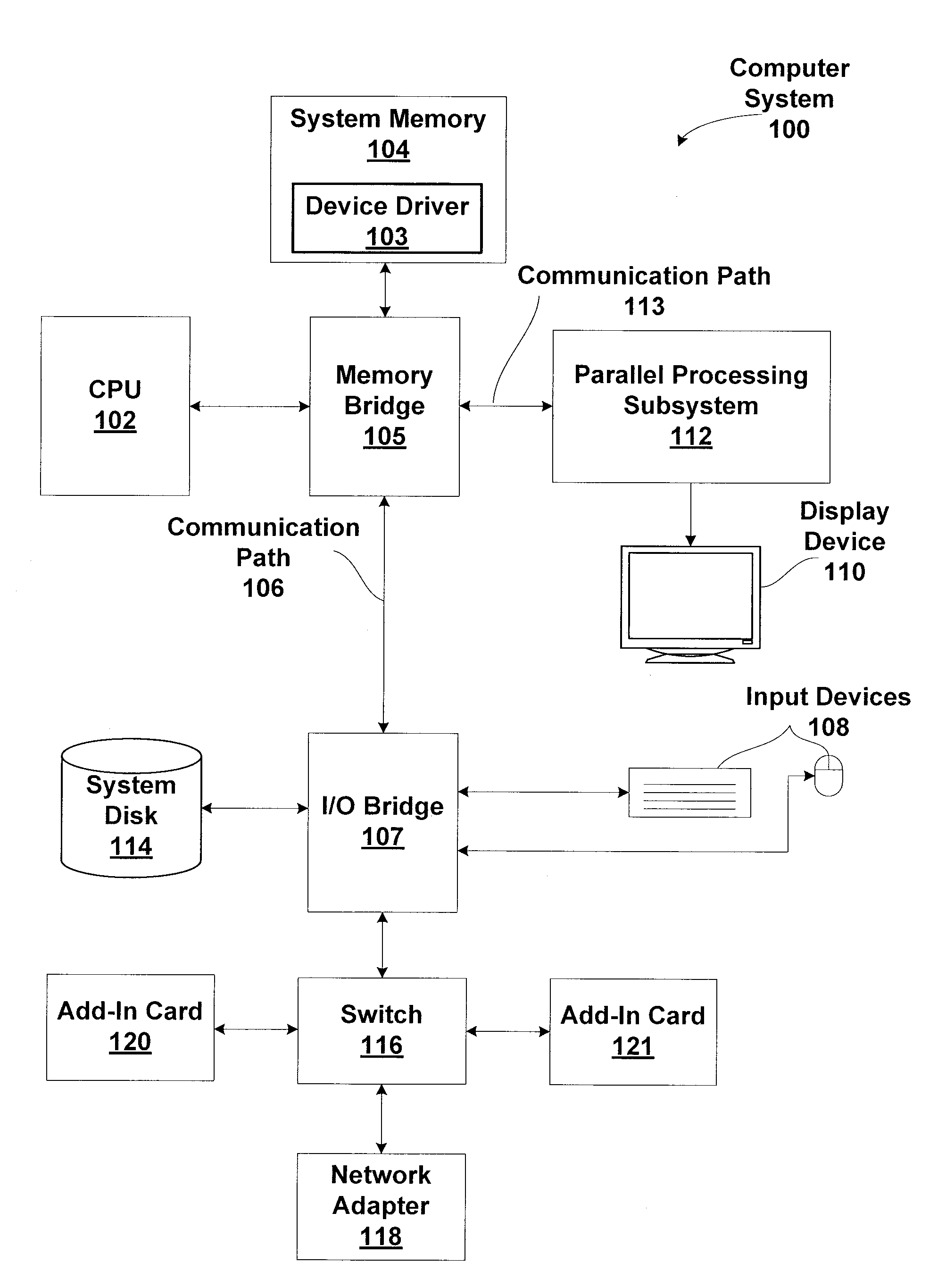
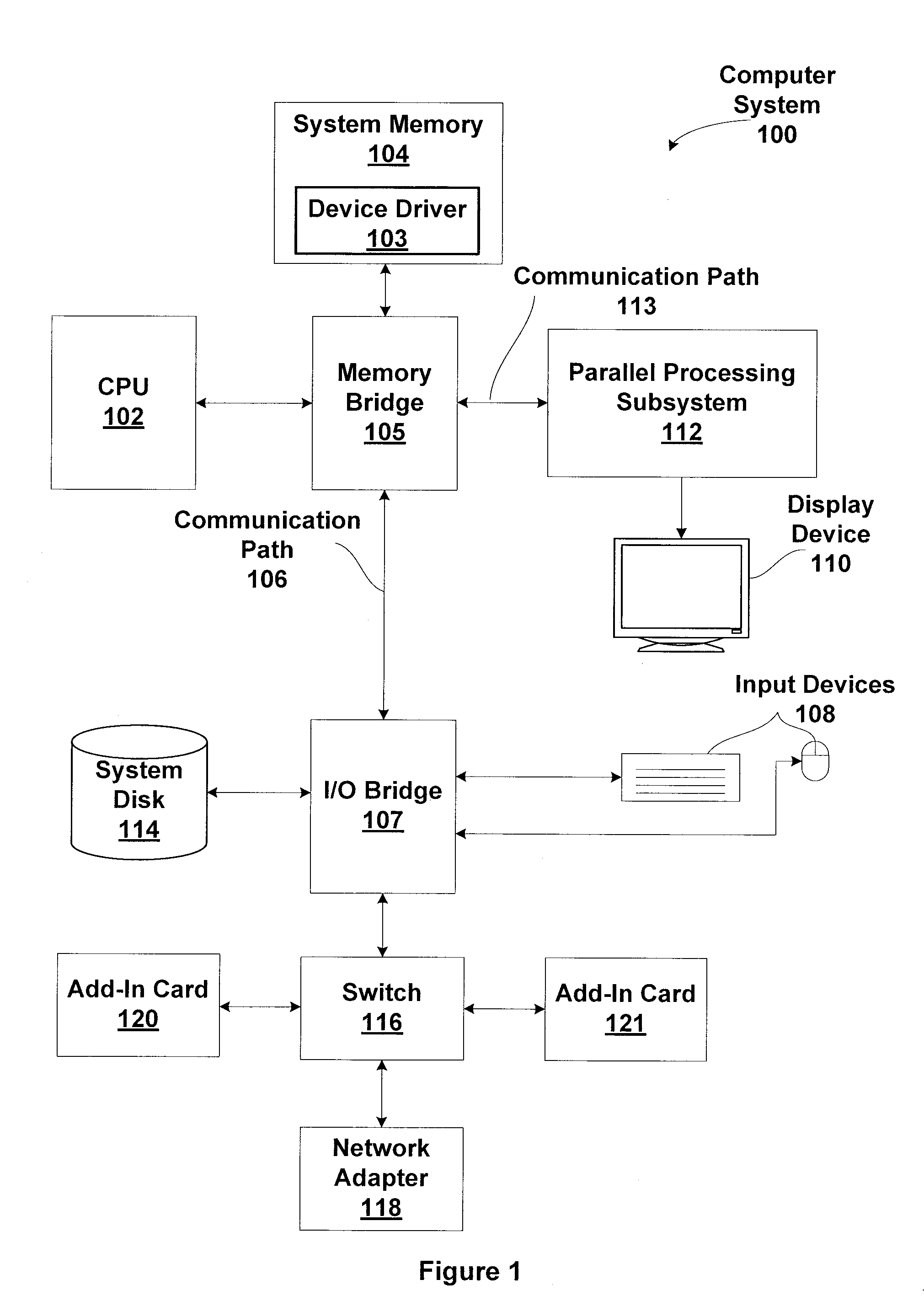
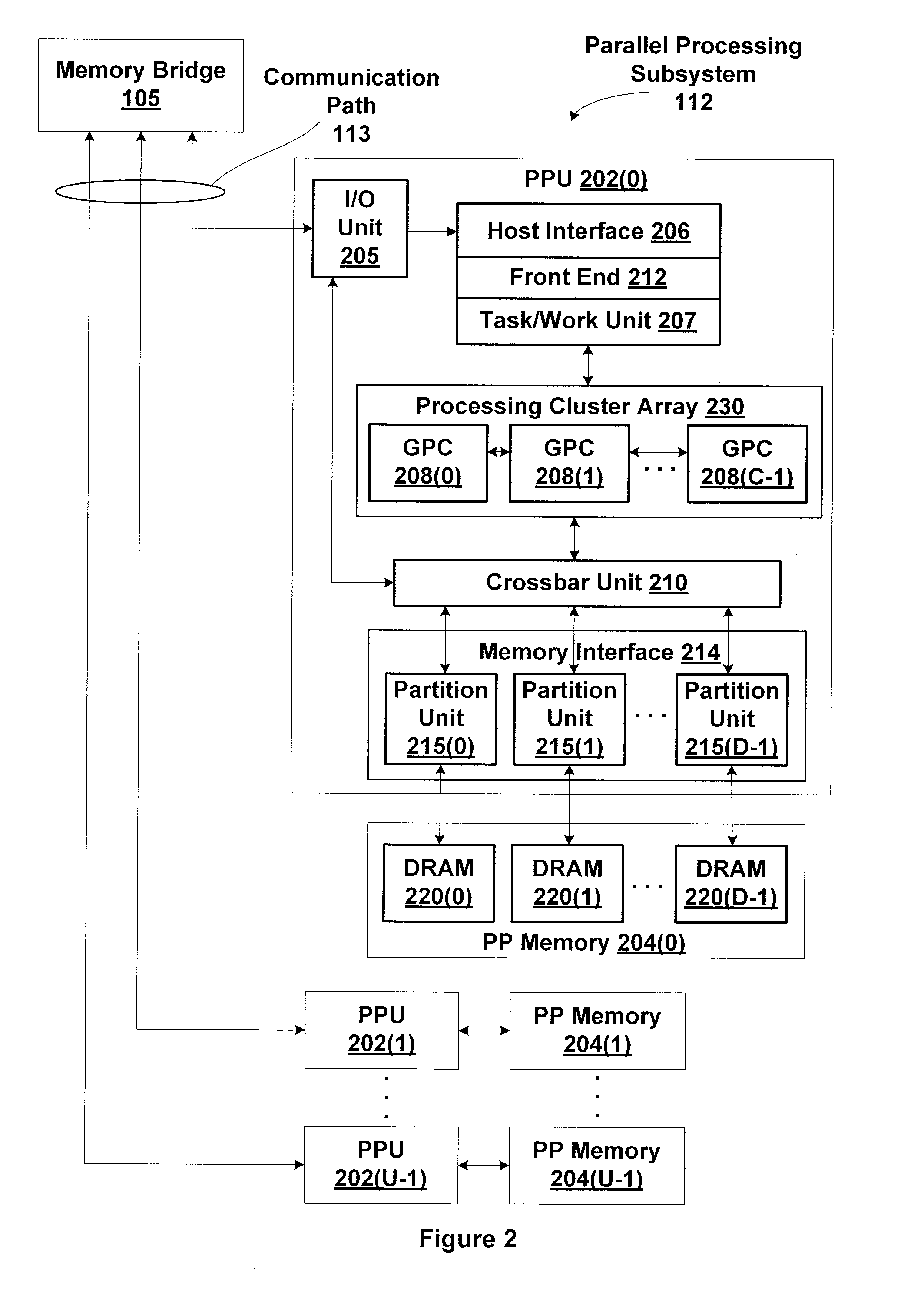
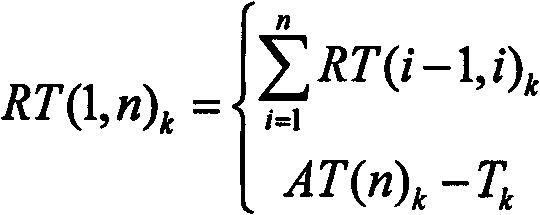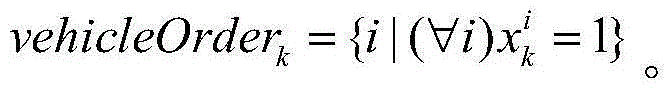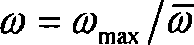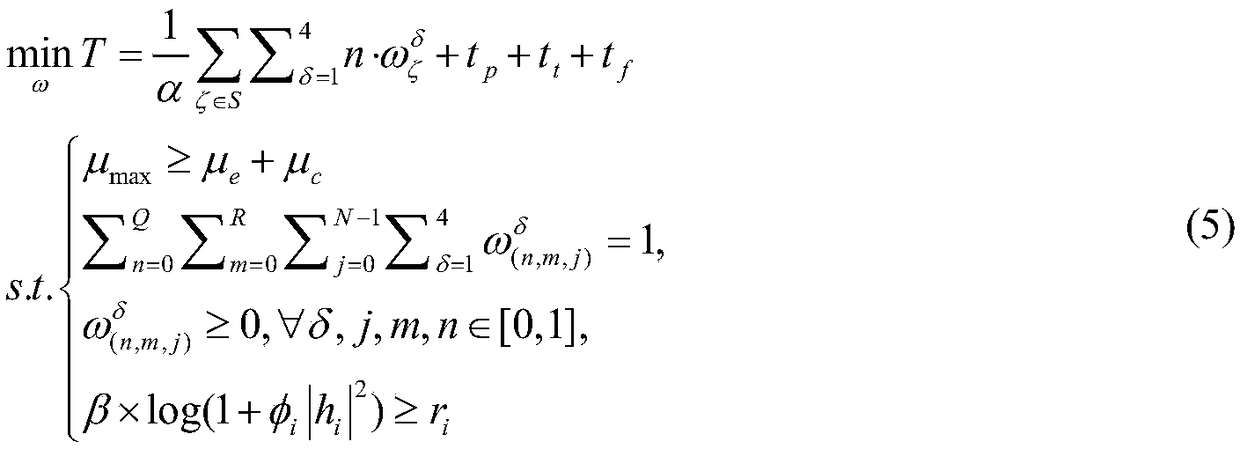Patents
Literature
555 results about "Dynamic dispatch" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In computer science, dynamic dispatch is the process of selecting which implementation of a polymorphic operation (method or function) to call at run time. It is commonly employed in, and considered a prime characteristic of, object-oriented programming (OOP) languages and systems.
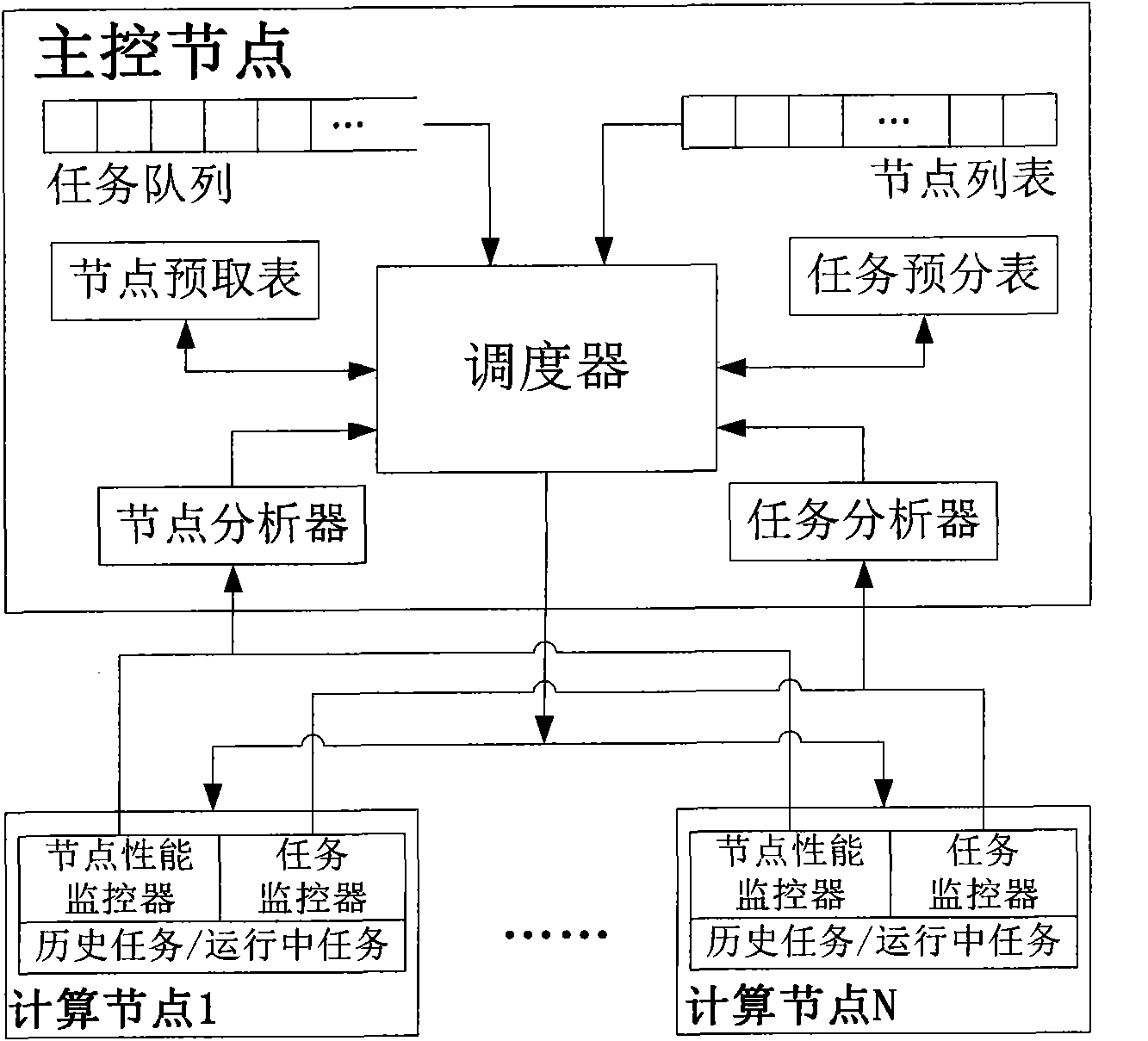
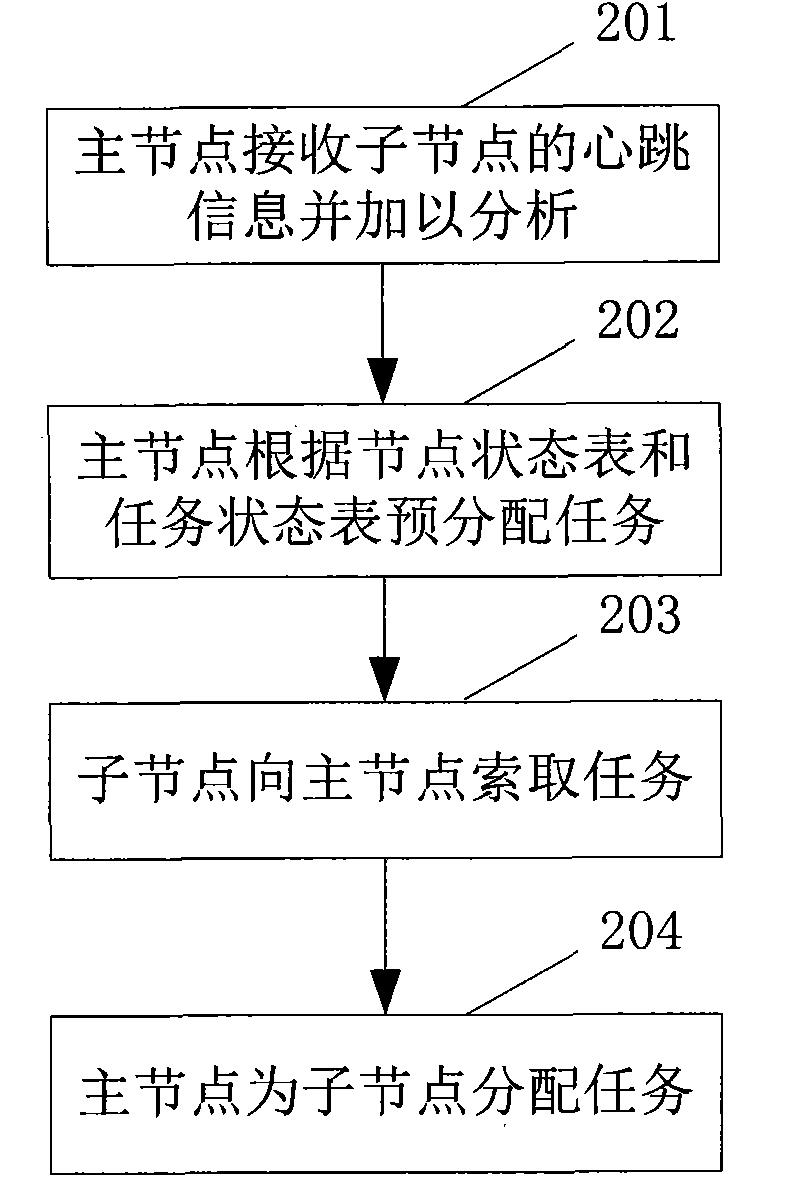
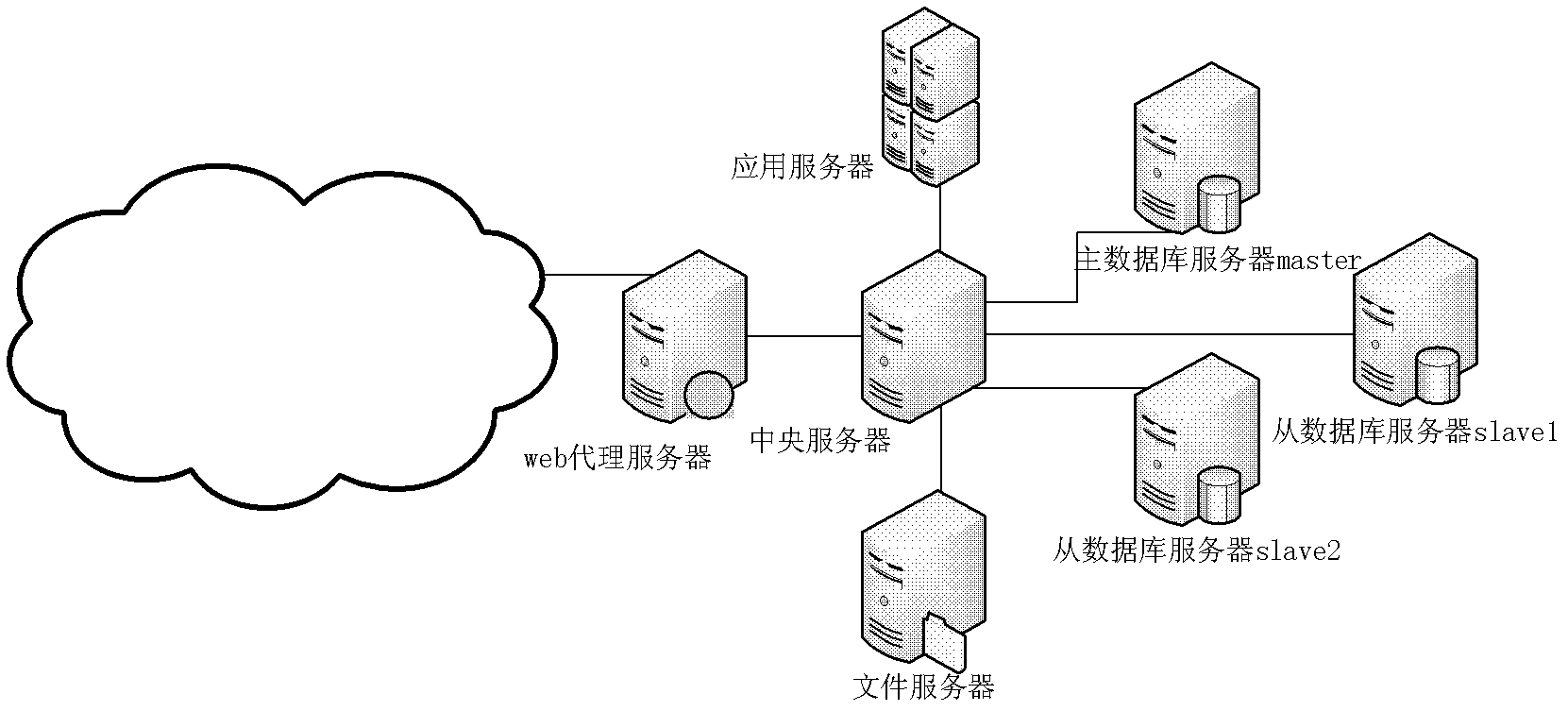
Task-dynamic dispatching method under distributed computation mode in cloud computing environment
InactiveCN102073546AReasonable distributionSolve bottlenecksResource allocationResource utilizationCloud computing
The invention provides a task-dynamic dispatching method under a distributed computation mode in a cloud computing environment, which comprises the following four steps: 1. a main node receives and analyzes heartbeat information of a subsidiary node; 2. the main node previously distributes the task according to a node state table and a task state table; 3. the subsidiary node demands the task from the main node; and 4. the main node distributes the task to the subsidiary node. The method firstly considers the resource demand of the task and the performance information of the nodes, and dynamically controls the distribution of the task under the condition that the requirement is met, so that the response speed of the work and the resource utilization of the nodes are improved. The method has wide practical value and application prospect in the technical field of the distributed computation in the cloud computing environment.
Owner:SHANGHAI JUNESH INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
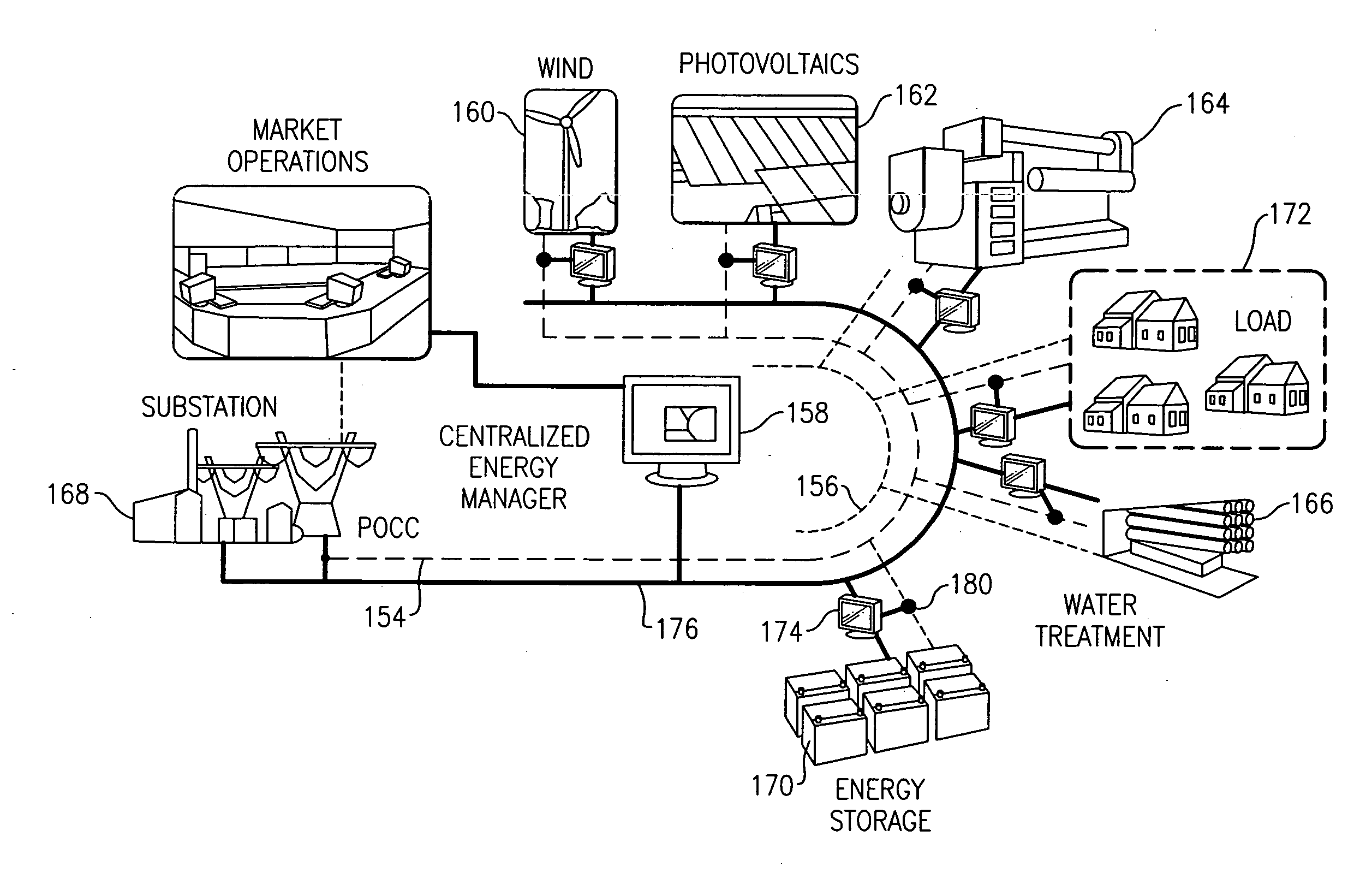
Hybrid robust predictive optimization method of power system dispatch
ActiveUS20090062969A1OptimizationMechanical power/torque controlLevel controlPower system schedulingPredictive function
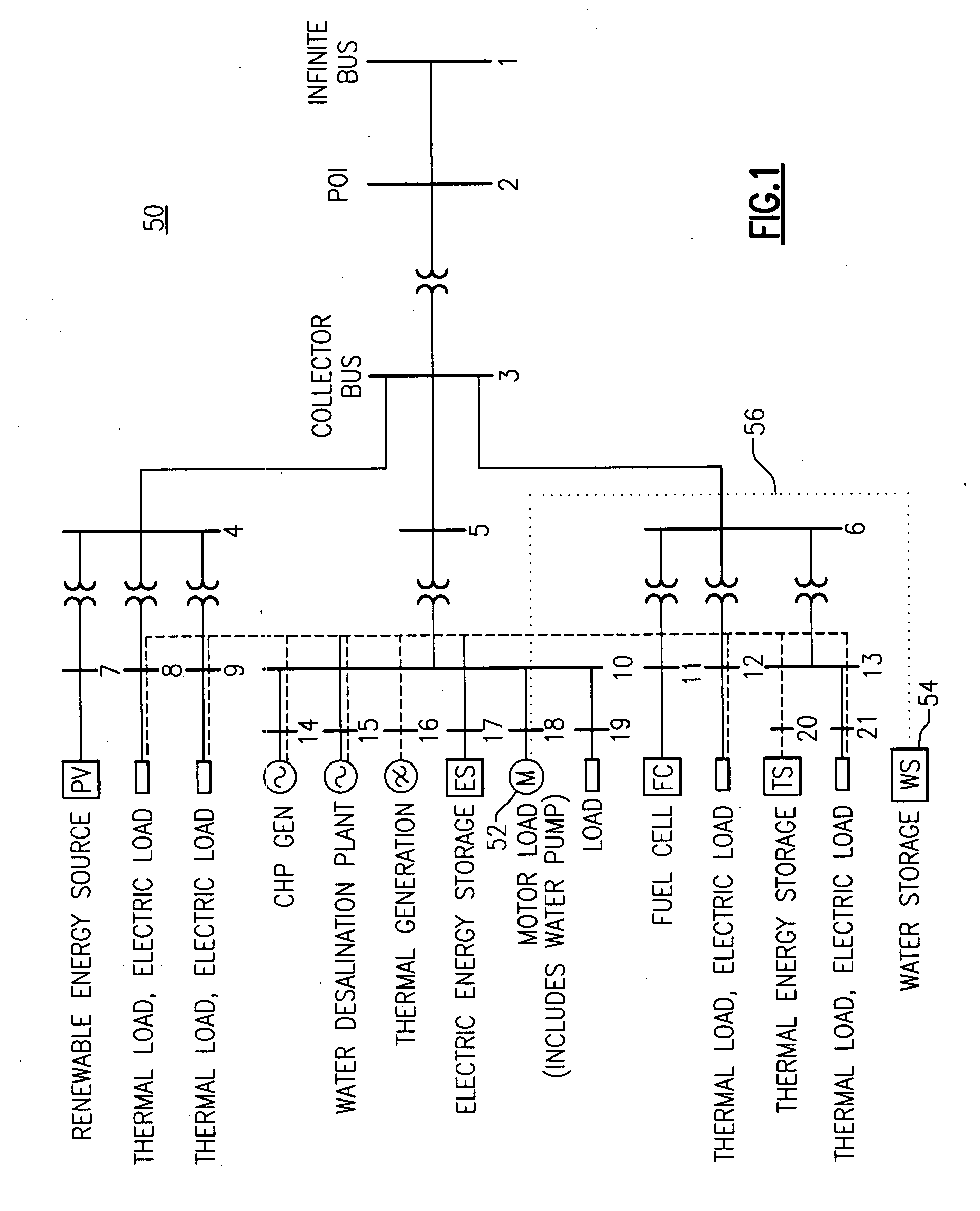
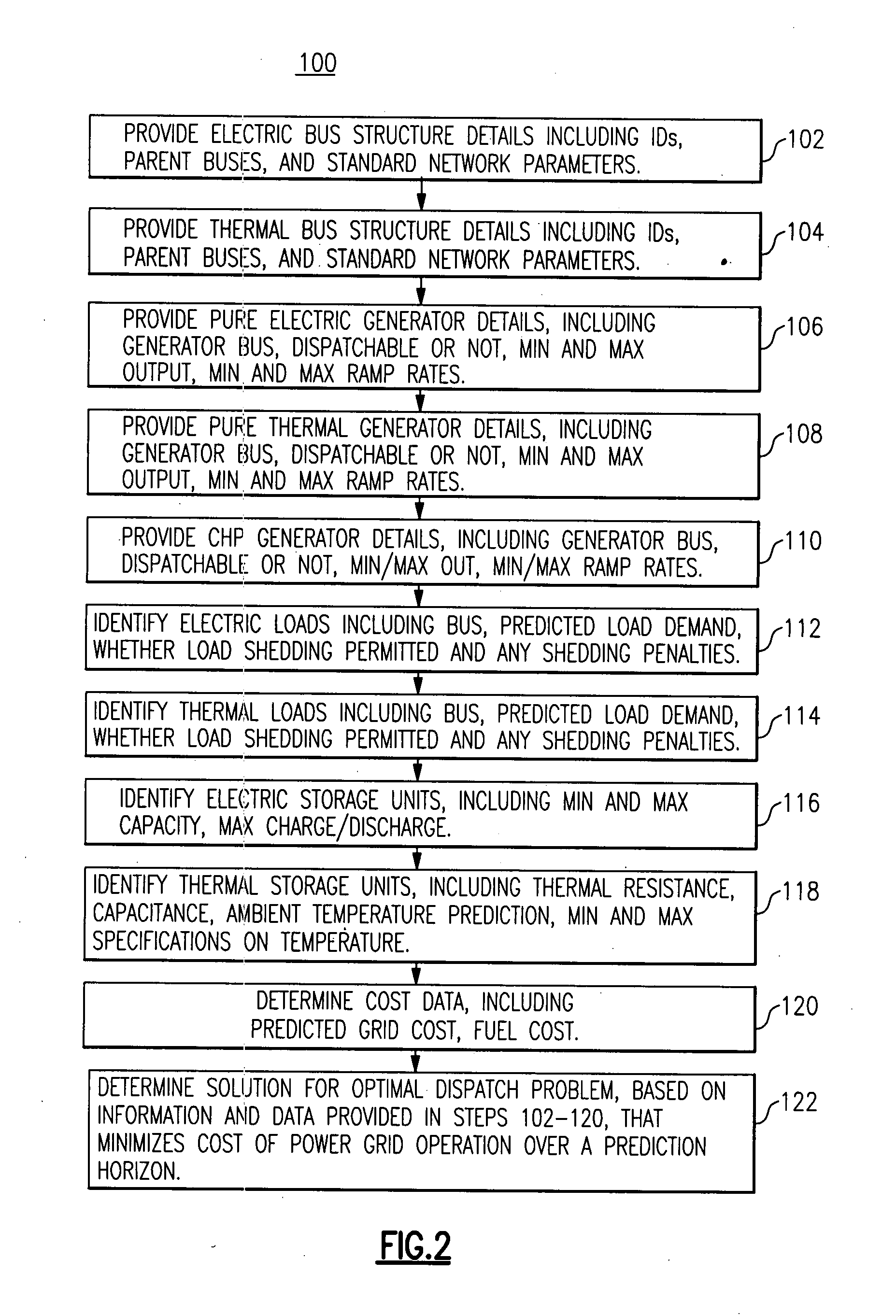
A method of power system dispatch control solves power system dispatch problems by integrating a larger variety of generation, load and storage assets, including without limitation, combined heat and power (CHP) units, renewable generation with forecasting, controllable loads, electric, thermal and water energy storage. The method employs a predictive algorithm to dynamically schedule different assets in order to achieve global optimization and maintain the system normal operation.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
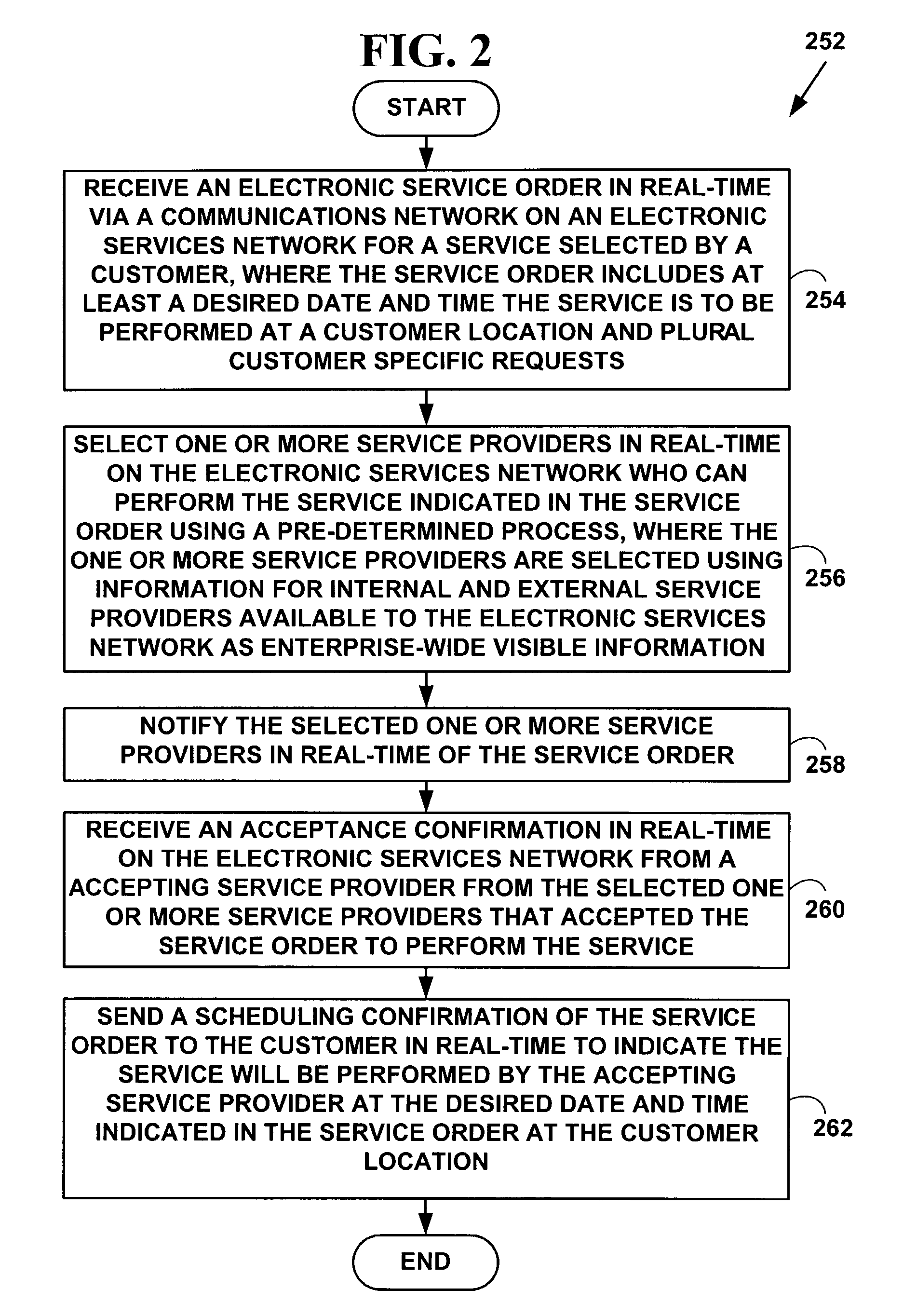
Method and system to select, schedule and purchase home services
InactiveUS7580862B1Expand selectionImprove schedulingOffice automationMarketingVisibilityService provision
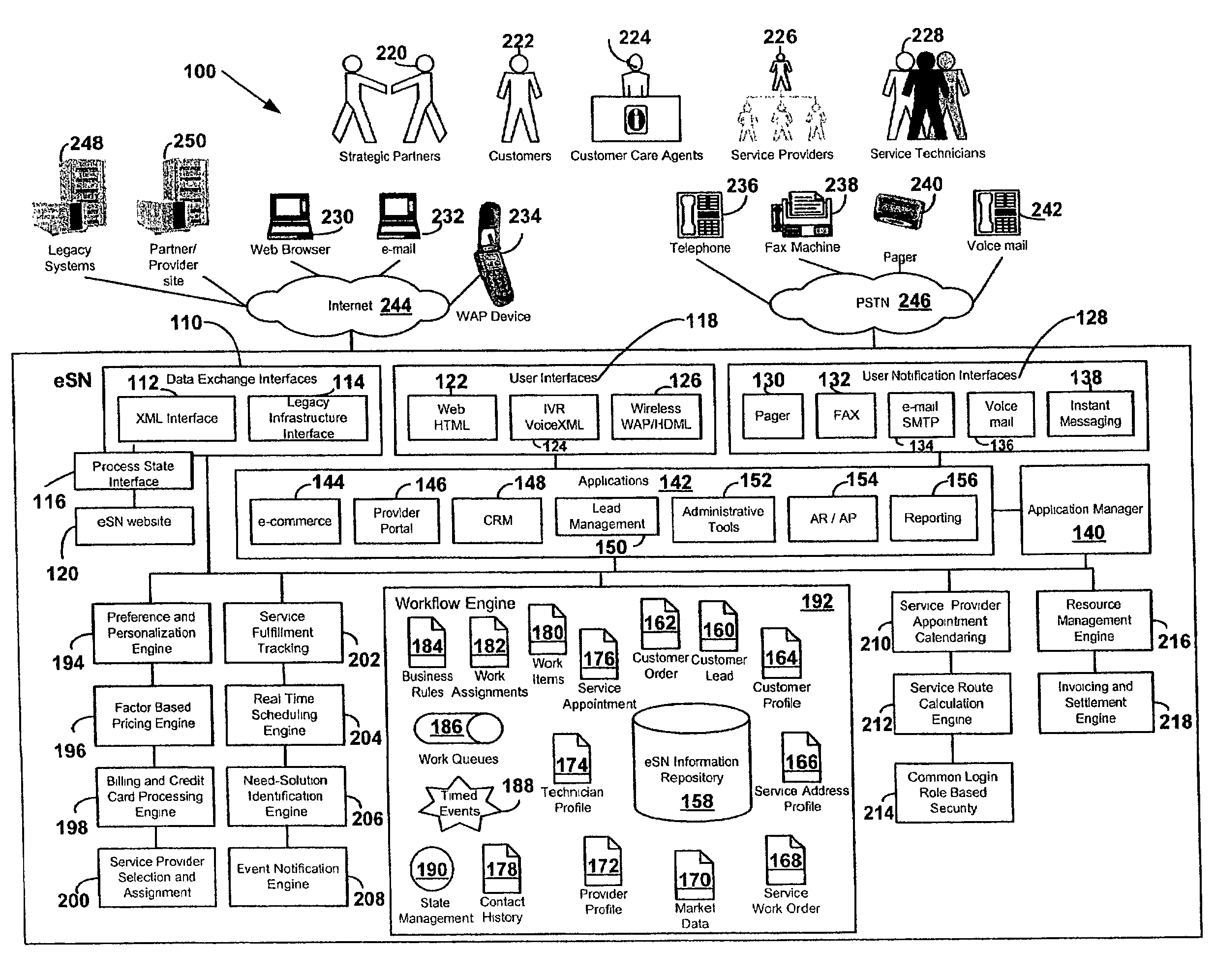
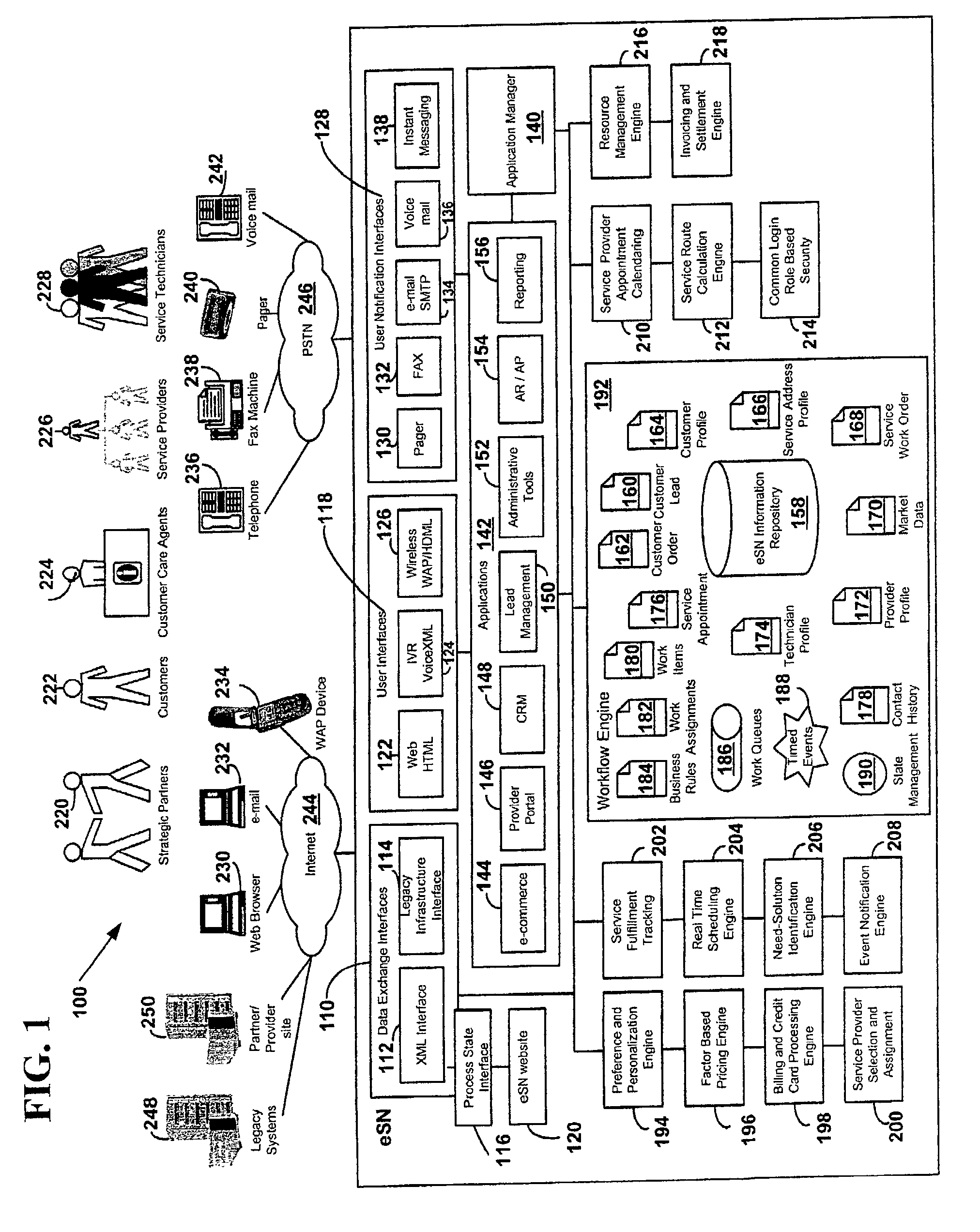
A method and system to select, schedule, purchase, confirm, invoice, bill and settle service orders, such as home services orders from customers. The method and system accept electronic service orders as well as customer leads for services, selects service providers and schedule services in real-time via a computer network, confirms scheduling of service delivery in real-time, handles administrative and business details for both customers and service providers, as well as fulfills, tracks and settle service orders. The method and system also provide customized information for services available via an electronic services network and dynamically schedule services using plural electronic appointment calendars from plural service providers. The method and system includes customer service order and customer lead information and enterprise-wide visibility and management of business processes. The method and system may also be used for goods.
Owner:SERVICEMASTER CLEAN RESTORE SPE LLC
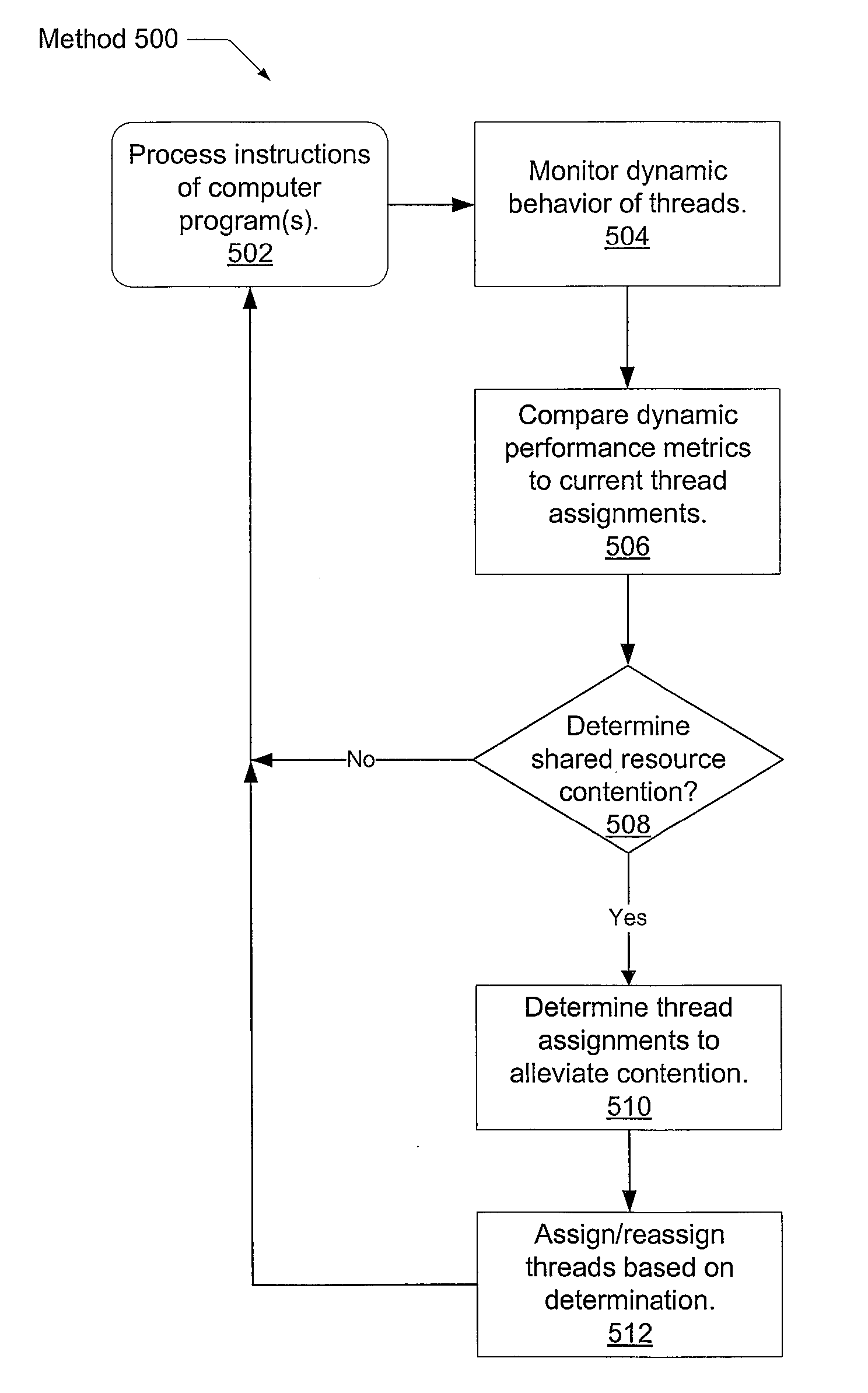
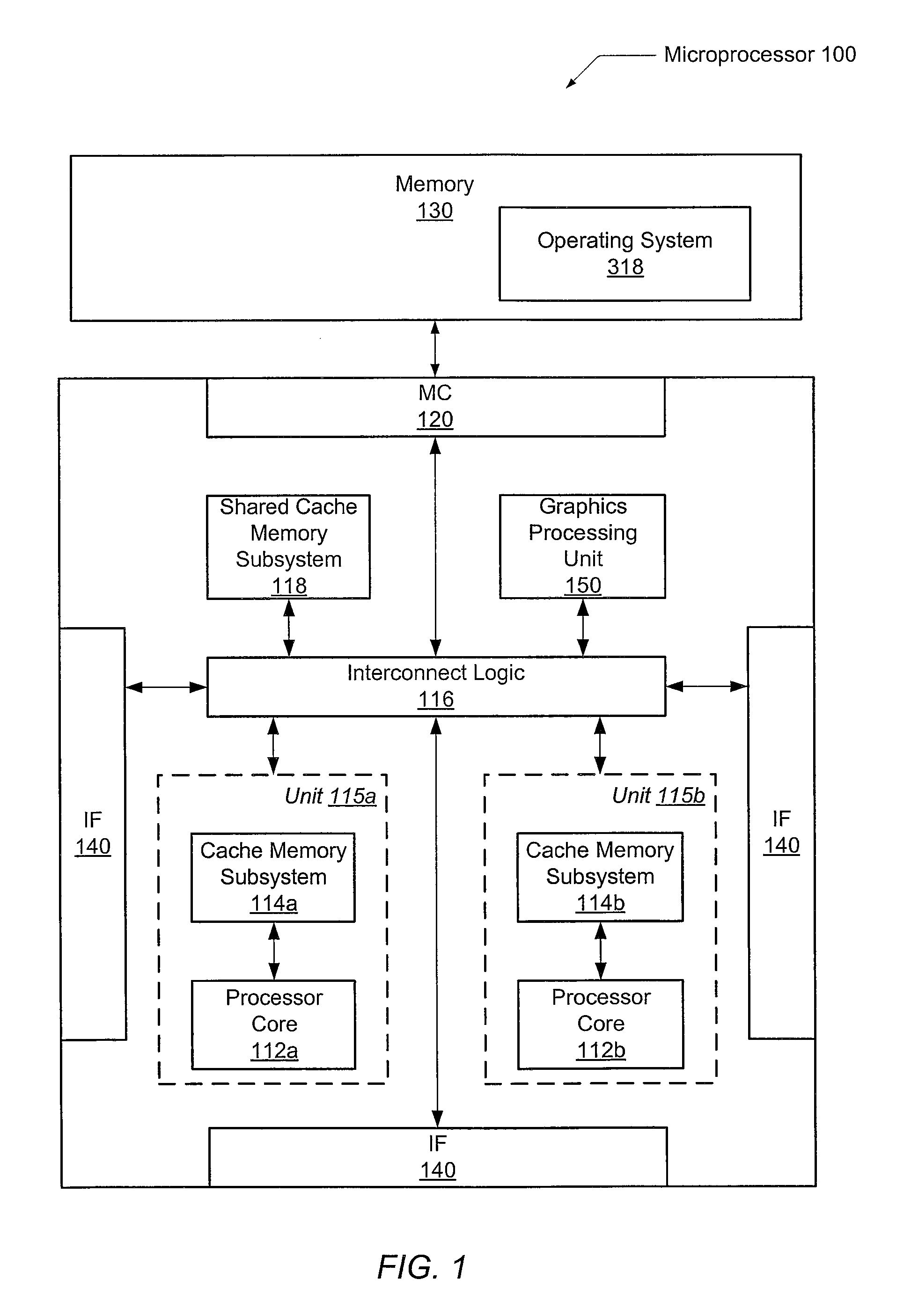
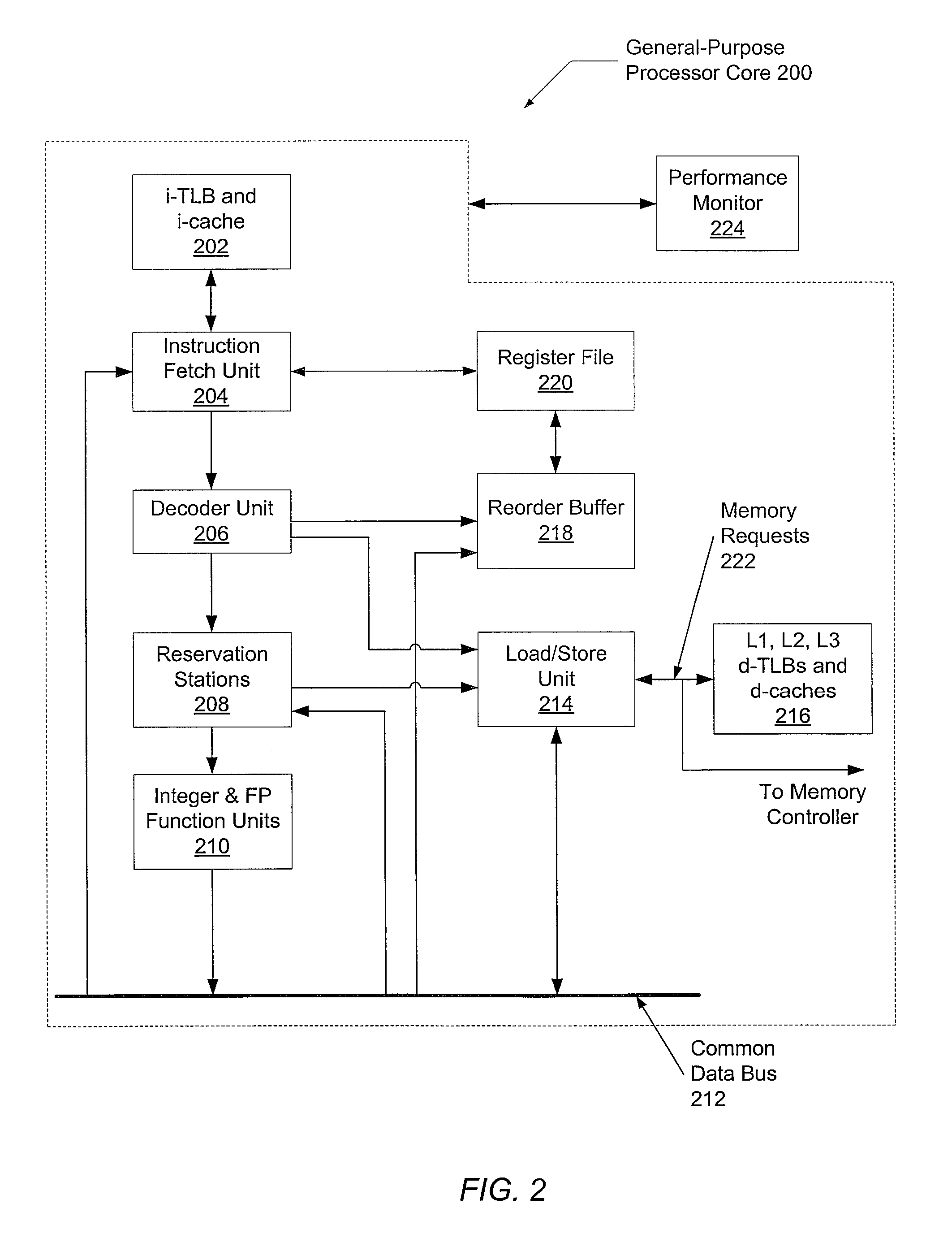
Optimized thread scheduling via hardware performance monitoring
A system and method for efficient dynamic scheduling of tasks. A scheduler within an operating system assigns software threads of program code to computation units. A computation unit may be a microprocessor, a processor core, or a hardware thread in a multi-threaded core. The scheduler receives measured data values from performance monitoring hardware within a processor as the one or more processors execute the software threads. The scheduler may be configured to reassign a first thread assigned to a first computation unit coupled to a first shared resource to a second computation unit coupled to a second shared resource. The scheduler may perform this dynamic reassignment in response to determining from the measured data values a first measured value corresponding to the utilization of the first shared resource exceeds a predetermined threshold and a second measured value corresponding to the utilization of the second shared resource does not exceed the predetermined threshold.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
System for switching data using dynamic scheduling
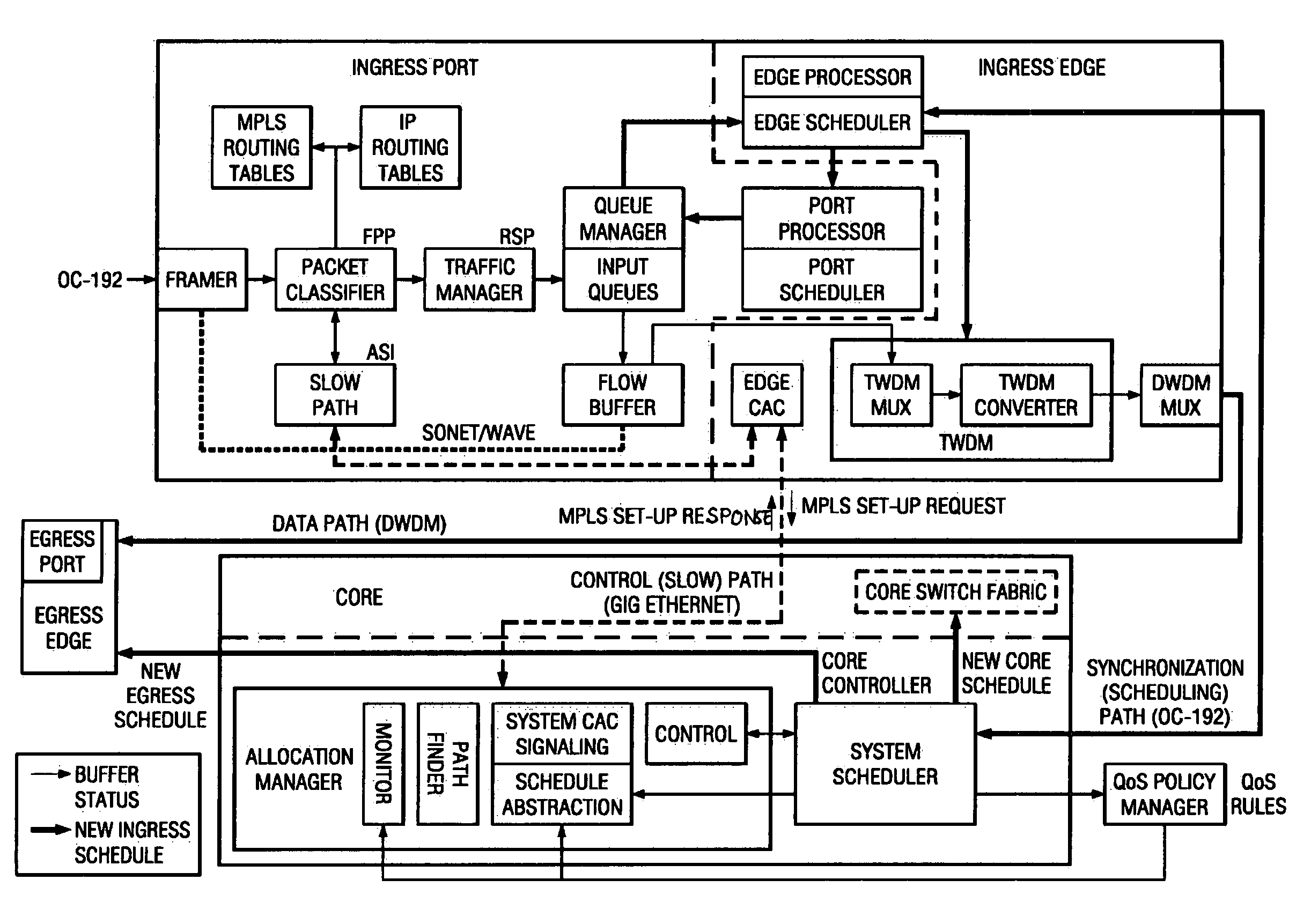
ActiveUS7218637B1Lower latencyImprove performanceData switching by path configurationTime scheduleData interchange
An architecture and related systems for improving the performance of non-blocking data switching systems. In one embodiment, a switching system includes an optical switching core coupled to a plurality of edge units, each of which has a set of ingress ports and a set of egress ports. The switching system also contains a scheduler that maintains two non-blocking data transfer schedules, only one of which is active at a time. Data is transferred through the switching system according to the active schedule. The scheduler monitors the sufficiency of data transferred according to the active schedule and, if the currently active schedule is insufficient, the scheduler recomputes the alternate schedule based on demand data received from the edges / ports and activates the alternate schedule. A timing mechanism is employed to ensure that the changeover to the alternate schedule is essentially simultaneous among the components of the system.
Owner:UNWIRED BROADBAND INC
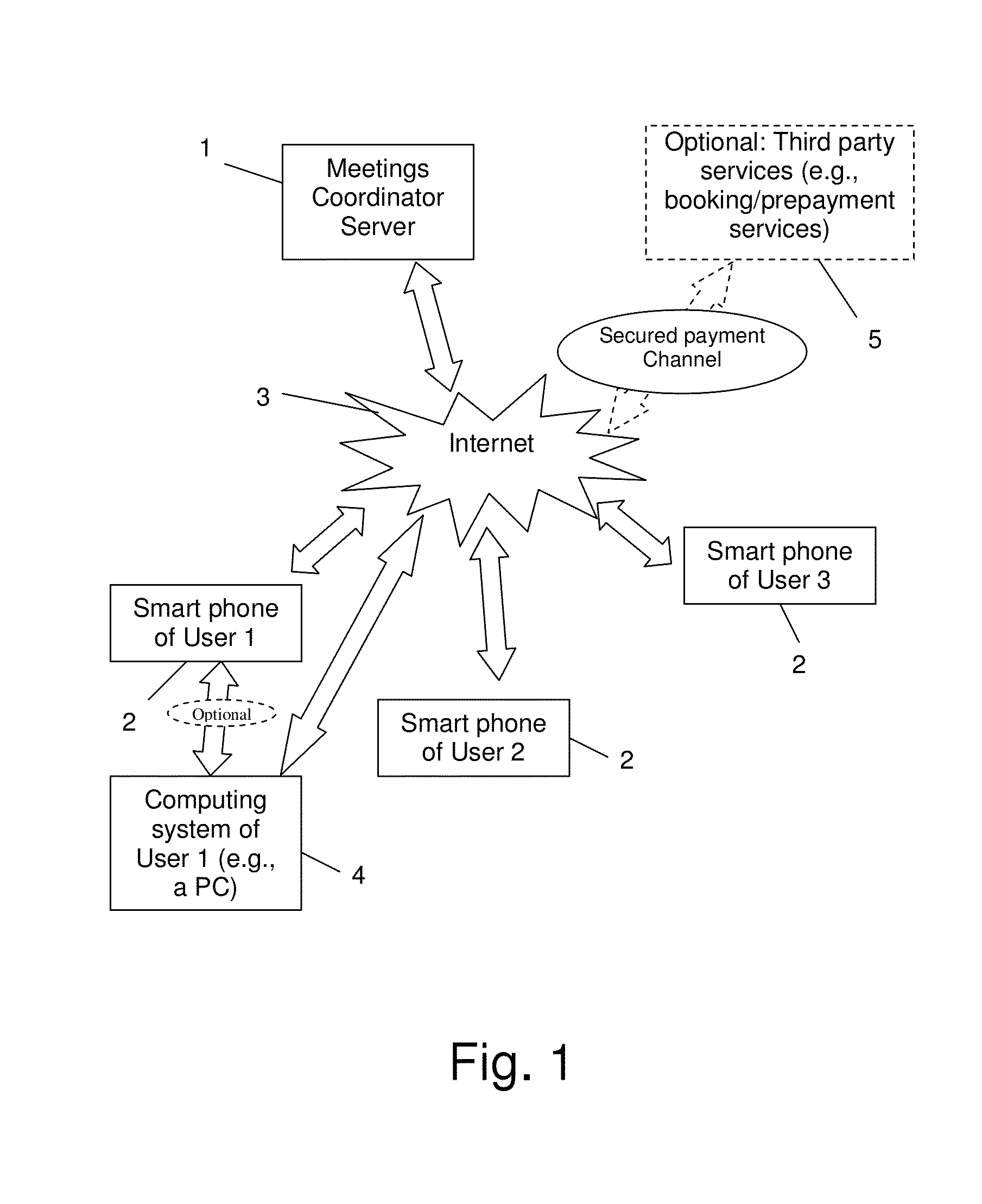
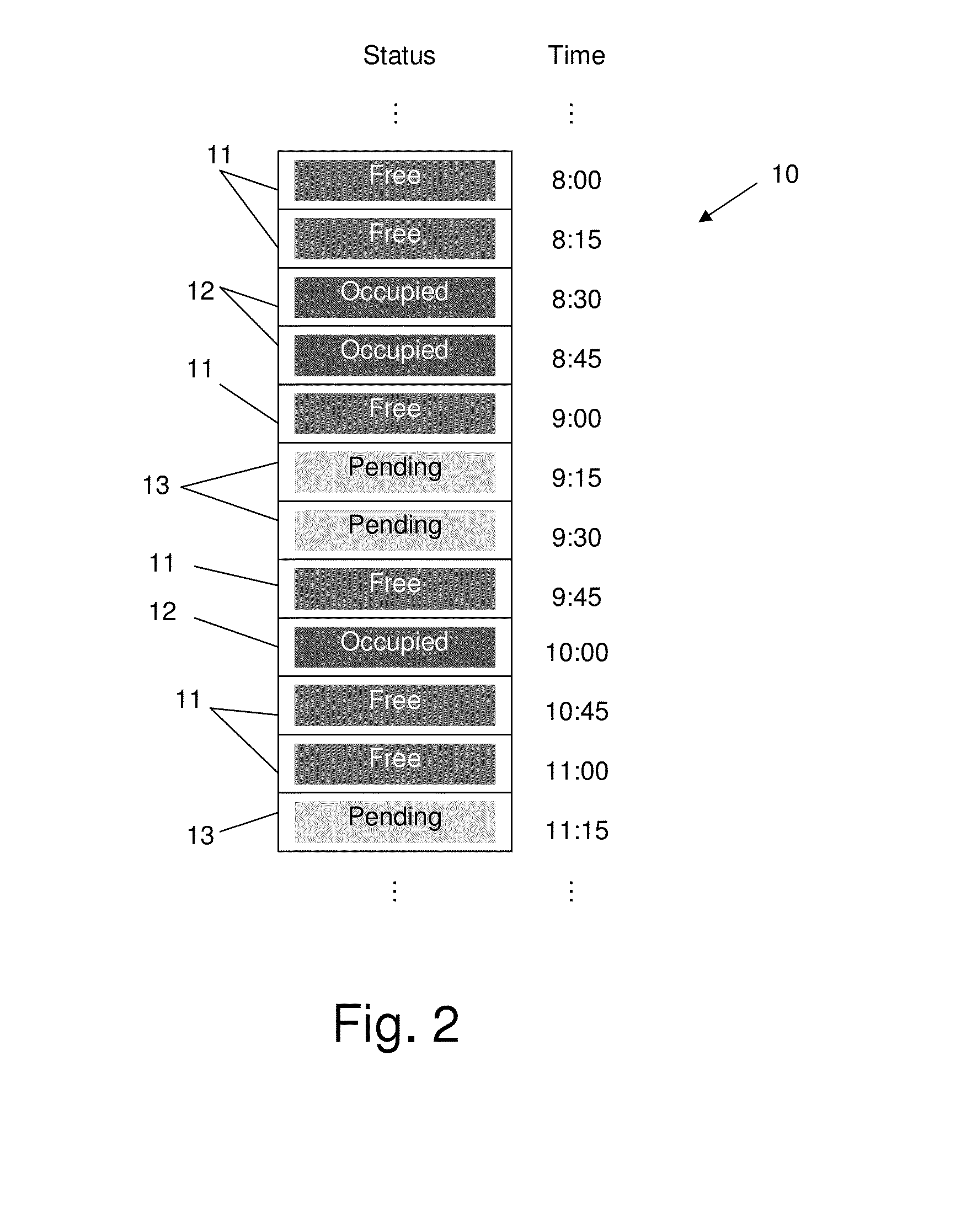
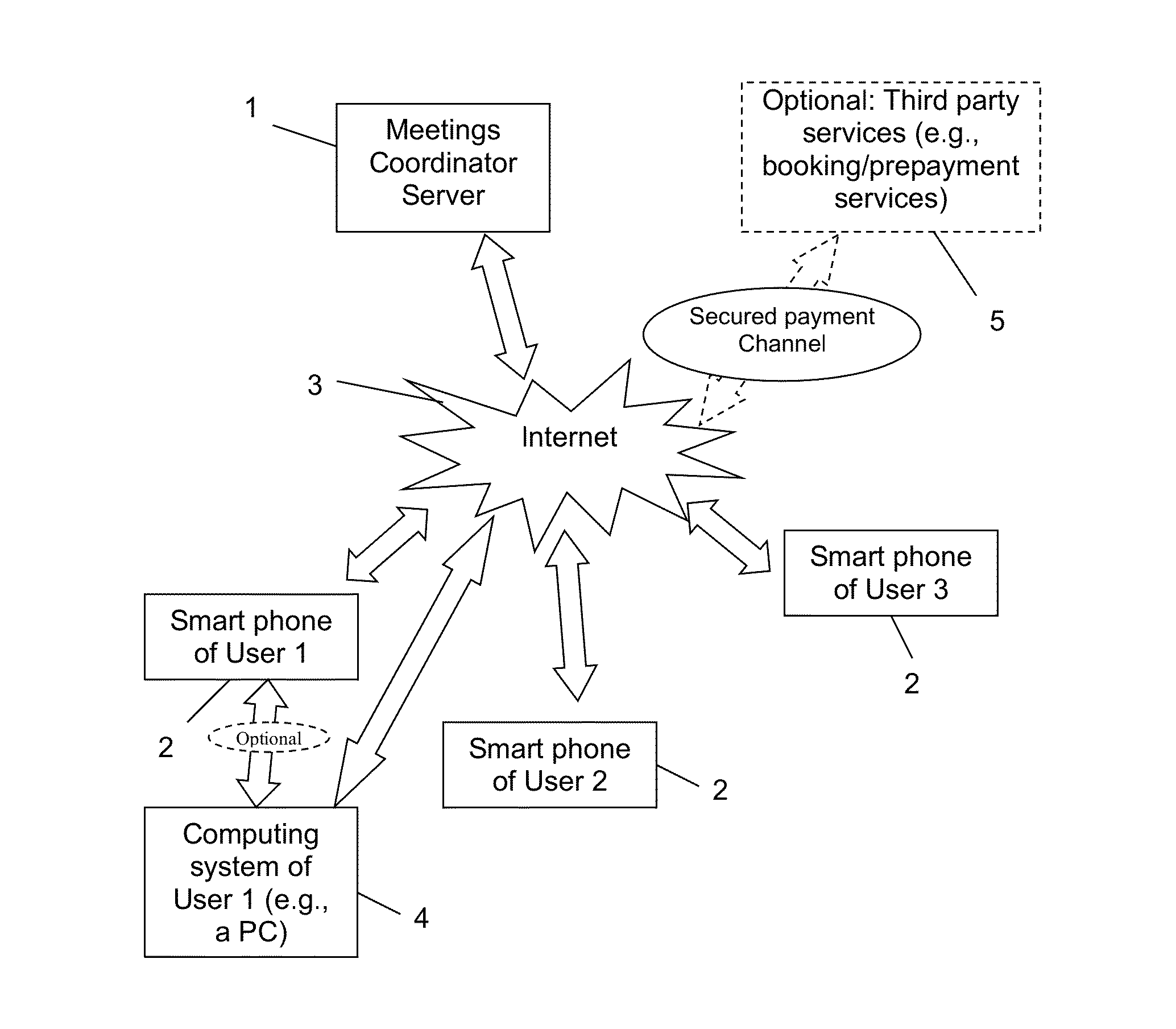
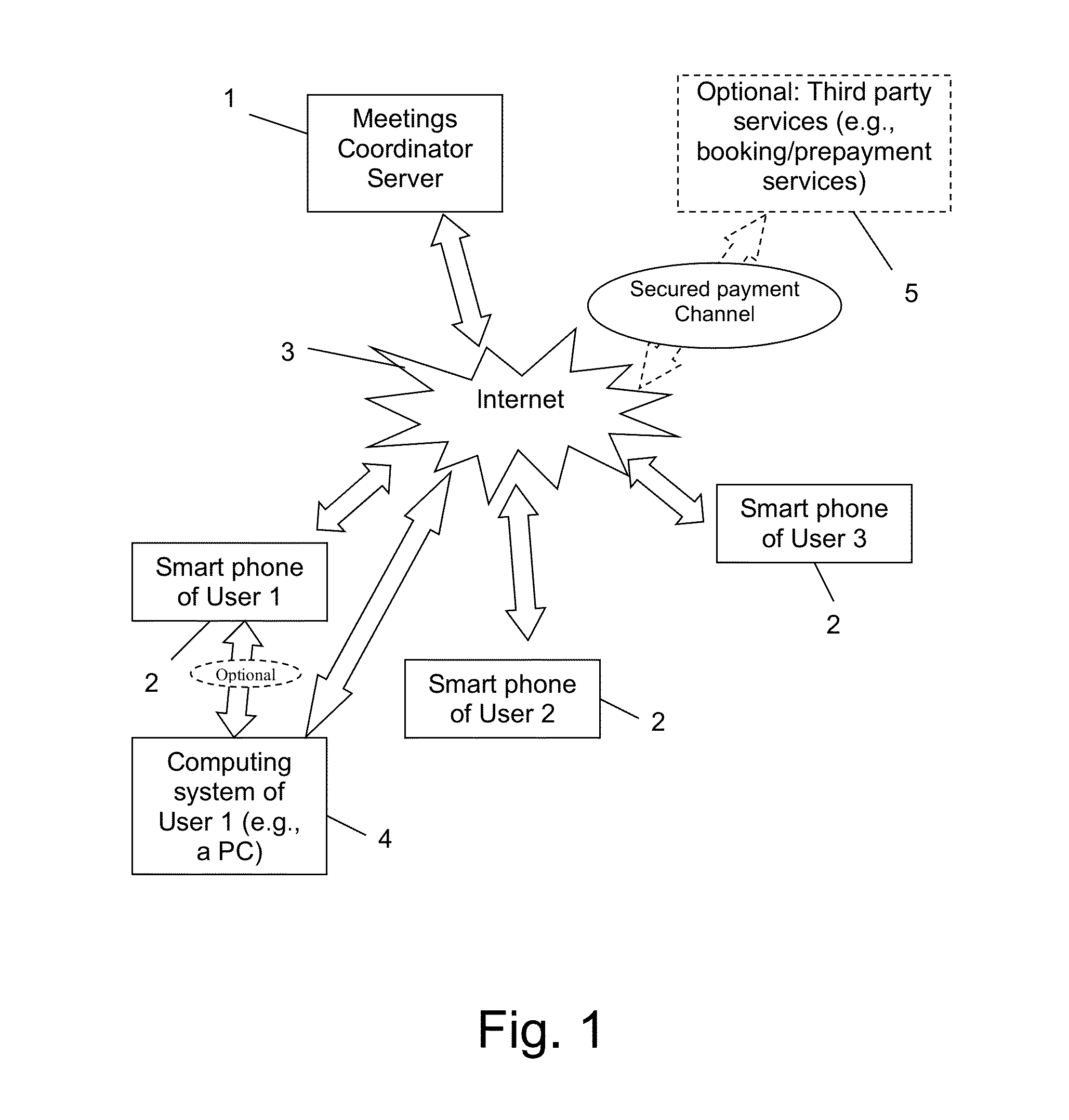
Meetings and Events Coordinating System and Method
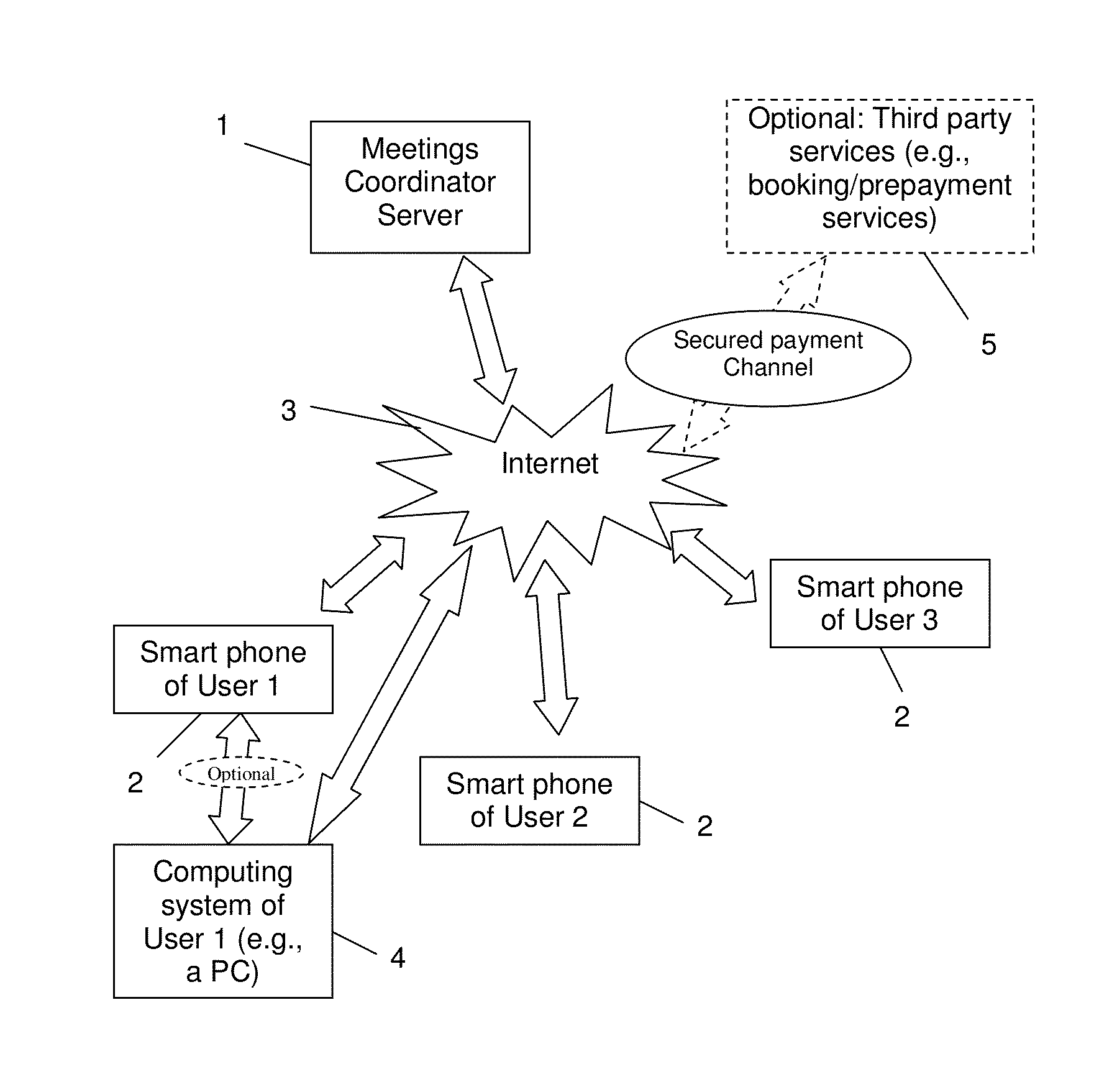
InactiveUS20140074536A1Raise the importanceAvoid difficult choicesOffice automationChronological timeComputer terminal
A calendaring method and system providing dynamic scheduling services by synchronizing calendars in a confidential and anonymous manner without the need for sharing calendar content with others. One can divide their calendar into time cubes chronologically, define each time cube according to availability states, allow a user to send data representing an invitation to an event to one or more contacts for approval, and when an invitation of one or more contacts has been approved, opening a secure “private room” in a meeting and event coordinating server adapted for synchronizing between users' calendars in a confidential and anonymous manner. Also a meeting coordinating server adapted for synchronizing between users' calendars via a secure “private room” without using any calendaring content except the availability status of each user, and according to a level of importance, and a dedicated application adapted for running / executing on a user's terminal.
Owner:MEUSHAR DANA +1
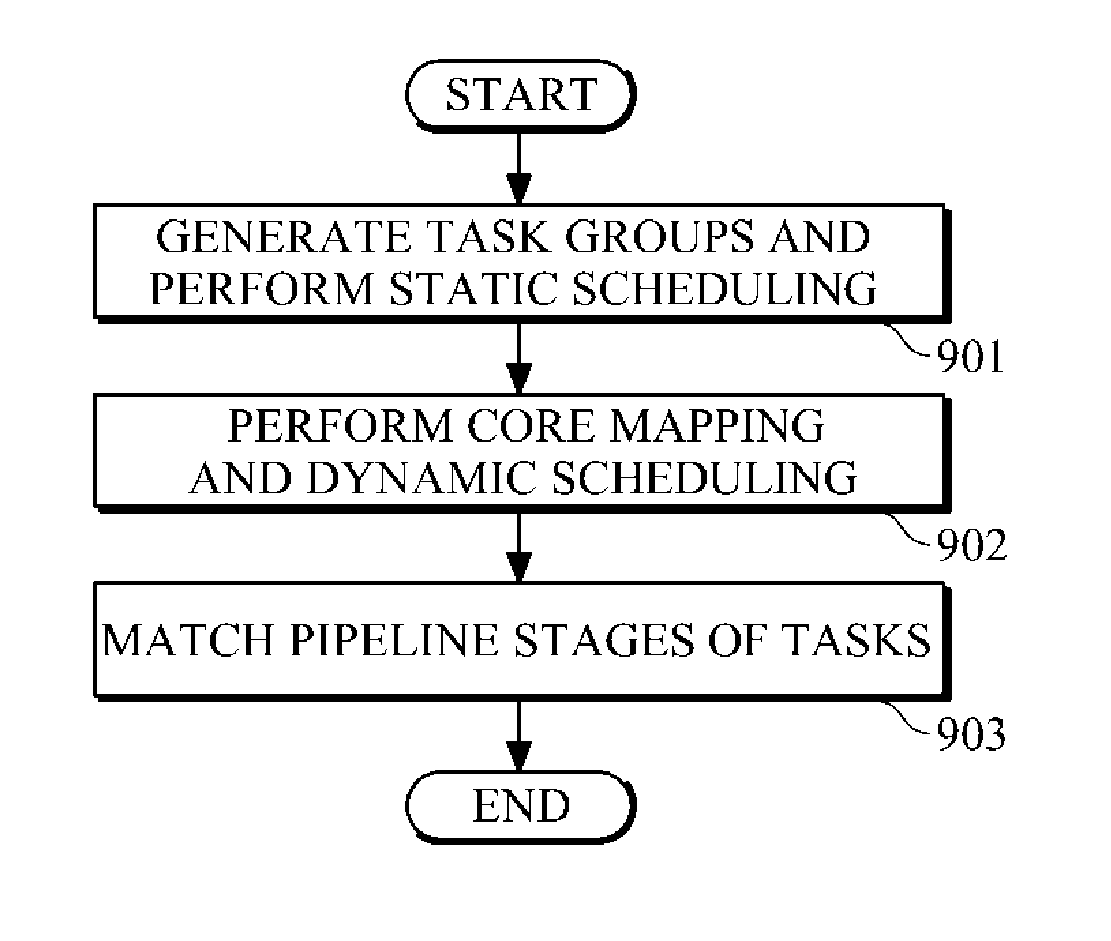
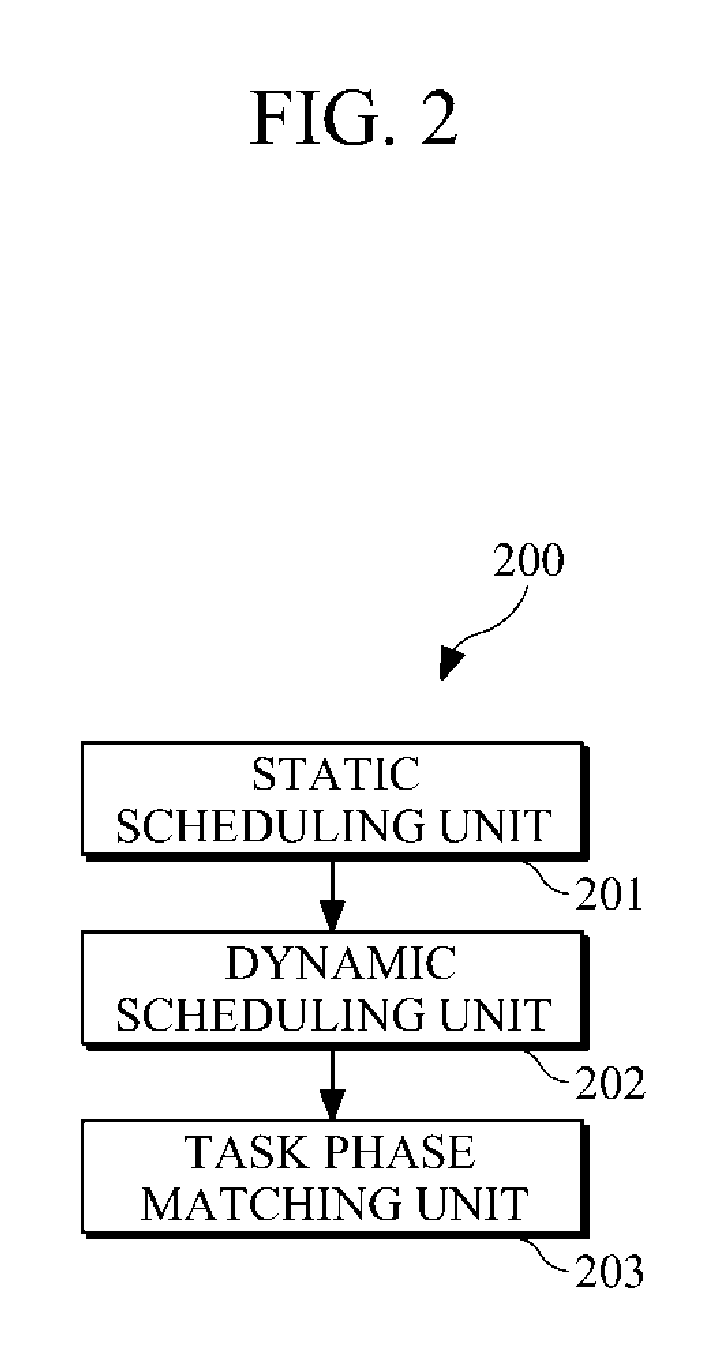
Compiling apparatus and method of a multicore device
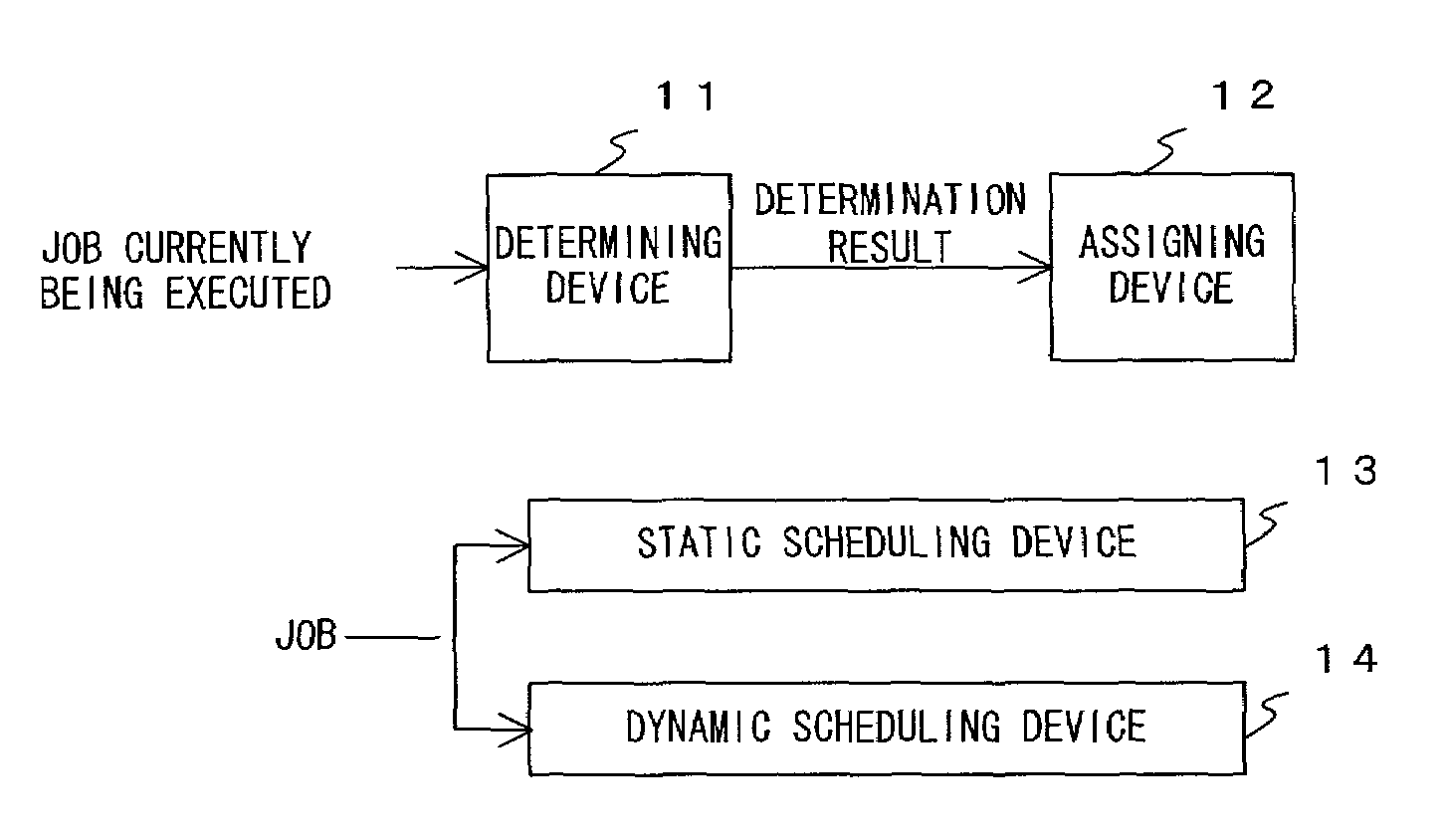
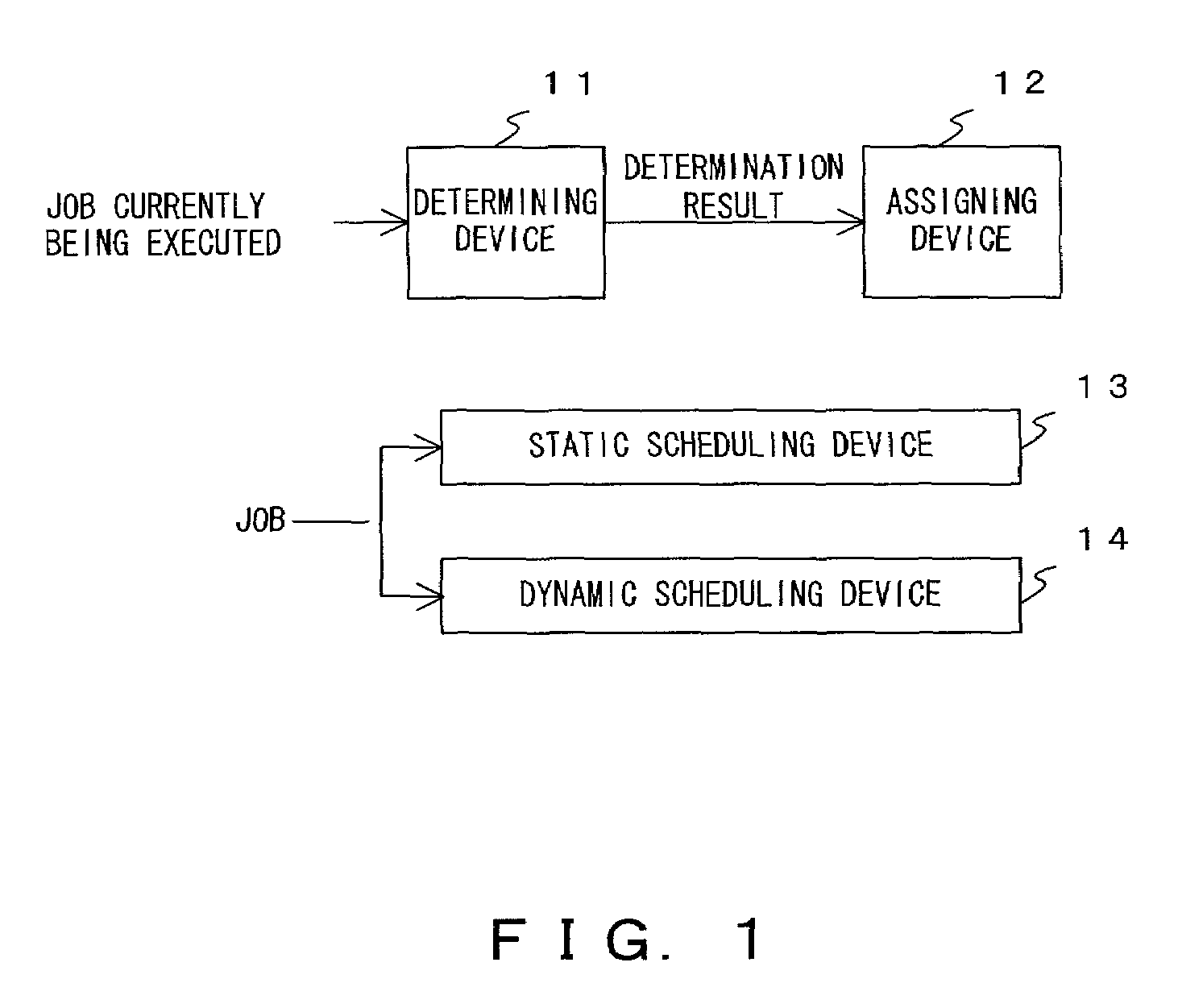
ActiveUS20120159507A1Increase the number ofResource allocationSoftware engineeringStatic dispatchOperating system
An apparatus and method capable of reducing idle resources in a multicore device and improving the use of available resources in the multicore device are provided. The apparatus includes a static scheduling unit configured to generate one or more task groups, and to allocate the task groups to virtual cores by dividing or combining the tasks included in the task groups based on the execution time estimates of the task groups. The apparatus also includes a dynamic scheduling unit configured to map the virtual cores to physical cores.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
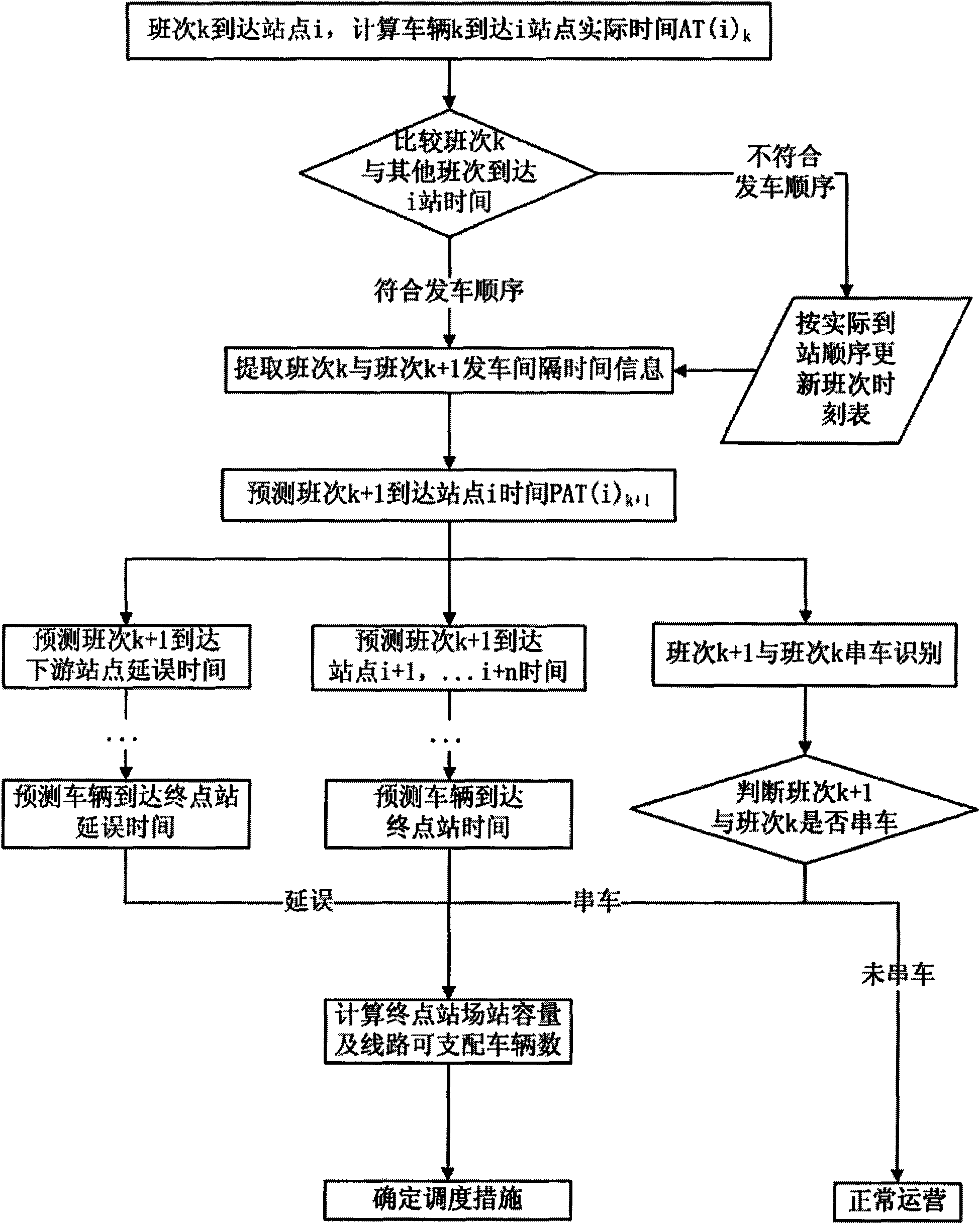
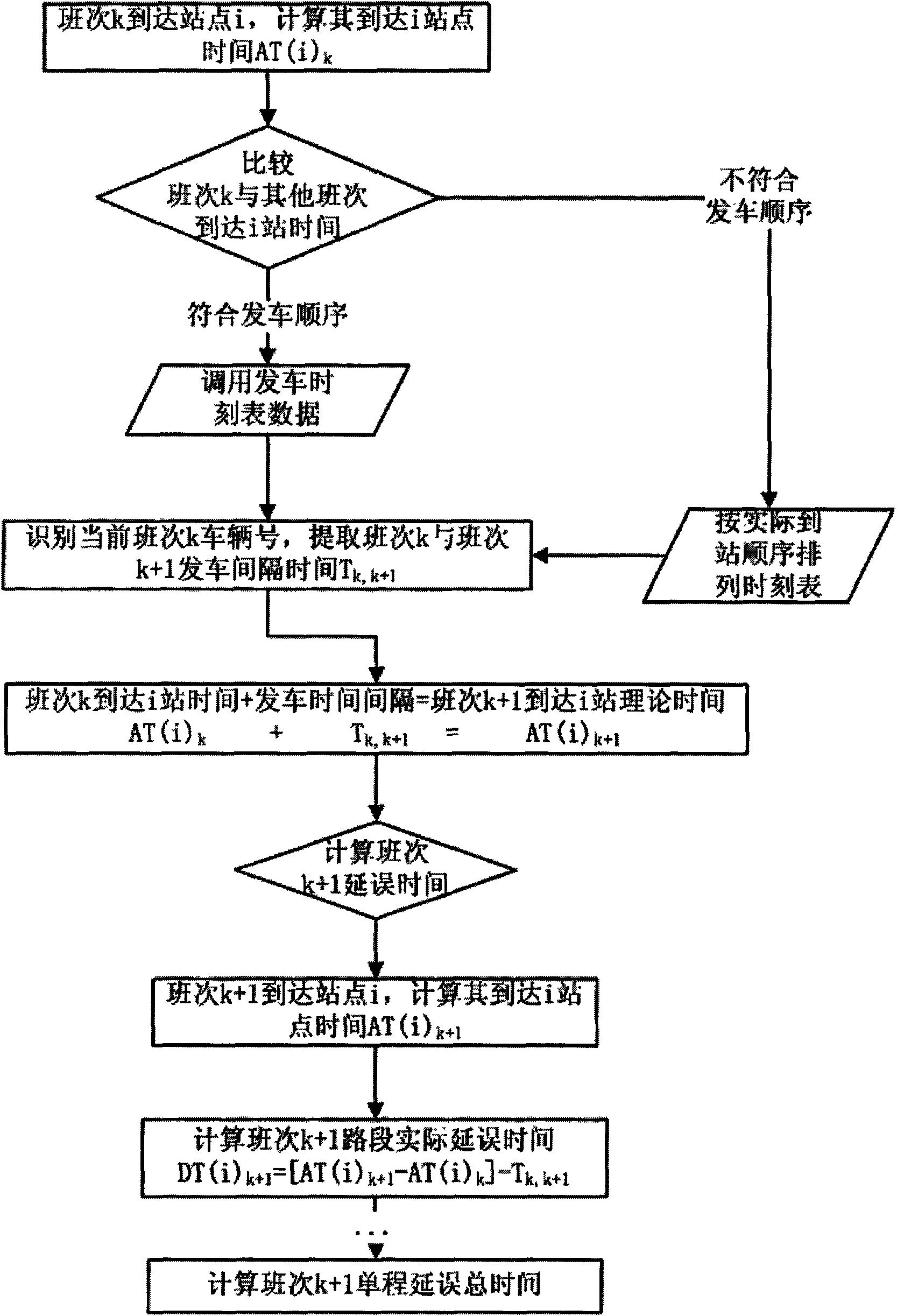
Real-time information processing method in bus dynamic dispatching
InactiveCN101615340AImprove dynamic scheduling efficiencyDetection of traffic movementTime informationReal time information processing
The invention relates to a real-time information processing method in bus dynamic dispatching, which is specially used for dynamic dispatching of bus single or area multi-line of the ground. The real-time information comprises vehicle positioning information and passenger flow information; acquiring equipment comprises a GPS vehicle-mounted terminal and an IC card POS machine terminal; a processing method comprises the following steps: acquiring and transmitting real-time information; processing and preprocessing real-time information; carrying out secondary processing to the acquired data; taking relevant technologies of ITS and the computer of the bus vehicle positioning technology, the bus passenger flow acquisition technology, the network communication technology, WebGIS and the like as support, acquiring real-time information of ground bus line operation, carrying out processing on the real-time information, calculating operating state of vehicle delay time, section passenger flow, load factor and the like, and carrying out vehicle bunching recognition; and using a Kalman filtering model to predict the arrival time and delay time of the bus vehicle, and providing decision basis for dynamic dispatching measures.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Scheduling method of cloud computing open platform
ActiveCN102681889AHigh speedImprove responsivenessResource allocationMulti core computingOpen platform
The invention discloses a scheduling method of a cloud computing open platform, which particularly characterized in that call requests of mass users are monitored through maintaining a central server; business service and data service of a cluster server are dynamically scheduled; and meanwhile, detachable service components are called and a multithread ability of a multi-core processor is scheduled and distributed according to use levels of the users. Through using the method, the defects that the traditional open platform is short of expansibility and flexibility can be effectively corrected, two targets of rapidly constructing and deploying an application and operation environments and dynamically adjusting the application and operation environments are established, the existing equipment is maximally utilized and the service is maximally constructed; and meanwhile, through adopting a multi-core computing manner and a multithread technology, the scheduling speed and the response ability of the system service are improved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
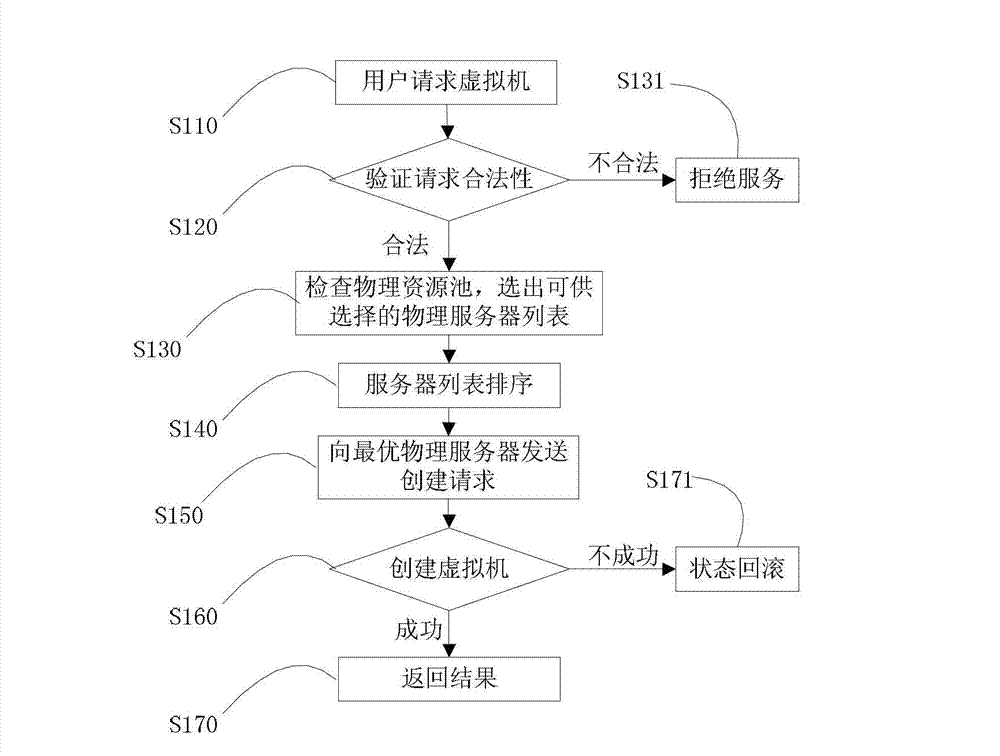
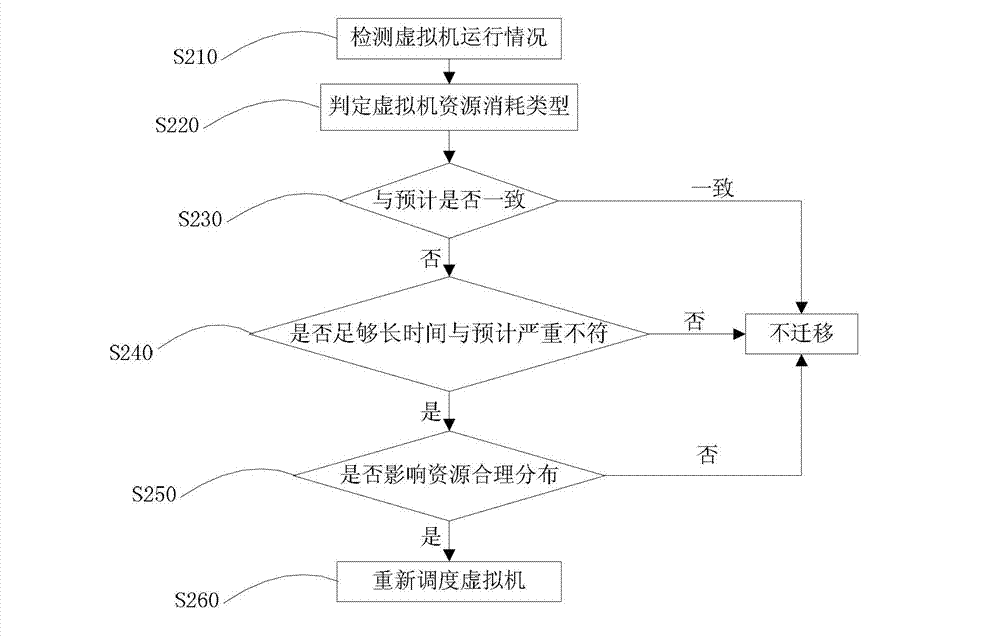
Method and system for dynamic scheduling management of virtualized resources in virtualized desktop system
ActiveCN103164283AOptimize dynamic loadRaise the level of experienceResource allocationSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationVirtualizationResource consumption
The invention aims to disclose a method and a system for dynamic scheduling management of virtualized resources in a virtualized desktop system. Compared with the prior art, the system carries out reasonable assignment on a virtual machine according to the resource consumption type of the virtual machine requested by a user, so that the resource demands of the virtual machine can be matched with the capacity of a host machine, the operating performance of the virtual machine is promoted, and the load balance of cluster resources is optimized. In the operating process of the virtual machine, the operating conditions of the virtual machine are monitored in real time, virtual machines which are not even in assignment is rescheduled appropriately, and dynamic load balance of resources is achieved. An appropriate chance to reschedule the virtual machine is selected, the adjustment of the load can not affect normal operation of other parts of the system, while the resource utilization is optimized, the user experience level of the system is promoted, and the purposes of the method and the system are achieved.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUILIU CLOUD COMPUTING TECH CO LTD
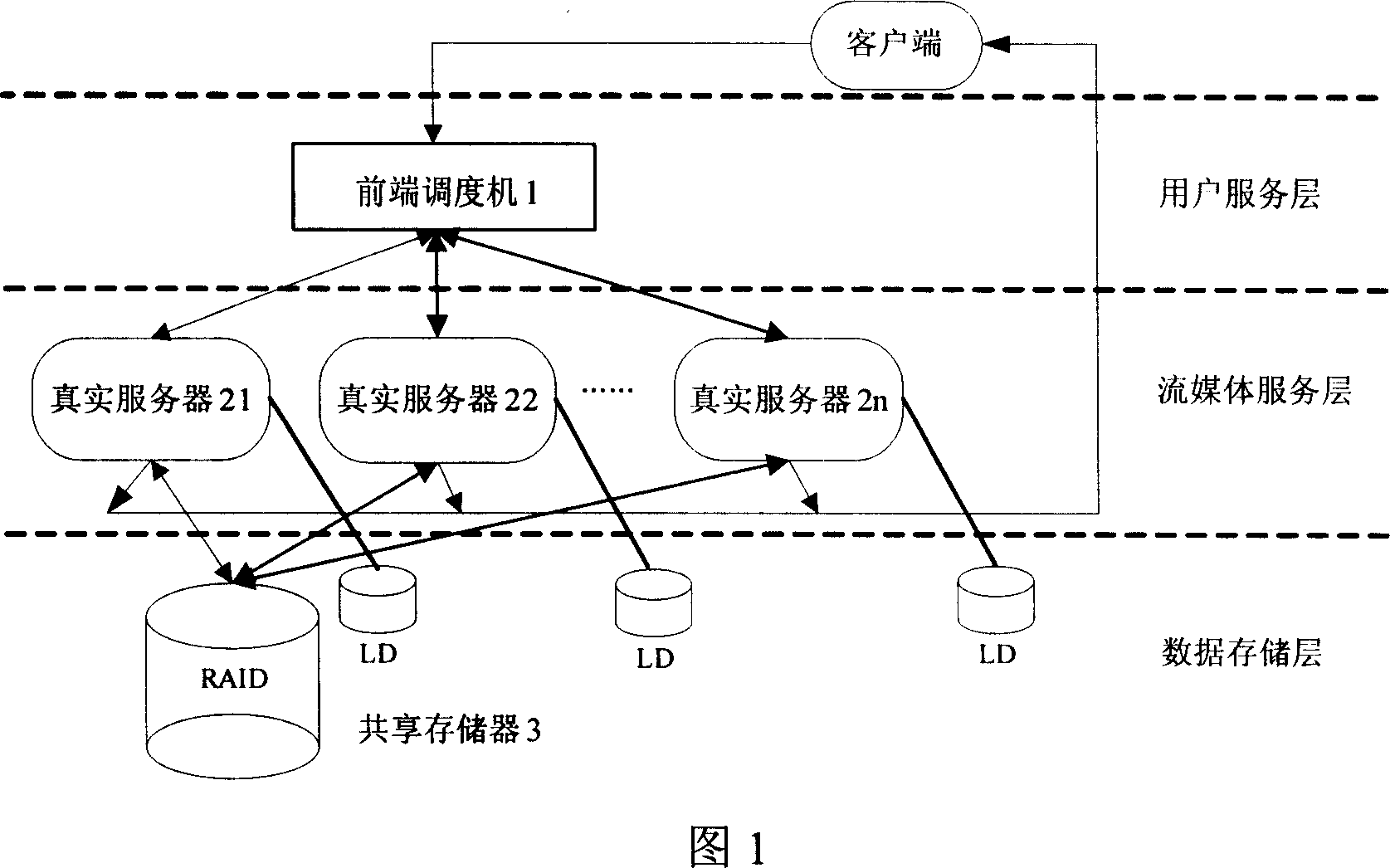
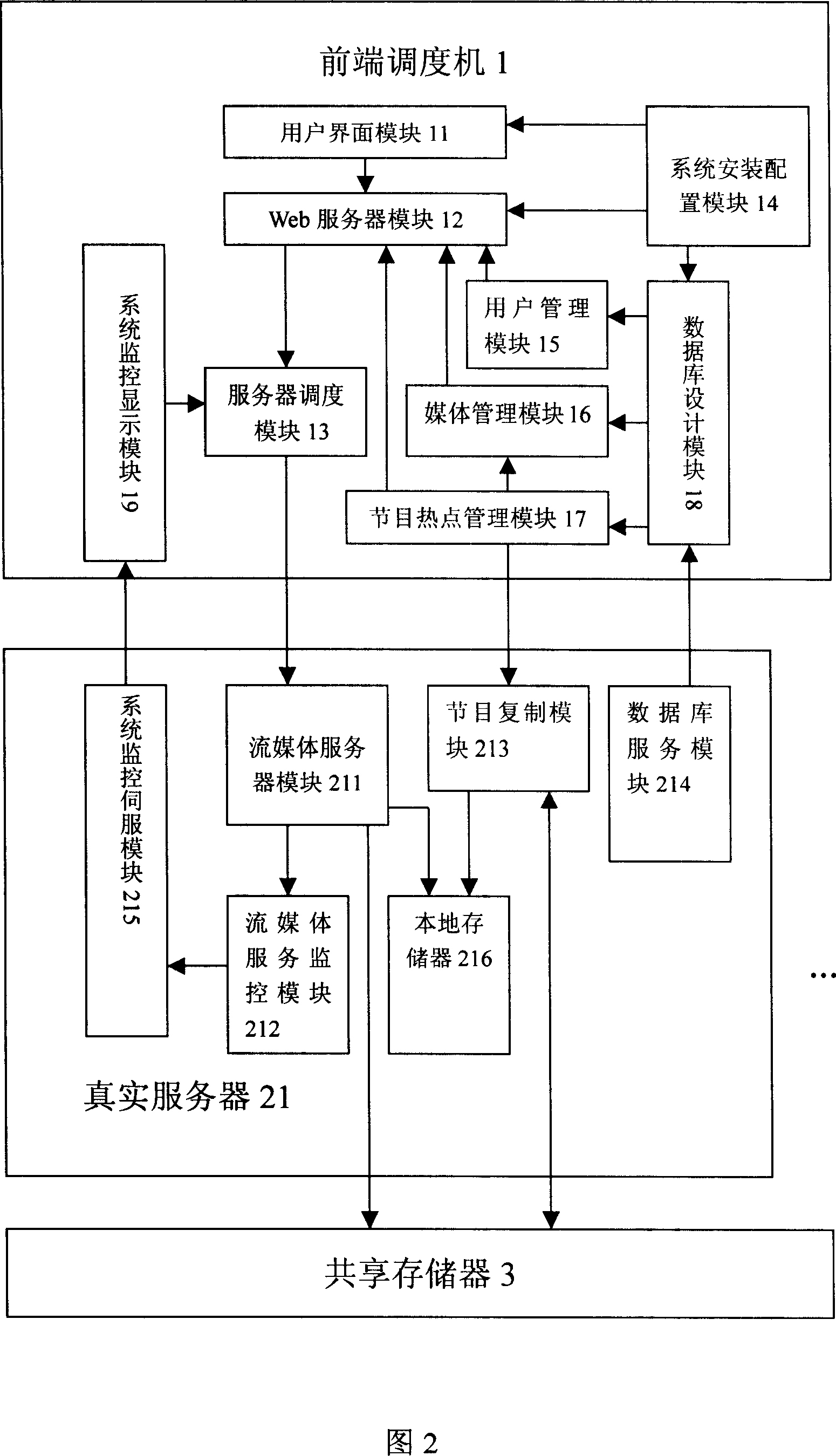
A stream media server system based on cluster balanced load
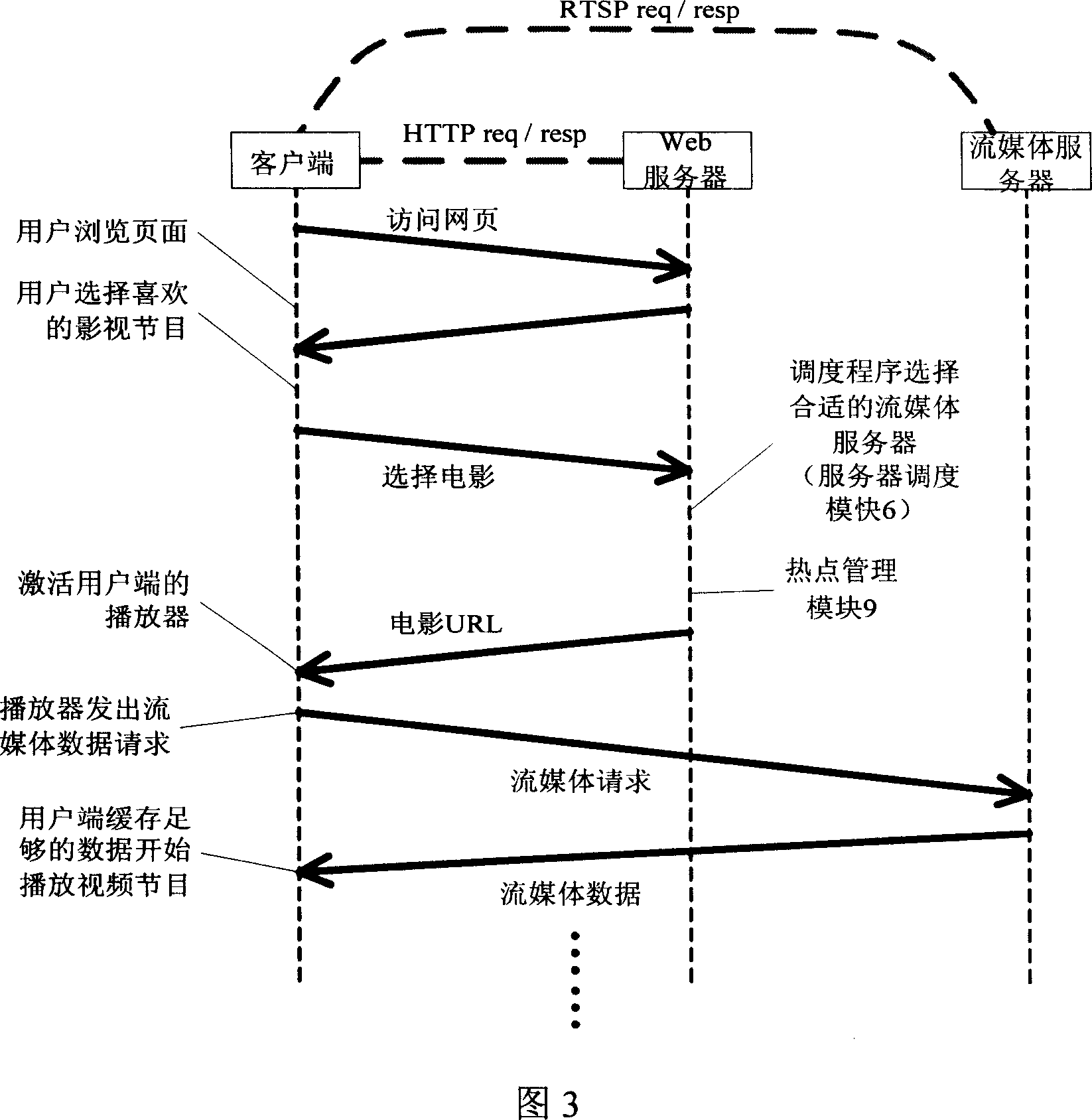
This invention relates to flow media servo system based on group balance load, which comprises front transfer machine, n real servo and common memory, wherein, the transfer machine provides user visit interacting interface and system manager entrance and selects minimum load for user according to current each real servo status; real servo receives front transfer visual frequency point require to provide media service for user and for utility rate onto local database; in system spare, according to hot video information copying information from common memory into real servo local memory.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
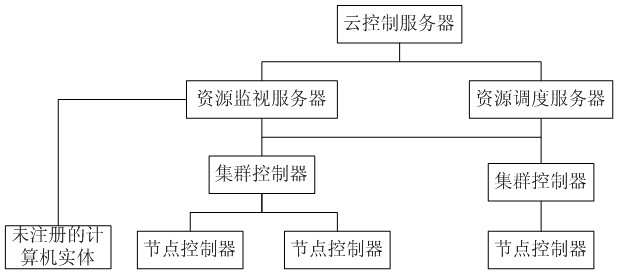
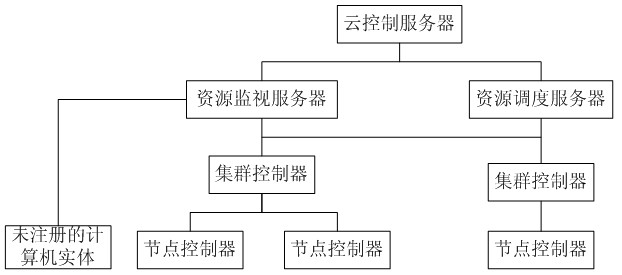
Method and system for dynamic scheduling of virtual resources in cloud computing network
InactiveCN102170474AEfficient use ofLoad balancingData switching networksDistributed computingDynamic priority scheduling
The invention provides a method and system for dynamic scheduling of virtual resources in a cloud computing network, the system comprises a cloud control server, a resource monitoring server, a resource scheduling server, at least one cluster controller and at least one node controller, and the method comprises: the resource monitoring server collects running information and sends the running information to the cloud control server; the node controller in which a virtual machine is positioned sends a real-time migration request to the cloud control server when achieving virtual resource bottleneck; the cloud control server sends the running information to the resource scheduling server; and the resource scheduling server searches the node controller with sufficient scheduling resources in the running information for performing real-time migration. The dynamic scheduling of the virtual resources is realized by adopting the real-time migration method, load balancing is dynamically realized, and the virtual resources in a cloud are utilized with high efficiency through the high-efficient load balancing.
Owner:GCI SCI & TECH
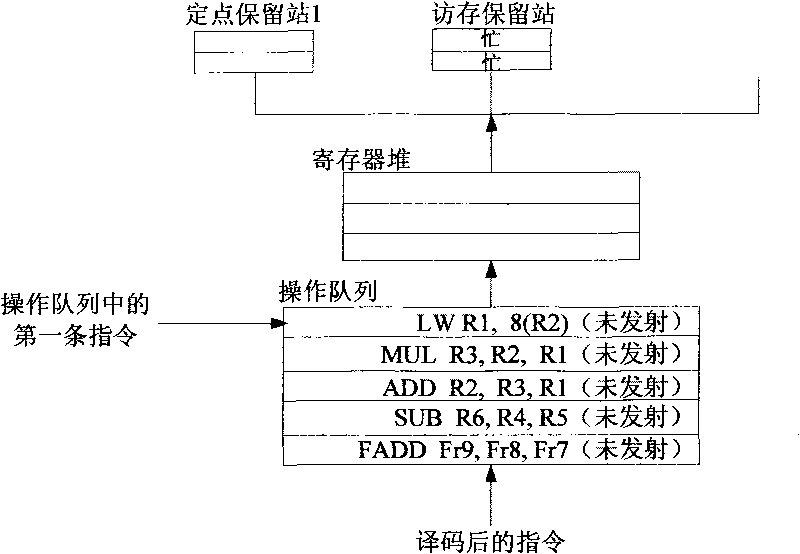
Device and method for instruction scheduling
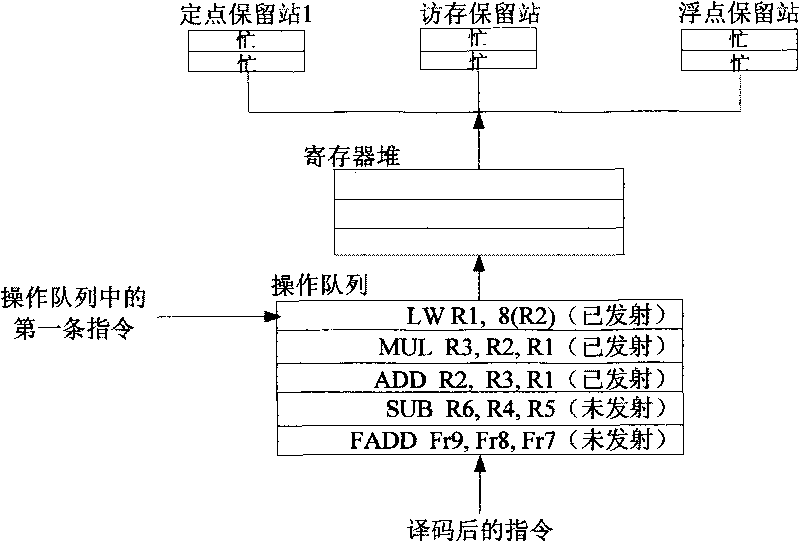
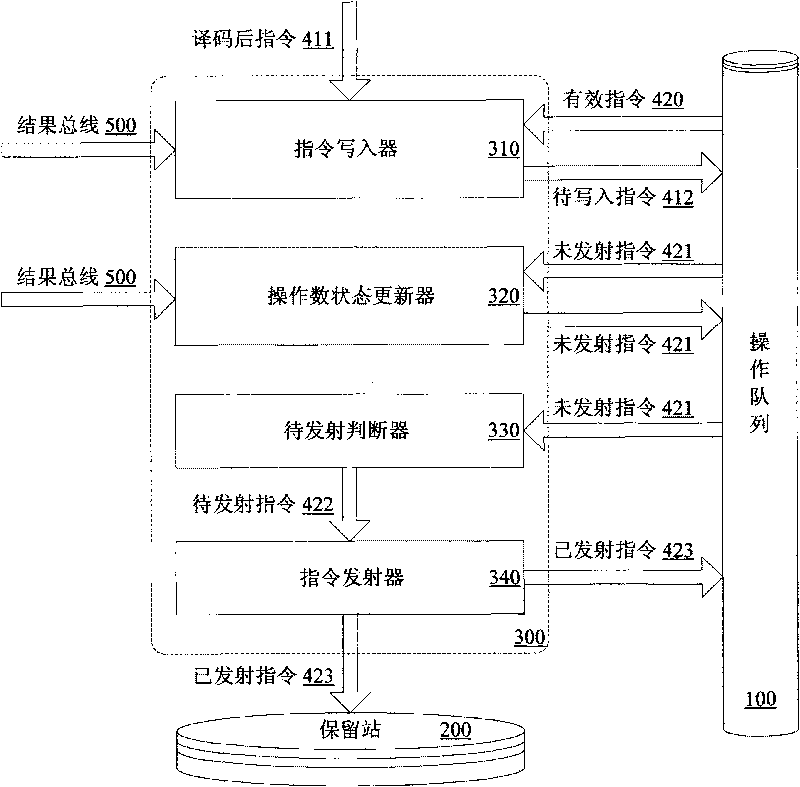
ActiveCN101710272AImprove efficiencyImprove performanceConcurrent instruction executionReservation stationScheduling instructions
The invention provides a device and a method for dynamically scheduling instructions transmitted from an operation queue to a reservation station in a microprocessor. The method comprises the following: a step of writing instructions, which is to set and then write the operand states of the decoded instructions on the basis of data correlation between the decoded instructions to be written into the operation queue and effective instructions in the operation queue, as well as instruction execution results which have been written back and are being written; a step of updating the operand states, which is to update the operand state of each instruction not transmitted on the basis of the data correlation between each instruction not transmitted and the instructions being written back of instruction execution results; a step of judging to-be-transmitted instructions, which is to judge whether the to-be-transmitted instructions with all operands ready exist on the basis of the operand state of each instruction not transmitted; and a step of transmitting instructions, which is to transmit the judged to-be-transmitted instructions to the reservation station when the reservation station has vacancies. Pipeline efficiency can be effectively improved by transmitting the instructions with the operands ready to the reservation station on the basis of the data correlation between the instructions.
Owner:LOONGSON TECH CORP
System and method for slaves in a master-slave wireless network to dynamically develop affinity to a time slot
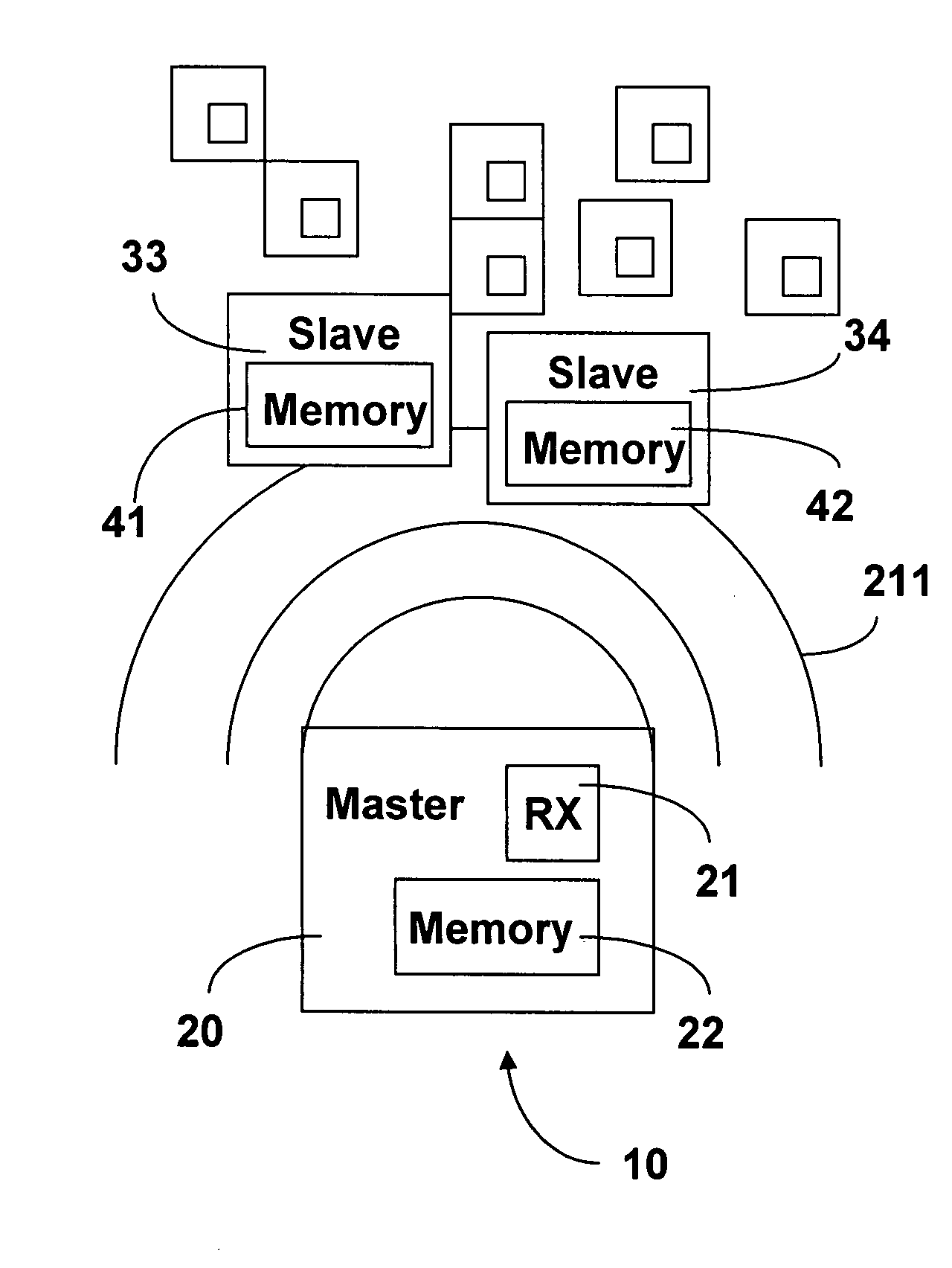
A method to dynamically schedule communication between a master and slaves in a variable slave population in a master-slave wireless network. The method includes receiving a first interrogation phase command signal from the master, transmitting a response signal to the master responsive to the first interrogation phase command signal after a current time interval, the current time interval based on a current time slot selection, receiving an acknowledgment list from the master responsive to the transmitted response signal, determining whether the current time slot selection matches a master-filled time slot based on the acknowledgement list, and modifying an affinity value based on the determination.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Decoupling parallel scheduling method for rely tasks in cloud computing
InactiveCN102591712AStrong parallelismLoad balancingMultiprogramming arrangementsTransmissionParallel computingPerformance index
The invention belongs to the field of cloud computing application, and relates to method for task rely relation description, decoupling, parallel scheduling and the like in cloud service. Rely task relations are provided, and a decoupling parallel scheduling method of rely tasks are constructed. The method comprises first decoupling the task rely relations with incoming degree being zero to construct a set of ready tasks and dynamically describing tasks capable of being scheduled parallelly at a moment; then scheduling the set of the ready tasks in distribution type and multi-target mode according to real time resource access so as to effectively improve schedule parallelism; and during the distribution of the tasks, further considering task execution and expenditure of communication (E / C) between the tasks to determine whether task copy is used to replace rely data transmission so as to reduce the expenditure of communication. The whole scheduling method can schedule a plurality of tasks in the set of the ready tasks in dynamic parallel mode, well considers performance indexes including real time performance, parallelism, expenditure of communication, loading balance performance and the like, and effectively improves integral performance of the system through the dynamic scheduling strategy.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Meetings and Events Coordinating System and Method
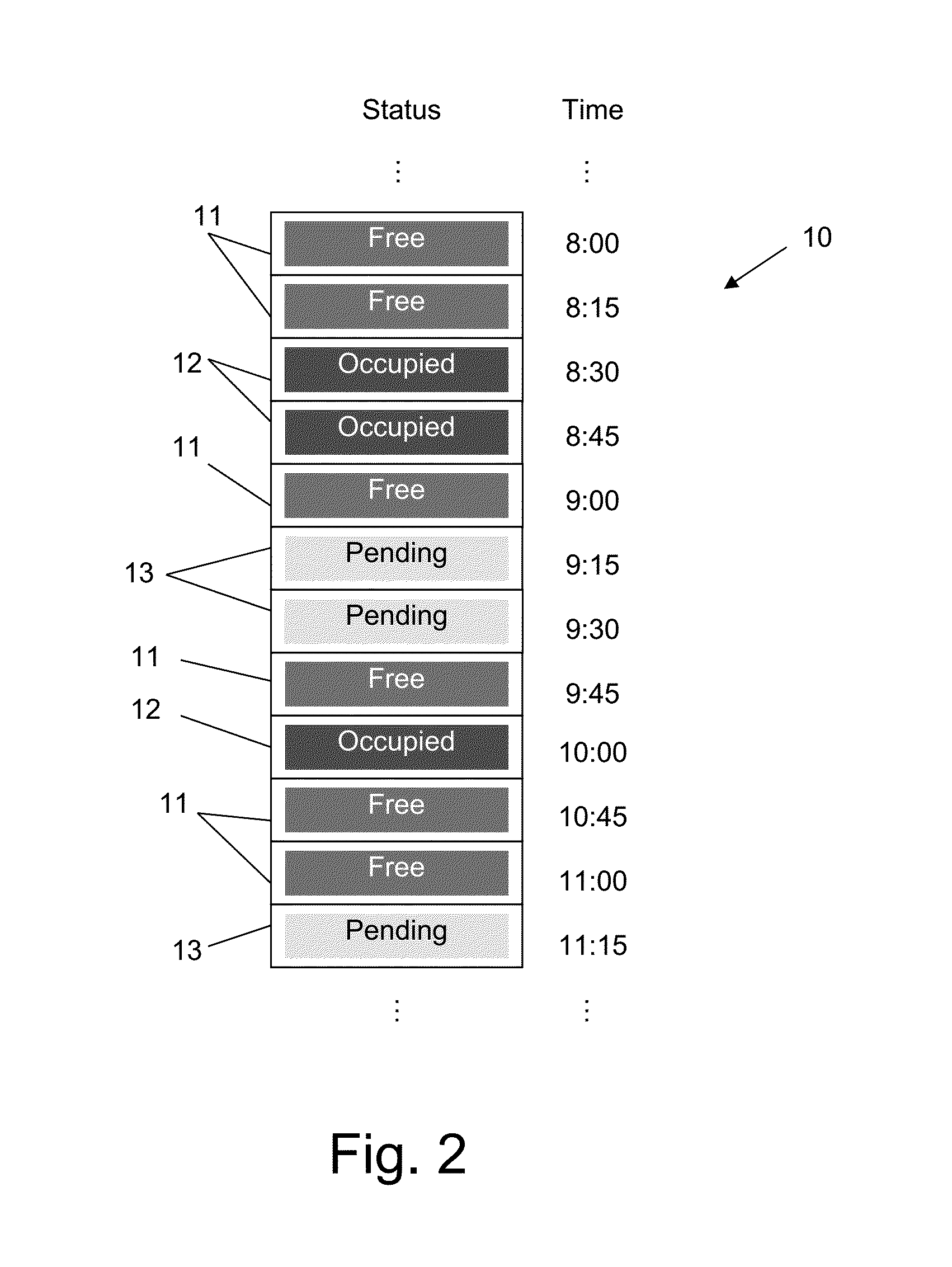
Providing dynamic scheduling services without sharing calendar content, involving retrieving real time availability data and terms applied to calendar time cubes for an invitation to an event with one or more invited users, simultaneously synchronizing between calendars of the invited users in a meeting and event coordinating server to find a combination of common available matching time cubes while considering the terms including arrival time calculations (the common available matching time cubes defined as either “free”, “occupied”, “pending”, ane having a lower level of importance than the event currently created), setting the state of the matched time cubes as occupied at the calendar of each invited user; and rescheduling an event that was previously associated with the sequence of “occupied”, “pending” states with the lower level of importance, the already existing events being automatically subject to changes constantly and immediately.
Owner:PRIVATE SEC
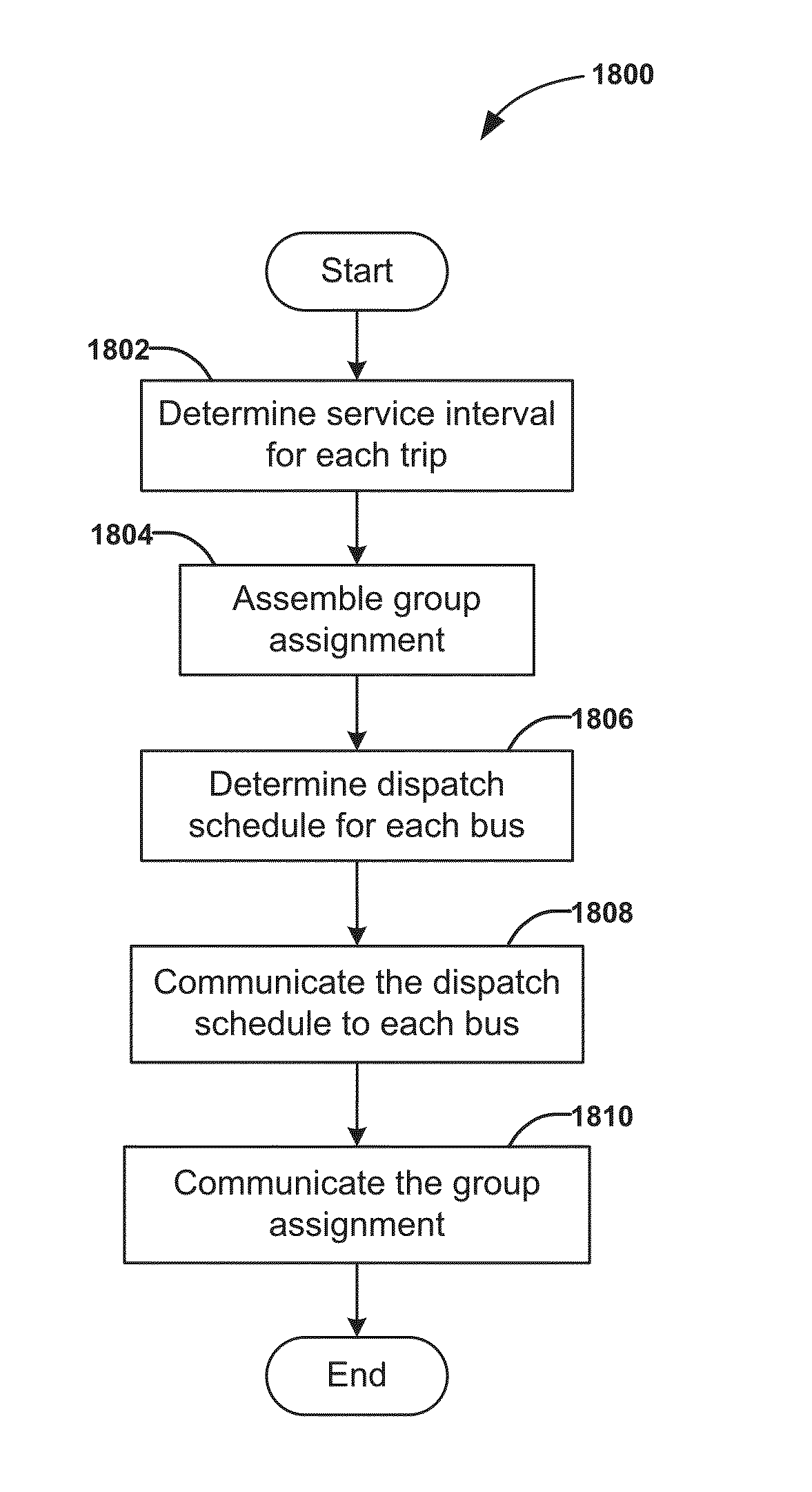
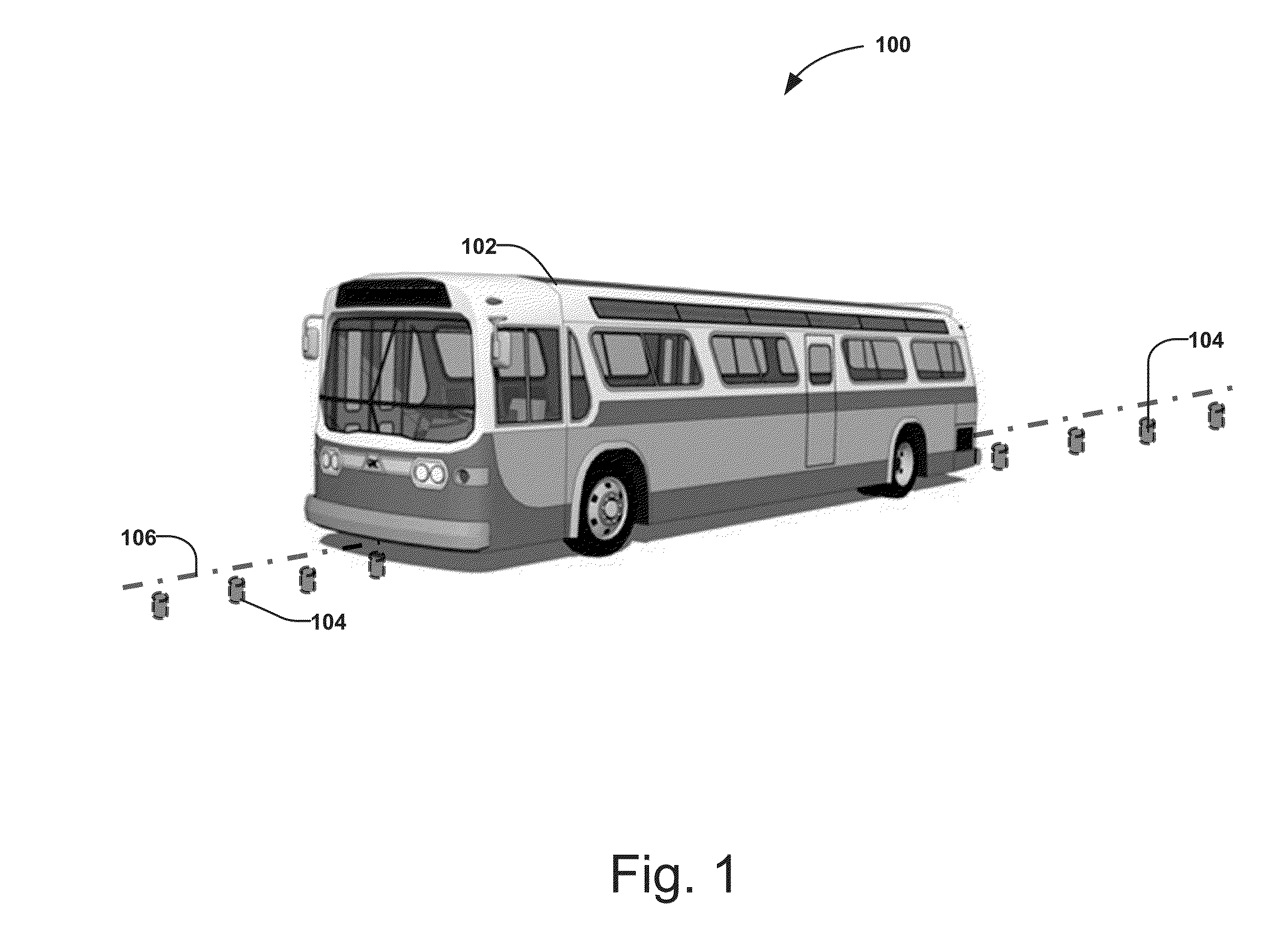
Dynamic dispatching and schedule management methods for an intelligent transit system with electronic guided buses
InactiveUS20150294430A1Increasing driver workloadIncreasing transit operational costDigital data processing detailsExternal condition input parametersGuided busTransit system
A method for dispatching buses in groups for a bus transit system comprising determining a service interval for each trip of the bus transit system, assembling group assignments based on the service interval for each trip, determining a dispatch schedule for each bus based on the service interval and the group assignment, communicating the dispatch schedule to each bus, and communicating group assignment information to each of a plurality of the buses in a group. The group assignment assigns a plurality of the buses into a group on a segment of the trip shared by the plurality of buses such that multiple buses for different trips can dock at a station at the same time like a train to facilitate transferring passengers.
Owner:TOMORROWS TRANSPORTATION TODAY
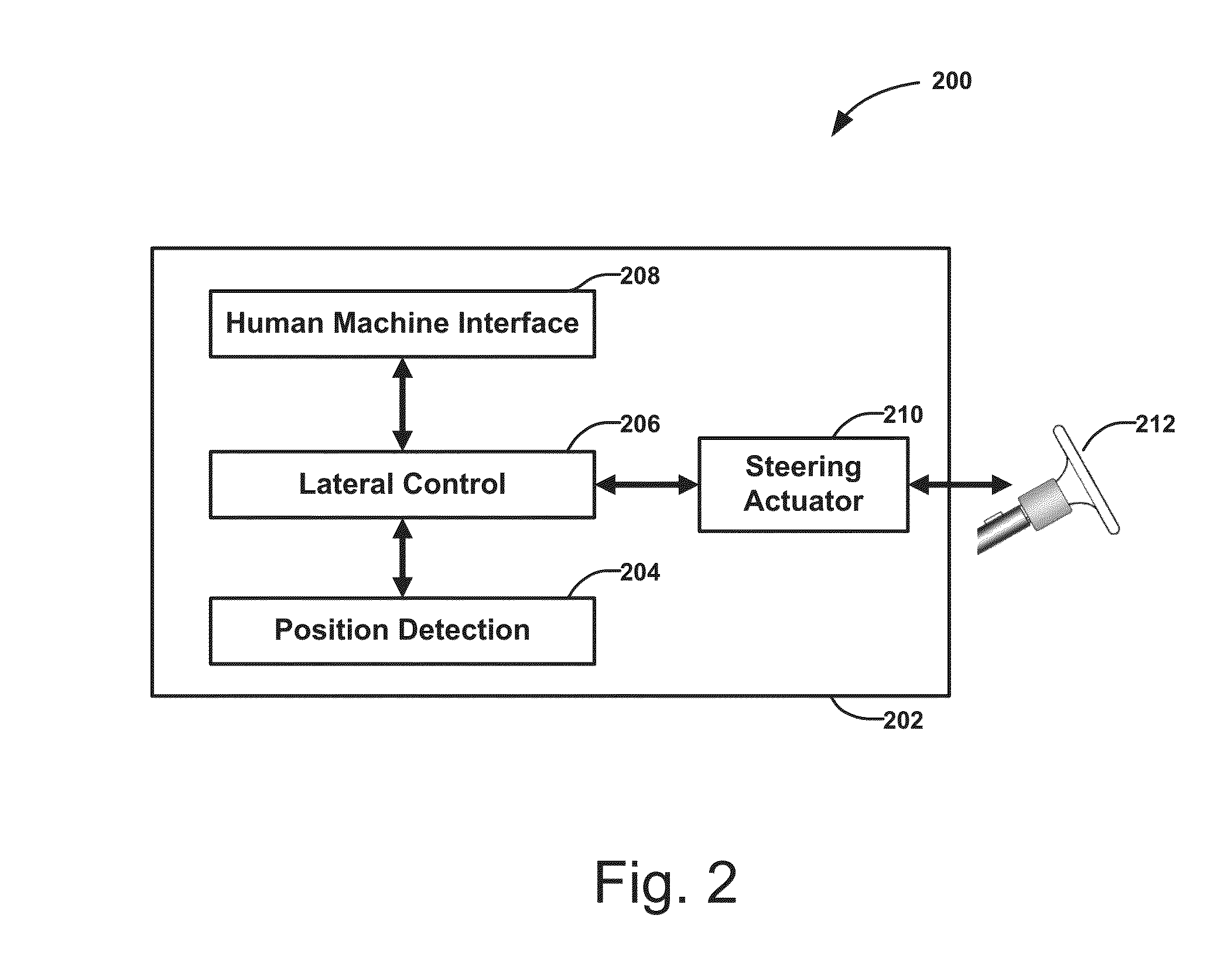
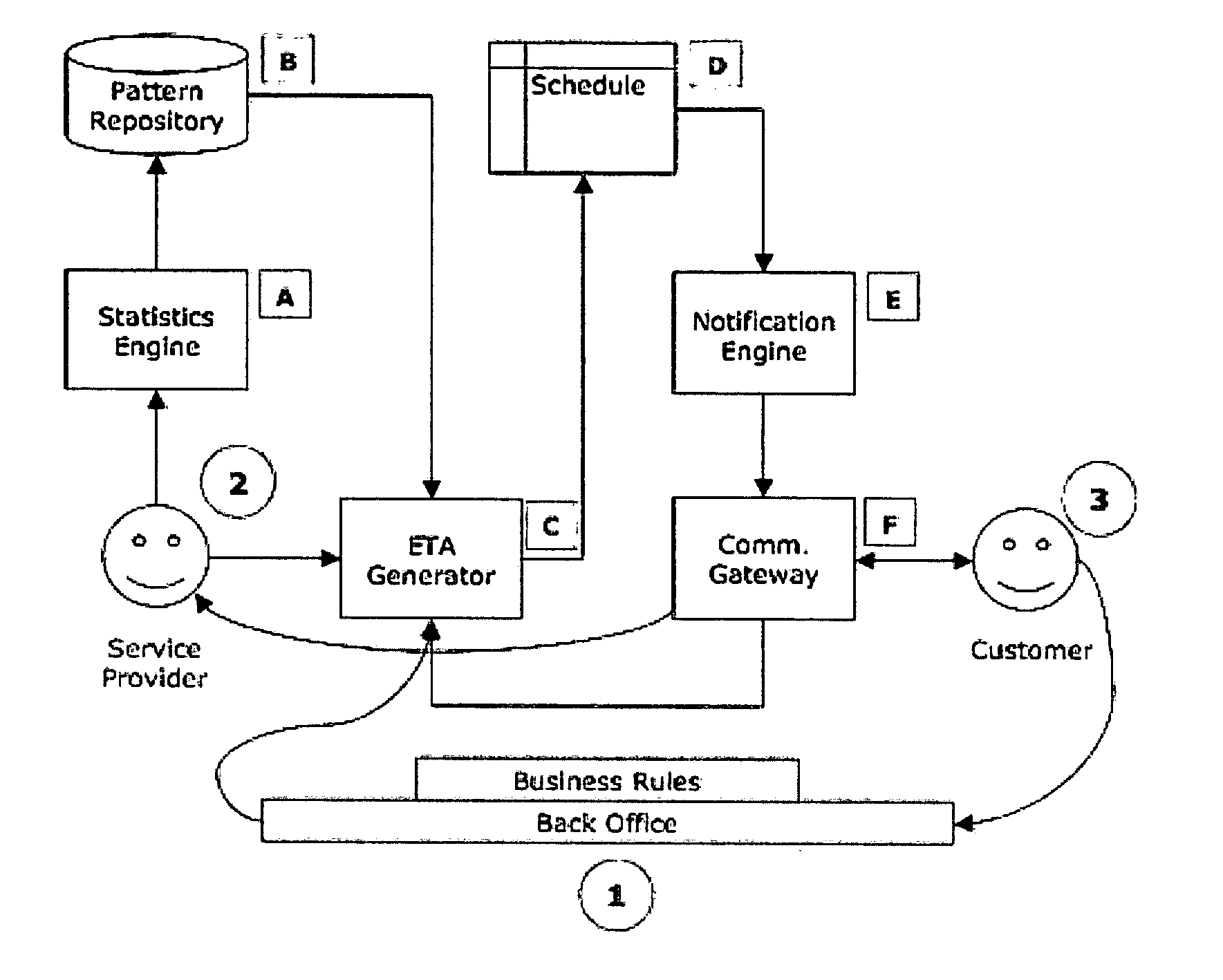
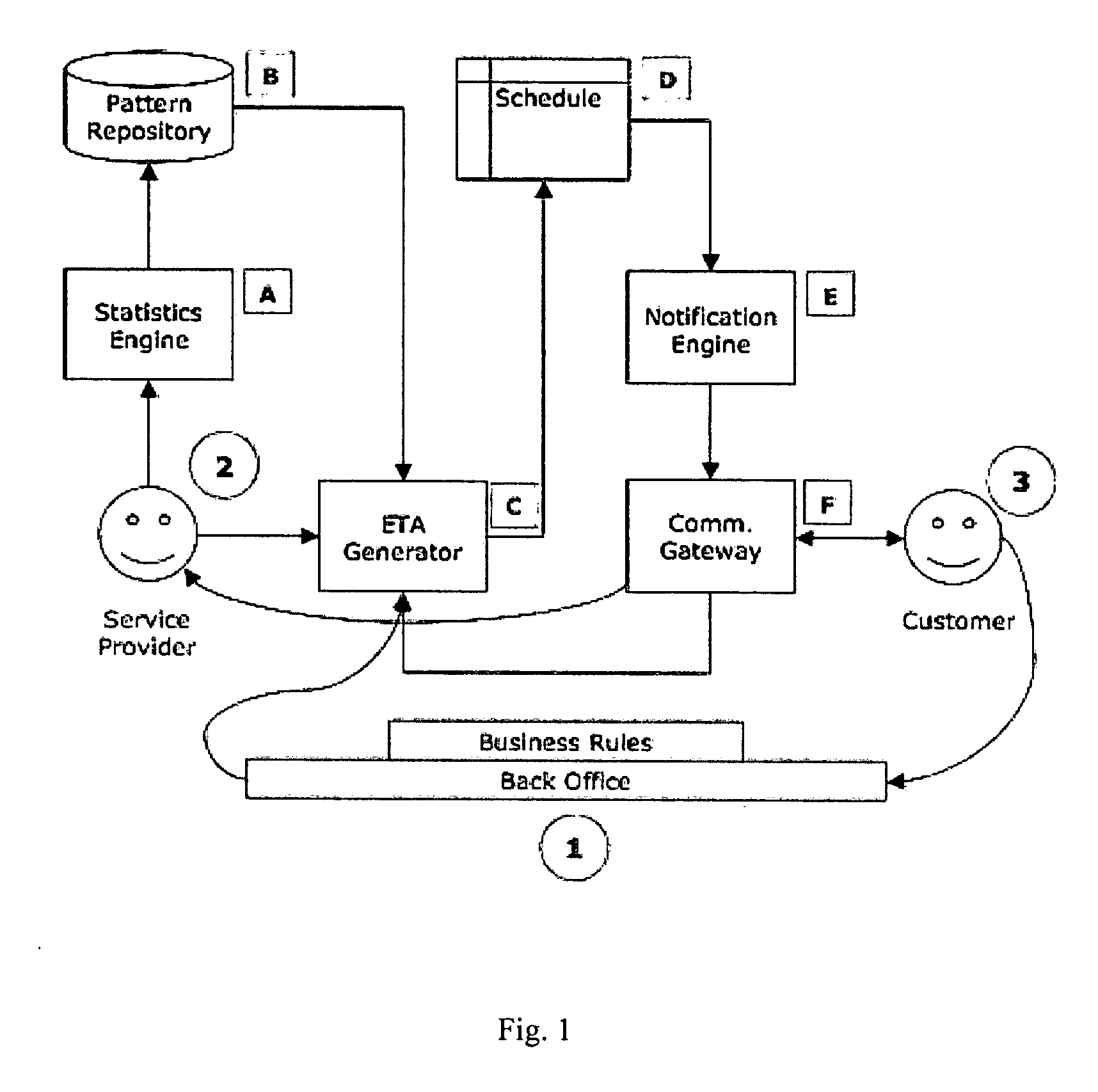
Dynamic schedule mediation
ActiveUS20060111957A1Digital computer detailsSpecial data processing applicationsAppointment timeStatistical analysis
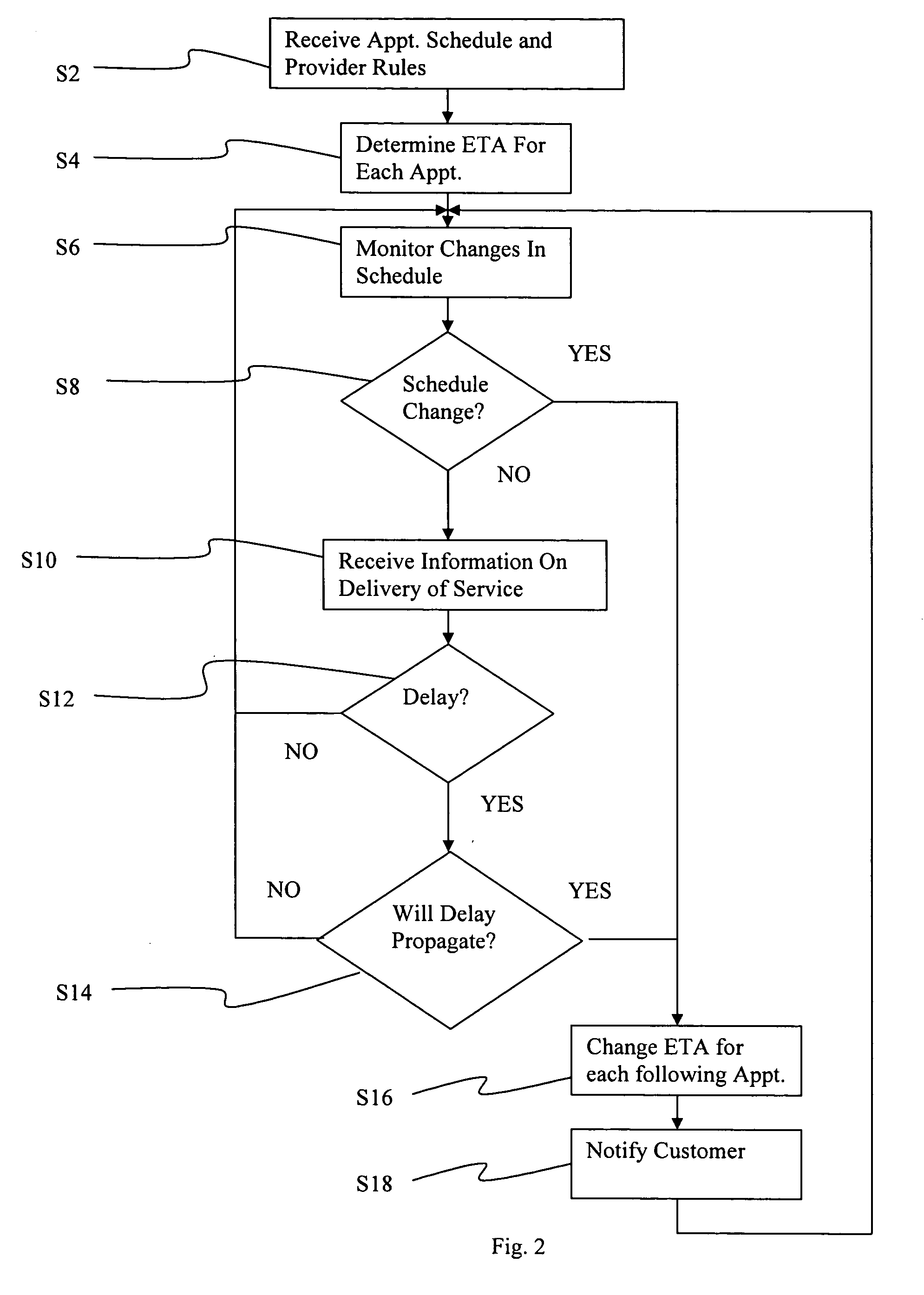
An apparatus and method provides dynamic schedule mediation by scheduling and monitoring appointments between a service provider and customers. The apparatus and method uses a statistical analysis to determine a best appointment time based on at least one of: historical performance patterns, the type of service requested during the appointment, geographic location of the customer or the service provider, time of day, time of year, weather, skills of the service provider, and automobile traffic conditions. The system and method continuously monitors changes to the appointment initiated by the customer or the service provider and notifies the other. Reminders are also sent to the customer and confirmation prompts may also be sent to the customer. The apparatus and method also provides the ability to select service providers based on their historical performance or other factors. The statistical information of a service provider may also be used to evaluate the rules of the service provider and to evaluate individual field service personnel of the service provider.
Owner:TOA TECH
Managing hierarchical authority to access files in a shared database
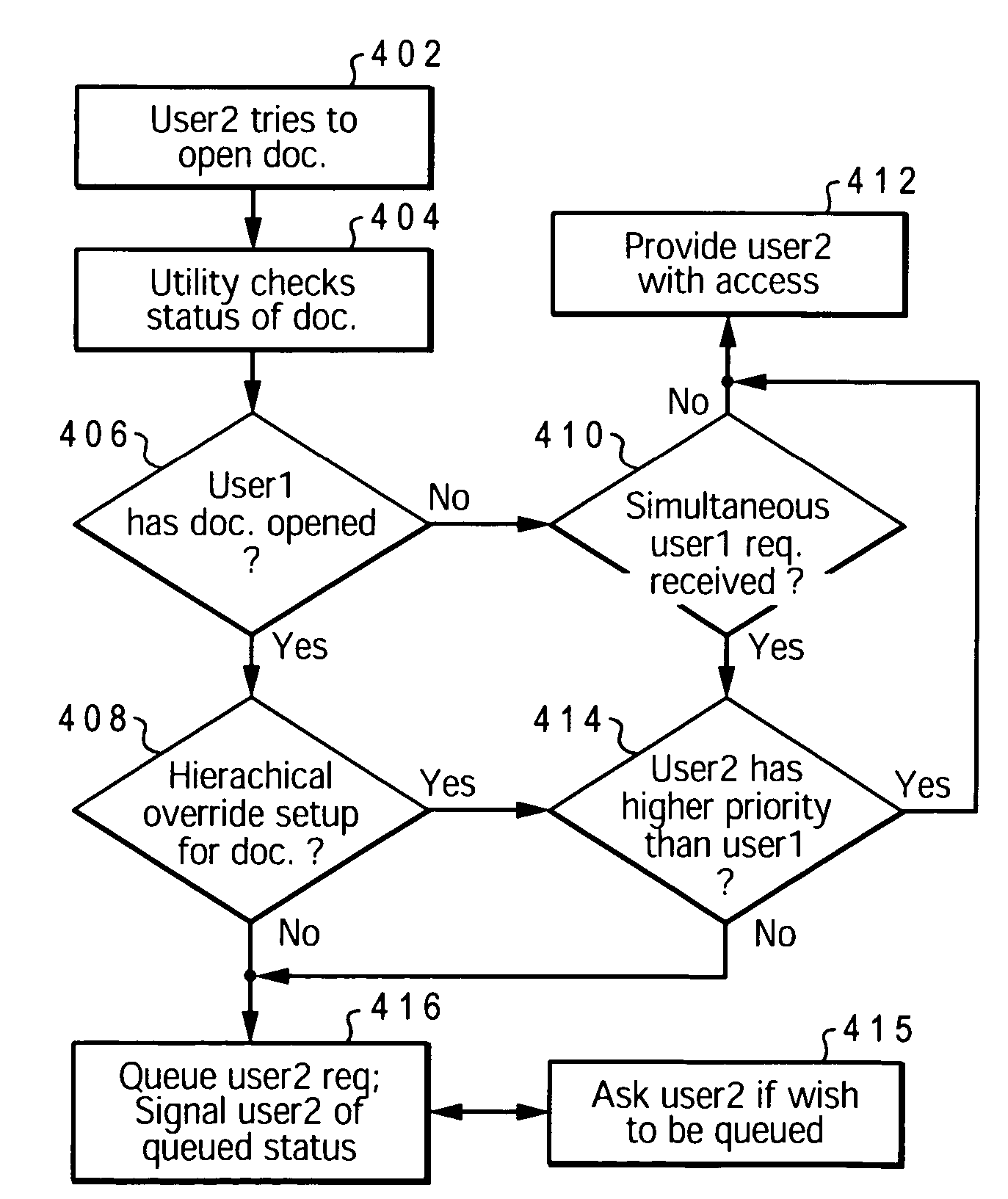
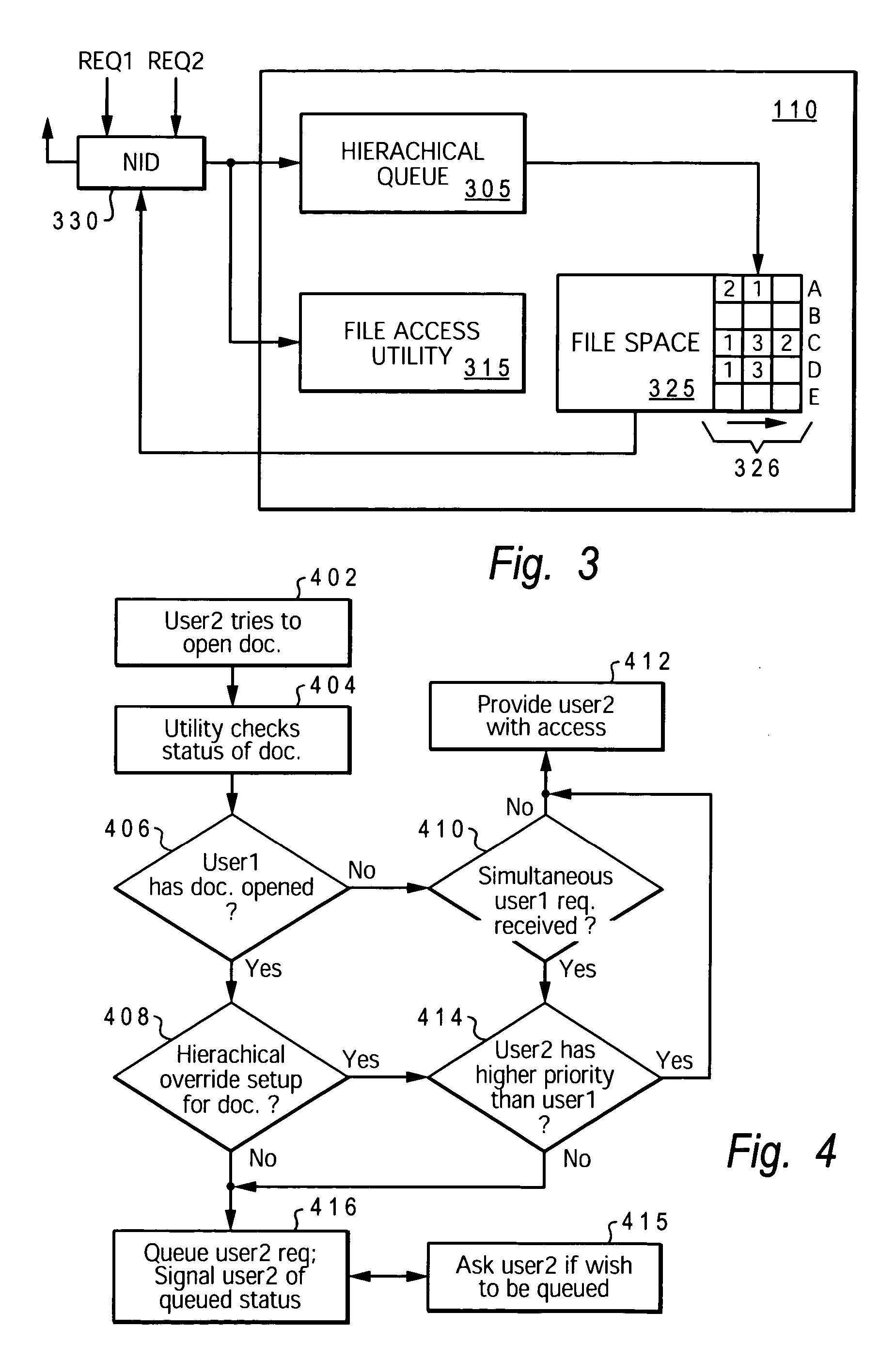
InactiveUS20060155705A1Timely controlSpecial data processing applicationsFile systemsNetwork dataUser identifier
A method, system, and program product that enable dynamic scheduling / arranging of access by multiple users to a single electronic file. A network-database access management utility (NAMU) is provided, which manages / schedules network-level access to the electronic file. NAMU includes an access-request queue that schedules / arranges the user identifier (IDs) for each of multiple users that have requested access to the file while the file was checked out to a previous user. When the first user completes his access to the file and closes the file, an alert is generated for the next user in queue. This alert informs the next user that the first user has closed the file and that he / she may now access the electronic file.
Owner:IBM CORP
Dynamic scheduling method for customized buses and car pooling based on passenger appointments
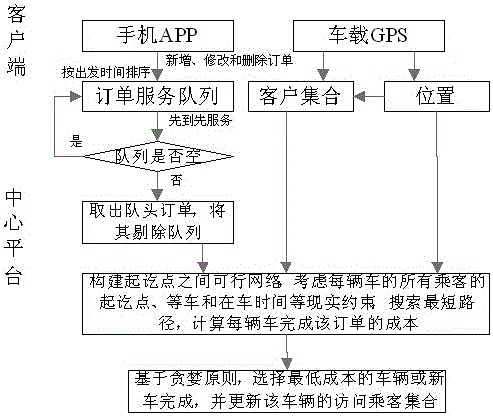
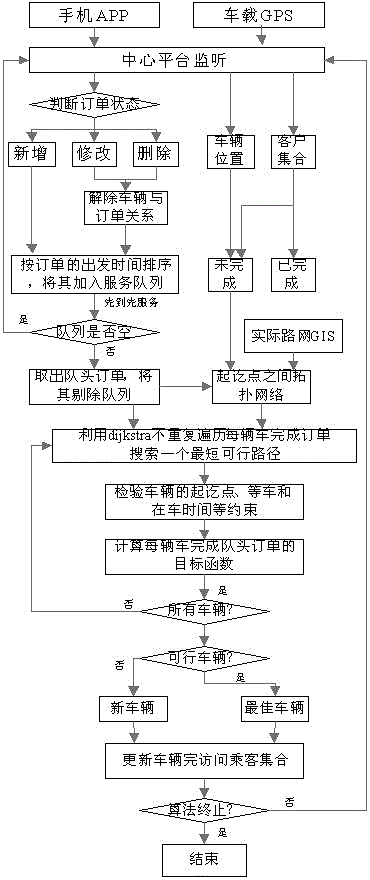
The invention provides a dynamic scheduling method for customized buses and car pooling based on passenger appointments. Adding modifying and deleting orders are completed on a cell phone App, and an order service queue is established on a central platform for orders of all clients based on departure time. Based on the strategy of first come first serve, each order on the front of a queue is processed gradually. A possible path between starting points is calculated with shortest distance algorithm and constraint examination object functions by taking the position information of onboard GPS terminals and all order messages assigned to a customized bus before into consideration. The cost for each customized bus to complete the order is calculated, and the bus with the lowest cost is chosen to complete the order based on the greedy principle. The accessing passenger set of the customized bus is updated. The process is repeated to assign all passenger appointment to buses. Reliable technical support is provided for dynamic scheduling customized buses and car pooling based on passenger appointments.
Owner:重庆南大苏富特智能科技有限公司
Self-adapting selection dynamic production scheduling control system accomplished through computer
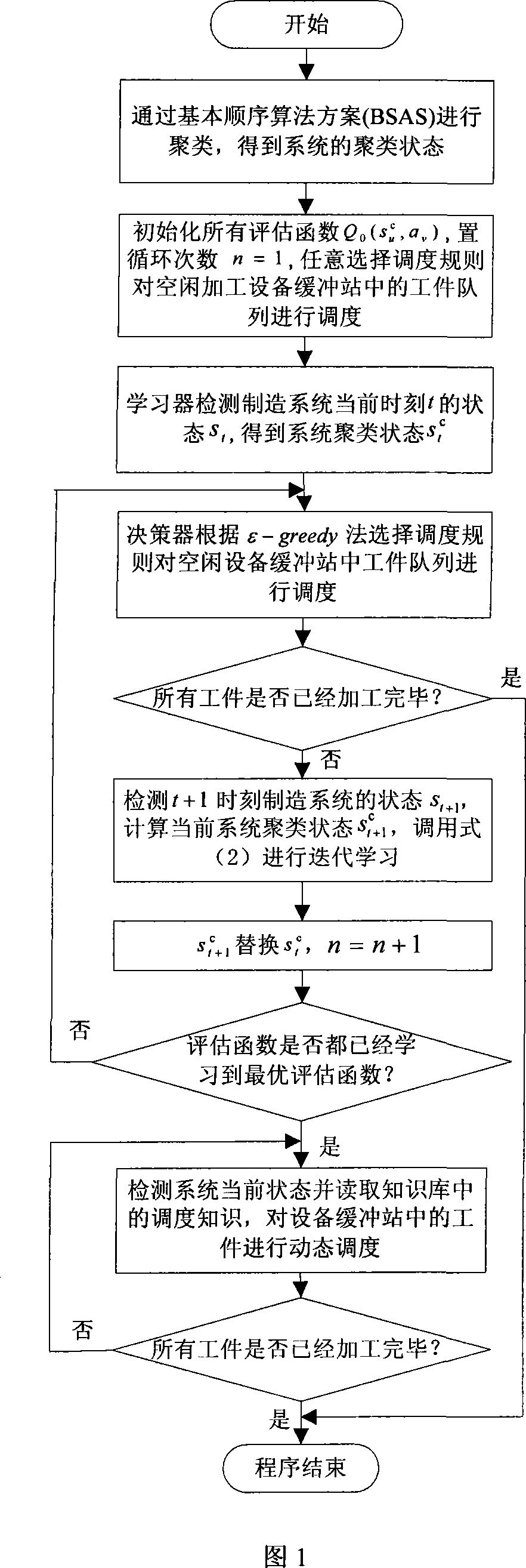
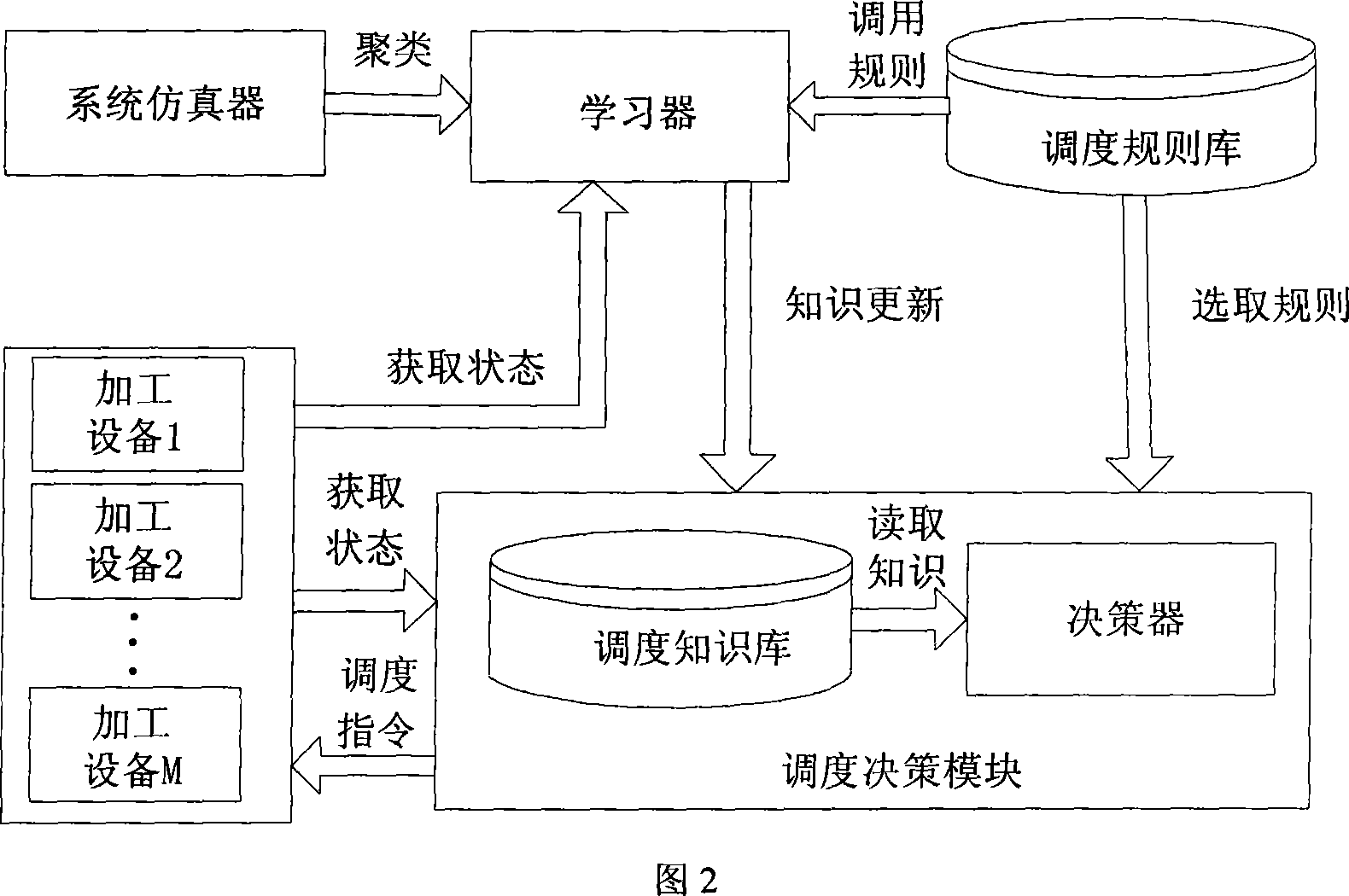
InactiveCN101216710AReduce delaysReduce average time overdueTotal factory controlProgramme total factory controlLearning machineProduction schedule
A self-adaptive selection dynamic production scheduling control system, which is realized via a computer, is characterized in that: the system comprises a system emulator, a learning machine, a decision-making machine, a scheduling rules base, a scheduling knowledge base, a carrier, processing equipments and a buffer station thereof; the buffer station is provided with an optical grating, a sensor and a detection equipment; when a working piece reaches the buffer station and is processed, the learning machine detects the current system status for learning, so as to acquire dynamic scheduling knowledge about the system and update the knowledge in the scheduling knowledge base; when one processing equipment needs to be scheduled, the decision-making machine reads corresponding scheduling knowledge in the scheduling knowledge base according to the detected system status, acquires new scheduling knowledge through continuous interactive learning with the processing system, dynamically selects the scheduling rules based on the status of the processing equipments and the working piece in the system, and chooses the optimized scheduling rules to schedule the processing equipments. The invention can adapt to instable time-varying workshop dynamic production environments, obtain a better working-piece arrangement than prior rule-based scheduling technology, effectively reduce the process waiting time, and improve the fill rate of product delivery time.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Method and apparatus for cooperative multithreading
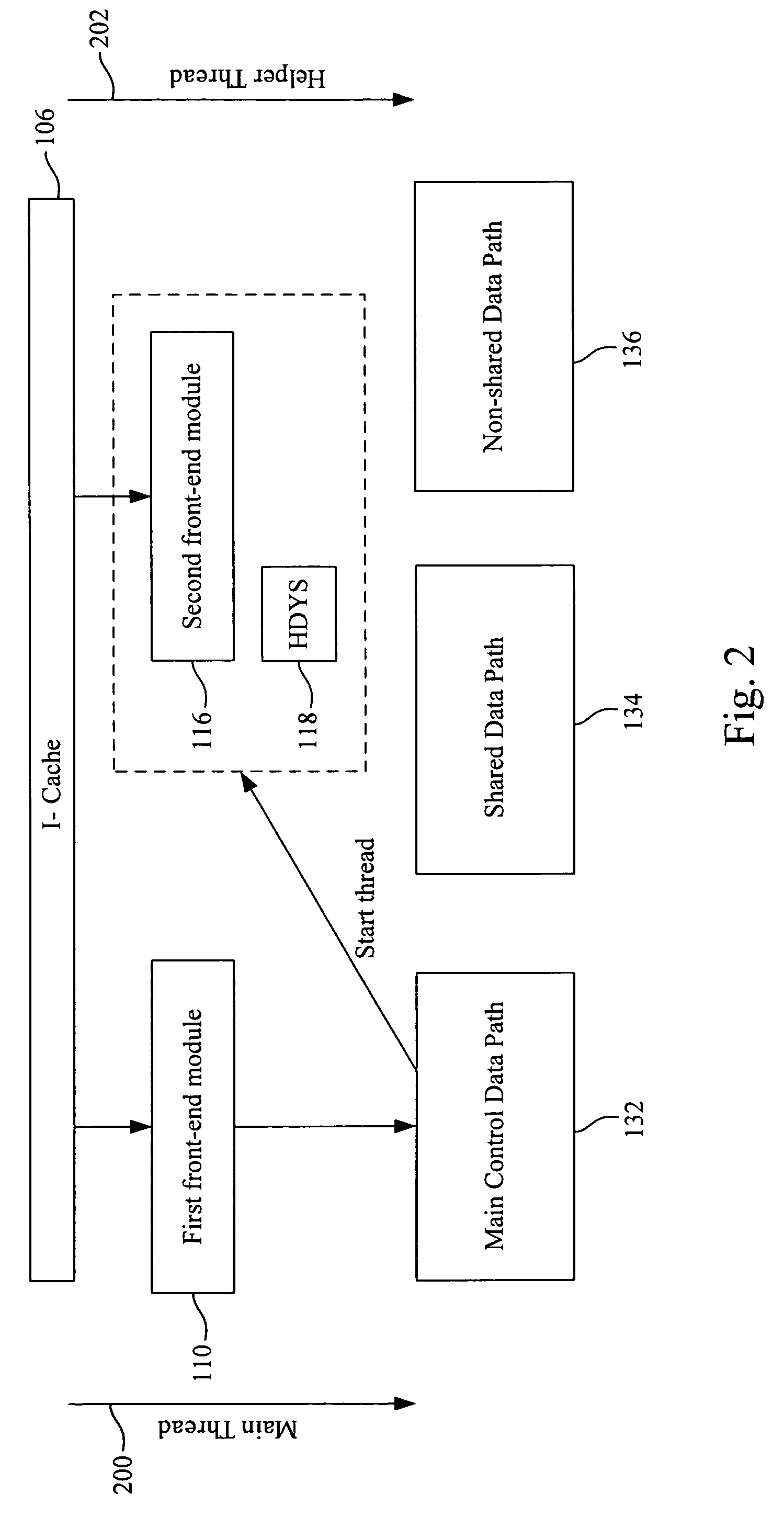
InactiveUS20080046689A1Register arrangementsGeneral purpose stored program computerDatapathSpeculative multithreading
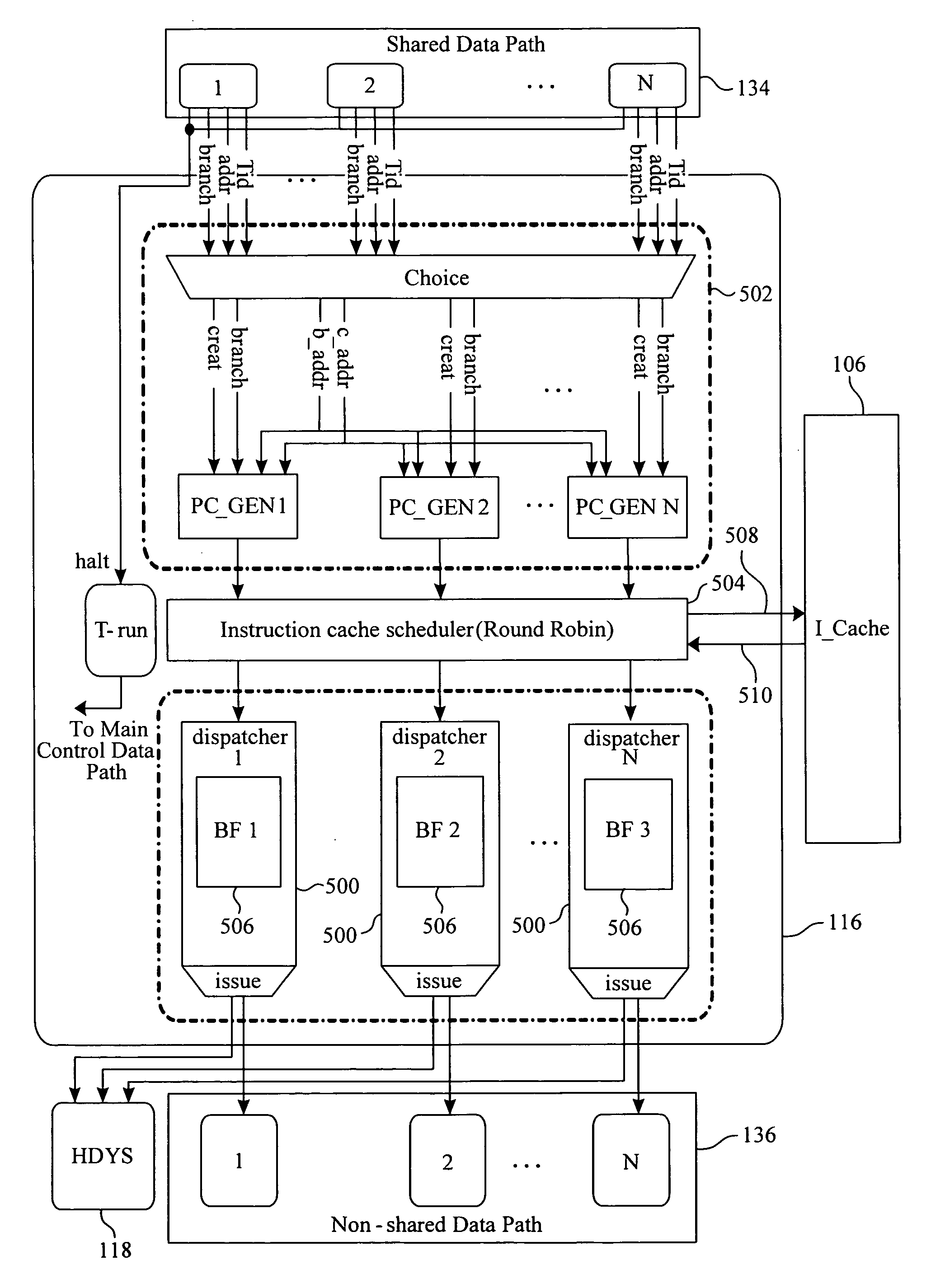
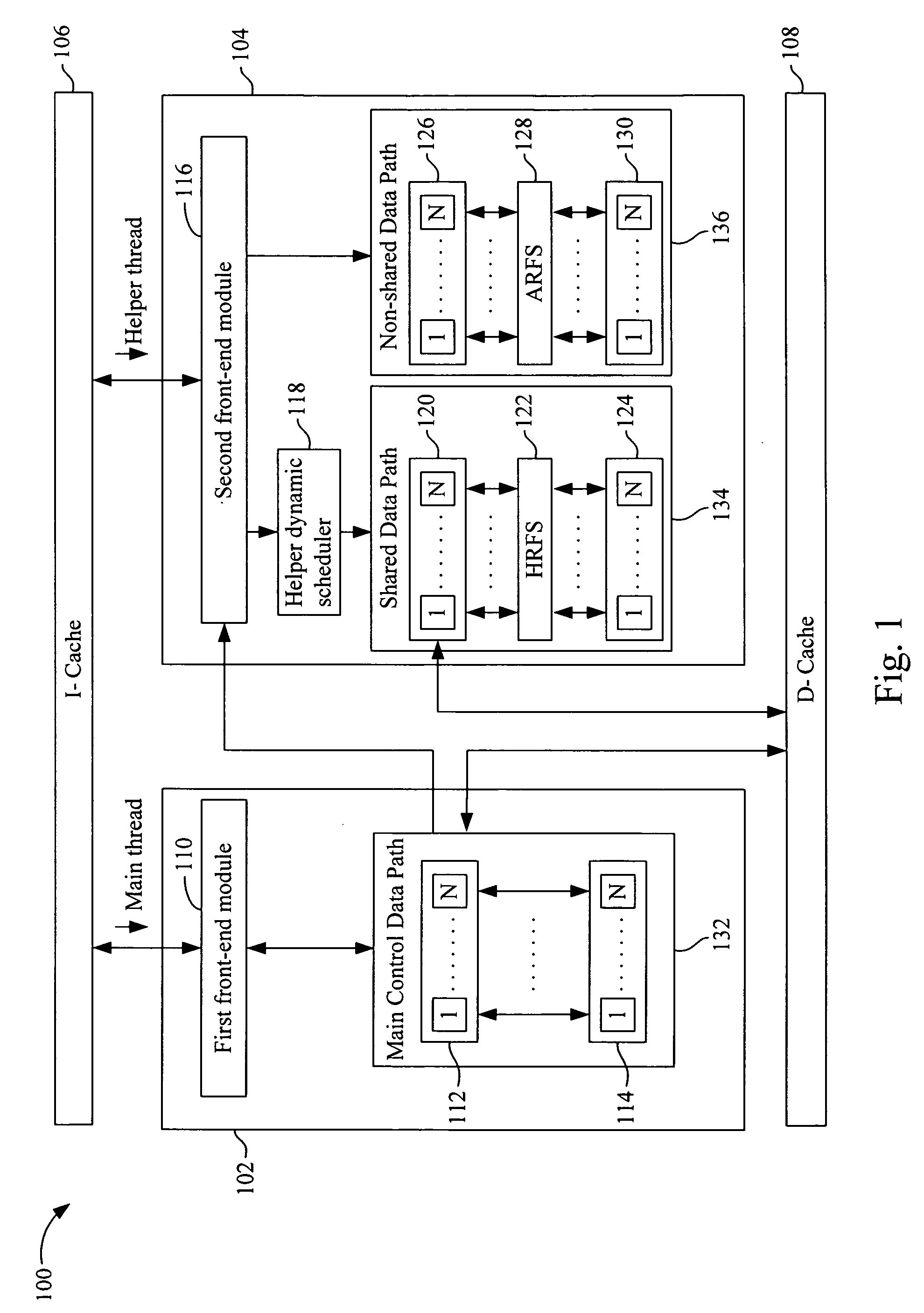
A cooperative multithreading architecture includes an instruction cache, capable of providing a micro-VLIW instruction; a first cluster, connects to the instruction cache to fetch the micro-VLIW instruction; and a second cluster, connects to the instruction cache to fetch the micro-VLIW instruction and capable of execution acceleration. The second cluster includes a second front-end module, connects to the instruction cache and capable of requesting and dispatching the micro-VLIW instruction; a helper dynamic scheduler, connects to the second front-end module and capable of dispatching the micro-VLIW instruction; a non-shared data path, connects to the second front-end module and capable of providing a wider data path; and a shared data path, connected to the helper dynamic scheduler and capable of assisting a control part of the non-shared data path. The first cluster and the second cluster carry out execution of the respective micro-instructions in parallel.
Owner:CHEN TIEN FU
Dynamic Workflow Scheduling
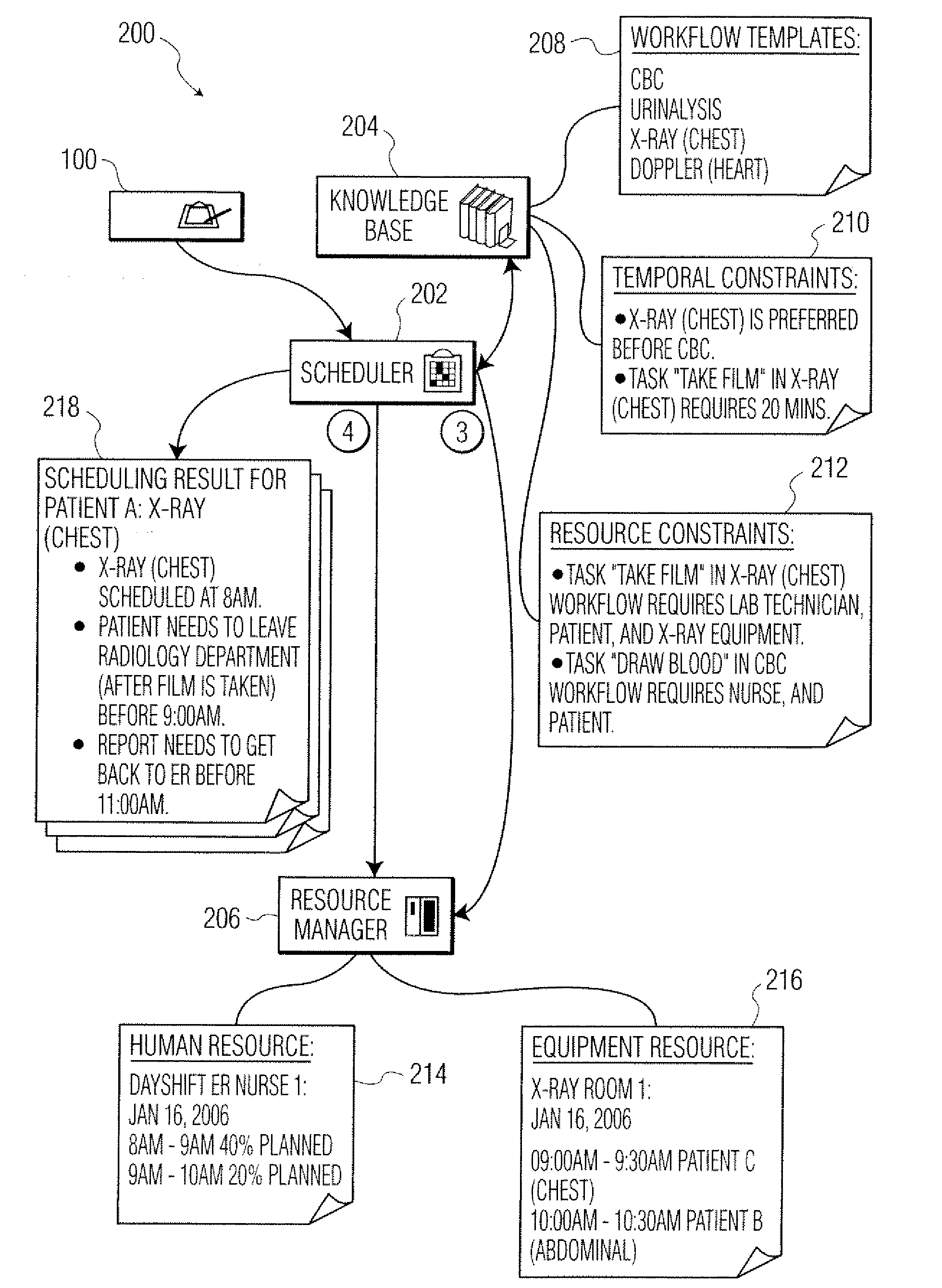
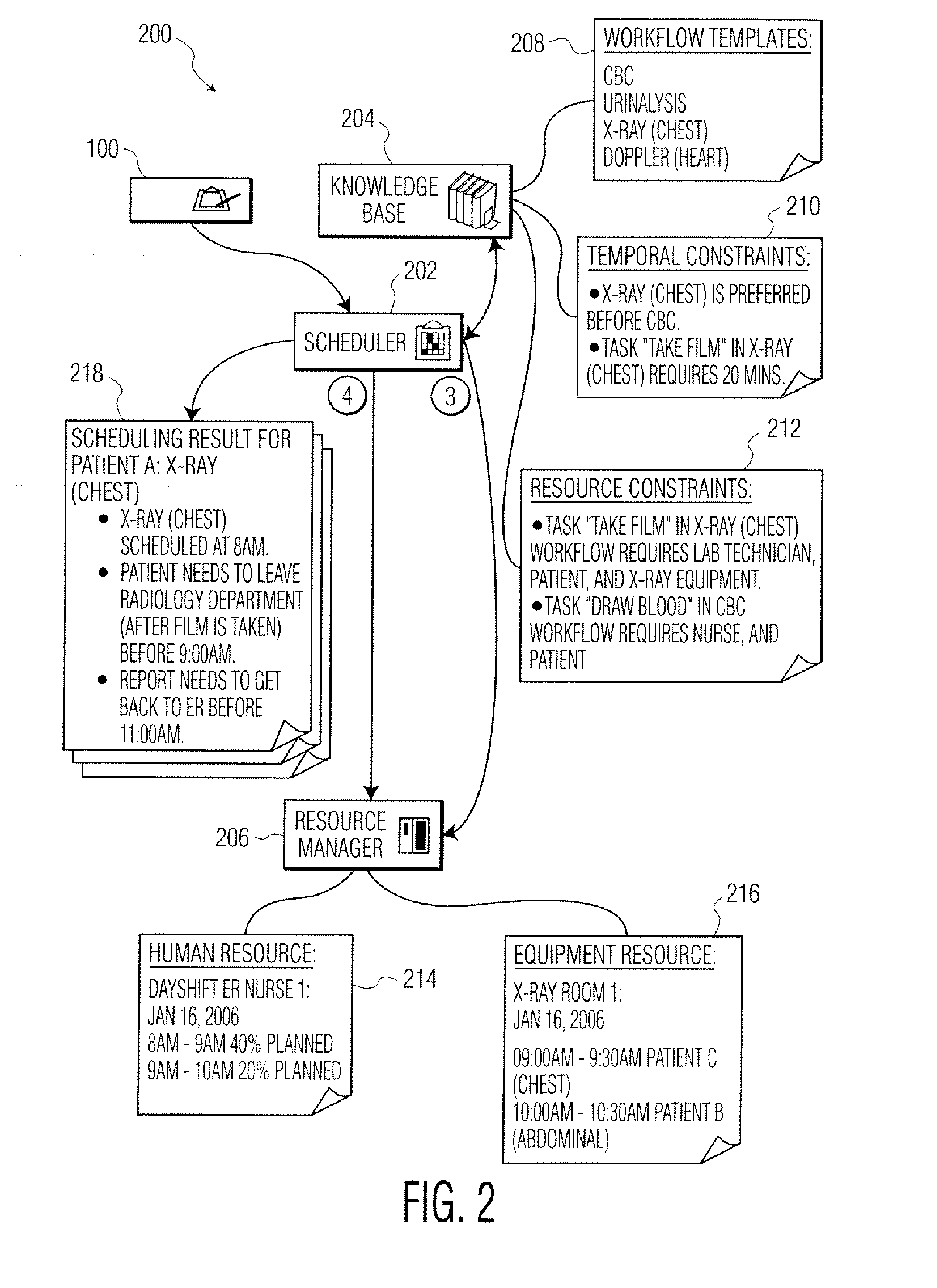
InactiveUS20070282476A1Hospital data managementHealthcare resources and facilitiesComputerized systemWorkflow scheduling
Methods and apparatus are disclosed for workflow scheduling. A workflow scheduling system, such as a computer system, is used to coordinate and schedule tasks in complex scheduling environments. The system accepts incoming orders and dynamically schedules them according to the constraints of the resources required for the order and any constraints of the orders themselves.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
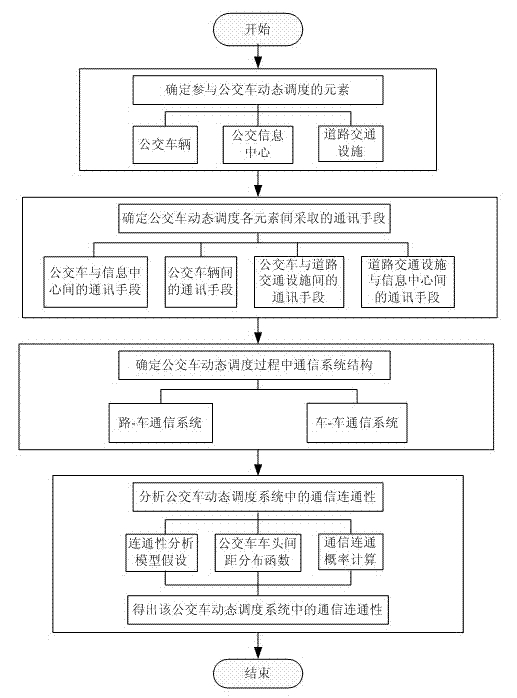
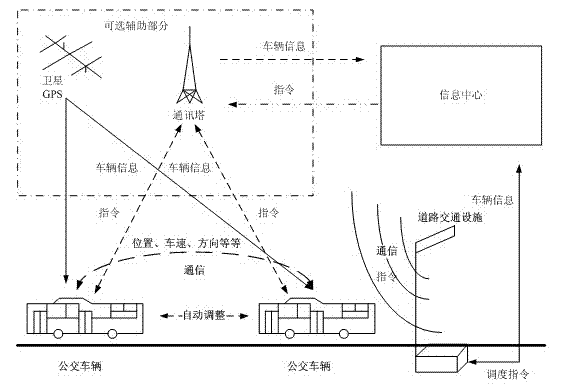
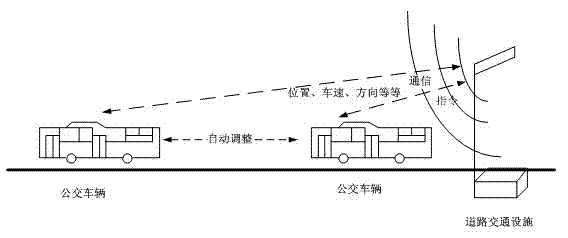
Communication connectivity analysis method for bus dynamic scheduling under internet of vehicles environment
ActiveCN102737503APrevention of cross-traffic phenomenonAccurately master connectivity reliabilityRoad vehicles traffic controlNetwork topologiesTechnical communicationCommunications system
The invention discloses a communication connectivity analysis method for bus dynamic scheduling under an internet of vehicles environment, and the method is a method for analyzing the intra-area wireless communication connectivity under the situation of bus dynamic scheduling of a vehicle ad hoc networks (VANET). The method comprises steps of firstly determining elements participating in the bus dynamic scheduling under the internet of vehicles environment; determining a communication method adopted among the elements of the bus dynamic scheduling; classifying a communication structure in the bus dynamic scheduling process into a route-vehicle communication system and a vehicle-vehicle communication system so as to analyze the basic structural characteristics of the communication connectivity in the scheduling process; and finally under the limitation of relevant proposal condition, calculating a wireless communication connectivity probability of the bus dynamic scheduling within a given regional range to obtain the connectivity of the intra-area wireless communication.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
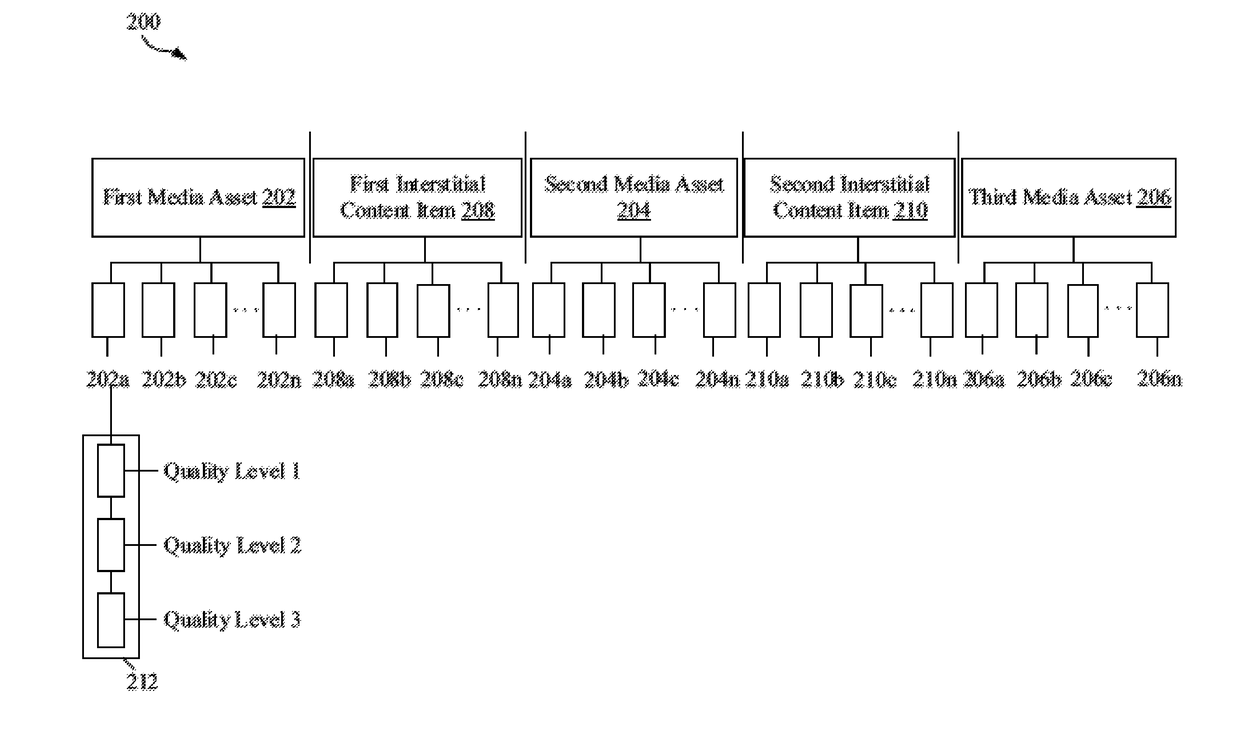
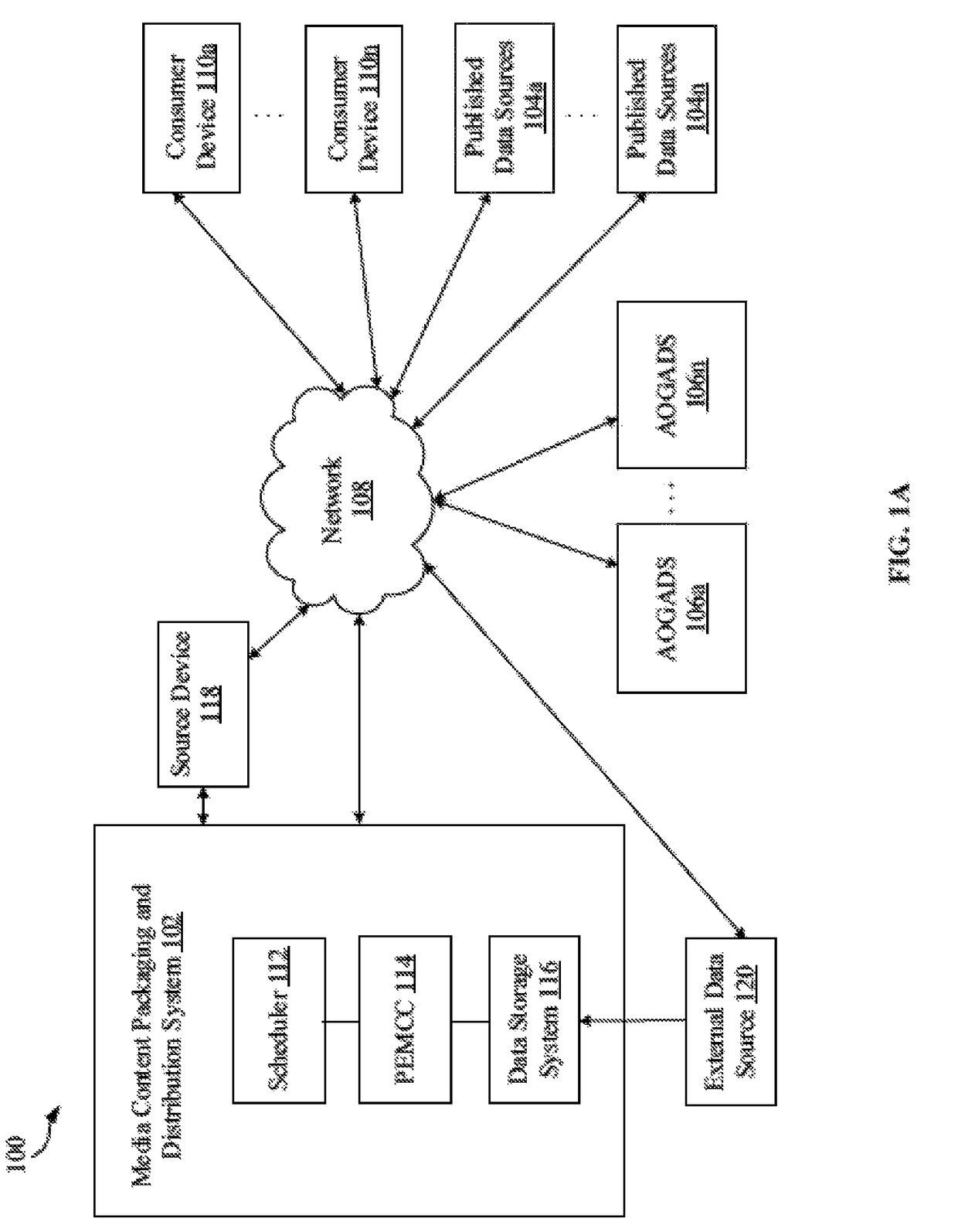
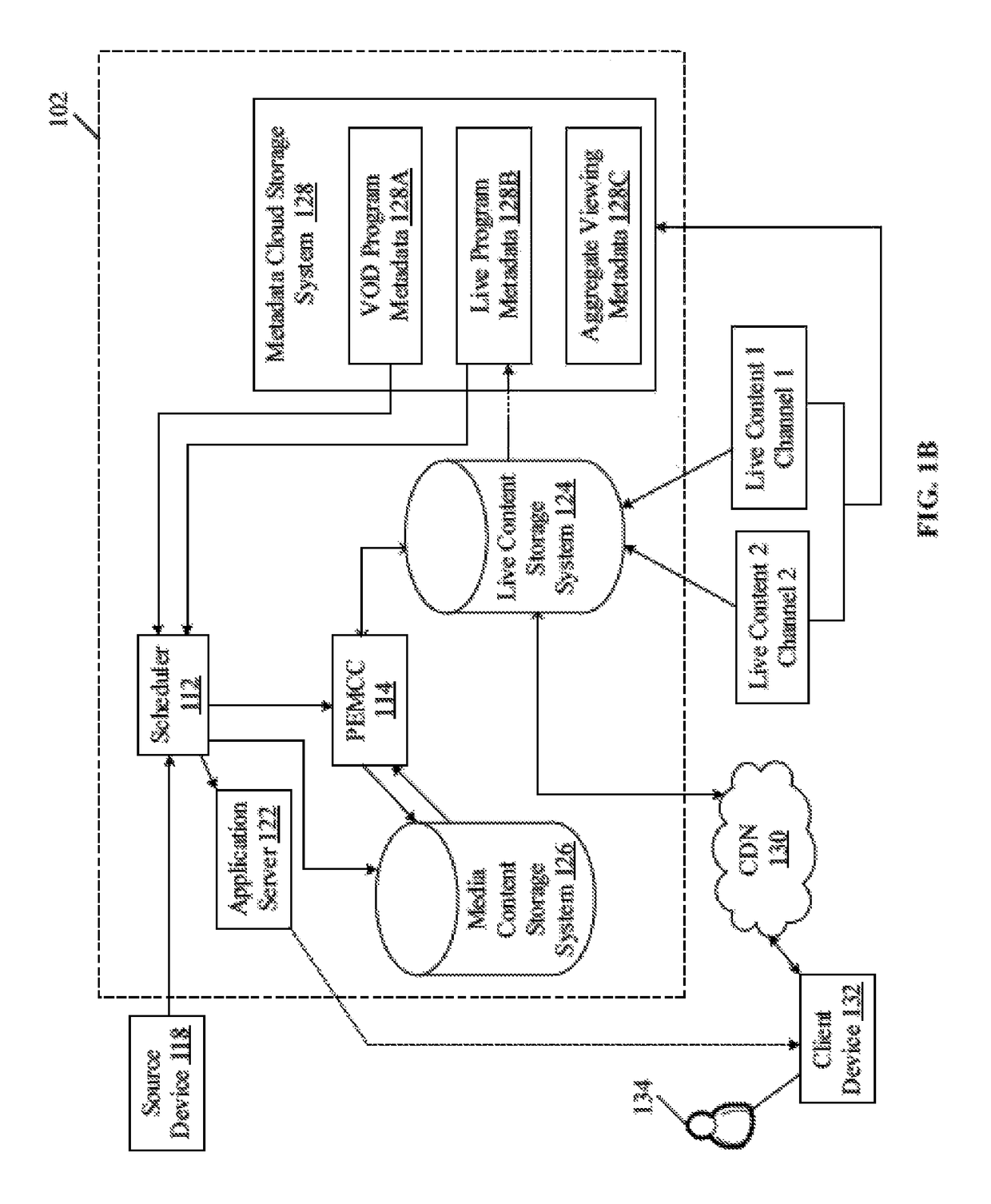
Dynamic scheduling and channel creation based on user selection
ActiveUS10075753B2Selective content distributionElectrical cable transmission adaptationUser inputDistribution system
A content packaging and distribution system that handles distribution of channels to be viewed on a plurality of consumer devices, receives a media feed and a first programming schedule of a first channel from a source device. An input that corresponds to a user-selection is received on a first consumer device of the plurality of consumer devices over a distribution system, and a media item to be inserted in the media feed of the first channel is determined based on criteria related to the user-selection. The determined media item may be dynamically scheduled in the media feed of the first channel to be delivered over the distribution system to be viewed on the first consumer device, based on the user-selection related criteria. The user-selection includes a first criterion that corresponds to a real time or a near-real time user input corresponding to the user-selection on the first consumer device.
Owner:TURNER BROADCASTING SYST INC
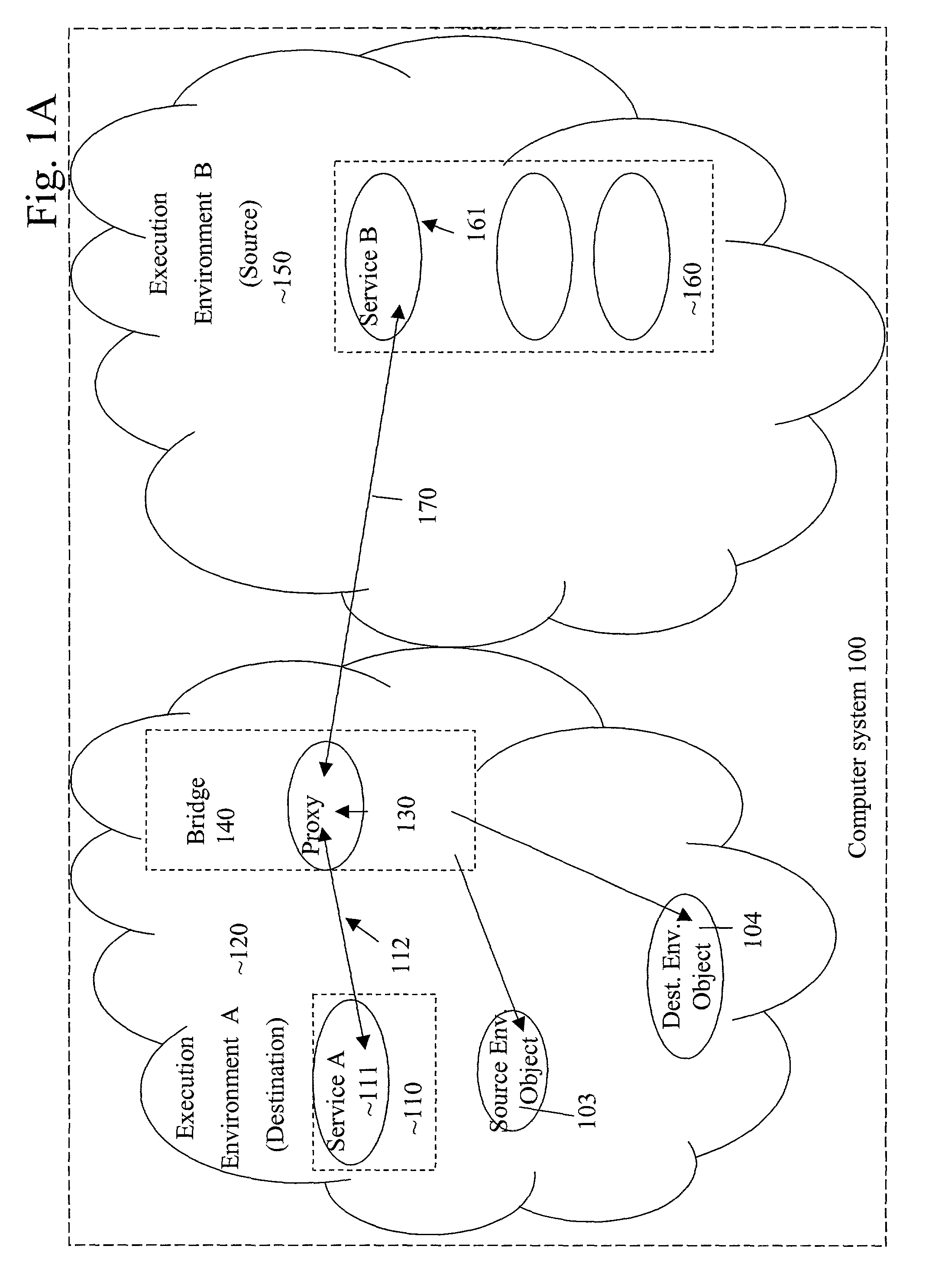
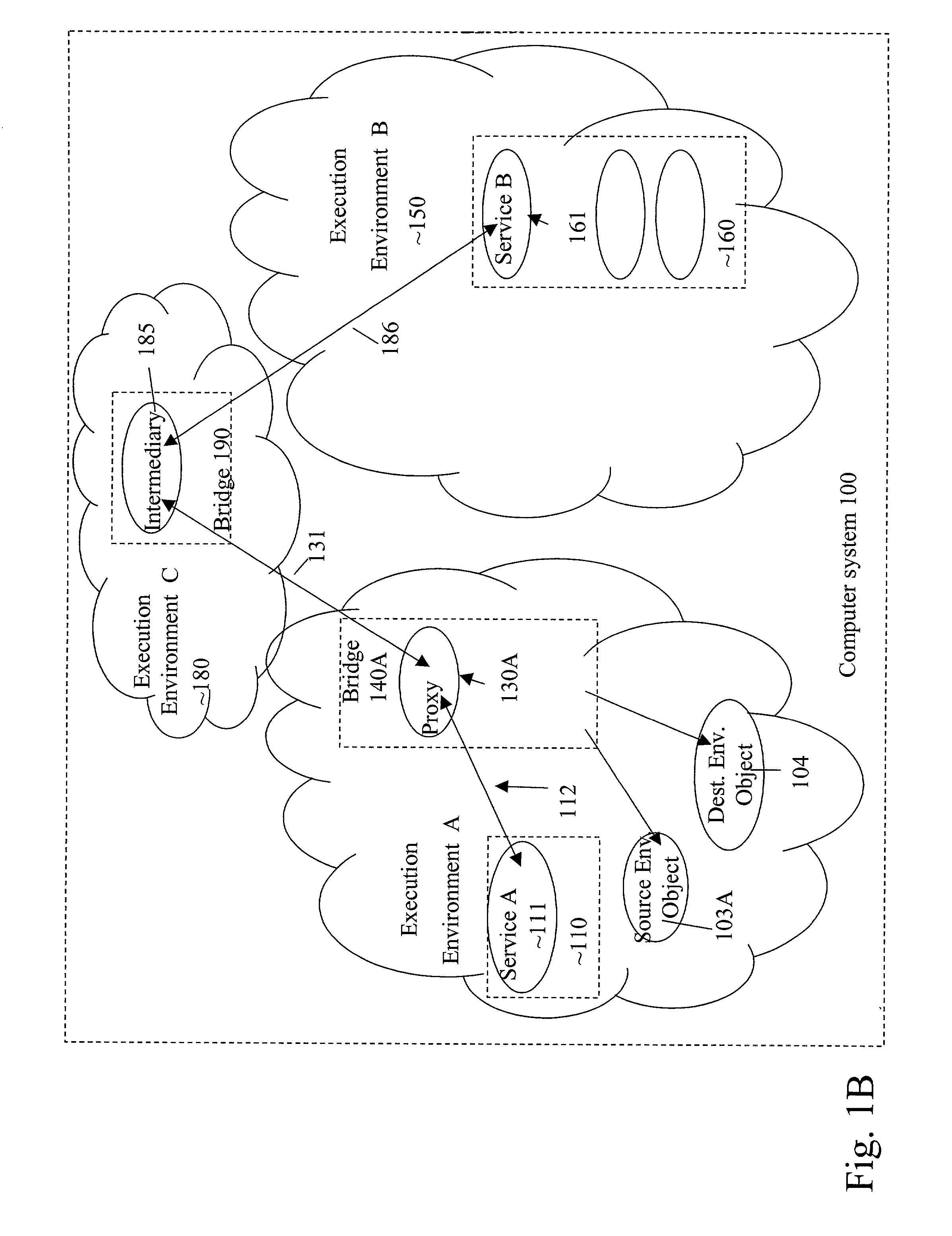
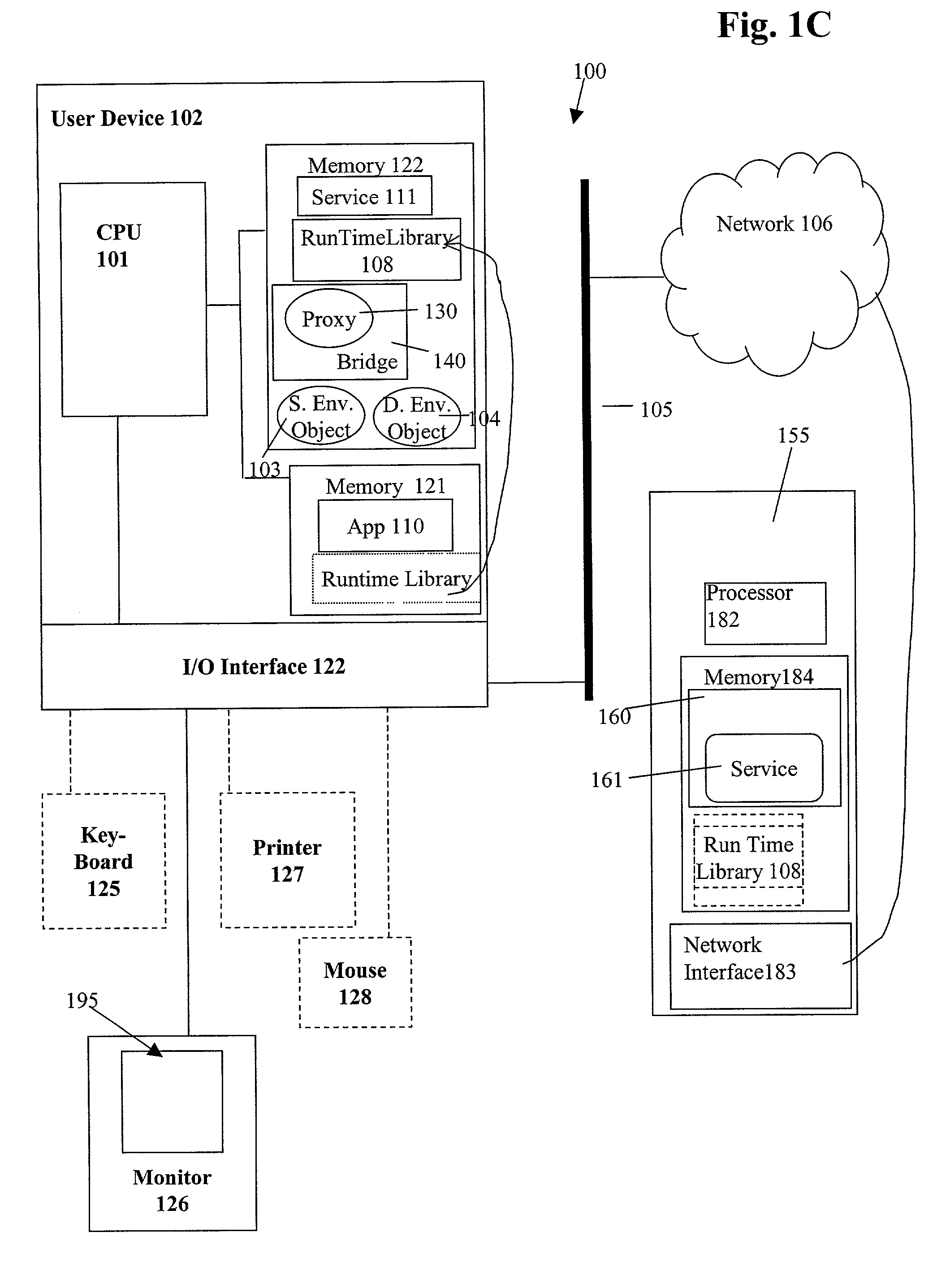
Method and system for dynamically dispatching function calls from a first execution environment to a second execution environment
A method for enabling a first software program using a first binary specification in a first execution environment to employ a limited functionality of a second software program using a second binary specification in a second execution environment first creates a bridge in the first execution environment. Using the bridge, a proxy wrapping an interface to the limited functionality of the second software program in the second execution environment is created in the first execution environment. The proxy is used to access the limited functionality of the second software program in the second execution environment.
Owner:SUN MICROSYSTEMS INC
Scheduling apparatus performing job scheduling of a parallel computer system
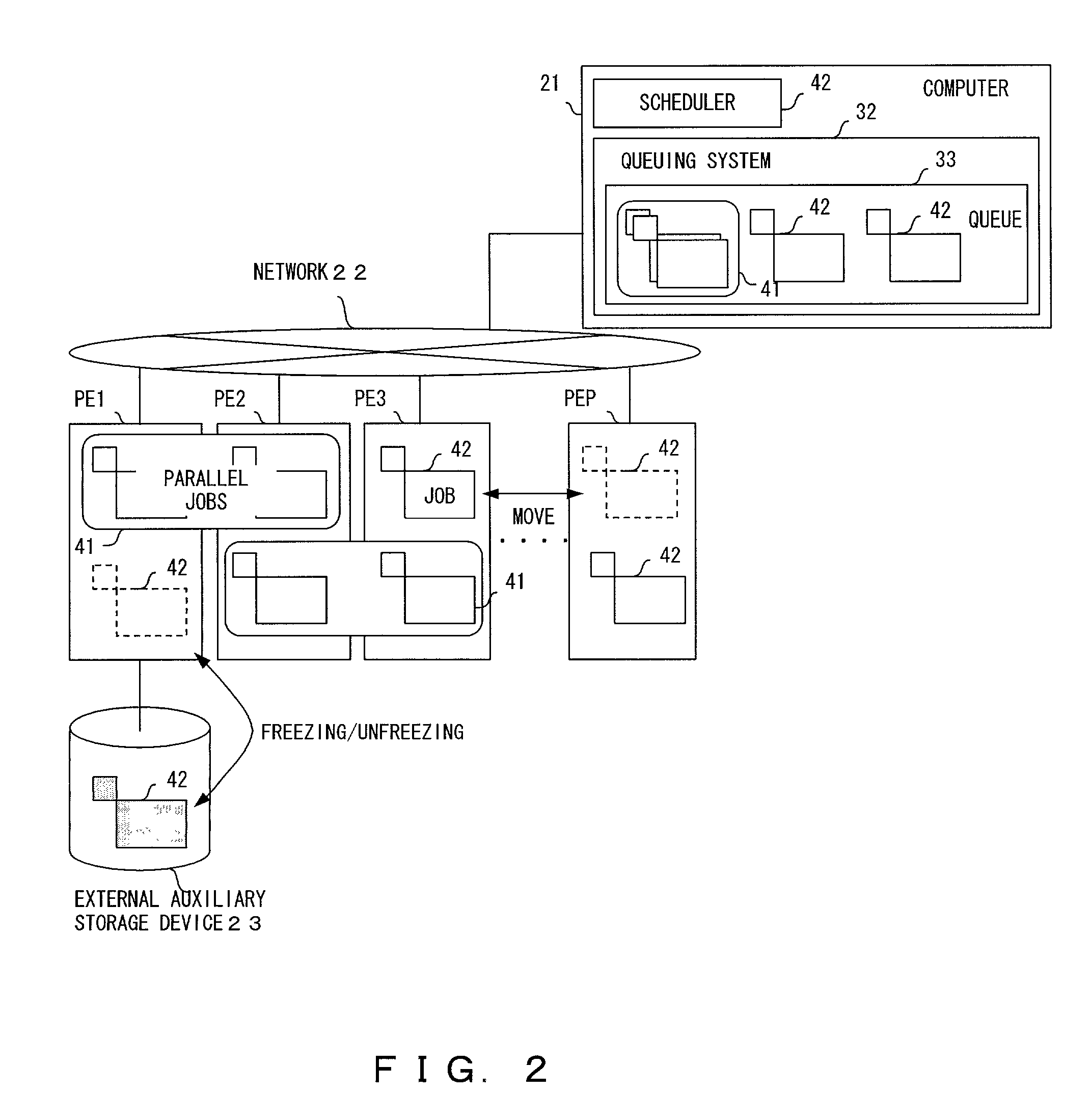
InactiveUS7024671B2Reduce errorsImprove efficiencyResource allocationDigital computer detailsProcessor elementJob shop scheduling
A job entered into a processor element (PE) of a parallel computer system is moved to a different PE, or written to an external auxiliary storage device by being frozen, with dynamic scheduling. A scheduler estimates the remaining time of execution of each job, compares with a migration / freezing cost, and determines a job to be moved / frozen.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Scheduling and management of compute tasks with different execution priority levels
InactiveUS20130074088A1Fast executionMemory systemsProgram saving/restoringMulti processorDistributed computing
One embodiment of the present invention sets forth a technique for dynamically scheduling and managing compute tasks with different execution priority levels. The scheduling circuitry organizes the compute tasks into groups based on priority levels. The compute tasks may then be selected for execution using different scheduling schemes, such as round-robin, priority, and partitioned priority. Each group is maintained as a linked list of pointers to compute tasks that are encoded as queue metadata (QMD) stored in memory. A QMD encapsulates the state needed to execute a compute task. When a task is selected for execution by the scheduling circuitry, the QMD is removed for a group and transferred to a table of active compute tasks. Compute tasks are then selected from the active task table for execution by a streaming multiprocessor.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
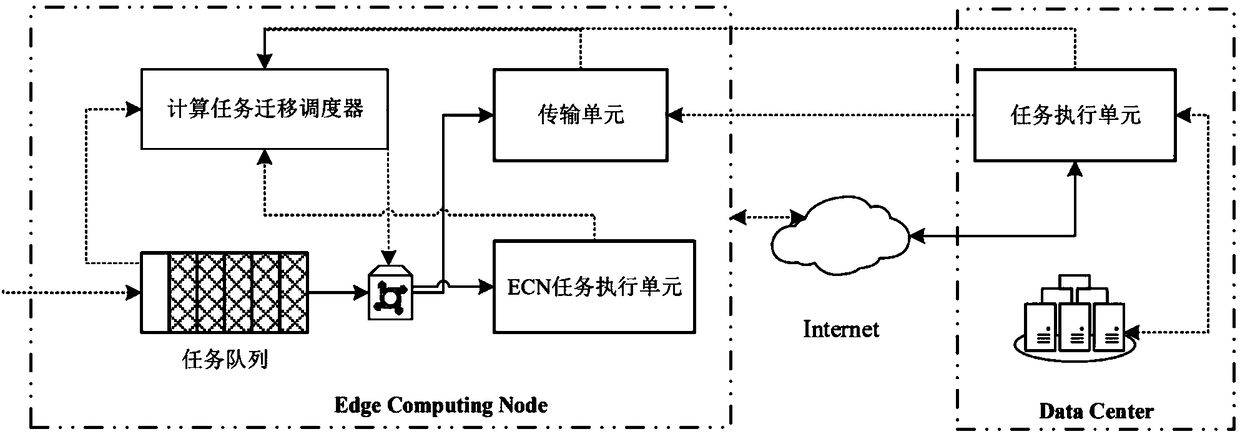
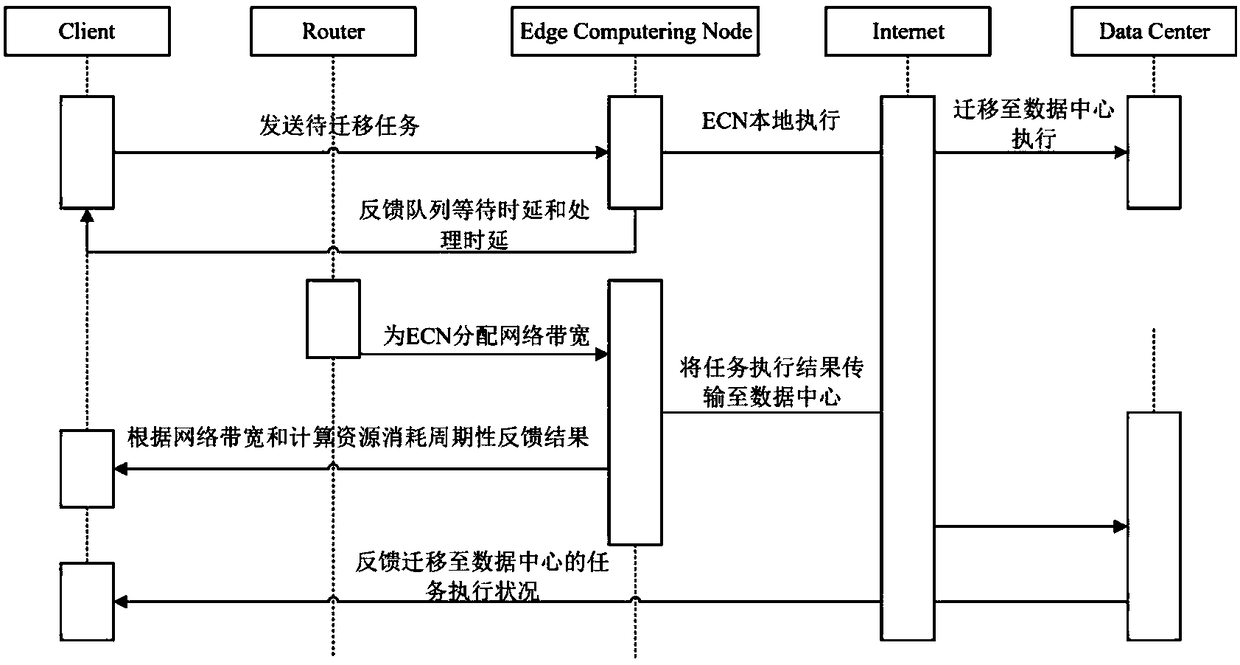
Dynamic migration method of video tasks in edge computing environment
ActiveCN108509276AIncrease profitReduce overheadProgram initiation/switchingResource allocationTask analysisService experience
The invention discloses a dynamic migration method of video tasks in an edge computing environment. Multiple ECNs (Edge Compute Nodes) are selected in an ECN cluster under the edge environment to runa task scheduling migration scheduler to be responsible for distribution and scheduling work of the tasks, and the other ECNs in the cluster undertake task migration work and provide computing resources. The computing task migration scheduler executes task migration decision in each scheduling cycle to determine whether the tasks are executed locally in the ECNs or migrated to a data center, and tasks needing to be migrated to the data center are directly sent to a task execution unit of the remote-end data center through an ECN transmission unit for analysis processing. According to the method, the tasks are dynamically scheduled and processed on the basis of meeting network bandwidth and calculation costs, goals of reducing transmission time delay of edge data and improving task analysisprocessing speed are achieved, thus low delay time and high response of a task migration process are effectively guaranteed, and video service experience of users is improved while higher video service quality is realized.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
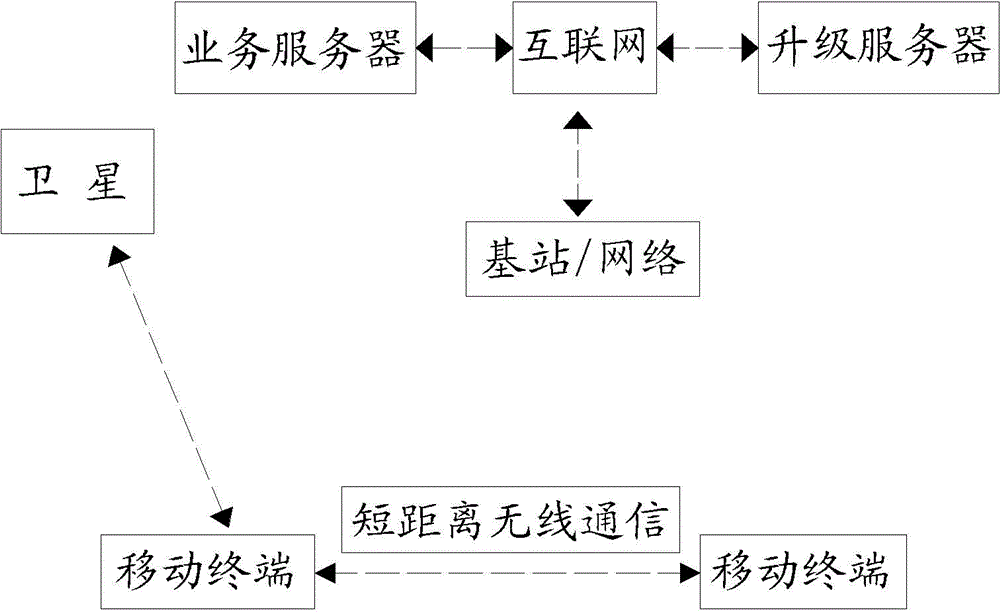
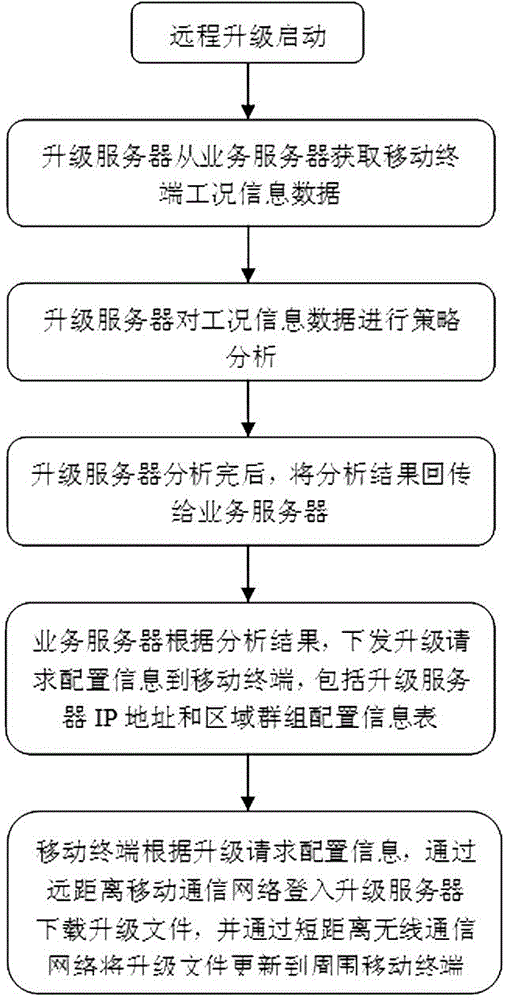
Remote software upgrade method for clustered mobile terminals
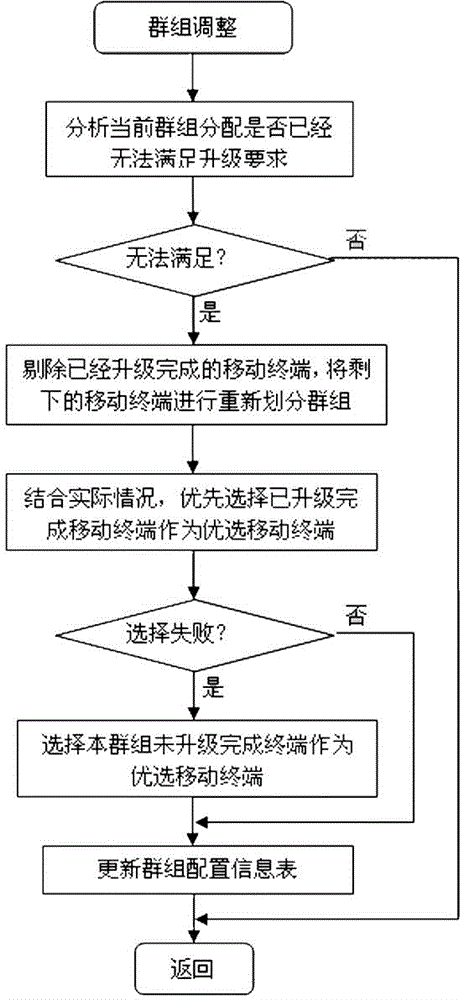
ActiveCN103607456AReal-time dynamic adjustment of download strategySolve the problem that cannot be upgraded remotelyProgram loading/initiatingTransmissionShortest distanceComputer terminal
The invention discloses a remote software upgrade method for clustered mobile terminals. The method comprises steps that: step 1, condition information data of the mobile terminals is acquired by an upgrade server in real time from a business server; step 2, dynamic strategy analysis on the condition information data is carried out by the upgrade server; step 3, upgrade request configuration information is issued by the business server to the mobile terminals according to the analysis result of the upgrade server; and step 4, the preferable mobile terminal registers the upgrade server to download an upgrade file according to the upgrade request configuration information, upgrade updating on self software is carried out, and the upgrade file is updated to surrounding mobile terminals through a short distance wireless communication network. According to the method, characteristics of slow speed of long distance mobile communication and fast speed of short distance wireless communication are utilized, real-time dynamic strategy analysis in combination with the condition information data of the mobile terminals is carried out, downloading strategy is dynamically adjusted in real time during a downloading process, and scientific dynamic scheduling and reasonable distribution are realized. The remote software upgrade method is applied to rapid reliable upgrade of mobile terminal software.
Owner:XIAMEN YAXON NETWORKS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com