Deep-sea sediment-sourced esterase EST4 as well as encoding gene and application thereof
A technology of esterase and gene, applied in the field of esterase EST4 derived from deep sea sediments, can solve the problems of inability to reproduce the in-situ habitat conditions of microorganisms, obtain pure culture, limit the exploration and application of marine microbial genetic resources, and achieve excellent enzymatic characteristics Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] The acquisition of embodiment 1 esterase gene est4
[0024] Deep-sea sediment samples were collected from the margins of Pacific seamounts in 2008 by a deep-sea visual multi-tube sampler. Metagenomic library construction using CopyControl TM HTP fosmid library production kit (Epicentre Biotechnologies, USA), the host strain is E.coliEPI300 (Epicentre Biotechnologies, USA), and the vector is pCC2FOS fosmidvector (Epicentre Biotechnologies, USA). The size of the inserted fragment was detected by pulsed field electrophoresis, which was 36-48kb.
[0025]The clones with esterase gene were screened by esterase screening plate. The esterase screening medium formula is LB medium (10g / L tryptone, 5g / L yeast extract, 10g / L sodium chloride, pH 7.2) adding 10g / L tributyrin; after sterilization, Aseptically add chloramphenicol to a final concentration of 12.5 μg ml -1 . Take 10 μl of the library bacteria solution and dilute it to 100 μl, spread it on the esterase screening pla...
Embodiment 2
[0030] The construction of the recombinant expression plasmid of embodiment 2 esterase gene est4 and recombinant bacterial strain
[0031] The esterase gene est4 obtained in the present invention is cloned into an expression vector to construct a recombinant expression strain. Based on the open reading frame sequence of the esterase gene obtained by the ORF analysis of NCBIORF Finder, the upstream primer E4F (5'-TCGC GGATCC GTGGCGGACGGCGAGGC-3', BamHI) and downstream primer E4R (5'-TCCG CTCGAG CTAGAGGTCGTCGATCCTGTC-3', XhoI), PCR amplification confirmed the full-length sequence of the gene. The expression plasmid was constructed by enzyme digestion cloning, that is, the PCR product was double-digested with BamHI and XhoI, and the purified fragment was ligated with the plasmid pSMT3 that had been double-digested with BamHI and XhoI. 2 The transformation method was transformed into E.coliDH5α, and positive clones were screened for kanamycin resistance. A plasmid extraction ...
Embodiment 3
[0032] Embodiment 3 Utilizes recombinant expression strain to express recombinant esterase gene est4
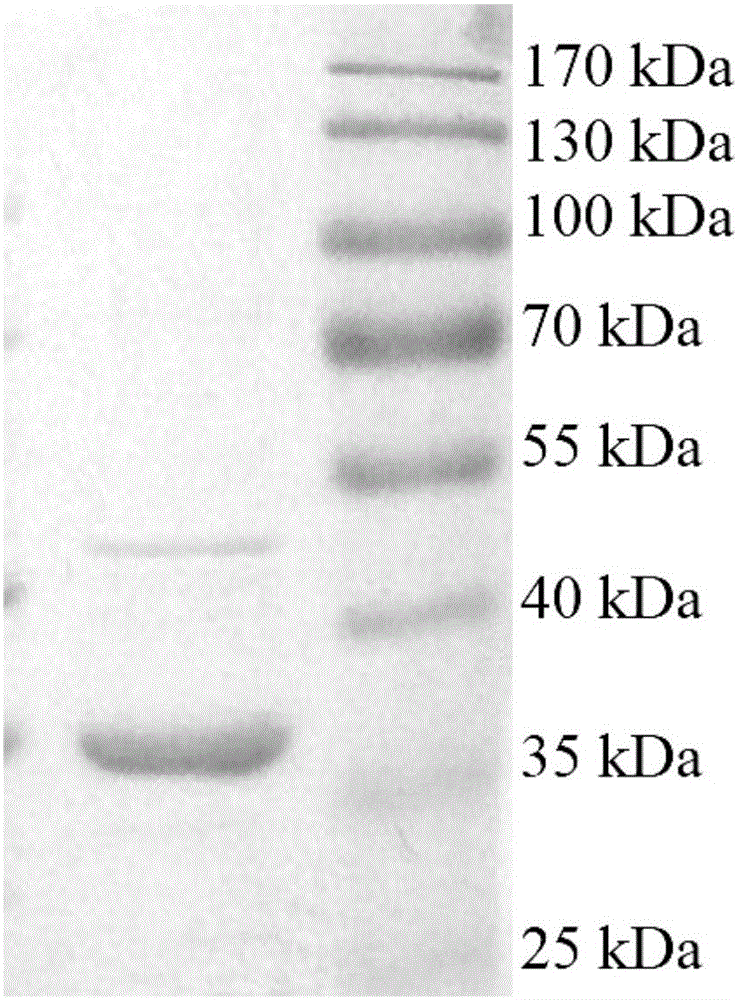
[0033] Transfer 3ml of the constructed recombinant expression strain to 100ml of LB liquid medium containing 20μg / ml kanamycin and 34μg / ml chloramphenicol, and shake at 37°C until OD 600 When it reaches 0.6, add IPTG with a final concentration of 0.5mM to induce expression, transfer to 25°C and shake at 150r / min for 8h. The cells were collected by low-temperature centrifugation, resuspended in NTA-10 solution (500 mM sodium chloride, 10 mM imidazole, 20 mM Tris hydrochloric acid, pH 8.0), and subjected to sonication on ice. Centrifuge at low temperature to collect supernatant, use NTA-Ni 2+ The expressed protein was purified by affinity column chromatography. The expressed recombinant protein contains a 6×His tag at the N-terminal, which can be affinity-adsorbed to the layer suction column, and is eluted through gradient elution with different concentrations of imidazole so...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Absorbance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com