Method for self-calibrating a rotary encoder
A rotary encoder and self-calibration technology, which is applied in the direction of converting sensor output, instruments, and using electric/magnetic devices to transfer sensing components, etc., can solve the problems of increasing calibration effort and time, reduce cost and complexity, and eliminate centrifugal effect of error
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
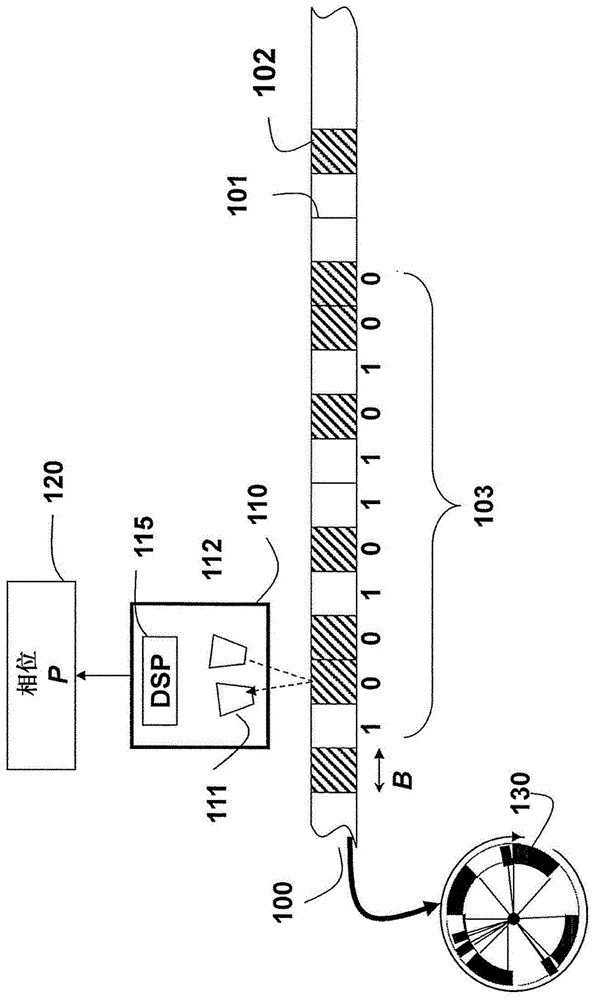
[0028] Embodiments of the present invention provide a monorail absolute rotary encoder. The read head can be a linear charge coupled device (CCD) or complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS) to obtain a 1D image of the rotating circular scale. The 1D image comprises a linear array of pixels. The scale comprises reflective and non-reflective areas arranged according to the deBruijn sequence. The deBruijn sequence is a good fit because the pattern itself is circular in nature.
[0029] Absolute Round Dial
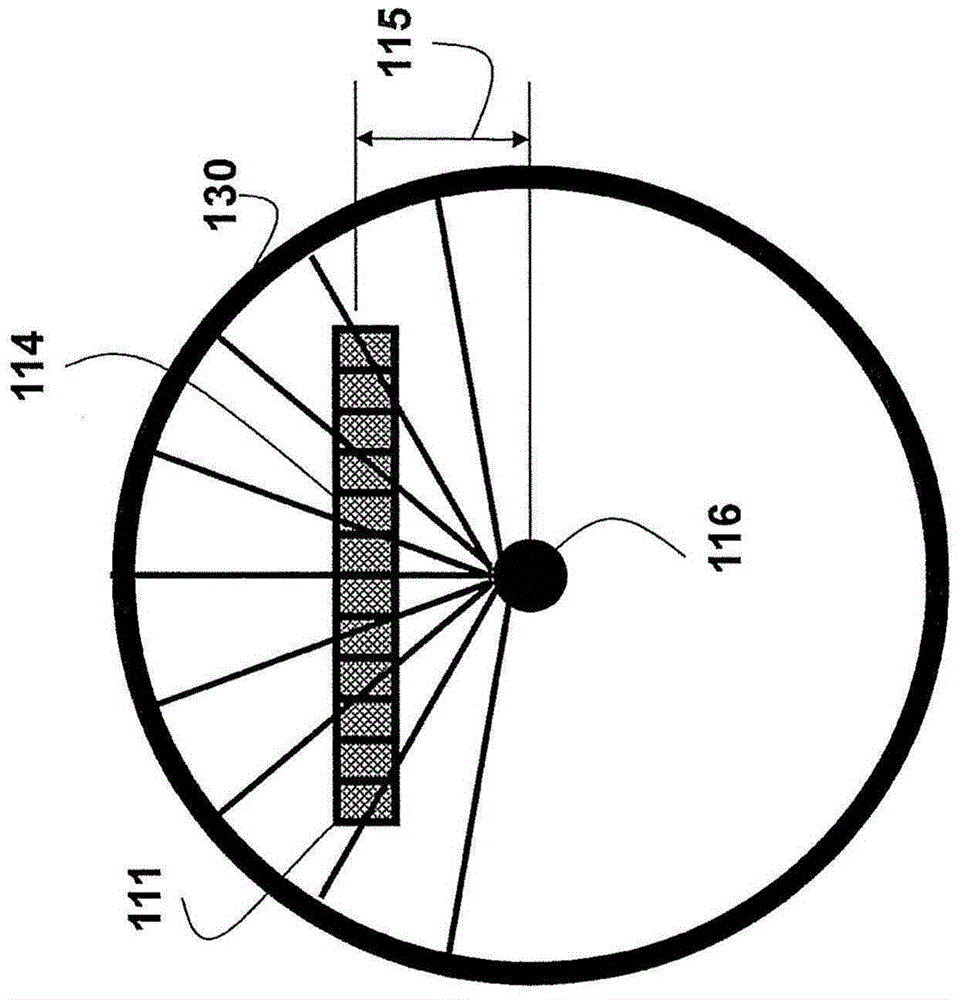
[0030] Figure 1 shows a small part of a circular scale 100 of an absolute encoder of an embodiment of our invention. Details of the dial are described in US application 13 / 100092. This dial is used to determine the high resolution phase P120.
[0031] The dial may include alternating light reflective 101 and non-reflective 102 marks or digits. The markings may also alternate between opaque and transparent depending on the relative position of the light source with ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com