Patents
Literature
34 results about "Speculative multithreading" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
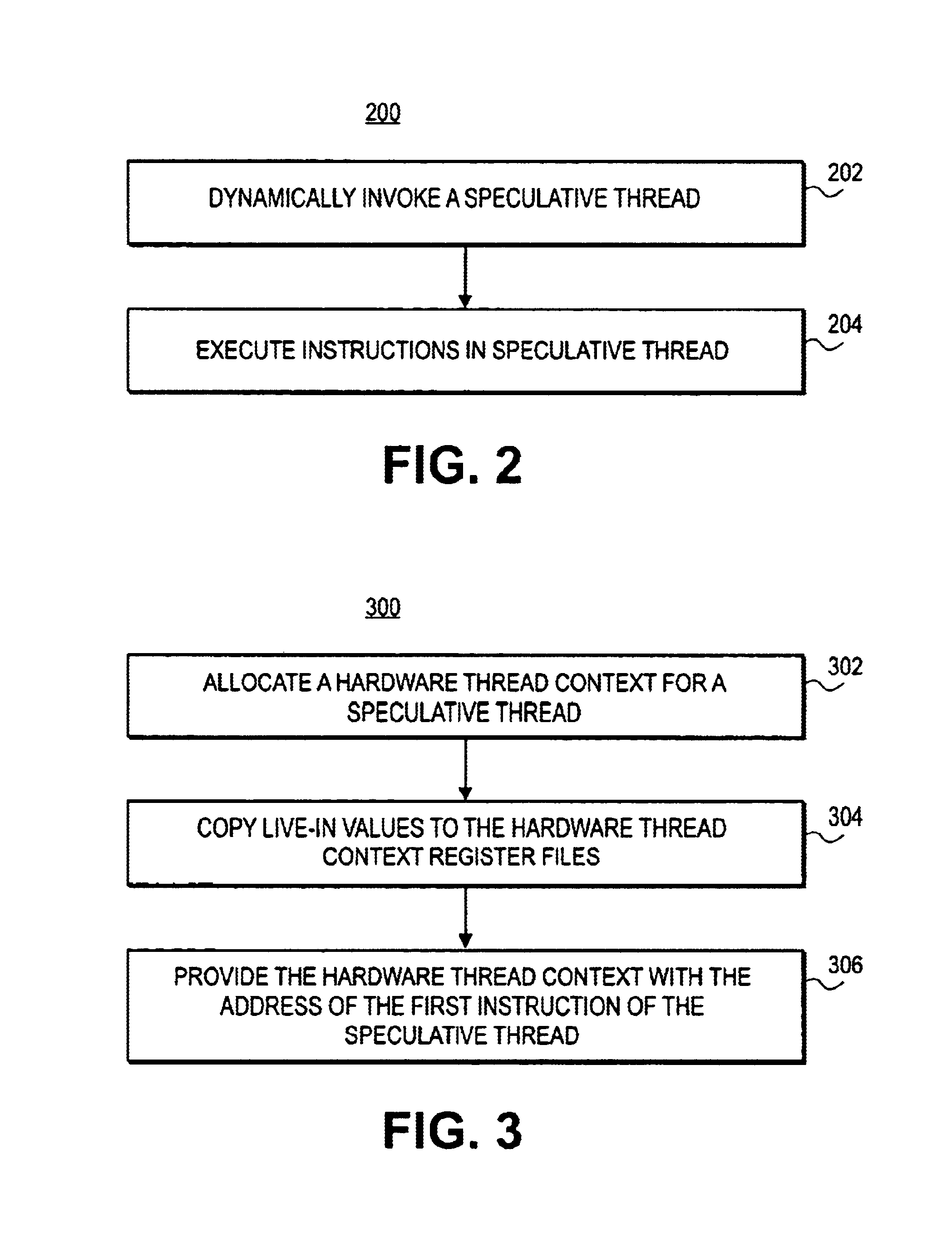
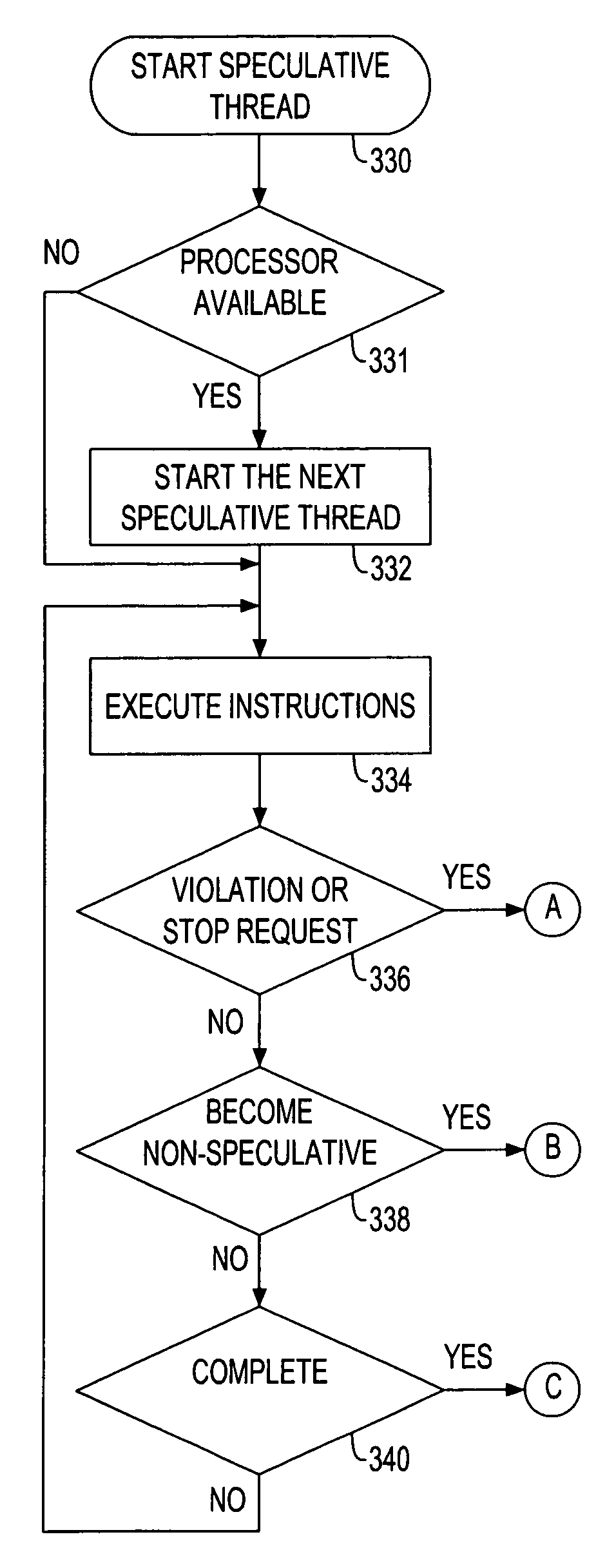
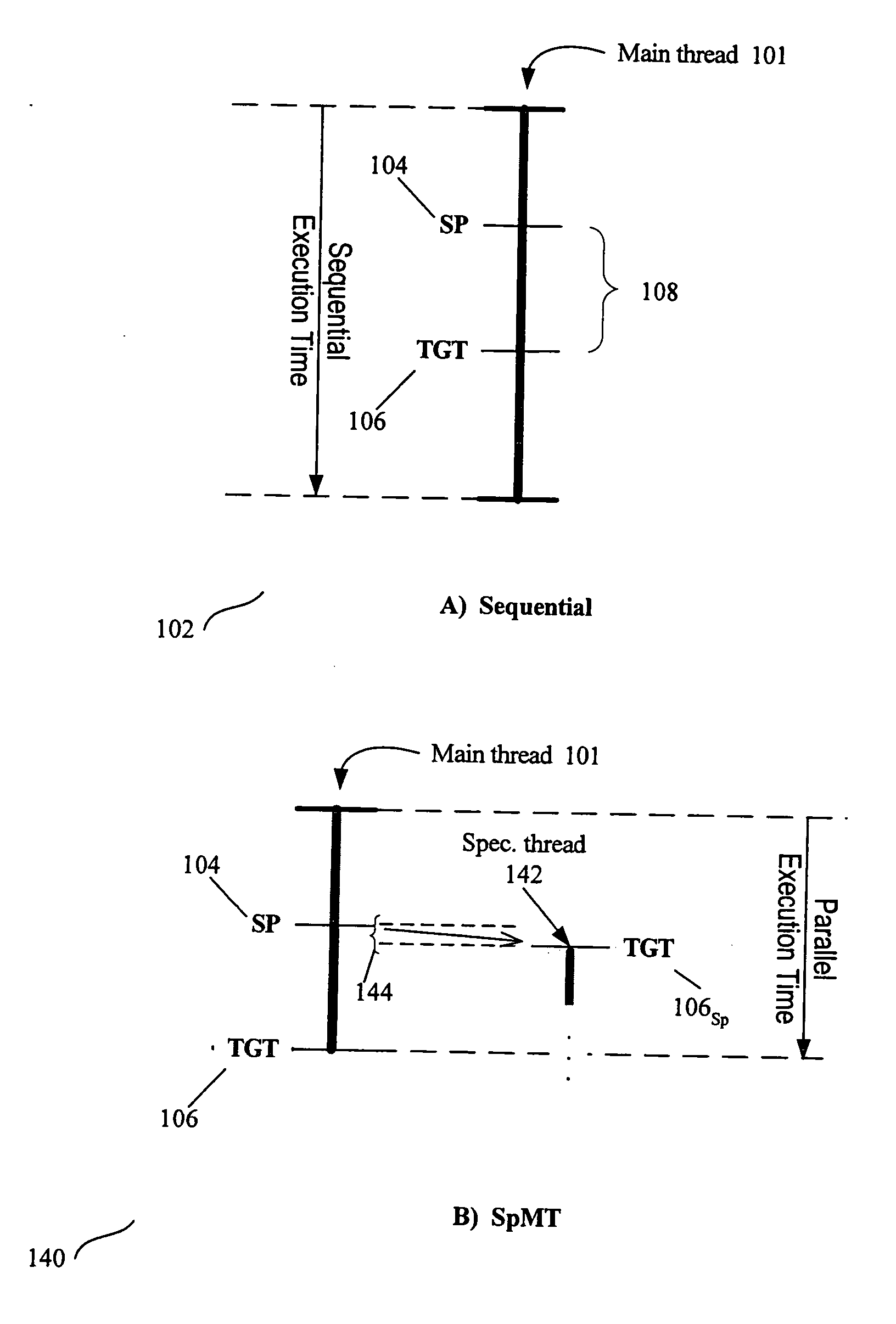
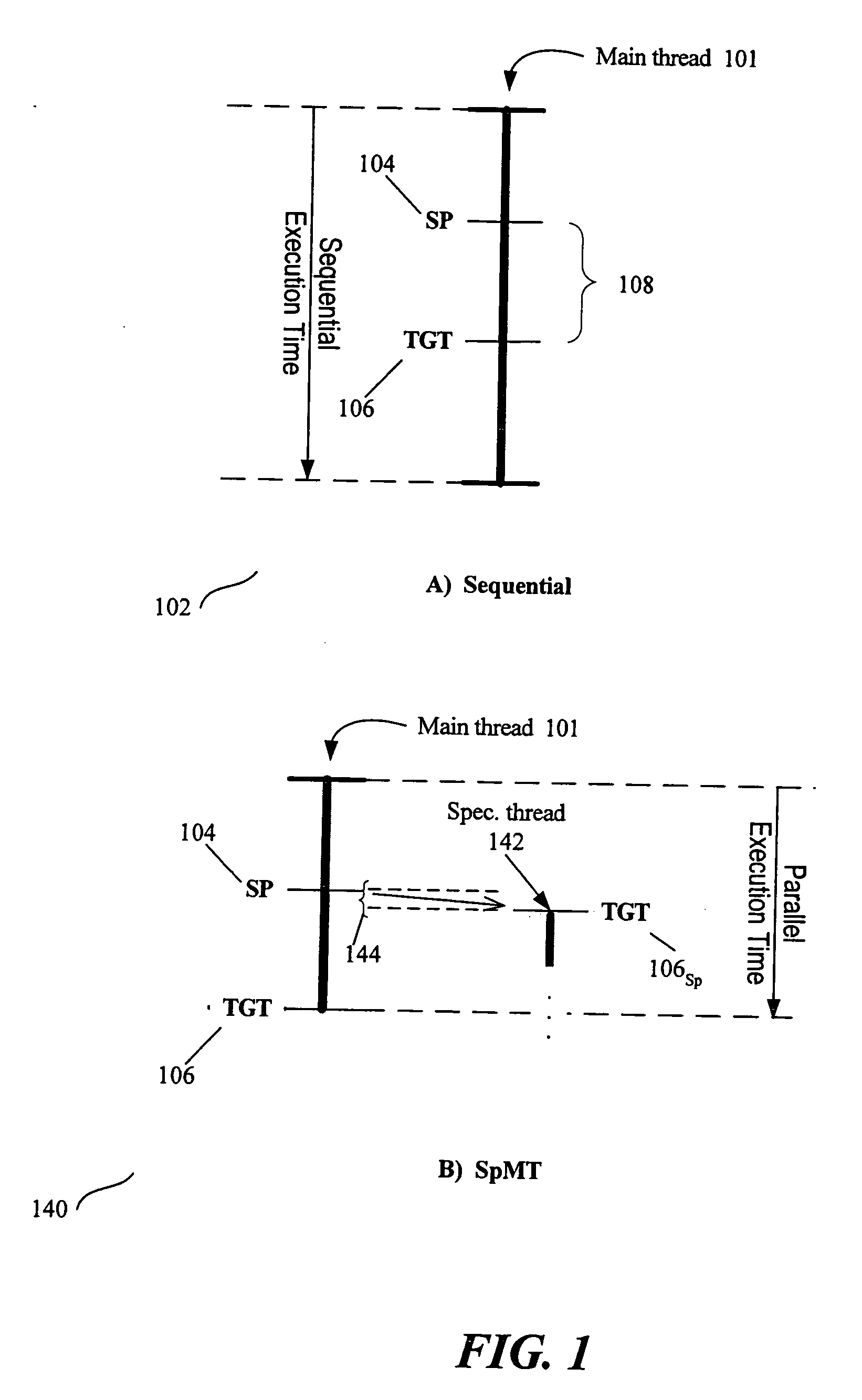
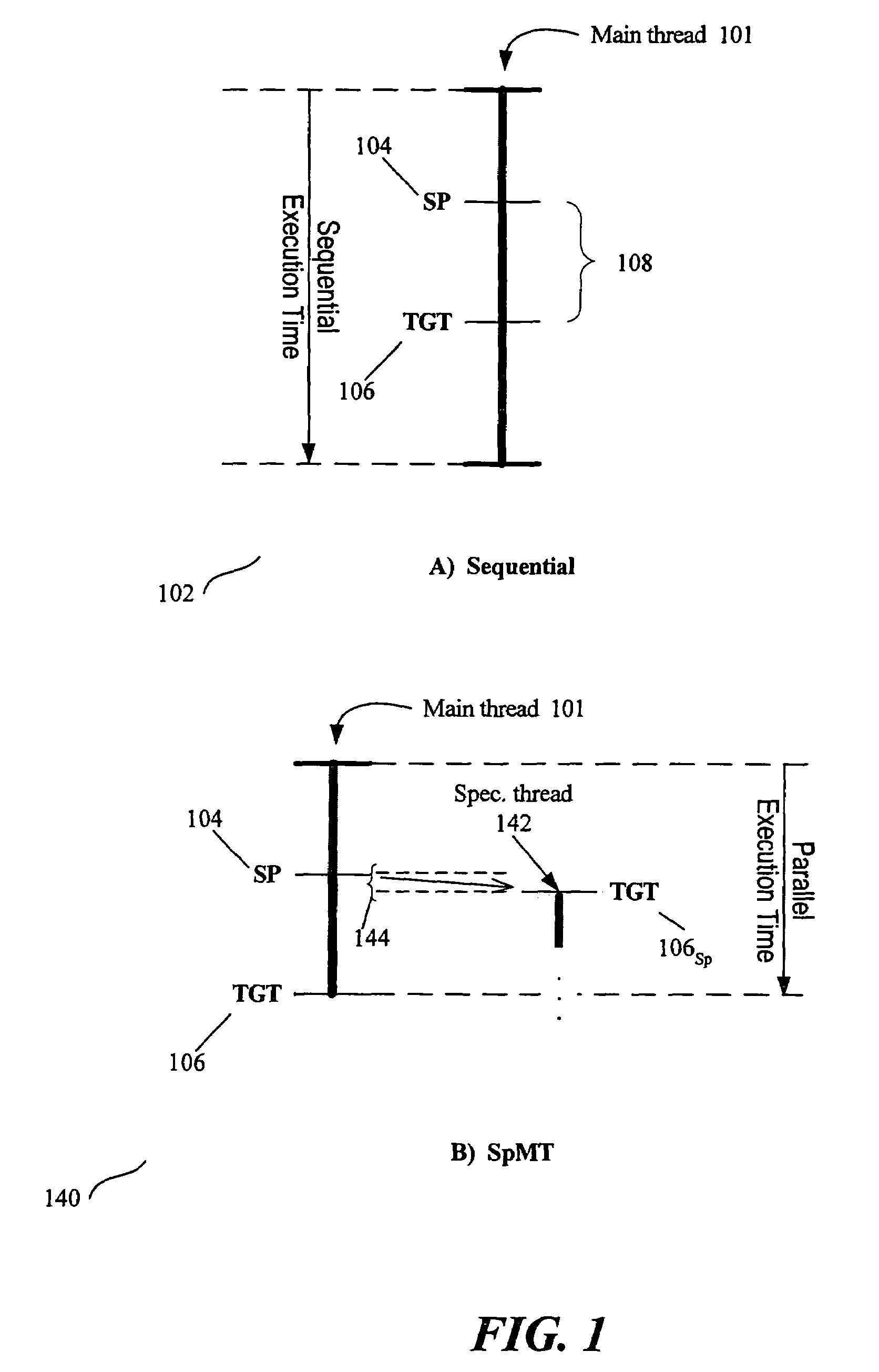
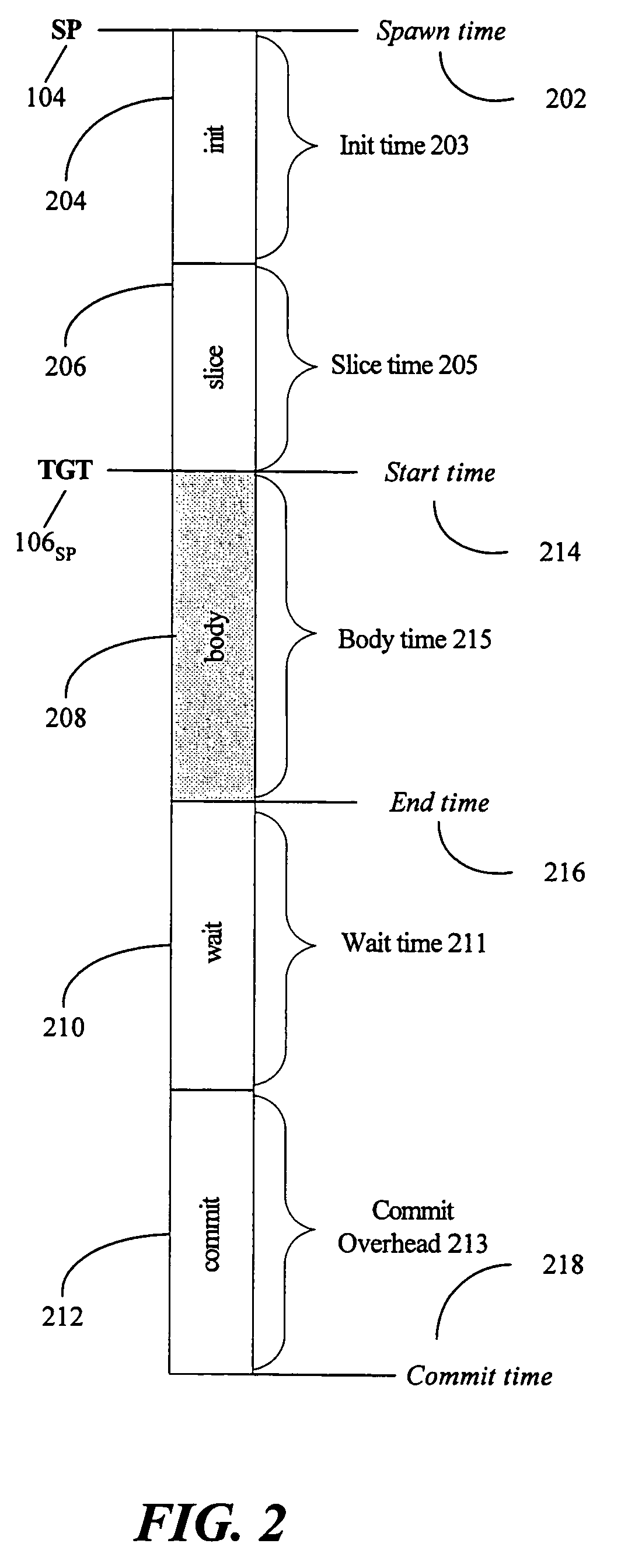
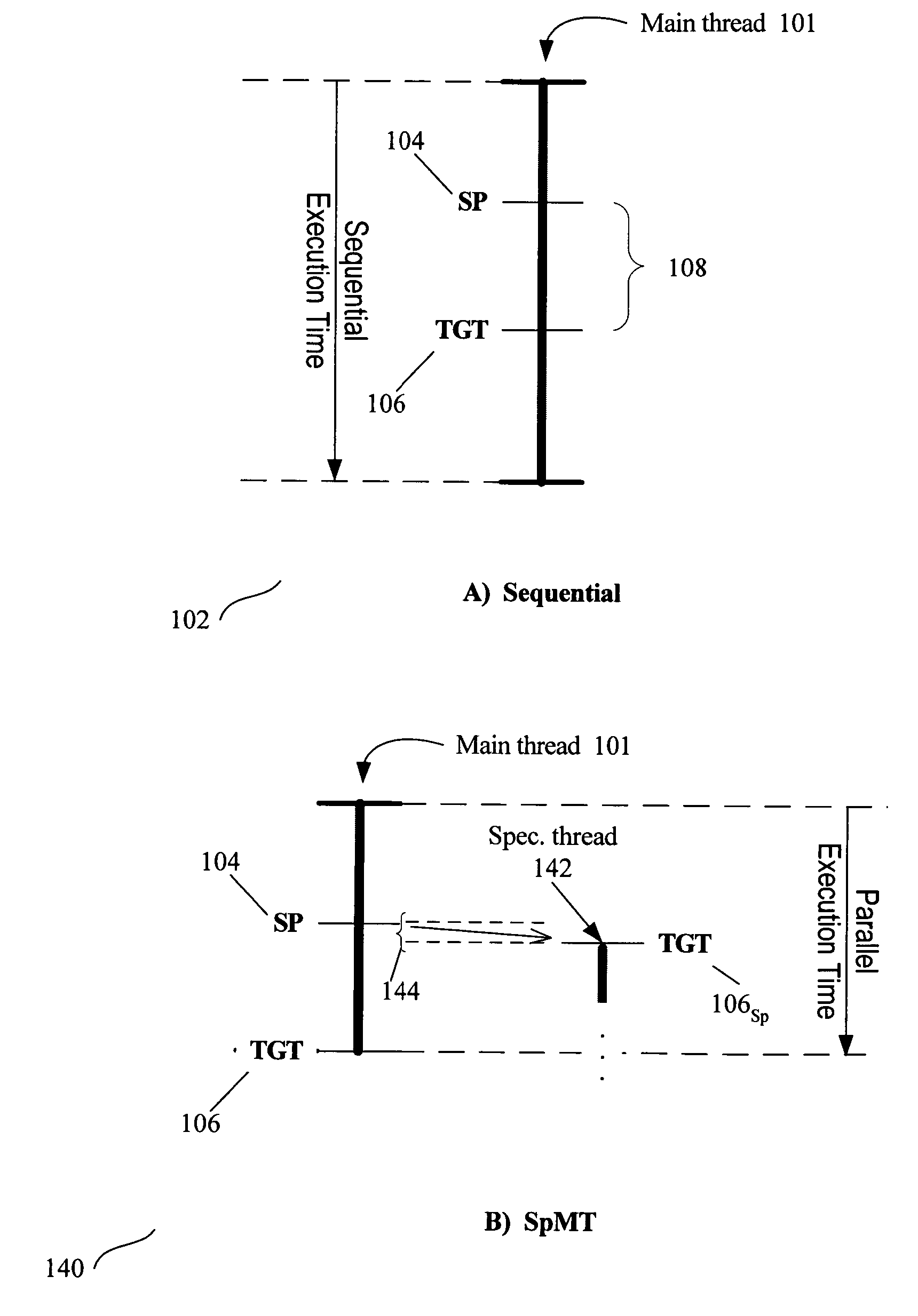
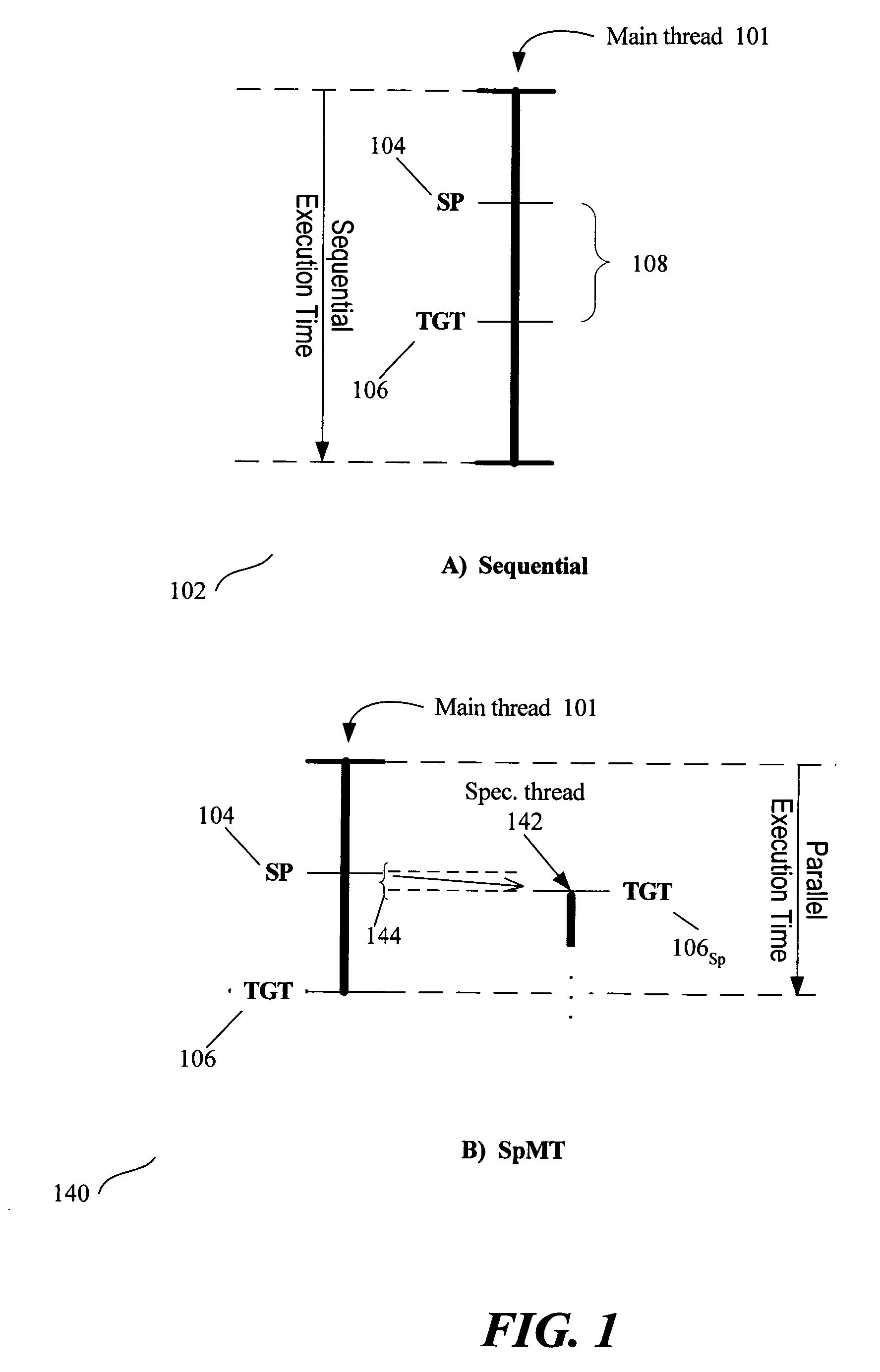
Thread Level Speculation (TLS) is a technique to speculatively execute a section of computer code that is anticipated to be executed later in parallel with the normal execution on a separate independent thread. Such a speculative thread may need to make assumptions about the values of input variables. If these prove to be invalid the speculative thread will need to be discarded and squashed. If the assumptions are correct the program can complete in a shorter time provided the thread was able to be scheduled efficiently.
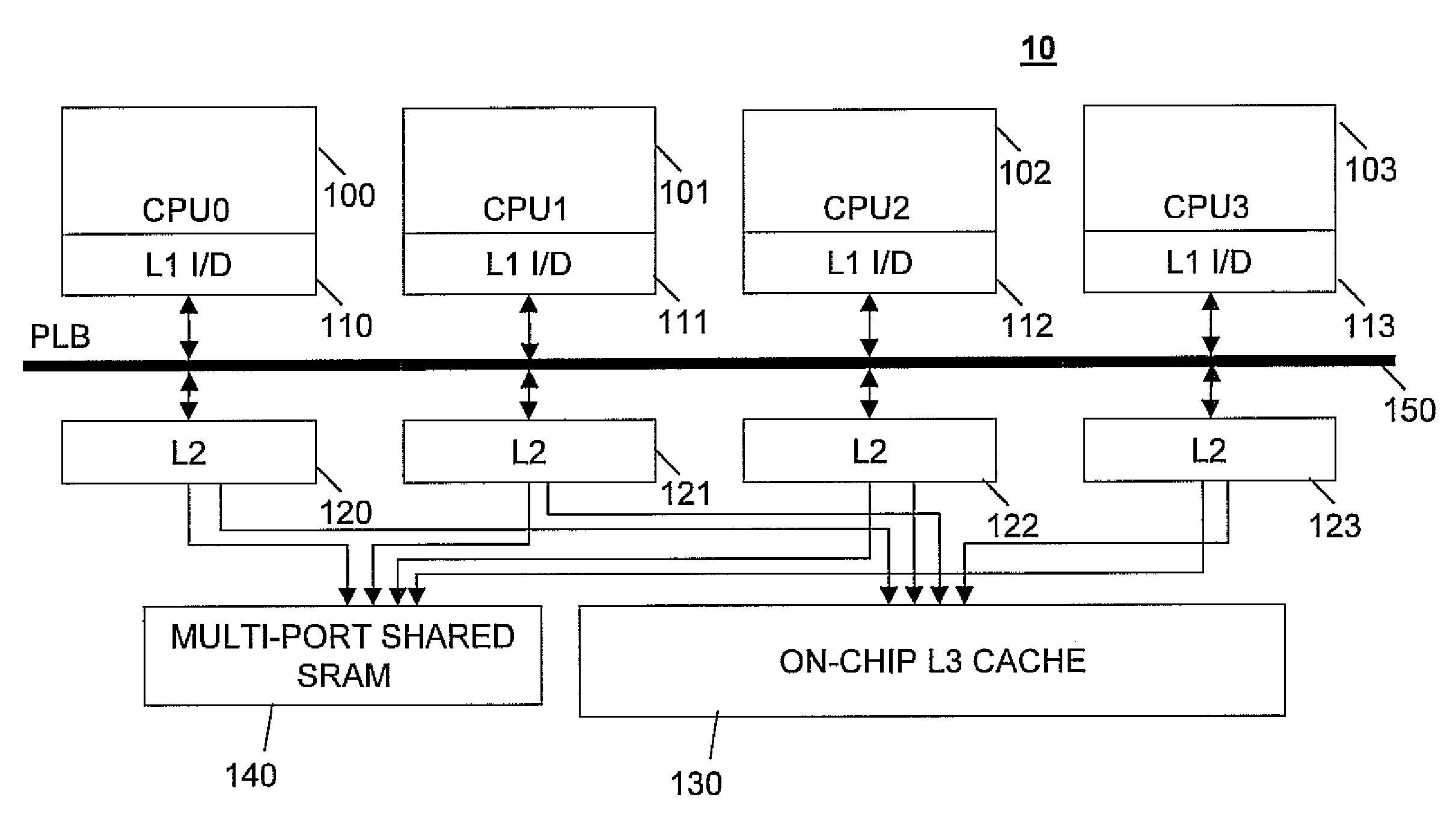
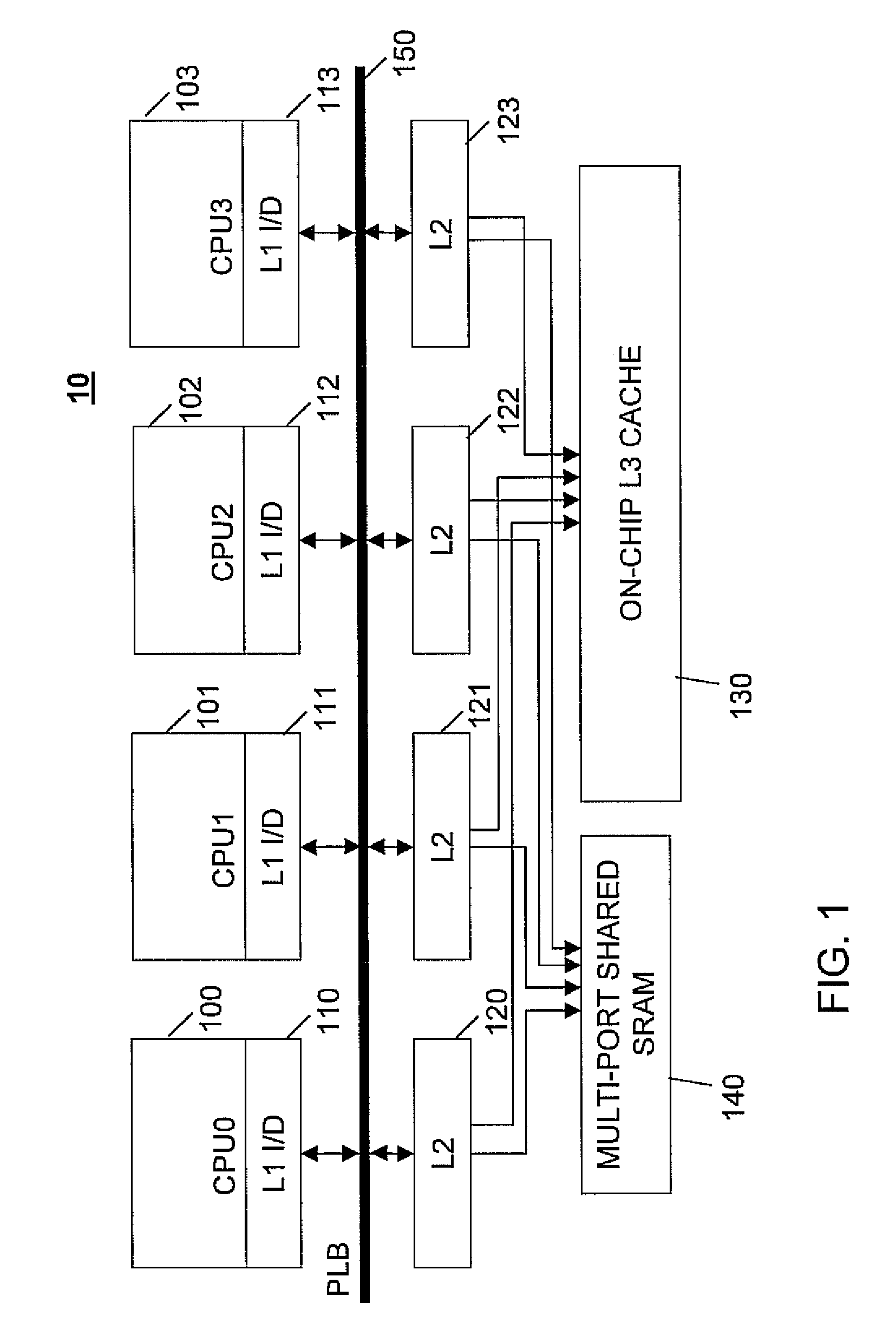
Low complexity speculative multithreading system based on unmodified microprocessor core
InactiveUS20070192545A1Efficient use ofMemory architecture accessing/allocationProgram controlMemory hierarchySpeculative execution
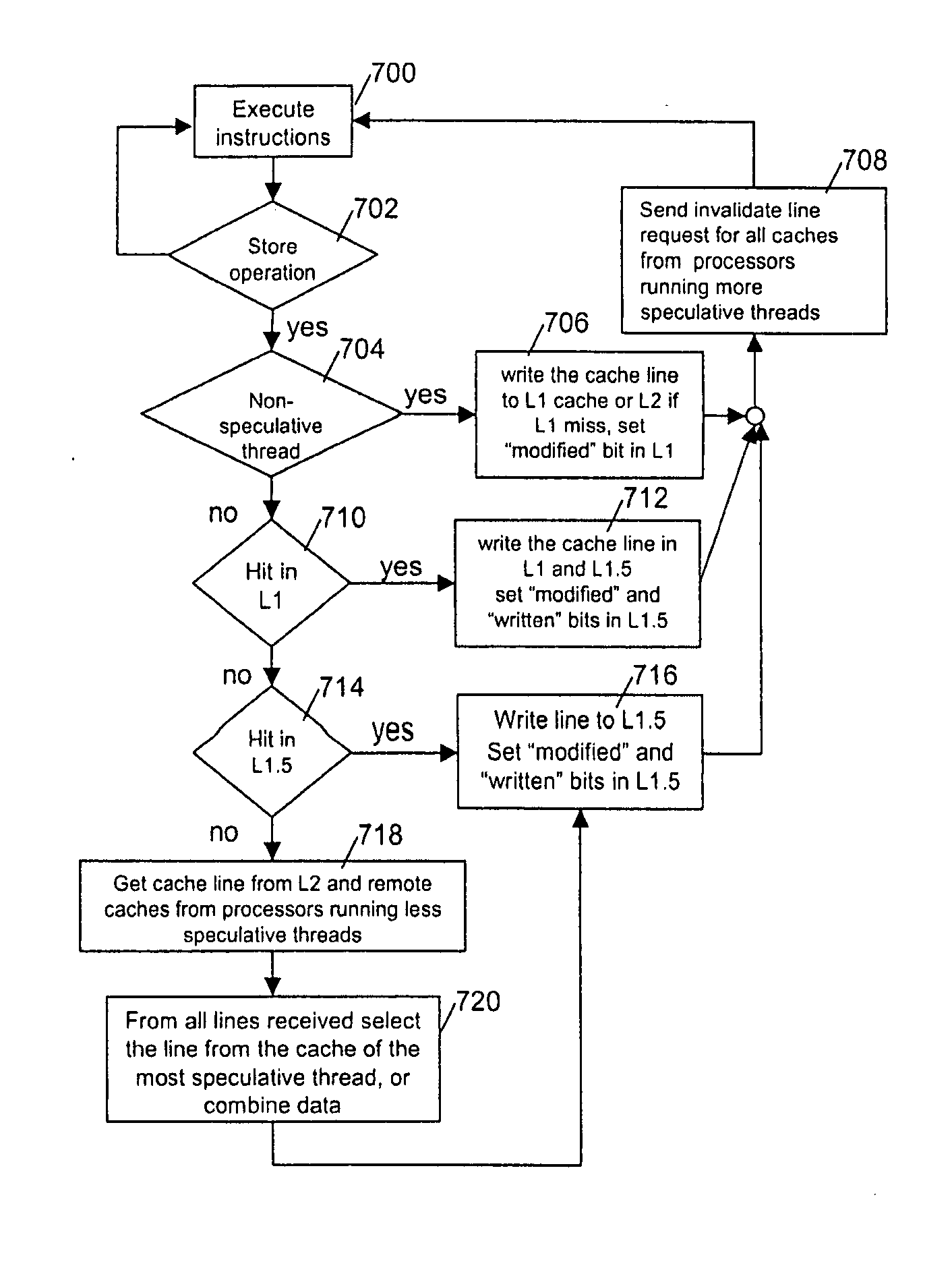
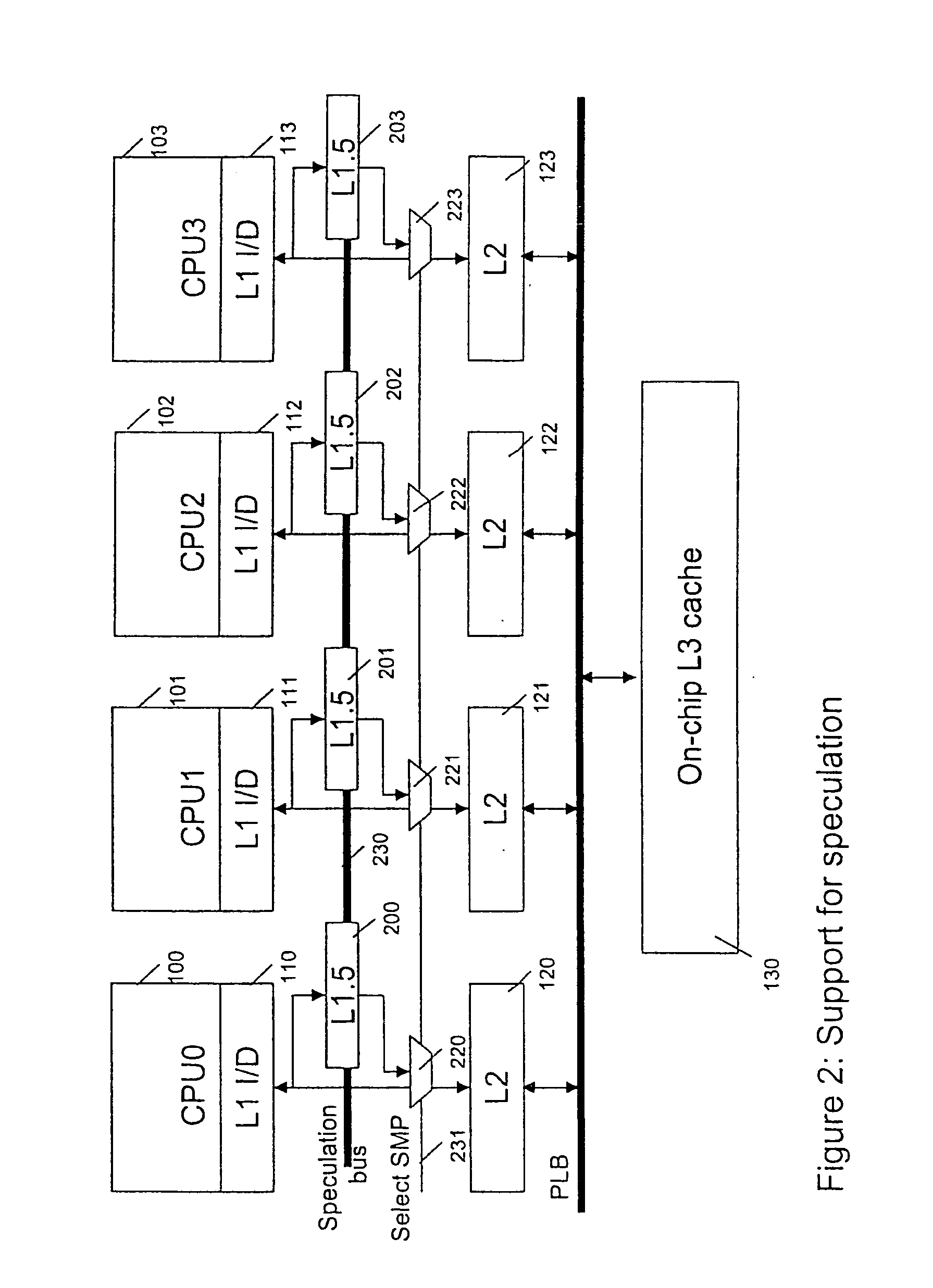
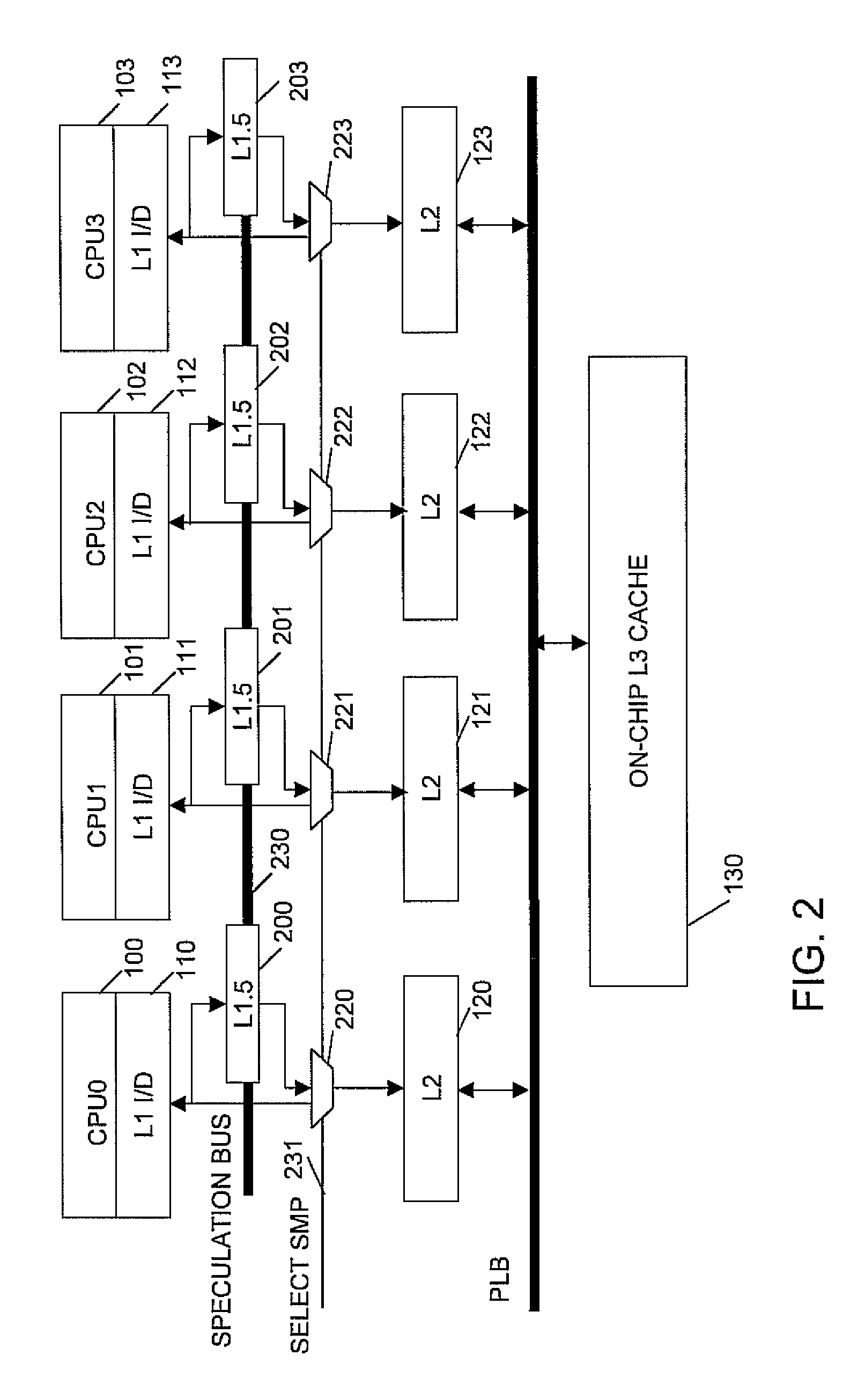
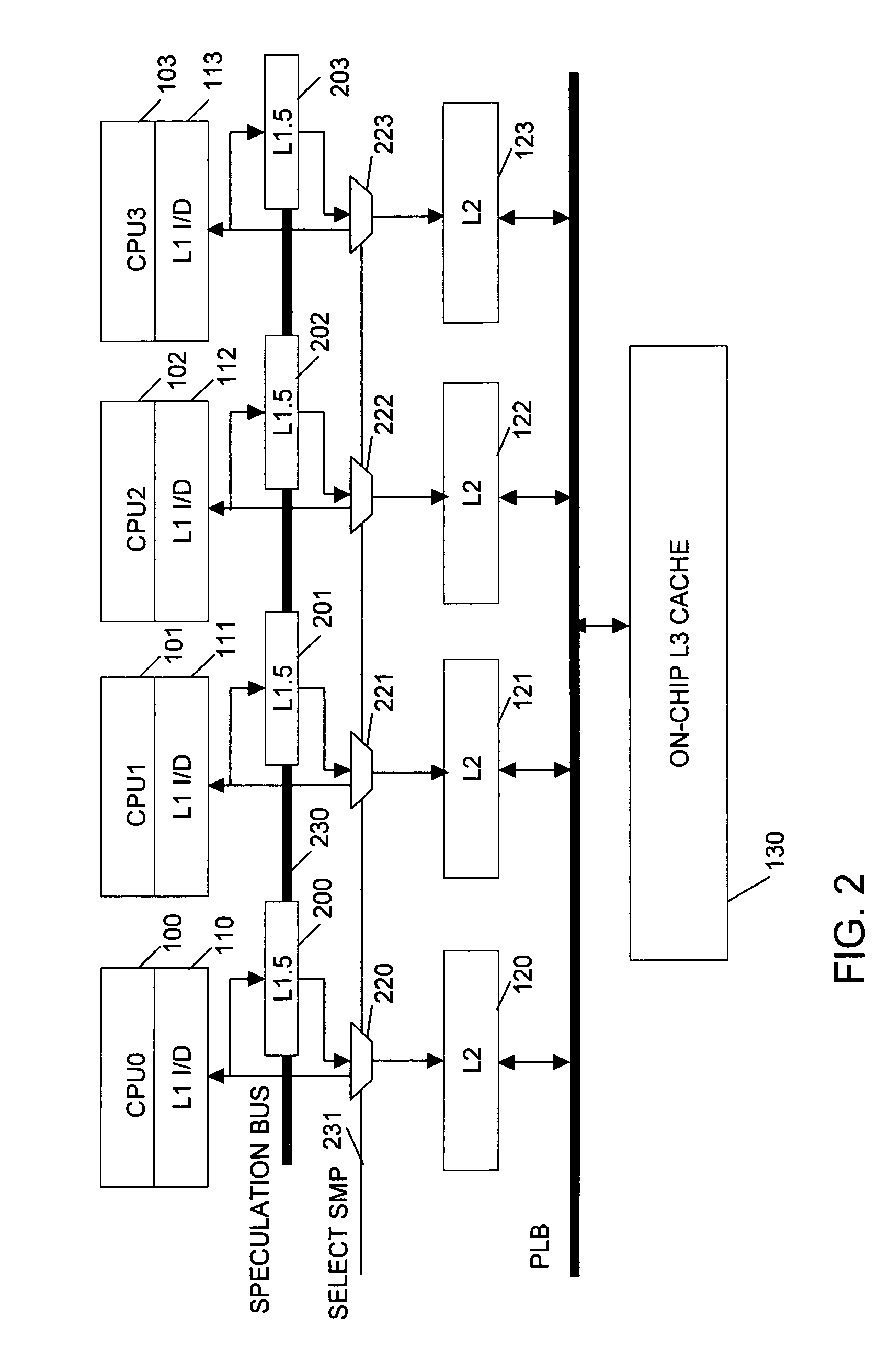
A system, method and computer program product for supporting thread level speculative execution in a computing environment having multiple processing units adapted for concurrent execution of threads in speculative and non-speculative modes. Each processing unit includes a cache memory hierarchy of caches operatively connected therewith. The apparatus includes an additional cache level local to each processing unit for use only in a thread level speculation mode, each additional cache for storing speculative results and status associated with its associated processor when handling speculative threads. The additional local cache level at each processing unit are interconnected so that speculative values and control data may be forwarded between parallel executing threads. A control implementation is provided that enables speculative coherence between speculative threads executing in the computing environment.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method and apparatus for cooperative multithreading
InactiveUS20080046689A1Register arrangementsGeneral purpose stored program computerDatapathSpeculative multithreading
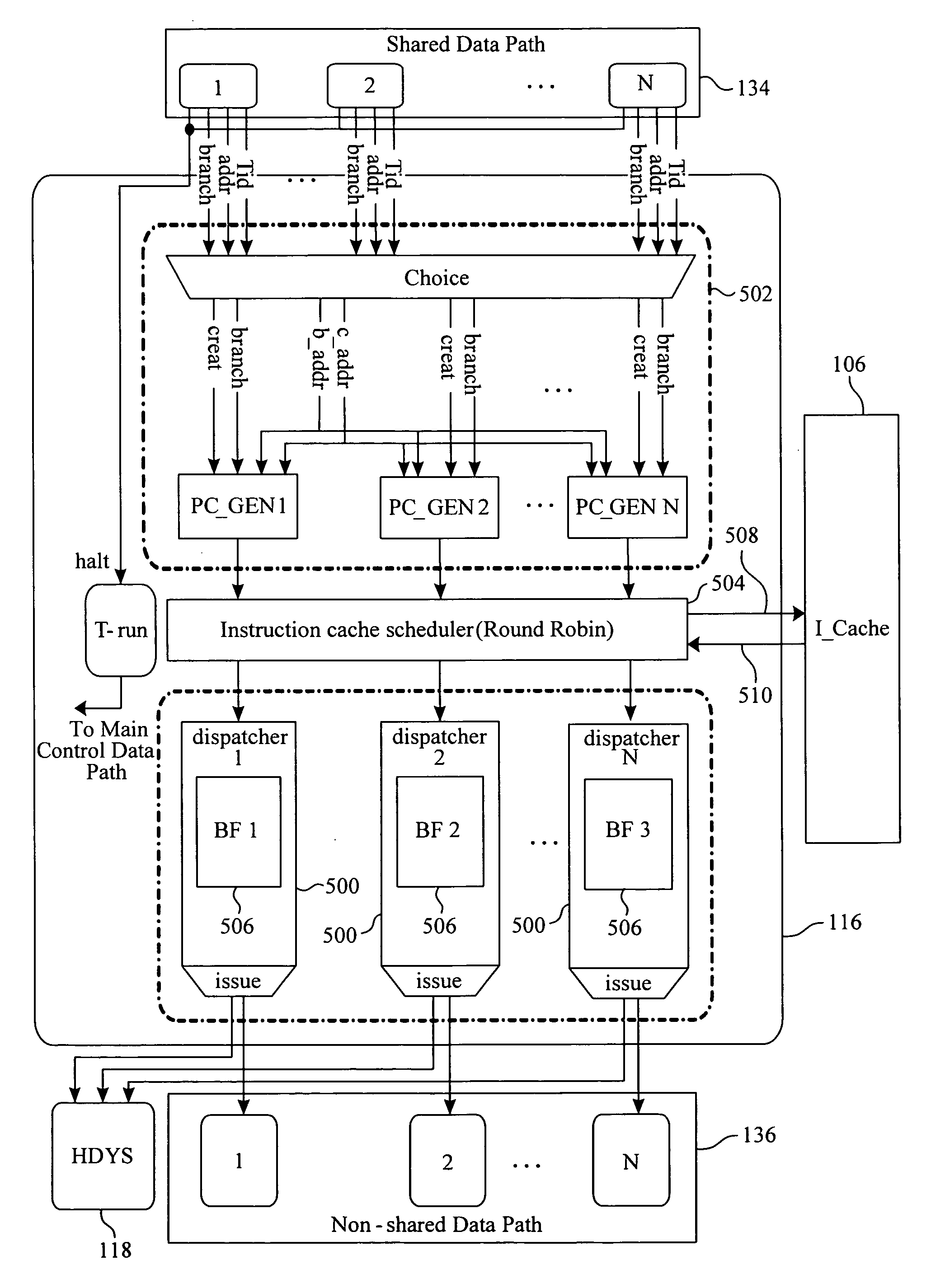
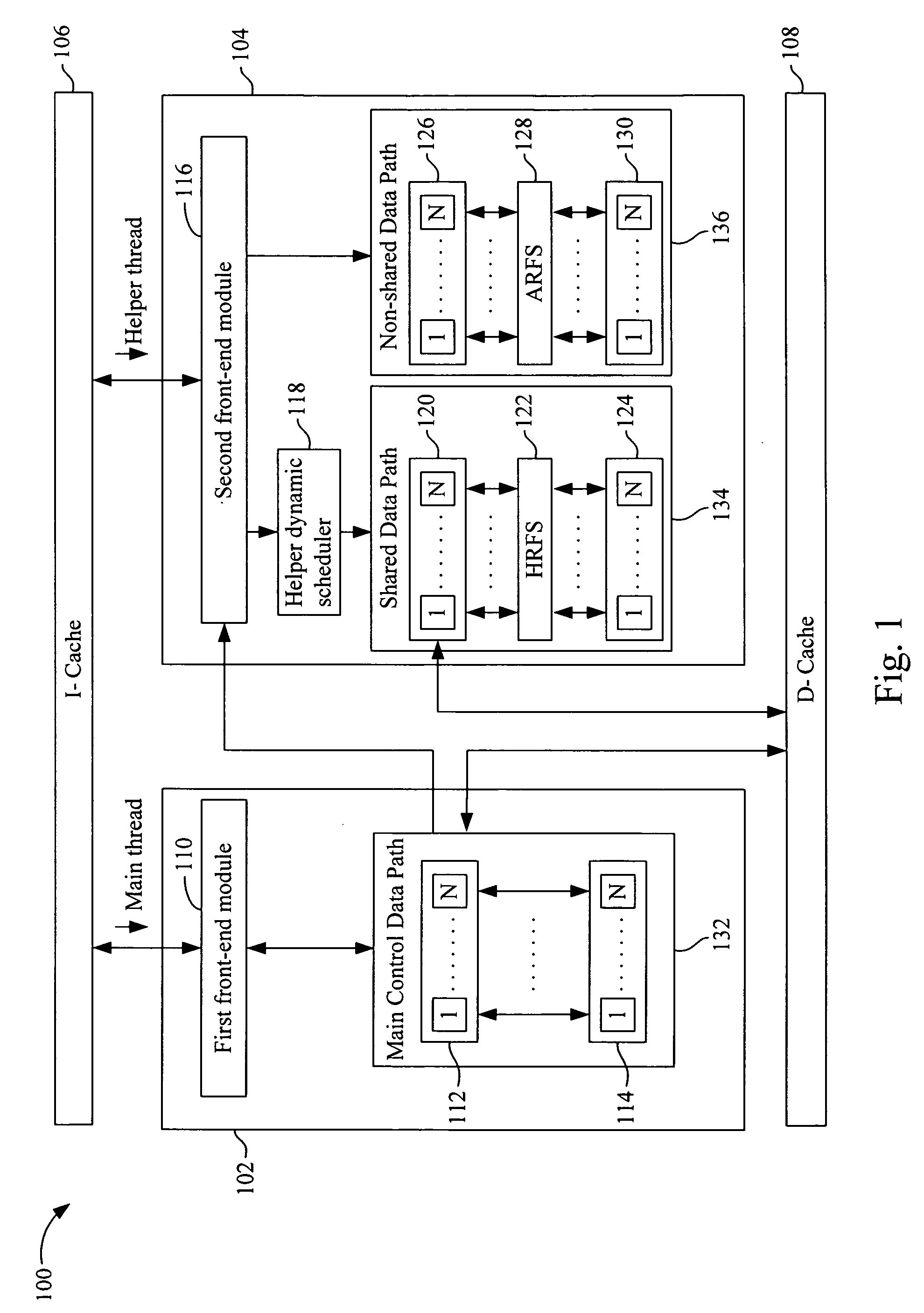
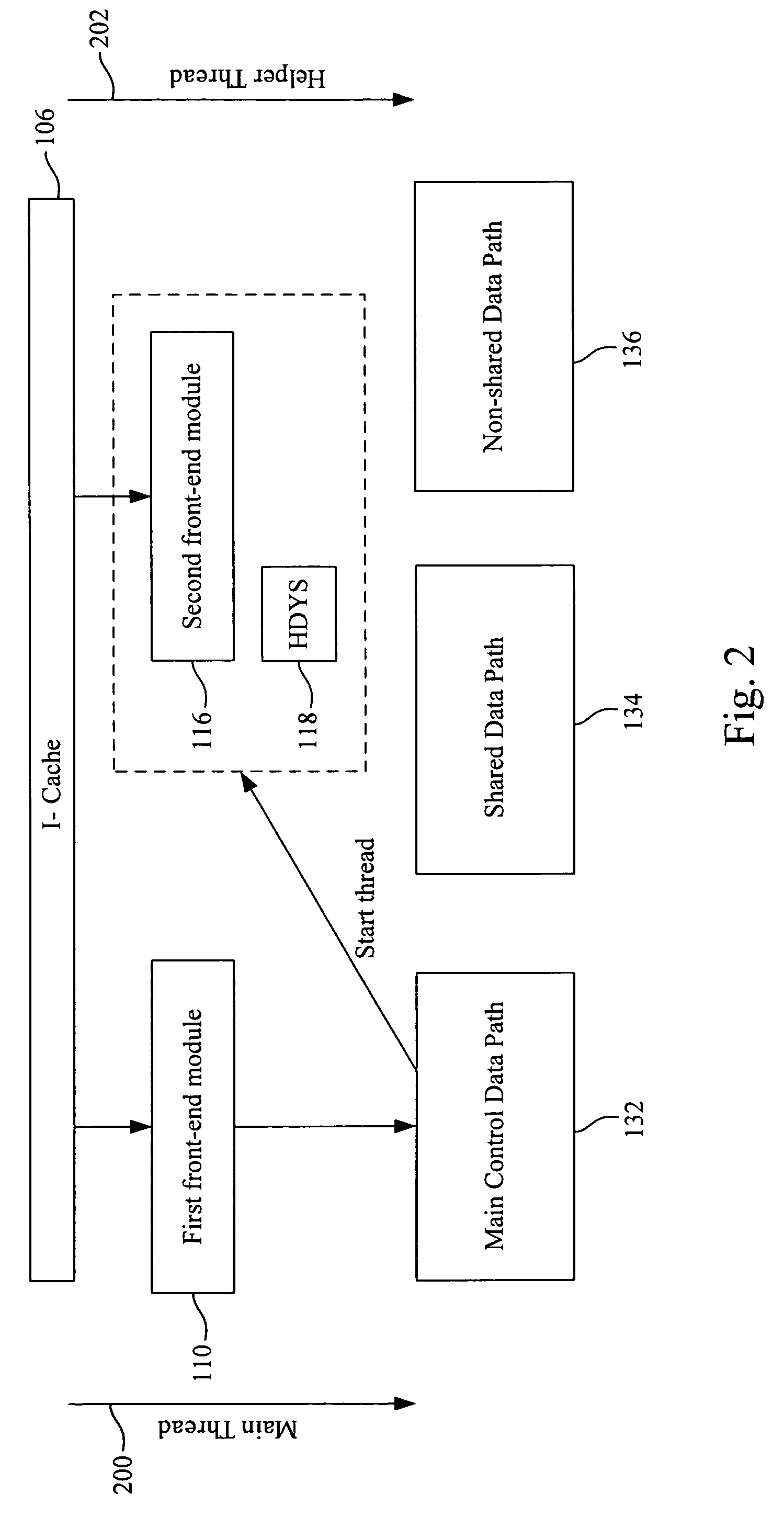
A cooperative multithreading architecture includes an instruction cache, capable of providing a micro-VLIW instruction; a first cluster, connects to the instruction cache to fetch the micro-VLIW instruction; and a second cluster, connects to the instruction cache to fetch the micro-VLIW instruction and capable of execution acceleration. The second cluster includes a second front-end module, connects to the instruction cache and capable of requesting and dispatching the micro-VLIW instruction; a helper dynamic scheduler, connects to the second front-end module and capable of dispatching the micro-VLIW instruction; a non-shared data path, connects to the second front-end module and capable of providing a wider data path; and a shared data path, connected to the helper dynamic scheduler and capable of assisting a control part of the non-shared data path. The first cluster and the second cluster carry out execution of the respective micro-instructions in parallel.
Owner:CHEN TIEN FU
Software-based speculative pre-computation and multithreading
InactiveUS6928645B2General purpose stored program computerMultiprogramming arrangementsParallel computingSpeculative multithreading
Speculative pre-computation and multithreading (SP), allows a processor to use spare hardware contexts to spawn speculative threads to very effectively pre-fetch data well in advance of the main thread. The burden of spawning threads may fall on the main thread via basic triggers. The speculative threads may also spawn other speculative threads via chaining triggers.
Owner:INTEL CORP
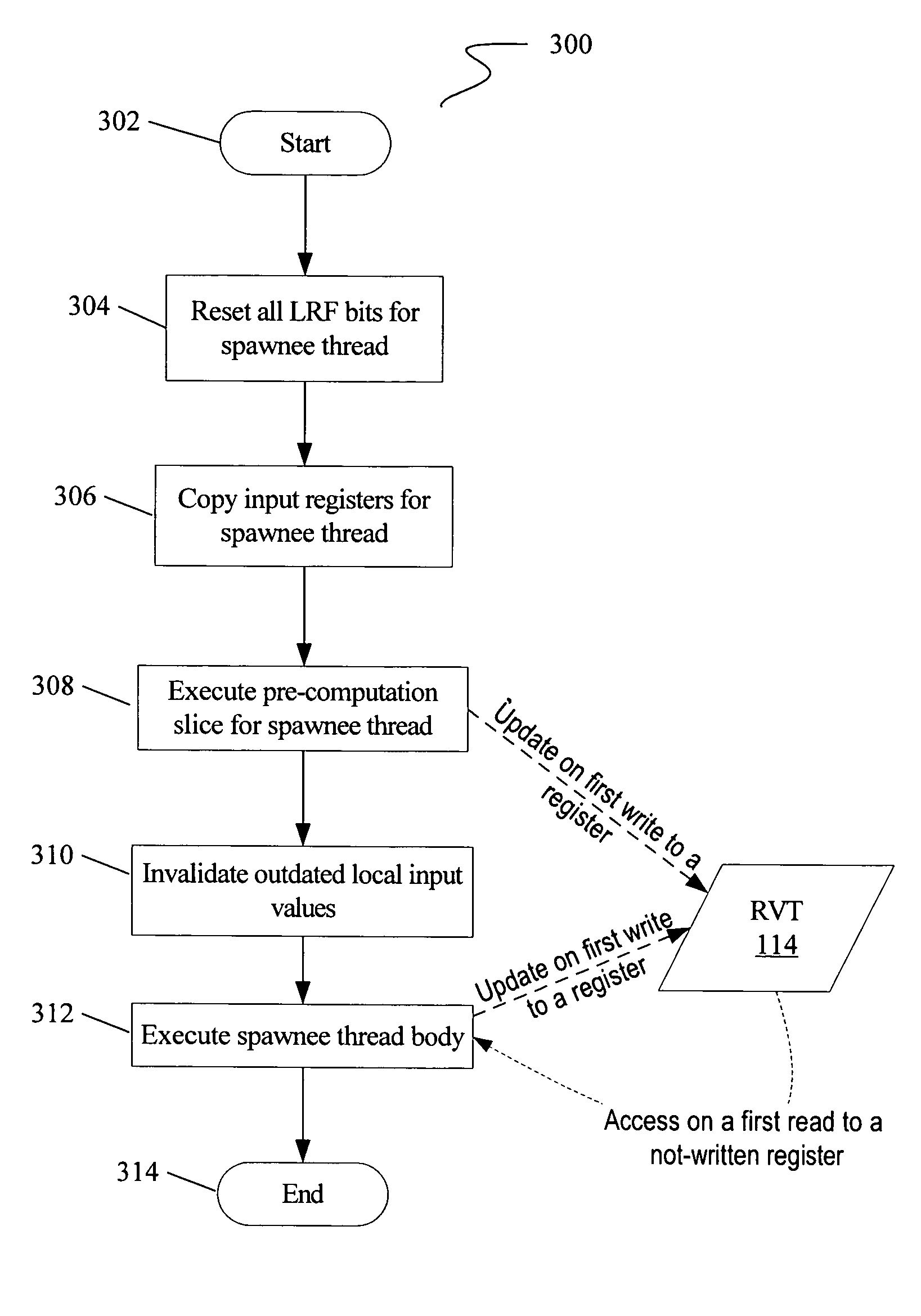
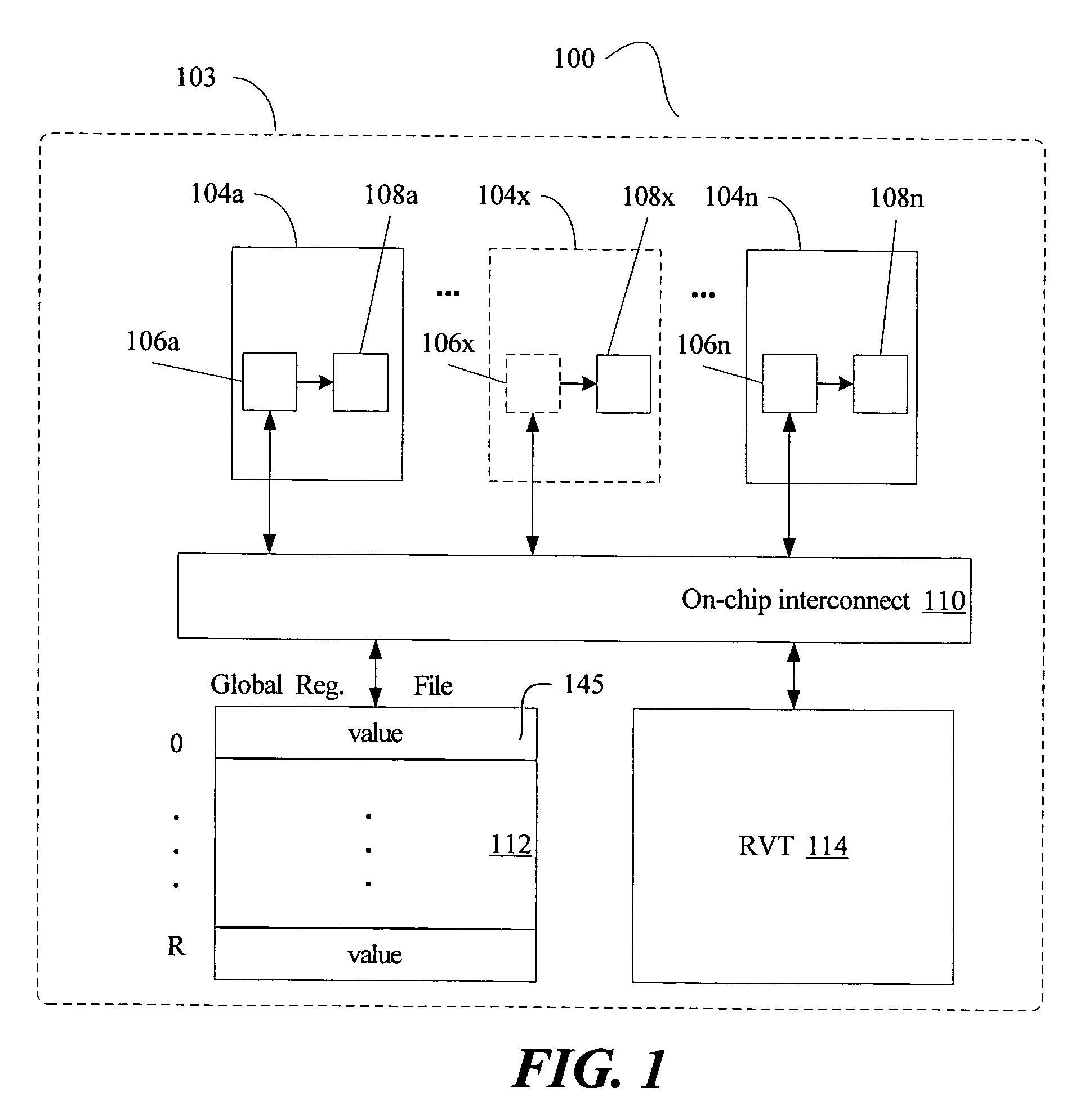
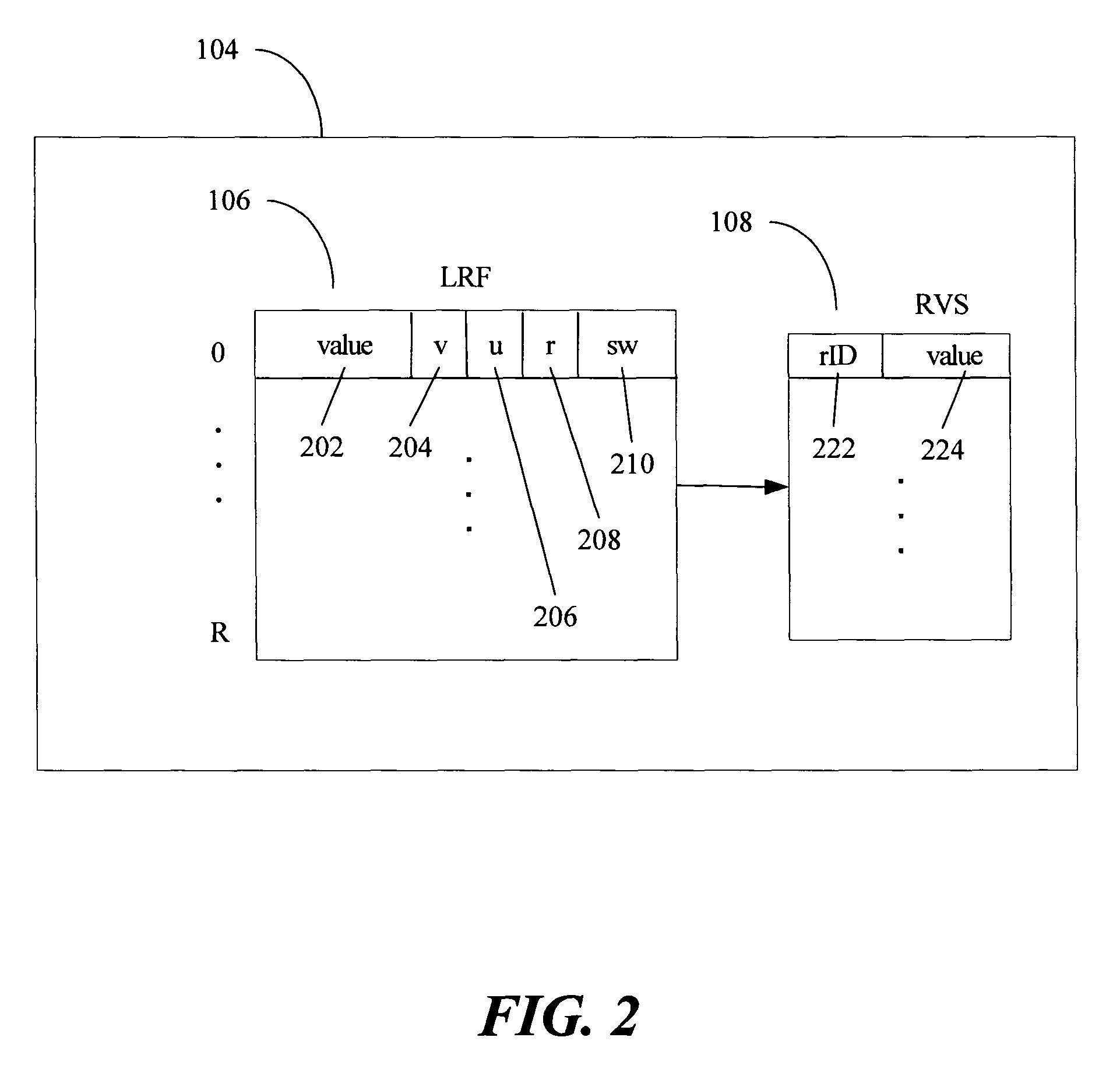
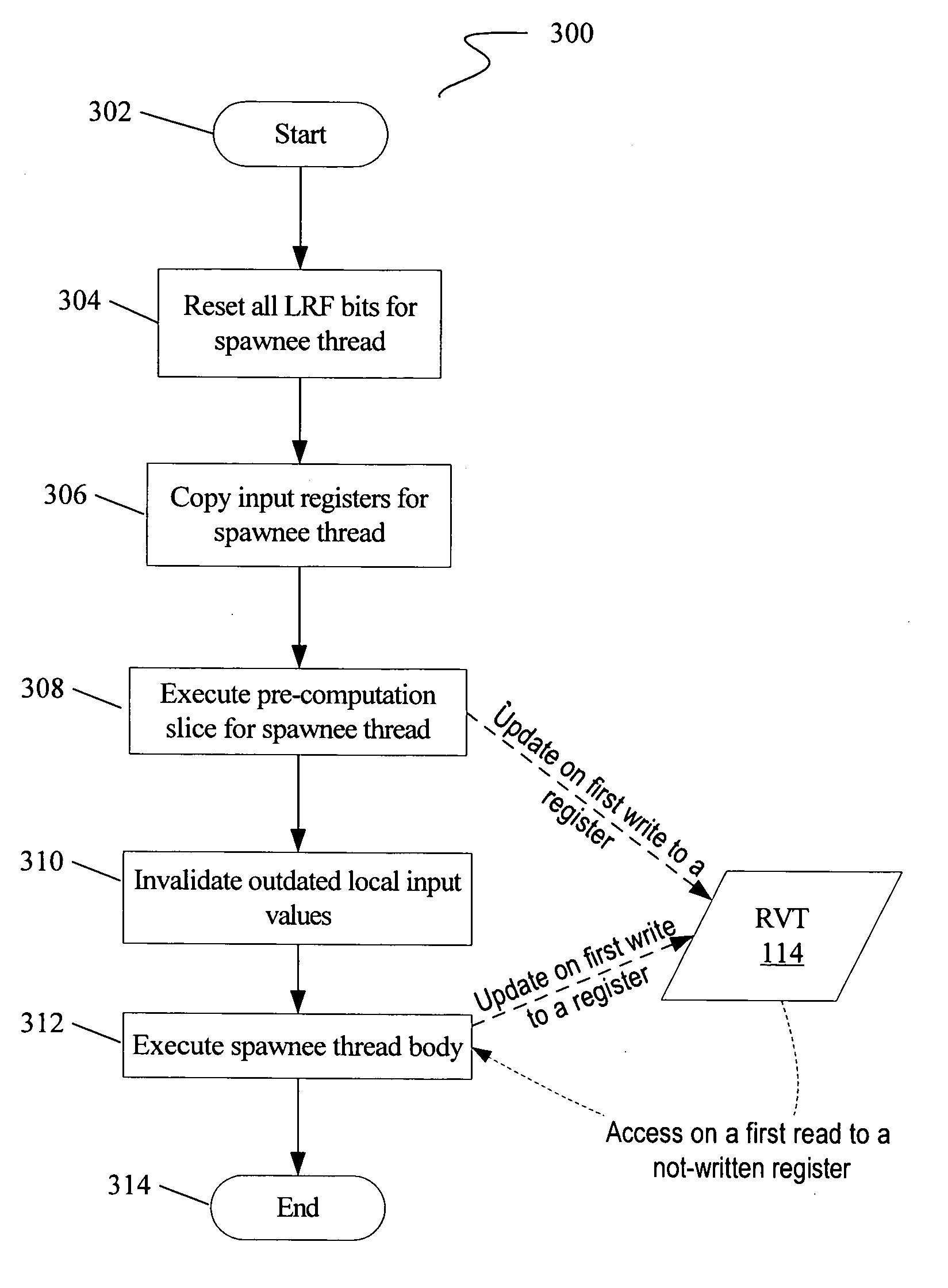
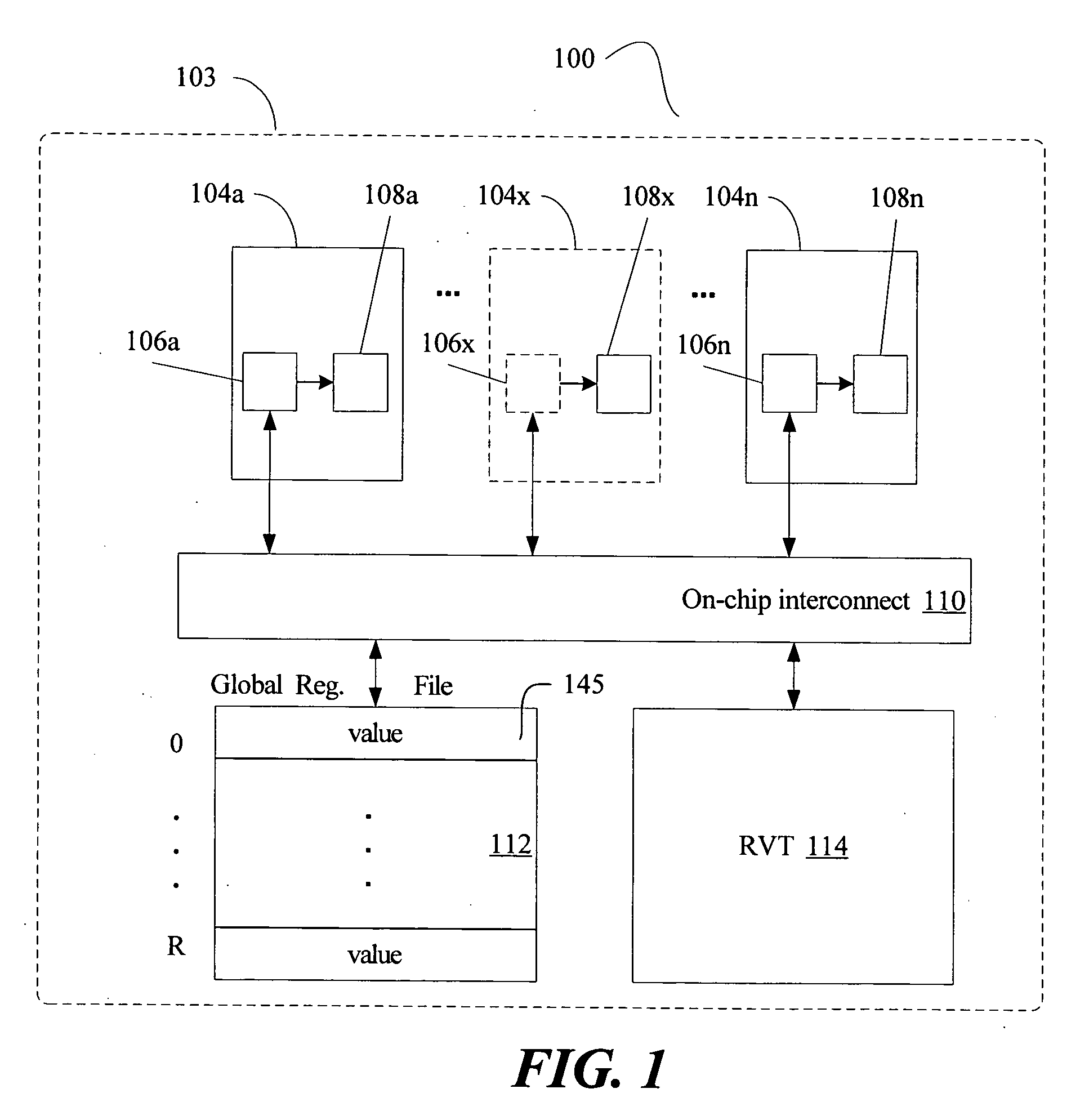
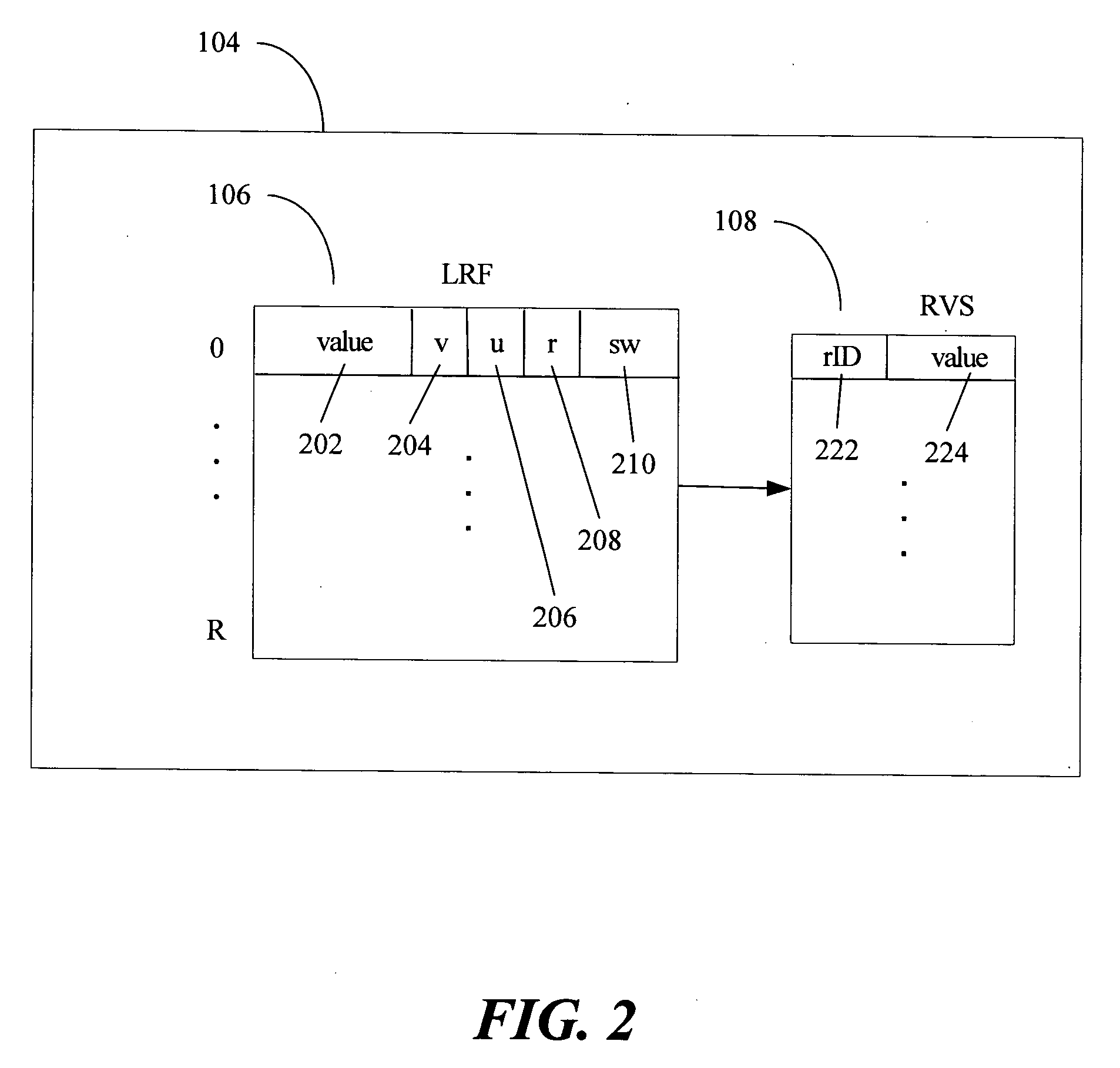
Multi-version register file for multithreading processors with live-in precomputation
Disclosed are selected embodiments of a processor that may include a plurality of thread units and a register file architecture to support speculative multithreading. For at least one embodiment, live-in values for a speculative thread are computed via execution of a precomputation slice and are stored in a validation buffer for later validation. A global register file holds the committed architecture state generated by a non-speculative thread. Each thread unit includes a local register file. A directory indicates, for each architectural register, which speculative thread(s) have generated a value for the architectural register. Other embodiments are also described and claimed.
Owner:BEIJING XIAOMI MOBILE SOFTWARE CO LTD
Speculative loading of buffers within a port of a network device
InactiveUS6920106B1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsComputer scienceSpeculative multithreading
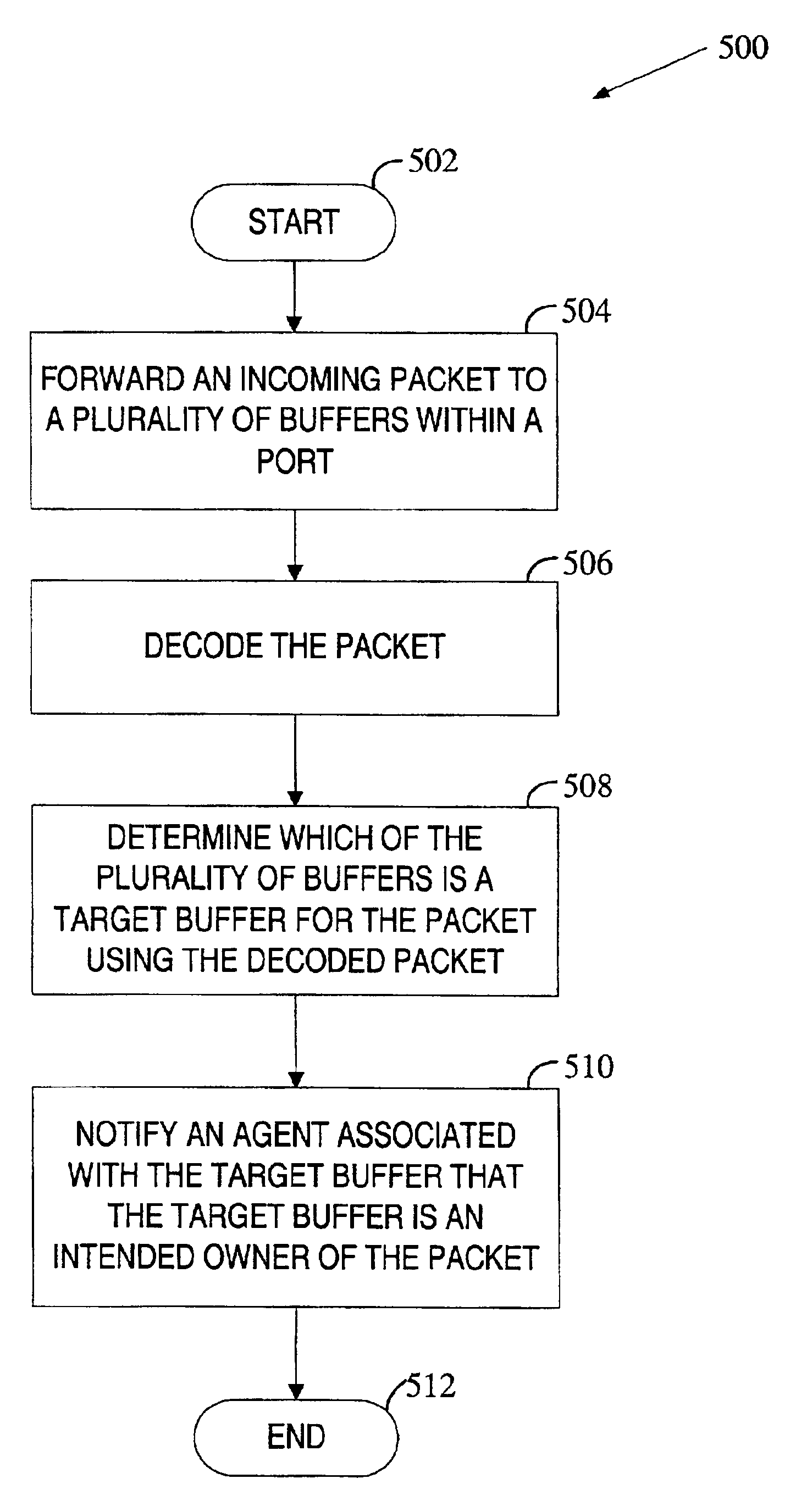
In one embodiment a method for processing an incoming packet in a port of an interconnect device includes speculatively forwarding the incoming packet to multiple buffers within the port prior to determining which of the multiple buffers is a target buffer for the packet, decoding the packet, and determining which of the multiple buffers is the target buffer for the packet using the decoded packet. The method further includes notifying an agent associated with the target buffer that the target buffer is an intended owner of the data packet. In one embodiment, agents associated with the multiple buffers are designated to process packets that are not subject to a credit-based flow control method.
Owner:MICROSEMI SOLUTIONS (US) INC
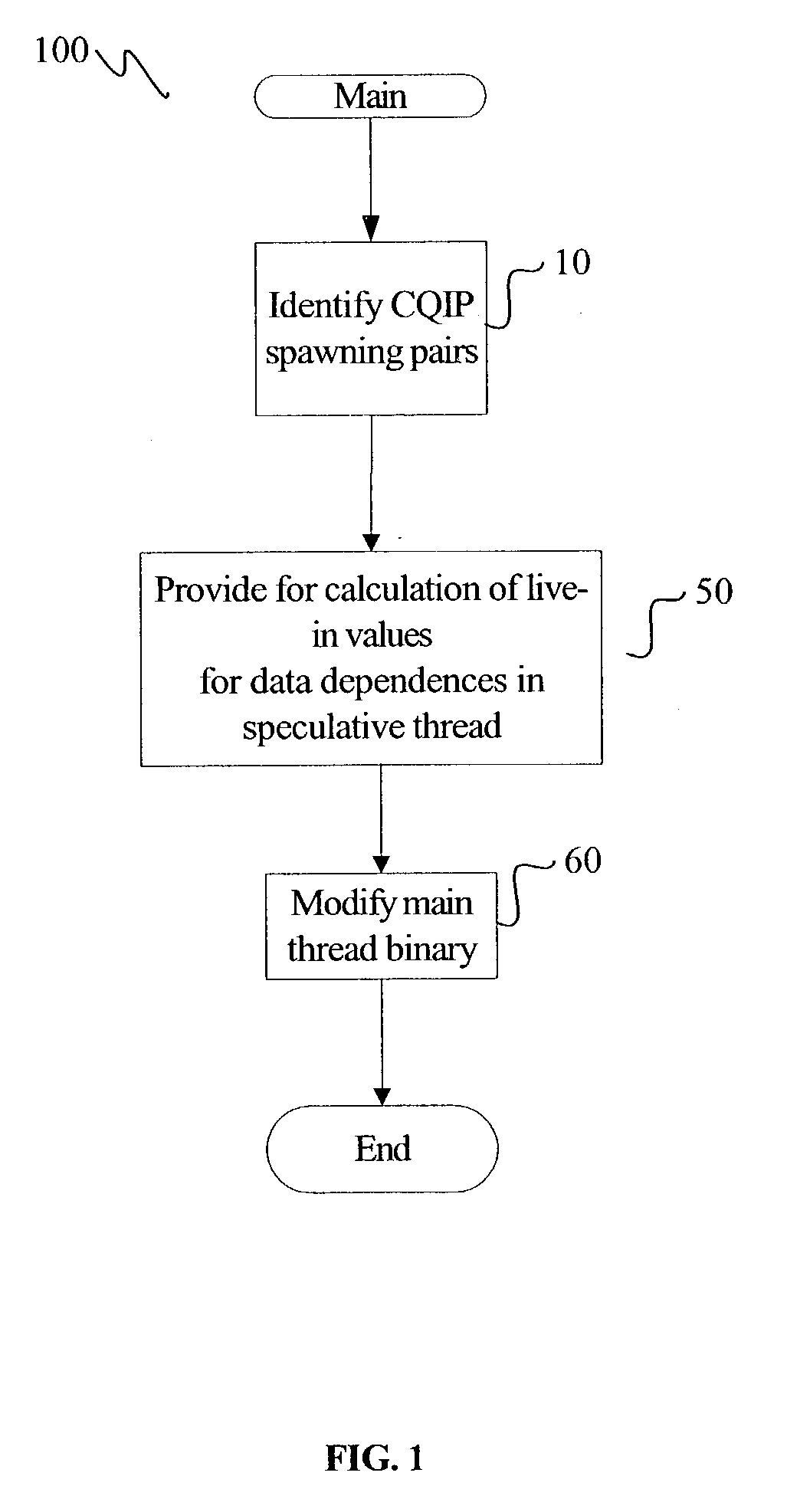
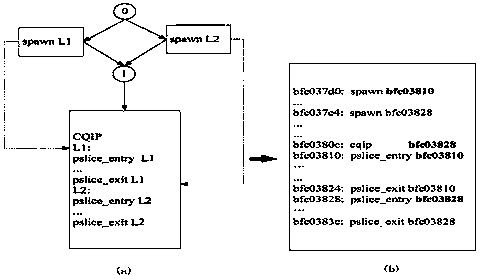
Control-quasi-independent-points guided speculative multithreading
InactiveUS20040154010A1Program initiation/switchingSoftware engineeringPrecomputationExecution control
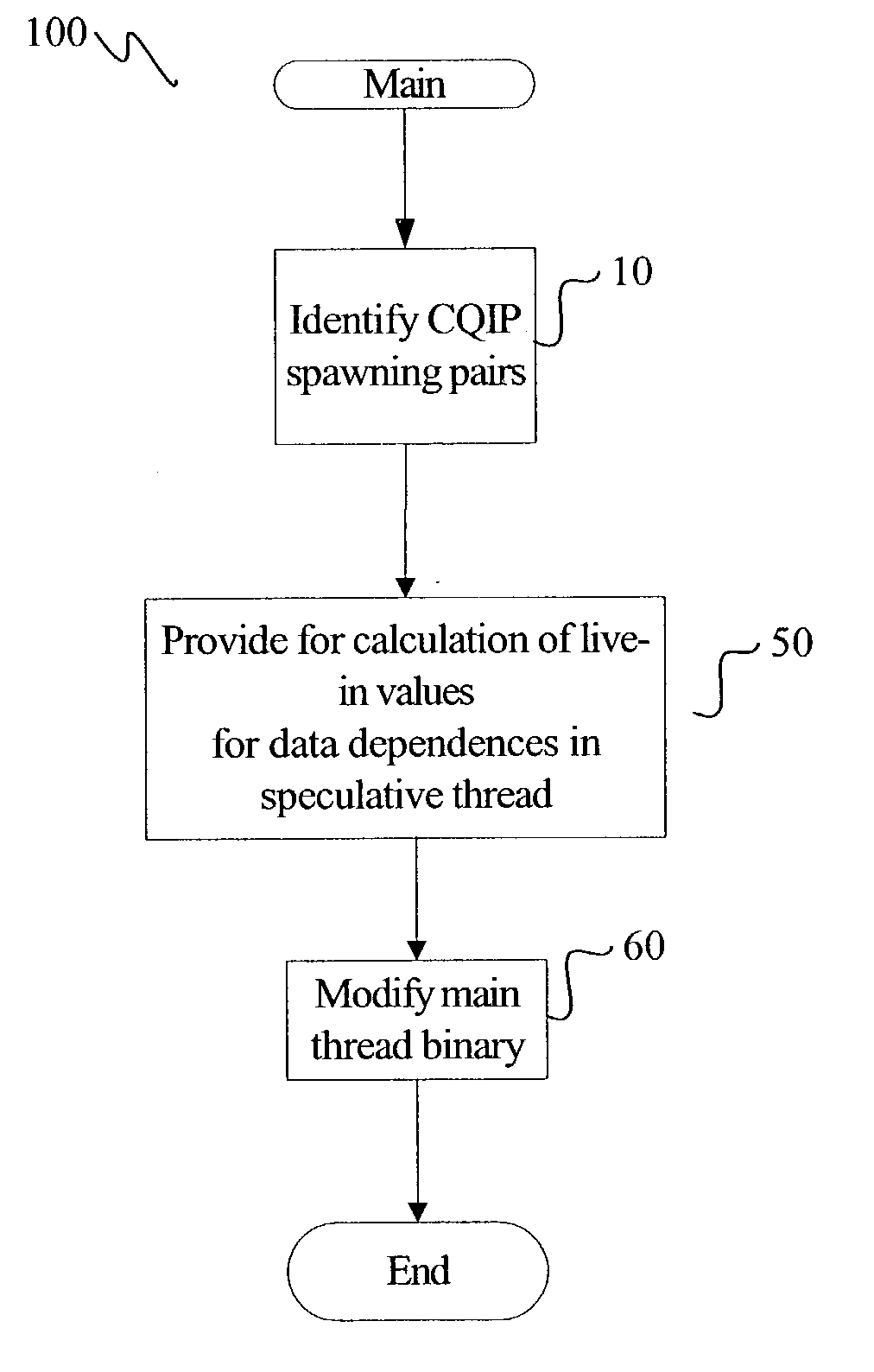
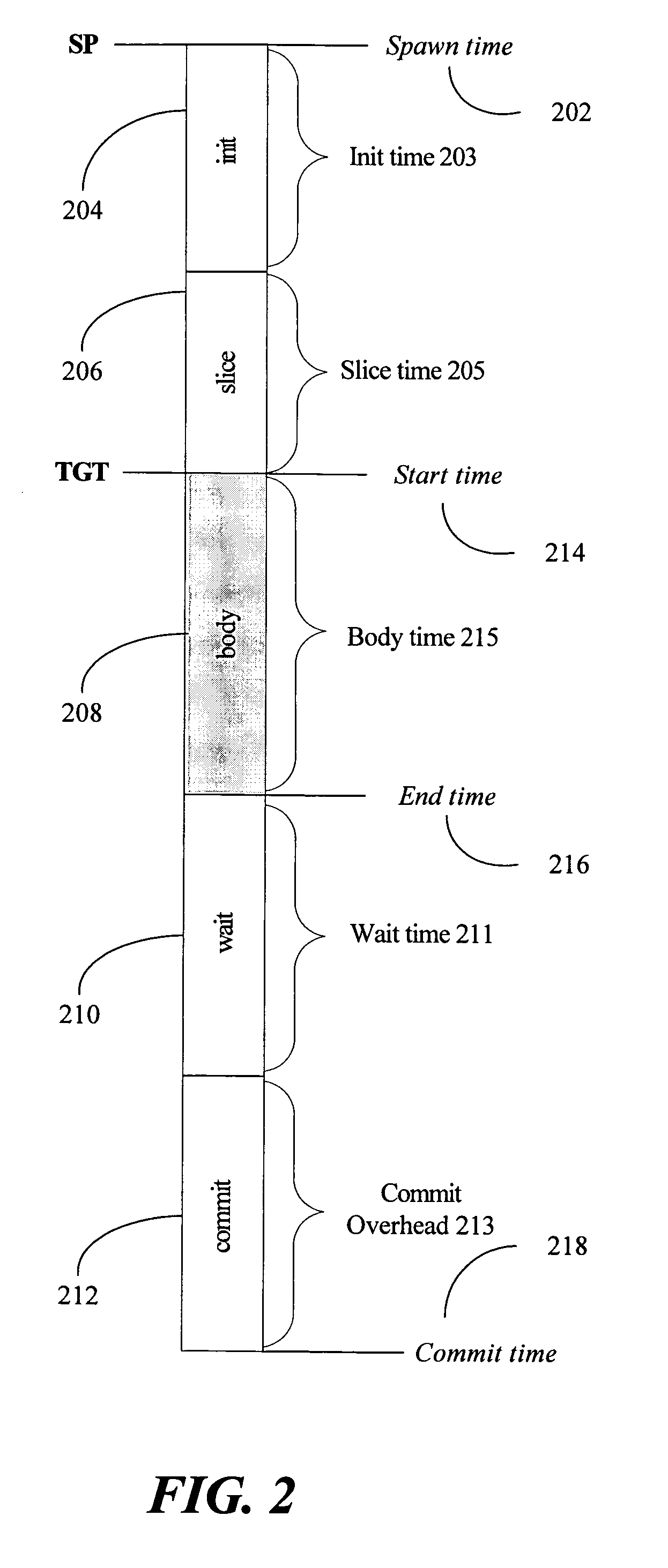
A method for generating instructions to facilitate control-quasi-independent-point multithreading is provided. A spawn point and control-quasi-independent-point are determined. An instruction stream is generated to partition a program so that portions of the program are parallelized by speculative threads. A method of performing control-quasi-independent-point guided speculative multithreading includes spawning a speculative thread when the spawn point is encountered. An embodiment of the method further includes performing speculative precomputation to determine a live-in value for the speculative thread.
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
Low complexity speculative multithreading system based on unmodified microprocessor core
InactiveUS20080263280A1Efficient use ofMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationMemory hierarchySpeculative execution
A system, method and computer program product for supporting thread level speculative execution in a computing environment having multiple processing units adapted for concurrent execution of threads in speculative and non-speculative modes. Each processing unit includes a cache memory hierarchy of caches operatively connected therewith. The apparatus includes an additional cache level local to each processing unit for use only in a thread level speculation mode, each additional cache for storing speculative results and status associated with its associated processor when handling speculative threads. The additional local cache level at each processing unit are interconnected so that speculative values and control data may be forwarded between parallel executing threads. A control implementation is provided that enables speculative coherence between speculative threads executing in the computing environment.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Low complexity speculative multithreading system based on unmodified microprocessor core
InactiveUS7404041B2Efficient use ofMemory architecture accessing/allocationProgram controlSpeculative executionMain processing unit
A system, method and computer program product for supporting thread level speculative execution in a computing environment having multiple processing units adapted for concurrent execution of threads in speculative and non-speculative modes. Each processing unit includes a cache memory hierarchy of caches operatively connected therewith. The apparatus includes an additional cache level local to each processing unit for use only in a thread level speculation mode, each additional cache for storing speculative results and status associated with its associated processor when handling speculative threads. The additional local cache level at each processing unit are interconnected so that speculative values and control data may be forwarded between parallel executing threads. A control implementation is provided that enables speculative coherence between speculative threads executing in the computing environment.
Owner:IBM CORP
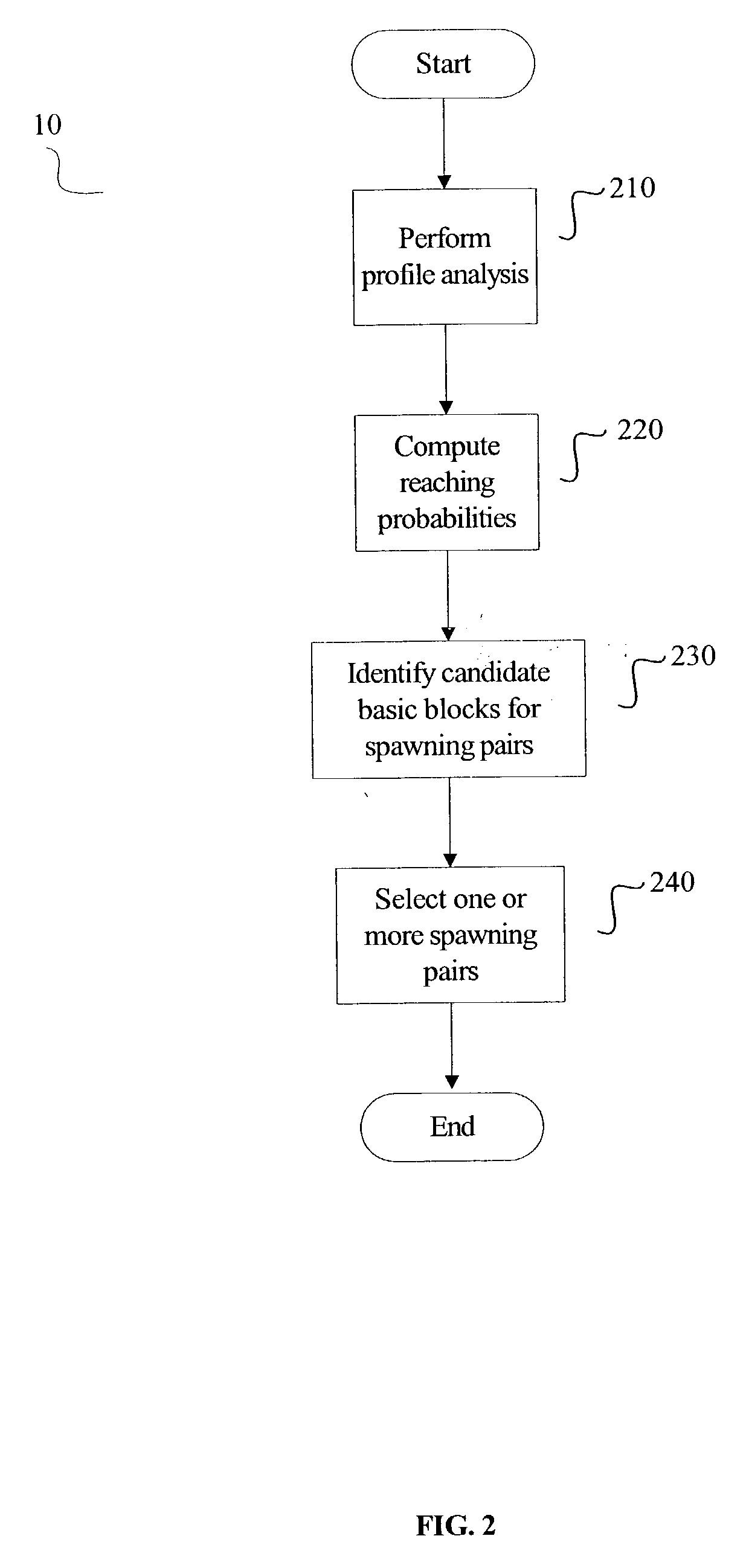
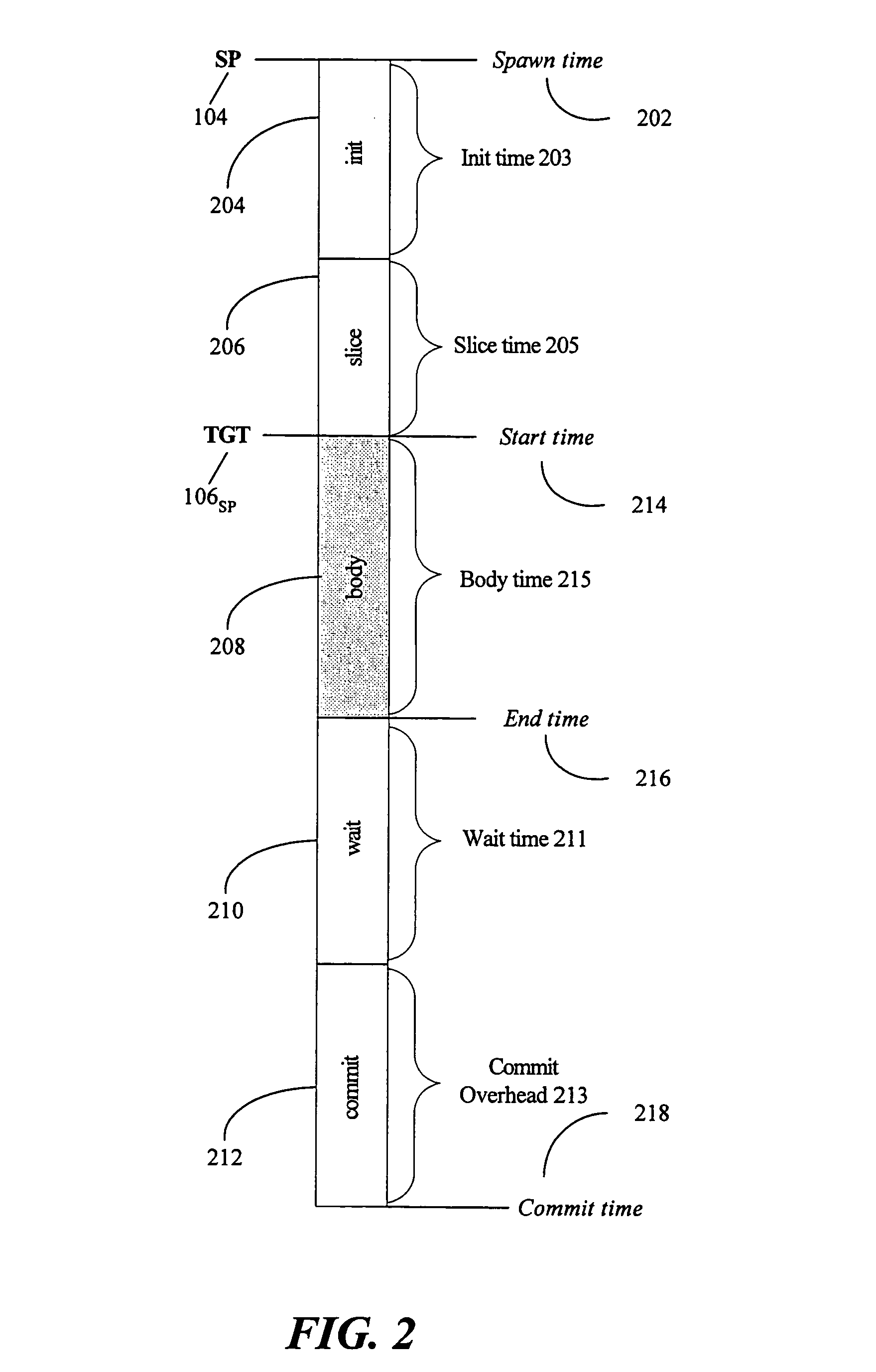
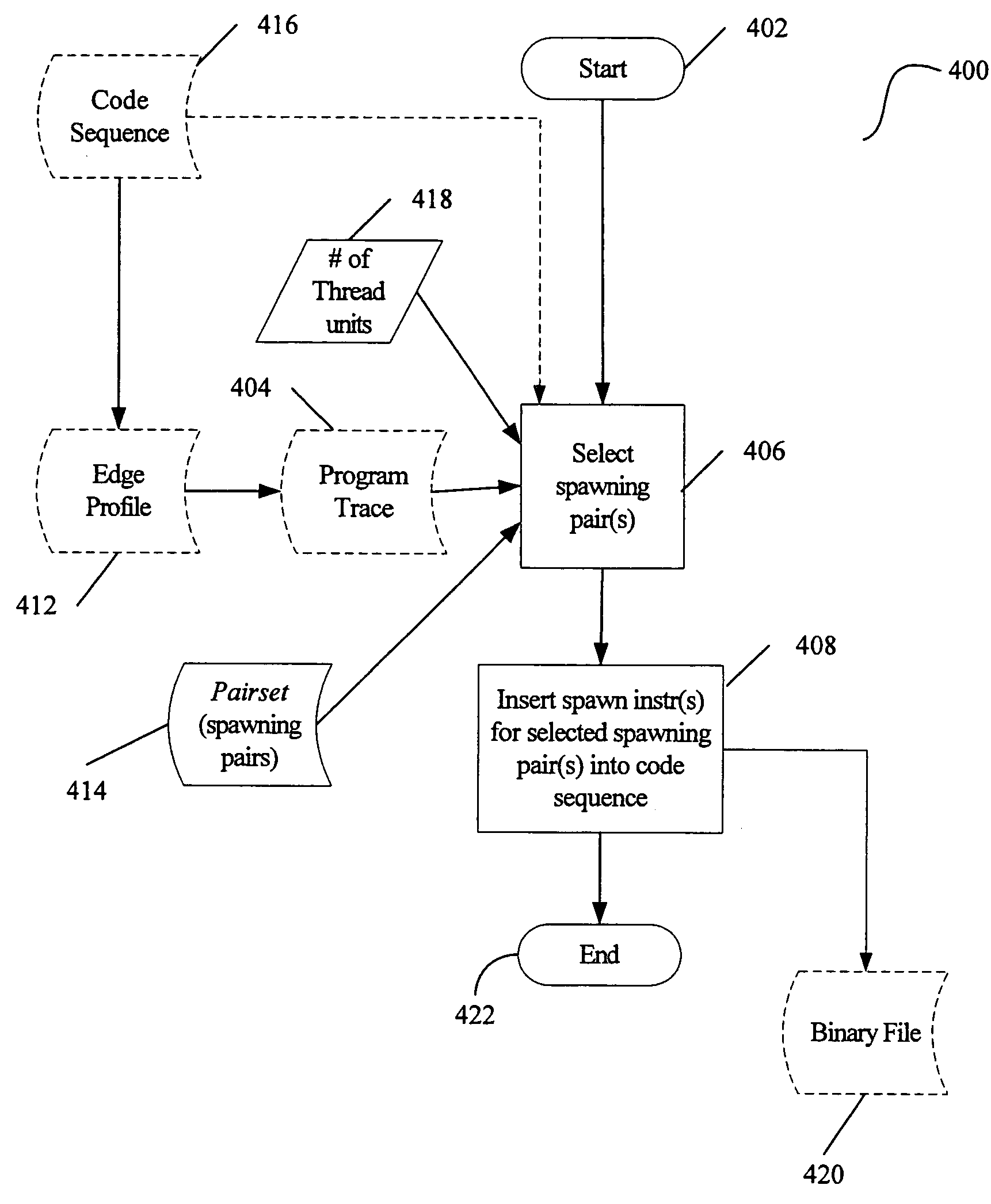
Selection of spawning pairs for a speculative multithreaded processor
ActiveUS20060064692A1Multiprogramming arrangementsSpecific program execution arrangementsProgram instructionPerformance enhancement
A method for analyzing a set of spawning pairs, where each spawning pair identifies at least one speculative thread. The analysis may be practiced via software in a compiler, binary optimizer, standalone modeler, or the like. The analysis may include determining a predicted execution time for a sequence of program instructions, given the set of spawning pairs, for a target processor having a known number of thread units, where the target processor supports speculative multithreading. The method is further to select a spawning pair, according to a greedy approach, if the spawning pair provides a performance enhancement, in terms of decreased execution time due to increased parallelism, when the speculative thread is spawned during execution of a code sequence. Other embodiments are also described and claimed.
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
Selection of spawning pairs for a speculative multithreaded processor
ActiveUS7458065B2Multiprogramming arrangementsSpecific program execution arrangementsPerformance enhancementProgram instruction
A method for analyzing a set of spawning pairs, where each spawning pair identifies at least one speculative thread. The analysis may be practiced via software in a compiler, binary optimizer, standalone modeler, or the like. The analysis may include determining a predicted execution time for a sequence of program instructions, given the set of spawning pairs, for a target processor having a known number of thread units, where the target processor supports speculative multithreading. The method is further to select a spawning pair, according to a greedy approach, if the spawning pair provides a performance enhancement, in terms of decreased execution time due to increased parallelism, when the speculative thread is spawned during execution of a code sequence. Other embodiments are also described and claimed.
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
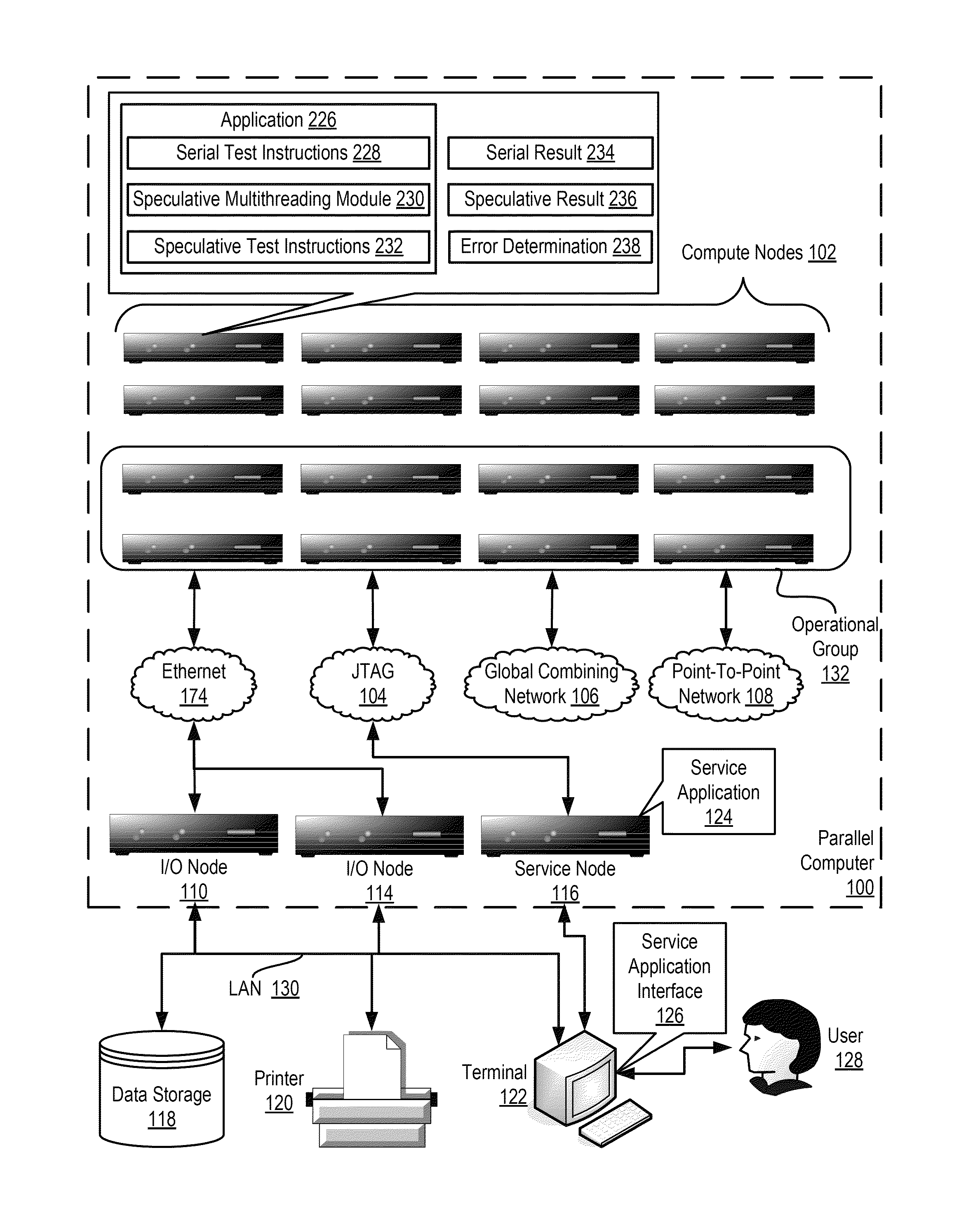
Verifying Speculative Multithreading In An Application
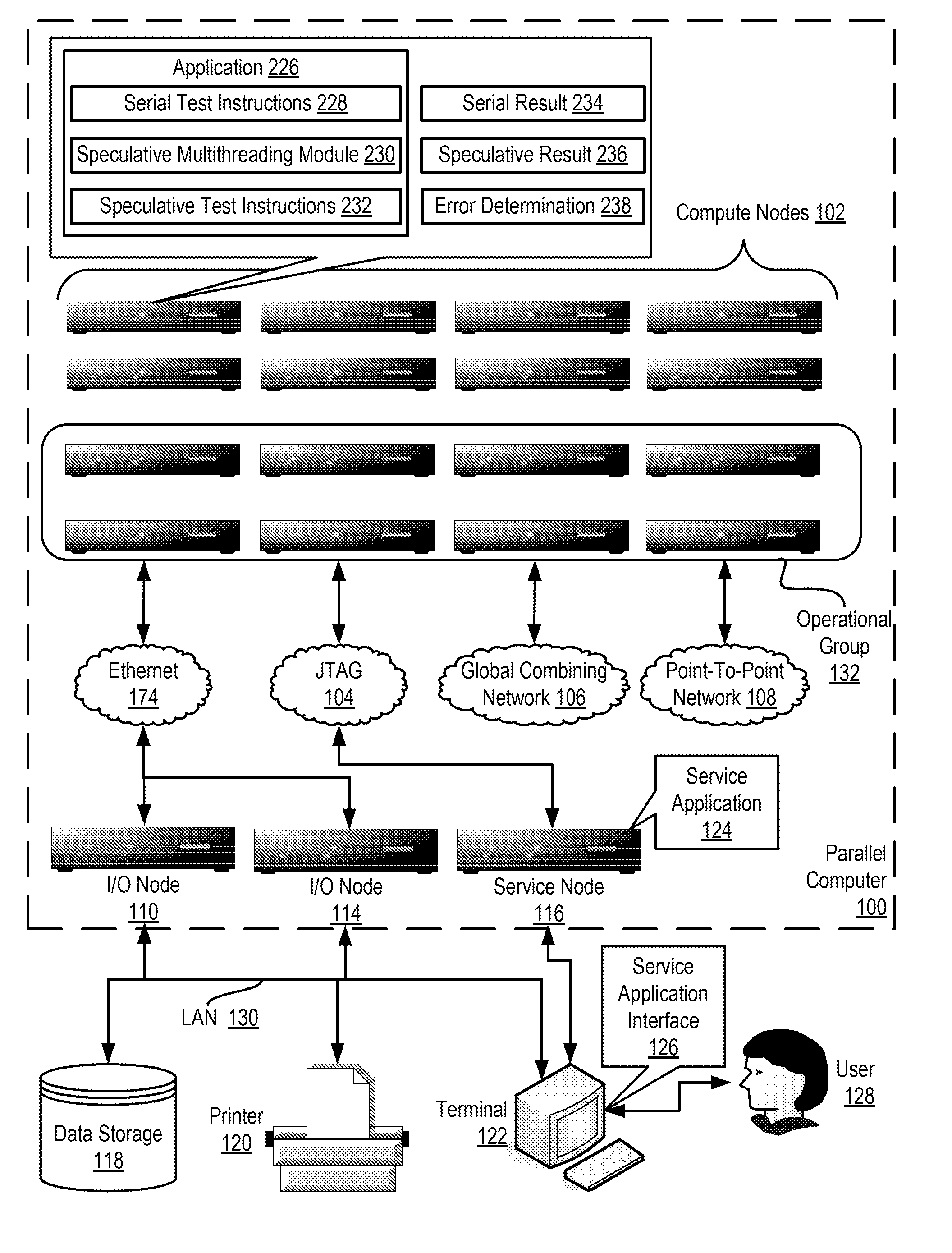
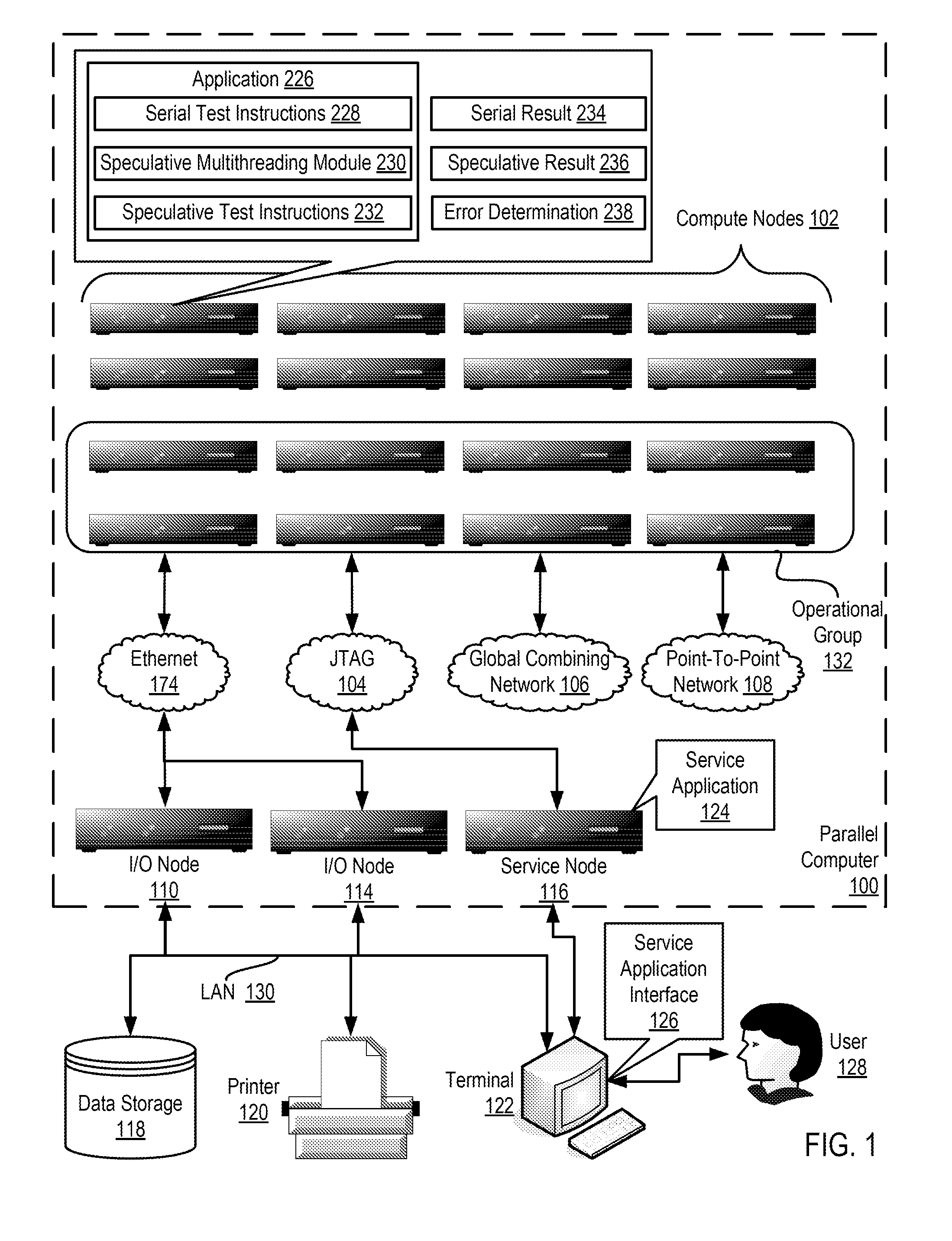
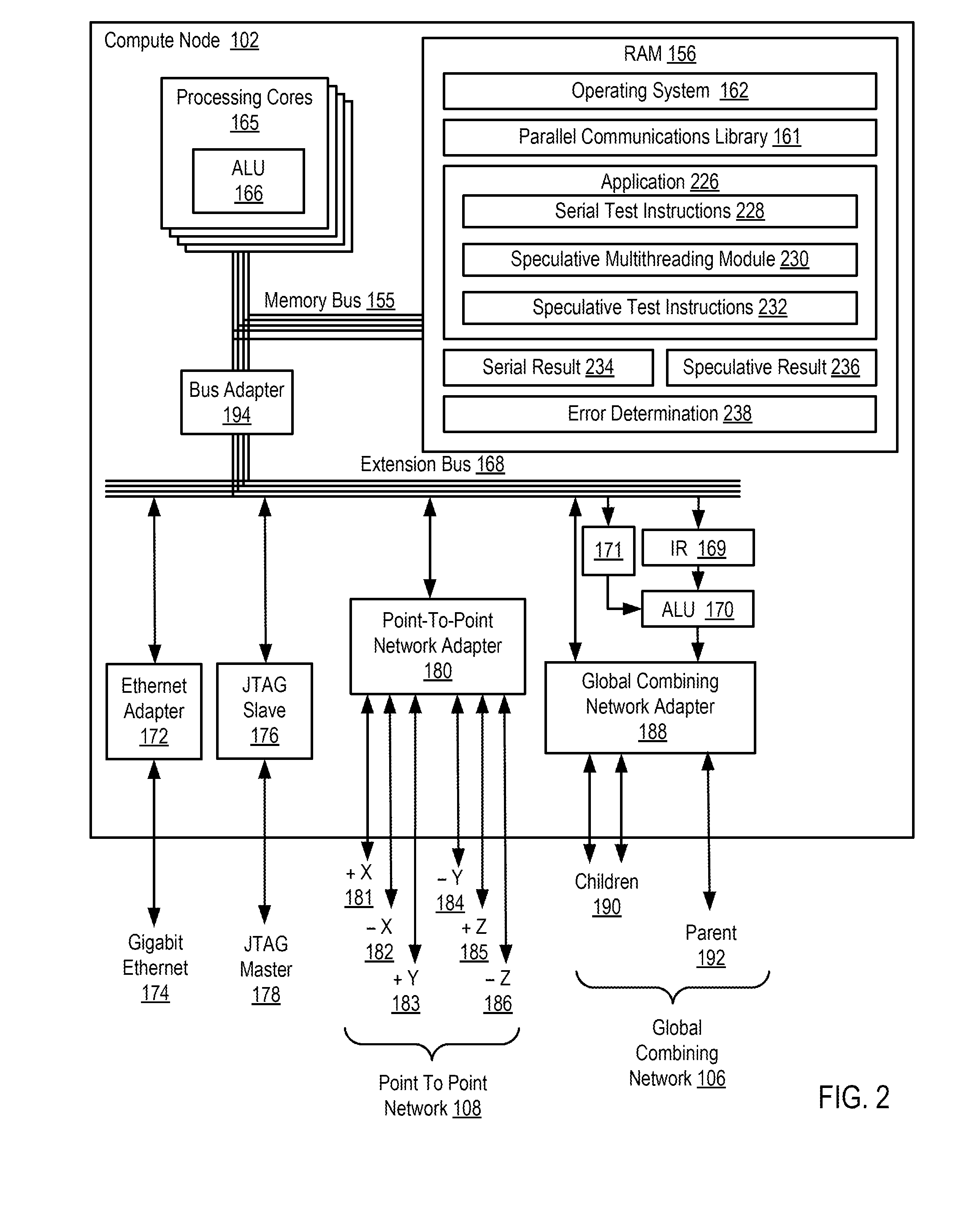
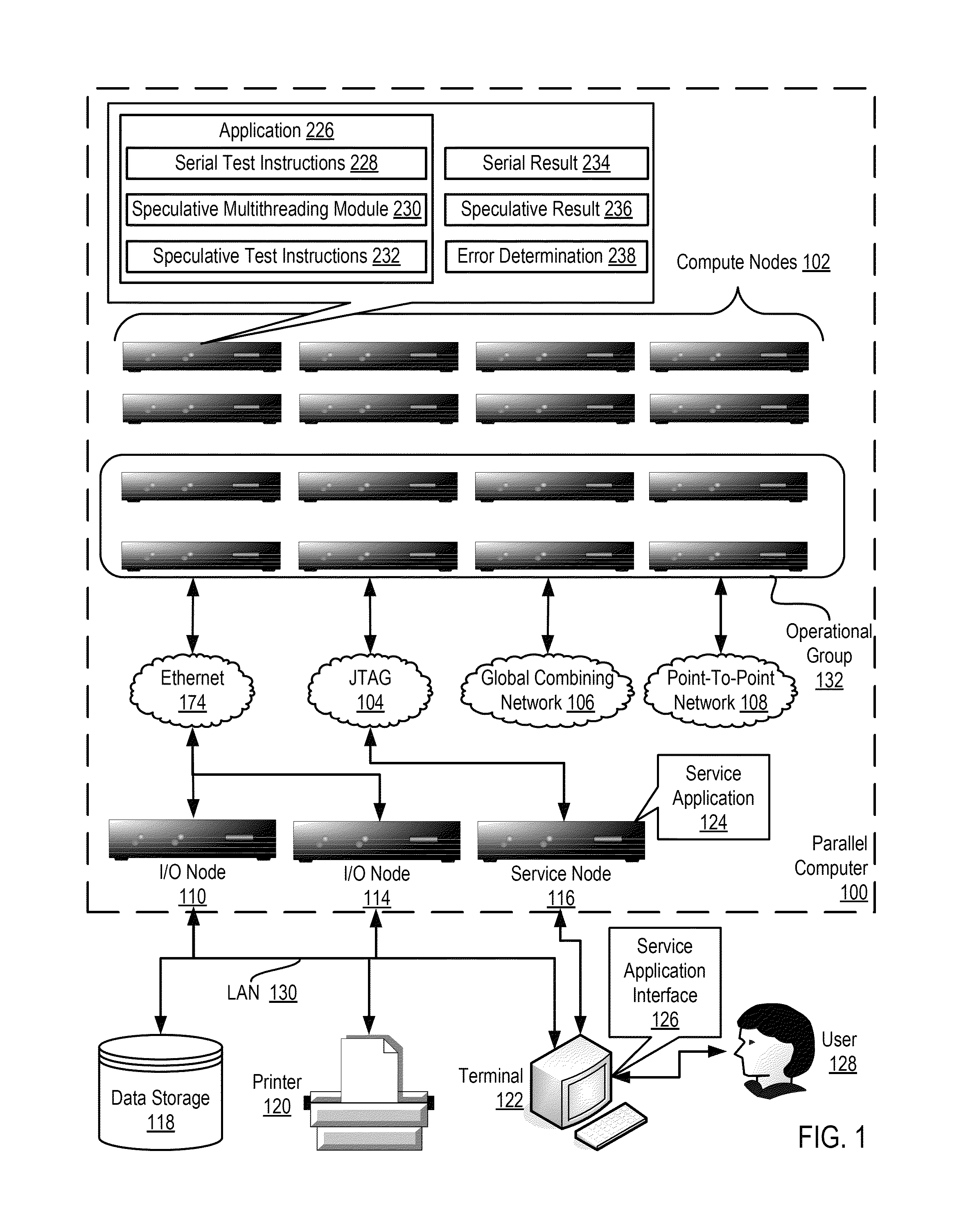
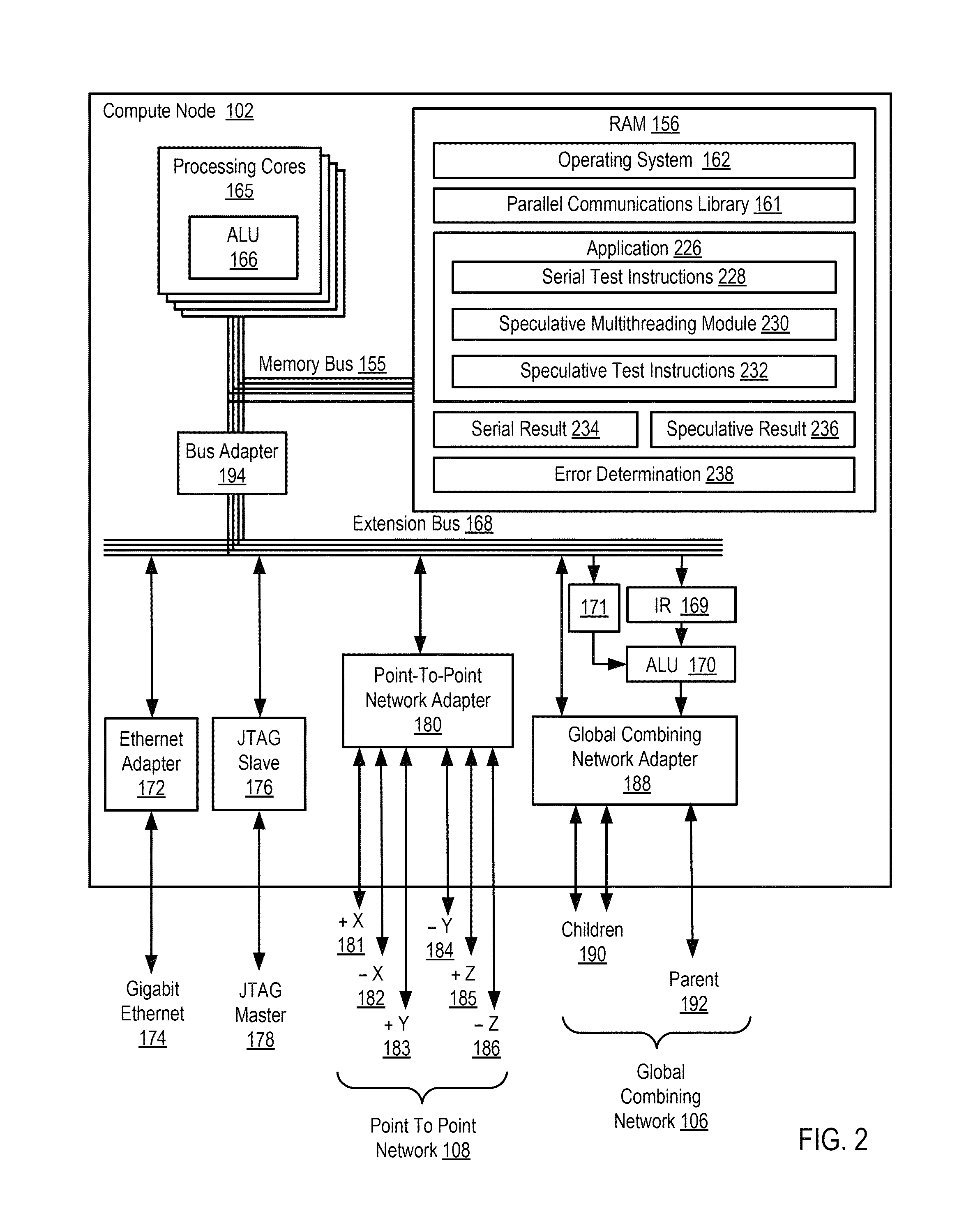
ActiveUS20130159772A1Software testing/debuggingMachine execution arrangementsApplication softwareSpeculative multithreading
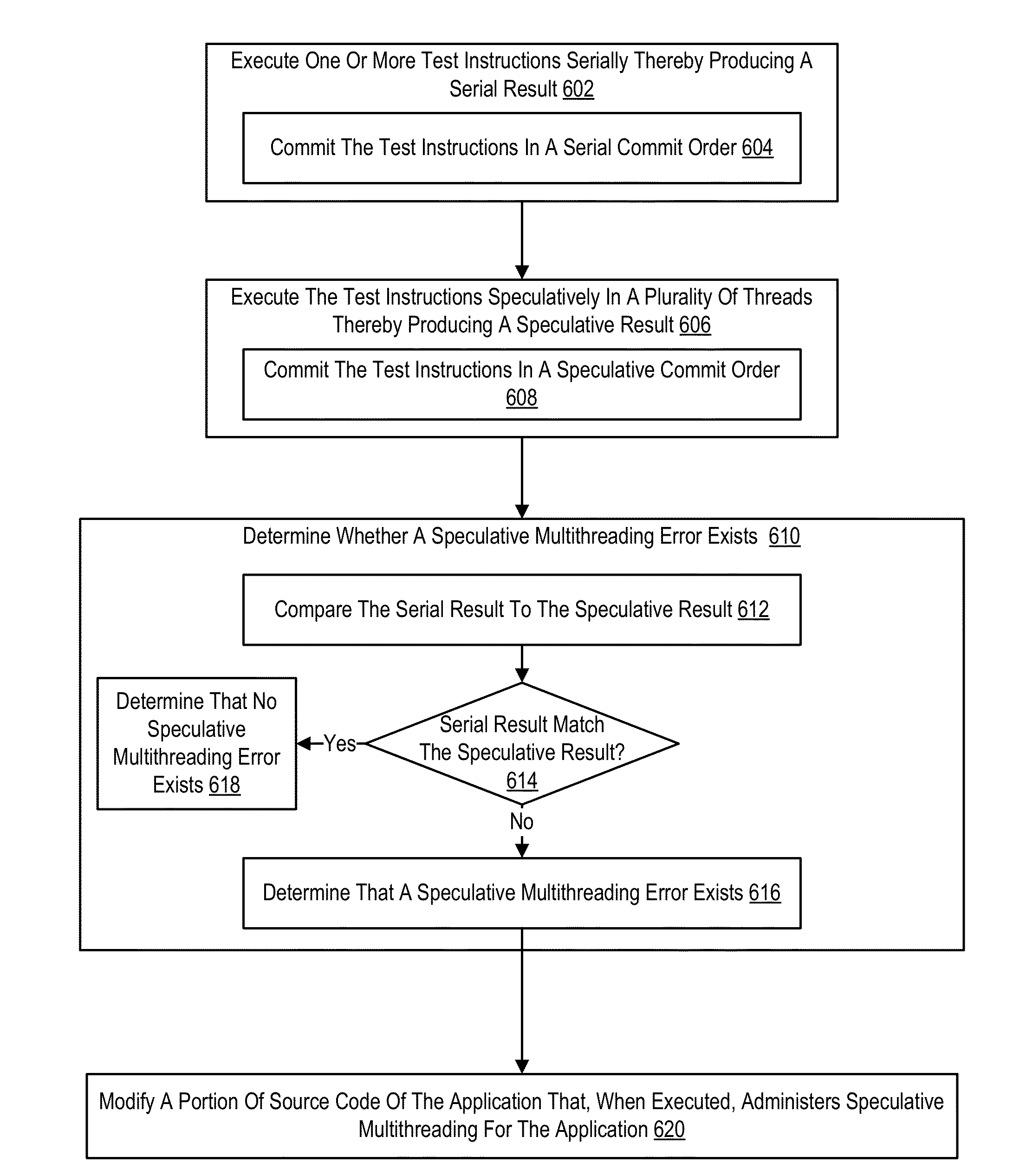
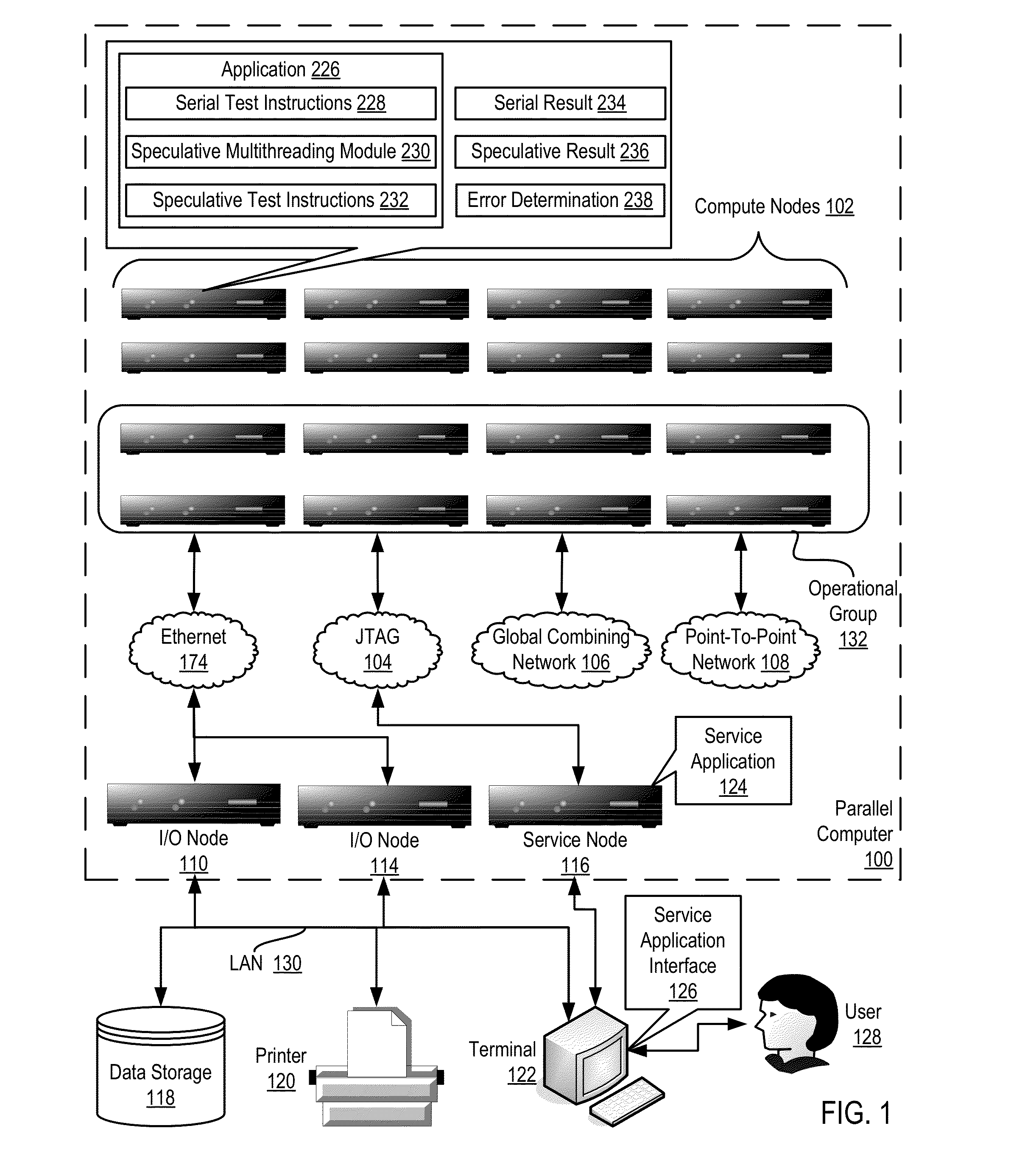
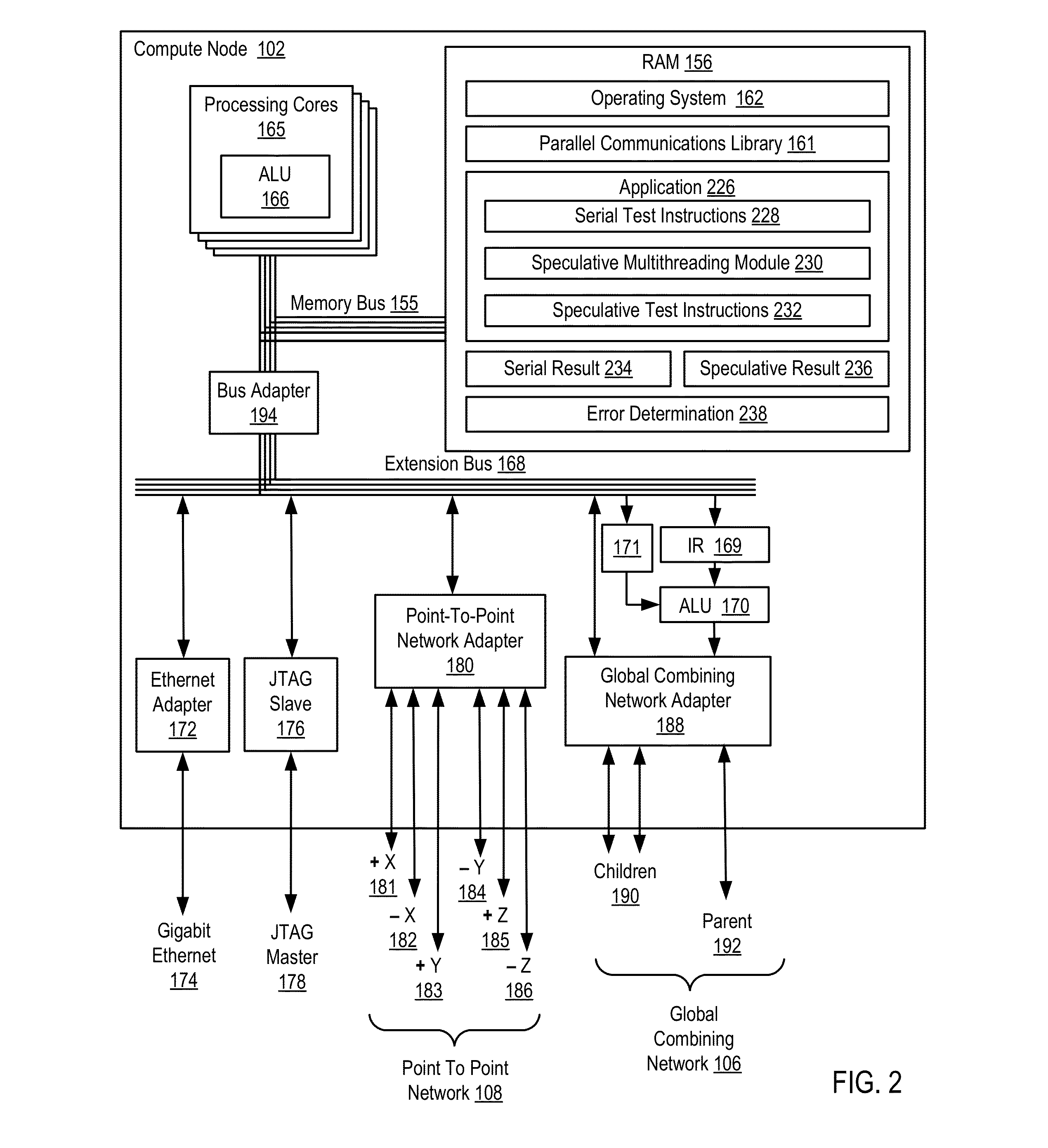
Verifying speculative multithreading in an application executing in a computing system, including: executing one or more test instructions serially thereby producing a serial result, including insuring that all data dependencies among the test instructions are satisfied; executing the test instructions speculatively in a plurality of threads thereby producing a speculative result; and determining whether a speculative multithreading error exists including: comparing the serial result to the speculative result and, if the serial result does not match the speculative result, determining that a speculative multithreading error exists.
Owner:IBM CORP
Analyzer for spawning pairs in speculative multithreaded processor
A method for analyzing a set of spawning pairs, where each spawning pair identifies at least one speculative thread. The method, which may be practiced via software in a compiler or standalone modeler, determines execution time for a sequence of program instructions, given the set of spawning pairs, for a target processor having a known number of thread units, where the target processor supports speculative multithreading. Other embodiments are also described and claimed.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Multi-version register file for multithreading processors with live-in precomputation
Disclosed are selected embodiments of a processor that may include a plurality of thread units and a register file architecture to support speculative multithreading. For at least one embodiment, live-in values for a speculative thread are computed via execution of a precomputation slice and are stored in a validation buffer for later validation. A global register file holds the committed architecture state generated by a non-speculative thread. Each thread unit includes a local register file. A directory indicates, for each architectural register, which speculative thread(s) have generated a value for the architectural register. Other embodiments are also described and claimed.
Owner:BEIJING XIAOMI MOBILE SOFTWARE CO LTD
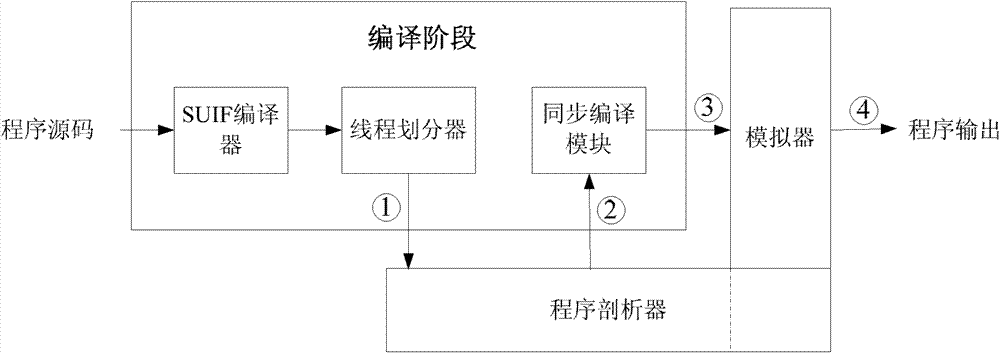
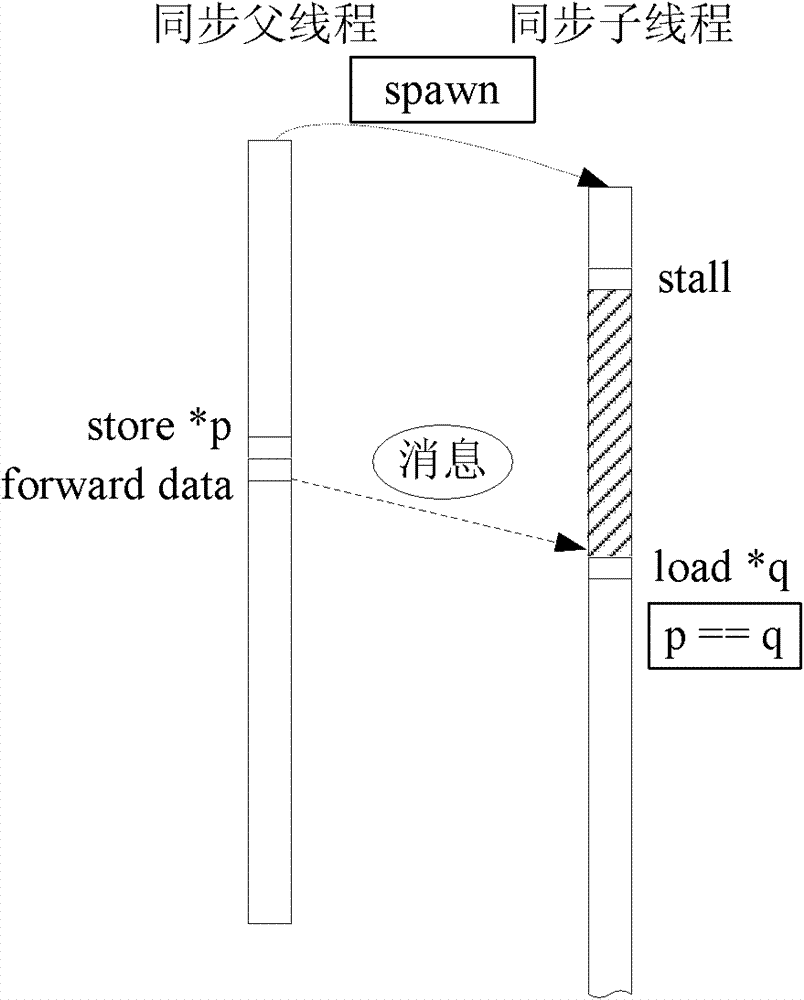
Speculative multithreading memory data synchronous execution method under support of compiler and device thereof
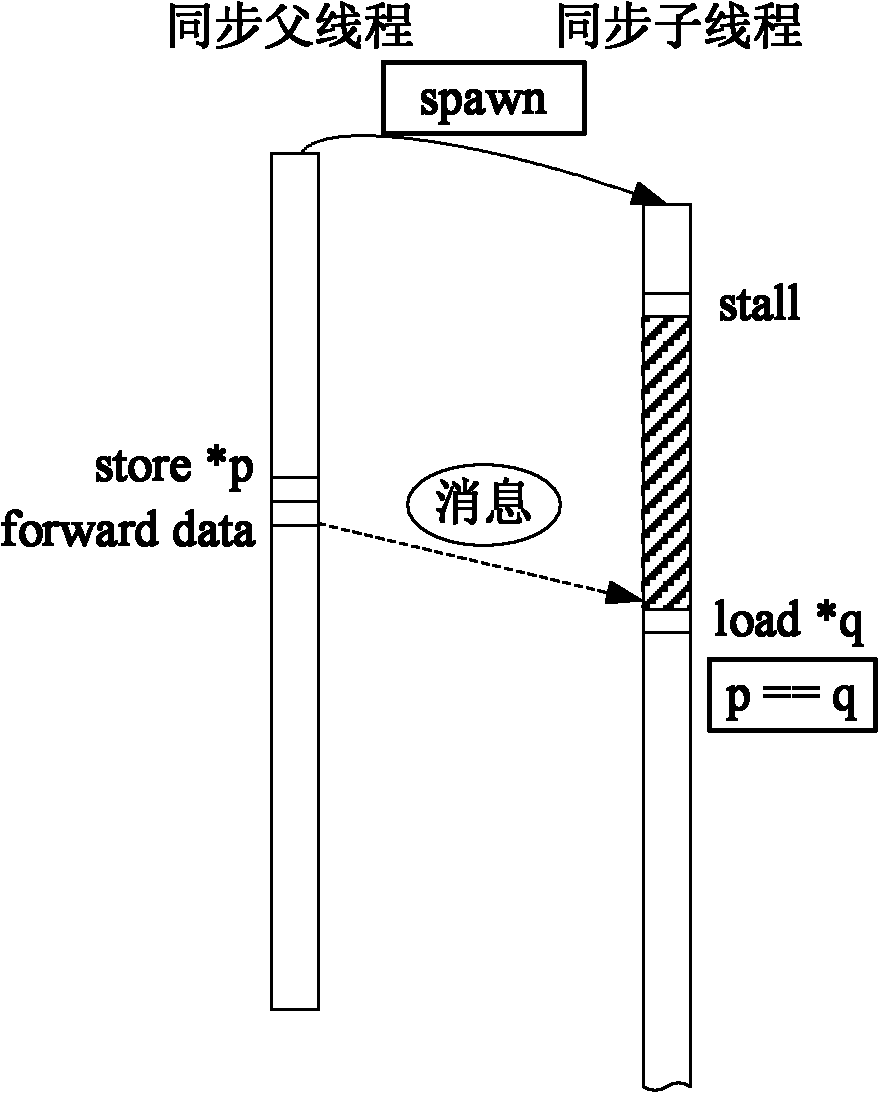
InactiveCN101833440AHigh speedupReduce the number of timesConcurrent instruction executionData synchronizationSpeculative execution
The invention discloses a speculative multithreading memory data synchronous execution method under the support of a compiler and a device thereof, which can synchronize selected read / write memory instructions when a program is operated, reduce the frequency of read / write data dependency violation and improve the integral speedup ratio of multithreading synchronous operation. The method comprisesthe following steps of: adding a stall instruction before a read instruction after a candidate read / write instruction pair is obtained, replacing the read instruction into a synchronous read instruction synload, adding one or more forward instructions behind a write instruction and adding a synset instruction behind a thread initiating instruction spawn of a thread in which the write instruction is positioned; finally operating on a simulator after an executable file generated through compilation linking is loaded; and speculatively executing a multithreading program in a synchronous mode to obtain an operation result and a higher speedup ratio.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
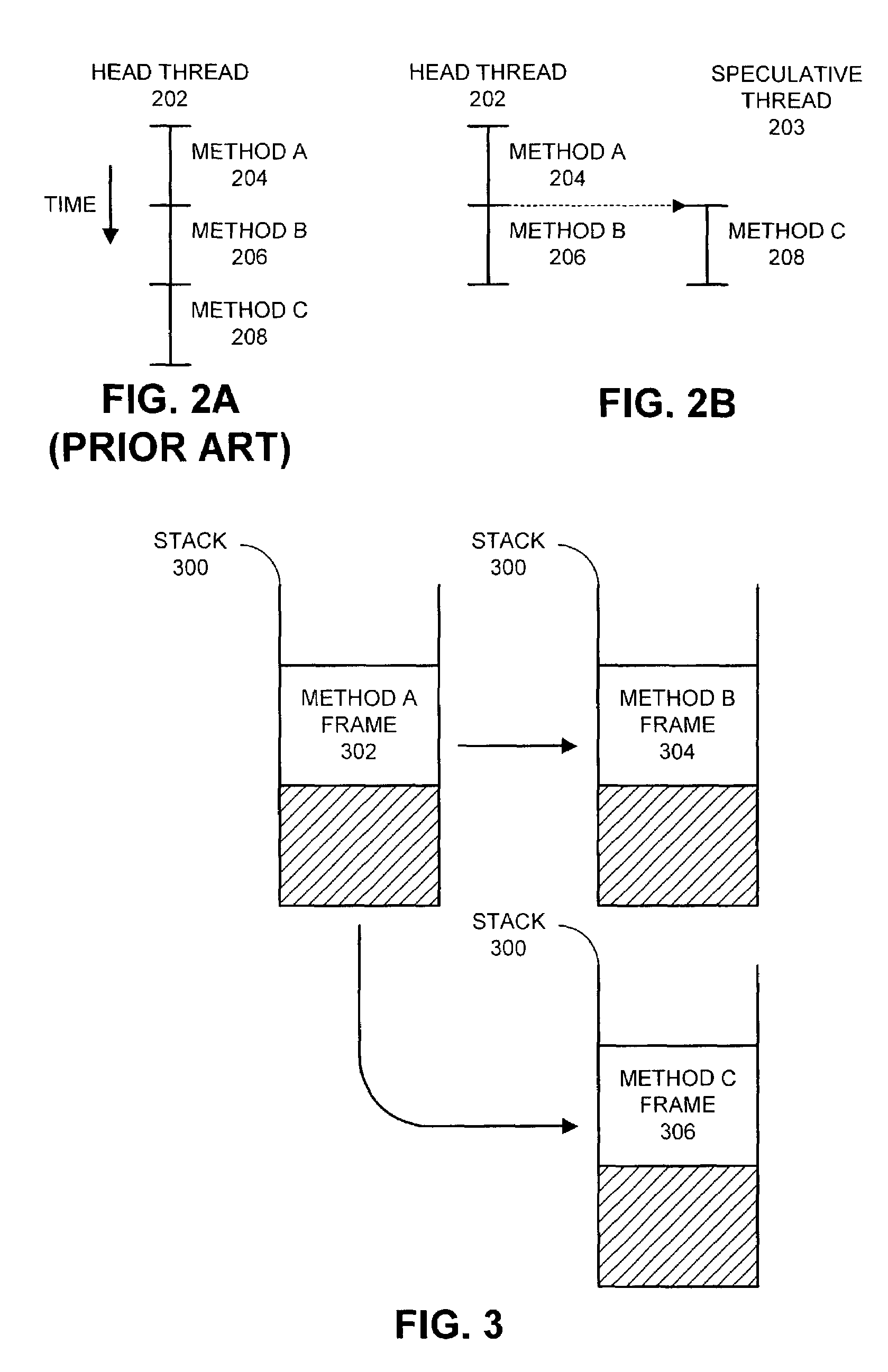
Facilitating efficient join operations between a head thread and a speculative thread
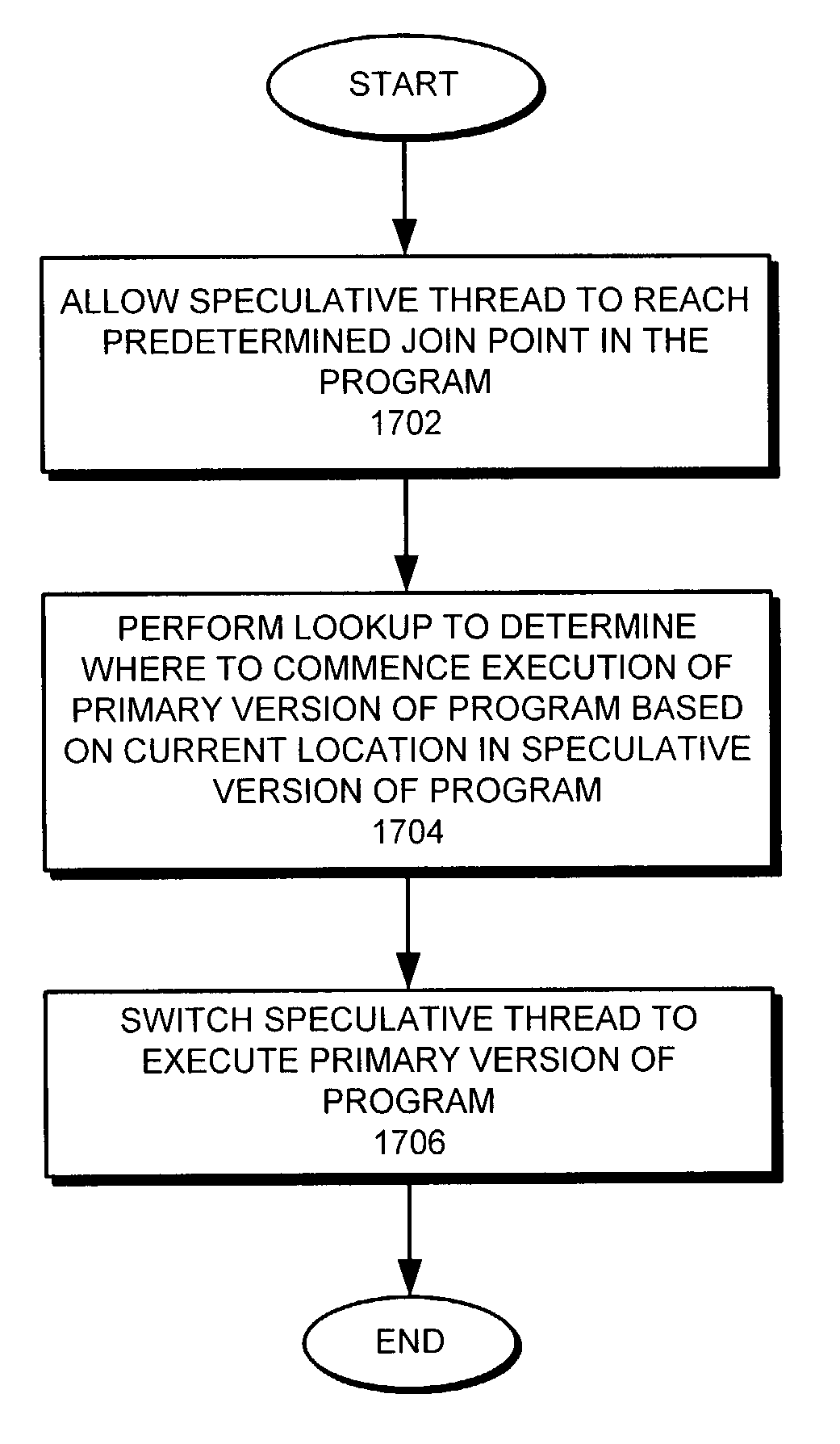
InactiveUS7168076B2Facilitates efficient join operationEasy to operateProgram initiation/switchingDigital computer detailsProgram instructionParallel computing
One embodiment of the present invention provides a system that facilitates efficient join operations between a head thread and a speculative thread during speculative program execution, wherein the head thread executes program instructions and the speculative thread executes program instructions in advance of the head thread. The system operates by executing a primary version of a program using the head thread, and by executing a speculative version of the program using the speculative thread. When the head thread reaches a point in the program where the speculative thread began executing, the system performs a join operation between the head thread and the speculative thread. This join operation causes the speculative thread to act as a new head thread by switching from executing the speculative version of the program to executing the primary version of the program. To facilitate this switching operation, the system performs a lookup to determine where the new head thread is to commence executing within the primary version of the program based upon where the speculative thread is currently executing within the speculative version of the program.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
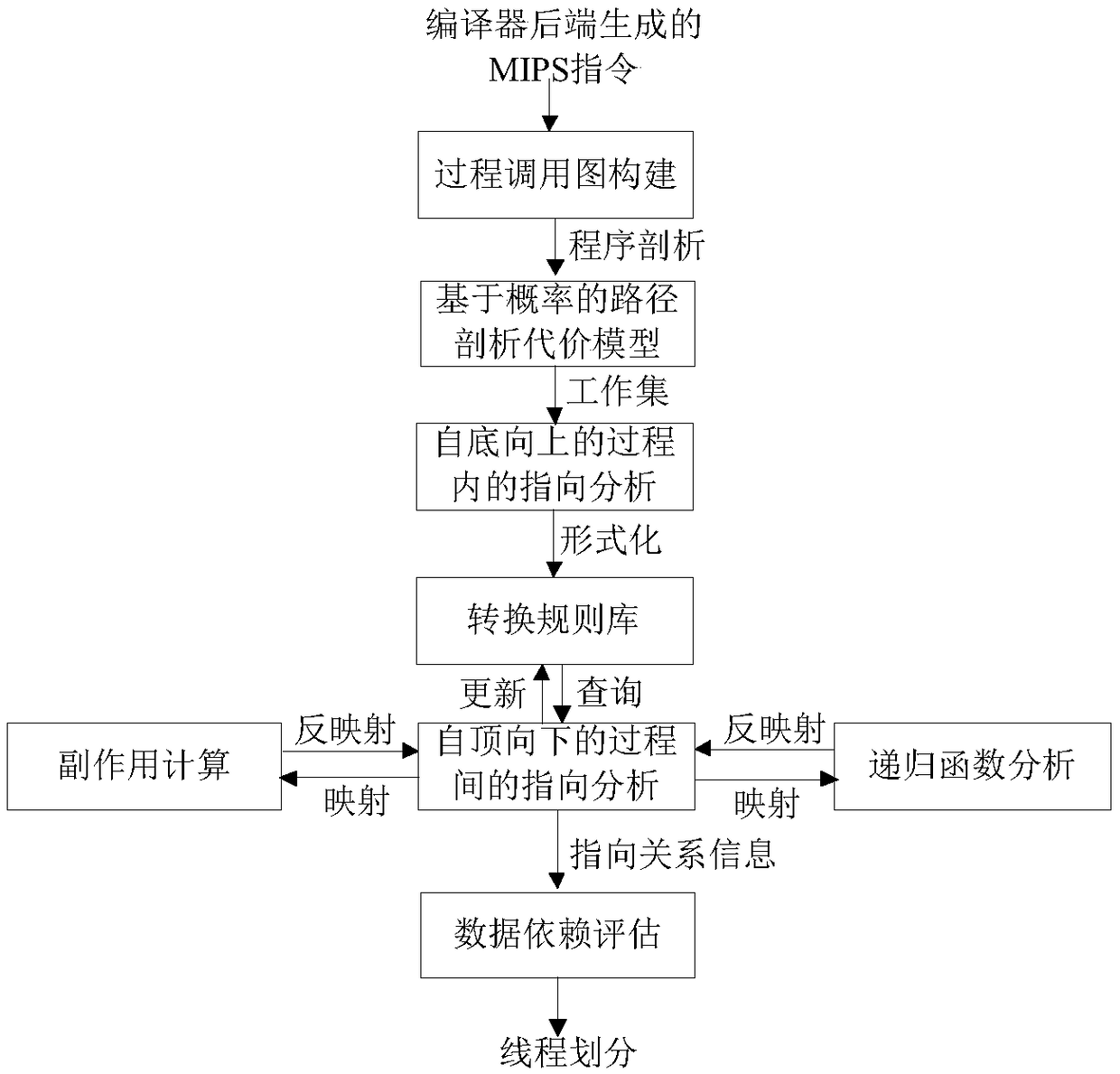
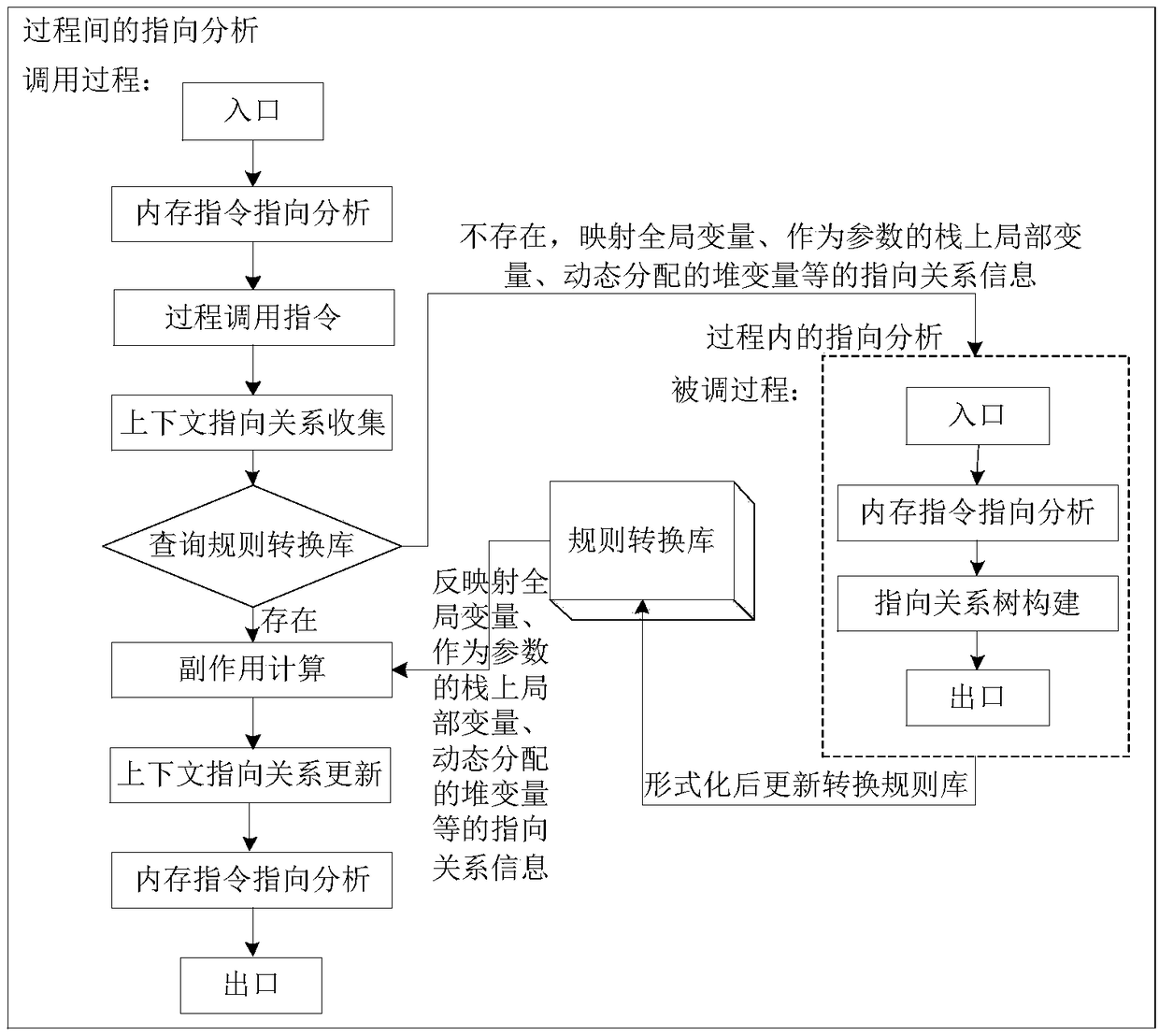
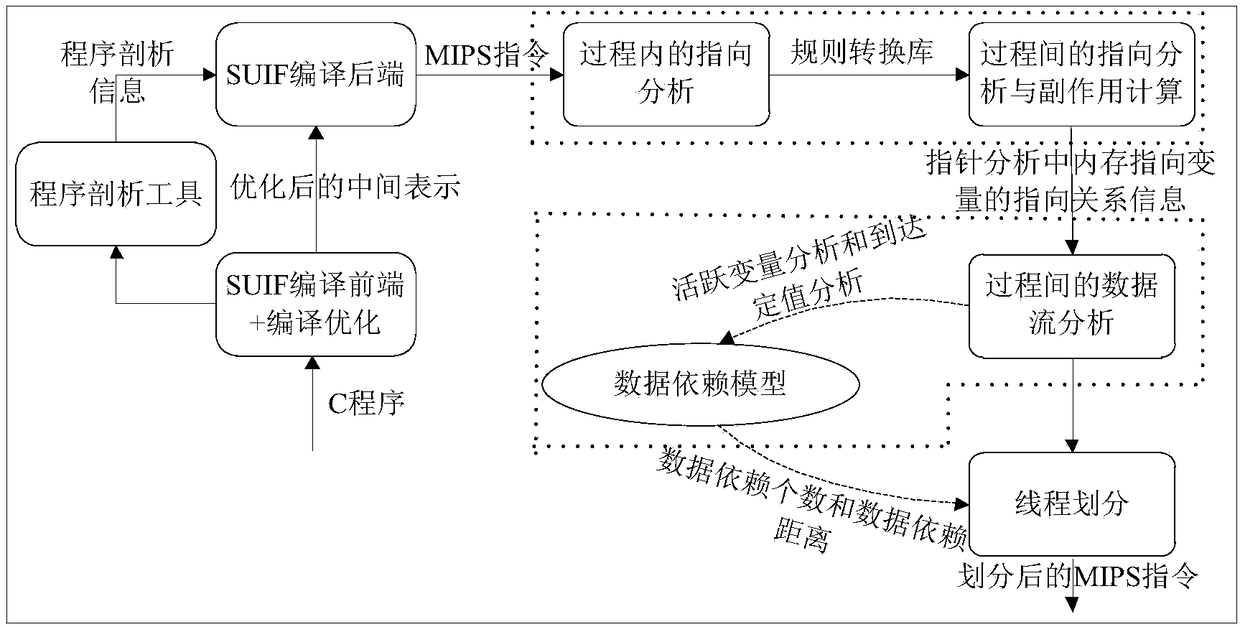
Assembly level interprocedual pointer analysis method based on speculative multithreading
ActiveCN108932137ARefine Data DependenciesAccurate analysisInstruction analysisConcurrent instruction executionProcedure callsPath profile
The invention discloses an assembly level interprocedual pointer analysis method based on speculative multithreading. Through assembly level interprocedual points-to analysis, a procedure call graph of all processes is established in a source program before the interprocedual points-to analysis is carried out, and after establishment, points-to analysis is carried out in two stages. The method comprises: in the first stage, firstly, establishing a path profiling cost model based on probability, extracting speculative paths selected by all process nodes in the procedure call graph, and then performing points-to analysis in a process; in the second stage, performing interprocedual points-to analysis and interprocedual side-effect calculation, on each process calling point, performing mappingand inverse mapping on points-to relations using a points-to analysis result in a process, to obtain an interprocedual side-effect calculation result, and realize context points-to relation update ofa calling procedure. On this basis, the method guides a whole procedure to perform interprocedual data flow analysis, evaluates data dependence degree among pointer variable memory points-to relations, and obtains a more accurate thread partitioning result.
Owner:XIAN AERONAUTICAL UNIV
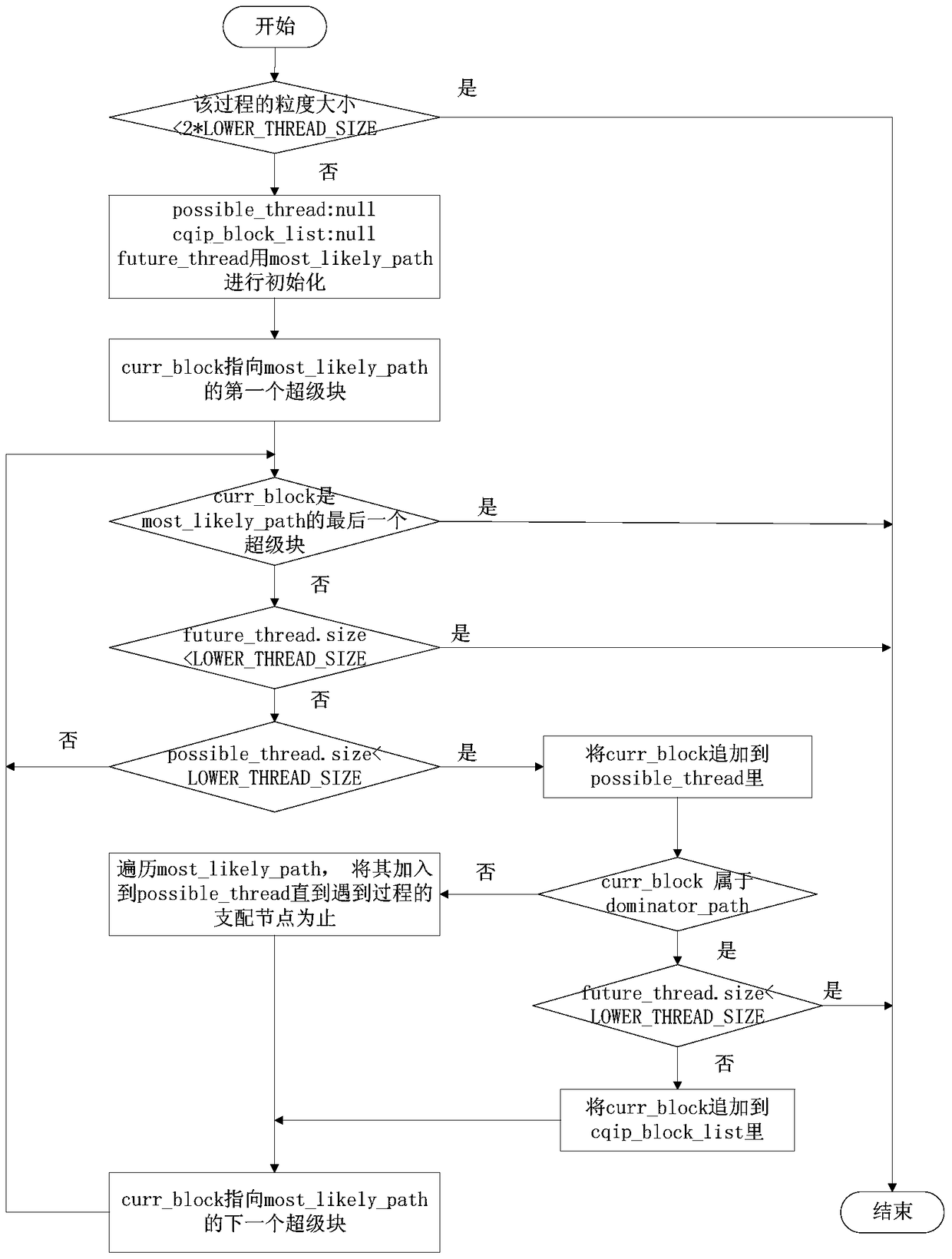
CMP (Chip Multiprocessor)-based multi-speculative path thread partitioning method under speculative multithreading mechanism
InactiveCN105138309AExpand branch coverageMining potential parallelismConcurrent instruction executionParallel computingSpeculative multithreading
The invention discloses a CMP (Chip Multiprocessor)-based multi-speculative path thread partitioning method under a speculative multithreading mechanism. According to the method, a process is taken as a unit in thread partitioning; for each process, control-independence nodes of thread end points in the process are limited during partitioning; mutual exclusion path segments of thread excitation points in the process are limited, so that excitation of the thread is relatively strictly limited; meanwhile, the excitation points on the mutual exclusion path segments are made to correspond to the same thread end point; a plurality of continuous pre-computation slices are inserted behind the thread end points; the contents of the pre-computation slices are mutually different along with the changes of the speculative paths and the excitation points; and a simulator carries out different speculative paths when running, and selects corresponding pre-computation slices for executionaccording to the corresponding excitation points on the speculative paths. According to the method, thread partitioning can be carried out on a plurality of paths, so that the branch coverage rate of speculative parallel execution is increased.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Verifying speculative multithreading in an application
ActiveUS8892946B2Error detection/correctionMachine execution arrangementsApplication softwareSpeculative multithreading
Verifying speculative multithreading in an application executing in a computing system, including: executing one or more test instructions serially thereby producing a serial result, including insuring that all data dependencies among the test instructions are satisfied; executing the test instructions speculatively in a plurality of threads thereby producing a speculative result; and determining whether a speculative multithreading error exists including: comparing the serial result to the speculative result and, if the serial result does not match the speculative result, determining that a speculative multithreading error exists.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
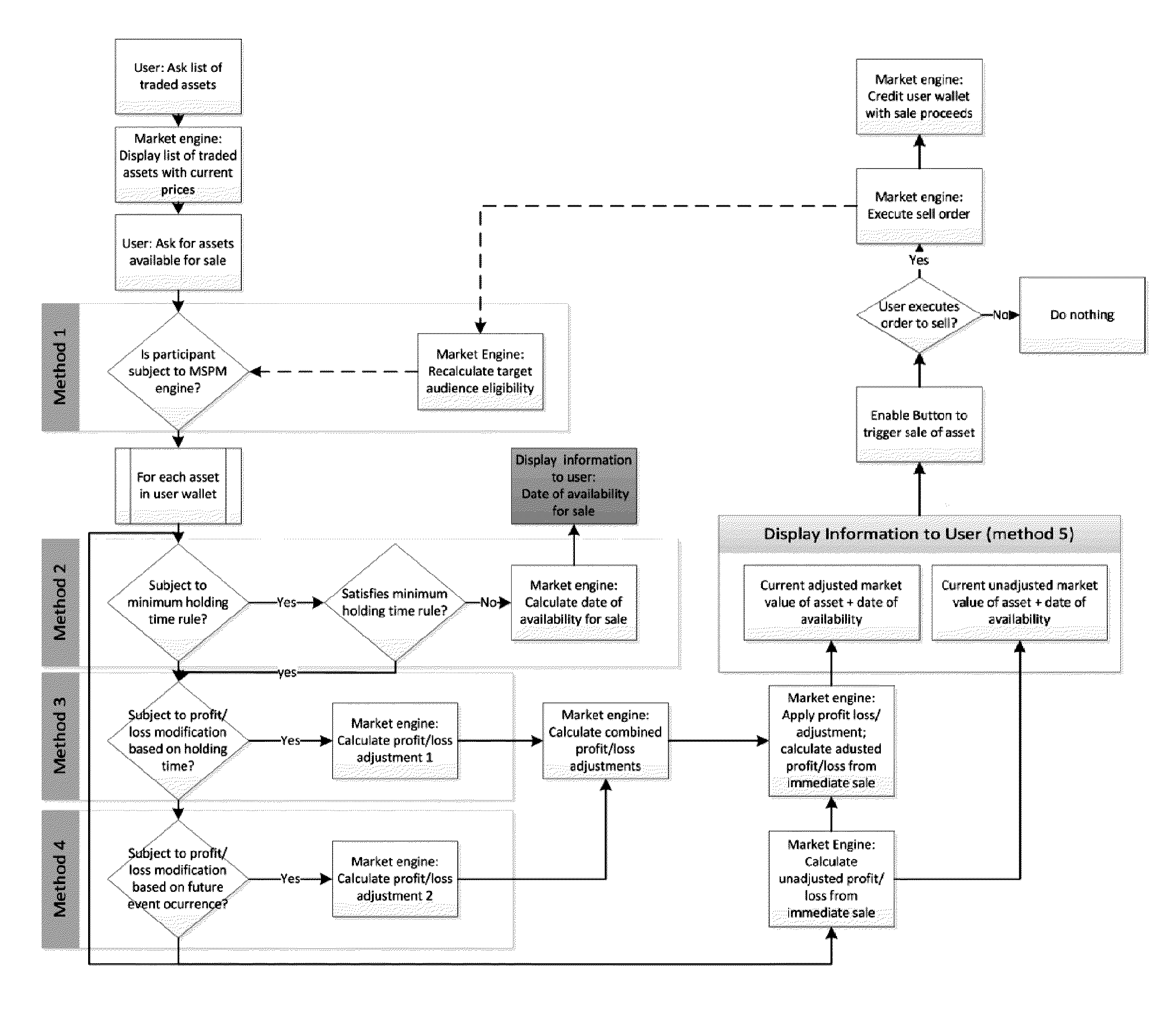
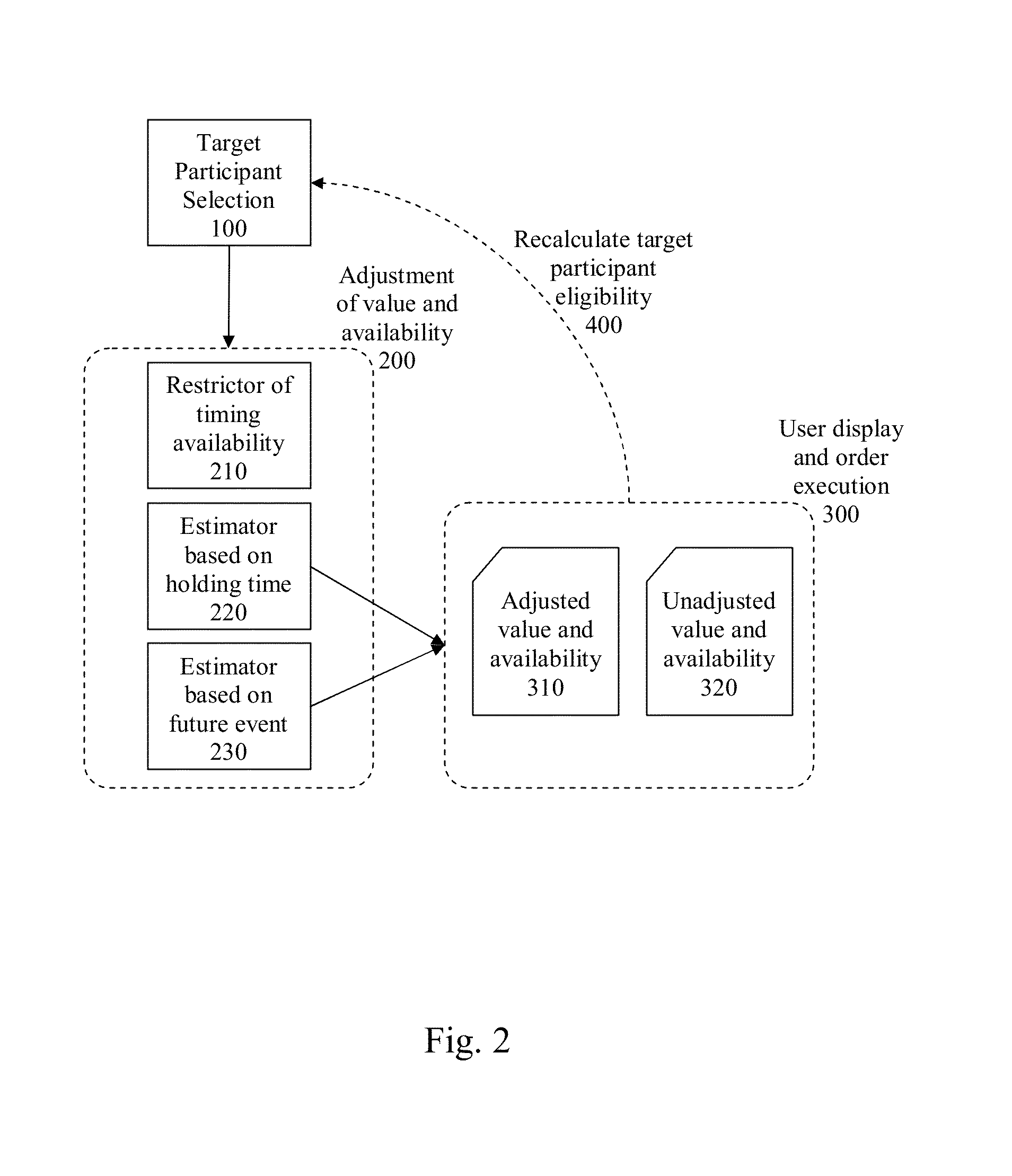
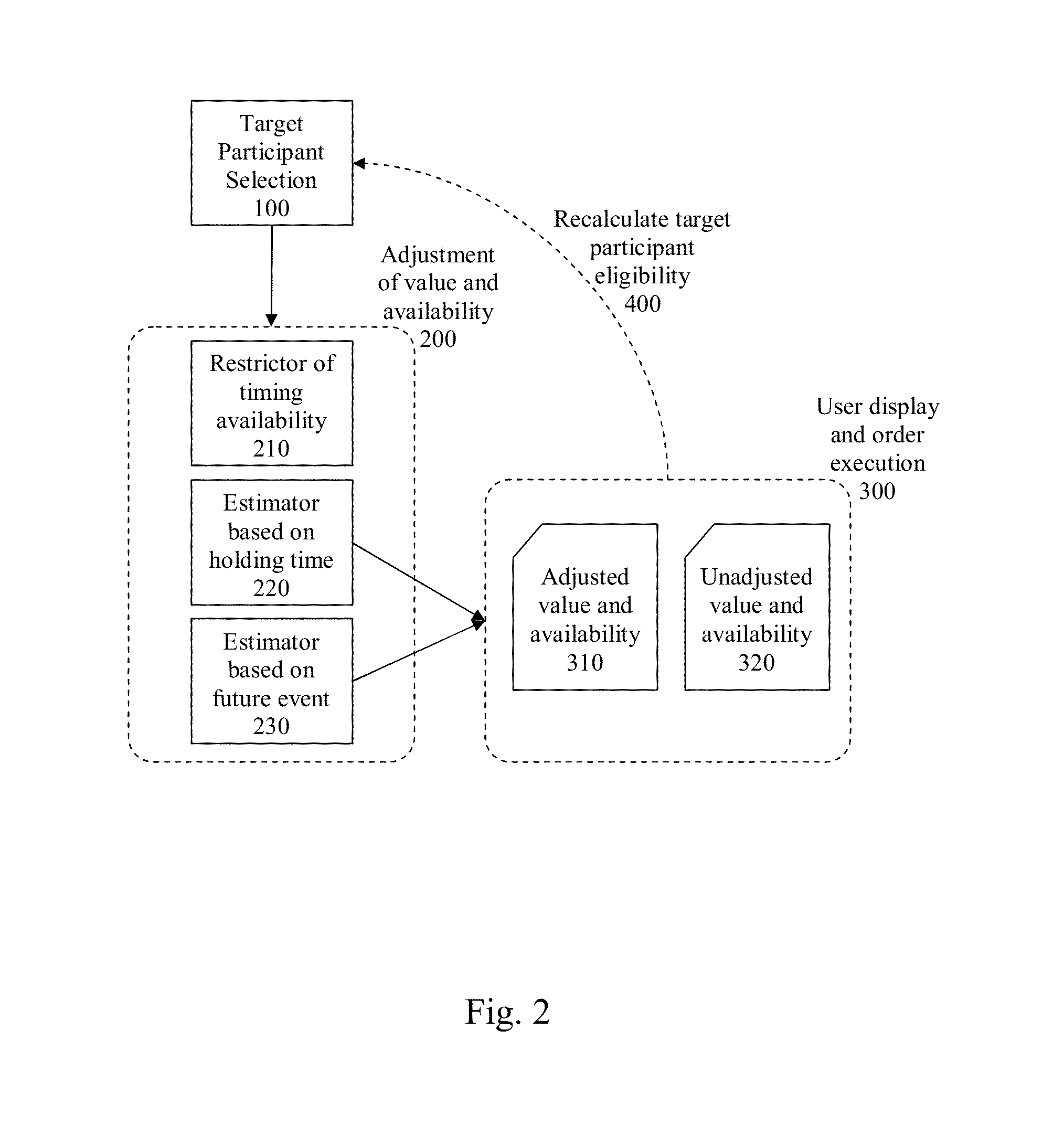
System and method for adjusting asset value and availability in data records for mitigating speculative trading in a prediction market
The present subject-matter belongs to the field of system and methods for automatic and electronic transaction control, namely in introducing minimum holding times and forcing transaction outcomes in a market. The system and method include adjusting asset value and availability for mitigating speculative market manipulation and pure speculative trading transactions outcomes in a prediction market. The modules introduce pure delays, selective delays or force the transaction outcome evaluations such that these goals are addressed. One of the principles used in these methods and modules is that by increasing the risk of the purely speculative or manipulative trading strategies, their expected payoff will be reduced. Thus participants will have less incentive to use them and their occurrence and impact will be greatly reduced.
Owner:EXAGO VENTURES
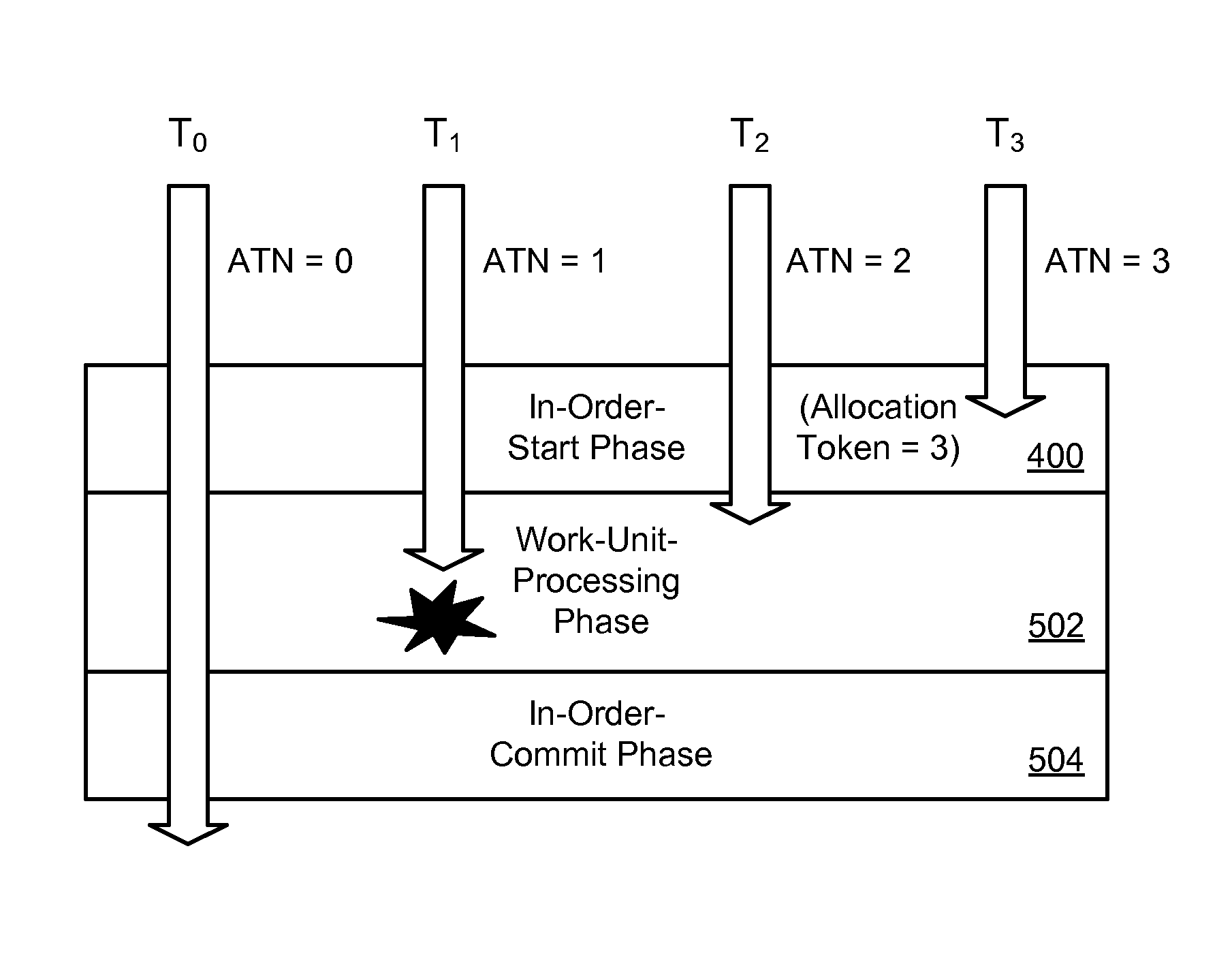
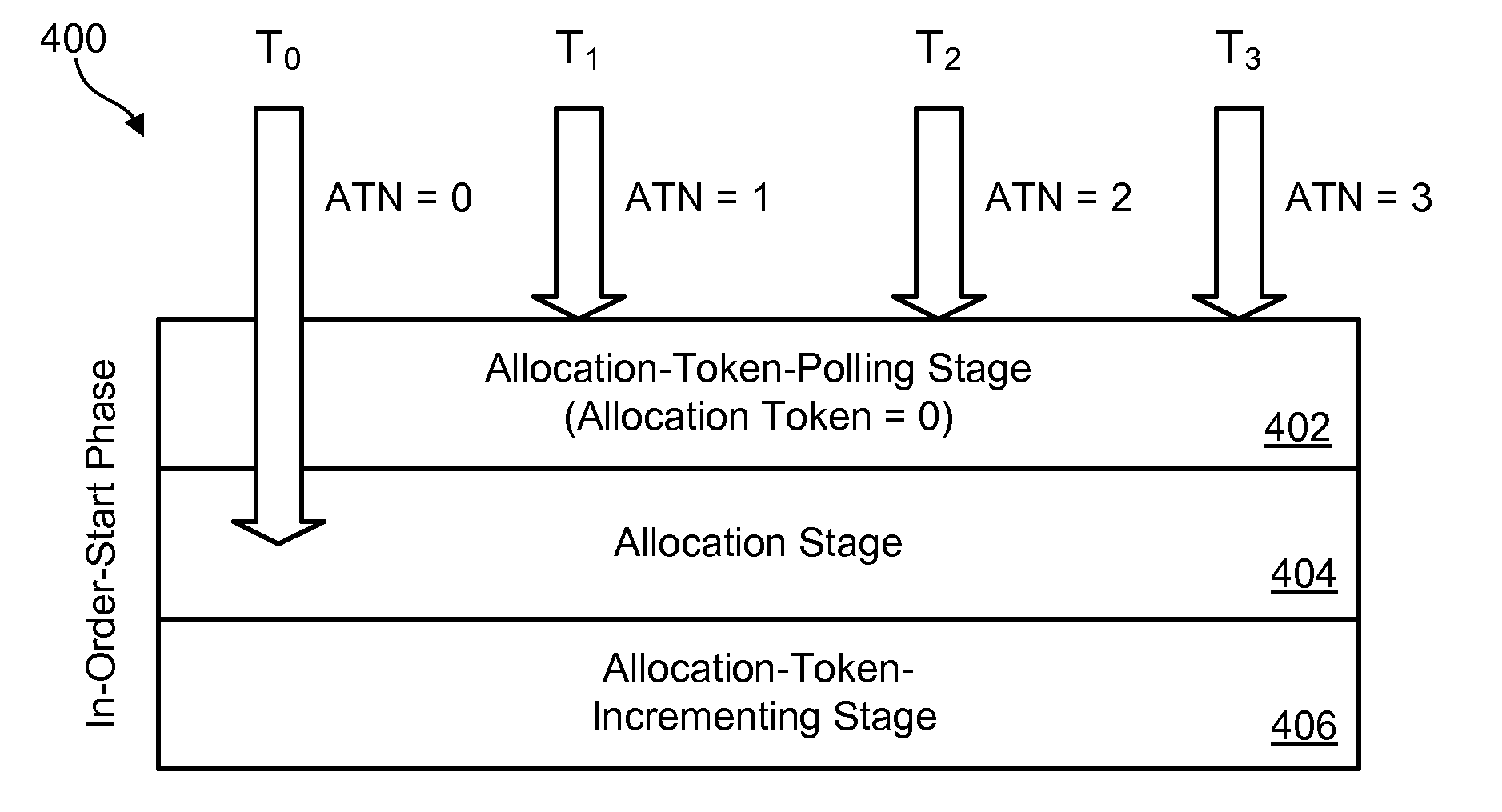
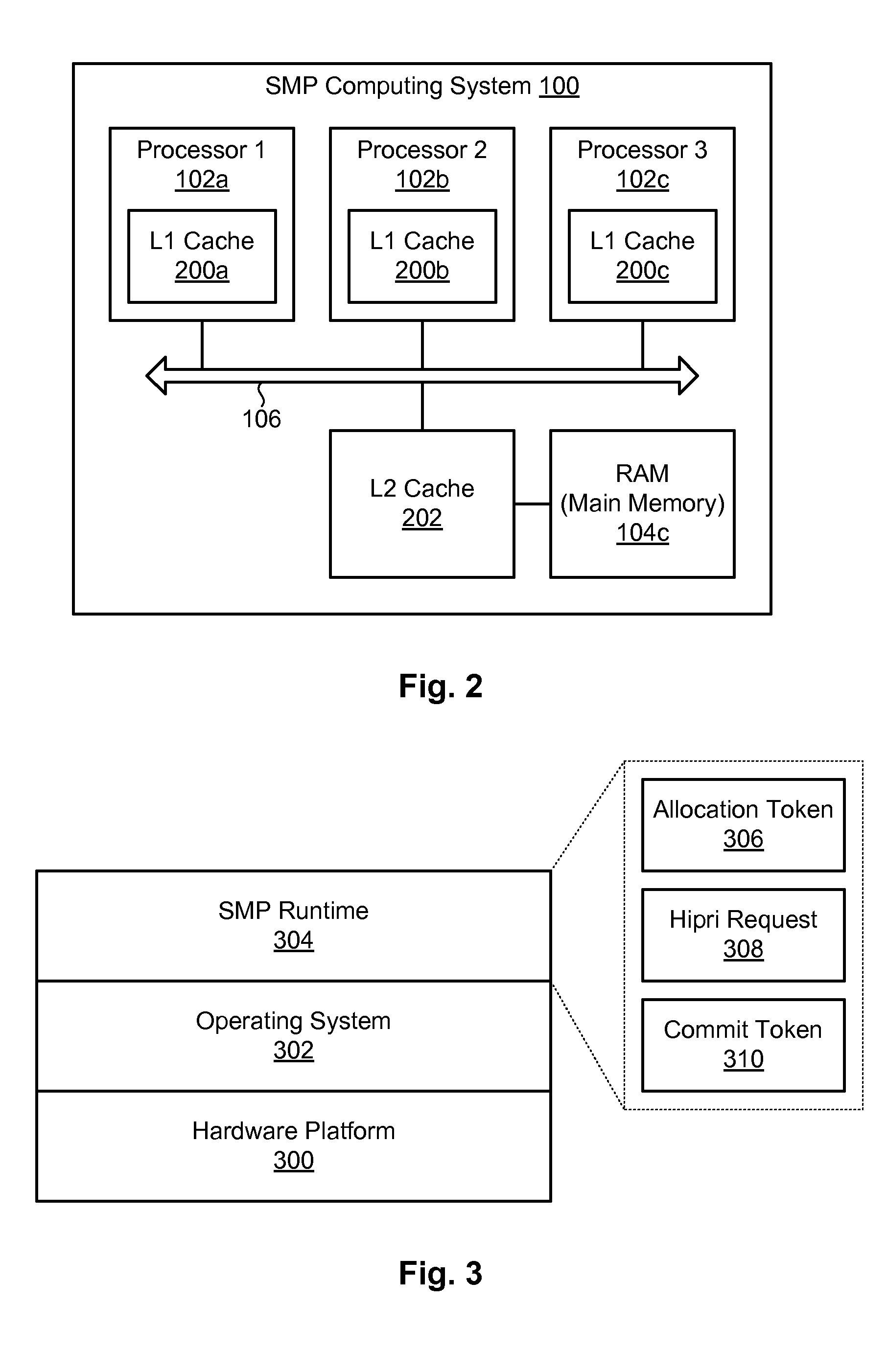
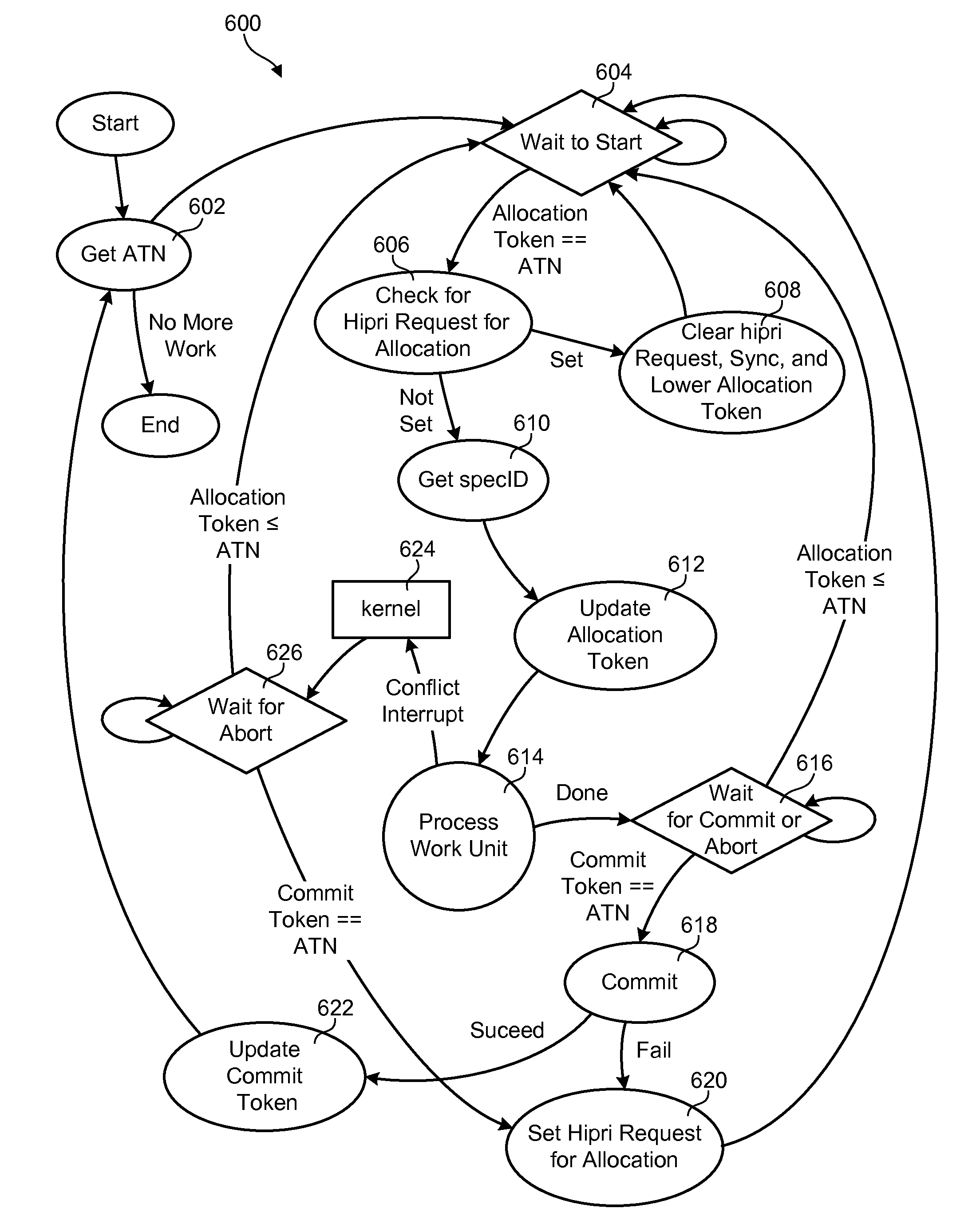
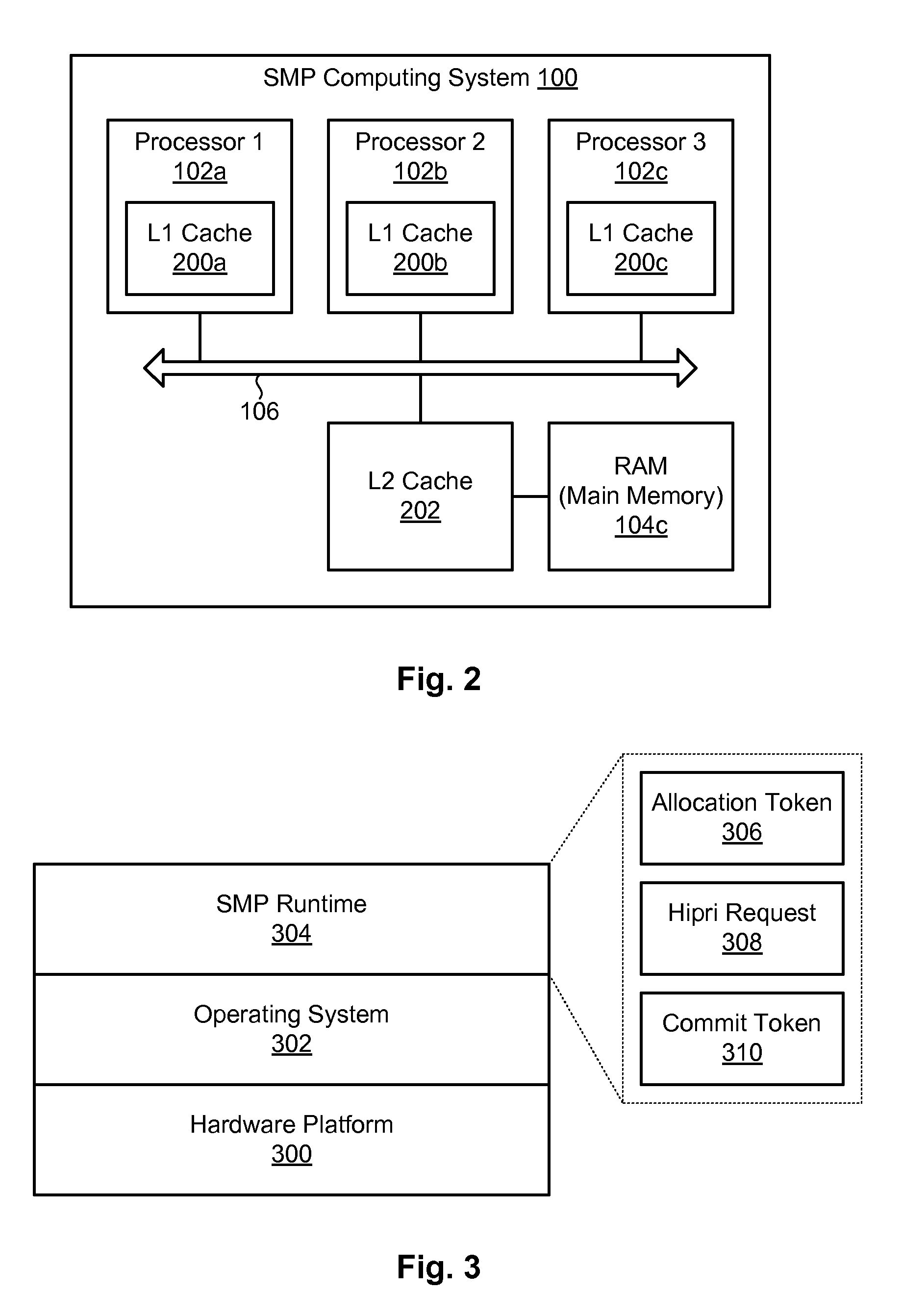
Efficient rollback and retry of conflicted speculative threads using distributed tokens
InactiveUS8990819B2Program initiation/switchingProgram synchronisationParallel computingSpeculative multithreading
A method for rolling back speculative threads in symmetric-multiprocessing (SMP) environments is disclosed. In one embodiment, such a method includes detecting an aborted thread at runtime and determining whether the aborted thread is an oldest aborted thread. In the event the aborted thread is the oldest aborted thread, the method sets a high-priority request for allocation to an absolute thread number associated with the oldest aborted thread. The method further detects that the high-priority request is set and, in response, modifies a local allocation token of the oldest aborted thread. The modification prompts the oldest aborted thread to retry a work unit associated with its absolute thread number. The oldest aborted thread subsequently initiates the retry of a successor thread by updating the successor thread's local allocation token. A corresponding apparatus and computer program product are also disclosed.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
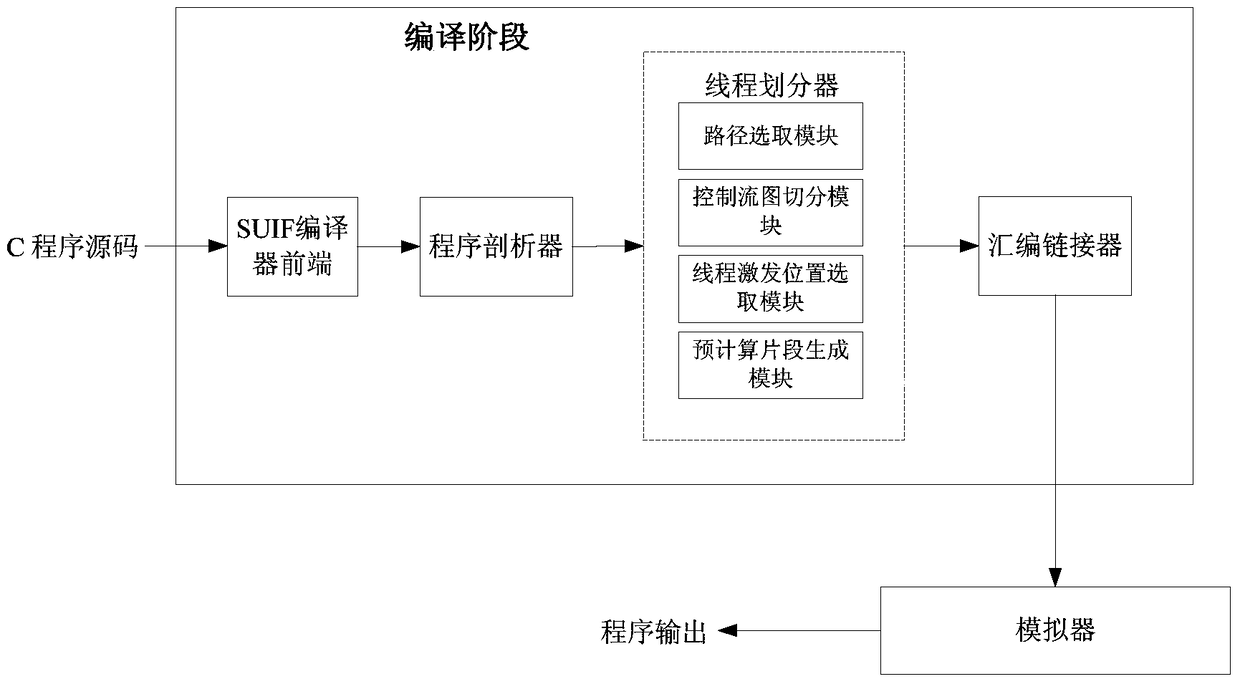
A Speculative Multithreading Partitioning Method Based on Machine Learning
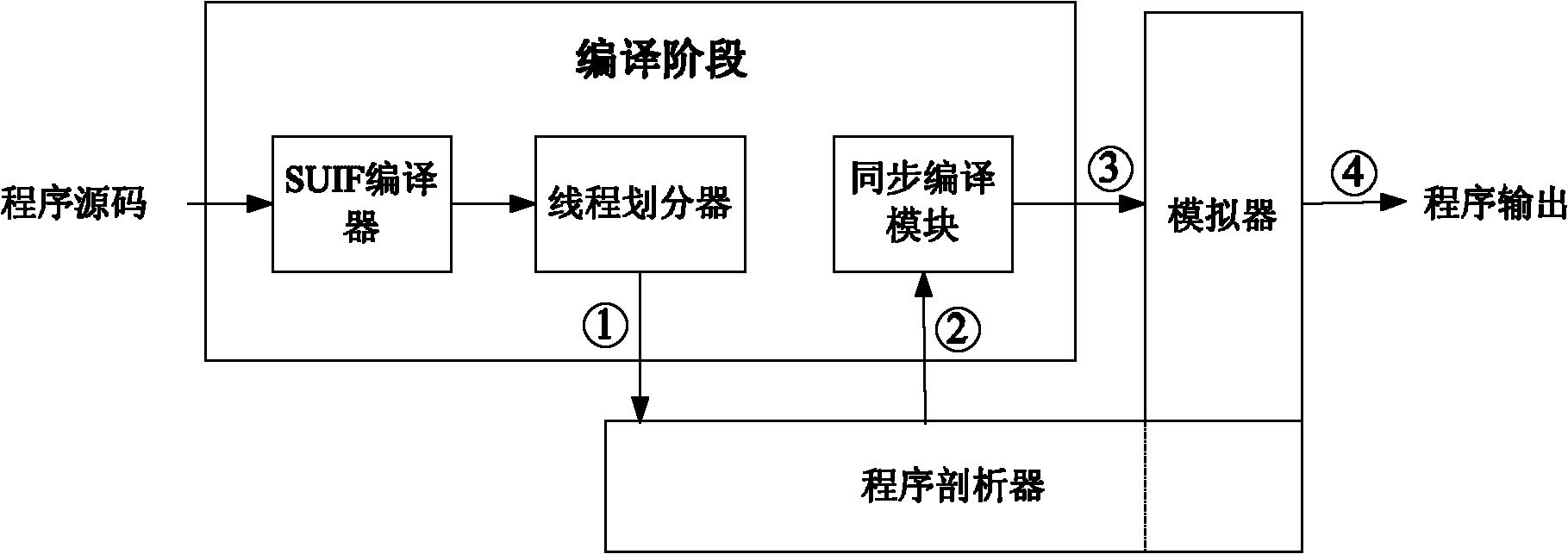
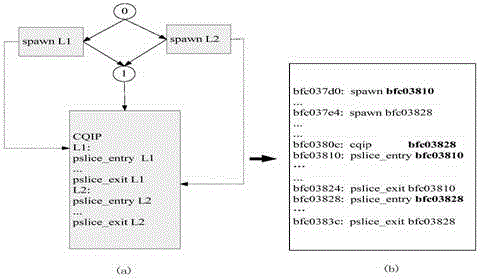
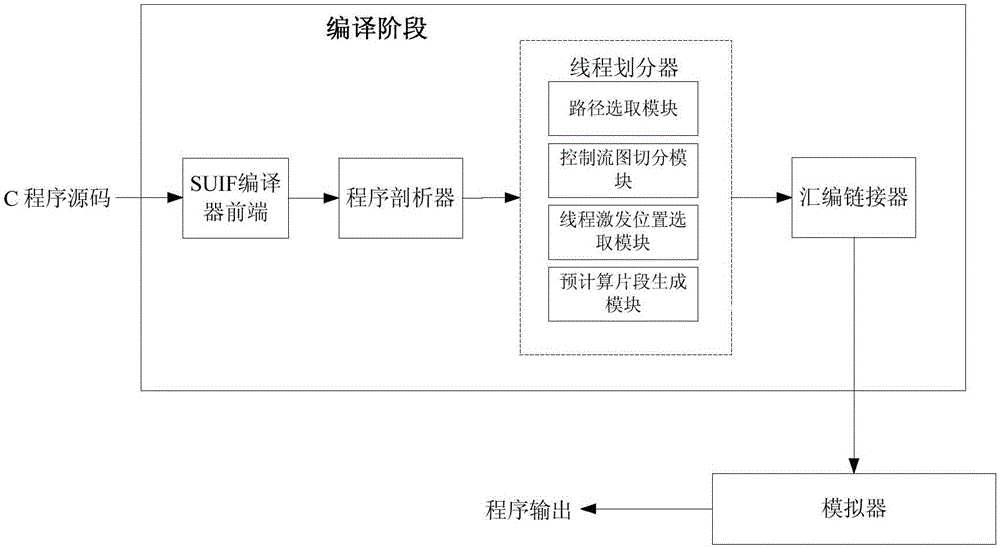
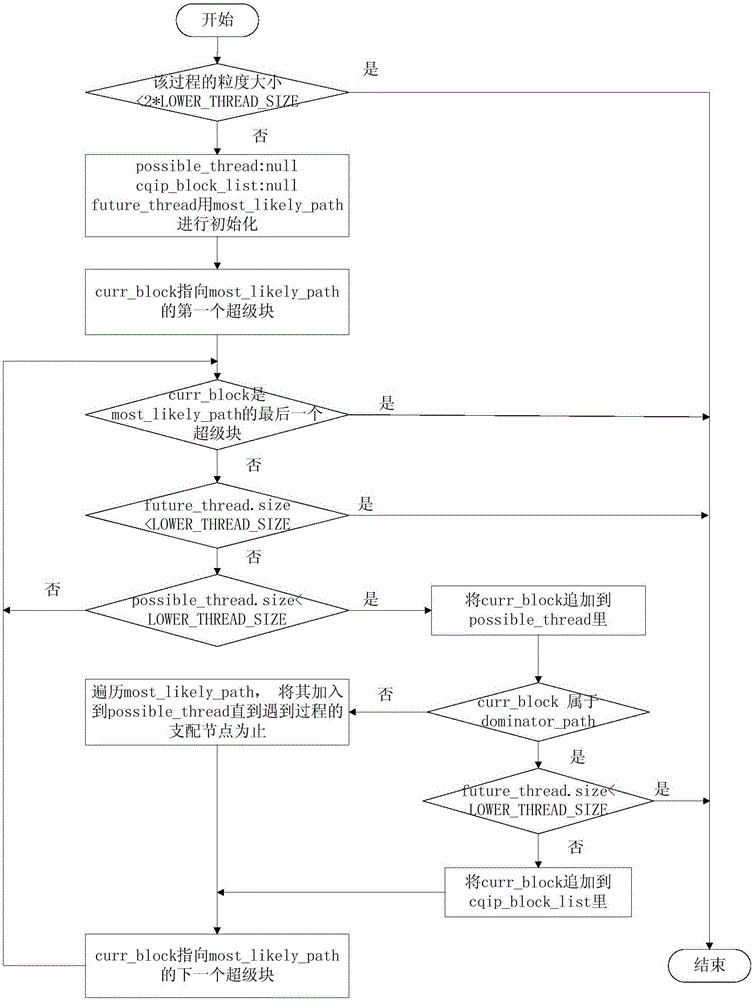
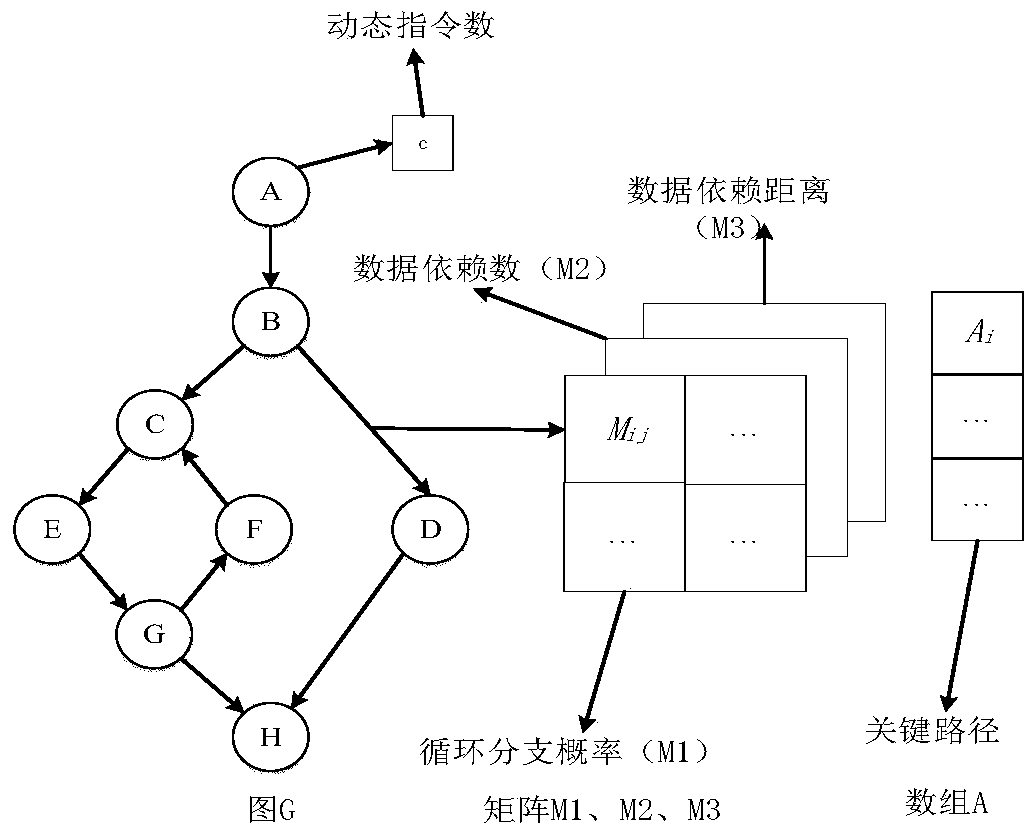
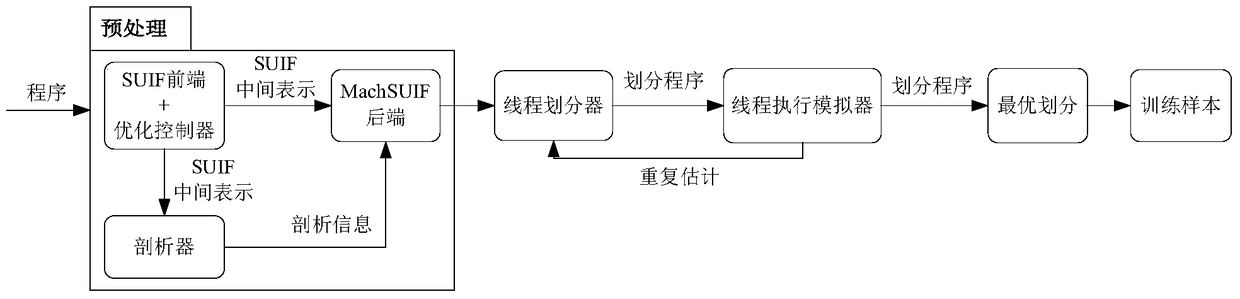
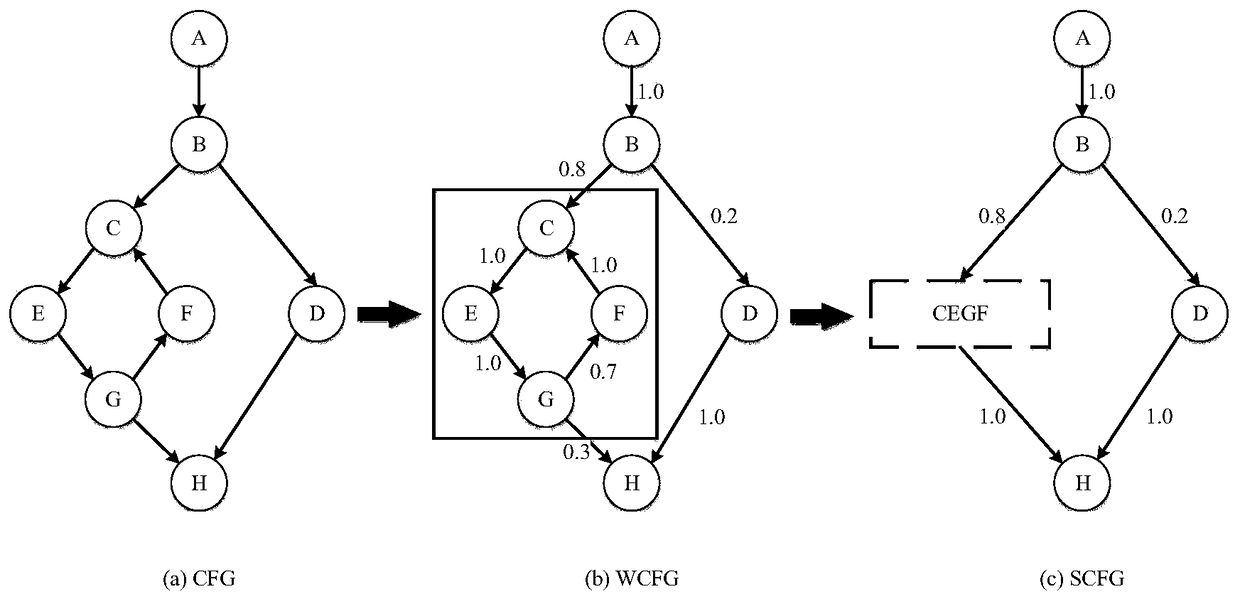
InactiveCN105373424BOvercome limitationsImprove adaptabilityProgram initiation/switchingResource allocationTheoretical computer scienceSpeculative multithreading
The invention discloses a speculative multithreading division method based on machine learning. The speculative multithreading division method comprises the following steps: extracting program characteristics from an irregular program set, and combining a CFG (Control Flow Graph) with comments with a key path to show the program characteristics; then, constructing a program CFG by a SUIF compiler, converting the program CFG into a weighted CFG and a super block CFG, carrying out threading division, which aims at a cyclic part and an acyclic part, on the program set to obtain a training sample set formed by the program characteristics and an optimal division scheme; and finally, extracting the characteristics of an irregular program to be divided, calculating similarity between the characteristics of the irregular program to be divided and the program characteristics in the training samples, and carrying out weighted calculation on the division threshold values of a plurality of most similar sample programs to obtain an optimal division scheme suitable for the irregular program. The similarity between the program to be divided and the sample program is compared on the basis of the program characteristics, a similar sample division scheme is applied to the program to be divided, and therefore, the speculative multithreading division method exhibits better adaptability on each class of parallel irregular programs.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Efficient rollback and retry of conflicted speculative threads with hardware support
InactiveUS20140123152A1Resource allocationProgram synchronisationParallel computingSpeculative multithreading
A method for rolling back speculative threads in symmetric-multiprocessing (SMP) environments is disclosed. In one embodiment, such a method includes detecting an aborted thread at runtime and determining whether the aborted thread is an oldest aborted thread. In the event the aborted thread is the oldest aborted thread, the method sets a high-priority request for allocation to an absolute thread number associated with the oldest aborted thread. The method further detects that the high-priority request is set and, in response, clears the high-priority request and sets an allocation token to the absolute thread number associated with the oldest aborted thread, thereby allowing the oldest aborted thread to retry a work unit associated with the absolute thread number. A corresponding apparatus and computer program product are also disclosed.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
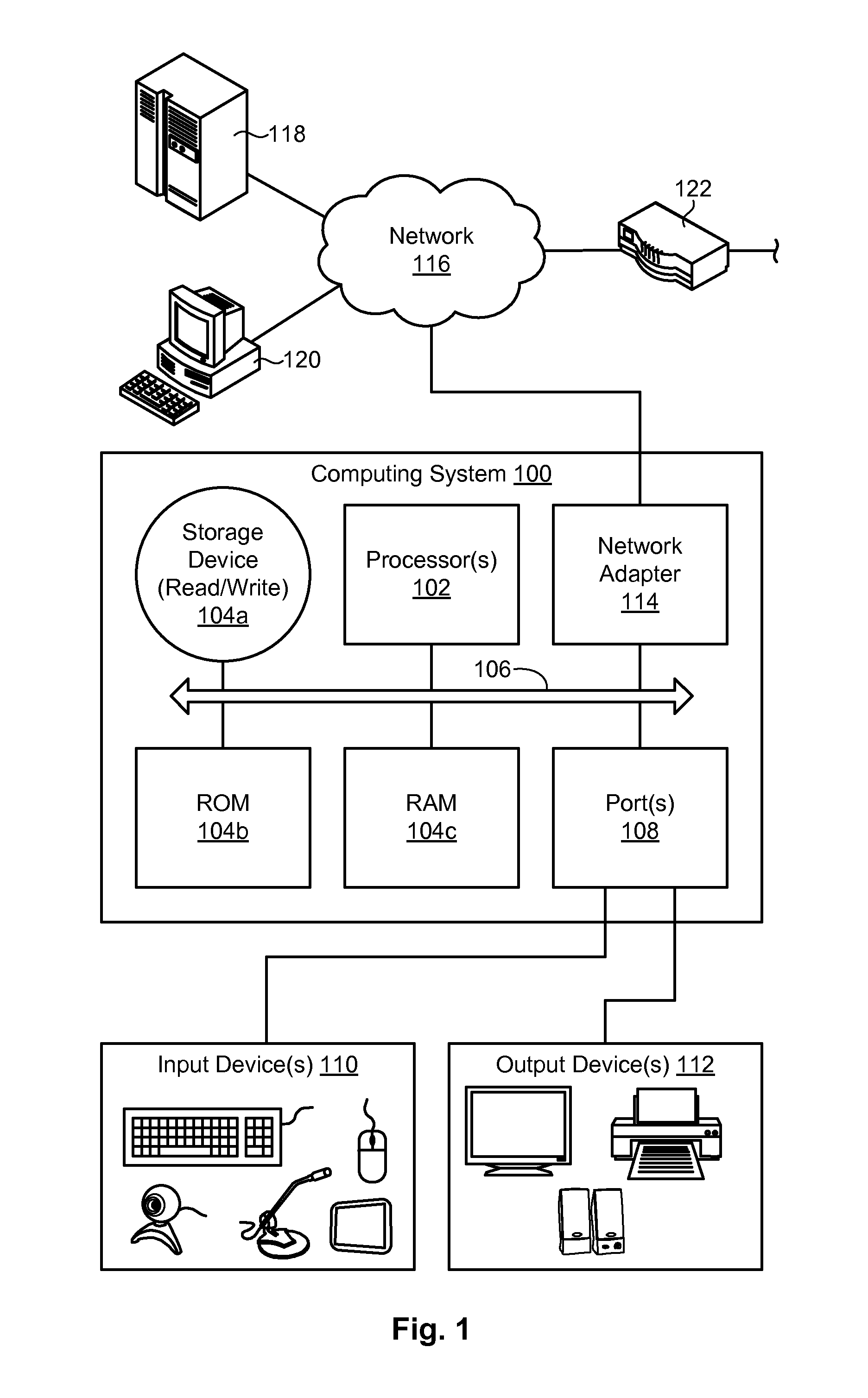
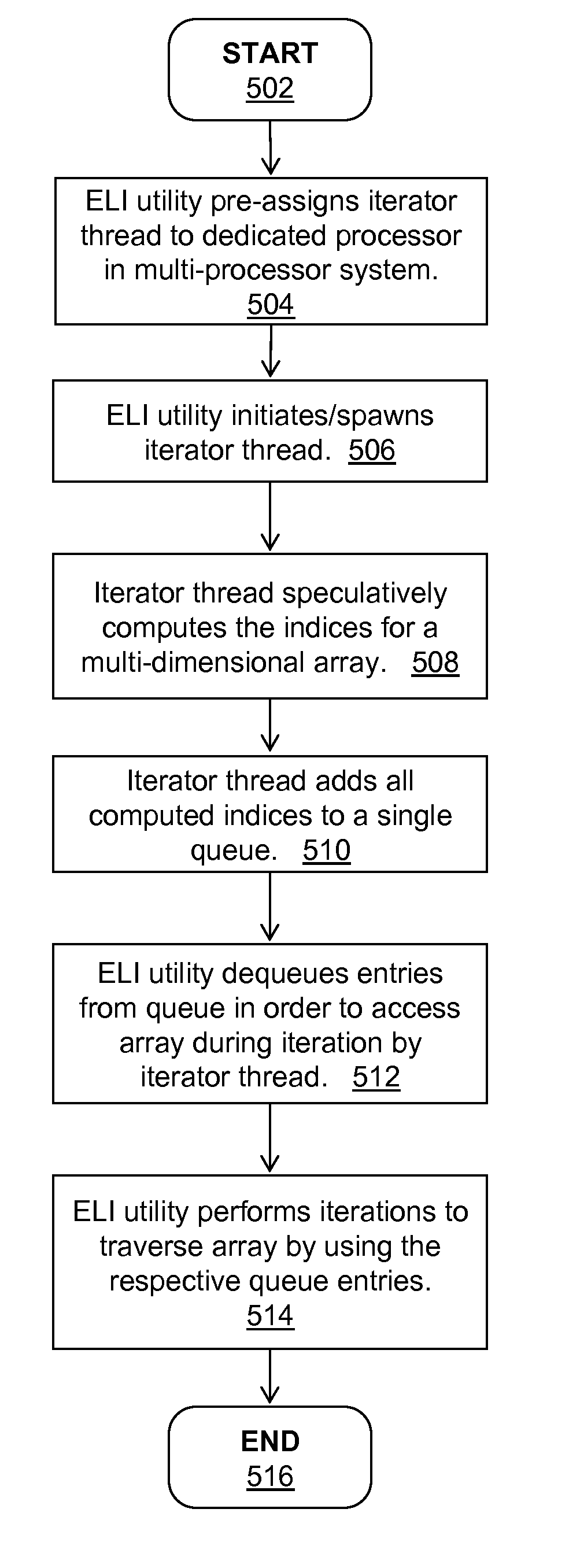
Accelerating generic loop iterators using speculative execution
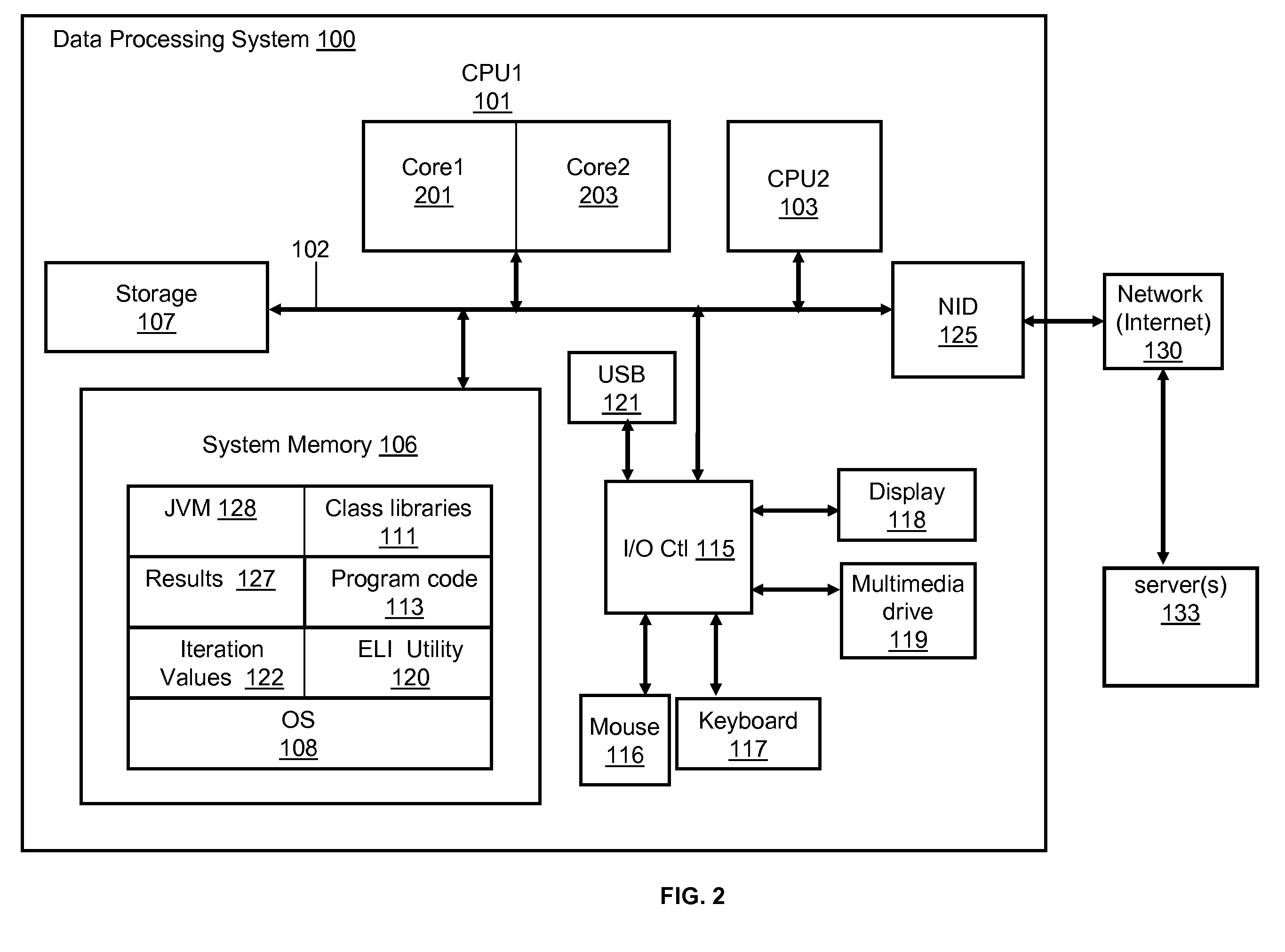
InactiveUS8701099B2Effective expansionEfficient replacementProgram control using stored programsMemory systemsCoding blockSpeculative execution
A method, a system and a computer program product for effectively accelerating loop iterators using speculative execution of iterators. An Efficient Loop Iterator (ELI) utility detects initiation of a target program and initiates / spawns a speculative iterator thread at the start of the basic code block ahead of the code block that initiates a nested loop. The ELI utility assigns the iterator thread to a dedicated processor in a multi-processor system. The speculative thread runs / executes ahead of the execution of the nested loop and calculates indices in a corresponding multidimensional array. The iterator thread adds all the precomputed indices to a single queue. As a result, the ELI utility effectively enables a multidimensional loop to be replaced by a single dimensional loop. At the beginning of (or during) each iteration of the iterator, the ELI utility “dequeues” an entry from the queue to use the entry to access the array upon which the ELI utility iterates. The ELI utility performs concurrent iterations on the array by using the queue entries.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
System and method for adjusting asset value and availability in data records for mitigating speculative trading in a prediction market
The present subject-matter belongs to the field of system and methods for automatic and electronic transaction control, namely in introducing minimum holding times and forcing transaction outcomes in a market. The system and method include adjusting asset value and availability for mitigating speculative market manipulation and pure speculative trading transactions outcomes in a prediction market. The modules introduce pure delays, selective delays or force the transaction outcome evaluations such that these goals are addressed. One of the principles used in these methods and modules is that by increasing the risk of the purely speculative or manipulative trading strategies, their expected payoff will be reduced. Thus participants will have less incentive to use them and their occurrence and impact will be greatly reduced.
Owner:EXAGO VENTURES
Verifying speculative multithreading in an application
InactiveUS20130159681A1Error detection/correctionDigital computer detailsData dependenceSpeculative multithreading
Verifying speculative multithreading in an application executing in a computing system, including: executing one or more test instructions serially thereby producing a serial result, including insuring that all data dependencies among the test instructions are satisfied; executing the test instructions speculatively in a plurality of threads thereby producing a speculative result; and determining whether a speculative multithreading error exists including: comparing the serial result to the speculative result and, if the serial result does not match the speculative result, determining that a speculative multithreading error exists.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method and device for improving speculative multithreading
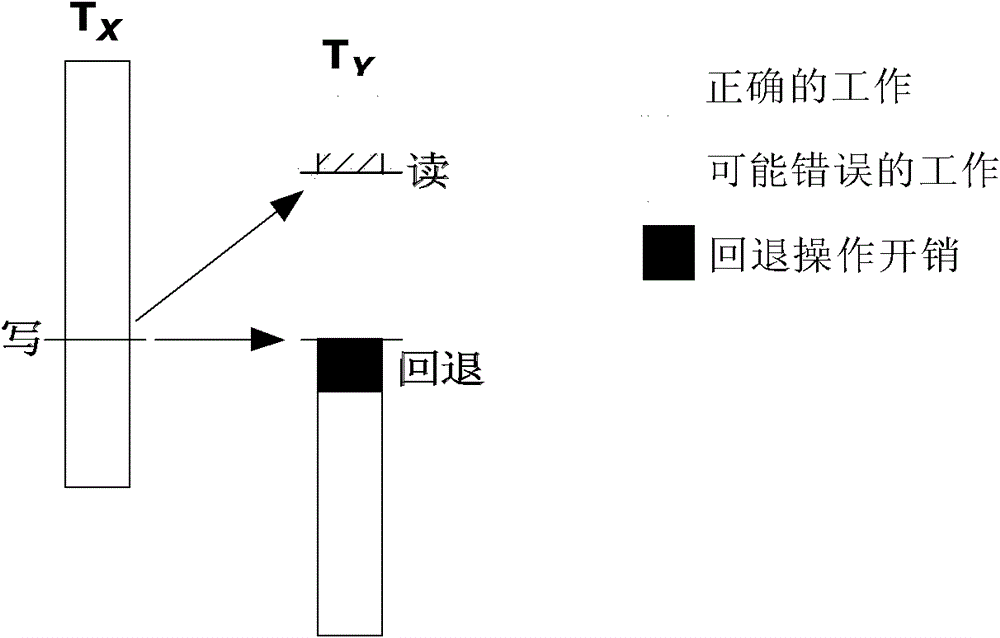
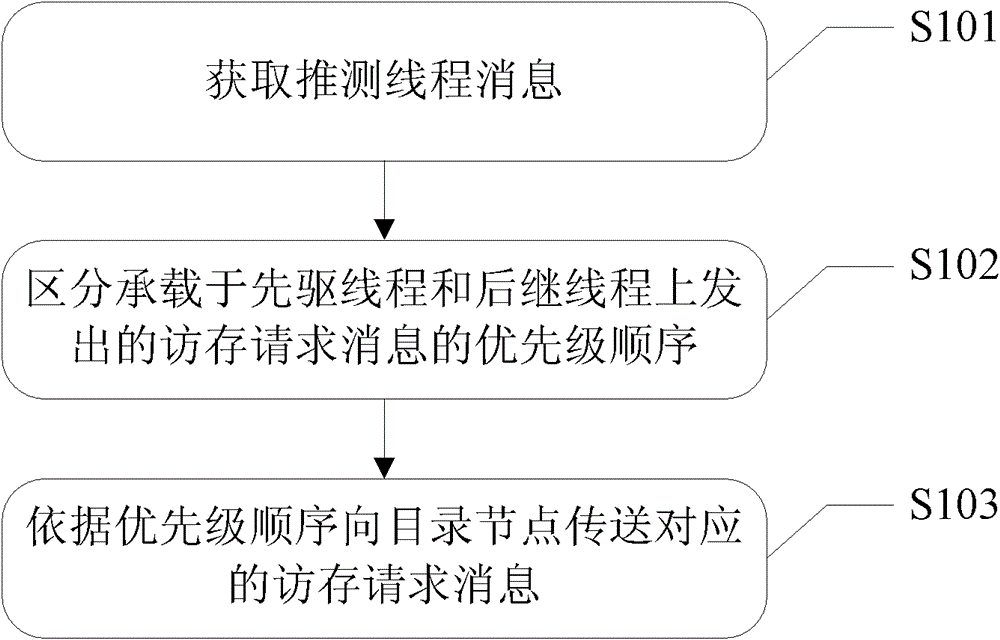
ActiveCN102799414BReduce bounce ratePrevent rollbackConcurrent instruction executionImproved methodSpeculative multithreading
The invention discloses an improved thread level speculation (TLS) method and an improved TLS device. The method comprises the following steps of: acquiring a thread speculation message in a network message, and distinguishing and arranging the priorities of access request messages which are sent by a previous thread and a subsequent thread to determine a priority sequence, wherein the priority of the access request message which is sent by the previous thread is higher than that of the access request message which is sent by the subsequent thread; and transmitting the corresponding access request messages to directory nodes according to the determined priority sequence, and reading or writing data at the directory nodes. By adoption of the method provided by the invention, the priorities of access requests in the thread speculation message are distinguished, the priorities of a plurality of threads in a program are distinguished, and the data at the directory nodes can be read or written according to the priority sequence, so squash of the threads is avoided, the squash rate of the threads and the power consumption of TLS are reduced, and the performance of the TLS is stabilized and improved.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
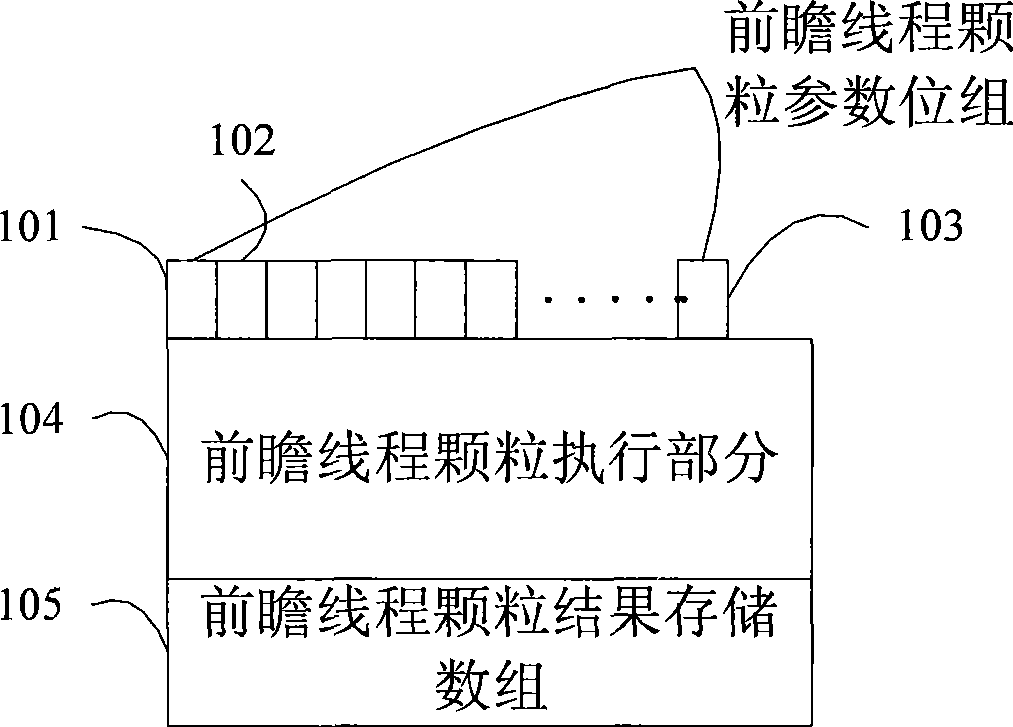
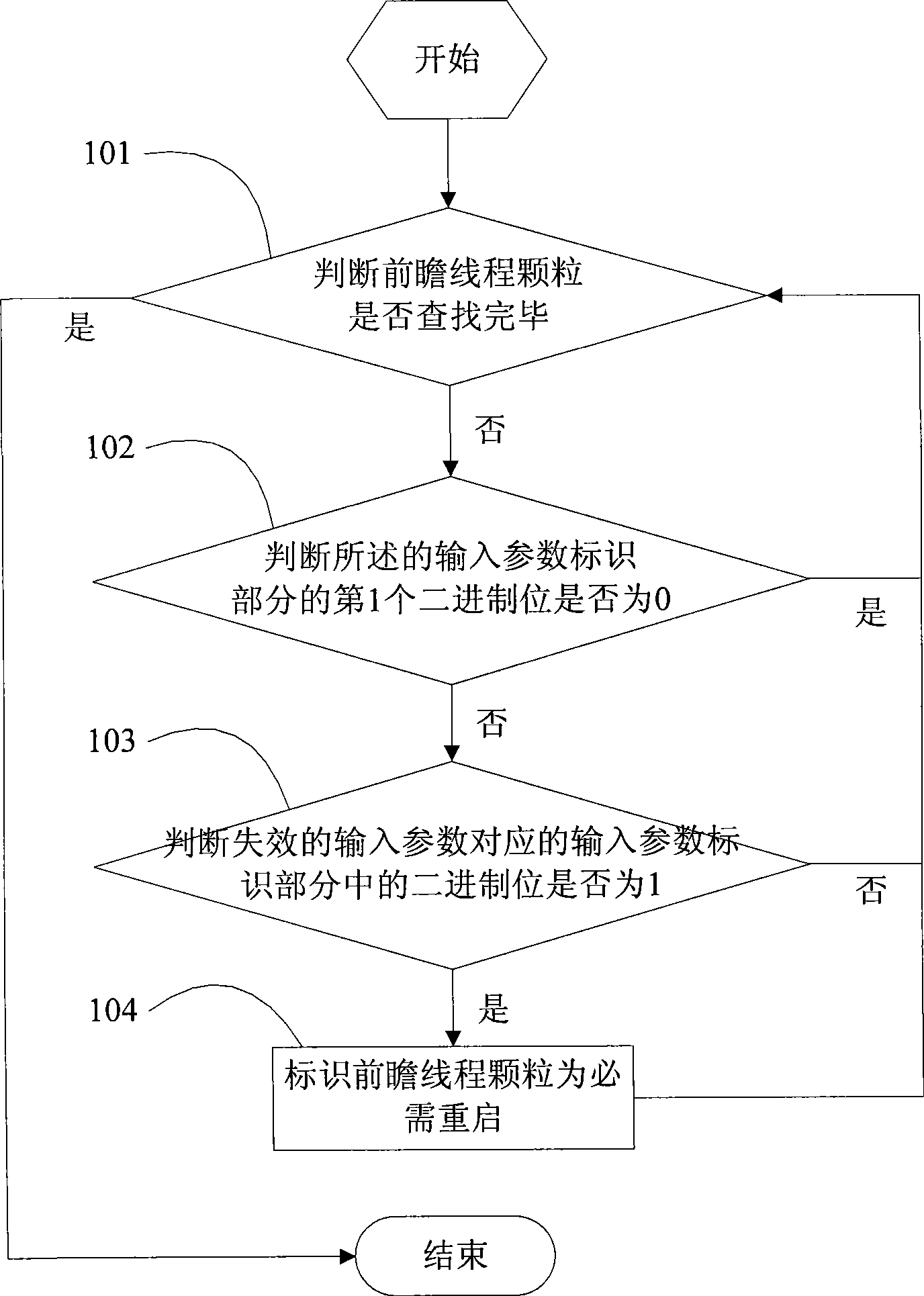
Speculative thread particle with restart optimization and restart optimization method thereof
The invention discloses a speculative thread particle with restart optimization and a restart optimization method thereof. The speculative thread particle consists of an input parameter identification part, an execution part, and a result storage part, wherein the input parameter identification part consists of N+1 binary digits which are orderly arranged, and is used for identifying whether the speculative thread particle uses an input parameter corresponding to an input parameter identification byte; the execution part consists of a plurality of program statements in speculative thread, and is used for storing executive statements of the speculative thread particle; and the result storage part is used for storing an execution result of the speculative thread particle. The restart optimization method has the following operation steps of: A, detecting disabled speculative thread input parameters; B, searching speculative thread particles which depend on the failed speculative thread input parameters in step A; and C, restarting the speculative thread particles found in step B. The restart optimization method has the advantages that the restart optimization method can quickly judge the speculative thread particles which must be restarted when the speculative fails, and reduce the cost for thread restart.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Multi-speculative path thread division method under the speculative multi-thread mechanism based on cmp
InactiveCN105138309BExpand branch coverageMining potential parallelismConcurrent instruction executionParallel computingSpeculative multithreading
The invention discloses a CMP (Chip Multiprocessor)-based multi-speculative path thread partitioning method under a speculative multithreading mechanism. According to the method, a process is taken as a unit in thread partitioning; for each process, control-independence nodes of thread end points in the process are limited during partitioning; mutual exclusion path segments of thread excitation points in the process are limited, so that excitation of the thread is relatively strictly limited; meanwhile, the excitation points on the mutual exclusion path segments are made to correspond to the same thread end point; a plurality of continuous pre-computation slices are inserted behind the thread end points; the contents of the pre-computation slices are mutually different along with the changes of the speculative paths and the excitation points; and a simulator carries out different speculative paths when running, and selects corresponding pre-computation slices for executionaccording to the corresponding excitation points on the speculative paths. According to the method, thread partitioning can be carried out on a plurality of paths, so that the branch coverage rate of speculative parallel execution is increased.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Efficient rollback and retry of conflicted speculative threads with hardware support
InactiveUS20140096142A1Program synchronisationMemory systemsParallel computingSpeculative multithreading
A method for rolling back speculative threads in symmetric-multiprocessing (SMP) environments is disclosed. In one embodiment, such a method includes detecting an aborted thread at runtime and determining whether the aborted thread is an oldest aborted thread. In the event the aborted thread is the oldest aborted thread, the method sets a high-priority request for allocation to an absolute thread number associated with the oldest aborted thread. The method further detects that the high-priority request is set and, in response, clears the high-priority request and sets an allocation token to the absolute thread number associated with the oldest aborted thread, thereby allowing the oldest aborted thread to retry a work unit associated with the absolute thread number. A corresponding apparatus and computer program product are also disclosed.
Owner:IBM CORP
Speculative multithreading memory data synchronous execution method under support of compiler and device thereof
InactiveCN101833440BHigh speedupReduce the number of timesConcurrent instruction executionData synchronizationSpeculative execution
The invention discloses a speculative multithreading memory data synchronous execution method under the support of a compiler and a device thereof, which can synchronize selected read / write memory instructions when a program is operated, reduce the frequency of read / write data dependency violation and improve the integral speedup ratio of multithreading synchronous operation. The method comprisesthe following steps of: adding a stall instruction before a read instruction after a candidate read / write instruction pair is obtained, replacing the read instruction into a synchronous read instruction synload, adding one or more forward instructions behind a write instruction and adding a synset instruction behind a thread initiating instruction spawn of a thread in which the write instruction is positioned; finally operating on a simulator after an executable file generated through compilation linking is loaded; and speculatively executing a multithreading program in a synchronous mode to obtain an operation result and a higher speedup ratio.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com