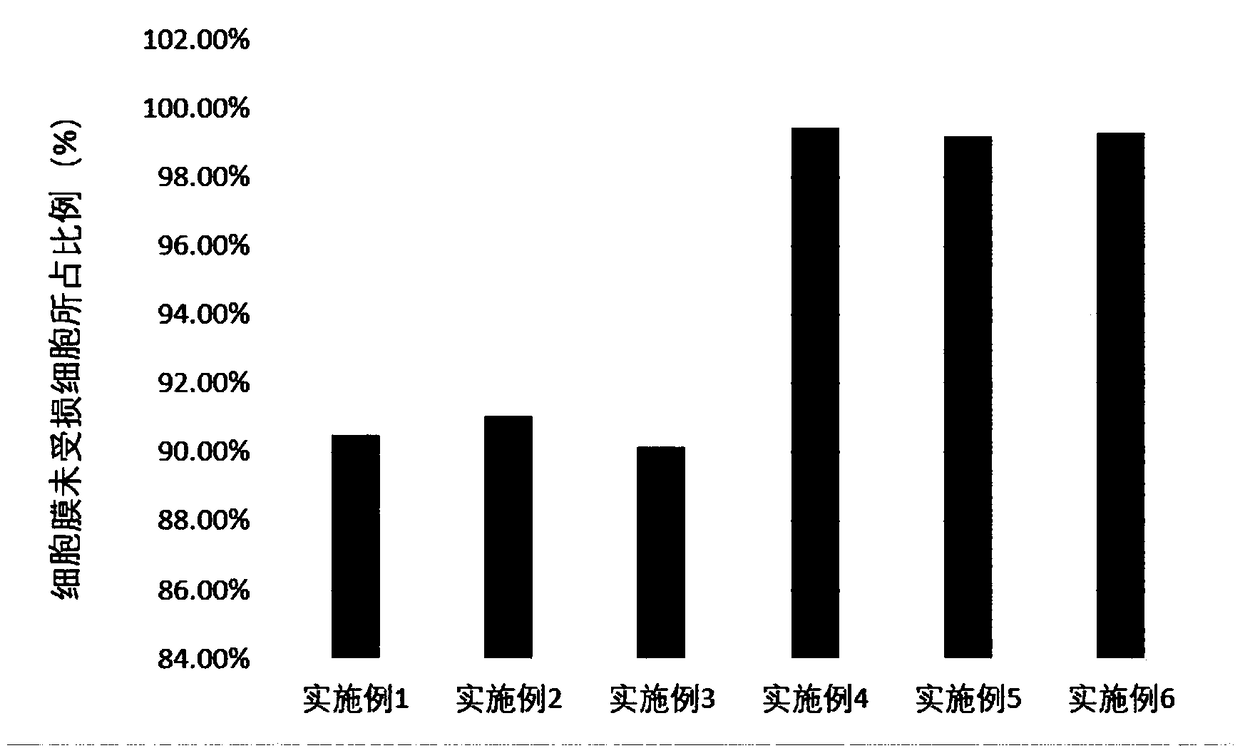
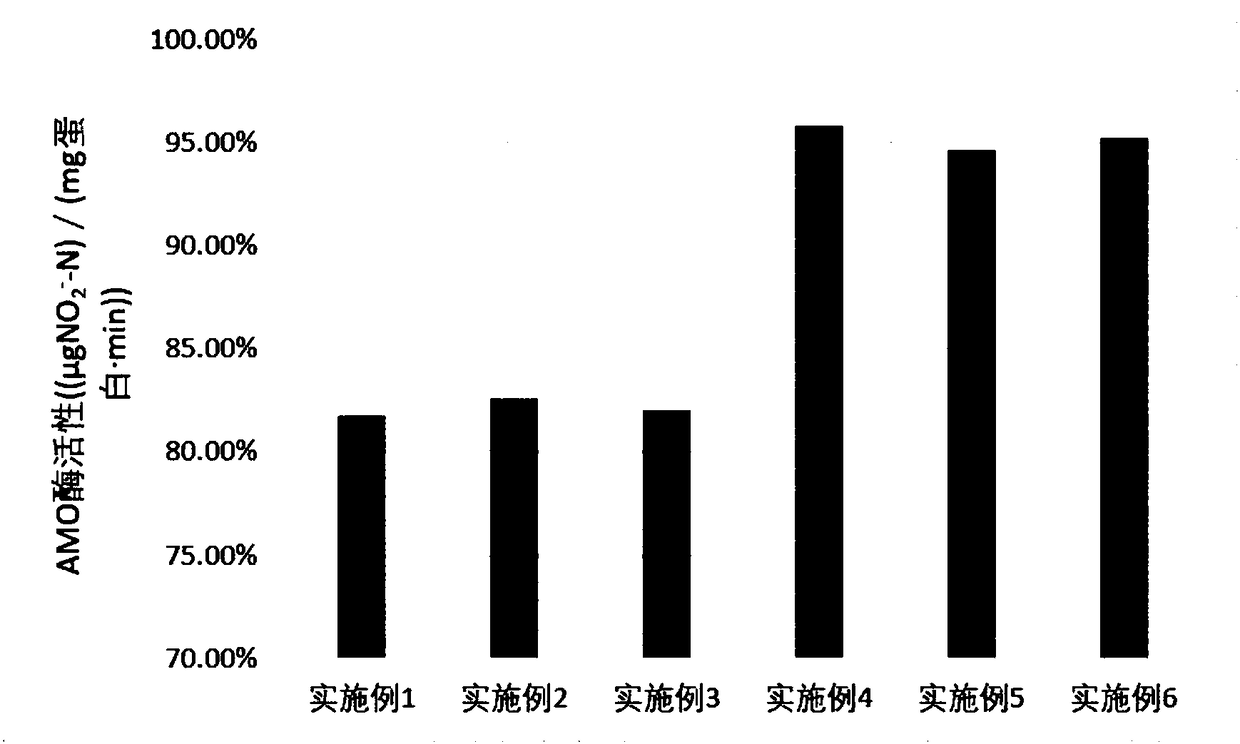
Method for collecting nitrosobacteria
A nitrosative bacteria, cryopreservation technology, applied in the direction of preservation of microorganisms, bacteria, etc., can solve the problems of uncontrollable two-way exchange of extracellular and extracellular substances, increase of van der Waals force between molecules, increase of cell membrane permeability, etc., to achieve excellent performance retention and flow improvement The effect of sex and stability of membrane protein structure
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] Preservation method of nitrosative bacteria:
[0029] 1) Prepare the protective agent: add 3 parts of sodium glutamate, 20 parts of tripotassium phosphate and 2 parts of cysteine to 100 parts of sterile water, mix well to obtain the protective agent;
[0030] 2) Adding bacterial cells: Add 160 parts of nitrosative bacterial cells to 110 parts of the protective agent obtained in step 1), shake and resuspend to obtain a mixed solution;
[0031] 3) Cold and heat stress treatment: heat-treat the obtained mixture at 35°C for 12 minutes, and then at 6°C for 1.7 hours;
[0032] 4) Cryopreservation: freeze-dry the mixed solution obtained in step 3), freeze-preserve at -80° C., and perform activation transfer every 8-12 months. The freeze-drying process is: pre-freezing: -30°C for 4 hours; freeze-drying: -60°C, 40Pa freeze-drying for 6 hours, -20°C, 70Pa freeze-drying for 2.2 hours; sublimation drying: 10°C, 150Pa sublimation drying for 3.5 hours; Drying: 16°C, 4Pa analytical ...
Embodiment 2
[0034] Preservation method of nitrosative bacteria:
[0035] 1) Prepare the protective agent: add 3.5 parts of sodium glutamate, 22 parts of tripotassium phosphate and 2 parts of cysteine to 110 parts of sterile water, mix well to obtain the protective agent;
[0036] 2) Add bacterial cells: add 140 parts of nitrosative bacterial cells to 100 parts of the protective agent obtained in step 1), shake and resuspend to obtain a mixed solution;
[0037] 3) Cold and heat stress treatment: heat-treat the obtained mixture at 37°C for 10 minutes, and then at 7°C for 1.2 hours;
[0038] 4) Cryopreservation: freeze-dry the mixed liquid obtained in step 3), freeze-preserve at -85°C, and perform activation transfer every 8-12 months. The freeze-drying process is as follows: pre-freezing: -30°C for 4 hours; freeze-drying: -58°C, 40Pa freeze-drying for 6 hours, -20°C, 70Pa freeze-drying for 2.2 hours; sublimation drying: 10°C, 150Pa sublimation drying for 3.5 hours; Drying: 16°C, 4Pa ana...
Embodiment 3
[0040] Preservation method of nitrosative bacteria:
[0041] 1) Prepare the protective agent: add 2.8 parts of sodium glutamate, 20 parts of tripotassium phosphate and 2 parts of cysteine to 100 parts of sterile water, mix well to obtain the protective agent;
[0042] 2) Adding cells: Add 150 parts of nitrosative bacteria cells to 100 parts of the protective agent obtained in step 1), shake and resuspend to obtain a mixture;
[0043] 3) Cold and heat stress treatment: heat-treat the obtained mixture at 37°C for 10 minutes, and then at 7°C for 1.2 hours;
[0044] 4) Cryopreservation: freeze-dry the mixed solution obtained in step 3), freeze-preserve at -80° C., and perform activation transfer every 8-12 months. The freeze-drying process is as follows: pre-freezing: -35°C for 4 hours; freeze-drying: -60°C, 40Pa freeze-drying for 6 hours, -20°C, 70Pa freeze-drying for 2.2 hours; sublimation drying: 10°C, 140Pa sublimation drying for 3.5 hours; Drying: 16°C, 4Pa analytical dry...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com