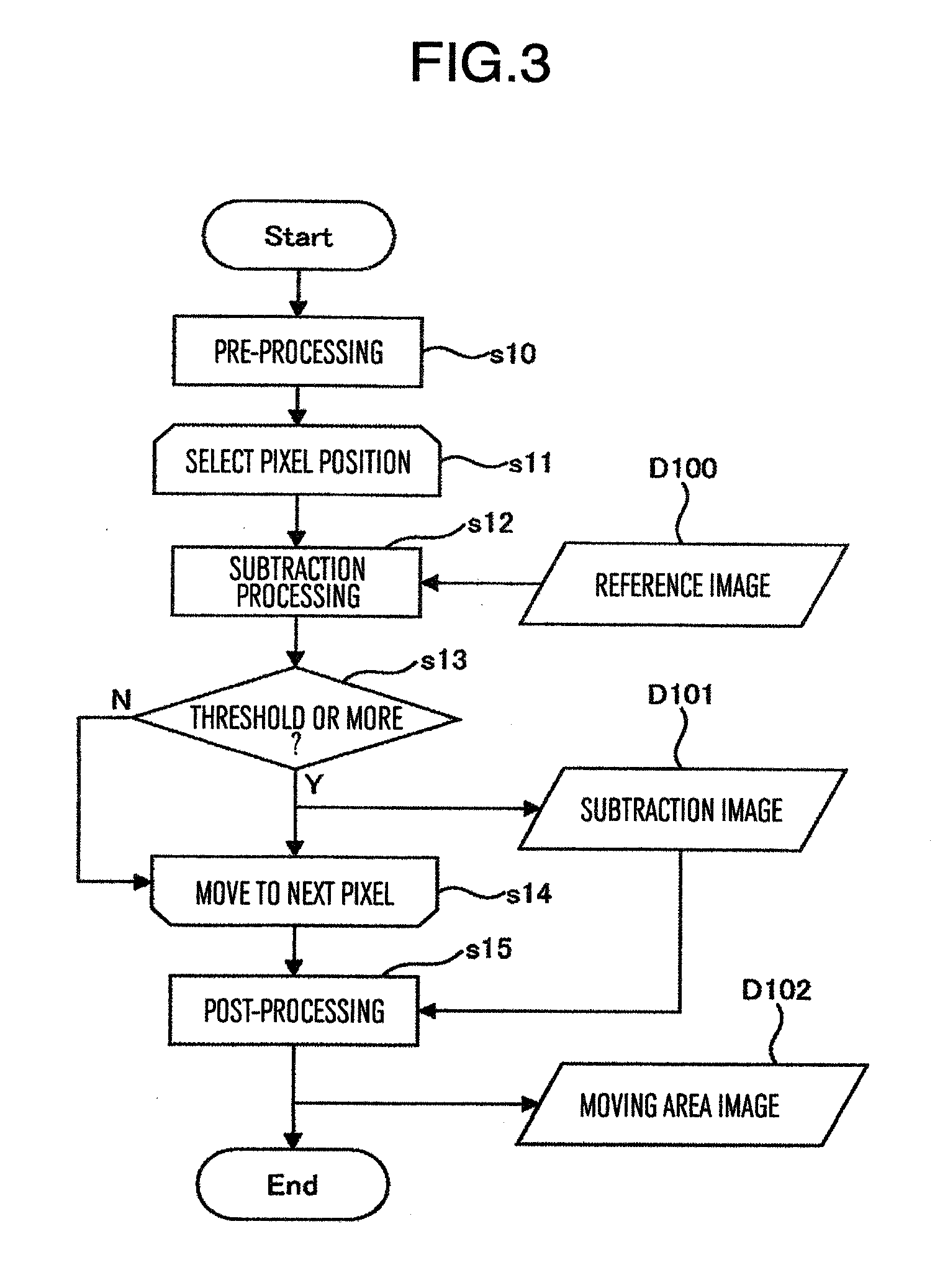
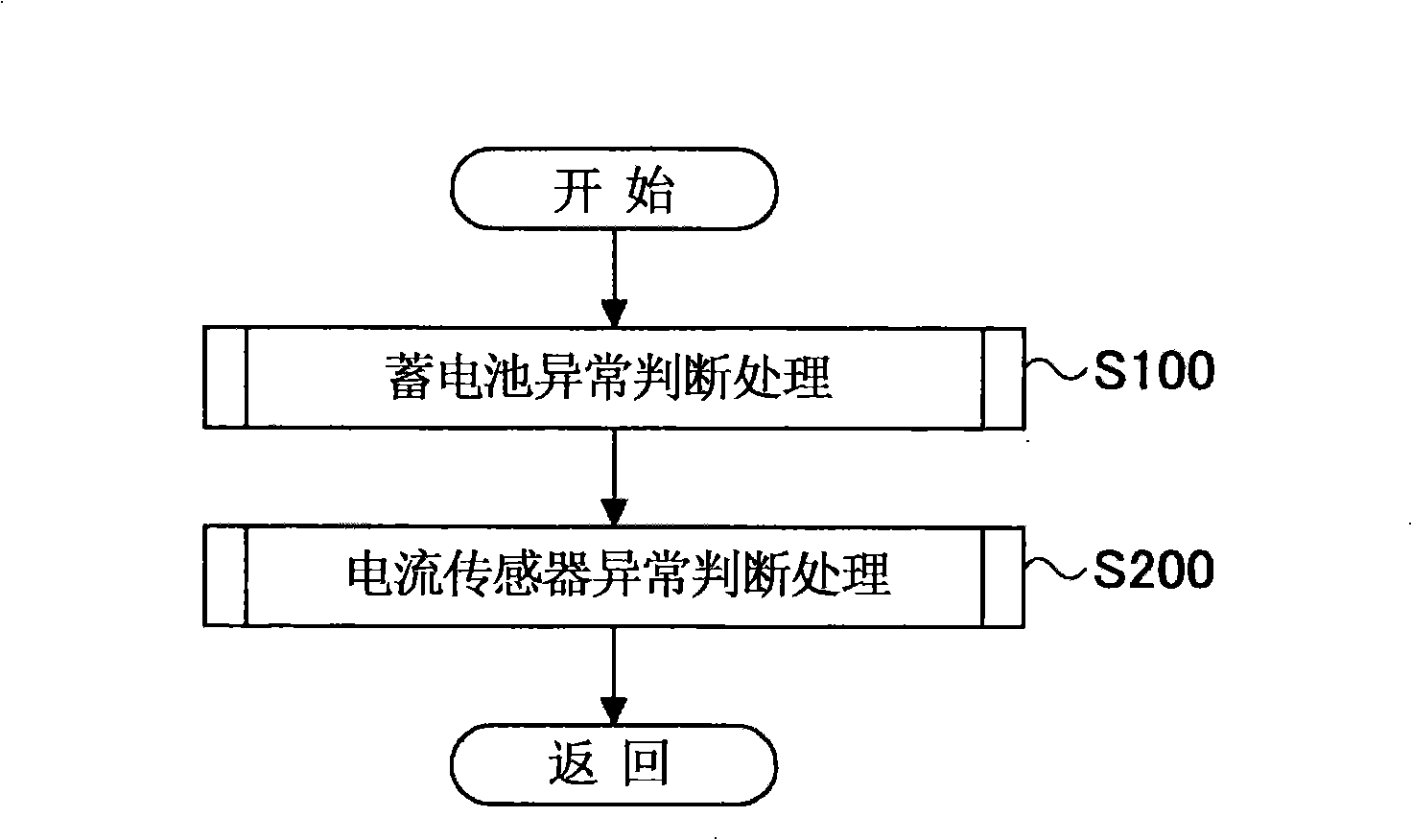
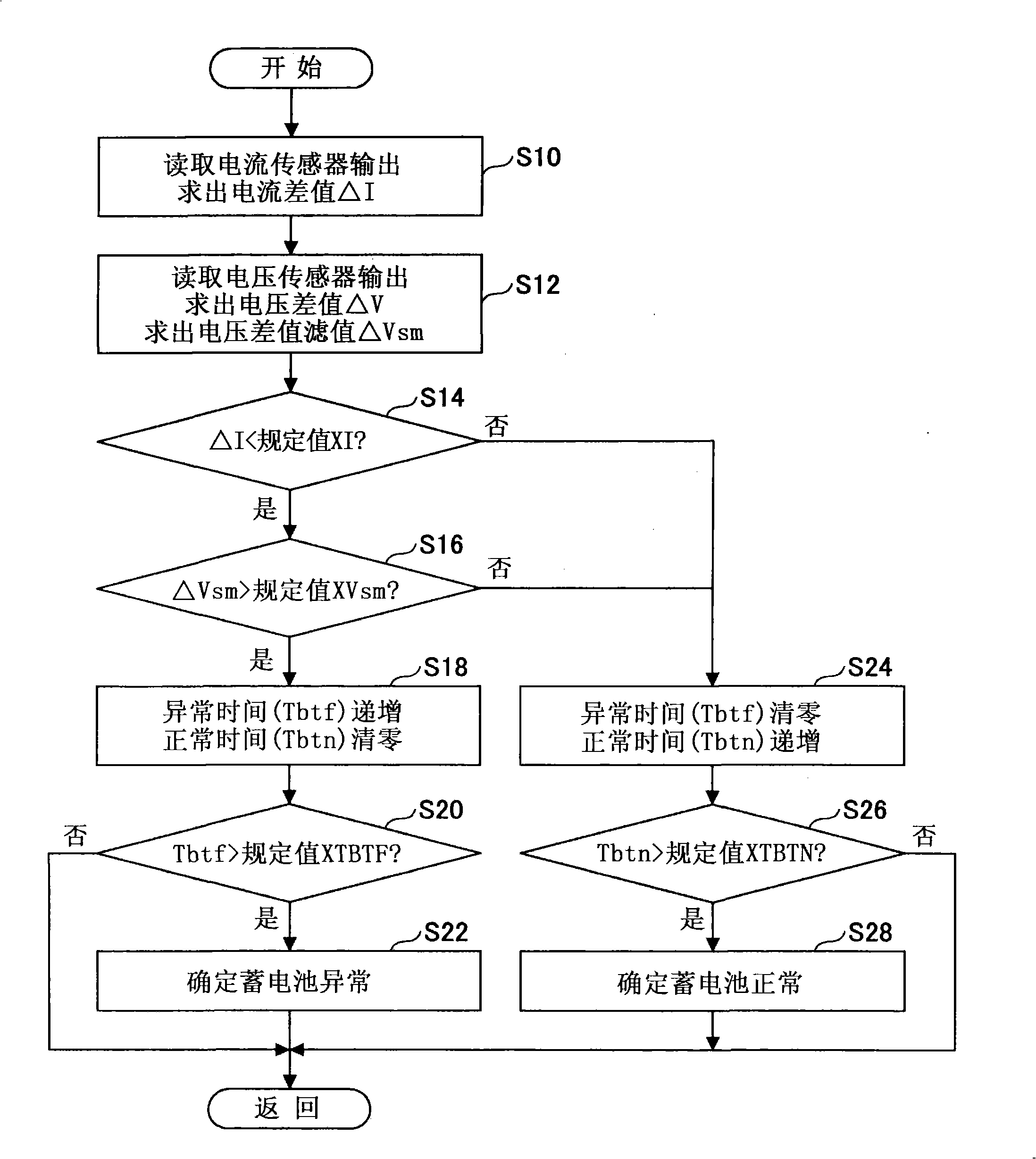
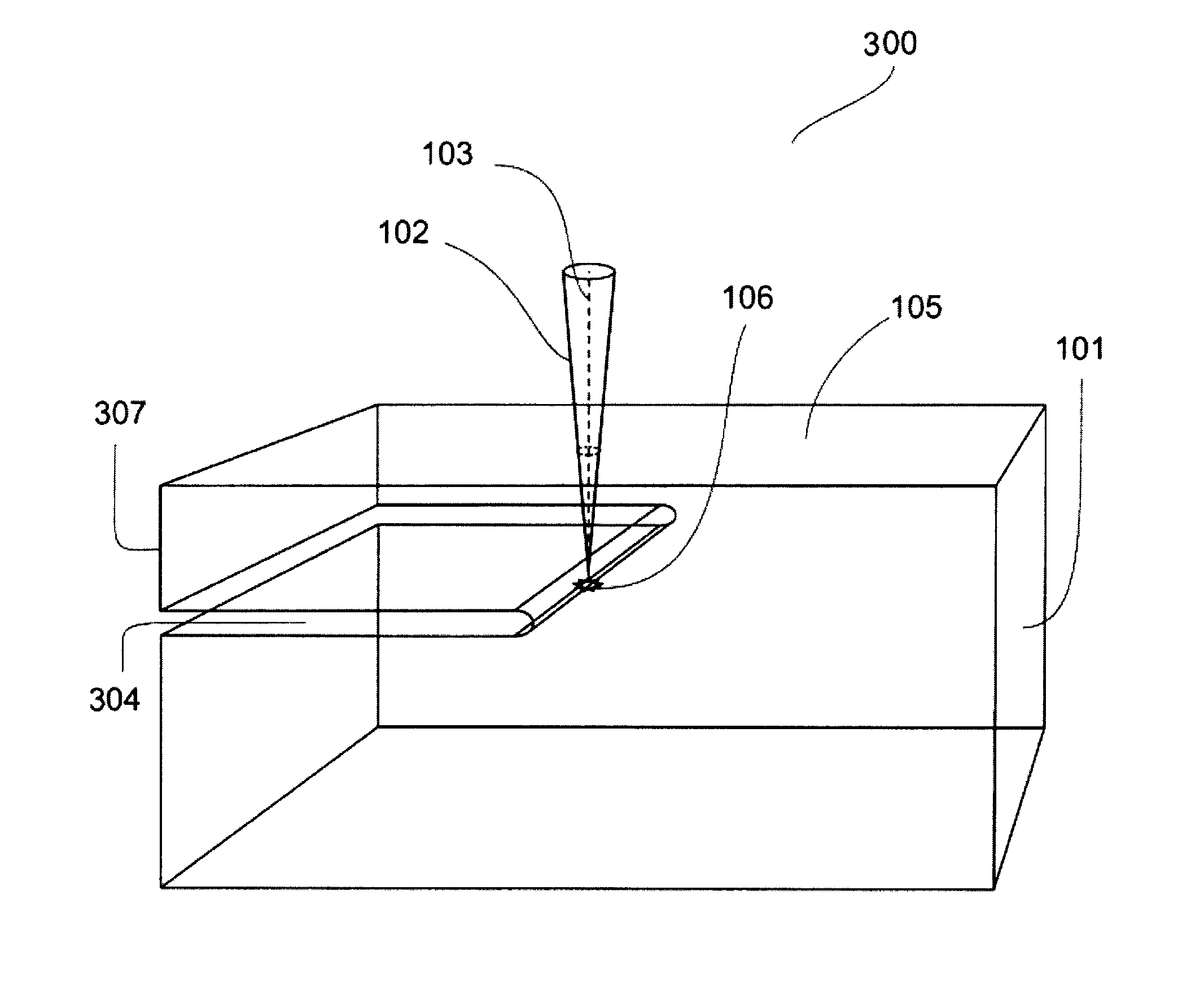
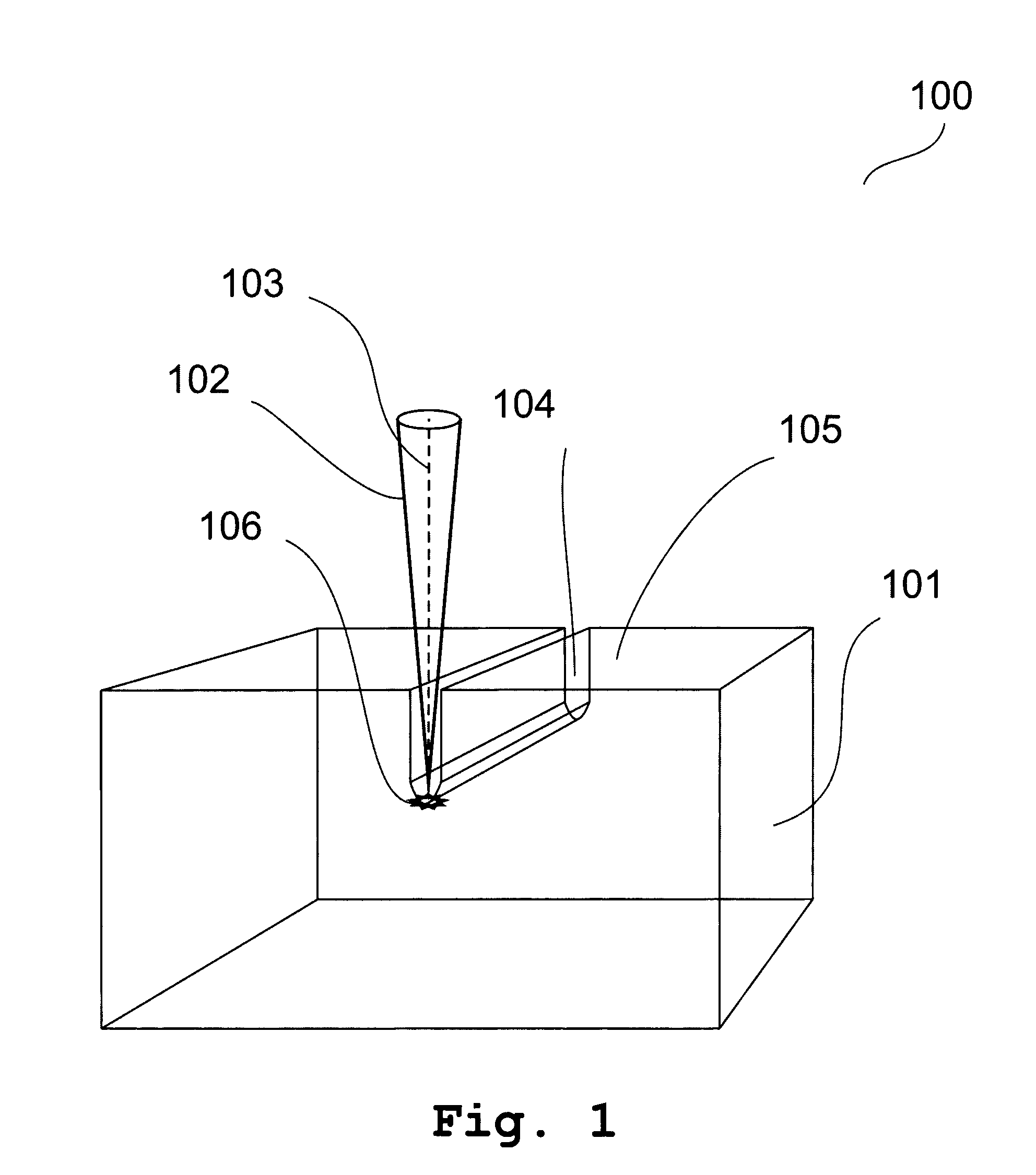
Patents
Literature
209 results about "First variation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In applied mathematics and the calculus of variations, the first variation of a functional J(y) is defined as the linear functional δJ(y) mapping the function h to δJ(y,h)=limɛ→₀(J(y+ɛh)-J(y))/ɛ=.d/dɛJ(y+ɛh)|ɛ₌₀, where y and h are functions, and ε is a scalar. This is recognizable as the Gateaux derivative of the functional.
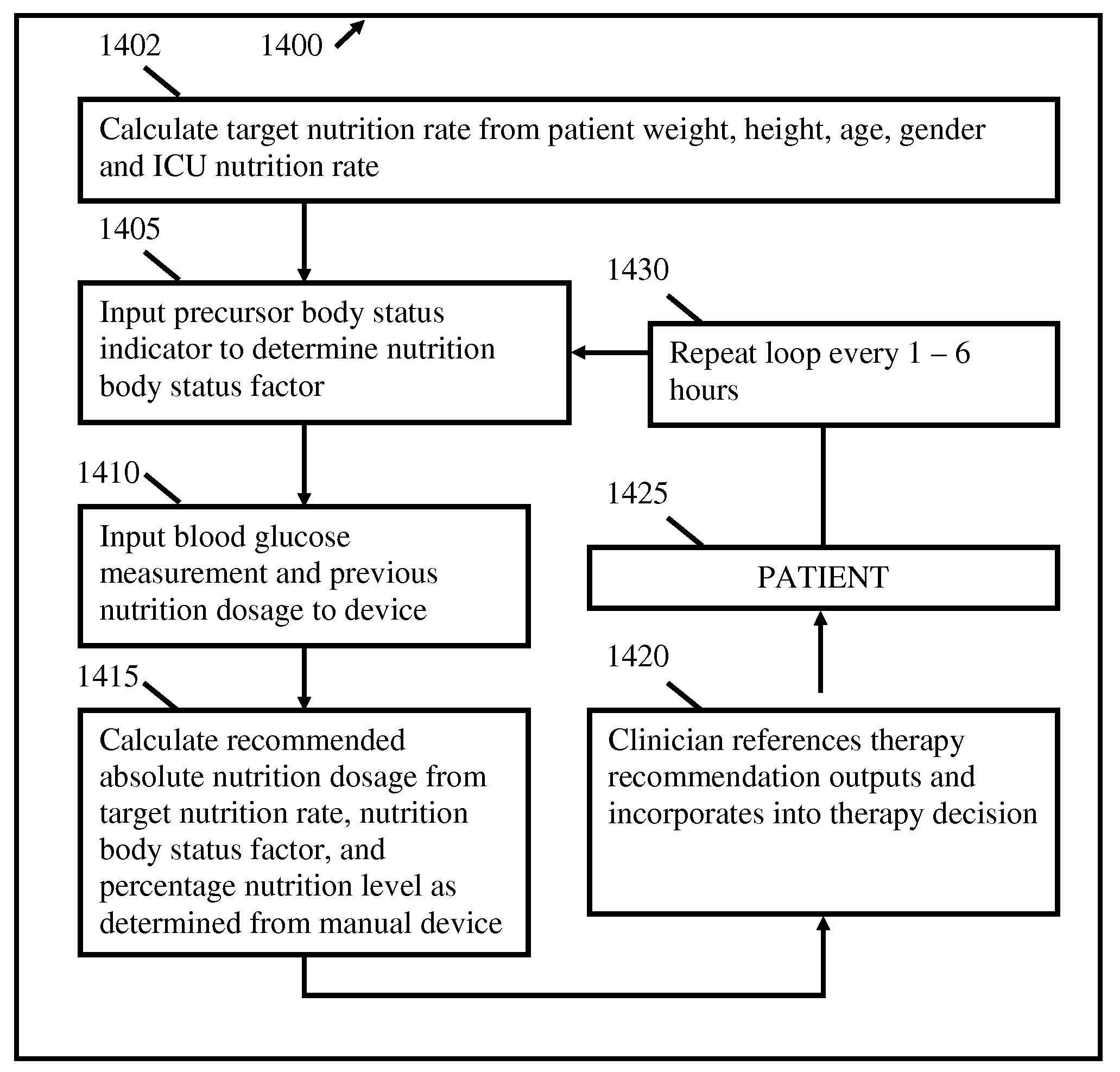
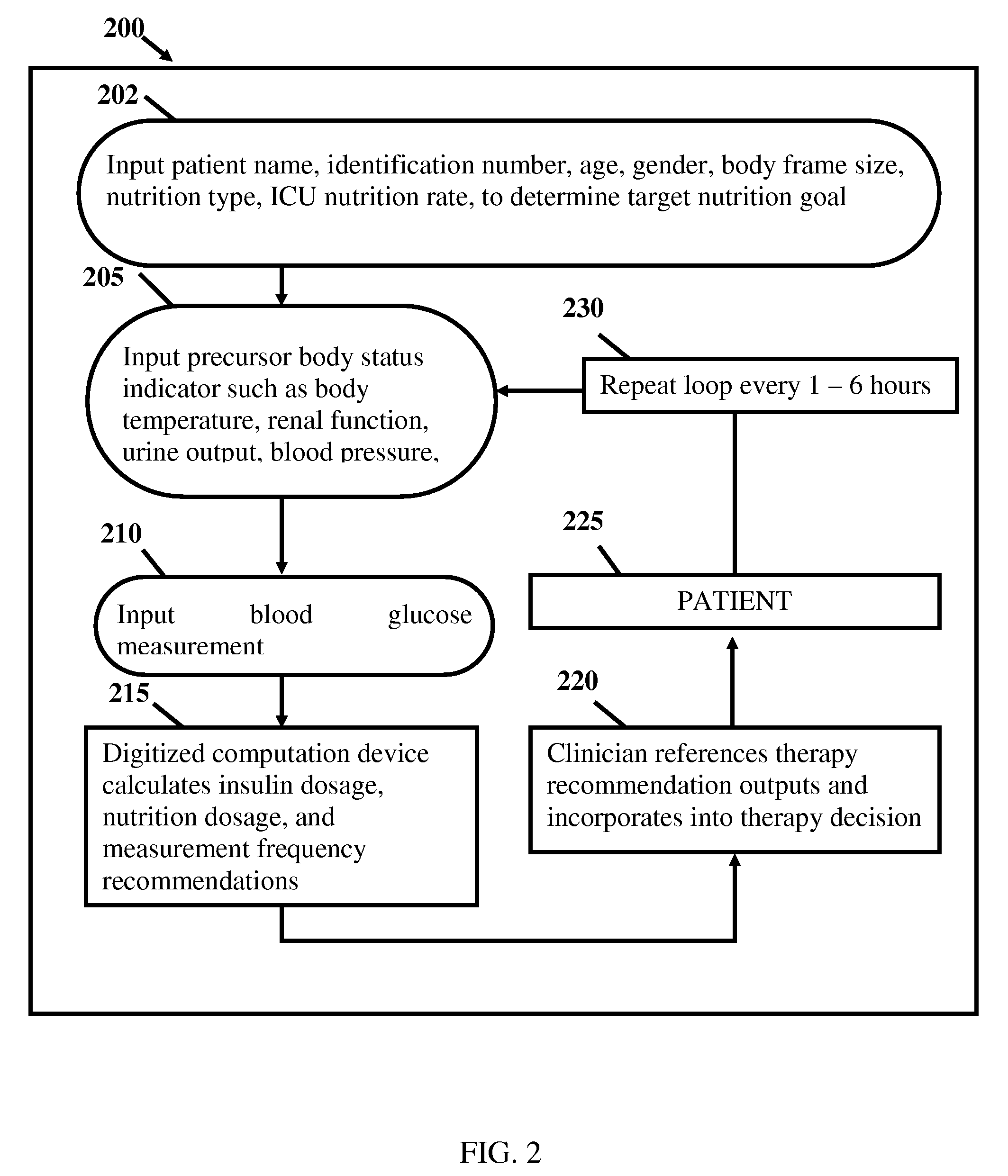
Calculation device for metabolic control of critically ill and/or diabetic patients
InactiveUS20080306353A1Improve insulin resistanceTight controlLocal control/monitoringDrug and medicationsCritically illEmergency medicine
A method of providing blood glucose therapy for a critically ill patient includes calculating a baseline nutrition feed requirement based on an algorithm that incorporates at least one of age, gender, and body size of the patient: determining a first blood glucose level; determining a second blood glucose level after a preselected time interval: determining a first body temperature reading: comparing the blood glucose levels: and administering either nutrition or insulin. The amount of nutrition administered to the patient is based on a first change in blood glucose level, the current body temperature reading, and a predetermined feed algorithm based on the second blood glucose level as well as the baseline nutritional feed requirement. The amount of insulin administered is based on a second change in blood glucose level, body temperature, and a predetermined insulin algorithm that incorporates at least one of the patient's body frame size, age, and gender.
Owner:INTERSECTION LIFESCI +1
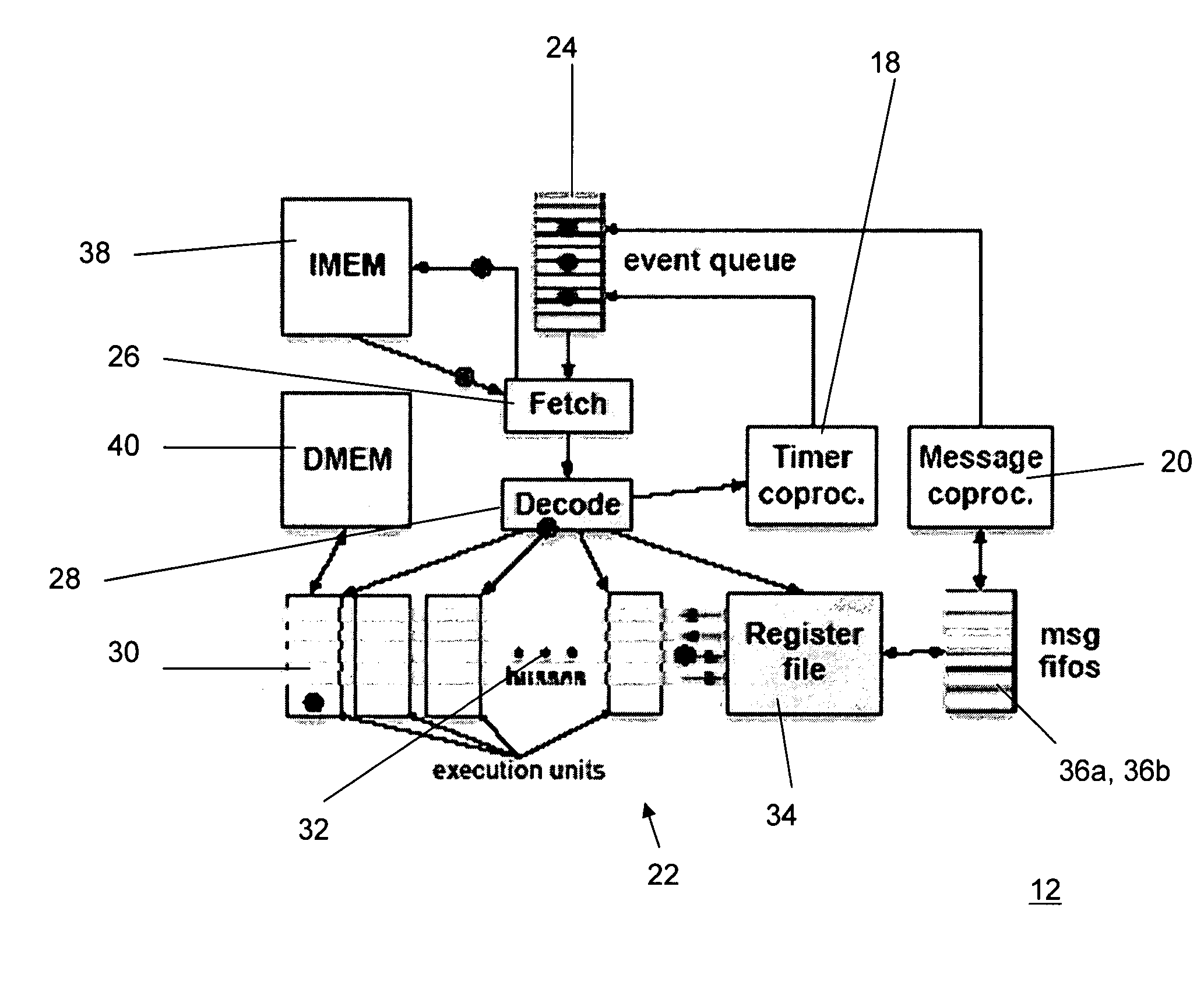
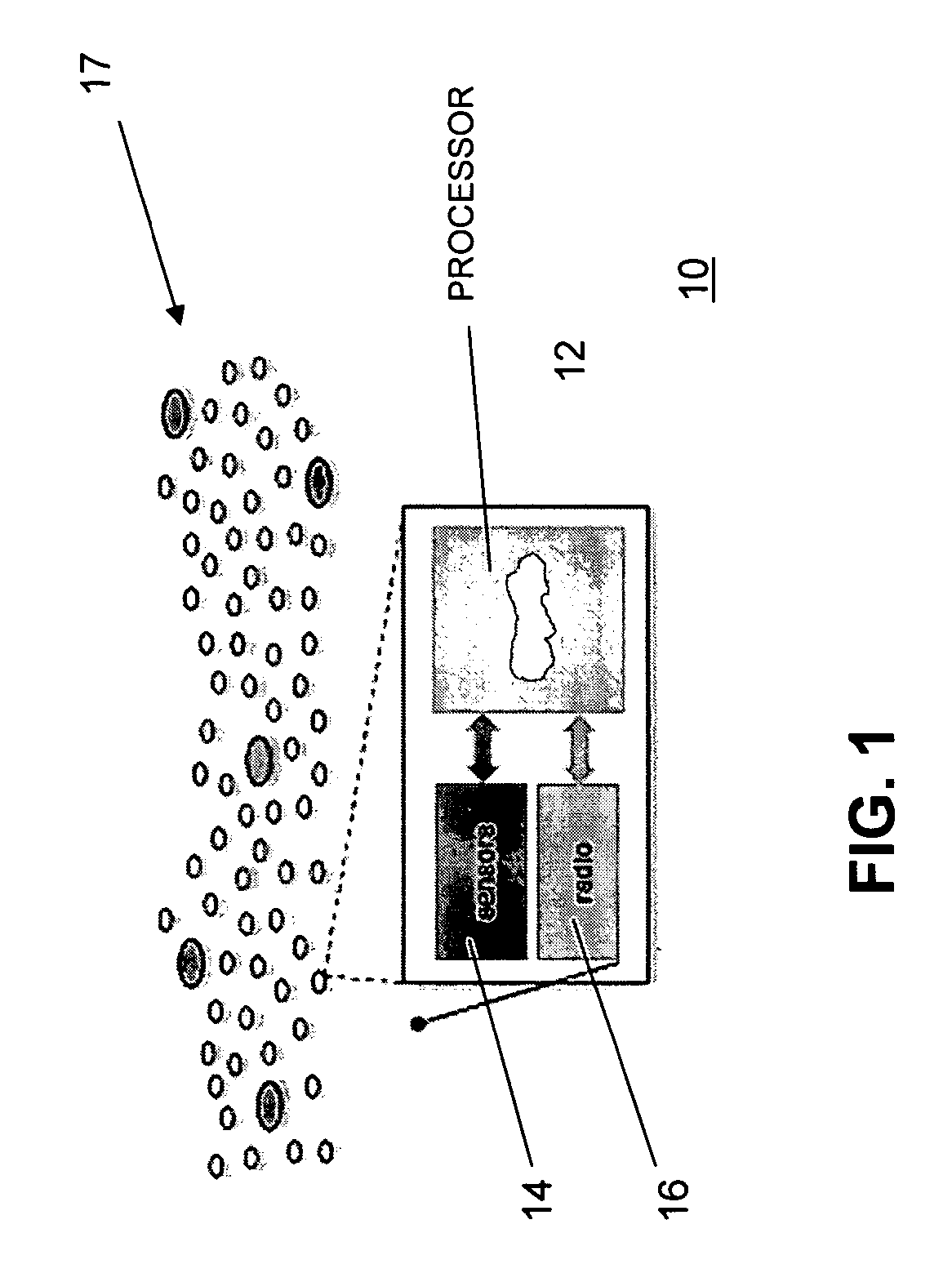
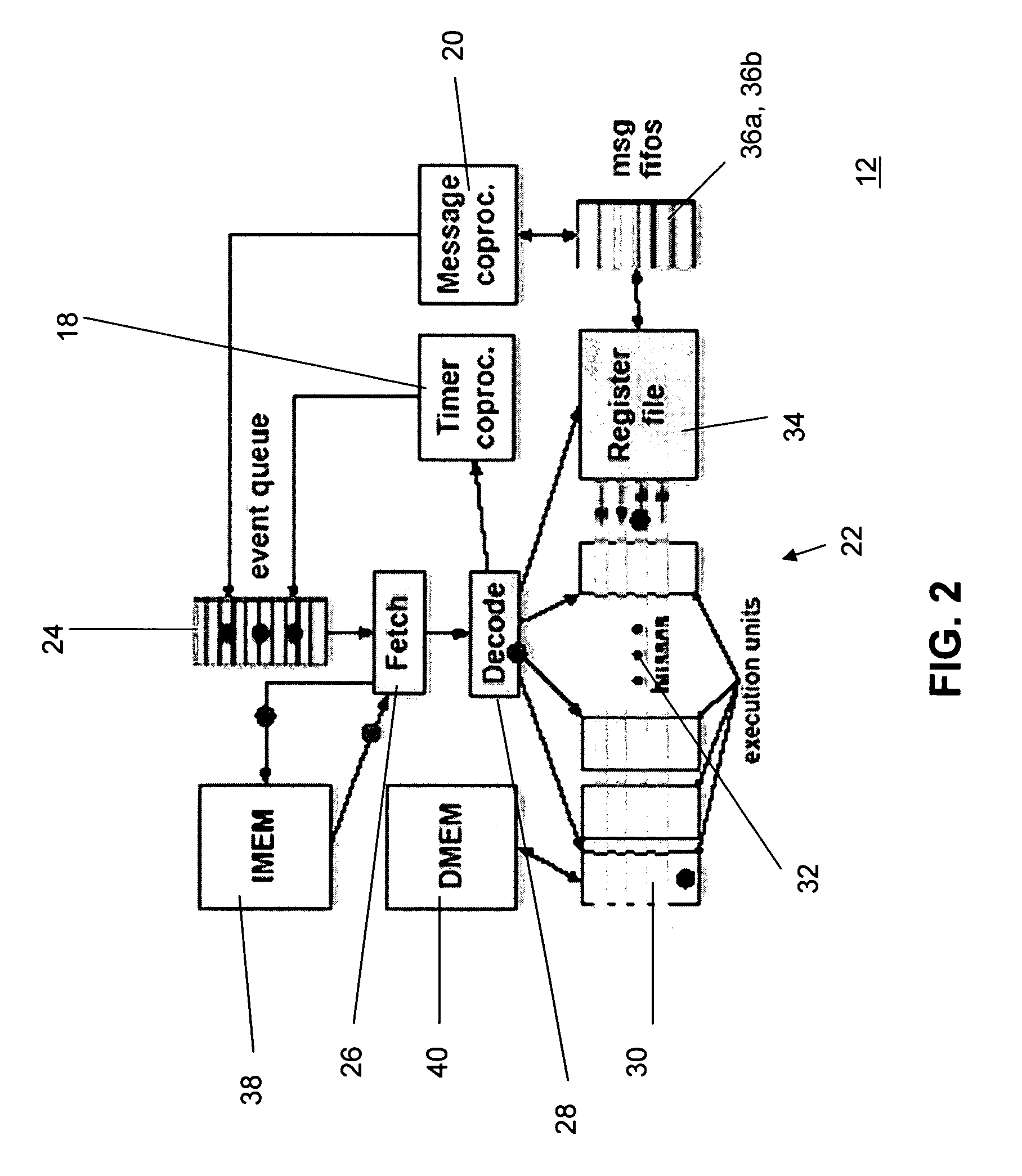
Sensor-network processors using event-driven architecture
InactiveUS20060075210A1Life maximizationLow-overhead transitionsPower managementMeasurement devicesMultiple sensorNetwork simulation
Event-driven processor architectures are particularly suited for use in multiple sensor node networks and simulators of such networks. A first variation of the processor is particularly suited for use in a sensor node in a wireless sensor network. Through use of the event-driven architecture and special message and timing coprocessors, this embodiment of the invention is optimized for low energy requirements and data monitoring operations in sensor networks. A second embodiment of the invention includes modifications necessary for use of the processor in a network simulation protocol.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
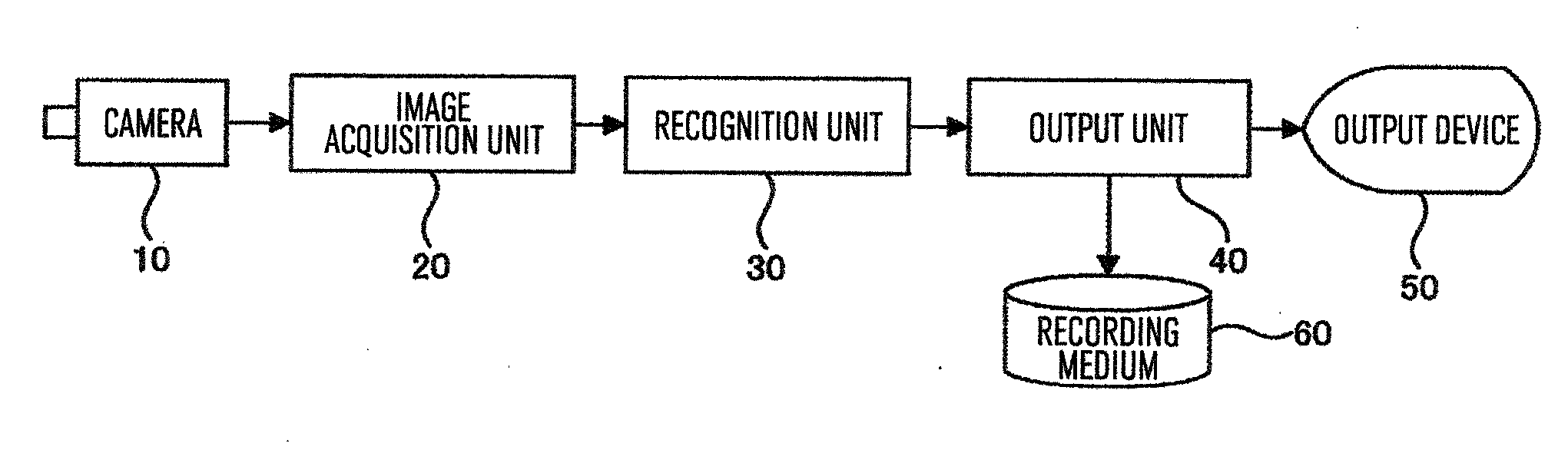
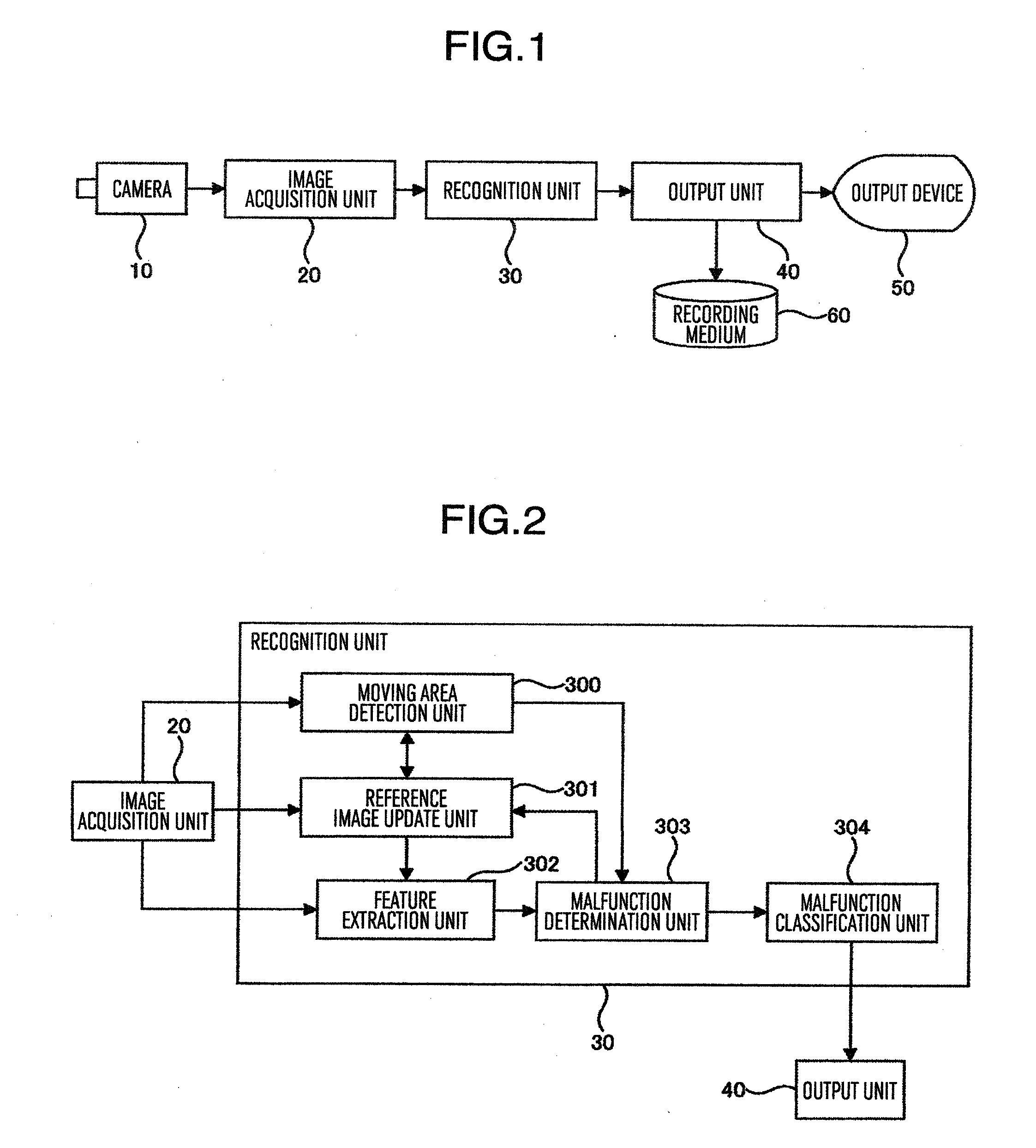
Surveillance camera system having camera malfunction detection function
InactiveUS20120026326A1Improve efficiencySupport job efficiencyCharacter and pattern recognitionColor television detailsFeature extractionSurveillance camera
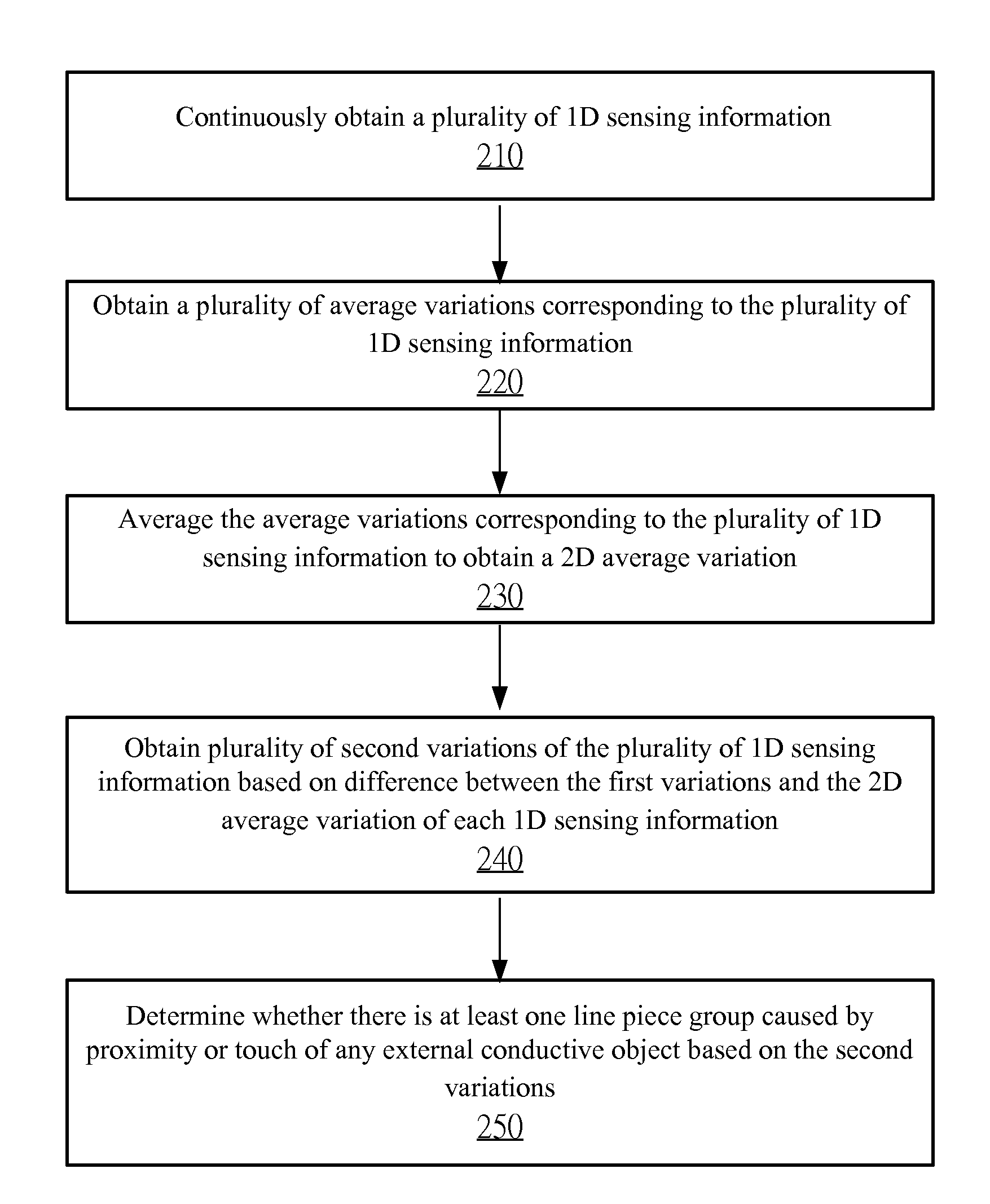
A camera surveillance system having a camera malfunction function includes an entire feature extraction unit to extract each entire feature from an input image and a reference image; a block feature extraction unit to extract block features being features of each block from images after the block division of the input image and the reference image divided into blocks by a block division unit; and a malfunction determination unit to calculate a first variation between the entire features of the reference image and the entire features of the input image, and a second variation between the block features of the reference image and the block features of the input image, to determine a camera malfunction by using a threshold, and output information indicating a type of the camera malfunction for each block.
Owner:HITACHI INFORMATION & CONTROL SOLUTIONS LTD
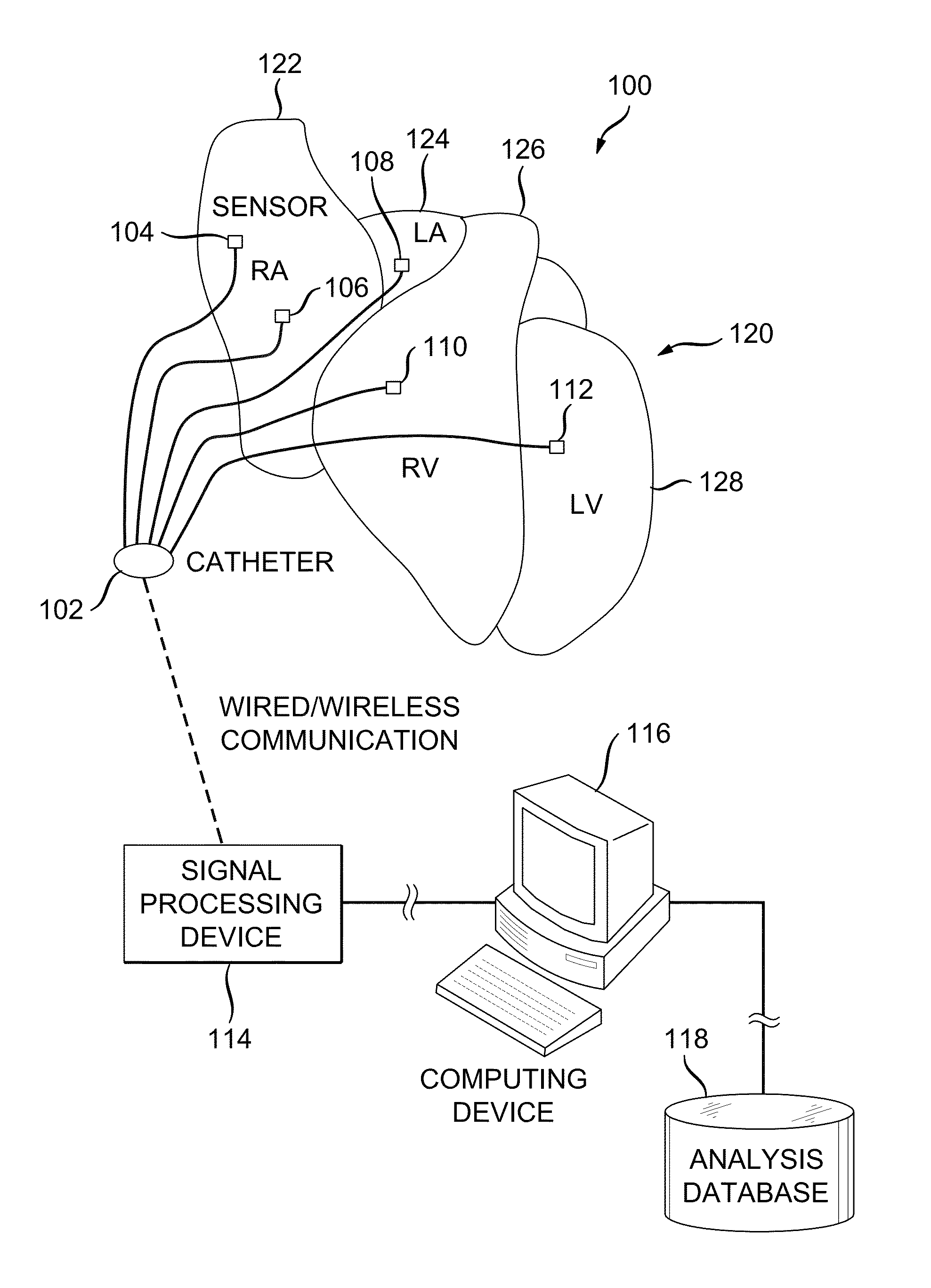
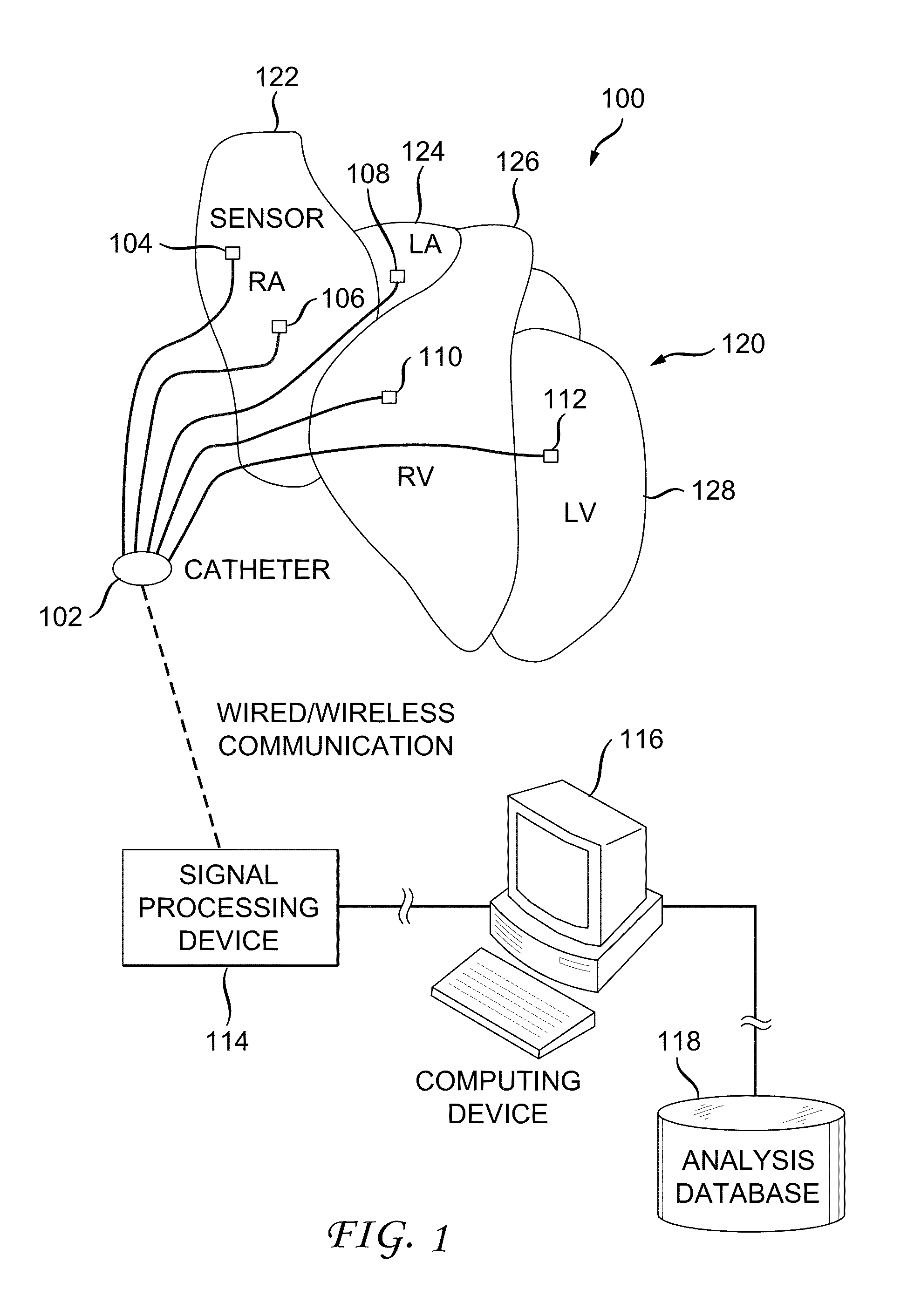
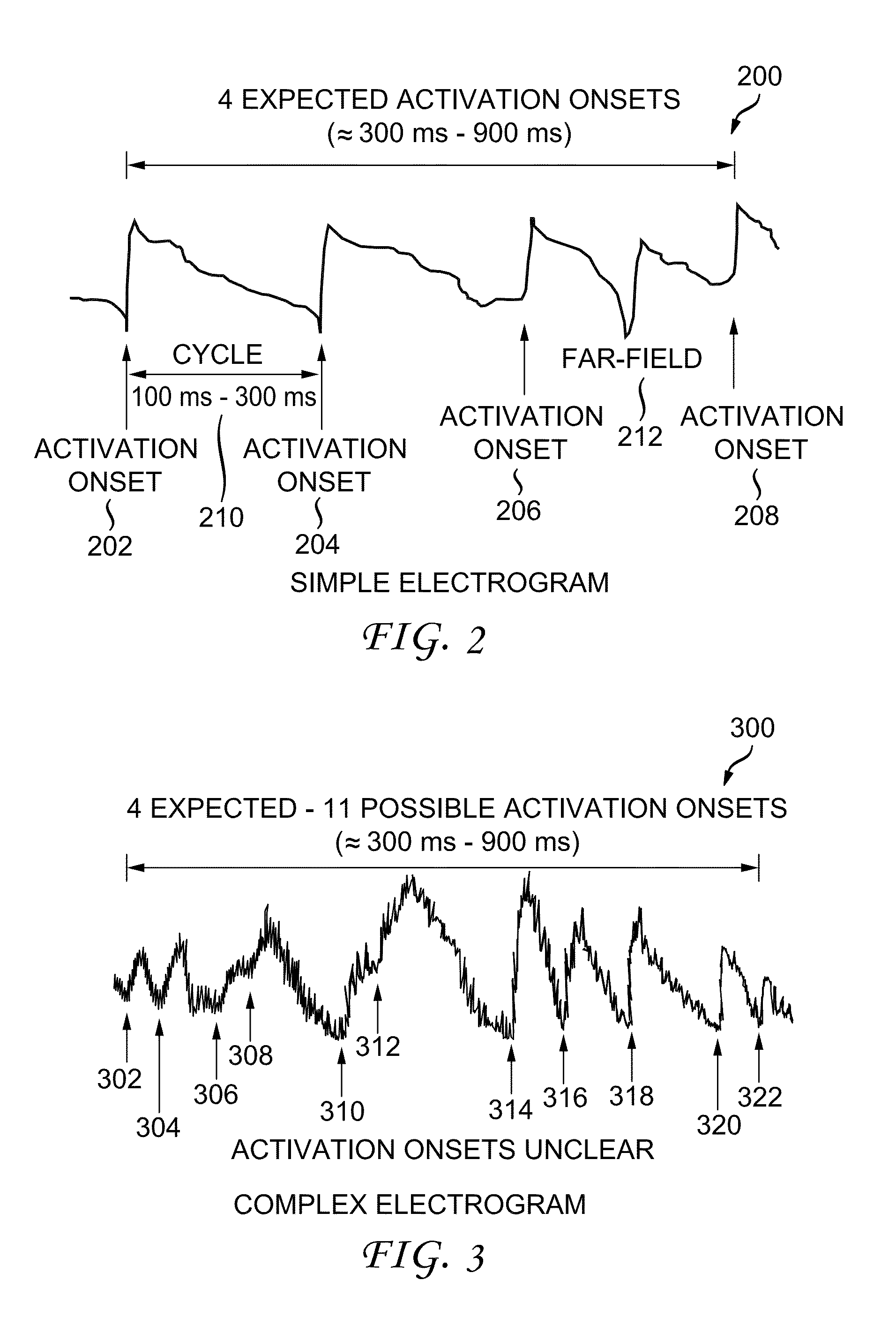
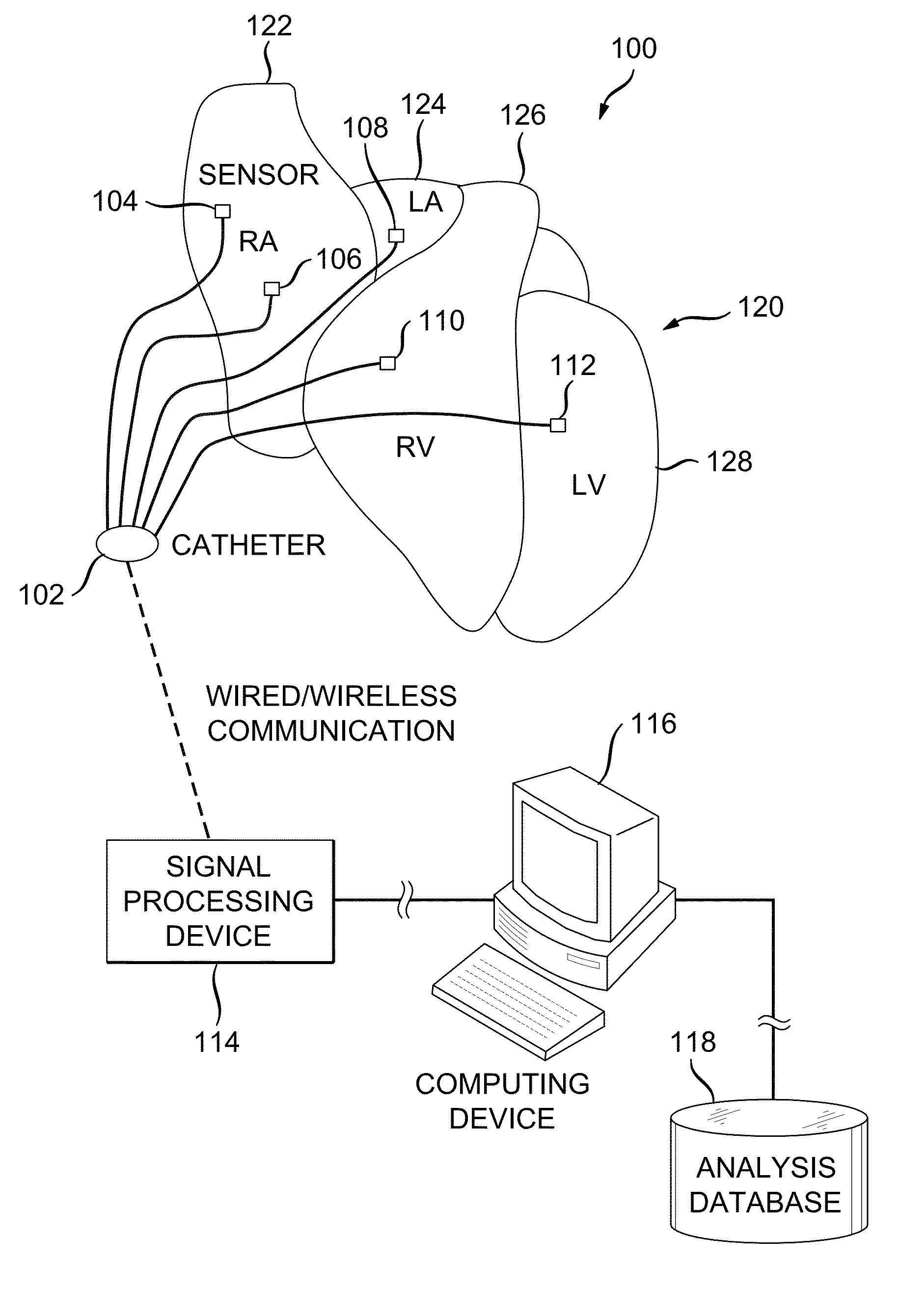
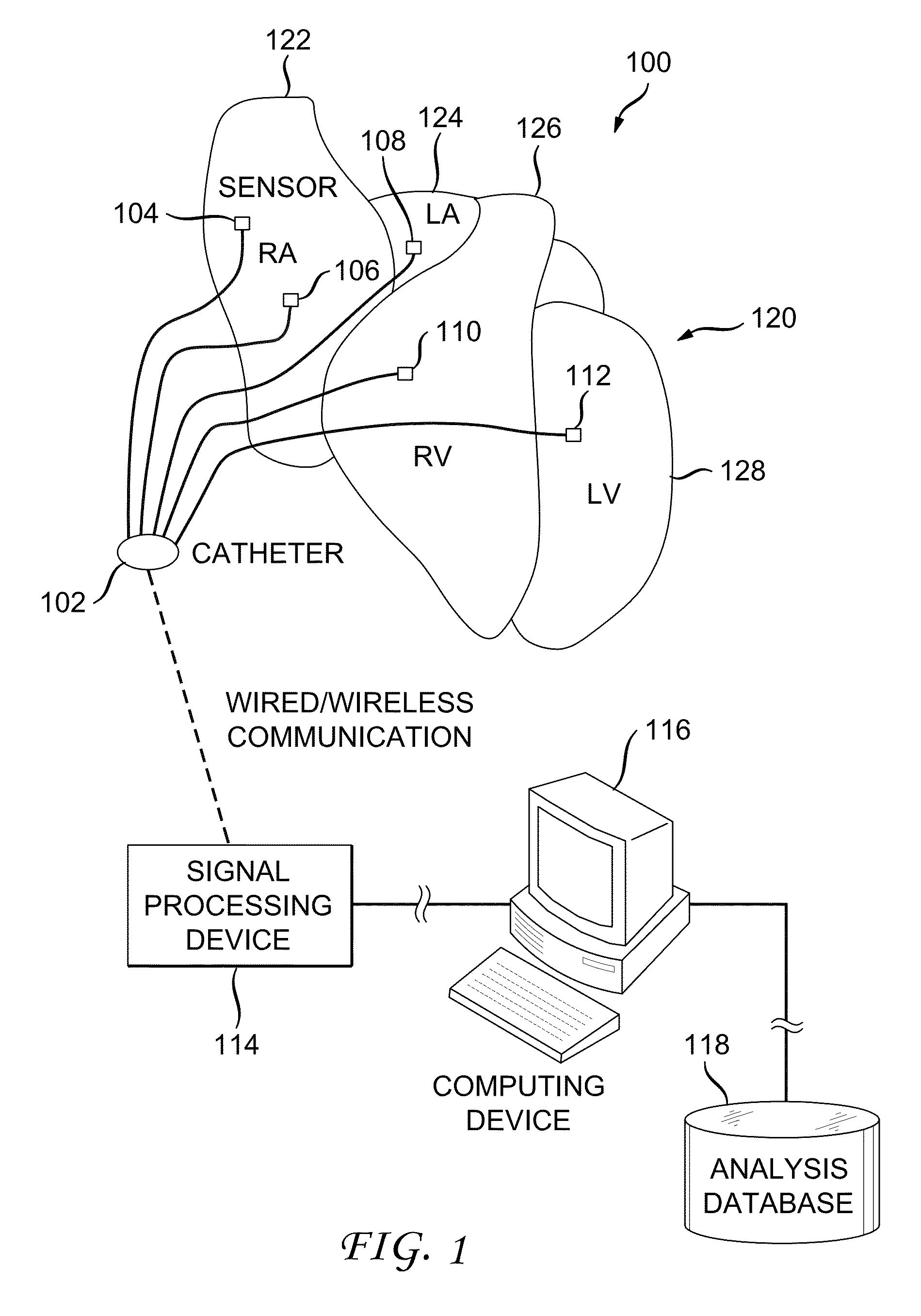
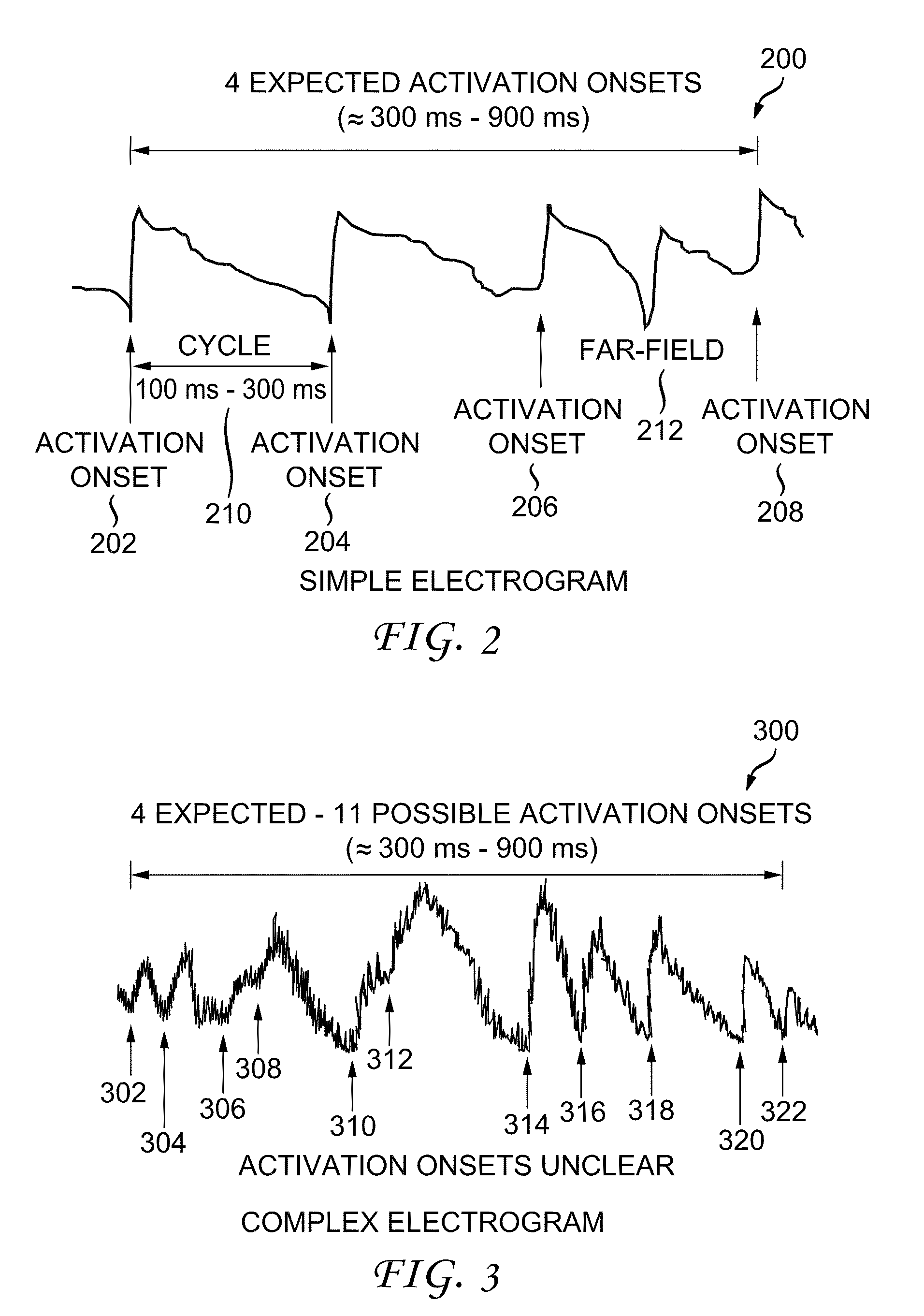
System and method for reconstructing cardiac activation information
ActiveUS20130226016A1Ameliorate disorderCure disorderElectrocardiographyCatheterStart timeBiological activation
An example system and method of reconstructing cardiac activation information are disclosed. An analysis signal and a reference signal are processed to determine whether there is a first point of change in a first selected-order derivative of the analysis signal with respect to a first selected-order derivative of the reference signal above a first threshold. The analysis signal and the reference signal are processed to determine whether there is a second point of change in a second selected-order derivative of the analysis cardiac signal with respect to a second selected-order derivative of the reference cardiac signal above a second threshold. An activation onset time is assigned in the analysis cardiac signal at a point based on a mathematical association of the first point of change and the second point of change to define cardiac activation indicating a beat in the analysis cardiac signal.
Owner:TOPERA +2
System and method for reconstructing cardiac activation information
ActiveUS9050006B2Ameliorate disorderCure disorderElectrocardiographyCatheterStart timeBiological activation
An example system and method of reconstructing cardiac activation information are disclosed. An analysis signal and a reference signal are processed to determine whether there is a first point of change in a first selected-order derivative of the analysis signal with respect to a first selected-order derivative of the reference signal above a first threshold. The analysis signal and the reference signal are processed to determine whether there is a second point of change in a second selected-order derivative of the analysis cardiac signal with respect to a second selected-order derivative of the reference cardiac signal above a second threshold. An activation onset time is assigned in the analysis cardiac signal at a point based on a mathematical association of the first point of change and the second point of change to define cardiac activation indicating a beat in the analysis cardiac signal.
Owner:TOPERA +2
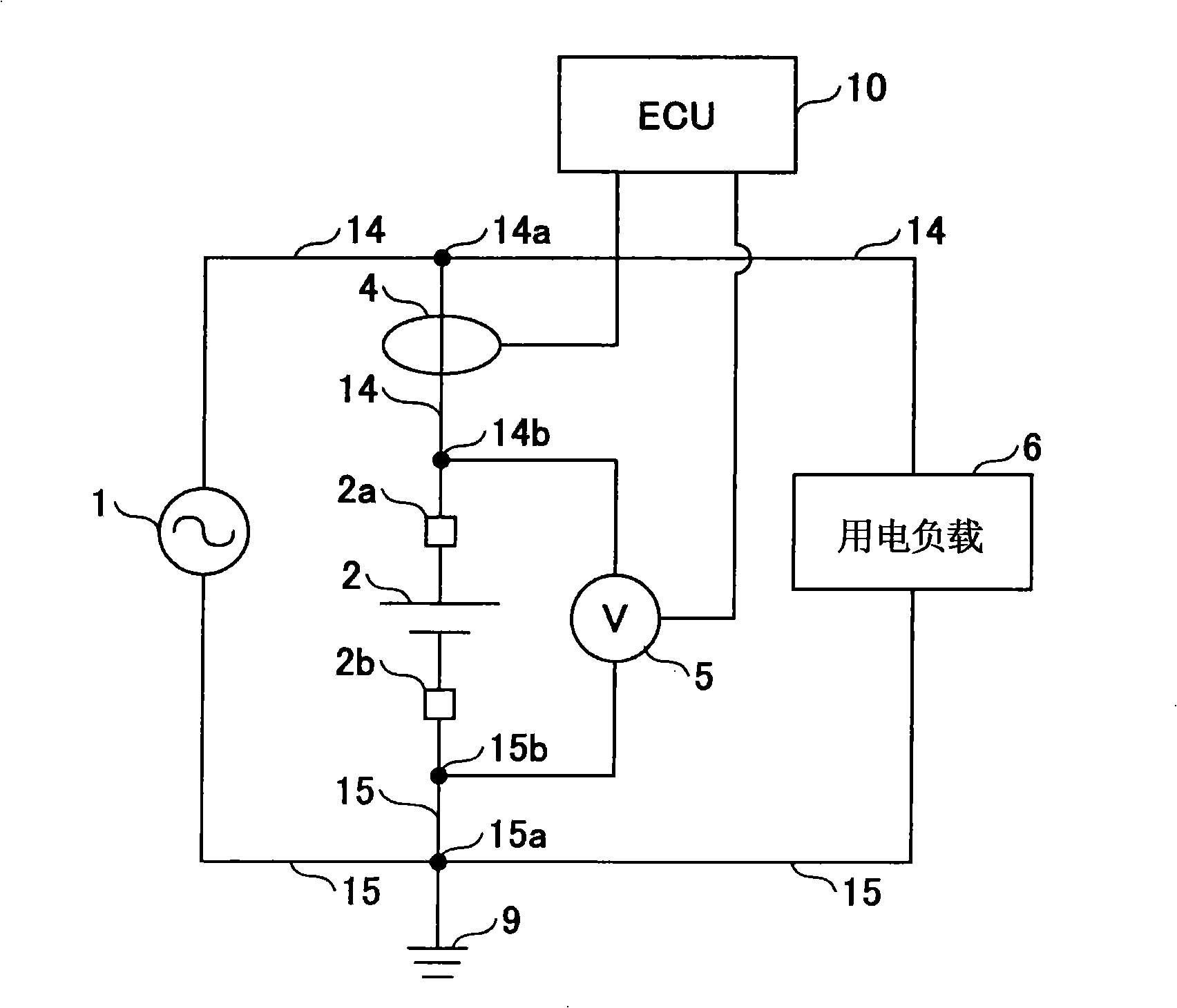
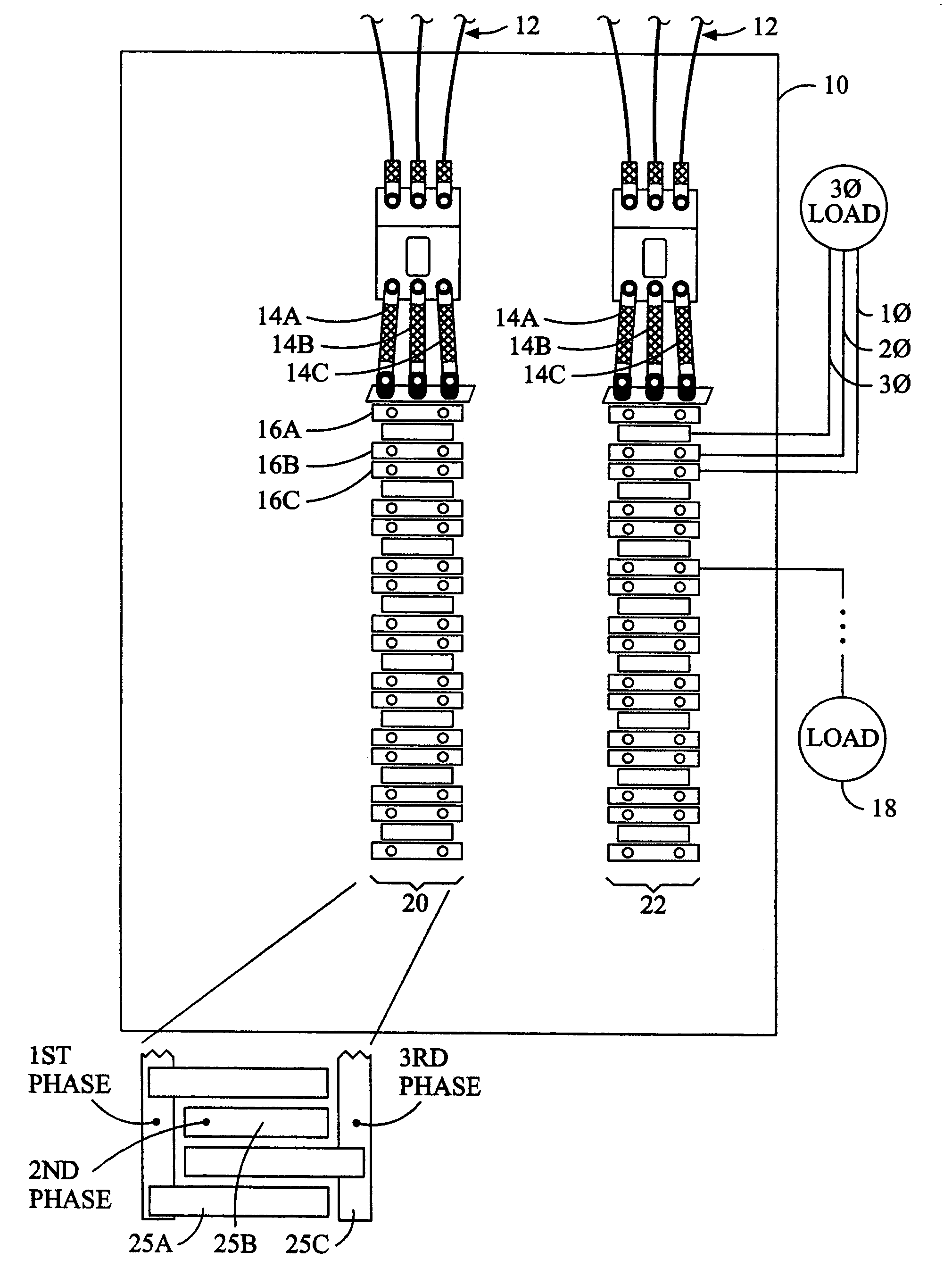
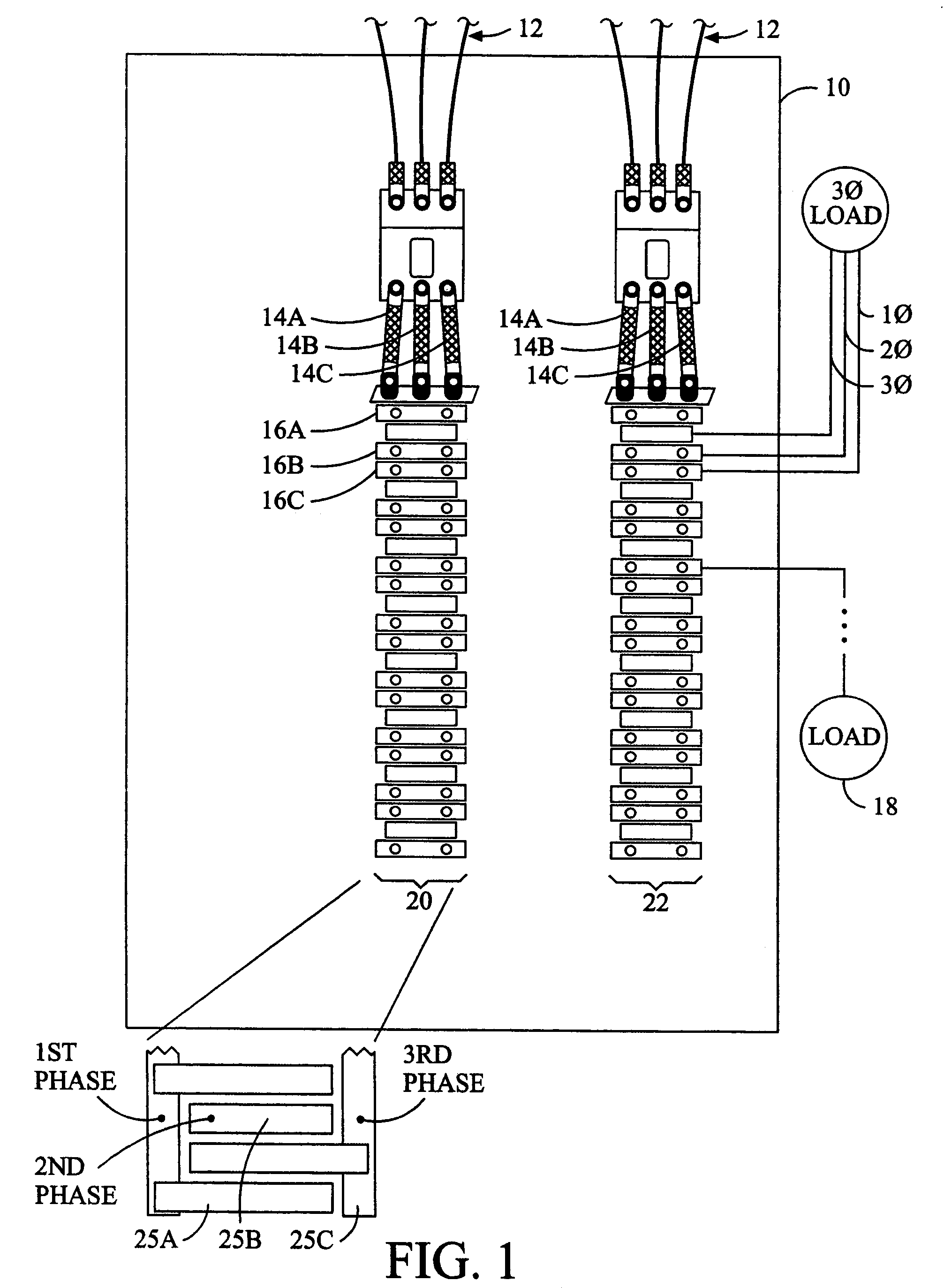
Abnormality judgment device and abnormality judgment method of power supply unit
In a power supply unit comprising a battery (2) for supplying power to an electric load (6), a current sensor (4) for detecting the current of the battery (2), and a voltage sensor (5) for detecting the voltage of the battery (2), a decision is made that open fault has occurred in the battery (2) if a voltage detected by the voltage sensor (5) is larger than a predetermined first variation and a current detected by the current sensor (4) is smaller than a predetermined second variation, and a decision is made that intermediate fixed fault has occurred in the current sensor (4) if a decision is not made that open fault has occurred in the battery (2) and when the internal resistance of the battery (2) is not lower than a predetermined value.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
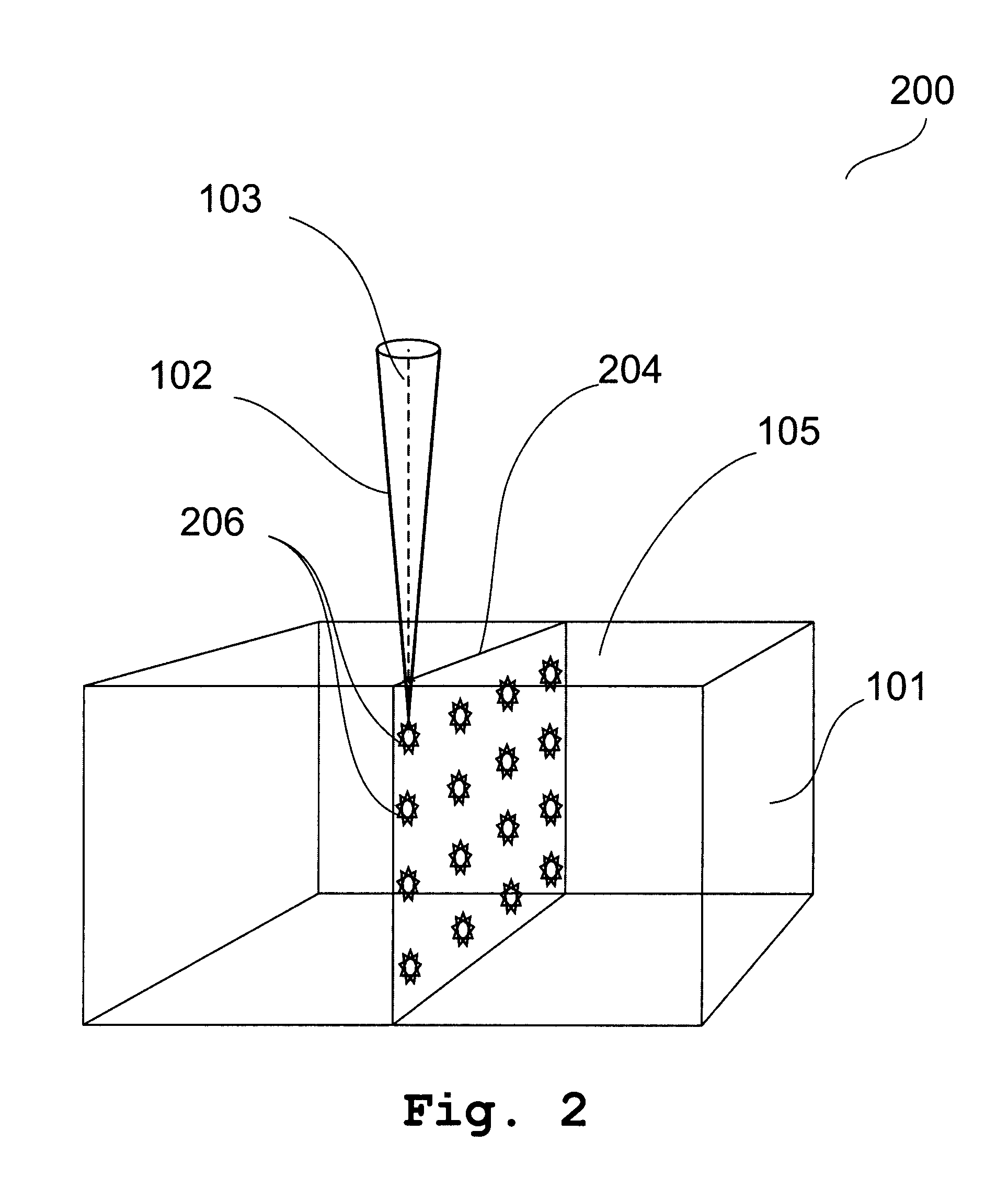
Method of Separating Surface Layer of Semiconductor Crystal Using a Laser Beam Perpendicular to the Separating Plane
ActiveUS20130248500A1Low mechanical strengthPolycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsSurface layerLight beam
This invention provides two variations of methods of separating a surface layer (307) of the semi-conductor crystal (101). In the first variation of the method, a focused laser beam (102) is directed onto the crystal (101) in such a way that focus is placed in the layer separation plane (304) perpendicular to the axis (103) of said beam (102), the laser beam (102) is moved with scanning the layer separation plane (304) with focus in the direction from the open side surface of the crystal (101) deep into the crystal with forming a continuous slit width of which is increased with every pass of the laser beam (102), the previous operation is performed up to separation of the surface layer (307). In the second variation of the method, pulse laser emission is generated; a focused laser beam is directed onto the crystal in such a way that focus is placed in the layer separation plane perpendicular the axis of said beam, a laser beam is moved in such a way that focus is moved in the layer separation plane with forming the non-overlapping local regions with a disturbed topology of the crystal structure and with reduced interatomic bonds, wherein said local regions is distributed over the whole said plane, an external action disturbing said reduced interatomic bonds is applied to the separable layer.
Owner:SHRETER YURY GEORGIEVICH +2
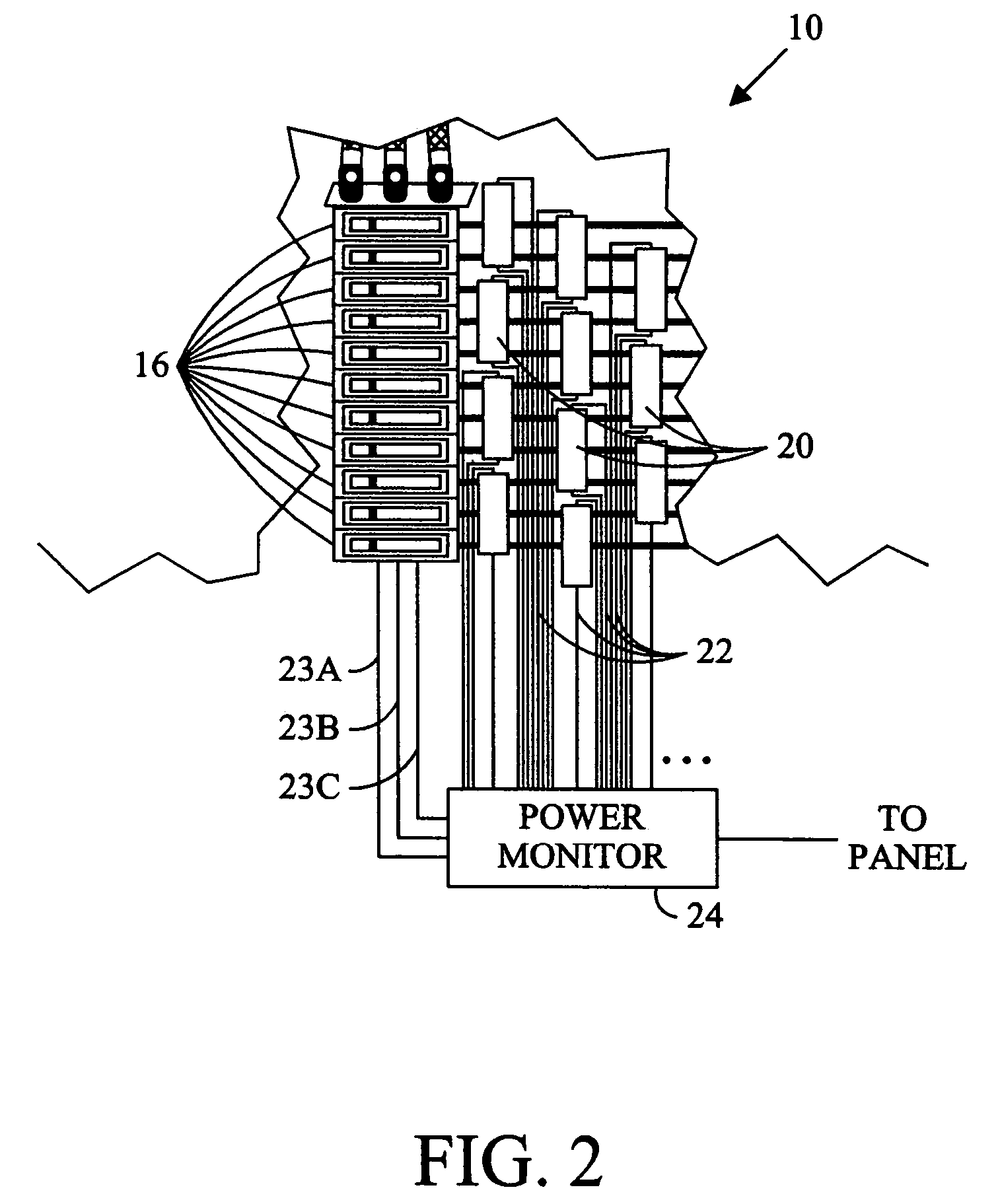
Power monitoring system that determines phase using a superimposed signal
A power monitoring system comprising a first current sensor suitable to sense first changing electrical current within a first conductor to a first load and a first conductor. A second conductor sensing a first voltage potential provided to the first load. A power monitor superimposes a first signal on the first conductor and first current sensor such that the first signal is sensed on the other of the first conductor and first current sensor. Associating the first voltage potential with first changing electrical current in the power usage calculation of the first load.
Owner:VERIS INDS
MEMS resonant accelerometer having improved electrical characteristics
ActiveUS20110056294A1Improved physical and electrical characteristicAcceleration measurement using interia forcesClassical mechanicsFirst variation
A MEMS resonant accelerometer is disclosed, having: a proof mass coupled to a first anchoring region via a first elastic element so as to be free to move along a sensing axis in response to an external acceleration; and a first resonant element mechanically coupled to the proof mass through the first elastic element so as to be subject to a first axial stress when the proof mass moves along the sensing axis and thus to a first variation of a resonant frequency. The MEMS resonant accelerometer is further provided with a second resonant element mechanically coupled to the proof mass through a second elastic element so as to be subject to a second axial stress when the proof mass moves along the sensing axis, substantially opposite to the first axial stress, and thus to a second variation of a resonant frequency, opposite to the first variation.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
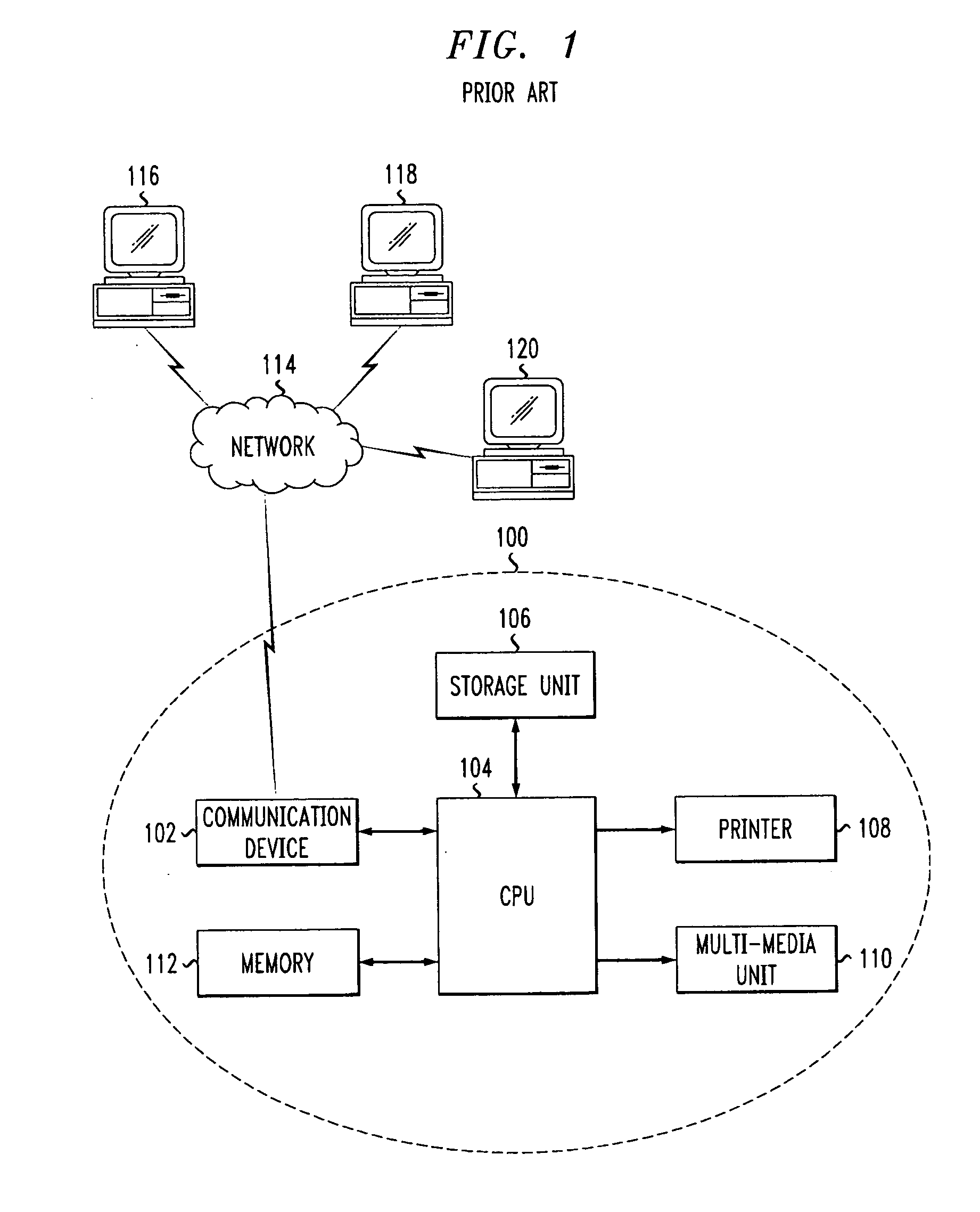
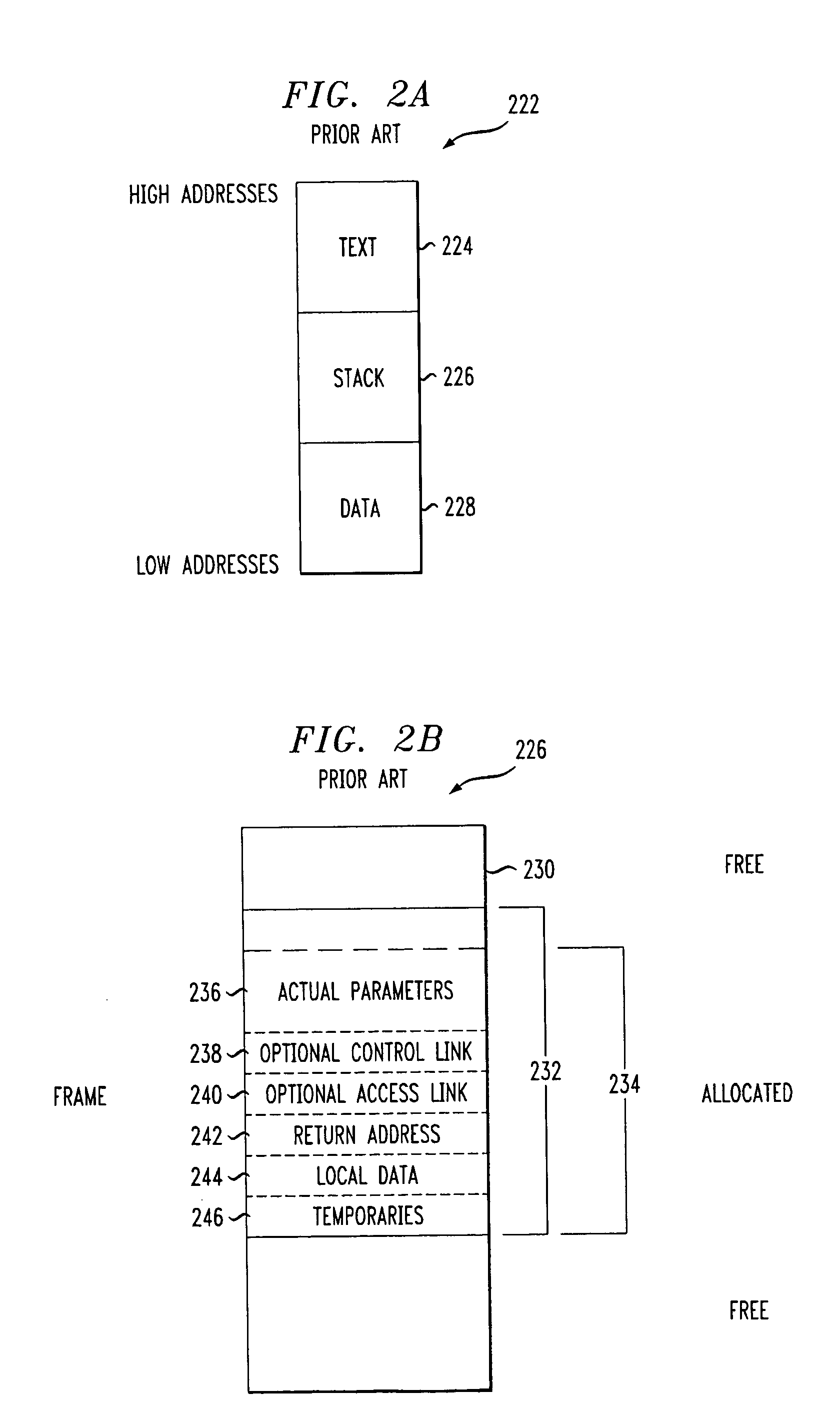
Buffer overflow protection and prevention
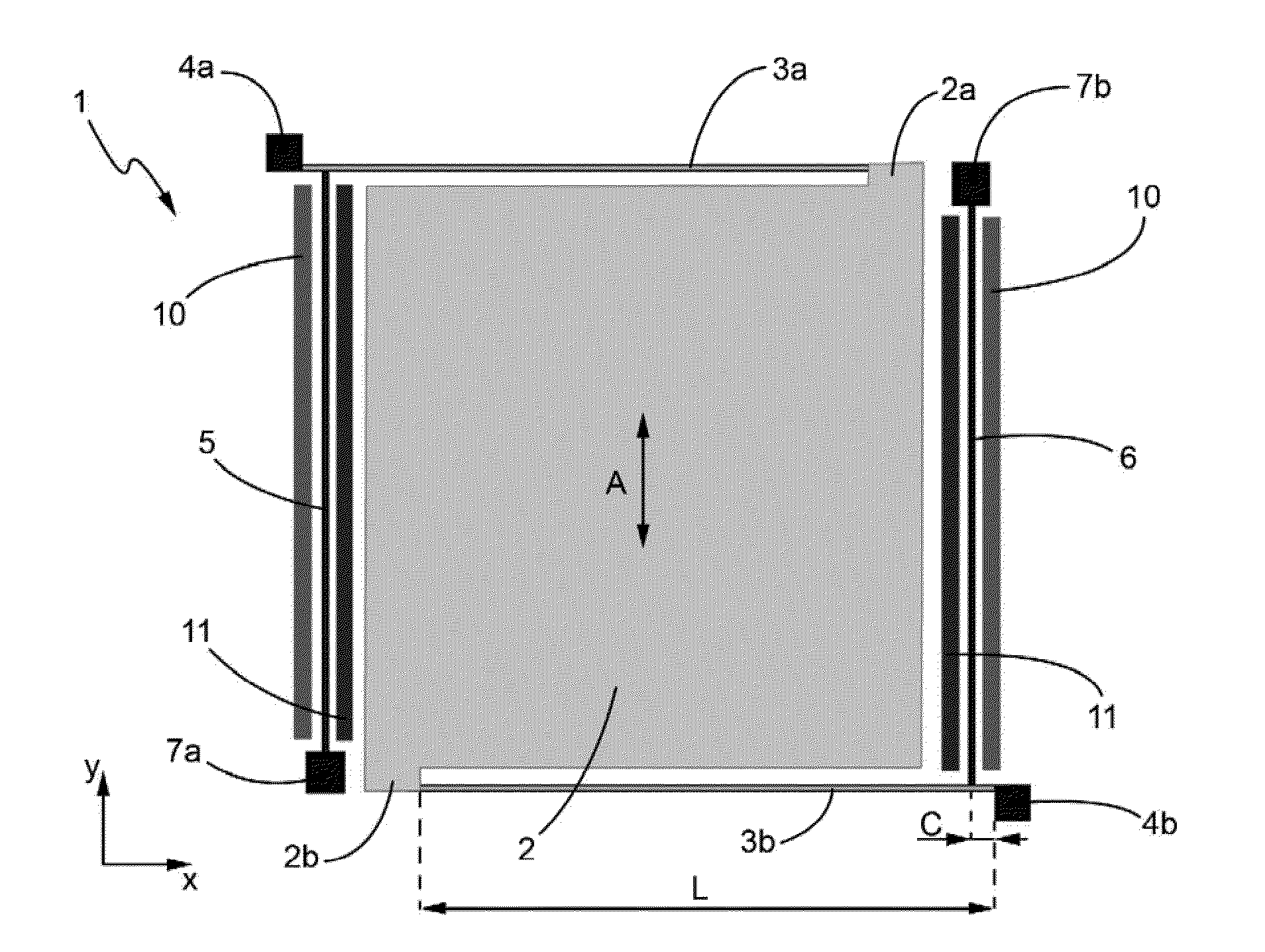
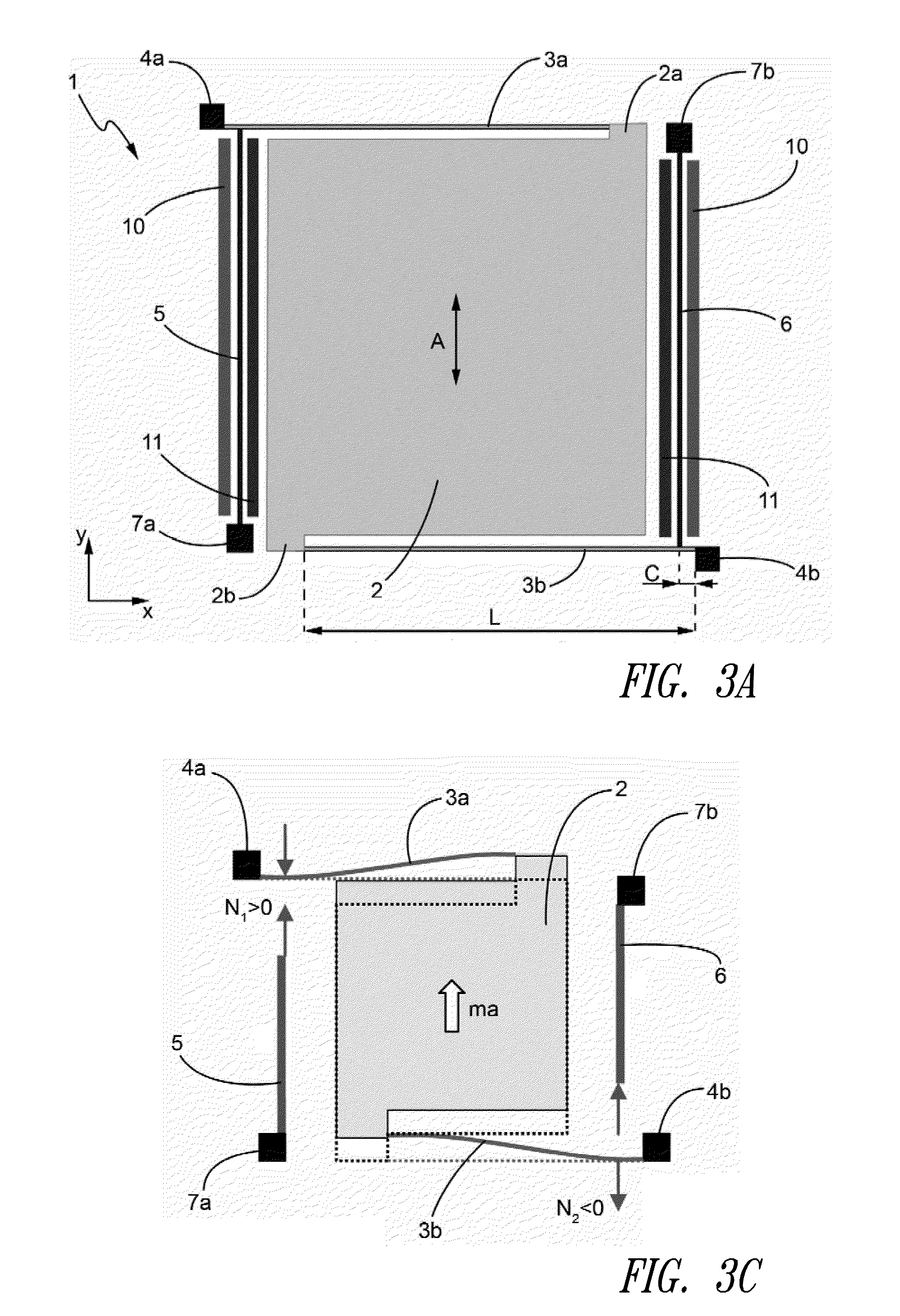
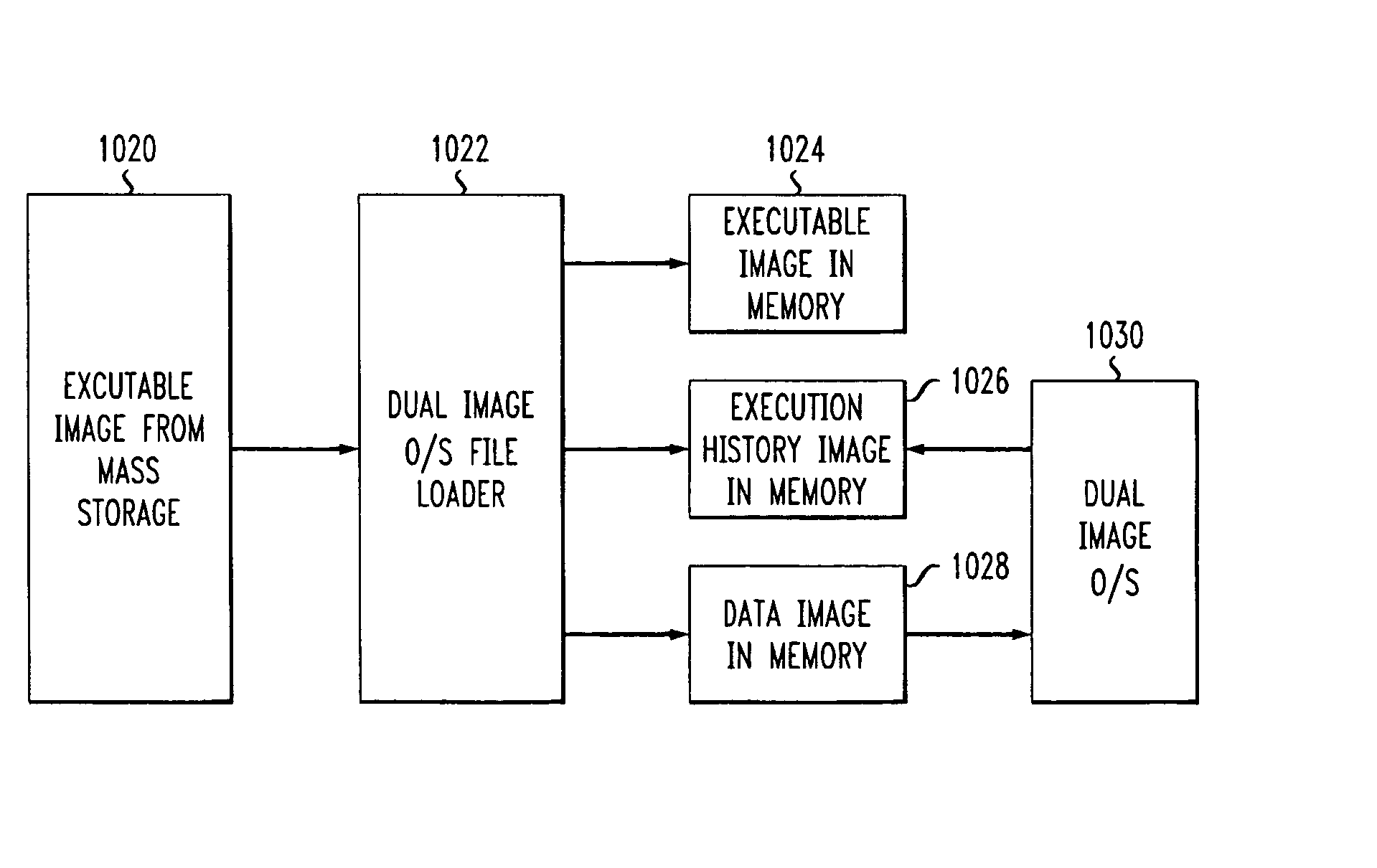
InactiveUS20050022172A1Unauthorized memory use protectionHardware monitoringOperational systemBuffer overflow protection
A method and apparatus for protecting against a buffer over flow attack. In one variation, an executable software program is divided into an executable image, a data image, and an execution history image. The operating system processes an executable statement in the executable image. Other statements are processed in the data image. In a second variation, the execution history image is made use of in addition to the tasks of the first variation. Each statement is classified as either mutable or immutable. The usage of statements is recorded in the execution history image. If a mutable statement has over-written an immutable statement memory location, then the program is terminated. Optionally, the entire program is re-mapped using the execution history image such that immutable statements cannot over-write mutable statements.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
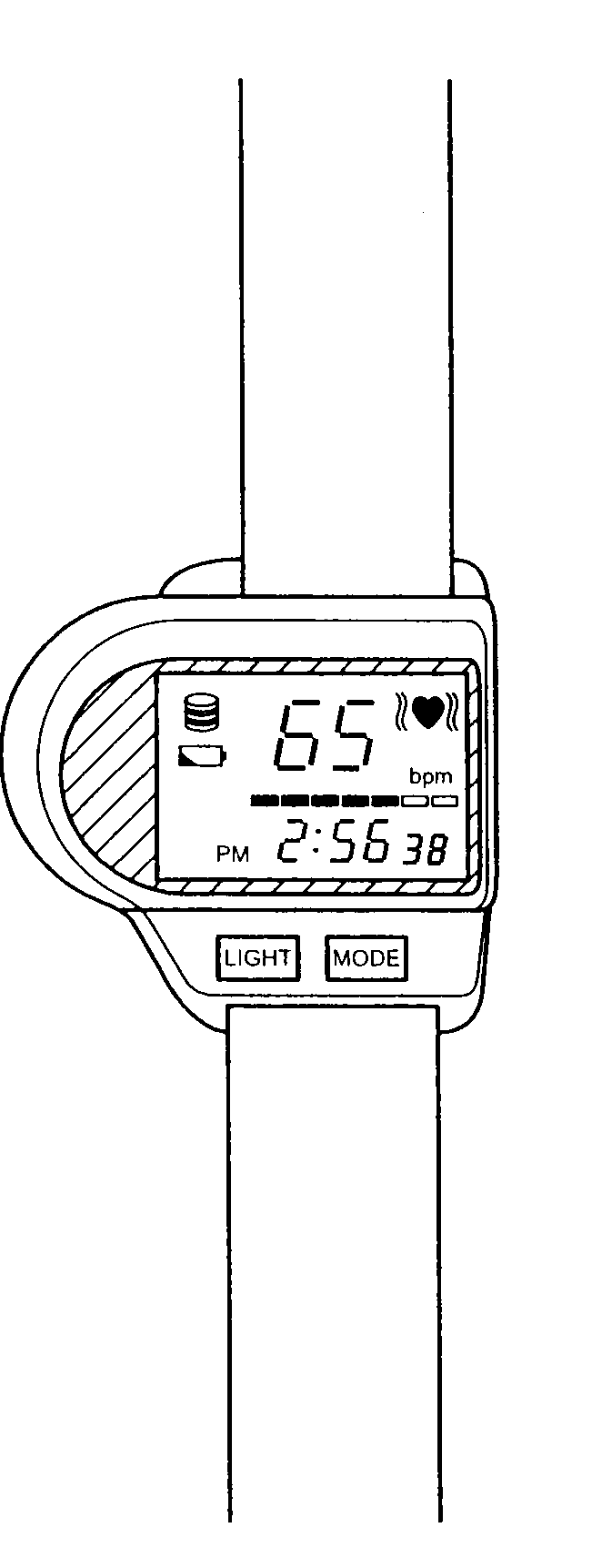
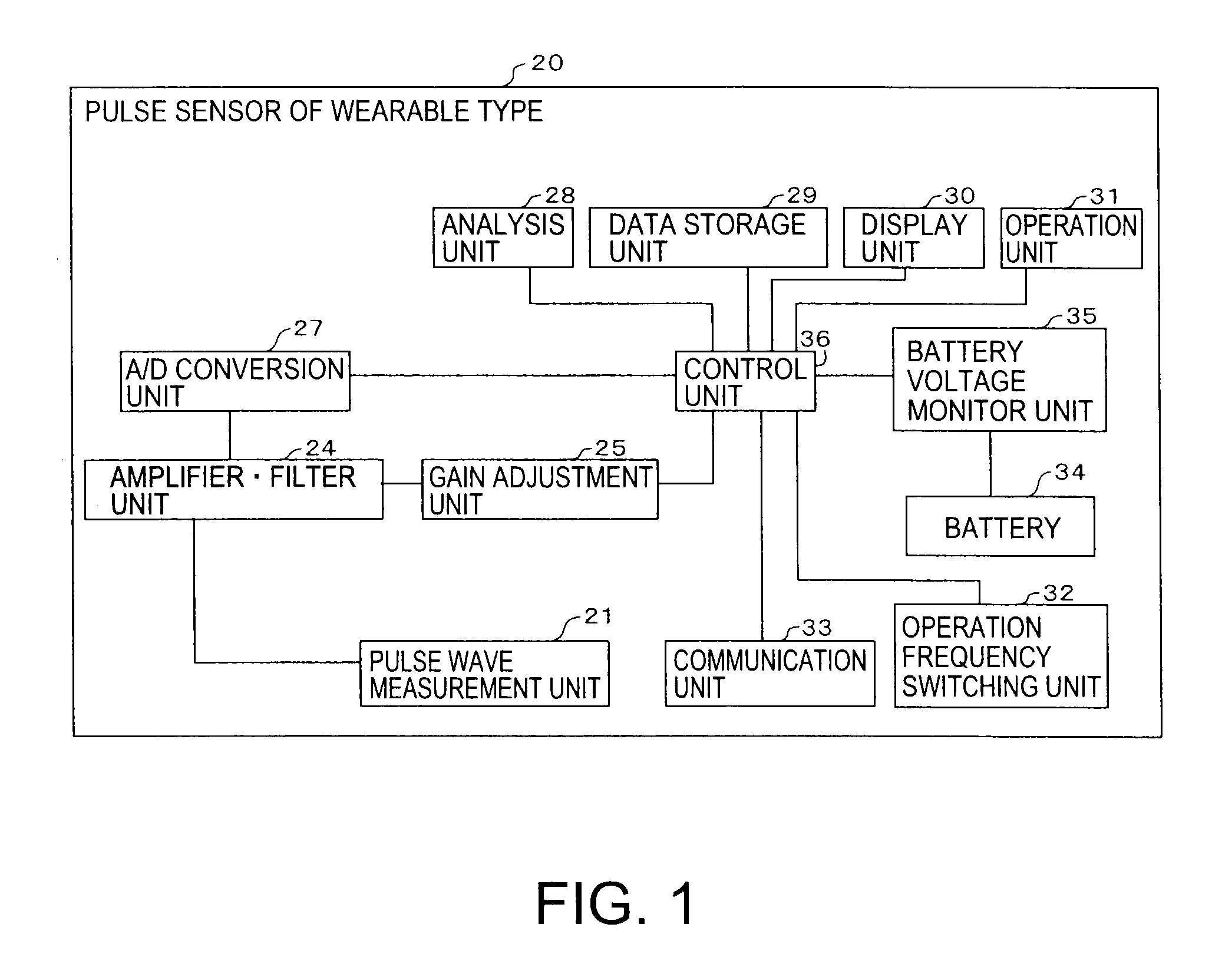
Apparatus and method for measuring pulse waves
Pulse waves of a subject are detected in time sequence. Amplitude of the pulse waves is detected, and an interval between two pulse waves adjacent along a time axis is detected. A first change ratio of the interval along the time axis, and a second change ratio of the amplitude divided by the interval along the time axis are calculated respectively. By comparing the first change ratio and the second change ratio with a first threshold and a second threshold respectively, it is decided whether the pulse waves of the subject are irregular.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
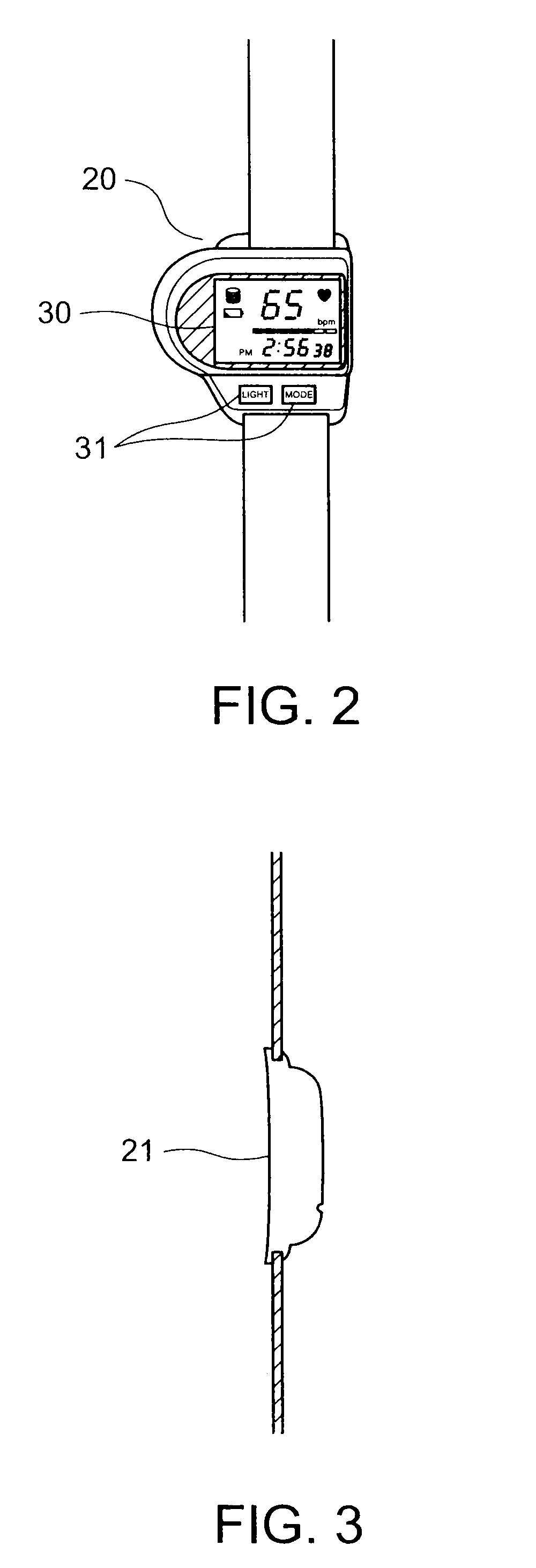
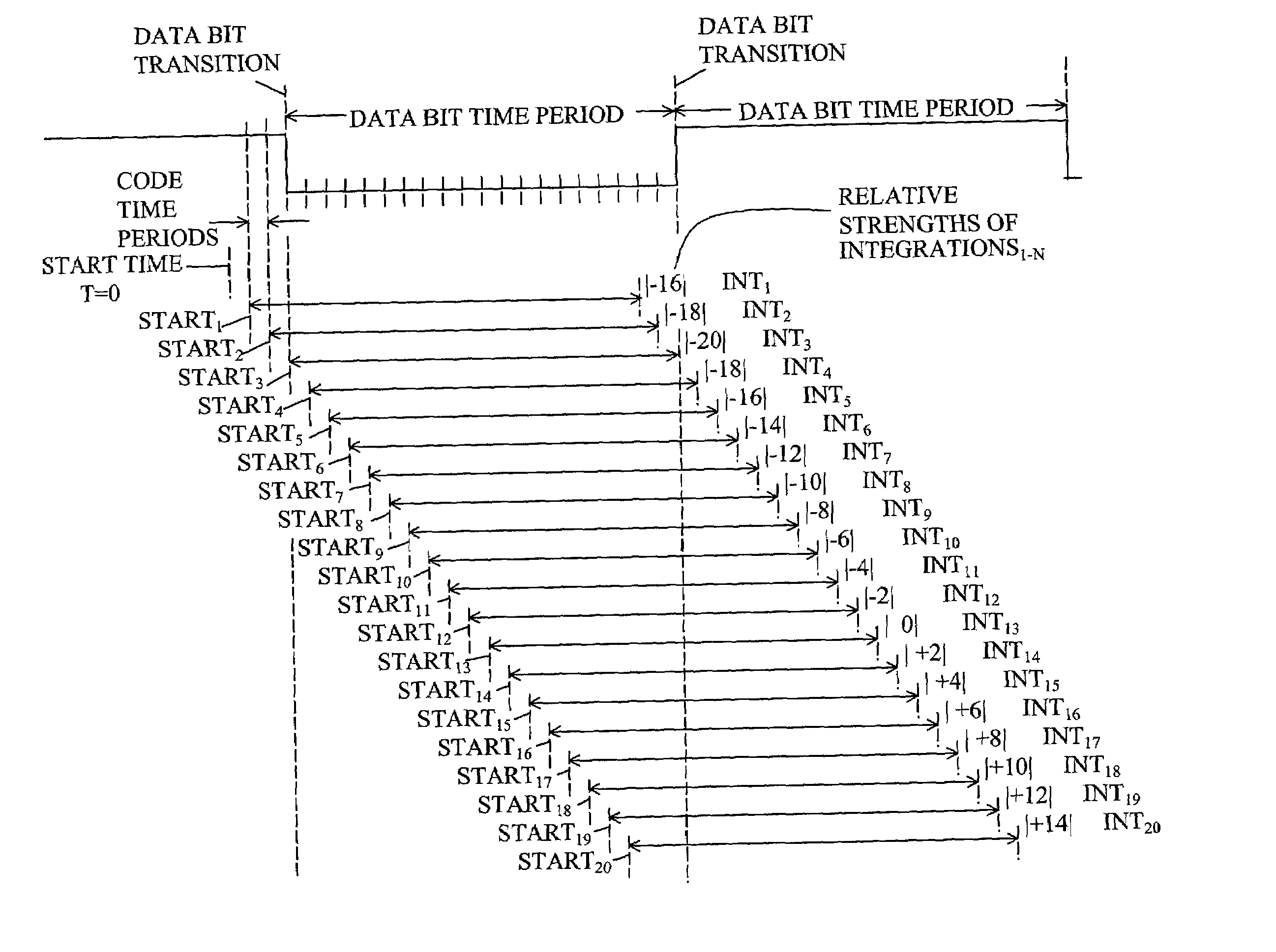
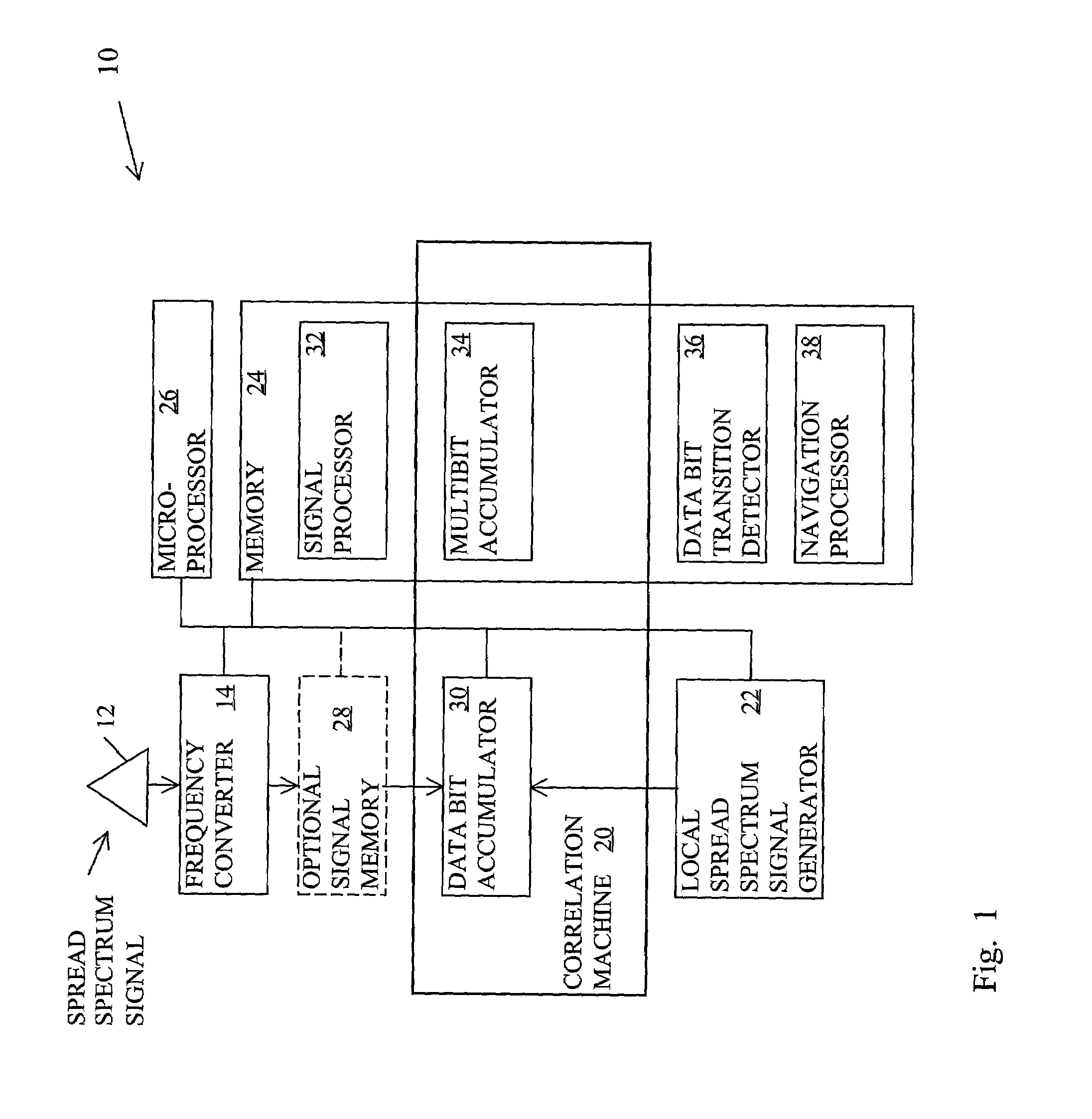
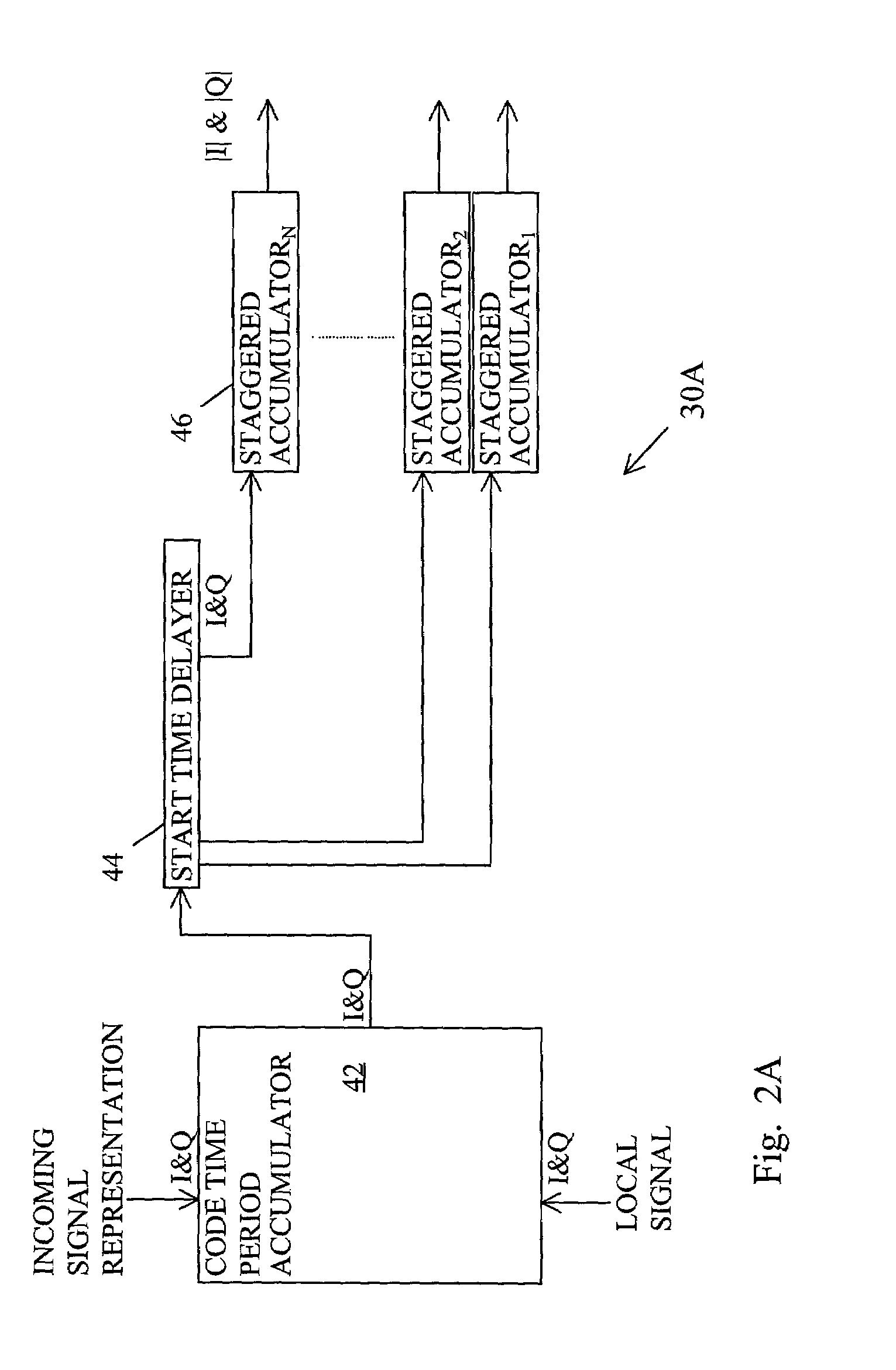
Method for determining data bit transitions for a low level spread spectrum signal
Apparatus and methods for determining the timing of the data bit transitions. “N” assumptions of data bit transitions are used for determining N integrations of an incoming spread signal for data bit time periods where N is the data bit time period divided by the code time period. In a first variation, the N assumptions use N start times separated by code time periods. In a second variation, the N assumptions use N sign inversion times separated by code time periods. In either variation the unsigned values of the N integrations, respectively, may be combined for several data bit time periods. The assumed transition timing that results in the strongest of the N integrations is indicative of the timing of the data bit transitions.
Owner:TRIMBLE NAVIGATION LTD
Method for scanning projective capacitive touch panel
InactiveCN101840294AEasy-to-understand technical featuresInput/output processes for data processingHigh resistanceCapacitance
The invention discloses a method for scanning a projective capacitive touch panel, which comprises the following steps of: (A) dividing all mutual capacitors into two groups according to resistance-capacitance constants to an integrator, and setting a first standard voltage value and a first variation difference of each group of mutual capacitors and a second standard voltage value and a second variation difference of each mutual capacitor respectively; (B) applying higher single-frequency excitation signals to the group of mutual capacitors with lower resistance-capacitance constants and applying lower single-frequency excitation signals to the group of mutual capacitors with higher resistance-capacitance constants to perform scanning so as to obtain first current voltage values of all the mutual capacitors in each group, and comparing the first current voltage values with the first standard voltage value corresponding to the group to judge suspicious mutual capacitors beyond the range of the first variation difference; and (C) applying low-frequency excitation signals to the suspicious mutual capacitors to obtain second current voltage values of the suspicious mutual capacitors, and comparing the second current voltage values with the second standard voltage value corresponding to the mutual capacitors to judge the mutual capacitors beyond the range of the second variation difference and affected by touch. The method is quick to scan and accurate to position.
Owner:TPK TOUCH SOLUTIONS (XIAMEN) INC +1
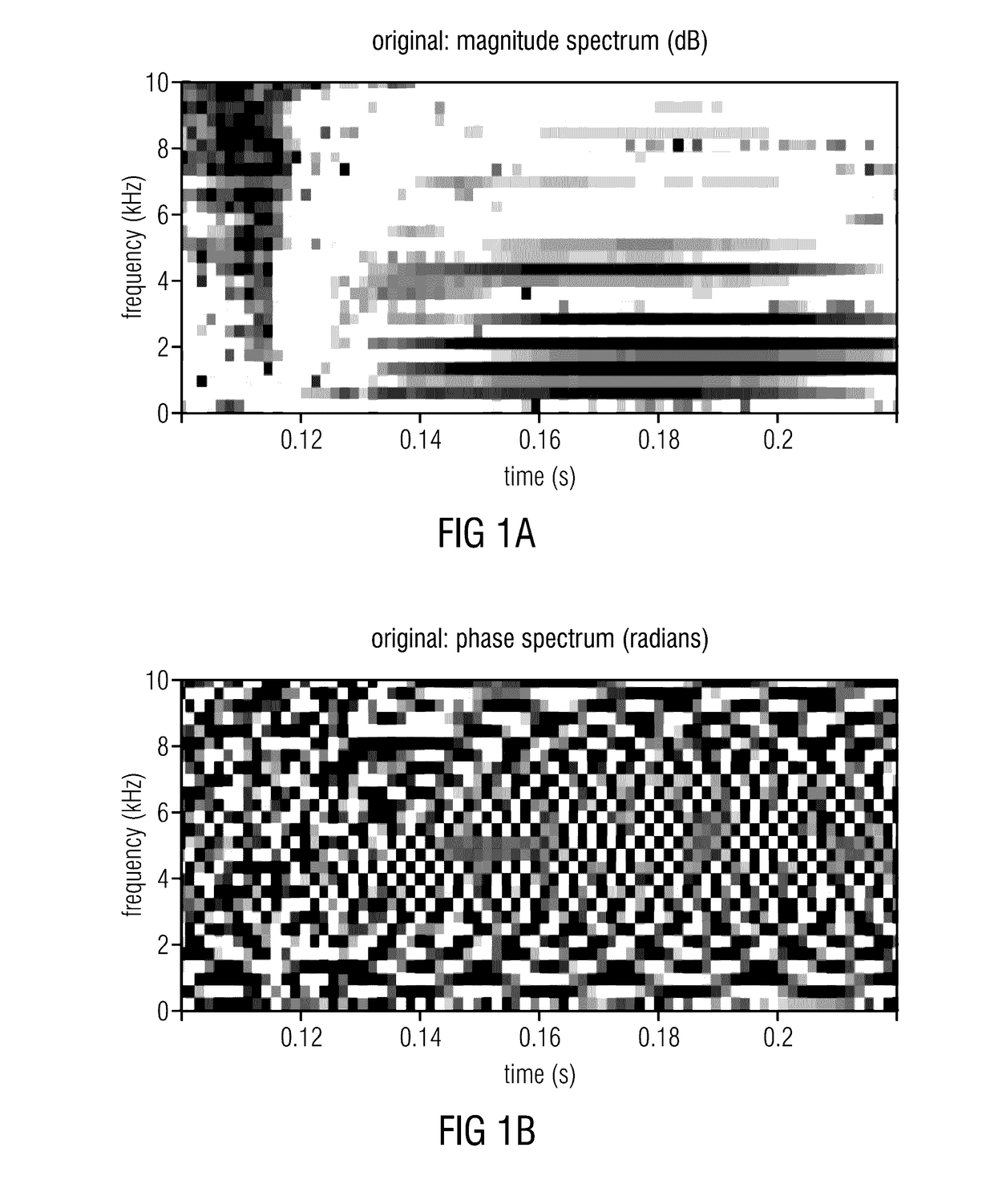
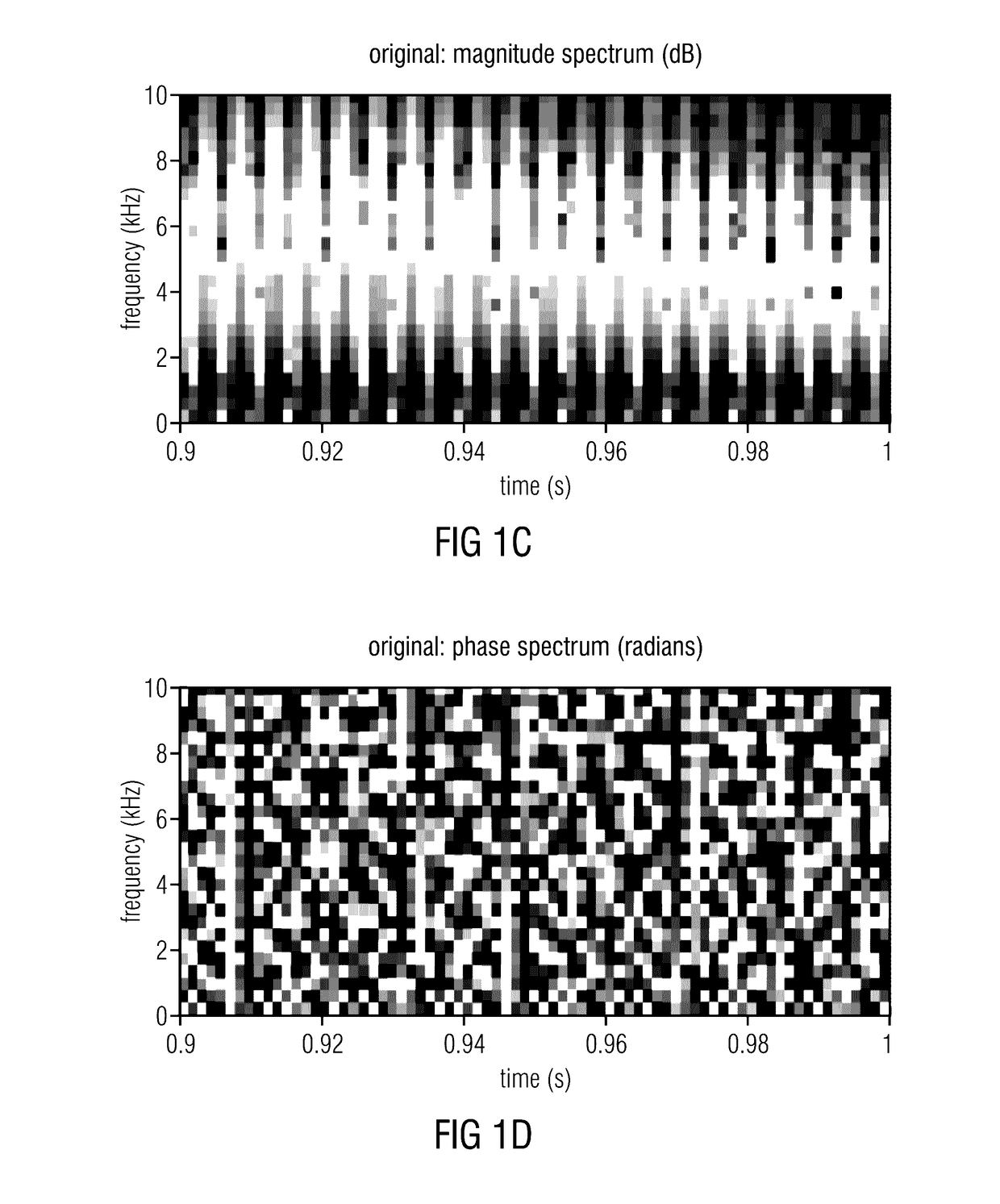
Calculator and method for determining phase correction data for an audio signal
A calculator for determining phase correction data for an audio signal includes a variation determiner for determining a variation of a phase of the audio signal in a first and a second variation mode, a variation comparator for comparing a first variation determined using the first variation mode and a second variation determined using the second variation mode, and a correction data calculator for calculating the phase correction data in accordance with the first variation mode or the second variation mode based on a result of the comparing.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
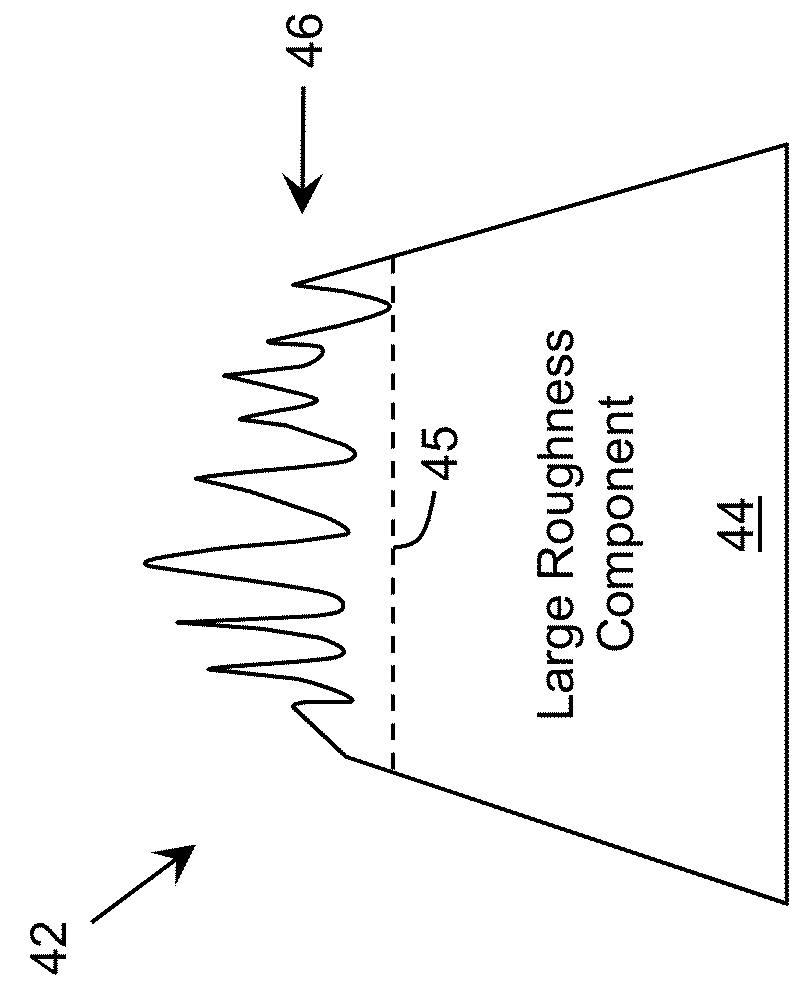
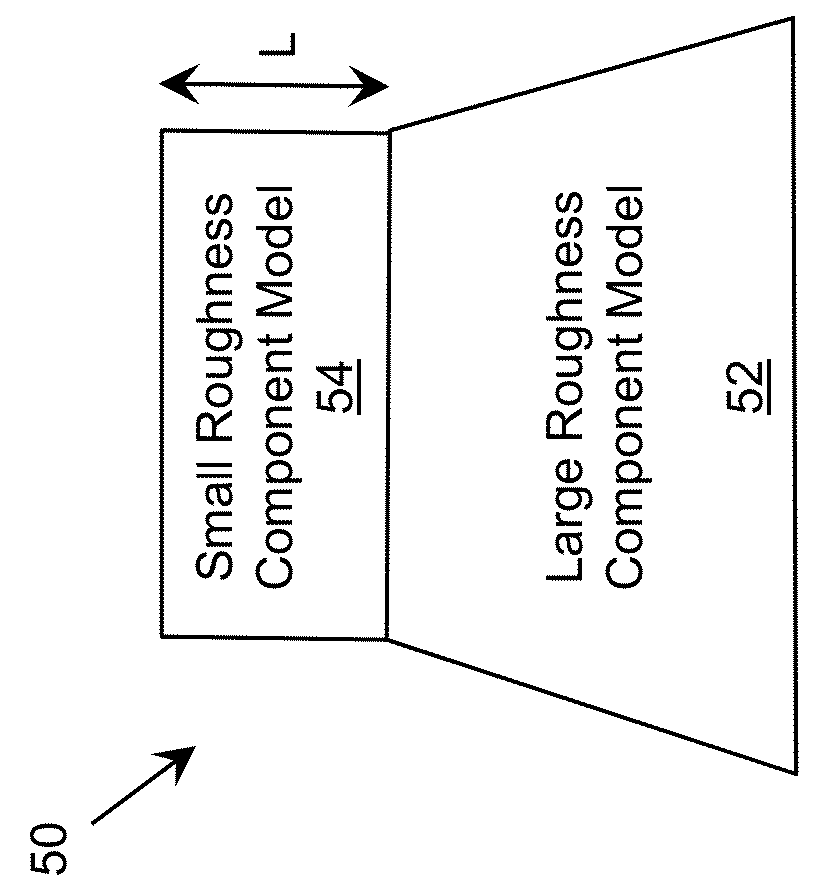
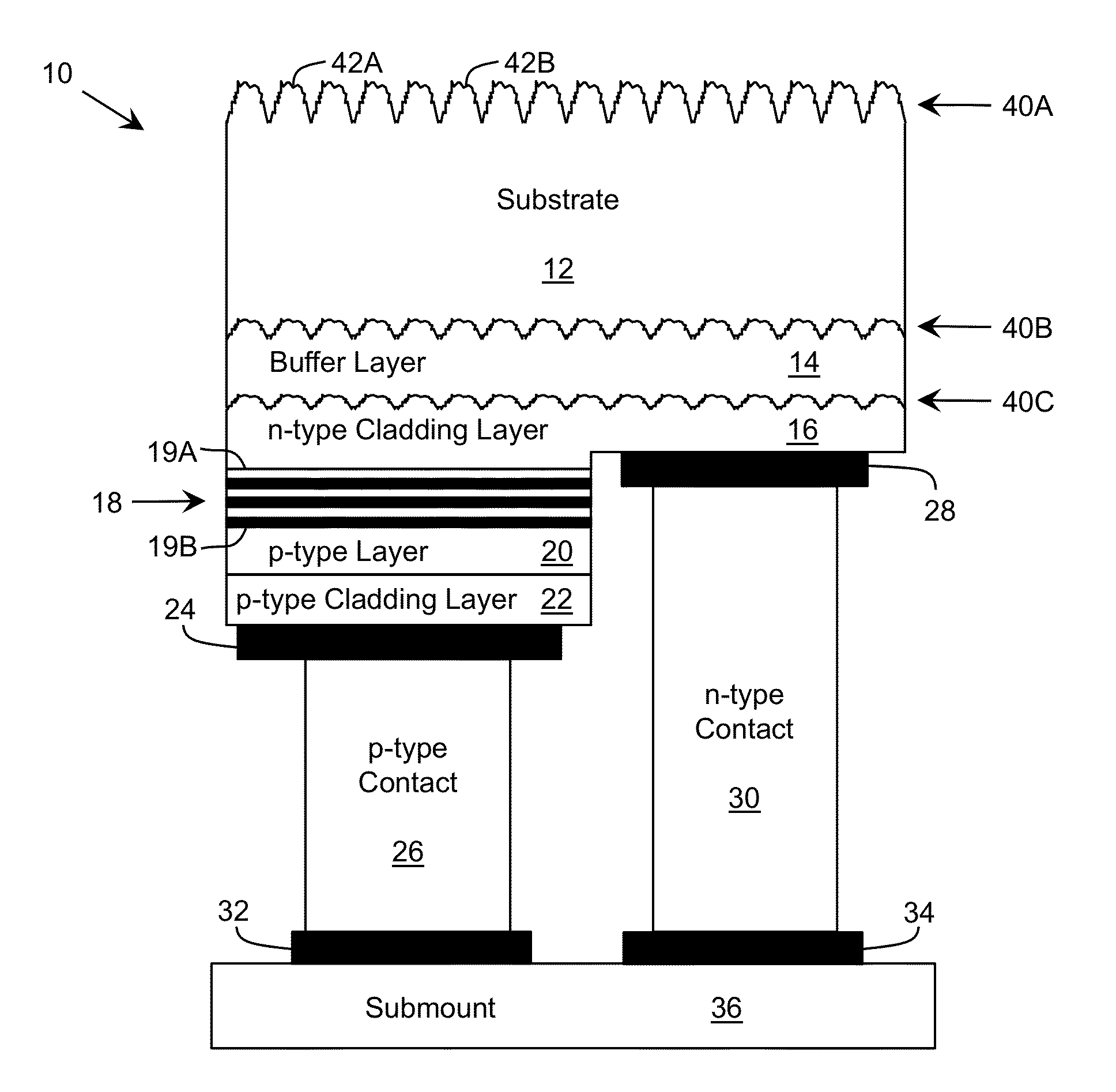
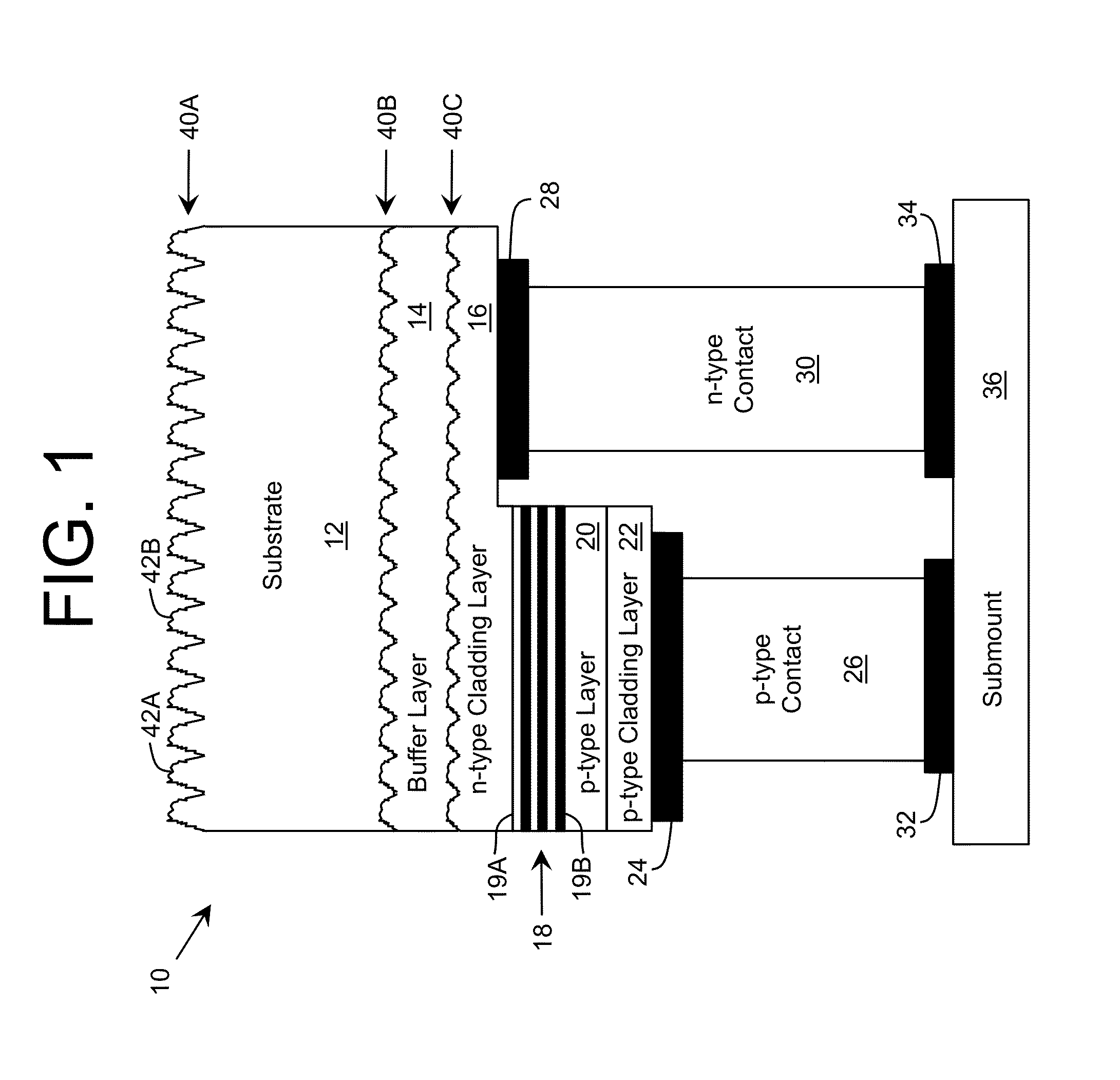
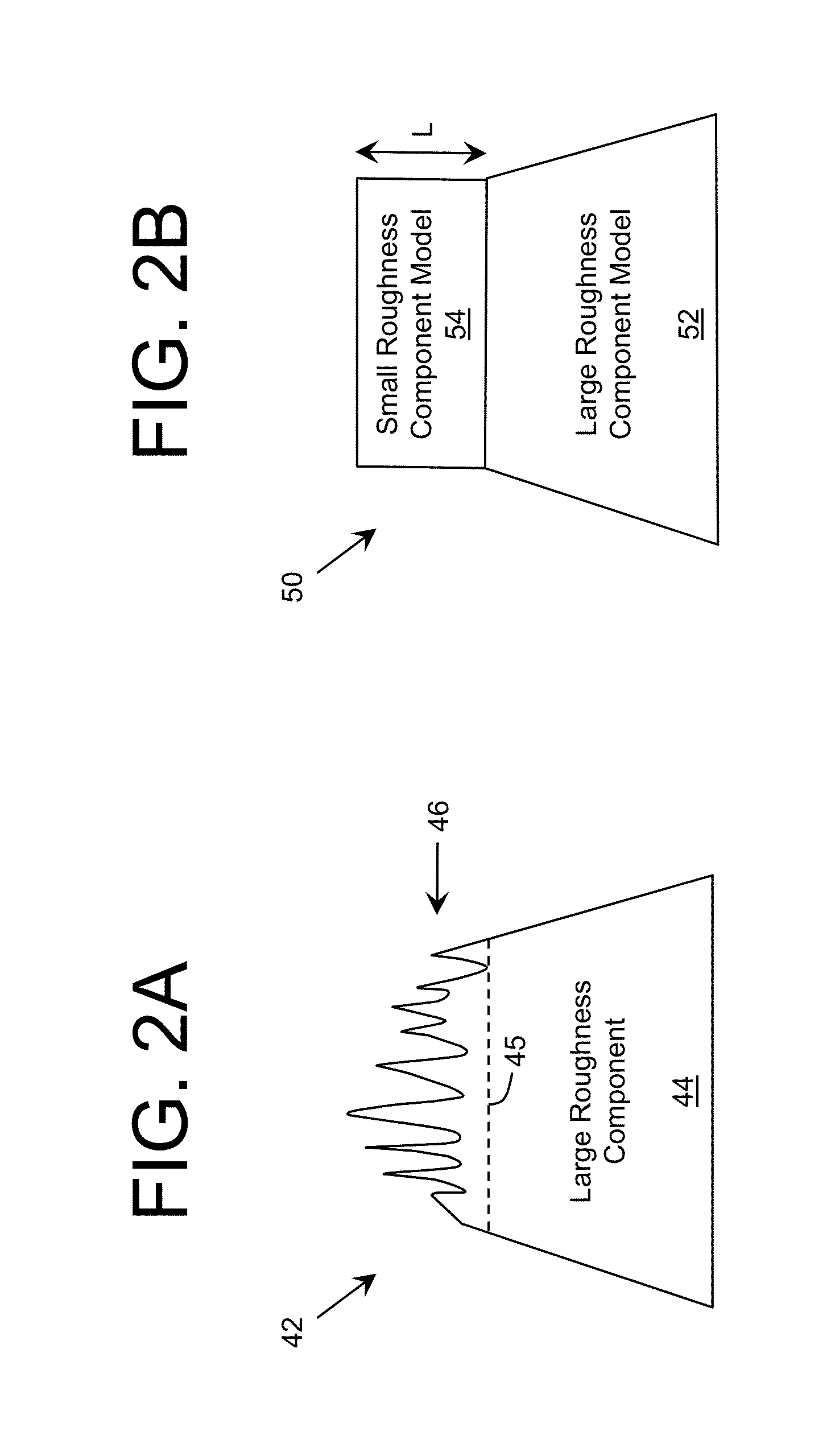
Emitting device with improved extraction
A profiled surface for improving the propagation of radiation through an interface is provided. The profiled surface includes a set of large roughness components providing a first variation of the profiled surface having a characteristic scale approximately an order of magnitude larger than a target wavelength of the radiation. The set of large roughness components can include a series of truncated shapes. The profiled surface also includes a set of small roughness components superimposed on the set of large roughness components and providing a second variation of the profiled surface having a characteristic scale on the order of the target wavelength of the radiation.
Owner:SENSOR ELECTRONICS TECH
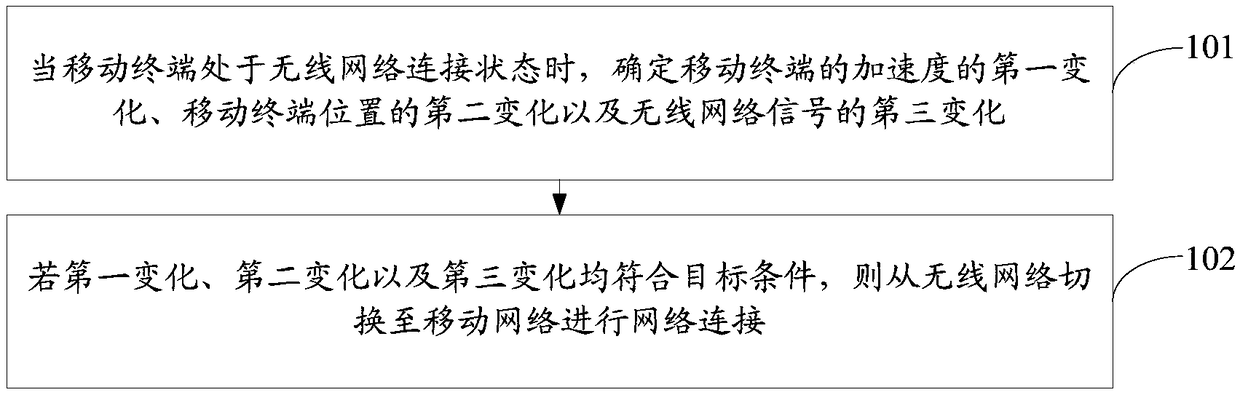
A mobile terminal operation method and a mobile terminal
ActiveCN109041148AGuaranteed stabilityImprove user experienceWireless communicationTelecommunicationsWireless mesh network
The embodiment of the invention provides a mobile terminal operation method and a mobile terminal. The method comprises the following steps: when the mobile terminal is in a wireless network connection state, determining a first change of the acceleration of the mobile terminal, a second change of the position of the mobile terminal and a third change of the wireless network signal; If the first variation, the second variation, and the third variation meet the target conditions, the network connection is switched from the wireless network to the mobile network. If the first variation, the second variation, and the third variation meet the target conditions, the mobile terminal is in the scene of getting on and off the elevator, and the wireless network signal is poor in the process of getting on and off the elevator, so the mobile terminal switches from the wireless network connection to the mobile network connection, and the automatic switching is realized without manual switching ofthe user, and the stability of the network connection can be maintained, and the user's use experience can be improved.
Owner:VIVO MOBILE COMM CO LTD
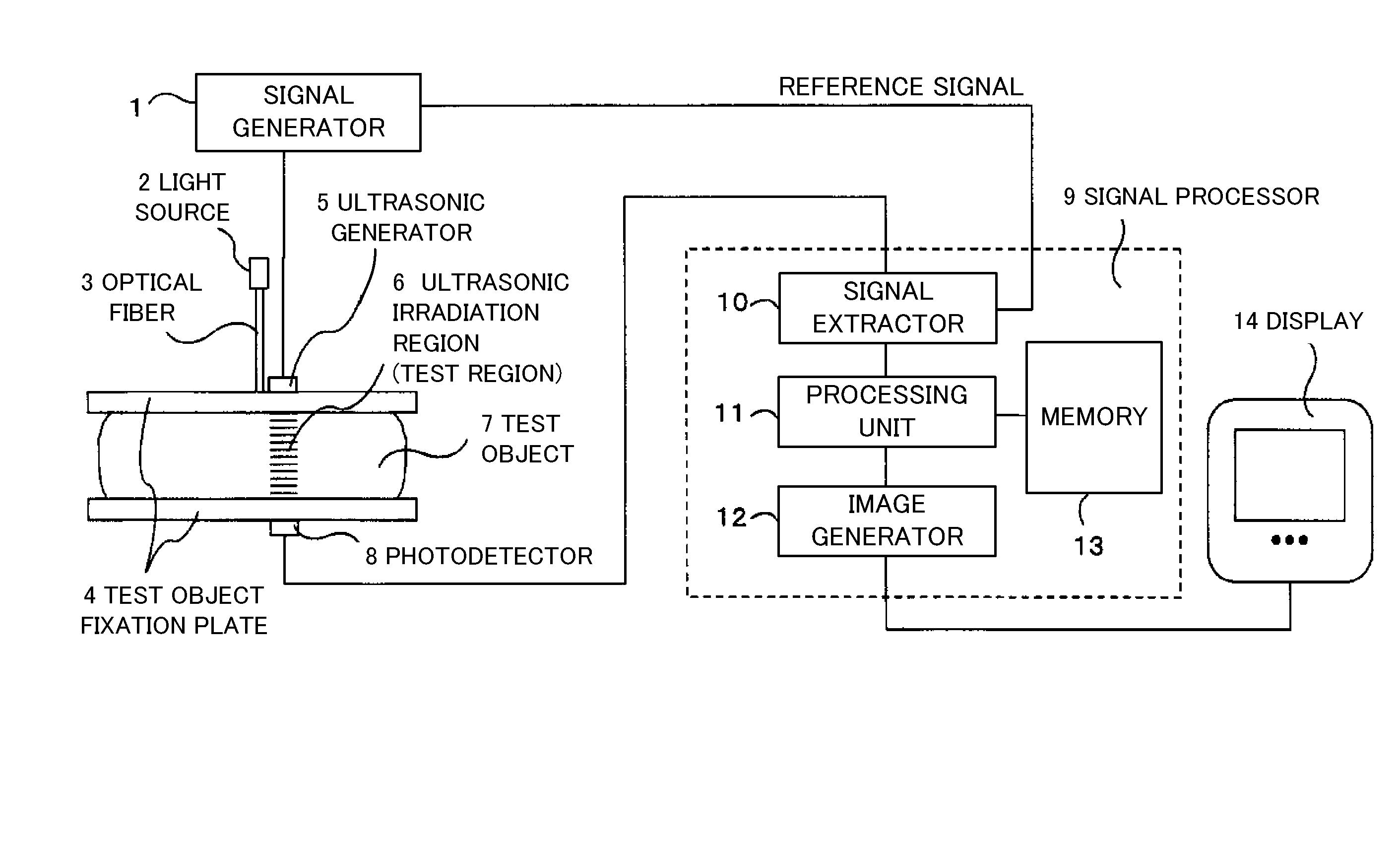
Measurement apparatus and measurement method
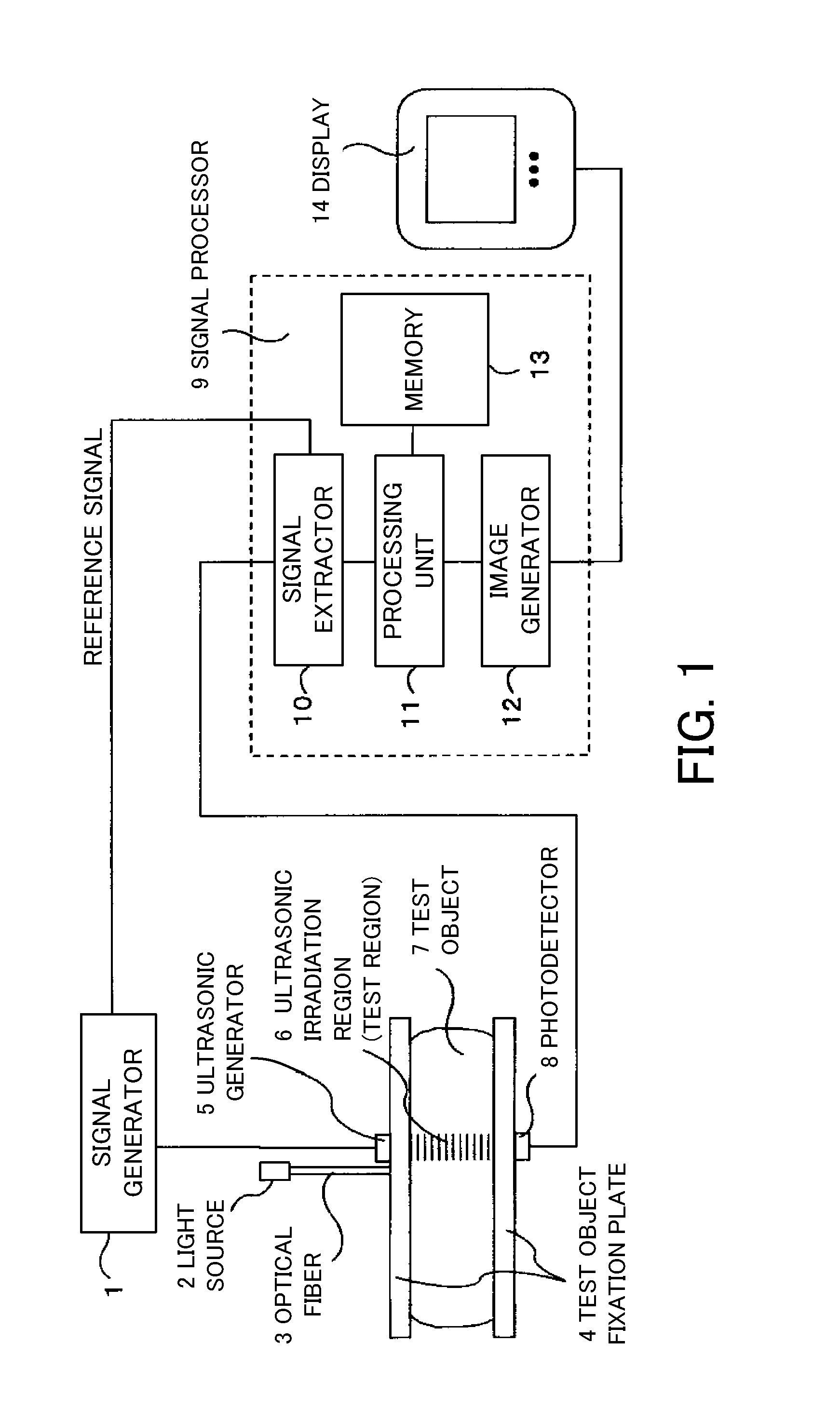
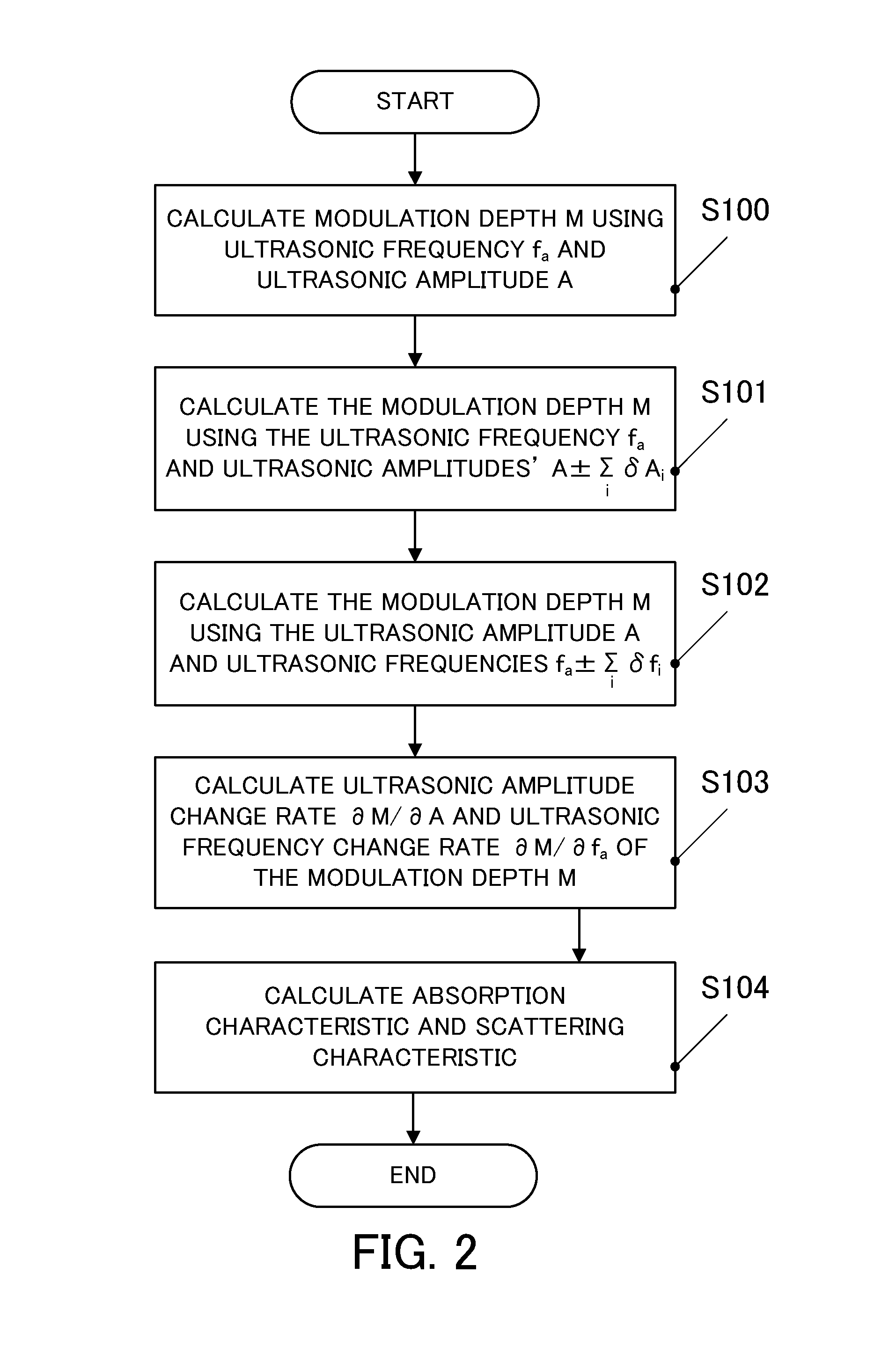
InactiveUS20100069750A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsDiagnostics using lightMeasurement deviceAcousto-optics
A measurement apparatus includes a measurement unit configured to irradiate three types of ultrasonic waves and light upon a test region in a test object, and to measure modulated light and non-modulated light, the modulated light being modulated by an acousto-optical effect, and a signal processor configured to calculate a modulation depth that is an intensity of the modulated light divided by an intensity of the non-modulated light for the one, and at least one of a scattering characteristic and an absorption characteristic of the test region in the test object by utilizing a first change rate of the modulation depth to an amplitude of the one or an amount corresponding to the first change rate, and a second change rate of the modulation depth to a frequency of the one or an amount corresponding to the second change rate.
Owner:CANON KK
Touch sensing method, processor and system
ActiveUS20140062949A1Avoid noiseInput/output processes for data processingTouch SensesComputer science
Owner:EGALAX EMPIA TECH INC
Devices and methods for determining relative motion
Devices and methods are disclosed for determining relative motion. In one implementation, an interferometer is provided. The interferometer may include a body, a light source configured to project a coherent light to an opposing surface, a plurality of pairs of light detectors configured to convert reflections of the coherent light into photocurrents, and a processor. The processor may be configured to detect changes in the photocurrents, wherein a first change in the photocurrents, which occurs in response to a relative motion between the body and the opposing surface, represents a motion signal, and a second change in the photocurrents represents a noise signal. The processor may also determine the relative motion between the body and the opposing surface based on the first change in the photocurrents when a ratio between a power of the motion signal and a power of the noise signal is below about 10.
Owner:OTM TECH
Method and apparatus for controlling bias point of optical transmitter
InactiveUS20070092266A1Solve problemsRecord information storageElectromagnetic transmittersEngineeringOptical transmitter
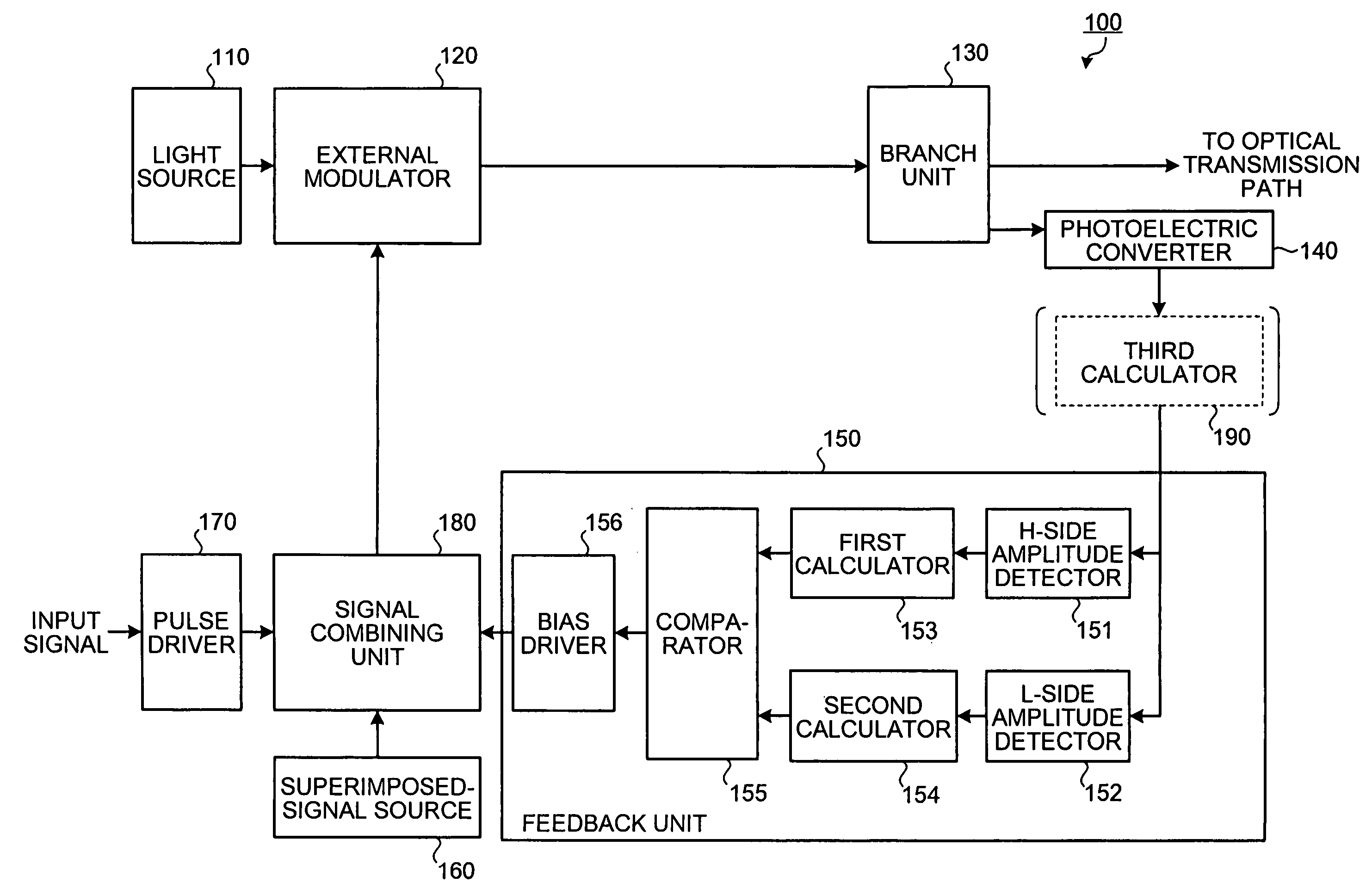
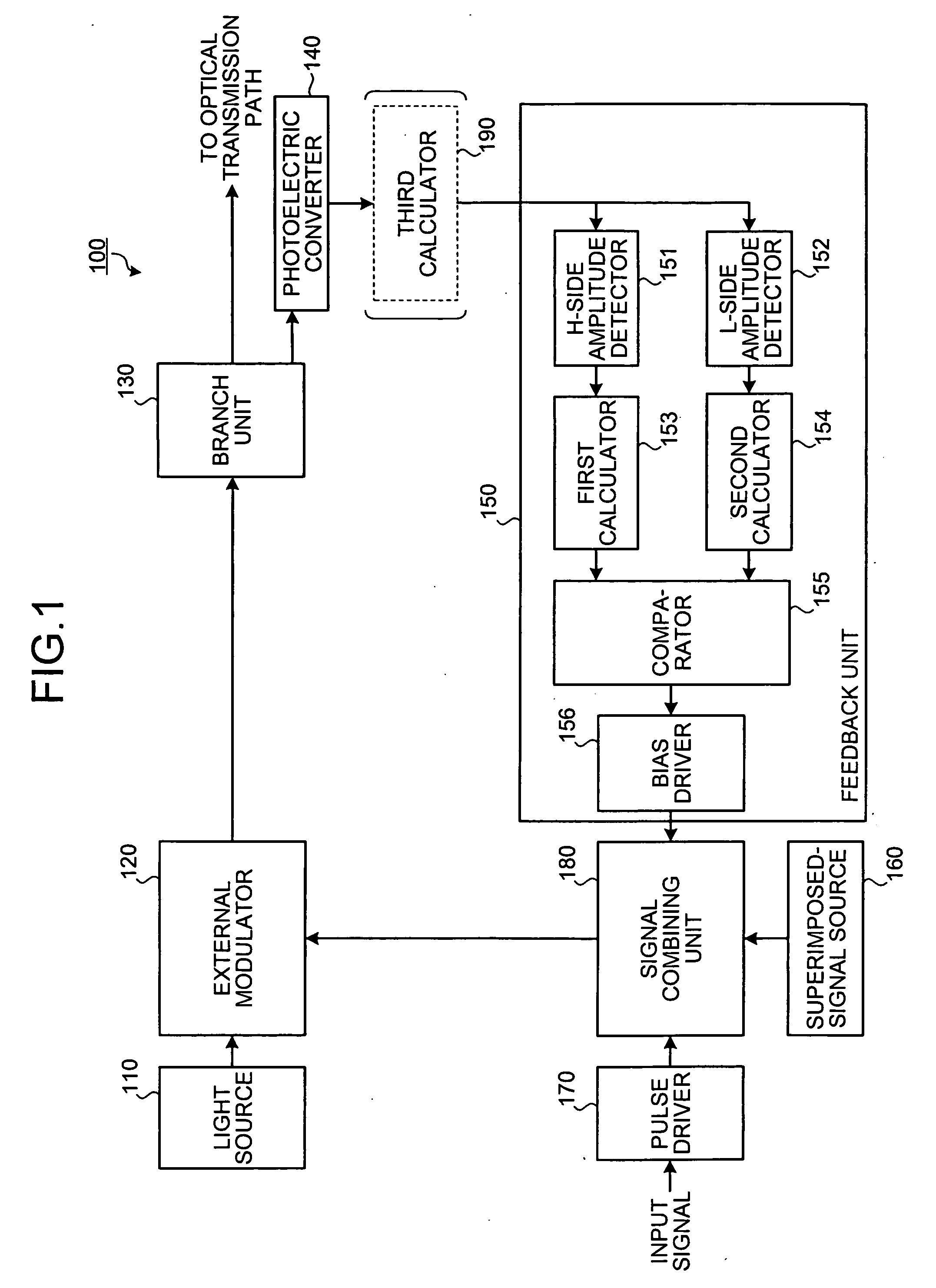
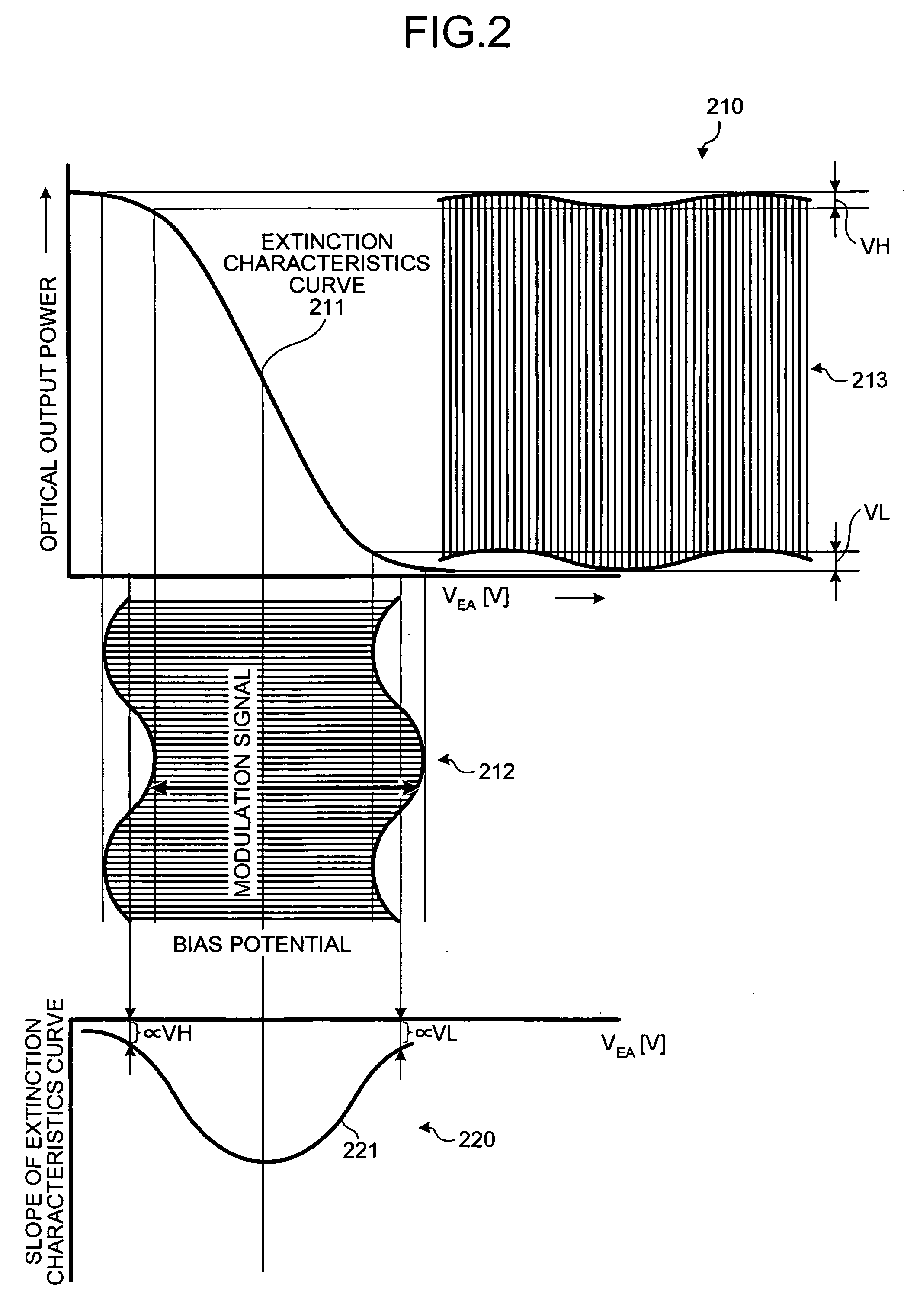
An optical transmitter includes: a modulating unit that modulates an optical signal based on an electric signal; a first detecting unit that detects a first variation width of a maximum output of the modulated optical signal; a second detecting unit that detects a second variation width of a minimum output of the modulated optical signal; a comparing unit that performs a comparison of the first variation width and the second variation width; and an adjusting unit that adjusts a bias potential of the electric signal based on a result of the comparison.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
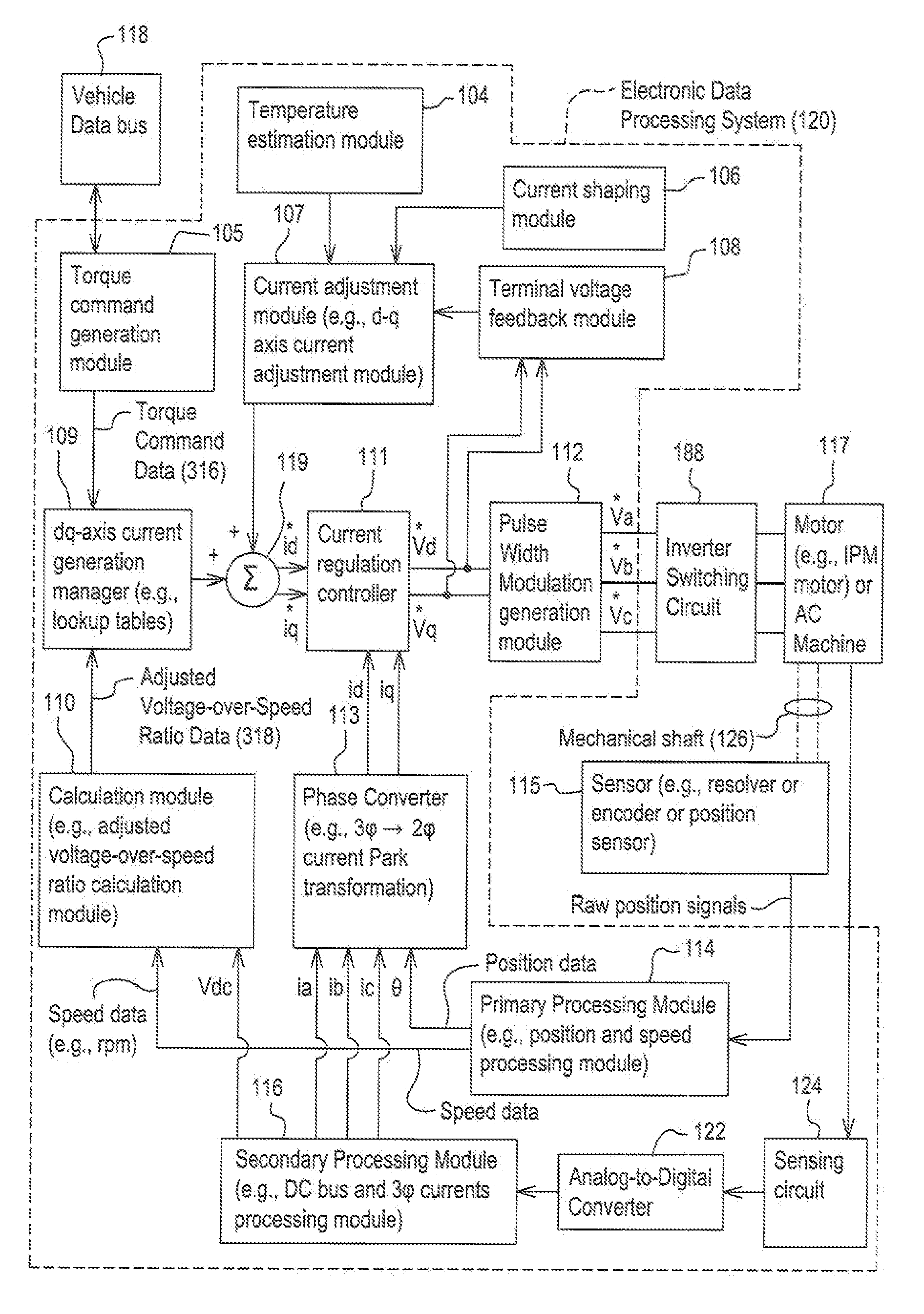
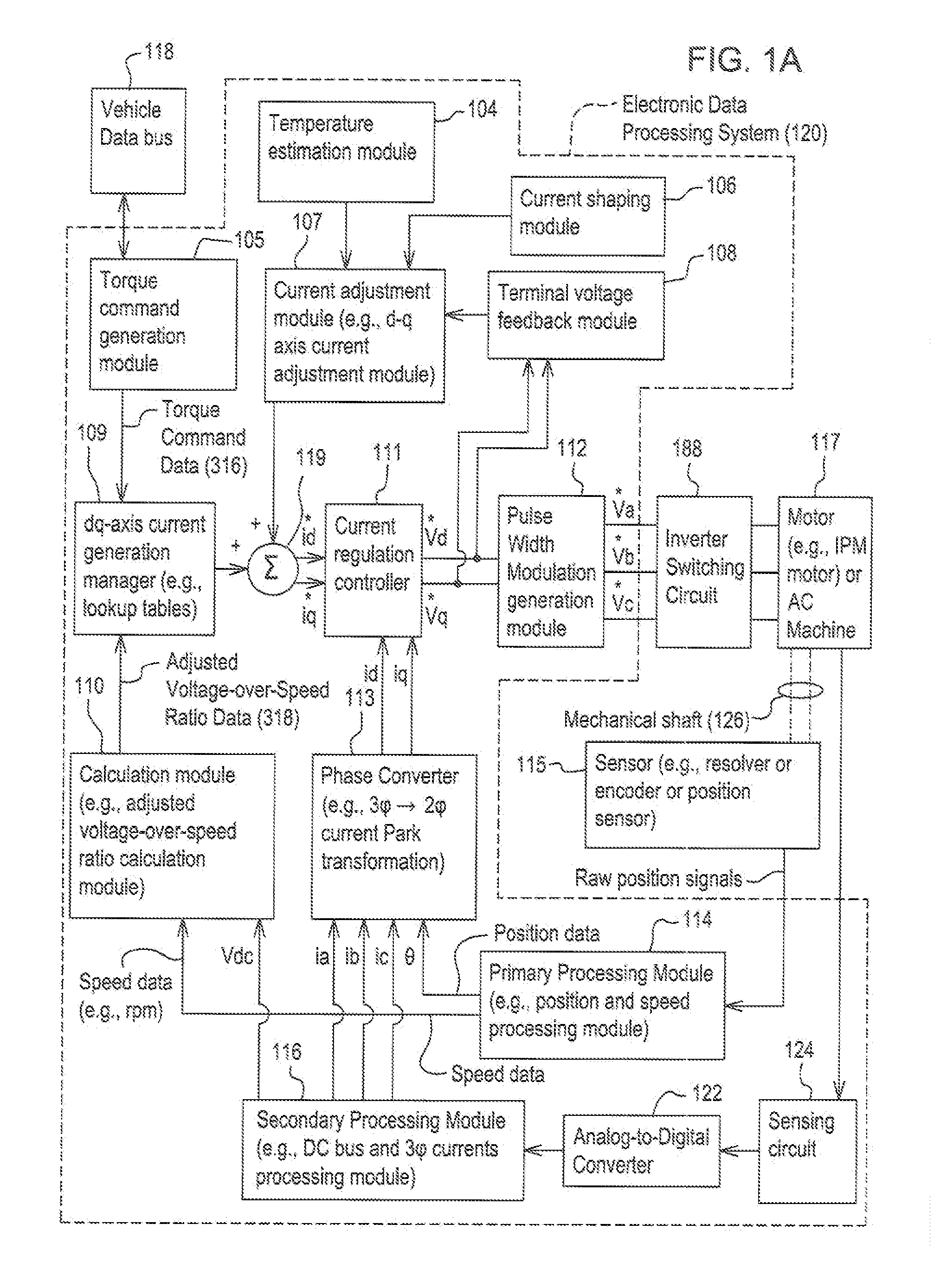
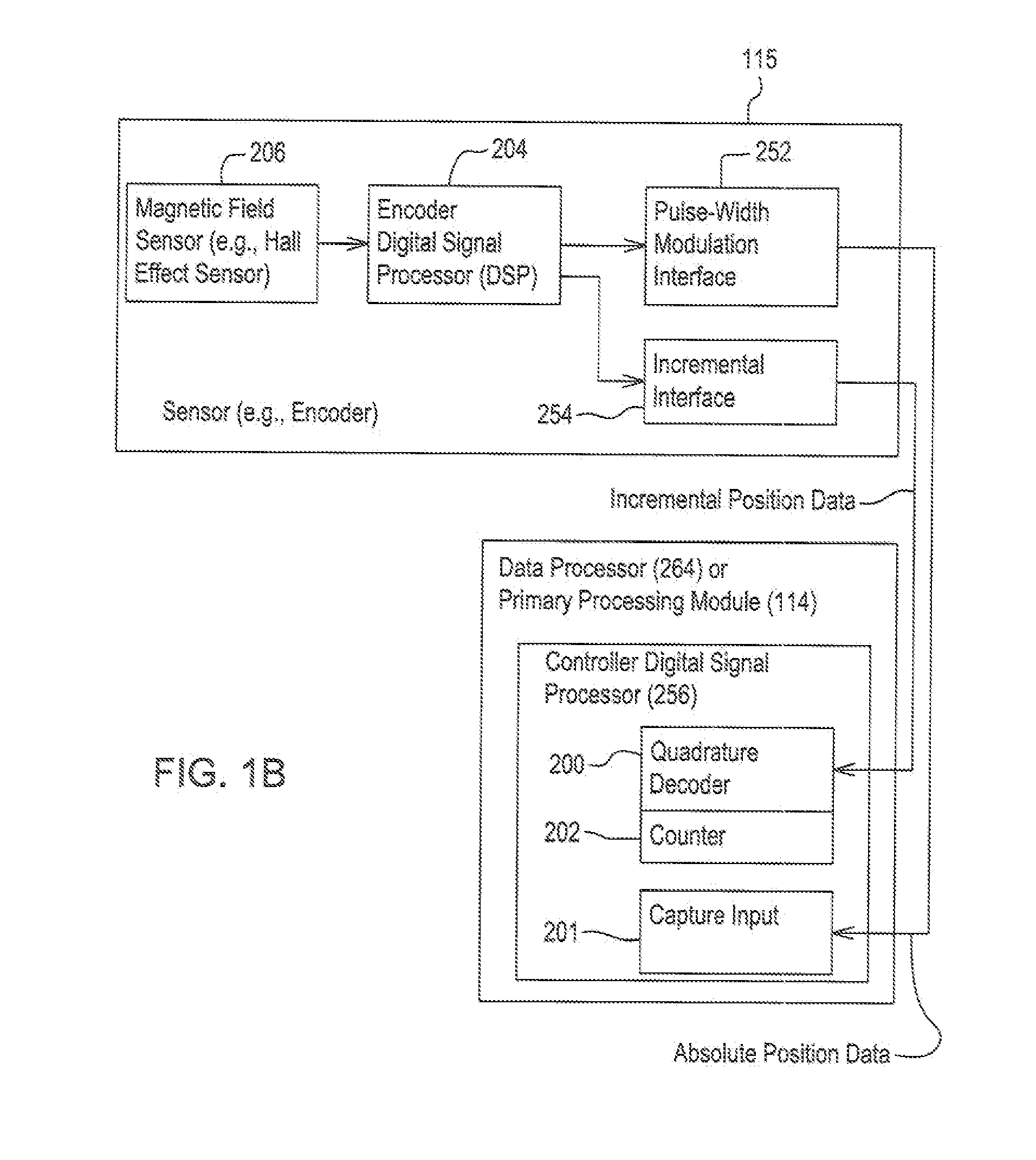
Method and system estimating rotor angle of an electric machine
ActiveUS20130093372A1Motor/generator/converter stoppersSynchronous motors startersElectric machineRotor angle
Position samples are stored from an encoder coupled to a permanent magnet electric machine. A data processor determines first changes in position between successive position samples and second changes between successive first changes in position. A data processor determines whether each first change in position is generally increasing, decreasing or constant. A corrective motion factor is applied to each stored position sample based on whether the first change in position is generally increasing or decreasing. The data processor estimates a final rotor angle of the electric machine based on a particular one of the position samples and a corresponding first change in position associated with the particular one of the position samples corresponding to a respective time.
Owner:DEERE & CO
Emitting Device with Improved Extraction
A profiled surface for improving the propagation of radiation through an interface is provided. The profiled surface includes a set of large roughness components providing a first variation of the profiled surface having a characteristic scale approximately an order of magnitude larger than a target wavelength of the radiation. The profiled surface also includes a set of small roughness components superimposed on the set of large roughness components and providing a second variation of the profiled surface having a characteristic scale on the order of the target wavelength of the radiation.
Owner:SENSOR ELECTRONICS TECH
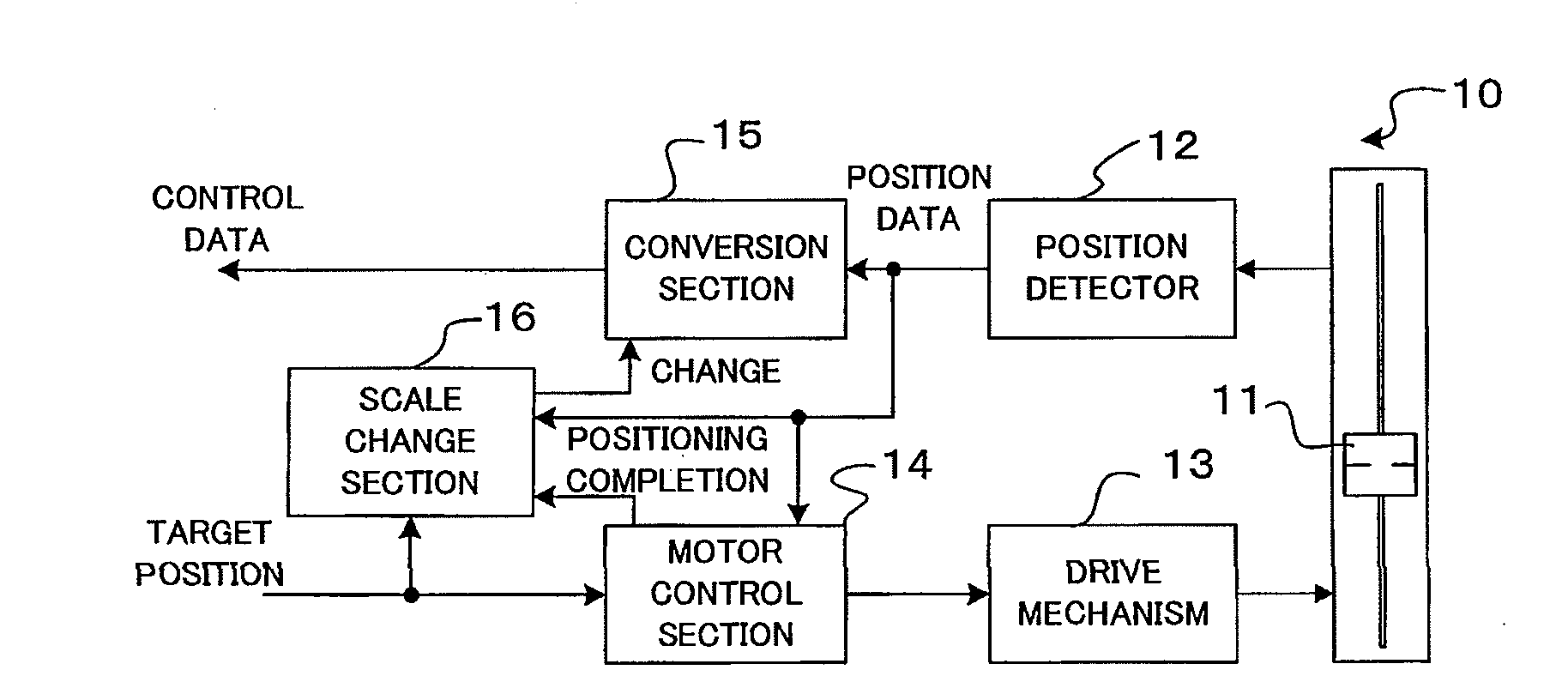
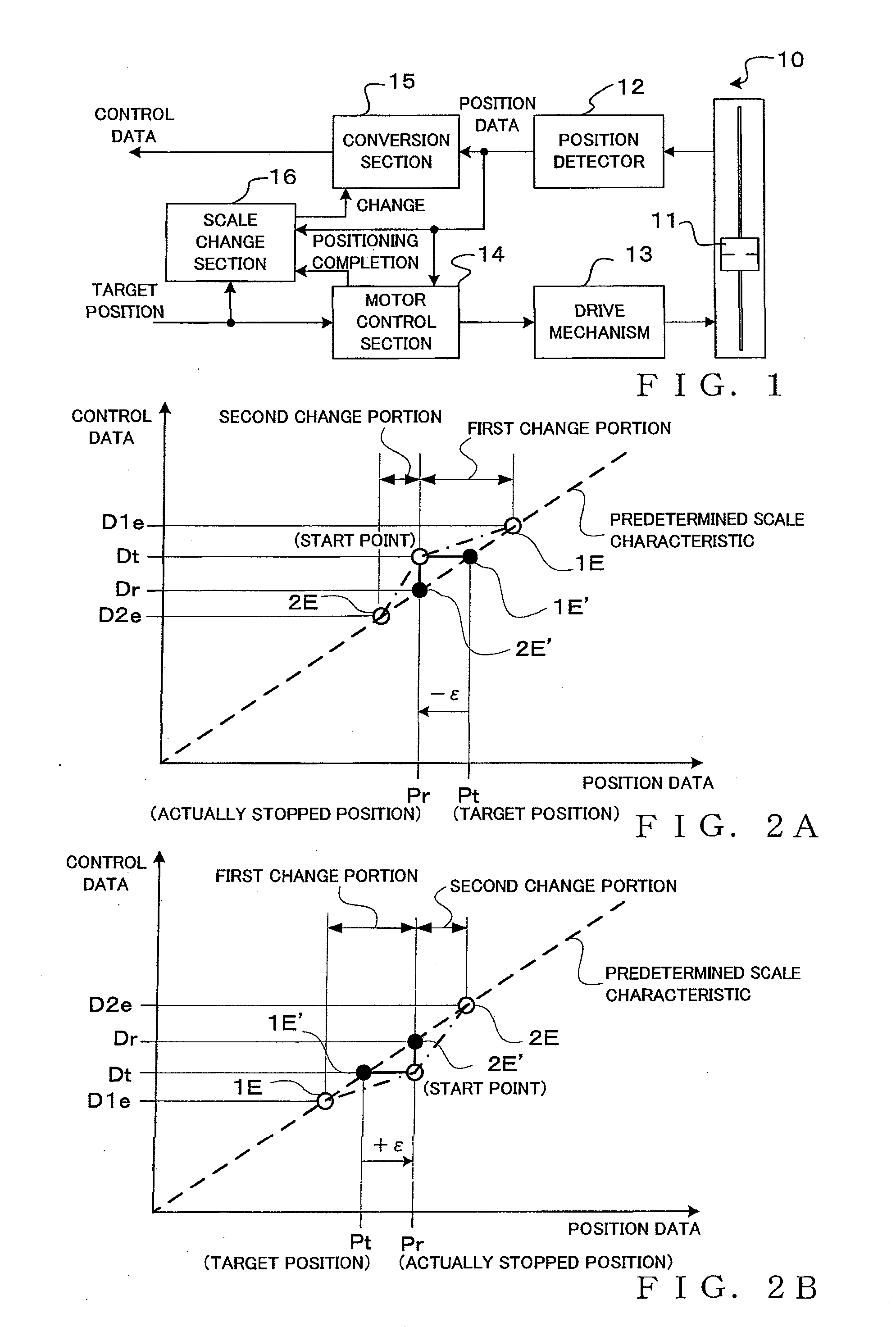
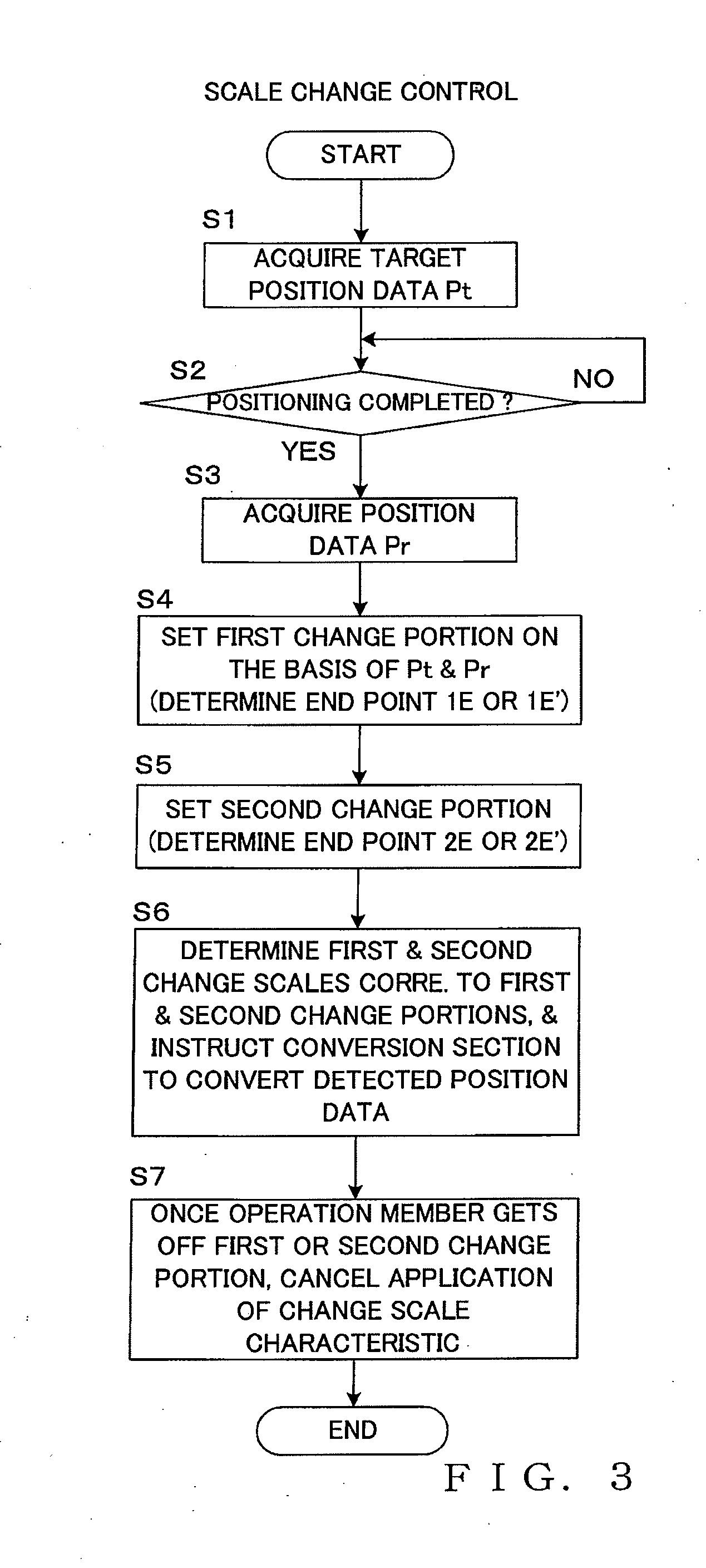
Control Data Generation Device and Method
InactiveUS20100034400A1Removed positioningEffective and efficient utilizationElectronic editing digitised analogue information signalsCarrier indicating arrangementsControl dataData mining
Control data is generated in response to generation, from a position detector, of position data in accordance with a predetermined scale characteristic. Change scale characteristic is applied in manual operation performed immediately after an operation member has been automatically positioned to a target position. In the change scale characteristic, a start point is established such that control data, corresponding to the target position, of the predetermined scale characteristic is outputted in correspondence with the position data outputted at the time of completion of the positioning, but also a first change portion, including a portion extending from a position of the start point at least up to the target position, is established, so that the control data outputted in correspondence with the position data output gradually varies from data corresponding to the start point to data of the predetermined scale characteristic corresponding to an end point of the first change portion.
Owner:YAMAHA CORP
Ground object change detection method, ground object change detection system and terminal
ActiveCN110378224AImprove robustnessImprove stabilityImage enhancementImage analysisImaging processingFirst variation
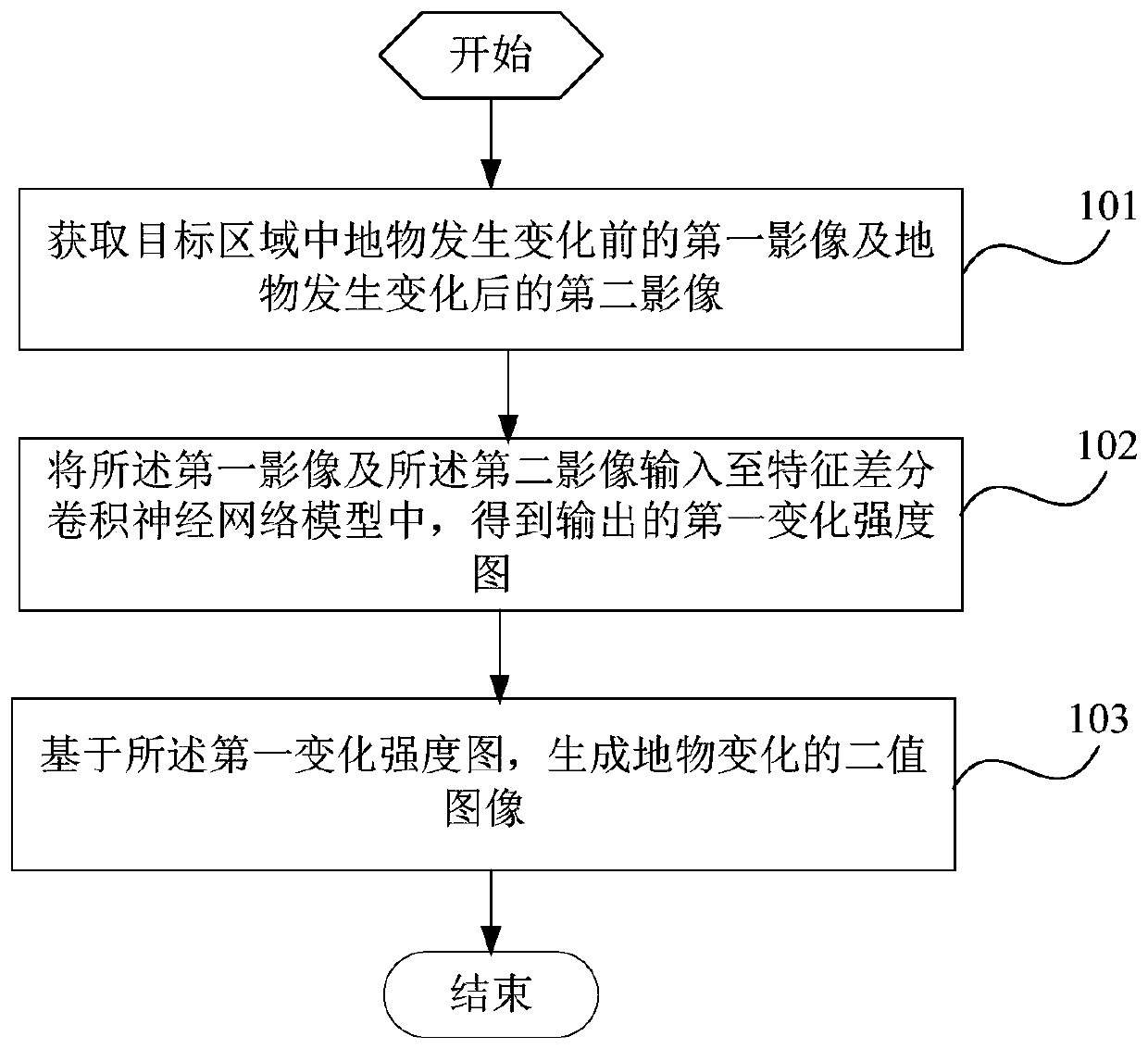
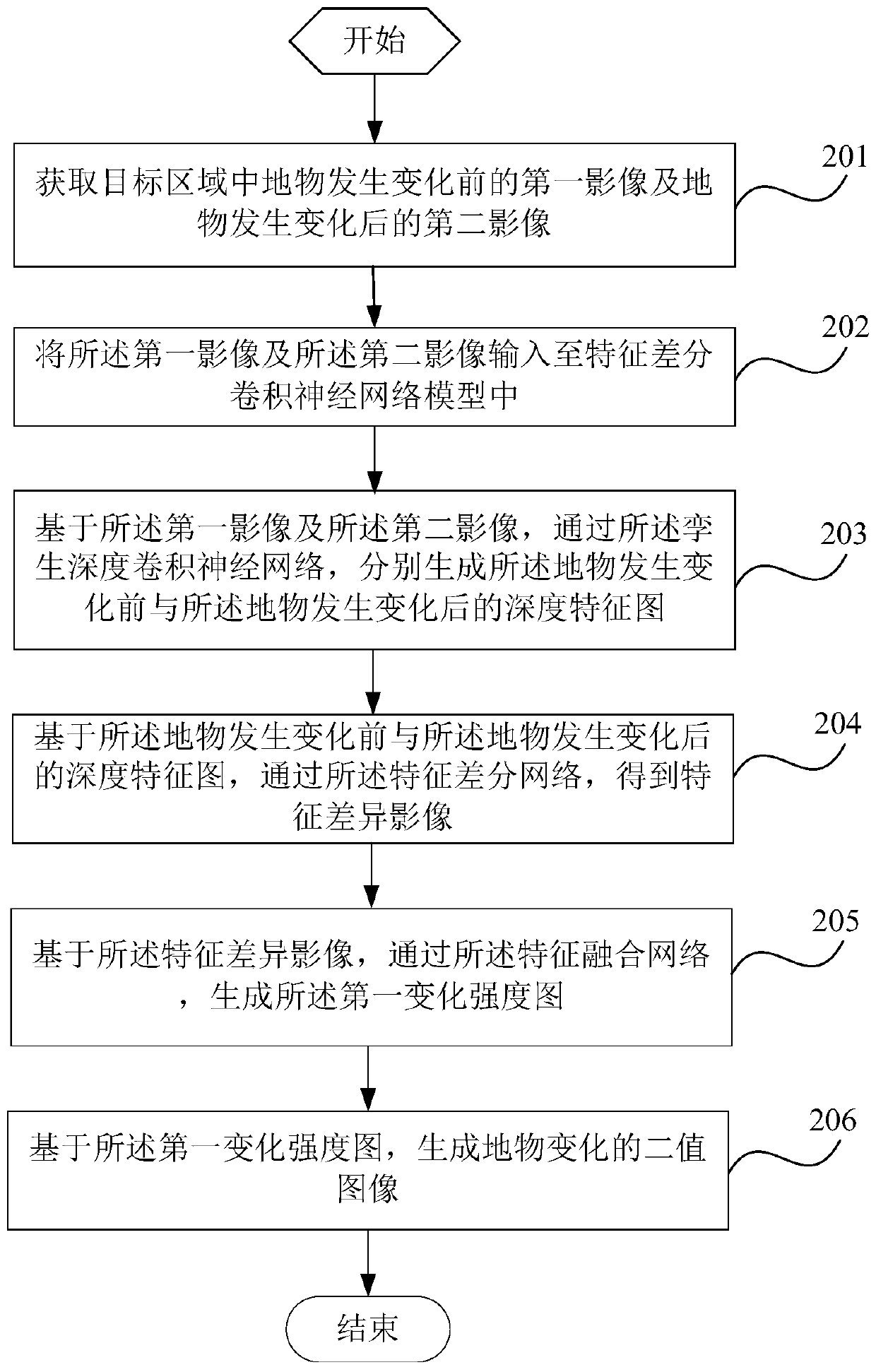
The invention is suitable for the technical field of image processing, and provides a ground object change detection method, a ground change detection system and a terminal, and the method comprises the steps: obtaining a first image before a ground object changes and a second image after the ground object changes in a target region; inputting the first image and the second image into a feature differential convolutional neural network model to obtain an output first change intensity graph; and based on the first change intensity map, generating a binary image of ground object change. The method, the system and the terminal improve the robustness and stability of remote sensing image change detection, and improve the precision of change detection.
Owner:THE HONG KONG POLYTECHNIC UNIV SHENZHEN RES INST
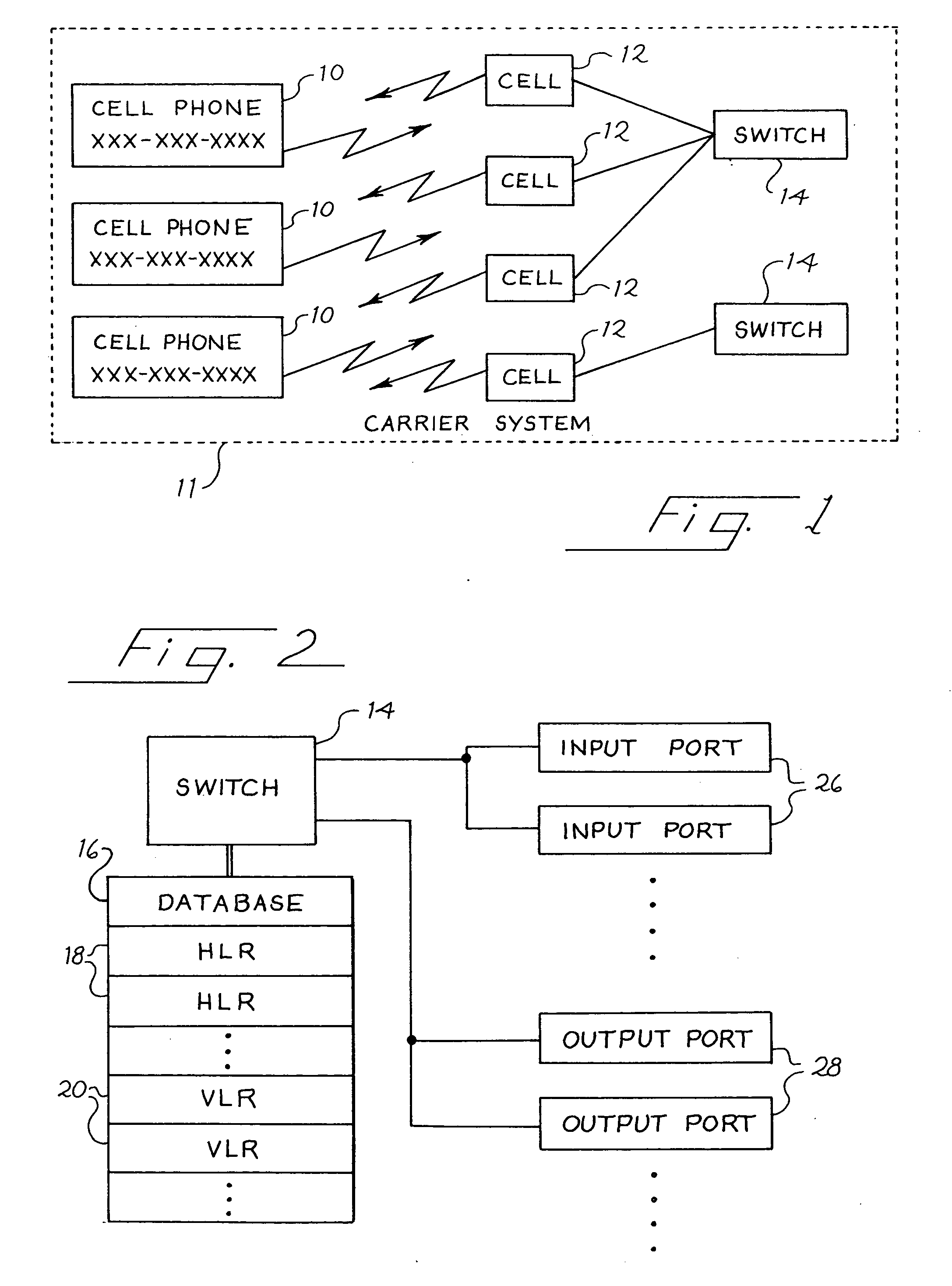
Communications system having pre-defined calling group
InactiveUS20050014522A1Satisfies needSolid-state devicesSpecial service for subscribersCommunications systemCommunication device
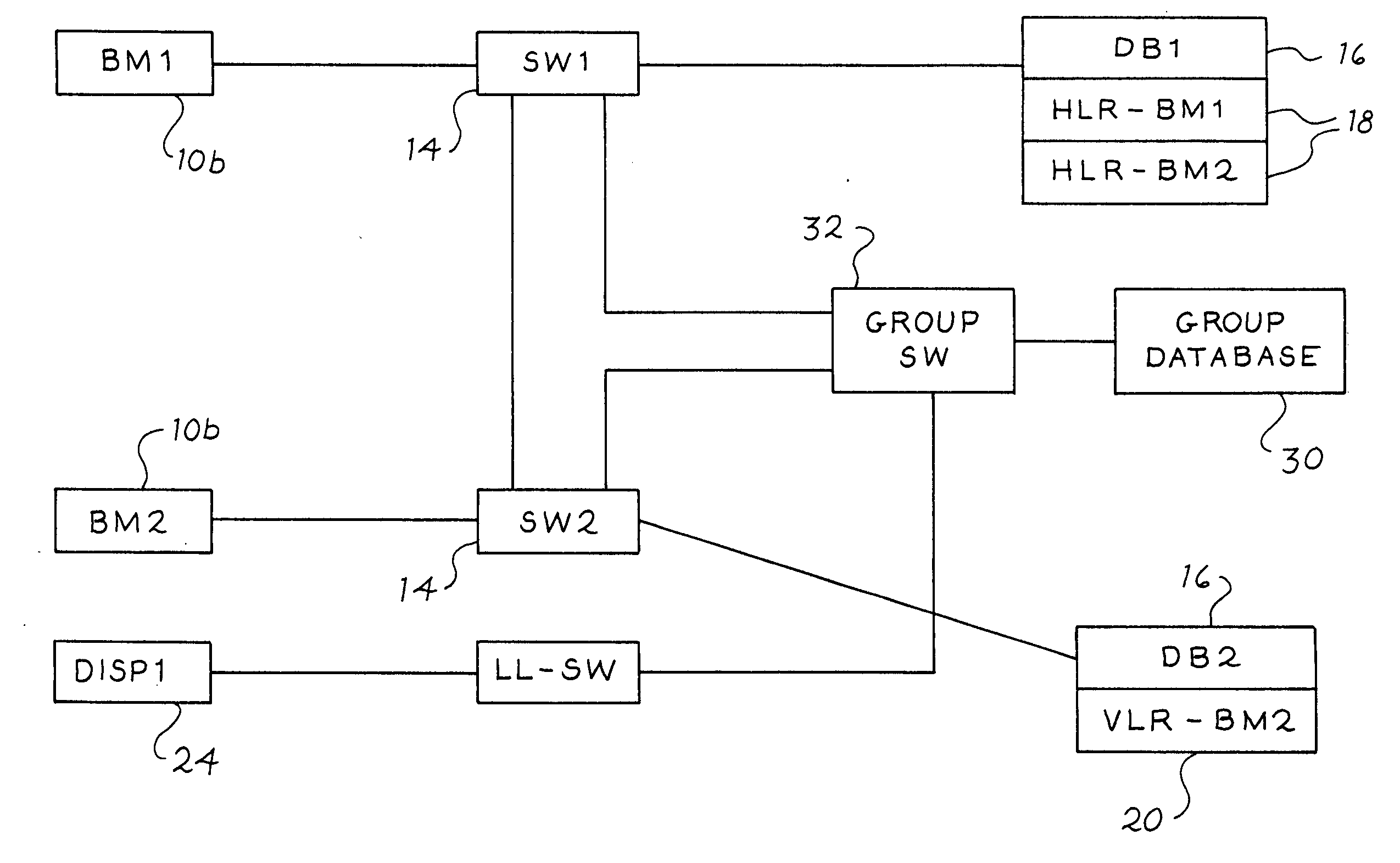
A communications system having a pre-defined calling group with a plurality of members is disclosed. A plurality of personal communication devices (PCDs) each have a system ID and a group ID, and each member of the group is assigned one of the PCDs. The system ID and the group ID both have a predetermined characteristic, where each system ID has a first variation thereof and each group ID has a second variation. A first group -member having a first PCD contacts a second member having a second PCD by entering into the first PCD the second PCD group ID. The first PCD transmits the first PCD system ID and the second PCD group ID to a communications switch. Based on the first PCD system ID, the communications switch locates a record for the first PCD in a switch database and determines therefrom that the first PCD can contact the second PCD by way of the second PCD group ID. A group database in switchable communication with the communications switch has the system ID and group ID for each group member PCD. The communications switch forwards the contact and the second PCD group ID to the group database for further processing. The group database determines that the second PCD group ID is located therein, locates the second PCD system ID based on the second PCD group ID, and forwards the attempted contact and the second PCD system ID to an appropriate communications switch for further processing.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
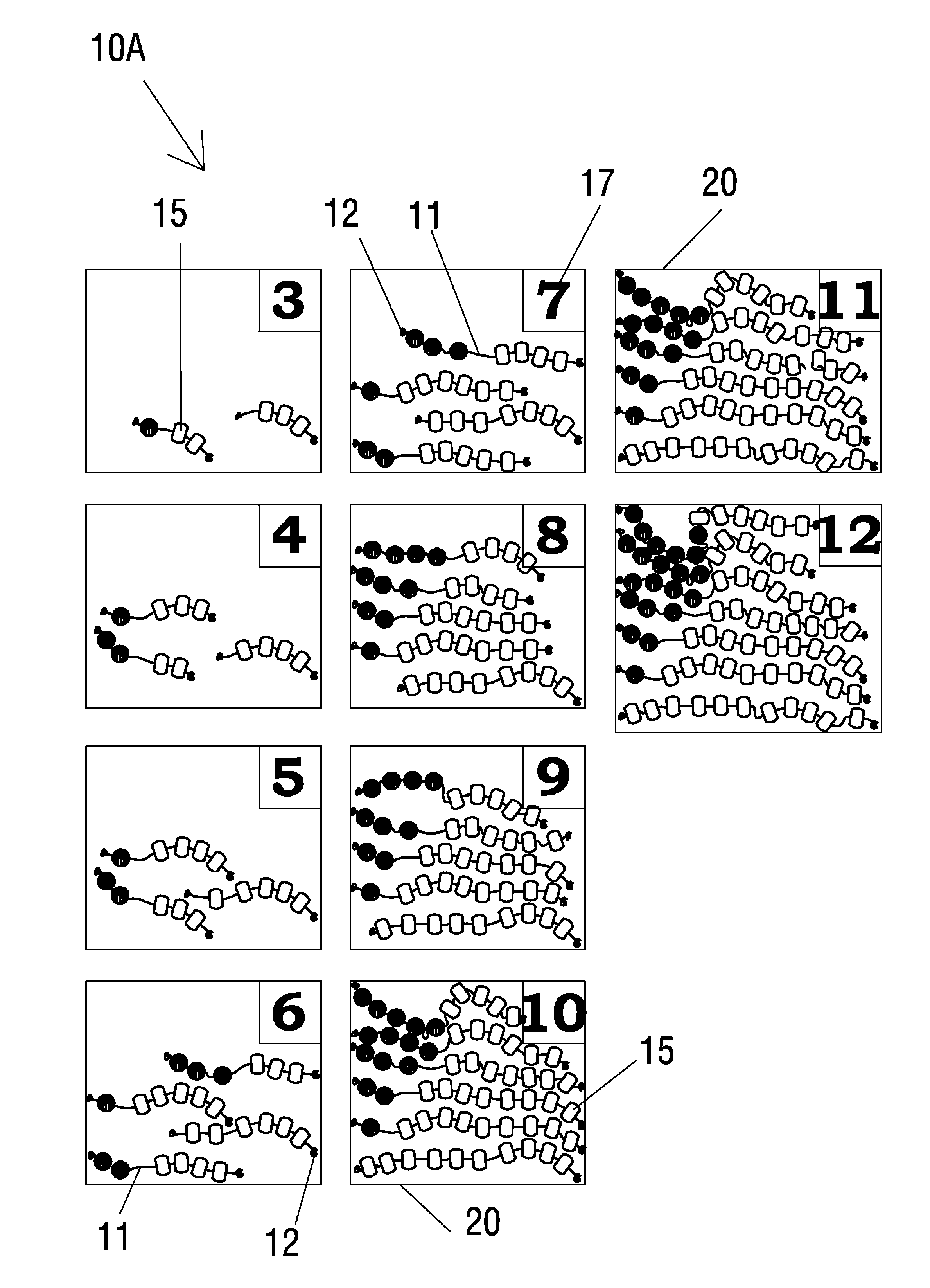
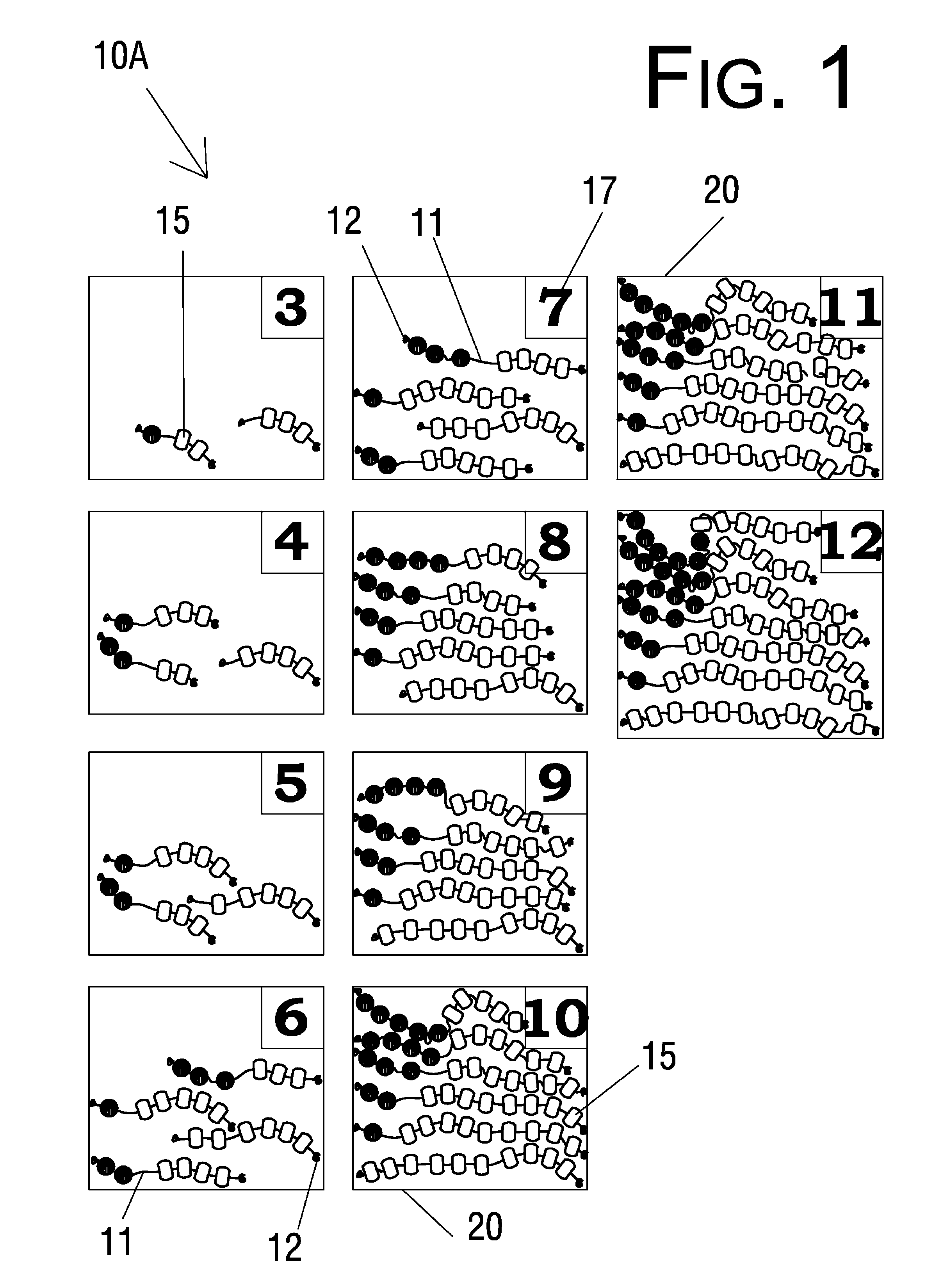
String math manipulative system and method
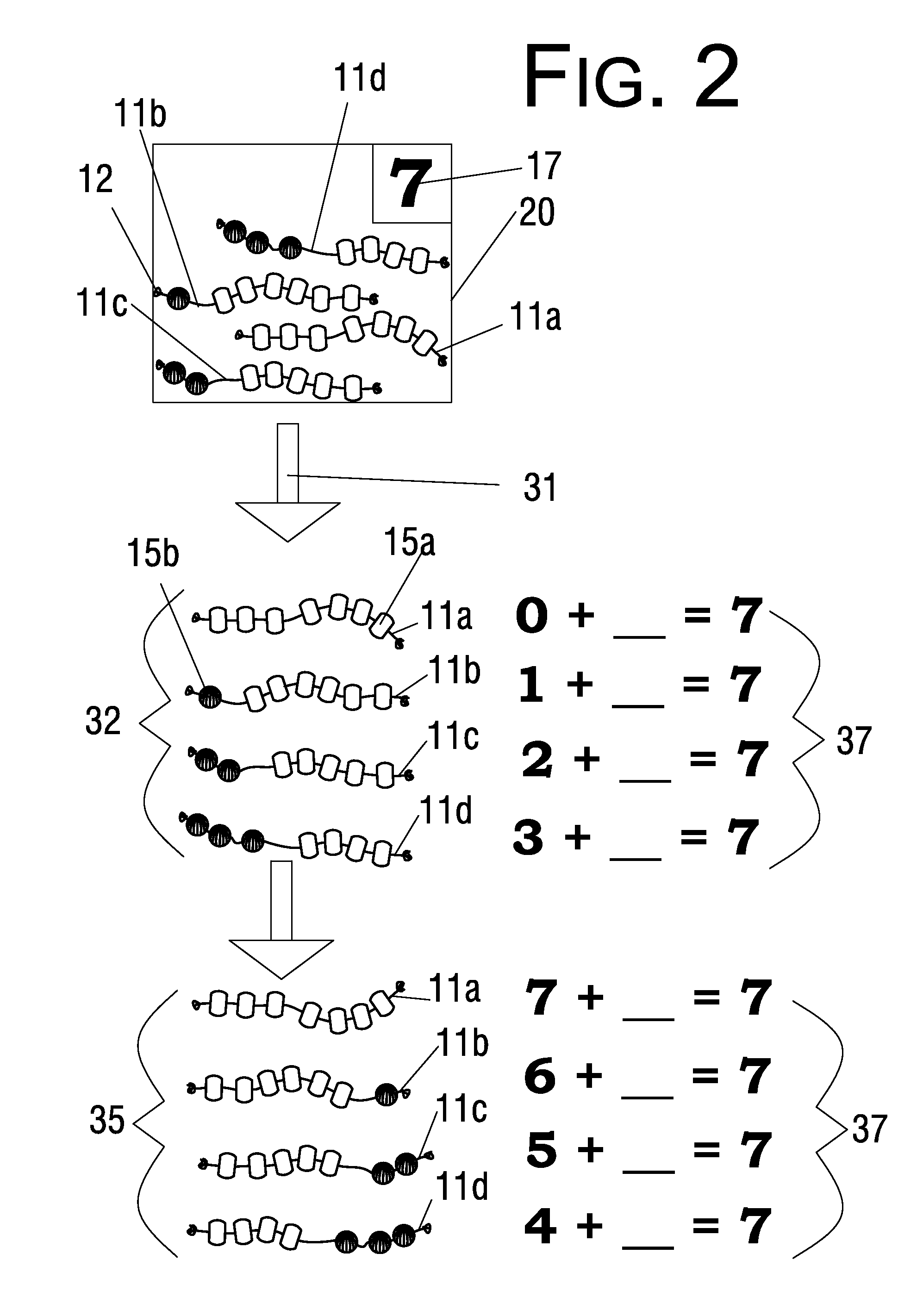
ActiveUS8021159B1Easy to useEasy to learnComputing aidsTeaching apparatusTheoretical computer scienceFirst declension
A string math manipulative system and method is provided including series of a particular number of holed objects threaded on strings. The holed objects comprise one or more variations in color and / or shape and / or material, with the variations configured to represent math facts. For example, to illustrate the number family summing to 5, three strings would be included in the set; one string having all holed objects of a first variation representing 5+0=5 or 0+5=5, one string having one holed object of the first variation and four holed objects of a second variation representing 4+1=5 or 1+4=5, and one string having two holed objects of the first variation and three holed objects of the second variation representing 4+1=5 or 1+4=5.
Owner:STRING MATH
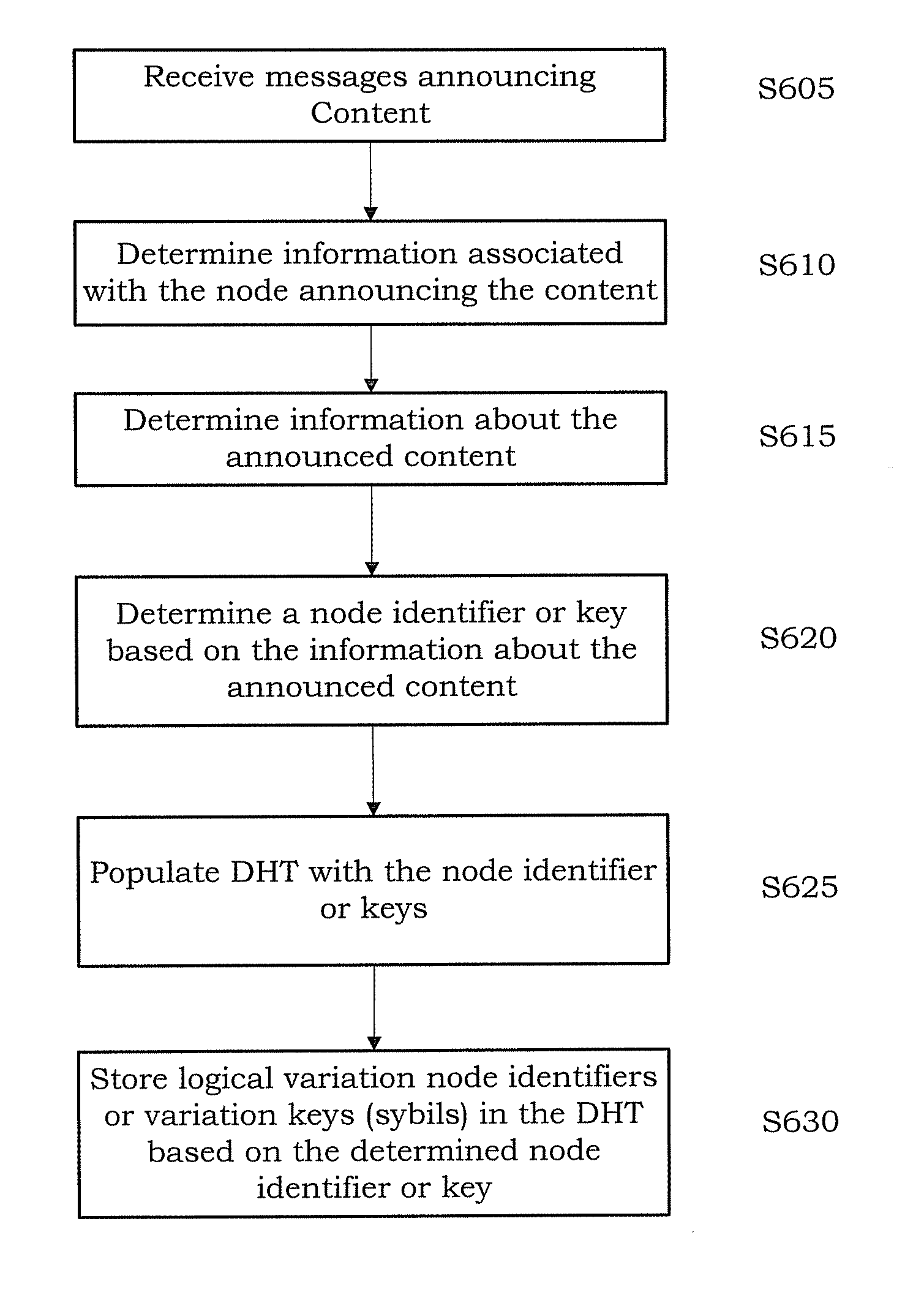
Peer to peer localization for content in a distributed hash table
Provided is a method for localizing content in a peer-to-peer network. The method includes receiving a message announcing first content. Storing a <key, value> pair in a table based on the message. The key represents content information and the value represents node information. The node information identifies a node announcing the content, and the content information identifying the content. Storing a plurality of first variation keys in the table. Each of the plurality of first variation keys being a variation of the stored first key. The method further includes intercepting a request message and sending a response to a sender of the request message. The response message including the list of nodes, the list of nodes based on a key based on a destination address of the request message and the table.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
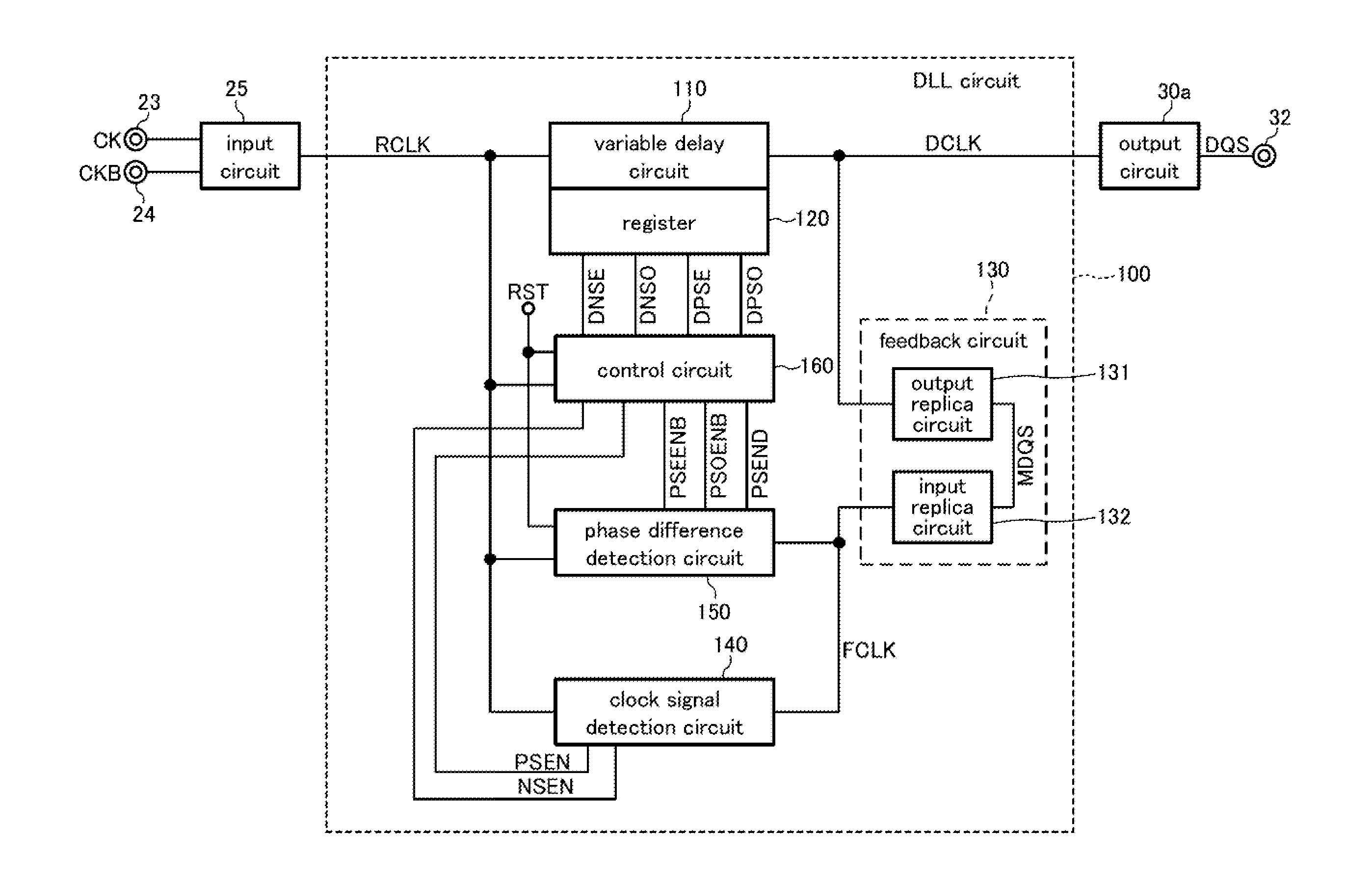
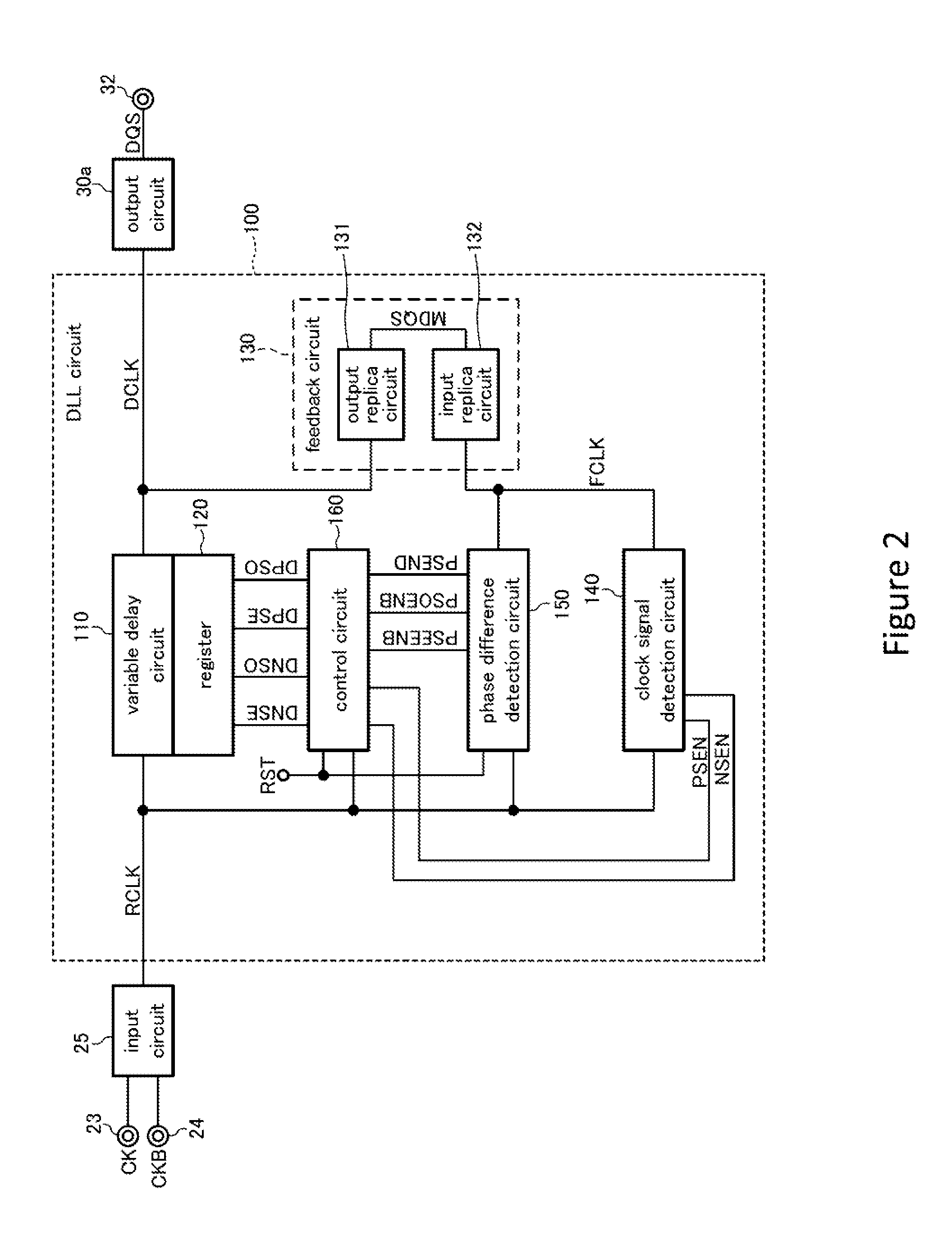
Semiconductor device including a clock adjustment circuit
Disclosed herein is a semiconductor device that includes a first circuit comprising a plurality of first logic elements coupled in cascade and configured, in response to first and second clock signals and a control signal, to produce control information that indicates a first number of the first logic elements through which the control signal has been propagated during a period defined by a first change in logic level of the first clock signal and by a second change in logic level of the second clock signal, the first and second changes occurring adjacently to each other in same directions as each other, and a second circuit comprising a delay circuit configured to receive the first clock signal and the control information and to produce a third clock signal by delaying the first clock signal by an amount responsive to the control information.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Acoustic flowmeter and method for determining the flow in an object
ActiveCN104870949AMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesVolume/mass flow measurementSonificationBobbin
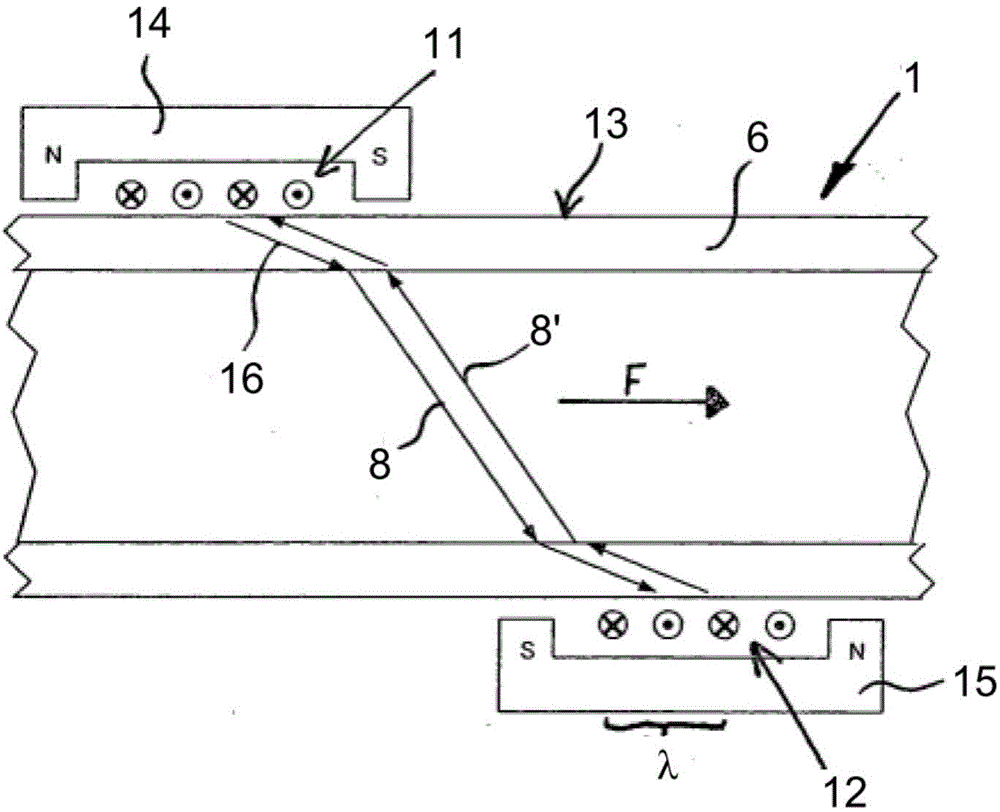
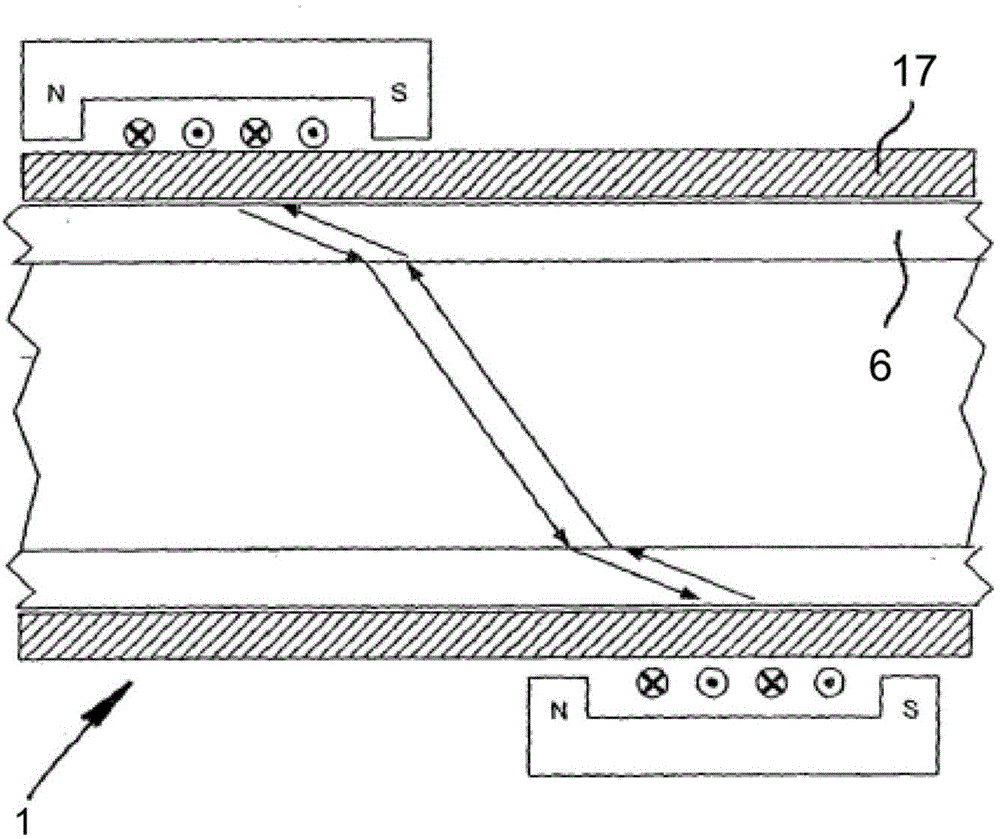
The invention relates to a method for determining the flow or the flow rate of a medium in an electrically conductive object, in particular a pipe (1) or a pipeline, through which a medium flows. At least one ultrasonic wave (16) is produced by means of a transmitting transducer (11) in the object and is injected into the medium as a longitudinal wave (8) on an inner side of the object, and an ultrasonic signal, coming at least partially from the longitudinal wave (8), is received by the receiving transducer (12), at a spatial distance from the injection point and is used to evaluate the flow or the flow rate. Said transmitting transducer (11) produces, preferably in the absence of an acoustic coupling with the surface of the object, a first variable magnetic field in an area close to the surface of the object, in particular metallic, and a first ultrasonic wave is produced in said area by means of the interaction of said variable magnetic field with a static or quasi-static magnetic field. Said transmitting transducer (11) also produces an additional variable magnetic field in the area of the object and an additional ultrasonic wave is produced in said area by means of the interaction of the variable magnetic field with a static or quasi-static magnetic field, said other ultrasonic wave is superimposed on the first ultrasonic wave such that an amplitude of a resulting wave in the direction of the receiving transducer (12) is increased and is reduced in the direction away from said receiving transducer (12). Preferably, the first and the second magnetic fields are produced by two high frequency bobbins (18, 19) of the transmitting transducer (11). The invention also relates to a device for carrying out said inventive method.
Owner:ROSEN SWISS
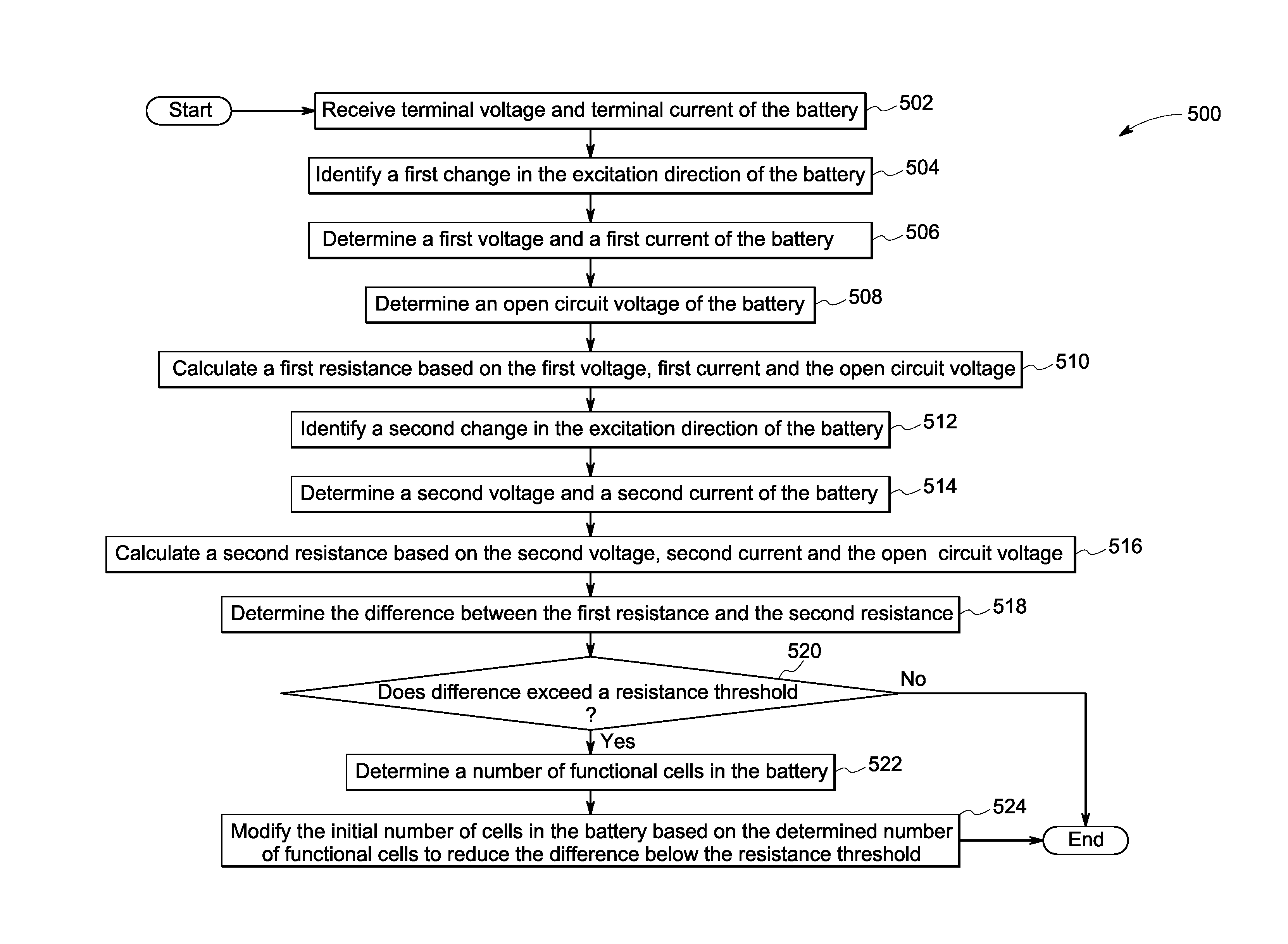
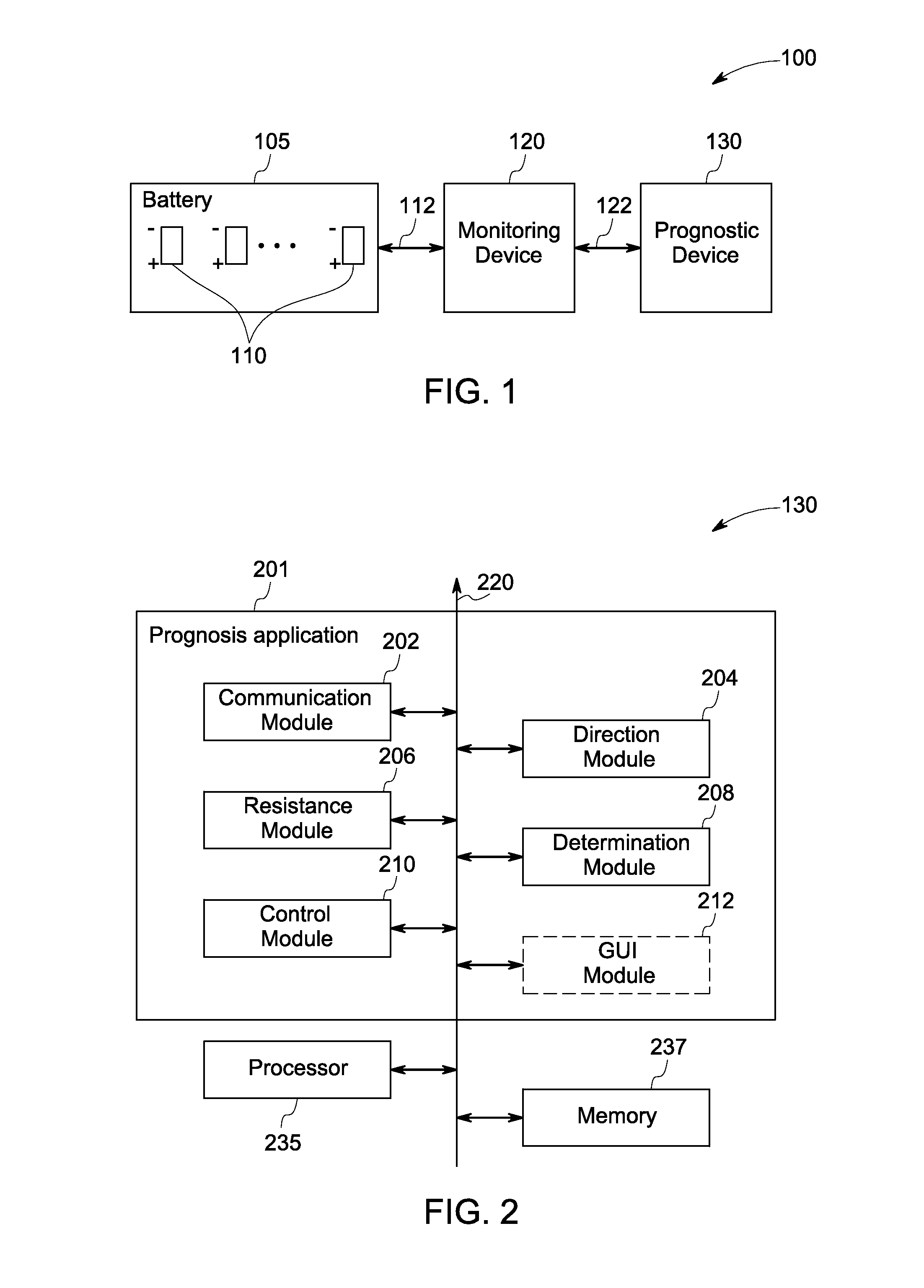
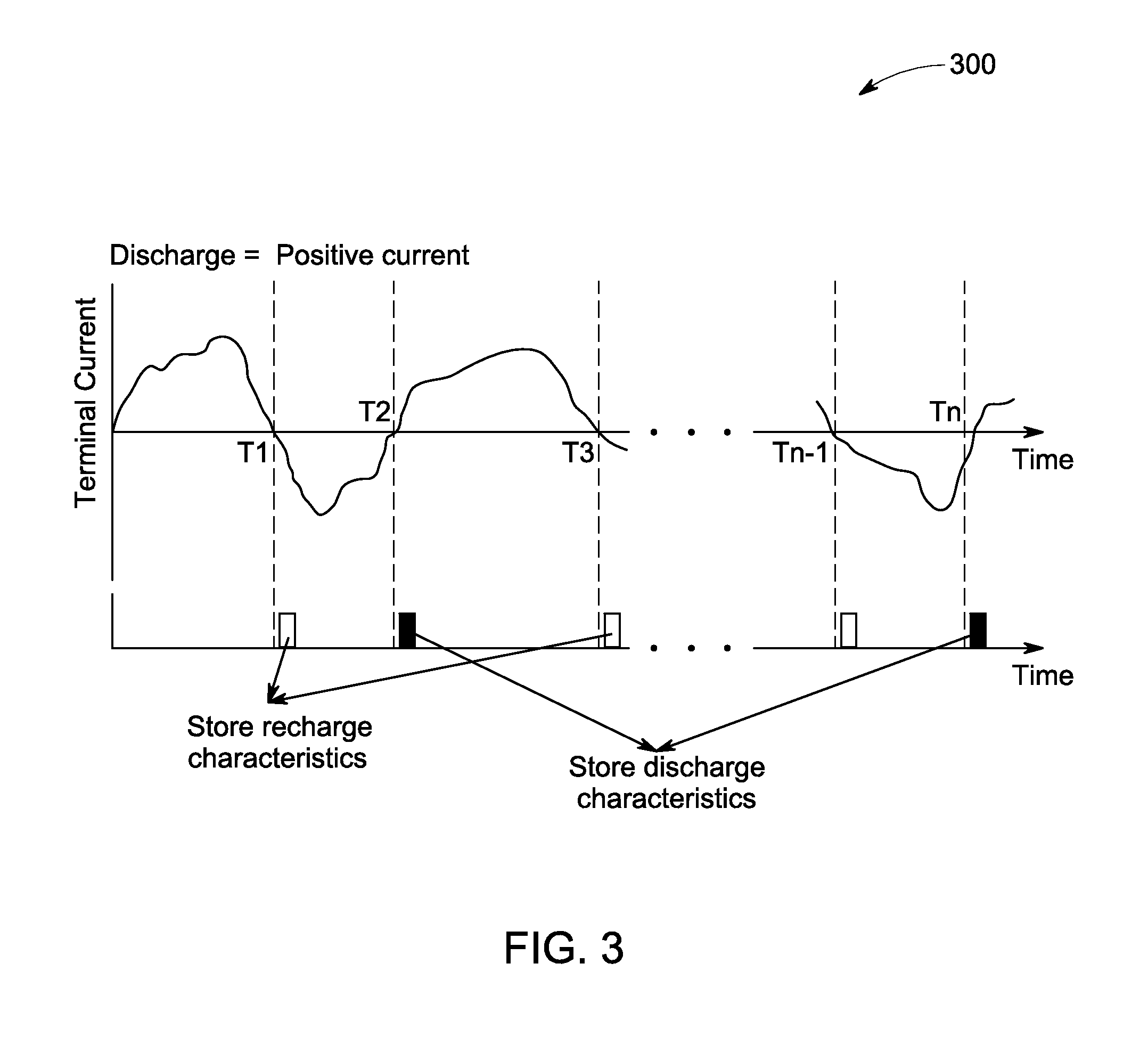
System and method for prognosis of batteries
ActiveUS20140176147A1Material analysis by electric/magnetic meansElectrical testingCell basedIndustrial engineering
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com