A log number counter is incremented. A log representing the data item and the chance is created. The log includes data regarding the type of change, the network identifier, the unique identifier of the synchronization module, the relative path, the unique value, and the log number.
Owner:KINGLITE HLDG INC
High-precision Ethernet timing device
ActiveCN101789627AIncrease the level of automationMeet the time synchronization requirements of power servicesCircuit arrangementsTime-division multiplexProcess moduleSynchronization networks
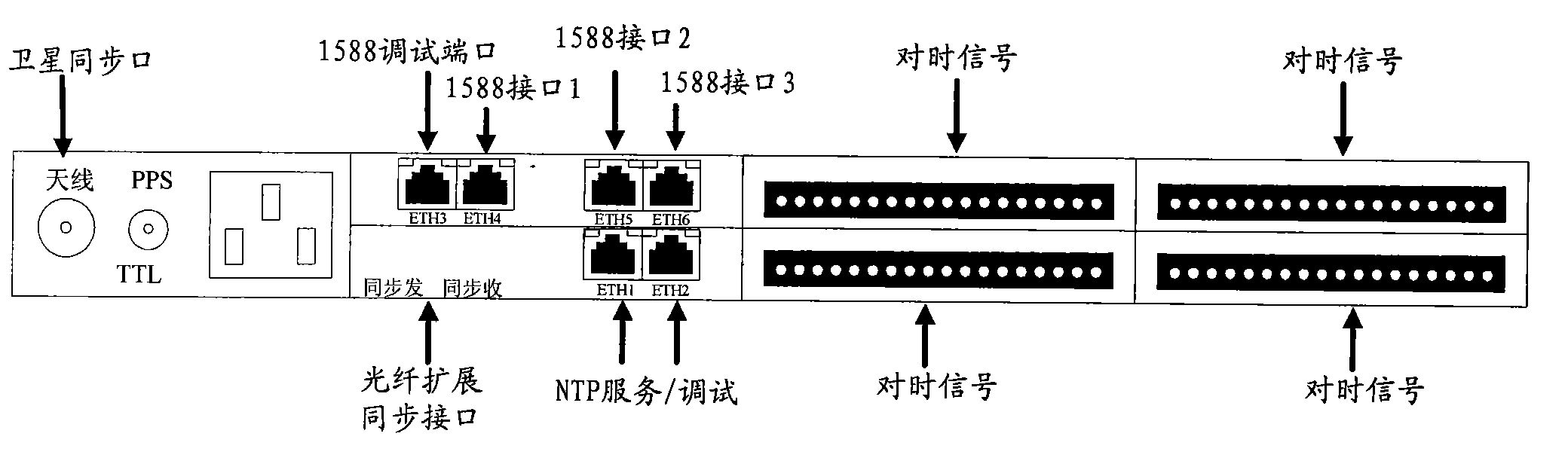
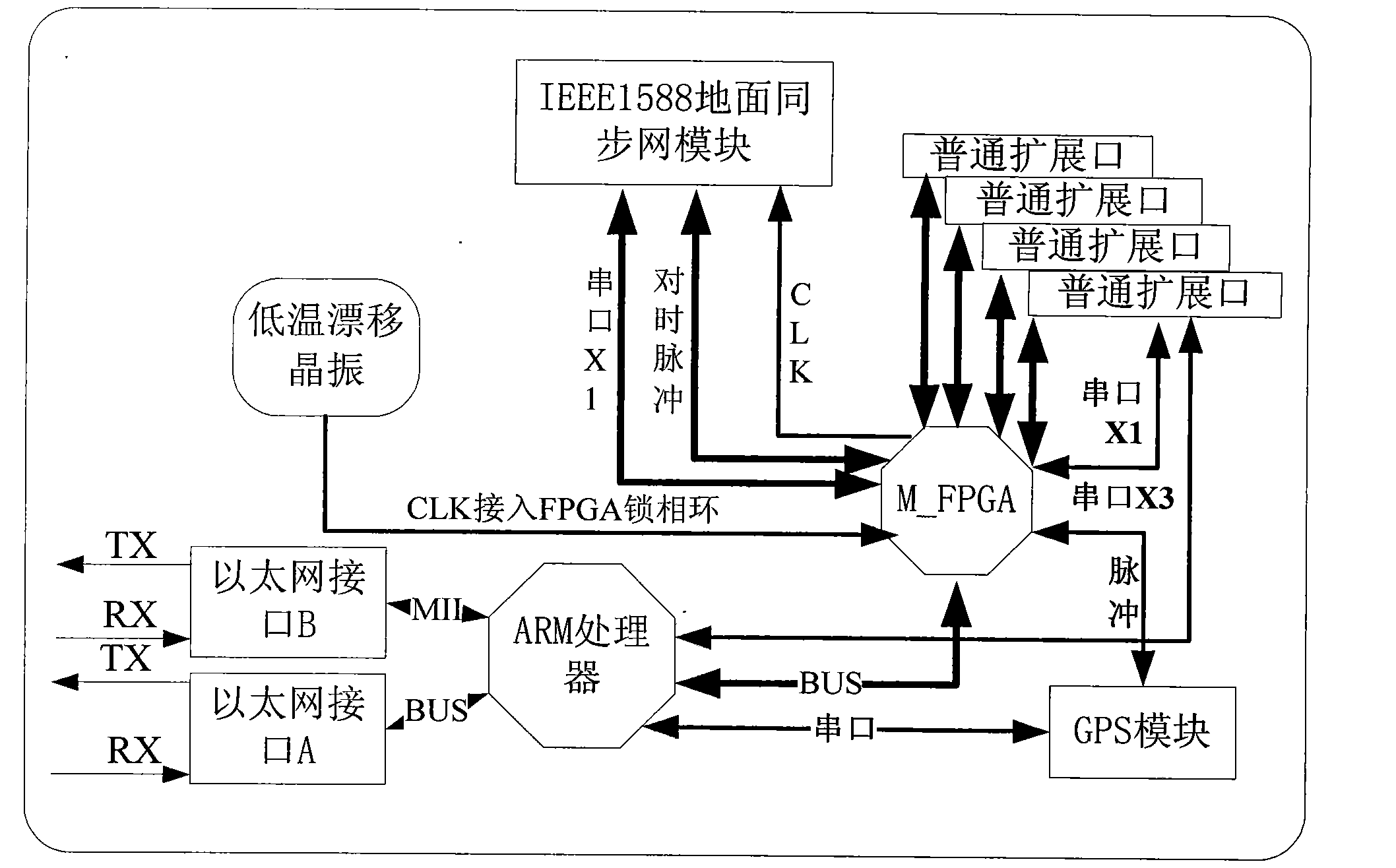
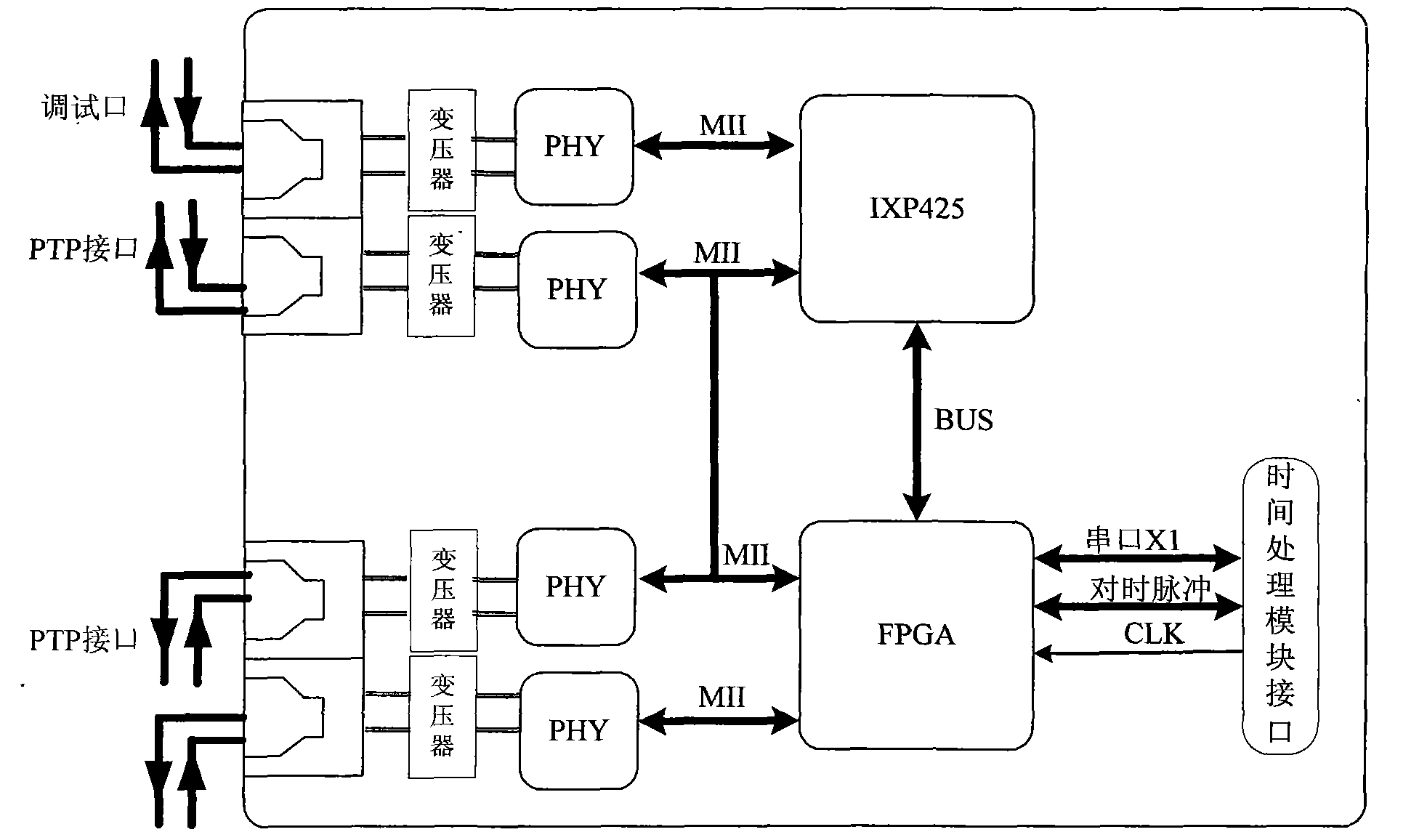
The invention discloses a high-precision Ethernet timing device which is characterized in that hardware comprises a time processing module CPU (central processing unit), the time processing module CPU is connected with a time processing field programmable gate array (FPGA) through a BUS and is connected with a GPS (global position system) receiving module through a serial port as well as connected with an IEEE1588 (Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineers 1588) ground synchronization network module through a timing signal; the IEEE1588 ground synchronization network module comprises an IXP425 processor and an IEEE1588 FPGA port, a low-temperature drift crystal oscillator is used as a crystal oscillator source to be accessed into an FPGA phase-locked loop, and a time clock port FPGA, the IEEE1588 ground synchronization network module and the time processing module CPU are provided with timing signal output ports. The invention can be used for building an IEEE1588 ground time synchronization network and supporting clock mutual automatic switching, and can achieve timing precision of 100us in an electric system II region Ethernet under the condition of not supporting IEEE1588 by a router switch and the like.
Owner:JIANGSU FRONTIER ELECTRIC TECH +1
Intelligent power grid distributed self-supporting photovoltaic power supply system
ActiveCN103199564AReduce shockMake sure grid-tied mode is runningBatteries circuit arrangementsSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsElectricitySynchronization networks
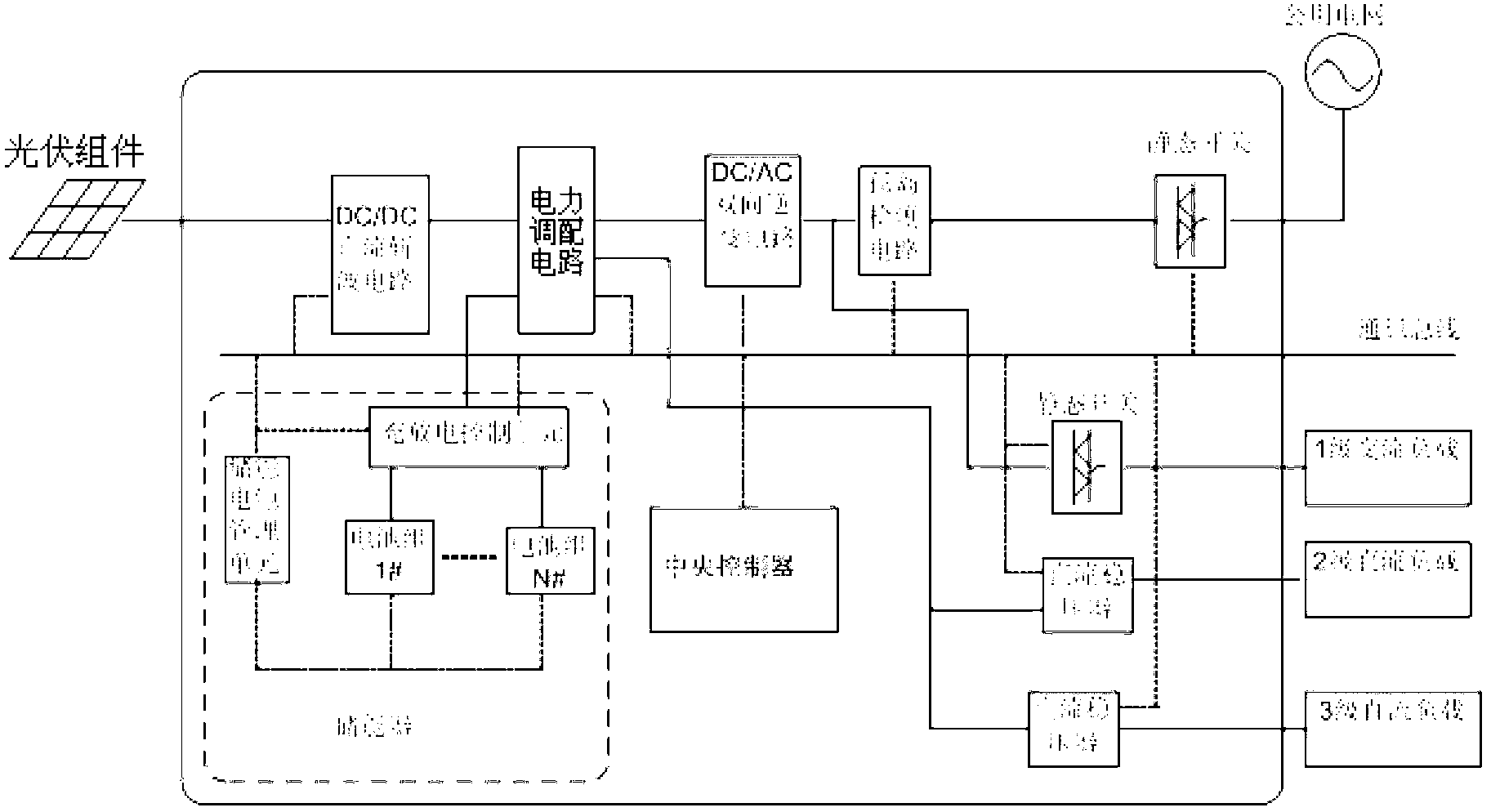
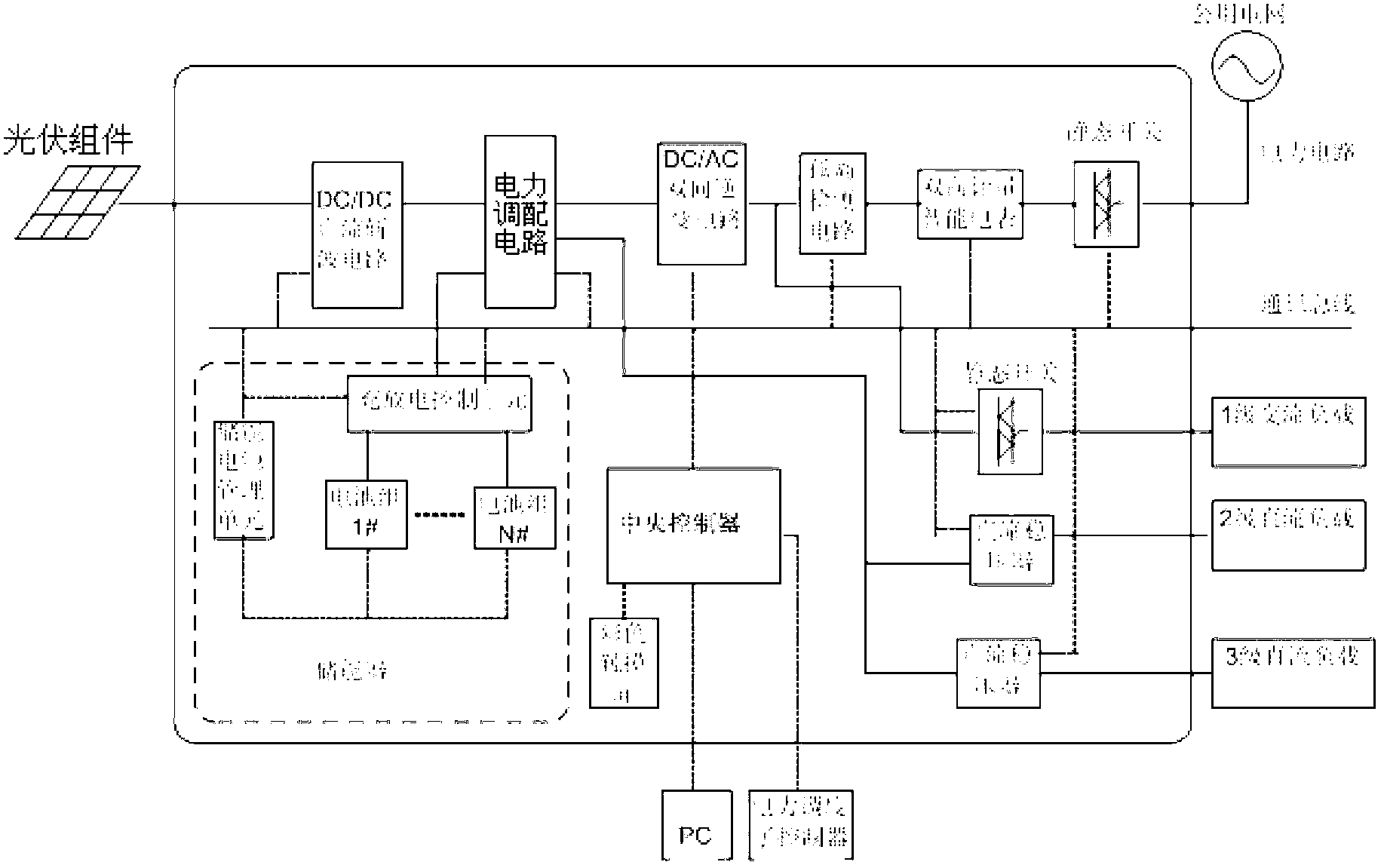
The invention discloses an intelligent power grid distributed self-supporting photovoltaic power supply system. The system comprises a central controller, a DC / DC (direct current to direct current) direct chopper circuit, a power dispensable circuit, a DC / AC (direct current to alternating current) bidirectional inverter circuit, an island detection circuit and an energy accumulator, wherein the central controller is used for collecting data in real time, and controlling the DC / DC direct current chopper circuit, the power dispensable circuit, the DC / AC bidirectional inverter circuit, the island detection circuit and the energy accumulator through analytic calculation, so that the seamless switching between synchronization network and off network can be realized, the synchronization mode operation when a public utility grid is normal can be guaranteed, the system can quickly perform the automatic off-line and off-network mode operation when power is down, the remote dispatching acceptability to a public power grid, the power interaction between the system and the power grid, the off-peak power consumption of load and economical operation of the system can be realized, the power supply quality can be improved, the safety and the reliability of loaded power consumption can be guaranteed, the spontaneous self-supply rate of the system can be improved, and the impact of intermittency and fluctuation of photovoltaic power output to the power grid can be reduced.
Owner:SHANDONG SACRED SUN POWER SOURCES
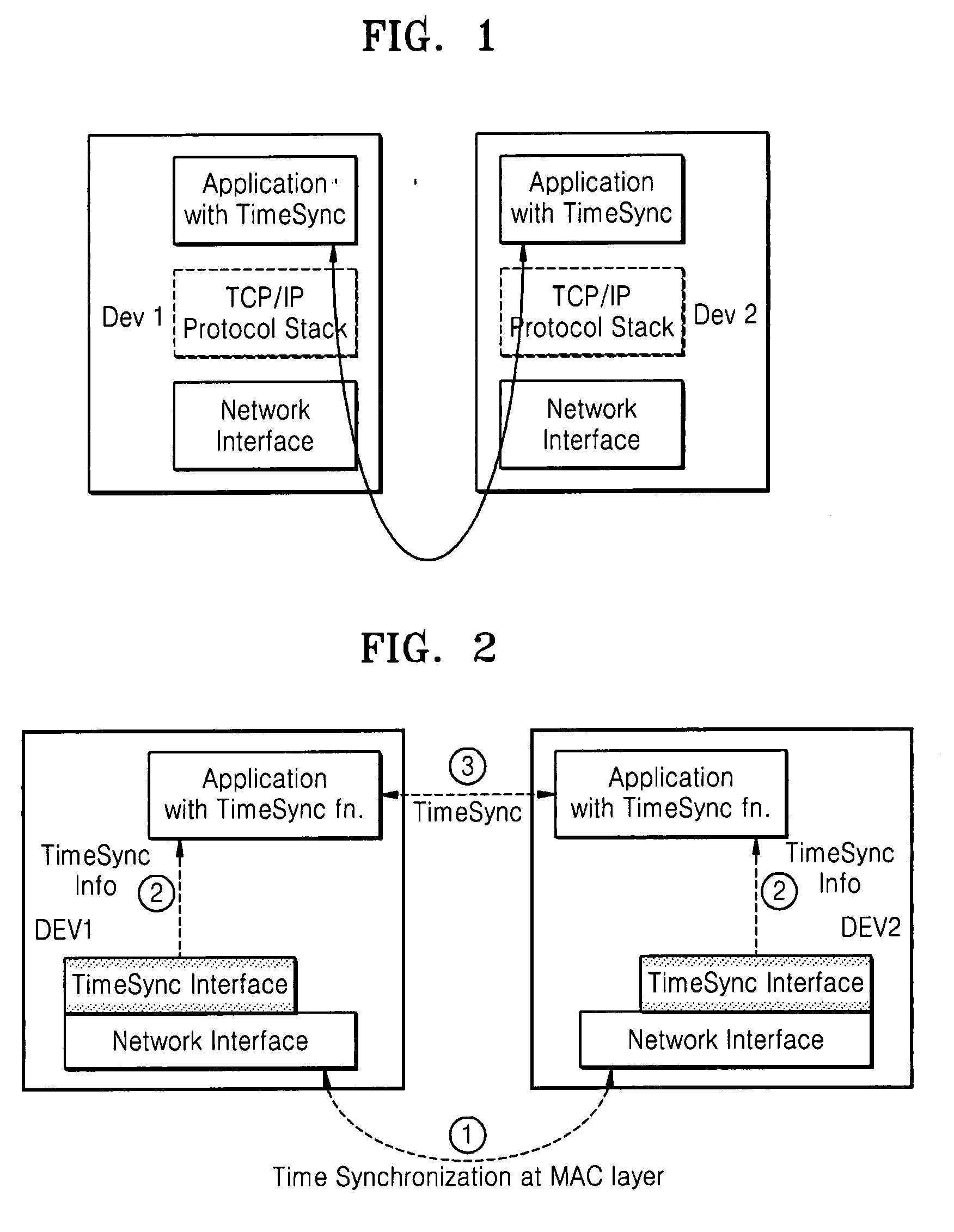
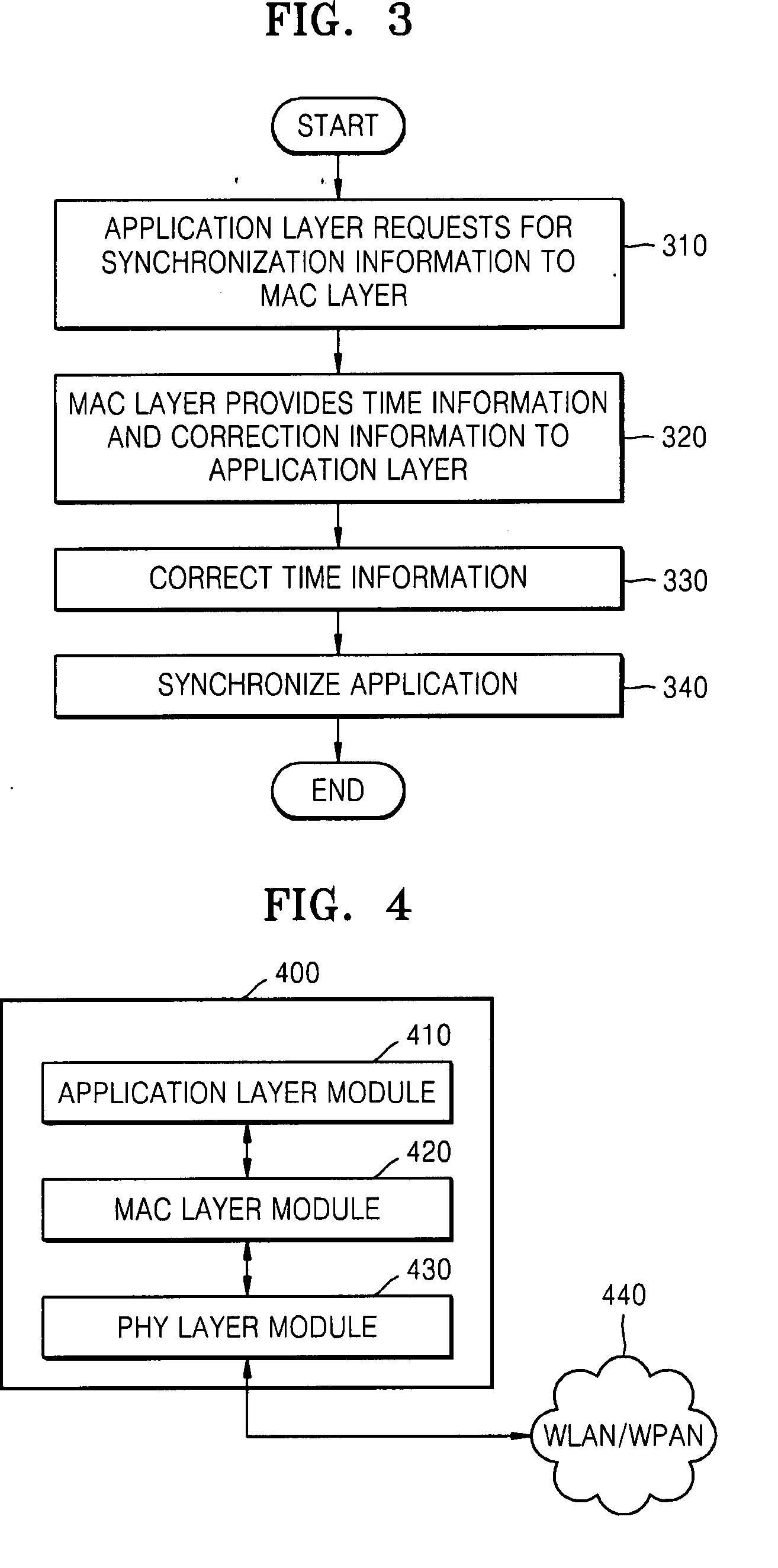
Method and apparatus for synchronizing applications of terminals in communication network
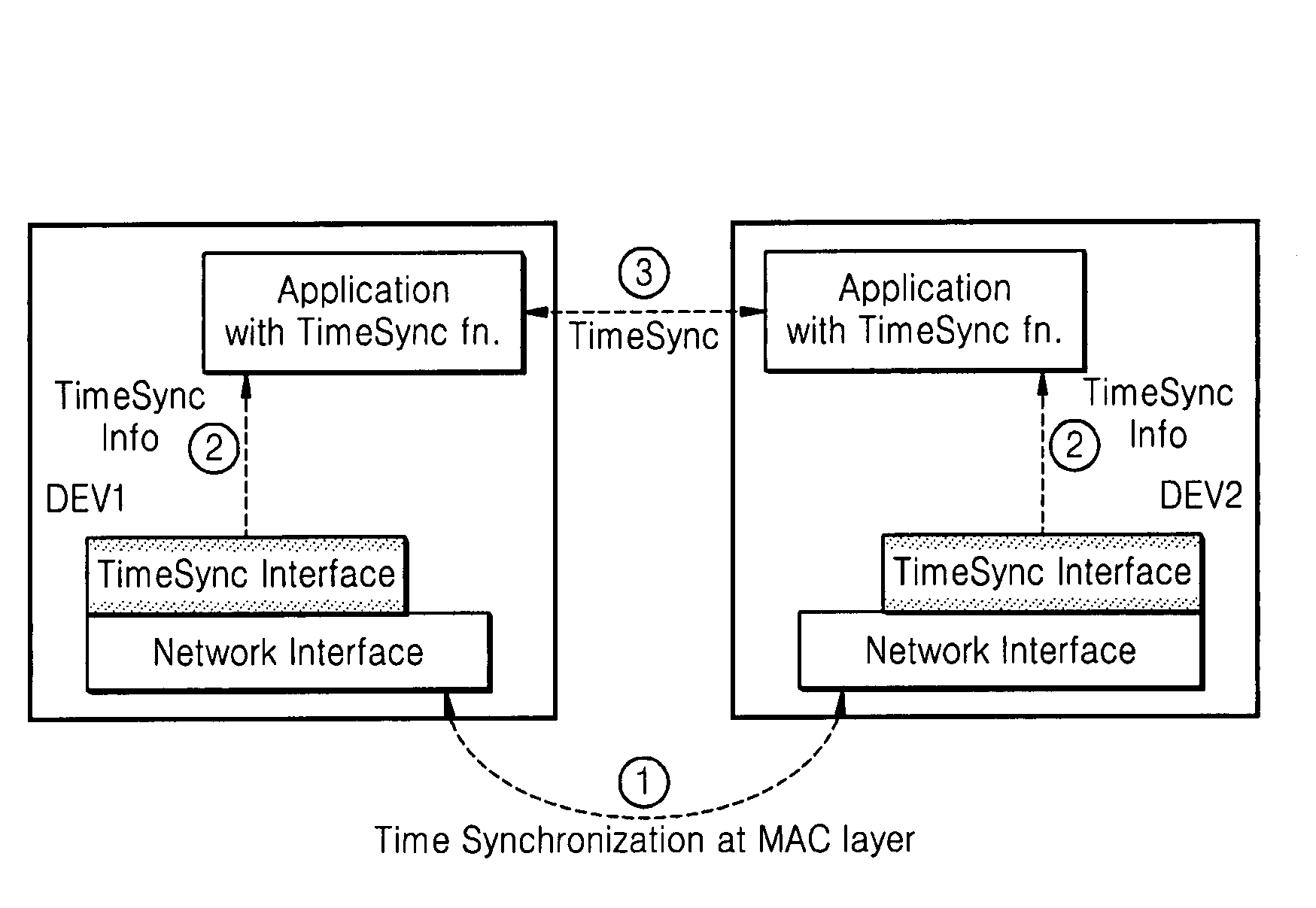
ActiveUS20080075126A1Time-division multiplexWireless network protocolsTime informationSynchronization networks
A method and apparatus for synchronizing applications of network terminals are provided. Time information, which is synchronized and managed with other terminals for controlling use of media in the network in a media access control (MAC) layer, is transmitted to an application layer so as to directly execute the application using a synchronization interface. Accordingly, it is possible to synchronize applications without exchanging packets for obtaining synchronization information of terminals using a TCP / IP protocol.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
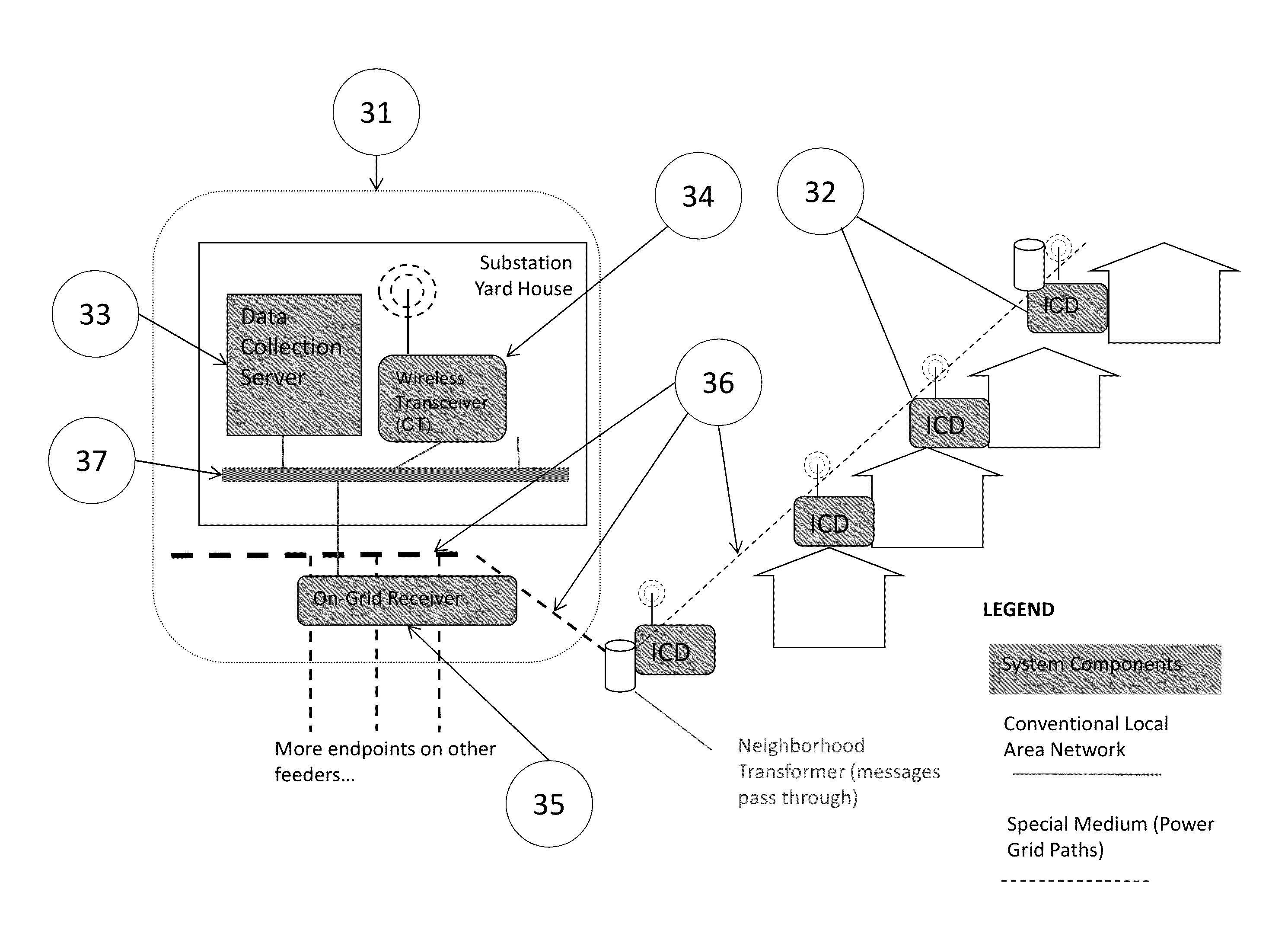
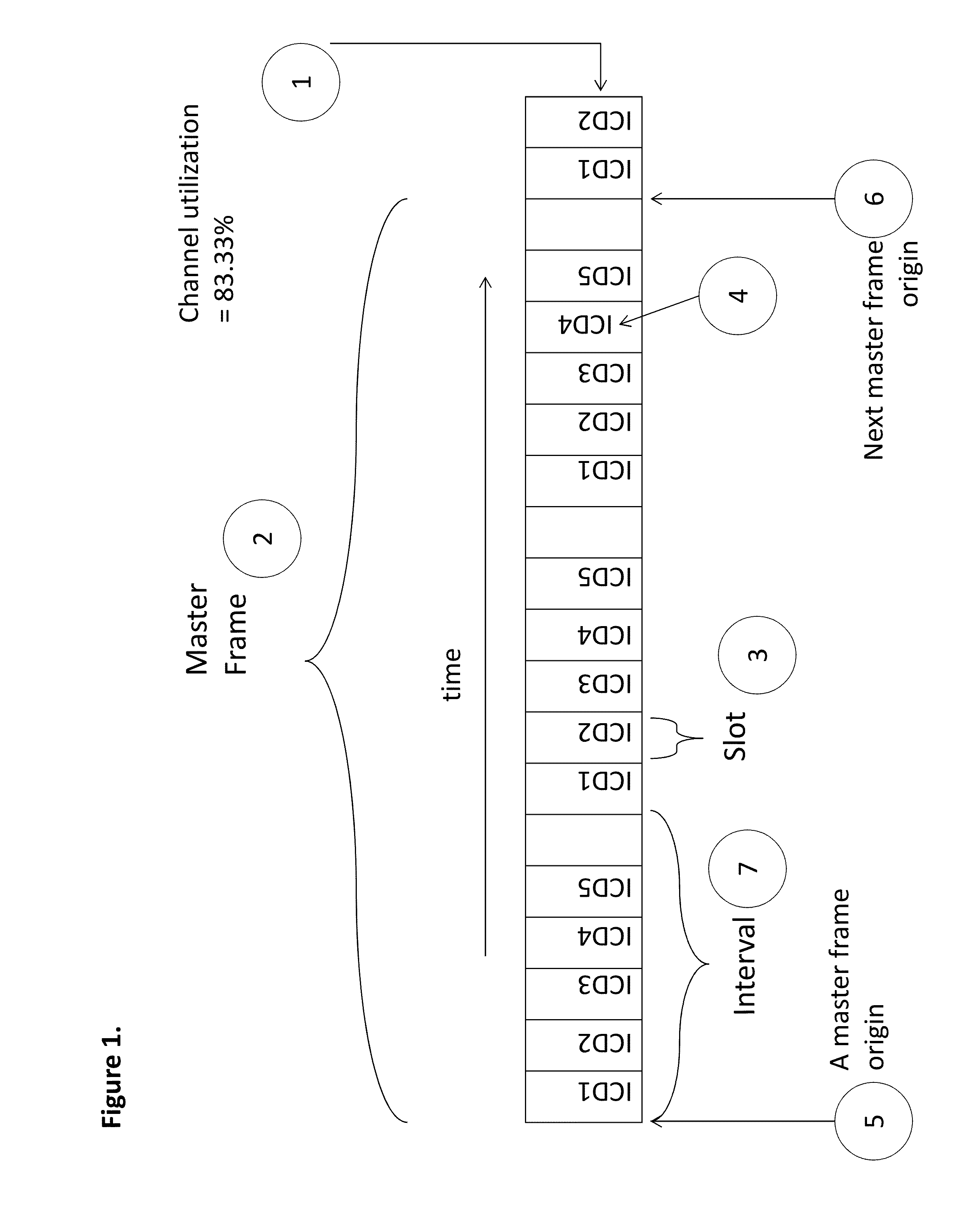
System and methods for synchronizing edge devices on channels without carrier sense
ActiveUS20130034086A1Synchronisation arrangementNetwork traffic/resource managementSynchronization networksCarrier signal
A system and method are disclosed for synchronizing edge devices on a network, wherein the network has limited bandwidth and does not support a practical carrier sense mechanism. The edge devices transmit, using a slotted protocol, to a server located at a central data aggregation point. The server also controls a Central Transmitter, which sends messages to the edge devices to assign transmission slots and provide timing information to the edge devices to ensure that transmissions sent by devices sharing the same communication channel do not collide.
Owner:DOMINION ENERGY TECH +1
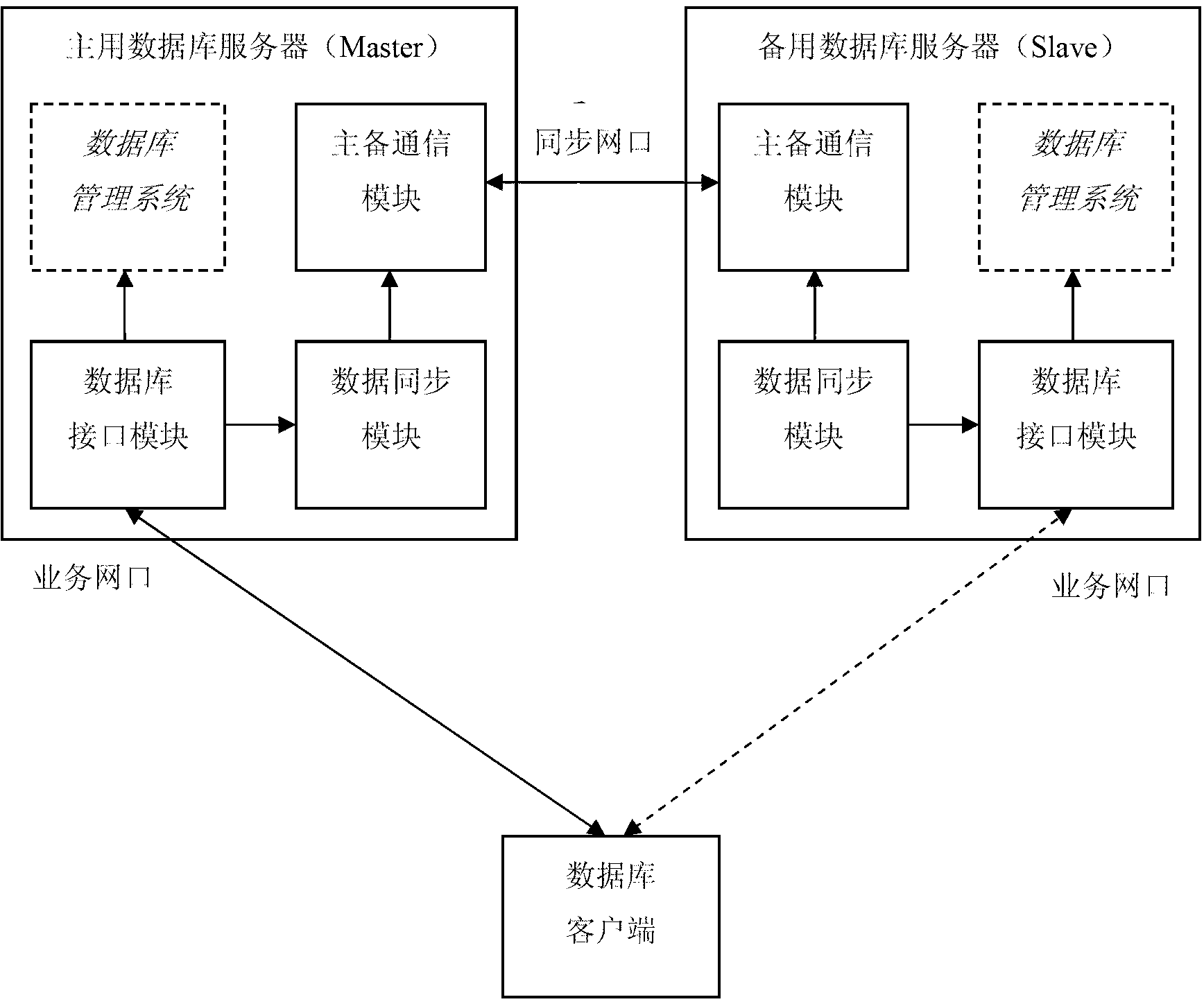
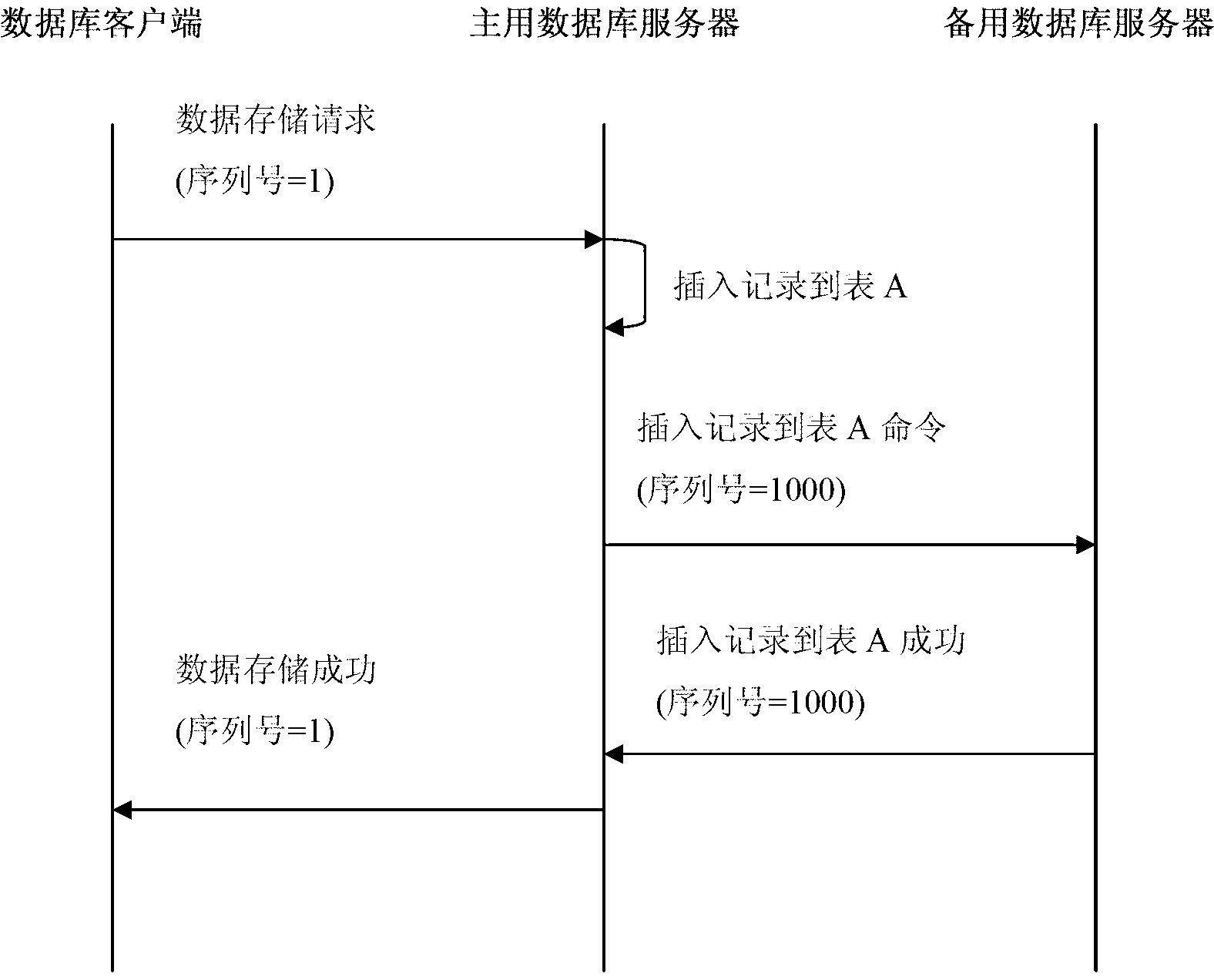
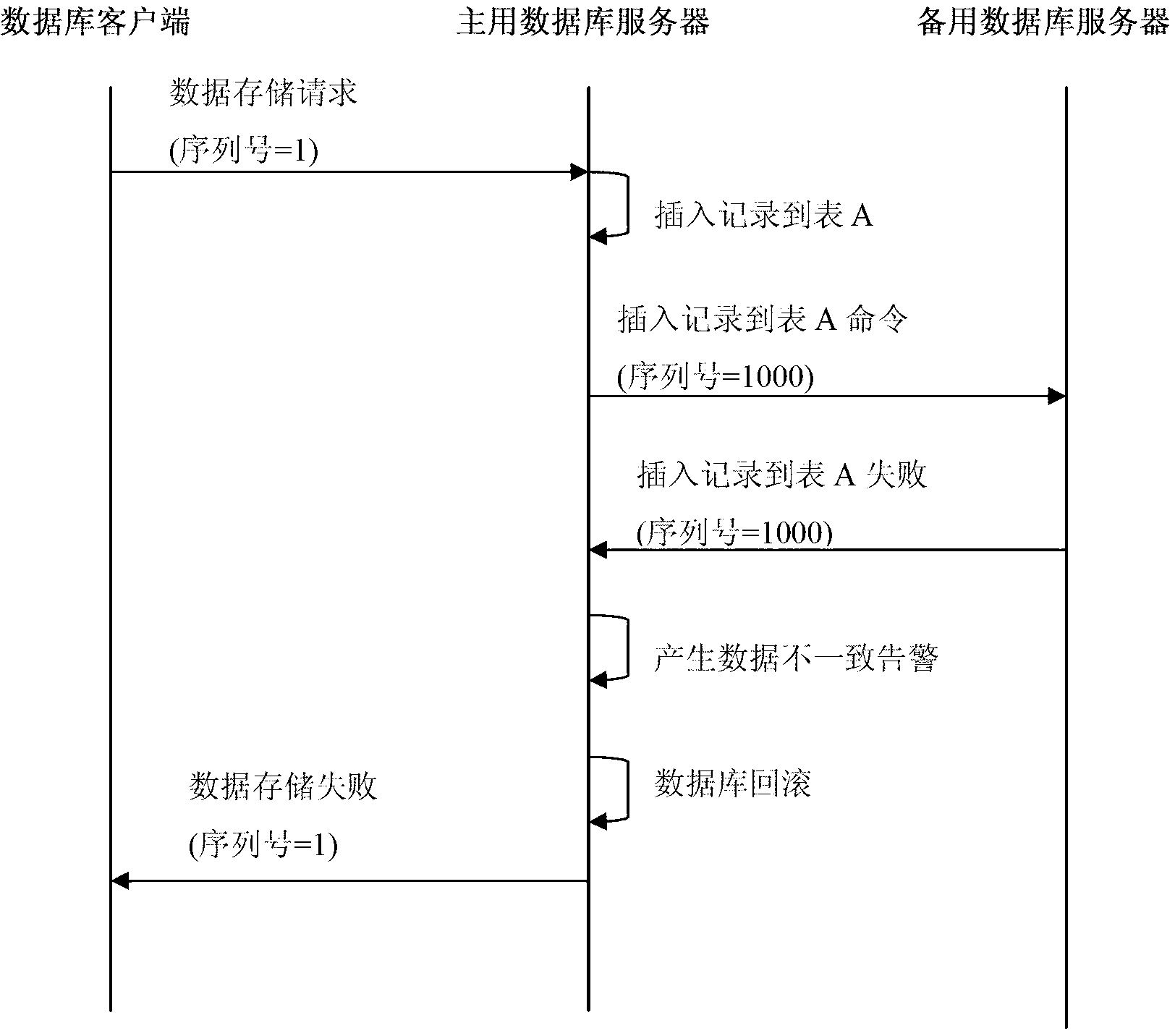
Method for hot standby of dual database servers
InactiveCN103077242AImprove integrityAchieve consistencyData switching networksSpecial data processing applicationsData synchronizationSynchronization networks
The invention provides a method for the hot standby of dual database servers in the technical field of database systems. A system comprises an active database server and a standby database server. The two servers perform regular handshake, master-slave negotiation, data access and data synchronization through a synchronization network port. A server network port of the active database server employs a virtual Internet protocol (IP) address to externally provide server service, and a service network port of the standby database server does not externally provide database service. A database client accesses the active database server through the virtual IP address by adopting a transmission control protocol (TCP). A flexibly selectable real-time / quasi-real-time database synchronization mechanism, a comprehensive data consistency detection method for the active and standby database servers and a selectable data consistency recovery means are provided by the invention.
Owner:BEIJING JIAXUN FEIHONG ELECTRIC CO LTD
Time synchronization system and method
ActiveCN102237941AAddress high-precision time synchronization requirementsSolve problems such as high-precision time synchronization requirementsTime-division multiplexData synchronizationSynchronization networks
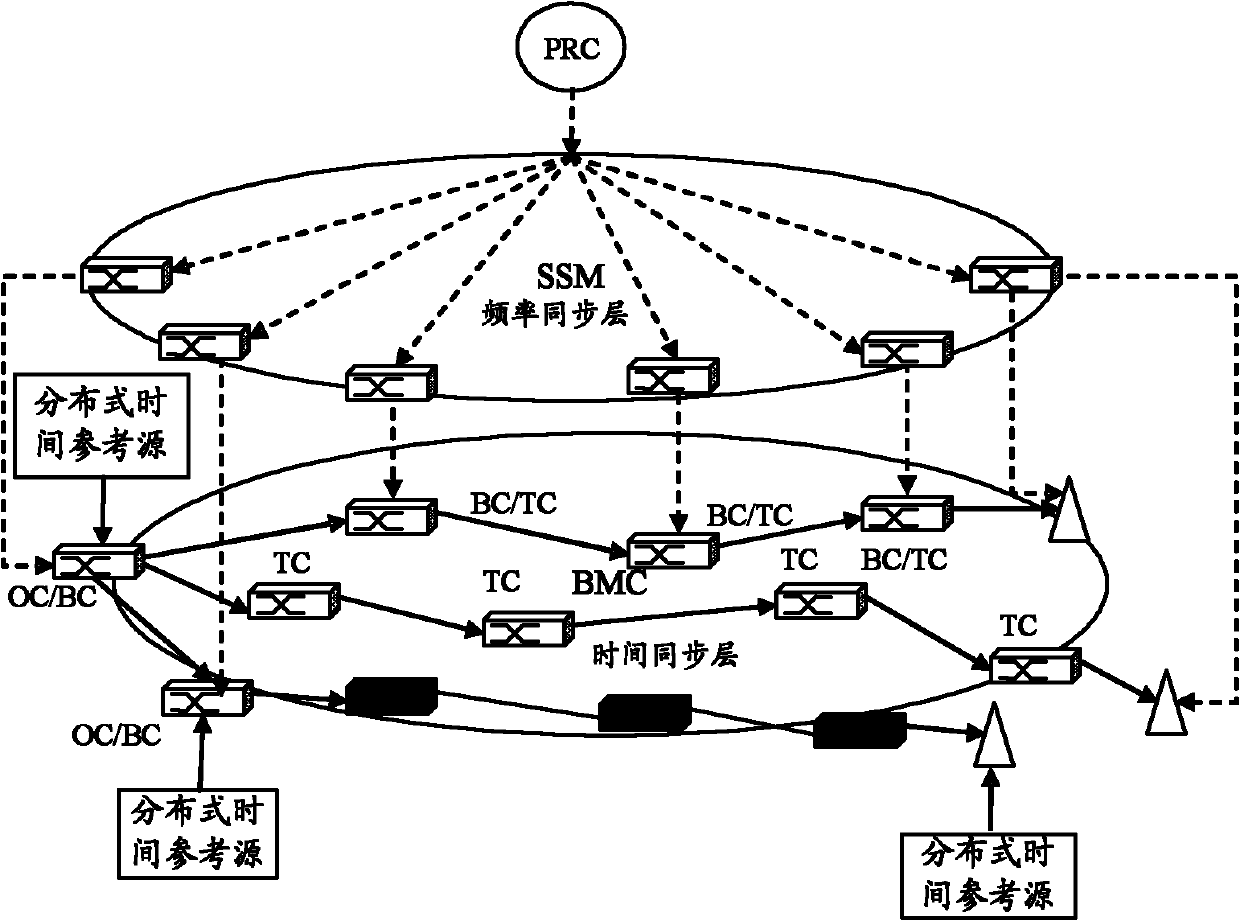
The invention discloses a time synchronization system and method. The system comprises a frequency synchronization network and a time synchronization network, wherein the frequency synchronization network is used for transmitting a frequency synchronization signal to the time synchronization network after implementing frequency synchronization of every network element; and the time synchronization network is used for receiving the frequency synchronization signal from the frequency synchronization network, carrying out time counting according to the frequency synchronization signal to establish local time, and exchanging a time synchronization protocol message to calibrate the local time. According to the technical scheme disclosed by the invention, the high-precision time synchronization requirement can be satisfied; meanwhile, the time synchronization network and the frequency synchronization network are relatively independent logically in the aspects of frequency / time reference source selection mechanism, synchronous route computing mechanism and protective switching mechanism, and the layered architectures of the two networks in such a structure can be separated physically or logically; and thus, the system is very easy to maintain and manage, and the time synchronization network can be allocated according to the specific network environment, thereby enhancing the internetworking flexibility.
Owner:NANJING ZHONGXING XIN SOFTWARE CO LTD
Sensing RF environment to synchronize network elements
InactiveUS20080085721A1Synchronisation arrangementTime-division multiplexSynchronization networksRadio frequency signal
Providing a frequency reference to a mobile telecommunications base station is disclosed. A radio frequency signal that includes a periodic component having a known frequency is received. A frequency reference is derived from the received radio signal, based at least in part on the periodic component. The frequency reference is used to transmit from the base station at an assigned frequency.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
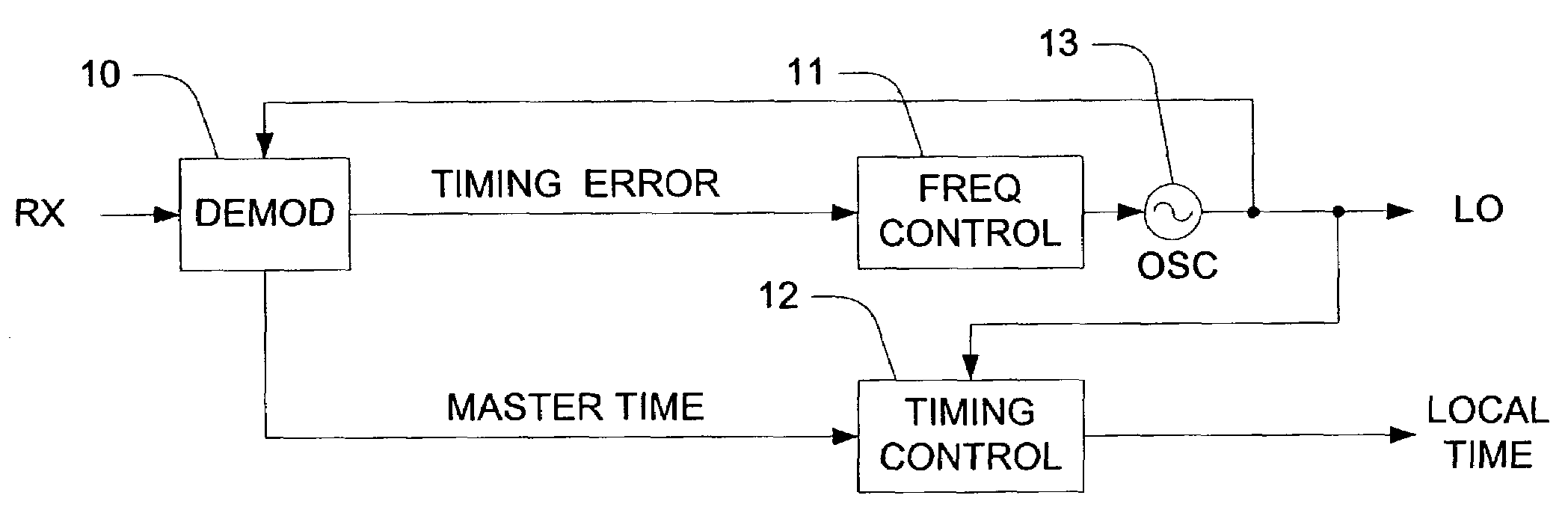
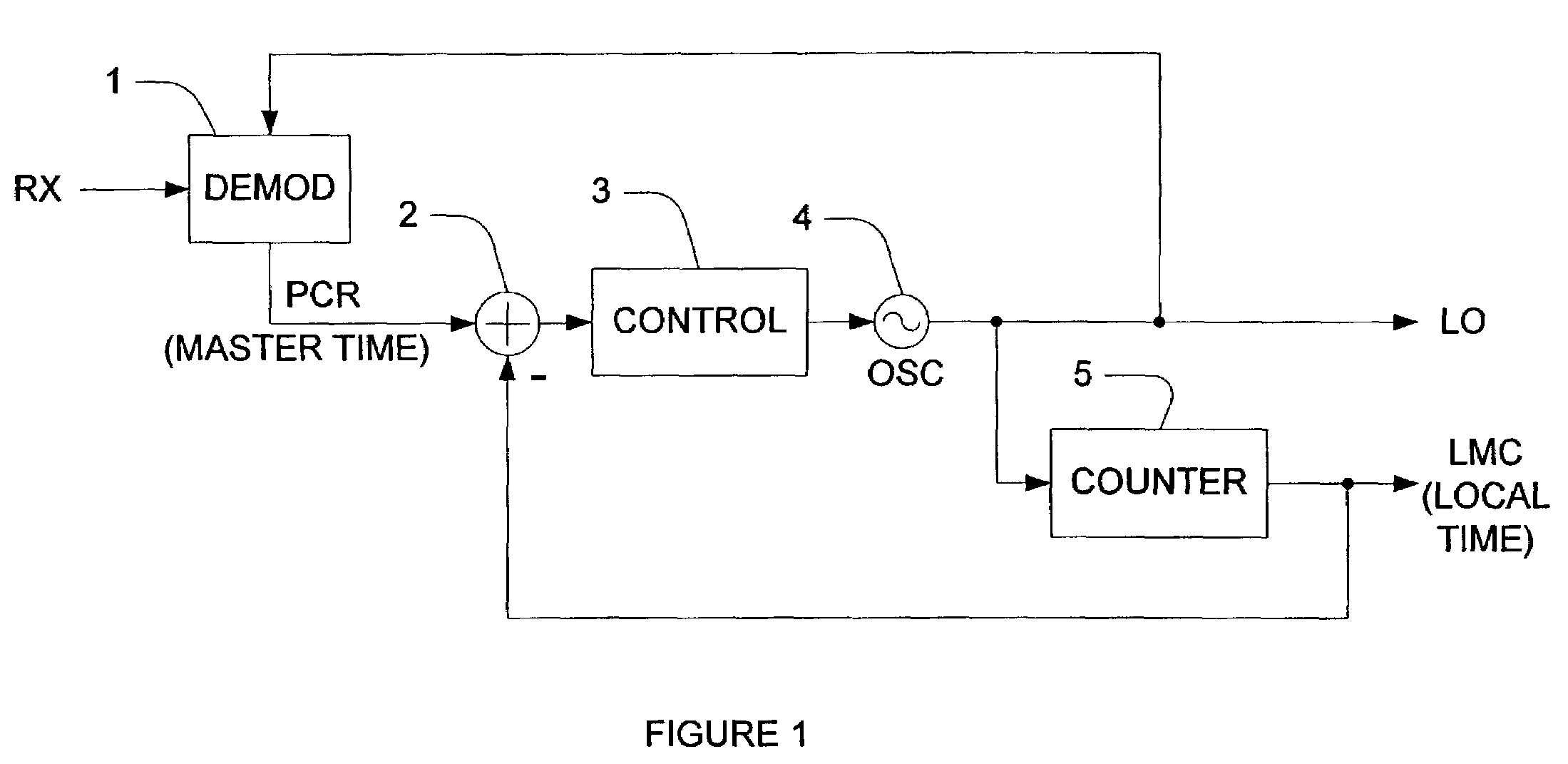
System and method of timing and frequency control in TDM/TDMA networks
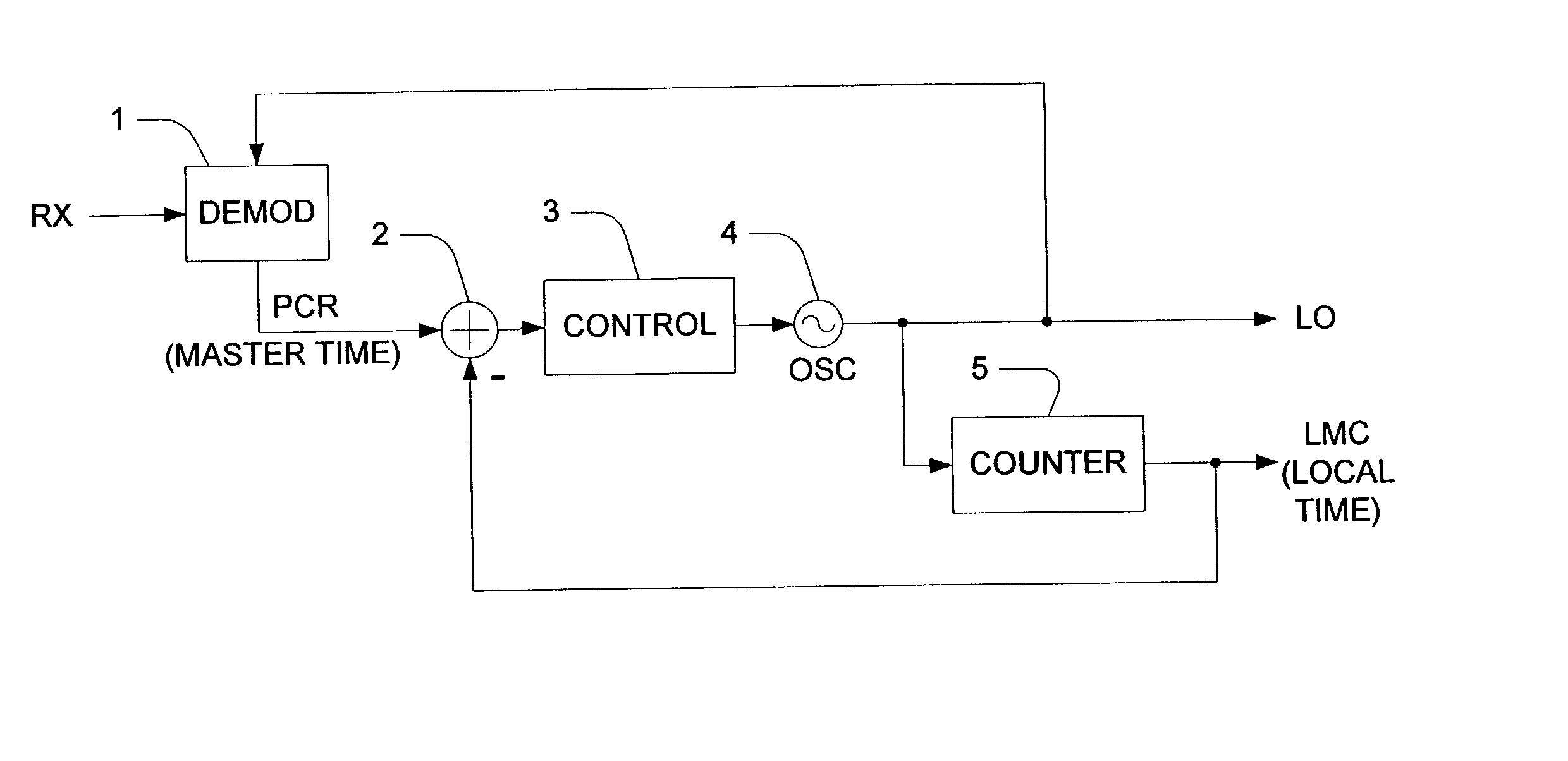
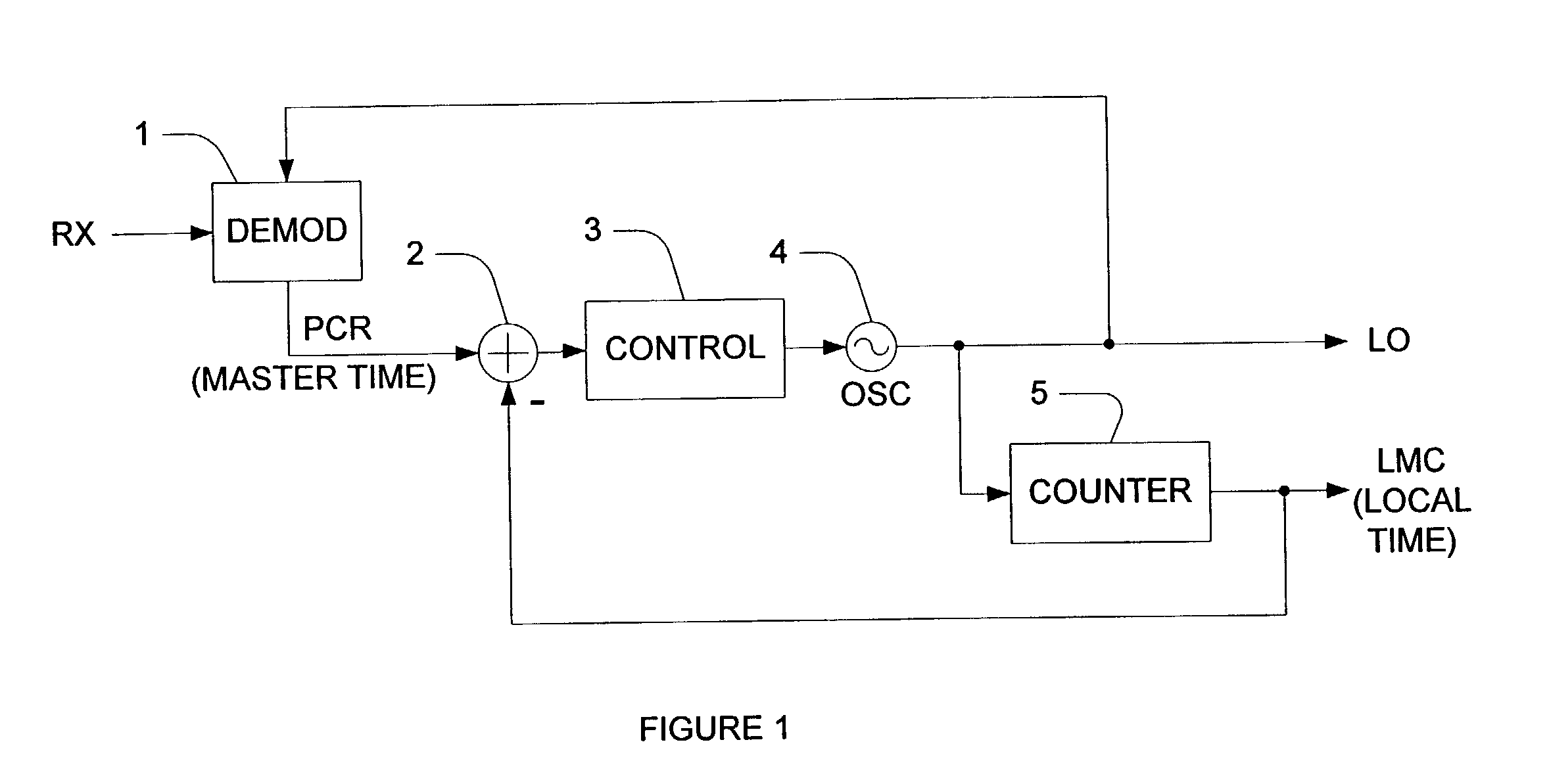
ActiveUS20030147426A1Broadcast information characterisationSynchronisation error detectionProgram clock referenceLoop filter
A method and system of synchronizing two nodes of a network uses a demodulated output signal of a time division multiplex (TDM) demodulator to perform frequency and timing synchronization independently. Frequency synchronization is performed without using a program clock reference, by detecting a symbol timing loop error of the TDM demodulator. The error is filtered by an oscillator control loop filter if the error is within a predetermined range. Thus, an output voltage of a digital to analog converter that receives the filtered output controls an oscillator. In the timing synchronizer, an error between a program clock reference (PCR) and a value of a counter in the terminal is computed if the PCR is a not a first PCR, and the error is filtered with a timing loop control filter. A processor then adjusts a value of the counter in the terminal based on the filtered output.
Owner:VIASAT INC
Fast frequency adjustment method for synchronizing network clocks
ActiveUS7379480B2Eliminate jumpingEasy to controlTime-division multiplexNetwork clockSynchronization networks
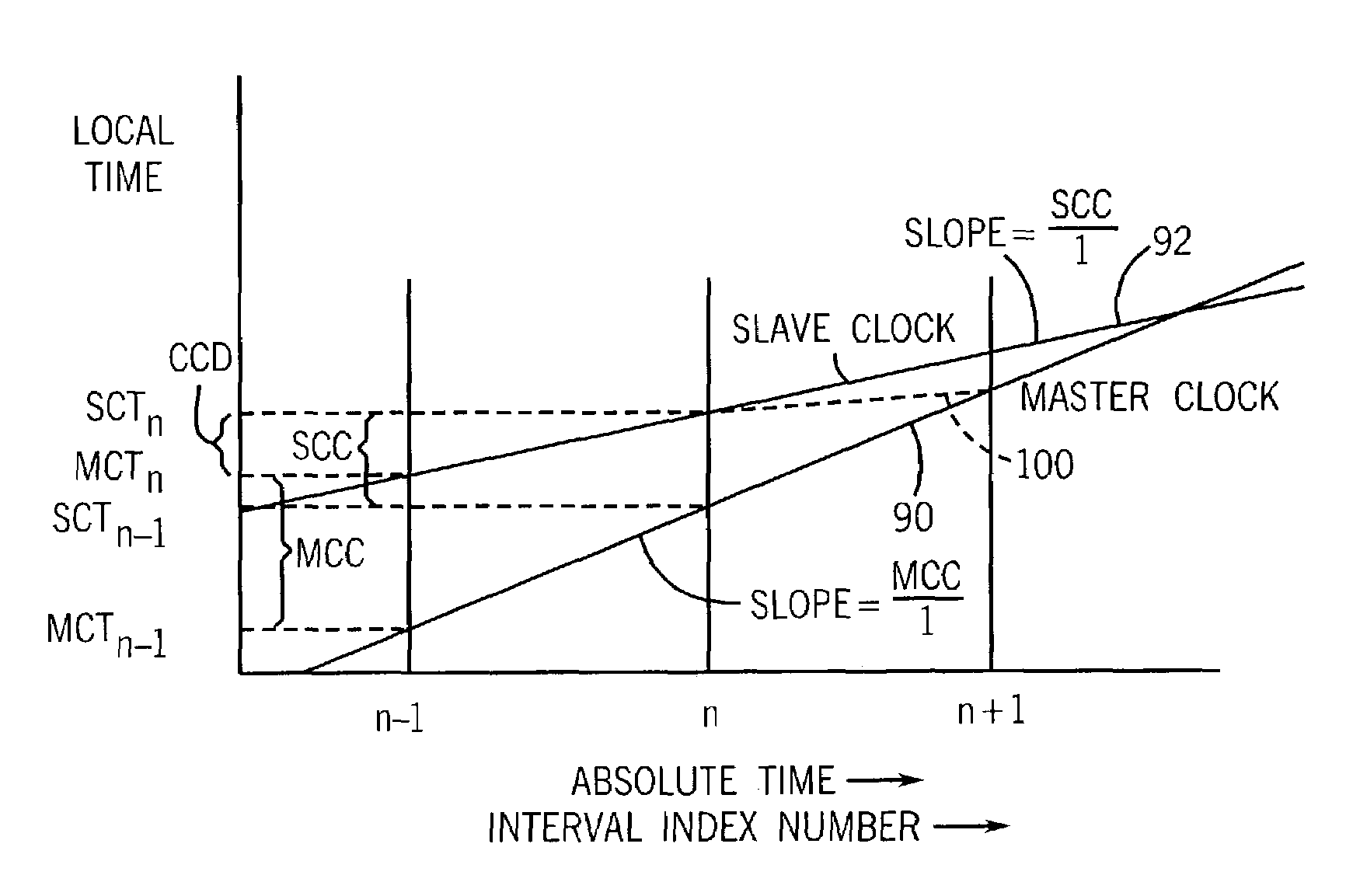
A method of precisely synchronizing clocks held in separate nodes on a communication network is provided that adjusts clock frequency based on a measure of relative clock rates and absolute clock offsets. In one embodiment, clock convergence is obtained with one synchronization session.
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
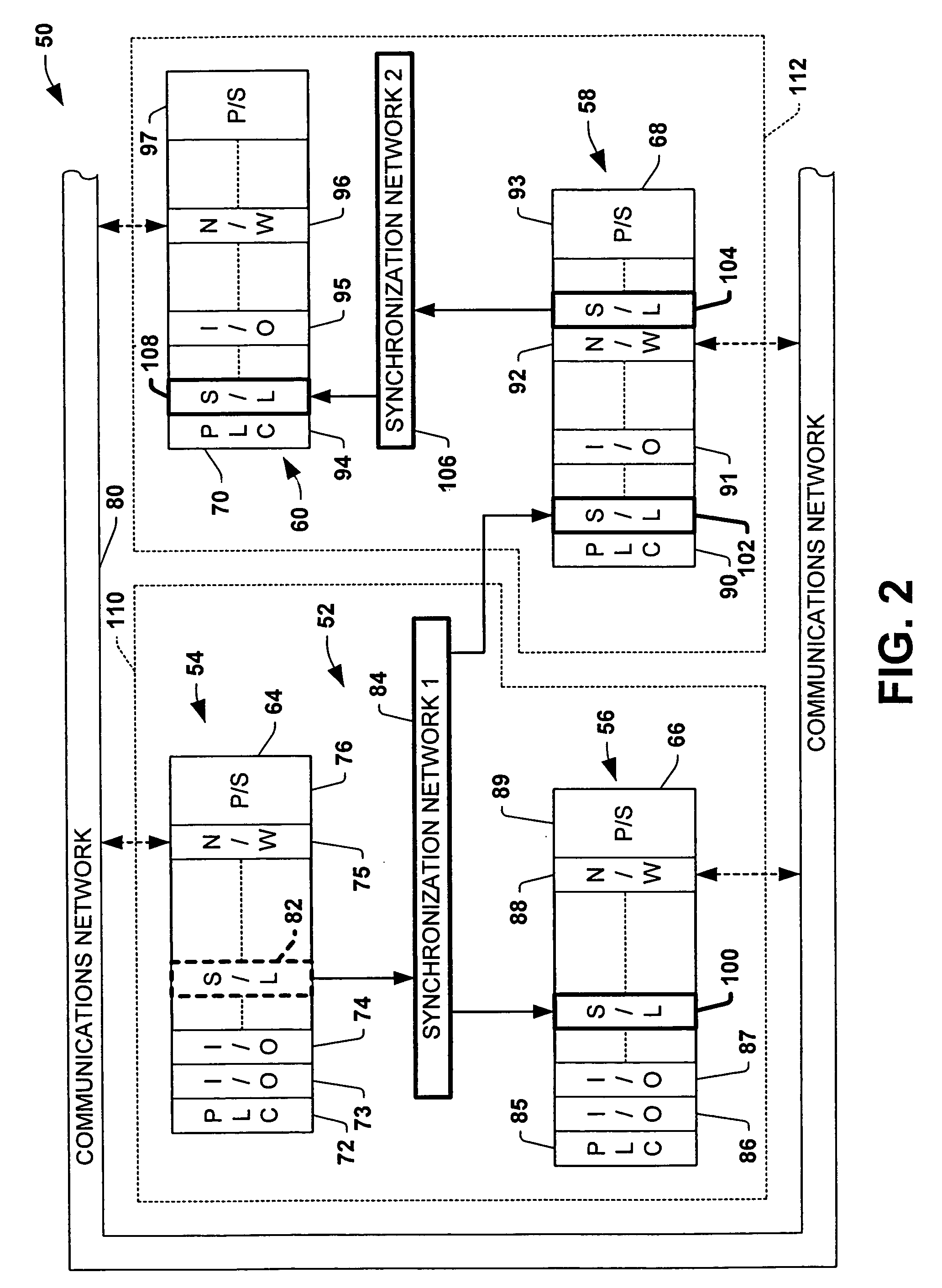
System and method for multi-chassis configurable time synchronization
InactiveUS7457322B1Time-division multiplexProgramme control in sequence/logic controllersControl systemSynchronization networks
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
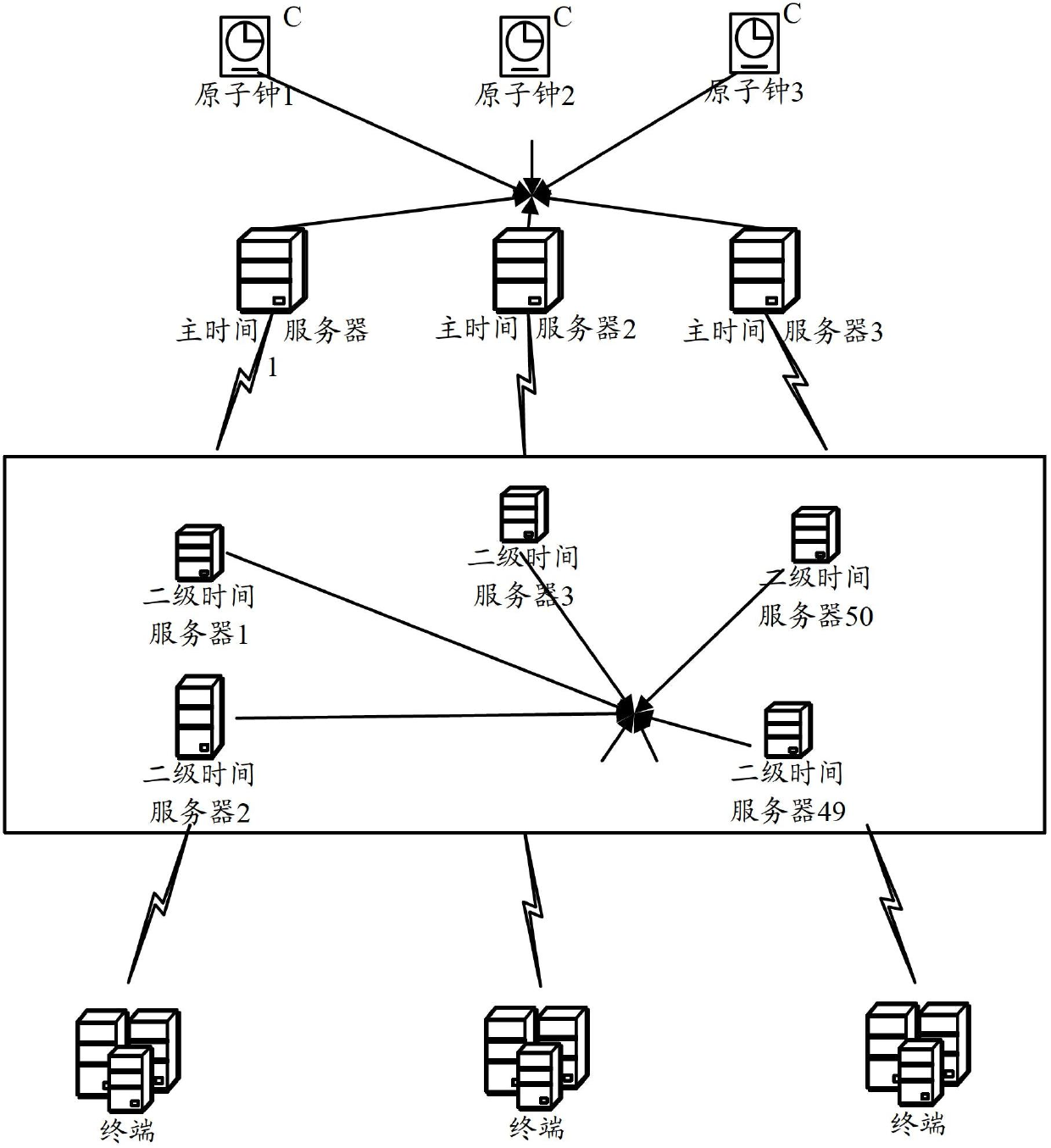
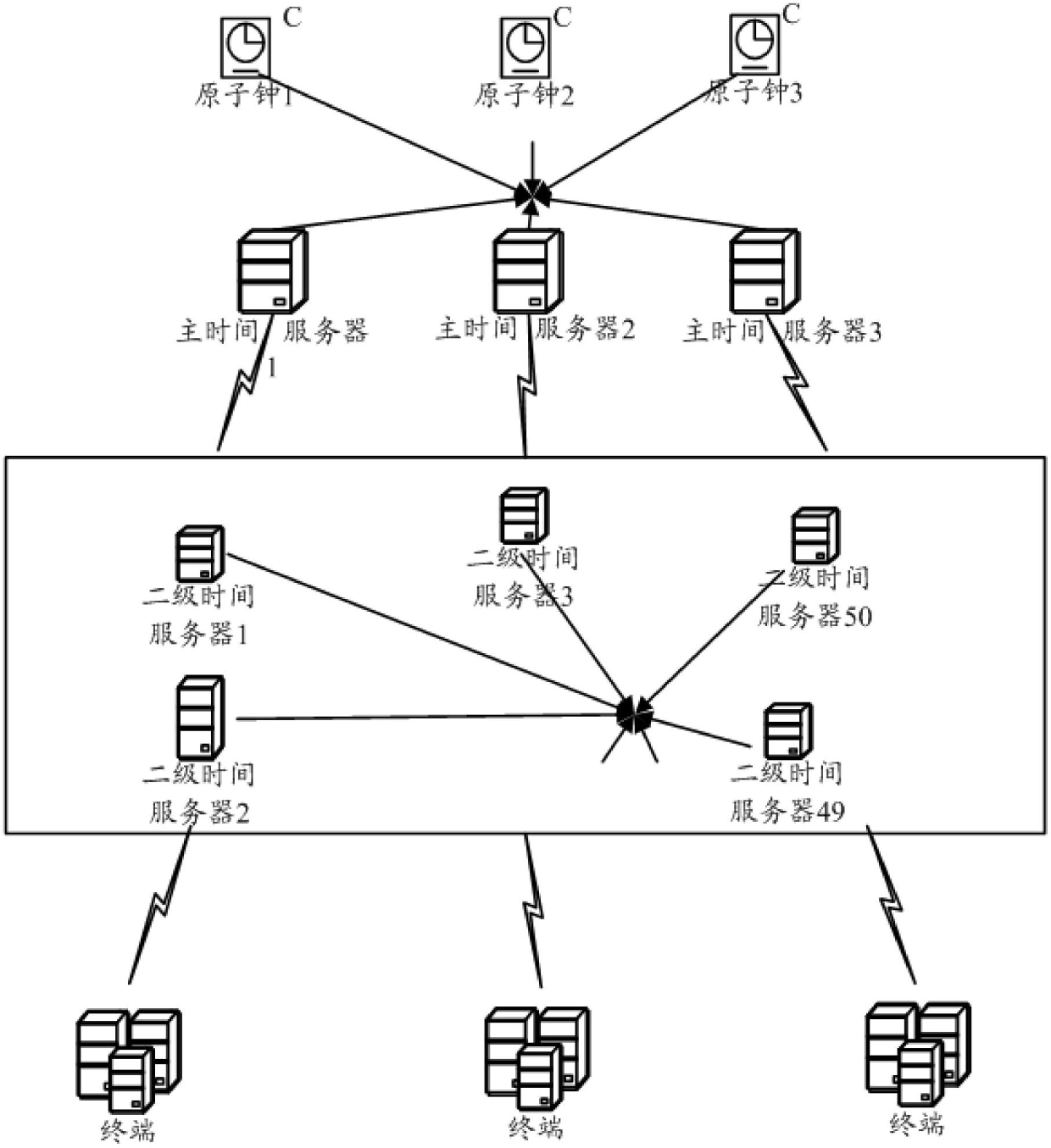
Self-adaptive clock synchronous system
InactiveCN102684808AImprove stabilityAdaptableTime-division multiplexClear LayerSynchronization networks
The invention discloses a self-adaptive clock synchronous system which comprises a main service layer, a secondary service layer and a client layer, wherein the main service layer comprises one or more main time servers; the main time servers are externally connected with an atomic clock; the secondary service layer comprises a plurality of secondary time servers; one part of secondary time servers and the main time servers are subjected to time synchronization; the other part of secondary time servers are mutually subjected to time synchronization; the client layer comprises a plurality of terminals; and the terminals are used for sending time synchronization requests to the secondary time servers to carry out time synchronization. According to the invention, when a reference time source goes wrong, a suitable time source can be automatically searched, so that the system automatically completes the configuration of a synchronization network and the time synchronization network has sufficient stability and robustness and has strong self-adaptive capacity; and meanwhile, a self-adaptive clock synchronous system has higher safety. The self-adaptive clock synchronous system adopts a hierarchical system structure, has clear layers and clear layout as well as strong expandability and is suitable for growth of services.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
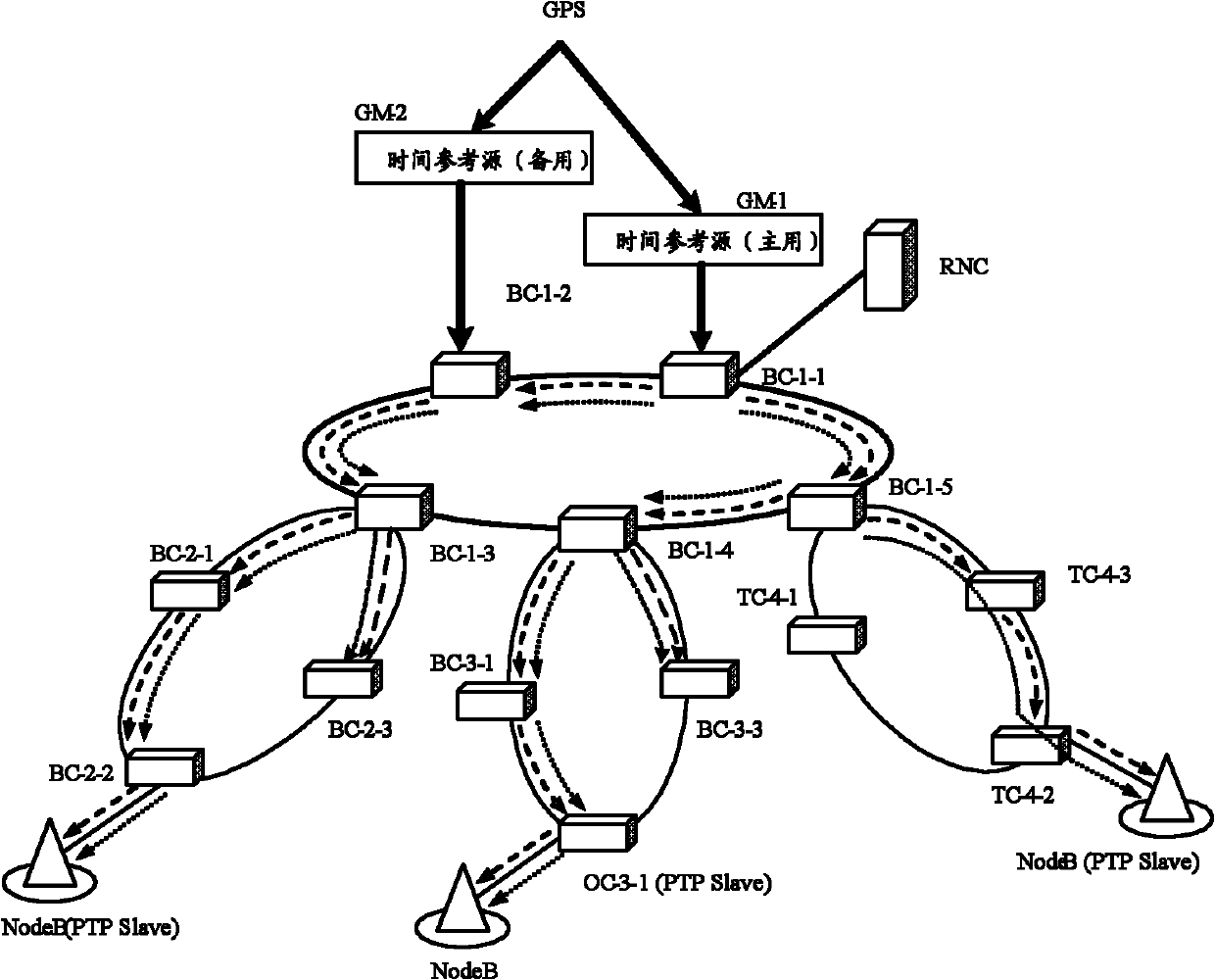
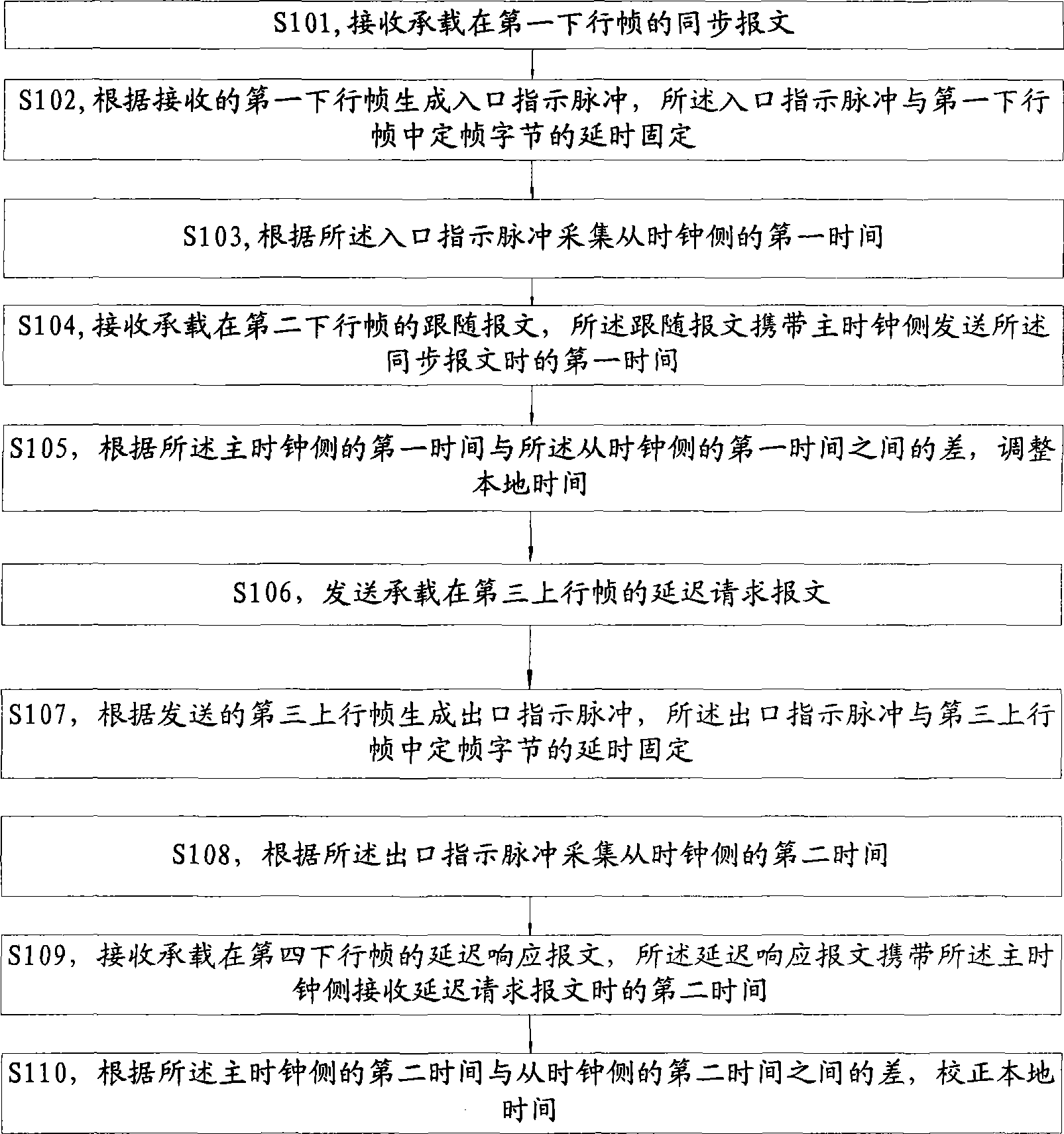
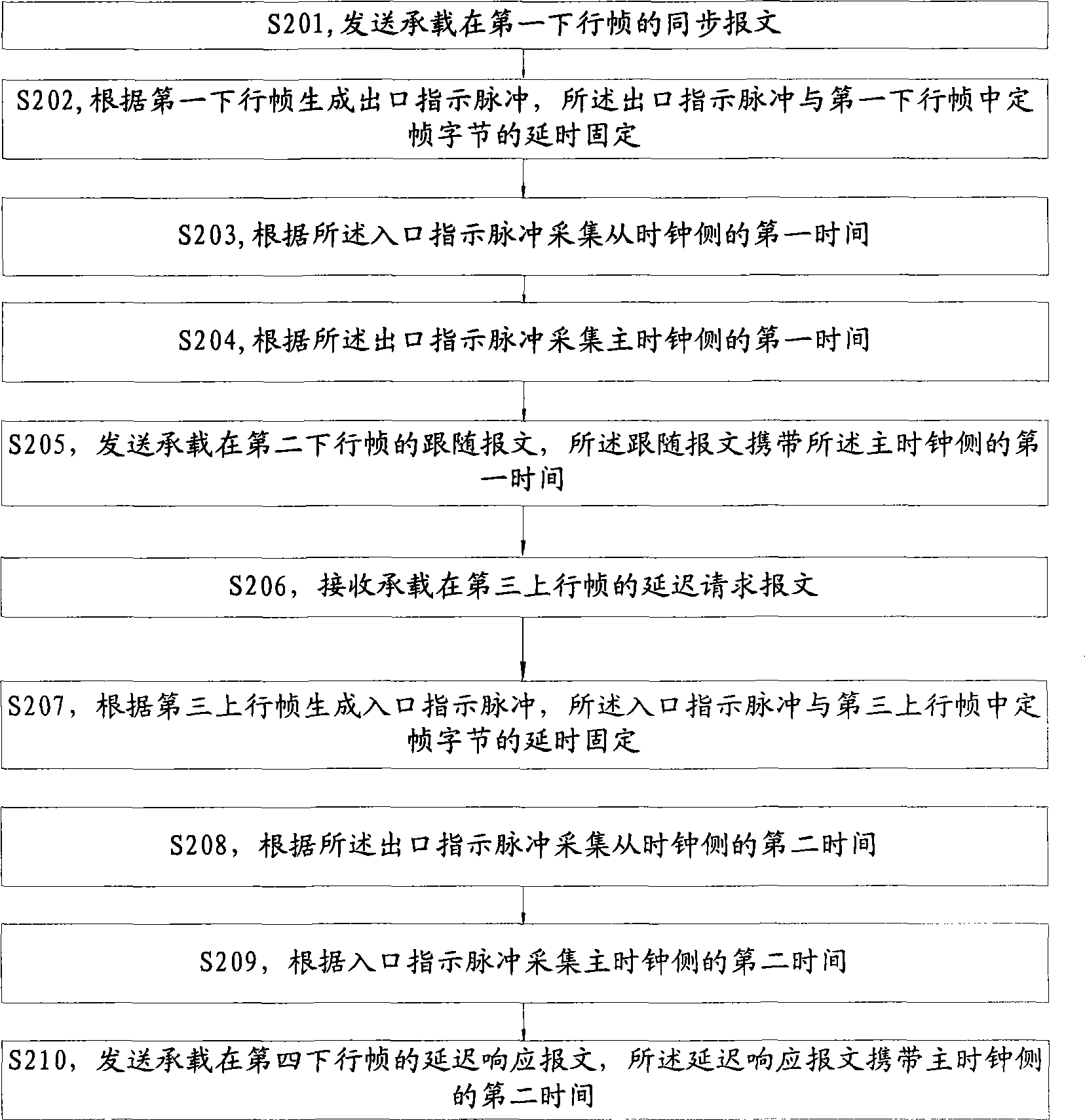
Time synchronizing method, apparatus and system for master, slave time clock side in synchronous network
ActiveCN101364863ATime synchronizationTime-division multiplexSetting time indicationSynchronization networksSlave clock
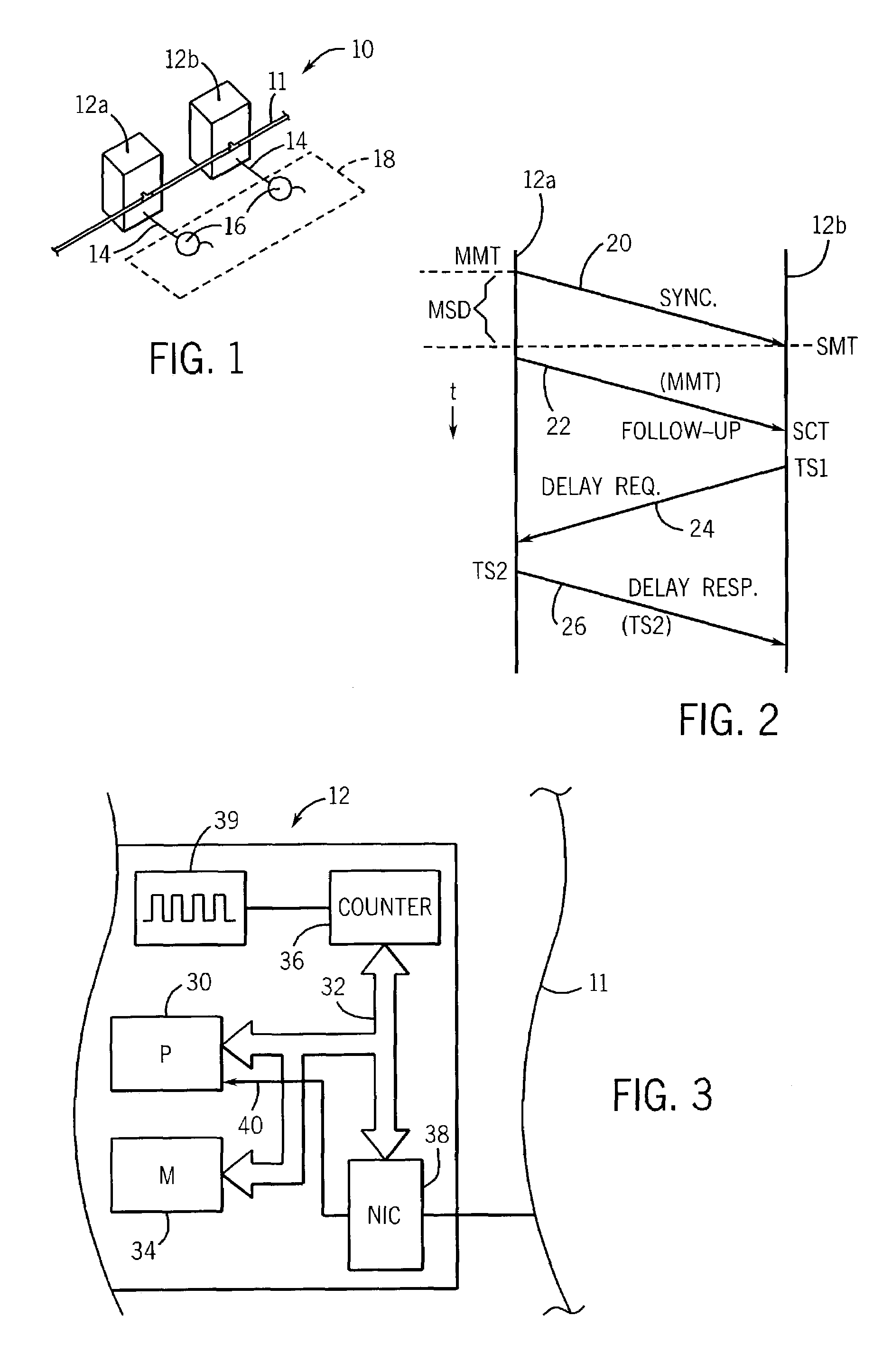
The inventive embodiment discloses a method, a device and a system for synchronizing time on a main clock side and a slave clock side in a synchronization network, which belong to the communication field and are designed to solve the technical problem in achieving time synchronization of the synchronization network. The method synchronizing time on the slave clock side in the synchronization network comprises the following steps: receiving a synchronous message supported on a first downlink frame; generating an entrance indication pulse according to the received first downlink frame, the entrance indication pulse being fixed with the time delay of fixed-frame bytes in the first downlink frame; collecting a first time on the slave clock side according to the entrance indication pulse; receiving a following message supported on a second downlink frame, the following message carrying a first time for transmitting the synchronous message on the main clock side; and adjusting the local time according to the difference between the first time on the main clock side and the first time on the slave clock side.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
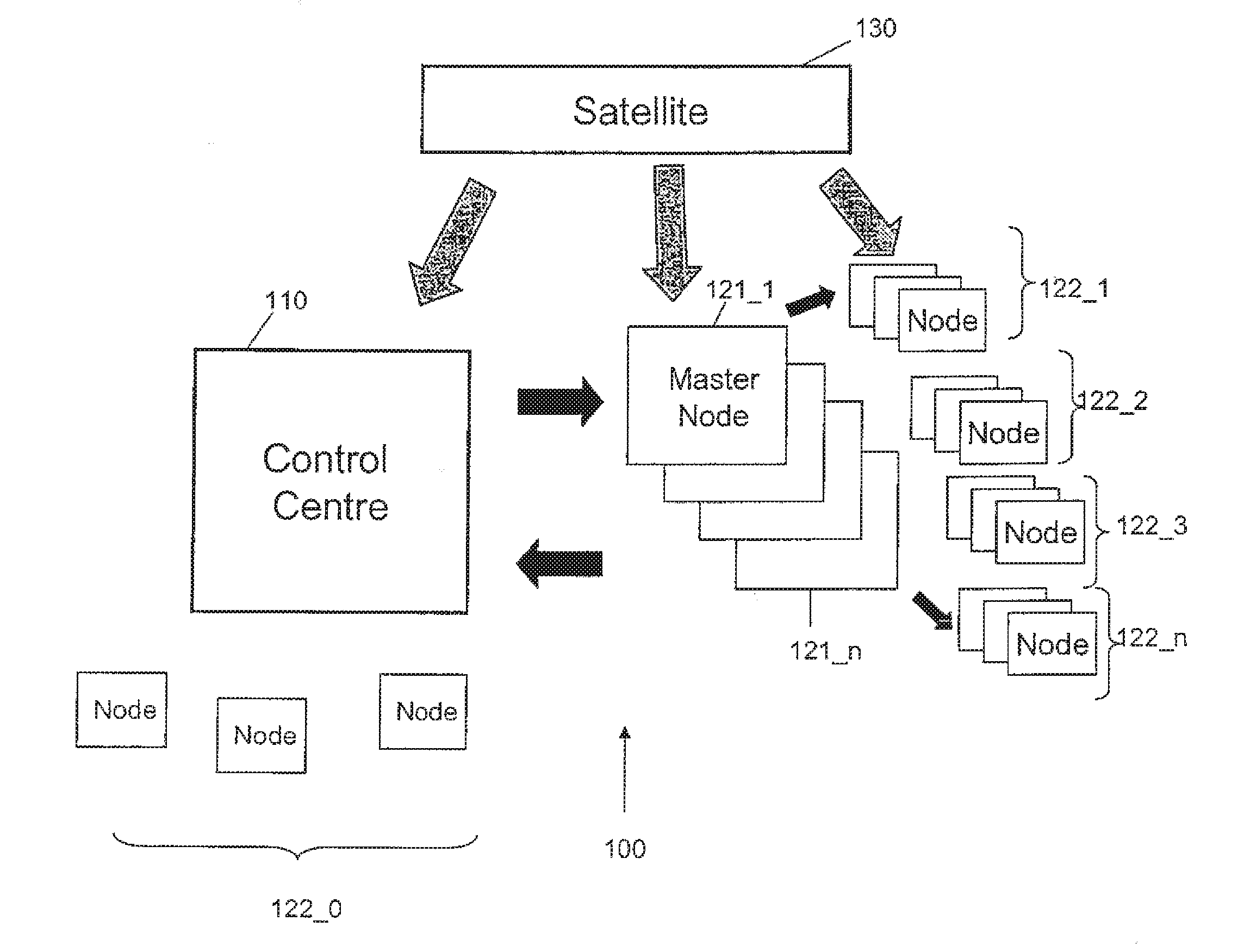
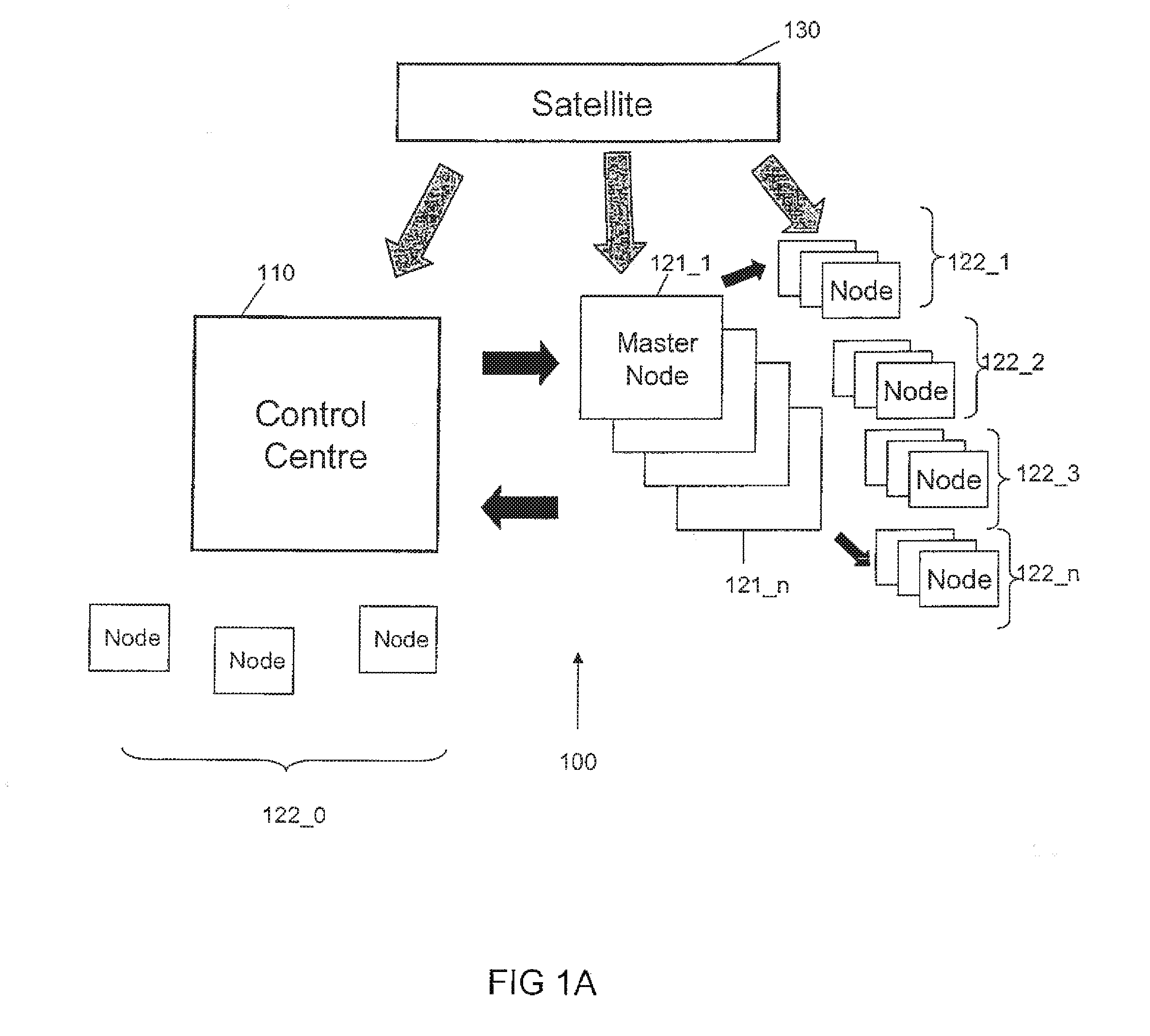
Method of Synchronising Nodes of a Network, and System and Device Therefor
ActiveUS20100245172A1Provide scalabilityImprove accuracyDirection finders using radio wavesTime-division multiplexSynchronization networksRanking
A method of and a system for synchronising a plurality of spaced apart nodes of a network to a reference time of a control centre, the method comprising receiving measurement data from each of the plurality of nodes; ranking the plurality of nodes with respect to one another according to the measurement data; selecting one or more master nodes from the plurality of nodes according to the ranking; assigning each of the plurality of nodes to a corresponding master node; determining a first time offset between the local time measured at each node and the local time measured at its corresponding master node and determining a second time offset between each of the master nodes and the reference time such that the time offset between the local time measured at each node and the reference time can be determined.
Owner:THALES ALENIA SPACE ITAL SPA
Verifiable and adjustable full synchronous communication network, and implementation method thereof
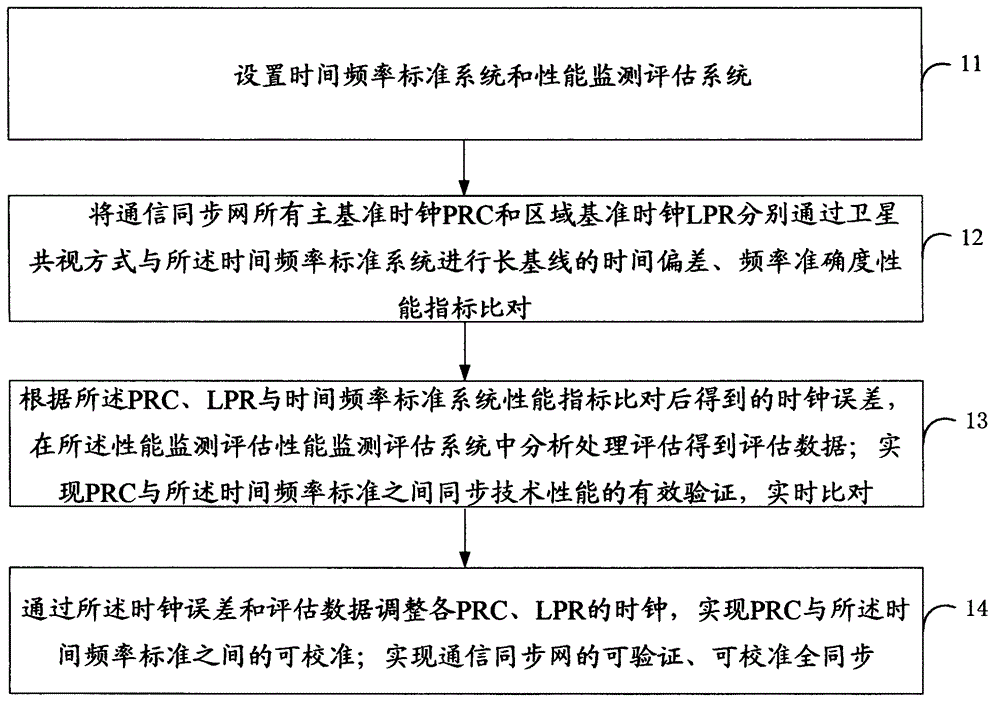
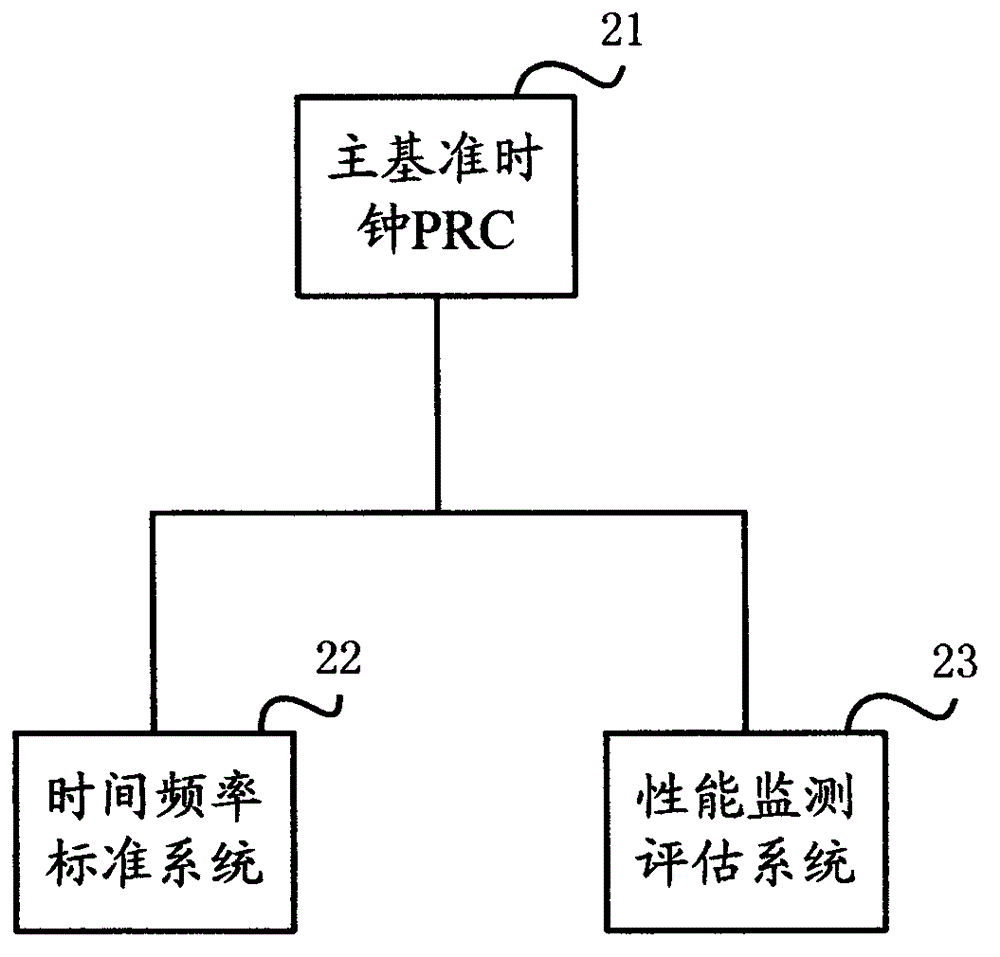
InactiveCN105991205AFully synchronizedAchieving Trusted VerificationTime-division multiplexData switching networksSynchronization networksFrequency standard
The invention discloses a verifiable and adjustable full synchronous communication network, and an implementation method thereof. The implementation method of the verifiable and adjustable full synchronous communication network comprises the steps: setting a time frequency standard system and a performance monitoring and evaluation system; comparing all the PRCs (Primary Reference Clock), LPRs (Local Primary Reference) and the like of the whole network respectively with the time frequency standard system in a common view satellite mode; according to the obtained clock error through common view comparison between the PRCs and LPRs and the time frequency standard system, calculating, processing and evaluating the technical performance in the performance monitoring and evaluation system; and adjusting the clock of each PRC and each LPR through the clock error so as to realize full synchronization of the communication synchronization network. The implementation method of the verifiable and adjustable full synchronous communication network belongs to a communication synchronization network full synchronizing method based on satellite common view, can establish a high accuracy time frequency measuring system, a synchronization performance evaluation system and a synchronous calibration system, can realize trusted verification and calibration of the synchronization performance quality, and can realize full synchronous operation of the full synchronous communication network based on the above capabilities.
Owner:于天泽
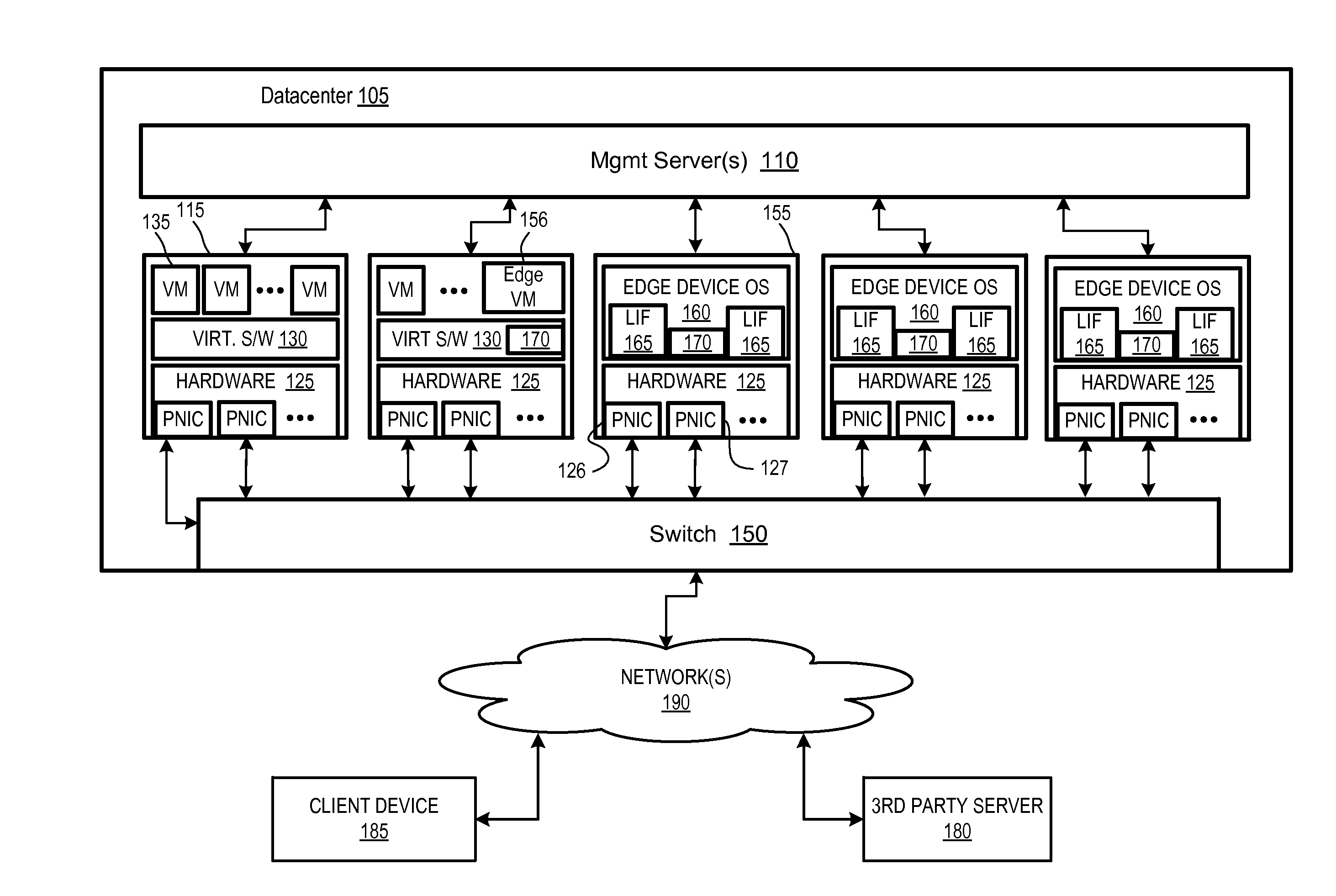
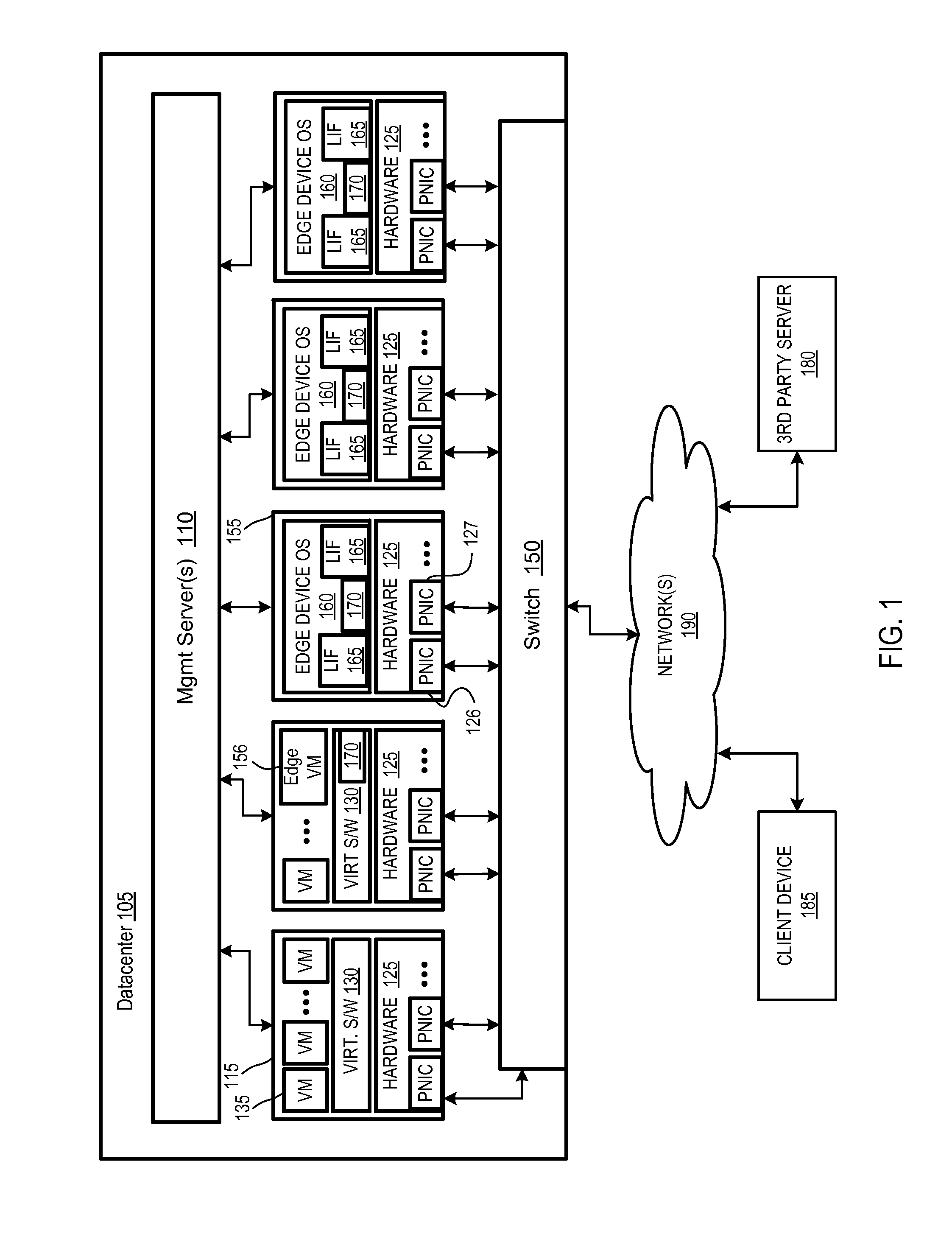
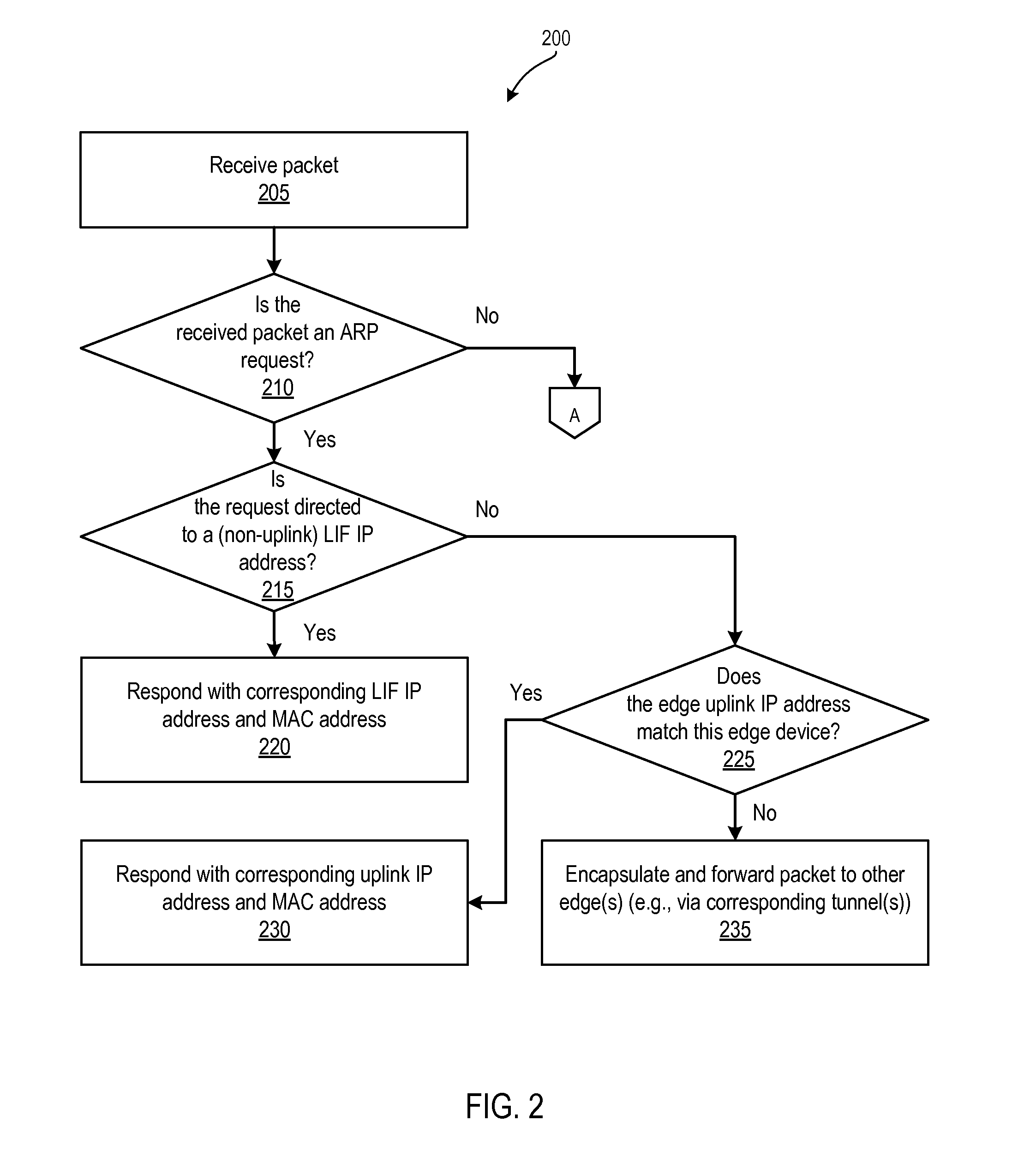
Managing link aggregation traffic in edge nodes
Exemplary methods, apparatuses, and systems include a first network edge device configuring a physical network interface to be included within a link aggregation group (LAG). The physical network interface of a second network edge device is also included within the LAG. The first network edge device receives, via the LAG, a first address resolution packet including a source and a destination. The first network edge device determines that the destination of the address resolution packet is a networking address assigned to a logical interface that is unique to the second network edge device. In response, first network edge device transmits the address resolution packet from a synchronization network interface to a synchronization network interface of the second network edge device. The synchronization network interface of each network edge device is excluded from sharing a LAG with network edge device ports of the other network edge device.
Owner:NICIRA
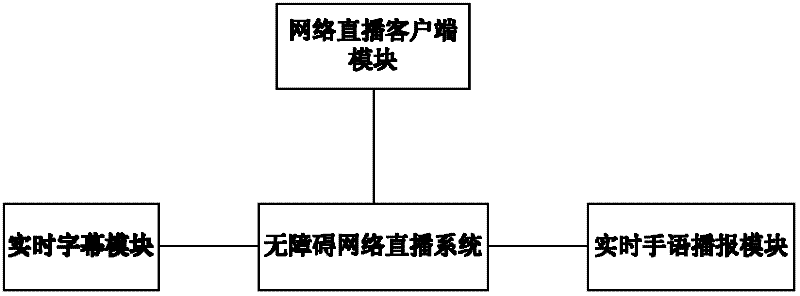
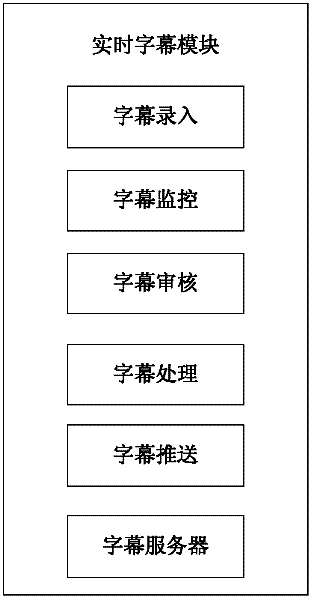
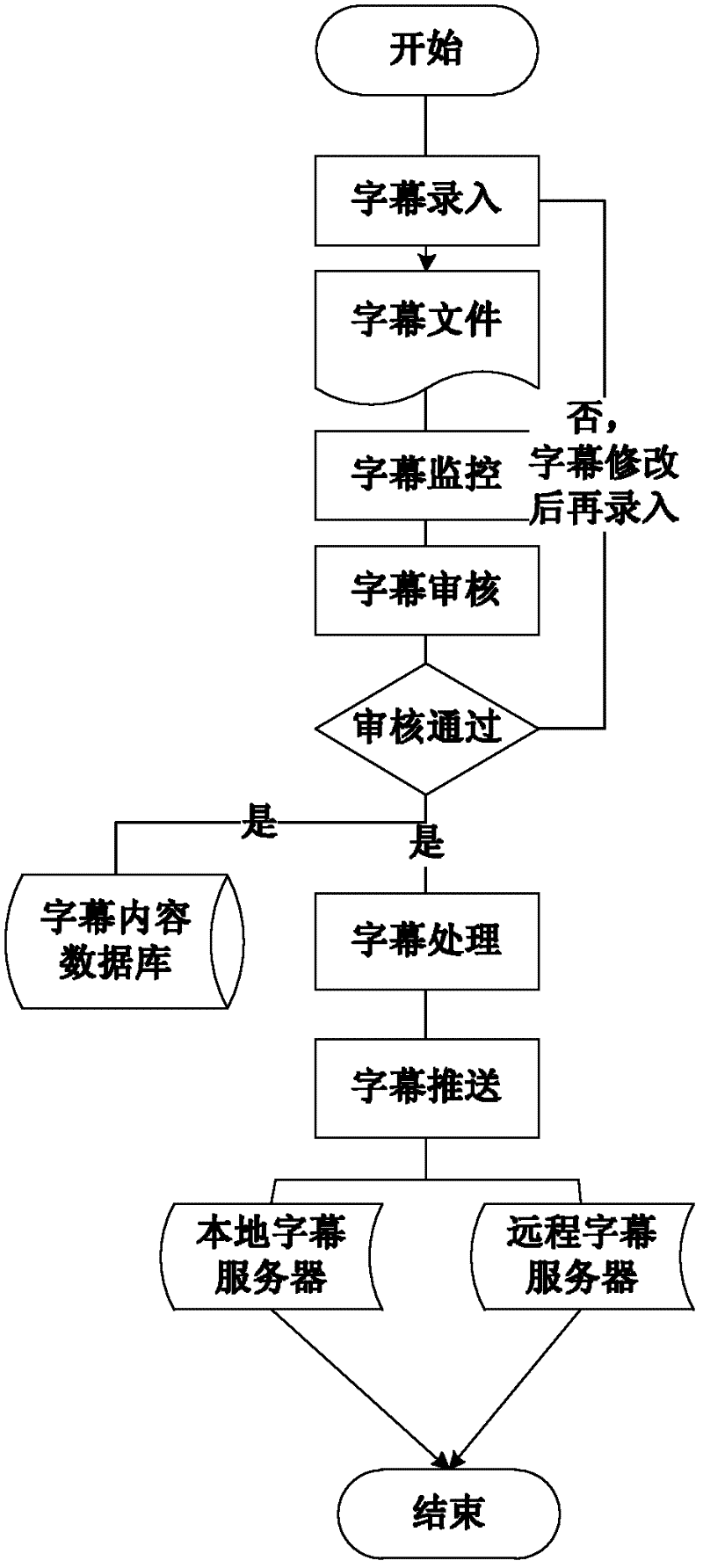
Method and system for adding real-time subtitle and sign language services to live program based on P2P (Peer-to-Peer) network
InactiveCN102655606AReal-timeAchieve accuracySelective content distributionTelecommunicationsSynchronization networks
The invention provides a method and system for adding real-time subtitle and sign language services to a live program based on a P2P (Peer-to-Peer) network. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: 1) making corresponding real-time subtitles according to a television direct transmission or field of the live program; 2) making the corresponding real-time sign language according to the television direct transmission or field of the live program; and 3) respectively synchronizing the subtitle and the sign language with the network live program, and playing. The system is used for realizing the method to the network live programs, and comprises a real-time subtitle module for generating the real-time subtitle for a live video program, a real-time sign language module for generating a real-time sign language for the live video program, and a network live client module for directly broadcasting a network program, synchronizing a network live program with the real-time subtitle, and synchronizing the network live program and a real-time sign language video.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
System and method of timing and frequency control in TDM/TDMA networks
ActiveUS7263090B2Phase noise specifications for the TCXO can be relaxedBroadcast information characterisationSynchronisation error detectionProgram clock referenceLoop filter
A method and system of synchronizing two nodes of a network uses a demodulated output signal of a time division multiplex (TDM) demodulator to perform frequency and timing synchronization independently. Frequency synchronization is performed without using a program clock reference, by detecting a symbol timing loop error of the TDM demodulator. The error is filtered by an oscillator control loop filter if the error is within a predetermined range. Thus, an output voltage of a digital to analog converter that receives the filtered output controls an oscillator. In the timing synchronizer, an error between a program clock reference (PCR) and a value of a counter in the terminal is computed if the PCR is a not a first PCR, and the error is filtered with a timing loop control filter. A processor then adjusts a value of the counter in the terminal based on the filtered output.
Owner:VIASAT INC
DPLL circuit having holdover function
InactiveUS20070182467A1Suppresses frequency changesPulse automatic controlGenerator stabilizationSynchronization networksComputer science
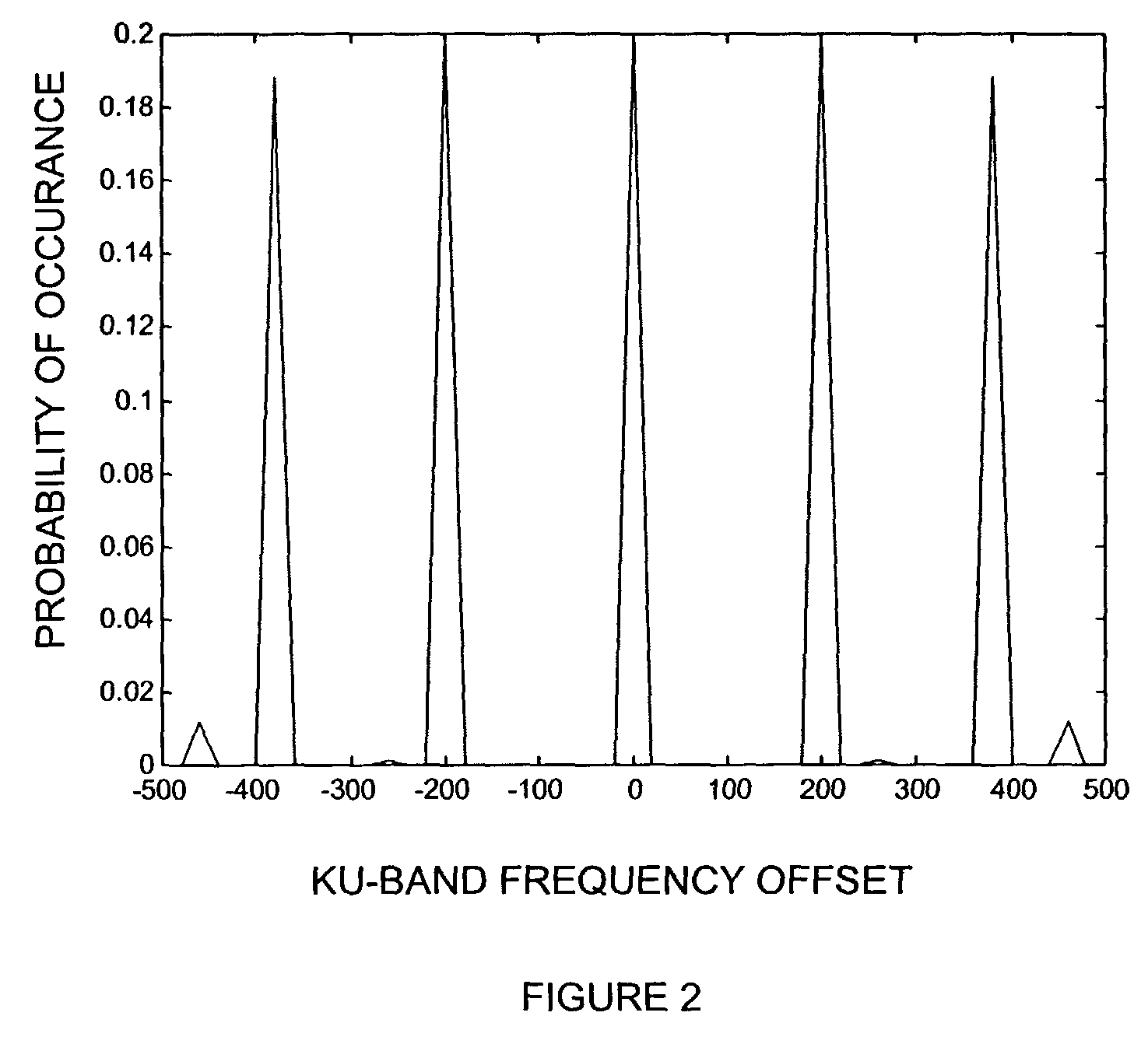
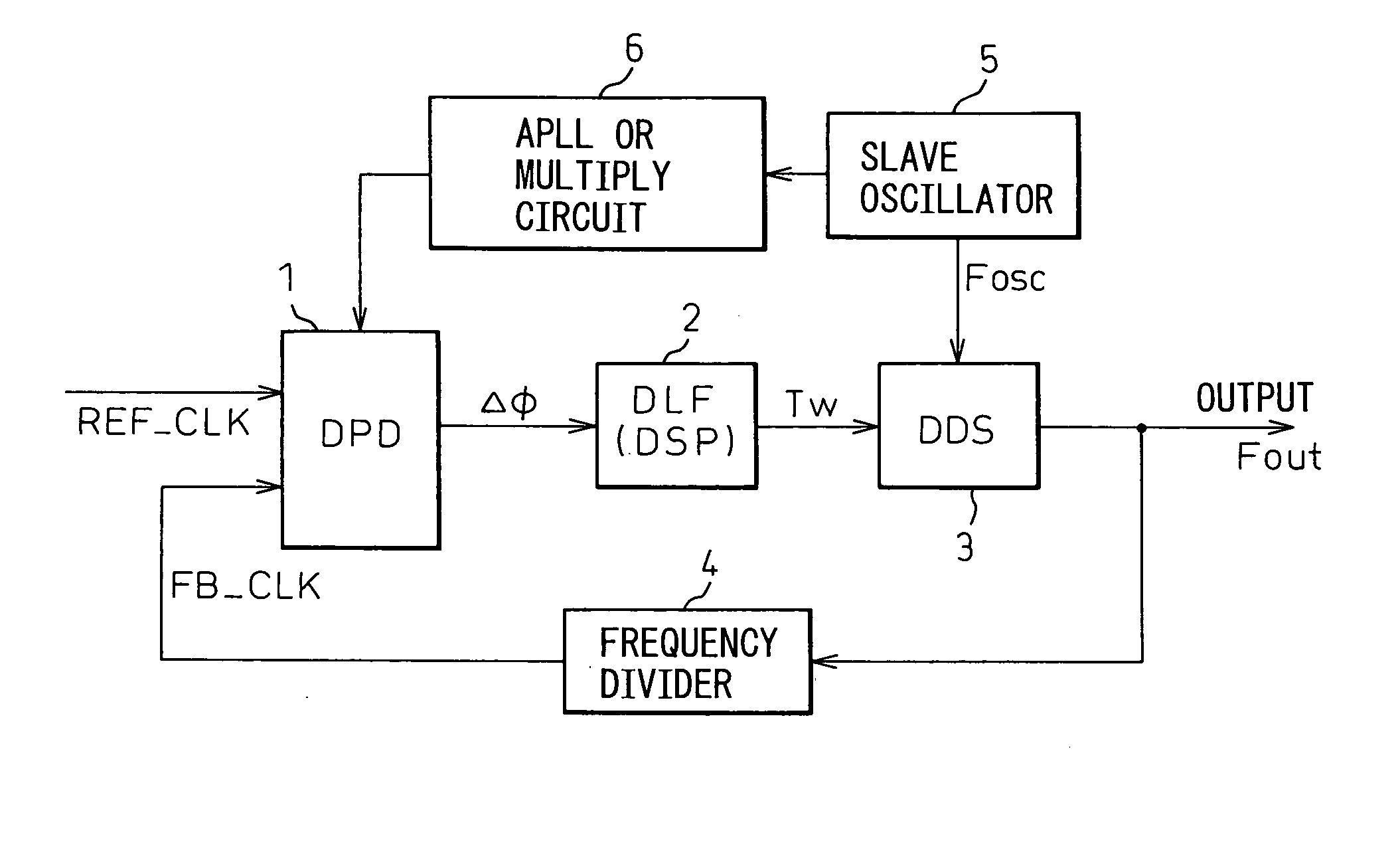
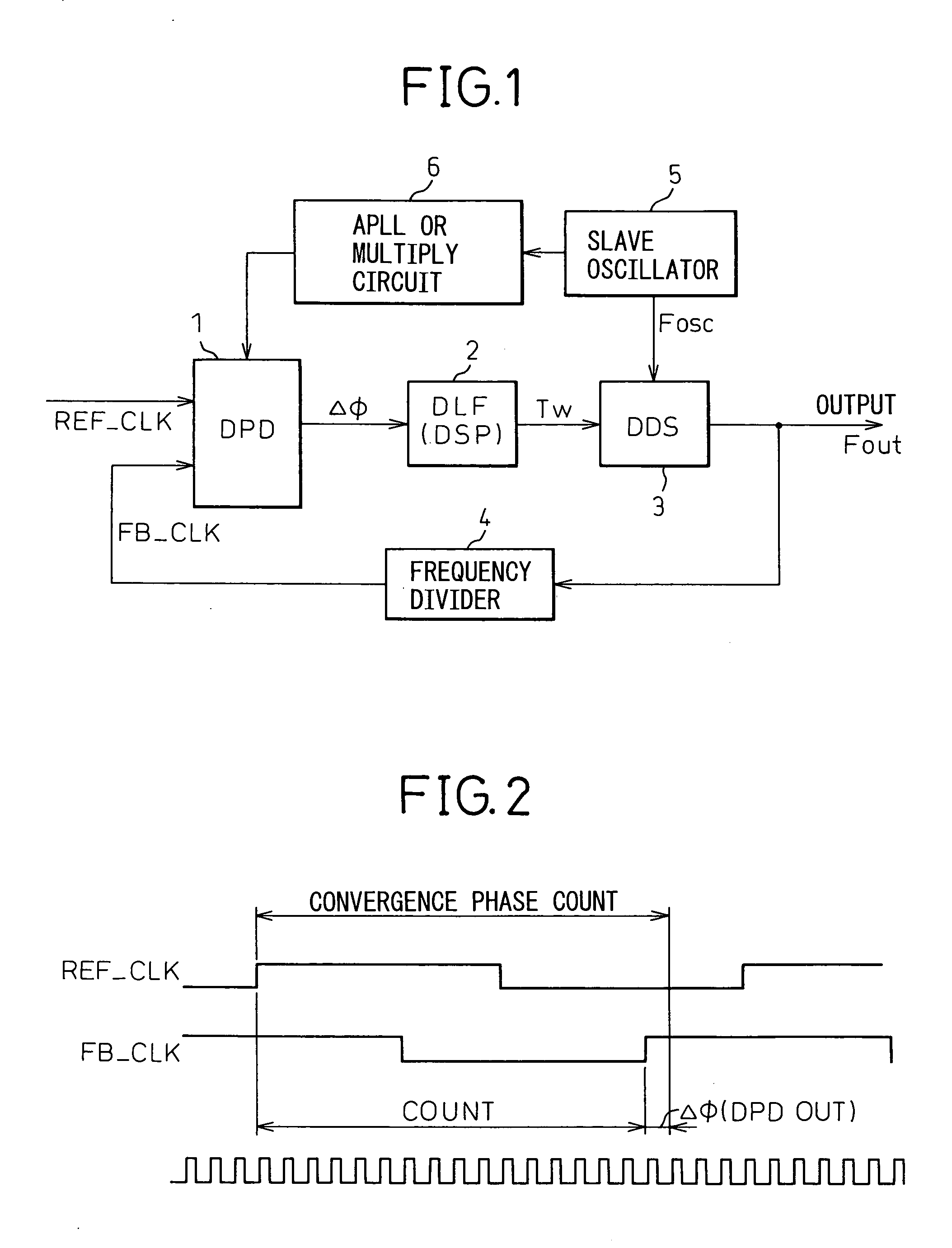
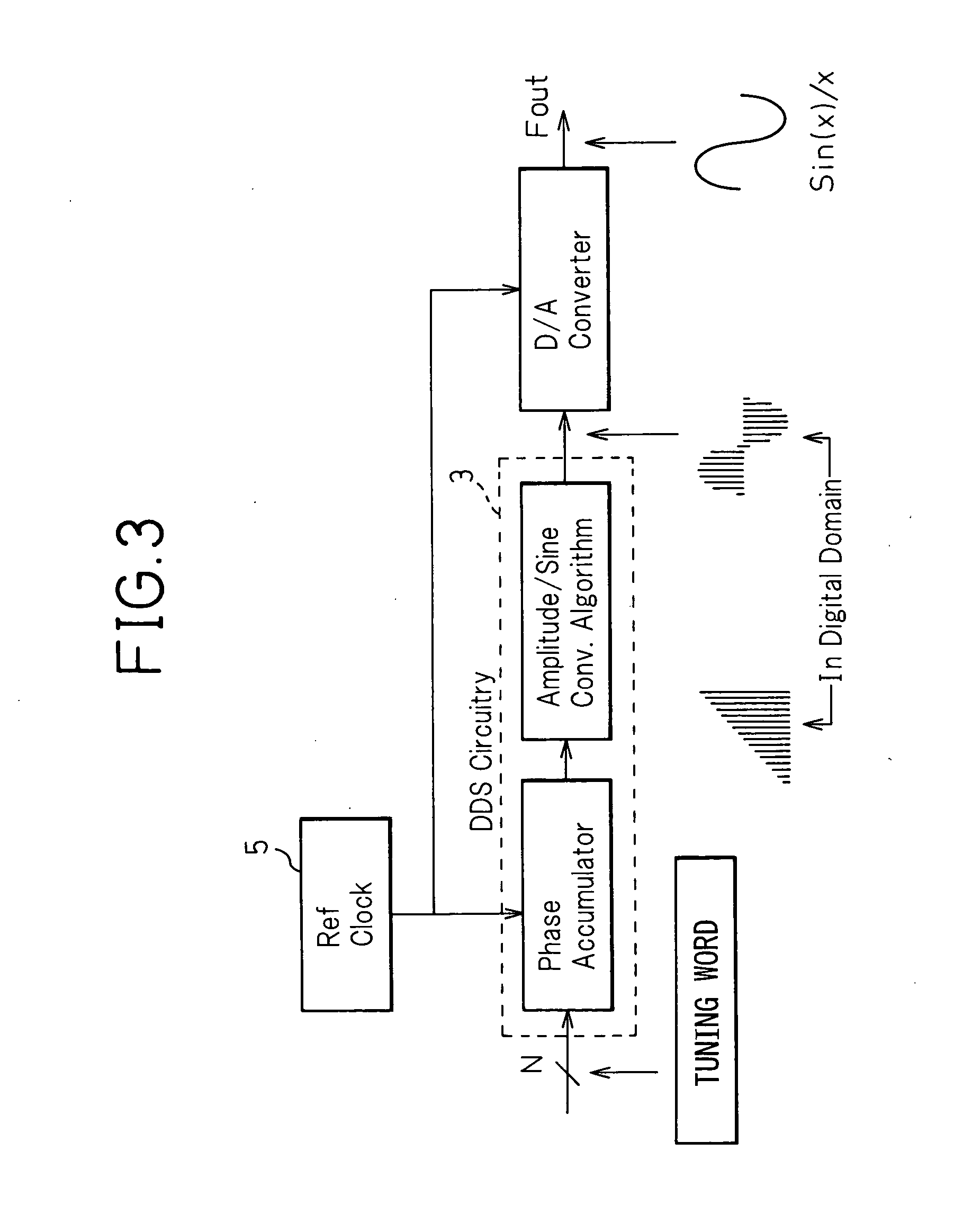
The invention relates to a digital synchronization network, and provides a DPLL circuit having a holdover function that generates a high-precision reference clock with a temperature correction to perform a free-running frequency control at a holdover time. In a holdover mode of the DPLL circuit using a DDS, the DPLL circuit having a holdover function adds a correction value calculated from a temperature characteristic of a slave oscillator to a fixed DDS control value during a detection of a holdover, thereby changing the DDS control value according to the temperature characteristic.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
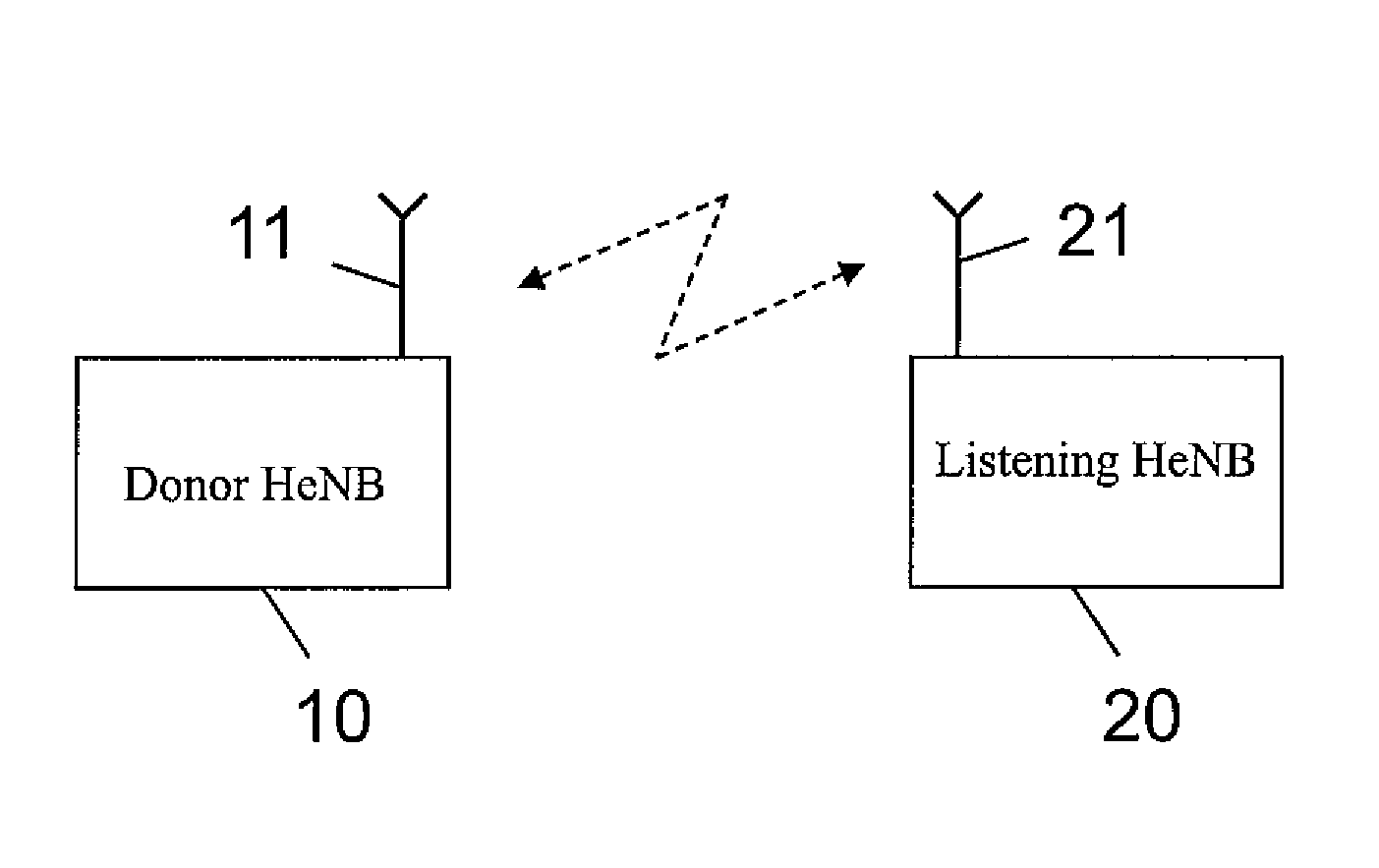
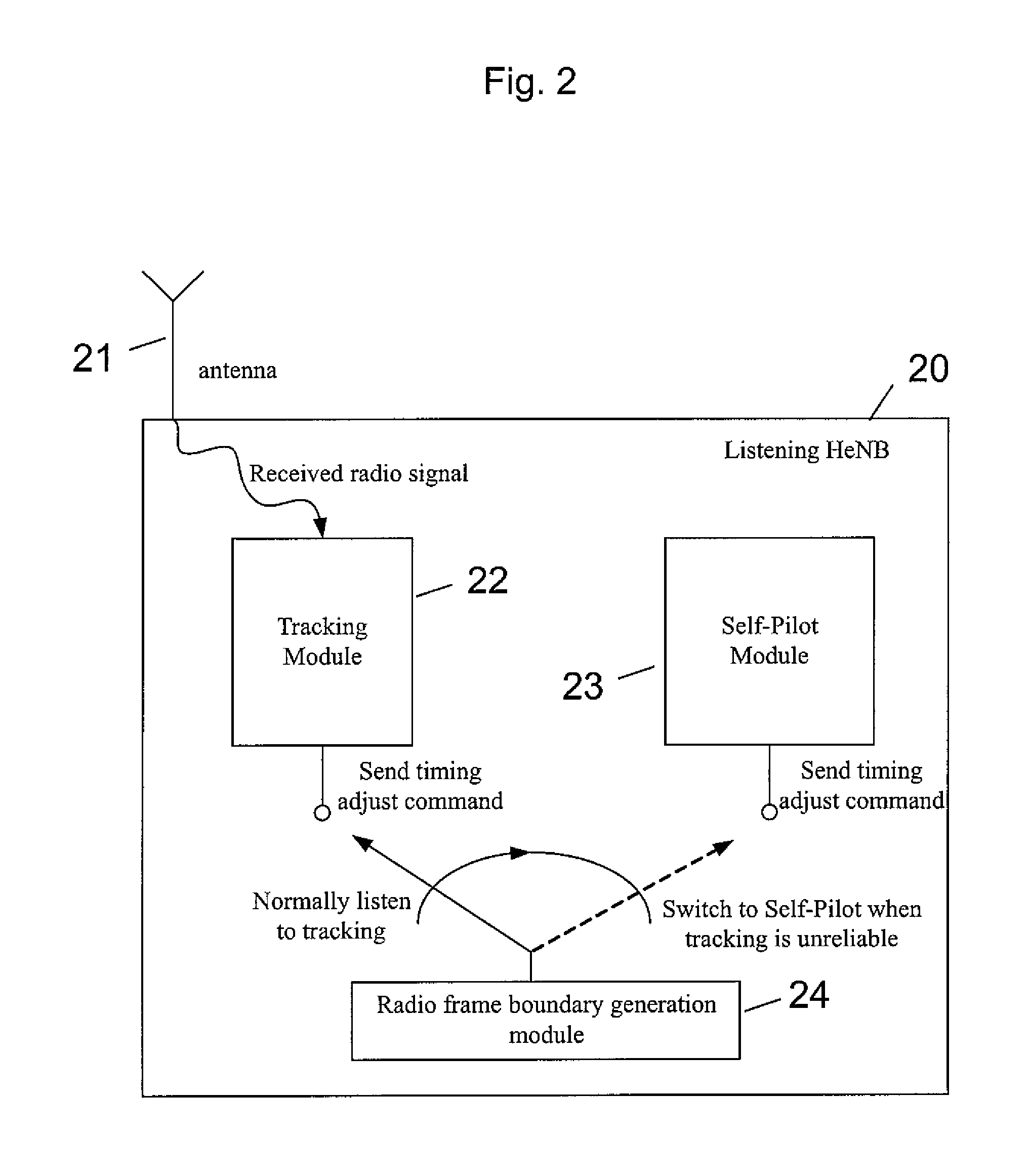
Fast Recovering for Network Listening Schemes in Synchronization Over Air for Small Cells
InactiveUS20150173033A1Promote recoverySynchronisation arrangementOrthogonal multiplexSynchronization networksSmall cell
The present invention provides methods, apparatuses and a program relating to fast recovering for network listening schemes in synchronization over air for small cells. The present invention includes tracking, at a first base station, a reference signal of a second base station, determining, whether the reference signal can be tracked, if it is determined that the reference signal can be tracked, adjusting, at the first base station, a system clock of the first base station based on the reference signal of the second base station, and estimating and storing parameters relating to a frequency difference between the system clock of the first base station and a system clock of the second base station, and if it is determined that the reference signal cannot be reliably tracked, adjusting the system clock of the first base station based on the stored parameters.
Owner:NOKIA SOLUTIONS & NETWORKS OY
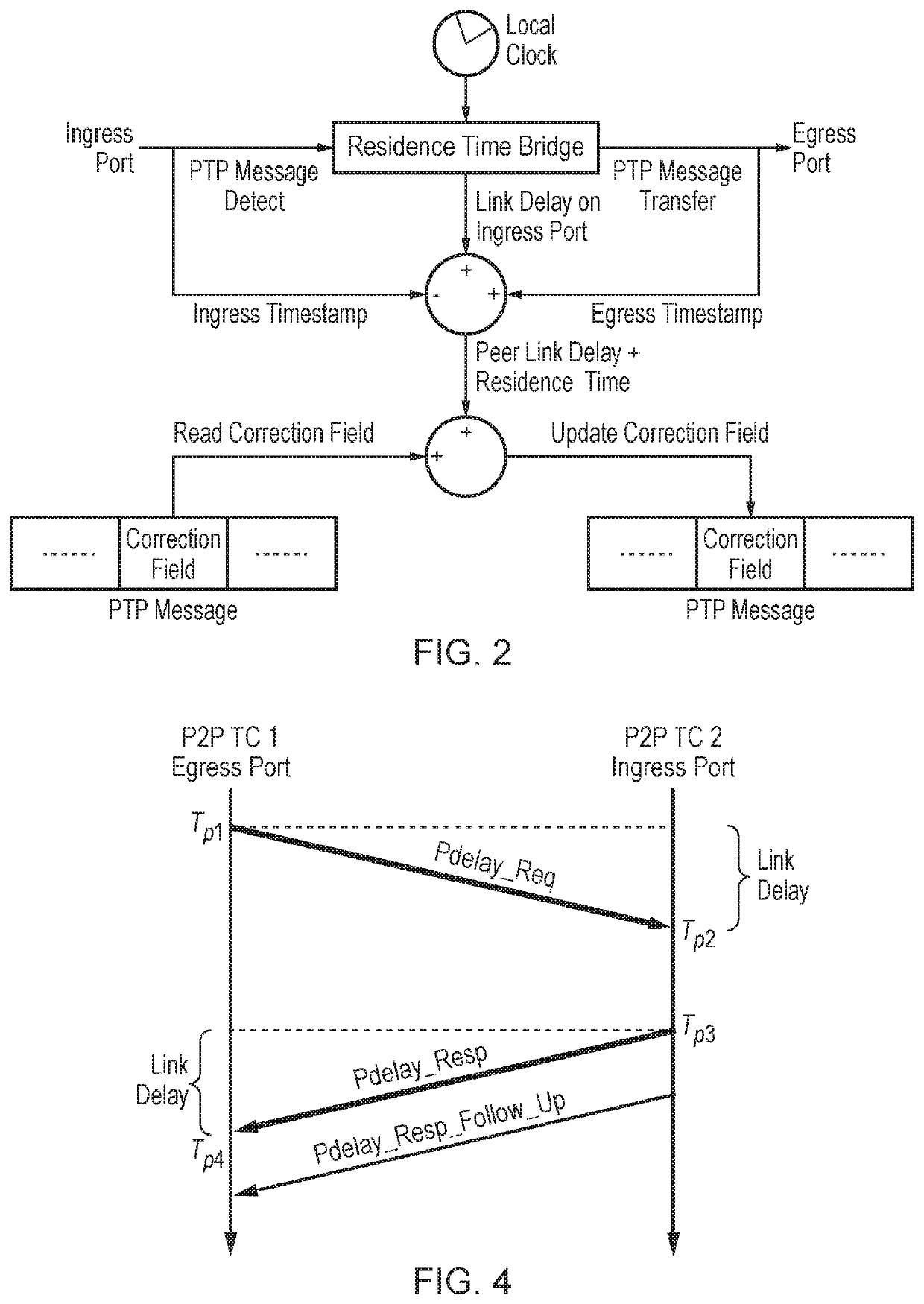
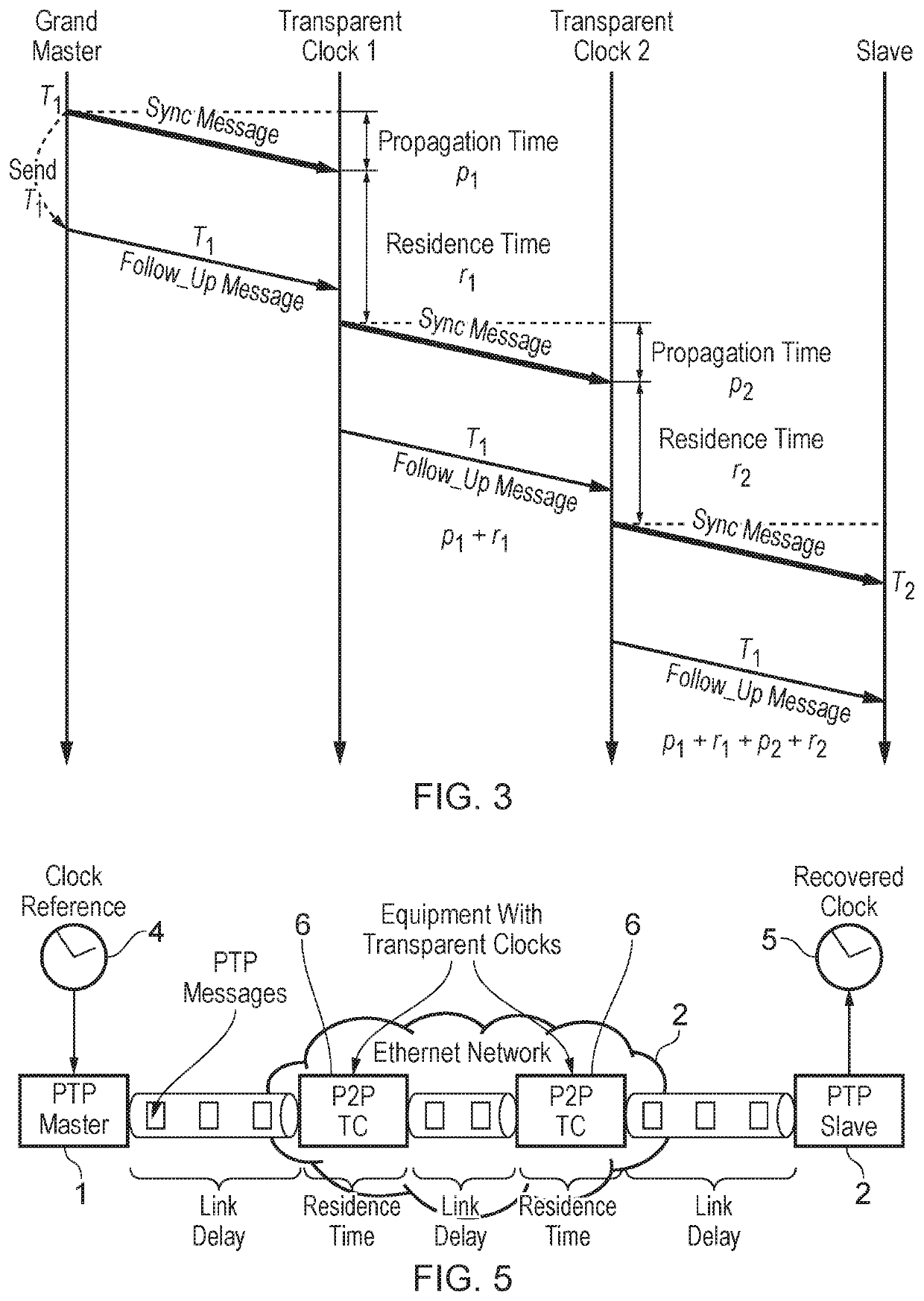
Peer-to-peer transparent clocks and methods of estimating skew in peer-to-peer transparent clocks
This invention relates to peer-to-peer transparent clocks and methods of estimating skew in peer-to-peer transparent clocks. Embodiments of the invention relate to techniques for estimating clock skew between a free-running clock in a transparent clock and a master clock, in particular by using the timing information embedded in timing messages passing through the transparent clock. Further embodiments of the invention set out uses of these estimates to modify the residence times computed by the transparent clock and a synchronization network including such transparent clocks.
Owner:BRITISH TELECOMM PLC +2
Unified network architecture for scalable super-calculus systems
ActiveUS20130239121A1Reduce latencyReduce trafficInterprogram communicationDigital computer detailsSupercomputerSynchronization networks
A network architecture is used for the communication between elementary calculus units or nodes of a supercomputer to execute a super-calculus processing application, partitionable and scalable at the level of calculus power in the range of PetaFLOPS. The supercomputer comprises a plurality of modular structures, each of which comprises a plurality of elementary calculus units or nodes defined by node cards, a backplane, a root card, and a node communication network of the switched fabric fat tree type; ii) a synchronization architecture comprising a plurality of distinct node communication networks, configured for the communication of specific synchronization information different from network to network and with different characteristics; iii) a re-configurable Programmable Network Processor that implements the nodes both of the n-toroidal network and those of the synchronization networks.The node communication networks of the n-toroidal type and of the switched fabric fat tree type can be used alternately or simultaneously for the transmission between the calculus nodes of the same type of data and information also in a configuration of system partitions in order to achieve the desired interconnection topology of the nodes.
Owner:EUROTECH
Tdoa based positioning with calculation of correction factors for compensating the clock offsets of unsynchronized network stations
InactiveUS20130137452A1Synchronisation error detectionPosition fixationUser deviceSynchronization networks
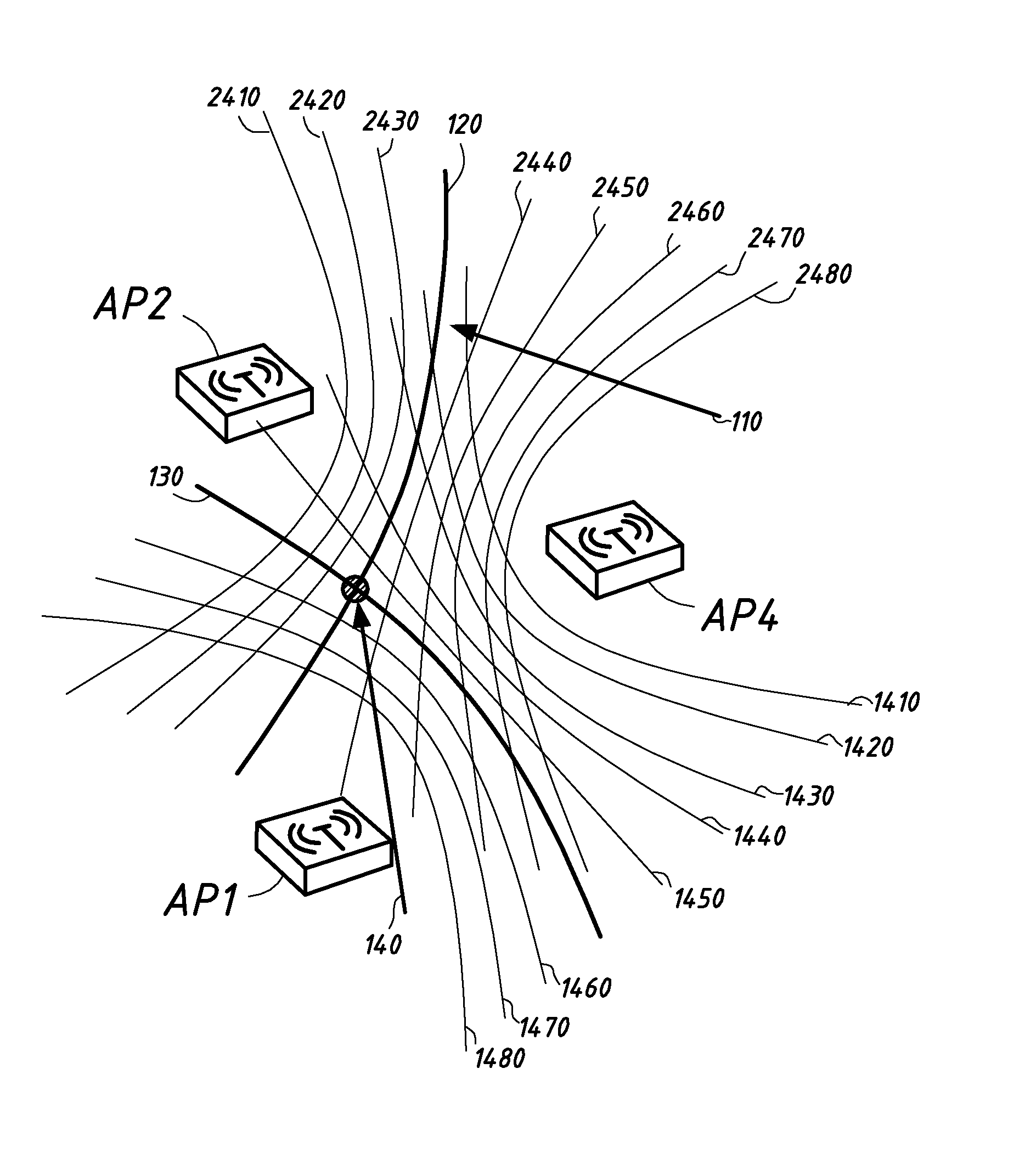
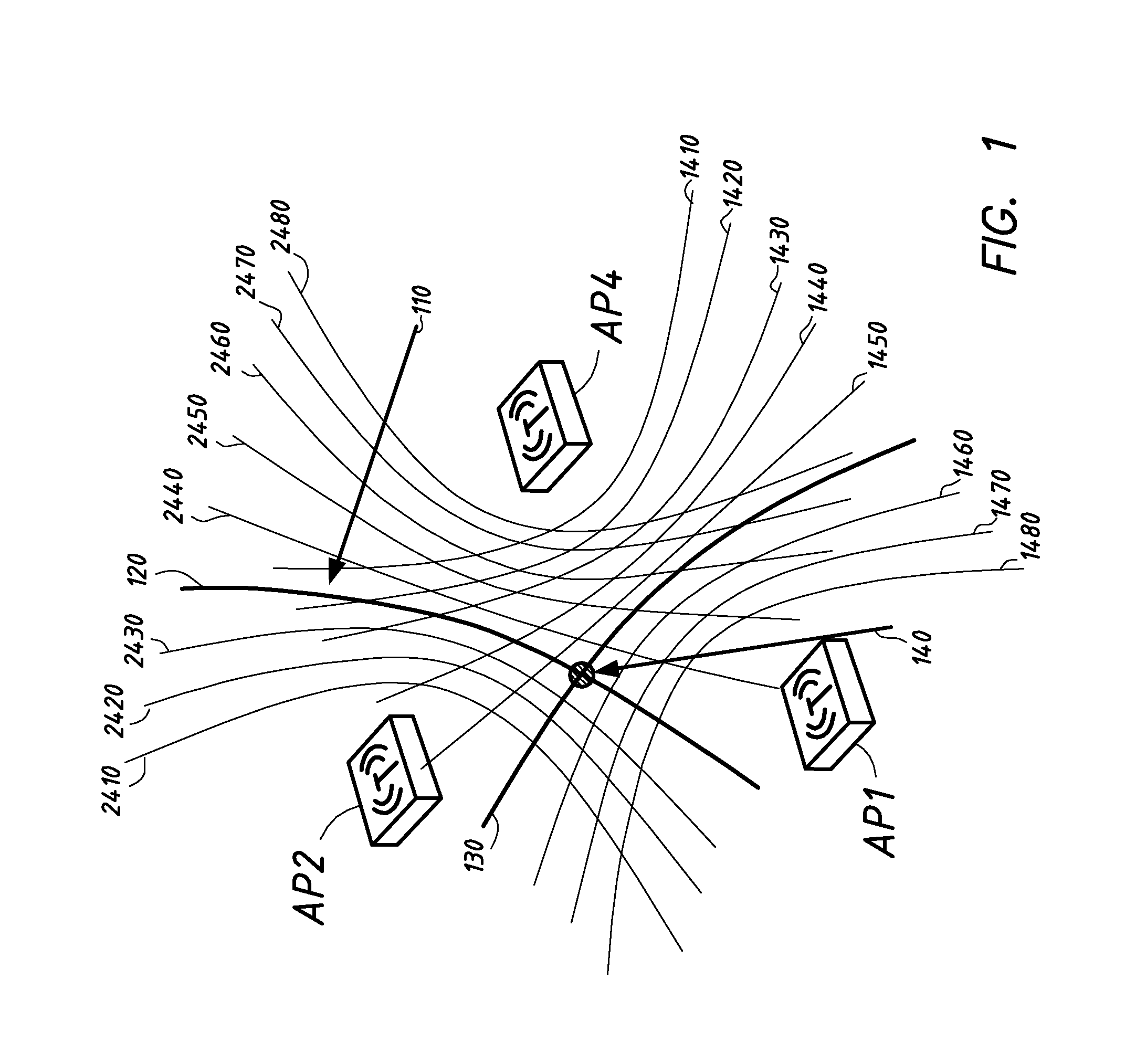
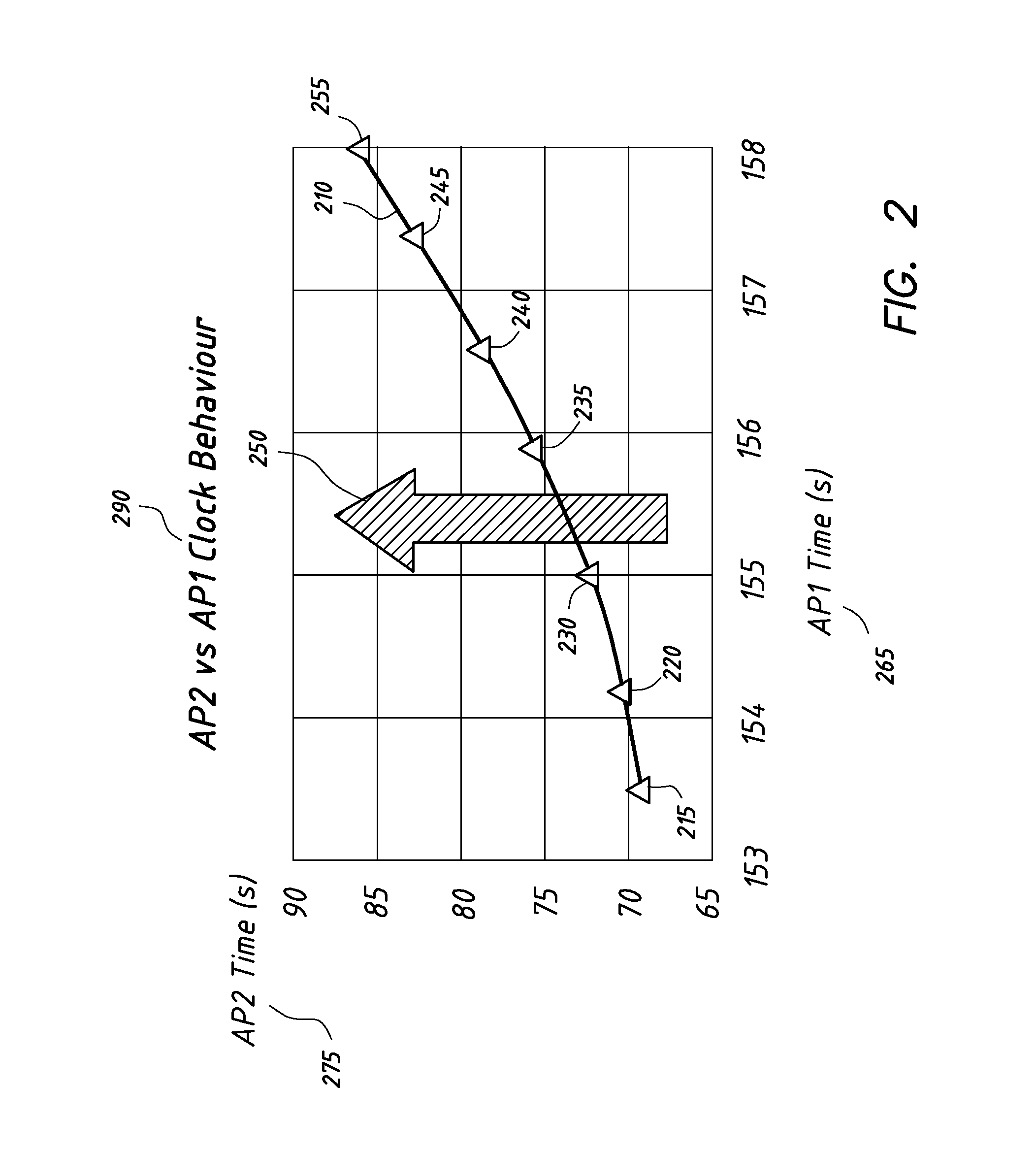
The present invention presents a method, arrangement and computer program product for clocking exploiting the relative behavior of clocks of individual receiving stations as well as a corresponding modeling to derive a time difference of arrival of a signal from a user device which can be used to correct the time difference of arrival based on the modeled clock behavior and leads to a correct clocking of received user signals without the need of synchronization of the clocks in the various receiving stations. This principle is applicable to a plurality of pairs of receiving stations and beacon signals transmitted amongst them and allows for a correct location estimation of a user device.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
High-speed optical fiber ring network communication network control topology of large-capacity power electronic system
InactiveCN103916187ASmall swingHigh communication rateRing-type electromagnetic networksFibre transmissionElectronic systemsSynchronization networks
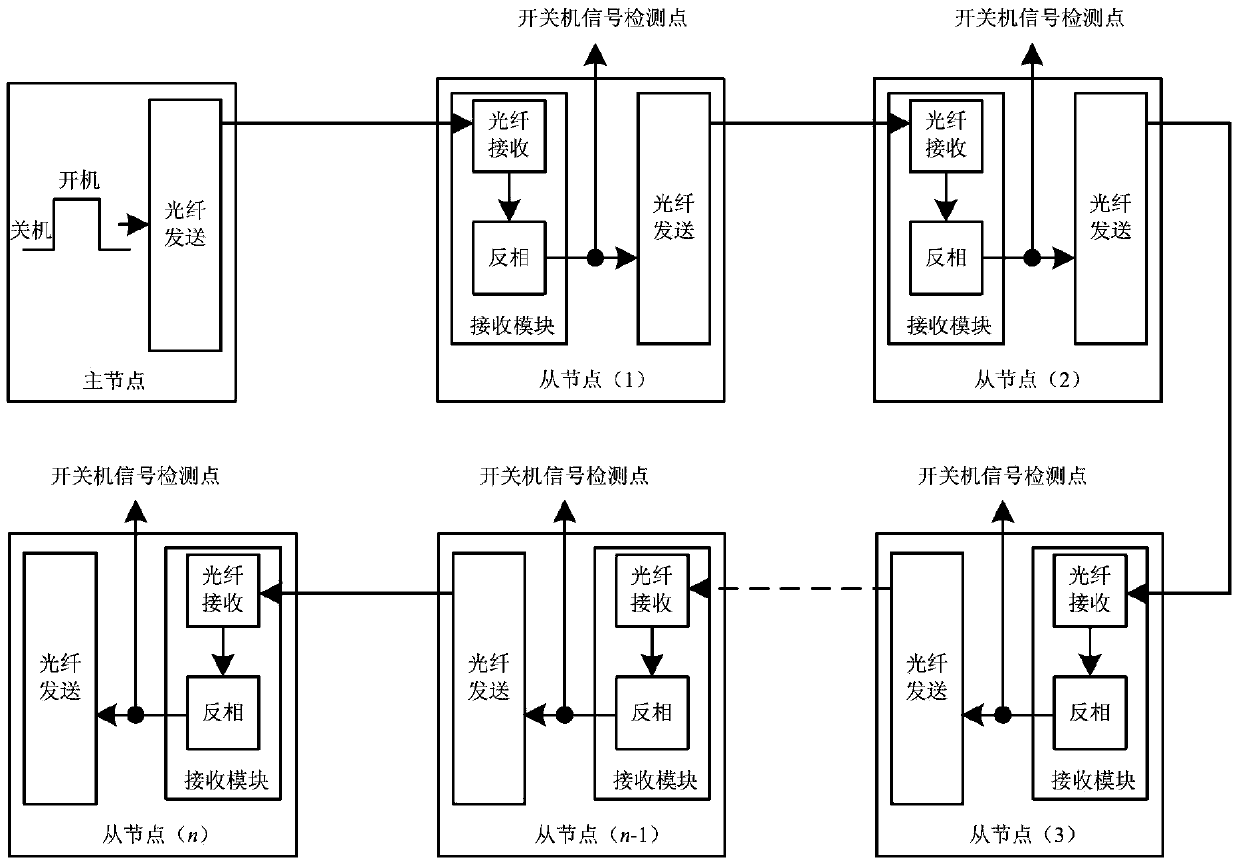
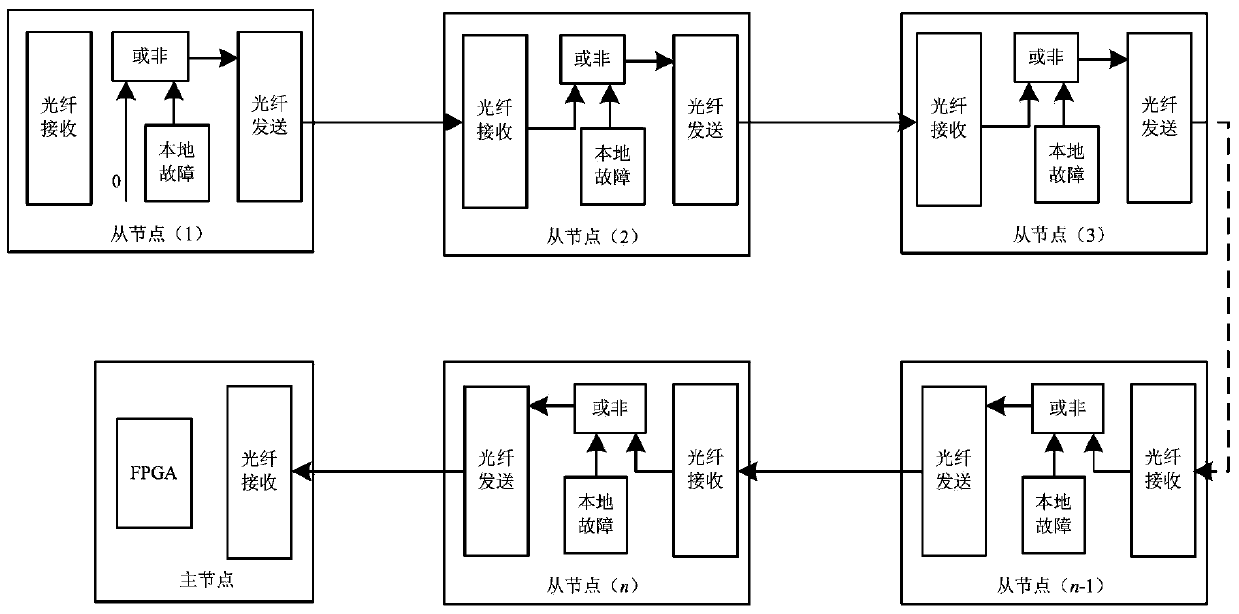
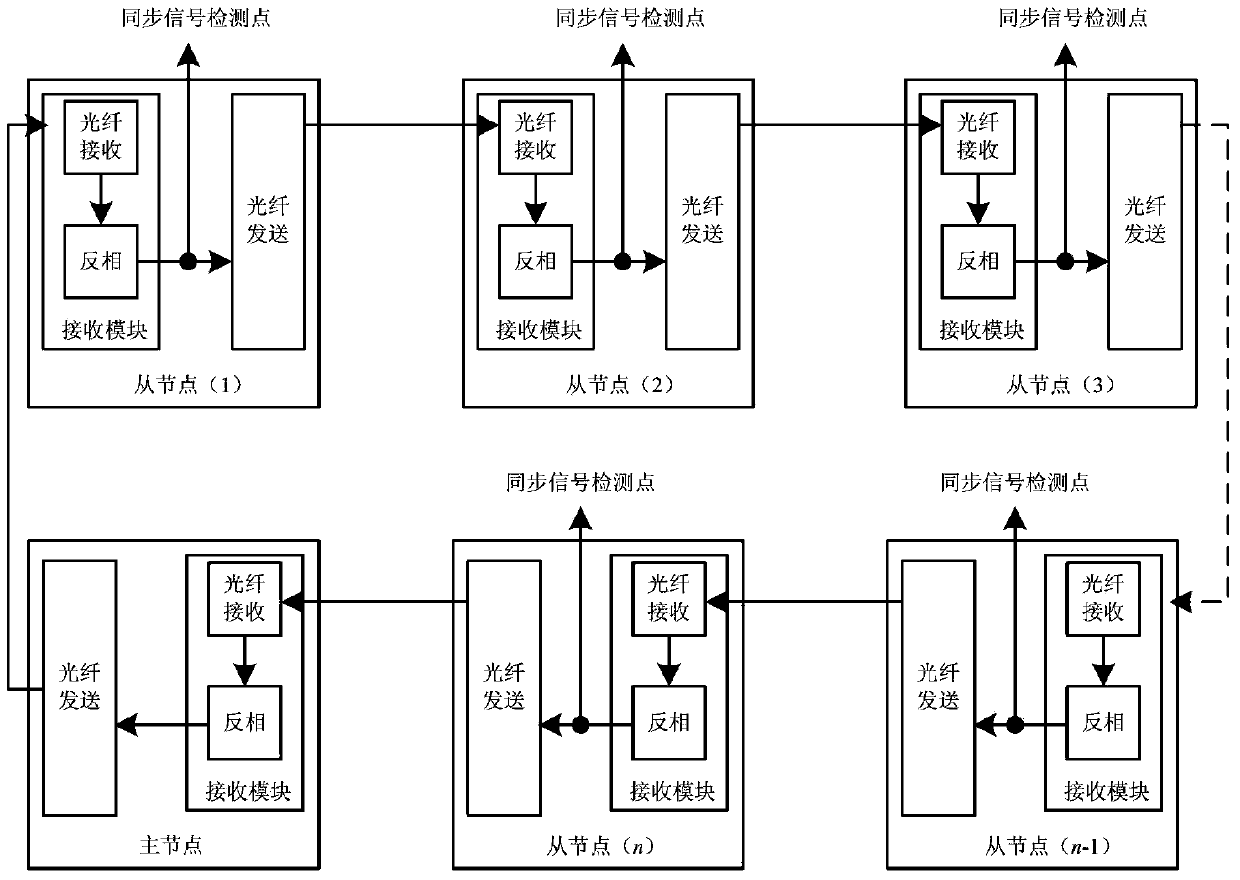
The invention discloses a high-speed optical fiber ring network communication network control topology of a large-capacity power electronic system. The control topology comprises a main node, multiple slave nodes, an on-off machine network, a fault protective network, a synchronization network and a high-speed data communication network. The control topology is high in communication speed, simple in structure, good in synchronization effect, high in distributed modularization and high in reliability.
Owner:NAVAL UNIV OF ENG PLA
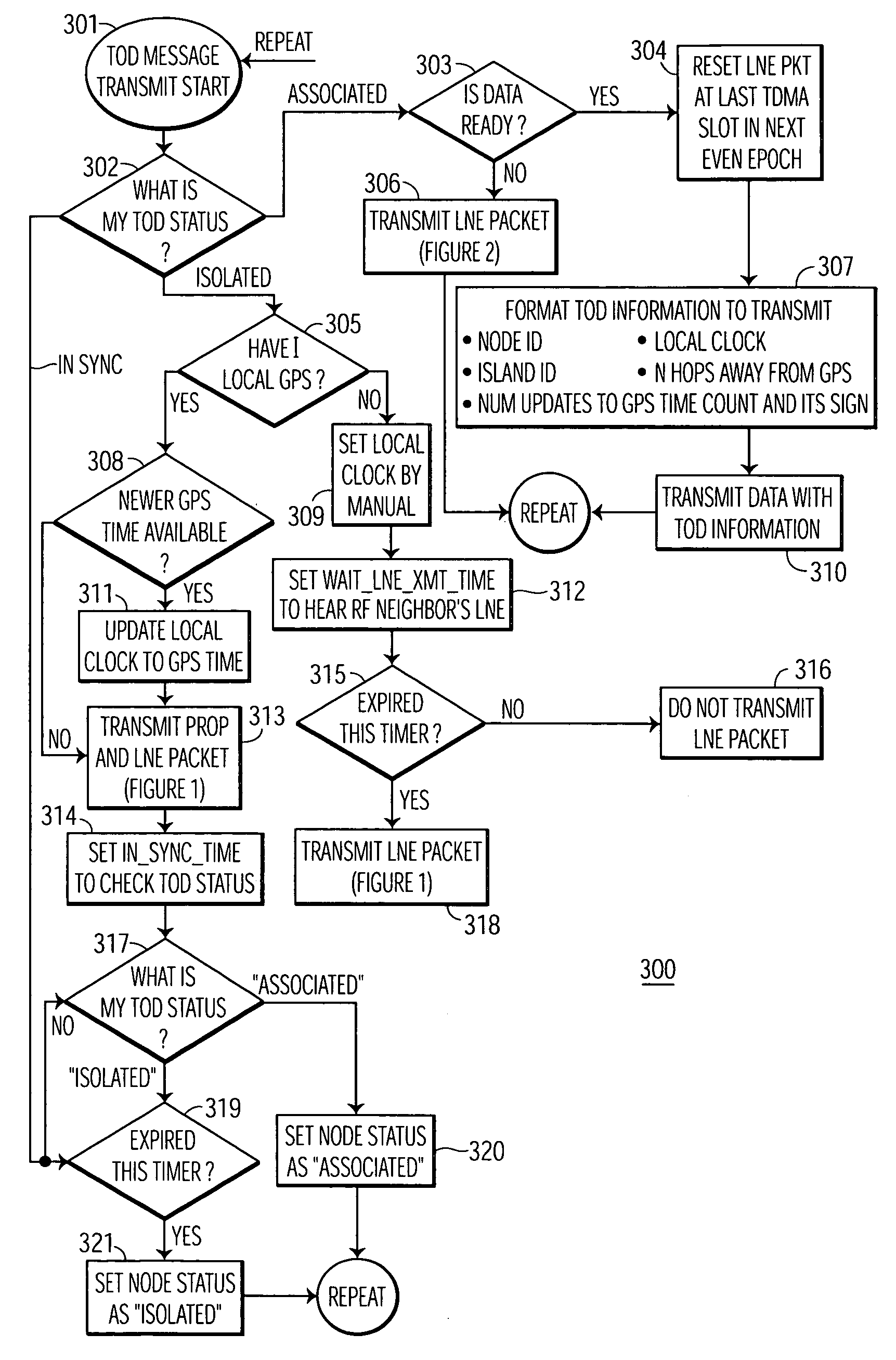
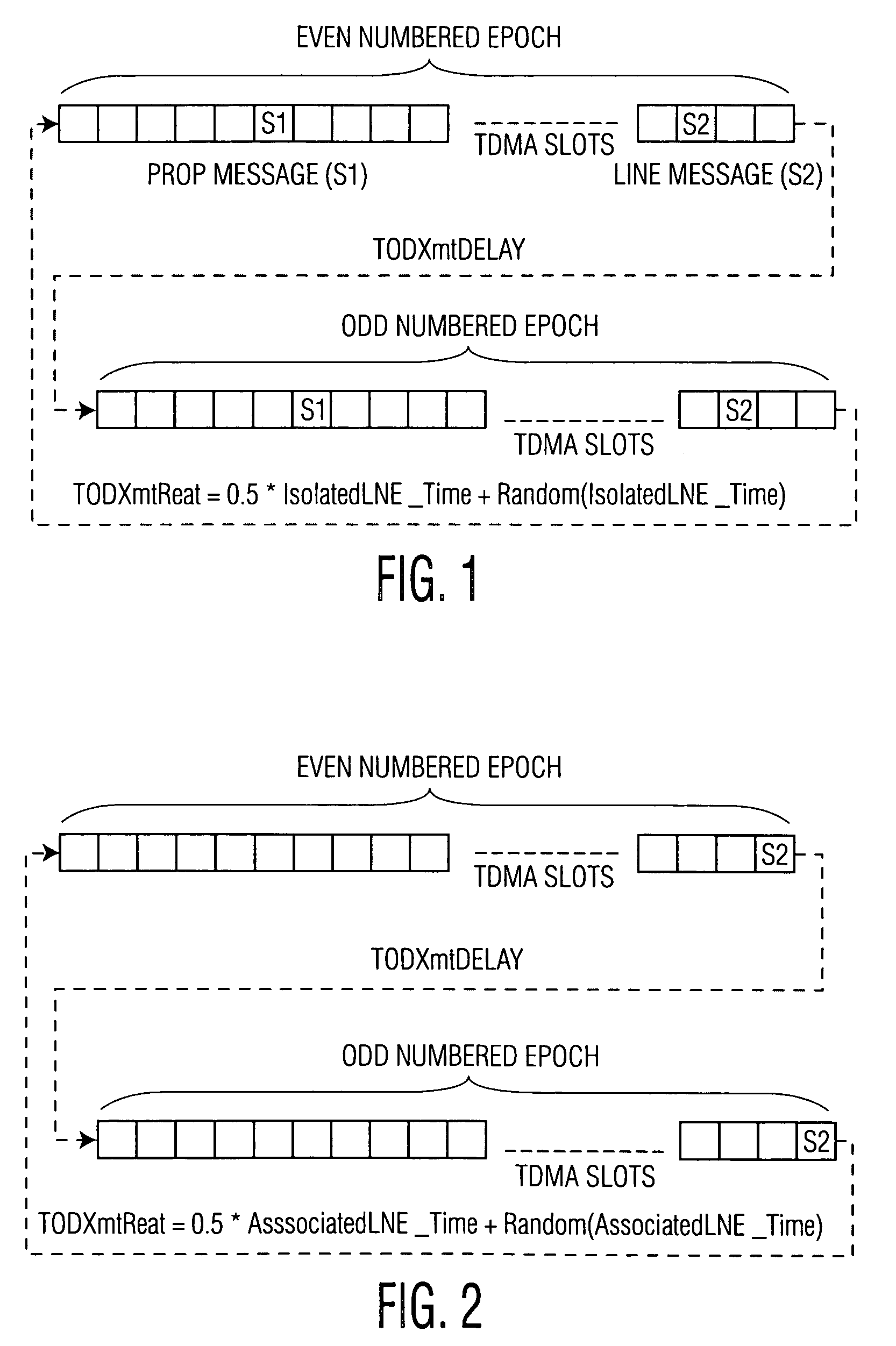
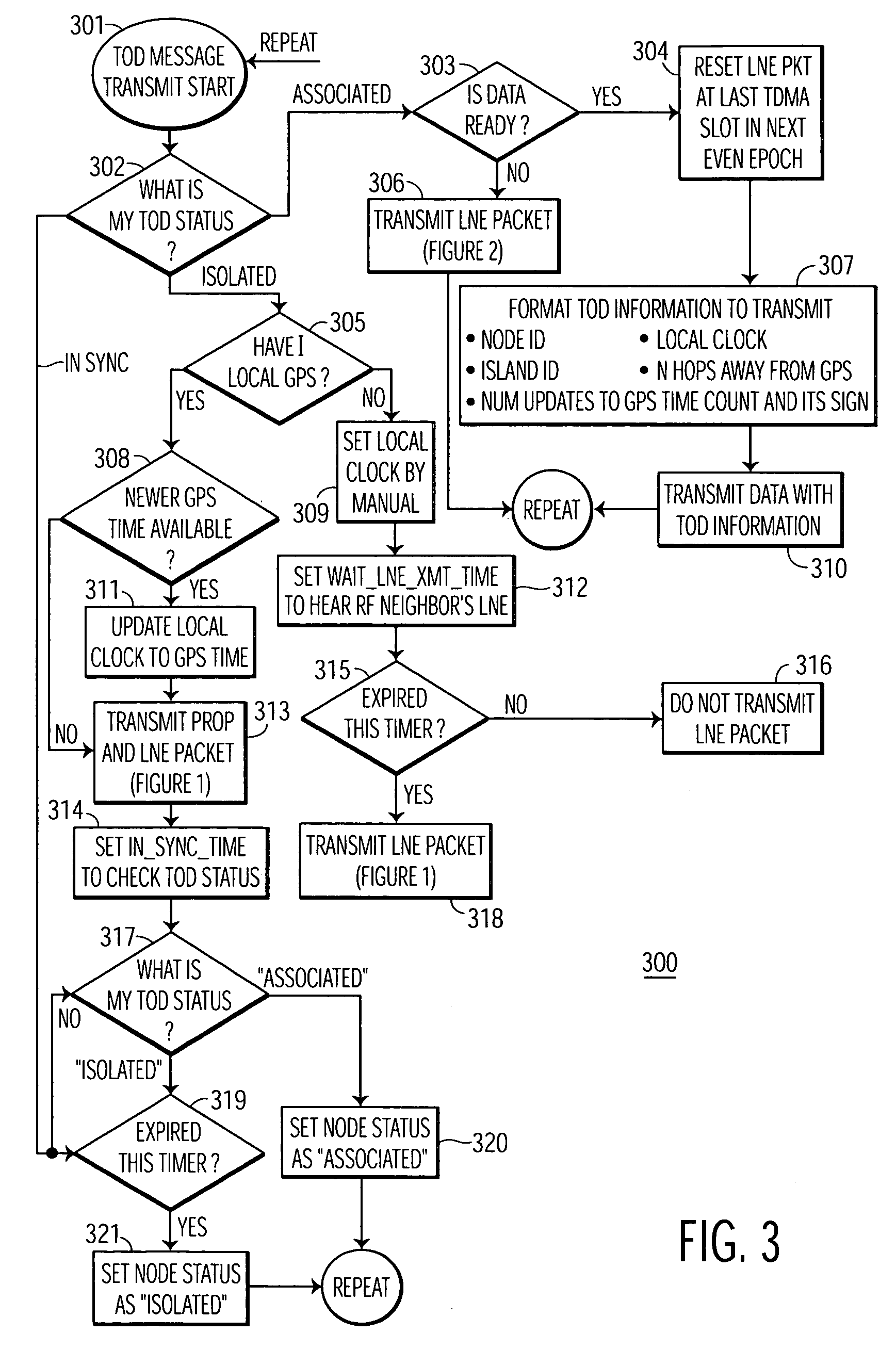
Apparatus and method of flywheel time-of-day (TOD) synchronization
ActiveUS7304981B2Synchronisation arrangementTime-division multiplexSynchronization networksTime management
A wireless communications network including multiple nodes, and a local node having GPS-based time for synchronization of time-of-day (TOD) in the network. The network includes at least the local node and a neighbor node communicating in the network. The local node includes a clock generator for generating a local TOD, and a time management unit, coupled to the clock generator, for adjusting the local TOD. A receiver in the local node receives from the neighbor node a message including a neighbor TOD. A counter in the local node computes and provides an integer value corresponding to a number of update values for synchronization of the neighbor TOD to the GPS-based time. A transmitter in the local node transmits to the neighbor node the integer value provided by the counter, whereby the time management unit adjusts the local TOD to the neighbor TOD and then transmits the adjusted local TOD and the integer value to the neighbor node for synchronization of the neighbor TOD to the GPS-based time.
Owner:HARRIS GLOBAL COMM INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com