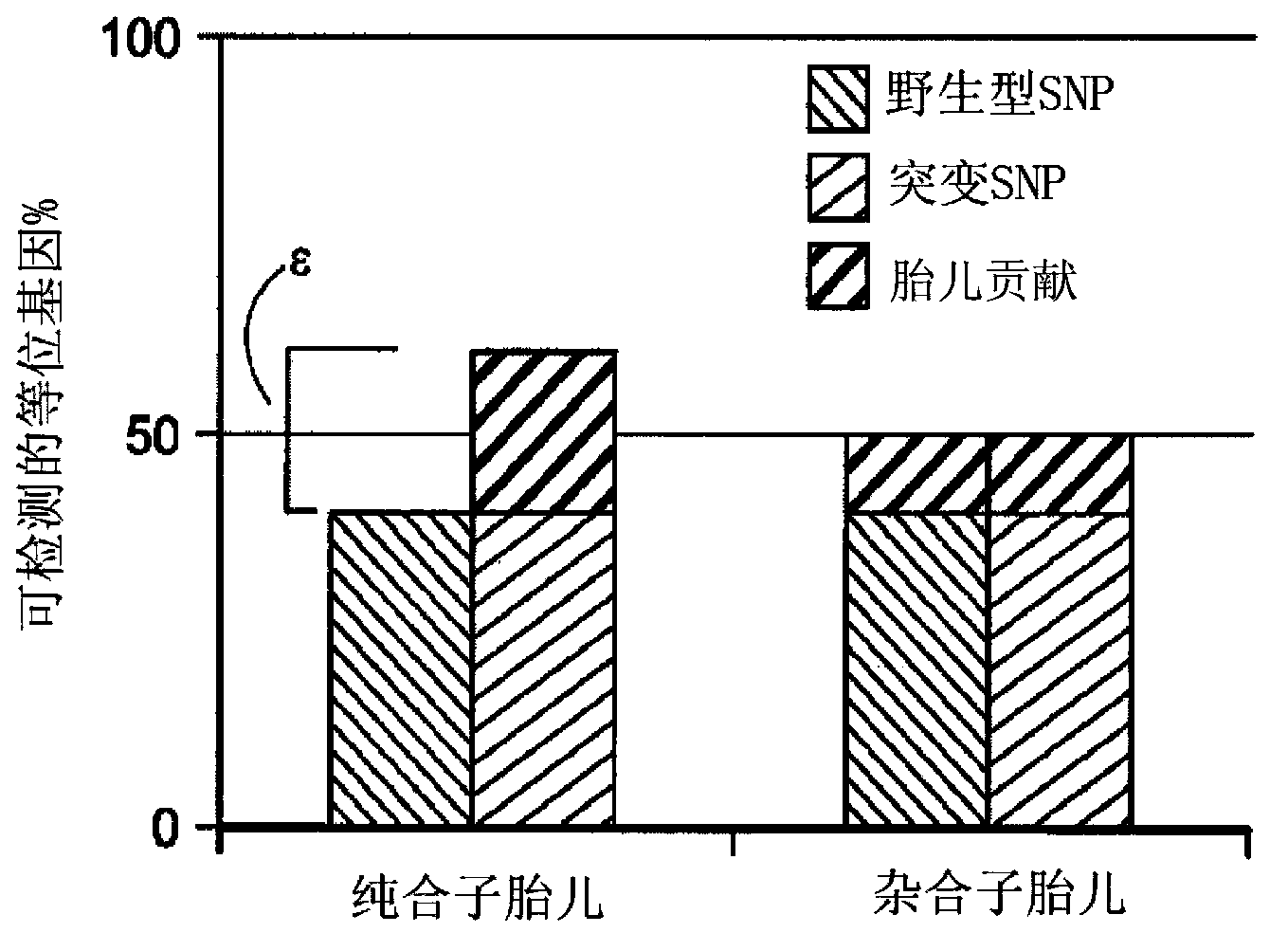
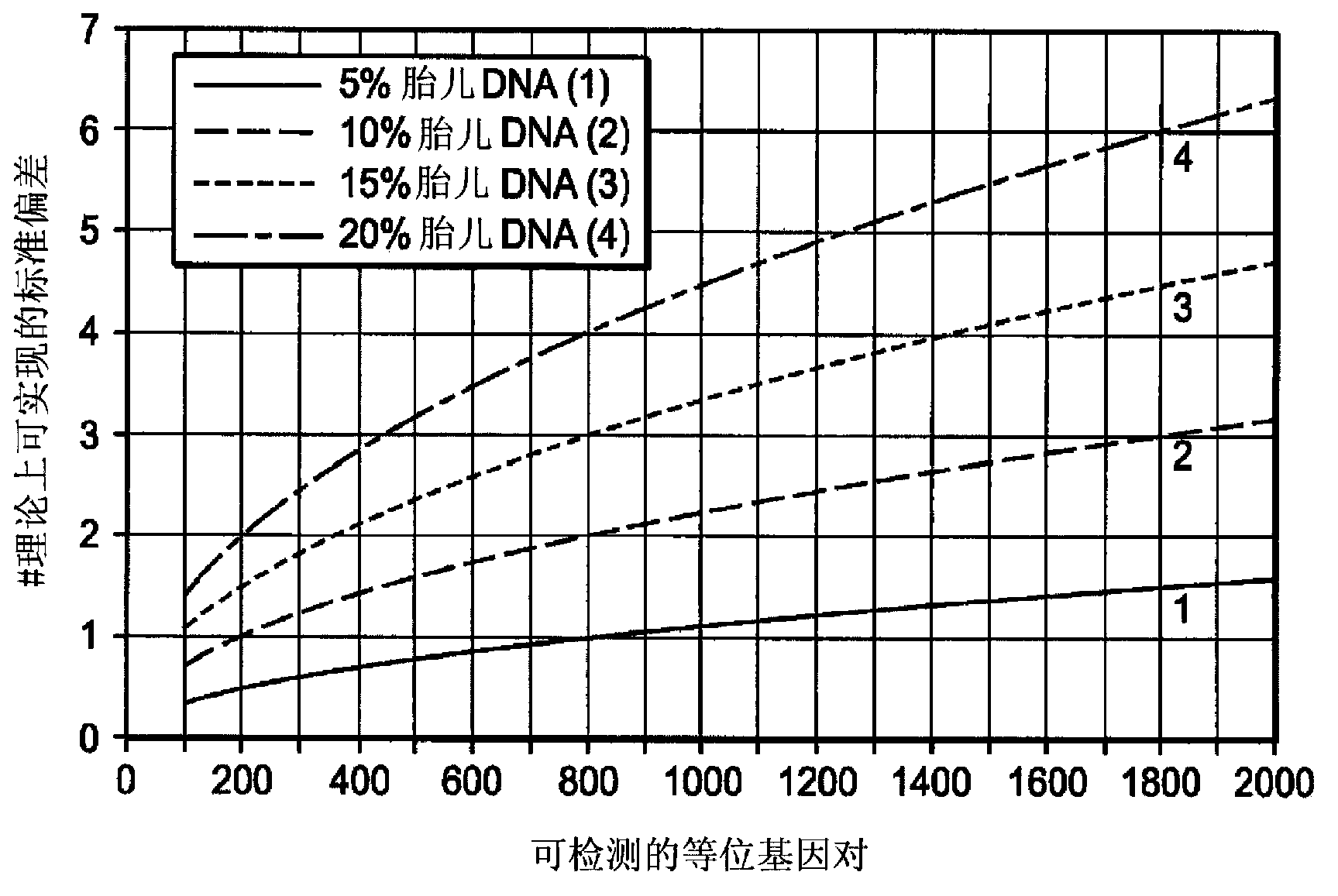
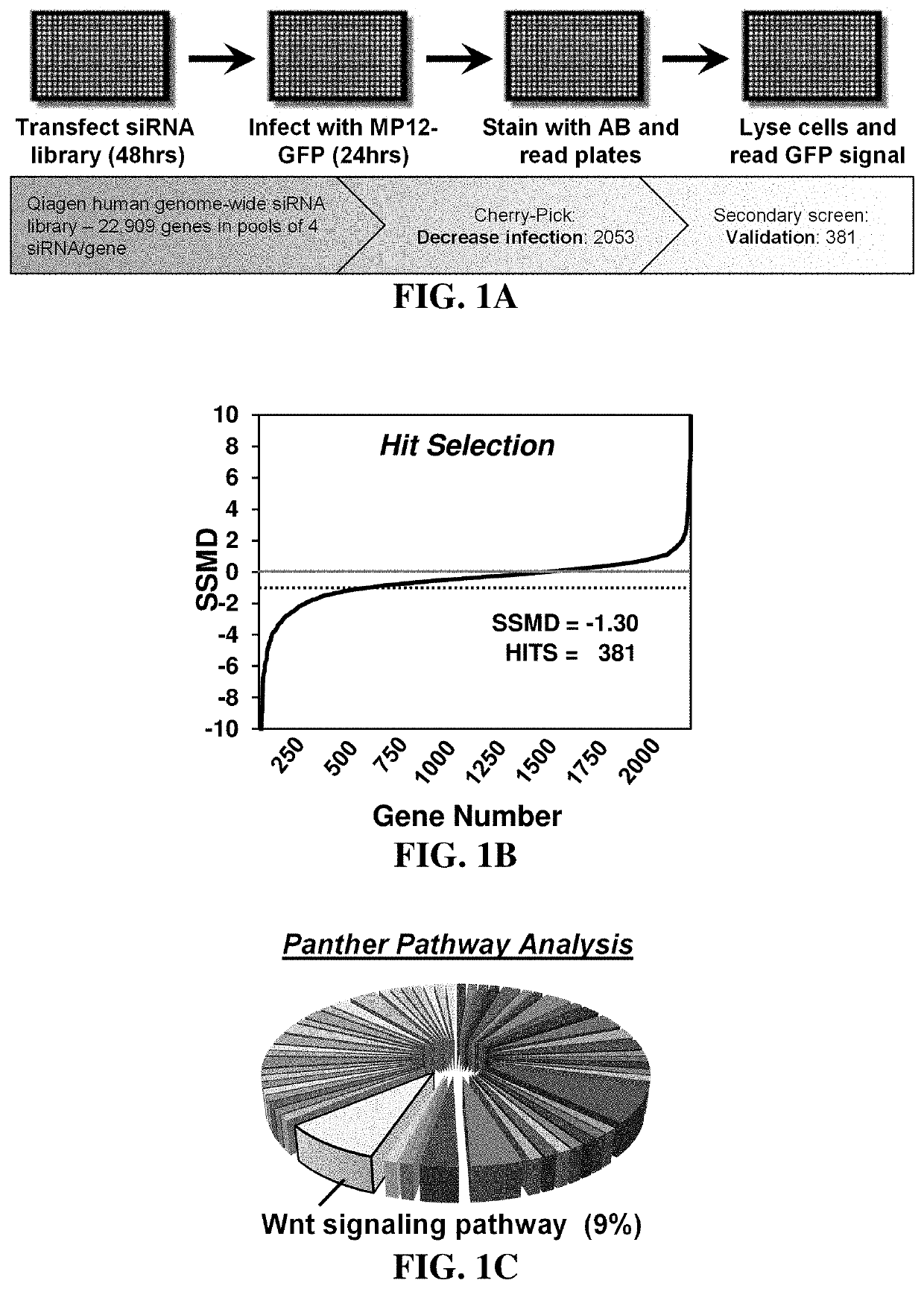
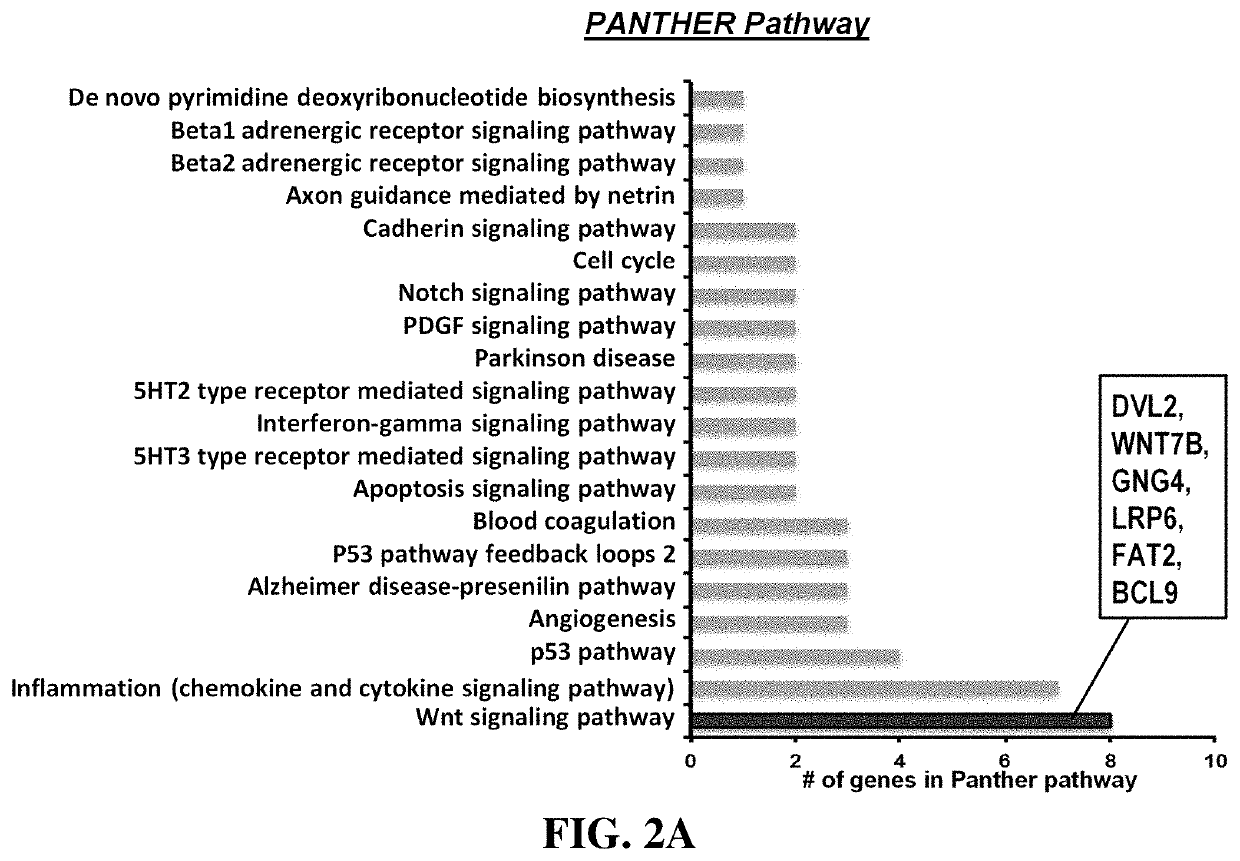
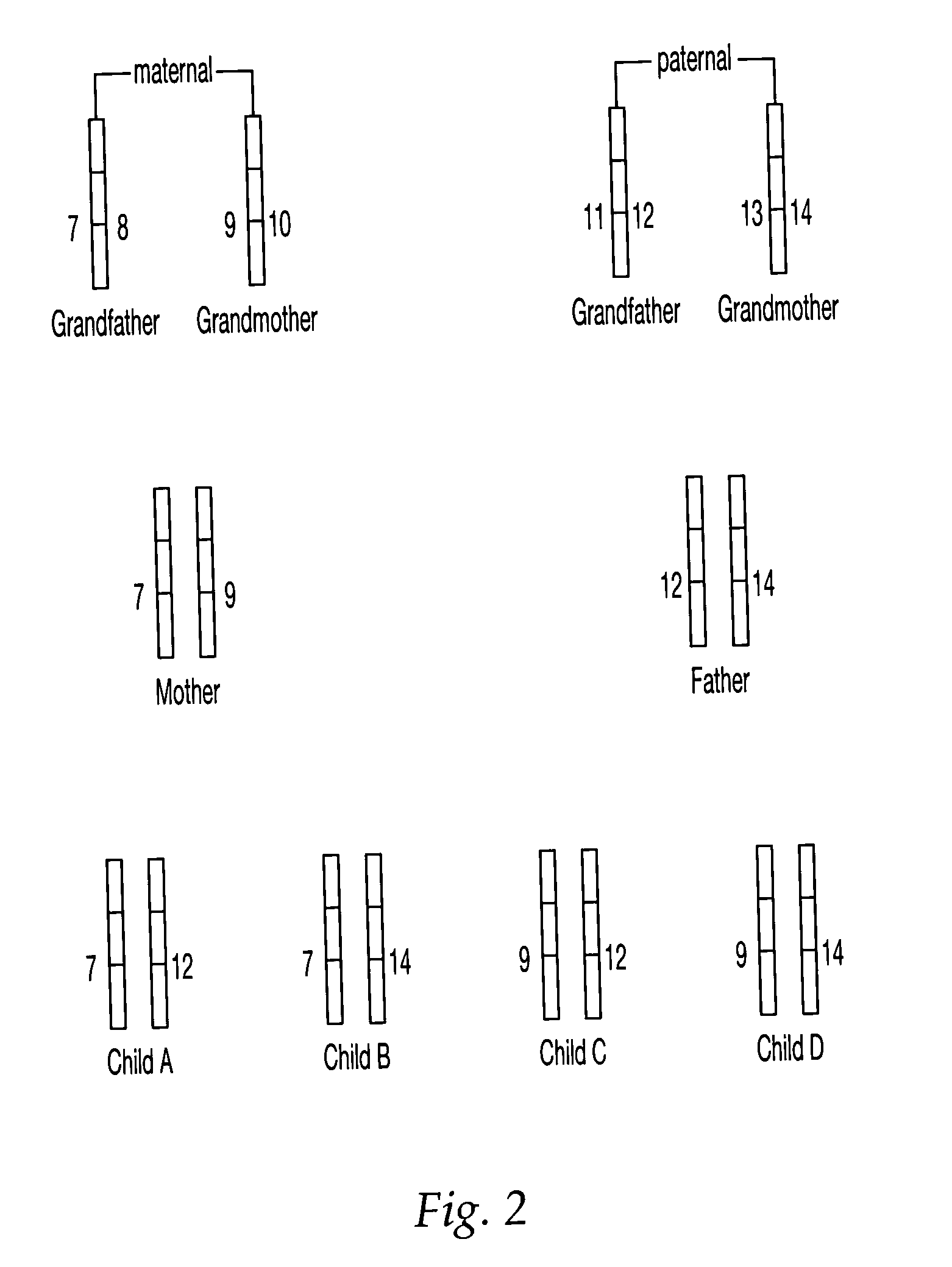Patents
Literature
57 results about "Genomic screening" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Genetic screen. A genetic screen or mutagenesis screen is an experimental technique used to identify and select for individuals who possess a phenotype of interest in a mutagenized population. Hence a genetic screen is a type of phenotypic screen.
Microfluidic sequencing systems
InactiveUS7238323B2Minimize contaminationIncrease speedBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsGenomic screeningSoftware
Owner:CAPLIPER LIFE SCI INC
Methods and apparatus for sample tracking
InactiveUS20040157220A1Reduce chanceMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationPrenatal diagnosisGenotype
A method and apparatus are provided for identifying a biological sample obtained during either paternity screening, genetic screening, prenatal diagnosis, presymptomatic diagnosis, diagnosis to detect the presence of a target microorganism carrier detection analysis, forensic chemical analysis, or diagnosis of a subject to determine whether a subject is afflicted with a particular disease or disorder, or is at risk of developing a particular disorder, wherein the result obtained from the analysis is associated with the unique DNA fingerprint biological barcode of the genotype of the subject being analyzed. The methods and apparatus of the invention have application in the fields of diagnostic medicine, disease diagnosis in animals and plants, identification of genetically inherited diseases in humans, family relationship analysis, forensic analysis, and microbial typing.
Owner:HANDYLAB
Microfluidic devices and methods for optimizing reactions
InactiveUS6440722B1Increase speedMinimize contaminationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsGenomic screeningSoftware
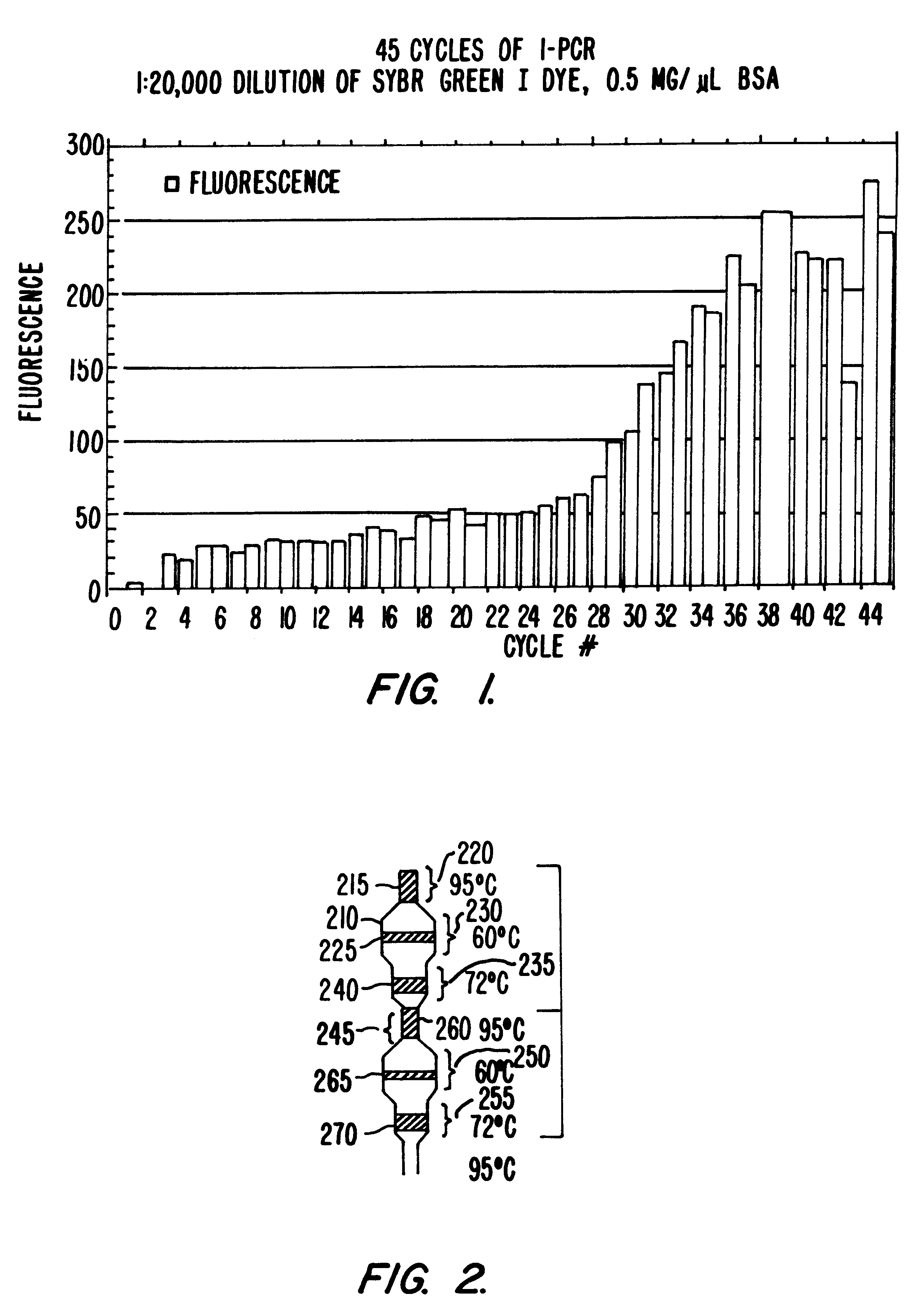
Integrated systems, apparatus, software, and methods for performing biochemical analysis, including DNA sequencing, genomic screening, purification of nucleic acids and other biological components and drug screening are provided. Microfluidic devices, systems and methods for using these devices and systems for performing a wide variety of fluid operations are provided. The devices and systems of are used in performing fluid operations which require a large number of iterative, successive or parallel fluid manipulations, in a microscale, or sealed and readily automated format.
Owner:CAPLIPER LIFE SCI INC
Microfluidic sequencing methods
InactiveUS6849411B2Minimize contaminationIncrease speedBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsGenomic screeningDNA sequencing
Integrated systems, apparatus, software, and methods for performing biochemical analysis, including DNA sequencing, genomic screening, purification of nucleic acids and other biological components and drug screening are provided. Microfluidic devices, systems and methods for using these devices and systems for performing a wide variety of fluid operations are provided. The devices and systems of are used in performing fluid operations which require a large number of iterative, successive or parallel fluid manipulations, in a microscale, or sealed and readily automated format.
Owner:CAPLIPER LIFE SCI INC
Pathogenic microorganism genome database and establishment method thereof
ActiveCN110473594AReduce data volumeAvoid false positivesBioinformaticsInstrumentsPathogenic microorganismHemidesmosome assembly
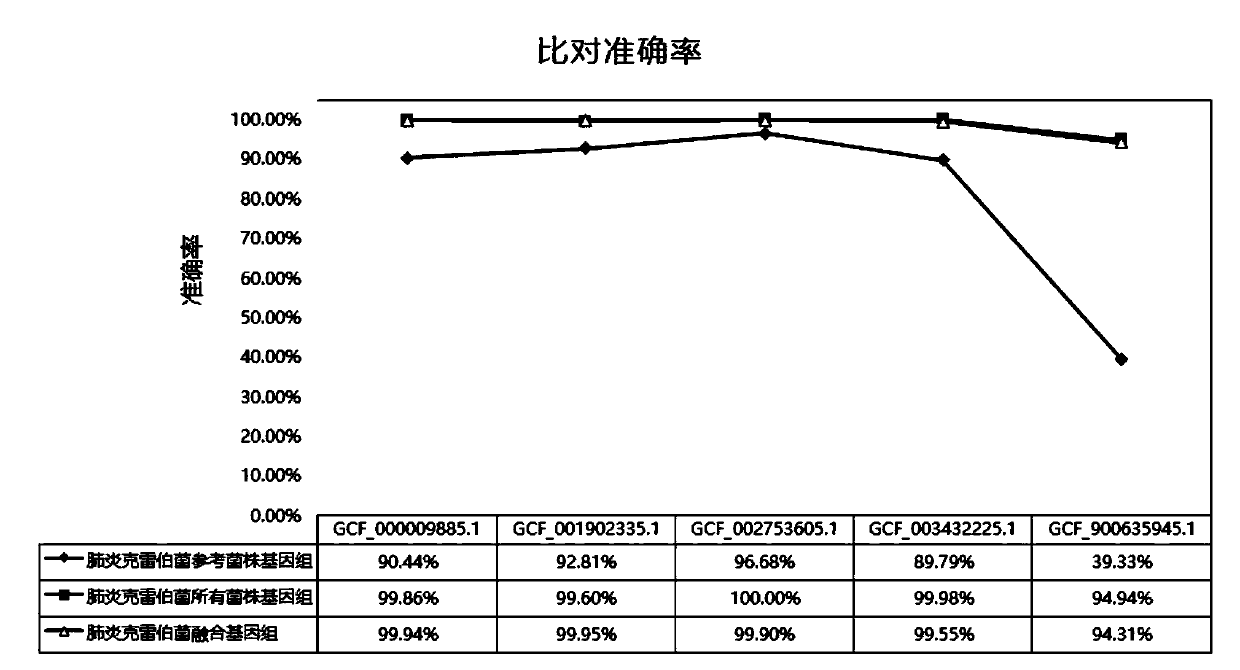
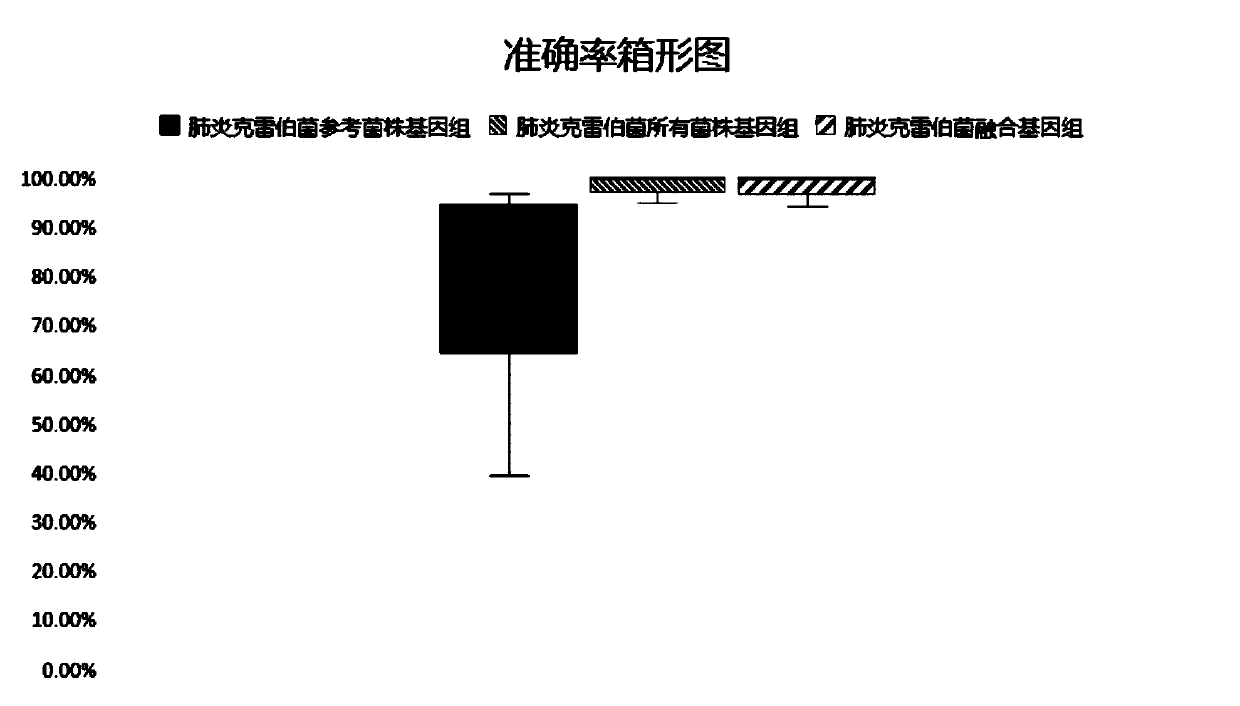
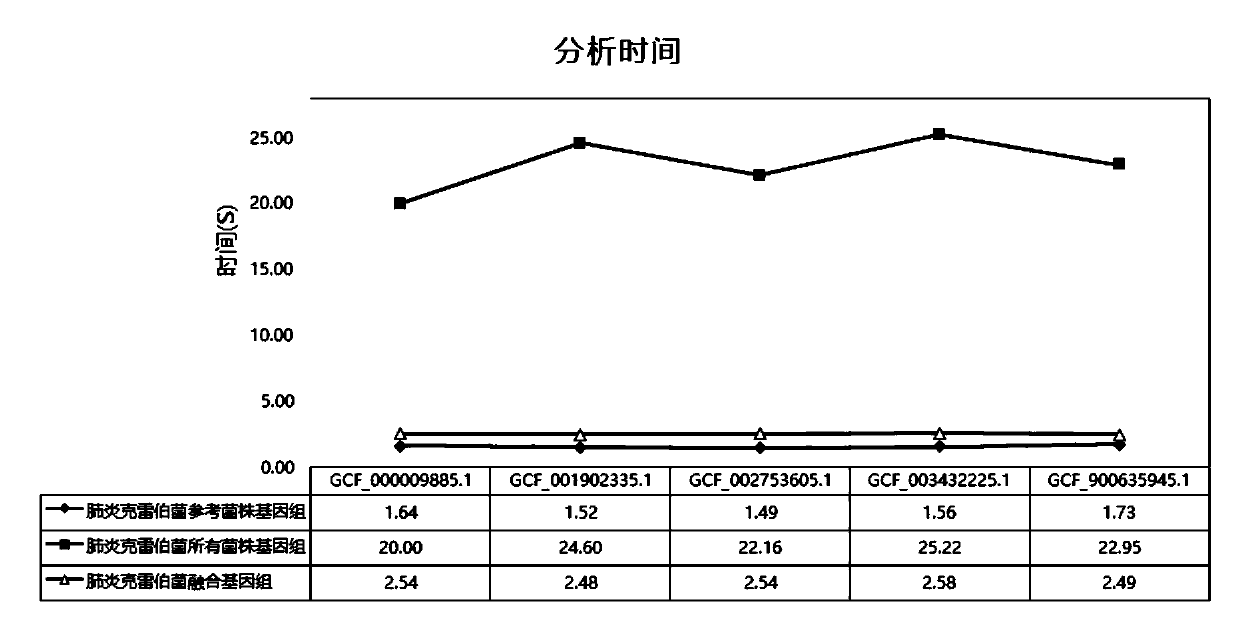
The invention relates to a pathogenic microorganism genome database and an establishment method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of meta-genomes. The method comprises the following steps ofdata acquisition, wherein pathogenic microorganism genome data is obtained; strain genome screening, wherein species strain genomes are selected according to a predetermined screening rule; plasmid sequence removal, wherein plasmid sequences existing in the strain genomes obtained in the last step are removed; filtration, wherein according to a predetermined filtering rule, strains with incorrectlabeling information, incomplete chromosome assembly and incorrect classification are removed to obtain a reference strain genome of the species; fusion genome construction, wherein the reference strain genome is interrupted, redundancy is removed, reassembly is performed, and the sequences are reassembled to obtain a fusion genome of the species; database assembly, wherein the above steps are repeated to obtain the fusion genome of the predetermined species, summary is performed, and the pathogenic microorganism genome database is obtained. The genome database has the advantages of not onlyhaving a high precision rate, but also having short analysis time and reducing the cost.
Owner:GZ VISION GENE TECH CO LTD +4
Methods of predicting pathogenicity of genetic sequence variants
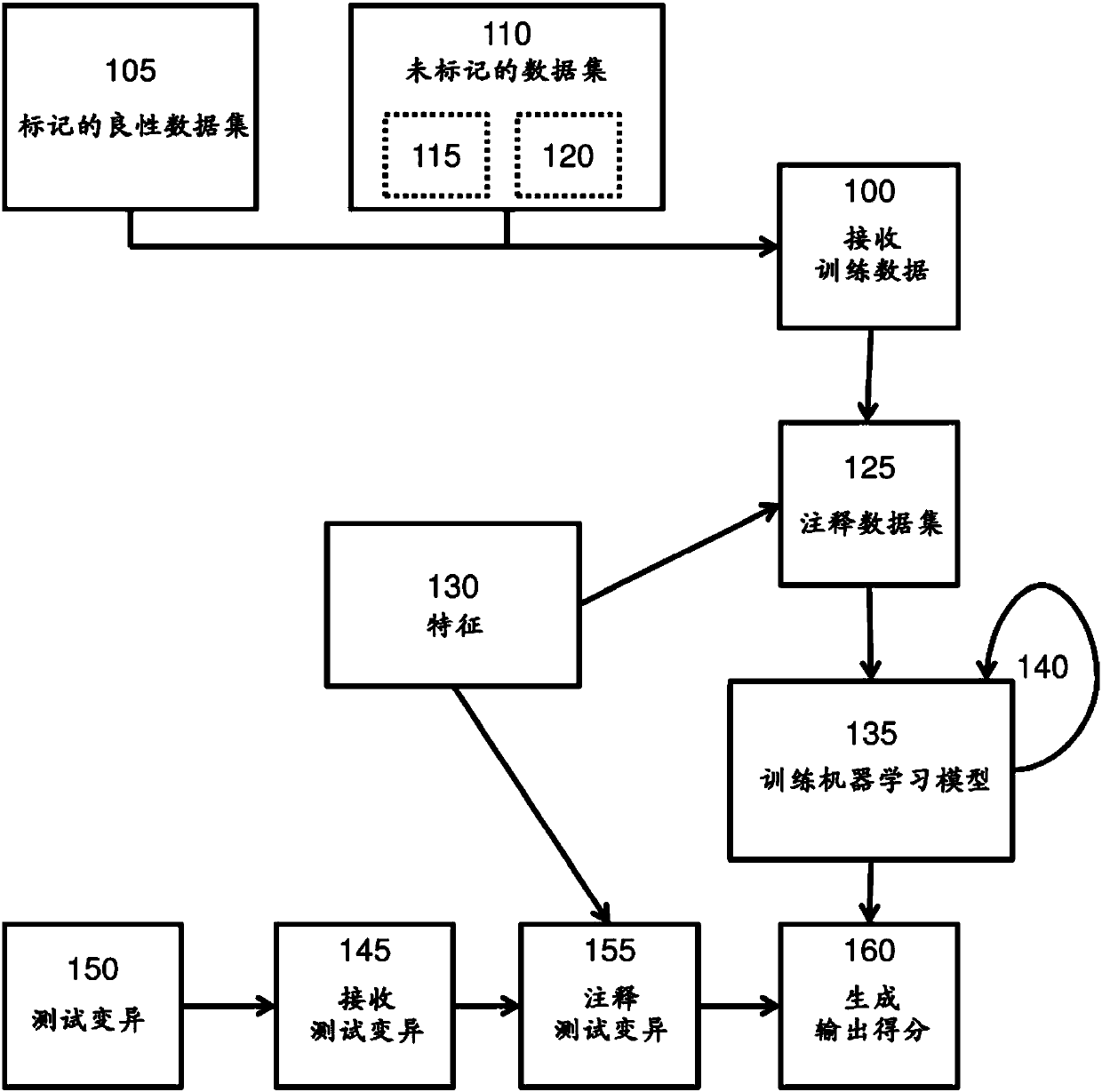
Recent developments in cost-effective DNA sequencing allows for individualized genomic screening of a subject for genetic sequence variants. Training a pathogenicity prediction model using semi-supervised training methods produces a better model for predicting the pathogenicity of a test genetic sequence variant. Provided herein are methods for predicting the pathogenicity of a test genetic sequence variant by utilizing a training data set comprising labeled benign genetic sequence variants unlabeled genetic sequence variants, the unlabeled genetic sequence variants comprising a mixture of benign genetic sequence variants and pathogenic genetic sequence variants. The genetic sequences are annotated with one or more features and a machine learning model is trained in a semi-supervised process based on the training data. The test genetic sequence is then annotated using the one or more features and the probability that the test genetic sequence variant is pathogenic is predicted based onthe trained machine learning model.
Owner:COUNSYL INC
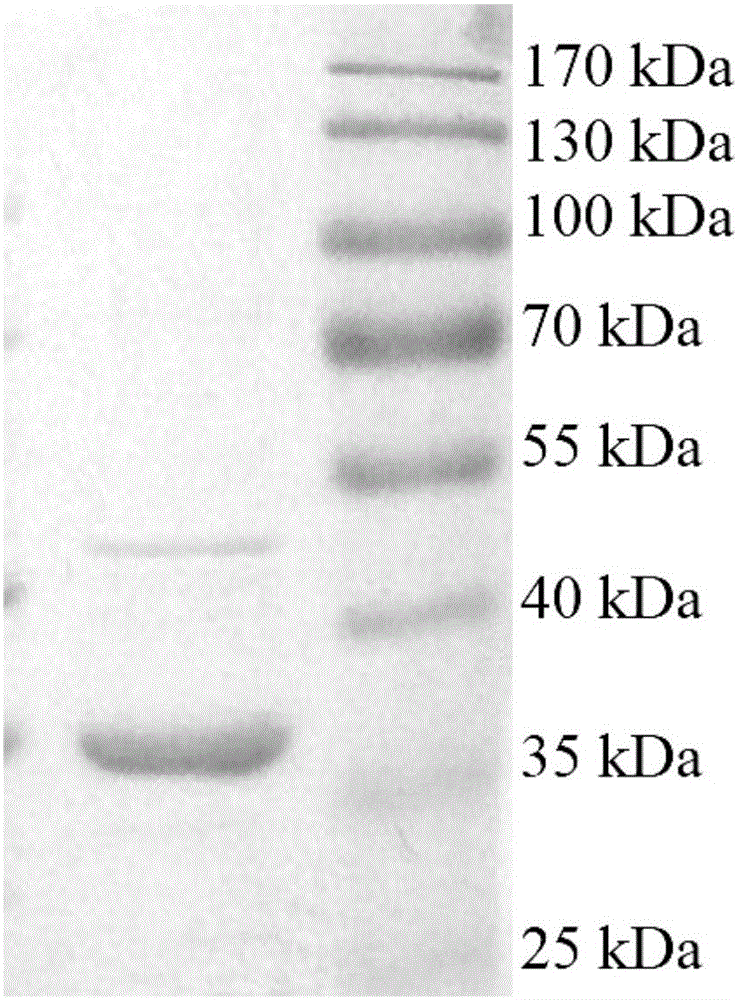
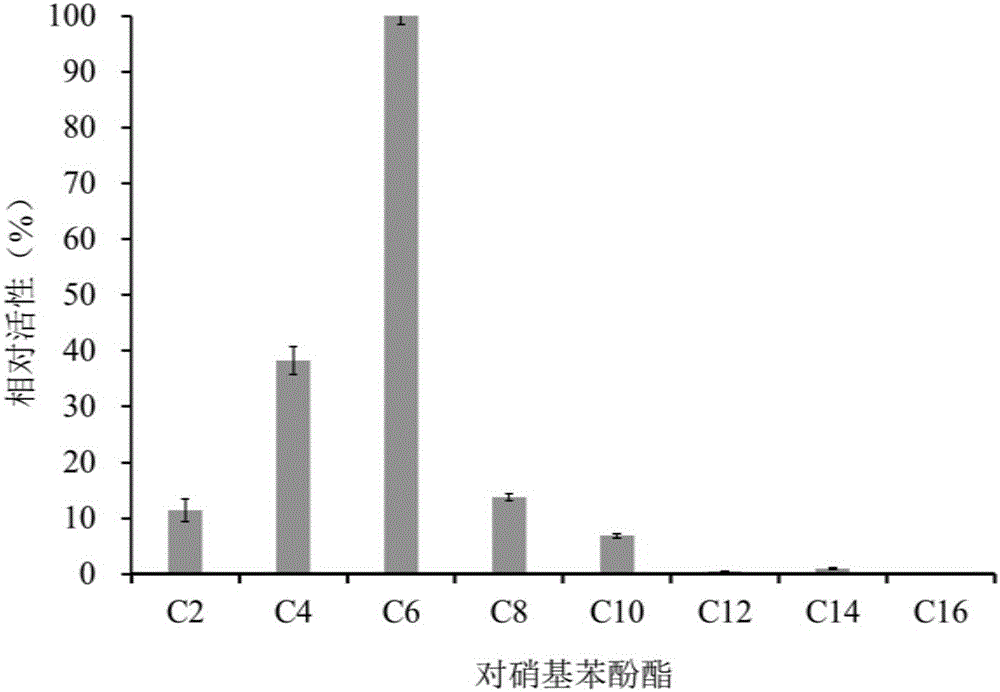
Deep-sea sediment-sourced esterase EST4 as well as encoding gene and application thereof
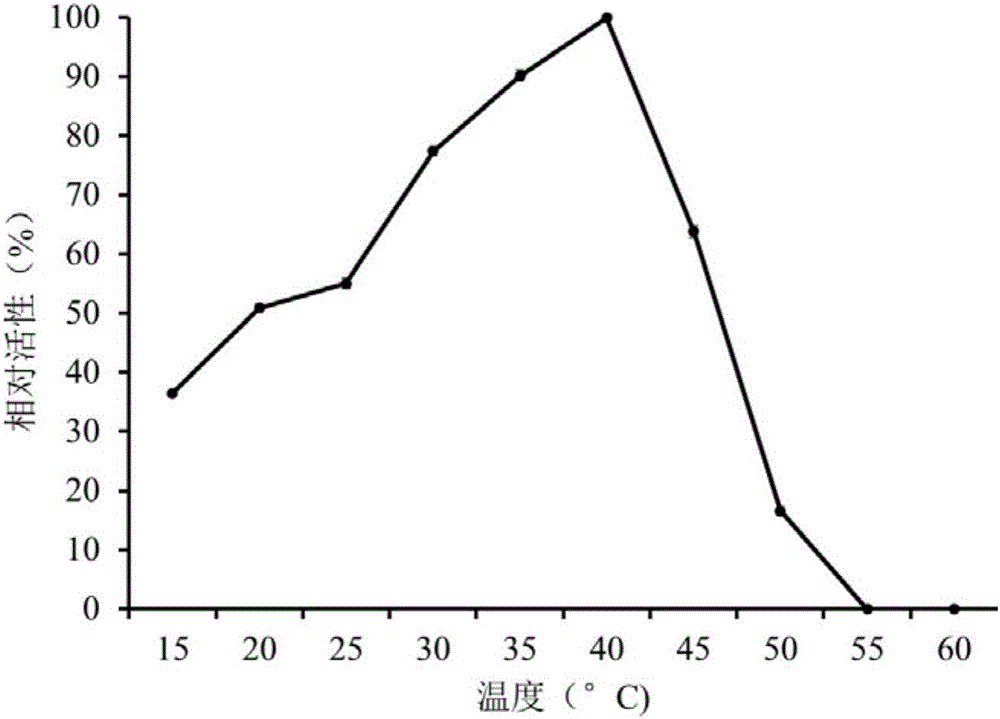
The invention discloses a deep-sea sediment-sourced novel esterase EST4 as well as an encoding gene and application thereof. A deep-sea sediment-sourced esterase gene est4 is obtained by screening a metagenome and has a nucleotide sequence shown as SEQ ID NO. 1, and the esterase EST4 encoded thereby has an amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID NO. 2. After heterologous expression of the esterase gene provided by the invention, the catalytic activity is highest when a substrate is p-nitrophenol caproate (C6) and the enzymatic activity is 56.1U / mg. The optimum temperature for catalytic hydrolysis of the esterase EST4 is 35-40 DEG C; in the presence of Ca<2+>, Co<2+>, Sr<2+> and Zn<2+>, the enzymatic activity is increased. The esterase can be applied to chiral medicine synthesis, food processing and food flavor modification, wastewater treatment and washing industry and other industrial productions.
Owner:SECOND INST OF OCEANOGRAPHY MNR
Rice fingerprint constructing method based on SSR marking and capillary electrophoresis technology
InactiveCN103911442ASolve identification difficultiesAccurate identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementCapillary electrophoresisGel electrophoresis
The invention provides a rice fingerprint constructing method. The method includes: extracting rice genome DNA, screening SSR fluorescent primers with high polymorphism, subjecting the rice variety DNA to PCR amplification, detecting the PCR product by utilization of capillary gel electrophoresis, analyzing data to obtain a 0-1 matrix graph and converting the 0-1 matrix graph into a fingerprint mode mapping. By adoption of the characteristics of the SSR polymorphism and the high resolution of the capillary gel electrophoresis technology, the method can recognize two polymorphism bands with a band difference being 1 bp. The method is prone to automation, simple in operation, stable and reliable in results, and prone to large-scale multi-batch data integration and analysis, and is suitable for construction of a large number of rice variety fingerprints.
Owner:广西益谱检测技术有限公司 +3
Targeted screening for mutations
InactiveUS20160281171A1Microbiological testing/measurementDNA preparationInternal tandem duplicationProtein translocation
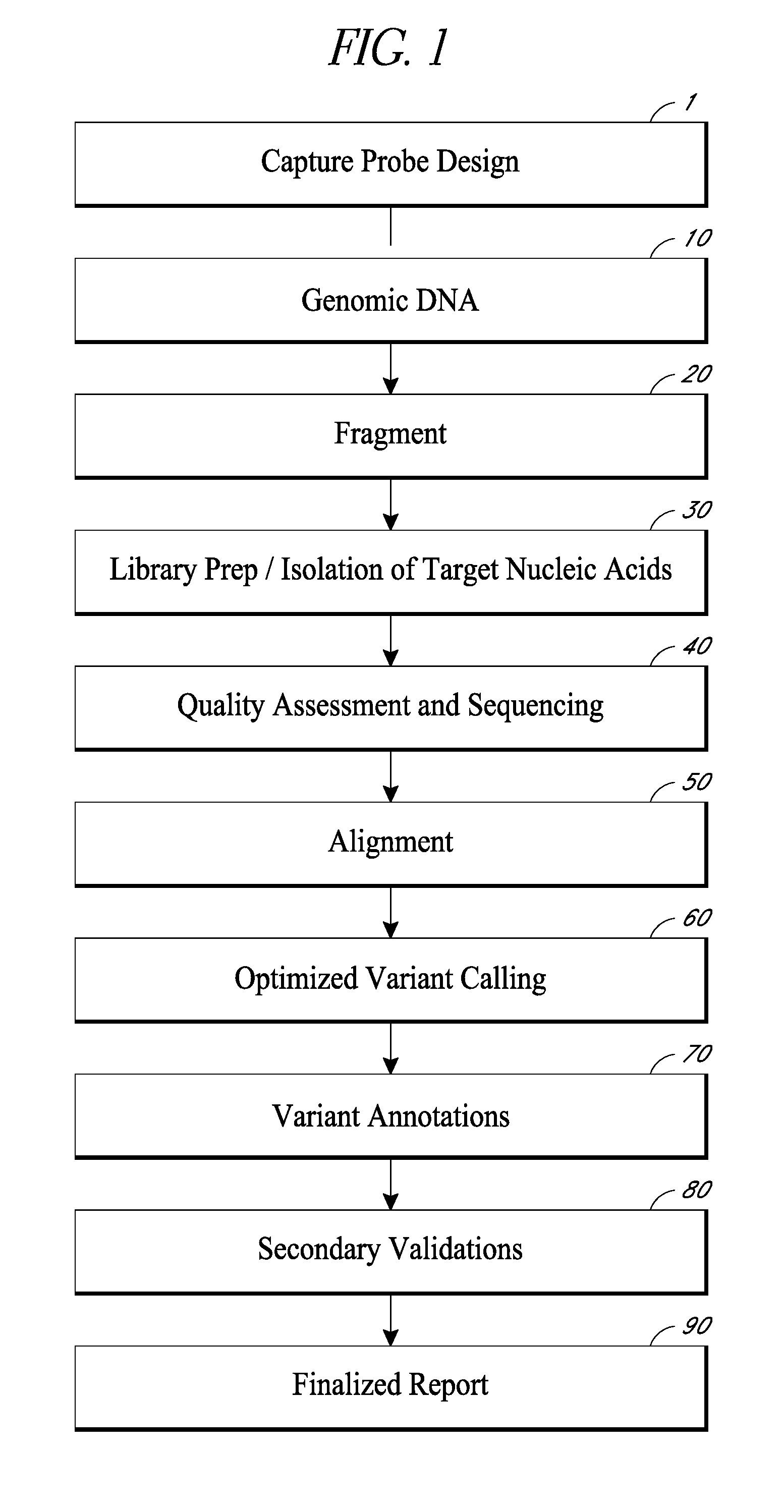
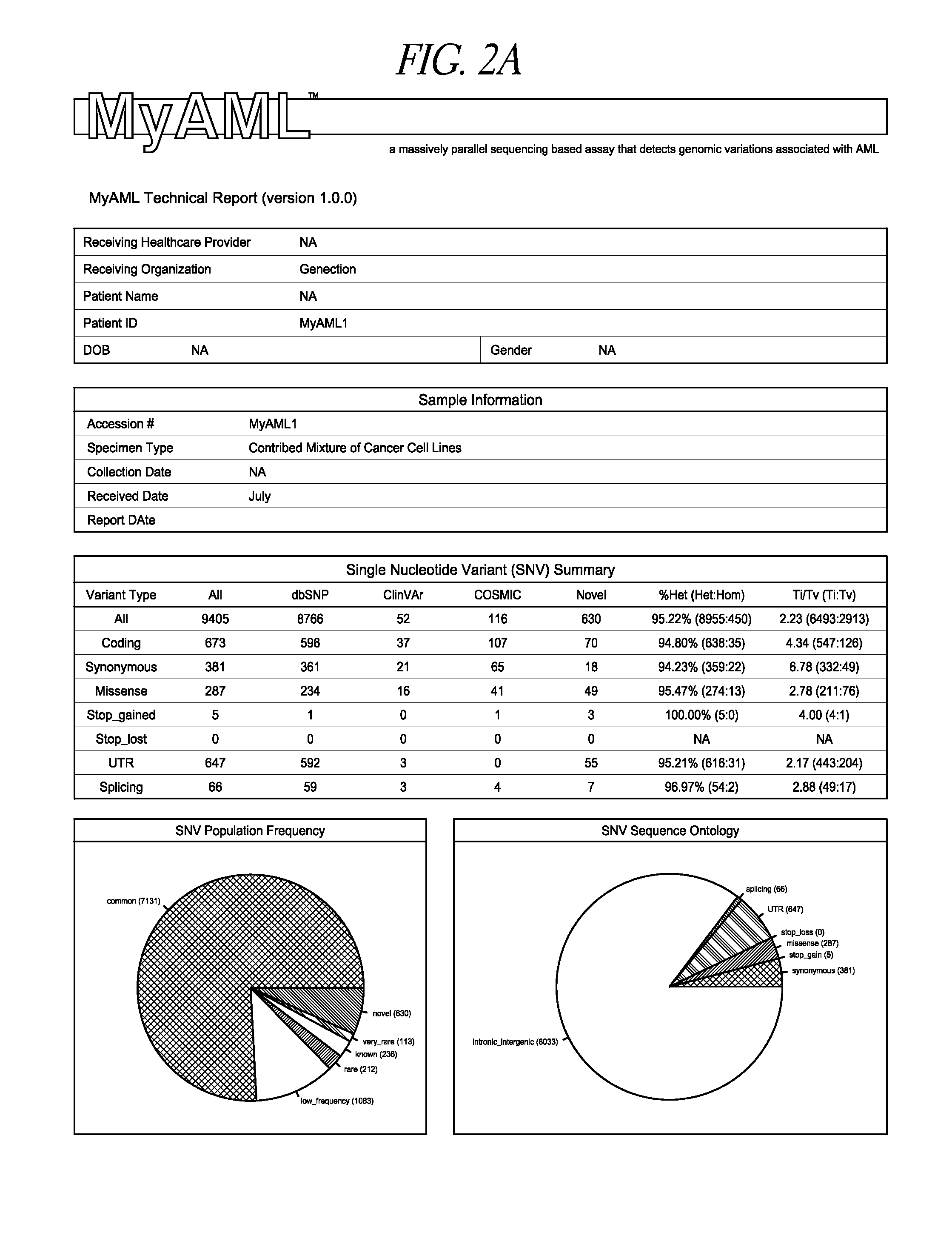
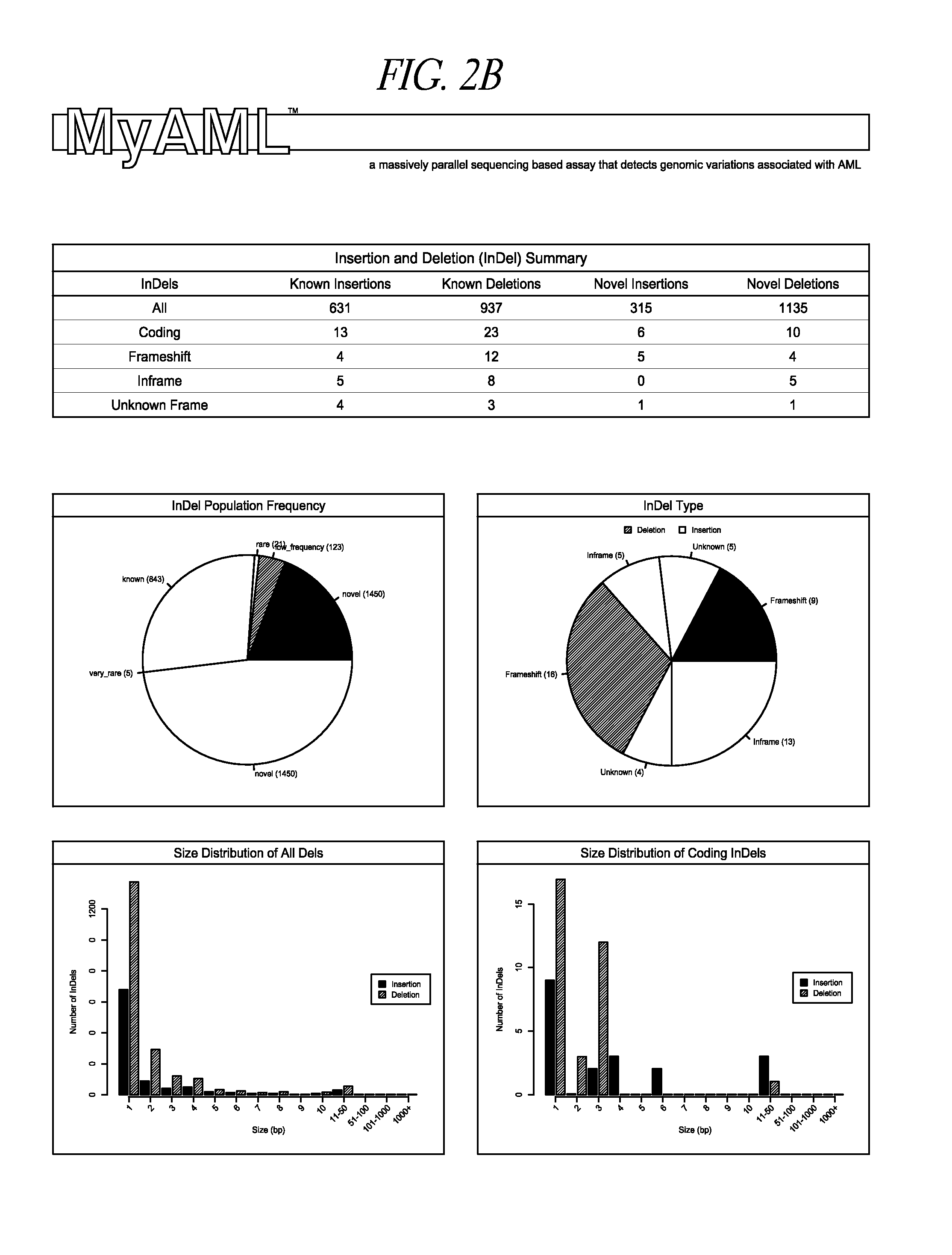
Compositions, methods and kits for genomic screening, genetic analysis, and gene discovery. In some embodiments the disclosed methods can detect large internal tandem duplications, or novel translocations, as well as identify the genomic breakpoint of novel translocations when only one of the two fusion partners is known or targeted. This is accomplished by employing a series of carefully selected capture probes to target genome-specific and disease-specific areas of target genes that harbor disease related somatic mutations, insertions / deletions or are involved in translocations.
Owner:INVIVOSCRIBE TECH
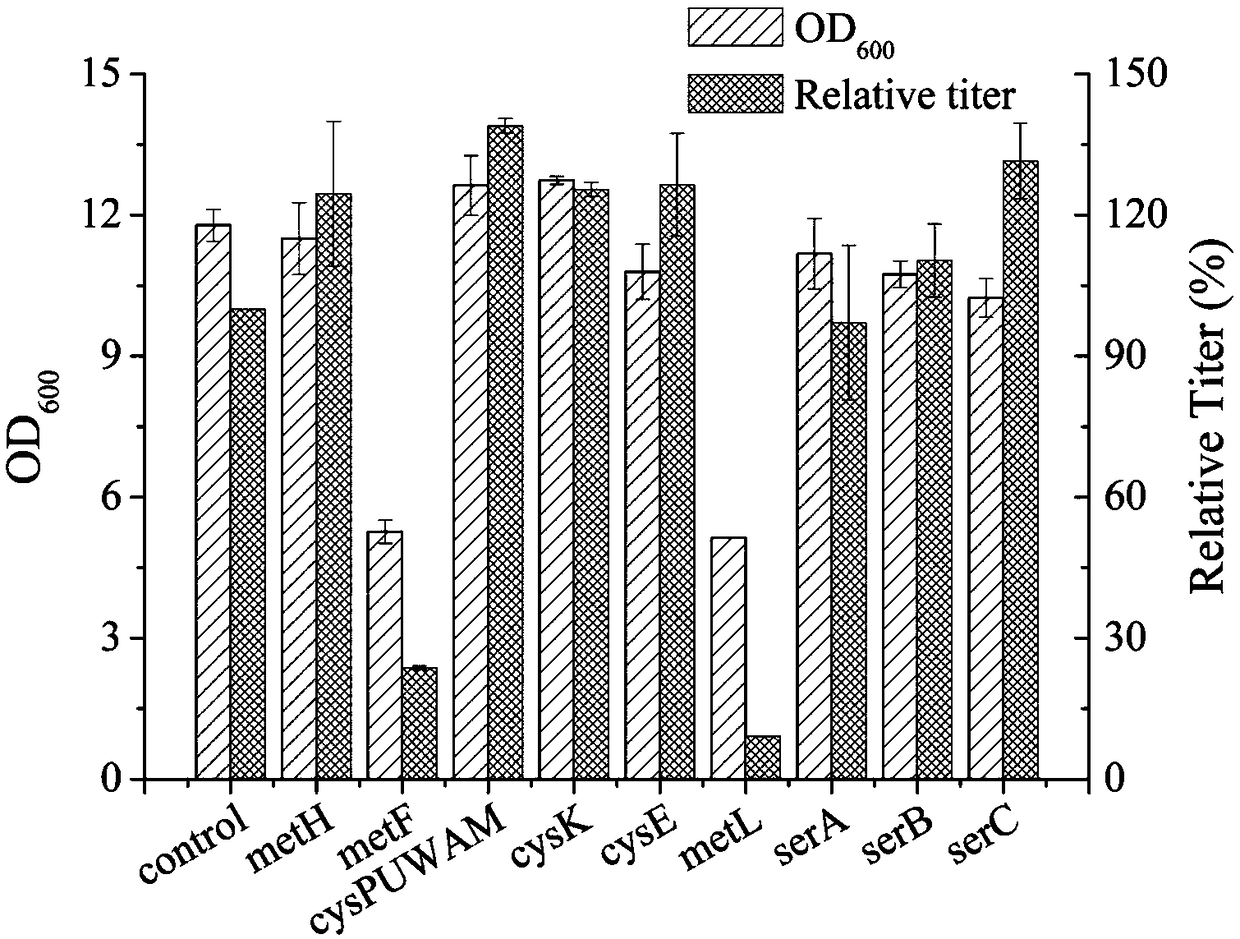
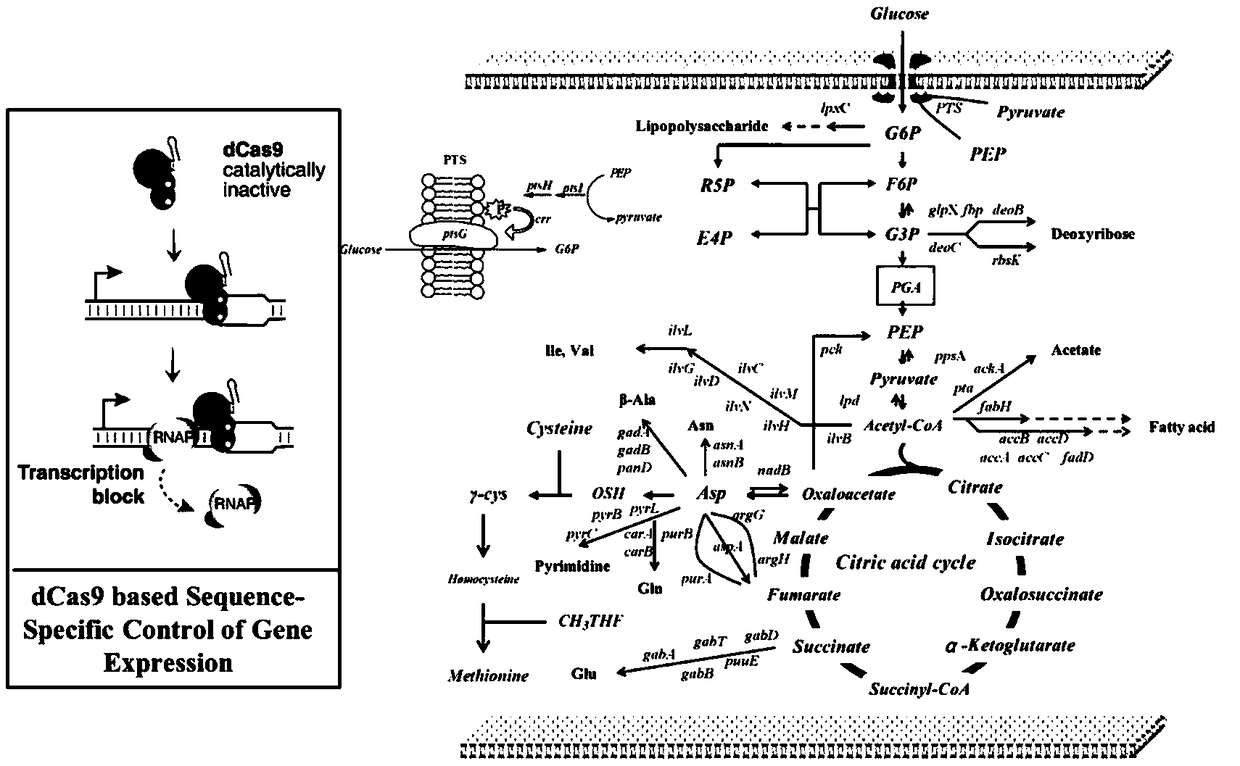
Recombinant escherichia coli capable of high-yielding L-methionine and application thereof
ActiveCN109055289AHigh potencyImprove fermentation titerBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliRecombinant escherichia coli
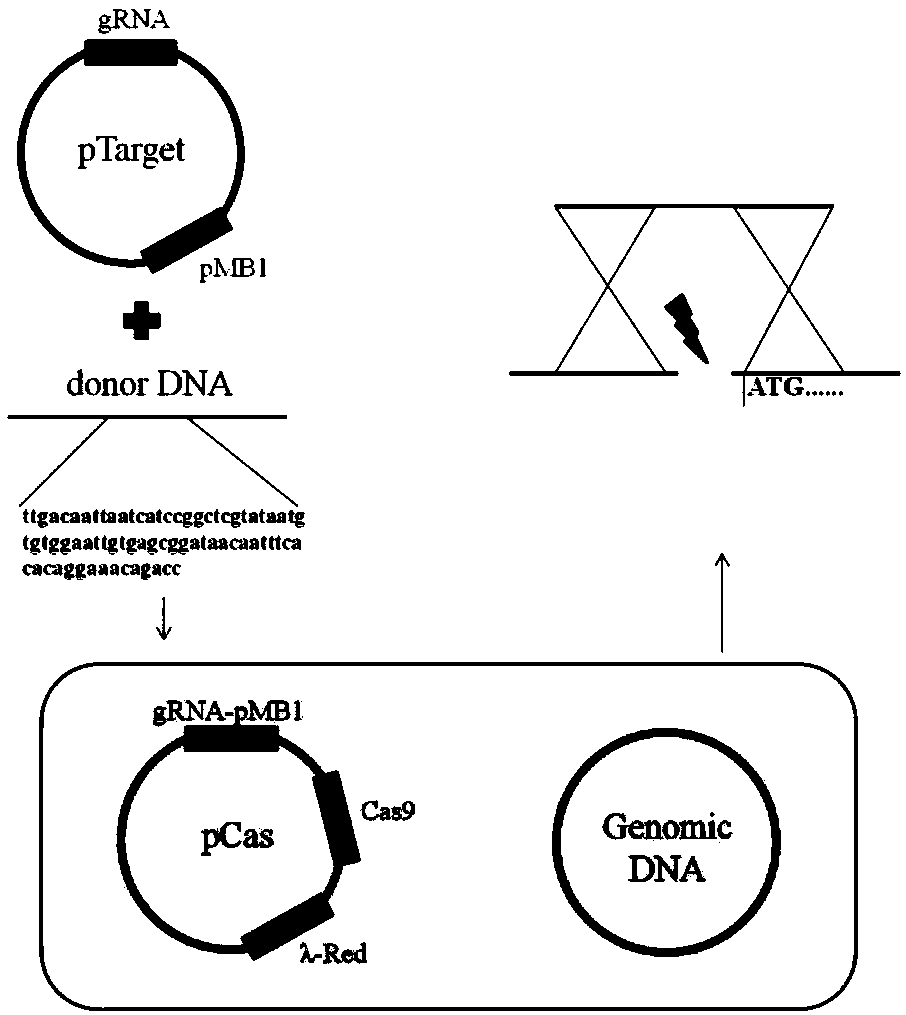
The invention discloses a recombinant escherichia coli capable of high-yielding L-methionine and an application thereof. The recombinant escherichia coli is constructed according to a method as follows: adopting a CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing technology for respectively replacing L-methionine synthase gene promoters with trc promoters in escherichia coli genomes, introducing a host strain genome and screening, thereby acquiring the recombinant escherichia coli capable of high-yielding L-methionine. The host strain is E.coli W3110 Delta metJ Delta metI / pTrc99A / metA* / yjeH which is constructed by knocking out metJ and metI in escherichia coli E.coli W3110 and then introducing a pTrc99A / metA* / yjeH plasmid. The maximal titer of L-methionine can reach up to 2.8g / L and DAP of by-products is obviouslyreduced to above 60% (reduced from 1g / L to below 0.4g / L).
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
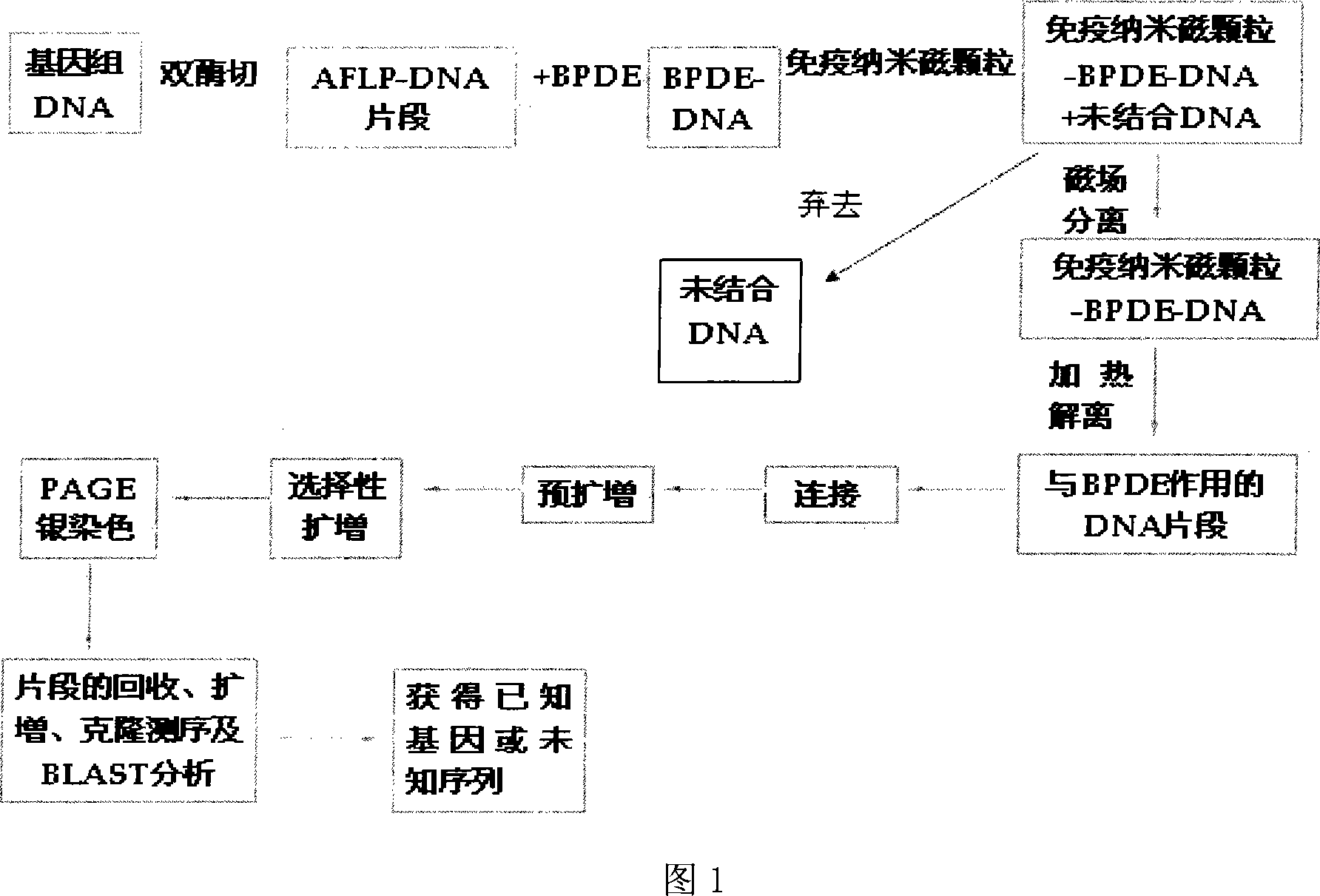
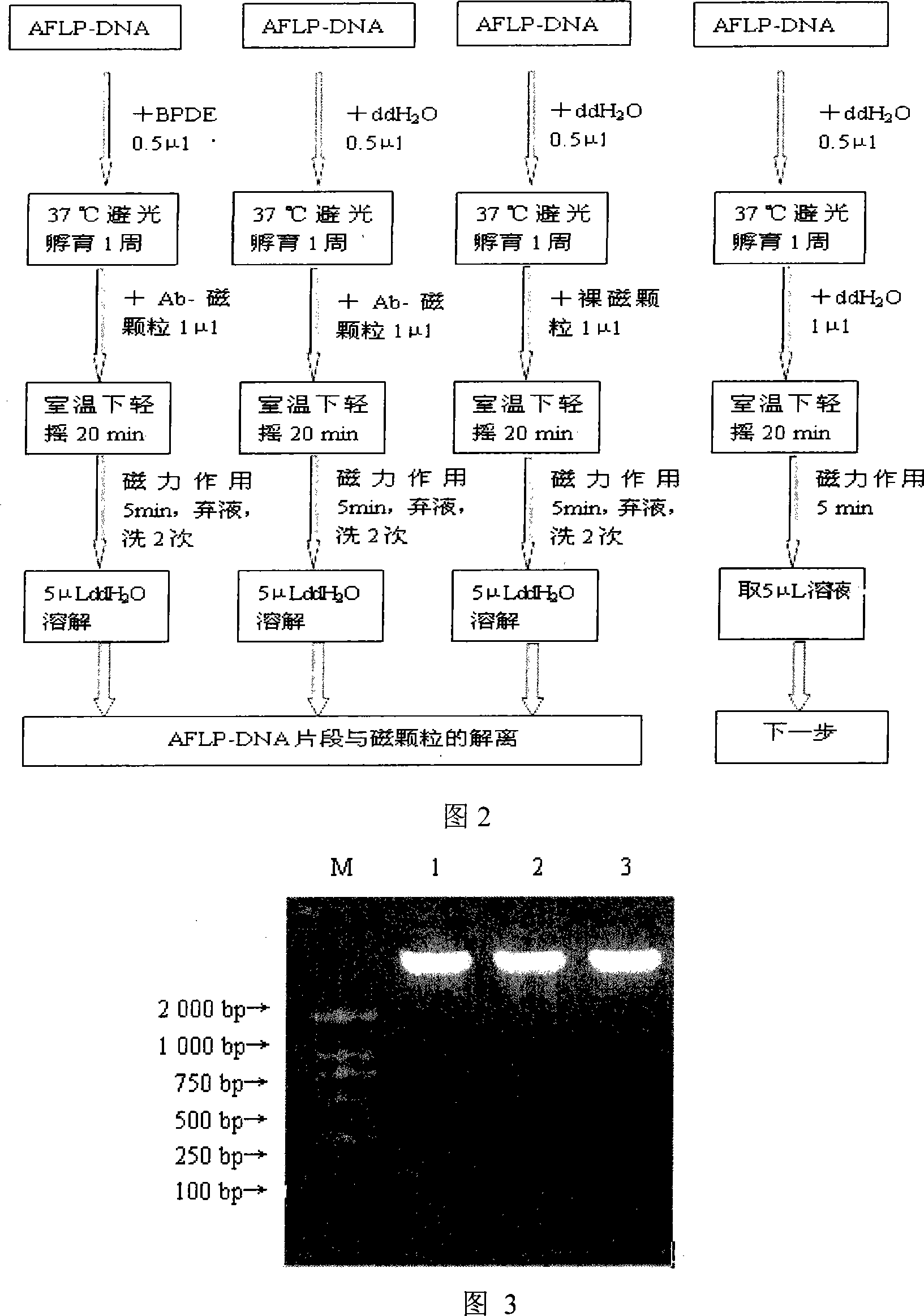
Whole-genom sifting method for BPDE carcinogen related gene
InactiveCN101113474AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationCarcinogenScreening method
The invention discloses a whole genome screening method for screening relative BPDE oncogenes and comprises the steps that: (1) genome DNA is extracted from normal lung tissue; (2) AFLP DNA fragment is prepared; (3) immunomagnetic of AFLP DNA fragment interacting with BPDE is enriched and separated; (4) AFLP PCR is increased; (5) denatured polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and silver stain visualization are done to selective PCR amplification products of AFLP; (6) differential fragment is recycled, amplified, cloned and tested for sequence and homologous similarity and analysis are done. The whole genome screening method for screening relative BPDE oncogenes of the invention is the high effective and specific method and more BPDE susceptible oncogenes are screened in the whole genome level, which provides a basis for stating BPDE carcinogenic molecular mechanism.
Owner:INST OF HYGIENE & ENVIRONMENTAL MEDICINE PLA ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL
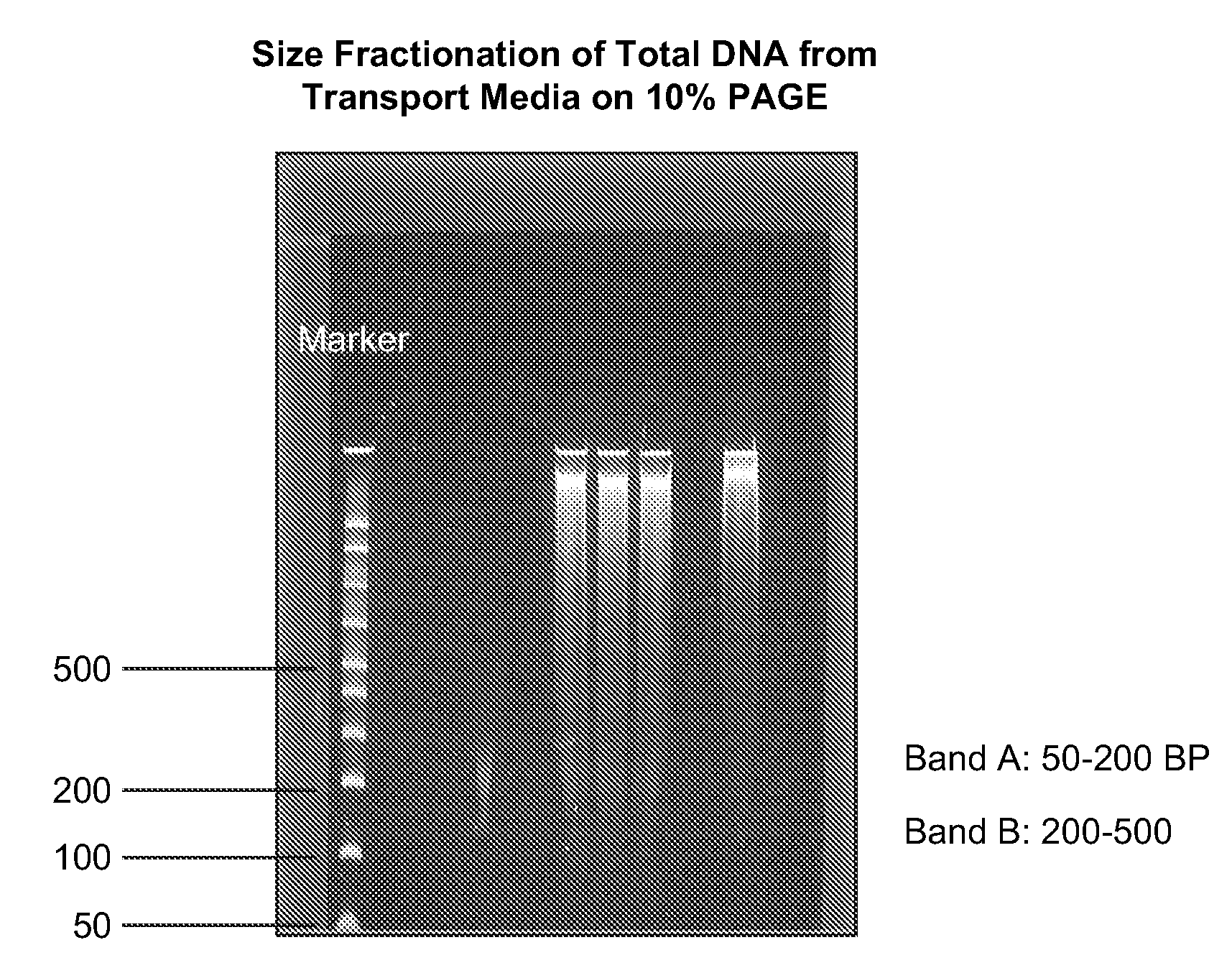
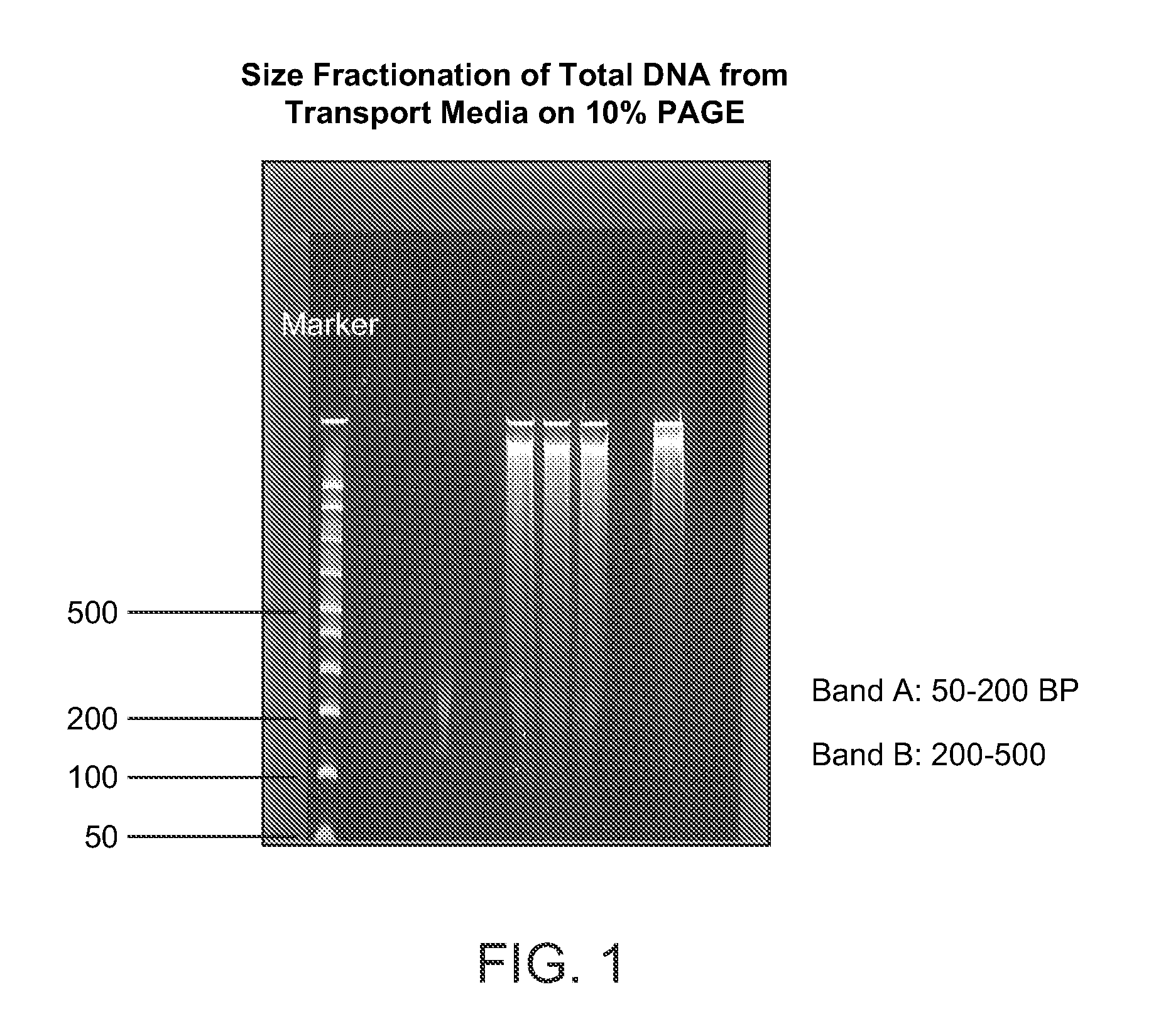
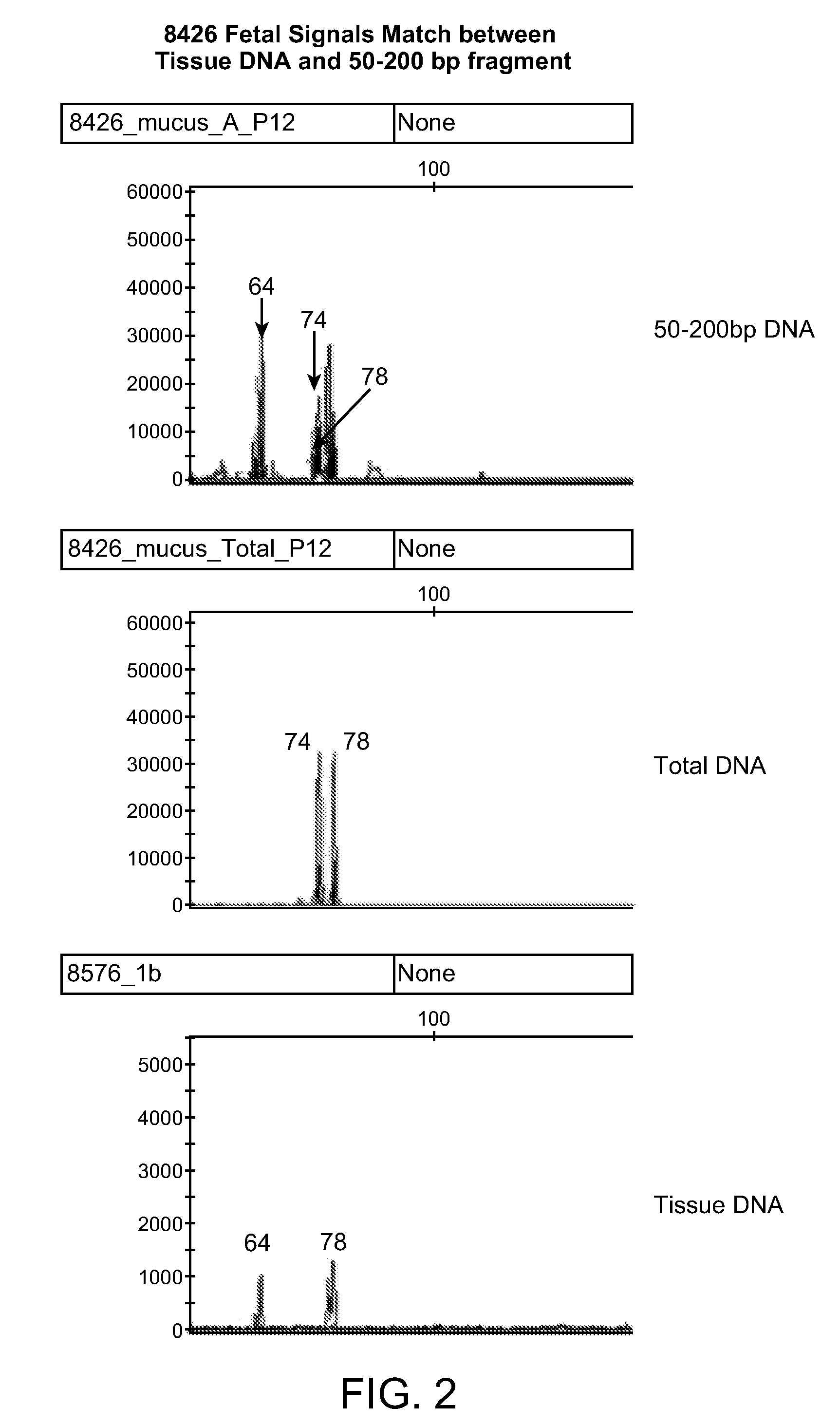
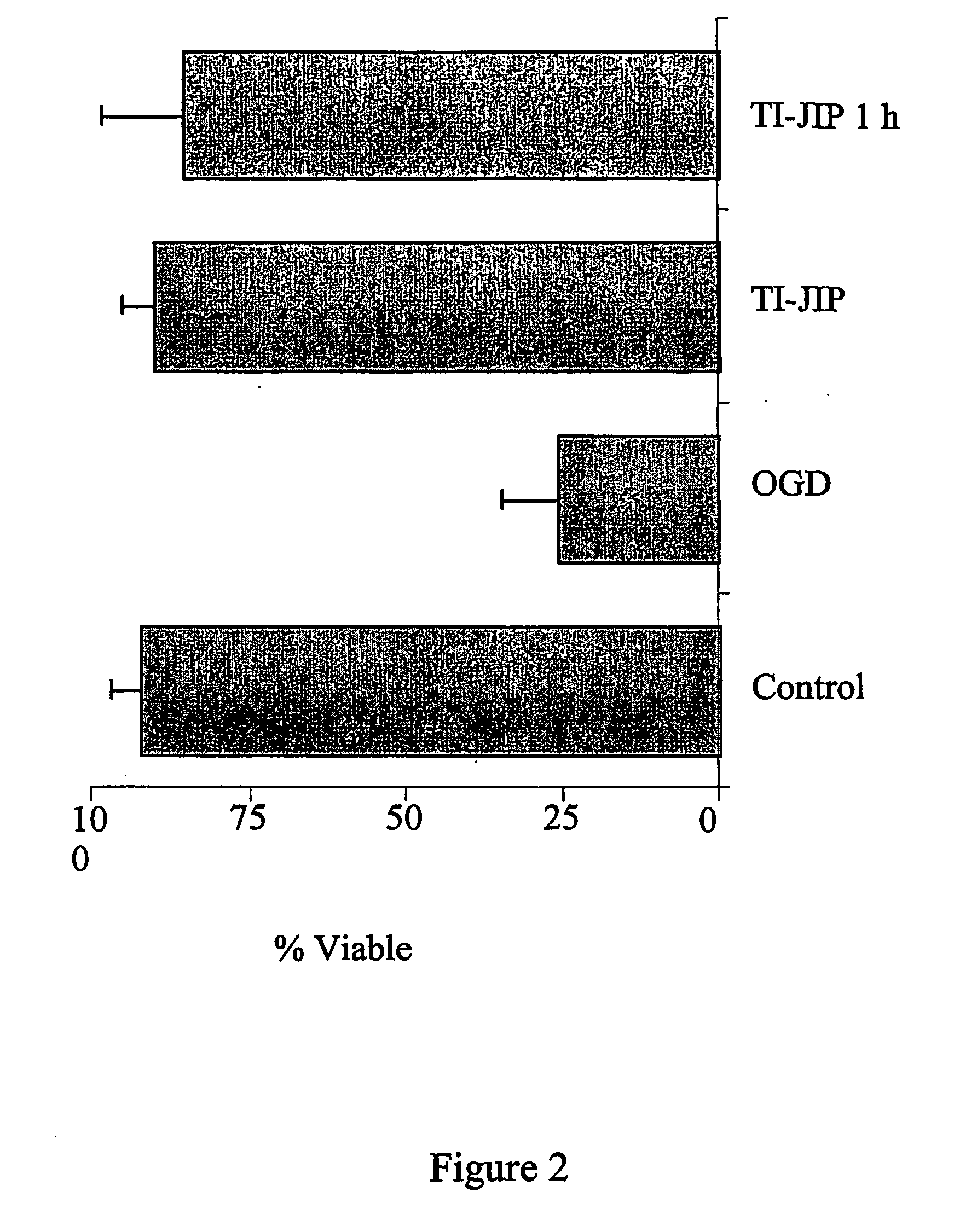
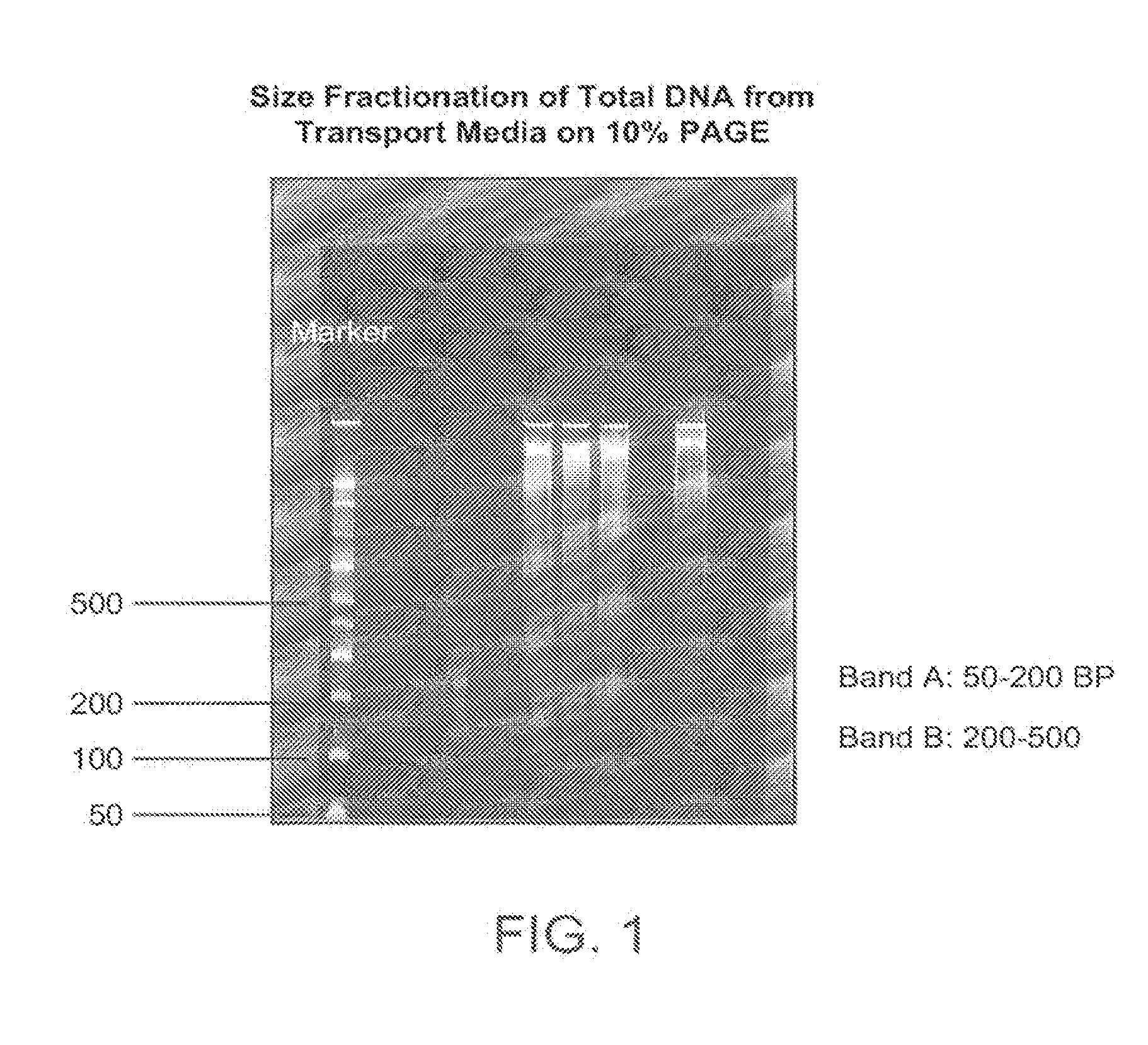
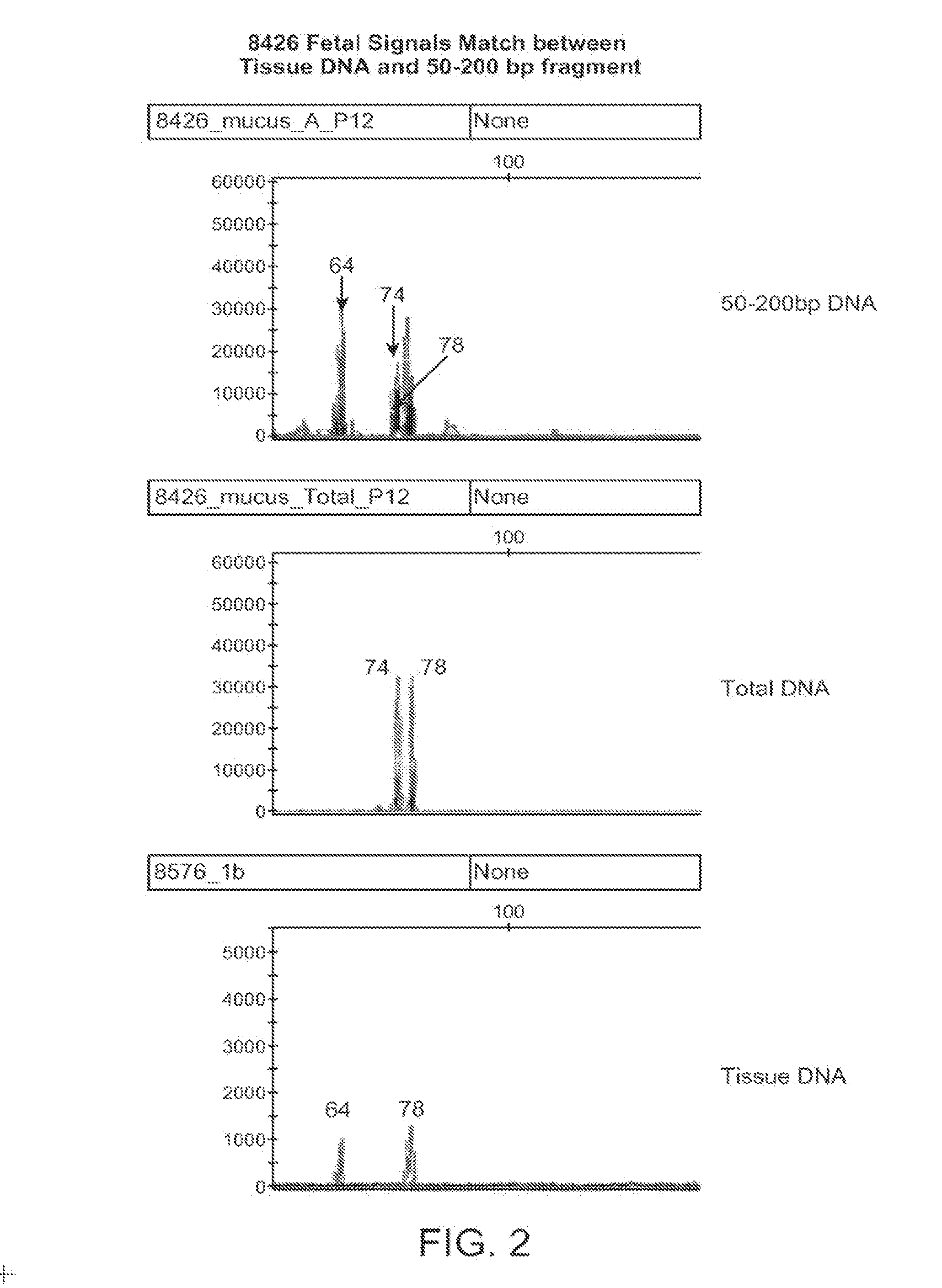
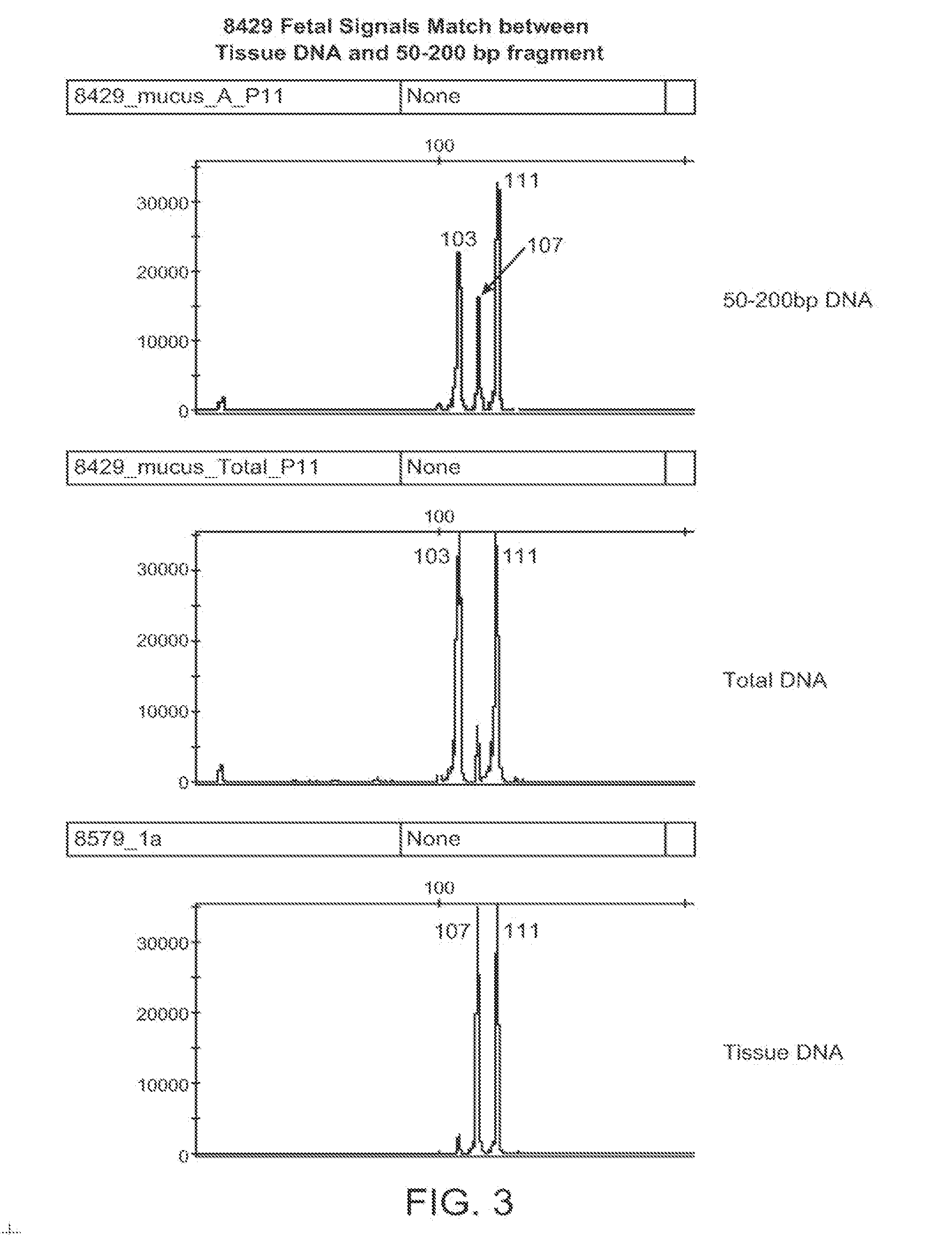
Non-invasive prenatal genetic screen
The present invention provides methods and kits useful for genetic testing or screening of fetuses using nucleic acid samples isolated from cervical mucus samples of fetus hosts.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
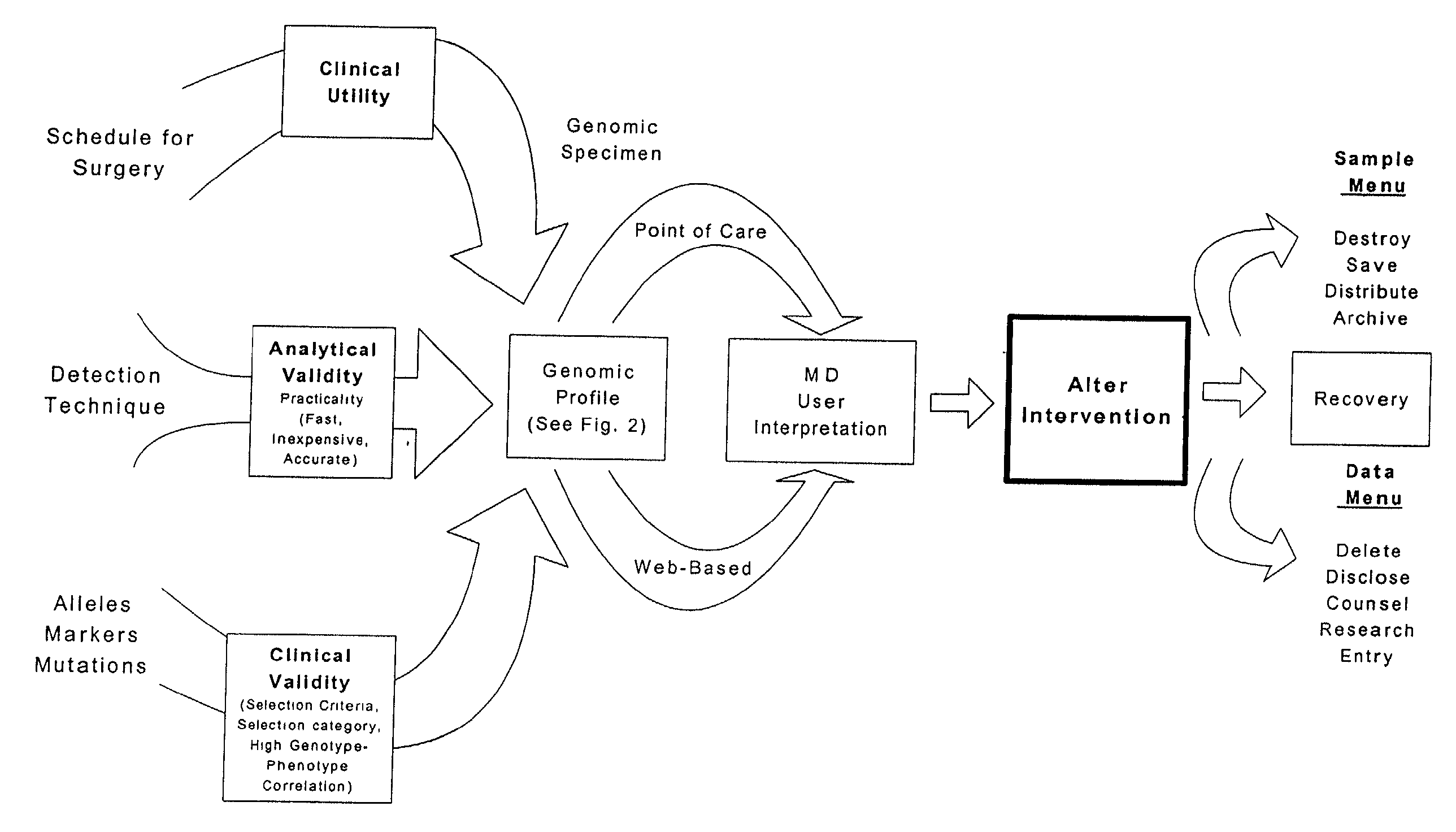
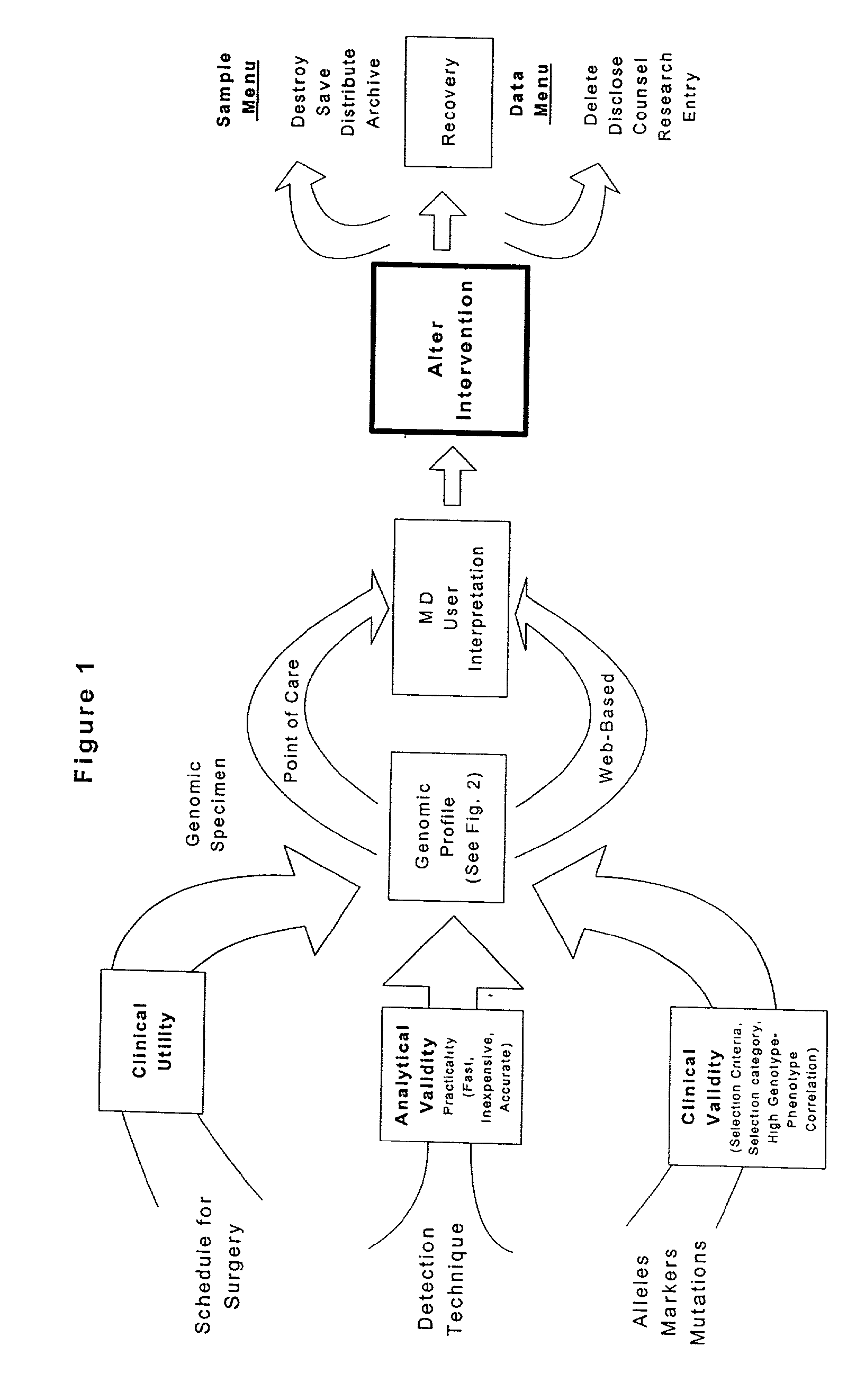
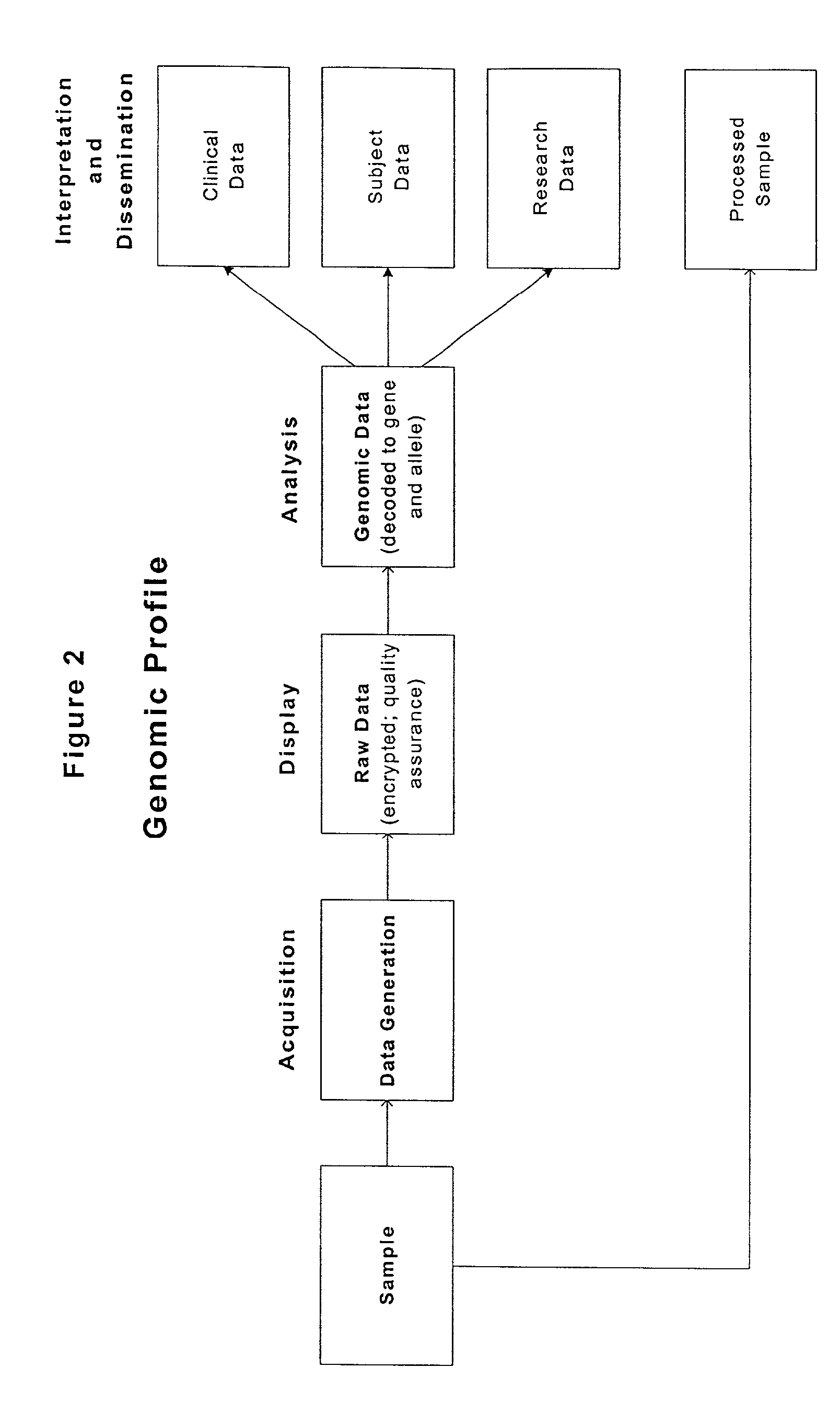
Methods and compositions for perioperative genomic profiling
InactiveUS20110183335A1Microbiological testing/measurementRecombinant DNA-technologySurgical treatmentScreening method
The present invention relates to methods for perioperative genomic screening of subjects, in particular to perioperative screening for markers indicative of responses to anesthesia and other perioperative or operative treatments and procedures. The present invention also provides compositions for use in screening methods. The methods and compositions of the present invention find use in tailoring a subject's medical or surgical treatment to reflect genetic information that predicts a subject's response to medications or techniques used in the procedure.
Owner:HOGAN KIRK
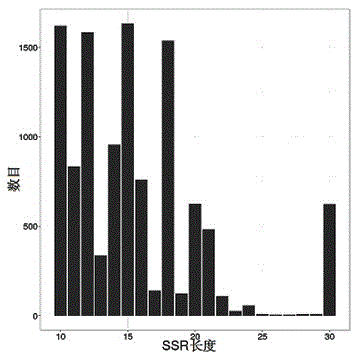
Method for developing SSR (Simple Sequence Repeat) molecular mark of nibea albiflora for population identification
InactiveCN105624322AImprove work efficiencyReduce screening costsMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationGenomic DNAGrowing season
The invention discloses a method for developing an SSR (Simple Sequence Repeat) molecular mark of nibea albiflora for population identification. The method comprises the following steps: extracting RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) by using a nibea albiflora mixed tissue of a plurality of nibea albiflora, performing RNA sequencing, performing splicing to obtain a nibea albiflora expression gene sequence, and obtaining a potential SSR mark with a bioinformatics method; designing primers by utilizing an SSR flanking sequence, extracting genomic DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) by using fins from a random sample, and screening the SSR primers; and performing PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification on different nibea albiflora DNA templates by using each pair of the SSR primers, performing capillary electrophoresis detection on an amplification product by using a Qsep100 full-automatic nucleic acid analysis system, screening out primers with different amplification results, calculating allelic composition and allelic frequency by utilizing PopGene, and analyzing a nibea albiflora population relationship and a genetic structure. The SSR molecular mark method for identifying and verifying nibea albiflora groups, provided by the invention, is stable and reliable, is not influenced by ages, gender and growth seasons, and provides scientific bases for group analysis as well as species identification, breeding and evaluation of the nibea albiflora.
Owner:JIMEI UNIV
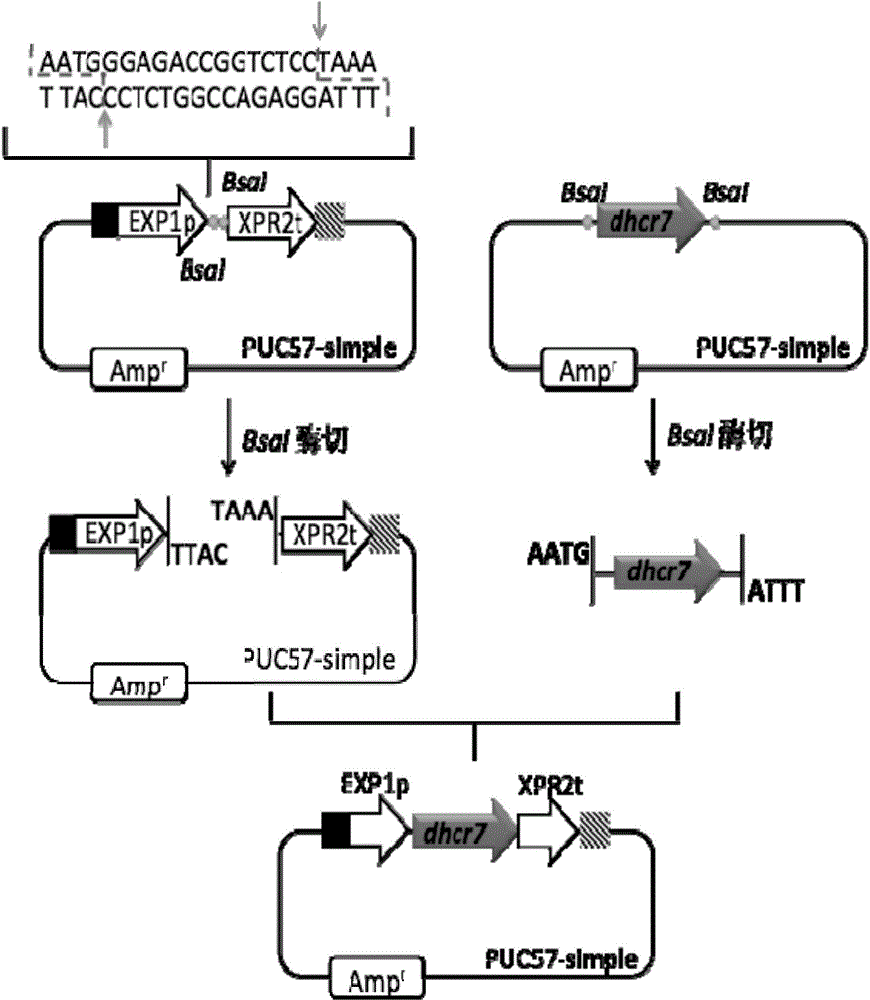
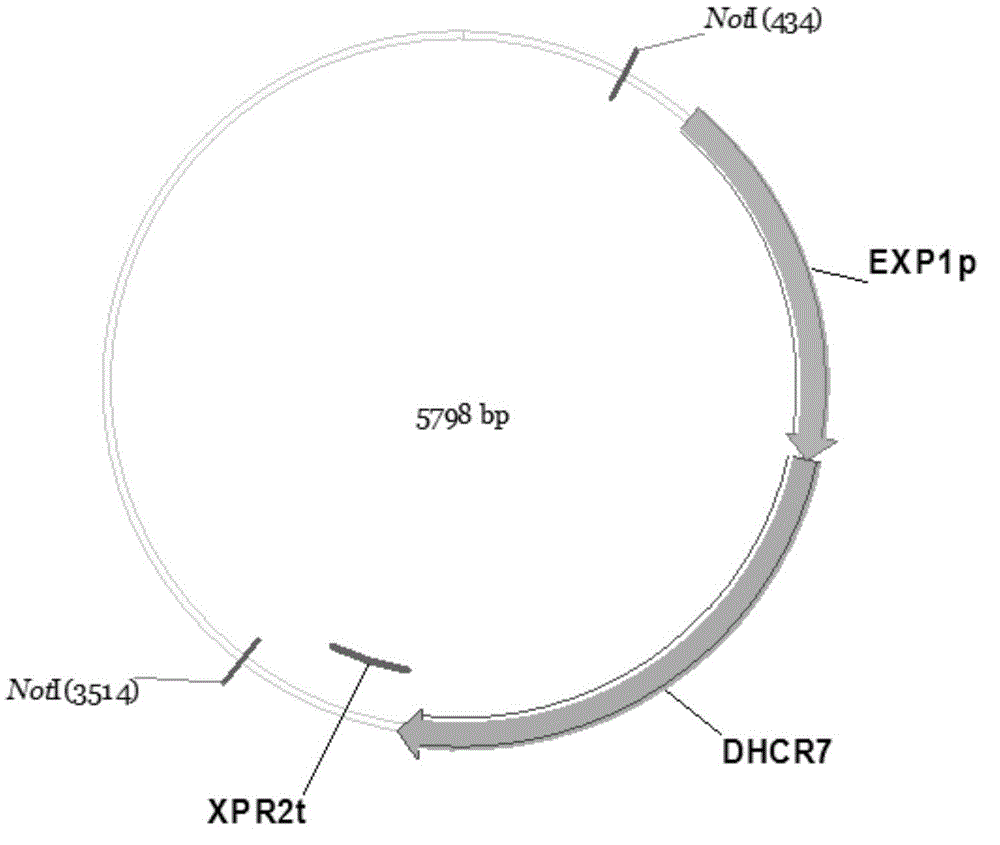
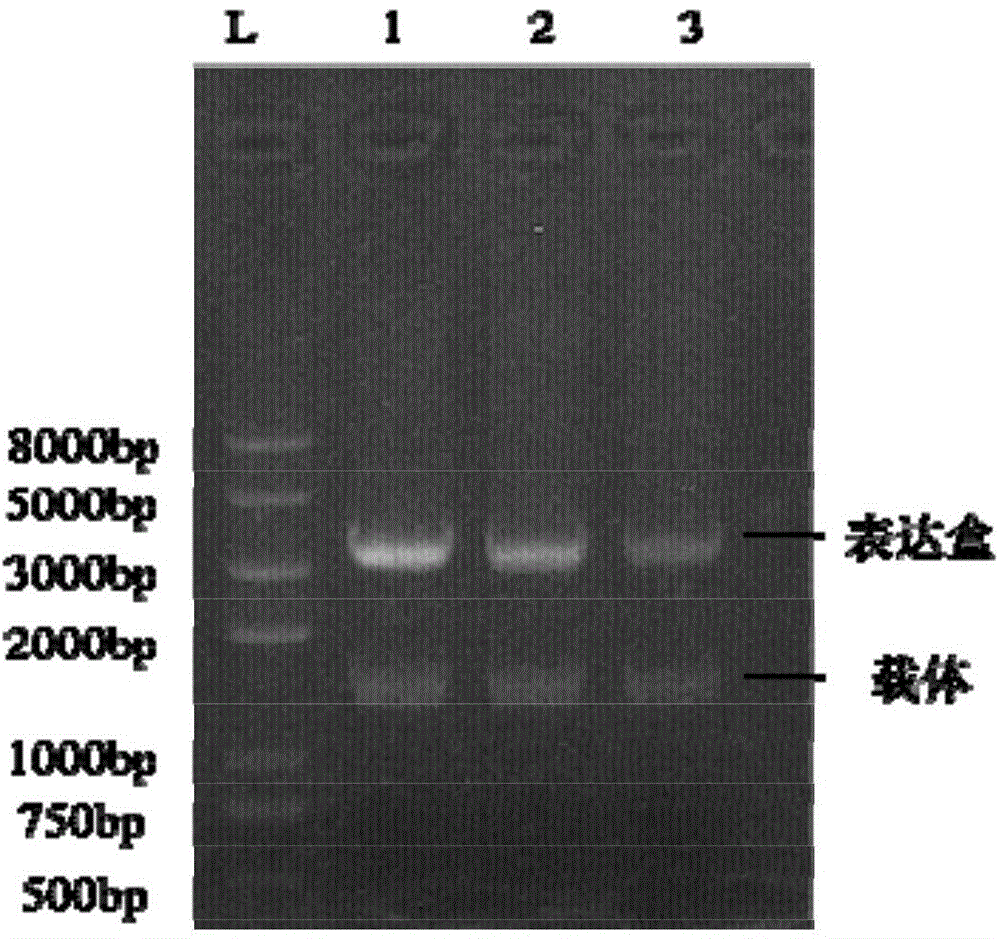
Recombinant yarrowia lipolytica bacterial strain as well as construction method and application thereof
The invention relates to the technical field of genetic engineering and particularly discloses a recombinant yarrowia lipolytica bacterial strain as well as a construction method and an application thereof. A genome of the recombinant yarrowia lipolytica bacterial strain comprises a nucleotide sequence as shown in any one of SEQ ID NO: 1-3. The construction method comprises the following steps of constructing a key gene dhcr7 in a biosynthesis way of campesterol expressed by a single-gene expression cassette through an OE-PCR (overlap extension-polymerase chain reaction) method; cutting down the single-gene expression cassette through restriction enzyme, transferring the single-gene expression cassette into yeast at one time to perform homologous recombination among fragments and integration of a special erg5 lotus of the genome, screening a completely-assembled converter through an auxotrophic culture medium and genome PCR to obtain a novel recombinant yarrowia lipolytica bacterial strain. The novel recombinant yarrowia lipolytica bacterial strain can be applied to biosynthesis of campesterol, and a relatively high yield can be kept.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
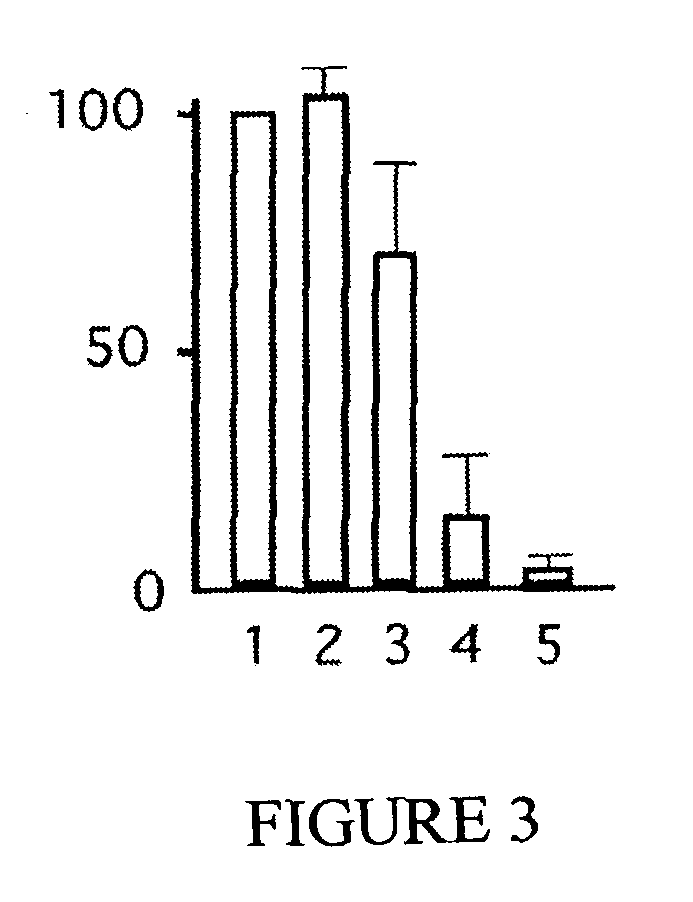
High throughput functional genomic screening methods for osteoarthritis
InactiveUS20060188885A1Microbiological testing/measurementSkeletal disorderFunctional assayGene product
High-throughput functional screening assays are provided that identify genes and gene products that are associated with the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis (OA) in chondrocytes. In addition, genes and gene products identified by such functional assays are also provided. The genes and gene products provided herein are useful inter alia for diagnosing OA in individuals and as drug targets for identifying drugs to treat OA.
Owner:BODIAN DALE +4
Vectors having replication, immunogenicity and/or pathogenicity under stress promoter regulation and use thereof
InactiveUS20020168771A1Small genomeConvenient genetic constructionVectorsGenetic material ingredientsBacteroidesImmunogenicity
The present invention relates to modified vectors, e.g. plasmids, viruses or microbia sucsh as yeast or bacteria, wherein the replication, immunogenicity and / or pathogenicity is placed under the control of at least one stress gene regulating element. In preferred embodiments, these modified vectors are used for gene therapy, in vaccines, or for functional genomic screening.
Owner:GAMERMAN GARY ERIC
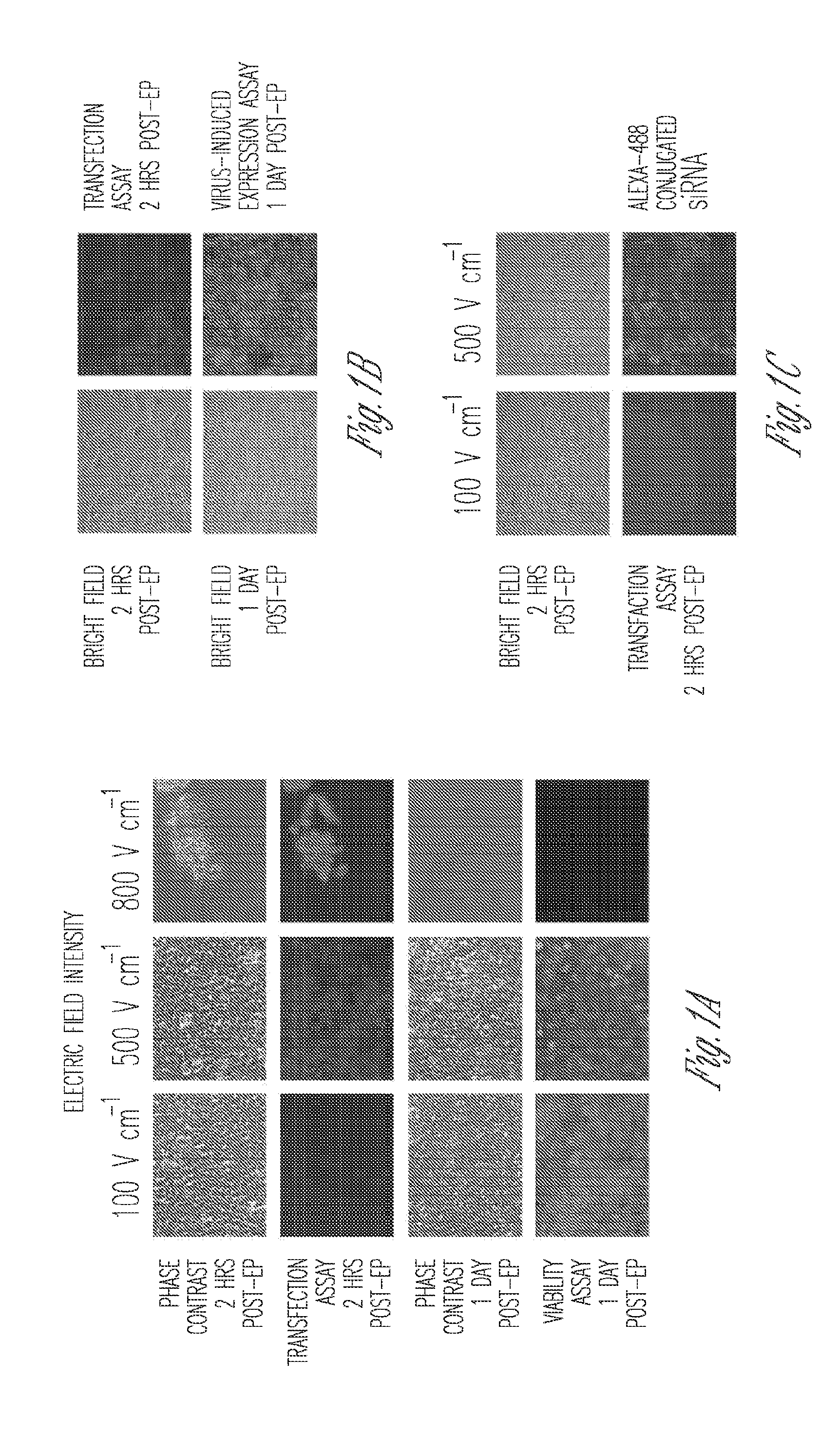
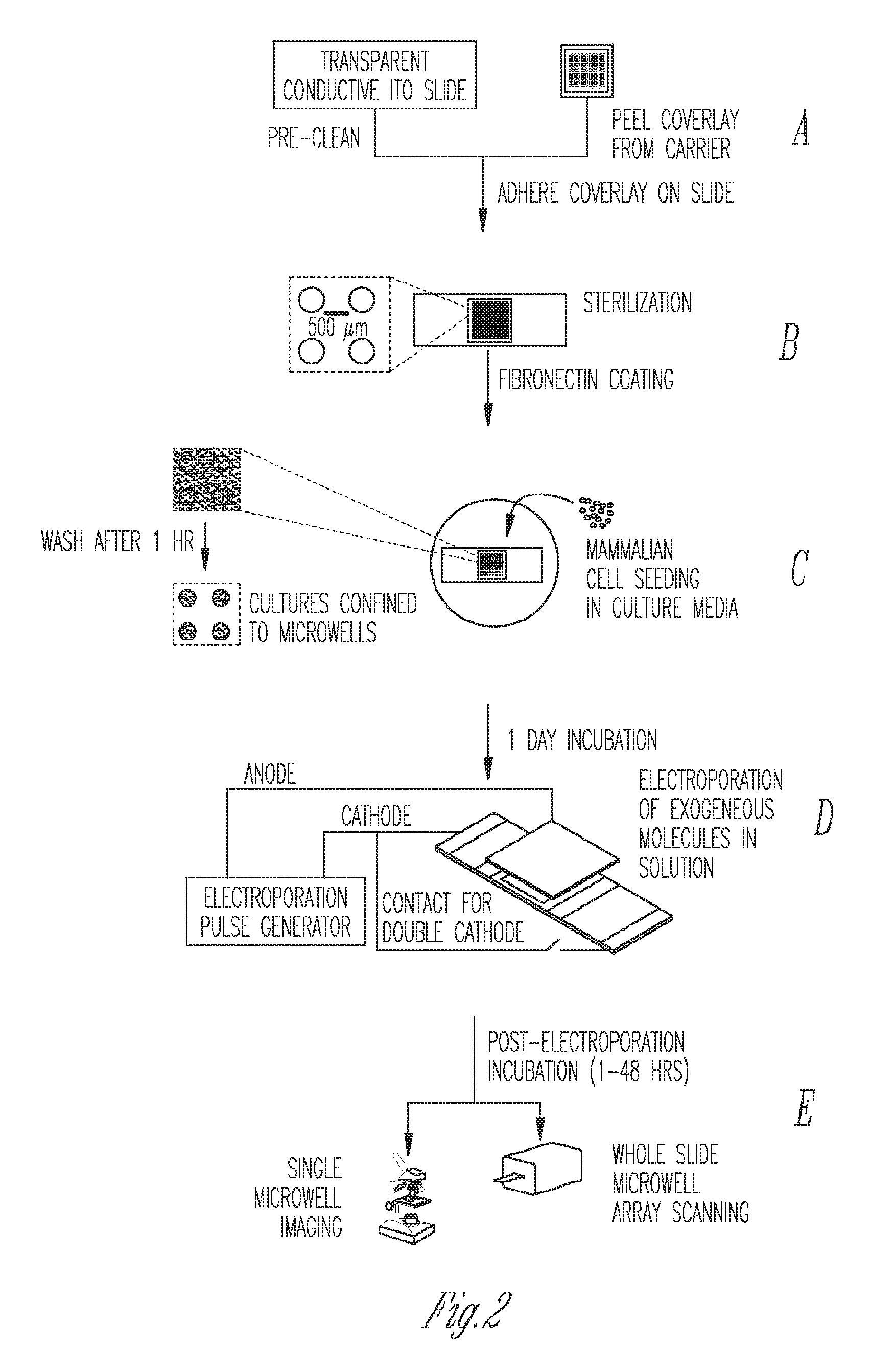
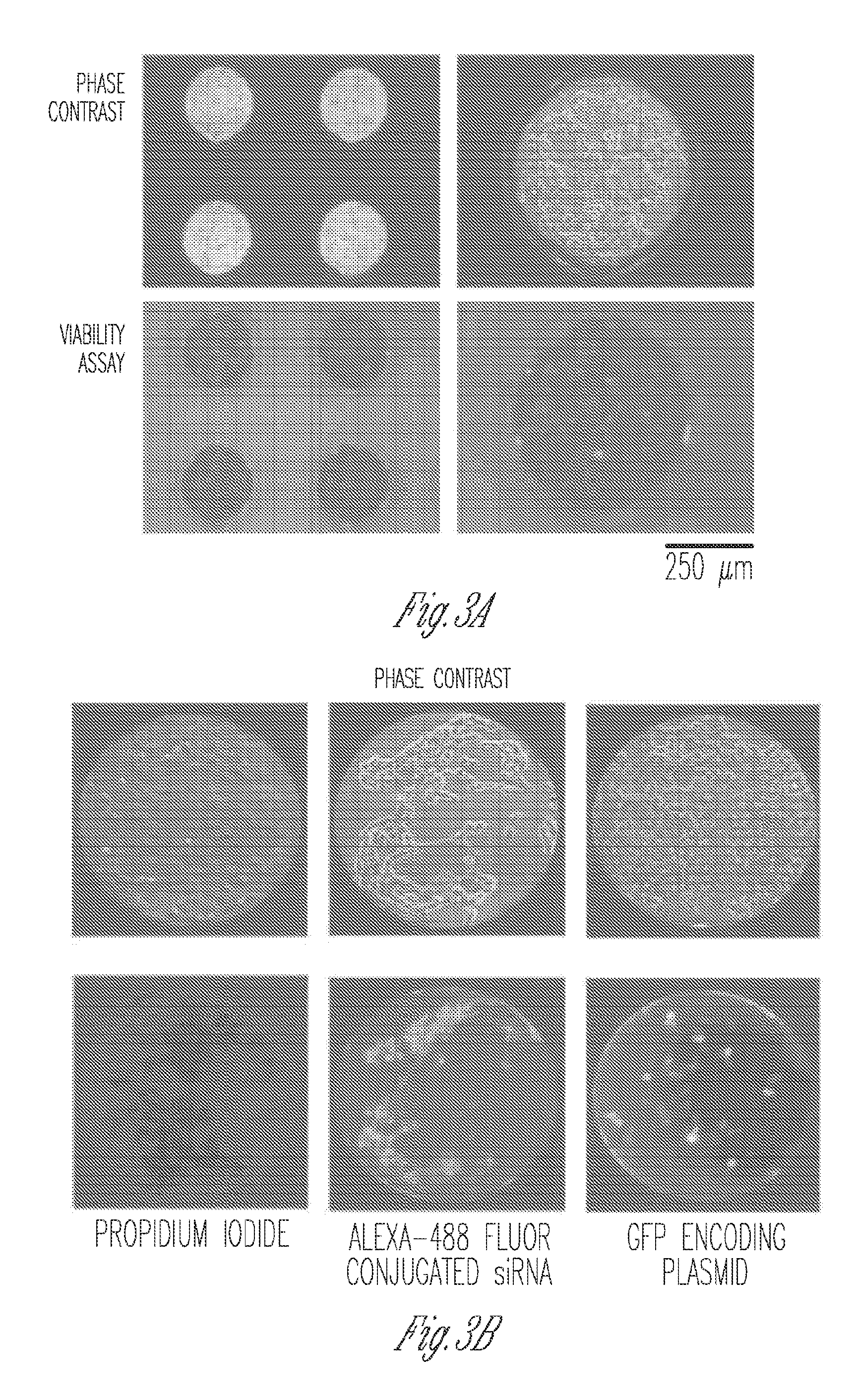
Miniaturized electroporation-ready microwell aray for high-throughput genomic screening
InactiveUS20120231517A1Highly efficient parallel introductionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMiniaturizationPrimary cell
Methods of introducing exogenous molecules into cells including cell lines and primary cells are provided. Additionally, miniaturized electroporation-ready microwell arrays are provided. These tools provide a miniaturized high-throughput functional genomics screening platform to carry out genome-size screens in a variety of cell types.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
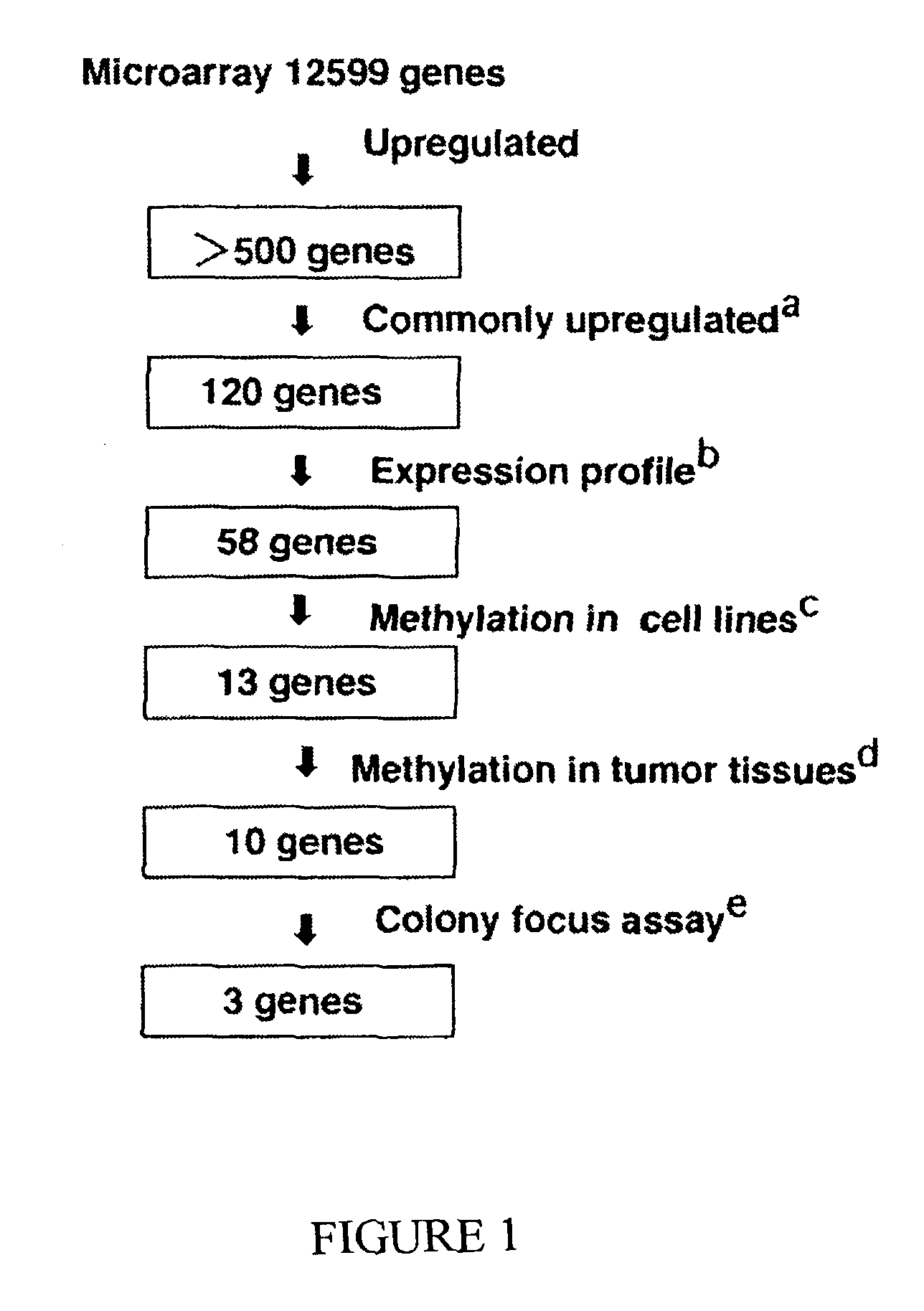
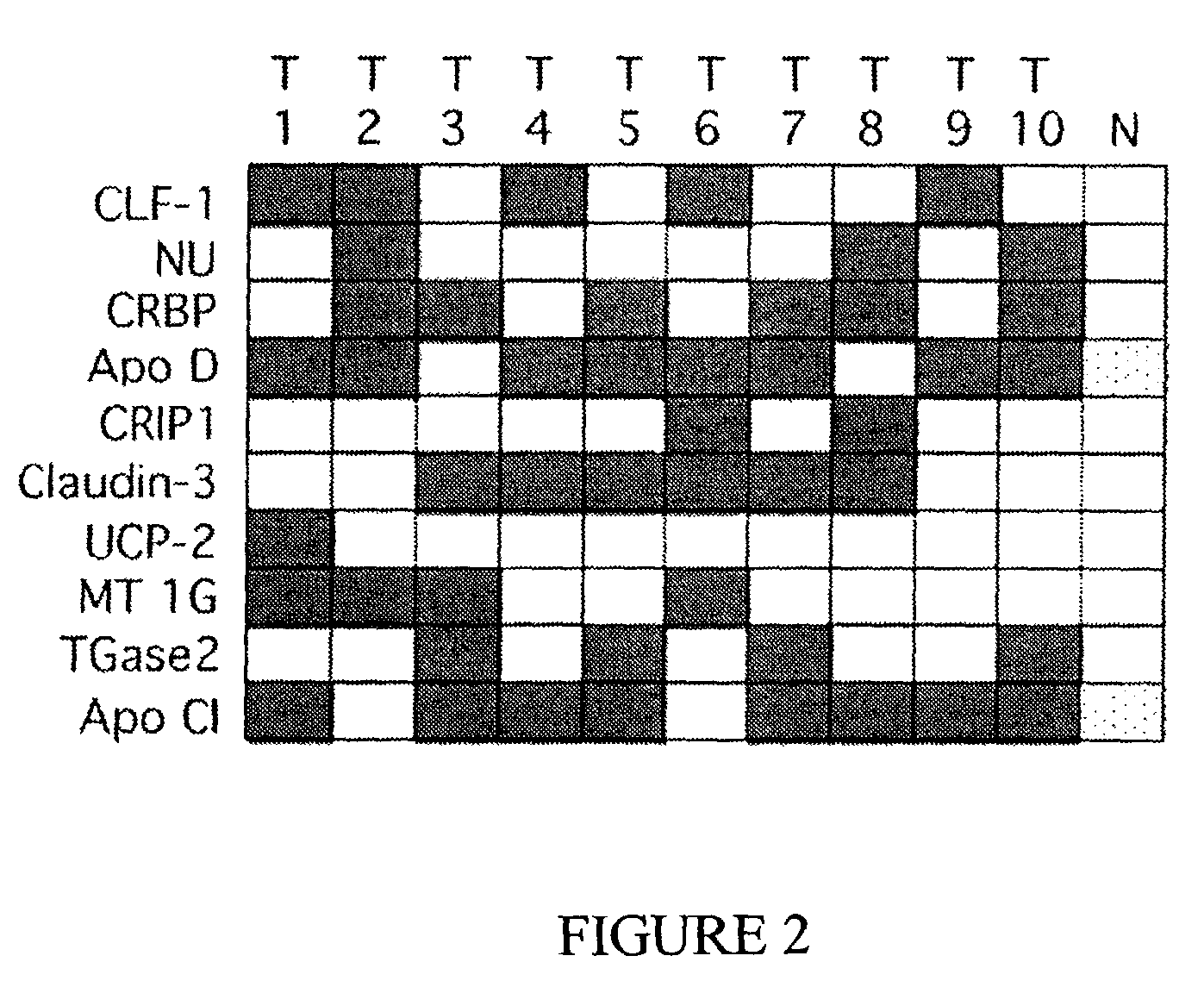
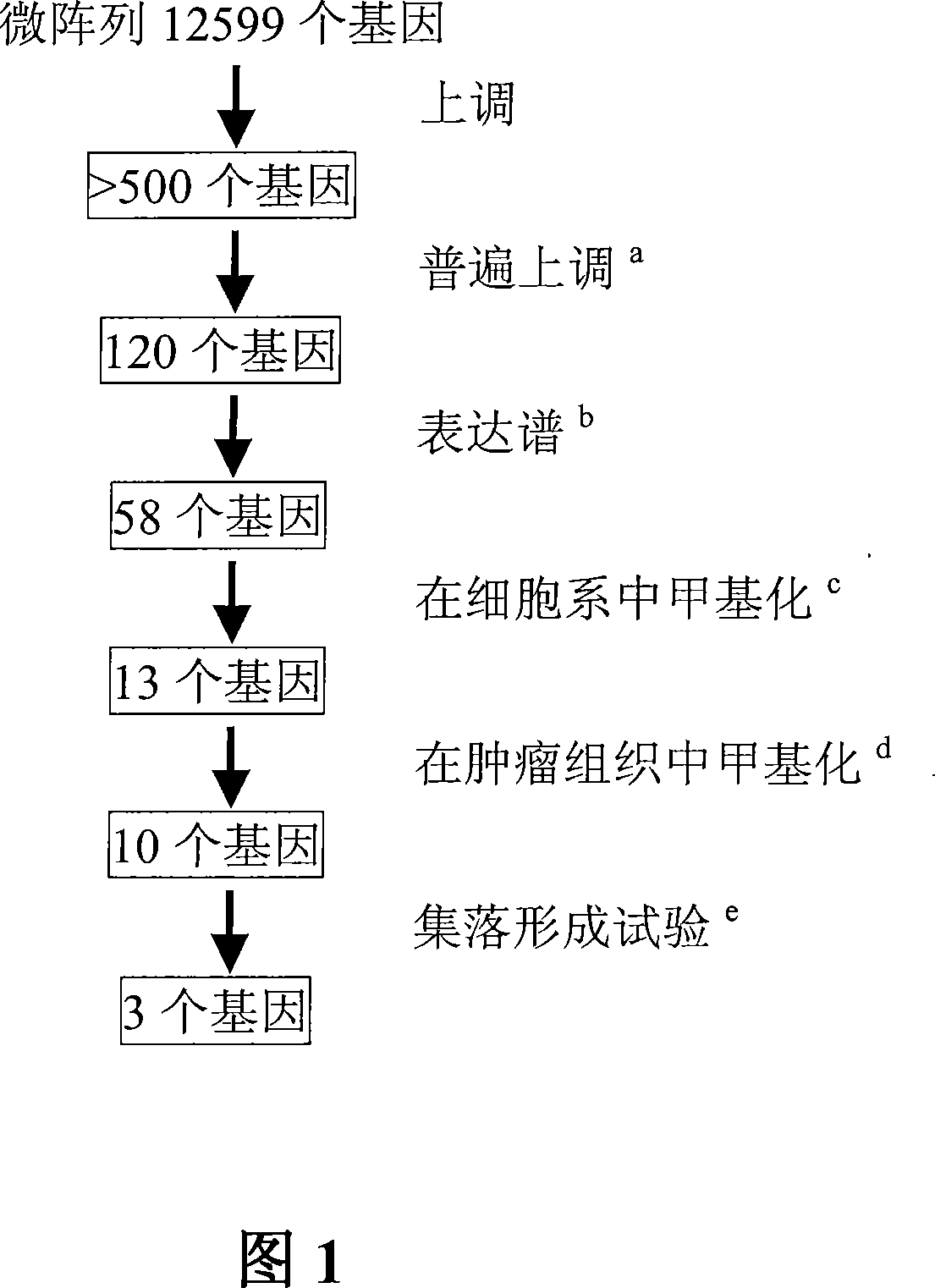
Genomic screen for epigenetically silenced tumor suppressor genes
Methods of genomic screening to identify epigenetically silenced genes, including epigenetically silenced tumor suppressor genes are provided. Also provided are methods of detecting a cancer, for example, an esophageal squamous cell carcinoma or a head and neck squamous cell carcinoma, as are methods of treating a subject having such a cancer.
Owner:THE JOHNS HOPKINS UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
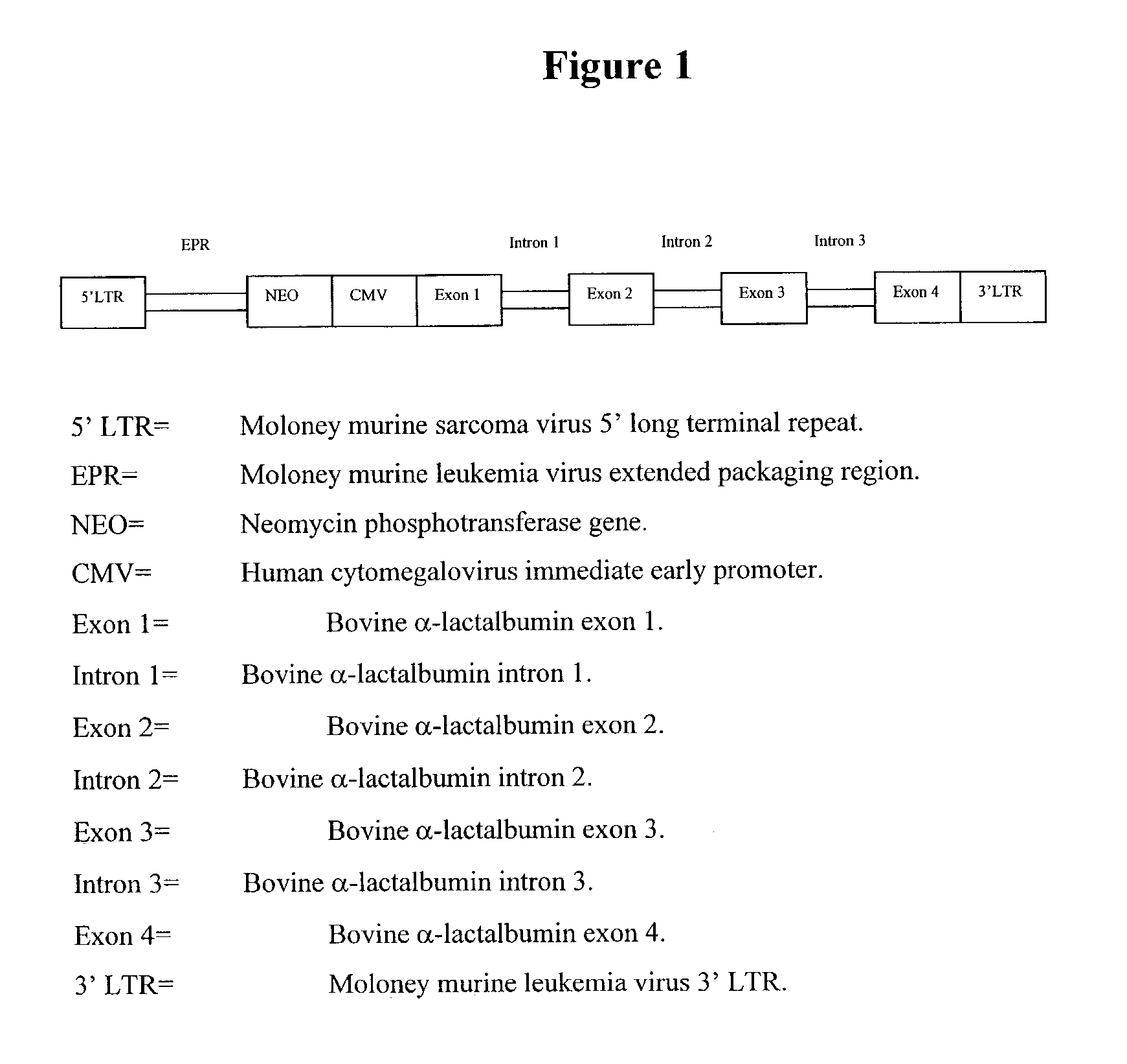
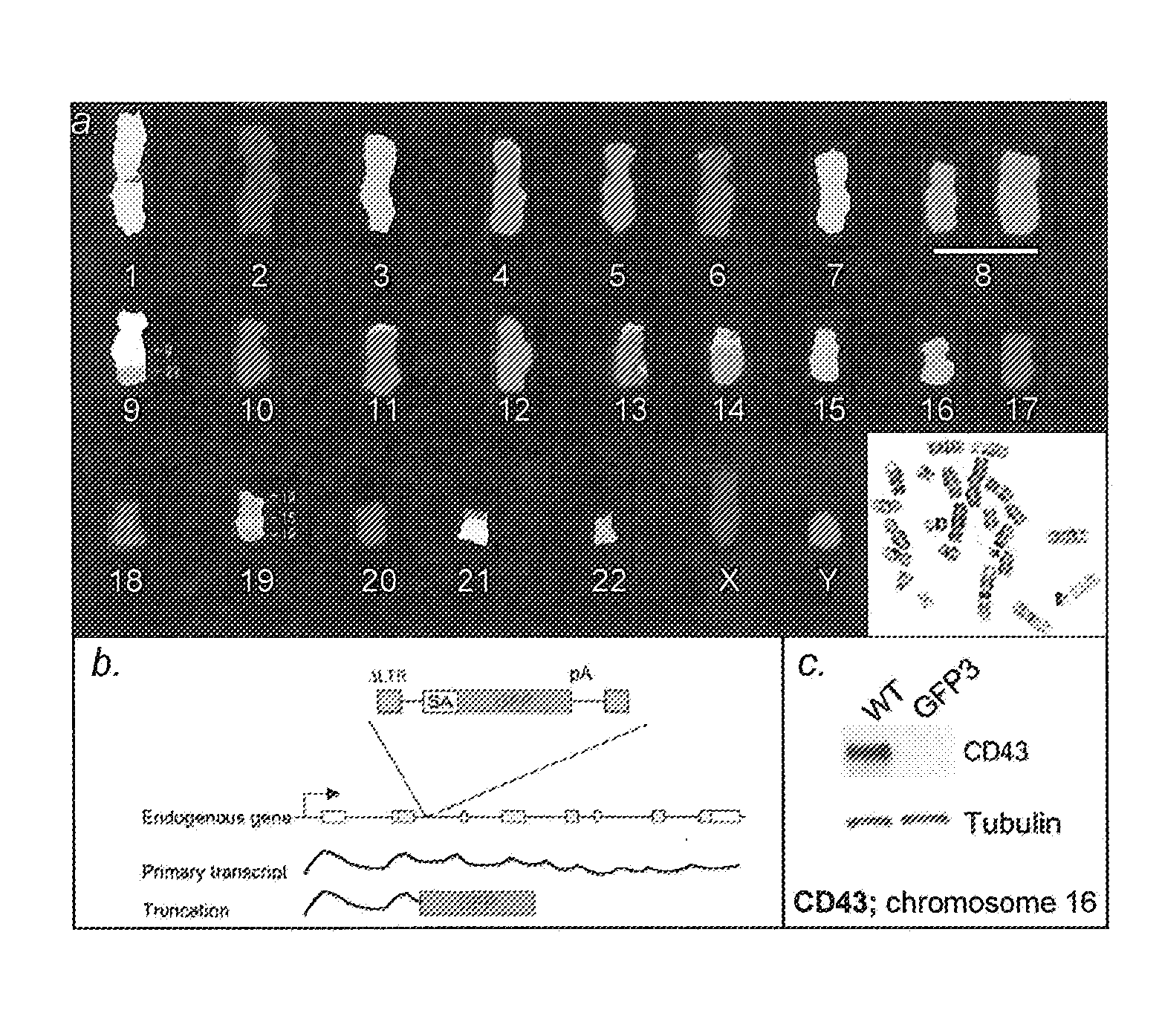
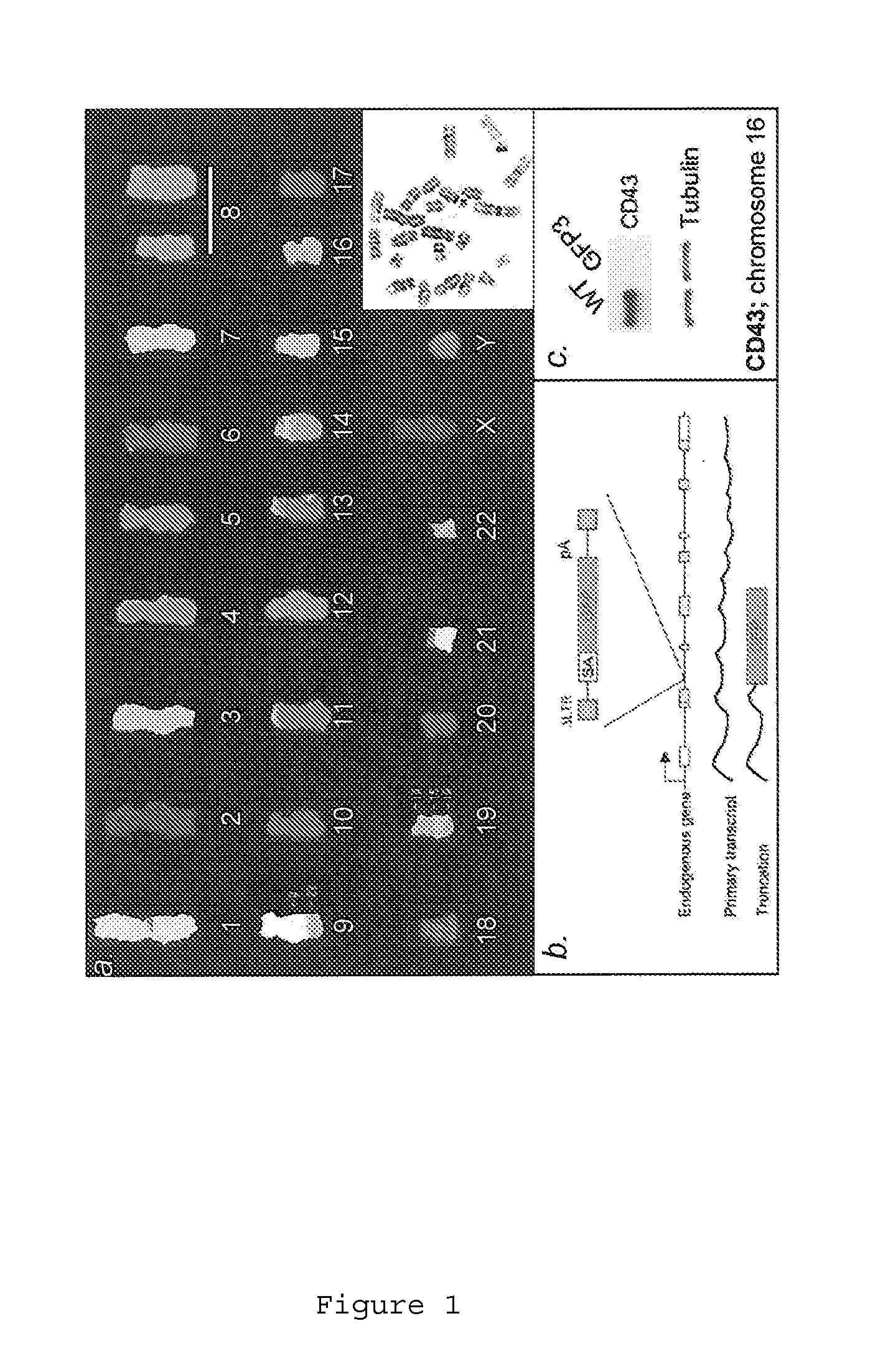
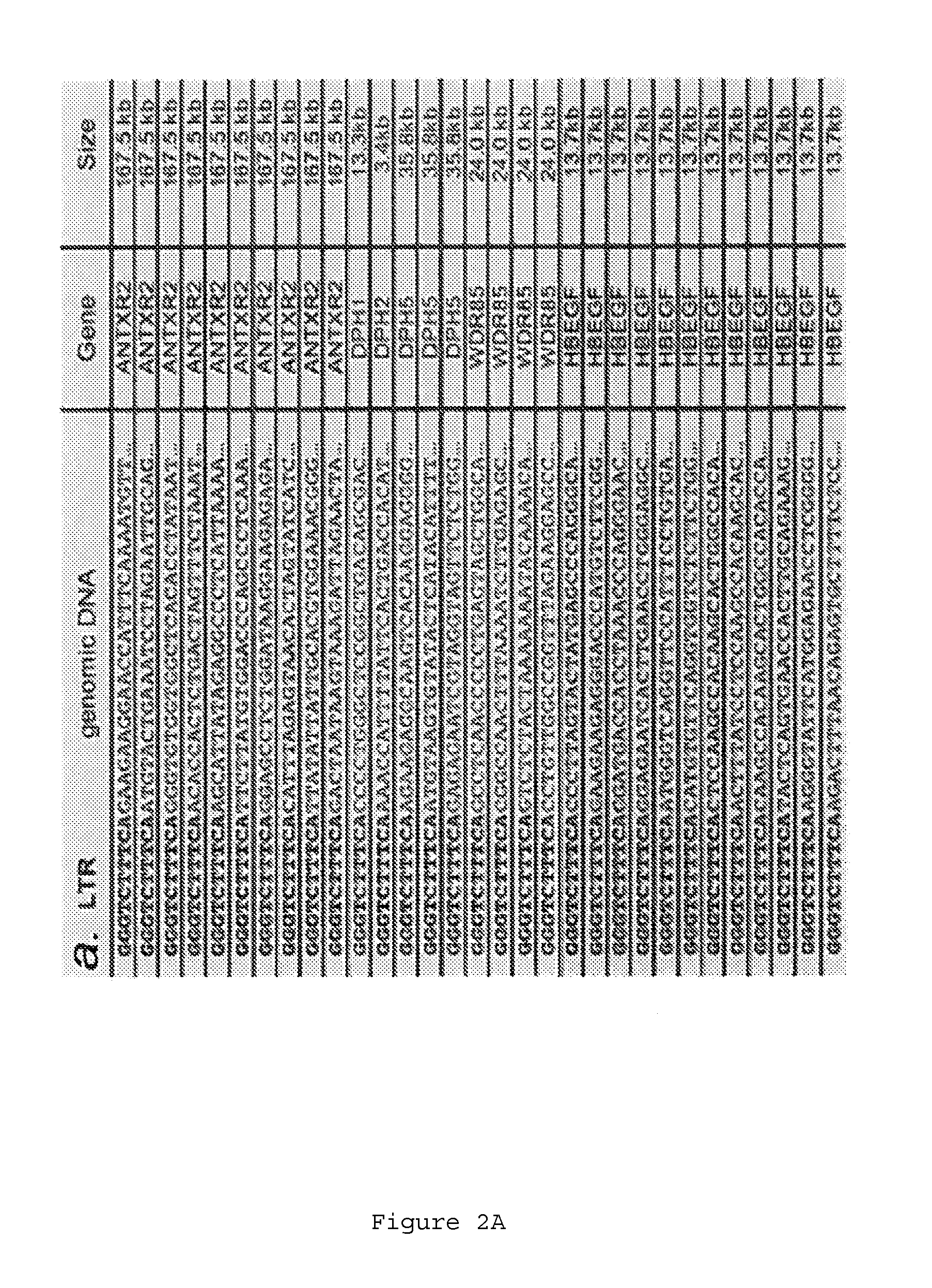
Retrovirus-based genomic screening
The present invention relates to the expression and screening of genomic DNA sequences encoding uncharacterized genes and proteins. The present invention provides systems utilizing unique features of retroviral replication to analyze uncharacterized genes derived from genomic DNA samples. In preferred embodiments, a segment of genomic DNA is inserted between 5′ and 3′ viral long terminal repeats (LTRs) in a vector (e.g., a plasmid, cosmid, or artificial chromosome vector). The resulting vector (or library of vectors containing a plurality of independent genomic sequences) is then introduced into a retroviral packaging cell. The resulting provirus or proteins expression from the provirus are then analyzed.
Owner:CATALENT USA WOODSTOCK INC +3
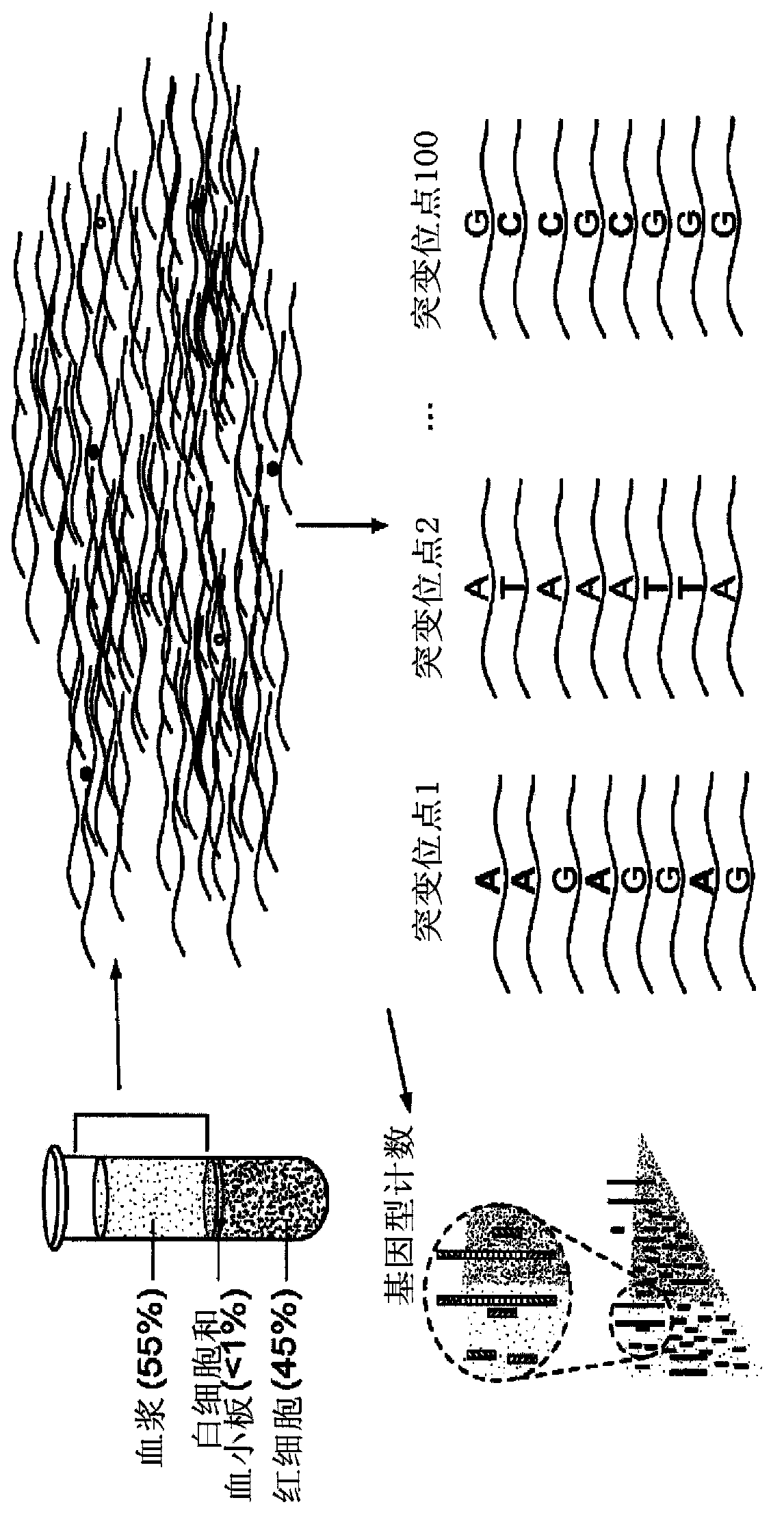
Non-invasive fetal genetic screening by sequencing analysis
InactiveCN103534591AImprove detection rateSignificant clinical effectMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingSequence analysisNucleotide level
The invention provides a non-invasive technique for the differential detection of multiple genotypes and / or mutations for a plurality of target genes in a biological sample containing genetic material from different genomic sources. Methods are conducted using multiplex amplification of a plurality of target sequences from the biological sample, and sequencing is used to detect and enumerate genetic mutations and chromosomal abnormalities at the single nucleotide level.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Methods for treating diseases related to the wnt pathway
ActiveUS10624949B1Relieve symptomsDiminishment of extentPeptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementGenomeDisease status
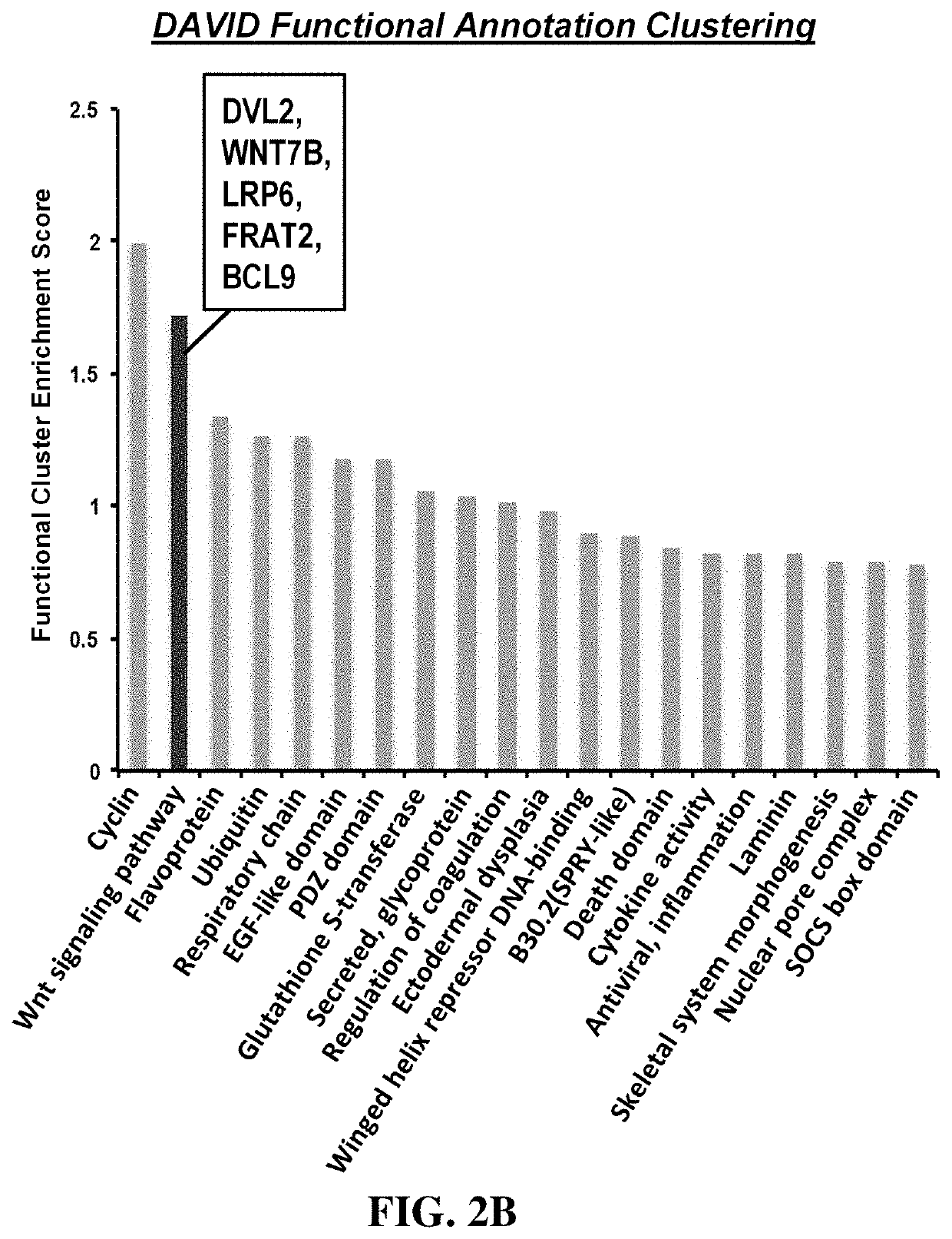
The present invention relates to methods for treating a disease, in which the disease arises from dysregulation of the Wnt signaling pathway. In some instances, the disease can be treated by administering a Wnt pathway inhibitory compound. In other instances, the method optionally includes conducting a genome-wide screening to determine one or more genes resulting in a reduced disease state and then identifying the gene(s) as being involved in the Wnt signaling pathway.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
Susceptibility gene for alzheimer's disease
InactiveUS20070072184A1Increased riskReduction in age of onset of AlzheimerSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGeneticsGenotyping
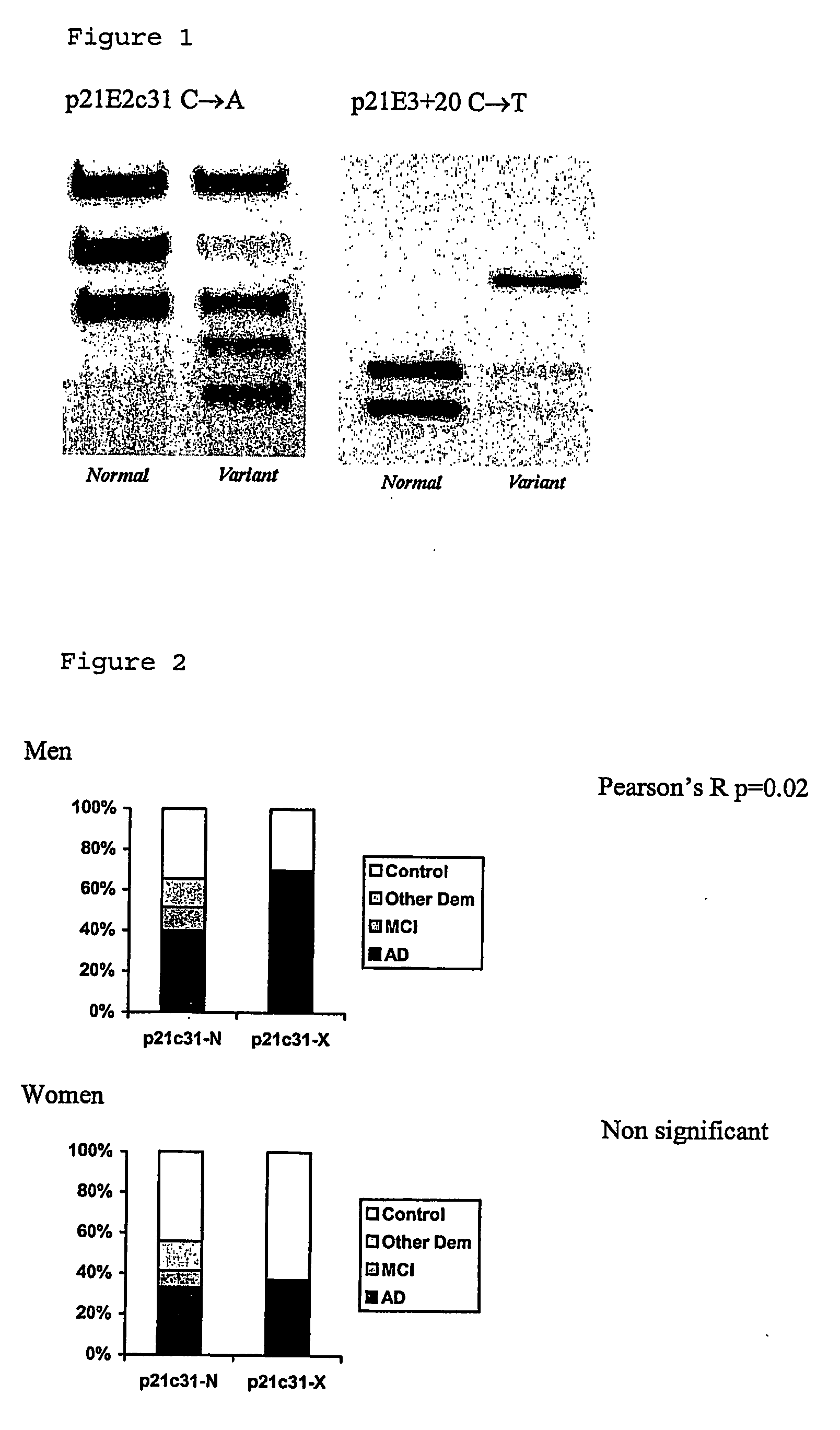
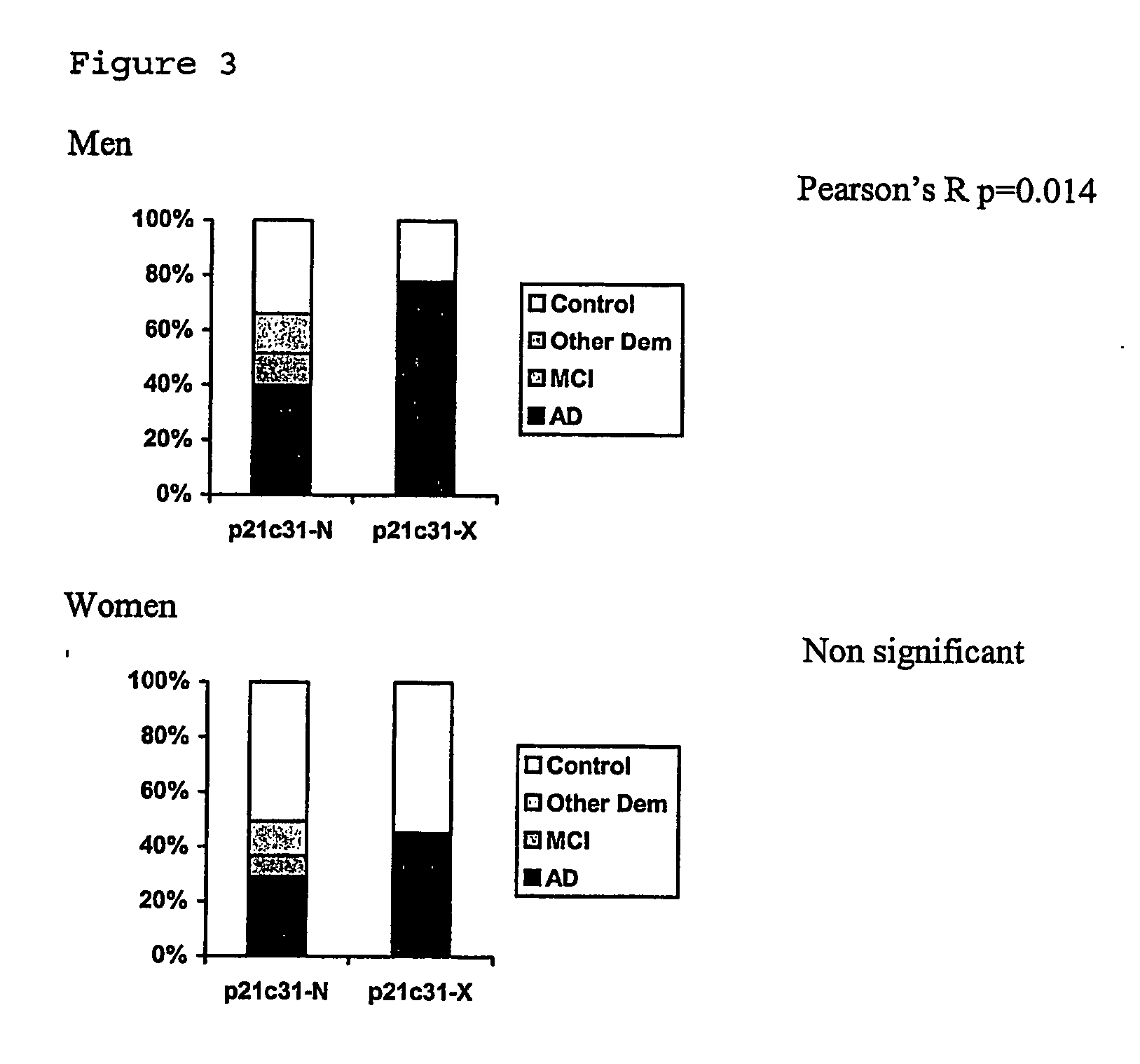
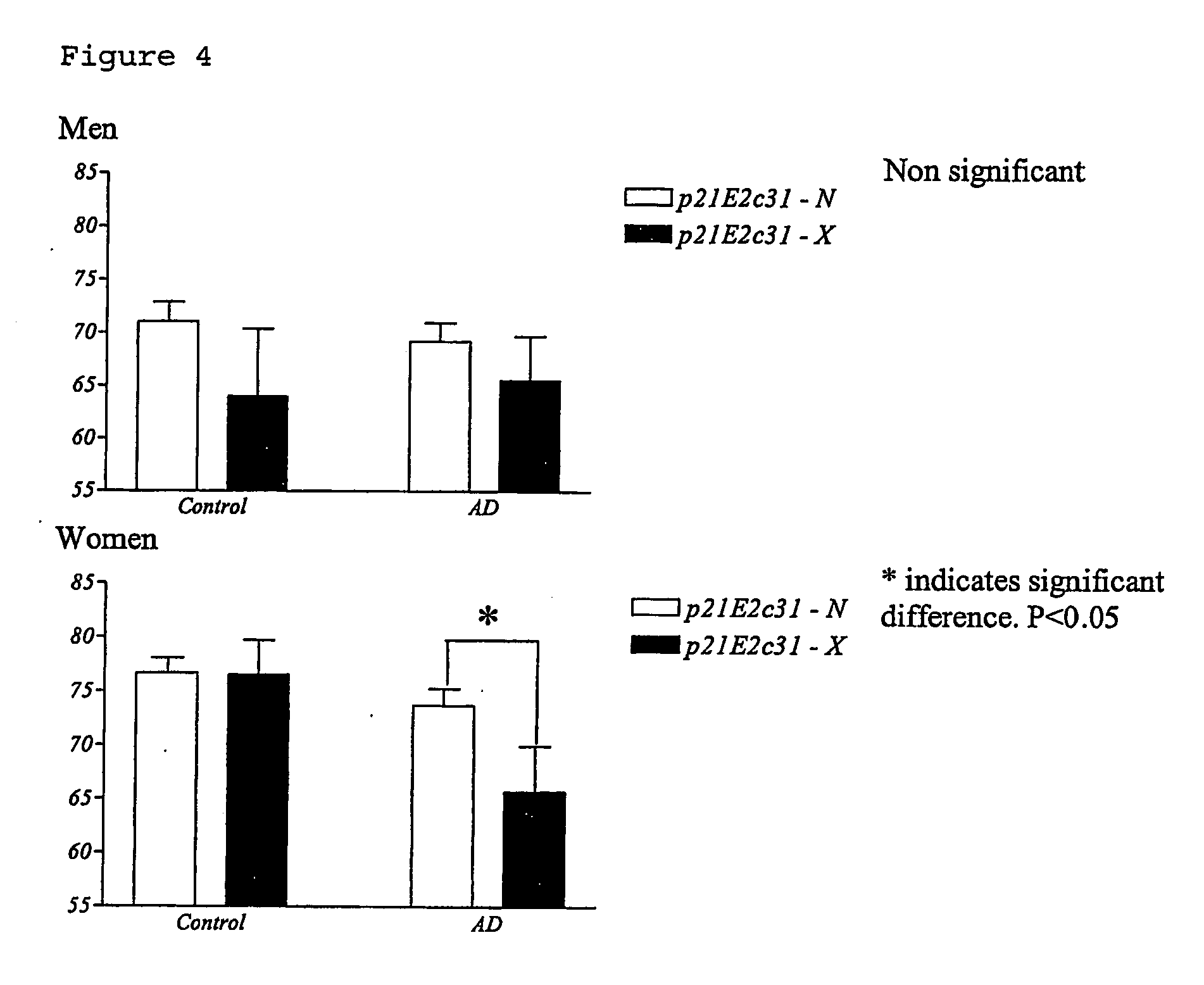
The invention relates to genetic screens for susceptibility to Alzheimer's disease. In particular, the invention provides genetic screens based on genotyping of the p21E2c31 polymorphism and / or the p21E3+20 C / T polymorphism in the p21cip 1 gene.
Owner:OXFORD UNIV INNOVATION LTD
Compositions and methods for mammalian genetics and uses thereof
InactiveUS20120190011A1Microbiological testing/measurementNucleic acid vectorGene productMammalian cell
The invention provides compositions and methods for performing mammalian cell genetics, e.g., genetic screens, using near-haploid cells. The invention further provides genes and gene products isolated using the inventive methods and methods of use thereof.
Owner:WHITEHEAD INST FOR BIOMEDICAL RES
Genomic screen for epigenetically silenced tumor suppressor genes
InactiveCN101080499AOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsTumour suppressor geneParanasal Sinus Carcinoma
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Genetic Screen for Interaction Interface Mapping
InactiveUS20080044815A1Quick identificationReduce in quantityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationAssayInteraction interface
Owner:PHYLOGICA
Non-invasive prenatal genetic screen
InactiveUS20100261188A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGenetic Screening (procedure)Non invasive
The present invention provides methods and kits useful for genetic testing or screening of fetuses using nucleic acid samples isolated from cervical mucus samples of fetus hosts.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
Genetic screening method for negative regulatory factor of streptomyces biosynthesis gene cluster
PendingCN108611361AReduce false positivesReduce verification effortMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid vectorMetaboliteBiosynthetic genes
The invention provides a screening method for a negative regulatory factor of a novel biosynthesis gene cluster of streptomyces. The screening method comprises the following steps: constructing a promoter-mediated reporting system of genes of self-interest in a streptomyces cell, then using a random mutation system based on a transposon Himar1 to mutate the streptomyces with the reporting system,intensively screening a mutant streptomyces strain to obtain a streptomyces strain with high expression of target genes, performing bacteriophage packaging on genomes of the streptomyces strain with high expression of target genes and screening out cosmids with randomly inserted fragments, sequencing DNA of the cosmids to determine the location of the randomly inserted fragments in the genomes ofthe streptomyces strain with high expression of target genes. The screening method, provided by the invention, is stable in screening environment, high in screening flux, low in false positive, high in efficiency, accurate and convenient to operate, and can be widely used in the field of high-yield screening and transformation of industrial streptomyces metabolites, and the screened and transformed streptomyces metabolites are high in yield, good in genetic stability and suitable for industrial production.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
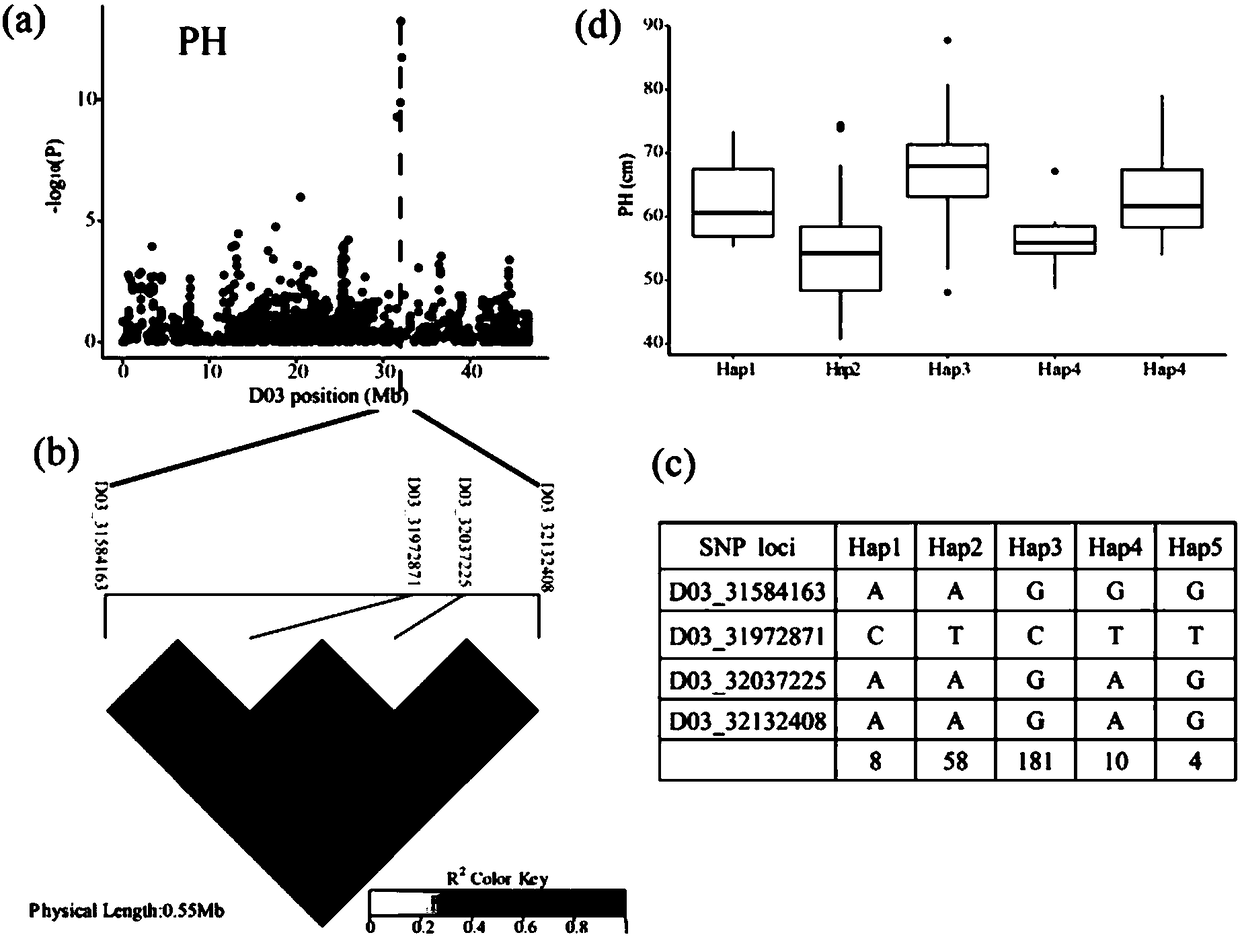
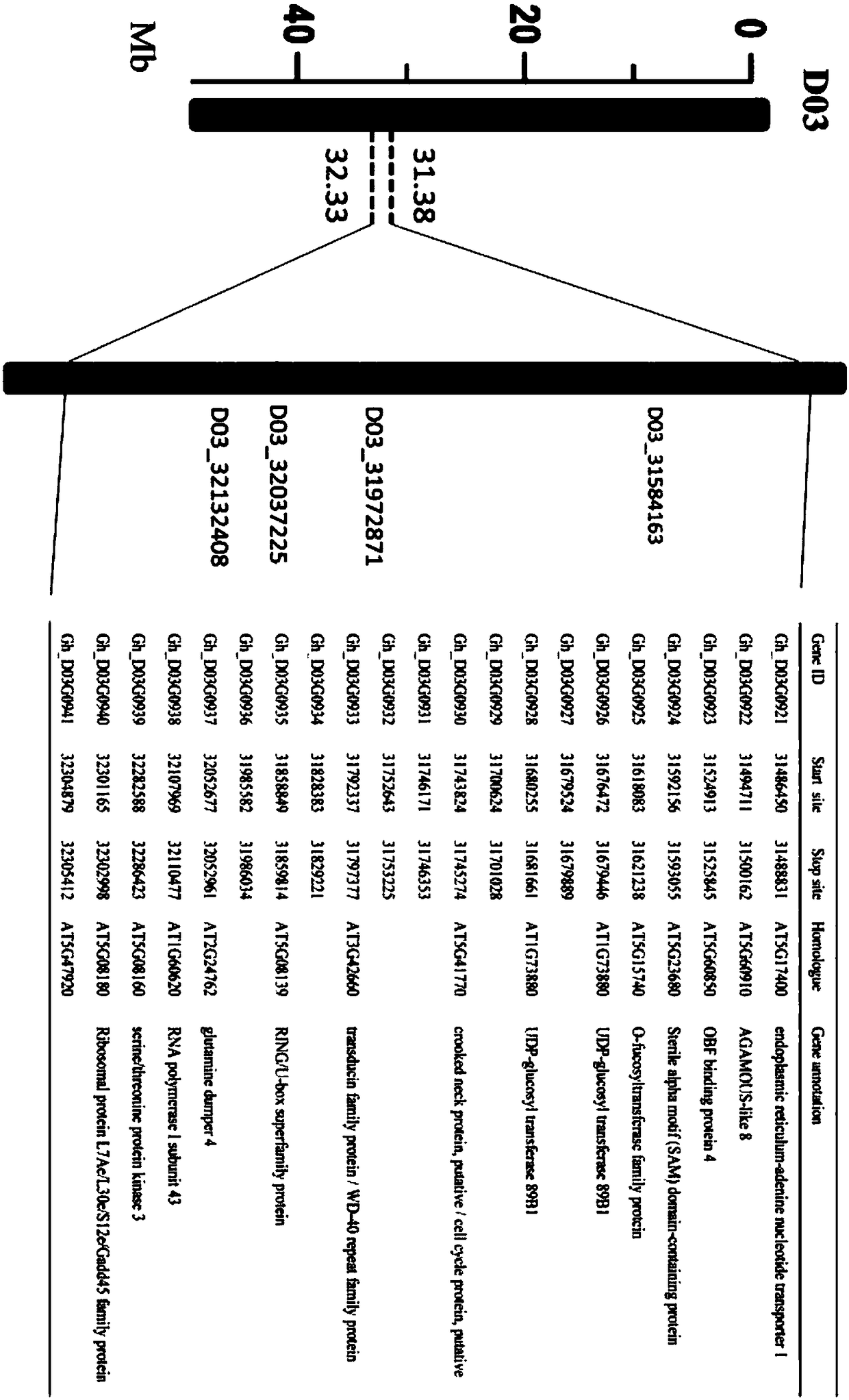
Gene for regulating plant height of Gossypium hirsutum, and application thereof
InactiveCN108396031AStrong specificityRealize regulationPlant peptidesFermentationGenomic sequencingMolecular breeding
The invention relates to the field of plant height genes, and concretely relates to a gene for regulating the plant height of Gossypium hirsutum, and an application thereof. The base sequence of the CDS of the gene for regulating the plant height of Gossypium hirsutum is represented by SEQ ID NO.1, and a specific base sequence of the gene is represented by SEQ ID NO.2. A large number of SNPs covering the whole genome of Gossypium spp. are developed based on an SLAF-seq reduced representation sequencing technology by utilizing 355 natural populations of Gossypium hirsutum, genetic genes of theplant height are parsed by adopting a GWAS technology through the 3-year and 2-site phenotypic identification of plant height traits, and the genetic screens are screened to obtain the gene for regulating the plant height of Gossypium hirsutum. A result of verification of the functions of the gene by using a virus-induced gene silencing technology shows that the plant height can be controlled by regulating the expression of the gene, so the gene lays a foundation for developing the molecular breeding of the Gossypium hirsutum.
Owner:GANSU AGRI UNIV +1
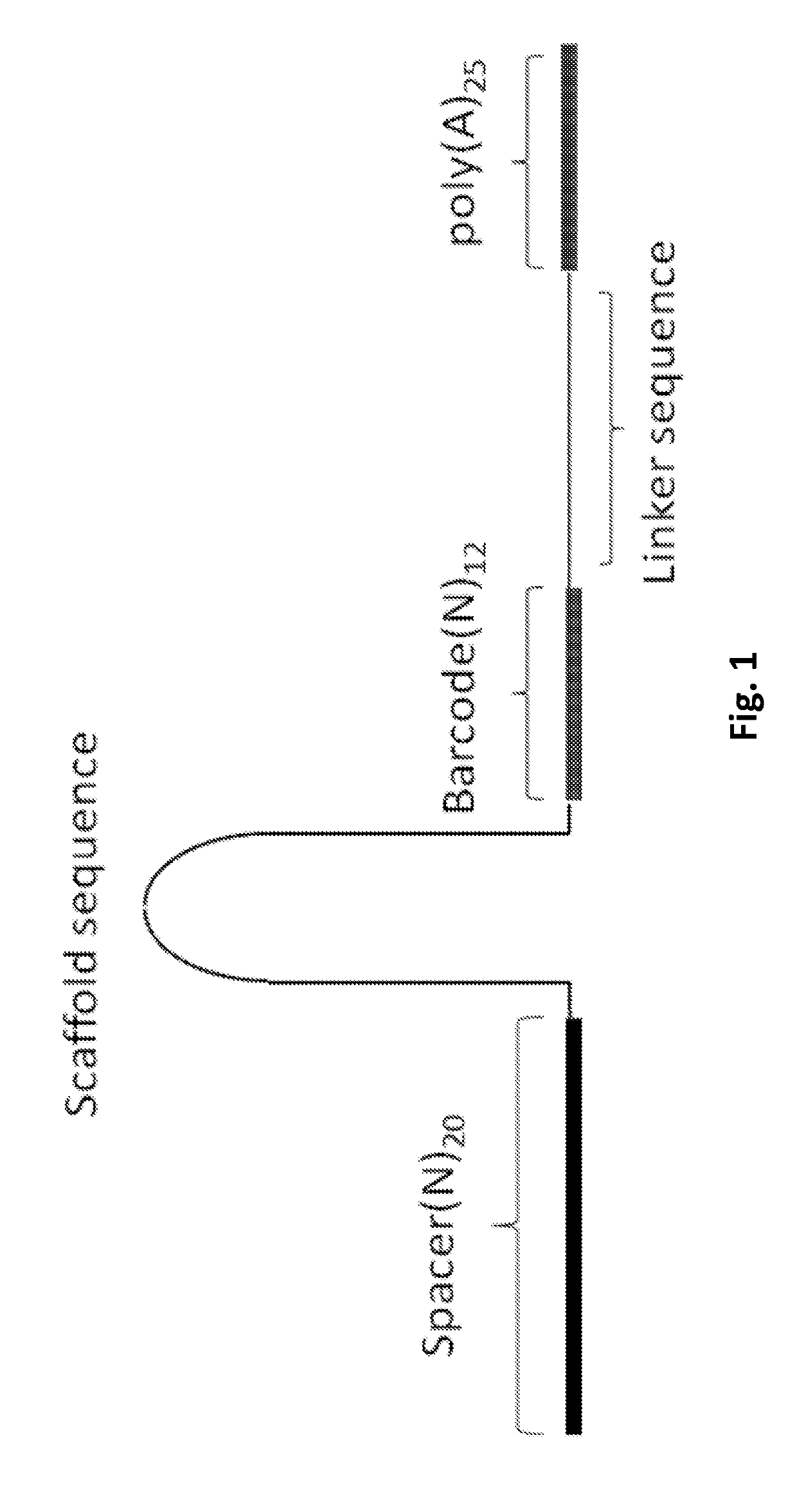
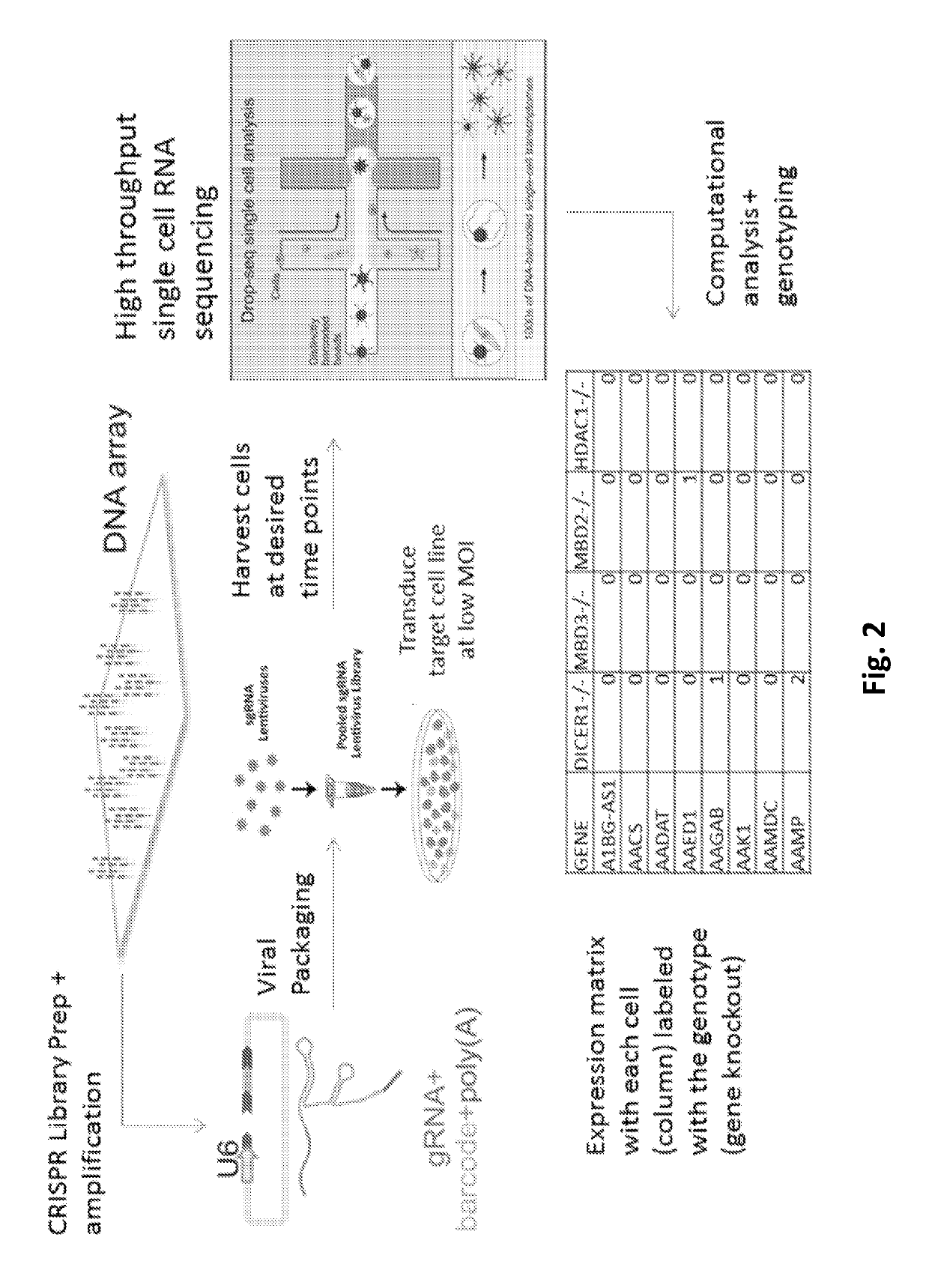
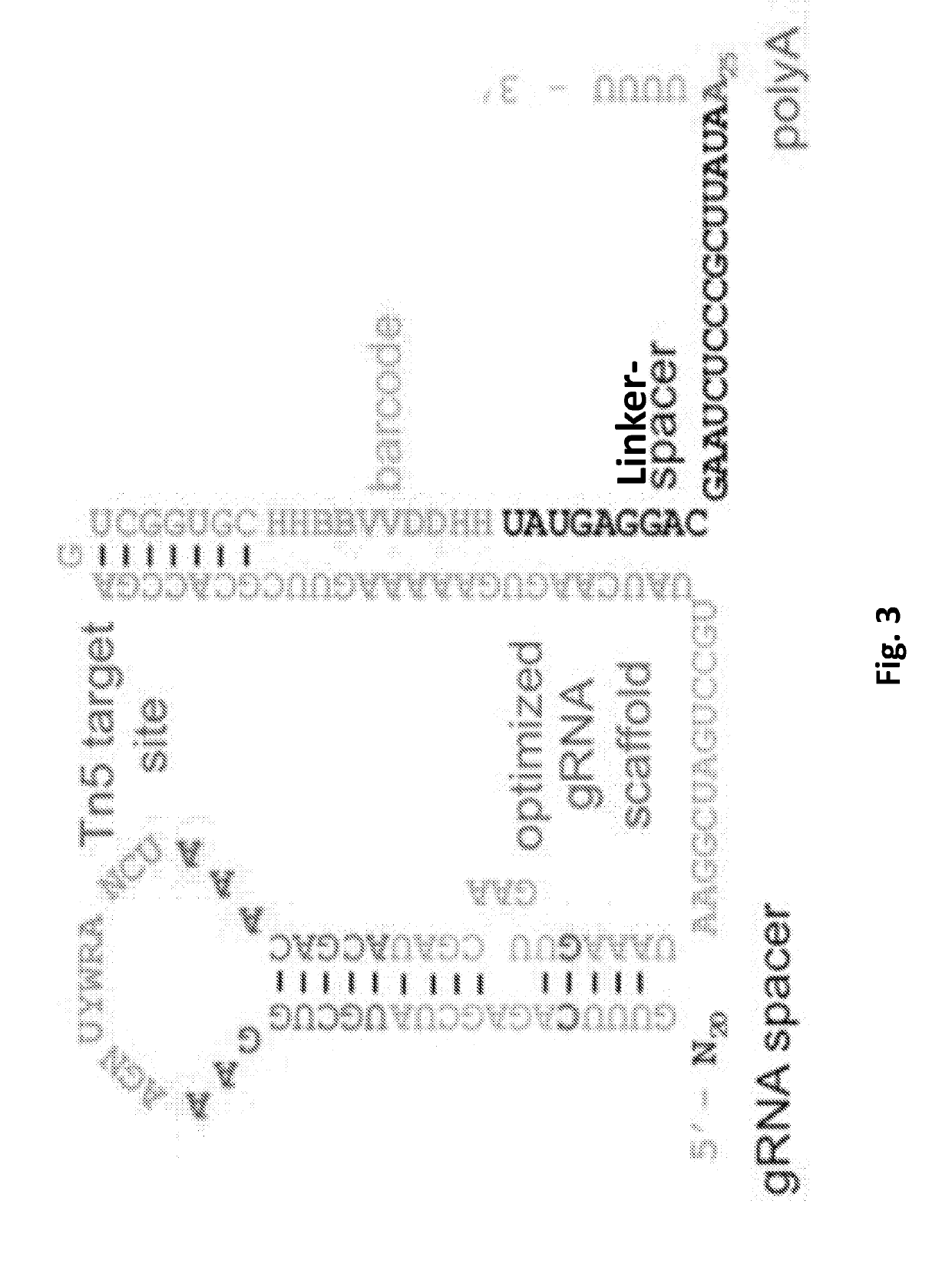
Efficient genetic screening method
PendingUS20190330661A1Easy to handleImprove efficiencyHydrolasesStable introduction of DNADiseaseBarcode
A guide RNA comprising: a gRNA spacer sequence at the 5′ end of the guide RNA, wherein the spacer sequence is complementary to a target gene, a scaffold sequence that binds to Cas9, and an RNA capture and sequencing domain comprising: a barcode sequence, and a primer binding sequence; nucleic acids and vectors encoding the guide RNA; cells expressing the guide RNA; and a library comprising a plurality of guide RNAs. Also disclosed are methods of introducing a genetic perturbation into a cell, methods of assessing an effect of at least one genetic perturbation on RNA expression in a cell, methods of identifying nucleic acid sequences associated with a disease state and a method of identifying candidate therapeutic agents.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com