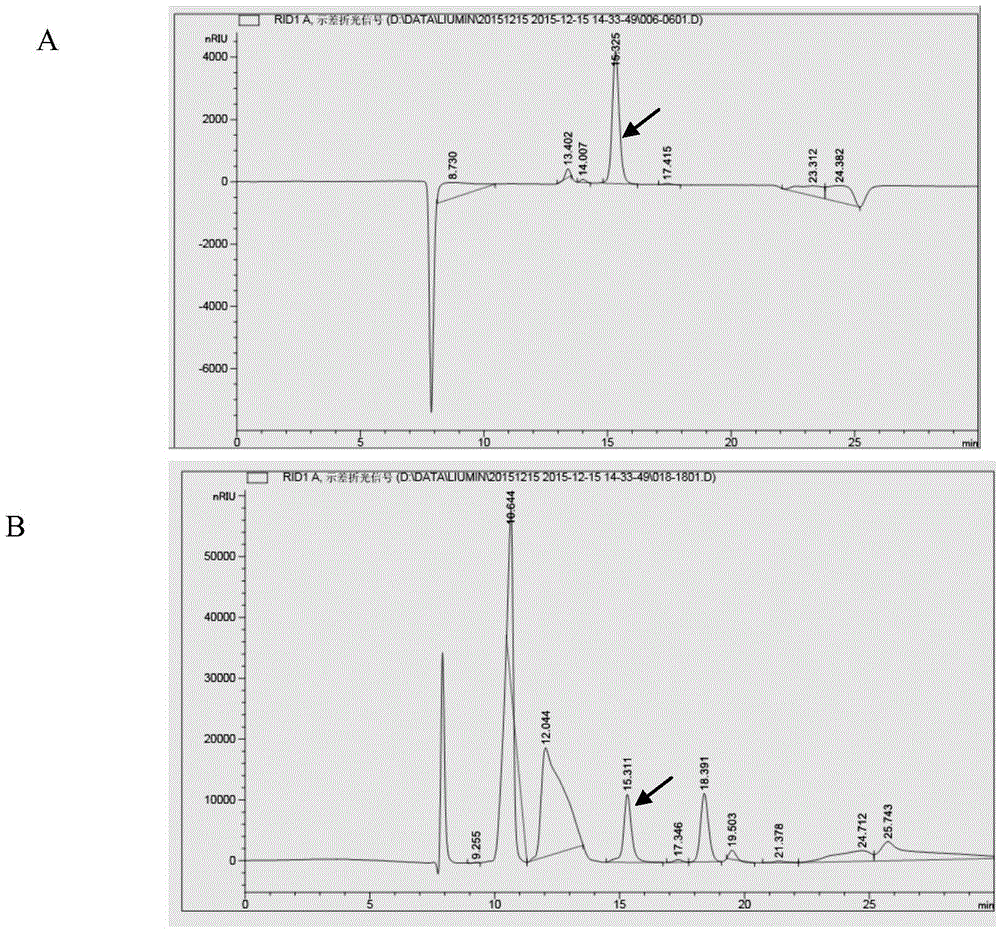
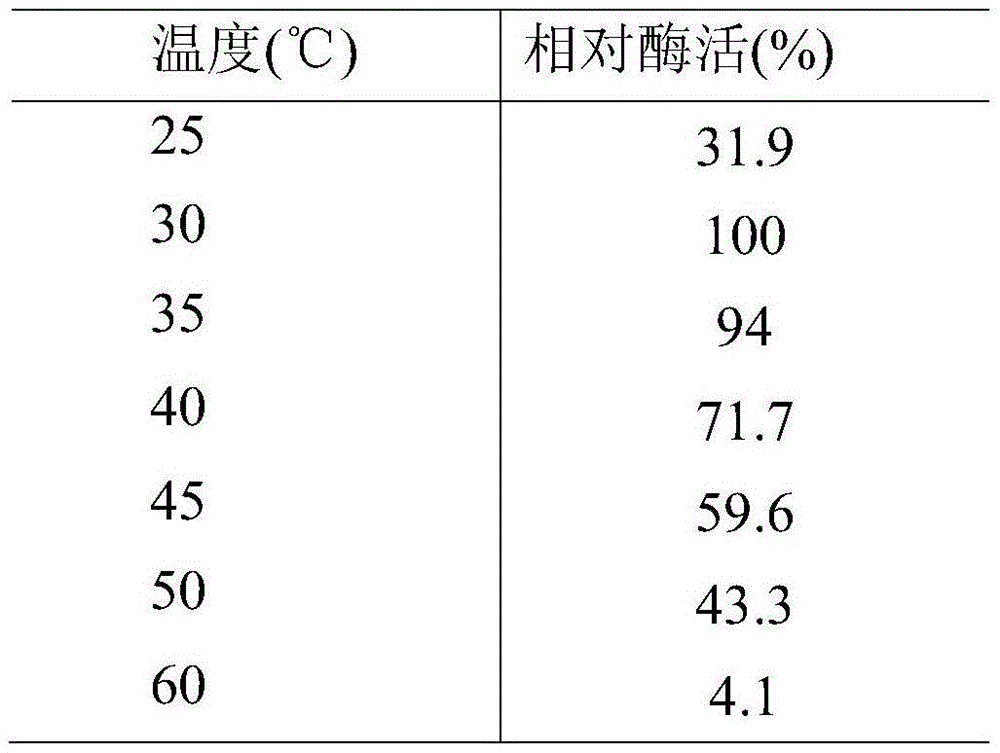
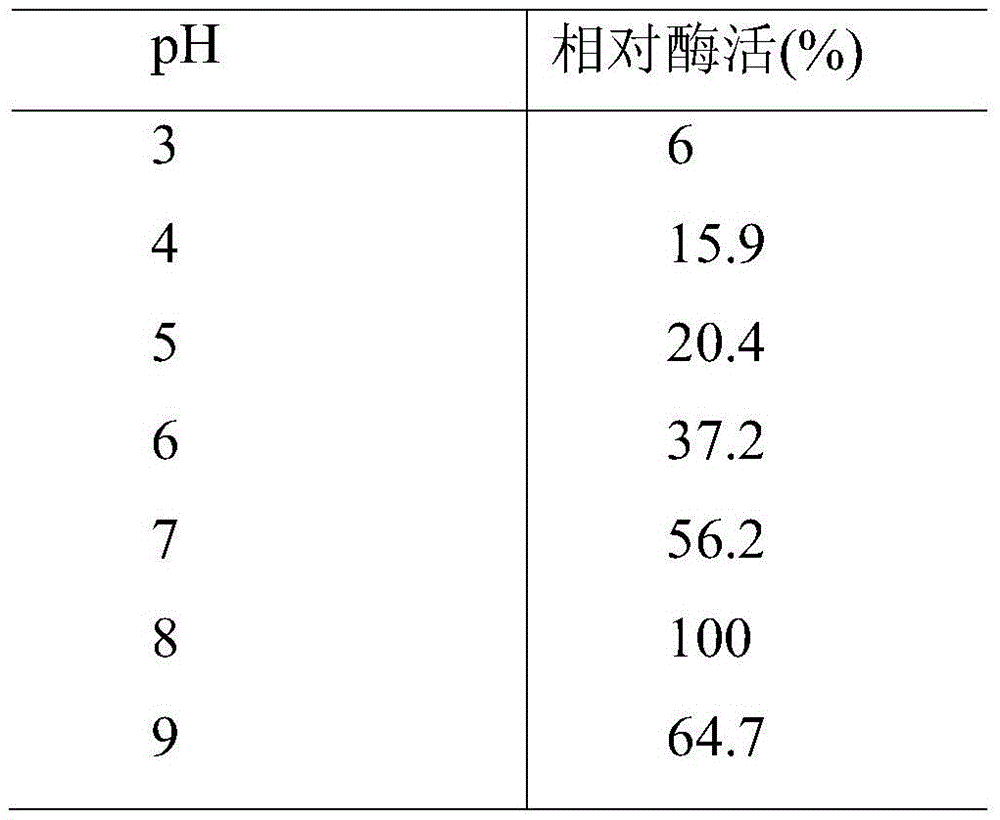
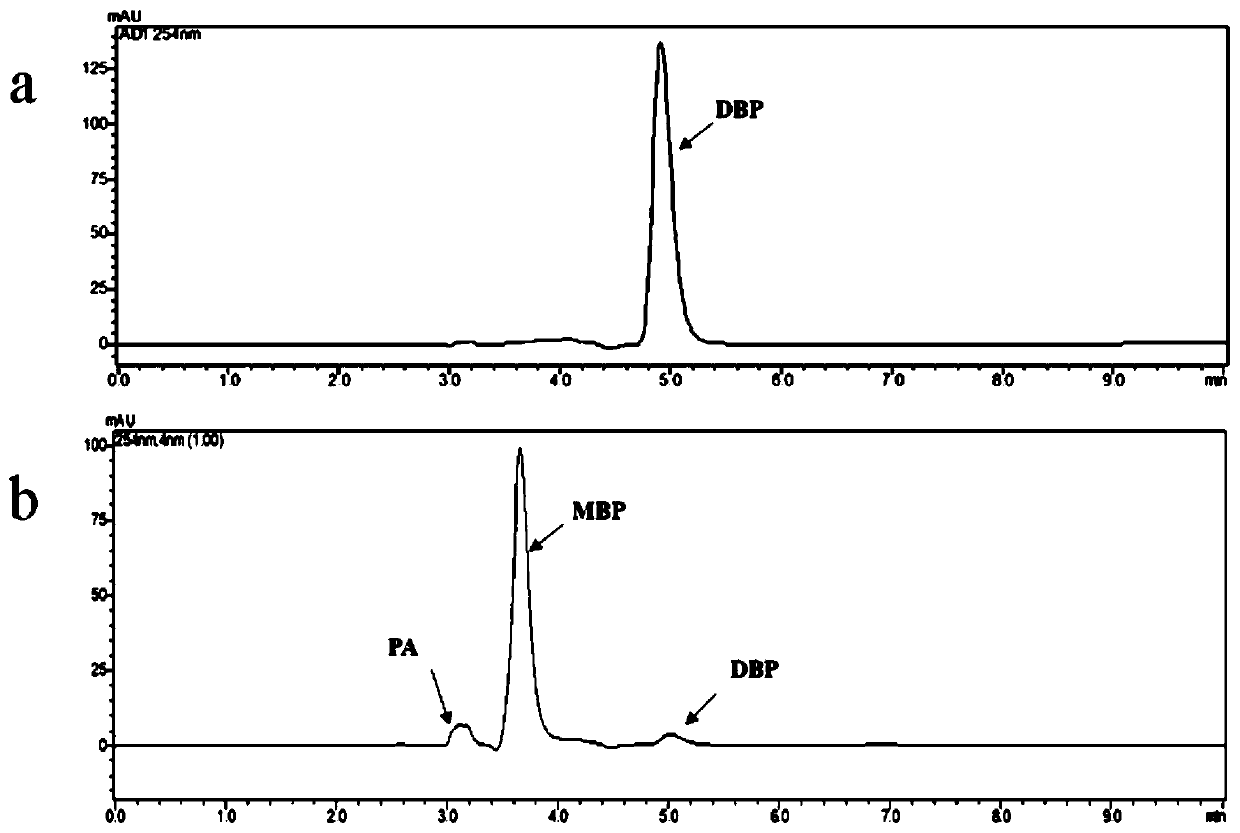
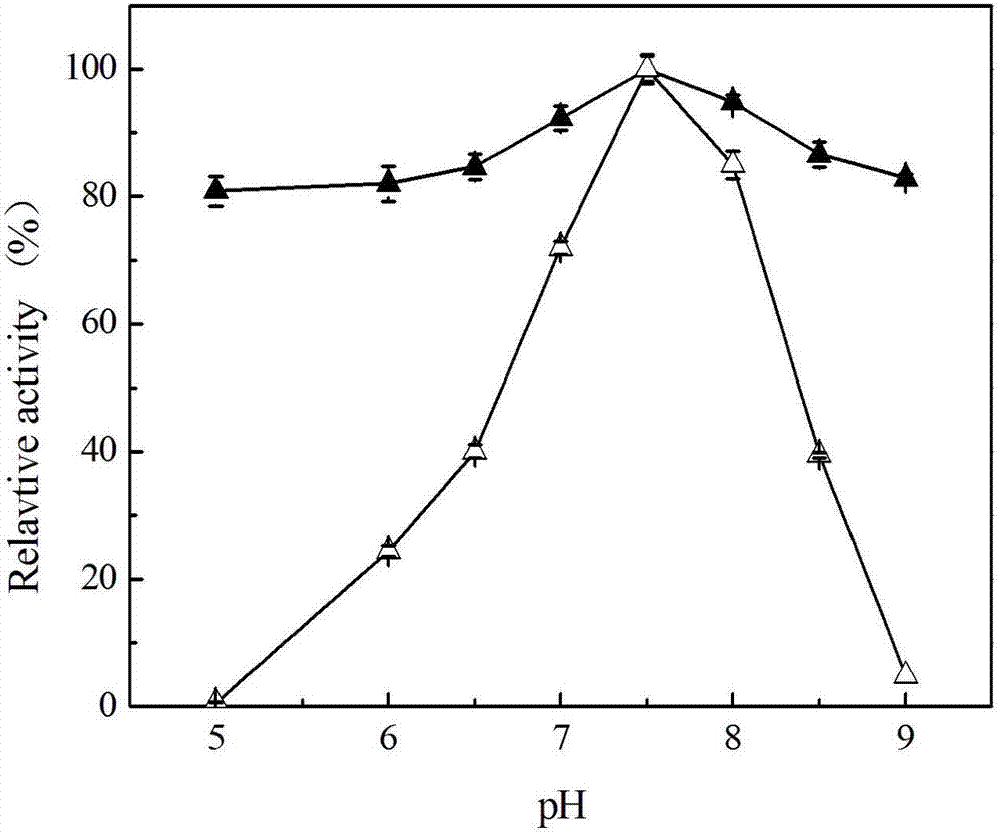
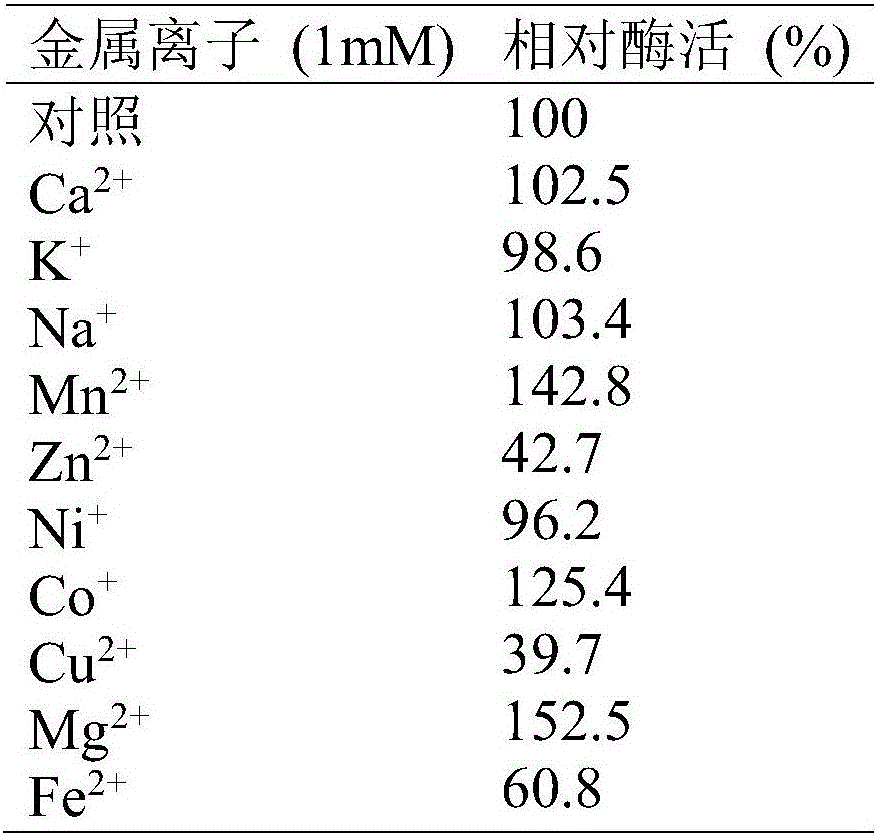
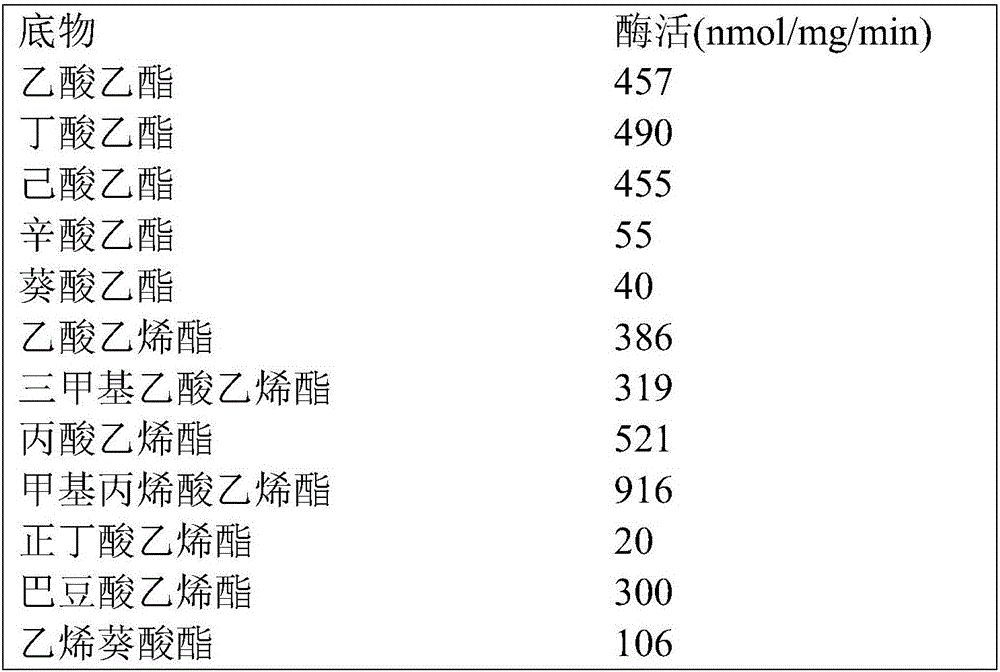
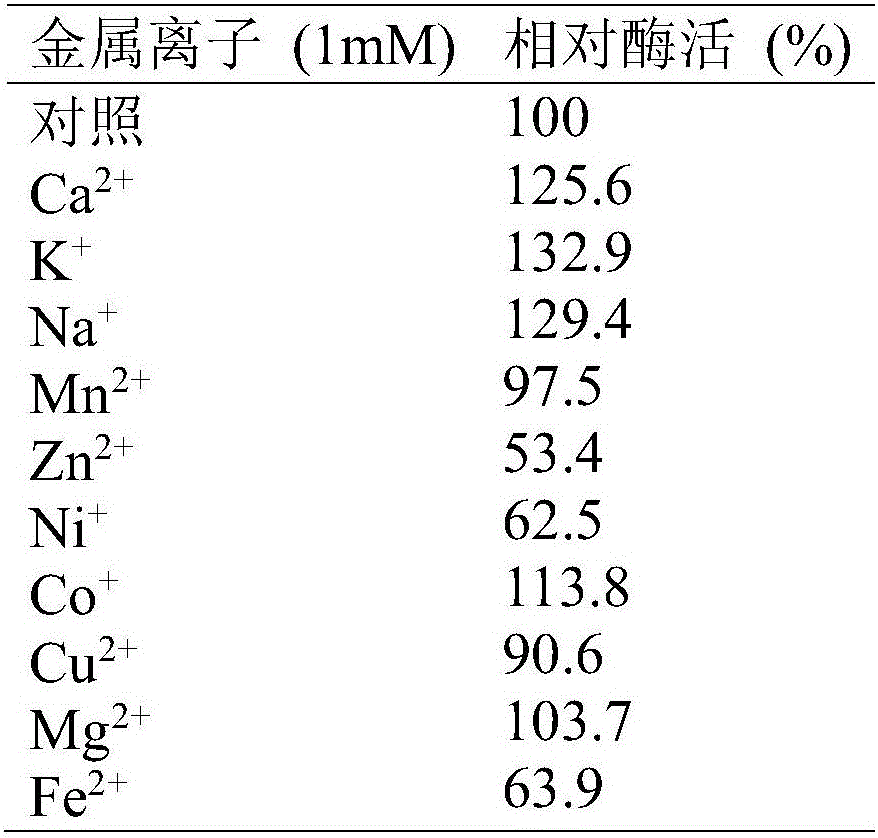
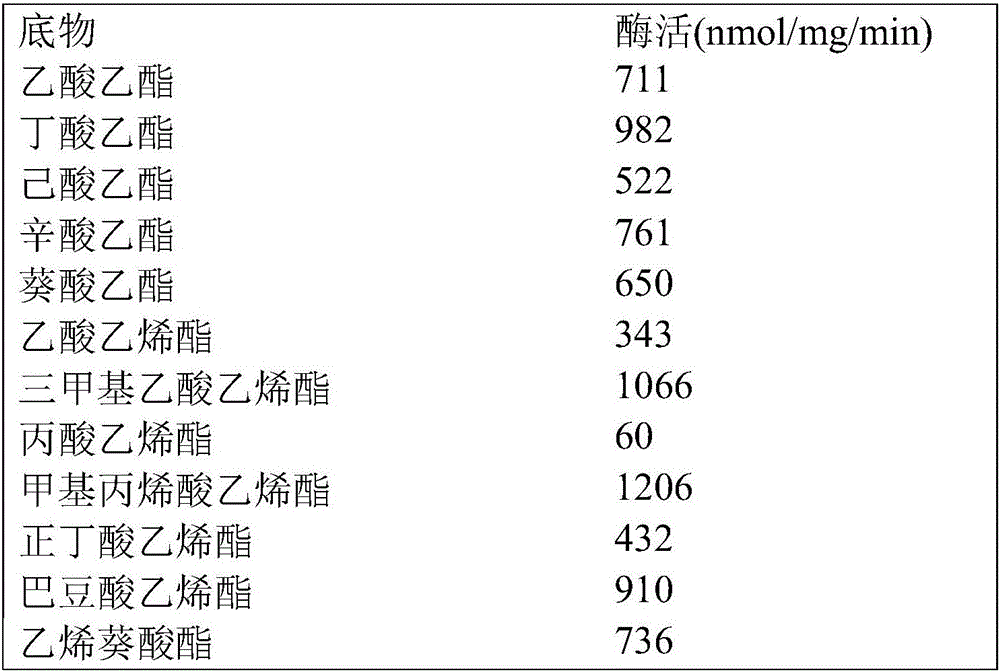
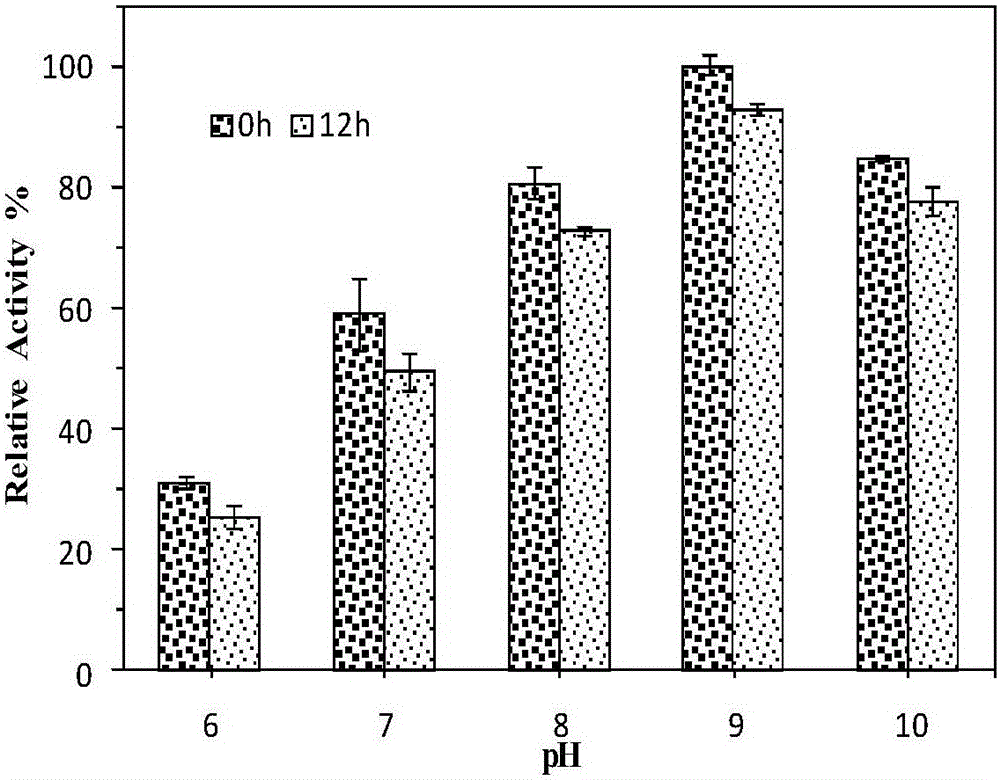
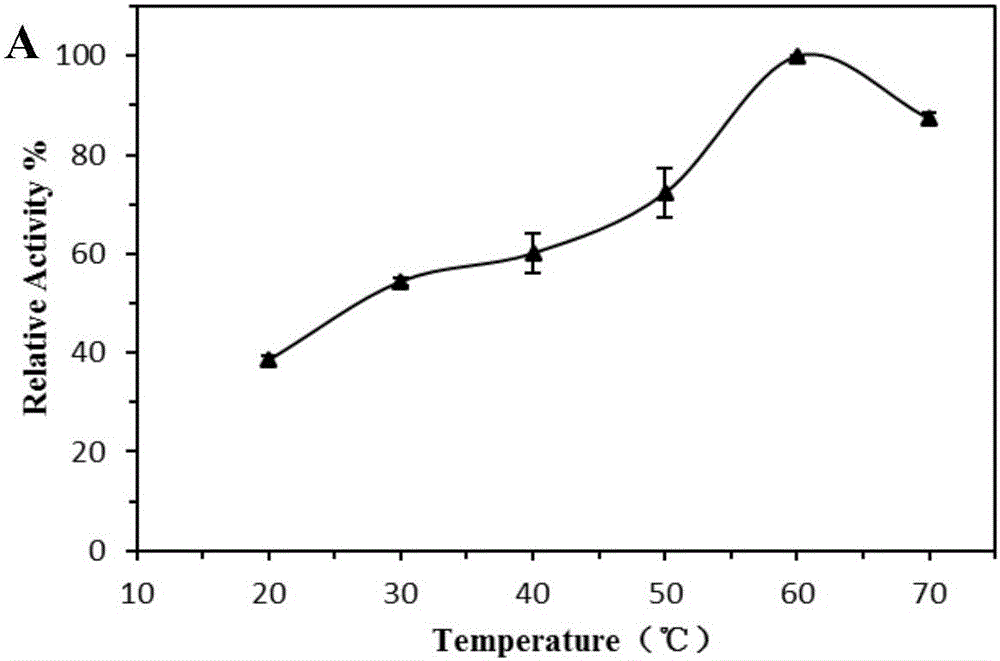
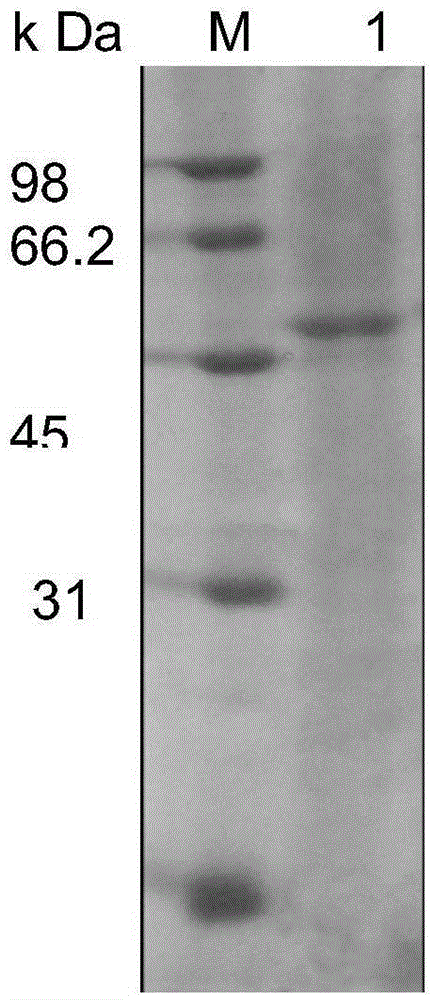
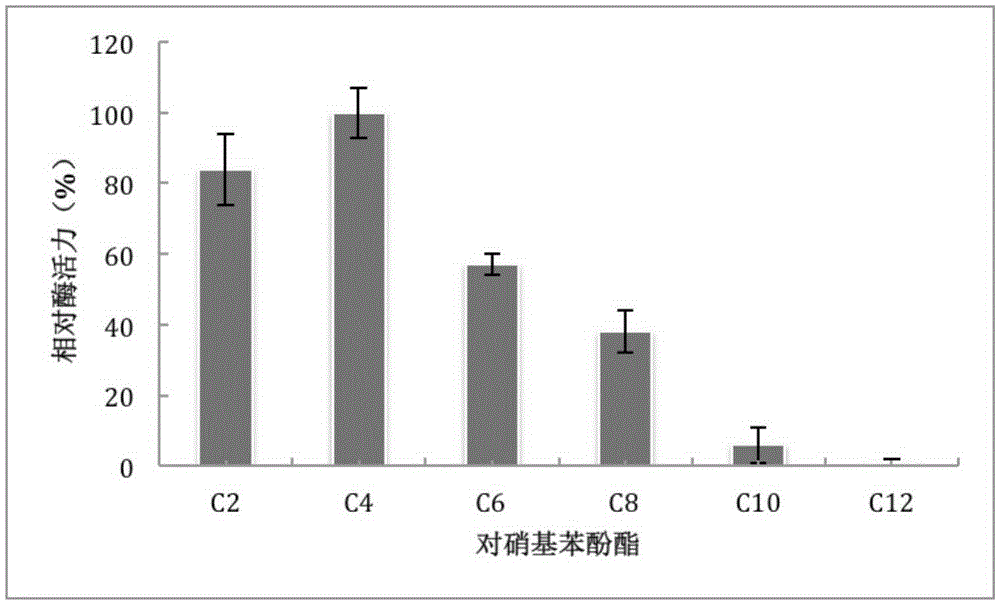
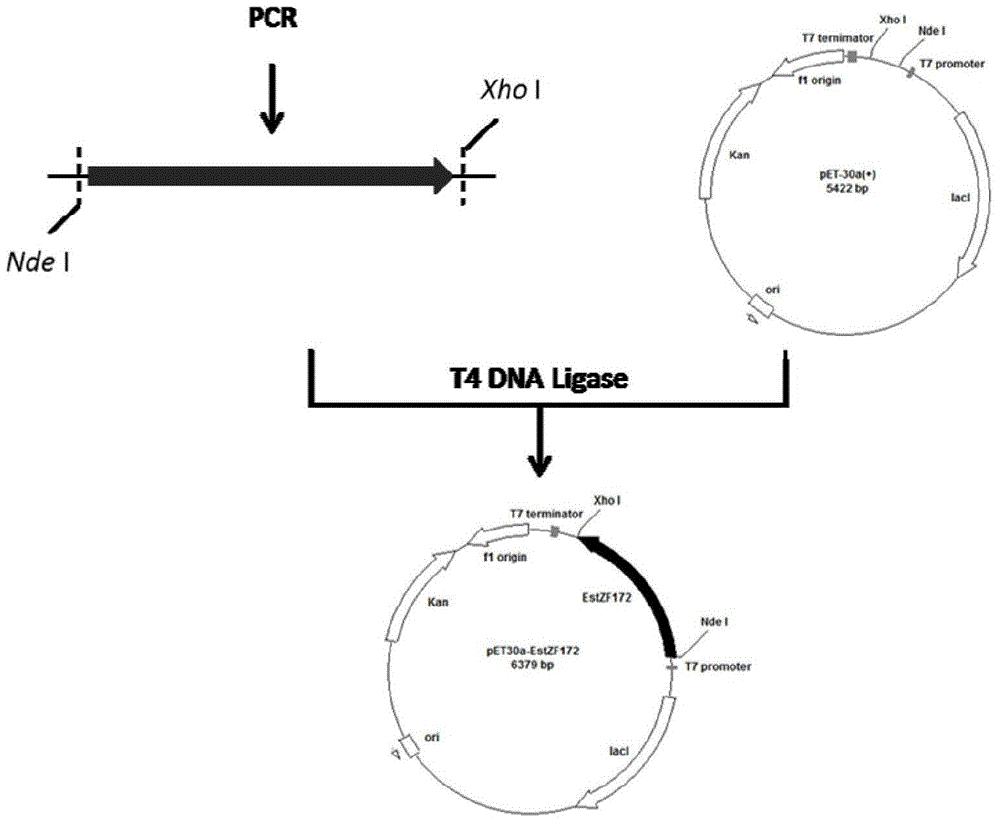
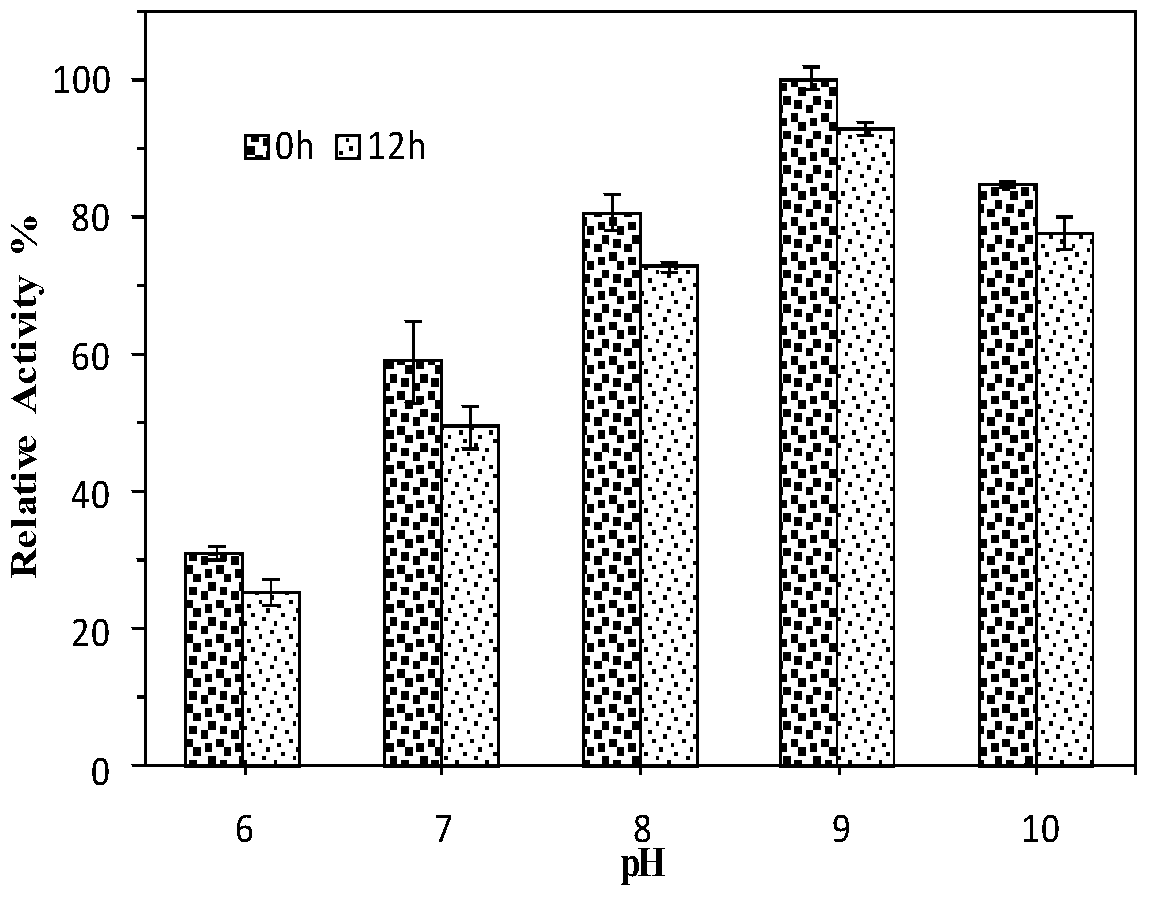
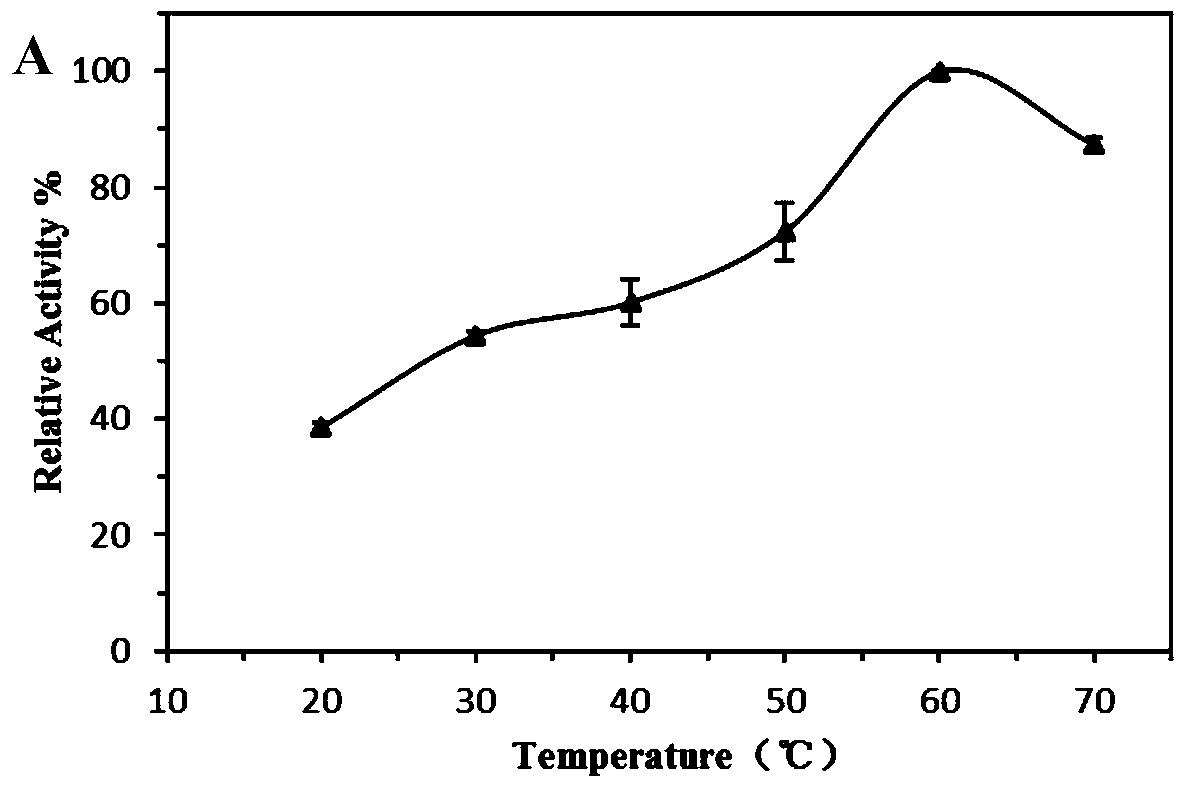
Patents
Literature
109 results about "Esterase Gene" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Esterase Genes encode Esterases that catalyze hydrolysis of ester bonds to produce alcohol and acid reaction products. (NCI)
Acyl-acp thioesterase genes and uses therefor
InactiveUS20110020883A1High activityIncrease volumeSugar derivativesHydrolasesBiotechnologyMicroorganism
The present invention provides novel genes encoding Class II acyl-ACP thioesterases and variants thereof that are active on C8, C10, C12, C14, C16, and C18 acyl-ACP substrates. The thioesterases can be introduced into transgenic organisms, including microorganisms and photosynthetic organisms, for producing fatty acids and fatty acid products.
Owner:SYNTHETIC GENOMICS INC
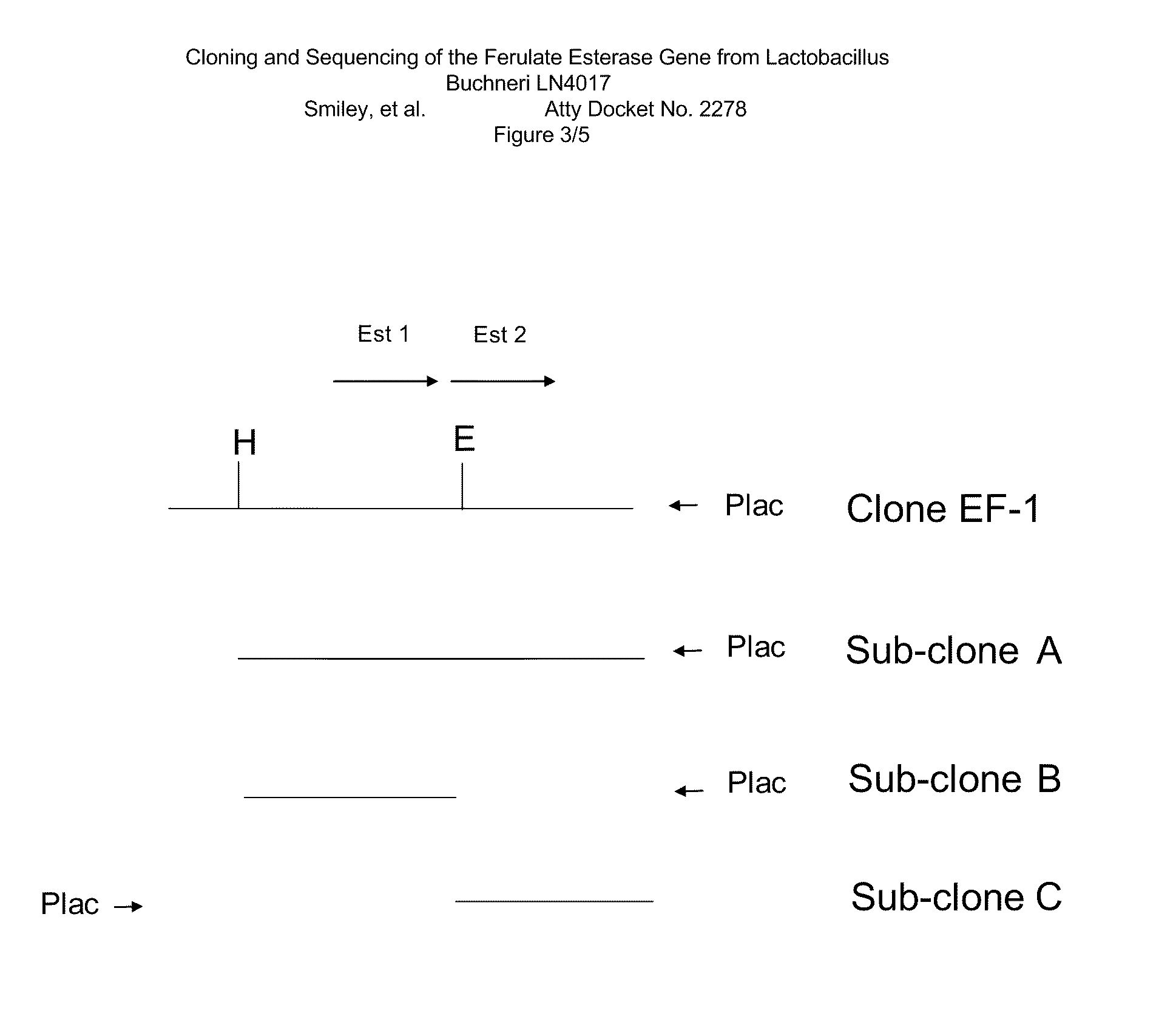
Cloning and sequencing of the ferulate esterase gene from Lactobacillus buchneri LN4017
Embodiments of the present invention include polypeptides having ferulate esterase activity and the nucleic acid sequences that encode them. Methods of the embodiments utilize these ferulate esterase polypeptides and nucleic acid sequences to enhance the digestibility of plant cell walls and the accessibility of carbohydrates in plants. The invention provides for transgenic plants transformed with expression vectors containing a DNA sequence encoding ferulate esterase from Lactobacillus buchneri. Methods of using same to enhance plant fiber digestion in animals, are disclosed. Uses of this invention include, but are not limited to, forage and silage with improved digestibility for livestock, and enhanced biomass conversion.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Deep-sea sediment-sourced esterase EST4 as well as encoding gene and application thereof
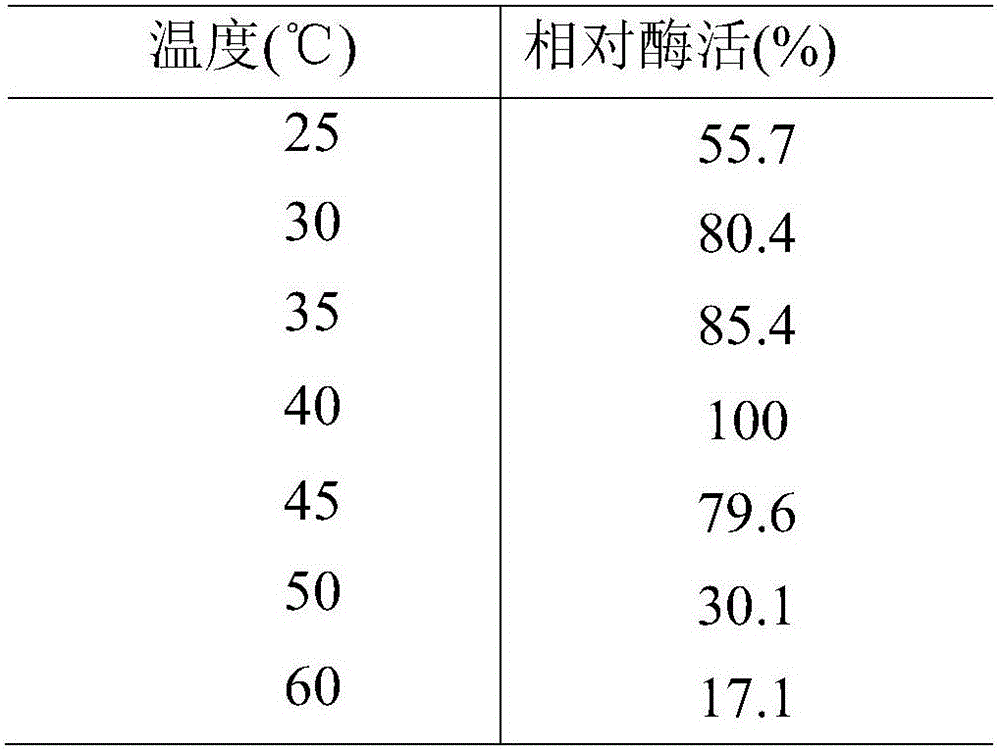
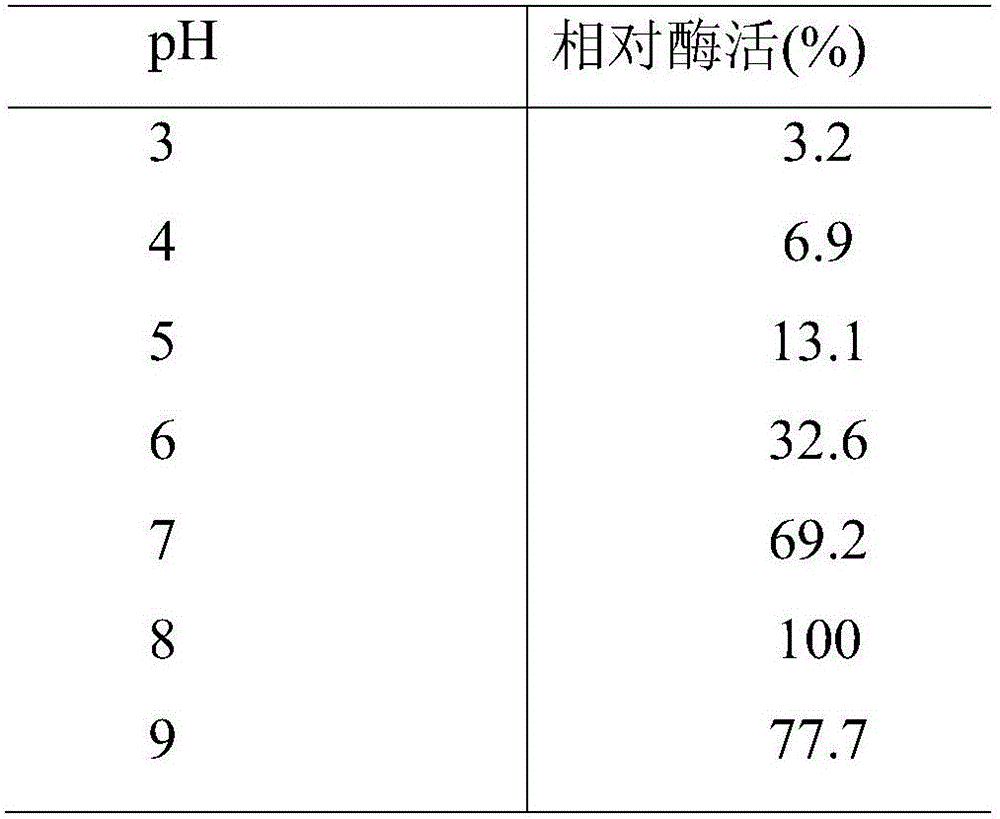
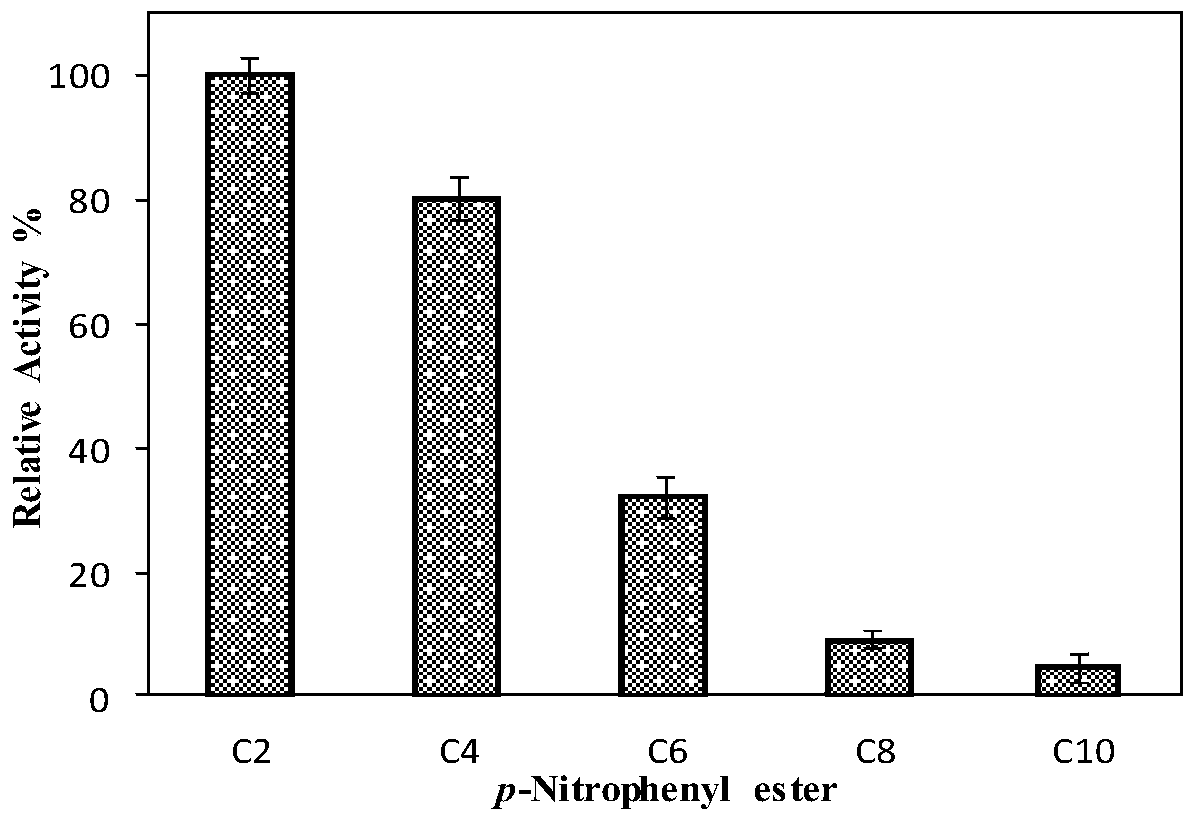
The invention discloses a deep-sea sediment-sourced novel esterase EST4 as well as an encoding gene and application thereof. A deep-sea sediment-sourced esterase gene est4 is obtained by screening a metagenome and has a nucleotide sequence shown as SEQ ID NO. 1, and the esterase EST4 encoded thereby has an amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID NO. 2. After heterologous expression of the esterase gene provided by the invention, the catalytic activity is highest when a substrate is p-nitrophenol caproate (C6) and the enzymatic activity is 56.1U / mg. The optimum temperature for catalytic hydrolysis of the esterase EST4 is 35-40 DEG C; in the presence of Ca<2+>, Co<2+>, Sr<2+> and Zn<2+>, the enzymatic activity is increased. The esterase can be applied to chiral medicine synthesis, food processing and food flavor modification, wastewater treatment and washing industry and other industrial productions.
Owner:SECOND INST OF OCEANOGRAPHY MNR
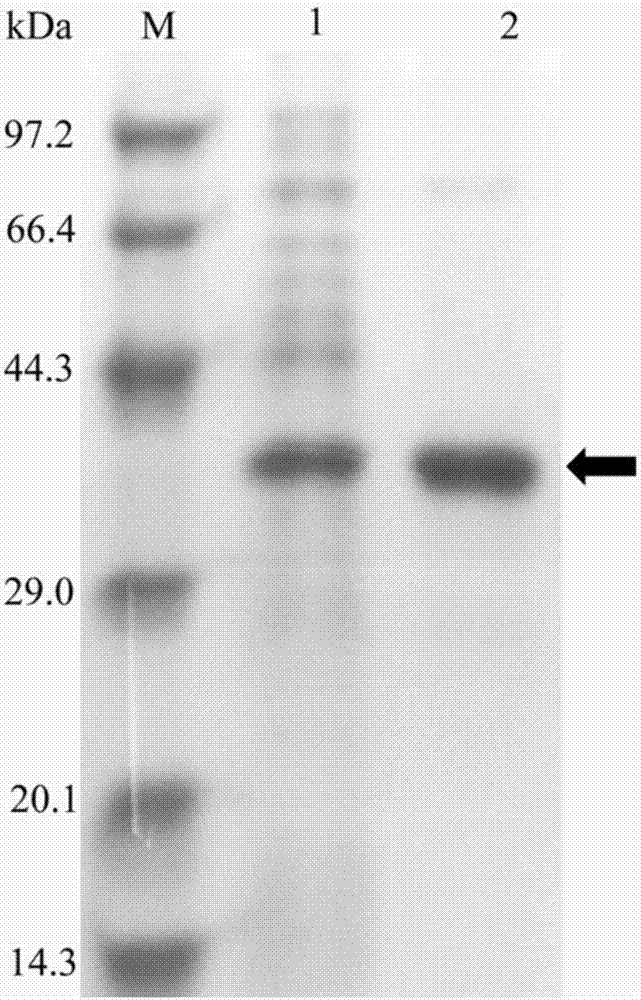
Feruloyl esterase and preparing method and application thereof
ActiveCN109652392AIncrease enzyme activityHigh hydrolytic activityBacteriaHydrolasesEscherichia coliCefazolin
The invention provides feruloyl esterase and a preparing method and application thereof. A feruloyl esterase gene coming from a soil macro gene library have the nucleotide sequence and amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.1 and SEQ ID NO.2. The gene contains a tetrapeptide SXXK sequence motif which is rarely seen, and after the esterase gene is inserted into plasmid pET28a(+), the gene is transformed into escherichia coli BL21(DE3) to achieve heterogeneous expression. The molecular weight of purified recombinase (DLFae4) is 38.3 kDa. Besides, it is put forward for the first time that novel feruloyl esterase can hydrolyze penbritin, penicillin, cefazolin and other lactam antibiotics. As is shown by site-directed mutagenesis experiments, a catalysis triplet of DLFae4 is composed of serine(S11), histidine (H74) and aspartic acid (D302), and the mutation of any of serine (S11), histidine (H74) and aspartic acid (D302) can cause loss of the catalysis capability of DLFae4. DLFae4 has a high hydrolytic activity on methyl ferulate and has good heat stability. In the presence of cellulase, DLFae4 can obviously increase the amount of ferulic acid released from destarched wheat bran. Due to peculiar activities and enzymatic characteristics of novel feruloyl esterase, novel feruloyl esterase can be applied to feed, paper making, food, pharmacy and other fields.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Recombinant bacteria using xylose to produce glycollic acid and building method and application of recombinant bacteria
The invention discloses recombinant bacteria using xylose to produce glycollic acid and a building method and application of the recombinant bacteria and belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering. The xylose dehydrogenase gene, xylonic acid lactonase gene, xylonic acid dehydratase gene, 3-deoxygenation-D-glycerin ketopentose acid aldolase gene and glycolic aldehyde dehydrogenase gene in the recombinant bacteria using the xylose to produce the glycollic acid are overexpressed. Meanwhile, the invention further provides a preparation method of the recombinant bacteria and a method using the recombinant bacteria to produce the glycollic acid. By the recombinant bacteria, the biological synthesizing path using D-xylose as the carbon source to form the glycollic acid through glycolic aldehyde conversion is achieved for the first time.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
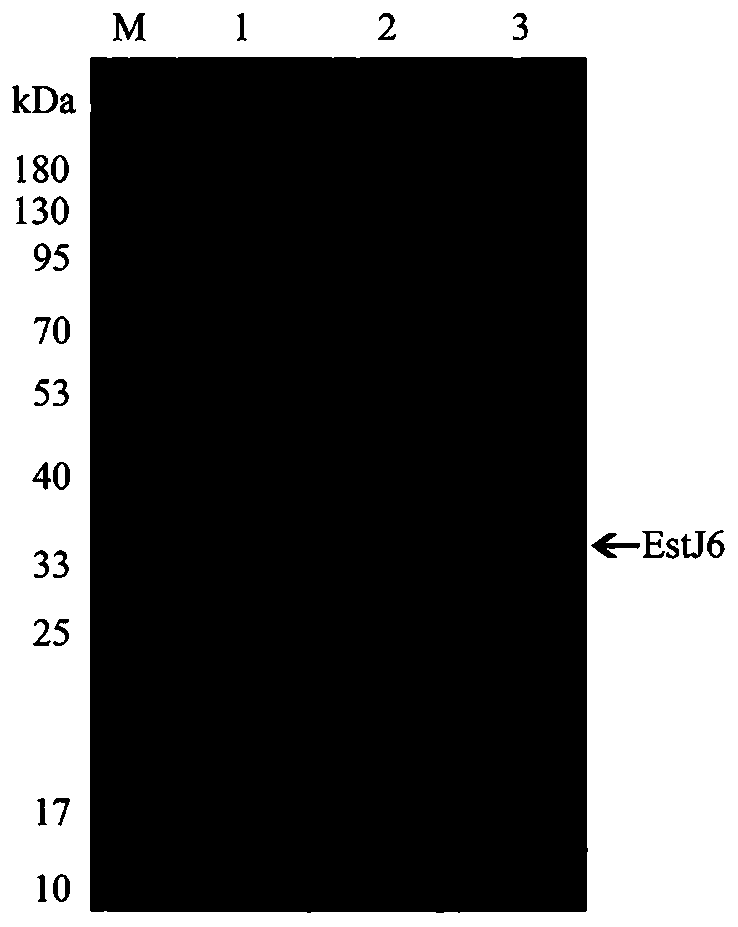
Novel phthalate hydrolase EstJ6 as well as coding gene and application thereof
ActiveCN110982803AImprove space utilizationBroad substrate specificityBacteriaHydrolasesEscherichia coliHeterologous
The invention provides a novel phthalate hydrolase gene derived from a soil metagenome library. The nucleotide sequence and an amino acid sequence of the novel phthalate hydrolase gene are shown as SEQ ID NO.1 and SEQ ID NO.2. After the esterase gene is connected to an expression vector pET28a (+), the esterase gene is transformed into escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) to realize heterologous expression. The molecular weight of the purified recombinase (EstJ6) is 33.31 kDa. The EstJ6 has wide substrate specificity on phthalate, and the EstJ6 not only can hydrolyze phthalate with a simple side chain,but also can hydrolyze diethyl hexyl phthalate and monoethyl hexyl phthalate with complex and longer side chains. In addition, site-specific mutagenesis experiments show that the catalytic triad residue of EstJ6 is S146-E240-H270, and mutation of any amino acid in the three causes the EstJ6 to lose the catalytic ability. The novel phthalate hydrolase disclosed by the invention can be applied to the fields of food industry, agriculture, biotechnology and the like due to the specific activity and enzymatic characteristics of the novel phthalate hydrolase.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Application of esterase gene est816 and recombinant esterase thereof in degrading pyrethroid pesticides
InactiveCN107058362AEfficient soluble expressionRetain relative enzyme activityFungiBacteriaCypermethrinHeterologous
The invention discloses an application of an esterase gene est816 and a recombinant esterase thereof in degrading pyrethroid pesticides. Specifically, the invention relates to heterologous expression of esterase gene est816 and a recombinant esterase thereof in degrading pyrethroid pesticides. A recombinant esterase Est816 is constructed via both an Escherichia coli expression system and a Pichia pastoris expression system, has efficient soluble expression in two expression systems, and has good thermal stability and acid and alkali resistance. The recombinant esterase est816 has a strong degradation effect on pyrethroid pesticides (such as cyhalothrin, cypermethrin, fenvalerate, deltamethrin, and so on), and the degradation rate is up to 90% or higher. Therefore, the esterase gene est816 and the recombinant esterase Est816 have broad application prospects in removing residual pyrethroid pesticides.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Phosphotriesterase mutant as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102796714AImprove hydrolysis activityHigh catalytic efficiencyBacteriaHydrolasesOrganophosphate poisonWild type
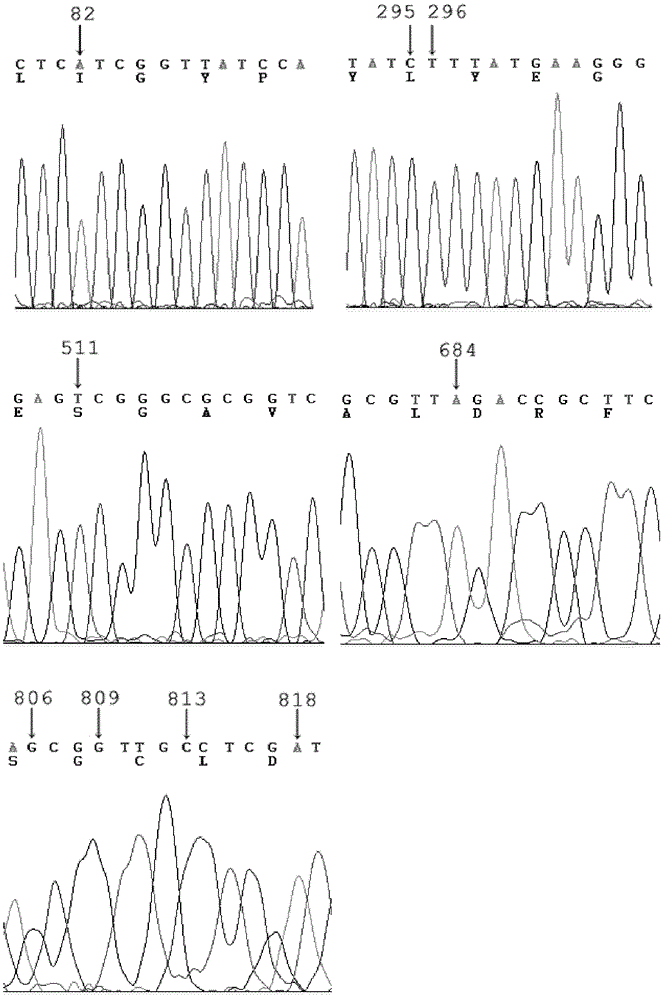
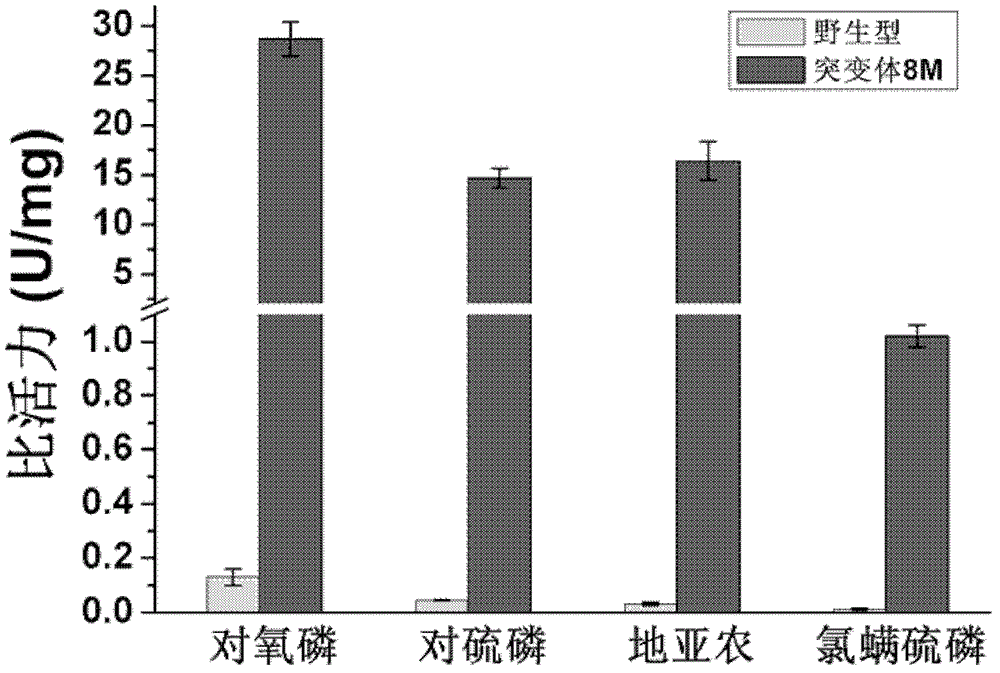
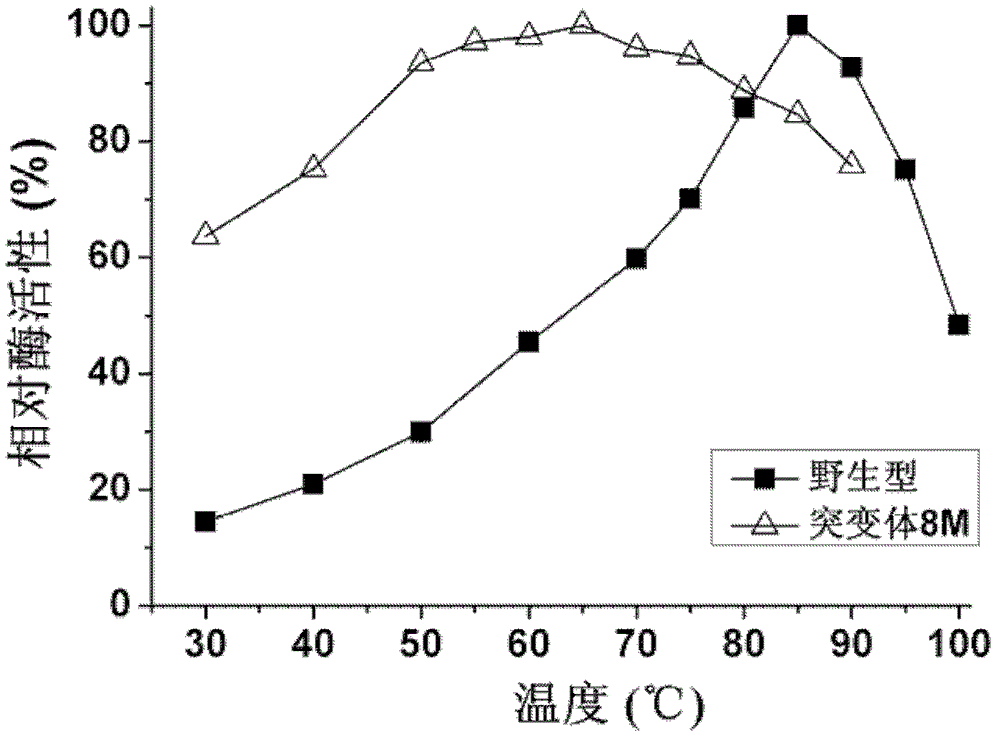
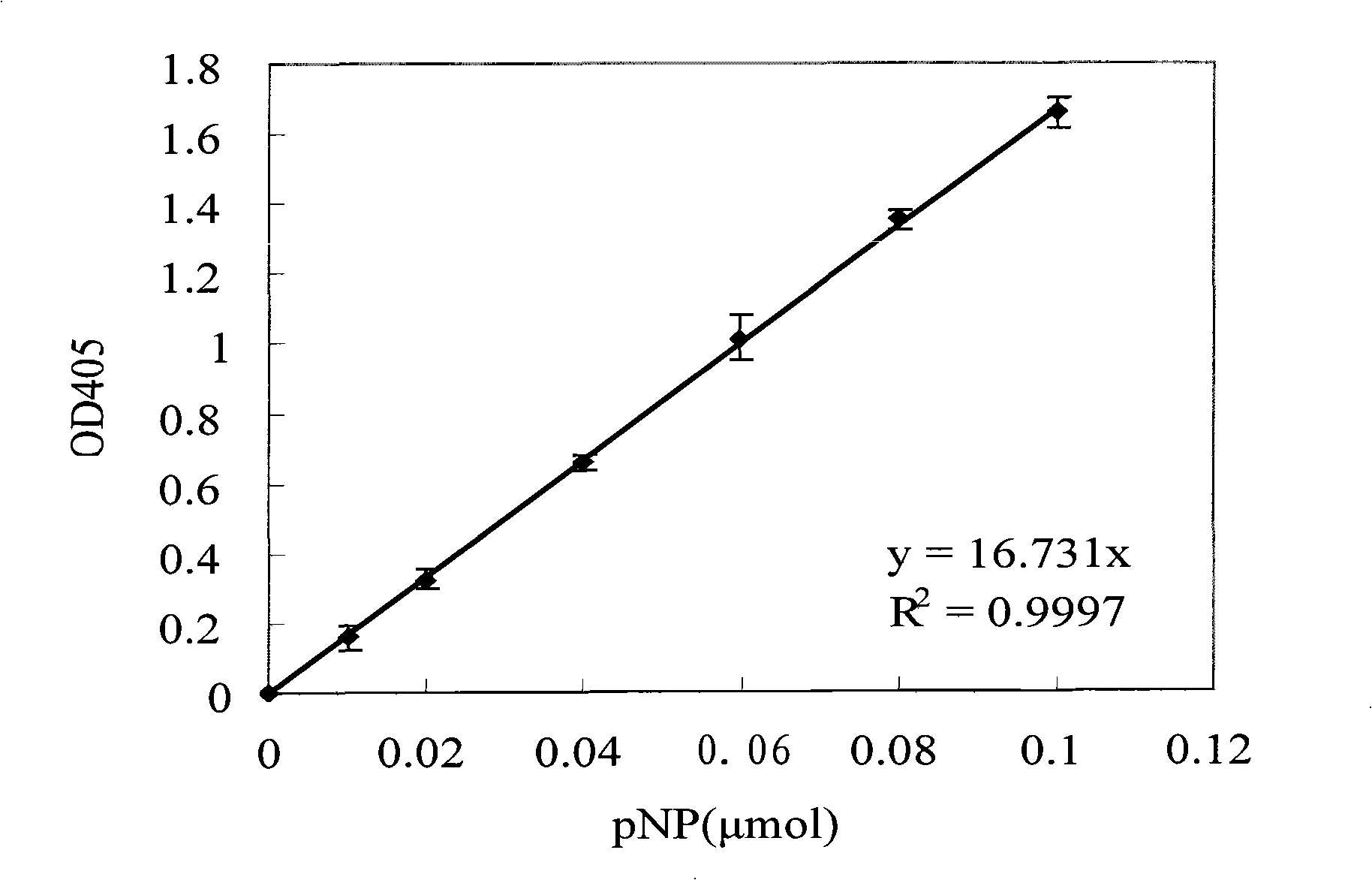
The invention provides a phosphotriesterase mutant as well as a preparation method and application of the phosphotriesterase mutant. According to the invention, a mutant with phosphotriesterase activity markedly improved is finally obtained by starting from a phosphotriesterase gene which is from Geobacillus kaustophilus HTA426 of thermophilic bacteria and then carrying out rounds of mutation and screening through an error-prone PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) method; and the mutations involved in amino acid sequence of the mutant are Phe28Ile, Tyr99Leu, Thr171Ser, Phe228Leu, Asn269Ser, Val270Gly, Trp271Cys and Gly273Asp. Compared with common organic phosphorous insecticides, the wild type specific activity of the mutant is markedly improved and the mutant has wide application prospect in the field of biodegradation of organic phosphorous poisions.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Novel gene of esterase and recombinant expression system
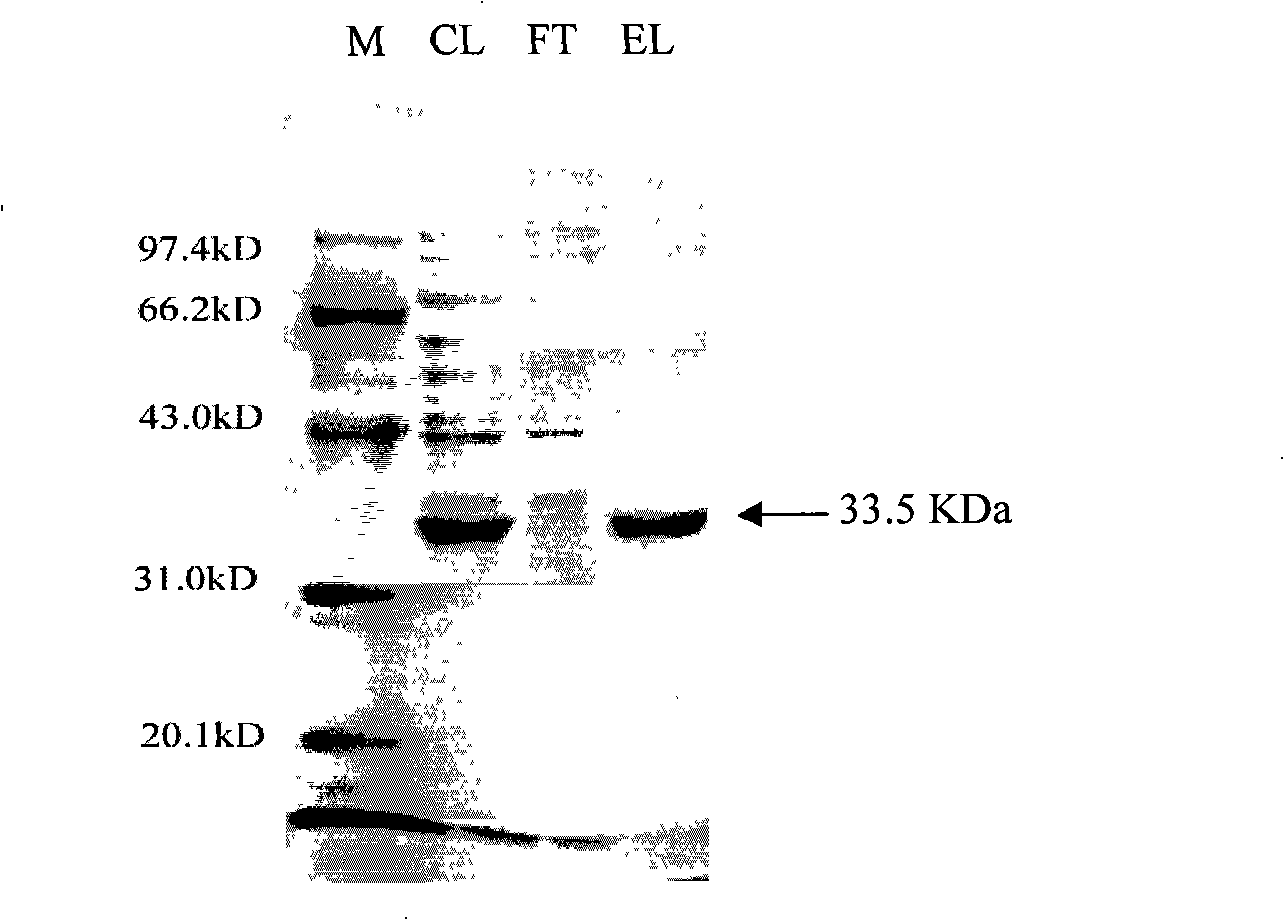
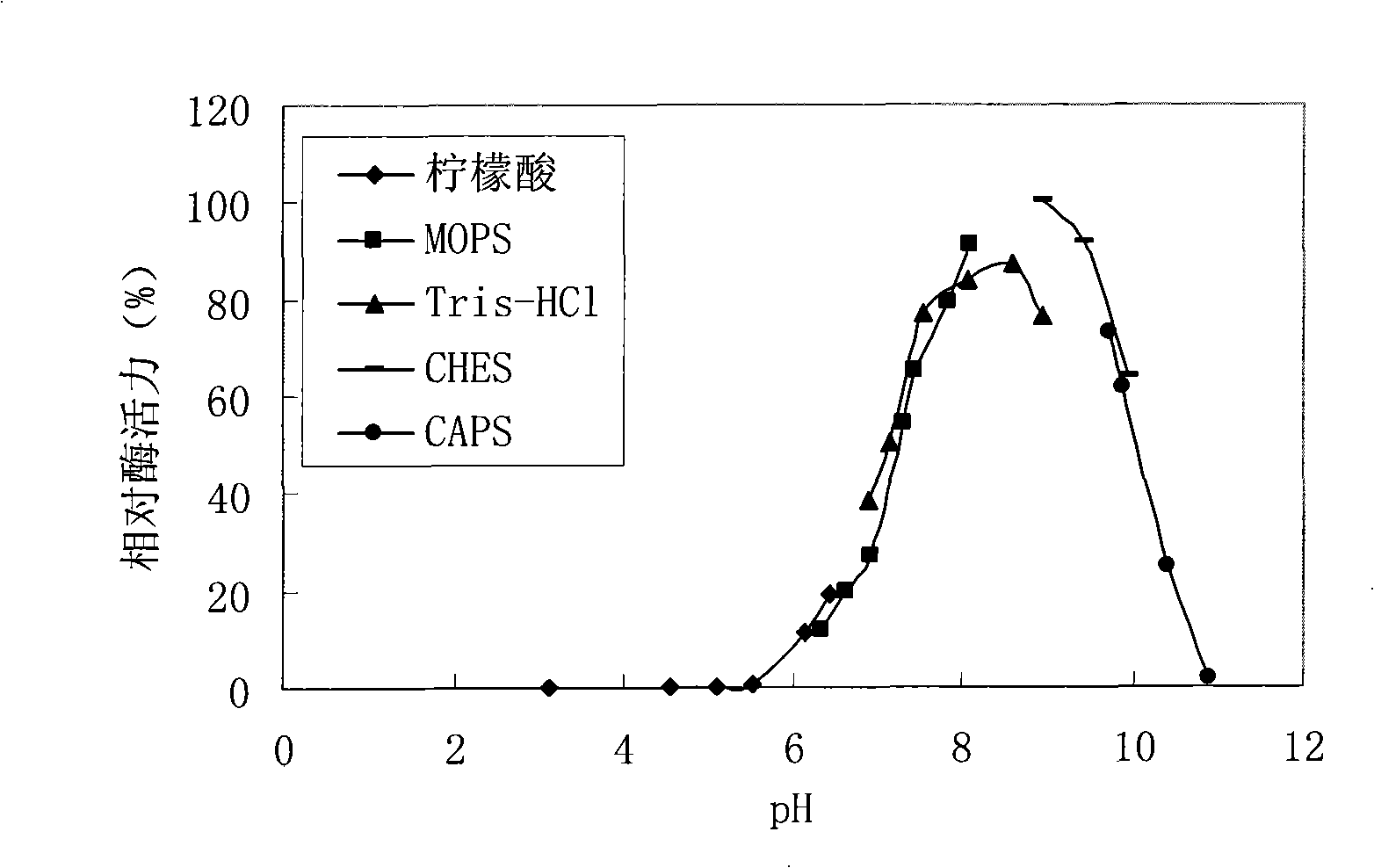
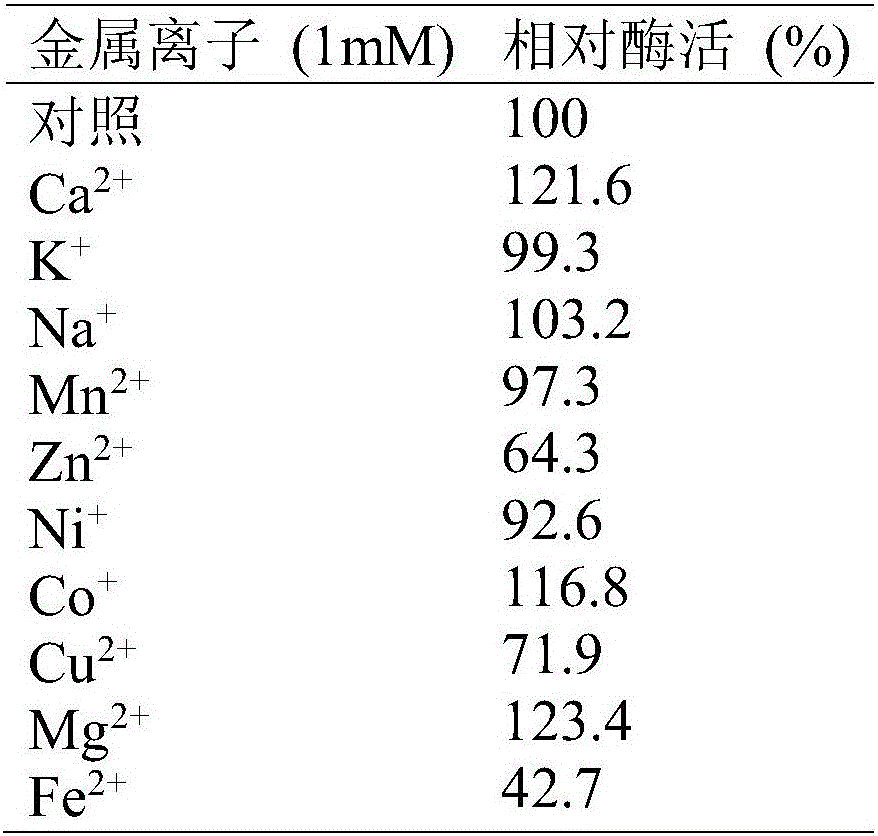
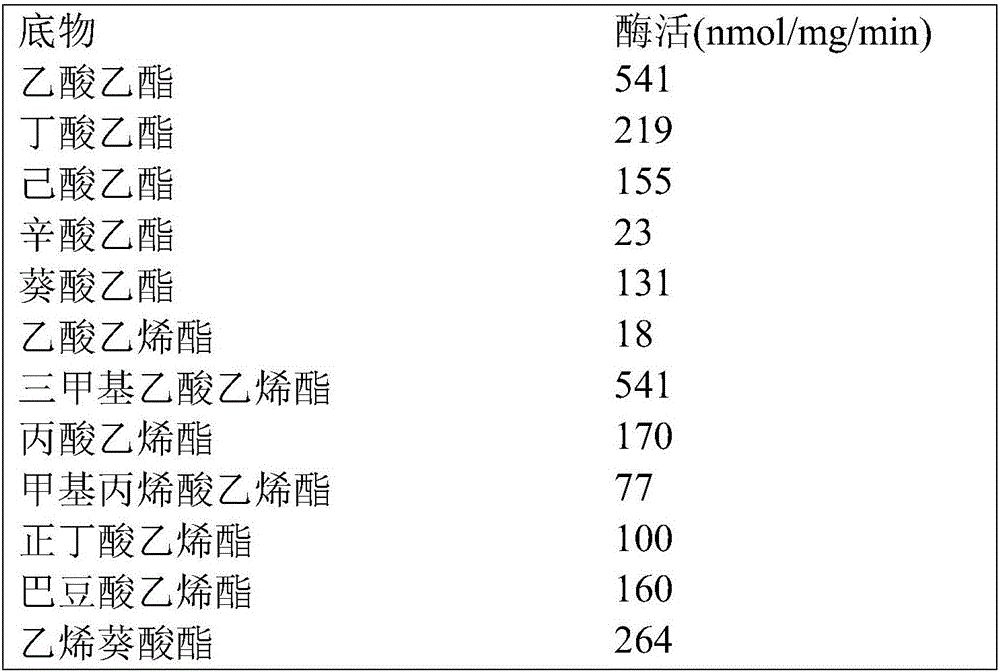
The invention provides a new esterase gene named Est_p1 and a recombination expression system thereof. The gene is cloned from the metagenomic library of the marginal mud 100 meters under the South China Sea. The gene is an 891bp long amino acid numbered 296, which successfully constructs a recombination expression system of a colon bacillus named pET28a-Est_p1 / BL21. The molecular weight of a target protein is 33.5 kD. With pNP-butyric ester as catalyzing substrates, the Est_p1 is proved to be a mildly alkaline medium temperature esterase. The Est_p1 has strong catalytic activity for short esters and is applicable to esterification and transesterification industries.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Acyl-ACP thioesterase genes and uses therefor
InactiveUS8956834B2Increase volumeHigh activitySugar derivativesHydrolasesBiotechnologyMicroorganism
The present invention provides novel genes encoding Class II acyl-ACP thioesterases and variants thereof that are active on C8, C10, C12, C14, C16, and C18 acyl-ACP substrates. The thioesterases can be introduced into transgenic organisms, including microorganisms and photosynthetic organisms, for producing fatty acids and fatty acid products.
Owner:SYNTHETIC GENOMICS INC
Esterase and application thereof
The invention relates to acquisition of an esterase gene, and cloning and expression and application thereof, which belong to the field of bioengineering. The invention discloses a substrate characteristic of the esterase gene. An esterase has a wide function and an important industrial application value.
Owner:卓虹超源生物科技(郑州)有限公司
Marine bacterial novel esterase, as well as preparation method and application thereof
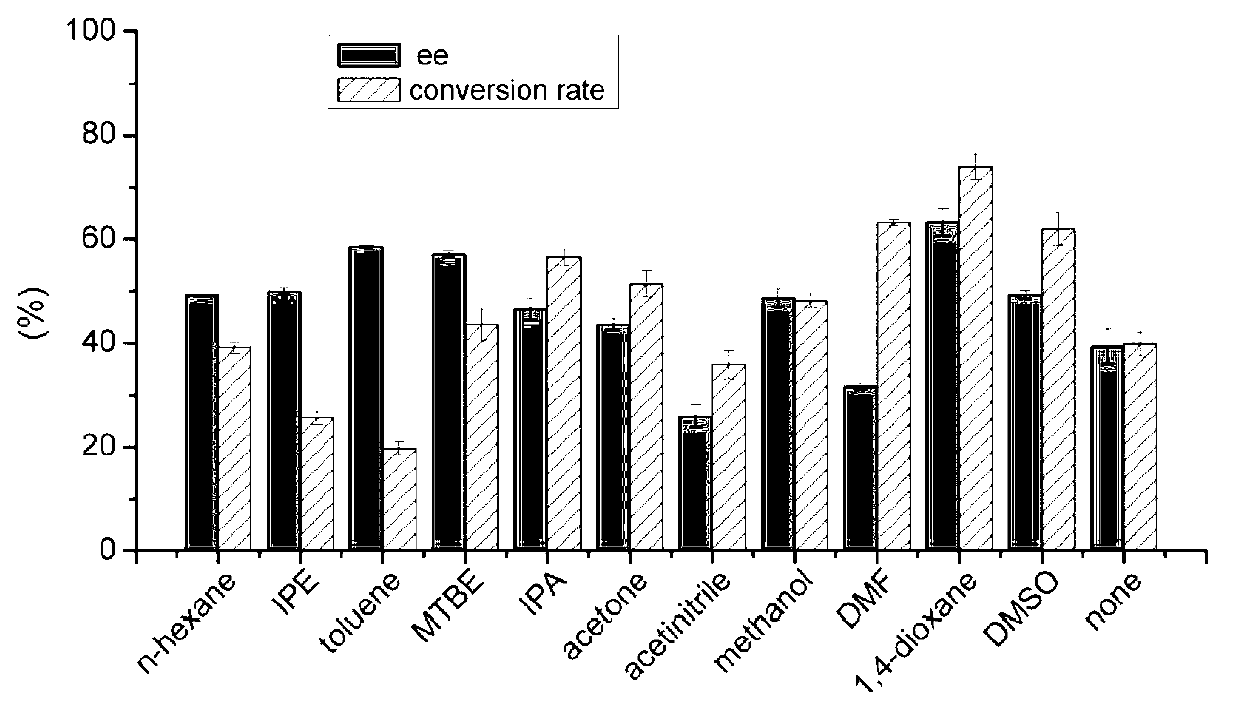
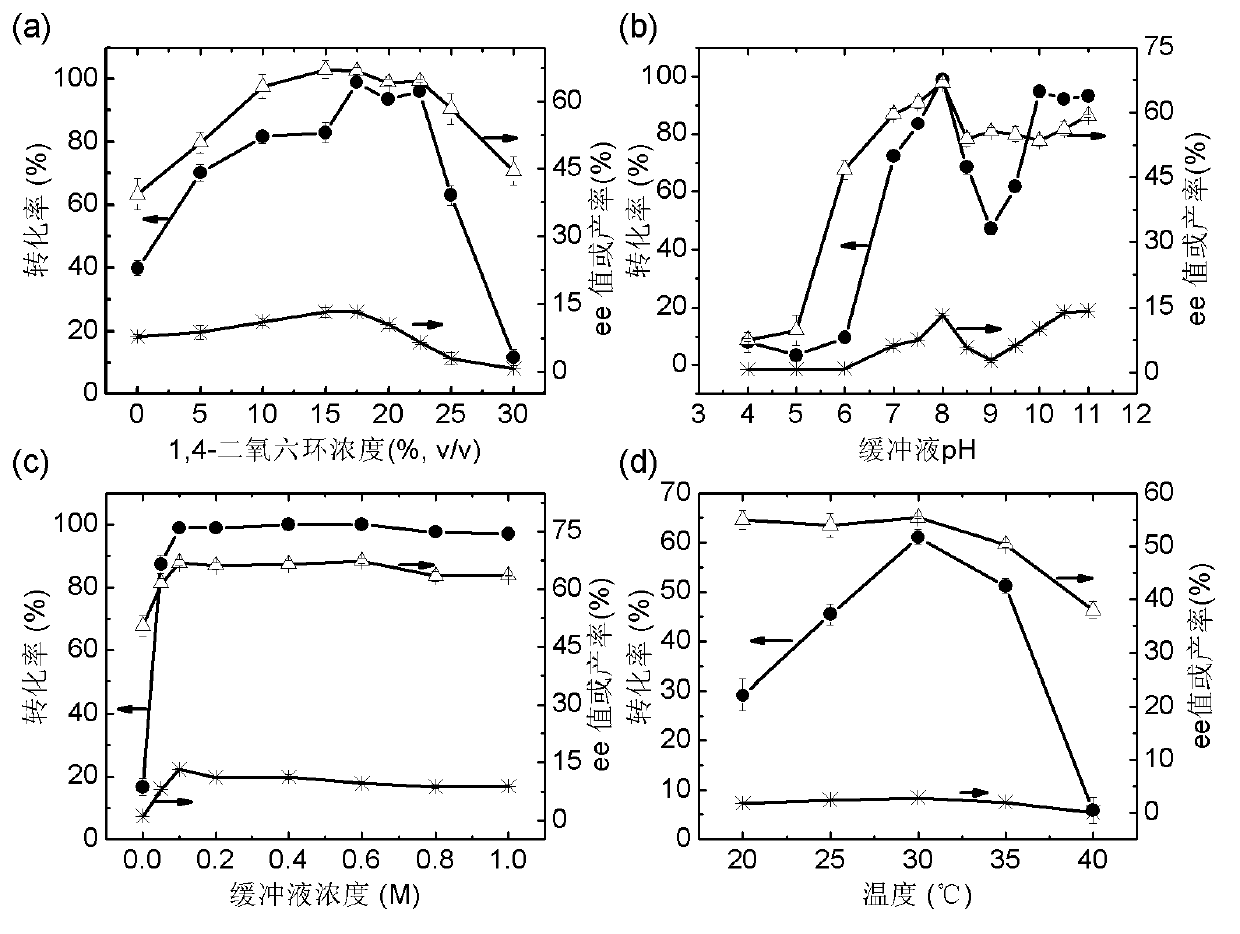
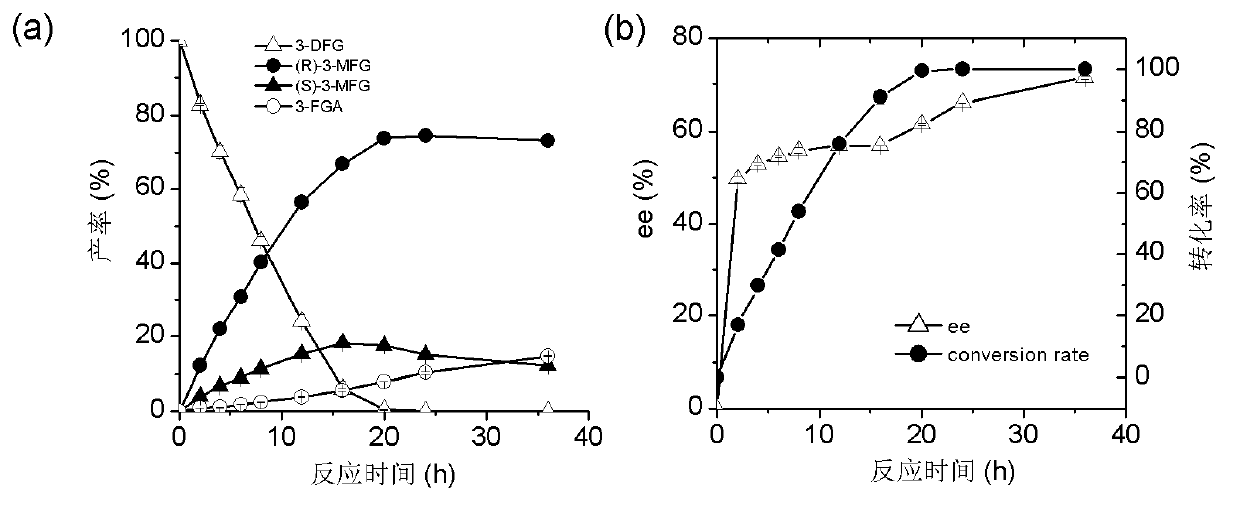
The invention discloses a marine bacterial novel esterase, and a method for producing a drug intermediate (R)-3-(4-fluorophenyl) monomethyl glutarate by chirally catalyzing 3-(4-fluorophenyl) methyl glutarate by using the esterase. The gene of the esterase is cloned to an expression plasmid to transform escherichia coli Rosetta. As the esterase can be highly and solubly expressed in an expression strain, and shows excellent salt resistant, alkali resistance and chiral selectivity, the esterase can be used as potential enzyme for industrial production of the antidepressant drug intermediate (R)-3-(4-fluorophenyl) monomethyl glutarate. As long as the reaction conditions are optimized, the esterase can be used for catalyzing 3-(4-fluorophenyl) methyl glutarate to produce the drug intermediate (R)-3-(4-fluorophenyl) monomethyl glutarate; and as a result, the transformation ratio and chiral selectivity of the esterase are greatly improved.
Owner:SECOND INST OF OCEANOGRAPHY MNR +1
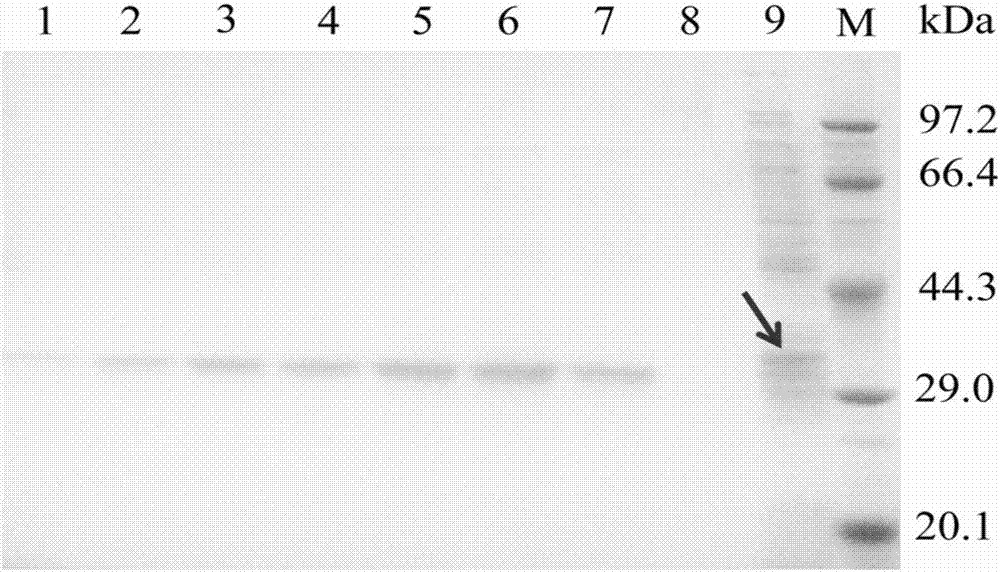
Novel feruloyl esterase and preparation method and application thereof
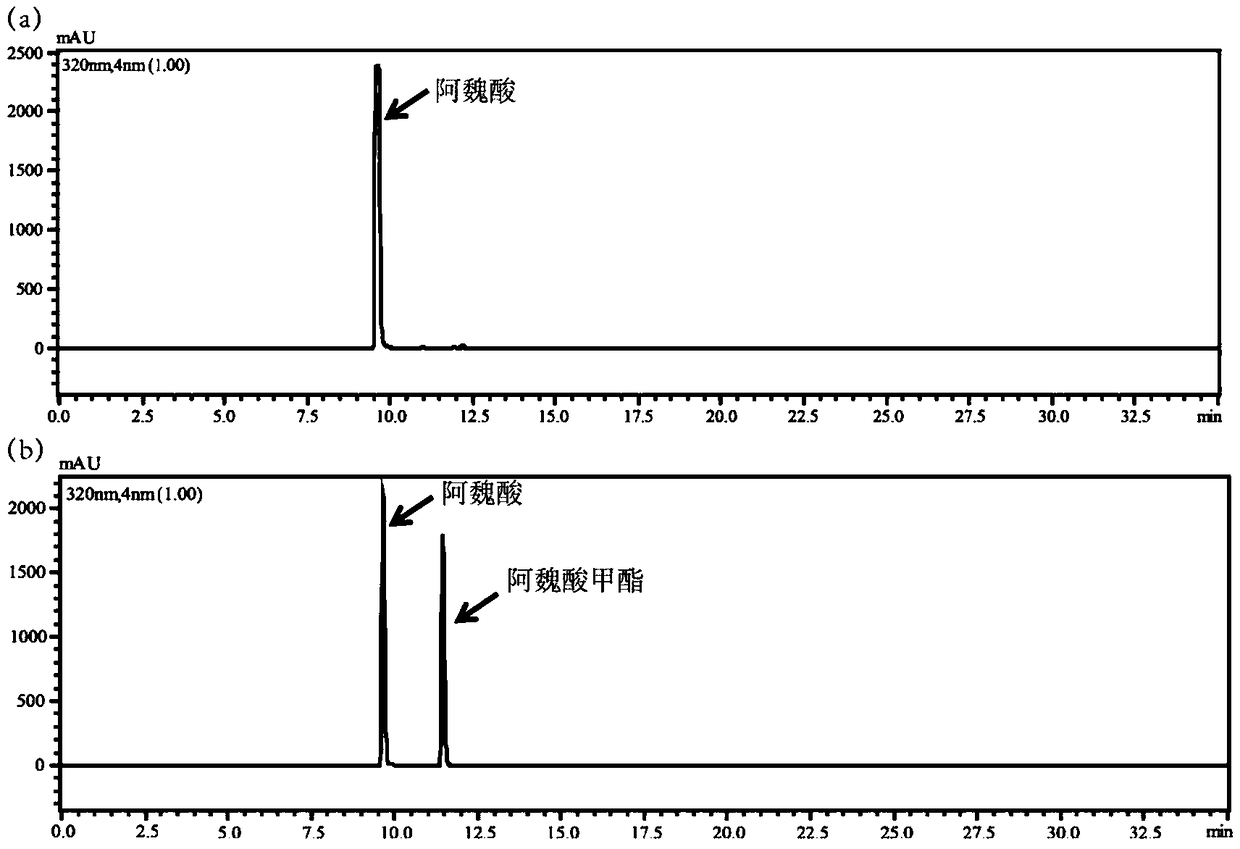
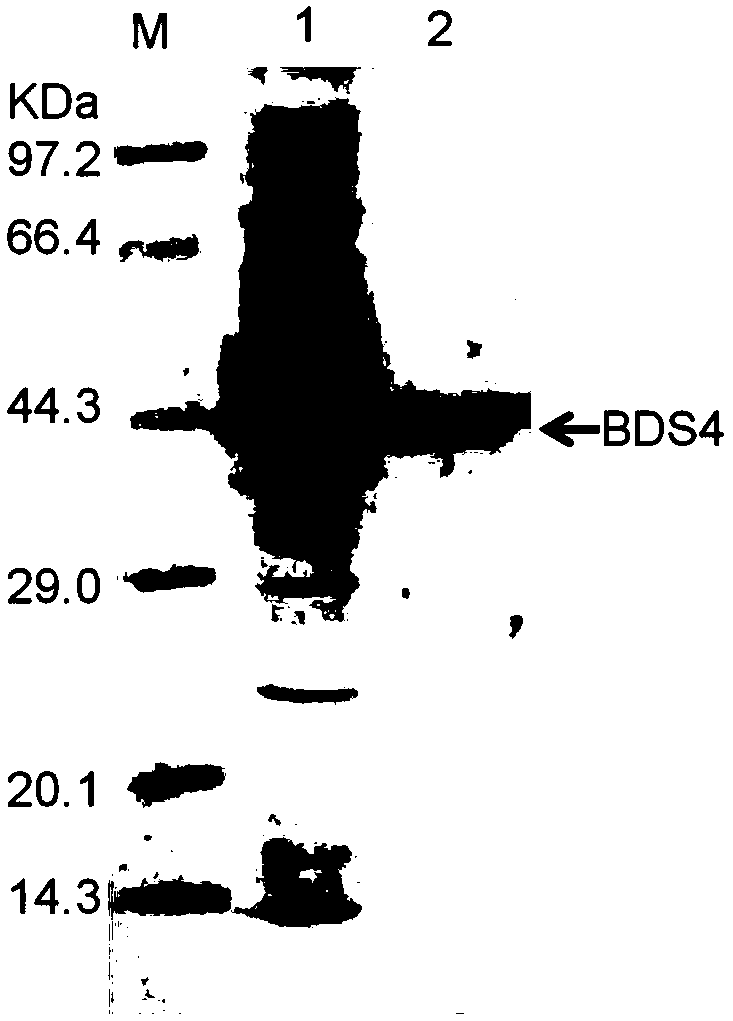
The invention provides a feruloyl esterase gene derived from a soil macrogene library. The nucleotide sequence and amino acid sequence of the feruloyl esterase gene are shown as SEQ ID NO.1 and SEQ IDNO.2. The esterase gene is inserted into a plasmid pET-28a(+) and transformed into escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) to achieve heterologous expression. The molecular weight of a purified recombinant enzyme (BDS4) is 38.8 kDa. In addition, it is proposed for the first time that novel feruloyl esterase can hydrolyze various plasticizers such as dimethyl phthalate, diethyl phthalate and dibutyl phthalate. It is shown through site-directed mutagenesis experiments that a catalytic triplet of BDS4 consists of serine (S158), aspartic acid (D256) and histidine (H286), and the mutation of any of the threeamino acids can lead to the loss of catalytic capability of BDS4. In the presence of xylanase, BDS4 can significantly increase the amount of ferulic acid released from de-starched wheat bran. The novel feruloyl esterase can be applied in the fields of feed, paper making, food, pharmacy and the like due to the unique activity and enzymatic properties of the novel feruloyl esterase.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Bacteria and method for synthesizing fatty acids
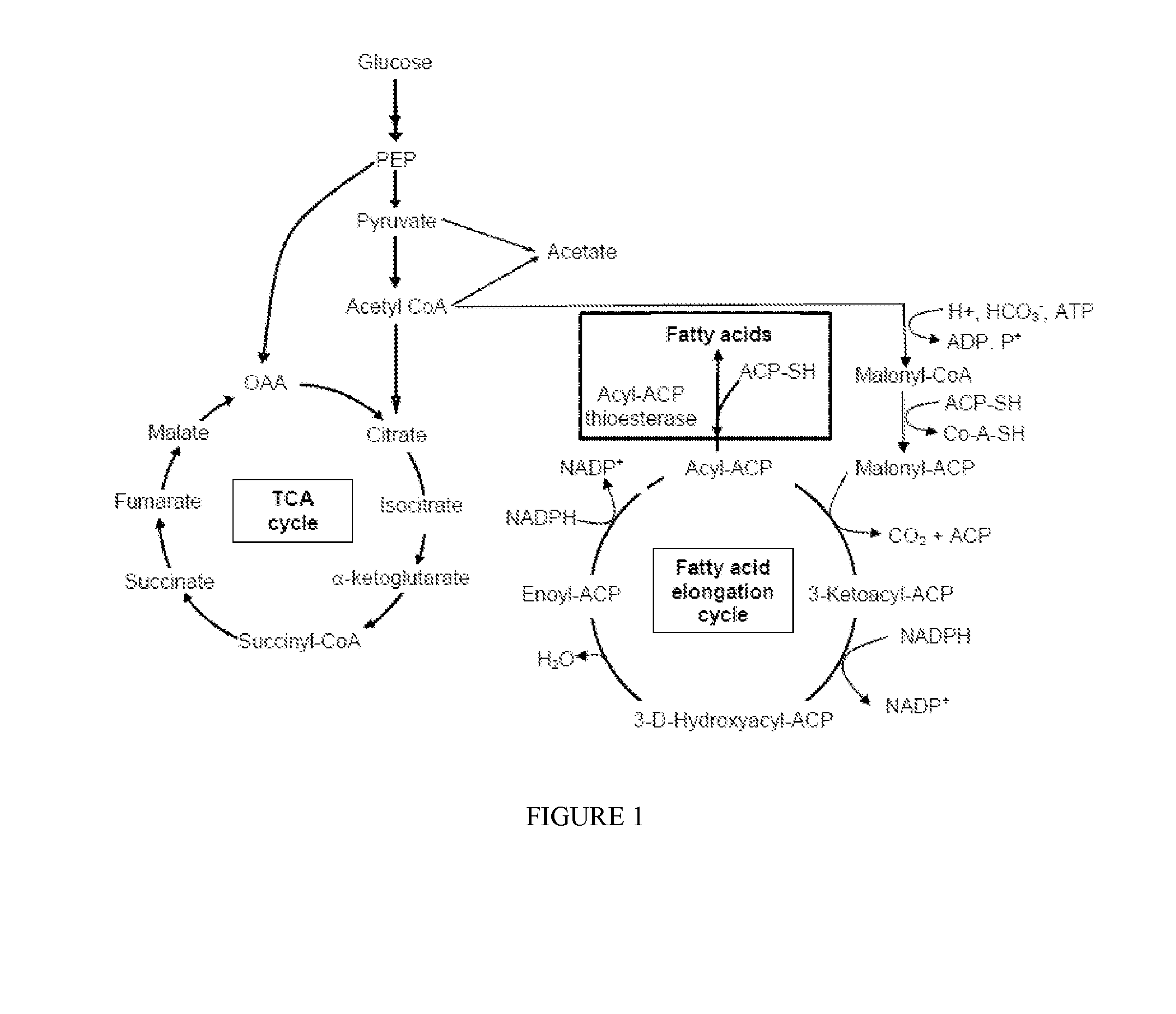
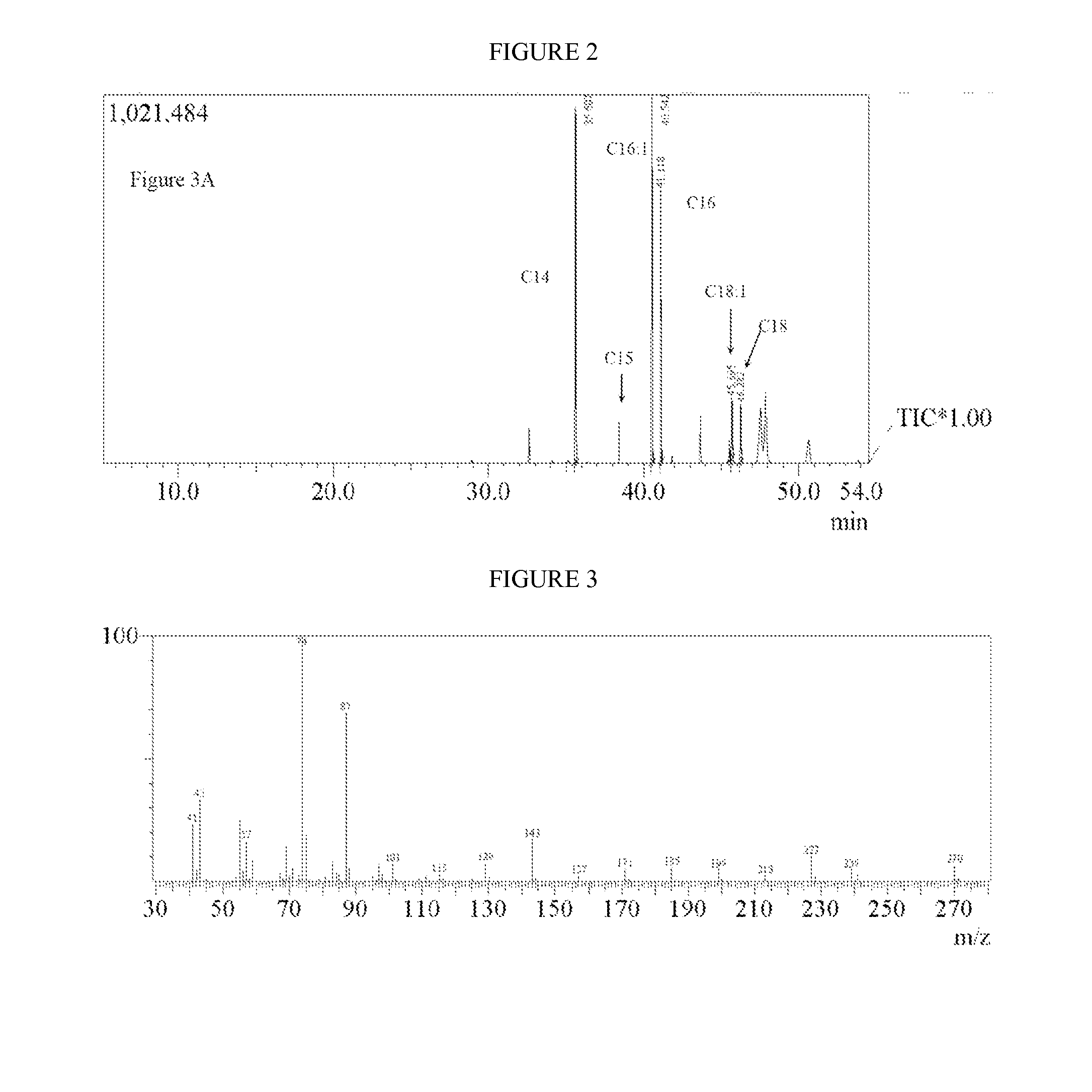
ActiveUS20140093921A1Increasing production of fatty acidIncrease synthesisBacteriaSugar derivativesTricarboxylic acidAcyl group
There is provided a recombinant bacterium comprising at least one overexpressed acyl-ACP thioesterase gene, and wherein at least one gene from the tricarboxylic acid cycle or glycolysis or both is inactivated. There is also provided a method for producing fatty acids, said method comprising culturing bacteria comprising at least one overexpressed acyl-ACP thioesterase gene in a growth medium in a container having walls; allowing said bacteria to secrete fatty acids; and collecting said fatty acids. Acid supplementation is also shown to increase productivity.
Owner:RICE UNIV
Novel deep-sea low-temperature salt-tolerant esterase and application
ActiveCN105400750ARealize industrial productionLow costFungiBacteriaHeterologousCroceicoccus marinus
The invention discloses novel deep-sea low-temperature salt-tolerant esterase E10 and a coding gene and application thereof. The invention relates to the esterase gene e10 coming from deep-sea bacteria Croceicoccus marinus E4A9T, and a nucleotide sequence is shown in SEQ ID No.1. After heterologous expression is conducted on an esterase gene, when a substrate is p-nitro phenol caproate (C6), the catalytic activity is the maximum, and the enzyme activity is 29.4 U / mg. The optimum temperature of esterase catalytic hydrolysis of the esterase E10 ranges from 15 DEG C to 20 DEG C; the activity remains 80 percent or above in 1 mol / L NaCl; under the condition of adding organic solvent of dimethyl sulfoxide, glycerin and isopropanol, the enzyme activity is increased. The esterase has the advantages of being low in temperature, resistant to salt and capable of being applied to industrial production such as chiral drug synthesis, food processing and food flavor improvement, wastewater treatment and washing industry under the low-temperature salt-containing condition.
Owner:SECOND INST OF OCEANOGRAPHY MNR +1
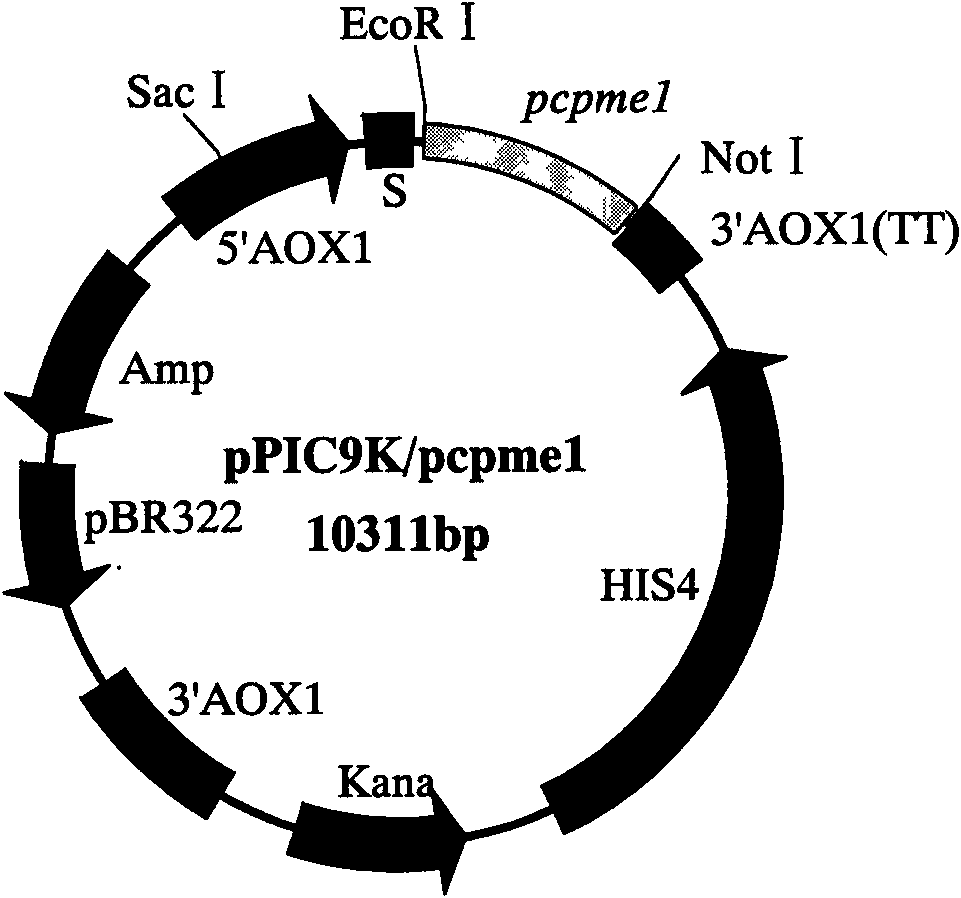
Phytophthora capsici pectin methylesterase Pcpme l gene as well as preparation method of protein and application thereof
InactiveCN101671684AObvious symptomsSufficient technical reservesHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease courseCell wall
The invention provides a pectin methylesterase gene Pcpme l cloned from phytophthora capsici and a preparation technique of a protein thereof, belonging to the technical field of biology. The invention proves that the pectin methylesterase gene Pcpme l effectively participates in the processes of infecting a host by the phytophthora capsici and causing the disease course of phytophthora capsici leonian on the basis of gene and protein levels and also proves that the protein coded by the pectin methylesterase gene Pcpme l has property of destroying leaf tissue cells and cell wall structures thereof to enable destroyed parts to generate obvious symptoms on the basis of a cell chemistry technique, thus the pectin methylesterase gene Pcpme l is an important target pathogenic gene of a coded phytophthora capsici pectin methylesterase gene cluster. The invention provides sufficient technical reserve for further researching a germ molecule detection technique.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Novel esterase and its application
InactiveCN102732539AEfficient expressionHeat stableHydrolasesFermentationBiotechnologyEscherichia coli
The invention discloses DNA of a novel esterase. The novel esterase DNA has a nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO.1 and an amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO.3. The invention also discloses an expression vector containing the novel esterase gene, a recombinant esterase and application of the recombinant esterase in degradation of homoserinelactone signal molecules. The novel esterasehas efficient soluble expression in an Escherichia coli expression system and good thermal stability, and has a strong degradation effect on homoserinelactone signal molecules.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Esterase and application thereof
The invention relates to acquisition of esterase genes as well as cloning and expression and an application of the esterase genes, and belongs to the field of bioengineering. The invention discloses substrate characteristics of esterase. The esterase has broad actions, and the esterase has an important industrial application value.
Owner:卓虹超源生物科技(郑州)有限公司
Esterase and applications thereof
The invention relates to obtaining, cloning expression and applications of an esterase gene, belongs to the field of biological engineering, and discloses substrate properties, wherein the esterase has wide effects and important industrial application values.
Owner:卓虹超源生物科技(郑州)有限公司
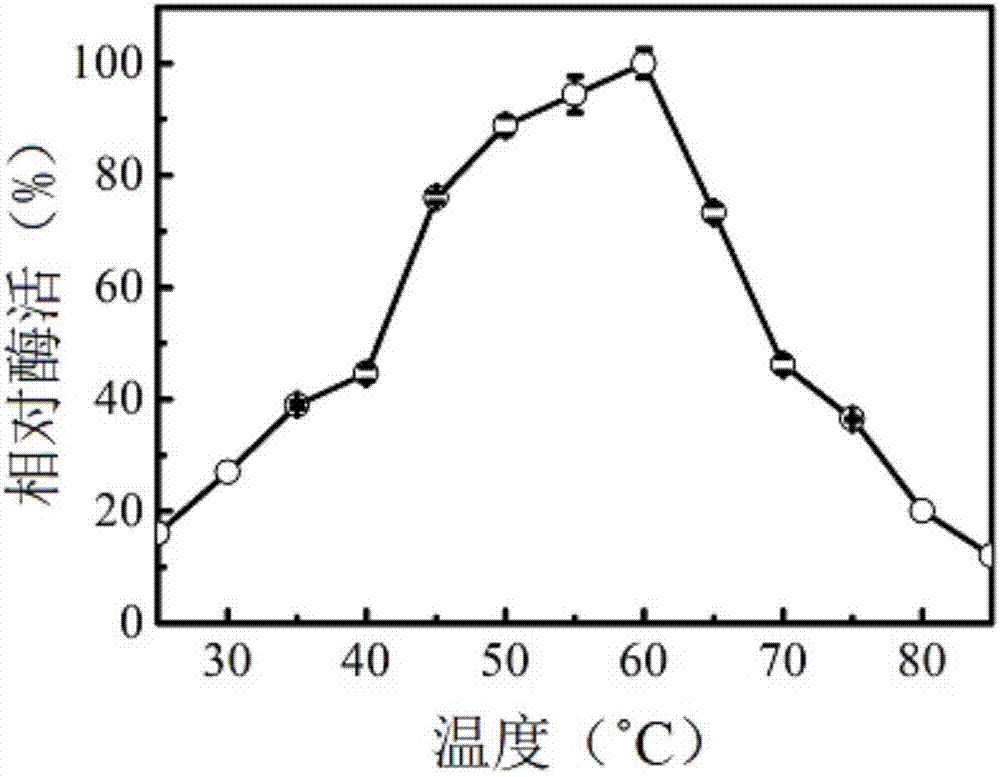
Ocean cold-adapted esterase as well as coding gene E40 and application thereof
The invention relates to ocean cold-adapted esterase as well as a coding gene E40 and an application thereof. The nucleotide sequence of the gene E40 of ocean cold-adapted esterase is shown by SEQ ID No.1. The esterase E40 provided by the invention has relatively high catalytic efficiency at 0-20 DEG C and can hydrolyze butterfat at a low temperature or normal temperature to generate short-chain fatty acid, and the substances can enhance the flavor of the dairy product and avoid the influence of long-time high temperature on the food quality and the taste and nutritional ingredients; and meanwhile, when the cold-adapted esterase E40 is used for treating the ester-containing waste and wastewater from the catering, the application is safe and efficient and is of very positive significance to environmental protection.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
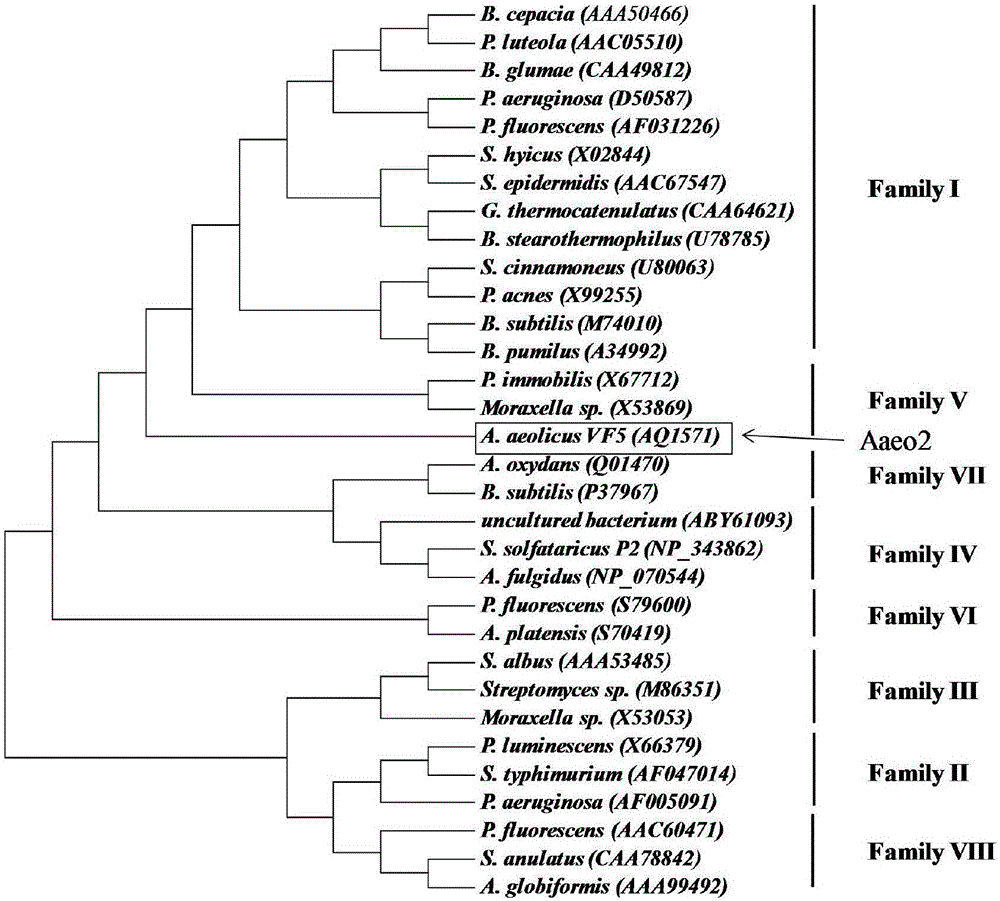
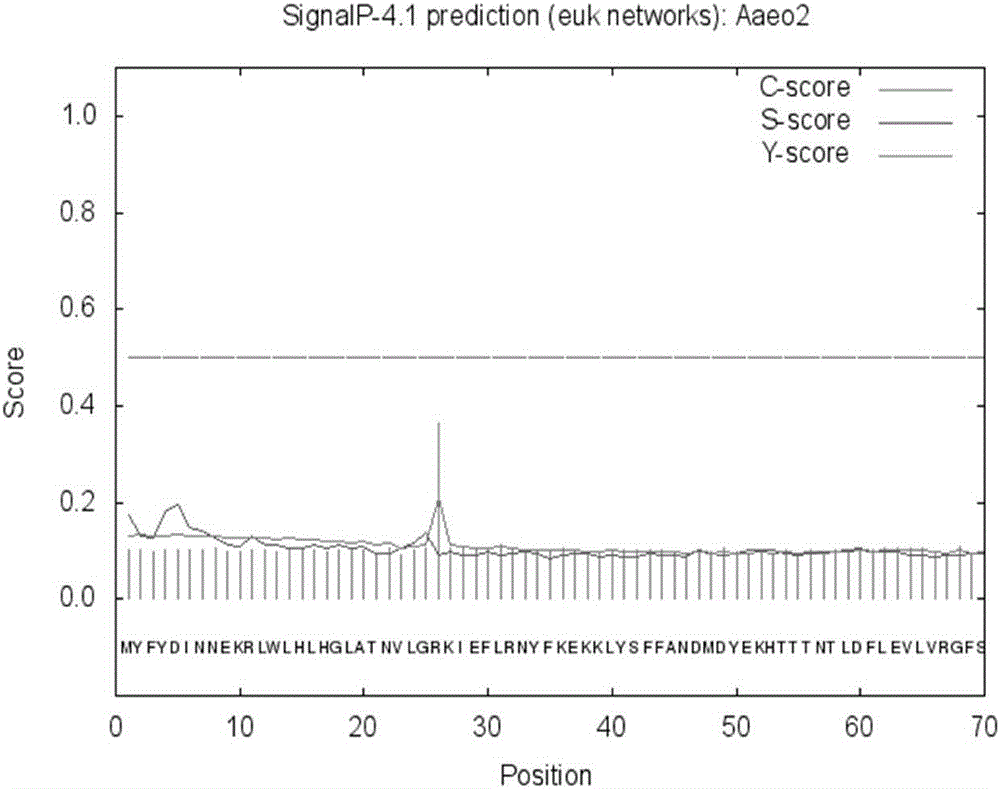
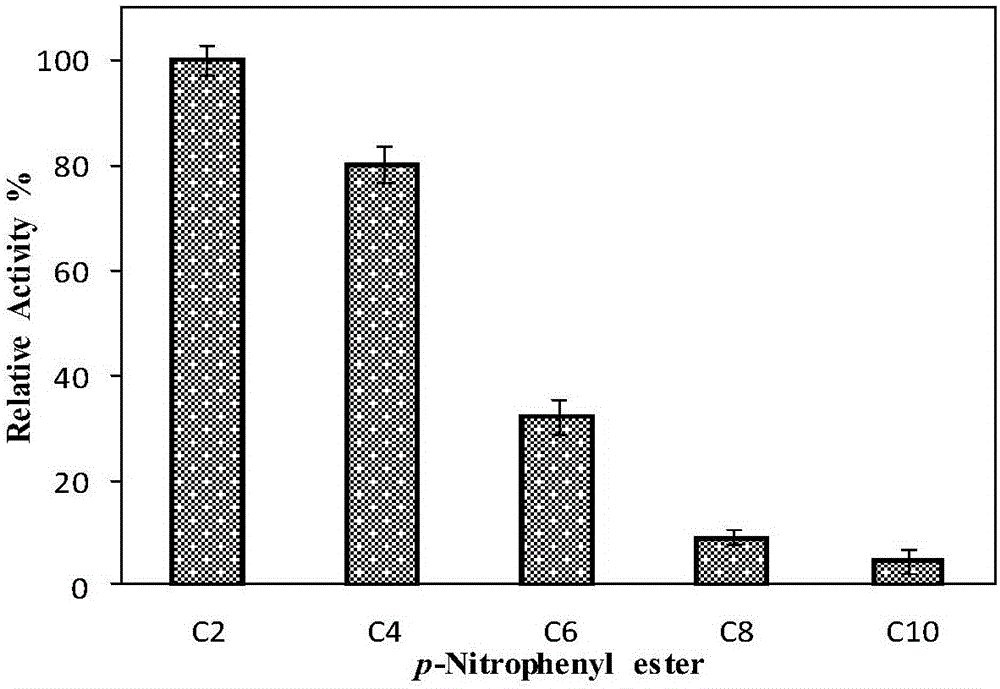
Thermophilic esterase derived from aquifex aeolicus strain and functional verification of thermophilic esterase
The invention discloses thermophilic esterase derived from an aquifex aeolicus strain and functional verification of the thermophilic esterase, and belongs to the field of bioengineering technology. According to the invention, a novel thermophilic esterase gene is discovered, three expression systems are constructed, and efficient expression and research of enzymatic properties are achieved. Construction of an eukaryotic expression system: preferably, a vector pPIC9K is adopted for expression vector construction, and a pichia pastoris host, preferably GS115, is transformed, so that efficient expression is achieved; construction of a prokaryotic escherichia coli expression system: preferably, a vector MBP3 is adopted for expression vector construction, and escherichia coli hosts, preferably BL21 and Origami2, are transformed, so that efficient expression is achieved; and construction of a prokaryotic bacillus megaterium expression system: preferably, a vector pHIS1525 is adopted for expression vector construction, and a bacillus megaterium host, preferably YYBm1, is transformed, so that efficient expression is achieved. The recombinant enzyme (the thermophilic esterase) has the advantages of esterase activity, ,thermophilic characteristic, thermal stability and the like; and the recombinant enzyme has a great potential in industrial application under a high-temperature condition.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Esterase PHE14 as well as encoding gene and application thereof
The invention discloses esterase PHE14 as well as an encoding gene and an application thereof. A novel enzyme gene PHE14 is developed from (Pseudomonadaceae oryzihabitans) HUP022, the whole length is 645bp, and the esterase PHE14 encoded by using the gene contains 214 amino acids. By cloning the esterase gene PHE14 and connecting the gene with an expression vector pET-28a (+) and converting escherichia coli BL21 (DE3), after culture and inducible expression, the recombinant expressed esterase PHE14 can be obtained. The esterase PHE14 can be used for preparing chiral methyl lactate, the esterase PHE14 of recombinant expression is taken as a catalyst, and (S)-methyl lactate of which the optical purity is greater than 99% can be prepared. The esterase PHE14 has very high application values in fields such as biochemical engineering and biological medicines.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Salt-tolerant esterase, coding gene of salt-tolerant esterase and application of salt-tolerant esterase
ActiveCN105368802AHigh catalytic activityGreat application potentialHydrolasesFermentationBiotechnologyNucleotide
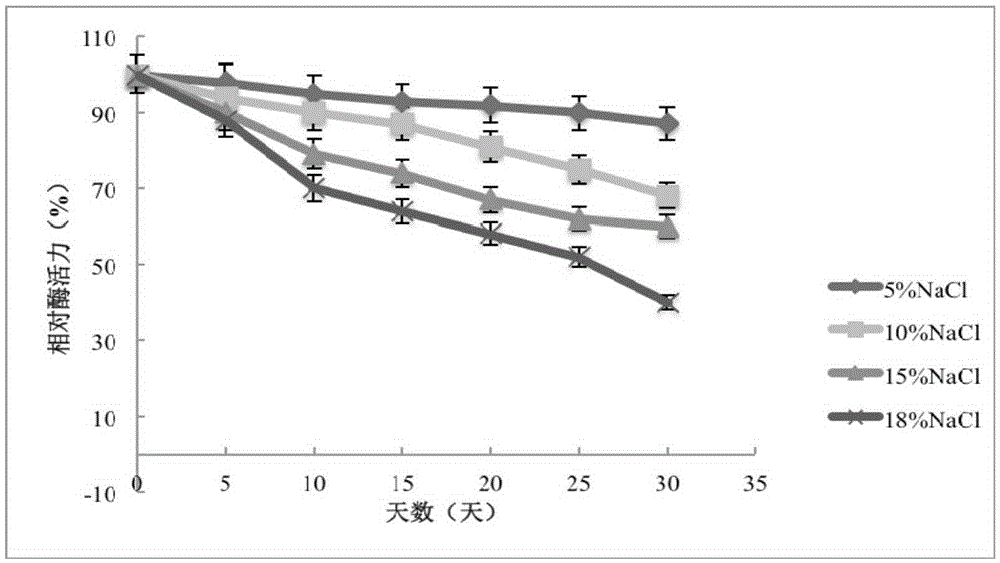
The invention provides a salt-tolerant esterase, a coding gene of the salt-tolerant esterase and application of the salt-tolerant esterase. An amino acid sequence of a protein molecule of the esterase is shown as SEQ ID NO:2, and a nucleotide sequence of an esterase gene is shown as SEQ ID NO:1. The new esterase gene is obtained by screening from a Chinese traditional food fermentation environment metagenomic library, excellent enzymatic characteristics of a coding protein of the gene are detected, a catalytic hydrolysis / synthesis temperature range is 25-50 DEG C, and a pH value is 5.5-8.0. The esterase has a main advantage that the excellent enzymatic characteristics of the esterase protein can be kept under the condition of 10-18% NaCl. Catalysis of acetic acid, propanoic acid, pentanoic acid, hexanoic acid, ethyl alcohol, propyl alcohol, butyl alcohol, pentyl alcohol and hexyl alcohol to realize synthesis of corresponding short-chain aromatic ester compounds such as ethyl acetate, propyl propionate and butyl pentanoate is realized, and esterification rates can reach 80%-90% mostly. The salt-tolerant esterase can be applied to industrial biosynthesis of short-chain aromatic ester flavorings and has significant economic and social values in foods and daily chemical products.
Owner:GUANGDONG IND TECHN COLLEGE
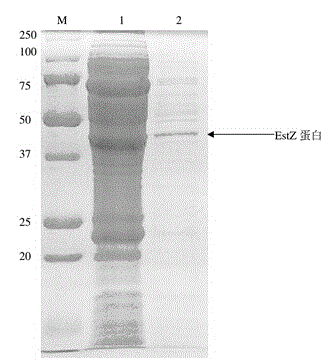
Esterase gene estZ, esterase gene estZ encoded protein and application of esterase gene estZ
ActiveCN104694558AImprove qualityIncrease added valueBacteriaHydrolasesCypermethrinEcological environment
The invention discloses an esterase gene estZ, an esterase gene estZ encoded protein and application of the esterase gene estZ. The esterase gene estZ has a total length of 1,206bp, has a G and C content of 65.2% and has a nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO. 1. The esterase gene estZ is an encoded product and contains 401 amino acids, and the sequence of the amino acids is shown in SEQ ID NO. 2. The esterase gene estZ is capable of catalyzing and degrading ester bond containing pesticides like beta cypermethrin, lambda cyhalothrin, deltamethrin, cypermethrin, fenpropathrin, bifenthrin, kresoxim-methyl, pyraclostrobin and azoxystrobin. An enzyme preparation produced from the esterase gene estZ can be used for removing pesticide residue in agricultural products such as vegetables, fruits, tea leaves, cotton and tobacco so that the quality of the agricultural products can be improved and the additional value of the agricultural products can be increased. The esterase gene estZ can be further used for producing genetically modified crops so that the problem of excessive pesticide residue in agricultural products can be solved and pollution-free green agricultural products can be produced. The esterase gene estZ can be also used for restoring pesticide contaminated soil so that the problem of environmental pollution can be solved and the ecological environment and the human health can be protected.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Esterase as well as encoding genes and application thereof
The invention discloses esterase as well as encoding genes and application thereof. The amino acid sequence of the esterase is shown in SEQ ID NO.2. The esterase genes are obtained by cloning from pseudomonas Pseudomonas CGMCC NO.4184, and the esterase expressed by the genes has the characteristics of high expression quantity, high selectivity and chiral selectivity. The engineering bacteria containing the esterase genes are applied to a method for catalyzing hydrolysis of rac-2-carboxyethyl-3-cyano-5-methyl ethyl caproate so as to prepare 2-carboxyethyl-(S)-3-cyano-5-methyl ethyl caproate, and when the conversion rate of the reaction is controlled to exceed 50 percent, the unhydrolyzed high-purity 2-carboxyethyl-(S)-3-cyano-5-methyl ethyl caproate can be obtained.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Preparation method for archaea thermophilic esterase and (S)-ketoprofen
InactiveCN103194467AHigh purityHigh resolution activityHydrolasesFermentationEscherichia coliBiotechnology
The invention discloses a preparation method for archaea thermophilic esterase and (S)-ketoprofen. The method comprises preparation of a strain, a plasmid, enzymes and a culture medium, PCR amplification and construction of recombinant plasmid, and inducible expression of a gene and purification of protein. Specifically, the method comprises the following steps: (1) designing a pair of primers, carrying out amplification with a whole genome sequence of Thermotogamaritima as a template, carrying out enzyme digestion with endonuclease, connecting the primers to pET15b which has undergone enzyme digestion by same endonuclease, transforming ligation productsinto escherichia coli DH5 alpha, carrying out screening to obtain a recombinant plasmid and carrying out double digestion and sequencing confirmation; and (2) carrying out inducible expression of the gene and purification of the protein so as to obtain the archaea thermophilic esterase. According to the invention, through usage of a genetic engineering method, the gene of the esterase is cloned and expressed in escherichia coli, the protein of the esterase is prepared, and the protein has a high purity (more than 95%). The optimal reaction temperature and the reaction pH value of the esterase are 70 DEG C and 5.0 to 5.5, respectively; the esterase has good acid resistance and can maintain about 50% of its activity when treated for 60 min in a reaction system where the temperature is 70 DEG C and the pH value is 4.5.
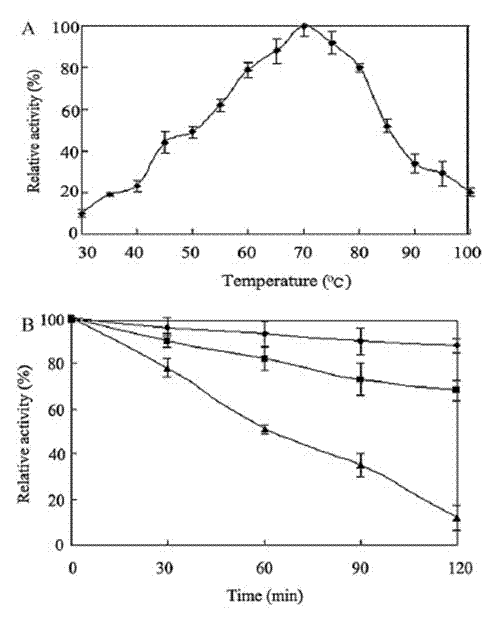
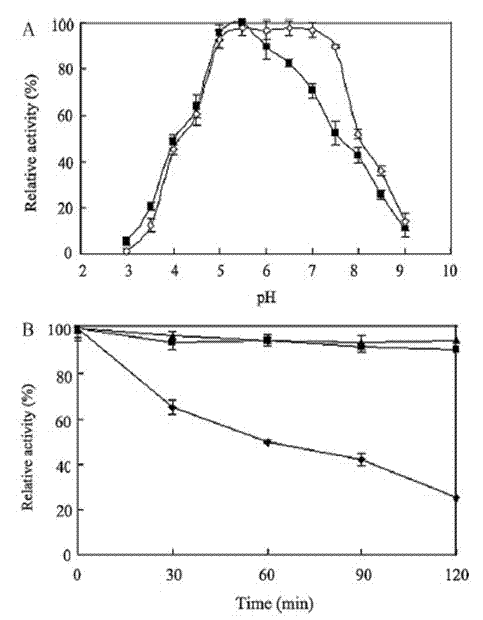
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIVERSITY OF LIGHT INDUSTRY
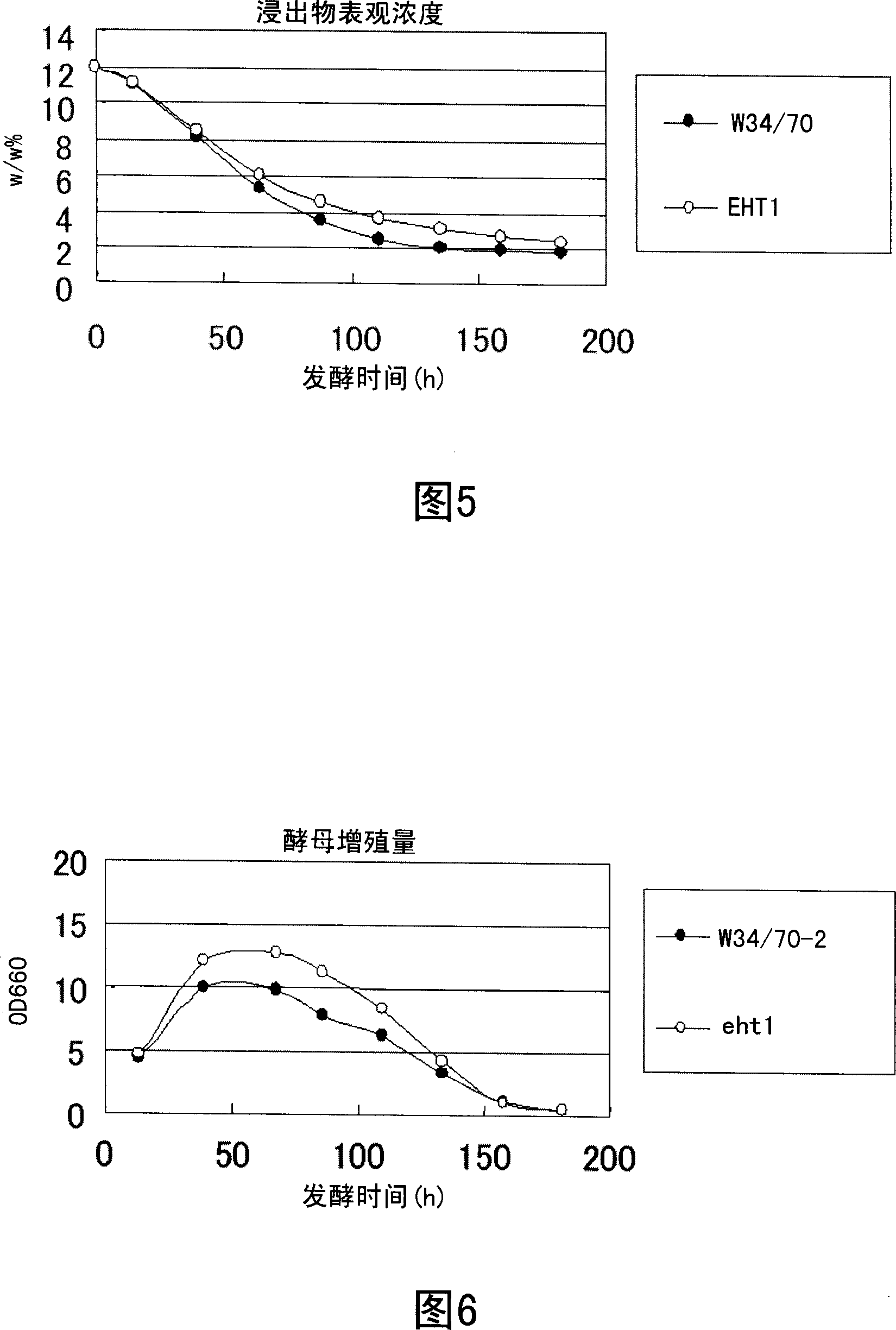
Acyl-CoA: ethanol O-acyltransferase/esterase gene and use thereof
Owner:SUNTORY HLDG LTD
A kind of esterase phe14 and its coding gene and application
The invention discloses esterase PHE14 as well as an encoding gene and an application thereof. A novel enzyme gene PHE14 is developed from (Pseudomonadaceae oryzihabitans) HUP022, the whole length is 645bp, and the esterase PHE14 encoded by using the gene contains 214 amino acids. By cloning the esterase gene PHE14 and connecting the gene with an expression vector pET-28a (+) and converting escherichia coli BL21 (DE3), after culture and inducible expression, the recombinant expressed esterase PHE14 can be obtained. The esterase PHE14 can be used for preparing chiral methyl lactate, the esterase PHE14 of recombinant expression is taken as a catalyst, and (S)-methyl lactate of which the optical purity is greater than 99% can be prepared. The esterase PHE14 has very high application values in fields such as biochemical engineering and biological medicines.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com