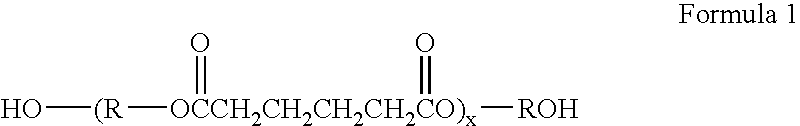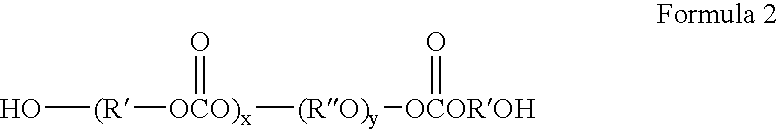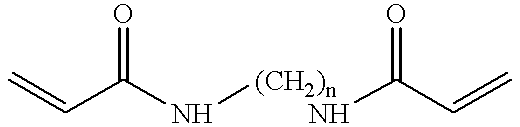Patents
Literature
4211results about "Burettes/pipettes" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
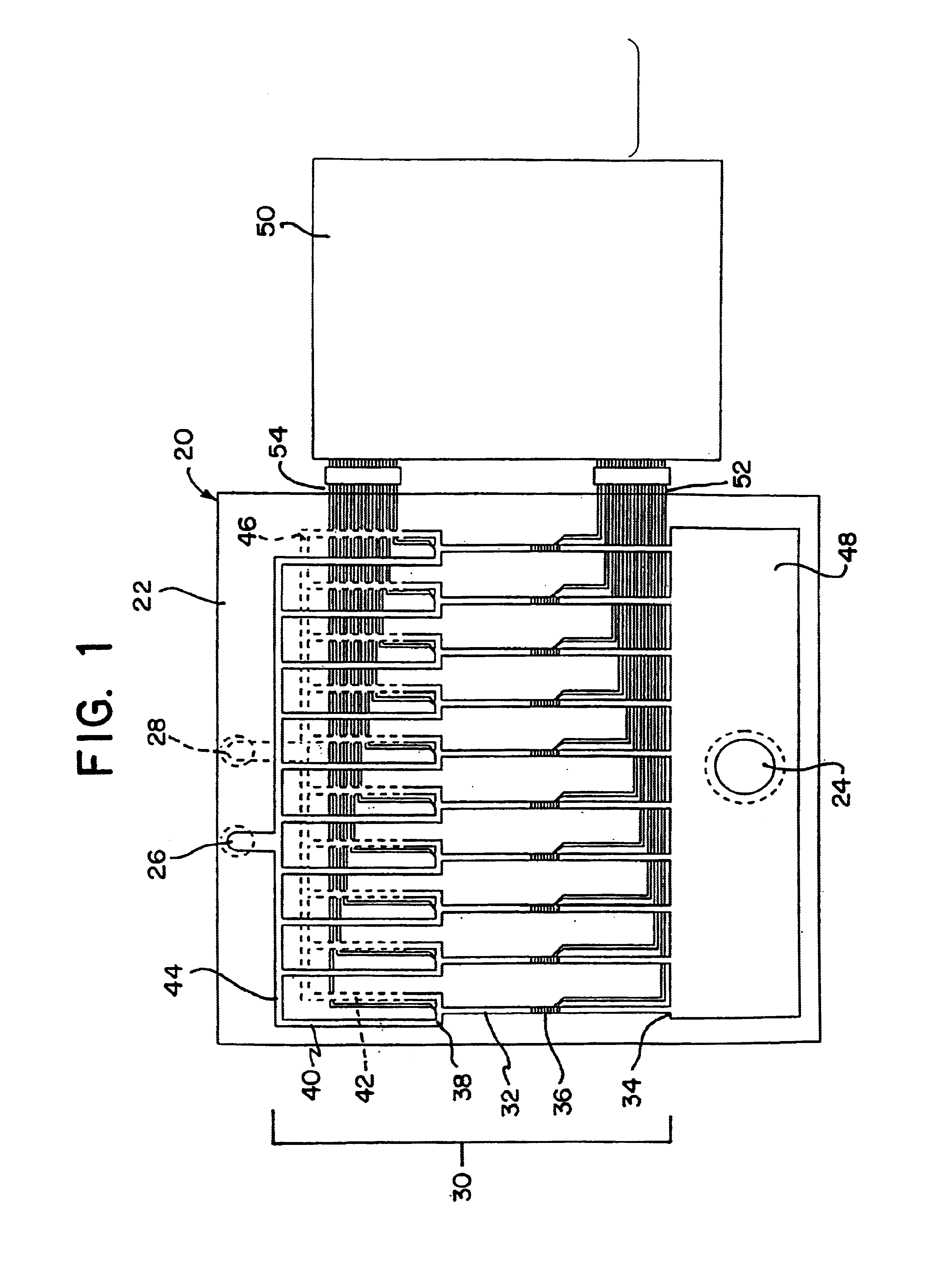
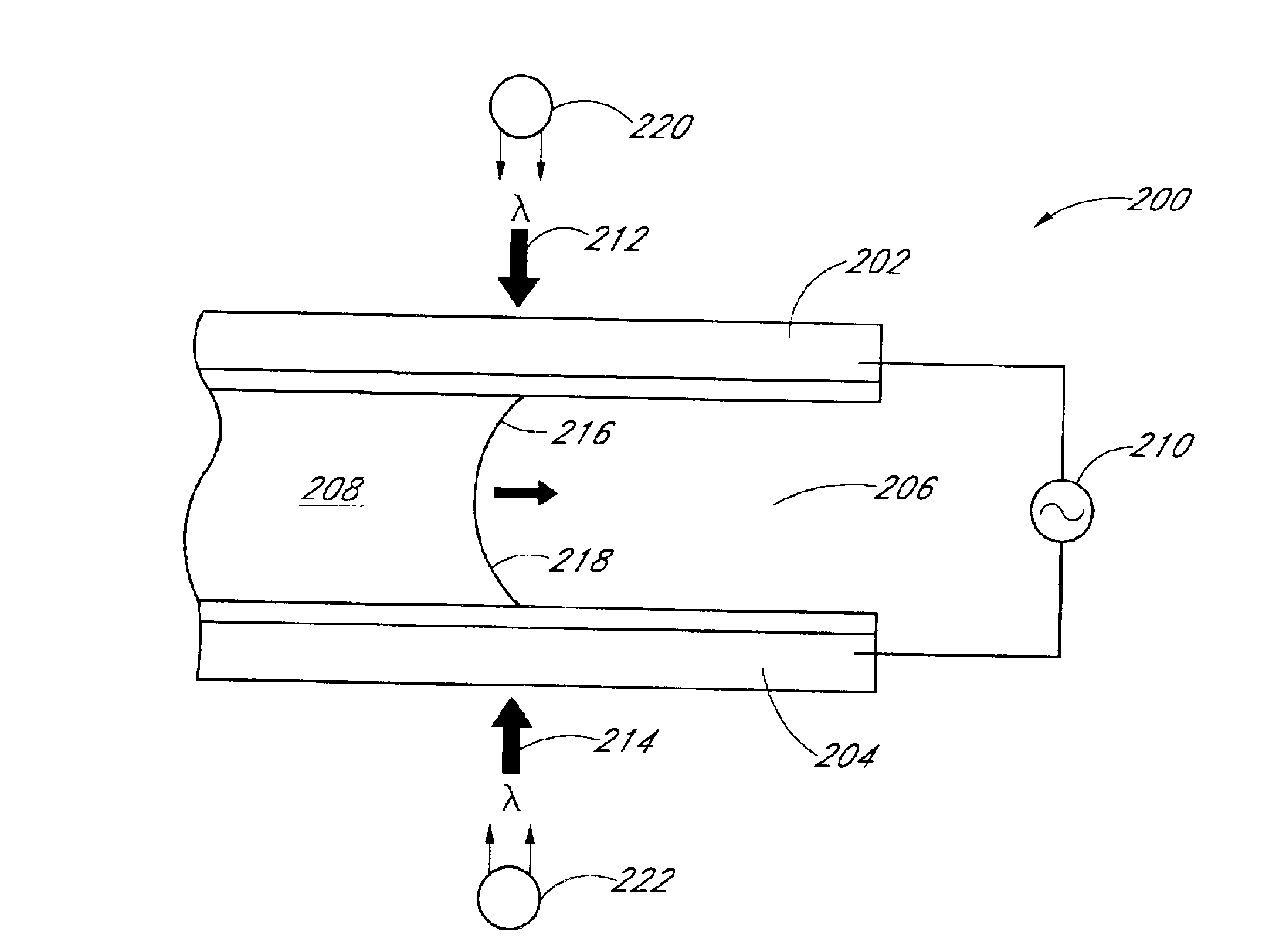
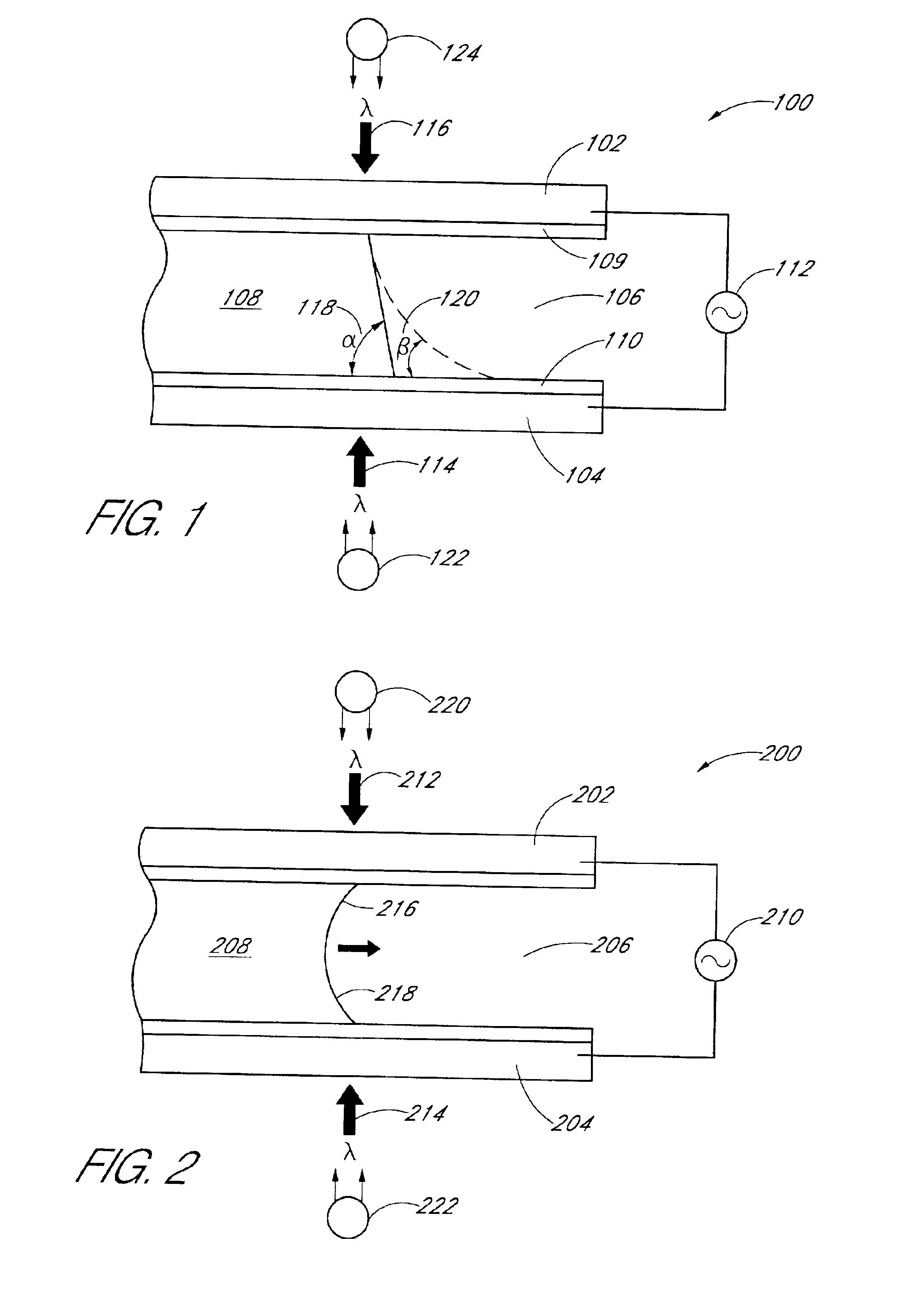
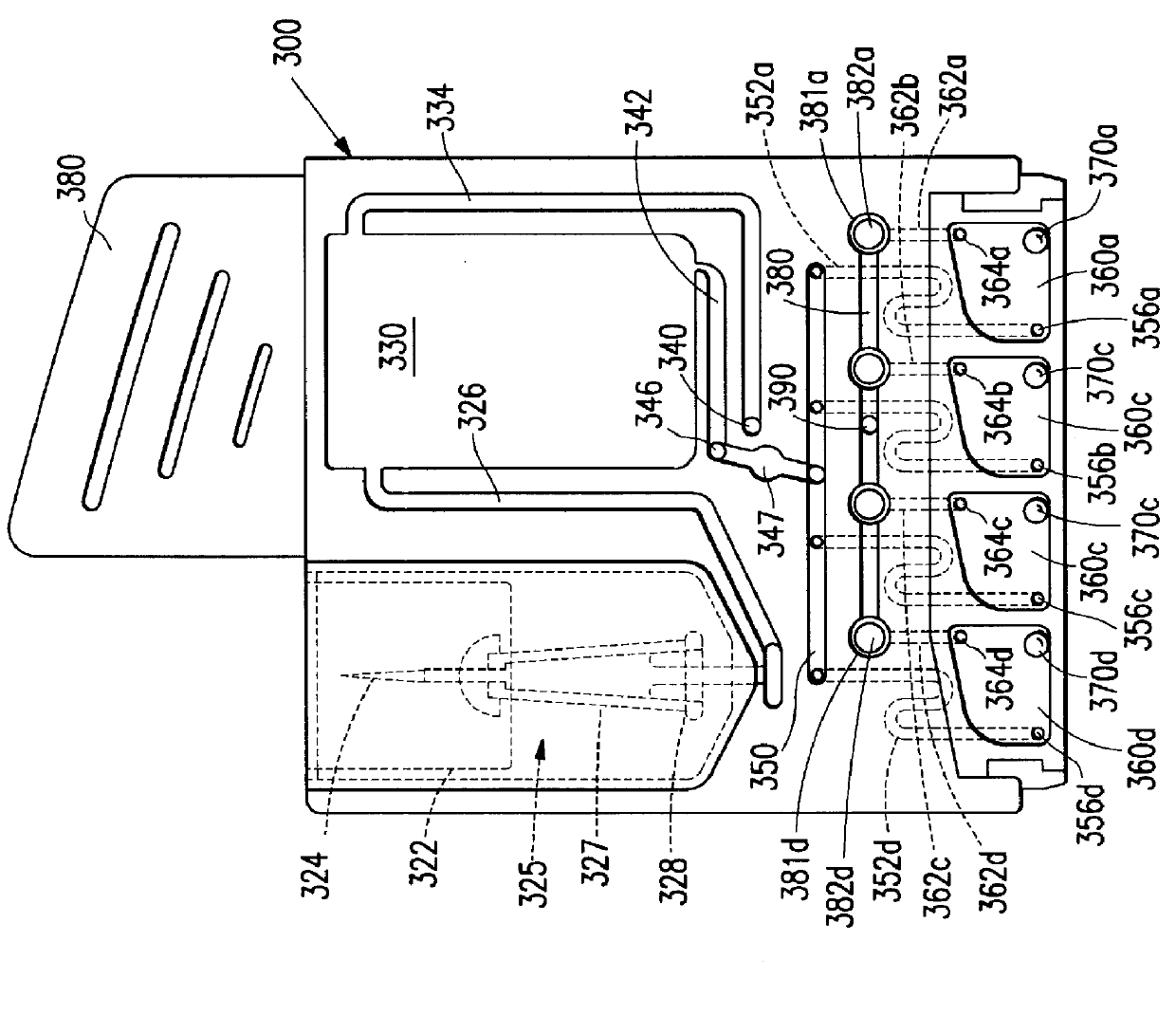
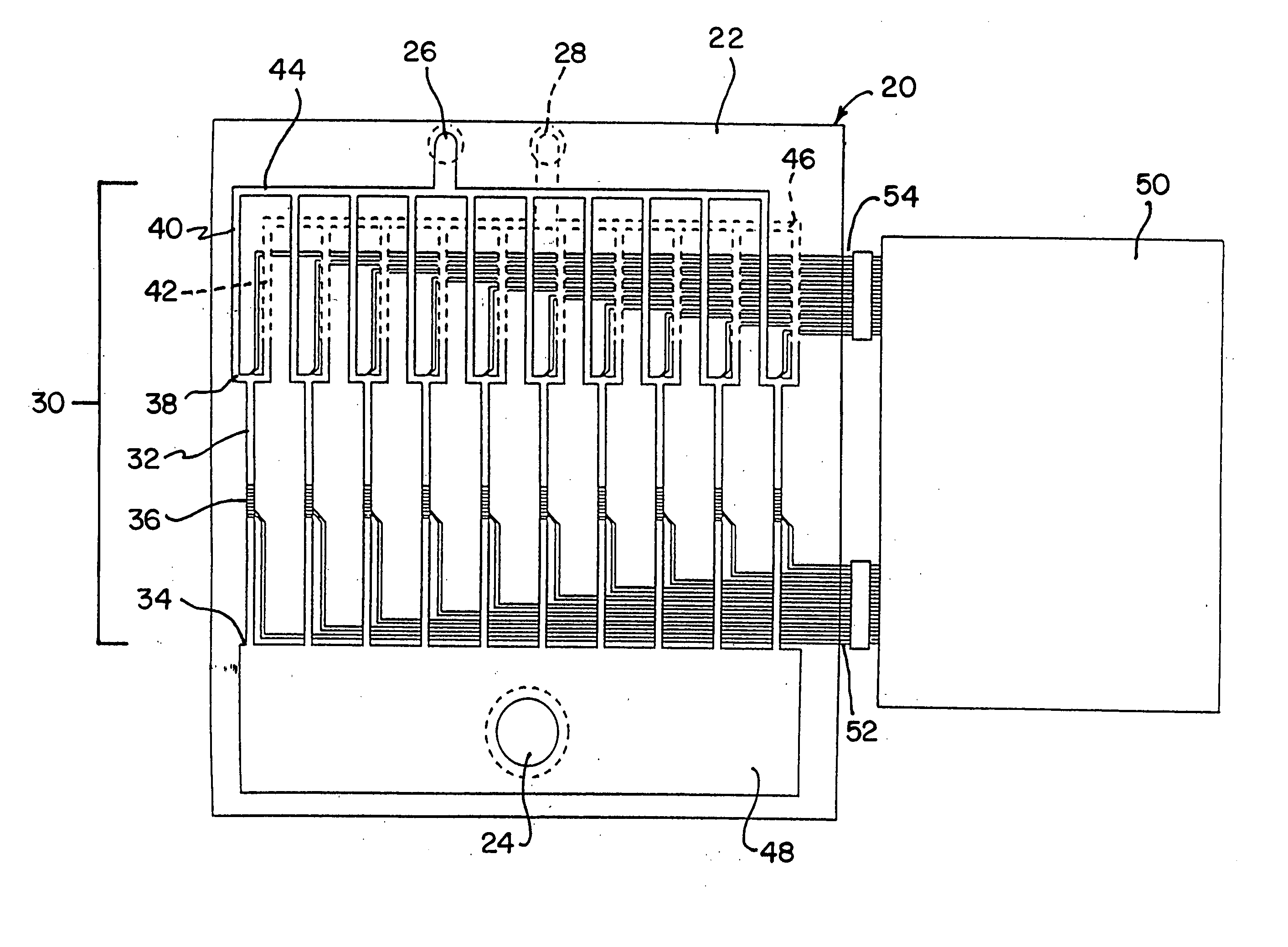
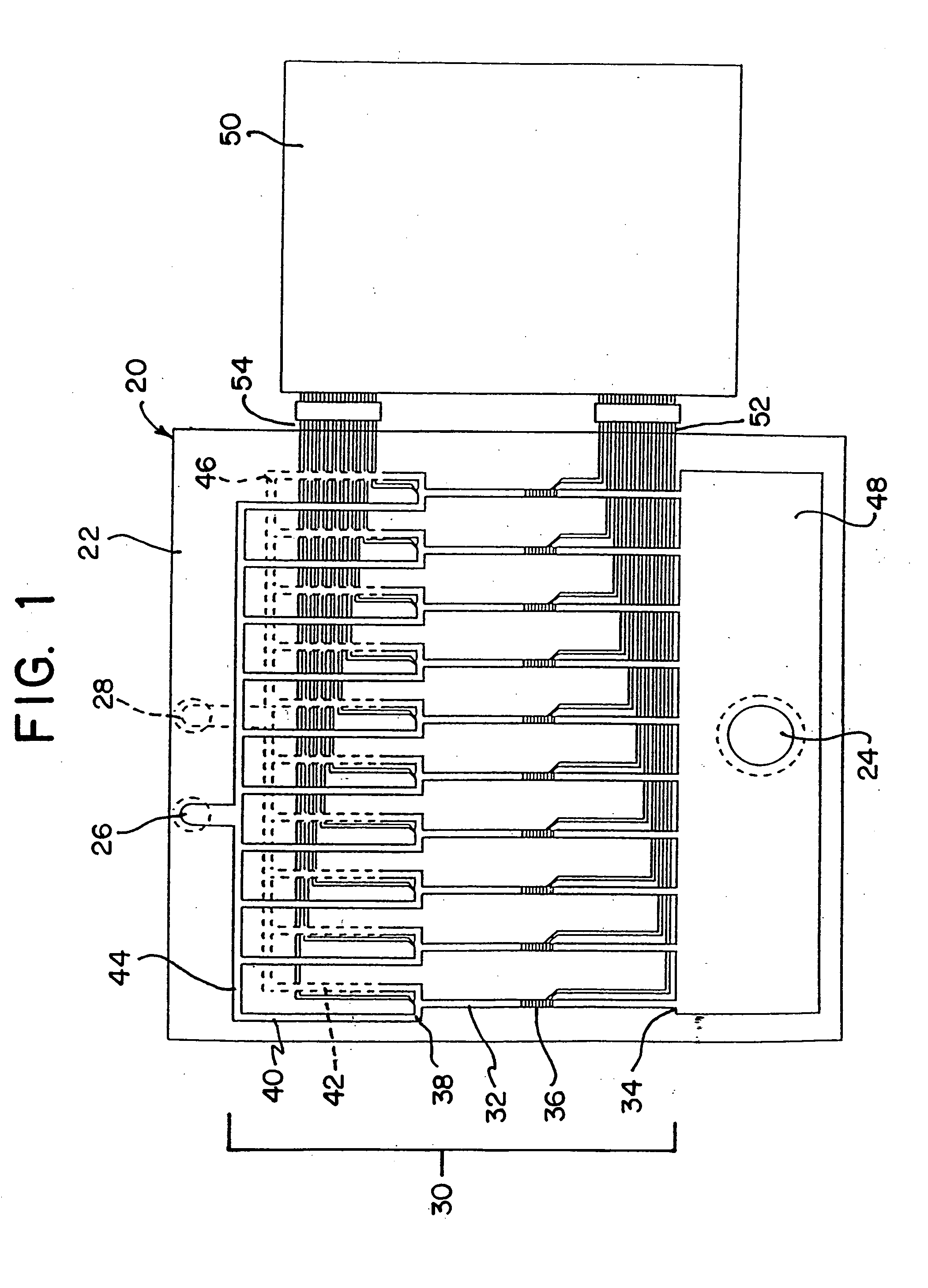
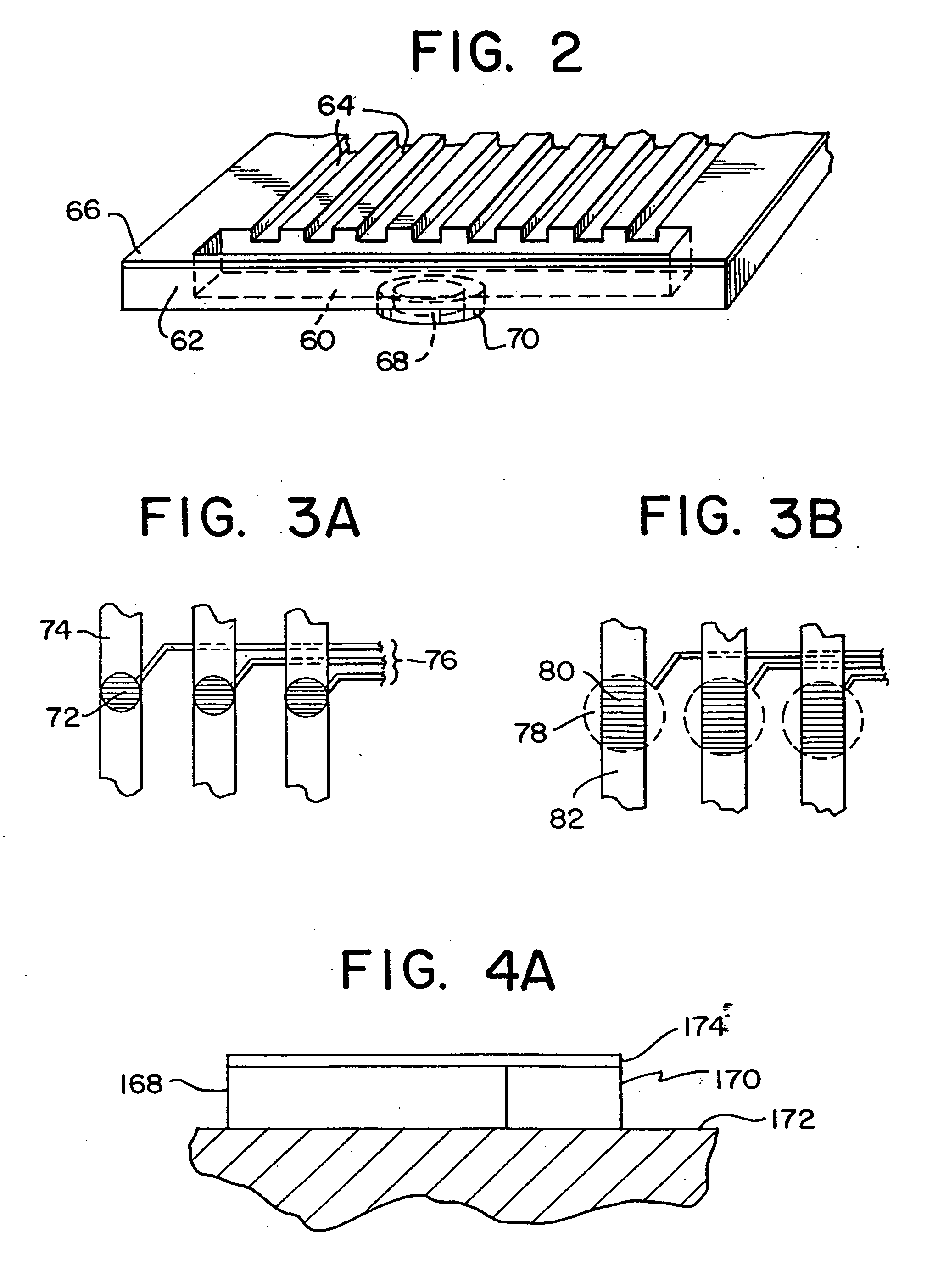
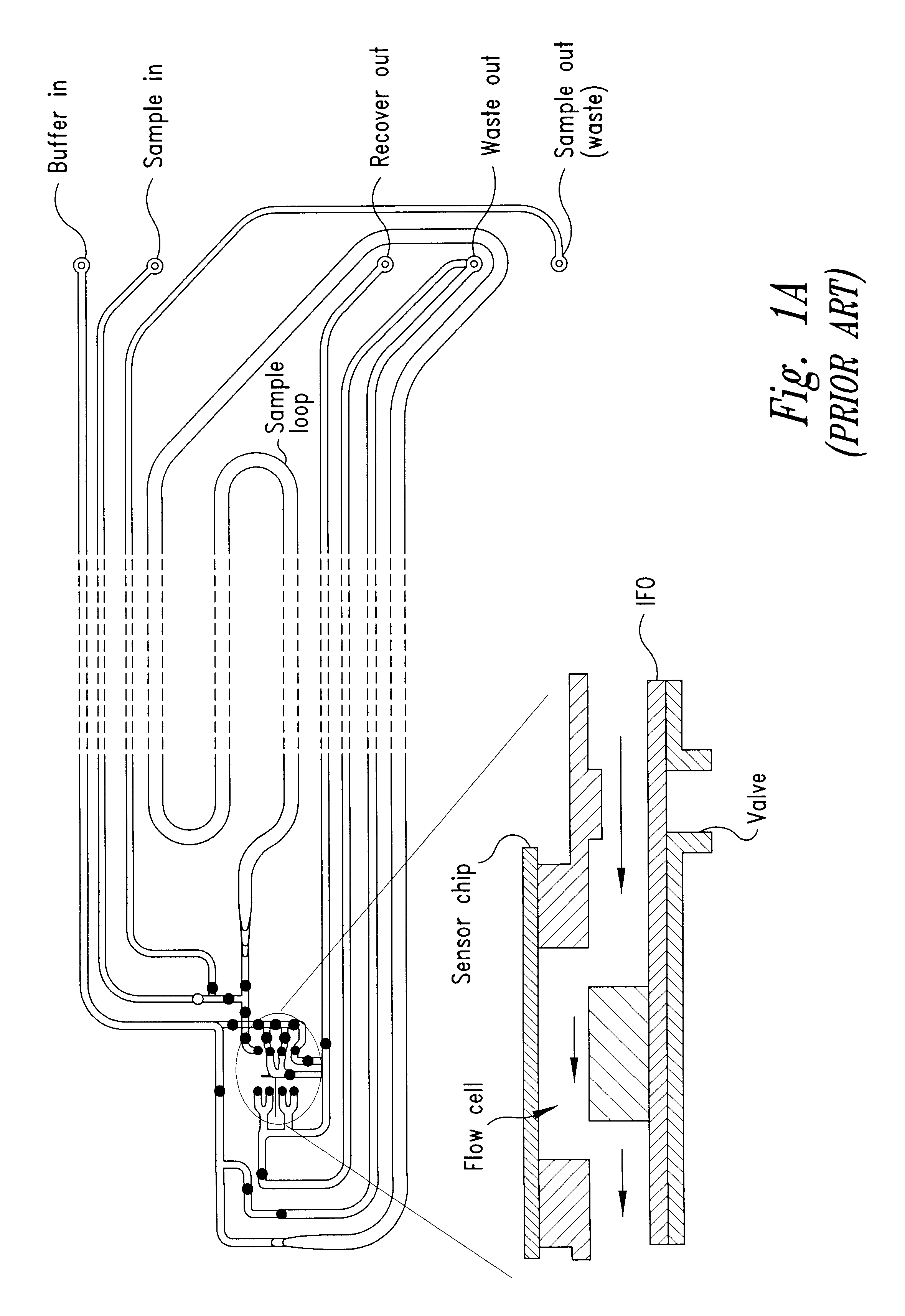
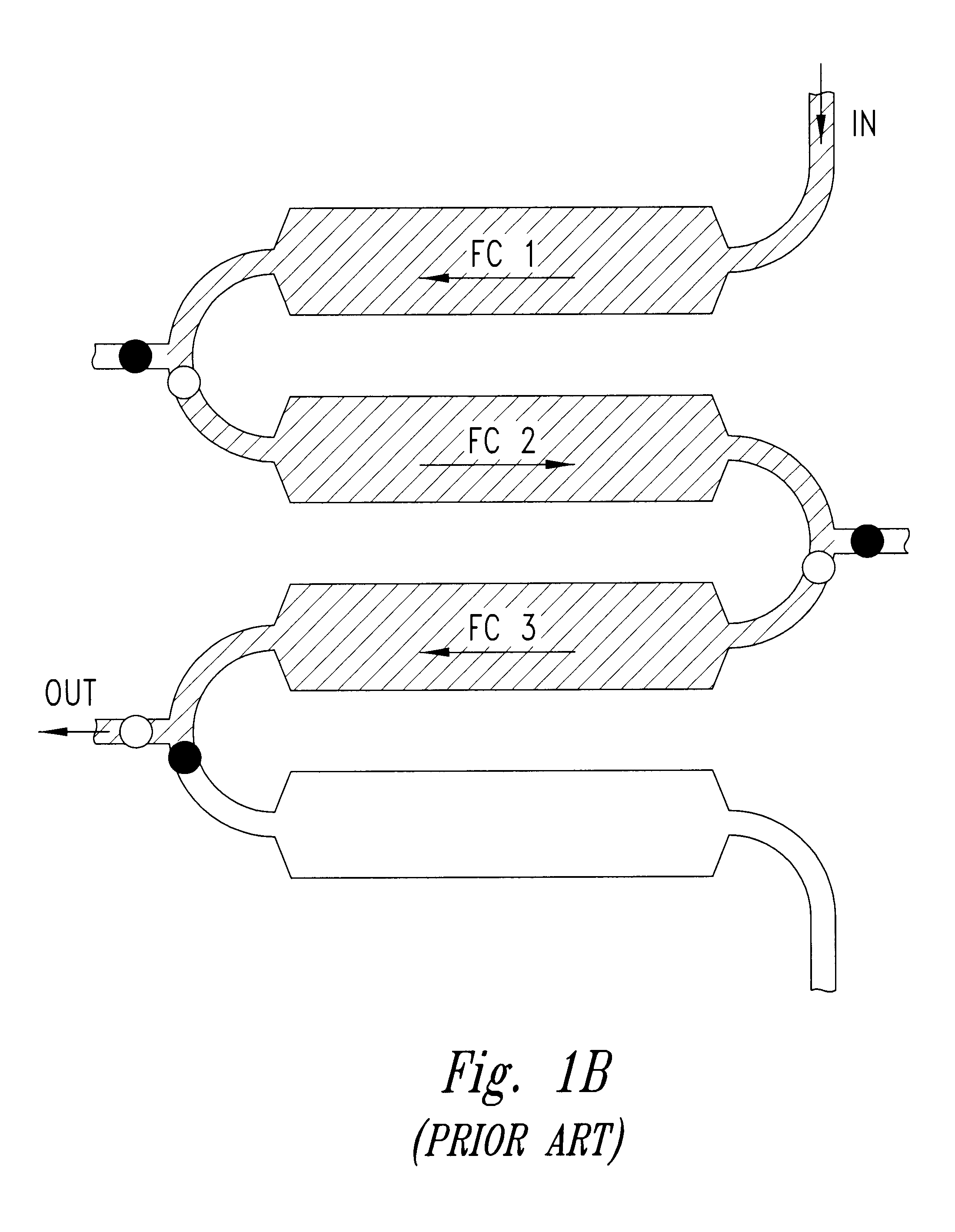
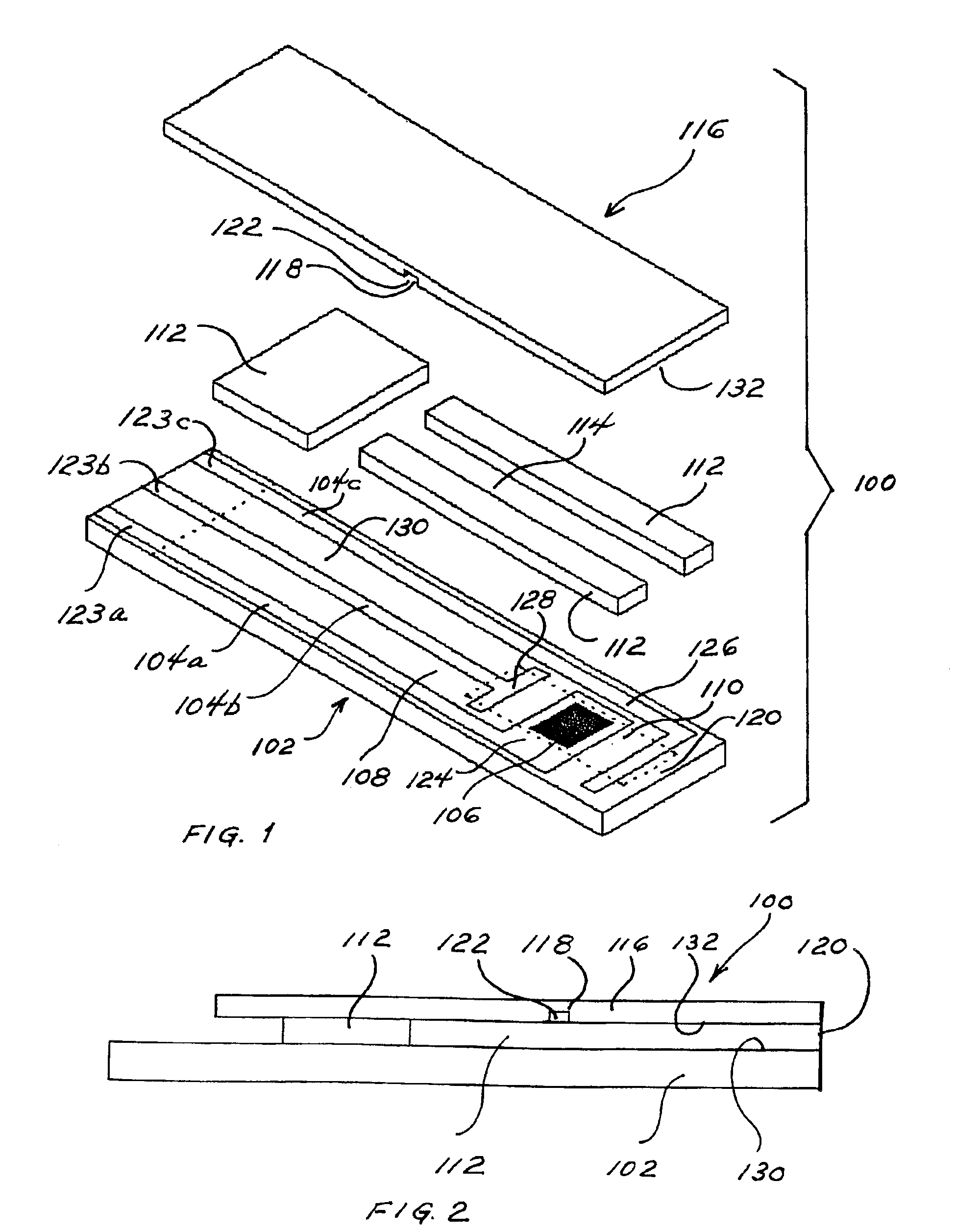
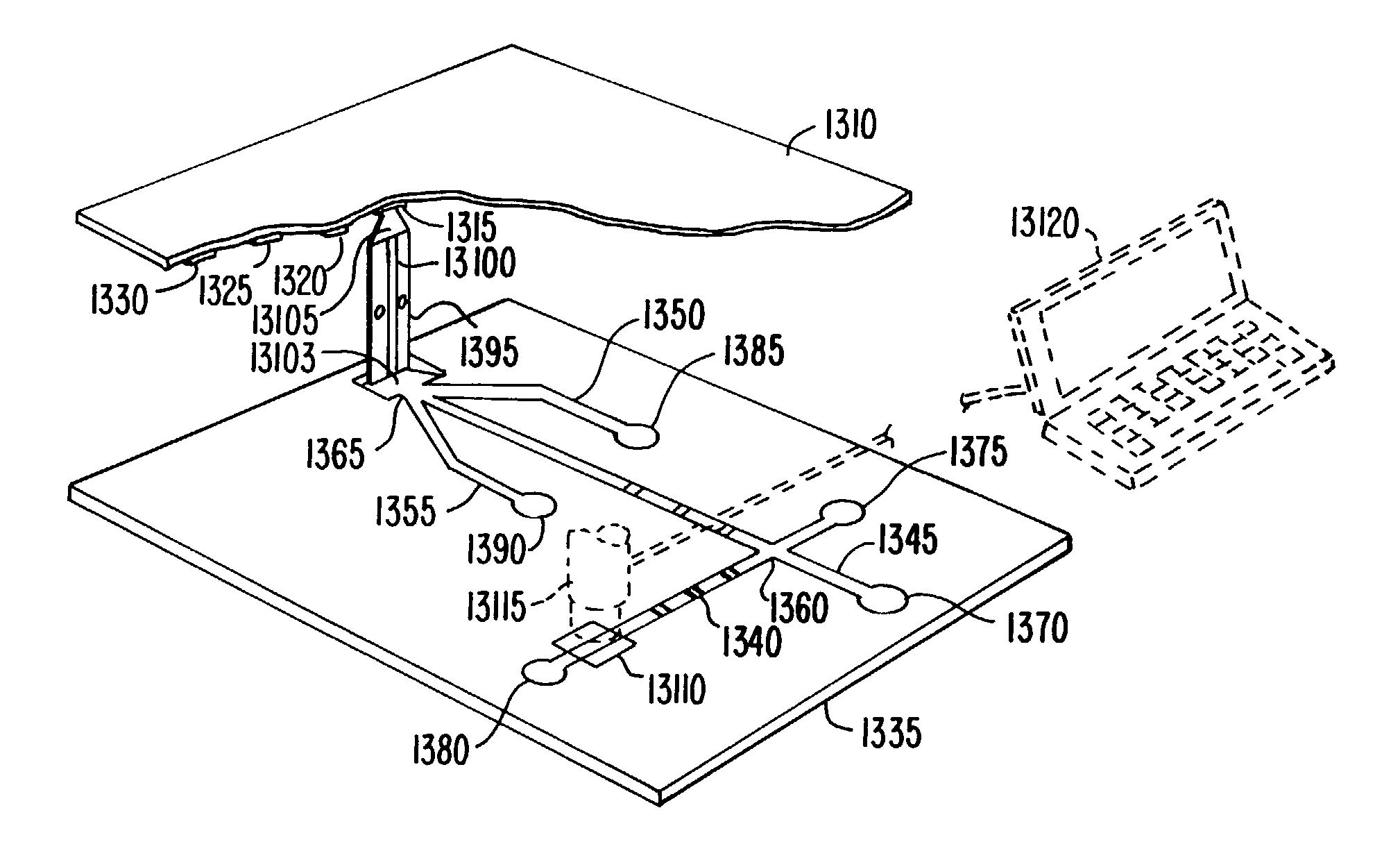
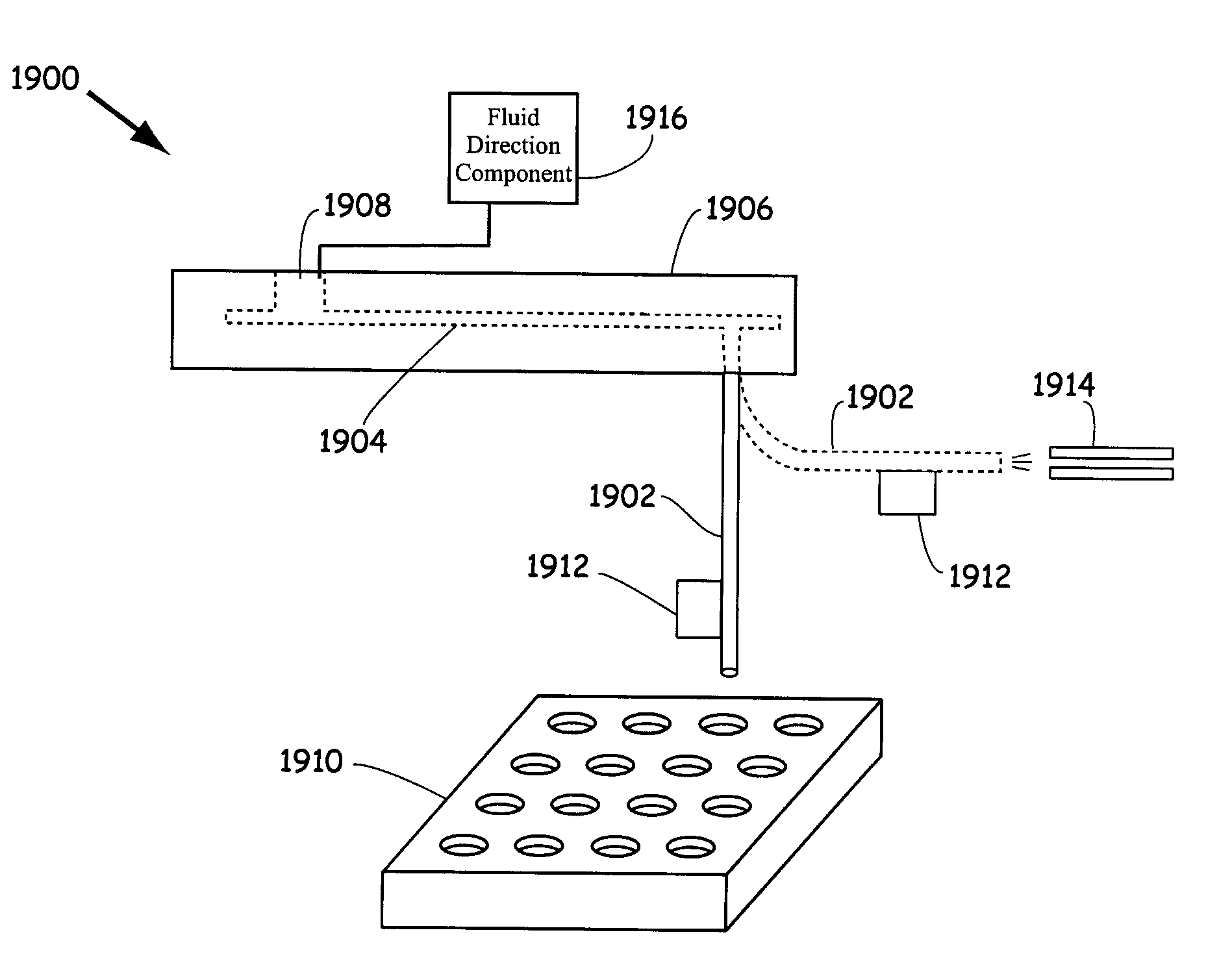
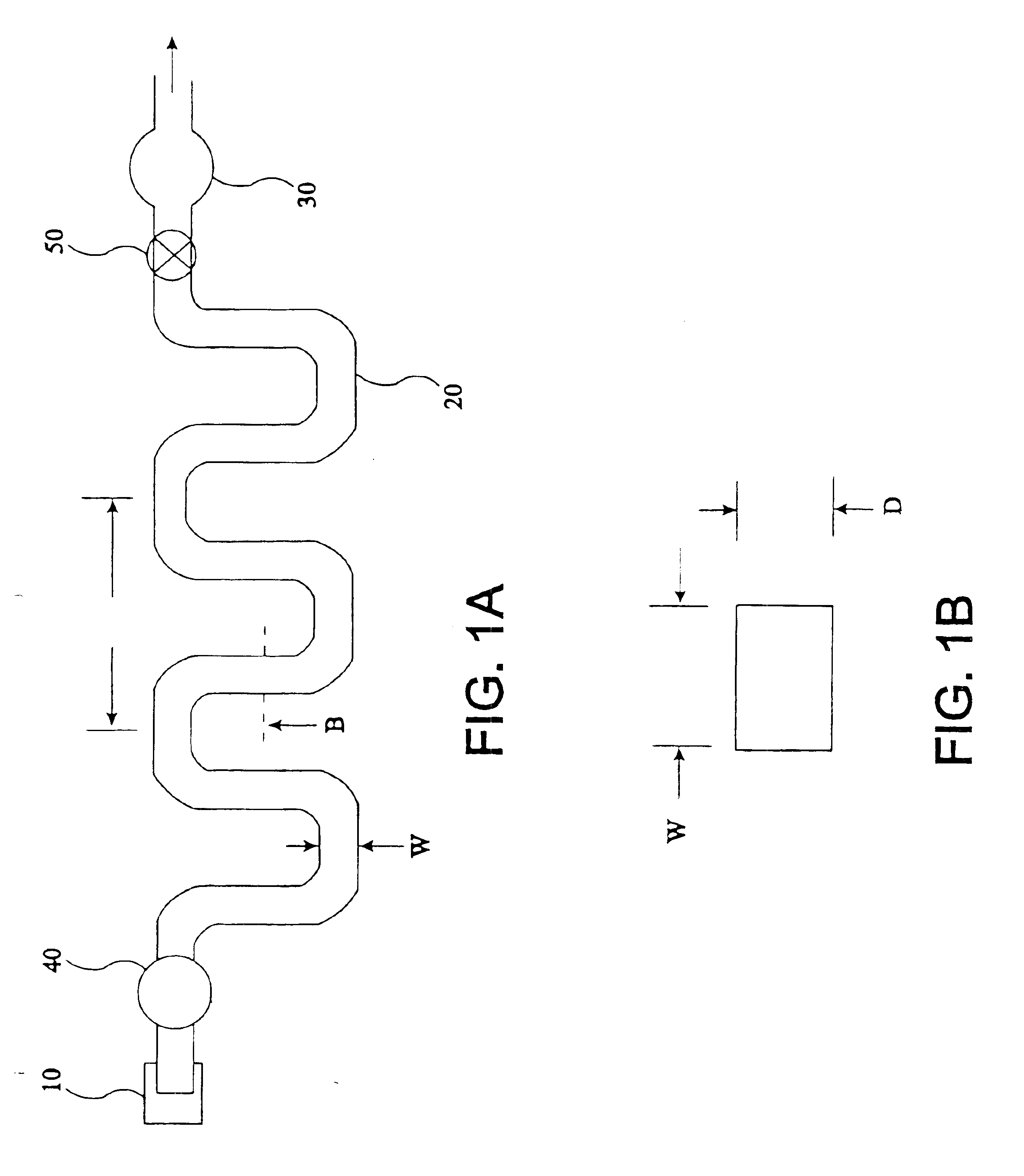
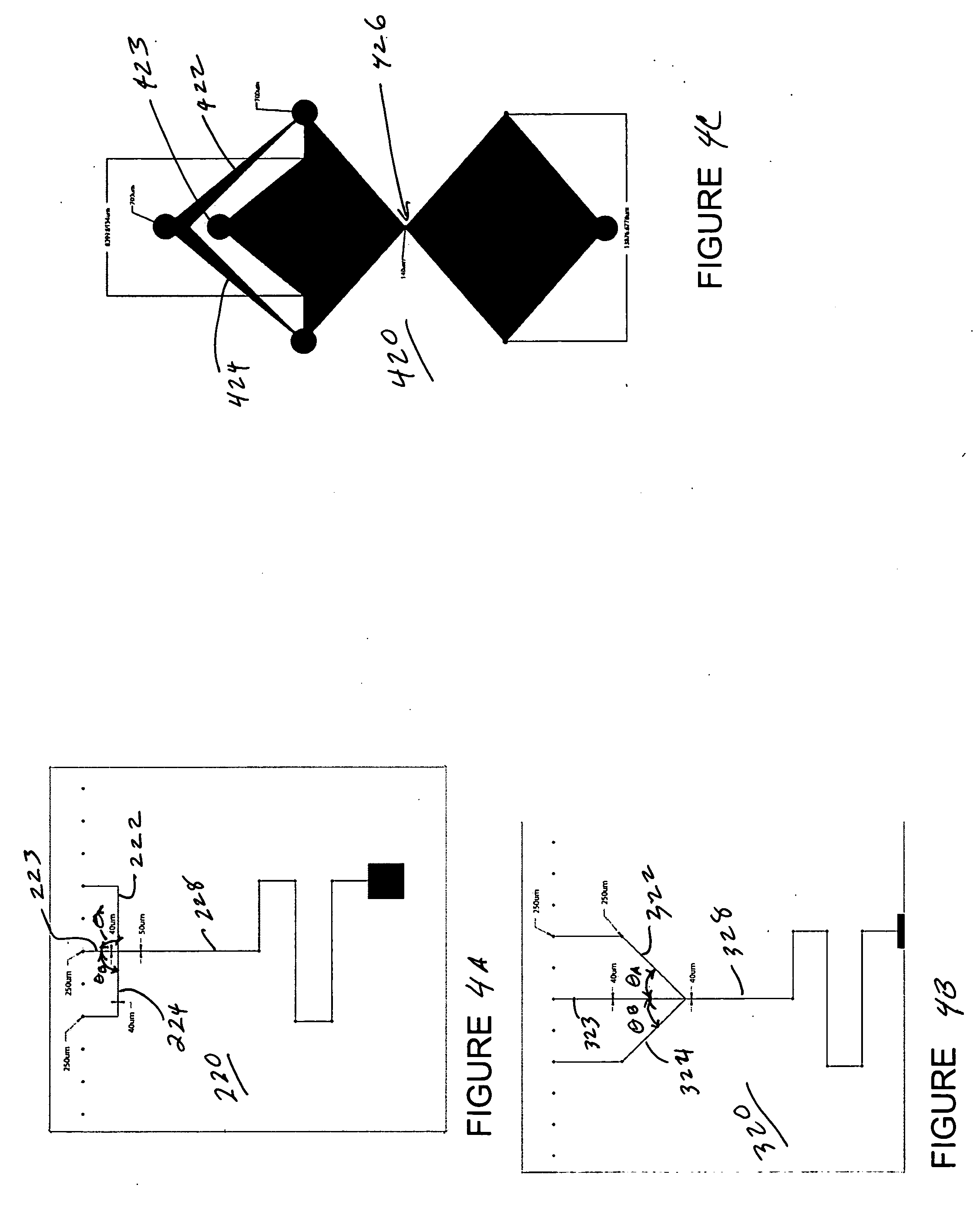
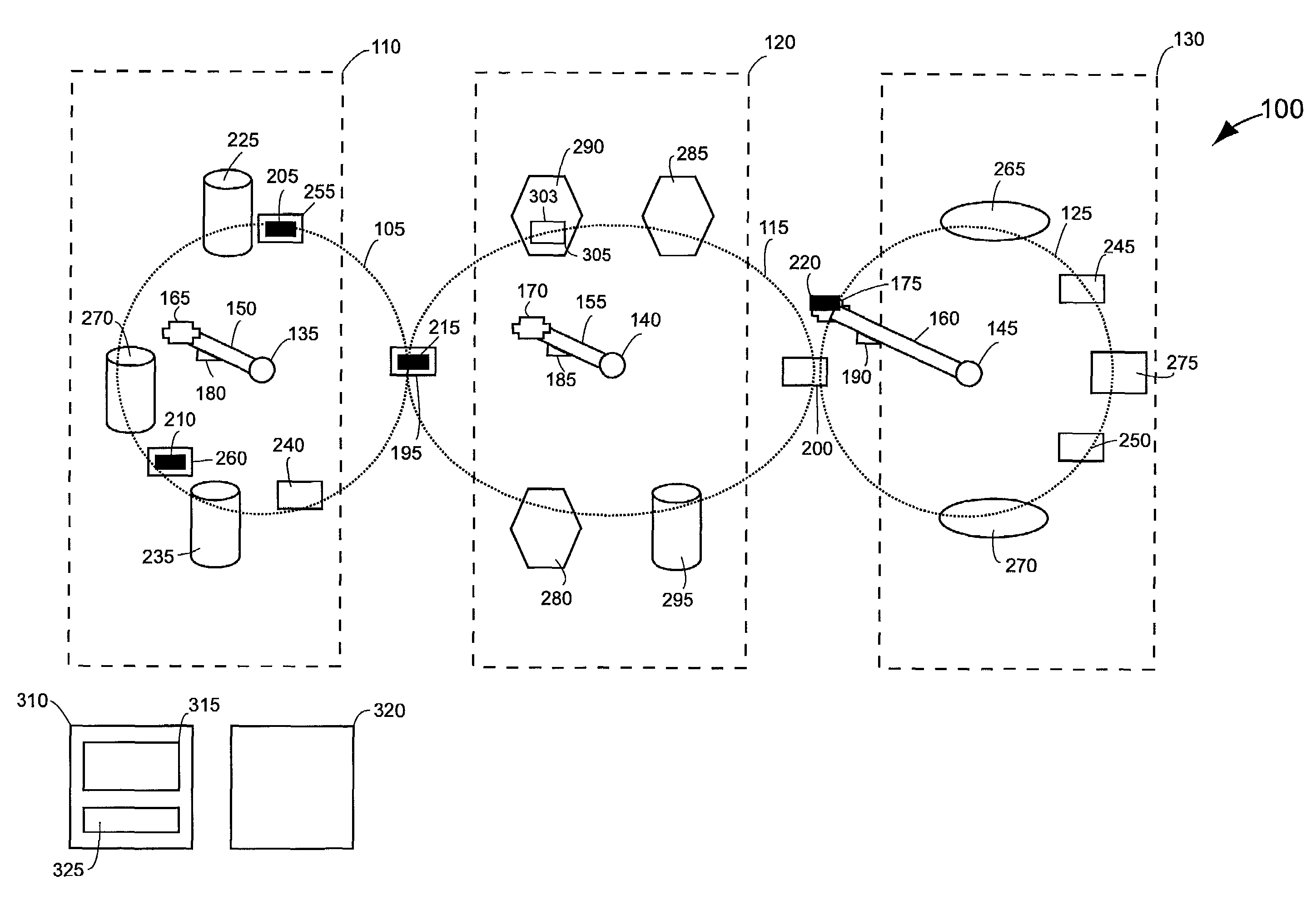
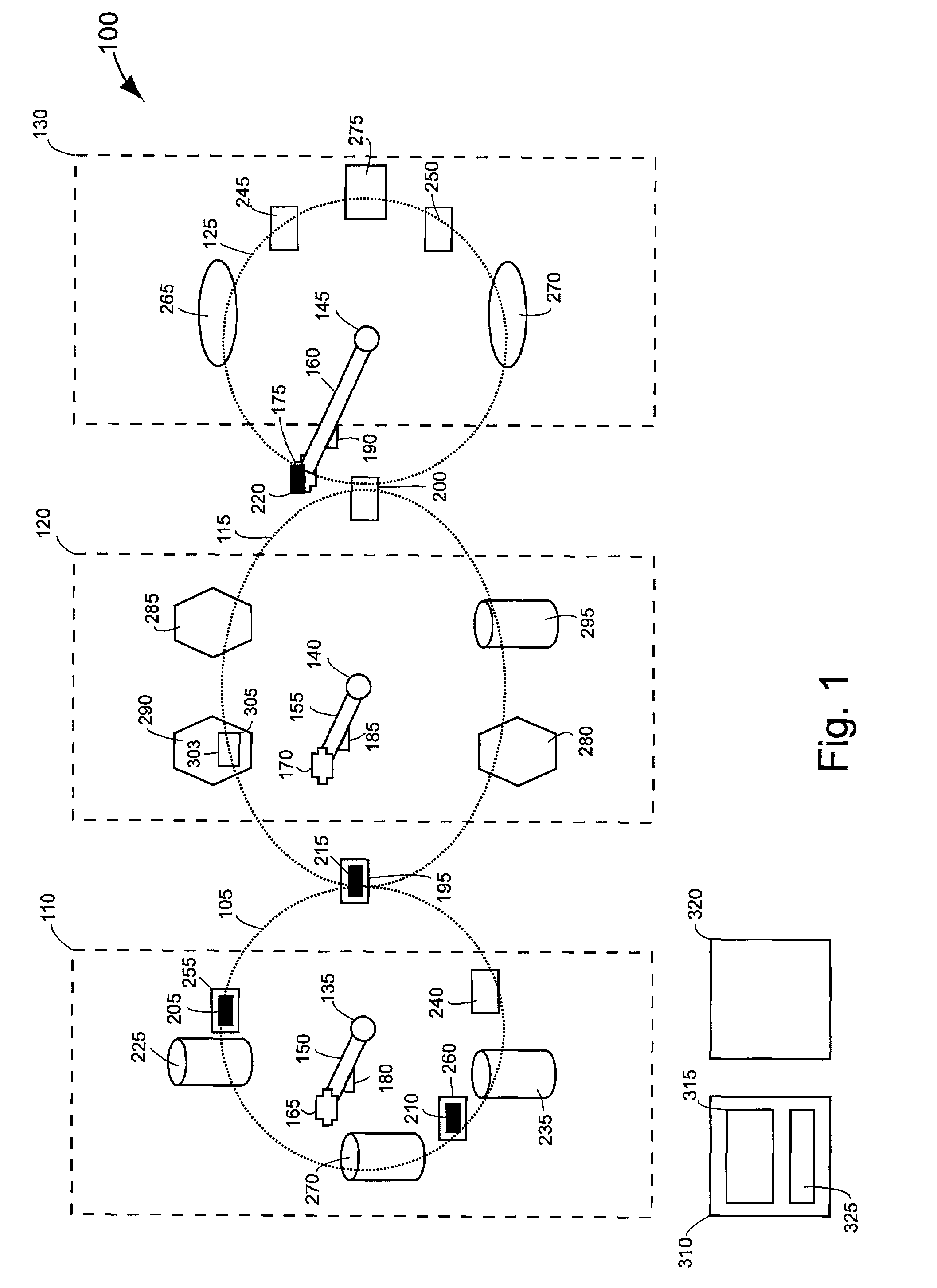
Integrated active flux microfluidic devices and methods
InactiveUS6767706B2Rapid and complete exposureQuick and accurate and inexpensive analysisBioreactor/fermenter combinationsFlow mixersAntigenHybridization probe
The invention relates to a microfabricated device for the rapid detection of DNA, proteins or other molecules associated with a particular disease. The devices and methods of the invention can be used for the simultaneous diagnosis of multiple diseases by detecting molecules (e.g. amounts of molecules), such as polynucleotides (e.g., DNA) or proteins (e.g., antibodies), by measuring the signal of a detectable reporter associated with hybridized polynucleotides or antigen / antibody complex. In the microfabricated device according to the invention, detection of the presence of molecules (i.e., polynucleotides, proteins, or antigen / antibody complexes) are correlated to a hybridization signal from an optically-detectable (e.g. fluorescent) reporter associated with the bound molecules. These hybridization signals can be detected by any suitable means, for example optical, and can be stored for example in a computer as a representation of the presence of a particular gene. Hybridization probes can be immobilized on a substrate that forms part of or is exposed to a channel or channels of the device that form a closed loop, for circulation of sample to actively contact complementary probes. Universal chips according to the invention can be fabricated not only with DNA but also with other molecules such as RNA, proteins, peptide nucleic acid (PNA) and polyamide molecules.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Capillary electroflow apparatus and method
The present invention concerns an apparatus for conducting a microfluidic process. The apparatus comprises integral first and second plates. The first plate comprises an array of sample receiving elements for receiving a plurality of samples from an array of sample containers and dispensing the samples. The second plate comprises a planar array of microfluidic networks of cavity structures and channels for conducting a microfluidic process. Also disclosed is a method for processing an array of samples. At least a portion of each sample in an array of sample wells is simultaneously transferred to a corresponding array of microfluidic networks of cavity structures and channels by means of a corresponding array of sample receiving elements that is in integral fluid communication with the array of microfluidic networks. The samples are then processed. Also disclosed is a device for conducting a microfluidic process wherein the device comprising a planar substrate having a planar array of microfluidic networks of cavity structures and channels for conducting a microfluidic process. A plurality of such devices may be present on a continuous sheet. The invention further includes kits for carrying out microfluidic processes comprising an apparatus as described above.
Owner:ACLARA BIOSCIENCES INC
Apparatus and method for transferring liquids
InactiveUS6284113B1Sequential/parallel process reactionsSludge treatmentElectricityMechanical engineering
The present invention concerns devices, apparatus and methods for transferring liquids. One aspect of the present invention is a device comprising a plate having a plurality of transfer elements. Each of the transfer elements comprises an aperture in the plate where the aperture is capable of being electrically activated. The plate has one of more attaching elements for attaching the plate to a multiwell plate to form a sealed system except for the apertures of the transfer elements. Usually, the device is adapted for sealing attachment to a multiwell plate. In a method in accordance with the present invention a quantity of liquid is disposed to a second side of a plate having a plurality of apertures in the plate. The apertures are capable of being electrically activated. The liquid is present in a closed well except for the apertures in the plate. To simultaneously expel liquid from the apertures, the apertures are electrically activated. Also disclosed are kits comprising a device in accordance with the present invention.
Owner:MONOGRAM BIOSCIENCES
Method and apparatus for fluid dispersion
Owner:THE GOVERNING COUNCIL OF THE UNIV OF TORONTO +1
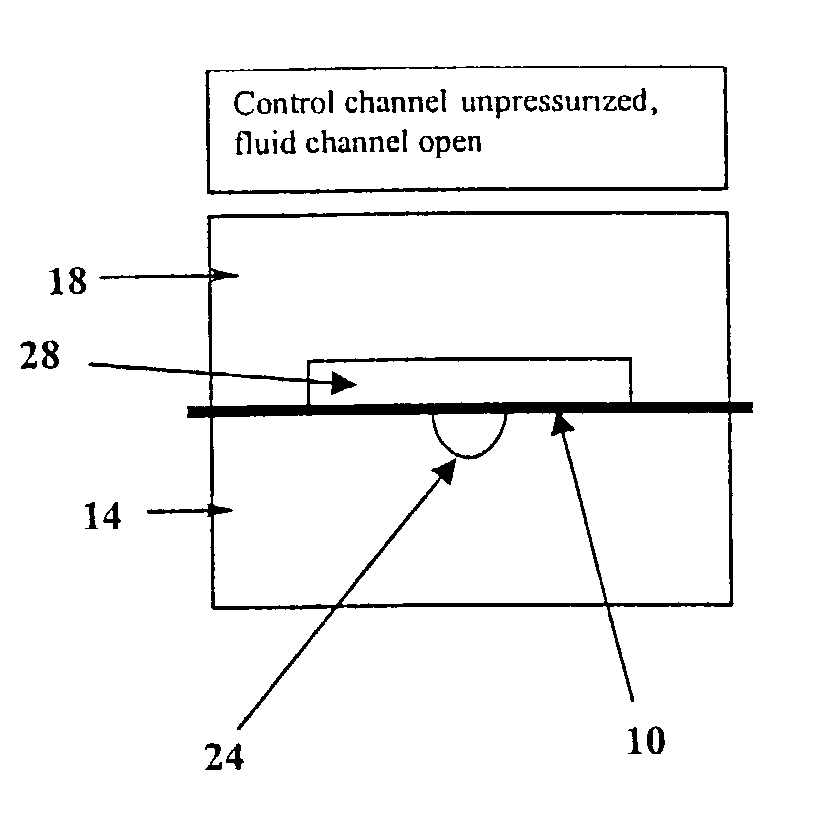
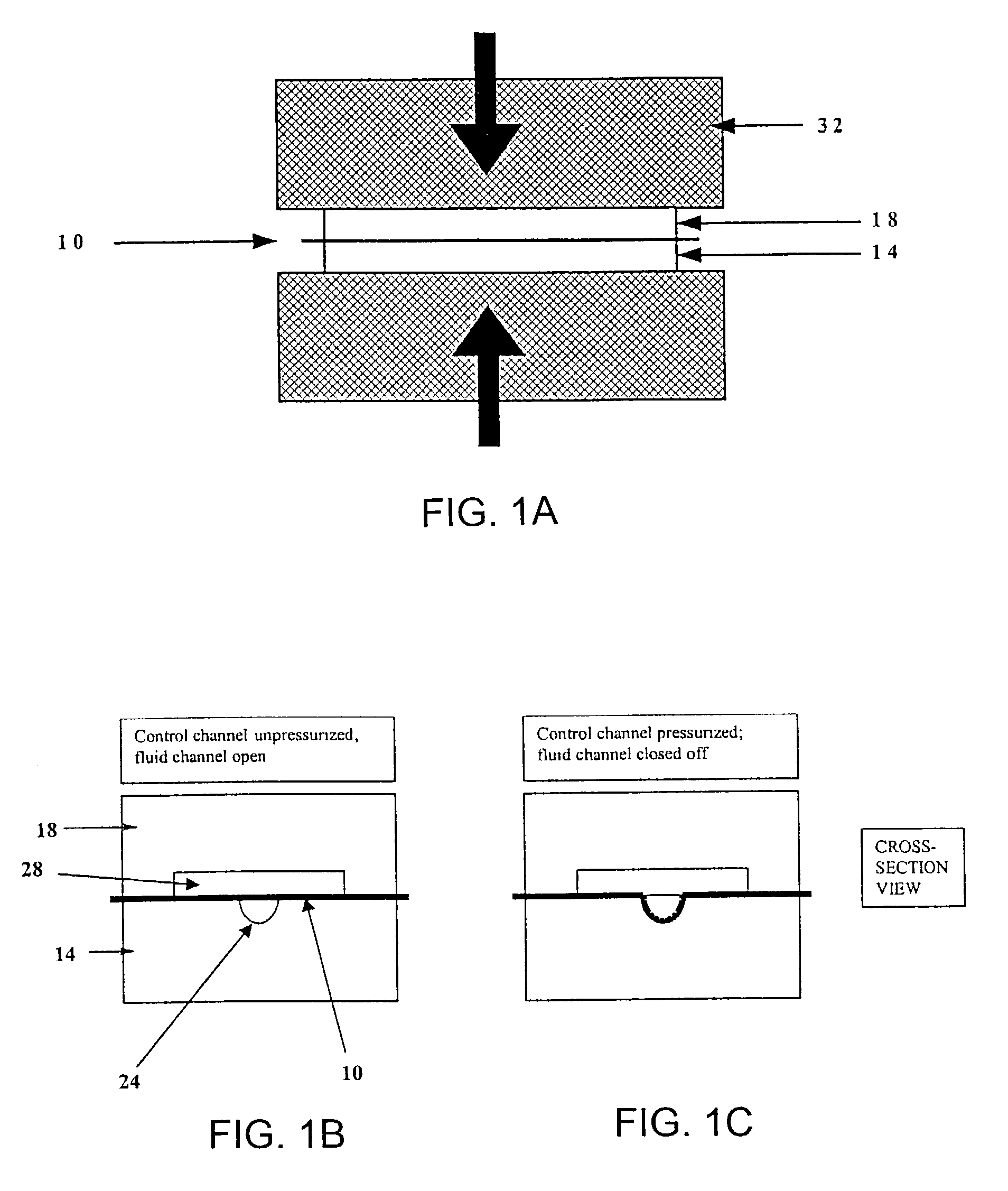
Methods and systems for control of microfluidic devices
InactiveUS20020143437A1Overcome deficienciesFixed microstructural devicesVolume/mass flow measurementControl systemLow voltage
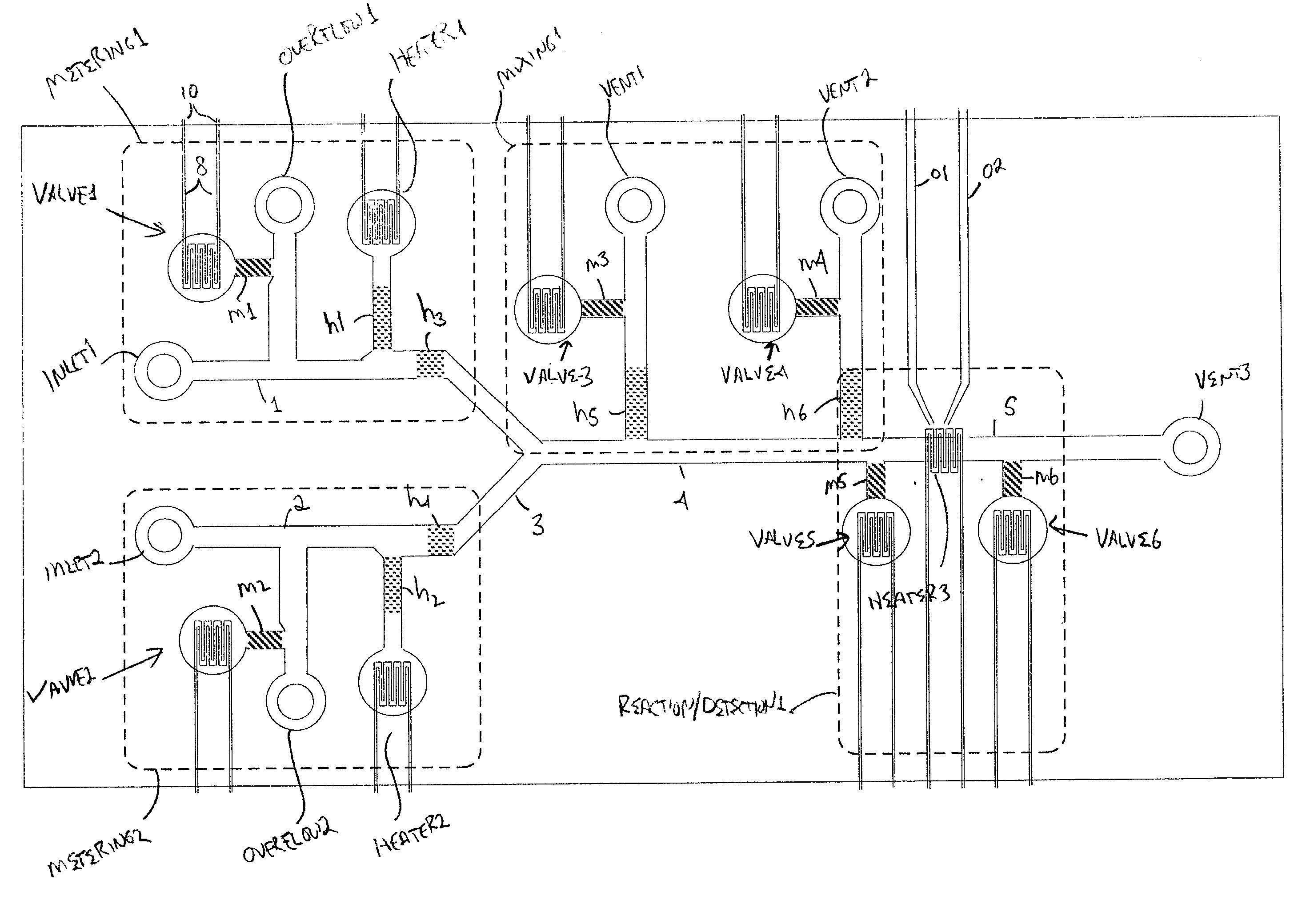
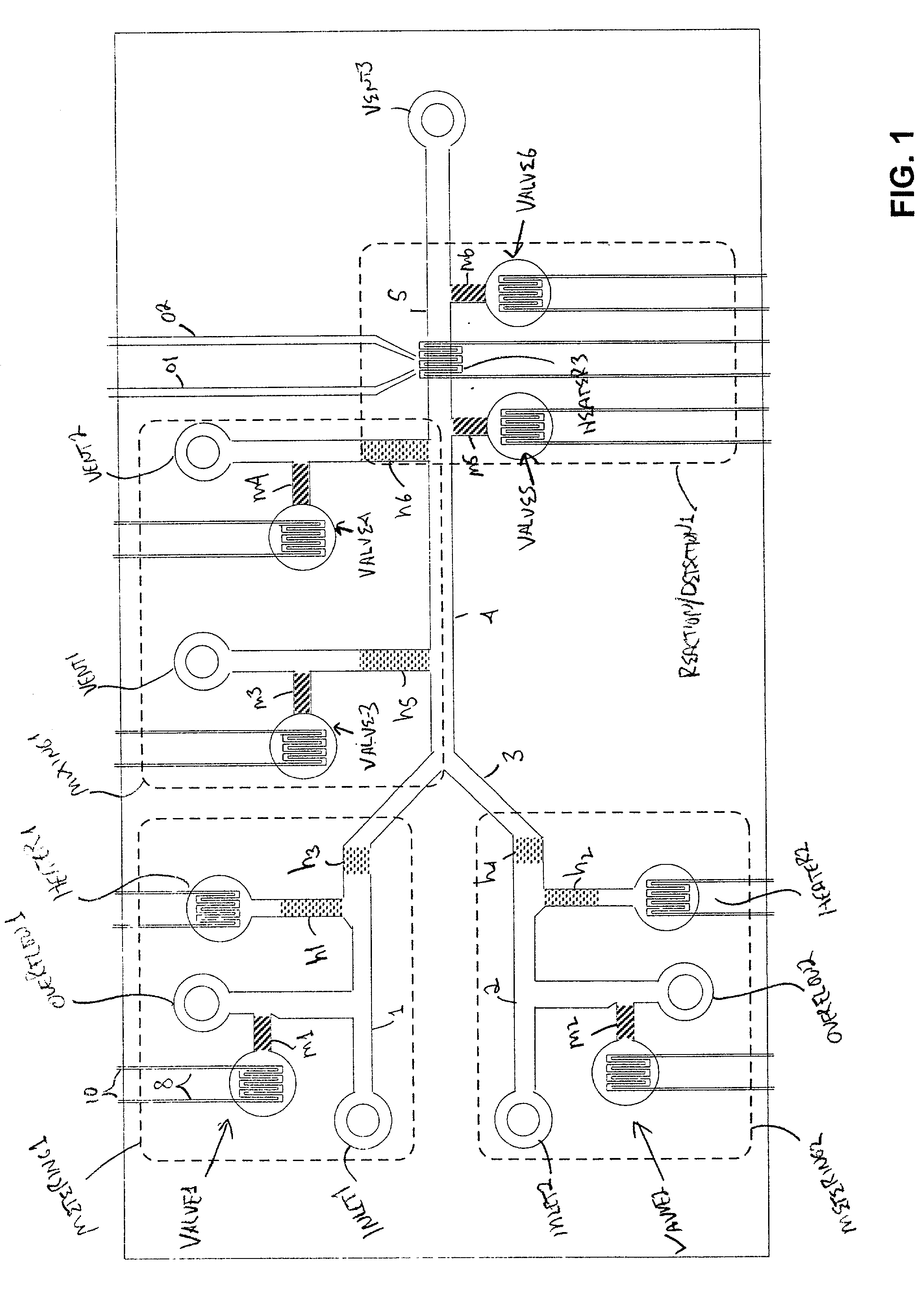
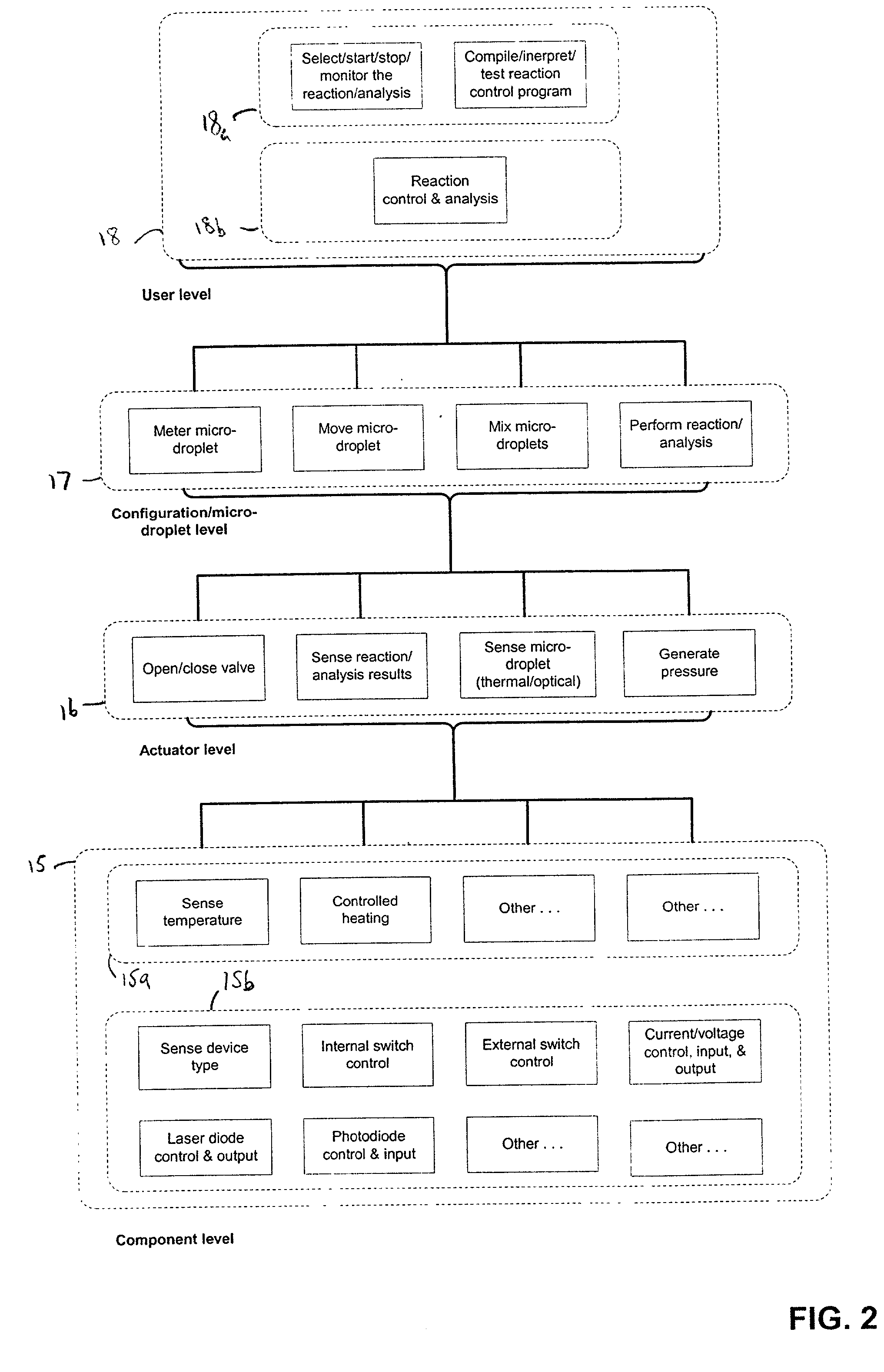
The present invention provides control methods, control systems, and control software for microfluidic devices that operate by moving discrete micro-droplets through a sequence of determined configurations. Such microfluidic devices are preferably constructed in a hierarchical and modular fashion which is reflected in the preferred structure of the provided methods and systems. In particular, the methods are structured into low-level device component control functions, middle-level actuator control functions, and high-level micro-droplet control functions. Advantageously, a microfluidic device may thereby be instructed to perform an intended reaction or analysis by invoking micro-droplet control function that perform intuitive tasks like measuring, mixing, heating, and so forth. The systems are preferably programmable and capable of accommodating microfluidic devices controlled by low voltages and constructed in standardized configurations. Advantageously, a single control system can thereby control numerous different reactions in numerous different microfluidic devices simply by loading different easily understood micro-droplet programs.
Owner:HANDYLAB
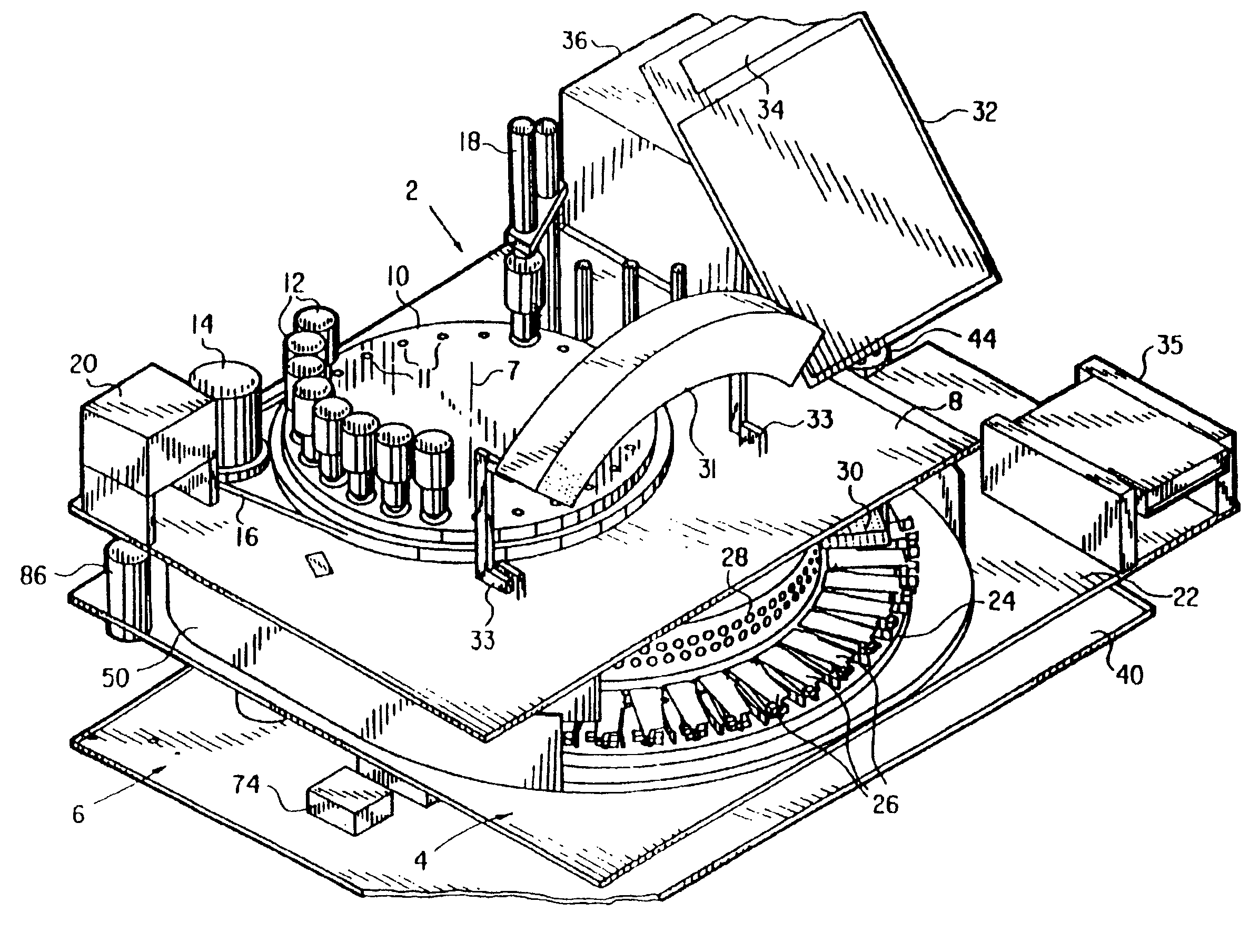
Automated biological reaction apparatus
An automated immunostaining apparatus having a reagent application zone and a reagent supply zone. The apparatus has a carousel slide support supporting a plurality of slide supports thereon, and drive means engaging the carousel slide support for consecutively positioning each of a plurality of slide supports in the reagent application zone. The apparatus also has a carousel reagent support having a plurality of reagent container supports thereon, and drive means engaging the carousel for rotating the carousel and positioning a preselected reagent container support in the reagent supply zone. The apparatus also has a reagent delivery actuator means positioned for engaging a reagent container positioned on a container support in the reagent delivery zone and initiating reagent delivery from the reagent container to a slide supported on a slide support in the reagent receiving zone.
Owner:VENTANA MEDICAL SYST INC
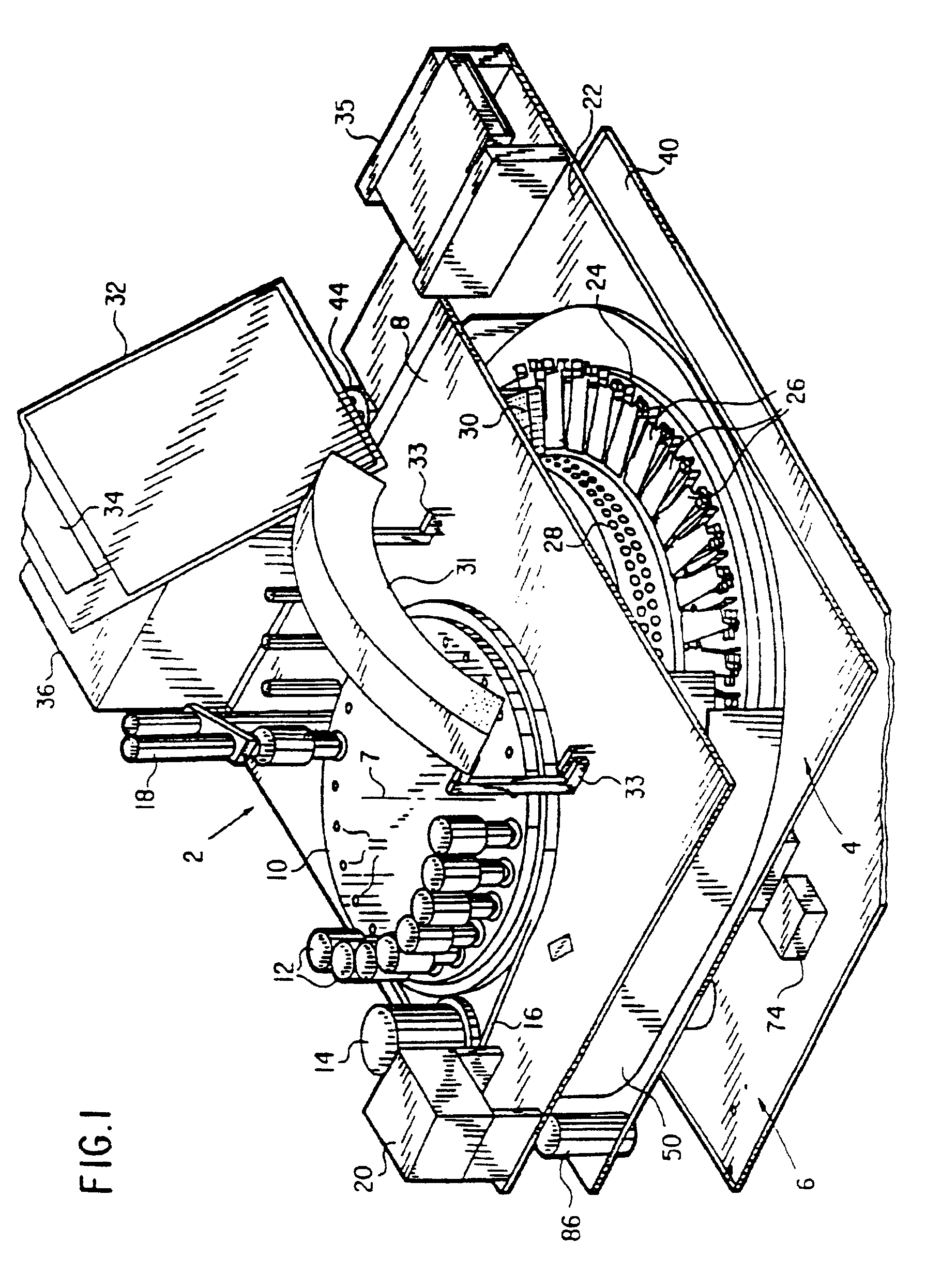
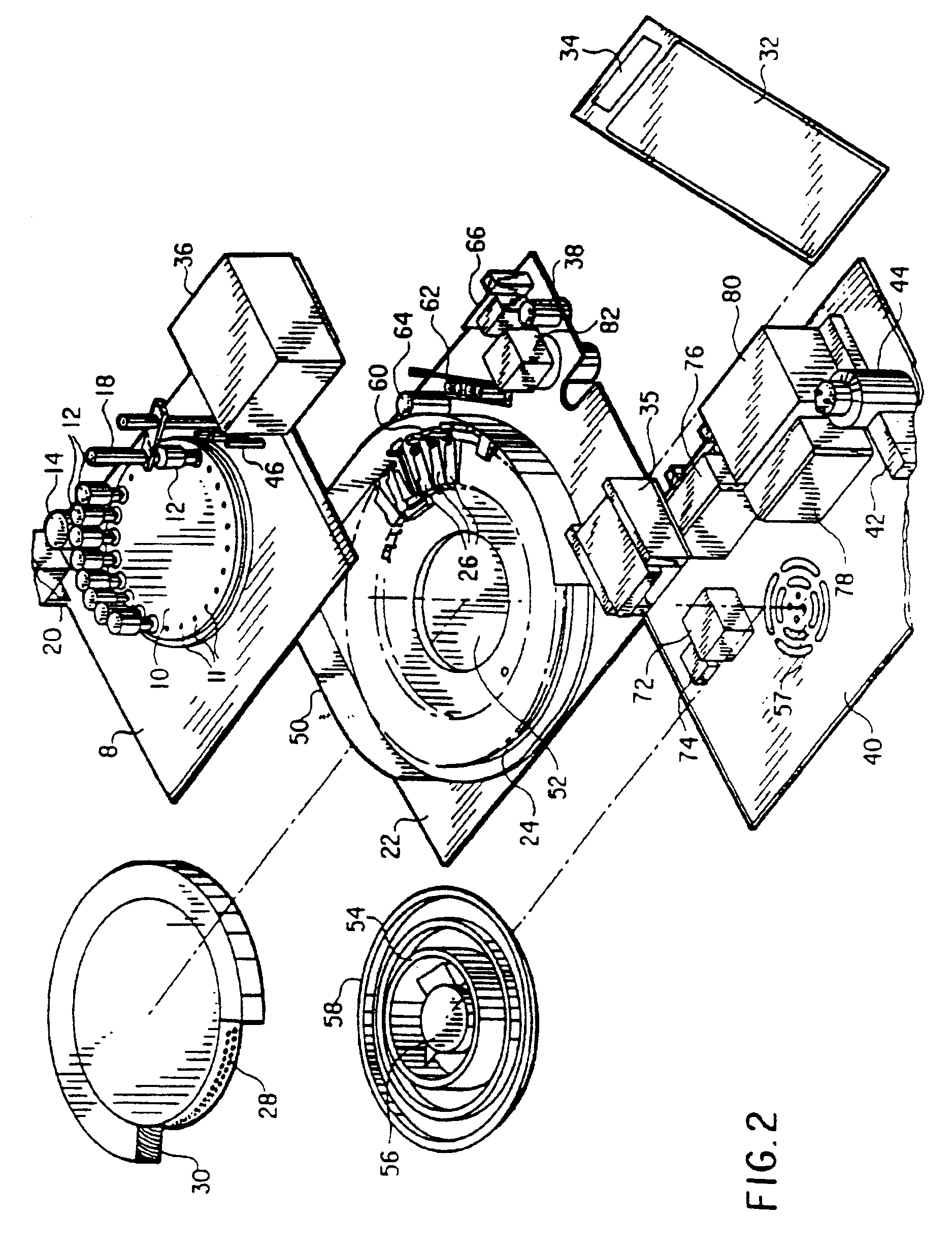
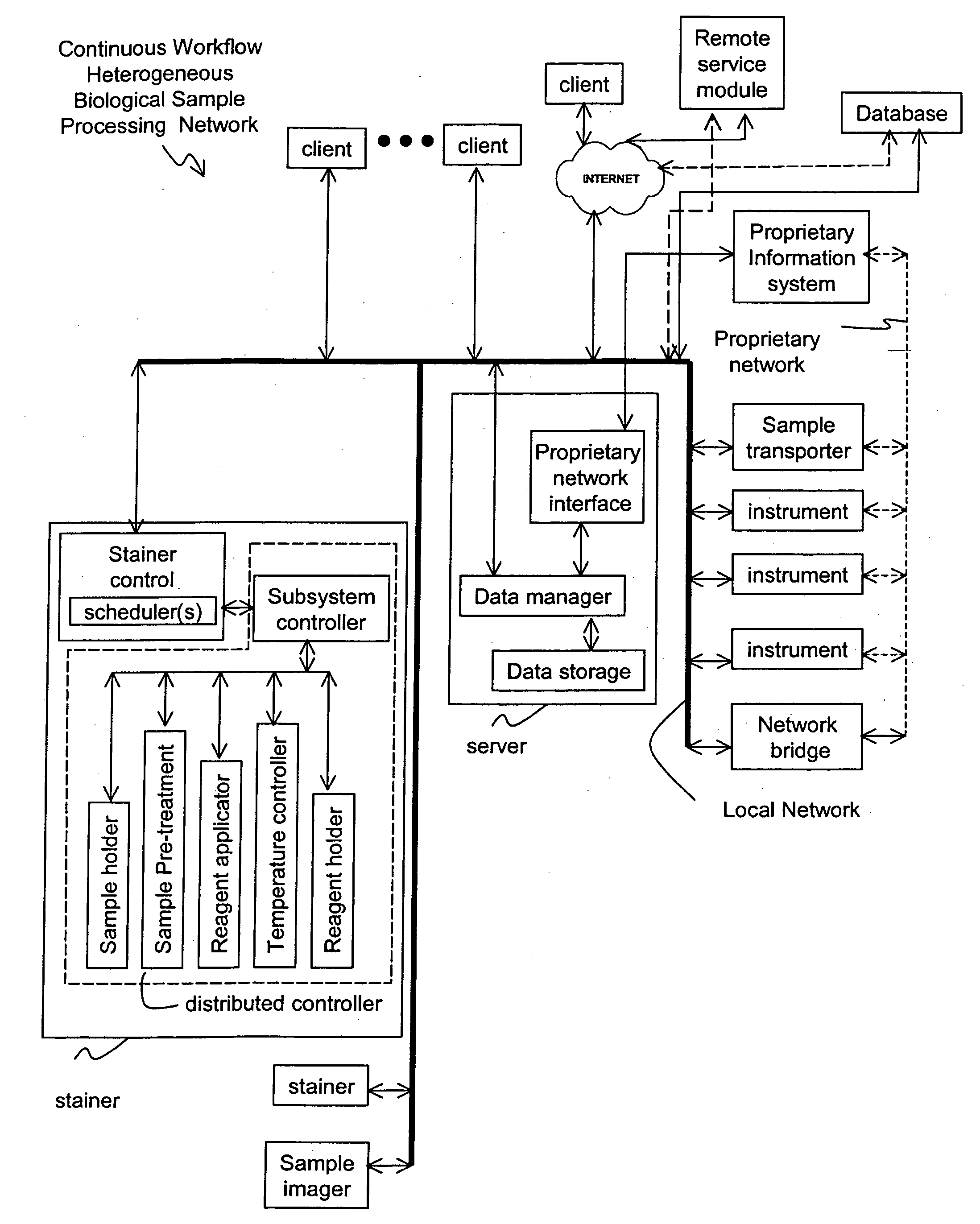
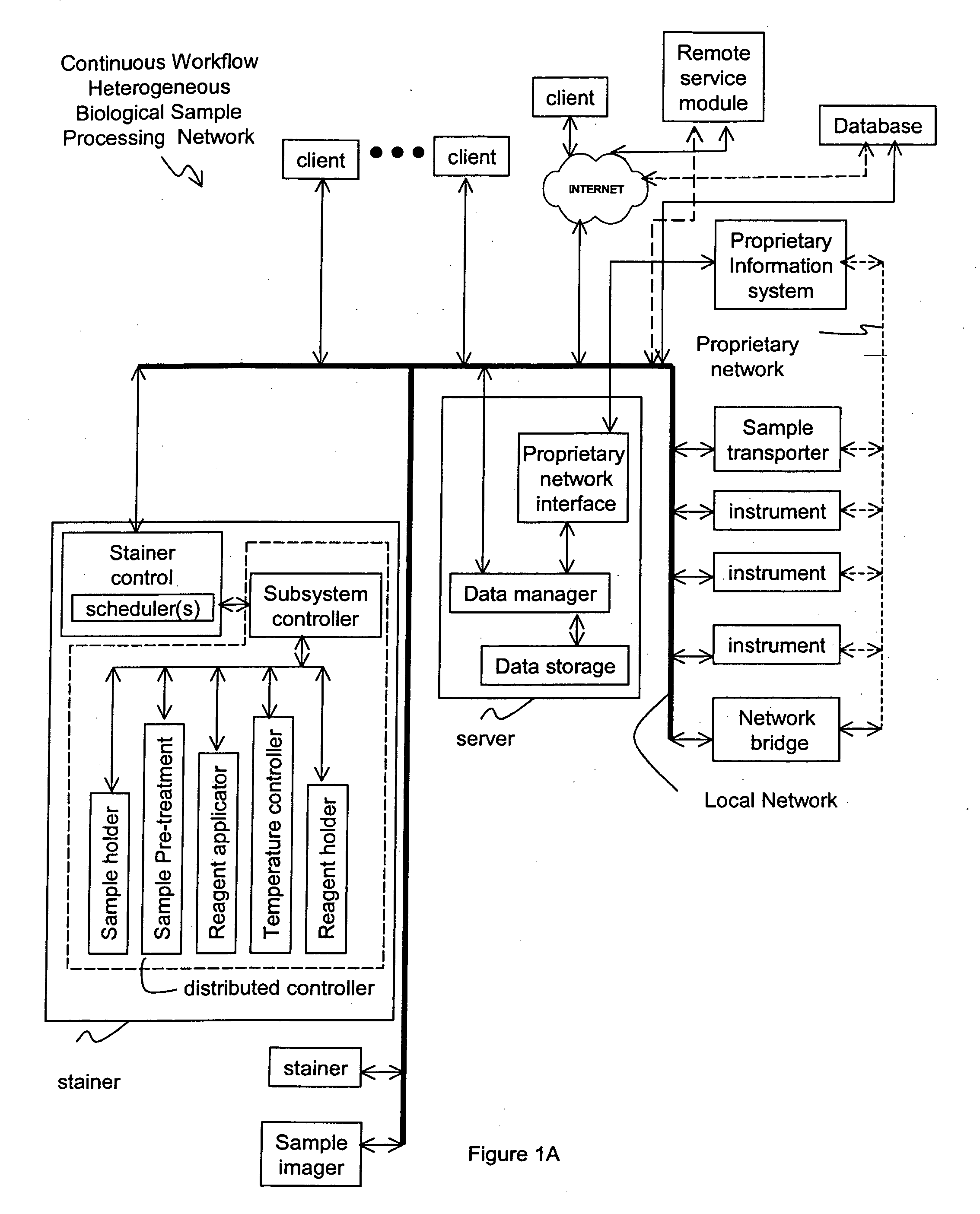
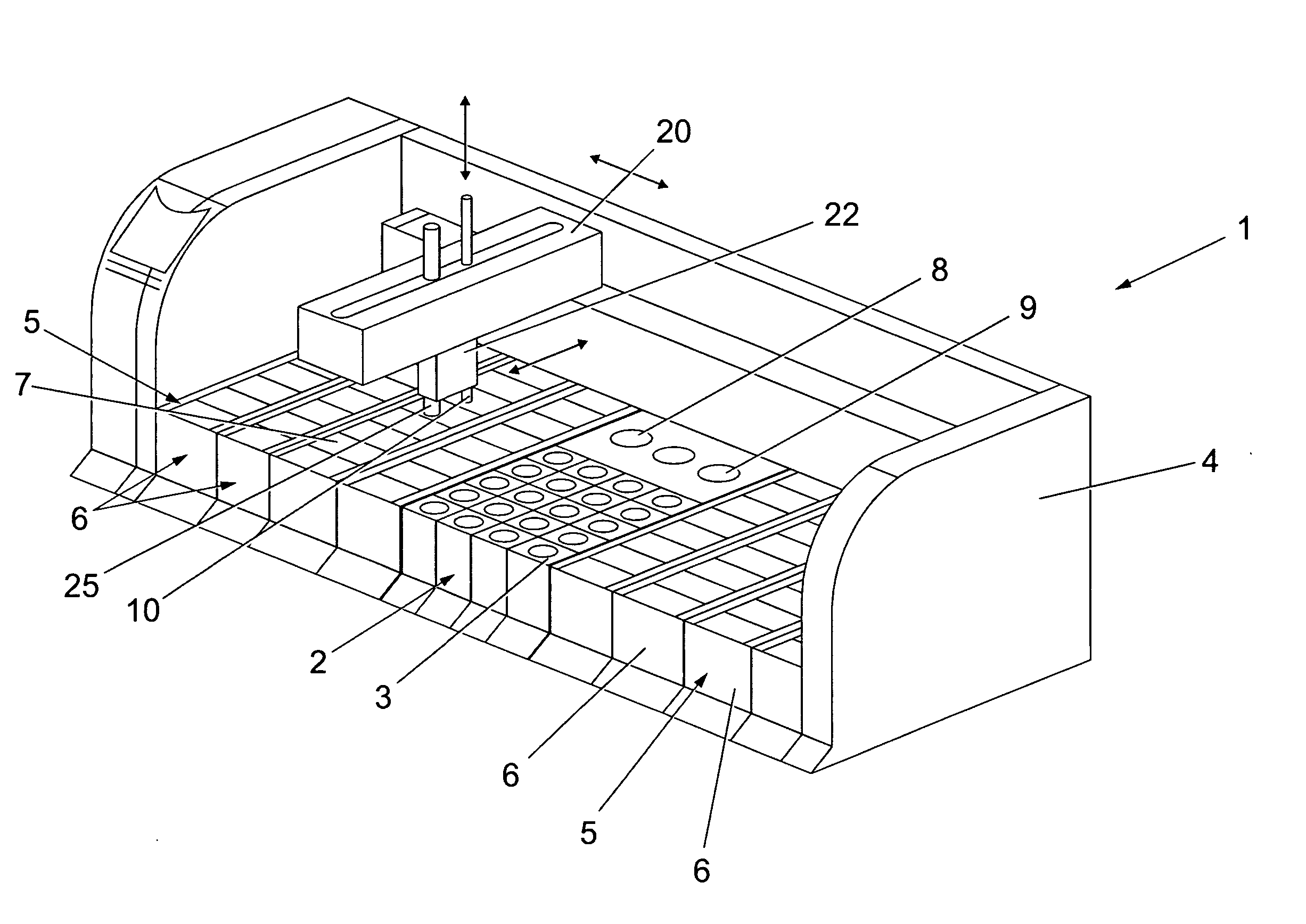
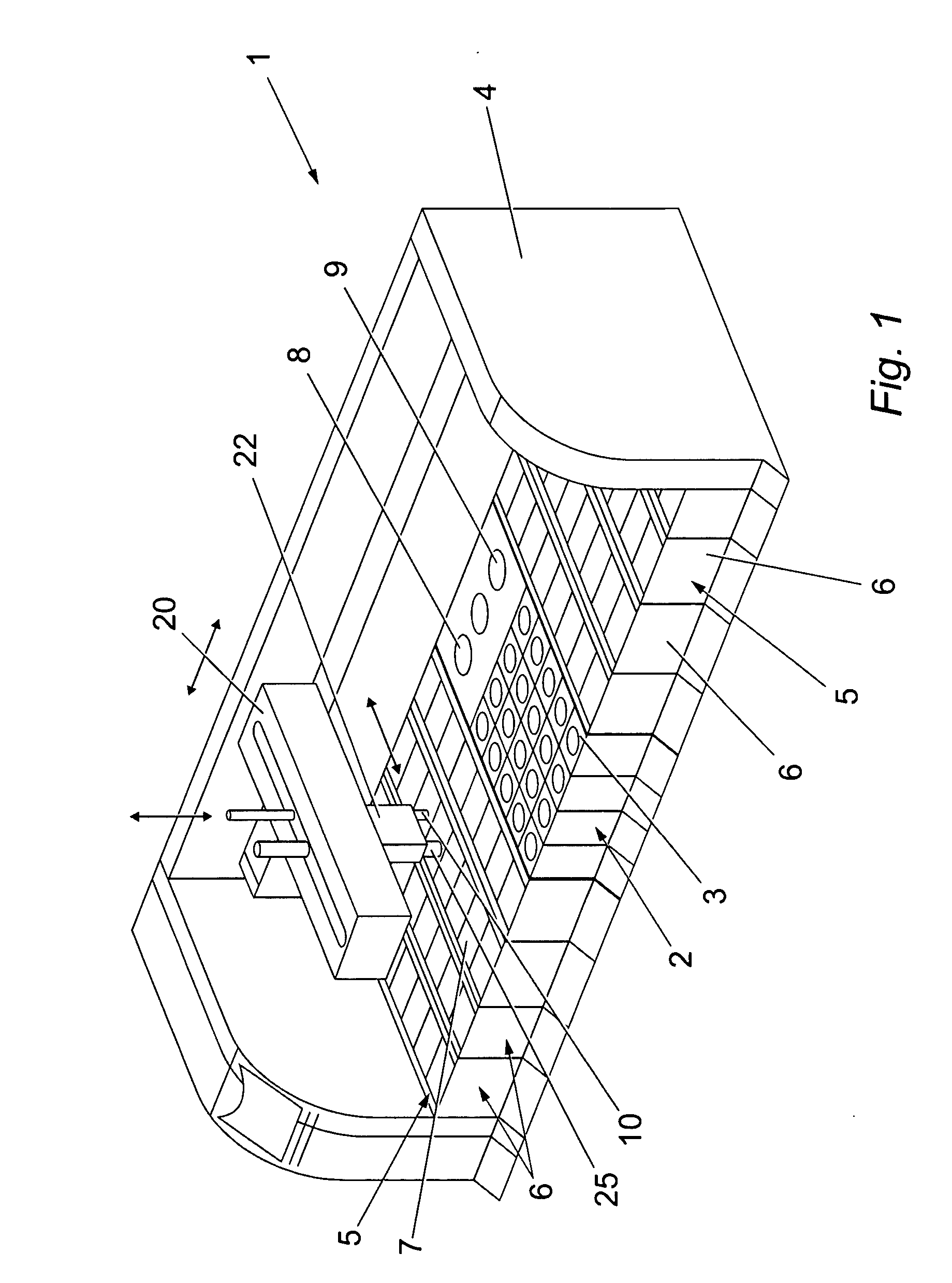
Method and apparatus for automated pre-treatment and processing of biological samples
ActiveUS20060148063A1Maximize throughputImprove efficiencyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPre treatmentComputer science
A method and apparatus for continuous workflow processing of biological samples. In one embodiment, the appratus includes a probe for dispensing one or more reagents from one or more reagent containers onto one or more biological sample carriers. The method and apparatus includes processing each biological sample according to a respective sequence of protocol steps which may be ordered by a scheduler protocol. The method and apparatus also includes network capability for connectivity with additional equipment for receiving or transmitting pertinent data via the network.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Method and apparatus for programmable fluidic processing
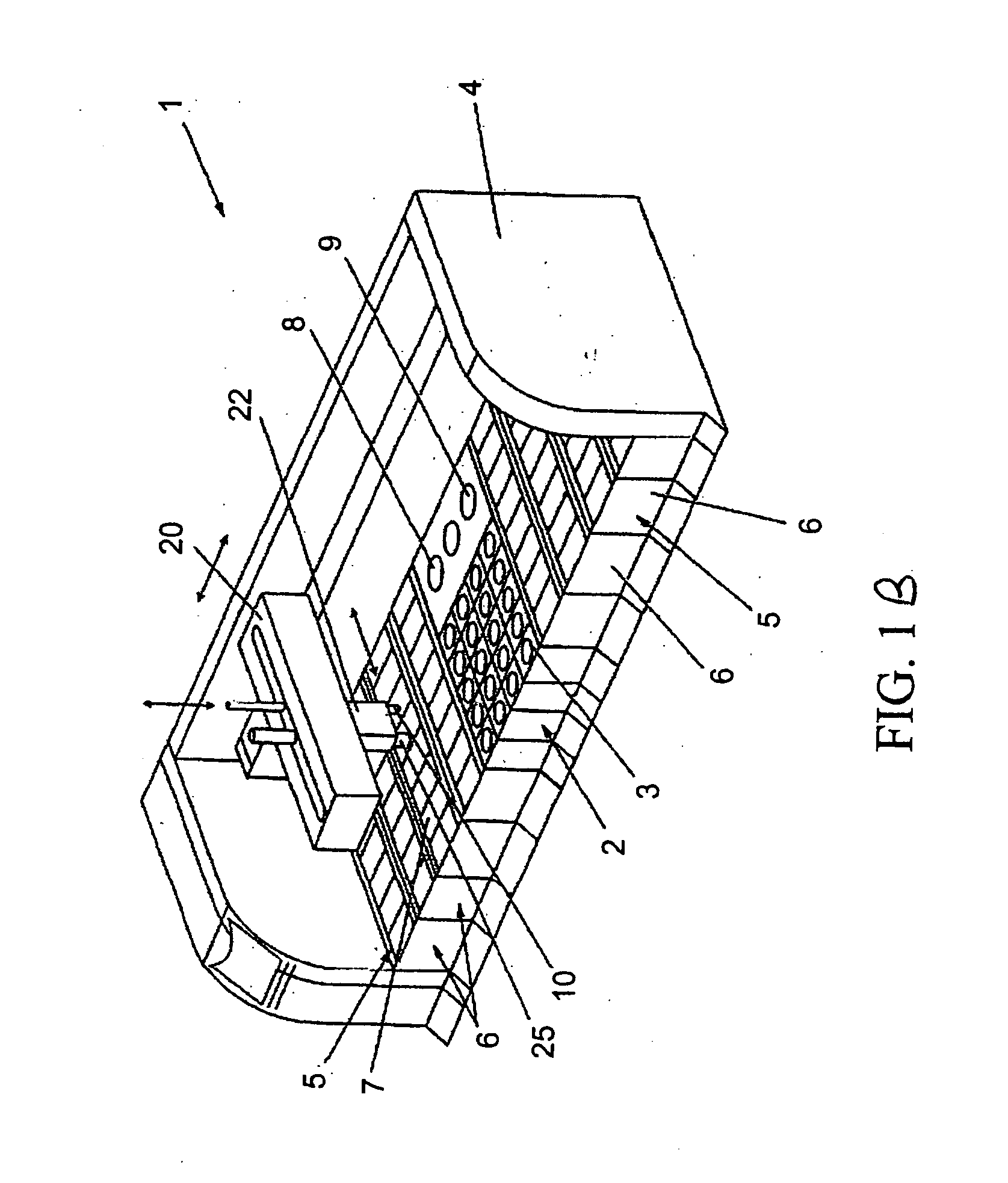
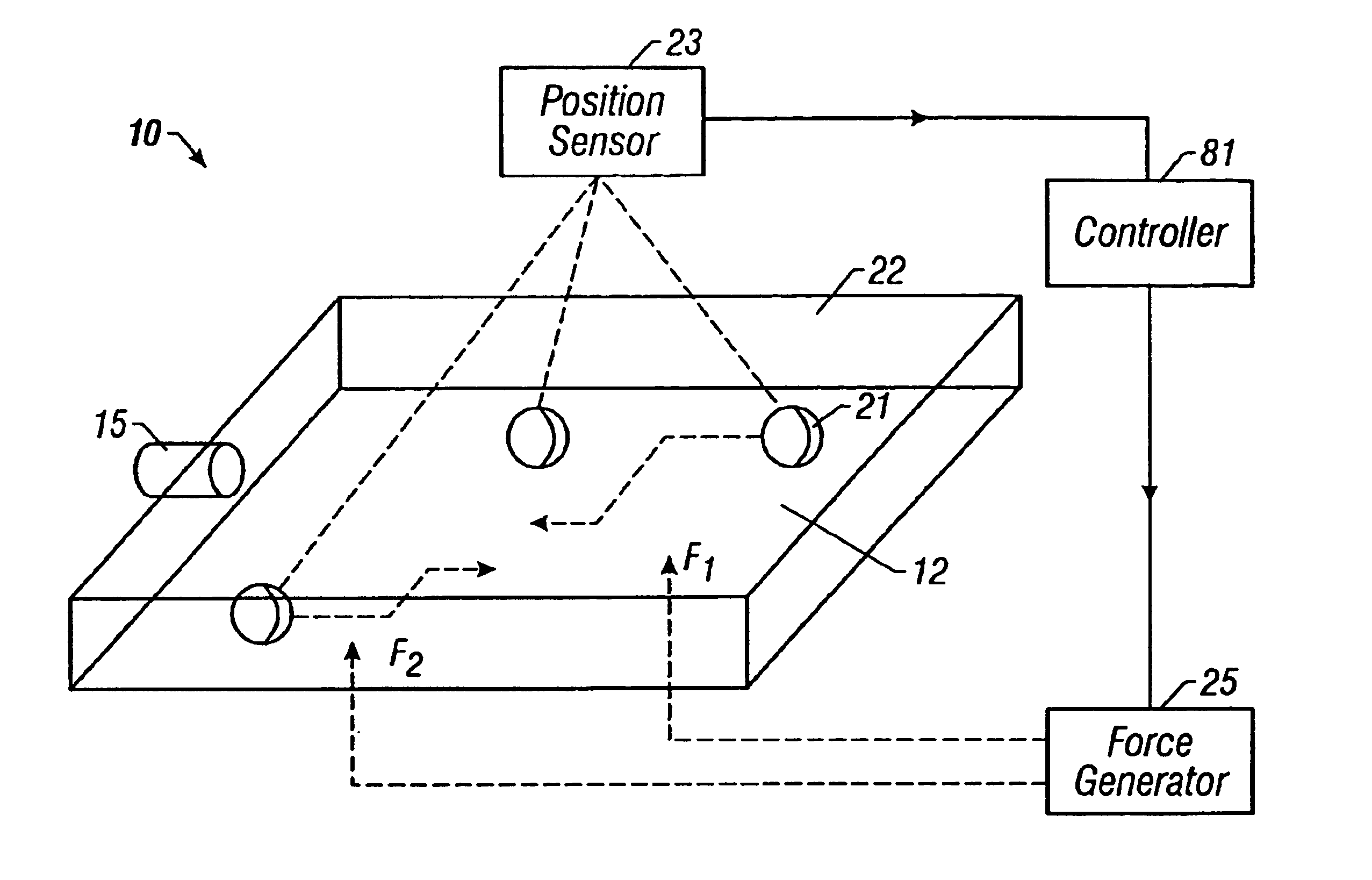
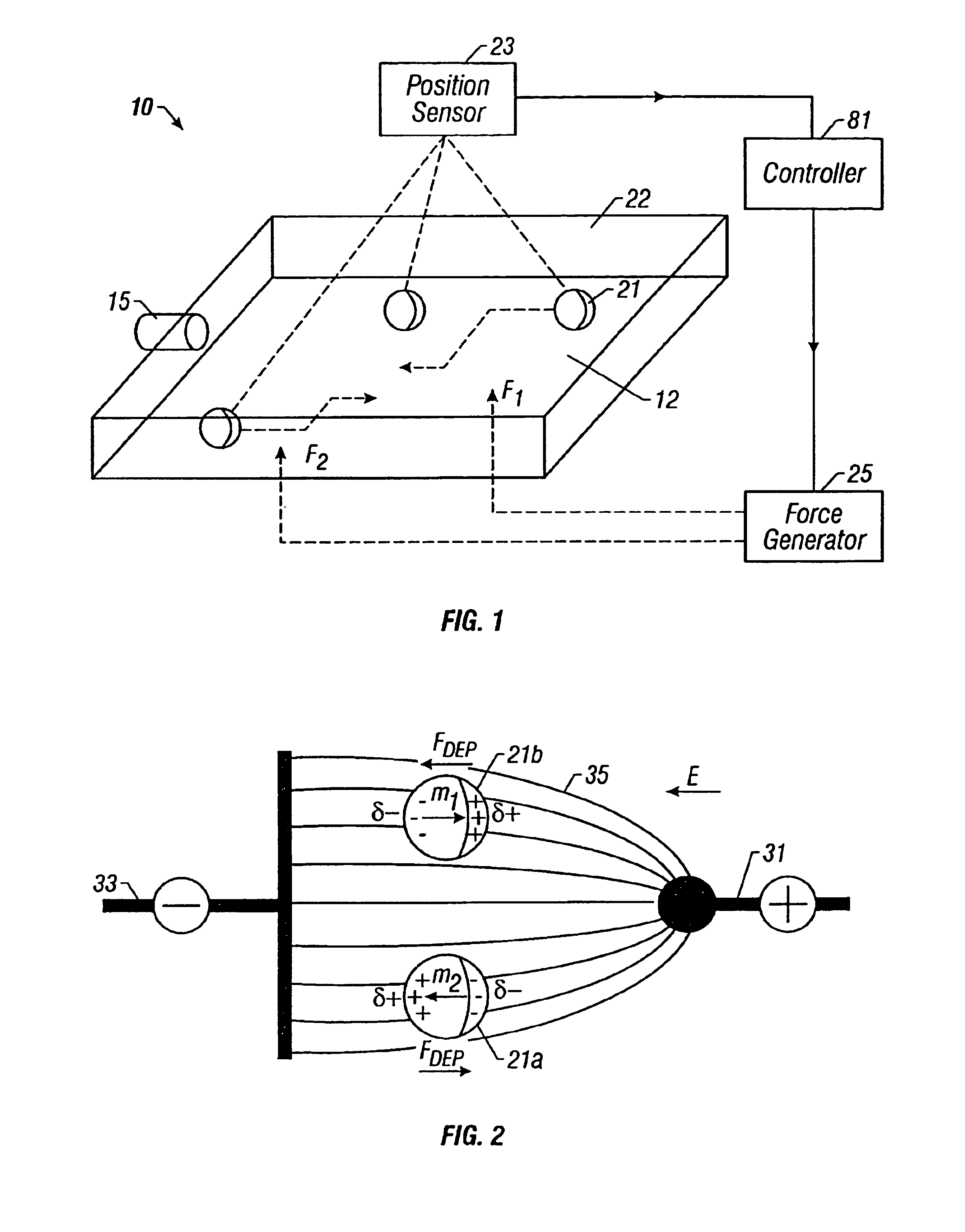
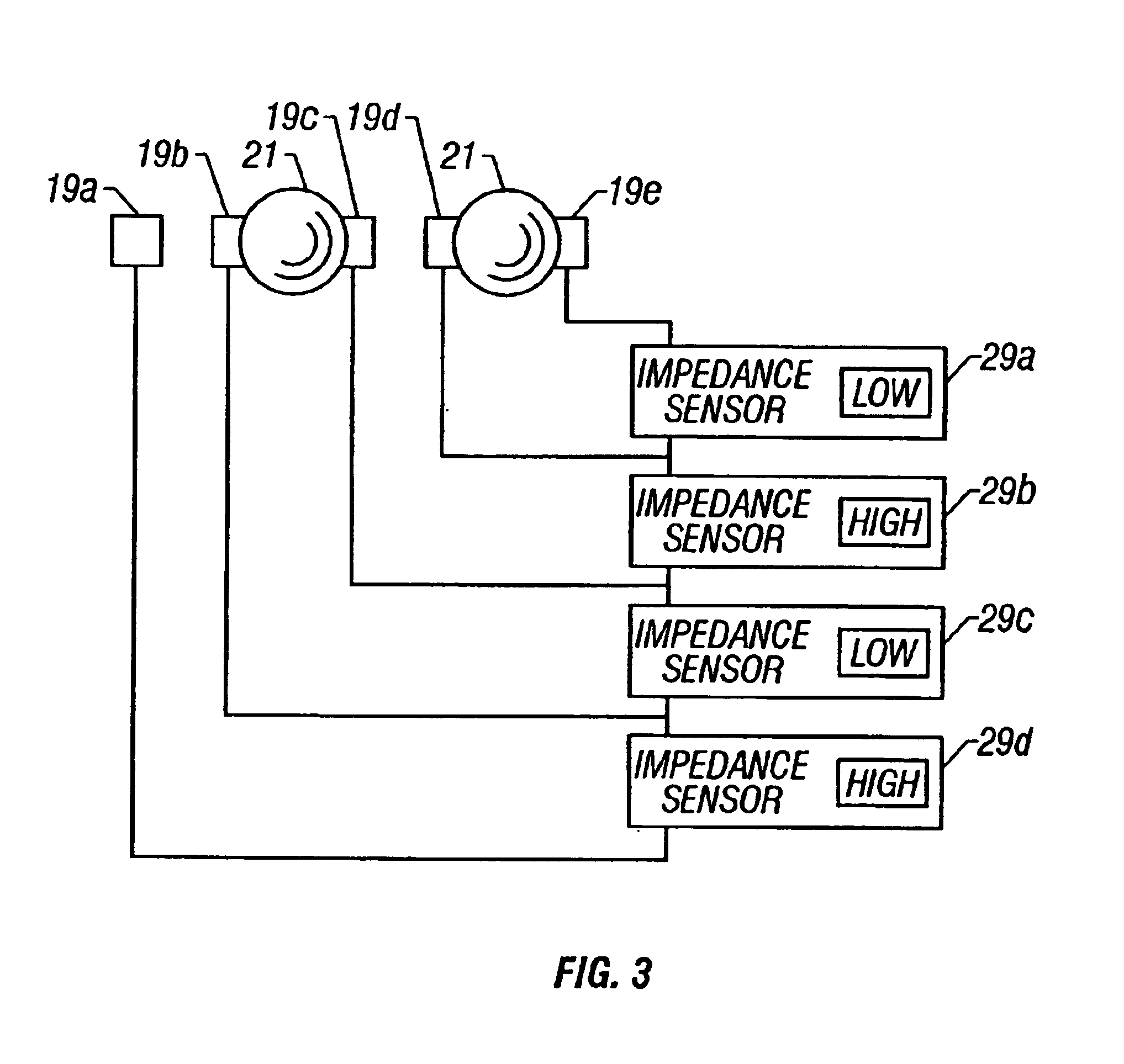
A method and apparatus for microfluidic processing by programmably manipulating a packet. A material is introduced onto a reaction surface and compartmentalized to form a packet. A position of the packet is sensed with a position sensor. A programmable manipulation force is applied to the packet at the position. The programmable manipulation force is adjustable according to packet position by a controller. The packet is programmably moved according to the programmable manipulation force along arbitrarily chosen paths.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Systems and methods for optical actuation of microfluidics based on opto-electrowetting
InactiveUS6958132B2Improve performanceSludge treatmentMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansElectricityMicrofluidics
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Self-sealing materials and devices comprising same
InactiveUS20040052689A1Analysis using chemical indicatorsOther chemical processesPorous substratePipette
This invention relates to gas- or liquid-permeable materials that seal when exposed to water and methods of making such materials. In general, materials of this invention comprise a hydrogel adhered to pore walls of a porous substrate. The invention further relates to devices comprising self-sealing materials including, but not limited to, pipette tips, containers, intravenous liquid delivery systems, and syringe caps.
Owner:POREX TECHNOLOGIES CORP
Device for receiving and processing a sample
The present invention concerns devices for receiving and processing a sample. The device comprises a sample receiving element adapted to establish fluid communication with and receive a sample directly from a sample container. The sample receiving element also allows for introduction of a sample into the device. A first chamber is in fluid communication with the sample receiving element. One or more second chambers are in fluid communication with the first chamber. The device also comprises first and second ports. The first port provides for venting the device. The second port provides for establishing communication between the device and means for moving the sample from the sample receiving element to the first chamber and for moving the sample from the first chamber to the one or more second chambers. Also included as part of the device is means for controlling the precise amount of the sample introduced into each of the second chambers. The first chamber and / or one or more of the second chambers are adapted for processing the sample. Also disclosed are kits containing the above devices and methods of using the devices to process a sample.
Owner:ACCUMETRICS INC
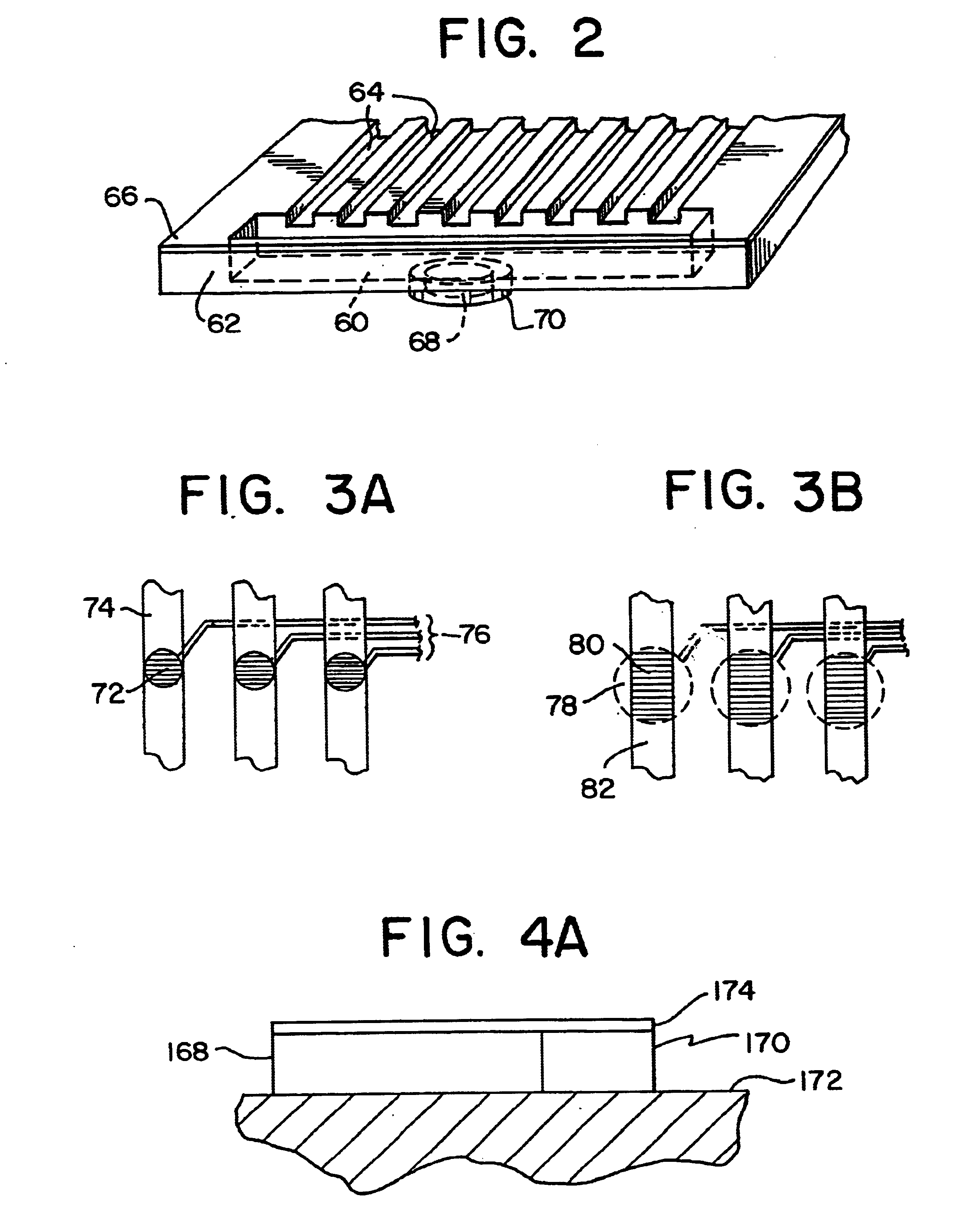
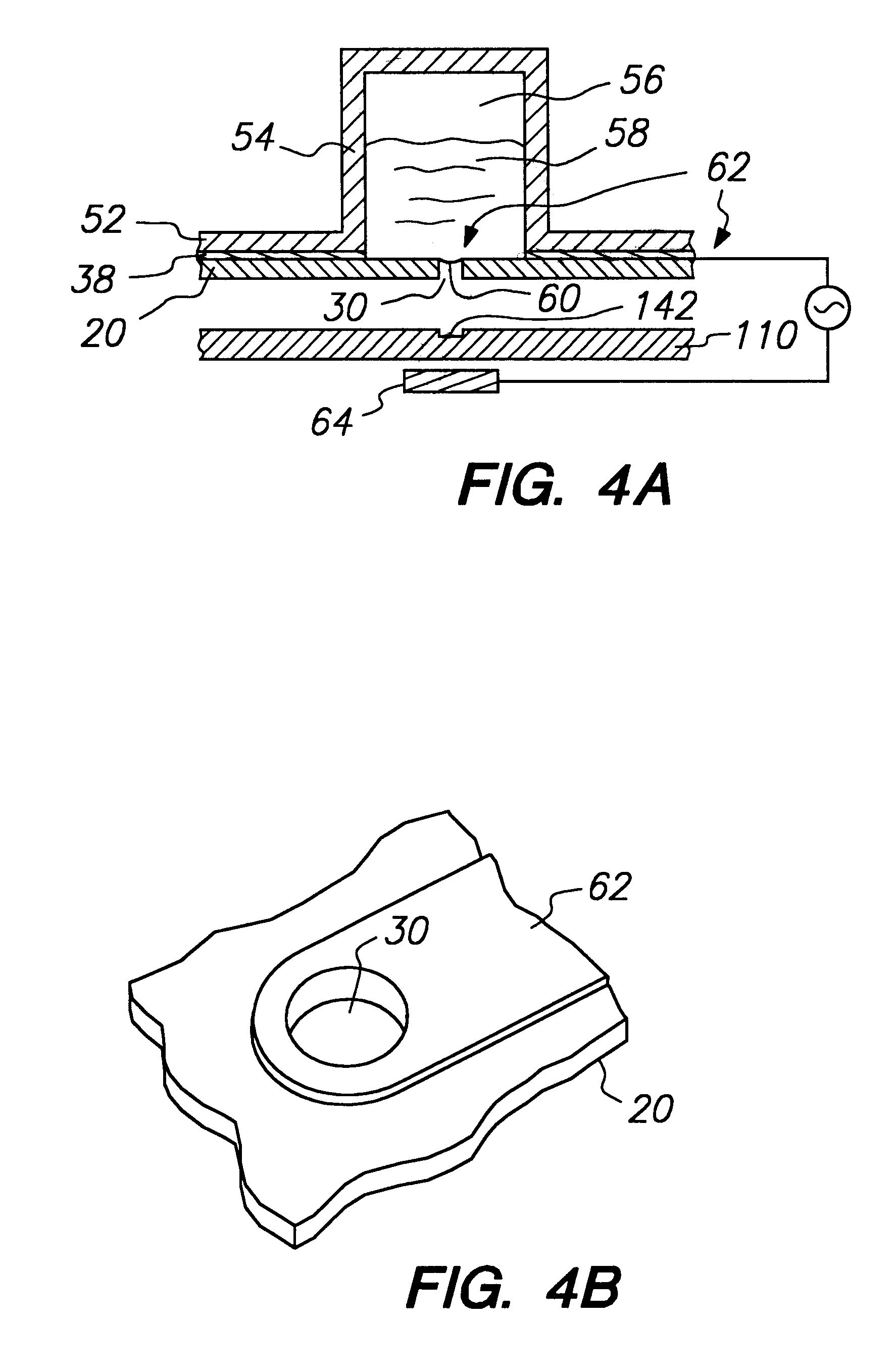
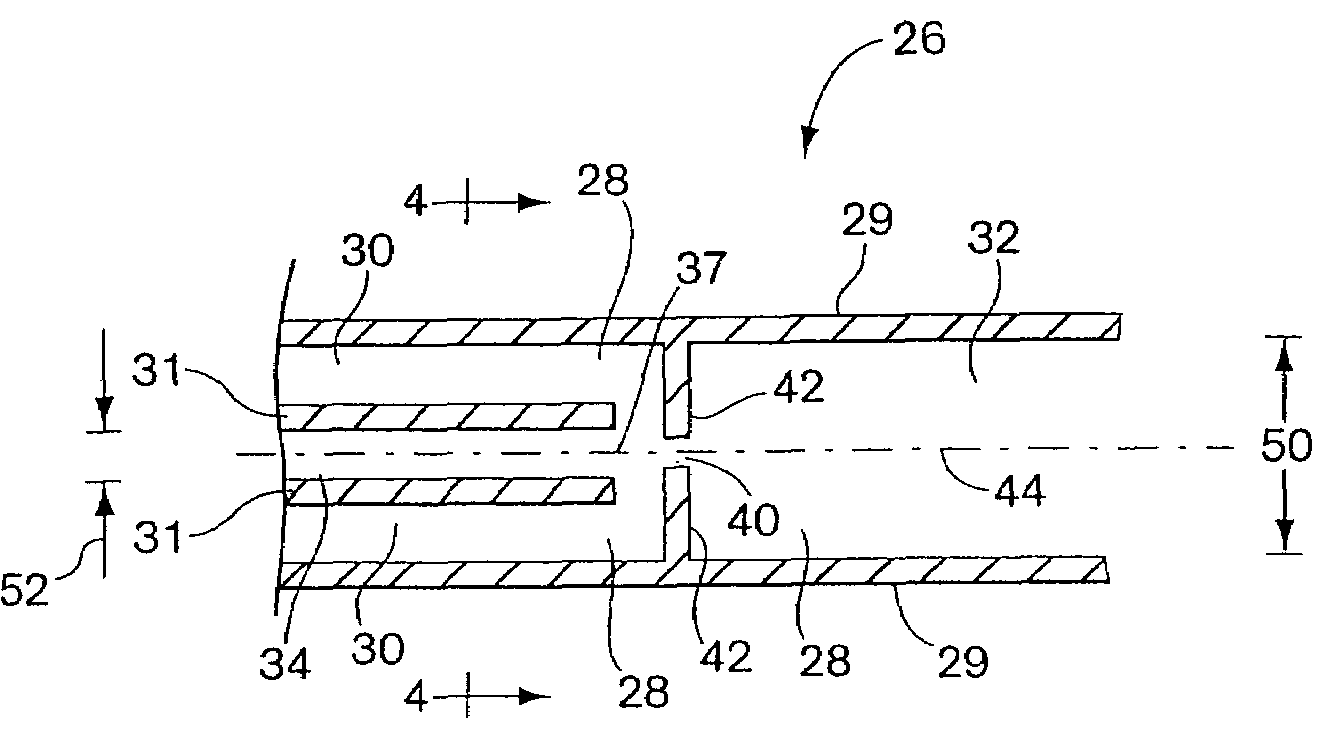
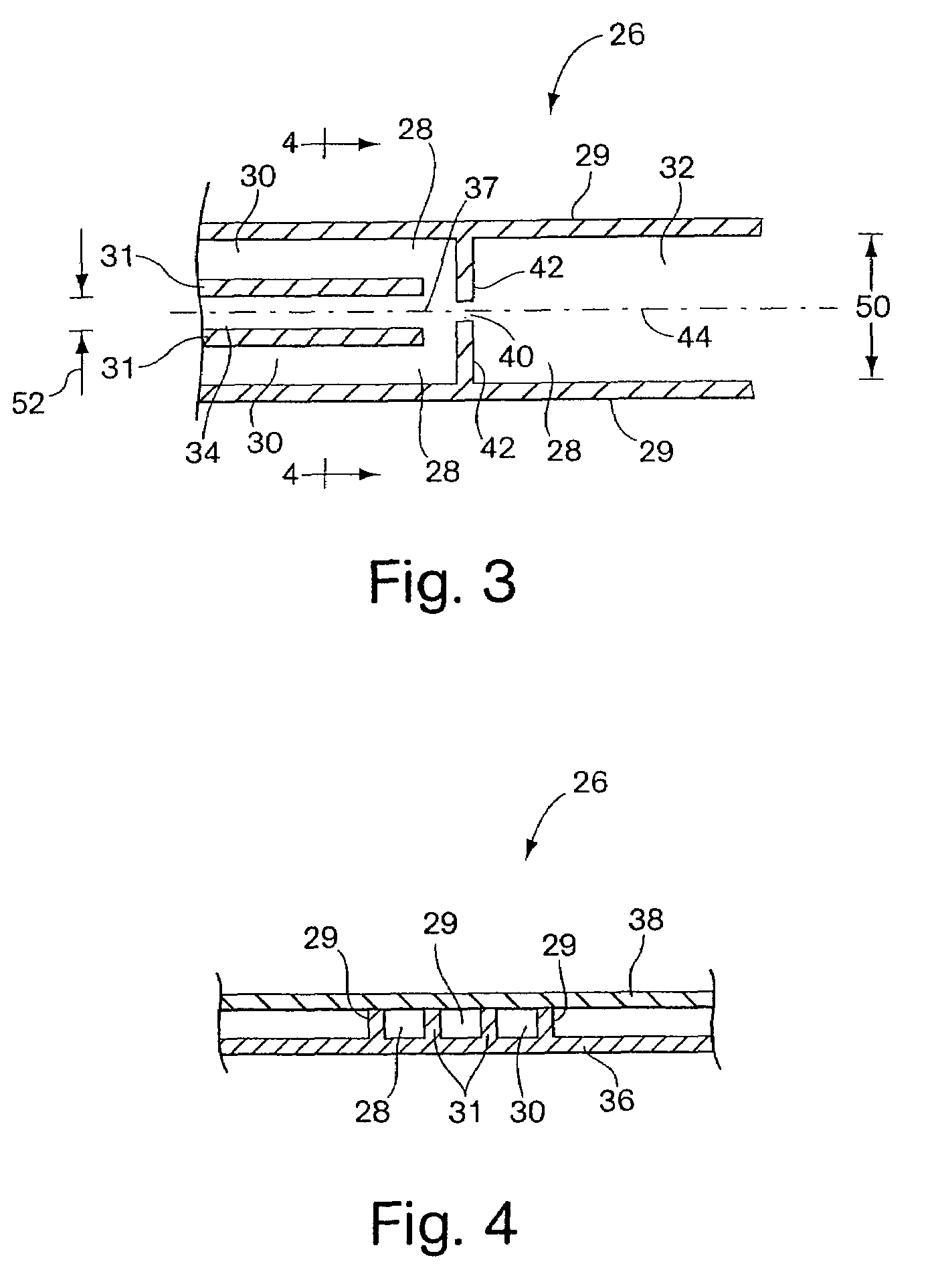
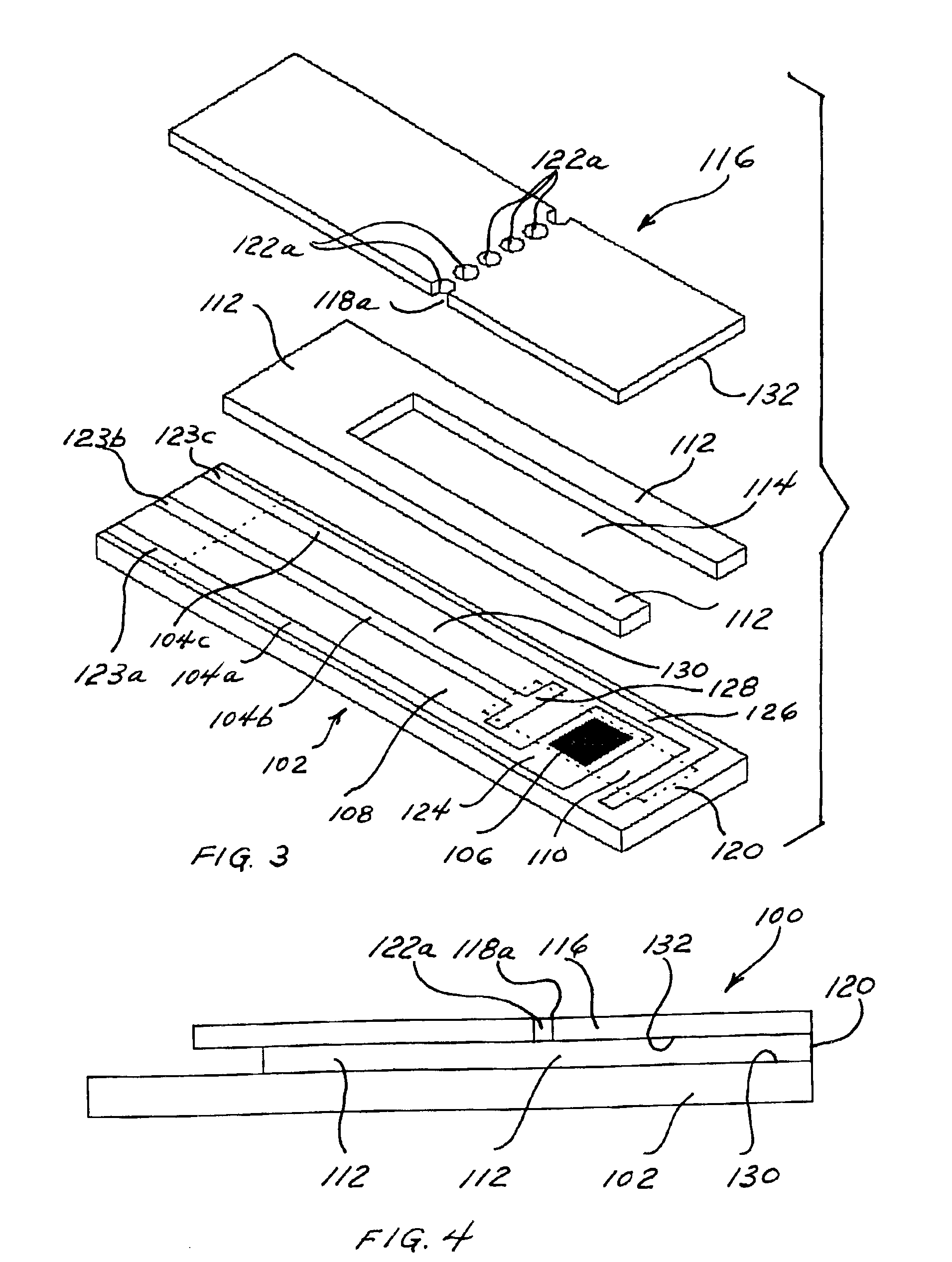
Integrated active flux microfluidic devices and methods
InactiveUS20040248167A1Increase speedImprove accuracyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsFlow mixersAntigenHybridization probe
The invention relates to a microfabricated device for the rapid detection of DNA, proteins or other molecules associated with a particular disease. The devices and methods of the invention can be used for the simultaneous diagnosis of multiple diseases by detecting molecules (e.g. amounts of molecules), such as polynucleotides (e.g., DNA) or proteins (e.g., antibodies), by measuring the signal of a detectable reporter associated with hybridized polynucleotides or antigen / antibody complex. In the microfabricated device according to the invention, detection of the presence of molecules (i.e., polynucleotides, proteins, or antigen / antibody complexes) are correlated to a hybridization signal from an optically-detectable (e.g. fluorescent) reporter associated with the bound molecules. These hybridization signals can be detected by any suitable means, for example optical, and can be stored for example in a computer as a representation of the presence of a particular gene. Hybridization probes can be immobilized on a substrate that forms part of or is exposed to a channel or channels of the device that form a closed loop, for circulation of sample to actively contact complementary probes. Universal chips according to the invention can be fabricated not only with DNA but also with other molecules such as RNA, proteins, peptide nucleic acid (PNA) and polyamide molecules.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
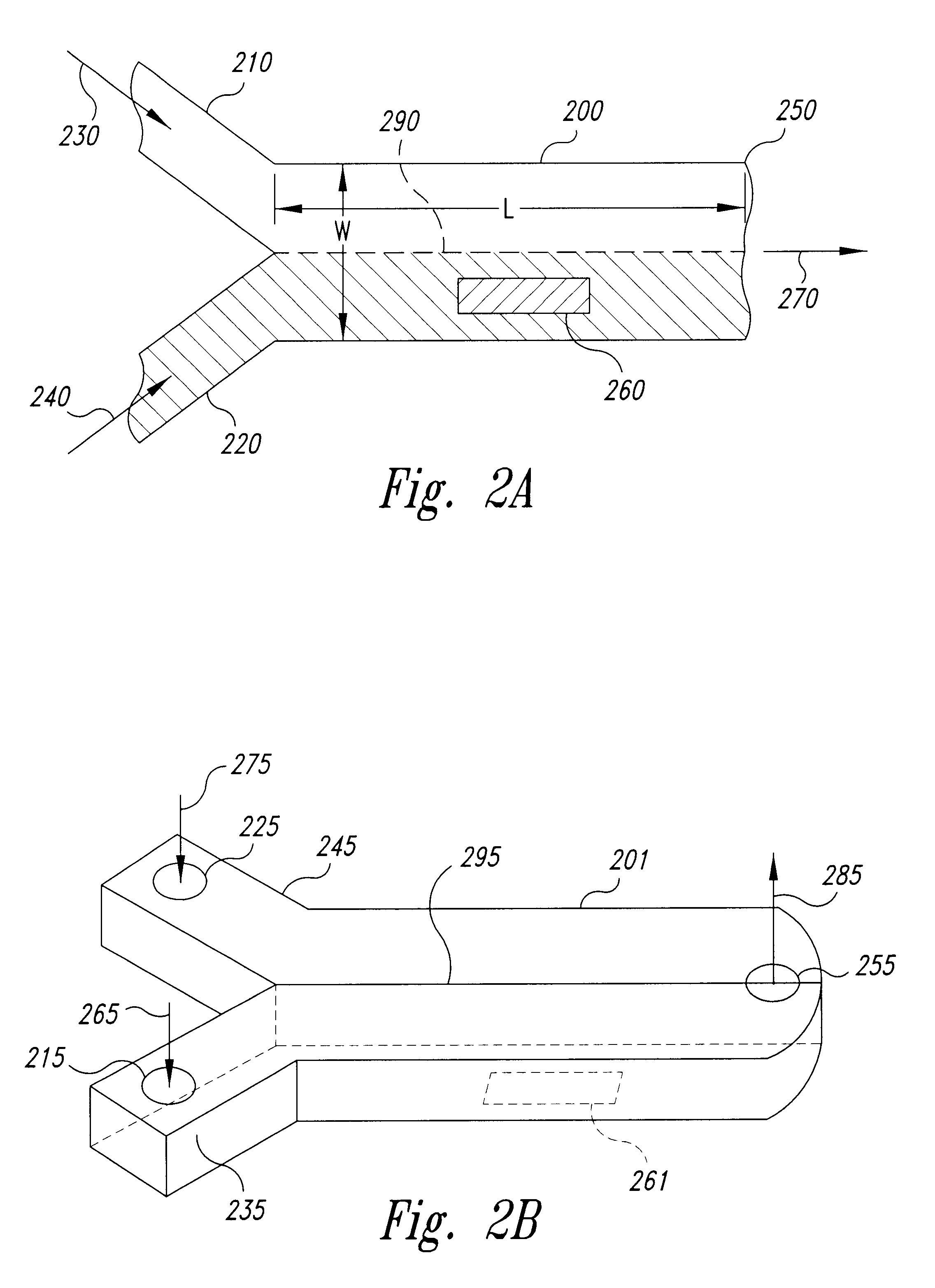
Method and device for laminar flow on a sensing surface
Methods and devices are provided for controlling a fluid flow over a sensing surface within a flow cell. The methods employ laminar flow techniques to position a fluid flow over one or more discrete sensing areas on the sensing surface of the flow cell. Such methods permit selective sensitization of the discrete sensing areas, and provide selective contact of the discrete sensing areas with a sample fluid flow. Immobilization of a ligand upon the discrete sensing area, followed by selective contact with an analyte contained within the sample fluid flow, allows analysis by a wide variety of techniques. Sensitized sensing surfaces, and sensor devices and systems are also provided.
Owner:GE HEALTHCARE BIO SCI CORP
Device having a flow channel
InactiveUS6939450B2High strengthImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsOptical measurementsEngineering
A device having a flow channel, wherein at least one flow-terminating interface is used to control the flow of liquid in the flow channel. The flow-terminating interface prevents the flow of the liquid beyond the interface. In one aspect, the invention provides a sensor, such as, for example, a biosensor, in the form of a strip, the sensor being suitable for electrochemical or optical measurement. The sensor comprises a base layer and a cover layer, and the base layer is separated from the cover layer by a spacer layer. The base layer, cover layer, and spacer layer define a flow channel into which a liquid sample is drawn therein and flows therethrough by means of capillary attraction. The flow of the sample is terminated by a flow-terminating interface positioned in the flow channel.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
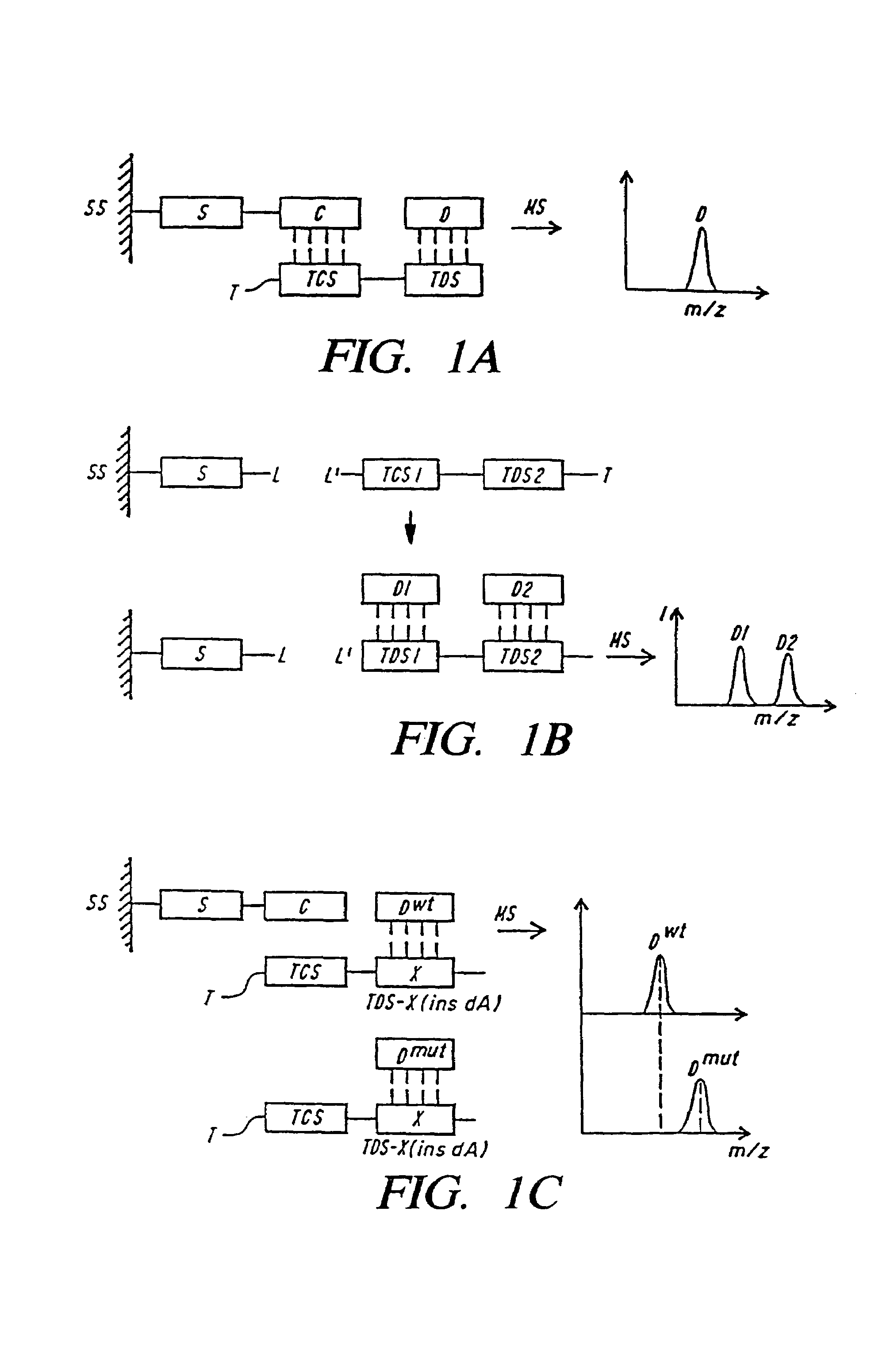
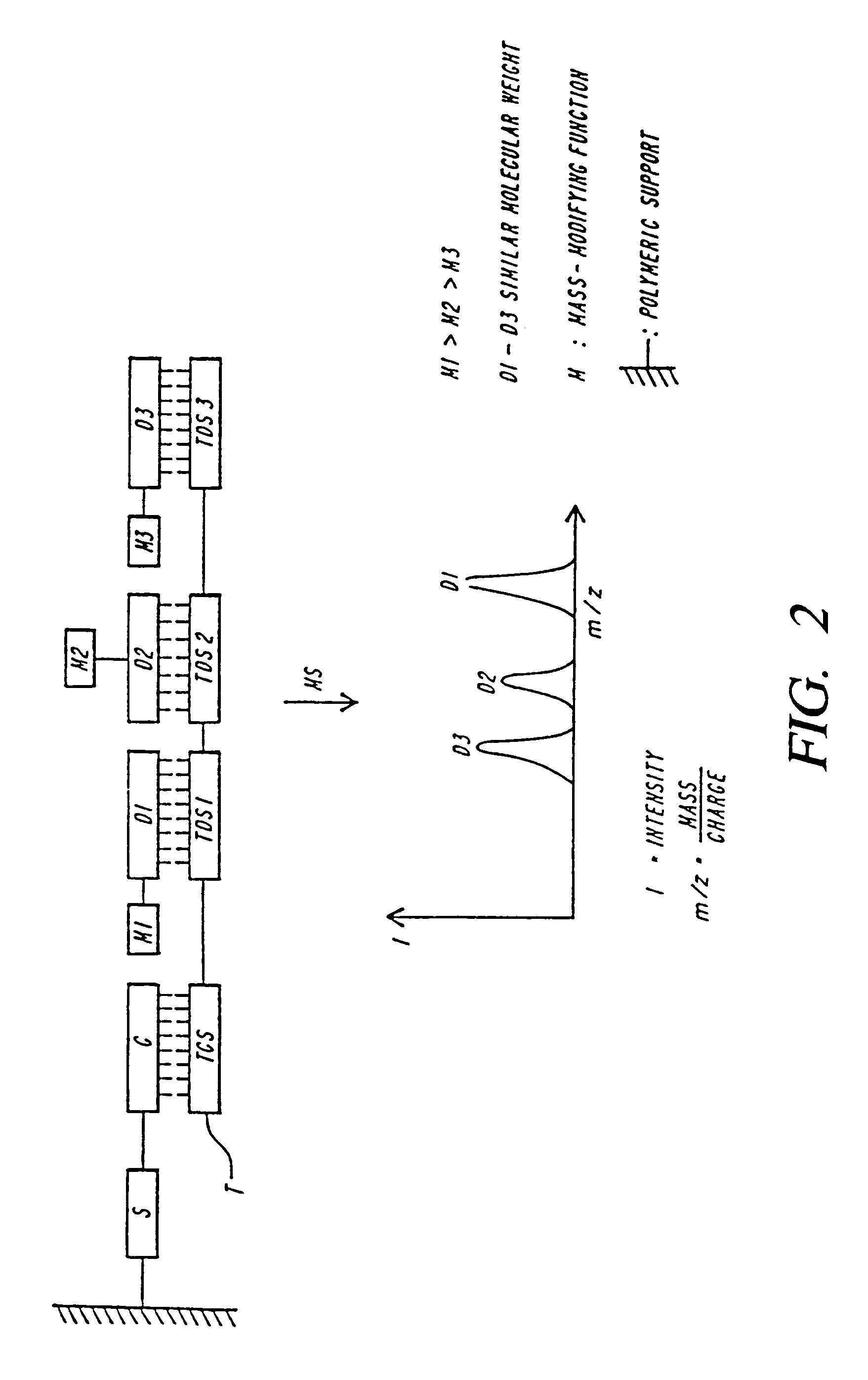
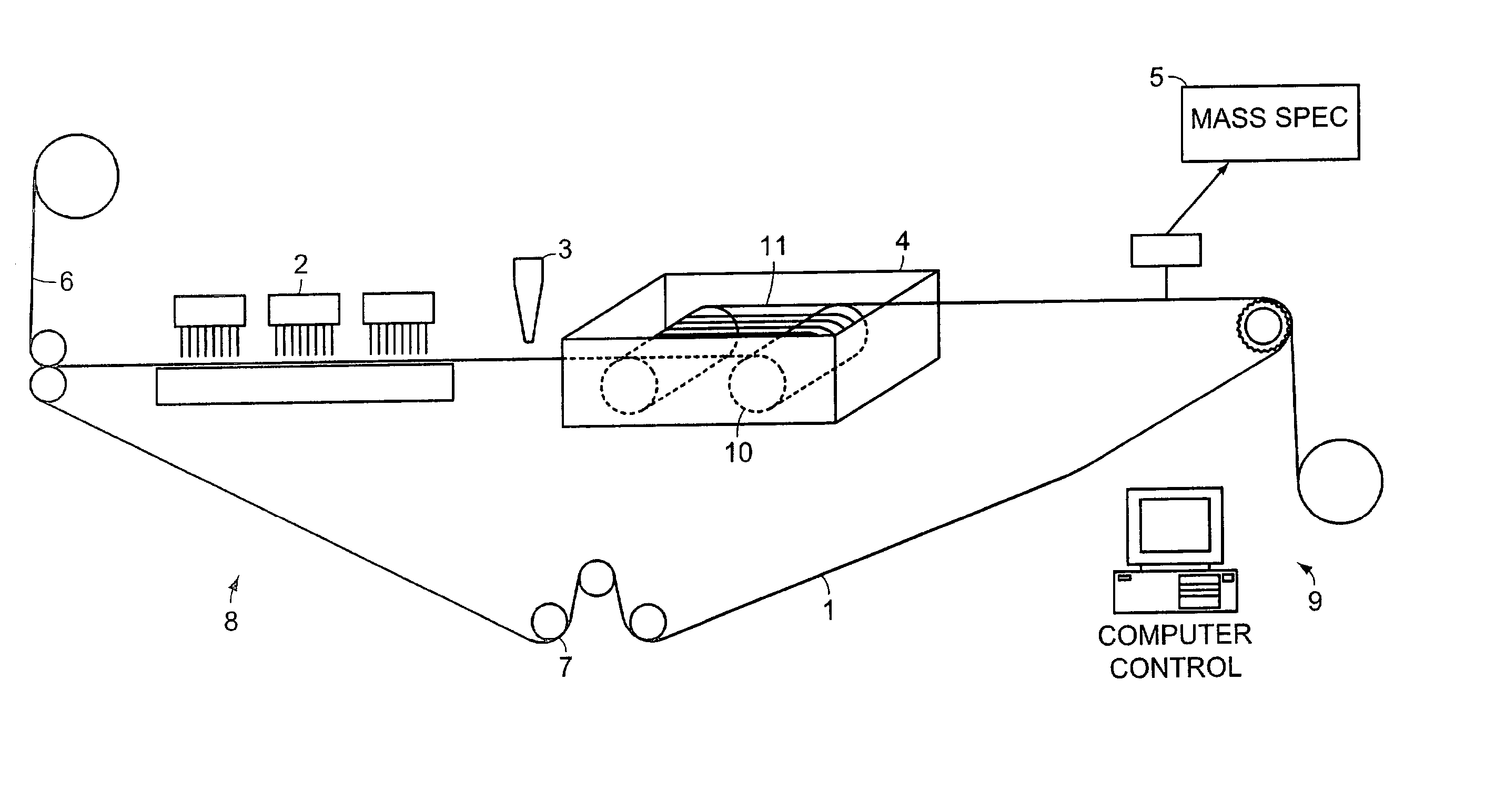
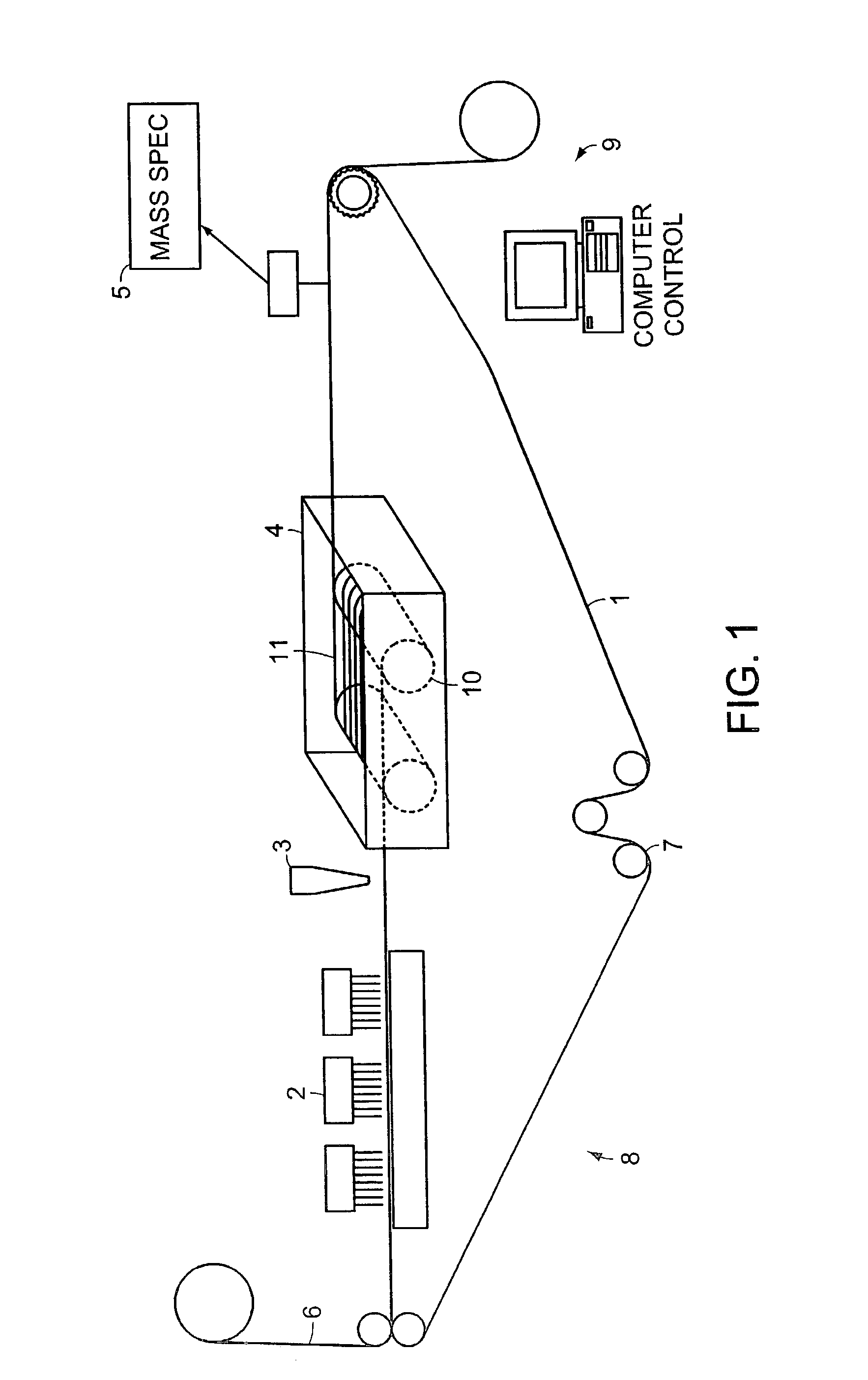
DNA diagnostics based on mass spectrometry
InactiveUS7198893B1Increase mass resolution massIncrease mass mass accuracyPeptide librariesSequential/parallel process reactionsMass spectrometry imagingOrganism
Fast and highly accurate mass spectrometry-based processes for detecting a particular nucleic acid sequence in a biological sample are provided. Depending on the sequence to be detected, the processes can be used, for example, to diagnose a genetic disease or chromosomal abnormality; a predisposition to a disease or condition, infection by a pathogenic organism, or for determining identity or heredity.
Owner:AGENA BIOSCI
Sample Preparation System And Method for Processing Clinical Specimens
ActiveUS20080247914A1Reduce turnaround timeLow efficiencyAnalysis using chemical indicatorsMicrobiological testing/measurementRobotic systemsMolecular analysis
A system and method for automated handling of vials containing liquid medical specimens is disclosed. The robotic system processes the specimens for further downstream molecular analysis. The processing comprises automated vial cap removal, pipetting of the vial contents, transfer of the vial contents to a destination tray such as a multiwell plate, and recapping of the vial.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Microfluidic sequencing systems
InactiveUS7238323B2Minimize contaminationIncrease speedBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsGenomic screeningSoftware
Owner:CAPLIPER LIFE SCI INC
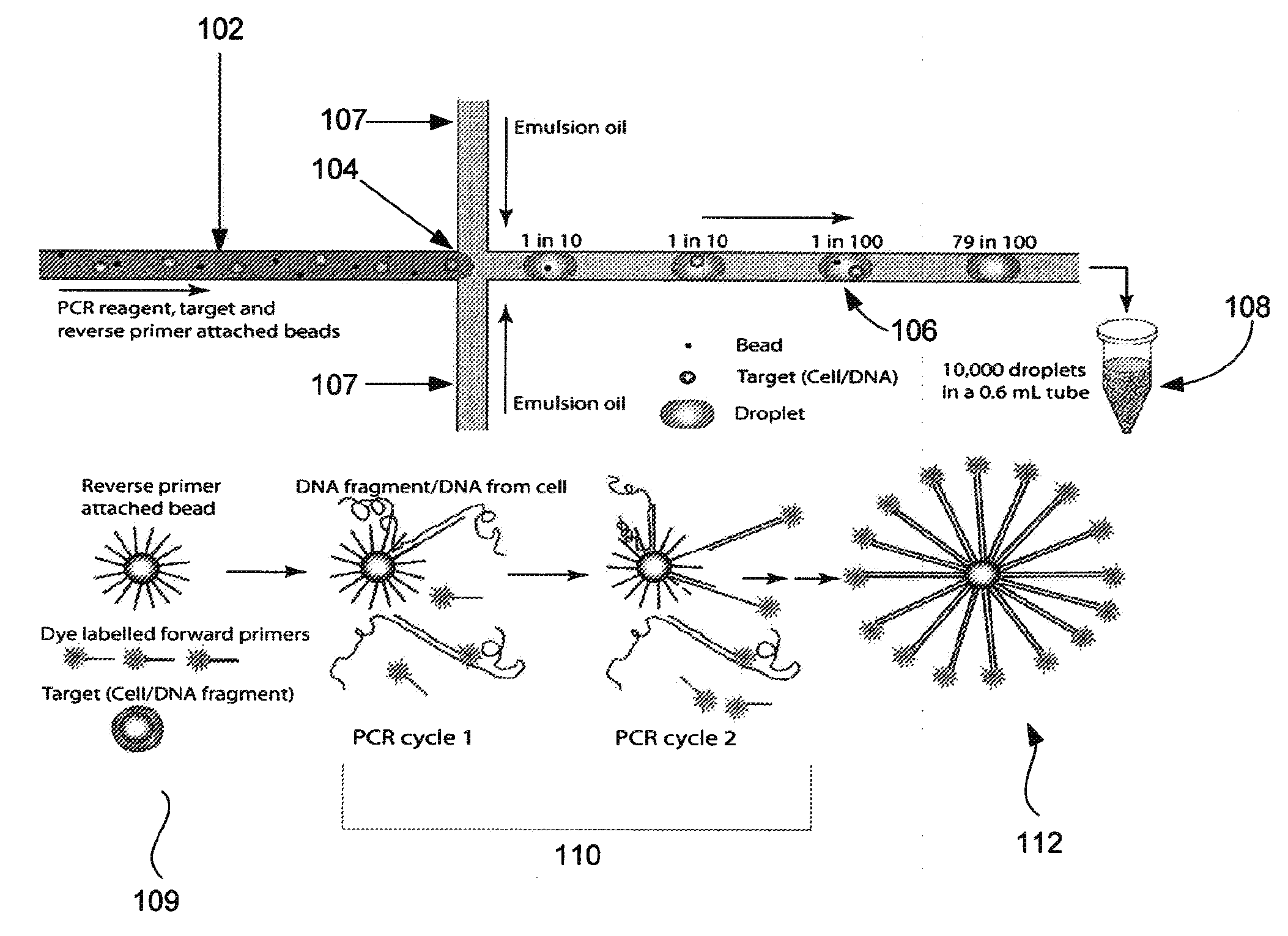
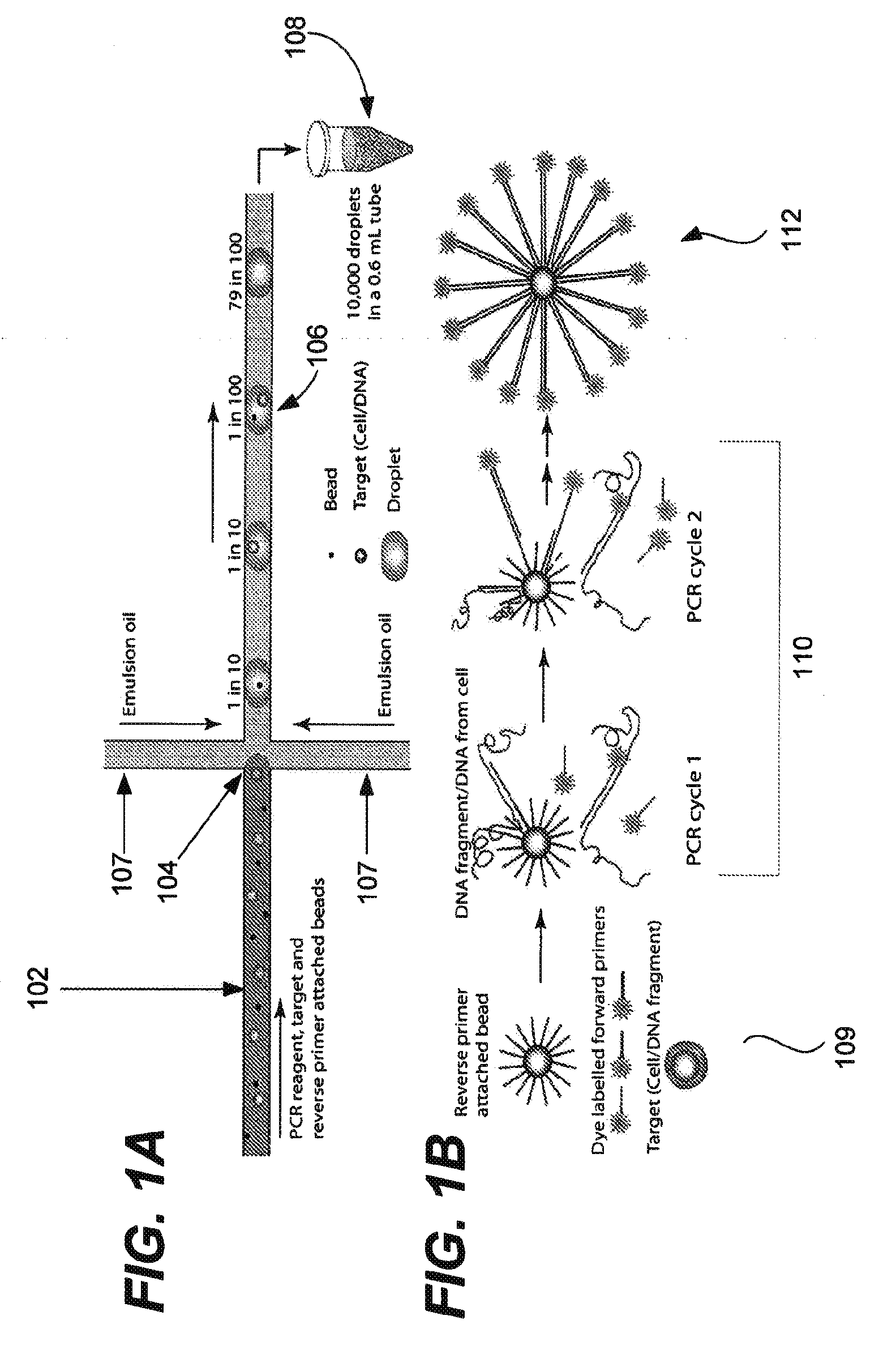
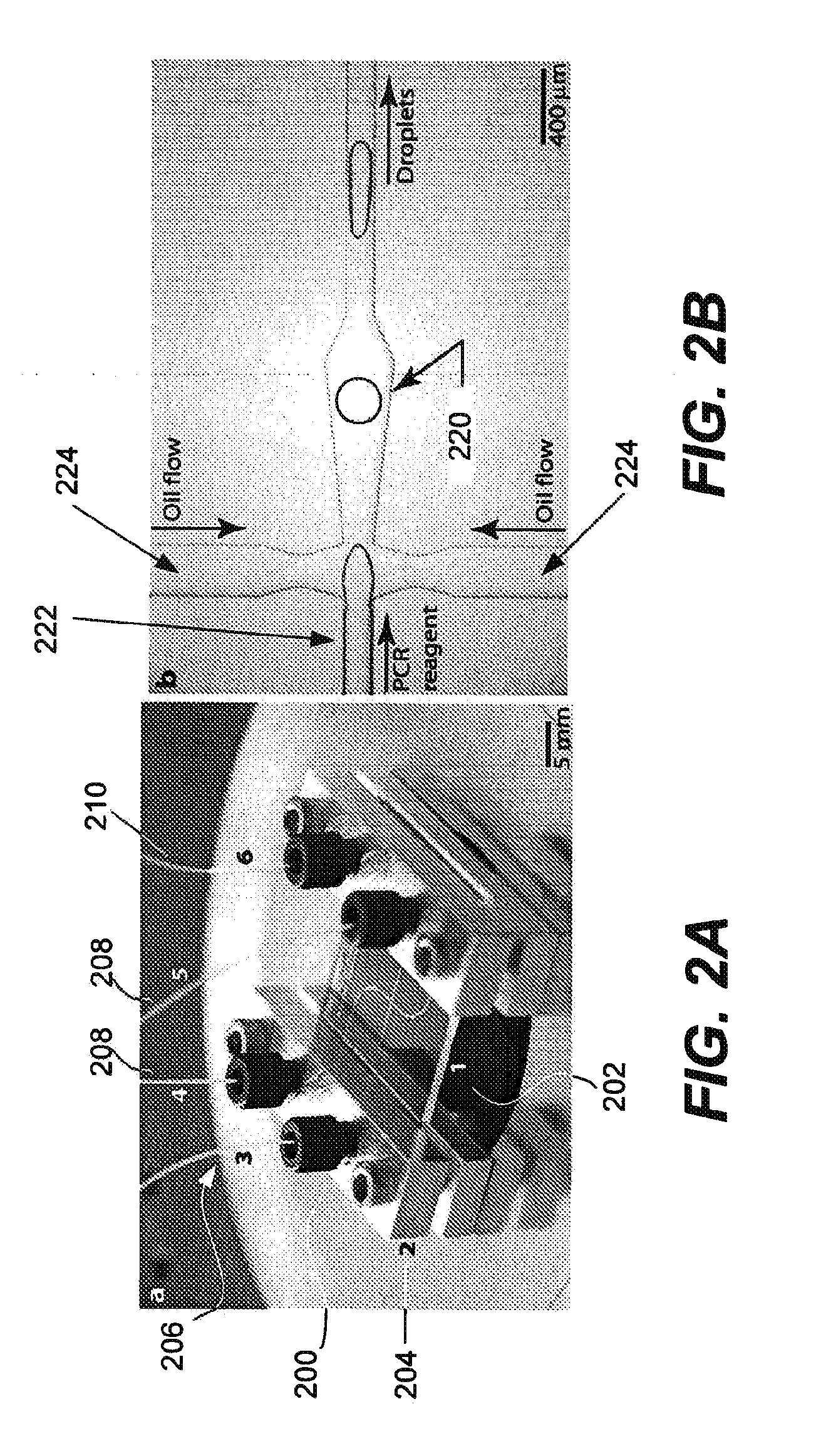
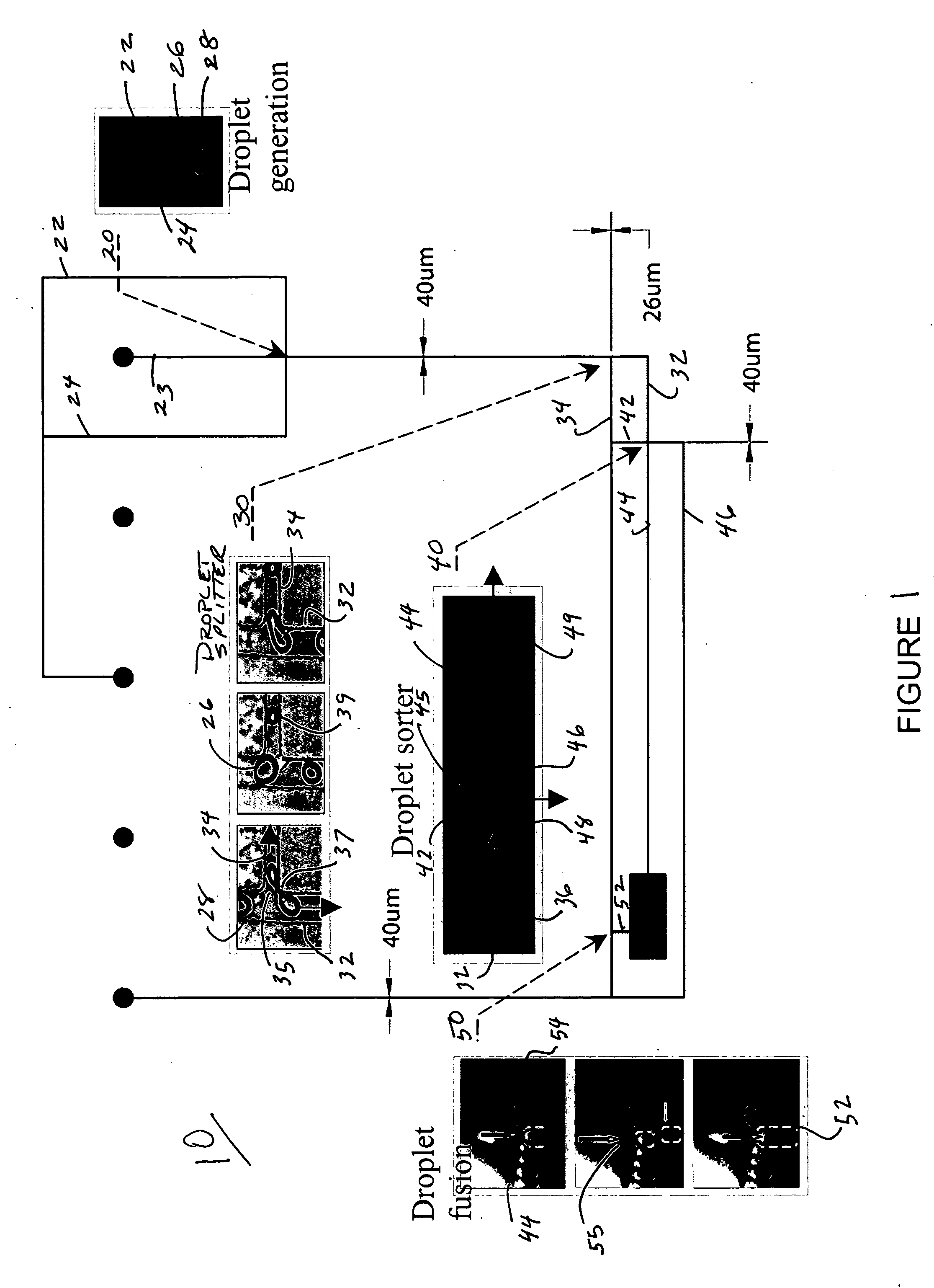
Microfabricated droplet generator for single molecule/cell genetic analysis in engineered monodispersed emulsions
ActiveUS20100285975A1Efficient routingEfficient single-molecule amplificationTransportation and packagingLibrary screeningEmulsionMicroparticle
Provided are microfluidic designs and methods for rapid generation of monodisperse nanoliter volume droplets of reagent / target (e.g., molecule or cell) mix in emulsion oil. The designs and methods enable high-throughput encapsulation of a single target (e.g., DNA / RNA molecules or cells) in controlled size droplets of reagent mix. According to various embodiments, a microfabricated, 3-valve pump is used to precisely meter the volume of reagent / target mix in each droplet and also to effectively route microparticles such as beads and cells into the device, which are encapsulated within droplets at the intersection of the reagent channel and an oil channel. The pulsatile flow profile of the microfabricated pumps provides active control over droplet generation, thereby enabling droplet formation with oils that are compatible with biological reactions but are otherwise difficult to form emulsions with.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Methods for microdispensing patterened layers
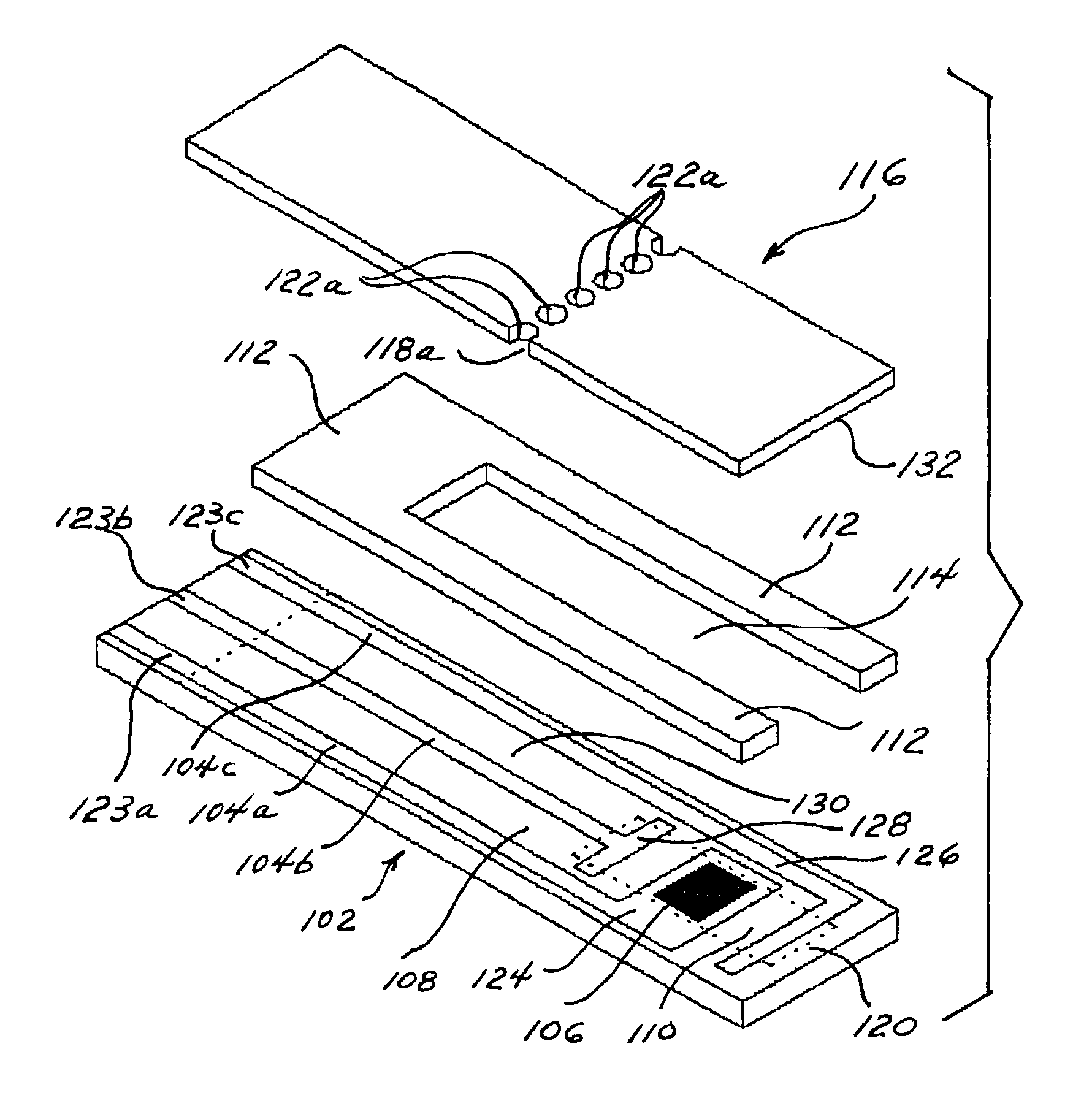
InactiveUS6306594B1Efficient couplingShort response timeMicrobiological testing/measurementBurettes/pipettesAnalyteClinical settings
An efficient method for the microfabrication of electronic devices which have been adapted for the analyses of biologically significant analyte species is described. The techniques of the present invention allow for close control over the dimensional features of the various components and layers established on a suitable substrate. Such control extends to those parts of the devices which incorporate the biological components which enable these devices to function as biological sensors. The materials and methods disclosed herein thus provide an effective means for the mass production of uniform wholly microfabricated biosensors. Various embodiments of the devices themselves are described herein which are especially suited for real time analyses of biological samples in a clinical setting. In particular, the present invention describes assays which can be performed using certain ligand / ligand receptor-based biosensor embodiments. The present invention also discloses a novel method for the electrochemical detection of particular analyte species of biological and physiological significance using an substrate / label signal generating pair which produces a change in the concentration of electroactive species selected from the group consisting of dioxygen and hydrogen peroxide.
Owner:I STAT CORP
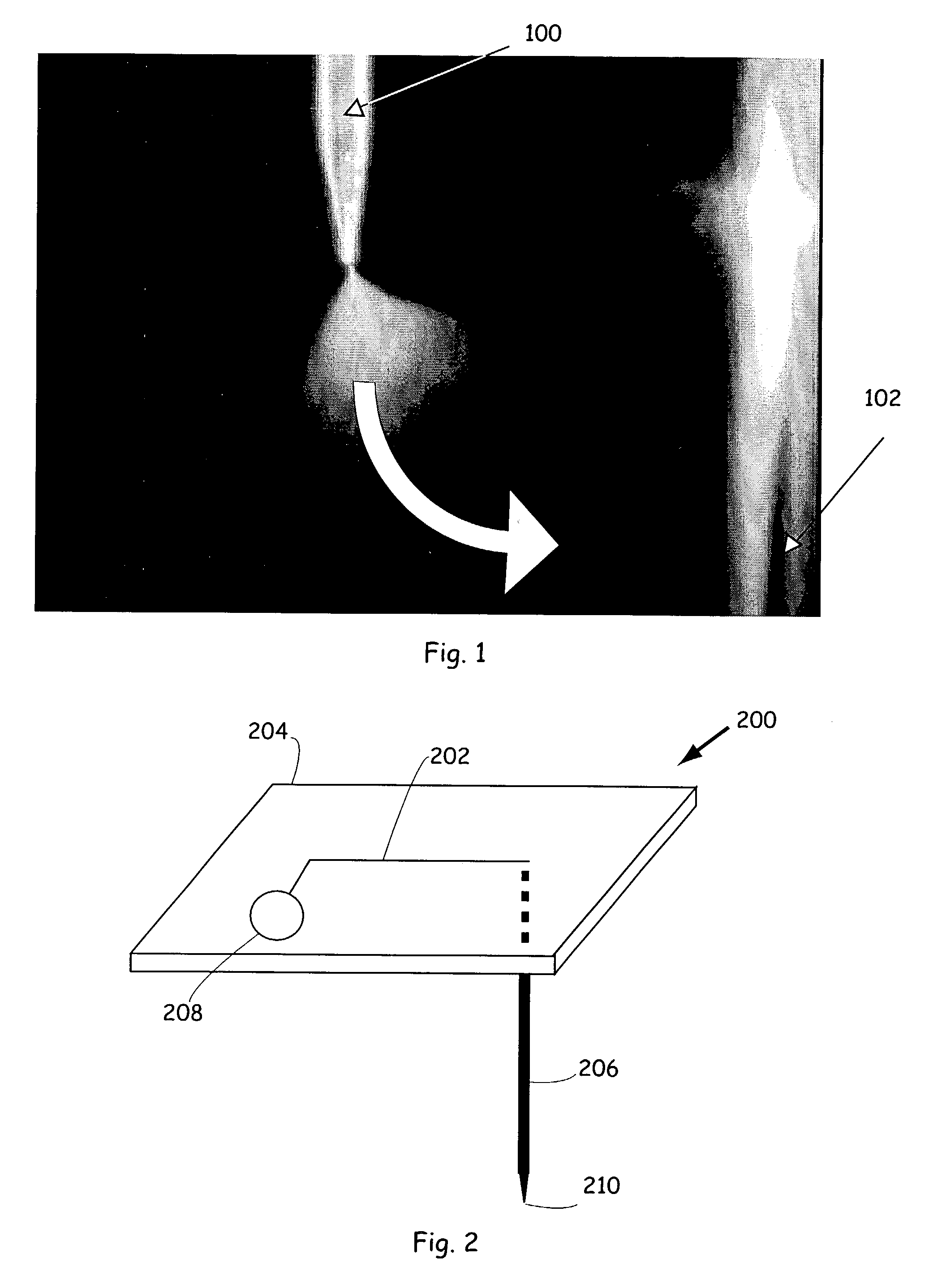
Microfluidic sample delivery devices, systems, and methods
ActiveUS7303727B1Improve throughputResidue reductionParticle separator tubesComponent separationSpray nozzleMass spectrometry
Methods and apparatus for delivering fluidic materials to sample destinations, including mass spectrometers for analysis are provided. In preferred embodiments, sample aliquots are electrosprayed from tapered spray tips of capillary elements into the orifices of mass spectrometric inlet systems. In certain embodiments, fluidic samples are orthogonally sprayed from capillary elements or other fluid conduits, whereas in other embodiments samples are sprayed after devices are rotated or otherwise translocated from sample sources to sample destinations. In still other embodiments, samples are sprayed from flexed or deflected capillary elements at selected sample destinations.
Owner:CAPLIPER LIFE SCI INC
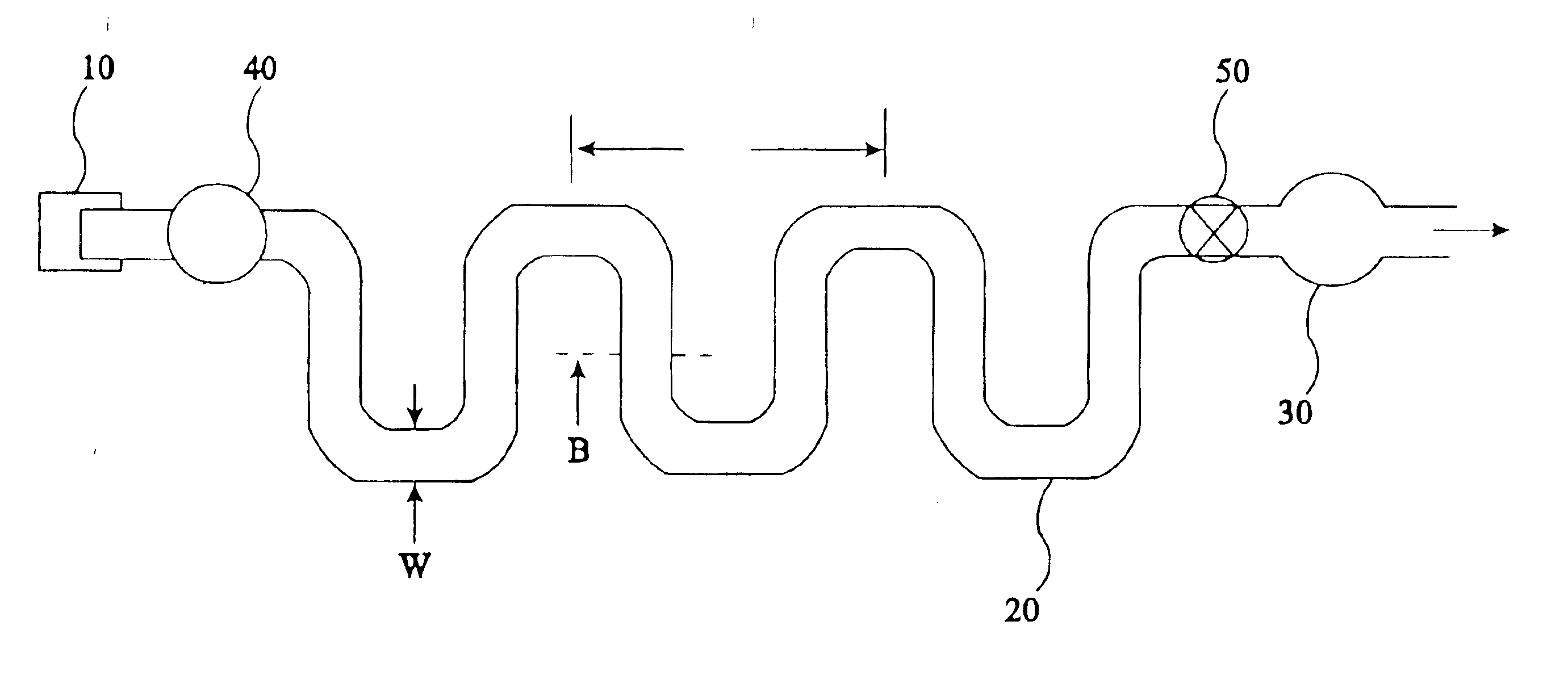
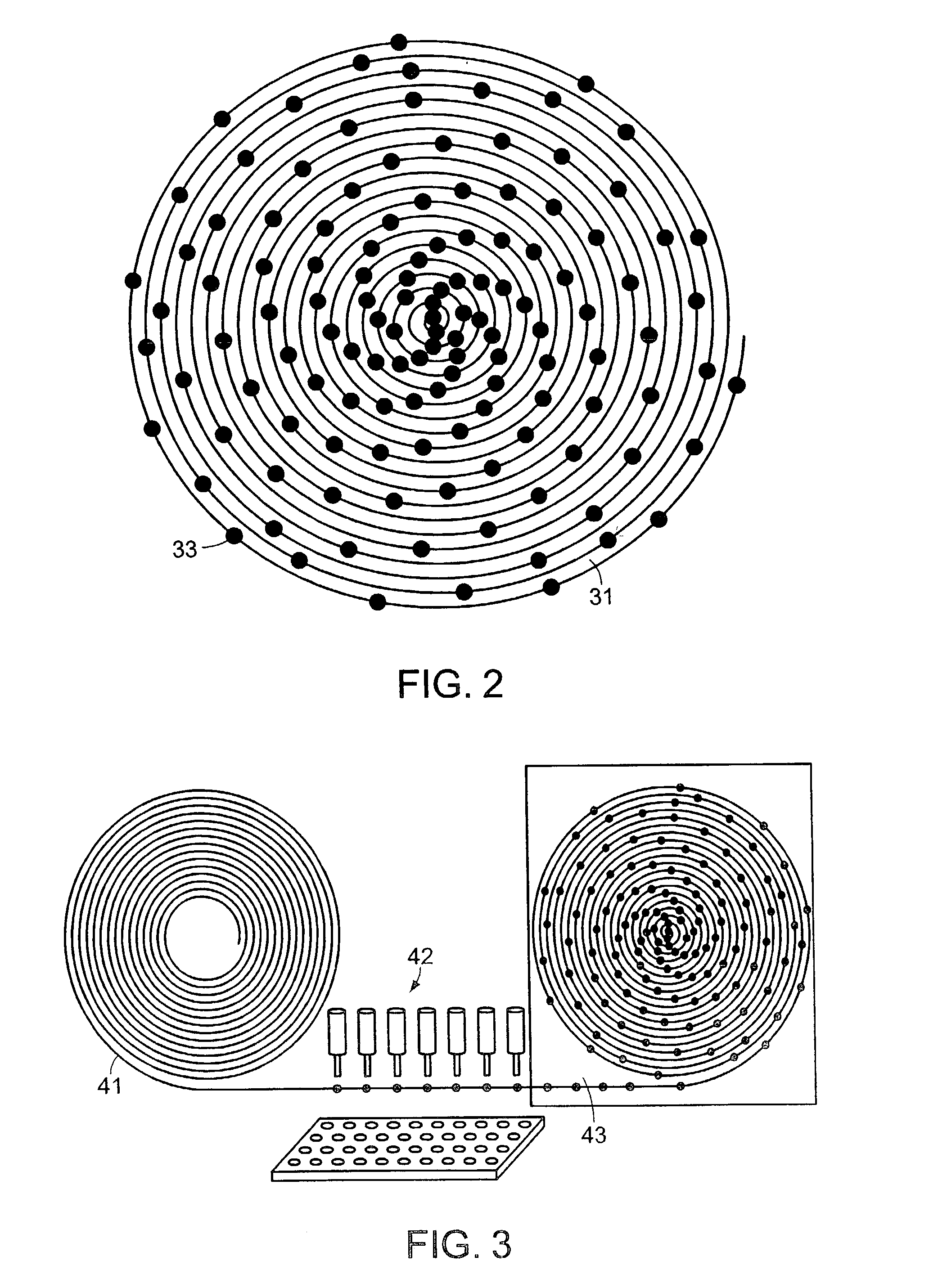
Liquid analysis cartridge
InactiveUS6852284B1Rapidly and effectively reconstituteEasy to reorganizeFlow mixersTransportation and packagingShell moldingDiluent
The present invention provides an apparatus and method for storing a particle-containing liquid. The storage apparatus comprises a microfluidic convoluted flow channel having a plurality of article capture regions. The storage channel is preferably an isotropic spatially periodic channel. Sedimented particles can be resuspended following storage. This invention further provides a microfluidic analysis cartridge having a convoluted storage channel therein. The sample analysis can use optical, electrical, pressure sensitive, or flow sensitive detection. A plurality of analysis channels can be included in a single cartridge. The analysis channels can be joined to reagent inlets for diluents, indicators or lysing agents. A mixing channel can be positioned between the reagent inlet and the analysis region to allow mixing and reaction of the reagent. The cartridge can include additional valves and pumps for flow management. The analysis cartridge can be a self-contained disposable cartridge having an integral waste storage container. This invention further provides a sheath flow assembly. The sheath flow assembly includes a sample channel and first and second sheath fluid channels positioned on either side of and converging with the sample channel. The assembly also includes upper and lower sheath fluid chambers positioned above and below and converging with the sample channel. The flow cartridges of this invention can be formed by molding, machining or etching. In a preferred embodiment they are laminated. This invention further provides a method of fabricating a laminated microfluidic flow device. In the method, flow elements are formed in rigid sheets and abutting surfaces of the sheets are bonded together.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
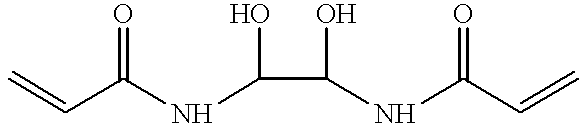
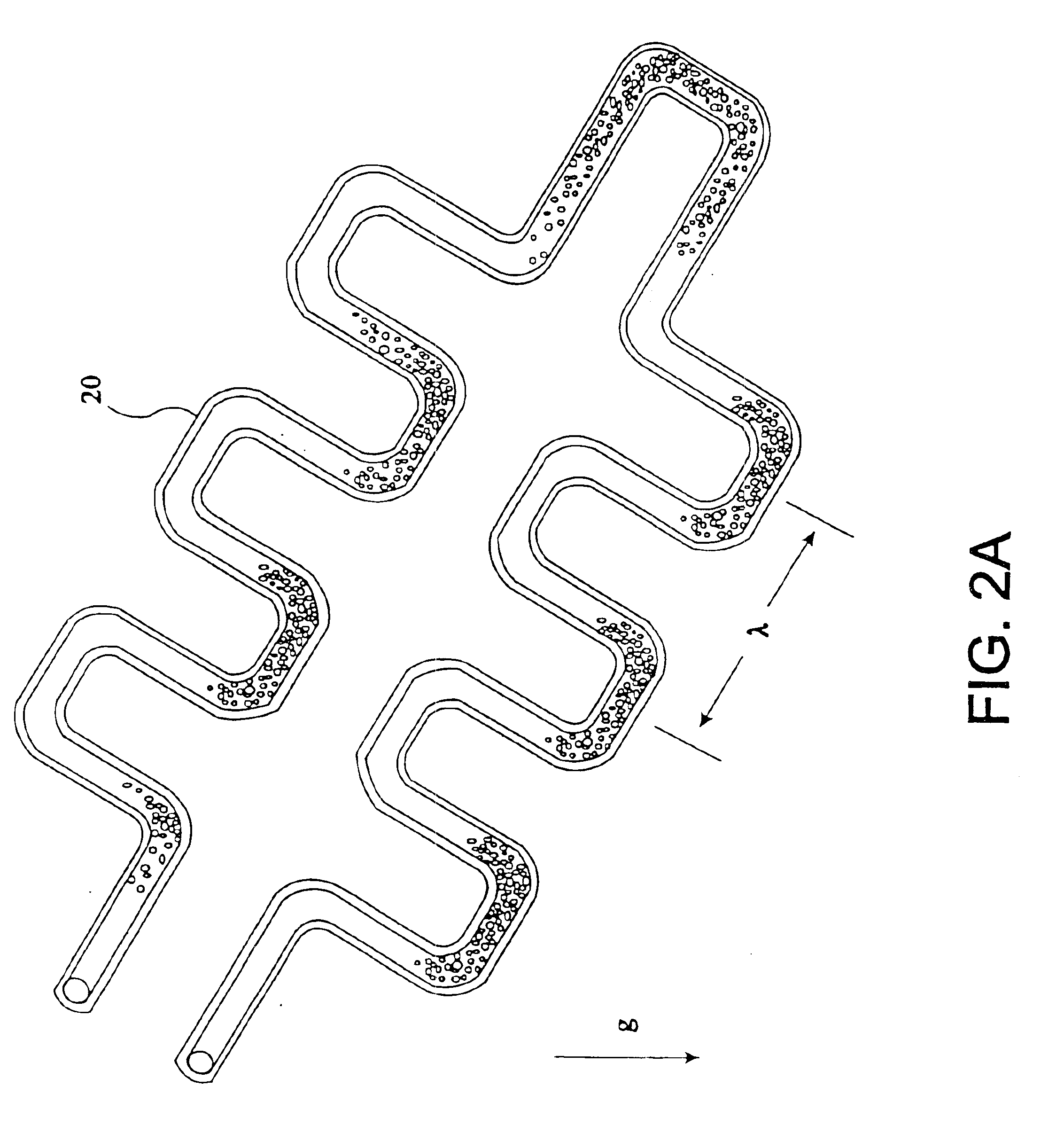
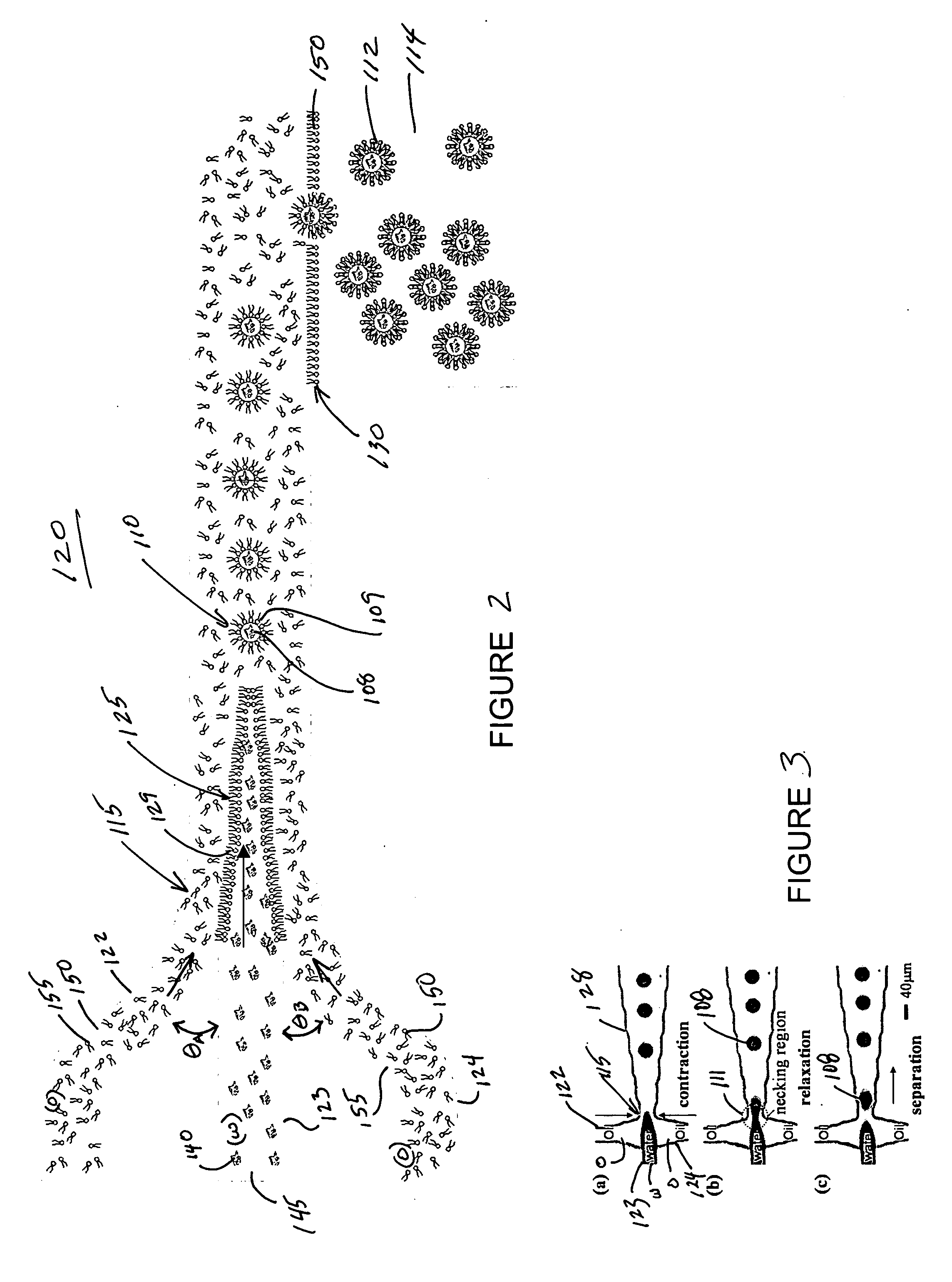
Microfluidic devices for controlled viscous shearing and formation of amphiphilic vesicles
ActiveUS20050032240A1Facilitates programmable control of sizeIncrease shear forceMixing methodsTransportation and packagingViscous shearEngineering
Systems and methods that control the size and composition of emulsified droplets, multi-lamellar and asymmetric vesicles, encapsulation of reagents, membrane proteins, and sorting of vesicles / droplets. More particularly, microfluidic devices for controlled viscous shearing of oil-water emulsions of micro- and nano-scale droplets, the subsequent formation of amphiphilic vesicles such as liposomes, polymer vesicles, micelles, and the like, the post-assembly and post-processing of the droplets including splitting, fusing, sorting and the like, polymer emulsions, and the integration of amphiphilic vesicle production-line on a single microfluidic chip. Preferably, the microfluidic device enables oil-water co-flows with tunable viscous shear forces higher than the immiscible interfacial tension forces that generate favorable conditions for droplet formation.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
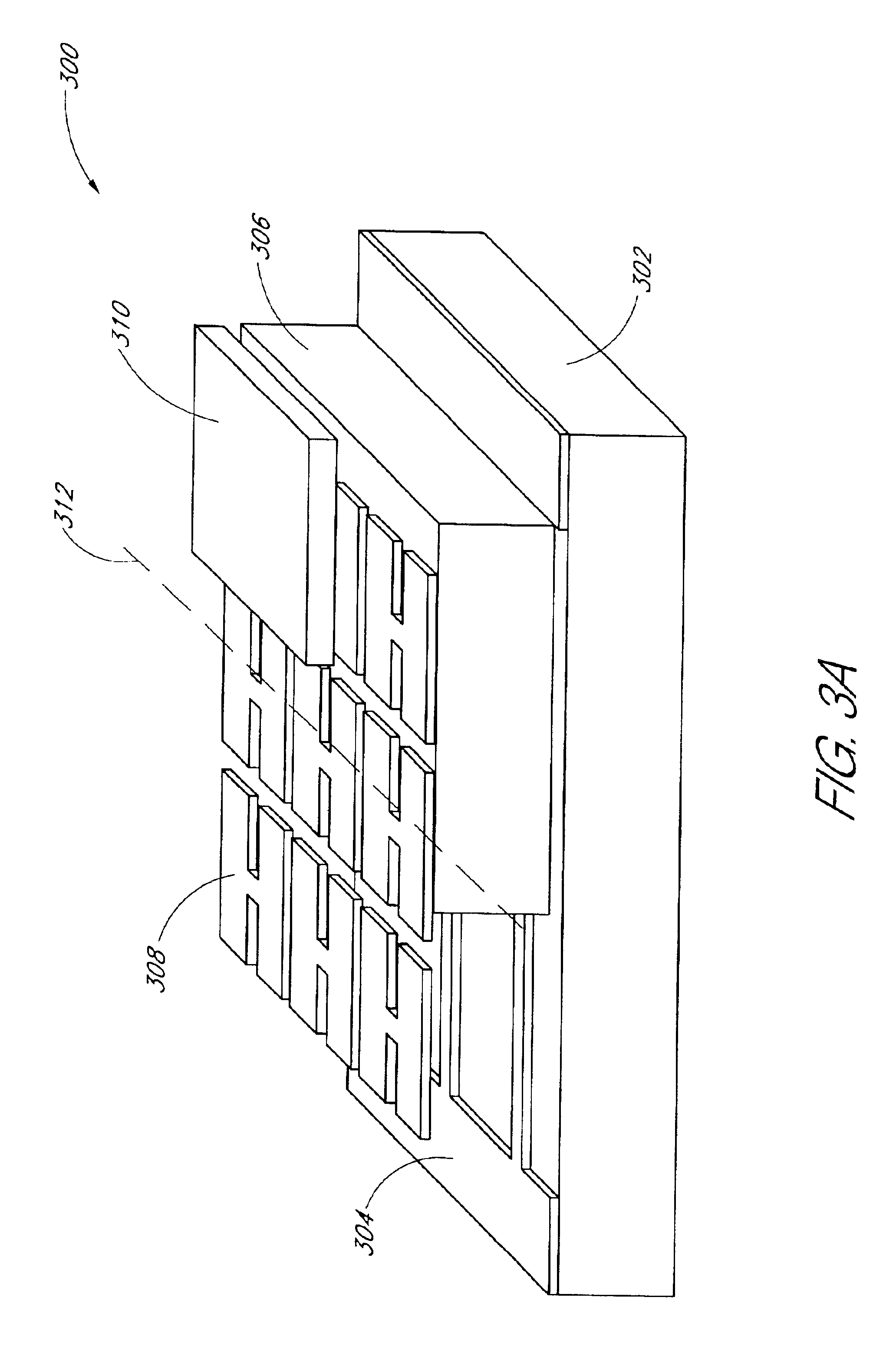
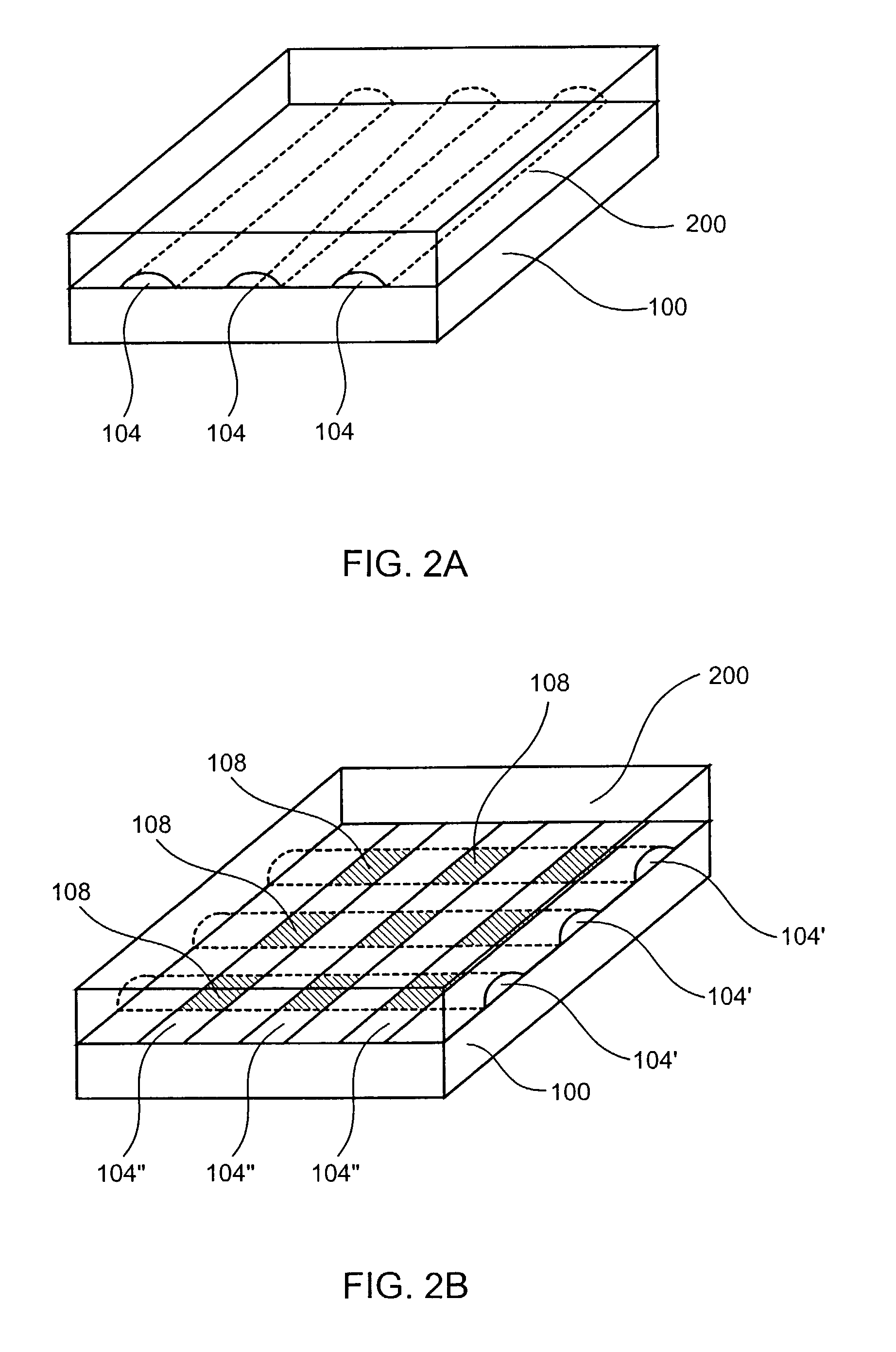
Combinatorial synthesis system
InactiveUS7097809B2Material nanotechnologySequential/parallel process reactionsControl channelEngineering
The present invention provides a microfluidic device for synthesizing an array of compounds and methods for using the same. In particular, the microfluidic device of the present invention comprises a solid support base, an elastomeric layer attached to the solid support, and a plurality of flow channels located within the interface between the solid support and the elastomeric layer. In addition, the solid support comprises a functional group for forming a bond with a reactive reagent. In some embodiments, the microfluidic device further comprises a second plurality of flow channels that intersect the first plurality of flow channels. A plurality of control channels are also present in the microfluidic devices of the present invention. The control channels can be actuated to regulate flow of fluids within the flow channel(s).
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
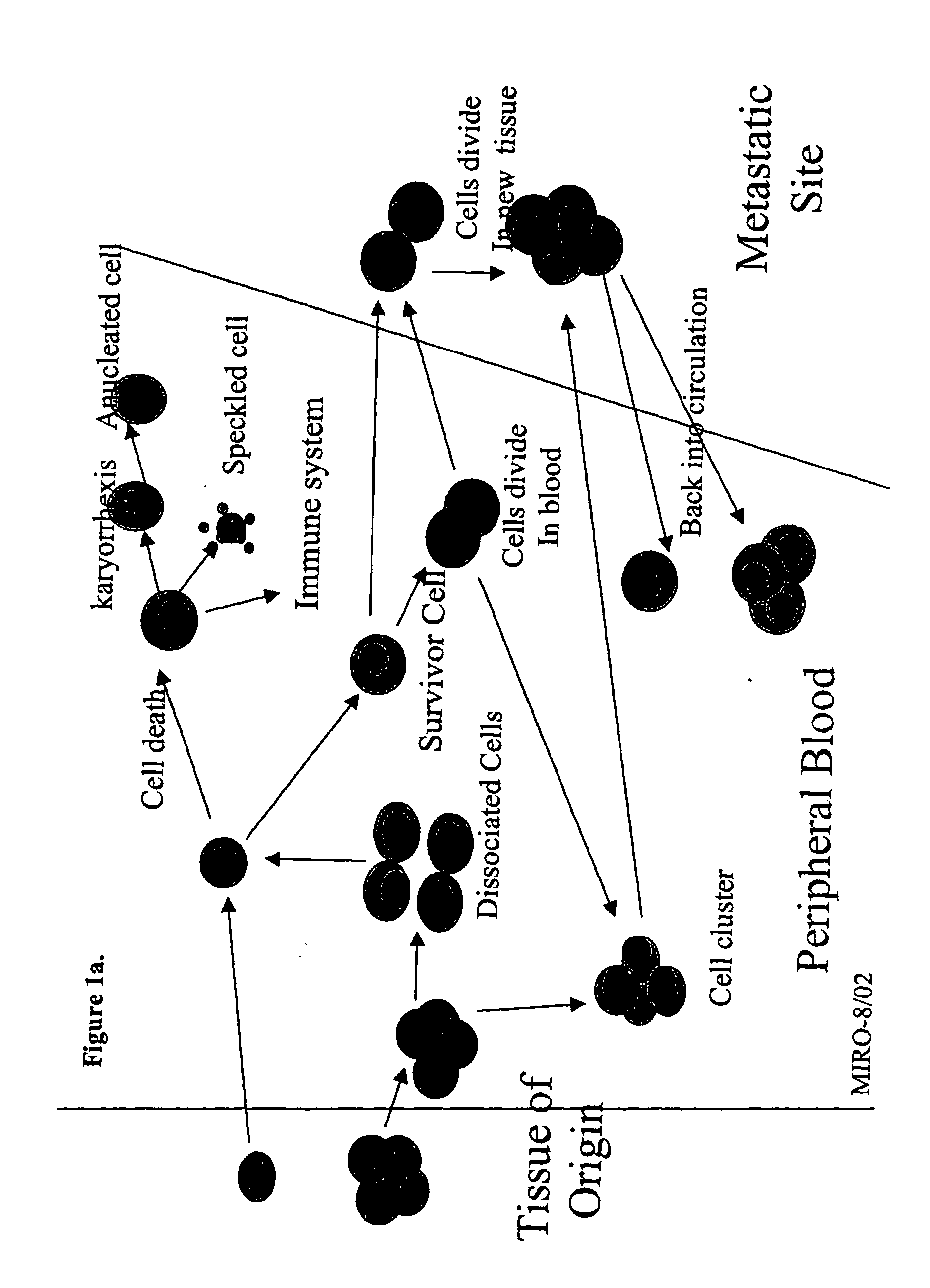
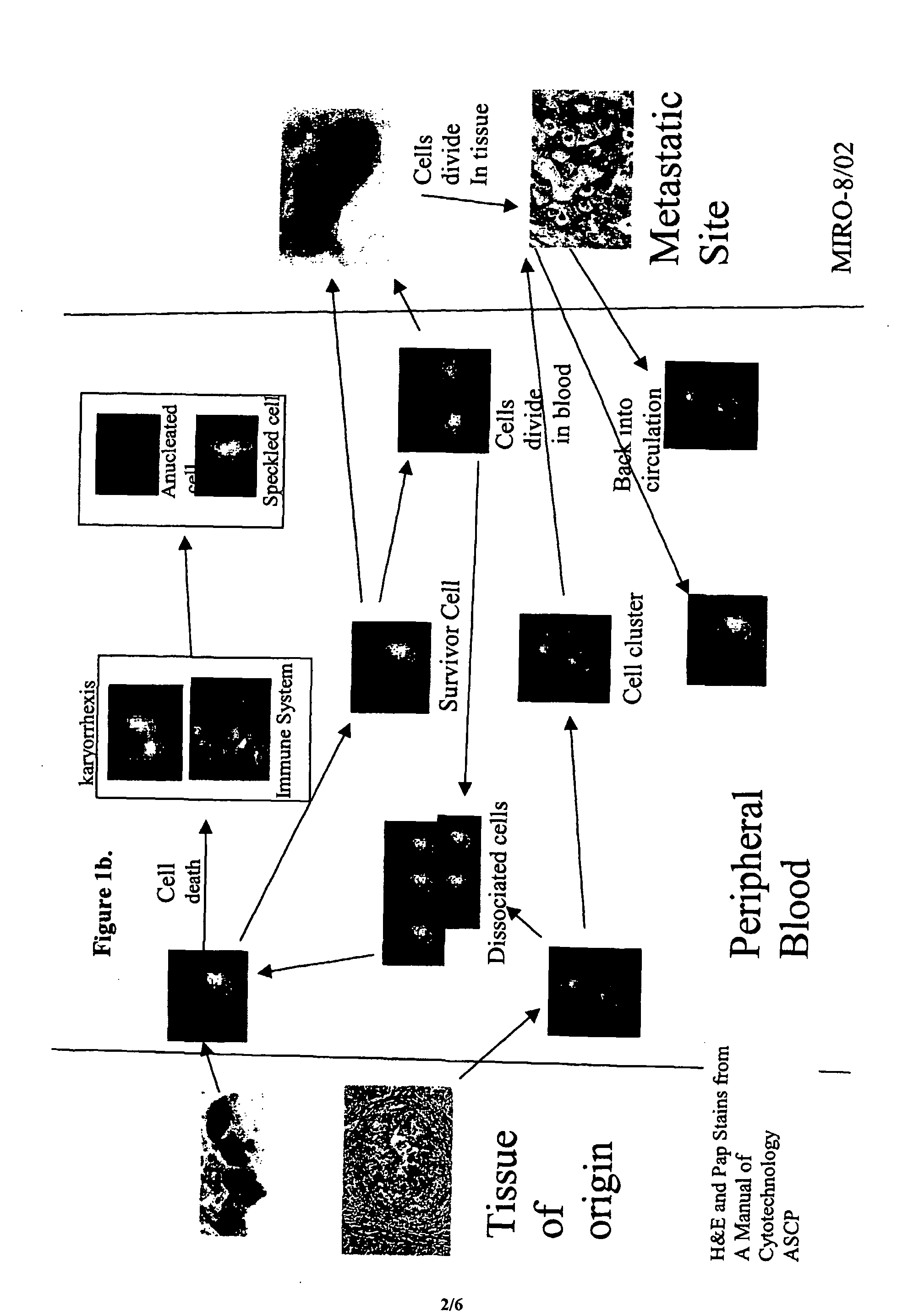
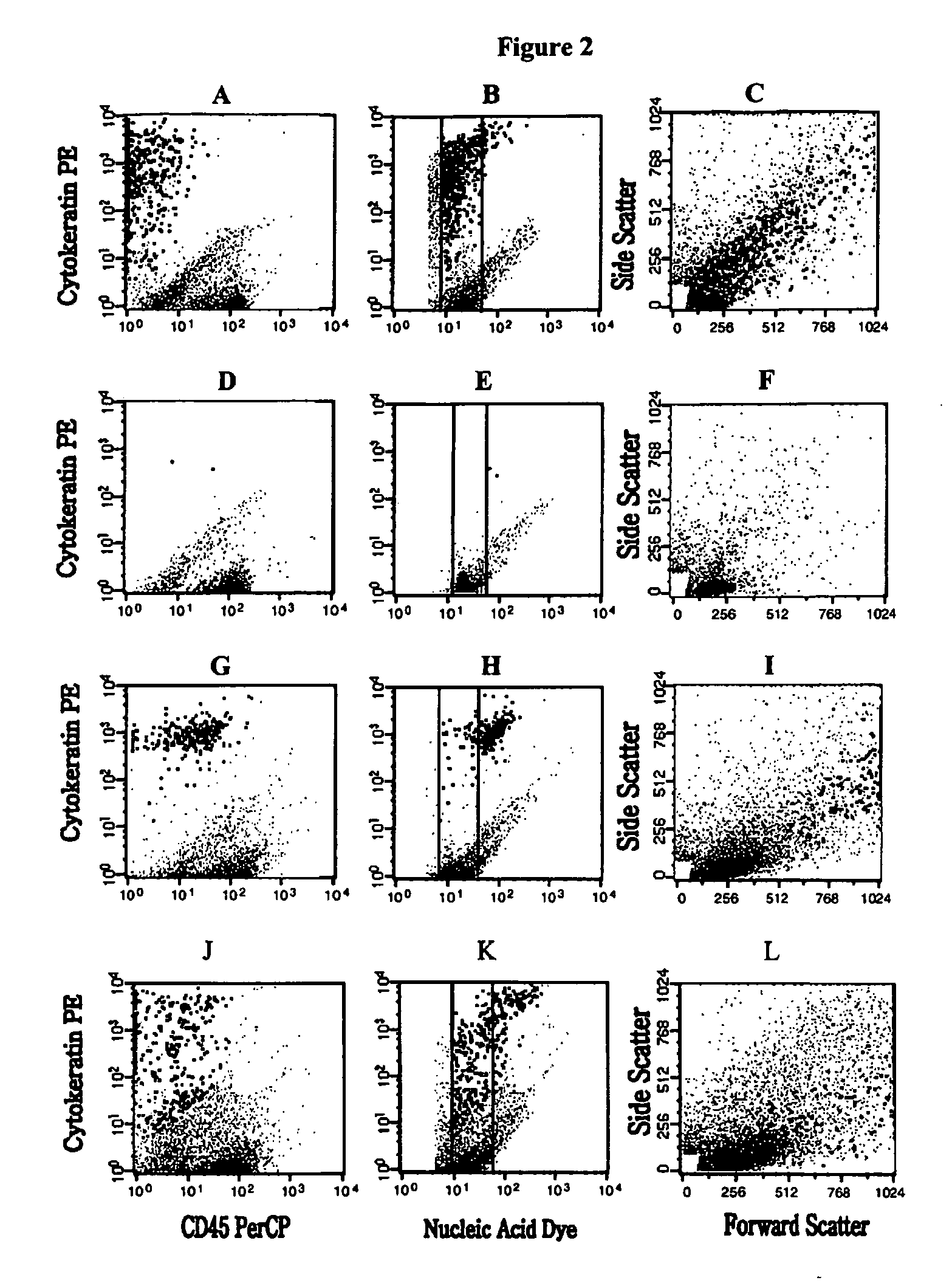
Analysis of circulating tumor cells, fragments, and debris
InactiveUS20050181463A1Avoid further damageInhibit further damageBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsFluorescenceApoptosis
The methods and reagents described in this invention are used to analyze circulating tumor cells, clusters, fragments, and debris. Analysis is performed with a number of platforms, including flow cytometry and the CellSpotter® fluorescent microscopy imaging system. Analyzing damaged cells has shown to be important. However, there are two sources of damage: in vivo and in vitro. Damage in vivo occurs by apoptosis, necrosis, or immune response. Damage in vitro occurs during sample acquisition, handling, transport, processing, or analysis. It is therefore desirable to confine, reduce, eliminate, or at least qualify in vitro damage to prevent it from interfering in analysis. Described herein are methods to diagnose, monitor, and screen disease based on circulating rare cells, including malignancy as determined by CTC, clusters, fragments, and debris. Also provided are kits for assaying biological specimens using these methods.
Owner:MENARINI SILICON BIOSYSTEMS SPA
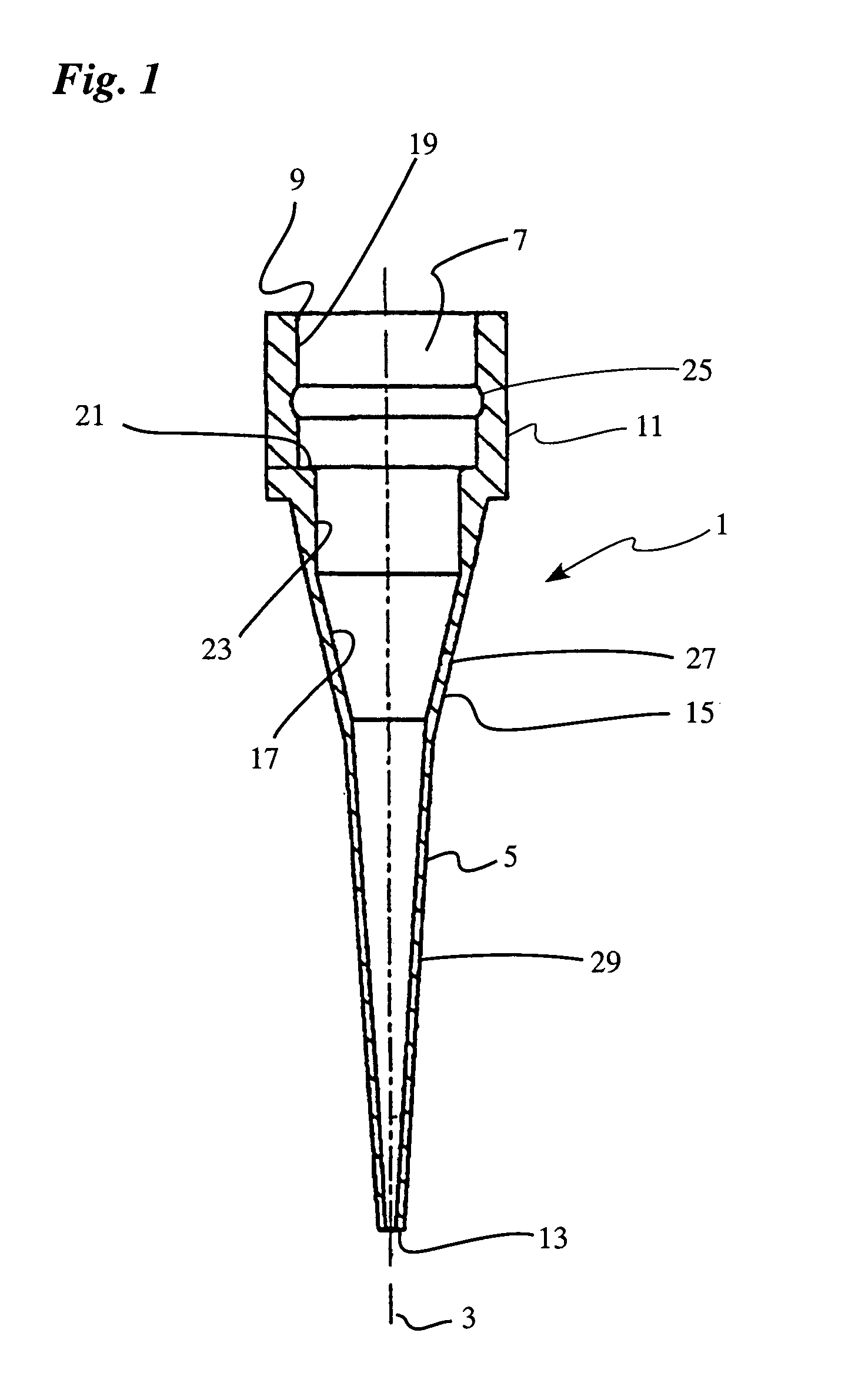
Ergonomic pipette tip and adapters
ActiveUS7335337B1Easily and securely mountedLittle generationWithdrawing sample devicesBurettes/pipettesBiomedical engineeringExpansion joint
An ergonomically designed pipette tip that can be securely mounted to a barrel of a pipetter yet is designed to substantially reduce the axial force necessary to install and eject the pipette tip from the pipetter. The ergonomic pipette tip includes molded-in expansion joints and / or the addition of a second elastic material to decrease the amount of force necessary to radially expand the entrance to the pipette tip when the pipetter barrel is guided and stability oriented towards the sealing region of the pipette tip. Also disclosed is an ergonomic adapter with similar features as the tip that can also be mounted to the barrel of the pipetter and attached to a standard pipette tip or a combination of tips. Therefore, the relatively small axial forces necessary for mounting and ejecting the new ergonomic tip and adapter can substantially help to reduce the hand and thumb forces, that due to repeated use, will sometimes result in repetitive stress injury.
Owner:SMITH JAMES C
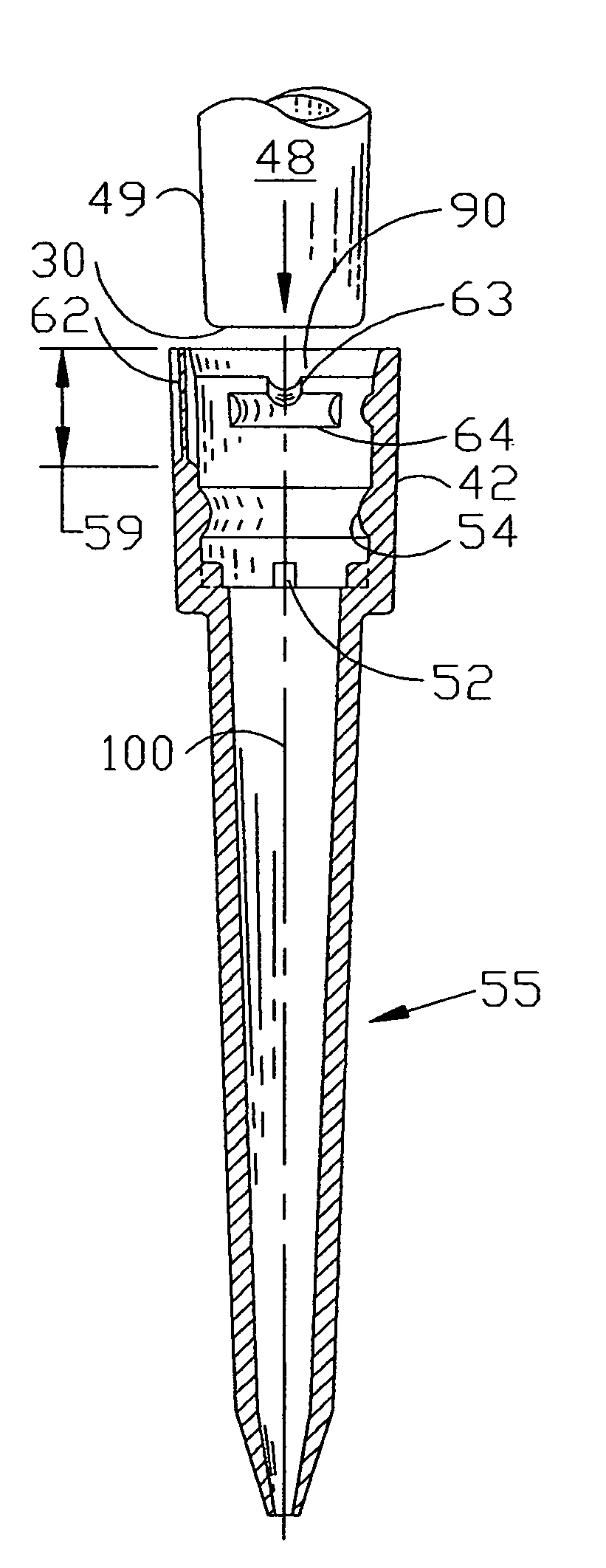
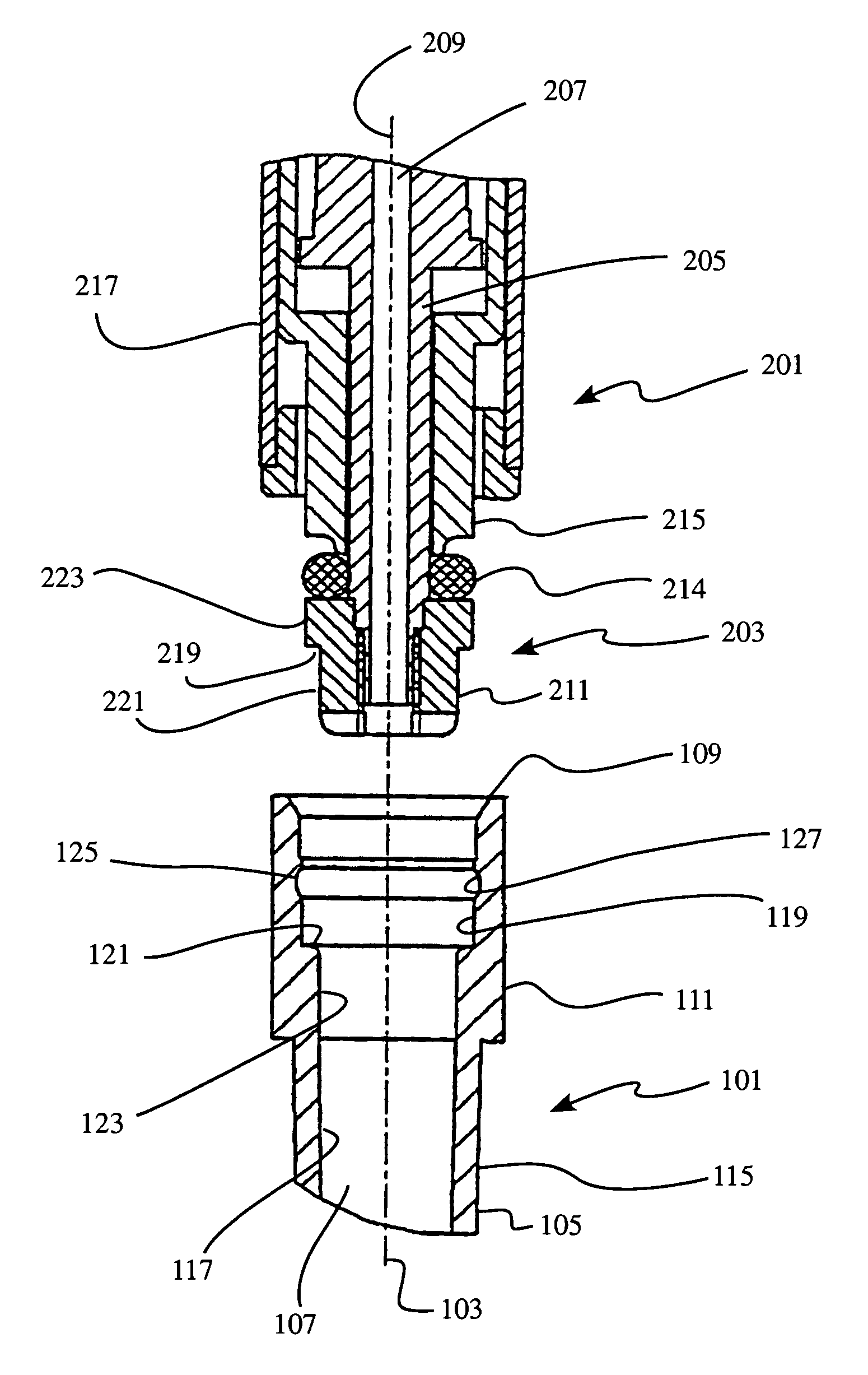
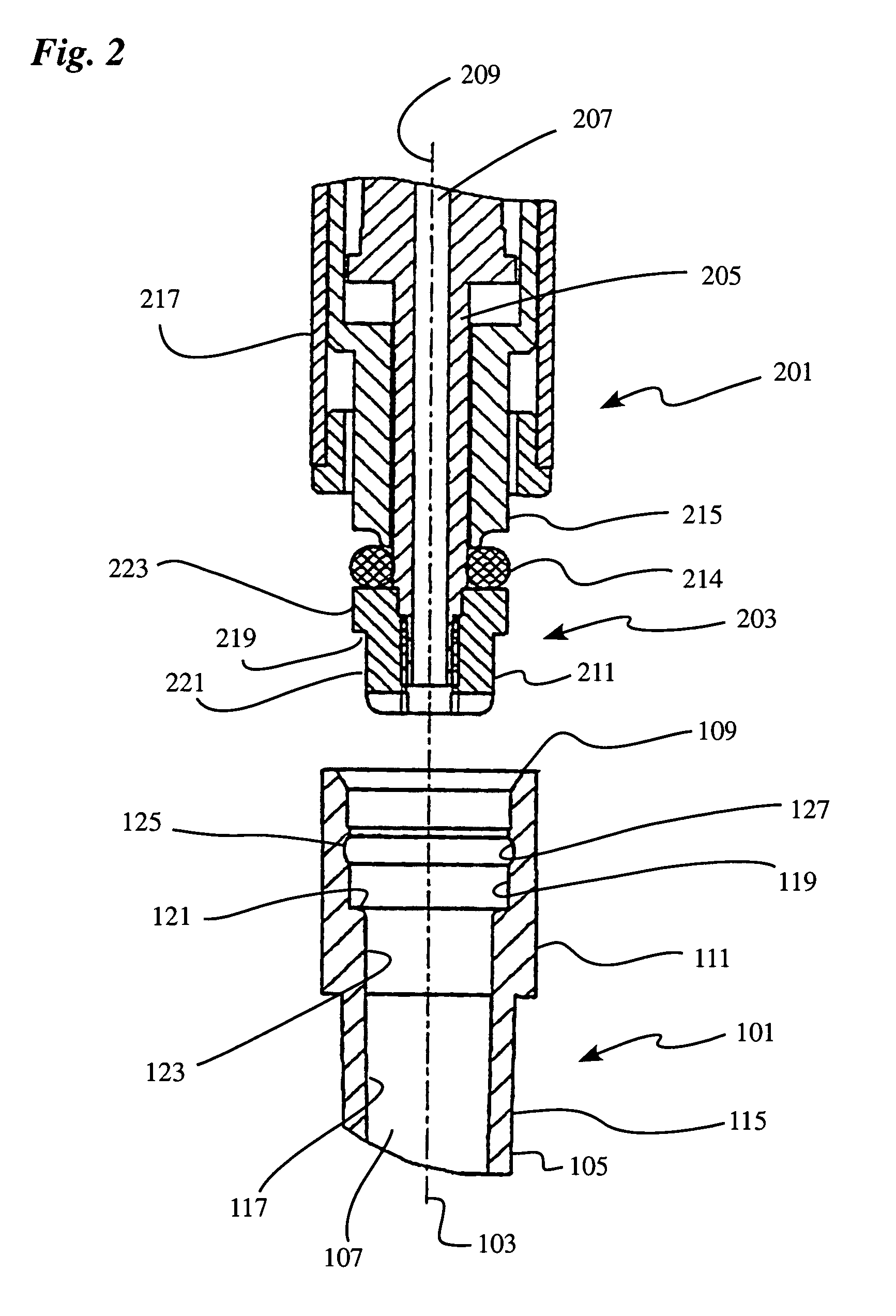
Pipette tip, pipetting device and combination consisting of a pipette tip and pipetting device
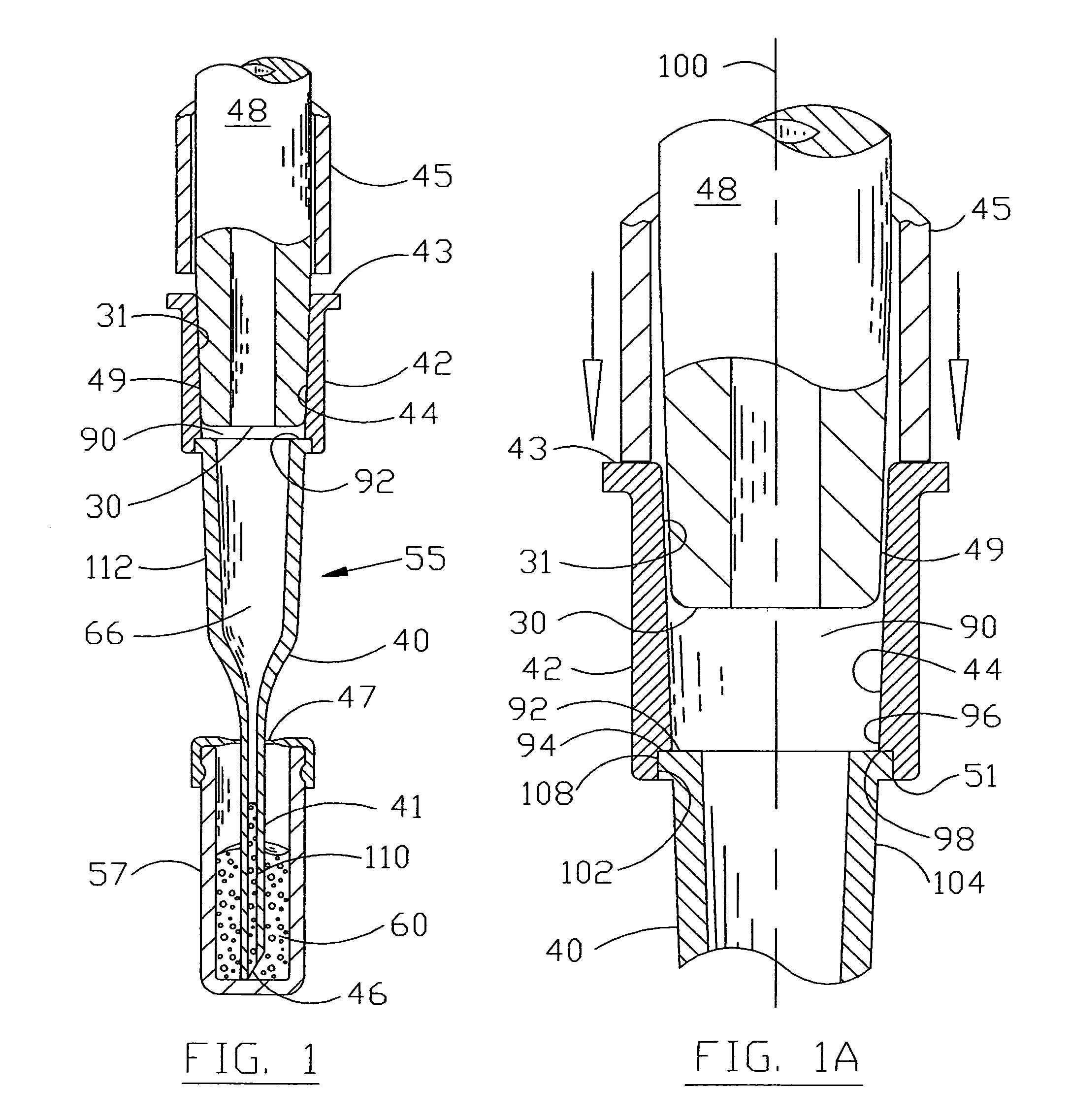
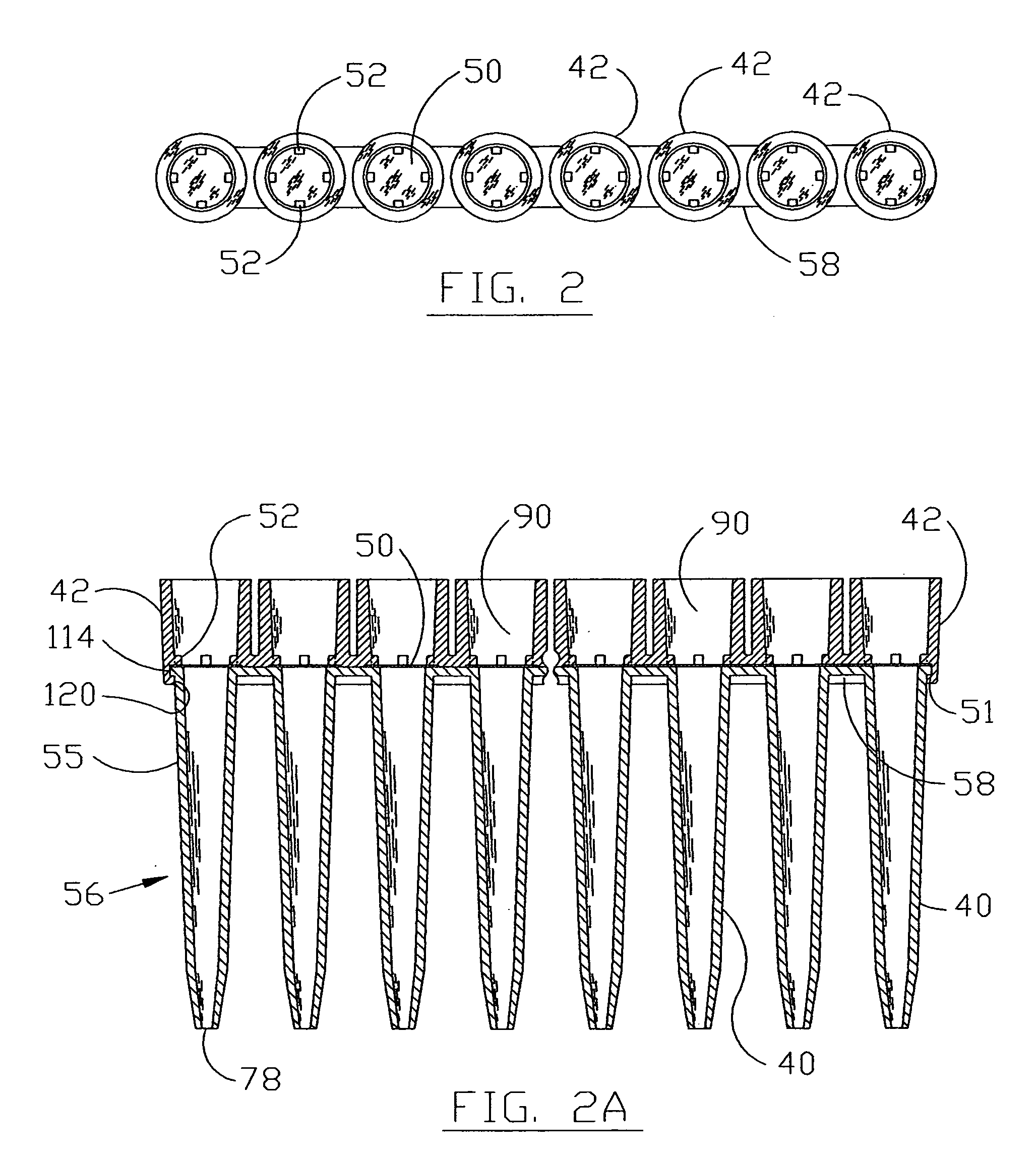
InactiveUS7033543B1Extended service lifeStable supportWithdrawing sample devicesBurettes/pipettesPipetteCoupling
A pipette device has a coupling stud on which a pipette tip can be stuck in a slipping-on direction for coupling. The coupling stud has an adjustable pre-stress member that can be adjusted into a prestress state and a release state via an actuation device which is provided in the coupling stud. The pipette tip has an axial stop which interacts with a counter-stop of the coupling stud in an axial coupling position of the pipette tip. The prestress member in its prestress state acts upon a working surface of the stuck-on pipette tip having a surface component of the pipette tip, which extends radially inward, turned away from the stuck on direction, in such a way that it abuts sealingly on the working surface, and prestresses the pipette tip on the pipette unit into the axial coupling position. The prestress member, in its releasing state, substantially releases the working surface of the pipette tip (101).
Owner:HAMILTON BONADUZ AG
Integrated sample-processing system
InactiveUS6902703B2Ruthenium organic compoundsChemical analysis using titrationFluidicsProcess engineering
The invention provides an integrated sample-processing system and components thereof for preparing and / or analyzing samples. The components may include a transport module, a fluidics module, and an analysis module, among others.
Owner:MOLECULAR DEVICES
High throughput processing system and method of using
Briefly, the present invention provides a system and method for high throughput processing using sample holders. The system has a plurality of work perimeters, with a rotational robot preferably associated with each work perimeter. At least one transfer station area is provided between adjacent work perimeters to facilitate robotic transfer of sample holders from one work perimeter to another area. Each work perimeter typically includes a plurality of defined station locations, with each station location positioned to be accessible by the robot associated with that area. In addition, each station location is typically configured to receive a device, such as an automated instrument or a holding nest. Device components are arranged at selected station locations according to specific application requirements to provide a flexible, robust, reliable, and accurate high throughput processing system.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
System and method for high throughput screening of droplets
InactiveUS20030119193A1Sequential/parallel process reactionsComponent separationHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsHigh flux
A system and method for high throughput screening of fluid samples. A reduced pressure is applied, via an injection valve, to a sample aspiration tube. A first fluid and a second fluid are alternatively aspirated, via the sample aspiration tube, the first fluid for filling a sample loop with samples, the second fluid for flushing the sample aspiration tube. Excess fluid aspirated from the first fluid source and all fluid aspirated from the second fluid source is captured in an inline trap.
Owner:BIOCIUS LIFE SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com