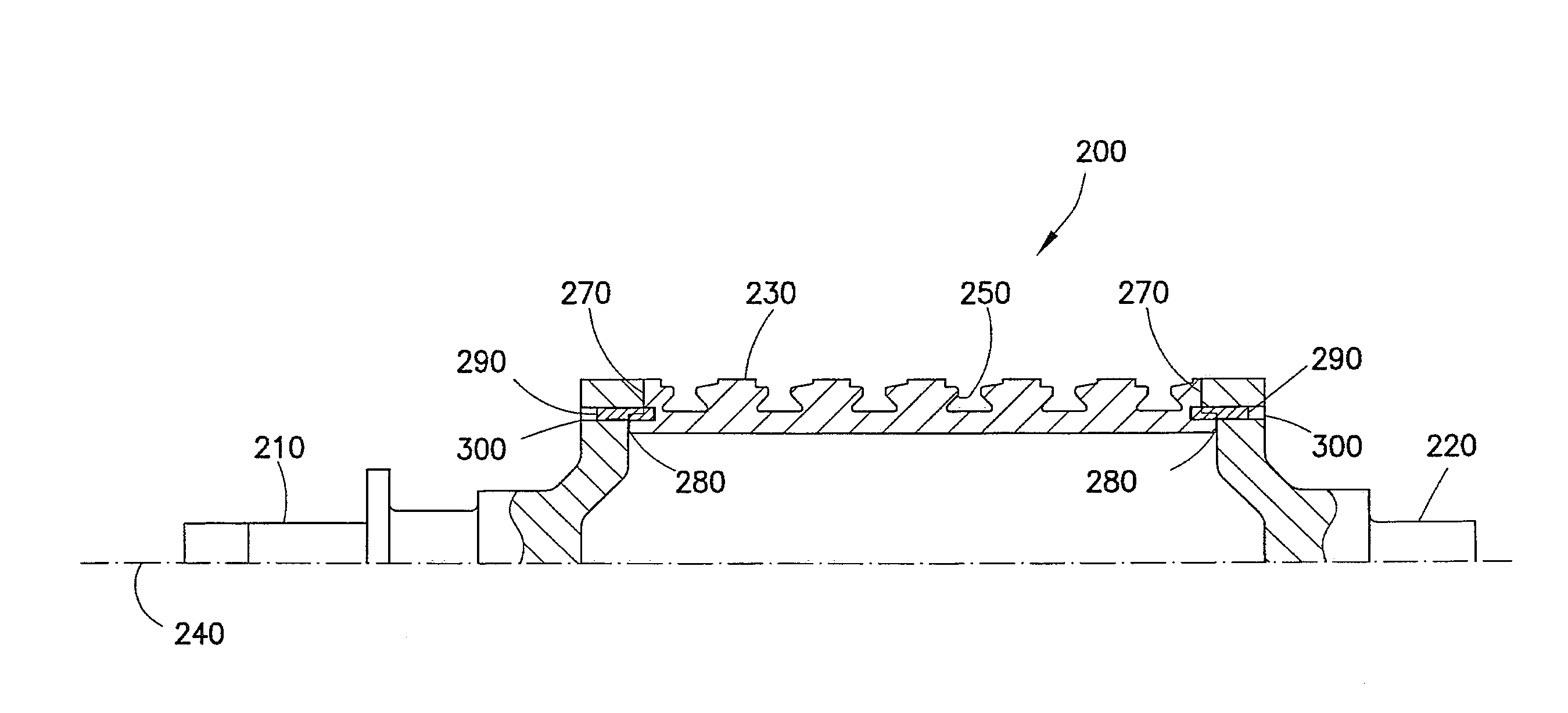
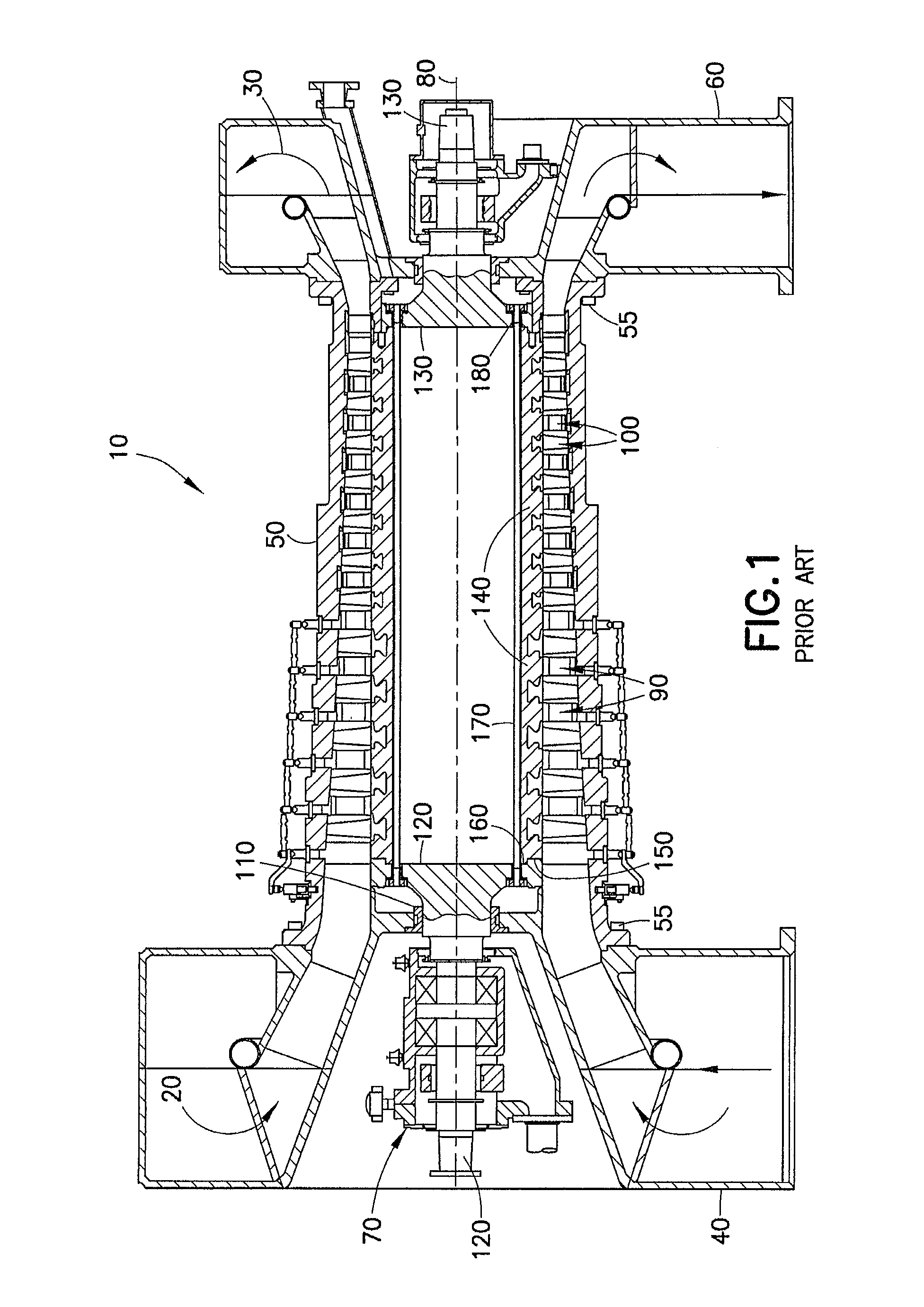
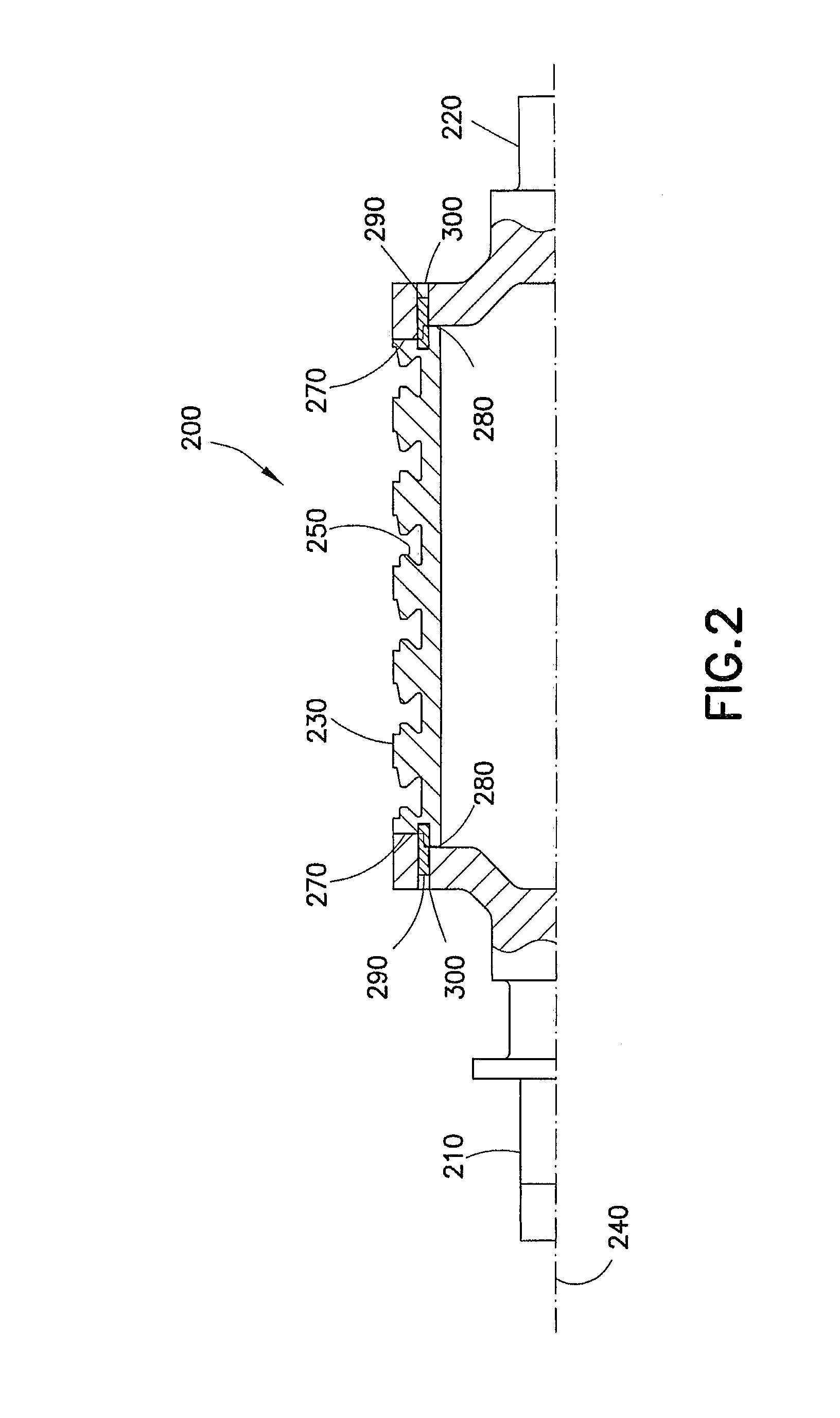
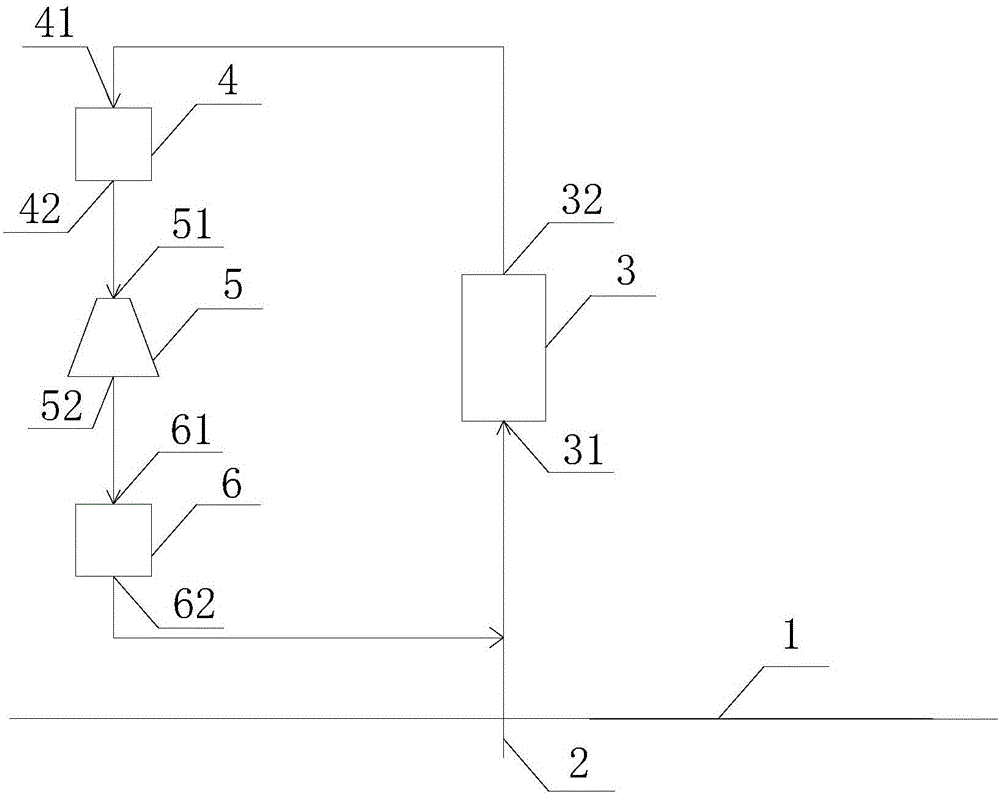
Patents
Literature
48results about "Self-contained rotary compression machines" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
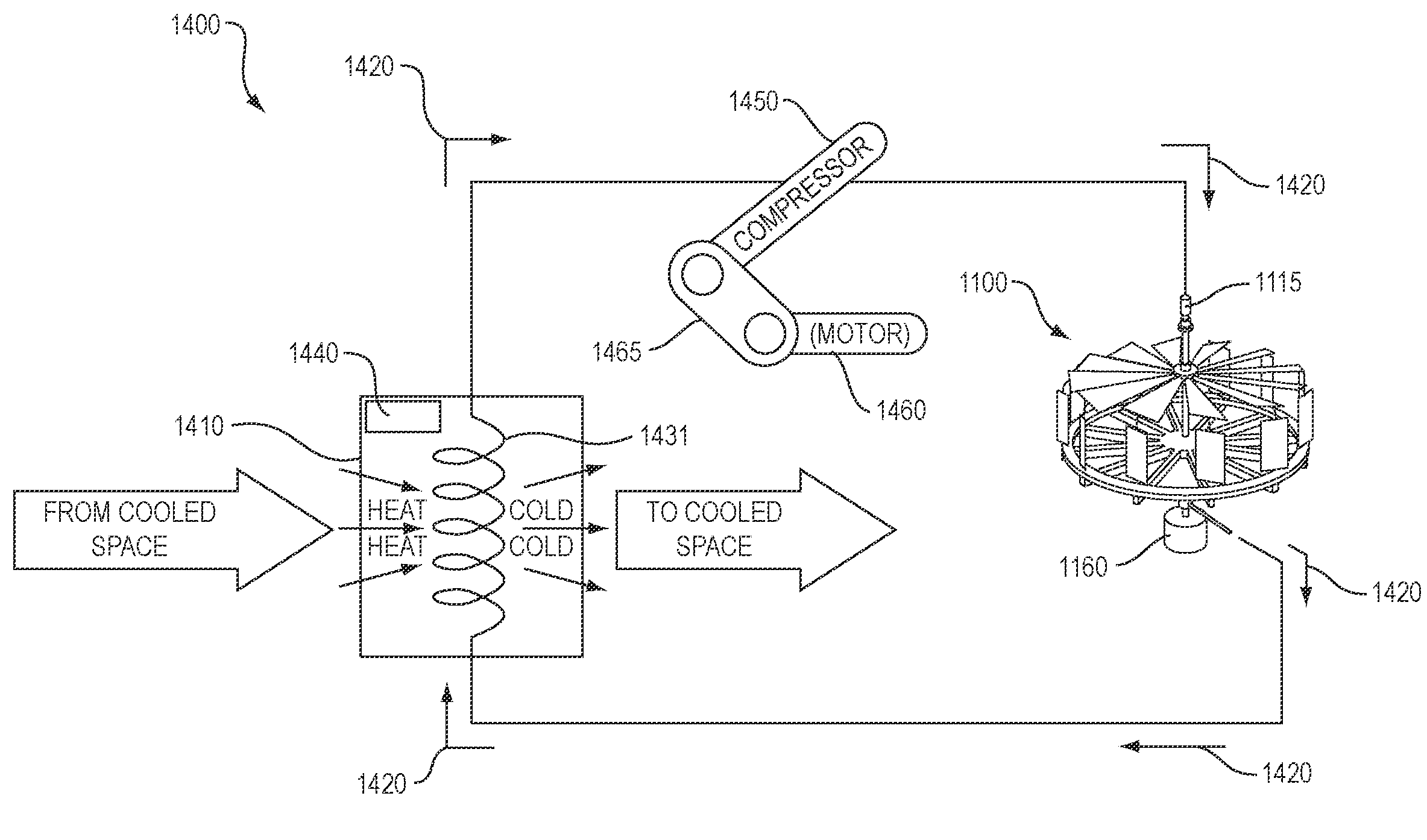
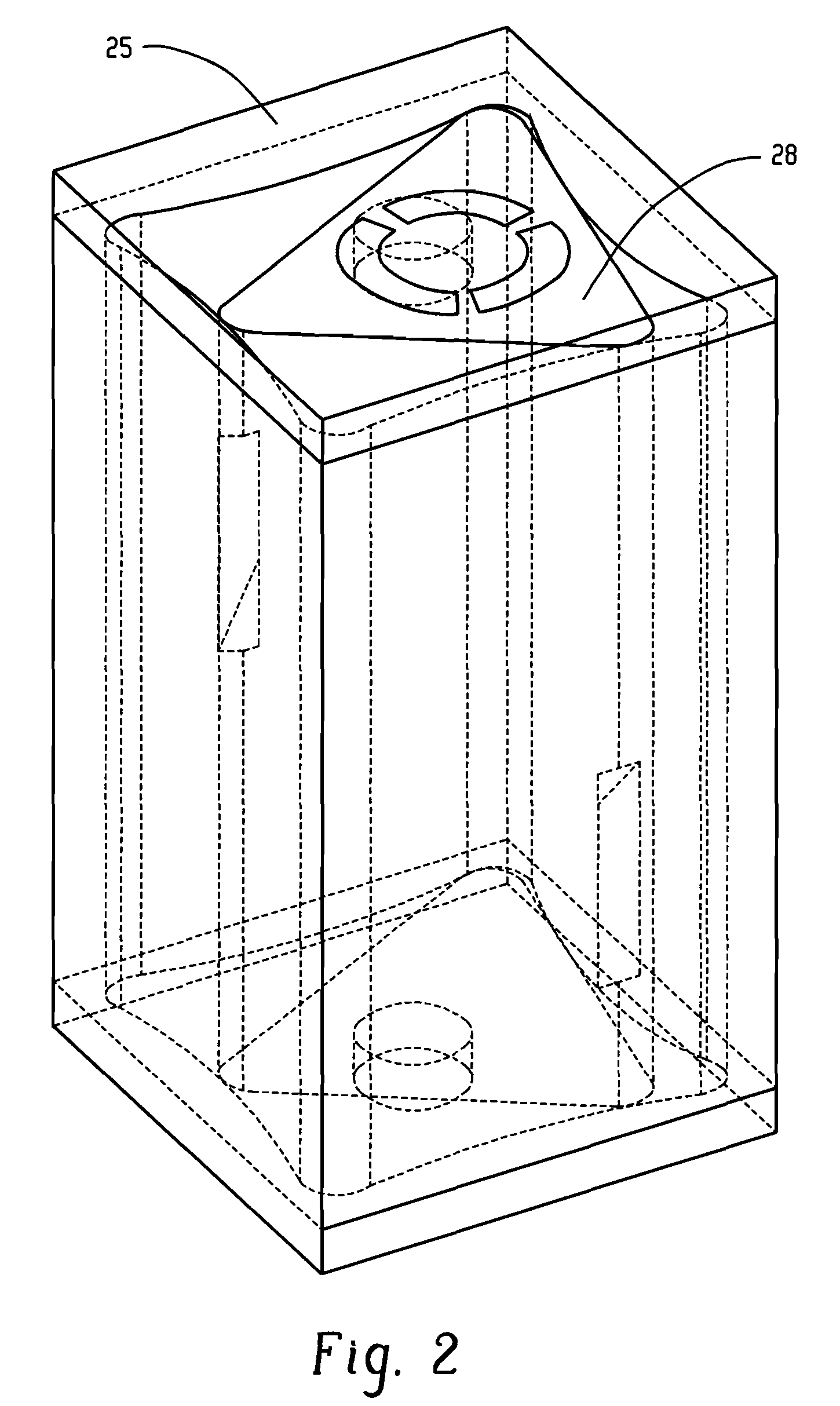
System and method for cooling a compressor motor
ActiveUS7181928B2Unacceptable compromises to system efficiencyImprovement in motor coolingCompressorPump componentsEngineeringAir compressor
Apparatus and methods are provided for cooling motors used to drive gas and air compressors. In particular, the cooling of hermetic and semi-hermetic motors is accomplished by a gas sweep using a gas source located in the low-pressure side of a gas compression circuit. The gas sweep is provided by the creation of a pressure reduction at the compressor inlet sufficient to draw uncompressed gas through a motor housing, across the motor, and out of the housing for return to the suction assembly. The pressure reduction is created by means provided in the suction assembly, such as a nozzle and gap assembly, or alternatively a venturi, located upstream of the compressor inlet. Additional motor cooling can be provided by circulating liquid or another cooling fluid through a cooling jacket in the motor housing portion adjacent the motor.
Owner:JOHNSON CONTROLS TYCO IP HLDG LLP
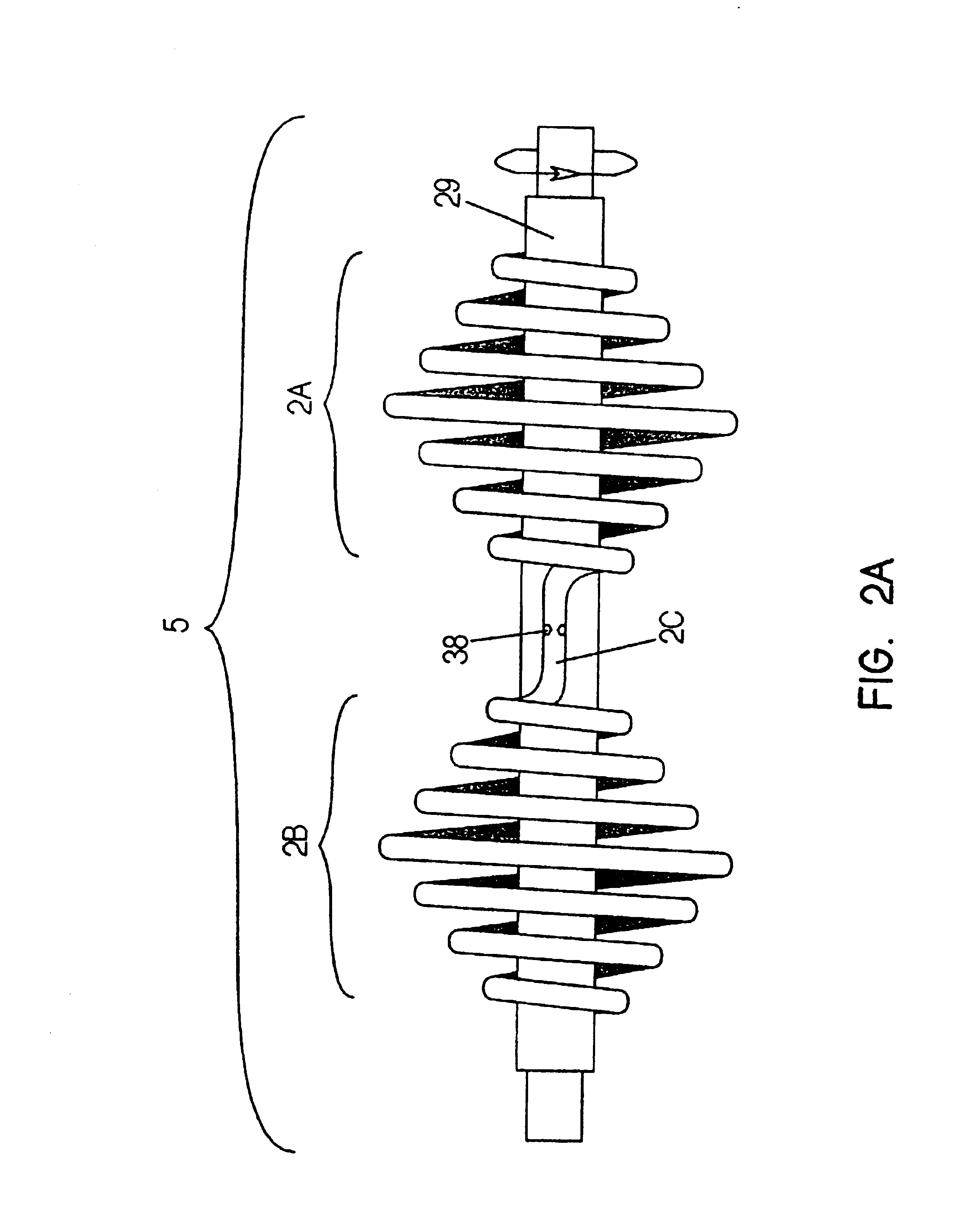
Centrifugal heat transfer engine and heat transfer systems embodying the same
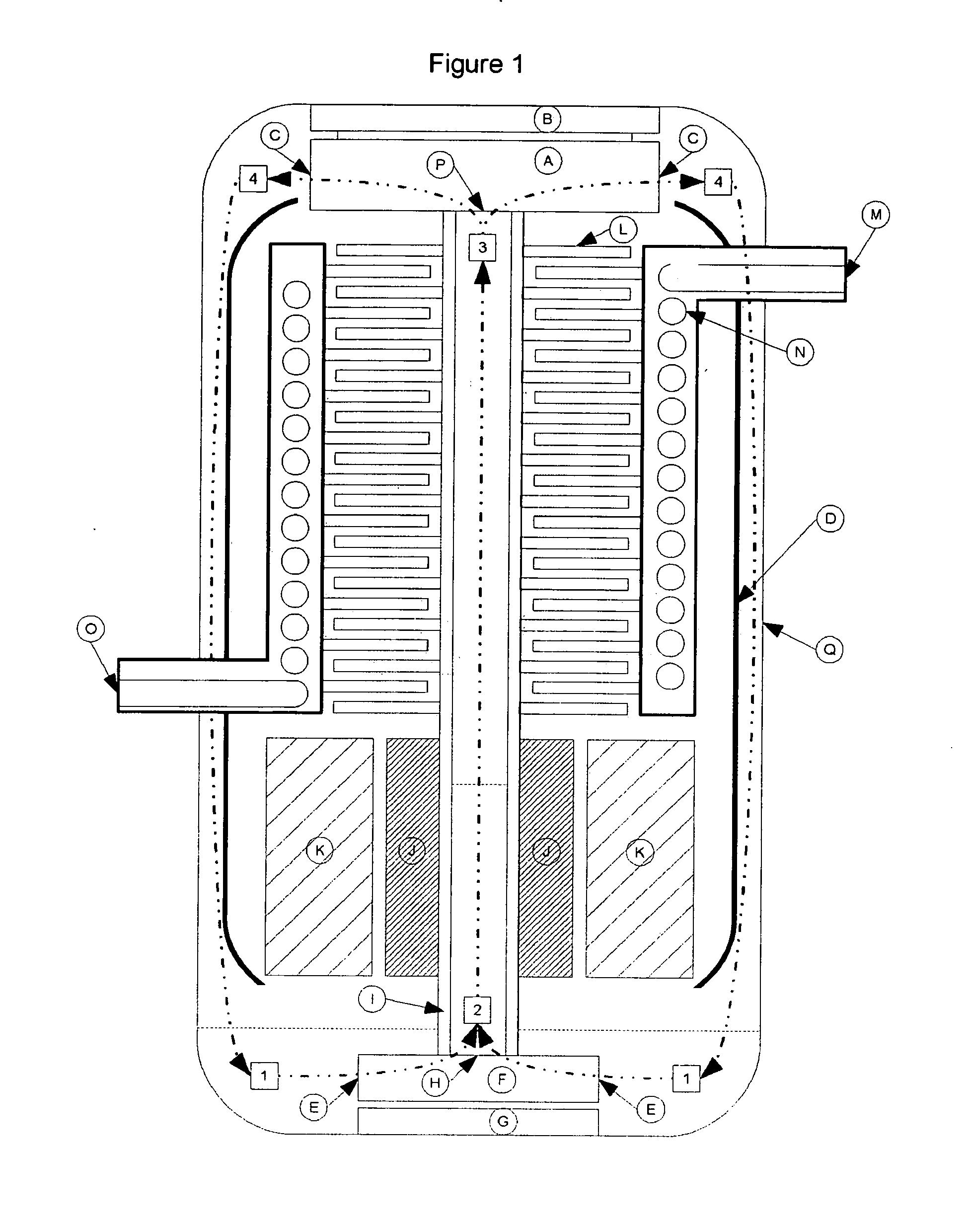
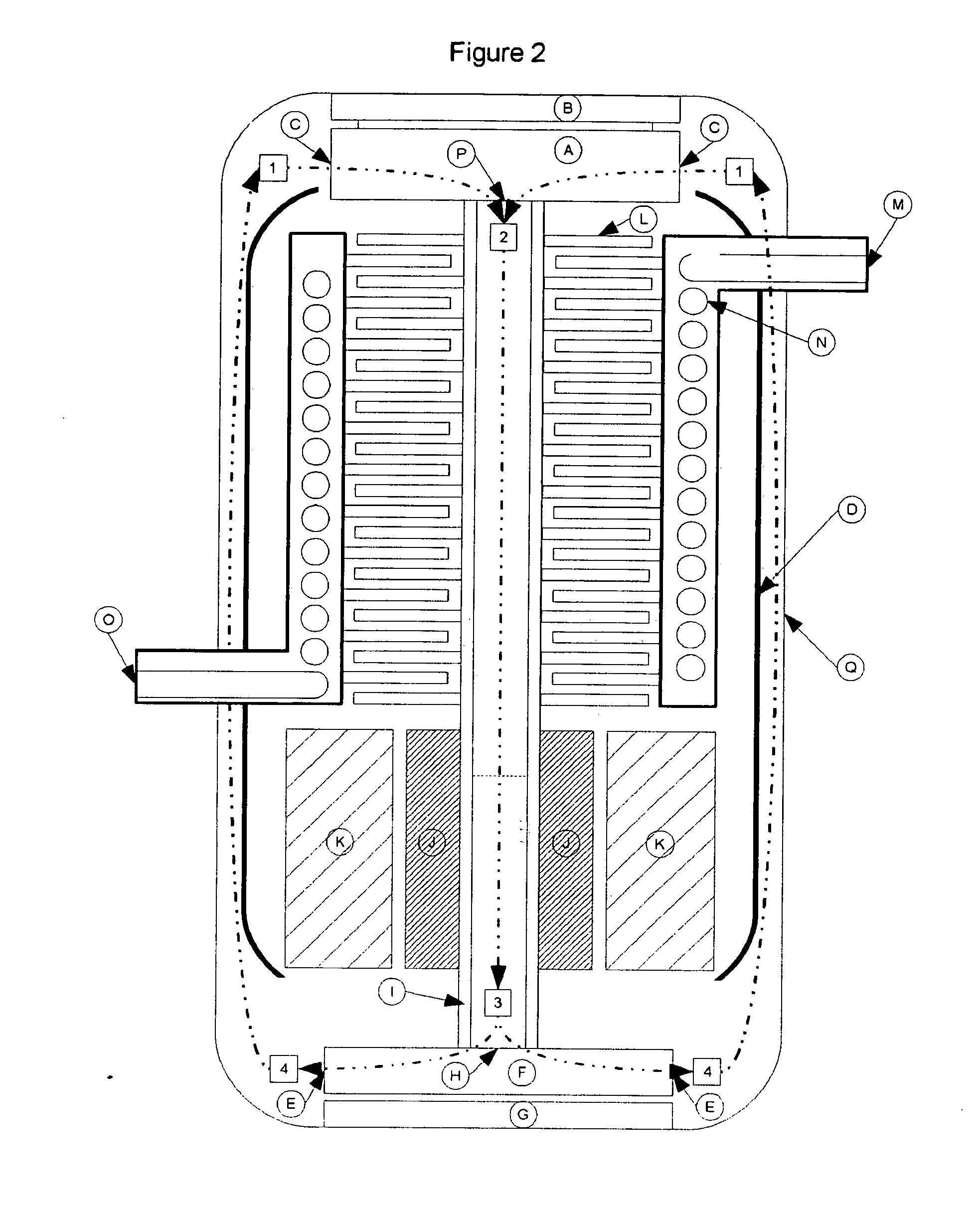
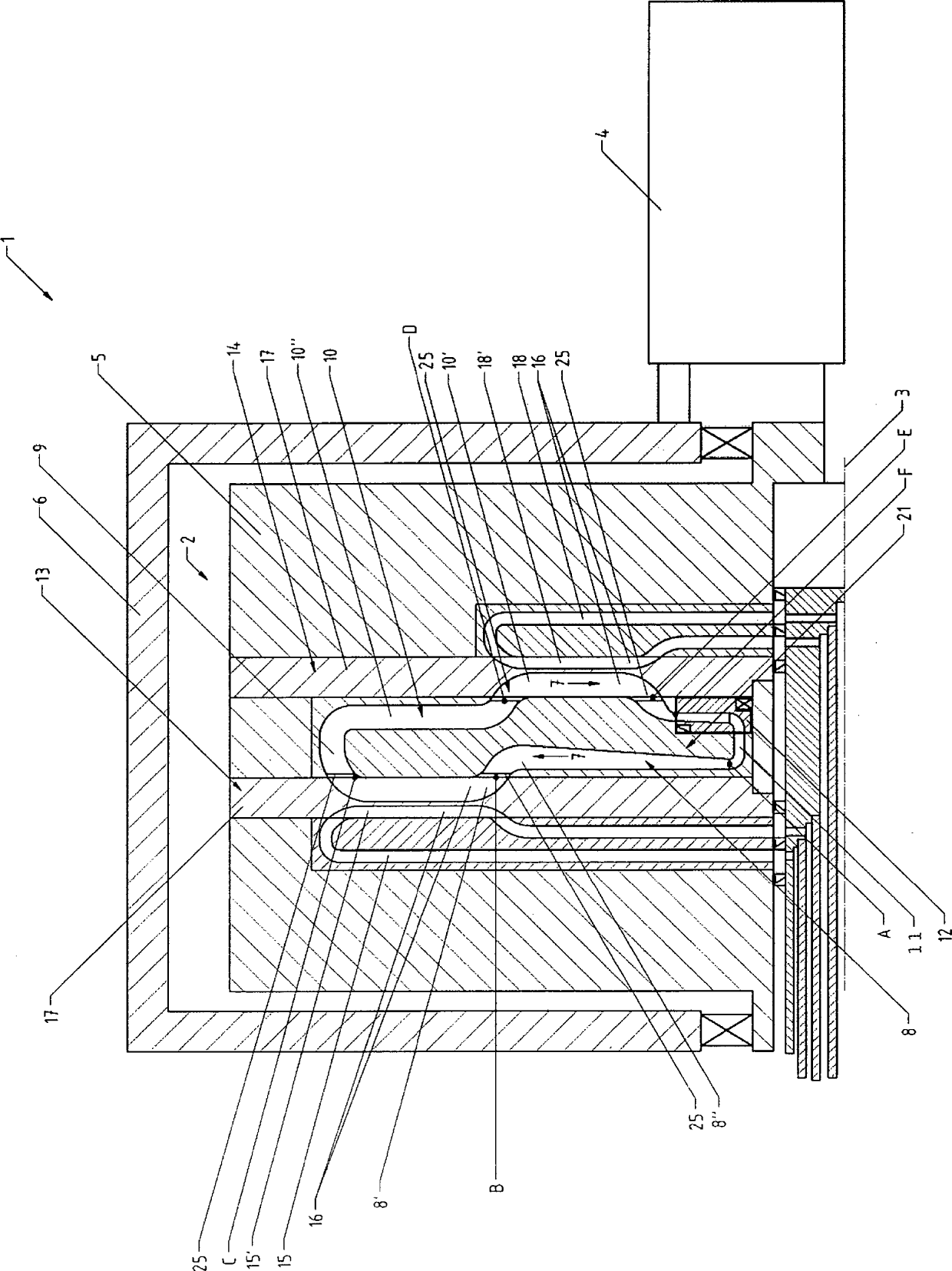
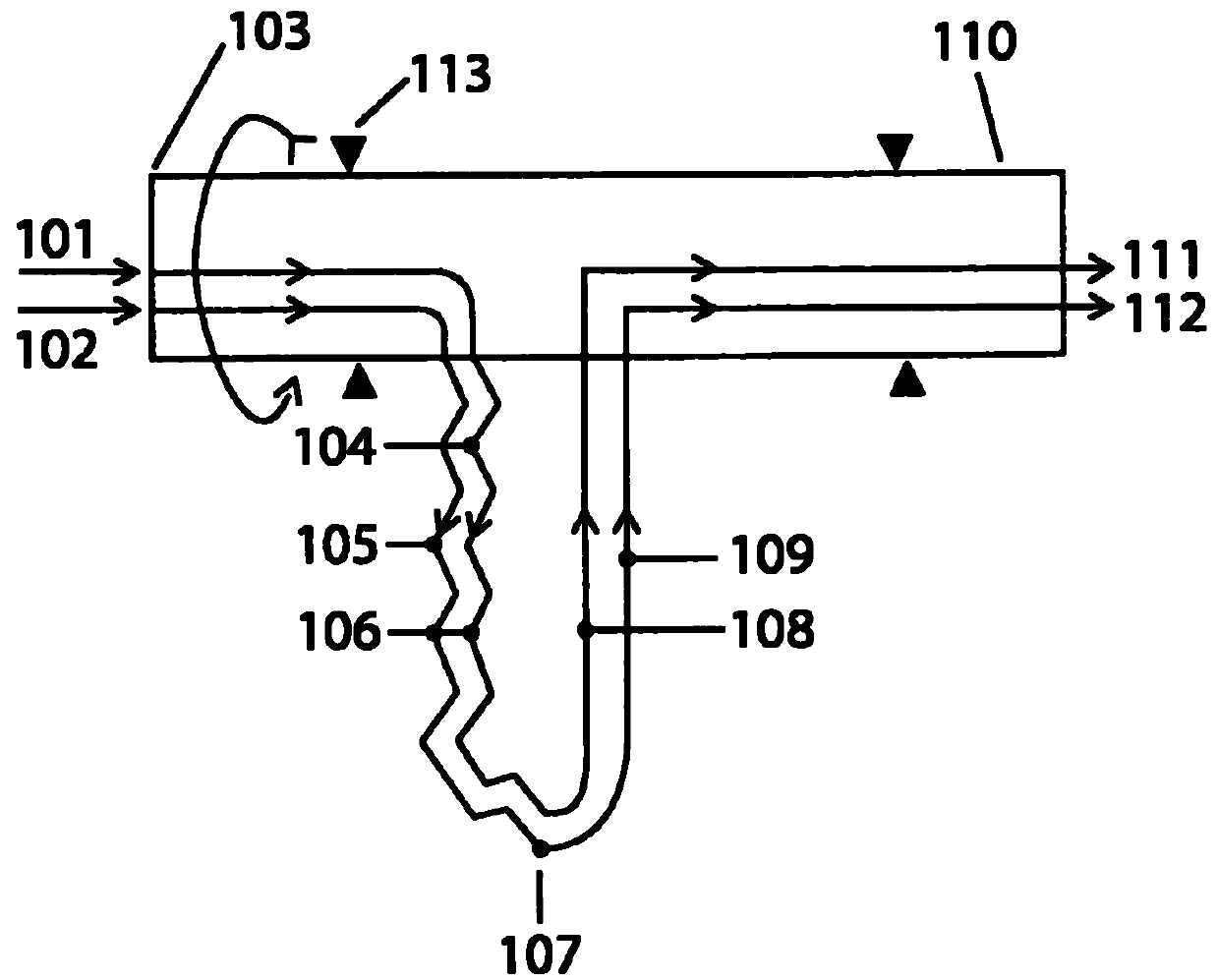
InactiveUS20030145621A1Simple methodReduce the introductionSelf-contained rotary compression machinesCompression machines with non-reversible cycleRotational axisThermal isolation
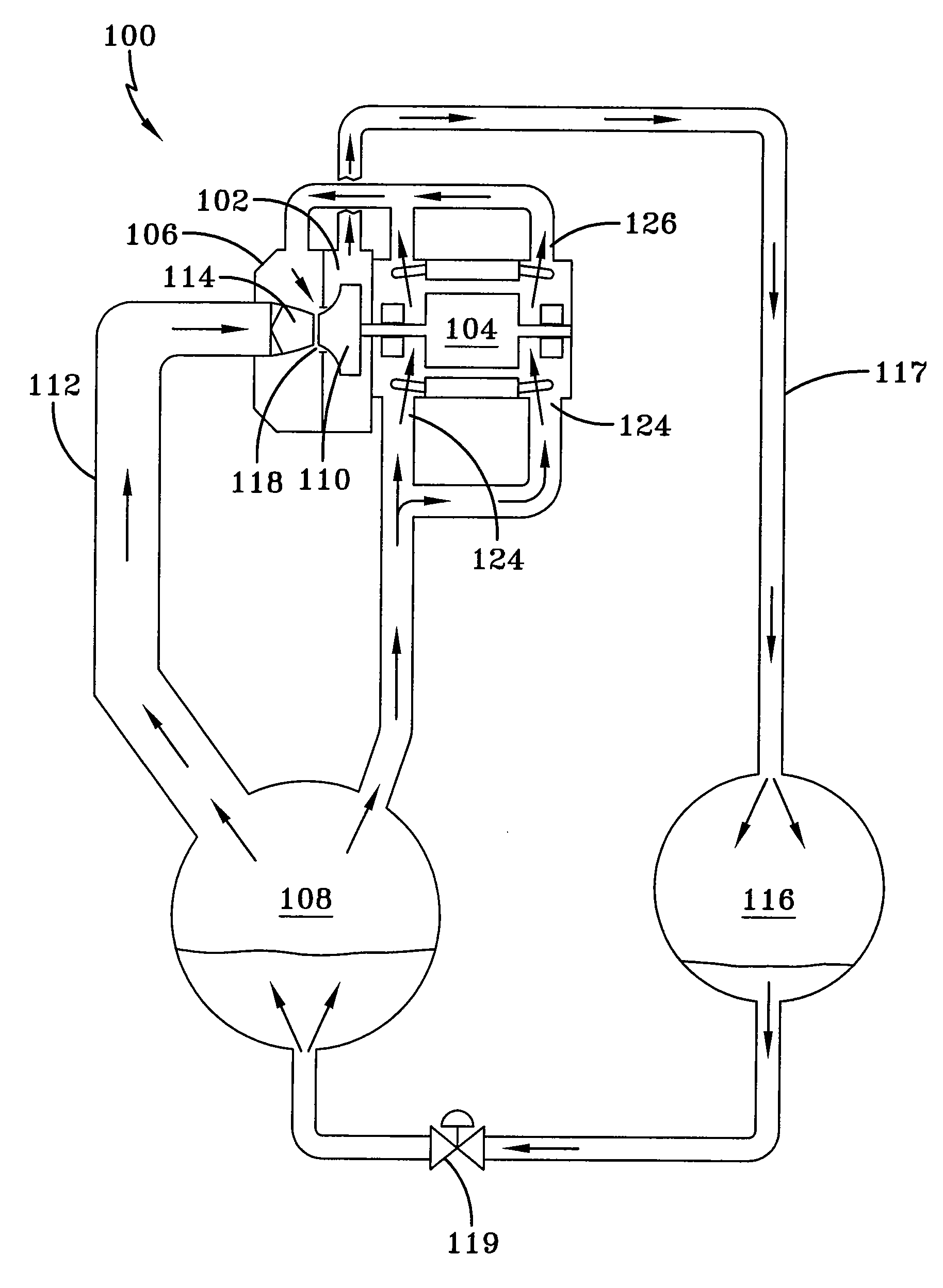
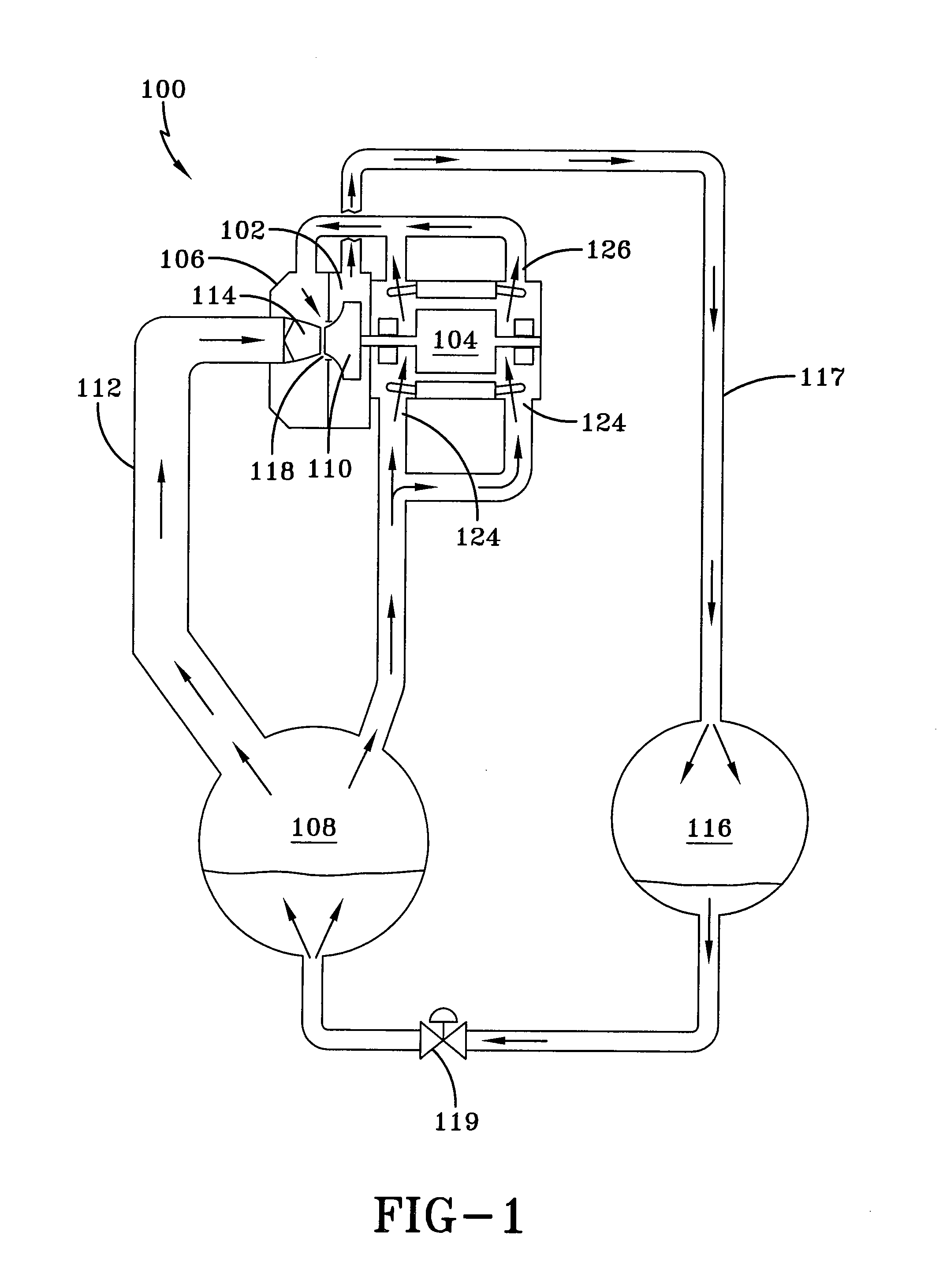
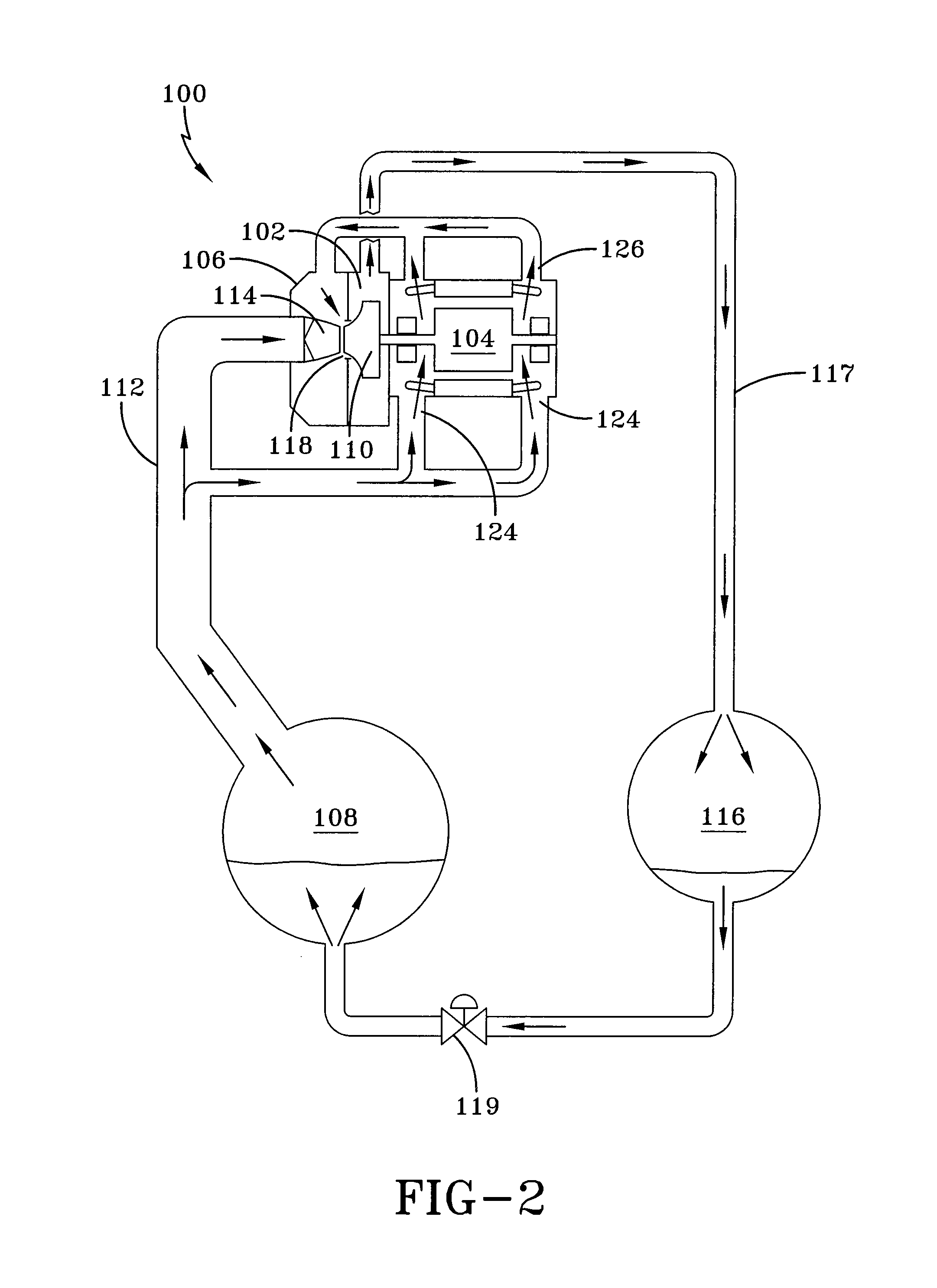
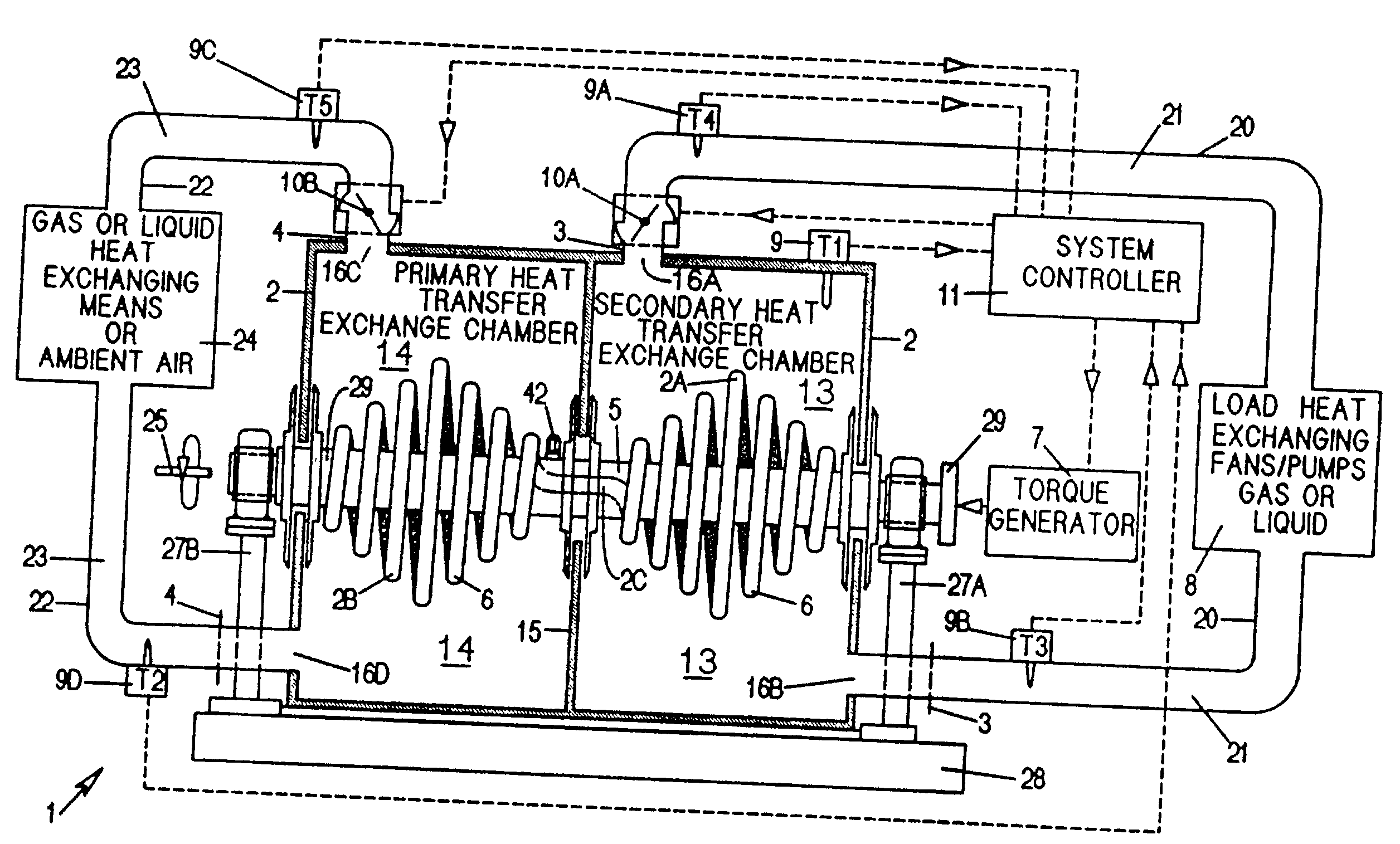
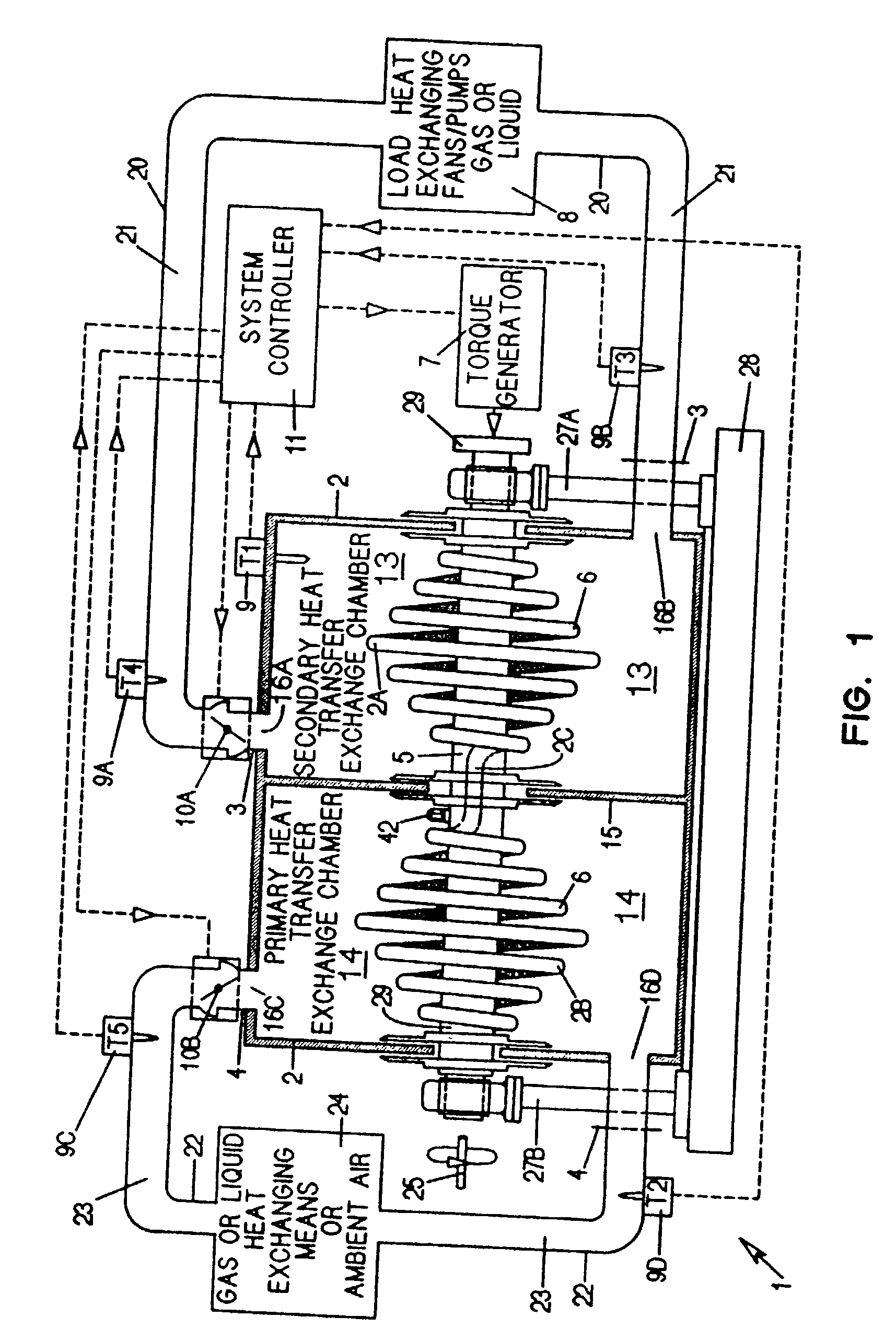
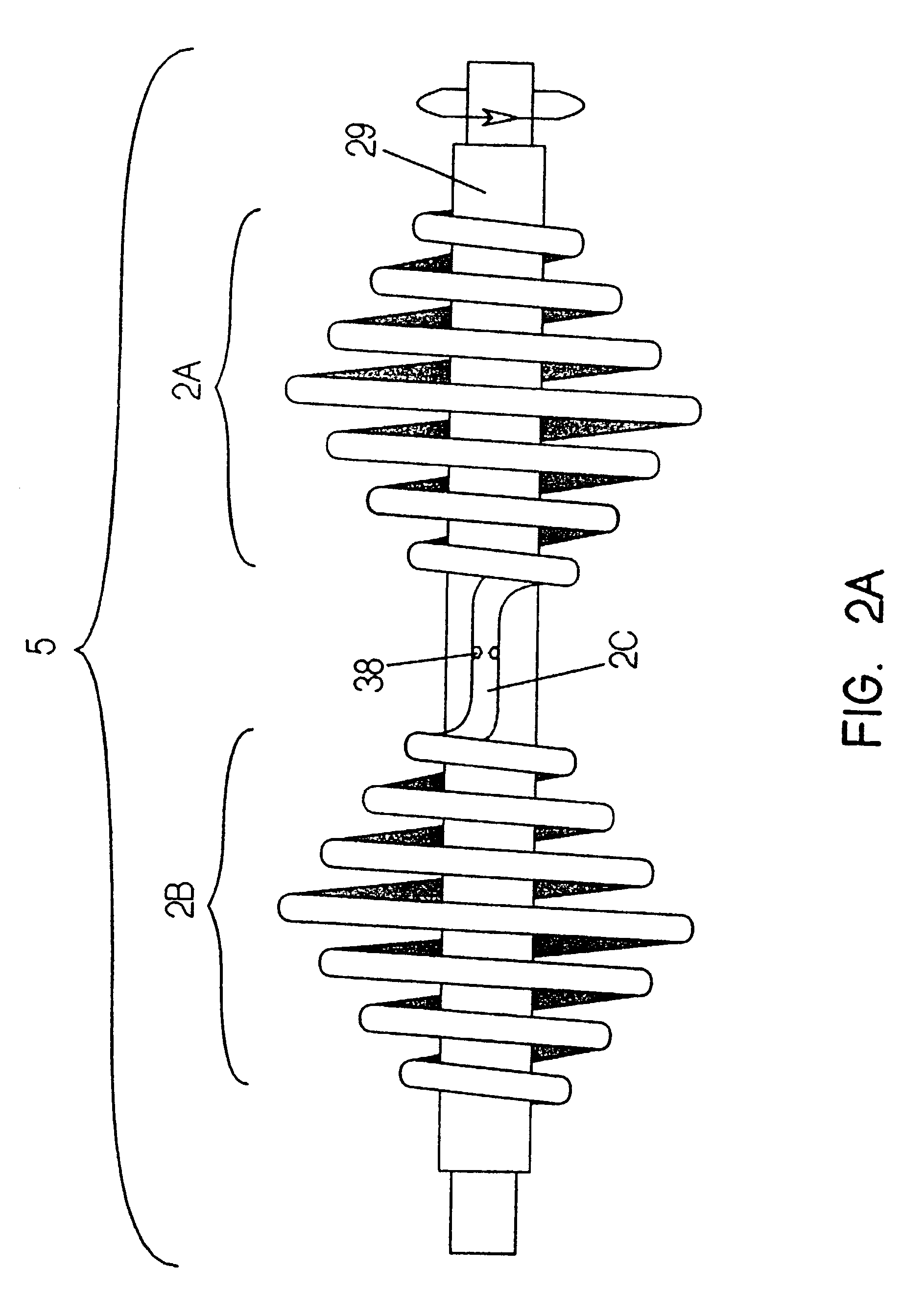
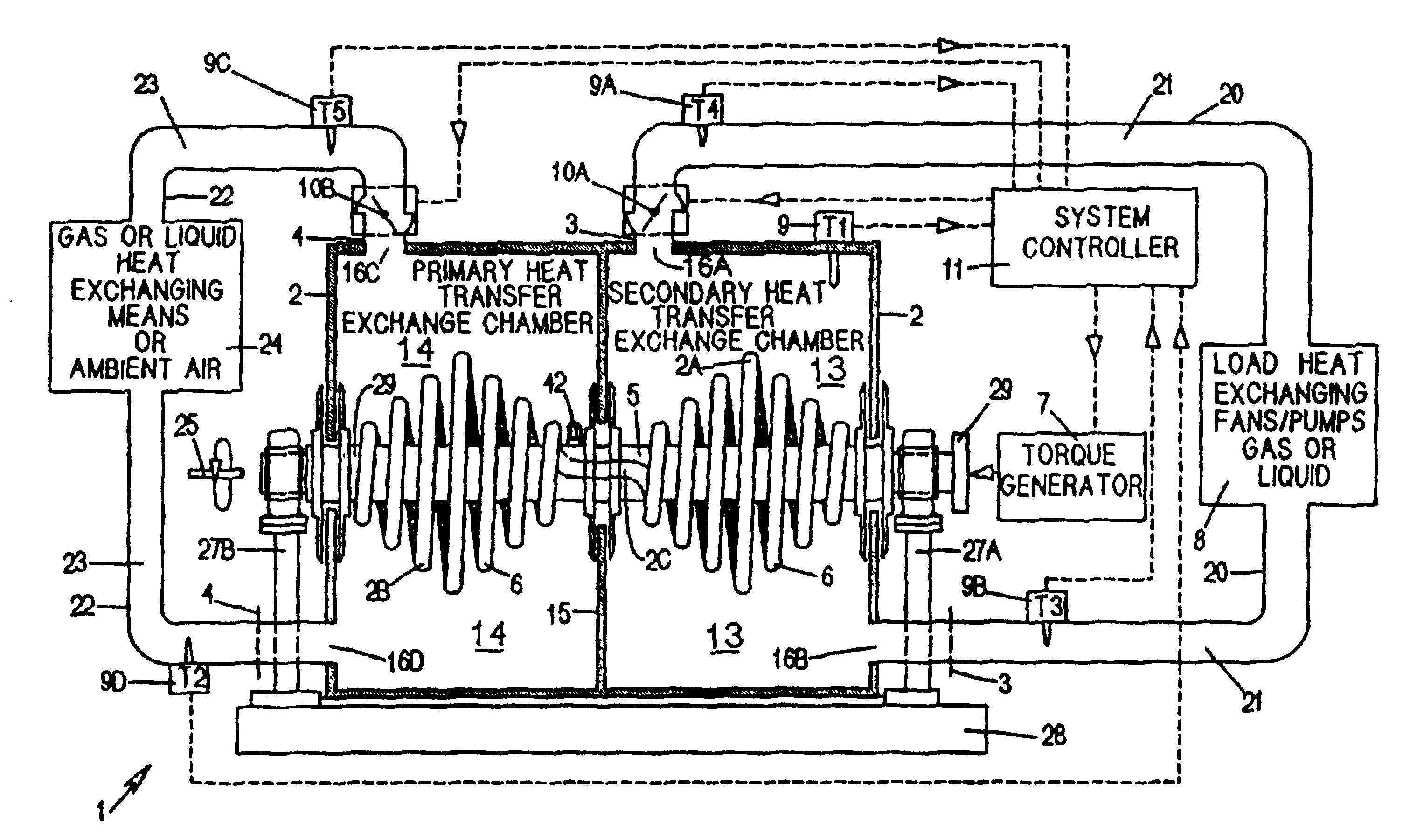
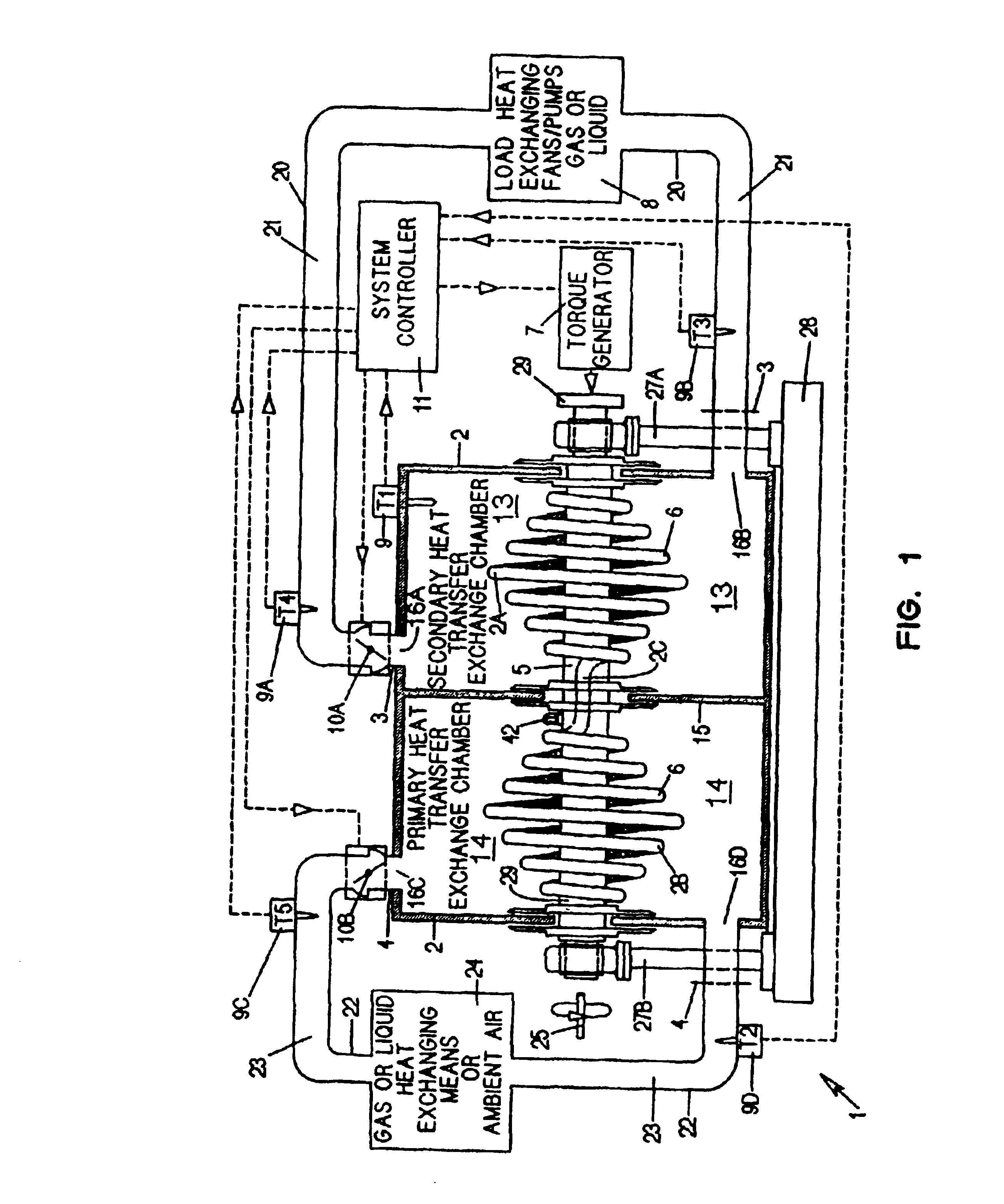
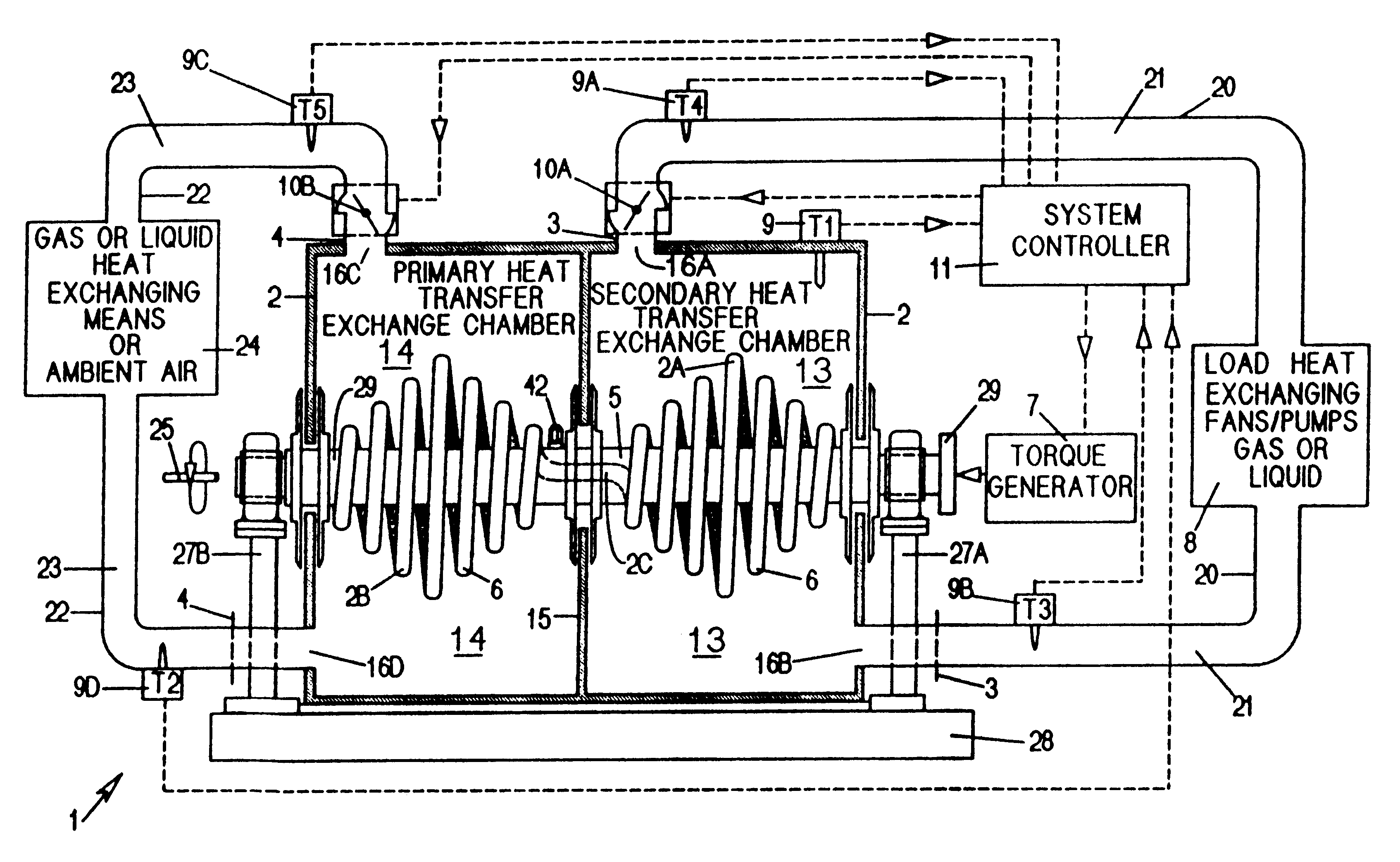
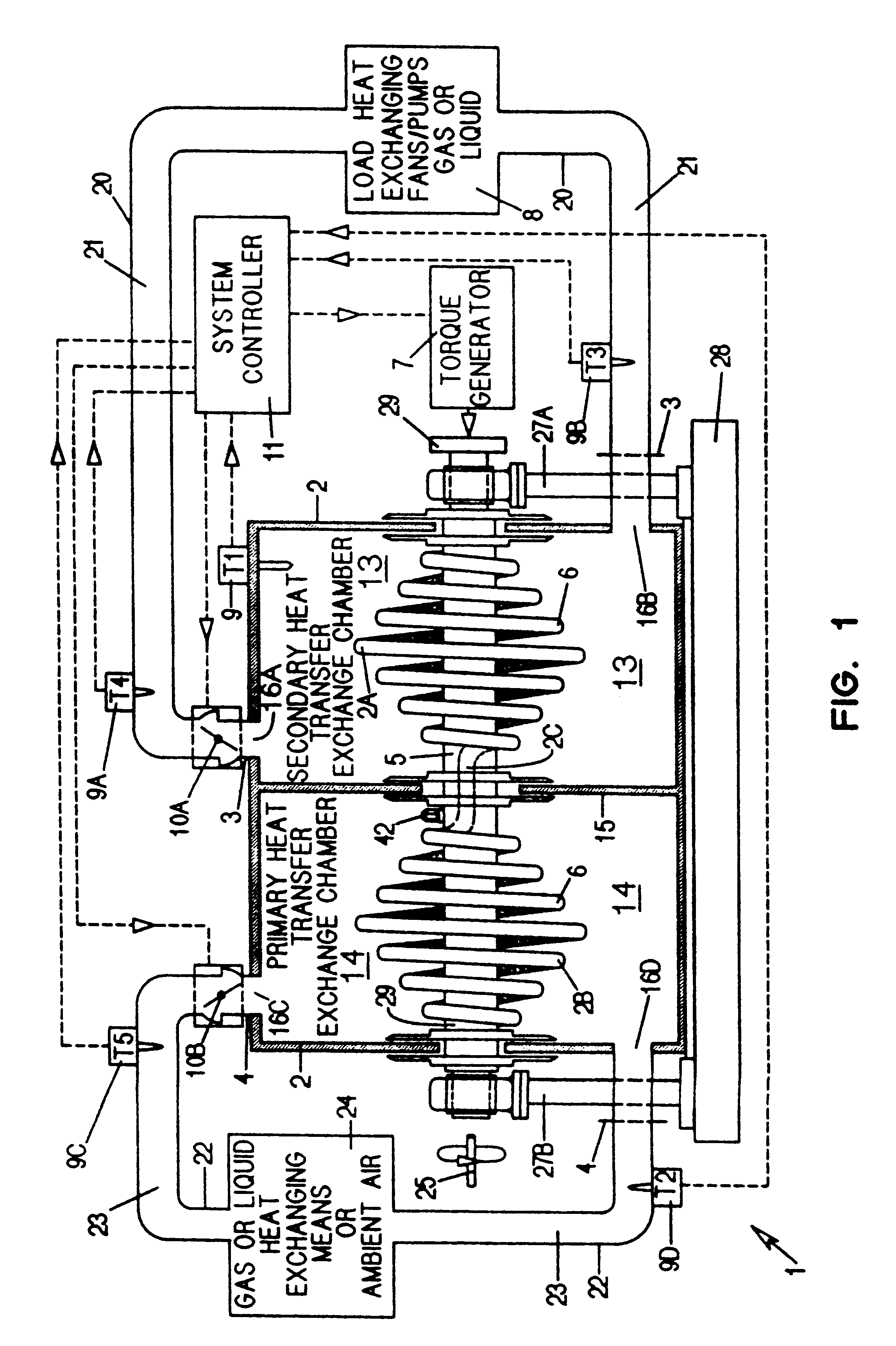
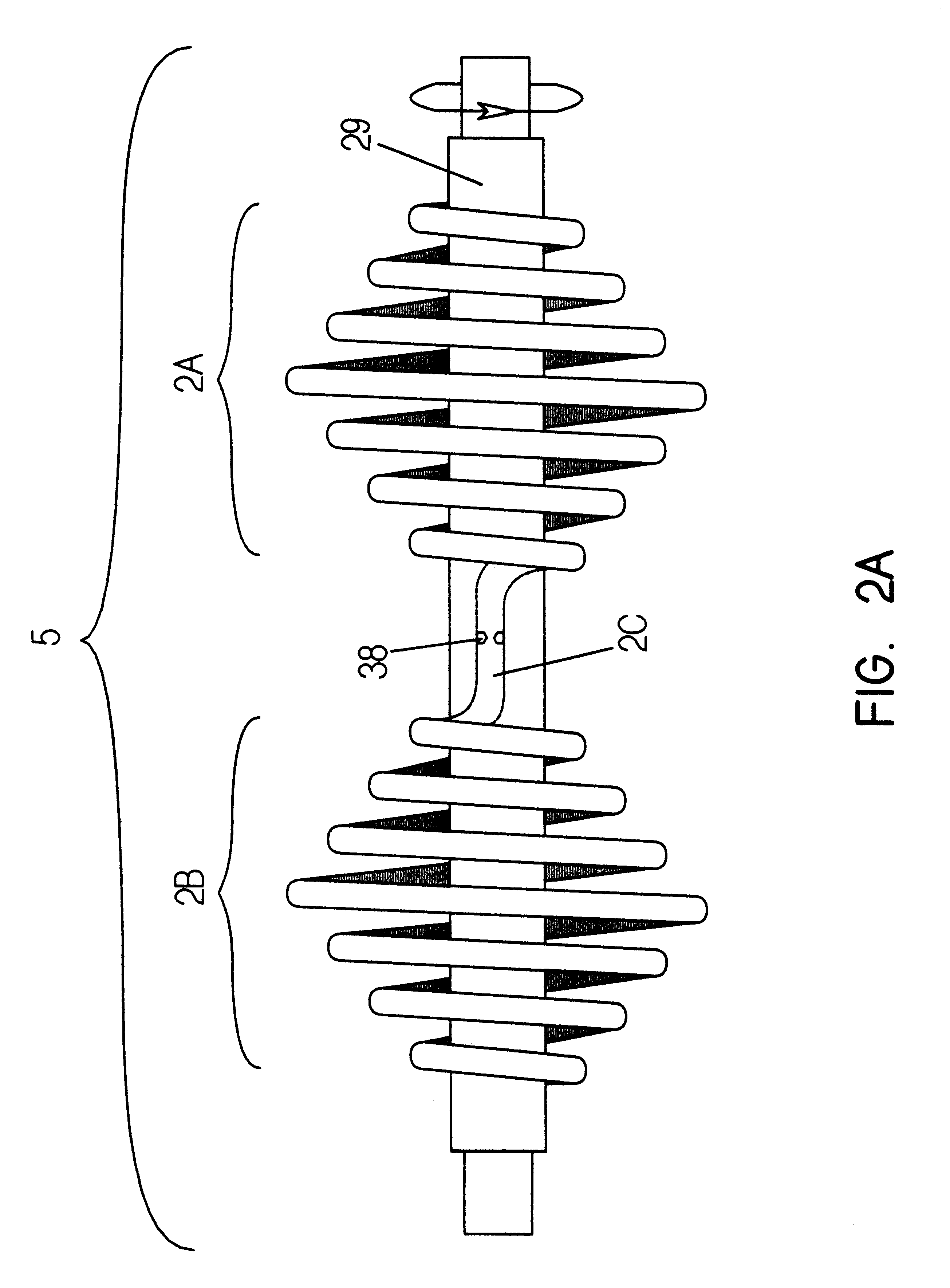
A heat transfer engine having cooling and heating modes of reversible operation, in which heat can be effectively transferred within diverse user environments for cooling, heating and dehumidification applications. The heat transfer engine of the present invention includes a rotor structure which is rotatably supported within a stator structure. The stator has primary and secondary heat exchanging chambers in thermal isolation from each other. The rotor has primary and secondary heat transferring portions within which a closed fluid flow circuit is embodied. The closed fluid flow circuit within the rotor has a spiraled fluid-return passageway extending along its rotary shaft, and is charged with a refrigerant which is automatically circulated between the primary and secondary heat transferring portions of the rotor when the rotor is rotated within an optimized angular velocity range under the control of a temperature-responsive system controller. During the cooling mode of operation, the primary heat transfer portion of the rotor carries out an evaporation function within the primary heat exchanging chamber of the stator structure, while the secondary heat transfer portion of the rotor carries out a condenser function within the secondary heat exchanging chamber of the stator. During the cooling mode of operation, a vapor-compression refrigeration process is realized by the primary heat transfer portion of the rotor performing an evaporation function within the primary heat exchanging chamber of the stator structure, while the secondary heat transfer portion of the rotor performs a condenser function within the secondary heat exchanging chamber of the stator. During the heating mode of operation, a vapor-compression refrigeration process is realized by the primary heat transfer portion of the rotor performing a condenser function within the primary heat exchanging chamber of the stator structure, while the secondary heat transfer portion of the rotor performs an evaporation function within the secondary heat exchanging chamber of the stator. By virtue of the present invention, a technically feasible heat transfer engine is provided which avoids the need for conventional external compressors, while allowing the use of environmentally safe refrigerants. Various embodiments of the heat transfer engine are disclosed, in addition to methods of manufacture and fields and applications of use.
Owner:KELIX HEAT TRANSFER SYST
Centrifugal heat transfer engine and heat transfer systems embodying the same
InactiveUS6964176B2Simple methodReduce the introductionSelf-contained rotary compression machinesCompression machines with non-reversible cycleRotational axisThermal isolation
A heat transfer engine having cooling and heating modes of reversible operation, in which heat can be effectively transferred within diverse user environments for cooling, heating and dehumidification applications. The heat transfer engine of the present invention includes a rotor structure which is rotatably supported within a stator structure. The stator has primary and secondary heat exchanging chambers in thermal isolation from each other. The rotor has primary and secondary heat transferring portions within which a closed fluid flow circuit is embodied. The closed fluid flow circuit within the rotor has a spiraled fluid-return passageway extending along its rotary shaft, and is charged with a refrigerant which is automatically circulated between the primary and secondary heat transferring portions of the rotor when the rotor is rotated within an optimized angular velocity range under the control of a temperature-responsive system controller.
Owner:KELIX HEAT TRANSFER SYST
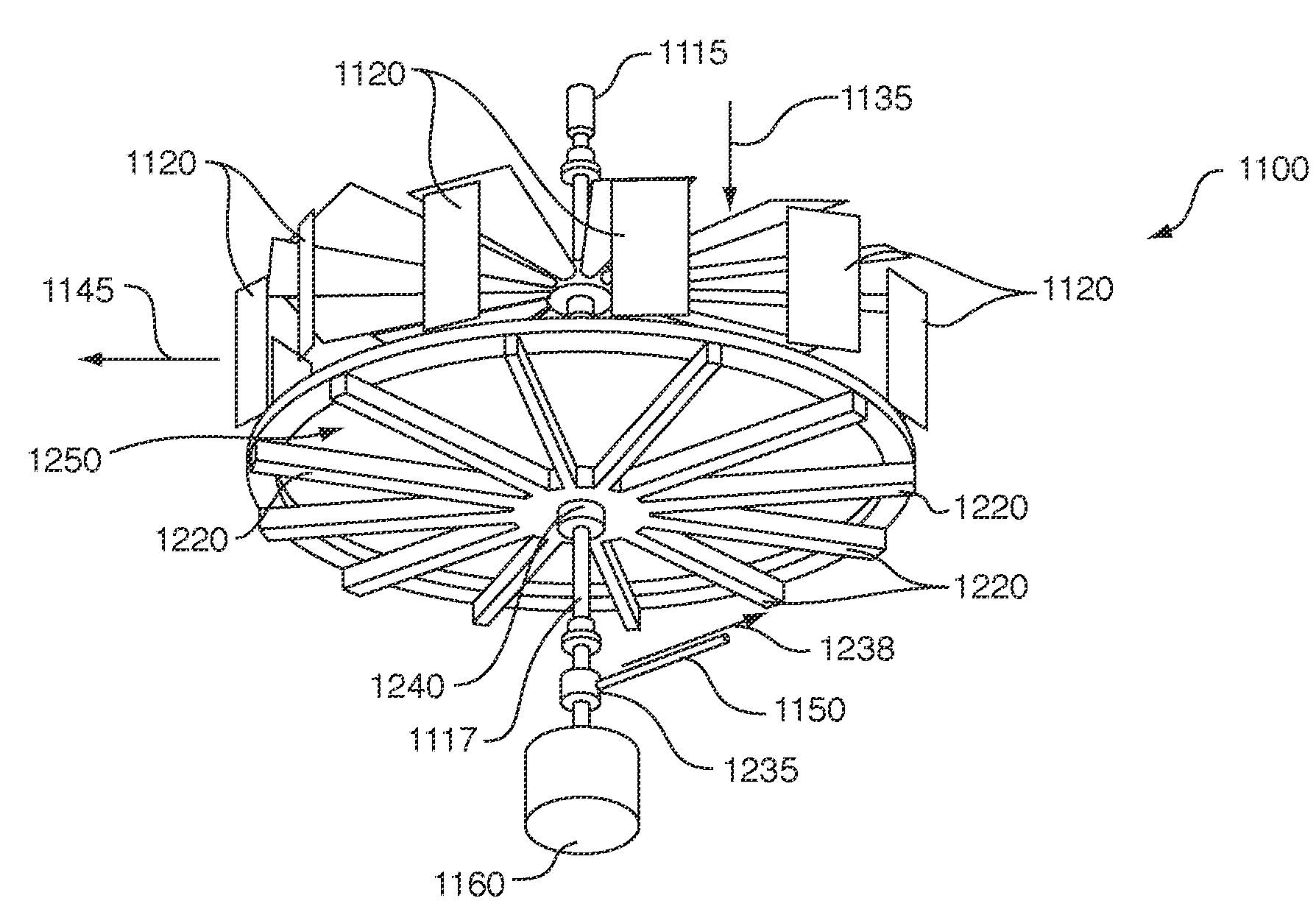
Turbo-compressor-condenser-expander
ActiveUS20100180631A1Improve featuresImprove heat transfer characteristicsCompressorPump componentsOpen frameworkEngineering
This invention provides an isothermal turbocompressor and a combined turbo-compressor-condenser-expander arrangement, which includes heat-transferring blades that are mounted on, or surround, individual conduits to promote air exchange and heat transfer. In operation, the open framework rotates in free air to promote heat exchange. This optimizes contact with free air during rotation. The assembly includes a first plurality of spokes extending radially outwardly from a first central hub to an outer perimeter with first radial conduits that transport refrigerant under centrifugal force and compression from the hub to the outer perimeter. The first radial conduits include heat exchanging blades. A second plurality of spokes extend radially outwardly from a second central hub at an axial spacing from the first central hub. This second plurality of spokes each includes a second thermally-insulated conduit that transports refrigerant from the outer perimeter to the second central hub. Axial conduits extend axially at the outer perimeter, and each interconnects each first radial conduit and each second radial conduit. At least some of the plurality of axial conduits include an axial blade in thermal communication with the conduit that promotes heat exchange radially. A motor rotates a central axis of the turbo-compressor-condenser-expander.
Owner:APPOLLO WIND TECH
Compositions comprising tetrafluoropropene and difluoromethane and uses thereof
The present invention relates to compositions for use in refrigeration, air-conditioning and heat pump systems wherein the composition comprises tetrafluoropropene and difluoromethane. The compositions of the present invention are useful in processes for producing cooling or heat, as heat transfer fluids, foam blowing agents, aerosol propellants, fire suppression, fire extinguishing agents, as power cycle working fluids and in methods for replacing HFC-134a, R410A, \R404A, or R507.
Owner:THE CHEMOURS CO FC LLC
Gas heat pump type air conditioner
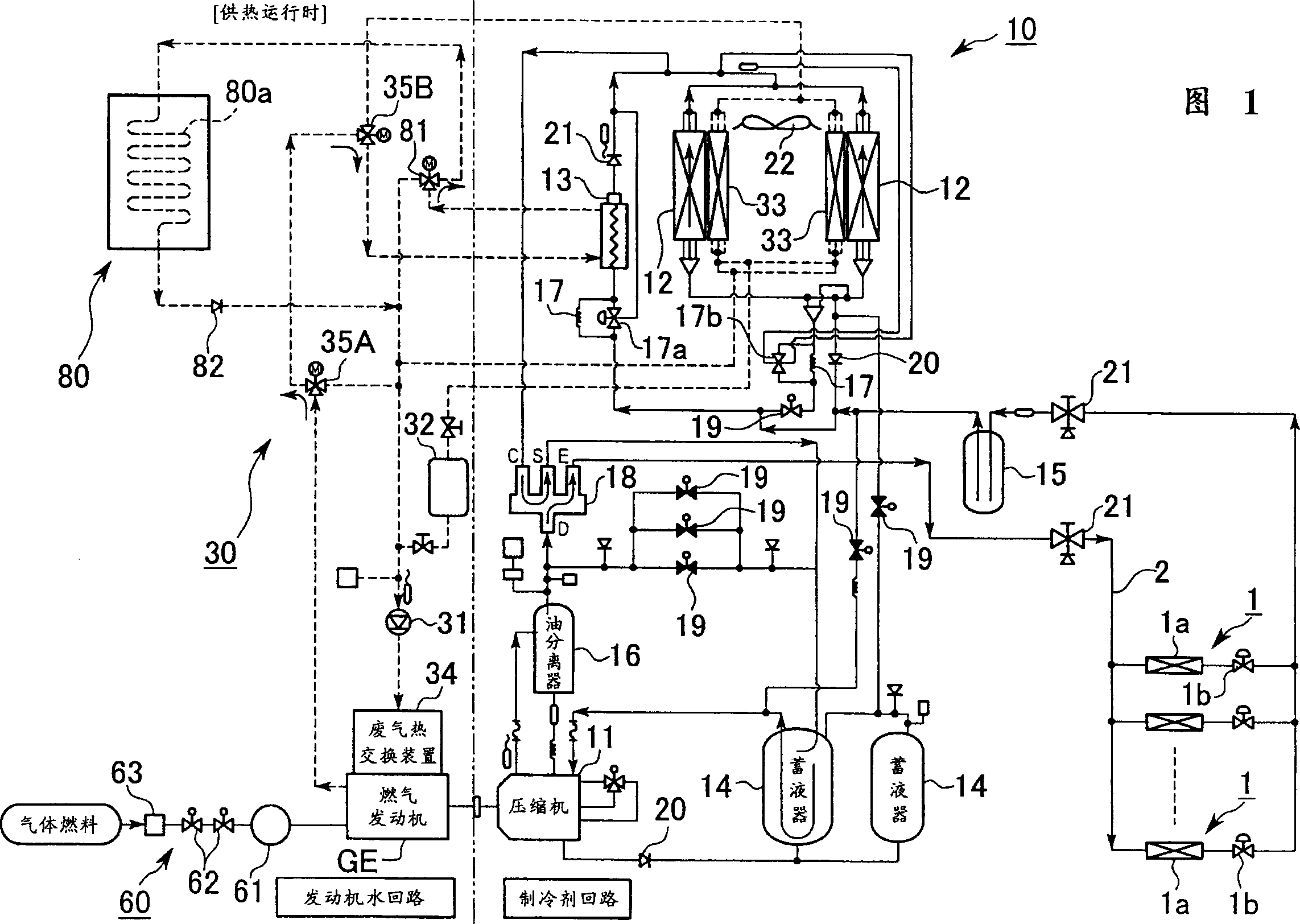
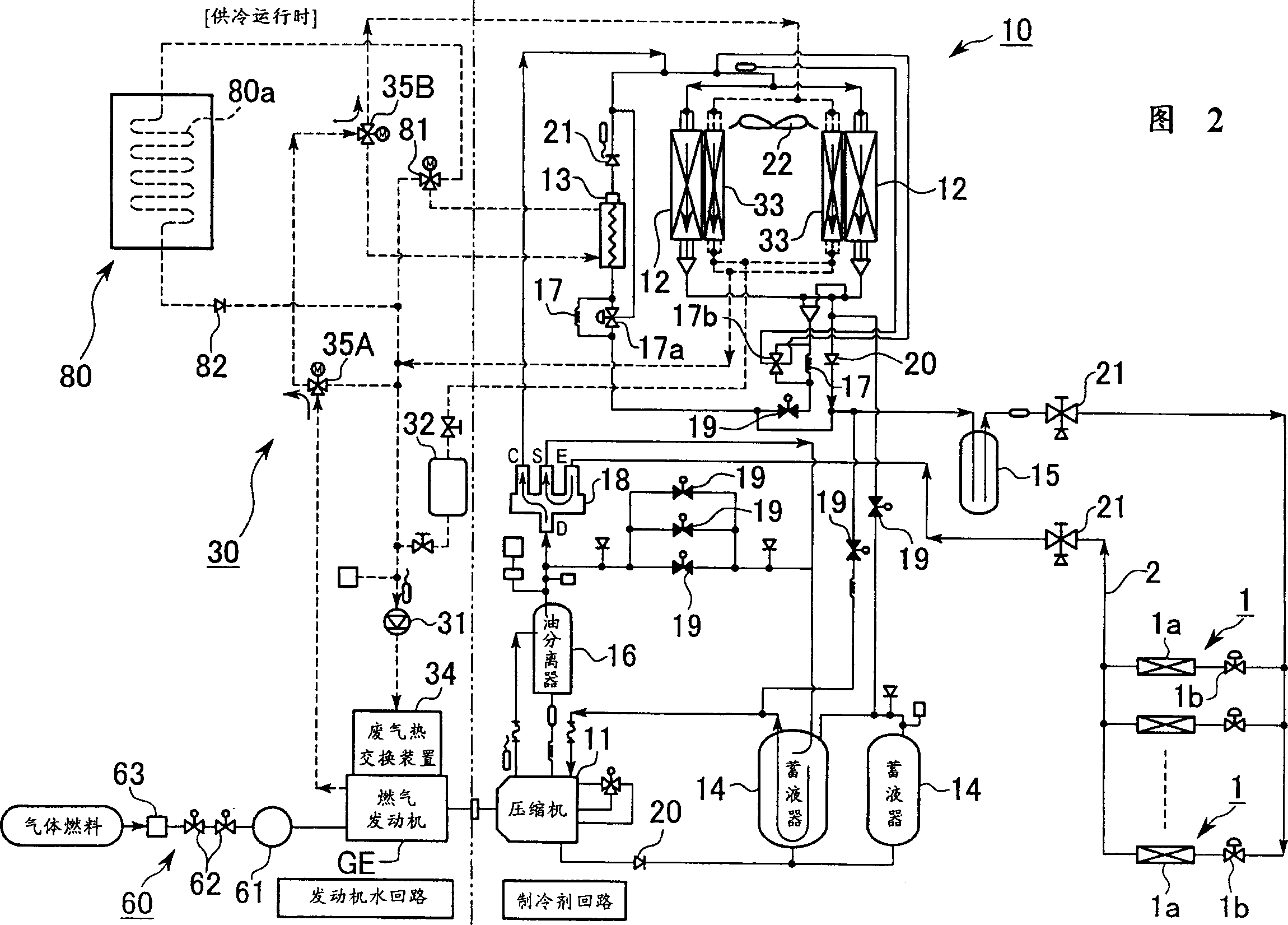
InactiveCN1403765AEasy accessIncreased ability to use waste heat to melt snowHeat pumpsInternal combustion piston enginesCompression deviceEngineering
In order to provide a gas heat pump type air conditioning device in which accessibility and maintenance operation are not disturbed due to snow in snowy areas, a gas heat pump type air conditioning device comprises a compression device (11) for which the driving source is a gas engine and forms a refrigerating cycle by circulating a refrigerant, a bypass pipe channel section (80) which is provided around space where an outdoor unit is installed and is separated from an engine-coolant-water system (30) of the gas engine via a channel change switching device (81), wherein waste heat exhausted from the gas engine is collected back into the engine-coolant-water, and the refrigerant is heated by the engine-coolant-water so as to enhance air heating capacity.
Owner:MITSUBISHI HEAVY IND LTD
Compact energy cycle construction utilizing some combination of a scroll type expander, pump, and compressor for operating according to a rankine, an organic rankine, heat pump, or combined organic rankine and heat pump cycle
InactiveUS20130232975A1More compactLow costRotary/oscillating piston combinations for elastic fluidsHeat pumpsWorking fluidOrganic Rankine cycle
A compact energy cycle construction that operates as or in accordance with a Rankine, Organic Rankine, Heat Pump, or Combined Organic Rankine and Heat Pump Cycle, comprising a compact housing of a generally cylindrical form with some combination of a scroll type expander, pump, and compressor disposed therein to share a common shaft with a motor or generator and to form an integrated system, with the working fluid of the system circulating within the housing as a torus along the common shaft and toroidally within the housing as the system operates.
Owner:AIR SQUARED
Centrifugal heat transfer engine and heat transfer systems embodying the same
InactiveUS6321547B1Simple methodImprove heat transfer performanceSelf-contained rotary compression machinesIndirect heat exchangersMajor and minorRotational axis
A heat transfer engine having cooling and heating modes of reversible operation, in which heat can be effectively transferred within diverse user environments for cooling, heating and dehumidification applications. The heat transfer engine of the present invention includes a rotor structure which is rotatably supported within a stator structure. The stator has primary and secondary heat exchanging chambers in thermal isolation from in each other. The rotor has primary and secondary heat transferring portions within which a closed fluid flow circuit is embodied. The closed fluid flow circuit within the rotor has a spiralled fluid-return passageway extending along its rotary shaft, and is charged with a refrigerant which is automatically circulated between the primary and secondary heat transferring portions of the rotor when the rotor is rotated within an optimized angular velocity range under the control of a temperature-responsive system controller. During the cooling mode of operation, the primary heat transfer portion of the rotor carries out an evaporation function within the primary heat exchanging chamber of the stator structure, while the secondary heat transfer portion of the rotor carries out a condenser function within the secondary heat exchanging chamber of the stator. During the cooling mode of operation, a vapor-compression refrigeration process is realized by the primary heat transfer portion of the rotor performing an evaporation function within the primary heat exchanging chamber of the stator structure, while the secondary heat transfer portion of the rotor performs a condenser function within the secondary heat exchanging chamber of the stator. During the heating mode of operation, a vapor-compression refrigeration process is realized by the primary heat transfer portion of the rotor performing a condenser function within the primary heat exchanging chamber of the stator structure, while the secondary heat transfer portion of the rotor performs an evaporation function within the secondary heat exchanging chamber of the stator. By virtue of present invention, a technically feasible heat transfer engine is provided which avoids the need for conventional external compressors, while allowing the use of environmentally safe refrigerants. Various embodiments of the heat transfer engine are disclosed, in addition to methods of manufacture and fields and applications of use.
Owner:KELIX HEAT TRANSFER SYST
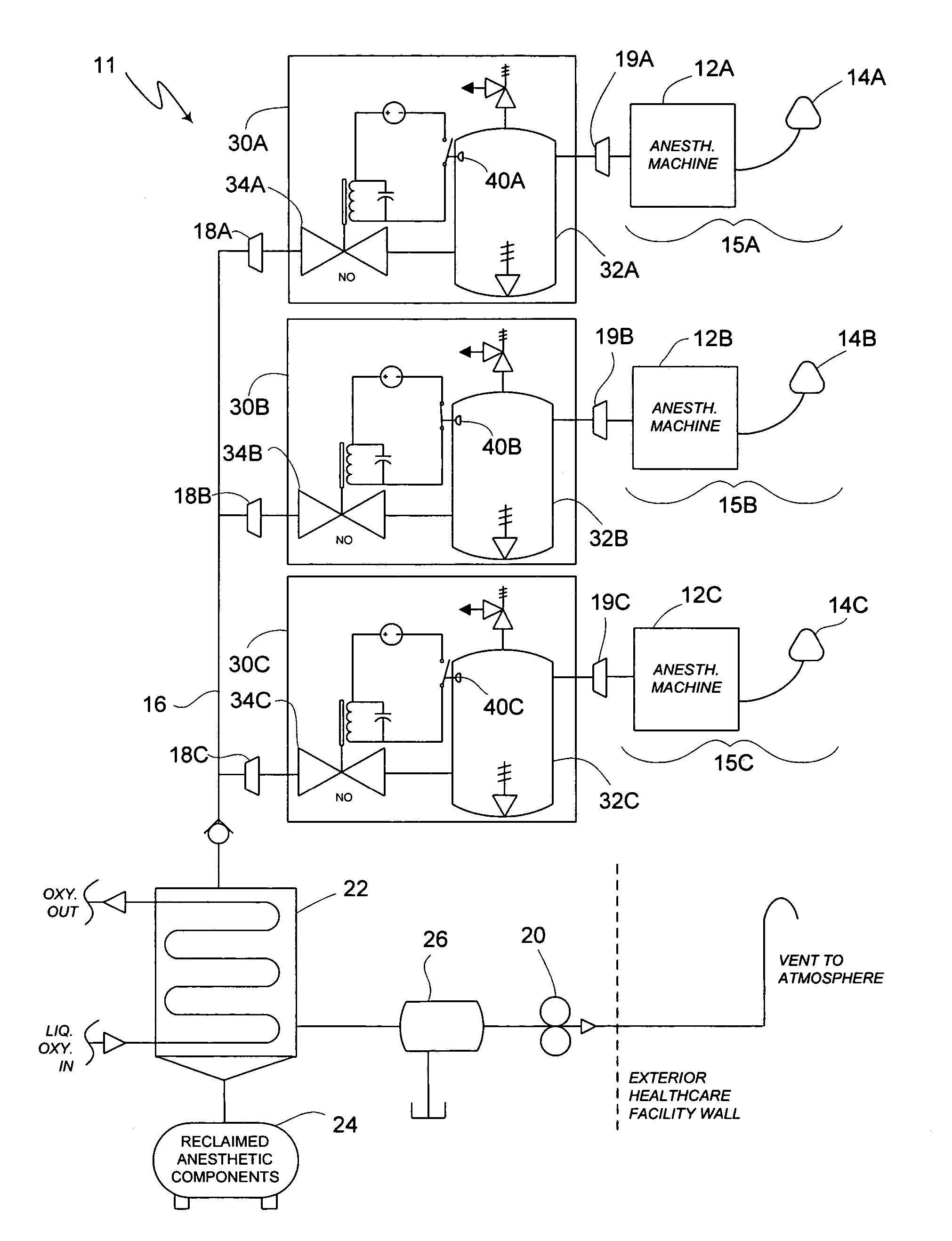
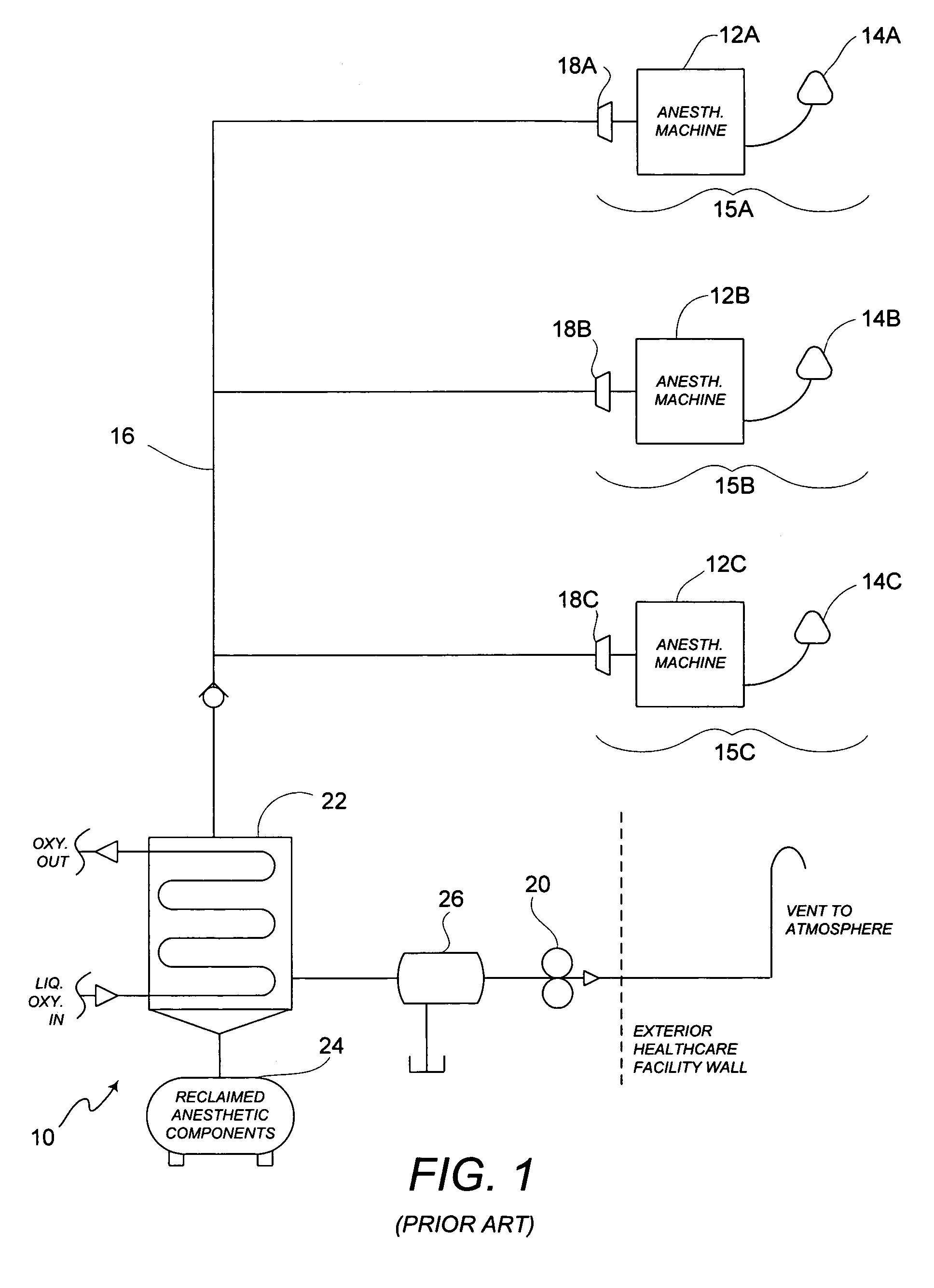
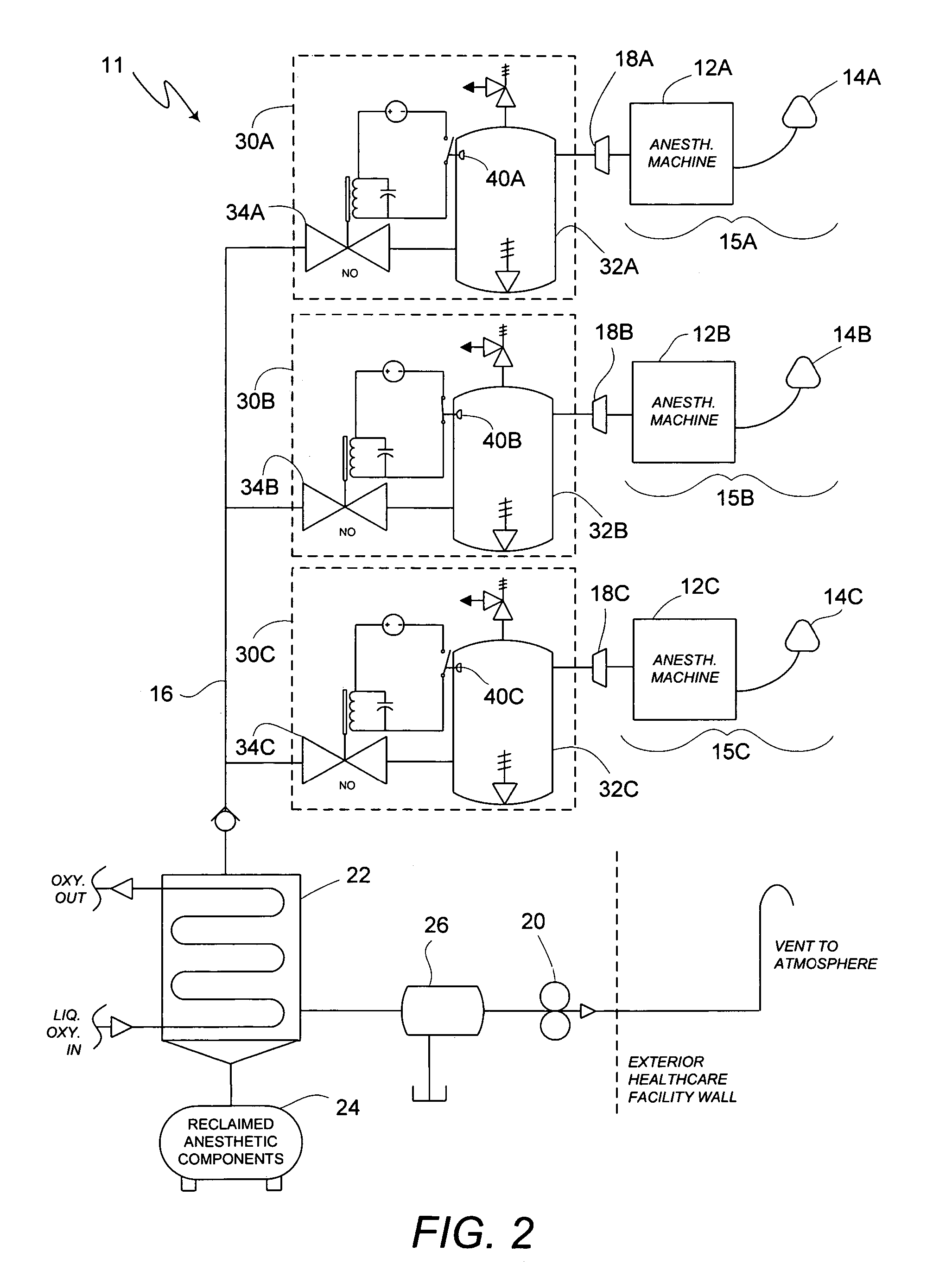
Method of low flow anesthetic gas scavenging and dynamic collection apparatus therefor
A method and system for removal of nitrous oxide and volatile halocarbon gas components from waste anesthetic gases using a low-flow scavenging or reclamation system preferably including an intelligent waste anesthetic gas collection unit fluidly coupled between each individual anesthetic machine and the waste gas evacuation manifold. Through a system including a collection chamber, a pressure detector, and a exhaust valve which is actuated based on the detected pressure in the collection chamber, the waste anesthetic gas collection unit allows flow to the waste suction manifold only in the presence of waste gas and interrupts all flow into the suction manifold when no waste gas is present.
Owner:ANESTHETIC GAS RECHAMATION LLC
Centrifugal heat transfer engine and heat transfer systems embodying the same
InactiveUS6334323B1Simple methodImprove heat transfer performanceSelf-contained rotary compression machinesIndirect heat exchangersThermal isolationRotational axis
A heat transfer engine having cooling and heating modes of reversible operation, in which heat can be effectively transferred within diverse user environments for cooling, heating and dehumidification applications. The heat transfer engine of the present invention includes a rotor structure which is rotatably supported within a stator structure. The stator has primary and secondary heat exchanging chambers in thermal isolation from in each other. The rotor has primary and secondary heat transferring portions within which a closed fluid flow circuit is embodied. The closed fluid flow circuit within the rotor has a spiralled fluid-return passageway extending along its rotary shaft, and is charged with a refrigerant which is automatically circulated between the primary and secondary heat transferring portions of the rotor when the rotor is rotated within an optimized angular velocity range under the control of a temperature-responsive system controller. During the cooling mode of operation, the primary heat transfer portion of the rotor carries out an evaporation function within the primary heat exchanging chamber of the stator structure, while the secondary heat transfer portion of the rotor carries out a condenser function within the secondary heat exchanging chamber of the stator. During the cooling mode of operation, a vapor-compression refrigeration process is realized by the primary heat transfer portion of the rotor performing an evaporation function within the primary heat exchanging chamber of the stator structure, while the secondary heat transfer portion of the rotor performs a condenser function within the secondary heat exchanging chamber of the stator. During the heating mode of operation, a vapor-compression refrigeration process is realized by the primary heat transfer portion of the rotor performing a condenser function within the primary heat exchanging chamber of the stator structure, while the secondary heat transfer portion of the rotor performs an evaporation function within the secondary heat exchanging chamber of the stator. By virtue of present invention, a technically feasible heat transfer engine is provided which avoids the need for conventional external compressors, while allowing the use of environmentally safe refrigerants. Various embodiments of the heat transfer engine are disclosed, in addition to methods of manufacture and fields and applications of use.
Owner:KIDWELL ENVIROMENTAL LTD INC
Rotary compressor with fluidic passages in rotor
The problems of prior compressor structures relying upon conventional check valves are obviated by using, instead, flow control passages which operate to control flow while avoiding mechanical moving elements which may become problematical.
Owner:LENOVO PC INT
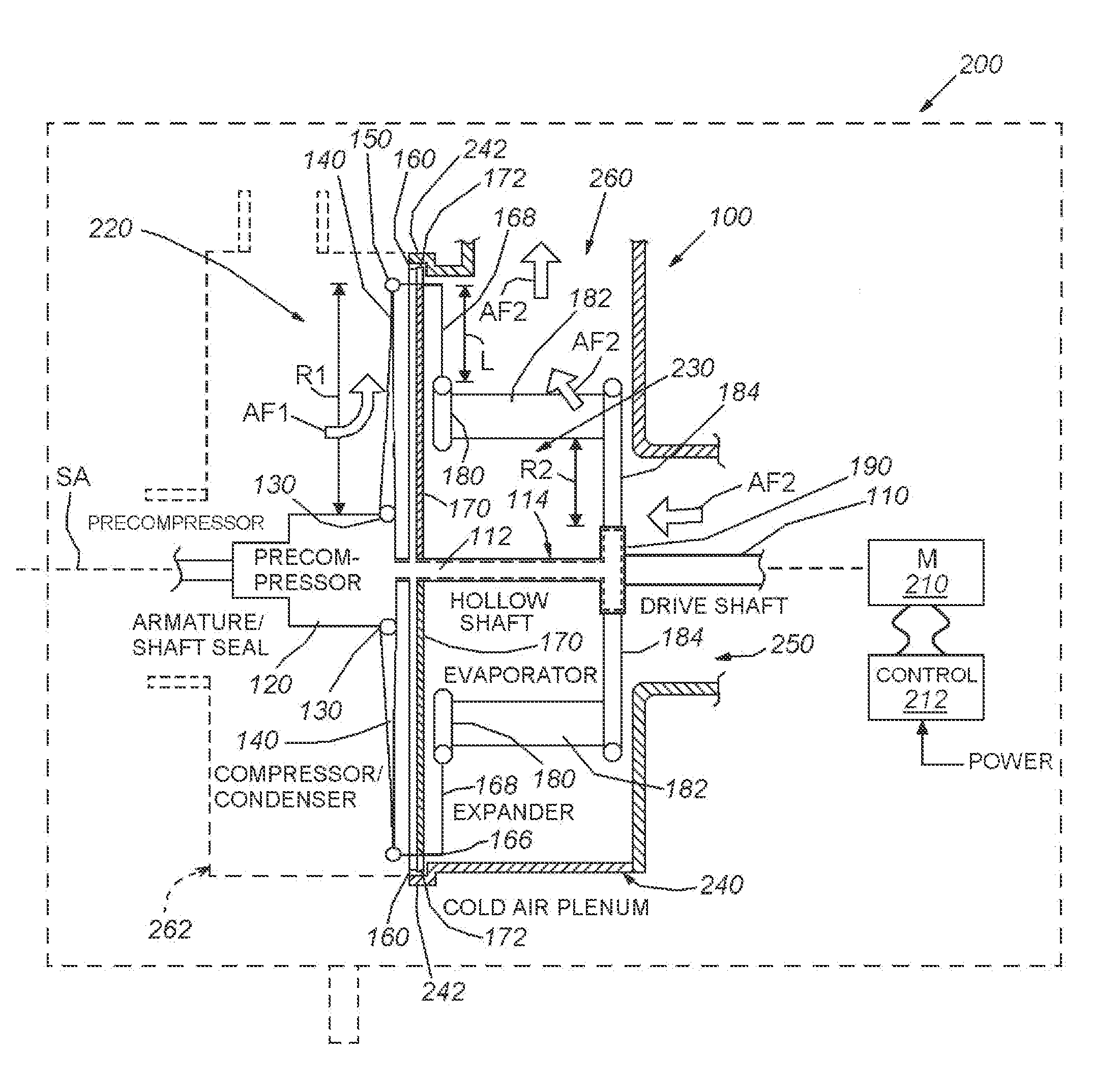
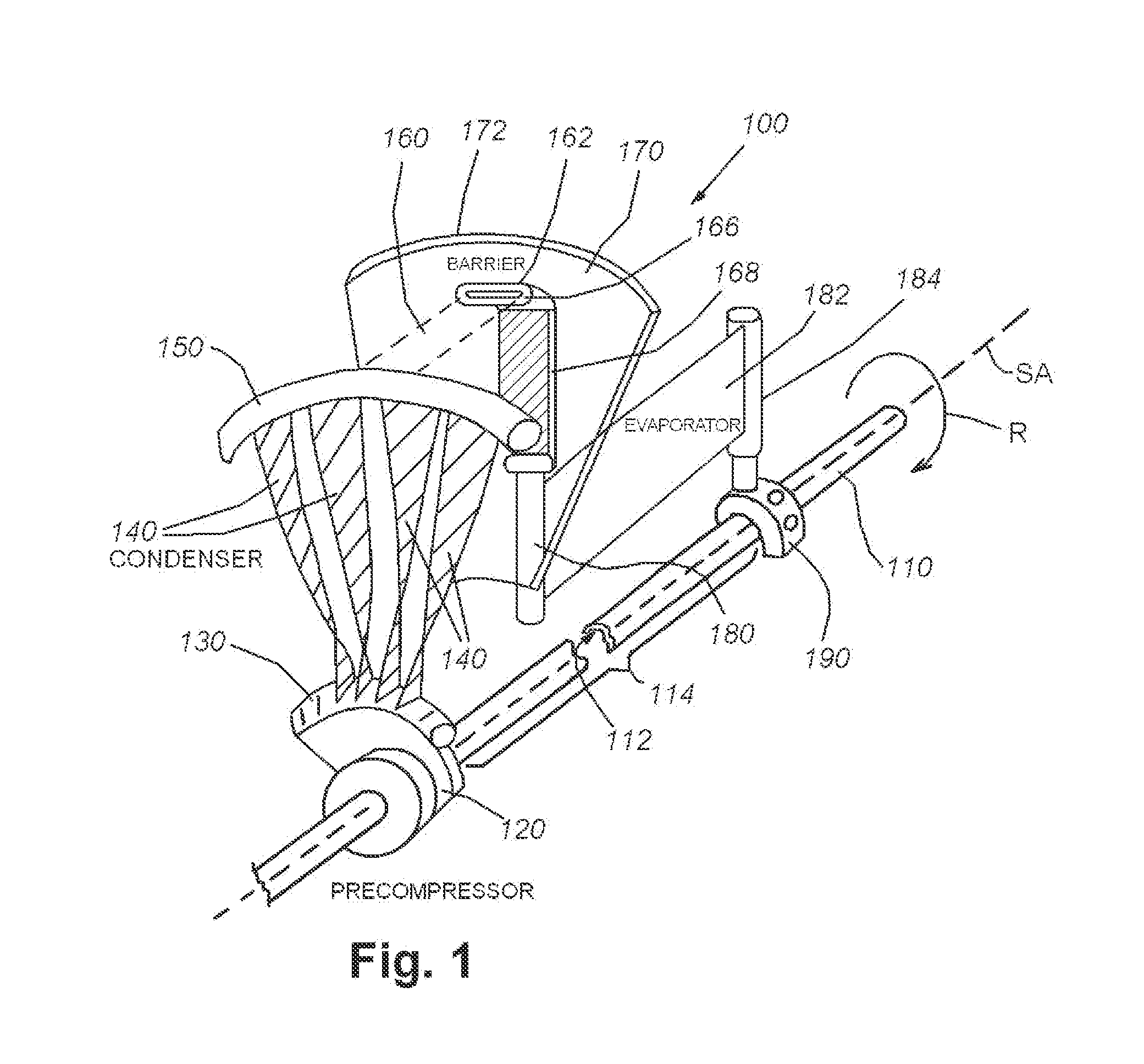
Isothermal-turbo-compressor-expander-condenser-evaporator device
InactiveUS20160138815A1Minimize air leakageSelf-contained rotary compression machinesCompression machines with non-reversible cycleEvaporationEngineering
This invention provides an isothermal turbo-compressor-expander-condenser-evaporator in a single integral arrangement that is suitable for a variety of compact arrangements, such as a window air-conditioner and / or automotive-based unit. This arrangement avoids the use of rotary fluid joints and maintains the entire fluid cycle, including compression, condensation, expansion and evaporation within a single rotating shaft-based structure, with the compressor / condenser section and the expansion / evaporator section separated from each other in separate spaces and / or plena by a rotating, insulated barrier disc and associated seal.
Owner:APPOLLO WIND TECH
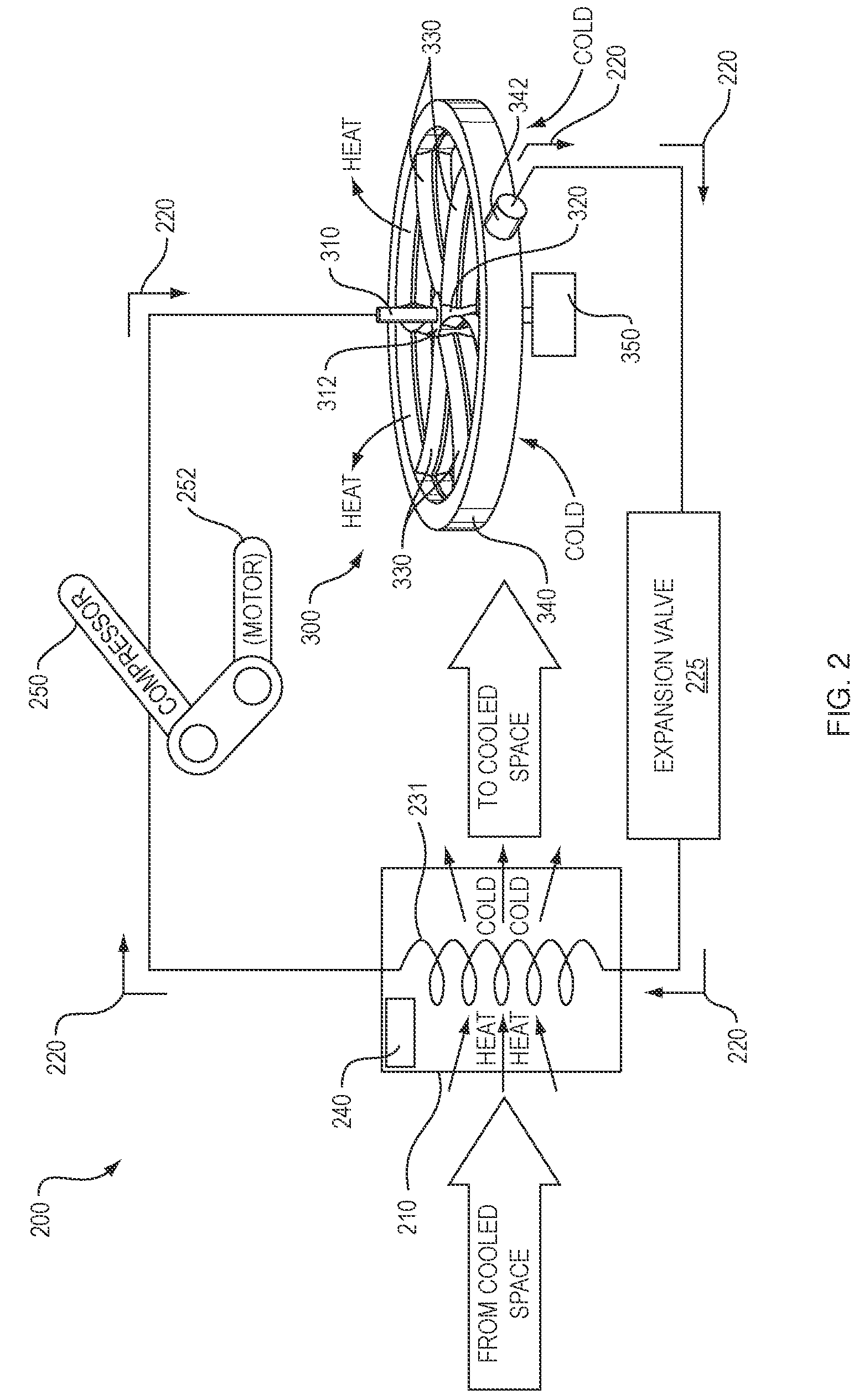
Rotating air conditioner and method
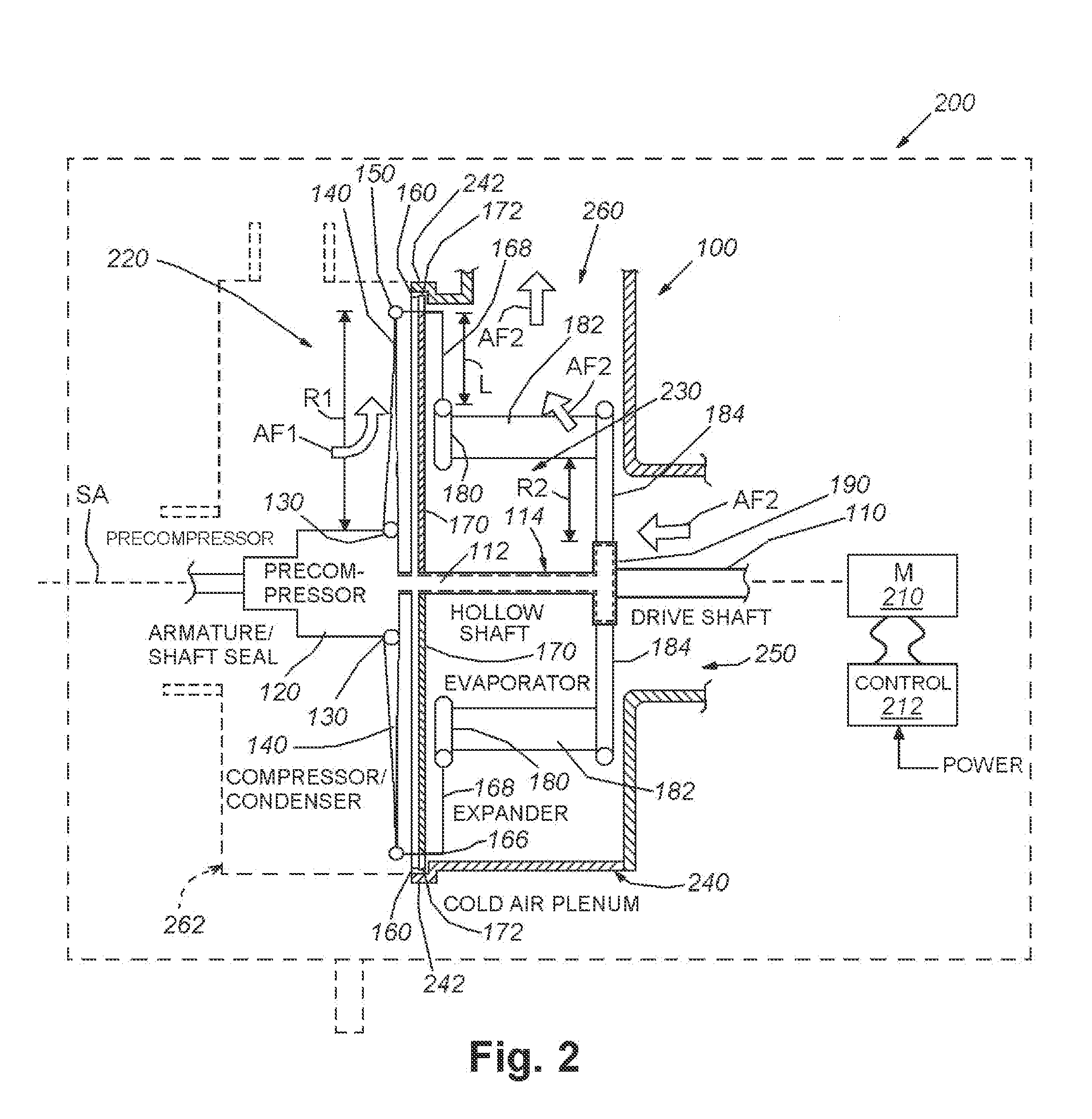
ActiveUS20150089973A1Reduce maintenanceSmall and portableSelf-contained rotary compression machinesCompression machines with non-reversible cycleEngineeringEvaporator
A rotating air conditioner apparatus and method comprising an elongated shaft, whereby one or more of a condenser coil, an evaporator coil, and a compressor rotate around the elongated shaft. In one embodiment, balancing weights rotate with the shaft and are positioned to prevent uneven rotation of rotating air conditioner during operation. The evaporator and condenser contain a plurality of fins and / or fan blades and coils for refrigerant. Inlets and / or adjustably directed outlets on the evaporator and / or the condenser provide for circulation of air through the rotating air conditioner apparatus.
Owner:KOBAYASHI HERBERT S
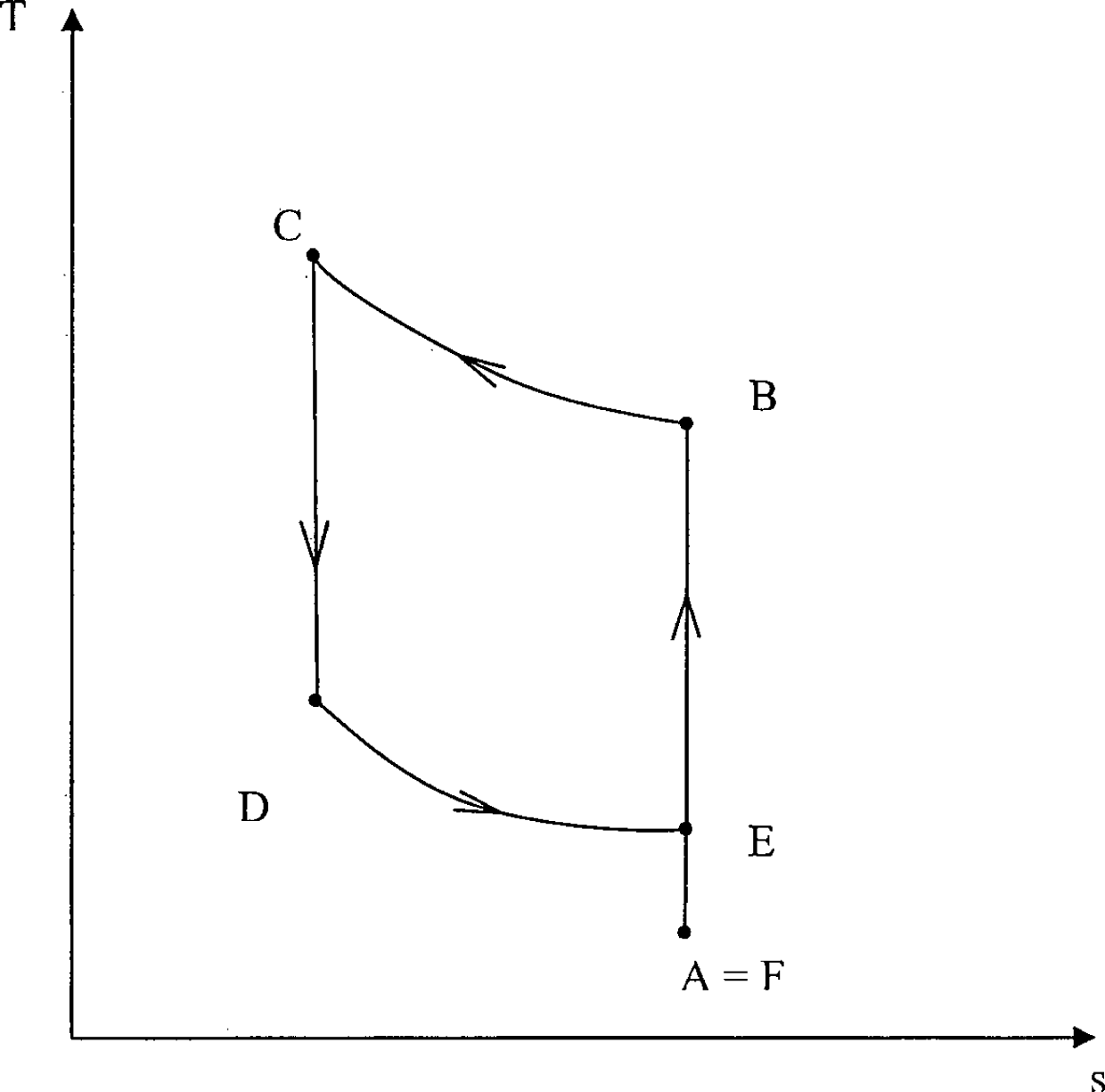
Method for converting thermal energy at a low temperature into thermal energy at a relatively high temperature by means of mechanical energy, and vice versa
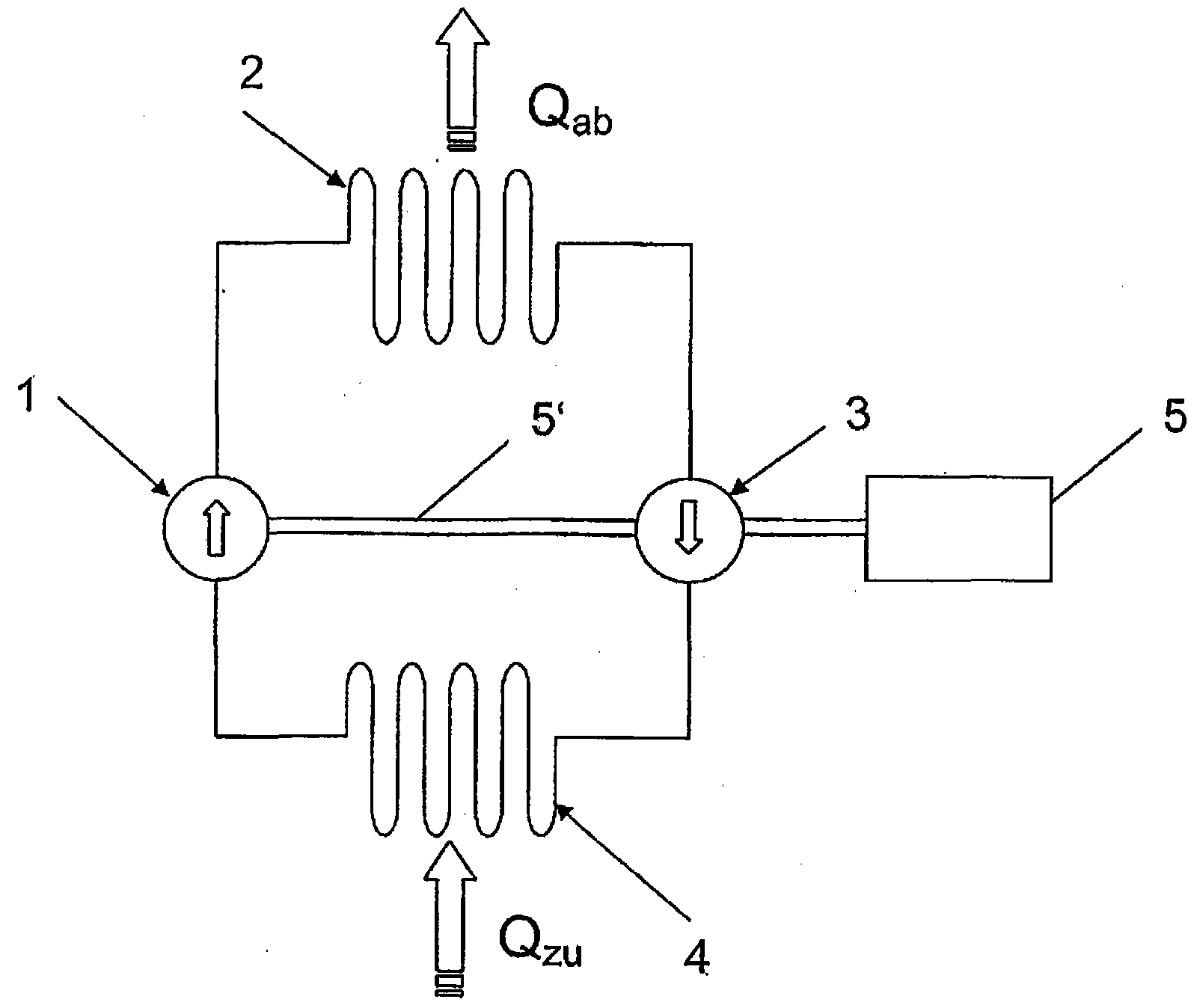
ActiveCN101883958AIncrease pressureKeep the energy flowingSelf-contained rotary compression machinesCyclic processThermal energy
Method for converting thermal energy at a low temperature into thermal energy at a relatively high temperature by means of mechanical energy, and vice versa, with a working medium which runs through a closed thermodynamic circulation process, wherein the circulation process has the following working steps: - reversible adiabatic compression of the working medium, - isobaric conduction away of heat from the working medium, - reversible adiabatic relaxing of the working medium, - isobaric supply of heat to the working medium, and wherein the increase or decrease in pressure of the working medium is produced during the compression or relaxing, increasing or decreasing the centrifugal force acting on the working medium, with the result that the flow energy of the working medium is essentially retained during the compression or relaxing process.
Owner:风和日暖科技有限责任公司
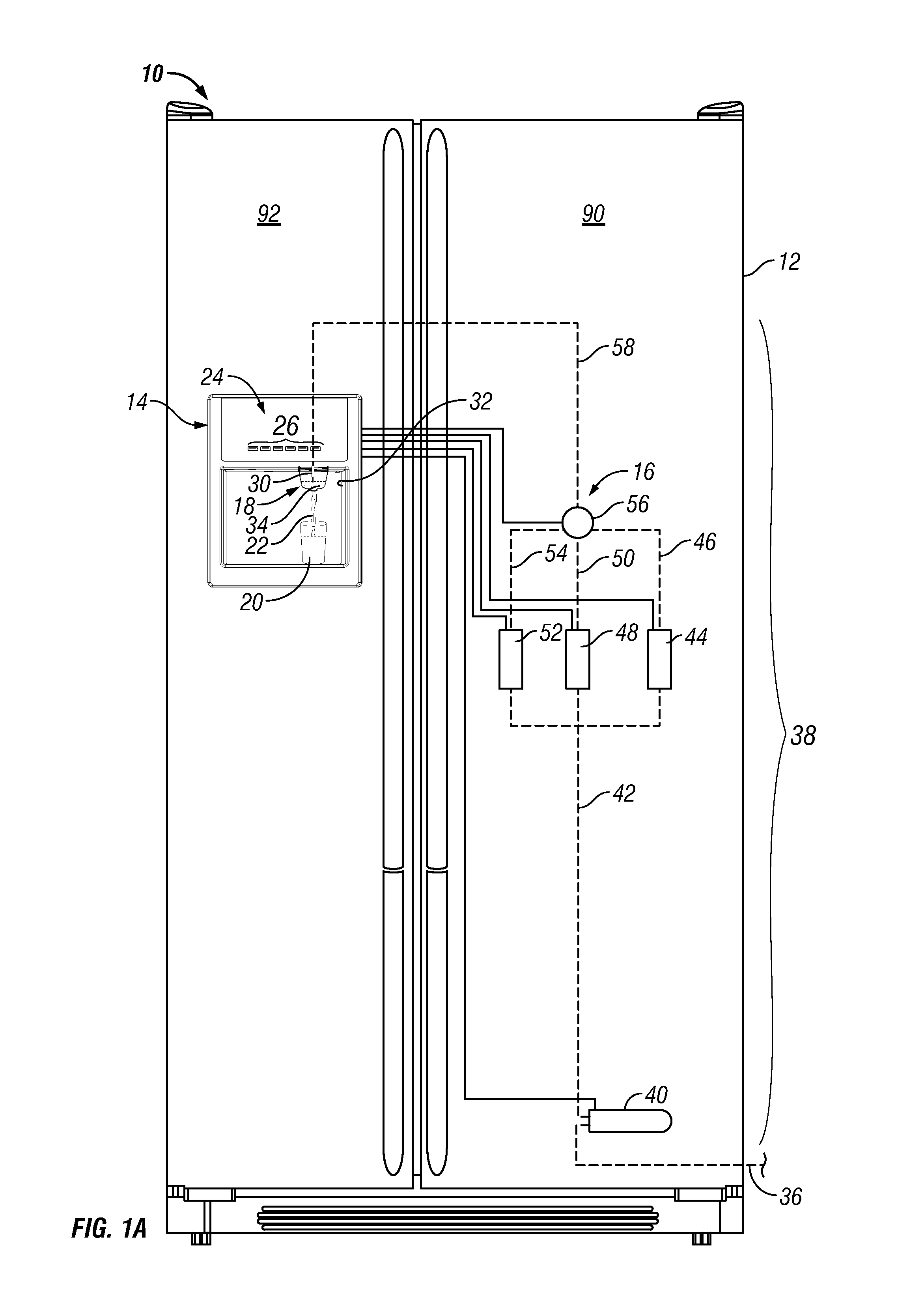
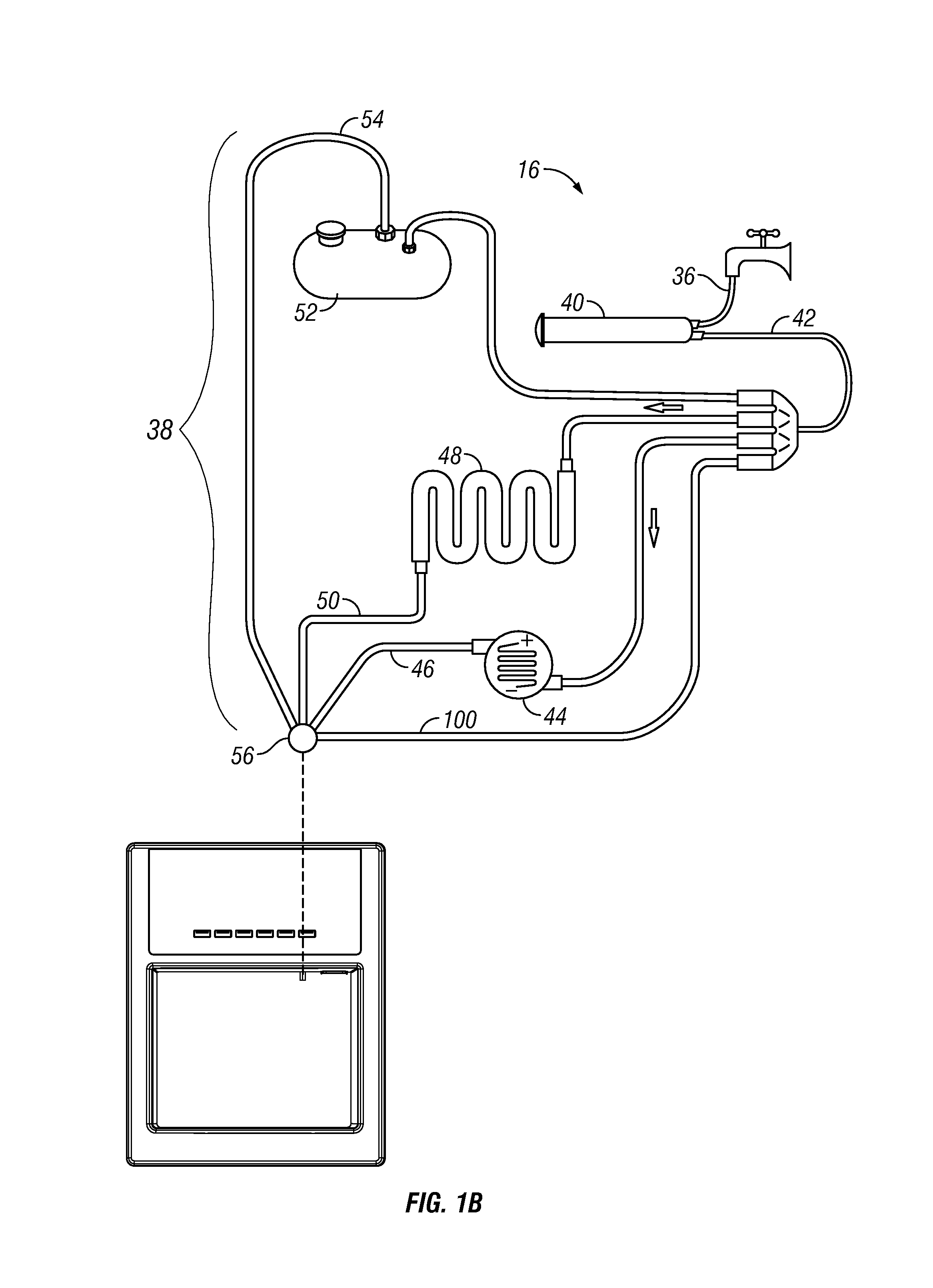
Apparatuses and methods for a refrigerator having liquid conditioning and enhancement components for enhanced beverage dispensing
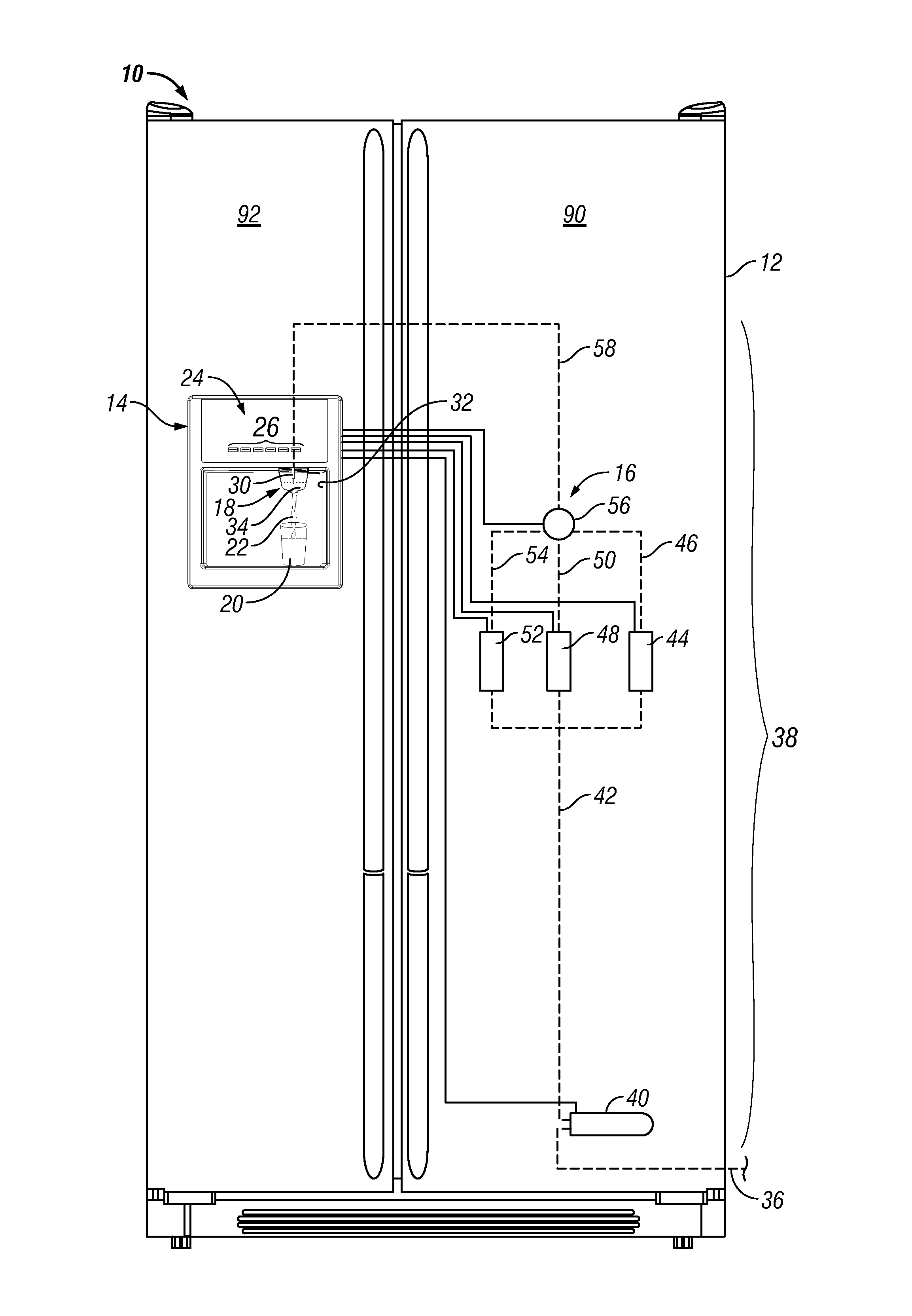
ActiveUS9556011B2Minimize potential for back contaminationOpening closed containersBottle/container closureEngineeringRefrigerated temperature
Apparatuses and methods for conditioning a liquid stream with a liquid dispensing system associated with a refrigerator, preparing an enhanced beverage using one or more of the individually conditioned liquid streams and a liquid enhancement device and minimizing the potential for back contamination of the liquid dispensing system are provided.
Owner:WHIRLPOOL CORP
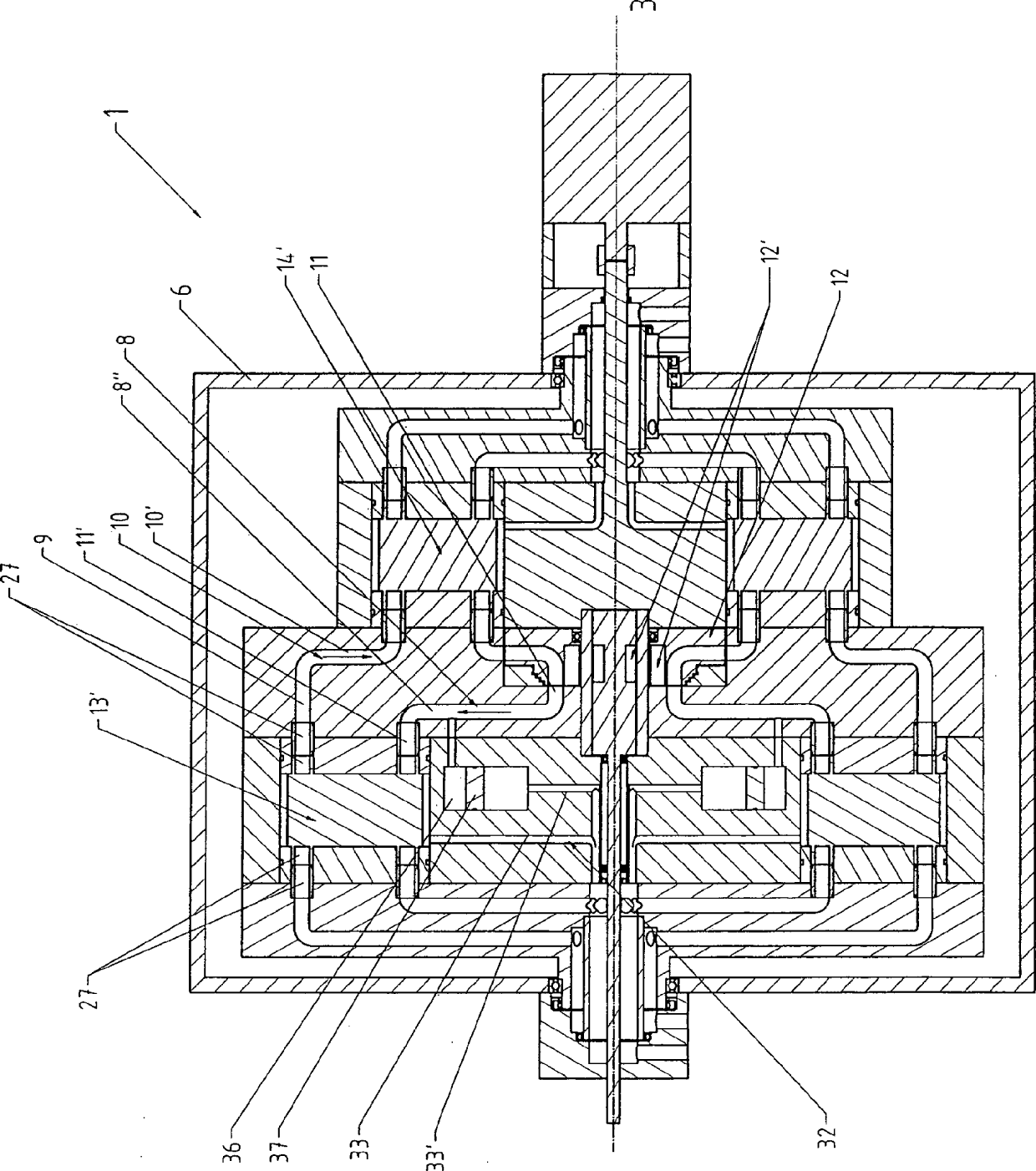
Device and method for converting thermal energy
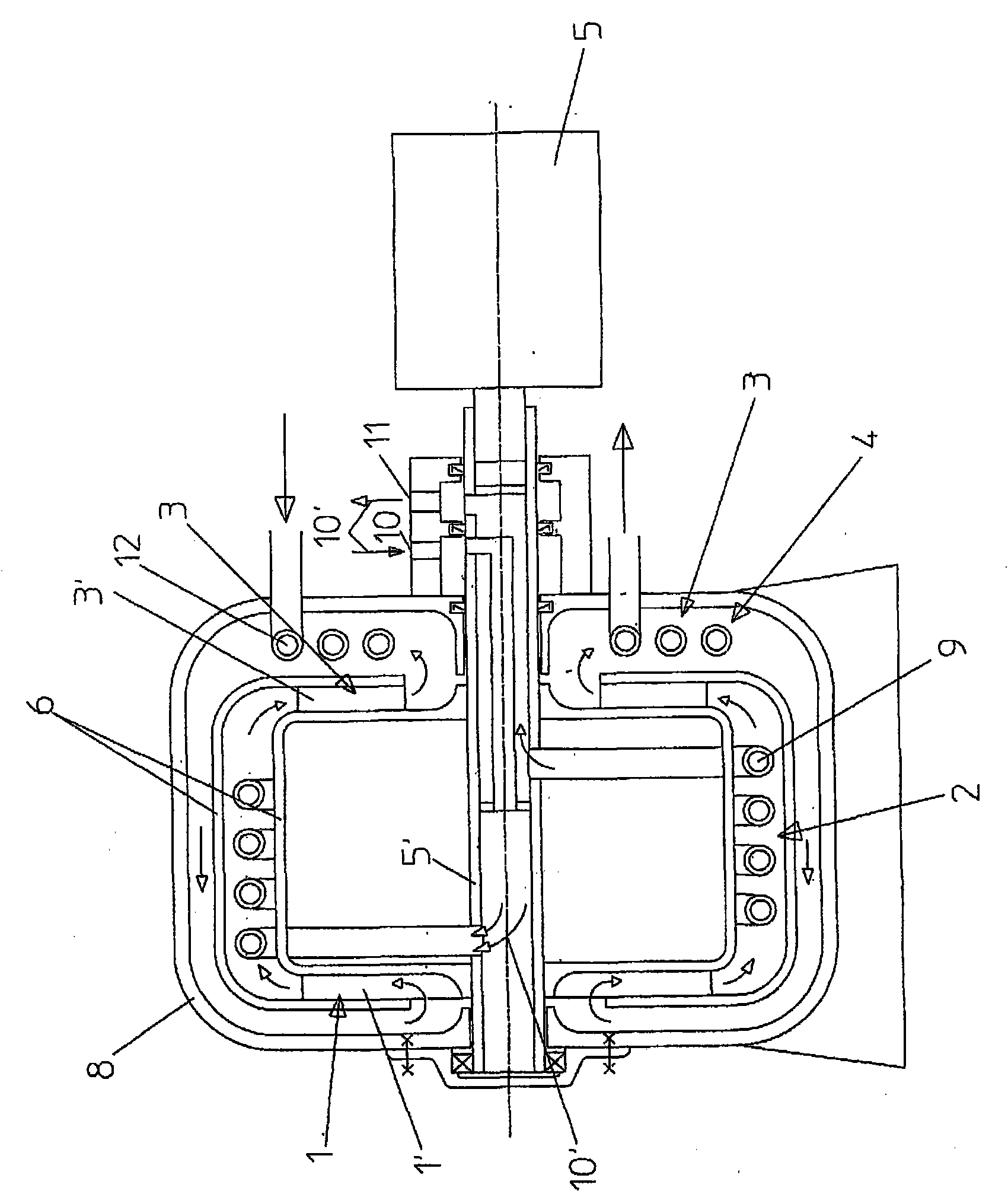
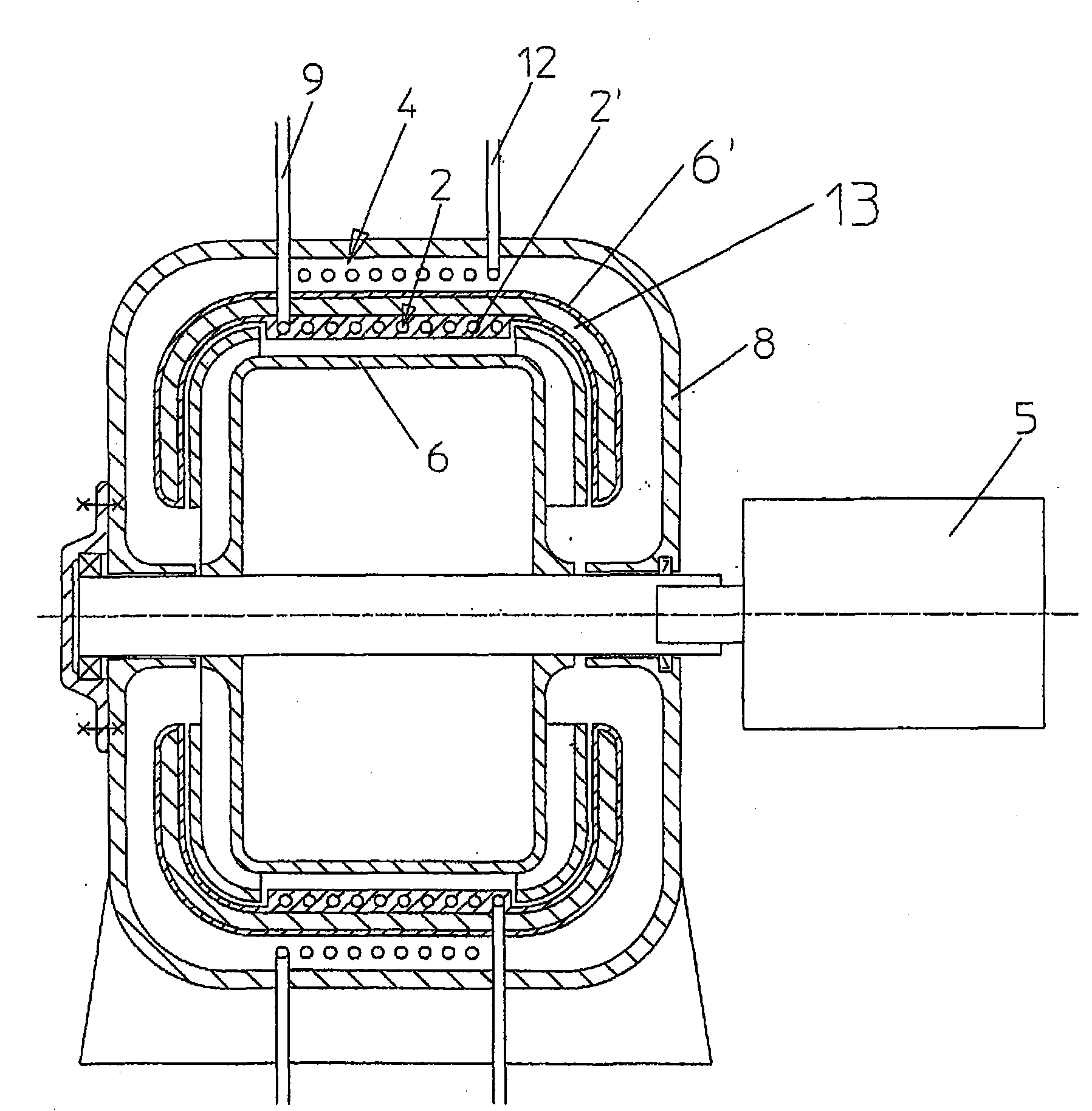
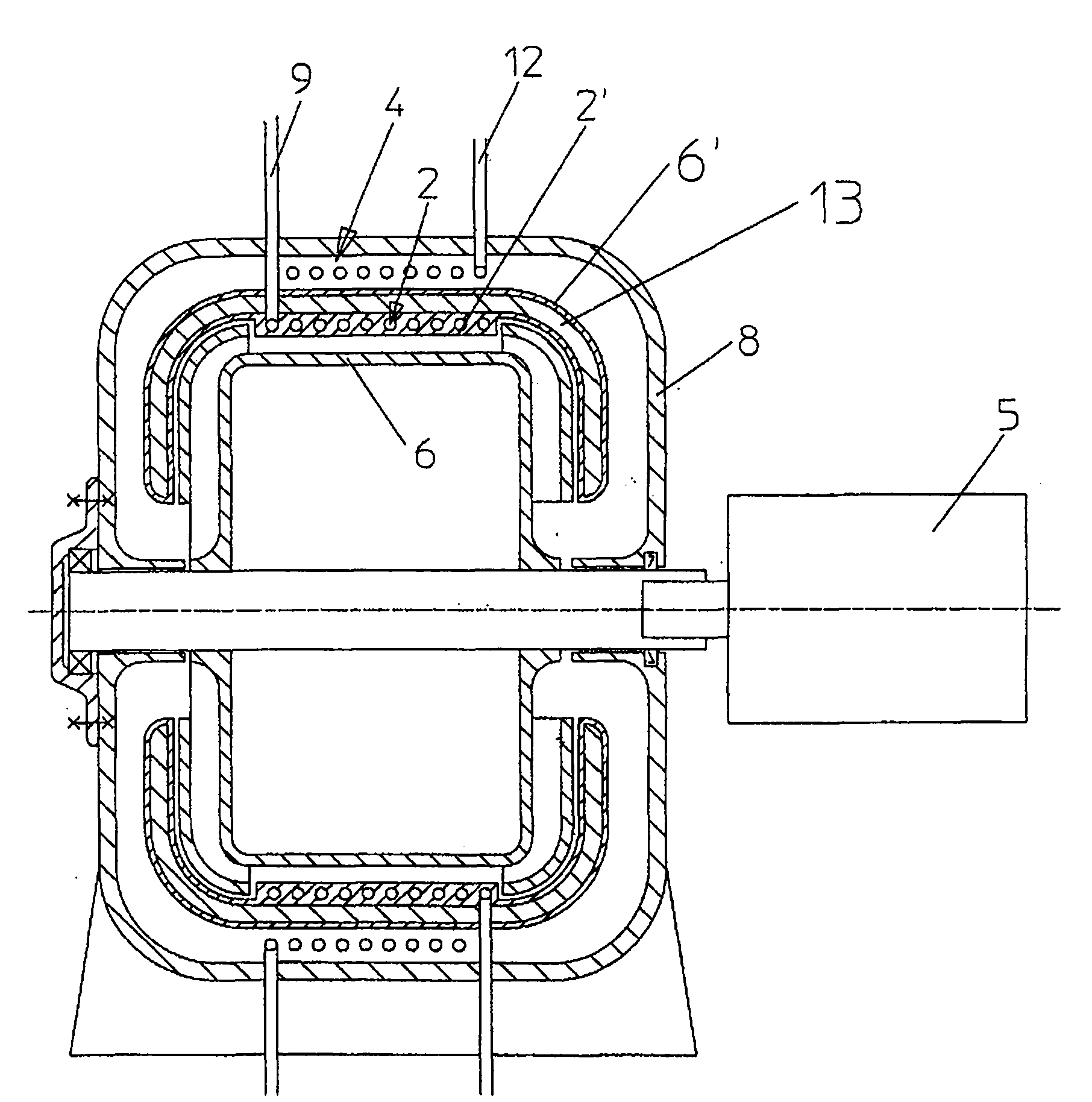
ActiveCN102893103AReduce layoutImprove stabilitySelf-contained rotary compression machinesThermal energyCyclic process
The invention relates to a device (1) and a method for converting thermal energy of low temperature to thermal energy of high temperature by means of mechanical energy and vice versa, said device comprising a rotor (2) that is rotatably supported about a rotational axis (3), a flow channel for a working medium that runs through a closed cycle being provided in the rotor, wherein the flow channel has a compression channel (8), a relaxation channel (10), and two connection channels (9, 11) extending substantially parallel to the rotational axis (3), and furthermore heat exchangers (13, 14) for exchanging heat between the working medium and a heat-exchange medium are provided, wherein the compression channel (8) and the relaxation channel (10) each have a heat-exchange segment (8', 10'), each of which has a heat exchanger (13, 14) that rotates together with the compression channel (8); or the relaxation channel (10) associated therewith, said heat exchanger being formed by at least one heat-exchange channel (15, 18) that conducts the heat-exchange medium.
Owner:风和日暖科技有限责任公司
Pulsed flow for capacity control
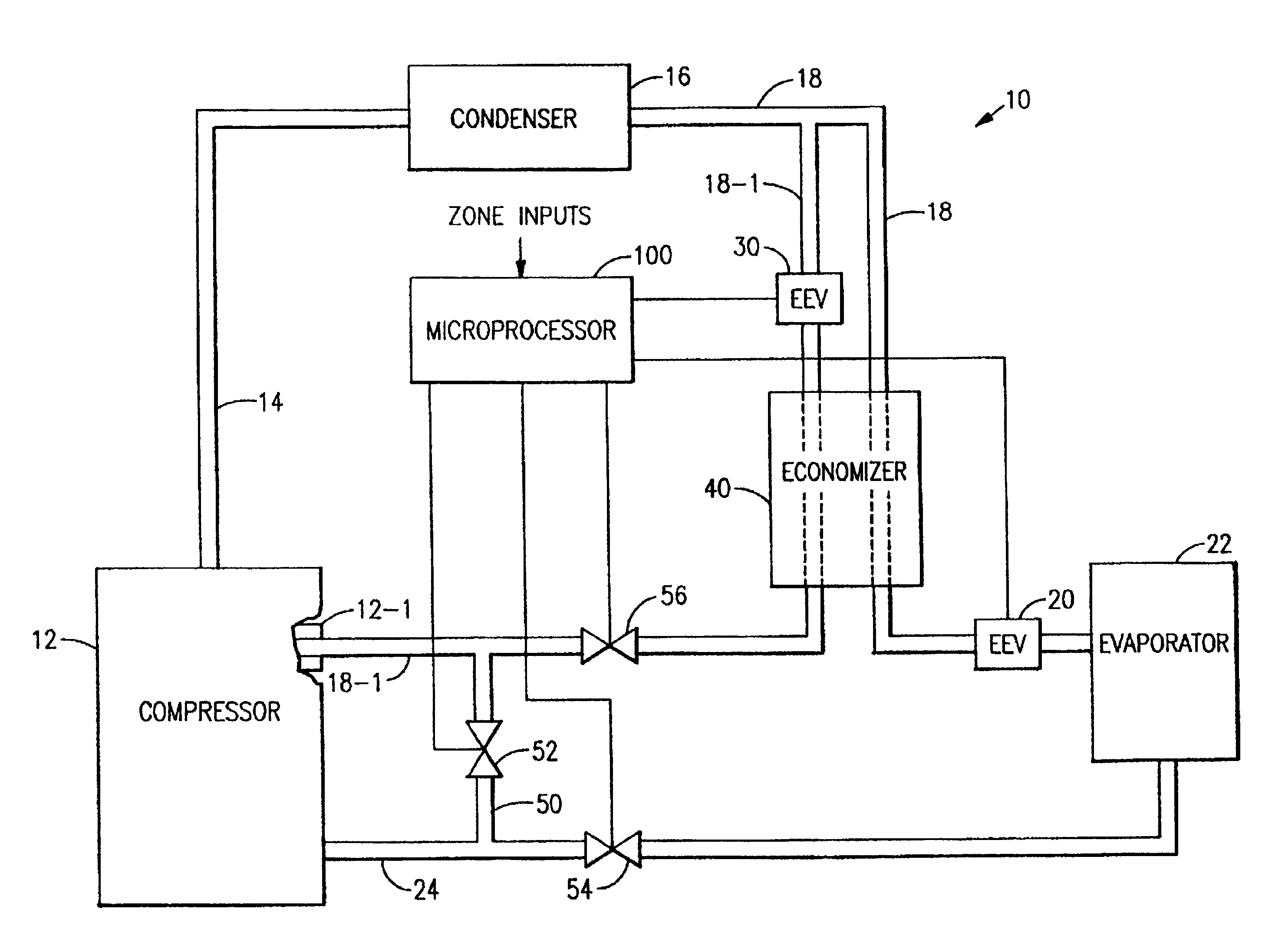
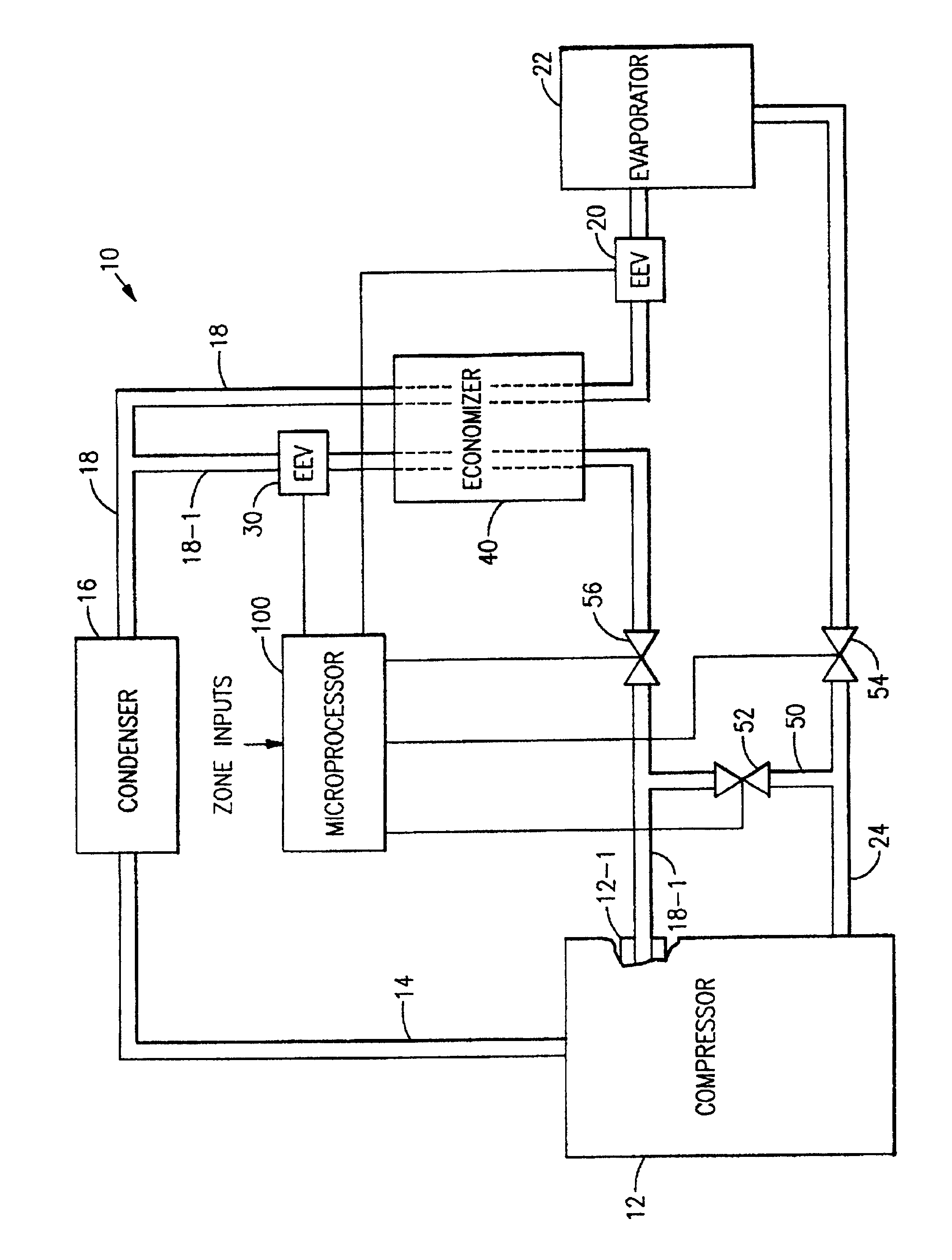
InactiveUSRE40499E1Less expensiveOperating means/releasing devices for valvesSelf-contained rotary compression machinesSolenoid valveAir conditioning
Step control in capacity modulation of a refrigeration or air conditioning circuit is achieved by rapidly cycling a solenoid valve in the suction line, economizer circuit or in a bypass with the percent of “open” time for the valve regulating the rate of flow therethrough. A common port in the compressor is used for economizer flow and for bypass.
Owner:CARRIER CORP
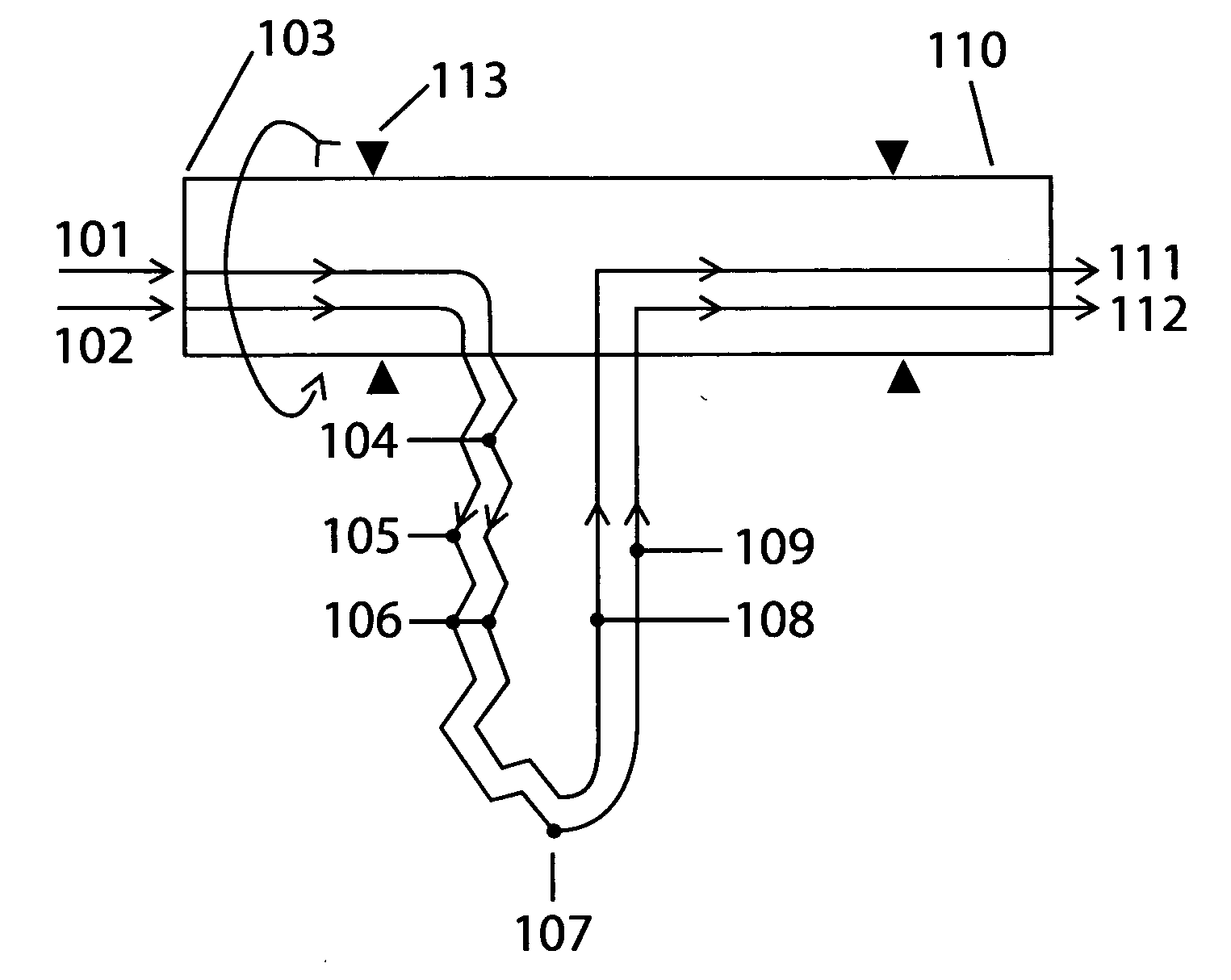
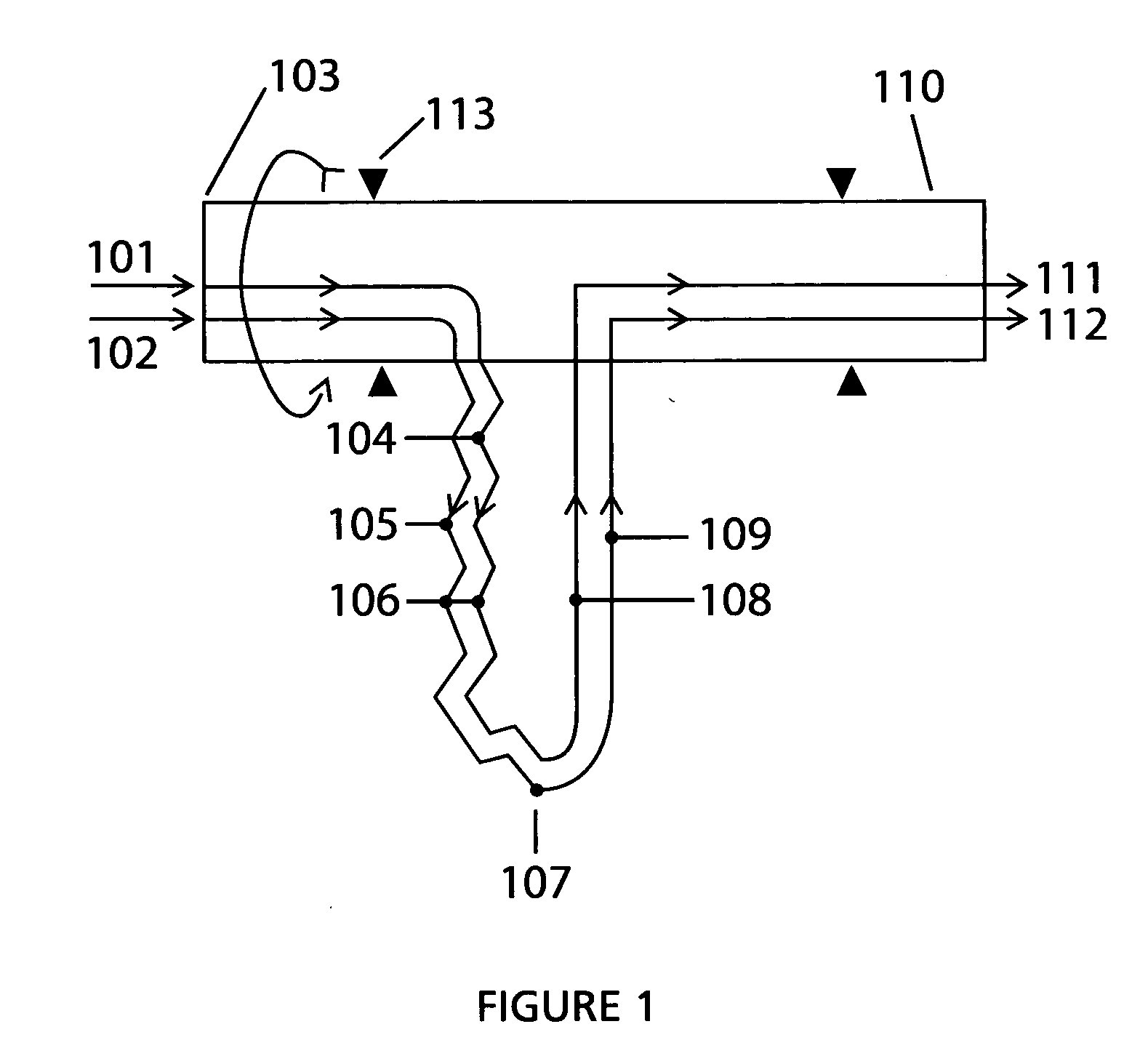
A device and method for transport heat
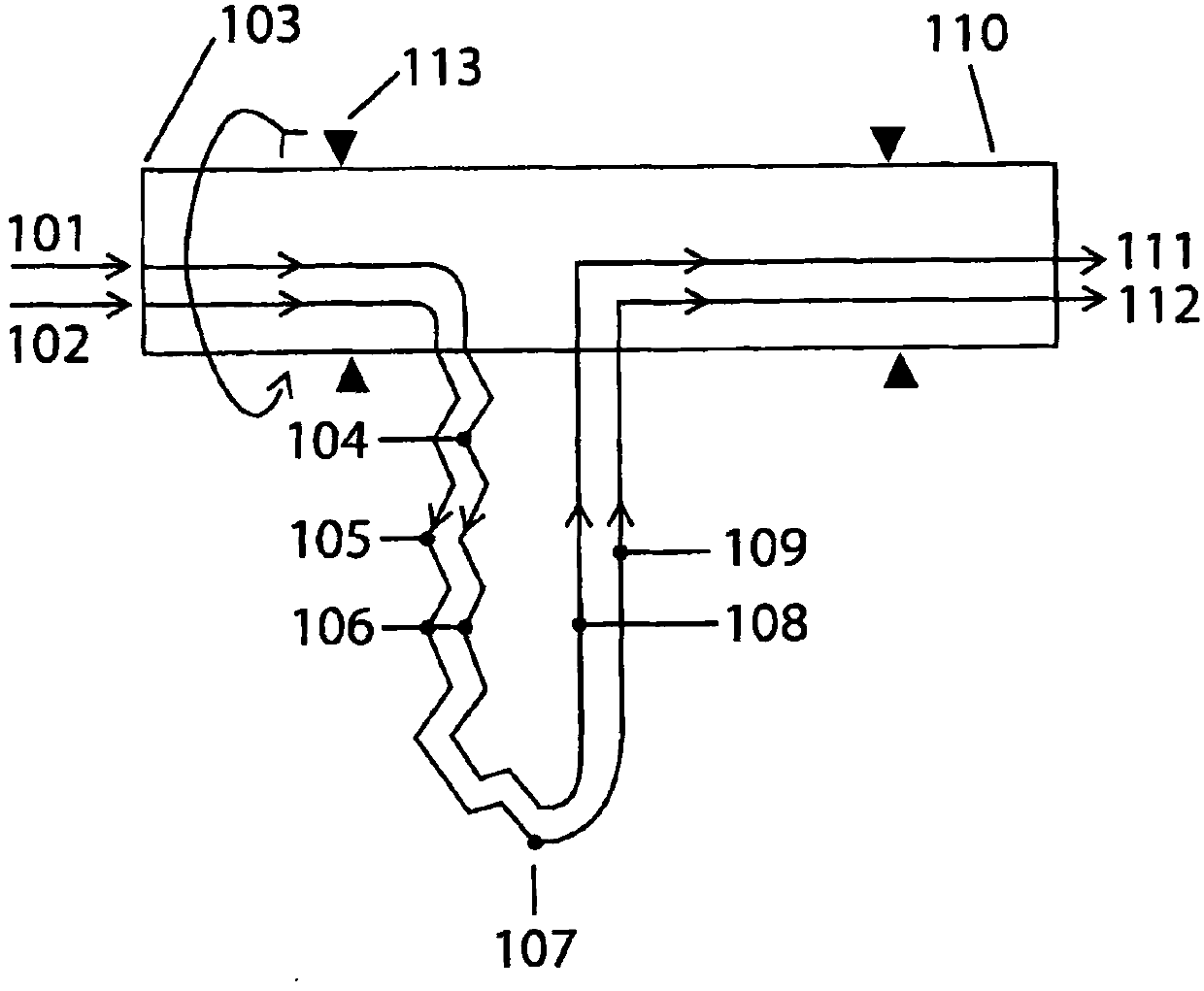
InactiveCN102007362AImprove efficiencySelf-contained rotary compression machinesStationary tubular conduit assembliesCentrifugationEngineering
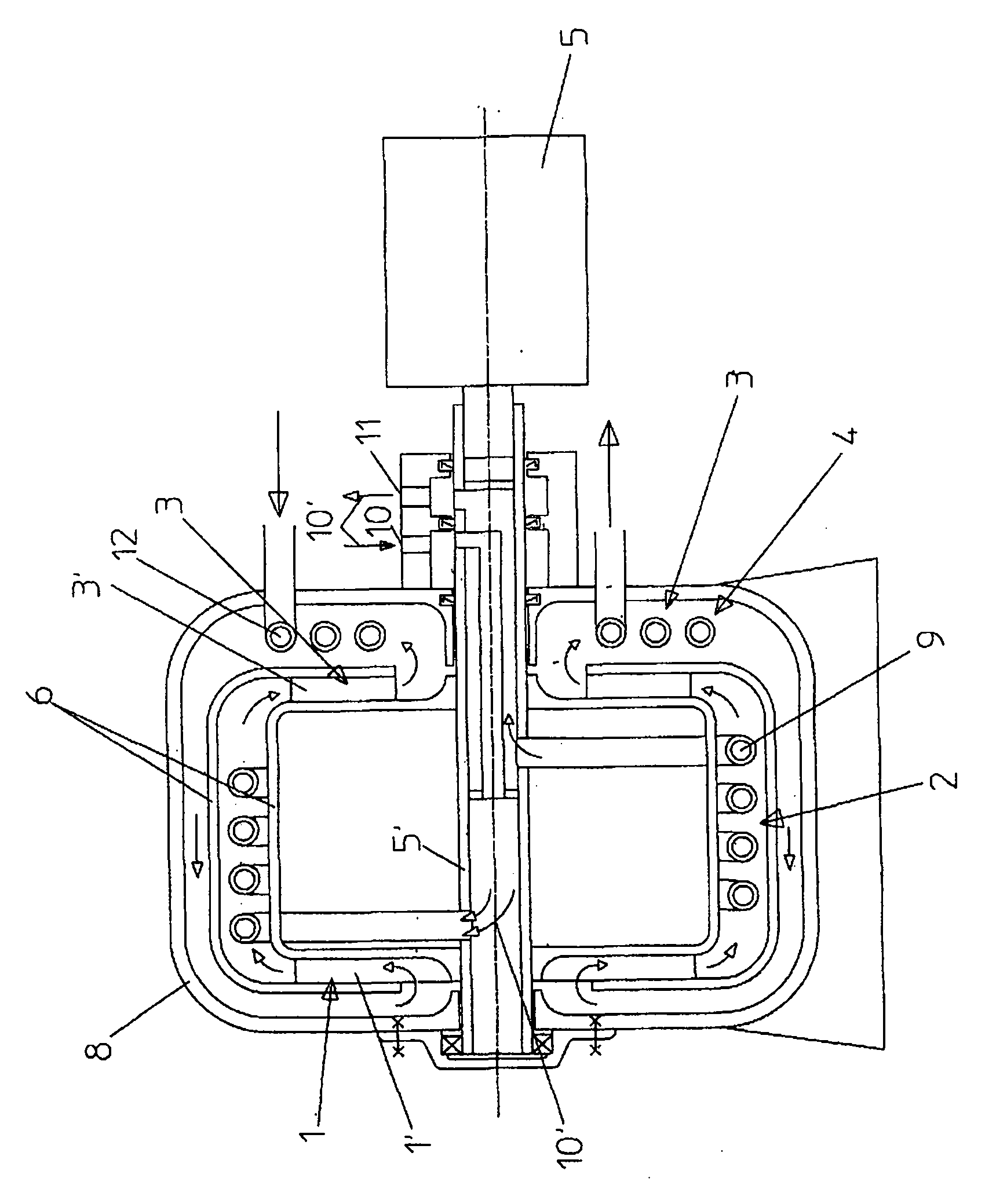
It is a purpose for the invention to provide a rotating device (107) to generate heat, cold and pressure from the outlet at the rotation axis, by centrifugation pressurized fluid in that it include at least two under-supported U-channel structures (107) where one of the channels (104, 105) from each U-channel structure (107) toward the periphery (107) is in thermal contact, forming a heat exchanger (106) where one of the channels (105) contains a compressible cooling fluid which develops heat from the centrifugal compression in the channel (105), and the heat is transferred to a heating fluid with a lower temperature in the second channel (104) in heat exchanger (106) toward the periphery (107) where heat exchanging ceases, and the U-channels (107) is connected to its inlet - (101, 102) and outlet channels (111, 112 ) at the rotation axis for the transport of said fluid through the U-channels (104, 105, 108, 109) via the periphery (107), which after the outlet (111 ) for heating fluid is heat-exploited, and cooling fluid (112) is cold-exploited, and the heating fluid before the outlet(111) is pressurized by the heat received in the heat exchangers (106), and the cooling fluid is compressed with an adapted circulation pressure before inlet (102) to compensate against emitted heat in heat exchangers (106), and an expansion work of the heating fluid reduces the supplied energy to the compression work of the cooling fluid, and U-channel structures is rotated by appropriate means, and the U-channels are arranged radial and in balance around the rotation axis.
Owner:ROTOBOOST AS
Turbo-compressor-condenser-expander
ActiveUS8578733B2Improve heat transfer characteristicsCompressorPump componentsOpen frameworkGuide tube
A turbo-compressor-condenser-expander arrangement, including heat-transferring blades mounted on or surrounding individual conduits. The open framework rotates in free air to promote heat exchange. A first hub, a first set of radial conduits, axial conduits, a second set of radial conduits, and a second hub are included; a motor rotates a central axis of the turbo-compressor-condenser-expander.
Owner:APPOLLO WIND TECH
Compact Energy Cycle Construction Utilizing Some Combination of a Scroll Type Expander, Pump, and Compressor for Operating According to a Rankine, an Organic Rankine, Heat Pump, or Combined Orgainc Rankine and Heat Pump Cycle
ActiveUS20160069219A1More compactLow costRotary/oscillating piston combinations for elastic fluidsHeat pumpsWorking fluidProcess engineering
A compact energy cycle construction that operates as or in accordance with a Rankine, Organic Rankine, Heat Pump, or Combined Organic Rankine and Heat Pump Cycle, comprising a compact housing of a generally cylindrical form with some combination of a scroll type expander, pump, and compressor disposed therein to share a common shaft with a motor or generator and to form an integrated system, with the working fluid of the system circulating within the housing as a torus along the common shaft and toroidally within the housing as the system operates.
Owner:AIR SQUARED
Method for converting thermal energy at a low temperature into thermal energy at a relatively high temperature by means of mechanical energy, and vice versa
Owner:风和日暖科技有限责任公司
Hybrid absorption-compression chiller
InactiveCN103649649ASelf-contained rotary compression machinesBoiler absorbersHybrid typeAbsorption compression
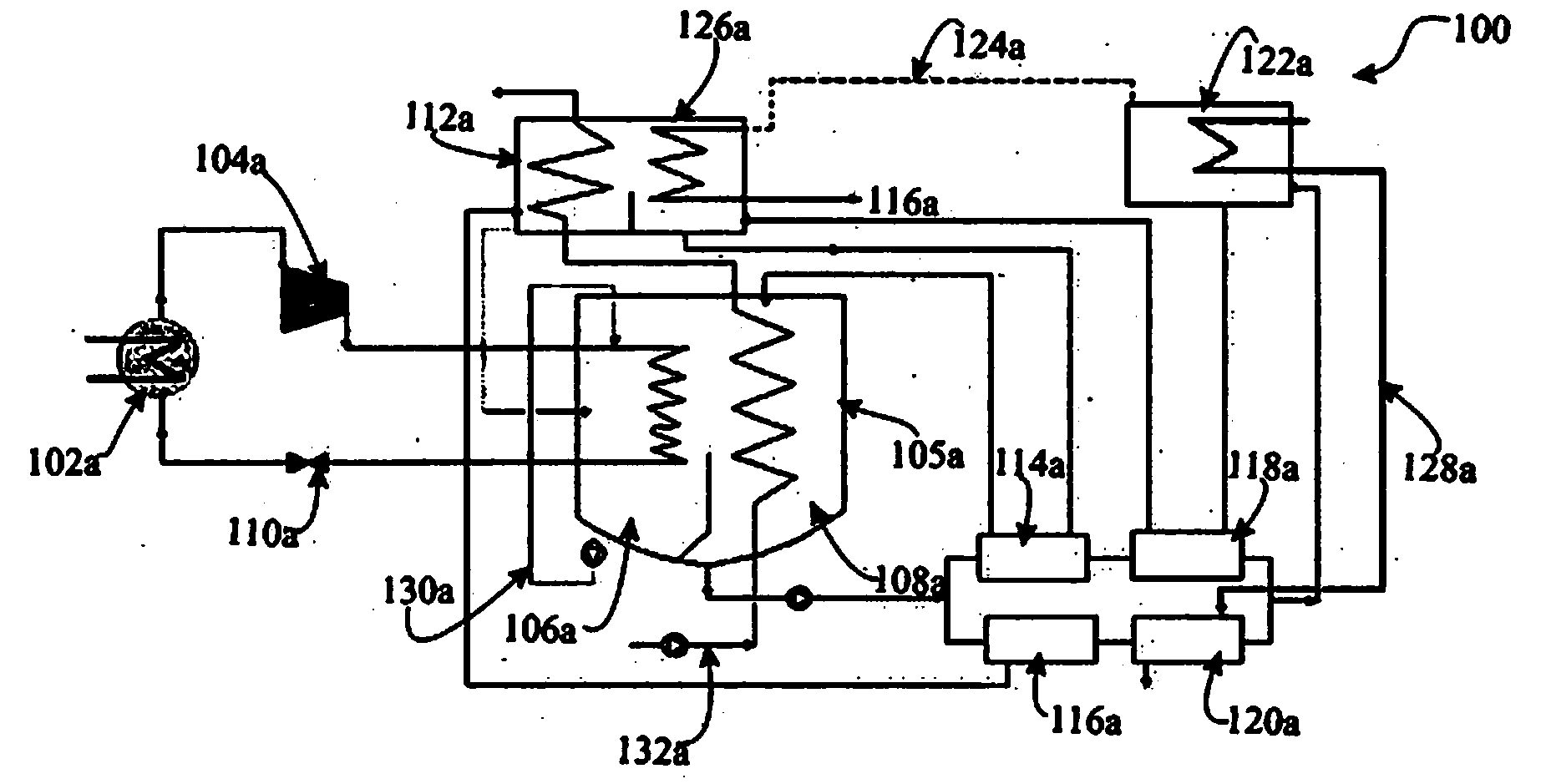
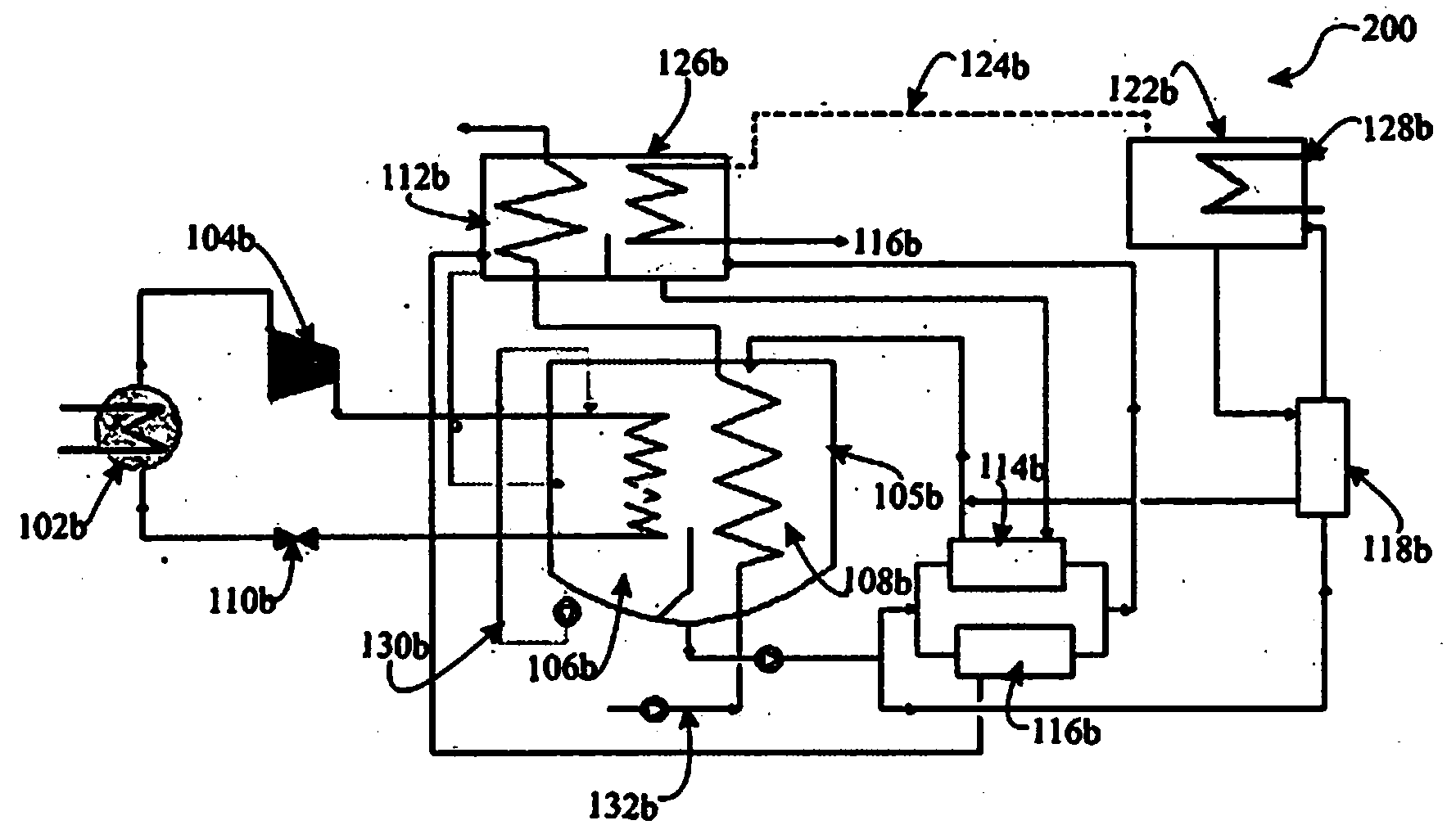
The present invention envisages a hybrid absorption-compression chiller comprising: a vapor-compression system providing a refrigeration effect in a primary evaporator (102a) by extracting heat from a medium to be cooled in a condensed primary refrigerant, and a vapor-absorption system in operative communication with the vapor-compression system for receiving primary refrigerant vapors via a compressor (104a), these vapors are cooled by a condensed secondary refrigerant in a secondary evaporator (106a) to provide cold condensed primary refrigerant which is recycled to the vapor-compression system. The hybrid absorption-compression chiller of the present invention is energy-efficient and provides a higher (coefficient of performance) COP in comparison with the conventional chillers.
Owner:TEMAX CO LTD
Rotating air conditioner and method
ActiveUS9242525B2Small and portableMaintenanceAir-treating devicesSelf-contained rotary compression machinesEngineeringEvaporator
A rotating air conditioner apparatus and method comprising an elongated shaft, whereby one or more of a condenser coil, an evaporator coil, and a compressor rotate around the elongated shaft. In one embodiment, balancing weights rotate with the shaft and are positioned to prevent uneven rotation of rotating air conditioner during operation. The evaporator and condenser contain a plurality of fins and / or fan blades and coils for refrigerant. Inlets and / or adjustably directed outlets on the evaporator and / or the condenser provide for circulation of air through the rotating air conditioner apparatus.
Owner:KOBAYASHI HERBERT S
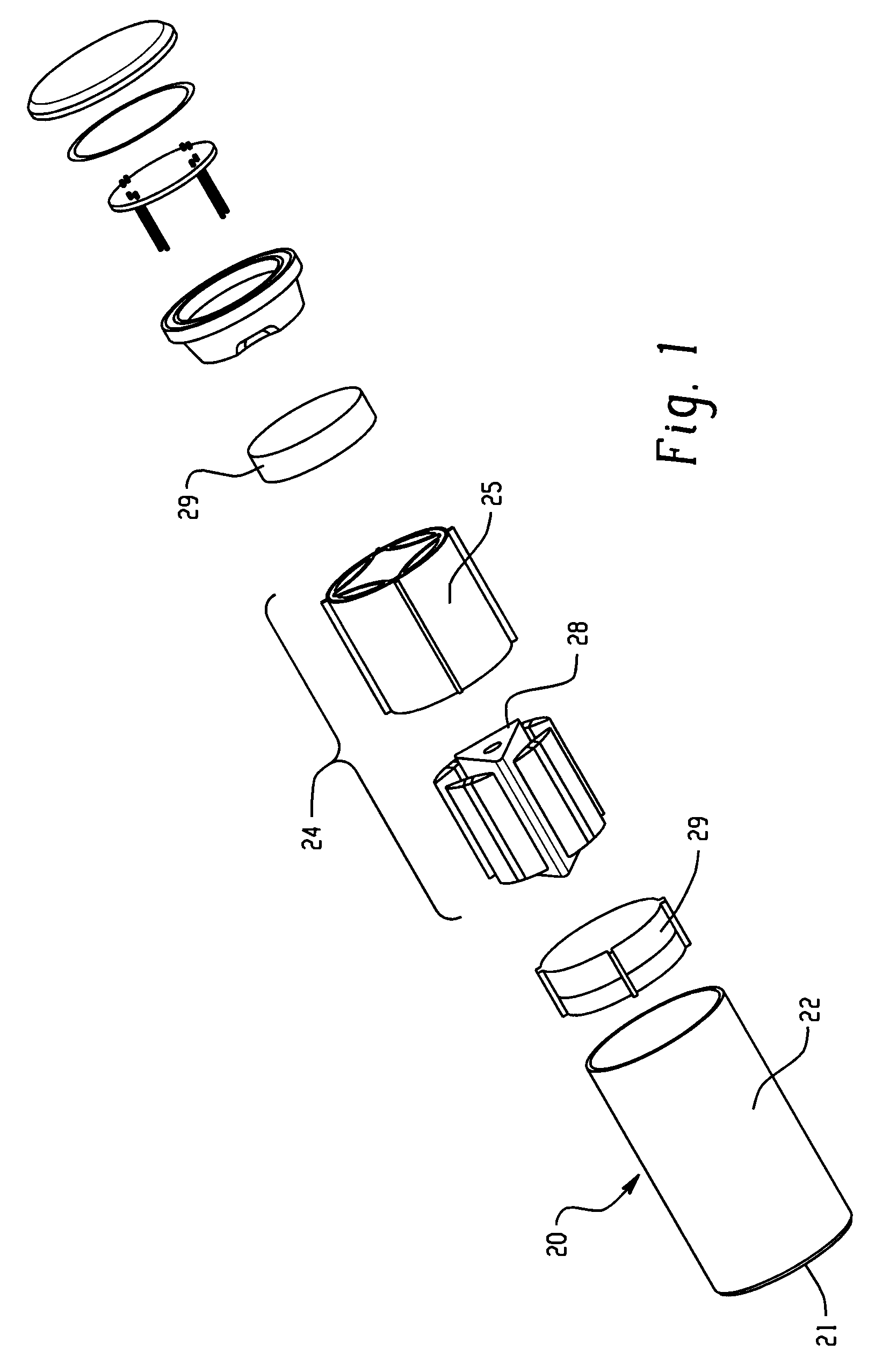
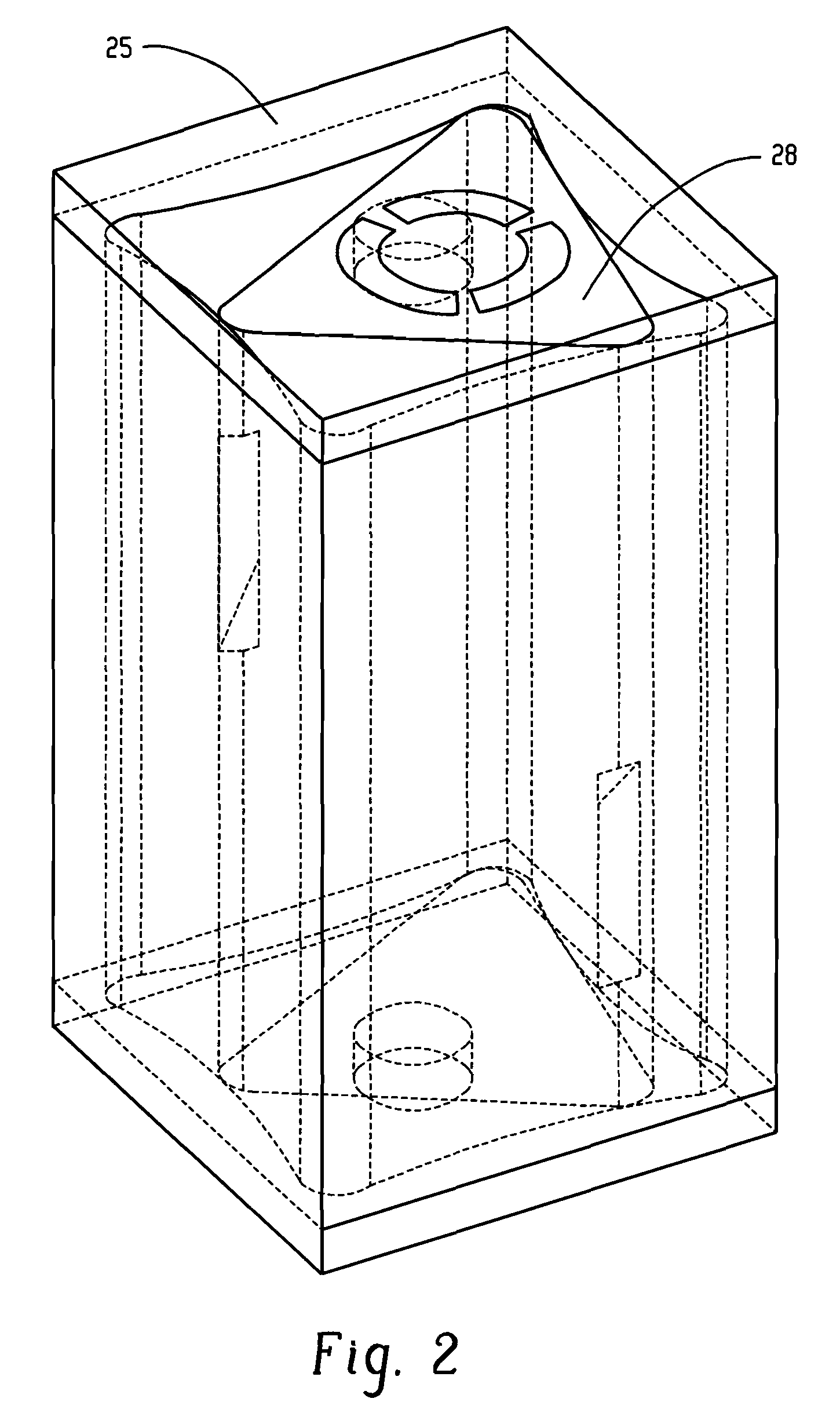
Assembly and method of attaching stub shaft to drum of axial compressor rotor shaft
InactiveUS20130309087A1Reduce manufacturing costReduce maintenance costsSelf-contained rotary compression machinesPump componentsAxial compressorMechanical engineering
An assembly and method for an axial compressor includes an axial shaft extending between an inlet casing and a discharge casing along the longitudinal length of a compressor housing. The axial shaft assembly includes a first stub shaft, a second stub shaft, and a hollow shaft drum having a longitudinal axis. The first stub shaft and the second stub shaft are coupled to opposing ends of the shaft drum along its longitudinal axis. A plurality of keys is disposed in a radial arrangement near the outer circumference of the first and second stub shafts and the shaft drum. A plurality of pins engage the plurality of keys, whereby the pins prevent the shaft drum from rotating axially relative to the first stub shaft and the second stub shaft and prevent the shaft drum from axially and radially separating from the stub shafts.
Owner:ELLIOTT CO
Compression-driven double-temperature supergravity refrigeration heat pump system and method
ActiveCN106679213ANo mixing lossSelf-contained rotary compression machinesGas cycle refrigeration machinesClosed loopEngineering
The invention discloses a compression-driven double-temperature supergravity refrigeration heat pump system. The system comprises a supergravity generation mechanism and a refrigeration device with working media flowing. The supergravity generation mechanism comprises a rotary base and a rotary shaft. The rotary shaft is arranged in the axis of the rotary base. The refrigeration device is of a closed loop structure formed by sequentially connecting a first evaporator, a second evaporator, a compressor and a condenser through a pipeline. The first evaporator is arranged in the axis of the rotary base. The second evaporator, the compressor and the condenser are arranged at the edge of the rotary base. An outlet of the first evaporator and an inlet of the second evaporator are connected. An outlet of the second evaporator and an inlet of the compressor are connected. An outlet of the compressor and an inlet of the condenser are connected. An outlet of the condenser and an inlet of the first evaporator are connected. The invention further provides a compression-driven double-temperature supergravity refrigeration heat pump method by adoption of the system.
Owner:辽宁辉达制冷空调工程有限公司
Compositions comprising tetrafluoropropene and difluoromethane and uses thereof
The present invention relates to compositions for use in refrigeration, air-conditioning and heat pump systems wherein the composition comprises tetrafluoropropene and difluoromethane. The compositions of the present invention are useful in processes for producing cooling or heat, as heat transfer fluids, foam blowing agents, aerosol propellants, fire suppression, fire extinguishing agents, as power cycle working fluids and in methods for replacing HFC-134a, R410A, \R404A, or R507.
Owner:THE CHEMOURS CO FC LLC
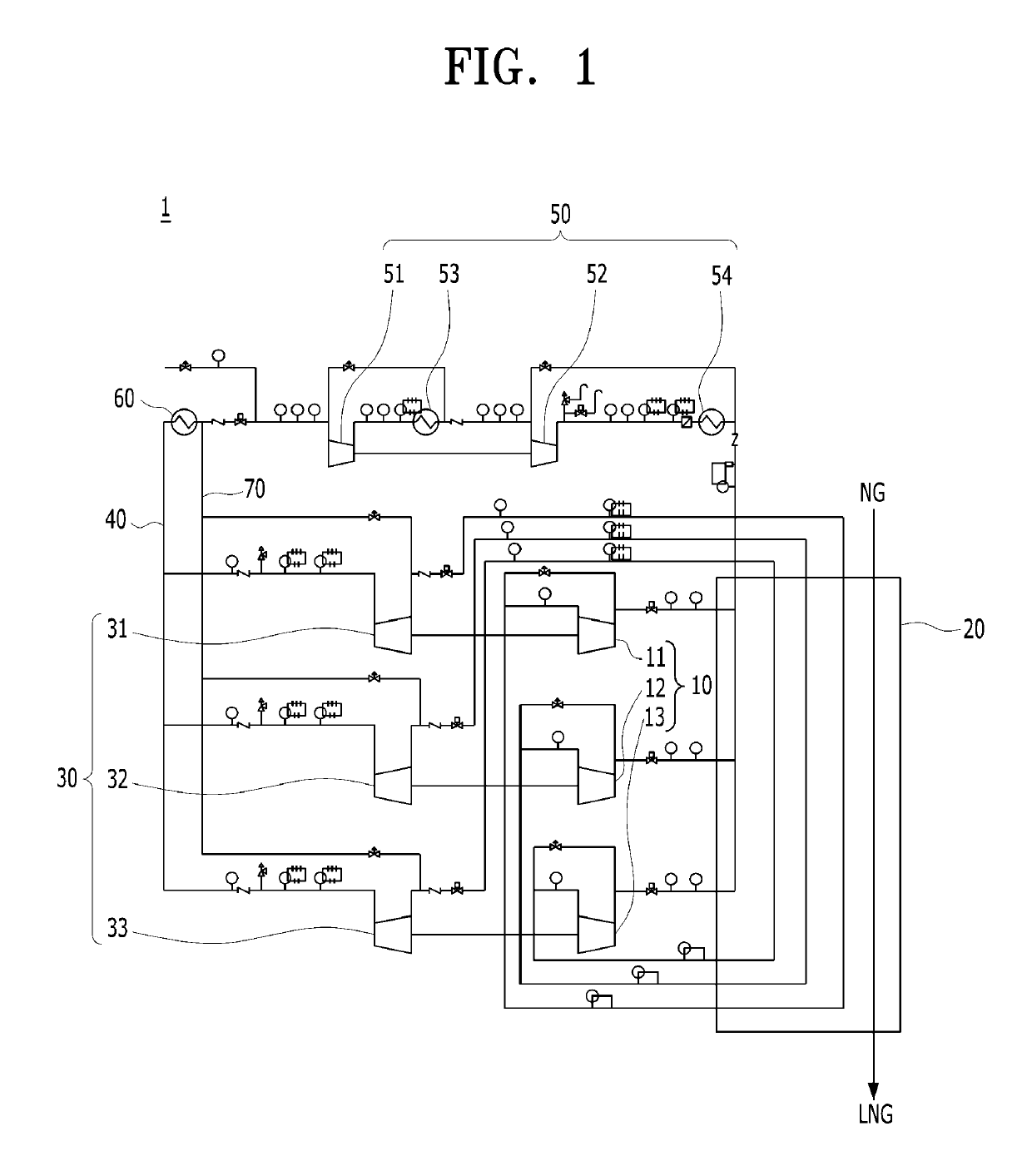
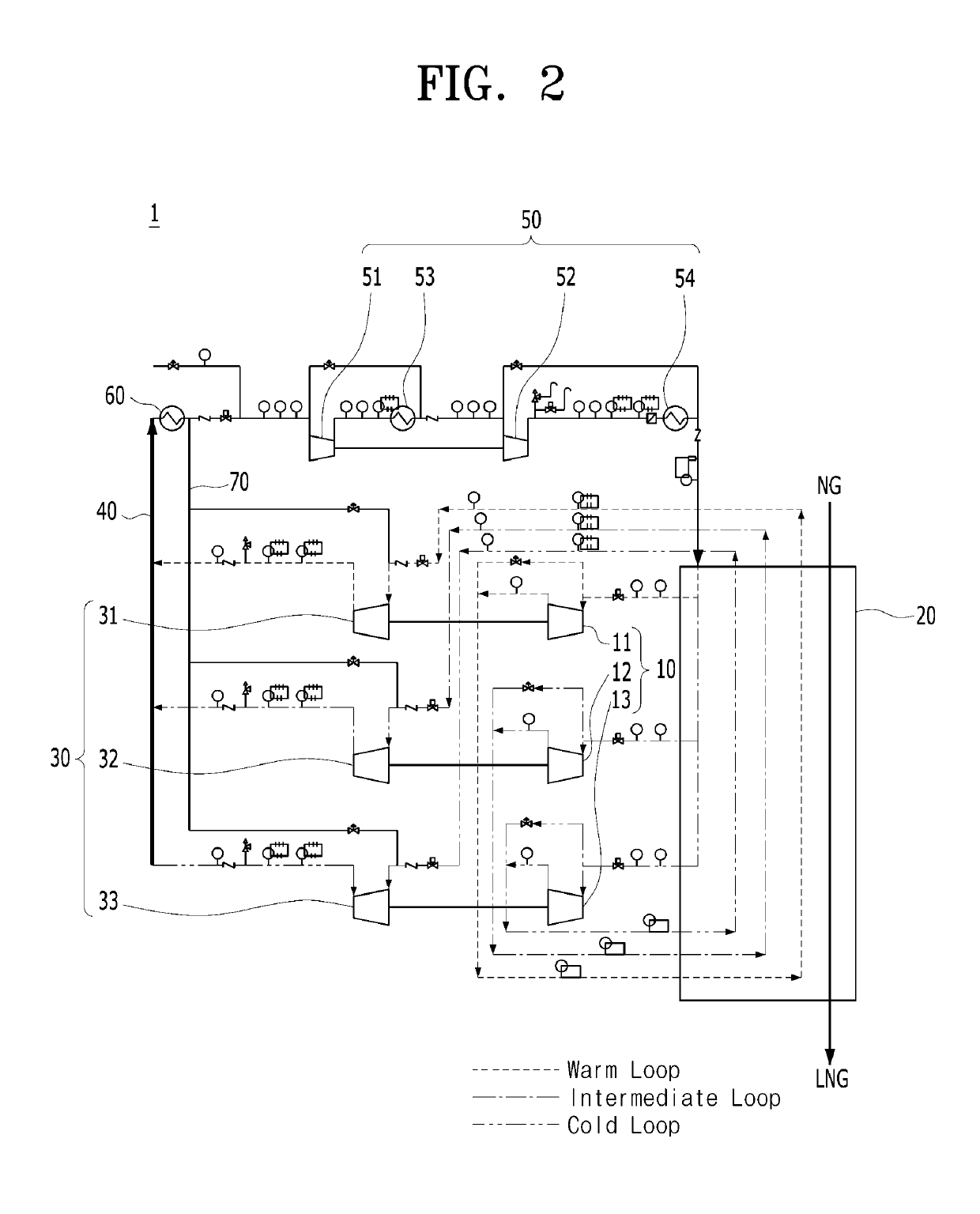
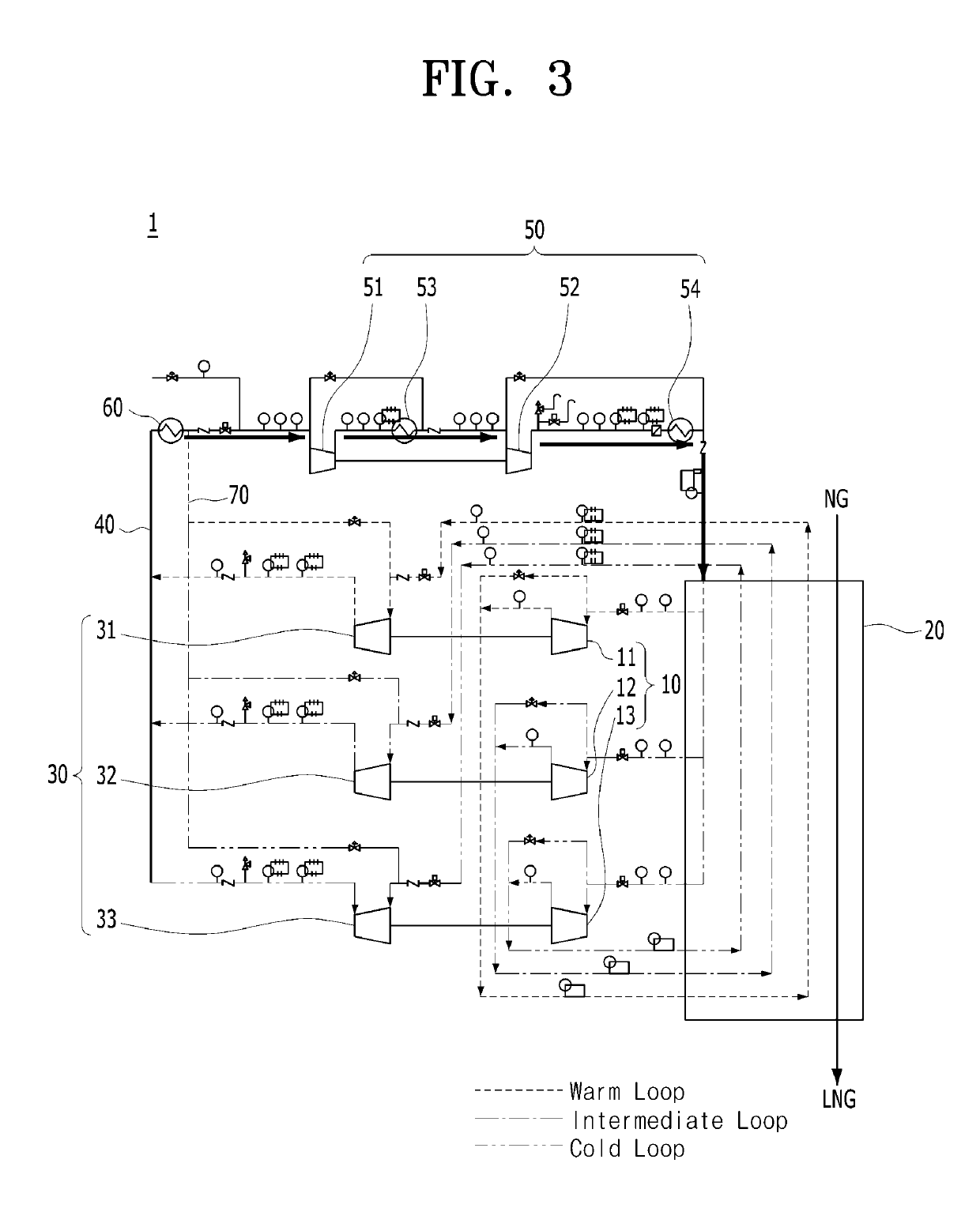
Fluid cooling apparatus
PendingUS20190195536A1Operation efficiency can be improvedArrangement relationshipCompressorSolidificationEngineeringRefrigerant
A fluid cooling apparatus capable of improving liquefaction efficiency of a fluid by appropriately cooling the fluid in various temperature ranges through a simple process. The fluid cooling apparatus includes an expansion unit including a plurality of expanders, which receive refrigerants through a plurality of paths to expand the refrigerants and discharge the expanded refrigerants having different temperatures, a heat exchanger receiving the refrigerants having different temperatures from the expansion unit to cool the fluid in multistages, a precompression unit including a plurality of precompressors, which receive the refrigerants passing through the heat exchanger to compress the refrigerants and discharge the compressed refrigerants at the same pressure, a mixing tube configured to mix the refrigerants discharged from the precompression unit to supply the mixed refrigerant, and a main compression unit connected to the mixing tube to compress the mixed refrigerant and supply the compressed refrigerant to the expansion unit.
Owner:SAMSUNG HEAVY IND CO LTD
Compression-driven dual-temperature supergravity refrigeration heat pump system and method
ActiveCN106679213BNo mixing lossSelf-contained rotary compression machinesHeating and refrigeration combinationsClosed loopRefrigeration
The invention discloses a compression-driven double-temperature supergravity refrigeration heat pump system. The system comprises a supergravity generation mechanism and a refrigeration device with working media flowing. The supergravity generation mechanism comprises a rotary base and a rotary shaft. The rotary shaft is arranged in the axis of the rotary base. The refrigeration device is of a closed loop structure formed by sequentially connecting a first evaporator, a second evaporator, a compressor and a condenser through a pipeline. The first evaporator is arranged in the axis of the rotary base. The second evaporator, the compressor and the condenser are arranged at the edge of the rotary base. An outlet of the first evaporator and an inlet of the second evaporator are connected. An outlet of the second evaporator and an inlet of the compressor are connected. An outlet of the compressor and an inlet of the condenser are connected. An outlet of the condenser and an inlet of the first evaporator are connected. The invention further provides a compression-driven double-temperature supergravity refrigeration heat pump method by adoption of the system.
Owner:辽宁辉达制冷空调工程有限公司
Flow Control
ActiveUS20080229781A1Eliminate the problemInternal combustion piston enginesCheck valvesControl flowEngineering
The problems of prior compressor structures relying upon conventional check valves are obviated by using, instead, flow control passages which operate to control flow while avoiding mechanical moving elements which may become problematical.
Owner:LENOVO PC INT
Device and Method for Transporting Heat
ActiveUS20110067847A1Improve efficiencySelf-contained rotary compression machinesStationary tubular conduit assembliesCentrifugationEngineering
It is a purpose for the invention to provide a rotating device (107) to generate heat, cold and pressure from the outlet at the rotation axis, by centrifugation pressurized fluid in that it include at least two under-supported U-channel structures (107) where one of the channels (104, 105) from each U-channel structure (107) toward the periphery (107) is in thermal contact, forming a heat exchanger (106) where one of the channels (105) contains a compressible cooling fluid which develops heat from the centrifugal compression in the channel (105), and the heat is transferred to a heating fluid with a lower temperature in the second channel (104) in heat exchanger (106) toward the periphery (107) where heat exchanging ceases, and the U-channels (107) is connected to its inlet—(101, 102) and outlet channels (111, 112) at the rotation axis for the transport of said fluid through the U-channels (104, 105, 108, 109) via the periphery (107), which after the outlet (111) for heating fluid is heat-exploited, and cooling fluid (112) is cold-exploited, and the heating fluid before the outlet (111) is pressurized by the heat received in the heat exchangers (106), and the cooling fluid is compressed with an adapted circulation pressure before inlet (102) to compensate against emitted heat in heat exchangers (106), and an expansion work of the heating fluid reduces the supplied energy to the compression work of the cooling fluid, and U-channel structures is rotated by appropriate means, and the U-channels are arranged radial and in balance around the rotation axis.
Owner:ROTOBOOST AS
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com