Improved shortest path bridging in a multi-area network
A multi-path and area technology, applied in the field of Ethernet networks, can solve the problems of network design that cannot be easily decoupled from each other, lack of specificity, and computational complexity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0024] In the following description, numerous specific details are set forth. However, it is understood that embodiments of the invention may be practiced without these specific details. In other instances, well-known circuits, structures and techniques have not been shown in detail in order not to obscure the description. However, it will be understood by those skilled in the art that the present invention may be practiced without such specific details. Those of ordinary skill in the art, using the included descriptions, will be able to implement appropriate functionality without undue experimentation.
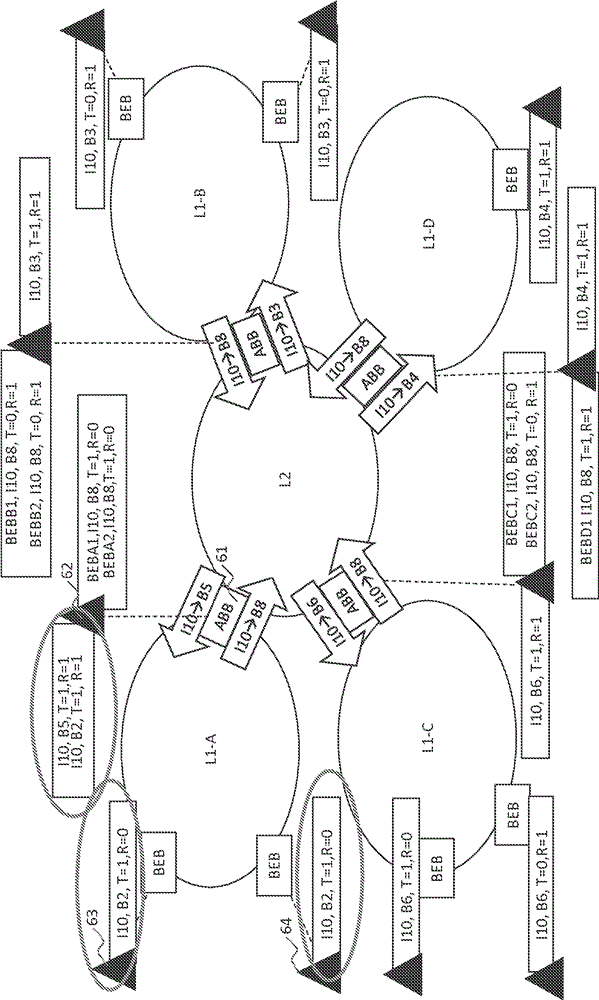
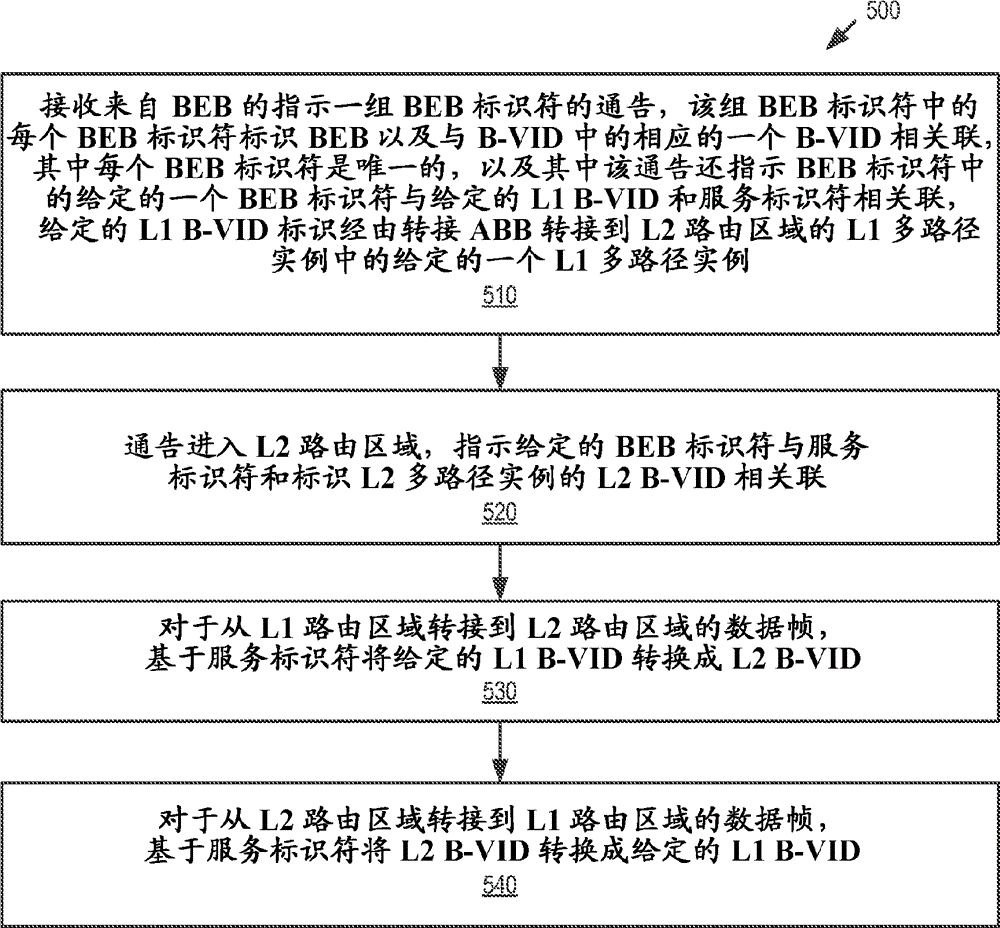
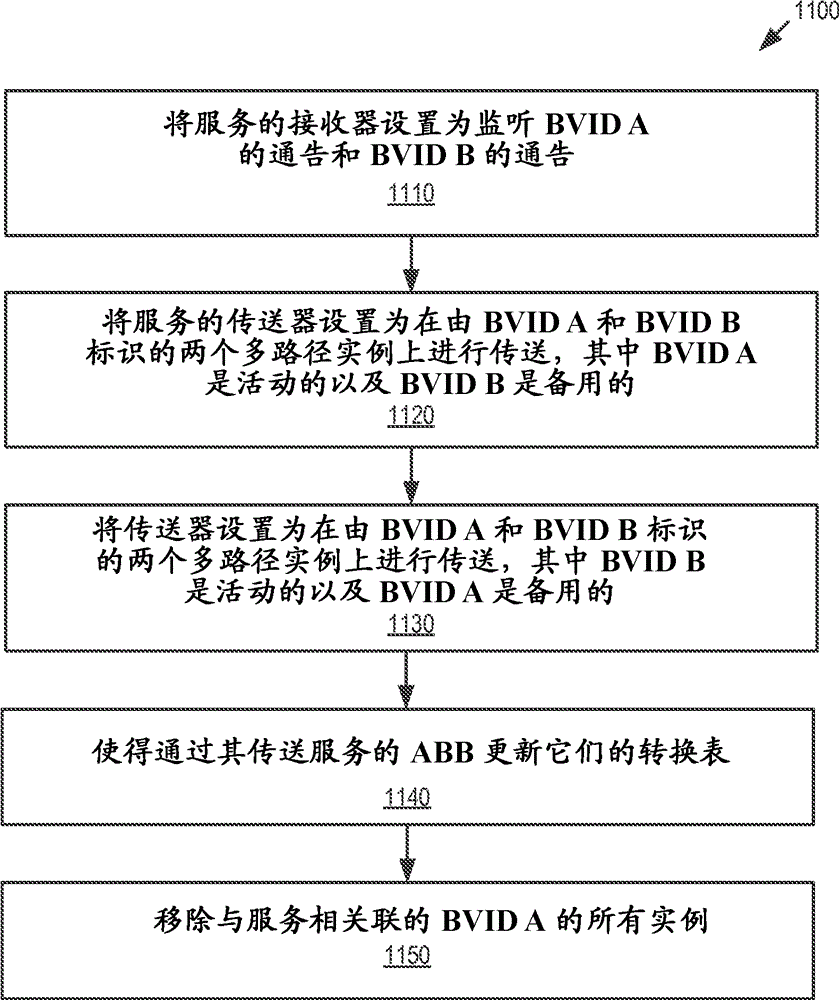
[0025]The multi-area network structure described in this paper is , which simplifies the task of providing loop-free symmetric connectivity between nodes in different areas. For Ethernet, a loop in the forwarding path can be disastrous if the forwarding path is a multicast path. Therefore, the use of routing hierarchies is advantageous, as opposed to peer-to-peer mesh inte...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com