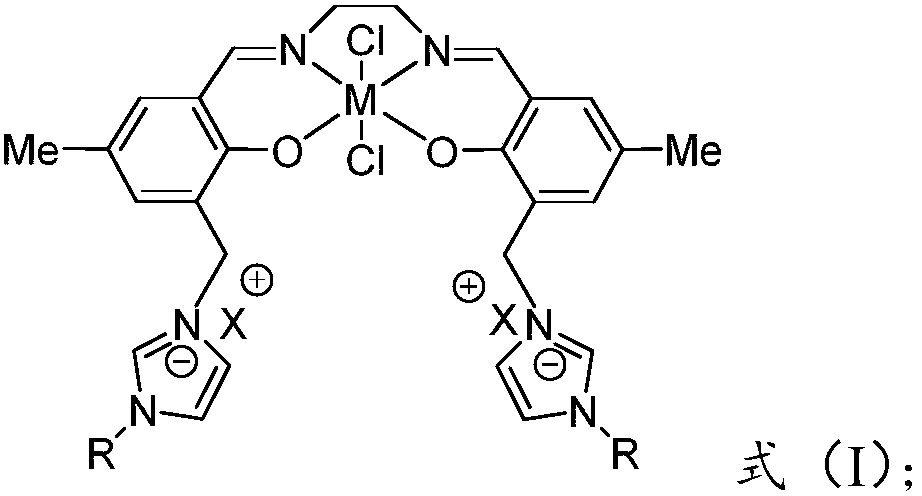
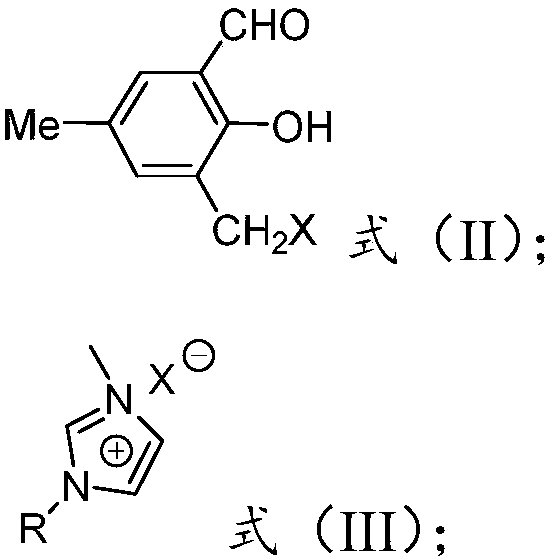
Patents
Literature
105 results about "Methyl lactate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
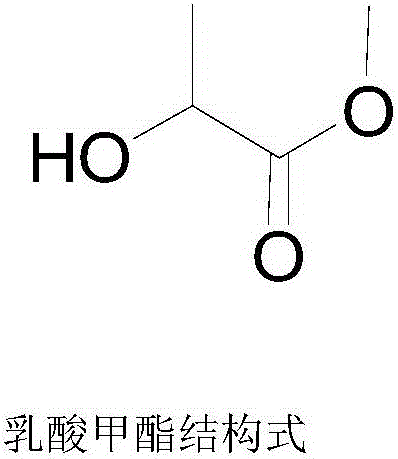
Methyl lactate, also known as lactic acid methyl ester, is a monobasic ester formed from lactic acid and methanol, commonly used as a solvent. Methyl lactate belongs to the lactate ester group of compounds that are considered nontoxic and highly and readily biodegradable.
Absorbent article comprising a synthetic polymer derived from a renewable resource and methods of producing said article
An element of an absorbent article is provided. The element has a bio-based content of at least about 50% based on the total weight of the element, and comprises a synthetic polymer derived from a renewable resource via a first intermediate compound selected from the group consisting of crotonic acid, propiolactone, ethylene oxide, i-propanol, butanol, butyric acid, propionic acid, 2-acetoxypropanoic acid, methyl 2-acetoxypropanoate, methyl lactate, ethyl lactate, polyhydroxybutyrate, and a polyhydroxyalkanoate comprising 3-hydroxypropionate monomers. An absorbent article comprising the element and a method of making an element for an absorbent article also are provided.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
New process for synthesizing tenofovir disoproxil fumarate
InactiveCN101648974AShorten the reaction stepsEasy to getGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsAntiviralsAlcoholAntiviral drug
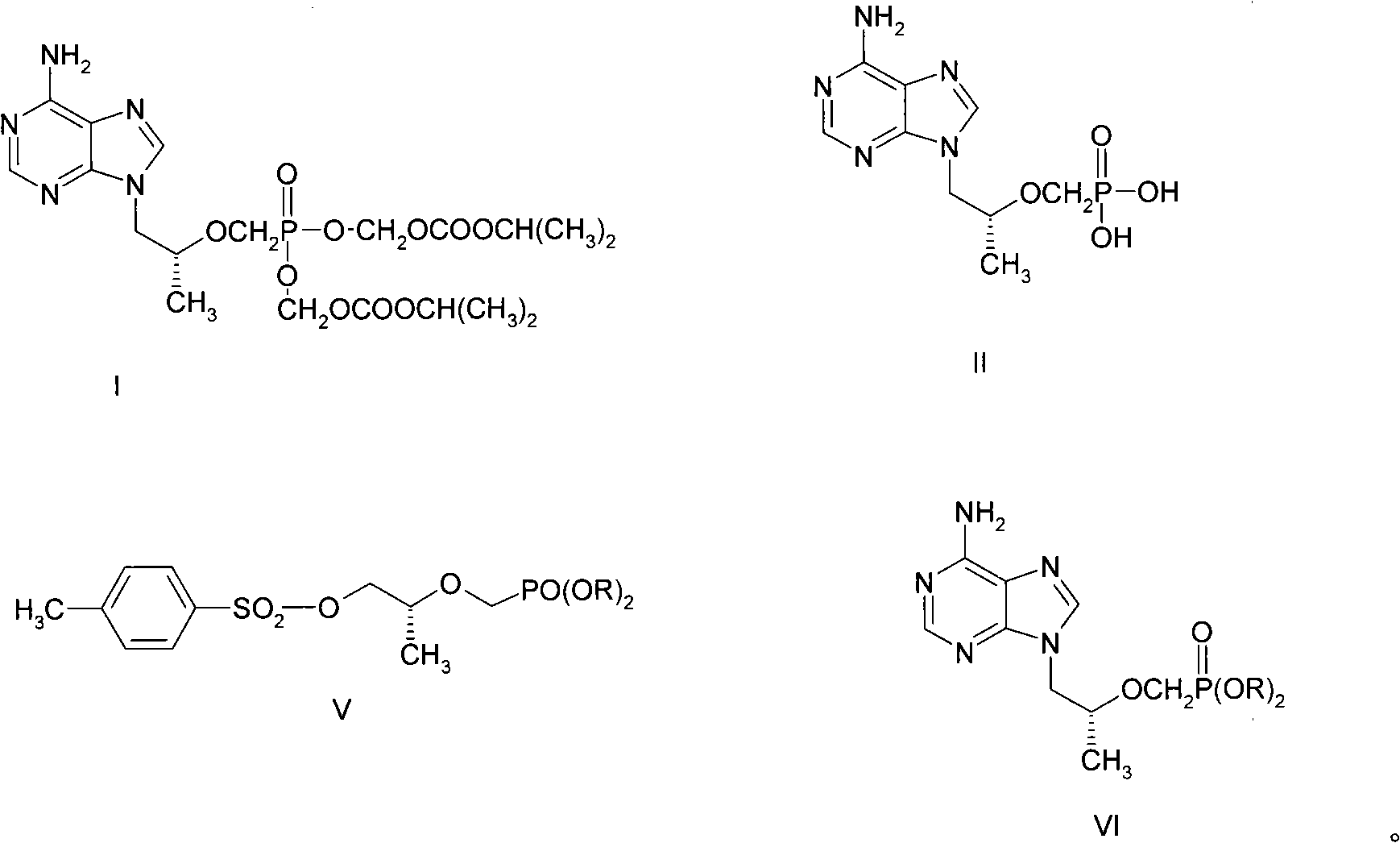
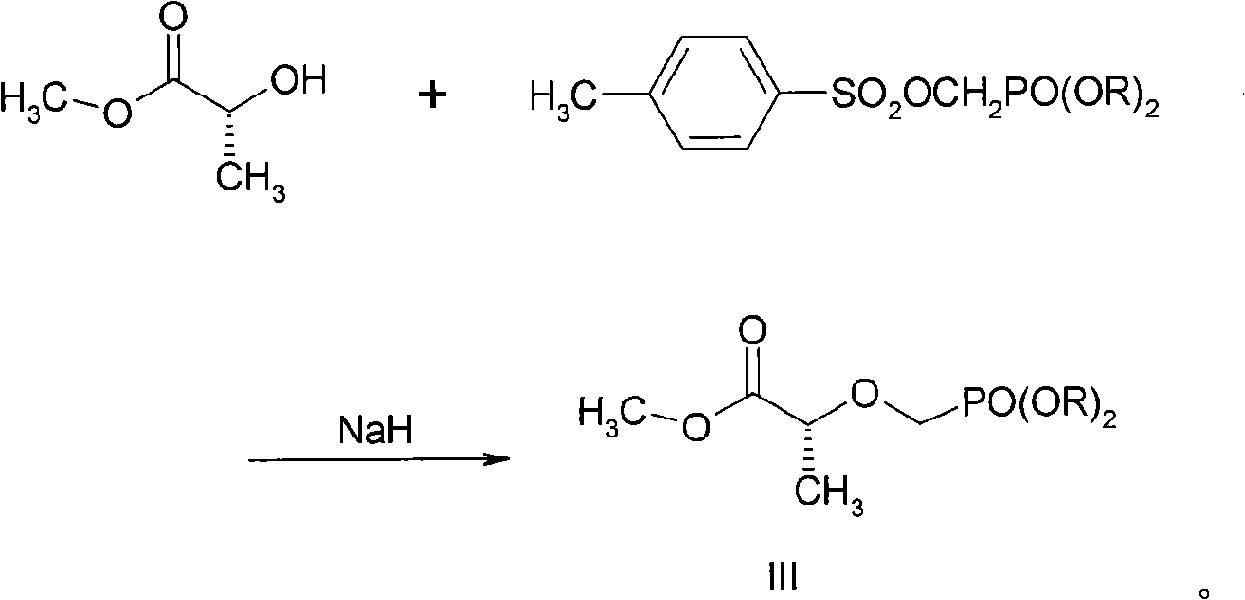
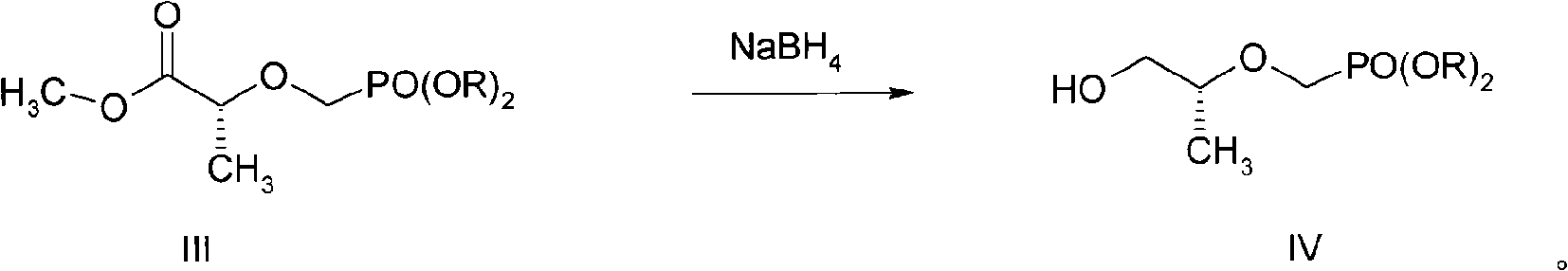
The invention discloses a new process for sysnthesizing tenofovir disoproxil fumarate as an antiviral medicament. The invention greatly reforms the preparation process of tenofovir disoproxil as a keyintermediate for synthesizing the tenofovir disoproxil fumarate and establishes a new process suitable for industrial production. The new process includes the following steps: firstly (R)-methyl lactate and diisopropyl-p-ethyl methyl-phosphonate are condensed so that diisopropyl oxygroup- phosphonyl-methyl is introduced and the condensate can be used as a protection group of hydroxyl, and then the reaction step is shortened; secondly, carboxylic ester can be selectively reduced into alcohol by NaBH4 without affecting the phosphonate; and thirdly, adenine and 2-O-( diisopropyl oxygroup- phosphonyl-methyl)-(R)- isopropyl p-toluenesulfonic acid are condensed. Through hydrolysis, the enofovir disoproxil (II) as the key intermediate can be conveniently obtained, and the optical purity can reach more than 98%.
Owner:广东京豪生物制药有限公司
Carbodiimide compound, carbodiimide composition and aqueous coating composition
ActiveUS20110021679A1Improve adhesionNice appearanceIsocyanic acid derivatives preparationOrganic compound preparationCross-linkAcetic acid
A water-soluble or water-dispersible carbodiimide compound is hydrophilicized by incorporating methyl glycolate or methyl lactate, which serves a moiety similar to the moiety which aqueous urethane resin, aqueous acrylic resin, or the like possesses, into an end of a starting carbodiimide compound. The invention provides a carbodiimide compound and a carbodiimide composition, which, when added as a cross-linking agent to aqueous resin, can enhance water resistance, solvent resistance, and adhesion of the resin, while maintaining the conventionally attained pot life, and an aqueous coating composition containing the carbodiimide compound or composition.
Owner:HISSHINBO HOLDINGS INC
Neutral blocking remover composition for oilfield oil extraction and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104293333AImprove plugging efficiencyRestore permeabilityDrilling compositionButanedioic acidMethyl lactate
The invention relates to a neutral blocking remover composition for oilfield oil extraction, which is prepared from the following components in parts by weight: 30-35 parts of acrylic acid-methyl acrylate copolymer, 44-50 parts of diethylene triamine pentaacetic acid, 30-35 parts of sodium polyepoxysuccinate, 30-35 parts of amine malate, 10-14 parts of sodium alkyl sulfonate, 5-8 parts of amine hydroxy ethylidene diphosphate, 10-14 parts of hydrolyzed polyacrylamide, 12-17 parts of atlapulgite, 20-25 parts of sodium persulfate, 7-10 parts of sodium lignosulfonate, 5-8 parts of tannin, 12-16 parts of sodium malate, 5-8 parts of sodium sulfosuccinate, 5-8 parts of starch, 9-12 parts of methyl lactate, 0.2-0.3 part of vanadium pentoxide and 0.1-0.3 part of diisobutyl carbinol. The neutral blocking remover composition for oilfield oil extraction has the advantages of high blocking removal speed, no corrosivity due to neutrality and no dead area, can quickly dissolve the material scales, clean the oilfield stratum and remove blocking, and does not generate the phenomenon of precipitation or secondary blocking; and the cleaning waste liquid does not need to be subjected to sewage treatment after returning to the ground.
Owner:兰州熙瑞化工科技有限公司
Mint-flavored nicotine liquid and electronic cigarette with same
InactiveCN104489900AUnique mint natural aromaUnique cool tasteTobacco treatmentTobacco devicesBiotechnologyMentha spicata extract
The invention belongs to the field of electronic cigarettes and particularly relates to mint-flavored nicotine liquid and an electronic cigarette with the same. The mint-flavored nicotine liquid is made from, by weight, 5% to 10% of mint extract, 0.5% to 2% of nicotine, 0.15% to 0.6% of methyl lactate, 0.02% to 0.06% of eucalyptus oil, 0.02% to 0.06% of lemon oil, 0.06% to 0.16% of spice mix, 3% to 11% of ethyl alcohol, 3% to 5% of deionized water, 10% to 13% of glycerol, and the balance of propanediol. The mint-flavored nicotine liquid has the unique natural flavor and coolness of mint; the mint-flavored nicotine liquid has the smoking effect similar to that of the traditional mint cigarettes. The mint-flavored nicotine liquid produces no tar and CO and causes no mint-flavored nicotine liquid damage, and harm to consumers is greatly decreased.
Owner:CHINA TOBACCO ZHEJIANG IND
Method for fine purification of lactic acid
InactiveCN101492367AHigh esterification rateAchieve complete esterificationOrganic compound preparationChemical industryHigh energyReboiler
The invention relates to a method for refining lactic acid by cation resin column bed catalysis and reactive rectification technology. The method solves the problems that the traditional esterification-hydrolysis technology uses concentrated sulfuric acid as a catalyst, thereby causing the environmental pollution, and high energy consumption, etc. Crude lactic acid after the pretreatment and concentration is subjected to the esterification reaction with methanol or ethanol by a cation resin column; then a mixture after the esterification reaction is subjected to reduced pressure distillation to obtain a mixture A of methyl lactate or ethyl ester, the methanol or the ethanol, water and the like and a distillation residue B; and B is mixed with the methanol or the ethanol and introduced into the cation resin column to take the esterification reaction. Subsequently, A is mixed with deionized water and introduced into the other cation resin column to be hydrolyzed to obtain a hydrolysis mixture C. The hydrolysis mixture C is introduced into a reaction rectifying tower to continue hydrolysis, the methanol or the ethanol is eluted from the top of the tower, lactic acid aqueous solution is obtained from a reboiler, and a high purity lactic acid product is obtained after concentration and can reach (Chinese and American) pharmacopoeia grade standard.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Method for preparing ester by catalytic oxidization of 1,3-propanediol
InactiveCN101906038AHigh selectivityEasy to separate and purifyMolecular sieve catalystsOrganic compound preparation3-Hydroxypropionic acidGas phase
The invention discloses a method for preparing an ester by catalytic oxidization of 1,3-propanediol. The catalyst adopted is a supported noble metal catalyst (gold or palladium); a carrier is made from metal oxides of different shapes and sizes or mixed oxides (such as CeO2, gamma-Al2O3, CuO, MgO, ZnO, ZSM-5, MoO3, V2O5 and the like), or a silicon dioxide-containing material or a carbon material; after the catalyst is treated by different preparation and treatment methods, the selective oxidization reaction of the 1,3-propanediol for preparing 3-methyl lactate, dimethyl malenate, 3-methoxypropionate and methyl acrylate is performed under a mild liquid-phase or liquid- and gas-phase reaction condition. The highest yield of the produced 3-methyl lactate is 81.5 percent (the conversion rate is 97.0 percent and the selectivity is 84.0 percent); the highest yield of the produced dimethyl malenate is 58.2 percent ( the conversion rate is 99.6 percent and the selectivity is 58.4 percent); and the highest yield of produced 3-methoxypropionate is 53.0 percent (the conversion rate is 97.0 percent and the selectivity is 58.4 percent) and the highest yield of produced methyl acrylate is 38.4 percent (the conversion rate is 92.2 percent and the selectivity is 41.6 percent).
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
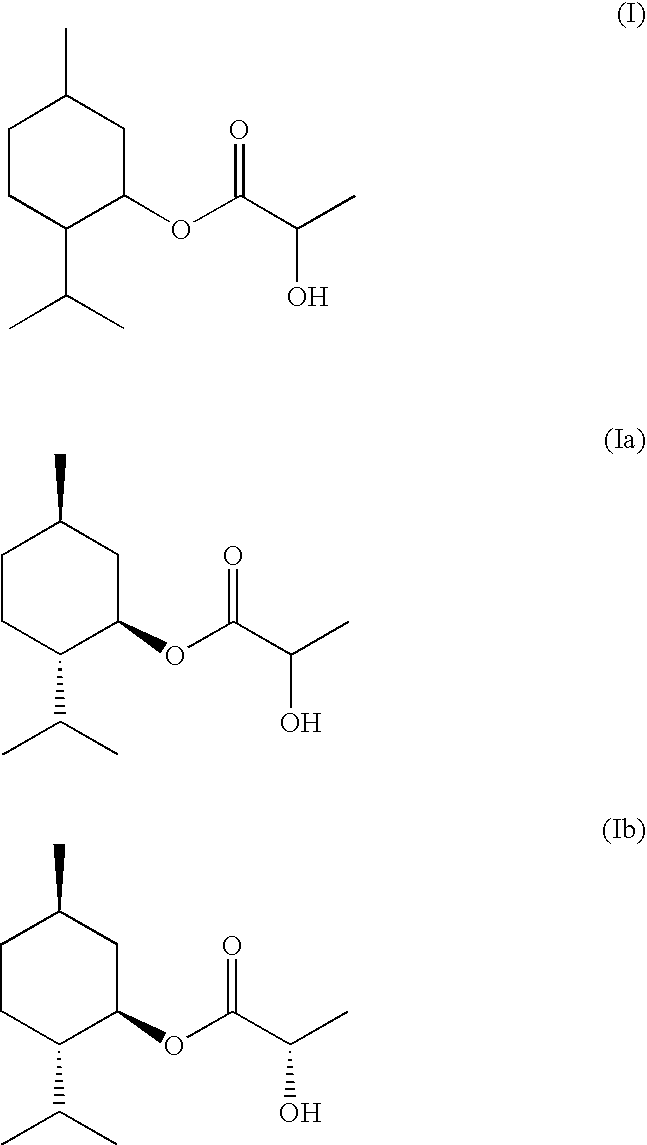
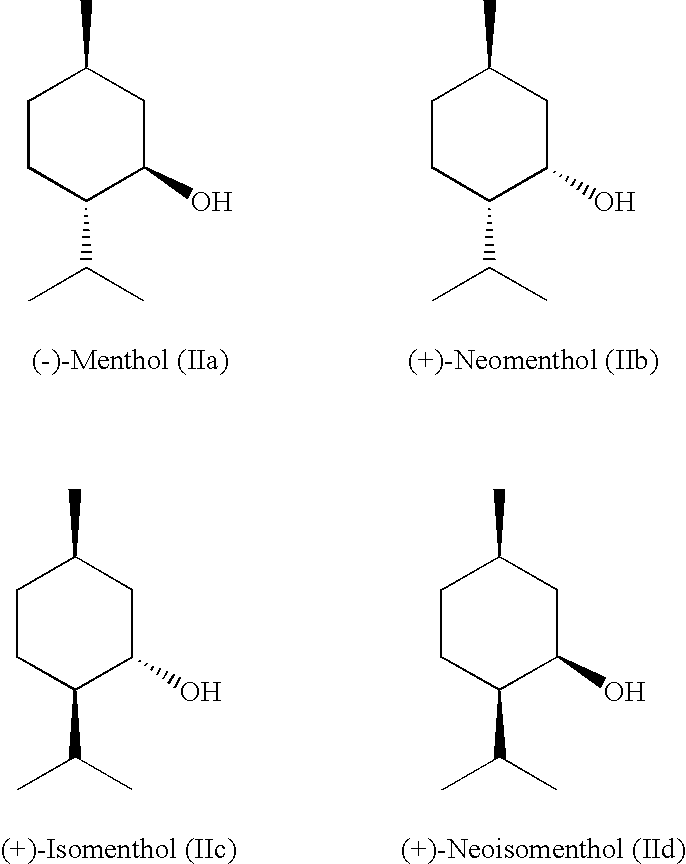
Composition of Menthyl Lactate and a Mixture of Menthol Isomers
InactiveUS20080085247A1Small smellStrong overall senseCosmetic preparationsBiocideMethyl lactateMedicinal chemistry
Described is a composition (i) comprising or (ii) essentially consisting of or (iii) consisting of (a) methyl lactate, (b) neomenthol, and (c) menthol, and optionally (d) neoisomenthol and / or (e) isomenthol, wherein said composition has a solidification point below +5° C.
Owner:SYMRISE GMBH & CO KG
Novel method for synthesis of (S)-propisochlor
ActiveCN101367746ALow costMild responseOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid amides preparationMethyl lactateAniline
The present invention relates to a novel method of synthesizing (S)-metolachlor, and discloses a complete synthesis route which adopts chiron. In the novel method, (D)-methyl lactate or (D)-ethyl lactate is used as a raw material and reacts with p-toluenesulfonyl chloride to generate (R)-2-(p-tolylsulfonyl oxyl) propionate; the (R)-2-(p-tolylsulfonyl oxyl) propionate reacts with 2-methyl-6-ethyl aniline to prepare S-(-)-N-(2-methyl-6-ethyl benzyl) alanine ester; the S-(-)-N-(2-methyl-6-ethyl benzyl) alanine ester reacts with a reducing agent C to prepare S-(-)-N- (1'-methyl-2'-ethylol)-2-methyl-6-ethyl aniline; and the S-(-)-N- (1'-methyl-2'-ethylol)-2-methyl-6-ethyl aniline is acylated with chloroacetic chloride and ultimately methylated to prepare the (S)-metolachlor. The present invention has the advantages that no resolution is required in the whole process, the reaction is mild, the yield rate is high, the optical purity is good, the reaction time is short, the raw materials are inexpensive and can be easily acquired, and the cost is low.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH +1
New thioxanthone carboxylic ester photoinitiator and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104910131AOvercome the weakness of poor transesterification activityMild reaction conditionsOrganic chemistryTrans esterificationAlkoxy group
The invention discloses a new thioxanthone carboxylic ester photoinitiator and a preparation method thereof. The invention relates to a preparation method of thioxanthone carboxylic ester. The thioxanthone carboxylic ester is a compound with the structure of a formula (I) as shown in the specification, wherein the carboxylic ester substituent group of the thioxanthone is at position 2 and position 4; each R1 is independently selected from hydrogen, halogen, C1-C12 alkyl, C3-C6 naphthenic base and C1-C12 alkoxy; each of R2 and R3 is independently selected from hydrogen, halogen, C1-C18 alkyl, C3-C6 naphthenic base and C1-C18 alkoxy; X is independently selected from multi-hydroxyl micromolecular compound (wherein the hydroxyl number is 2-6) and C1-C18 alkoxy; and m is 1-6. The preparation method overcomes the defect that the generally used thioxanthone carboxylic ester has low ester exchange activity by introducing a methyl lactate group and improving the condition of ester exchange reaction; the reaction condition is mild and ester exchange can be finished in a short time; and the preparation method is suitable for industrialized production.
Owner:TIANJIN JIURI NEW MATERIALS CO LTD
Preparation method for immobilized Lewis acid
InactiveCN103464196AWide applicabilitySolve the problem of immobilized Lewis preparationSugar derivativesMolecular sieve catalystsMolecular sieveFructose
The invention discloses a preparation method for immobilized Lewis acid, belonging to the field of catalysis in organic synthesis. The immobilized Lewis acid referred to in the invention comprises Sn-Beta, Ti-Beta, In-Beta, Cu-Beta, Zn-Beta, Cr-Beta, etc. Solid acid with activity of Lewis acid is prepared by reacting a salt solution of a metal with a dealuminated molecular sieve and then carrying out sintering. The invention has the following advantages: raw materials are cheap and easily available, a generation period is short, the preparation method has high yield, the immobilized Lewis acid is easy to separate, reaction conditions are simple, and the immobilized Lewis acid can be extensively applied in the Baeyer-Villiger oxidation reaction, a reaction for preparation of methyl lactate from 1,3-dioxyacetone or a reaction for preparation of fructose from glucose.
Owner:GUANGZHOU CHEM CO LTD CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
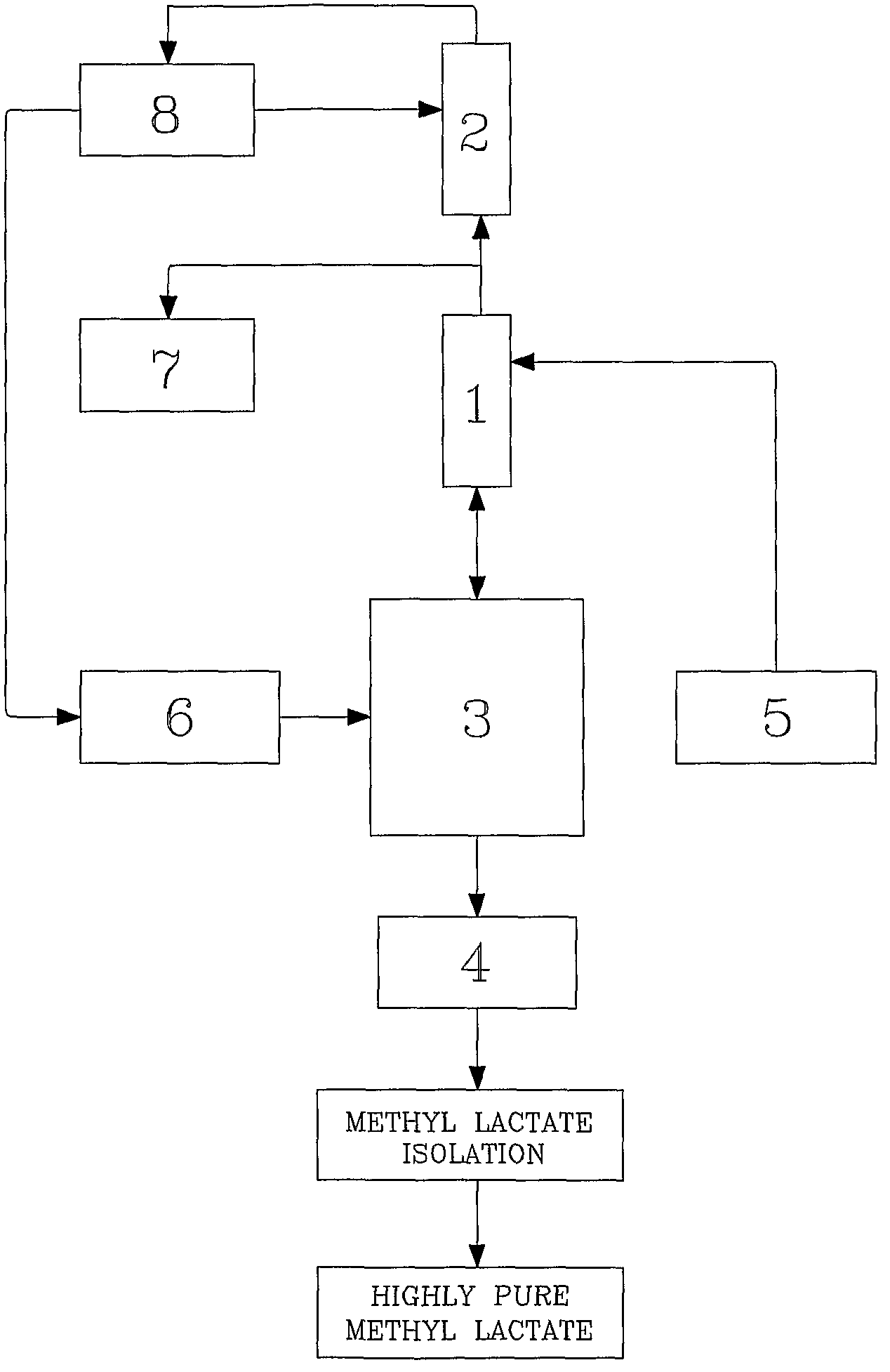
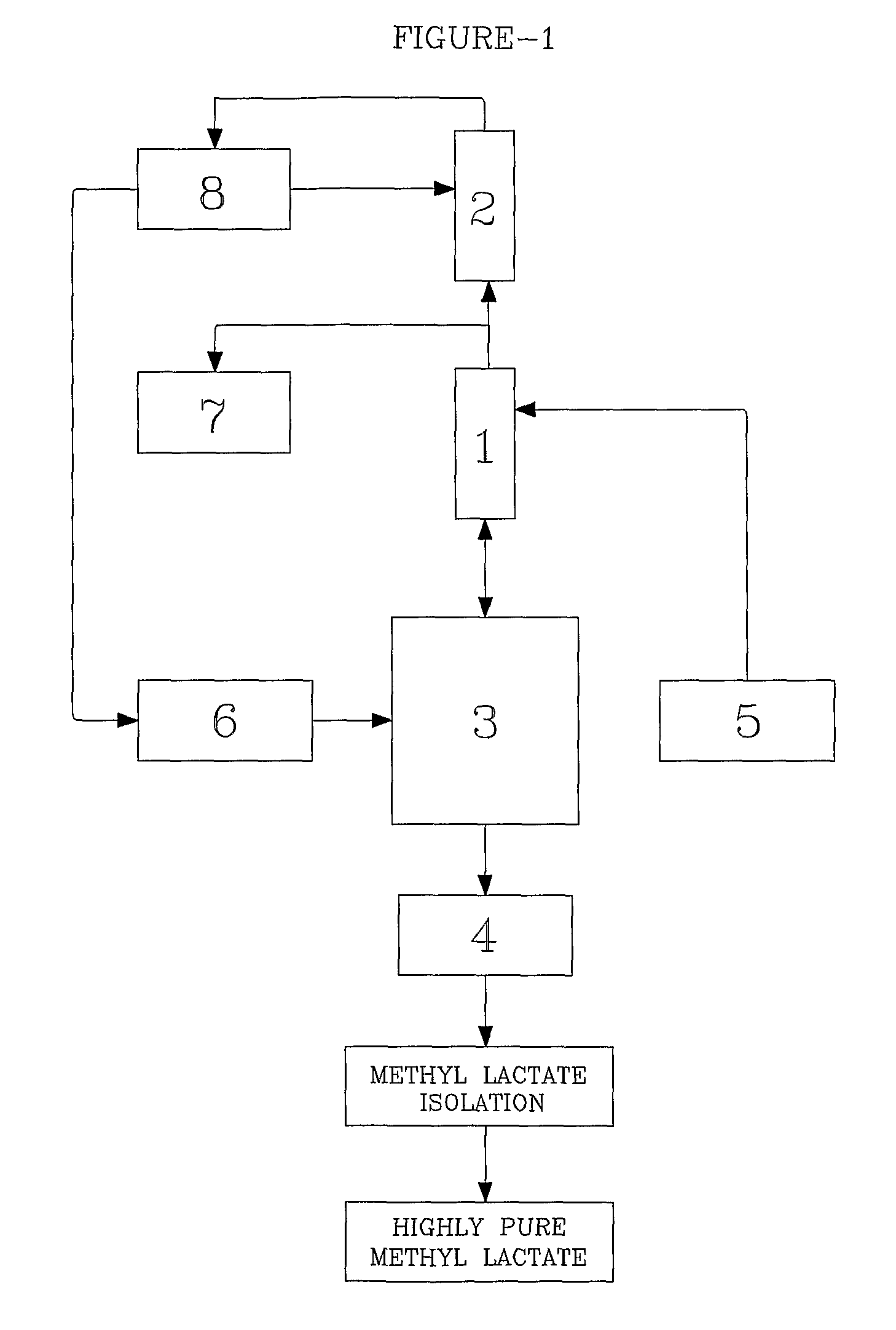
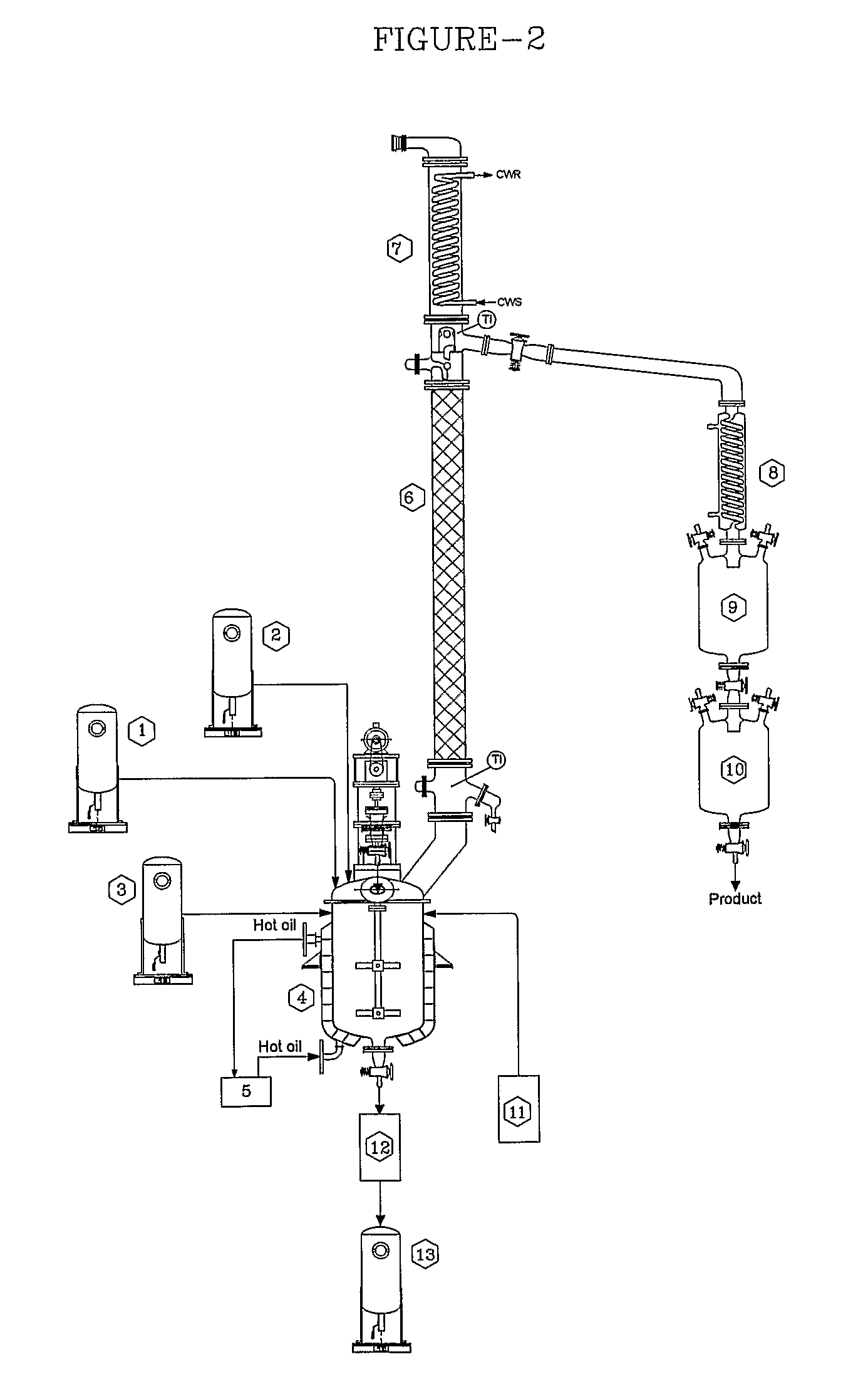
Method for producing methyl lactate with high content and high optical purity in two steps
ActiveCN101914022AReduce moisture contentConfiguration flipPreparation by ester-hydroxy reactionDepolymerizationOligomer
The invention relates to a method for producing methyl lactate with high content and high optical purity from lactide and methanol through ester exchange reaction in two steps. The method comprises the following steps of: adding a catalyst to a lactic acid to carry out polycondensation reaction to obtain the lactate oligomer with the molecular weight of 1,000-2,500; adding a catalyst to the lactate oligmer to carry out depolymerization reaction to obtain the crude lactide; refining the lactide, and carrying out full-reflux reaction on the refined lactide and the absolute methanol to obtain the methyl lactate. The process is simple, the content of synthesized methyl lactate is more than 99.5%, and the optical purity can achieve more than 99%.
Owner:XIAOGAN ESUN NEW MATERIAL
Method for catalytic alcoholysis of PLA (Polylactic Acid) by CaO/MCF (Mesocellular silica Foam) mesoporous basic molecular sieve
ActiveCN107382718ALarge hole volumeLarge and adjustable apertureMolecular sieve catalystsPreparation by ester-hydroxy reactionMolecular sieveDistillation
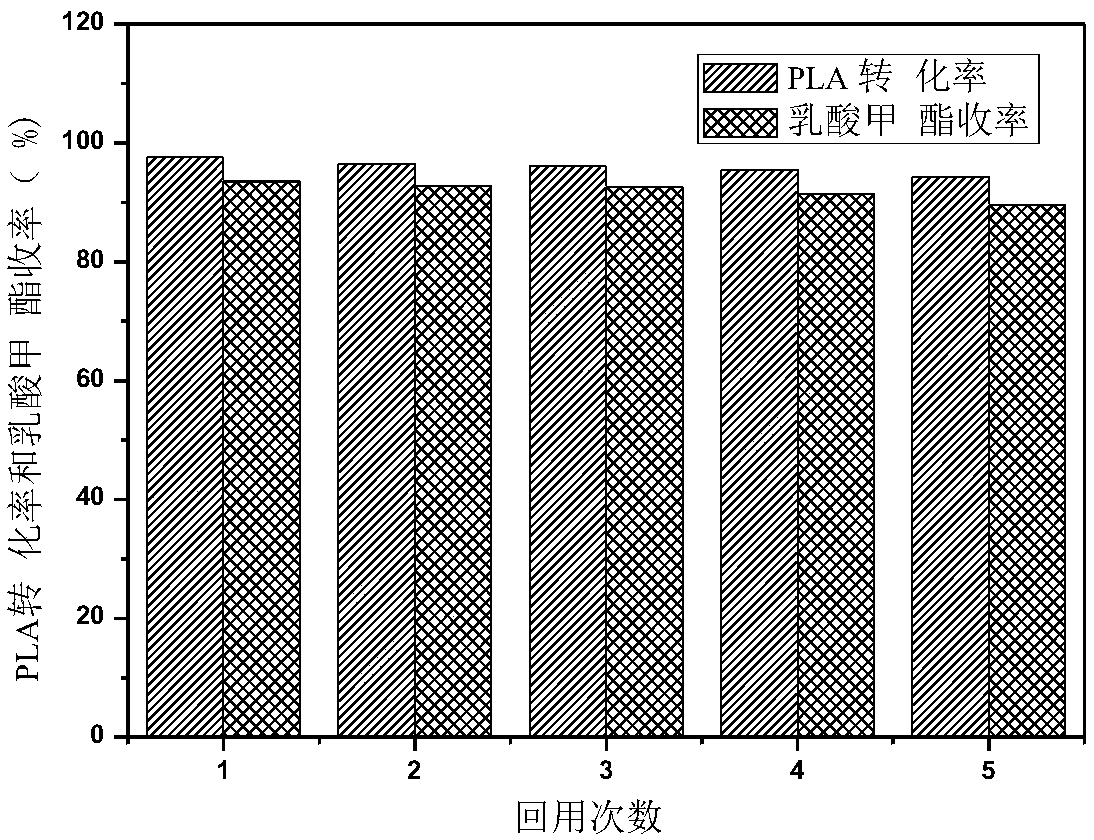
The invention discloses a method for the catalytic alcoholysis of (Polylactic Acid PLA) by a CaO / MCF (Mesocellular silica Foam) mesoporous basic molecular sieve, and belongs to the technical field of the high-value conversion of waste resources. The method is a reaction of degrading the PLA by using the CaO / MCF mesoporous basic molecular sieve as a catalyst and methanol as a reactant; after the reaction is finished, a methyl lactate product is recovered through operations of filtration, distillation and the like; the alcoholysis rate of the PLA can reach 98 percent or above; the selectivity of the product methyl lactate can reach 90 percent or above. According to the method, CaO / MCF is used as the catalyst; the methanol is used as a reactive raw material; a reaction condition is mild; a reaction method is simple; the price of the raw material is low; a process of recovering the product is simple; the catalyst can be repeatedly utilized; the degradation efficiency is high; the cost of degrading the PLA can be greatly industrially decreased; the method is actually an economical and effective way, and is worth popularizing.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Purification method of lactic acid ester
ActiveCN101456812AHigh purityReduce hydrolysisPreparation by ester-hydroxy reactionDepolymerizationPurification methods
The invention discloses a method for purifying lactate. The method comprises: dissolving the lactate containing dimer and polymer in a solvent of lower alcohol, adding a catalytic amount of alkali, carrying out the ester exchange reaction at a temperature of between 0 and 80 DEG C, converting the dimer or polymer into lactate products and methyl lactate or ethyl lactate, and adding acid for neutralization or adopting cation resin for ion exchange so as to neutralize the reaction product; and recovering the solvent, and obtaining the finished product by recrystallization or reduced pressure distillation. The method has the advantages that the method can effectively lower hydrolysis of the lactate simultaneously carried out during depolymerization of the dimer or polymer in the purificationprocess, the reaction can be carried out at normal temperature, and the production cost can be effectively lowered, along with simple operation, safety and high efficiency; moreover, the purity of the obtained target product reaches more than 98 percent, so that the method has industrial application values.
Owner:南京枫华投资管理有限公司
Second-stage reaction process for preparing propenoic acid or ester from lactic acid or ester
InactiveCN101306990AOrganic compound preparationCatalyst regeneration/reactivationSodium phosphatesFixed bed
The invention relates to a two-section reaction method for preparing acrylic acid or propylene ester by lactic acid or lactic ester, belonging to the biological matrix chemical product field. A two-stage vertical type fixed bed reactor is adopted; a front part of an upper-section reactor is connected with a material carburetor; a lower-section reactor is connected with a gas-liquid separator; catalyzers A,B,C and D are adopted, wherein, the catalyzer A is an X-type molecular sieve; a NaY-type molecular sieve is roasted, subject to ion exchange by a potassium nitrate solution to prepare the catalyzer B; a nitrate solution and sodium phosphate are used to prepare phosphate as the catalyzer C; and a mixture of CaSO4 and CuSO4 and phosphate are mixed to prepare the catalyzer D; the catalyzer A or B is positioned in the upper-section reactor; the catalyzer C or D is positioned in the lower-section reactor; air in the reactors is exhausted by nitrogen; the nitrogen flow speed is between 5 and 100 ml / min; the temperature of the carburetor is 235 DEG C; the upper-section reaction temperature is between 275 and 350 DEG C; the lower-section reaction temperature is between 350 and 450 DEG C; and a condensed liquid of the gas-liquid separator is kept at a temperature of 2 DEG C; after the temperature is stabilized, raw material is pumped to the carburetor; the raw material is an aqueous solution of the ethyl lactate and the methyl lactate or a lactic acid aqueous solution added with a polymerization inhibitor of 0.5 percent of the raw material mass; and the sampling speed of the raw material is between 0.5 and 2 ml / h. The method develops the advantages of different catalyzers and improves the selectivity of a target product.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
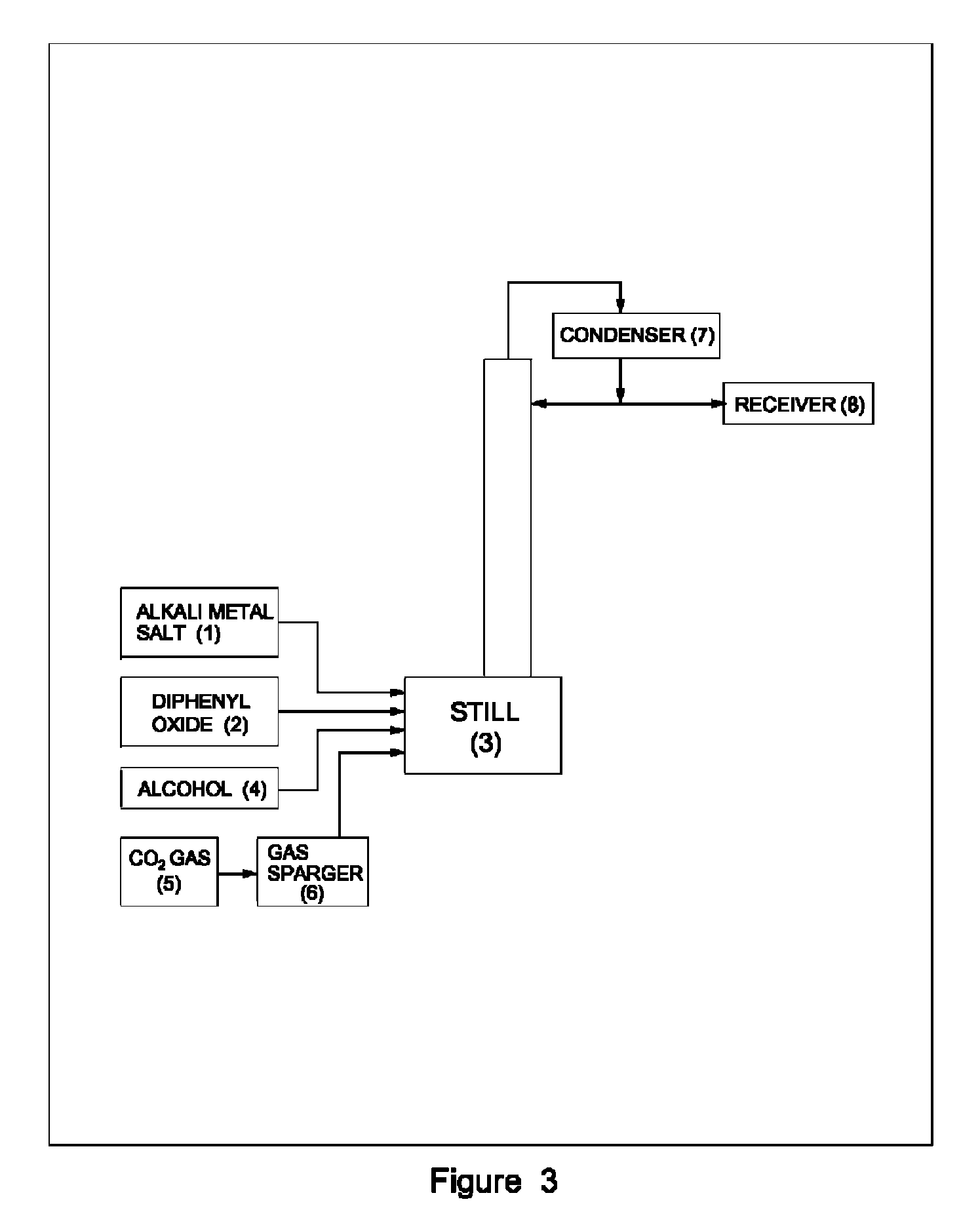
Process for preparation of pure alkyl esters from alkali metal salt of carboxylic acid
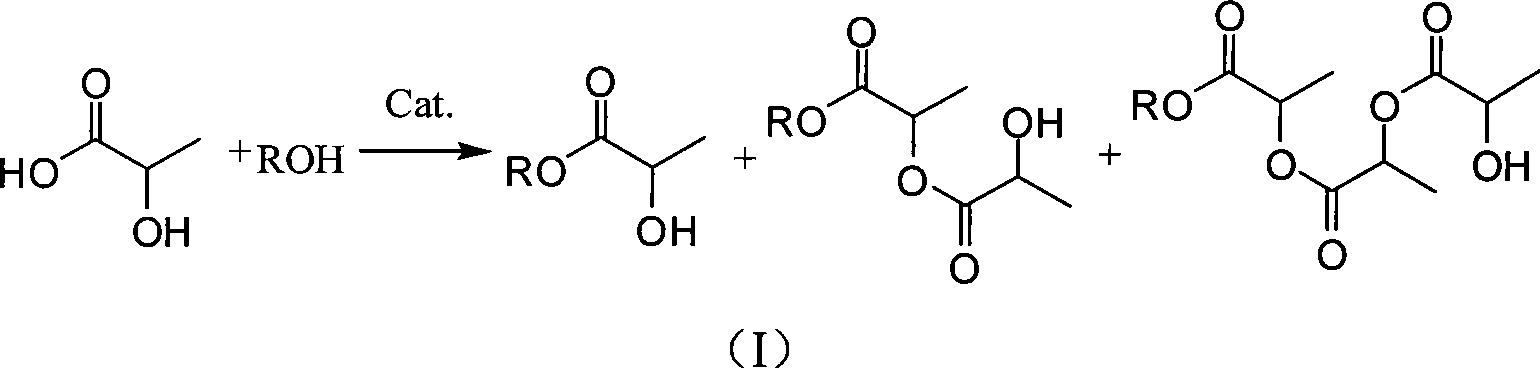
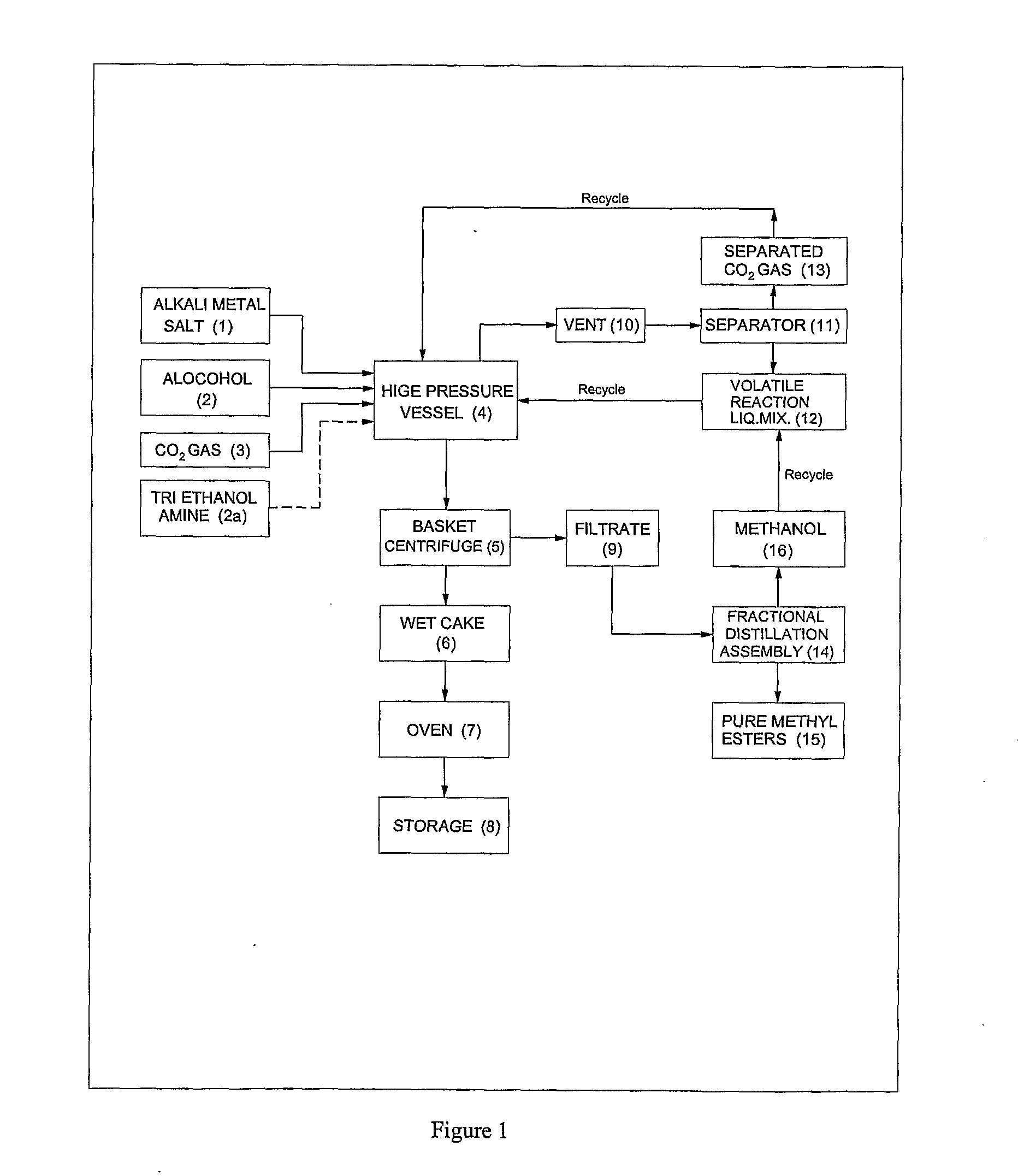
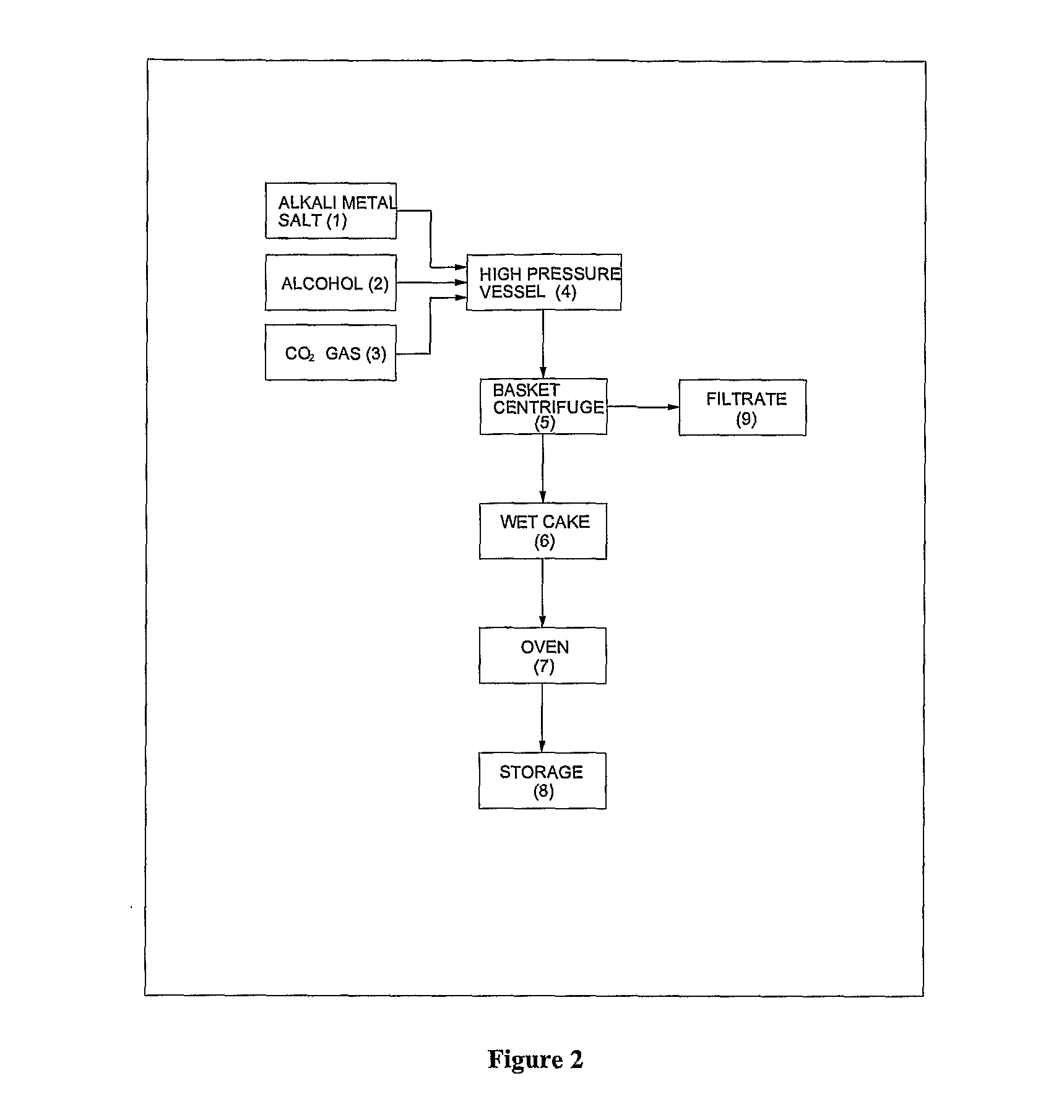
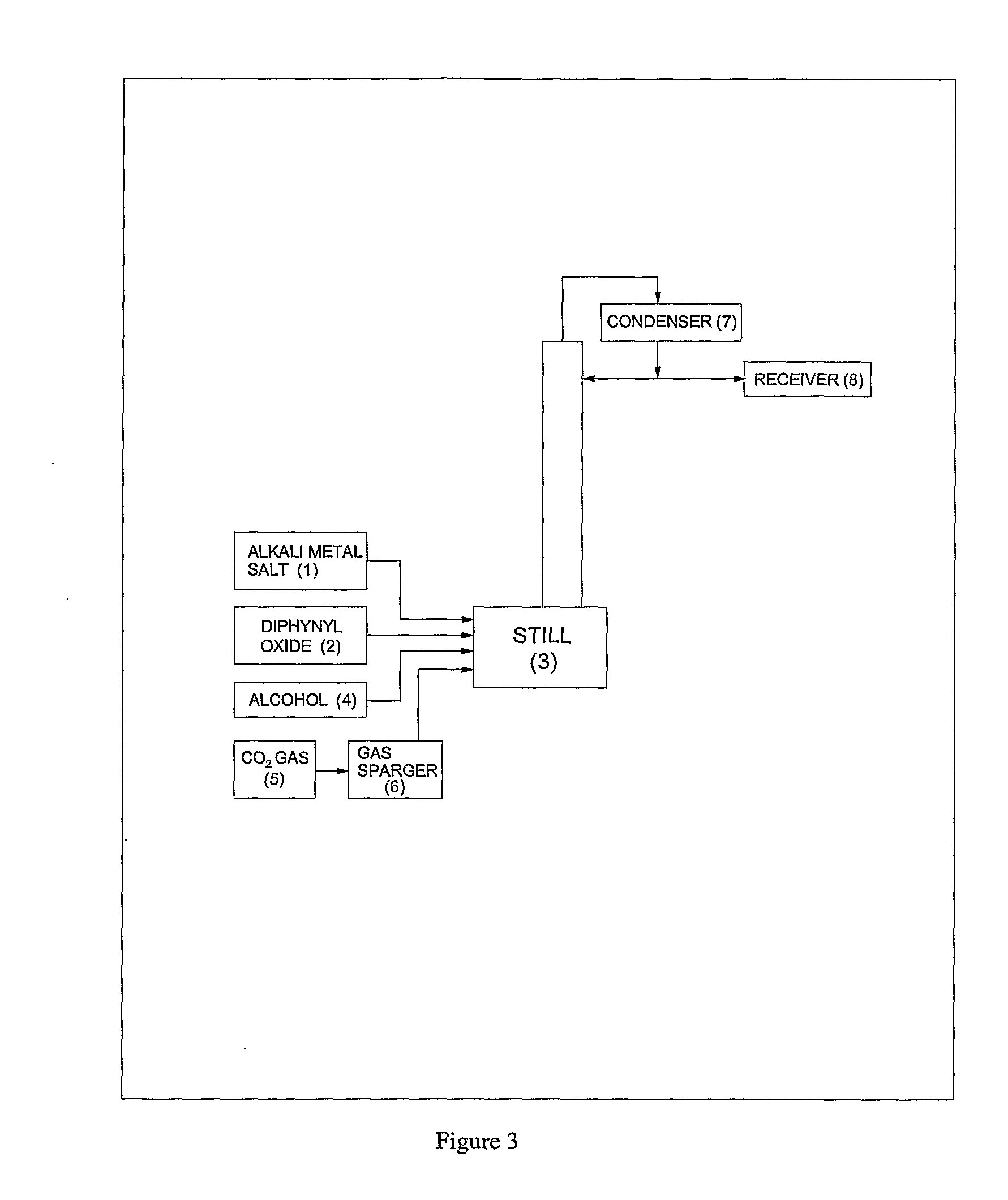
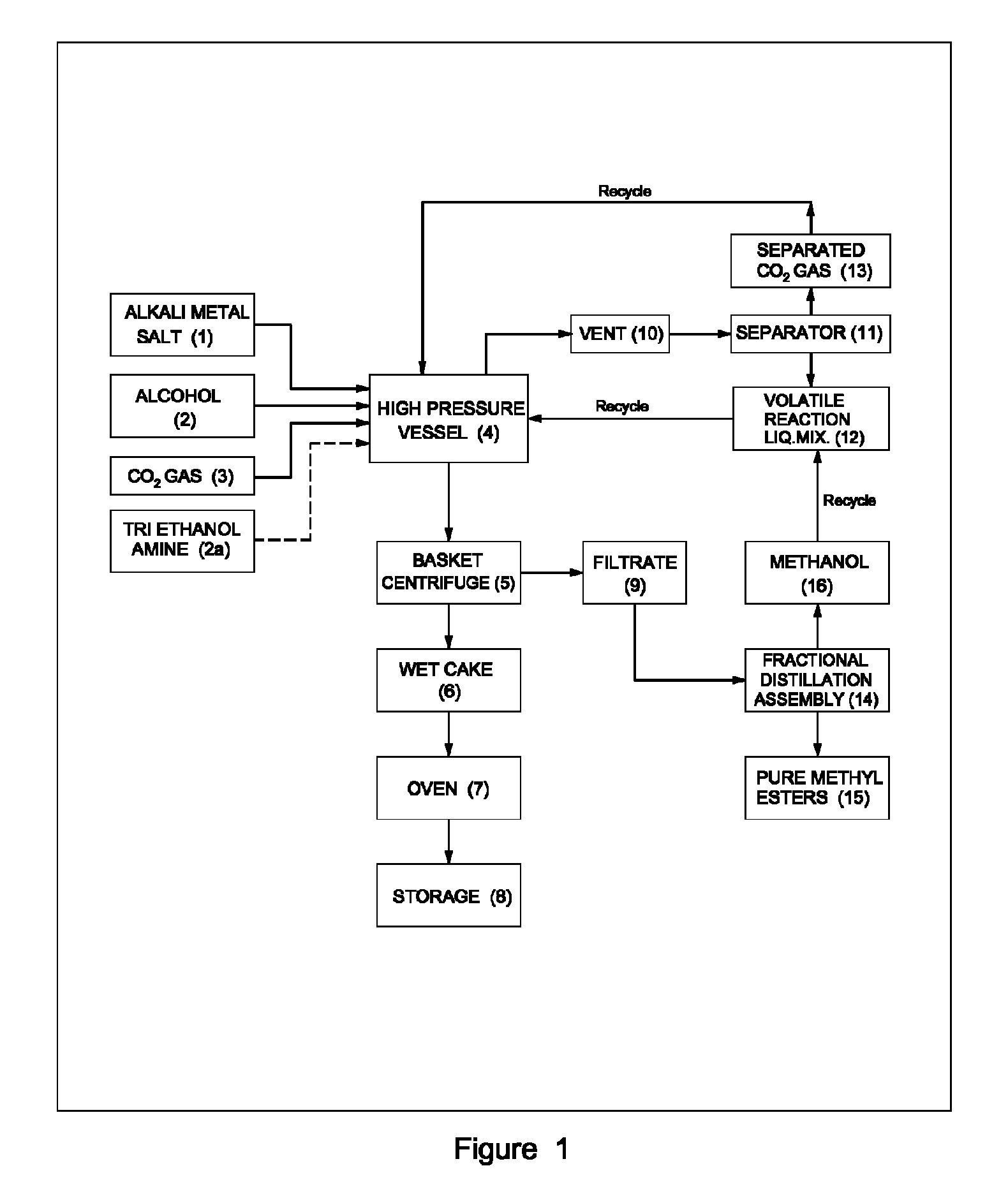
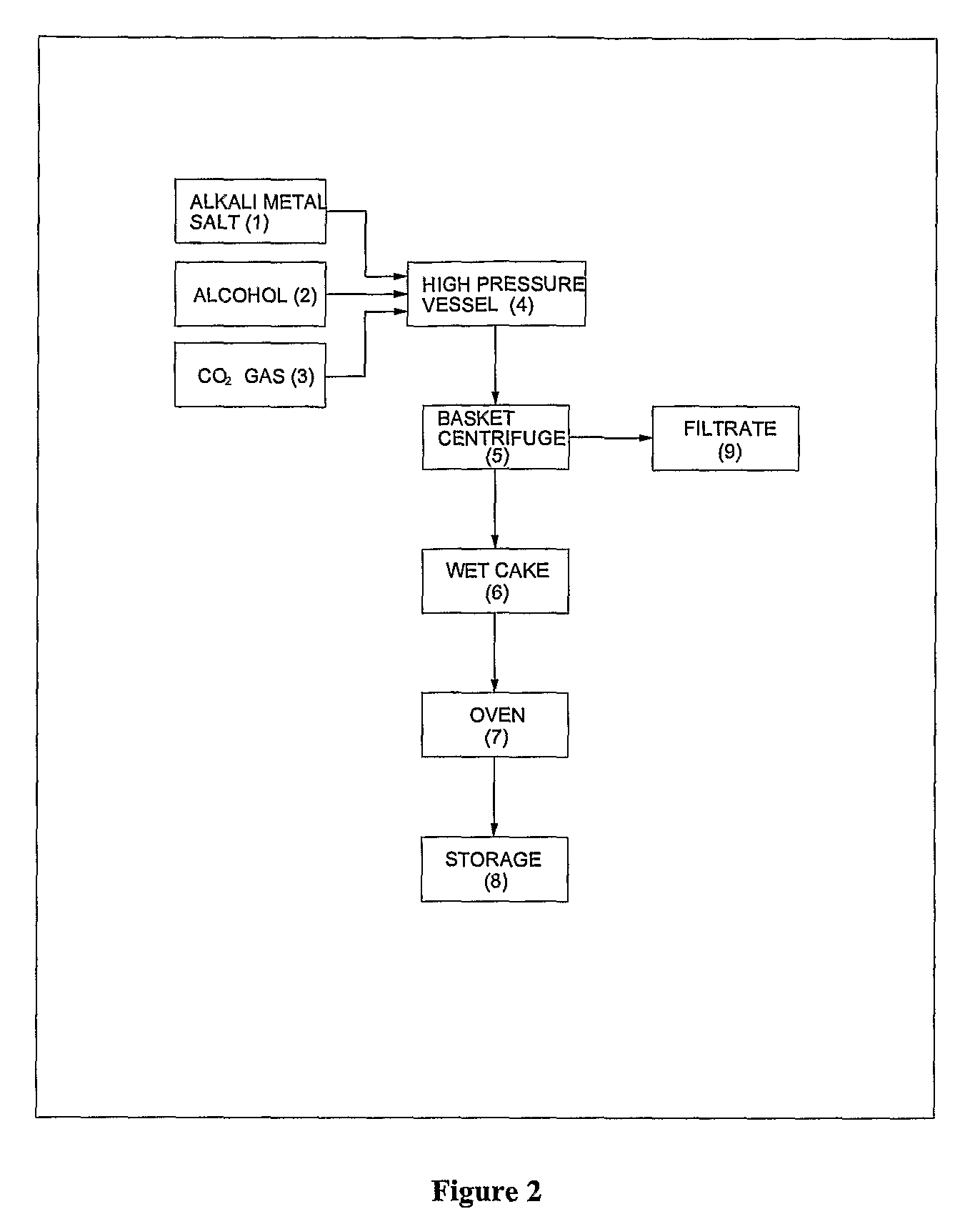
ActiveUS20120296110A1Organic compound preparationOrganic chemistry methodsSodium acetateSodium lactate
The dehydrated alkali metal salts of carboxylic acid are dissolved in the alcohol such as methanol or ethanol or butanol to make their solution in corresponding alcohol. The solution alcohol is further treated with carbon dioxide under pressure or at atmospheric pressure at elevated temperature such as 150 to 200° C. The carboxylic acid gets converted into corresponding alkyl ester and calcium carbonate or sodium carbonate or potassium carbonate as the byproduct. Calcium lactate or Sodium lactate or Sodium acetate or Sodium benzoate or Sodium salicylate as alkali metal salt solution prepared in Methanol or Ethanol or Butanol when treated with carbon di-oxide under pressure or at atmospheric pressure at elevated temperature gets converted to Methyl lactate or Ethyl lactate or Methyl acetate or Methyl benzoate or Methyl salicylate as product.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Synthesis method of high-purity D-2-chloropropionyl chloride
ActiveCN103408416ALower requirementOperational securityOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic compound preparationSynthesis methodsMethyl lactate
The invention provides a synthesis method of high-purity D-2-chloropropionyl chloride. A process path of chlorination, hydrolysis and chloroacylation of L-methyl lactate is adopted. Specifically, the synthesis method sequentially comprises the following steps: (1) the synthesis of D-methyl-2-chloropropionate: dropwise adding thionyl chloride into the mixed solution of the L-methyl lactate and pyridine, carrying out vacuum stirring, increasing the temperature to 55-90 DEG C, reacting for 1-5h, reducing the temperature to 25-35 DEG C, exhausting air, washing and separating, wherein the L-methyl lactate and the thionyl chloride are used as raw materials and the pyridine is used as a catalyst; (2) the synthesis of D-2-chloropropionic acid: hydrolyzing methyl-2-chloropropionate under the action of a sodium hydroxide solution, and carrying out chloroform extraction; and (3) the synthesis of D-2-chloropropionyl chloride: dropwise adding the thionyl chloride into the mixed solution of D-2-chloropropionic acid and the catalyst, increasing the temperature to 70-80 DEG C, reacting for 3-5 hours, and carrying out vacuum rectification to obtain a target product. The process path has the advantages that raw materials are easily available; synthesis steps are simple, safe and reliable; the waste gas generated in the production can be easily disposed; therefore, the process path is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:SHANDONG JINCHENG PHARMACEUTICAL GROUP CO LTD
Carbodiimide compound, carbodiimide composition and aqueous coating composition
ActiveUS8604154B2Improve adhesionNice appearanceIsocyanic acid derivatives preparationOrganic compound preparationCross-linkWater dispersible
A water-soluble or water-dispersible carbodiimide compound is hydrophilicized by incorporating methyl glycolate or methyl lactate, which serves a moiety similar to the moiety which aqueous urethane resin, aqueous acrylic resin, or the like possesses, into an end of a starting carbodiimide compound. The invention provides a carbodiimide compound and a carbodiimide composition, which, when added as a cross-linking agent to aqueous resin, can enhance water resistance, solvent resistance, and adhesion of the resin, while maintaining the conventionally attained pot life, and an aqueous coating composition containing the carbodiimide compound or composition.
Owner:HISSHINBO HOLDINGS INC
Method for preparing 1,3 propanediol by 3-methyl lactate
InactiveCN101993352AEasy to operateEasy to manufactureOrganic compound preparationHydroxy compound preparation3-Hydroxypropionic acidMethyl lactate
The invention discloses a method for preparing 1,3 propanediol by 3-methyl lactate. Under the presence of a reaction solvent, an activated solvent and a catalyst, 3-methyl lactate and hydrogen carries out hydrogenation, and active components of the catalyst can be oxides of Cu, Mn and Zr. The 1,3 propanediol is prepared by using the following methods: mixing Cu, Mn and Zr salt with water to obtain a solution with the total mass concentration of 10-20 percent; titrating and coprecipiting the solution and the alkali precipitator at 25 DEG C-90 DEG C while stirring; aging the precipitate for 2-20 hours at 40 DEG C-95 DEG C; washing, drying and baking for 2-6h at 300-900 DEG C; and pulverizing for over 200 meshes to obtain the catalyst, wherein the molar rate of Cu to Mn to Zr in Cu, Mn and Zr salt is 1 to (0.0.25-1.2) to (0.8-2), and the mass ratio of the alkali precipitator to the total mass of three monomers of Cu, Mn and Zr salt is 1 to (1-1.5). The invention is simple for operation, can be realized under the milder condition and can better inhibit the dehydration side reaction of beta-bit with hydroxide radicals.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF PETROCHEMICAL TECH
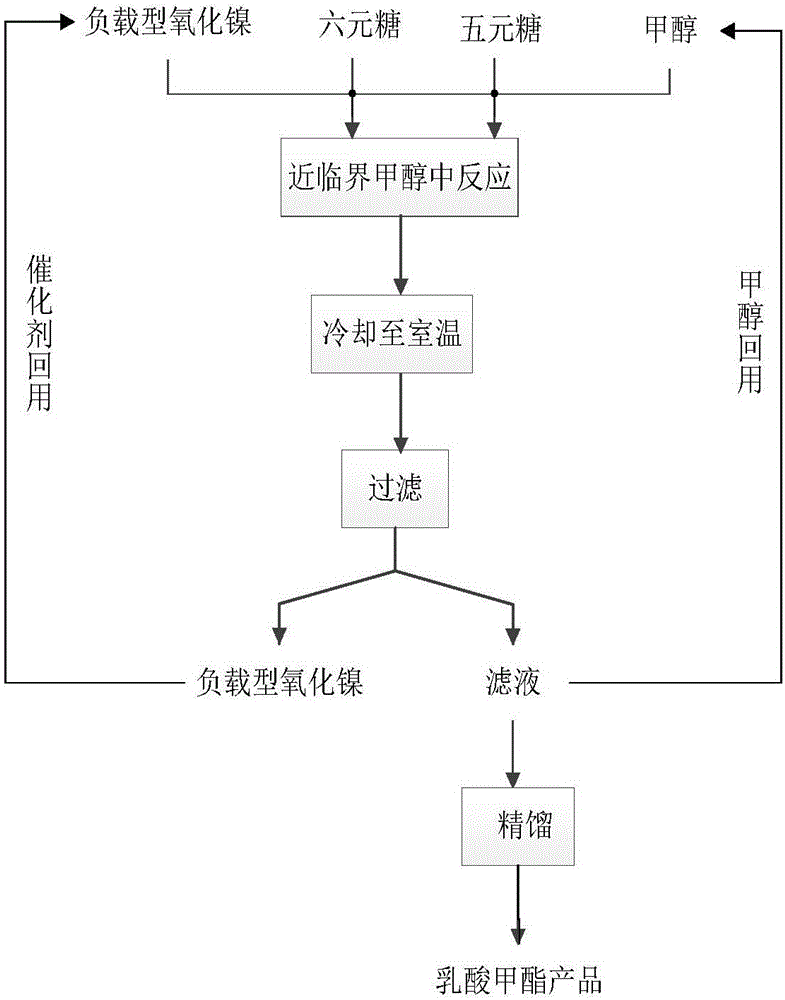
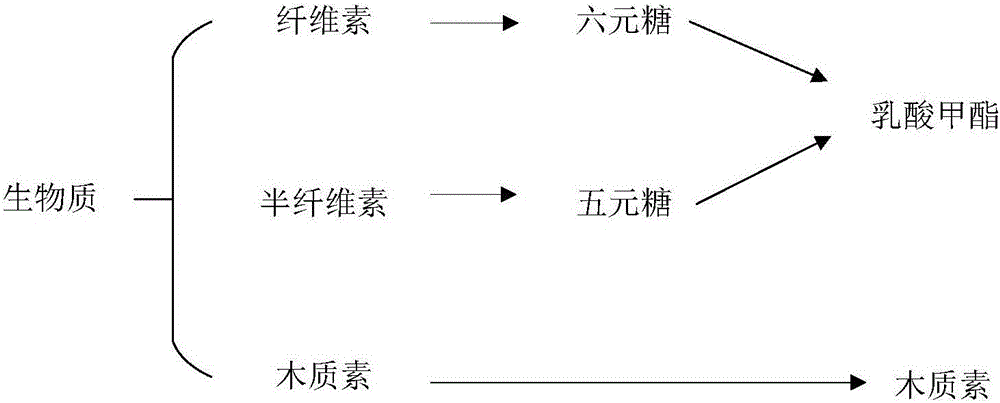
Method for preparing methyl lactate through supported nickel oxide catalyzed monosaccharide conversion in near critical methanol medium
ActiveCN105949053AHigh yieldIncrease profitOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationMethyl lactateSolvent
The invention discloses a method for preparing methyl lactate through supported nickel oxide catalyzed monosaccharide conversion in a near critical methanol medium. The method comprises the following steps: 1, adding monosaccharide, methanol and a supported nickel oxide catalyst to a high-temperature and high-pressure reaction kettle with a stirring function, wherein the monosaccharide is five-membered sugar, six-membered sugar or a five-membered sugar and six-membered sugar mixture; 2, starting stirring, heating above added materials to 140-240DEG C, and reacting the materials for 1-12h; and 3, cooling a material obtained after the reaction ends to room temperature, filtering the cooled material, rectifying the obtained filtrate to obtain a methyl lactate product and methanol for reuse, washing filter residues containing the catalyst with methanol, and drying the catalyst for reuse. The method for preparing methyl lactate through monosaccharide conversion has the advantages of high raw material utilization rate, high methyl lactate yield, and great reduction of the separation cost, low price and good reusability of the catalyst supported nickel oxide, good mass transfer performance of the near critical methanol used as a solvent and a reactant, greenness and good industrial application prospect.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Process for the preparation of 2-hydroxy carboxylic acids
InactiveUS20050143600A1Mild reaction conditionsOrganic compound preparationPreparation from carboxylic acid esters/lactonesPalladium catalystMethyl lactate
A two step preparation for hydroxy carboxylic acid (e.g. lactic acid) is disclosed. An enol ester (e.g. vinyl acetate) is carbonylated in the presence of a hydroxyl compound (e.g. methanol) using a palladium catalyst having one or more O-, N- and / or P-containing ligands (e.g. PdCl2(PPh3)2), and a solvent at 50-150° C. / 50-2000 psig to yield hydroxy ester (e.g. methyl lactate) and acetoxy ester (e.g. methyl-2-acetoxy propionate). The second step involves hydrolyzing the products of the carbonylation step using acid catalysts (e.g. TsOH, aq HCl, resin) at 10-125° C. to produce 2-hydroxy carboxylic acids (e.g. lactic acid). The carbonylation and hydrolysis catalysts may be separated and recycled.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Catalyst capable of performing alcoholysis on polylactic acid and method
ActiveCN108837847ALow costEasy to makePreparation by ester-hydroxy reactionOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsAlcoholMethyl lactate
The invention belongs to an alcoholysis reaction of polylactic acid and discloses a catalyst capable of catalyzing alcoholysis of polylactic acid to recover methyl lactate and a method. The method comprises the following steps: taking a deep-eutectic solvent ChClZn(OAc)2 as a catalyst, and carrying out an alcoholysis reaction between the polylactic acid and alcohol, thereby obtaining the lactate.According to the catalyst and method provided by the invention, the alcoholysis rate of the PLA and the yield of lactate can be effectively improved, and the catalyst is simple in synthetic method, low in cost, extremely less in usage amount and favorable for industrial production.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Process for preparation of pure alkyl esters from alkali metal salt of carboxylic acid
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Esterase PHE14 as well as encoding gene and application thereof
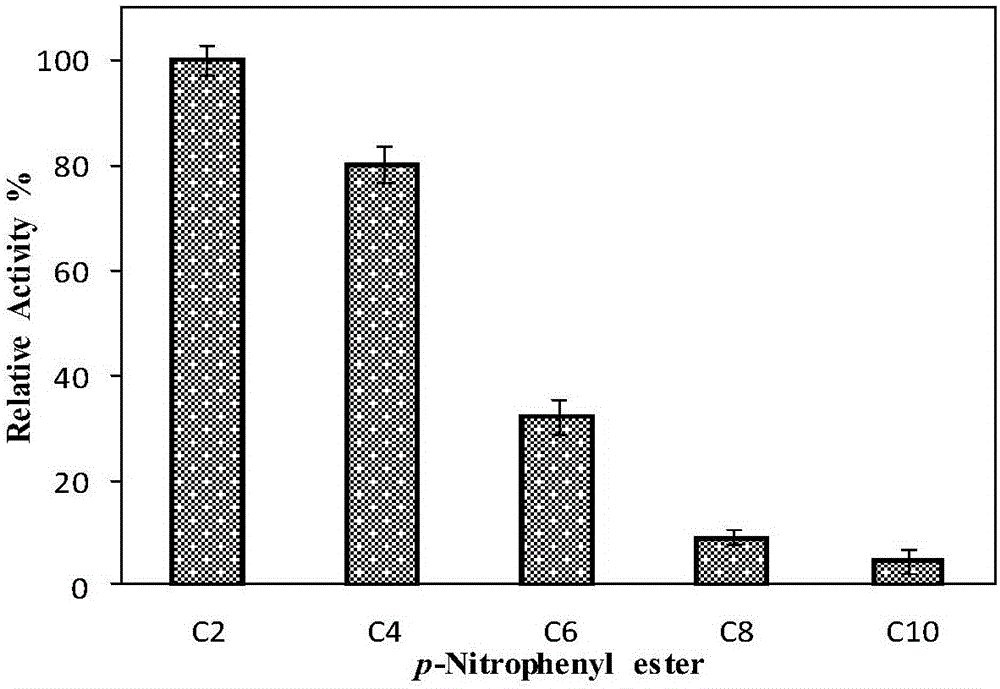
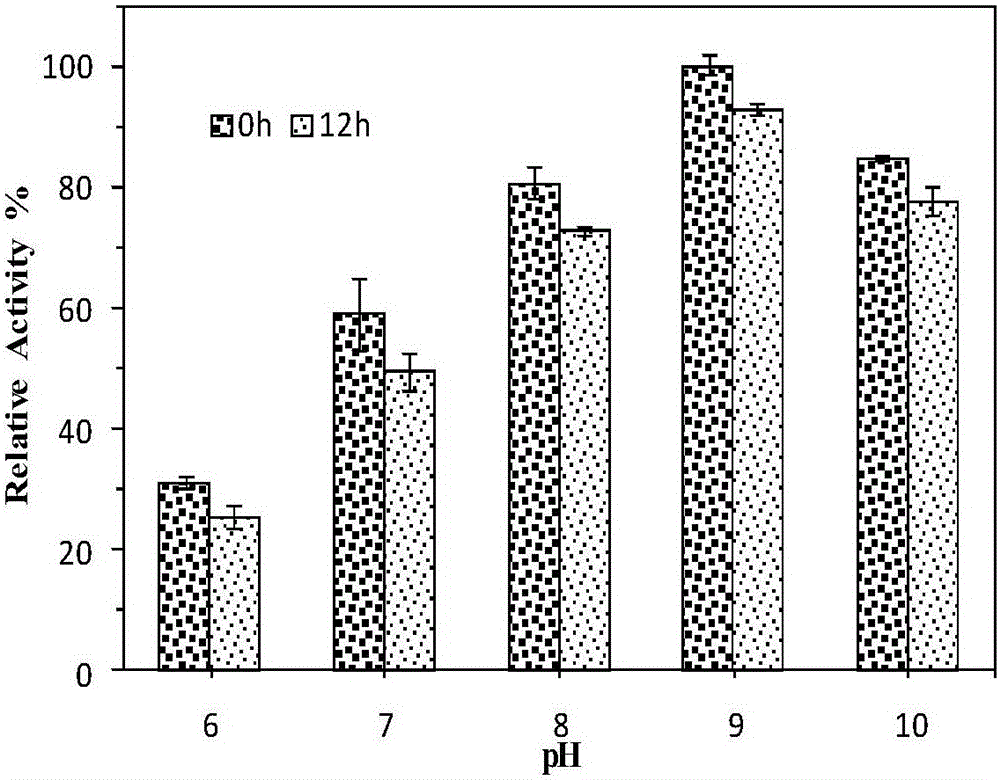
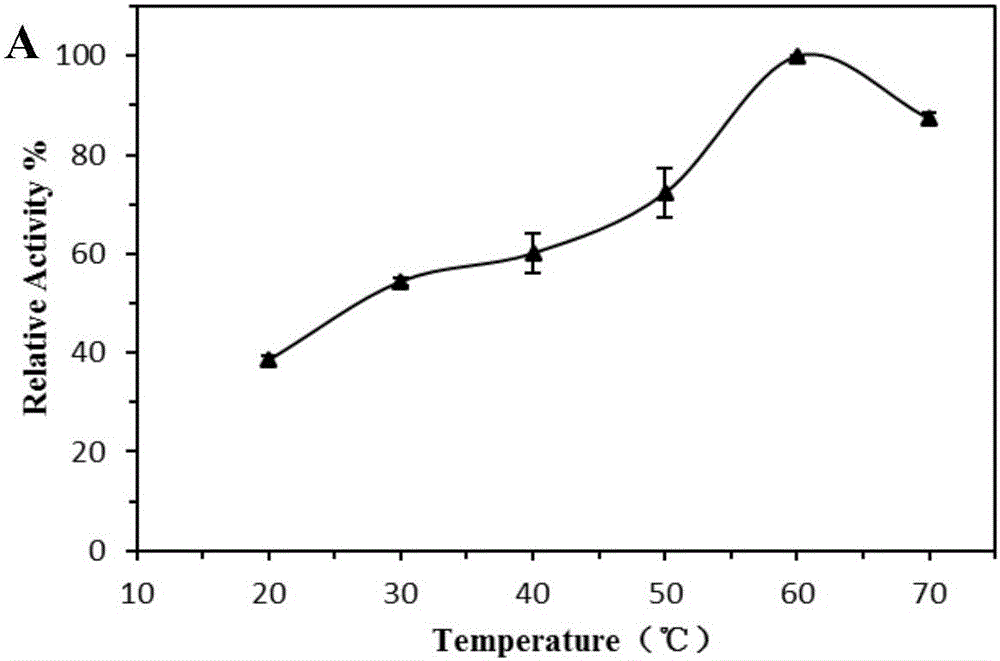
The invention discloses esterase PHE14 as well as an encoding gene and an application thereof. A novel enzyme gene PHE14 is developed from (Pseudomonadaceae oryzihabitans) HUP022, the whole length is 645bp, and the esterase PHE14 encoded by using the gene contains 214 amino acids. By cloning the esterase gene PHE14 and connecting the gene with an expression vector pET-28a (+) and converting escherichia coli BL21 (DE3), after culture and inducible expression, the recombinant expressed esterase PHE14 can be obtained. The esterase PHE14 can be used for preparing chiral methyl lactate, the esterase PHE14 of recombinant expression is taken as a catalyst, and (S)-methyl lactate of which the optical purity is greater than 99% can be prepared. The esterase PHE14 has very high application values in fields such as biochemical engineering and biological medicines.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
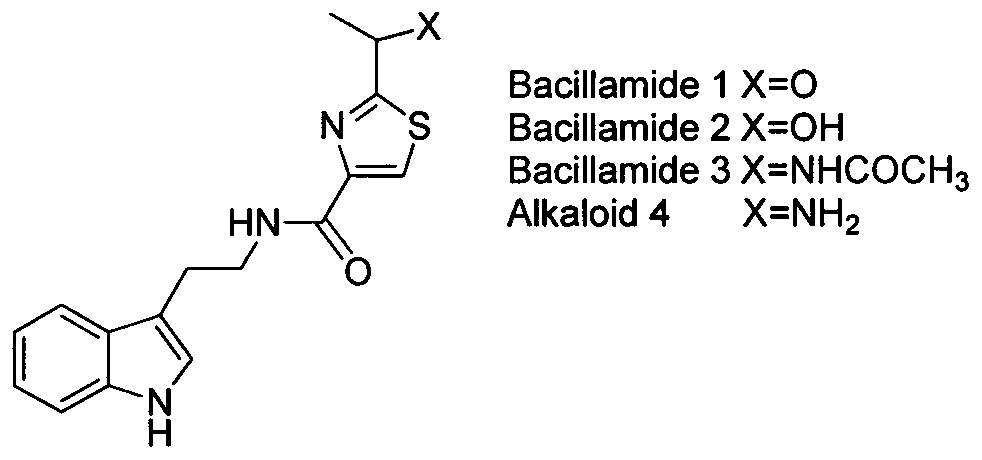
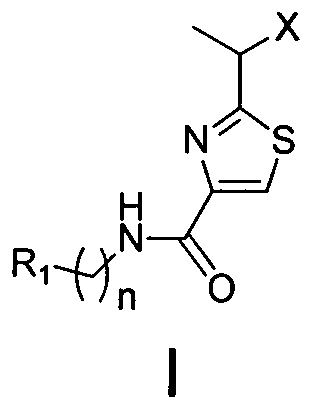
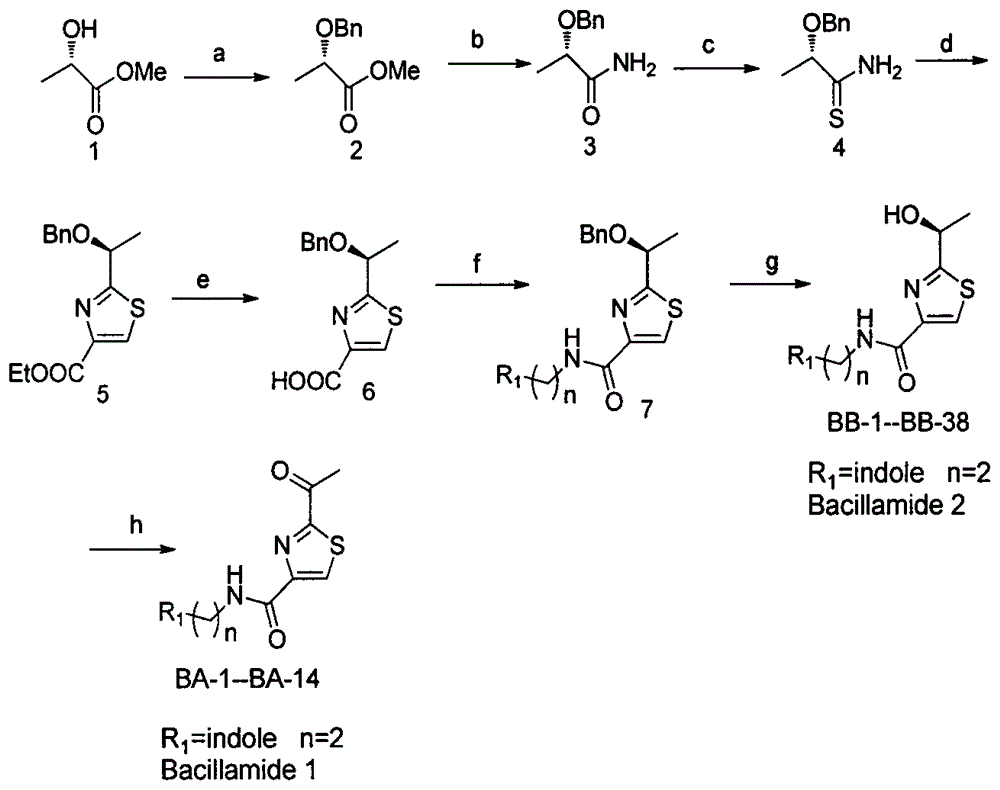
2-(1-ethoxyl).2-acetylthiazole-4-formamide compounds and application
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Salen metal complex catalyst, as well as preparation method and application thereof
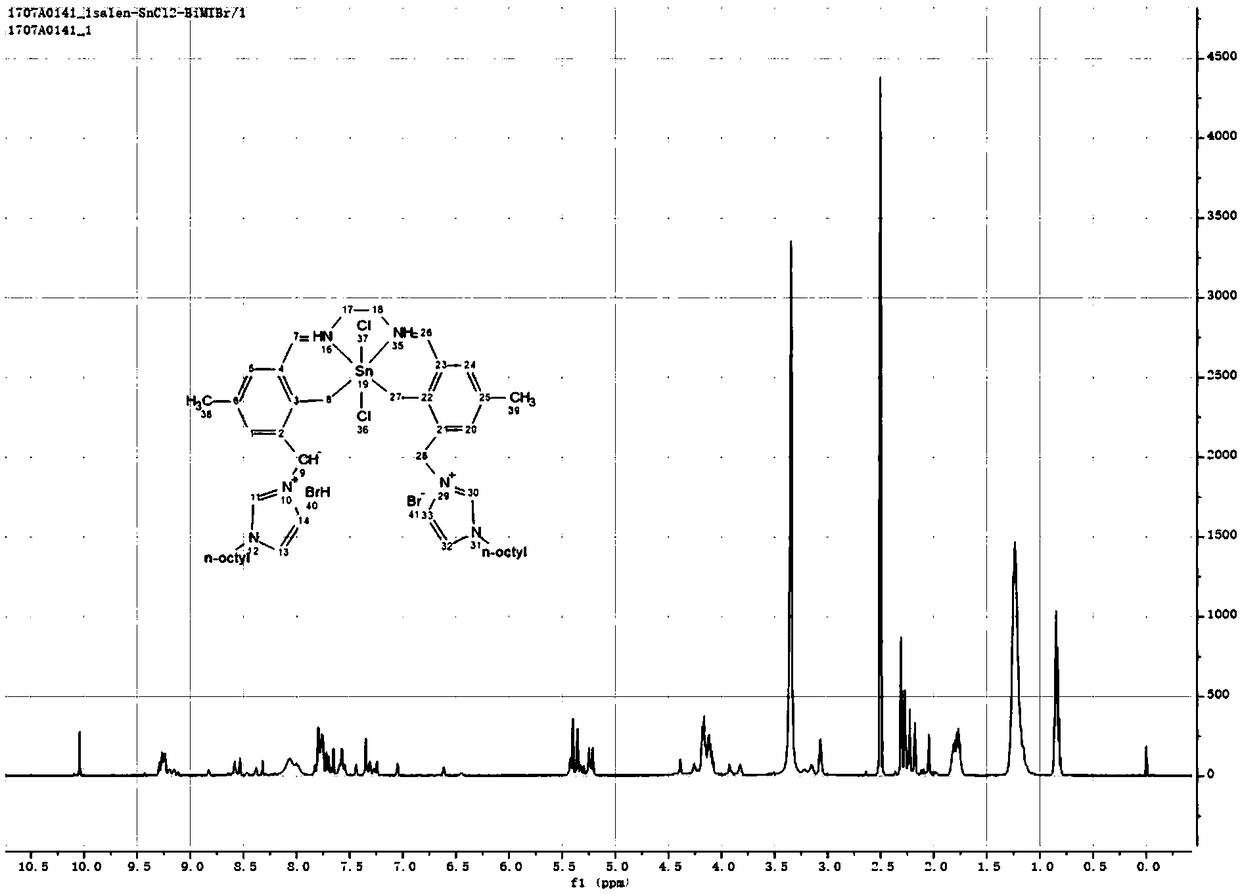
ActiveCN108636456AImprove stabilityEasy to prepareTin organic compoundsOrganic compound preparationEthylenediamineBromine
The invention relates to the technical field of catalysts, and particularly relates to a salen metal complex catalyst, as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The salen metal complexcatalyst is prepared by the following steps: modifying salicylaldehyde by adding a bromide salt and performing reacting the modified salicylaldehyde with ethylenediamine and a metal compound. The catalyst has good stability and good catalysis for biomass-based carbohydrate, can be recycled, and is economical and environmentally friendly. The preparation method of the catalyst is simple, has low cost and high yield, the structure of the salen metal complex is changed by a substitution reaction, so the activity and selectivity of the catalyst can be adjusted; and the catalyst is creatively applied to preparation of methyl lactate from the biomass-based carbohydrate, and the biomass-based carbohydrate has high conversion rate, and methyl lactate has high yield.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
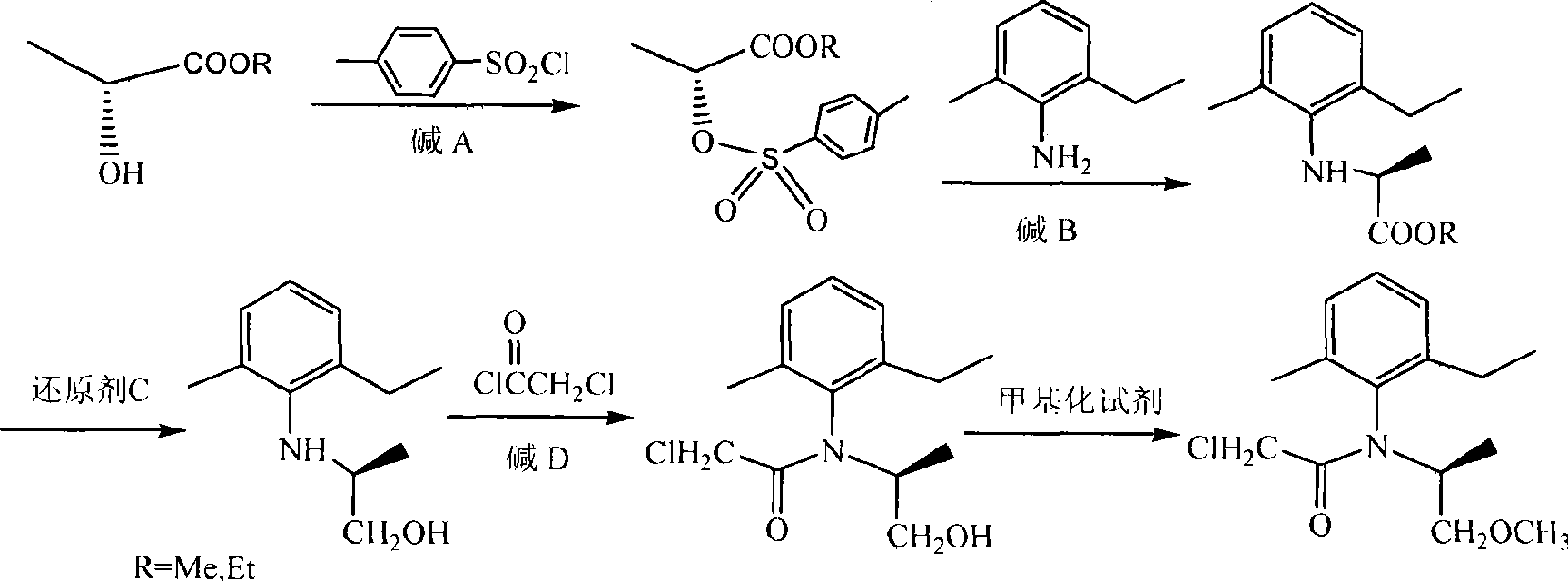
Synthesis method of S-metolachlor
InactiveCN102010346AOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid amides preparationSynthesis methodsMethyl lactate
The invention discloses a synthesis method of S-metolachlor, comprising the following steps: 1) reacting (R)-methyl lactate or (R)-ethyl lactate with methanesulfonyl chloride to generate (R)-2-(mesyloxy)propionate; 2) reacting the obtained (R)-2-(mesyloxy)propionate with 2-methyl-6-ethylphenylamine to obtain (S)-N-(2-methyl-6-ethyl phenyl) phenylalanine ester; 3) reducing an ester group into corresponding alcohol by a reducing agent; 4) obtaining acyamino alcohol by performing acylation on the alcohol and chloroacetic chloride; and 5) obtaining the S-metolachlor through methylation reaction. The S-metolachlor produced by the synthesis method is low in production cost and good in optical purity, the ee value reaches 90-93%, and the yield is up to 86-89%. The synthesis method is simple to operate and easy to realize industrialization.
Owner:江苏常隆化工有限公司
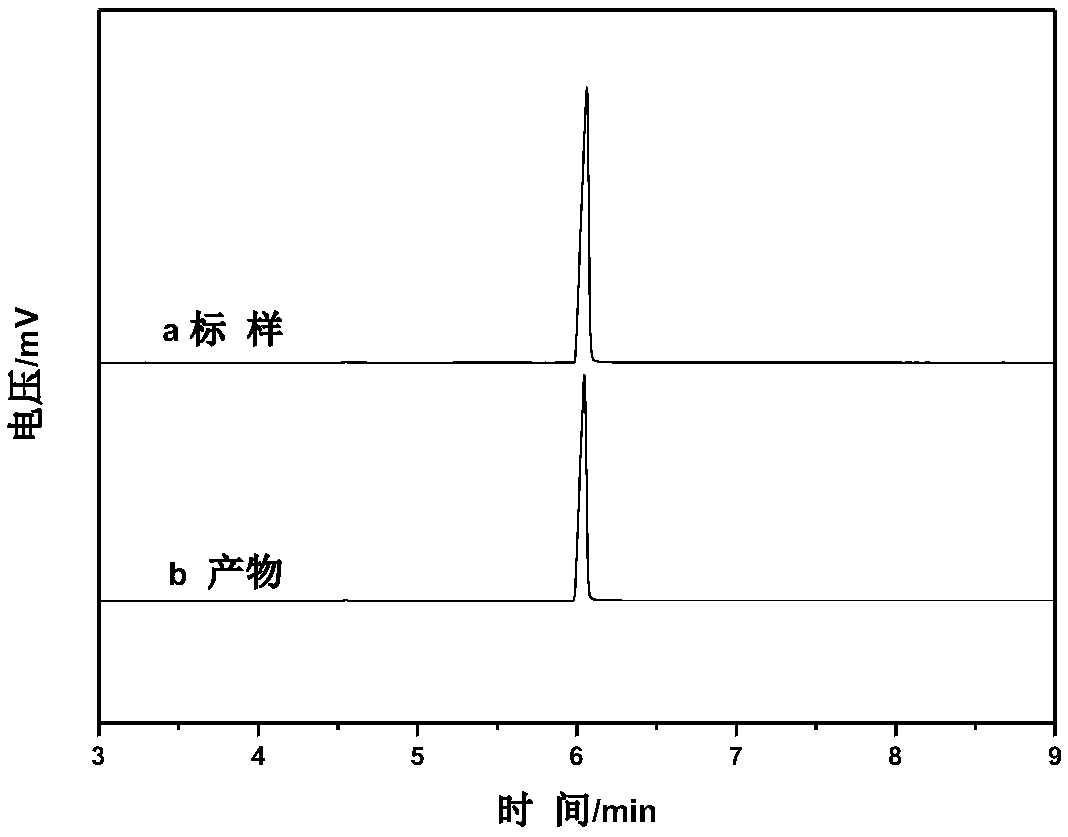
Method for chiral separation and measurement of methyl lactate optical isomers by capillary gas chromatography
The invention discloses a method for chiral separation and measurement of methyl lactate optical isomers by chiral capillary column gas chromatography. The preferred chromatographic conditions are as follows: chiral capillary column having inner wall coated with 2,3,6-tri-O-capryl-beta-cyclodextrin as chiral stationary phase; chromatographic column with length of 20-30 m, inner diameter of 250-320 micrometer, and stationary phase film thickness of 0.31 micrometer; inert gas as mobile phase with flow rate of 25-35 cm / s; hydrogen flame ionization detector; injection port temperature of 200-280 DEG C; detector temperature of 250-280 DEG C; and chromatographic column temperature of 50-80 DEG C. The inventive method can completely achieve baseline separation of D-methyl lactate and L-methyl lactate enantiomer chromatographic peaks, with separation degree of 5.49. The method can be utilized for simultaneous quantitative determination of D-methyl lactate and L-methyl lactate isomers.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Preparation method for ravuconazole intermediate
The invention belongs to the technical field of medicines, and particularly relates to a preparation method for a ravuconazole intermediate. The preparation method comprises the following steps: enabling D,L-methyl lactate, morpholine and 3,4-dihydropyran to react; enabling a reactant and a Grignard reagent of 2,4-difluorobrmorobenzene to react to prepare a compound III; enabling the compound III to react through asymmetric kortchaikovsky under the catalysis of a catalyst B, namely, L-menthol, and triphenylphosphine; enabling a compound IV to react with 1,2,4-triazole to react; dewatering to cyclise to obtain a ravuconazole intermediate compound V. According to the preparation method for the ravuconazole intermediate, D,L-methyl lactate is used and a catalyst is added for inducing production of a chiral centre; the raw material cost of the reaction is greatly reduced; the yield is high; the purity is high; the preparation method is easy to control, and is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:VALIANT CO LTD
Process for preparing L- (+) -lactic acid
InactiveUS7820859B2High purityPrevent oxidationOrganic compound preparationChemical industrySodium bicarbonateMethyl pyruvate
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com