Load balancing in shortest-path-bridging networks
A shortest path bridging and network technology, applied in the field of data communication network, can solve problems such as incompatibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0026] It should be understood that the following description, while indicating several embodiments of the invention, is given by way of illustration only. Various changes and modifications within the scope of the invention as claimed will become apparent to those skilled in the art upon reading the following description and upon viewing the accompanying drawings.
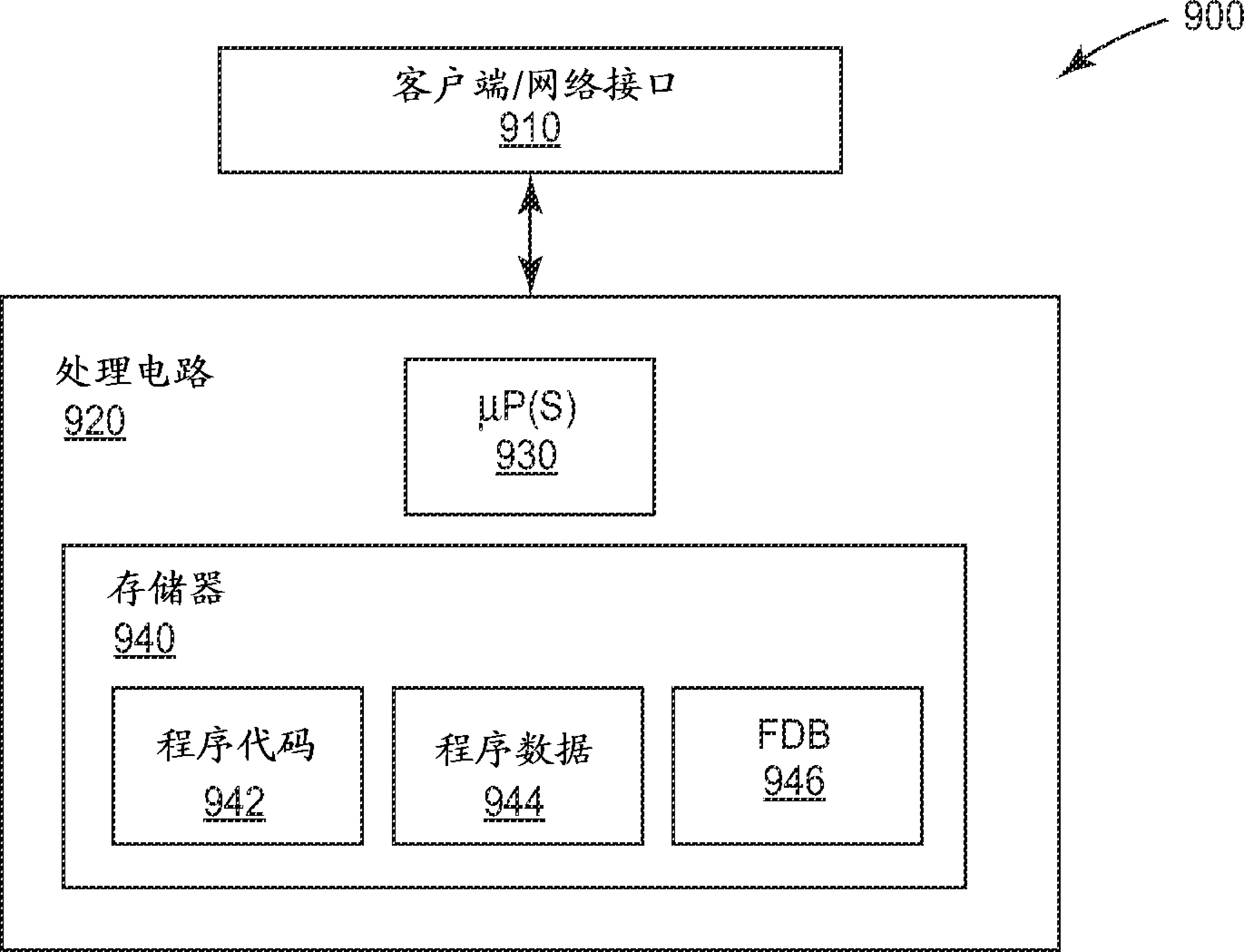
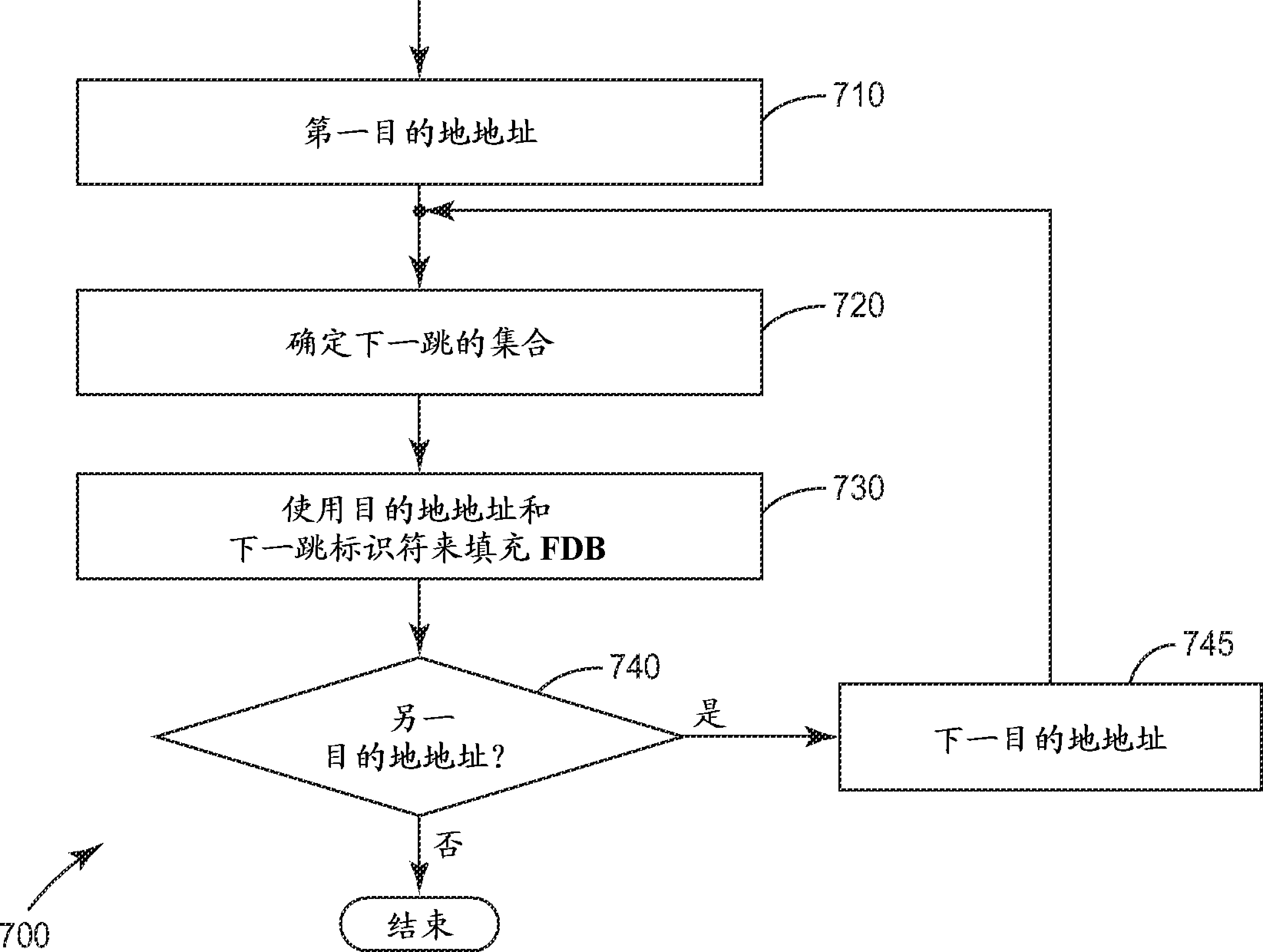
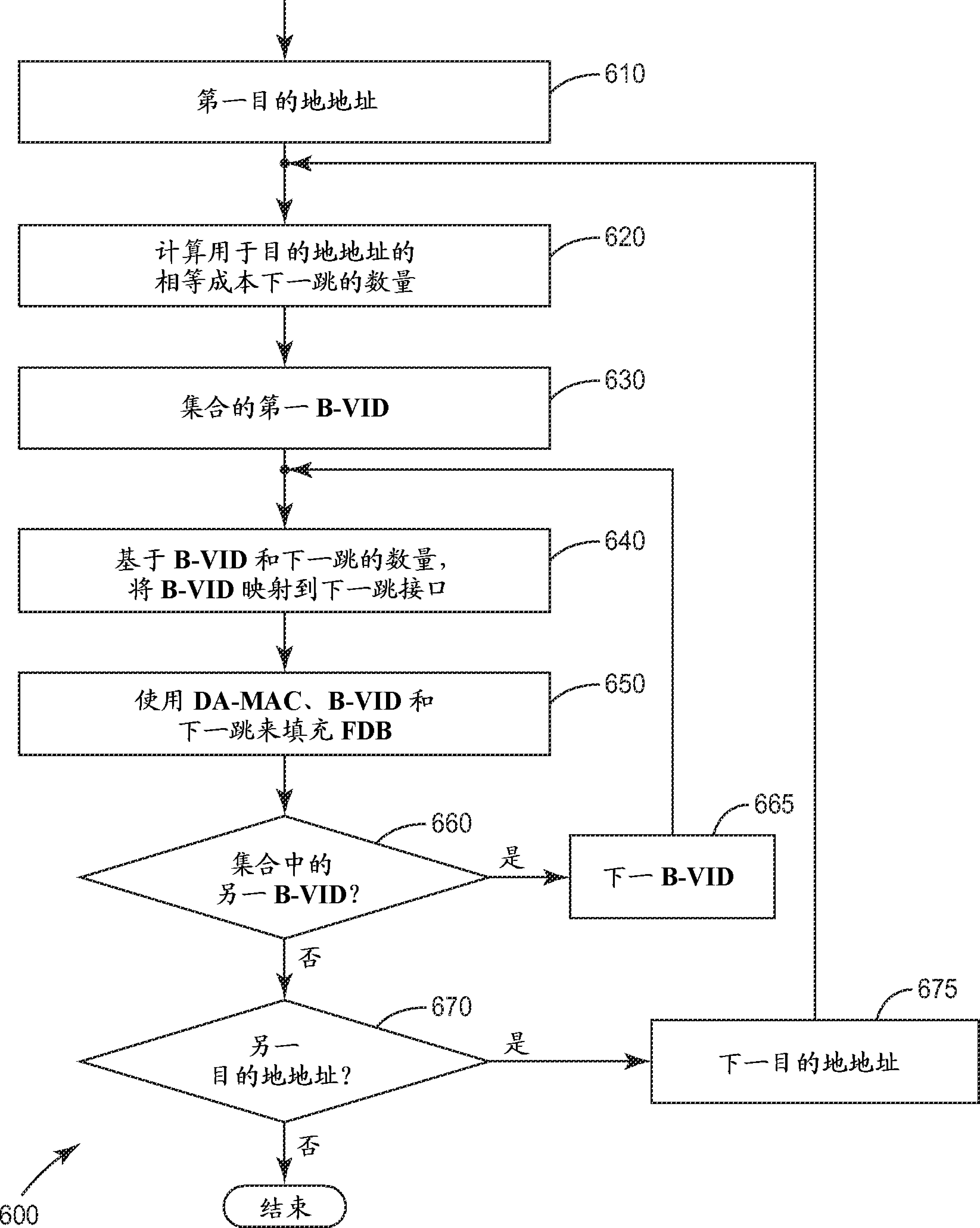
[0027] The IEEE has developed the 802.1aq standard for shortest path bridging to provide logical Ethernet networks over native Ethernet infrastructure. 802.1aq-enabled nodes (SPB-capable bridges) advertise network topology and membership in logical networks using the Intermediate System-to-Intermediate System (ISIS) link-state protocol. This well-known routing protocol allows nodes in a network to automatically determine the shortest paths between nodes. In effect, each bridge advertises the nodes it knows to all other nodes, so that all bridges in the network end up having a similar view of the network. Each nod...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com