Method for manufacturing rotary type sensor used for rapidly, sensitively and specifically detecting trace small RNAs
A sensor, rotary technology, used in the field of biosensors
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
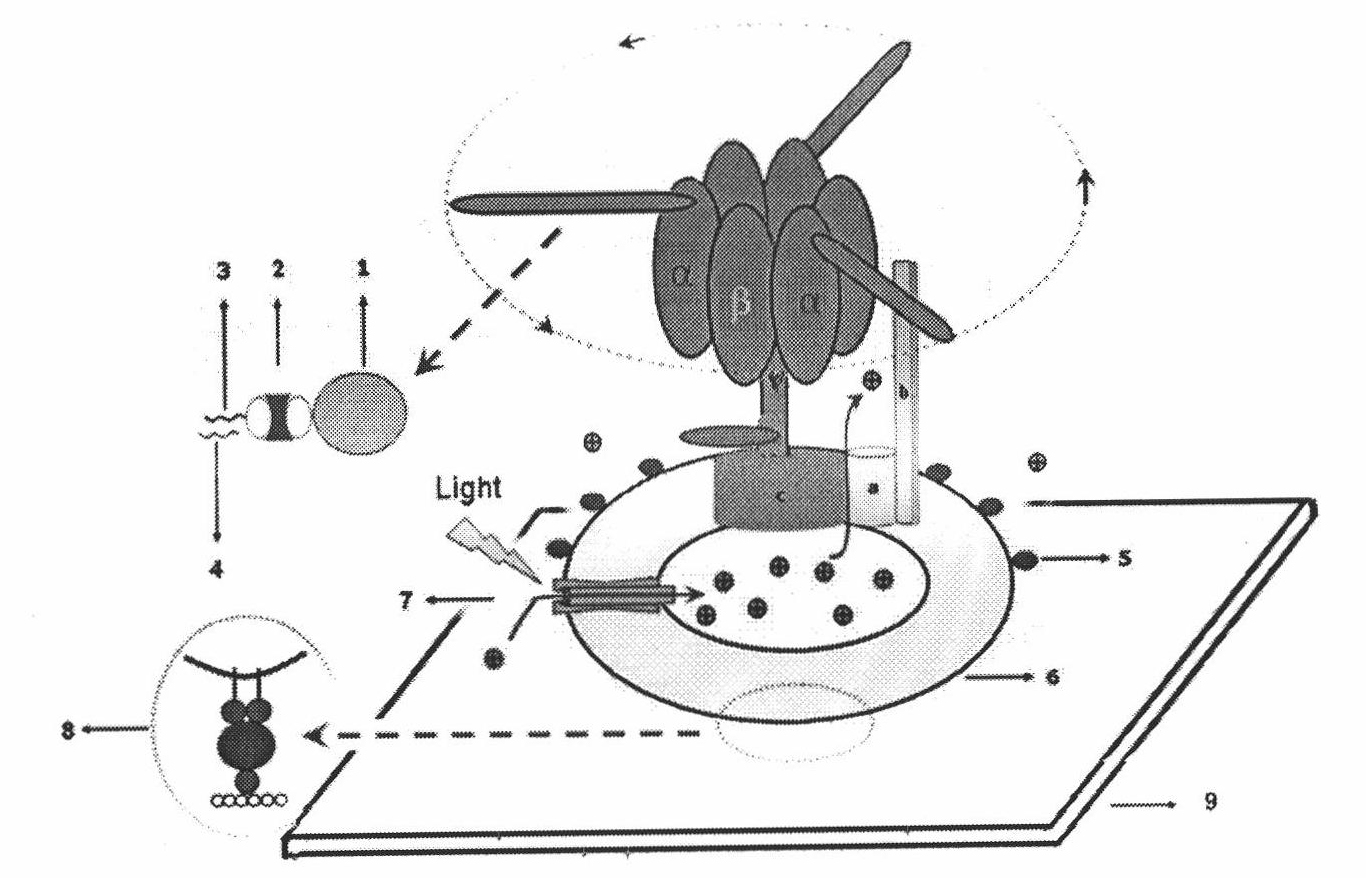
[0027] Example 1. Preparation, labeling and assembly of molecular motor sensors
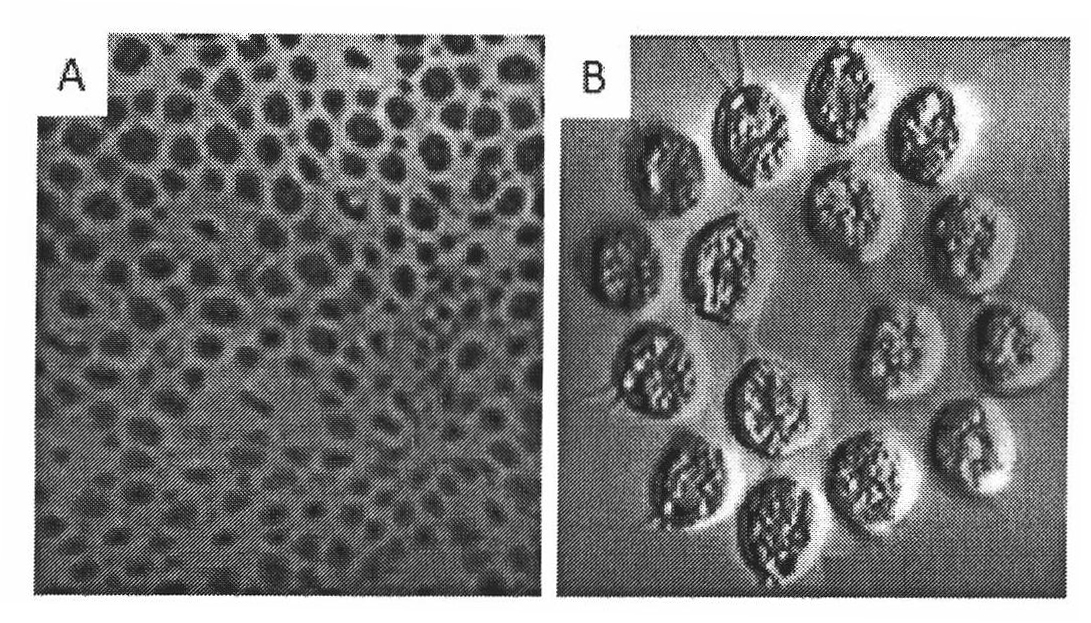
[0028] Extraction of photosynthetic bacteria chromophore [2, 3]: Use 5g of cultured R.rubrum cells (provided by Dr. Zhang Xujia) with 50ml TSM buffer (50mM Tricine-NaOH, pH 8.0, 0.25M sucrose, 4mM MgCl) 2 ) Suspended. Use ultrasound to break cells: large probe, 25% intensity, over 5s, stop for 5s, ultrasound for 10-12min, which can prevent the denaturation and inactivation of biological macromolecules caused by the overheating reaction caused by ultrasound. Then centrifuge at 25,000g for 30min; centrifuge the supernatant in FicollPM400 (GE Healthcare, USA) at 145,000g for 90min to obtain a uniform precipitation band, that is, photosynthetic bacterial chromatophores with higher purity ( Figure 4 ). Then suspend the precipitate in 1ml TSM buffer, add an equal volume of glycerin, and store at -20°C or -80°C.
[0029] LiCl treatment of the chromophore: take 0.8ml of the newly extracted chromophore (wit...
Embodiment 2
[0034] Example 2. Biosensor feasibility test
[0035] Previous studies have shown that the addition of the proton channel permeability agent CCCP can make the membrane permeable inside and outside, thereby inhibiting the non-delta subunit F o F 1 -The rotation of ATPase [11]. In addition, F o Channel inhibitor DCCD (purchased from Sigma) is able to interact with F o The carboxyl group of aspartic acid at position 61 of the upper c subunit is covalently bound, thereby blocking the outflow of protons and causing the fluorescence to no longer increase. In the experiment, the sample was incubated with 20μM DCCD at room temperature for one hour. Due to the inhibitory effect of DCCD, the fluorescence will not increase after the temperature is increased to 37℃ ( Figure 5 ). The above results prove that the increase in fluorescence is the result of proton pumping out of the membrane, not an artifact.
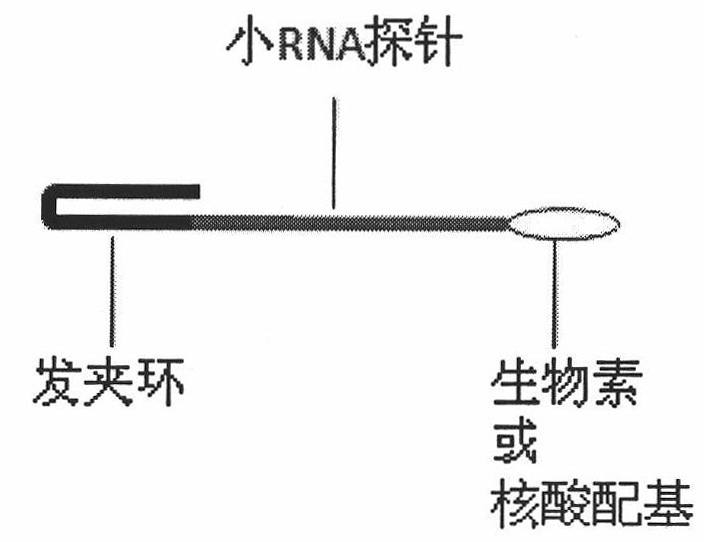
[0036] Determine the light time: Before detection, the miRNA detection system is illu...
Embodiment 3
[0042] Example 3. Sensitivity of the biosensor
[0043] Previous studies have shown that mir-145 is a tumor suppressor gene in breast cancer cells, so the expression level is lower than that of normal cells [15]. Therefore, this experiment chose to detect the low content of mir-145 in human breast cancer cells MCF-7 for research. We prefer to use Trizol (purchased from invitrogen) to extract total cellular RNA to detect mir-145 in this complex environment. Figure 7 The middle curves (a, b, c, d, e, f, g) respectively represent the effects of adding different amounts of load on the changes in fluorescence of the biosensor at 37°C. The curve a represents that the control sample probe system is completely connected, and only the target miRNA is not bound. Experiments show that when adding 10 6 The slope of miR-145 curve after the total RNA of the above cells 6 The slope of the curve of total RNA of each cell is the same. Through the above results, the saturation concentration of ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com