SAR target recognition method based on sparse least squares support vector machine
A sparse least squares and support vector machine technology, applied in the field of target recognition, can solve problems such as lack of sparsity and increase in the recognition time of SAR target recognition, and achieve the effect of reducing the amount of calculation and saving recognition time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
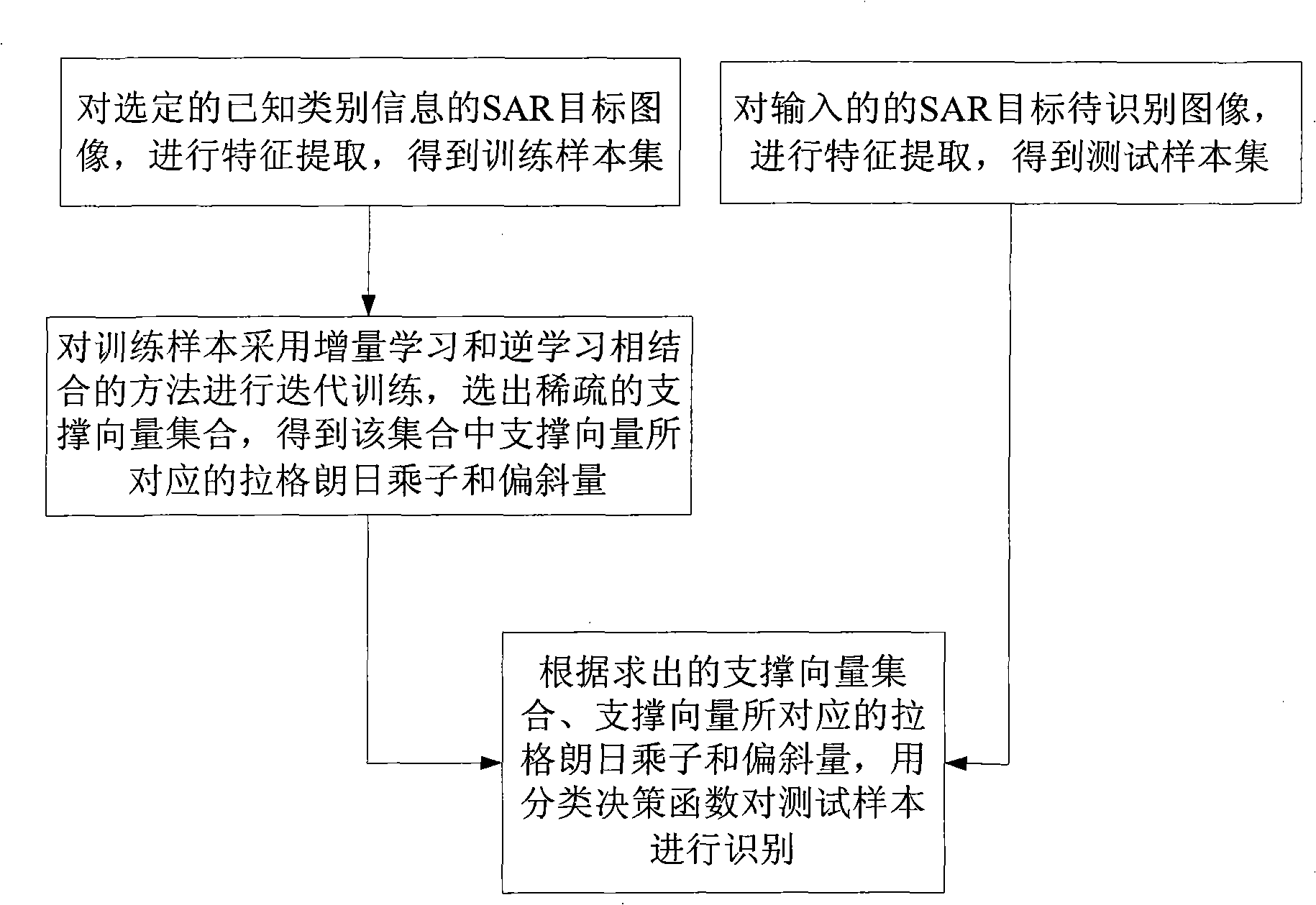
[0024] refer to figure 1 , the specific implementation steps of the present invention are as follows:
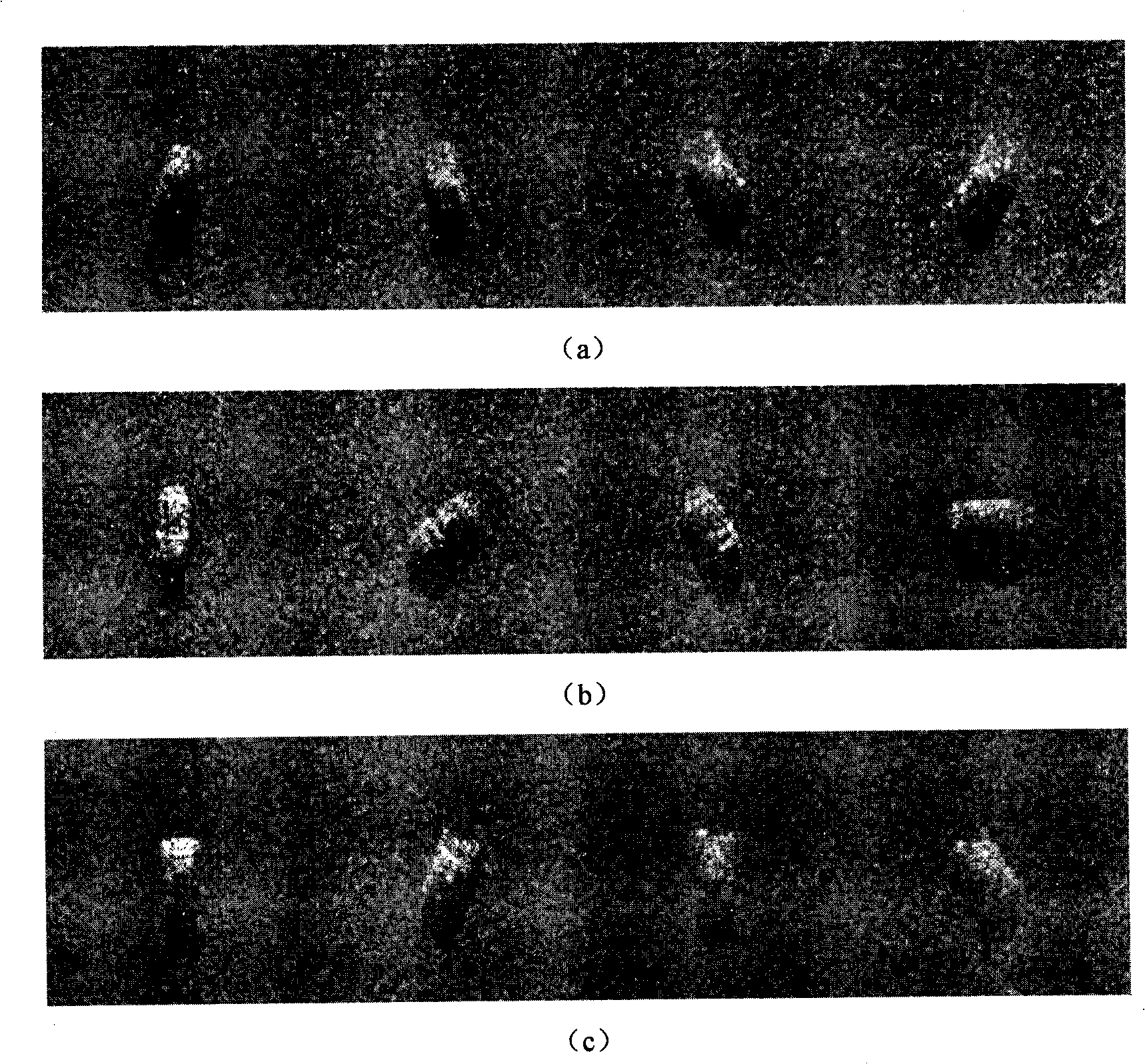
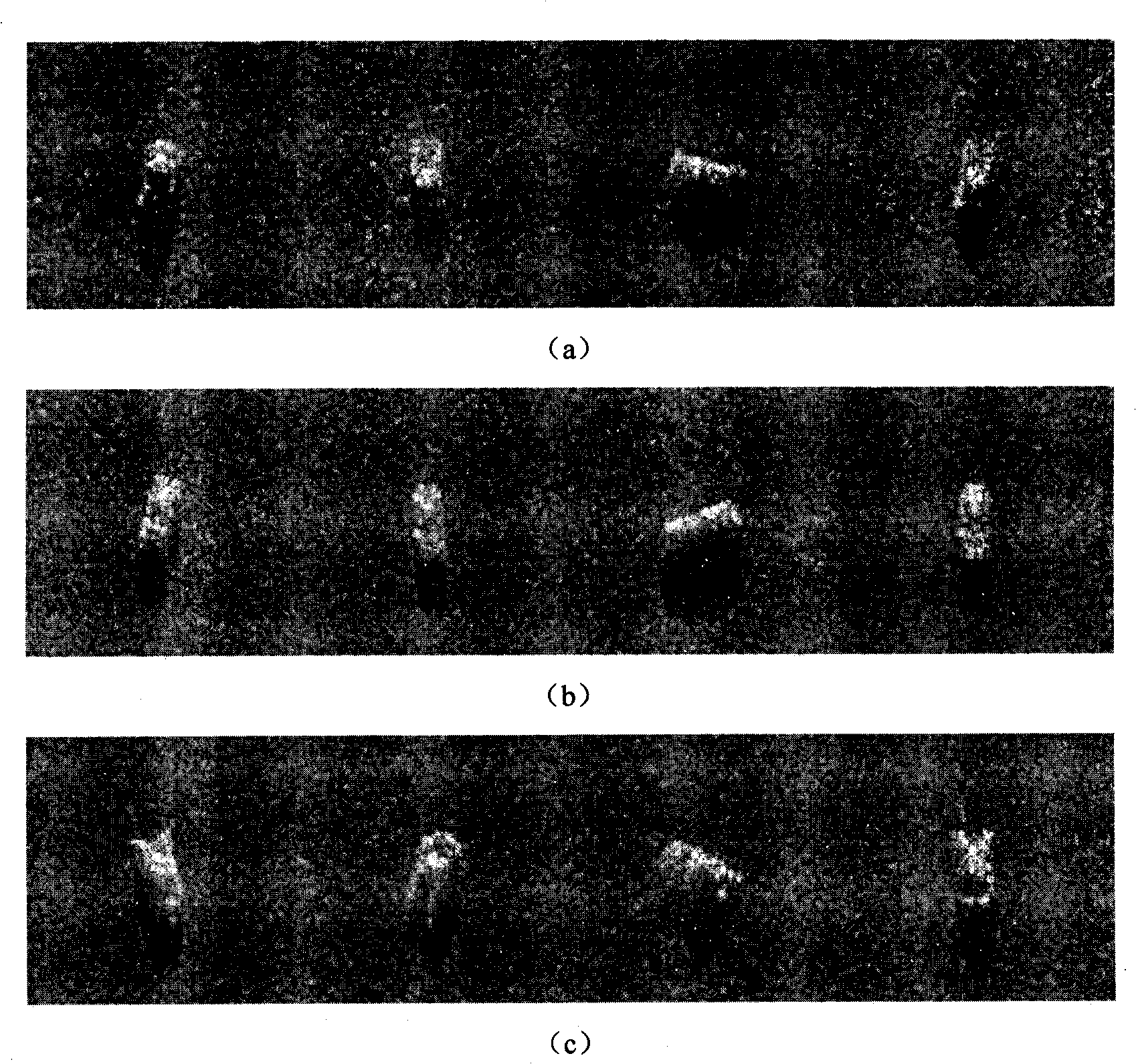
[0025] Step 1. For the image of 17° overlooking angle in the input MSTAR data, cut out a 60×60 area from the center of the original 128×128 image, and use the kernel principal component analysis method for feature extraction to obtain the training sample set {x k ,y k} k=1 n , where n is the number of samples in the training sample set, x k Represents the kth sample, represented by a row vector, y k is with sample x k corresponding label.
[0026] Step 2: For the image with a 15° overlooking angle in the input MSTAR data, a 60×60 area is cut from the center of the original 128×128 image, and the kernel principal component analysis method is used for feature extraction to obtain the test sample set {x′ k ,y′ k} k=1 n ’, where n’ is the number of samples in the training sample set, x’ k Represents the kth sample, represented by a row vector, y' k is the sample x′ ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com