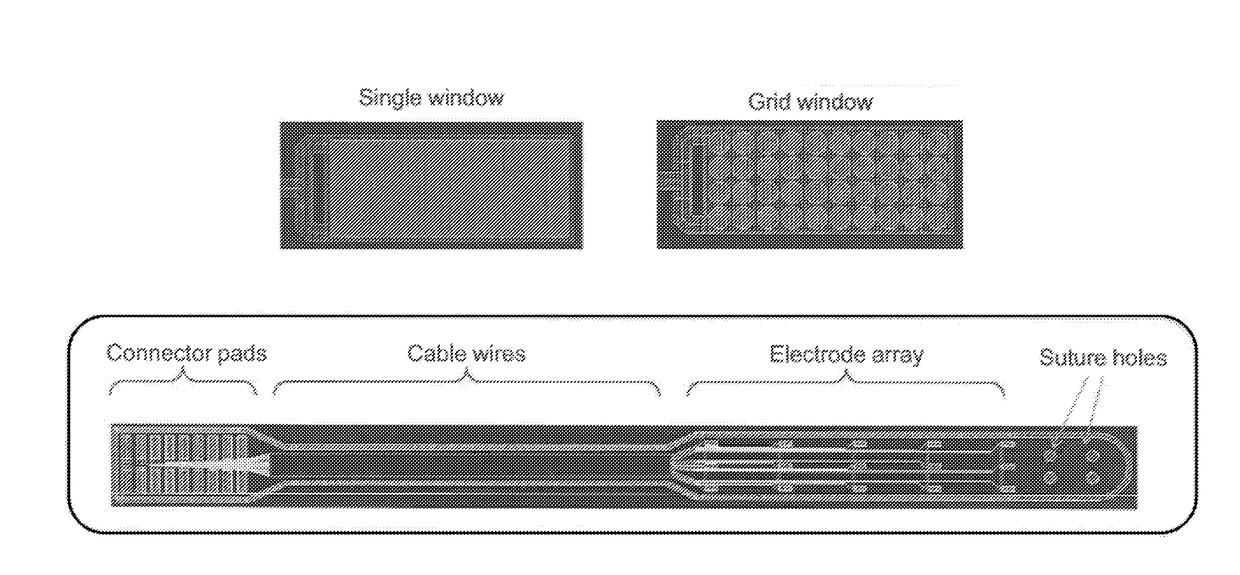
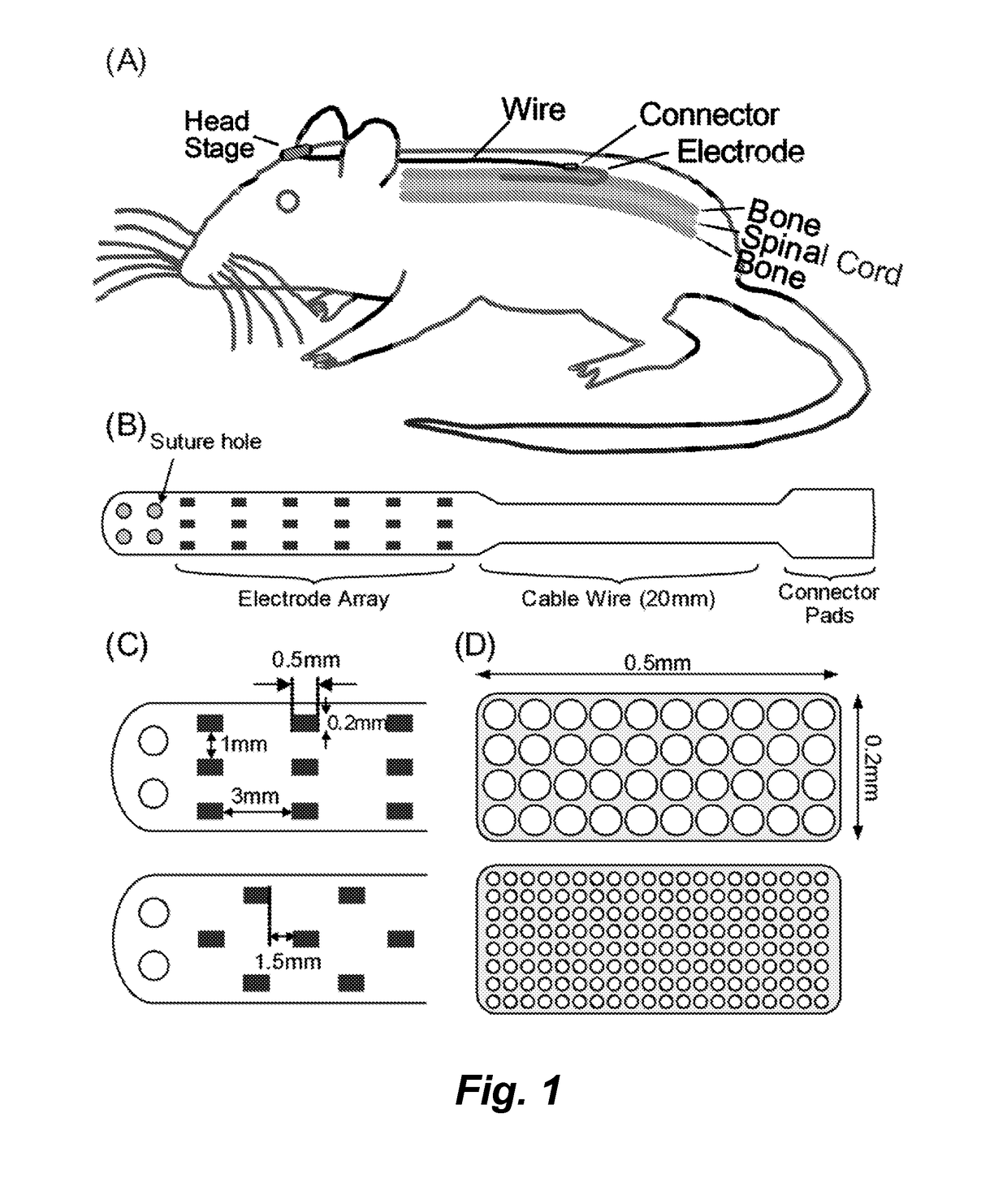
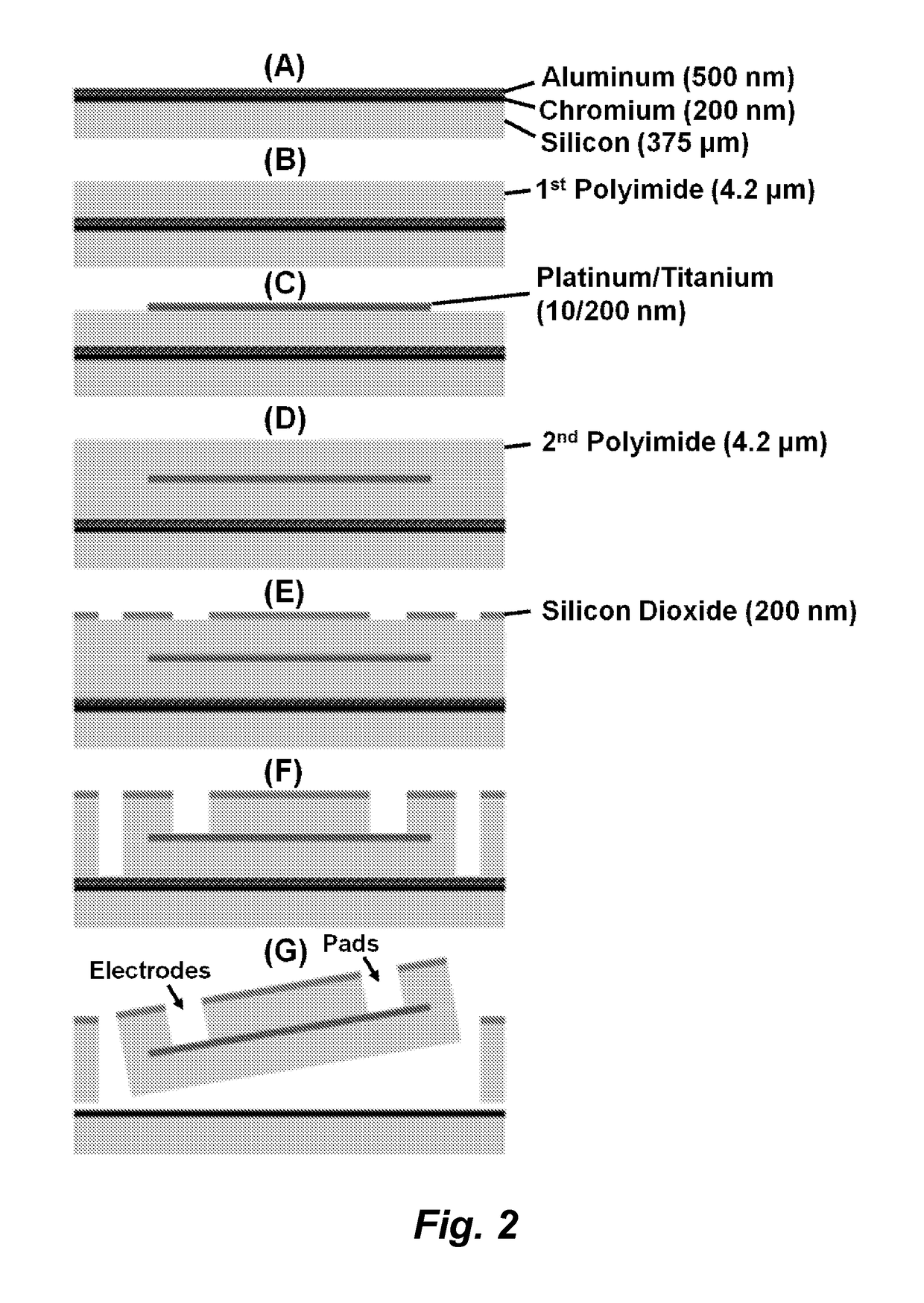
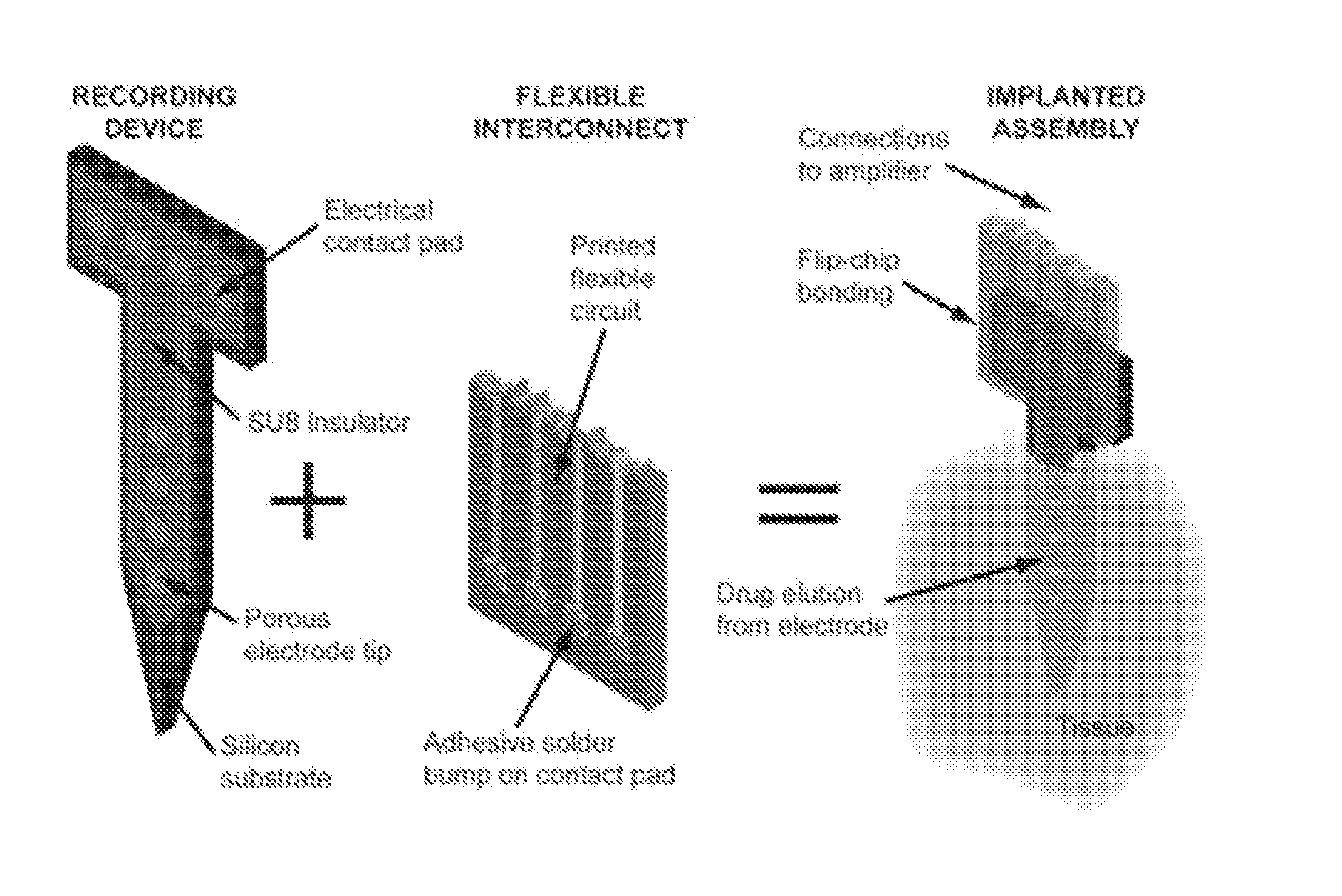
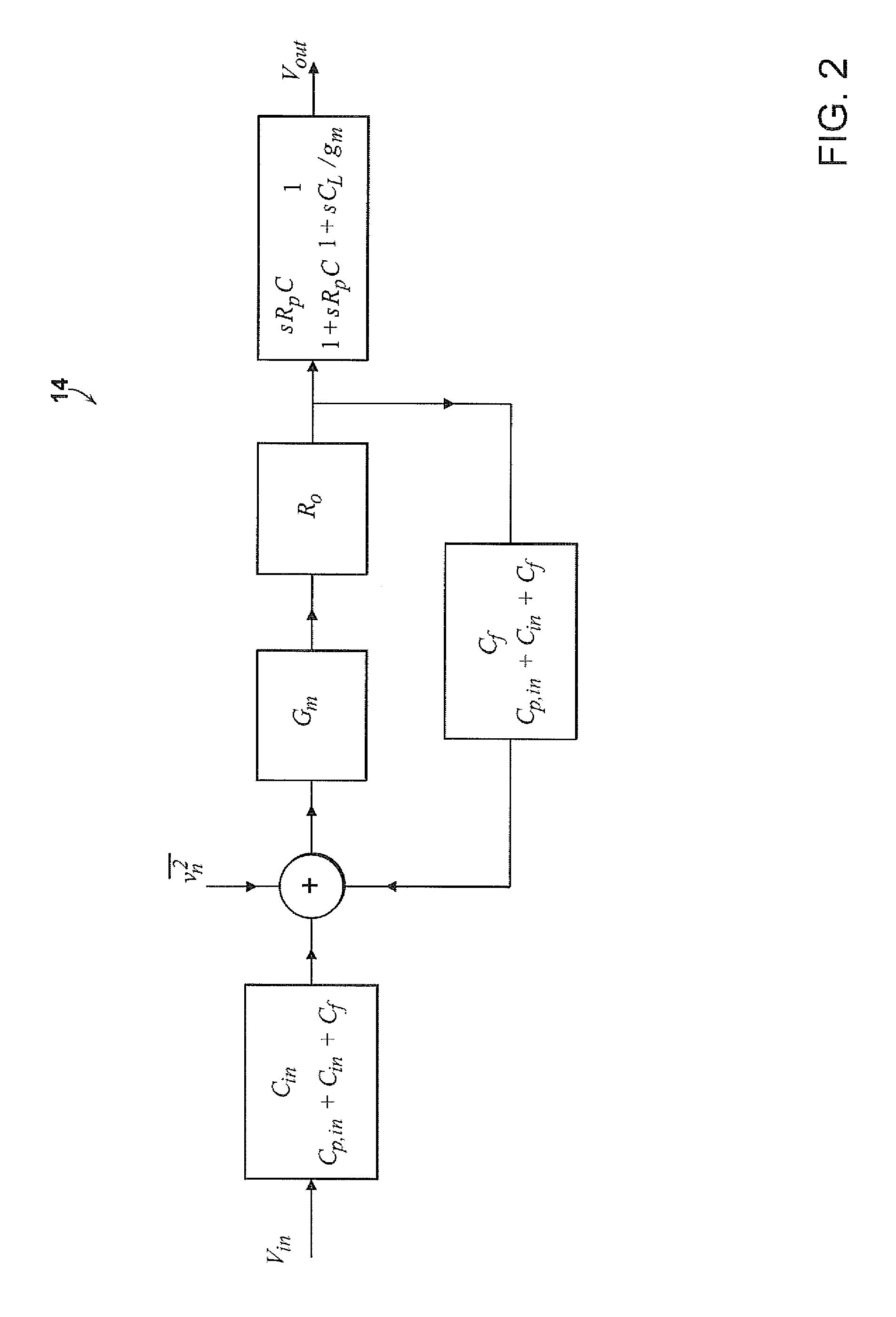
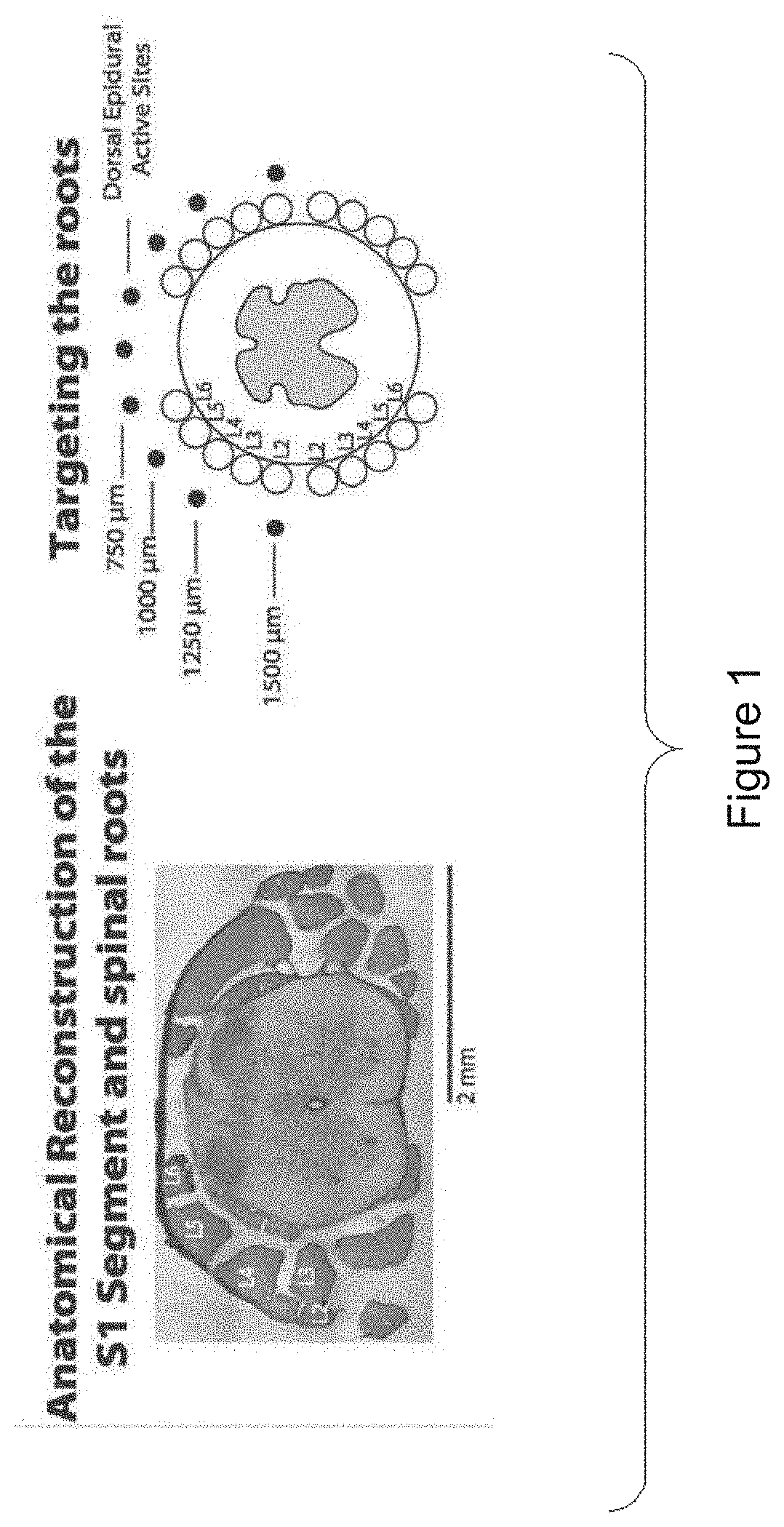
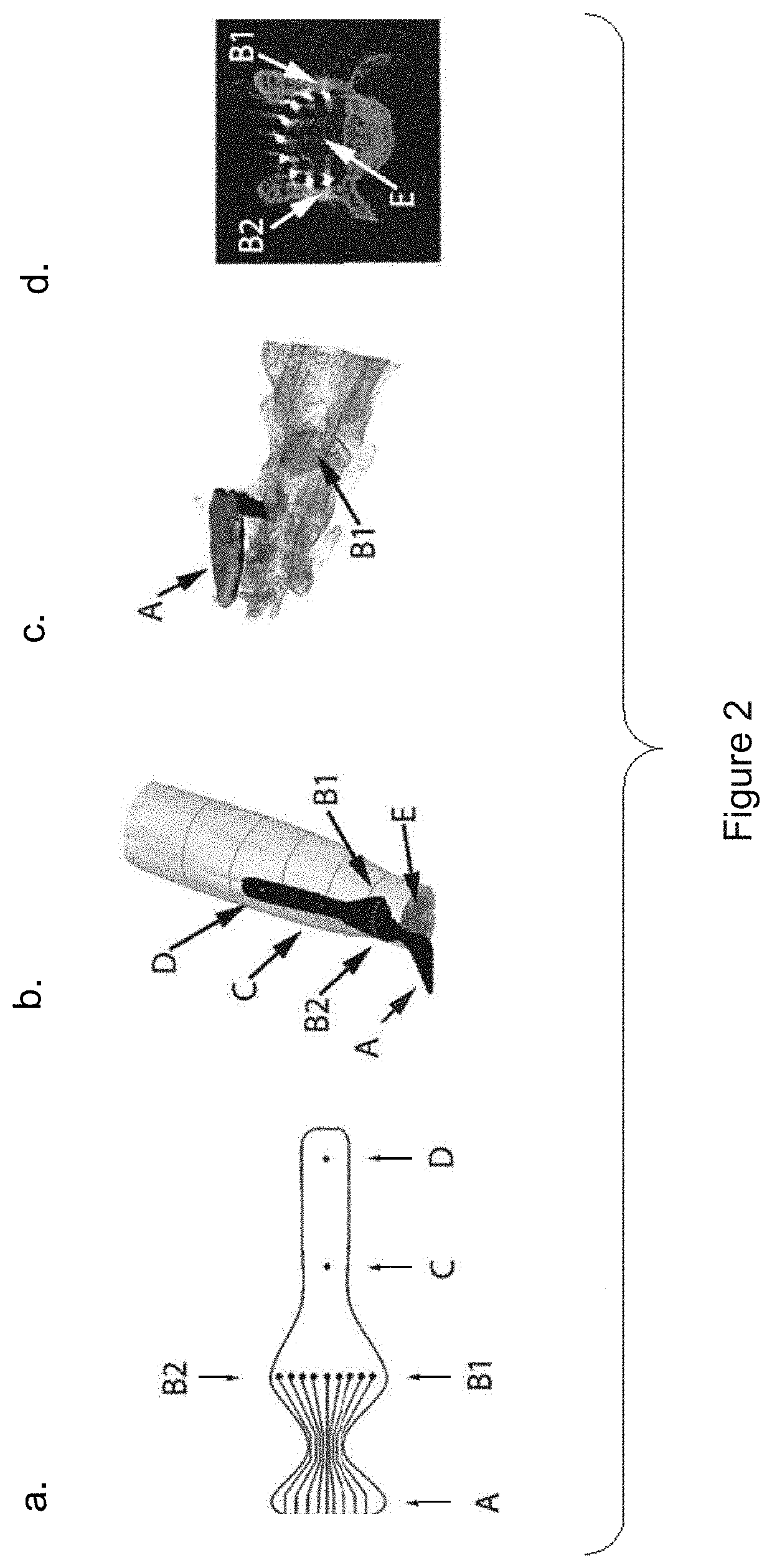
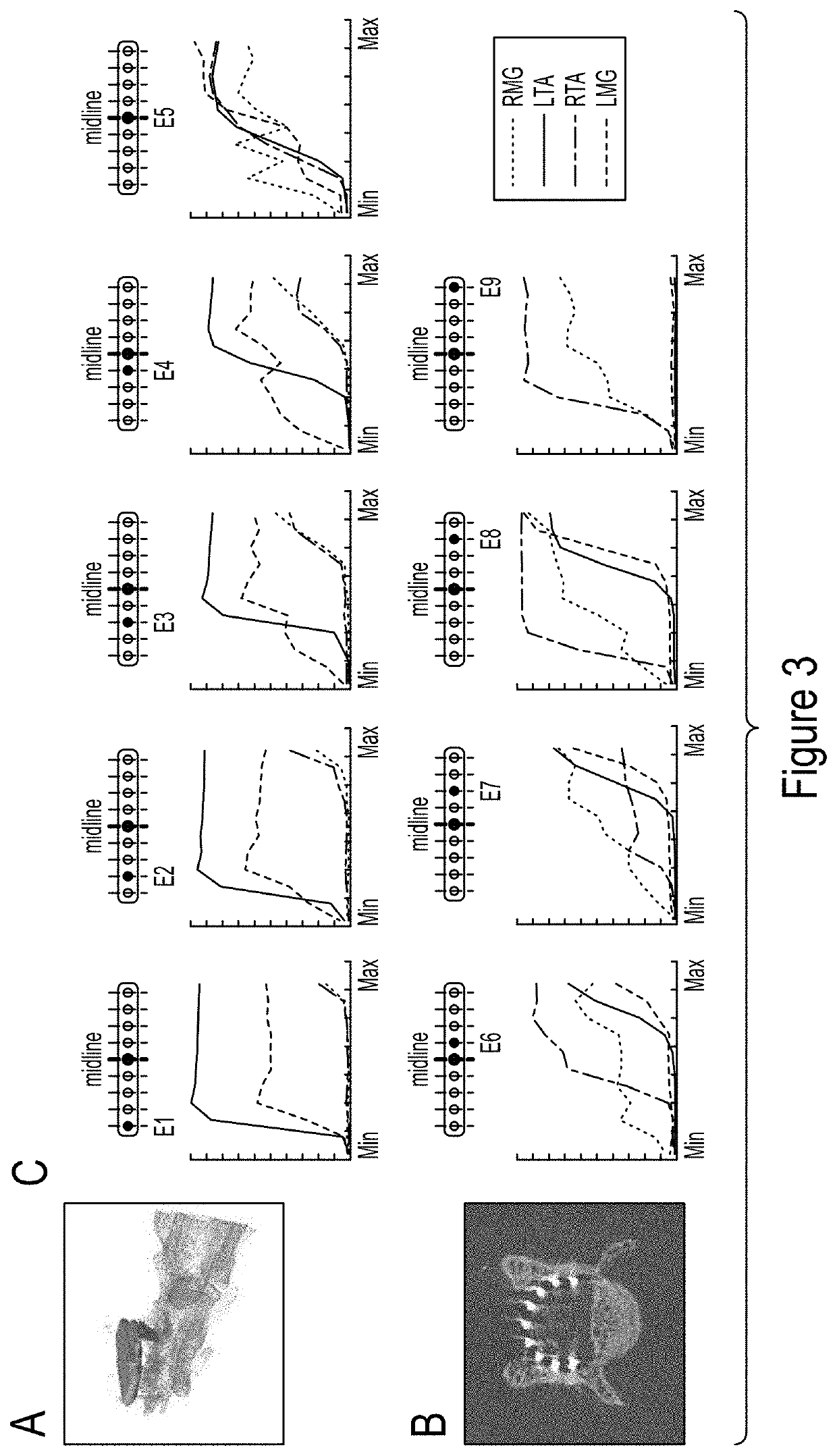
Patents
Literature
73 results about "Multielectrode array" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Microelectrode arrays (MEAs) (also referred to as multielectrode arrays) are devices that contain multiple (tens to thousands) microelectrodes through which neural signals are obtained or delivered, essentially serving as neural interfaces that connect neurons to electronic circuitry. There are two general classes of MEAs: implantable MEAs, used in vivo, and non-implantable MEAs, used in vitro.
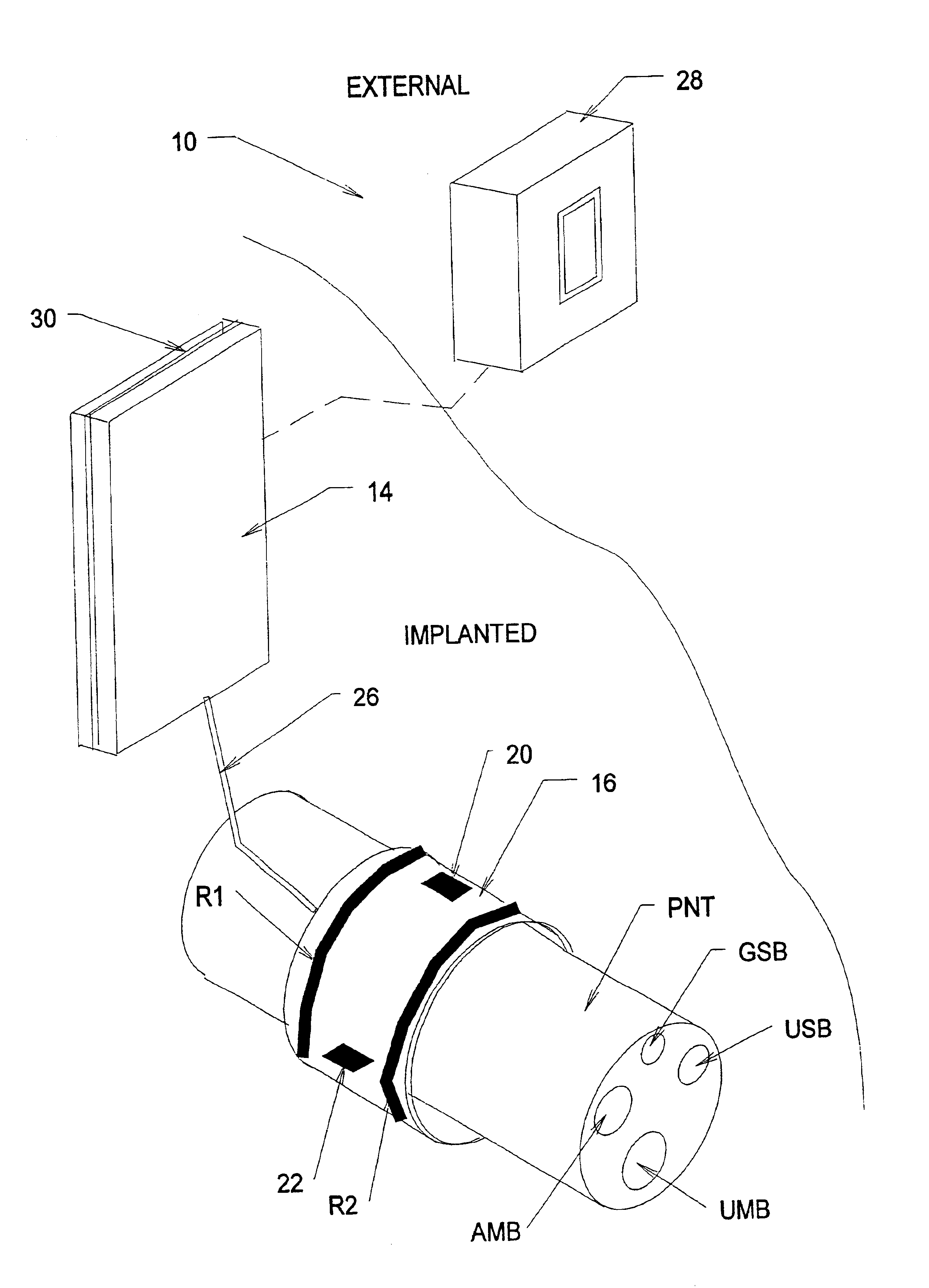
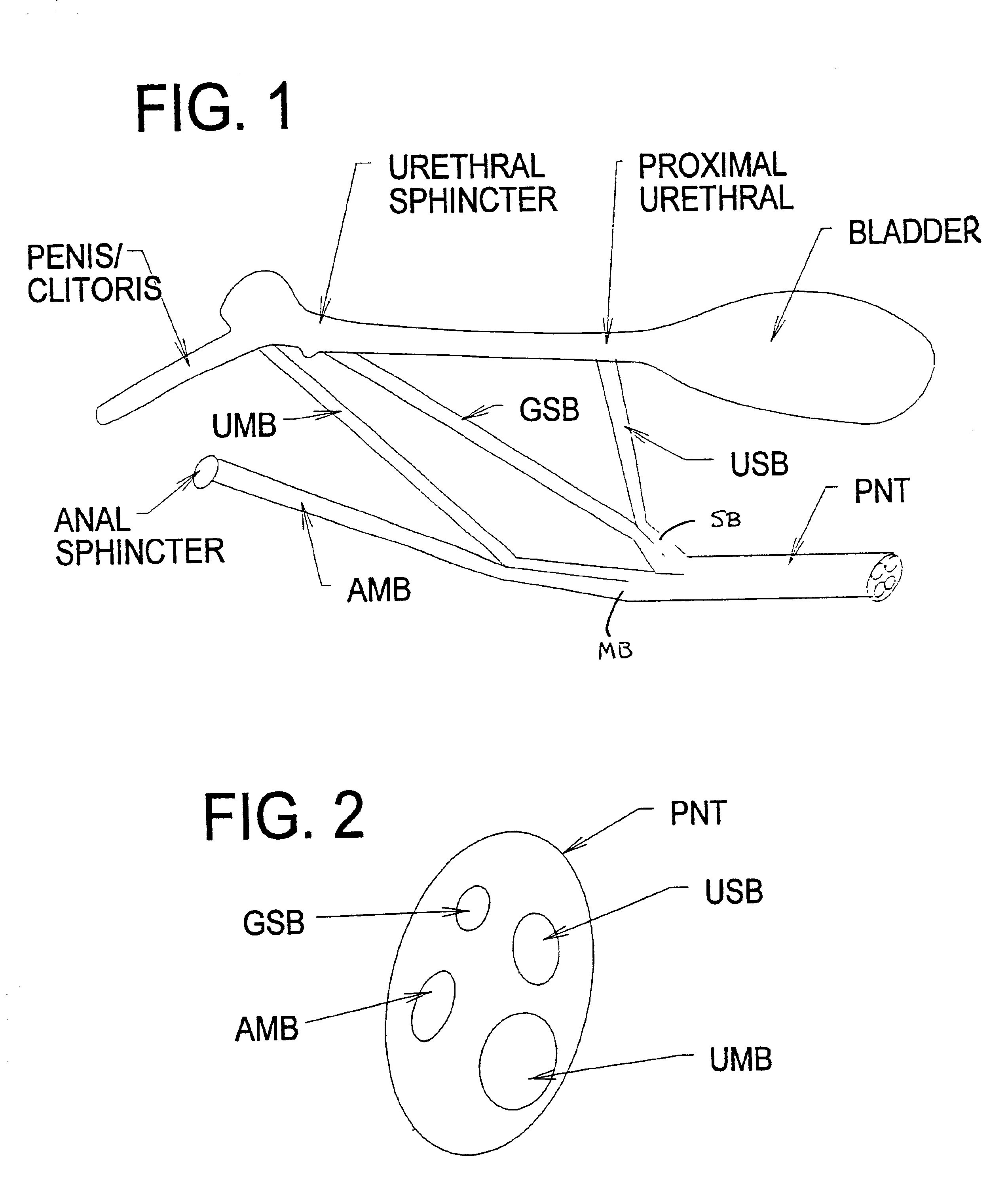
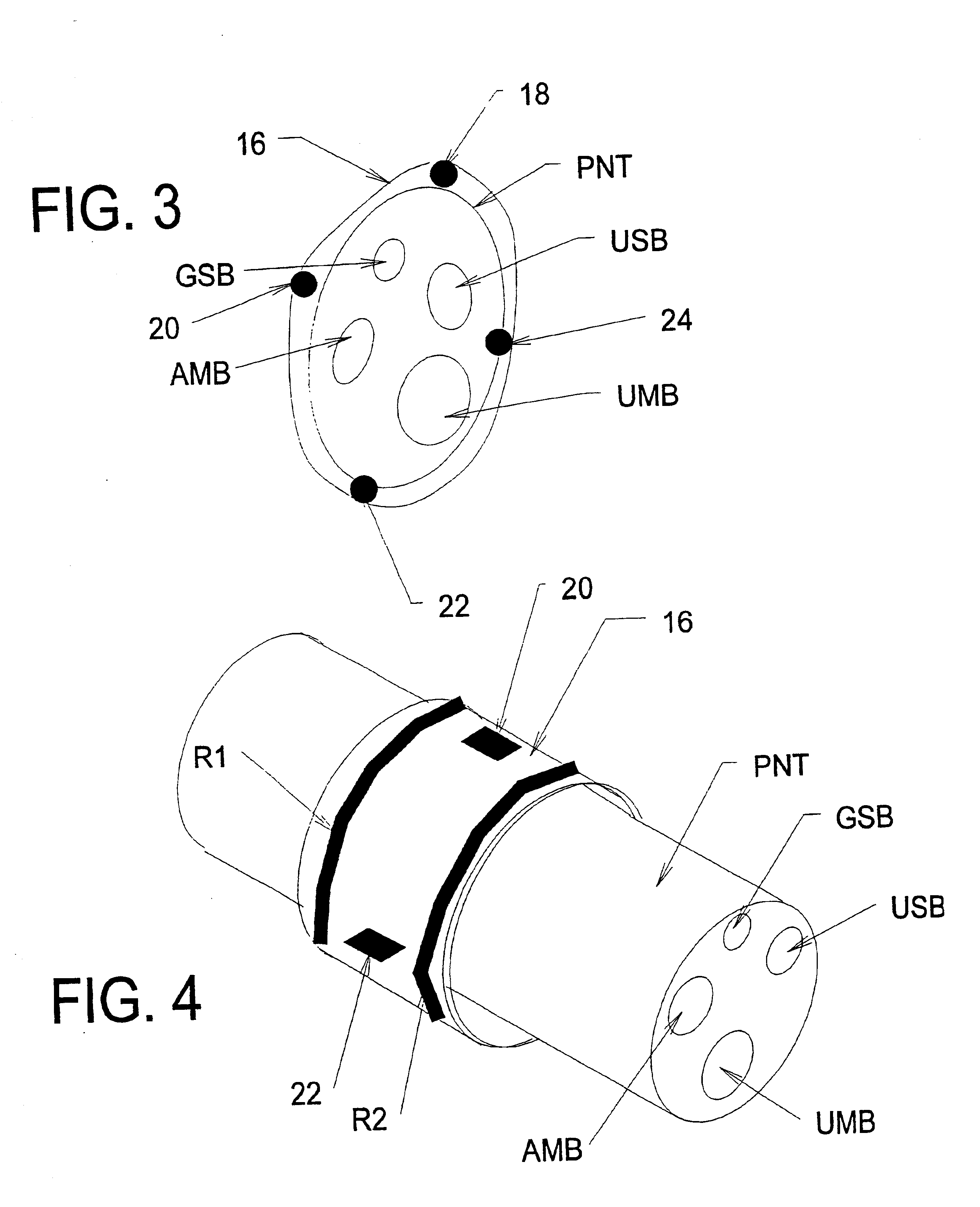
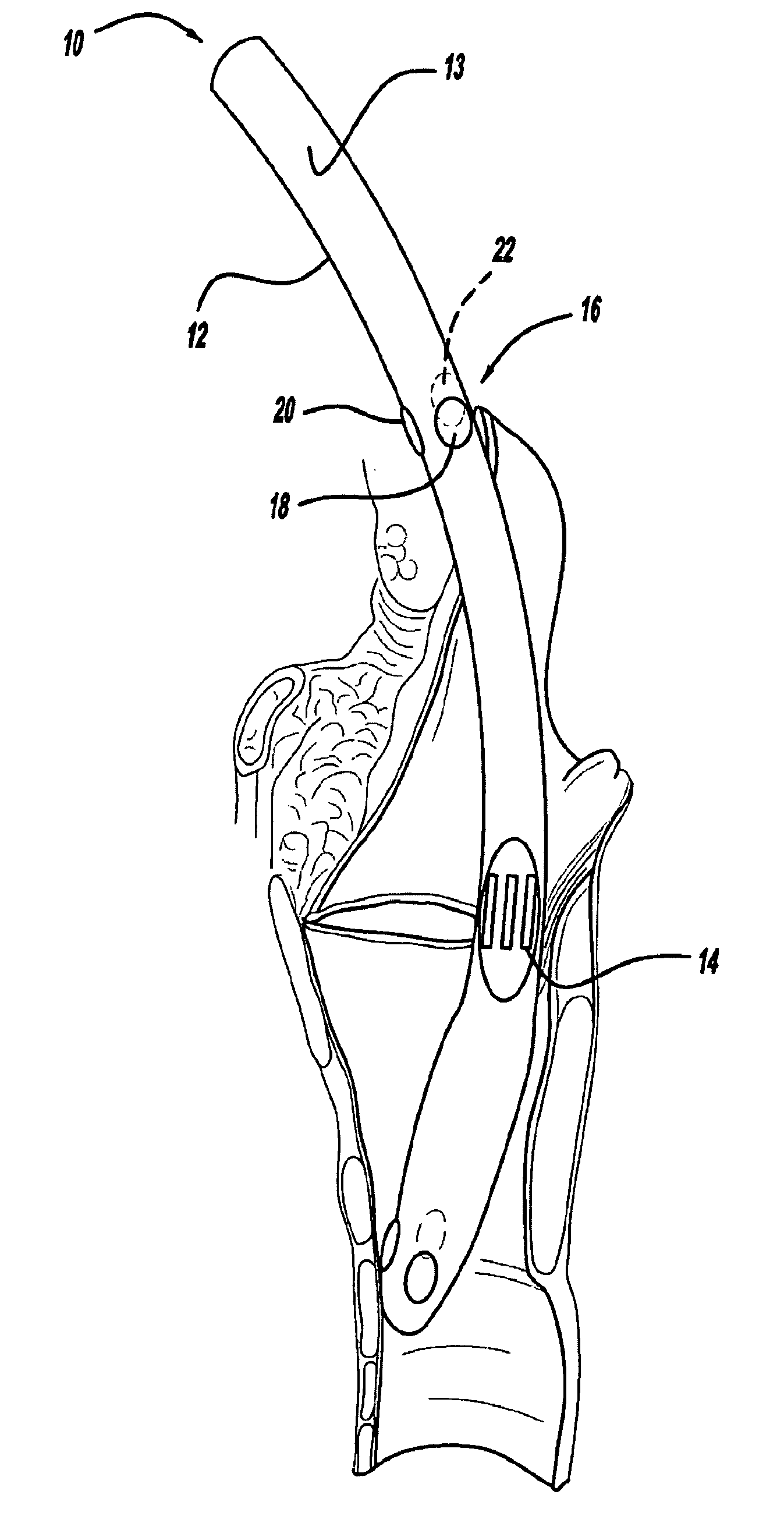
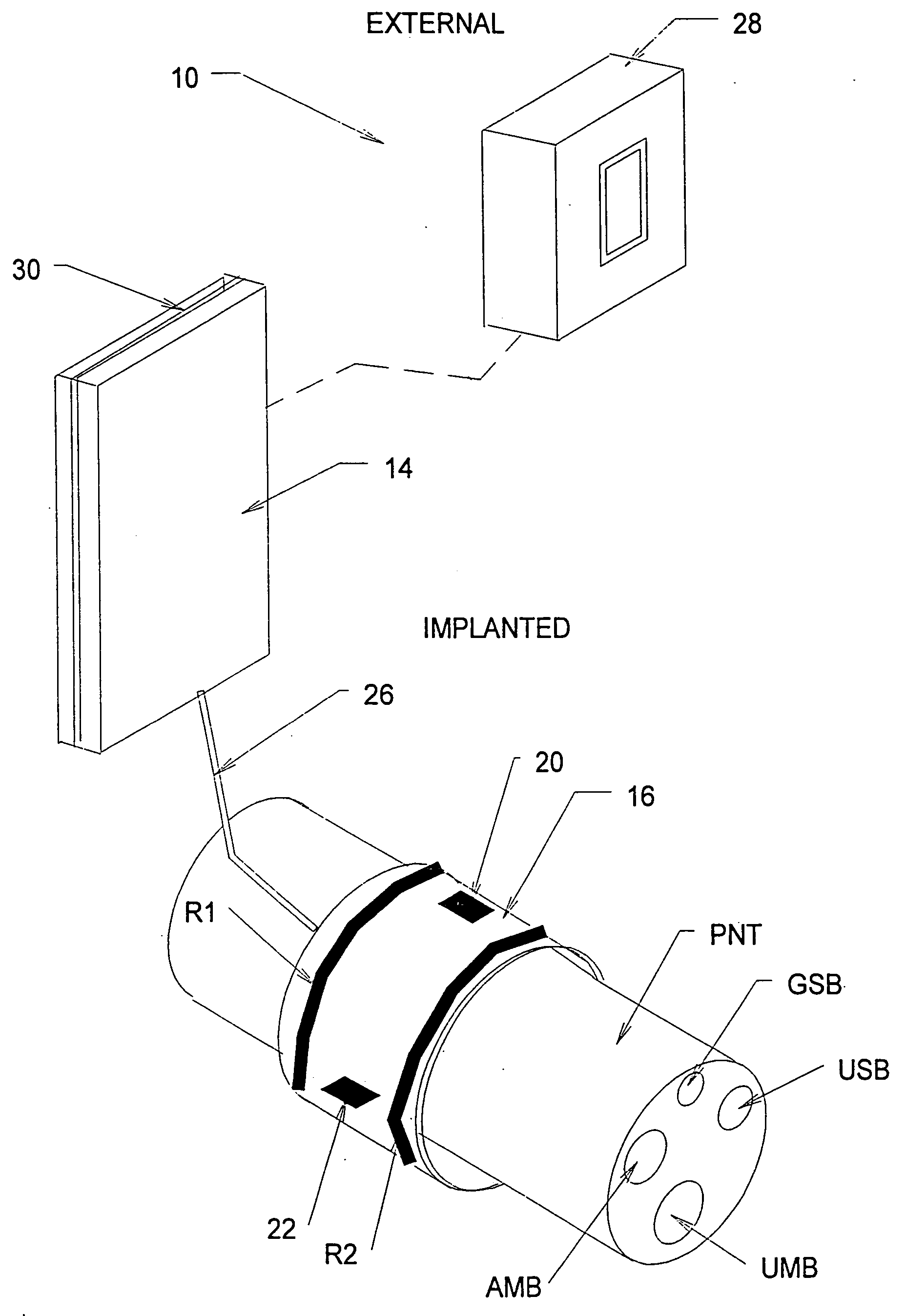
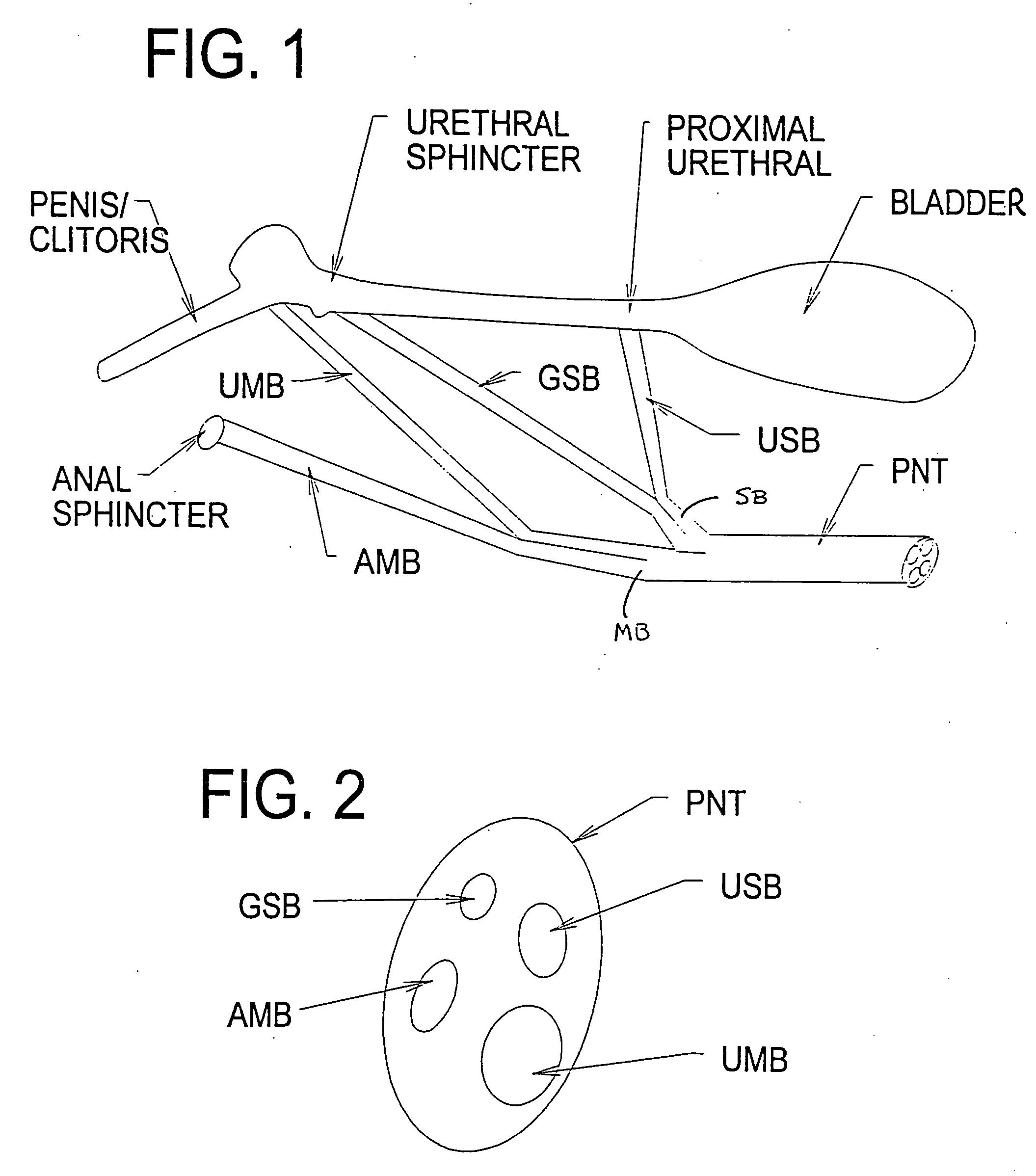
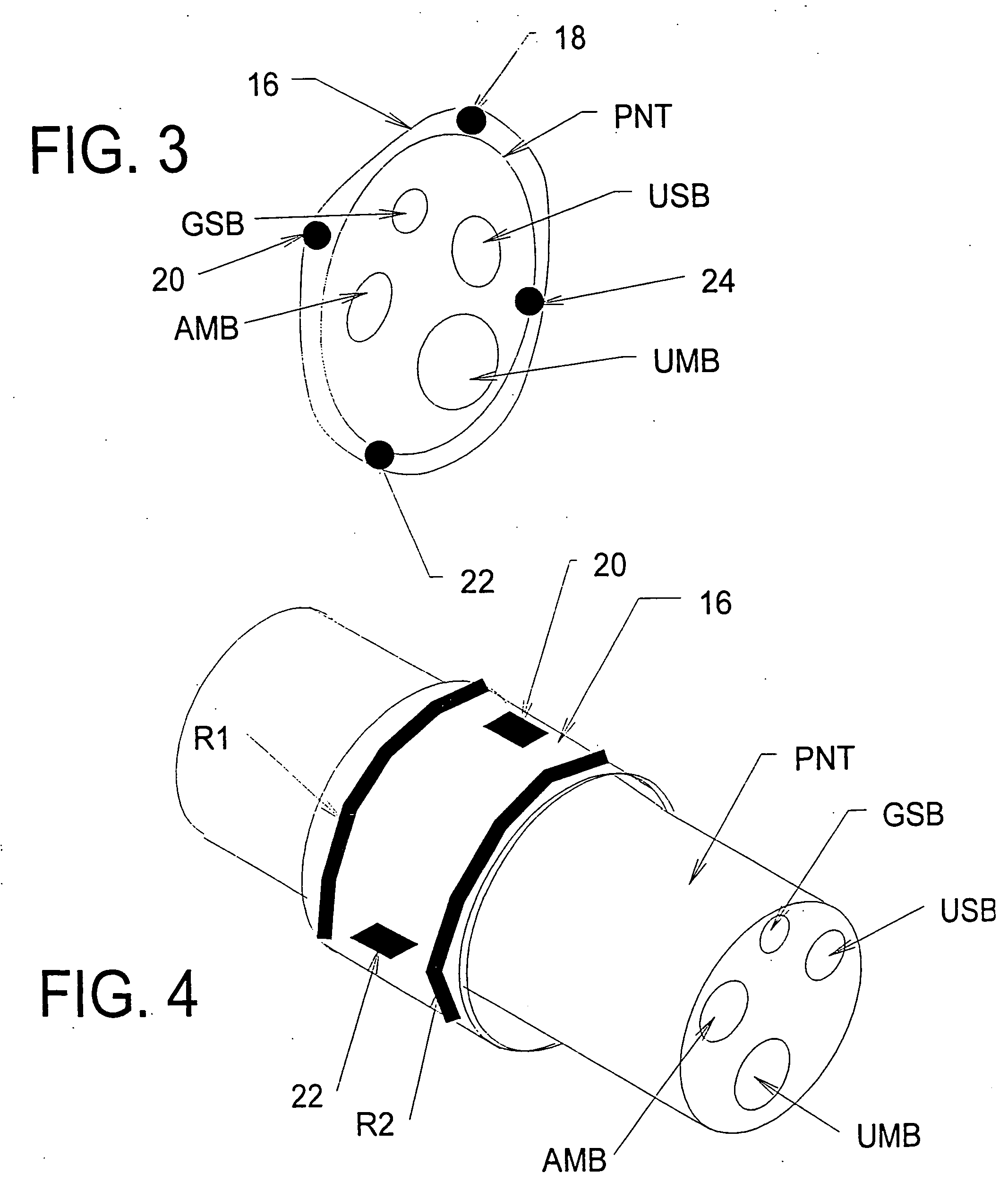
Systems and methods for selectively stimulating components in, on, or near the pudendal nerve or its branches to achieve selective physiologic responses
ActiveUS6907293B2Easy to defecatePromote contractionSpinal electrodesExternal electrodesMedicineMultielectrode array
Systems and methods selectively stimulate components of the pudendal nerve away from the sacral root to evoke desired physiologic responses in persons who lack the ability to otherwise produce these responses—e.g., maintain continence and / or produce micturition, and / or provide male / female sexuality responses, and / or provide bowel responses. The systems and methods use a multiple electrode array, or individual electrodes, placed on, in, or near the pudendal nerve. The electrode array, or individual electrodes, in association with a pulse generator, provide selective stimulation of individual fascicles within the pudendal nerve, to achieve different physiologic responses.
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
Leadless neurostimulation device and method including the same
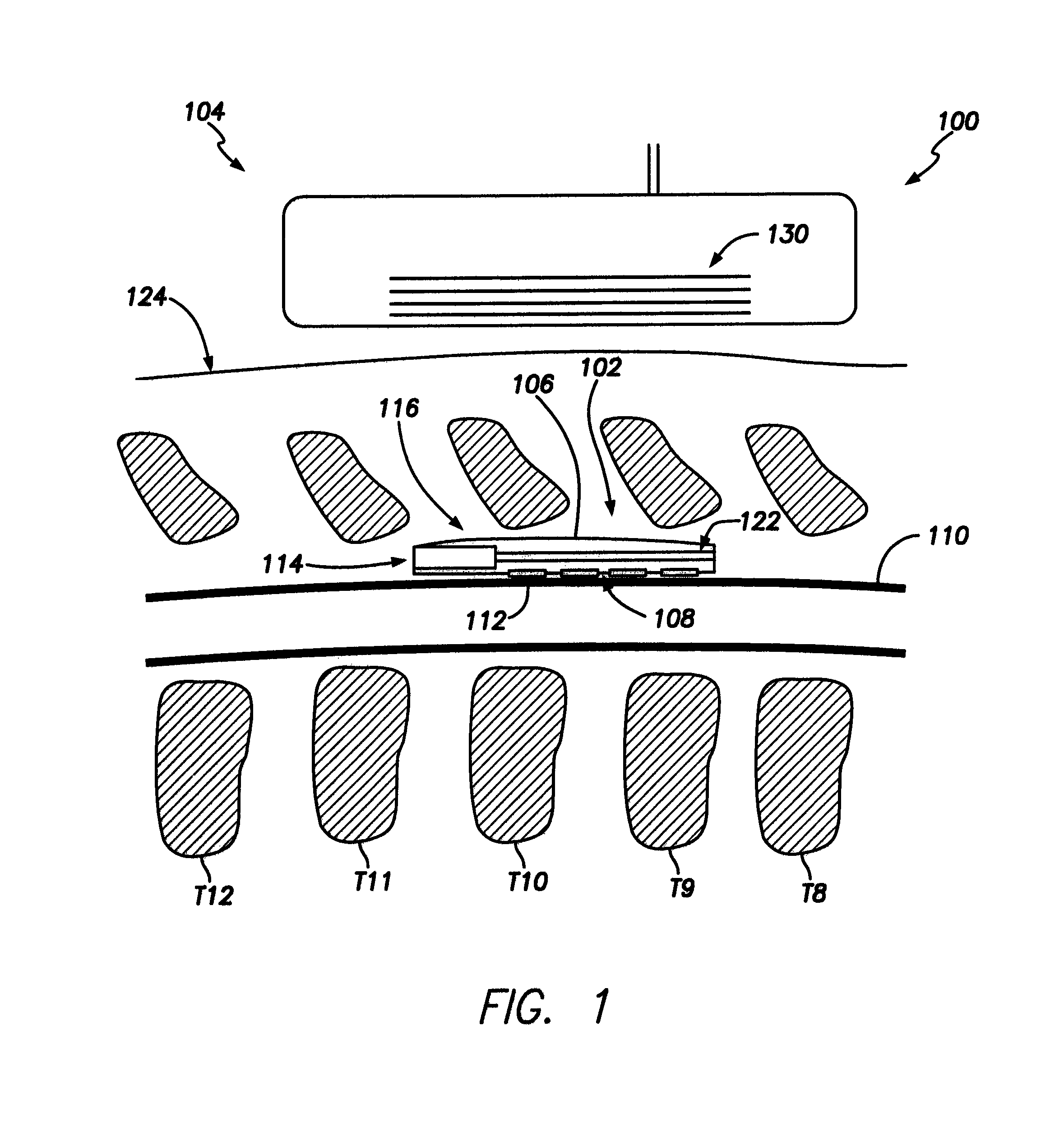
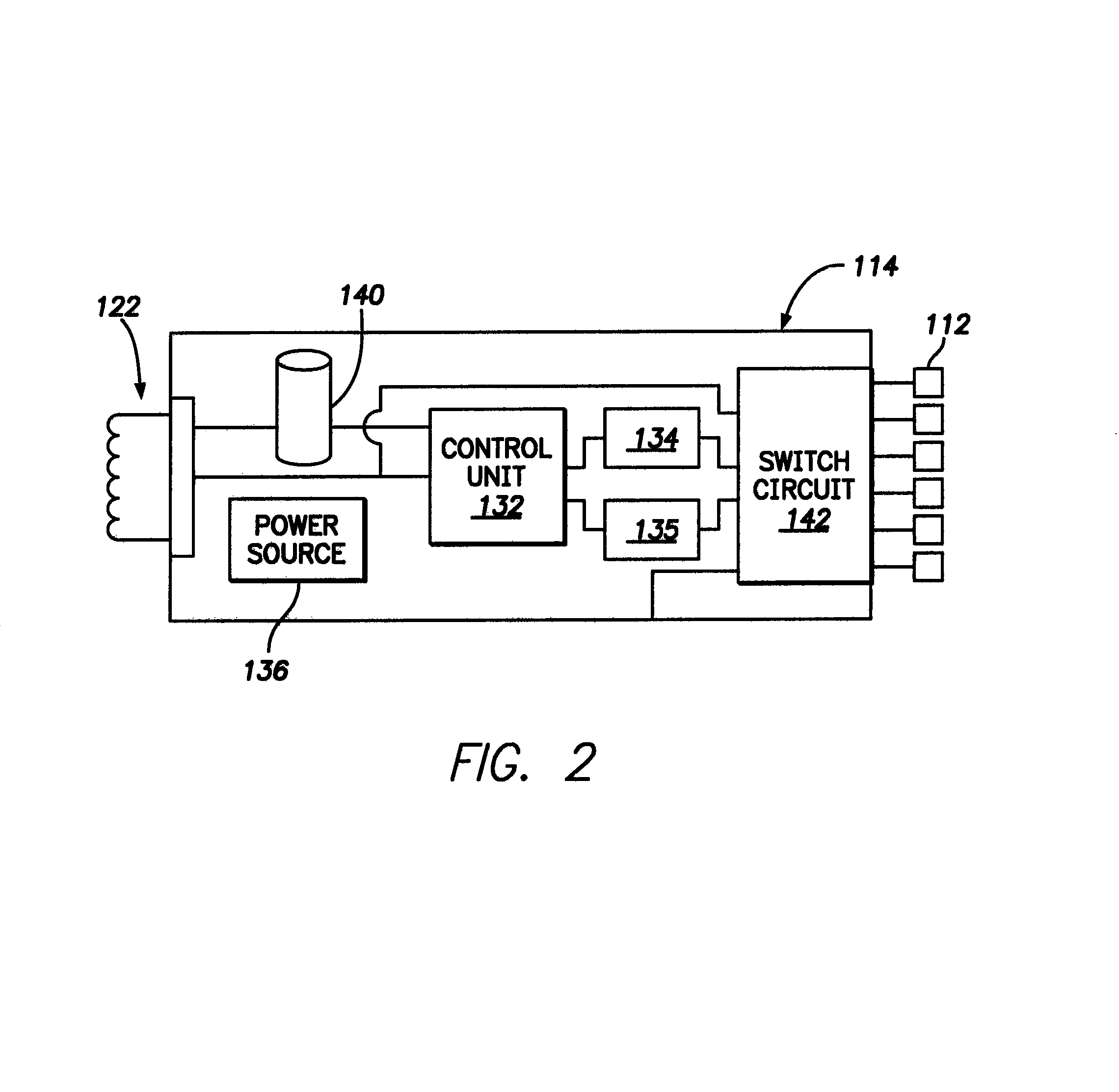
Leadless neurostimulation (NS) device including a device body and electrodes positioned along an active side of the device body. The electrodes form a multi-electrode array that is configured to interface with nervous tissue of a patient and supply electrical pulses to the nervous tissue. The NS device also includes an electronic sub-system that is coupled to the device body. The electronic sub-system includes switching circuitry, a power source, and an inductive coil that is operably coupled to the power source. The inductive coil is configured to receive electrical power through inductive coupling with an external coil. The device body, including the inductive coil coupled thereto, is sized and shaped to be disposed within an epidural space of a patient.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
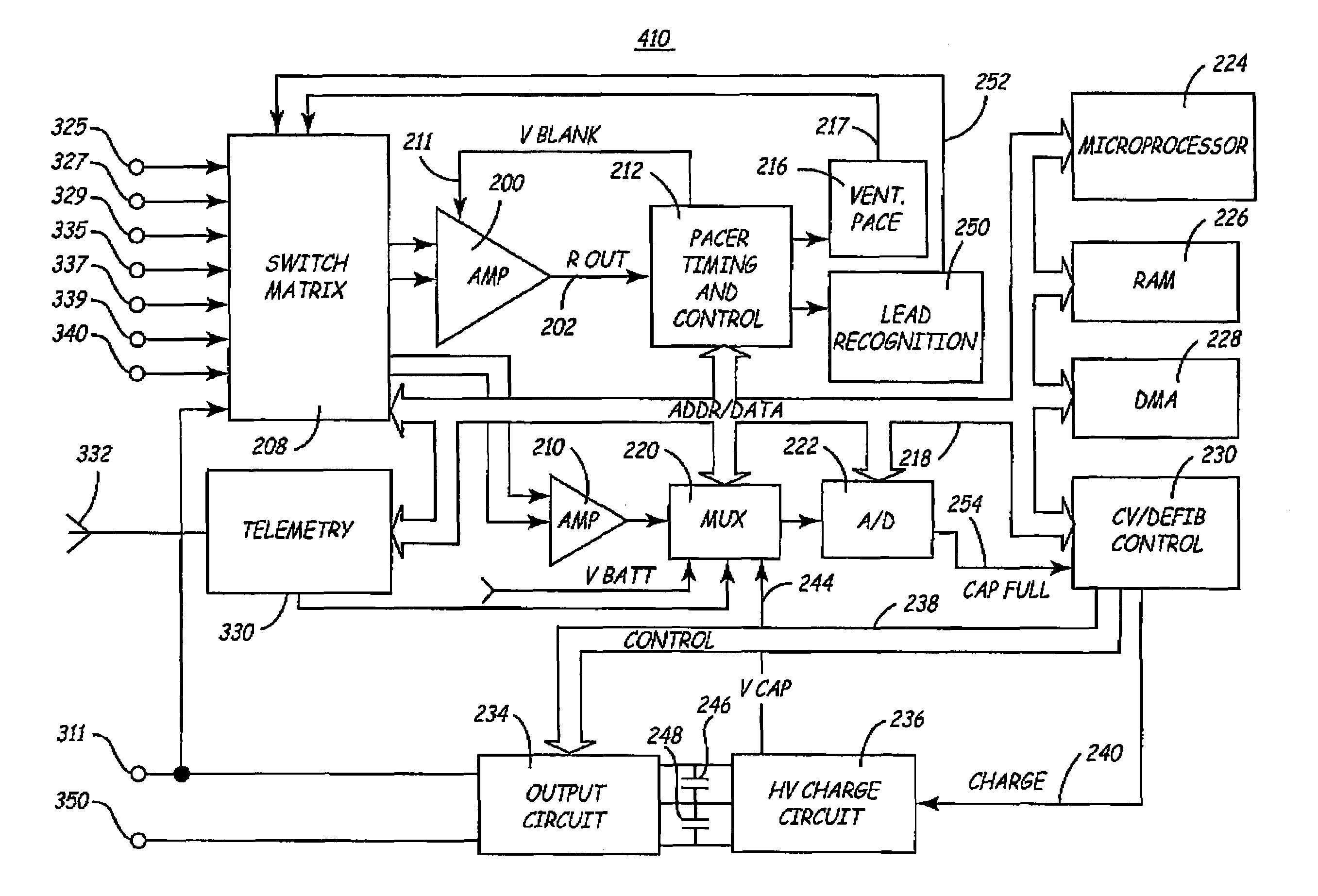
Method and apparatus for selecting an optimal electrode configuration of a medical electrical lead having a multiple electrode array
InactiveUS6978178B2ElectrocardiographyTransvascular endocardial electrodesElectrical conductorElectrode Contact
An electrical medical lead is provided having two or more electrodes, electrically insulated from each other and electrically coupled to individually insulated filars in a multi-filar coiled conductor. When the lead is used with a medical device equipped with a switch matrix, electrodes are selected individually or simultaneously to serve as an anode or cathode in any unipolar, bipolar or multi-polar configuration for delivering stimulation and / or sensing signals in excitable tissue. In one embodiment, a tip electrode array is expandable for improving electrode contact with targeted tissue and stabilizing lead position.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Method and device for image processing and learning with neuronal cultures
InactiveUS20060094001A1Microbiological testing/measurementCharacter and pattern recognitionElectricityImaging processing
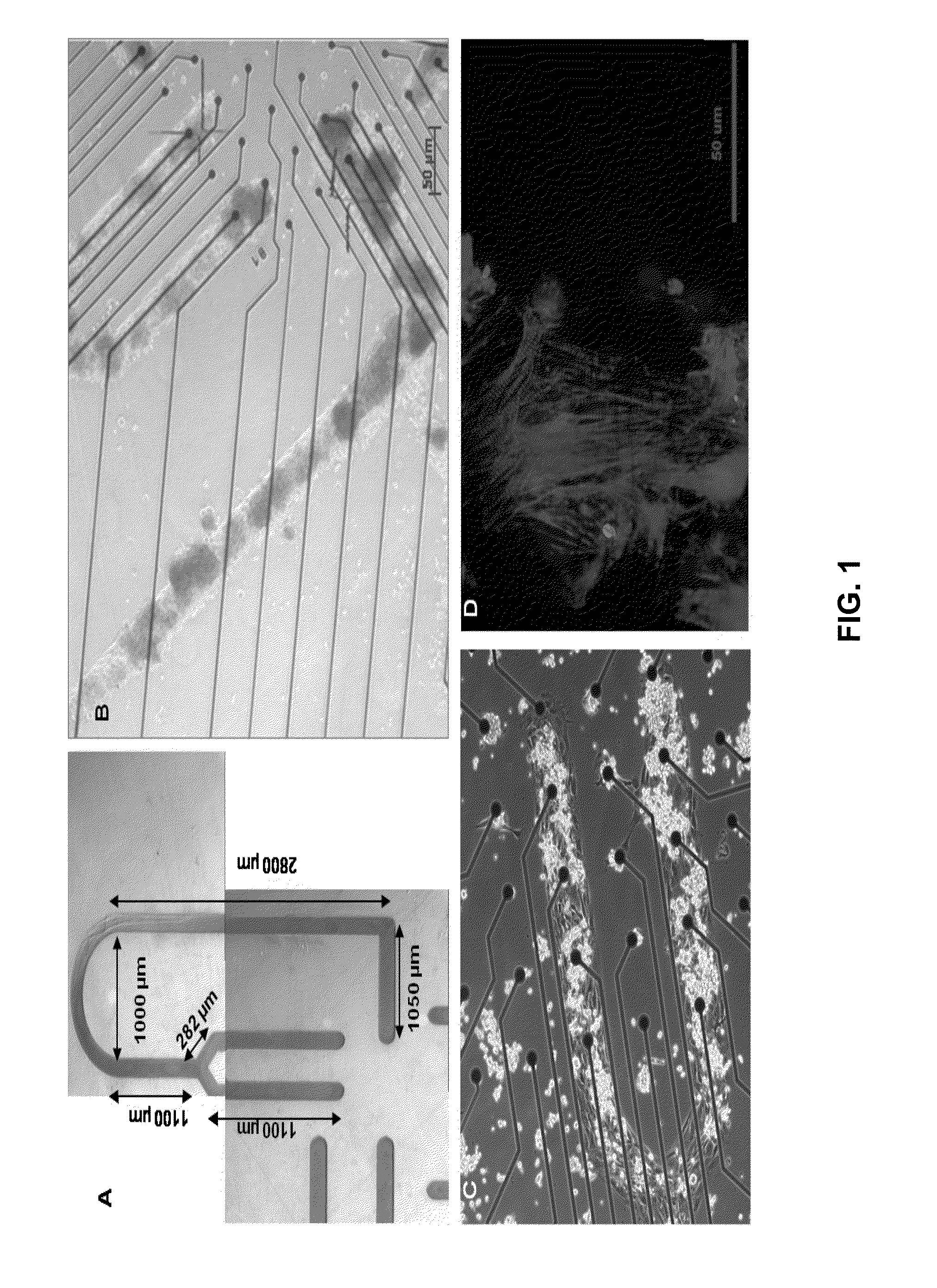
It is disclosed a device for image processing and learning comprising at least a “multi electrode array” (MEA), over which an homogeneous culture of interconnected neurons, so that forming a cell network, is grown on, wherein said MEA is able to stimulate and record the electric activity of said neurons. Methods for image processing and learning utilizing the device are disclosed too.
Owner:S I S SCUOLA INTERNAZ SUPERIORE DI STUDI AVANZATI
Conformally Encapsulated Multi-Electrode Arrays With Seamless Insulation
ActiveUS20130345780A1Opportunities decreaseImprove adhesionSpinal electrodesHead electrodesMicrofabricationMultielectrode array
Thin-film multi-electrode arrays (MEA) having one or more electrically conductive beams conformally encapsulated in a seamless block of electrically insulating material, and methods of fabricating such MEAs using reproducible, microfabrication processes. One or more electrically conductive traces are formed on scaffold material that is subsequently removed to suspend the traces over a substrate by support portions of the trace beam in contact with the substrate. By encapsulating the suspended traces, either individually or together, with a single continuous layer of an electrically insulating material, a seamless block of electrically insulating material is formed that conforms to the shape of the trace beam structure, including any trace backings which provide suspension support. Electrical contacts, electrodes, or leads of the traces are exposed from the encapsulated trace beam structure by removing the substrate.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
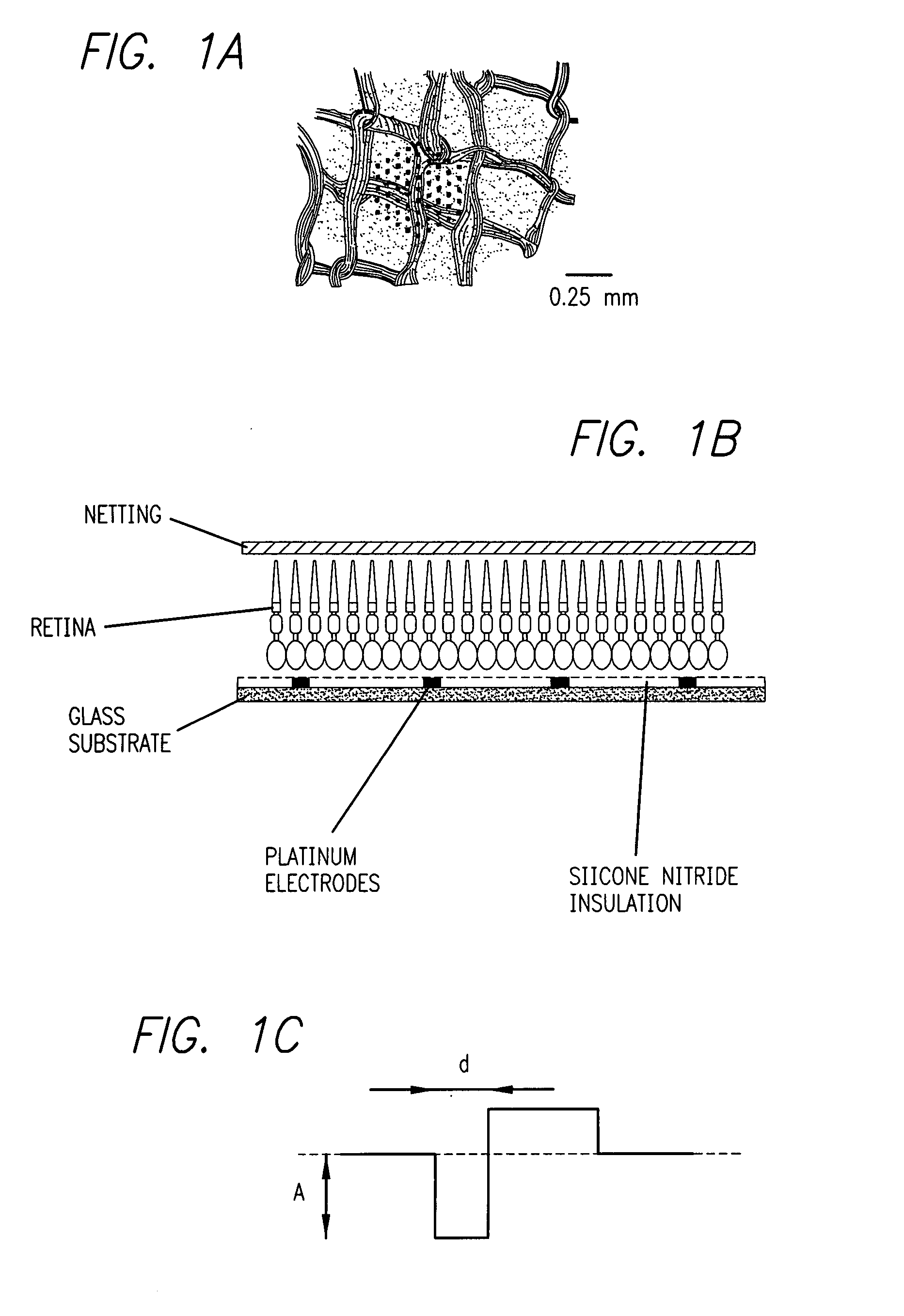
Method and apparatus for visual neural stimulation
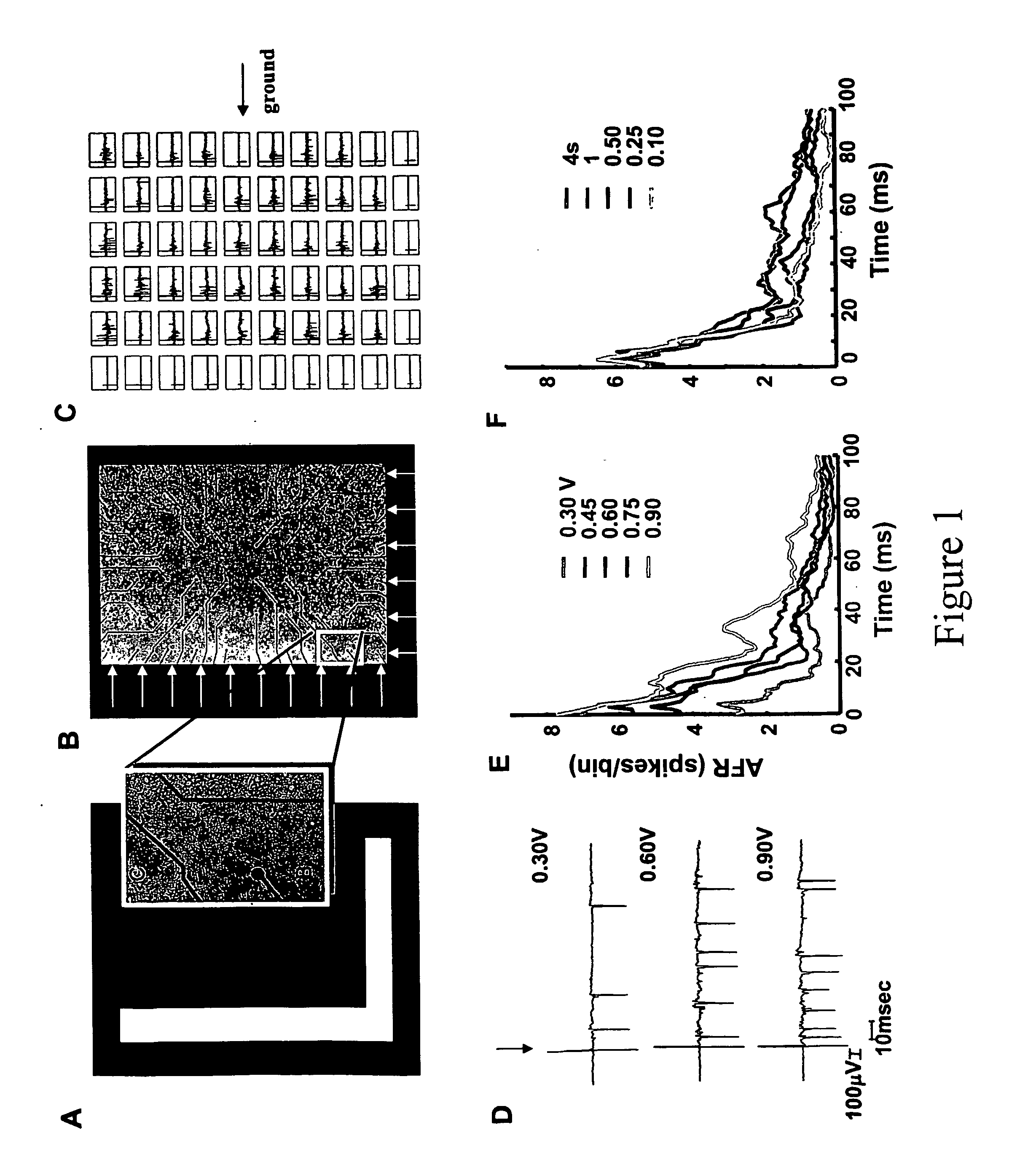
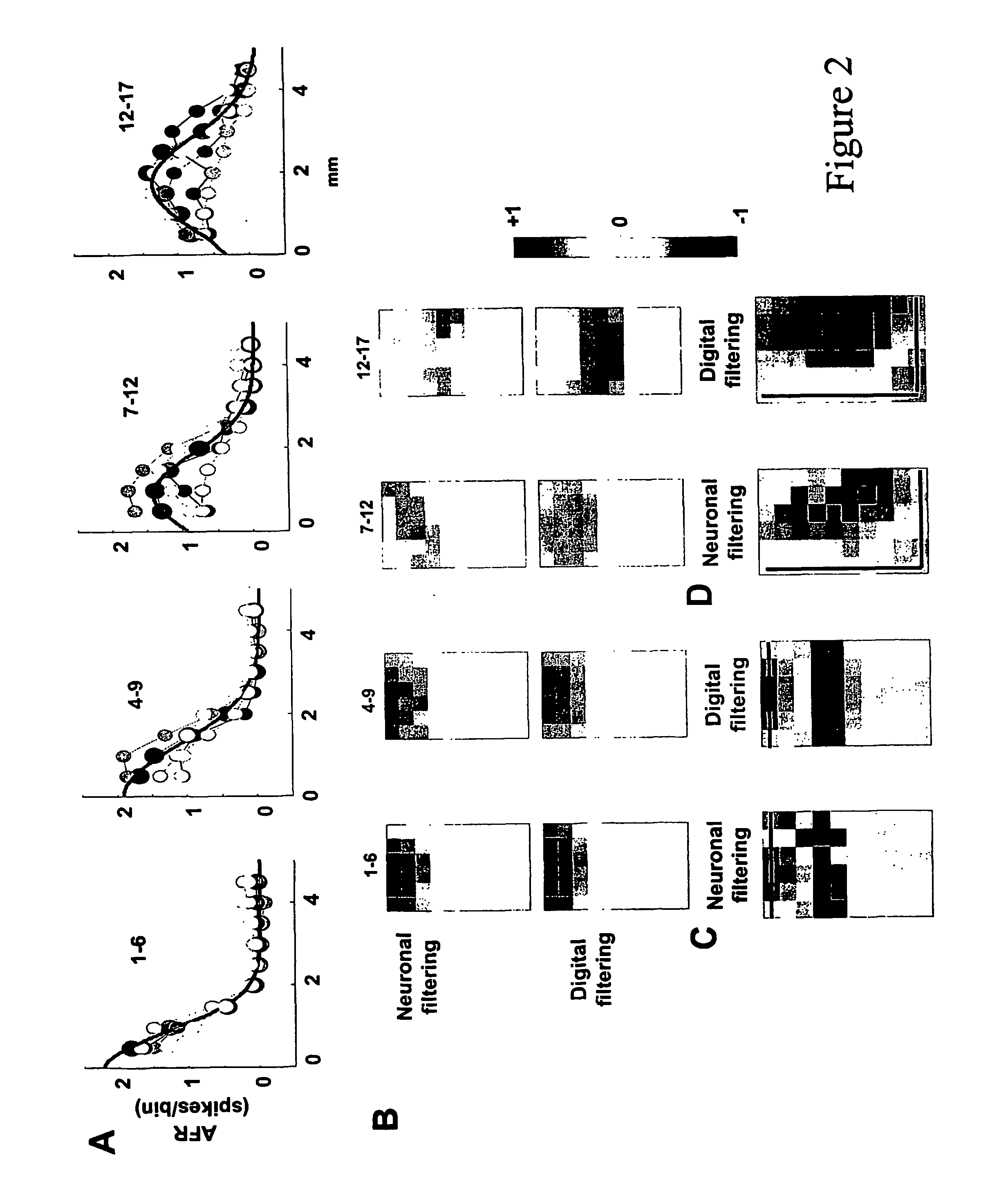
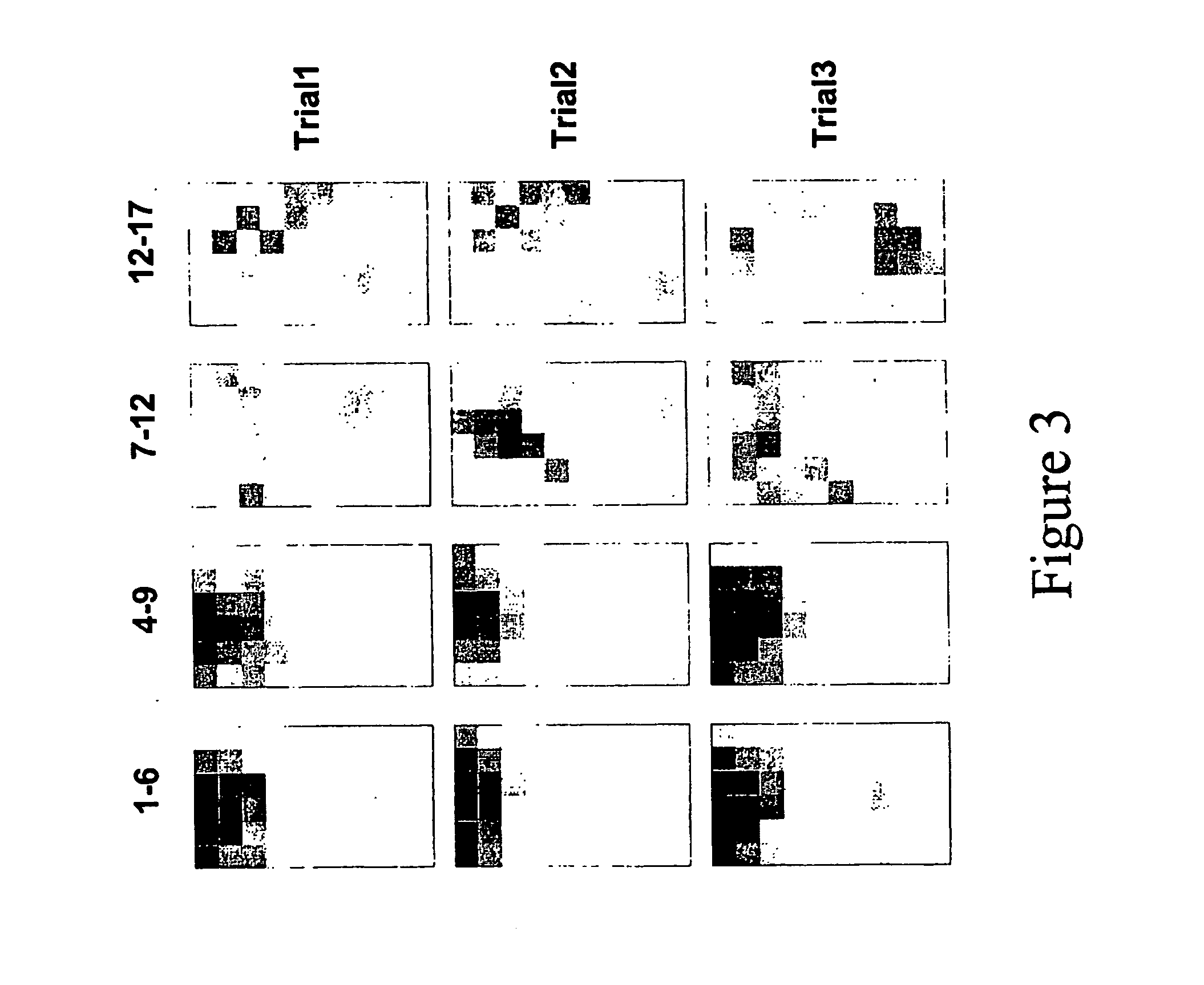
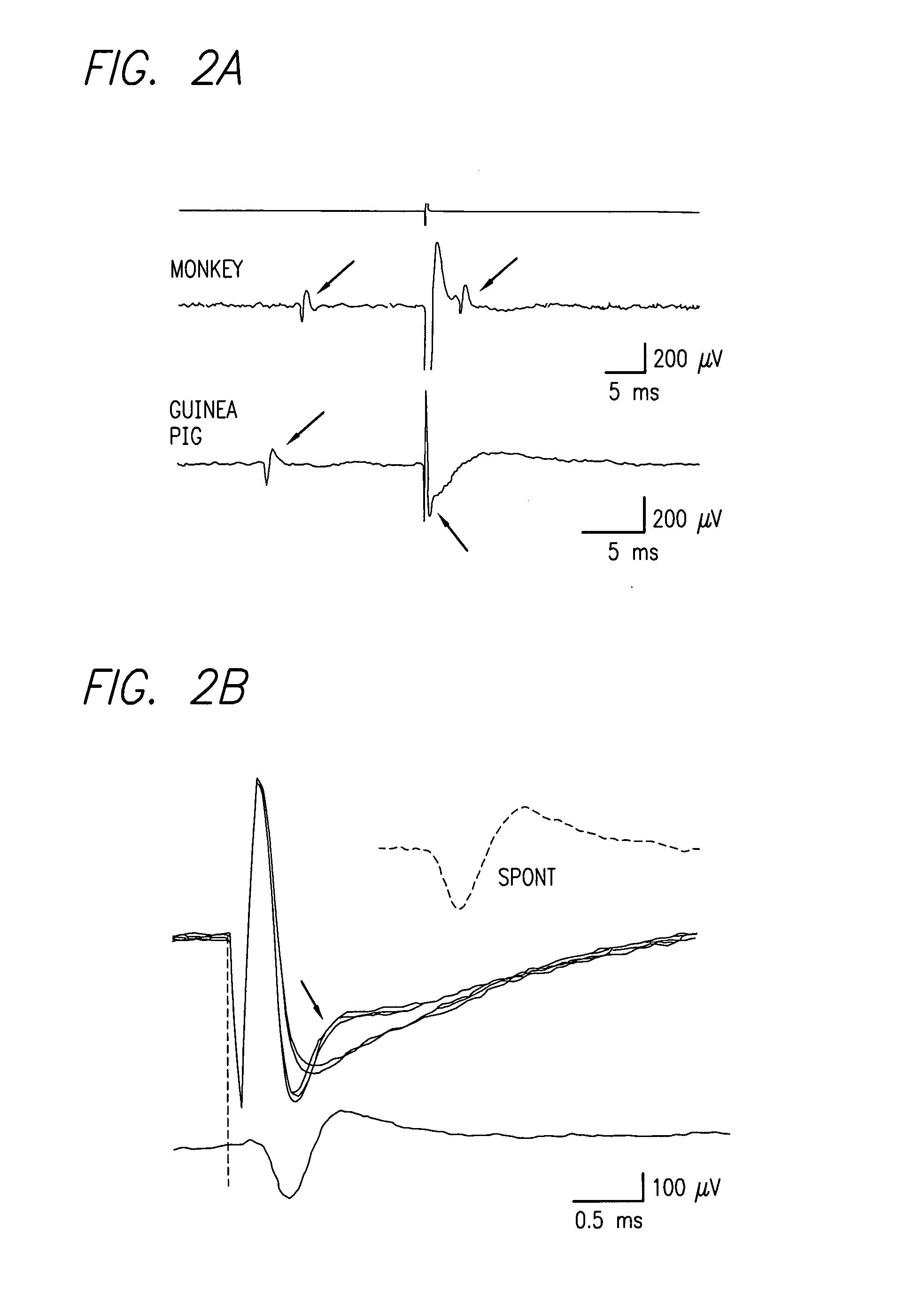
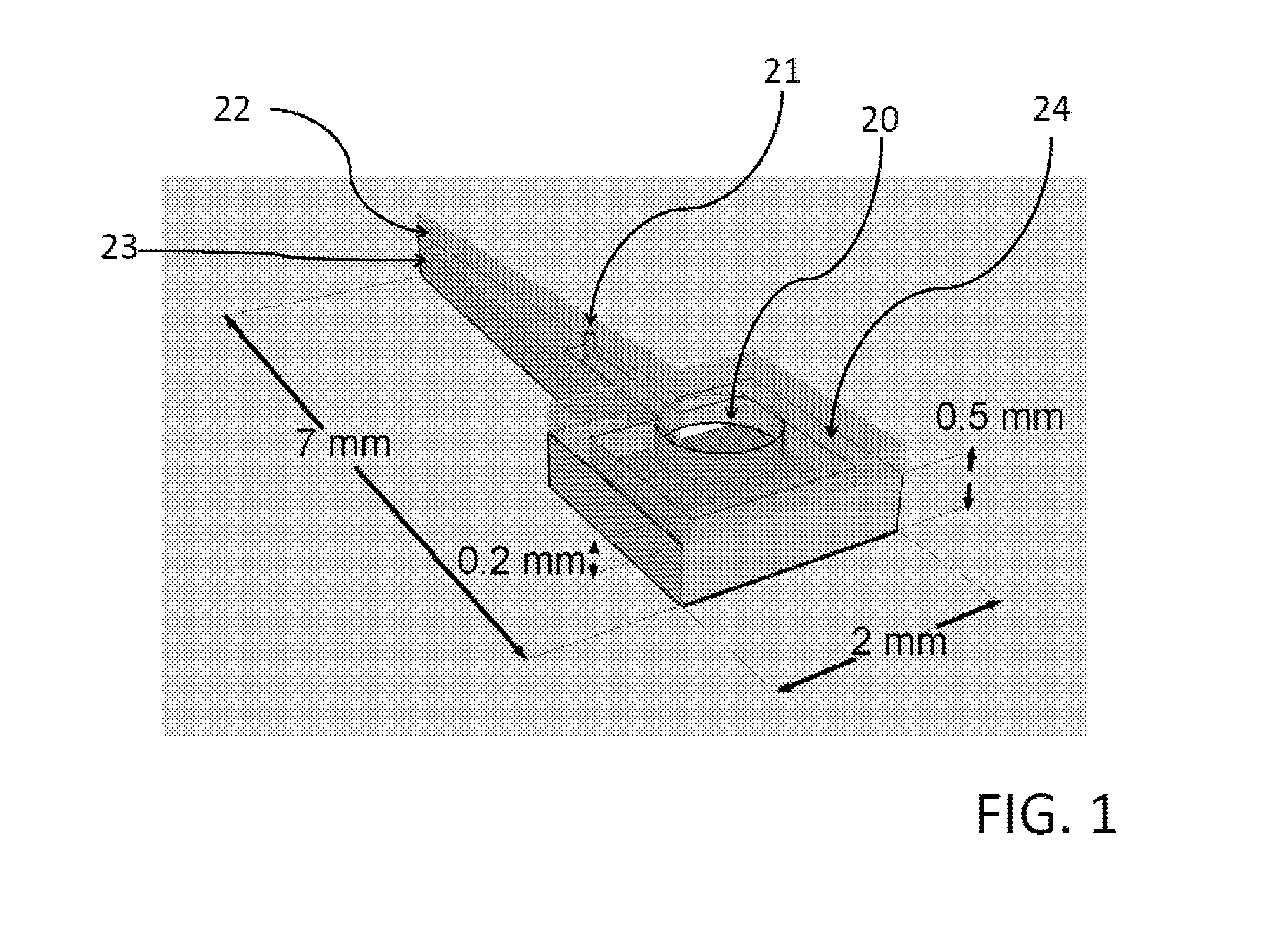
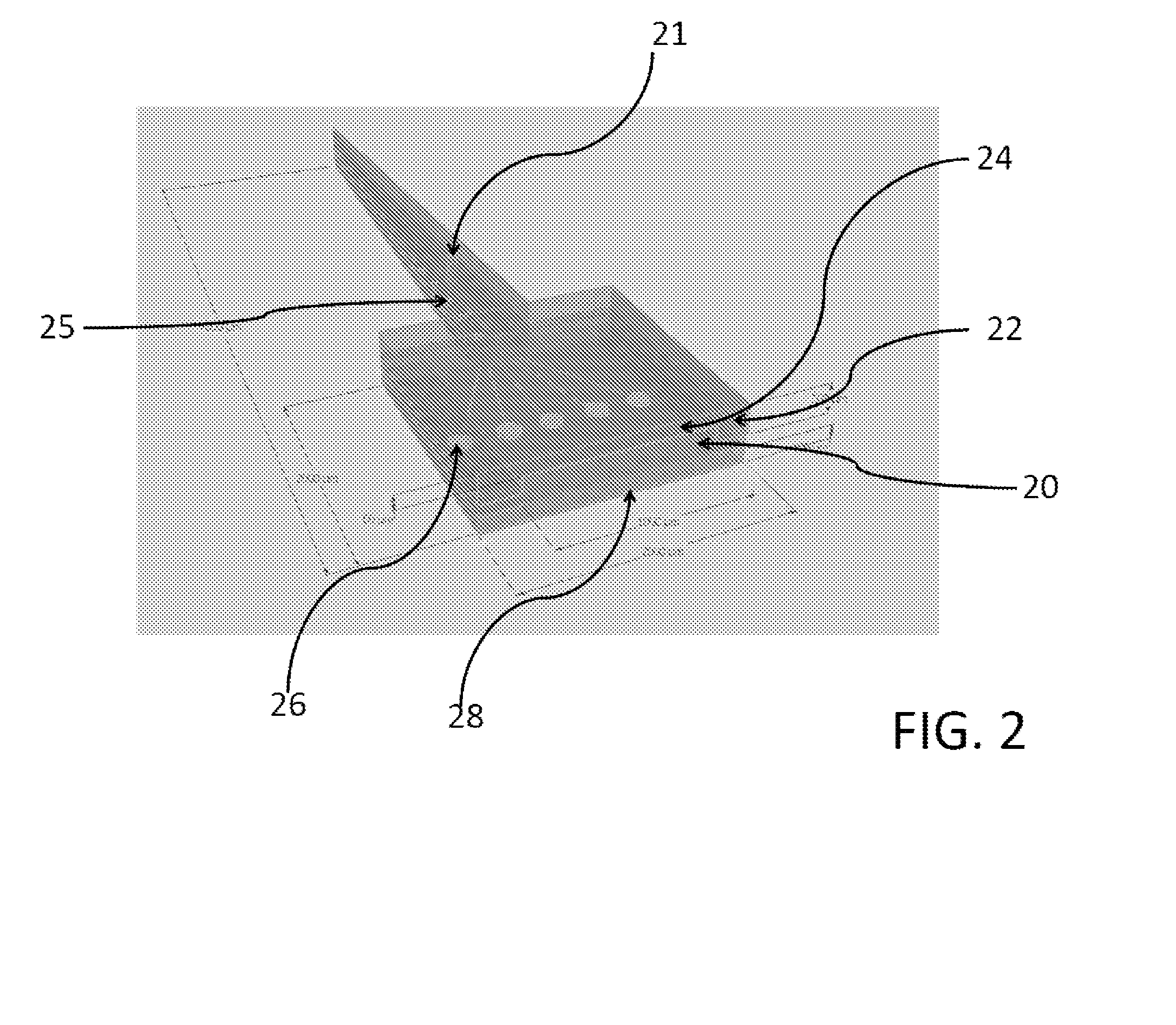
Existing epiretinal implants for the blind are designed to electrically stimulate large groups of surviving retinal neurons using a small number of electrodes with diameters of several hundred μm. To increase the spatial resolution of artificial sight, electrodes much smaller than those currently in use are desirable. In this study we stimulated and recorded ganglion cells in isolated pieces of rat, guinea pig, and monkey retina. We utilized micro-fabricated hexagonal arrays of 61 platinum disk electrodes with diameters between 6 and 25 μm, spaced 60 μm apart. Charge-balanced current pulses evoked one or two spikes at latencies as short as 0.2 ms, and typically only one or a few recorded ganglion cells were stimulated. Application of several synaptic blockers did not abolish the evoked responses, implying direct activation of ganglion cells. Threshold charge densities were typically below 0.1 mC / cm2 for a pulse duration of 100 μs, corresponding to charge thresholds of less than 100 pC. Stimulation remained effective after several hours and at high frequencies. To demonstrate that closely spaced electrodes can elicit independent ganglion cell responses, we utilized the multi-electrode array to stimulate several nearby ganglion cells simultaneously. From these data we conclude that electrical stimulation of mammalian retina with small-diameter electrode arrays is achievable and can provide high temporal and spatial precision at low charge densities. We review previous epiretinal stimulation studies and discuss our results in the context of 32 other publications, comparing threshold parameters and safety limits.
Owner:SALK INST FOR BIOLOGICAL STUDIES +1
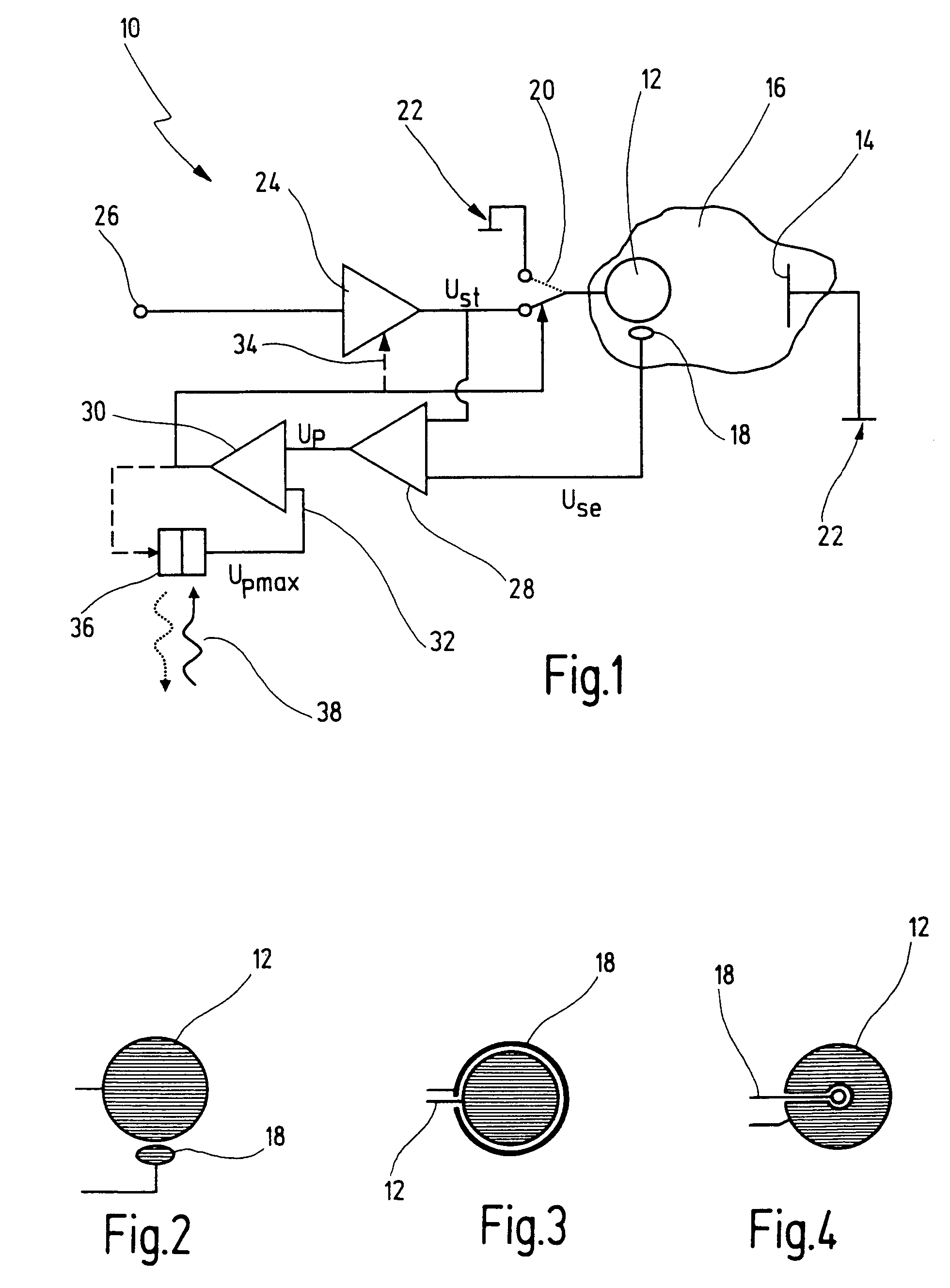
Electrode arrangement for electrical stimulation of biological material, and a multi-electrode array for use in such an electrode arrangement
InactiveUS20040267344A1Without further computational stepSimple methodHead electrodesDiagnostic recording/measuringElectricityMultielectrode array
An electrode arrangement for electrical stimulation of biological material has at least one stimulation electrode via which the biological material can be fed a stimulus signal. Furthermore, a counter electrode is present which forms a counter pole to the stimulation electrode, one sensor electrode is provided with the aid of which it is possible to determine a polarization voltage across the stimulation electrode.
Owner:RETINA IMPLANT GMBH
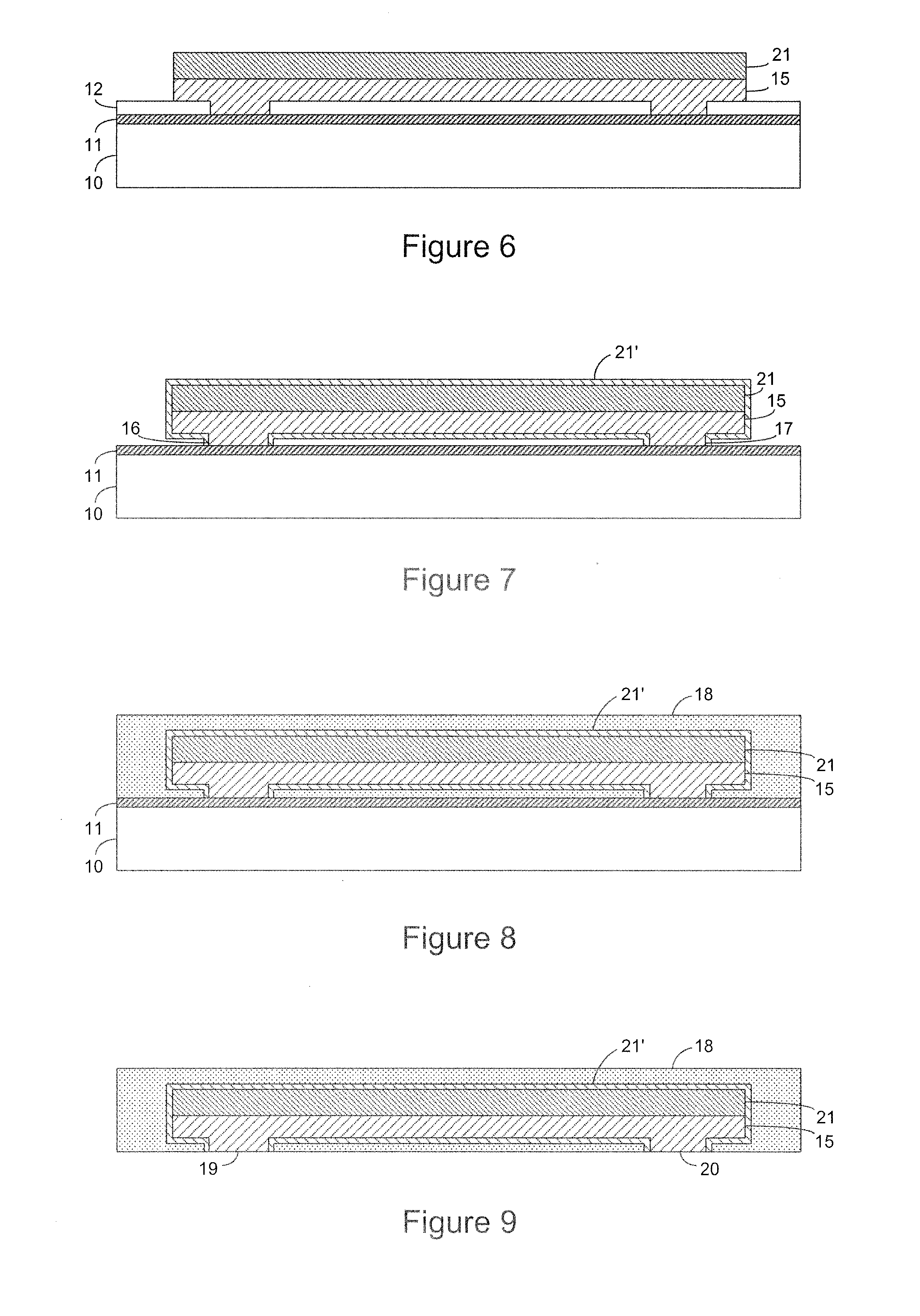
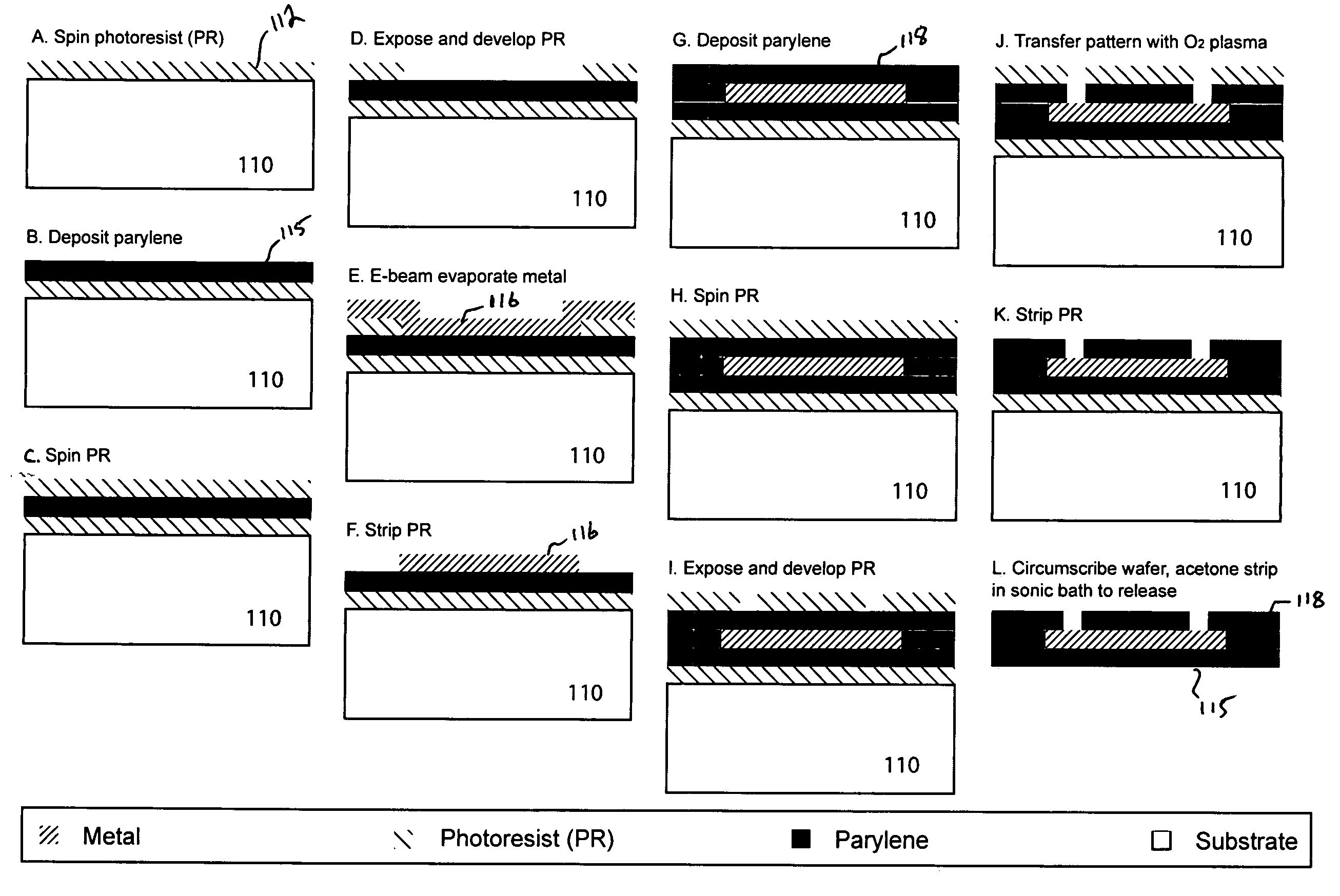
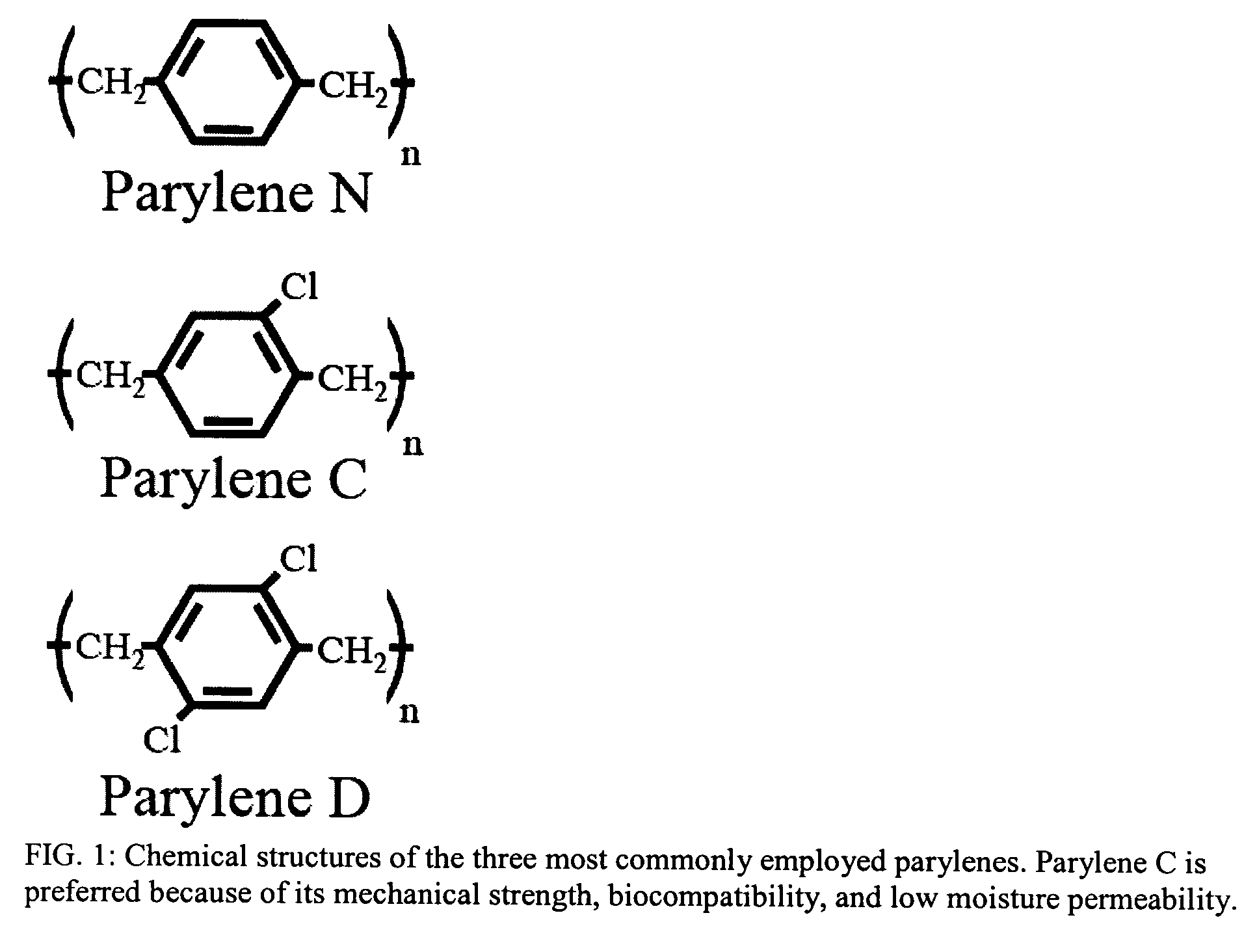
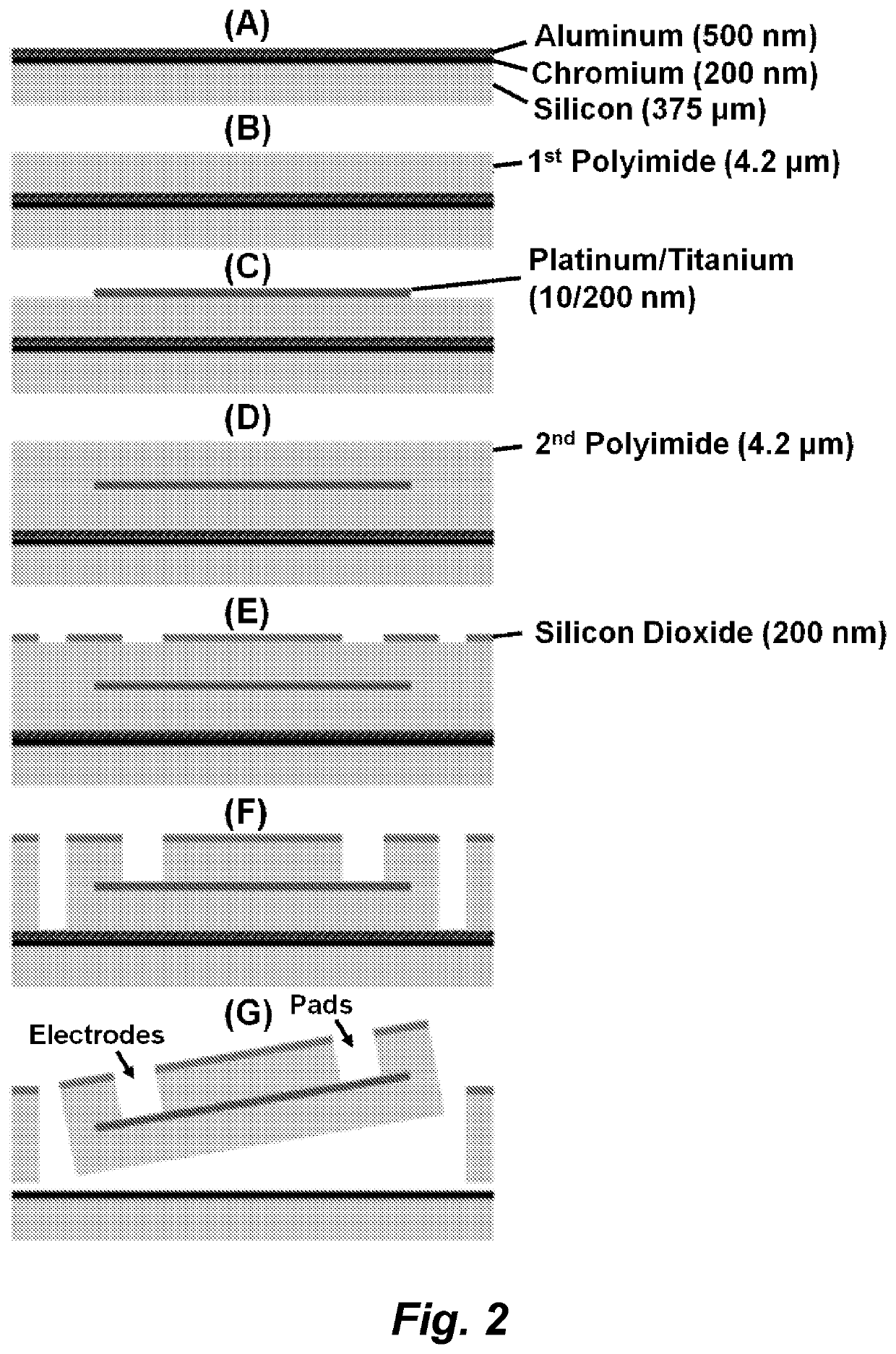
Parylene-based flexible multi-electrode arrays for neuronal stimulation and recording and methods for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS7326649B2Environment can be compatibleSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesNeuronal stimulationParylene
Method for manufacturing a parylene-based electrode array that includes an underlying parylene layer, one or more patterned electrode layers comprising a conductive material such as a metal, and one or more overlying parylene layers. The overlying parylene is etched away or otherwise processed to expose the electrodes where stimulation or recording is to occur. All other conductive material in the device is occluded from the environment by the two layers of parylene surrounding it.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA +1
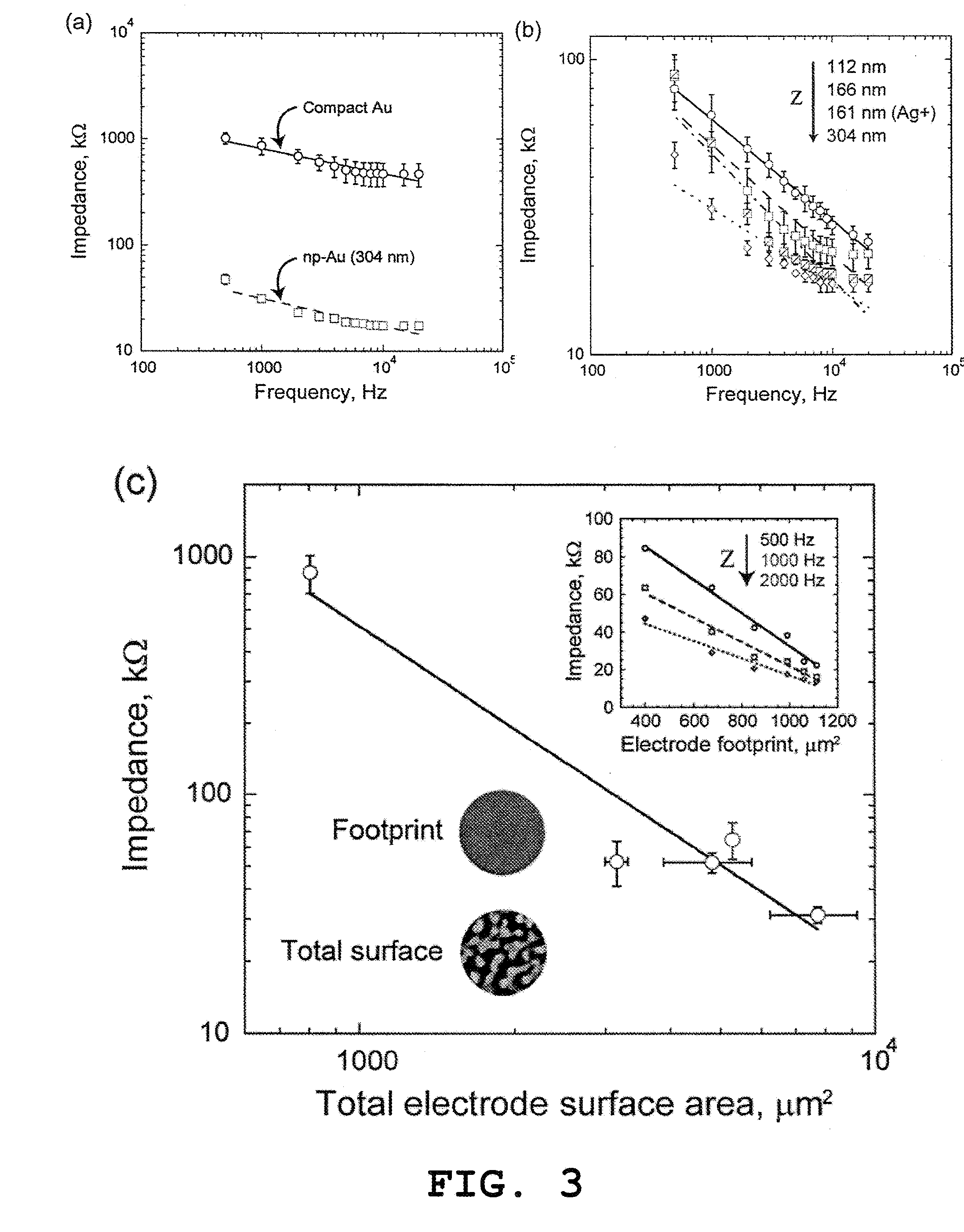
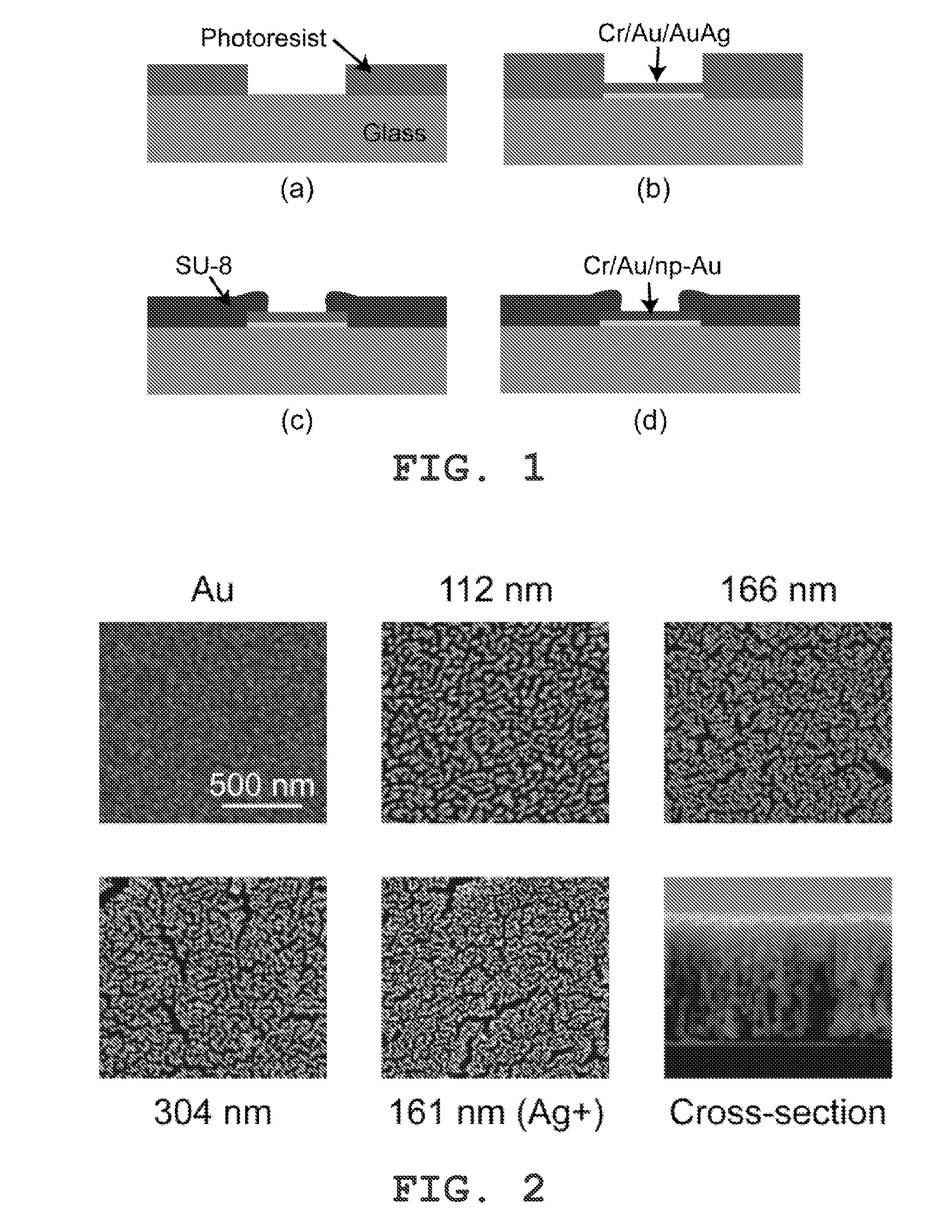
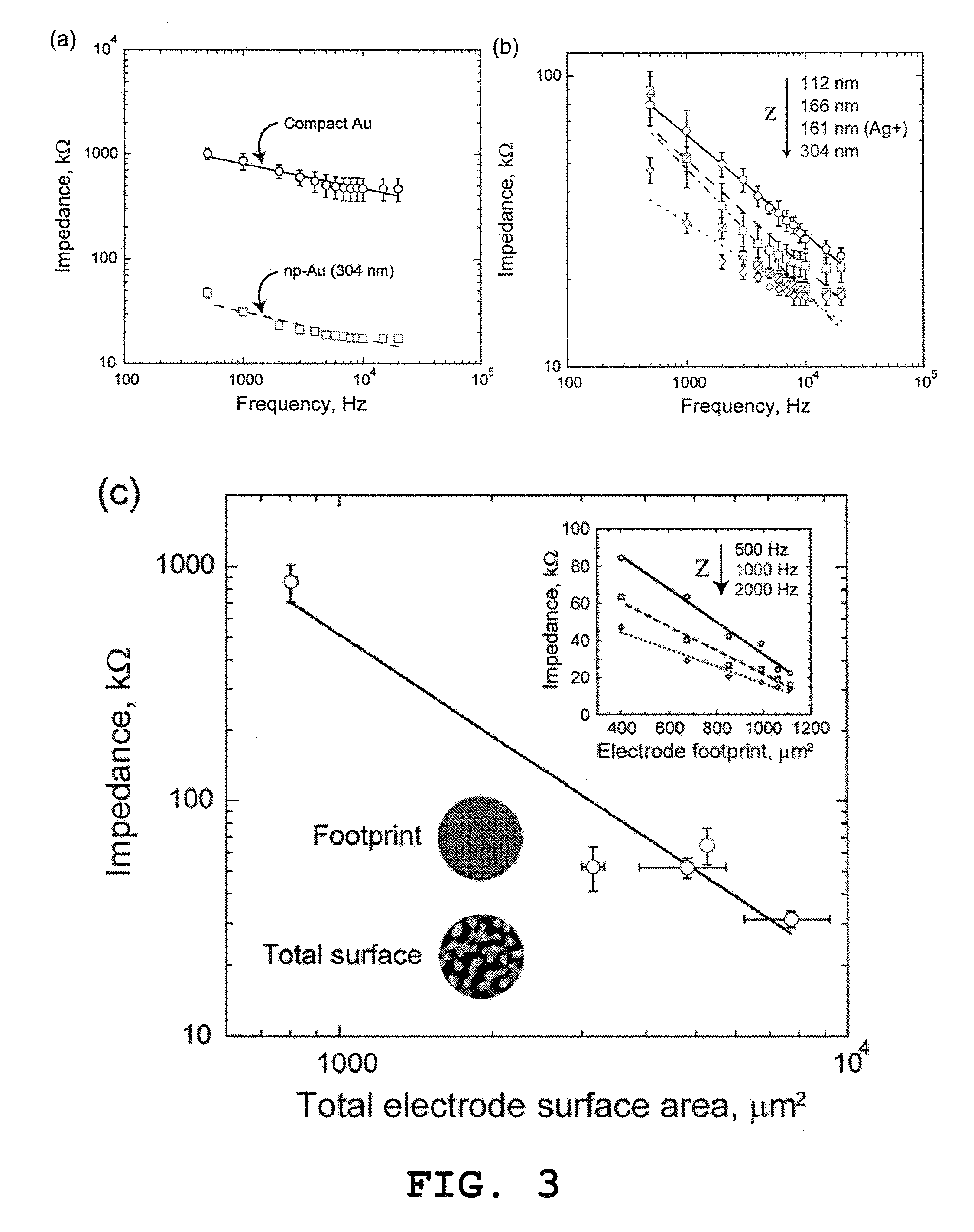
Nanoporous Metal Multiple Electrode Array and Method of Making Same
ActiveUS20130245416A1Improvement in electrode-electrolyte impedanceBetter signal to noise ratioElectromyographyInsulated cablesResistMetal alloy
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Nerve monitoring device
InactiveUS20100063376A1Rotational errorAccurate monitoringSensorsNeuroelectric signal measurementRotational errorMultielectrode array
The present invention provides a nerve monitoring device. The device includes a cannula, a sensor for monitoring the nerve and an alignment device. The cannula can be any surgical cannula, and is preferably an endotracheal tube. The sensor can be an electrode or other sensor that is capable of sensing nerve activity. The alignment device is a device that ensures that after insertion of the nerve sensor into a patient, the sensors are aligned to properly monitor the target nerve or muscle. The internal alignment device may communicate externally to surgeon by using electromagnetic energy as either a transmittor or a receiver. The mismatch of triangular laryngeal anatomy to circular cannula anatomy can be compensated for by a) altering the geometry (external shape) of the cannula and b) using soft, felt-like expandable electrodes. Rotational error can be compensated for by using a multi-electrode array wherein the optimized recording montage can be simply selected on the external recording device.
Owner:THE MAGSTIM
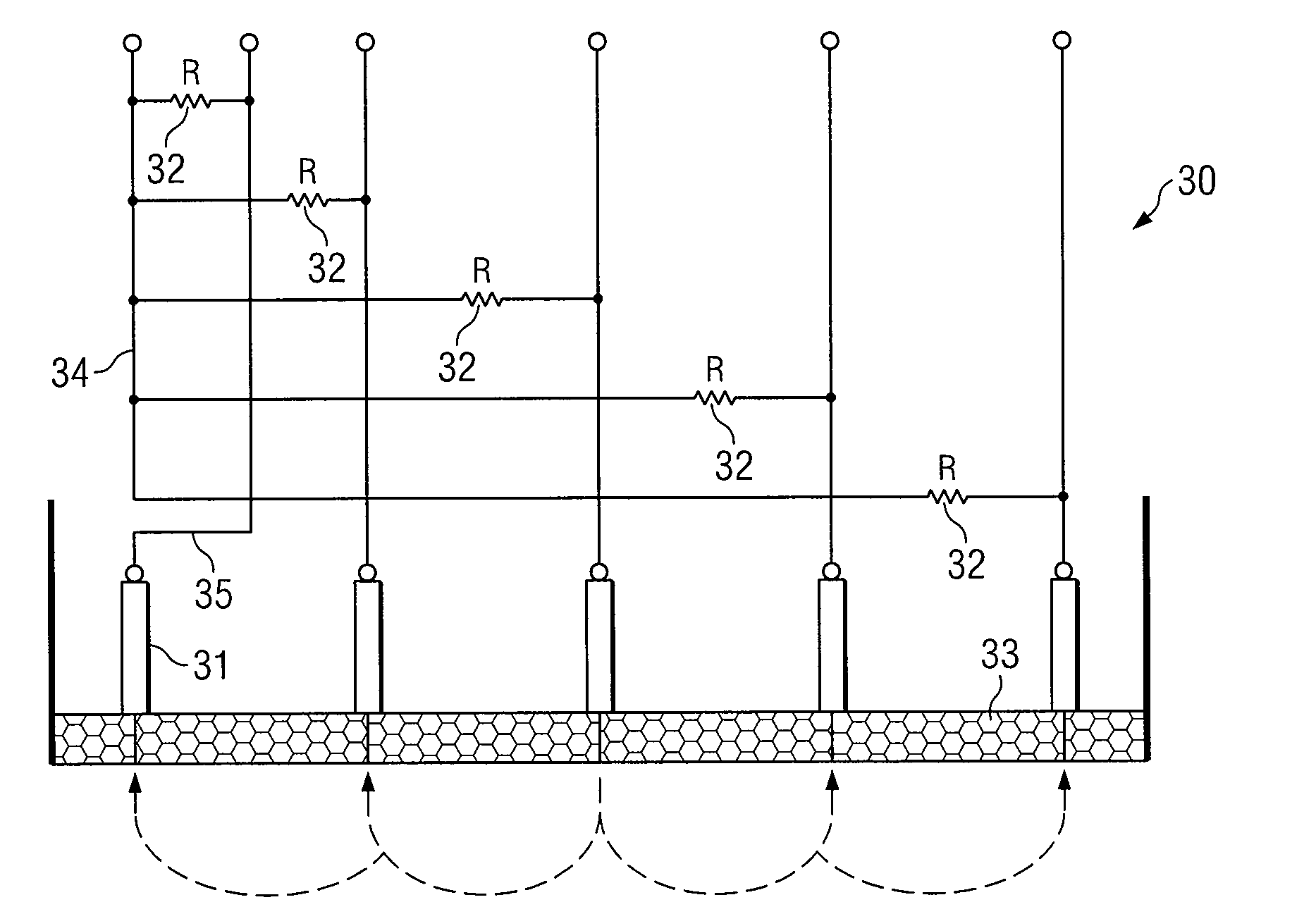
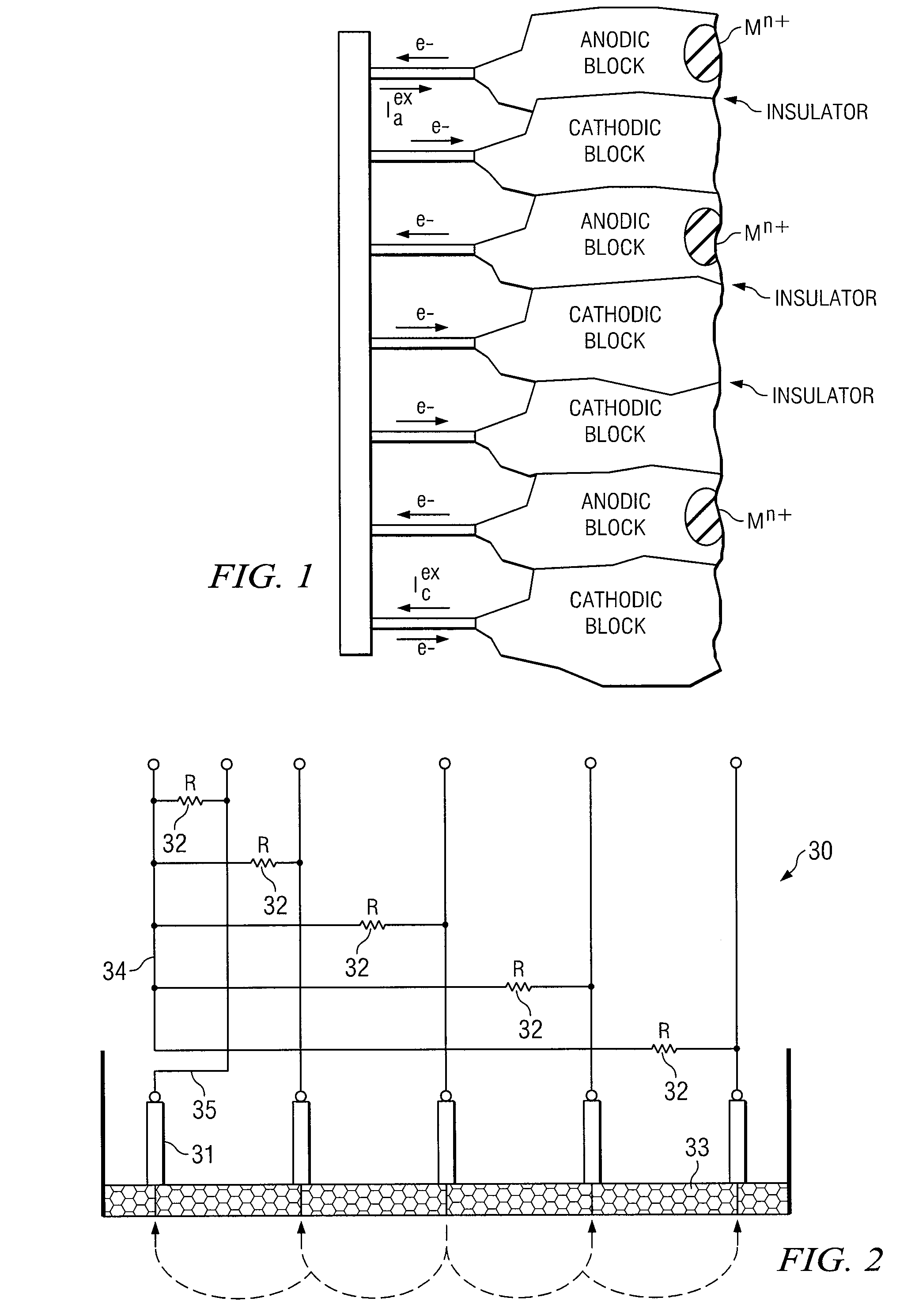
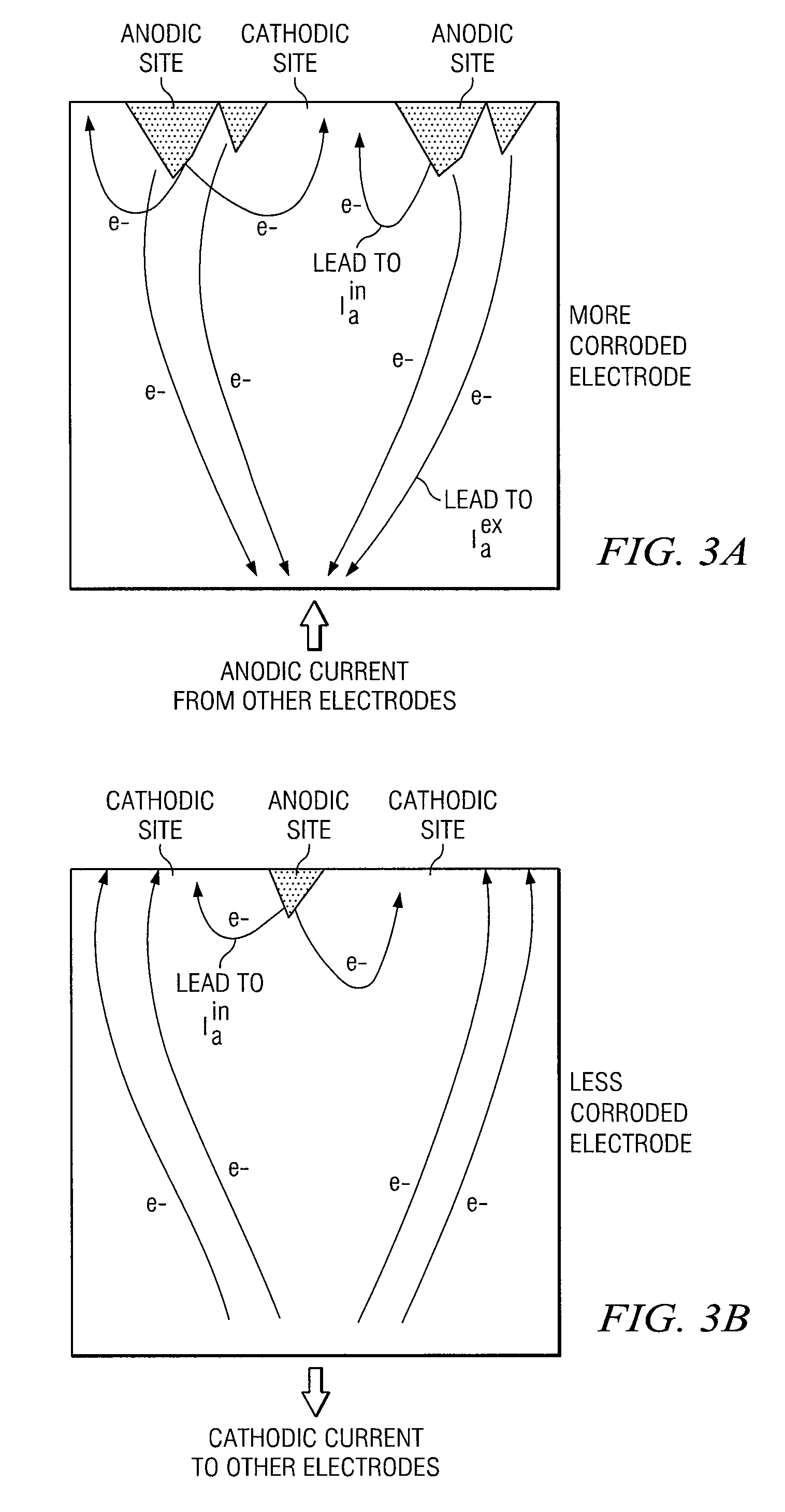
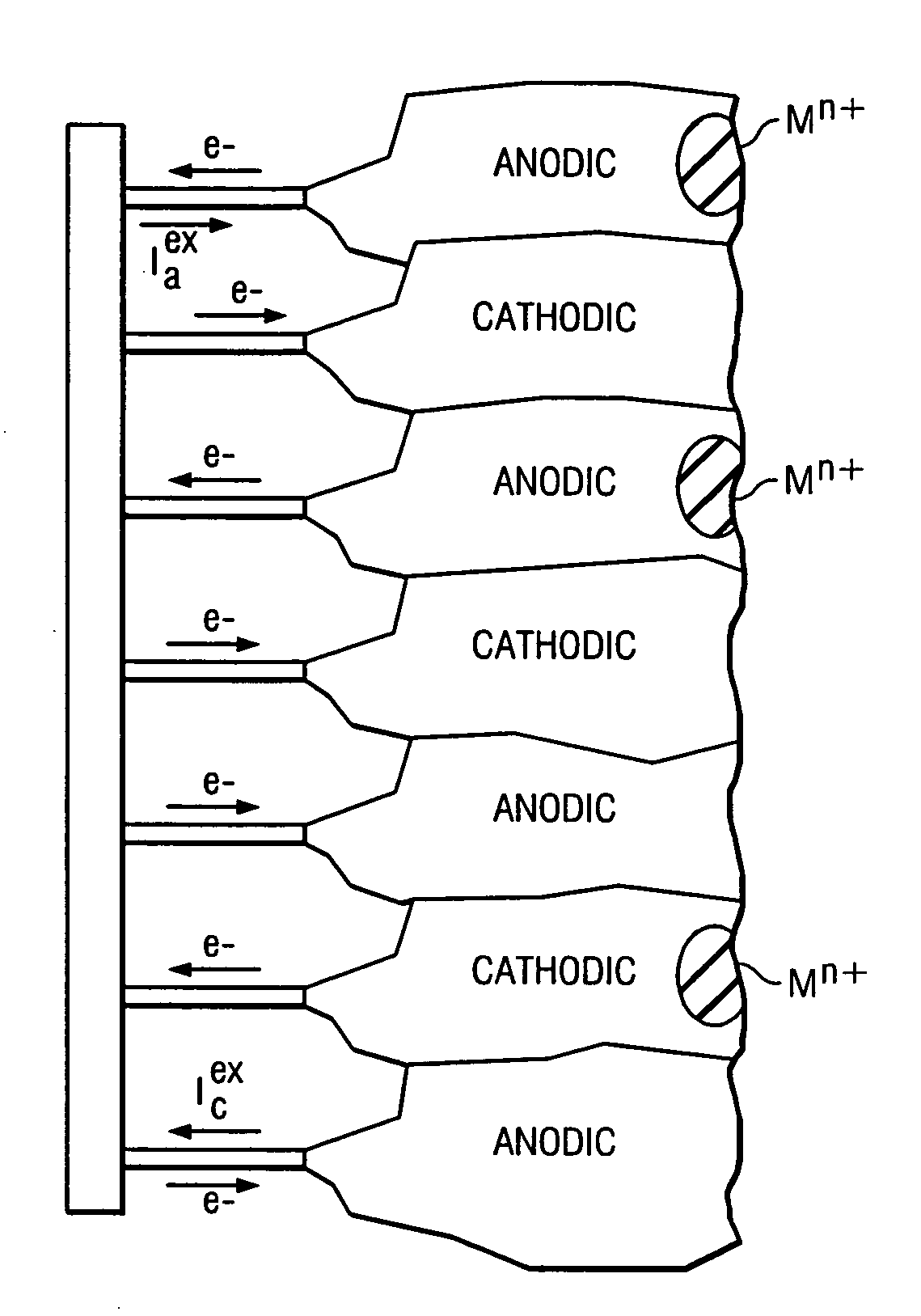
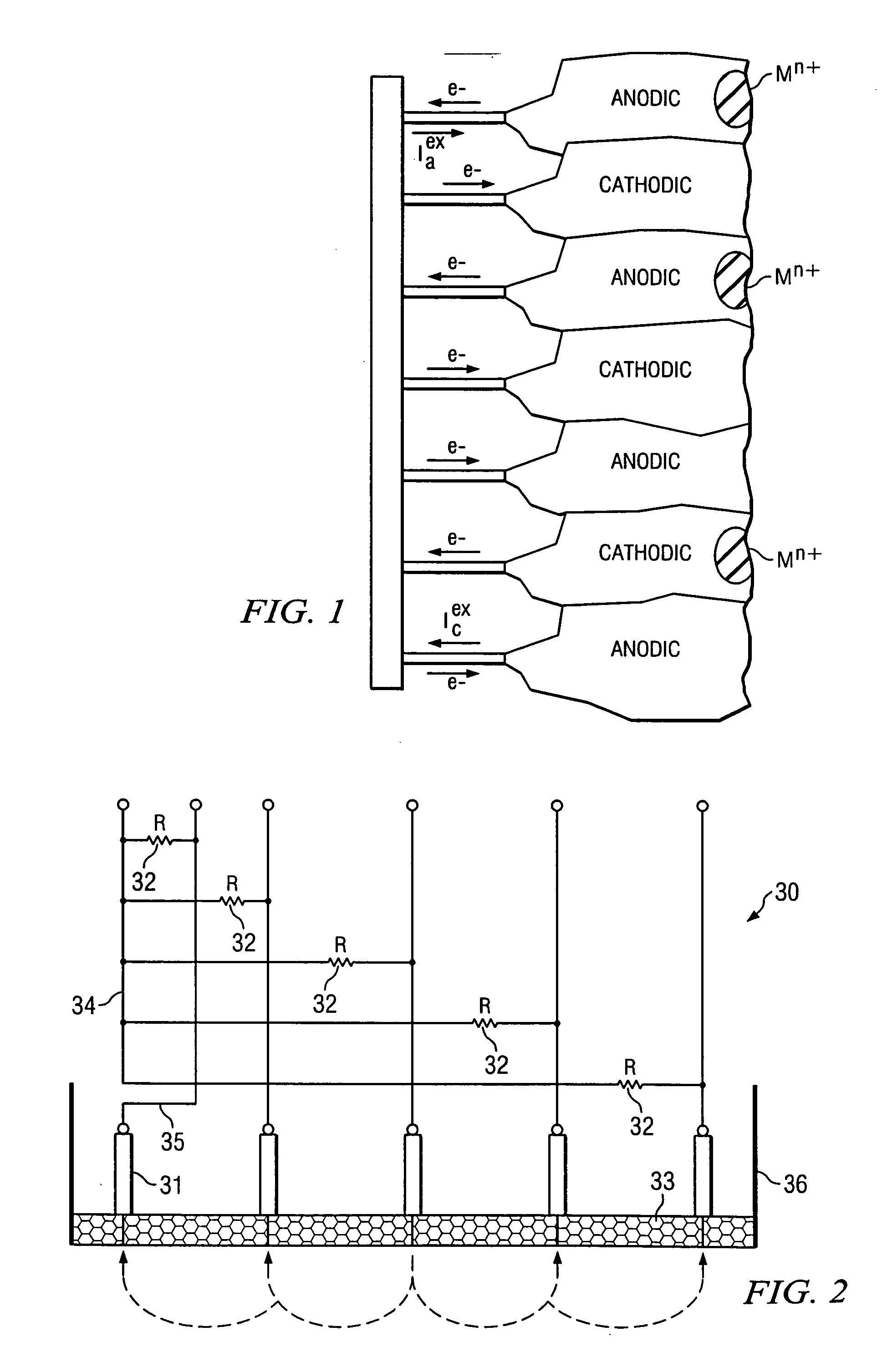
Method for measuring localized corrosion rate with a multi-electrode array sensor
ActiveUS7309414B2Weather/light/corrosion resistanceResistance/reactance/impedenceMultielectrode arrayElectrode array
A method of measuring localized corrosion, using a multi-electrode array sensor. The method eliminates the effect of internal current in corroded electrodes, and thus provides a more accurate corrosion measurement. In one embodiment, the potential of a common node of the sensor is adjusted so that the sensor's most cathodic current is close to zero.
Owner:SOUTHWEST RES INST
Electrode arrangement for electrical stimulation of biological material, and a multi-electrode array for use in such an electrode arrangement
InactiveUS7272447B2Reliable suppressionHead electrodesDiagnostic recording/measuringElectricityMultielectrode array
Owner:RETINA IMPLANT GMBH
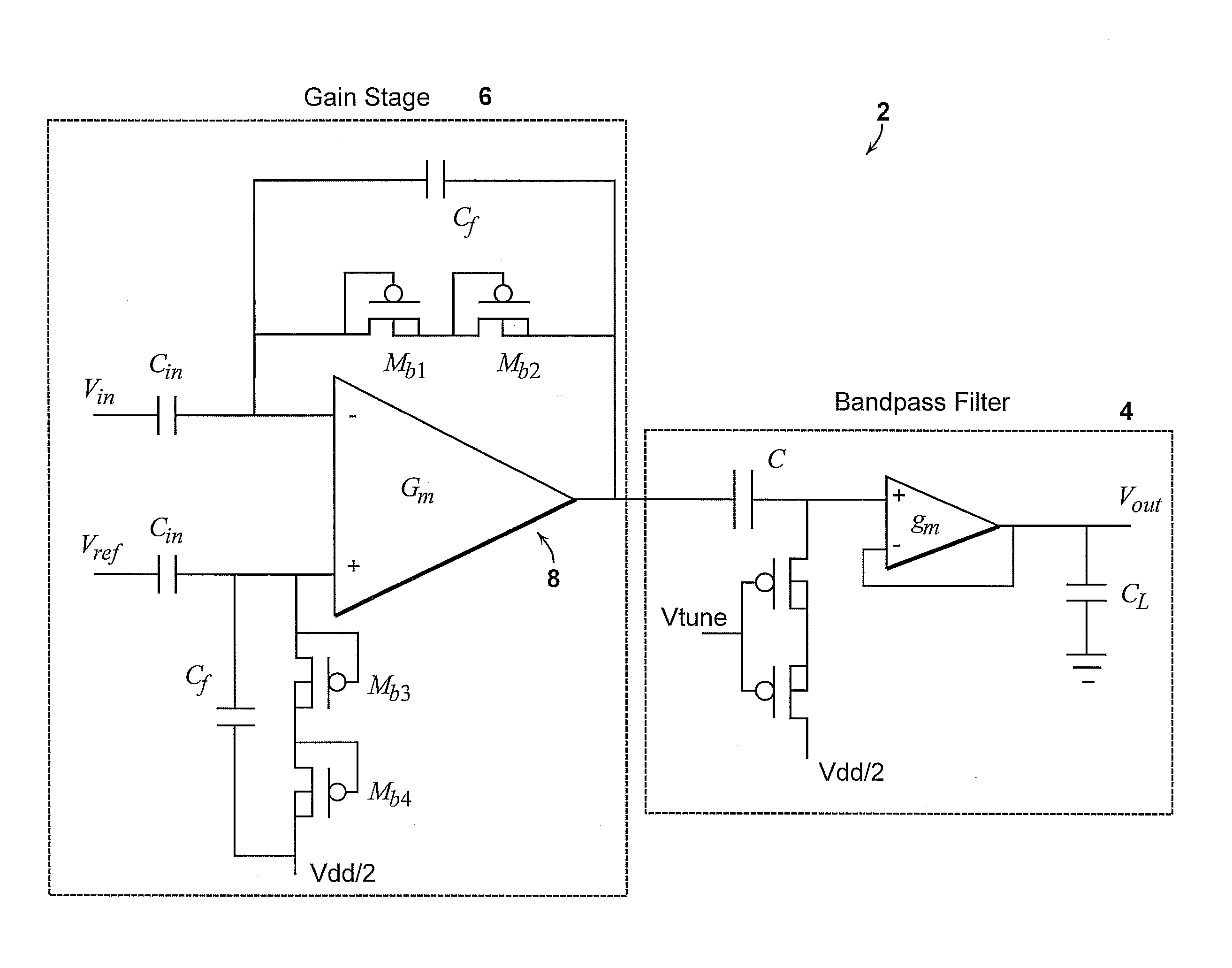
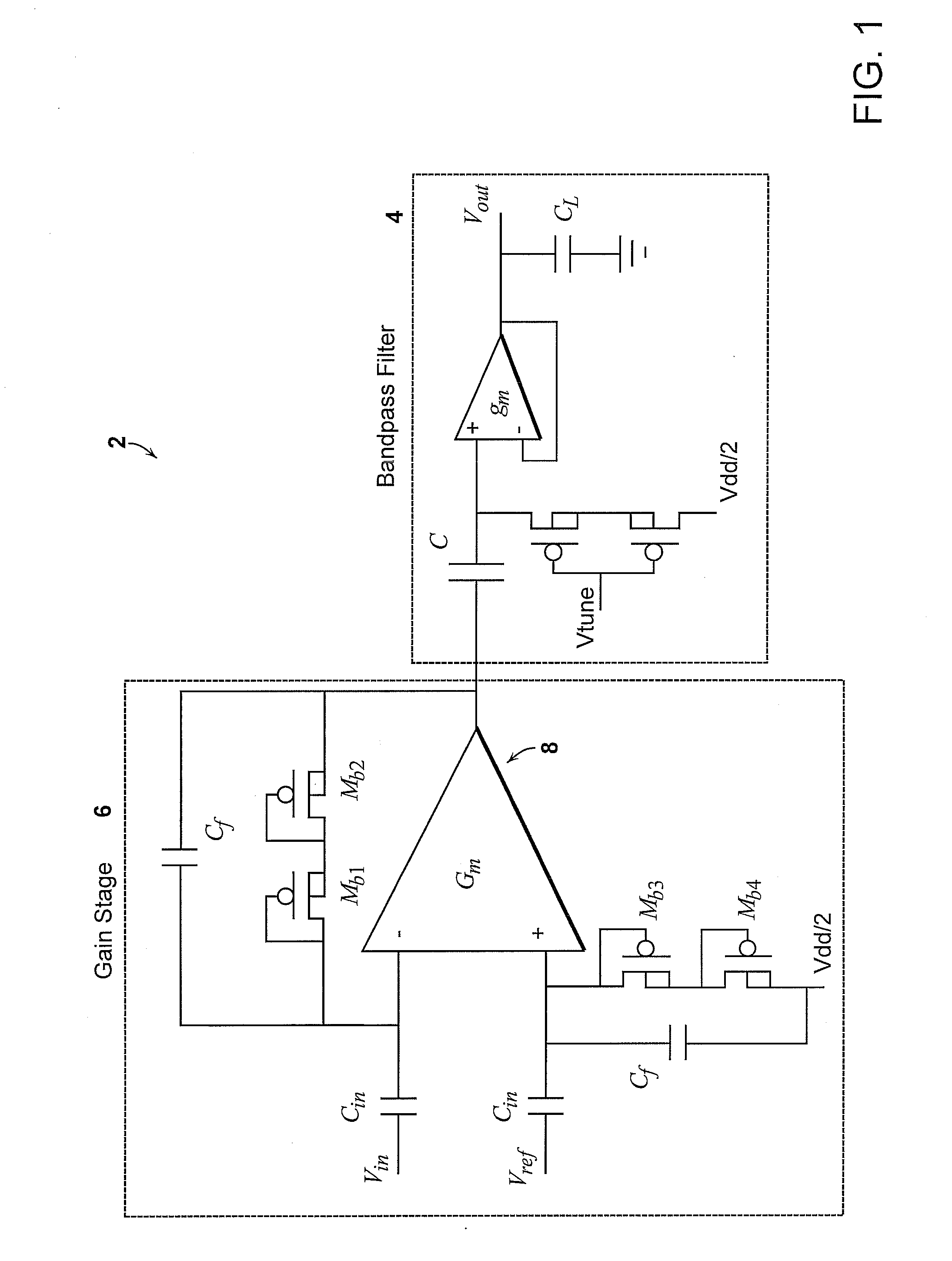
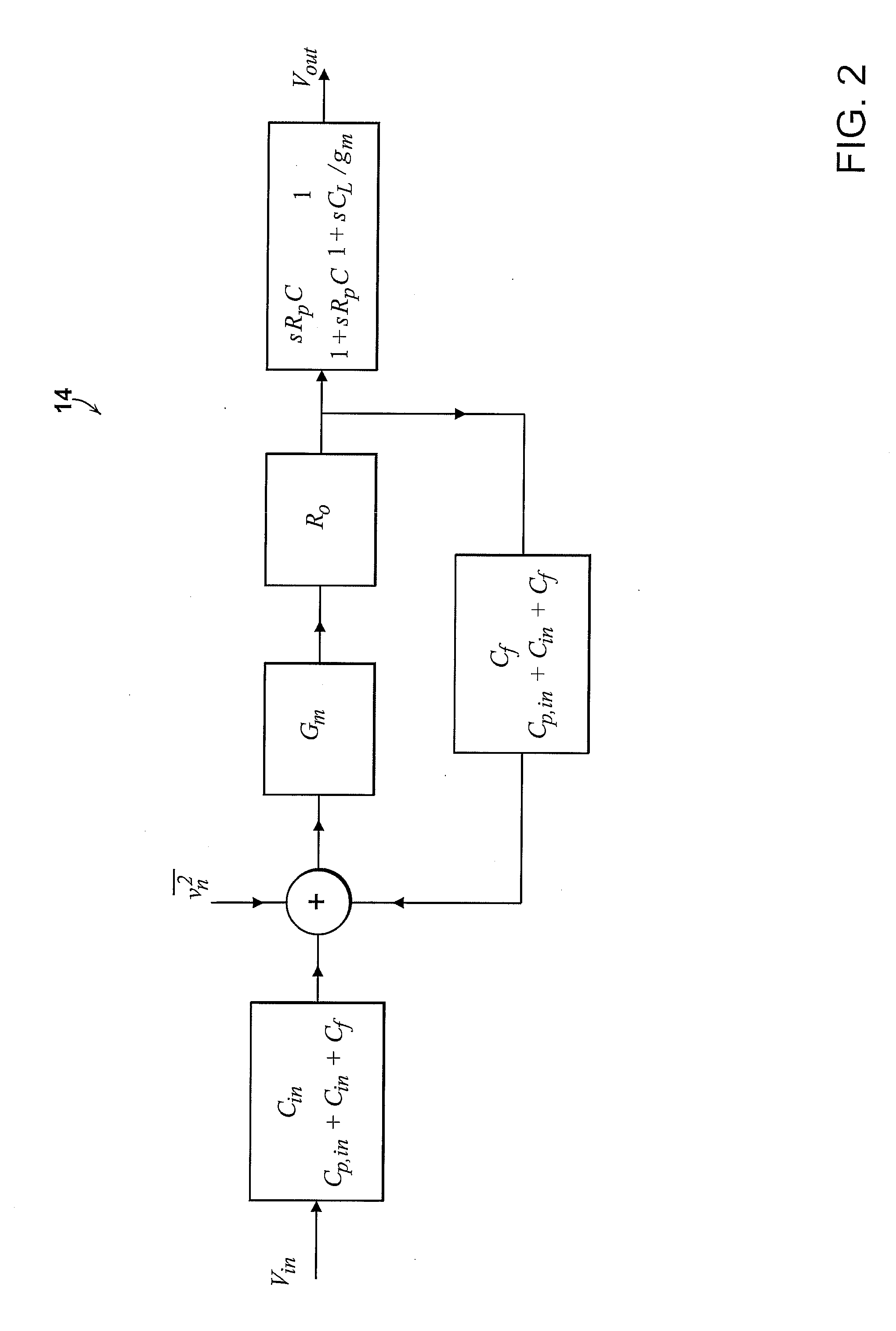
Micropower neural amplifier with adaptive input-referred noise
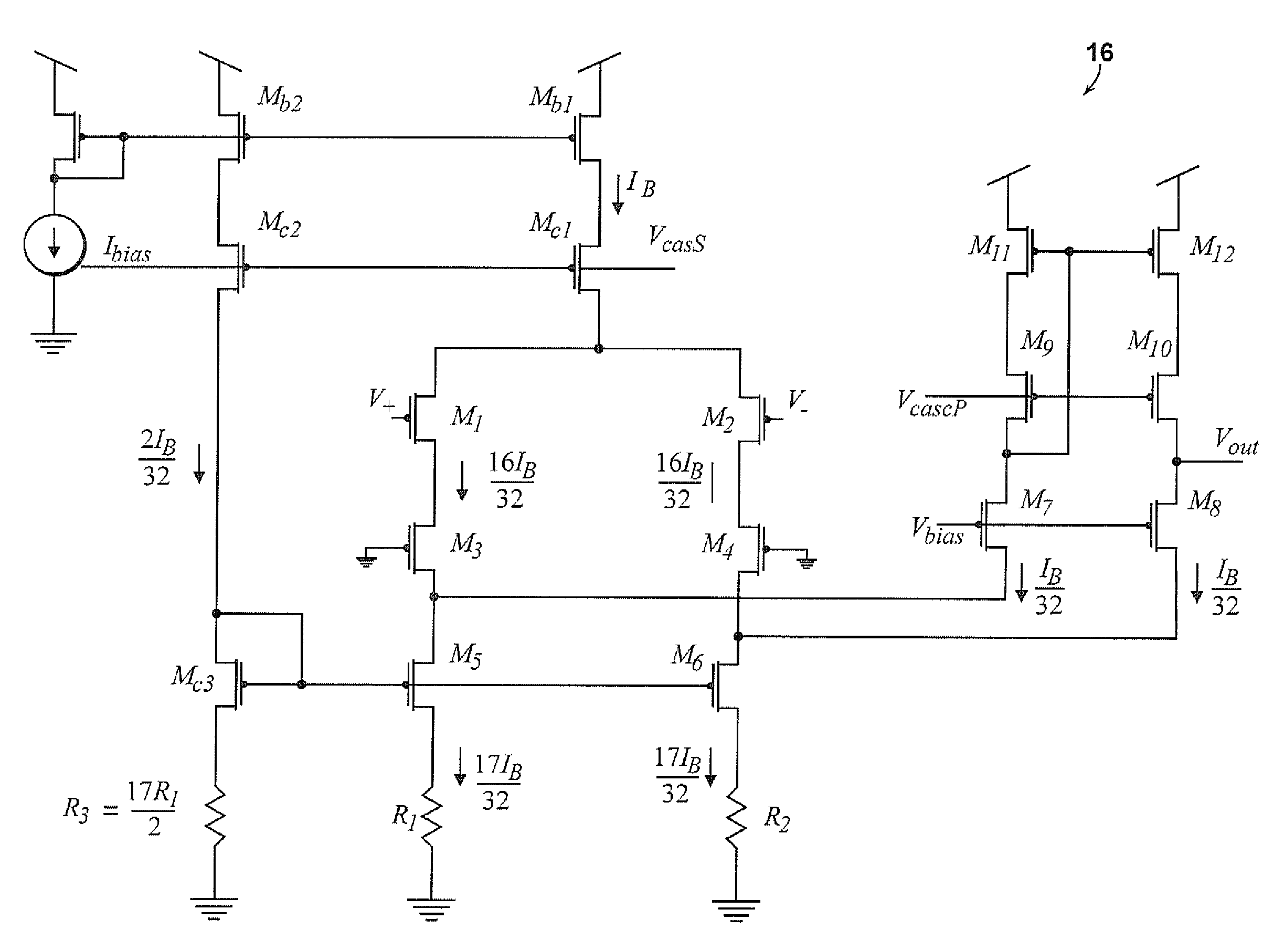
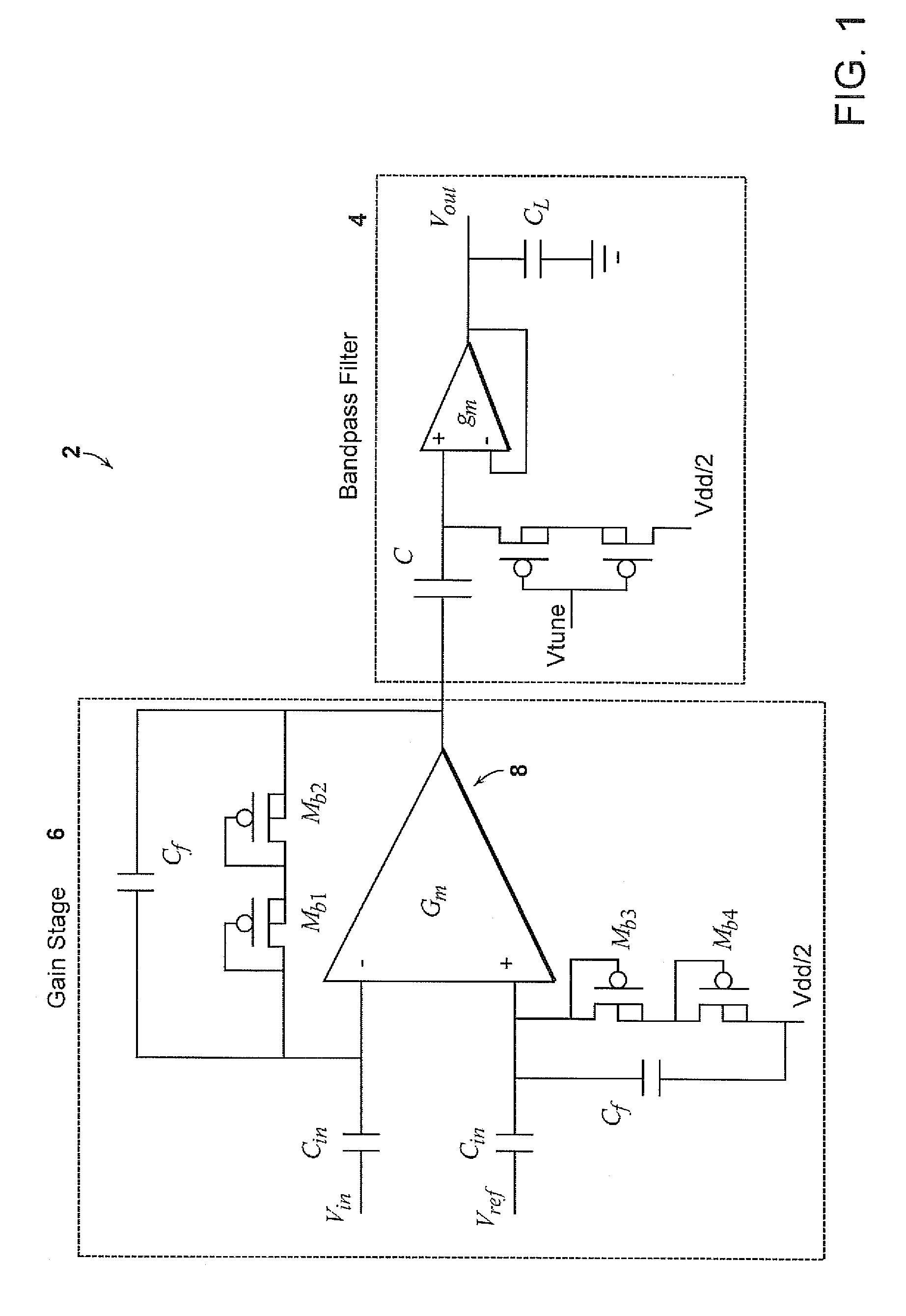
ActiveUS20080290944A1Low noise gainImprove low noiseAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDiagnostic recording/measuringAudio power amplifierMultielectrode array
A micropower neural amplifier with adaptive power biasing for use in multi-electrode arrays is provided. The micropower neural amplifier includes a low noise gain stage. The low noise gain stage is implemented using an amplifier and pseudoresistor elements.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
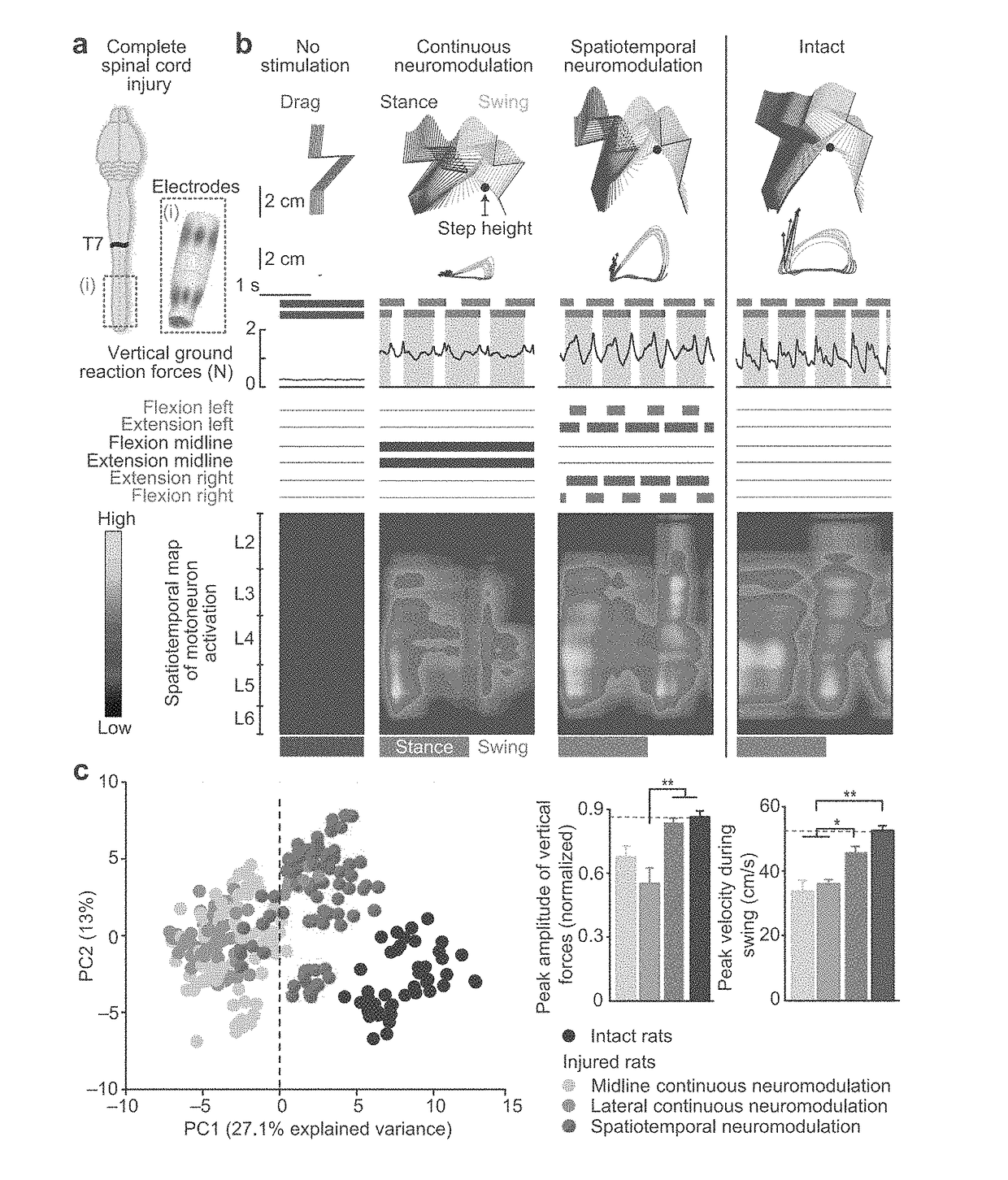
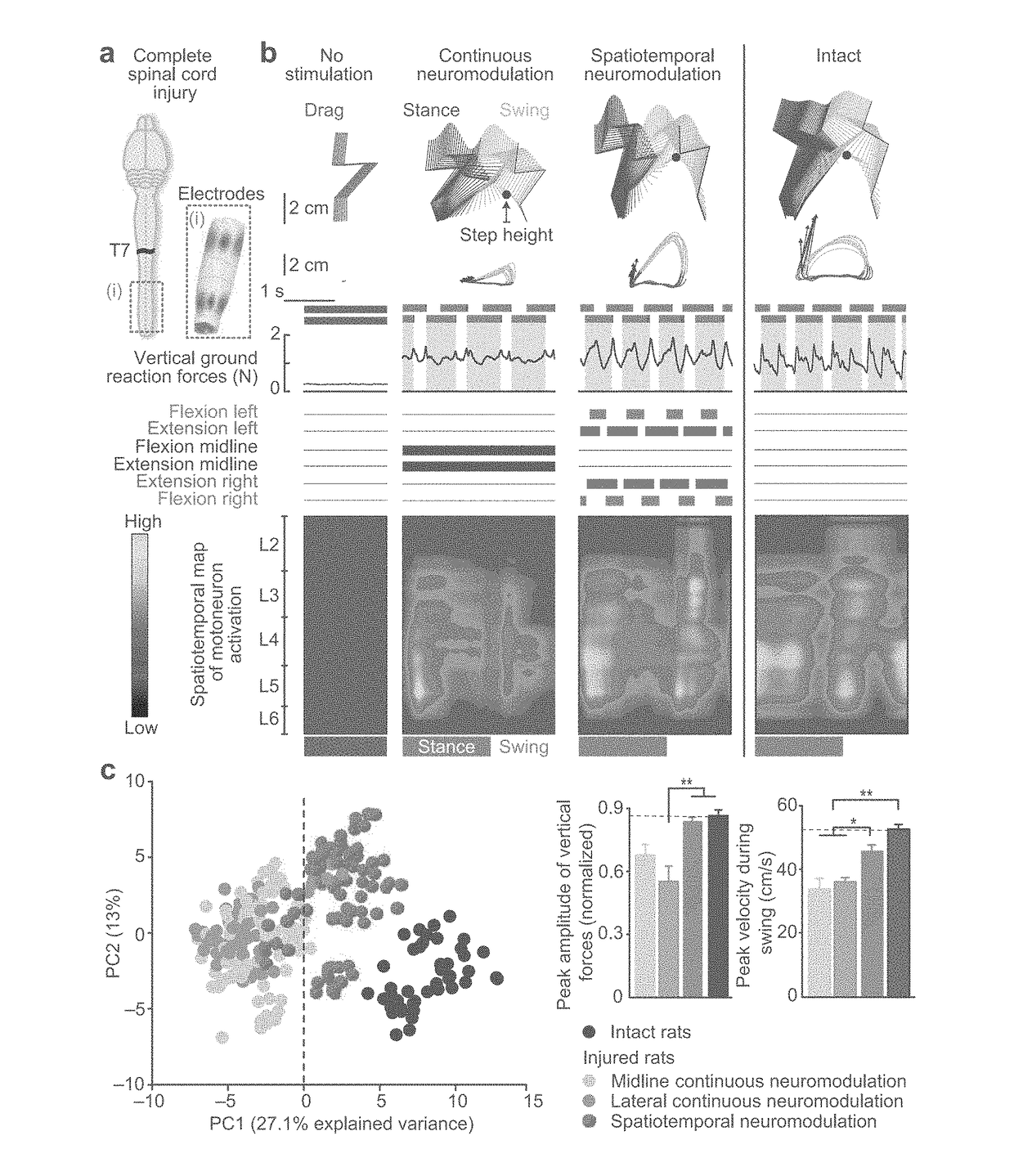
System for selective spatiotemporal stimulation of the spinal cord
ActiveUS20170173326A1Fine control of movementEasy to controlSpinal electrodesElectromyographySpinal columnVoltage pulse
The present disclosure refers to systems for electrical neurostimulation of a spinal cord of a subject in need of nervous system function support. In one example, a system comprises a signal processing device configured to receive signals from the subject and operate signal-processing algorithms to elaborate stimulation parameter settings; one or more multi-electrode arrays suitable to cover a portion of the spinal cord of the subject; and an Implantable Pulse Generator (IPG) configured to receive the stimulation parameter settings from the signal processing device and simultaneously deliver independent current or voltage pulses to the one or more multiple electrode arrays, wherein the independent current or voltage pulses provide multipolar spatiotemporal stimulation of spinal circuits and / or dorsal roots. Such system advantageously enables effective control of nervous system functions in the subject by stimulating the spinal cord, such as the dorsal roots of the spinal cord, with spatiotemporal selectivity.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
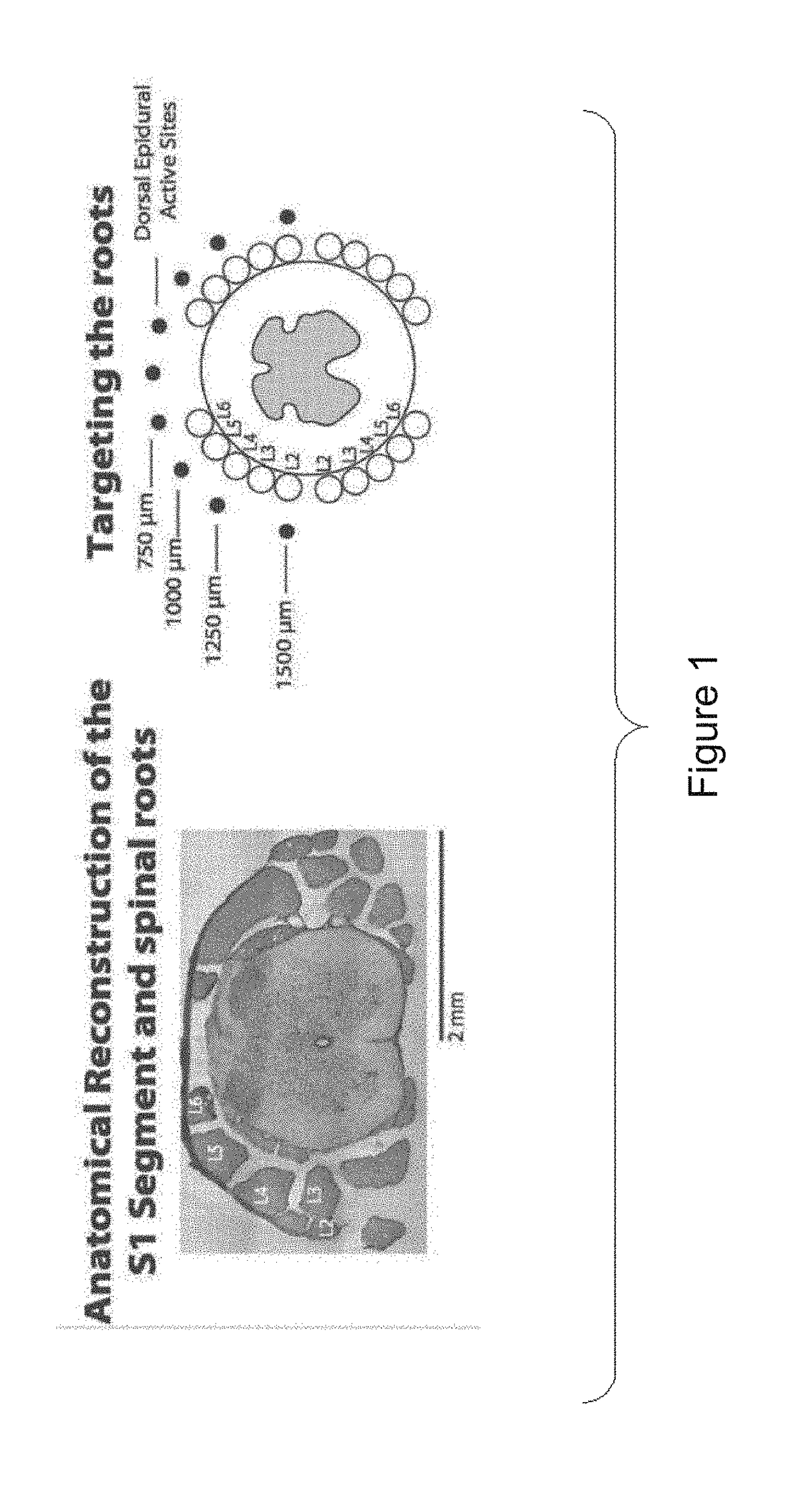
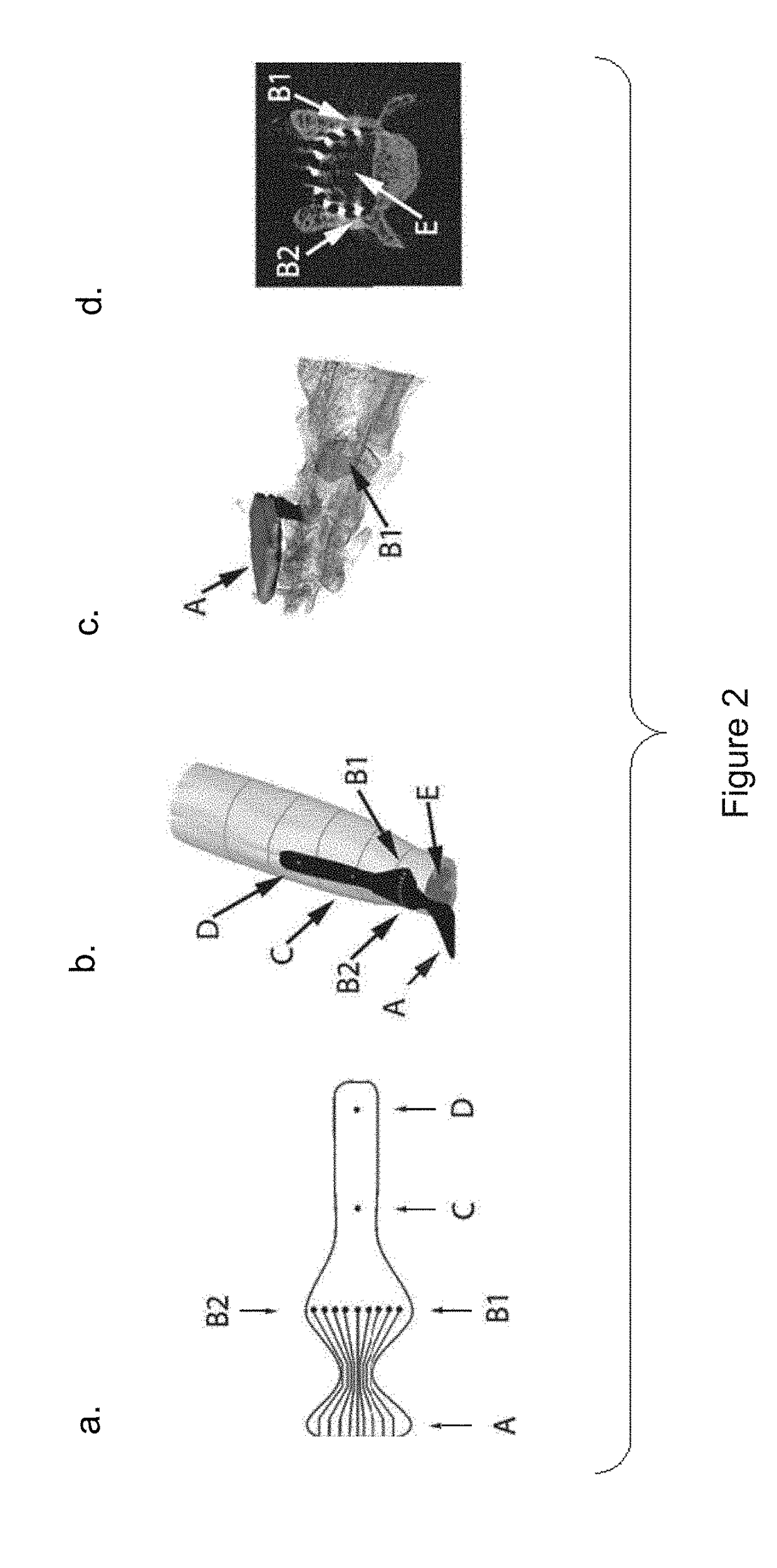
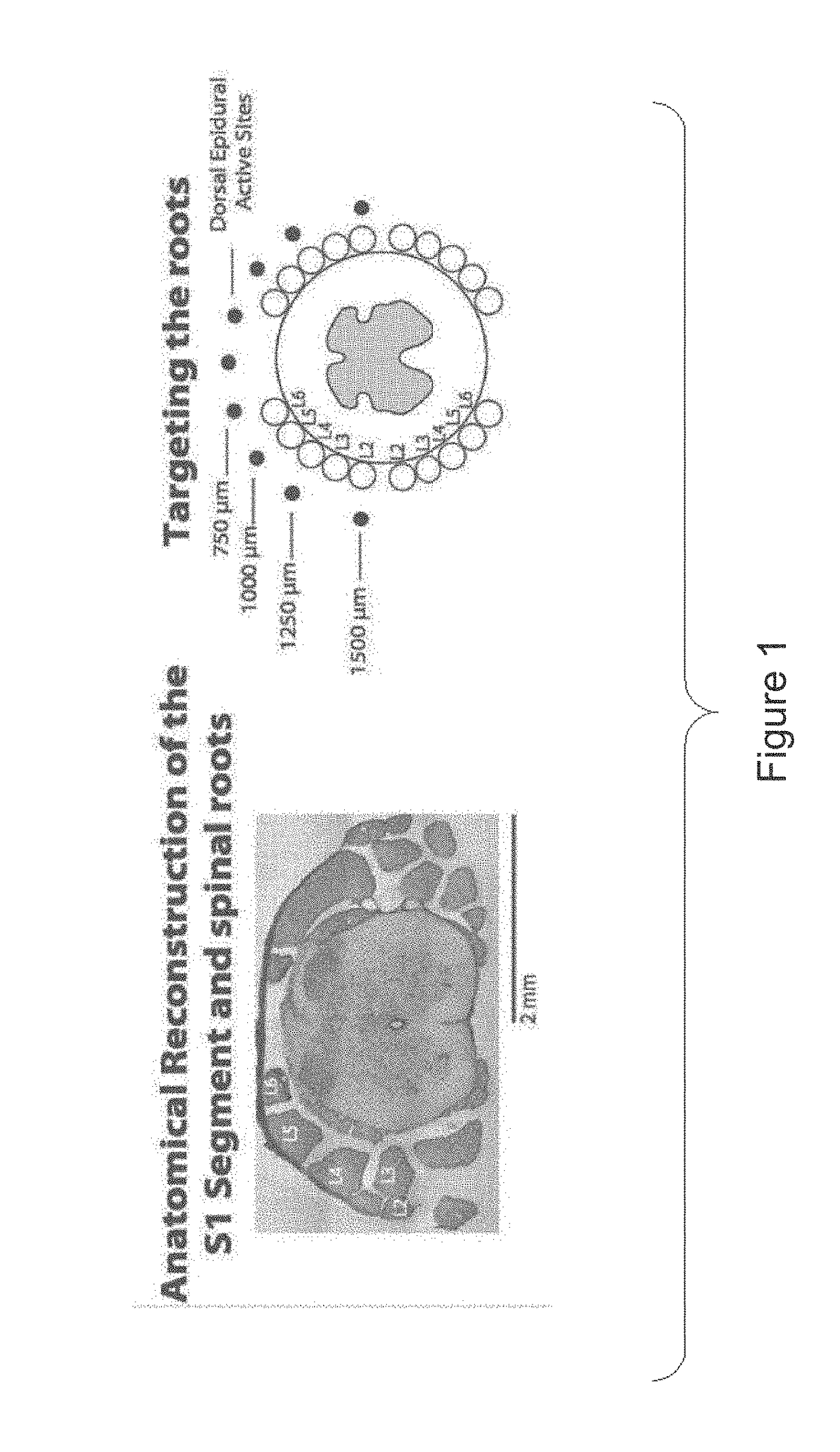
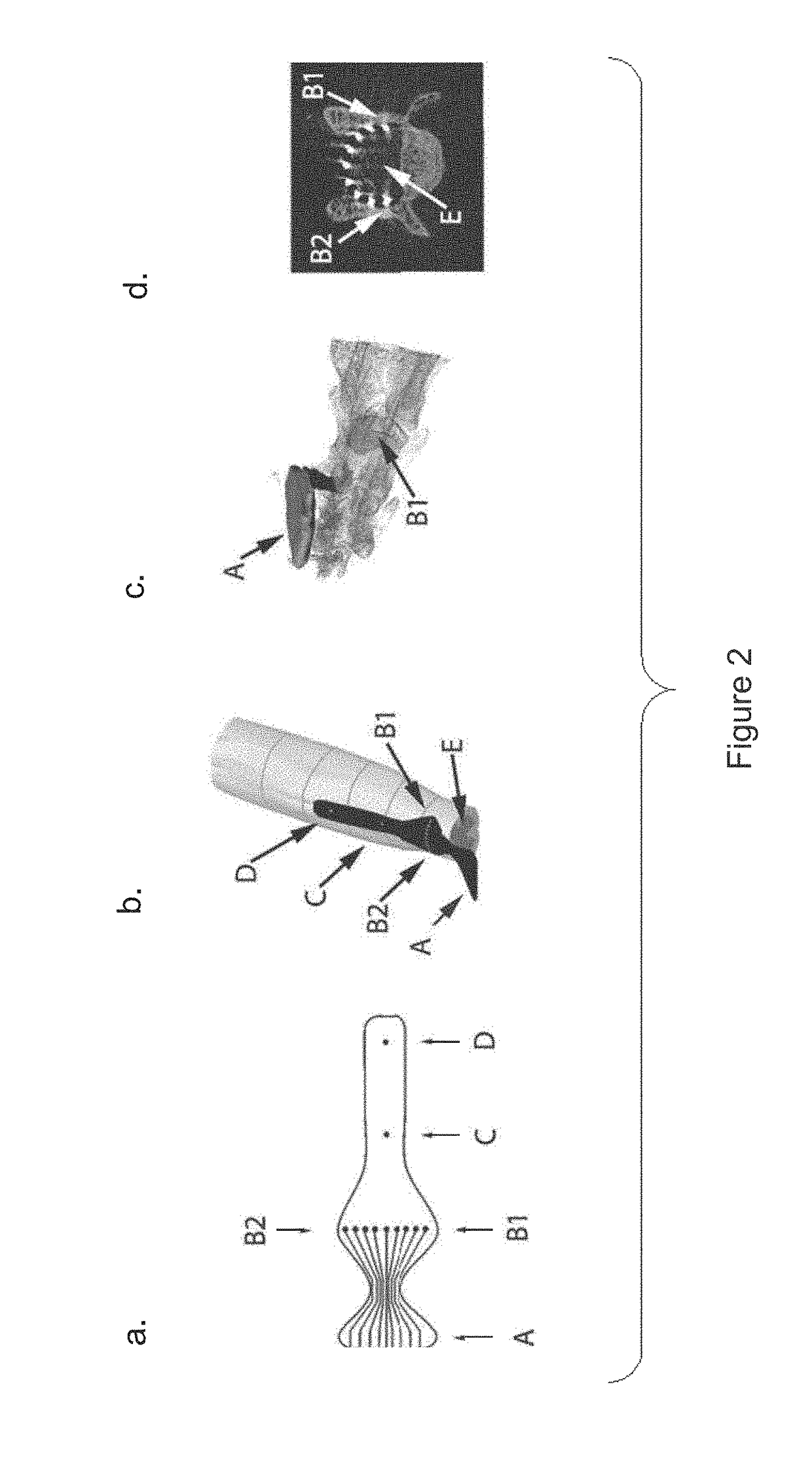
Multi-electrode array for spinal cord epidural stimulation
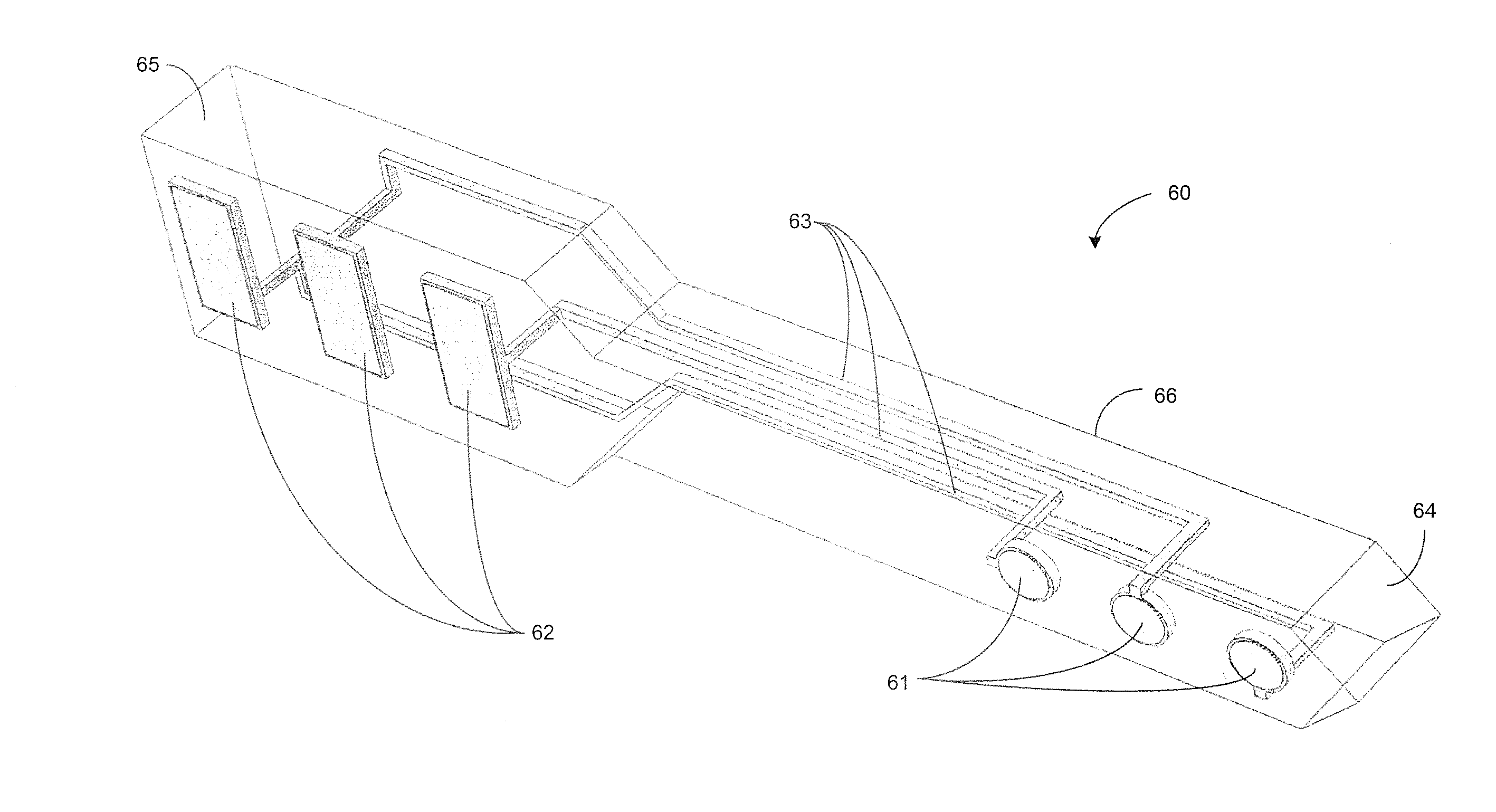
ActiveUS20170246452A1Solve the lack of durabilitySolve the lack of flexibilitySpinal electrodesExternal electrodesPolymer substrateMultielectrode array
In certain embodiments an electrode array for epidural stimulation of the spinal cord is provided where the array comprises a plurality of electrodes disposed on a flexible polymer substrate; said electrodes being electrically connected to one or more lead wires and / or connection points on an electrical connector; where the electrodes of said array are bonded to said polymer so that the electrodes can carry an electrical stimulation signal having a voltage, frequency, and current sufficient to provide epidural stimulation of a spinal cord and / or brain in vivo or in a physiological saline solution, without separation of all or a part of an electrode from the polymer substrate.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Nanoporous metal multiple electrode array and method of making same
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Method for measuring localized corrosion rate with a multi-electrode array sensor
ActiveUS20050274628A1Weather/light/corrosion resistanceResistance/reactance/impedenceMultielectrode arrayElectrode array
A method of measuring localized corrosion, using a multi-electrode array sensor. The method eliminates the effect of internal current in corroded electrodes, and thus provides a more accurate corrosion measurement. In one embodiment, the potential of a common node of the sensor is adjusted so that the sensor's most cathodic current is close to zero.
Owner:SOUTHWEST RES INST
System and method for providing a combined bioprosthetic specification of goal state and path of states to goal
InactiveUS20060241788A1Maximum flexibilityEasy to produceProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlKaiman filterMultielectrode array
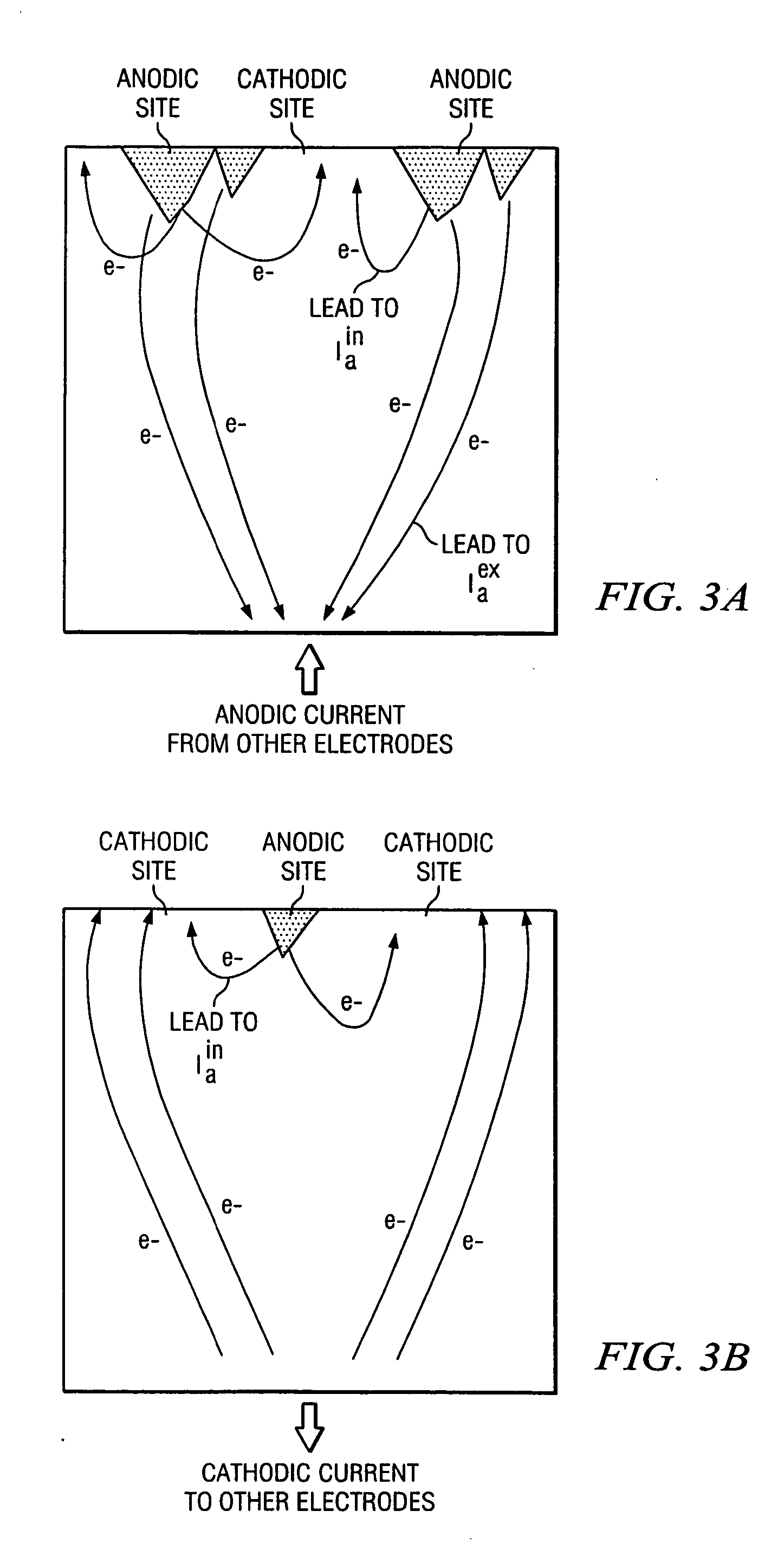
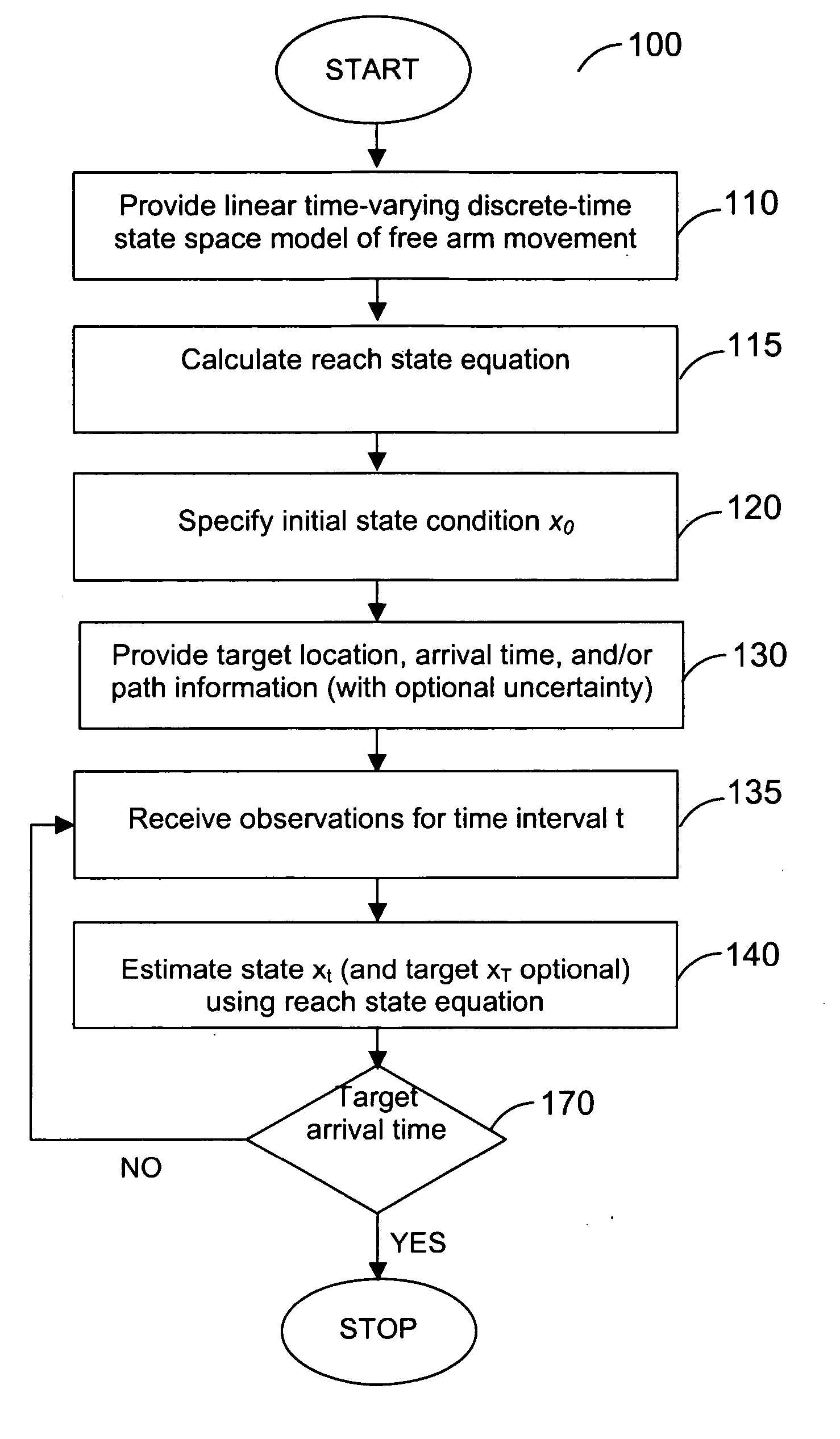
The exemplary embodiments of the method, system and arrangement according to the present invention enables an estimation of reaching movements. For example, using the exemplary embodiments of the present invention, it is possible to derive a Bayesian-optimal discrete time state equation to support real-time filters that incorporate observations about the target position and arm trajectory. The exemplary embodiments of the present invention may be compatible with any filtering method, such as point process or Kalman filters, and any recording methods, such as multielectrode arrays, intracortical EEG, or eye trackers.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
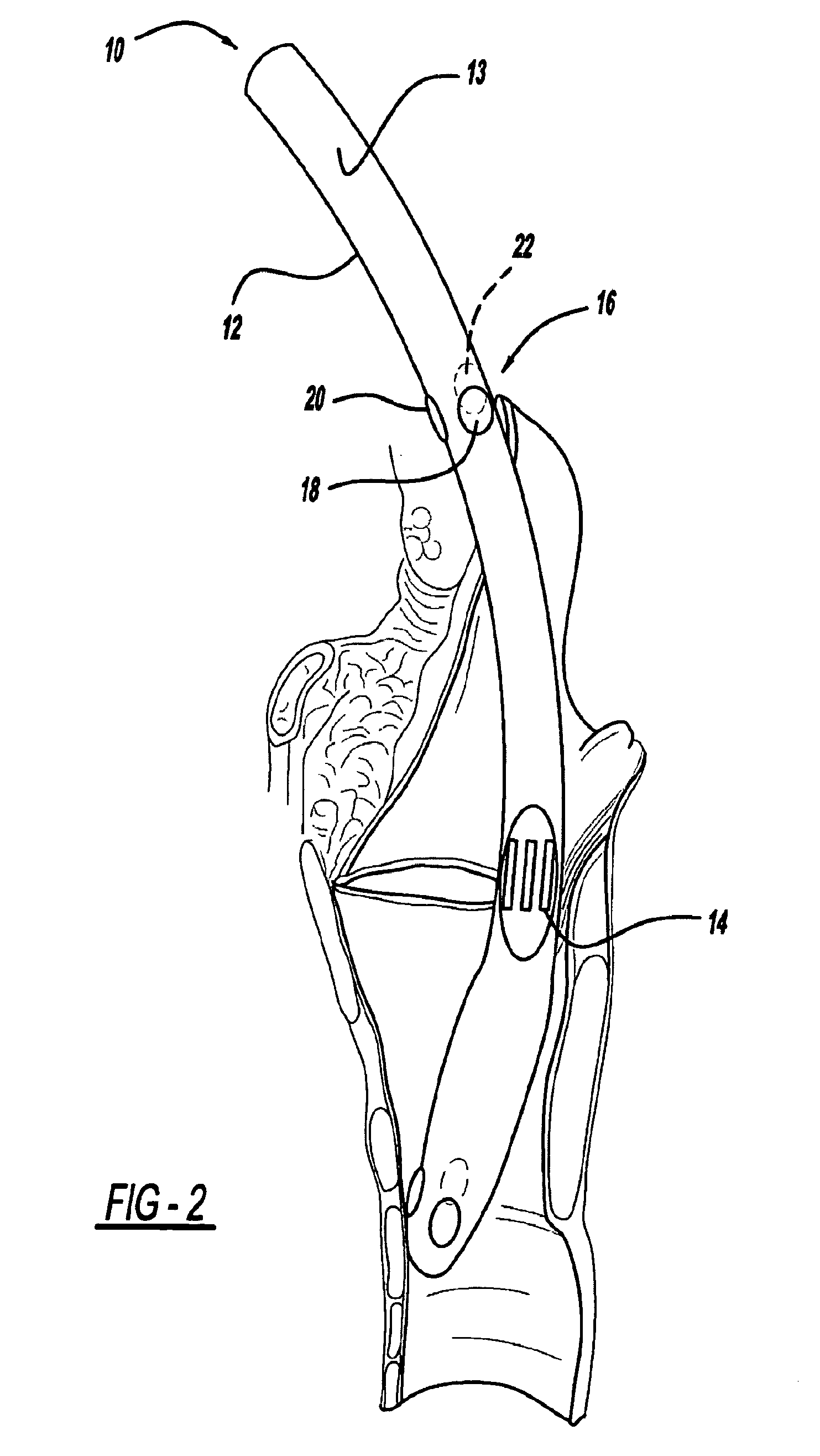
Systems and methods for selectively stimulating components in, on, or near the pudendal nerve or its branches to achieve selective physiologic responses
InactiveUS20050222636A1Promote contractionReduced activitySpinal electrodesExternal electrodesMedicineMultielectrode array
Systems and methods selectively stimulate components of the pudendal nerve away from the sacral root to evoke desired physiologic responses in persons who lack the ability to otherwise produce these responses—e.g., maintain continence and / or produce micturition, and / or provide male / female sexuality responses, and / or provide bowel responses. The systems and methods use a multiple electrode array, or individual electrodes, placed on, in, or near the pudendal nerve. The electrode array, or individual electrodes, in association with a pulse generator, provide selective stimulation of individual fascicles within the pudendal nerve, to achieve different physiologic responses.
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
System for selective spatiotemporal stimulation of the spinal cord
ActiveUS20170354819A1Easy to moveEasy to controlSpinal electrodesElectromyographySpinal columnNervous system
The present disclosure refers to systems for electrical neurostimulation of a spinal cord of a subject in need of nervous system function support. In one example, a system comprises a signal processing device configured to receive signals from the subject and operate signal-processing algorithms to elaborate stimulation parameter settings; one or more multi-electrode arrays suitable to cover a portion of the spinal cord of the subject; and an Implantable Pulse Generator (IPG) configured to receive the stimulation parameter settings from the signal processing device and simultaneously deliver independent current or voltage pulses to the one or more multiple electrode arrays, wherein the independent current or voltage pulses provide multipolar spatiotemporal stimulation of spinal circuits and / or dorsal roots. Such system advantageously enables effective control of nervous system functions in the subject by stimulating the spinal cord, such as the dorsal roots of the spinal cord, with spatiotemporal selectivity.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
Multi-electrode array for spinal cord epidural stimulation
ActiveUS10773074B2Solve the lack of durabilitySolve the lack of flexibilitySpinal electrodesExternal electrodesMultielectrode arraySpinal cord
In certain embodiments an electrode array for epidural stimulation of the spinal cord is provided where the array comprises a plurality of electrodes disposed on a flexible polymer substrate; said electrodes being electrically connected to one or more lead wires and / or connection points on an electrical connector; where the electrodes of said array are bonded to said polymer so that the electrodes can carry an electrical stimulation signal having a voltage, frequency, and current sufficient to provide epidural stimulation of a spinal cord and / or brain in vivo or in a physiological saline solution, without separation of all or a part of an electrode from the polymer substrate.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
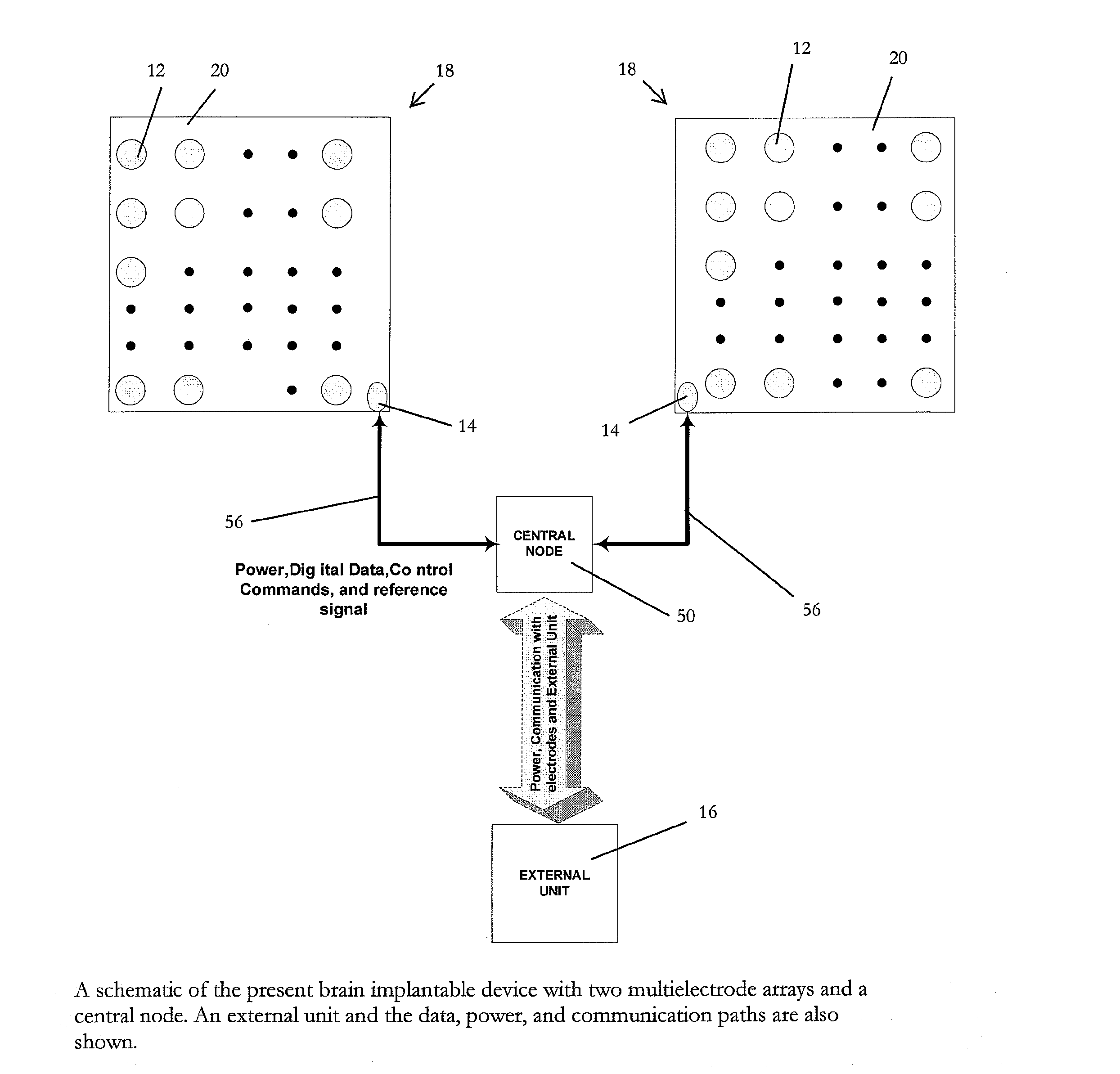
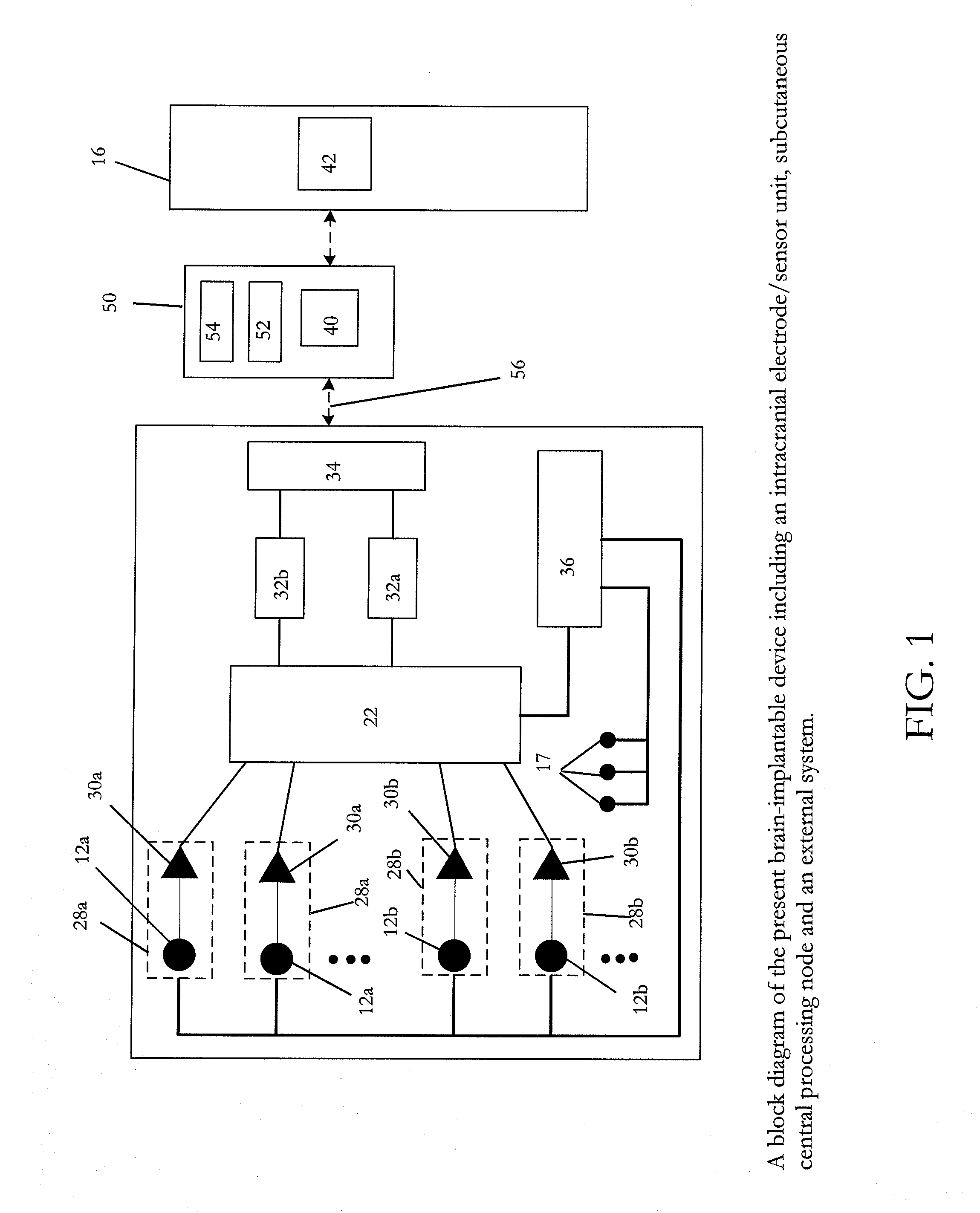
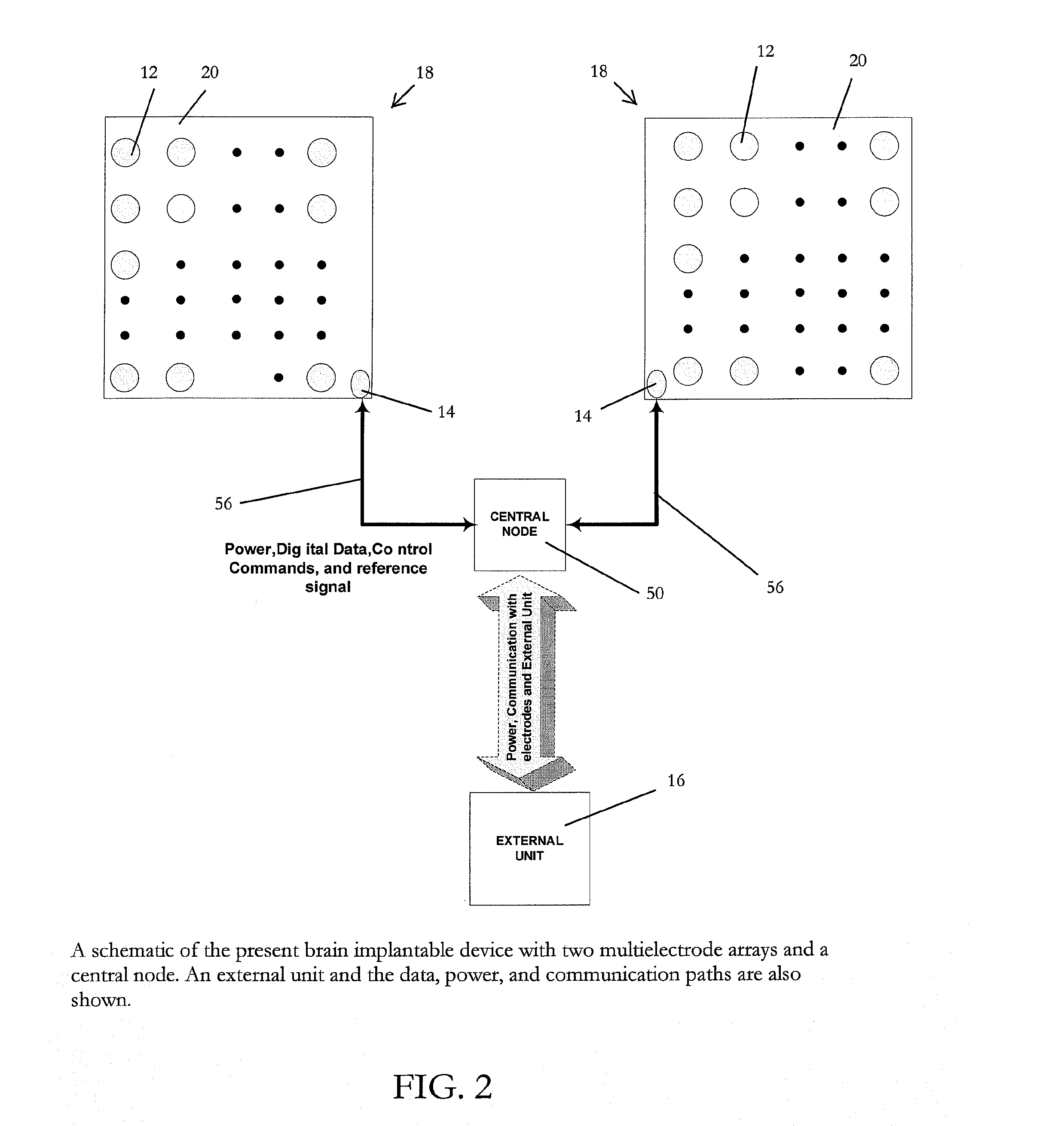
Fault-tolerant multielectrode array for brain implantable device
A multielectrode array with fault-tolerance for use in conjunction with a brain implantable device includes a sensor grid composed of a plurality of sensors, the plurality of sensors including primary sensors and spare sensors. The multielectrode array also includes signal processing circuitry associated with the plurality of sensors and a control system associated with the sensor grid for replacing faulty primary sensors with spare sensors.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL +1
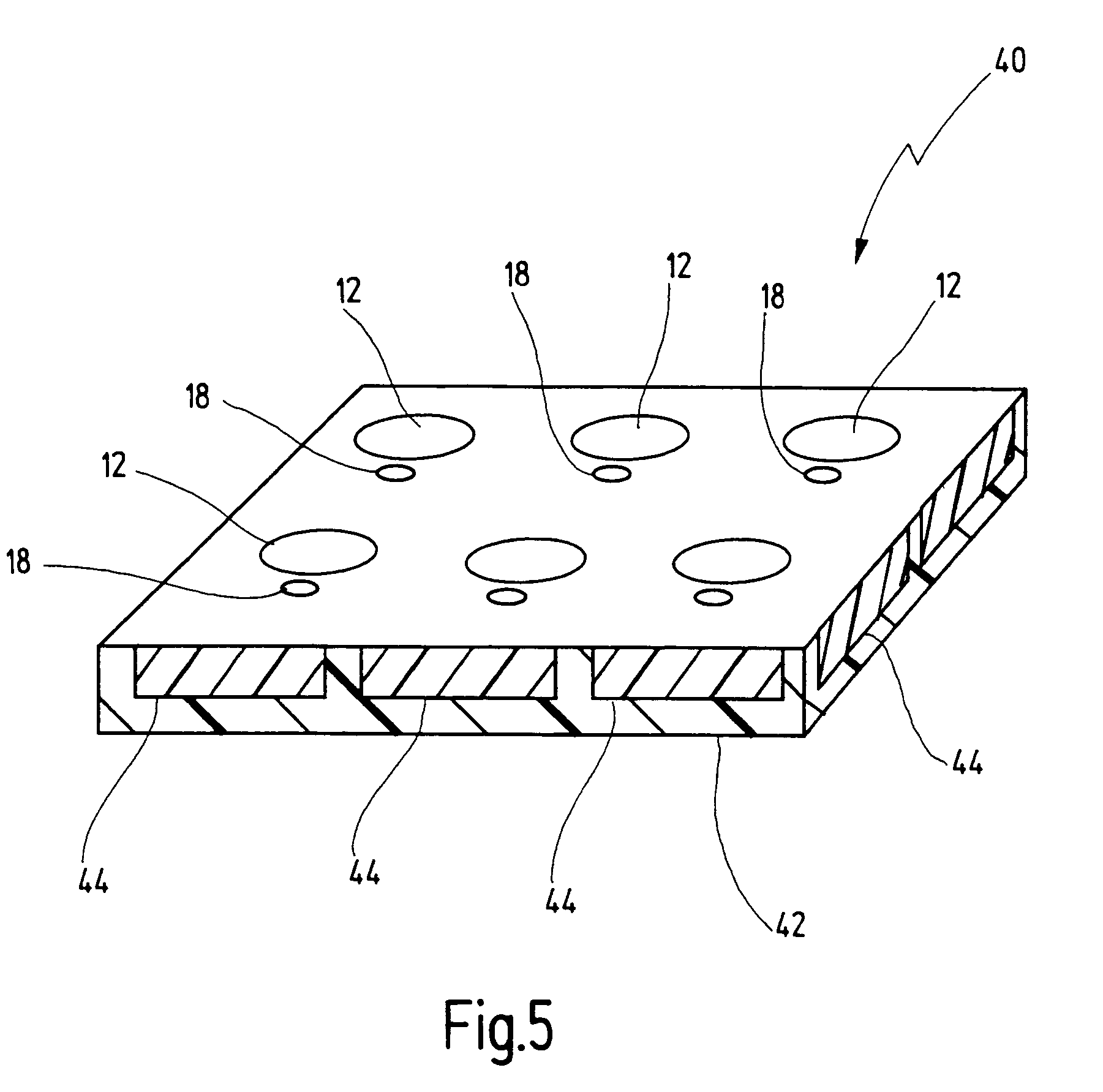
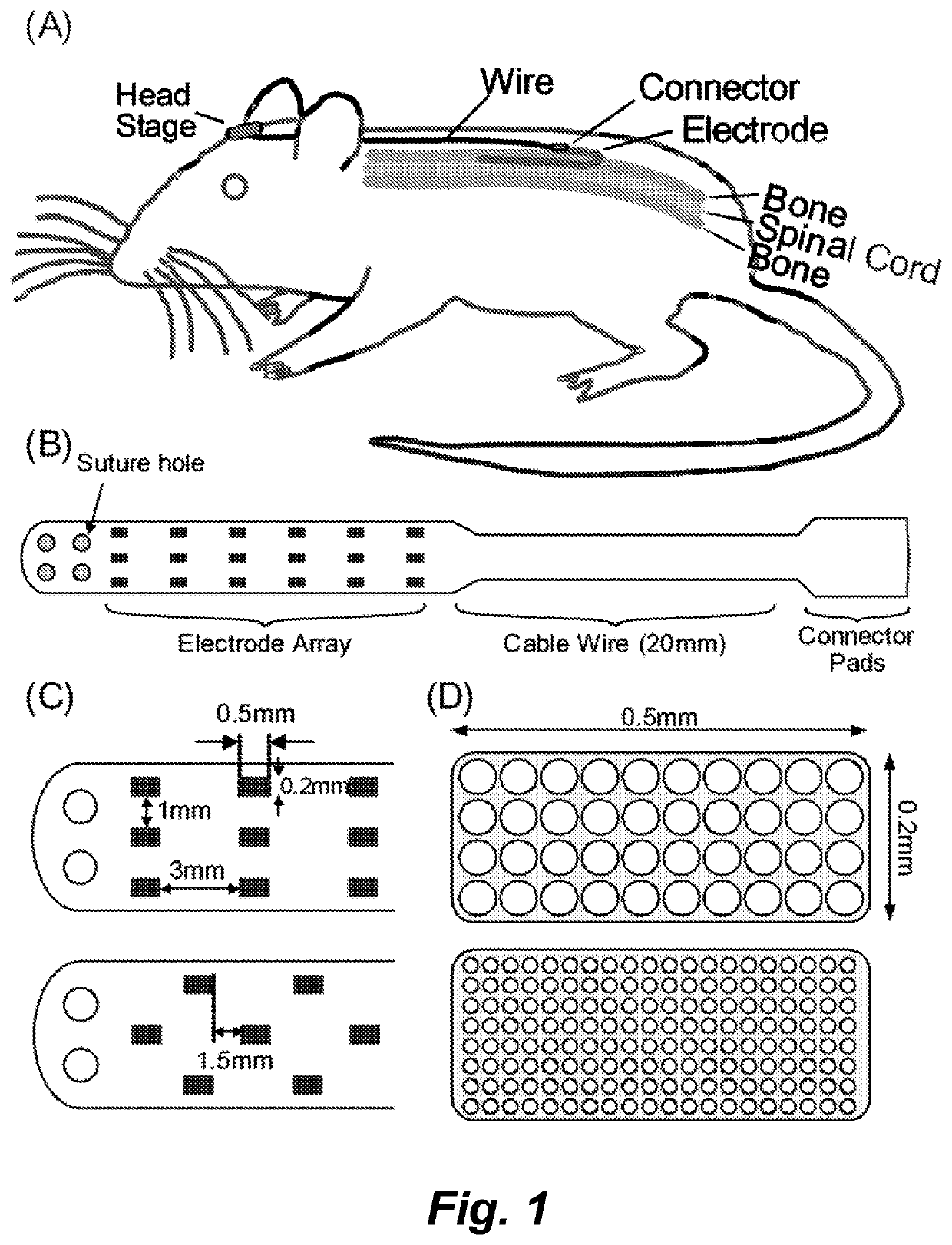
Multiple electrode array and manufacturing method
InactiveCN1600264ASmall electrode spacingReduce spacingDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsMultielectrode arrayEngineering
Owner:INSITUTE OF BIOPHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCIENCES
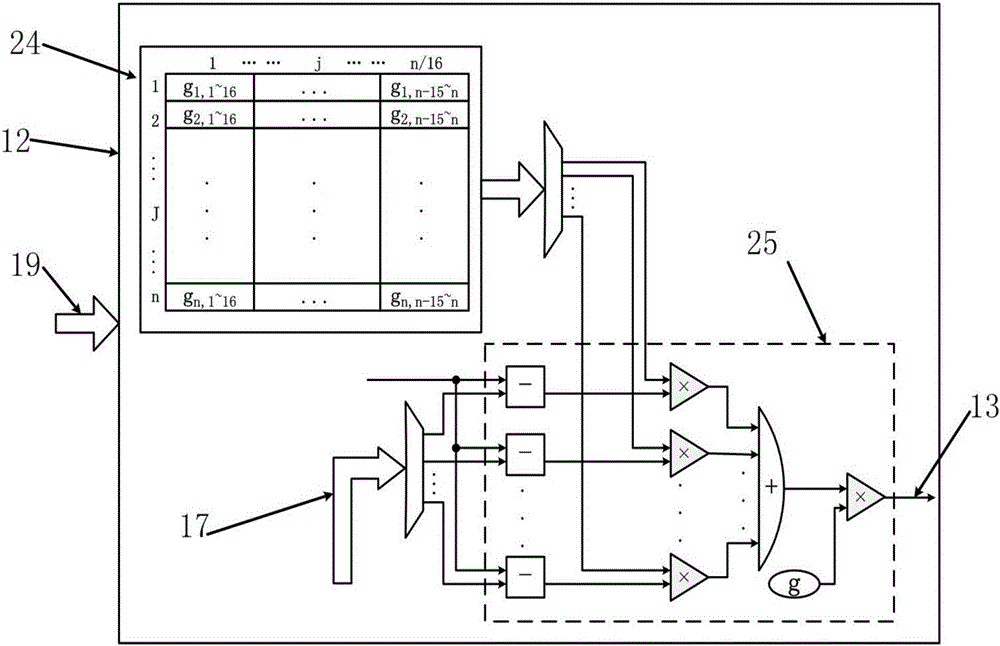
FPGA-based multi-electrode array simulation experiment platform
The invention provides an FPGA-based multi-electrode array simulation experiment platform. The experiment platform comprises an FPGA development board and a principal computer which are connected with each other via a USB interface. The FPGA development board is used for implementing an STN neuron network model and a multi-electrode array algorithm. The software interface of the principal computer is designed based on LabVIEW, and the principal computer communicates with the FPGA development board. With the FPGA neural network experiment platform which is taken as a biological neuron network, free of animal experiment and based on high-speed operation, synchronous record of multiple sites of the field potential of a neuron network through a multi-electrode array is realized, and the consistency with real biological neurons in time scale can be ensured. A visual study platform closer to a real neural network is provided for the study of the discharge mechanism of a sub-thalamic nucleus STN nuclei and the study of a multi-electrode array. The platform is of important practical value to the study and treatment of a variety of neurological diseases including the Parkinson's disease.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Patterned cardiomyocyte culture on microelectrode array
ActiveUS9404140B1Microbiological testing/measurementSkeletal/connective tissue cellsElectricityMultielectrode array
The invention provides a culture of patterned cardiomyocytes, the culture including a support substrate bearing a multielectrode array, a negative surface resistant to cell attachment and deposited on the support substrate covering the multi-electrode array, a pattern ablated on the negative surface, a positive surface promoting cell attachment deposited on the pattern ablated on the negative surface; and cardiomyocytes adherent to the positive surface and growing aligned along the pattern ablated on the negative surface. The invention also includes a method of making the culture of patterned cardiomyocytes and a method of in vitro method of testing the effect of a compound on cardiac function by measuring electrical output from the patterned cardiomyocytes.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC
Multielectrode array and method of fabrication
ActiveUS20150126843A1Lower immune responseEnhance neural growthInternal electrodesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLithographic artistMultielectrode array
A multielectrode array with a fluidic channel and its method of fabrication are presented here. In accordance with various embodiments, the present invention allows for scalability, reproducibility, and precision dimension control by utilizing a lithography dependent process. In one embodiment, the present invention provides for a microelectrode that is a neural implant, with the microelectrode configured for connection to a fluidic channel. In another embodiment, the fluidic channel may deliver growth factors and / or drugs.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Micropower neural amplifier with adaptive input-referred noise
ActiveUS8200325B2Amplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDiagnostic recording/measuringAudio power amplifierMultielectrode array
A micropower neural amplifier with adaptive power biasing for use in multi-electrode arrays is provided. The micropower neural amplifier includes a low noise gain stage. The low noise gain stage is implemented using an amplifier and pseudoresistor elements.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
System for selective spatiotemporal stimulation of the spinal cord
ActiveUS20190344075A1Fine control of movementEasy to controlElectrotherapyDiagnostic recording/measuringSpinal columnNervous system
The present disclosure refers to systems for electrical neurostimulation of a spinal cord of a subject in need of nervous system function support. In one example, a system comprises a signal processing device configured to receive signals from the subject and operate signal-processing algorithms to elaborate stimulation parameter settings; one or more multi-electrode arrays suitable to cover a portion of the spinal cord of the subject; and an Implantable Pulse Generator (IPG) configured to receive the stimulation parameter settings from the signal processing device and simultaneously deliver independent current or voltage pulses to the one or more multiple electrode arrays, wherein the independent current or voltage pulses provide multipolar spatiotemporal stimulation of spinal circuits and / or dorsal roots. Such system advantageously enables effective control of nervous system functions in the subject by stimulating the spinal cord, such as the dorsal roots of the spinal cord, with spatiotemporal selectivity.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
Detection device and method for multi-electrode array corrosion sensor micro current
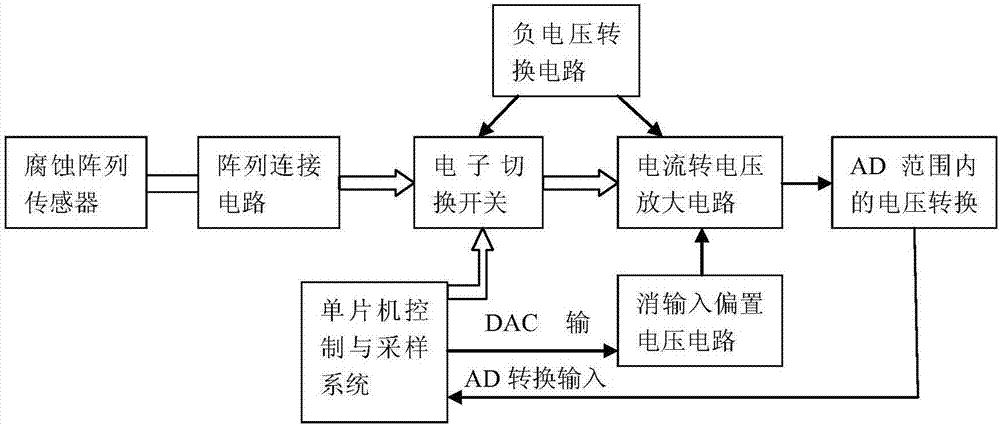
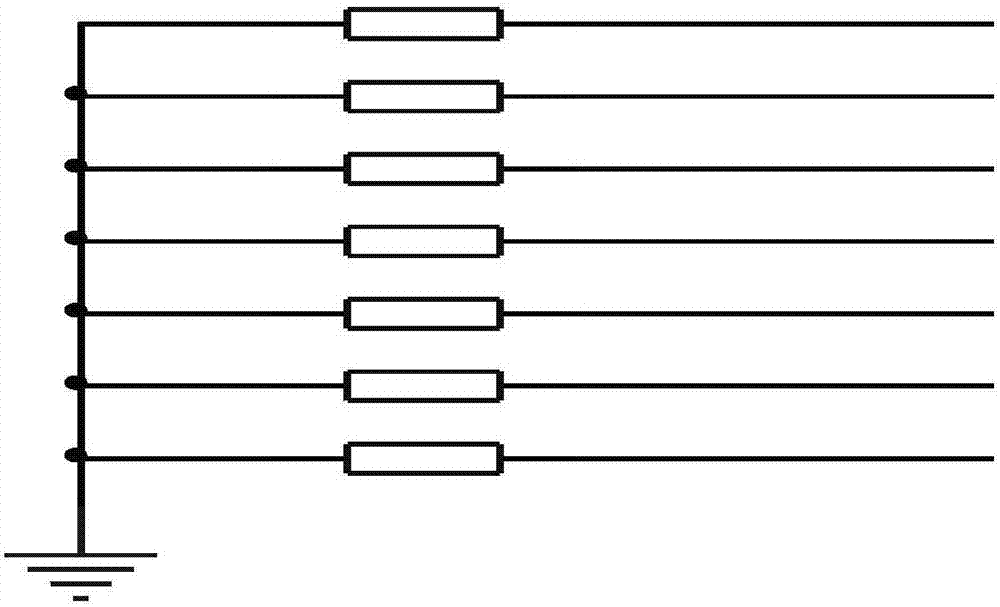
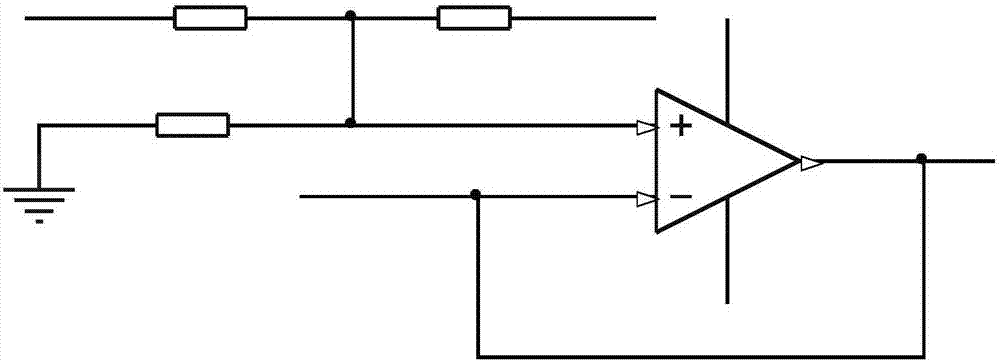
ActiveCN107356521AEliminate Op Amp Offset VoltageReal-time switch comparisonWeather/light/corrosion resistanceMicrocontrollerTime switching
The invention relates to a detection device and method for multi-electrode array corrosion sensor micro current. The detection device consists of a corrosion array connection circuit, an electronic changeover switch circuit, a current-to-voltage amplifying circuit, a voltage conversion circuit within AD range and a single chip microcomputer control and sampling system that are connected in order. The single chip microcomputer control and sampling system is connected to the current-to-voltage amplifying circuit through an operational amplifier input offset voltage cancelling circuit, and is also connected to the electronic changeover switch circuit, and the electronic changeover switch circuit and the current-to-voltage amplifying circuit are also connected to a negative voltage conversion circuit simultaneously. Therefore, the device and the method provided by the invention have the advantages that: 1. DAC is utilized to eliminate the offset voltage of operational amplifier; and 2. real-time switching comparison is carried out to improve the measurement accuracy.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV OF TECH
Electrode measurement device based on electromyographic signals of genioglossus muscle
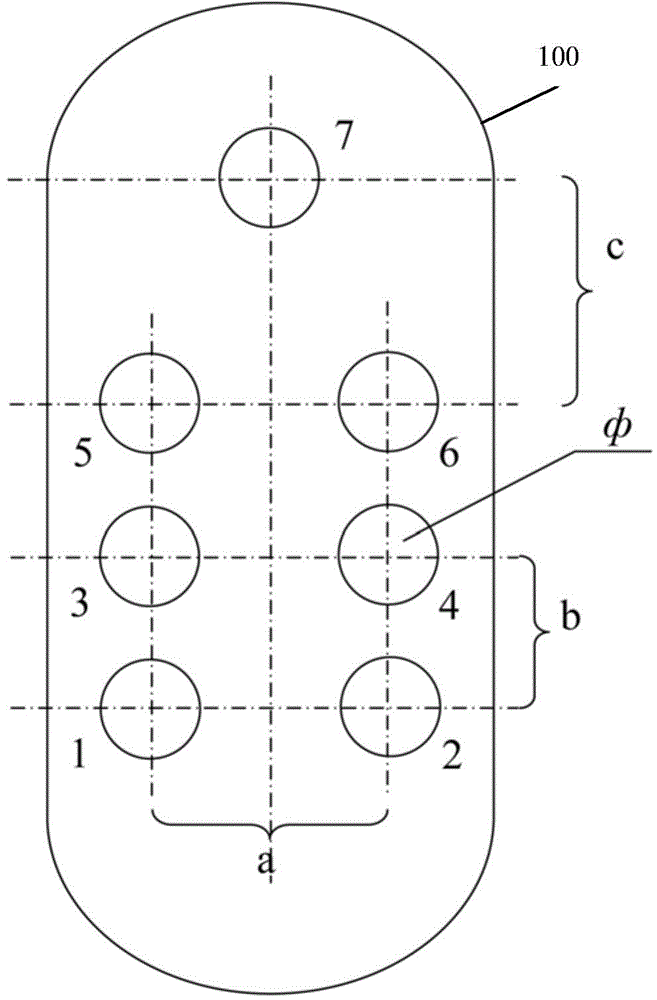
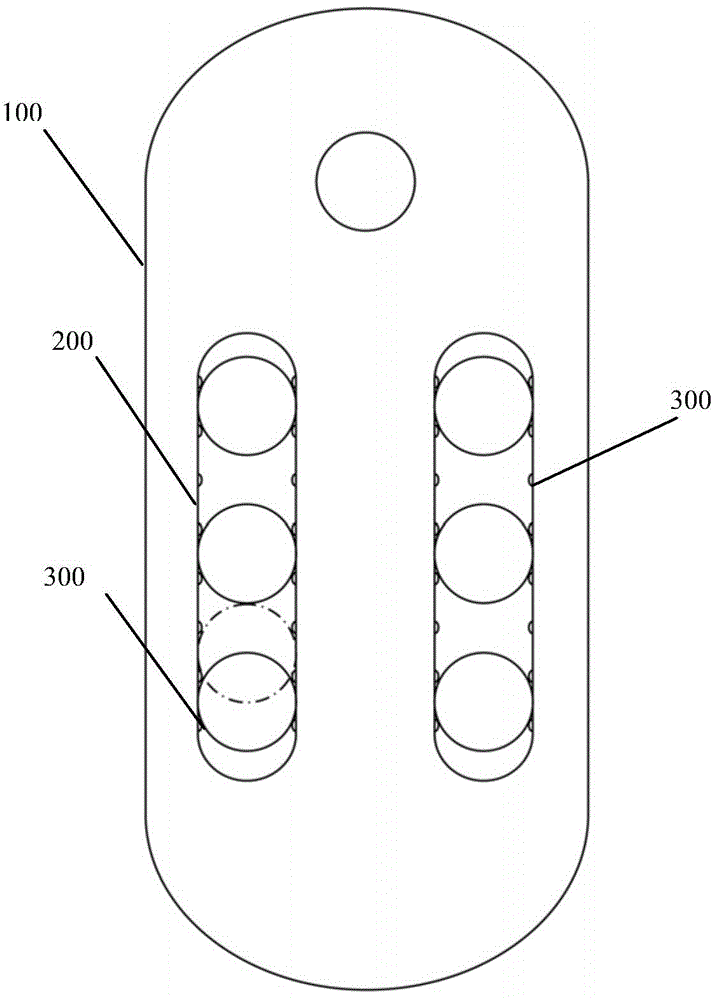
InactiveCN104783791AAccurate measurementReduce the effect of stackingDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsFiberHuman body
The invention discloses an electrode measurement device based on electromyographic signals of a genioglossus muscle. The electrode measurement device comprises a low jaw support, a reference electrode and array collection electrodes arranged in two rows and at least two lines, wherein the low jaw support is used for fixing the electrodes distributed on the low jaw support, the reference electrode is arranged in the middle of the upper portion of the lower jaw support and corresponds to the middle combination portion of the two side portions of the lower jawbone of a human body, and the array collection electrodes are sequentially arranged on the two sides of the lower portion of the reference electrode and correspond to the lower jaw tongue muscles of the human body. Compared with the prior art, the multi-electrode array measurement mode is adopted, the electrodes are large in number and wide in distribution range, the space resolution is high, the resolution ratio of the electromyographic signals of the genioglossus muscle can be increased, the electrodes are made of silver wire non-woven fabric fibers, the electrical resistivity is low, the polarized electromotive force is small, and the electrode measurement device is comfortable to wear.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com