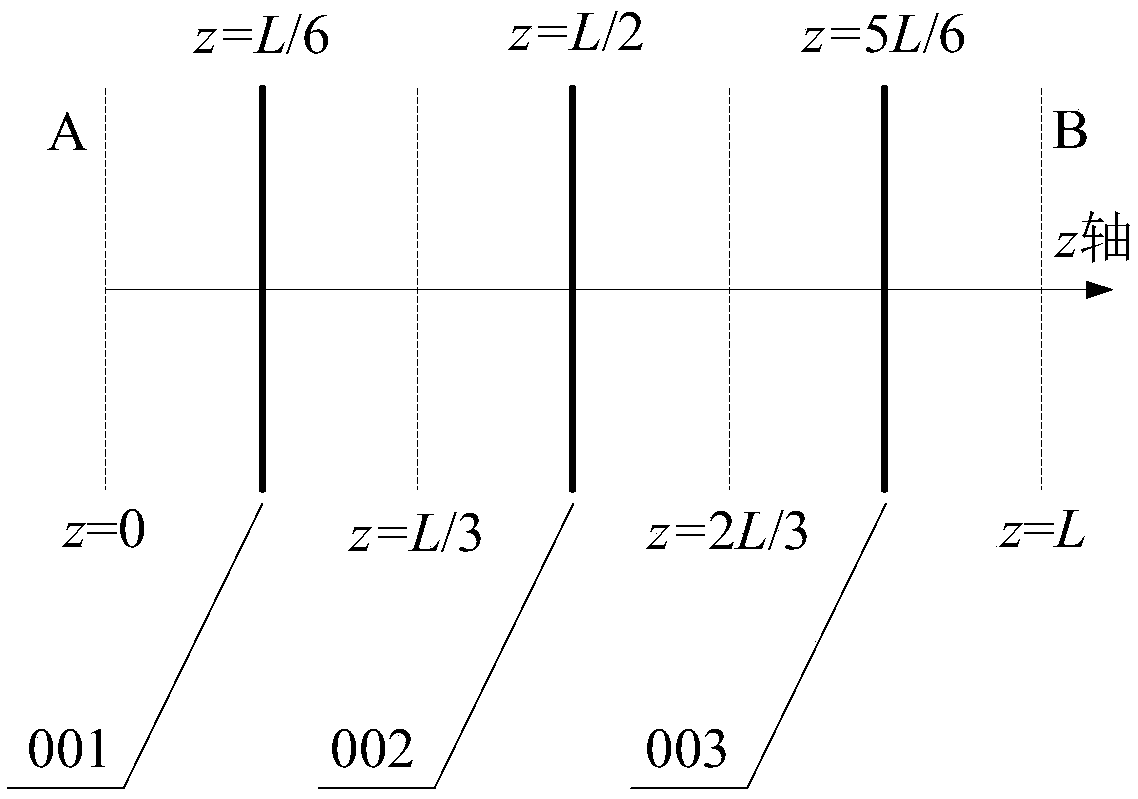Patents
Literature
42 results about "Path profile" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In telecommunication, a path profile is a graphic representation of the physical features of a propagation path in the vertical plane containing both endpoints of the path, showing the surface of the Earth and including trees, buildings, and other features that may obstruct the radio signal.
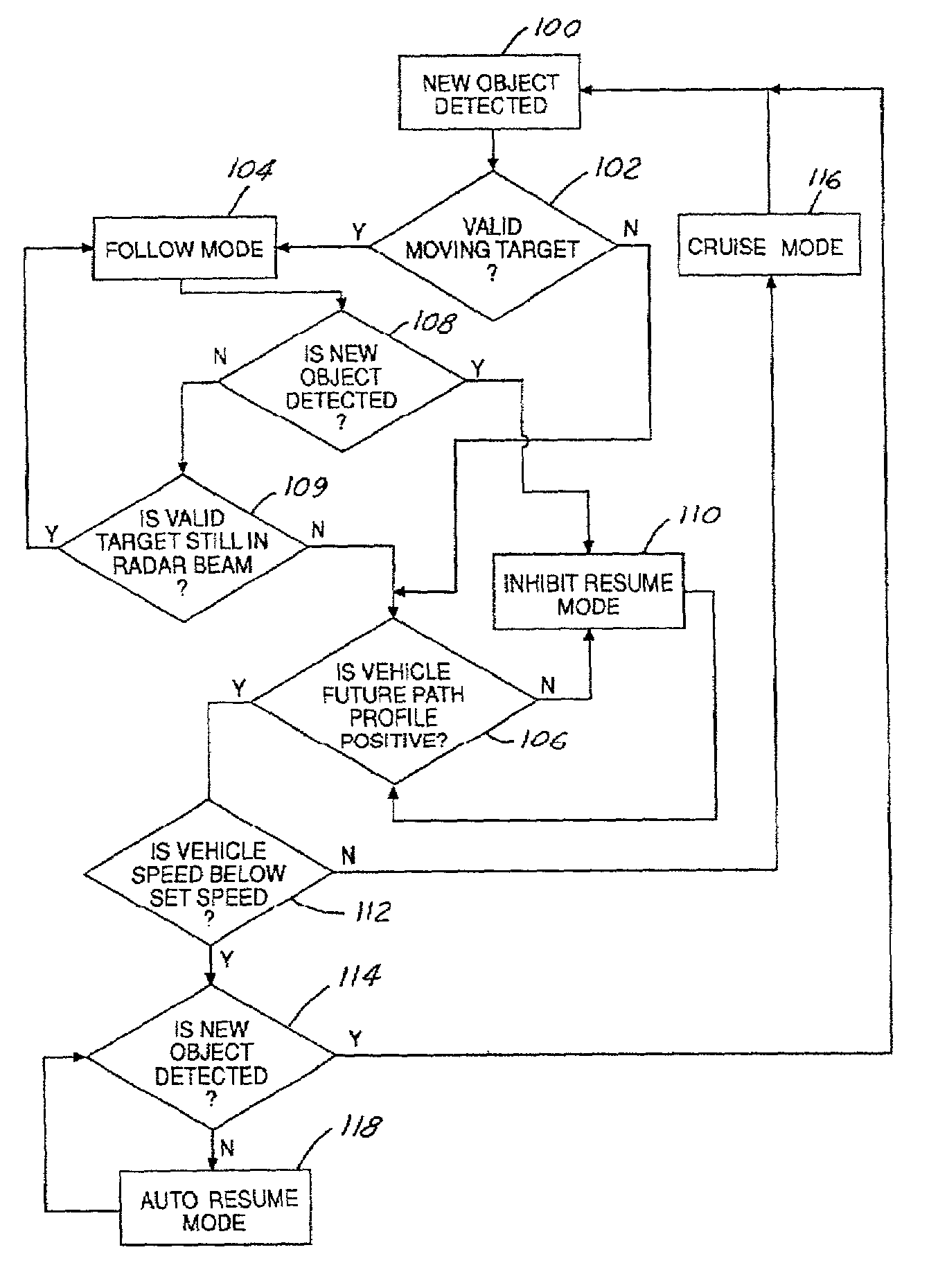
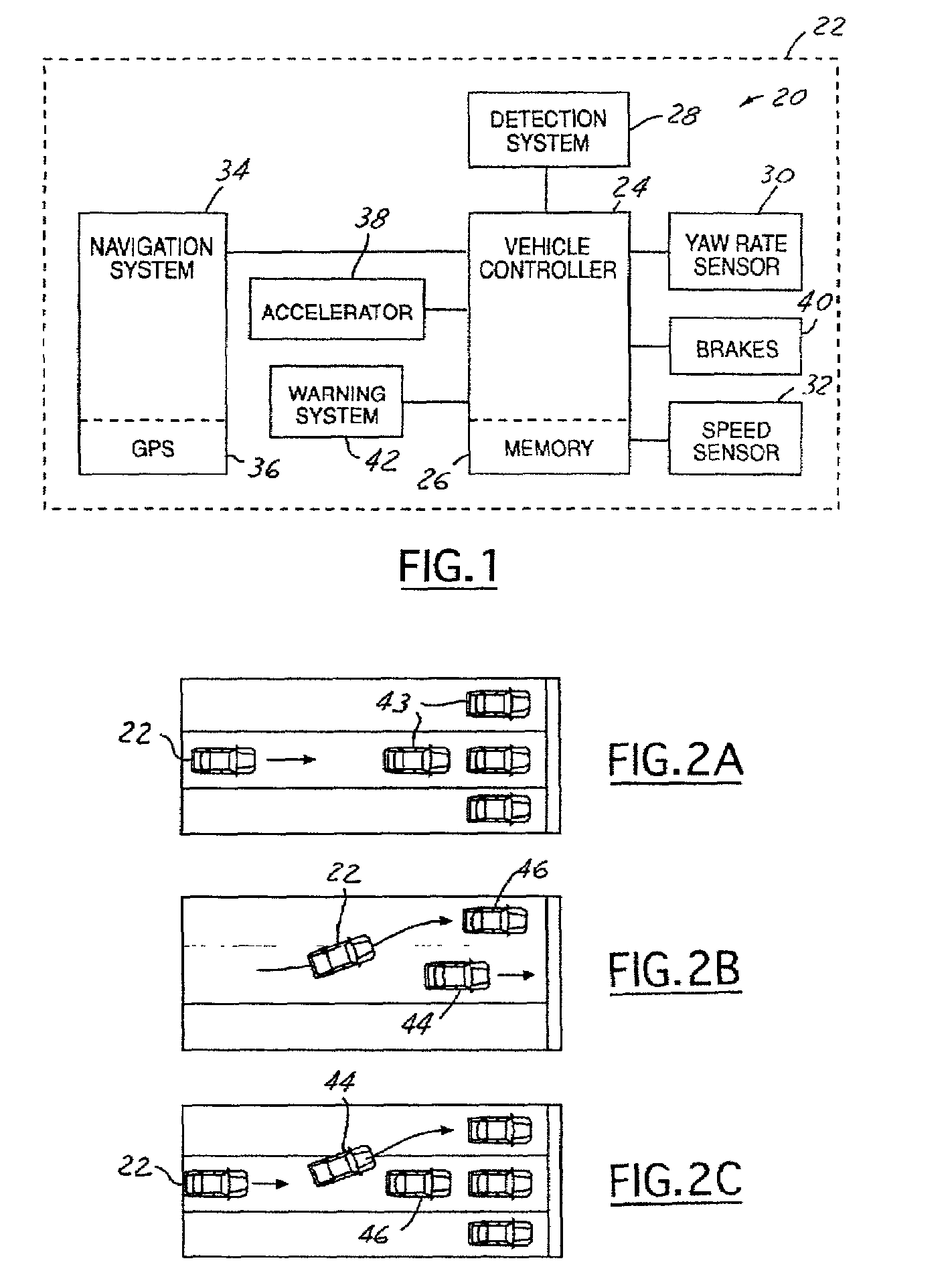
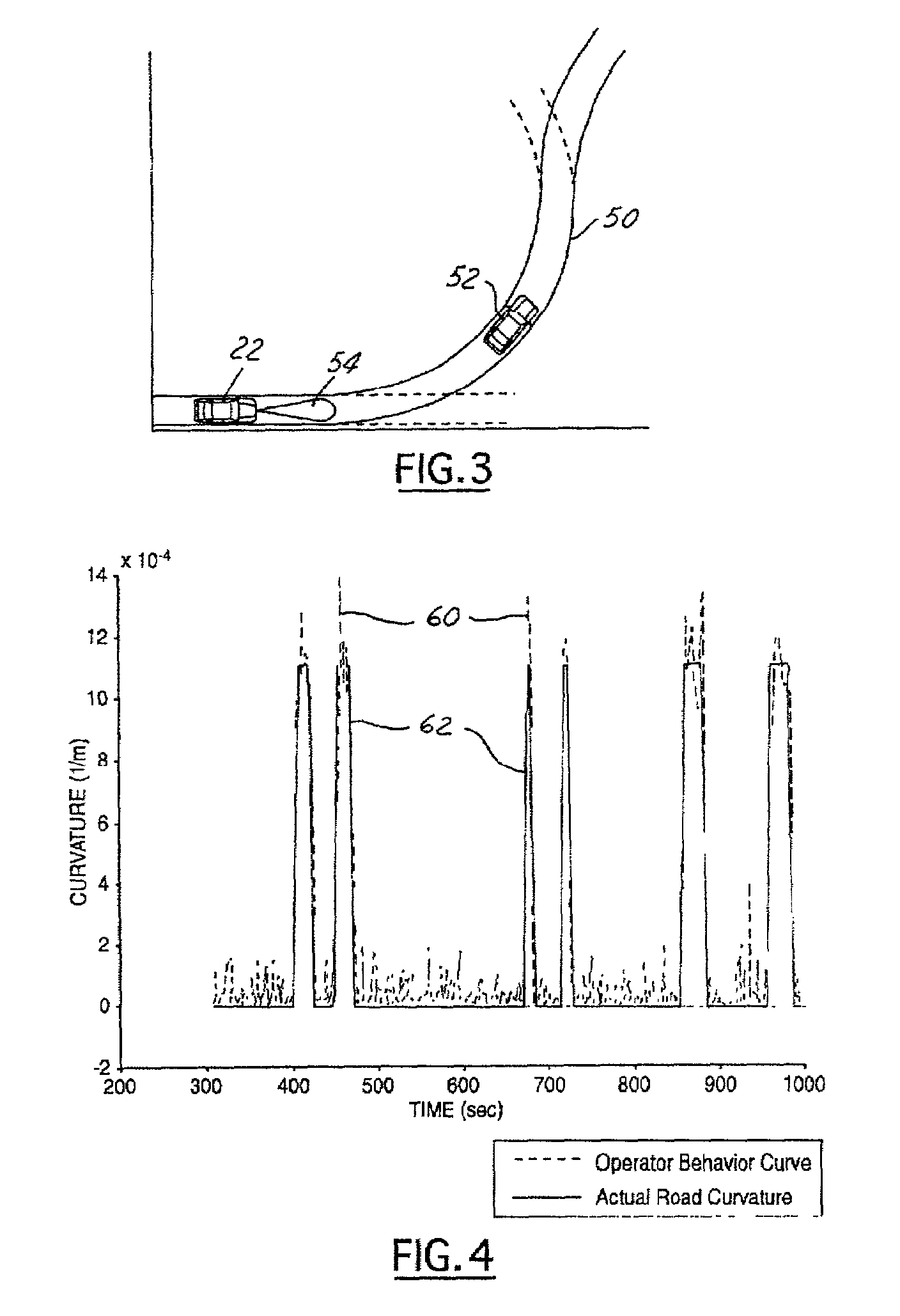
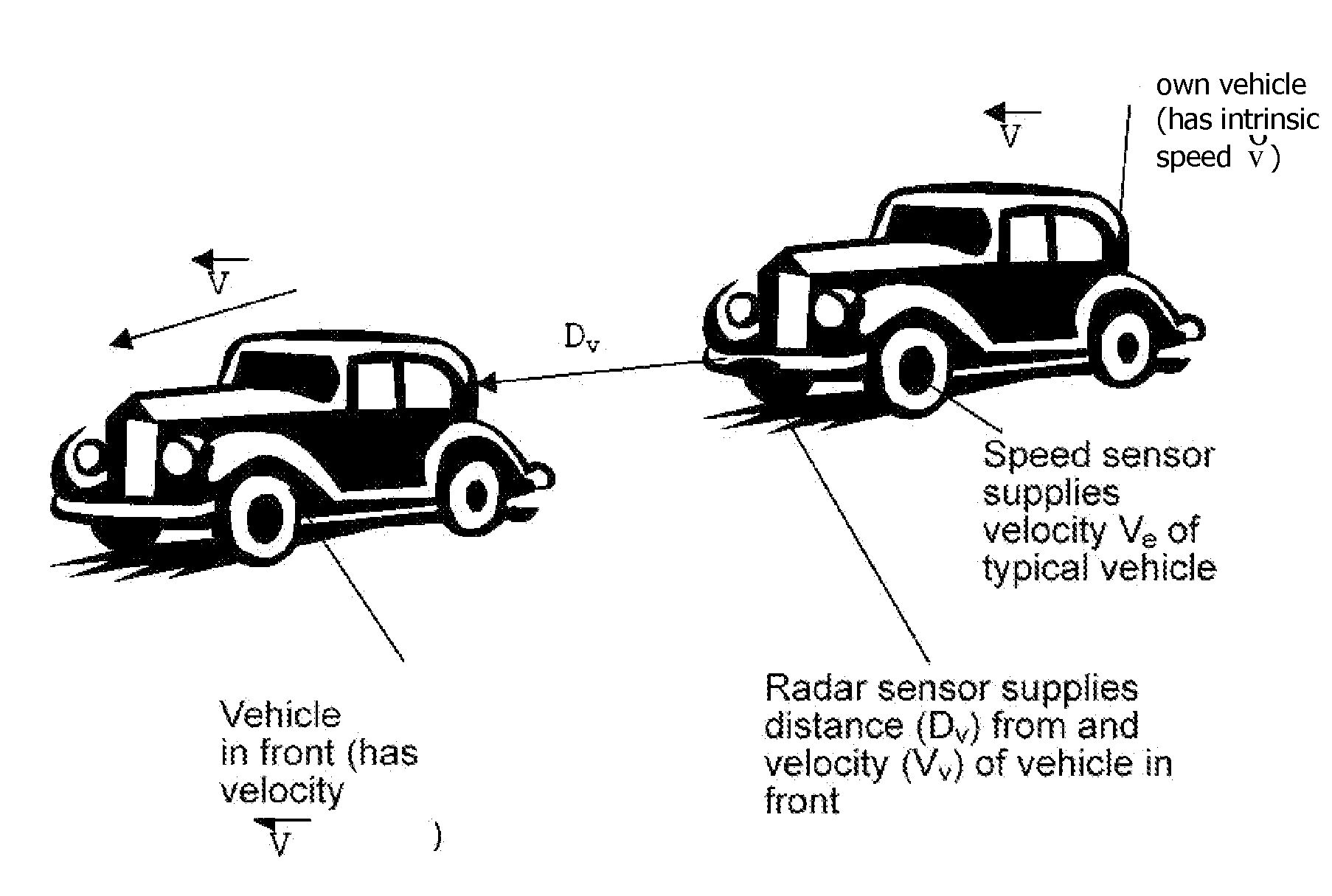
Object detection in adaptive cruise control
InactiveUS6968266B2Prevents false accelerationInstruments for road network navigationVehicle fittingsMobile vehicleRadar systems
A control system 20 for an automotive vehicle 22, such as an adaptive cruise control (ACC) system, is provided including a controller 24. The controller 24 is electrically coupled to a radar system and a navigation system. The detection system 28 detects an object and generates an object profile. The navigation system 34 generates a navigation signal. The controller 24 in response to the object profile and the navigation signal, generates a predicted future path profile and inhibits resume speed of the vehicle 22 in response to the predicted future path profile. An additional feature of the invention is that the controller 24 may also be electrically coupled to a yaw rate sensor 30. The yaw rate sensor 30 senses the yaw rate of the vehicle 22 and generates a yaw rate signal. The controller 24 in response to the yaw rate signal inhibits resume speed of the vehicle 22.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
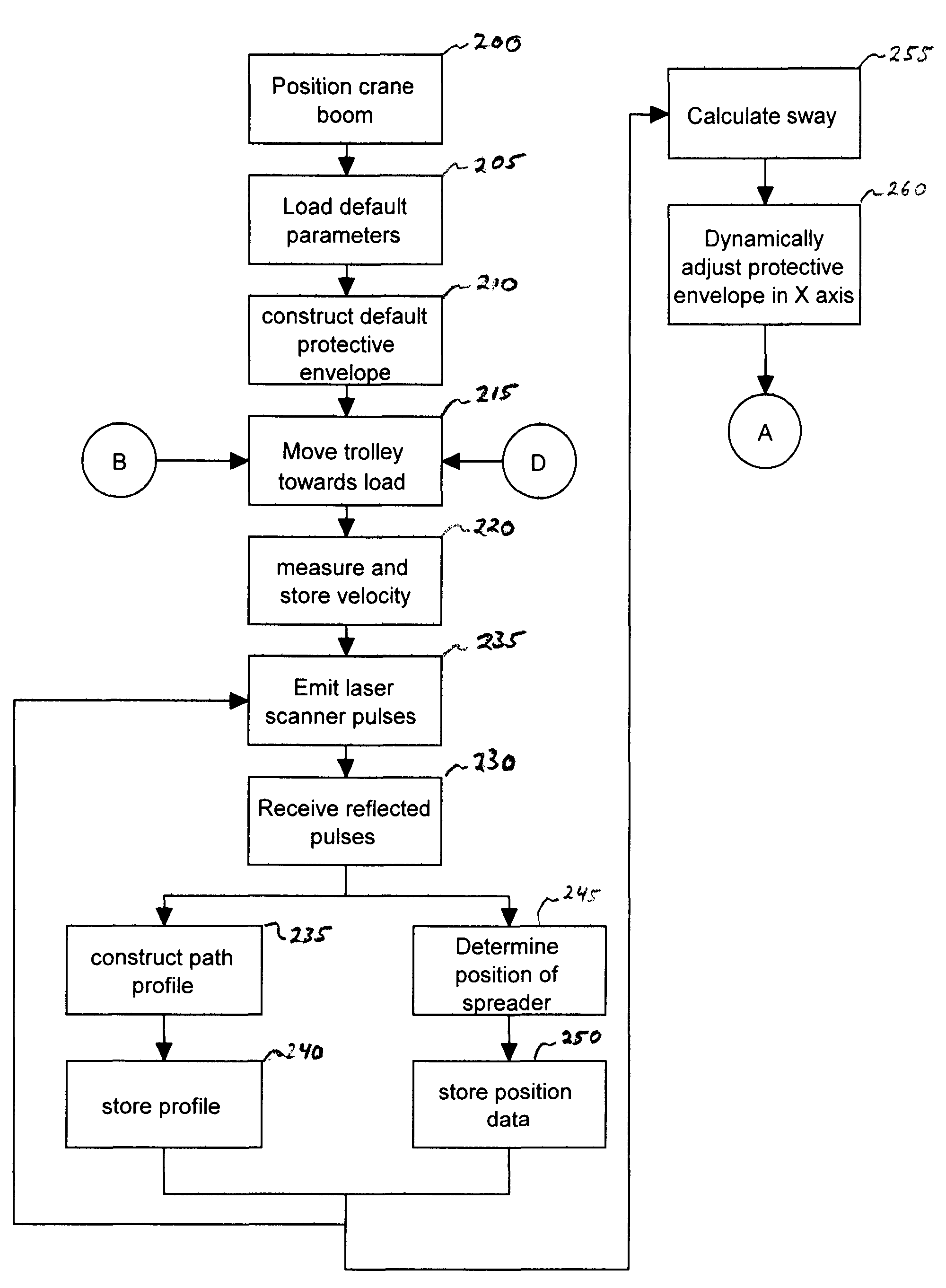
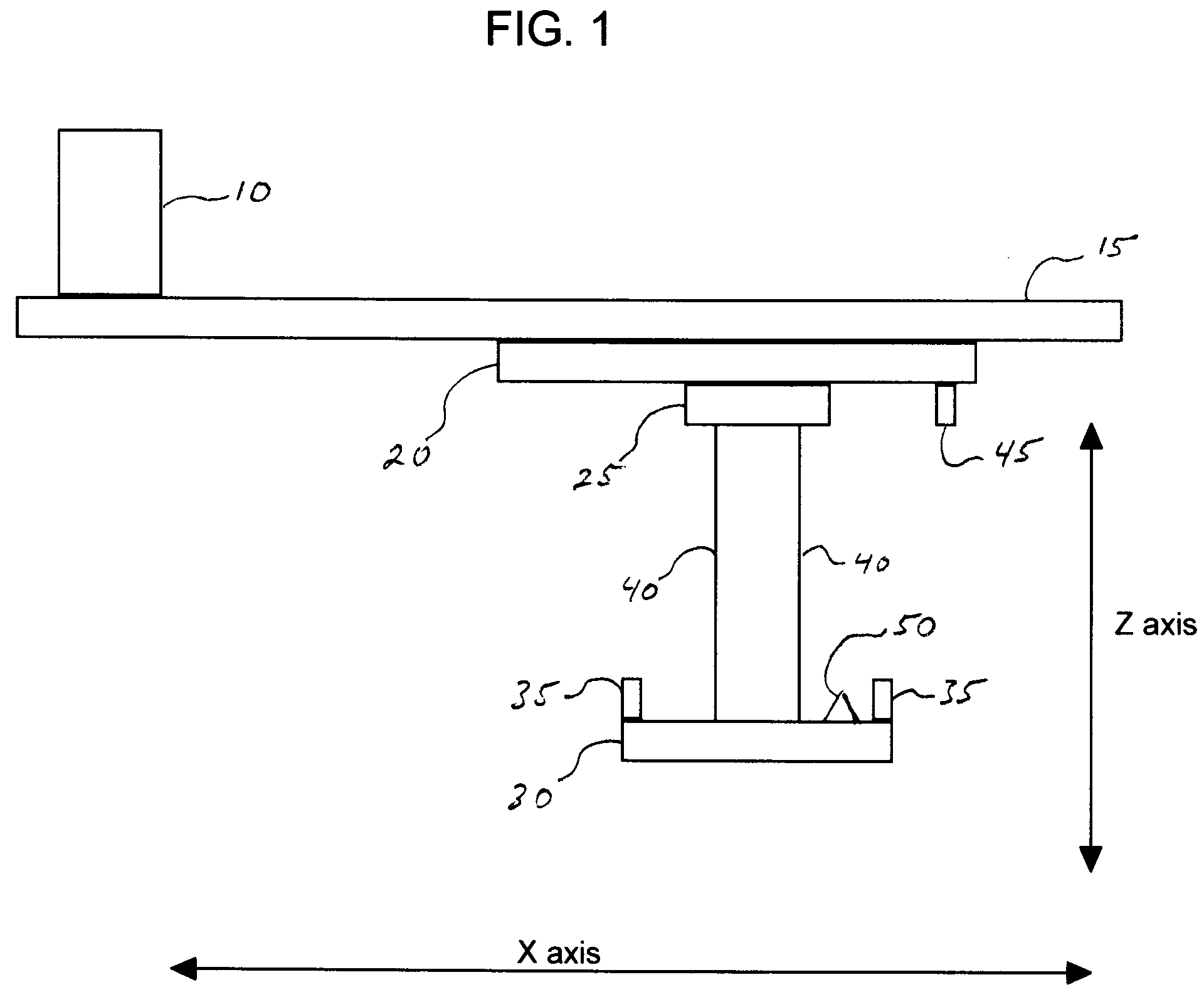
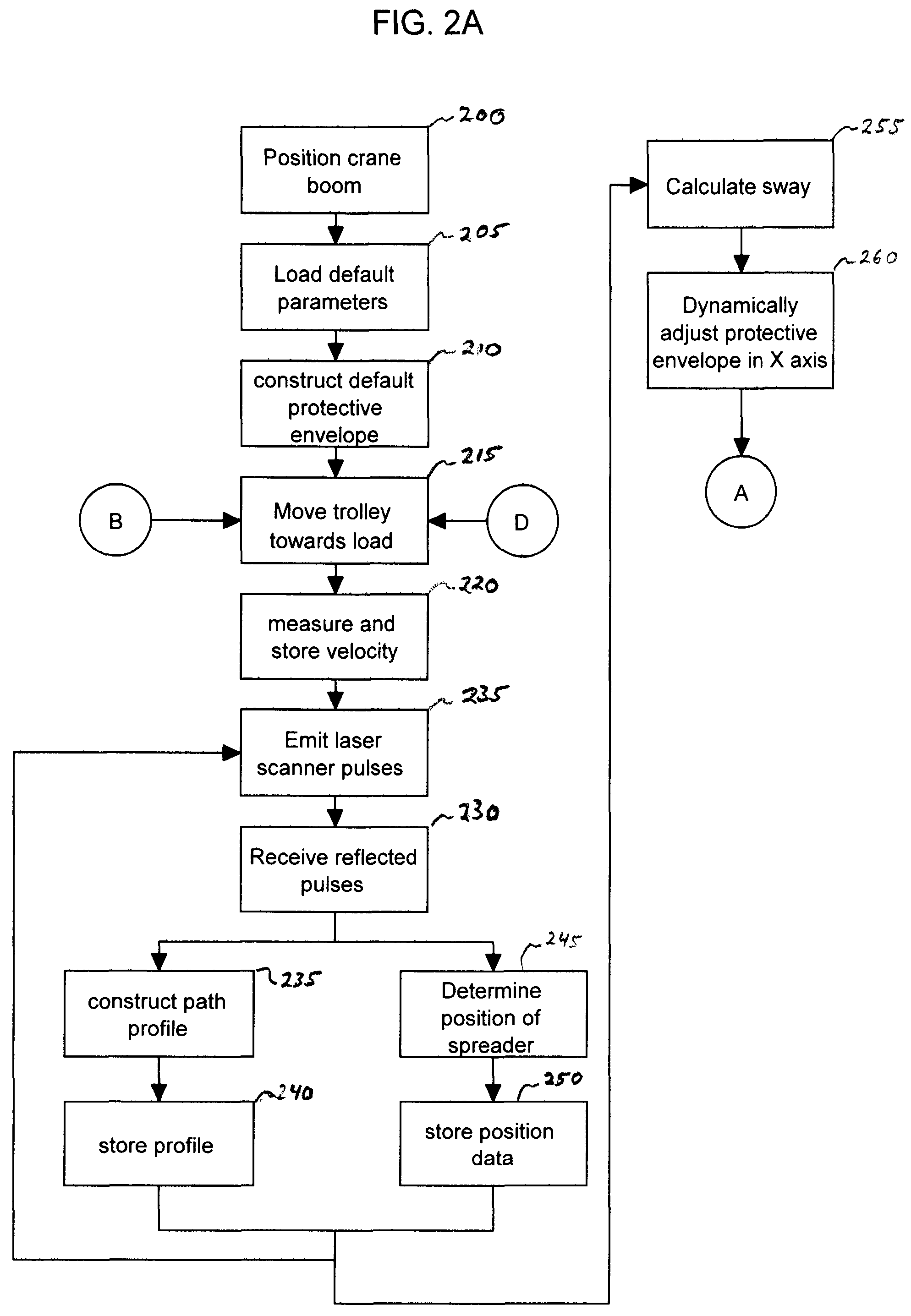
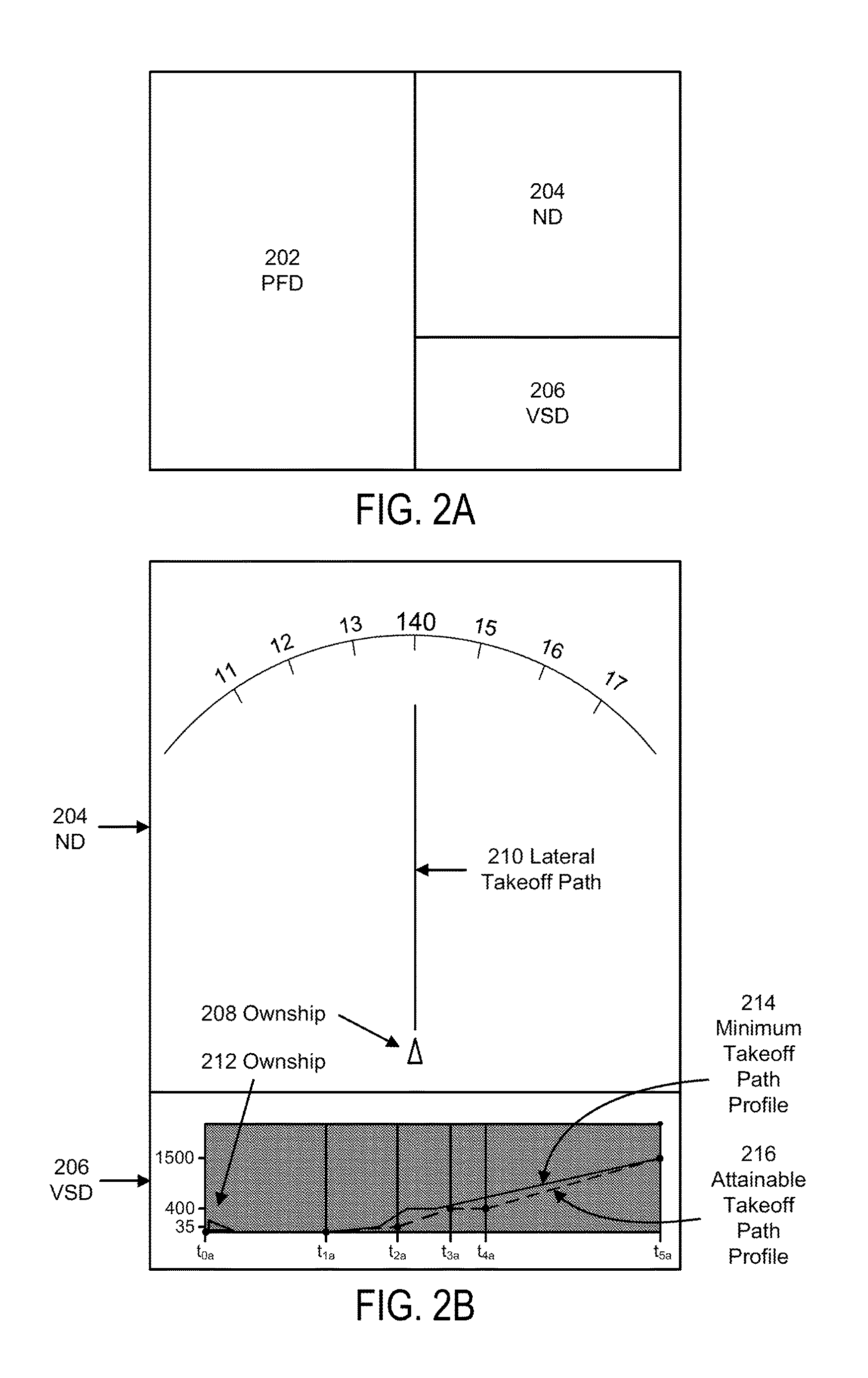
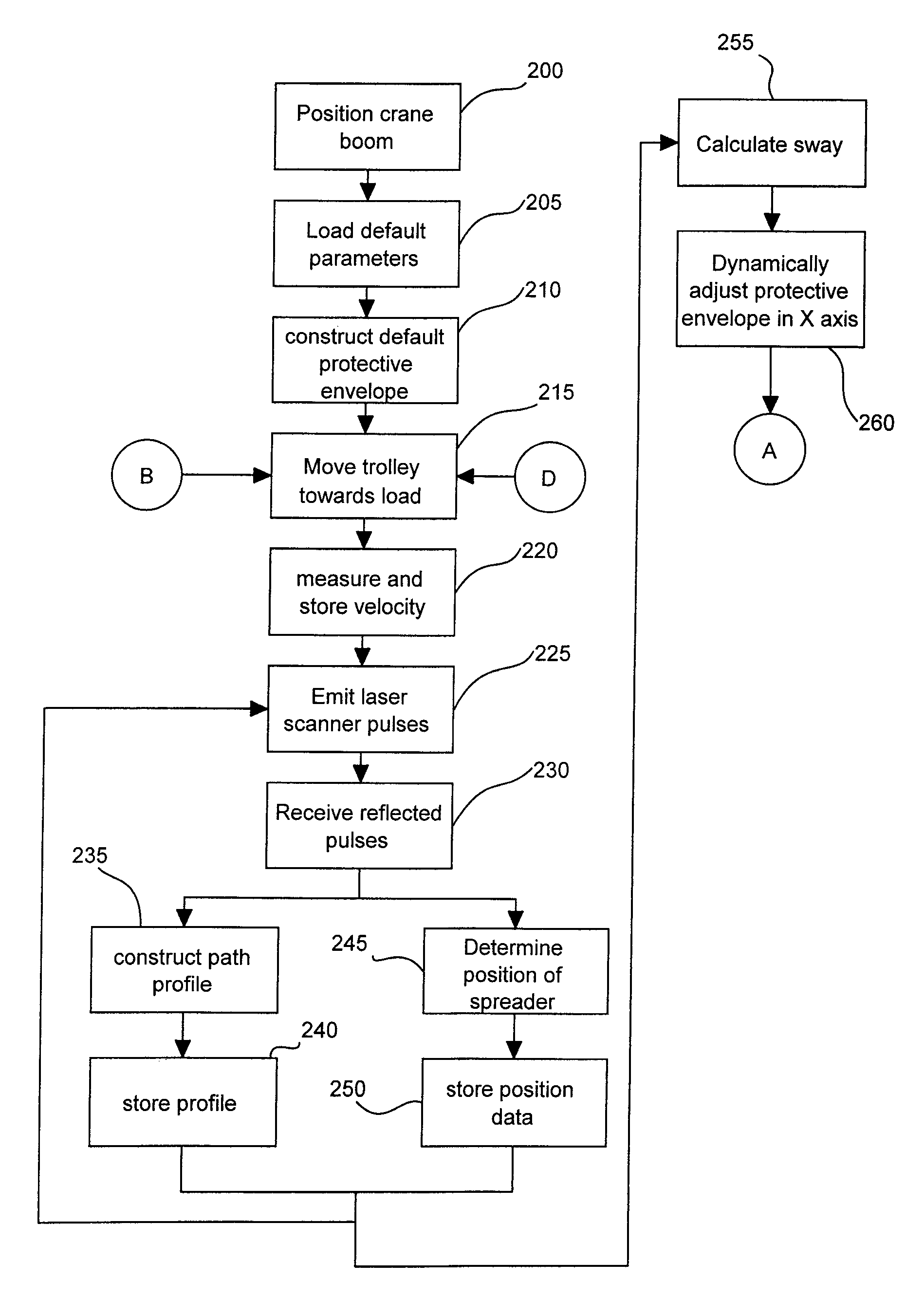
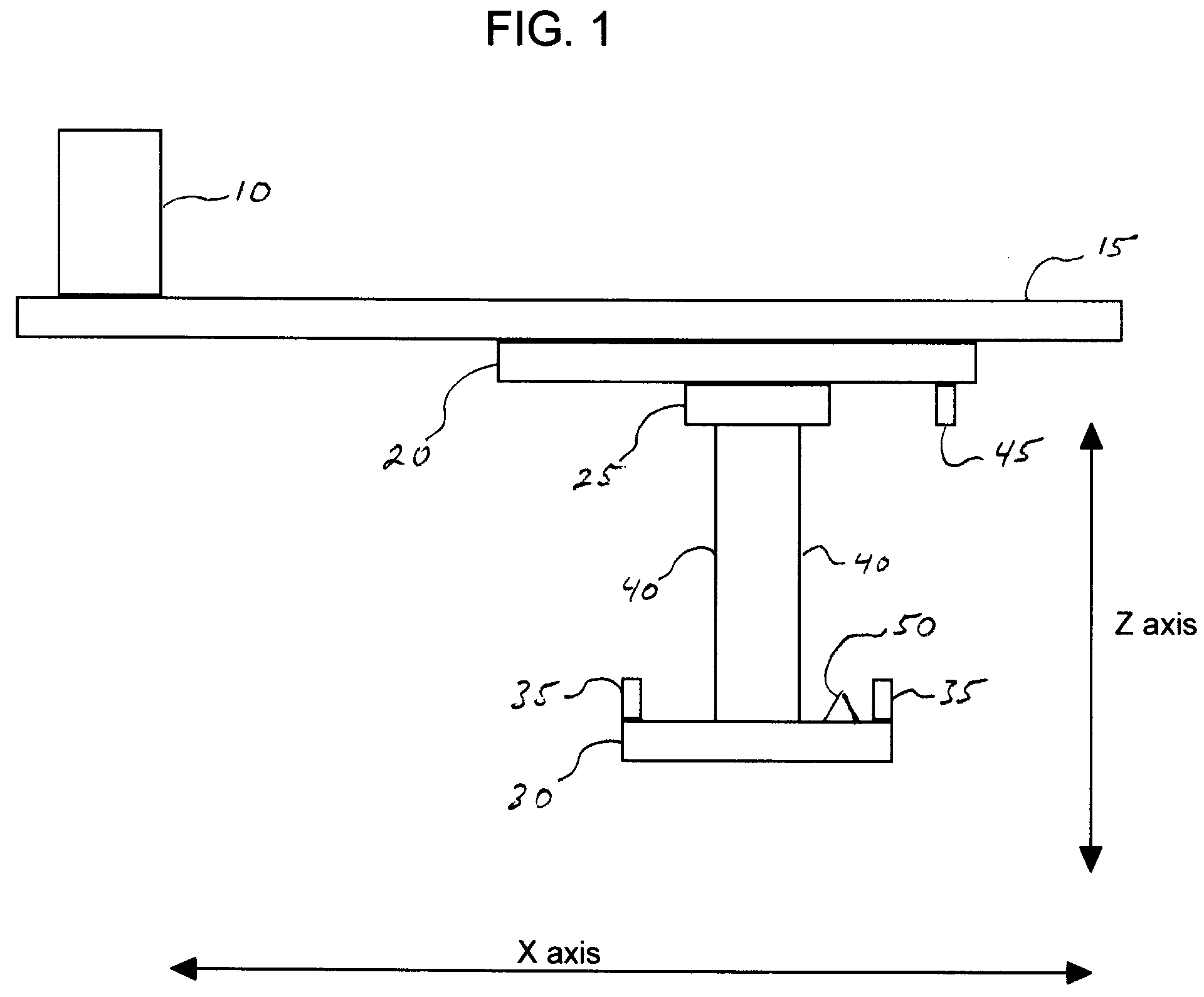
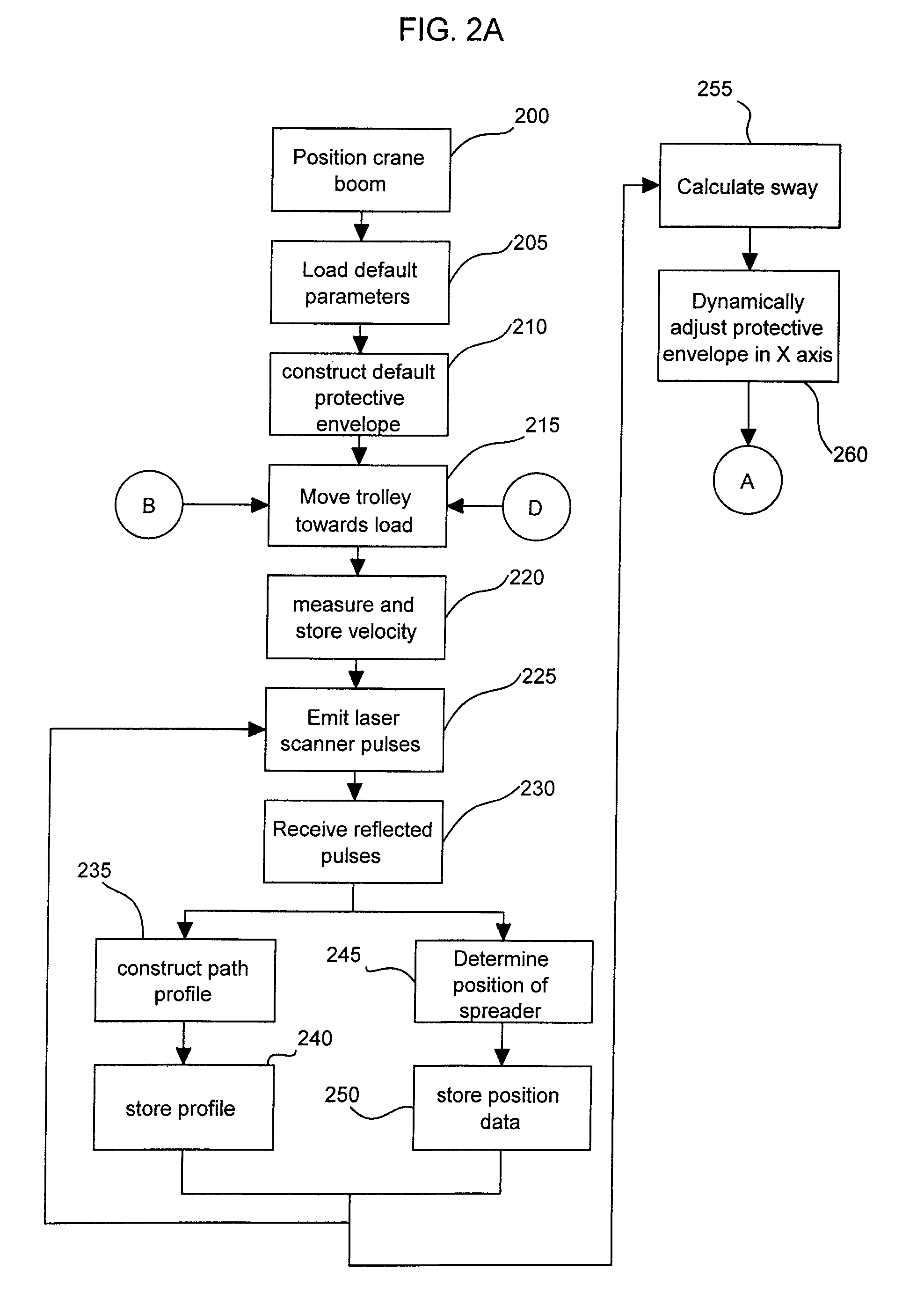
Dynamic Protective Envelope for Crane Suspended Loads
ActiveUS20110076130A1Avoid collisionAnalogue computers for trafficLifting devicesTransceiverMotor control
A system and method for using a gantry crane to efficiently and safely transport loads such as containers and ship hatch covers from one location to another along a known path while avoiding collisions between the loads and obstructing objects which may be situated in the known path. A transceiver emitting laser beams may be used to establish both the position of the spreader and its load and the profile of the known path. Continuous comparisons are made by computer between the location of a dynamic digital protective envelope constructed around the crane spreader and its load, if any, and a digital representation of the profile of the known path to be traveled by the spreader and its load, if any. In the event, the comparison indicates intersection of the protective envelope and the path profile, a speed limit is imposed on the motor controlling the movement in the X axis of the trolley or in the Z axis of the spreader, as required to prevent a collision.
Owner:TMEIC
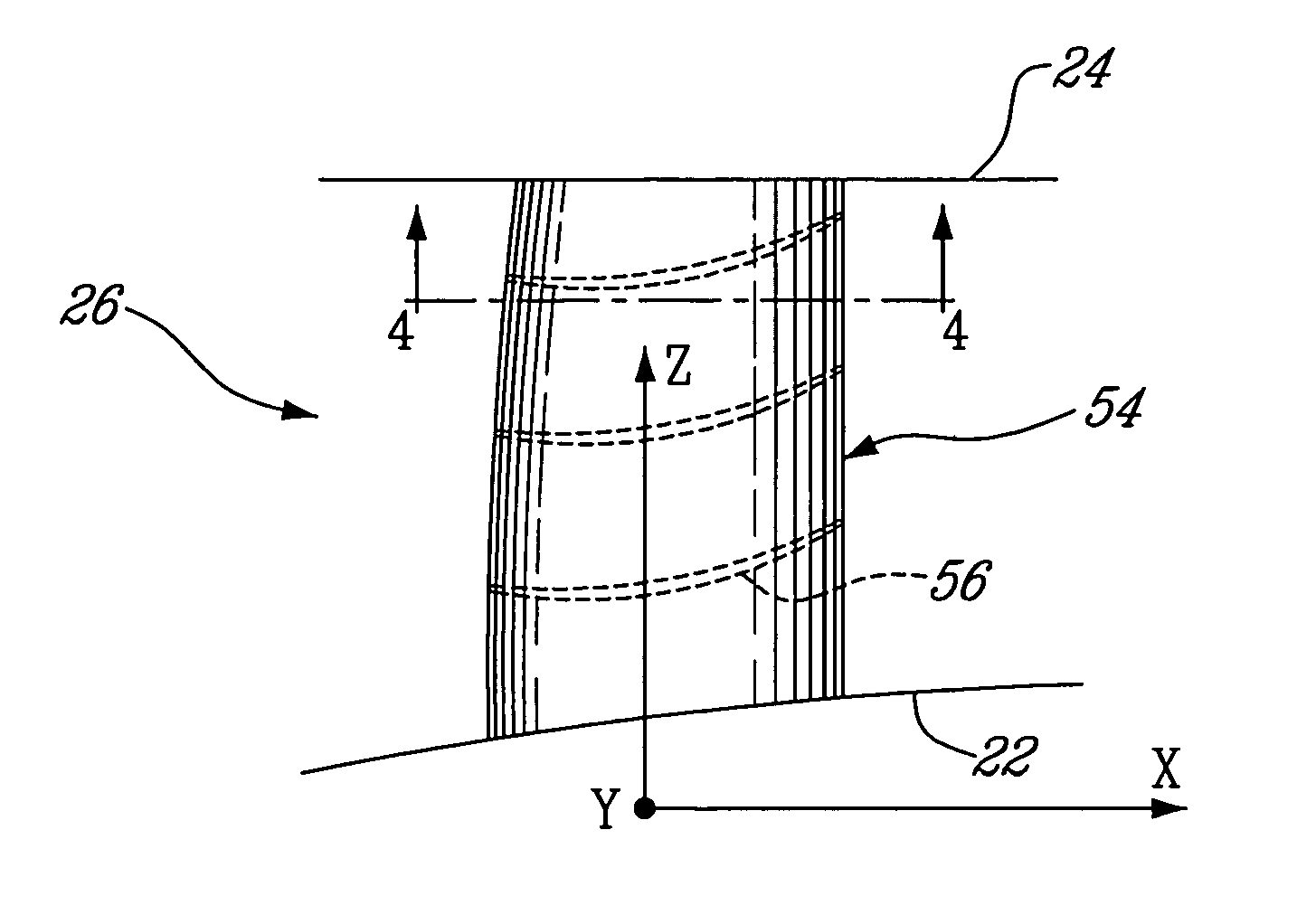
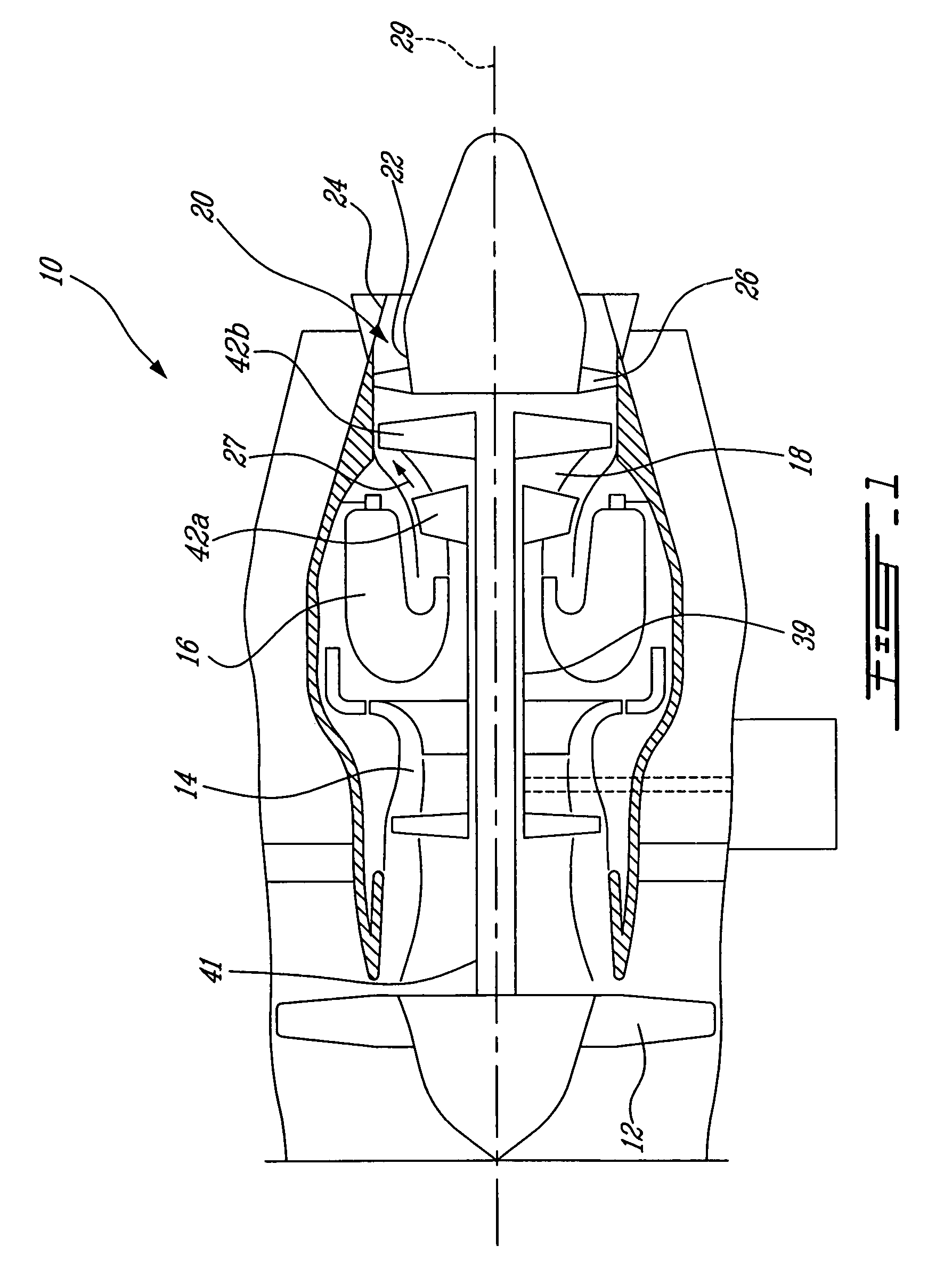
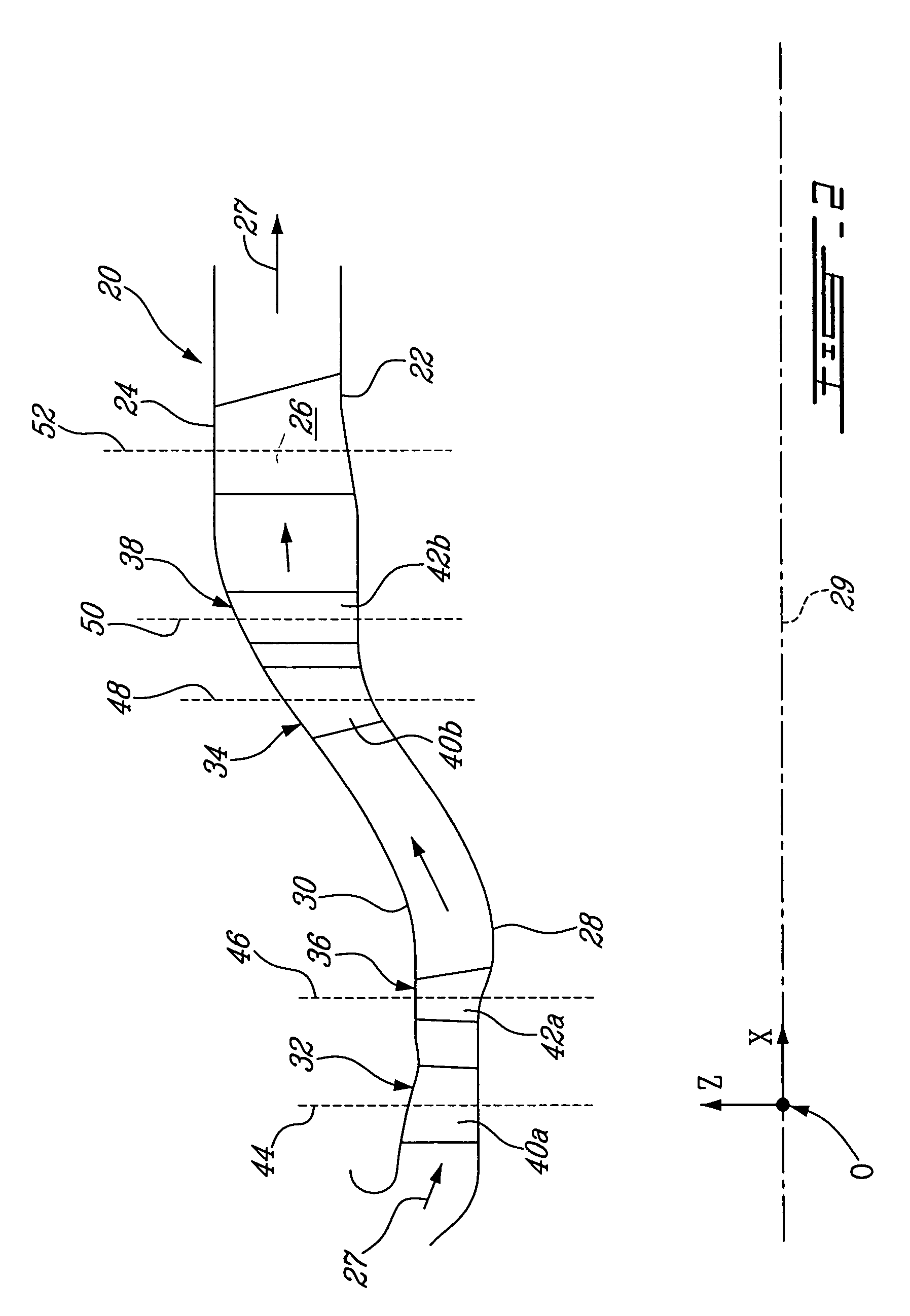
Turbine exhaust strut airfoil and gas path profile
ActiveUS7625182B2Remove large amount of residual swirlMore tolerant to manufacturing toleranceEngine manufactureOther chemical processesPath profileTurbine
A turbine exhaust thin strut includes an airfoil section having a profile substantially in accordance with at least an intermediate portion of the Cartesian coordinate values of X, Y and Z set forth in Table 2. The X and Y values are distances, which when smoothly connected by an appropriate continuing curve, define airfoil profile sections at each distance Z. The profile sections at each distance Z are joined smoothly to one another to form a complete airfoil shape.
Owner:PRATT & WHITNEY CANADA CORP
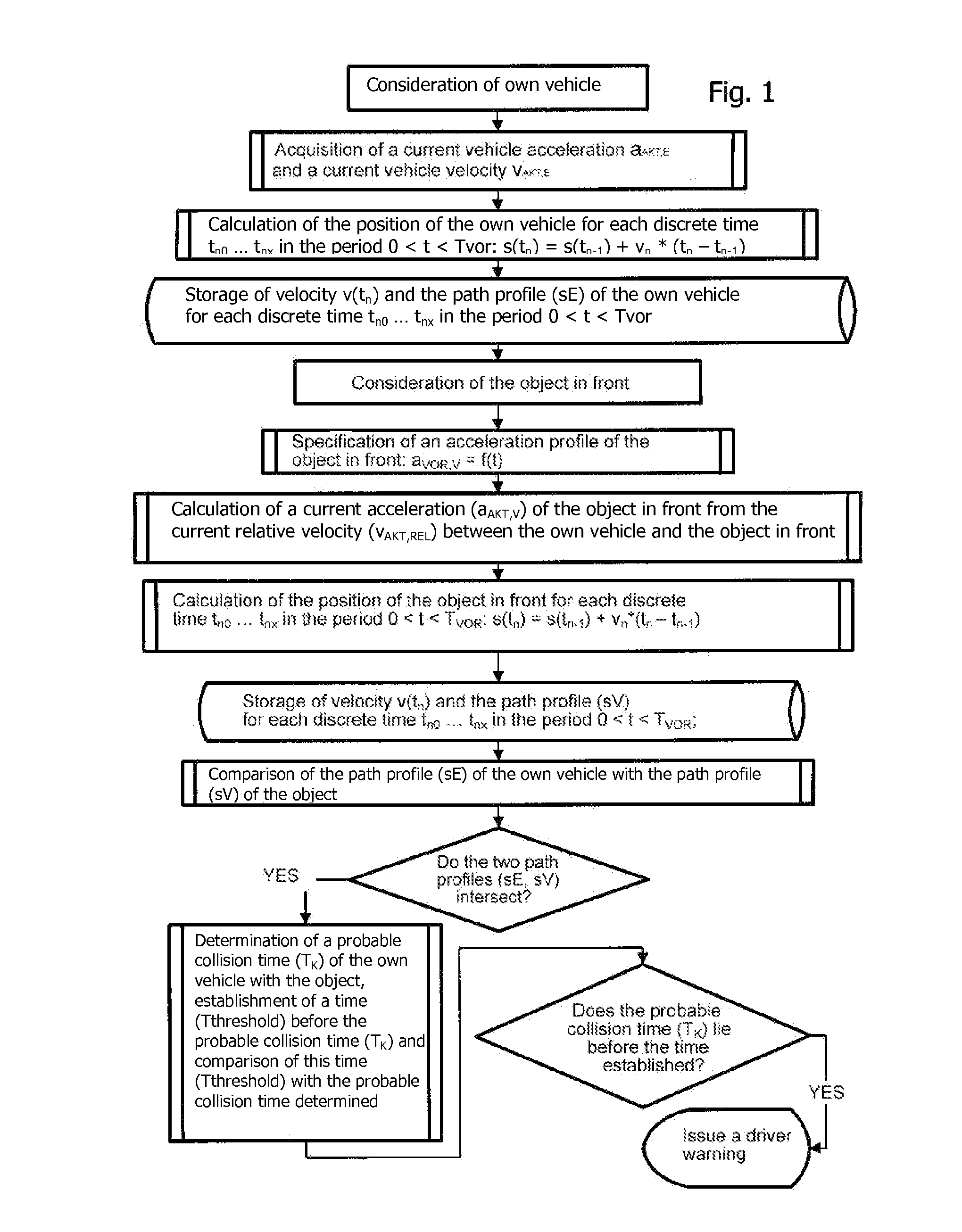
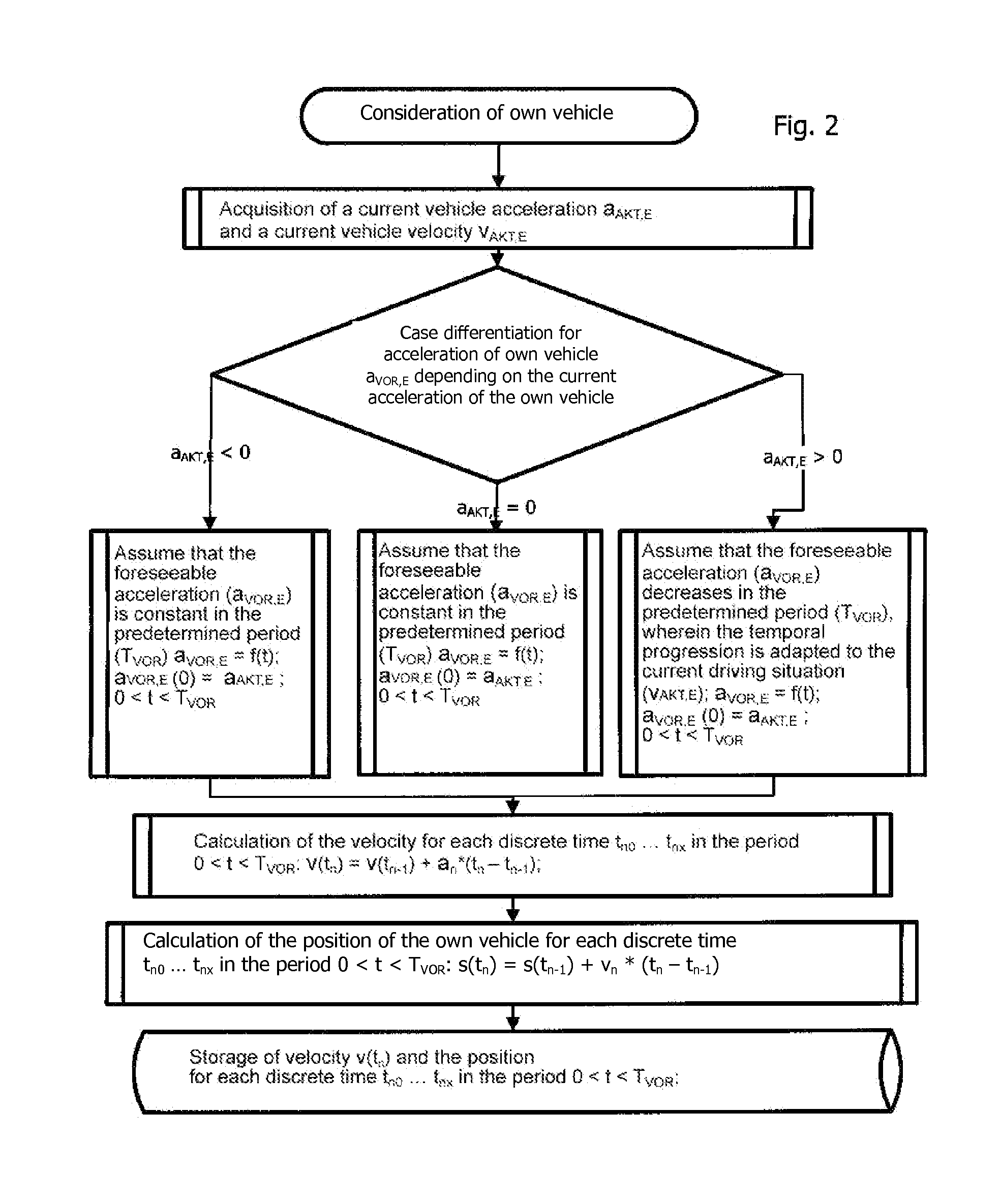
Method for Detecting Critical Driving Situations of Lorries or Passenger Vehicles and Method for Avoiding Collisions
ActiveUS20140032094A1Avoid collisionAnti-collision systemsAutomatic initiationsObject basedEngineering
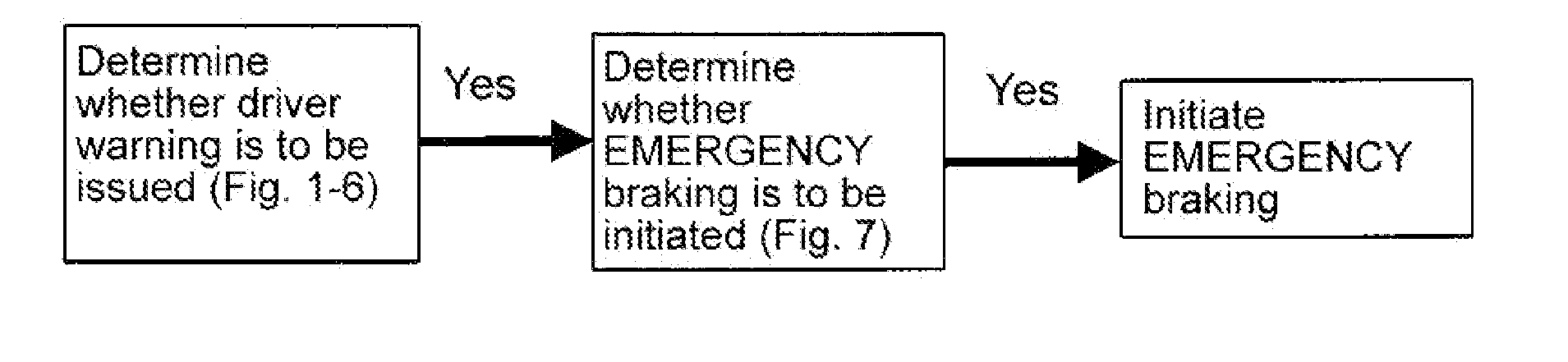
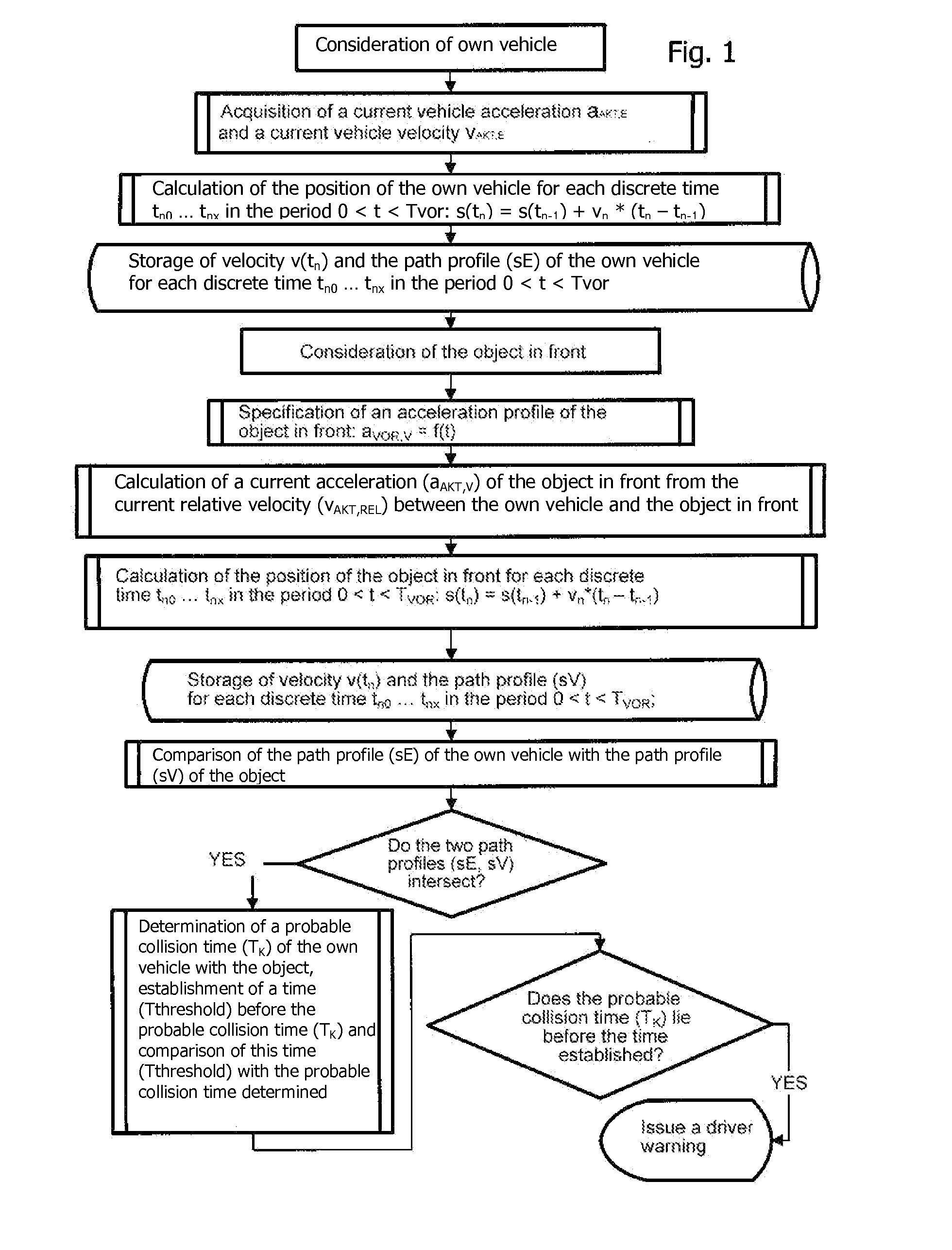
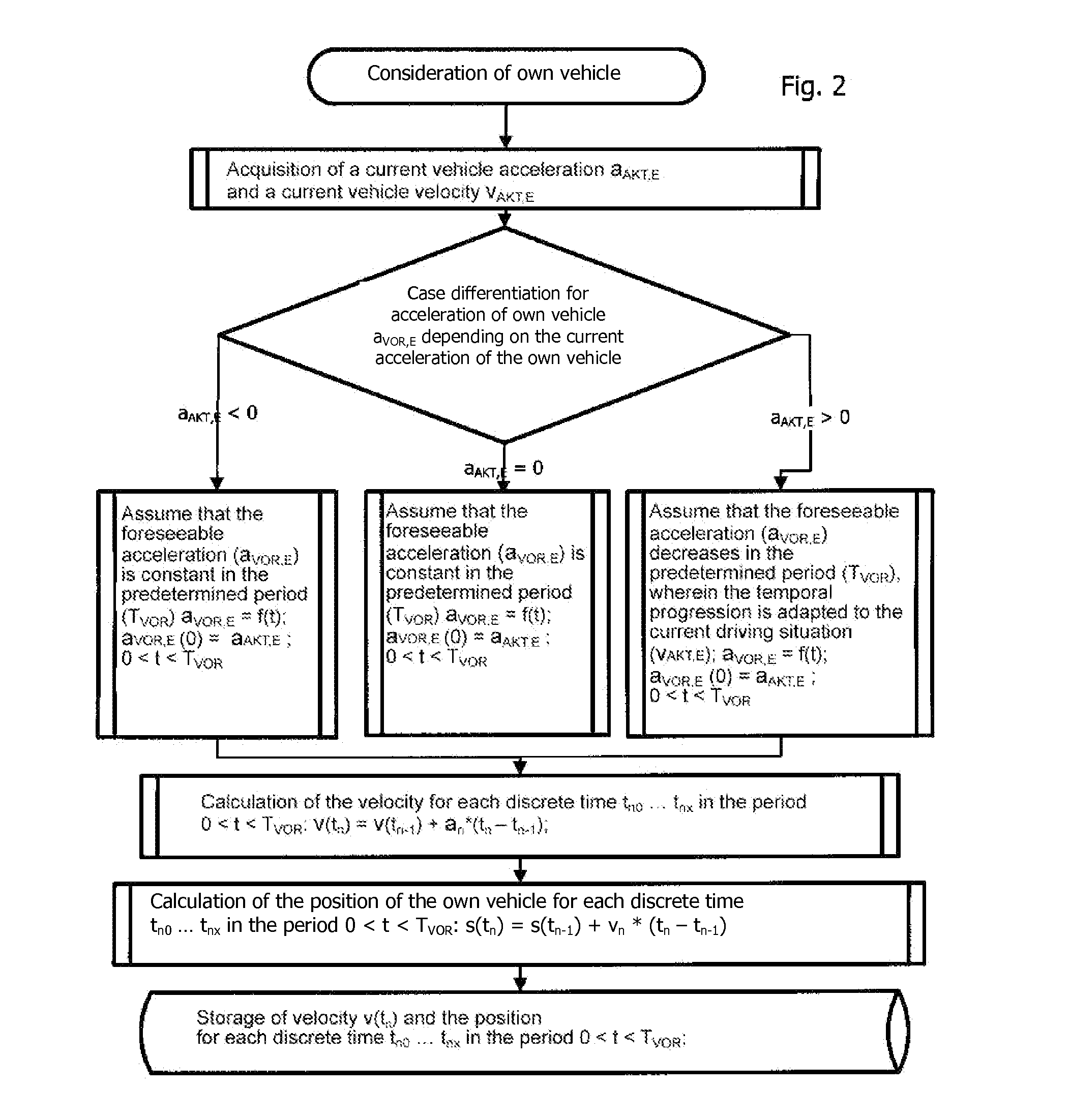
A method for detecting critical driving situations of motor vehicles, in particular for preventing collisions with an object in front of an own vehicle, has the following steps: detection of a current vehicle acceleration and a current vehicle velocity of an own vehicle; specification of an acceleration profile depending on driving variables of the own vehicle; assumption of a time progression of a foreseeable acceleration of the own vehicle based on its current acceleration; determination of a path profile of the own vehicle from the time progression of the foreseeable acceleration; acquisition of a current distance and a current relative velocity of an object in front of the own vehicle; calculation of the current absolute velocity of the object as well as of the absolute current acceleration of the object; assumption of a time progression of a foreseeable acceleration of the object based on its current acceleration; determination of a path profile of the object from the time progression of the foreseeable acceleration; comparison of the path profile of the own vehicle with the path profile of the object; and if the two path profiles intersect, determination of a probable collision time of the own vehicle with the object; establishment of a time before the probable collision time comparison of this time with the probable collision time determined; and if the probable collision time lies before the established time, issue of a warning to the driver of the own vehicle.
Owner:LUCAS AUTOMOTIVE GMBH
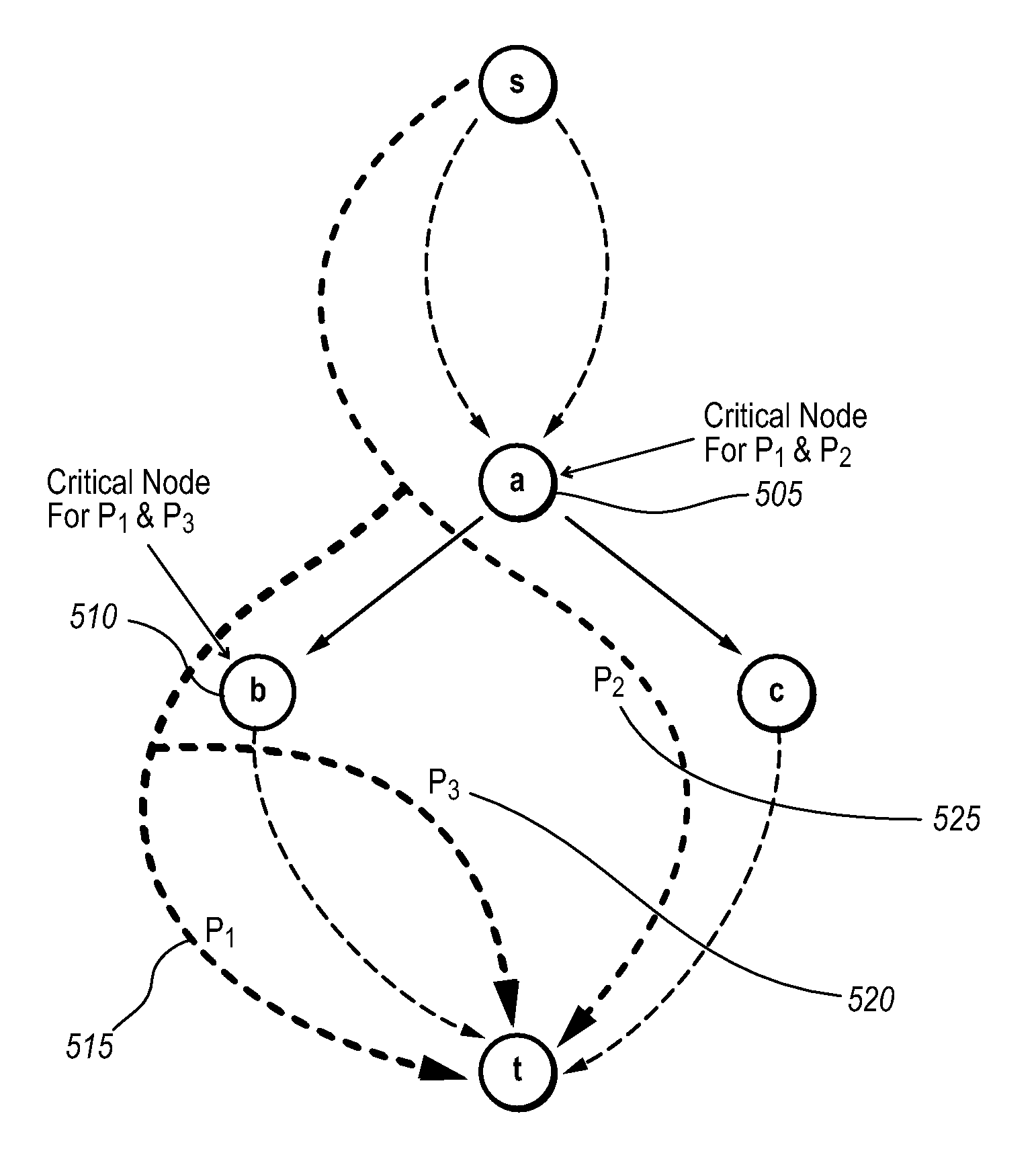
Preferential path profiling
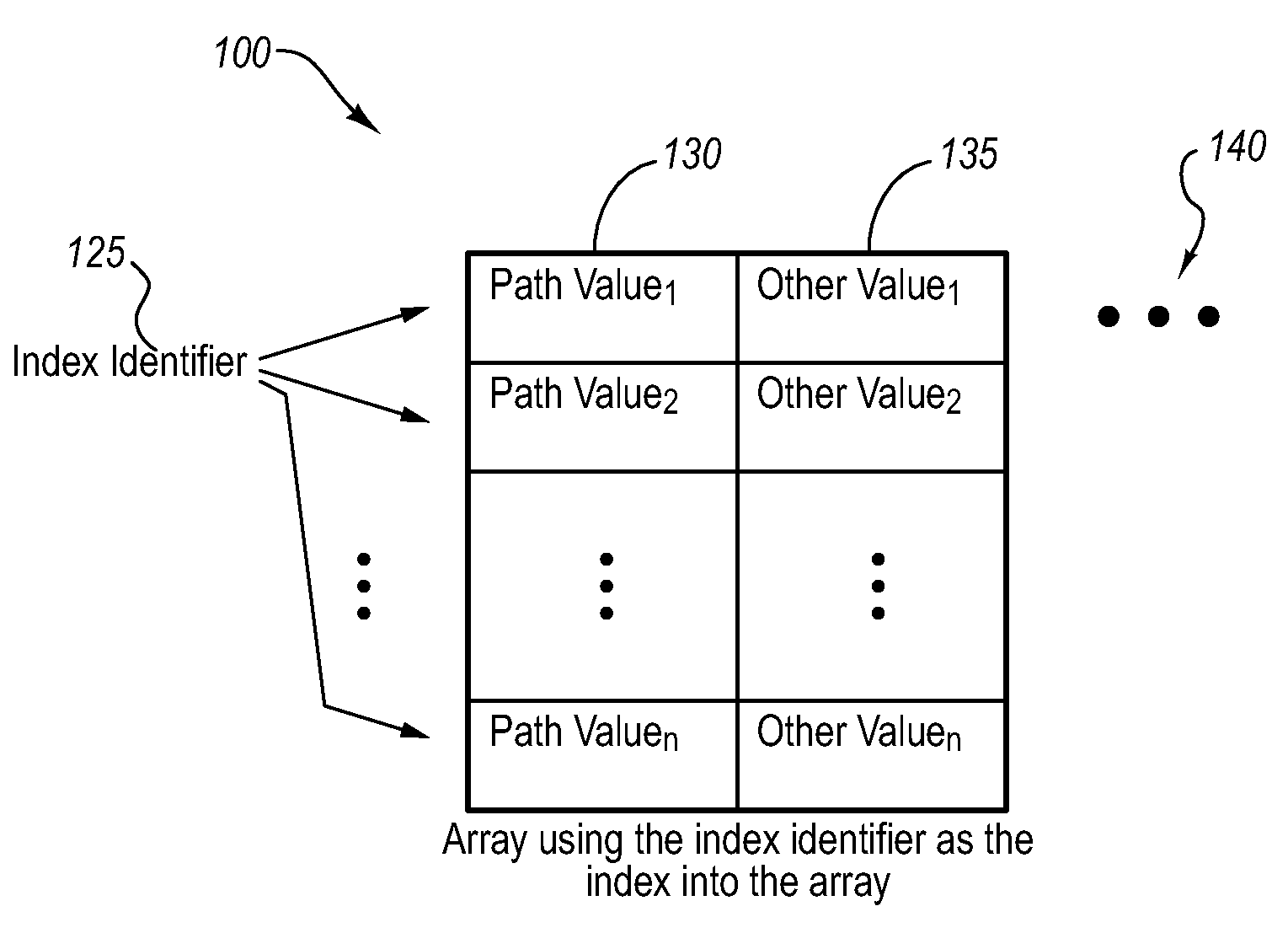
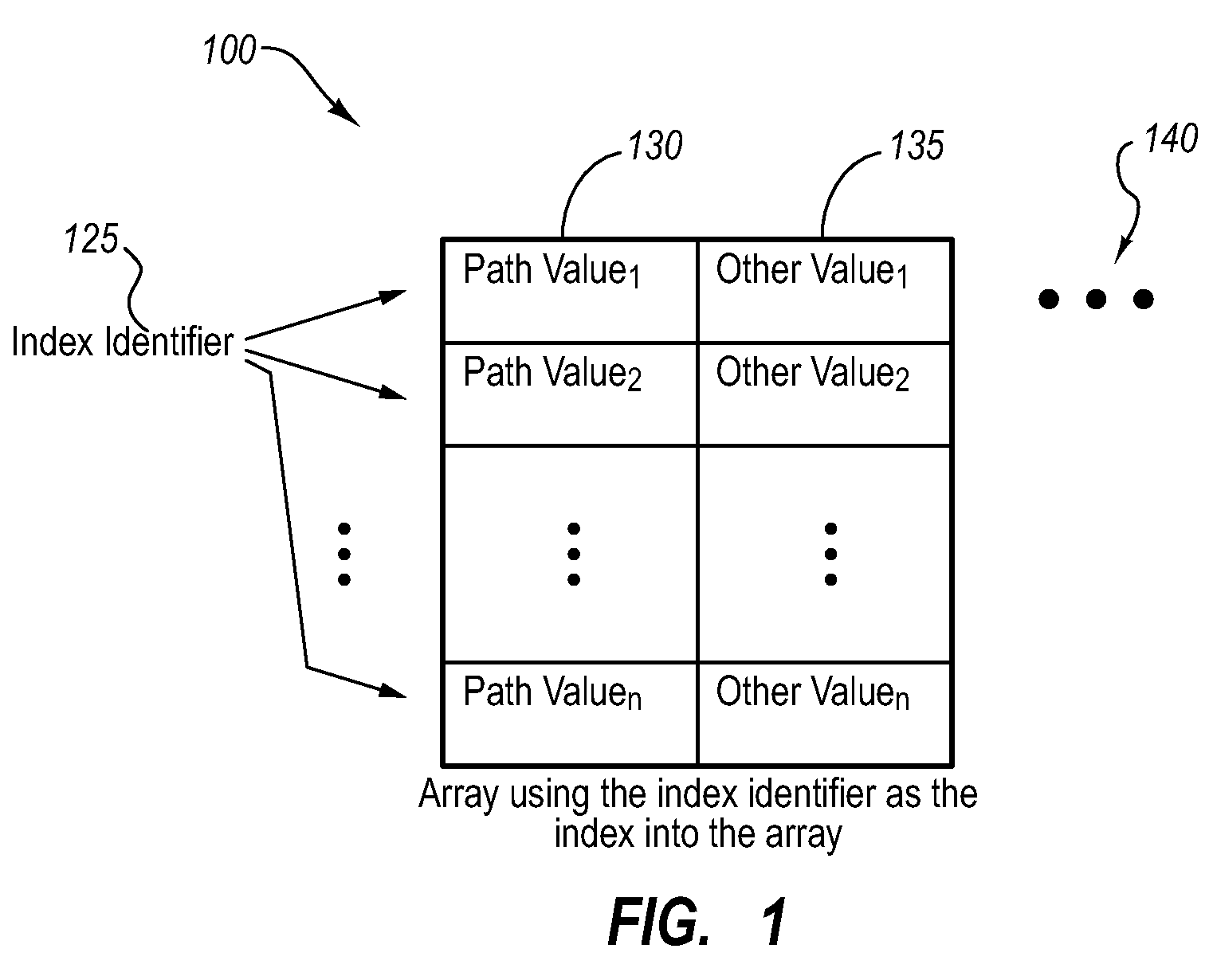
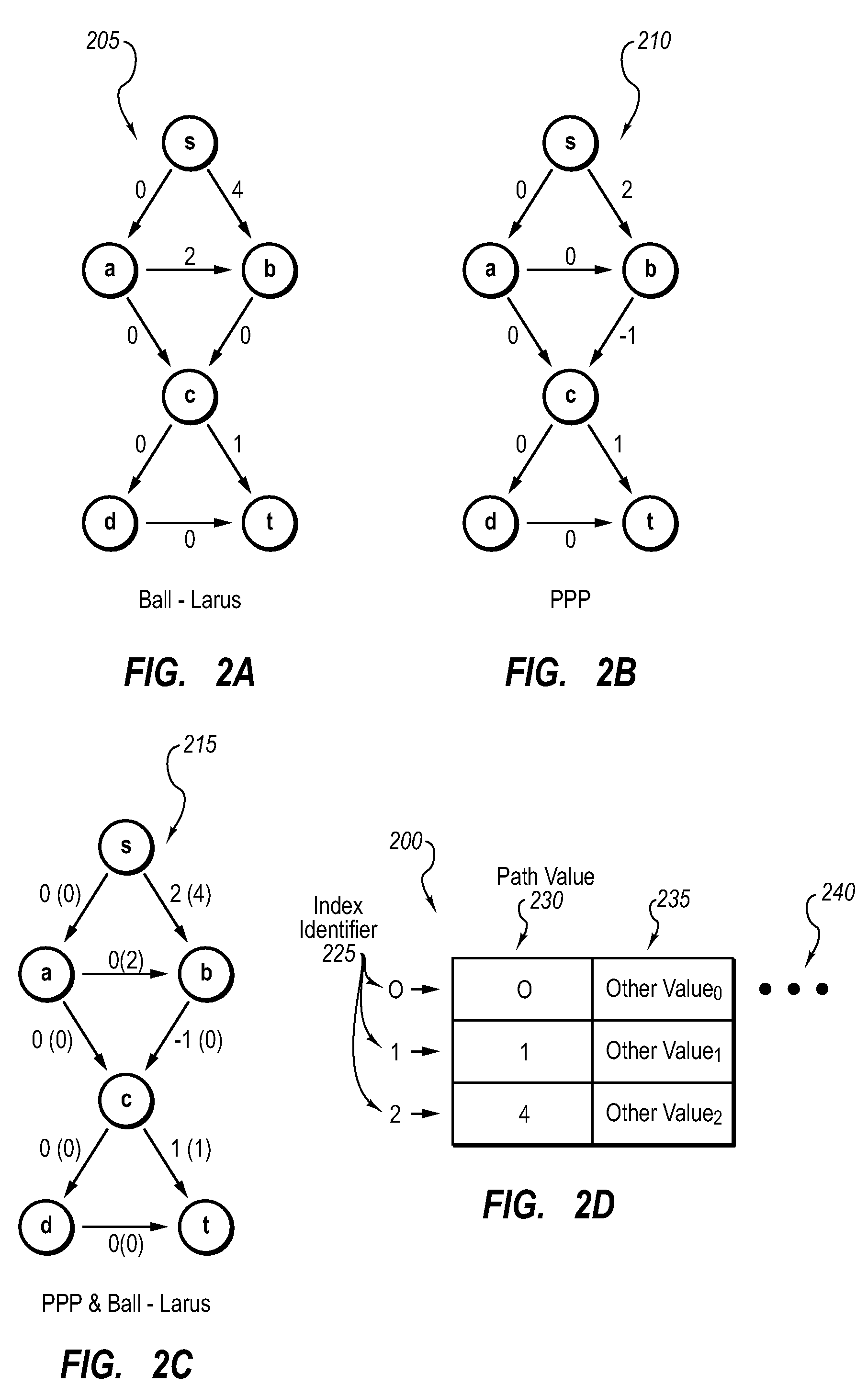
InactiveUS20080222614A1Reduce overheadError detection/correctionSpecific program execution arrangementsArray data structureParallel computing
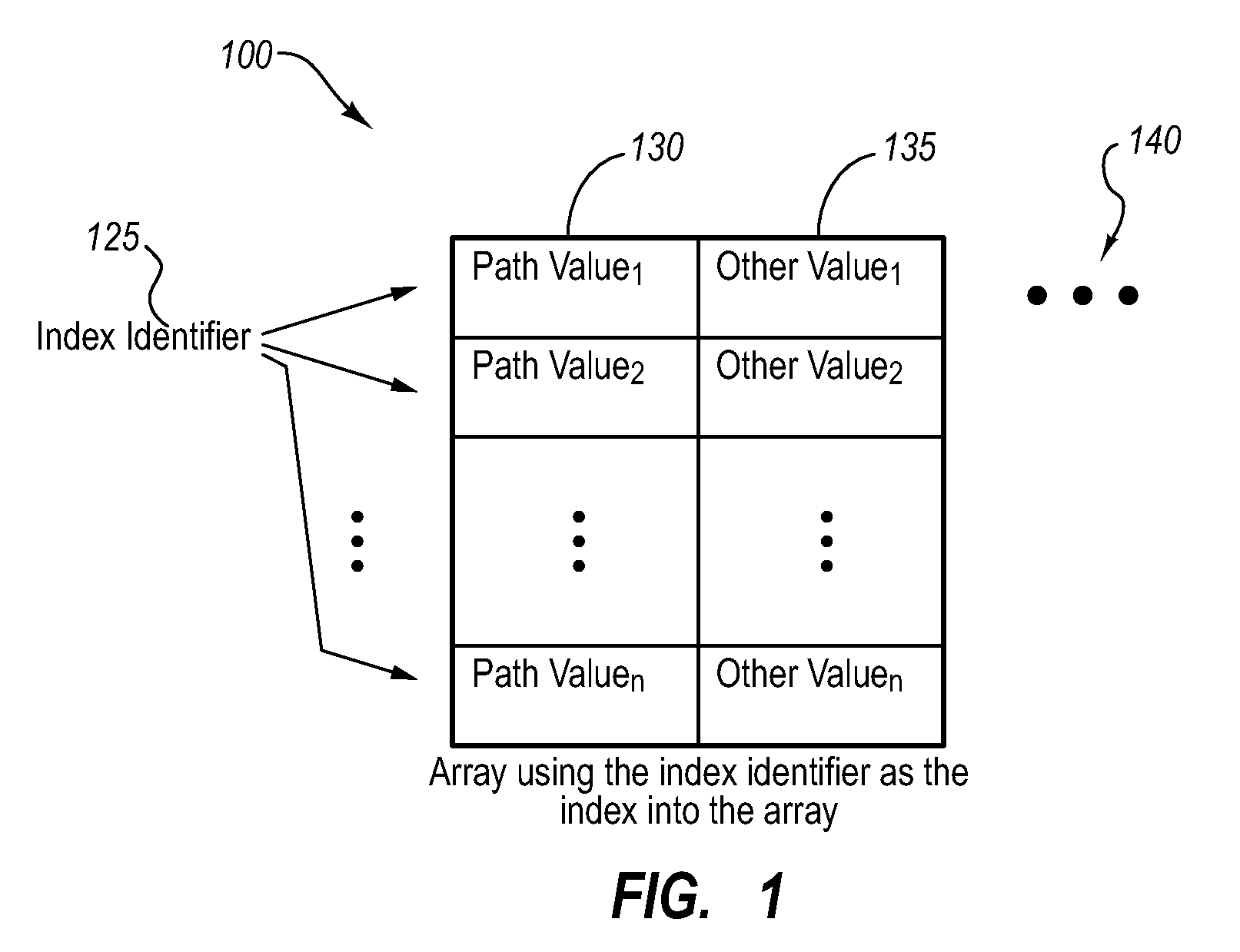
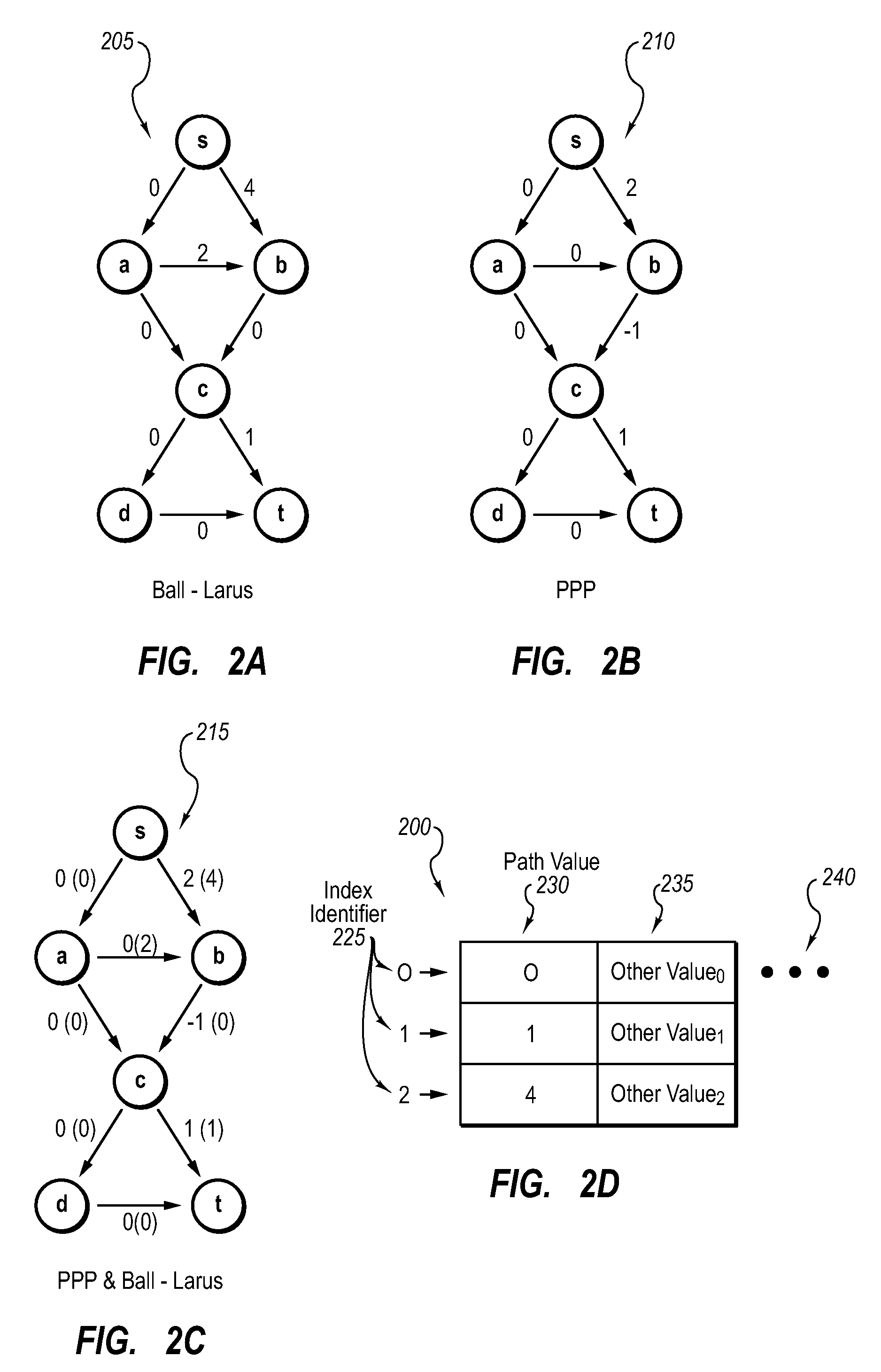
This paper describes preferential path profiling, which enables profiling a specified subset of all possible program paths with very low overhead. Preferential path profiling compactly identifies paths of interest using an array. More specifically, PPP assigns a unique and compact path index identifier to all interesting paths that can be used to index into a path array. The path array contains a second path value identifier that is used to distinguish interesting paths from other program paths This path numbering allows the implementation of preferential path profiling to use array-based counters instead of hash table-based counters for identifying paths of interest and gathering path profiles, which significantly reduces execution time and computational resource overhead during profiling.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
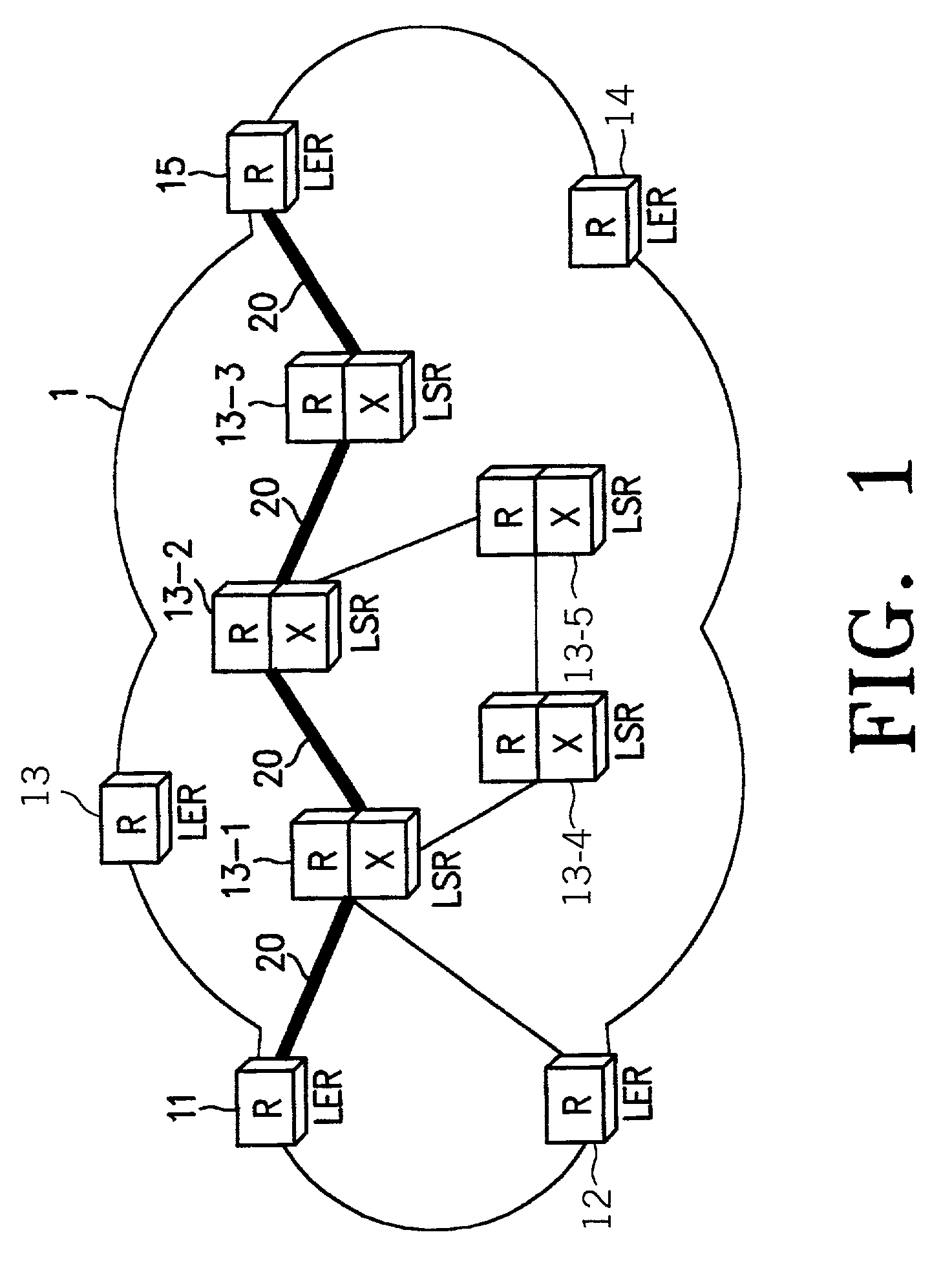
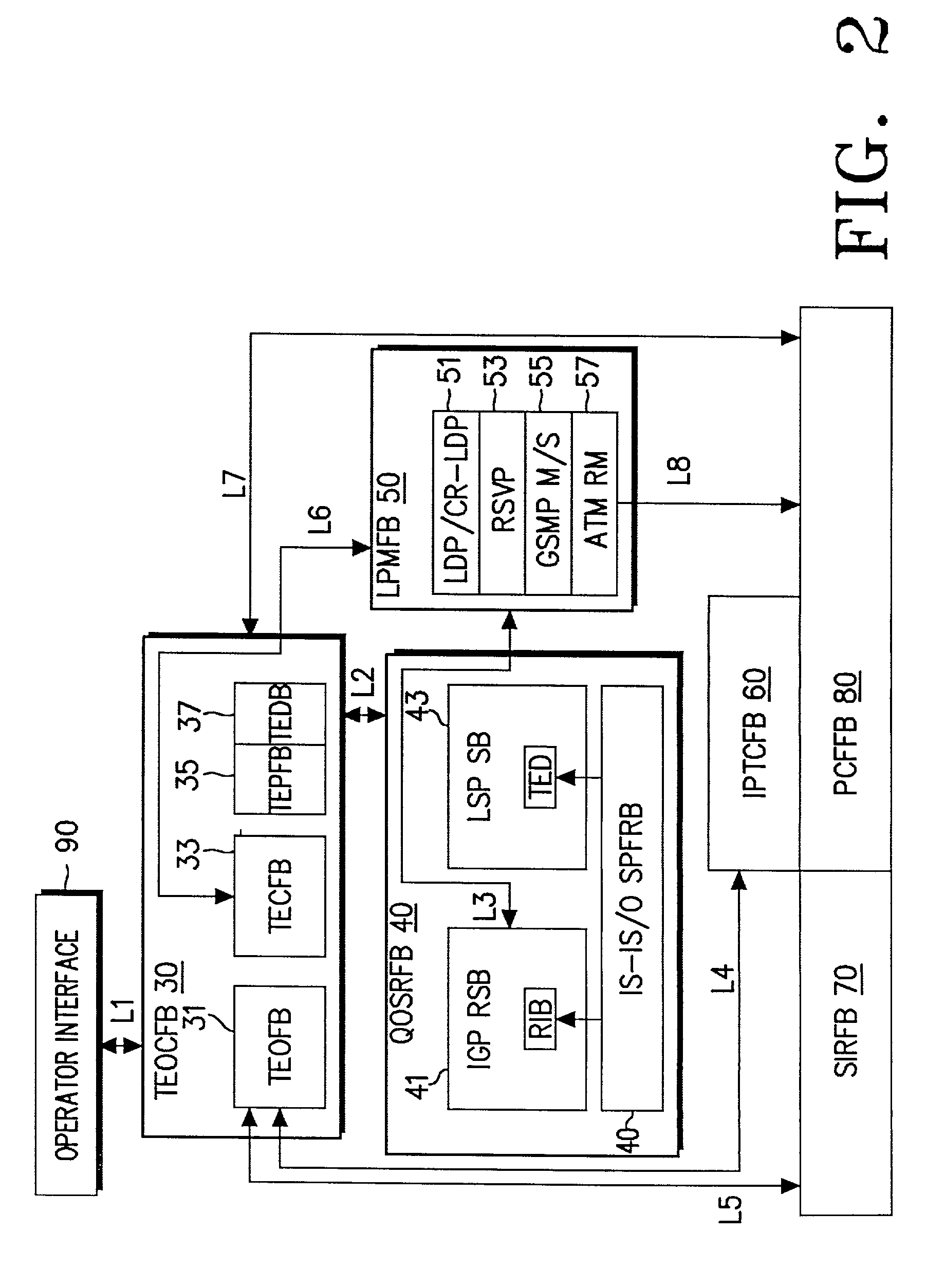
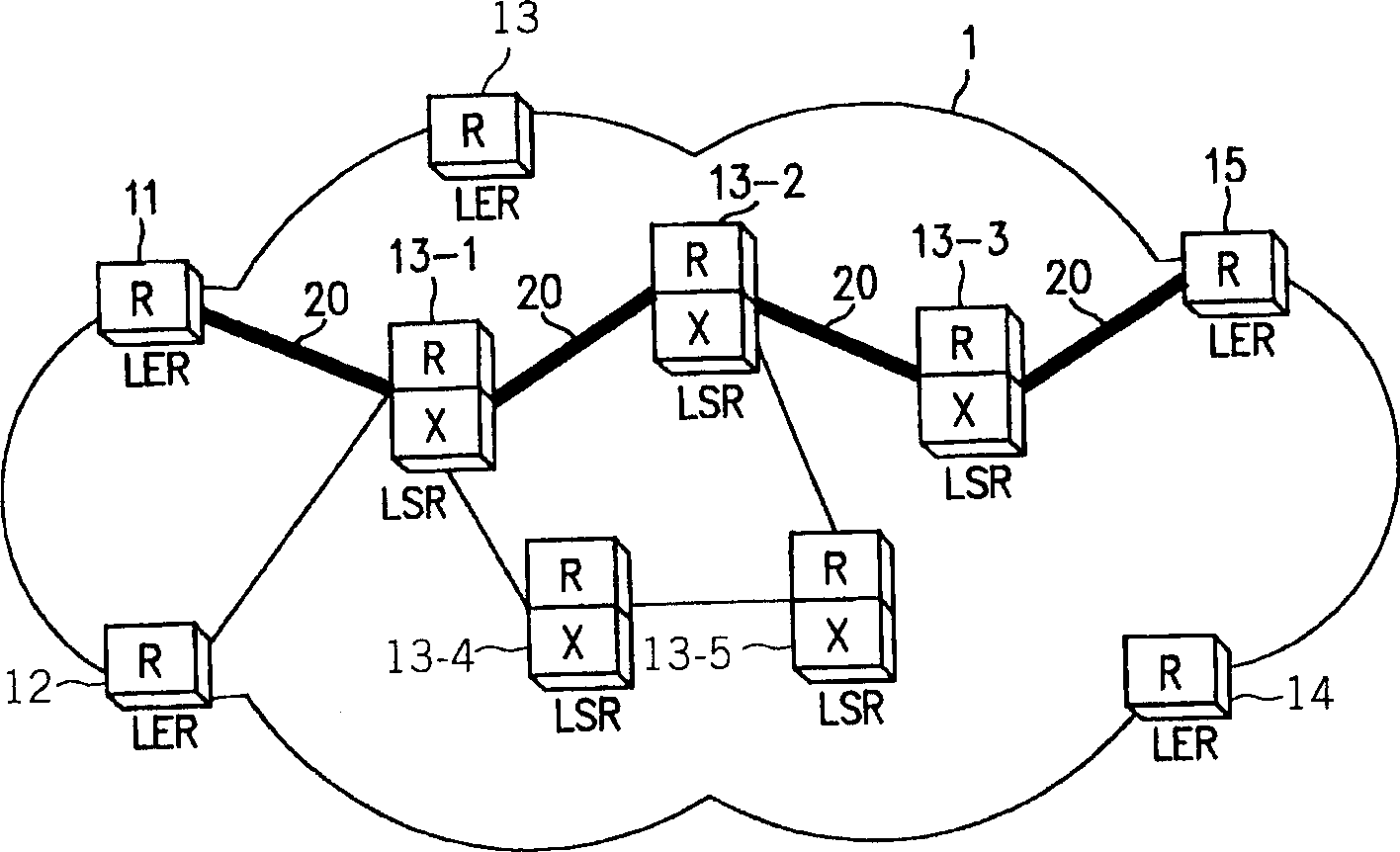
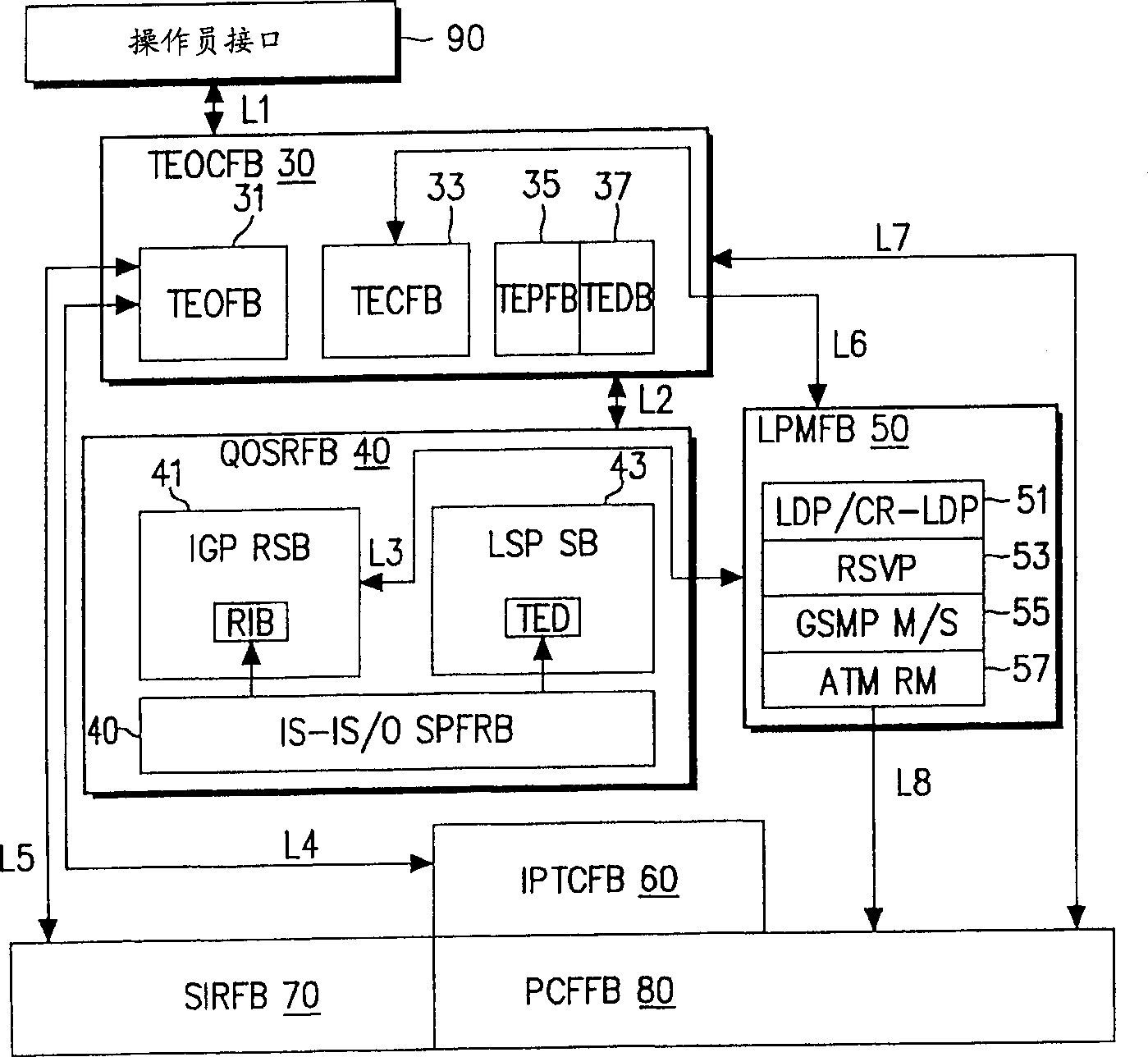
Data structure for implementation of traffic engineering function in multiprotocol label switching system and storage medium for storing the same
InactiveUS7065084B2Easy to manageQuality improvementData switching by path configurationStore-and-forward switching systemsForwarding equivalence classType-length-value
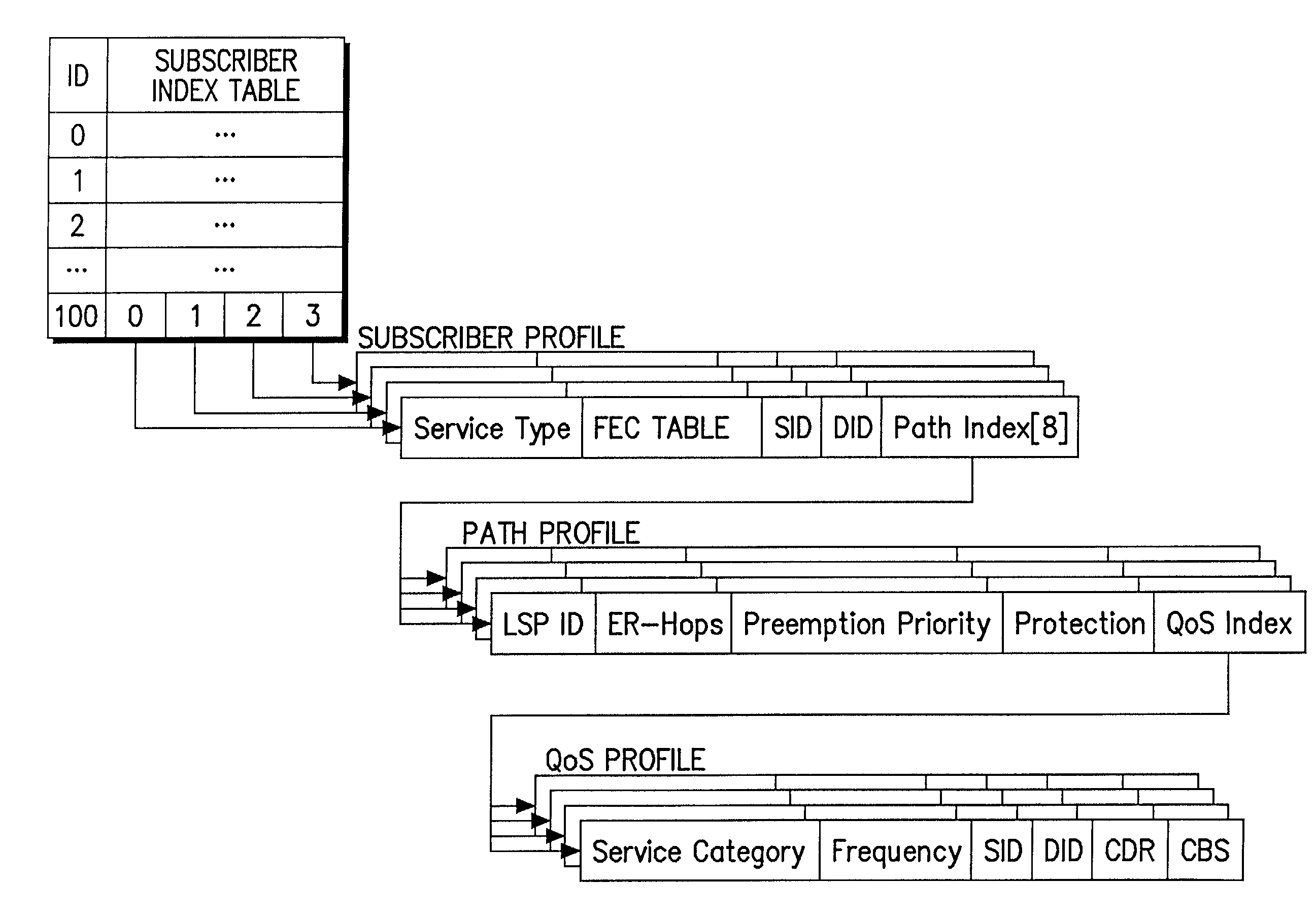
A data structure for implementing a traffic engineering function in a multiprotocol label switching system comprises: a subscriber profile including a plurality of entries for storing forwarding equivalence class (FEC) information required for setup of a label switched path (LSP) based on the traffic engineering function, the entries of the subscriber profile being sequentially assigned indexes corresponding to one traffic engineering service subscriber identification (ID); a path profile including a plurality of entries for storing respective path information items regarding a type length value (TLV) of a signal protocol required for setup of an explicit routed label switched ath (ER-LSP) based on the traffic engineering function, the entries of the path profile being sequentially assigned indexes corresponding to respective path information items; and a quality of service (QoS) profile including a plurality of entries for storing respective QoS information items regarding a TLV of a signal protocol required for setup of a constraint routed label switched path (CR-LSP) based on the traffic engineering function, the entries of the QoS profile being sequentially assigned indexes corresponding to respective QoS information items. The indexes assigned to the profile entries include a plurality of indexes set by an operator for interlinking corresponding ones of the subscriber profile entries, the path profile entries, and the QoS profile entries.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
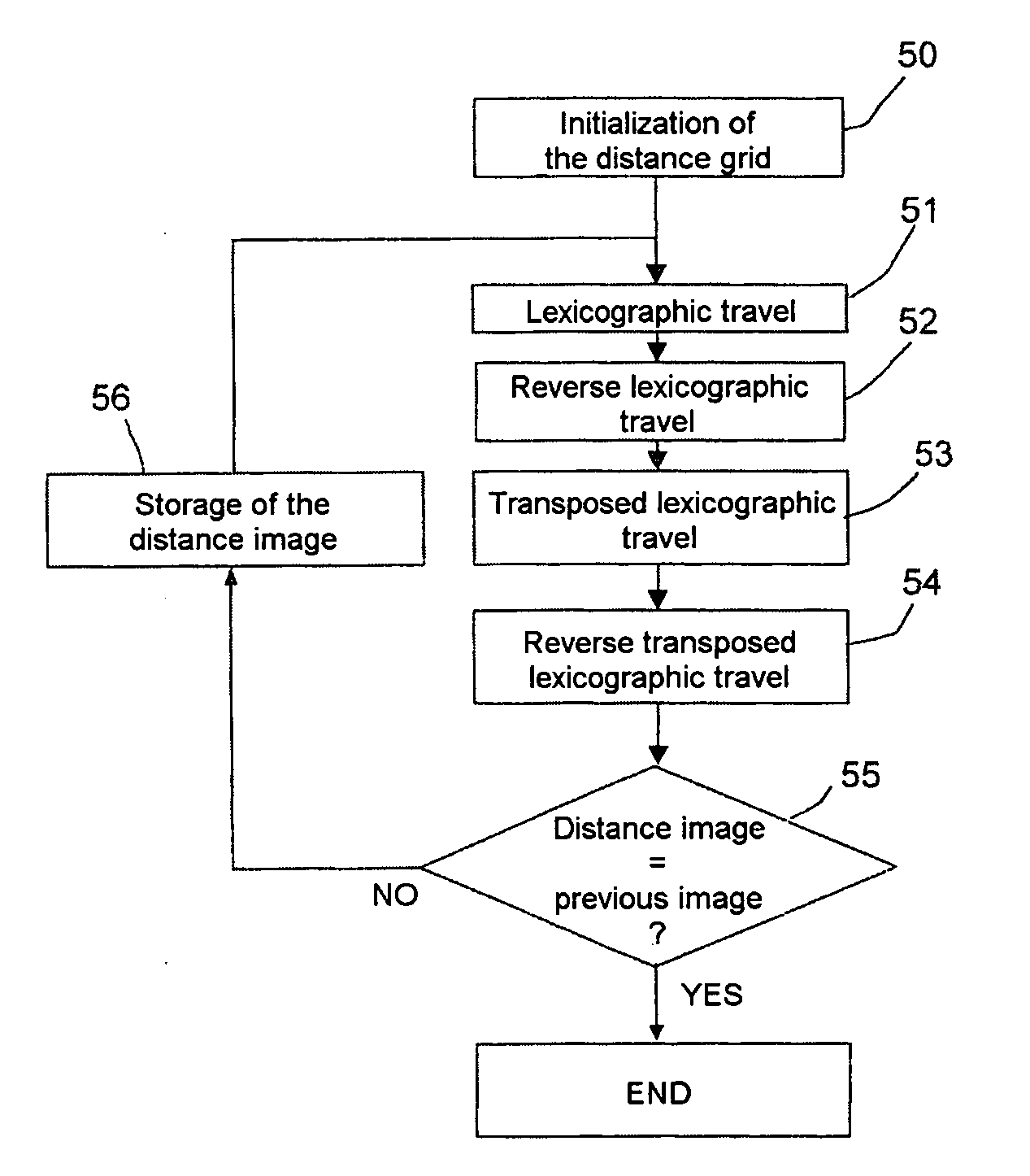
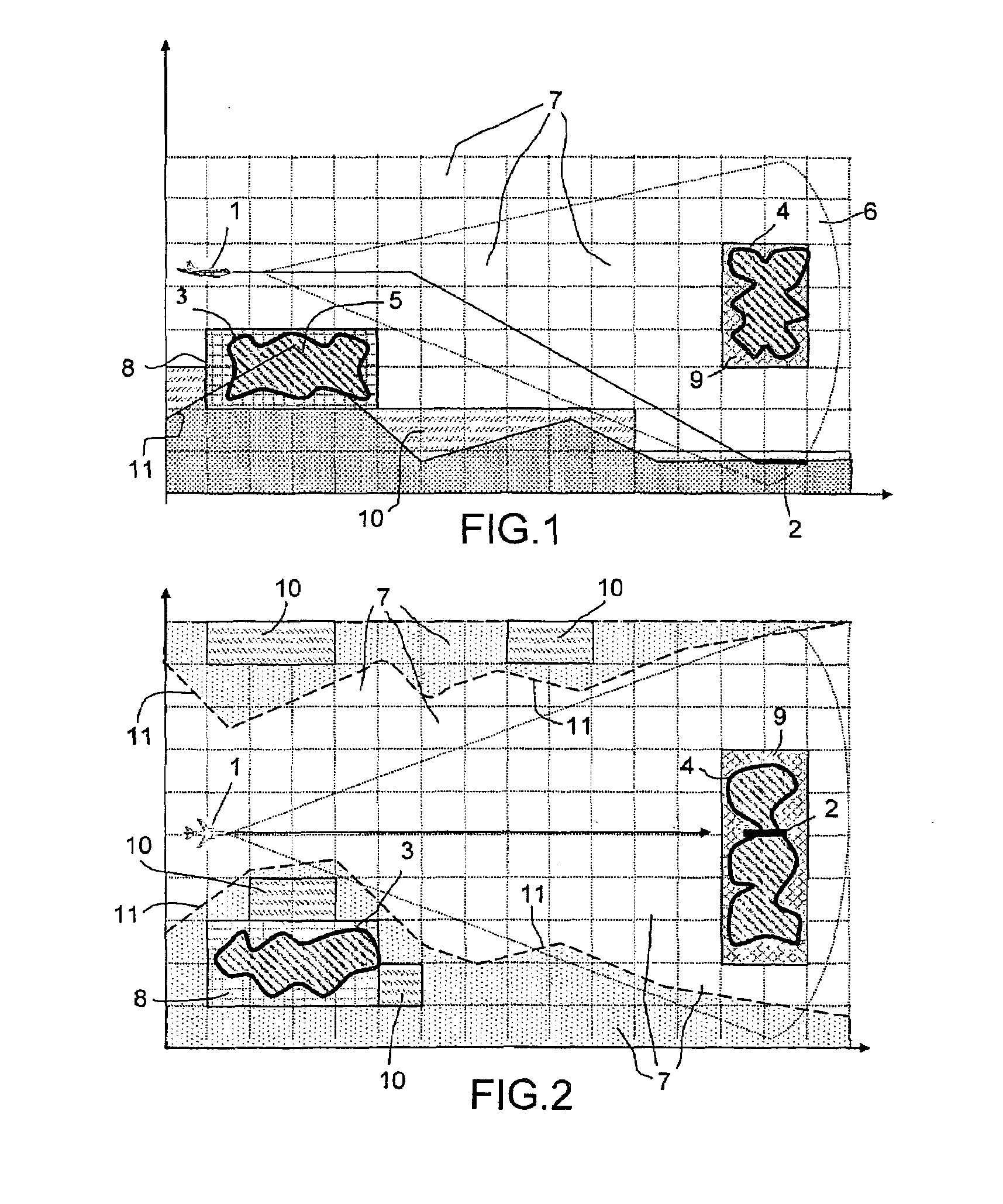
Distance estimation method for a moving object having a constrained vertical path profile
InactiveUS20080154493A1Road vehicles traffic controlNavigation instrumentsEstimation methodsChamfer distance
This method makes it possible to plot, from a terrain elevation database, a map of the distances of the points accessible to a moving object subject to constraints (inaccessible reliefs, unnegotiable obstacles, weather disturbances, path with an imposed vertical profile, etc.), the distances being measured only along paths that are practical for the moving object. It employs a chamfer distance transform applied to the image consisting of the projection on the horizontal plane of a 3D representation of the flying space of the moving object, which is likened to a mesh of elementary cubes associated with specific negotiation danger levels. It lists the typical paths without exceeding an acceptable danger threshold, going from a target point, the distance of which is to be estimated, to a source point, the origin of the distance measurements, and likens the distance of the target point to the length of the shortest practicable path or paths.
Owner:THALES SA
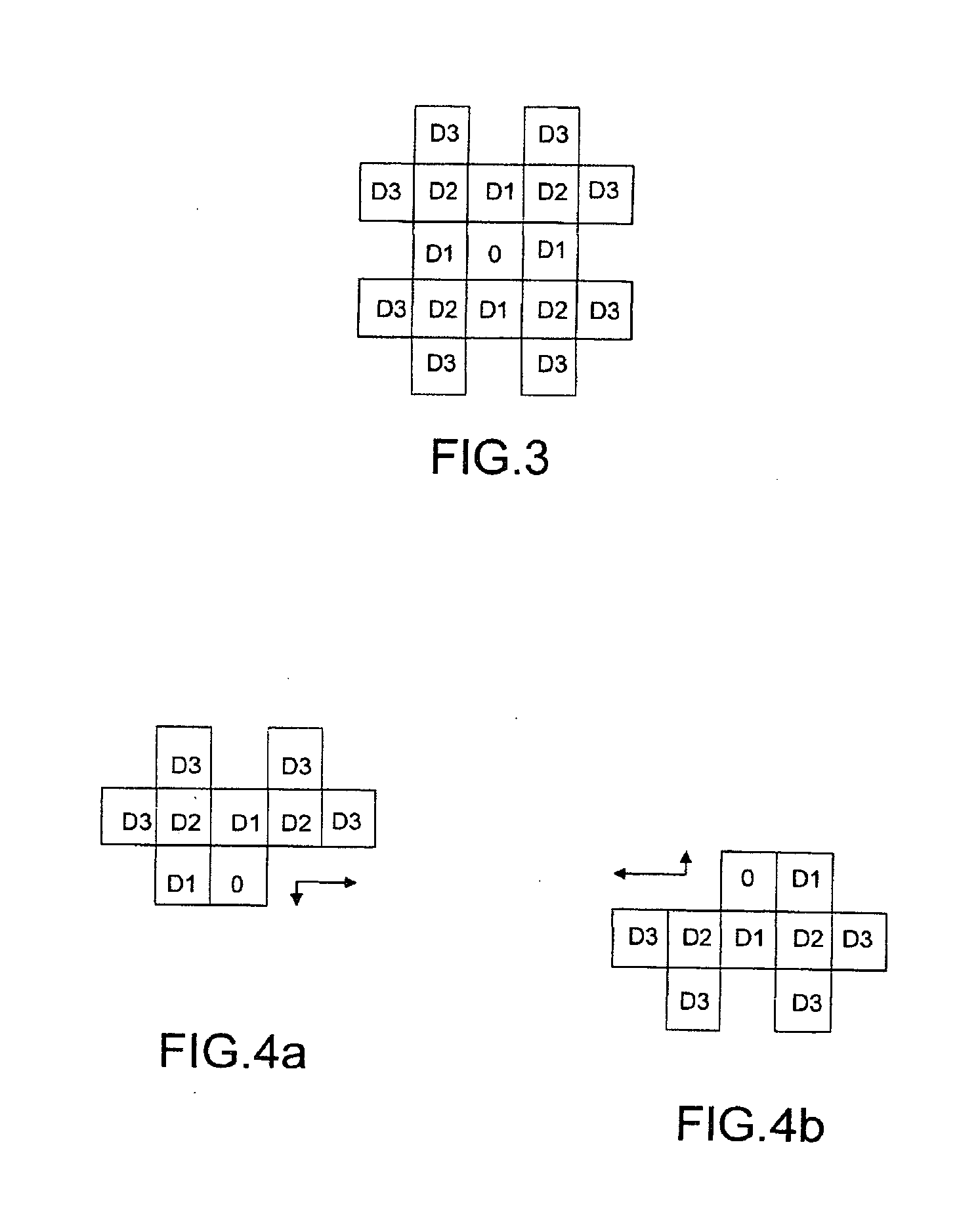
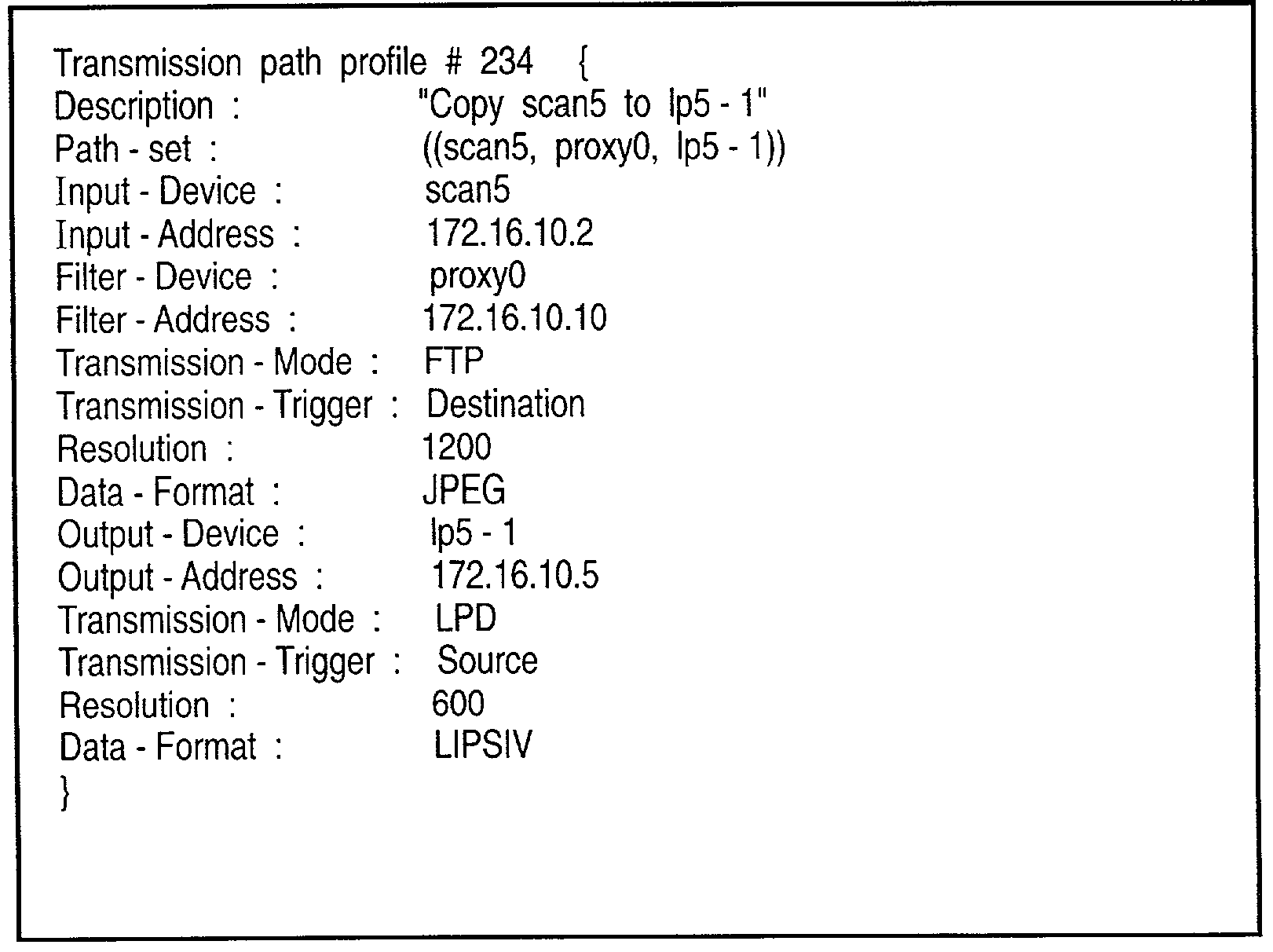
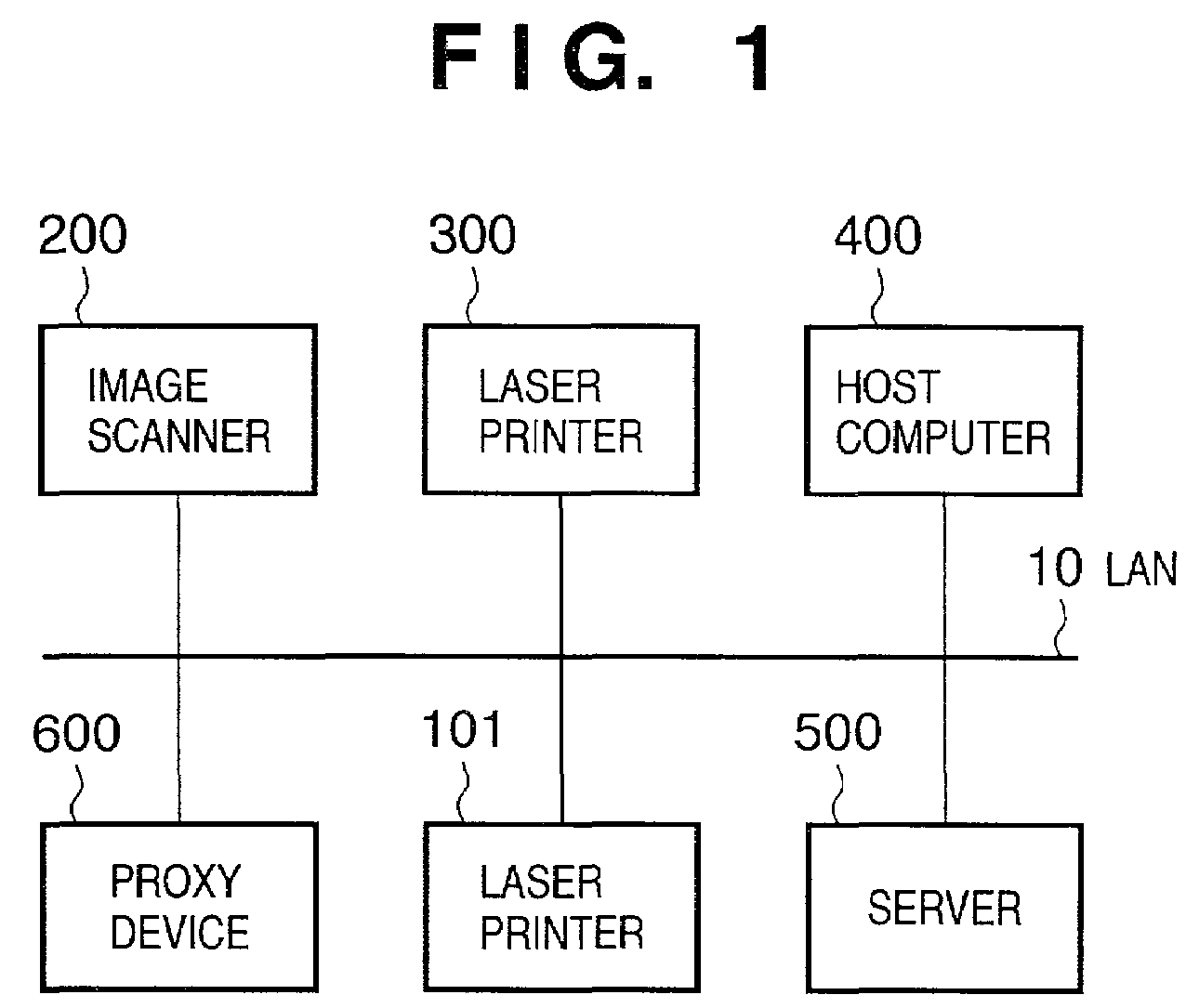
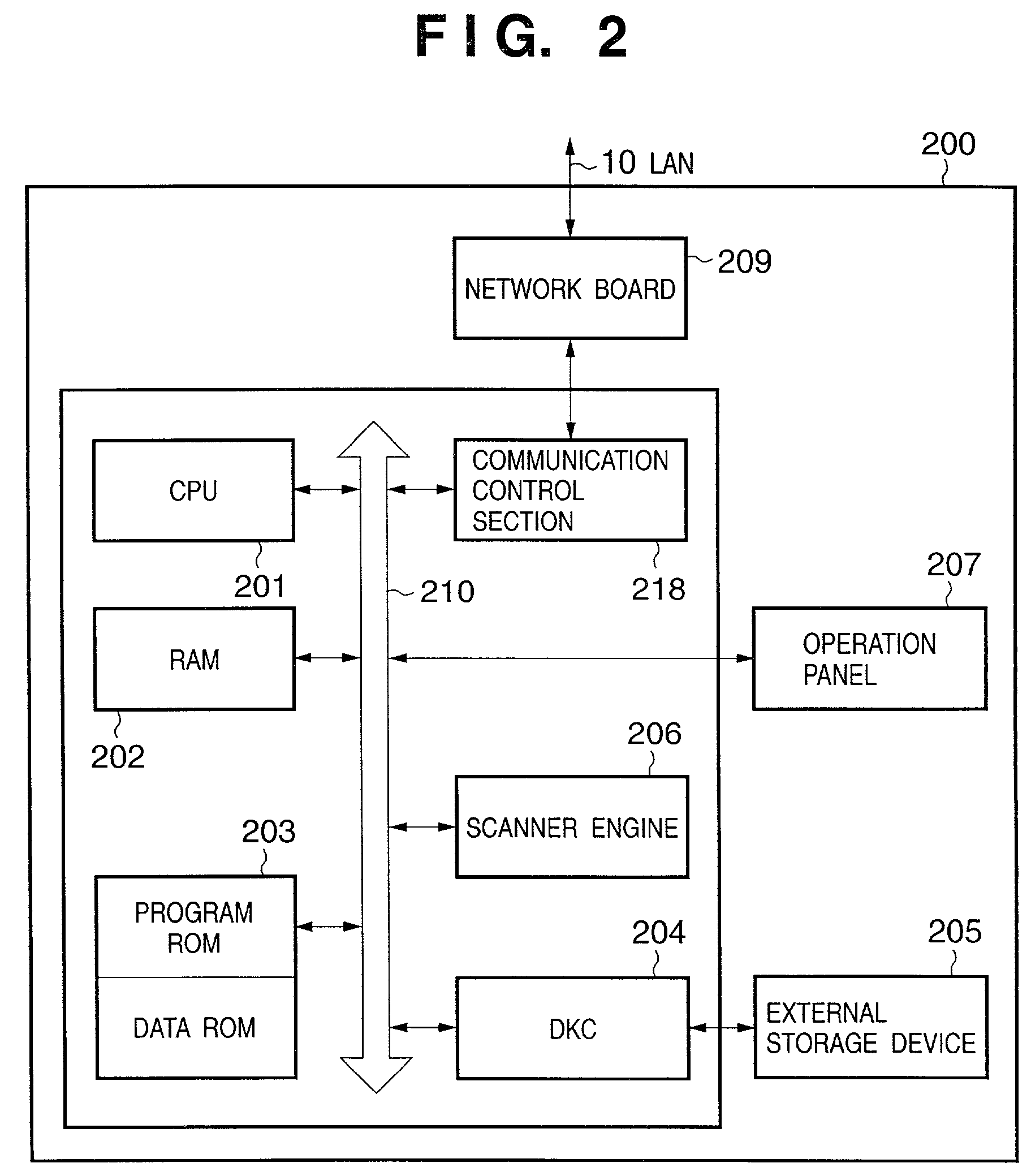
Image input/output system, image input/output control device, and control method therefor using device information indicating active execution of data communication or passive execution of data communication
InactiveUS7167258B2Simple compositionReduce loadDigitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsComputer hardwarePath profile
The present invention easily implements a virtual copying machine by connecting a scanner and printer on a network. When a passive scanner and passive printer are connected through a proxy device, the device profiles of the devices are collected to generate a transfer path profile. By referring to the transfer path profile, the proxy device issues an input request to the scanner to cause it read an image, receives the image data, issues an output request to the printer, and transfers the data received from the scanner to the printer to cause it to print the data.
Owner:CANON KK
Method for Detecting Critical Driving Situations of Lorries or Passenger Vehicles and Method for Avoiding Collisions
ActiveUS20140052355A1Analogue computers for trafficAnti-collision systemsDriver/operatorObject based
A method for detecting critical driving situations of motor vehicles, in particular for preventing collisions with an object in front of an own vehicle, has the following steps: detection of a current vehicle acceleration and a current vehicle velocity of an own vehicle; specification of an acceleration profile depending on driving variables of the own vehicle; assumption of a time progression of a foreseeable acceleration of the own vehicle based on its current acceleration; determination of a path profile of the own vehicle from the time progression of the foreseeable acceleration; acquisition of a current distance and a current relative velocity of an object in front of the own vehicle; calculation of the current absolute velocity of the object as well as of the absolute current acceleration of the object; assumption of a time progression of a foreseeable acceleration of the object based on its current acceleration; determination of a path profile of the object from the time progression of the foreseeable acceleration; comparison of the path profile of the own vehicle with the path profile of the object; and if the two path profiles intersect, determination of a probable collision time of the own vehicle with the object; establishment of a time before the probable collision time comparison of this time with the probable collision time determined; and if the probable collision time lies before the established time, issue of a warning to the driver of the own vehicle.
Owner:LUCAS AUTOMOTIVE GMBH
Mechanical chain tensioner with compliant blade spring
Owner:BORGWARNER INC
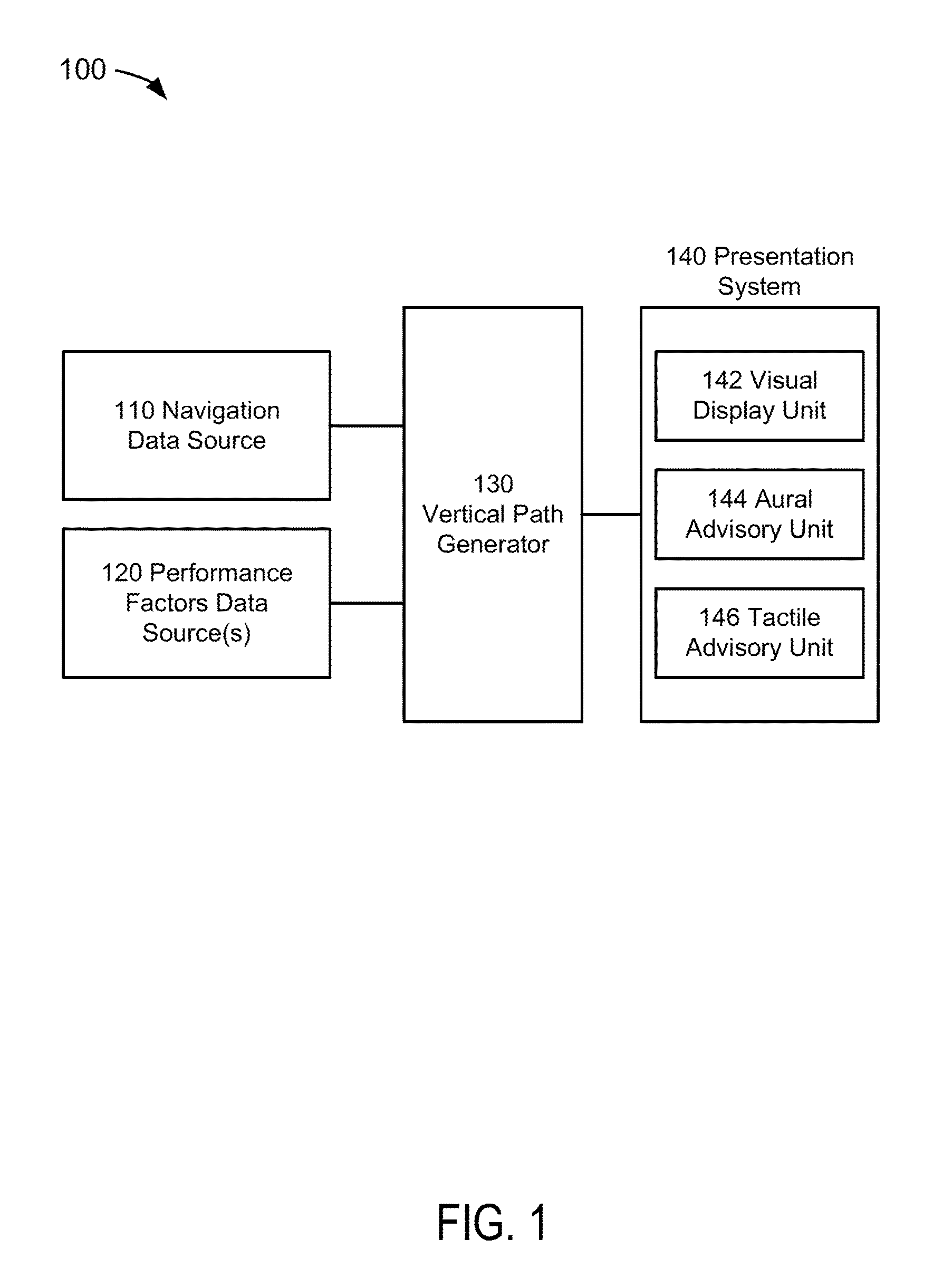
Vertical path profile generating system, device, and method
ActiveUS9583010B1Enhanced Situational AwarenessNavigation instrumentsVehicle position/course/altitude controlPath profileVisual perception
Present novel and non-trivial system, device, and method for generating a vertical path profile are disclosed. The vertical path profile generating system is comprised of a source of navigation data, a source of performance factors data, a vertical path generator (“VPG”) and a presentation system. The VPG may be configured to receive the navigation data representative of takeoff runway information; receive the performance data may be representative of aircraft performance factors; determine a first vertical path and / or second vertical path as a function of criteria employing the navigation data and the performance data; generate presentation data responsive to the determination; and provide the presentation data to one or more presentation devices comprised of, in part, a visual display unit configured to display a first takeoff path profile and / or a second takeoff path profile.
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
Dynamic protective envelope for crane suspended loads
A system and method for using a gantry crane to efficiently and safely transport loads such as containers and ship hatch covers from one location to another along a known path while avoiding collisions between the loads and obstructing objects which may be situated in the known path. A transceiver emitting laser beams may be used to establish both the position of the spreader and its load and the profile of the known path. Continuous comparisons are made by computer between the location of a dynamic digital protective envelope constructed around the crane spreader and its load, if any, and a digital representation of the profile of the known path to be traveled by the spreader and its load, if any. In the event, the comparison indicates intersection of the protective envelope and the path profile, a speed limit is imposed on the motor controlling the movement in the X axis of the trolley or in the Z axis of the spreader, as required to prevent a collision.
Owner:TMEIC
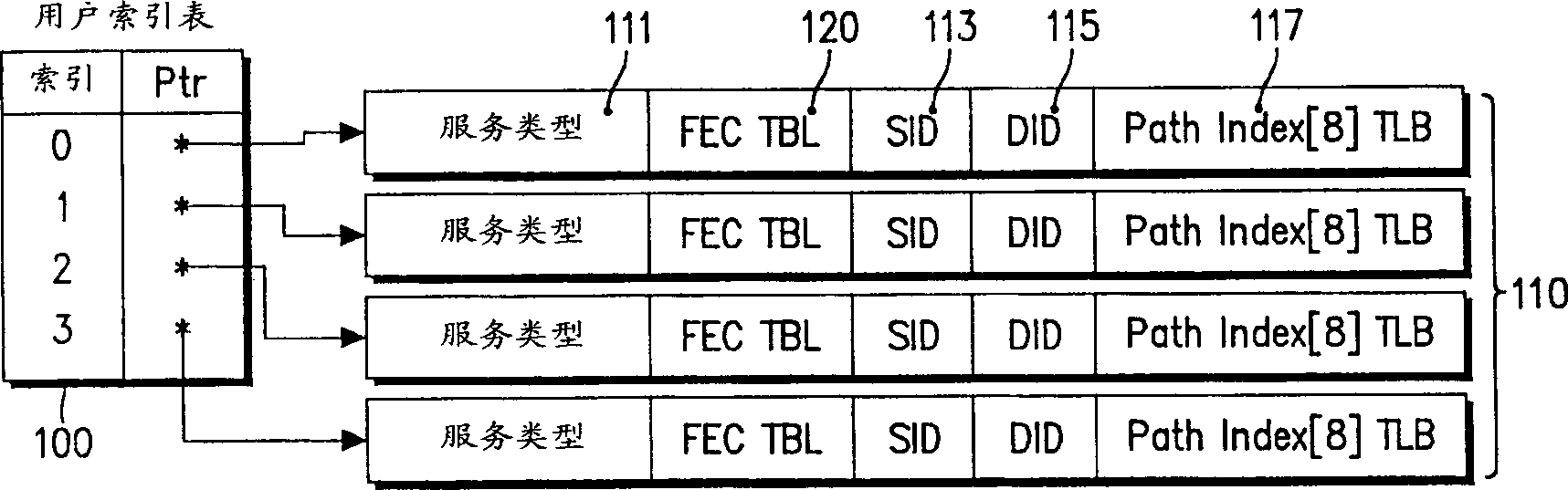
Data structure and storage medium for realizing multi-protocol habel exchange system engineering
InactiveCN1359218AQuality improvementHigh quality serviceMultiplex system selection arrangementsStore-and-forward switching systemsType-length-valueStore and forward
A data structure for implementing a traffic engineering function in a multiprotocol label switching system comprises: a subscriber profile including a plurality of entries for storing forwarding equivalence class (FEC) information, the entries of the subscriber profile being sequentially assigned indexes corresponding to one traffic engineering service subscriber identification (ID); a path profile including a plurality of entries for storing respective path information items regarding a type length value (TLV) of a signal protocol, the entries of the path profile being sequentially assigned indexes corresponding to respective path information items; and a quality of service (QoS) profile including a plurality of entries for storing respective QoS information items regarding a TLV of a signal protocol, the entries of the QoS profile being sequentially assigned indexes corresponding to respective QoS information items. The indexes assigned to the profile entries include a plurality of indexes set by an operator for interlinking corresponding ones of the subscriber profile entries, the path profile entries, and the QoS profile entries.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
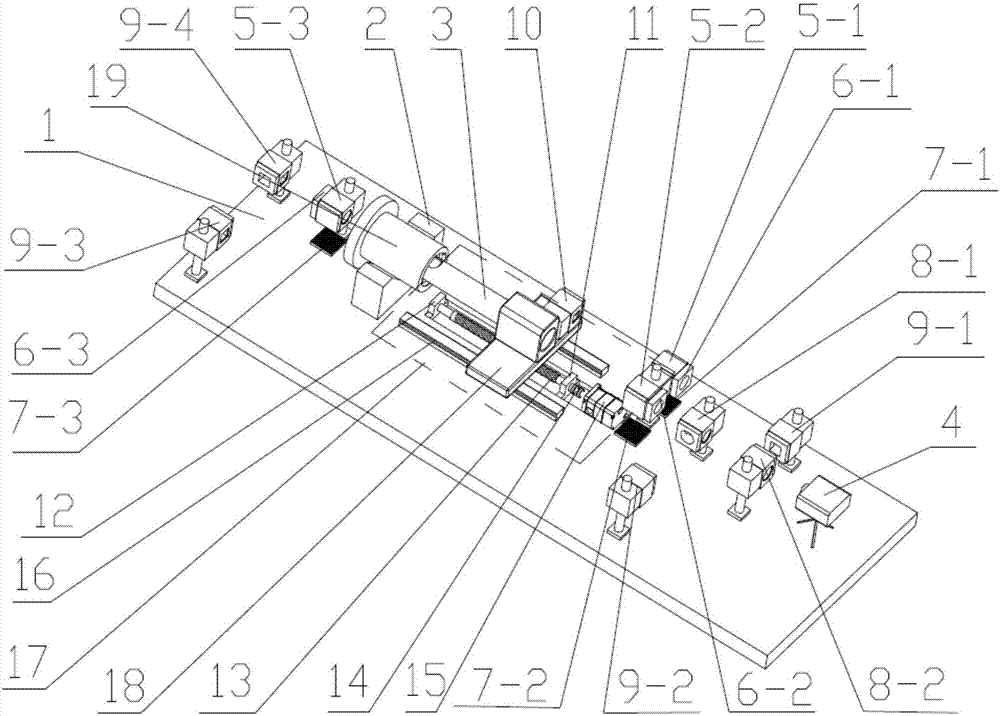
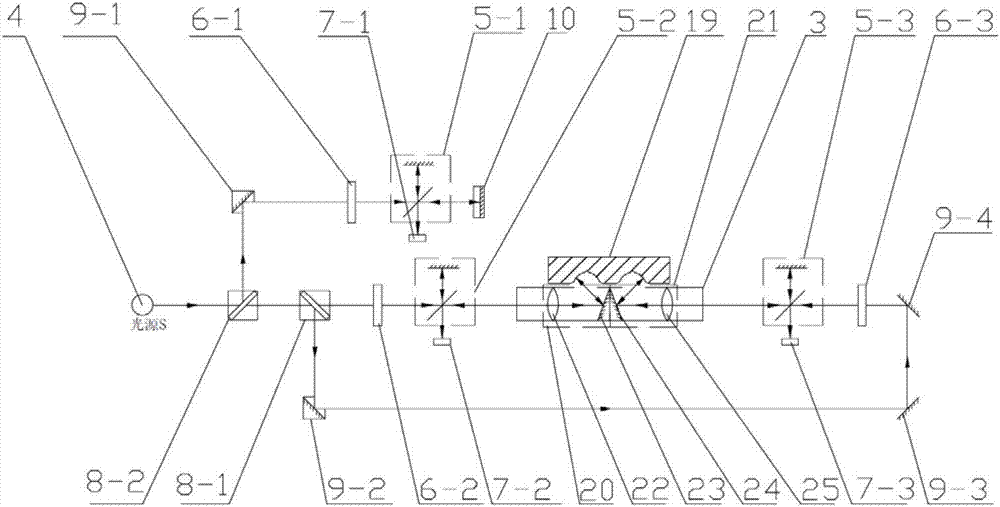
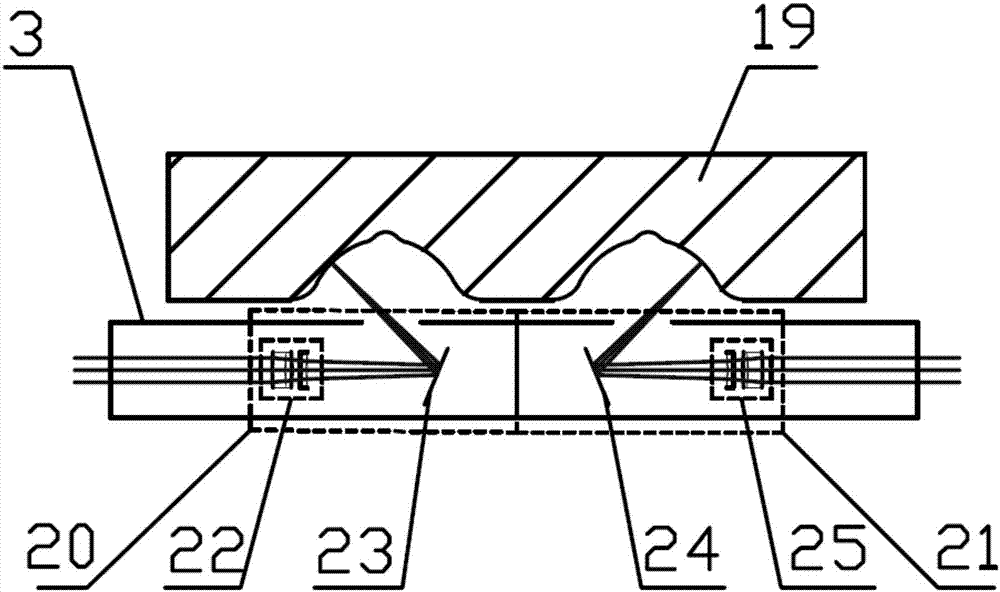
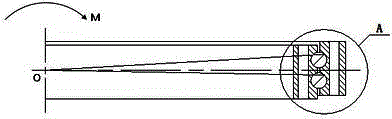
Novel device for detecting inner rolling path profile of ball screw nut, and method of device
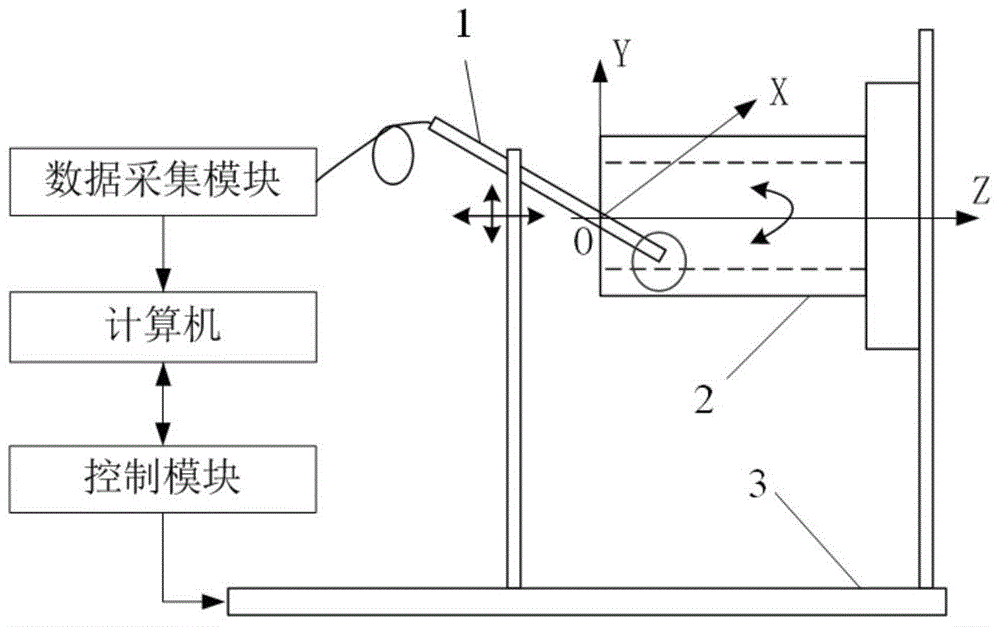
ActiveCN107014311ANo need for secondary adjustmentSuitable for automated production testing needsUsing optical meansPhotovoltaic detectorsBall screw
The invention discloses a device for detecting the inner rolling path profile of a ball screw nut, and the device comprises a marble platform, a nut clamping device and an X-axis linear movement platform, wherein the nut clamping device and the X-axis linear movement platform are disposed on the marble platform. The nut clamping device is provided with a to-be-detected part, and the laser light emitted by a double-frequency laser generator passes through a light splitter and a light right-angle reflector to reach a laser interferometer. The first laser interferometer is used for measuring the lateral displacement of a workbench. A second interferometer and a third interferometer play the same role, and the light passing through the second and third interferometers will generate diffuse reflection on a rolling path of the to-be-detected part. The returned light will be received by a photoelectric detector, and the contours of left and right arcs of the inner rolling path of the to-be-detected part are obtained with the movement of a measuring rod fixed on the X-axis linear movement platform. The device is high in precision, is high in measurement speed, does not damage the detected part, is high in automation degree, and meets the demands of automatic detection.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
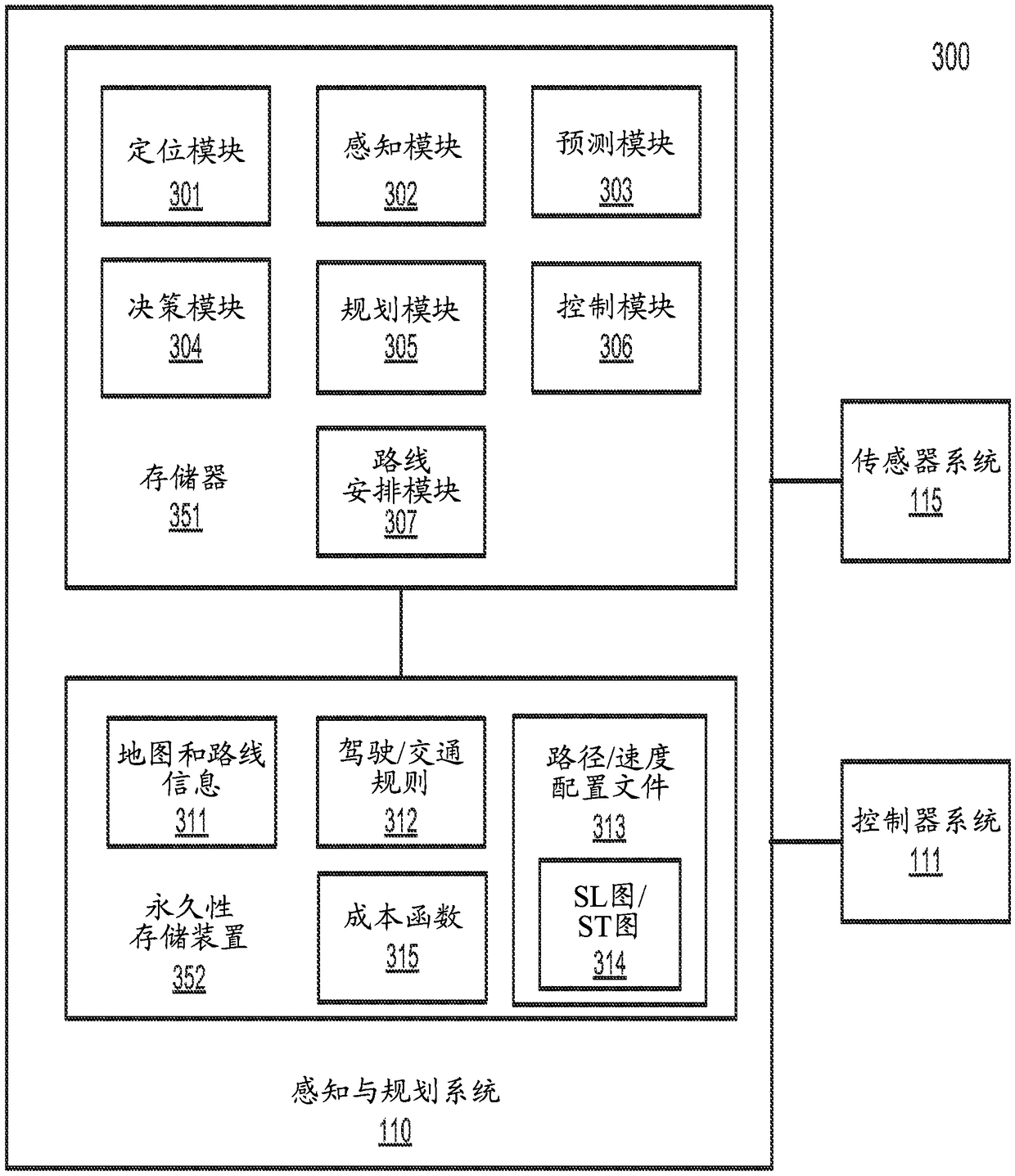
DP and QP based decision and planning for autonomous driving vehicles
ActiveCN109491377AControl safety arrangementsAutonomous decision making processSimulationPath profile
According to some embodiments, a system calculates a first trajectory based on a map and a route information. The system generates a path profile based on the first trajectory, traffic rules, and an obstacle information describing one or more obstacles perceived by the ADV. The system generates a speed profile based on the path profile, where the speed profile includes, for each of the obstacles,a decision to yield or overtake the obstacle. The system performs a quadratic programming optimization on the path profile and the speed profile to identify an optimal path with optimal speeds. The system generates a second trajectory based on the optimal path and optimal speeds to control the ADV autonomously according to the second trajectory.
Owner:BAIDU USA LLC
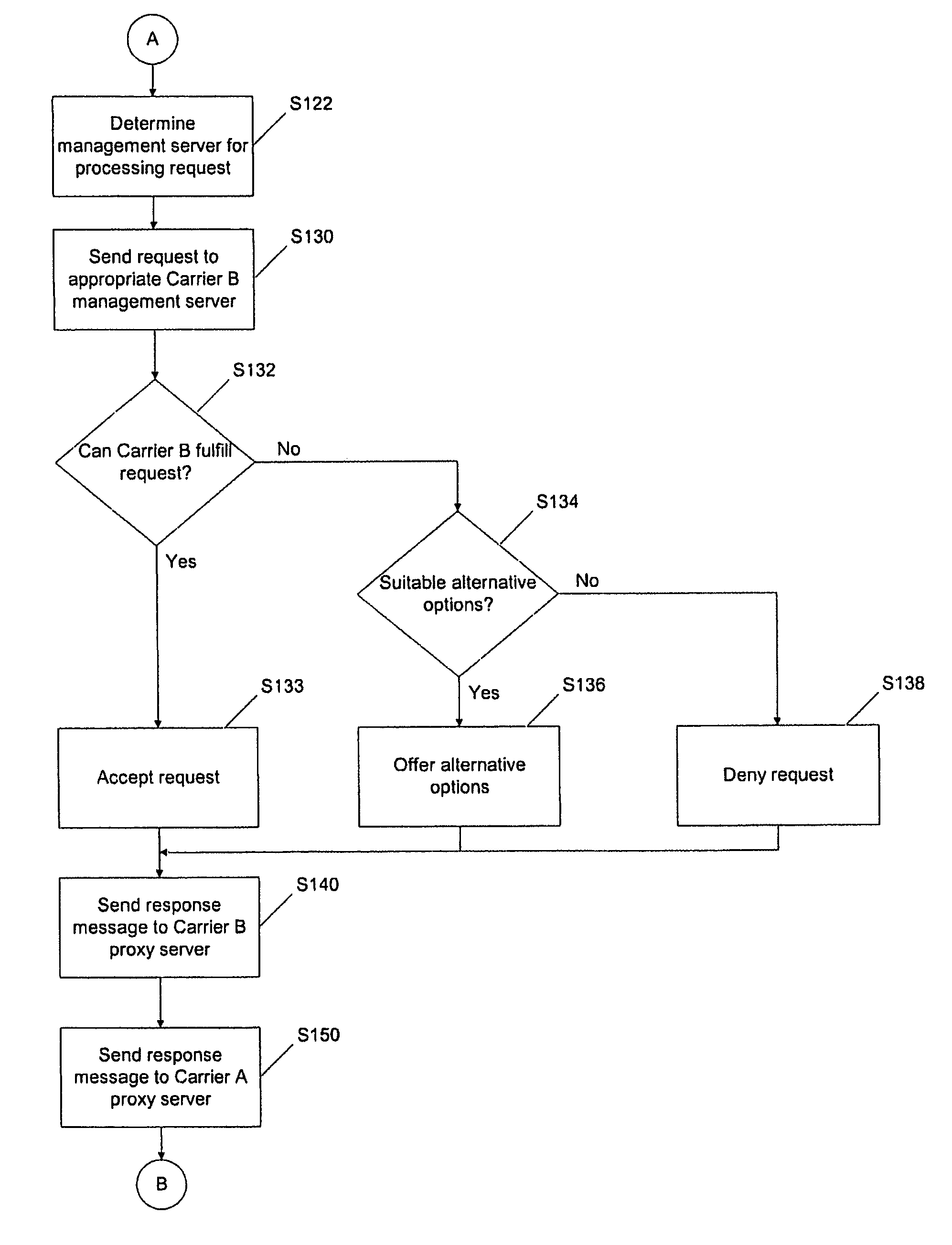
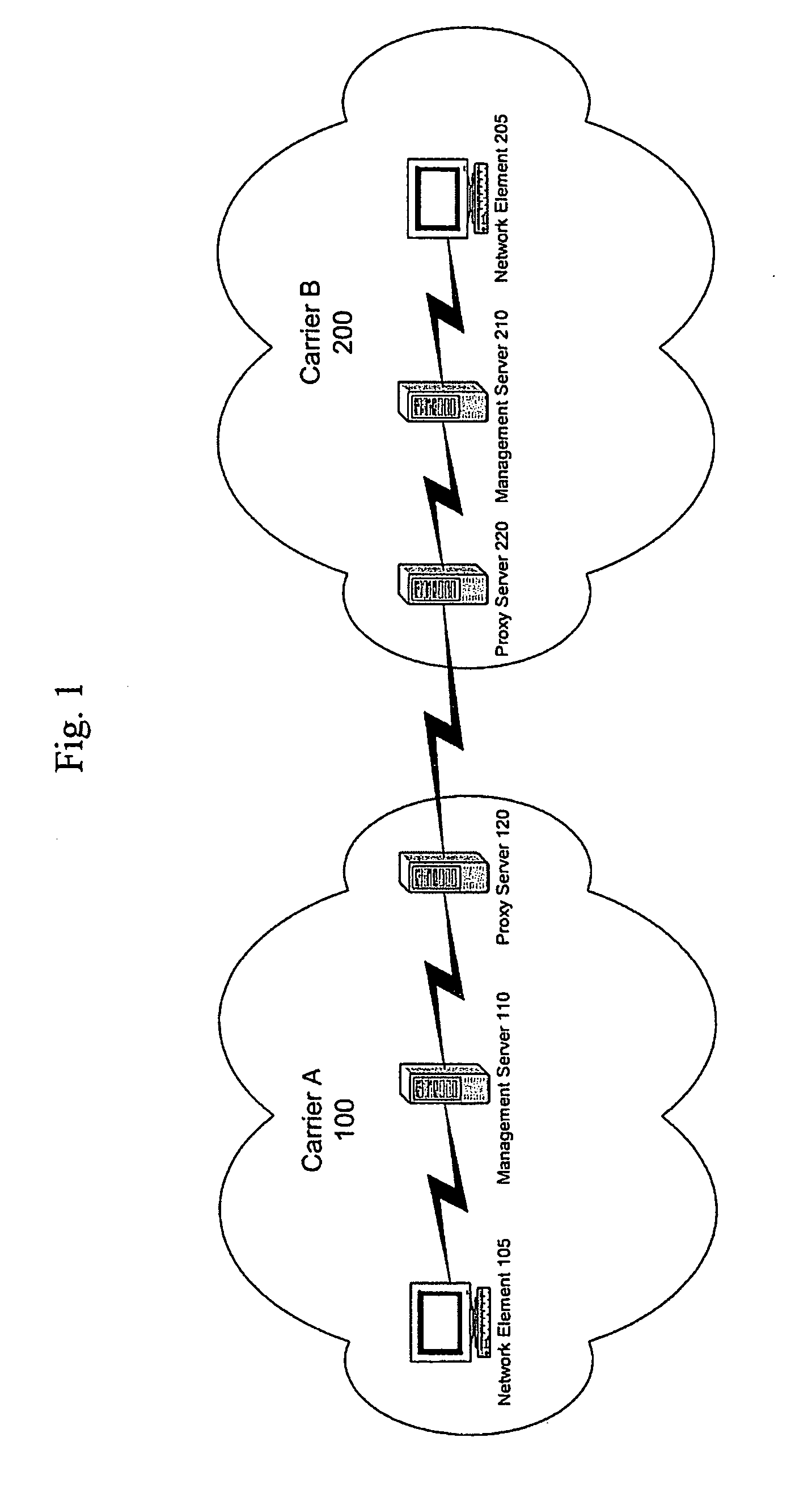
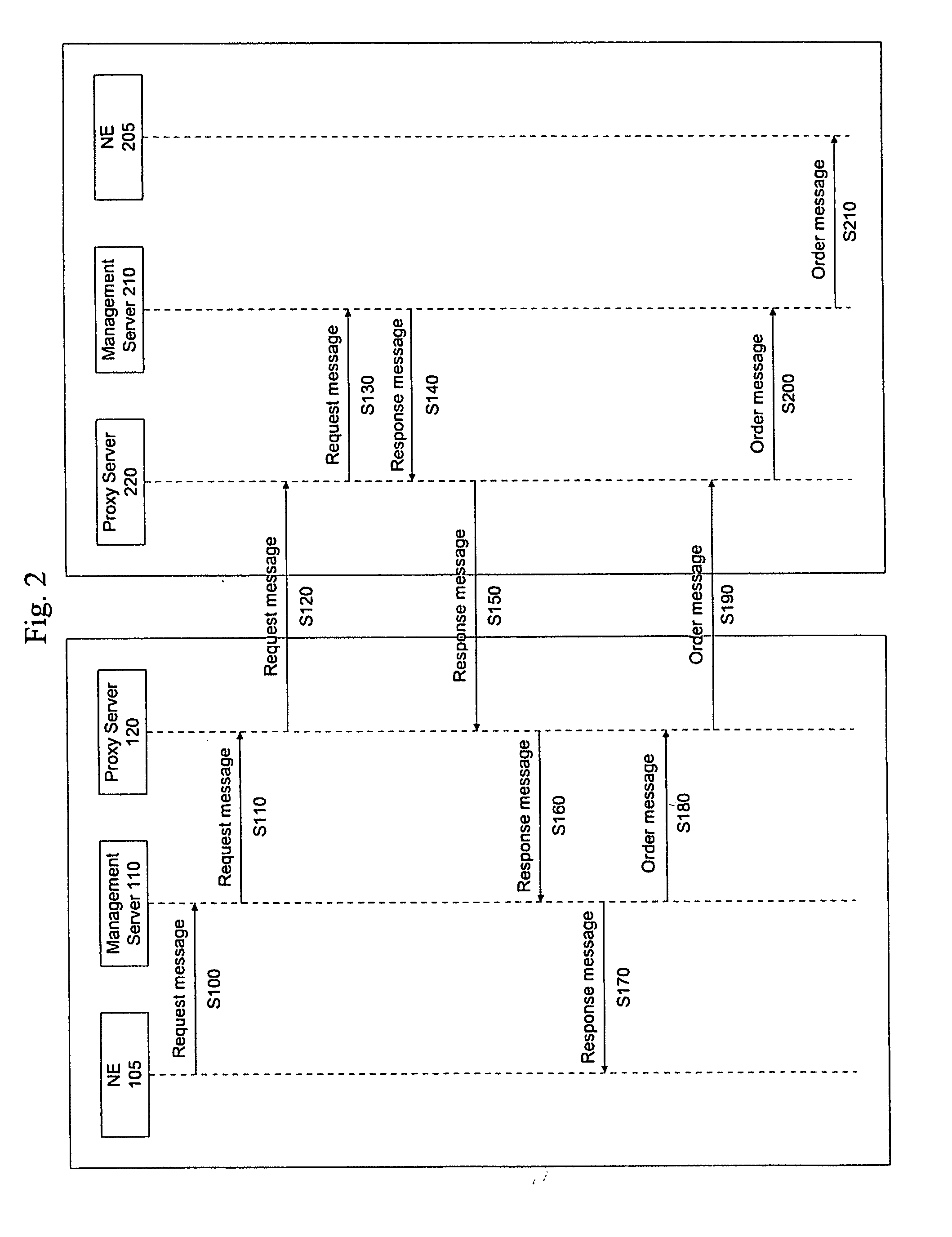
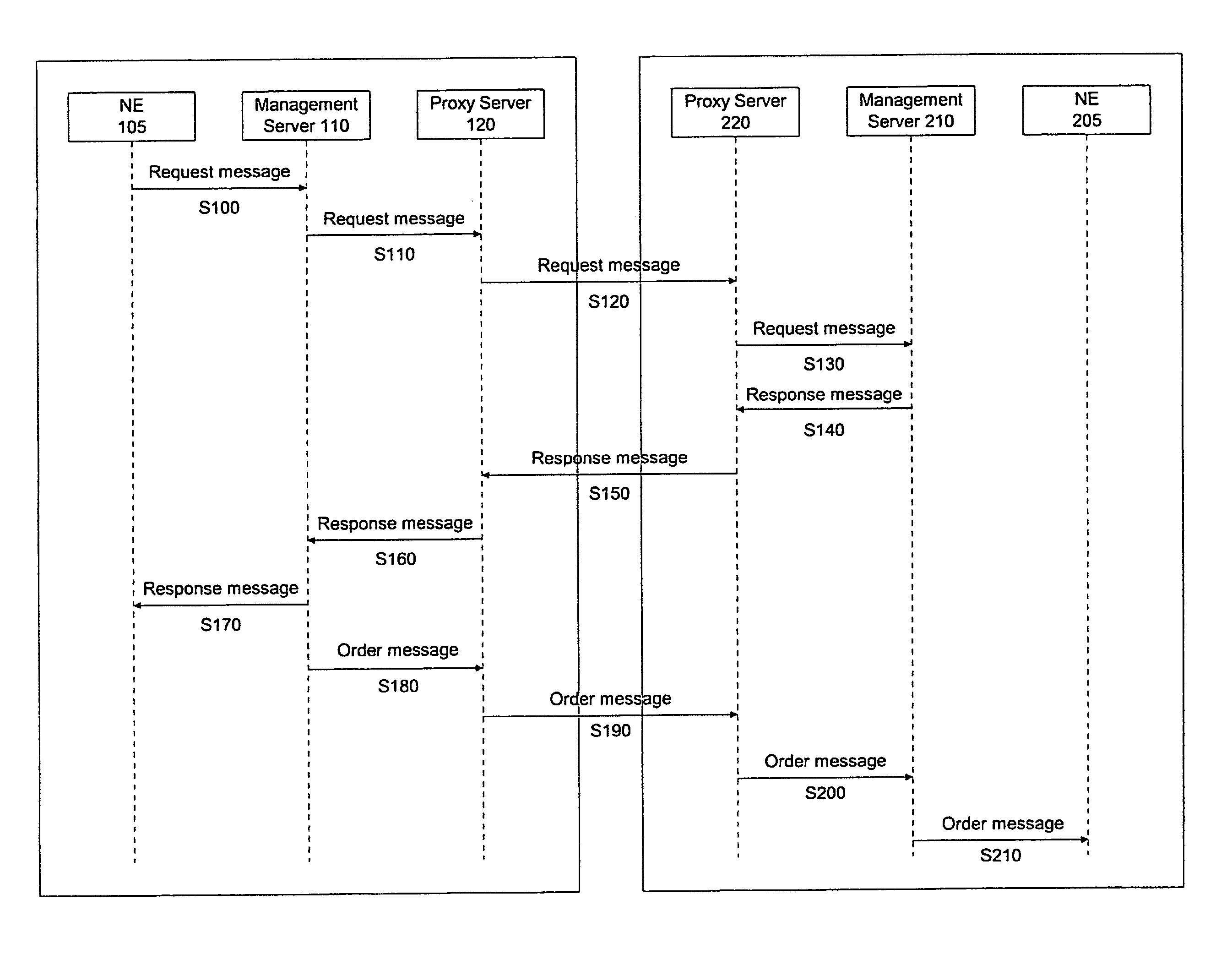
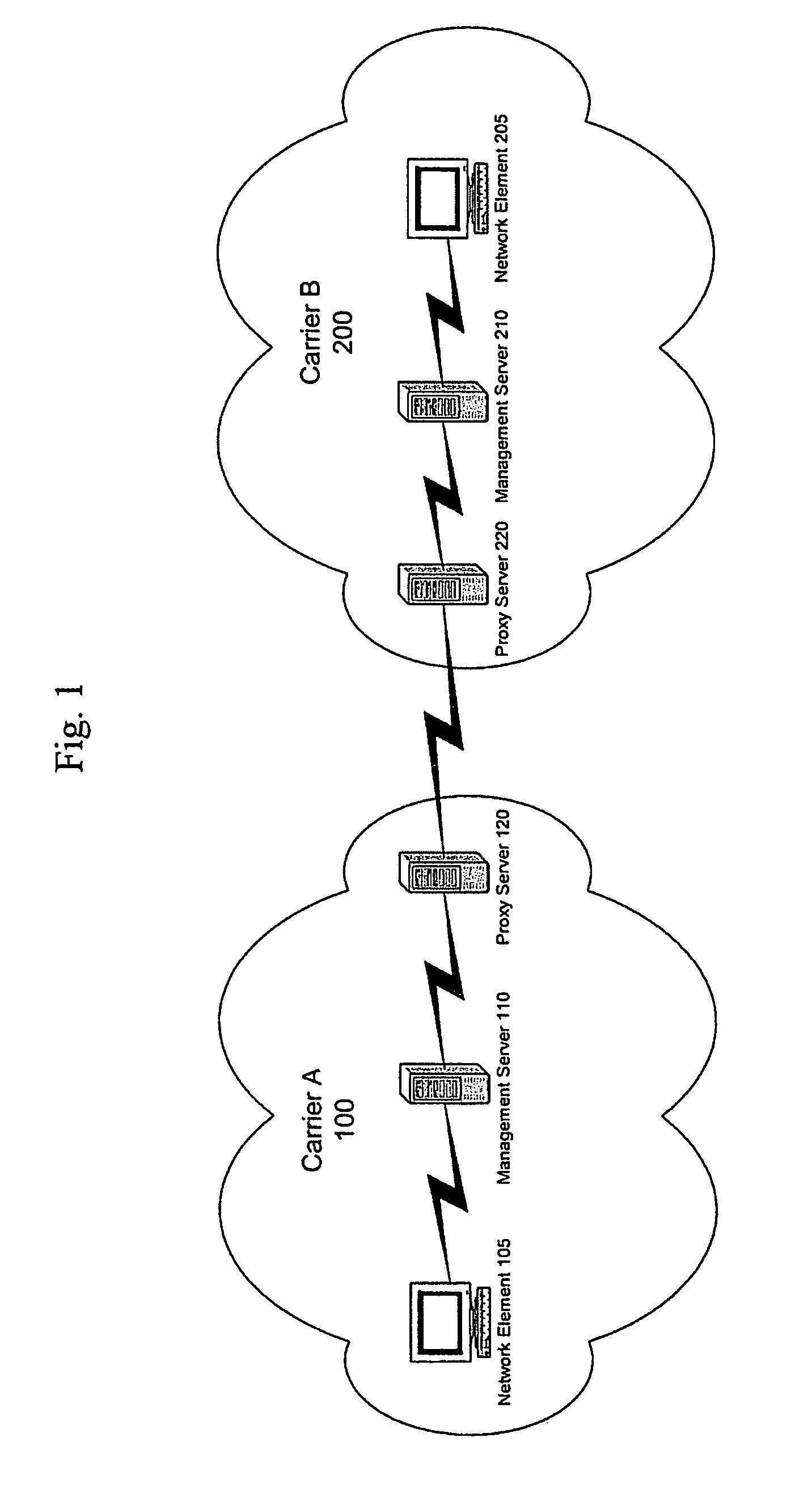
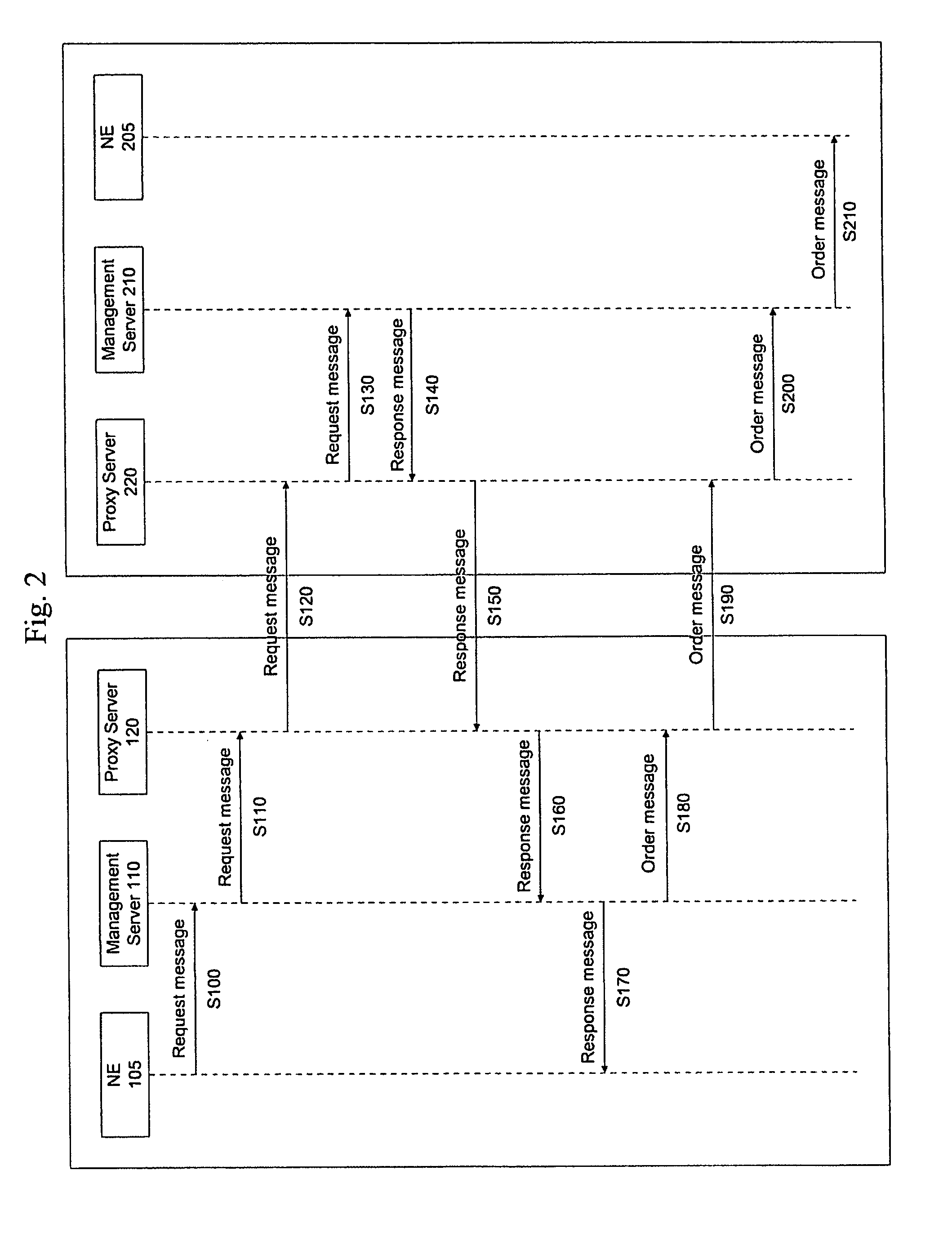
Carrier interoperability for critical services
A system processes communication path requests in an autonomous system. The system includes a proxy server that receives a request message from an external system requesting establishment of a communication path through the autonomous system. The request message includes a desired communication path profile including a desired level of redundancy. The system also includes a management server in the autonomous system that receives the request message from the proxy server, generates a response message indicating whether a communication path corresponding to the desired communication path profile is available, and sends the response message to the proxy server. The proxy server receives the response message and transmits the response message to the external system.
Owner:SBC KNOWLEDGE VENTURES LP
Preferential path profiling
InactiveUS8079020B2Error detection/correctionSpecific program execution arrangementsArray data structureParallel computing
This paper describes preferential path profiling, which enables profiling a specified subset of all possible program paths with very low overhead. Preferential path profiling compactly identifies paths of interest using an array. More specifically, PPP assigns a unique and compact path index identifier to all interesting paths that can be used to index into a path array. The path array contains a second path value identifier that is used to distinguish interesting paths from other program paths This path numbering allows the implementation of preferential path profiling to use array-based counters instead of hash table-based counters for identifying paths of interest and gathering path profiles, which significantly reduces execution time and computational resource overhead during profiling.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
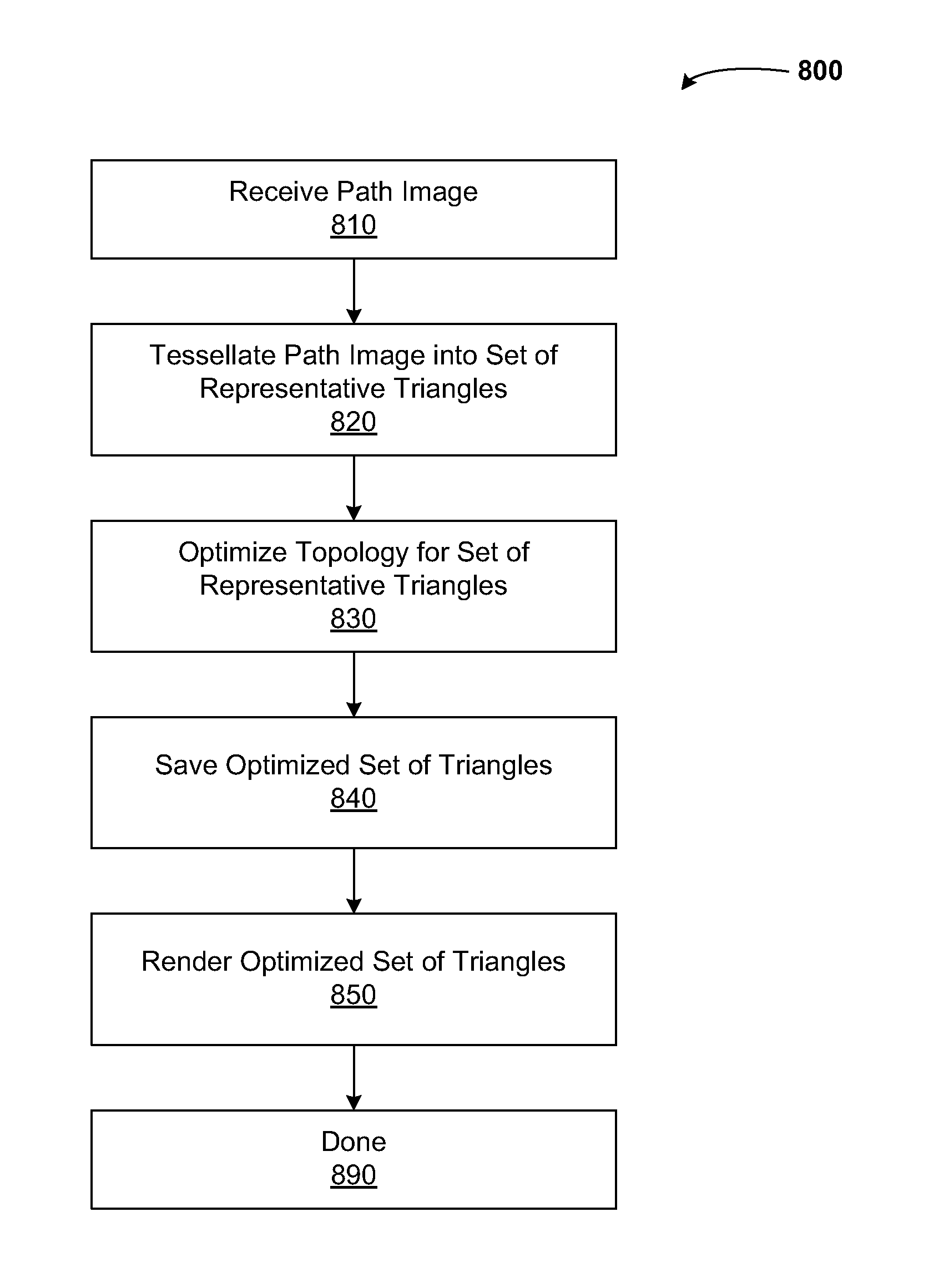
Optimizing triangle topology for path rendering
ActiveUS20140168222A1Efficient rasterizationLow costDrawing from basic elementsFilling planer surface with attributesComputer graphics (images)Path profile
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
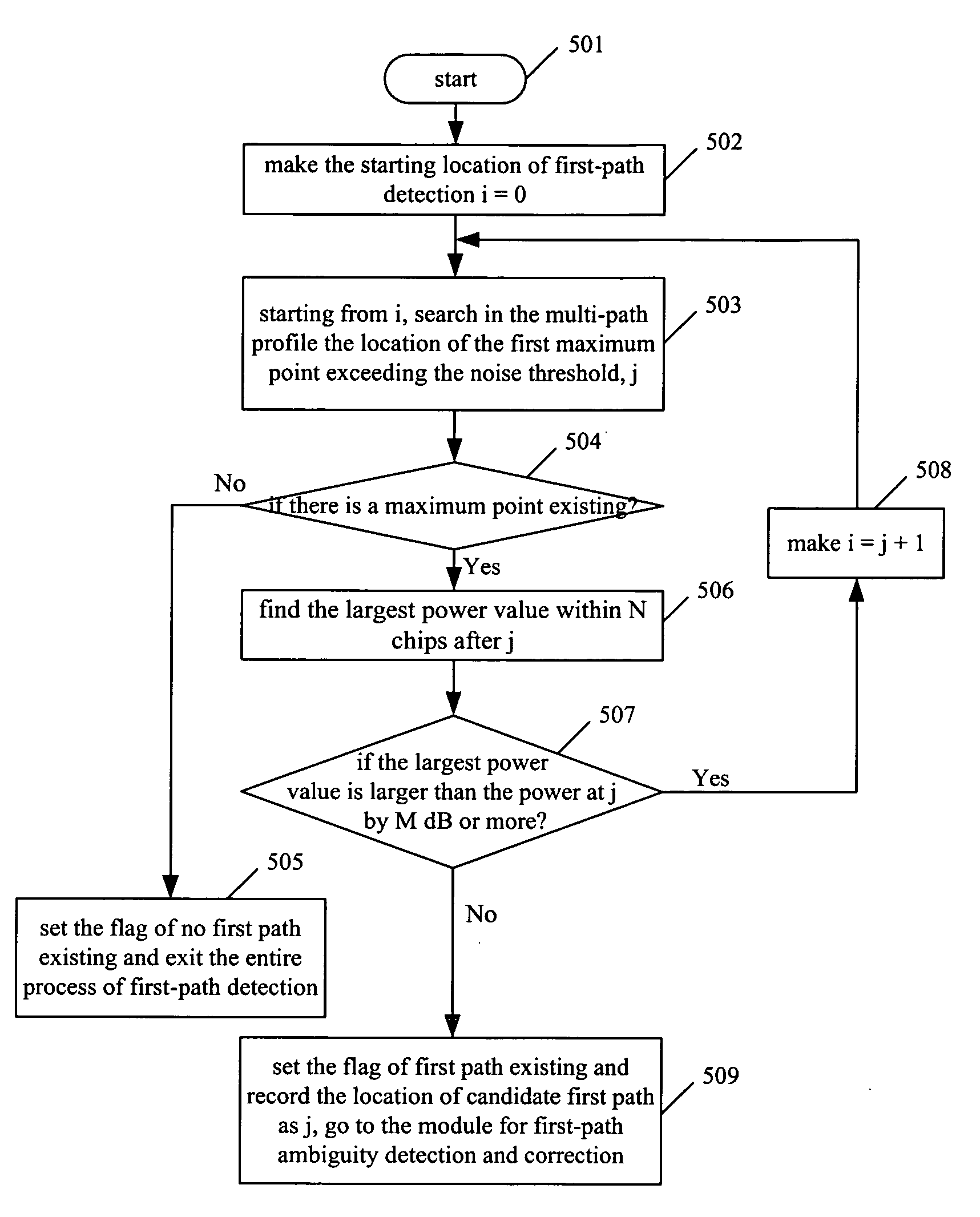
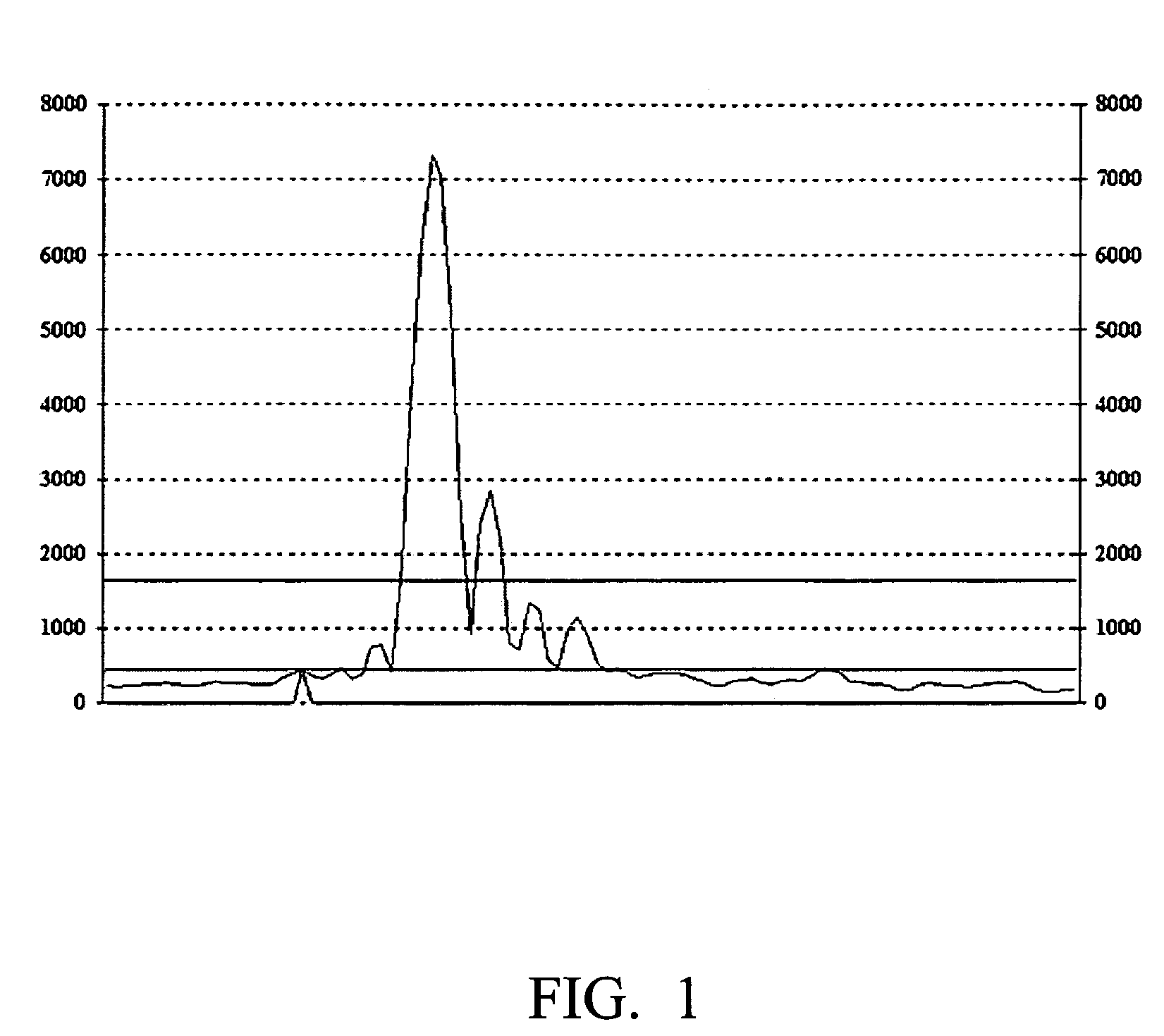
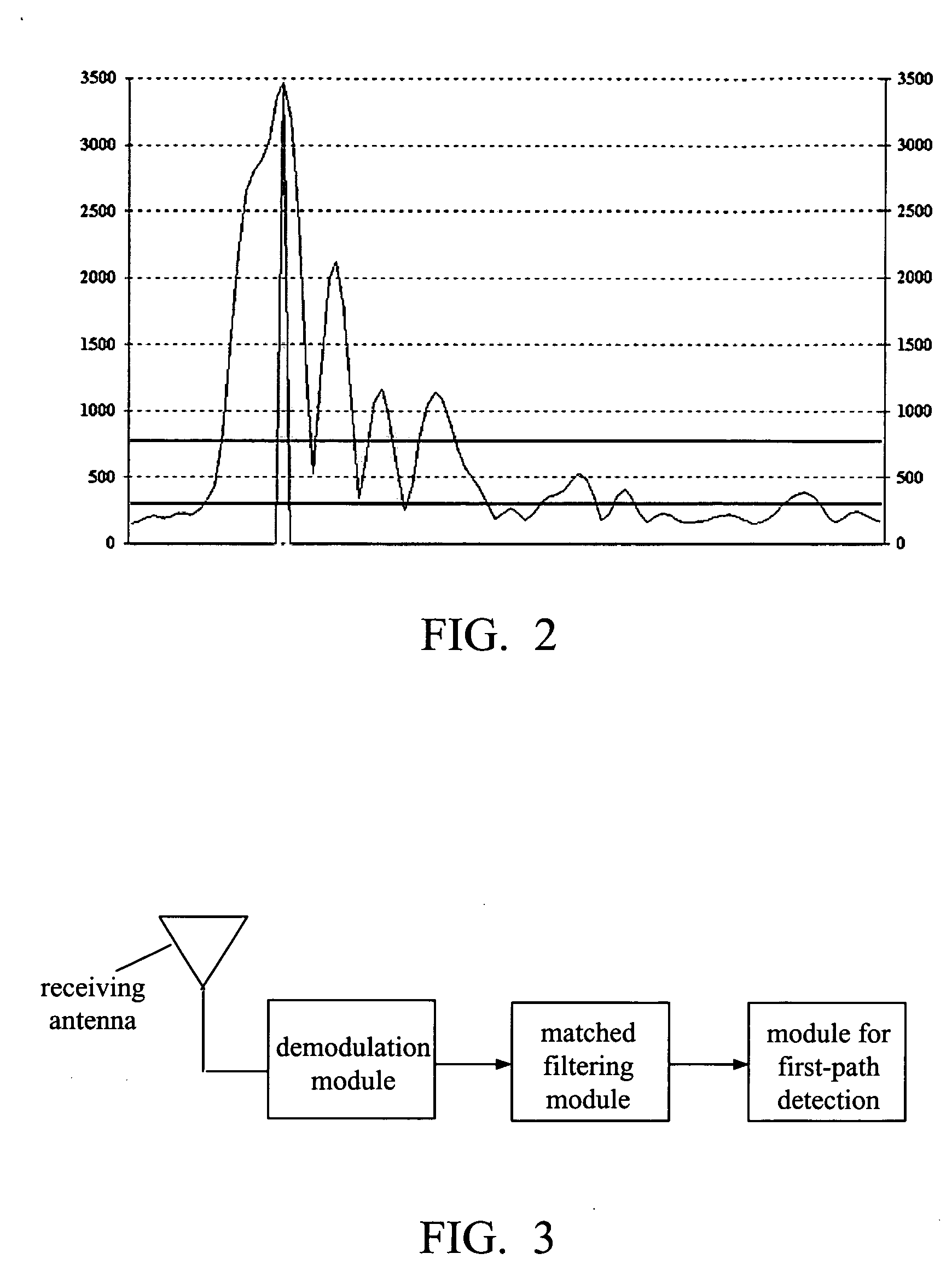
Method and apparatus for precise first-path detection in cdma mobile communications system
ActiveUS20070115870A1Accurate correctionHigh resolutionTransmission control/equalisingRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsCommunications systemSide lobe
The present invention relates to a method and apparatus of precise first-path detection in CDMA mobile communications systems, comprising the steps of: a. calculating the noise threshold for the first-path detection according to the multi-path profile; b. judging whether there is a maximum point exceeding the noise threshold in the multi-path profile, if yes, carrying out side-lobe suppression at this maximum point and obtaining the candidate first path; otherwise, setting the flag of no first path existing, and exiting the entire process of first-path detection; c. judging according to the location of the candidate first path whether the first path is ambiguous, if yes, carrying out correction of first-path ambiguity, obtaining the corrected location of final first path, and exiting the entire first-path detection process; otherwise, outputting the location of candidate first path as the location of final first path. The apparatus in accordance with this invention comprises at least a module for noise threshold calculation, a module for side-lobe suppression, and a module for first-path ambiguity detection and correction.
Owner:XFUSION DIGITAL TECH CO LTD
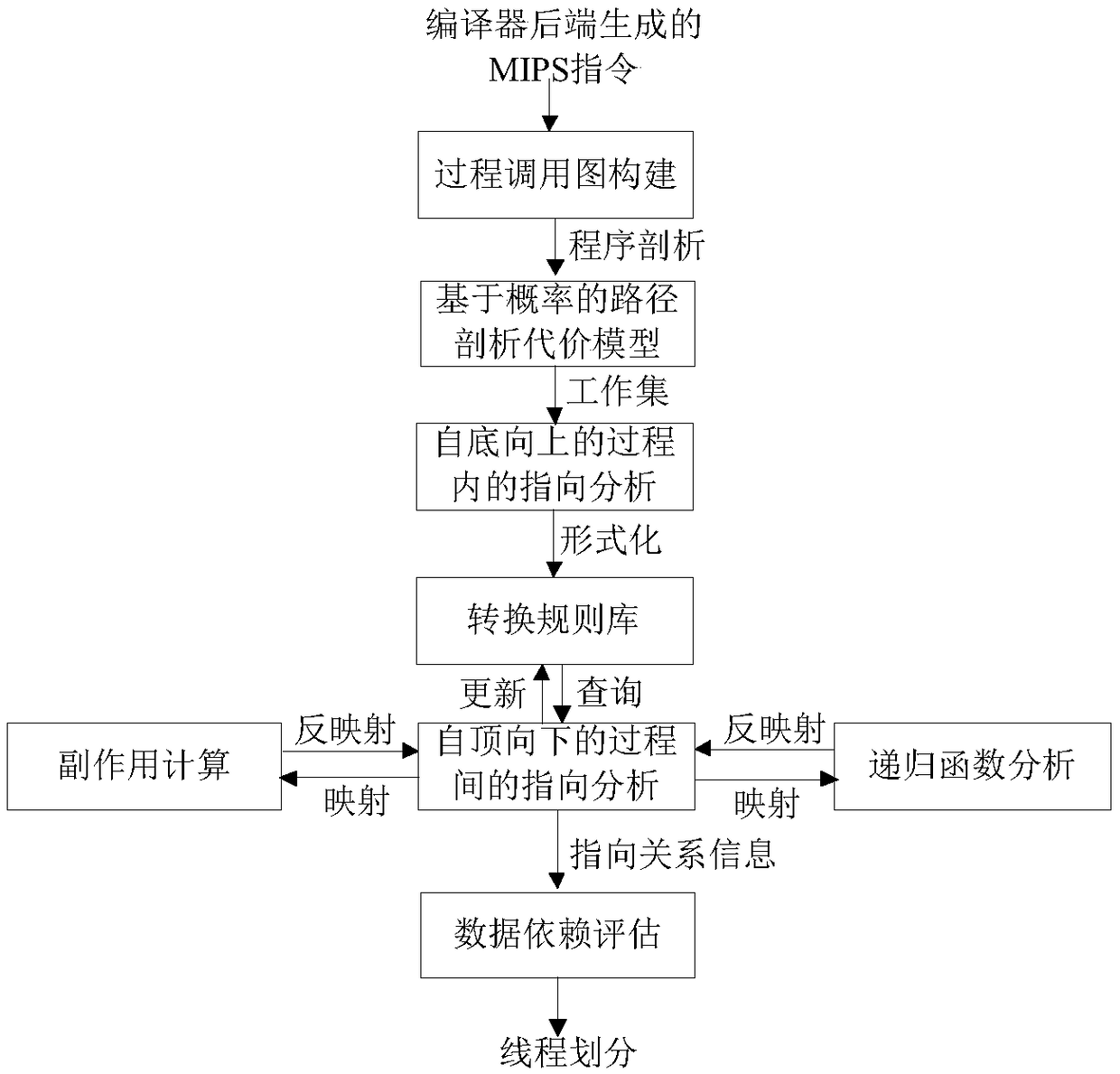
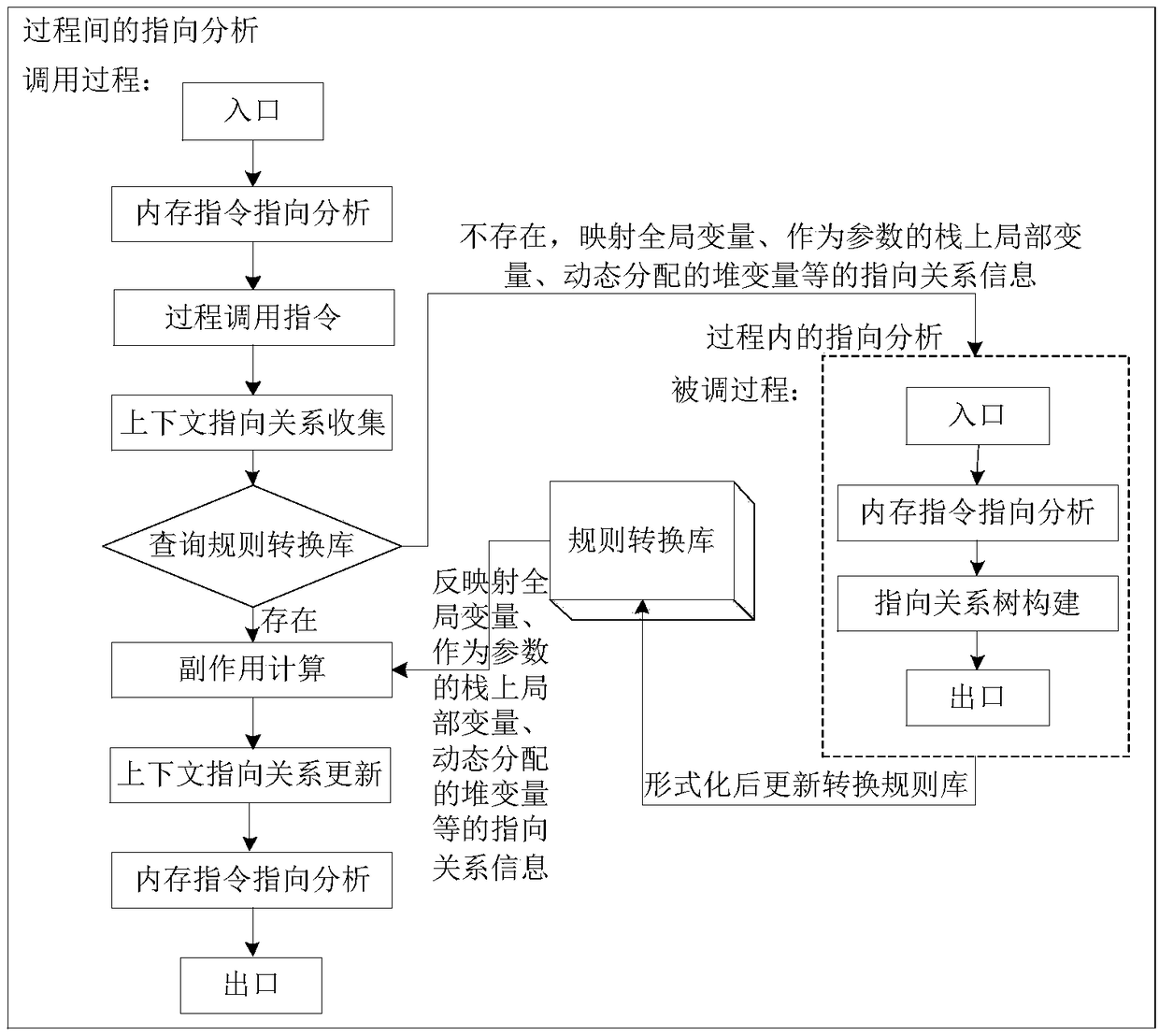
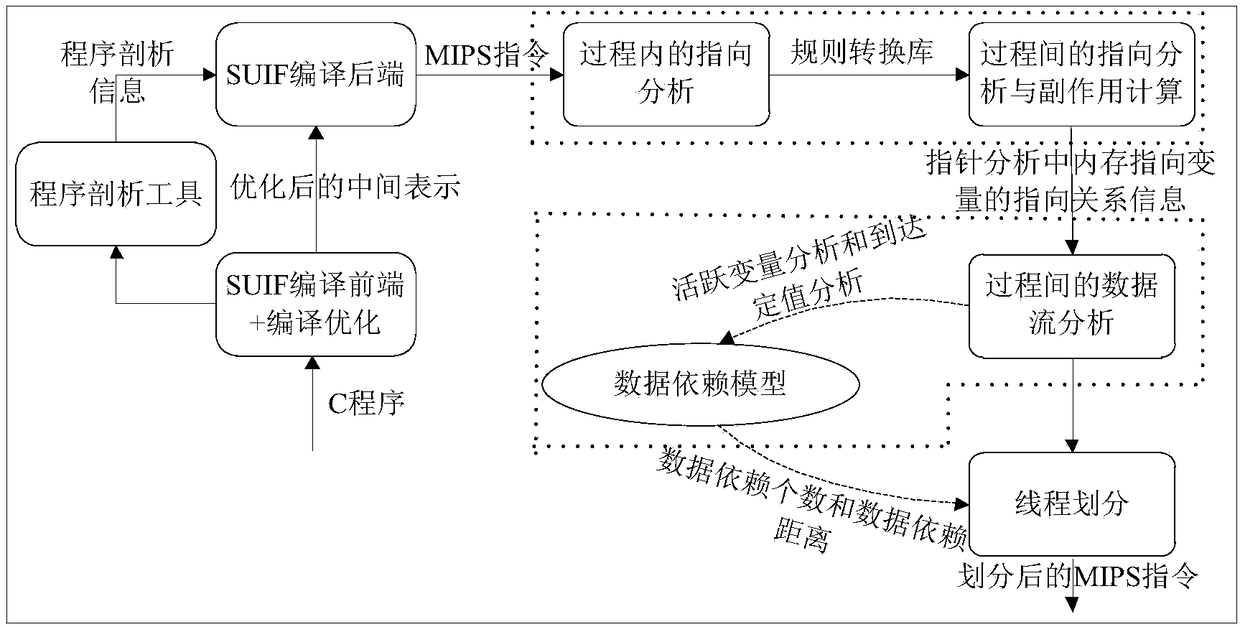
Assembly level interprocedual pointer analysis method based on speculative multithreading
ActiveCN108932137ARefine Data DependenciesAccurate analysisInstruction analysisConcurrent instruction executionProcedure callsPath profile
The invention discloses an assembly level interprocedual pointer analysis method based on speculative multithreading. Through assembly level interprocedual points-to analysis, a procedure call graph of all processes is established in a source program before the interprocedual points-to analysis is carried out, and after establishment, points-to analysis is carried out in two stages. The method comprises: in the first stage, firstly, establishing a path profiling cost model based on probability, extracting speculative paths selected by all process nodes in the procedure call graph, and then performing points-to analysis in a process; in the second stage, performing interprocedual points-to analysis and interprocedual side-effect calculation, on each process calling point, performing mappingand inverse mapping on points-to relations using a points-to analysis result in a process, to obtain an interprocedual side-effect calculation result, and realize context points-to relation update ofa calling procedure. On this basis, the method guides a whole procedure to perform interprocedual data flow analysis, evaluates data dependence degree among pointer variable memory points-to relations, and obtains a more accurate thread partitioning result.
Owner:XIAN AERONAUTICAL UNIV
Optimizing triangle topology for path rendering
ActiveUS9558573B2Efficient rasterizationLow costDrawing from basic elementsFilling planer surface with attributesComputer graphics (images)Path profile
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
Path profile approximation measurement method of refractive index structure constant of atmospheric turbulence
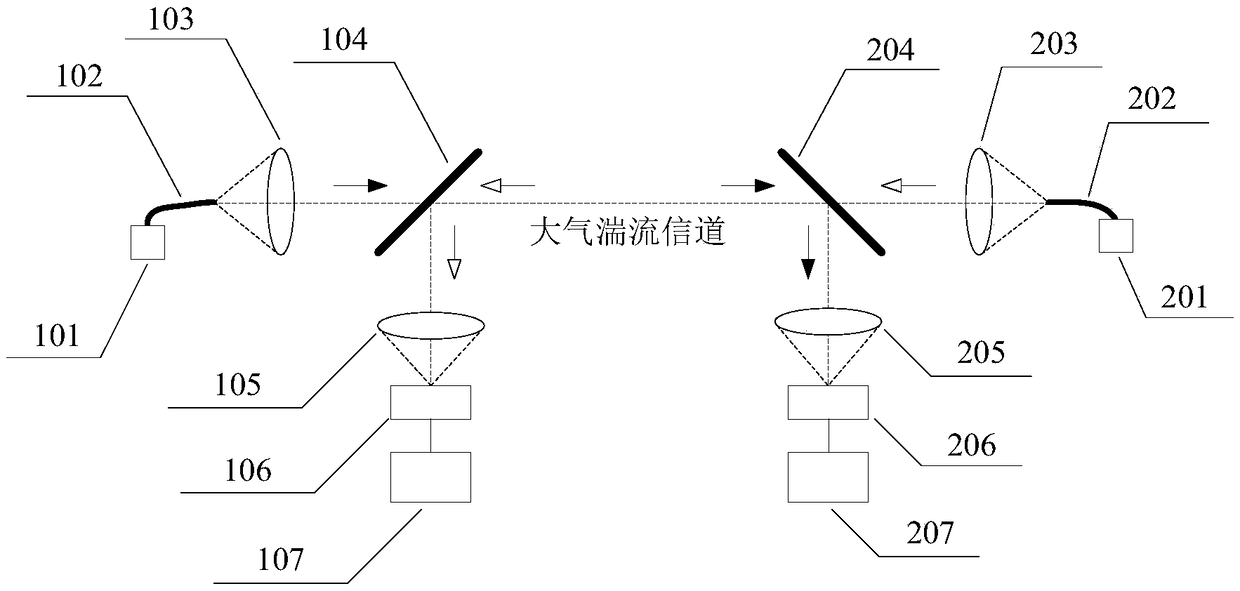
ActiveCN109342365APhase-affecting property measurementsDesign optimisation/simulationTransceiverPath profile
The invention discloses a path profile approximation measurement method of a refractive index structure constant of an atmospheric turbulence. According to the path profile approximation measurement method, a transmission path is divided into three segments, namely, a segment close to a transceiver A, a middle segment and a segment close to a transceiver B, and three discrete random phase screensare used for approximately describing the continuous atmospheric turbulence. By the path profile approximation measurement method, the effective refractive index structure constant of each random phase screen is obtained by measuring light wave intensity fluctuation and arrival angle fluctuation of a two-way transmission channel so as to describe general change characteristics of the refractive index structure constant of the atmospheric turbulence along the transmission path, so that a reference is provided for design of a light wave atmospheric transmission engineering system.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Coordination numerical control system and method for main shafts in different forms
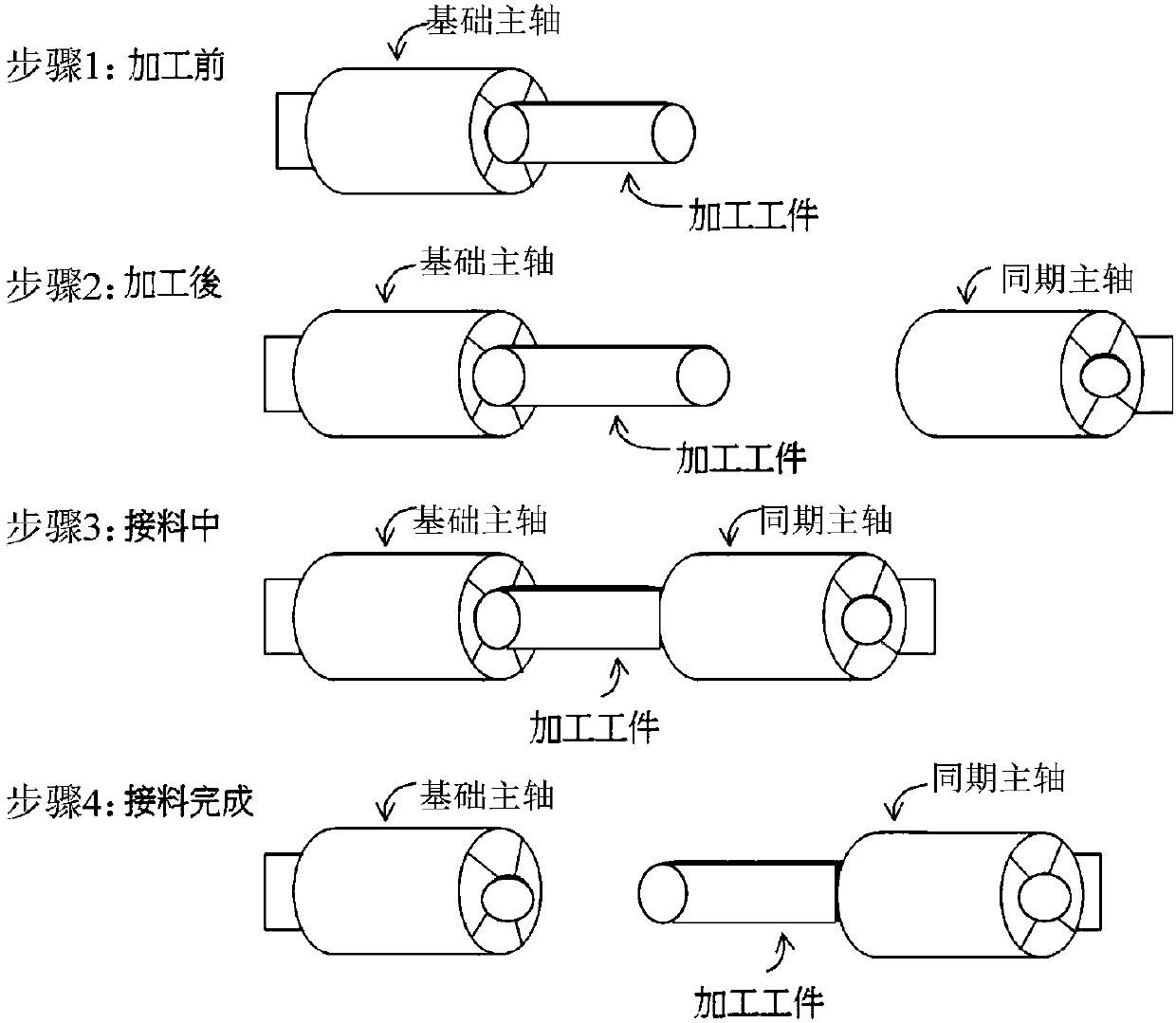
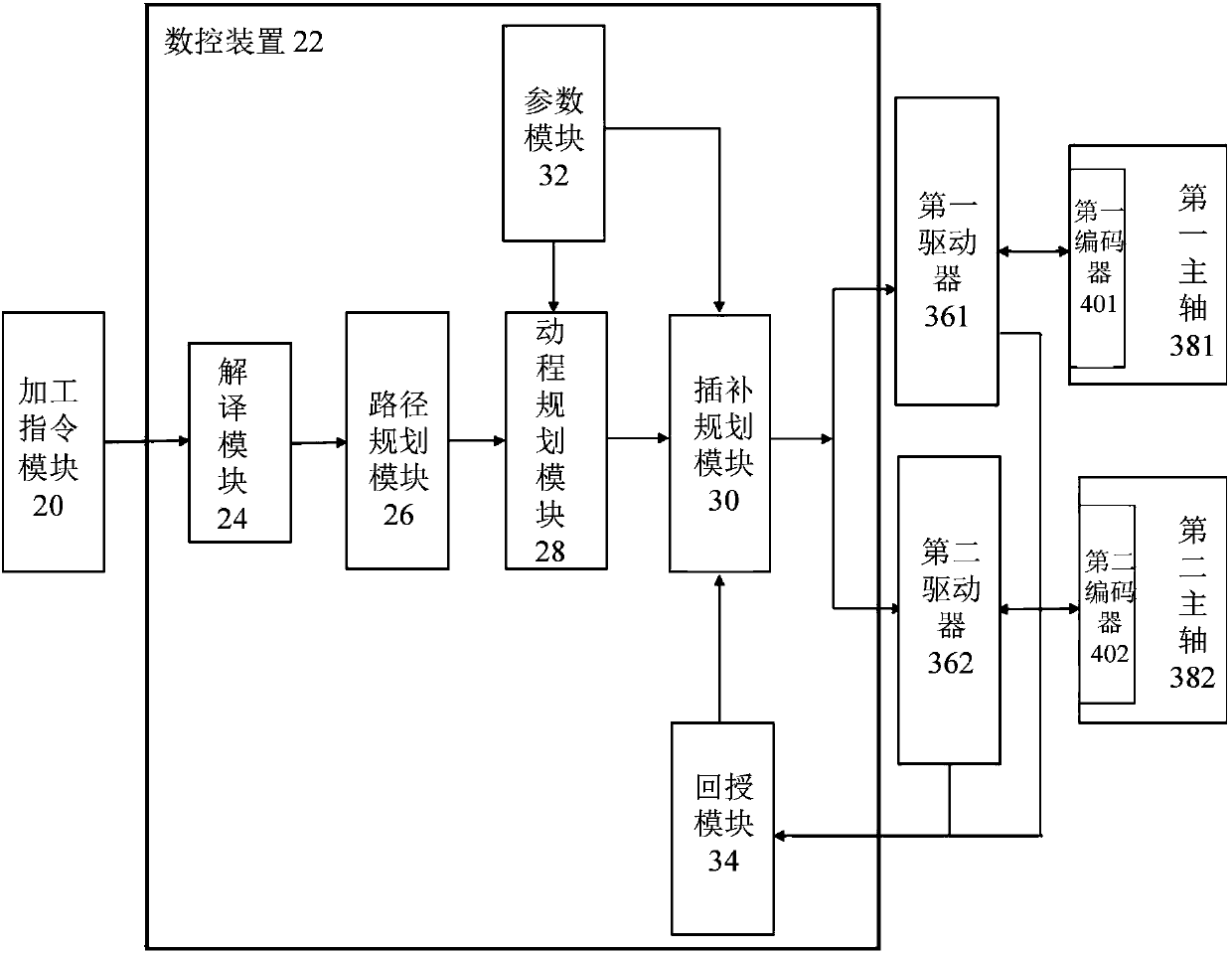
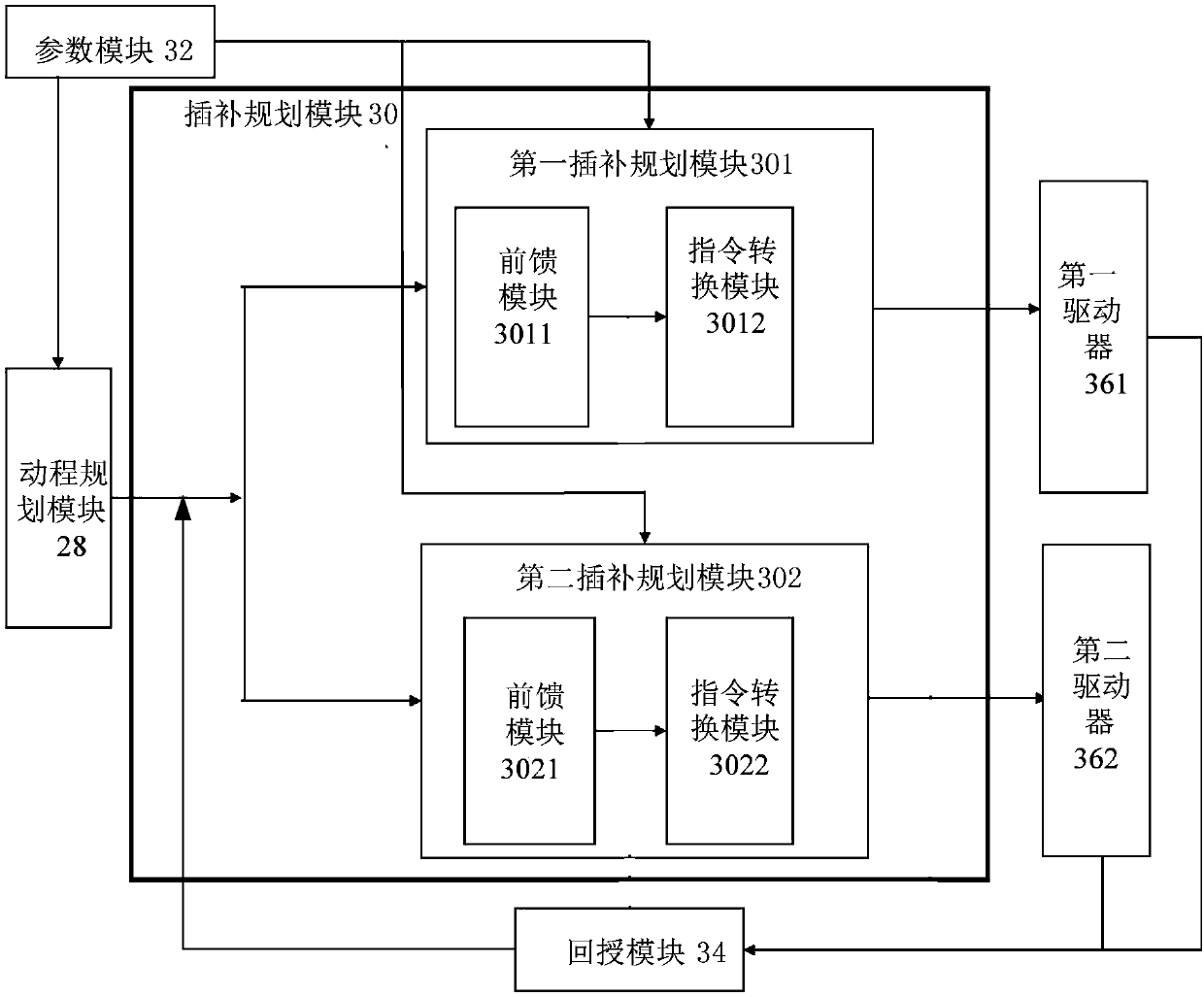
ActiveCN107728579AQuality improvementTo achieve the purpose of collaborative controlProgramme controlComputer controlComputer moduleMachine instruction
The invention relates to a coordination numerical control system and method for main shafts in different forms. The system comprises an interpretation module, a path planning module, a stroke planningmodule, an interpolation planning module and a feedback module, wherein the interpretation module selects a coordination instruction to interpret from a machining instruction module; the path planning module conducts path outline planning on the interpreted coordination instruction; the stroke planning module decides a first main shaft and at least one second main shaft from a parameter module and selects dynamic response parameters to conduct stroke command planning; the interpolation planning module is composed of feedforward modules and instruction conversion modules corresponding to the first main shaft and the second main shafts respectively; the feedback module receives dynamic signals through a first driver and at least one second driver, feeds the dynamic signals back to the interpolation planning module and calculates compensating command variables; the feedforward modules convert stroke commands into corresponding motion commands respectively; the instruction conversion modules add the corresponding motion commands to the compensating command variables respectively, results are converted into command formats and transmitted to the first main shaft and the second main shafts through the corresponding drivers, and the first main shaft and the second main shafts are in a coordination state, so that the purpose of coordination control is achieved.
Owner:新代科技(苏州)有限公司
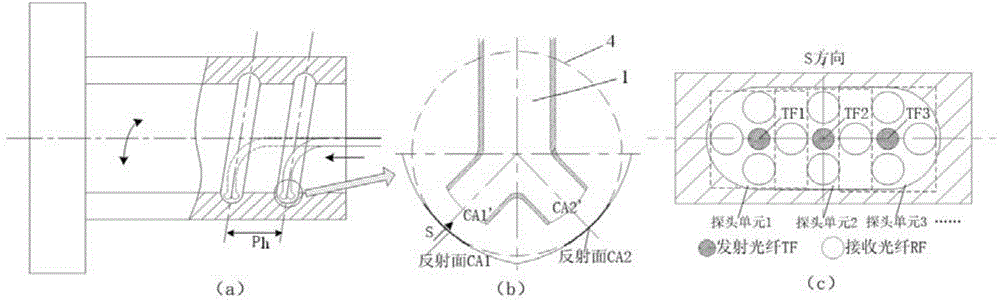
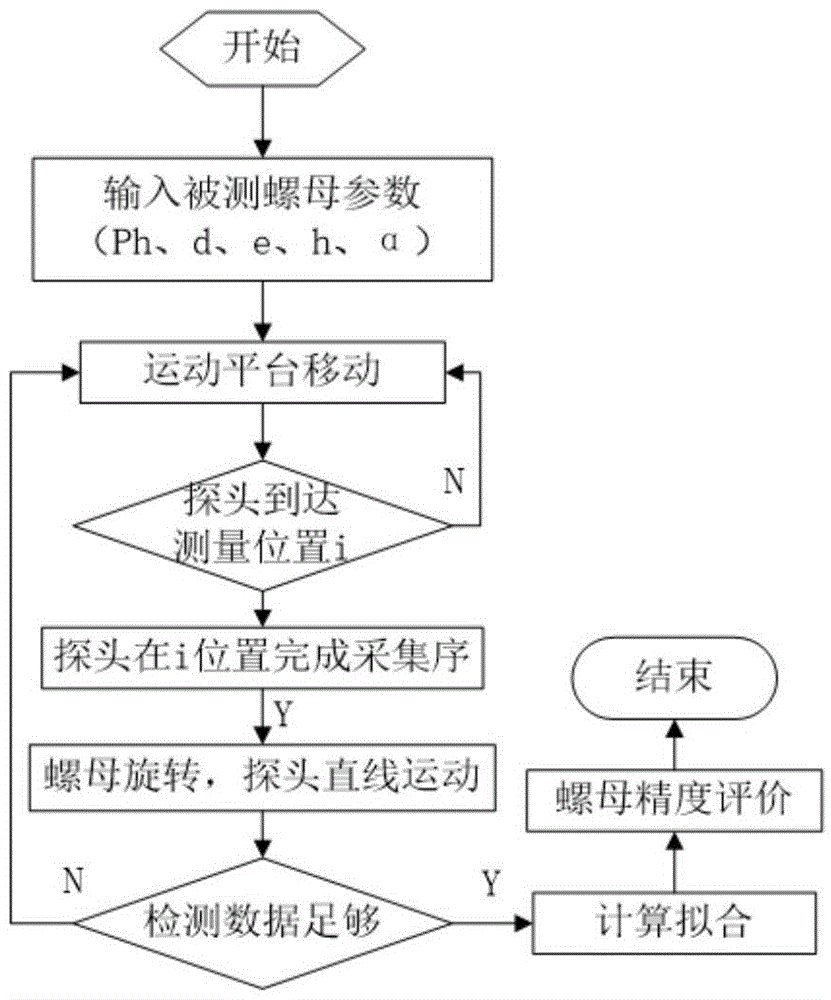
High-precision optical fiber detecting method for roller path curved surface in ball nut
ActiveCN104792276AEvaluate machining accuracyGuaranteed normal detection relationshipUsing optical meansHelical lineMathematical model
The invention discloses a high-precision optical fiber detecting method for a roller path curved surface in a ball nut. The high-precision optical fiber detecting method includes mounting the ball nut on a motion platform, and mounting an optical fiber sensor probe relative to the central axis of the ball nut by a helical angle of the ball nut; rotating the ball nut by the motion platform, enabling the optical fiber sensor probe to move linearly by one screw pitch of the ball nut by rotating the ball nut each circle, until the optical fiber sensor probe completes detection corresponding to the inner helical line along the roller path profile of the ball nut, modulating a mathematical model of the curved according to light strength of the optical fiber sensor probe, and calculating ranging data between the optical fiber sensor probe and the roller path profile; solving the actual internal helical line space coordinate according to the ranging data and transformation relation between the workpiece coordinate system of the ball nut and the normal section coordinate system of the roller path in the ball nut. Accordingly, machining accuracy of the ball nut can be completely analyzed and evaluated.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Evaluation of self-intersecting vector graphics objects via planar map profiles
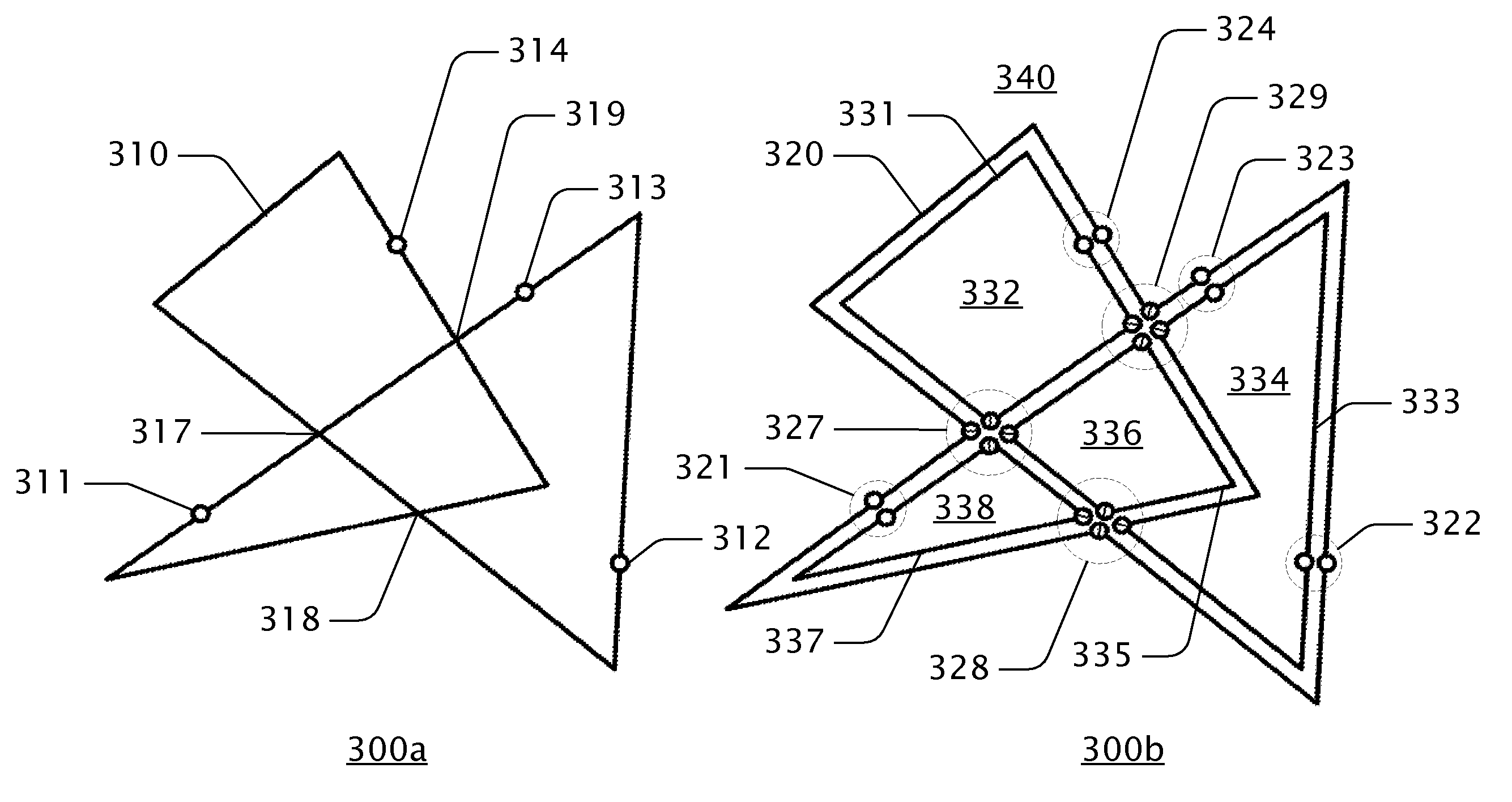
Systems and methods for converting vector graphic object path profiles into planar map profiles for efficient mean value coordinates evaluation wherein the nodes of resultant region paths include a set of quantities of arbitrary dimension.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
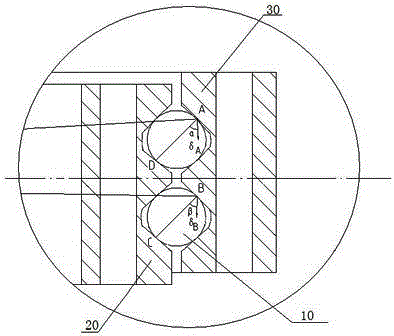
Method of improving double-row-contact ball-type revolve-bearing force situation
InactiveCN104832543AAvoid fatigue crackingEvenly distributedBall bearingsBearing componentsPath profileSteel ball
A method of improving a double-row-contact ball-type revolve-bearing force situation includes following steps: (1) regulating a rolling-path profile of a bearing outer ring to enable all contact points of a steel ball on the rolling-path profile of the bearing outer ring to be regulated in one spherical surface with a sphere center as a bearing center; and (2) regulating the rolling-path profile of a bearing inner ring so that a linking line between inner ring contact points and outer ring contact points corresponding to the inner ring contact points for transmitting force passes through the sphere center of the steel ball; or (1) regulating the rolling-path profile of the bearing inner ring to enable all inner ring contact points to be regulated in one spherical surface with the sphere center as the bearing center; and (2) regulating the rolling-path profile of the bearing outer ring so that the linking line between the outer ring contact points and the inner ring contact points corresponding to the outer ring contact points for transmitting force passes through the sphere center of the steel ball. The invention solves a problem that non-uniform distribution of contact force between rolling paths and steel balls in the same circumferential position in an upper row and a lower row.
Owner:杨晓莉
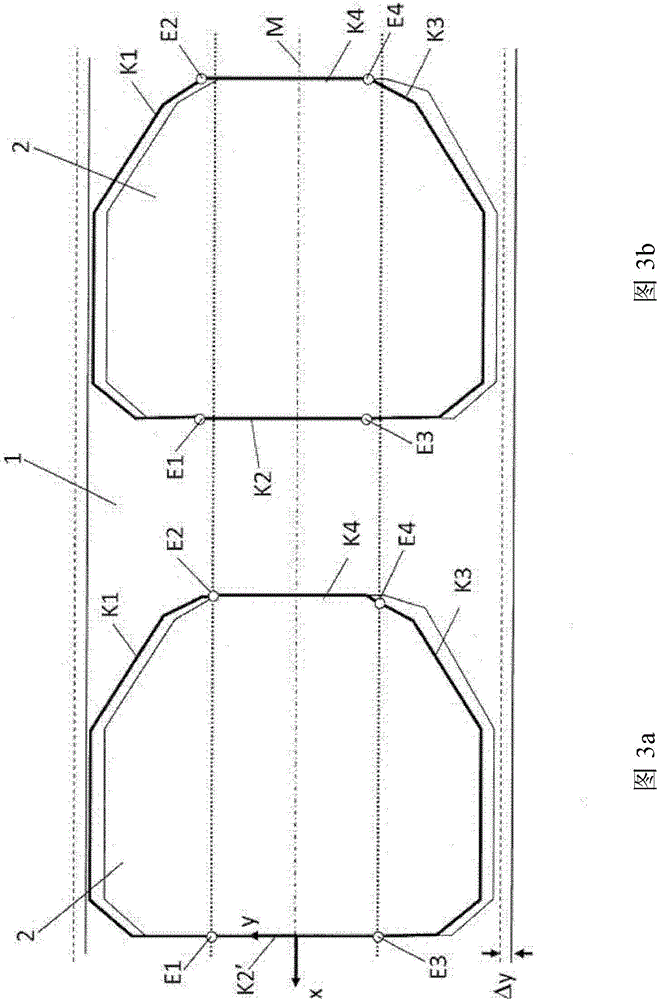
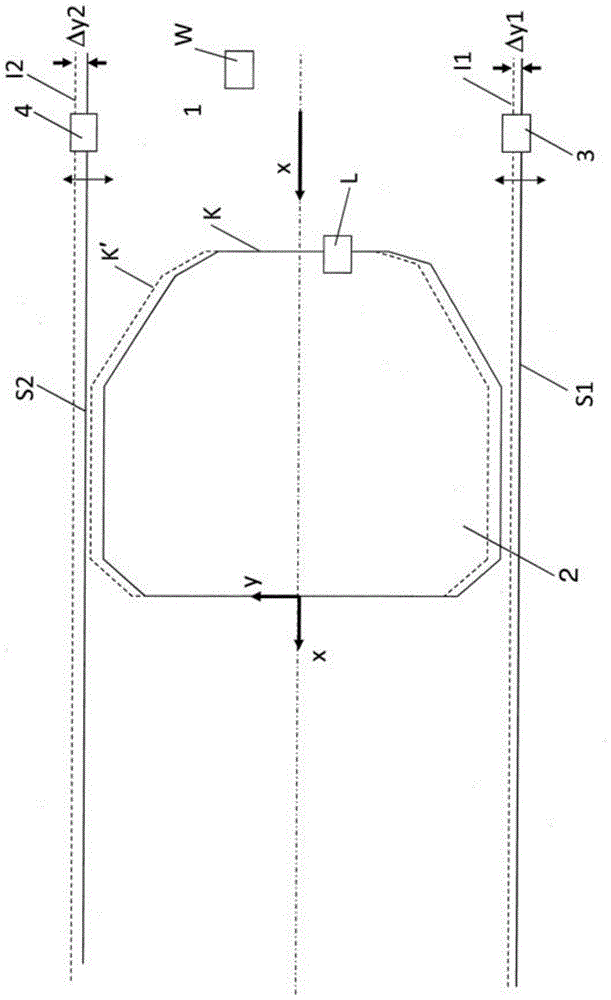
Method for cutting sheet metal stock
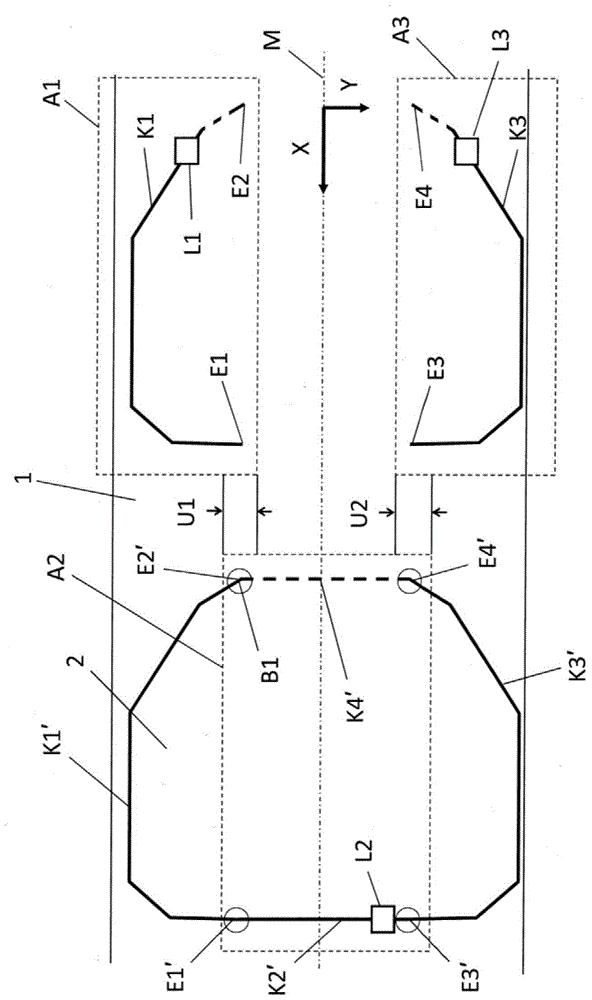
ActiveCN104520055BDetection securityReliable detectionLaser beam welding apparatusMetal stripsThin slab
The invention relates to a method for cutting a sheet metal blank (2) with a predetermined profile (K) from a sheet metal strip (1) conveyed continuously in a conveying direction (x), said method comprising the following steps : at least one laser cutting device is provided with at least one laser cutting head (L, L1, L2, L3) movable in said conveying direction (x) and in a y direction perpendicular to said conveying direction, and also having control means for controlling movement of said laser cutting head (L, L1, L2, L3) along a cutting path corresponding to said predetermined profile (K), by a first distance arranged upstream of said laser cutting means The measuring device continuously measures the first distance (I1) between the first strip edge of the metal sheet strip (1) and the fixed first measuring point in the y direction, and sends the measured first distance (I1) to the control device a distance value, using the predetermined cutting path and the measured first distance value, calculating a corrected cutting path by the control program of the control device, and moving the laser cutting machine along the corrected cutting path heads (L, L1, L2, L3) to create slits in said sheet metal strip (1).
Owner:SCHULER PRESSEN GMBH & CO KG
Dynamic Programming and Gradient Descent Based Decision and Planning for Autonomous Vehicles
ActiveCN109491376BNavigation instrumentsExternal condition input parametersDecision systemSimulation
According to some embodiments, the system calculates the first trajectory based on map and route information. The system generates a path profile based on the first trajectory, the traffic rules, and obstacle information describing the one or more obstacles perceived by the ADV, wherein, for each obstacle in the plurality of obstacles, the path profile includes yielding or Decision to skim to the left or right of the obstacle. The system generates a speed profile according to traffic rules based on the route profile. The system performs a gradient descent optimization based on the path profile and the velocity profile to generate a second trajectory representing the optimized first trajectory, and controls the ADV according to the second trajectory.
Owner:BAIDU USA LLC
Carrier interoperability for critical services
A system processes communication path requests in an autonomous system. The system includes a proxy server that receives a request message from an external system requesting establishment of a communication path through the autonomous system. The request message includes a desired communication path profile including a desired level of redundancy. The system also includes a management server in the autonomous system that receives the request message from the proxy server, generates a response message indicating whether a communication path corresponding to the desired communication path profile is available, and sends the response message to the proxy server. The proxy server receives the response message and transmits the response message to the external system.
Owner:SBC KNOWLEDGE VENTURES LP
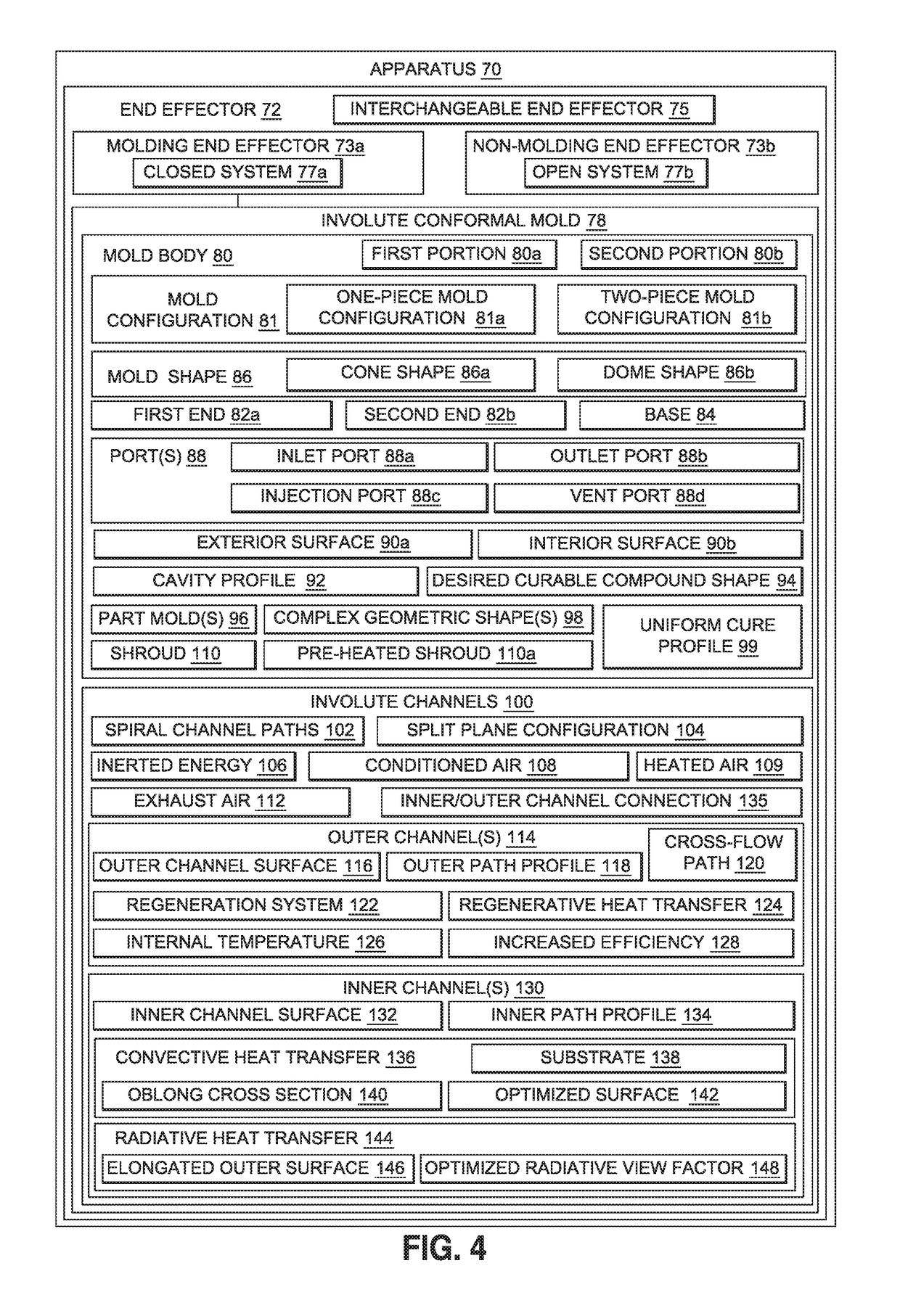
Apparatus, system and method for isolating a controlled environment for cure process control
An apparatus, system and method for isolating a controlled environment for cure process control of application and cure of one or more curable compounds to a structure. The apparatus has an end effector of an involute conformal mold having a mold body shaped to provide a shroud over an area covered with the one or more curable compounds on the structure, to isolate the area and the controlled environment. The mold body has an exterior surface, and an interior surface with a cavity profile corresponding to a desired curable compound shape. The mold body has one or more ports, and a plurality of involute channels with spiral flow paths. The involute channels include outer channel(s) having an outer path profile for regenerative heat transfer to the curable compound(s), and include inner channel(s) having an inner path profile for convective and radiative heat transfer to the curable compound(s).
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com