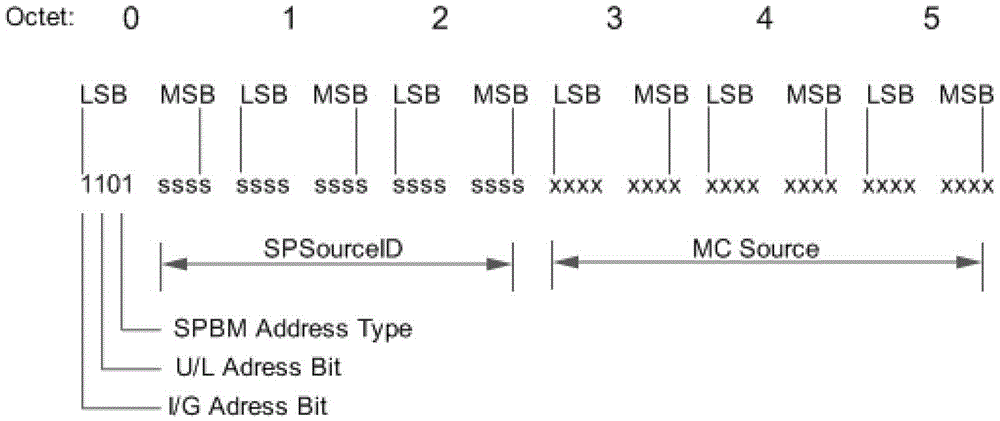
Patents
Literature
64 results about "Shortest path bridging" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Shortest path bridging (SPB or 802.1aq) is the IEEE’s specification for enabling multipath routing in the data center. Shortest path bridging is similar conceptually to its IETF counterpart, Transparent Interconnection of Lots of Links (TRILL) but differs from TRILL in its use of tree structures.
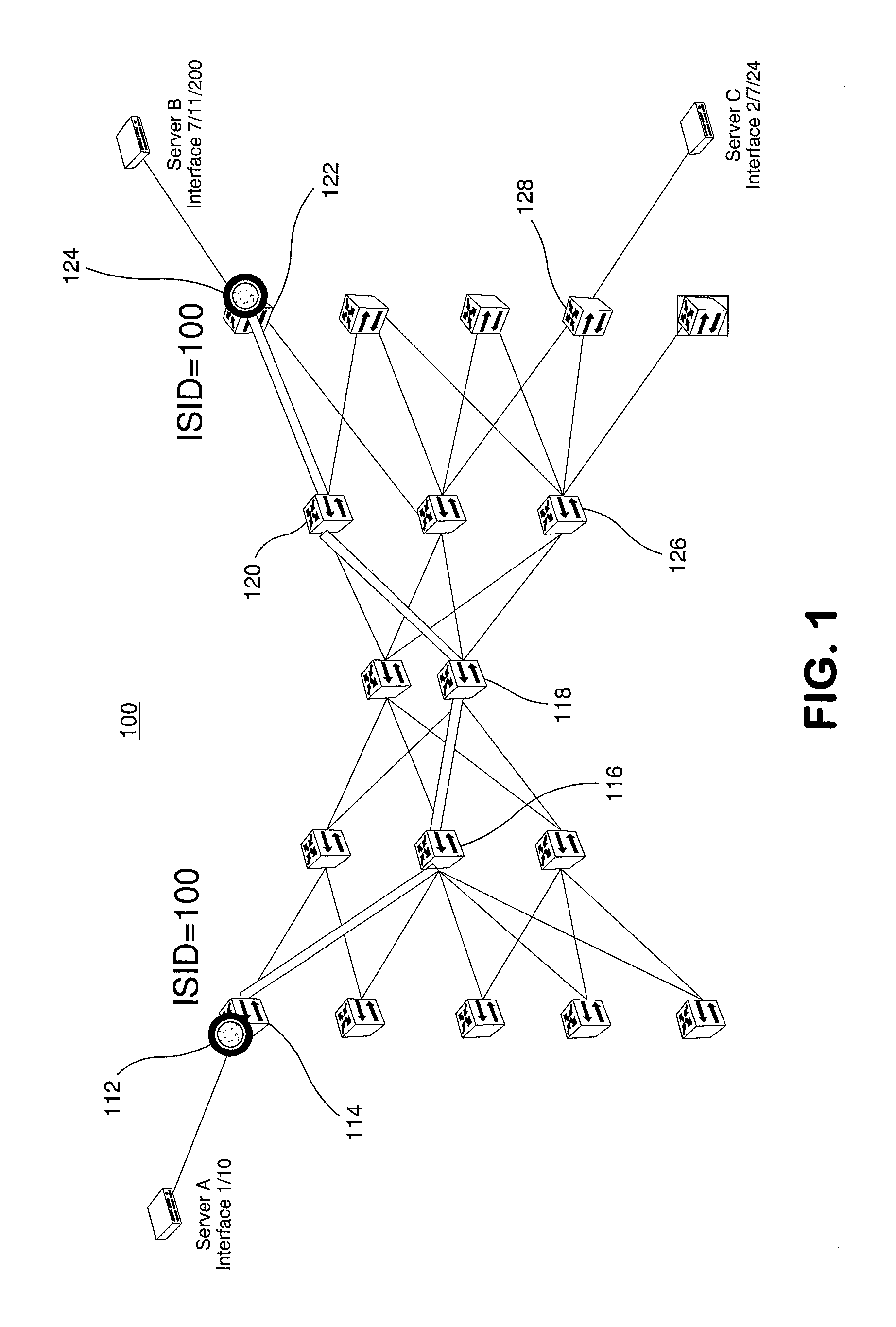
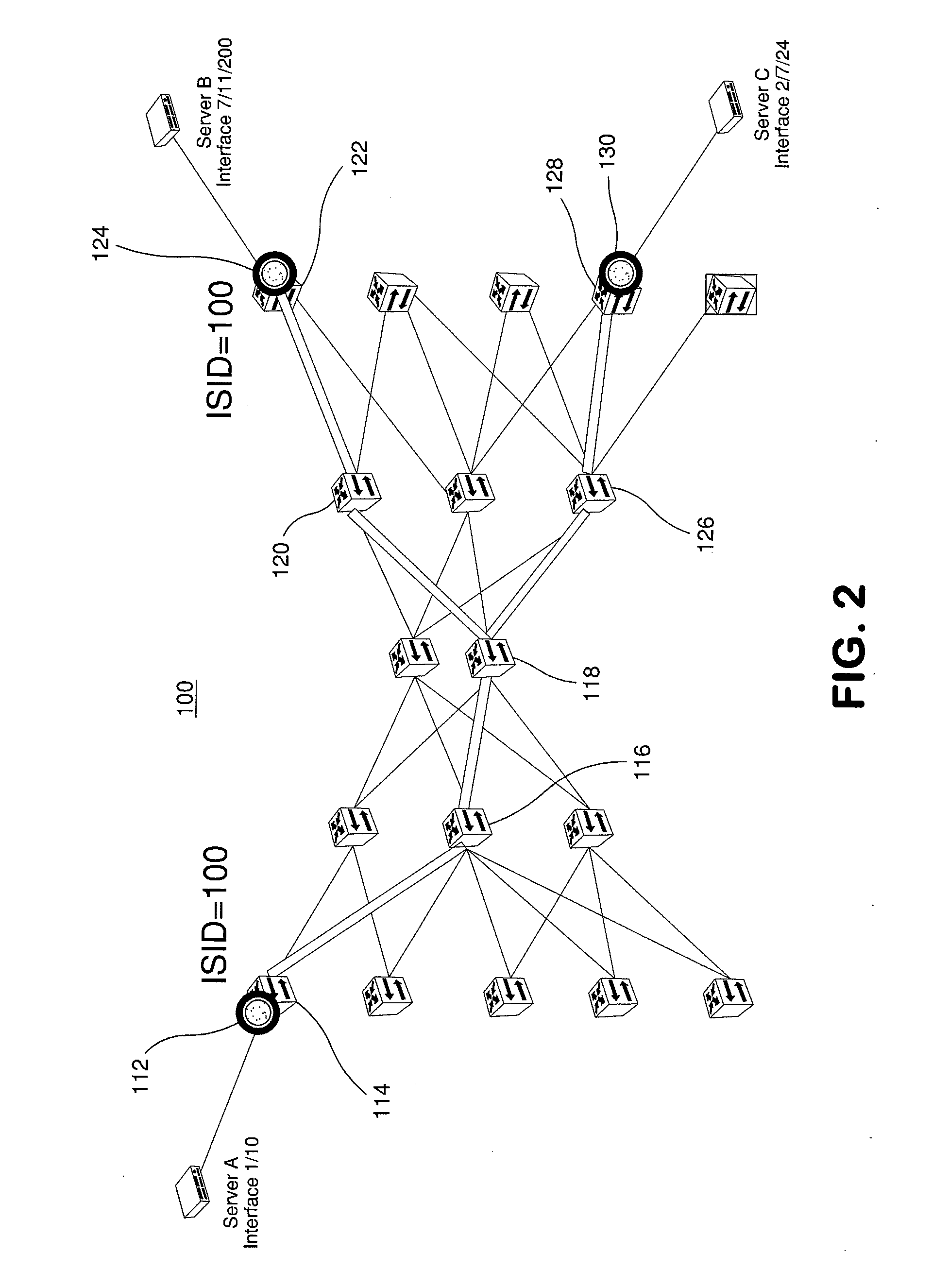
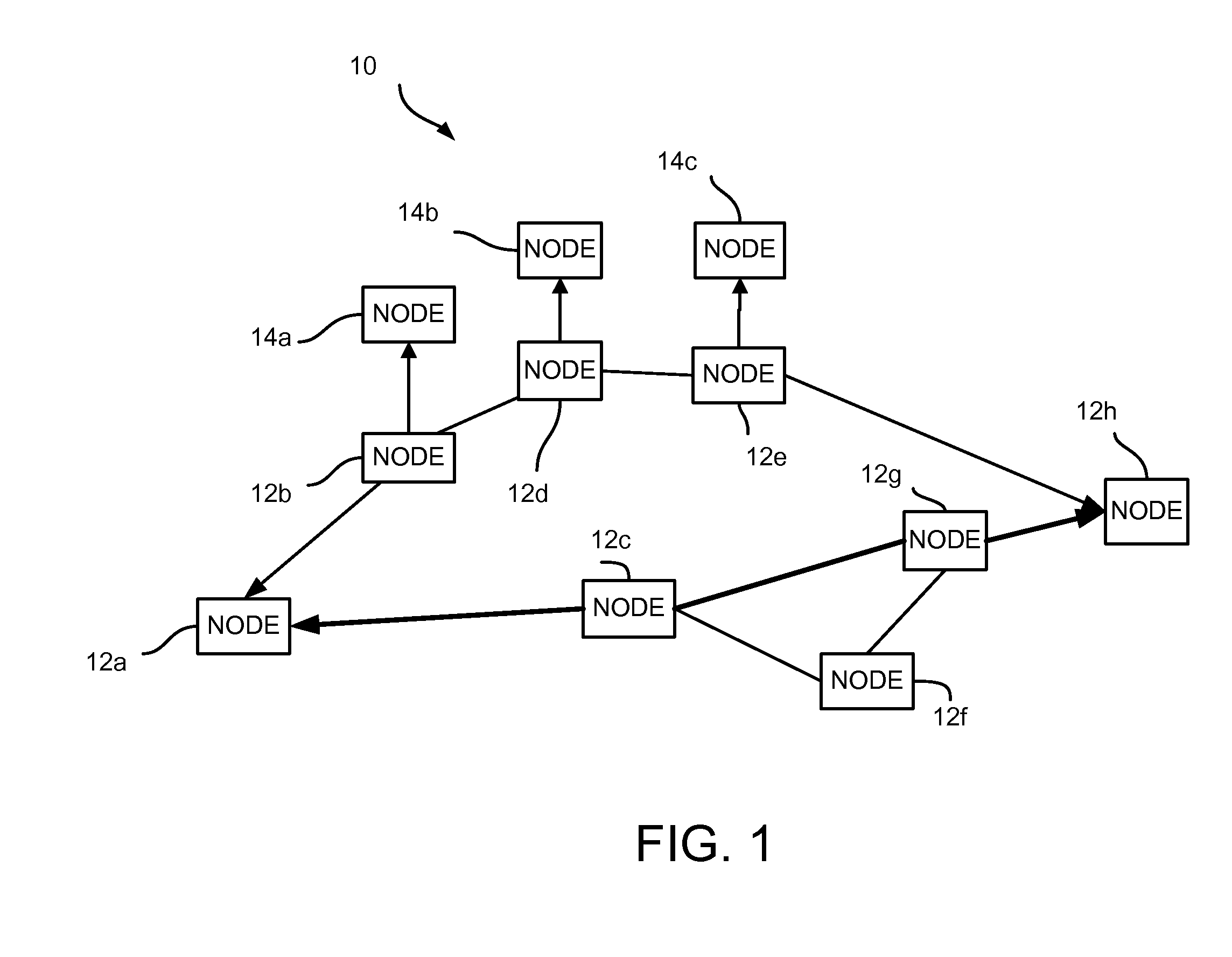
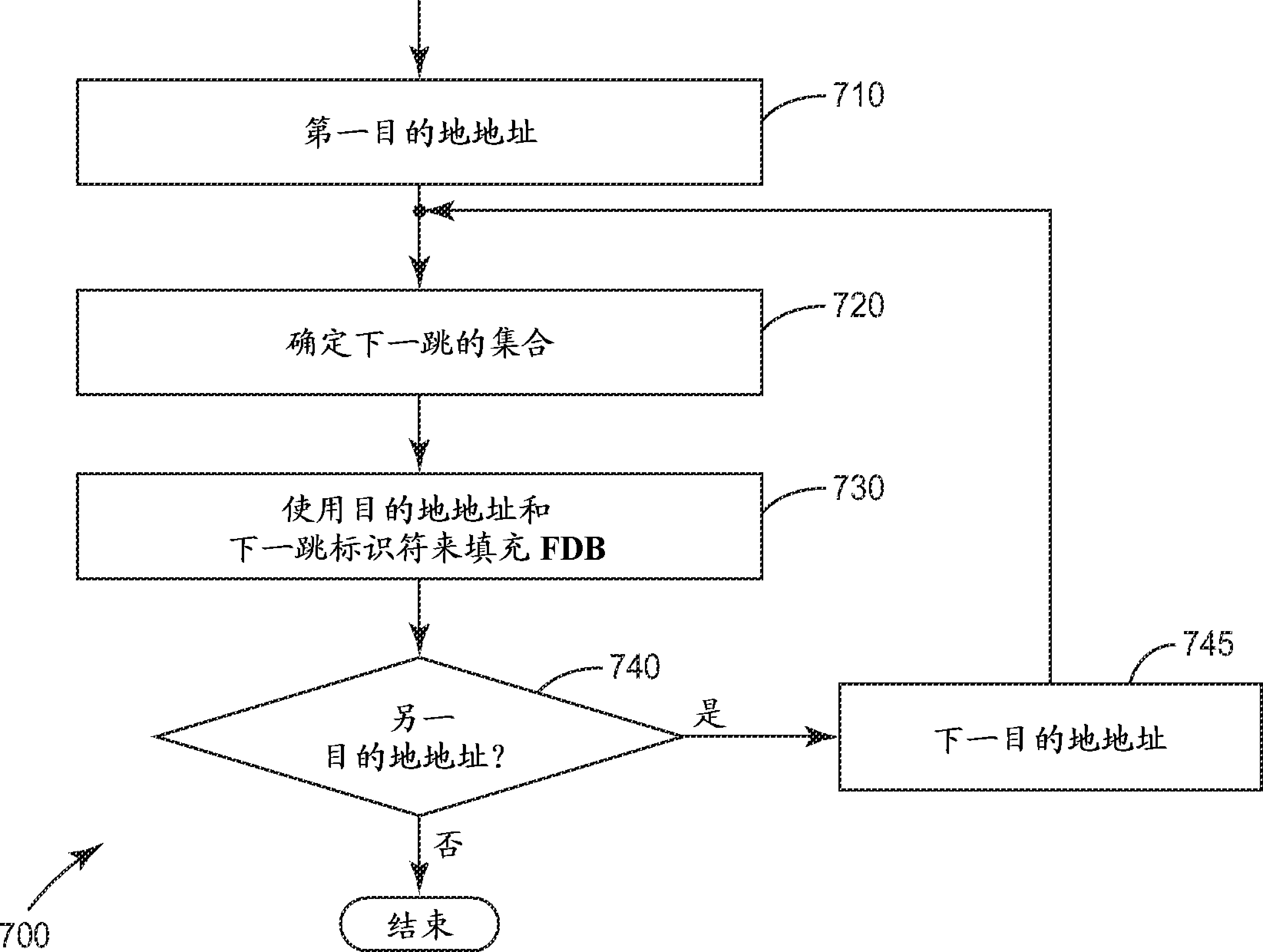
Forwarding frames in a computer network using shortest path bridging
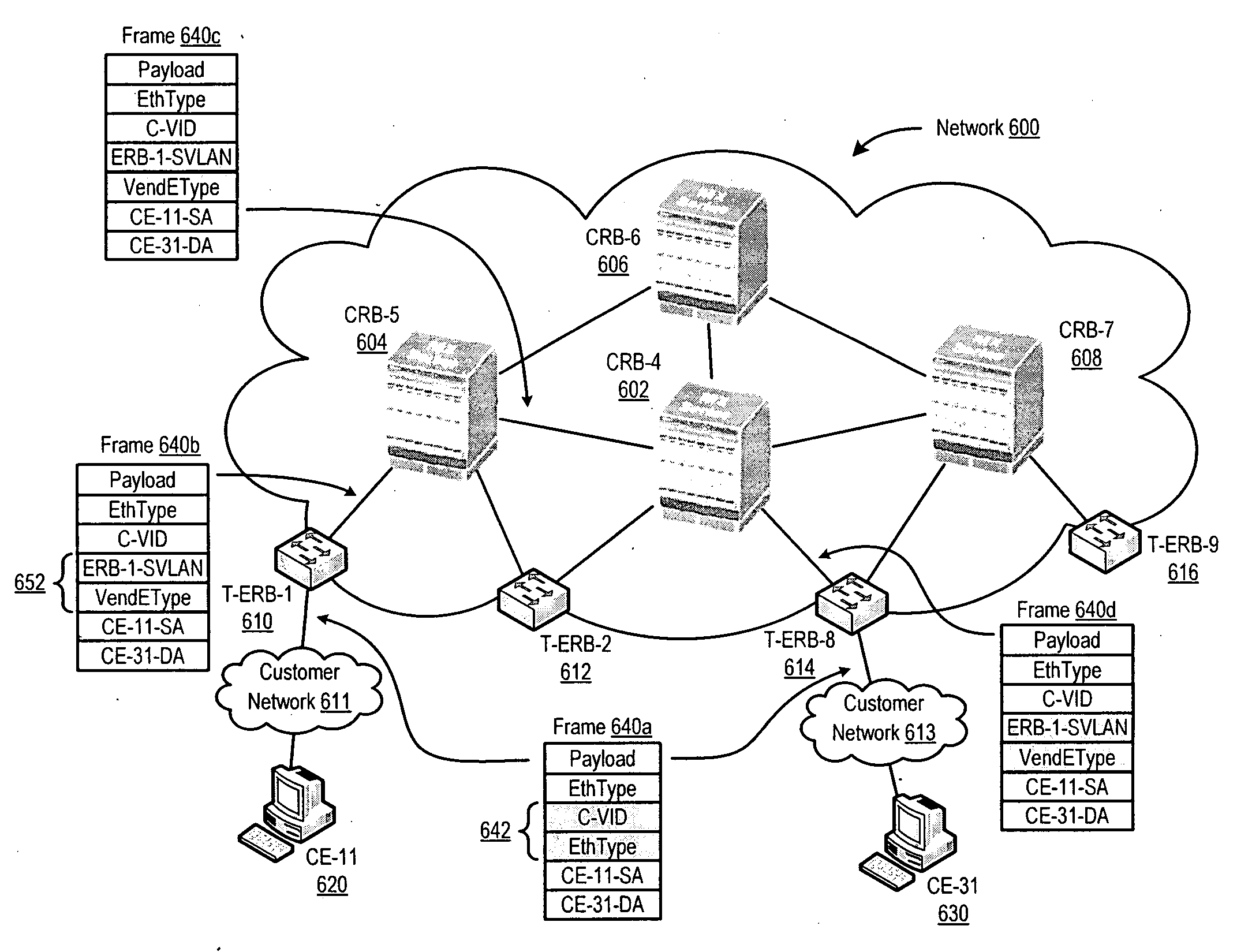
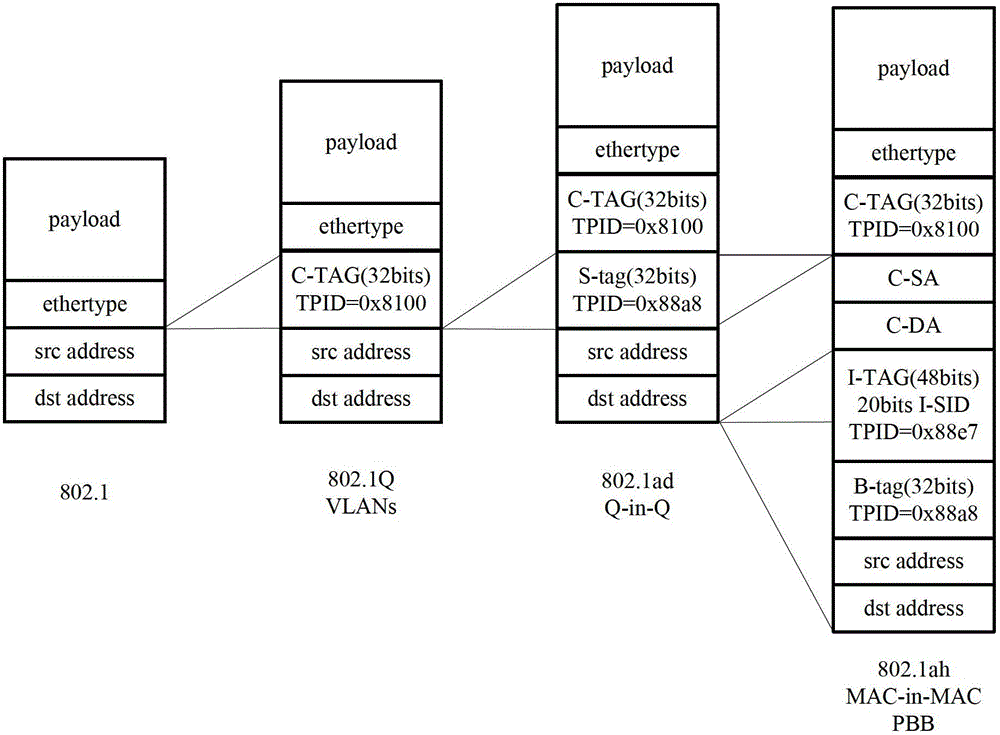
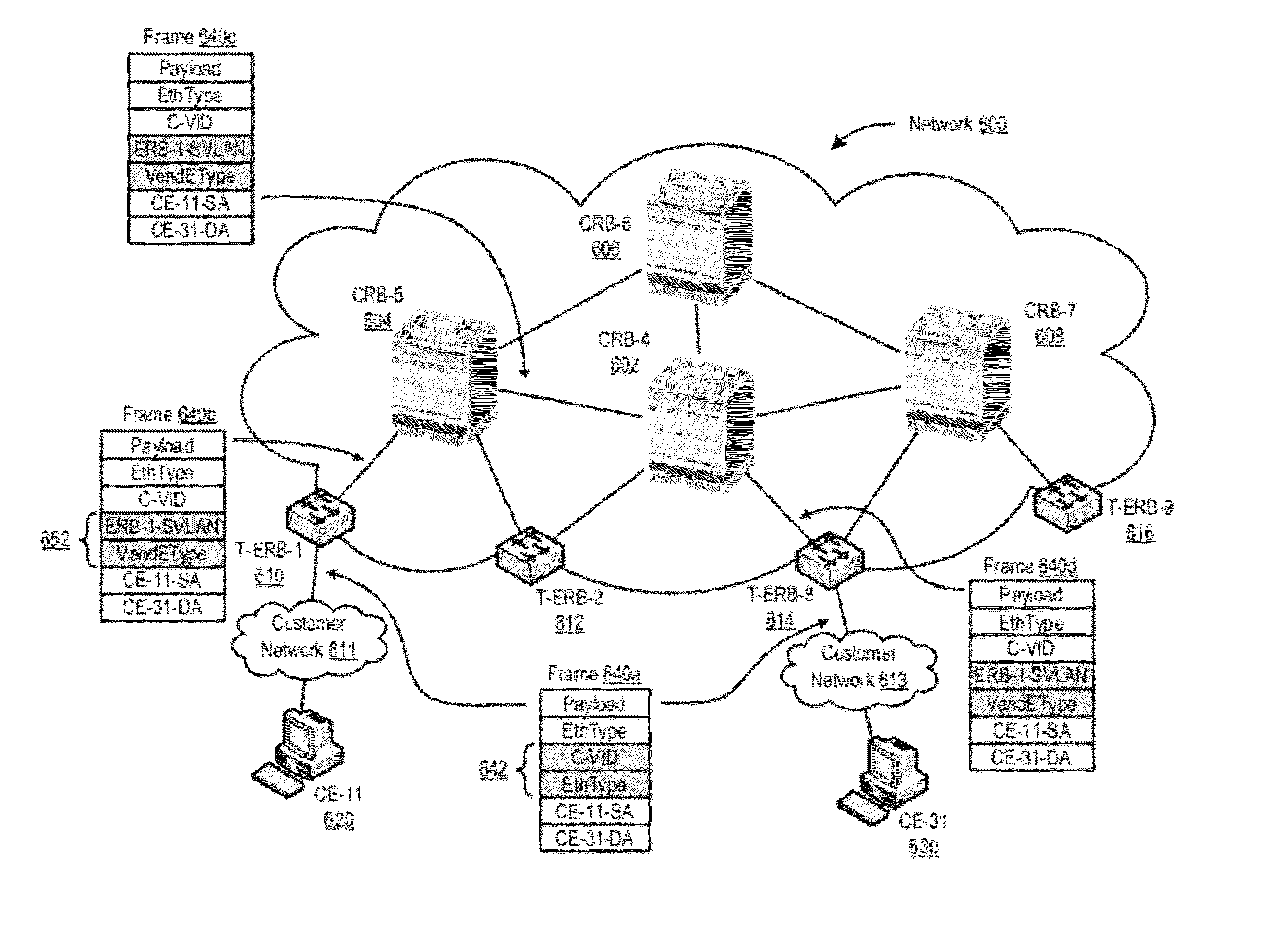
Methods, apparatus, and products are disclosed for forwarding frames in a computer network using shortest path bridging (‘SPB’). The network includes multiple bridges, and each edge bridge is assigned a unique service virtual local area network (‘VLAN’) identifier. One of the bridges receives a frame for transmission to a destination node. The received frame includes a service VLAN identifier for the ingress bridge through which the frame entered the network and a customer VLAN identifier. The one bridge identifies an SPB forwarding tree in dependence upon the service VLAN identifier. The SPB forwarding tree specifies a shortest route in the network from the ingress bridge through the one bridge to the other bridges in the network. The one bridge then forwards the received frame to the egress bridge without MAC-in-MAC encapsulation in dependence upon the SPB forwarding tree and the customer VLAN identifier.
Owner:JUMIPER NETWORKS INC
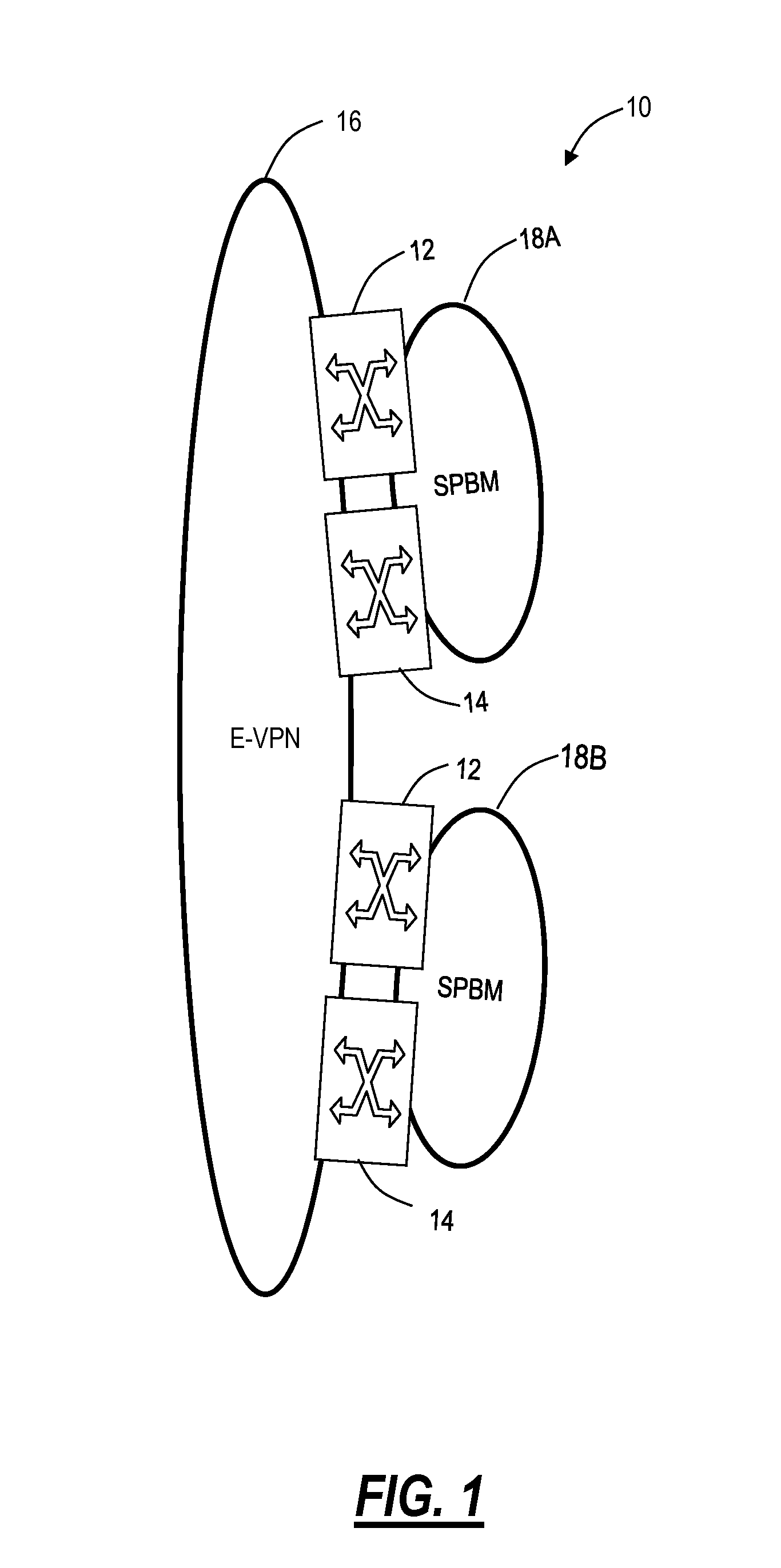
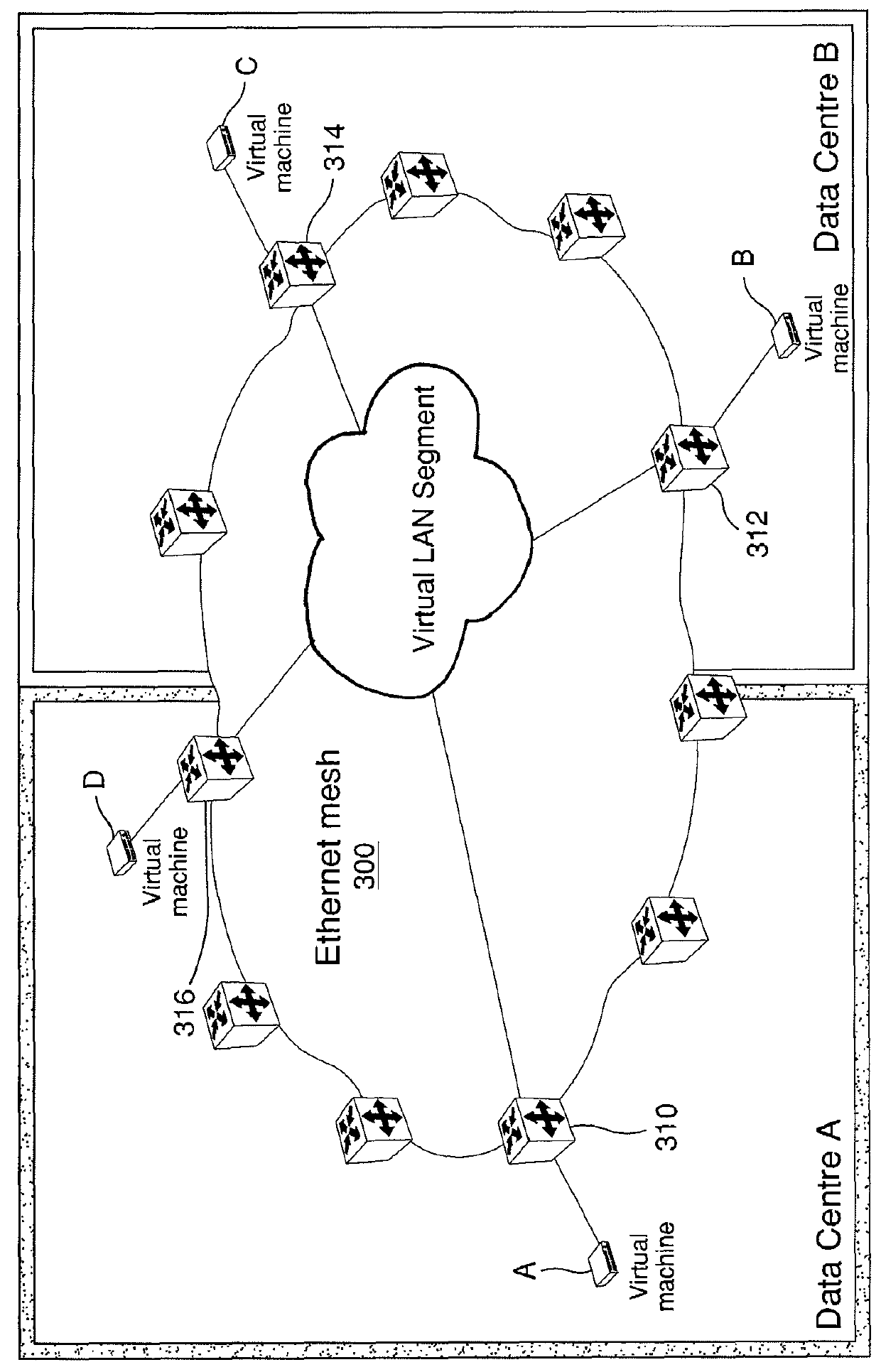
Dynamic Networking of Virtual Machines
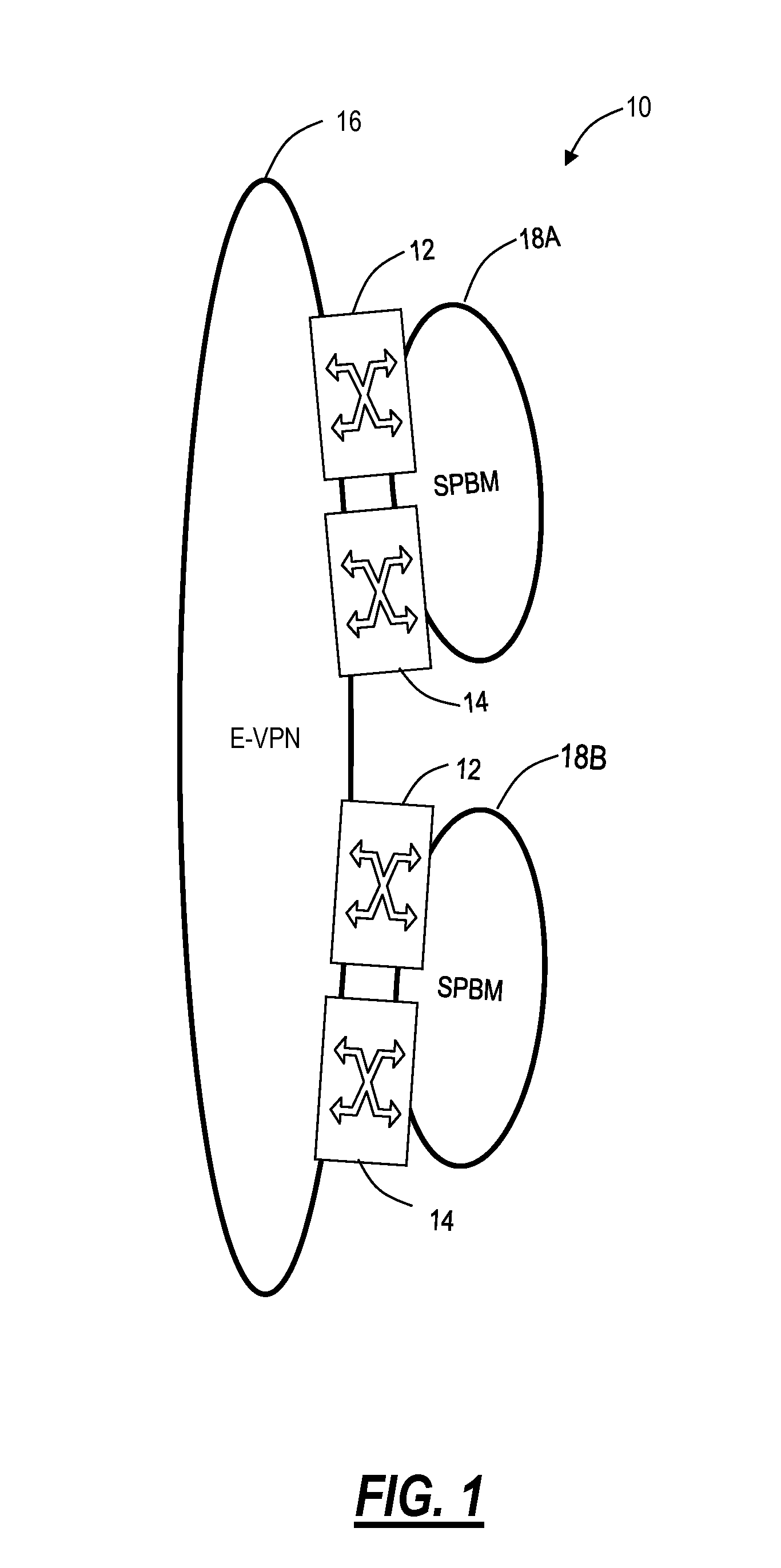
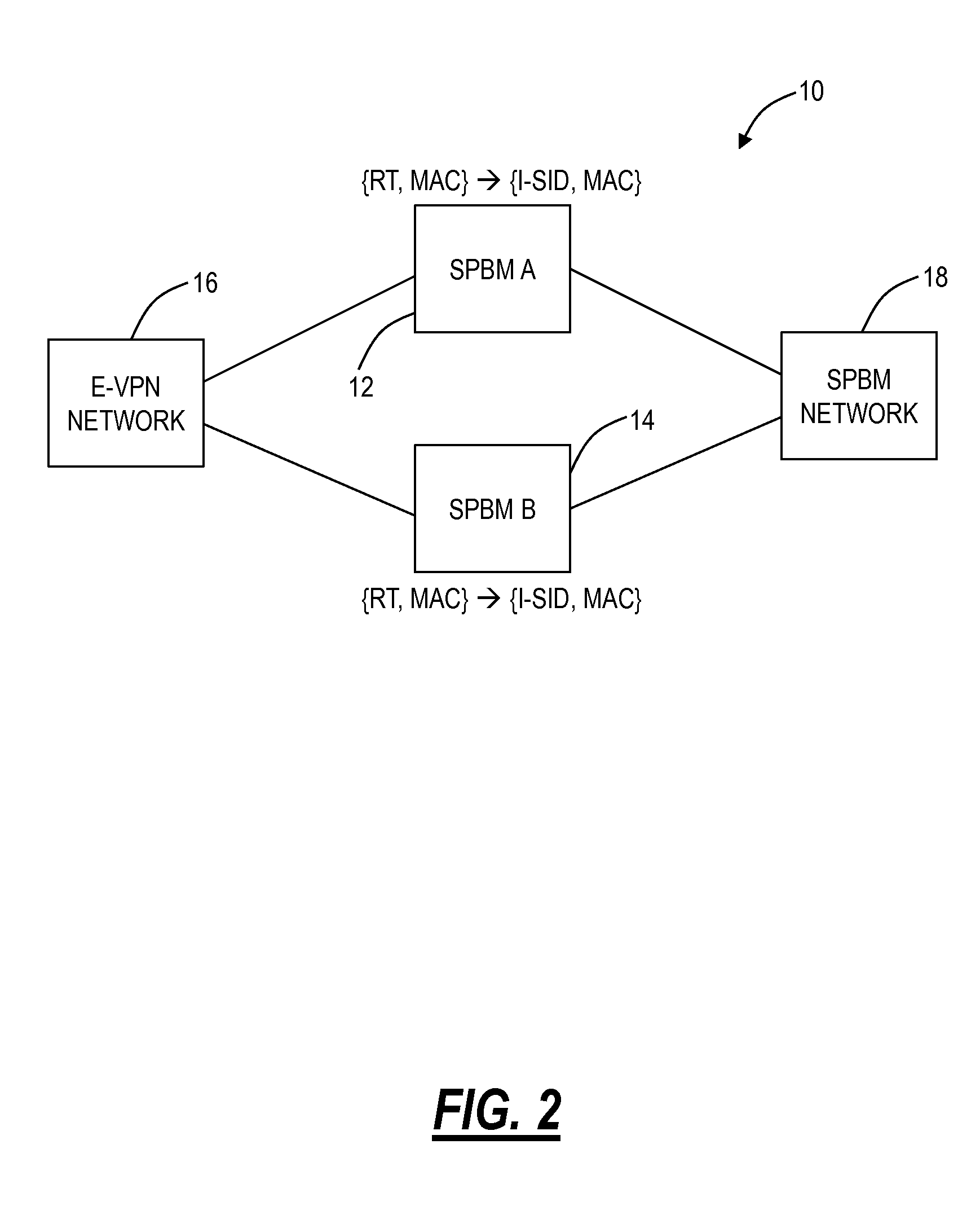
The invention is directed to the use of Provider Backbone Bridging (PBB) technology with Shortest Path Bridging, also called Provider Link State Bridging (PLSB) technology in the context of data centers and virtualized physical servers infrastructures. Virtual servers can be located anywhere inside the data center, or across different data centers, and still act as though they are physically adjacent and share the same Ethernet connectivity. Ethernet virtual machine VLan memberships are mapped to PBB Service Identifiers (I-SIDs). PBB I-SIDs extend the connectivity model to every Ethernet switches in the local, metropolitan or wide area networks. PLSB complements the connectivity by providing dynamic distribution and mapping of I-SID endpoints in the PBB domain. Virtual servers can then be added, removed or transferred to another point in the network and PLSB adjusts the VLan / I-SID specific connectivity pattern to match the physical distribution of the servers.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
Method and system for telecommunications including self-organizing scalable ethernet using is-is hierarchy
ActiveUS20100284418A1Data switching by path configurationLink-state routing protocolShortest path bridging
A first aggregation node in communication with the first network and the second network, the source node and internal nodes of the first network only having knowledge of each other and of the first aggregation node. The system includes a second aggregate node in communication with the second network and the third network, the internal nodes of the second network only having knowledge of each other and the first and second aggregate nodes, the destination node and the internal nodes of the third network only having knowledge of each other and the second aggregation node, the first and second aggregation nodes only having knowledge of each other, the destination node receiving the data from the source node using a link state routing protocol and shortest path bridging through the first second and third networks and the first and second aggregation nodes.
Owner:VIVO MOBILE COMM CO LTD
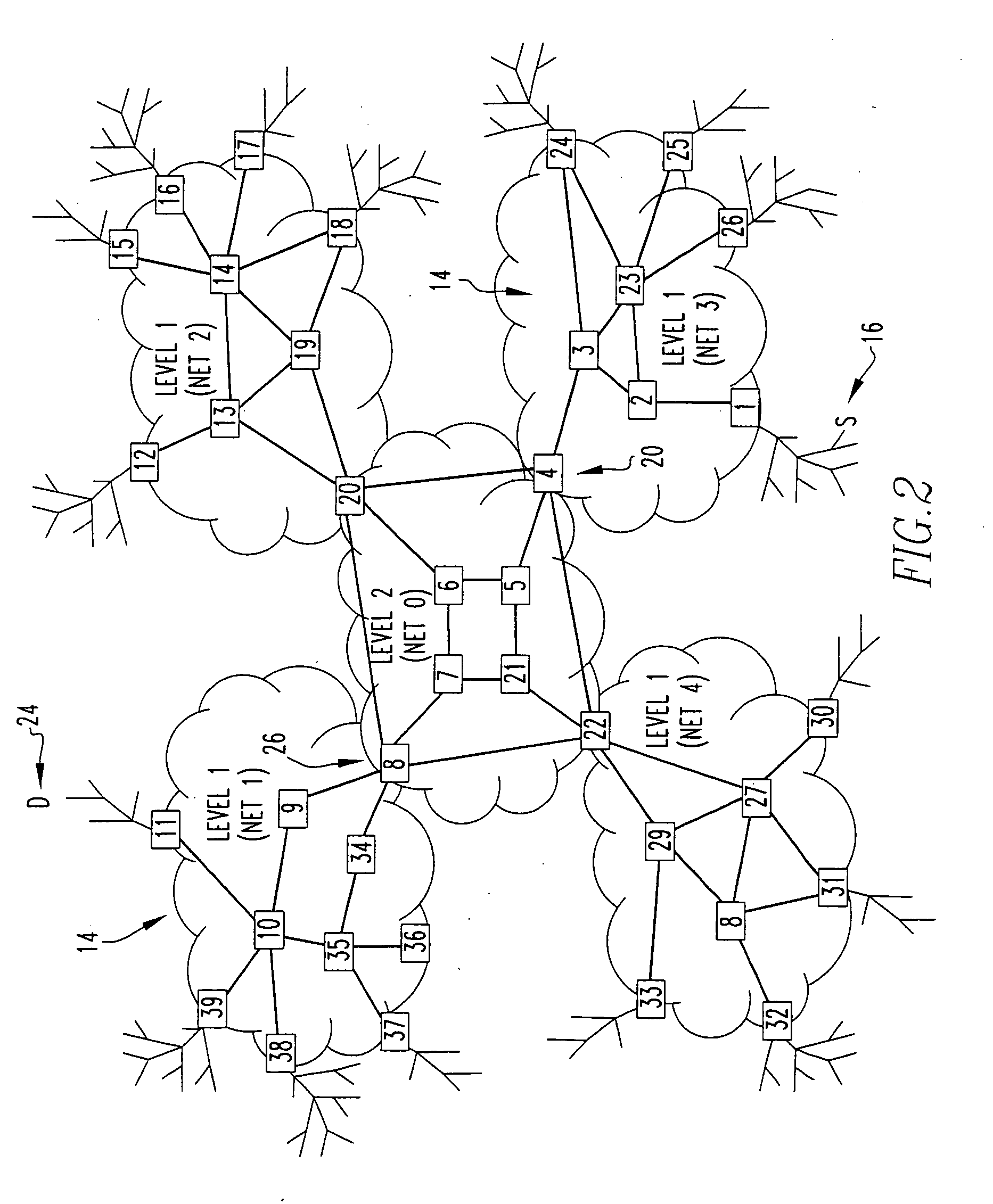
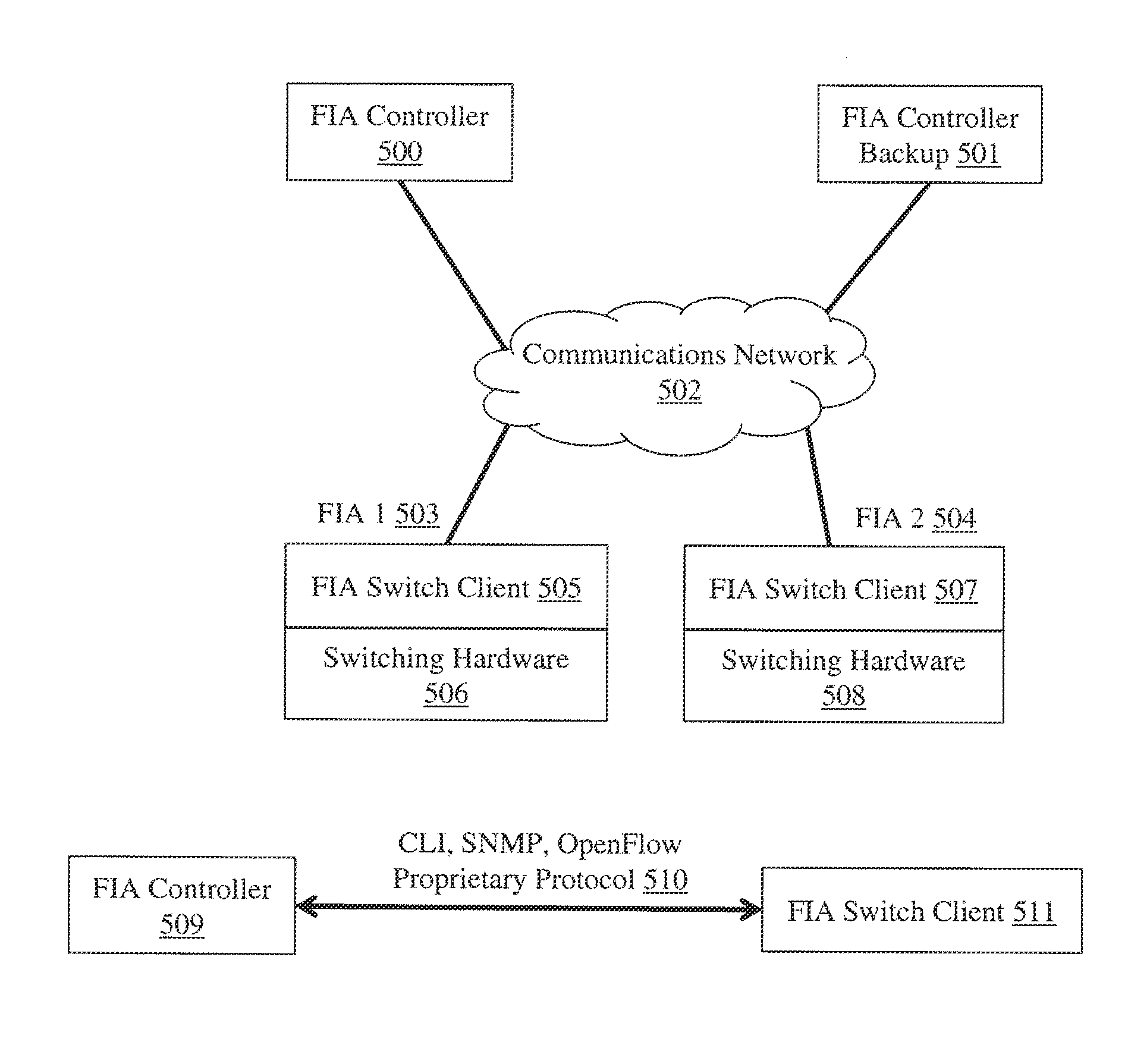
Methods, systems and apparatus for the interconnection of fibre channel over ethernet devices using shortest path bridging
InactiveUS20120177044A1Data switching by path configurationFibre Channel over EthernetInterconnection
Methods, apparatus and systems are provided for forwarding Fibre Channel over Ethernet (FCoE) frames over a Shortest Path Bridged network with a FCoE device interconnection apparatus (FIA). A FCoE frame is received from a FCoE device, the frame including at least destination Ethernet MAC address and source Ethernet MAC address fields. The destination Ethernet MAC address of the incoming frame is replaced with the MAC address of the remote FCoE device as determined by the Fibre Channel destination address identifier in the received FCoE frame. The source Ethernet MAC address of the incoming frame is replaced. The frame is encapsulated in a MAC header. The frame is forwarded to an egress FCoE device interconnection apparatus (FIA). Thereafter, the outer MAC header of the received frame is decapsulated into a FCoE frame. The decapsulated frame is forwarded to an attached FCoE device with the original destination and source Ethernet MAC addresses.
Owner:JEDA NETWORKS
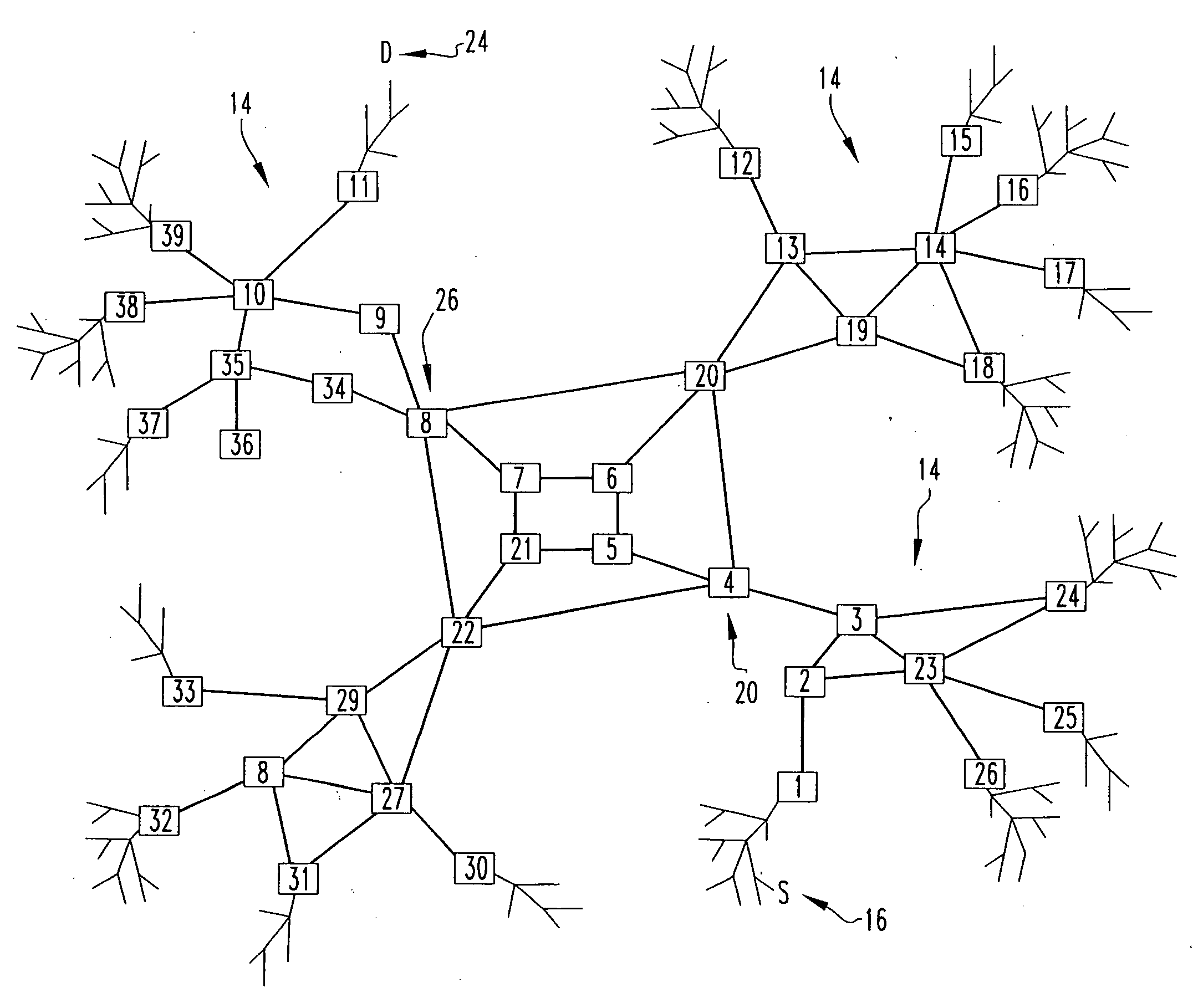
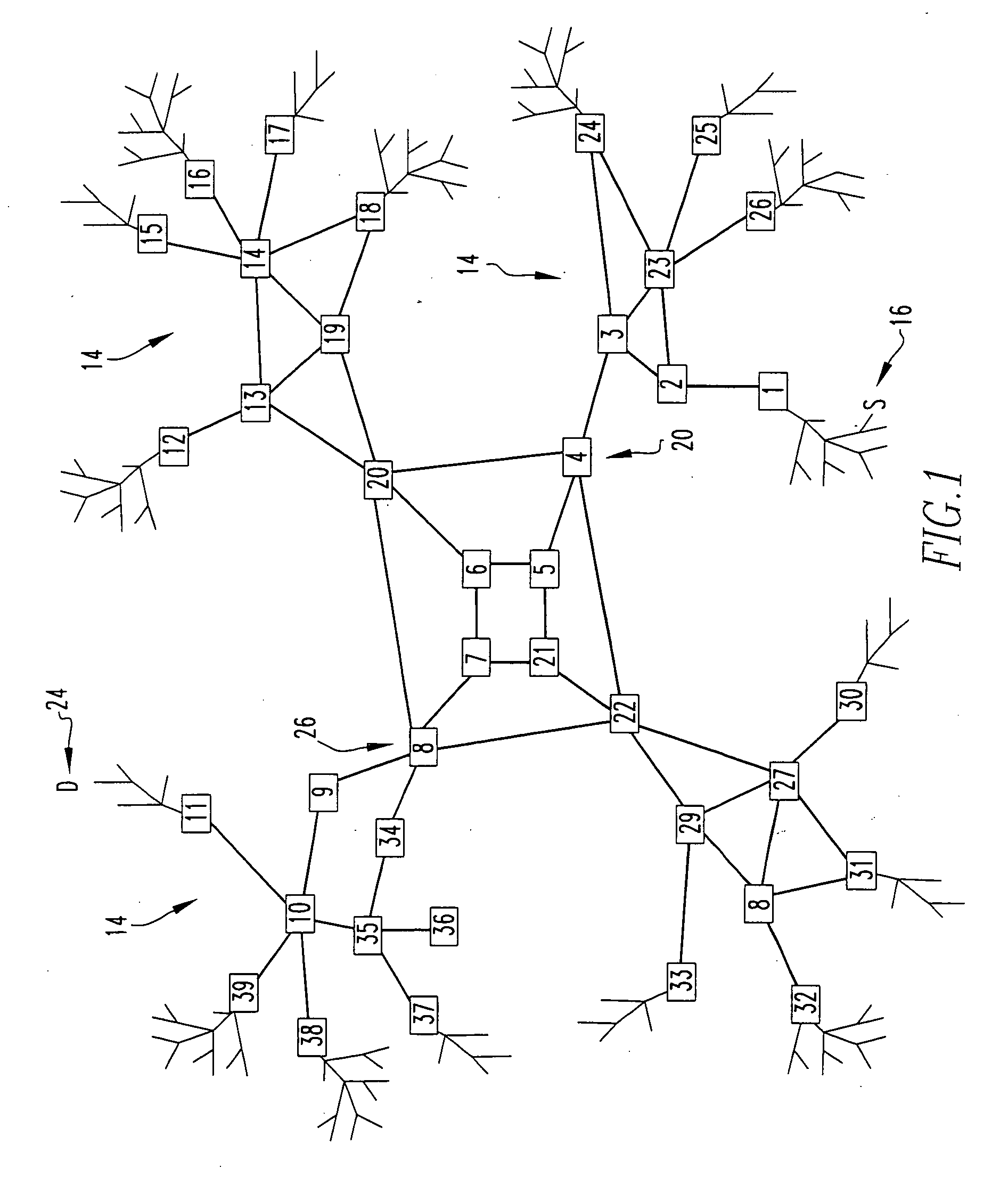
Method And System For Dynamic Routing And/Or Switching In A Network
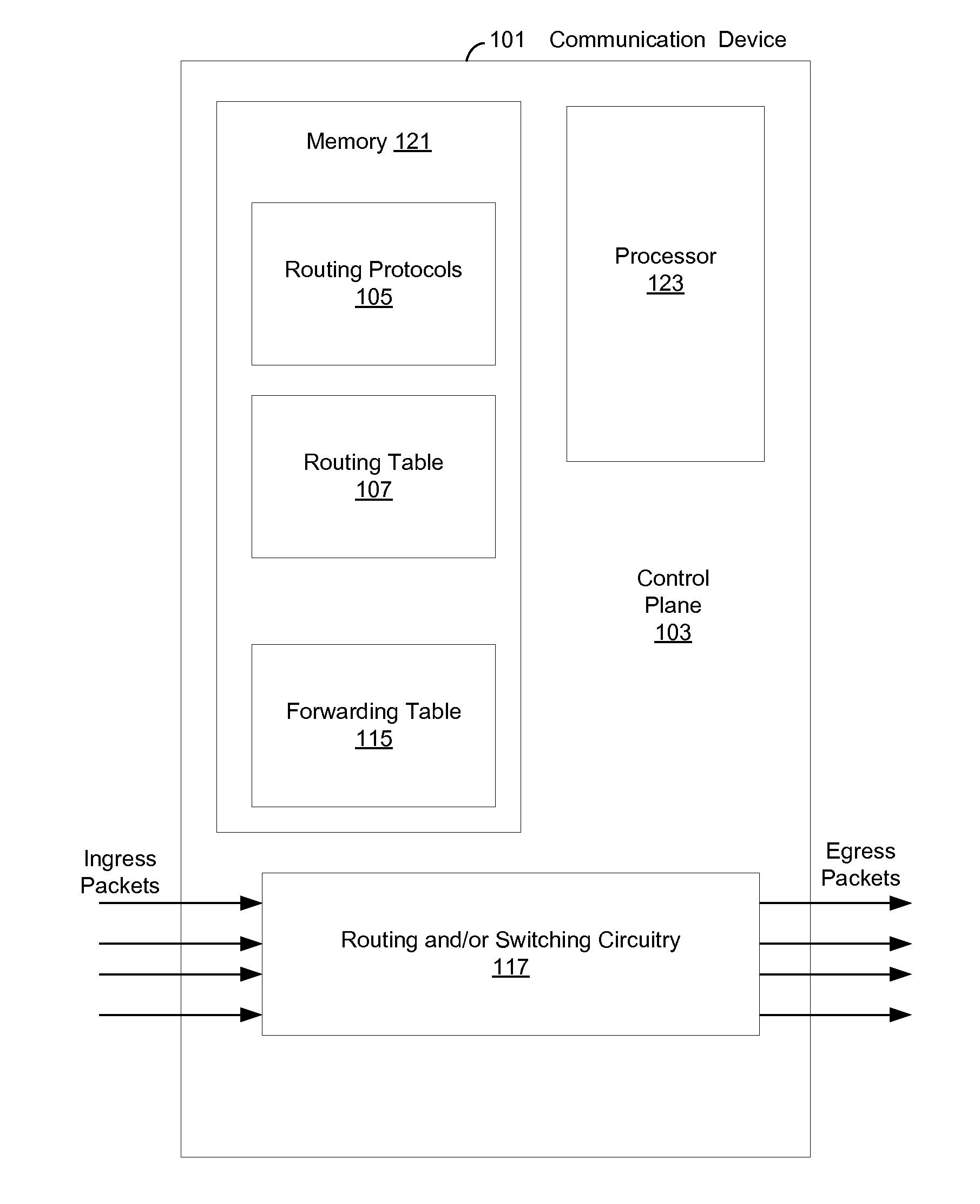
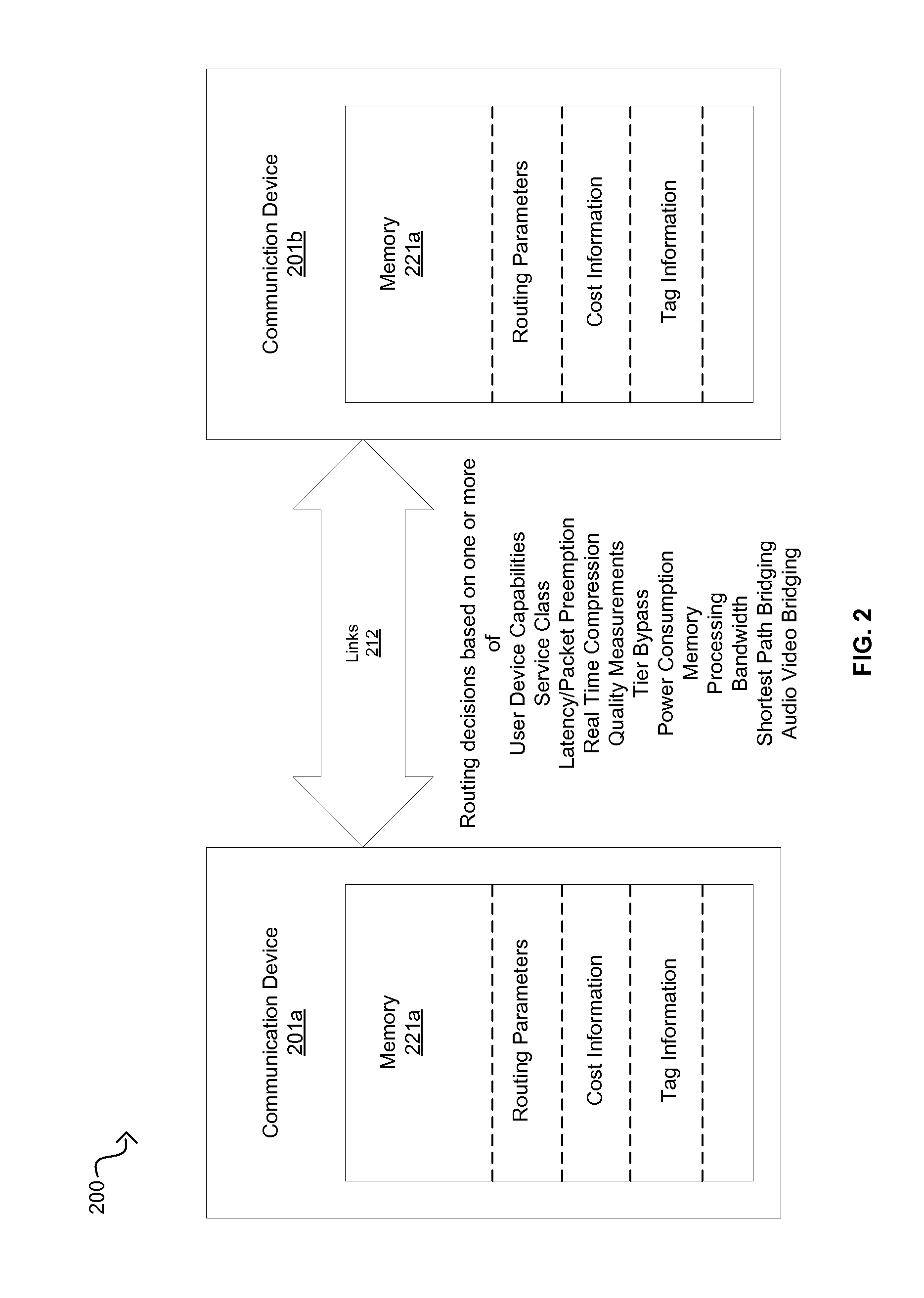
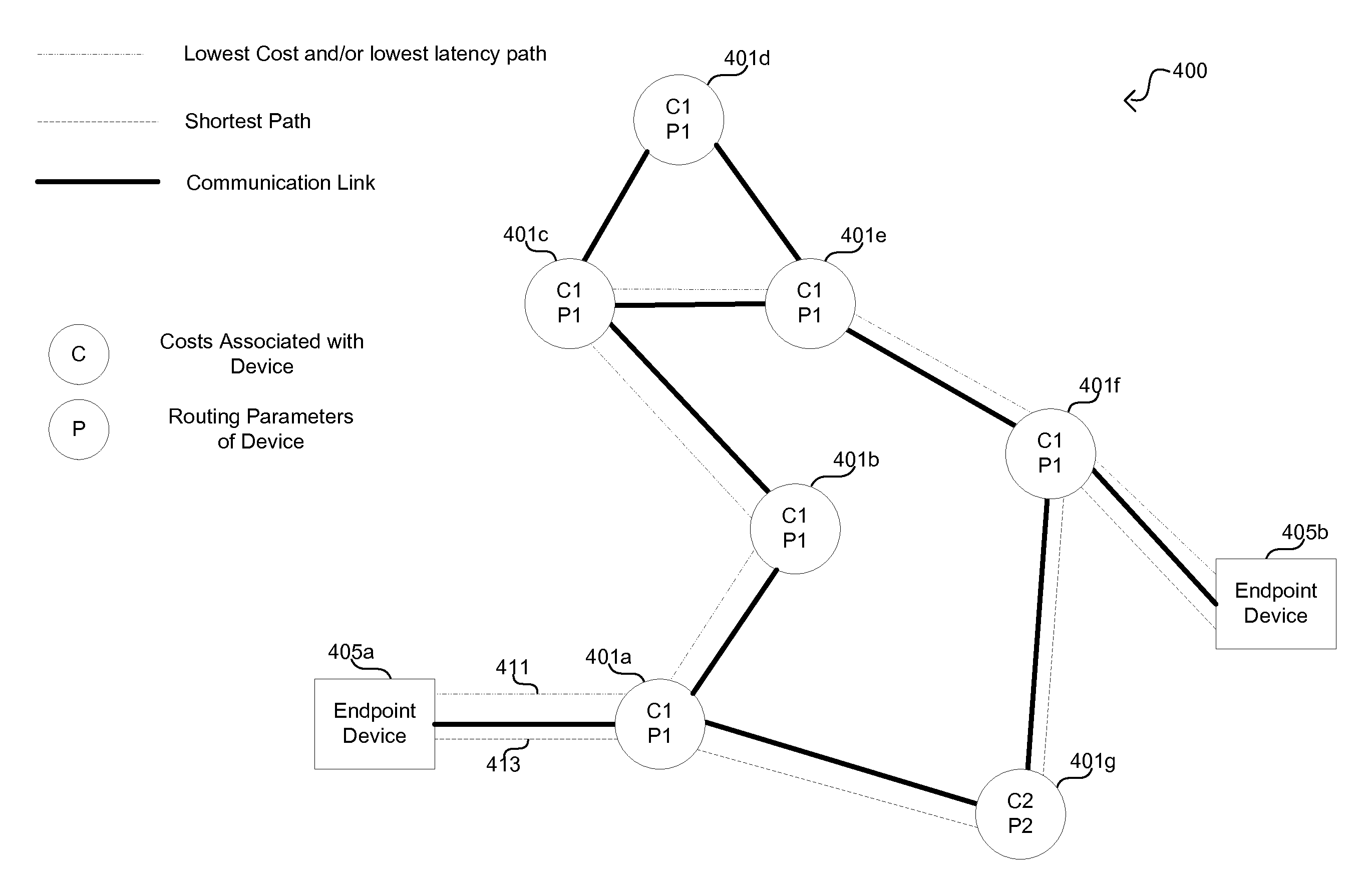
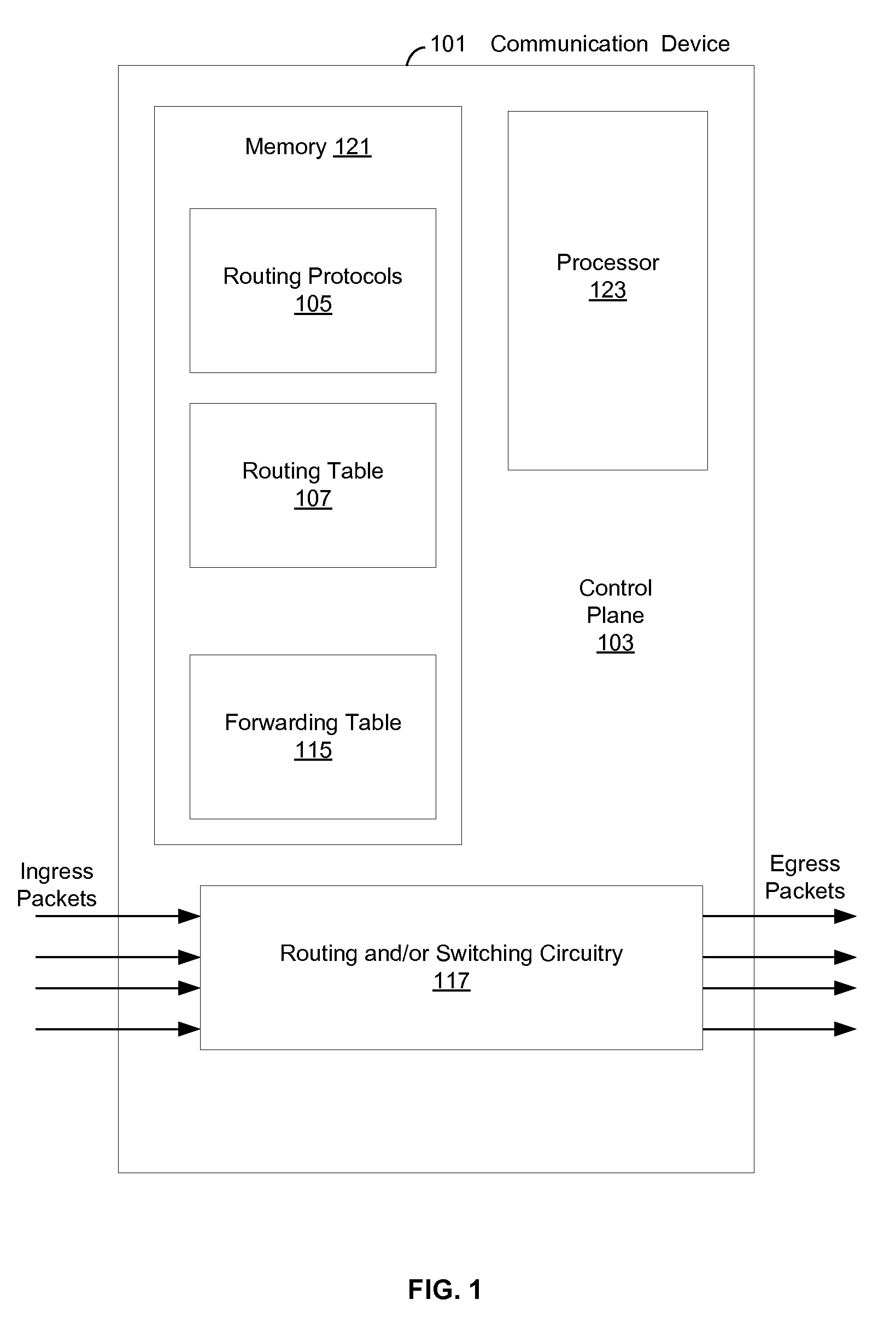
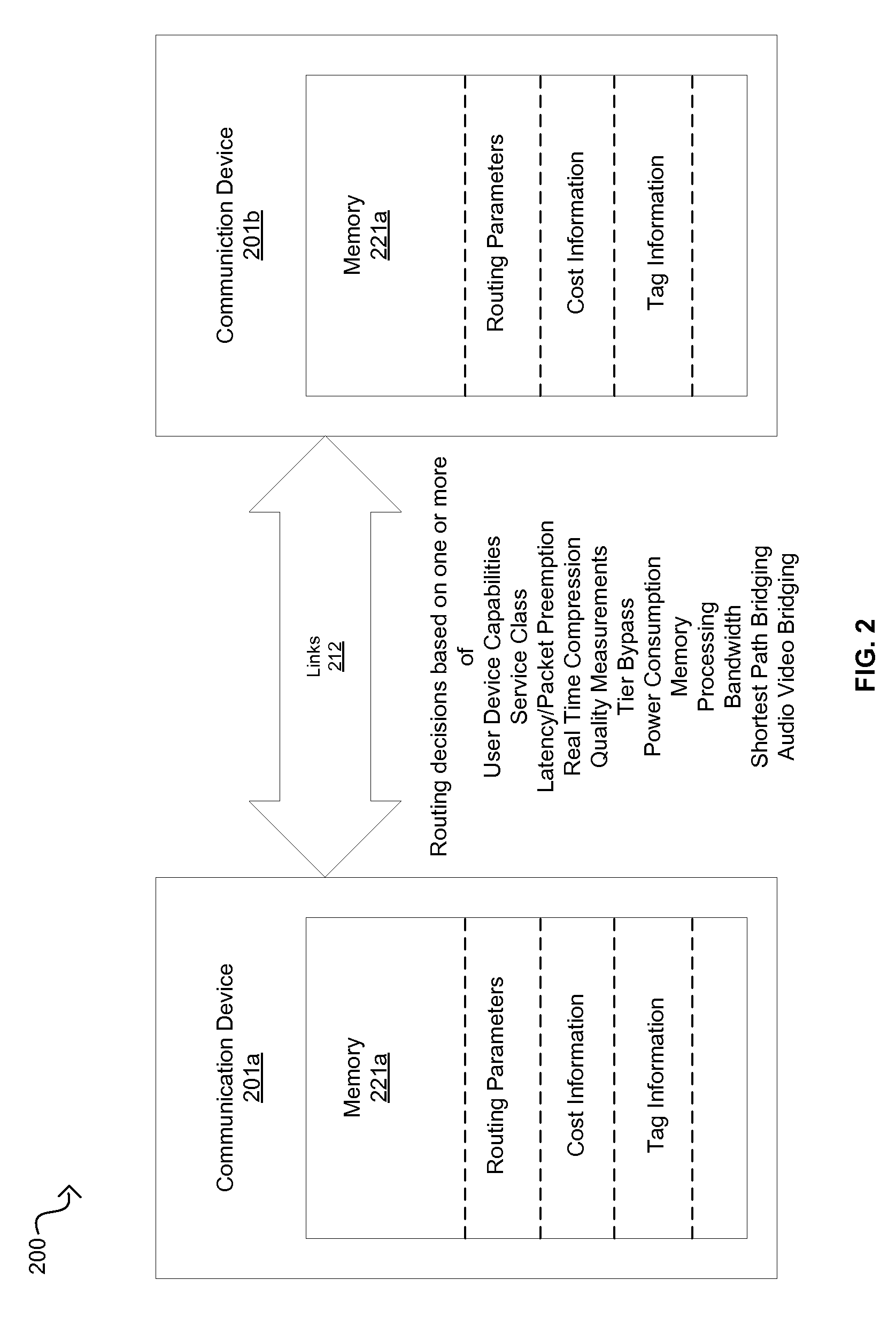
Communication devices may determine routes for packets based on packet marking, routing parameters and / or costs associated with routes. A route may be selected and the packets may be communicated via the selected route. The parameters may comprise service class, real time compression, packet preemption, quality measurements, tier bypass and / or power usage information. The costs may comprise capacity, efficiency and / or performance information for power usage, bandwidth, memory and / or processing. The marking may comprise traffic type, user device capabilities, service class, quality measurements, latency requirements and / or power usage information. Endpoint devices, software applications and / or service providers may insert the marking into packets. Routes may be determined and / or selected based on shortest path bridging, audio video bridging, the marking, the routing parameters and / or the costs. Parameters and / or costs may be received and / or discovered from communication devices. Packets and / or the marking may be parsed and / or inspected. Costs may be based on routing parameters.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Method and apparatus for traffic engineering in shortest path bridged networks
ActiveUS20120076014A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTraffic capacityInternet traffic engineering
A method and apparatus for diverting traffic in a communications network are disclosed. According to one aspect, the invention provides a communications network with a first node and a second node. Connecting these two nodes is a first set of intermediate nodes on a first path (the true shortest path) and a second set of intermediate nodes on a second alternate path. At a first node, a first processor determines whether a packet arriving at the first node must transit the second node. If so, the base virtual local area network (VLAN) identifier (VID) of the packet is replaced by a first VID, and the packet is transmitted along the second path through the second set of intermediate nodes to the second node. At the second node, a second processor determines whether a packet arriving at the second node must transit the first node. If so, the base VID of the packet is replaced by a second VID different from the first VID and different from the base VID, and the packet is transmitted along the second path through the second set of intermediate nodes to the first node.
Owner:CIENA
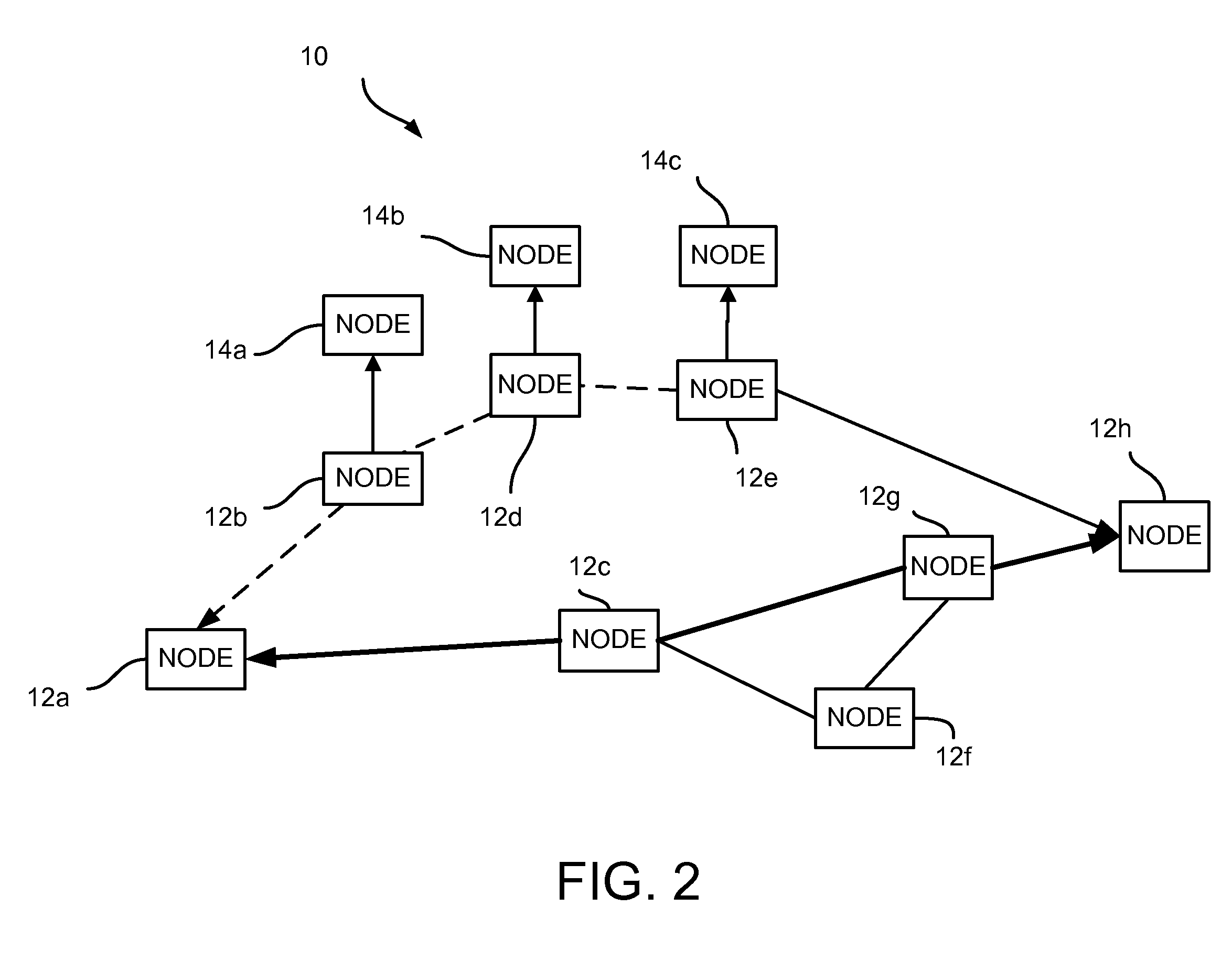
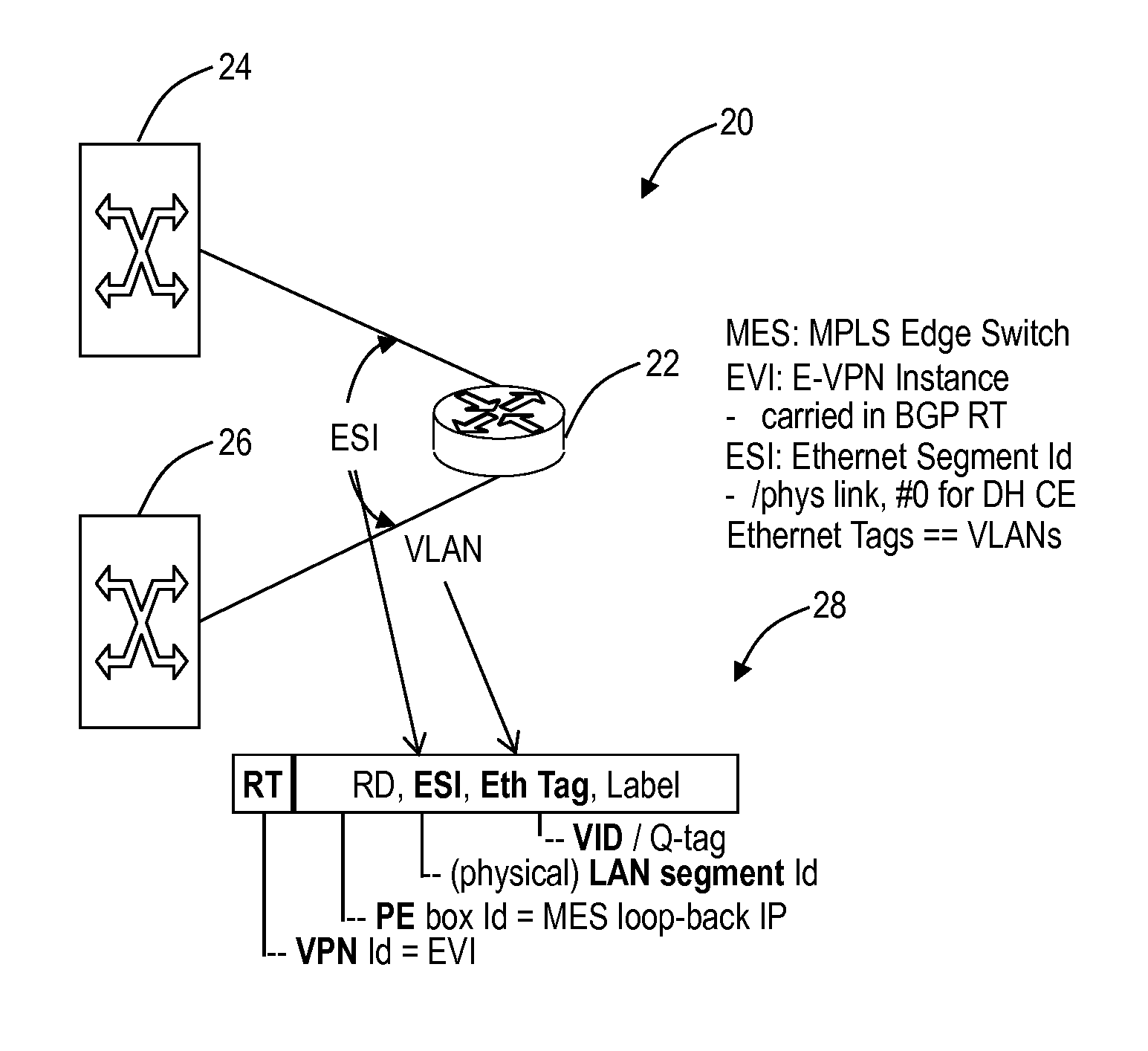
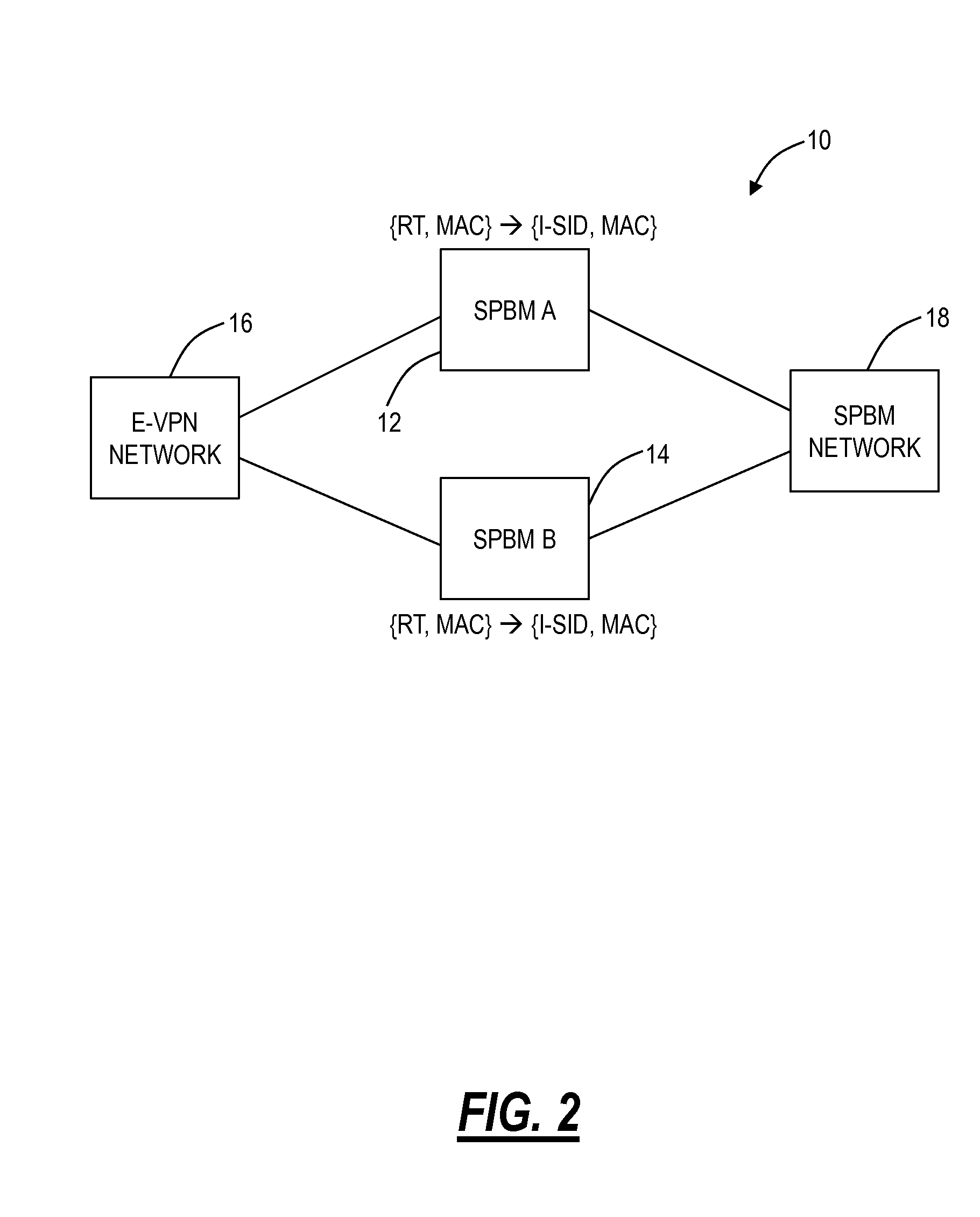
Resilient interworking of shortest path bridging and ethernet virtual private networks
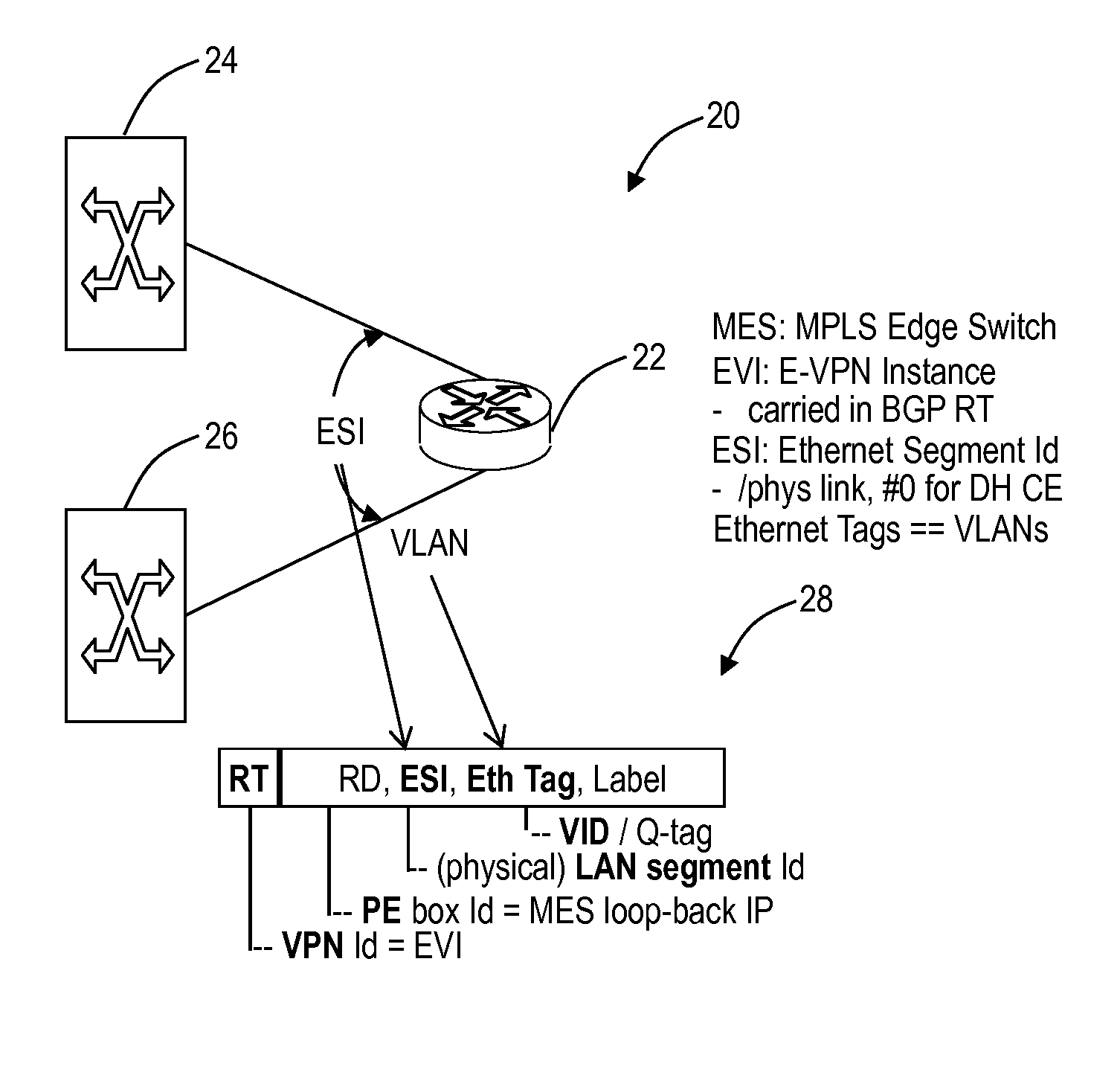
An Ethernet network, an Ethernet method, and an Ethernet node provide active-active dual-homed interworking between two Ethernet networks. The network, method, and node can include two nodes interconnected each to a Shortest Path Bridging (SPB) network and an Ethernet Virtual Private Network (E-VPN). The two nodes can utilize a same Ethernet Segment Identifier (ESI) for the E-VPN network to cause the dual-homed links to appear as a single link from an E-VPN perspective and a dummy node to advertise an extra node in the SPB network enabling two paths therein.
Owner:CIENA
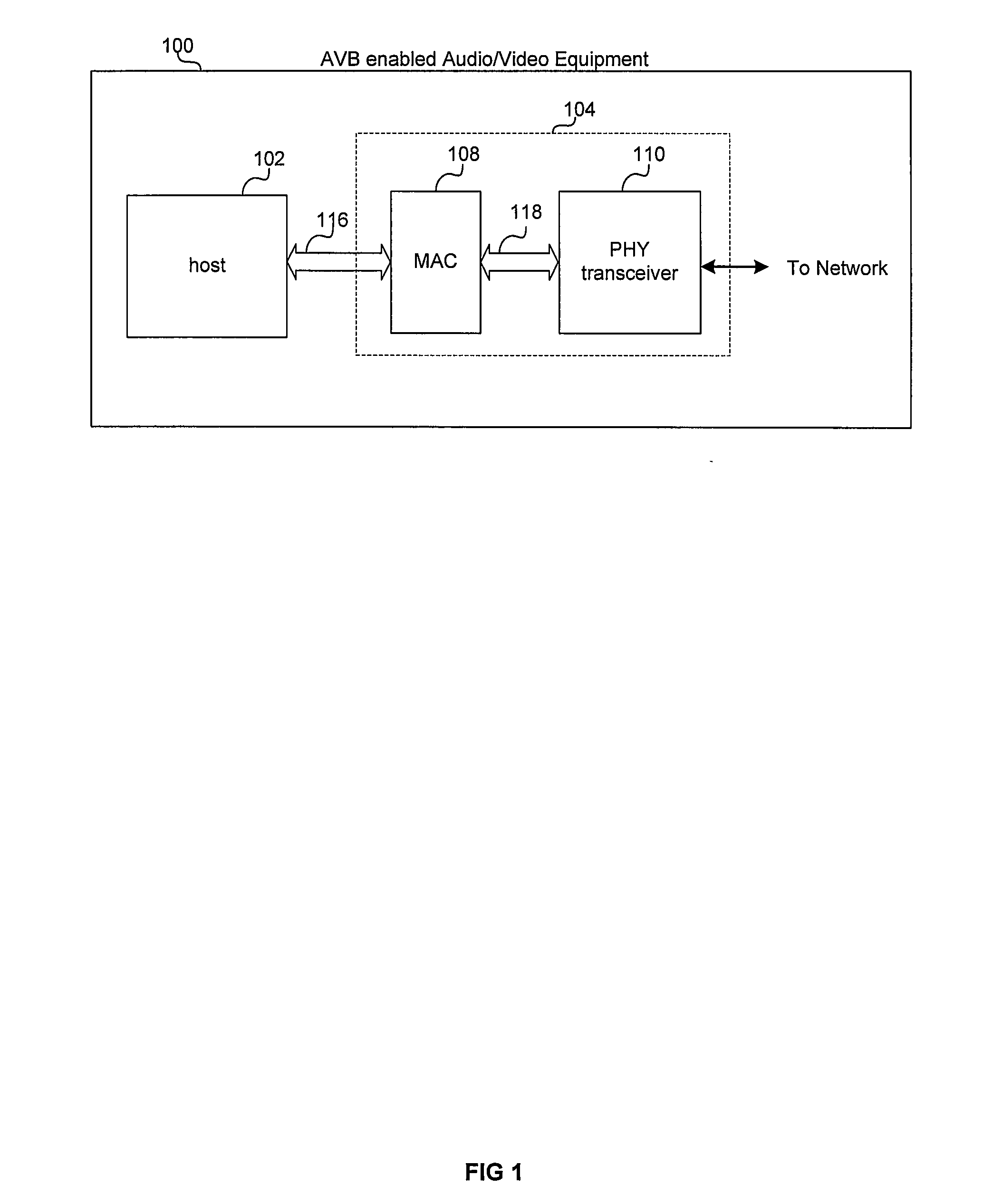
Method and system for audio/video bridging aware shortest path bridging
InactiveUS20080285459A1Least costEnergy efficient ICTTelevision system detailsQuality of serviceLeast cost
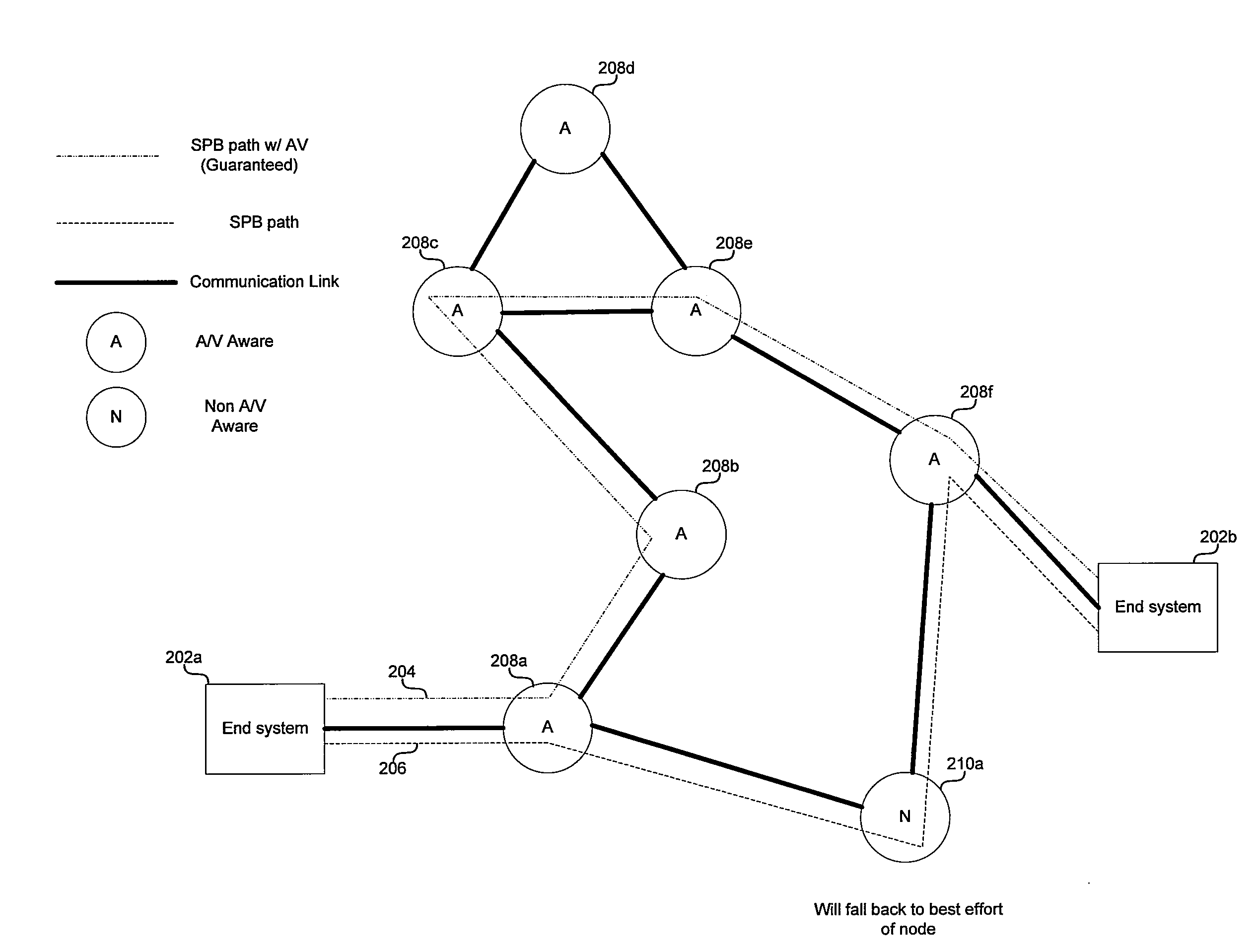
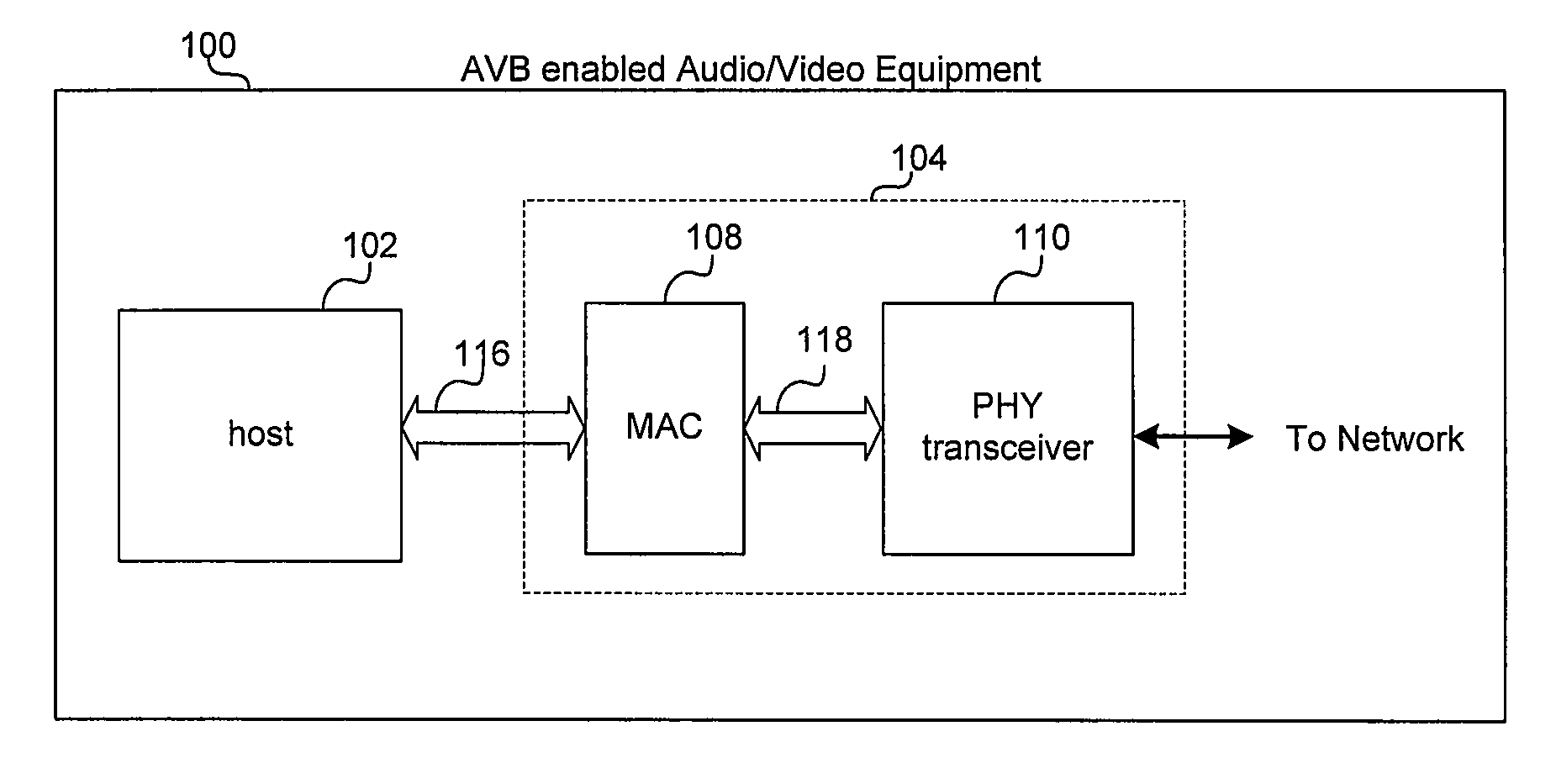
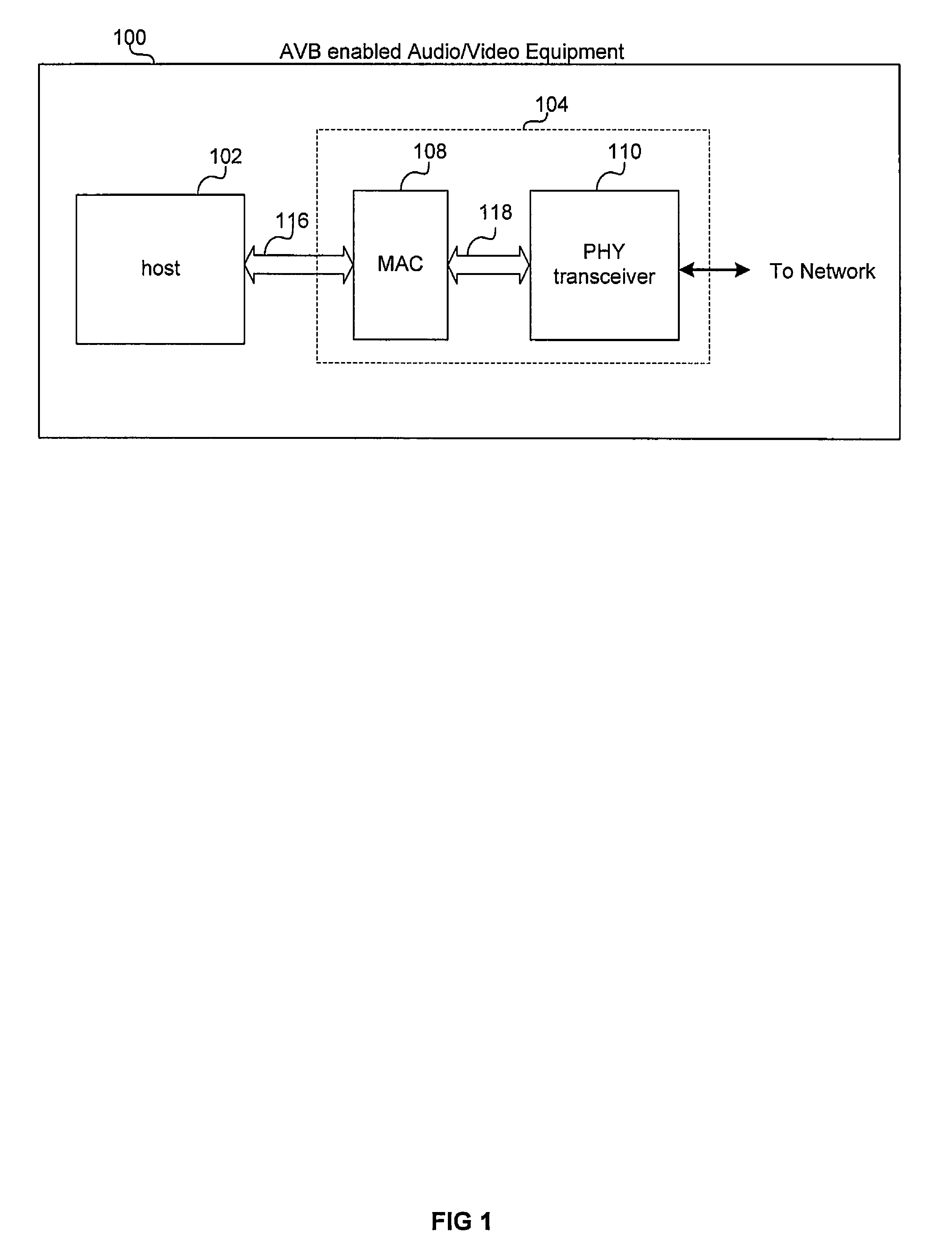
Aspects of a method and system for Audio / Video Bridging aware shortest path bridging are provided. In this regard, network nodes which are AVB enabled and capable of routing information based on a desired path cost and / or a desired quality of service (QoS) may be identified, and an AVB enabled path comprising one or more of the identified nodes may be established for communication over a network. In this regard, the desired cost may be a least cost and may be the “shortest path” between two nodes in a network. Additionally, the nodes maybe identified using Shortest path Bridging protocols and / or Audio Video Bridging protocols and / or extensions thereof. Also, bridge protocol data units may be exchanged to identify the nodes.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
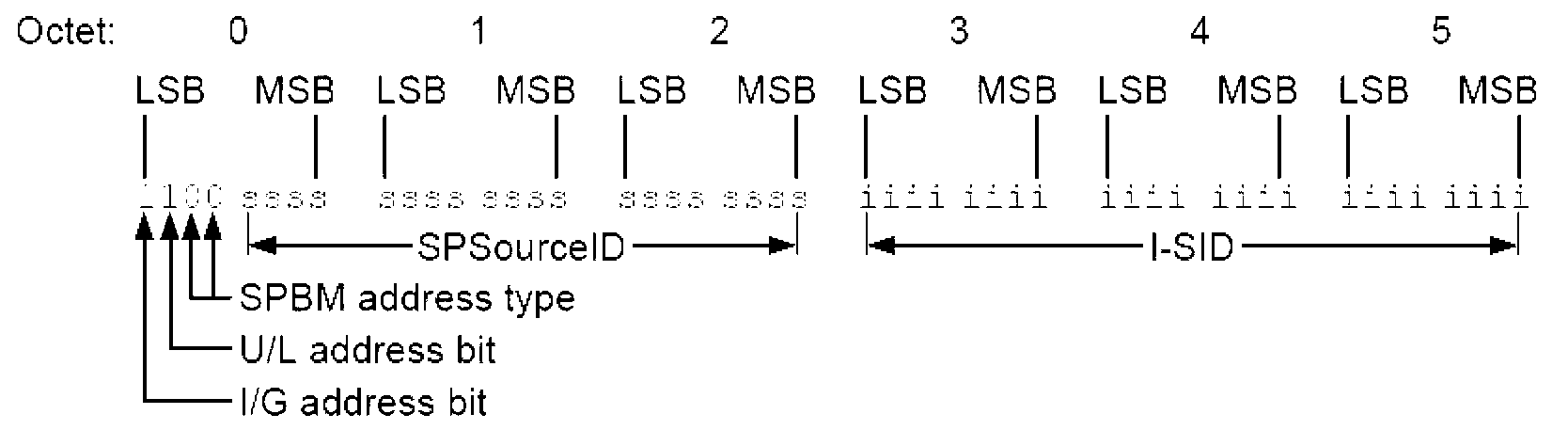
LSP (Layered Service Provider) information flooding method and equipment in SPBM (Shortest Path Bridging MAC)
ActiveCN102882784AFast convergenceIncrease the speed of floodingData switching networksLayered Service ProviderNetwork topology
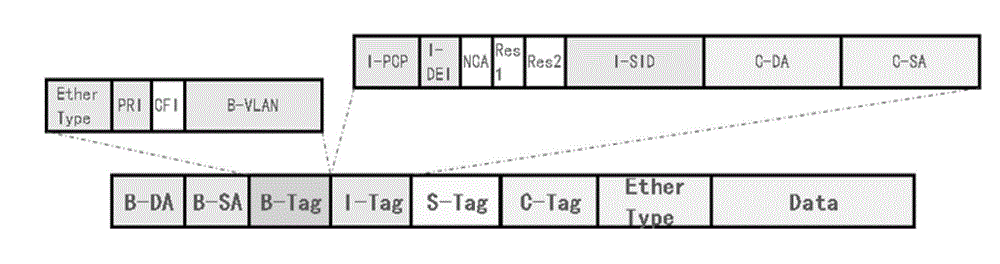
The invention discloses an LSP (Layered Service Provider) information flooding method and equipment in an SPBM (Shortest Path Bridging MAC). A data plane of each backbone network bridging equipment in the SPBM network is maintained by a unicast FDB (Forwarding Database) table. The method comprises the following steps of: generating new LSP information according to the variation of network topology after the variation of the network topology is detected; and using B-MAC (Multiplexed Analogue Components) addresses and corresponding B-VLANs (Virtual Local Area Network) of all the other backbone network bridging equipment locally saved to create an IS-IS (Intermediate System to Intermediate System) LSP message with the new LSP information and sending out the IS-IS LSP message by a transceiving port corresponding to the B-MAC address in the unicast FDB table, wherein the B-MAC address in the IS-IS LSP message refers to the B-MAC address of the other backbone network bridging equipment, and a B-VLAN tag is filled with the B-VLAN corresponding to the B-MAC address of the other backbone network bridging equipment. According to the invention, the flooding speed is raised, time spent in the flooding process is shortened, and the convergence performance of the SPBM network is improved.
Owner:紫光恒越技术有限公司
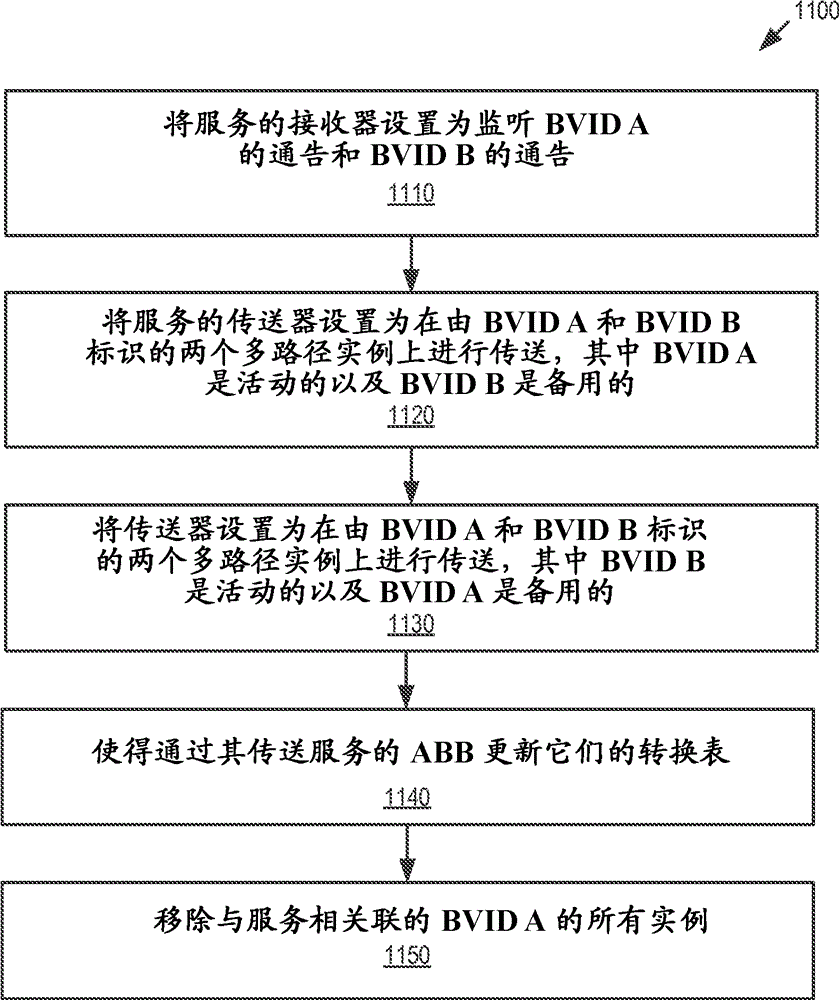
Load balancing in shortest-path-bridging networks
A flow classification process is used at the edge of the shortest path bridging network to determine a flow label (320) for attachment to a client frame (330) entering the network. Any of several flow labels (320) can be assigned to a client frame (330) traversing the network to a particular egress node, and the flow labels are used by forwarding nodes to select among multiple equal -cost paths. In several embodiments, the flow label is calculated as a function of the client frame contents, which provide an entropy source for randomizing the selection of the flow label. This entropy source comprises the Internet Protocol (IP) header in the client frame, in some embodiments, but may comprise other client frame content in other cases.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Method for separating different virtual LAN services
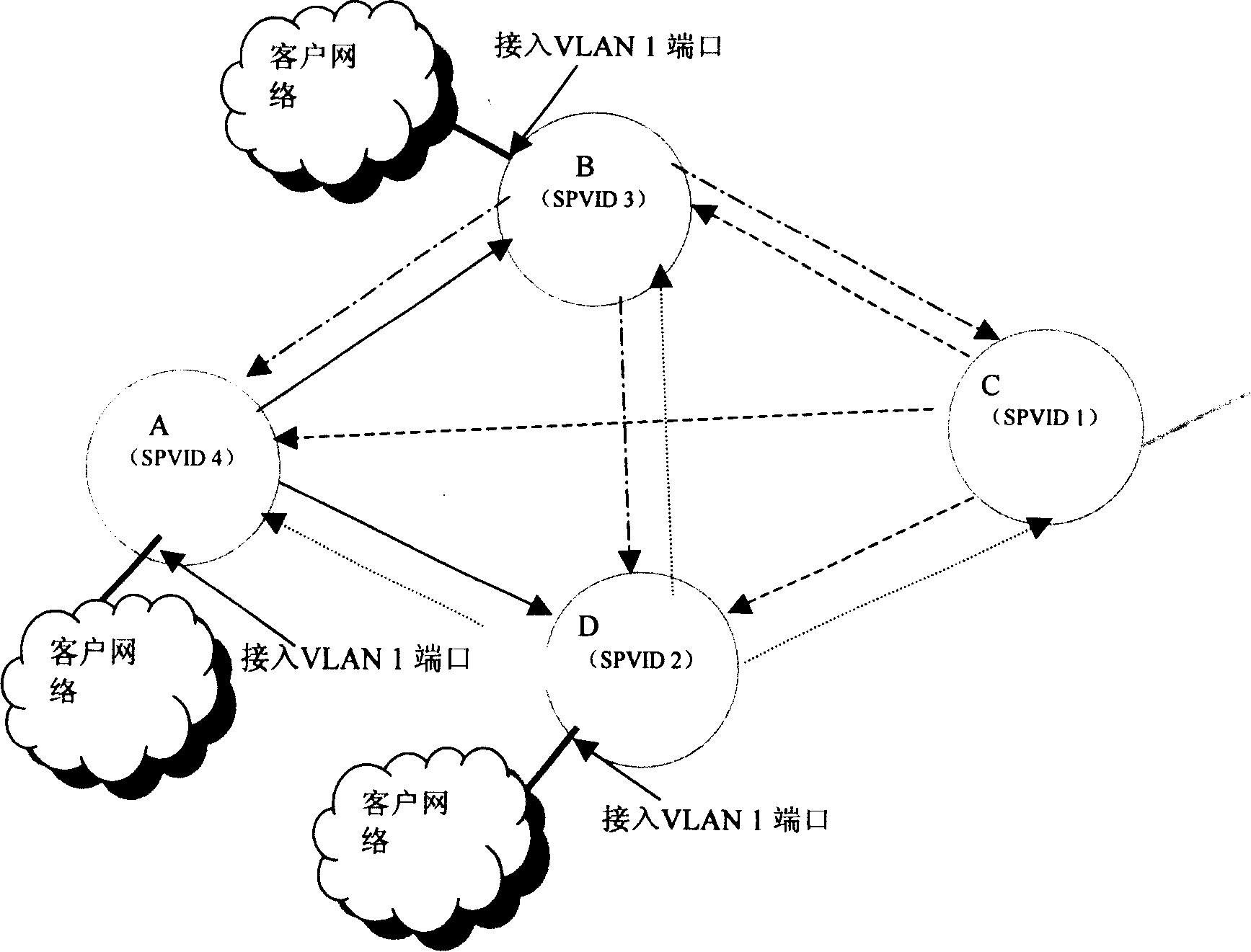
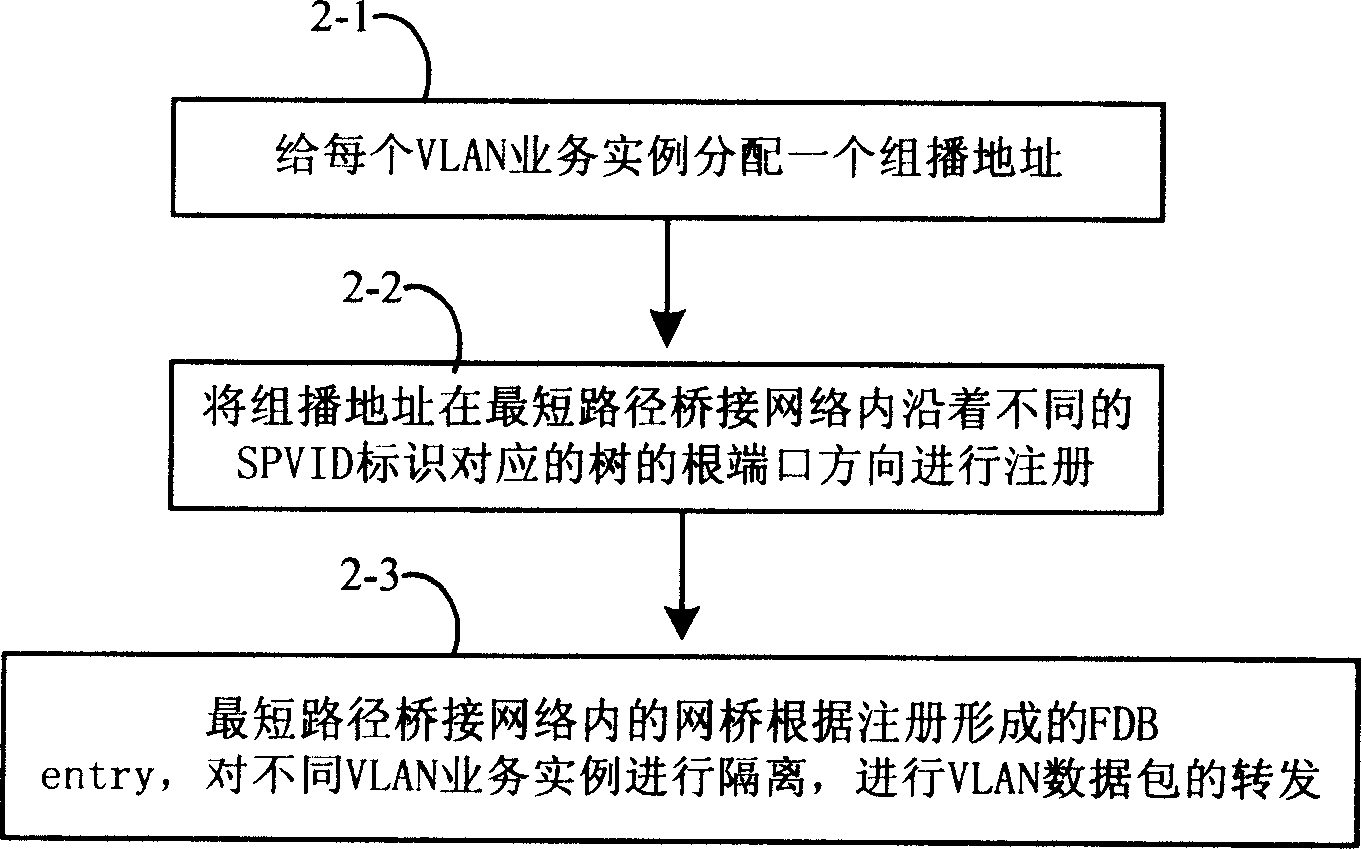
InactiveCN101166137AGuaranteed isolationRealize transparent processingNetworks interconnectionNetwork connectionsVirtual LANNetwork packet
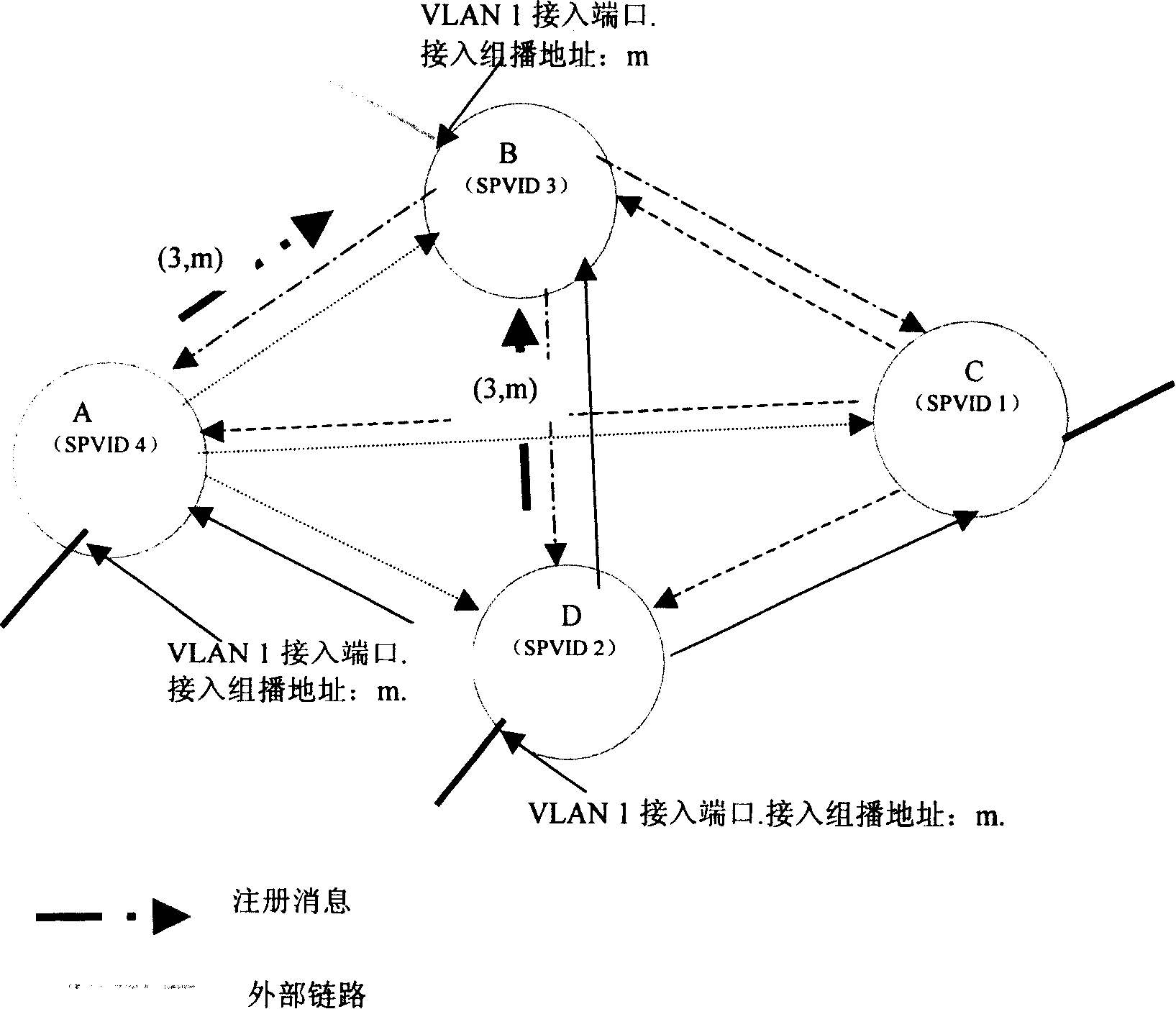
The method includes following steps: assigning ID information for service instance connected to virtual local area network (VLAN) in bridge network with shortest path (BNSP); the said access bridge transfers the said ID information along direction of root ports of different entry trees in BNSP; based on the said ID information received along direction of root port of entry tree, the access bridge in BNSP identifies VLAN service instance. The method can insulate different VLAN services in BNSP so as to guarantee that VLAN service data packets are transmitted within VLAN area.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Route bridging method, network bridge equipment and bridging network
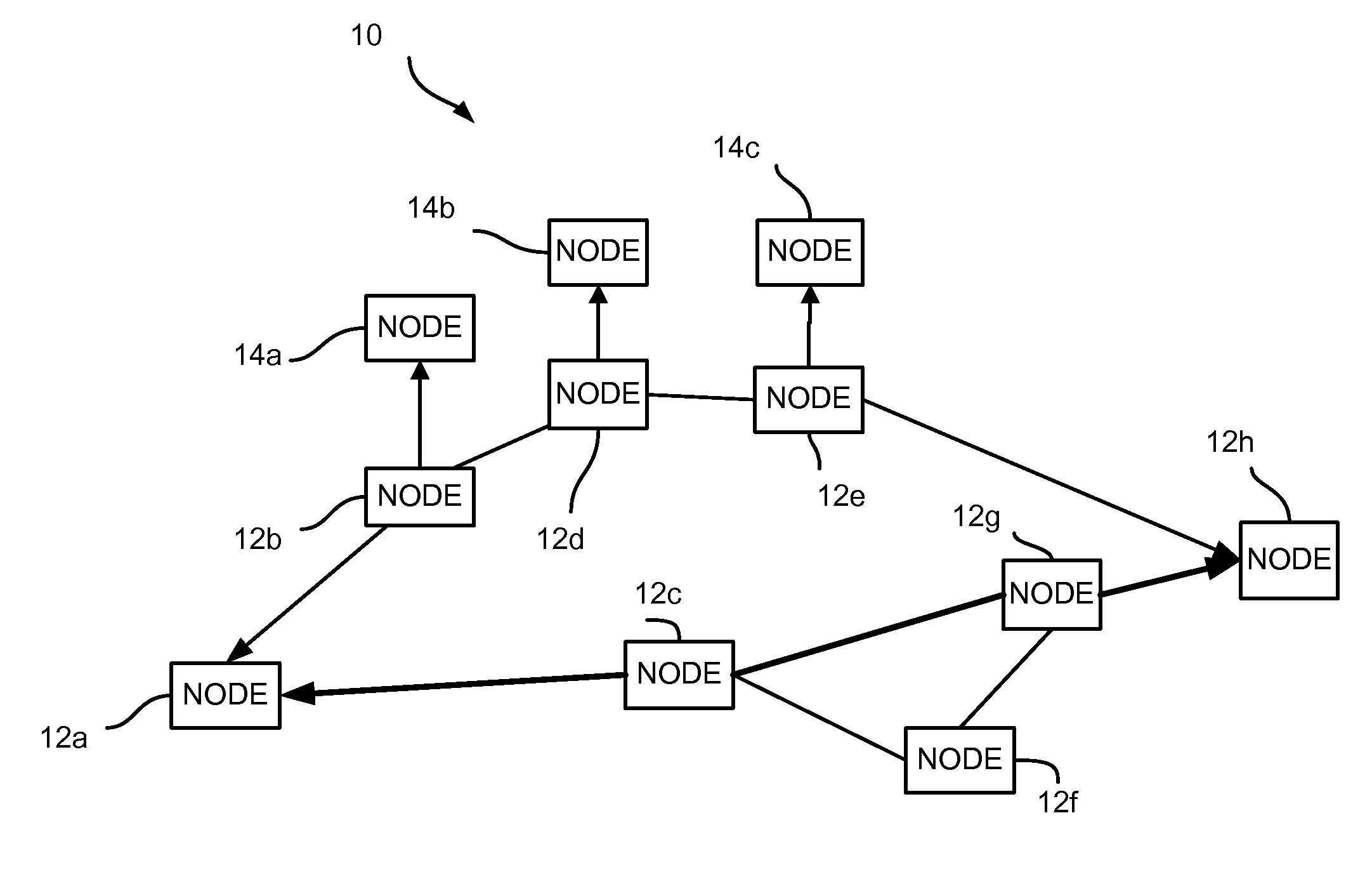
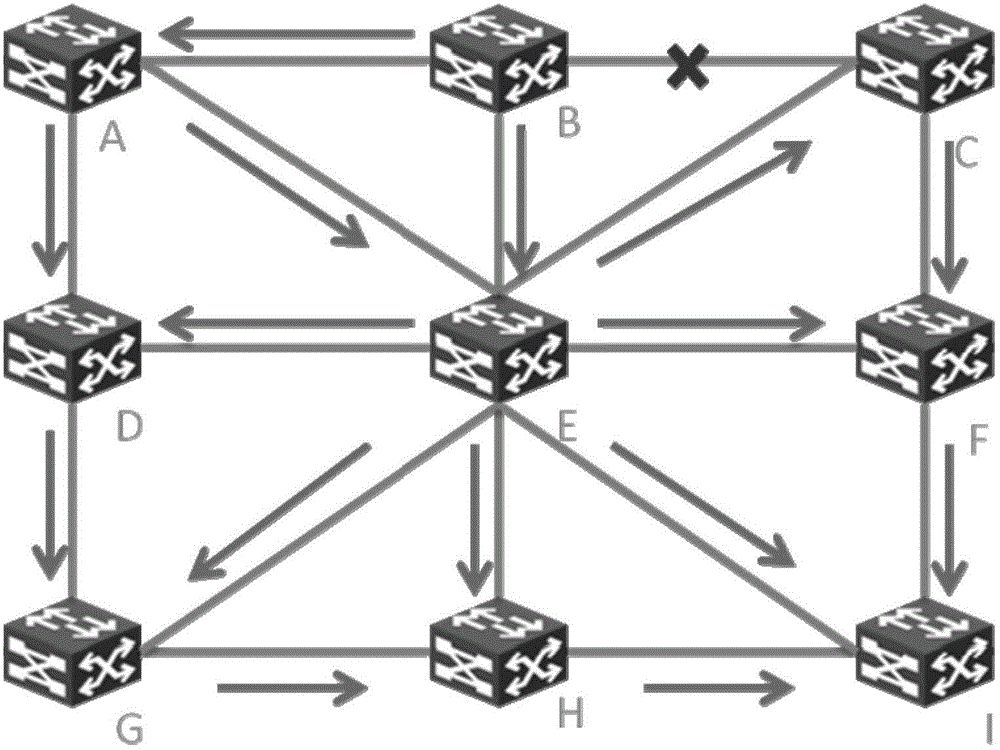
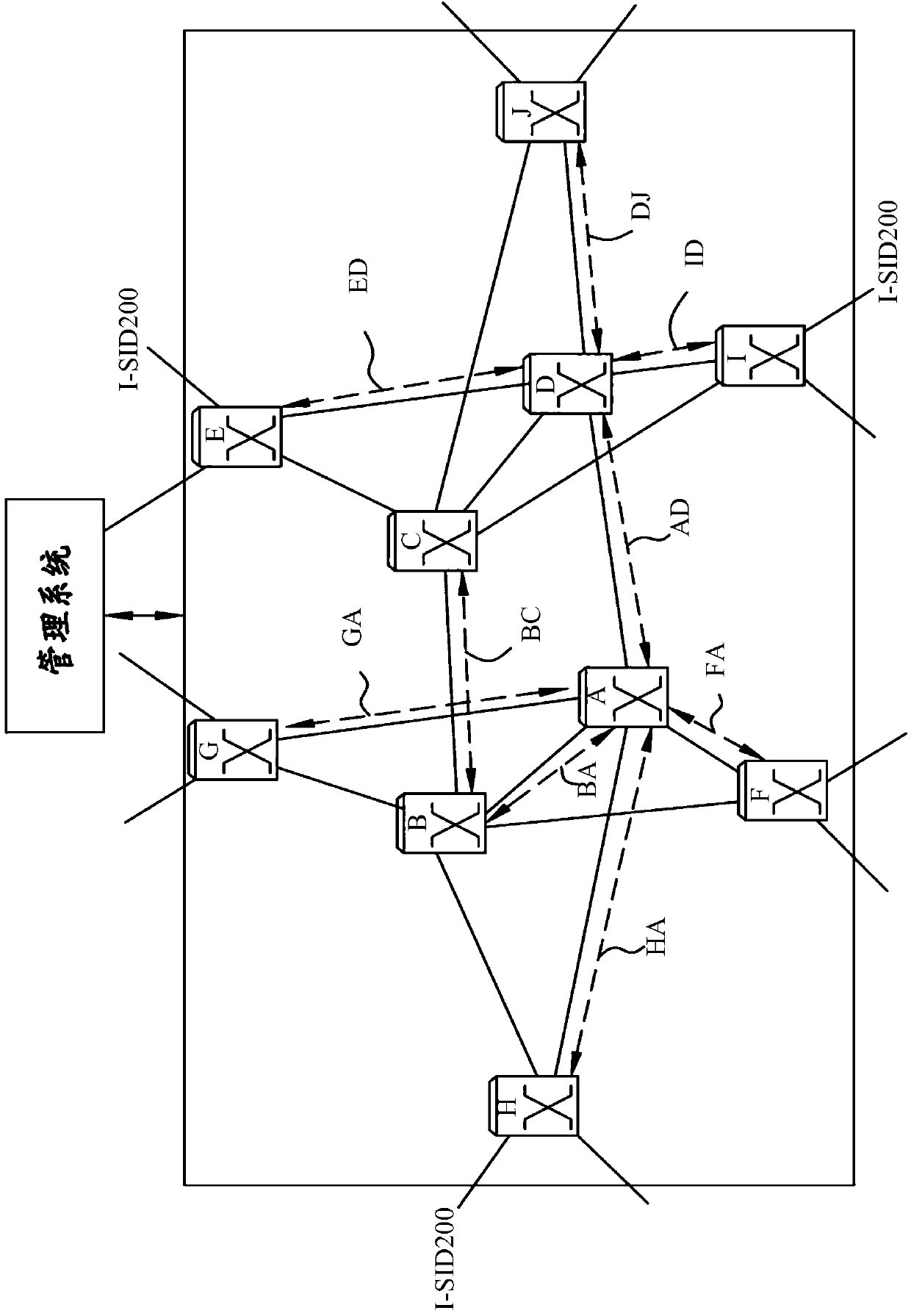
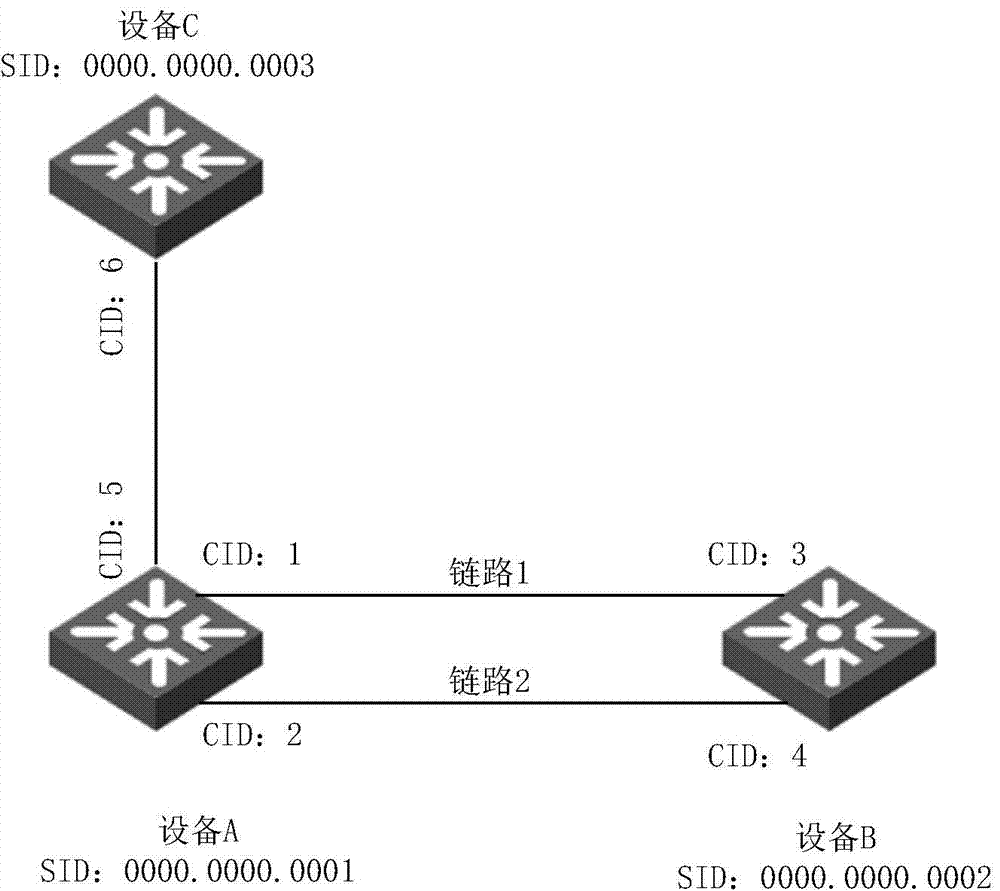
The invention discloses a path bridging method, network bridge equipment and a bridged network. The route bridging method comprises the steps that: all nodes in the bridged network respectively calculate the shortest path tree which takes the node as a root; a first node determines an output port reaching a second node according to the shortest path tree which takes the first node as the root and is calculated by the first node, and transmits a notification protocol message through the output port so as to lead the nodes receiving the notification protocol message to acquire that an input port of the notification protocol message belongs to a shortest path tree topology which takes the second node as the root; the first node determines the input port of the notification protocol message transmitted by other nodes; the first node adds the determined output port and input port to the shortest path tree topology which takes the second node as the root; and the first node transmits data frames according to the ports contained in the shortest path tree topology which takes the second node as the root. The shortest path tree topology can be based on VLAN, and also multicast MAC address. The implementation mode perfects the shortest path bridging technology.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
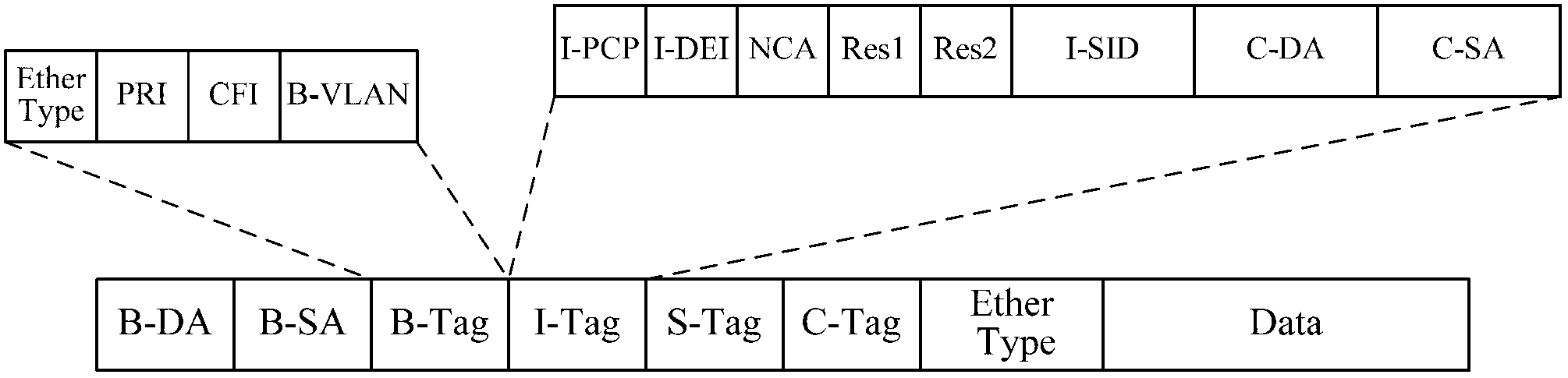
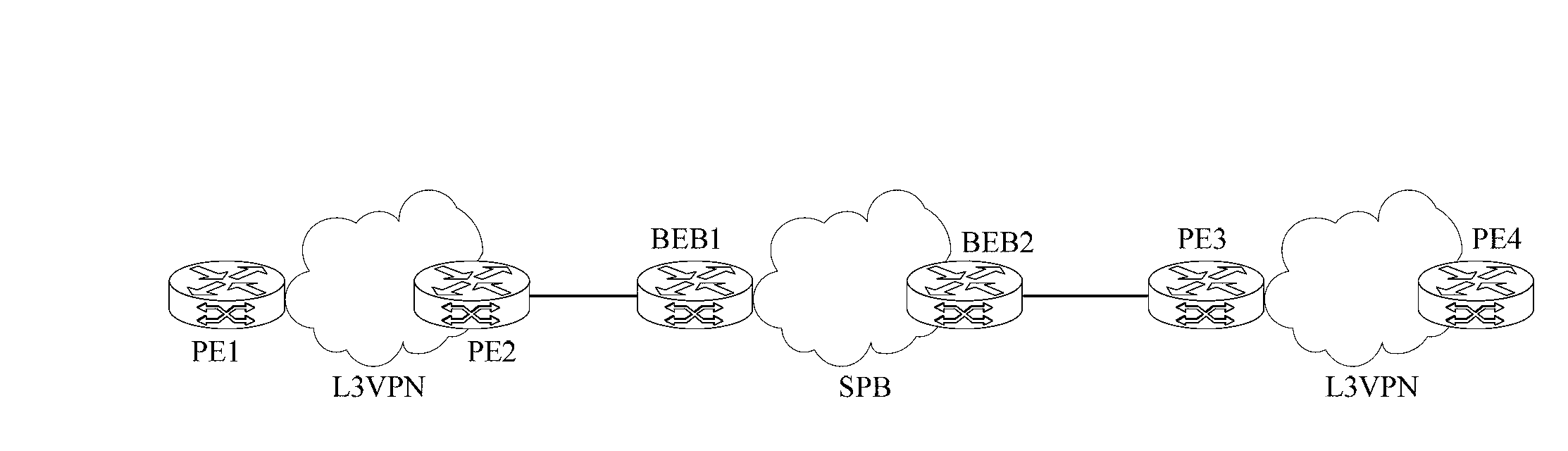
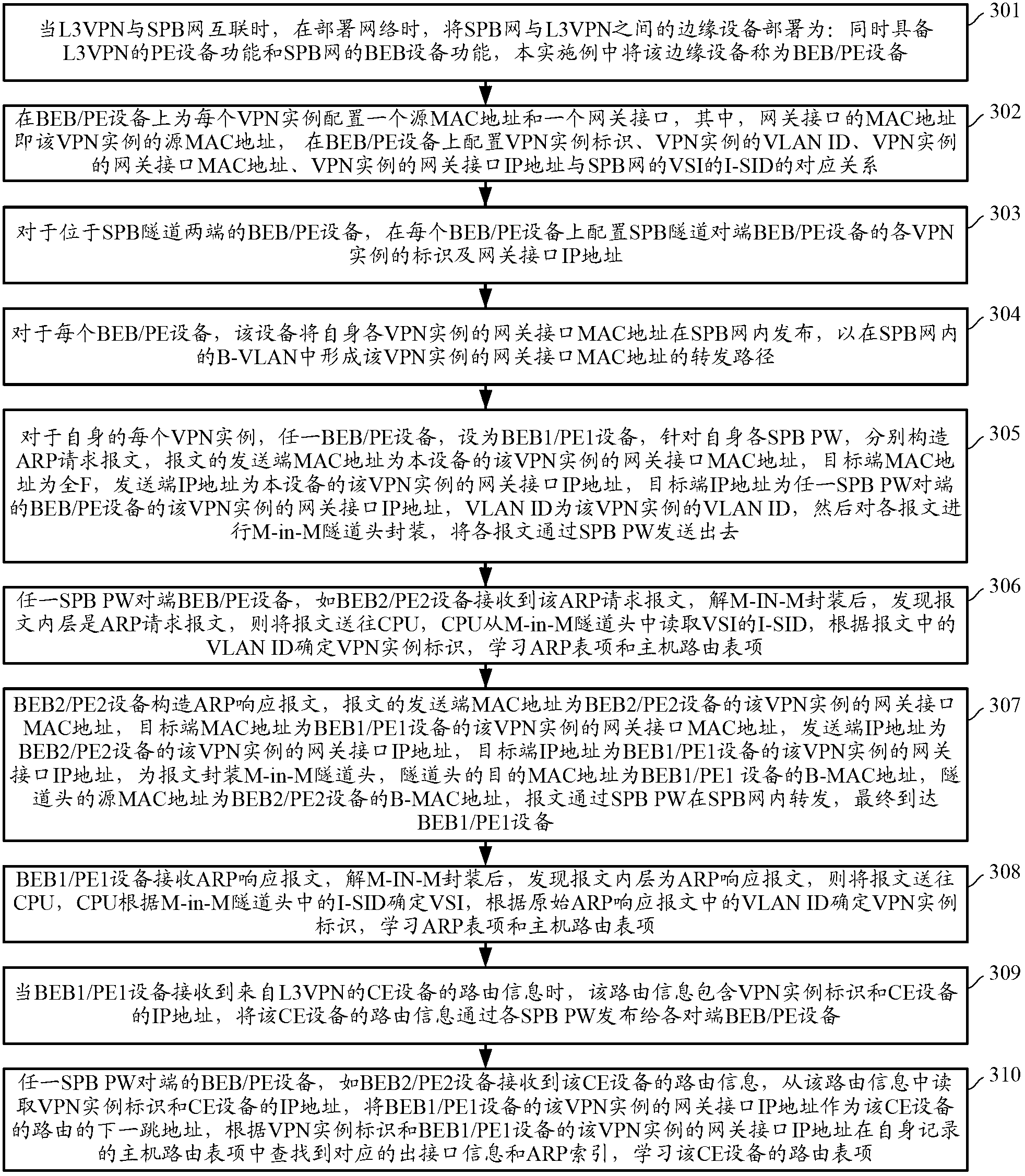
Intercommunication method of shortest path bridging network and Layer 3 virtual private network and common edge equipment
ActiveCN103227745ARealize direct exchange of visitsSave resourcesNetworks interconnectionRouting tableAddress resolution
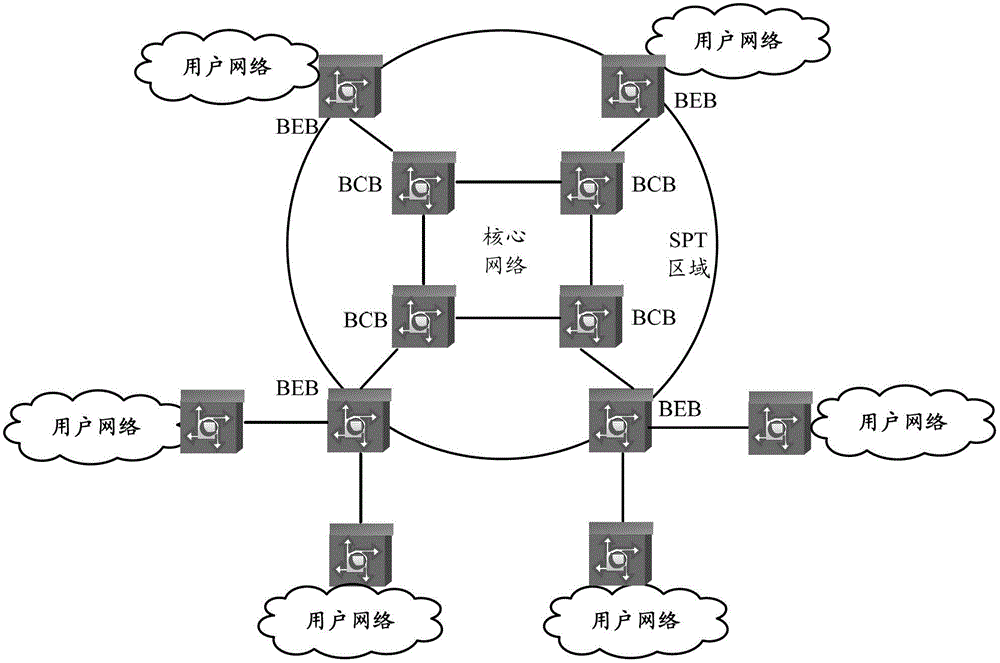
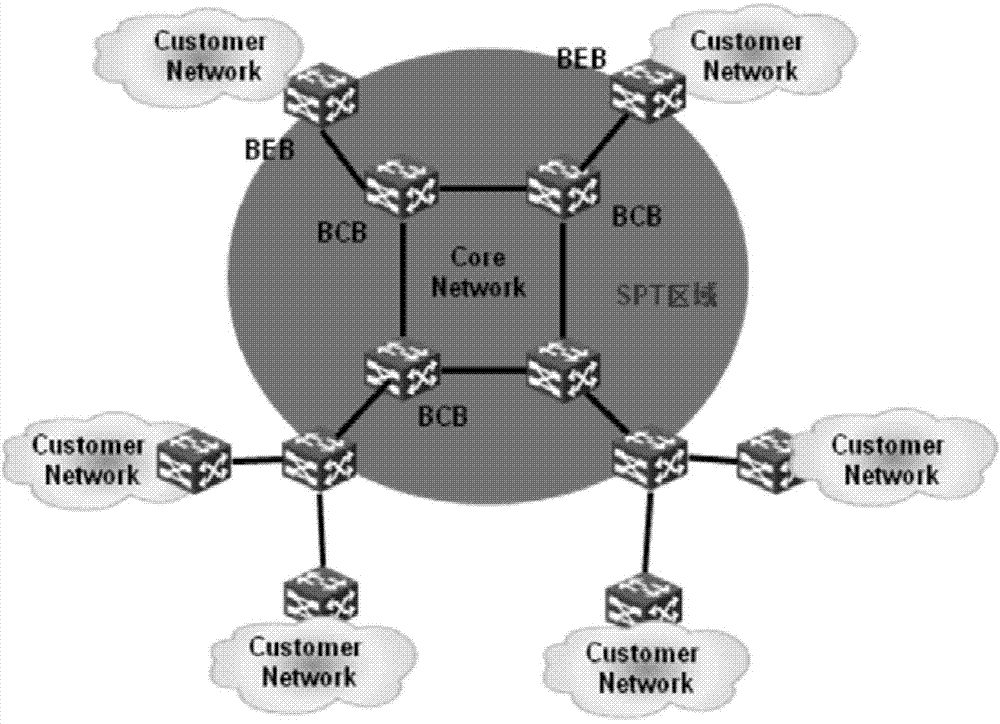
The invention discloses an intercommunication method of a shortest path bridging (SPB) network and a Layer 3 virtual private network (L3VPN), and common edge equipment. The method comprises the steps that the SPB network is connected with the L3VPN by the common edge equipment; the edge equipment serves as BEB (backbone edge bridge) equipment of the SPB network and PE (provider edge) equipment of the L3VPN simultaneously; association relationships between VPN instances and VSIs (virtual service instances) of the SPB network are configured on the edge equipment; each VPN instance is provided with a gateway interface; MAC (media access control) addresses of the gateway interfaces of the different VPN instances are different; for each VPN instance, the common edge equipment learns an IP (internet protocol) address resolution table entry and a host routing table entry of the common edge equipment at an SPB PW opposite end, learns a VPN routing table entry in the VPN instance of the common edge equipment at the opposite end according to the learned host routing table entry, and forwards a message from the VPN to the SPB network, or a message from the SPB network to the VPN according to the learned table entries. The equipment cost for the intercommunication of the SPB network and the L3VPN is lowered.
Owner:XINHUASAN INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
Method and system for fault resilience in networks with audio/video bridging aware shortest path bridging
Aspects of a method and system for fault resilience in Audio / Video Bridging (AVB) aware Shortest Path Bridging (SPB) networks are provided. In this regard, a path cost, which may be based at least on AVB compatibility, may be determined for each network path discovered between a first network node and a second network node. Additionally, a plurality of network paths may be selected based on the determined path cost, and a plurality of network connections may be established over the selected plurality of network paths. Also, a plurality of data streams may be transmitted and / or received via the established network connections, wherein at least one of data streams comprises data that is redundant to a first data stream. Furthermore, a primary data stream may be conveyed via a first network connection and one or more redundant data streams may be conveyed via a second network connection.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Method and equipment for sharing load in SPB (Shortest Path Bridging) network
InactiveCN103368863AEfficient use ofIncrease success rateData switching networksTraffic capacityMedia access control
The invention provides a method and equipment for sharing load in an SPB (Shortest Path Bridging) network. The method comprises the followings: BEB (Backbone Edge Bridge) equipment is provided with a main B-MAC (Backbone-Media Access Control) address and at least one load sharing B-MAC address, a main path and at least one load sharing path are established between the BEB equipment and neighboring BEB equipment; at initial period, flow transmission is performed through the main path between the BEB equipment and the neighboring BEB equipment; and when flow congestion is generated between the BEB equipment and neighboring BEB equipment, partial flow of the BEB equipment to the neighboring BEB equipment is switched on an unused load sharing path between the BEB equipment and the neighboring BEB equipment. The flow transmission efficiency in an SPB network is improved.
Owner:NEW H3C TECH CO LTD
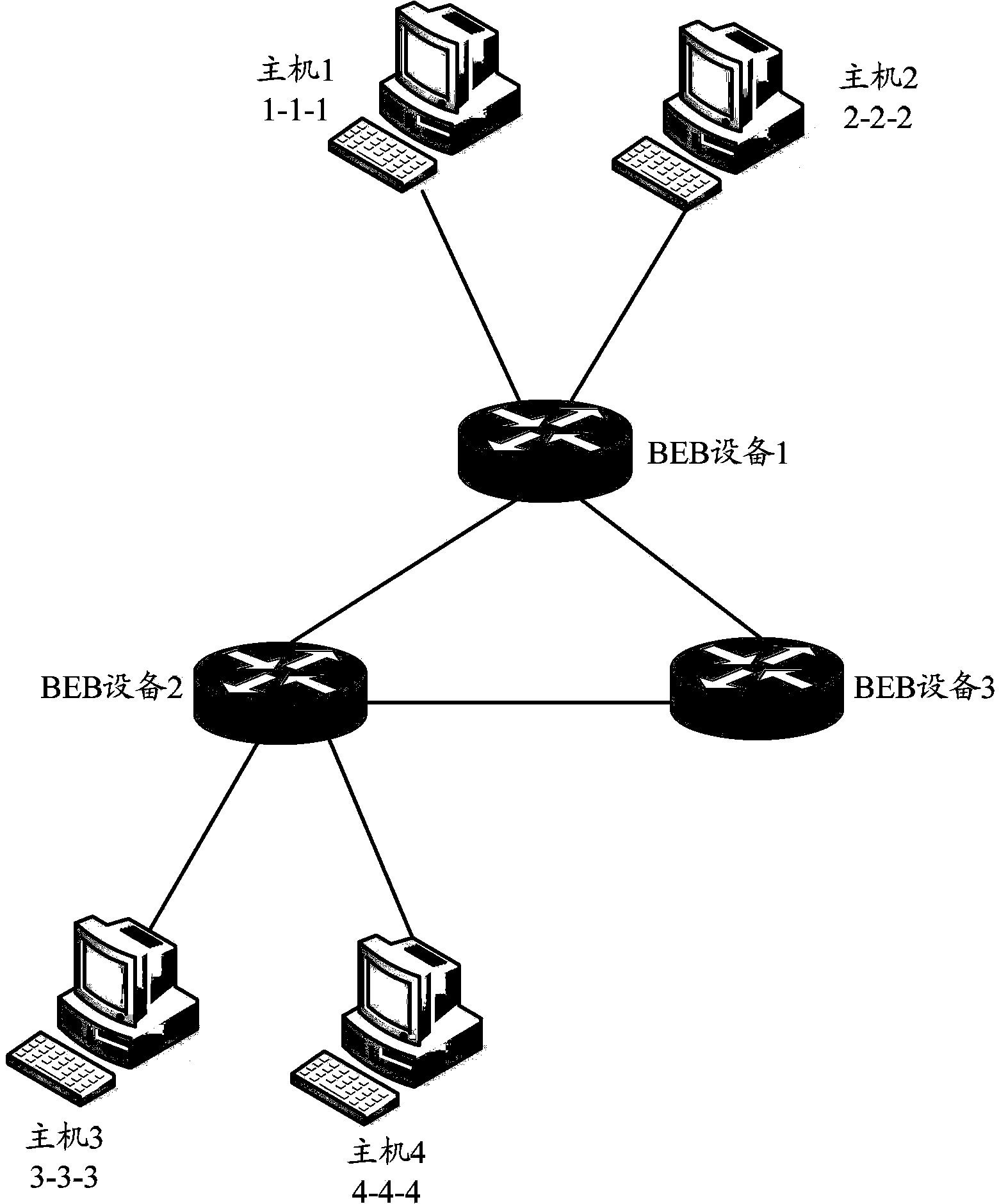
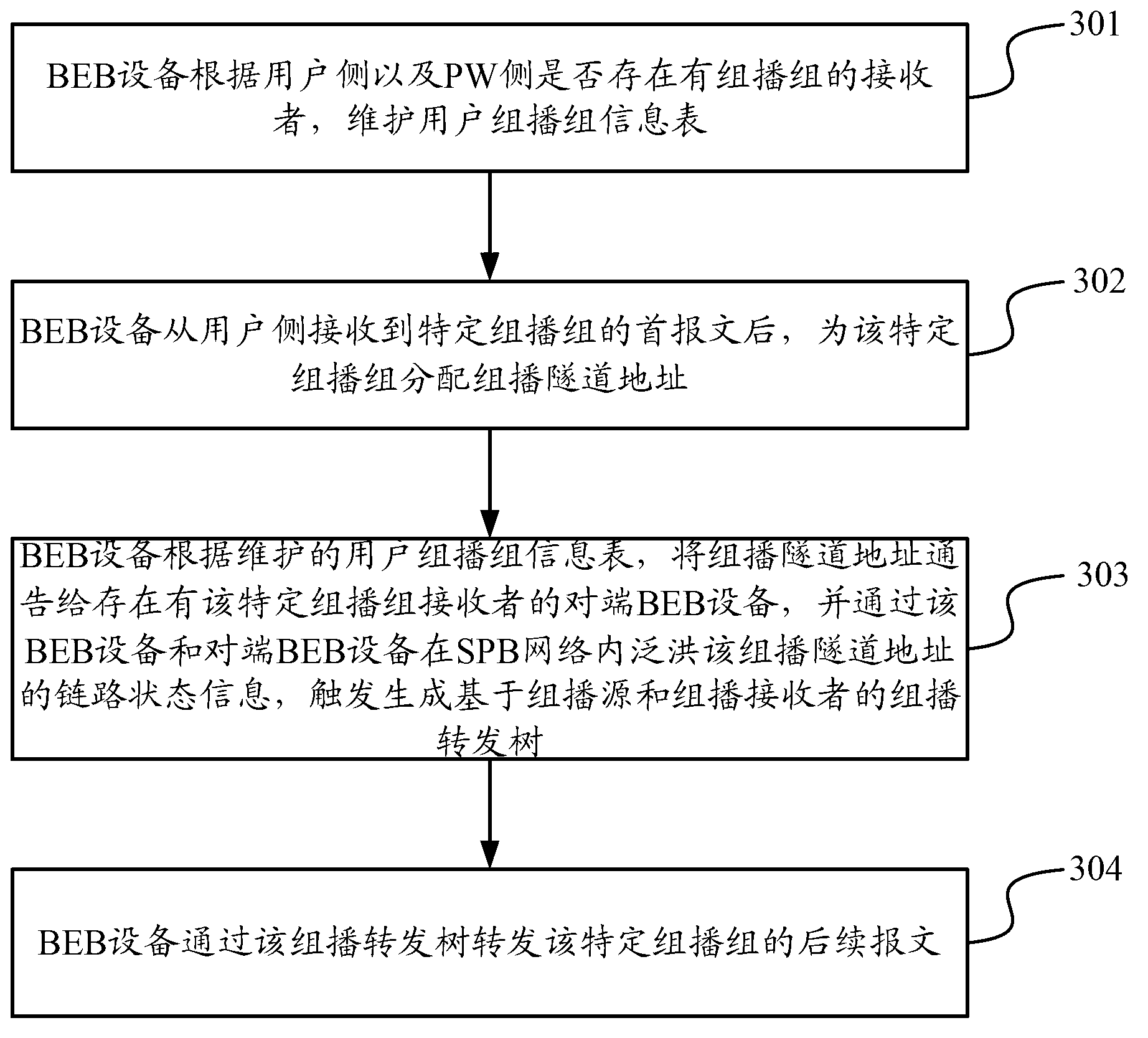
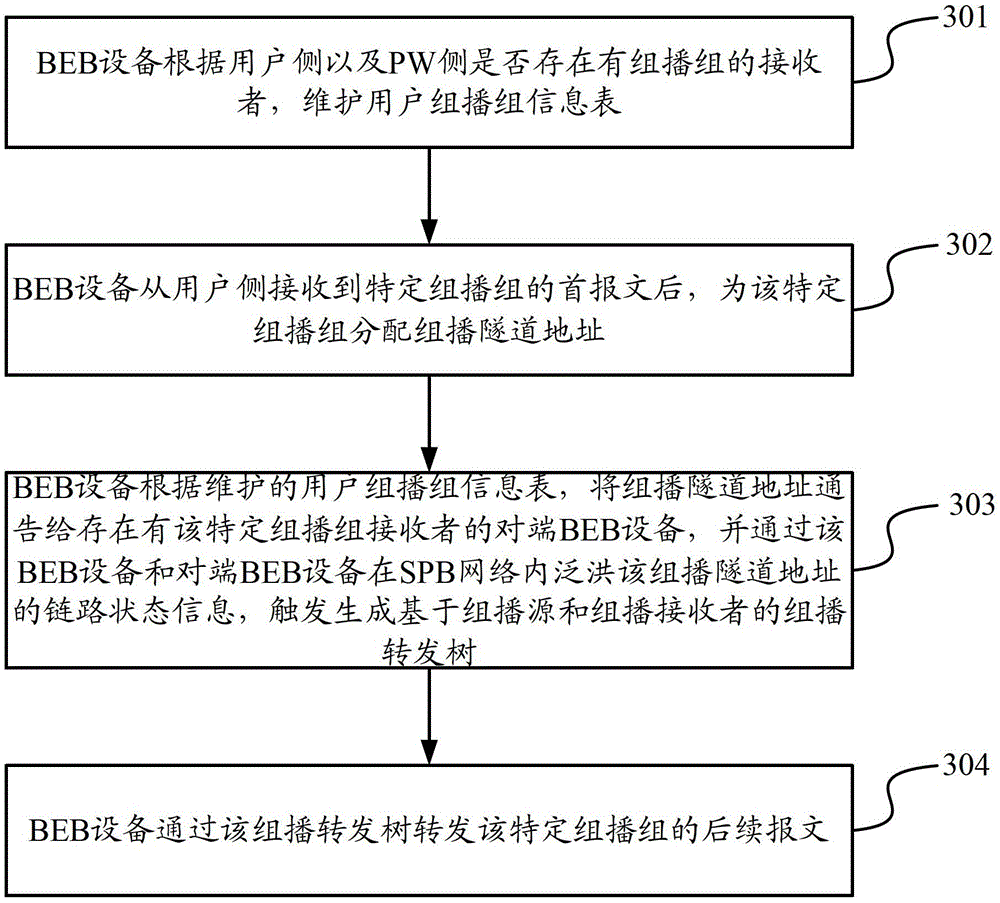
Multicast data transmission method and equipment
ActiveCN103067286ASave resourcesImprove stabilityNetworks interconnectionMulticast addressSystem stability
The invention discloses a multicast data transmission method and equipment. The method comprises the following steps that: BEB (Backbone Edge Bridge) equipment maintains a user multicast group information list according to that whether a receiver of a multicast group exists on a user side and a PW side or not; after receiving a first message of a special multicast group from the user side, the BEB equipment assigns a multicast tunnel address to the special multicast group; the BEB equipment announces the multicast tunnel address to opposite-end BEB equipment with a receiver of the special multicast group according to the maintained multicast group information list and implements flooding of link status information of the multicast tunnel address in an SPB (Shortest Path Bridging) network by the BEB equipment and the opposite-end BEB equipment so as to trigger and generate a multicast transmission tree based on a multicast source and the multicast receiver; and the BEB equipment transmits subsequent messages of the special multicast group through the multicast transmission tree. According to the multicast data transmission method and equipment disclosed by the invention, network resources are saved, and the system stability is improved.
Owner:XINHUASAN INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
Resilient interworking of shortest path bridging and Ethernet virtual private networks
An Ethernet network, an Ethernet method, and an Ethernet node provide active-active dual-homed interworking between two Ethernet networks. The network, method, and node can include two nodes interconnected each to a Shortest Path Bridging (SPB) network and an Ethernet Virtual Private Network (E-VPN). The two nodes can utilize a same Ethernet Segment Identifier (ESI) for the E-VPN network to cause the dual-homed links to appear as a single link from an E-VPN perspective and a dummy node to advertise an extra node in the SPB network enabling two paths therein.
Owner:CIENA
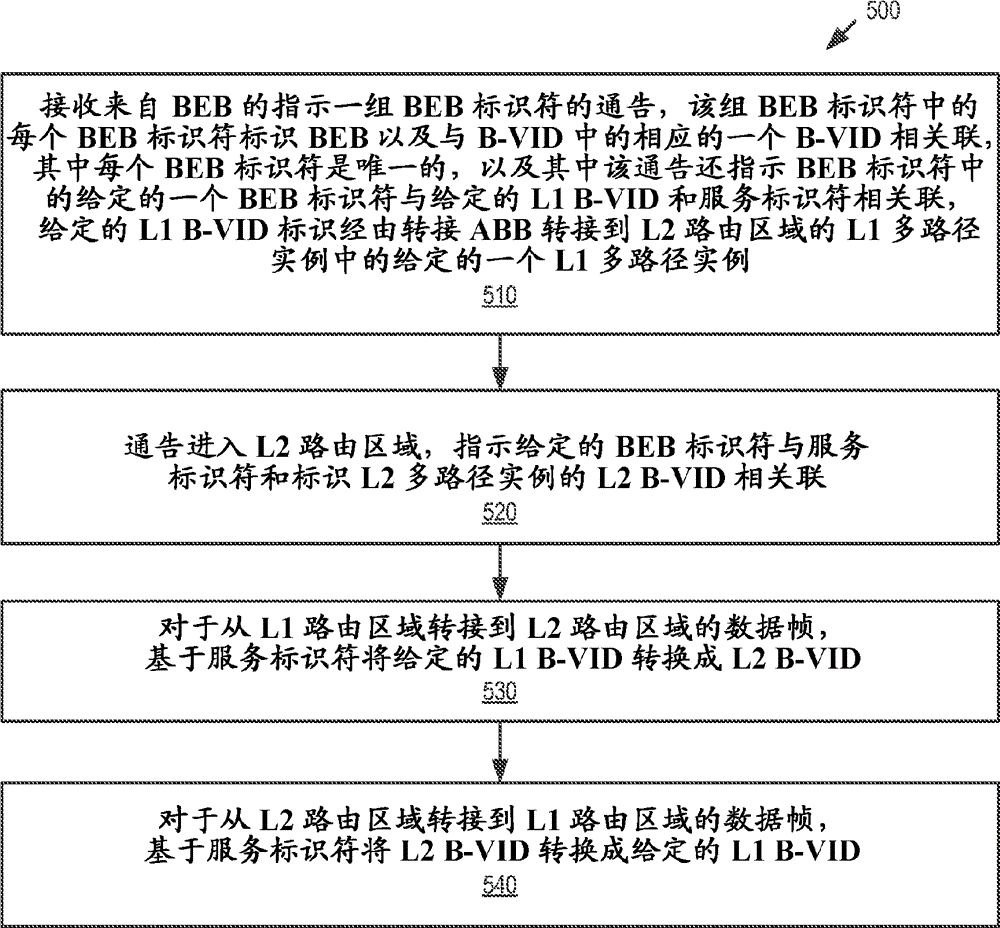
Improved shortest path bridging in a multi-area network
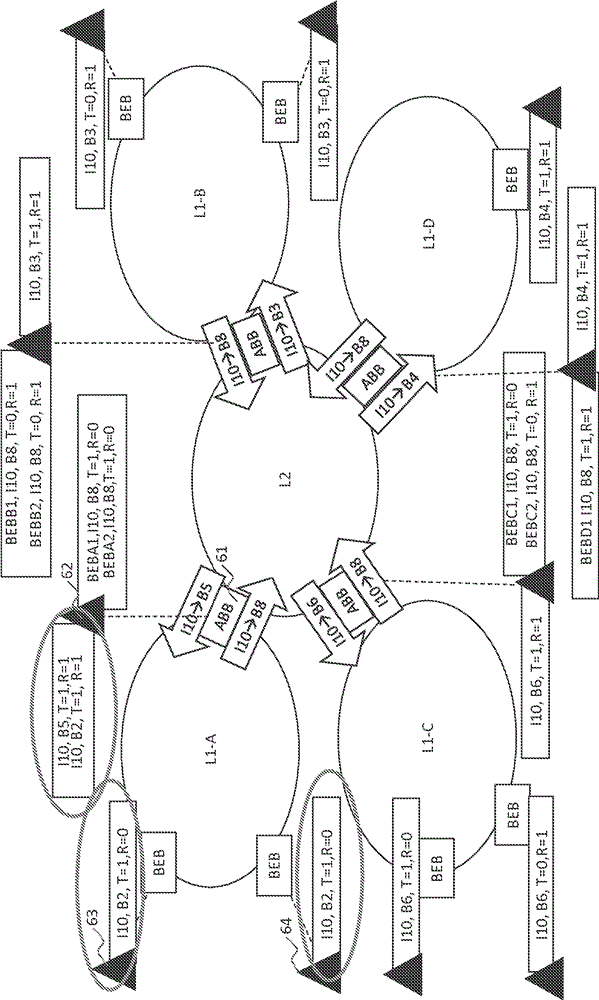
A method that improves multi-area routed Ethernet network design, in which multipath implementation in each of the areas is independent of each other area to allow optimal network design in each area. The network implements a shortest path bridging medium access control (SPBM) protocol. The areas include a Level 2 (L2) routing area coupled to a Level 1 (L1) routing area via multiple area border bridges (ABBs). The L1 routing area including a backbone edge bridge (BEB) coupled to the ABBs via multiple L1 multipath instances identified by respective backbone VLAN identifiers (B-VIDs). The ABBs receive an advertisement from the BEB that indicates a set of BEB identifiers, each of which identifies the BEB and is associated with a respective B-VID. Each of the BEB identifiers is unique. The ABBs also advertise into the L2 routing area, and translate the B-VIDs based on service identifiers for frames transiting the ABBs.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Dynamic networking of virtual machines
The invention is directed to the use of Provider Backbone Bridging (PBB) technology with Shortest Path Bridging, also called Provider Link State Bridging (PLSB) technology in the context of data centers and virtualized physical servers infrastructures. Virtual servers can be located anywhere inside the data center, or across different data centers, and still act as though they are physically adjacent and share the same Ethernet connectivity. Ethernet virtual machine VLan memberships are mapped to PBB Service Identifiers (I-SIDs). PBB I-SIDs extend the connectivity model to every Ethernet switches in the local, metropolitan or wide area networks. PLSB complements the connectivity by providing dynamic distribution and mapping of I-SID endpoints in the PBB domain. Virtual servers can then be added, removed or transferred to another point in the network and PLSB adjusts the VLan / I-SID specific connectivity pattern to match the physical distribution of the servers.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
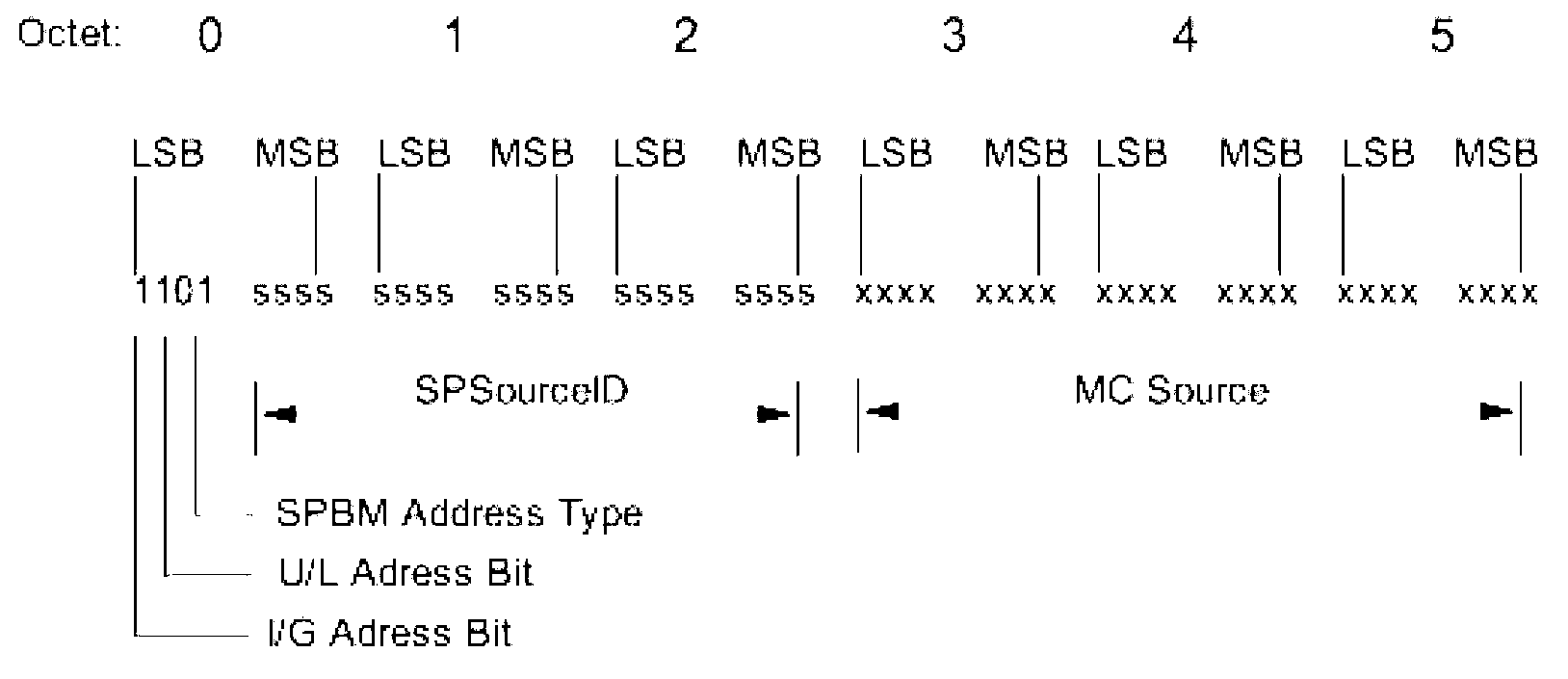
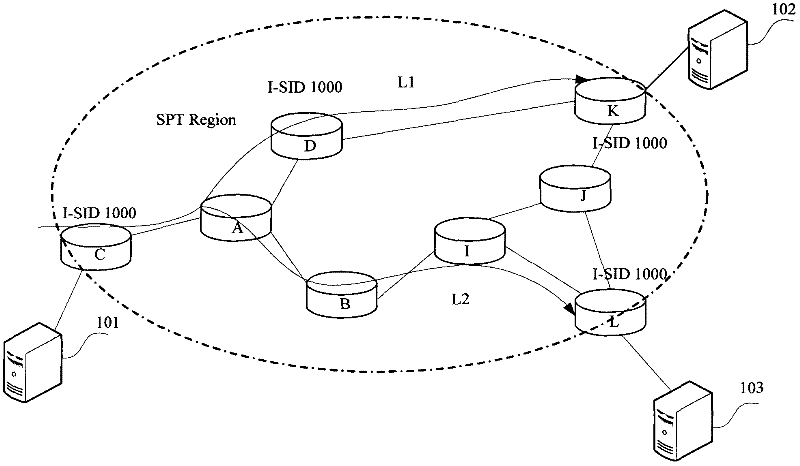
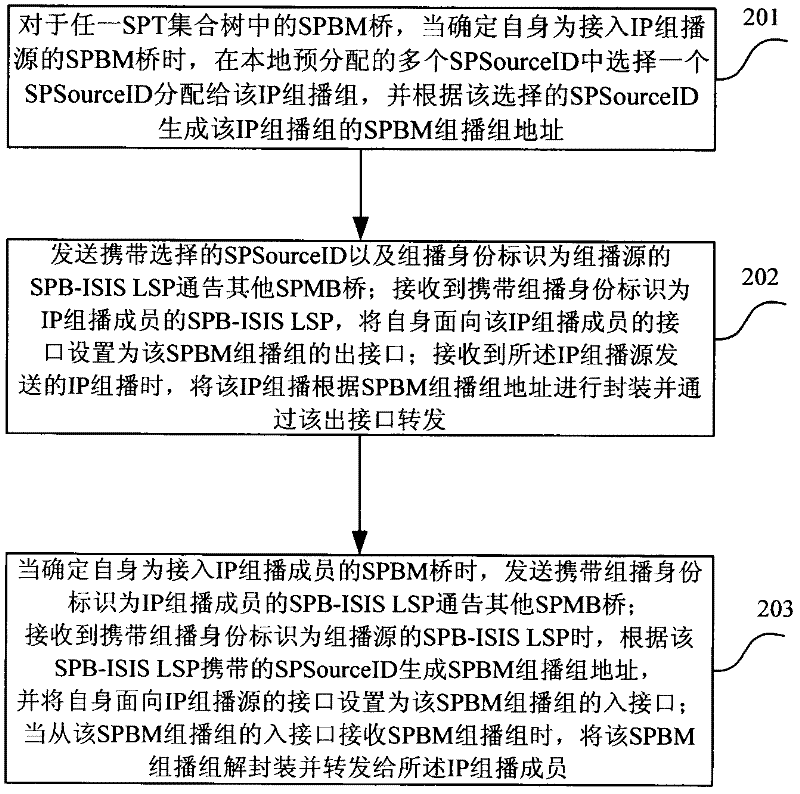
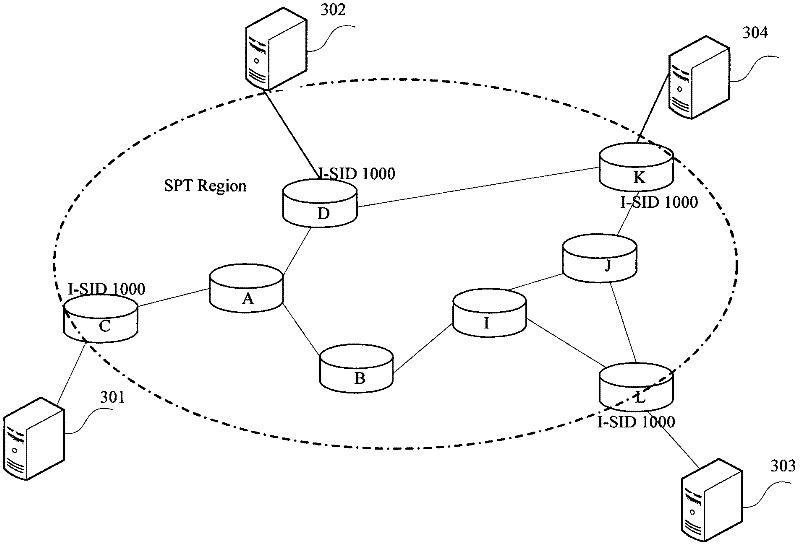
Multicast forwarding method based on SPB (Shortest Path Bridging) network and SPBM (MAC-in-MAC SPB) bridge
ActiveCN102413059AGood for forwardingSpecial service provision for substationIP multicastShortest path bridging
The invention discloses a multicast stream forwarding method based on an SPB (Shortest Path Bridging) network. The method comprises: all bridges in an SPBM (MAC-in-MAC SPB) network perform multicast listening so as to learn router and member information in an IP (Internet Protocol) multicast group, and the information is announced to all the bridges in the network through an SPBM-ISIS (Intermediate System-Intermediate System) LSP (Link State Protocol); and the SPBM bridges in the network receive and analyze the SPBM-ISIS LSP, and set input interfaces and output interfaces of the bridges so as to guide forwarding of the IP multicast group. The invention further provides an SPBM bridge based on the same conception. According to the invention, IP multicast forwarding is optimized and unnecessary multicast streams are prevented from reaching the SPBM bridges without corresponding IP multicast members.
Owner:NEW H3C TECH CO LTD
Forwarding frames in a computer network using shortest path bridging
Methods, apparatus, and products are disclosed for forwarding frames in a computer network using shortest path bridging (‘SPB’). The network includes multiple bridges, and each edge bridge is assigned a unique service virtual local area network (‘VLAN’) identifier. One of the bridges receives a frame for transmission to a destination node. The received frame includes a service VLAN identifier for the ingress bridge through which the frame entered the network and a customer VLAN identifier. The one bridge identifies an SPB forwarding tree in dependence upon the service VLAN identifier. The SPB forwarding tree specifies a shortest route in the network from the ingress bridge through the one bridge to the other bridges in the network. The one bridge then forwards the received frame to the egress bridge without MAC-in-MAC encapsulation in dependence upon the SPB forwarding tree and the customer VLAN identifier.
Owner:JUMIPER NETWORKS INC
Method and device for multicast data transmission
ActiveCN103067286BSave resourcesImprove stabilityNetworks interconnectionMulticast addressSystem stability
The present invention discloses a multicast data transmission method and equipment. The method comprises: a BEB equipment maintains a user multicast group information table according to whether there are receivers of the multicast group on the user side and the PW side; After receiving the first packet of a specific multicast group, the BEB device allocates a multicast tunnel address for the specific multicast group; the BEB device notifies the multicast tunnel address to the existing multicast group according to the maintained user multicast group information table The peer BEB device of the multicast group receiver, and floods the link state information of the multicast tunnel address in the SPB network through the BEB device and the peer BEB device, triggering the generation of A multicast forwarding tree; the BEB device forwards subsequent packets of the specific multicast group through the multicast forwarding tree. In the present invention, network resources are saved and system stability is improved.
Owner:XINHUASAN INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
Method and device for determining forwarding path in shortest path bridge network
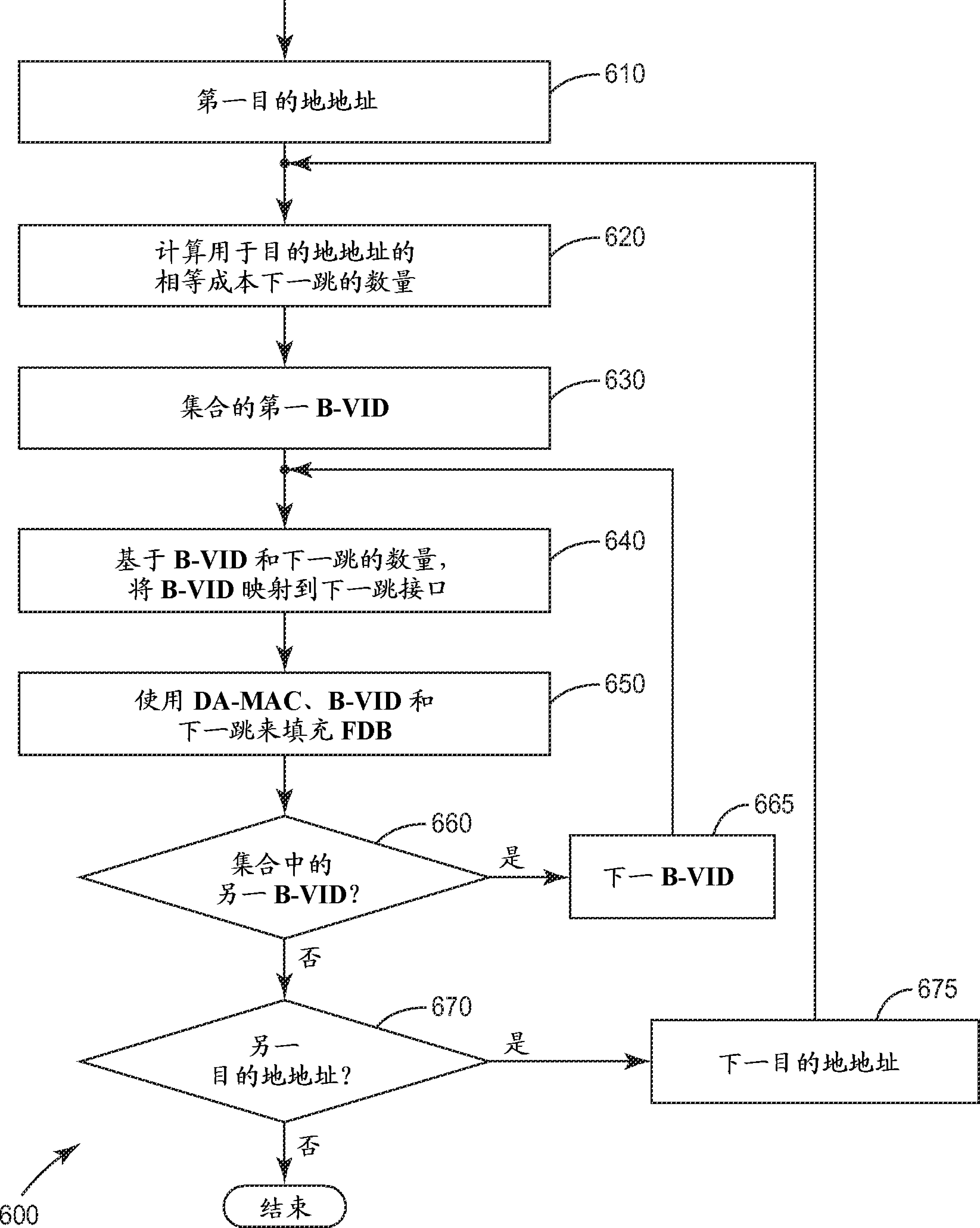
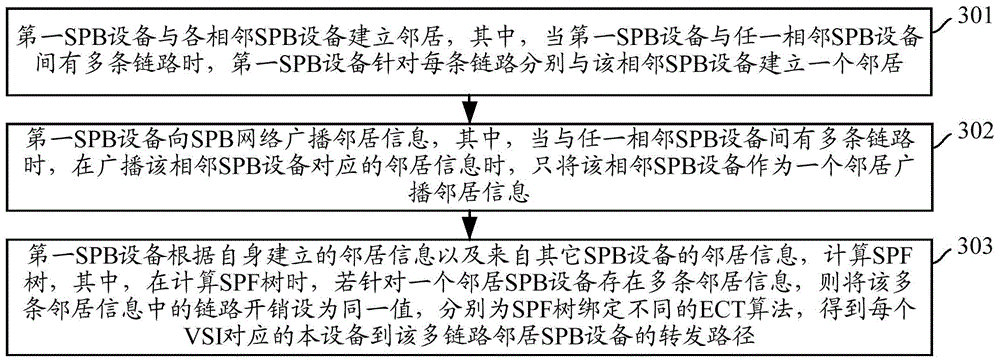
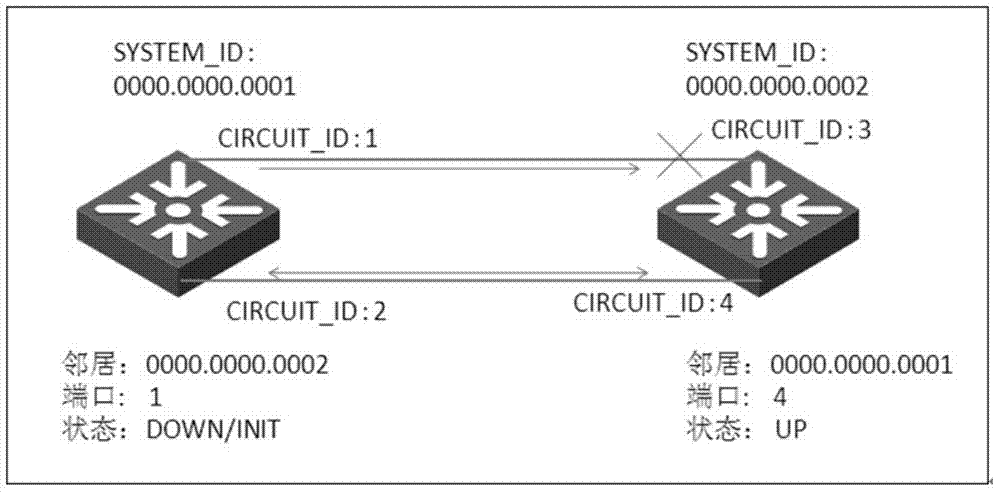
A method is described in which a first shortest path bridging (SPB) node and a neighboring second SPB node are connected via n links; a plurality of different neighborhoods are established between the first node and the second SPB node; and a shortest path first (SPF) tree is calculated in accordance with the links with the same cost.
Owner:NEW H3C TECH CO LTD
Data transmission method and device
ActiveCN103152257AForwarding control implementationData switching networksComputer hardwareExponential backoff
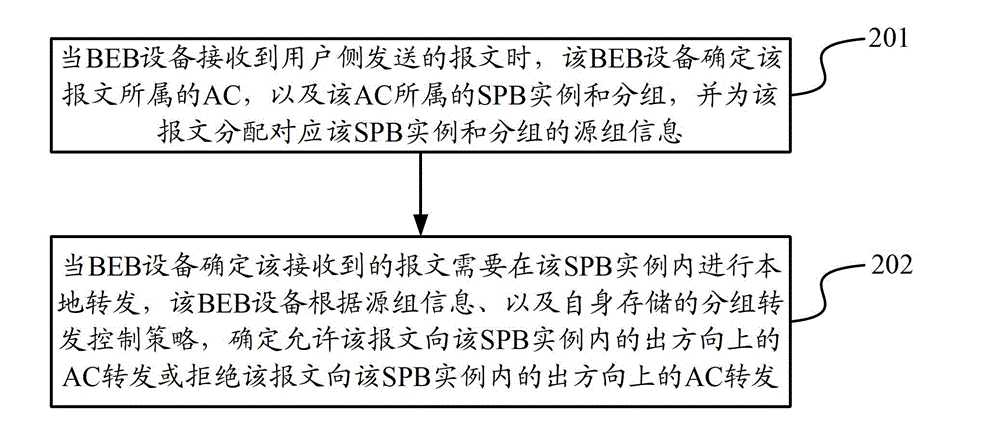
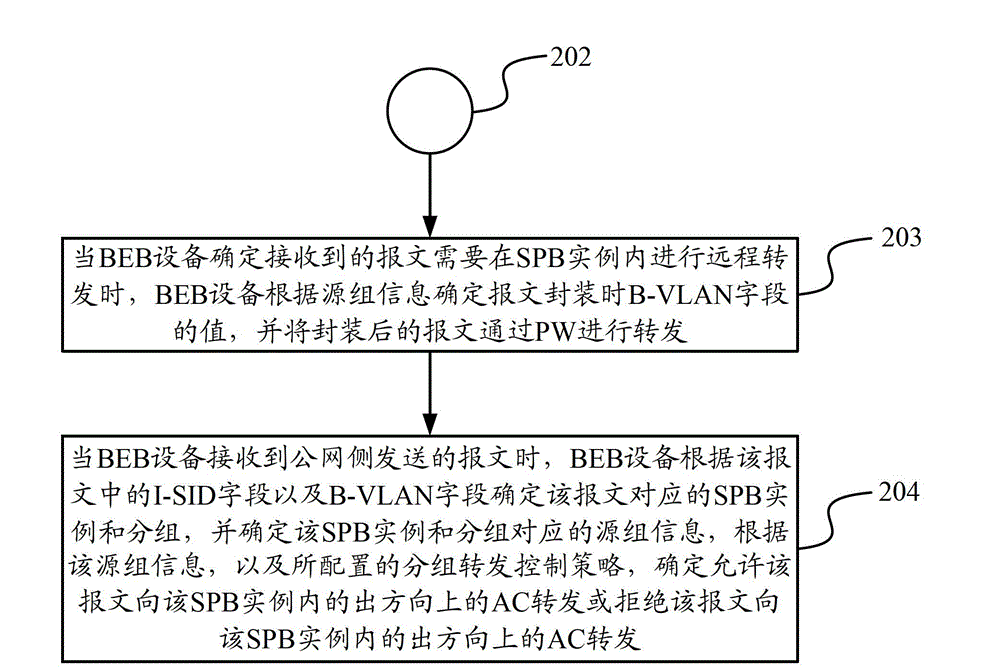
The invention discloses a data transmission method and device. The data transmission method comprises the following steps of: when BEB (Binary Exponential Backoff) equipment receives a message transmitted by a user side, determining an attachment circuit (AC) belonging to the message as well as an SPB (Shortest Path Bridging) case and groups belonging to the AC and allocating source group information corresponding to the SPB case and the groups for the message by the BEB equipment; and when the BEB equipment determines that the received message is required to be locally forwarded in the SPB case, determining to allow the message to be forwarded towards the AC in an egress direction in the SPB case or reject the message to be forwarded towards the AC in an egress direction in the SPB case according to the source group information and a grouping forwarding control strategy by the BEB equipment. According to the data transmission method and device disclosed by the invention, the message forwarding control over the AC in the SPB case is realized.
Owner:XINHUASAN INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
Method and system for dynamic routing and/or switching in a network
Communication devices may determine routes for packets based on packet marking, routing parameters and / or costs associated with routes. A route may be selected and the packets may be communicated via the selected route. The parameters may comprise service class, real time compression, packet preemption, quality measurements, tier bypass and / or power usage information. The costs may comprise capacity, efficiency and / or performance information for power usage, bandwidth, memory and / or processing. The marking may comprise traffic type, user device capabilities, service class, quality measurements, latency requirements and / or power usage information. Endpoint devices, software applications and / or service providers may insert the marking into packets. Routes may be determined and / or selected based on shortest path bridging, audio video bridging, the marking, the routing parameters and / or the costs. Parameters and / or costs may be received and / or discovered from communication devices. Packets and / or the marking may be parsed and / or inspected. Costs may be based on routing parameters.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
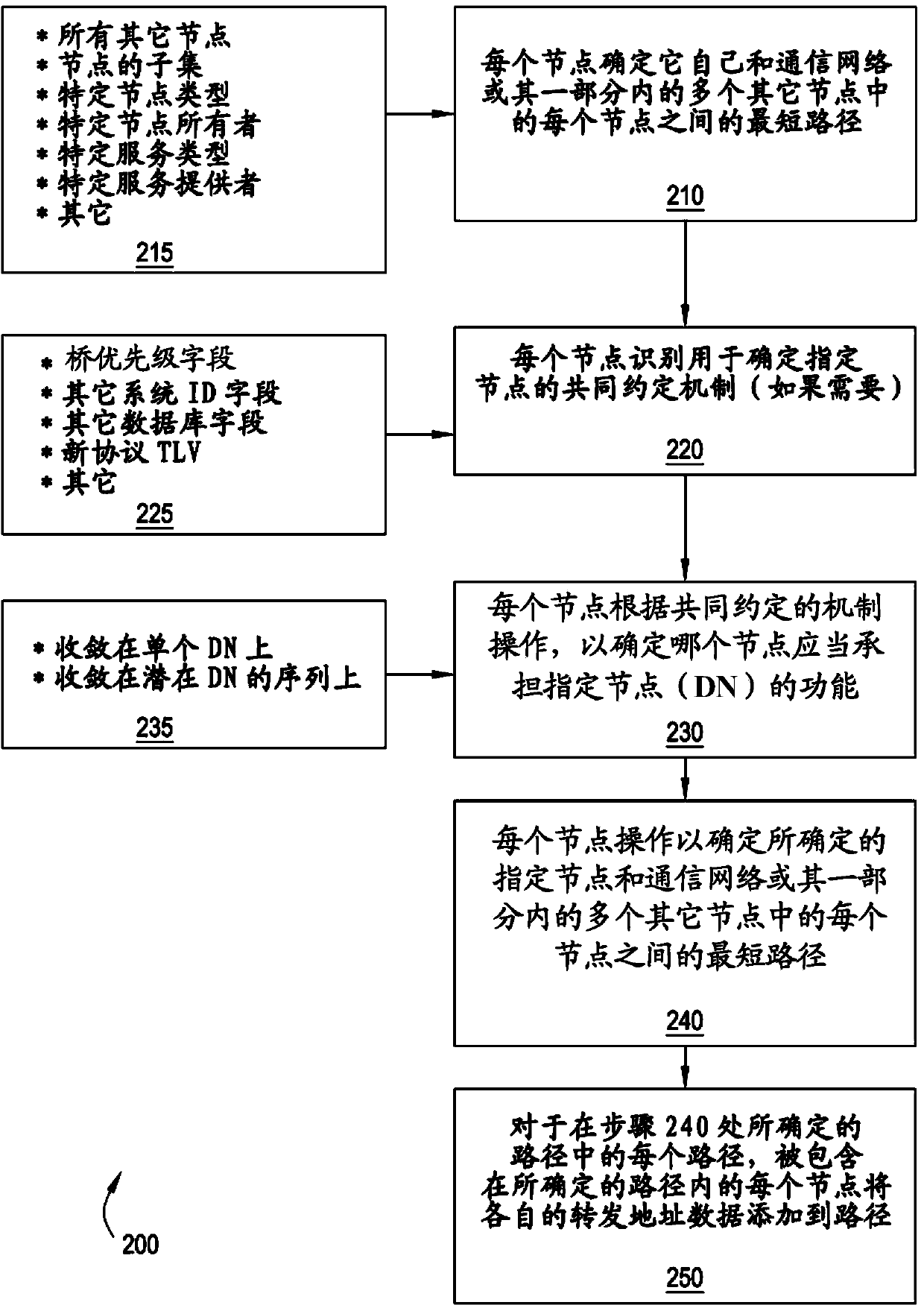
Method for shortest path bridging of multicast traffic
ActiveCN103828296ASpecial service provision for substationNetworks interconnectionComputer scienceShortest path bridging
Method for determining shortest path bridging (SPB) of multicast frames within a communications network comprises at each of a plurality of nodes within the network, determining a designated node (DN) according to a commonly agreed mechanism; at each of the plurality of nodes, determining a shortest path between the DN and each of the plurality of nodes; and at each of the plurality of nodes, selecting for inclusion in a respective forwarding tree for multicast only those determined shortest paths from the DN traversing the respective node.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Neighbor multilink processing method and device
ActiveCN103501275AAvoid the problem of not being able to achieve load sharingEfficient use ofData switching networksProtocol for Carrying Authentication for Network AccessComputer science
The invention provides a neighbor multilink processing method and a neighbor multilink processing device. The neighbor multilink processing method and the neighbor multilink processing device are applied to SPB (shortest path bridging) network equipment in an SPB network. The neighbor multilink processing method comprises the steps that a local port connected with neighbor equipment is determined according to a neighbor message transmitted by the neighbor equipment; when multiple local ports are connected with the neighbor equipment, the local ports are used as member ports to create a virtual port oriented to the SPB network; the virtual port is used as a neighbor port connected with the neighbor equipment, and the attribute information of the virtual port is broadcasted through a protocol message; when an SPB data message is forwarded, for the SPB data message taking the virtual port as the output port, one of the member ports in normal state, corresponding to the virtual port, is selected to transmit the SPB data message according to a preset load sharing algorithm. Compared with the prior art, the neighbor multilink processing method and the neighbor multilink processing device avoid the problem that the load sharing cannot be realized in the MSTP (multi-service transmission platform) routing process in the SPB network by introducing the virtual port.
Owner:NEW H3C TECH CO LTD
Method and system for fault resilience in networks with Audio/Video Bridging aware Shortest Path Bridging
Aspects of a method and system for fault resilience in Audio / Video Bridging (AVB) aware Shortest Path Bridging (SPB) networks are provided. In this regard, a path cost, which may be based at least on AVB compatibility, may be determined for each network path discovered between a first network node and a second network node. Additionally, a plurality of network paths may be selected based on the determined path cost, and a plurality of network connections may be established over the selected plurality of network paths. Also, a plurality of data streams may be transmitted and / or received via the established network connections, wherein at least one of data streams comprises data that is redundant to a first data stream. Furthermore, a primary data stream may be conveyed via a first network connection and one or more redundant data streams may be conveyed via a second network connection.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Ingress gateway selection for a shortest path bridging network to support inter domain multicast routing
ActiveUS20190014033A1Special service provision for substationNetwork connectionsShortest path bridgingInter-domain
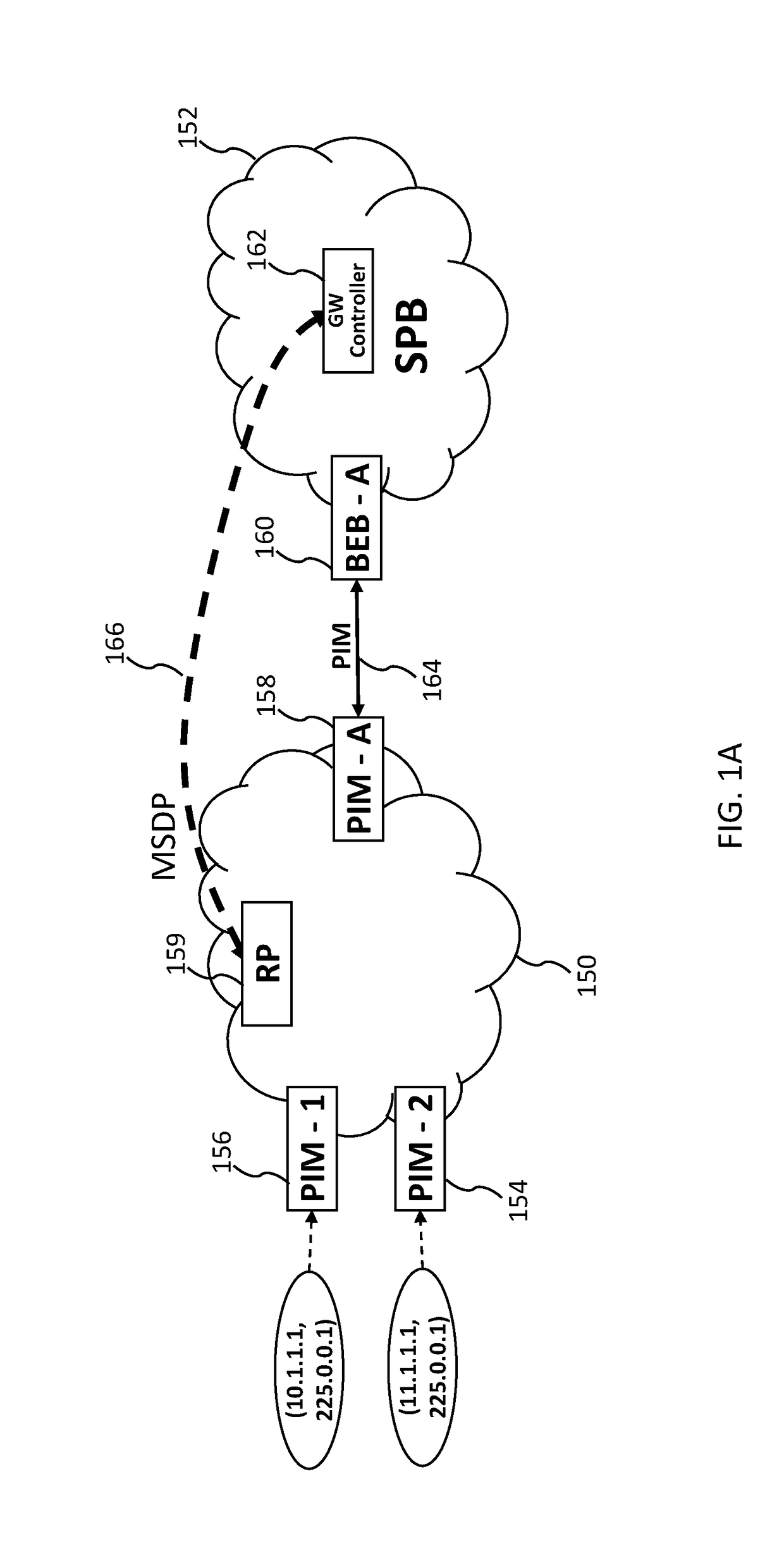
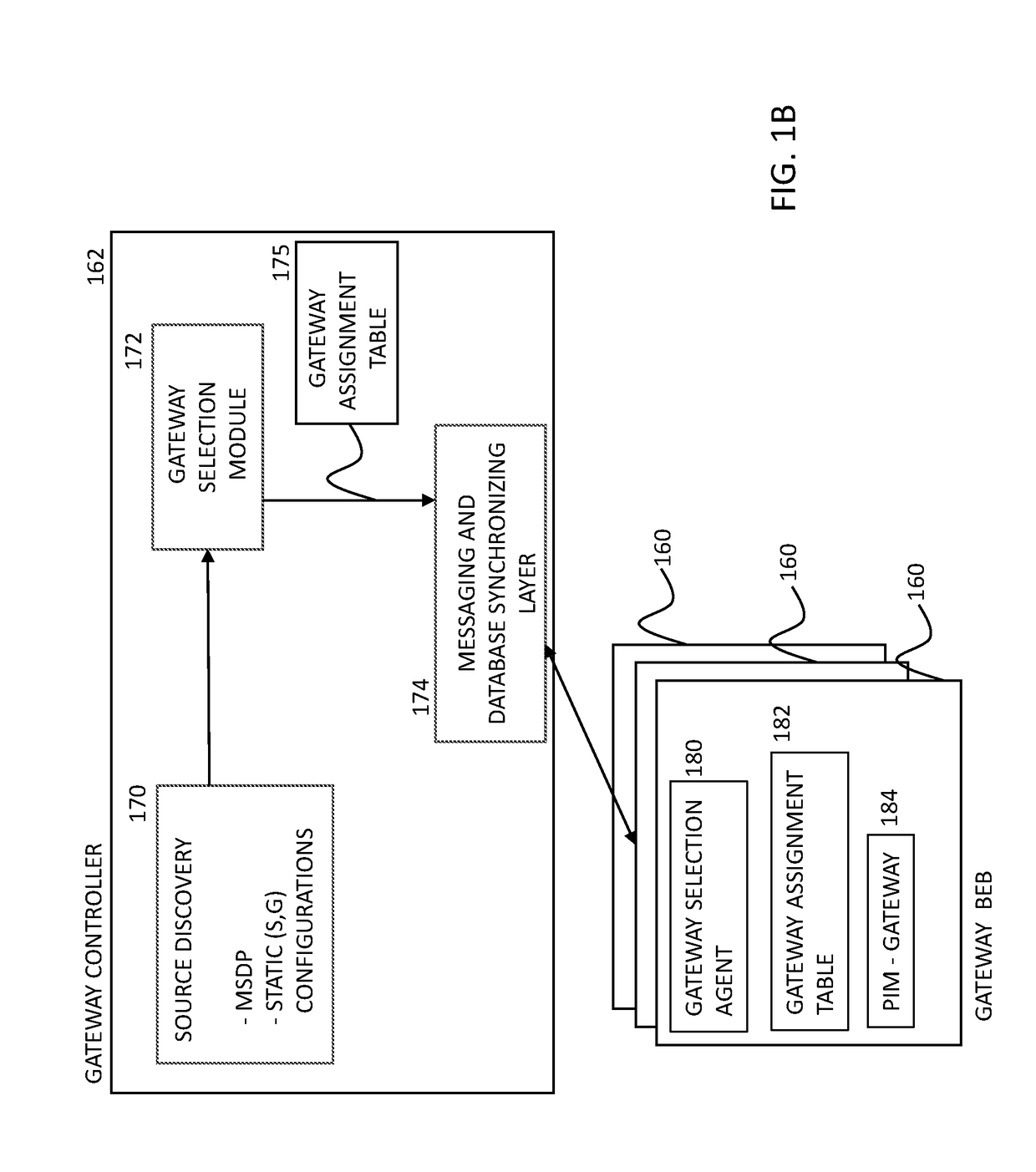
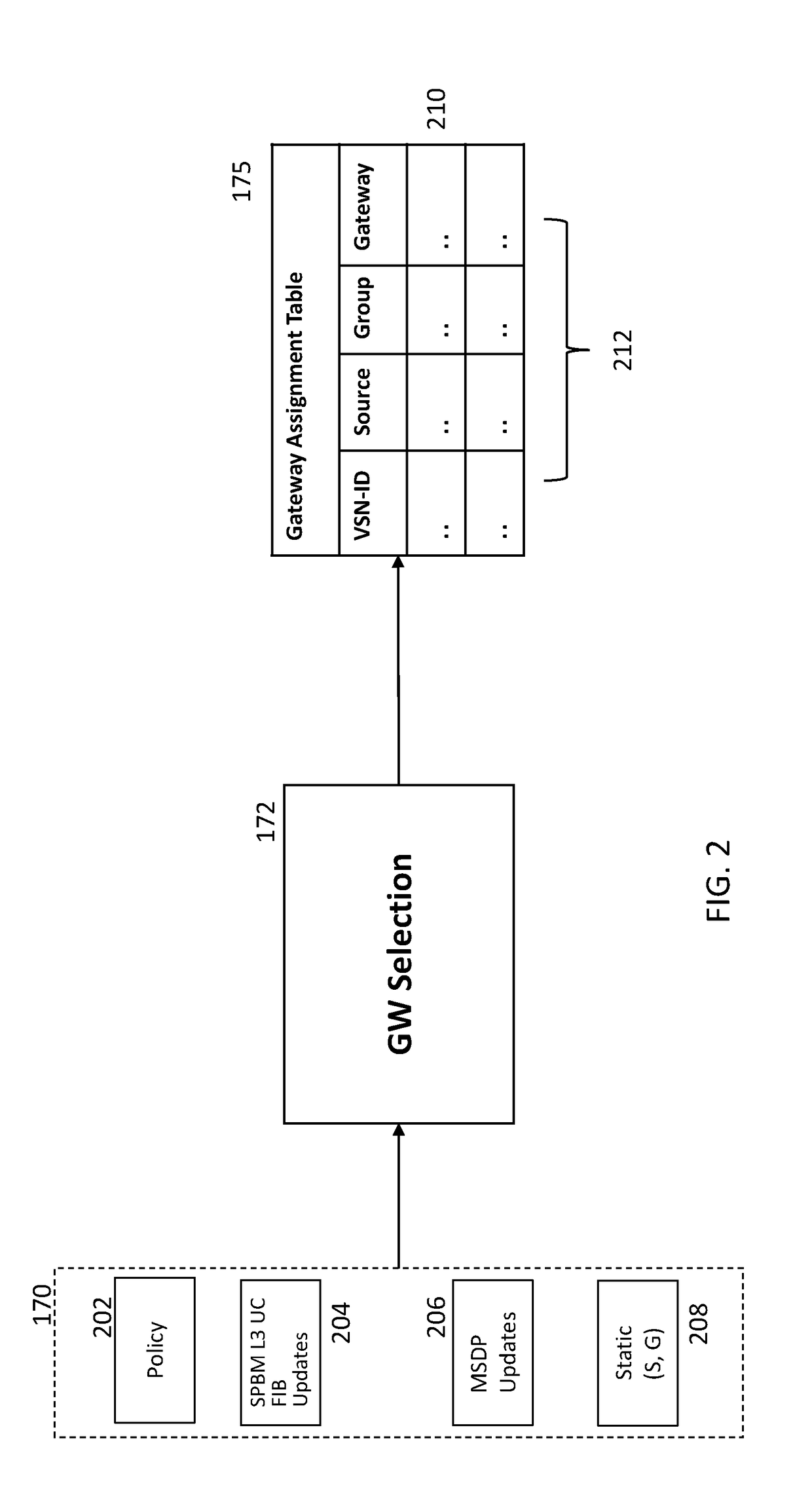
In a Shortest Path Bridge (SPB) network comprising a plurality of backbone edge bridges (BEBs), a gateway controller of the SPB network, establishes a link using Multicast Source Discovery Protocol (MSDP) with an external network domain; discovers via the link a source of a multicast stream originating outside of the SPB network; and determines a subset of the plurality of BEBs that are able to receive the multicast stream from the source. Once that occurs, the gateway controller selects a one of the subset of the plurality of BEBs to be a sole gateway BEB for the multicast stream; and then transmits to each of the subset of the plurality of BEBs an indication of the sole gateway BEB selected for the multicast stream.
Owner:EXTREME NETWORKS INC
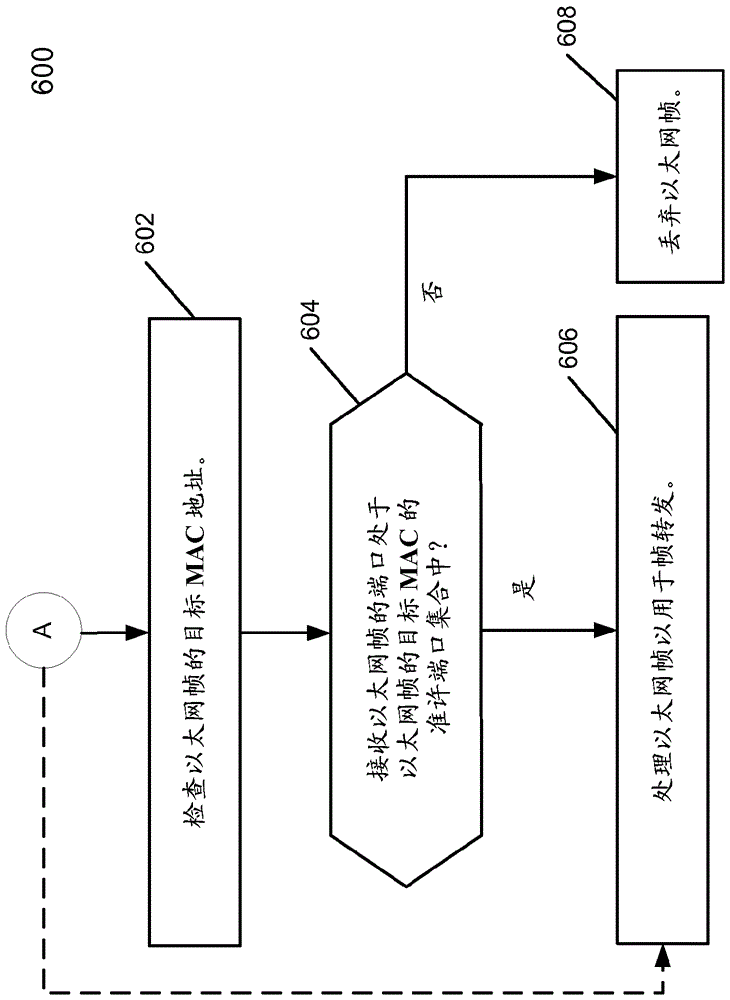
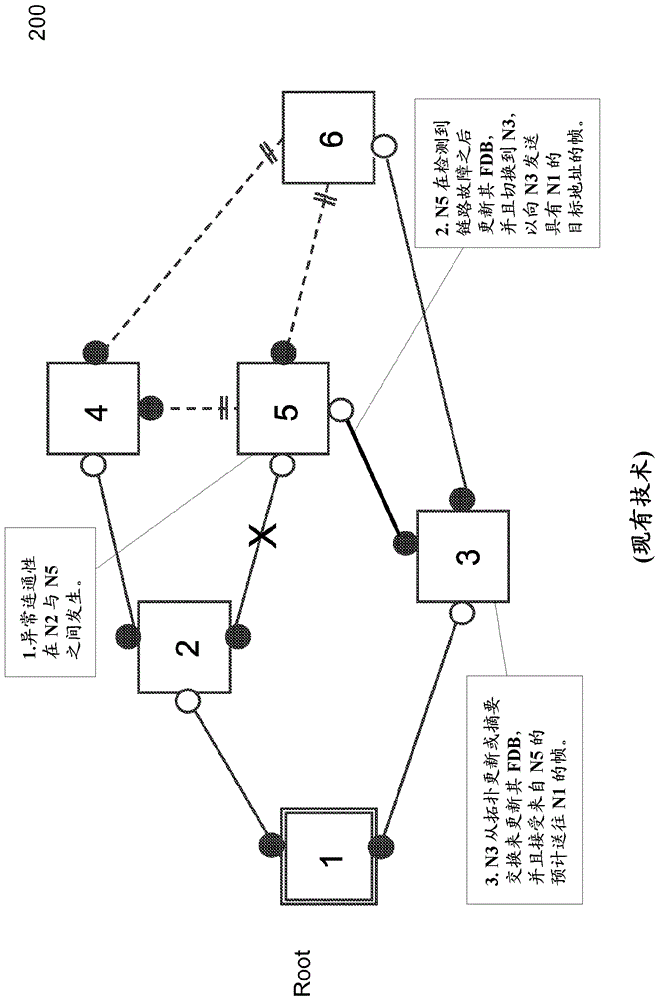
Method and system of shortest path bridging (SPB) enhanced resilience with loop mitigation
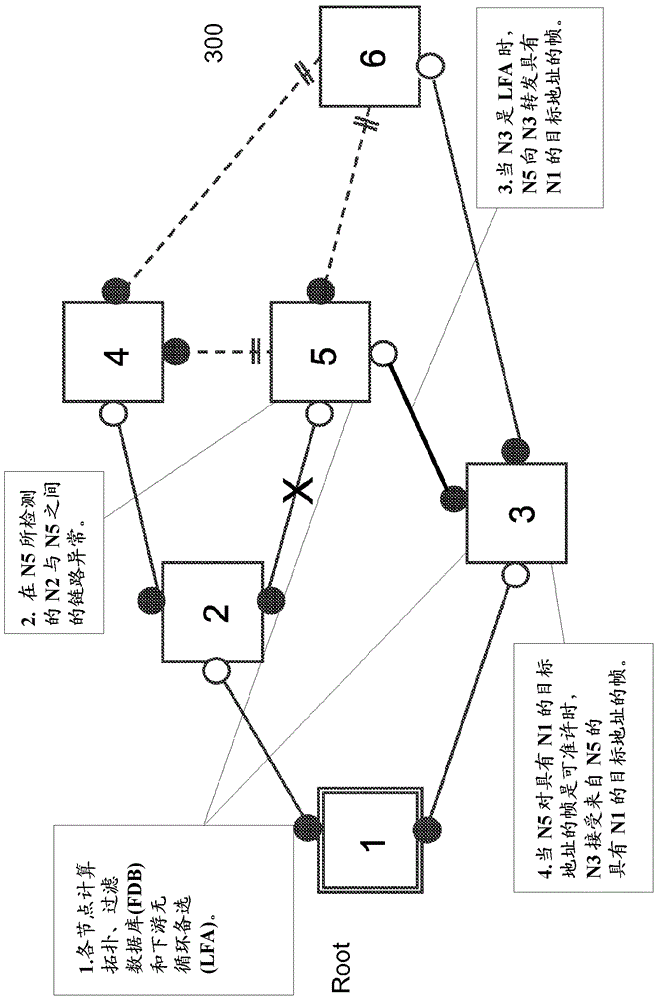
A method forward Ethernet frames at a node in a network supporting an implementation of shortest path bridging (SPB) protocol is disclosed. The method starts with a shortest path computation for the node (referred to as the computing node). The shortest path computation selects at least a shortest path to each destination node in the network, where a neighboring node on the shortest path to reach each node is recorded. Then it computes a downstream loop-free alternate (LFA) node for a destination node, where the LFA node is downstream of the computing node but not on the selected shortest path to the destination node from the computing node. Then when connectivity to the neighboring node on the computed shortest path is detected to be abnormal, the node forwards an Ethernet frame with a destination media access control (MAC) address corresponding to the destination node through the LFA node.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com