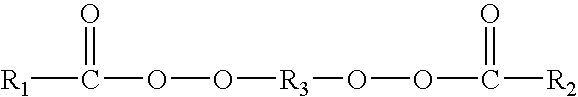Patents
Literature
118results about How to "Uniform charge" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
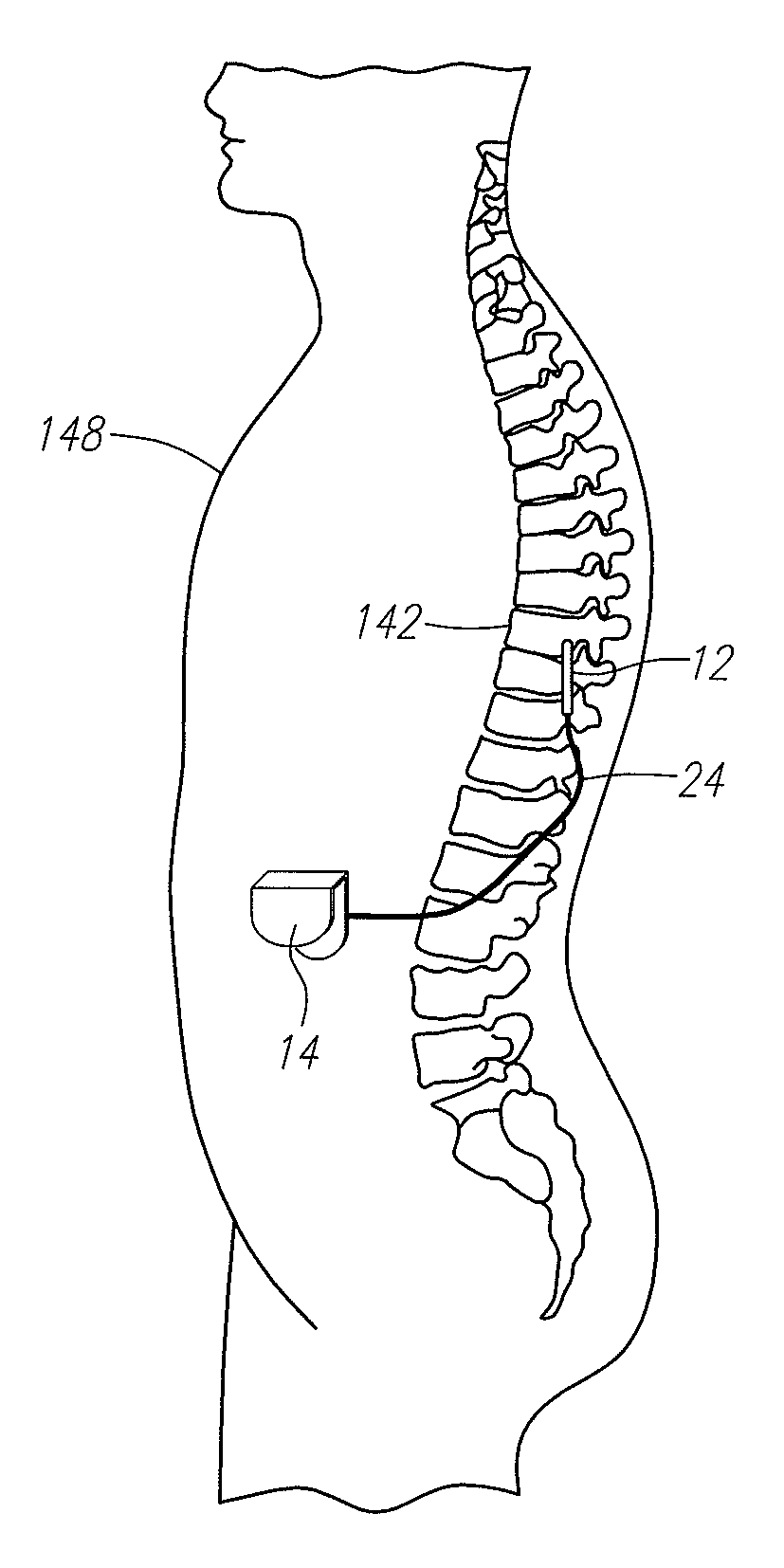
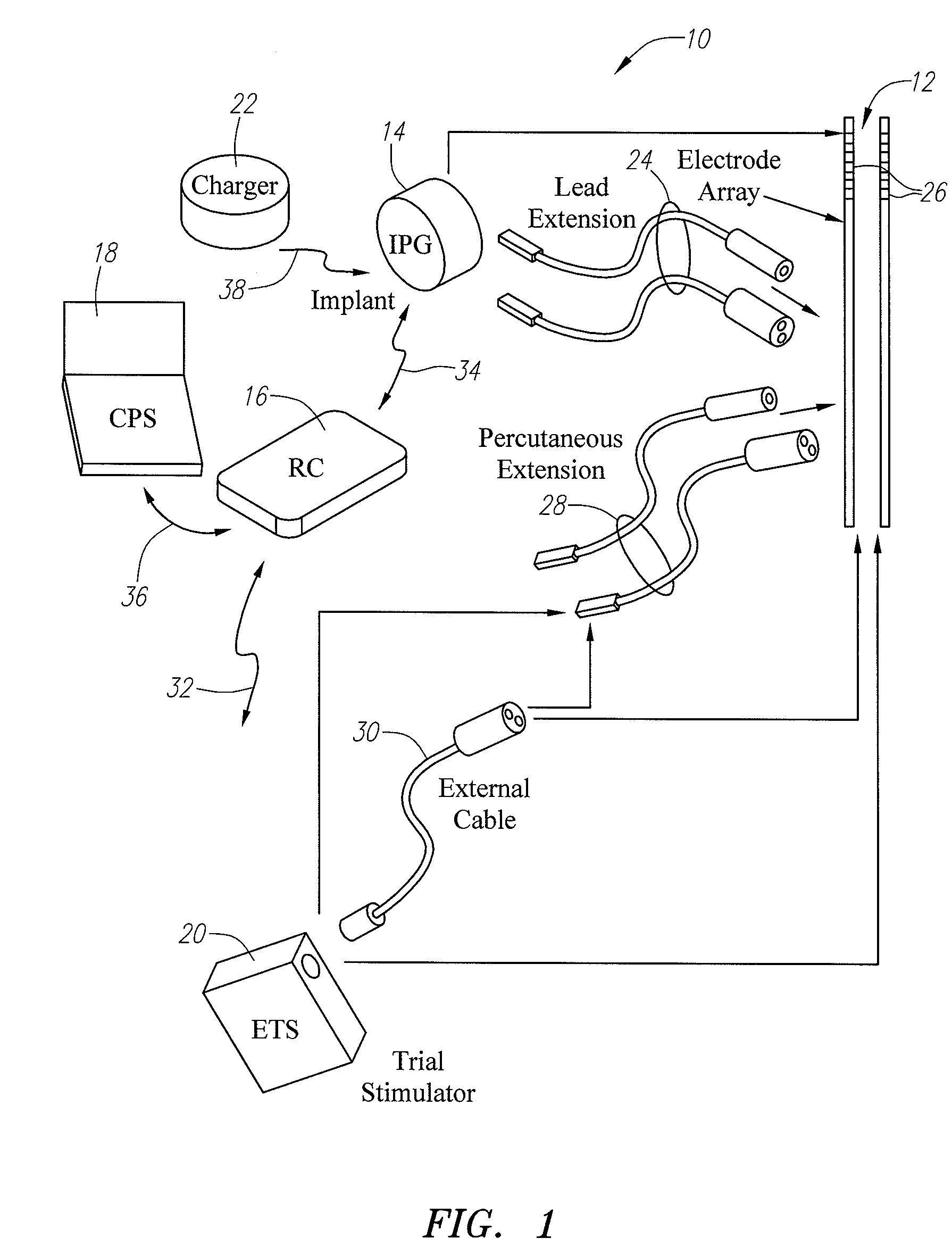
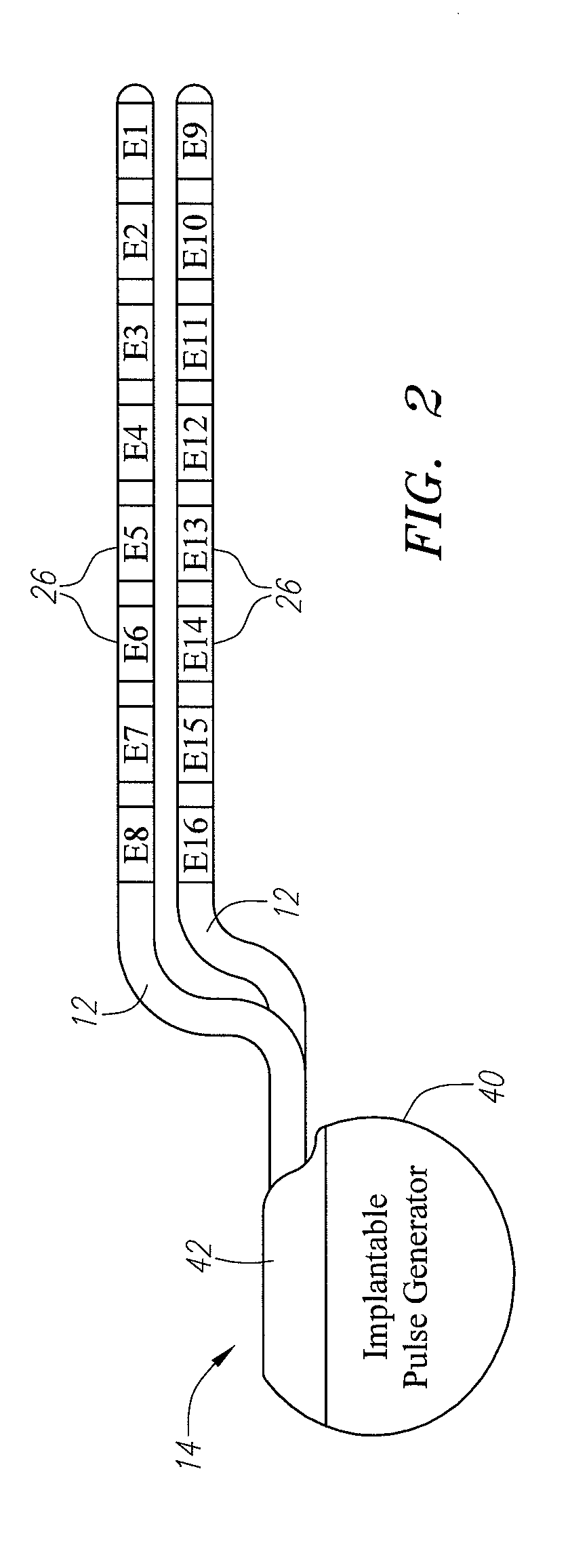
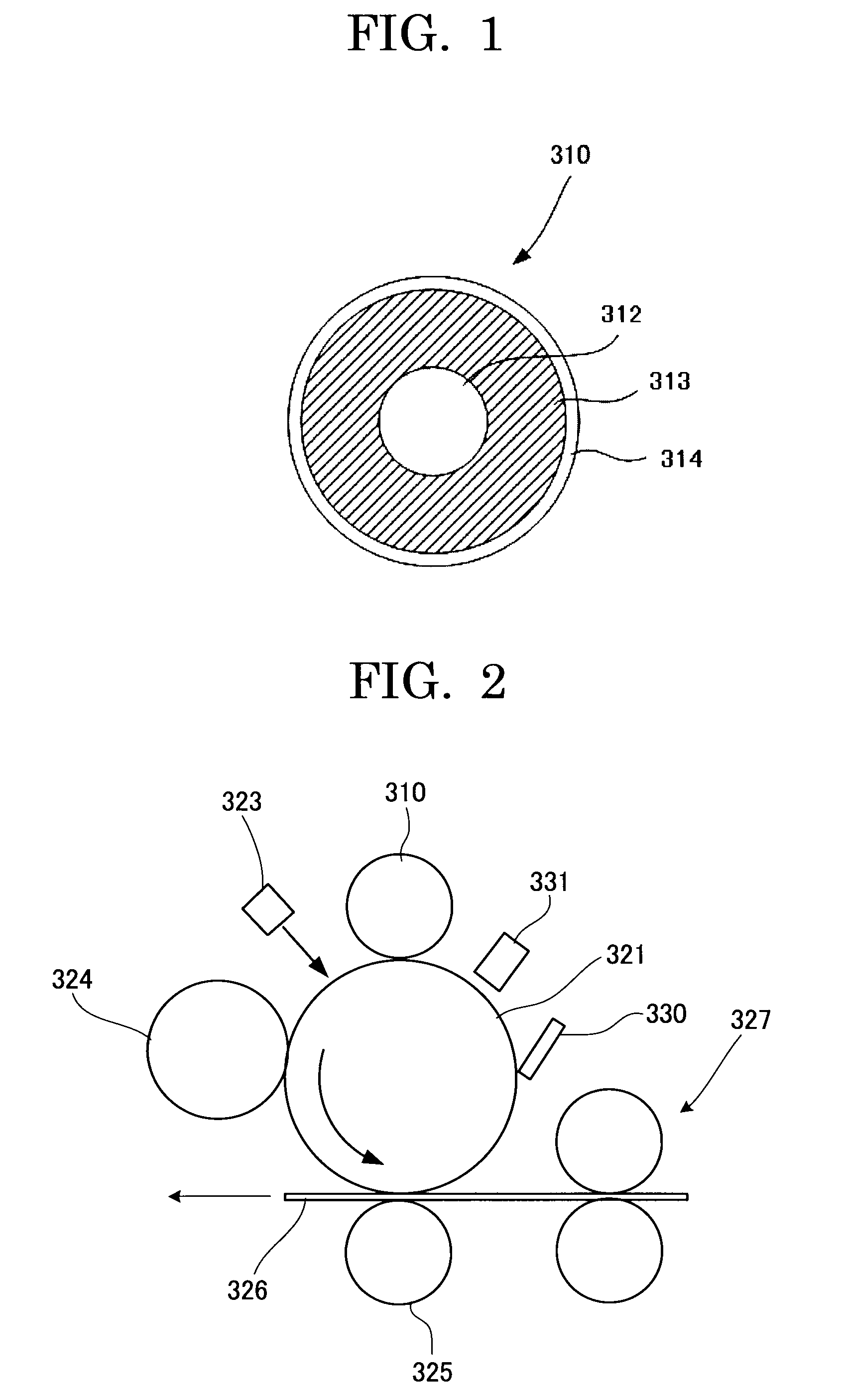
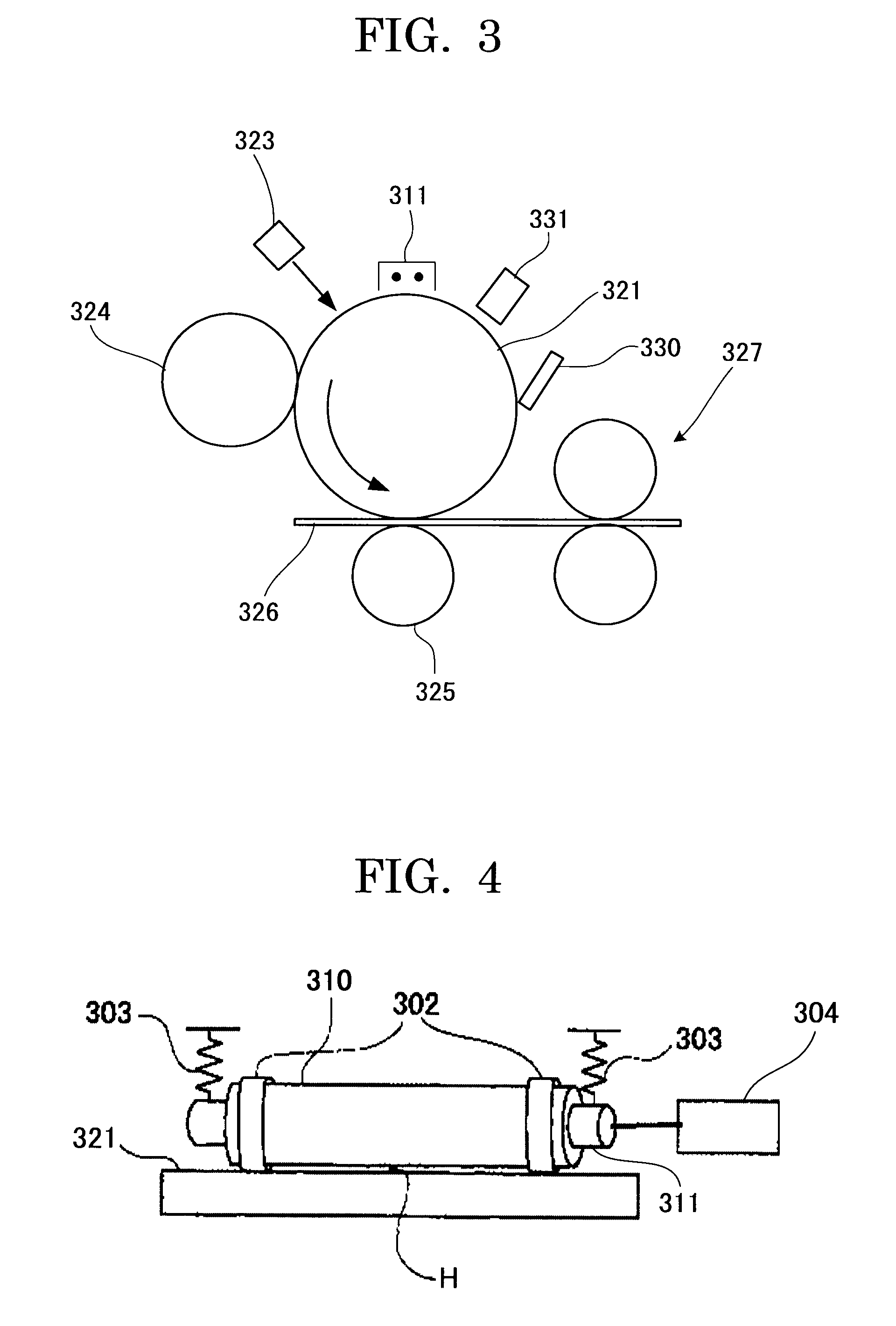
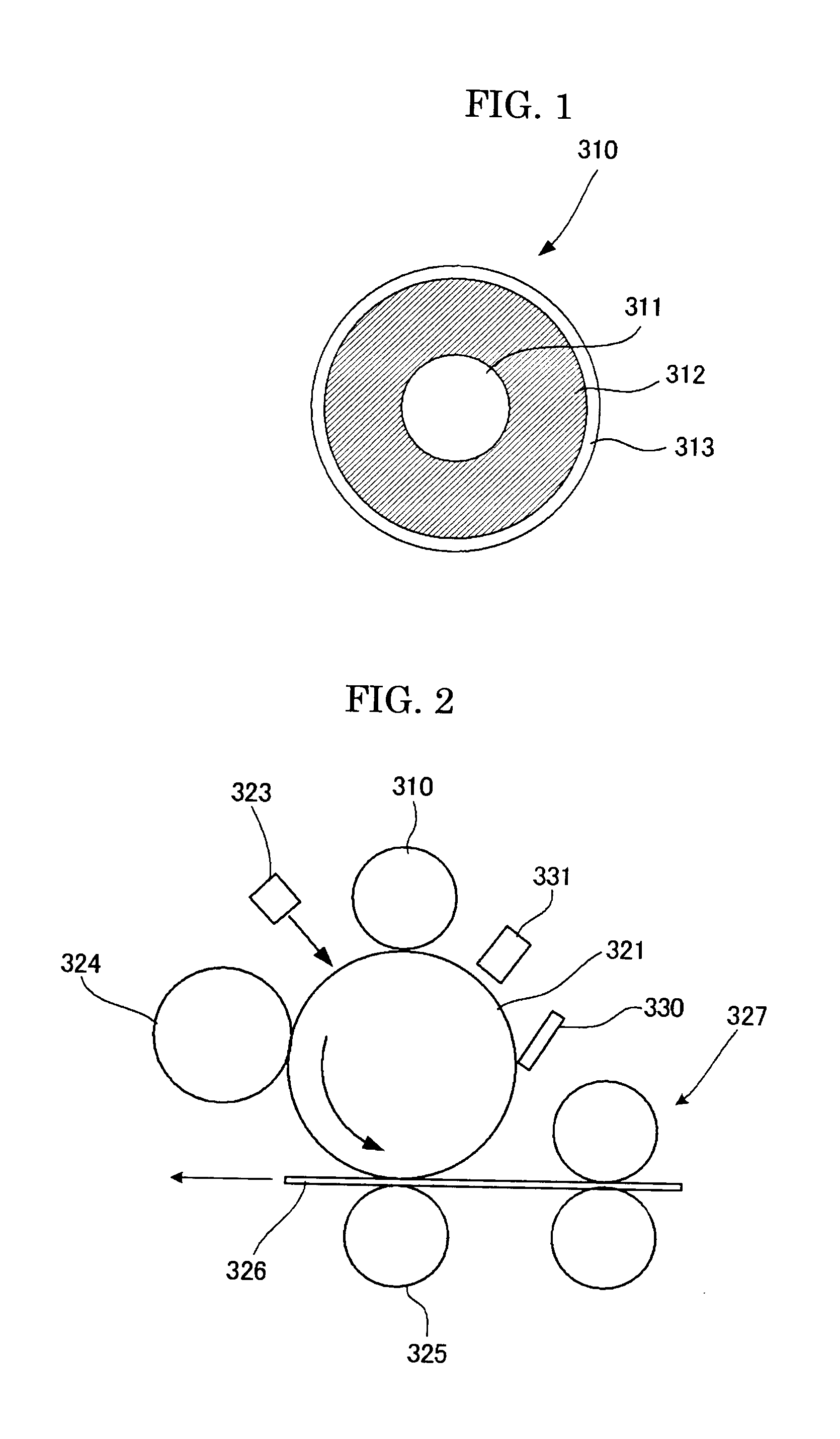
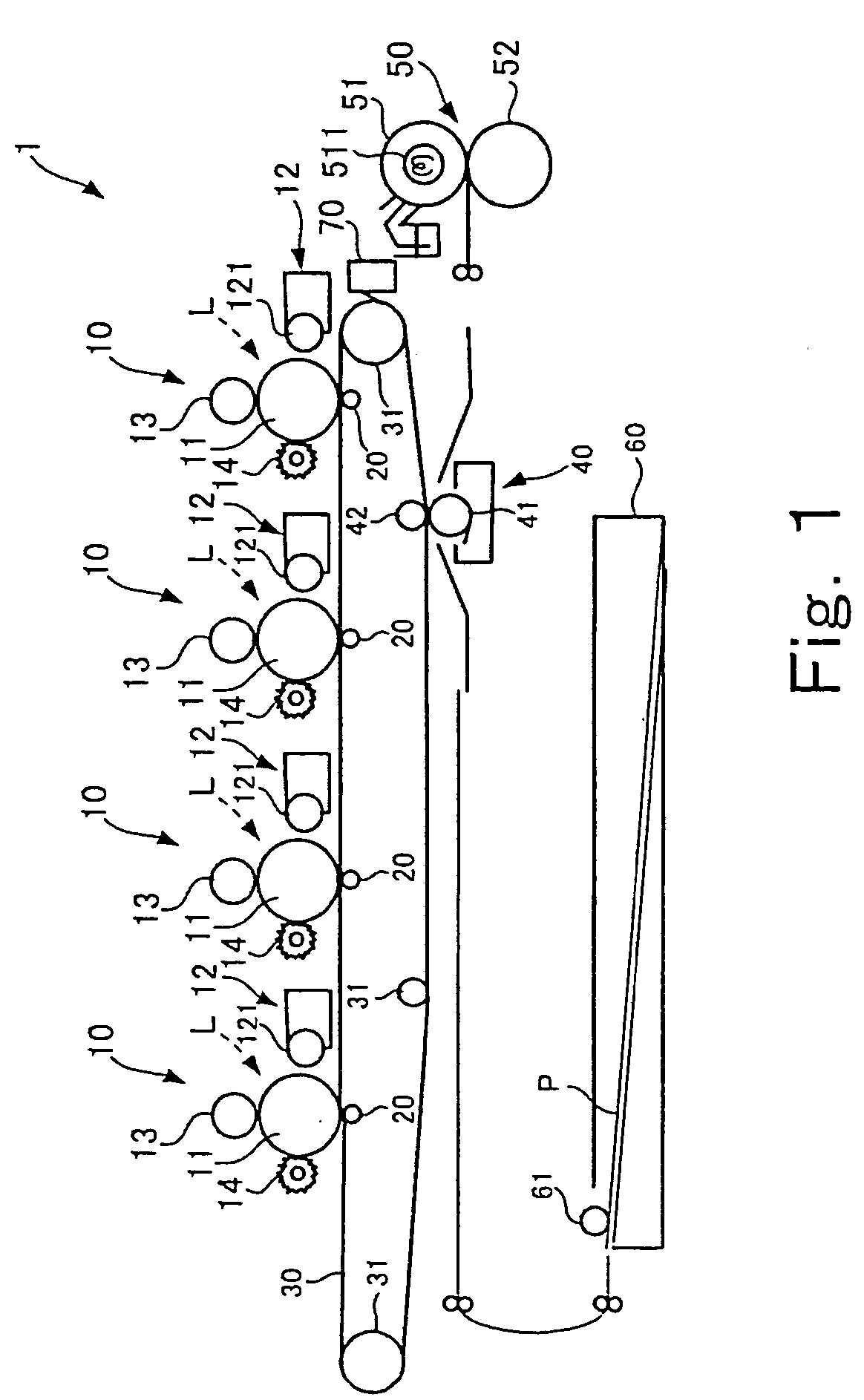
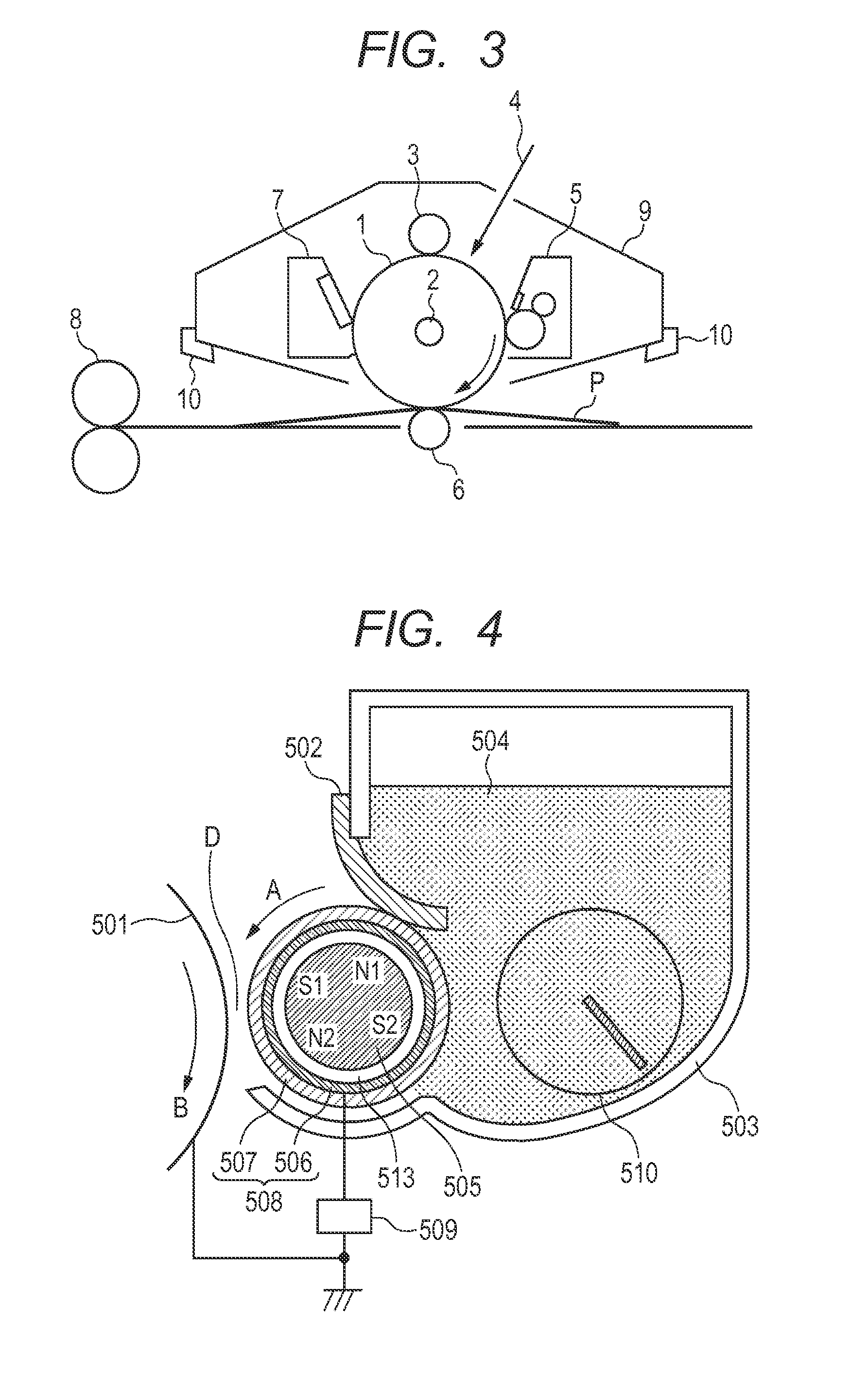
Use of stimulation pulse shape to control neural recruitment order and clinical effect
ActiveUS20090024189A1Uniform chargeImplantable neurostimulatorsArtificial respirationElectricityWave shape
A method, electrical tissue stimulation system, and programmer for providing therapy to a patient are provided. Electrodes are placed adjacent tissue (e.g., spinal cord tissue) of the patient, electrical stimulation energy is delivered from the electrodes to the tissue in accordance with a defined waveform, and a pulse shape of the defined waveform is modified, thereby changing the characteristics of the electrical stimulation energy delivered from the electrode(s) to the tissue. The pulse shape may be modified by selecting one of a plurality of different pulse shape types or by adjusting a time constant of the pulse shape.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
Toner, method of producing same and image forming device
A toner for developing an electrostatic image, including a colorant, a binder resin comprising a modified polyester, and fine resin particles having a weight average particle diameter of 50 to 300 nm and being present on an outer surface of the toner, wherein the toner has a BET specific surface area of 1.5 to 4.0 m2 / g.
Owner:RICOH KK
Toner, image forming apparatus, image forming method, and process cartridge using the toner
ActiveUS20080280219A1High quality imagingDecrease in image densityDevelopersElectrographic processes using charge patternImage formationCarboxylic acid
The present invention provides a toner containing at least a binder resin, a releasing agent, and a colorant, wherein the binder resin contains at least a polyester resin (A) having a softening point Tm(A) of 120° C. to 160° C., a polyester resin (B) having a softening point Tm(B) of 80° C. or more and less than 120° C. and a composite resin (C) containing a condensation polymerization monomer and an addition polymerization monomer, at least any one of the polyester resins (A) and (B) is a polyester resin prepared by condensation-polymerizing an alcohol component substantially composed of only aliphatic alcohol with a carboxylic acid component, and 65% or more of the alcohol component is 1,2-propanediol.
Owner:RICOH KK
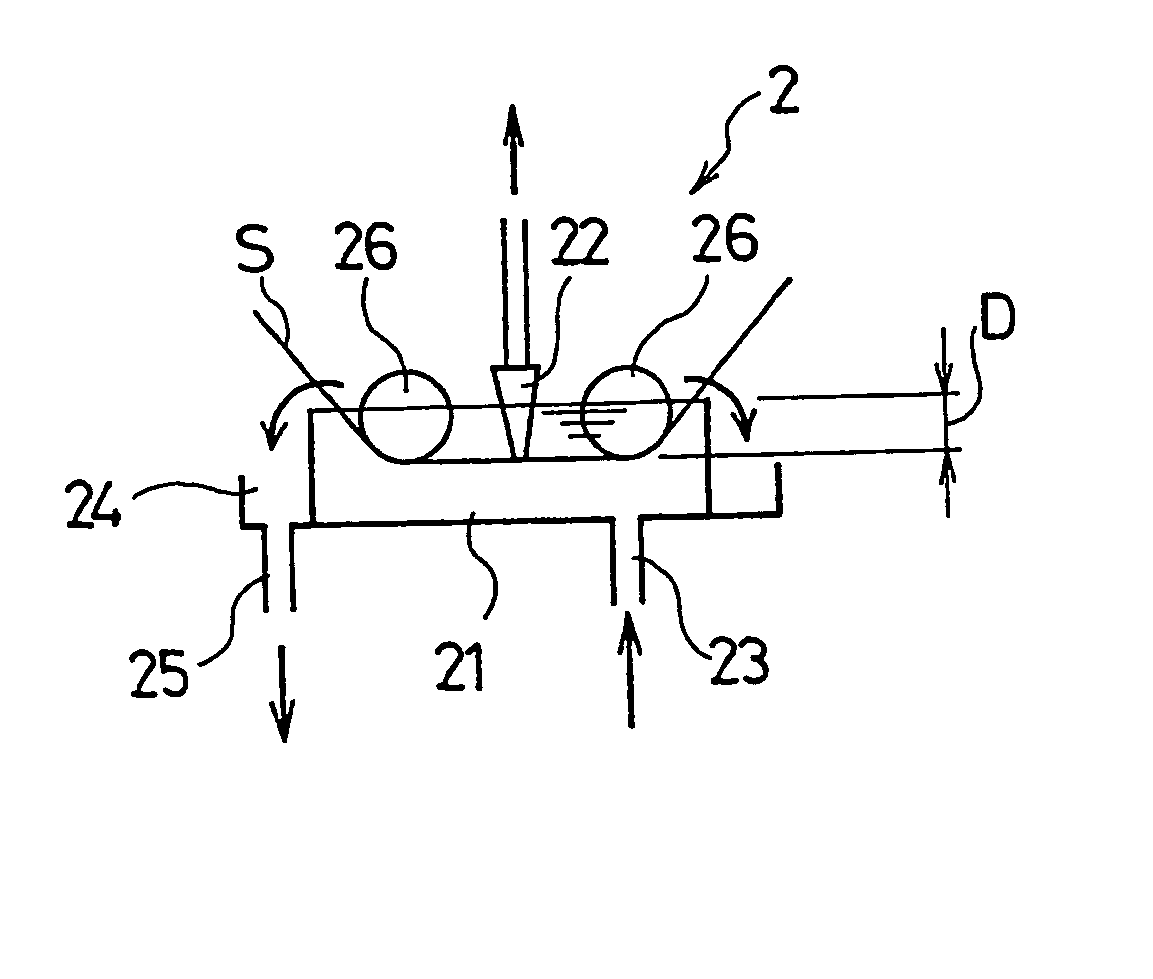
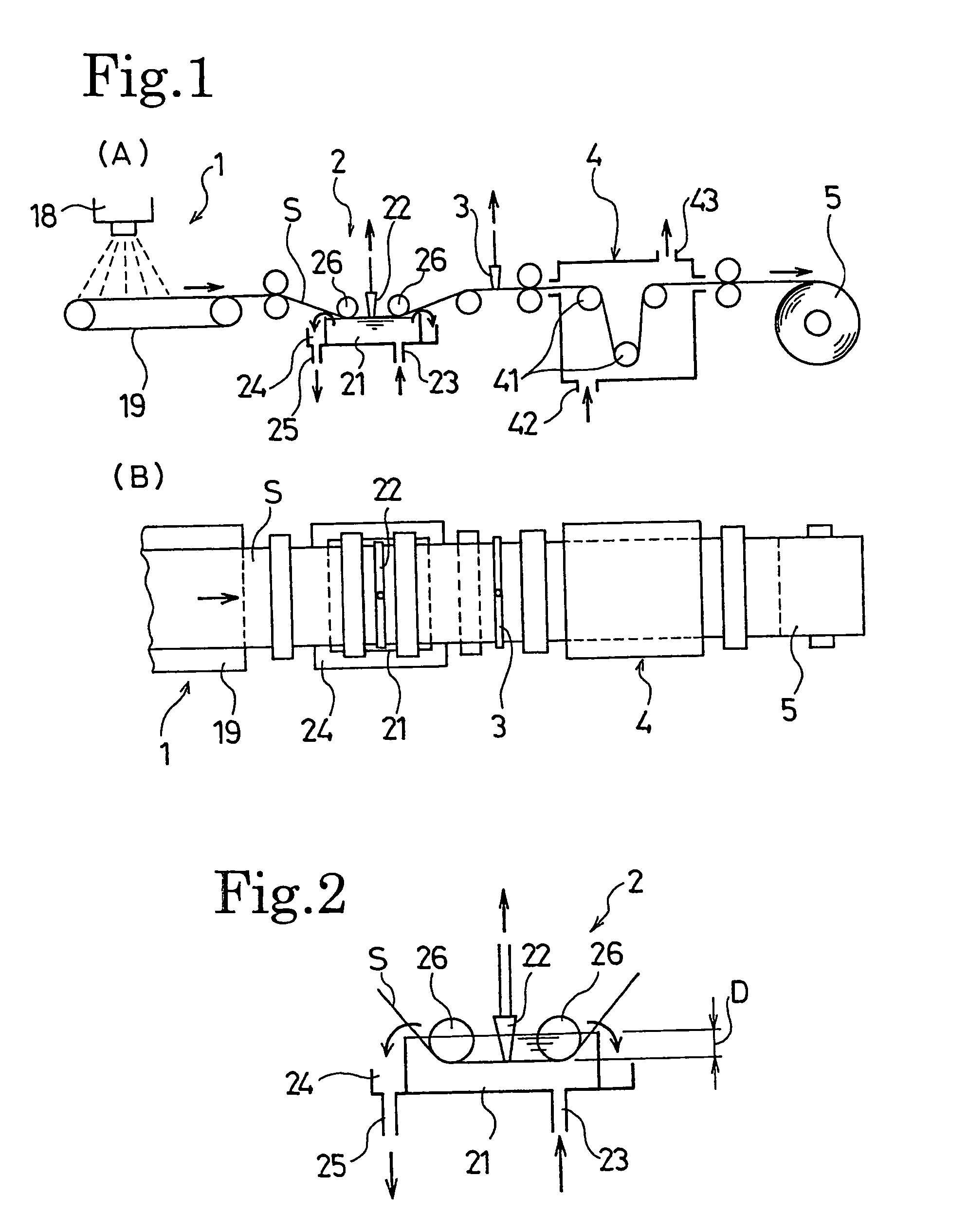
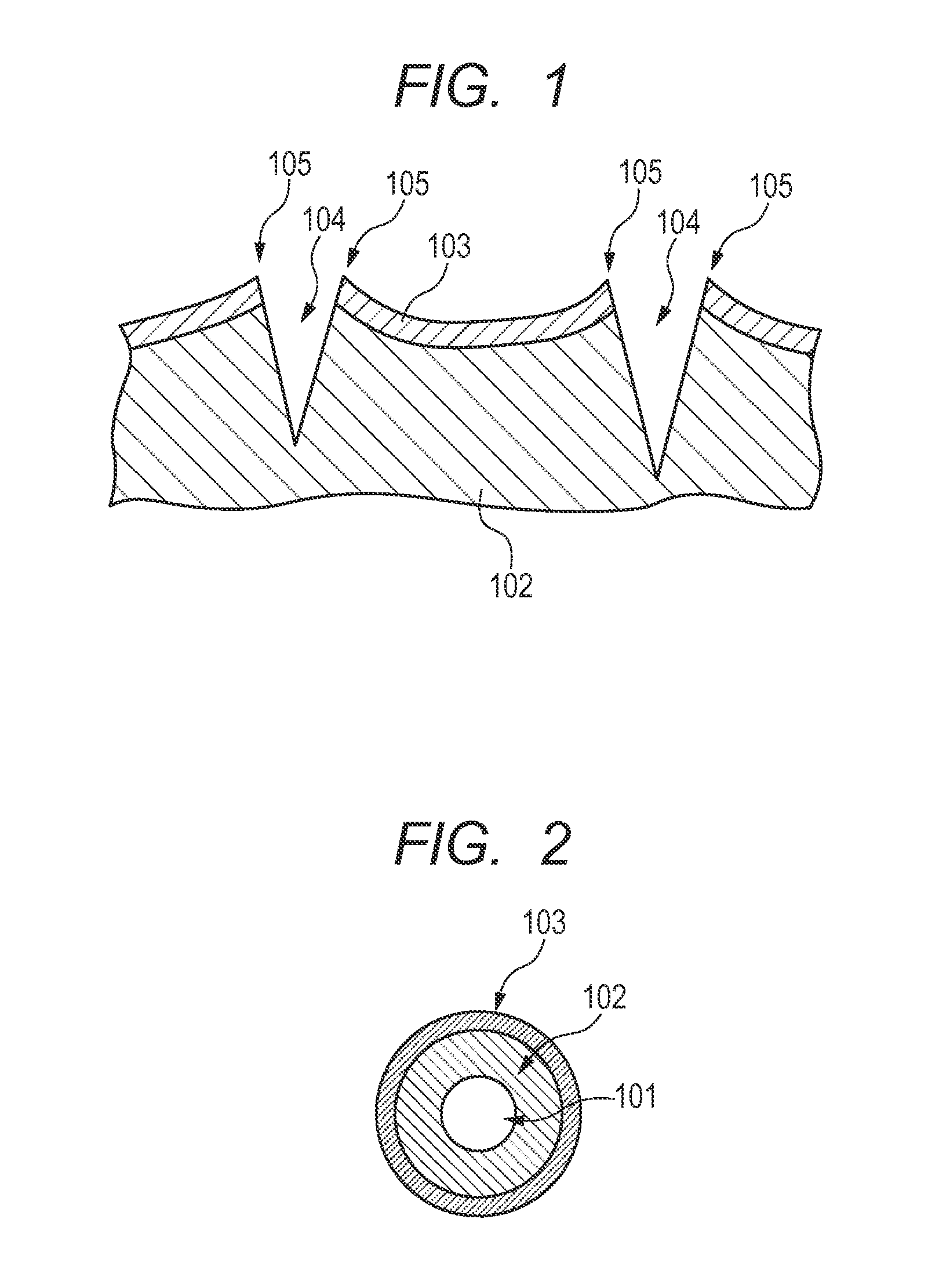
Manufacturing method and device for electret processed product
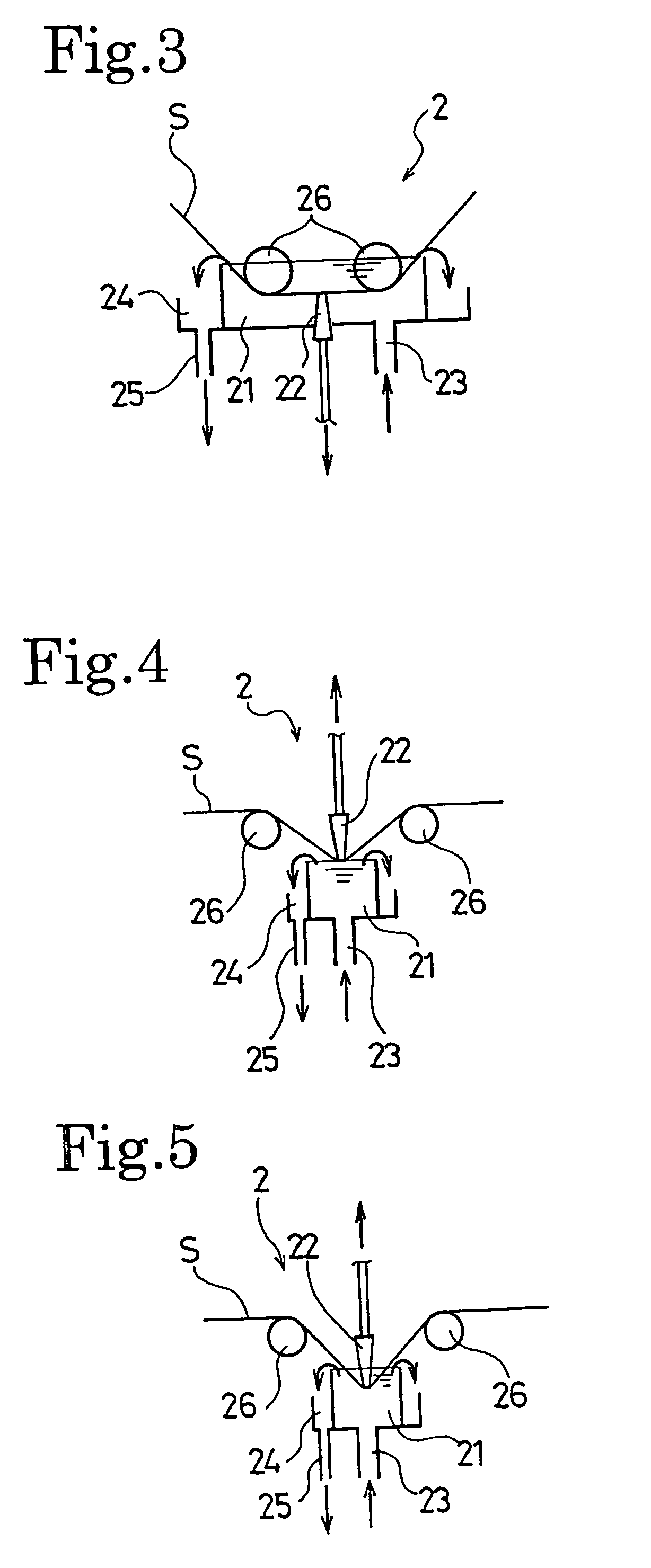
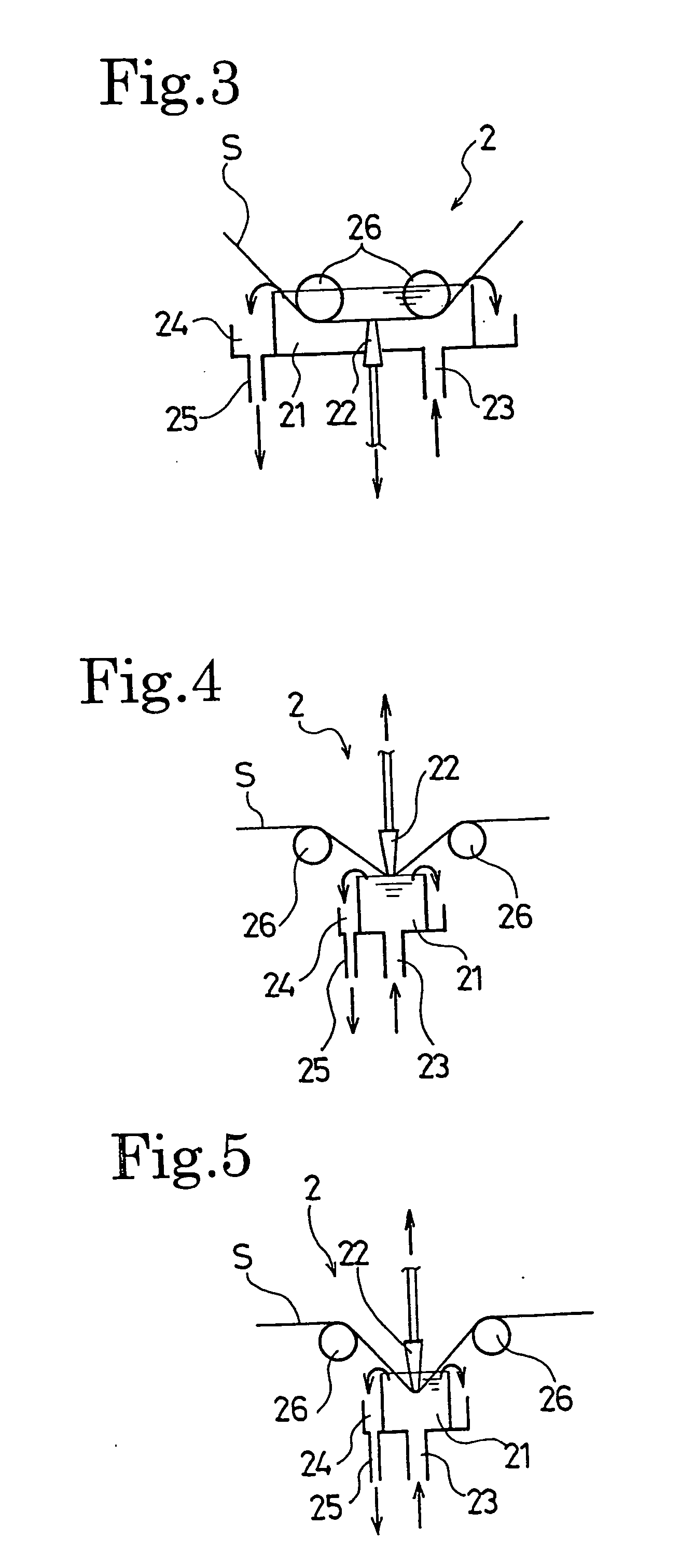
A manufacturing method of an electret processed product, comprising the steps of allowing a section nozzle (22) to come into contact with a nonconductive fiber sheet (S) so as to cross in the lateral direction of the sheet while running the sheet, allowing the surface of the sheet on the opposite side of the contact portion to come into contact with or to immerse into a water surface, sucking water from the suction nozzle (22) so that the water can be passed through the sheet in the thickness direction of the sheet to penetrate the water into the nonconductive fiber sheet (S), and drying the nonconductive fiber sheet (S), whereby a high quality and high performance electret processed product can be manufactured at a low cost.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
Conductive member, process cartridge, and electrophotographic apparatus
InactiveUS20120308261A1Evenly distributedUniform nip widthSynthetic resin layered productsElectrographic process apparatusConductive polymerIon exchange
Provided is a conductive member for electrophotography whose electrical resistance hardly increases even by long-term application of a high voltage. The conductive member for electrophotography is a conductive member for electrophotography, including: a conductive support; and a conductive elastic layer, in which: the elastic layer contains an A-B-A type block copolymer constituted of a non-ion conducting block (A block) and an ion conducting block (B block) having an ion exchange group; the block copolymer forms a microphase-separated structure; and the A block forms any structure selected from the group consisting of a spherical structure, a cylindrical structure, and a bicontinuous structure, and the B block forms a matrix for the structure.
Owner:CANON KK
Charging member, process cartridge and electrophotographic apparatus
InactiveUS20130034369A1Sufficient charging performanceUniform chargeElectrographic process apparatusWater-setting substance layered productSurface layerEngineering
A charging member is provided which can uniformly charge a photosensitive member without requiring any pre-exposure means in a low-, medium- or high-speed electrophotographic apparatus, and has a sufficient charging performance. An electrophotographic apparatus and a process cartridge are also provided which can keep multi-color ghost images from occurring and can form high-grade electrophotographic images stably. The charging member has a substrate, an elastic layer and a surface layer, which surface layer contains a high-molecular compound having an Si—O—Nb linkage; the high-molecular compound having a constitutional unit represented by the following formula (1) and a constitutional unit represented by the following formula (2).
Owner:CANON KK
Image forming apparatus, image forming method, and process cartridge
ActiveUS20070281237A1Easy to fixReduce odorElectrographic process apparatusDevelopersPolyesterPolymer science
To provide an image forming apparatus, image forming method and process cartridge, which are excellent in low-temperature fixation properties, storage stability, durability and filming resistance, can reduce generation of odor, and are capable of forming an extremely high quality image. The apparatus includes: a latent electrostatic image bearing member; a charging unit; an exposing unit; a developing unit; a transferring unit; and a fixing unit; wherein the toner comprises a binder resin and coloring agent, and the binder resin comprises a polyester-based resin (A) and polyester-based resin (B) having a melting point at least 10° C. higher than that of the polyester-based resin (A), and at least one of the polyester-based resins (A) and (B) is a resin derived from a (meth)acrylic acid modified rosin and includes a polyester unit obtained by condensation polymerization of an alcohol component and a carboxylic acid component containing a (meth)acrylic acid modified rosin.
Owner:RICOH KK
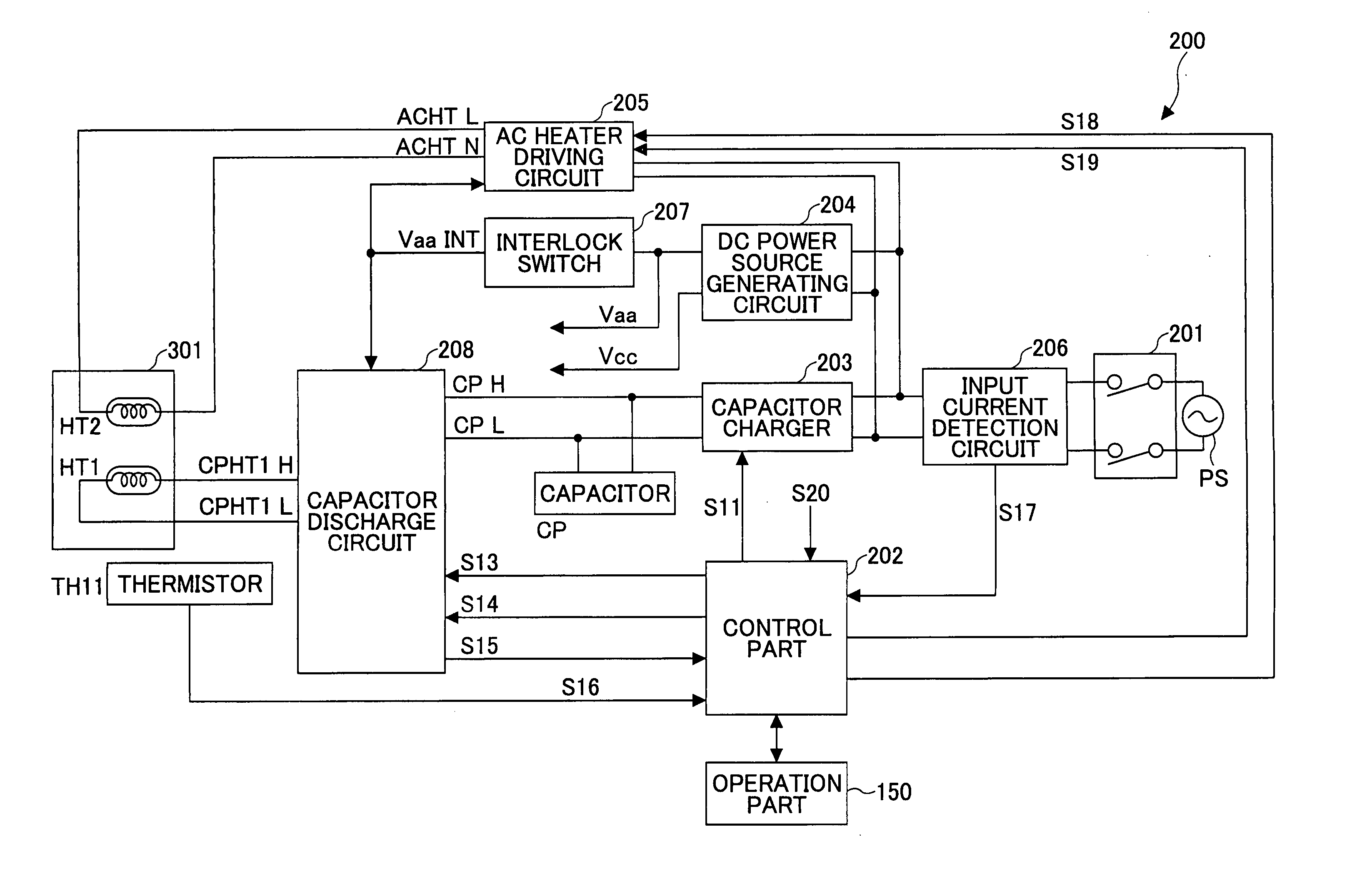
Auxiliary power source device, fixing device, image forming apparatus and charge operation control method
InactiveUS20050189923A1Large amount of chargeReduce chargeBatteries circuit arrangementsElectric powerEngineeringVoltage control
An auxiliary power source device includes: a first battery; a first charger receiving power supply from a commercial power source and charging the first battery; a second battery connected with the first battery in series; a second charger receiving power supply from the commercial power source and charging the second battery; a detecting circuit detecting voltages of the first battery and the second battery; and a control part switching charging operation between the first and second chargers for a final target voltage based on a detection result of the detecting circuit.
Owner:RICOH KK
Charging apparatus, and image forming apparatus equipped with same
InactiveUS20050271420A1Prevent image defectsSuppress fluctuationsElectrographic process apparatusCorona dischargeCharge currentImage formation
A charging apparatus, process cartridge, and image forming apparatus with which current fluctuation values in the charging current can be suppressed, and image defects caused by filming and the like can be prevented, by specifying a permissible gap fluctuation value by quantitatively ascertaining the relationship between the fluctuation value in charging current and the fluctuation value in the gap between the photosensitive body and the charging roller. In a charging apparatus equipped with a charging roller provided at a minute gap away from a photosensitive body, for performing charging, the relationship Gmax−Gmin≦30 (μm) is satisfied when the gap (μm) between the charged side of the photosensitive body and the charging side of the charging roller has a maximum value Gmax (μm) and a minimum value Gmin (μm).
Owner:RICOH KK
Charging member, process cartridge and electrophotographic apparatus
InactiveUS20140080691A1Little contaminationUniform chargeLiquid surface applicatorsElectrographic process apparatusSurface layerAbnormal discharge
The present invention provides a charging member that suppresses abnormal discharge which induces charging unevenness, and that has little contamination on a surface layer, to thereby enable uniform charging over a long period. The charging member includes a substrate, an elastic layer and a surface layer, wherein the surface layer contains a polymer compound having constitutional units represented by the following general formula (1), chemical formula (2) and general formula (3), and having a Si—O—Ti bond, a Ti—O-M bond and a Si—O-M bond. M is any atom selected from the group consisting of V, Nb and W.
Owner:CANON KK
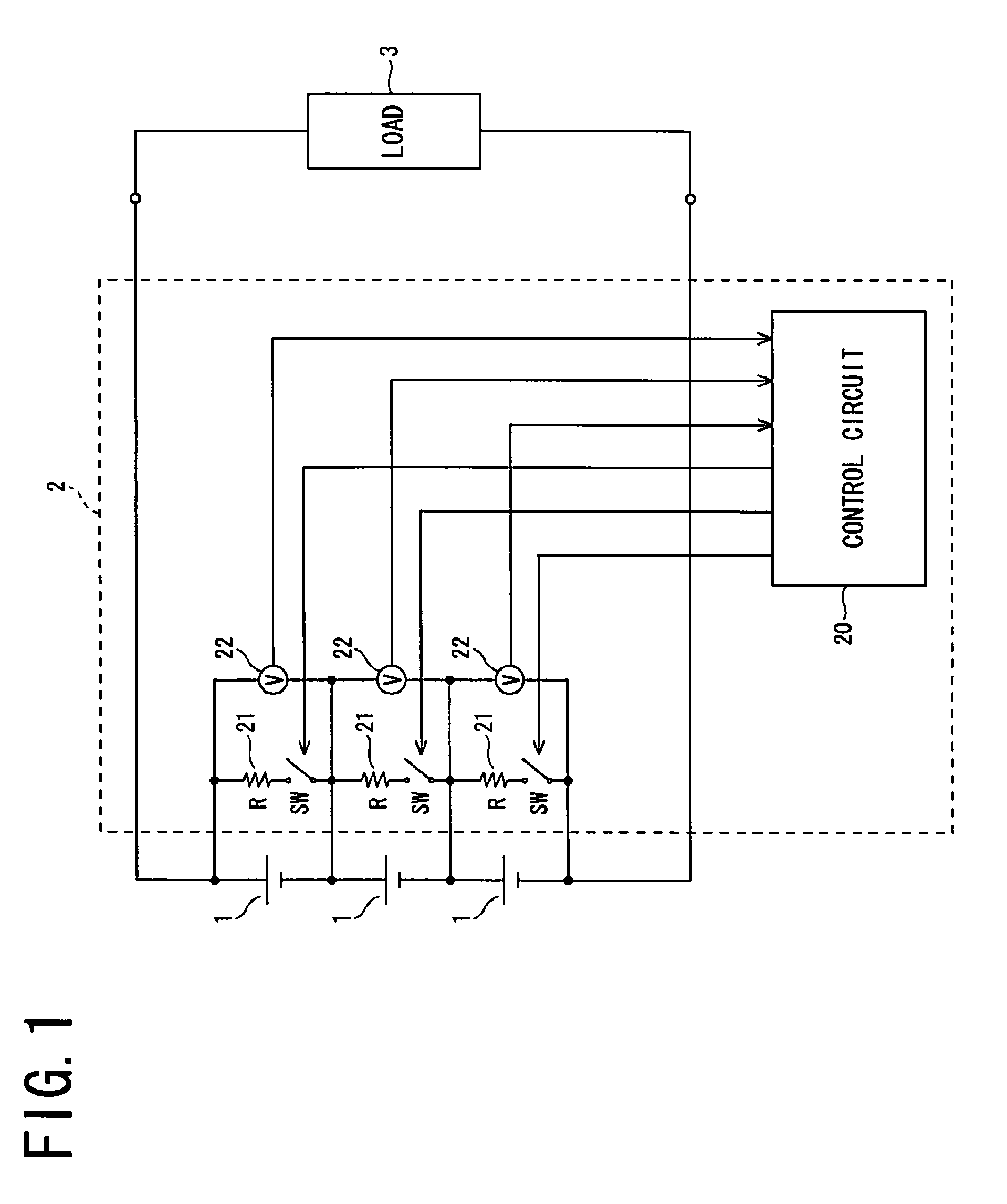
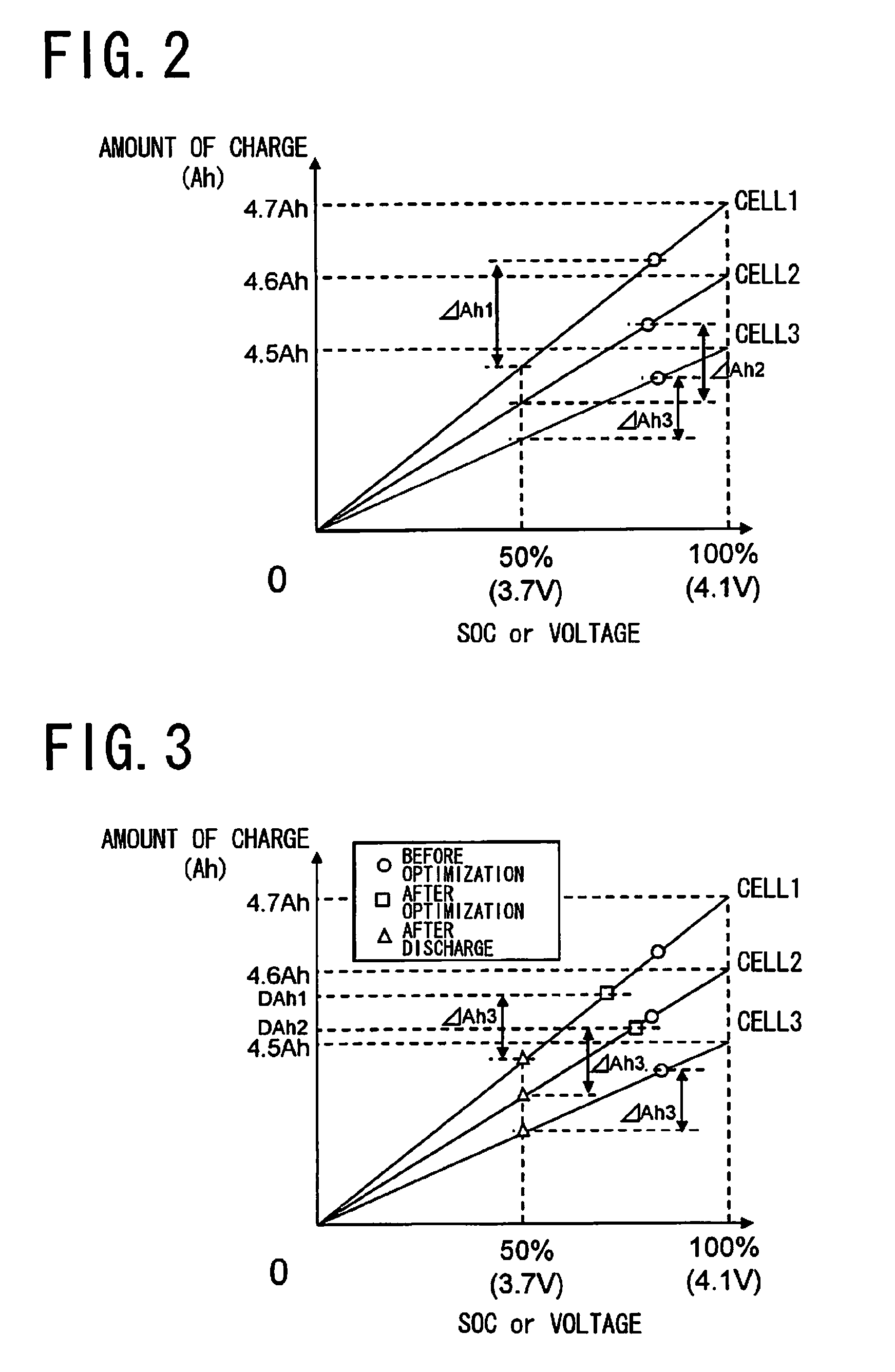
State of charge optimizing device and assembled battery system including same
ActiveUS20090085520A1Sufficient performanceElicit the performance of the assembled batteryCharge equalisation circuitMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansElectrical batteryState of charge
A state of charge optimizing device according to the present invention optimizes a state of charge of each of a plurality of cells which are connected in series to form an assembled battery, and conducts the optimization by discharging or charging a part or all of the plurality of cells so that the differences between the amount of charge after the optimization and the amount of charge in a predetermined state of charge become uniform.
Owner:PANASONIC ENERGY CO LTD
Image forming apparatus, image forming method, and process cartridge
ActiveUS20080318143A1Less odorQuality improvementDevelopersElectrographic process apparatusChemistryRosin
An image forming apparatus including a charging unit, an exposing unit, a developing unit, a transferring unit, and a fixing unit. A toner containing a colorant and a binder resin which contains a polyester resin (A) and a polyester resin (B) having a softening point 10° C. or more higher than that of the polyester resin (A); the polyester resin (A) is a (meth)acrylic acid-modified rosin derived resin having a polyester unit obtained by polycondensation of an alcohol component, which contains 65 mol % or more of 1,2-propanediol in a dihydric alcohol component, and a carboxylic acid component containing a (meth)acrylic acid-modified rosin; the polyester resin (B) is a purified rosin derived resin having a polyester unit obtained by polycondenstation of an alcohol component, which contains a total of 70 mol % or more of 1,2-propanediol and 1,3-propanediol in a dihydric alcohol component, and a carboxylic acid component containing purified rosin.
Owner:RICOH KK
Charging Device, Process Cartridge, Image Forming Apparatus, And Toner
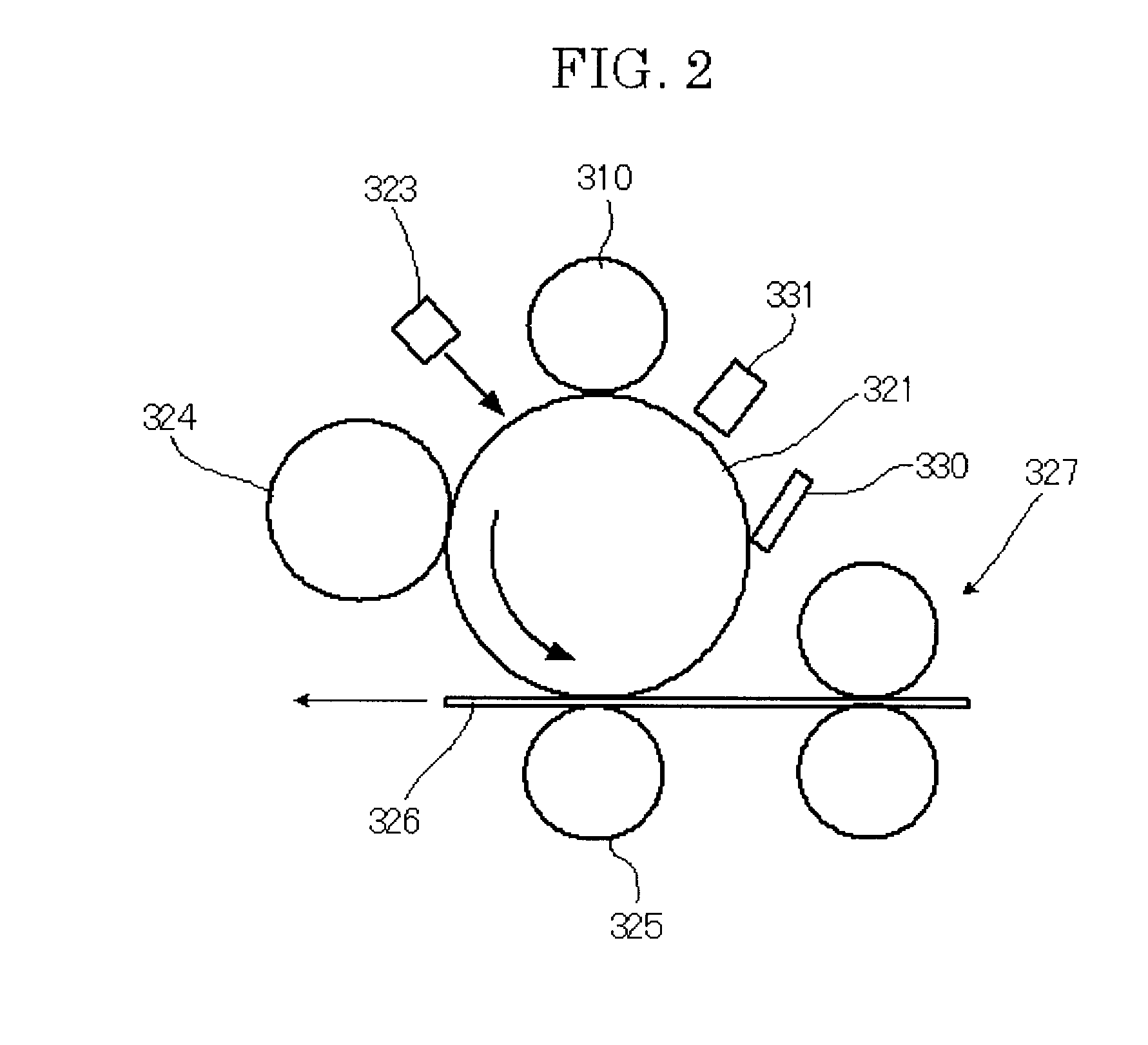
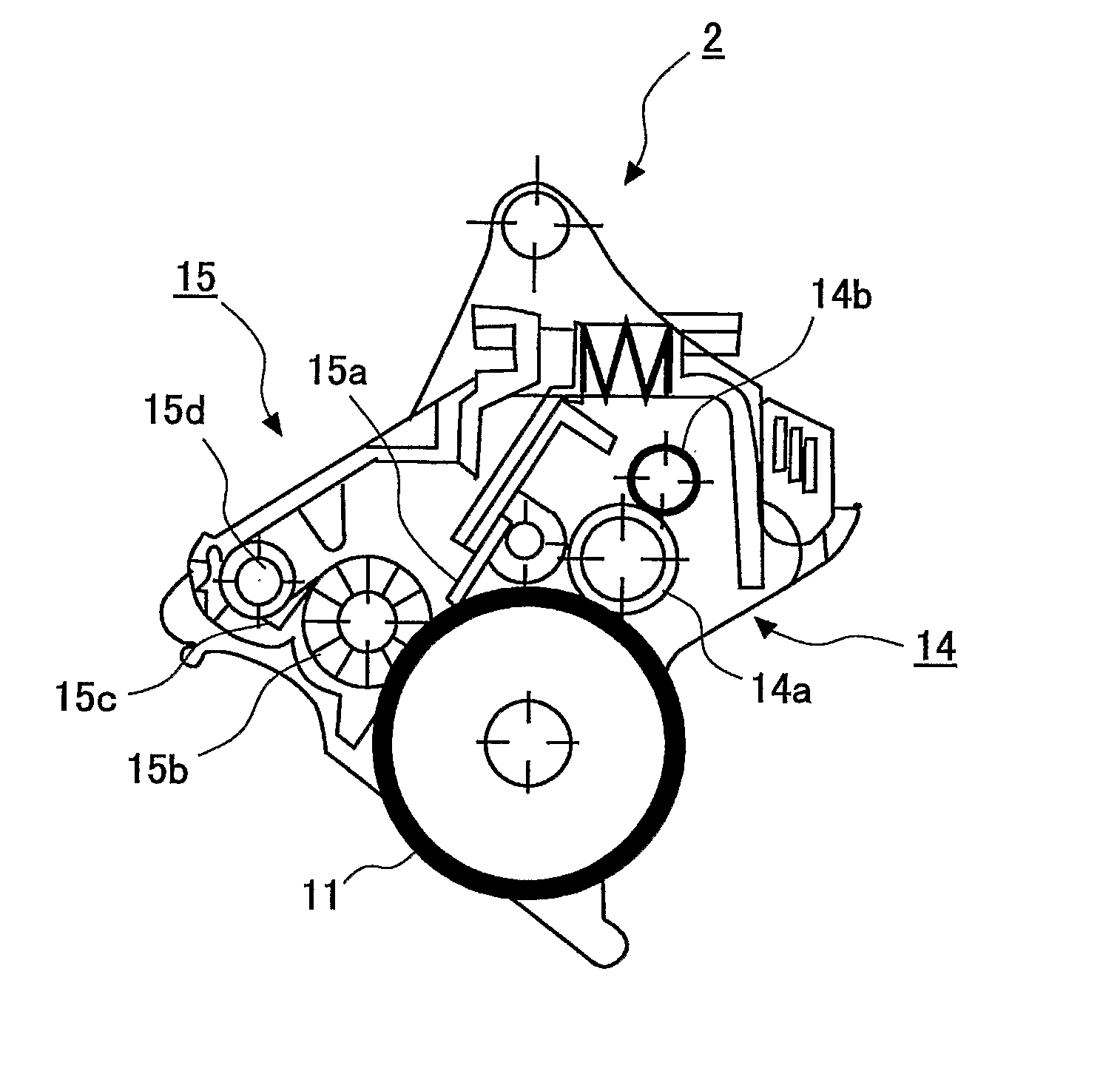
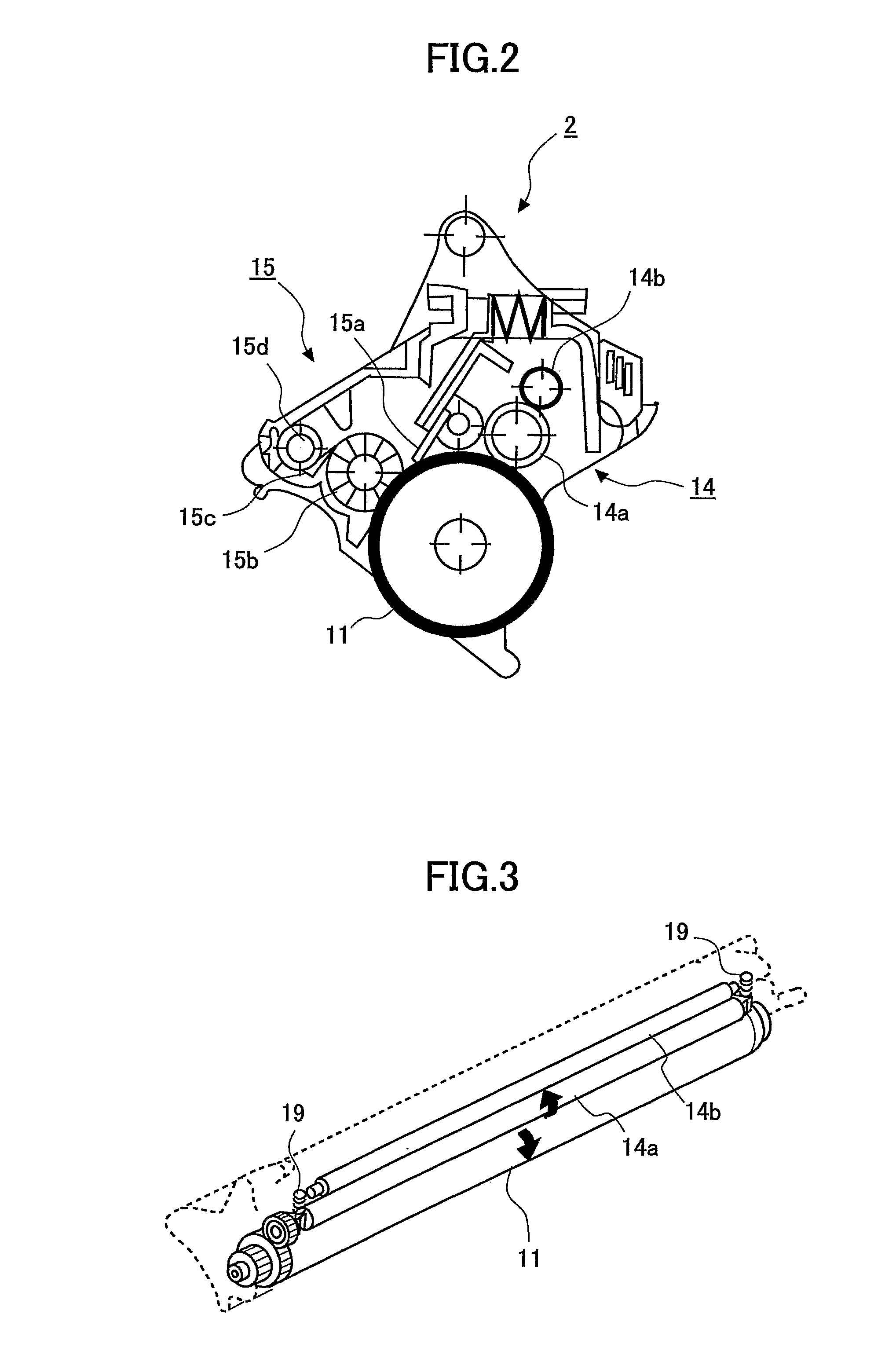
ActiveUS20070196123A1Maintains continuously cleaning performanceUniform chargeShaft and bearingsDevelopersElectrical resistance and conductanceImage recording
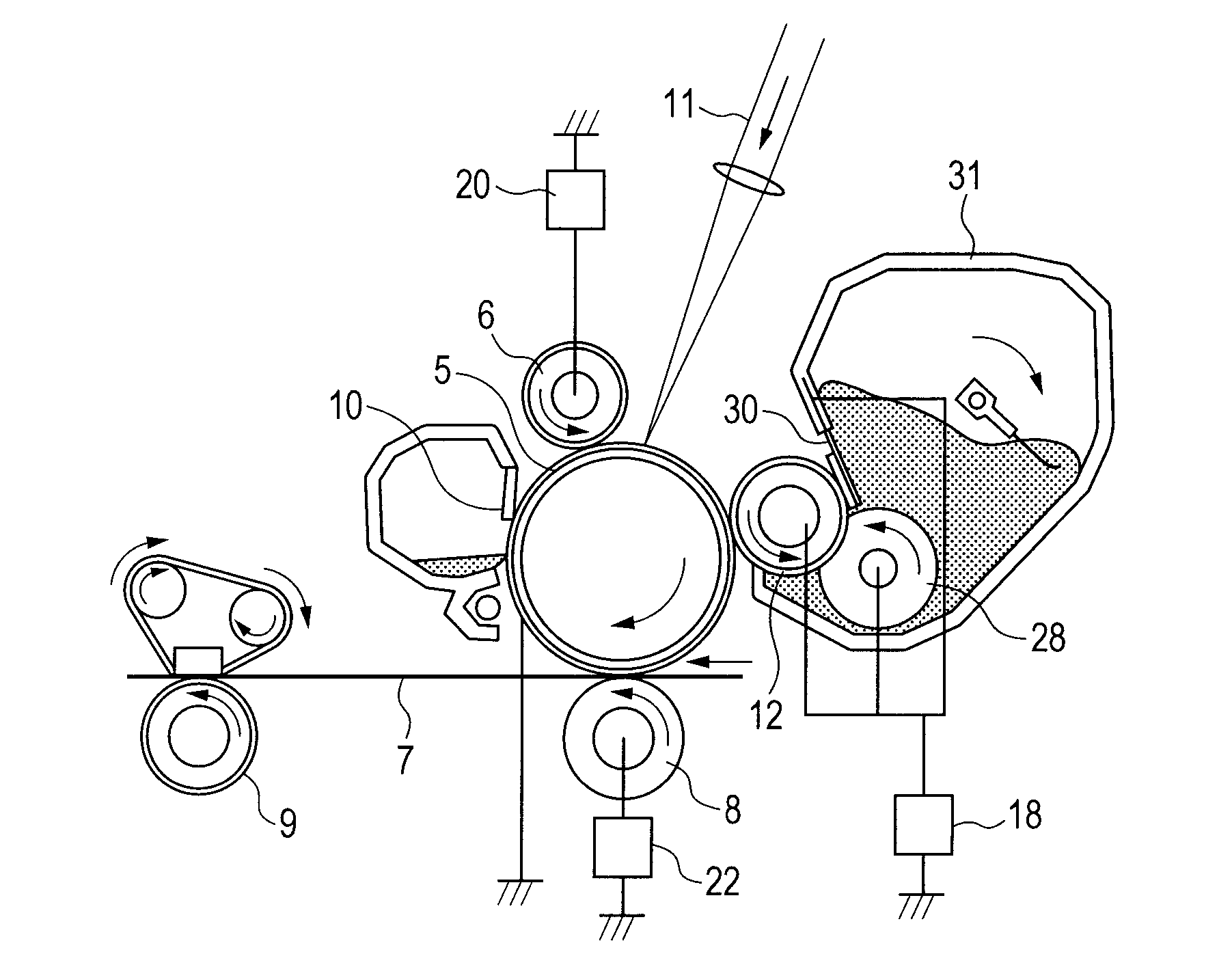
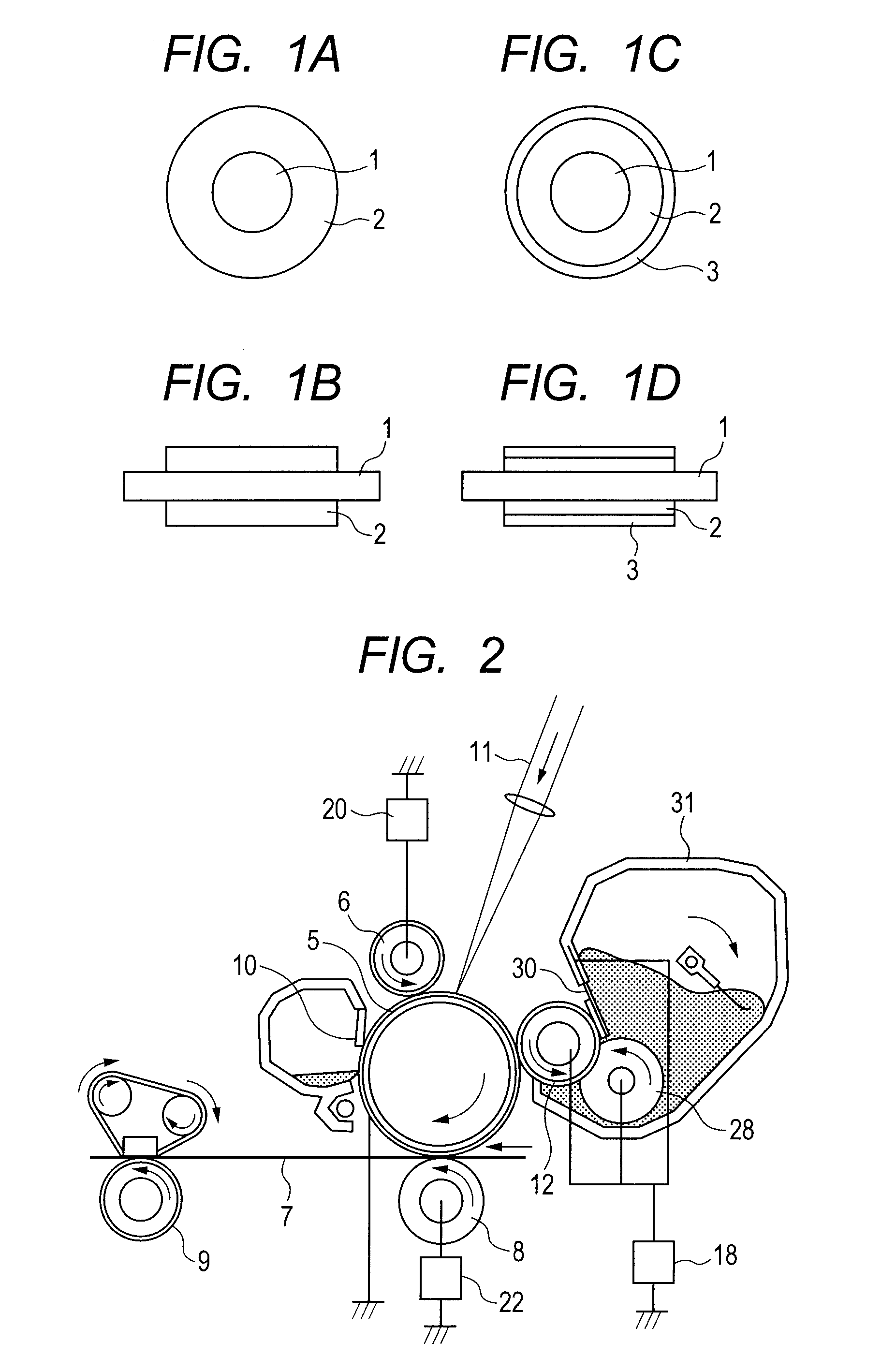
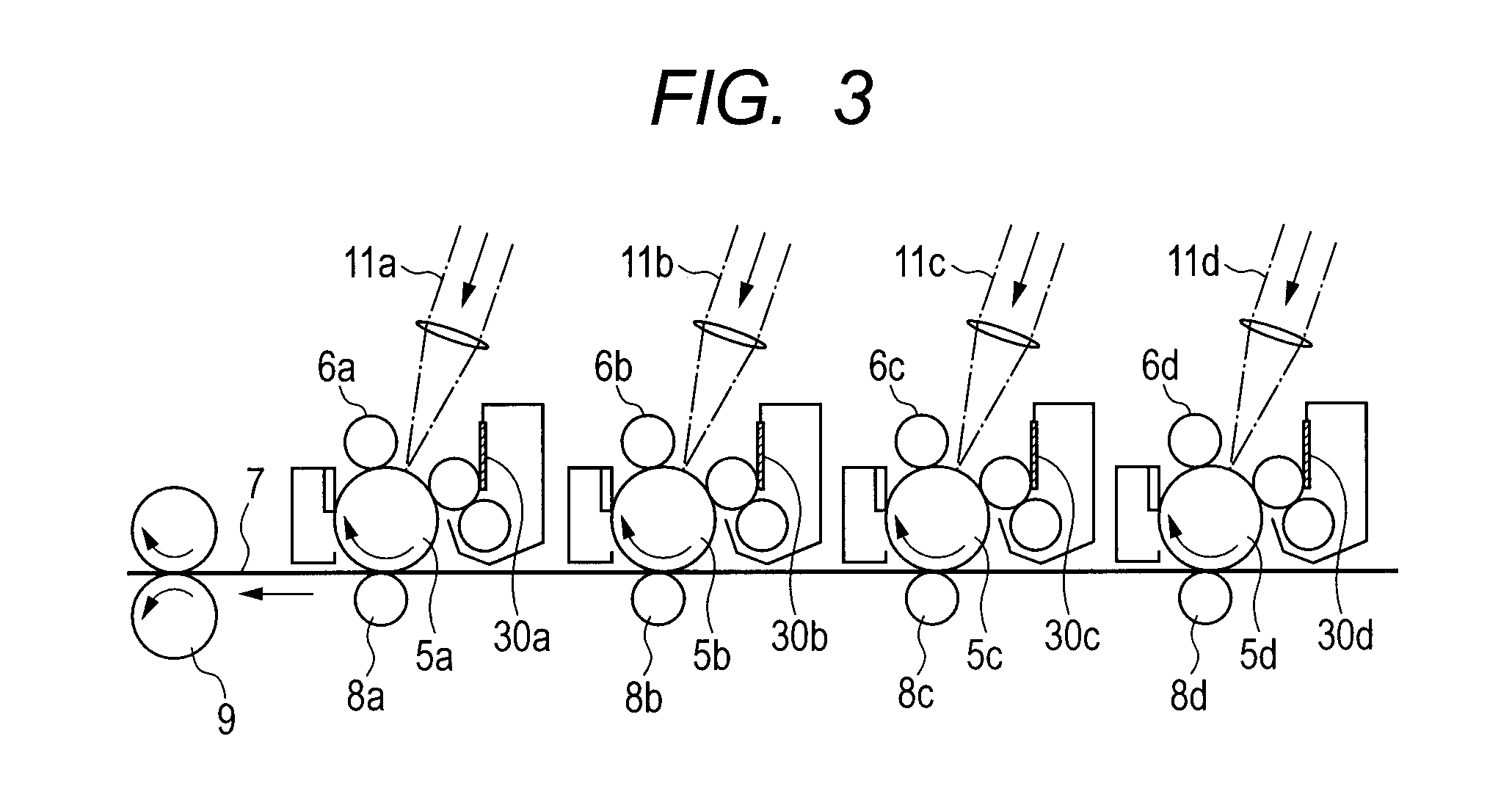
The present invention provides a charging device which comprises a charging roller (14a) and a cleaning component (14b). The charging roller charges a surface of an image-recording medium (11) with a voltage which is applied from an external source. The cleaning component cleans a surface of the charging roller. The charging roller includes a resistance adjustment layer which is made of a resin composite and formed on an outer periphery of a core metal. The hardness of the charging roller is 45 degrees or more in JIS D hardness. The cleaning component has a portion which is in contact with the charging roller This portion is made of resin foam which has a continuous foam structure. The density of the resin foam is 5 to 15 kg / m3 and its tensile strength is 1.7±0.5 kg / cm2.
Owner:RICOH KK
Image forming apparatus, image forming method and process cartridge
ActiveUS20070281236A1Quality improvementLow densityDevelopersElectrographic process apparatusPolyesterMeth-
To provide an image forming apparatus including a latent electrostatic image bearing member; a charging unit; an exposing unit; a developing unit; a transferring unit; and a fixing unit, wherein the binder resin of a toner comprises a polyester-based resin (A) and a polyester-based resin (B) having a melting point which is at least 10° C. higher than that of the polyester-based resin (A), the polyester-based resins (A) is a resin which is derived from a (meth)acrylic acid-modified rosin and which has a polyester unit obtained by condensation polymerization of an alcohol component and a carboxylic acid component containing a (meth)acrylic acid-modified rosin, and the polyester-based resin (B) is a resin derived from a fumaric acid / maleic acid-modified rosin and has a polyester unit obtained by condensation polymerization of an alcohol component and a carboxylic acid component containing any one of a fumaric acid-modified rosin and a maleic acid-modified rosin.
Owner:RICOH KK
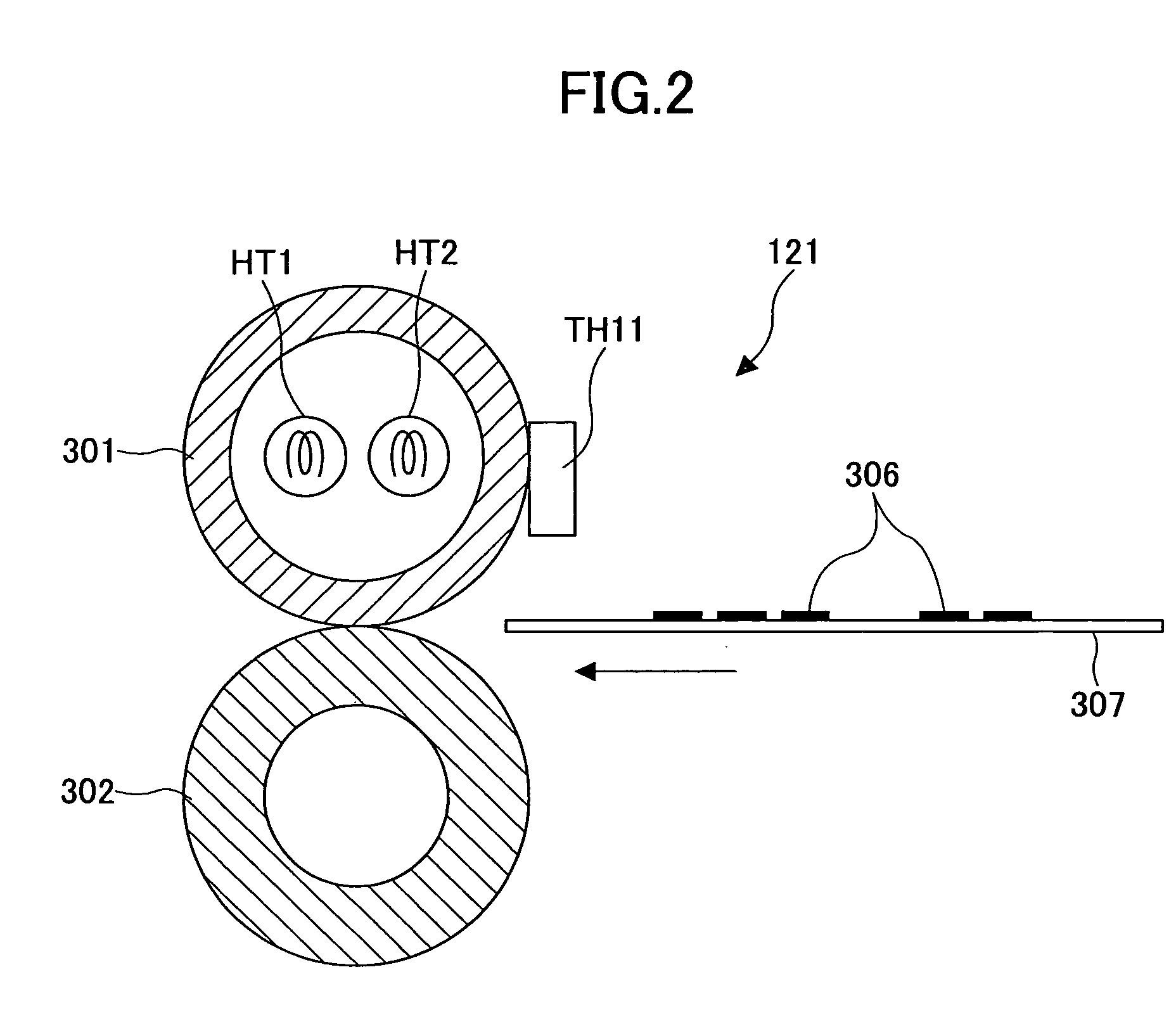
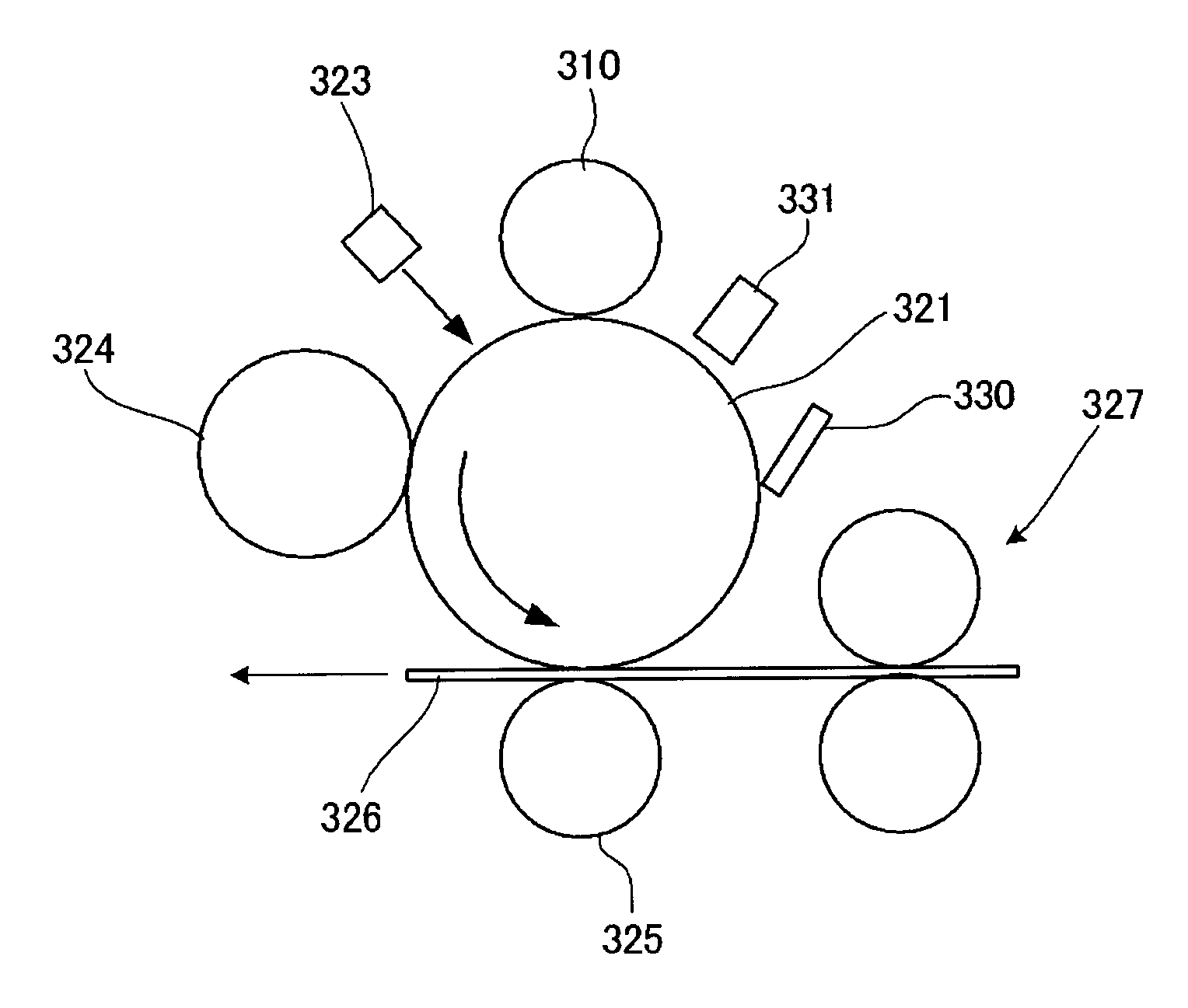
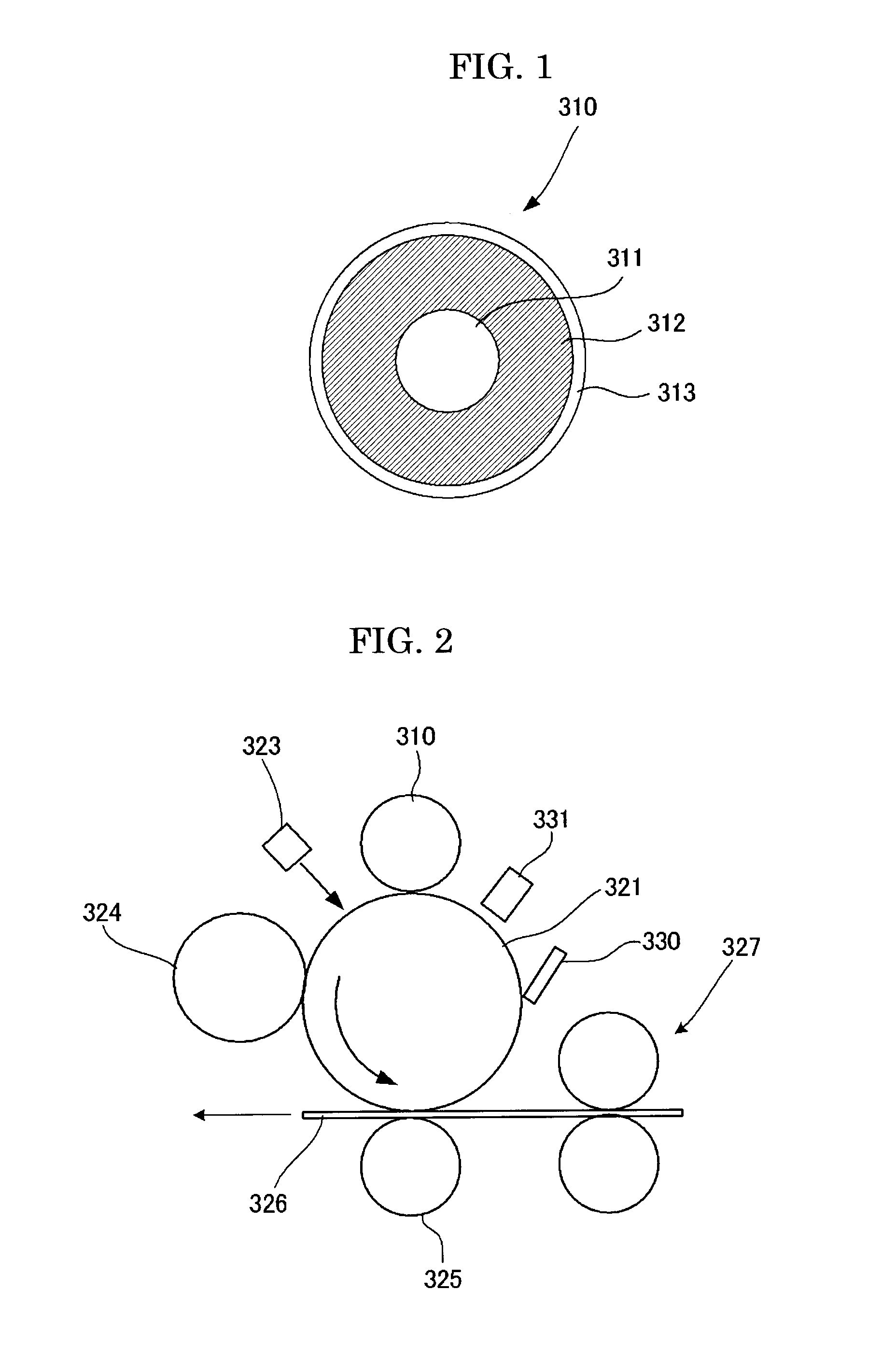
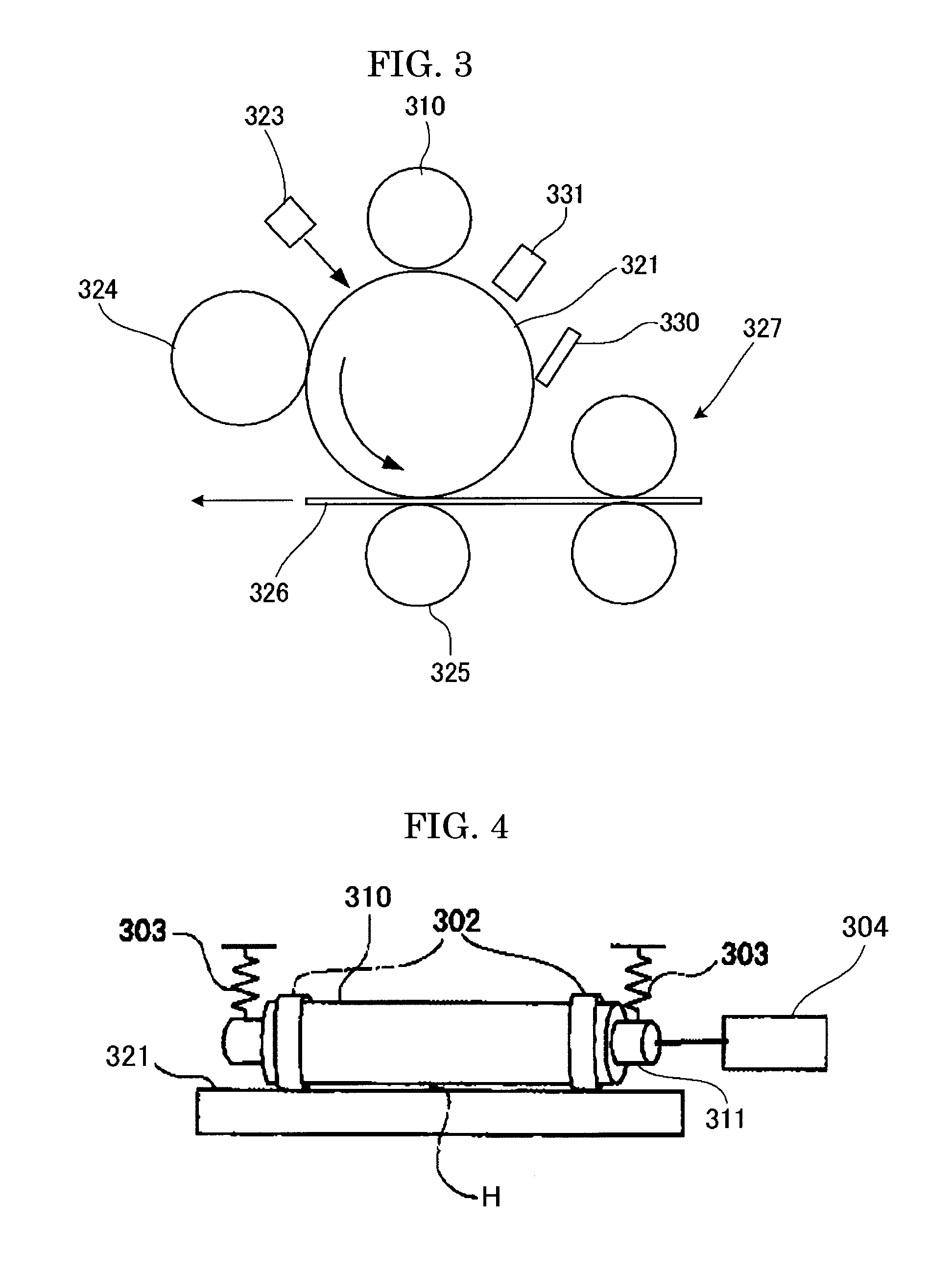
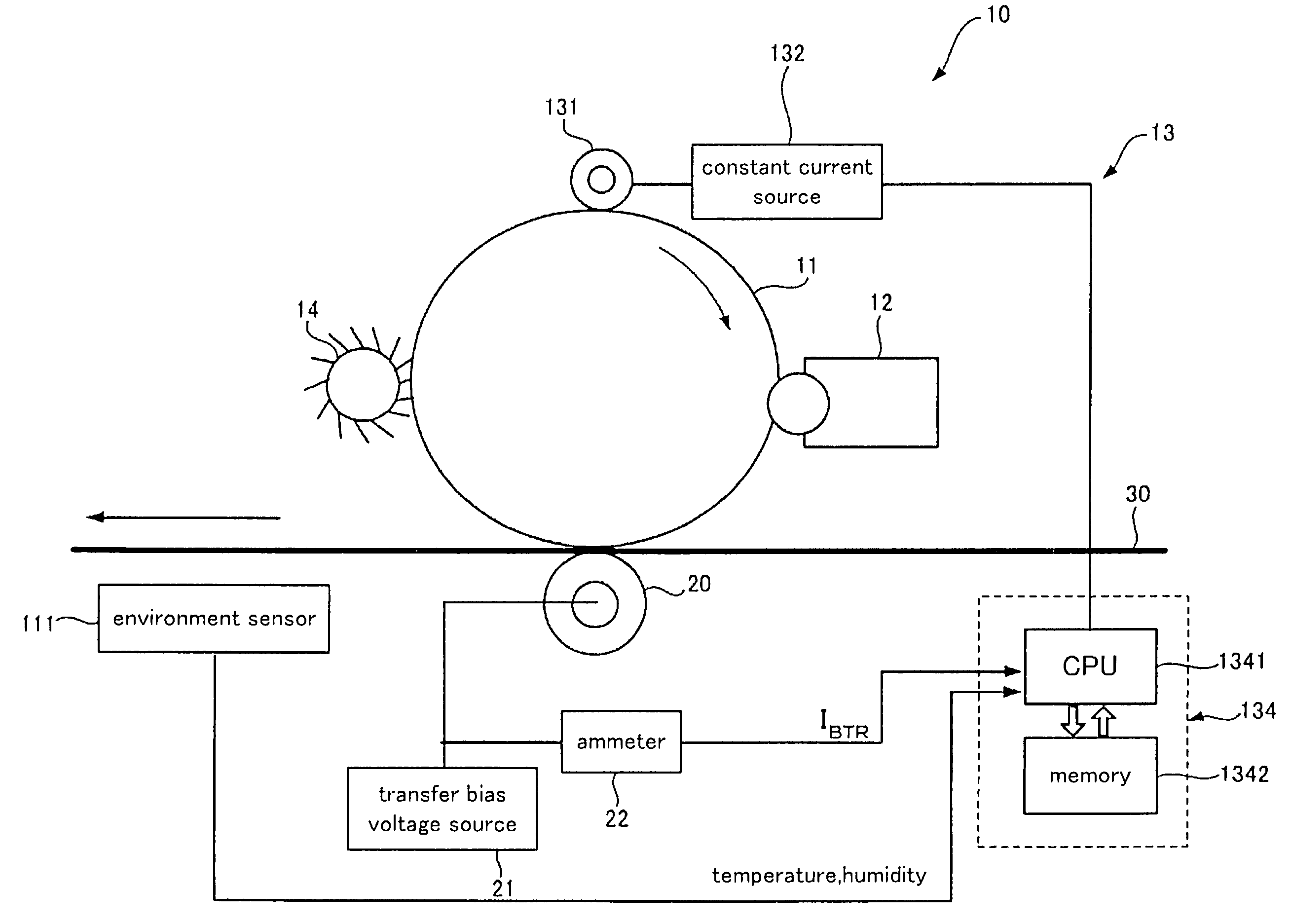
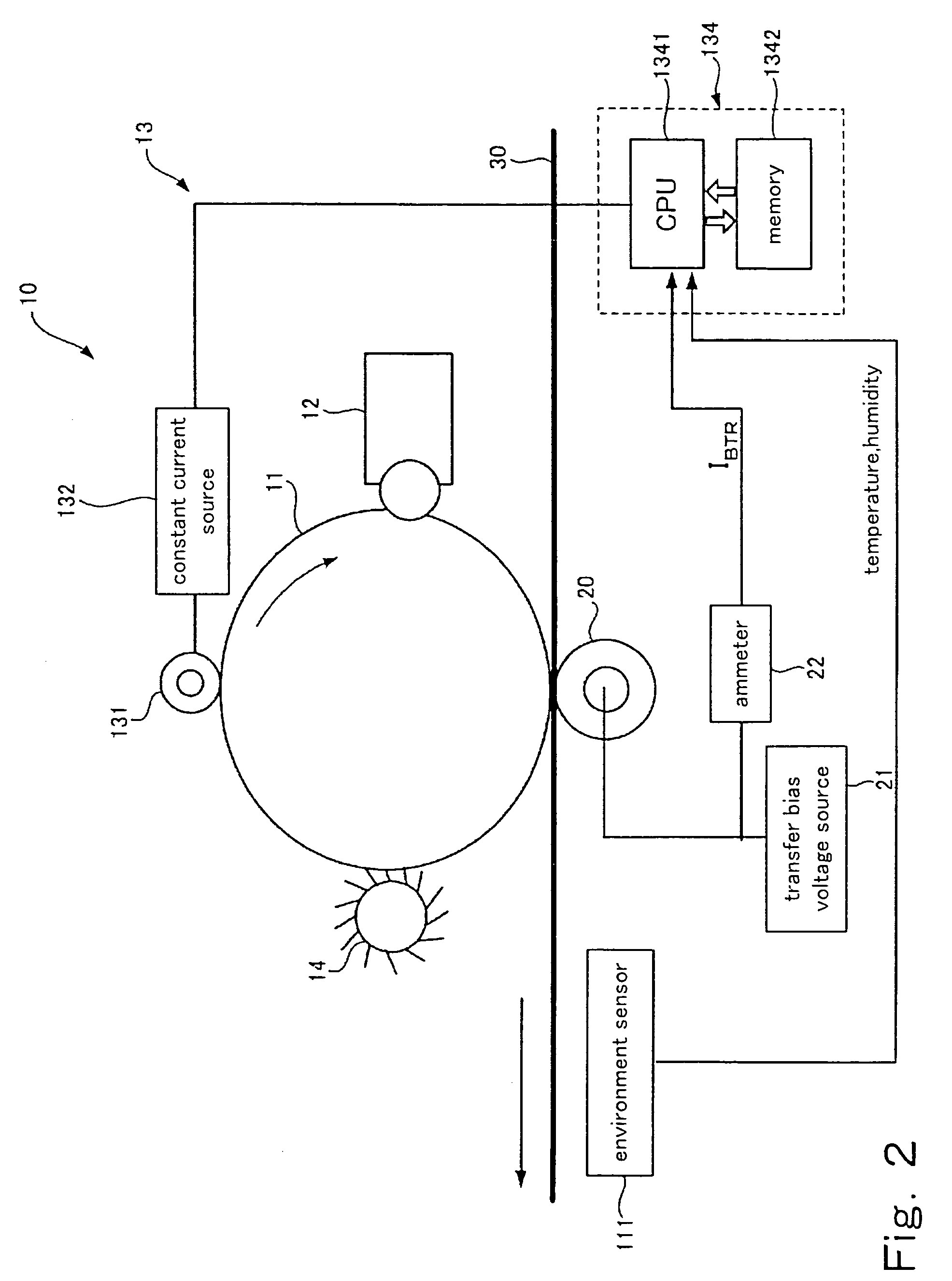
Charging device and image forming apparatus
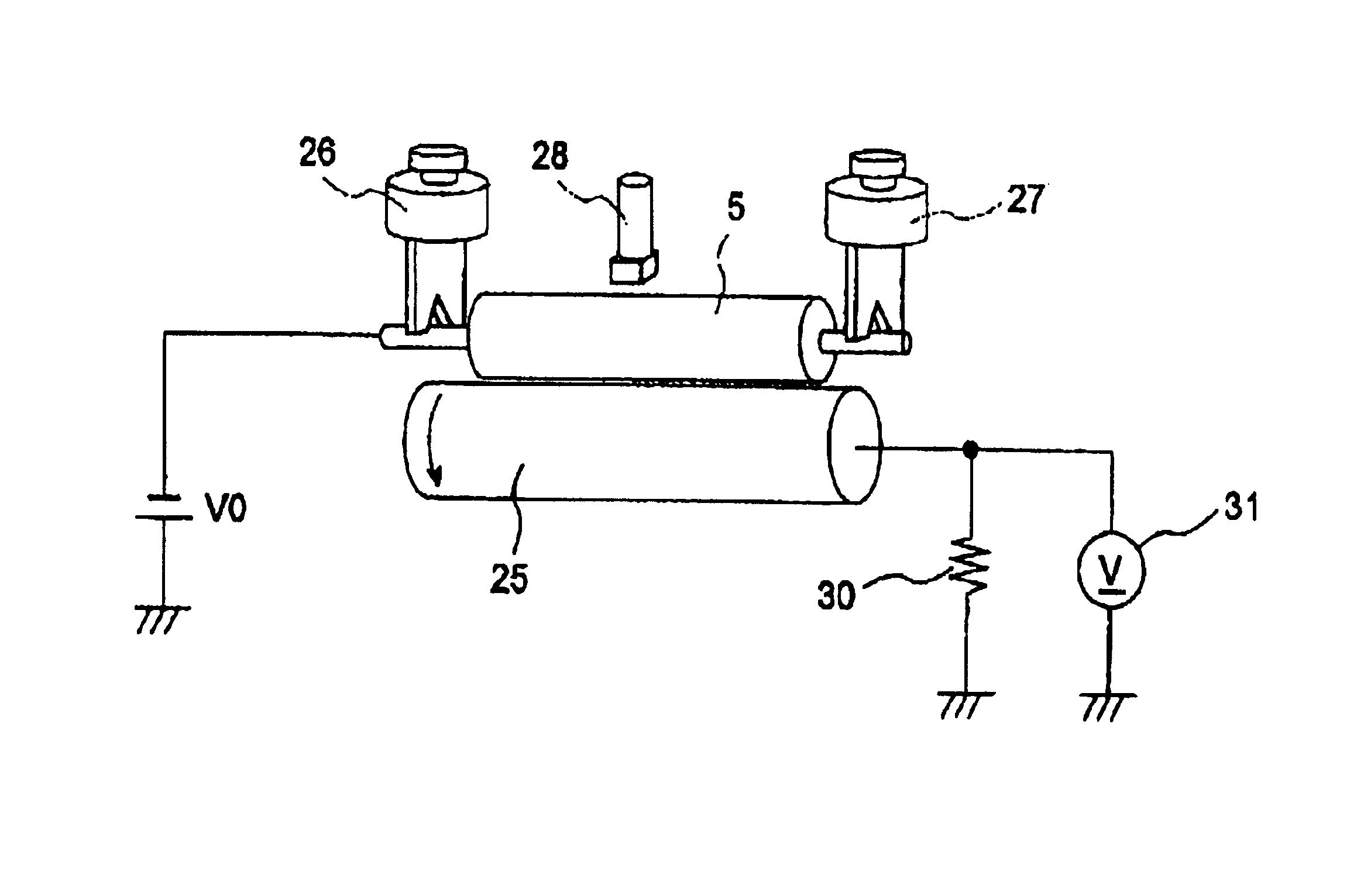
InactiveUS7024125B2Suppress excessive electric dischargeUniform chargeElectrographic process apparatusCorona dischargeCurrent meterImage formation
The present invention is a charging device that electrically charges an object that is charged while being moved in a predetermined direction and an image forming device having such a charging device. The charging device has: a charging member that electrically charges the charged object; a power source that supplies electric power to the charging member in order to electrically charge the charged object; a contact member arranged downstream relative to the charging member as viewed in the moving direction of the charged object and adapted to contact the charged object directly or by way of a predetermined intermediary medium; an ammeter that gauges an electric current caused to flow through the contact member due to an electric charge on the charged object electrically charged by the charging member; and a power source control section that controls the power source based on the electric current gauged by the ammeter.
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
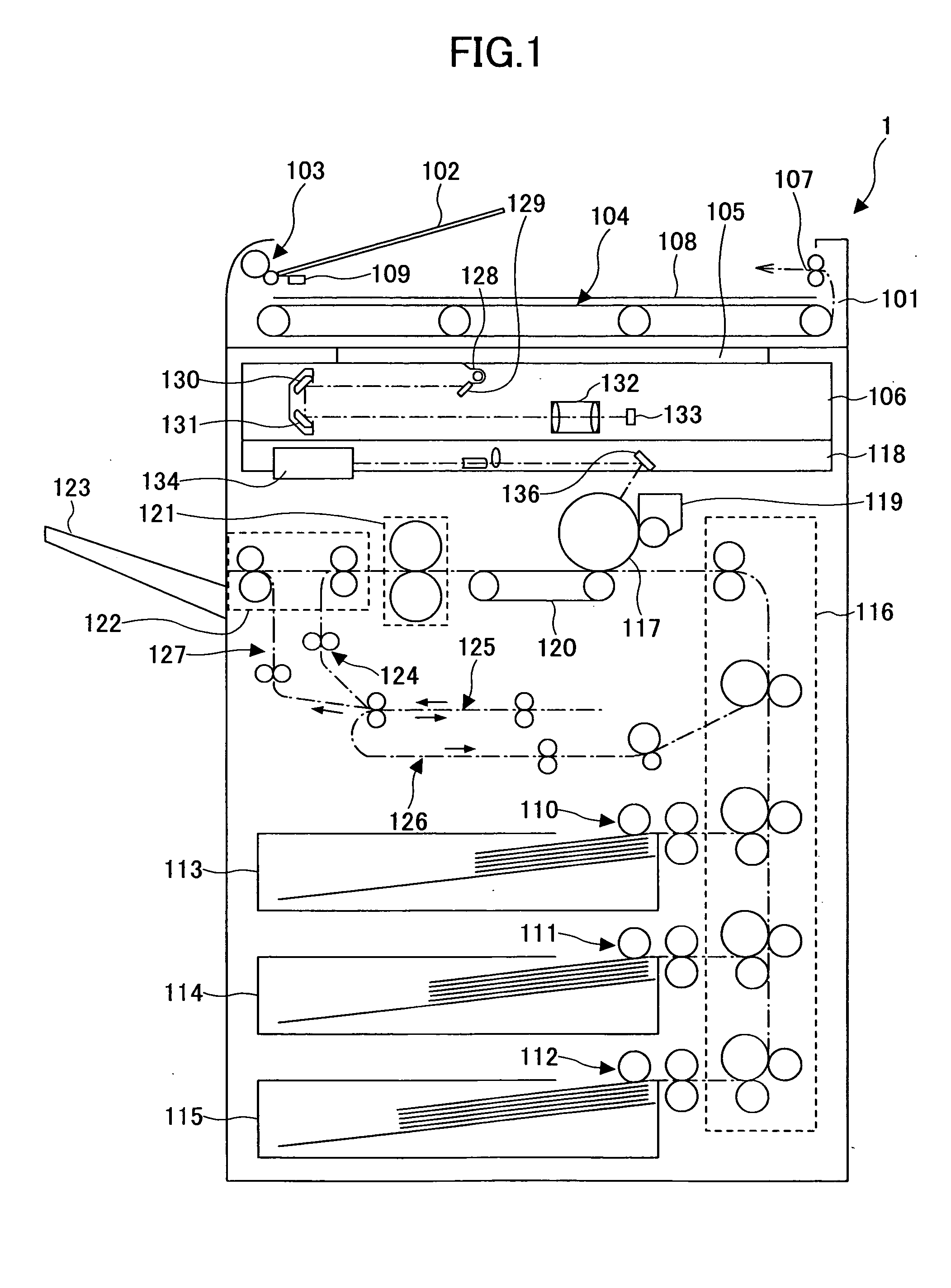
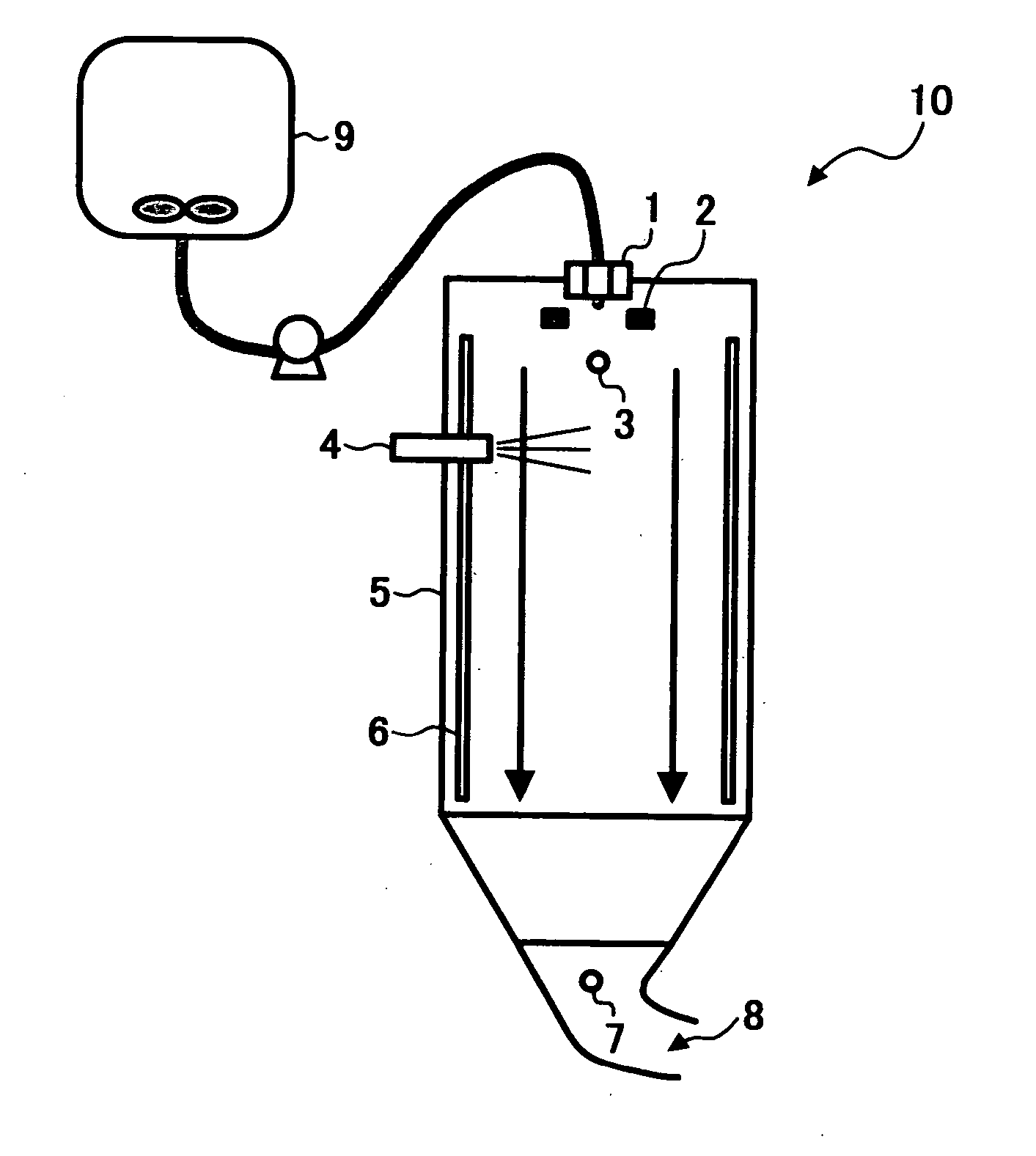
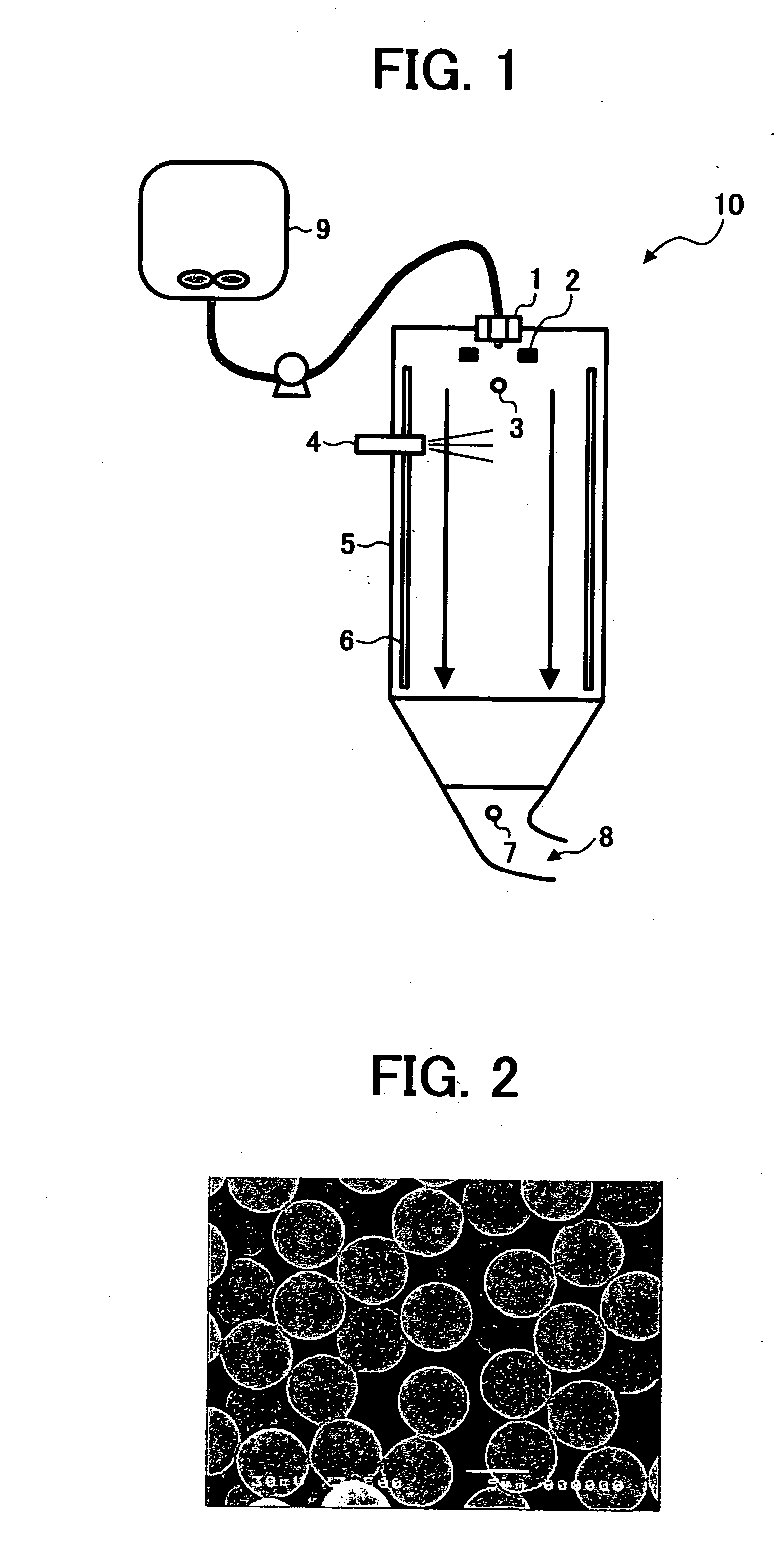
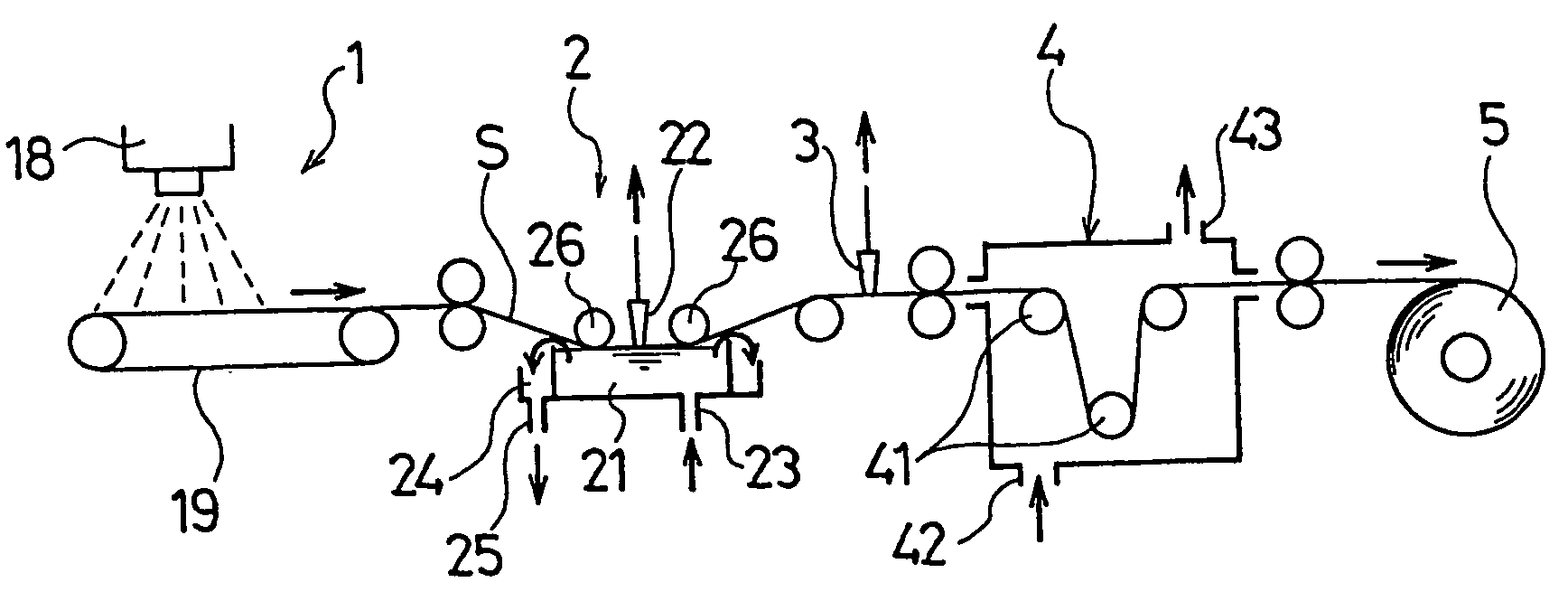
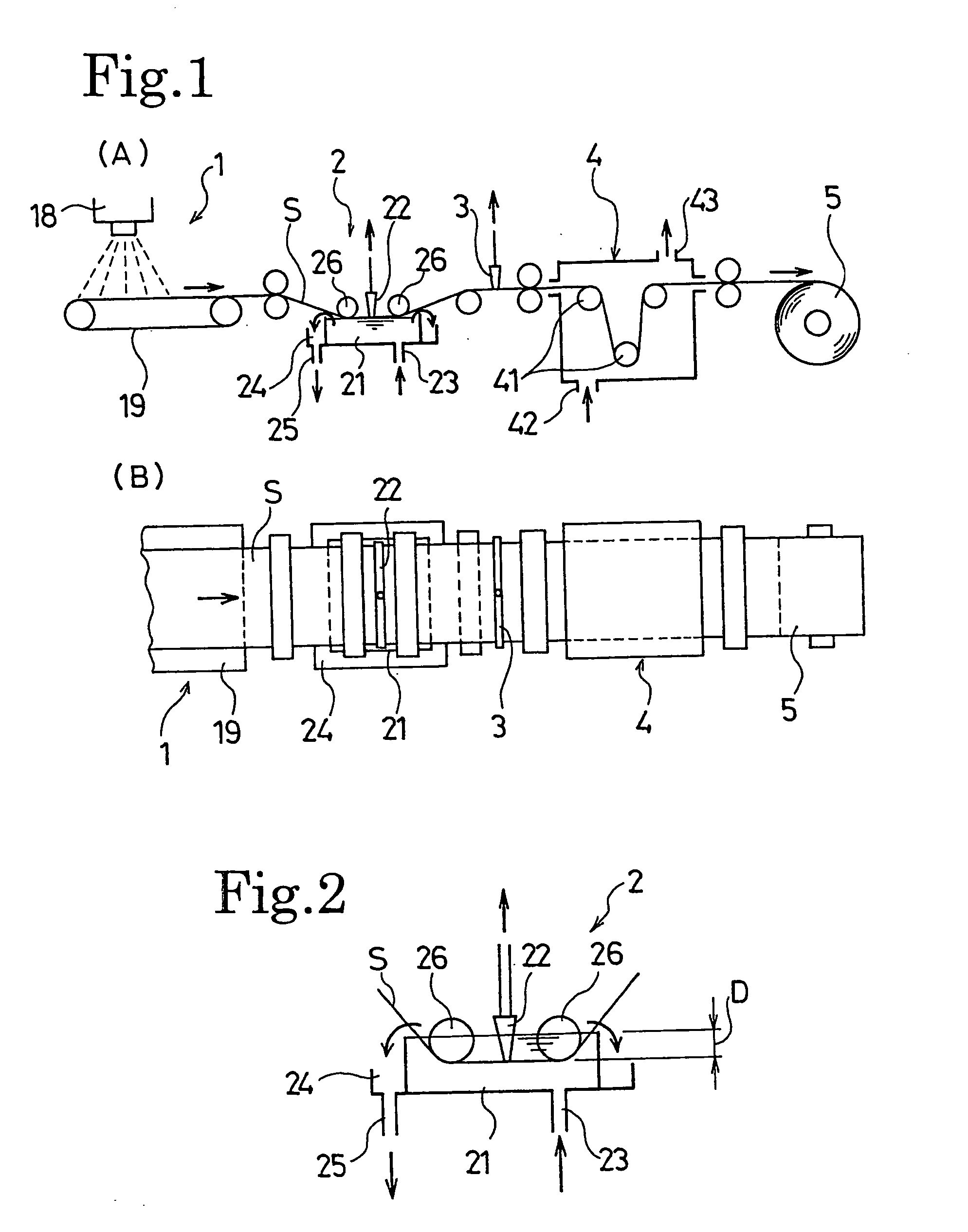
Toner, method of preparing the toner and apparatus for preparing the toner
InactiveUS20060240354A1Good storage stabilityUniform chargeLiquid surface applicatorsDevelopersConstant frequencyEngineering
A toner, a method of and an apparatus for preparing a permanently-charged electret toner, including discharging a solution or dispersion including a resin and a colorant through a nozzle vibrating at a constant frequency to form a droplet; applying a direct potential to an electrode facing the nozzle to positively or negatively charge the droplet by an induction phenomenon to form a charged droplet; and drying and solidifying the charged droplet to be permanently charged.
Owner:RICOH KK
Magnetic toner
A magnetic toner which has superior charging stability and charging uniformity, maintains stable developing performance without any dependence on service environments and may less cause any decrease in image density and any image defects such as fog and ghost, the magnetic toner has magnetic toner particles, each of the magnetic toner particles has magnetic toner base particle containing a binder resin and a magnetic material, and an inorganic fine powder, (a) the magnetic toner having, at a frequency of 100 kHz and a temperature of 30° C., a dielectric loss factor (∈″) of 2.5×10−1 pF / m or more and 7.0×10−1 pF / m or less and a dielectric dissipation factor (tan δL) of 3.0×10−2 or less, (b) the magnetic toner having, in a dielectric dissipation factor (tan δ) thereof at a frequency of 100 kHz, a maximum value (tan δH) within the temperature range of 60° C. to 140° C.; and the tan δH and the tan δL satisfying (tan δH−tan δL)≦3.0×10−2.
Owner:CANON KK
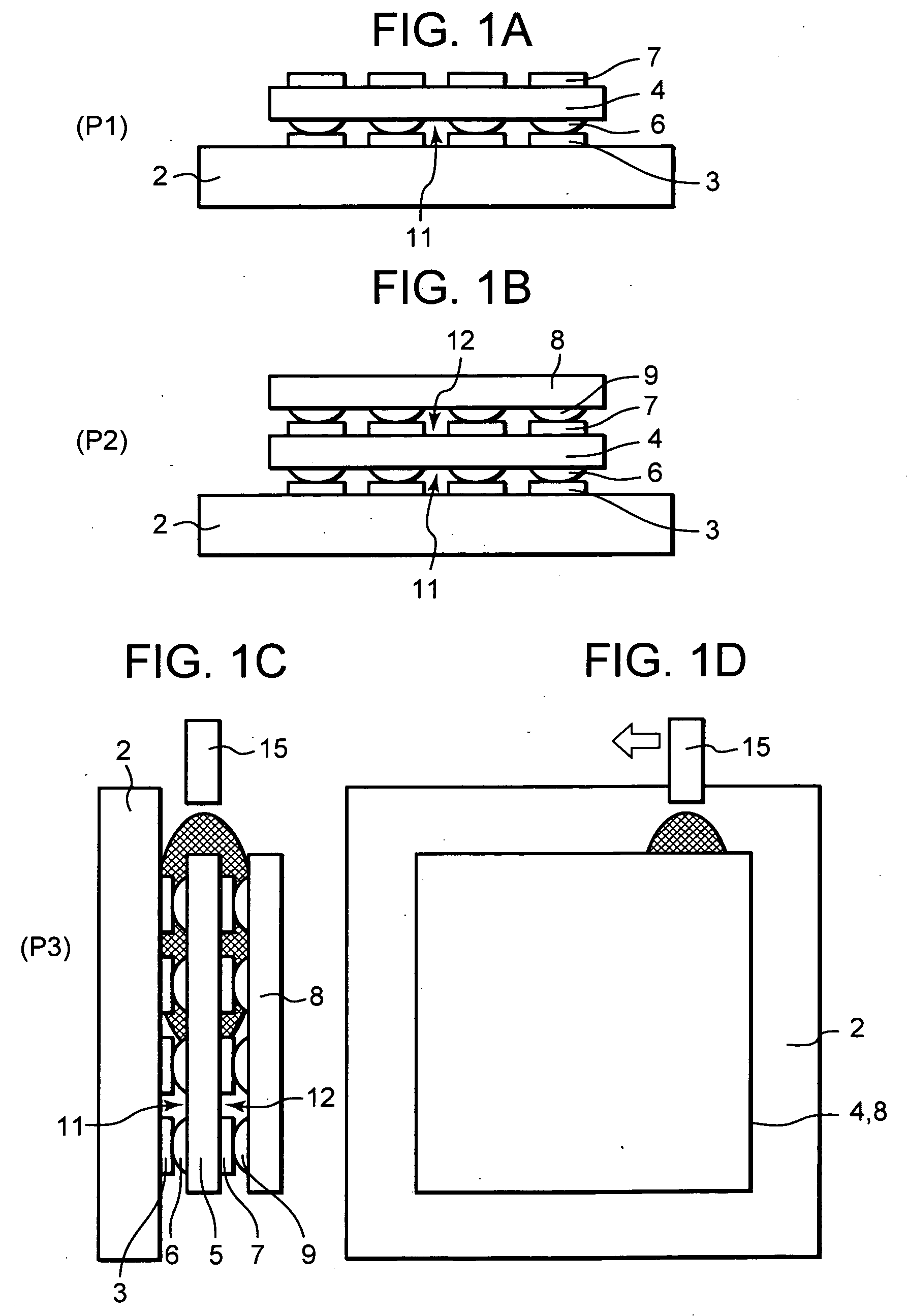
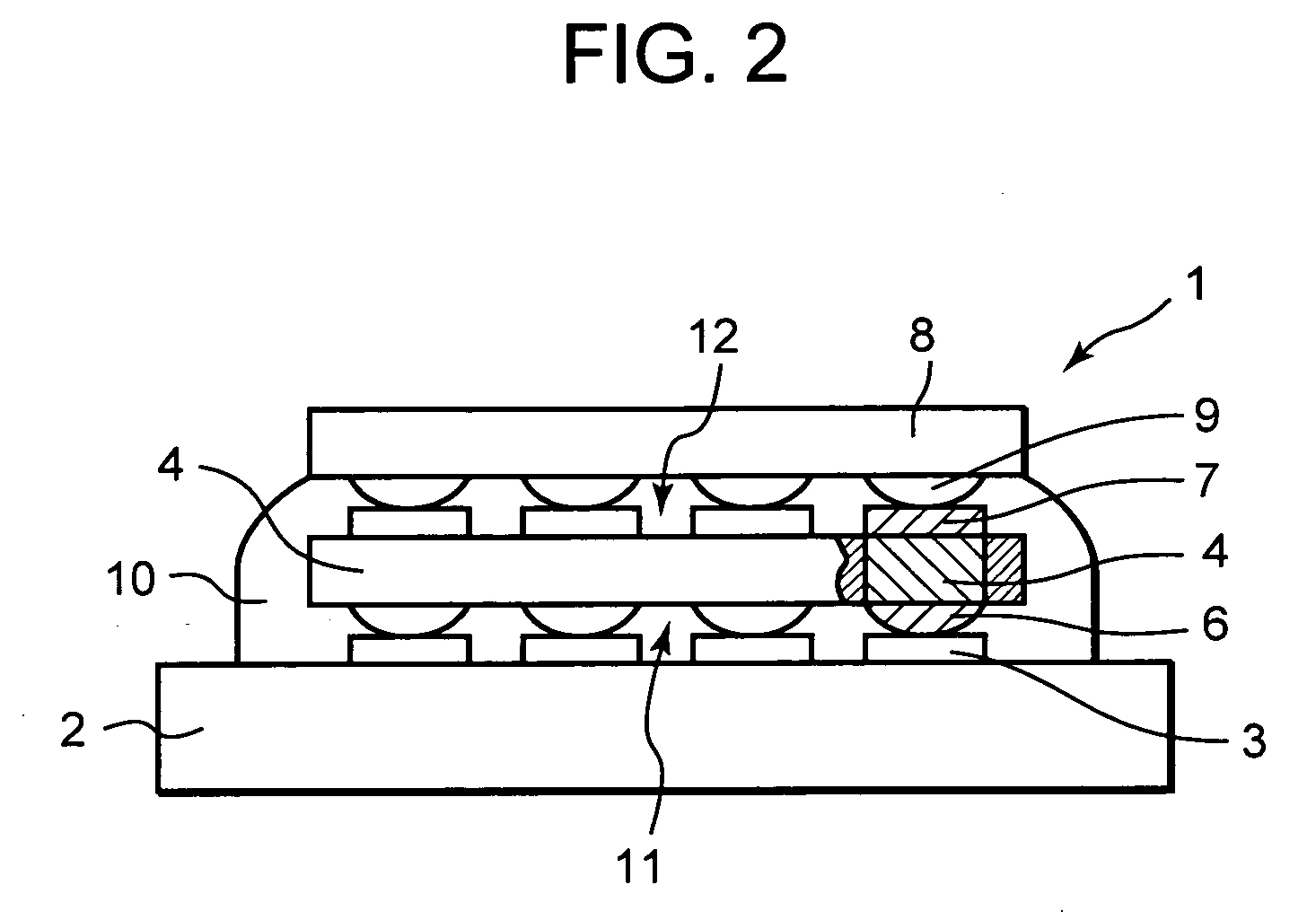
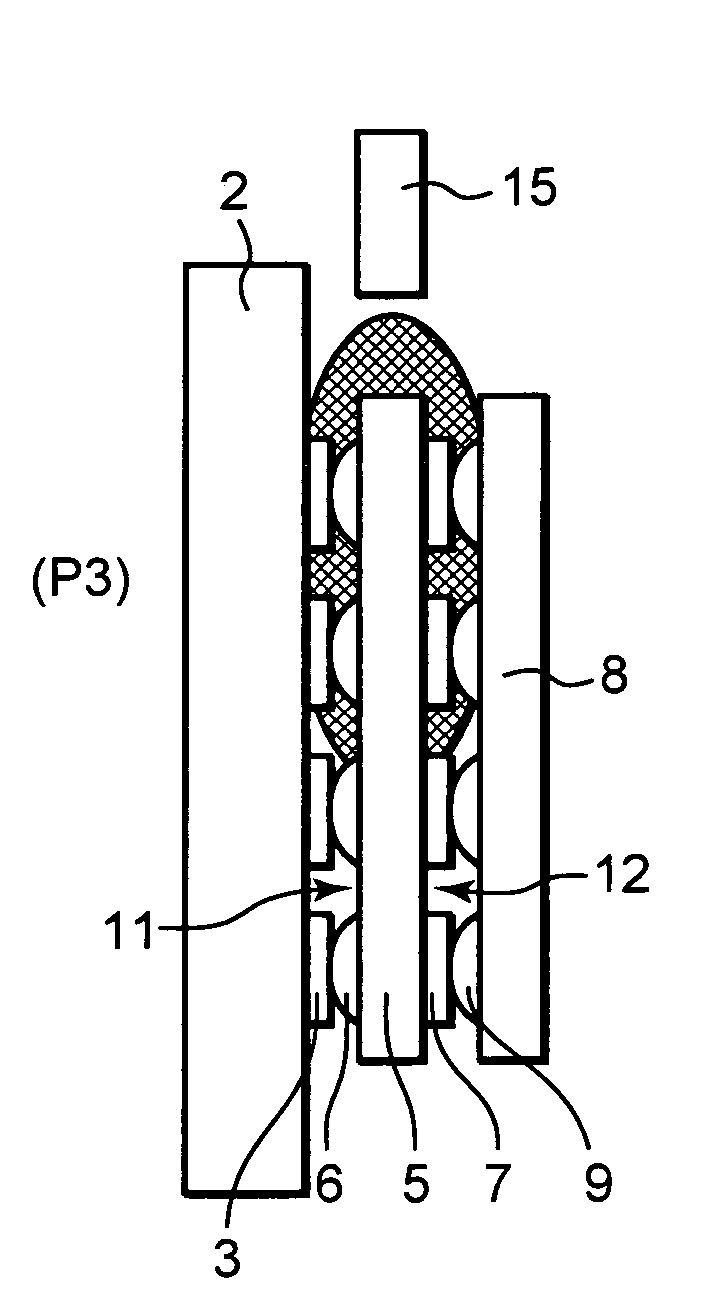
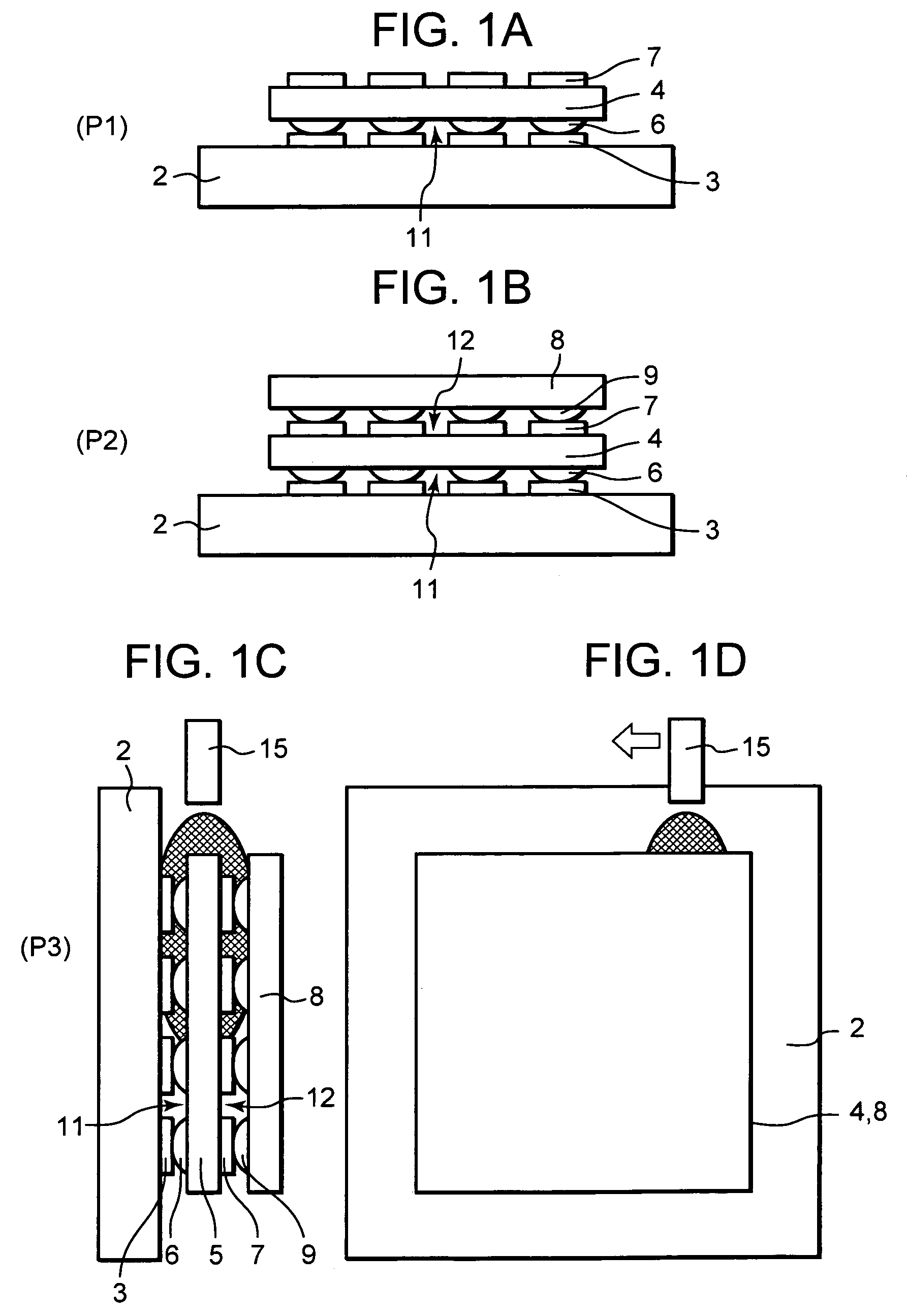
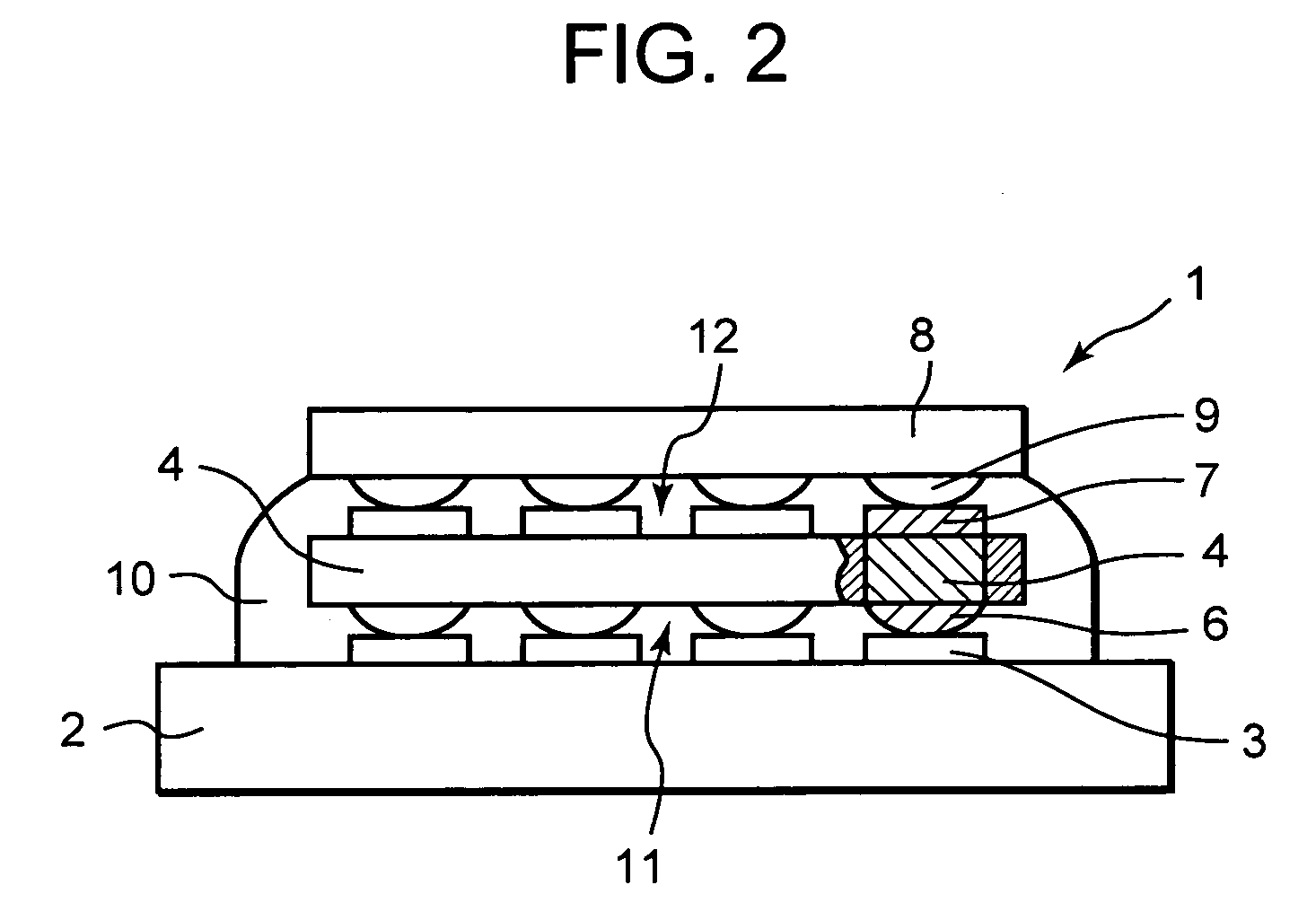
Method for manufacturing a semiconductor device
InactiveUS20060088957A1Uniform chargeSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDevice materialEngineering
A method for manufacturing a semiconductor device formed by stacking a plurality of semiconductor elements on a substrate, comprises the steps of stacking the plurality of semiconductor elements on the substrate to form plural stages, placing the substrate substantially vertically and charging an underfill agent into spaces defined between the substrate and the corresponding semiconductor element and spaces defined among the stacked semiconductor elements through a nozzle from above side faces of the stacked semiconductor elements, and curing the charged underfill agent.
Owner:LAPIS SEMICON CO LTD
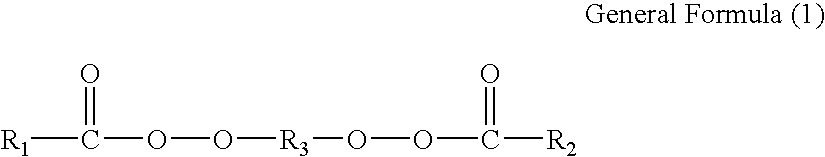
Method for producing polymerized toner, polymerized toner, method for producing binder resin for toner and binder resin for toner
ActiveUS8178275B2Eliminate the effects ofIncrease profitDevelopersMicroballoon preparationMonomer compositionPolymer science
The present invention provides a method for producing a toner that can suppress the production of the decomposition products derived from a polymerization initiator, and can suppress the remaining presence, in the toner particles, of the unreacted polymerizable monomer and decomposition product residues. On the basis of this method, the present invention provides a toner that is excellent in triboelectric charging stability and can yield stable images over a long term. The present invention provides a method for producing a polymerized toner including a step of producing a polymerized toner particle by dispersing in an aqueous medium a polymerizable monomer composition including at least a polymerizable monomer and a colorant and by polymerizing the polymerizable monomer by using a polymerization initiator in the aqueous medium, the method being characterized in that the polymerization initiator has a structure represented by the following General Formula:(wherein R1 and R2 each independently represent an optionally branched or substituted aliphatic hydrocarbon group having 1 to 6 carbon atoms, and R3 represents an optionally branched aliphatic hydrocarbon group having 3 to 12 carbon atoms).
Owner:CANON KK
Image forming apparatus, image forming method and process cartridge
ActiveUS7713672B2Low densityHigh quality imagingElectrographic process apparatusDevelopersPolyesterMeth-
To provide an image forming apparatus including a latent electrostatic image bearing member; a charging unit; an exposing unit; a developing unit; a transferring unit; and a fixing unit, wherein the binder resin of a toner comprises a polyester-based resin (A) and a polyester-based resin (B) having a melting point which is at least 10° C. higher than that of the polyester-based resin (A), the polyester-based resins (A) is a resin which is derived from a (meth)acrylic acid-modified rosin and which has a polyester unit obtained by condensation polymerization of an alcohol component and a carboxylic acid component containing a (meth)acrylic acid-modified rosin, and the polyester-based resin (B) is a resin derived from a fumaric acid / maleic acid-modified rosin and has a polyester unit obtained by condensation polymerization of an alcohol component and a carboxylic acid component containing any one of a fumaric acid-modified rosin and a maleic acid-modified rosin.
Owner:RICOH KK
Developing apparatus
InactiveUS6965743B2Stable quantityUniform chargeElectrographic process apparatusEngineeringMechanical engineering
A developer apparatus includes a developer carrying member, for carrying a developer to a developing portion, the developer carrying member including an electroconductive base and a resistance layer provided thereon; a developer feeding member for being supplied with a voltage to supply the developer to the developer carrying member; wherein a surface moving speed of the developer carrying member Vp [mm / sec], a resistance R1 (Ω) of the developer carrying member when an electric current applied the developer carrying member is 0.04 Vp [μA], and a resistance R2 (Ω) or the developer carrying member when the electric current applied to the developer carrying member is 4 Vp [μA], satisfy:r1 / R2<15.
Owner:CANON KK
Charging member and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20120107565A1Improve charging effectReduce thicknessLayered productsElectrographic process apparatusRough surfaceCrazing
Provided is a charging member having a rough surface, thereby suppressing adhesion of dirt on the surface. A charging member having a supporting member, an elastic layer and a surface layer, in which the surface layer contains a polymer compound, which has a Si—O-M bond and at least one structural unit selected from structural units represented by the following general formula (1) and the following general formula (2), and has a structural unit represented by the following general formula (3); the charging member has cracks developing from the surface thereof and reaching the elastic layer; and the cracks each have convexly raised edges, by which the surface thereof is roughened.MO4 / 2 General formula (1)
Owner:CANON KK
Method and device for manufacturing electret processed product
A manufacturing method of an electret processed product, comprising the steps of allowing a section nozzle (22) to come into contact with a nonconductive fiber sheet (S) so as to cross in the lateral direction of the sheet while running the sheet, allowing the surface of the sheet on the opposite side of the contact portion to come into contact with or to immerse into a water surface, sucking water from the suction nozzle (22) so that the water can be passed through the sheet in the thickness direction of the sheet to penetrate the water into the nonconductive fiber sheet (S), and drying the nonconductive fiber sheet (S), whereby a high quality and high performance electret processed product can be manufactured at a low cost.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
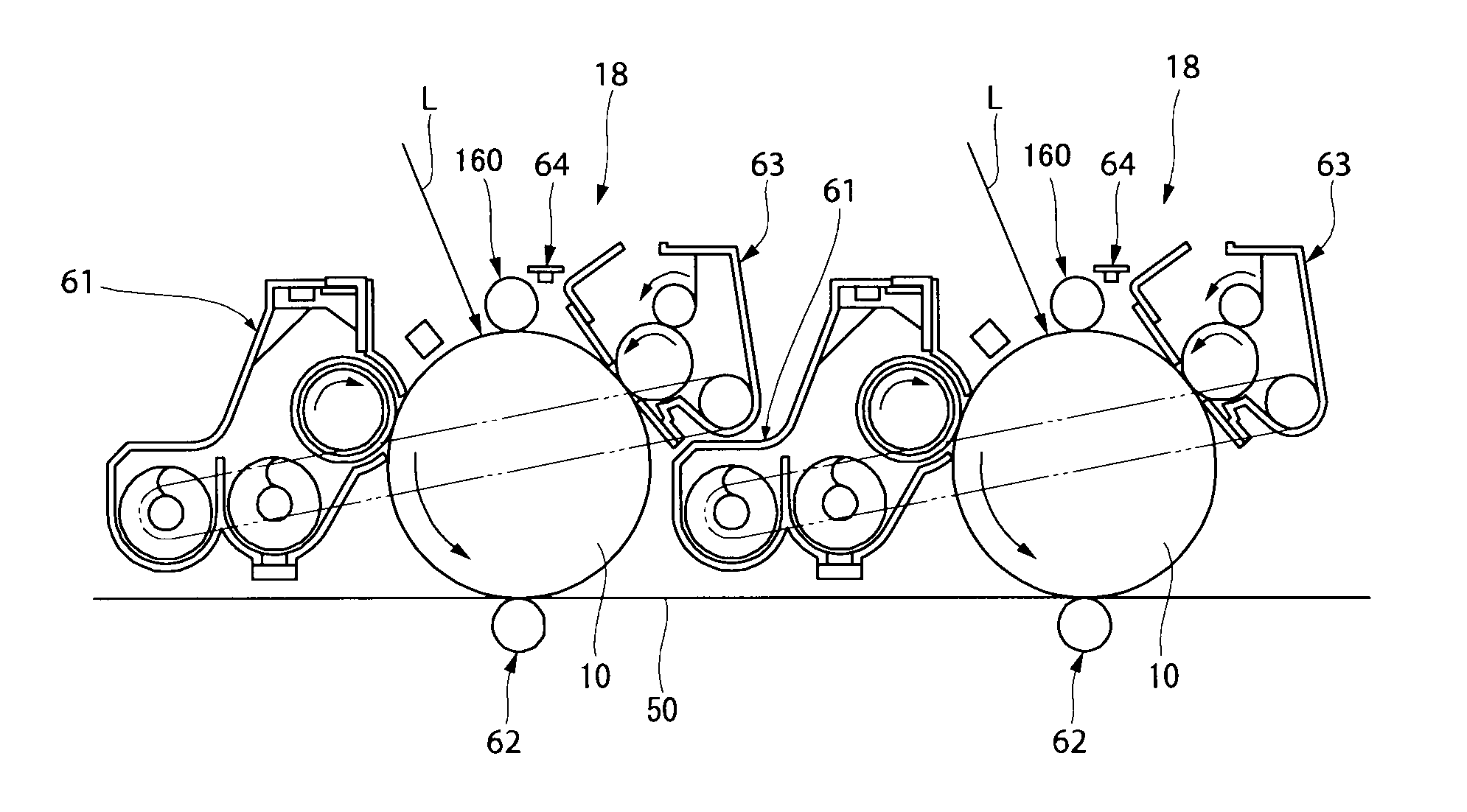
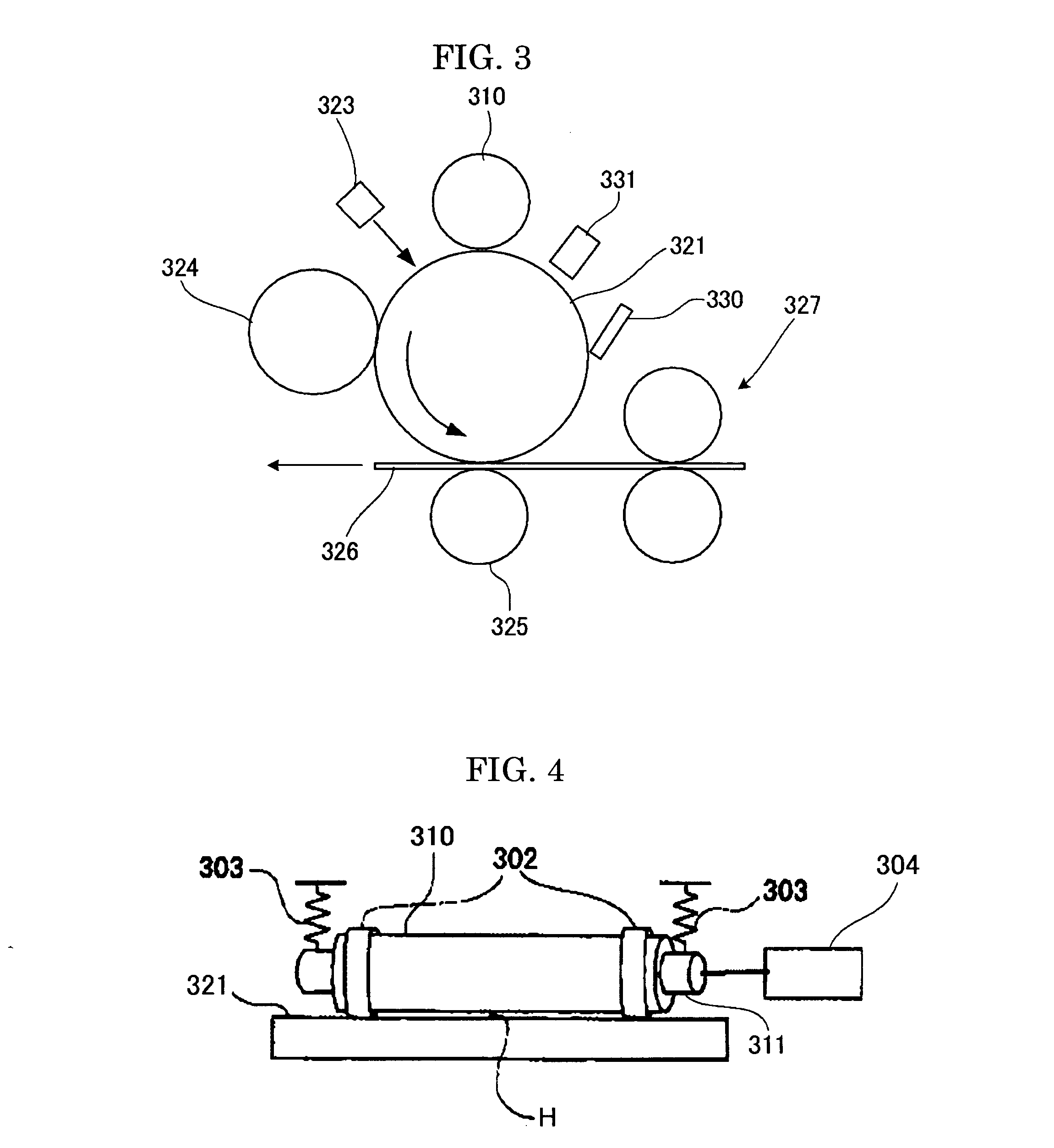
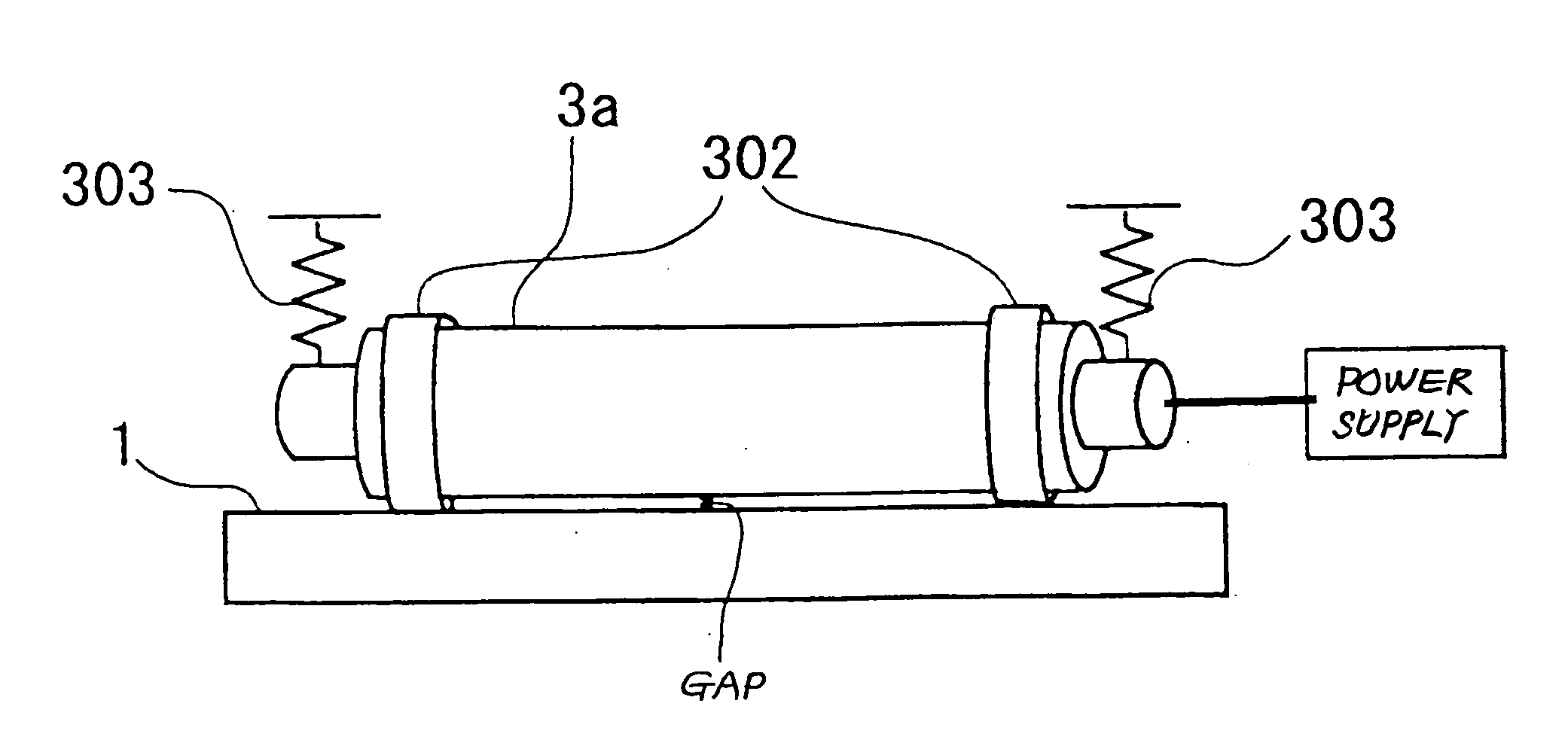
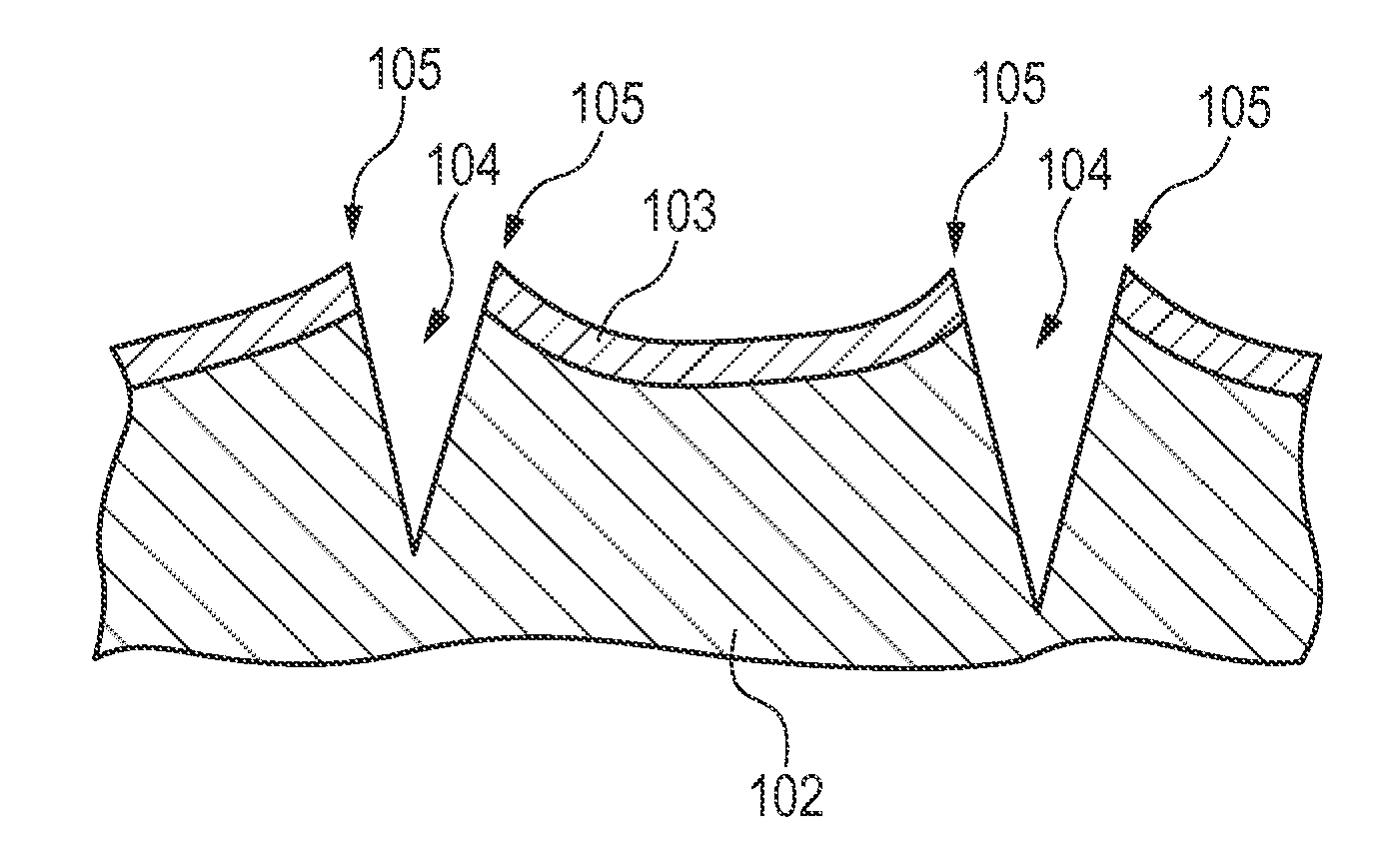
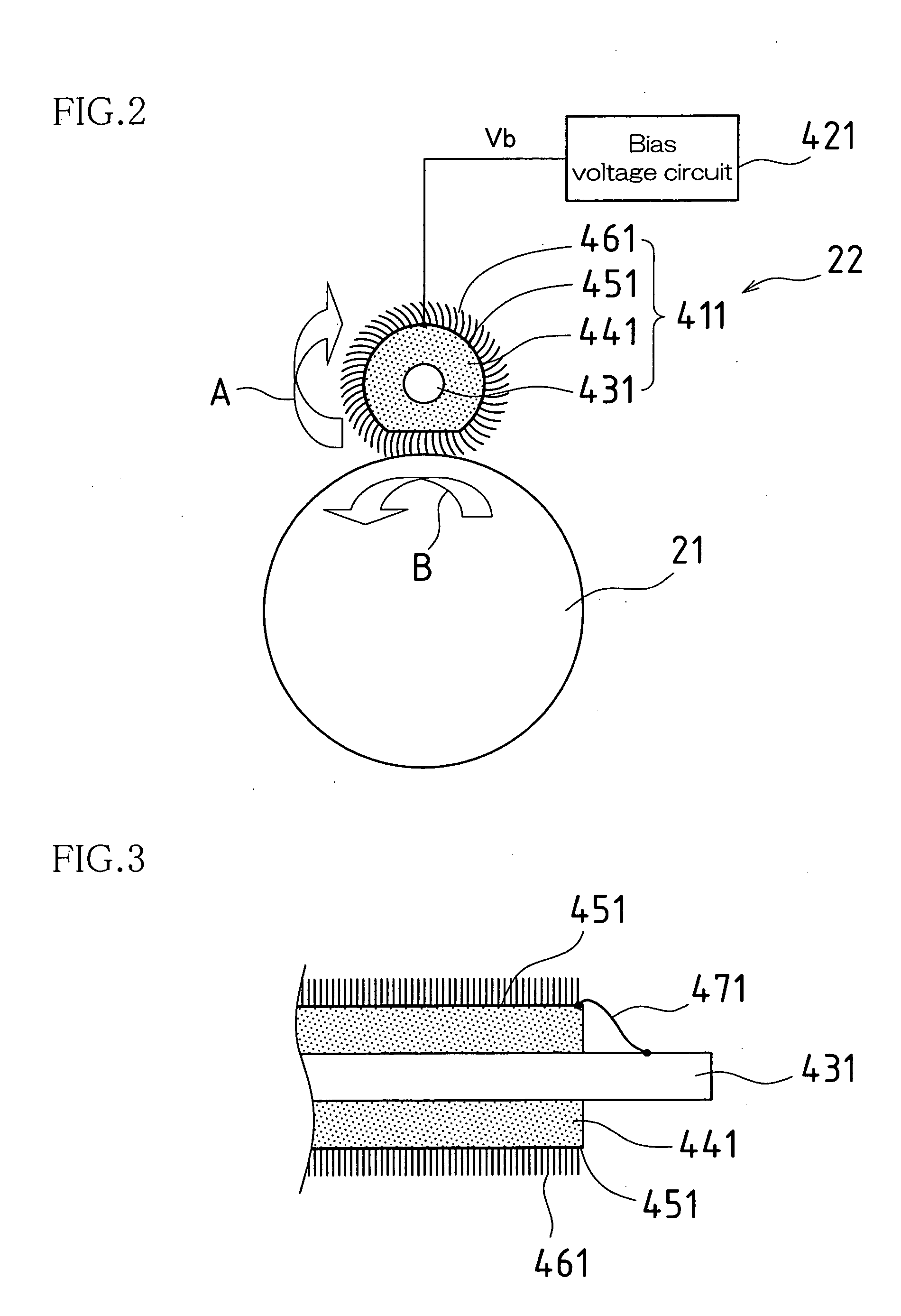
Rotatable brush manufacturing method, rotatable brush, charging apparatus, image forming apparatus, and cleaning apparatus for a rotatable brush
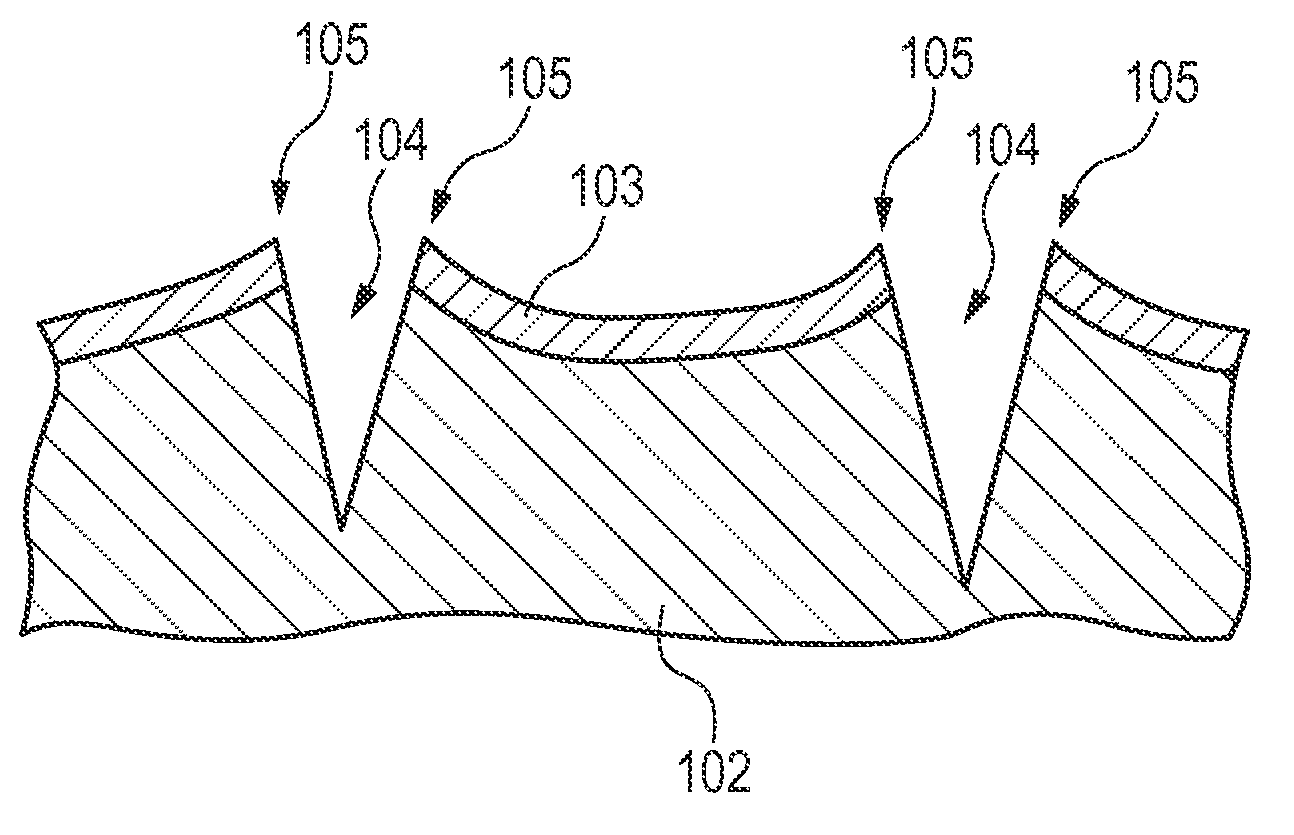
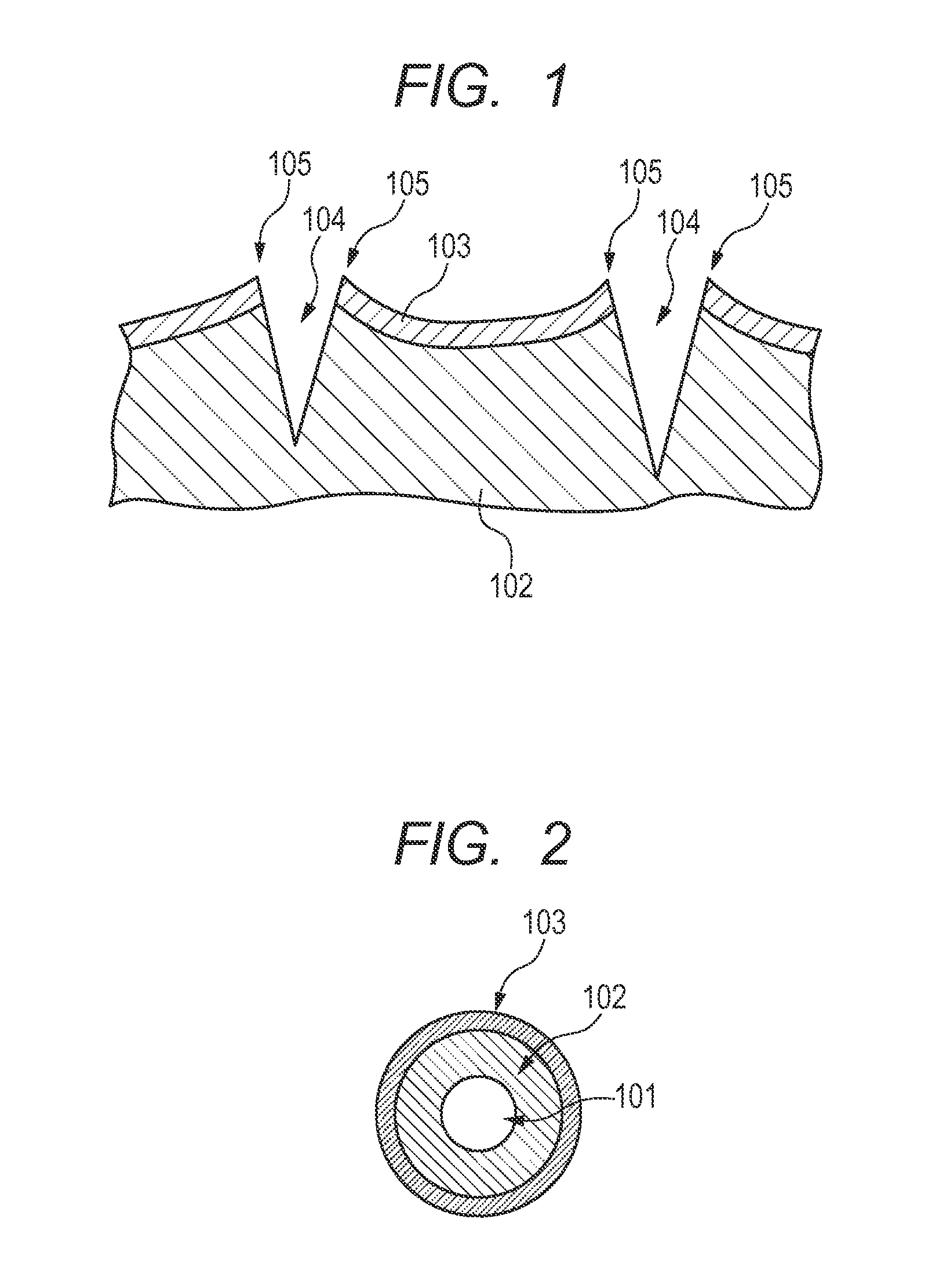
ActiveUS20050241092A1Improve removal efficiencyPreventing disturbance to lieLiquid surface applicatorsBrush bodiesBristleAdhesive
The periphery of a metal rotating shaft is covered with elastic foam material and the peripheral surface of the elastic foam material is coated with conductive adhesive. Before the layer of conductive adhesive hardens, a plurality of bristles is embedded vertically into the smooth material made of a layer of conductive adhesive, thus forming a bristle-embedded layer upon the periphery of the smooth material. Thereafter, the conductive adhesive to become the smooth material is hardened. Alternately, a metal shaft with an outside diameter slightly smaller than the inside diameter of the tube is inserted into the interior of the conductive tube, the tube is heated to cause heat shrinkage, thus tightly adhering the tube to the metal shaft, so that the metal shaft maintains the cylindrical shape of the tube. After the tube is coated with conductive adhesive, it is spirally wrapped with conductive brush cloth cut into strips. At this time, the tube is kept in a cylindrical shape, so the brush cloth is also kept wrapped in a cylindrical shape. The tube is removed from the metal shaft. The periphery of a rotating shaft is coated with elastic material, and the elastic material is pressed into the inside of the tube. Thus, as the charging brush rotates, the brushes of the charging brush are pressed against the contact face of the elastic foam material. At this time, the small holes in the contact face of the elastic foam material remove any developer or other fouling material adhering to the plurality of brushes of the charging brush, and the developer or other fouling material thus removed is transferred to the small holes in the contact face, and thus the bristles of the charging brush are cleaned from near their bases. Continuing on, the bristles of the charging brush are pressed against the smooth surface of the slide plate, thus aligning the bristles of the charging brush in the circumferential direction.
Owner:SHARP KK
Toner
InactiveUS20170123333A1Excellent low temperature fixabilityAdequate durability performanceDevelopersElastic modulusEngineering
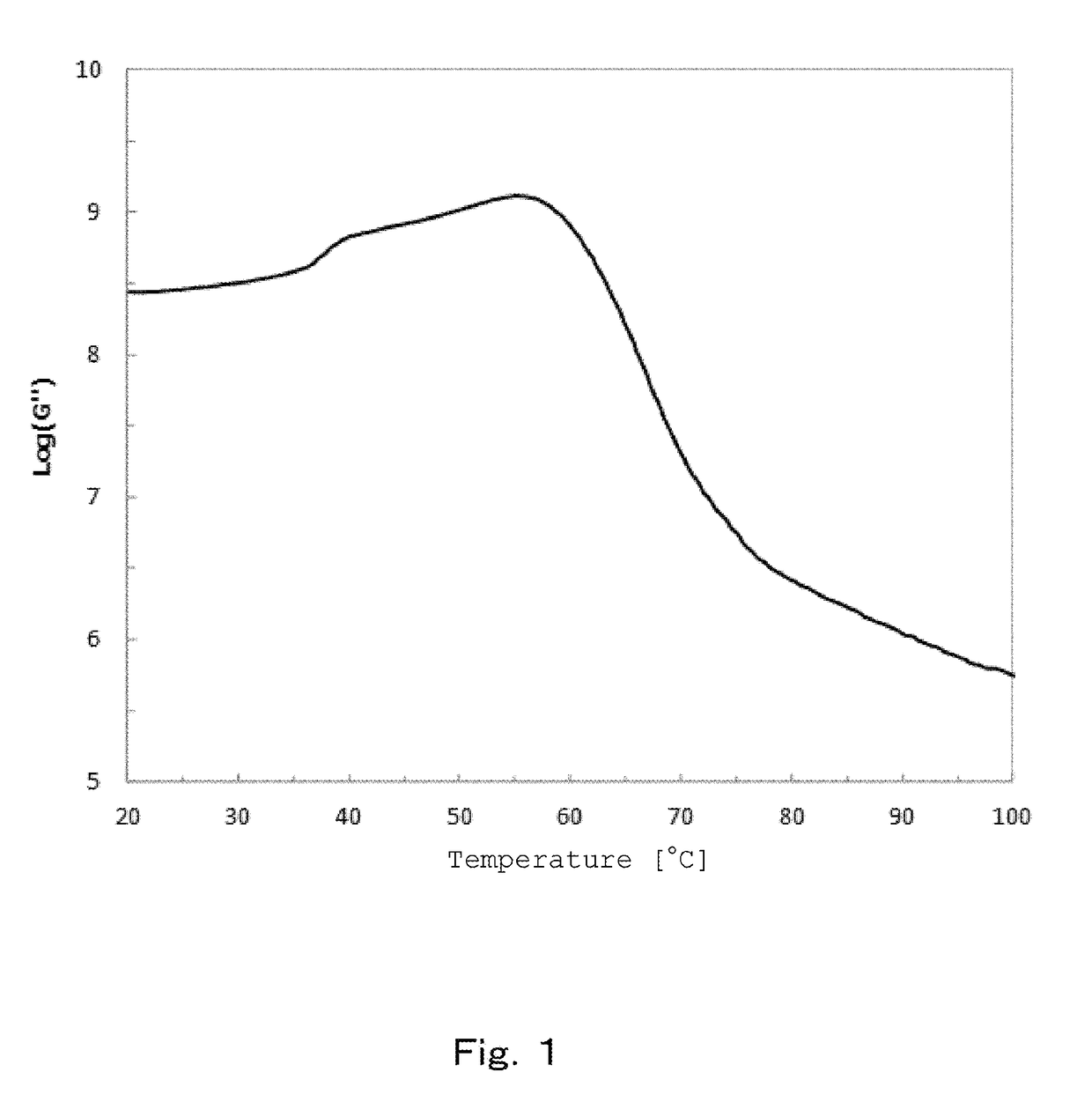
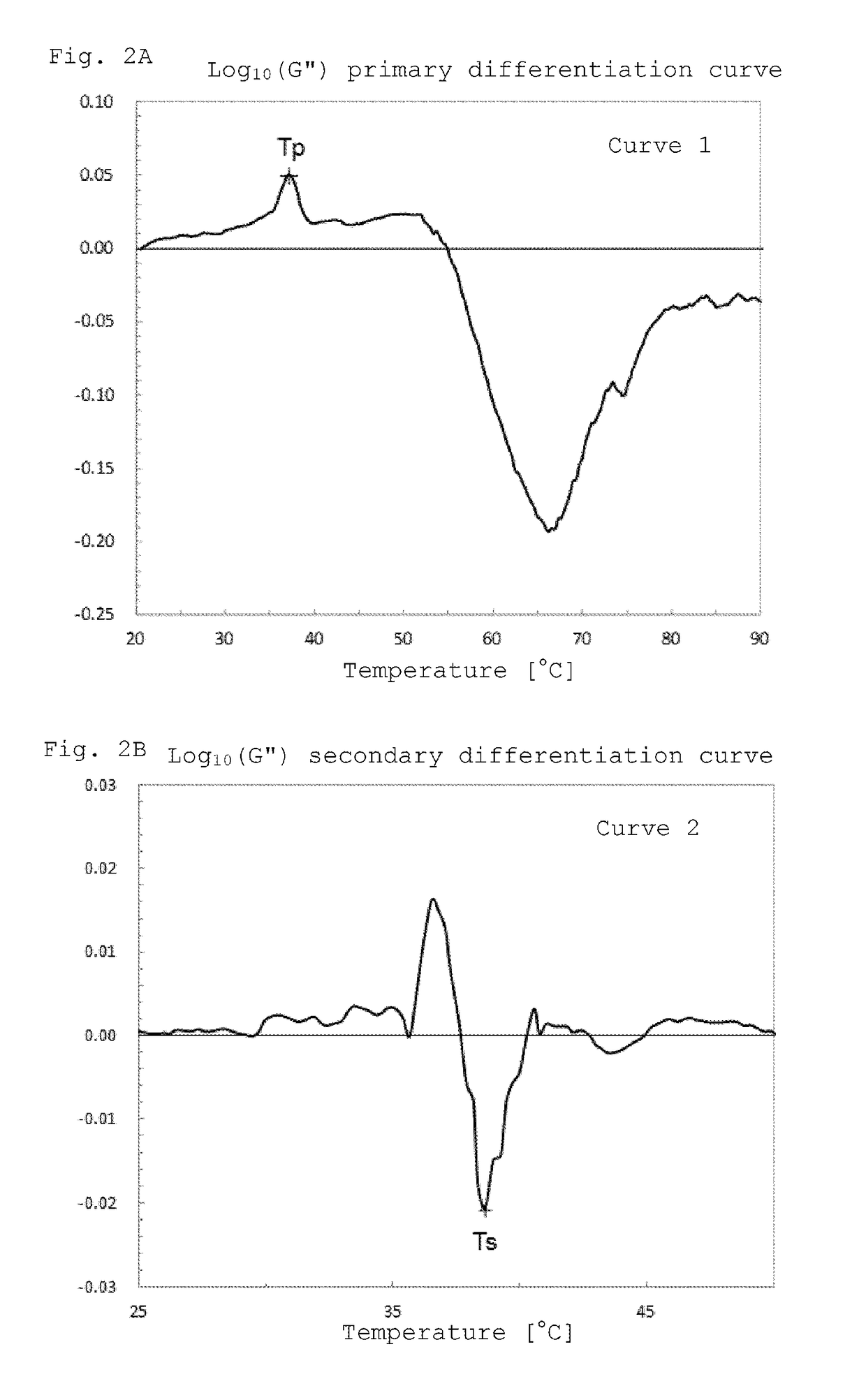
A toner comprising a toner particle containing a binder resin, a colorant and a crystalline resin, wherein the loss elastic modulus G″ of the toner at 20° C. is 1.5×108 Pa to 1.0×109 Pa, a shoulder appears at a temperature Tp (° C.) in the range of 30° C. to 45° C. in a temperature-loss elastic modulus curve, and, in Curve 1 obtained by differentiating the temperature-loss elastic modulus curve once by the temperature, the minimum value of the Curve 1 in the range of 60° C. or more is −0.30 to −0.15.
Owner:CANON KK
Storage element and method for the production thereof
InactiveUS20140205918A1Capacity uniformUniform stabilityFuel and secondary cellsCell electrodesCharge and dischargeOxide
A storage element for a solid electrolyte battery is provided. The storage element has a main member having a porous matrix of sintered ceramic particles in which particles that are made of a metal and / or a metal oxide and jointly form a redox couple are embedded. Along a preferred direction, the storage element has a certain concentration gradient of the particles made of the metal and / or the metal oxide and / or a certain gradient of a pore density and / or a pore size, thereby allowing the diffusion behavior of oxygen ions within the main member to be controlled and thus the charge and discharge kinetics, the life and the capacity of the battery to be improved.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY GLOBAL GMBH & CO KG
Magnetic toner
ActiveUS20120231384A1Uniformity in triboelectric chargingImprove charge stabilityDevelopersDielectric loss factorImage density
A magnetic toner which has superior charging stability and charging uniformity, maintains stable developing performance without any dependence on service environments and may less cause any decrease in image density and any image defects such as fog and ghost, the magnetic toner has magnetic toner particles, each of the magnetic toner particles has magnetic toner base particle containing a binder resin and a magnetic material, and an inorganic fine powder, (a) the magnetic toner having, at a frequency of 100 kHz and a temperature of 30° C., a dielectric loss factor (ε″) of 2.5×10−1 pF / m or more and 7.0×10−1 pF / m or less and a dielectric dissipation factor (tan δL) of 3.0×10−2 or less, (b) the magnetic toner having, in a dielectric dissipation factor (tan Δ) thereof at a frequency of 100 kHz, a maximum value (tan δH) within the temperature range of 60° C. to 140° C.; and the tan δH and the tan δL satisfying (tan δH−tan δL)≦3.0×10−2.
Owner:CANON KK
Lifting-hanging type bidirectional non-coupling presplitting blasting charge device and application method
The invention discloses a lifting-hanging type bidirectional non-coupling presplitting blasting charge device which comprises charge pull barrels, pull barrel connecting elements, a charge top barrel and a top cover. The charge pull barrels are sequentially connected through the pull barrel connecting elements. The charge top barrel is mounted at the uppermost end. The top cover is mounted at the upper end of the charge top barrel. Compared with the prior art, the lifting-hanging type bidirectional non-coupling presplitting blasting charge device has the beneficial effects that according to the lifting-hanging type bidirectional non-coupling presplitting blasting charge device, control over charge axial non-coupling and radial non-coupling coefficients can be achieved, explosive columns in presplitting holes achieve uniform charge, toes after blasting are avoided, excessive crushing of hole walls is reduced, and damage of blasting to rock bodies is effectively reduced; and materials used in the device are wide in source, the manufacturing cost is low, carrying is convenient during field use, operation is simple, and the device can be used for presplitting blasting of various blasting projects.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH LIAONING
Charging member and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS9372428B2Reduce contact areaRarely contaminated with dirtLayered productsElectrographic process apparatusRough surfaceCrazing
Provided is a charging member having a rough surface, thereby suppressing adhesion of dirt on the surface. A charging member having a supporting member, an elastic layer and a surface layer, in which the surface layer contains a polymer compound, which has a Si—O-M bond and at least one structural unit selected from structural units represented by the following general formula (1) and the following general formula (2), and has a structural unit represented by the following general formula (3); the charging member has cracks developing from the surface thereof and reaching the elastic layer; and the cracks each have convexly raised edges, by which the surface thereof is roughened.MO4 / 2 General formula (1)
Owner:CANON KK
Method for manufacturing a semiconductor device
InactiveUS7459348B2Uniform chargeSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor deviceSemiconductor components
A method for manufacturing a semiconductor device formed by stacking a plurality of semiconductor elements on a substrate includes the steps of stacking the plurality of semiconductor elements on the substrate to form plural stages, placing the substrate substantially vertically and charging an underfill agent into spaces defined between the substrate and the corresponding semiconductor element and spaces defined among the stacked semiconductor elements through a nozzle from above side faces of the stacked semiconductor elements, and curing the charged underfill agent.
Owner:LAPIS SEMICON CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com