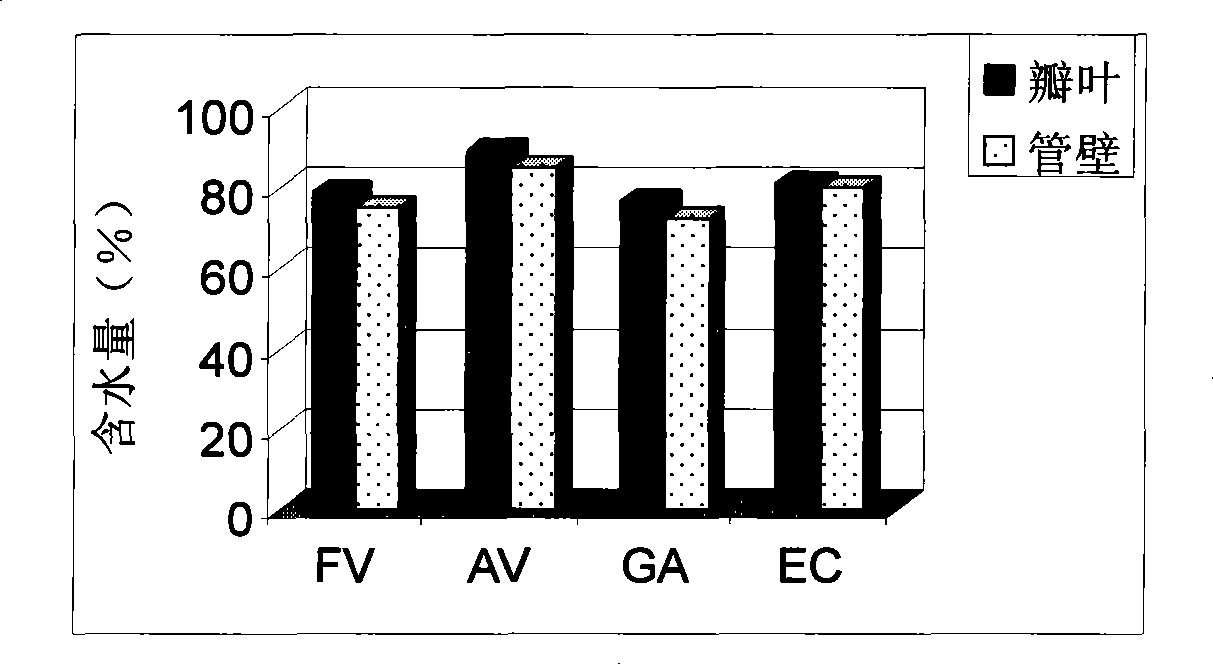
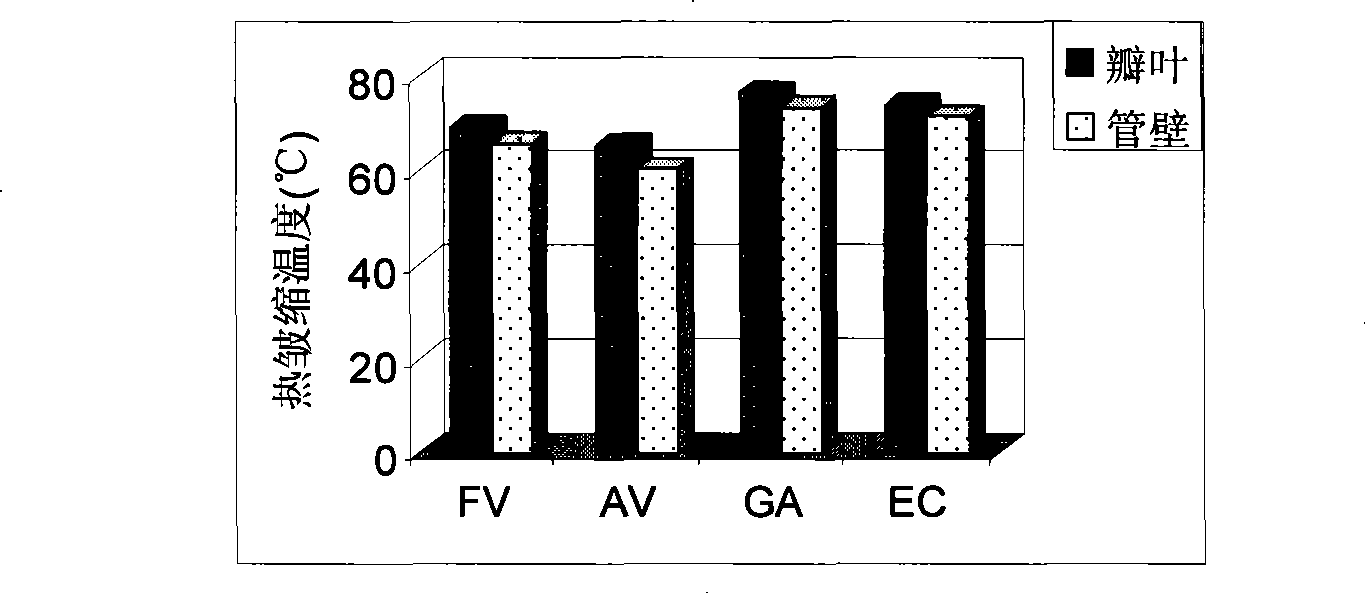
Method for improving de-cellular system engineering valve/blood vessel stent
A decellularized tissue and vascular stent technology, applied in the field of improved decellularized tissue engineering valves/vascular stents, can solve problems such as high cytotoxicity, no improvement in the biological and mechanical properties of decellularized stents, and inactivation of RGD polypeptide functions. To achieve the effect of enhancing anti-calcification and anti-degradation ability, improving biological and mechanical properties, and enhancing adhesion ability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0038] 1. Theoretical Basis
[0039] 1) The role of cell binding sites of extracellular matrix adhesion proteins in the adhesion and growth of seed cells
[0040] The study found that the adhesion of seed cells and scaffolds can be greatly increased through the specific binding of integrins on the cell surface and the binding sites of adhesion proteins in the extracellular matrix. The known adhesion proteins are mainly cells Soluble proteins in the external matrix: such as fibronectin (FN), laminin (laminin, LN) and so on. Studies have found that the cell adhesion sites of these proteins consist of only a few amino acids (RGD, arginine-glycine-aspartic acid). Therefore, peptides composed of these amino acids are widely synthesized and used to coat materials to improve adhesion to cells. RGD polypeptides are not only stable and non-immunogenic, but also can be modified in vitro, so the most widely used polypeptides contain RGD sequences.
[0041] 2) The role of integrins
...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com