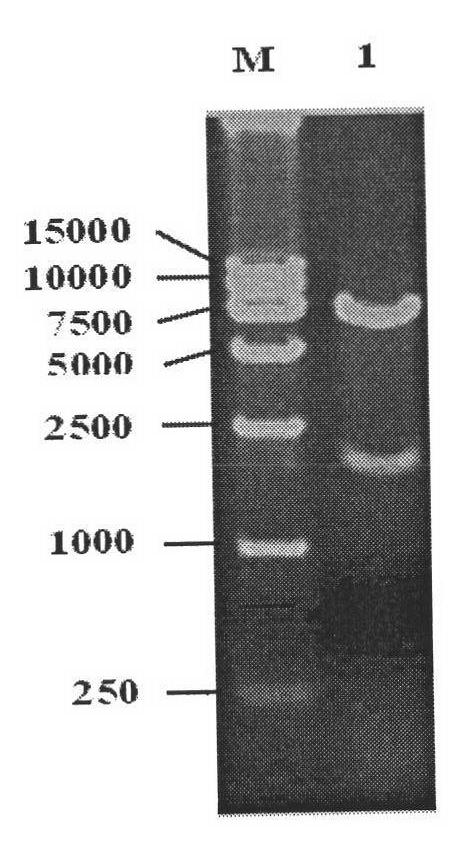
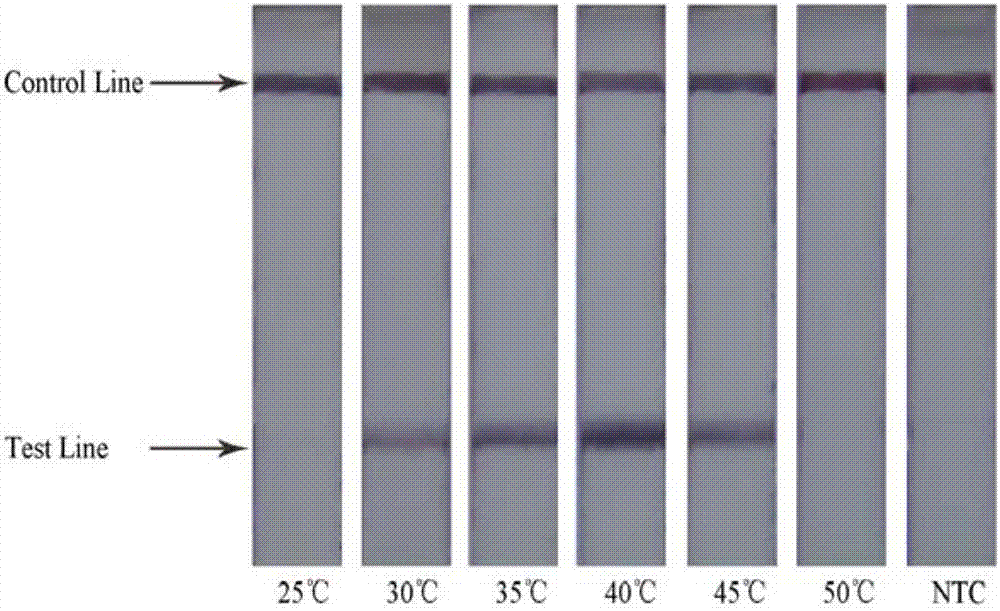
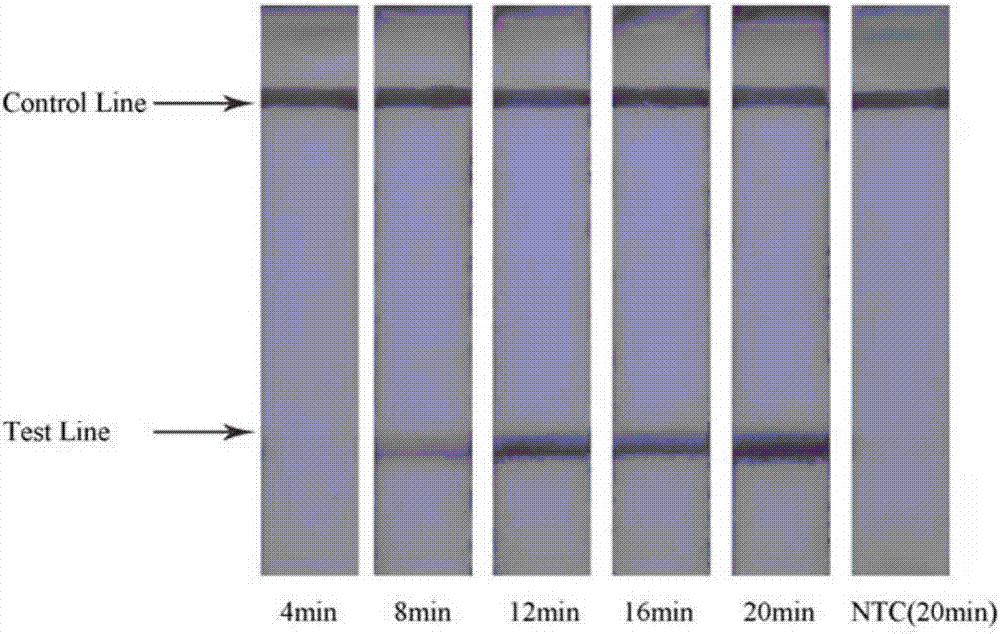
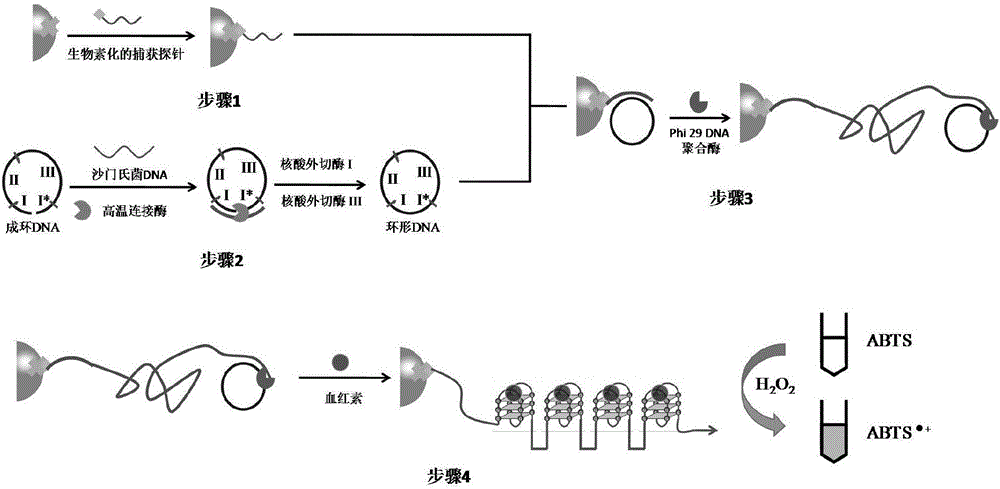
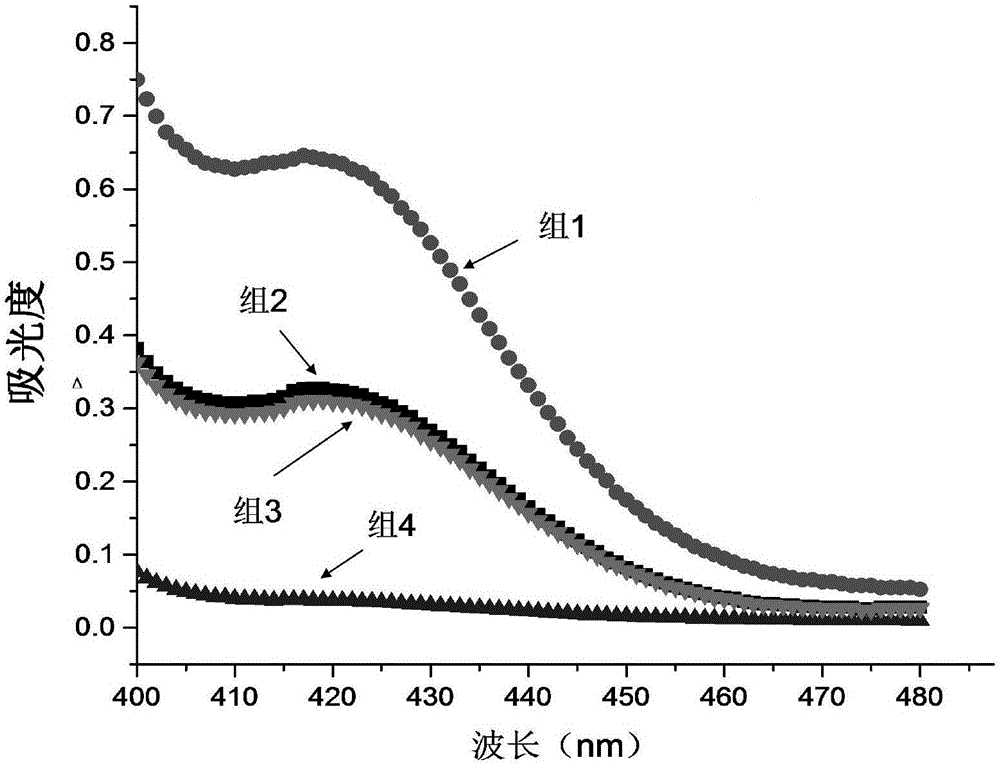
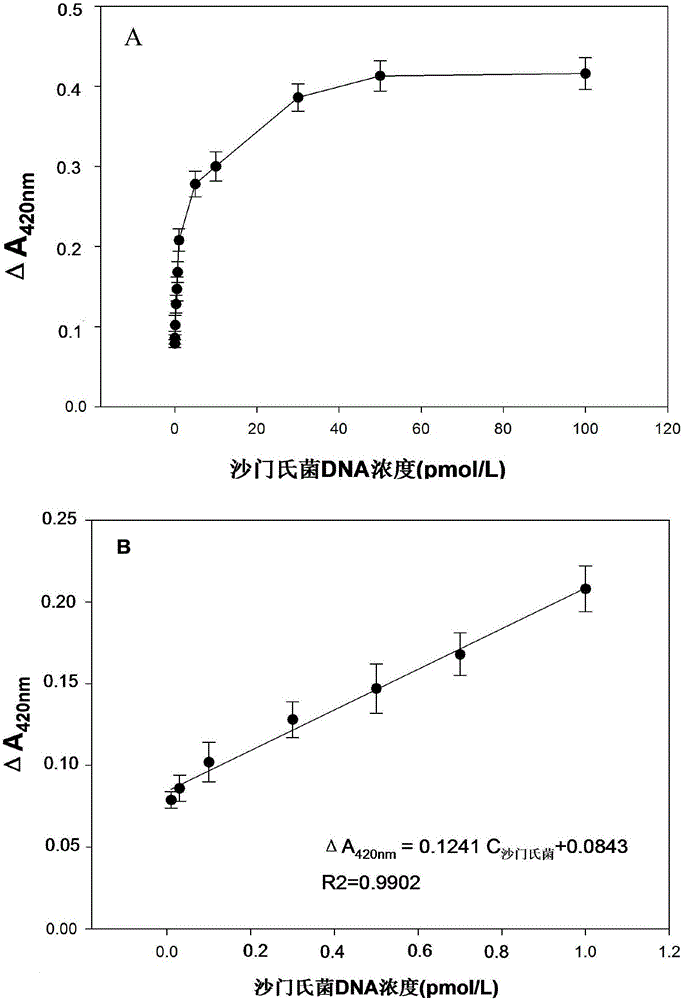
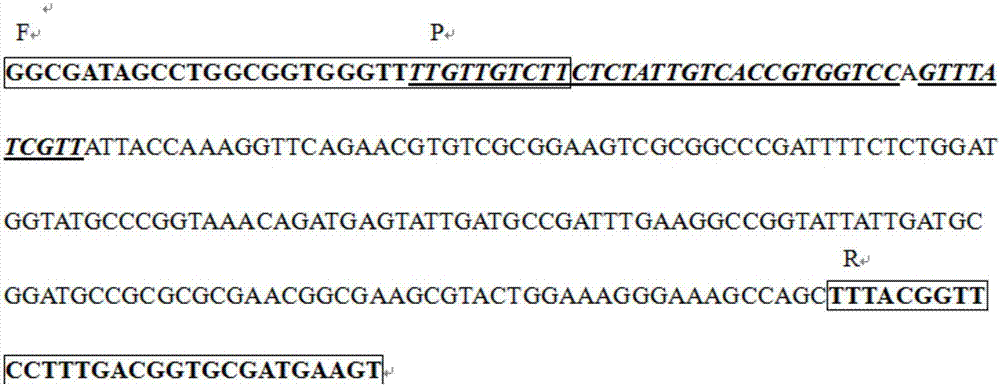Patents
Literature
141 results about "Salmonella Be" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Salmonella is rarely fatal, but if the bacteria enters your bloodstream, it can be life-threatening, especially for people with weakened immune systems, such as the elderly, the very young, and those with diseases like cancer and HIV/AIDS.
Genetically modified tumor-targeted bacteria with reduced virulence
InactiveUS6080849AImprove securityReduce capacityBiocideBacteriaTumor targetVirulent characteristics
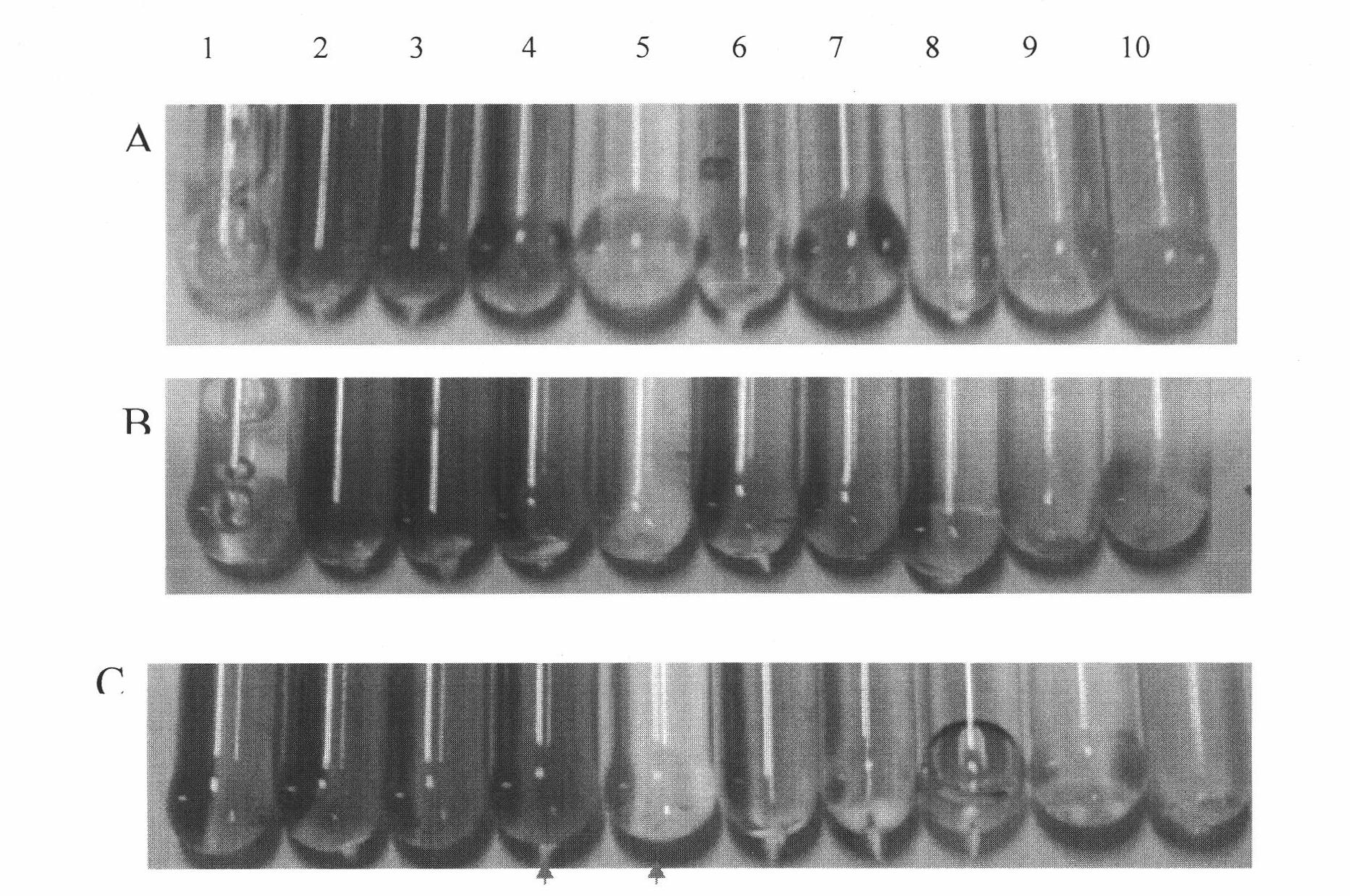
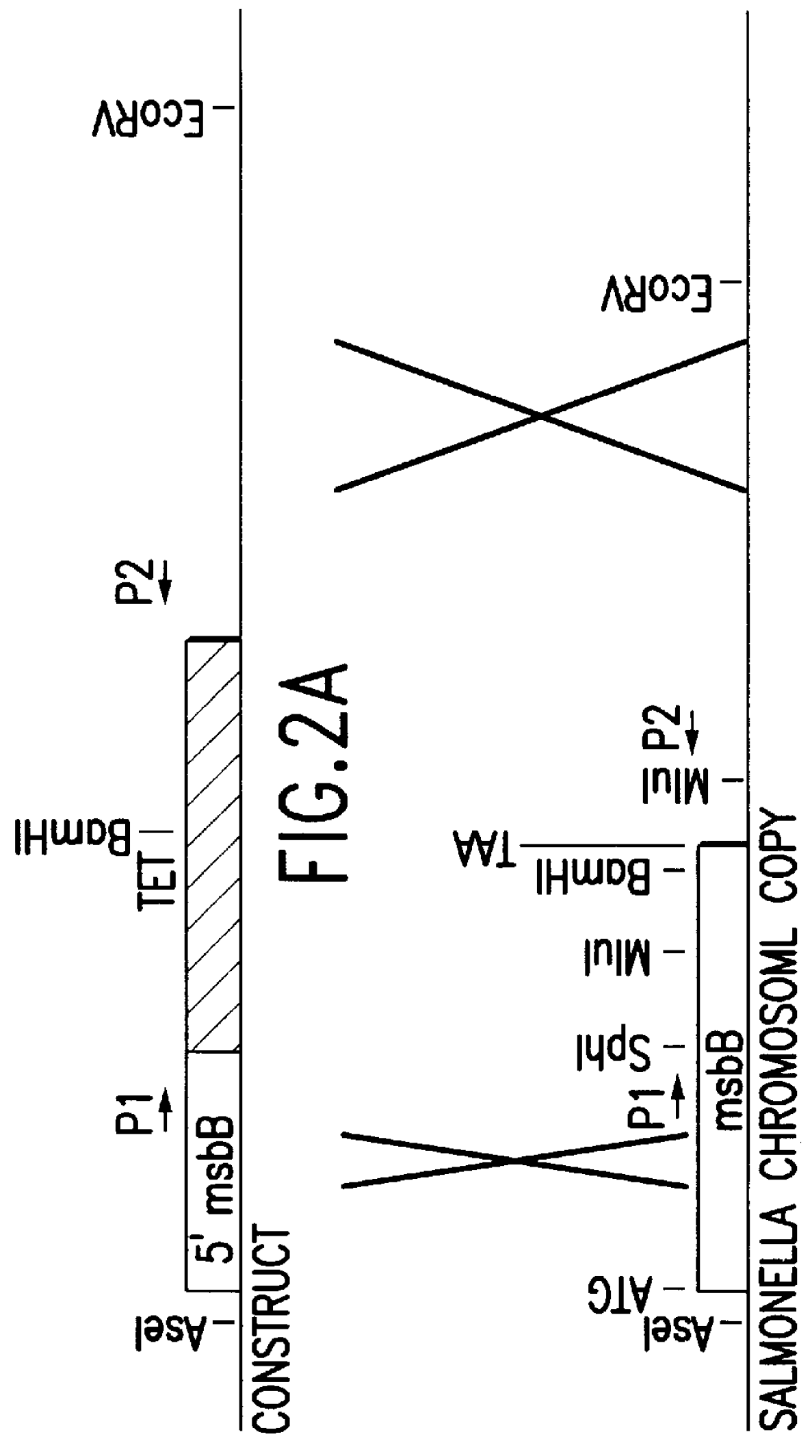
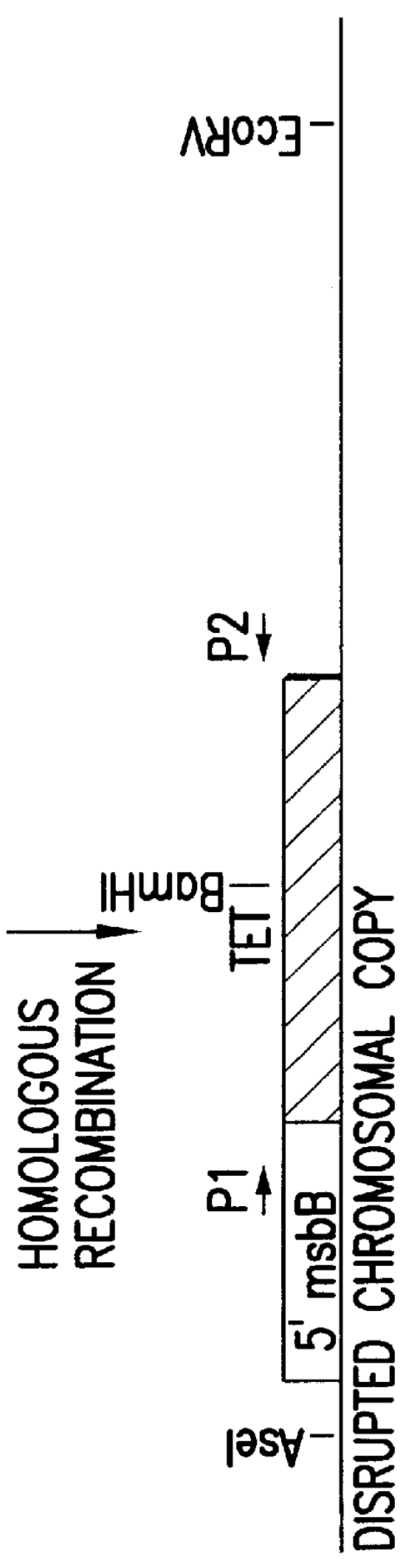
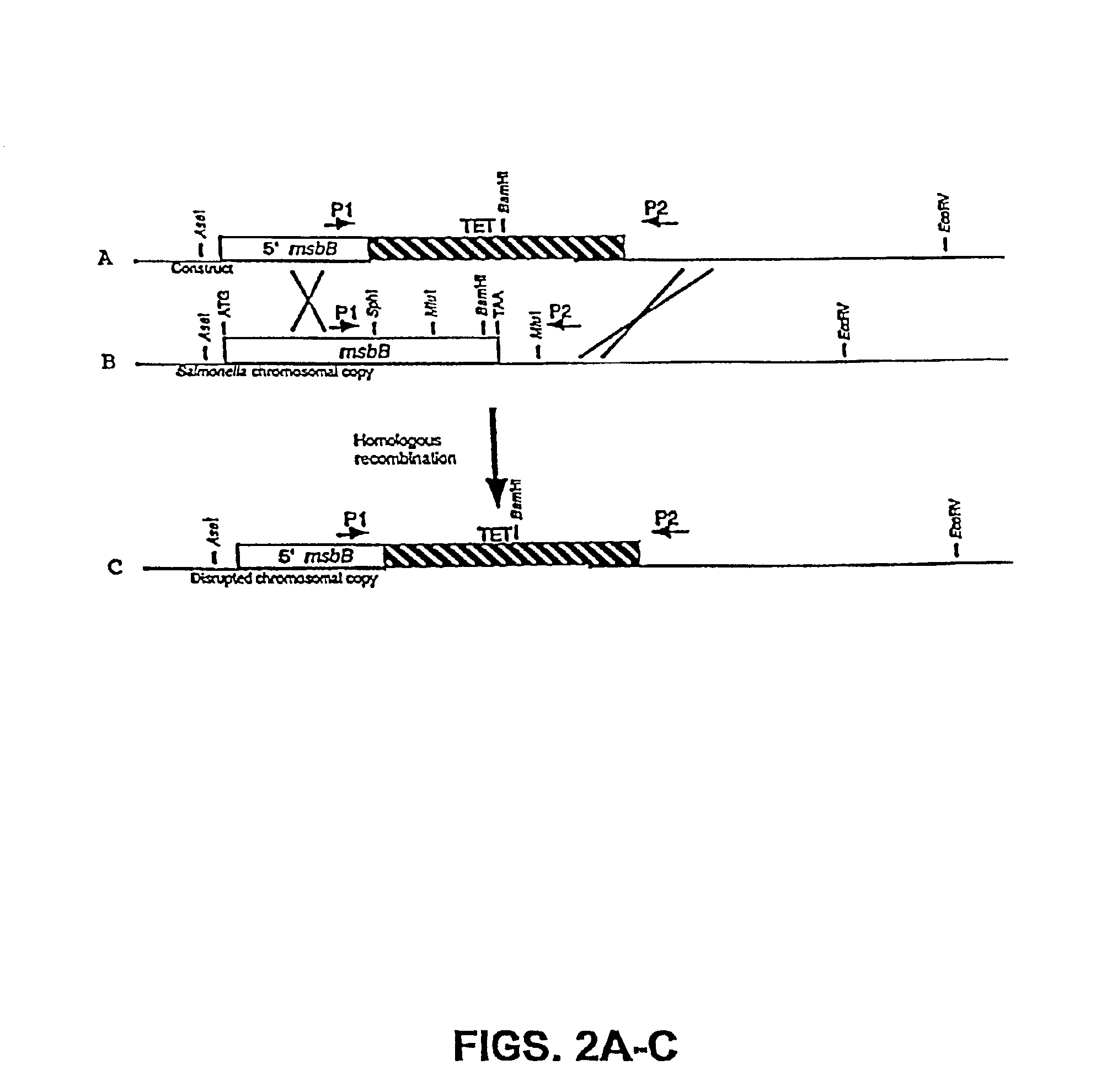
The present invention is directed to mutant Salmonella sp. having a genetically modified msbB gene in which the mutant Salmonella is capable of targeting solid tumors. The present invention further relates to the therapeutic use of the mutant Salmonella for growth inhibition and / or reduction in volume of solid tumors.
Owner:YALE UNIV +1
Genetically modified tumor-targeted bacteria with reduced virulence
InactiveUS6863894B2Effective concentration and/or duration of the therapeutic vectorBiocideBacteriaTumor targetVirulent characteristics
The present invention is directed to mutant Salmonella sp. having a genetically modified msbB gene in which the mutant Salmonella is capable of targeting solid tumors. The invention is also directed to Salmonella sp. containing a genetically modified msbB gene as well as an genetic modification in a biosynthetic pathway gene such as the purI gene. The present invention further relates to the therapeutic use of the mutant Salmonella for growth inhibition and / or reduction in volume of solid tumors.
Owner:VION PHARMA INC +1
Genetically modified tumor-targeted bacteria with reduced virulence
InactiveUS20030109026A1Improve securityReduce capacityBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsTumor targetVirulent characteristics
The present invention is directed to mutant Salmonella sp. having a genetically modified msbB gene in which the mutant Salmonella is capable of targeting solid tumors. The invention is also directed to Salmonella sp. containing a genetically modified msbB gene as well as an genetic modification in a biosynthetic pathway gene such as the purI gene. The present invention further relates to the therapeutic use of the mutant Salmonella for growth inhibition and / or reduction in volume of solid tumors.
Owner:VION PHARMA INC +1
Genetically modified tumor-targeted bacteria with reduced virulence
InactiveUS20020026655A1Improve securityReduce capacityBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsTumor targetVirulent characteristics
The present invention is directed to mutant Salmonella sp. having a genetically modified msbB gene in which the mutant Salmonella is capable of targeting solid tumors. The invention is also directed to Salmonella sp. containing a genetically modified msbB gene as well as an genetic modification in a biosynthetic pathway gene such as the purl gene. The present invention further relates to the therapeutic use of the mutant Salmonella for growth inhibition and / or reduction in volume of solid tumors.
Owner:YALE UNIV +1
Lactobacillus rhamnosus derived from human breast milk and application of lactobacillus rhamnosus
InactiveCN106754470AGrowth inhibitionMaintain gut healthBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliLactobacillus rhamnosus
The invention discloses lactobacillus rhamnosus derived from human breast milk and application of the lactobacillus rhamnosus. The lactobacillus rhamnosus Z5 disclosed by the invention is initially derived from the human breast milk and belongs a new subspecies of the lactobacillus rhamnosus. An experiment proves that the strain has the properties of acid resistance, bile salt resistance, and resistance on a simulated animal gastrointestinal tract environment, capability of inhibiting growth harmful bacteria including escherichia coli and salmonella in intestines and capability of being stuck on epithelial cells of human and animal intestines very well. The lactobacillus rhamnosus can be used for preparing health-care foods, fermented foods, vaccine adjuvants and animal feed so that the balance of intestinal flora of human and animals is easy to adjust and the health of the intestines of the human and animals is increased.
Owner:FEED RESEARCH INSTITUTE CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Salmonella sensor, preparation method and detection method of salmonella concentration
ActiveCN106770566AHigh sensitivityLow detection limitMaterial electrochemical variablesSemiconductor materialsOrganic semiconductor
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Fluorescence quantitative PCR (polymerase chain reaction) detection kit for salmonella and detection method thereof
ActiveCN102443629AMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceSalmonella frintropSalmonella Be
The invention relates to a fluorescence quantitative PCR (polymerase chain reaction) detection kit for salmonella, comprising a salmonella PCR reaction liquid, a Taq enzyme, a positive control and a negative control. The sequences of the specific primers of the fluorescence quantitative PCR detection kit for salmonella are as follows: the upstream primer is 5'-TGCGCCTGCCGTTATCAC-3'; the downstream primer is 5'-ATTTGAGCTGTTGGTTCAGTAACTC-3'; and the fluorescence probe sequence is 5'-CCAACGCCGCAGATATTTGATCGCC-3'. The detection for salmonella in a clinical excrement by using the kit disclosed by the invention has great specificity, sensitivity and stability, the whole detection process can be finished in 2-3 hours, and salmonella in foods or other cultures also can be rapidly and accurately detected.
Owner:广州华银医学检验中心有限公司
Puffed pet food and production method
InactiveCN102894205AEnsure safetySolve the problem of microbial germsAnimal feeding stuffFood safetyHazardous substance
The invention relates to the puffed pet food field, and especially relates to a puffed pet food which is capable of being added by a plurality of nutrients. The invention also relates to a production method of the puffed pet food, and especially relates to a production method of the puffed pet food which is capable of being added by a plurality of nutrients. According to the invention, a first purpose of the invention is to provide the puffed pet food having a plurality of vitamin, protein and fat, the puffed pet food supplements simple fat and is rich in a plurality of nutritional elements. According to the invention, a second purpose of the invention is to provide the production method of the pet food, various harmful substances such as mould and salmonella is removed and killed during the production method, thereby the security of the pet food is guaranteed. For the method, the high temperature three-segment disinfection is employed, thereby the microbial pathogens problem is comprehensively solved; the vitamin with high temperature resistance is ingeniously added, the nutrition can be guaranteed, and the food safety is guaranteed.
Owner:刘少伟 +2
Multi-PCR detection kit for poultry salmonella and non-diagnostic detection method of poultry salmonella
ActiveCN105648055AHigh sensitivityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBiologyMultiplex pcrs
The invention discloses a multi-PCR detection kit for poultry salmonella and a non-diagnostic detection method of the poultry salmonella. The kit comprises 10*PCR buffering liquid, 2.5 U / mu l Taq DNA polymerase, 10 Mm dNTPs, a multi-PCR detection primer group, a positive contrast material and a negative contrast material. The positive contrast material comprises salmonella enteritidis ATCC13076 genome DNA, salmonella typhimurium ATCC14028 genome DNA and salmonella gallinarum ATCC 9184 genome DNA; the negative contrast material is sterilized double distilled water. The invention further discloses a multi-PCR method for detecting the poultry salmonella by applying the kit. The method has the advantages of being rapid, simple, high in specificity and high in sensitivity, three types of salmonella can be detected and classified rapidly through a one-time PCR reaction, compared with traditional serological typing and ordinary PCR detection, great advantages are achieved on the aspect of detection time and detection cost, and the multi-PCR detection kit and the detection method are suitable for batch detection.
Owner:JIANGSU INST OF POULTRY SCI
Microorganism ability verification salmonella sample preparation method
ActiveCN105176823AImprove stabilityImprove survival rateBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementEscherichia coliFreeze-drying
The present invention relates to the technical field of microorganism ability verification, and discloses a microorganism ability verification salmonella sample preparation method. According to the method, salmonella is adopted as target bacteria, and Serratia marcescens, Citrobacter freundii and Escherichia coli are adopted as interference bacteria; the method comprises: (A) strain resuscitation and amplification; (B) strain isolation; (C) bacterial suspension preparation; and (D) freeze-drying and packaging; and the prepared samples comprise a simple-level negative sample, a simple-level positive sample, an intermediate-level negative sample, an intermediate-level positive sample, a difficult-level negative sample and a difficult-level positive sample, wherein the sample having the same level are subjected to paired use. According to the present invention, the sample prepared through the method has the good stability, the strain survival rate is high, and the reasonable level standards with different difficulties are provided.
Owner:舟山出入境检验检疫局综合技术服务中心
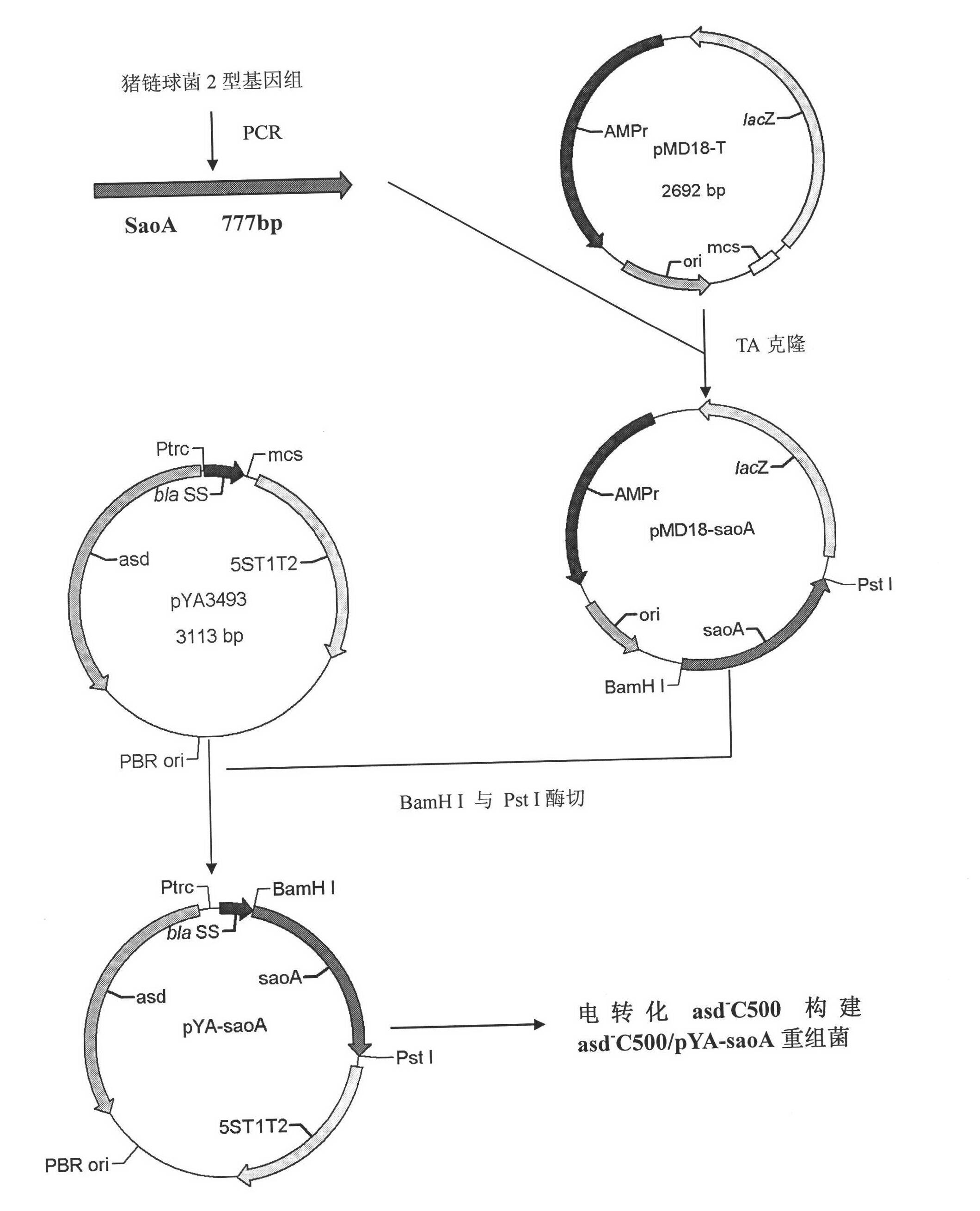
Recombinant Salmonella choleraesuis for expressing surface antigen gene sao of streptococcus suis type 2, vaccine and application
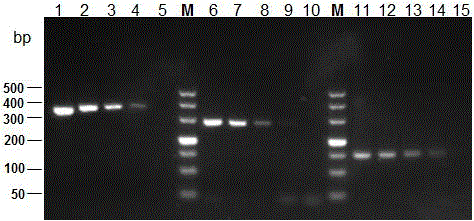
ActiveCN101979501AGood immune protectionPreserve immune efficiencyAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsBacteroidesAntigen
The invention belongs to the field of animal bacterium gene engineering, and in particular relates to construction of resistance marker-free recombinant Salmonella choleraesuis for expressing surface antigen sao gene segment of streptococcus suis type 2, preparation of a vaccine and application. The resistance marker-free recombinant Salmonella choleraesuis for expressing the surface antigen sao gene segment of the streptococcus suis type 2, namely asd-C500 / Pya-saoA is obtained, and the collection number is CCTCC NO: M2010156. The asd gene of the Salmonella choleraesuis is deleted in the recombinant strain, and the recombinant strain contains plasmid pYA-saoA capable of expressing the asd and the sao gene segment of the streptococcus suis type 2. The invention also discloses a method for preparing the recombinant strain and the vaccine, and application in preparing Salmonella choleraesuis-streptococcus suis type 2 vaccines.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV +1
Detection method of food-borne pathogenic bacteria salmonella
ActiveCN106868152ARapid on-site rapid detectionFast on-site safety detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesFood borneFood safety
Owner:宁波海洋研究院 +1
DNA vaccine for use in pancreatic cancer patients
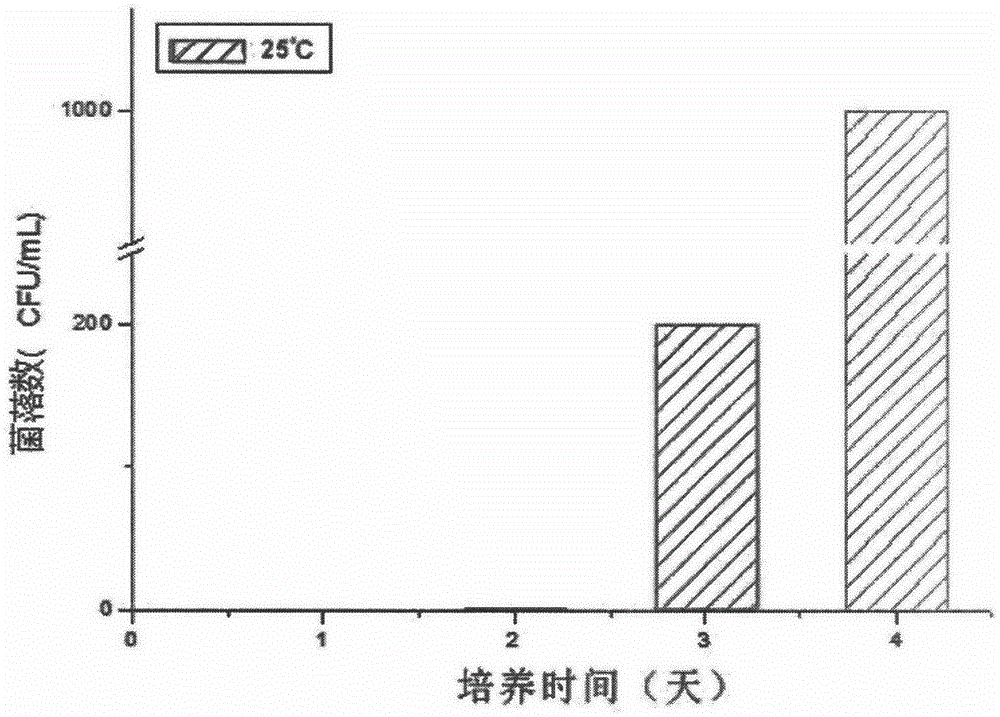
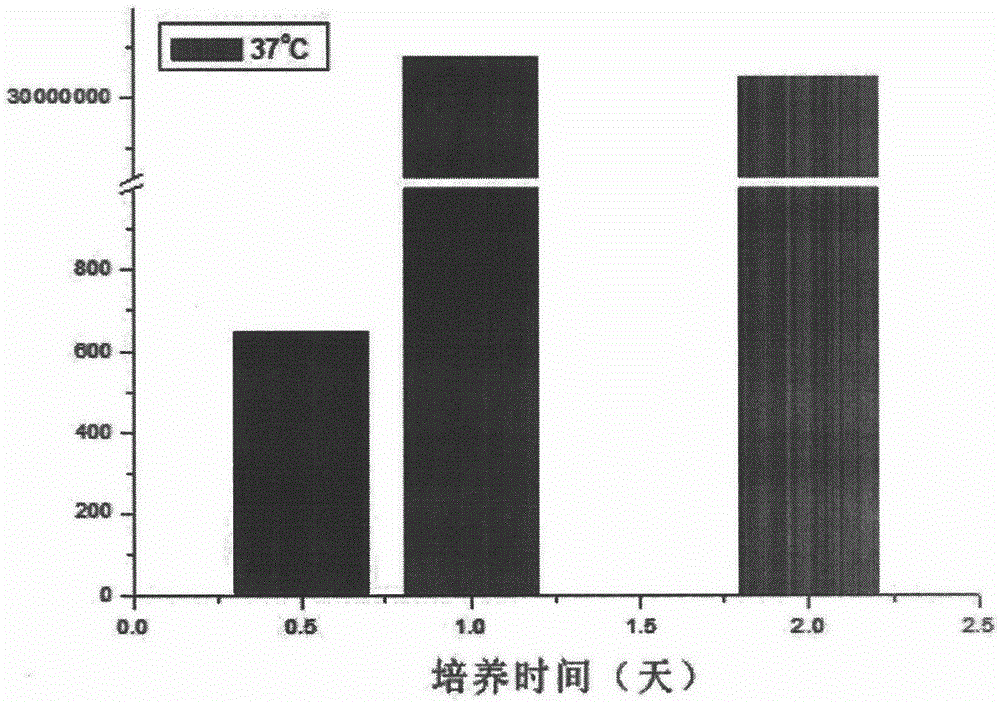
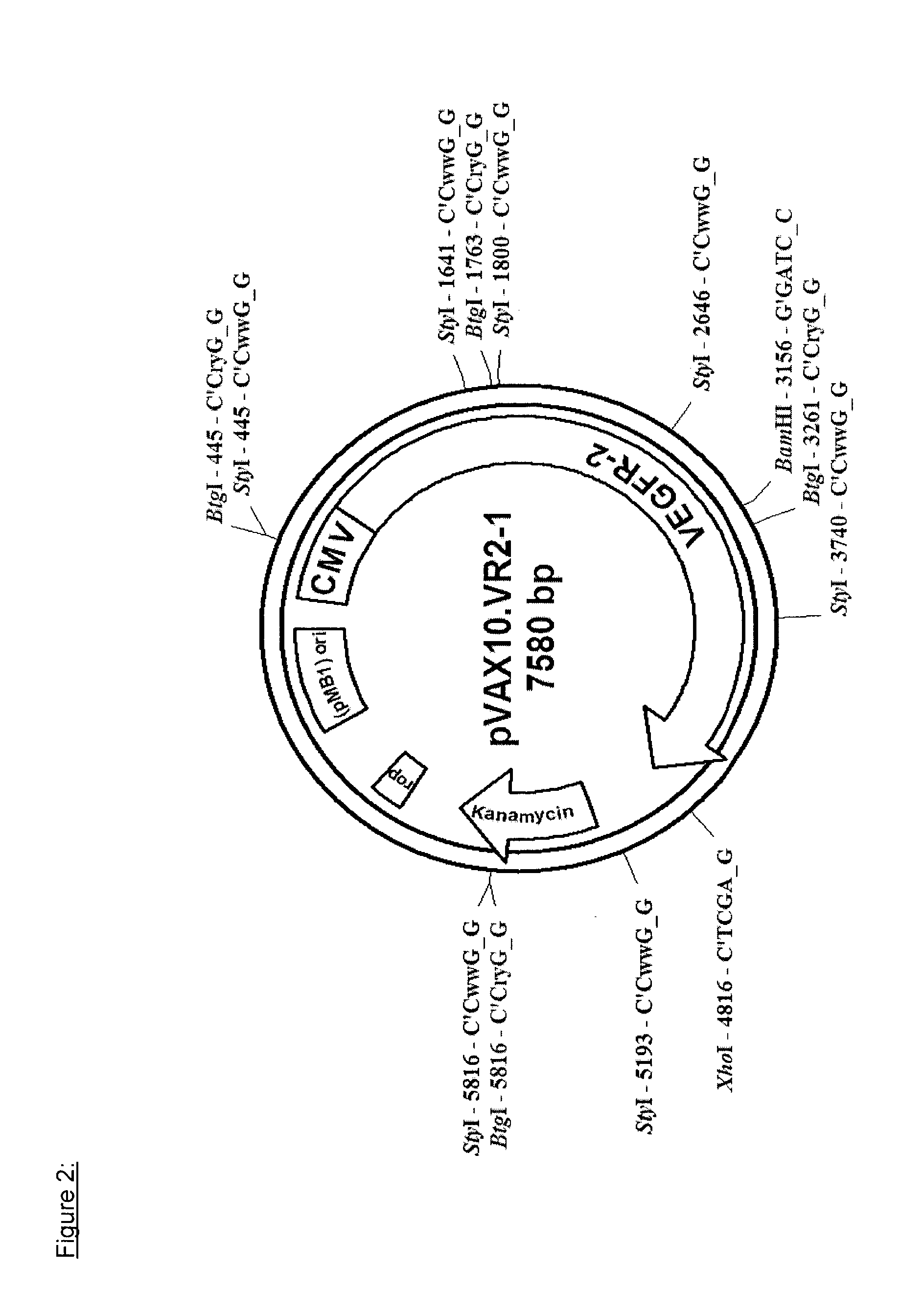
The present invention relates to an attenuated mutant strain of Salmonella comprising a recombinant DNA molecule encoding a VEGF receptor protein. In particular, the present invention relate to the use of said attenuated mutant strain of Salmonella in cancer immunotherapy.
Owner:VAXIMM
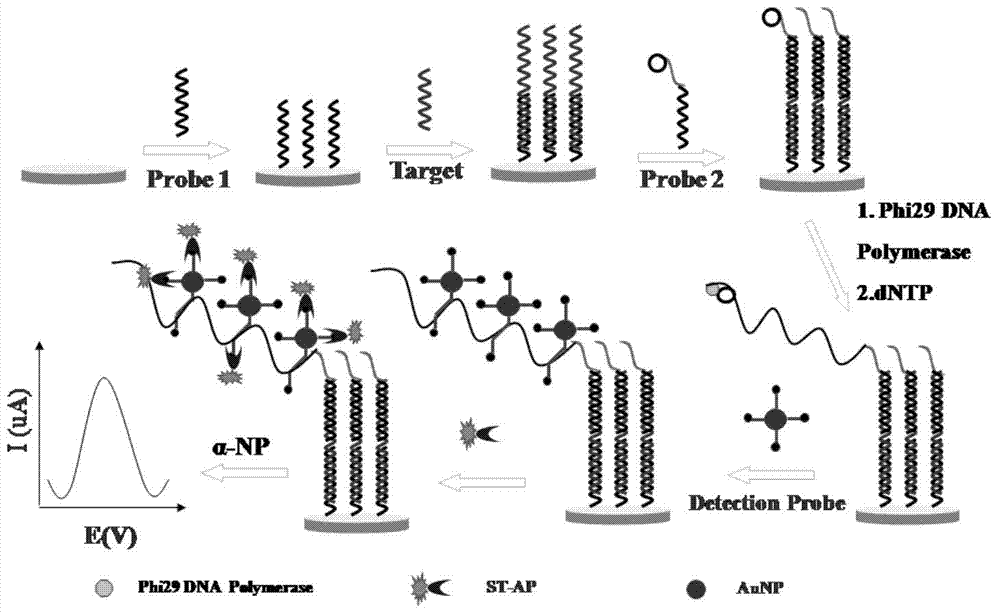
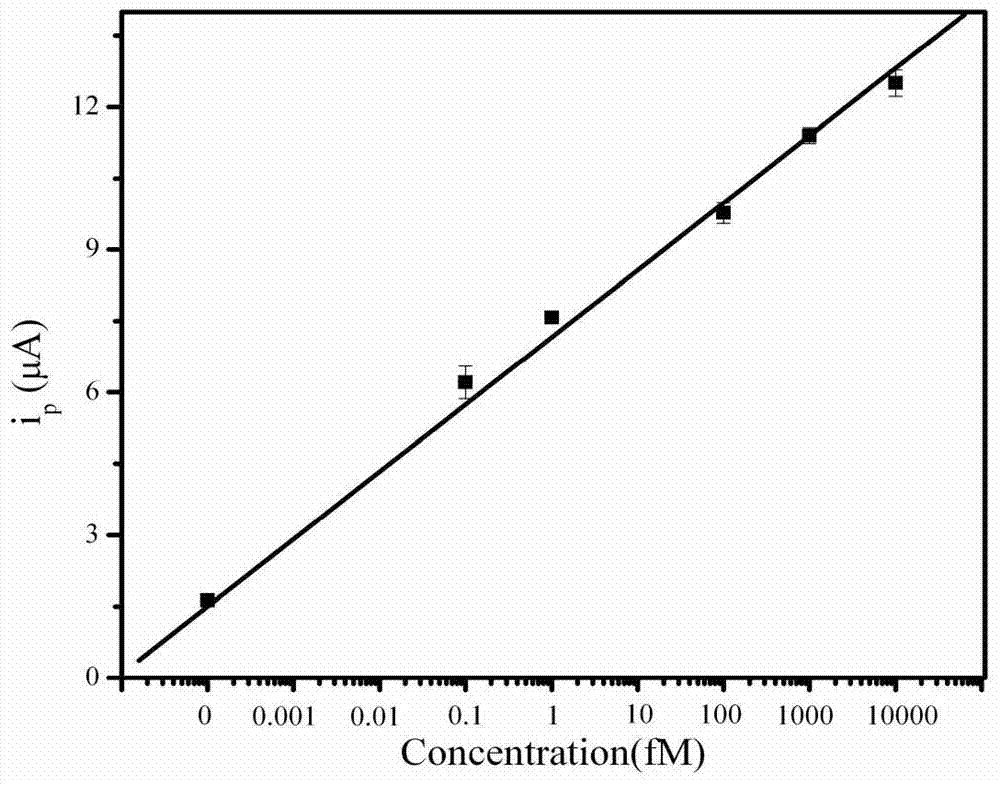
Method for detecting salmonella invA gene based on rolling circle amplification and gold nanoparticles
InactiveCN103614483AReduce testing costsHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesNanoparticleSalmonella Be
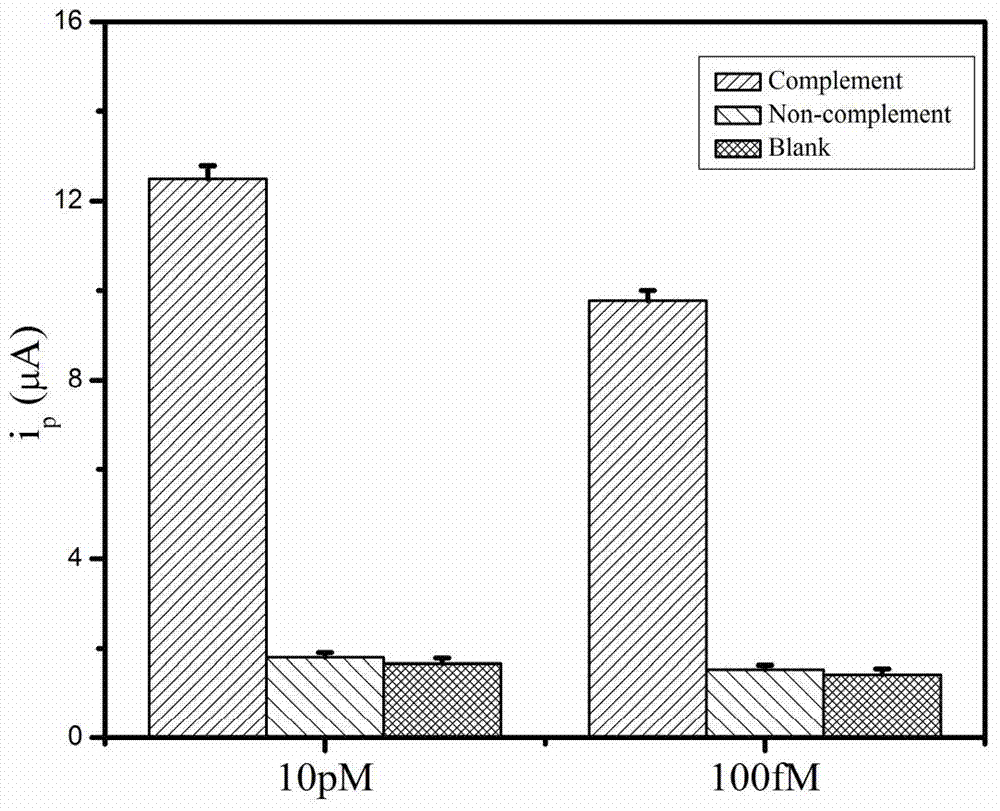
The invention discloses a method for detecting salmonella invA gene based on rolling circle amplification and gold nanoparticles. The method comprises the following steps: dropwise adding a capture probe on a clean gold electrode, placing the gold electrode in a refrigerator overnight, taking out and sealing the gold electrode, dropwise adding a sample to be detected on the gold electrode, dropwise adding cyclic DNA after the reaction, reacting, carrying out rolling circle amplification, adding a gold nanoparticle probe, hybridizing and detecting a DPV signal. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the highly conserved invA gene of the salmonella is selected, the probe specifically combined with the invA gene is designed, and the salmonella invA gene is detected by an electrochemical technology in combination with rolling circle amplification and gold nanoparticle technology, so that the sensitivity is greatly perfected, the linear detection range is extended to 100 aM to 10 pM, and the sensitivity is 100 aM. The salmonella detection range in polluted milk is 20 to 6*10<8> CFU ml<-1>, and the lowest detectable limit is 20 CFU ml<-1>. A method for quickly and ultra-sensitively detecting salmonella is created in the invention to greatly improve the detection sensitivity, and the method has the advantages of being miniaturized in detection equipment, convenient, rapid and low in detection cost.
Owner:CHONGQING MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Inert carrier salmonella and potential application thereof
ActiveCN110218668AHas inert carrier propertiesImprove and refine specificity bottlenecksBacteriaBiological material analysisAntigenSerum ige
The invention relates to an inert carrier salmonella and potential application thereof. The inert carrier salmonella is expected to be developed into a novel inert carrier bacterium. The inert carriersalmonella can be applied to development of an indirect agglutination test detection method for conveniently and rapidly detecting an antigen or an infection antibody. The inert carrier salmonella ispreserved at the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) at present, the preservation address is Beijing, China, the preservation number is CGMCC No.17340, the preservation date is March 18th, 2019, the classification name is Salmonella sp., and the strain number is S9. The salmonella is separated from a healthy chicken flock, the inert carrier is characterized in that bacteria under the high working concentration and serum of various chicken sources under different genetic backgrounds are not subjected to any macroscopic agglutination reaction, in other words, the bacteria and the chicken source serum are not subjected to a nonspecific agglutination reaction, and the salmonella is named as the inert carrier salmonella. The inert carrier salmonella and the potential application thereof are used for developing the novel convenient and rapid indirect agglutination detection method.
Owner:安徽荣达生物技术有限公司
Attenuated Salmonella pullorum and application thereof
InactiveCN102154184ALow toxicityImproving immunogenicityAntibacterial agentsBacteriaHorizontal transmissionMicroorganism
The invention discloses an attenuated Salmonella pullorum and application thereof. By using gene knockout technology, the in vivo colonization gene and the main virulence gene of Salmonella pullorum are deleted, thus obtaining an dual-gene-deleted attenuated Salmonella pullorum SM091-DED strain; and the microbiological preservation number of the strain is CGMCC NO.4604. The virulence of the attenuated Salmonella pullorum disclosed by the invention is obviously reduced, and the in vivo colonization time is short after the attenuated Salmonella pullorum is inoculated into a host; the herd infection test shows that the attenuated Salmonella pullorum has no horizontal transmission capability; the attenuated Salmonella pullorum provides full cross protection for homotype and allotype high-virulence Salmonella pullorum; and after SPF (Specific Pathogen Free) chicks are immunized, the infection of the high-virulence strain can be effectively eliminated, and the herd infection can not be caused. Thus, the invention provides a safe, fine-immunogenicity and low-virulence Salmonellosis avium attenuated live vaccine for preventing Salmonellosis avium.
Owner:HARBIN VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Series G-quadruplex-heme DNA enzyme label-free signal amplification method based on rolling-circle amplification
ActiveCN106367497AQuick checkReduce testing costsMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBiotin-streptavidin complexMicrosphere
The application provides a series G-quadruplex-heme DNA enzyme label-free signal amplification method based on rolling-circle amplification. The series G-quadruplex-heme DNA enzyme label-free signal amplification method comprises the steps of: 1) using affinity eluent and a biotinylated capture probe to treat functional microballs of streptavidin to obtain pretreated microballs; 2) cyclically amplifying and purifying the sample genomic DNA to obtain cyclic DNA; 3) mixing the pretreated microballs obtained in step 1) and the prepared cyclic DNA obtained in step 2) and then amplifying them in the rolling-circle to obtain rolling-circle amplification products; 4) mixing the rolling-circle amplification products with the heme to obtain the rolling-circle amplification products with signals amplified, and forming an amplified detection signal by the rolling-circle amplification products with signals amplified. In the step 1) and step 2) there is no time sequence. The detection limit of salmonella is 0.03 pmol / L, the detection cost is low, the operation is simple, the sensitivity is extremely high, the detection is rapid, and whether the salmonella is contained in the sample can be judged by the naked eye.
Owner:HUNAN INSTITUTE OF ENGINEERING
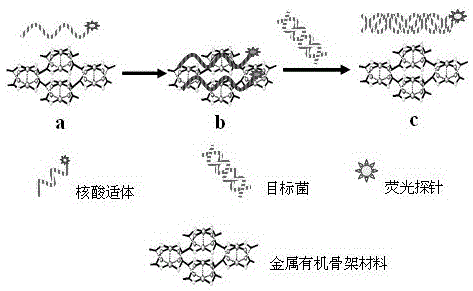
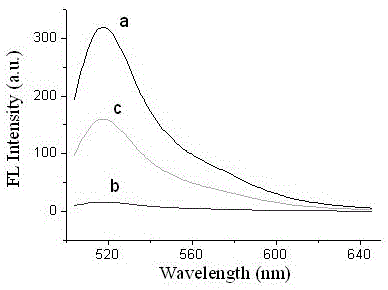
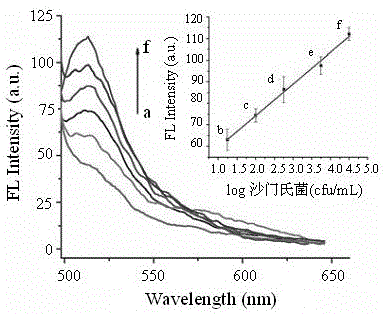
Method for detecting food-borne pathogenic bacteria on basis of metal organic framework material and aptamer fluorescence sensor
InactiveCN105021585AHigh affinityImprove specific recognition abilityFluorescence/phosphorescenceFood borneRelative standard deviation
The invention provides a method for detecting food-borne pathogenic bacteria on the basis of a metal organic framework material and aptamer fluorescence sensor. The fluorescence quenching characteristic of a metal organic framework material and the adsorbability of the framework material to aptamer are utilized, when the aptamer marked by a fluorescence probe is adsorbed to the metal organic framework material, fluorescence of the probe is quenched, a target bacterium is added into a system, the aptamer marked by the fluorescence probe leaves the metal organic framework material and is combined with the target bacterium to enhance fluorescence signals of the probe, and by means of the combination with high appetency and a high specific recognition ability of the aptamer, the method is constructed. Salmonellas are used as model analyte, the fluorescence intensity of the probe and the logarithm of target bacterium concentration form a good linear relation, the linearity range is 18-3.2*10<4> cfu / mL, the detection limit is 5 cfu / mL (S / N=3), the relative standard deviation (RSD) of standard adding experiments ranges from 3.6% to 7.5%, and the recovery rate is within the range of 90.0%-106.0%. The method for detecting the food-borne pathogenic bacteria has the advantages of being accurate, sensitive, high in specificity and the like.
Owner:SHENZHEN POLYTECHNIC
Anti-bacterial film modified by silver-lysozyme nano-cluster
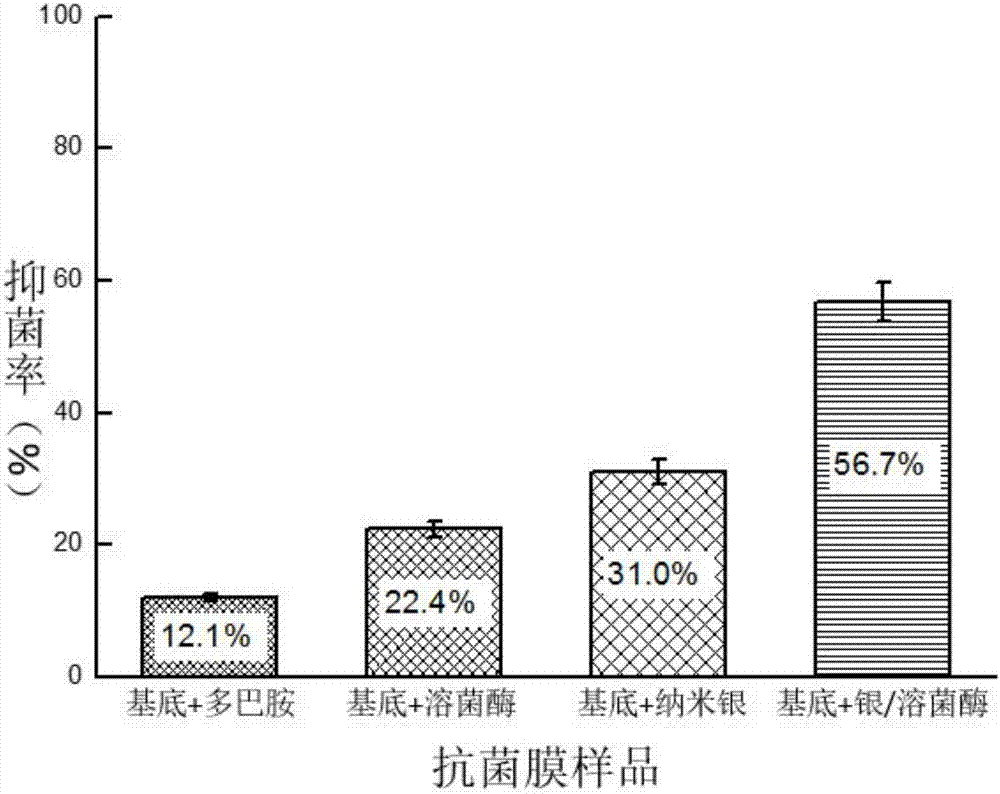
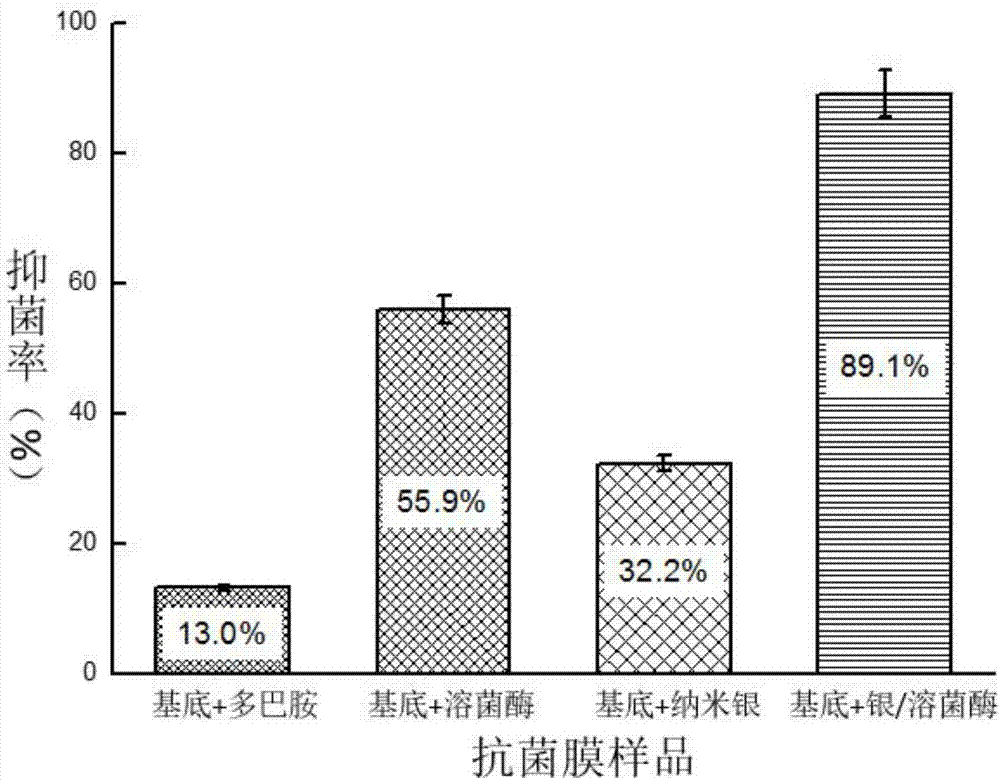
ActiveCN107018991AGood antibacterial effectBiocideDead animal preservationStaphylococcus aureusSalmonella Be
The invention discloses an anti-bacterial film modified by a silver-lysozyme nano-cluster, and belongs to the field of anti-bacterial materials. A preparation method of the anti-bacterial film comprises the following steps: modifying a layer of polydopamine on the surface of a substrate material; then, crosslinking a silver-lysozyme nano-cluster to the surface of the polydopamine through glutaraldehyde to obtain an efficient broad-spectrum antibacterial film material. According to different silver ion contents, the bacteriostasis rate of the anti-bacterial film on salmonella is 51.7 to 100 percent, and the bacteriostasis rate on staphylococcus aureus is 69.5 to 100 percent. In the anti-bacterial film, a substrate is modified by the silver-lysozyme nano-cluster, so that the stability of nano-silver is enhanced by adding lysozyme, the using amount of the silver is lowered greatly, the toxicity is lowered, the cost is controlled, and the reusing rate of the film is increased. The anti-bacterial film can be applied to preparation of food packaging materials and surface anti-bacterial films of medical anti-bacterial instruments.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Biosensor and method for detecting salmonella
InactiveCN110205394AImplement triggerRealize detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesPhosphorylationHemin
The invention relates to the technical field of molecular biology, and in particular, relates to a biosensor and method for detecting salmonella. The biosensor includes an RPA reaction reagent, a Lambda nucleic acid exonuclease cutting reaction reagent, an HCR reaction reagent and a chromogenic reagent. A double-stranded nucleic acid of salmonella is amplified by a multi-enzyme system, and dsDNA phosphorylated at the 5' end is obtained. 5'-phosphorylated strands in the dsDNA are digested by Lambda exonuclease, and RPA products become single strands. A universal junction is exposed, an HCR reaction is initiated, and released G-tetrad binds to Hemin to form G4 DNAzyme, colorless TMB is catalyzed to be oxidized into blue oxTMB visible to naked eyes by H2O2, and then salmonella is detected through the change of color and absorbance value. The biosensor has the advantages of visualization, versatility, rapidity and high sensitivity.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV +1
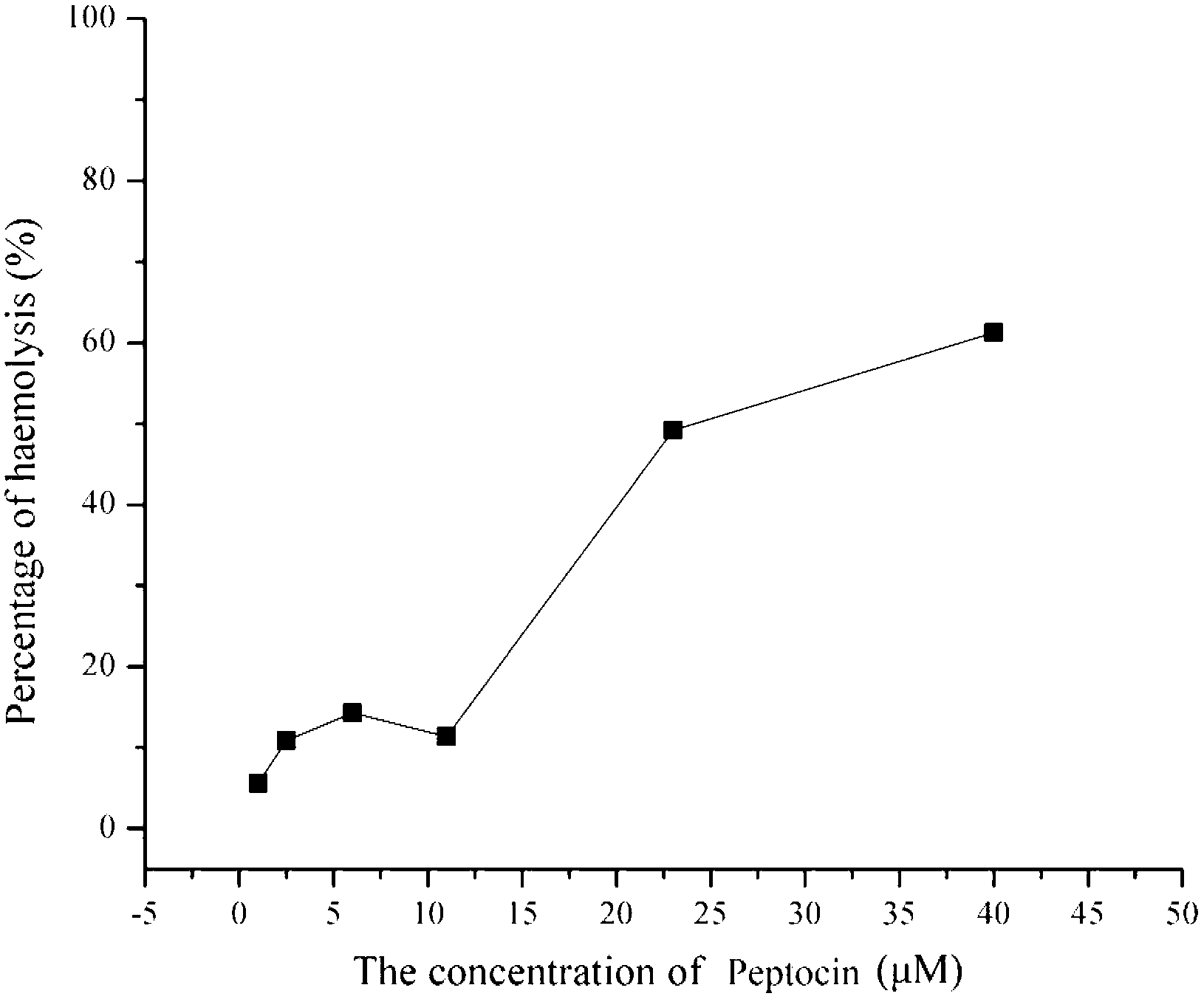
Antibacterial peptide of heterometrus spinifer and application of antibacterial peptide
InactiveCN103265628AImprove antibacterial propertiesBroad-spectrum antimicrobial activityAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsChemical synthesisDisease
The invention provides a Peptocin antibacterial peptide separated from heterometrus spinifer and obtained through a chemical synthesis method. The antibacterial peptide has a remarkable antibacterial effect on clinically-separated multi-drug resistant acinetobacter baumannii, and can be used for efficiently inhibiting the growth of the drug resistant acinetobacter baumannii; and meanwhile, human red blood cell toxicity tests also show that the antibacterial peptide is small in toxicity and can be applied to the preparation of drugs for treating or preventing diseases caused by the drug resistant acinetobacter baumannii and particularly to the preparation of drugs for treating serious infectious diseases such as ventilator-associated pneumonia, septicemia, meningitis, otitis media, skin soft-tissue infection, urinary system infection, central nervous system infection and the like caused by the drug resistant acinetobacter baumannii. The antibacterial peptide provided by the invention is remarkable in inhibiting effect on gram bacteria, unique in antibacterial mechanism and low in toxicity, and can also be applied to the preparation of drugs for treating or preventing diseases caused by micrococcus luteus, salmonella and other gram bacteria.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (WUHAN)
Method for rapidly detecting salmonellae
PendingCN106702016AEasy to operateShorten the timeMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesCouplingSalmonella Be
The invention belongs to the field of detection of pathogenic bacteria and discloses a method for rapidly detecting salmonellae. The method comprises steps as follows: (1) immunomagnetic beads and a to-be-detected sample in a form of liquid are mixed to capture possible salmonellae in the to-be-detected sample, and the immunomagnetic beads are obtained through coupling of antibodies and magnetic balls; (2) the immunomagnetic beads possibly capturing the salmonellae are mixed with a liquid culture medium, and the obtained mixture is cultured under the conditions under which salmonellae can be proliferated; (3) thalli obtained through culture in step (2) are subjected to PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification by use of specific primers of the salmonellae, and existence of the salmonellae in the to-be-detected sample is judged according to a PCR amplification product. The method is simple and rapid to operate, takes a short time, has higher sensitivity and accuracy and high applicability, is particularly favorable for application and popularization in a wide range and has great significance for safety monitoring and supervision of food.
Owner:BEIJING CENT FOR PHYSICAL & CHEM ANALYSIS
Method for eliminating multi-copy plasmid in salmonella by using suicide vector
ActiveCN106967744AElimination of multi-copy plasmidsA method for eliminating multi-copy plasmids, as well as specific single-copy plasmidsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismSalmonella Be
The invention belongs to the field of microorganisms, and in particular relates to a method for eliminating multi-copy plasmid in salmonella by using a suicide vector, and application of the method. According to the method, the multi-copy plasmid in the salmonella is eliminated by using an exogenous suicide vector. The whole process is simple, rapid, stable and efficient. A basis is made for studying functions of the plasmid.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
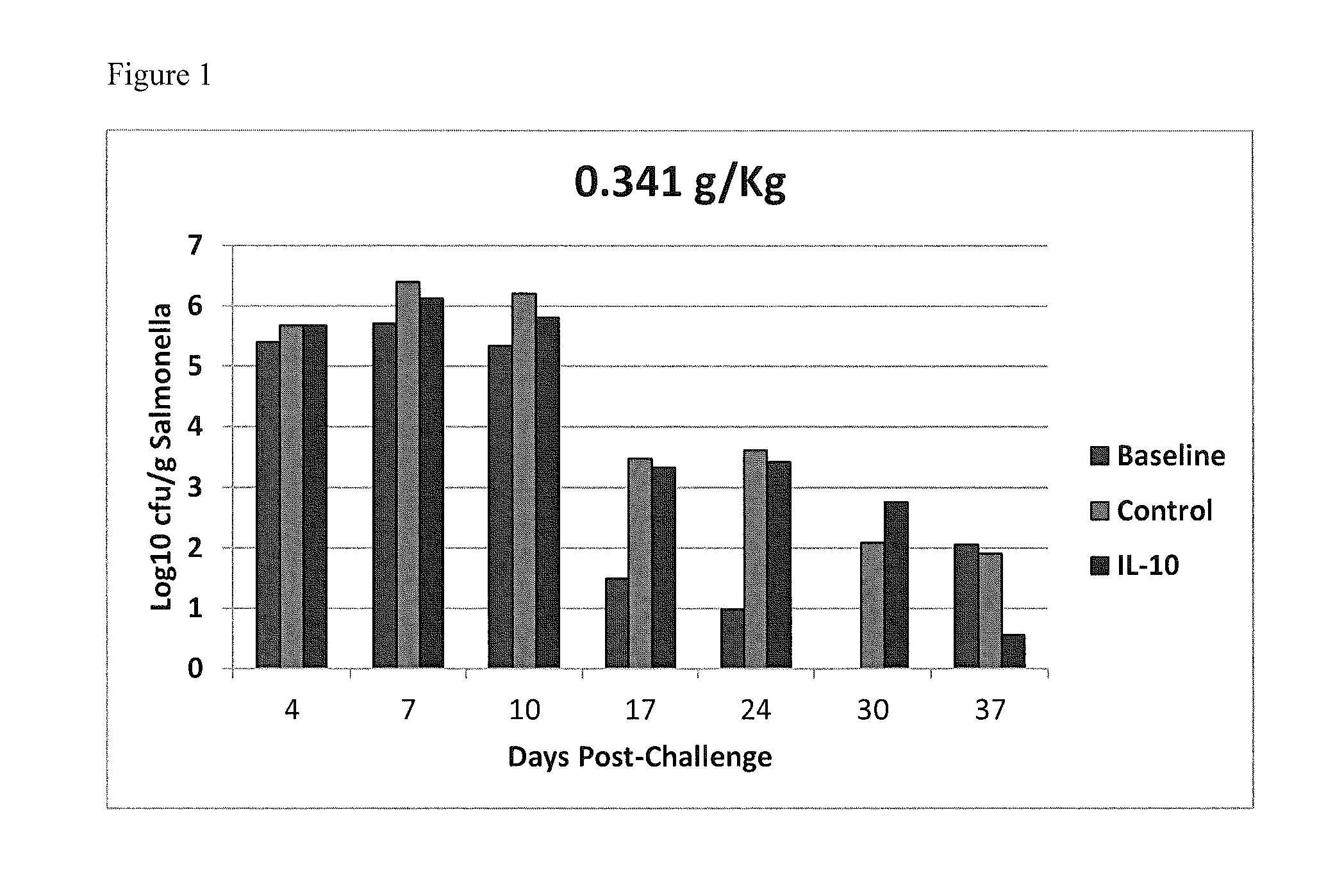
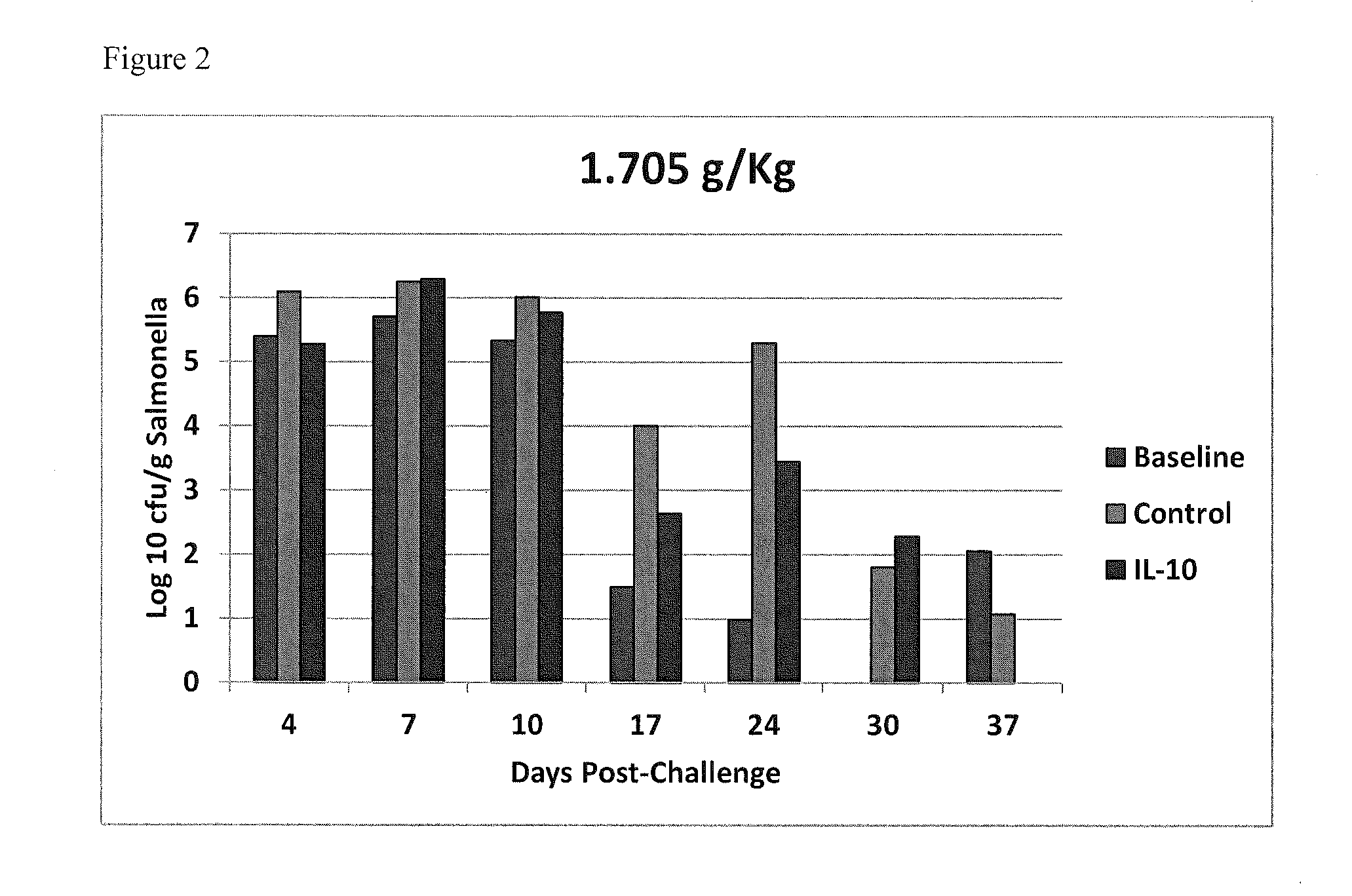
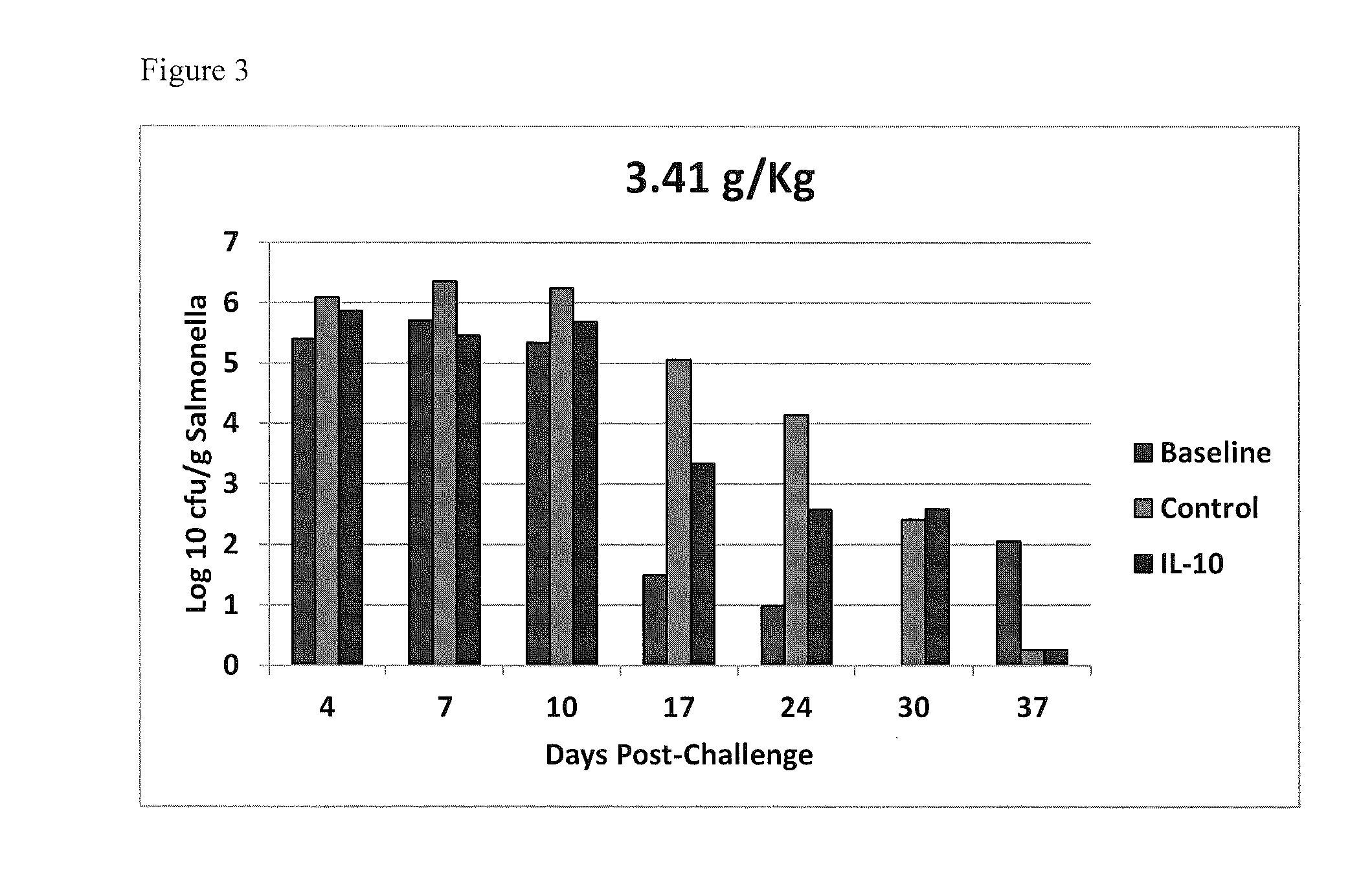
Methods of reducing salmonella in poultry
Described herein are methods of reducing Salmonella in the intestines of poultry in need thereof by administering to a poultry bird an effective amount of an interleukin-10 peptide or an isolated antibody that specifically binds an interleukin-10 peptide. Administering may be performed within 1 to 4 weeks of harvest of the poultry in order to reduce Salmonella transmission to human consumers. Also included herein are finishing feeds that include an interleukin-10 peptide or an isolated antibody that specifically binds an interleukin-10 peptide.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND +1
Inductive formation method for VBNC (viable but nonculturable) salmonella
ActiveCN105200034AIncrease awarenessSpeed up recoveryMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismFood safety
The invention discloses an inductive formation method for VBNC (viable but nonculturable) salmonella. The method comprises the following steps: salmonella is suspended in a liquid and uniformly mixed, the concentration of a bacterial liquid is enabled to be 107-108 CFU / mL, the bacterial liquid is treated with ultrasonic waves of 190-570 W at the constant temperature of 42-55 DEG C for 5-25 min, and whether the salmonella is induced into the VBNC state is detected. According to the method, understanding about the VBNC salmonella is expanded, and theoretical basis and technical support are provided for better application of the ultrasonic heat technology to food processing, microorganism control and food safety control.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
DNA vaccine for use in pancreatic cancer patients
ActiveUS20150165011A1Optimize treatment planOrganic active ingredientsBacteriaVEGF receptorsSalmonella Be
The present invention relates to an attenuated mutant strain of Salmonella comprising a recombinant DNA molecule encoding a VEGF receptor protein. In particular, the present invention relate to the use of said attenuated mutant strain of Salmonella in cancer immunotherapy.
Owner:VAXIMM
Salmonella detection primer group, method and kit based on RPA-LbCas12a-TTECDS system
InactiveCN113186313AChanging binding energyStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesNucleotideSalmonella
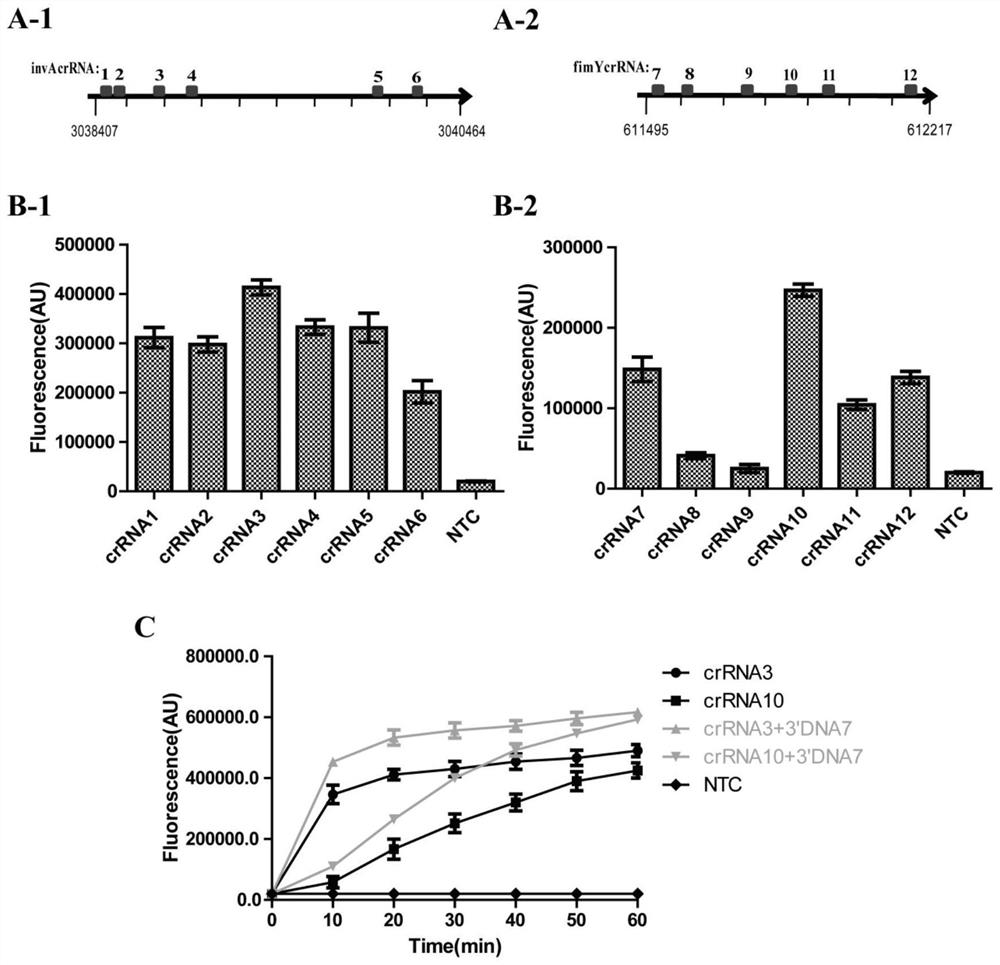
The invention provides a salmonella detection primer group, a salmonella detection method and a salmonella detection kit based on an RPA-LbCas12a-TTECDS system, and relates to the field of salmonella detection. Based on the combination of a recombinase polymerase amplification technology and a CRISPR gene detection technology, salmonella is detected through an optimized and modified crRNA double-target gene combination, crRNA is screened and optimized aiming at an invA gene and a fimY gene of the salmonella respectively, and upstream and downstream primers for RPA reaction are designed according to nucleotide sequences at two ends of a matched sequence of the crRNA, so that the primer group is obtained. According to the primer group and the crRNA, the RPA-LbCas12a-TTECDS system is designed, and t hesalmonella detection method and kit are established according to the system. The detection method and the kit provided by the invention are used for detecting actual samples, and have the advantages of strong specificity, rapid detection, high sensitivity and high precision.
Owner:常州市疾病预防控制中心
Foot and mouth disease virus inhibitor and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN101732710AQuick solveImprove the immunityAntiviralsAntibody medical ingredientsIntramuscular injectionSalmonella Be
The invention belongs to the genetic engineering field, in particular relates to a foot and mouth disease virus inhibitor which is designed by adopting RNAi technology and a preparation method and application thereof. The inhibitor is a recombinant live bacterial vaccine containing plasmid for expressing siRNA of foot and mouth disease virus and uses attenuated salmonella suipestifer as recipientbacterium. The recombinant live bacterial vaccine of the invention is convenient to store and use. The inhibitor can be given by injection as well as by mouth. The attenuated salmonella is used as carrier to transfer the expression plasmid of siRNA so that the organism can resist the targeting virus of siRNA and can also resist the infection of salmonella.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Method and kit for quickly detecting interior label of salmonella by adopting reverse transcription fluorescent quantitation
ActiveCN102676662AAvoid False Negative Missed TestsHigh detection specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesDiagnosis laboratorySalmonella
The invention discloses a quick detection method by using an interior label and taking a sigD / sigE gene of salmonella as a target through reverse transcription fluorescent quantitation PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction). In the quick detection method, an RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) interior label obtained by PCR amplification for three times is composed. In addition, the invention further provides a corresponding kit and application. The method disclosed by the invention can be widely applied to the fields such as research of laboratories, food safety and health and hygiene. The phenomenon of false negative missed detection can be avoided, so that the PCR amplification is effectively monitored; in addition, the detection specificity of salmonella is strong, so that dead bacteria and live bacteriacan be effectively distinguished; the quickness and high detection sensitivity are obtained; and the method can be applied to high-throughput screening of the salmonella in the food.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV +1
Salmonella constant temperature gene amplification fast detecting kit and method
InactiveCN101246126AStrong specificityRapid expansionMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorMicrobiological testing/measurementSalmonella BeGene
The present invention discloses a salmonella constant-temperature gene amplification fast detecting reagent kit and the method thereof, the reagent kit comprises the primer mixed liquid, the Bst DNA polyase, the reacting liquid, the sample pretreating liquid, the color developing agent, the positive comparison and negative comparison, wherein the sequence of the primer is the sequence such as SEQ ID NO.1, SEQ ID NO.2, SEQ ID NO.3 and SEQ ID NO.4. Through extracting the salmonella genome DNA, constant-temperature gene amplification reaction and judging the reaction product result with the reagent kit the high-specificity, quick, high-sensitivity and simple detecting to the salmonella is realized.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com