Patents
Literature
112results about How to "High utilization rate of visible light" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Preparation method and applications of biomass modified TiO2 visible light photocatalyst
ActiveCN103920479AEasy to controlLarge specific surface areaPhysical/chemical process catalystsWater/sewage treatment by irradiationAlcoholWastewater
The invention discloses a biomass modified TiO2 visible light photocatalyst. A preparation method of the biomass modified TiO2 visible light photocatalyst comprises the following steps: hydrolyzing titanium alkoxide to obtain sol, adding biomass in the sol and stirring, drying the sol to obtain gel, and calcining the gel. According to the preparation method, the reaction conditions are moderate and easy to control, raw materials are easily available, the synthesis process is simple, industrialized production is achieved easily, the prepared biomass modified TiO2 visible light photocatalyst has the performance of photocatalytically degrading organic substances by visible light and can be used for photocatalytically treating organic pollutants in air, soil and wastewater.
Owner:FUJIAN NORMAL UNIV
BiOCl-TiO2/diatomite photocatalyst and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105854906AInhibition of agglomerationReduce manufacturing costPhysical/chemical process catalystsDispersityHeterojunction
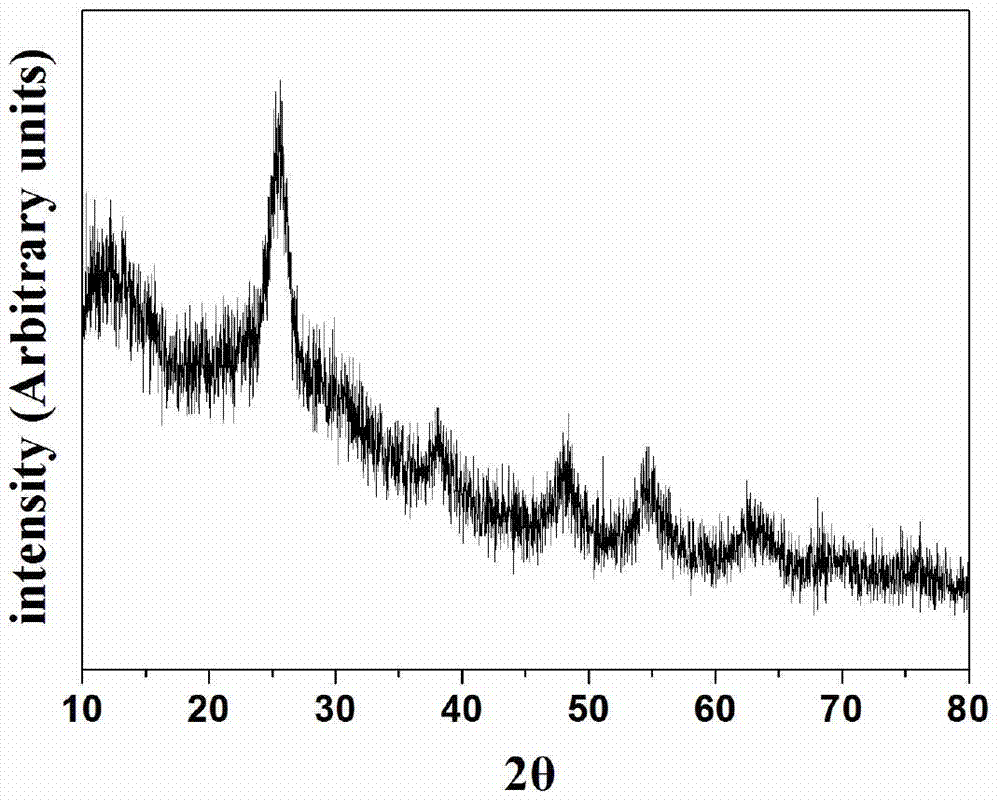
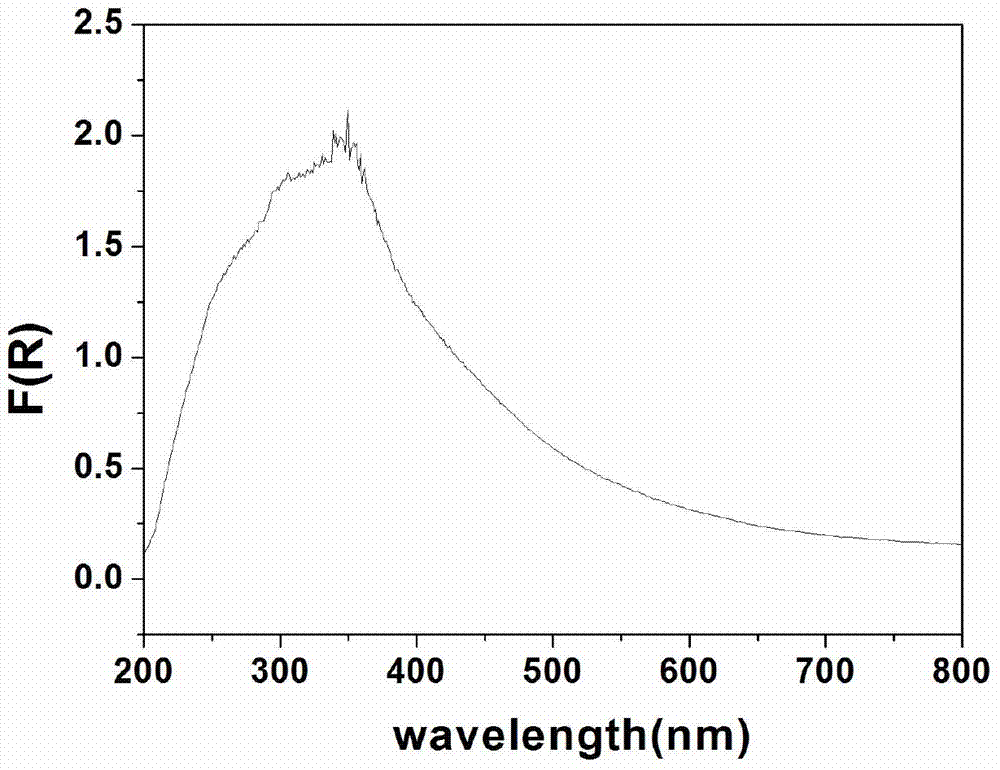
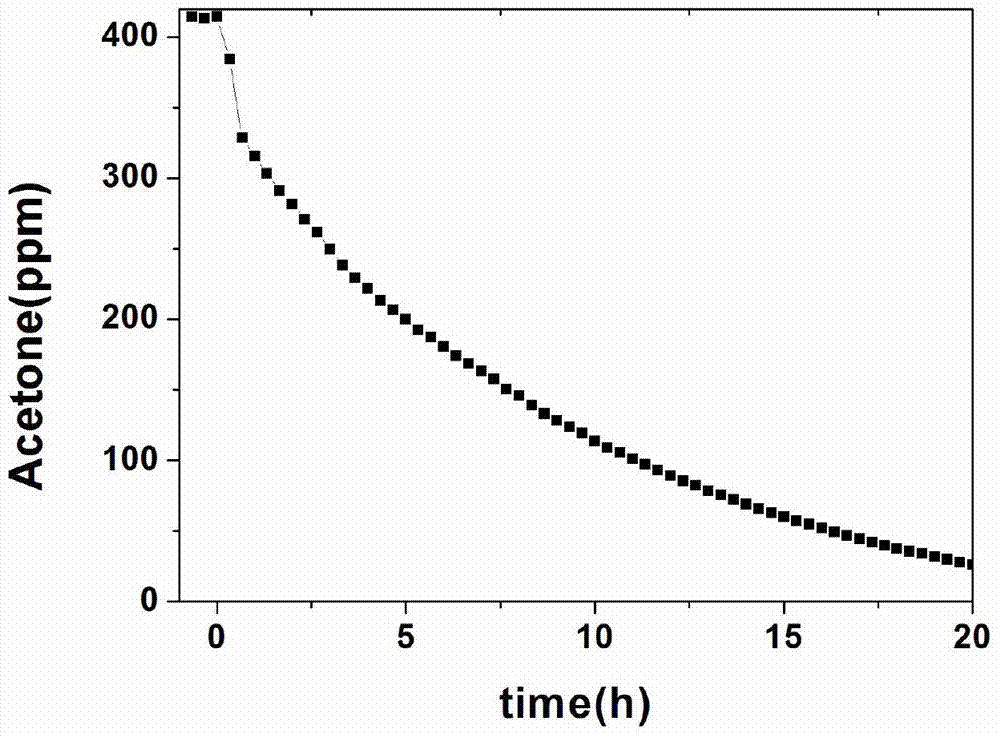
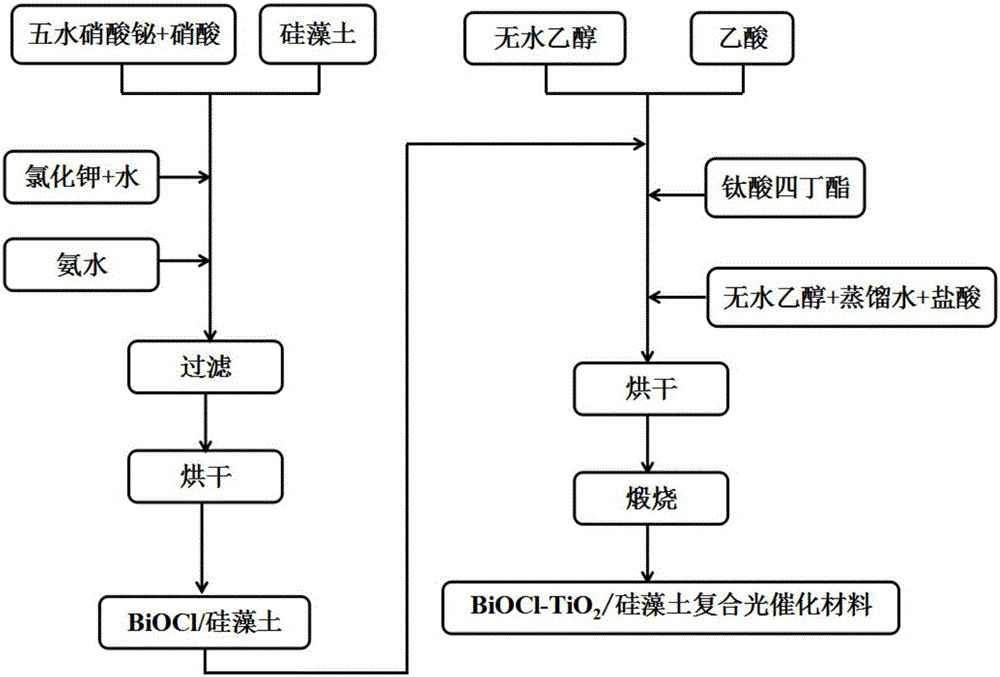
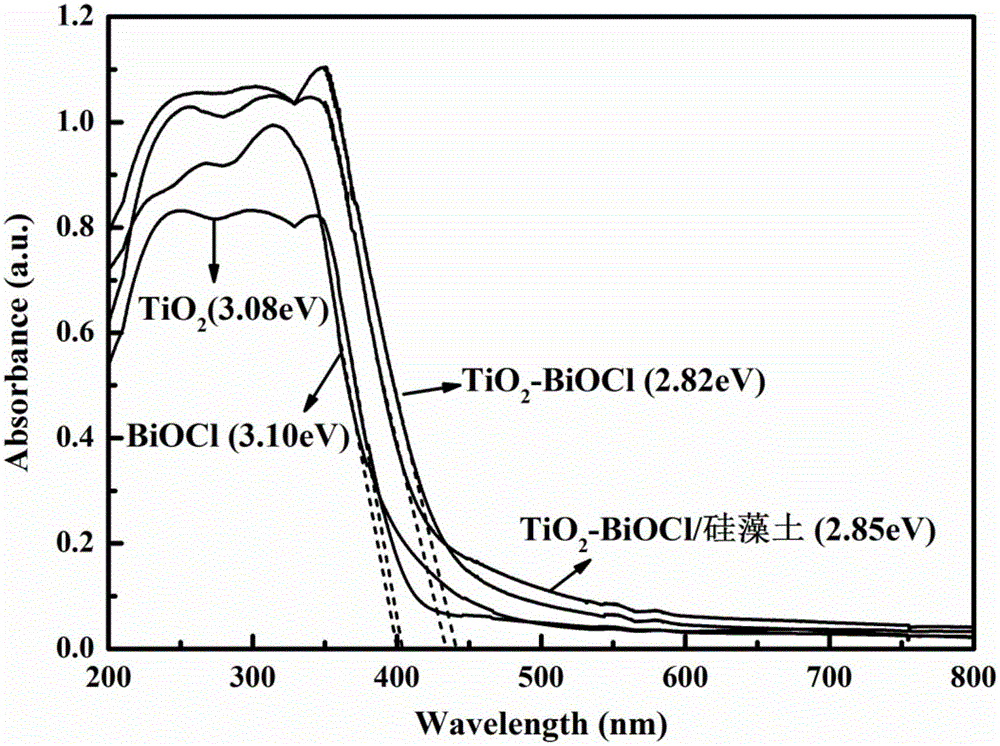
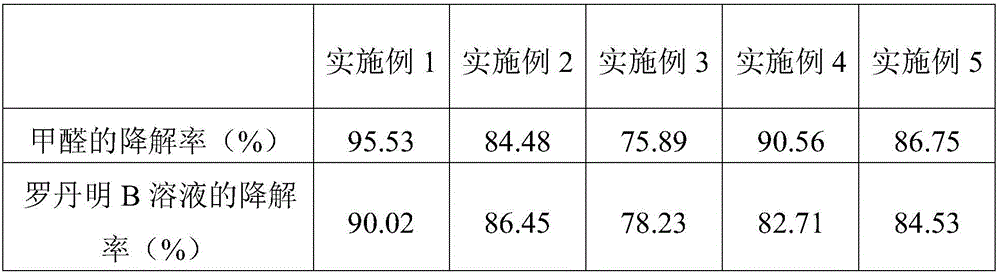
The invention relates to a BiOCl-TiO2 / diatomite photocatalyst and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the fields of nonmetal mine material deep processing and environmental engineering. The BiOCl-TiO2 / diatomite composite photocatalysis material with visible light response is obtained by taking diatomite as a catalyst carrier and loading a BiOCl-TiO2 heterojunction catalyst on the surface and in pore channels of diatomite through a sol-gel method and a calcination crystallization method. According to the method, diatomite and nano BiOCl-TiO2 heterojunction with visible light response are compounded, and the pollutant adsorption and capture performance of the material and the dispersity and photocatalysis activity of the catalyst are improved by virtue of diatomite carrier effect. The loading type photocatalysis material has excellent photocatalysis activity to gas formaldehyde and liquid dyes under visible light, and has great potential application value in the field of treatment of gas formaldehyde and liquid dyes.
Owner:浙江库实健康科技有限公司
Composite nanometer titanium dioxide photocatalysis material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101518730ALower redox potentialHigh utilization rate of visible lightOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsDeodrantsHYDROSOLSilicon dioxide
The invention discloses a composite nanometer titanium dioxide photocatalysis material and a preparation method thereof. The method includes the steps: titanium dioxide collosol, silicon dioxide collosol and propylene glycol monomethyl ether, of which the mass ratio is 1 to 4 to 10, are uniformly mixed to form composite collosol; porous ceramics are soaked in the composite collosol for 30 minutes; and the porous ceramics are taken out to be heated for 30 minutes at the temperature of 300 DEG C so as to obtain photocatalysis ceramics loaded titanium dioxide materials. Compared with the prior art, the invention has the technical scheme that modified silicon dioxide collosol is mixed in the titanium dioxide collosol, and the existing Ti-O-Ti bond is replaced by a Ti-O-Si bond, thereby reducing the titanium oxidation-reduction potential, enabling titanium dioxide light absorption wavelength to generate redshift, and improving the visible light utility ratio of titanium as well as the adhesive power and the hardness of a coating.
Owner:UNIVERSTAR SCI & TECH SHENZHEN
Titanium dioxide-boron modified carbon nitride catalyst and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105214708ALarge specific surface areaHigh utilization rate of visible lightPhysical/chemical process catalystsHydrocarbon from carbon oxidesModified carbonCarbon nitride
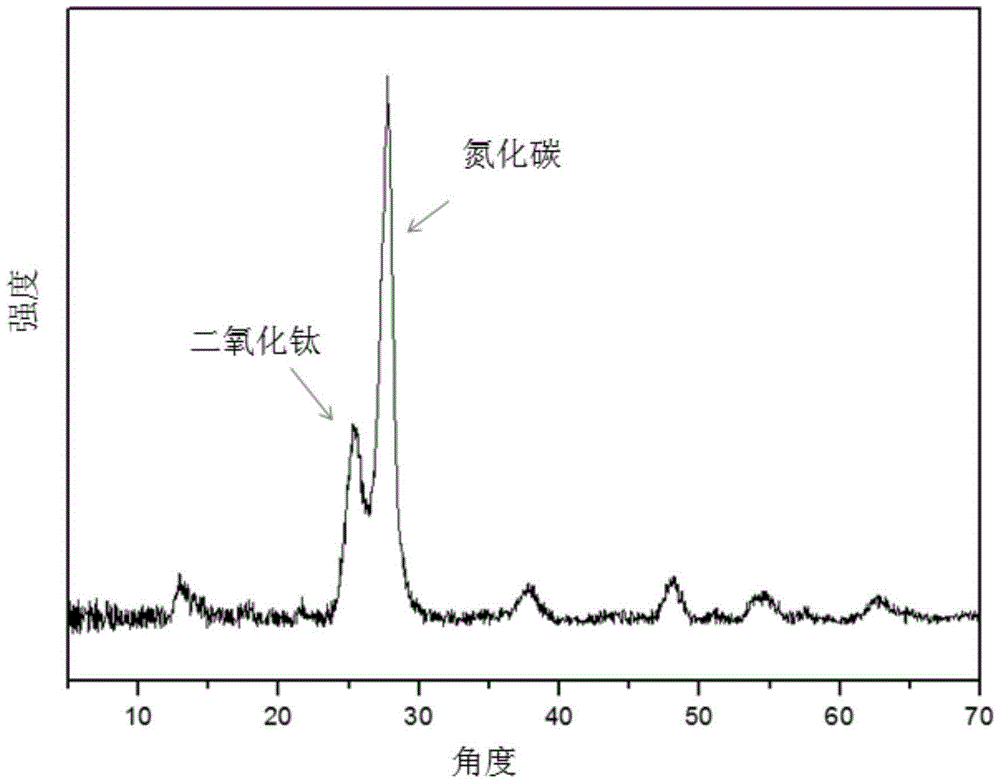
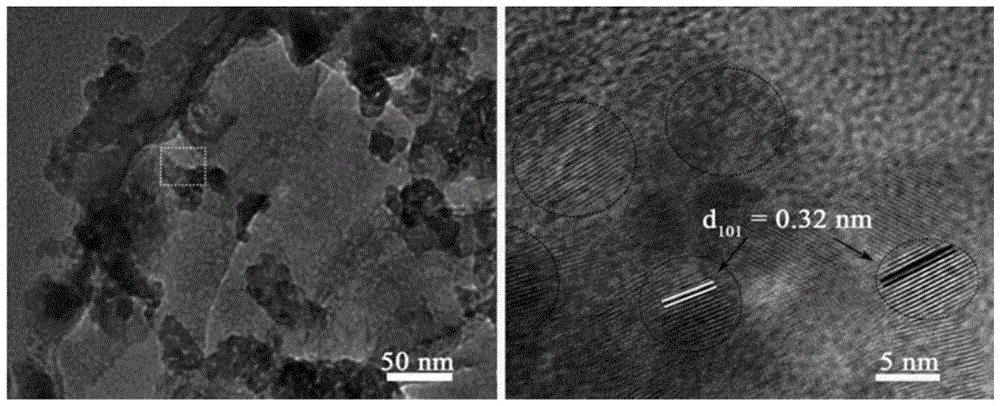
The invention relates to a preparation method of a high-activity titanium dioxide-boron modified carbon nitride catalyst and aims to solve the problems of low visible light utilization rate, serious charge recombination, difficulty in hole capture and poor light reducing capacity of a photocatalyst material prepared in the prior art. The preparation method of the high-activity titanium dioxide-boron modified carbon nitride catalyst is prepared in specific steps as follows: step one, preparation of a boron modified carbon nitride precursor solution; step two, preparation of boron modified carbon nitride; step three, preparation of titanium dioxide-boron modified carbon nitride composite, and the titanium dioxide-boron modified carbon nitride is obtained.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG UNIV
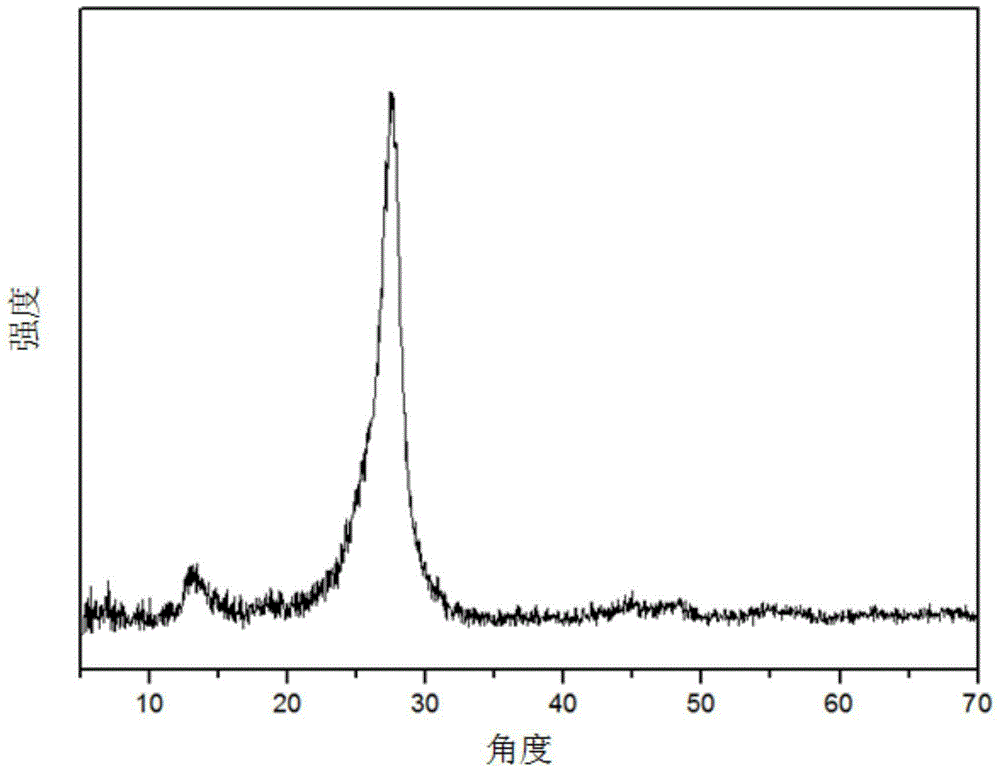
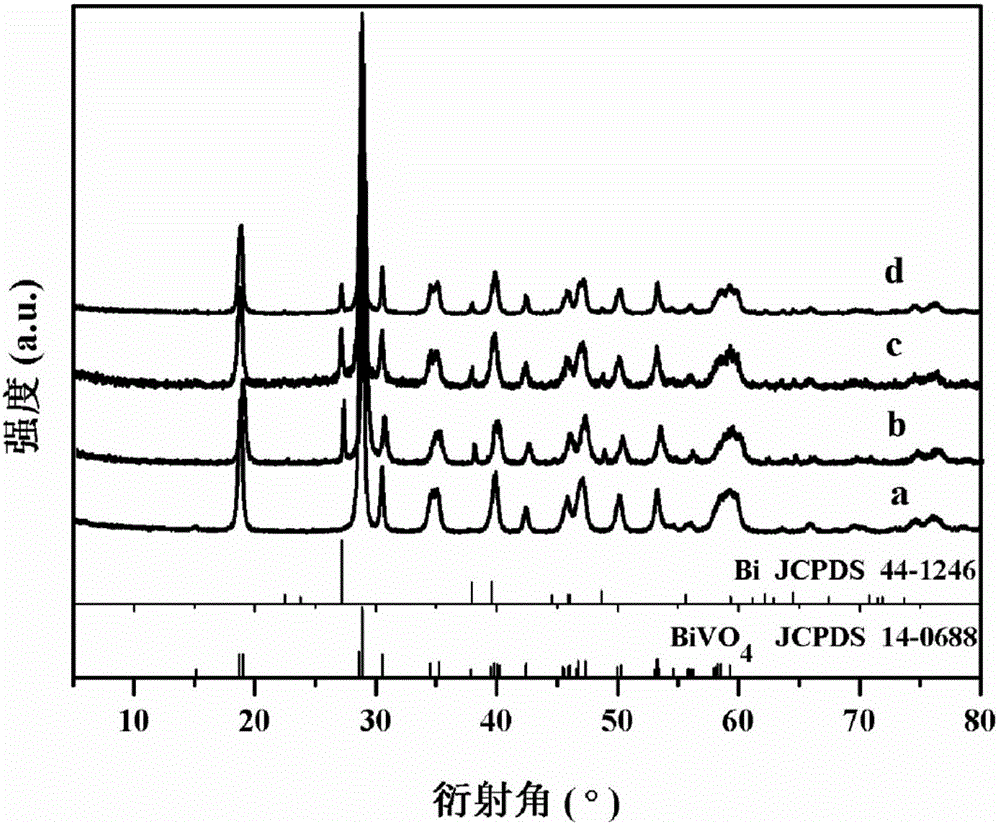
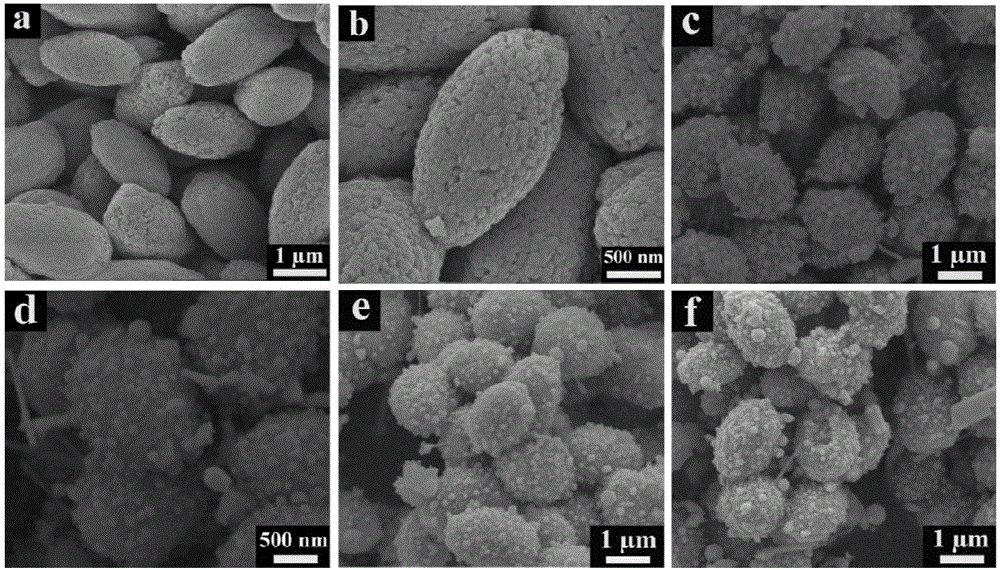
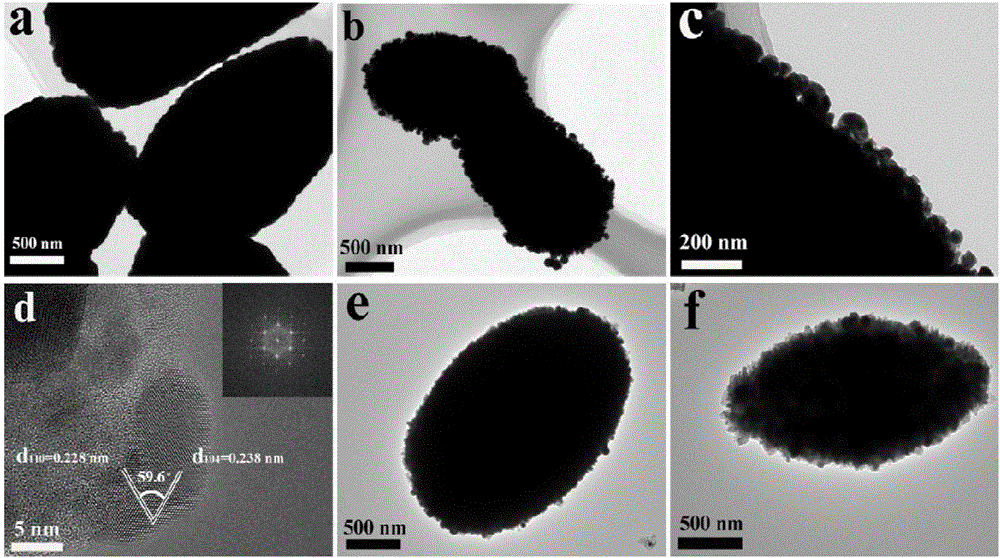
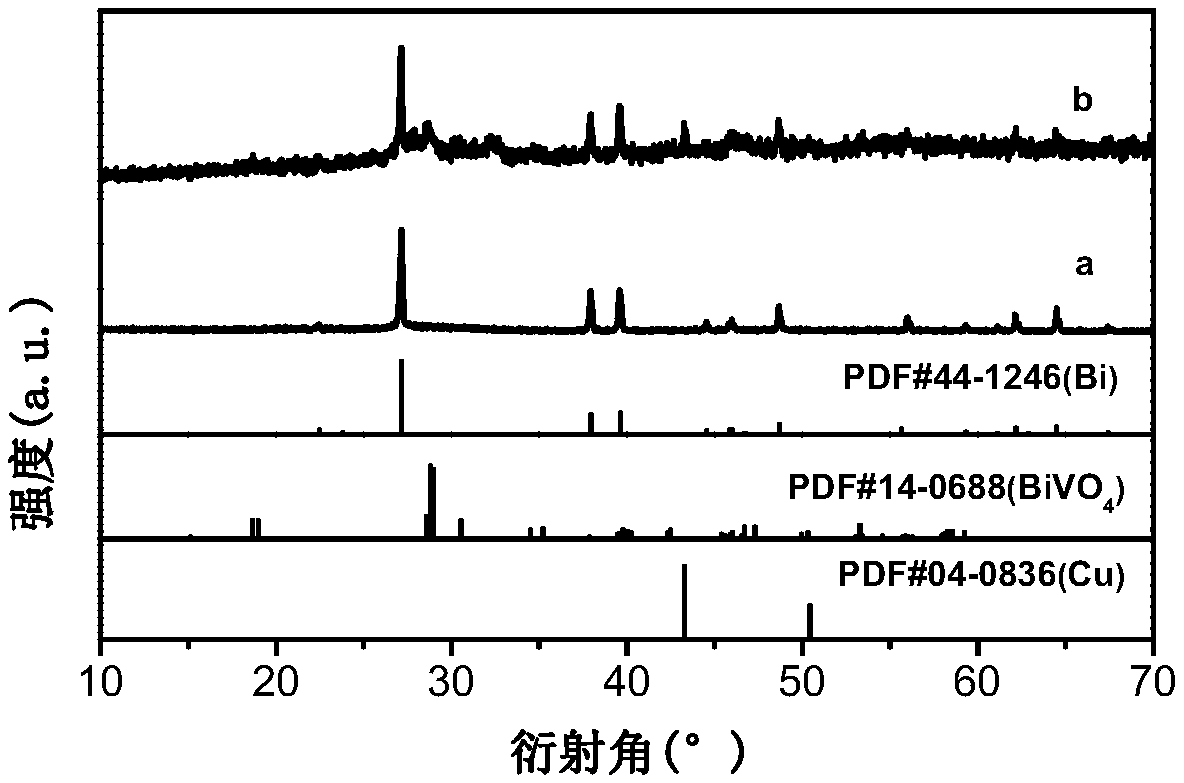
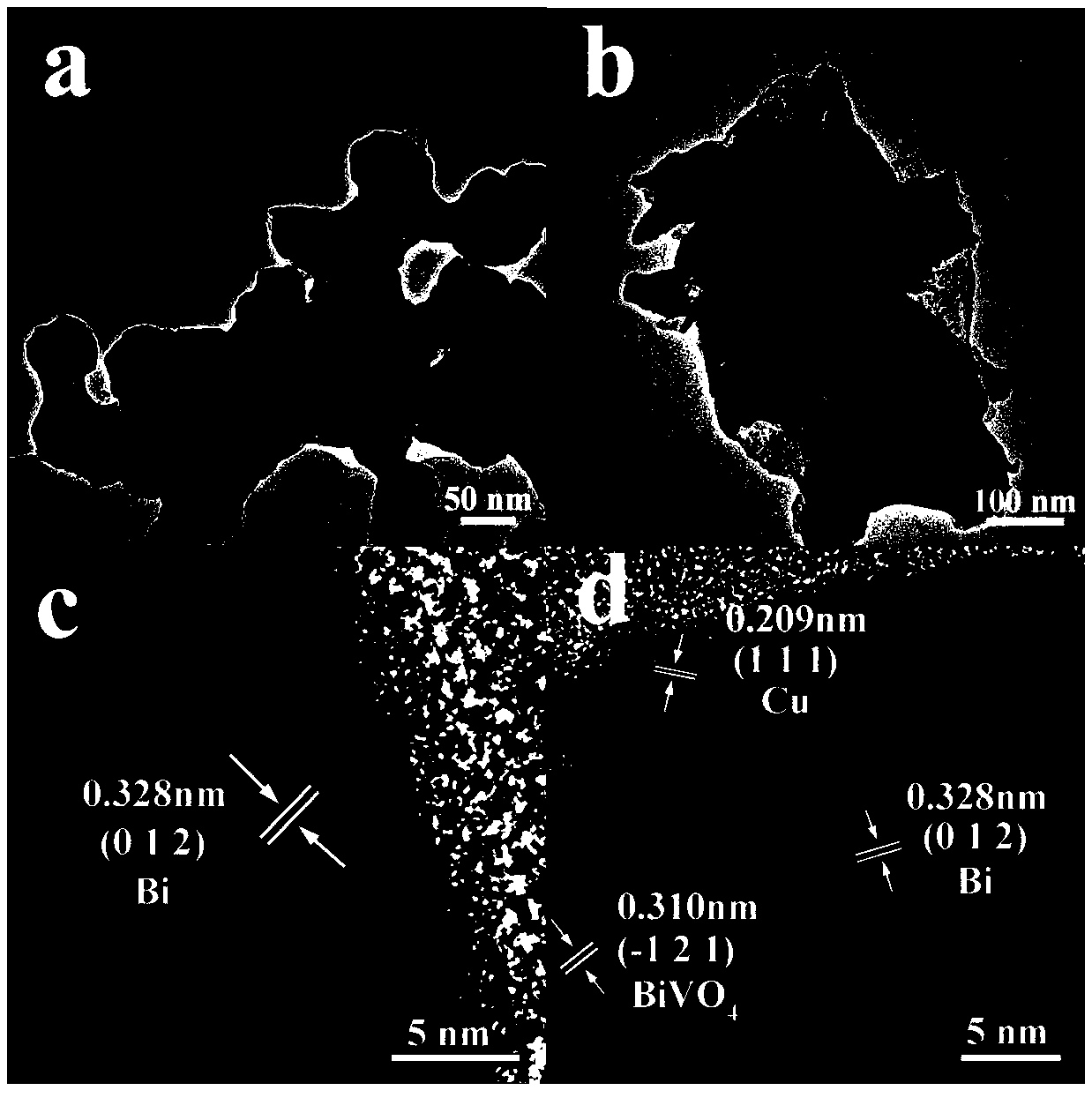
Bismuth/bismuth vanadate composite photocatalyst and preparation method and application thereof to photocatalytic degradation of organics
InactiveCN106732527AAvoid separationResponsive to visible lightWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater treatment compoundsSynthesis methodsBismuth vanadate
The invention discloses a bismuth / bismuth vanadate composite photocatalyst and a preparation method and application thereof to photocatalytic degradation of organics. The bismuth / bismuth vanadate composite photocatalyst is formed by in-situ growth of nano bismuth particles on surfaces of bismuth vanadate particles. The preparation method includes: mixing vanadium source containing aqueous solution and bismuth source containing ethylene glycol solution, and performing solvothermal reaction to obtain bismuth vanadate; dispersing the bismuth vanadate into water to obtain bismuth vanadate dispersion liquid; mixing the bismuth vanadate dispersion liquid with reductant solution, and performing hydrothermal reaction to obtain the bismuth / bismuth vanadate composite photocatalyst wide in light absorption range, high in visible light utilization rate and high in photocatalytic activity. Compared with bismuth vanadate catalysts, the bismuth / bismuth vanadate composite photocatalyst has the advantage of high catalytic activity in photocatalytic degradation of the organics. In addition, a synthesis method of the bismuth / bismuth vanadate composite photocatalyst is simple, raw materials are cheap and easy to acquire, and production cost is low.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
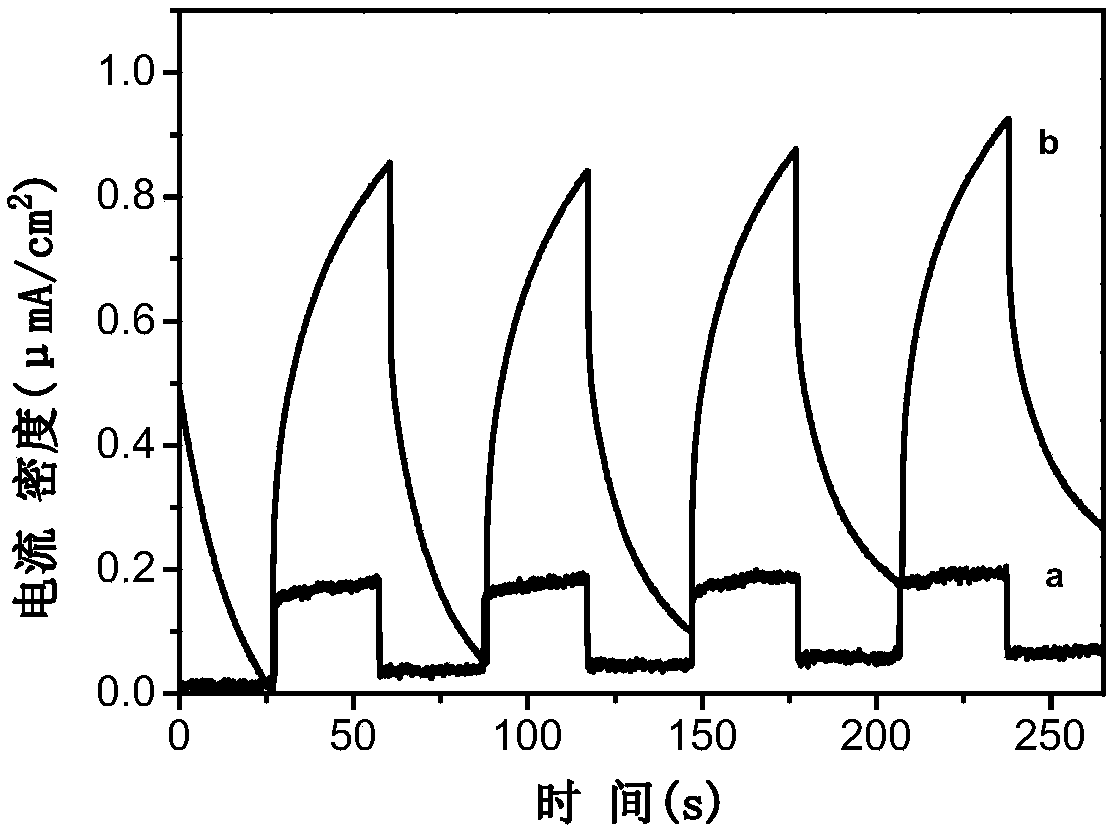
Preparation and application of copper-bismuth/bismuth vanadate composite photocatalyst
InactiveCN109364933AImprove photocatalytic performanceImprove separation efficiencyGas treatmentDispersed particle separationBismuth vanadateAmmonium metavanadate
The invention discloses a preparation method of a copper-bismuth / bismuth vanadate composite photocatalytic material, and belongs to the technical field of photocatalysis. The copper nanosheet-bismuthnanoparticle / bismuth vanadate composite photocatalytic material is formed in the mode that the surface of bismuth / bismuth vanadate with a mesh structure is coated with a copper nanosheet. The preparation method of the copper-bismuth / bismuth vanadate composite photocatalytic material comprises the steps: ammonium metavanadate and bismuth nitrate serve as raw materials to be subjected to a solvent thermal reaction in an ethylene glycol solution, and the mesh nanostructure of the bismuth / bismuth vanadate is obtained. After the bismuth / bismuth vanadate is dispersed in a copper acetate solution tobe mixed, a hydrothermal reaction is carried out, copper ions are reduced to copper simple substances through partial bismuth simple substances, meanwhile, amorphous bismuth vanadate is converted to crystalline bismuth vanadate, and thus the copper nanosheet-bismuth nanoparticle / bismuth vanadate composite photocatalyst is prepared. According to the composite photocatalyst, through the synergisticeffect of the bismuth vanadate, the bismuth and copper, the light response range is enlarged, the separation efficiency of light-generated electrons and hole pairs is improved, and thus the photocatalytic activity of photocatalytic reduction of carbon dioxide is improved.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
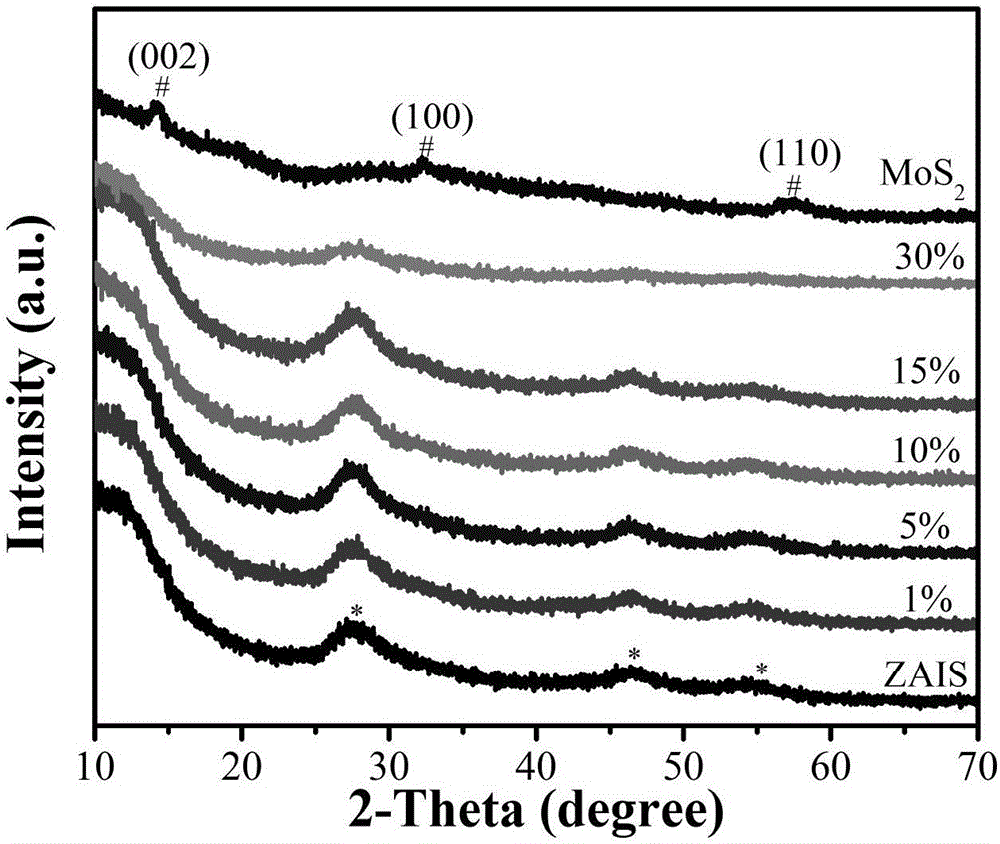
Method for preparing quaternary sulfide quantum dot based heterojunction efficient photocatalyst
ActiveCN105727999AFully crystallizedGood dispersionPhysical/chemical process catalystsHeterojunctionThiourea
The invention relates to I-III-VI group 2 sulfide and particularly relates to an AgIn5S8-ZnS / MoS2 heterojunction composite photocatalyst prepared by utilizing a simple and rapid hydrothermal method. The AgIn5S8-ZnS / MoS2 heterojunction composite photocatalyst can be used for degrading a rhodamine B dye under visible light. The AgIn5S8-ZnS / MoS2 heterojunction composite photocatalyst is prepared by mixing and stirring AgIn5S8-ZnS nano crystals, ammonium molybdate tetrahydrate and thiourea, carrying out a hydrothermal reaction for 8 hours at 200 DEG C, and filtering, washing and drying after the reaction is finished, wherein the mass ratio of the MoS2 to the AgIn5S8-ZnS nano crystals is 1%-30%, and the optimal mass ratio of the photocatalytic performance is 5%. An experiment of degrading rhodamine B (RhB) under the visible light shows that the prepared composite photocatalyst has good photocatalytic activity.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Composite visible-light-induced catalyst and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN107029777AHigh utilization rate of visible lightImprove photocatalytic performancePhysical/chemical process catalystsWater/sewage treatment by irradiationSilver citrateWastewater
The invention discloses a composite visible-light-induced catalyst and a preparation method and application thereof. The composite visible-light-induced catalyst is prepared from CNT-silver citrate and g-C3N4-PO43- through a precipitation method, wherein the CNT-silver citrate is prepared from CNT, sodium citrate and AgNO3 through surface complexing action, and the g-C3N4-PO43- is prepared from g-C3N4 and NaH2PO4 through surface phosphorylation. The preparation method includes the steps of preparation of the CNT-silver citrate, preparation of the g-C3N4-PO43- and preparation of CNT / Ag3PO4 / g-C3N4. The composite visible-light-induced catalyst can be applied to treatment of antibiotic wastewater and has the advantages of high visible light utilization rate, stable presence in water and stable photocatalytic performance.
Owner:CHANGSHA UNIVERSITY
Preparation method of visible light responded WO3/{001}TiO2 composite photocatalyst
InactiveCN104475082AVisible light catalytic activity is highImprove visible light catalytic performanceWater/sewage treatment by irradiationEnergy based wastewater treatmentHydrolysisTitanic acid
The invention relates to a preparation method of visible light responded WO3 / {001}TiO2 composite photocatalyst. The preparation method comprises the following steps: by adopting an improved sol-gel method, firstly preparing {001} surface-exposed anatase TiO2 at room temperature, then depositing a certain amount of WO3 on the surface of the anatase TiO2 to construct a WO3 / {001}TiO2 composite system. according to the preparation method, the {001} surface-exposed anatase TiO2 is prepared by adopting the simple sol-gel method, so that the original preparation concept of inhibiting the hydrolysis of a titanium-containing precursor can be changed, the amount of water is increased to promote the complete hydrolysis of butyl titanate and inhibit the polymerization, the original feeding sequence is changed, butyl titanate is dropwise added into an HF water solution, uniform {001} surface-exposed anatase TiO2 can be formed at room temperature, the preparation technology is simple, the reaction conditions are mild, the reaction speed is easily controlled, the cost is low, and the preparation method is suitable for industrial popularization and application.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Preparation method of oxide quantum dot modified graphene/titanium oxide photocatalysis material
ActiveCN107626296AImprove photocatalytic activityHelp to separateMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsHeterojunctionConductive polymer
The invention discloses a preparation method of an oxide quantum dot modified graphene / titanium oxide photocatalysis material. The preparation method comprises following steps: modification with a conductive polymer is adopted so as to obtain a conductive polymer coated graphene; sol-gel method is adopted so as to prepare a sol from conductive polymer coated graphene, butyl titanate, and an oxidequantum dot; and aging, gelling, drying, grinding, and heat treatment are adopted to obtain the quantum dot modified graphene / titanium oxide porous nanometer catalysis material. According to the preparation method, surface modification with the conductive polymer is capable of improving the dispersion performance and the surface activity of graphene, loading graphene nanosheets with titanium oxidenanometer particles uniformly, and controlling the particle size of the nanometer particles; and in addition, construction of a oxide quantum dot-titanium oxide heterojunction is adopted to widen thespectrum response range and the photocatalytic activity of the catalysis material.
Owner:湖南得成检测有限公司
Nonmetal-doped titanium dioxide, preparation method thereof and degradable plastic film
The invention discloses nonmetal-doped titanium dioxide, a preparation method thereof and degradable plastic film. The nonmetal-doped titanium dioxide is prepared by high-energy ball milling of nano titanium dioxide and a nonmetal doping source, wherein the weight of the nonmetal element is 0.1%-5.0% of the weight of the titanium element. The degradable plastic film can be prepared by subjecting the nonmetal-doped titanium dioxide and a polyolefin resin to belt blending and extrusion-blown molding, wherein the weight of the nonmetal-doped titanium dioxide is 0.1%-10.0% of the weight of the polyolefin resin. The nonmetal-doped titanium dioxide has characteristics of simple production technology, easily available raw materials, high photocatalytic activity, wide light absorption range, and the like. The degradable plastic film prepared by the nonmetal-doped titanium dioxide has characteristics of short degradation time, controllable stable periods, wide application range, and the like.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
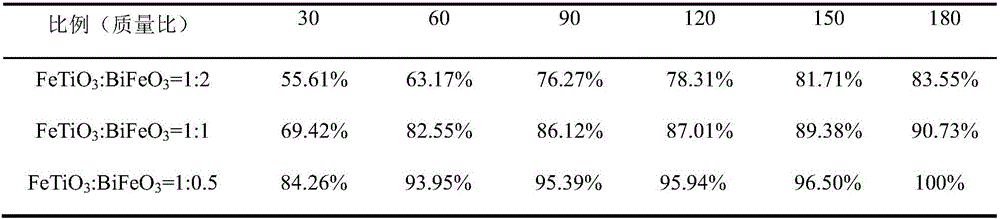
Composite bismuth ferrite photocatalyst and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN106807400AImprove visible light absorptionBroaden the photoresponse rangeWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater treatment compoundsUltraviolet lightsAntibiotic Y
The invention relates to a composite bismuth ferrite photocatalyst and a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method of Ag / FeTiO3 / BiFeO3 comprises the following steps: adding FeTiO3 to deionized water; stirring to obtain suspension; adding AgNO3 to the suspension; stirring for 20-30 minutes under a light-proof condition; then stirring for 10-20 minutes with the irradiating of an ultraviolet light; adding BiFeO3; ultrasonically dispersing; centrifugally separating; washing the obtained precipitate through deionized water; drying; and then roasting for 20-40 minutes through a muffle furnace at the temperature of 400-450 DEG C to obtain the target product. According to the preparation method, the BiFeO3 material is composited; antibiotics can be degraded through efficient photocatalyzing under the visible light effect.
Owner:LIAONING UNIVERSITY
Preparation method of supported visible-light response WO3/{001}TiO2 compound photocatalyst
InactiveCN104689855AImprove separation efficiencyHigh utilization rate of visible lightOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsEnergy levelSingle crystal
The invention relates to a preparation method of a supported visible-light response WO3 / {001}TiO2 compound photocatalyst, which comprises three steps of (1) pretreatment of a supporter, (2) preparation of {001} crystal face exposure anatase TiO2 single crystals, and (3) preparation of the supported compound photocatalyst, the support supported catalyst with TiO2 as a center and coated with a WO3 core-shell structure is prepared, the characteristic that the tungsten trioxide (WO3) is taken as a narrow-gap (2.8eV) n-type semiconductor, and can be excited in a visible light range is fully utilized, the energy level difference between two semiconductor materials is utilized to effectively separate charges, the separating efficiency of a photon-generated carrier and the utilization rate of visible light are improved, the photocatalytic activity is high and unlikely to be lost, the catalytic activity is preserved for a long time, furthermore, the preparation process is simple, the reaction condition is mild, the reaction speed is easy to control, the cost is low, and the method is applicable to industrial promotion and application.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
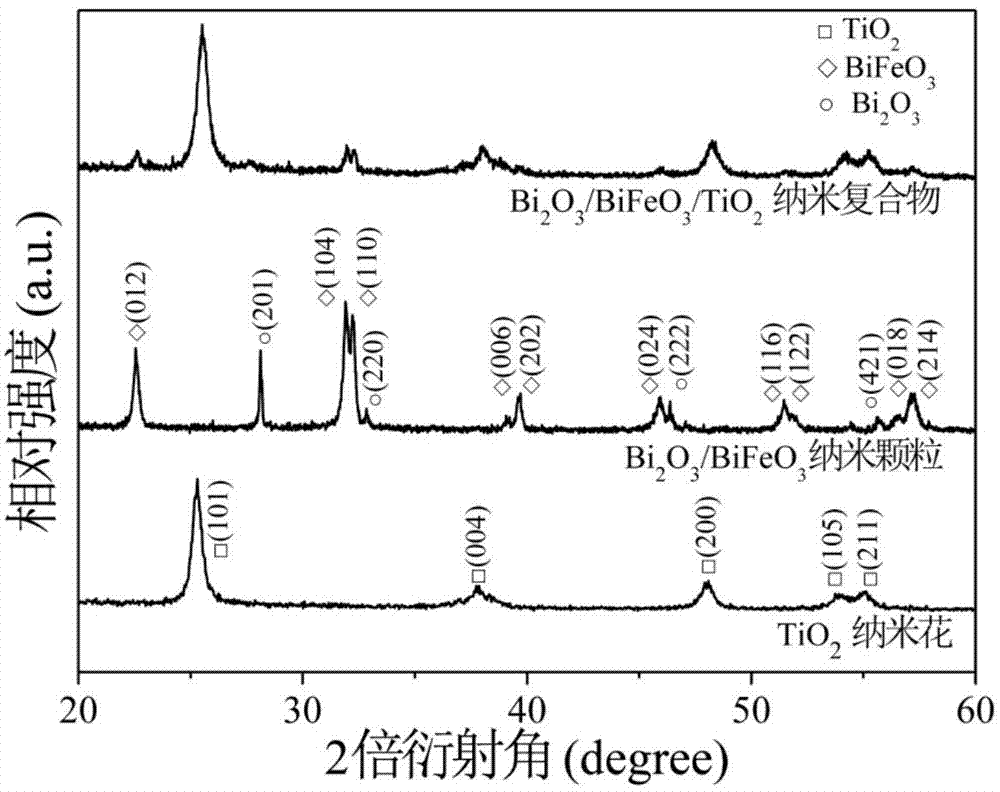
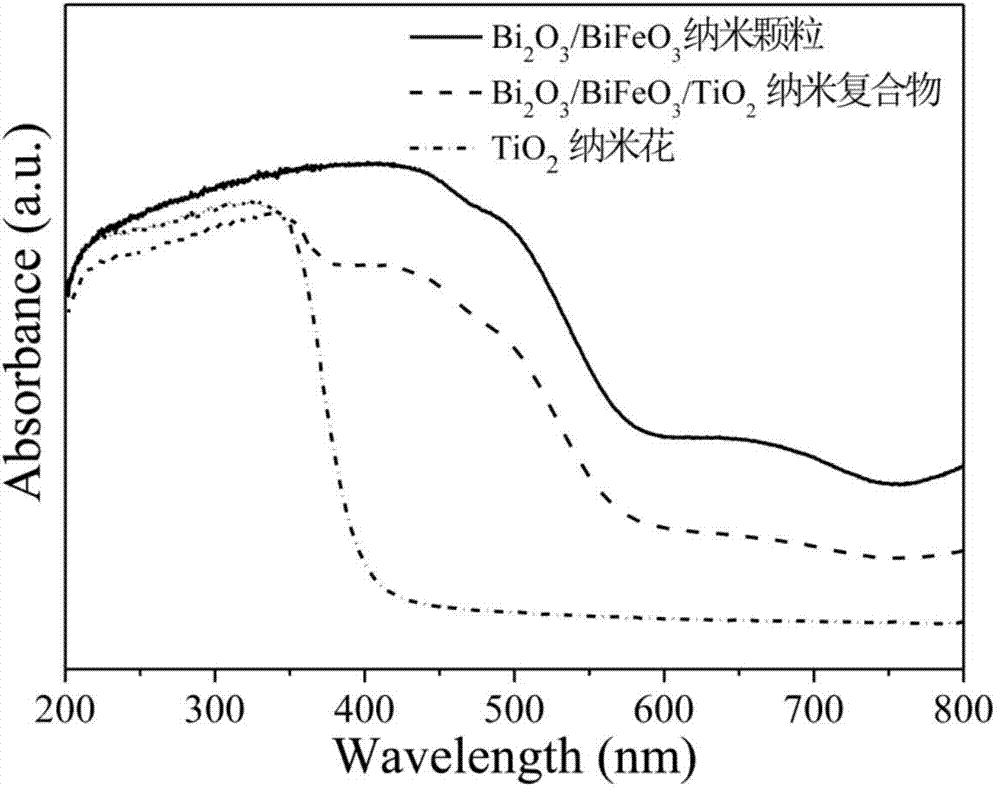
Bi2O3/BiFeO3/TiO2 nano-flower photocatalytic material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104772149AHigh utilization rate of visible lightImprove separation efficiencyMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsElectron holeMaterials preparation
The invention relates to a novel Bi2O3 / BiFeO3 / TiO2 nano-flower photocatalytic material and a preparation method thereof and belongs to the technical field of catalytic material and nano material preparation. The preparation method comprise the following steps: preparing TiO2 nano-flower and Bi2O3 / BiFeO3 particles by adopting a hydrothermal method and a sol-gel method and loading the Bi2O3 / BiFeO3 particles onto the surface of the TiO2 nano-flower through a bonding method to form a ternary structure, so as to improve the separation efficiency of photo-generated electrons-hole pairs and the utilization rate of solar light. The TiO2 nano-flower prepared through the hydrothermal method is uniform in appearance and grain size distribution; the Bi2O3 / BiFeO3 particles are uniformly dispersed on the surface of the TiO2 nano-flower to form the Bi2O3 / BiFeO3 / TiO2 nano-flower photocatalytic material. The preparation method is simple, feasible, cheap in raw material, low in equipment requirement and environment-friendly, and has certain application prospect and potential in the aspect of photocatalytic degradation of pollutants.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Bismuth phosphate-based heterojunction photocatalyst and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN112138700AEfficient separationUniform nucleationPhysical/chemical process catalystsHeterojunctionMicrowave method
The invention discloses a bismuth phosphate-based heterojunction photocatalyst and a preparation method thereof. The photocatalyst is a heterojunction photocatalyst constructed by bismuth phosphate and graphite-phase carbon nitride. The preparation method comprises the following steps: preparing nanorod-like BiPO4 by a microwave method, preparing light and thin g-C3N4 by a calcining method grinding and compounding g-C3N4 and BiPO4 through a ball milling method to obtain a heterojunction photocatalytic material g-C3N4 / BiPO4; the prepared heterojunction photocatalyst is high in activity, high inlight utilization rate, good in stability and reusability, simple in preparation process, economical, efficient and good in application prospect.
Owner:NANJING INST OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI MINIST OF ECOLOGY & ENVIRONMENT OF THE PEOPLES REPUBLIC OF CHINA +1
Foaming masterbatch with photocatalytic function and preparation method of foaming masterbatch
ActiveCN107096575ALarge specific surface areaHigh utilization rate of visible lightWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater treatment compoundsCalcium silicatePolyolefin
The invention discloses a foaming masterbatch with a photocatalytic function and a preparation method of the foaming masterbatch. The foaming masterbatch with the photocatalytic function is characterized by being prepared from 50-70 parts of a composite photocatalyst, 15-20 parts of carrier resin, 3-5 parts of a dispersing agent, 0.5-2 parts of a coupling agent, 1-2 parts of a lubricant and 1-20 parts of a foaming activator; inorganic powder is 100-5000 meshes in size and is one or a mixture of several of calcium carbonate, barium sulfate, kaoline, wet white carbon black, quartz powder, talcum powder, calcium silicate and mica; the method comprises the steps of taking polyolefin resin as a carrier, and adding the composite photocatalyst, the foaming activator, the dispersing agent, the coupling agent and the lubricant for extrusion and granulation. A photocatalytic material prepared from the masterbatch has the advantages that the material is high in catalytical efficiency and light in weight and can be recycled. The method is lower in cost, a preparation technology is simple, and industrialization can be achieved.
Owner:SHANXI LANHUA HUAMING NANO MATERIALS +1
Nanometer ferric oxide/nanometer titanium dioxide composite photocatalyst, and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN110394178AHigh utilization rate of visible lightReduce electron-hole recombination rateWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater treatment compoundsUltrasonic dispersionMaterials science
The invention discloses a nanometer ferric oxide / nanometer titanium dioxide composite photocatalyst, and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the field of photocatalysis environment restoration. The nanometer ferric oxide / nanometer titanium dioxide composite photocatalyst is composed through loading of the surfaces of titanium dioxide nanometer spheres with ferric oxide nanometer spheres.The preparation method comprises following steps: 1, 0.2 to 1.80g of iron nitrate nonahydrateis dissolved in distilled water, 0.10 to 0.80g of citric acid and a certain amount of sodium chloride are added into an obtained iron nitrate nonahydrate solution; 2, stirring is carried out to obtain a uniform solution; 3, commercially available P25 titanium dioxide powder is added in an obtained solution, and ultrasonic dispersion is carried out to prepare a suspension solution; 4, the suspension solution is introduced into a tubular furnace for combustion, after reaction, the reaction vessel to cooled to room temperature through natural cooling, and repeat washing is carried out; and 5, after washing, an obtained sample is placed in a vacuum drying box for 2h of drying at 60 DEG C.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
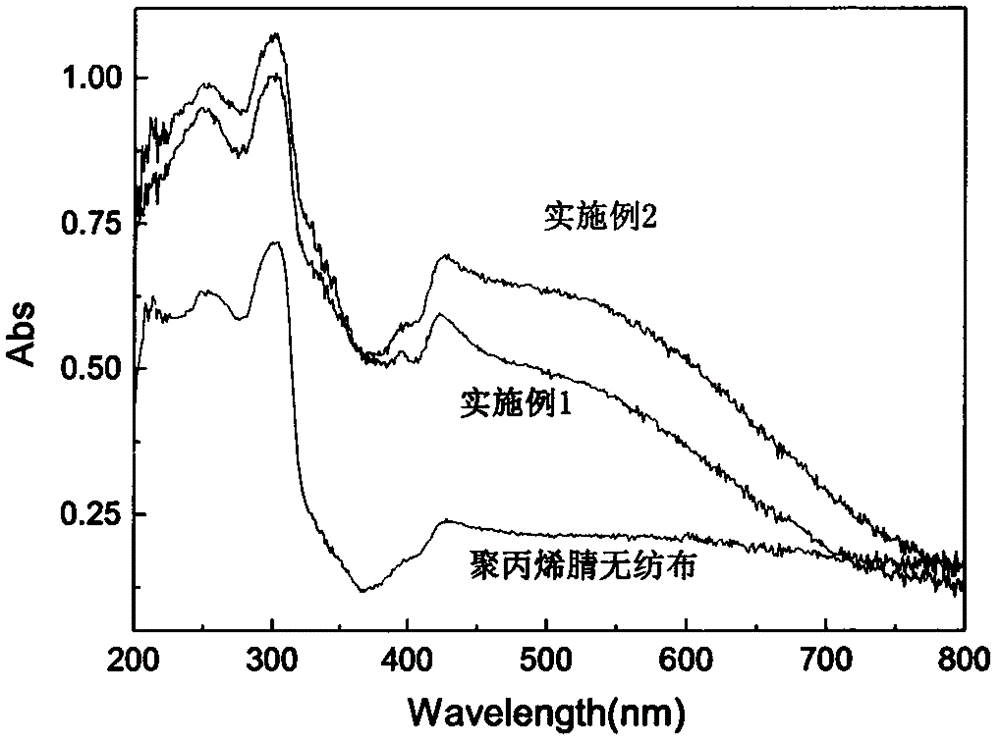
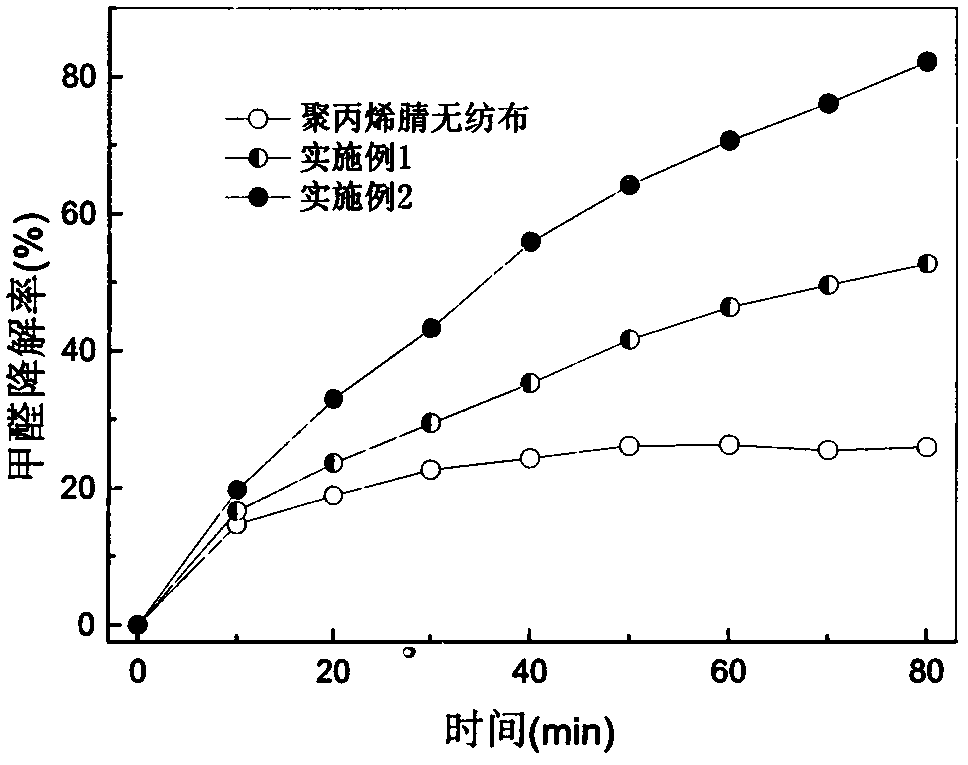
Fiber catalytic material for purifying formaldehyde gas and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104437657AGood flexibilityImprove practicalityOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsDispersed particle separationIonWoven fabric
The invention relates to a fiber catalytic material for purifying formaldehyde gas and a preparation method thereof. The fiber catalytic material is in a non-woven fabric shape and is formed after reaction of polyacrylonitrile non-woven fabric modified by hydroxylamine hydrochloride and iron ions, wherein the content of the iron ions is 15-270mg / g. The preparation method comprises the following steps: carrying out modification treatment on the polyacrylonitrile non-woven fabric by adopting the hydroxylamine hydrochloride, then carrying out reaction on the modified polyacrylonitrile non-woven fabric and aqueous solution of ferric chloride, and enabling the iron ions to be loaded on the polyacrylonitrile non-woven fabric by coordination action, thus obtaining the fiber catalytic material for purifying toxic and harmful gases such as the formaldehyde gas. The fiber catalytic material is applicable to a fiber-based filtering material of a core part in an air purifying system; and compared with the traditional nano TiO2 catalyst, the fiber catalytic material has the advantages of strong visible-light absorption, low preparation cost and easy recycling and the like, so that the fiber catalytic material has a potential application value.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
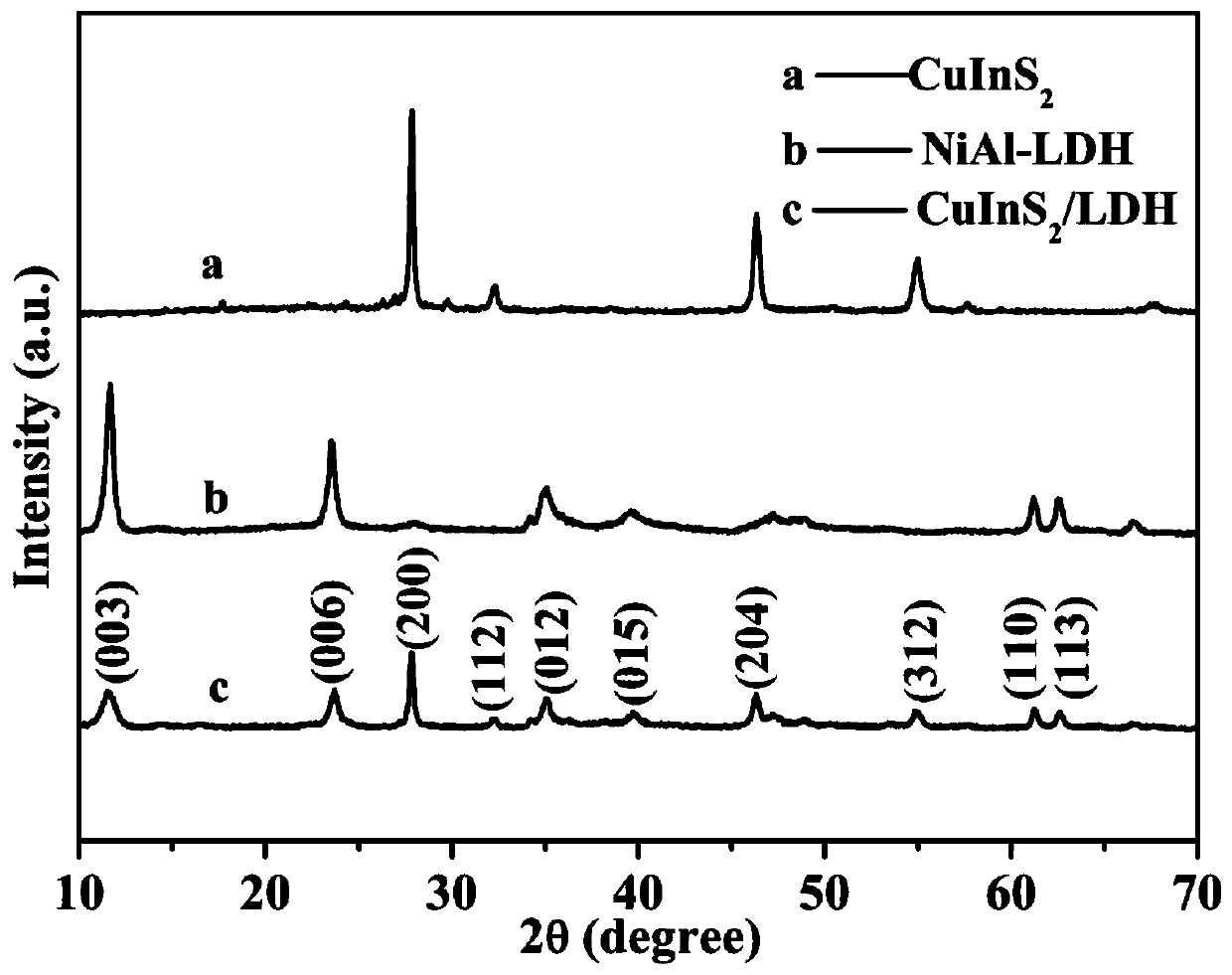
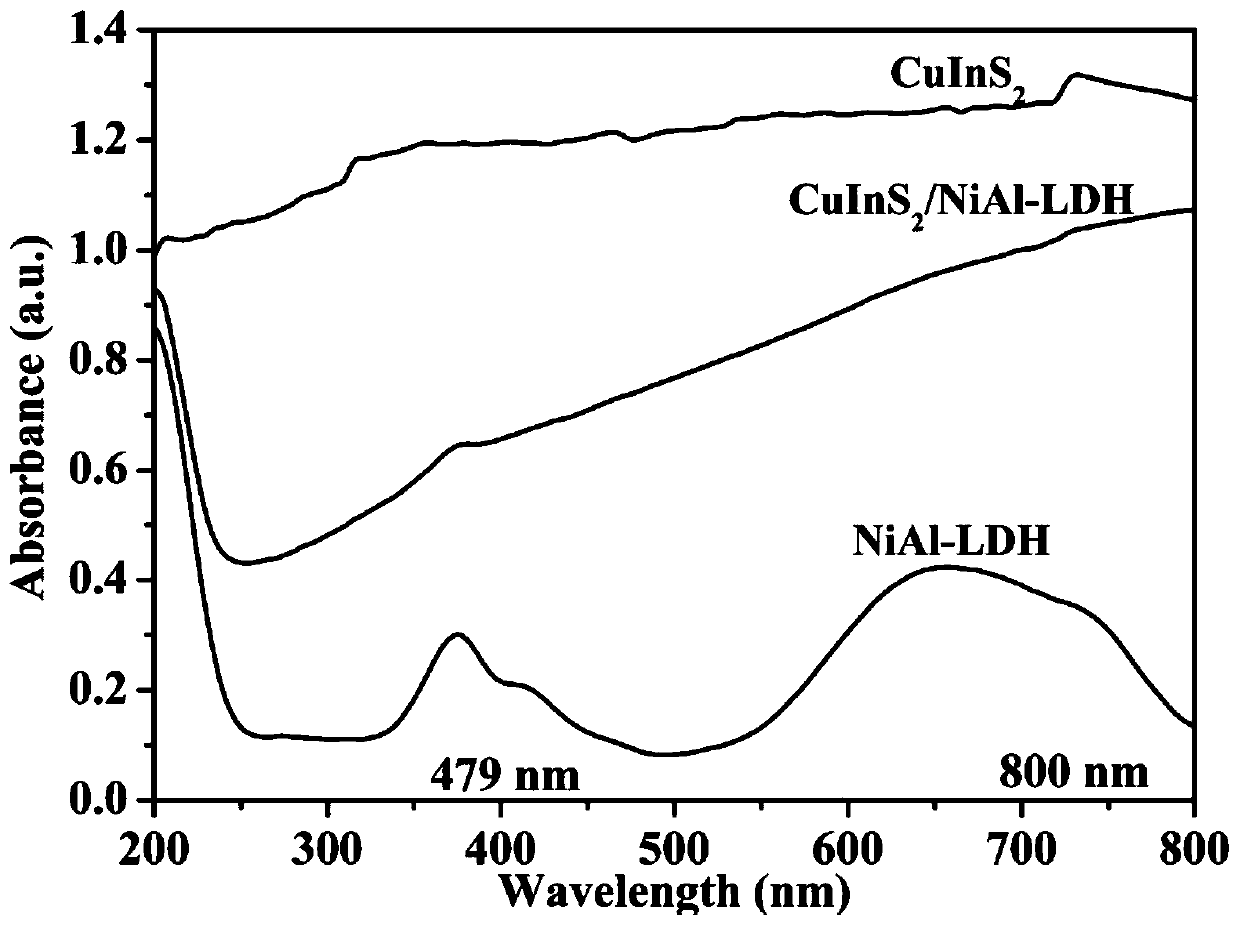
Preparation method and application of CuInS2 quantum dot/NiAl-LDH composite photocatalyst
ActiveCN110624566AImprove light responsivenessImprove separation efficiencyPhysical/chemical process catalystsWater/sewage treatment by irradiationHeterojunctionWastewater
The invention belongs to the technical field of preparation of environmental materials, and particularly relates to a preparation method and application of a CuInS2 quantum dot / NiAl-LDH composite photocatalyst. According to the invention, CuInS2 quantum dots and NiAl-LDH are loaded to form a CuInS2 quantum dot / NiAl-LDH heterojunction, so the recombination efficiency of electrons is greatly reduced, the photoresponse capability of the catalyst is greatly enhanced, and the CuInS2 quantum dot / NiAl-LDH composite photocatalyst has more excellent photocatalytic activity compared with a pure NiAl-LDHphotocatalys. The prepared CuInS2 quantum dot / NiAl-LDH photocatalyst can efficiently degrade 2,4-dichlorophenol wastewater, does not cause the wasting of resources and the formation of additional pollution, is simple and convenient to operate, and is an environment-friendly and efficient treatment technology.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
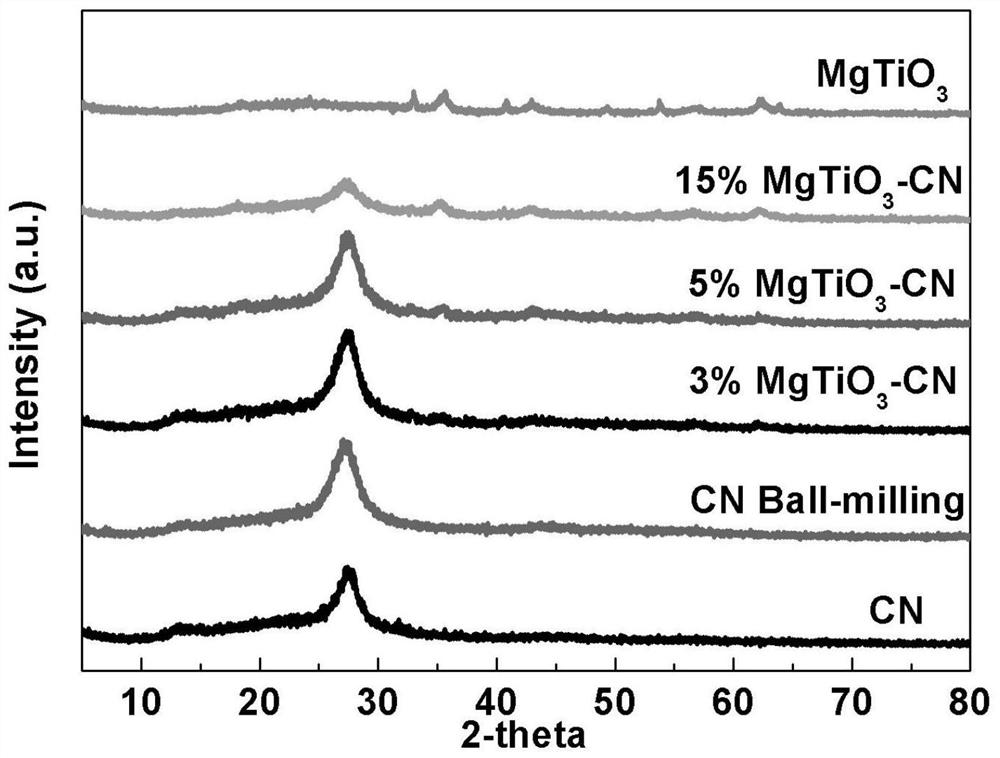
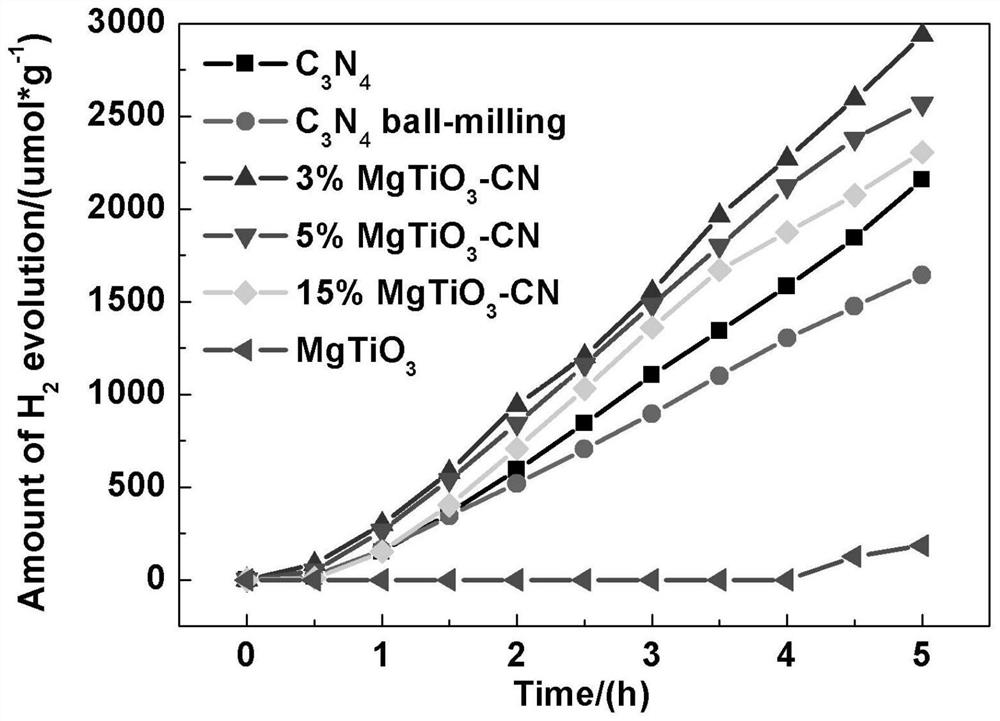
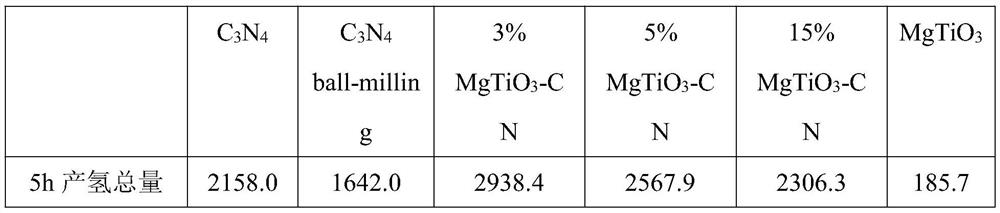
Preparation method and application of magnesium titanate/graphite-phase carbon nitride composite visible light photocatalyst
InactiveCN112295585AVisible light response range is wideHigh utilization rate of visible lightPhysical/chemical process catalystsHydrogen productionSpectral responsePerovskite (structure)
The invention discloses a preparation method and application of a magnesium titanate / graphite-phase carbon nitride composite visible light photocatalyst. The invention aims to solve the technical problem of non-ideal photocatalytic activity caused by relatively high recombination rate of existing g-C3N4 photo-induced electron holes. The preparation method comprises the following steps: synthesizing g-C3N4 with a relatively high specific surface area by adopting a pyrolysis method, then preparing magnesium titanate with a perovskite structure by adopting a hydrothermal method, and finally preparing the magnesium titanate / g-C3N4 composite visible light photocatalyst by adopting a ball milling method. According to the photocatalytic material disclosed by the invention, semiconductors with different band gap energy levels are compounded to form a heterostructure, so that the photocatalytic material has an excellent and adjustable photo-induced electron hole separation rate and a relativelywide spectral response range under visible light, and can be applied to visible light catalytic hydrogen production in the field of energy sources.
Owner:NANCHANG HANGKONG UNIVERSITY
Nano TiO2-diatomite composite photocatalyst and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105727921APicklingSave the craftPhysical/chemical process catalystsTitanium tetrachlorideAmmonium sulfate
The invention discloses a nano TiO2-diatomite composite photocatalyst and a preparation method thereof. The nano TiO2-diatomite composite photocatalyst is prepared from the following raw materials: raw diatomite, titanium tetrachloride, ammonium sulfate and iron salt, wherein the mass ratio of the raw materials is that the ratio of the raw diatomite to the titanium tetrachloride is 100 to (80-200), and the ratio of the titanium tetrachloride to the ammonium sulfate to the iron salt is 100 to (17-66) to (0-0.7). With the adoption of the composite photocatalyst, the problems in the prior art that the visible light utilization rate of the composite photocatalyst is low and the degradation capability on organic pollutants is low are solved, the visible light utilization rate of the composite photocatalyst is improved, and the degradation capability on the organic pollutants is improved.
Owner:CHINA BUILDING MATERIALS ACAD
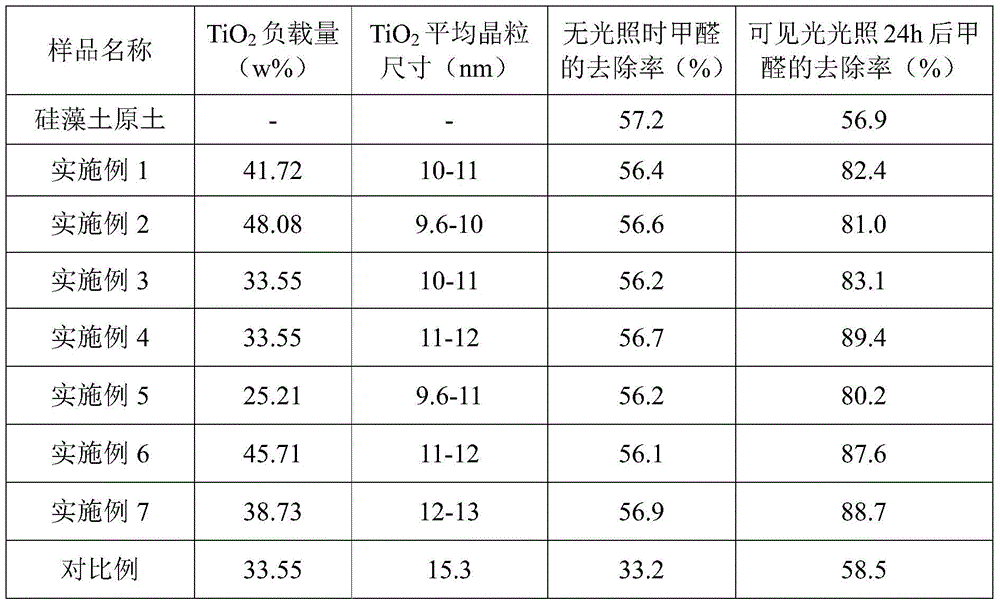
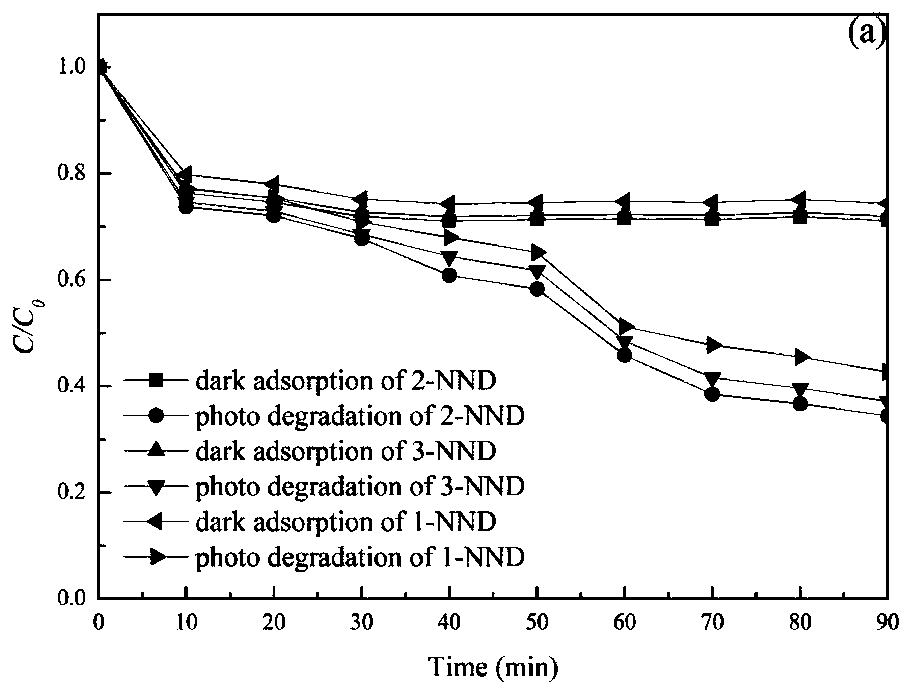
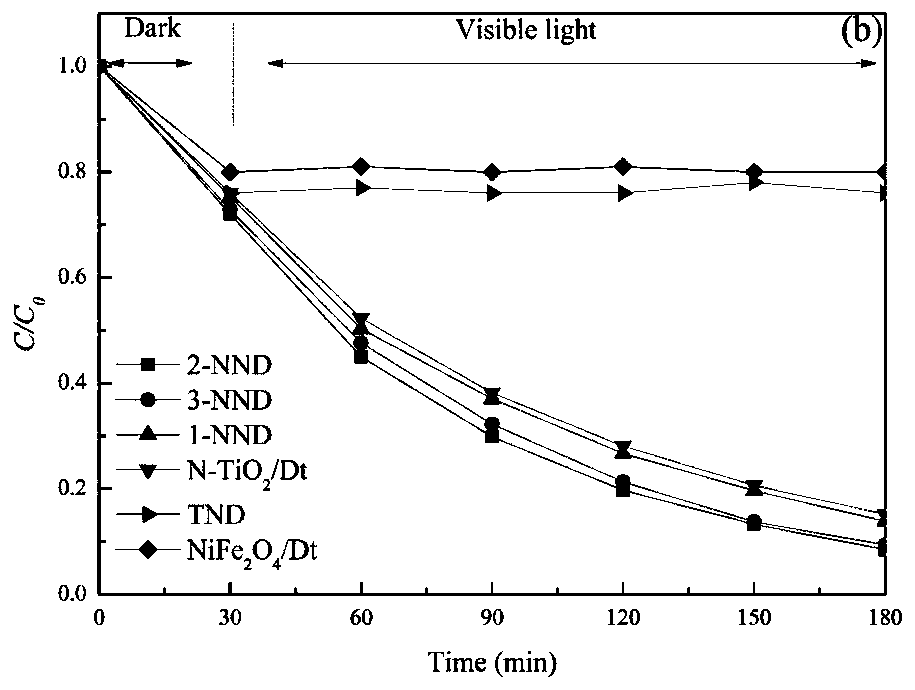
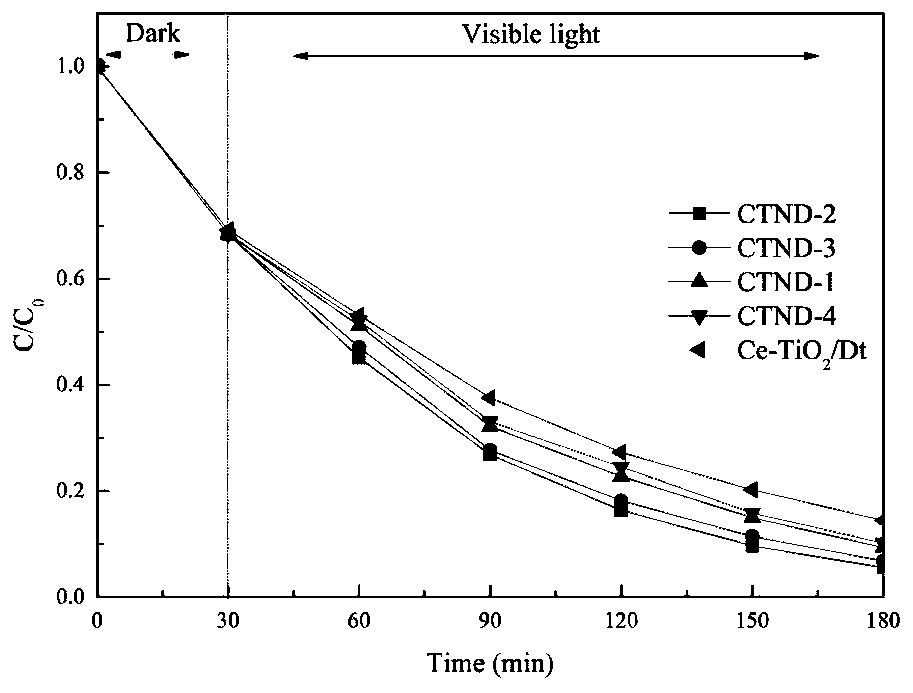
Magnetic Ce/N co-doped TiO2/diatomite composite material photocatalyst and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN109939720AHigh utilization rate of visible lightImprove photocatalytic performancePhysical/chemical process catalystsContaminated soil reclamationRare-earth elementElectron hole
The invention discloses a magnetic Ce / N co-doped TiO2 / diatomite composite material photocatalyst, which is based on a preparation process of N-doped composite powder, wherein cerium nitrate hexahydrate is selected as a Ce source, diatomite refined soil is adopted as a carrier, and NiFe2O4 nanoparticles with superparamagnetism are loaded on the surface of the catalyst by a sol-gel method. The doping modification of the rare earth element Ce is introduced into the TiO2, so that the visible light utilization rate of the TiO2 / diatomite composite powder and the separation efficiency of photo-generated electron hole pairs are improved, and the composite material shows excellent photocatalytic performance; due to the introduction of the nickel ferrite, the catalyst has magnetism, so that the recovery capacity of the catalyst is improved, and the catalyst has a wide prospect in the application of treating hard-degradation organic pollutants contained in soil in a high-pollution area.
Owner:LIAONING UNIVERSITY
Photocatalytic separation film for water treatment and preparation method
ActiveCN109126867AHigh utilization rate of visible lightImprove photocatalytic efficiencySemi-permeable membranesWater/sewage treatment by irradiationCvd grapheneChemistry
The invention belongs to the technical field of water treatment, and provides a photocatalytic separation film for water treatment and a preparation method. The method includes the steps that nano TiO2 and nano ZnO are generated in situ in the synthesis process of tertiary butyl thio[4]calixarene, then the nano TiO2 and the nano ZnO are compounded with graphene, a nano TiO2-nano ZnO-calixarene -graphene composite photocatalyst is prepared and further added into a polyether sulfone spinning solution, and the photocatalytic hollow fiber separation film is prepared through spinning. Compared witha traditional method, by means of the prepared photocatalytic separation film, the problem of film contamination in the film separation technology and the problem about nano powder recovery in the photocatalysis technology are solved at the same time, the utilization rate of visible light is high, the photocatalysis efficiency is high, and a catalyst can be evenly dispersed.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ZHIYUAN ENVIRONMENTAL TECH CO LTD
Preparation method and application of tungsten trioxide@molybdenum disulfide hollow tube composite catalyst
ActiveCN109201084AUnique shapeIncrease transfer ratePhysical/chemical process catalystsWater/sewage treatment by irradiationSodium molybdateOrganic dye
The invention provides a preparation method and application of a tungsten trioxide@molybdenum disulfide hollow tube composite catalyst, and relates to the preparation method and the application of a composite photocatalyst. The preparation method and the application aim at solving the problem that when the existing photocatalyst is applied to sewage purification, the visible light photocatalysis efficiency is low. The method comprises the steps that 1, rodlike WO3 is prepared; 2, after the rodlike WO3 is dispersed, sodium molybdate and thiourea are added; continuous stirring is performed; then, the mixture is transferred into a polytetrafluoroethylene inner liner; under the condition that the temperature is 160 to 200 DEG C, maintenance is performed for 2 to 24h; after the reaction is completed, natural cooling is performed to room temperature; washing is performed; drying is performed in a drying box; the tungsten trioxide@molybdenum disulfide hollow tube composite catalyst is obtained. The tungsten trioxide@molybdenum disulfide hollow tube composite catalyst is used for deeply purifying organic dye water bodies.
Owner:NORTHEAST INST OF GEOGRAPHY & AGRIECOLOGY C A S
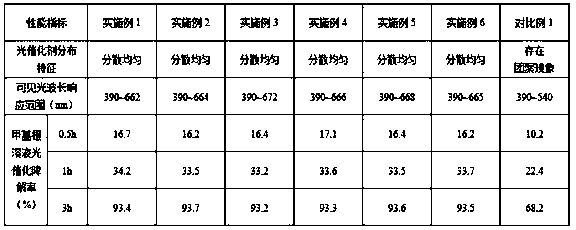
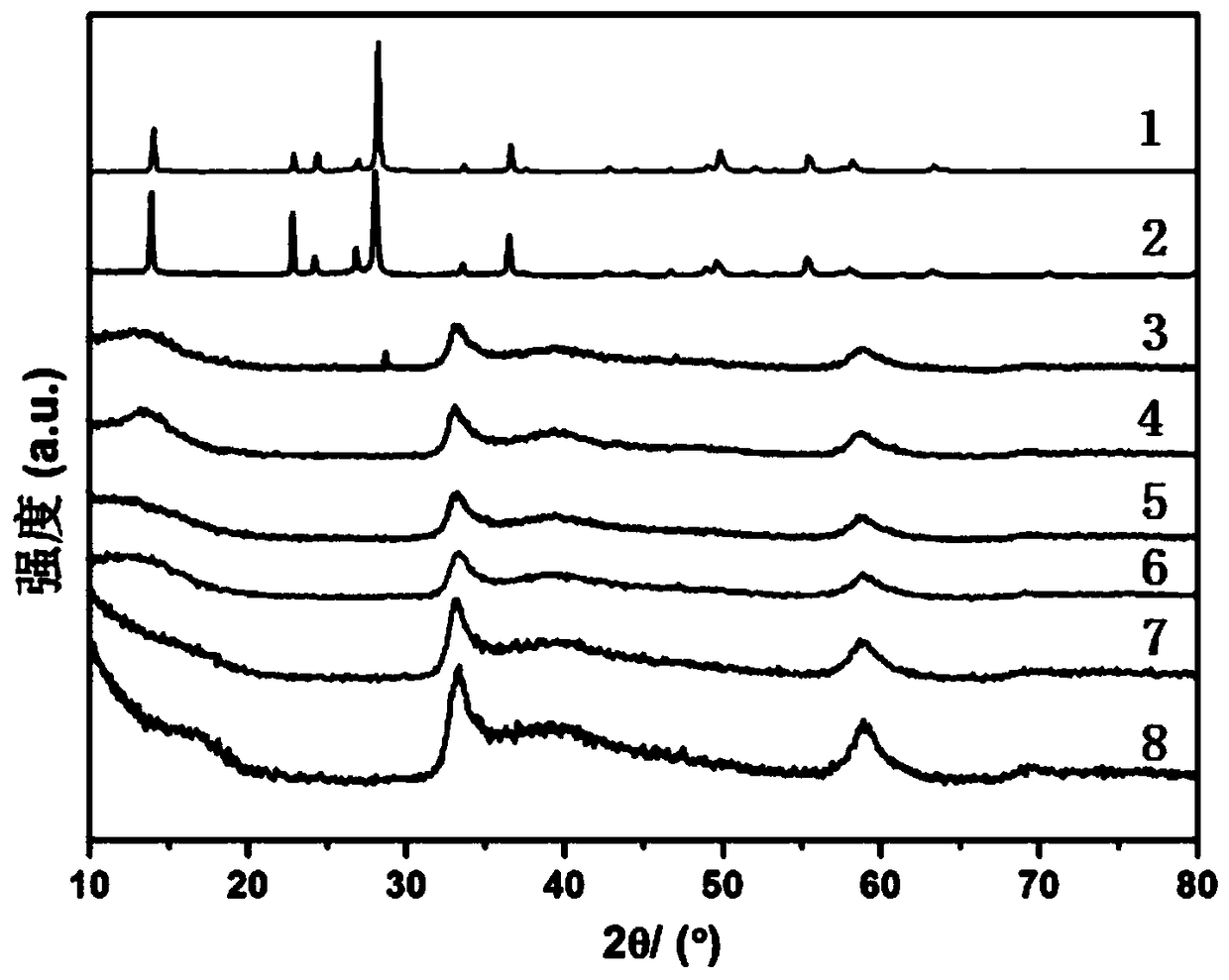
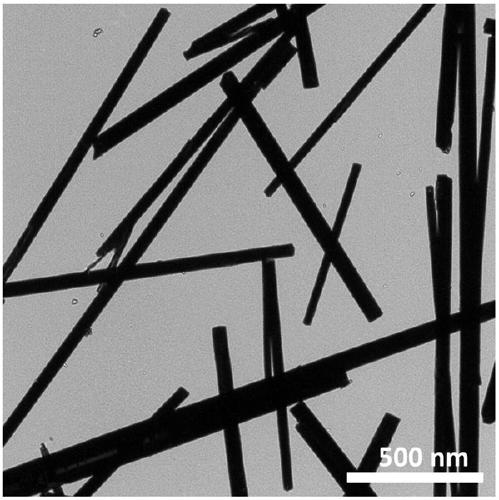
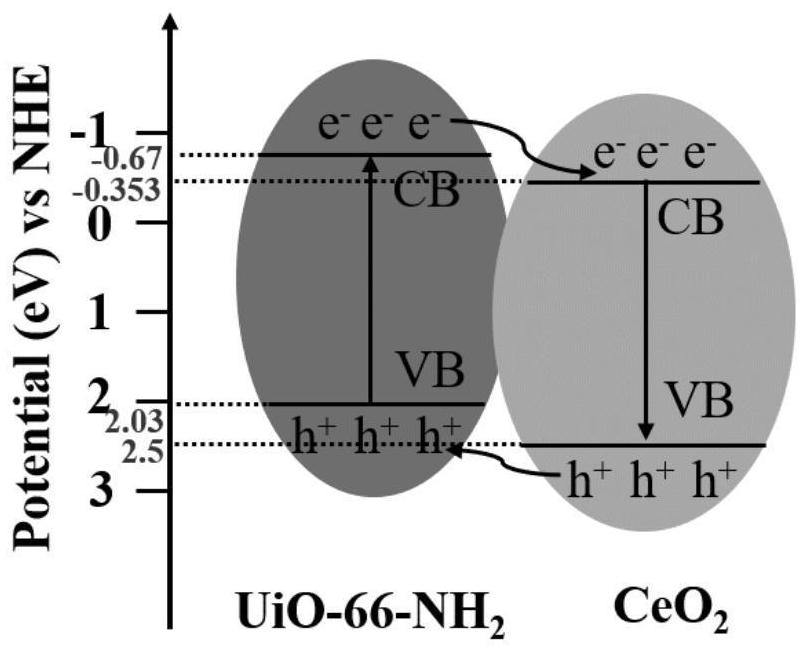
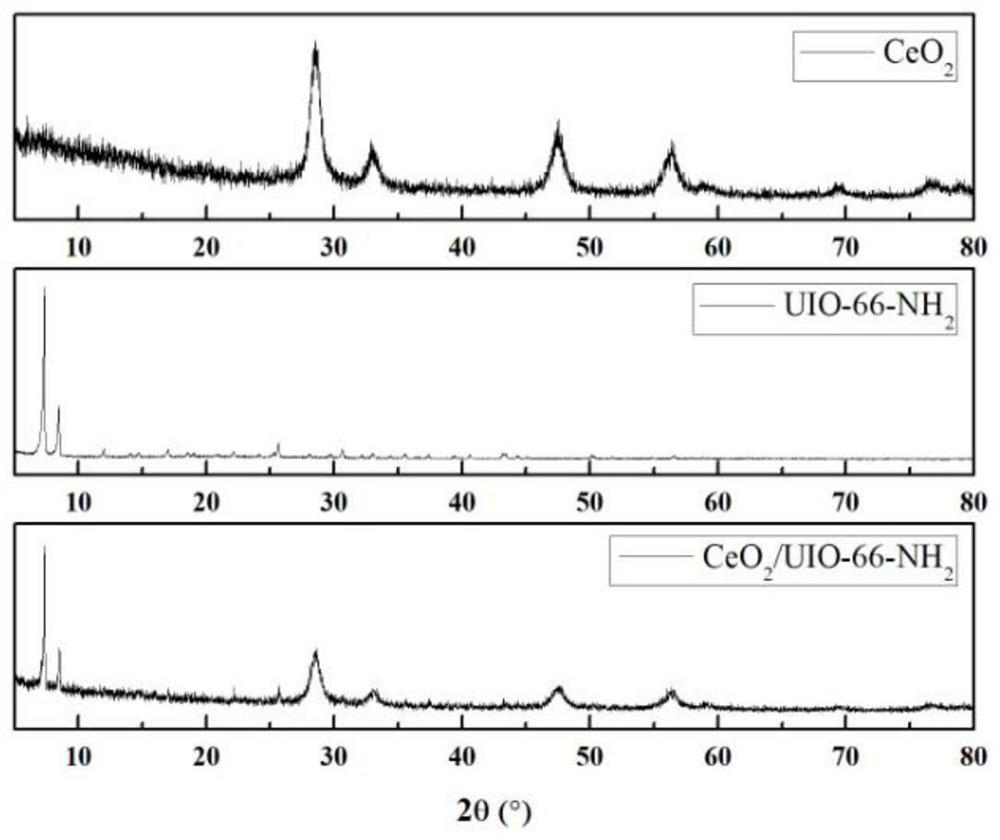
Flaky CeO2/UIO-66-NH2 composite photocatalytic material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN113318792APromote migrationExtend your lifeWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater treatment compoundsHeterojunctionTetrachloride
The invention provides a flaky CeO2 / UIO-66-NH2 composite photocatalytic material and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of photocatalyst preparation. The preparation method of the flaky CeO2 / UIO-66-NH2 composite photocatalytic material comprises the following steps: S1, preparing a CeO2 nanosheet precursor through a water bath synthesis method, and then calcining the CeO2 nanosheet precursor to obtain a CeO2 nanosheet; s2, ultrasonically dispersing zirconium tetrachloride and 2-amino-1,4 phthalic acid in a solvent, then adding the CeO2 nanosheet into the solvent, uniformly mixing the solution, preserving heat for 12-48 hours at the temperature of 100-180 DEG C, and then separating and drying the solution to obtain the flaky CeO2 / UIO-66-NH2 composite photocatalytic material. The flaky CeO2 and the UIO-66-NH2 are utilized to form a II-type heterojunction structure through surface-surface compounding, so that the separation efficiency of photo-induced electrons can be improved, and the photocatalytic activity of the composite material is favorably improved; meanwhile, the specific surface area of the composite material is increased, more active sites are favorably provided, and the photocatalytic performance is favorably improved.
Owner:哈尔滨邦定科技有限责任公司
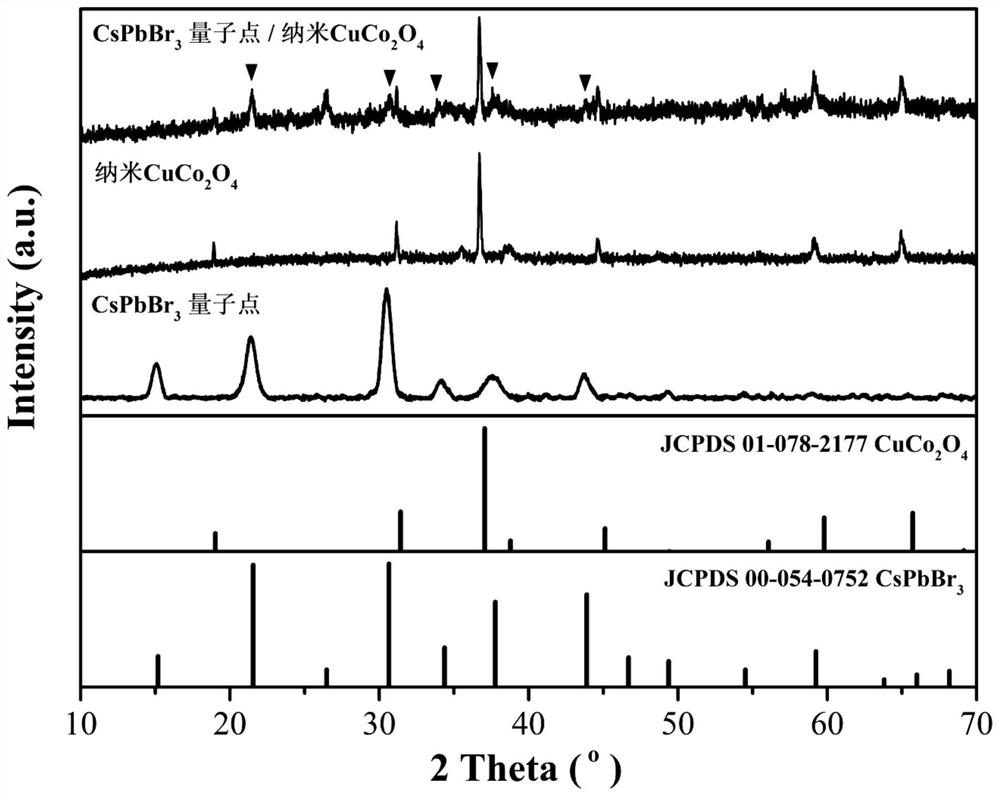
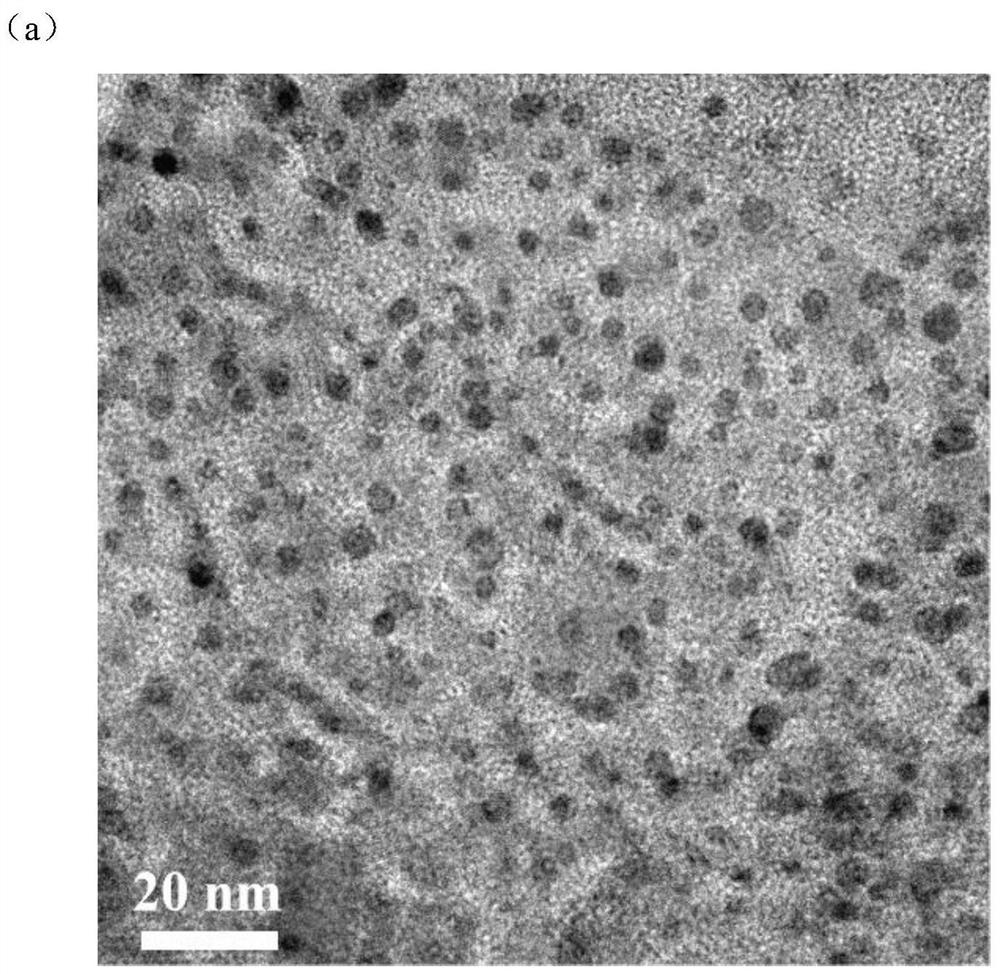
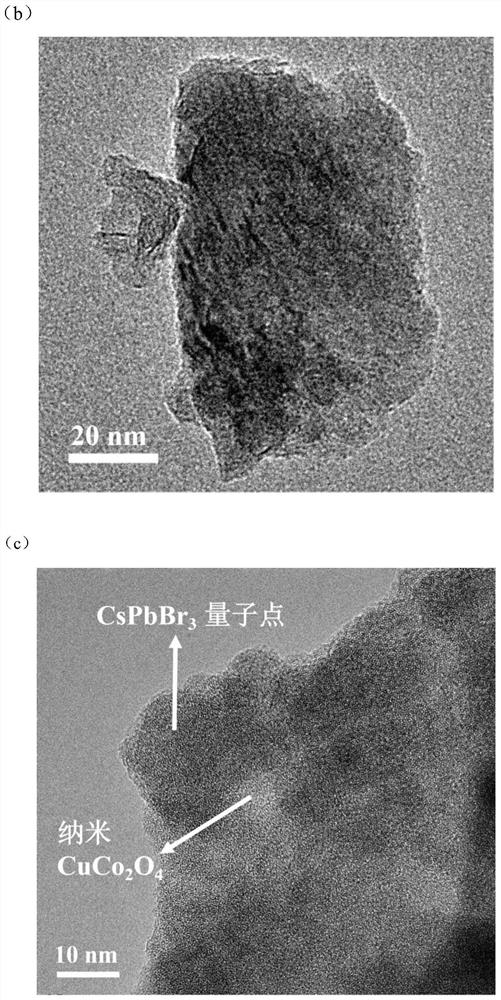
CsPbBr3 quantum dot/nano CuCo2O4 composite photocatalyst for CO2 reduction and preparation method of CsPbBr3 quantum dot/nano CuCo2O4 composite photocatalyst
ActiveCN113145141AGood monodispersityHigh utilization rate of visible lightCatalyst activation/preparationCarbon monoxideChemical physicsChemical reaction
The invention relates to a CsPbBr3 quantum dot / nano CuCo2O4 composite photocatalyst for CO2 reduction, the CsPbBr3 quantum dot / nano CuCo2O4 composite photocatalyst comprises CsPbBr3 quantum dots and nano CuCo2O4, and the ratio of the CsPbBr3 quantum dots to the nano CuCo2O4 is (0.2-2) mmol: (4-40) mg; and the invention further relates to a preparation method of the CsPbBr3 quantum dot / nano CuCo2O4 composite photocatalyst for CO2 reduction. The CsPbBr3 quantum dot / nano CuCo2O4 composite photocatalyst has the advantages of being high in visible light utilization rate and excellent in photocatalytic performance, CsPbBr3 quantum dots and nano CuCo2O4 are compounded through continuous ultrasonic treatment, sound waves of high-frequency vibration are transmitted to the surfaces of the CsPbBr3 quantum dots and the surfaces of the nano CuCo2O4, atoms on the surface layers of the CsPbBr3 quantum dots and the surfaces of the nano CuCo2O4 rub against one another, the key point of the method lies in the combination of atomic layers on the surfaces of the two materials, so that the CsPbBr3 quantum dots embedded into the CuCo2O4 nanosheets are not easy to fall off; the method does not involve chemical reaction, so that other impurities are not introduced; and the method is simple in process, good in reproducibility and low in cost, and meets environmental requirements.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Bismuth-based modified photocatalyst and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN105056978AEasy to prepareHigh utilization rate of visible lightPhysical/chemical process catalystsWater/sewage treatment by irradiationBismuthPollution
The invention discloses a bismuth-based modified photocatalyst and a preparation method and an application of the bismuth-based modified photocatalyst. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) dissolving alpha-Bi2O3 in water, carrying out ultrasonic dispersion to form suspension liquid, adding solid KI for reaction, and carrying out magnetic stirring to obtain reaction liquid; (2) adding silver nitrate solid to the reaction liquid obtained in step (1), and carrying out magnetic stirring for reaction; after the reaction is completed, adding graphene oxide, and sequentially carrying out ultrasonic dispersion and stirring; and (3) adding N2H4.H2O to the solution obtained after stirring in step (2), carrying out water-bath reaction to obtain turbid liquid, carrying out washing and centrifugation on the obtained turbid liquid, taking precipitate, and grinding the precipitate after drying to obtain the bismuth-based modified photocatalyst. The prepared photocatalyst is used in the treatment of chromium-containing wastewater and generates reaction under the irradiation of visible light without adjusting the pH value. The preparation method of the photocatalyst disclosed by the invention is simple, the photo-induced electron and hole separation effect is good, the photocurrent is high, and the effect of treatment for the chromium-containing wastewater is good, secondary pollution is avoided.
Owner:ZHEJIANG GONGSHANG UNIVERSITY
Composite nanometer phosphotungstic acid-titanium dioxide photocatalysis material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101518731BLower redox potentialHigh utilization rate of visible lightOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsDeodrantsHYDROSOLPropanediol
The invention discloses a composite nanometer phosphotungstic acid-titanium dioxide photocatalysis material and a preparation method thereof. The method includes the steps: firstly, titanium dioxide cThe invention discloses a composite nanometer phosphotungstic acid-titanium dioxide photocatalysis material and a preparation method thereof. The method includes the steps: firstly, titanium dioxide cstill be maintained.an still be maintained.ght; and further more, after the subsequent step of heating photocatalysis materials is accomplished, the keggin structure of the phosphotungstic acid is not affected, and high catalytic activity can ght; and further more, after the subsequent step of heating photocatalysis materials is accomplished, the keggin structure of the phosphotungstic acid is not affected, and high catalytic activity c liollosol, phosphotungstic acid and propylene glycol methyl ether, of which the mass ratio is 20 to 3 to 50, are uniformly mixed to form composite collosol; secondly, the composite collosol is heated foollosol, phosphotungstic acid and propylene glycol methyl ether, of which the mass ratio is 20 to 3 to 50, are uniformly mixed to form composite collosol; secondly, the composite collosol is heated for 30 minutes at the temperature of 300 DEG C to form dried gel; and finally, the dried gel is mechanically processed for two hours by ball milling so as to obtain phosphotungstic acid-titanium dioxider 30 minutes at the temperature of 300 DEG C to form dried gel; and finally, the dried gel is mechanically processed for two hours by ball milling so as to obtain phosphotungstic acid-titanium dioxidephotorecombination photocatalyst materials. Compared with the prior art, the phosphotungstic acids of the invention are combined into a stable netty structure in the form of W-O-P molecular linkages, photorecombination photocatalyst materials. Compared with the prior art, the phosphotungstic acids of the invention are combined into a stable netty structure in the form of W-O-P molecular linkages, thereby reducing the oxidation-reduction potential, enabling a titanium dioxide composite membrane photoabsorption wavelength to generate redshift, and improving the utility ratio of titanium visiblethereby reducing the oxidation-reduction potential, enabling a titanium dioxide composite membrane photoabsorption wavelength to generate redshift, and improving the utility ratio of titanium visibleli
Owner:UNIVERSTAR SCI & TECH SHENZHEN
Degradable synthetic fiber composition, preparation method thereof and product
InactiveCN106032422AImprove light utilizationHigh utilization rate of visible lightMonocomponent polystyrene artificial filamentArtifical filament manufacturePolyesterPolymer science
The invention relates to a degradable synthetic fiber composition, a preparation method thereof and a prepared biodegradable synthetic fiber product. The biodegradable synthetic fiber composition comprises a polymer and two or more transition metal salts dispersed in the polymer; and at least one of the transition metal salts is a polyvalent metal salt. The invention can degrade polyester, polyamide and styrene polymers, and selects more than two transition metal additives to produce synergistic effect, so as to directly improve the utilization rate of ultraviolet and visible light; and oxidation-biodegradation is applied to artificial fiber synthesis for the first time, and the existing equipment can be directly used for commercial production. The formula and method of the invention in particular can be directly applied to the non-woven fabric weaving technology to further reduce environmental pollution caused by wastes.
Owner:THE HONG KONG RES INST OF TEXTILES & APPAREL
Two-dimensional receptor molecule/hierarchical pore TiO2 composite photocatalyst, preparation method and photocatalytic application thereof
ActiveCN112354559AImprove photocatalytic hydrogen production activityEasy to separateOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCatalyst activation/preparationMicro nanoPtru catalyst
The invention discloses a photocatalyst obtained by compounding two-dimensional receptor molecules with porous TiO2, a preparation method and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field ofphotocatalysis. The two-dimensional receptor molecule composite porous TiO2 photocatalyst is formed by loading two-dimensional receptor molecules on the surface of porous TiO2. The preparation methodcomprises the following steps: taking degraded chitosan as a template agent, performing hydrothermal method and calcination to obtain porous TiO2 with micro-nano pore channels, dispersing the porousTiO2 into a solvent, dropwise adding a two-dimensional receptor molecule solution with a certain concentration, stirring overnight at 120 DEG C, and performing centrifugal washing and drying to obainthe product. According to the invention, the two-dimensional acceptor molecule / porous TiO2 composite photocatalyst increases the response range of the material to sunlight by utilizing the firm bonding effect between rich active sites on the surface of porous TiO2 and two-dimensional acceptor molecules with larger surface area, and the introduction of the two-dimensional acceptor molecules greatlypromotes the separation of photo-induced electron holes and the transmission of photoelectrons, so that the activity of hydrogen production by photocatalytic decomposition of water and the stabilityof the catalyst are improved, and the photocatalyst has a good application prospect in the field of photocatalysis.
Owner:HAINAN UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com