Method for shortest path bridging of multicast traffic
A technology of shortest path bridging and shortest path, which is applied in the field of transmission network and can solve problems such as inefficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
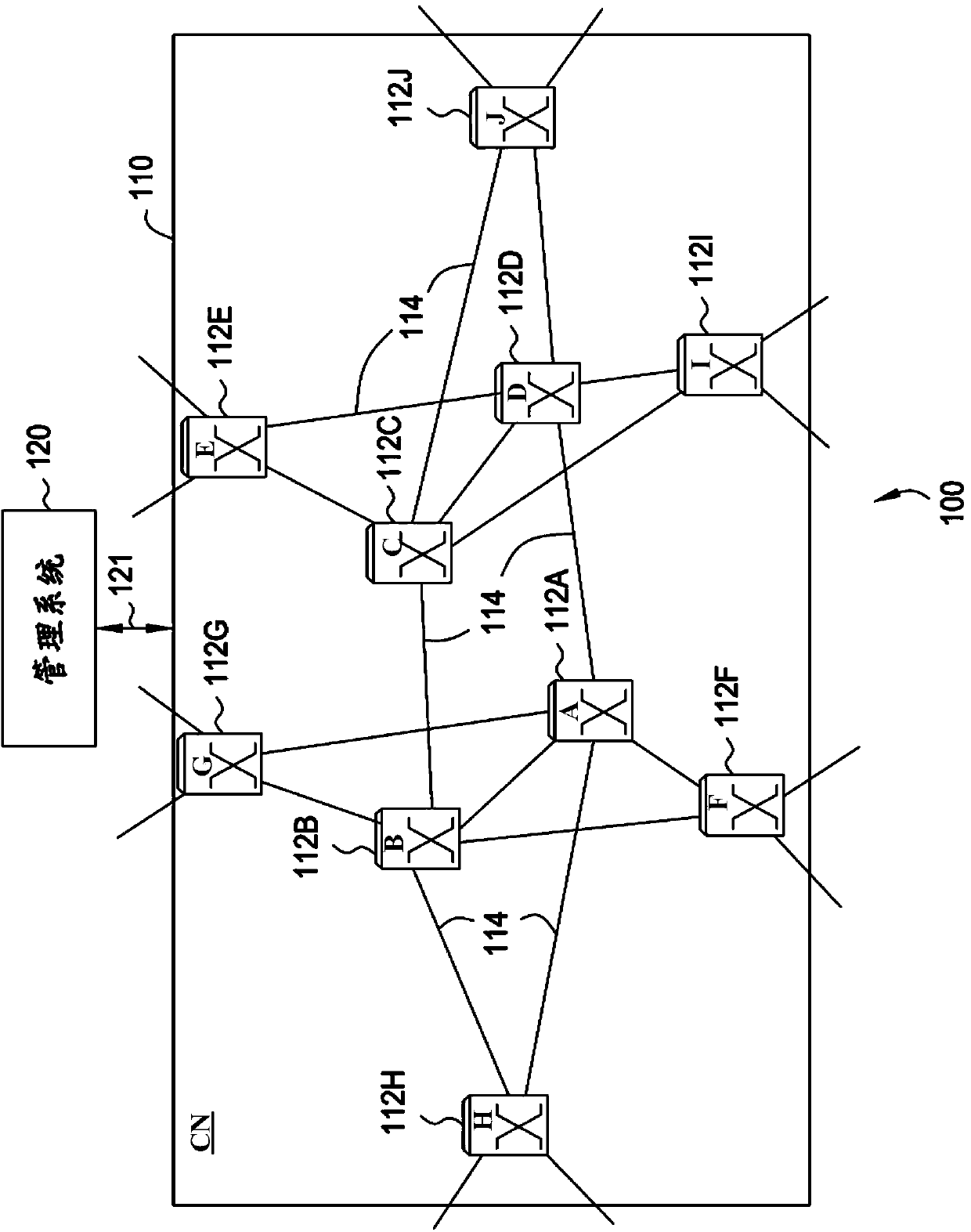
[0013] Various embodiments of the present invention are directed to determining shortest path bridging ( SPB).
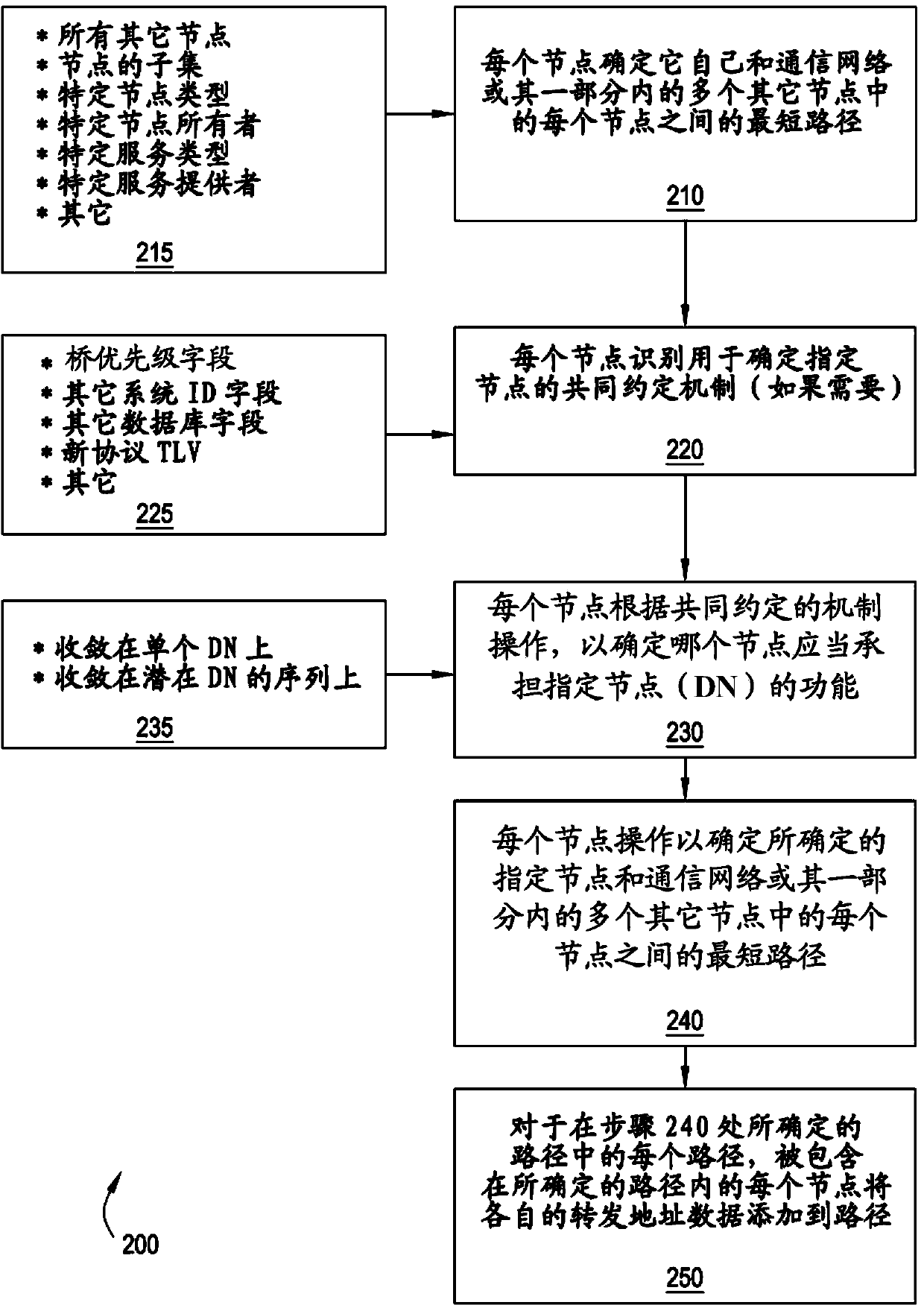
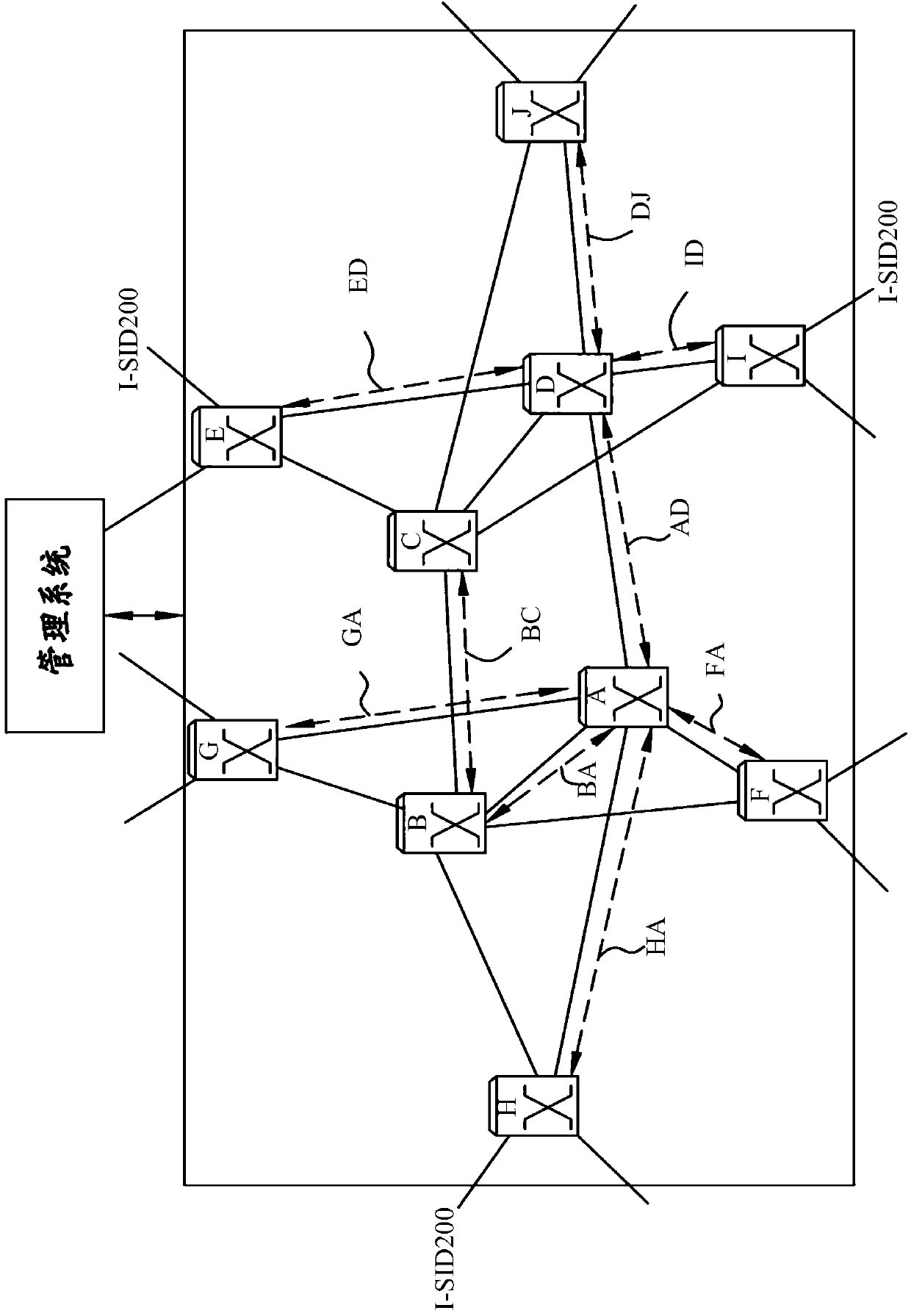
[0014] In various embodiments, different paths are allowed to support unicast and multicast traffic. In various embodiments, different cost factors for weights are associated with unicast and multicast paths or path elements. In various embodiments, each communication node (CN) computes once on one or more trees (referred to as "star, group trees" or "*, G trees") to define multicast paths, where according to common agreement The mechanism of computes the *,G-tree such that each of the respective nodes within a population of nodes, a subset of nodes of a population of nodes, a subset of service instances, etc. will converge on the common decision of the specified node(s).
[0015] Within the context of propagating unicast and multicast traffic within an Ethernet-based transport network, the determination of the SPB for unicast and multicast frames is primarily sho...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com