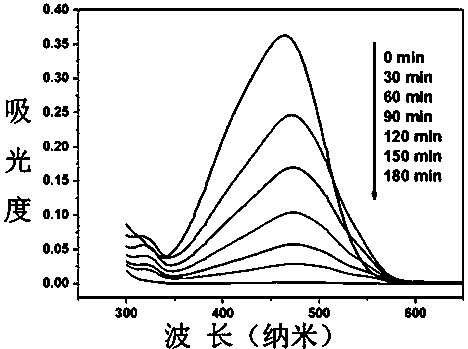
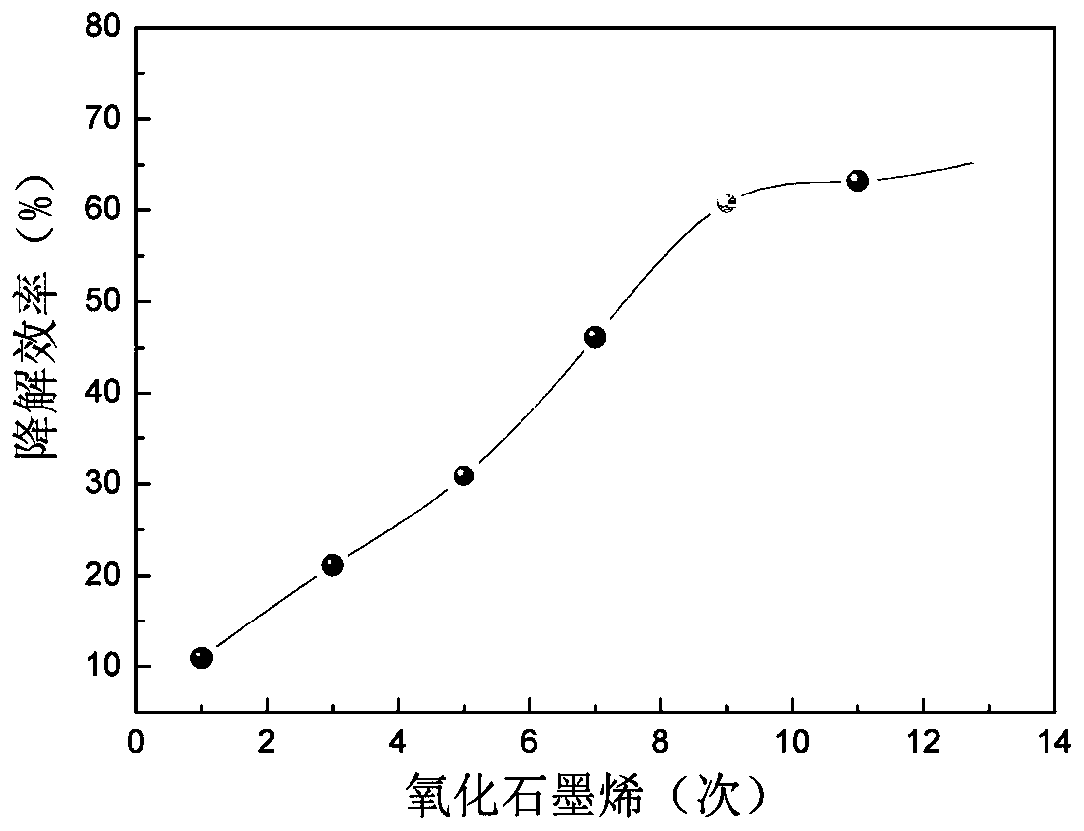
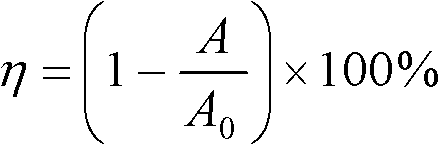Patents
Literature
120results about How to "Improve visible light catalytic performance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
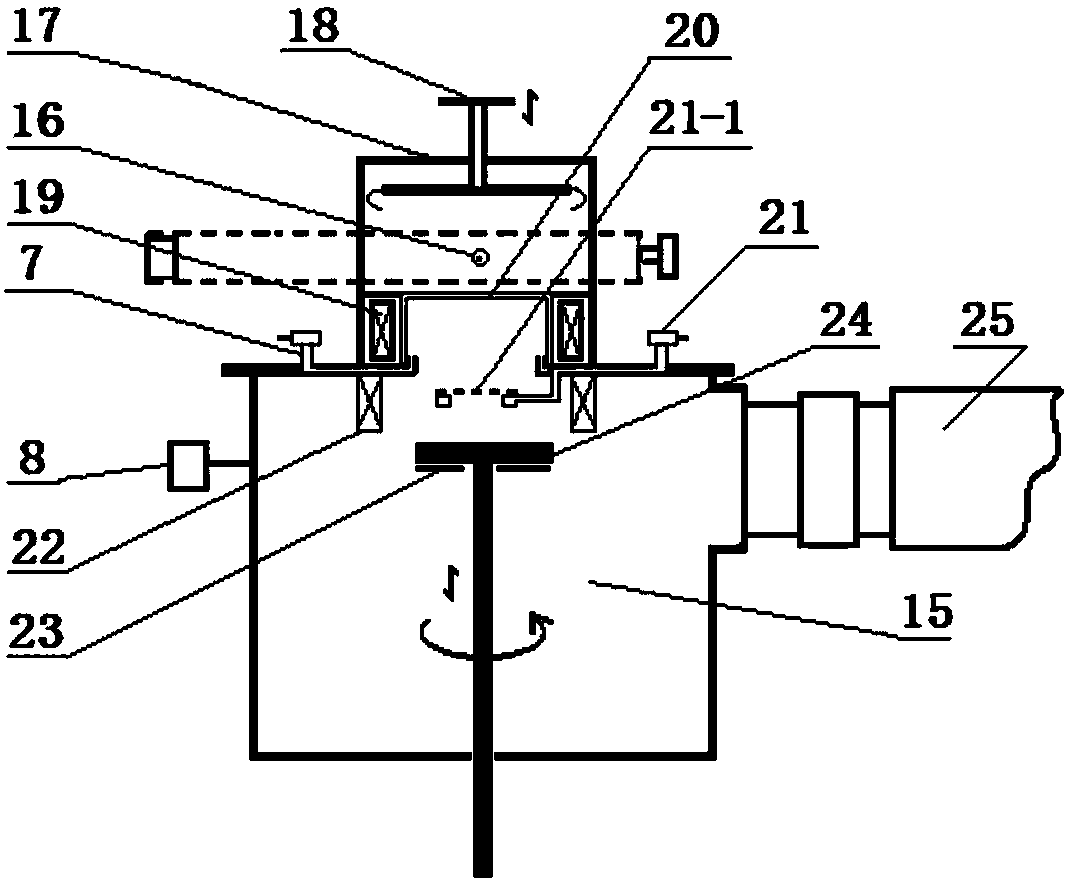
Preparation method of visible light catalyst
InactiveCN102247877AImprove protectionImprove visible light catalytic performancePhysical/chemical process catalystsPhoto catalyticSolvent
The invention discloses a preparation method of a visible light catalyst. Compared with the prior art, the invention adopts inexpensive, non-toxic and harmless urea as the raw material, with no need for highly toxic raw materials. By controlling the calcination temperature, C3N4 can be prepared, thus being in favor of environment protection. The invention also provides a preparation method of a visible light catalyst, comprising the steps of: preparing C3N4 according to the above process; mixing the obtained C3N4 with a modifier in a solvent for reaction, drying the reaction product, thus obtaining the visible light catalyst. The modifier can be an Fe source compound, a Cu source compound, a Zn source compound, a V source compound, a W source compound, a Pt source compound, an Au source compound or a Pd source compound. The method of the invention employs an immersion method for C3N4 metal ion modification, so that metal ions can adsorb the C3N4 surface, thus inhibiting photoinduced charge recombination. Therefore, the visible light catalyst prepared by the preparation method provided in the invention has a high photo catalytic performance.
Owner:CHONGQING TECH & BUSINESS UNIV +1
Preparation method of glass fiber loaded silver-silver bromide-titanium oxide composite material
ActiveCN103599800ASimple and fast operationEasy to scalePhysical/chemical process catalystsFiberVisible light photocatalytic
The invention provides a preparation method of a glass fiber loaded silver-silver bromide-titanium oxide composite material. The method comprises the following steps: with an organic or inorganic titanium compound as a titanium source and glass fibers as a carrier, obtaining a spherical titanium dioxide (TiO2) nano particle loaded threaded glass fiber composite material by a hydrolysis method under an acidic condition; impregnating the composite material in an ethylene glycol solution containing silver nitrate, and subsequently, adding dropwise an ethylene glycol solution containing potassium bromide to generate an AgBr-TiO2 / glass fiber composite material; and finally, reducing partial Ag<+1> in the AgBr-TiO2 / glass fiber composite material into metal Ag, thus obtaining an Ag-AgBr-TiO2 / glass fiber composite photocatalyst. The method provided by the invention realizes even loading of a nano-material having visible light catalytic activity on the surface of the threaded glass fibers by a two-step method; the method has the advantages of simple and convenient operation, easy large-scale production and the like; the obtained Ag-AgBr-TiO2 / glass fiber composite material has relatively high visible light catalytic activity.
Owner:中科瑞丽分离科技无锡有限公司
Photocatalytic electrode responding to visible lights and application thereof on chromium-containing wastewater treatment
InactiveCN103818986AImprove stabilityIncrease profitWater contaminantsEnergy based wastewater treatmentWastewaterTherapeutic effect
The invention discloses a photocatalytic electrode responding to visible lights and an application thereof on chromium-containing wastewater treatment. The preparation method of the photocatalytic electrode comprises the following steps: impregnating a TiO2-NTs electrode in a KI solution for 2 to 2.5 hours, taking out the TiO2-NTs electrode, impregnating the TiO2-NTs electrode in an AgNO3 solution with a pH value of 10.5 to 11.5 for 2 to 2.5 hours, washing the prepared electrode with deionized water, drying in the air, then soaking the electrode in a Bi(NO3)3 solution for 0.5 to 1 hour, taking out the electrode, drying in the air, and calcinating the electrode in a muffle furnace for 2 to 2.5 hours so as to obtain the Bi2O3 / AgI / TiO2-NTs electrode. The application of the electrode on a chromium-containing wastewater treatment comprises the following steps: adding wastewater containing hexavalent chromium into a reactor taking the Bi2O3 / AgI / TiO2-NTs electrode as the work electrode and Pt as the counter electrode, adjusting the reaction pH value by using an inorganic acid, stirring in the absence of light so as to ensure the absorption balance on the electrodes, applying a work voltage, and starting a light source to irradiate the system so as to carry out reactions. A photocatalytic electrode responding to visible lights is utilized, at the same time a certain amount of anode deflecting voltage is applied on the electrode so as to treat Cr(VI) through a photoelectric synergetic effect, and the treatment has the advantages of good treatment effect, rapid speed, and low cost.
Owner:ZHEJIANG GONGSHANG UNIVERSITY
Method for preparing nanometer composite with chrysanthemum structure
InactiveCN103521163AImprove adsorption capacityHigh photocatalytic degradation activityPhysical/chemical process catalystsWater/sewage treatment by irradiationVisible light photocatalyticUltrasonic dispersion
The invention relates to a nanometer composite, and particularly relates to a method for preparing a nanometer composite with a chrysanthemum structure. The method comprises the steps of adding titanium dioxide nanosheets into deionized water, carrying out ultrasonic dispersion, and obtaining a titanium dioxide dispersing liquid; under the condition of magnetic stirring, adding sodium molybdate and thioacetamide into the titanium dioxide dispersing liquid, and obtaining a mixed solution A; after finishing adding, stirring the mixed solution continuously, then transferring the mixed solution into a Teflon inner container, sealing the inner container in a stainless steel hydrothermal reaction kettle for hydrothermal reaction, after finishing the hydrothermal reaction, naturally cooling the reaction kettle to room temperature, centrifuging the obtained product, washing, vacuum drying and obtaining the composite. The method has the advantages that the source of raw materials is wide, and the method is simple and practicable and has low cost. The prepared titanium dioxide or molybdenum disulfide nanometer composite not only has good capacity in absorbing organic contaminants, but also has a good visible light photocatalytic degradation effect to organic contaminants.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Visible-light response hybrid aerogel and preparation method and application thereof in waste gas processing
ActiveUS20200016585A1Low costEasily recombinedMaterial nanotechnologyGas treatmentPollutionMaterials science
Visible-light response hybrid aerogel and a preparation method and application thereof in waste gas processing are disclosed. Dicyandiamide is taken as a precursor and is calcined in two times to prepare a carbon nitride nanosheet; the carbon nitride nanosheet is dispersed in water, silver metavanadate quantum dots are subjected to in-situ growth to prepare a silver metavanadate quantum dot / carbon nitride nanosheet composite material; the silver metavanadate quantum dot / carbon nitride nanosheet composite material and graphene oxide carry out hydrothermal reaction, and are then frozen and dried to prepare silver metavanadate quantum dot / carbon nitride nanosheet / graphene hybrid aerogel which is the visible-light response hybrid aerogel. The problems of large reduction dosage, serious secondary pollution, complexity in operation and the like generated when waste gas is processed by a traditional flue gas denitration technology are overcome.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
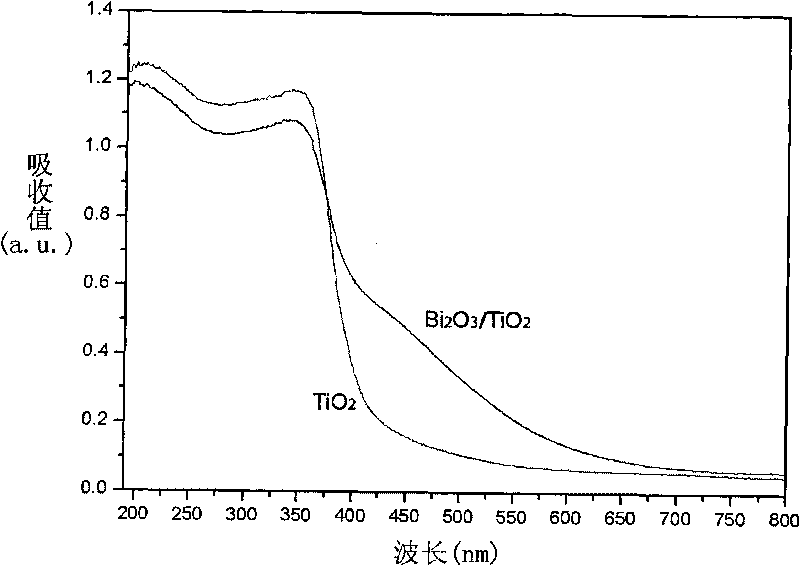
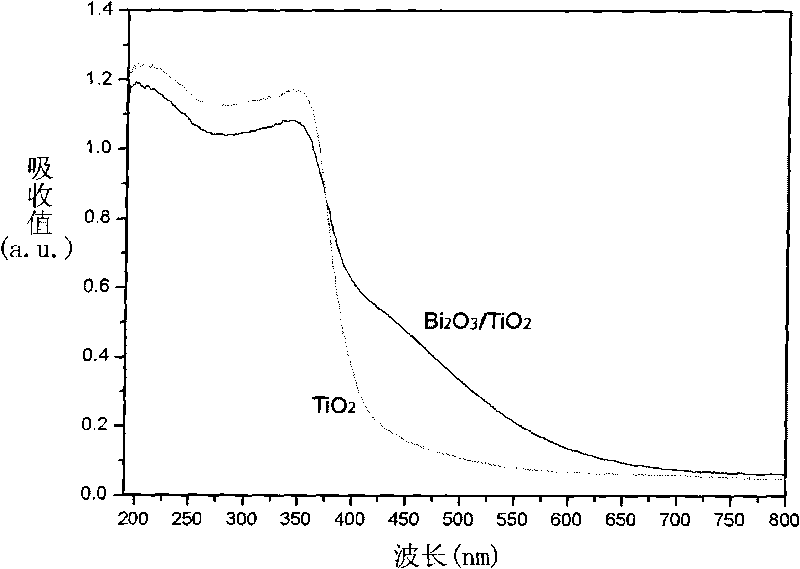
Method for preparing visible light photocatalyst Bi2O3/TiO
InactiveCN101745377AImprove quantum efficiencyEasy to operateCatalyst activation/preparationMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsCompound semiconductorVisible spectrum
The invention relates to a method for preparing visible light photocatalyst Bi2O3 / TiO2, comprising the following steps: (1) adding cetyl trimethyl ammonium bromide to anhydrous ethanol, and ultrasonically dissolving the cetyl trimethyl ammonium bromide to the anhydrous ethanol to form transparent solution A; (2) adding tetrabutyl titanate to the solution A, and ultrasonically dissolving the tetrabutyl titanate to the solution A to form light yellow transparent solution B; (3) heating the solution B to 75-85 DEG C, adding bismuth nitrate pentahydrate to the solution B, and ultrasonically dispersing the bismuth nitrate pentahydrate to the solution B to form light yellow sol; (4) standing the light yellow sol at 25-45 DEG C to form light yellow gel; (5) aging the light yellow gel at 80-100 DEG C to form light yellow particles; and (6) heating light yellow particles from the room temperature to 450-550 DEG C, calcining the light yellow particles for 5-8h, and cooling the calcined light yellow particles to room temperature naturally to obtain compound semiconductor with visible light catalytic activity. The method for preparing the visible light photocatalyst of Bi2O3 / TiO inhibits the combination of the light induced electrons and the hole, improves the quantum efficiency of the photocatalytic reaction and the utilization of solar energy, is easy to operate, has low cost and lays a foundation for the light catalytic technology to be practical. The photocatalyst Bi2O3 / TiO2 has high visible light catalytic performance.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Method for in-situ preparation of graphite-like-phase carbon nitride quantum dot/titanium dioxide nanotube array visible-light-induced photocatalyst
ActiveCN105854920AImprove separation efficiencyImprove visible light catalytic performancePhysical/chemical process catalystsTio2 nanotubeCarbon nitride
The invention discloses a method for in-situ preparation of a carbon nitride quantum dot / titanium dioxide nanotube array visible-light-induced photocatalyst. The method comprises the steps of 1, cleaning a pure titanium sheet to serve as a substrate for anodizing preparation of a titanium dioxide nanotube array; 2, adding a certain number of graphite-like-phase carbon nitride precursors to electrolyte adopted for anodizing preparation of the titanium dioxide nanotube array; 3, conducting heat treatment on the amorphous-state titanium dioxide nanotube array after anodizing, so that the graphite-like-phase carbon nitride quantum dot / titanium dioxide nanotube array visible-light-induced photocatalyst is obtained. The preparing method is simple and quick, economical and environmentally friendly, and the prepared graphite-like-phase carbon nitride quantum dot / titanium dioxide nanotube array visible-light-induced photocatalyst has high visible light catalysis property, stability and recyclability.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
Visible light catalytic material, and preparation method and application thereof
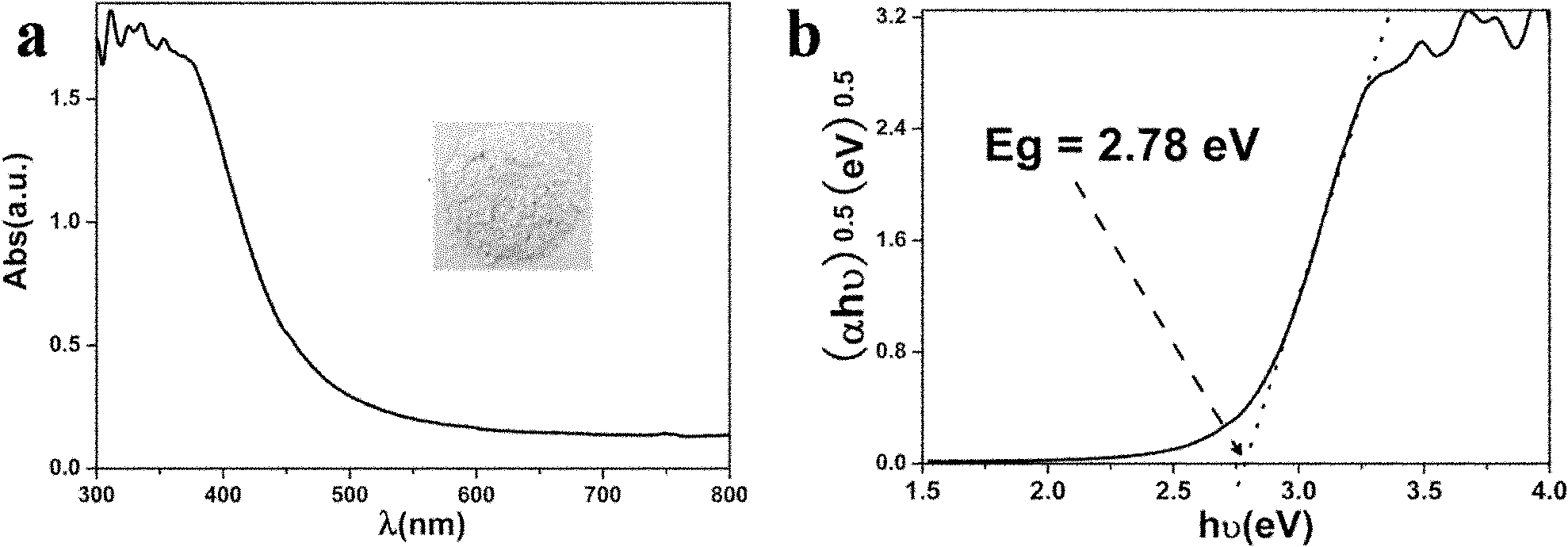
ActiveCN102080262AFast transferEasy to separatePolycrystalline material growthFrom normal temperature solutionsCrystallinityElectronic band structure
The invention discloses a visible light catalytic material used for environmental purification and a preparation method thereof. The visible light catalytic material is an indirect gas semiconductor with a dispersed energy band structure, is a crystalline nano material, comprises the chemical formula of Bi2Sn2O7, has the corresponding optical band gap width of 2.68 to 2.78eV and exhibits high visible light catalytic performance. In the preparation method provided by the invention, Bi2Sn2O7 nanoparticles can be prepared from readily-available raw materials with low cost under moderate conditions only by one-step hydrothermal reaction so as to avoid the coarsening and aggregation of the high-temperature sintered crystal particles; the preparation method is simple to operate; parameters are adjustable in a reaction process, and the crystallinity and material phase compositions of the product are easy to control; in addition, the sample provided by the invention exhibits high stability inphotocatalysis cycle tests of dye degradation and harmful gas purification, and is favorable for industrial application.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF CERAMIC CHEM & TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
BiOBr/Bi2WO6 composite photocatalyst with heterostructure and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105080579ASimple preparation processEasy to makePhysical/chemical process catalystsHeterojunctionMicro nano
Provided are a BiOBr / Bi2WO6 composite photocatalyst with a heterostructure and a preparation method thereof. The photocatalyst is formed by a P-type semiconductor BiOBr and an N-type semiconductor Bi2WO6 which have similar crystal structures and similar forbidden bandwidths in a composite mode, the molar ratio of the BiOBr to the Bi2WO6 is 1 to 1-1.5, a P-N heterojunction interface is formed between two crystal phases, the photocatalyst is nest-shaped and porous in appearance with micro-nano scales, and the average specific surface area is 110 m<2>.g<-1>. A one-step in-situ hydrothermal reaction process control technology is adopted, a P-N knot type composite semiconductor catalyst evenly mixed at the micro-nano scale level can be obtained only through a one-step reaction, the process is simpler and easy to control, the preparation time is shorter, and therefore the preparation cost is lower.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Graphite-phase carbon nitride sheet material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105126895ALarge specific surface areaImprove visible light catalytic performancePhysical/chemical process catalystsNitrogen and non-metal compoundsTube furnaceProduct gas
A preparation method of a graphite-phase carbon nitride sheet material comprises steps as follows: graphite-phase carbon nitride powder is provided, and the graphite-phase carbon nitride powder is flatly spread on a heated carrier; the heated carrier containing the graphite-phase carbon nitride powder is placed in a tubular furnace, the tubular furnace is heated to 150 DEG C-600 DEG C under the atmosphere of protective gas, the heated carrier containing the graphite-phase carbon nitride powder is kept at the temperature for 1 min-20 h in the ammonia gas atmosphere under negative pressure and finally cooled to the room temperature, and the graphite-phase carbon nitride sheet material is obtained. The invention further provides the graphite-phase carbon nitride sheet material prepared with the method.
Owner:SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL TSINGHUA UNIV
SiO2-WO3 composite aerogel and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102091589ALow densityLarge specific surface areaOther chemical processesAlkali metal oxides/hydroxidesAlkaneSilazane
The invention provides SiO2-WO3 composite aerogel and a preparation method thereof. The specific surface area of the SiO2-WO3 composite aerogel is 329 to 720m<2> / g, the pore volume is 0.6 to 1.8 cm<3> / g, the BJH most probable aperture is 4 to 10 nm and the average aperture is 4 to 9 nm. The preparation method mainly comprises: firstly, synthesizing SiO2-WO3 sol-gel by using sodium tungstate and industrial sodium silicate as raw materials; secondly, modifying a gel block by using modifying solution consisting organic silazane, organic siloxane and an alkane reagent; and finally, replacing pore water. The aerogel product has the characteristics of high specific surface area and high pore volume, the preparation method adopts cheap and readily available sodium tungstate and industrial sodium silicate raw materials and therefore can reduce production cost, and a normal pressure drying process is convenient and easy to implement and is suitable for industrial production and use.
Owner:DALIAN POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY
Alginate-based composite photo-catalytic aerogel material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN108816291AEasy to shapeHigh strengthOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCatalyst activation/preparationPhoto catalyticFreeze-drying
The invention discloses an alginate-based composite photo-catalytic aerogel material and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the steps: ultrasonically and uniformly dispersing a nanometer photocatalytic material into water to prepare a suspension liquid; then, adding soluble alginate, pouring a mixed solution obtained after carrying out vigorous stir into a die, and carrying out freeze-drying; and placing the freeze-dried block material into a curing agent solution for curing, and then, further carrying out freeze-drying to obtain the alginate-based composite photo-catalytic aerogel material. The alginate-based composite photo-catalytic aerogel material prepared by using the preparation method has the characteristics such as high strength, low density, large specific surface area, high water resistance and simplicity in recycle, is simple in preparation process and has a great potential application value on the aspect of advanced treatment of a polluted waterbody.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
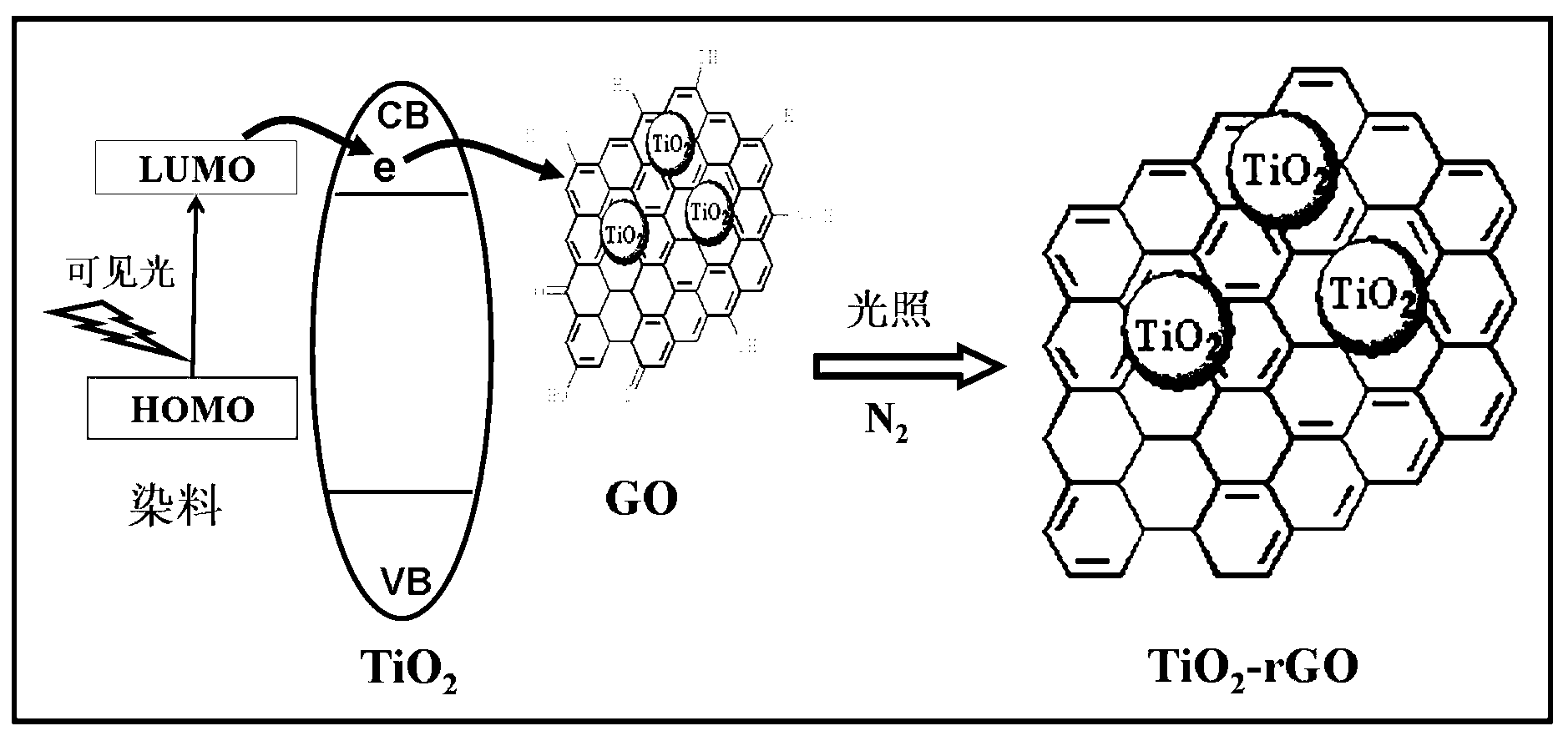
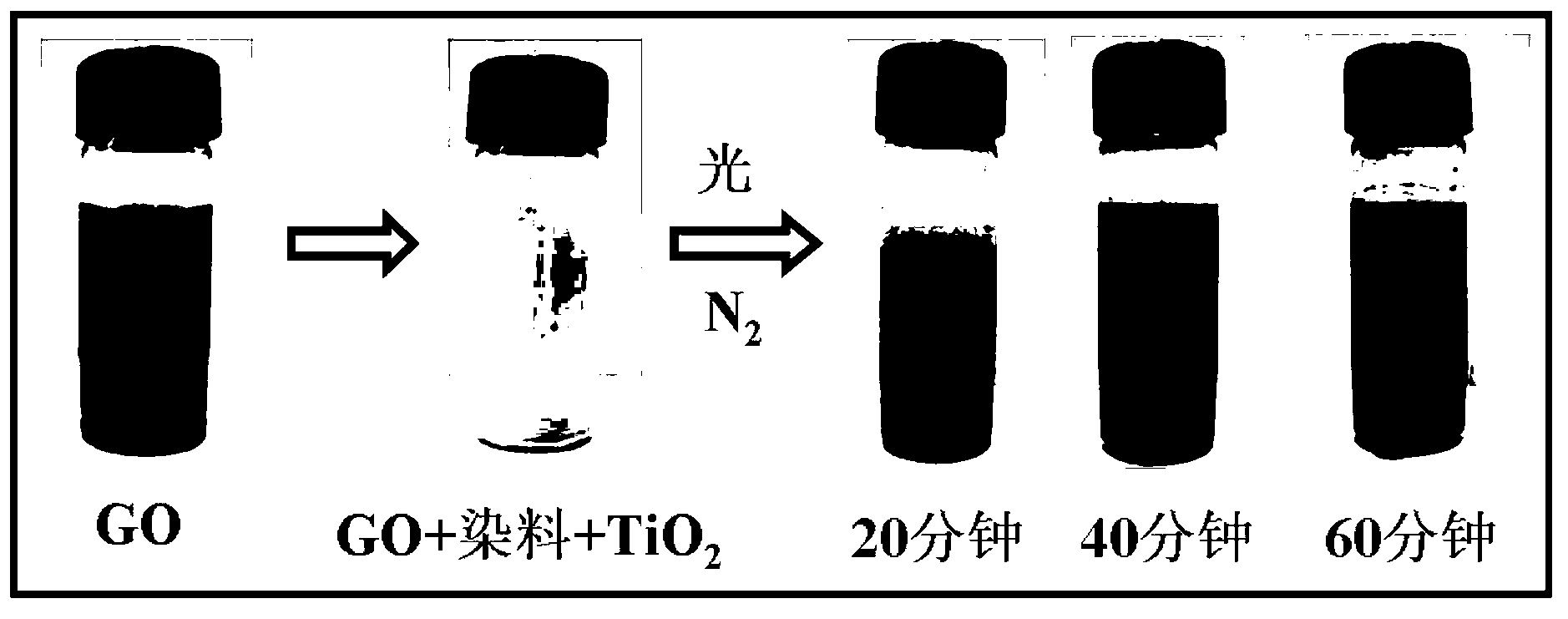
Visible light photosensitization preparation method of TiO2-rGO compound light catalyst
InactiveCN103055838AImprove photocatalytic performanceEfficient separationCatalyst activation/preparationPhoto catalysisReducing agent
The invention relates to a visible light photosensitization preparation method of TiO2-rGO compound light catalyst. The method comprises the following steps of: 1) thermally treating the commercial P25 TiO2 at high temperature; 2) ultrasonically dispersing an grapheme oxide in a de-ionized water to form an uniform solution; 3) mixing the Rhodamine B solution with the GO solution to form the uniform solution; 4) dispersing 1g of TiO2 nano particle in the uniform solution of the GO and Rhodamine B, and stirring uniformly; 5) irradiating the suspension liquid for 10-300 minutes in the presence of N2 by using the visible light, washing and drying the obtained product to obtain the TiO2-rGO compound light catalyst. The method provided by the invention has the advantages of environmental conservation and environmental friendliness without adding any organic additive as the reducing agent; meanwhile, the operation is simple, the device requirement is low, and the industrial production is easy to realize; and the prepared compound light catalyst has high photocatalysis, and the good social and economic benefit can be produced.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Method for carrying out photocatalytic degradation on bisphenol A (BPA) in water, and catalyst used in method
ActiveCN107649168AWidening of light absorption domainLarge specific surface areaPhysical/chemical process catalystsWater/sewage treatment by irradiationPhotocatalytic degradationBisphenol A
The invention discloses a method for carrying out photocatalytic degradation on bisphenol A (BPA) in water, and a catalyst used in the method. The method comprises the following steps: fully mixing aBPA solution with O-g-C3N4, firstly absorbing in a dark environment, and then carrying out catalytic degradation for 3h or more under the condition of visible light so as to realize a degradation rateof 60% or more, wherein the O-g-C3N4 is obtained by means of high temperature-oxidation-high temperature combined treatment. According to the method, melamine which is low in price and each to obtainis taken as a raw material, and the O-g-C3N4 product with excellent performance can be prepared by means of the path of high temperature-oxidation-high temperature combined treatment; the whole preparation process is simple and quick in operation steps and easier to popularize. Compared with the product treated by means of single treatment such as single oxidation or single high-temperature calcination, the O-g-C3N4 prepared by means of the path of high temperature-oxidation-high temperature combined treatment has improved O2 doping effect, enlarged specific surface area and obviously expanded light absorption domain; after the method is adopted, the photocatalytic degradation efficiency of the BPA in the water within a visible light region reaches 62.3% and is 7 times higher than the degradation efficiency obtained by using the product treated by means of the single treatment; therefore, the method provided by the invention has very good practicality.
Owner:JIANGSU PROVINCIAL ACAD OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI +1
Photocatalytic oil-water separation net film, preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN106186171AEasy to captureImprove transmission efficiencySemi-permeable membranesMembranesComposite filmElectrolysis
The invention discloses a photocatalytic oil-water separation net film, a preparation method and application thereof. The method comprises: firstly using diluted hydrochloric acid, anhydrous ethanol and deionized water to conduct ultrasonic cleaning on a copper net respectively and performing blow-drying with nitrogen; taking a tungstate solution as the electrolyte solution, using the cleaned copper net as the anode, and adopting an inert electrode as the cathode, connecting the anode and the cathode to the positive pole and negative pole of a power supply respectively, employing an anodic oxidation process to carry out constant-current electrolysis or constant-voltage electrolysis, then using deionized water to clean the anode and then performing drying, thus obtaining a copper net film covered by a cuprous oxide / copper tungstate composite film layer. The net film has super-hydrophilicity and underwater super-lipophobicity, and can efficiently separate oil-water mixtures. The invention utilizes the cuprous oxide / copper tungstate p-n junction structure to conduct photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants in water under visible light, and realize the separation and purification of oily wastewater containing organic pollutants. The preparation process is simple, the raw materials are environment-friendly, and the cost is low.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Composite visible-light-induced catalyst and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN107029777AHigh utilization rate of visible lightImprove photocatalytic performancePhysical/chemical process catalystsWater/sewage treatment by irradiationSilver citrateWastewater
The invention discloses a composite visible-light-induced catalyst and a preparation method and application thereof. The composite visible-light-induced catalyst is prepared from CNT-silver citrate and g-C3N4-PO43- through a precipitation method, wherein the CNT-silver citrate is prepared from CNT, sodium citrate and AgNO3 through surface complexing action, and the g-C3N4-PO43- is prepared from g-C3N4 and NaH2PO4 through surface phosphorylation. The preparation method includes the steps of preparation of the CNT-silver citrate, preparation of the g-C3N4-PO43- and preparation of CNT / Ag3PO4 / g-C3N4. The composite visible-light-induced catalyst can be applied to treatment of antibiotic wastewater and has the advantages of high visible light utilization rate, stable presence in water and stable photocatalytic performance.
Owner:CHANGSHA UNIVERSITY
Preparation method of visible light responded WO3/{001}TiO2 composite photocatalyst
InactiveCN104475082AVisible light catalytic activity is highImprove visible light catalytic performanceWater/sewage treatment by irradiationEnergy based wastewater treatmentHydrolysisTitanic acid
The invention relates to a preparation method of visible light responded WO3 / {001}TiO2 composite photocatalyst. The preparation method comprises the following steps: by adopting an improved sol-gel method, firstly preparing {001} surface-exposed anatase TiO2 at room temperature, then depositing a certain amount of WO3 on the surface of the anatase TiO2 to construct a WO3 / {001}TiO2 composite system. according to the preparation method, the {001} surface-exposed anatase TiO2 is prepared by adopting the simple sol-gel method, so that the original preparation concept of inhibiting the hydrolysis of a titanium-containing precursor can be changed, the amount of water is increased to promote the complete hydrolysis of butyl titanate and inhibit the polymerization, the original feeding sequence is changed, butyl titanate is dropwise added into an HF water solution, uniform {001} surface-exposed anatase TiO2 can be formed at room temperature, the preparation technology is simple, the reaction conditions are mild, the reaction speed is easily controlled, the cost is low, and the preparation method is suitable for industrial popularization and application.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for improving visible light catalytic performance of Ag3PO4
InactiveCN104014354AImprove visible light catalytic performanceSimple methodPhysical/chemical process catalystsAir atmosphereRoom temperature
The invention discloses a method for improving the visible light catalytic performance of Ag3PO4. The method comprises the following steps of putting silver phosphate into a muffle furnace, heating to 380-420 DEG C under an air atmosphere, performing heat-preservation sintering for 1-2 hours, and naturally cooling to the room temperature to obtain silver phosphate with the improved visible light catalytic performance. The silver phosphate is spherical silver phosphate or rhombic dodecahedron silver phosphate. The method is simple; the prepared silver phosphate is directly sintered, so that the visible light catalytic effect of a silver phosphate finished product is improved by 8-37.5 percent. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the specific atmosphere protection is not required, and the sintering can be performed under the air atmosphere only by using the common muffle furnace. The method is low in cost, high in efficiency and suitable for industrial application.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH
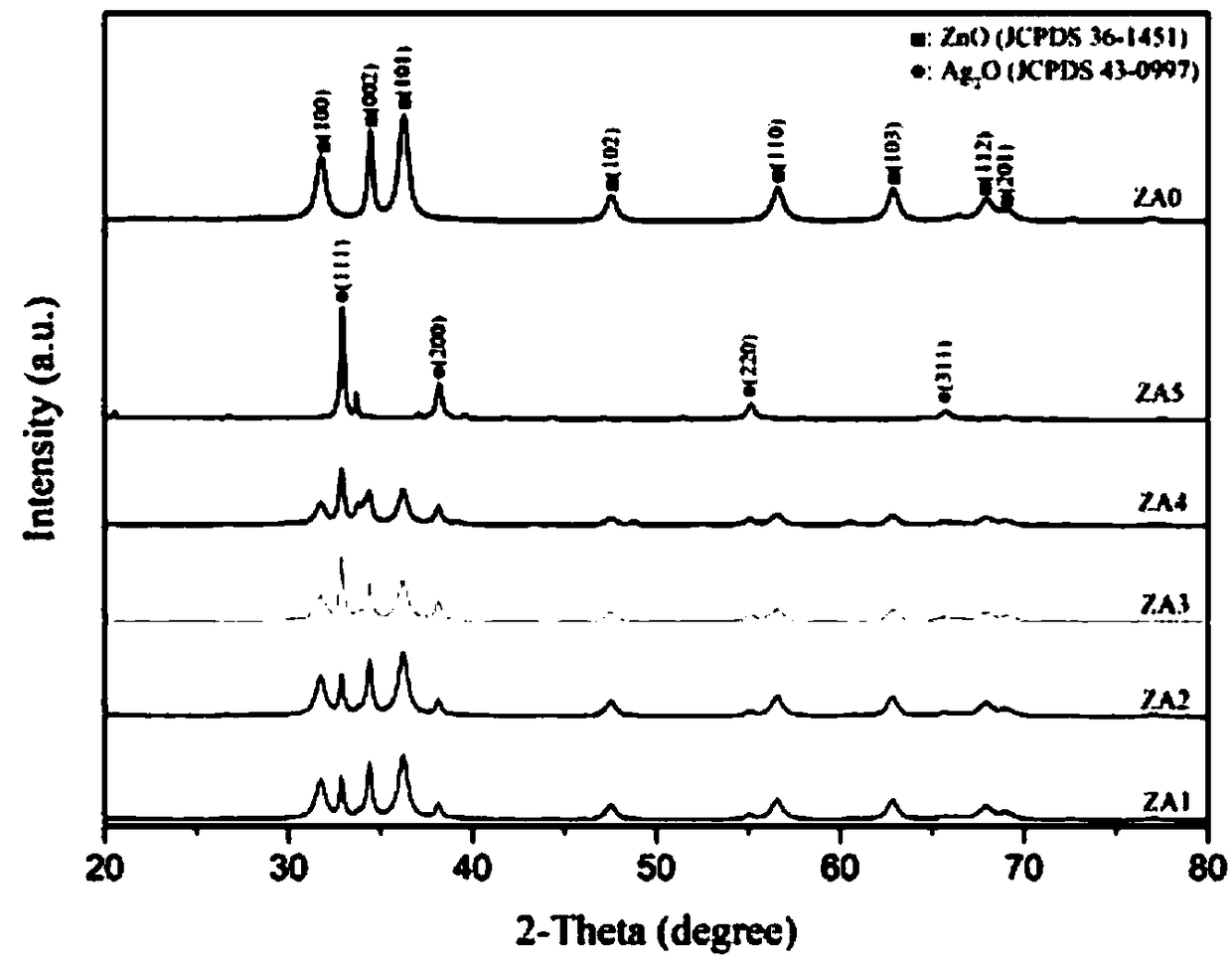
ZnO/Ag2O photocatalysis composite material, as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN108772062ANarrow bandgapImprove visible light catalytic performanceWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater treatment compoundsOrganic dyeElectron transfer
The invention discloses a ZnO / Ag2O photocatalysis composite material, as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The ZnO / Ag2O photocatalysis composite material, as well as the preparation method and the application thereof have the following technical effects that 1, the ZnO / Ag2O photocatalysis composite material is prepared by one step by adopting a solid phase grinding method, andthe preparation method has the remarkable advantages of simplicity in operation, low energy consumption, high efficiency, high yield, green and environmental protection, and recyclability of substratesodium nitrate, and is suitable for mass production; 2, a p-n node formed between zinc oxide and silver oxide is beneficial to interface electron transfer, the recombination of a photo-induced electron hole pair is reduced, and the catalytic performance is remarkably improved compared with a single semiconductor catalyst; on the other hand, the silver oxide is provided with narrower band gaps compared with the silver oxide, so that silver oxide nanoparticles can be used as an effective photosensitizer under the irradiation of sunlight, so that the visible light catalysis performance of the zinc oxide is improved; 3, the ZnO / Ag2O photocatalysis composite material can be used for degrading organic dye wastewater containing methylene blue, methyl orange and rhodamine B, and can be used for degrading 80 percent or more of target degradation products within 20 minutes at the soonest, so that the degradation rate can be improved by 13 times compared with single zinc oxide, and the excellentphotocatalytic activity is realized.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
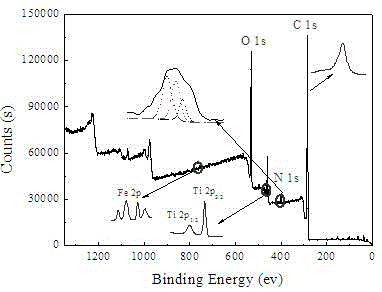
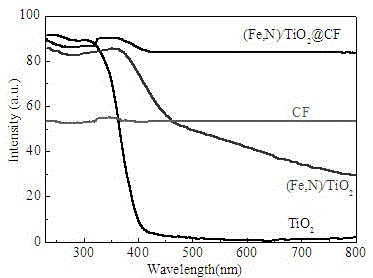
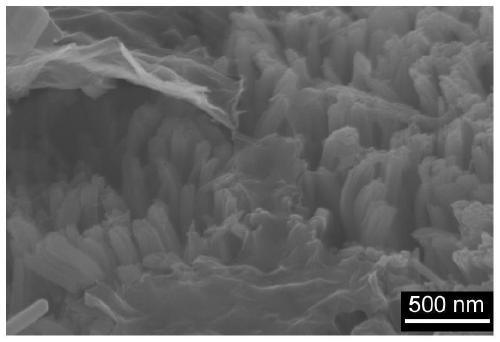
Iron-nitrogen-doped titanium dioxide-loaded carbon fiber composite photocatalyst and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105597805AImprove visible light absorptionEasy to recyclePhysical/chemical process catalystsFiberImpurity
The invention discloses an iron-nitrogen-doped titanium dioxide-loaded carbon fiber composite photocatalyst and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of photocatalysts. The iron-nitrogen-codoped titanium dioxide-loaded carbon fiber composite photocatalyst ((Fe,N) / TiO2@CF for short) is prepared through sol and gel and an impregnating method; by introducing iron atoms and nitrogen atoms into the photocatalyst, the impurity energy level is introduced between a conduction band and a valence band of TiO2, the band-gap energy of the photocatalyst is reduced, and the visible photocatalytic performance of the photocatalyst is improved; loaded carbon fibers (CF for short) are utilized, therefore, the material is easy to recycle, the reuse performance of the photocatalyst is improved, effective migration of photo-induced electrons is improved, the recombination probability of electron holes is decreased, and the photo quantum efficiency of a catalytic material is improved.
Owner:BINZHOU UNIV +1
Titanium dioxide loaded nickel ferrite and graphene oxide composite thin film, preparation method thereof, and application of titanium dioxide loaded nickel ferrite and graphene oxide composite thin film to wastewater treatment
InactiveCN109759065ALarge specific surface areaImprove visible light catalytic performanceWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater contaminantsTin dioxideComposite film
The invention discloses a titanium dioxide loaded nickel ferrite and graphene oxide composite thin film, a preparation method thereof, and application of the titanium dioxide loaded nickel ferrite andgraphene oxide composite thin film to wastewater treatment, and belongs to the technical field of wastewater treatment. The method comprises the steps: titanium dioxide is grown on fluorine doped tindioxide conductive glass through a hydrothermal method, and a nanorod array thin film with good discreteness is obtained; nickel ferrite nanoparticles are deposited on the titanium dioxide through animpregnated calcination method to obtain a titanium dioxide loaded nickel ferrite composite thin film, and the thin film has a good organic wastewater treatment effect under visible light; and a graphene oxide thin film is deposited on the titanium dioxide loaded nickel ferrite composite thin film through an impregnation method, and according to the titanium dioxide loaded nickel ferrite and graphene oxide composite thin film, compared with the titanium dioxide loaded nickel ferrite composite thin film, the visible light organic wastewater degradation efficiency is obviously improved. The treatment method is simple, the visible light catalysis performance is obviously improved, and the treatment method has wide application prospects in wastewater treatment.
Owner:ROCKET FORCE UNIV OF ENG
Surface-modified heterogeneous knot titanium dioxide photonic crystal catalyst and preparation thereof
InactiveCN106799218AImproved visible light responseEfficient separationPhysical/chemical process catalystsChemical reactionPhotonic bandgap
The invention discloses a surface-modified heterogeneous knot titanium dioxide photonic crystal thin film catalyst. The catalyst is of a three-dimensional ordered inverse opal structure and has an anatase / rutile heterogeneous knot crystal structure, and a photonic band gap is located at a visible light absorption region of the catalyst. The invention further discloses a preparation method of the surface-modified heterogeneous knot titanium dioxide photonic crystal thin film catalyst. The preparation method comprises the following steps: preparing TiO2 sol by virtue of an in-situ modification method; preparing polystyrene microsphere colloidal crystal template by virtue of a vertical deposition method; preparing a nano-TiO2 photonic crystal with the three-dimensional ordered inverse opal structure by virtue of a dipping-vertical pulling method; and carrying out high-temperature calcination, so as to obtain the surface-modified heterogeneous knot titanium dioxide photonic crystal thin film catalyst. The catalyst has very strong visible-light responsivity, and the visible light chemical reaction is enhanced by virtue of a slow photon effect of the photonic crystal; by utilizing the heterogeneous knot structure, the separation of photon-generated current carriers is promoted, and the visible light catalysis capacity is improved; and furthermore, equipment is simple and easy to operate.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for synthesizing molybdenum disulfide-carbon nitride composite photocatalytic material
ActiveCN108889324AImprove visible light catalytic performanceHas following advantage: synthetic method of the present invention has environmental protection characteristicPhysical/chemical process catalystsMuffle furnaceSolvent
The invention relates to a method for synthesizing a molybdenum disulfide-carbon nitride composite photocatalytic material. The method comprises the following steps: (1) calcining urea in a muffle furnace to obtain a carbon nitride powder material; 2) performing PEI (Polyetherimide) ultrasonic dispersion on the carbon nitride obtained in the step (1) and a cationic dispersant agent; (3) stirring the carbon nitride suspension obtained in the step (2) with sodium molybdate hydrate and cysteine in an aqueous solvent; (4) carrying out a hydrothermal reaction on the mixed solution in the step (3) in a high-pressure reactor, and performing suction filtration washing on the obtained solid product with absolute ethyl alcohol; and (4) calcining the dried solid product in a nitrogen furnace, therebyobtaining the molybdenum disulfide-carbon nitride composite material. According to the method disclosed by the invention, due to use of the novel cationic dispersant agent, the obtained molybdenum disulfide-carbon nitride composite material has a spherical structure, has an excellent visible light catalysis effect, and is a novel visible light catalytic material having potential application prospects.
Owner:FUJIAN JIANGXIA UNIV
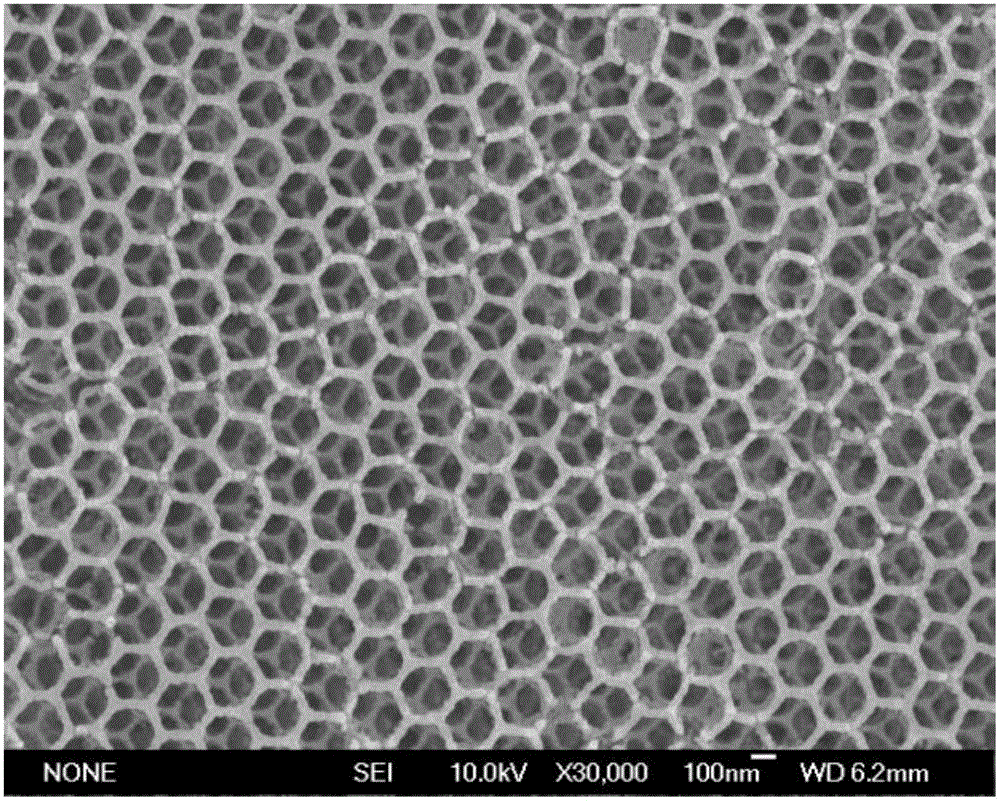
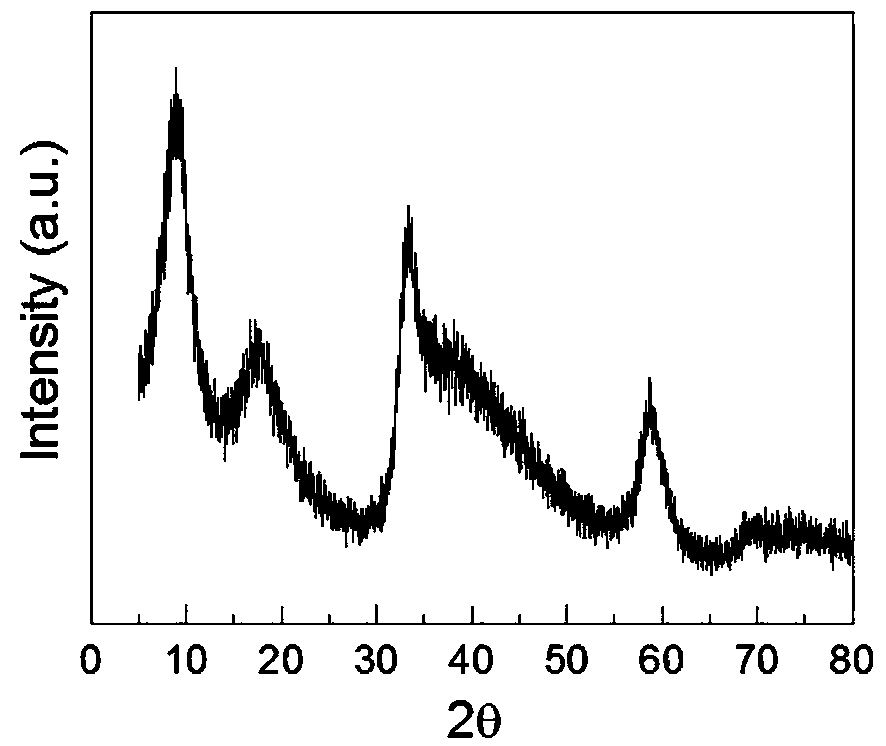
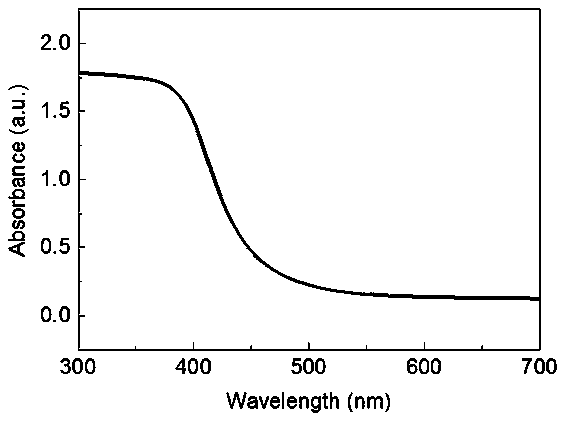
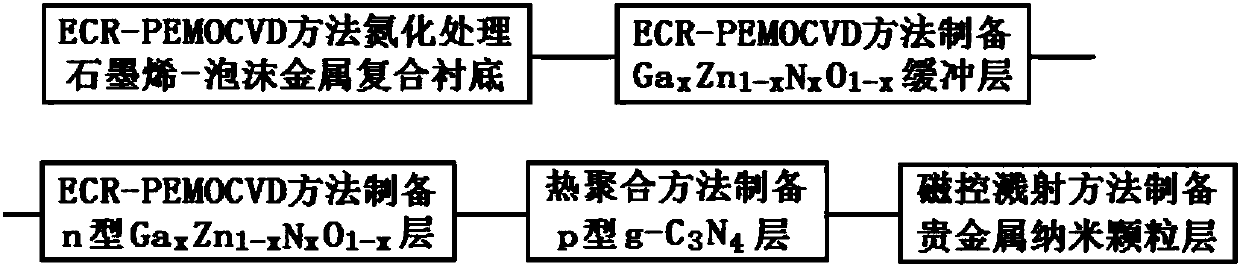
Photocatalytic thin film on foam metal-graphene composite substrate and preparation method
InactiveCN107649165AImprove mechanical propertiesUniform pore structureCatalyst activation/preparationHydrogen productionCvd grapheneNitrogen treatment
The invention belongs to the technical field of photocatalytic thin film manufacturing, and provides a photocatalytic thin film on a foam metal-graphene composite substrate and a preparation method. Concretely, the preparation method comprises the steps of taking a foam metal-graphene composite material as a substrate, firstly using an electron cyclotron resonance-plasma enhancing metal organic matter CVD (chemical vapor deposition) method to successively perform nitrogen treatment of the foam metal-graphene composite substrate, preparation of a GaxZnl-xNxO1-x buffer layer and preparation of an n-type GaxZn1-xNxO1-x layer, then using a thermal polymerization method to prepare a p-type g-C3N4 layer, and finally using a magnetron sputtering method to prepare a precious metal nanometer granular layer. The prepared photocatalytic thin film has a very good visible light photocatalysis effect, can be used for photolyzing water to produce hydrogen, degrading organic pollutant in waste water,removing harmful gas and purifying air, and has a broad application prospect.
Owner:秦永泽
TiO2 microsphere and preparation method therefor
InactiveCN103706347ANarrow size distributionImprove visible light catalytic performancePhysical/chemical process catalystsMicroballoon preparationMicrosphereCentrifugation
The invention discloses a TiO2 microsphere and a preparation method therefor. The particle size of the TiO2 microsphere is 1-8 mm. The preparation method is as follows: tetrabutyl titanate and octadecylamine are added into glycol at the room temperature, the tetrabutyl titanate concentration is controlled in 0.2 mol / L, the octadecylamine concentration is controlled in 0.06-0.4 mol / L, and a solution A is obtained; water and ethanol are mixed in that, the water concentration is controlled in 9.3-27 mol / L, and a solution B is obtained; the solution B is added into a high pressure reactor, then a container containing the solution A is placed in the high pressure reactor, the volume ratio of the solution A to the solution B is 6-10:5; the reactor is sealed, the temperature is controlled at the temperature of 140-220 DEG C, after the reaction is carried out for 12h, the reactor is cooled to the room temperature; centrifugation is carried out, precipitate is collected, washed and dried, and TiO2 microspheres are obtained. The TiO2 microspheres can be used for catalysis to p-nitrophenol, and the efficiency can reach 0-41%. The preparation method is advantaged by simple operation and mild conditions, and is suitable for large scale production.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECH
SiO2-WO3 composite aerogel and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102091589BLow densityLarge specific surface areaOther chemical processesAlkali metal oxides/hydroxidesAlkaneSilazane
The invention provides SiO2-WO3 composite aerogel and a preparation method thereof. The specific surface area of the SiO2-WO3 composite aerogel is 329 to 720m<2> / g, the pore volume is 0.6 to 1.8 cm<3> / g, the BJH most probable aperture is 4 to 10 nm and the average aperture is 4 to 9 nm. The preparation method mainly comprises: firstly, synthesizing SiO2-WO3 sol-gel by using sodium tungstate and industrial sodium silicate as raw materials; secondly, modifying a gel block by using modifying solution consisting organic silazane, organic siloxane and an alkane reagent; and finally, replacing porewater. The aerogel product has the characteristics of high specific surface area and high pore volume, the preparation method adopts cheap and readily available sodium tungstate and industrial sodiumsilicate raw materials and therefore can reduce production cost, and a normal pressure drying process is convenient and easy to implement and is suitable for industrial production and use.
Owner:DALIAN POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY
Preparation of Bi2WO6 spherical cluster with exposed {010} crystal plane families
InactiveCN104226212AImprove adsorption capacityMore activeOther chemical processesMicroballoon preparationCrystallographyCrystal plane
The invention discloses a preparation method of a Bi2WO6 spherical cluster with exposed {010} crystal plane families. The spherical cluster has a diameter of 2 to 4 microns and consists of Bi2WO6 nanosheets with a thickness of 15 to 30nm. The preparation method of the Bi2WO6 spherical cluster with the exposed {010} crystal plane families comprises the following processes: respectively dissolving Bi(NO3)3<.>5H2O and Na2WO4<.>2H2O into nitric acid and deionized water, wherein the molar ratio of Bi(NO3)3<.>5H2O to Na2WO4<.>2H2O is 2:1; after mixing, regulating pH of the obtained solution into a neutral value; finally, performing the hydrothermal reaction to obtain the Bi2WO6 spherical cluster with the exposed {010} crystal plane families. The preparation method is simple and easy to operate; the reaction is performed in the neutral solution; an organic additive does not need to be added; the prepared Bi2WO6 spherical cluster contains a great quantity of exposed {010} crystal plane families and is beneficial to attachment of dyes in the photocatalysis process and improvement of catalytic performance of visible light.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Iron sodium bismuthate-graphene visible-light-driven Fenton-like composite catalyst used for removing nonyl phenol and preparation method thereof
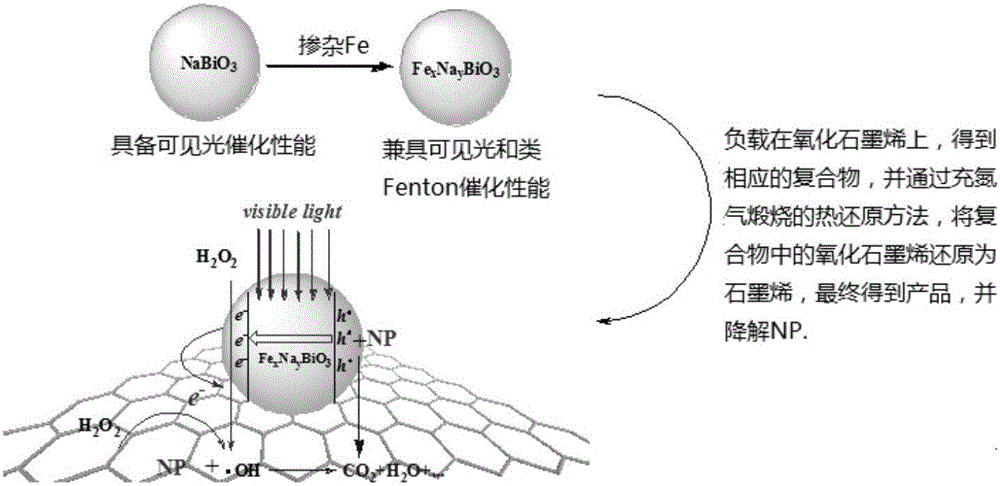
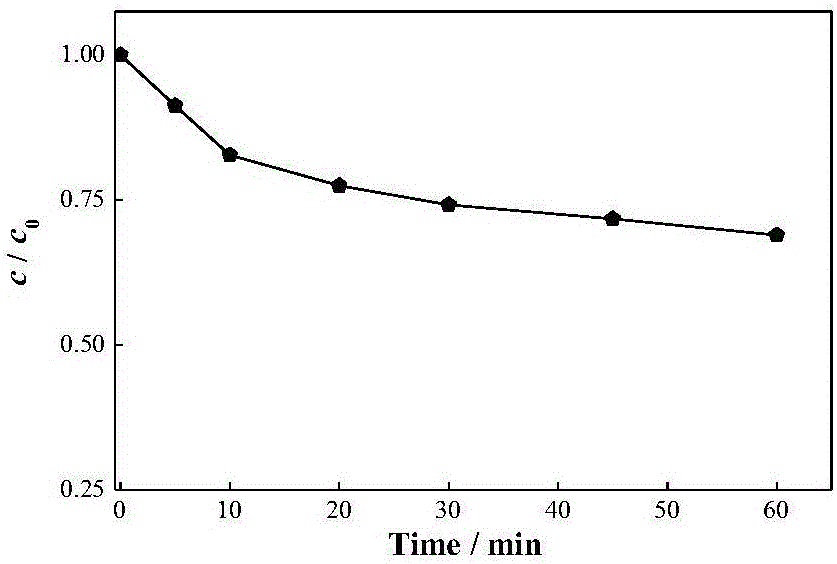
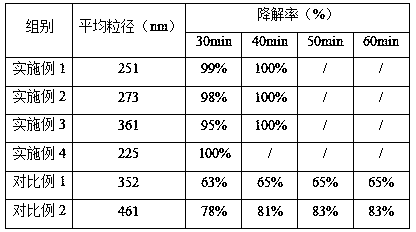
InactiveCN106362754AImprove adsorption capacityHas selective adsorption capacityWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater treatment compoundsInterfacial reactionLight driven
The invention provides an iron sodium bismuthate-graphene visible-light-driven Fenton-like composite catalyst used for removing nonyl phenol and a preparation method thereof. The composite catalyst is characterized in that the composite catalyst is prepared by compounding iron sodium bismuthate and graphene, wherein the mass content of iron sodium bismuthate FexNayBiO3 is 90 to 99.5% while the mass content of graphene is 10 to 0.5%. According to the invention, NaBiO3 (sodium bismuthate) is used as a basic catalyst and elemental Fe is doped to endow the basic catalyst with Fenton-like catalysis performance, so a nanometer catalyst, i.e., iron sodium bismuthate, with both visible-light-driven and Fenton-like catalysis performance is prepared; and then iron sodium bismuthate is loaded on micrometer graphene oxide, and graphene oxide in the compound is reduced into graphene through a hot reduction method so as to obtain the final product, i.e., the iron sodium bismuthate-graphene visible-light-driven Fenton-like composite catalyst. Under irradiation by visible light, nanometer FexNayBiO3 produces strong-oxidability substances like hydroxyl radicals under photocatalysis; graphene can improve affinity between the catalyst and a substrate, substantially strengthen adsorption of NP and enhance interfacial reaction capability in virtue of pi-pi interaction and hydrophobic action force, and graphene has excellent electron transport performance, which can promote separation and transfer of photogenerated holes and electrons on a heterophase boundary and further improve NP oxydative degradation capability.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV OF TECH
Preparation method of nitrogen-doped TiO2 microspheres with hollow core-shell structure
InactiveCN110605134AImprove photocatalytic efficiencyImprove stabilityWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater treatment compoundsMicrosphereDecomposition
The invention belongs to the field of photocatalytic nano materials. The invention provides a preparation method of nitrogen-doped TiO2 microspheres with a hollow core-shell structure. The preparationmethod comprises the following steps: (1) preparing titanium dioxide sol; (2) preparing PAM@TiO2 single-shell core-shell microspheres; (3) preparing SiO2@PAM@TiO2 double-shell core-shell microspheres; and (4) preparing SiO2@@TiO<2-x>Nx hollow core-shell structure microspheres. The preparation method comprises the following steps: mixing polyacrylamide for providing an N element with titanium dioxide to form the single-shell core-shell microspheres; coating a silicon dioxide shell with a film to form the double-shell core-shell microspheres; performing high temperature calcination so that polyacrylamide serving as a middle shell layer is subjected to thermal decomposition and removed to form a cavity and an N element is provided for thermal diffusion and doping into titanium dioxide afterthermal decomposition to obtain the nitrogen-doped TiO2 microspheres with the hollow core-shell structure. The preparation method is simple, titanium dioxide modification, core-shell structure titanium dioxide modification and core-shell structure integral forming are realized, the cost is reduced, and the photocatalysis efficiency and stability of a photocatalysis product are improved.
Owner:浙江迈实科技有限公司 +1
Graphene doped Cu/Cu2O nano photocatalytic coating and preparation method thereof
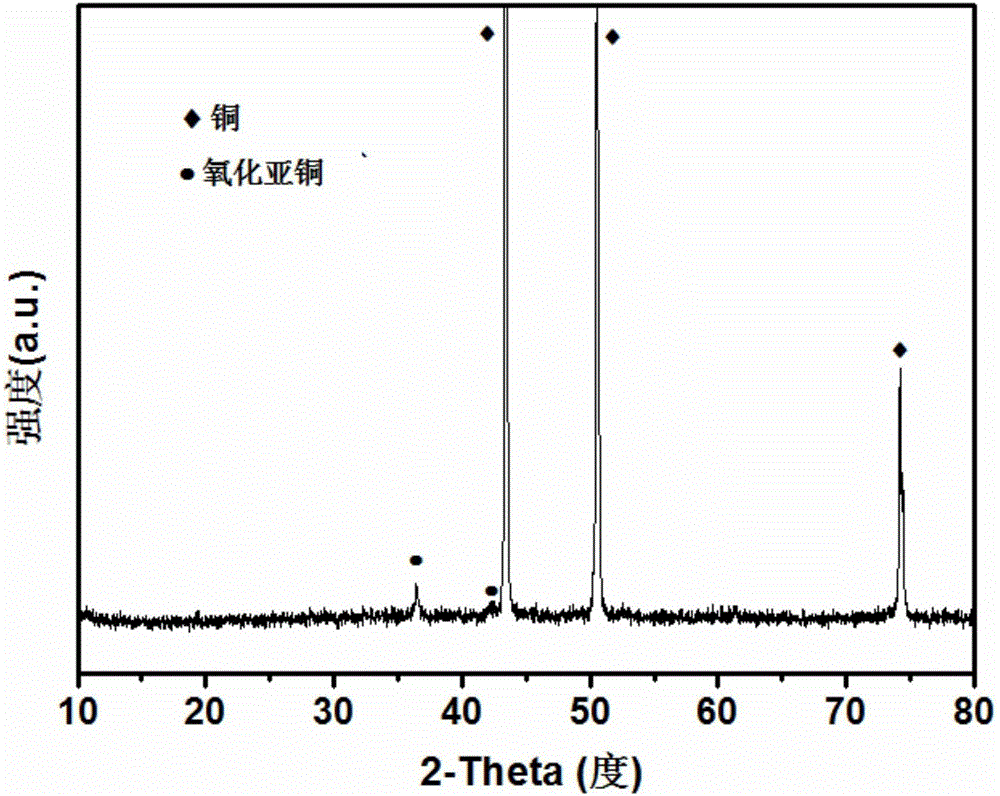
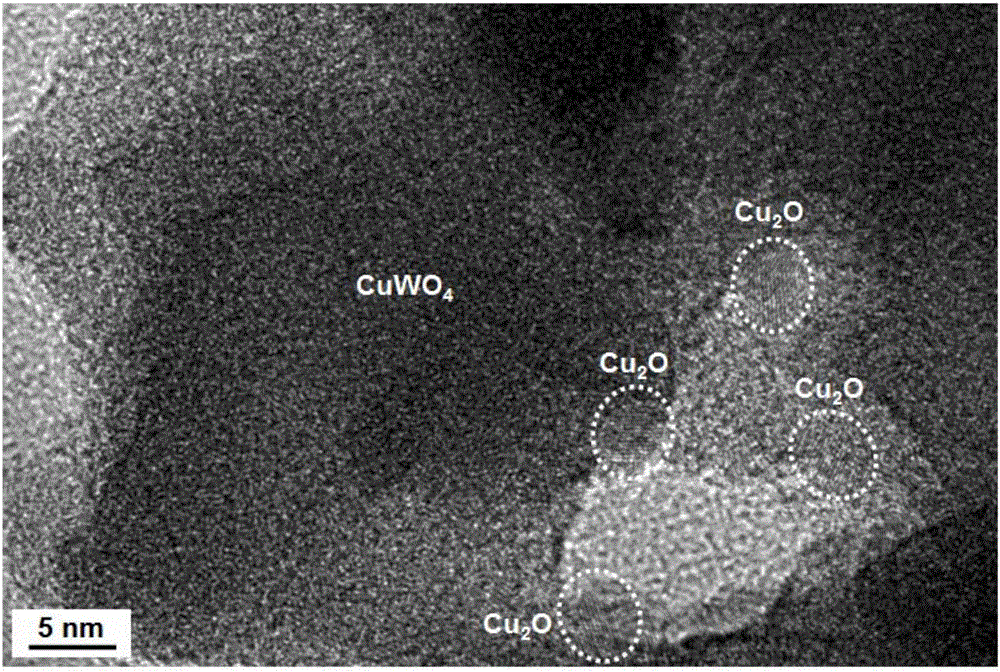
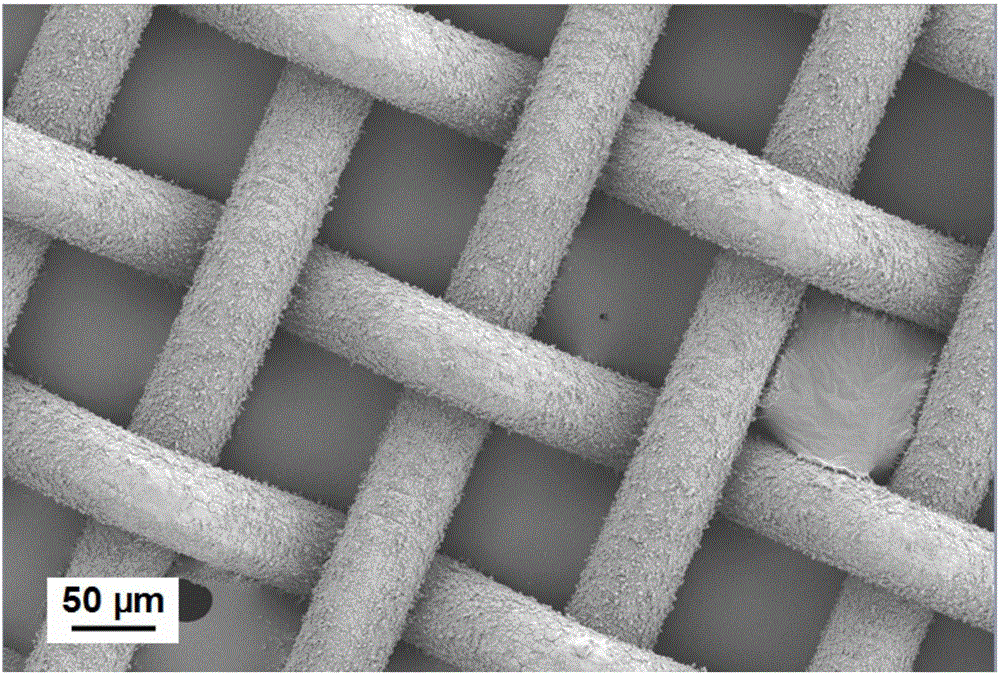
ActiveCN110508281AHigh specific surface areaEnhanced light absorptionWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater treatment compoundsCvd graphenePhotocatalytic coating
The invention discloses a graphene doped Cu / Cu2O nano photocatalytic coating and a preparation method thereof. The method includes: 1) pretreating a workpiece to remove dust, oil dirt and rust on thesurface of the workpiece; 2) preparing a graphene doped Cu / Cu2O composite slurry; 3) pressing the slurry on the surface of the pretreated workpiece through a mechanical roller to form a base layer; 4)adopting a vacuum induction sintering method, placing the workpiece with the formed base layer in a graphite integrated forming sintering mold, maintaining the pressure after the density of a pressedblank does not change any more, and starting sintering to form a preset layer on the surface of the workpiece; and 5) carrying out electron beam welding on the preset layer to obtain the graphene doped Cu / Cu2O nano photocatalytic coating. The method provided by the invention puts forward solar irradiation of the graphene doped Cu / Cu2O nano photocatalytic coating by a solar concentrating device, can solve the problem of shortening the forbidden bandwidth of a catalyst to expand an absorption spectrum to visible light so as to improve the solar energy utilization rate.
Owner:FUJIAN UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com