Control-quasi-independent-points guided speculative multithreading
a control-quasi-independent point and multi-threading technology, applied in the field of information processing systems, can solve the problems of affecting the efficiency and affecting the effectiveness of speculative thread execution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
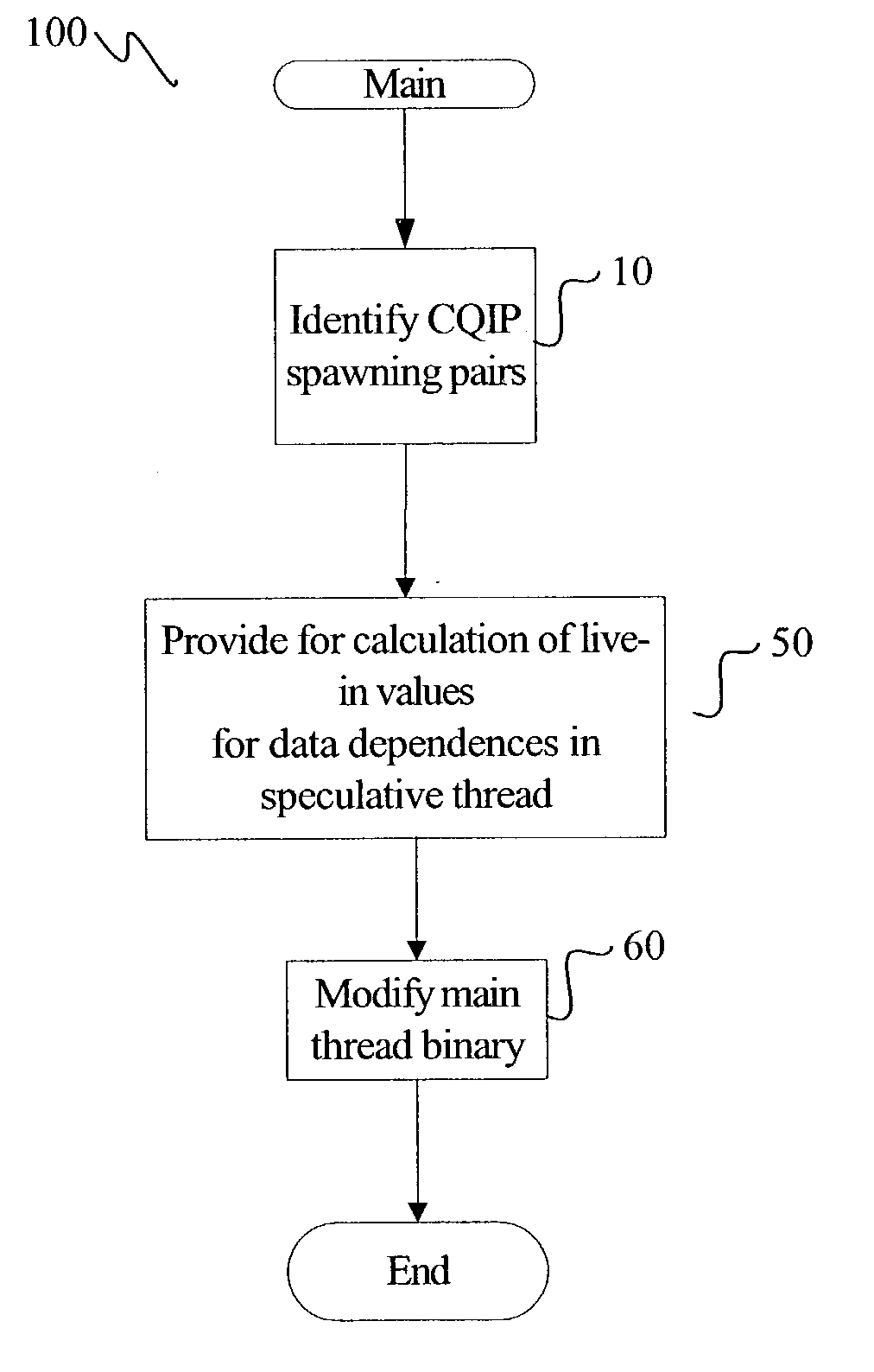
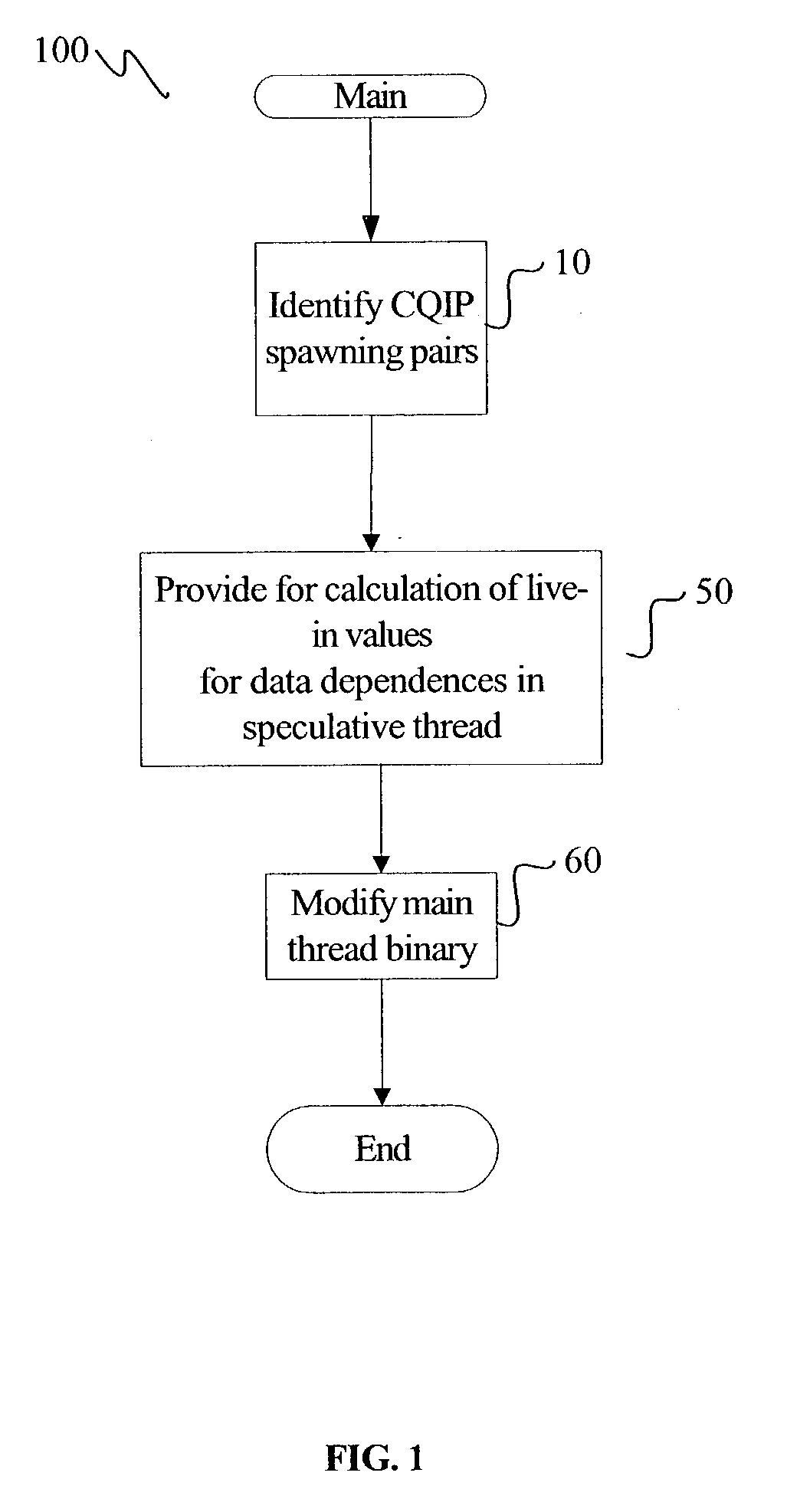
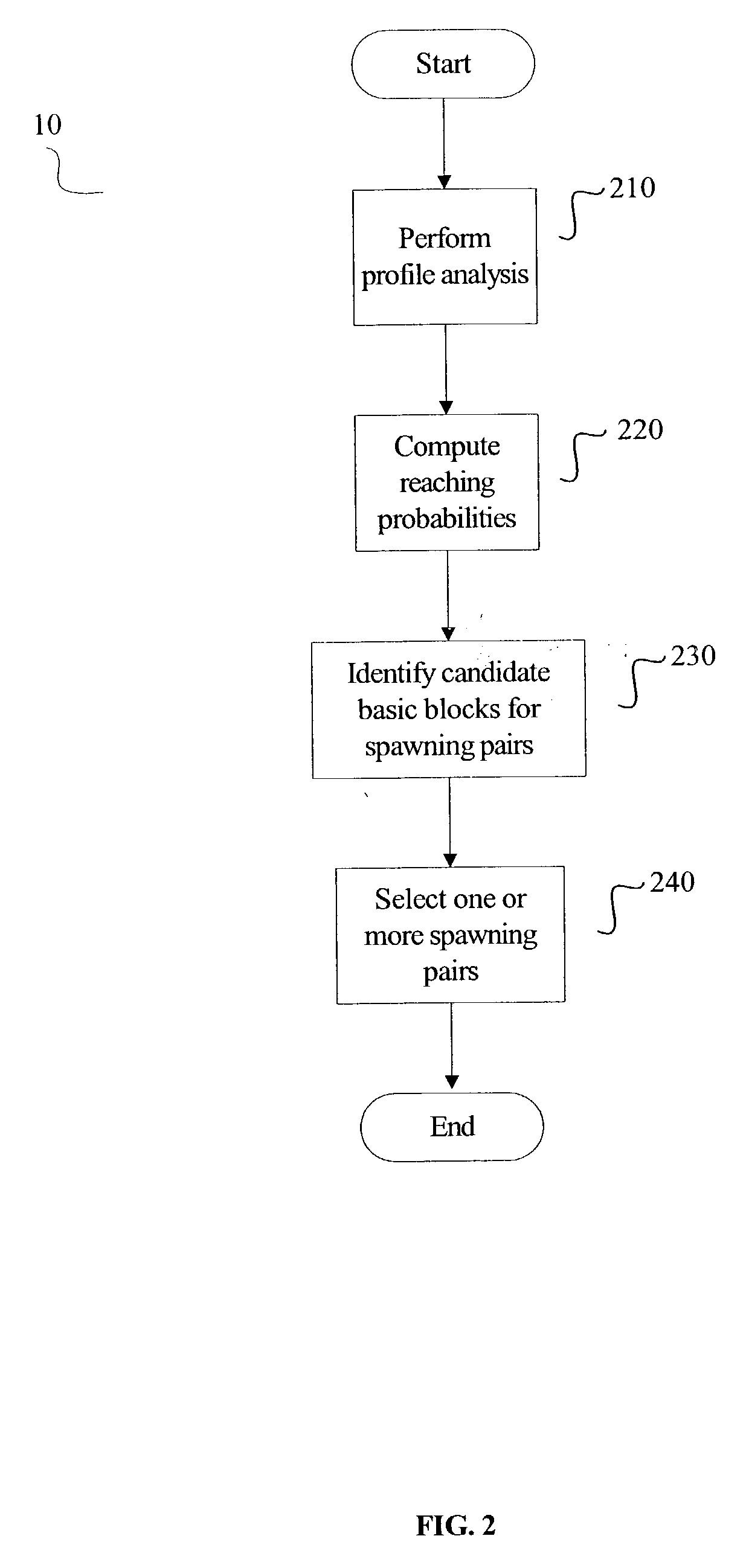
[0015] FIG. 1 is a flowchart illustrating at least one embodiment of a method for generating instructions to facilitate control-quasi-independen-t-points ("CQIP") guided speculative multithreading. For at least one embodiment of the method 100, instructions are generated to reduce the execution time in a single-threaded application through the use of one or more simultaneous speculative threads. The method 100 thus facilitates the parallelization of a portion of an application's code through the use of the simultaneous speculative threads. A speculative thread, referred to as the spawnee thread, executes instructions that are ahead of the code being executed by the thread that performed the spawn. The thread that performed the spawn is referred to as the spawner thread. For at least one embodiment, the spawnee thread is an SMT thread that is executed by a second logical processor on the same physical processor as the spawner thread. One skilled in the art will recognize that the met...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com