Patents
Literature
40results about How to "Ass quality" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
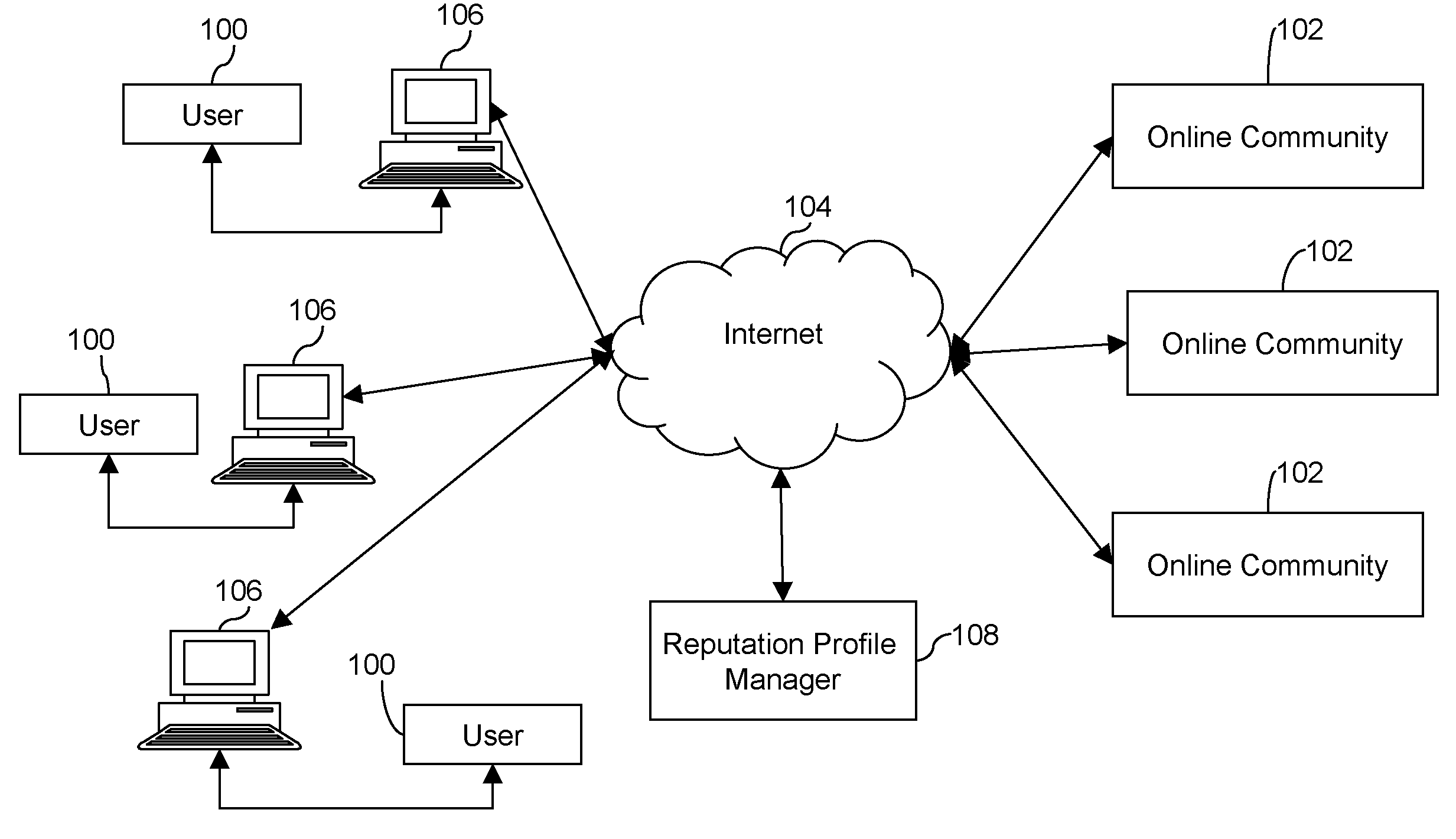
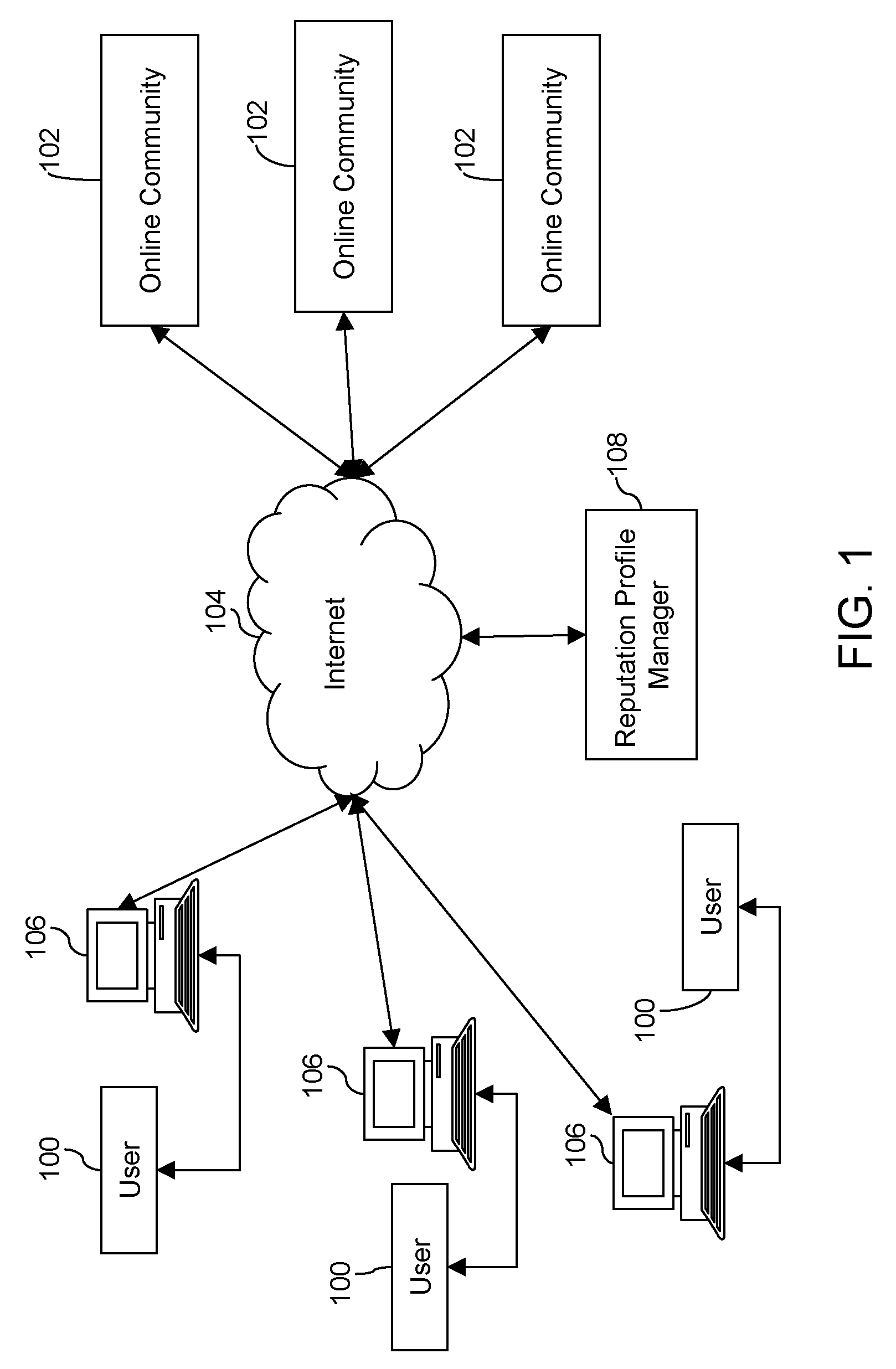
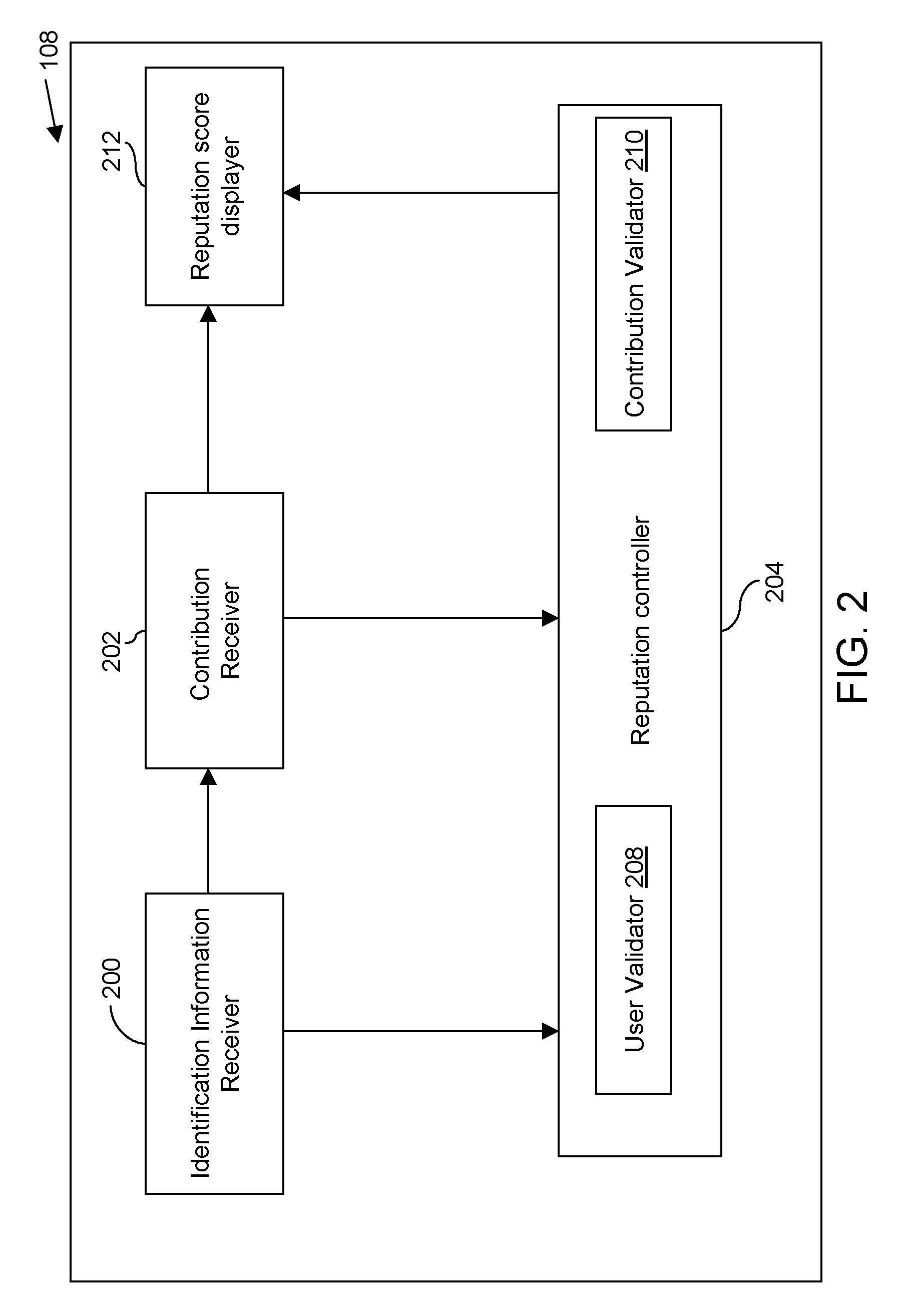
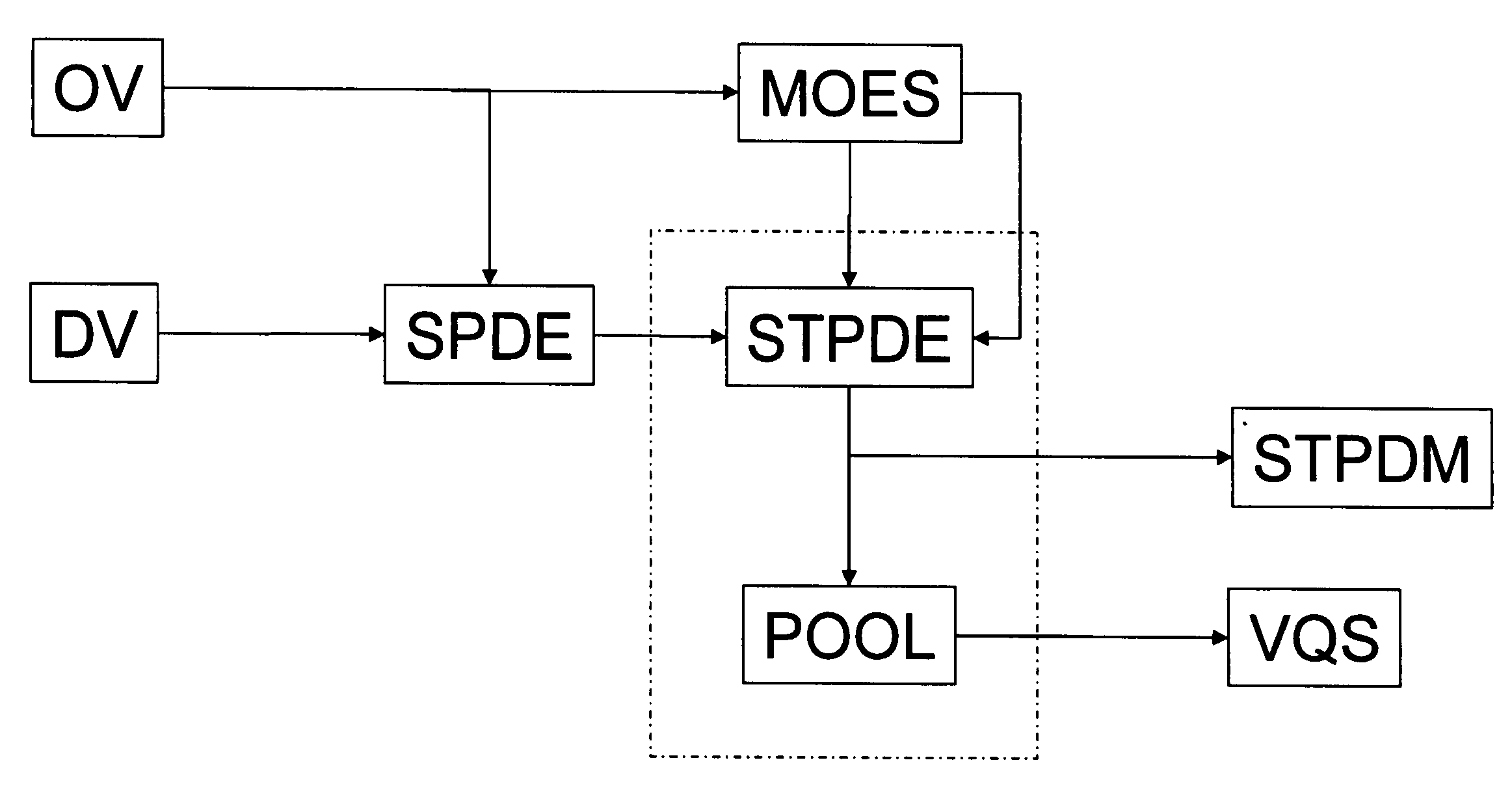
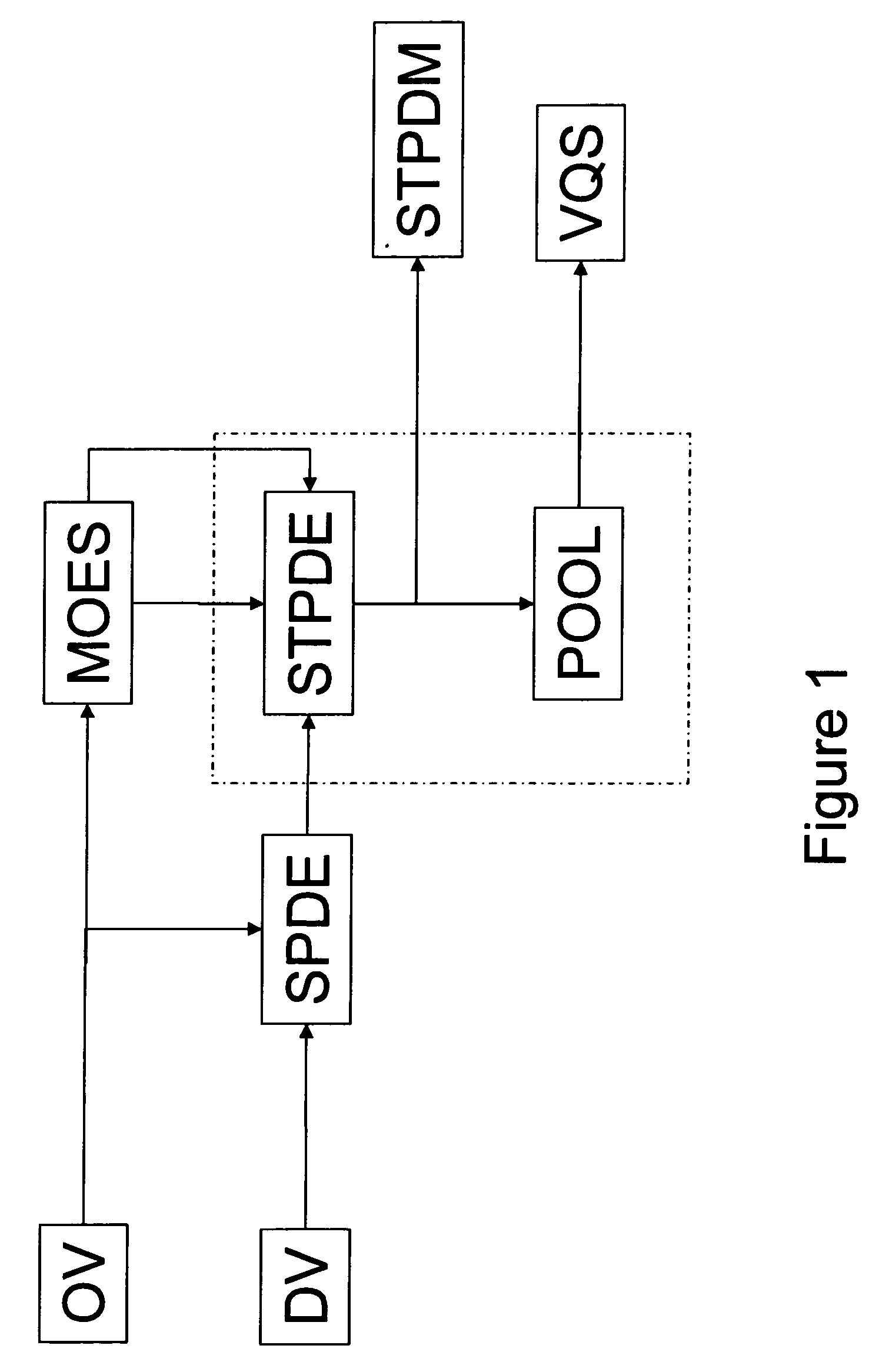
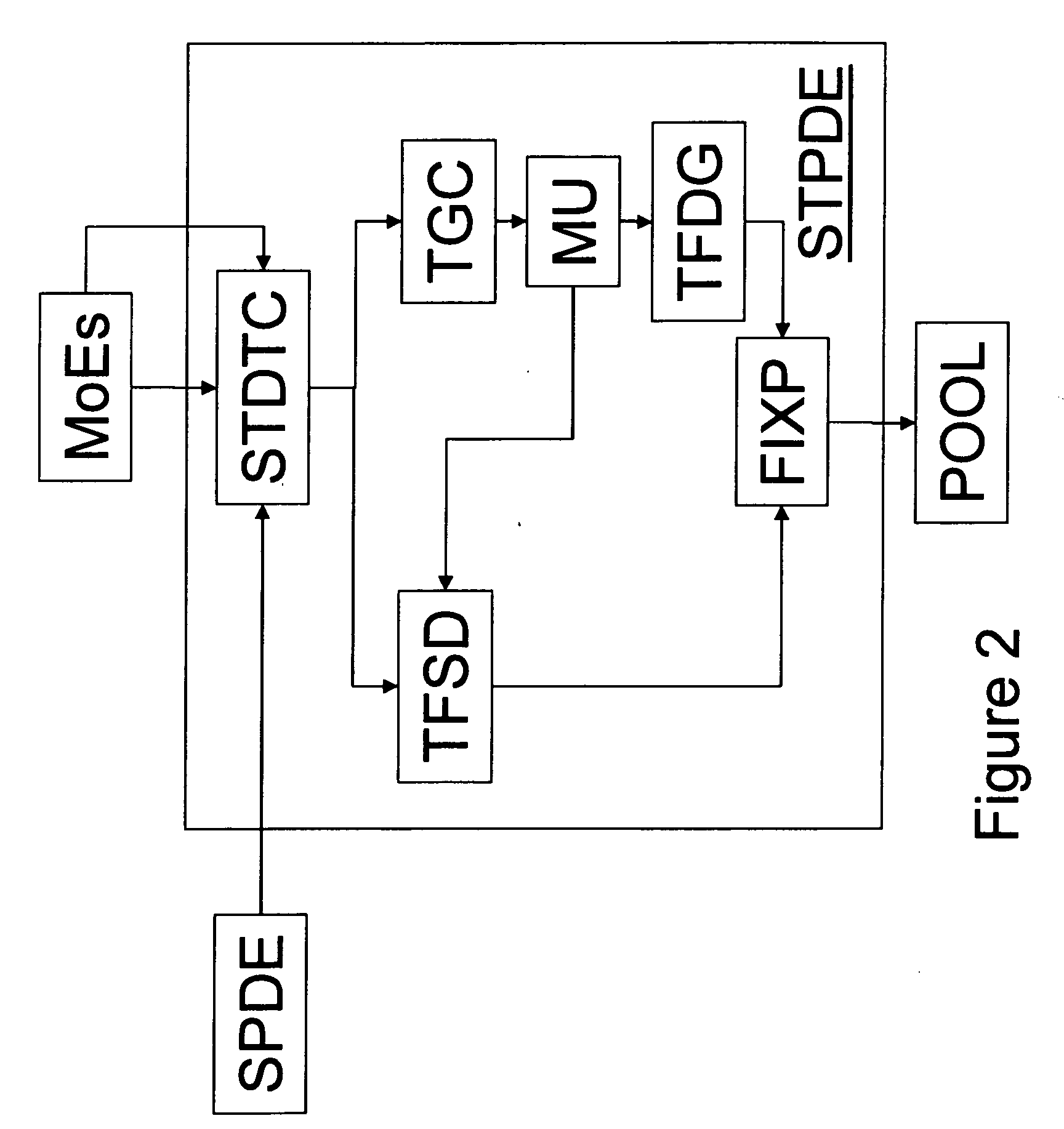
Method and system for managing reputation profile on online communities
InactiveUS20080109491A1Quality improvementAss qualityDigital data information retrievalOffice automationUser participationOnline community
A method and a system for evaluating the quality of a contribution made by a user in a distributed online community framework are disclosed. The quality of contribution is assessed by creating a reputation profile of the user across multiple online communities. The reputation profile contains a reputation score indicating the credibility of the user, user identification information, user participation statistics and user contribution information. Such reputation score is calculated based on the feedback provided by other users for the contribution made by the user. The system also allows maintaining and publishing a unique reputation profile across the distributed online communities. Maintaining the reputation profiles incentivizes users to contribute better quality content. This improves the overall quality of the community discourse.
Owner:SEZWHO
Aerosol drug formulations containing hydrofluoroalkanes and alkyl saccharides
InactiveUS6932962B1Function increaseGood dispersionPowder deliveryDispersion deliveryAerosol drugsActive agent
Aerosol formulations suitable for use in pressurised metered dose inhalers comprise a hydrofluoroalkane propellant, an medicament for inhalation and a surfactant which is a a C8–C16 fatty acid or salt thereof, a bile salt, a phospholipid, or an alkyl saccharide.
Owner:ASTRAZENECA AB
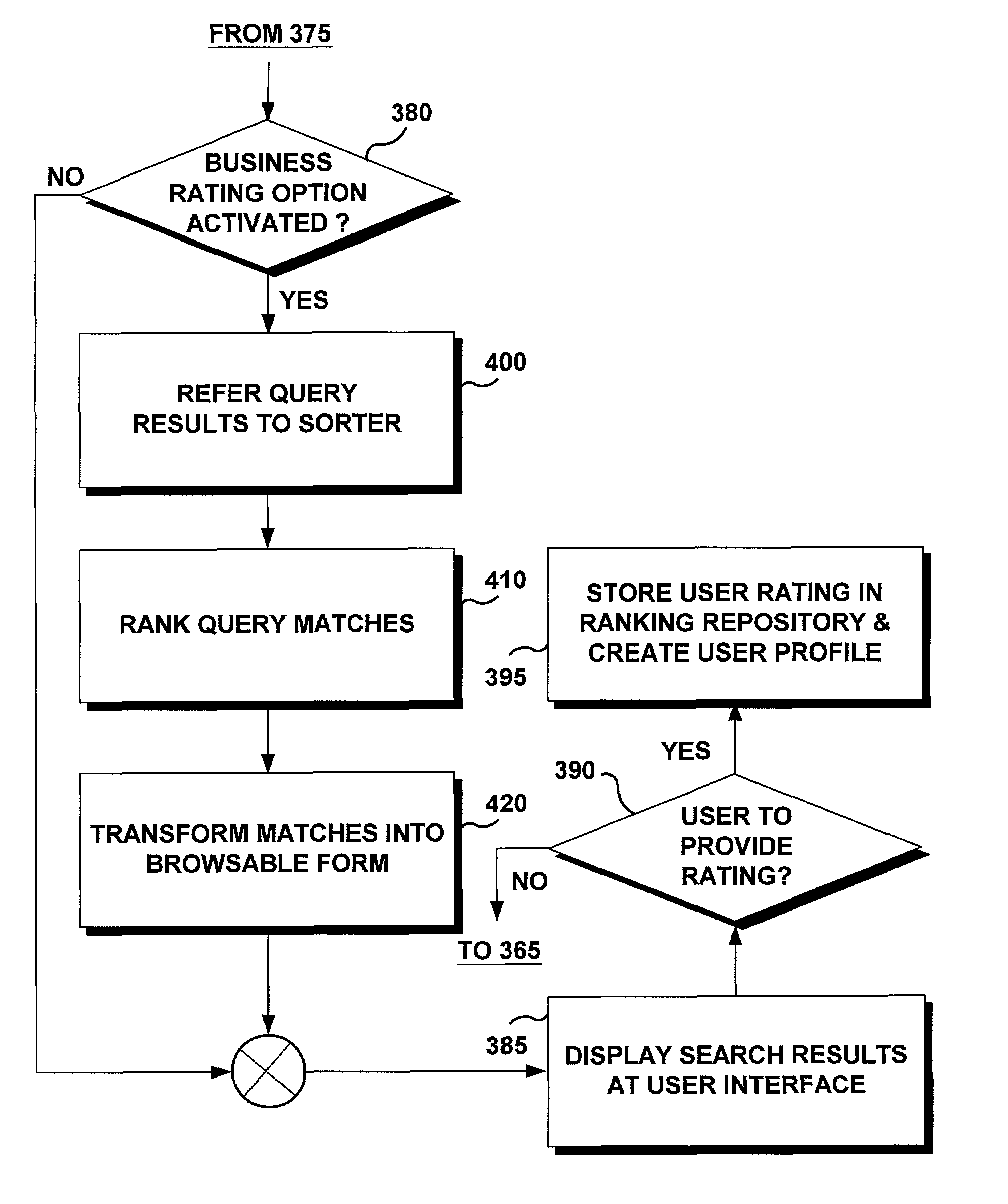
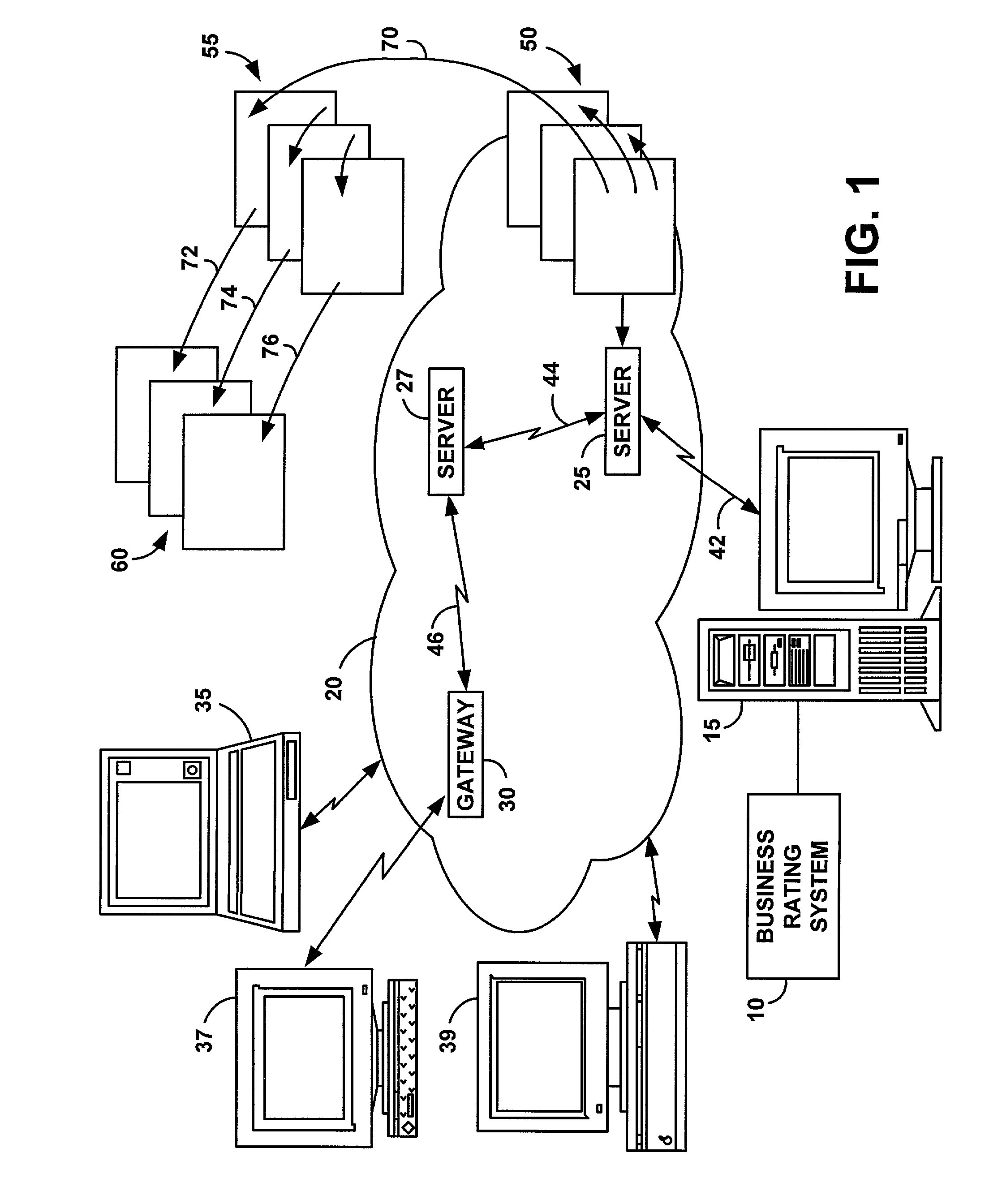
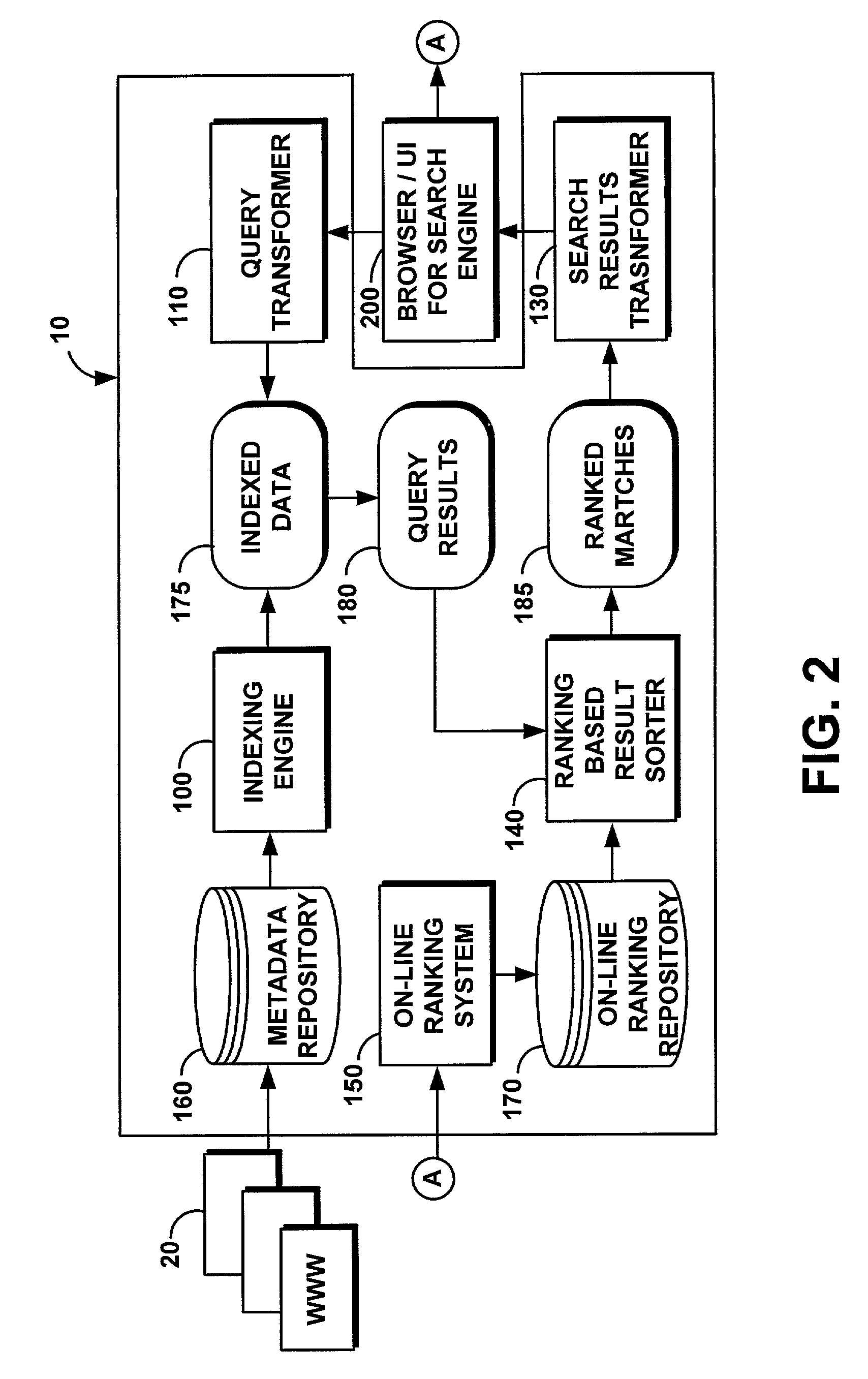
System and method for integrating on-line user ratings of businesses with search engines
A computer program product is provided as a business rating system to rank business that are relevant to a given Internet search topic. Business ratings are stored in a ranking repository that can be optionally searched by the user along with a user-defined search engine query. The business ratings are compiled from on-line questionnaires attached to the search engine results and / or on-line surveys obtained through other web based rating services. The business ratings assess the quality of the businesses in terms of “interactive” criteria such as customer satisfaction, professionalism, and cost and ease of use of the businesses' products or services. The business rating system is comprised of an on-line indexing engine, a query transformer, a search results transformer, a ranking based result sorter, an on-line ranking system, a metadata repository, and an on-line ranking repository. The business rating system integrates the ratings with the search results, and ranks the search results based on such business ratings. In this manner, the user of a search engine receives feedback from other users about businesses of interest. Eventually, businesses with higher ratings will be ranked at the top of the search list, while business with lower ratings will be ranked lower.
Owner:IBM CORP
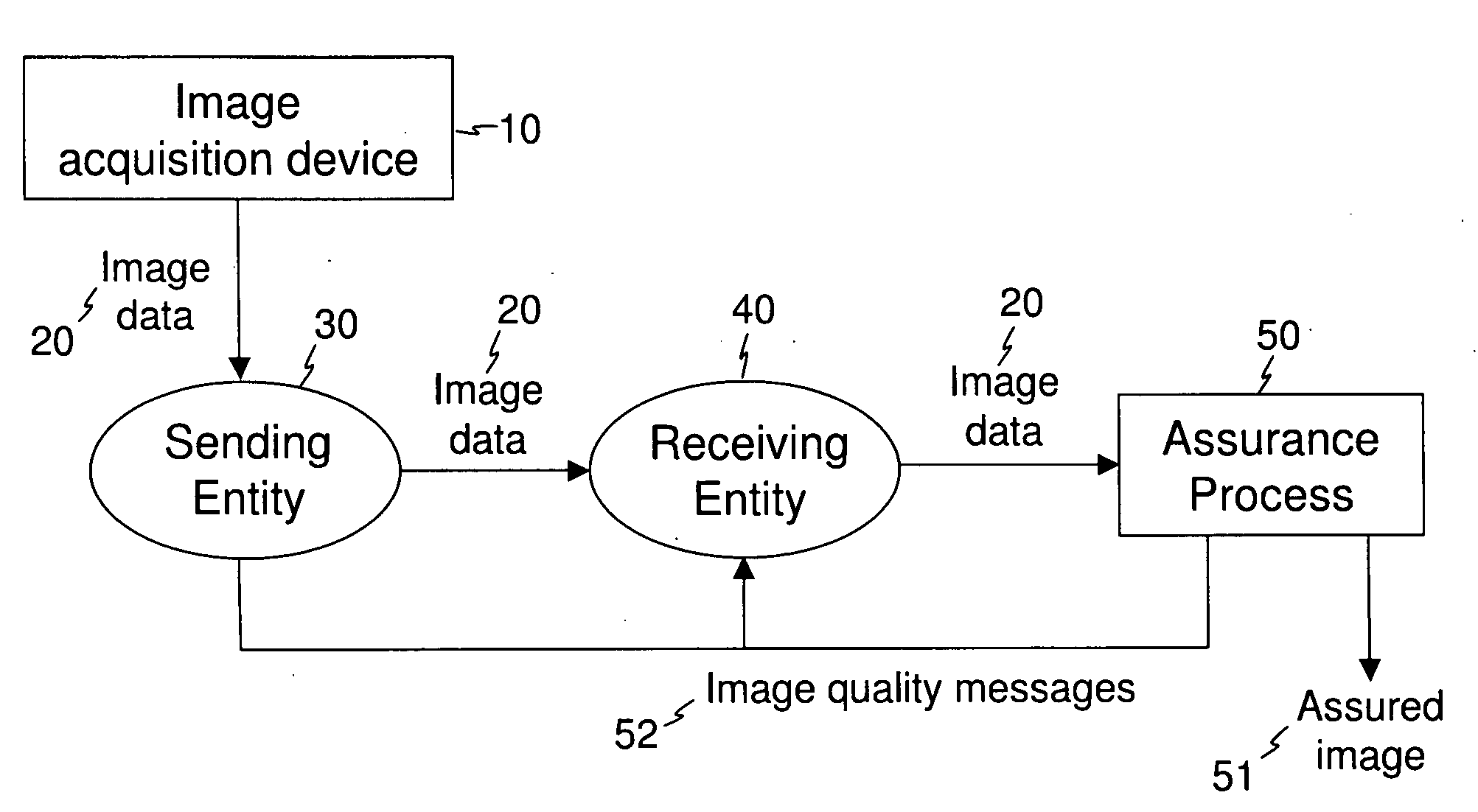
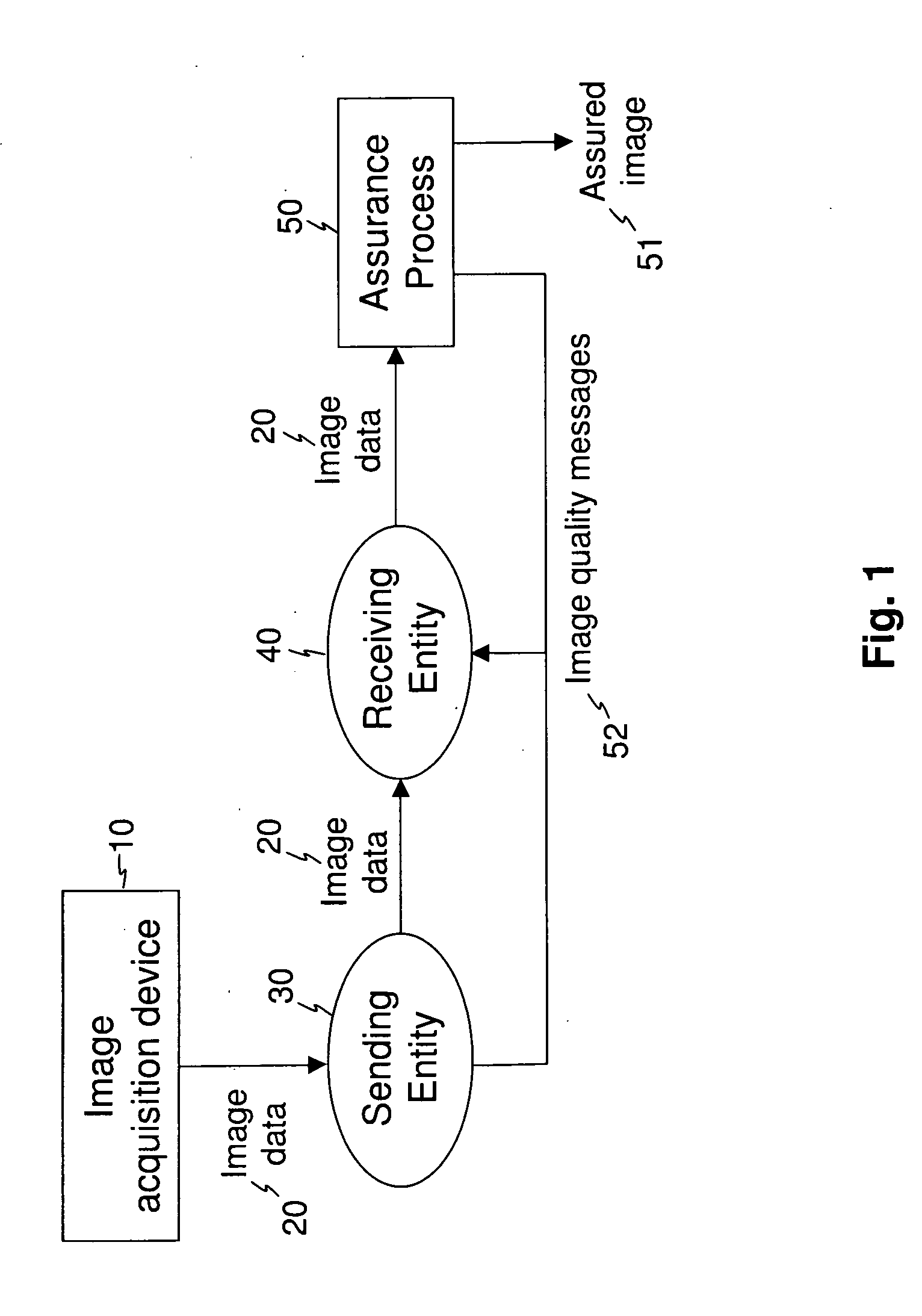
Image transfer with secure quality assessment
InactiveUS20090147988A1Verify integrityAss qualityCharacter and pattern recognitionPictoral communicationImage transferImaging quality
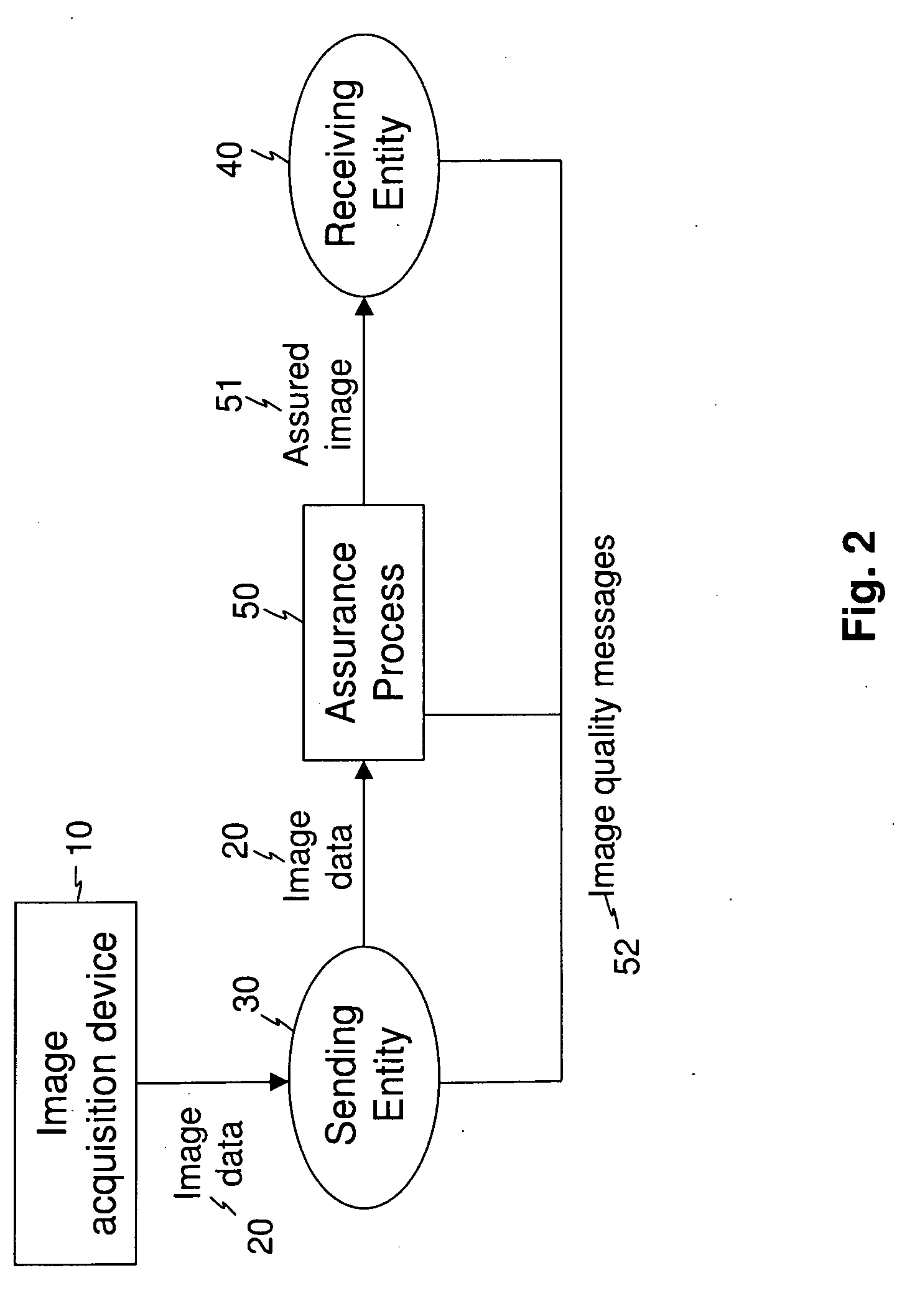
A method for producing an assured image from image data that is transferred from a first entity to a second entity acquires image data, transfers the acquired image data from the first entity to the second entity, forms secure assurance data according to image quality measurements obtained from the acquired image data, and forms an assured image that includes the acquired image data and the secure assurance data. At least one image quality message is generated that indicates the transfer of the acquired image data from the first entity to the second entity and is representative of the image quality measurements. The at least one image quality message is presented to at least one of the first entity and the second entity.
Owner:CERTIFI MEDIA
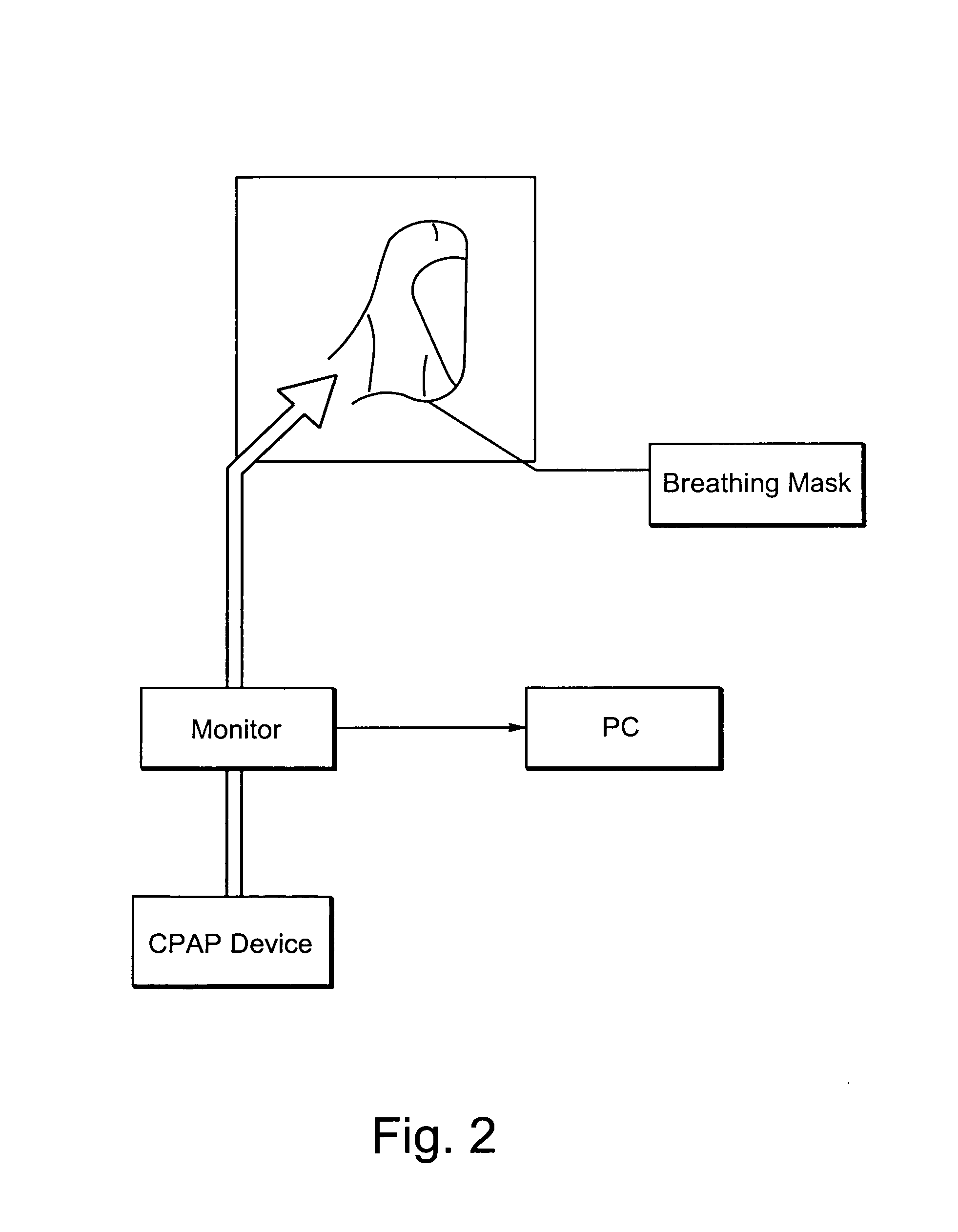
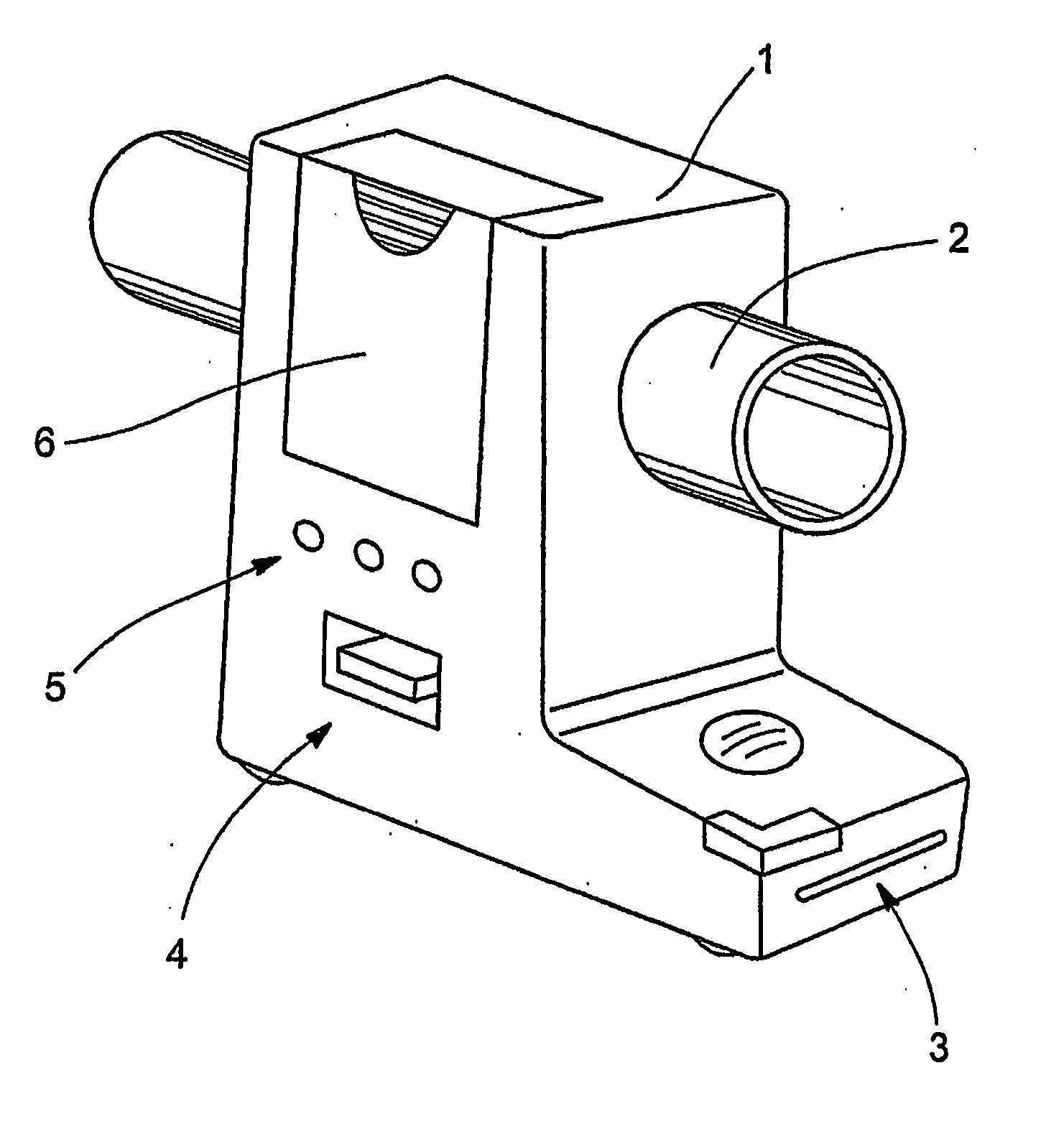
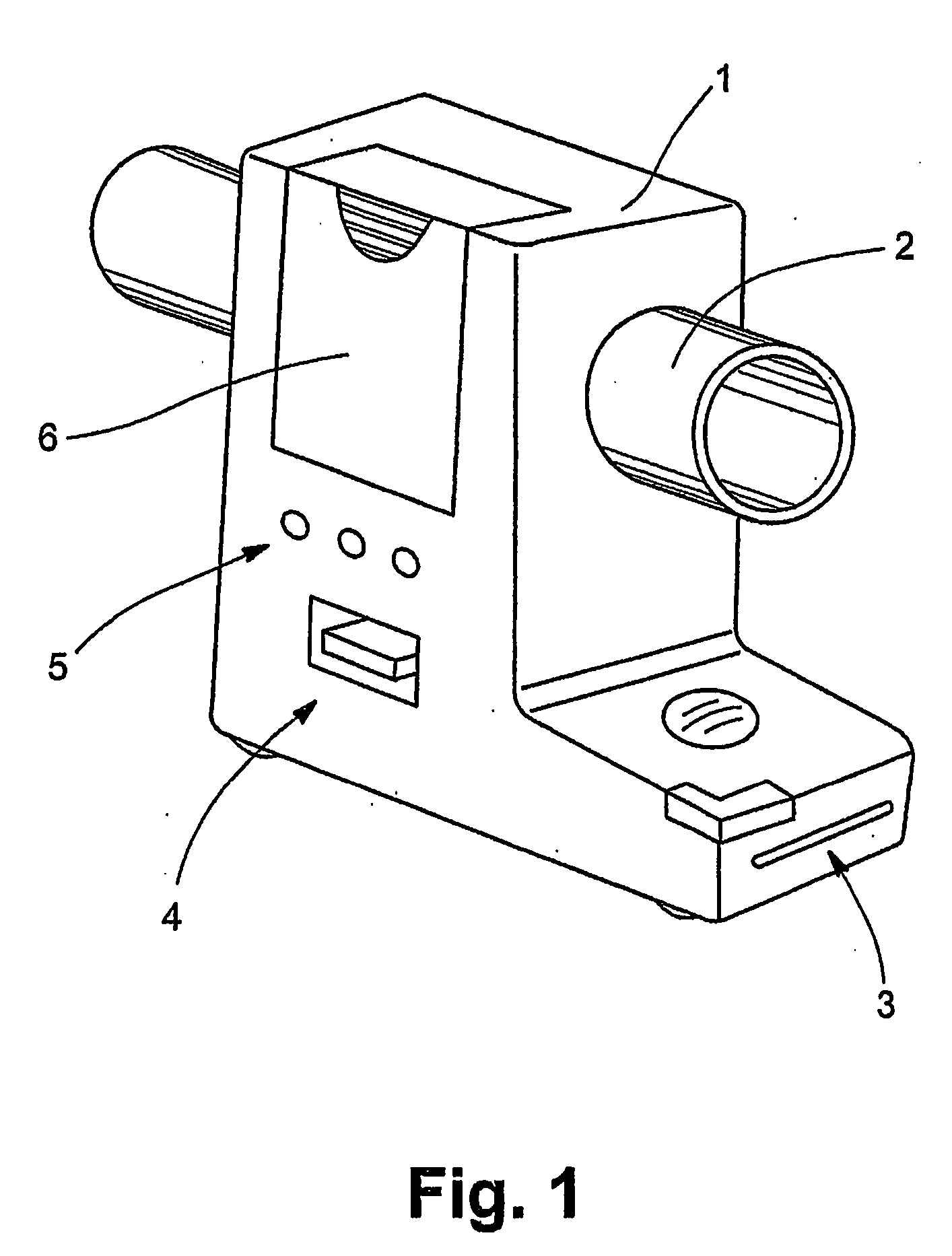
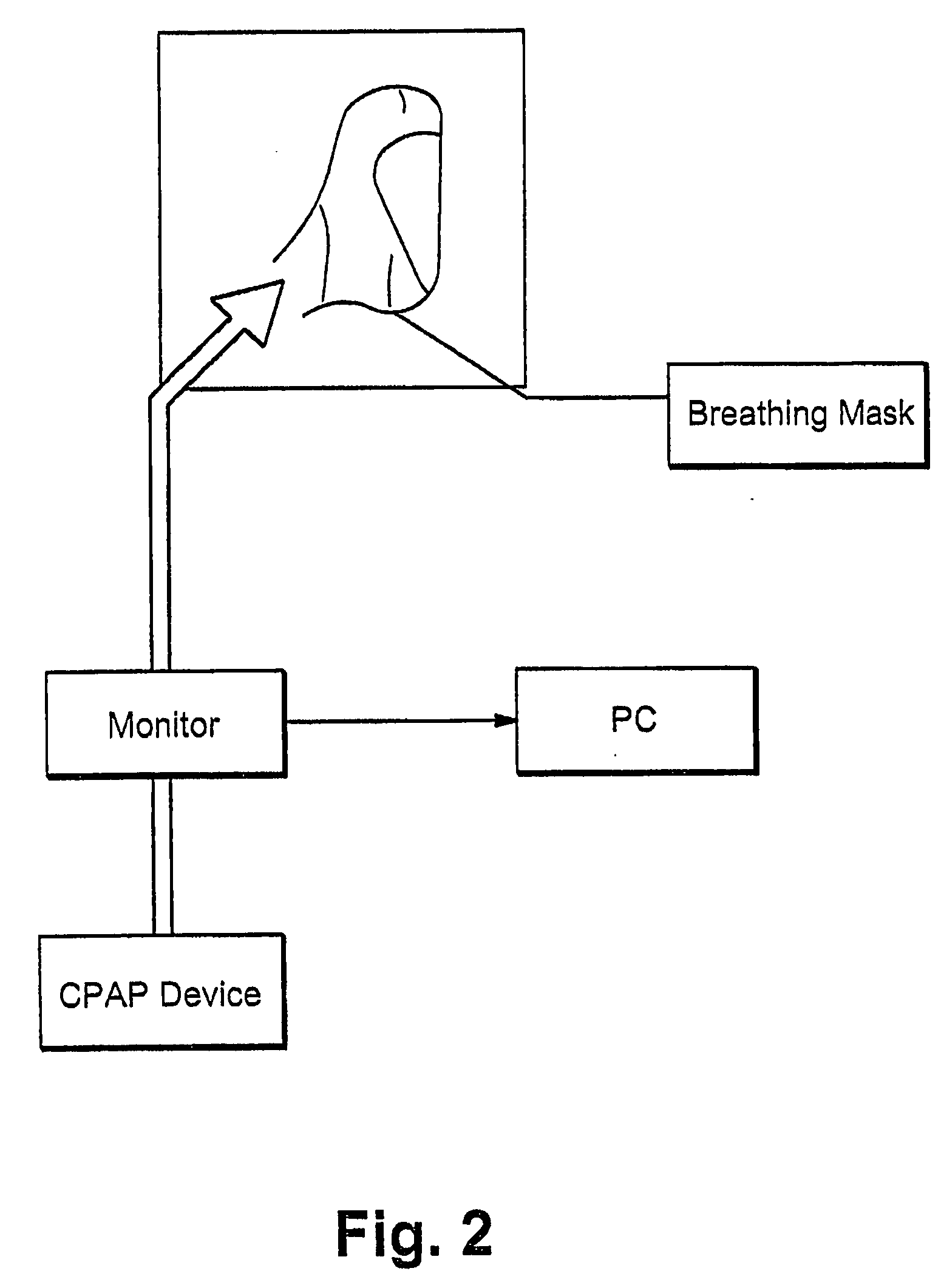
Monitor for CPAP/ventilator apparatus
InactiveUS20090020120A1Ass qualityAvoid pollutionRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesPositive airway pressure deviceVentilator equipment
A monitor includes a measurement line segment adapted to be coupled between a patient interface and a positive airway pressure device. The measurement line segment defines a gas flow path. A sensor includes two ports in communication with the gas flow path through the measurement line segment, and a recording device is adapted to record data collected by the sensor.
Owner:RESMED LTD +1
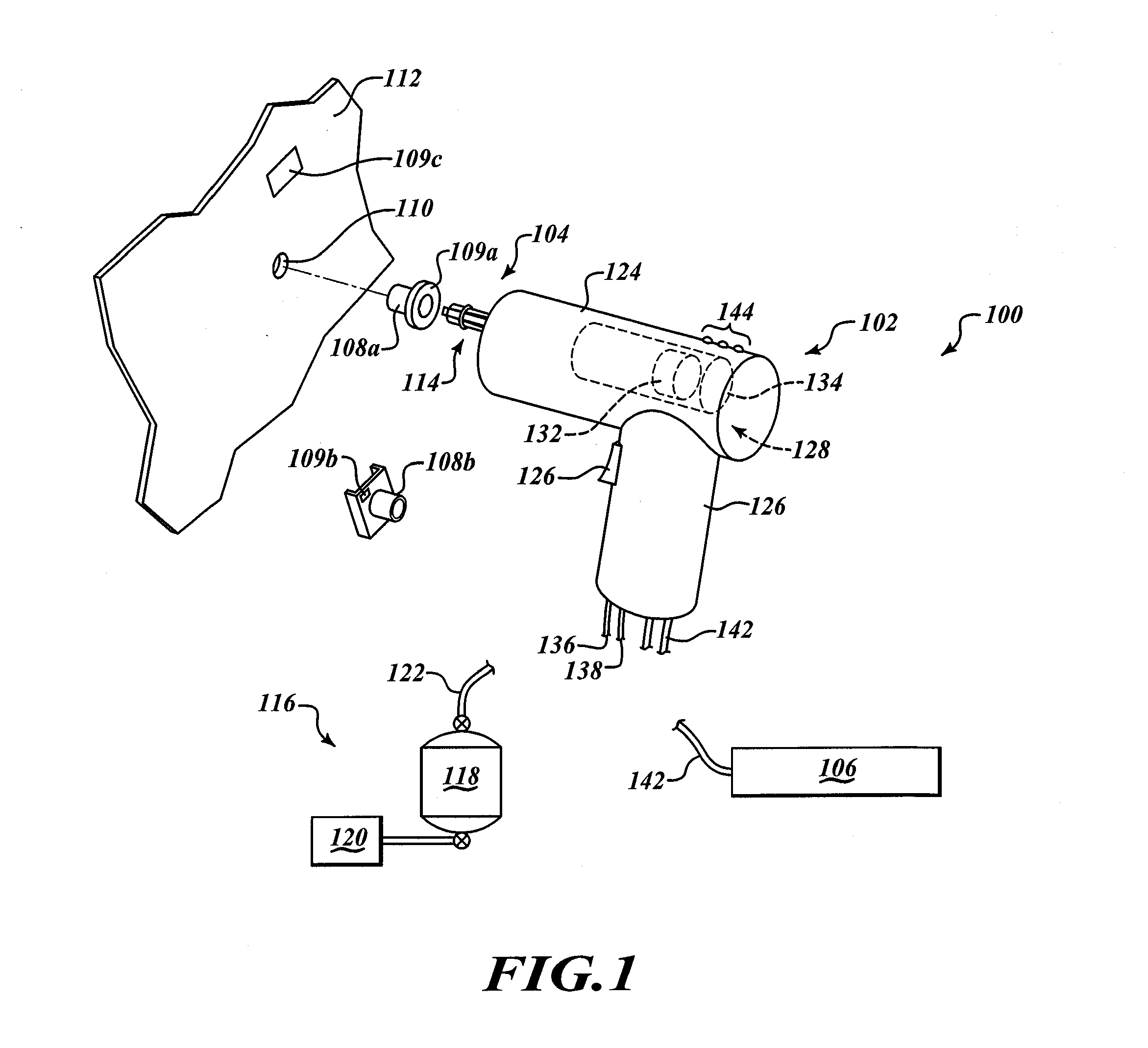
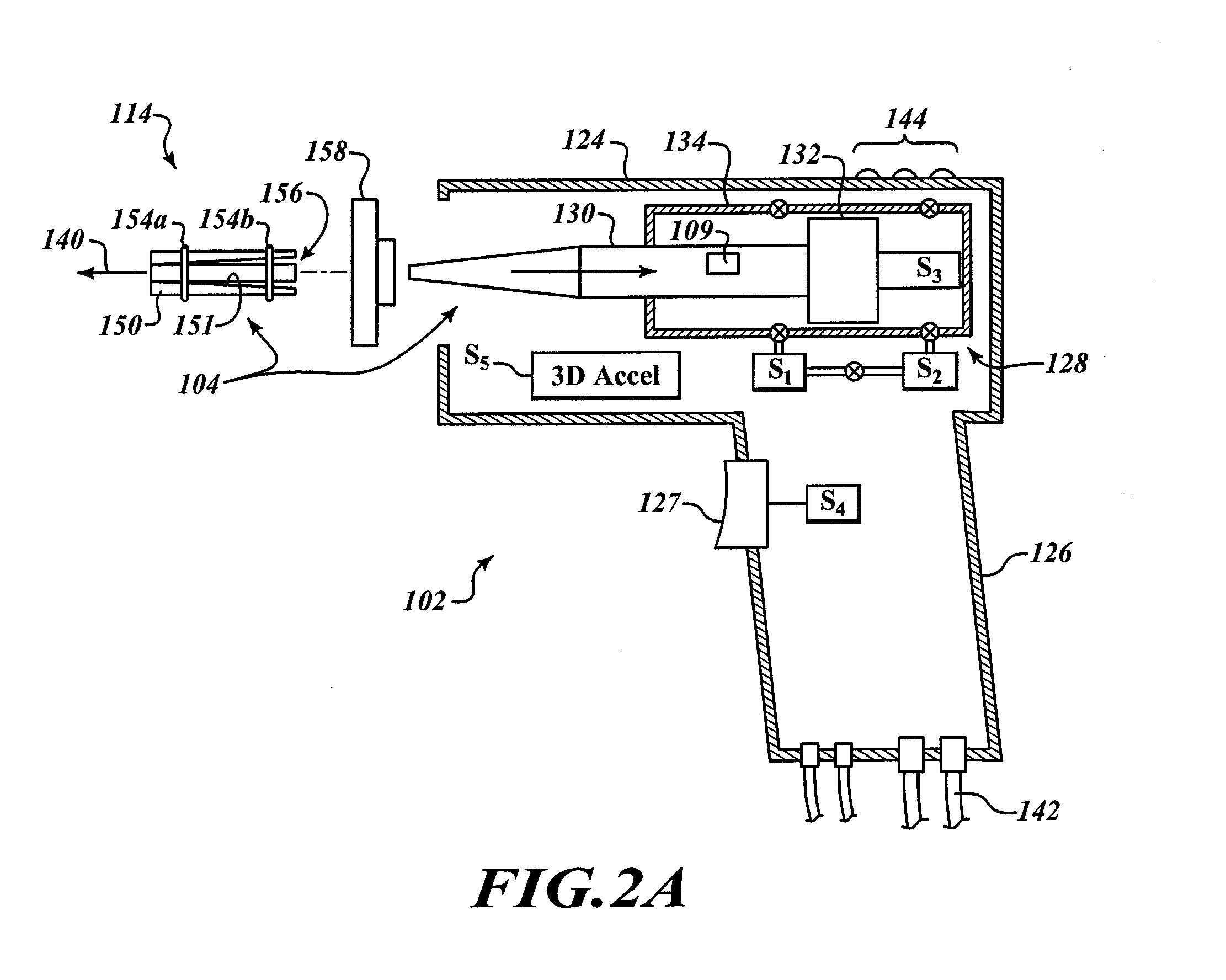
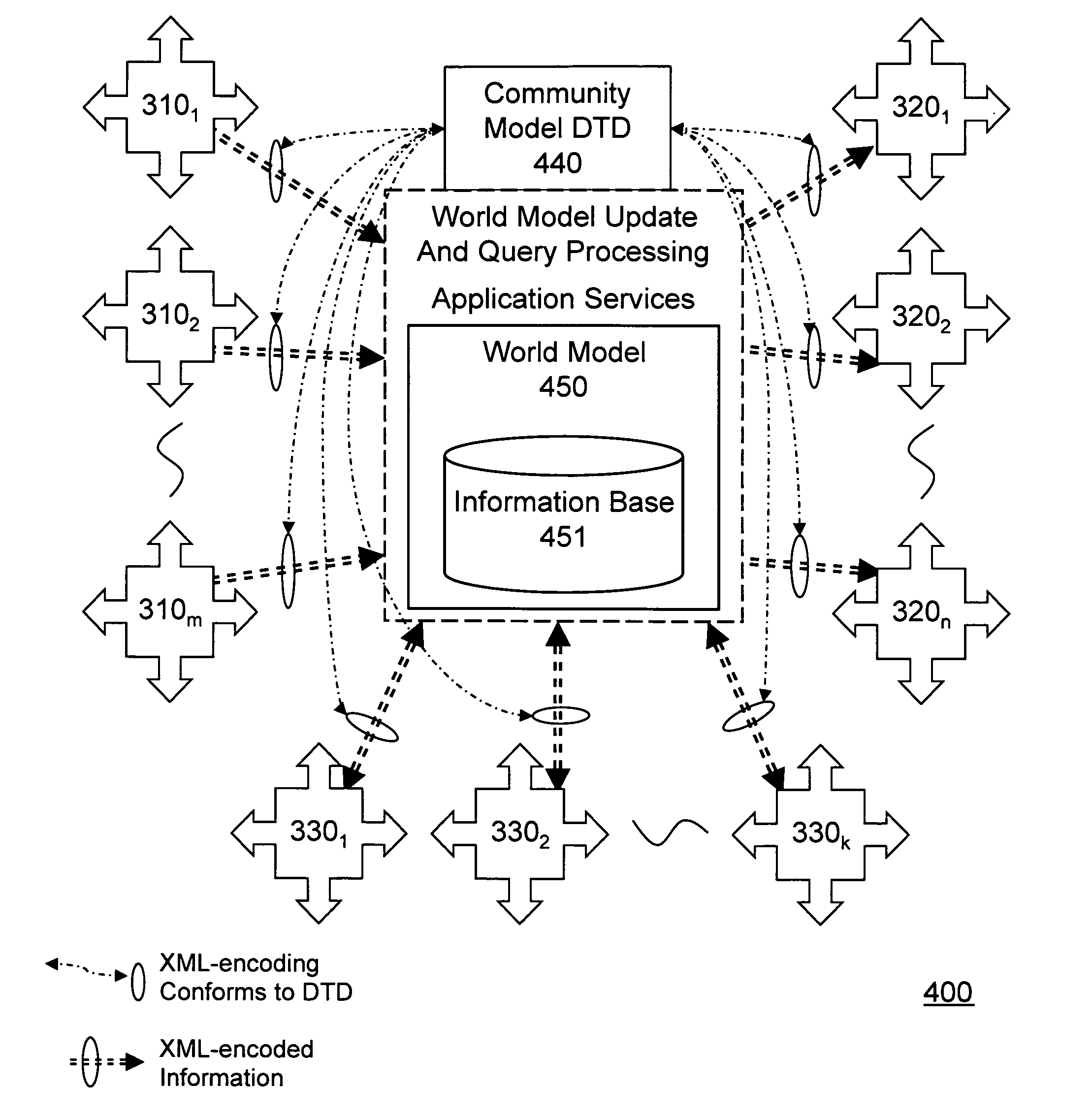
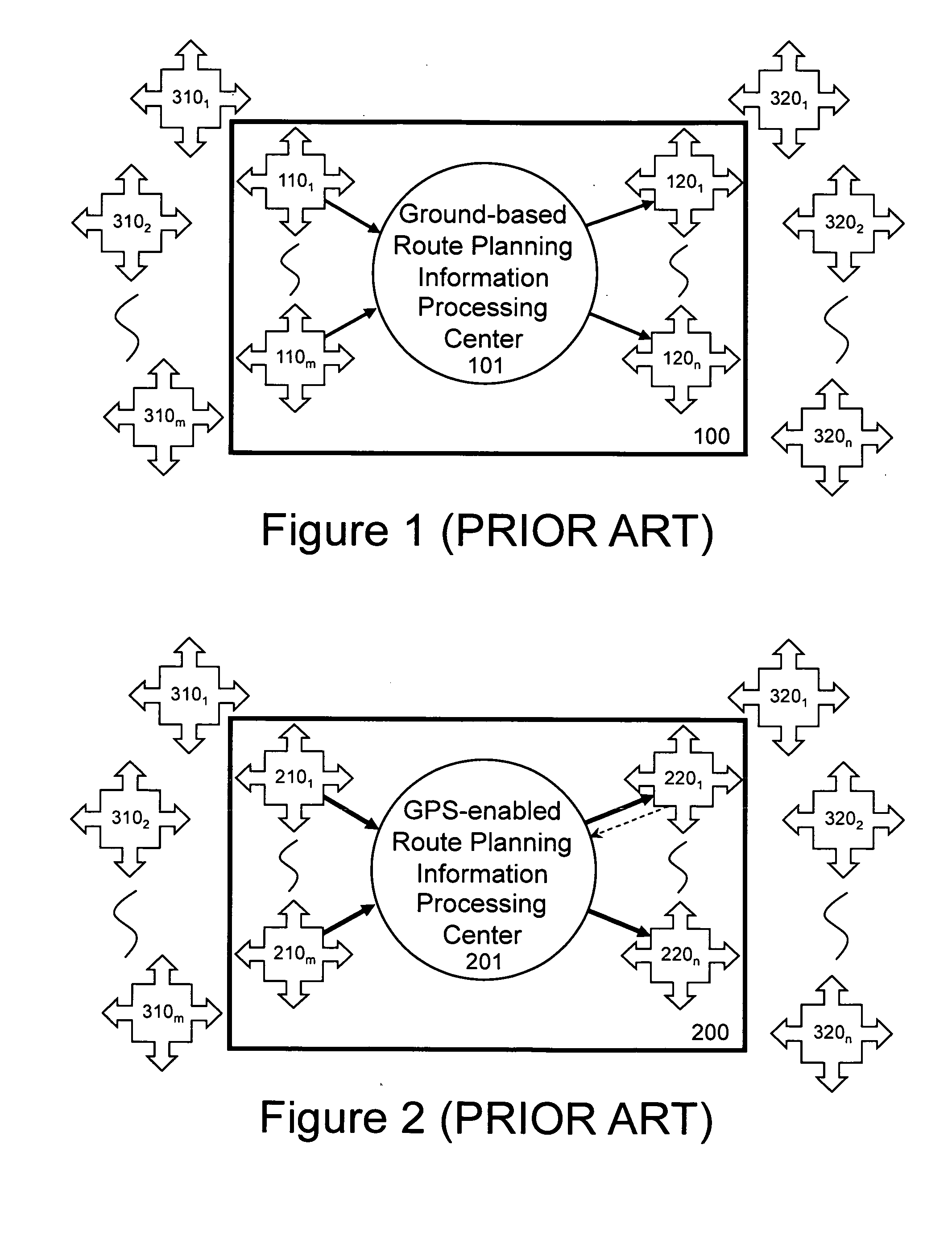
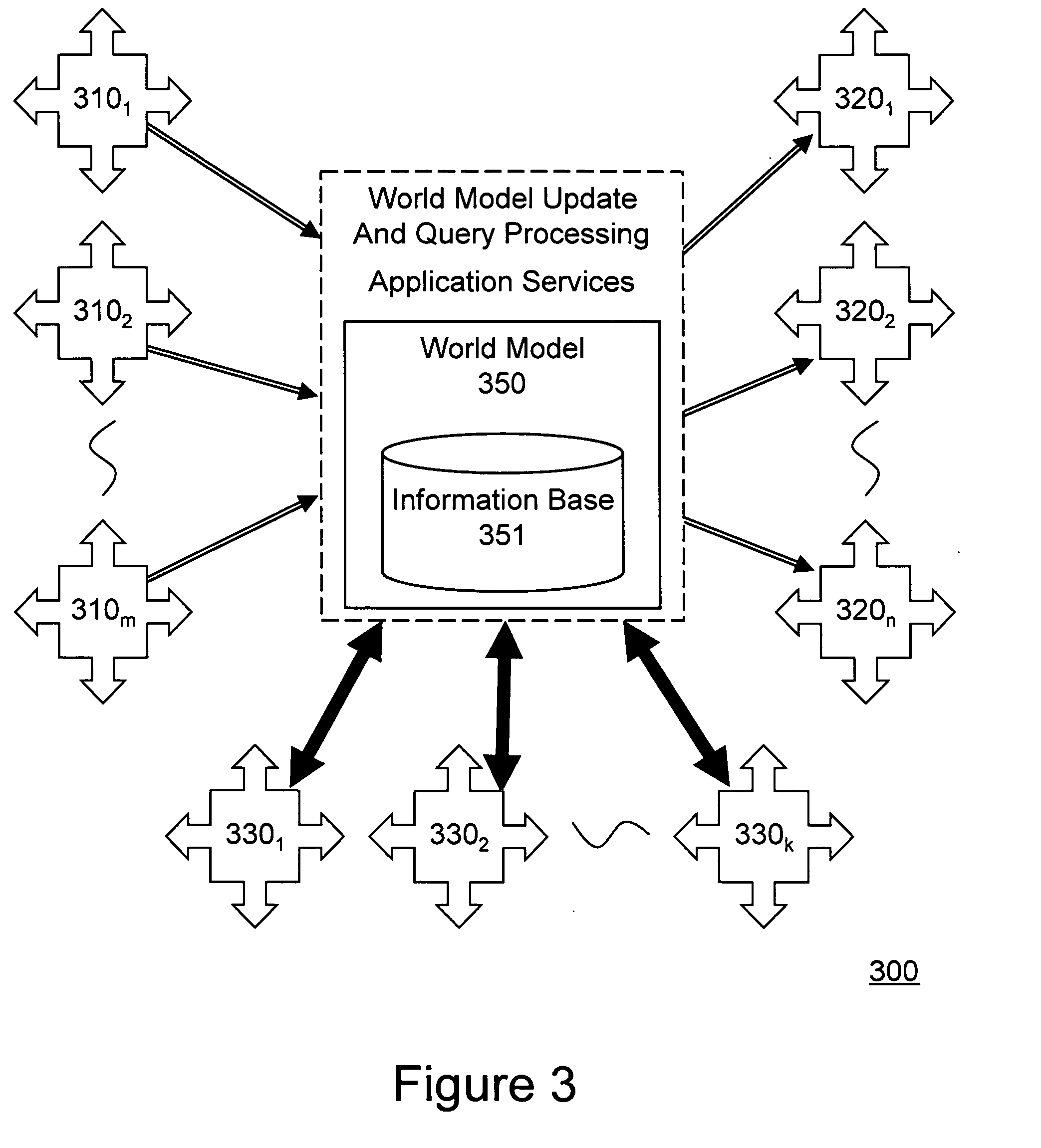
Open community model for exchanging information in dynamic environments
InactiveUS20050075921A1Limited privilegeEasy to liftFinanceResourcesRelevant informationOpen community
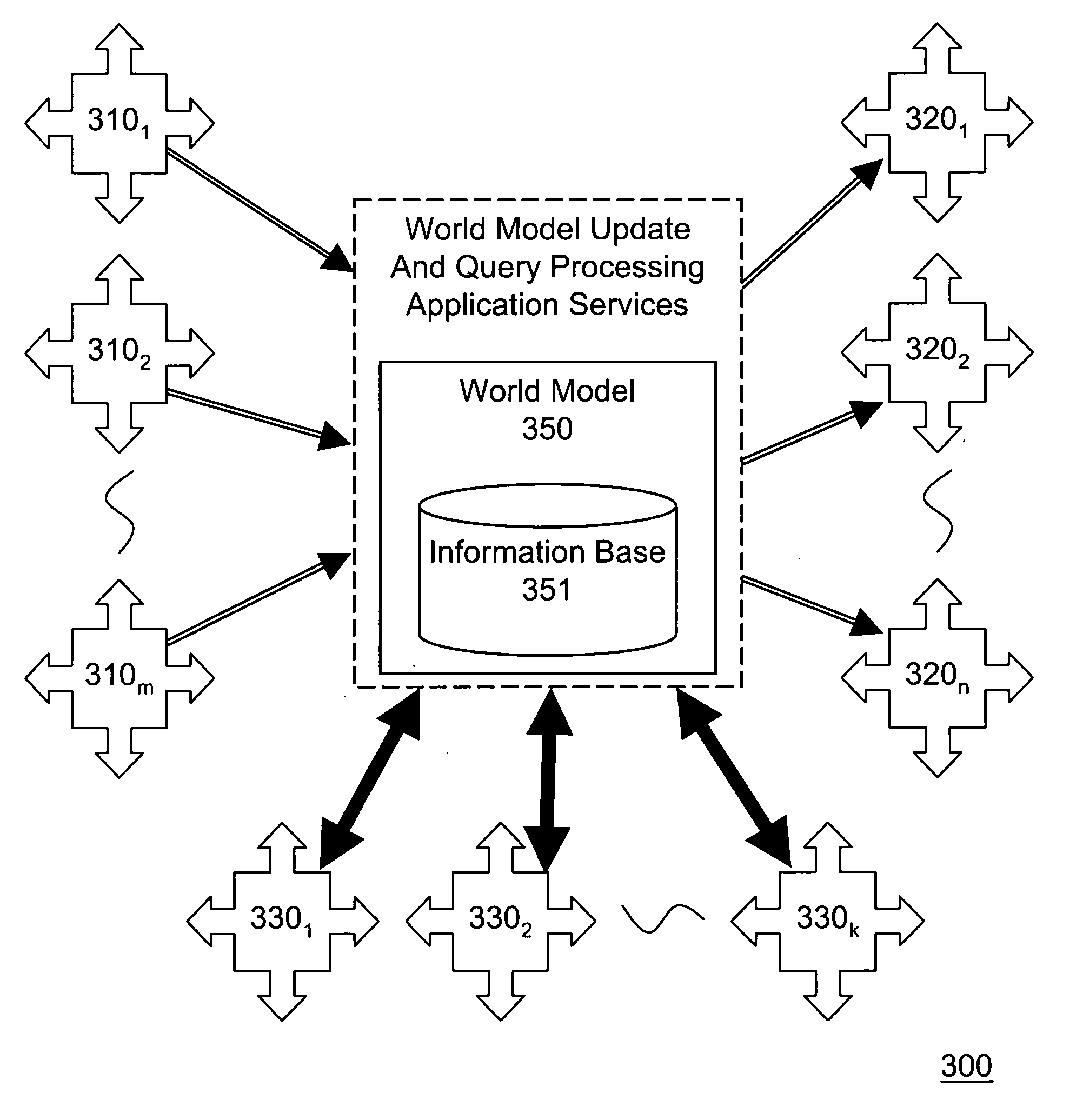
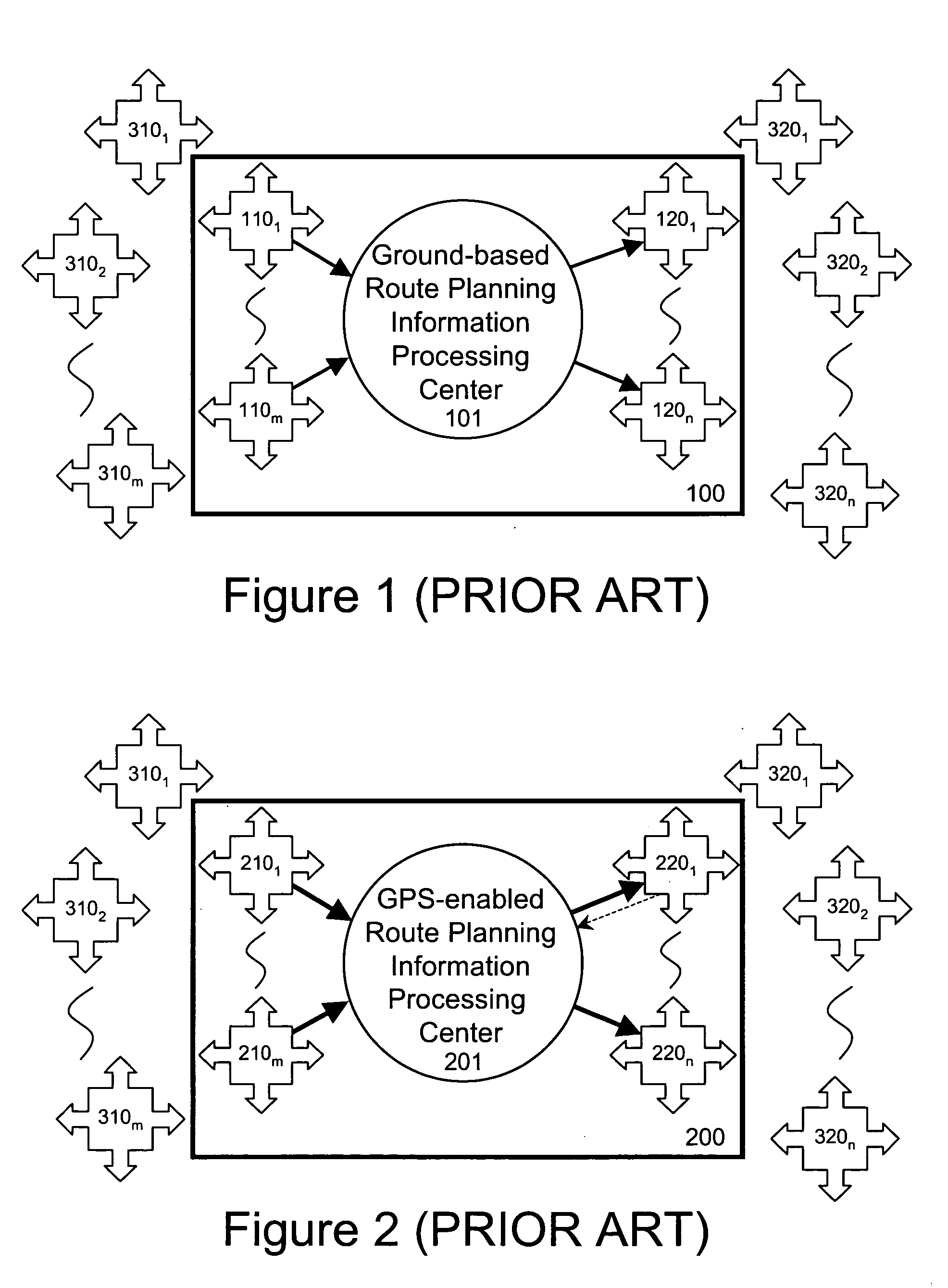
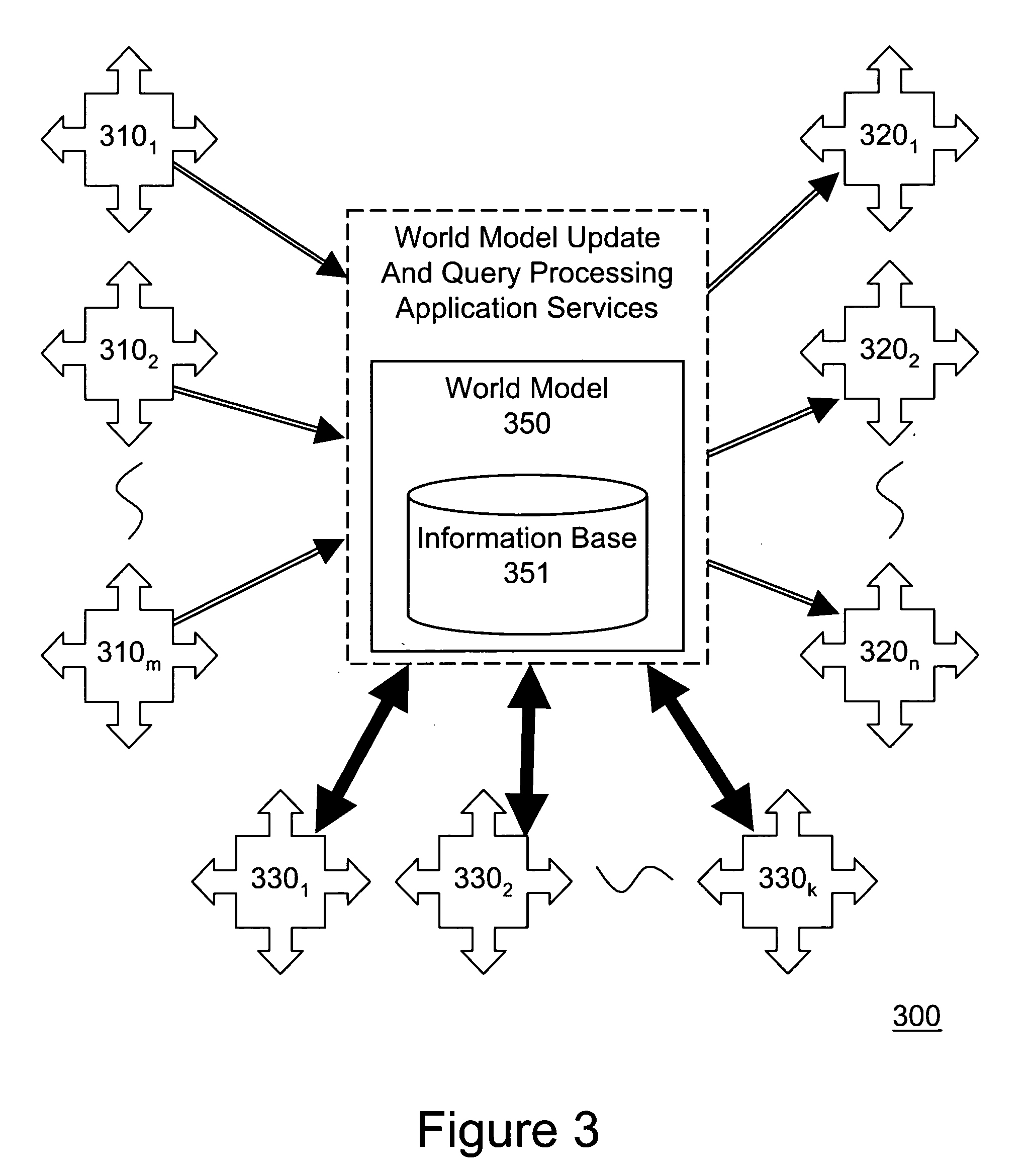
An open community model for information exchange enables individuals to plan and attain superior outcomes in a dynamic environment. A continually “world model” maintains information about the dynamic environment that is valuable for individuals of the open community. An open community model application publicizes a specification of relevant types of information it receives from suppliers and provides to consumers. Suppliers provide information consistent with the specification. Consumers utilize received information to reduce uncertainties or errors in the assumed environment so they can generate improved plans or improve their expected outcomes. Consumers give feedback to the open community model about the quality of information they received. A “world model” application combines information received to update and improve its understanding of the dynamic environment and its estimates of relevant parameters. The community model simplifies the creation and operation of information markets where innovative products are naturally selected and economically reinforced.
Owner:HAYES ROTH FAMILY TRUST THE UNDER AGREEMENT DATED SEPTEMBER 14 1987 AS AMENDED
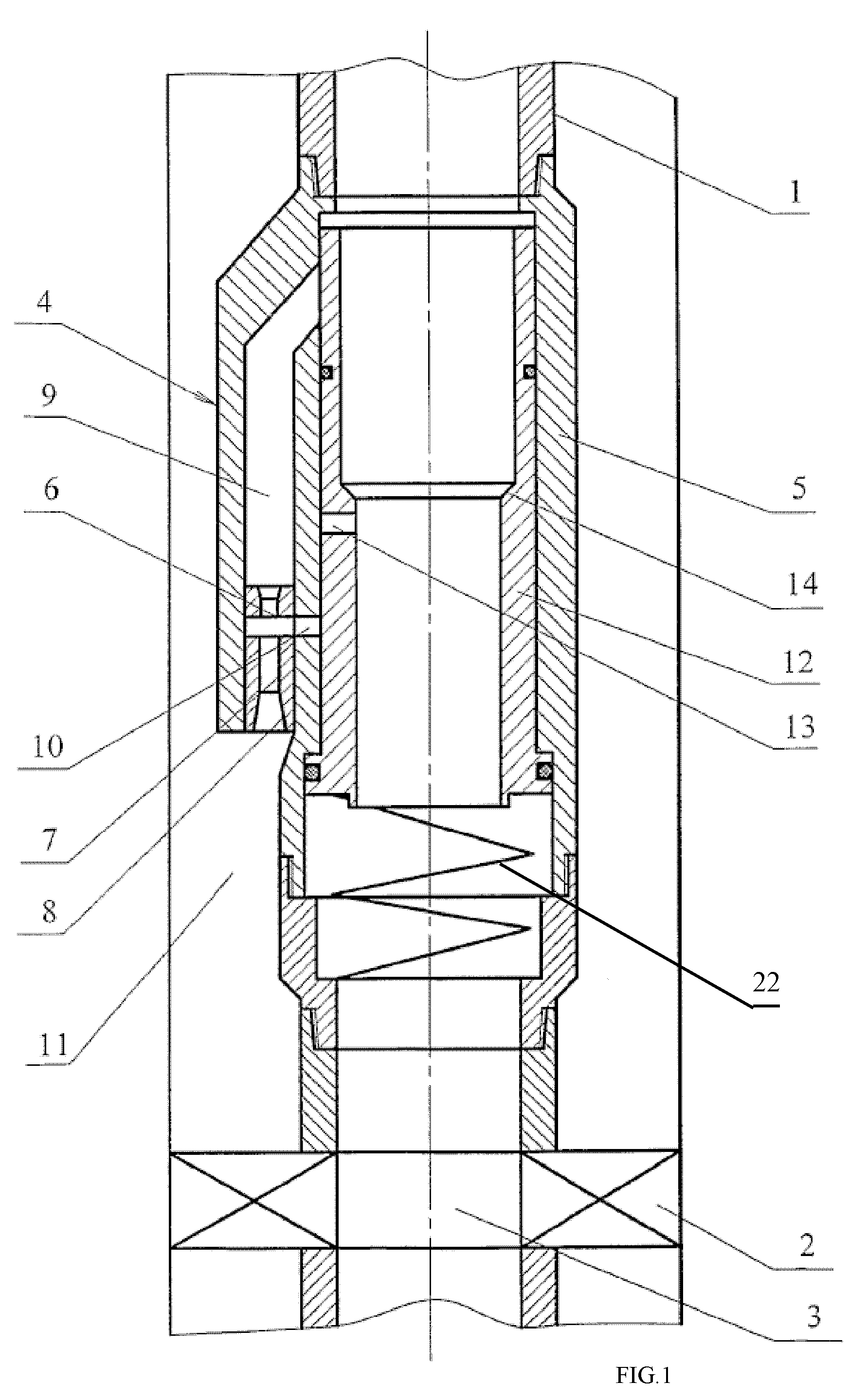
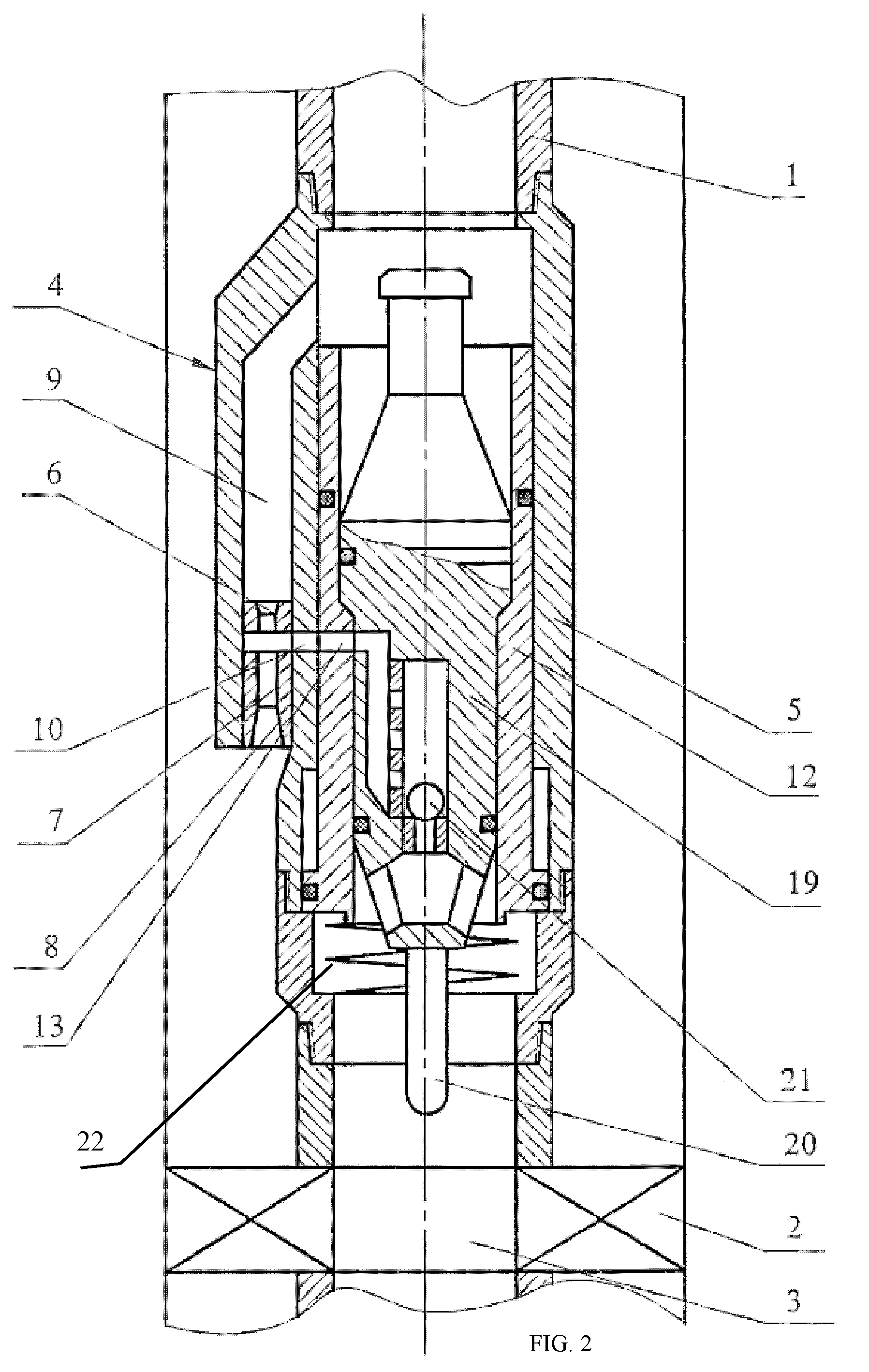
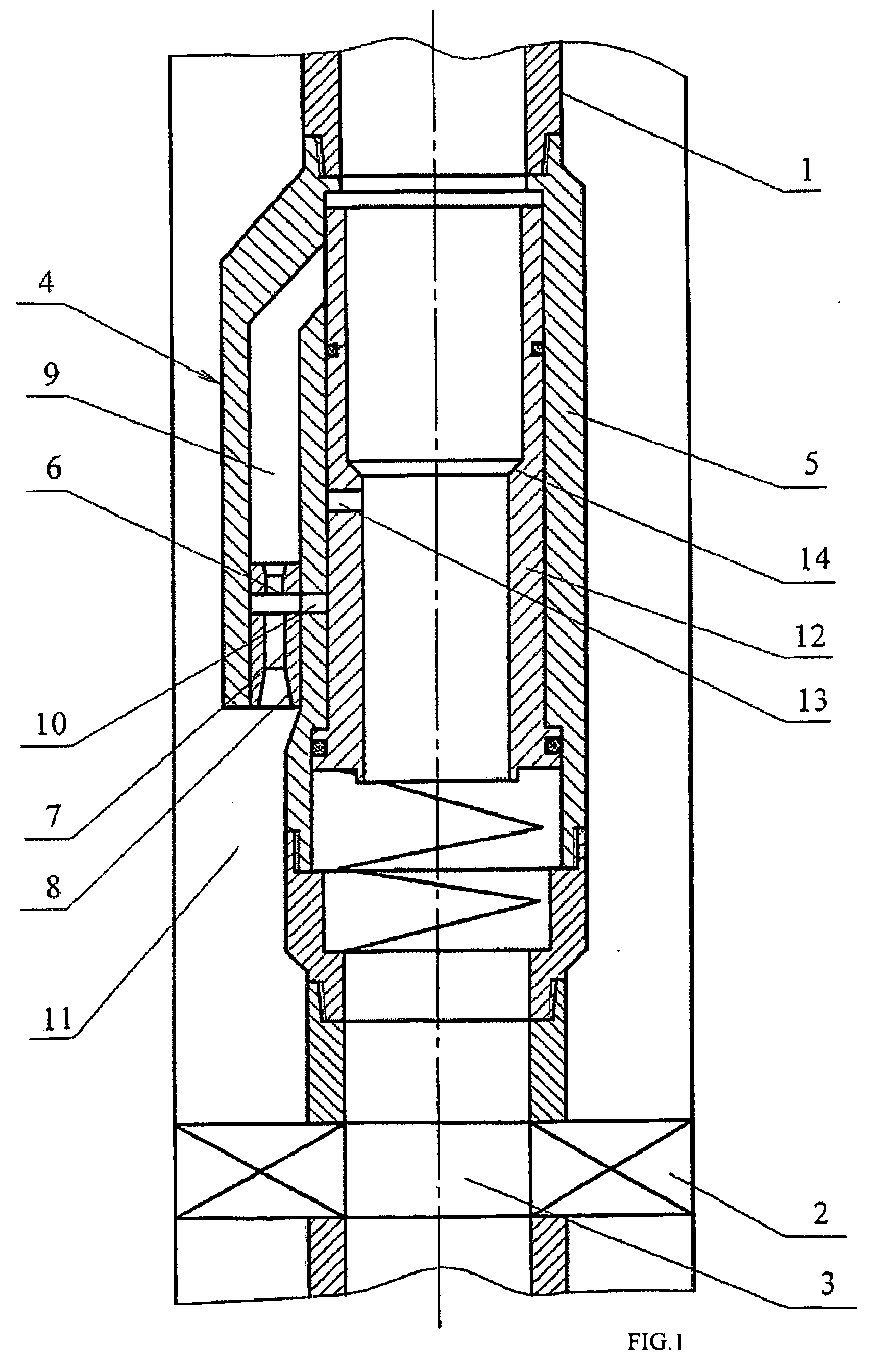
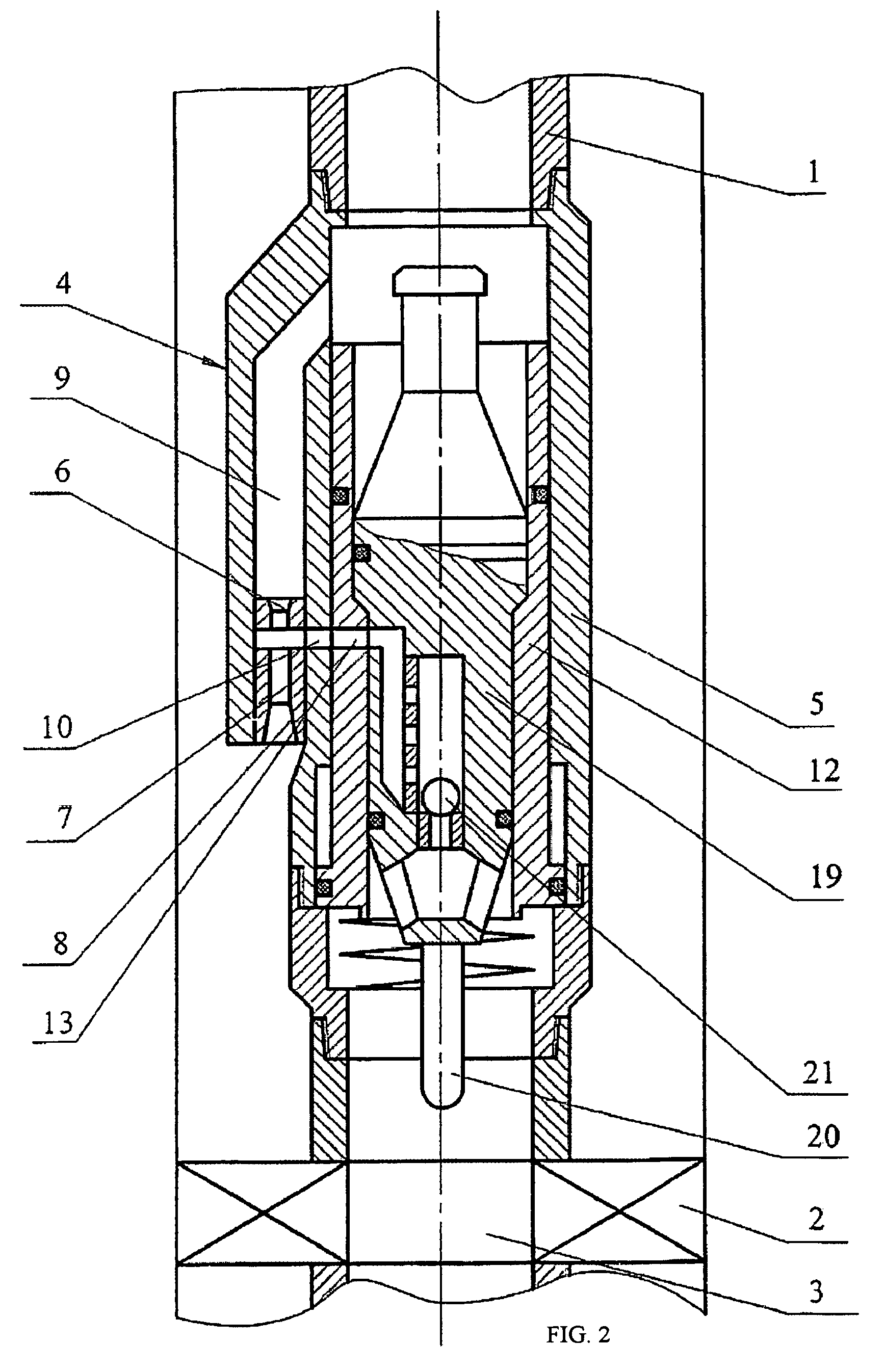
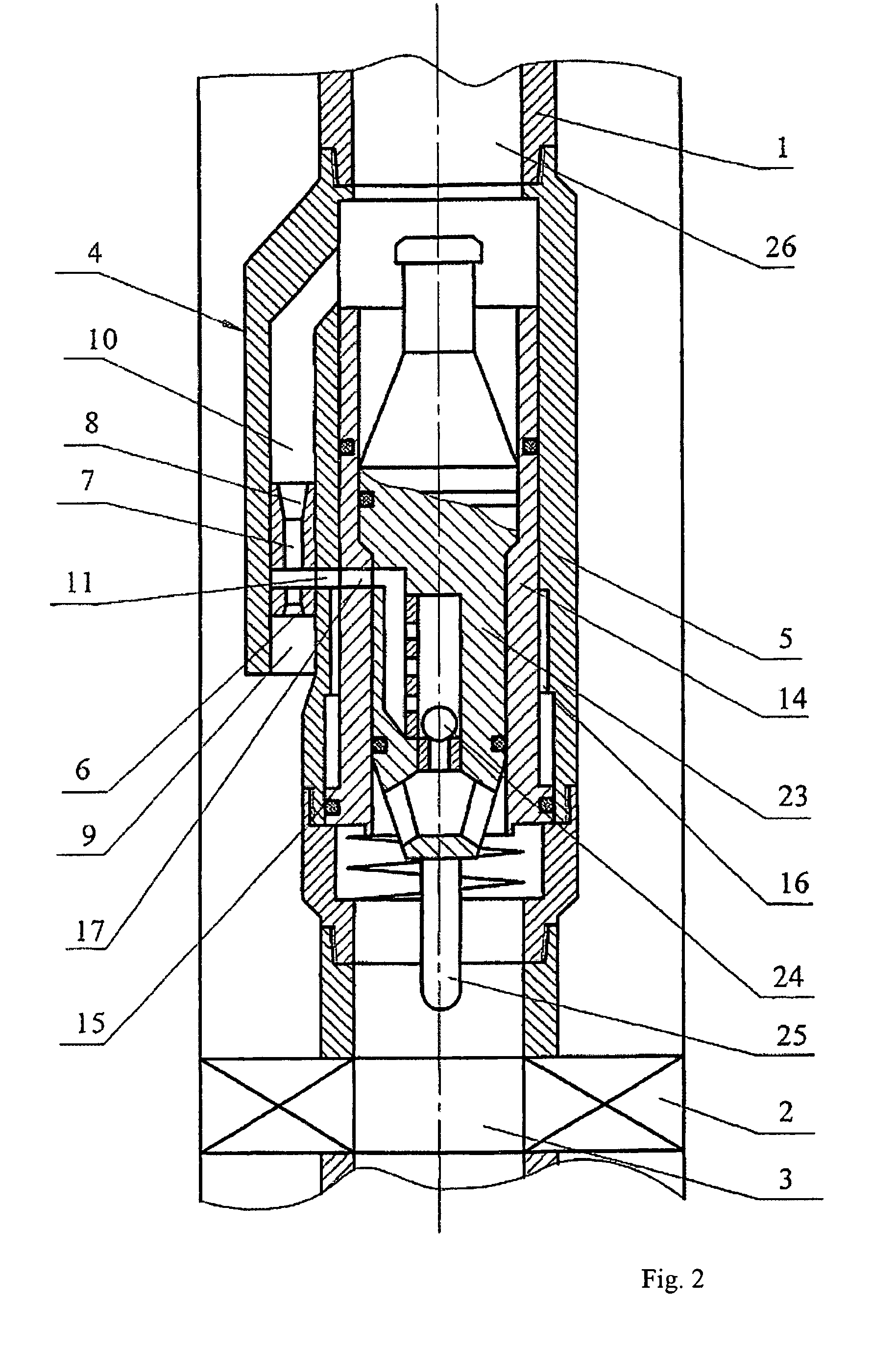
Well jet device and the operating method thereof
Owner:KHOMYNETS ZINOVIY DMITRIEVICH
Photochrome- or near ir dye-coupled polymeric matrices for medical articles
ActiveUS20120082713A1Promote formationImprove visualizationSurgical adhesivesAntipyreticBiocompatibility TestingCombined use
The invention provides polymers comprising pendent photochrome or near IR dye groups, as well as polymeric matrices made from these polymers, which can be used as or in association with a medical article. The polymers can be synthesized using methods that facilitate the preparation of medical articles having good biocompatibility. Exemplary polymeric matrices are in the form of lubricious coatings on medical devices, such as catheters. Visualization by irradiation of the photochrome or near IR dye can improve detection of the polymeric matrix on a device or in the body. This, in turn can improve aspects of a medical procedure, such as device insertion or matrix formation, as well as being useful for assessing the quality of the matrix.
Owner:SURMODICS INC
Smart installation/processing systems, components, and methods of operating the same
ActiveUS20130204422A1Less worryEliminate axial flow of materialProgramme controlUsing fluid meansEngineeringHandling system
A processing system employs a processing tool to process workpieces, for example cold working holes and / or installing expandable members into holes. Sensors sense various aspects of the processing. Information regarding performance of the process and / or materials may be stored, for example a hole-by-hole or a workpiece-by-workpiece basis, allowing validation of processing. Information also allows dynamic operation of the processing tool. Analysis of response relationships (e.g., pressure or force versus position or distance) may provide insights into the process and materials, and / or facilitate the real-time feedback including control, alerts, ordering replacement for consumable components.
Owner:FATIGUE TECH
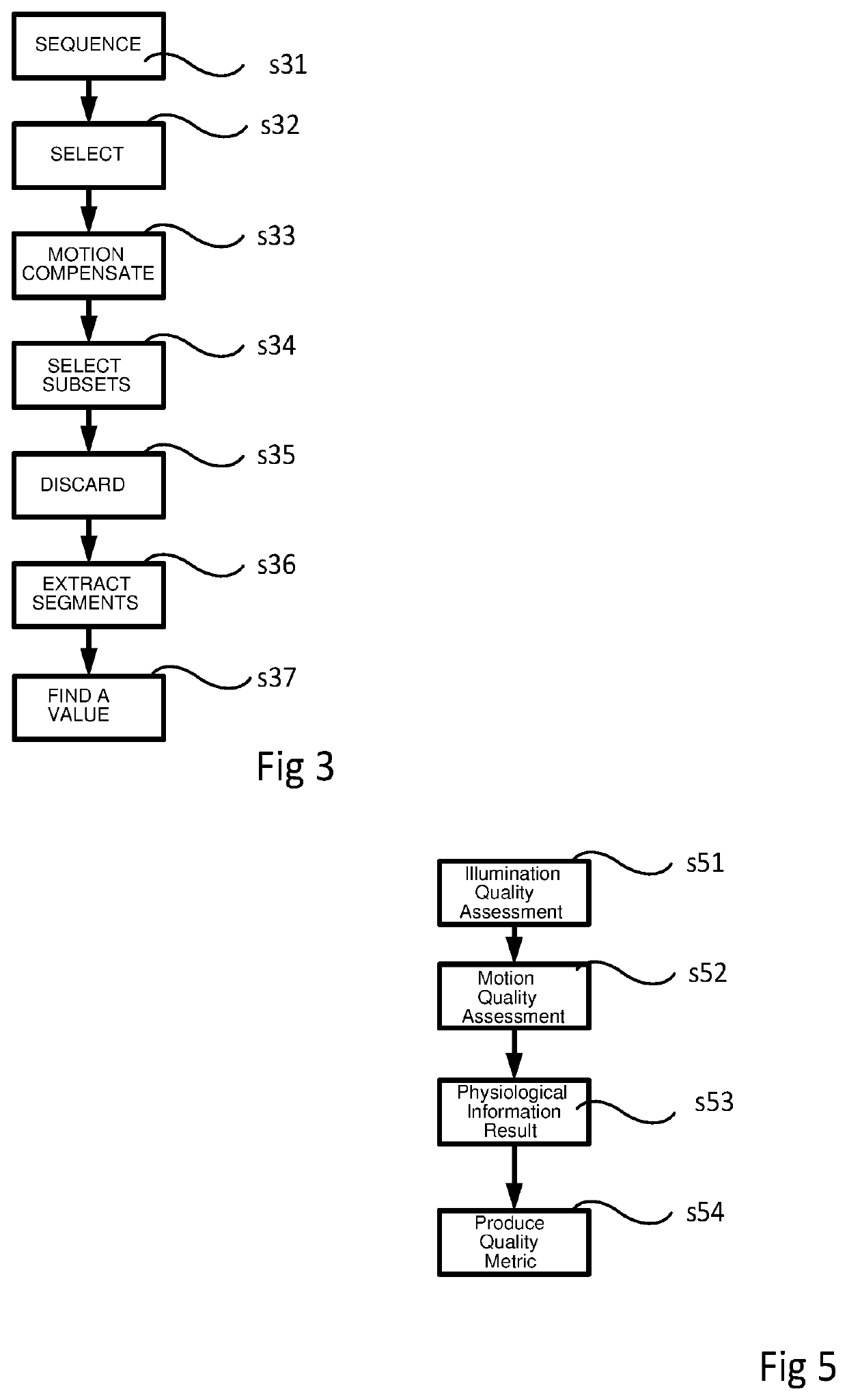
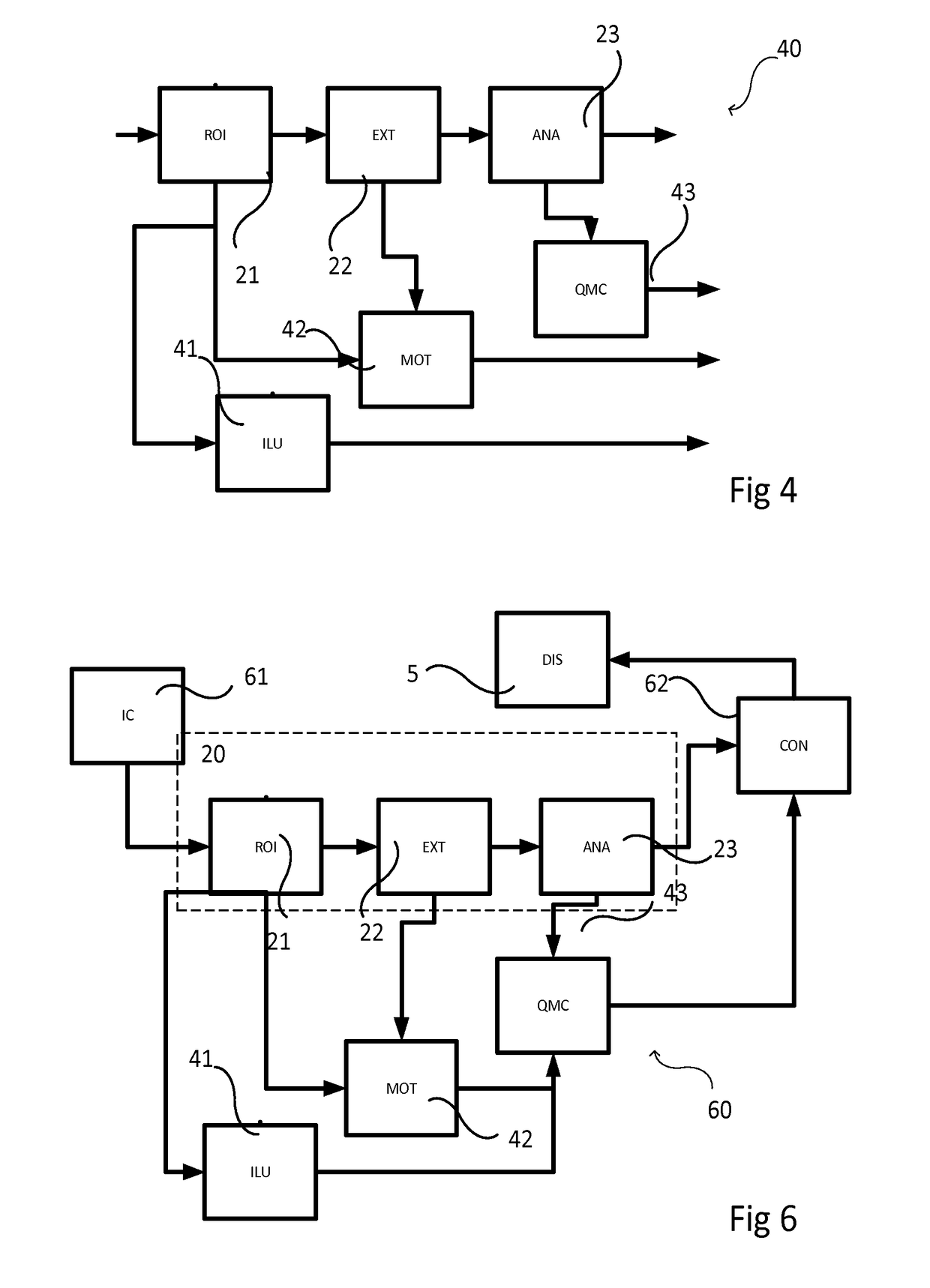
Method for assessing the quality of a distorted version of a frame sequence
InactiveUS20090274390A1Ass qualityQuality improvementImage enhancementImage analysisComputer hardwareFrame sequence
The invention is related to a method for video quality assessment.Said method comprises the steps of determining a last spatial distortion by comparing a block of a last frame (I6) of the sequence with a corresponding block of the distorted version of the last frame, determining, in a last-but-one frame, a best-matching block matching said block of the last frame best, determining a last-but-one spatial distortion by comparing the determined best-matching block of the last-but-one frame with a corresponding block of the distorted version of the last-but-one frame, determining a spatio-temporal perceptual distortion value associated with said block using said determined distortions and using the determined spatio-temporal perceptual distortion value for assessing the quality.The spatial distortion's temporal evolution improves video quality assessment.
Owner:MAGNOLIA LICENSING LLC
Smart installation/processing systems, components, and methods of operating the same
ActiveUS20130200543A1Reduce upsetImprove fatigue lifeProgramme controlUsing fluid meansEngineeringHandling system
A processing system employs a processing tool to process workpieces, for example cold working holes and / or installing expandable members into holes. Sensors sense various aspects of the processing. Information regarding performance of the process and / or materials may be stored, for example a hole-by-hole or a workpiece-by-workpiece basis, allowing validation of processing. Information also allows dynamic operation of the processing tool. Analysis of response relationships (e.g., pressure or force versus position or distance) may provide insights into the process and materials, and / or facilitate the real-time feedback including control, alerts, ordering replacement for consumable components.
Owner:FATIGUE TECH
Open community model for exchanging information in dynamic environments
InactiveUS20090240424A1Easy to liftProvide informationAnalogue computers for vehiclesInstruments for road network navigationRelevant informationOpen community
An open community model for information exchange enables individuals to plan and attain superior outcomes in a dynamic environment. A continually “world model” maintains information about the dynamic environment that is valuable for individuals of the open community. An open community model application publicizes a specification of relevant types of information it receives from suppliers and provides to consumers. Suppliers provide information consistent with the specification. Consumers utilize received information to reduce uncertainties or errors in the assumed environment so they can generate improved plans or improve their expected outcomes. Consumers give feedback to the open community model about the quality of information they received. A “world model” application combines information received to update and improve its understanding of the dynamic environment and its estimates of relevant parameters. The community model simplifies the creation and operation of information markets where innovative products are naturally selected and economically reinforced.
Owner:HAYES ROTH FAMILY TRUST THE UNDER AGREEMENT DATED SEPTEMBER 14 1987 AS AMENDED
Monitor For Cpap/Ventilator Apparatus
A monitor for surveying measurement values indicative of a person's breathing, to enable an improved assessment, in terms of conclusiveness and reliability, in the course of a treatment phase or a diagnosis. The monitor has a housing structure defining a gas flow path, a measurement line segment provided in the housing structure and structured to communicate with a breathing gas line segment, a sensor in communication with the gas flow path and structured to generate a signal indicative of the breathing gas flow flowing along the gas flow path, and an electronic recording device to record one or more signals indicative of the breathing gas flow, and / or information derived from them. It thus becomes advantageously possible, in treating a patient by using a CPAP device, for instance, to determine the quality of treatment in an objective and standardized way.
Owner:MAP MEDIZIN-TECHNOLOGIES GMBH
Analysing spectral data for the selection of a calibration model
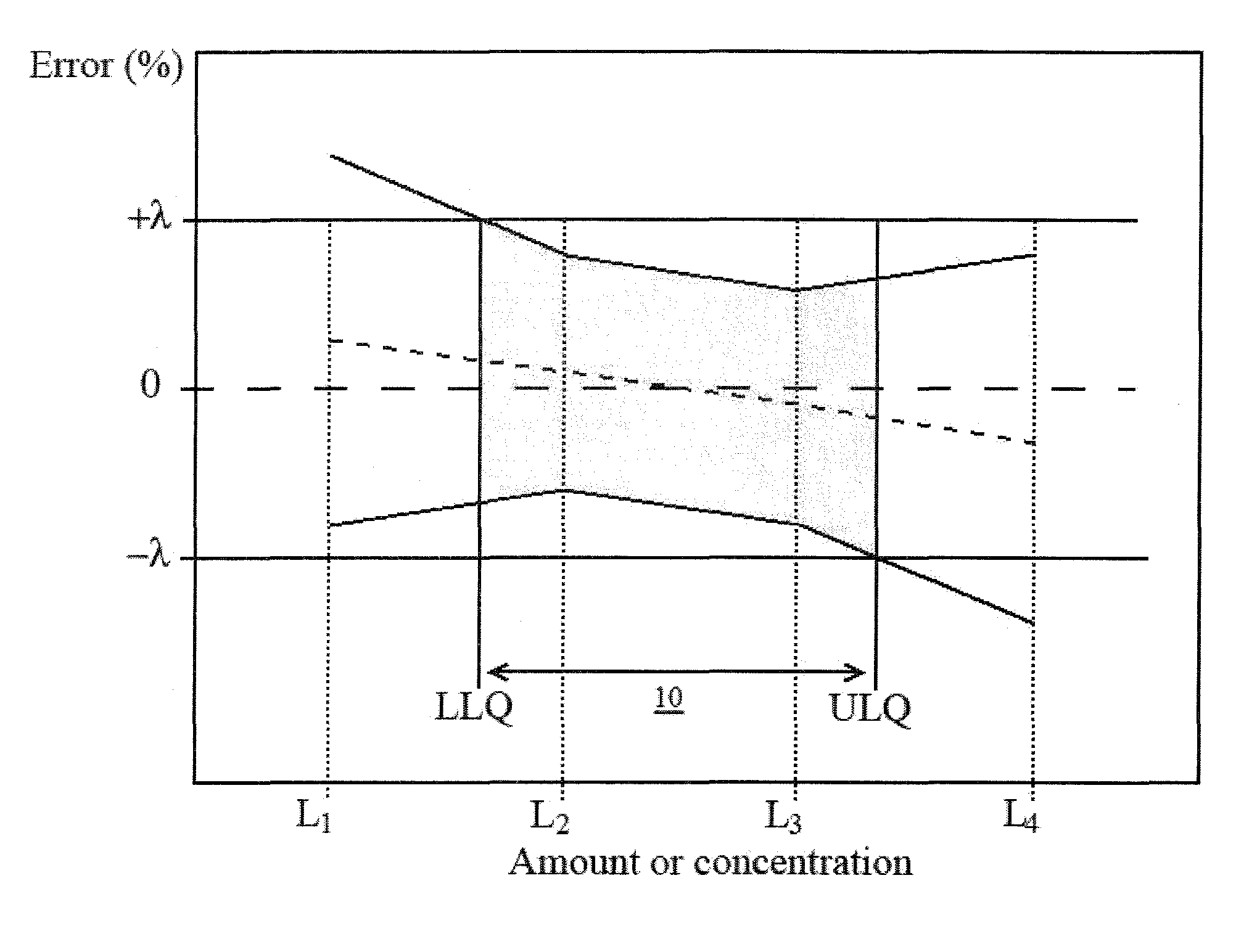
InactiveUS20110071807A1Easy to useAss qualityMaterial analysis by optical meansComputation using non-denominational number representationModel selectionTolerance interval
The invention relates to a method of analyzing spectral data for the selection of a calibration model, relating spectra of a substance to a physical or chemical parameter of the substance, over a predetermined range of the physical or chemical parameter, comprising the steps: a) capturing spectral data of the substance with respective values of the physical or chemical parameter over the predetermined range, b) creating a plurality of calibration models using the captured spectral data in dependence upon the values of the physical or chemical parameter based on the calibration data using statistical resampling methods, c) calculating tolerance intervals of the results at each reference level for each calibration model, and d) displaying the tolerance intervals at each reference level over the predetermined range for each calibration model. In this way, a possibility for analyzing spectra data is provided which is useful in spectroscopic applications for automated calibration model selection and makes analytical interpretation and evaluation easier and more accurate.
Owner:UNIV LIEGE +1
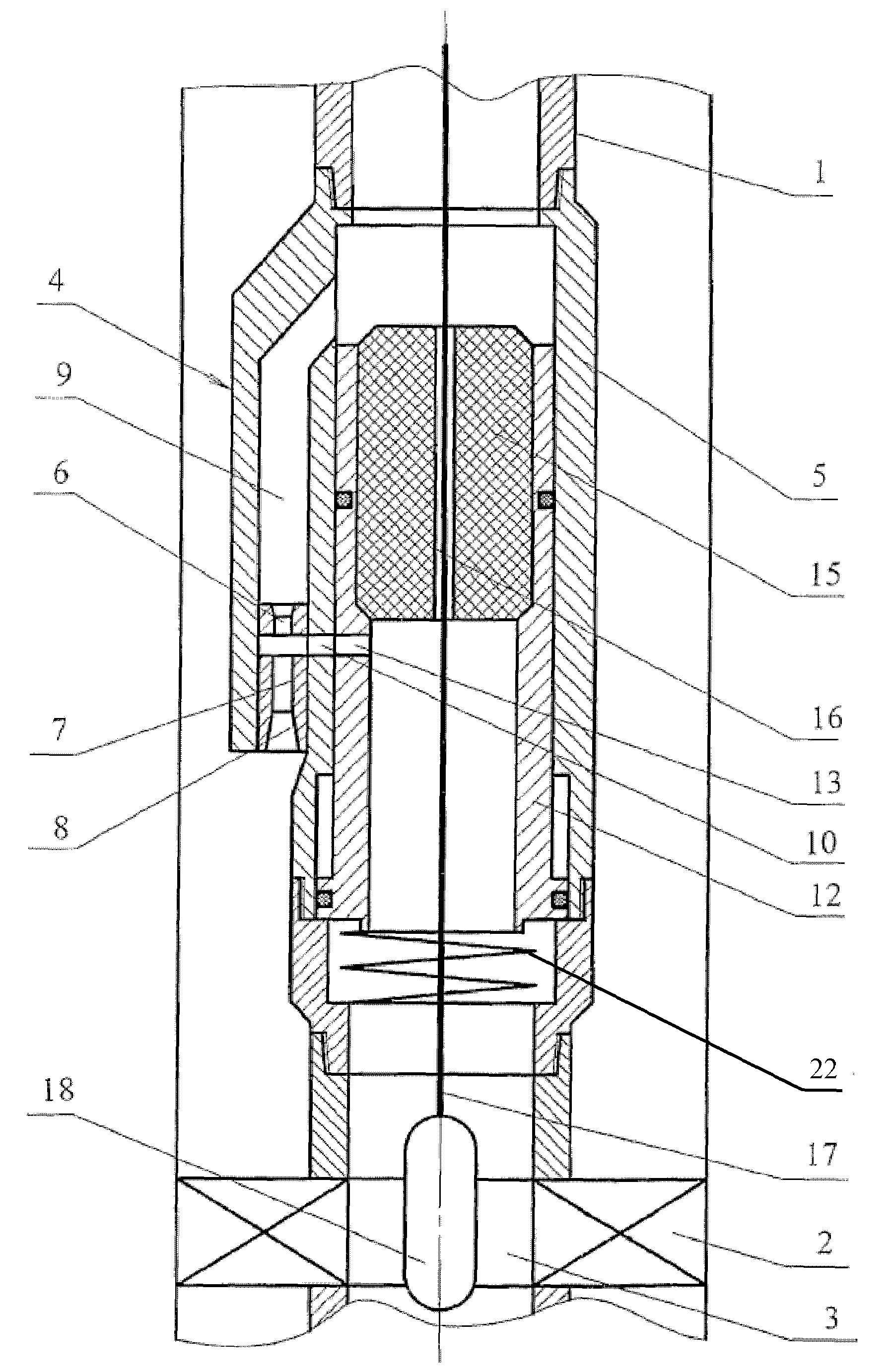
Well Jet Device and the Operating Method Thereof
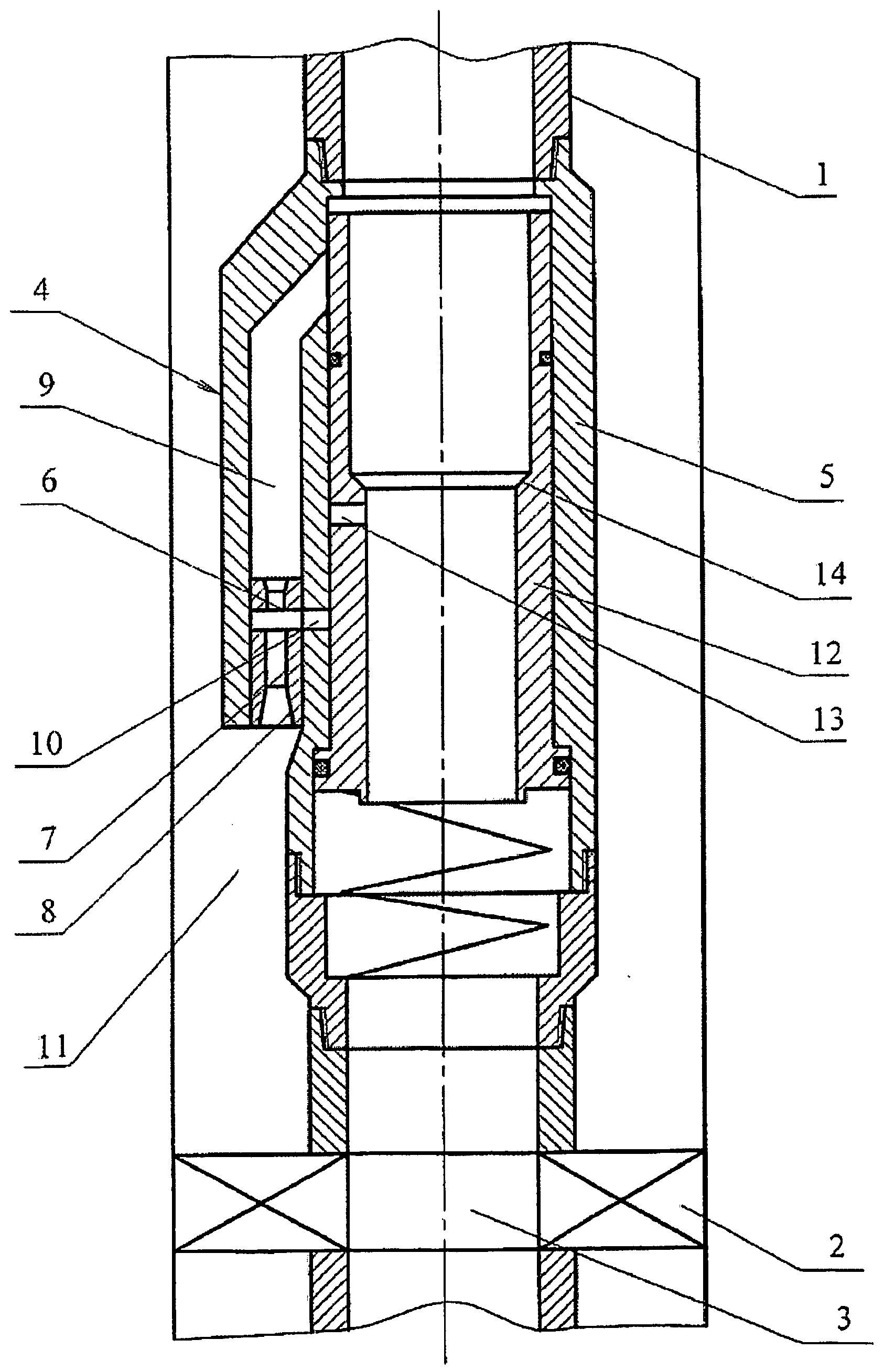
InactiveUS20080264634A1Quality improvementIncreasing well production rateSurveyJet pumpsReflux valveSpray nozzle
Well jet device comprises a packer on a pipe string, with a central channel and a jet pump, comprising channels for supplying a working medium to a nozzle and supplying a medium pumped from the well. A diffuser output connects to the annular space and the nozzle connects to the pipe string internal cavity on the side of the input thereof through the channels. The body has a movable steady bush, spring-loaded working medium flow switch. Steady bush bypass holes and mounting seat for mounting a sealing unit provided with a hole for passing a logging cable or for arranging a depression insert provided with autonomous instruments and a return valve are provided. The sleeve, in the top position, closes the channels and, in lower position, the top end face is positioned under the input into the channel. The bypass holes are connected to the input into the channel.
Owner:KHOMYNETS ZINOVIY DMITRIEVICH
Smart installation/processing systems, components, and methods of operating the same
ActiveUS8938886B2Improve Manufacturing TolerancesAss qualityProgramme controlComputer controlEngineeringHandling system
A processing system employs a processing tool to process workpieces, for example cold working holes and / or installing expandable members into holes. Sensors sense various aspects of the processing. Information regarding performance of the process and / or materials may be stored, for example a hole-by-hole or a workpiece-by-workpiece basis, allowing validation of processing. Information also allows dynamic operation of the processing tool. Analysis of response relationships (e.g., pressure or force versus position or distance) may provide insights into the process and materials, and / or facilitate the real-time feedback including control, alerts, ordering replacement for consumable components.
Owner:FATIGUE TECH
Analyzing spectral data for the selection of a calibration model
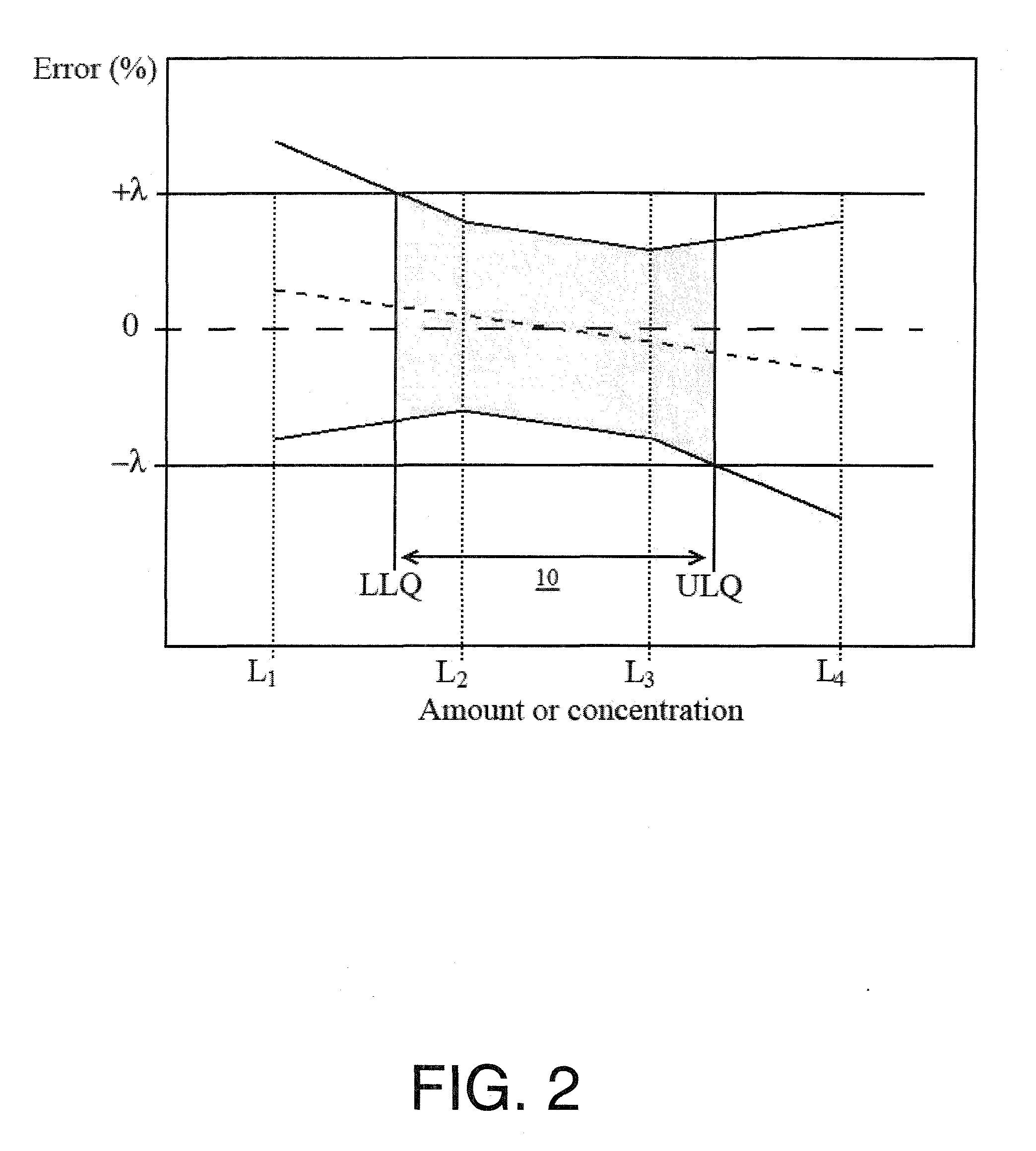
InactiveUS8494818B2Efficient use ofAss qualityMaterial analysis by optical meansComputation using non-denominational number representationModel selectionTolerance interval
The invention relates to a method of analyzing spectral data for the selection of a calibration model, relating spectra of a substance to a physical or chemical parameter of the substance, over a predetermined range of the physical or chemical parameter, comprising the steps: a) capturing spectral data of the substance with respective values of the physical or chemical parameter over the predetermined range, b) creating a plurality of calibration models using the captured spectral data in dependence upon the values of the physical or chemical parameter based on the calibration data using statistical resampling methods, c) calculating tolerance intervals of the results at each reference level for each calibration model, and d) displaying the tolerance intervals at each reference level over the predetermined range for each calibration model. In this way, a possibility for analyzing spectra data is provided which is useful in spectroscopic applications for automated calibration model selection and makes analytical interpretation and evaluation easier and more accurate.
Owner:UNIV LIEGE +1
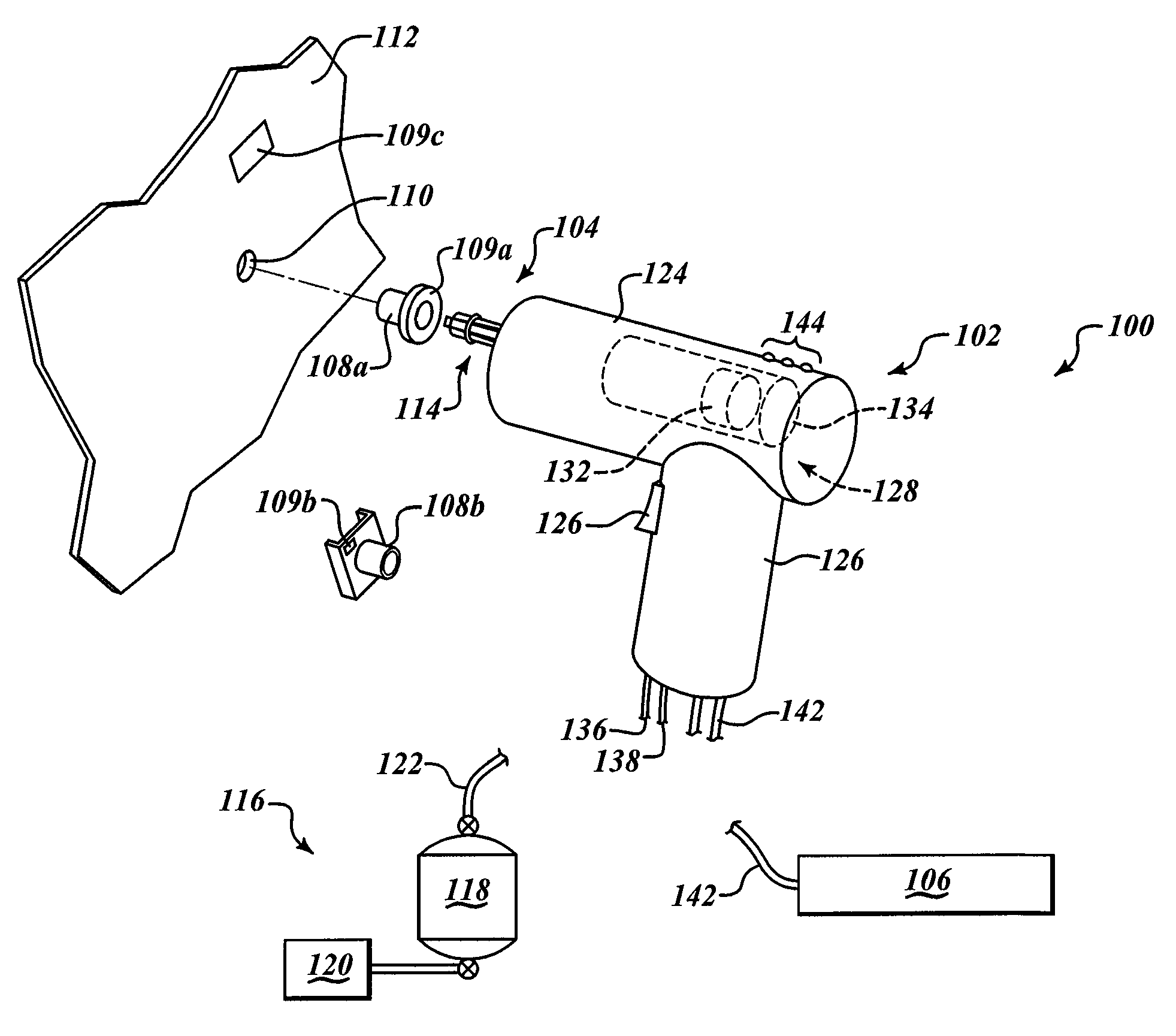
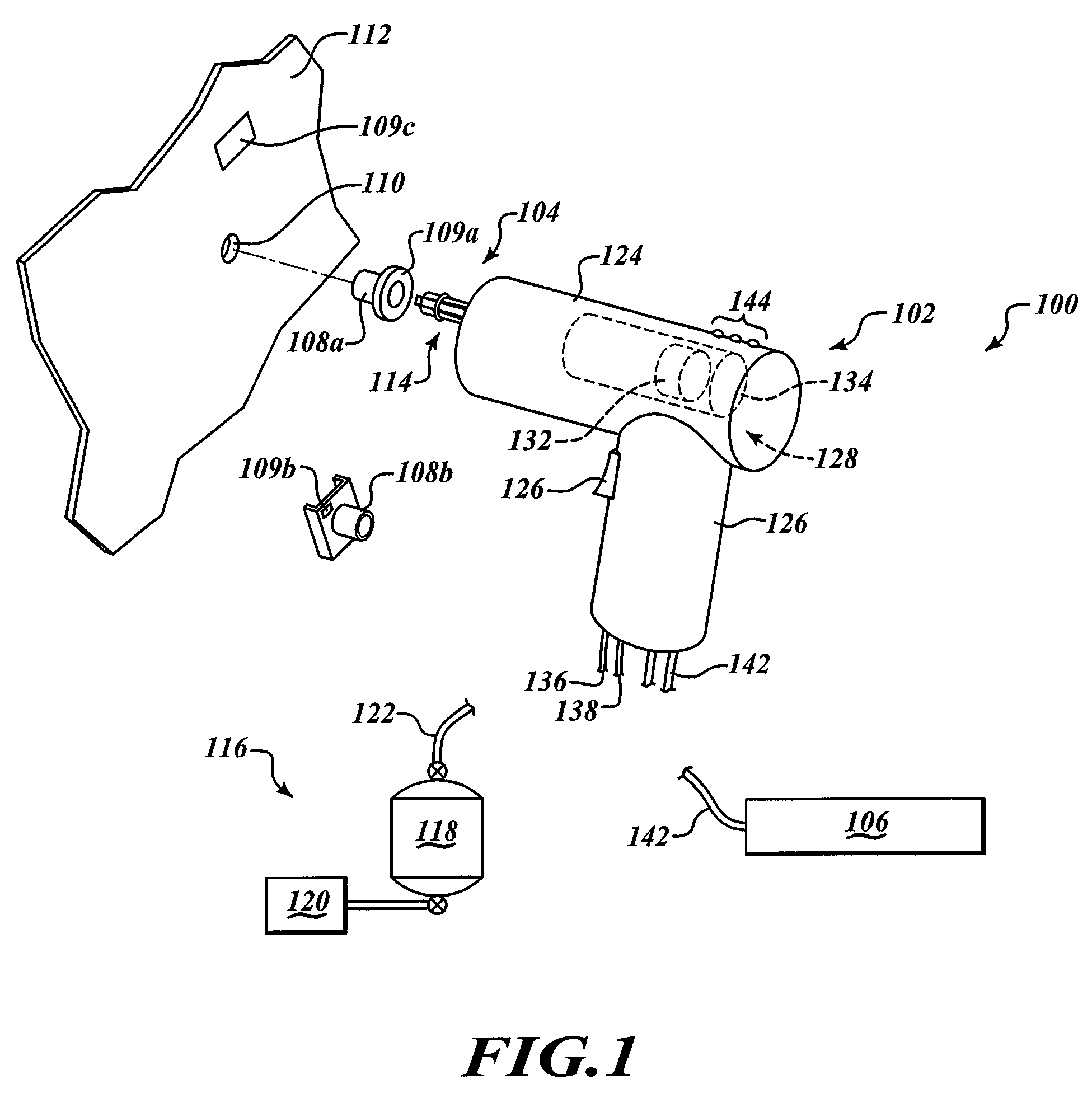
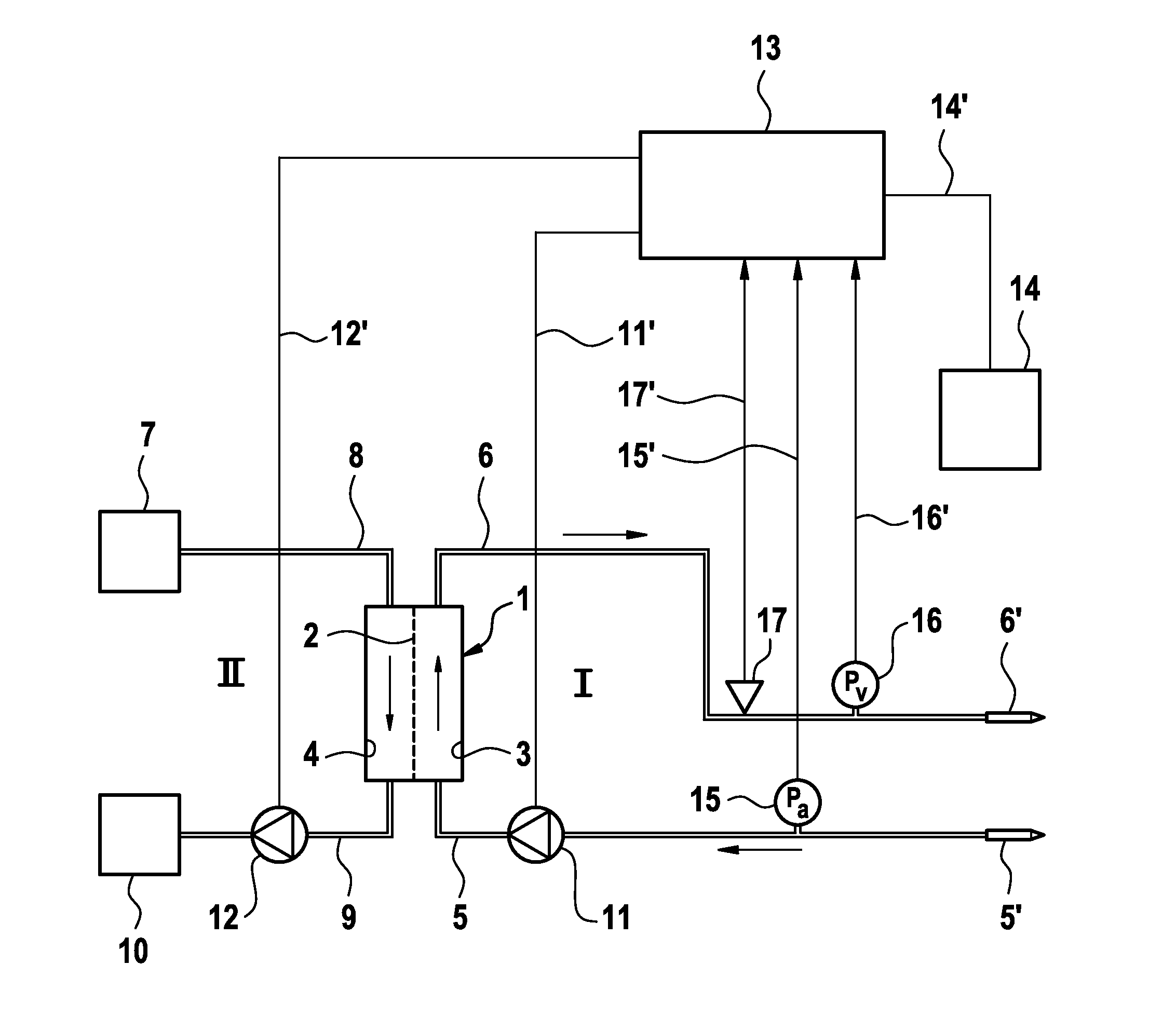
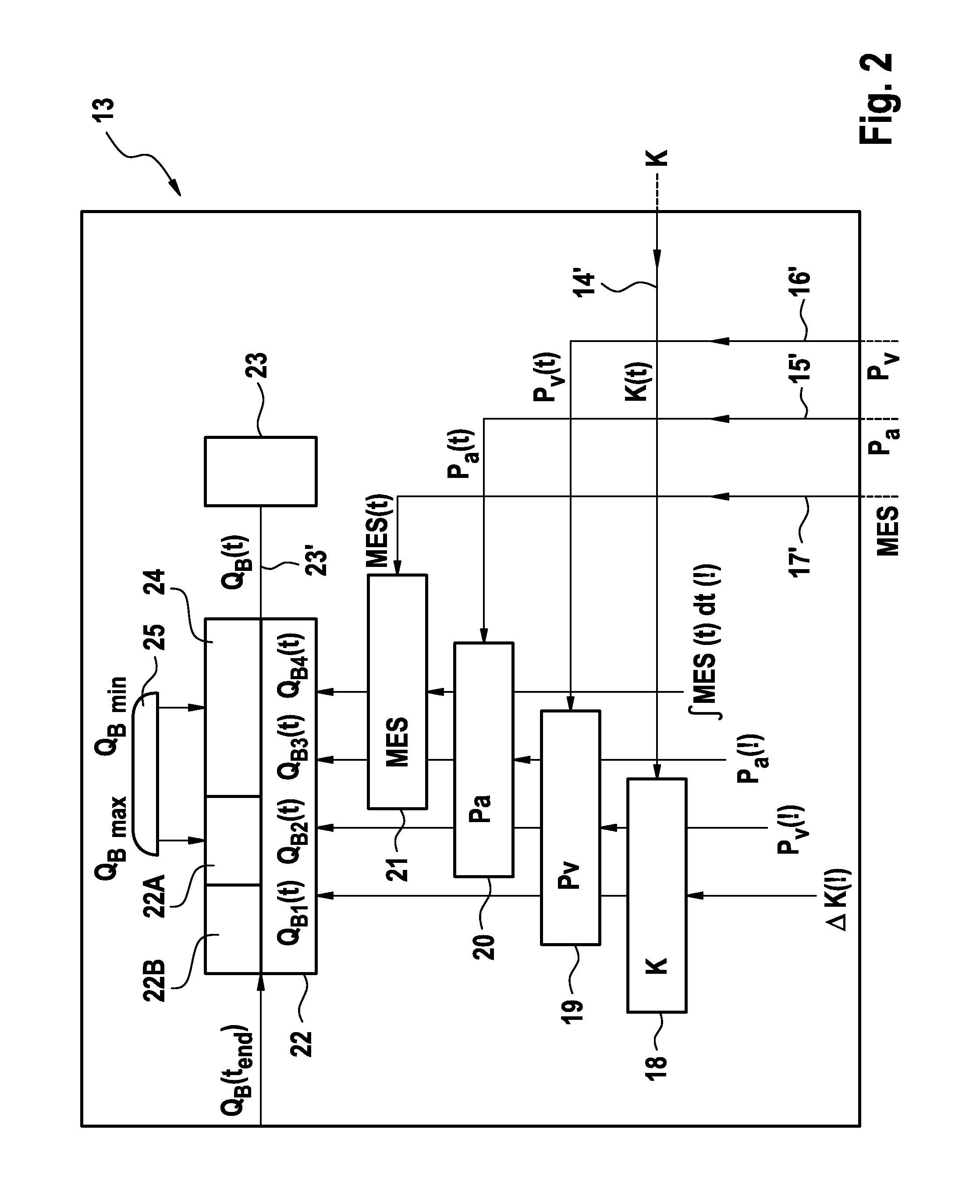
Apparatus for extra-corporeal blood treatment and method of determining a blood flow rate for an extra-corporeal blood treatment apparatus
ActiveUS20130303964A1Maximising metabolic performancePerformance maximizationDialysis systemsMedical devicesBlood treatmentsVein
An apparatus and method of determining the blood flow rate at which, in an extra-corporeal blood circuit of an extra-corporeal blood treatment apparatus, blood is pumped through the arterial blood line into the blood chamber of the dialyser and out of its blood chamber through the venous blood line is described. The method and apparatus provide for the determination of a plurality of parameters characteristic of the extra-corporeal blood treatment, with a given blood flow rate being determined in each case as a function of one of the characteristic parameters. A blood flow rate which is preset for the blood treatment is selected from the plurality of blood flow rates determined on the basis of the characteristic parameters. The blood flow rate to be preset is selected on the basis of a preset algorithm which may be implemented in software installed on a data processing unit or in hardware.
Owner:FRESENIUS MEDICAL CARE DEUTSCHLAND GMBH
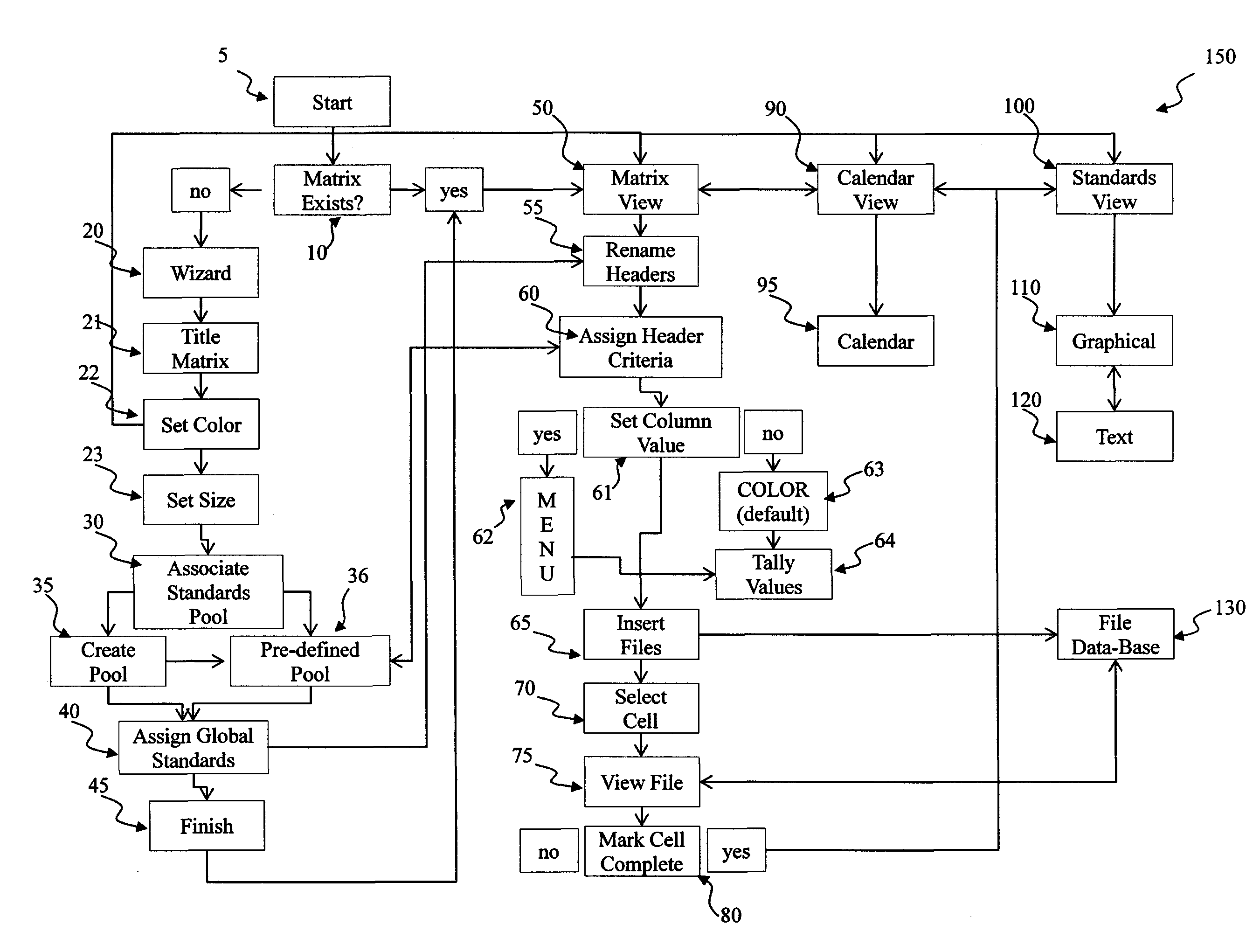
System and Method for Organizing, Managing, and Using Electronic Files
InactiveUS20090204921A1Easy to cleanEasy methodOffice automationInput/output processes for data processingDocumentation procedureInformation resource
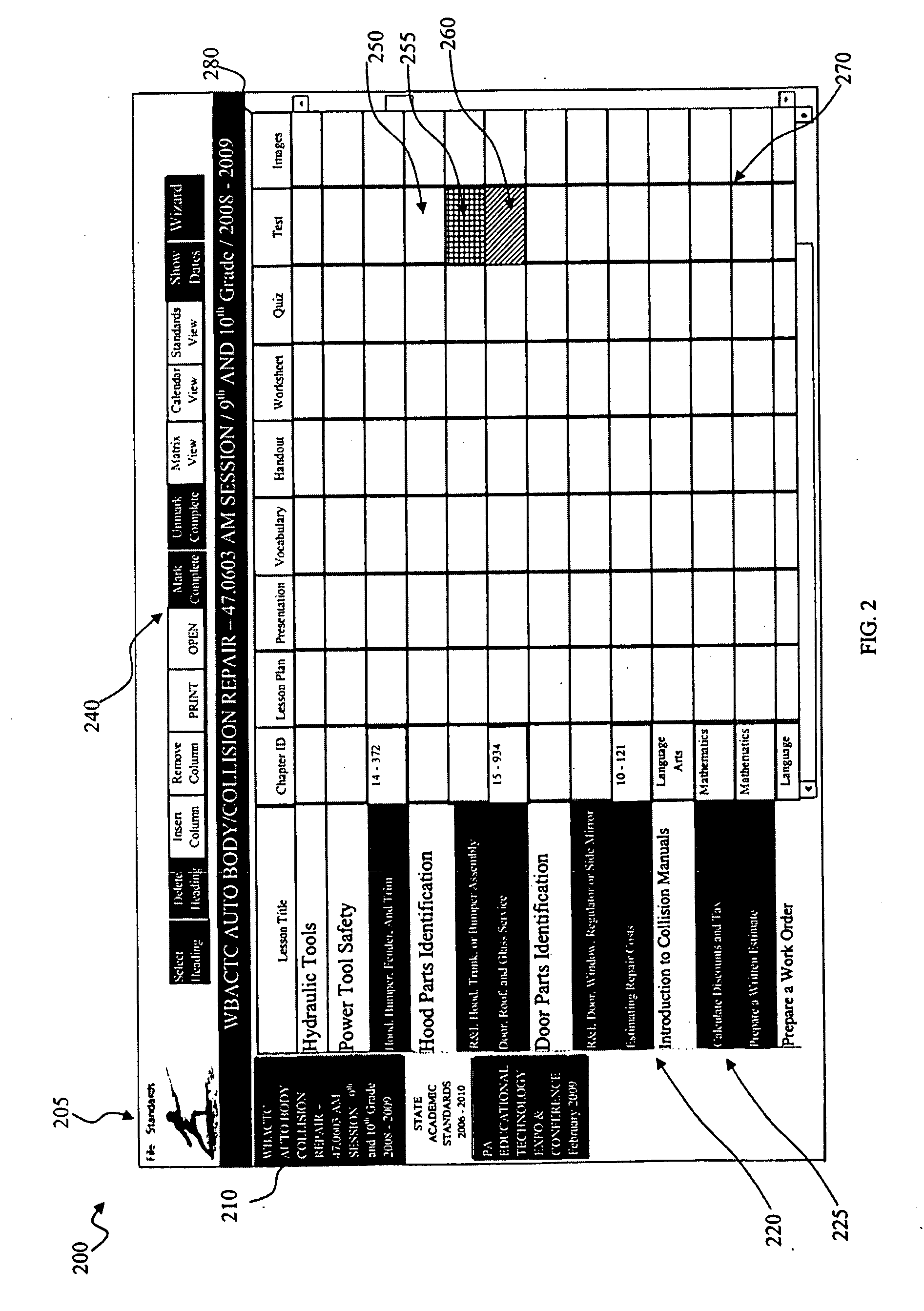
A system for organizing information resources electronically, preferably in the context of a lesson plan is disclosed. The system also provides a simple, clean, easy-to-use interface that creates a dynamic structure for storing document and other information files and for presenting the user with an easy method to retrieve and use the files. A preferred embodiment of the system according to the present invention allows teachers to visually assess the quality of their lesson plan(s) as created and utilized, to apply templates to standardize the teaching of students across multiple educators, and to provide reports on demand that provide details on the effectiveness and comprehensiveness of their lesson plans. At the same time, the system is flexible enough to allow educators to customize their lessons to meet individual students' needs.
Owner:VESTYCK ANTHONY R
Well jet device and the operating method thereof
Owner:KHOMYNETS ZINOVIY DMITRIEVICH
Instruments and Methods for the Implantation of Cell-Seeded Ultra-thin Substrates
A surgical instrument, and methods for its use, is described that includes clamp heads that can be nestled within or extended from a tubular sheath by longitudinal movement of the clamp heads' tines with respect to the tubular sheath. One of the tines includes an arch that slides against a mouth and inside wall of the tubular sheath, causing the clamp heads to open or close. The clamp heads close lightly, to within a predetermined (or zero) distance from one another, gently grasp an ultrathin polymer substrate seeded with cells, and pulls it within the sheath such that the substrate curls and folds to protect the cells.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Method and arrangement for outputting residual errors for a function customized to a set of points
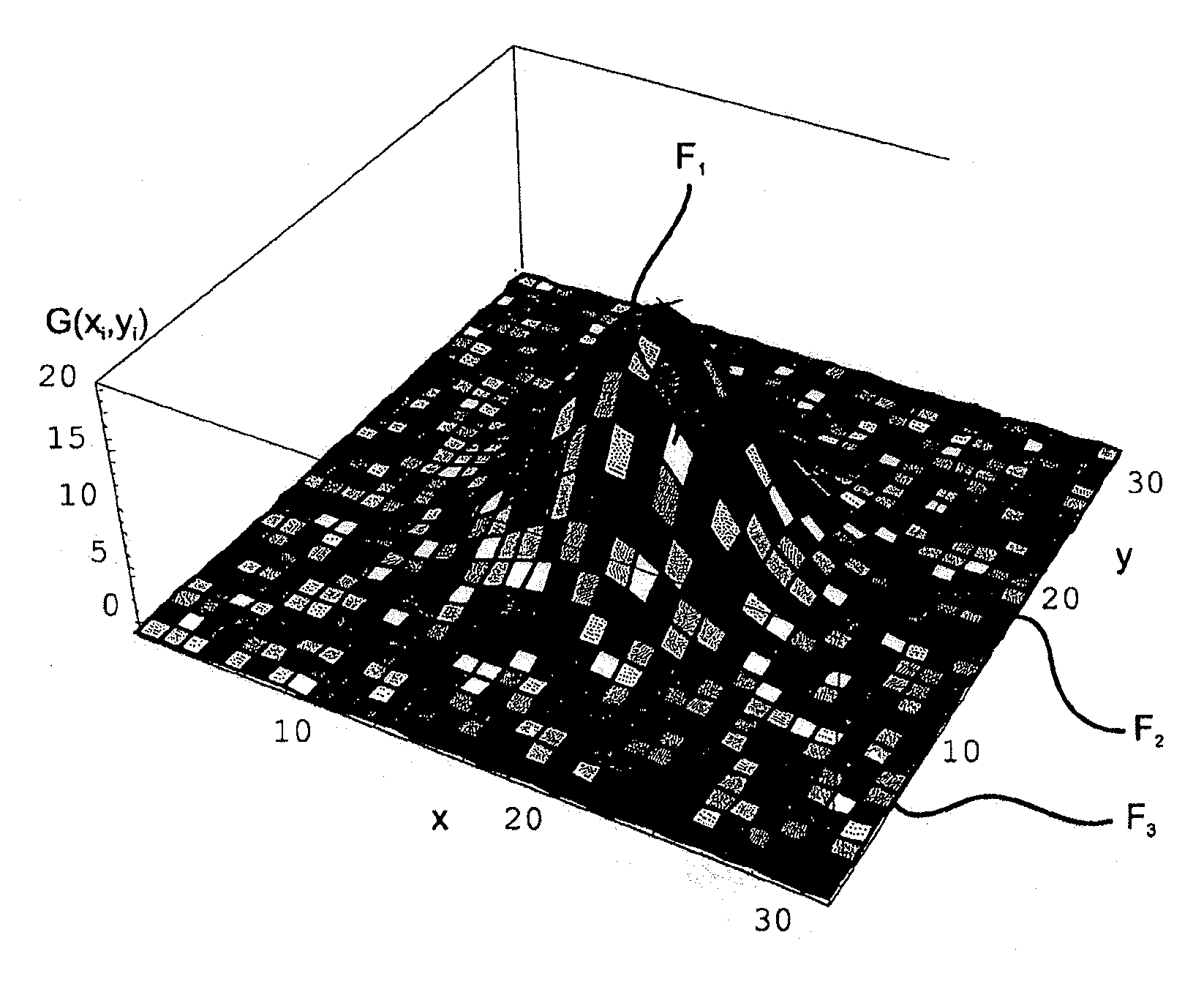
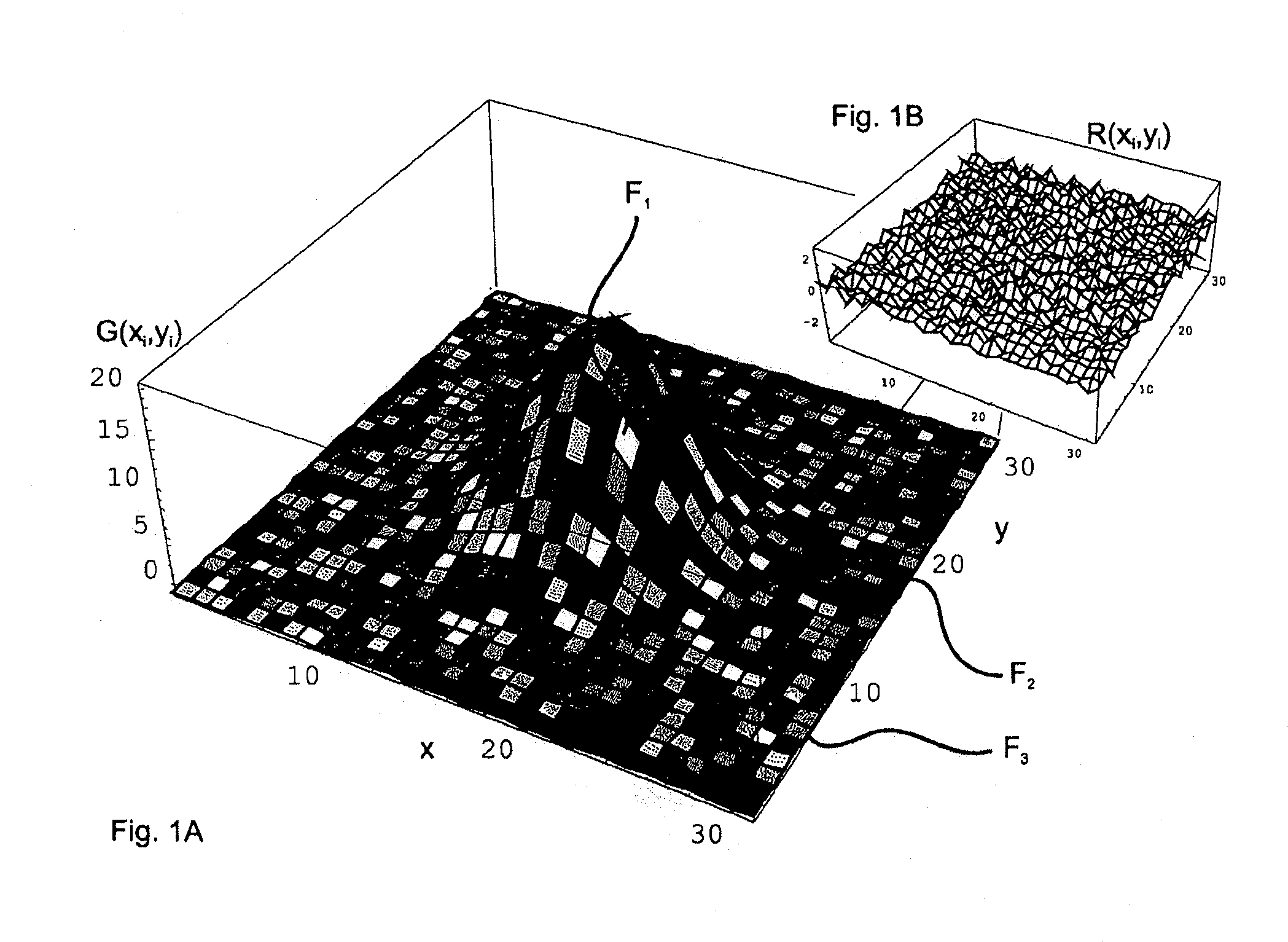
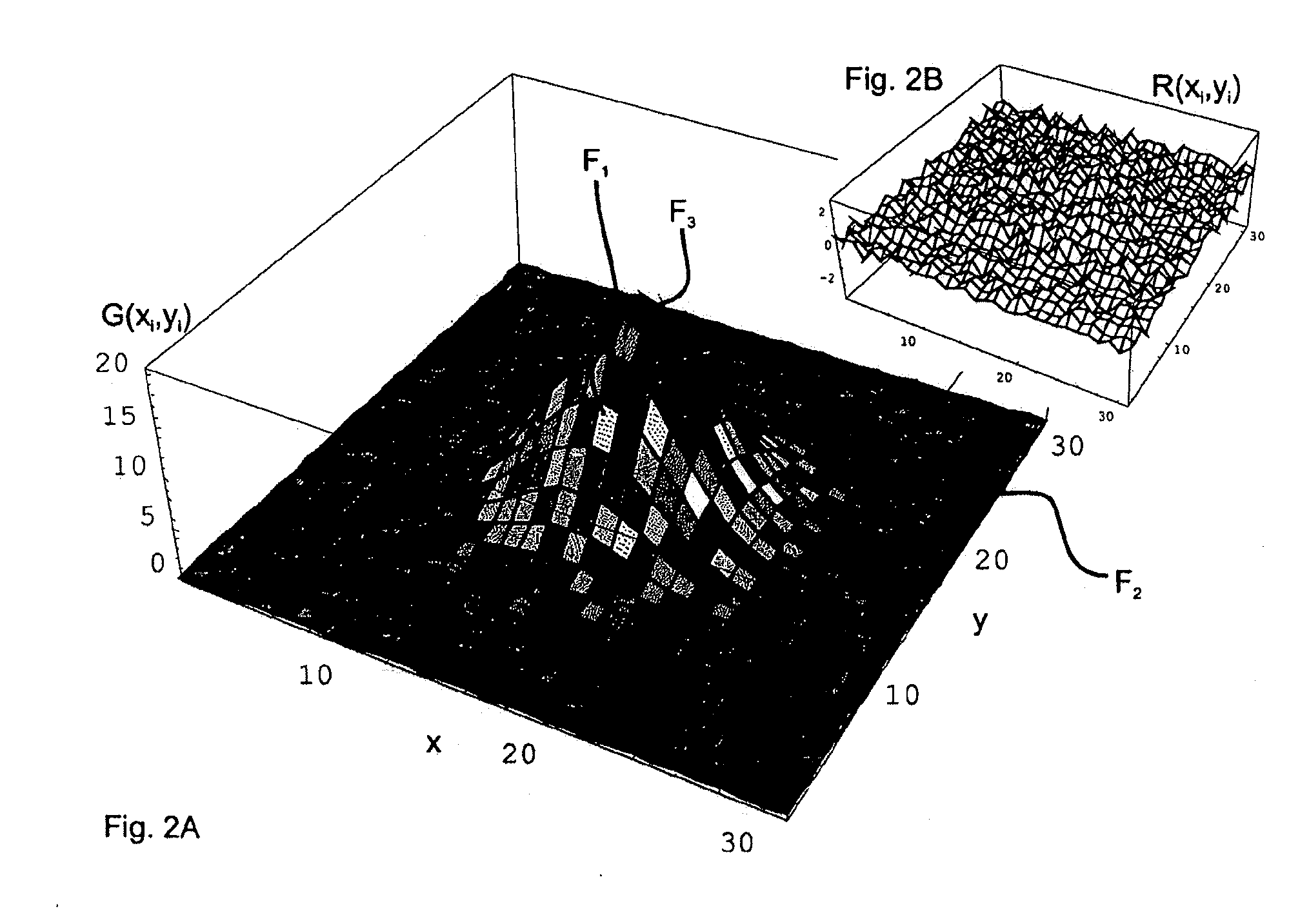
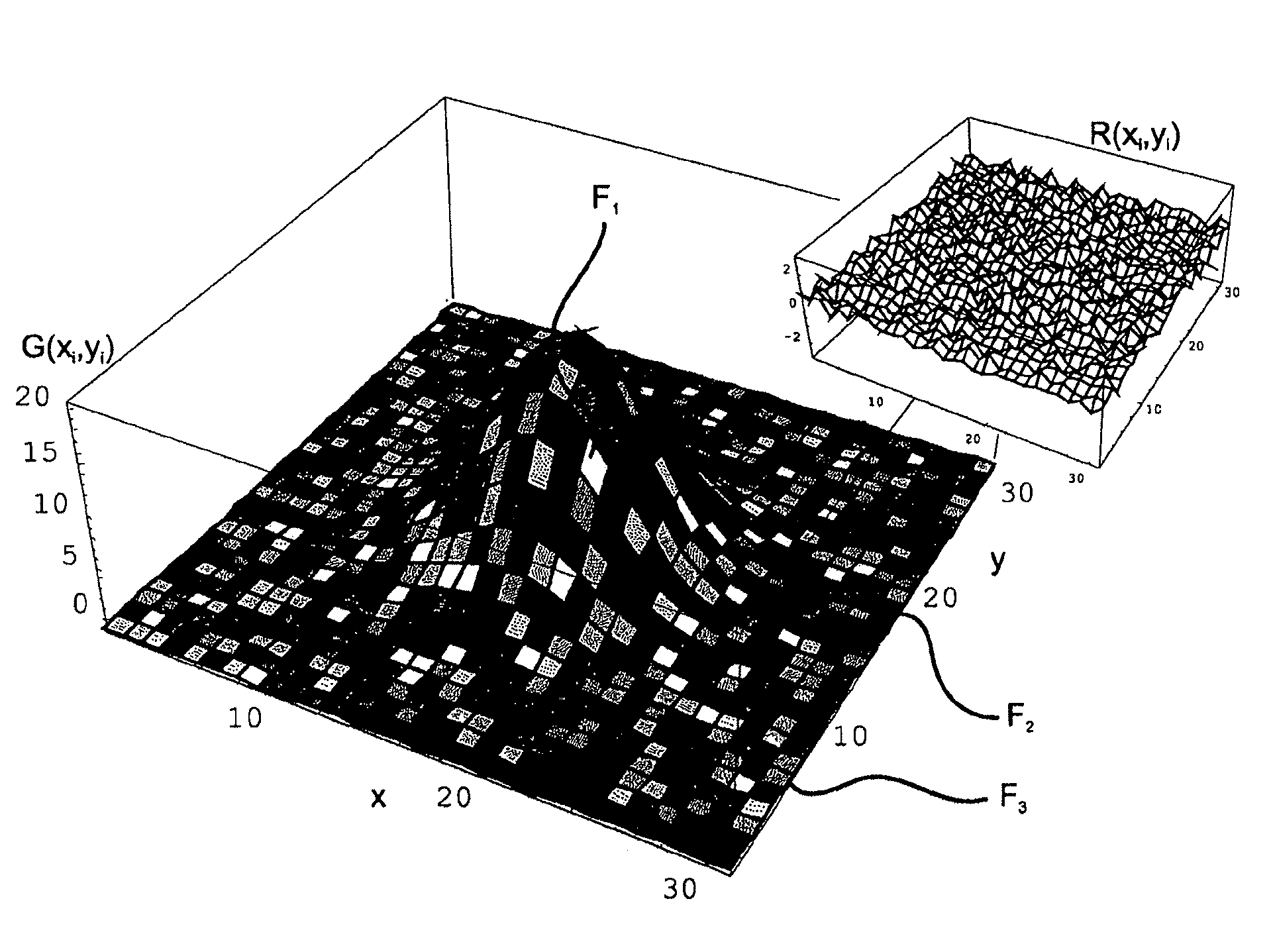
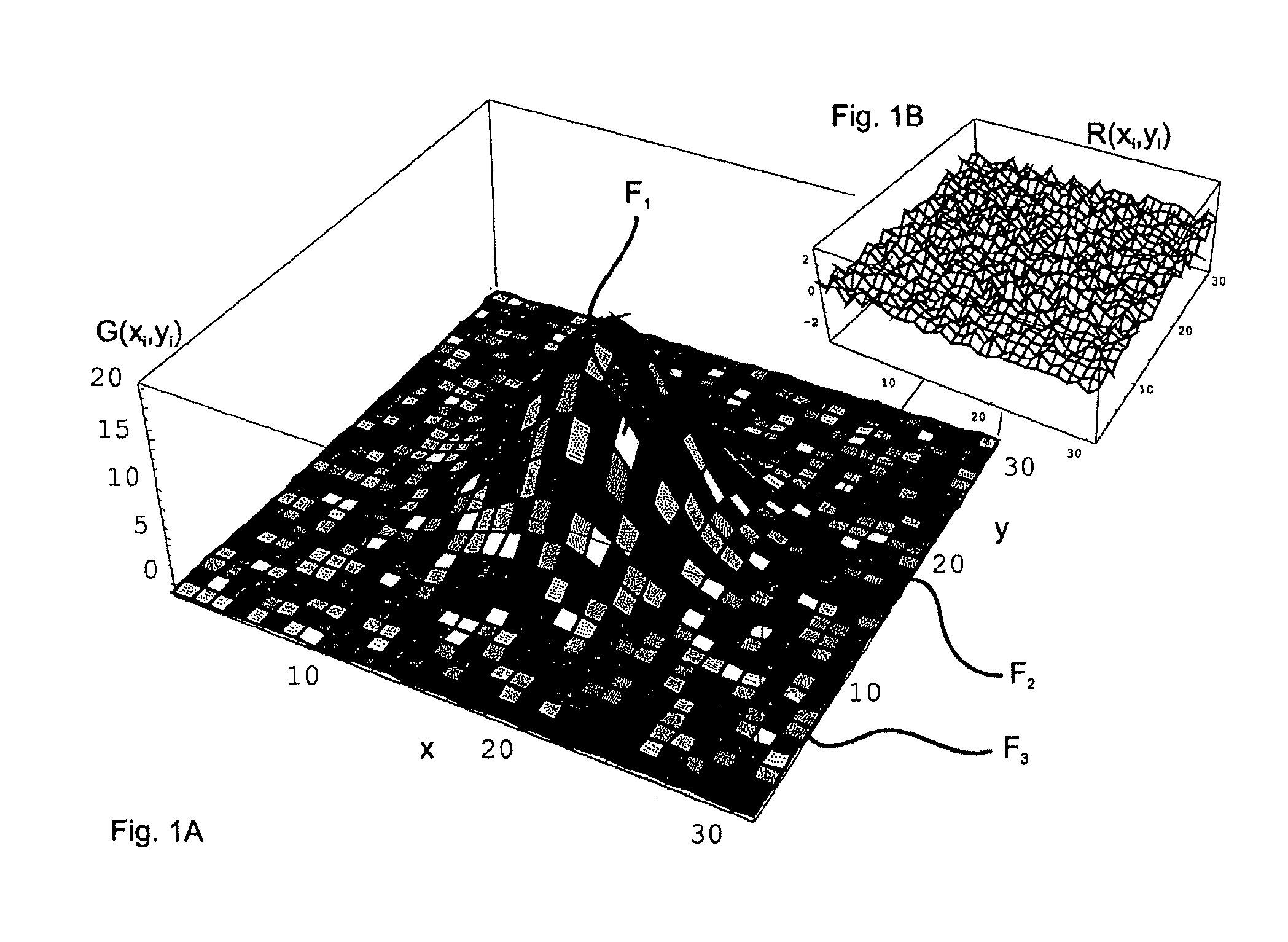
ActiveUS20100214297A1Simple and accurate visual assessment of qualitySimple and accurate visual assessment of quality of fitDrawing from basic elementsPoint setData point
The invention is directed to a method and an arrangement for displaying residual errors of a function which is fitted to a set of points. In the prior art, the residual errors are displayed in a separate graph apart from the function graph so that it is difficult for an observer to discern the quality of the fit of the function to the data points. An improved method and an improved arrangement make it possible to visually assess the quality of the fit in a simple, accurate manner. According to the invention, visual codes are assigned to the fitted function or to the data points of the point set piecewise or pointwise depending on the residual errors, and the fitted function is displayed graphically at an interface, wherein the fitted function is displayed piecewise or pointwise in the form of the assigned visual codes. The invention is preferably used for raster image spectroscopy with laser scanning microscopes.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MICROSCOPY GMBH
Apparatus and method for measuring the quality of an extracted signal
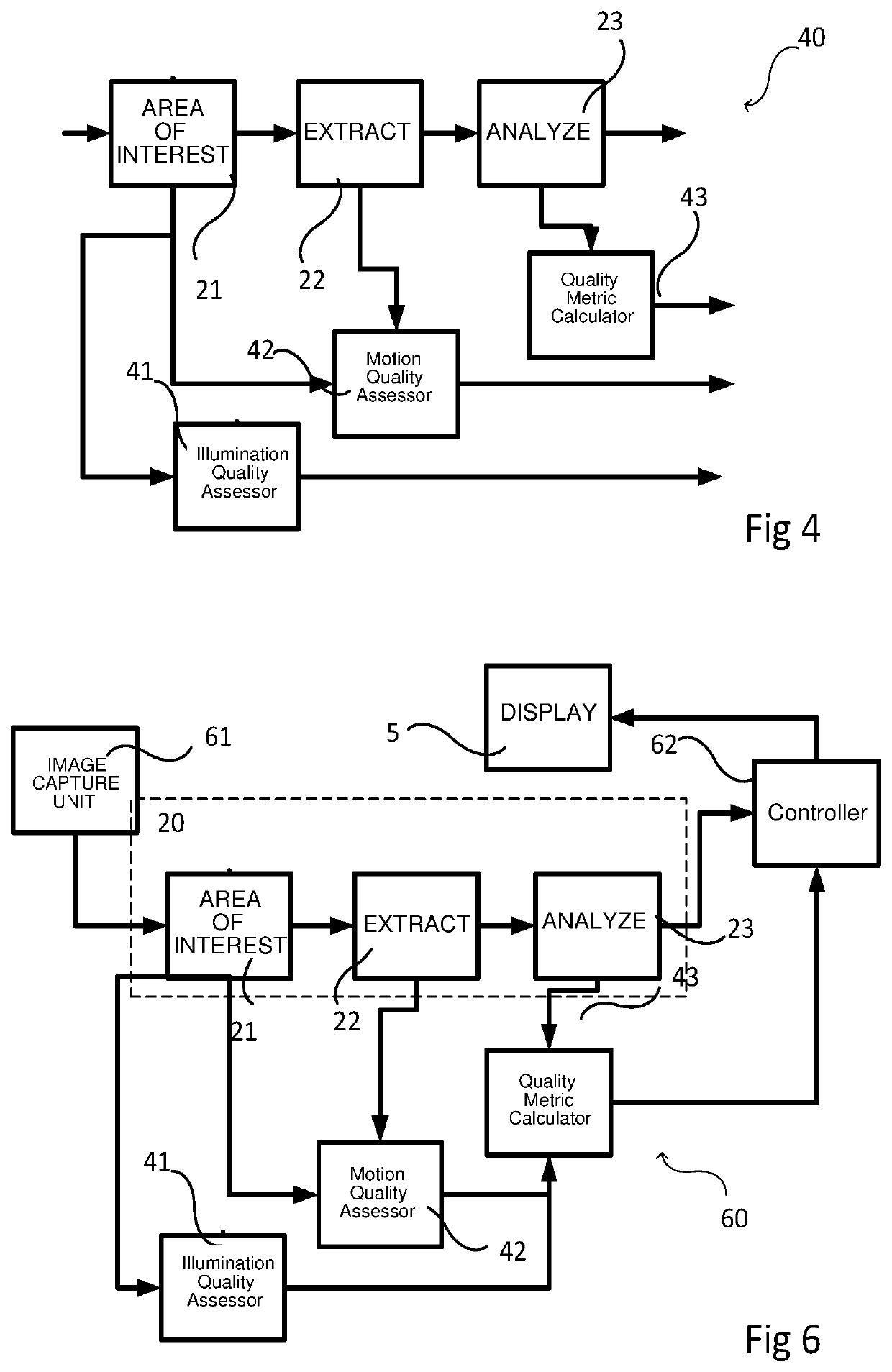
ActiveUS10667704B2Ass qualityEasy to implementImage enhancementImage analysisSignal qualityAlgorithm
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Apparatus and method for measuring the quality of an extracted signal
There is provided a system and method of assessing the quality of the extraction of the signal and the reliability of the physiological measurement by providing a system for producing a quality metric for physiological information extraction from a sequence of image frames, the system comprising a signal extraction unit configured to extract a signal representative of a physiological characteristic from a plurality of the image frames, a signal analyzer configured to calculate a plurality of physiological information results from the signal using a plurality of calculation functions, the plurality of calculation functions being comprised within a list of calculation functions, each physiological information result being calculated using a different calculation function, and a quality metric calculator for calculating a quality metric value based on a signal analysis metric derived from a comparison between the physiological information results of the plurality of physiological information results.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Well Jet Device and the Operating Method Thereof
InactiveUS20080245572A1Quality improvementIncreasing well production rateSurveyJet pumpsReflux valveEngineering
Well jet device comprises a packer mounted on a pipe string provided with a central channel embodied therein and jet pump. The pump has channels supplying a working medium to a nozzle, removing the media mixture and supplying a medium pumped from the well, respectively. Said nozzle is connected to the annular space by the channels and the channel is connected to the pipe string internal cavity through the channel on the side, where the diffuser of the pump enters and exits. A working medium flow switch is arranged in the body. An annular channel communicating with the channel via the channel and the nozzle is above said abutment flange and the steady bush comprises bypass holes and mounting seat for mounting a sealing unit with a hole for passing a logging cable with instruments therethrough or for arranging a depression insert provided with a return valve.
Owner:KHOMYNETS ZINOVIY DMITRIEVICH
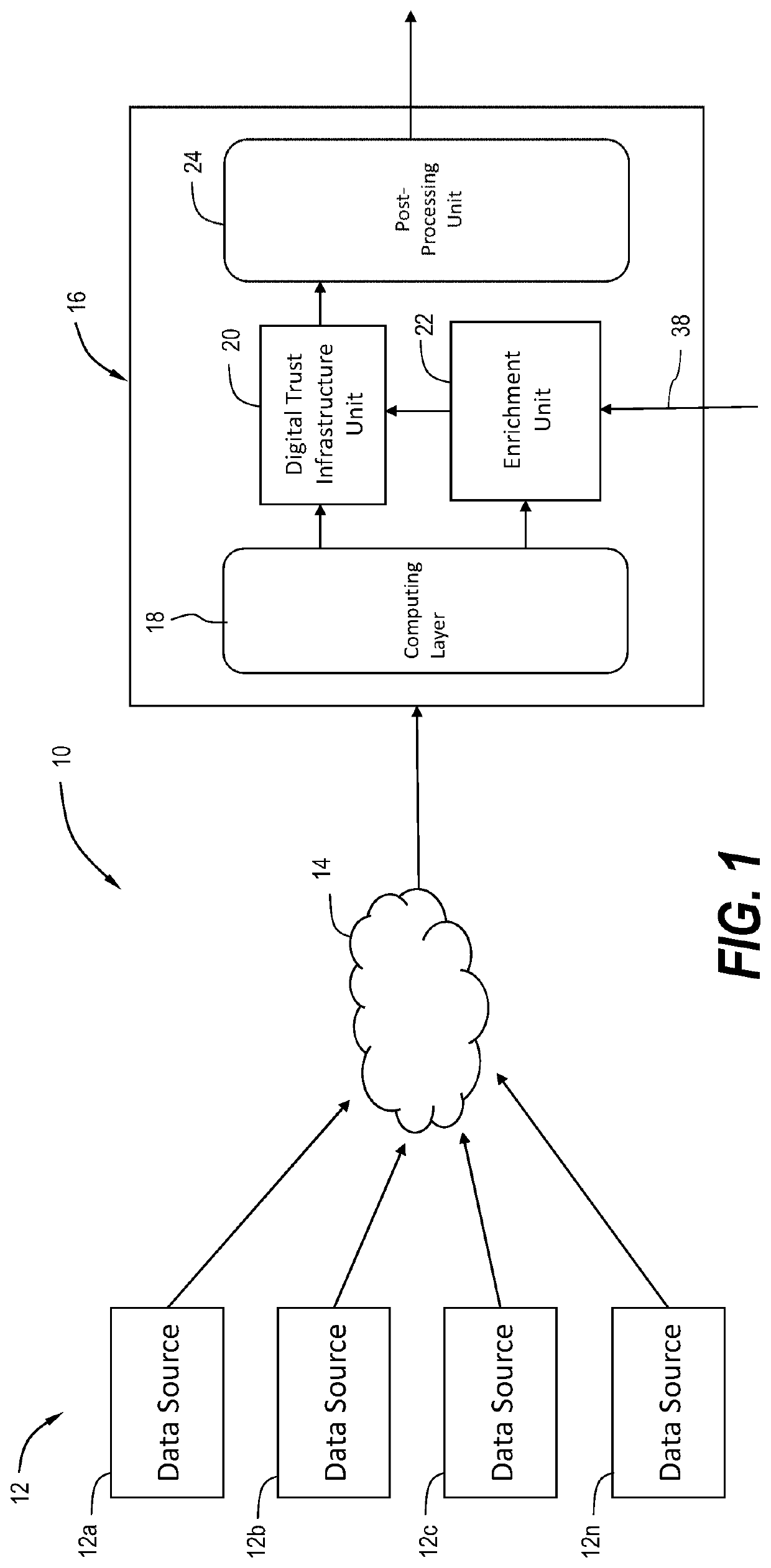
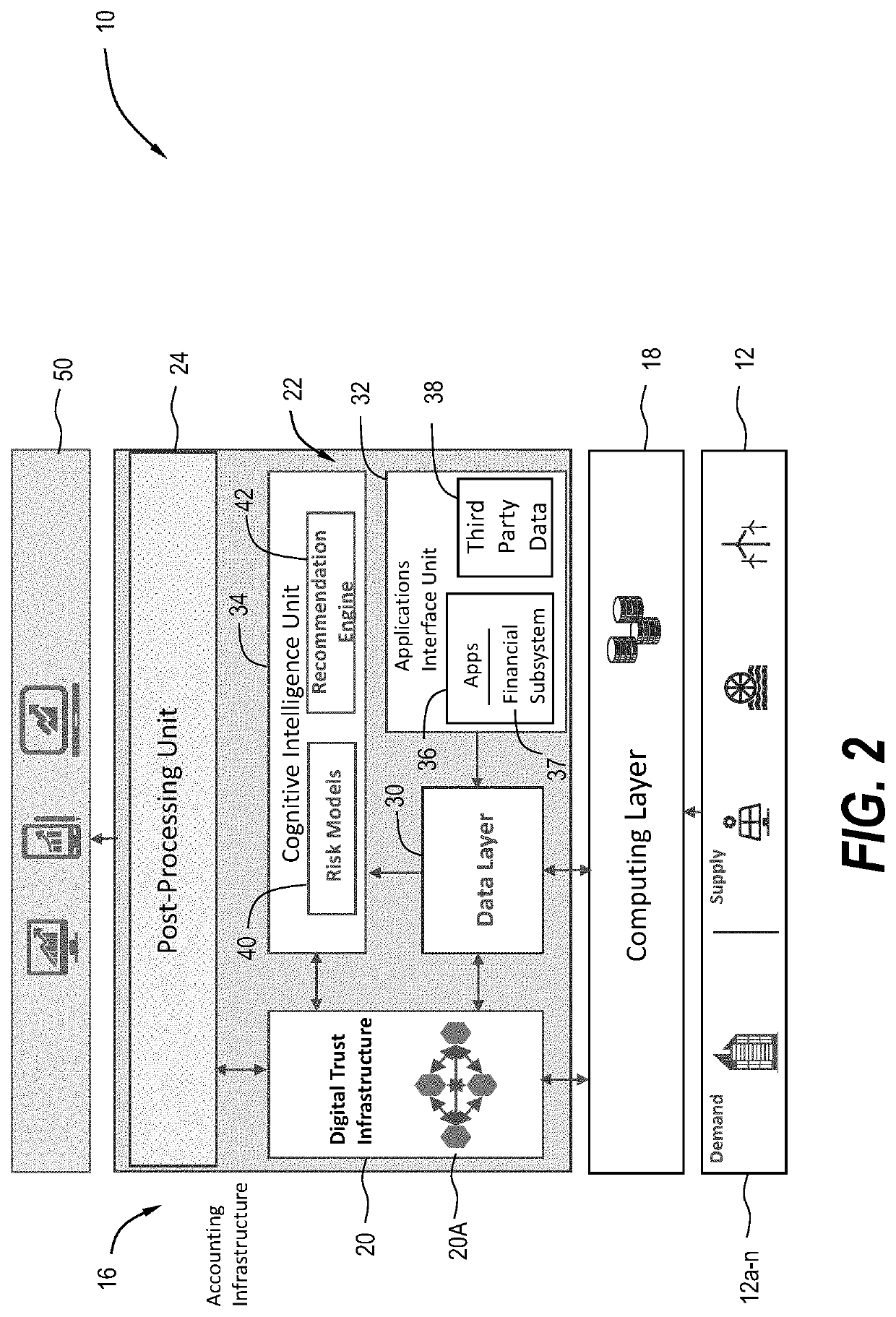
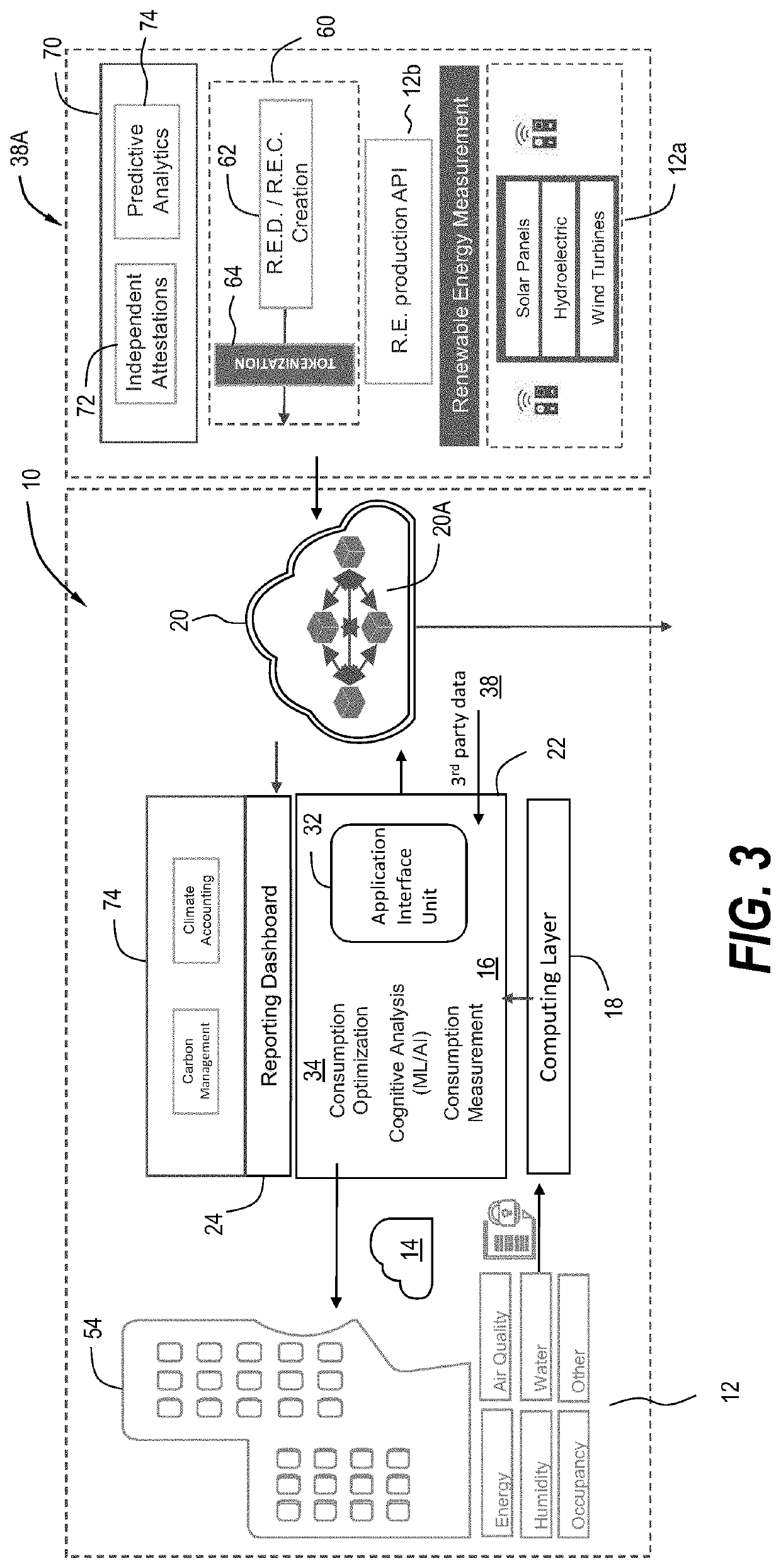
System and method for collecting and storing environmental data in a digital trust model and for determining emissions data therefrom
PendingUS20220327538A1Reduce carbon footprintReduce operating costsCryptography processingUser identity/authority verificationThird partyCarbon footprint
A system and method for monitoring and assessing the carbon footprint of an enterprise. The system aggregates data, such as for example environmental data, enriches the data and then stores the data along with additional information in a blockchain. The additional information stored in the blockchain can include third party data, the types of risk models and machine learning techniques employed by the system, emissions data, attribute data, and the like.
Owner:KPMG LLP
Method for assessing the quality of a distorted version of a frame sequence
InactiveUS8824830B2Ass qualityQuality improvementImage enhancementImage analysisComputer hardwareFrame sequence
A method for assessing the quality of a distorted version of a frame sequence includes the steps of determining a last spatial distortion by comparing a block of a last frame (I6) of the sequence with a corresponding block of the distorted version of the last frame, determining, in a last-but-one frame, a best-matching block matching said block of the last frame best, determining a last-but-one spatial distortion by comparing the determined best-matching block of the last-but-one frame with a corresponding block of the distorted version of the last-but-one frame, determining a spatio-temporal perceptual distortion value associated with said block using said determined distortions and using the determined spatio-temporal perceptual distortion value for assessing the quality.
Owner:MAGNOLIA LICENSING LLC
Method and arrangement for outputting residual errors for a function customized to a set of points
ActiveUS8654128B2Simple and accurate visual assessment of quality of fitVigorous suppression of statistical noiseDrawing from basic elementsGraphicsGrating
The invention is directed to a method and an arrangement for displaying residual errors of a function which is fitted to a set of points. In the prior art, the residual errors are displayed in a separate graph apart from the function graph so that it is difficult for an observer to discern the quality of the fit of the function to the data points. An improved method and an improved arrangement make it possible to visually assess the quality of the fit in a simple, accurate manner. According to the invention, visual codes are assigned to the fitted function or to the data points of the point set piecewise or pointwise depending on the residual errors, and the fitted function is displayed graphically at an interface, wherein the fitted function is displayed piecewise or pointwise in the form of the assigned visual codes. The invention is preferably used for raster image spectroscopy with laser scanning microscopes.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MICROSCOPY GMBH
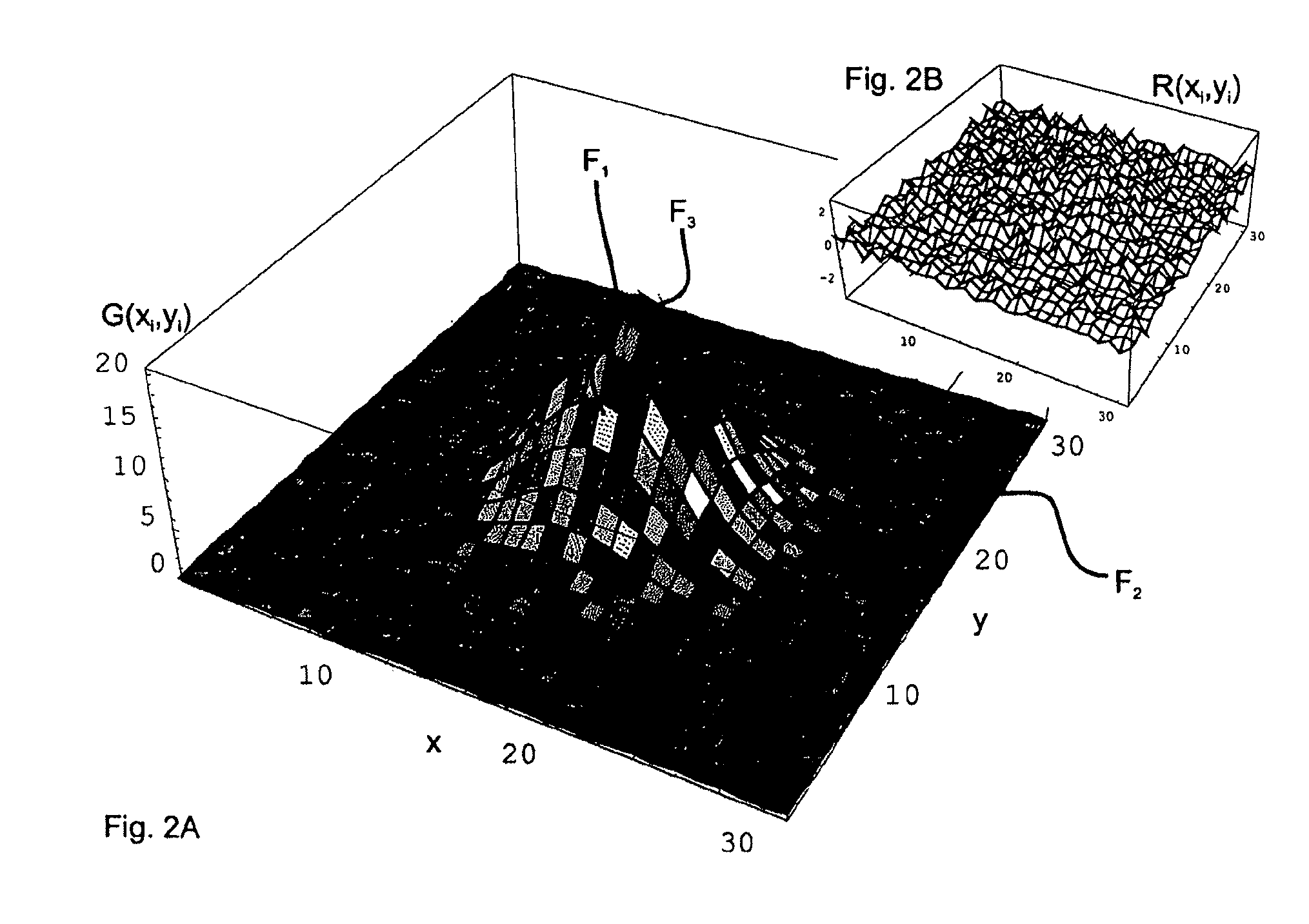
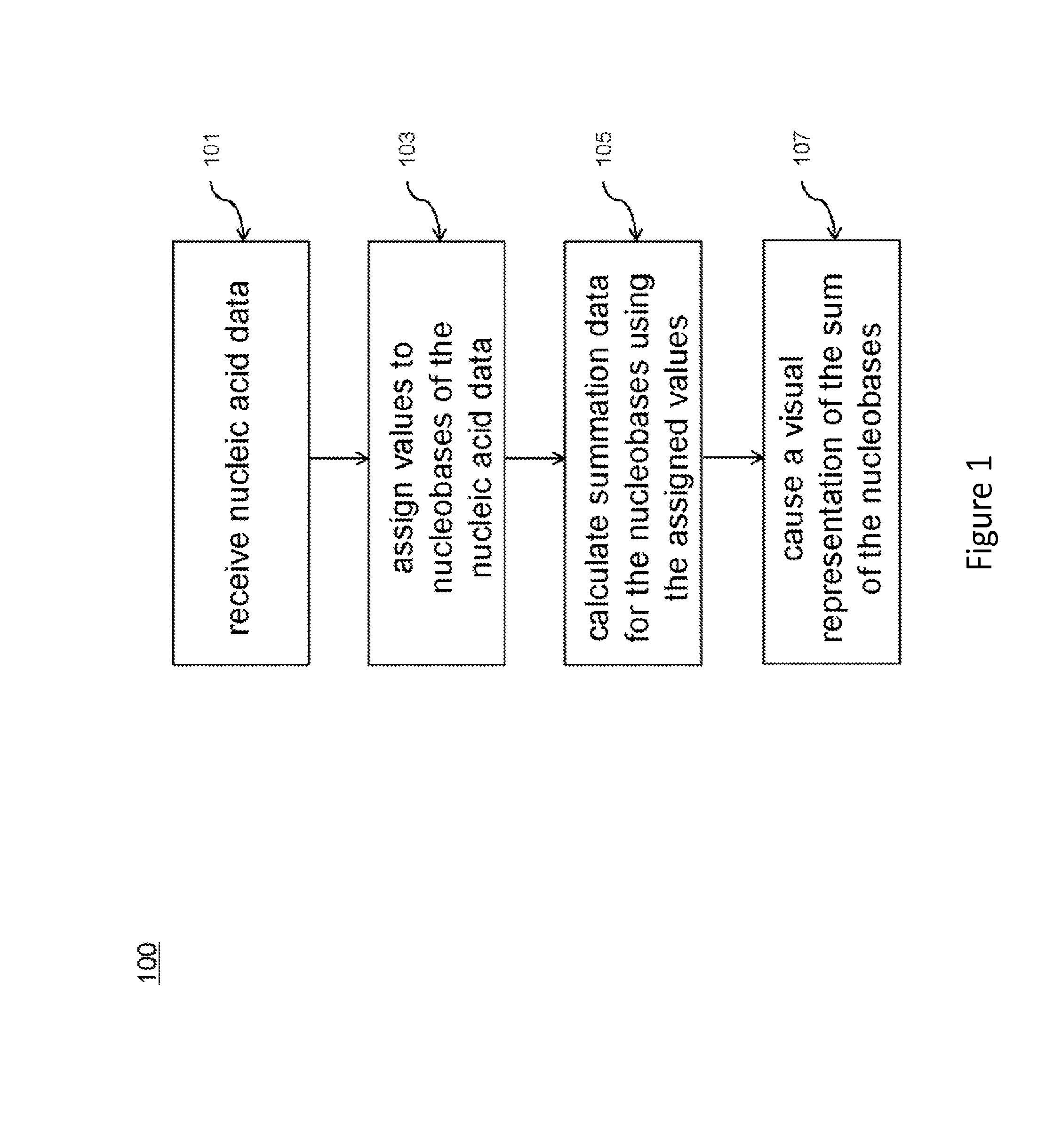
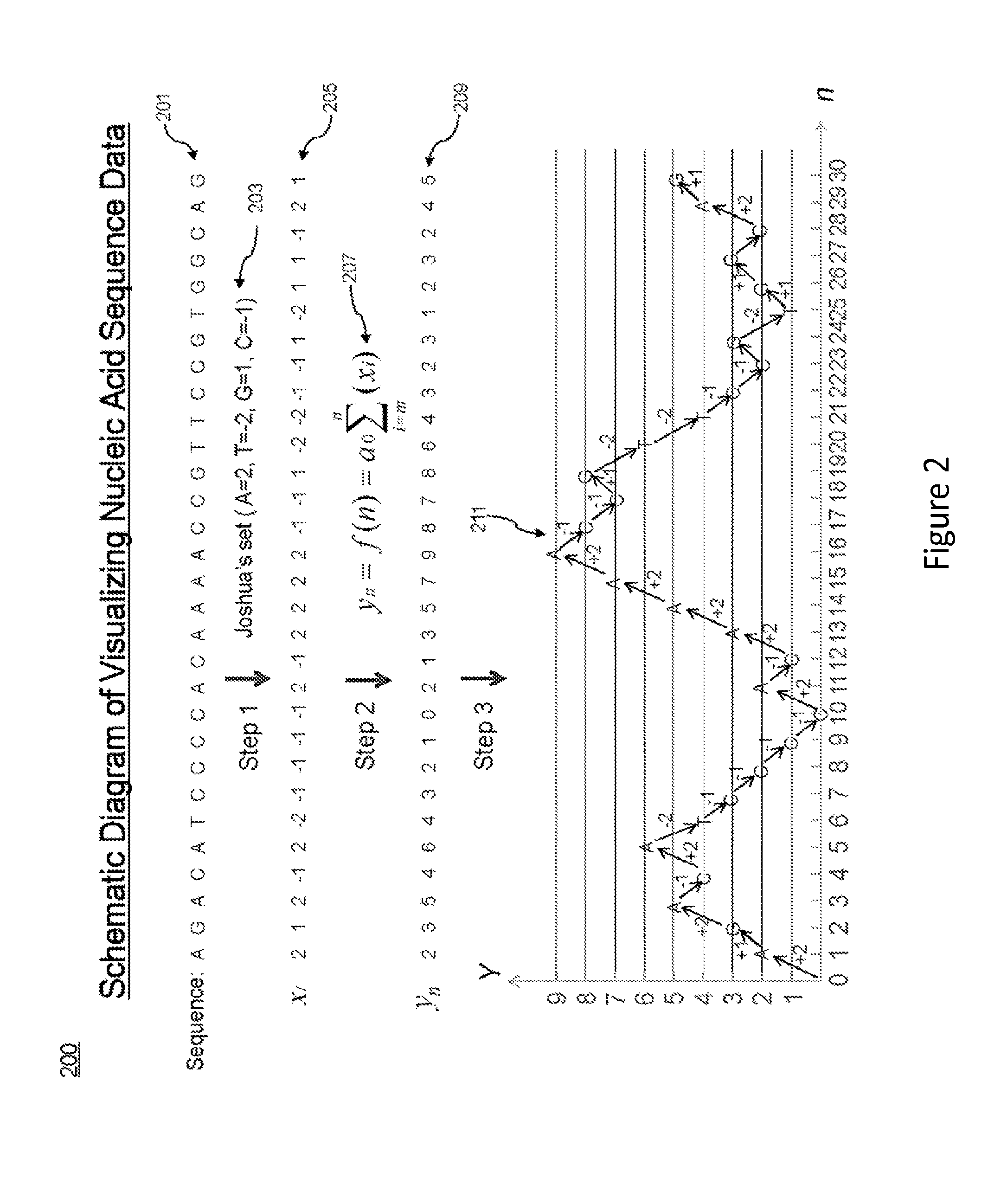
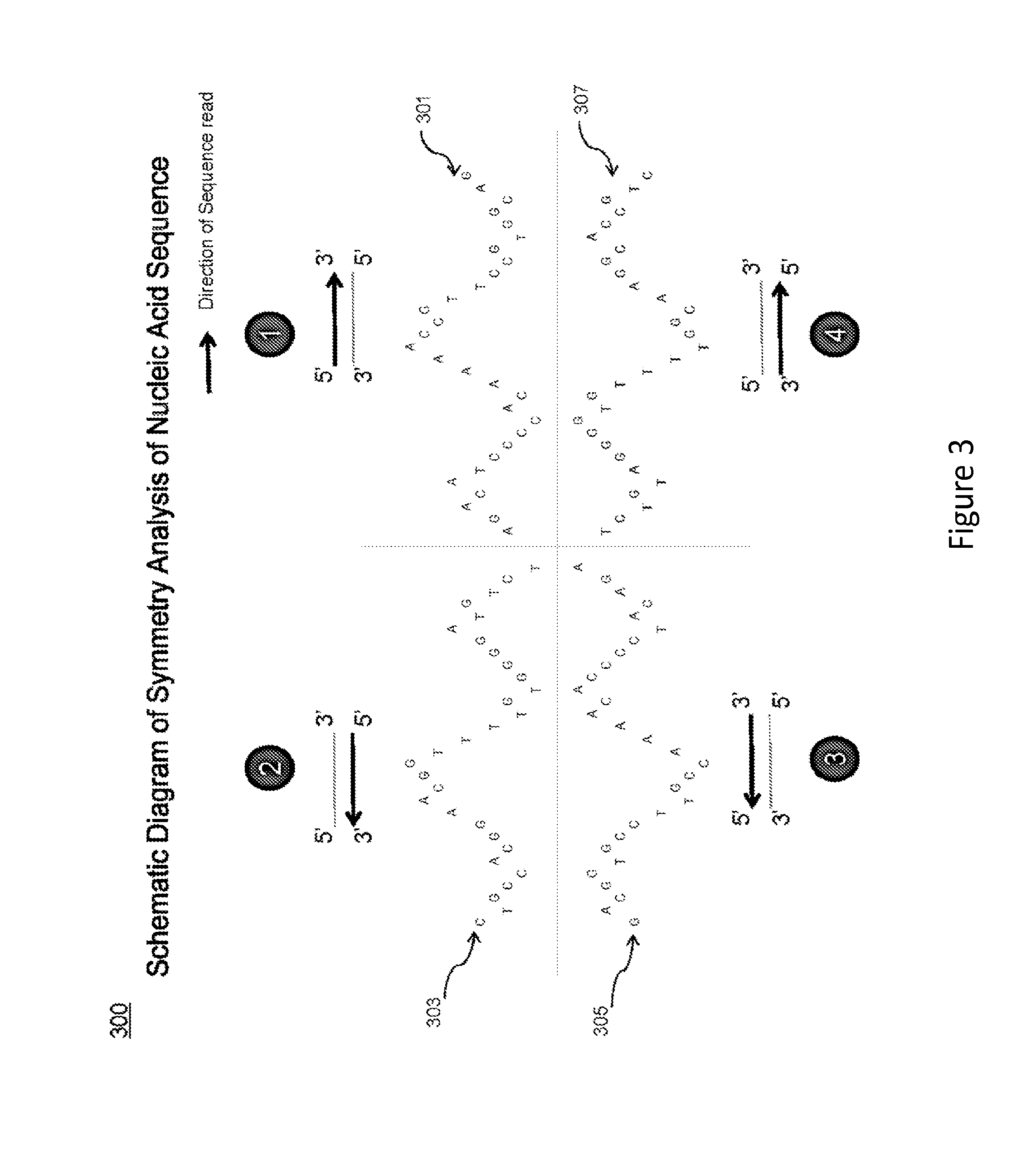
Visualization of nucleic acid sequences
InactiveUS20150331994A1Easy to analyzeEasy to identifyData visualisationBiological testingData setNucleotide
A system and process are provided for analyzing nucleic acid data. An example process can include receiving nucleic acid data including a set of sequence data. The nucleotides of the sequence data can be assigned numerical values. Using these assigned values, partial sums can be calculated for each position in the set of sequence data. The resulting sums can then be displayed in form of Charts or Maps which is so called sequence spectrum to make it easy to navigate and analyze the whole data set. In some examples, patterns or similar / identical sequence segments can be identified within a single set of sequence data or between different sets of sequence data in the spectrum.
Owner:ZHENG DALI
Method of detection of DNA end(s) and its use
PendingUS20200255884A1Ass qualitySensitive highMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideBinding site
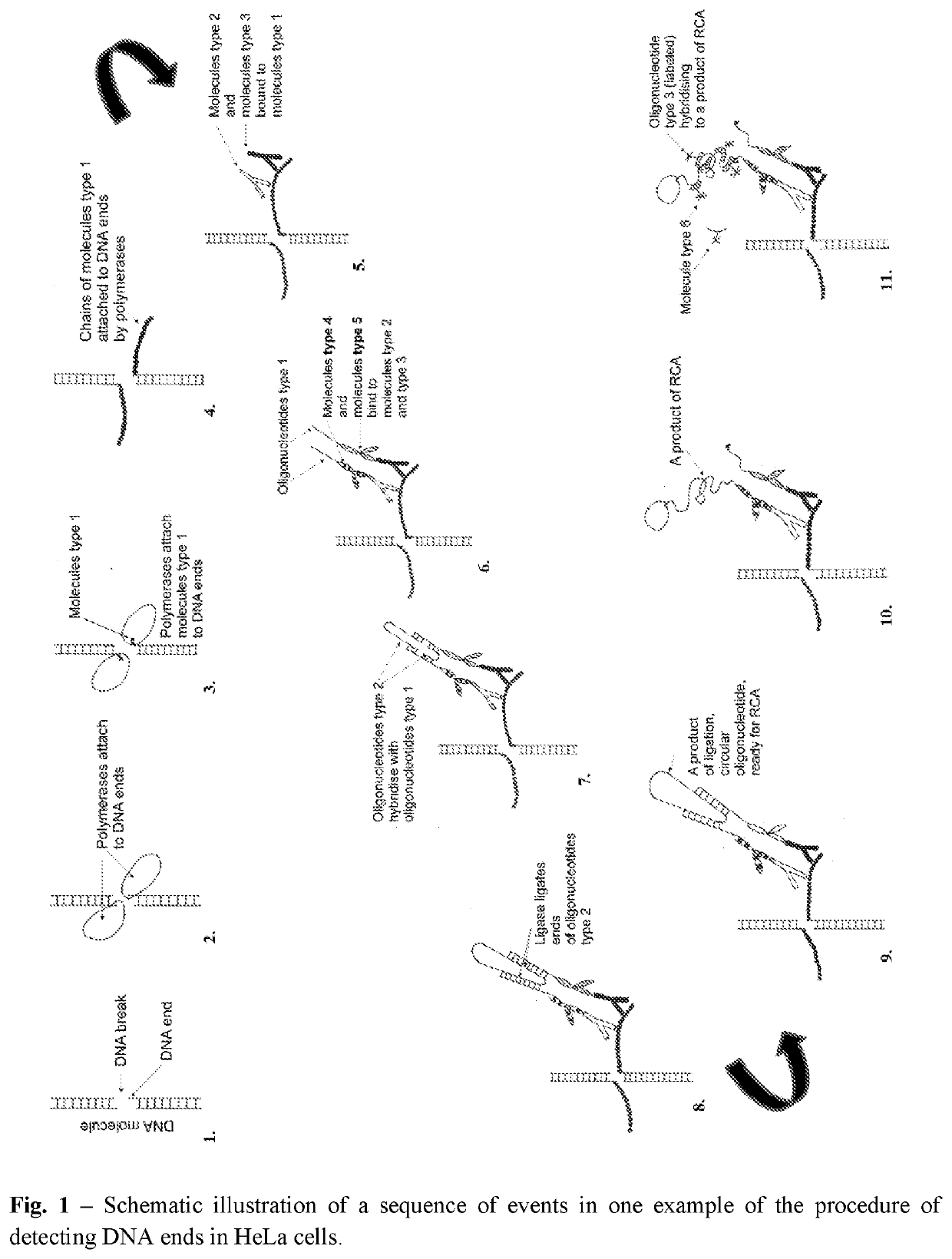
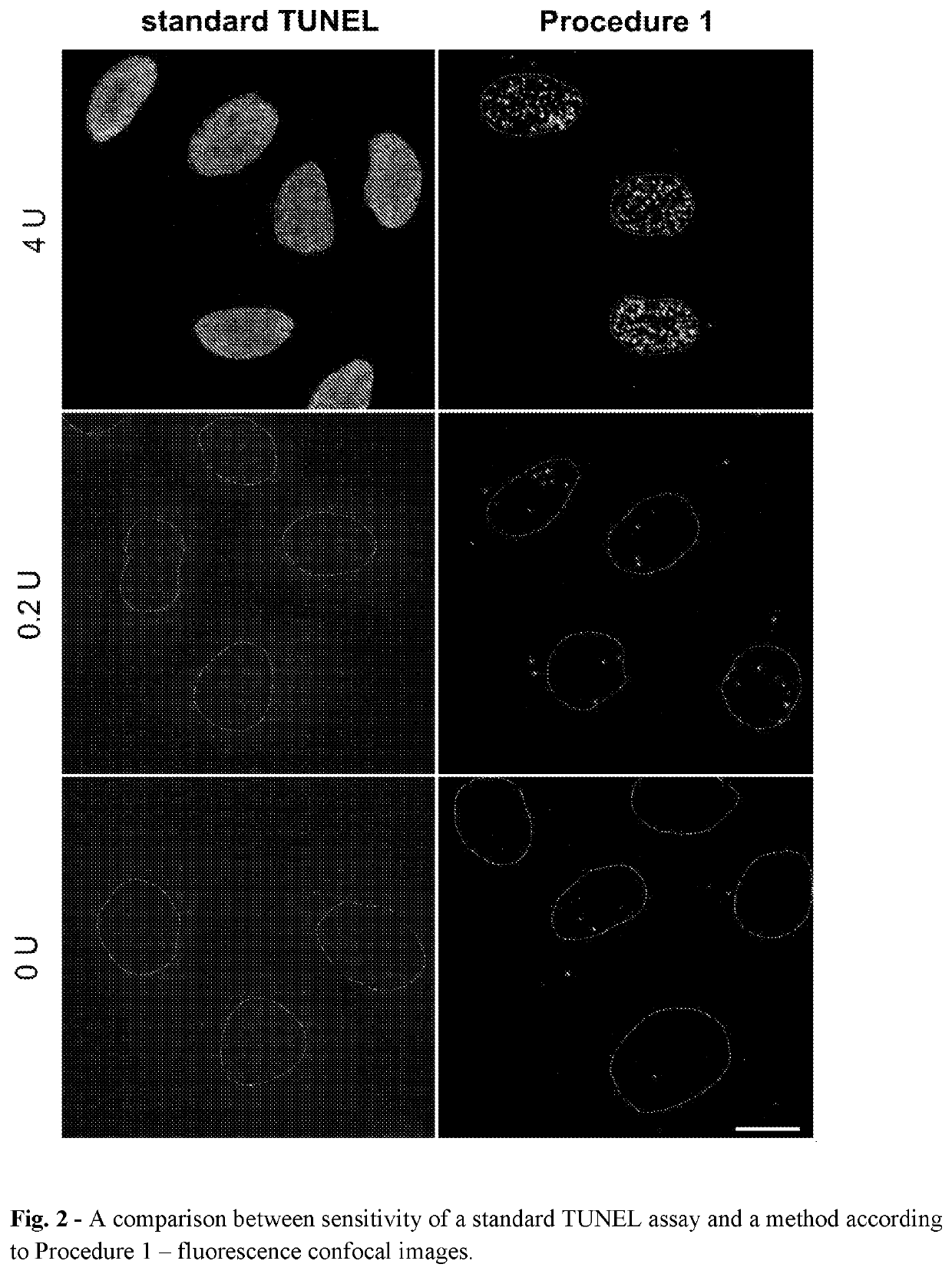
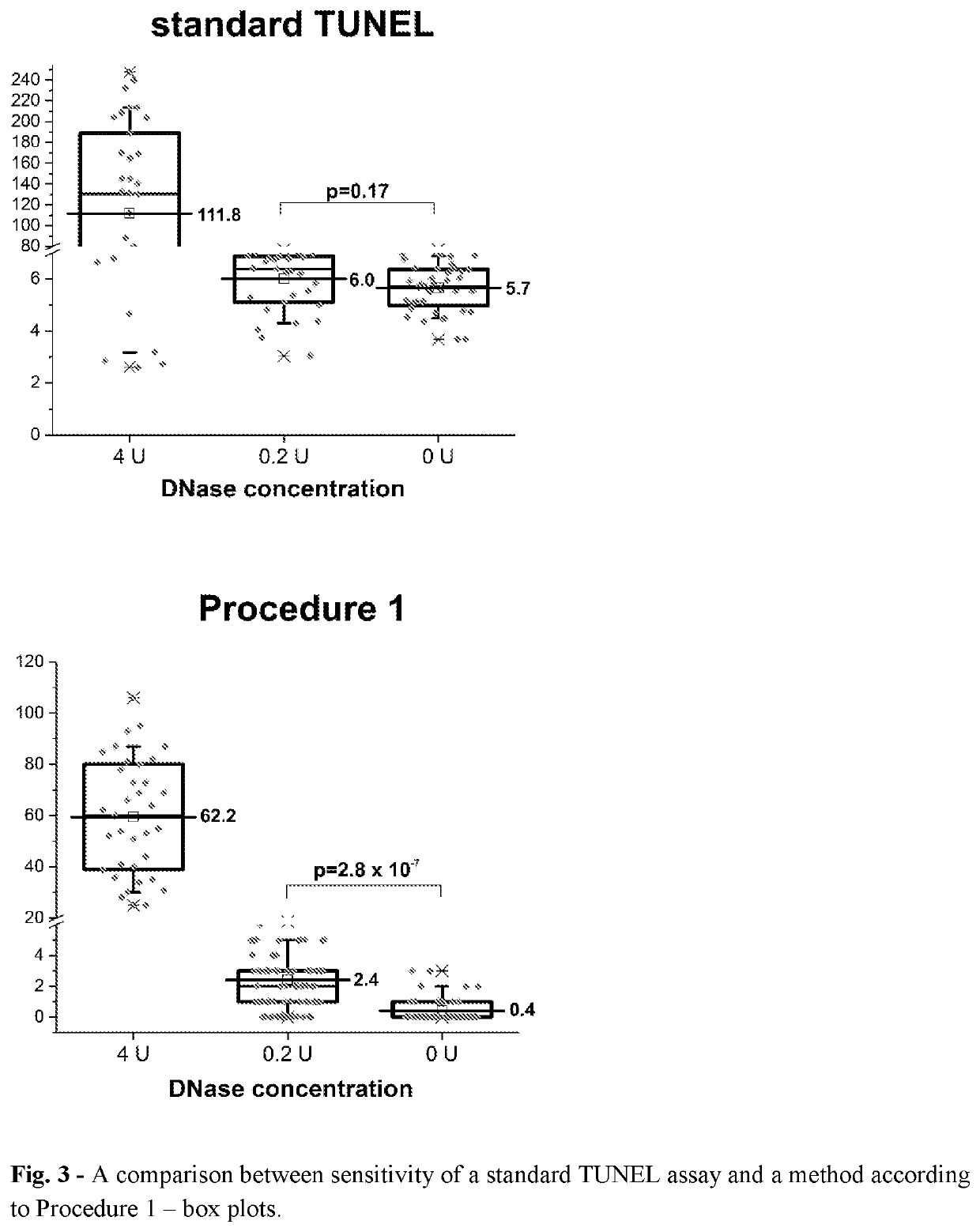
The invention concerns the method of detection of DNA end(s) in a biological material, comprising the following steps I III and at least one of sub-steps a-h of each of steps I-III: I. PREPARATION OF THE MATERIAL comprising a fixation and / or permeabilization and / or lysis and / or isolation and / or fractionation and / or immobilization of the biological material, b. increasing accessibility of DNA end(s), c. blocking nonspecific binding site(s) for molecules type 2-6, in the biological material; H. PROCESSING OF DNA END(S) comprising d.): modification of DNA end(s) by chemical or physical processing followed by binding molecules type 1 to the DNA end(s) by catalytic or noncatalytic means; blocking nonspecific binding site(s) for molecules type 2-6 in the biological material; III RECOGNITION AND DETECTION OF THE MODIFIED DNA END(S): incubation of the biological material from step II with at least two molecules type 2 and 3 which bind to the molecules type 1 in a manner that allows steps leading to rolling circle amplification (RCA) reactions, g. detection of DNA end(s) by: i. optionally contacting suitable molecules type 4 and / or 5 with molecules type 2 and 3, wherein the molecules type 4 and / or 5 are conjugated with the oligonucleotides type 1, ii. adding oligonucleotides type 2 and enzyme ligase to allow hybridization of said added oligonucleotides type 2 to the oligonucleotides type 1 already linked to molecules type 4 and / or 5, or to molecules type 2 and 3 if they are linked to oligonucleotides type 1, and subsequently performing DNA ligation of oligonucleotides type 2, iii. performing amplification by adding enzyme polymerase and a solution of nucleotides to allow rolling circle amplification (RCA) reactions, and molecules type 6 to allow subsequent hybridization of molecules type 6 to thus obtained product of RCA reactions, h. detection of molecules type 6; wherein when more than one sub-step a-c of step I is performed then they may occur in any order. The invention concerns also use of rolling circle replication for marking the presence and position of single DNA end(s) and use above-mentioned method for detection of DNA end(s) in a biological material.
Owner:INTODNA SPOLKA AKCYJNA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com