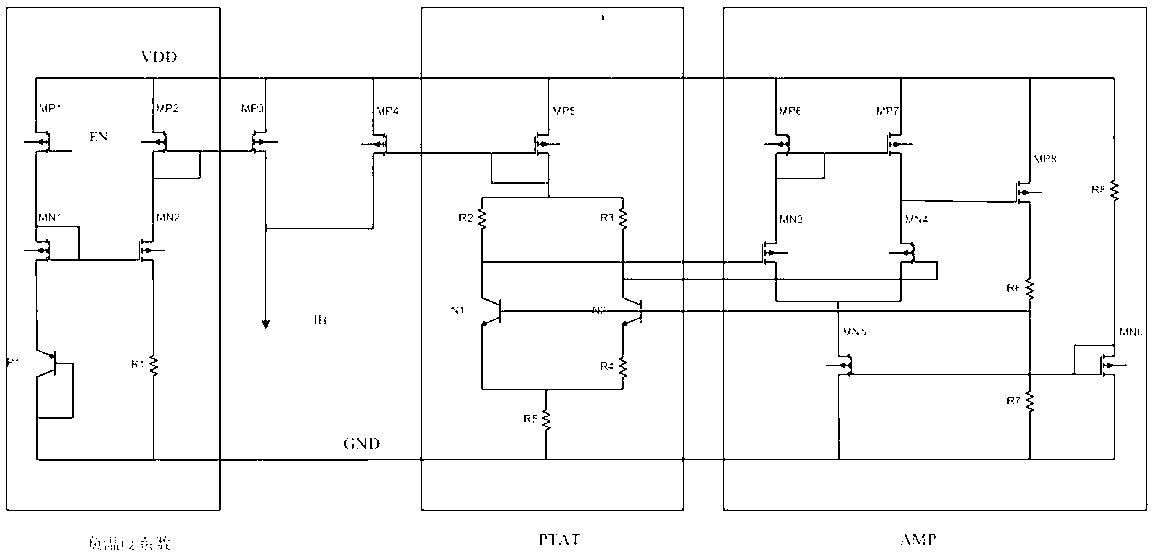
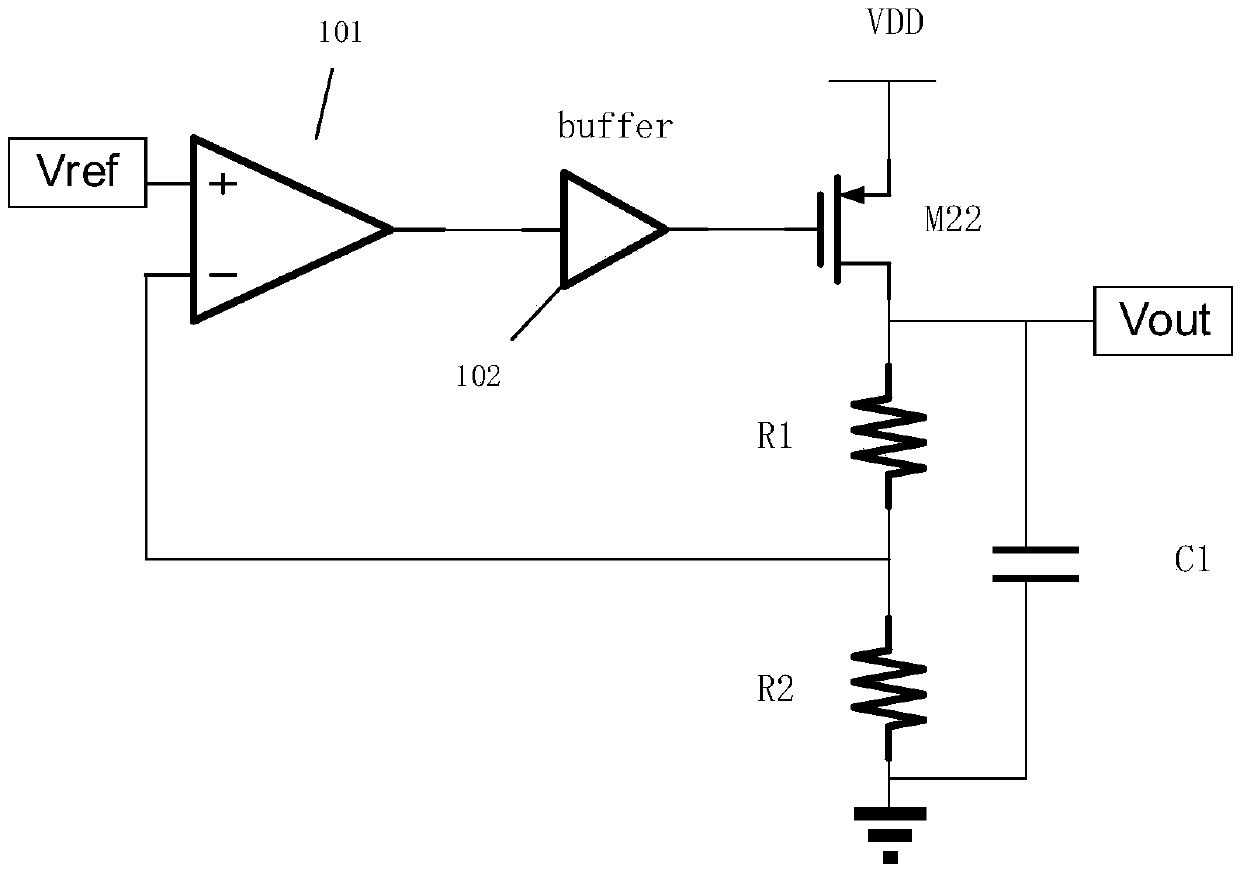
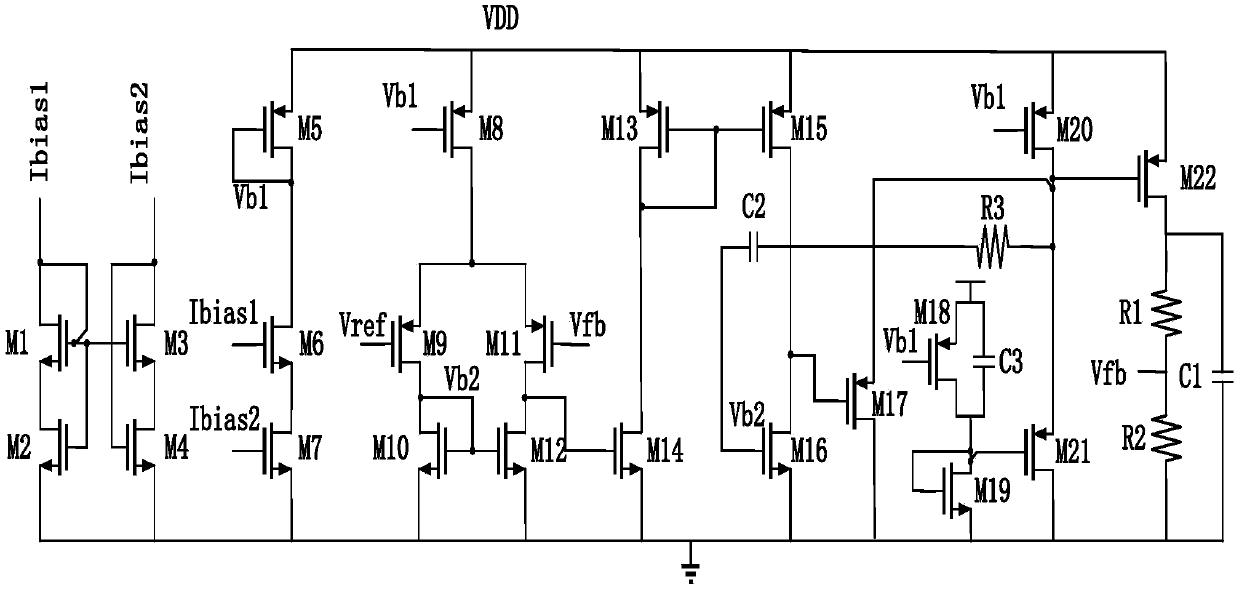
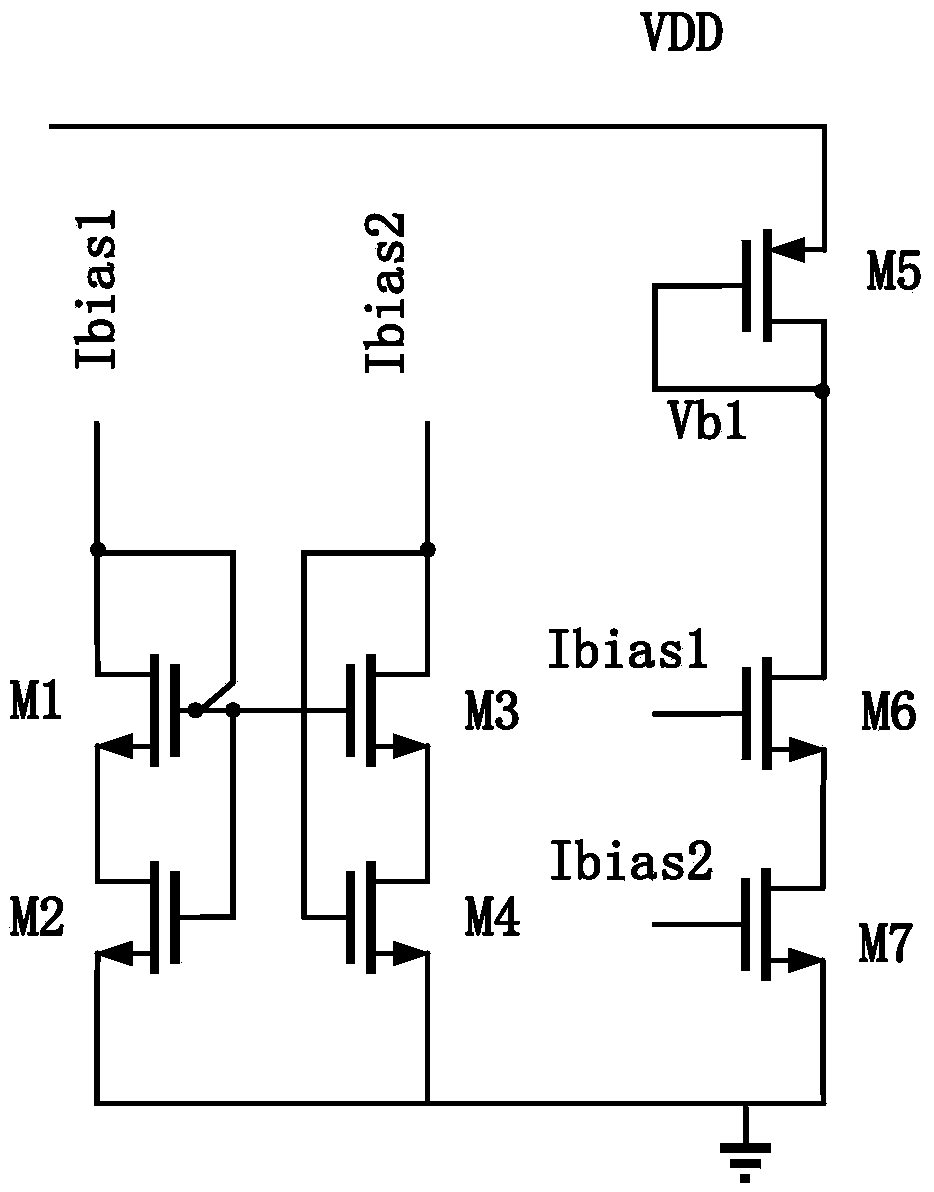
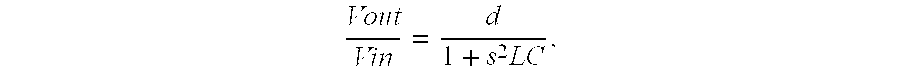Patents
Literature
134results about How to "Improve power supply rejection ratio" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
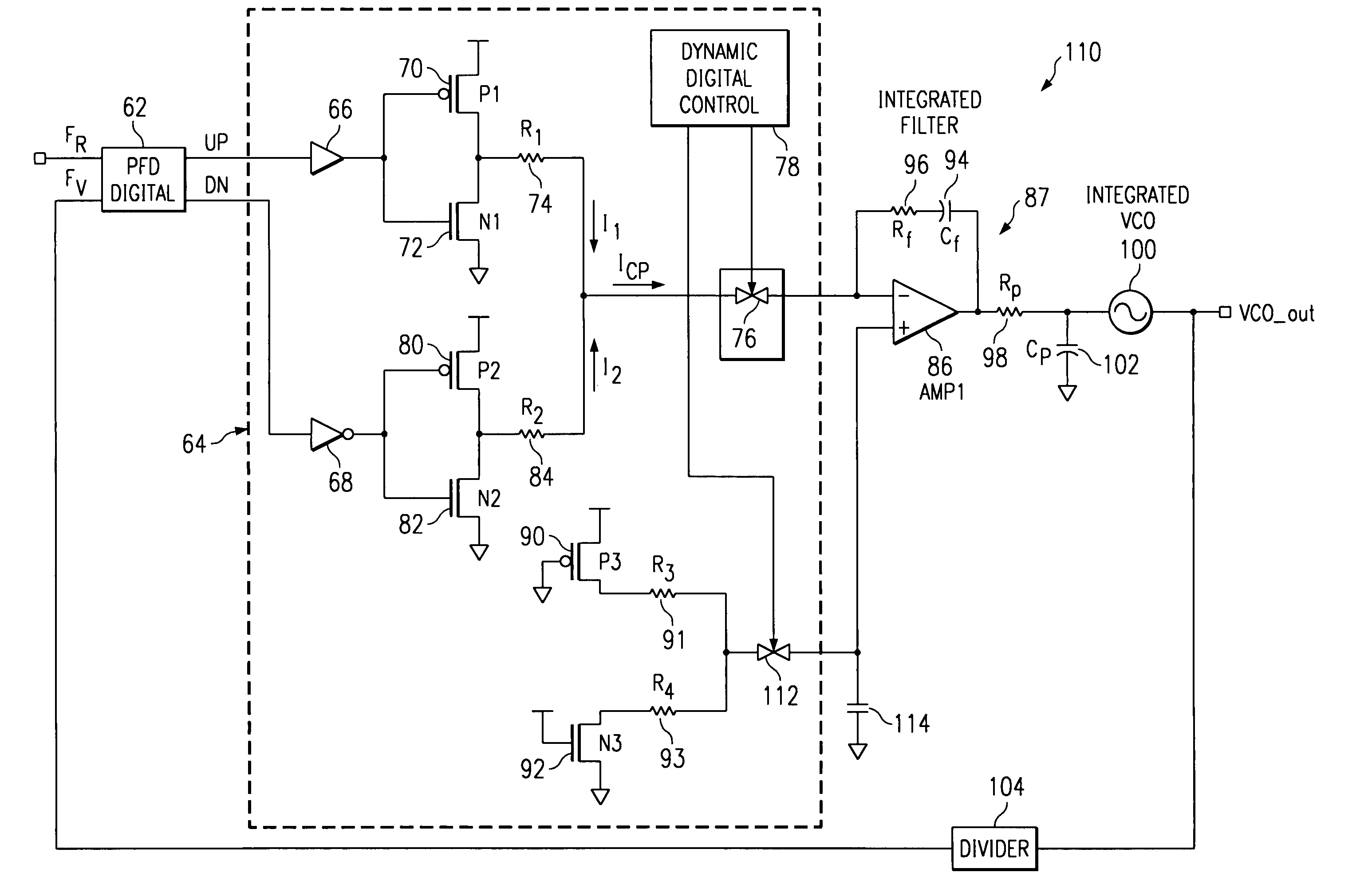
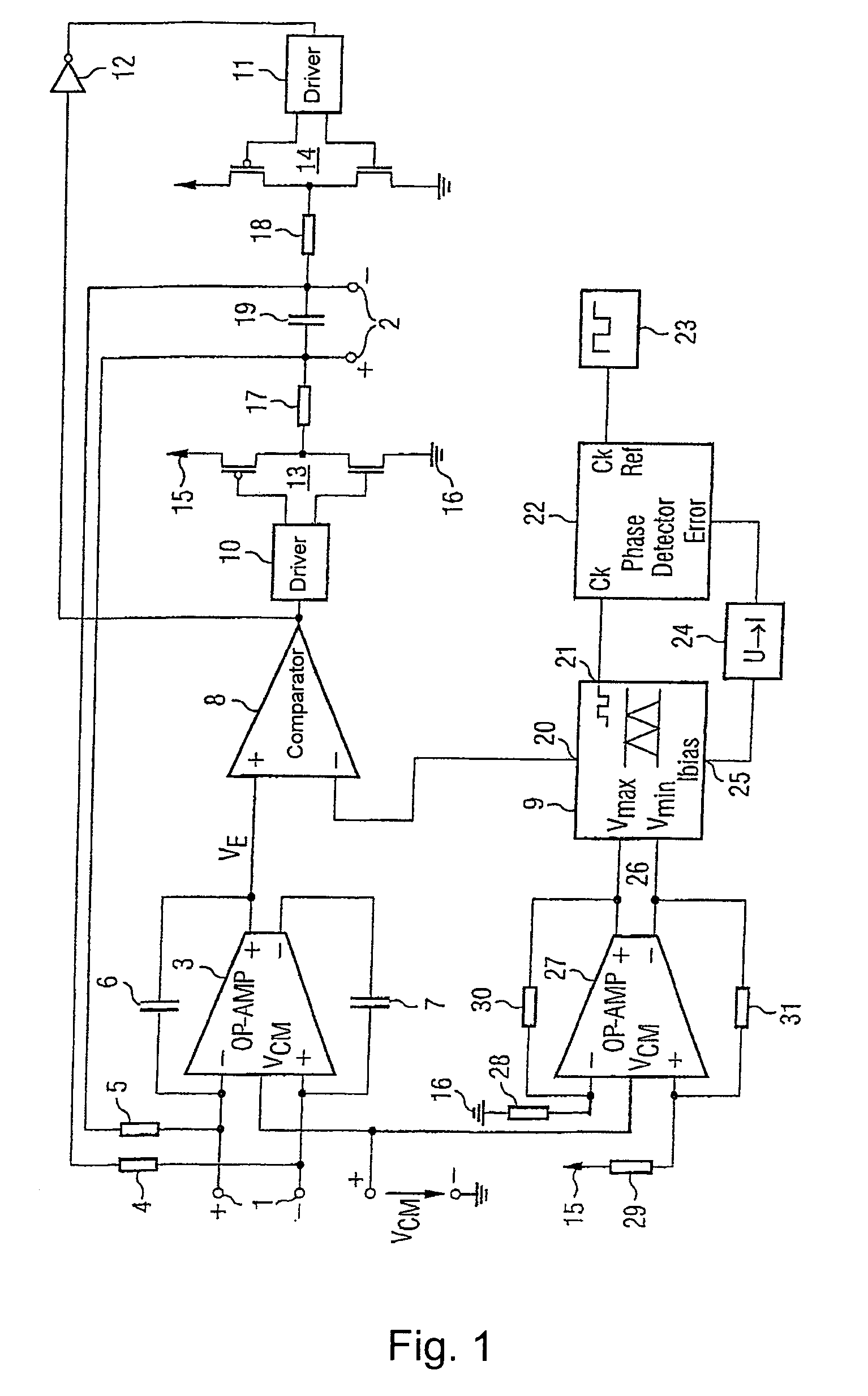
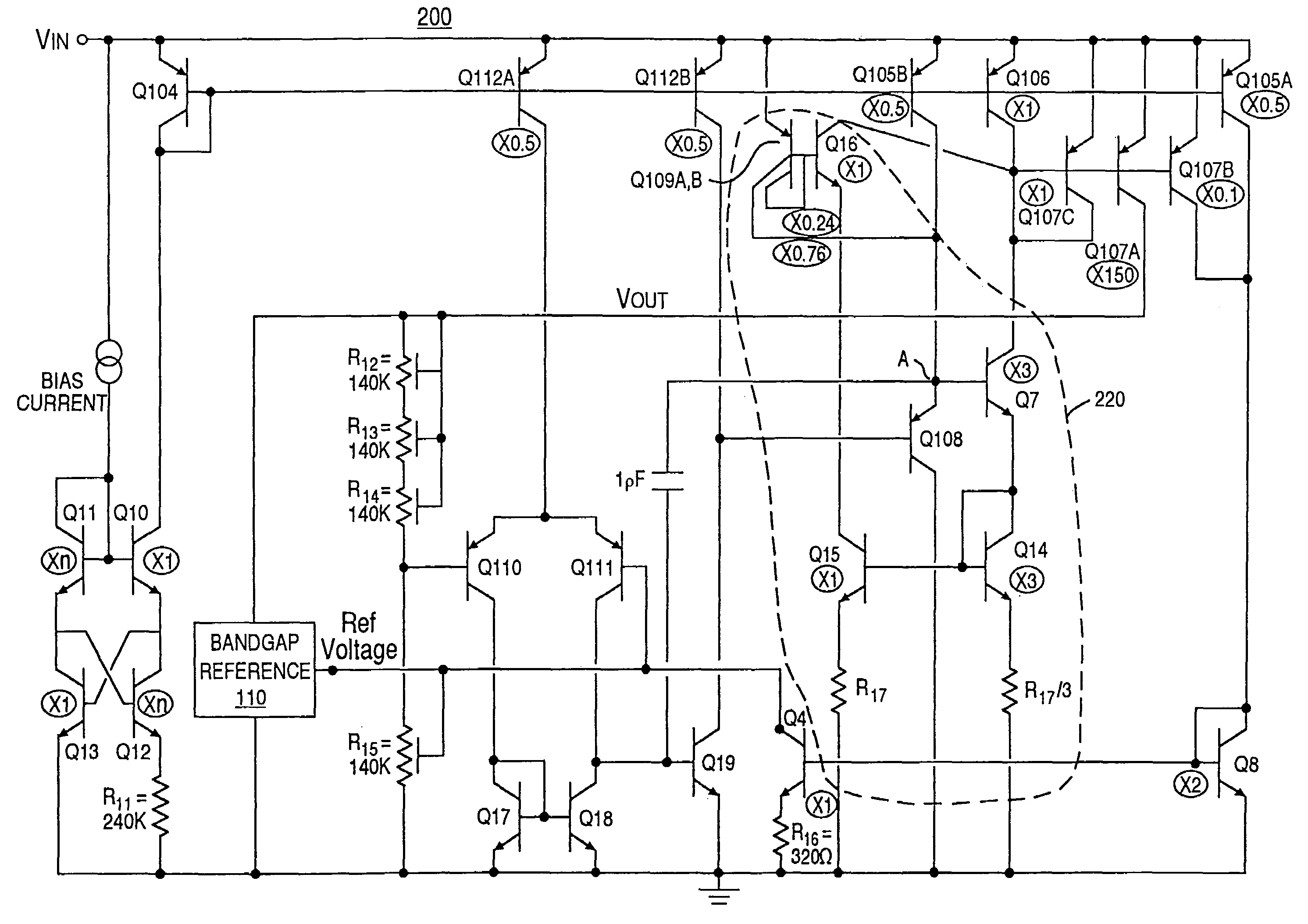
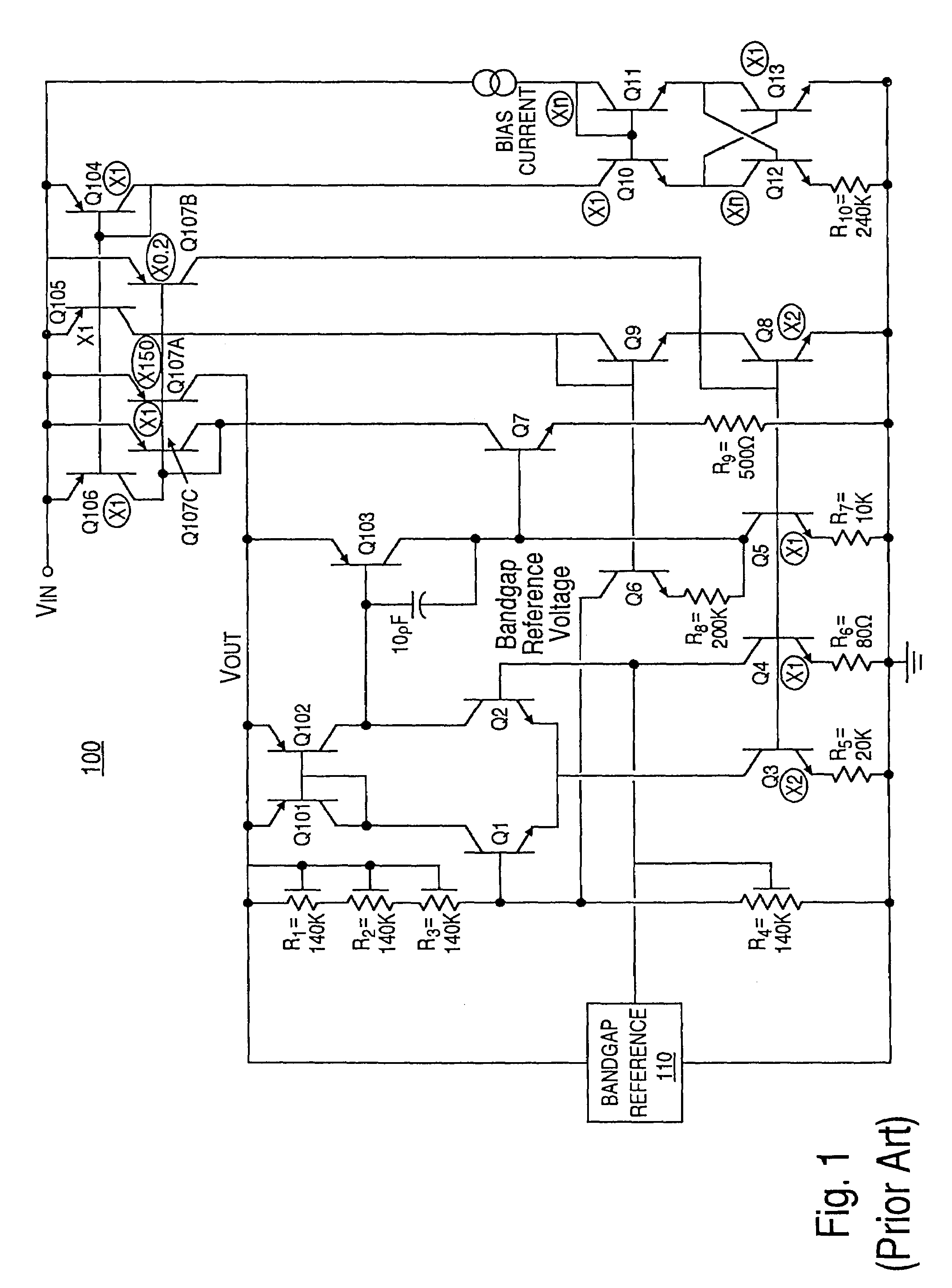
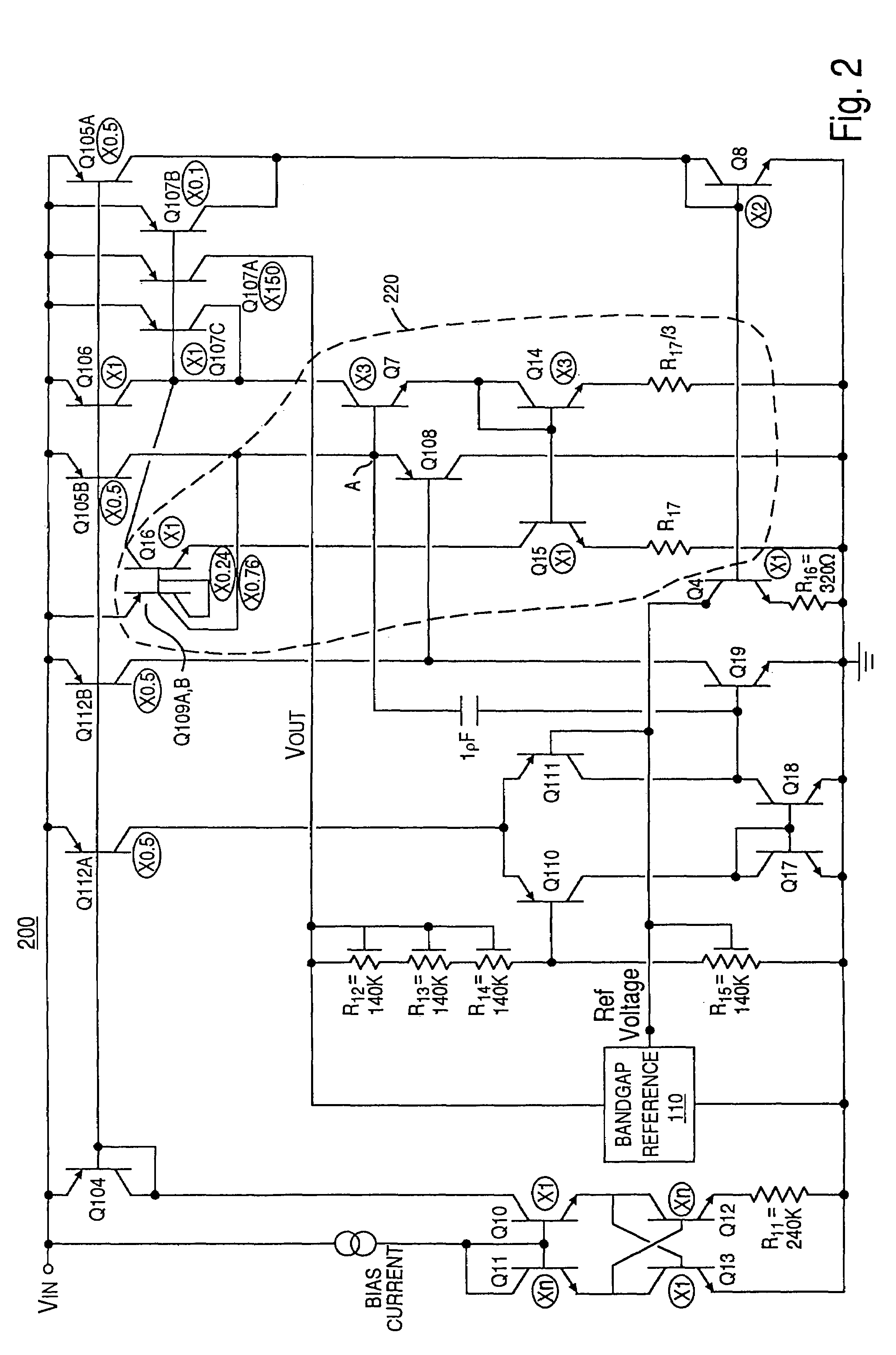
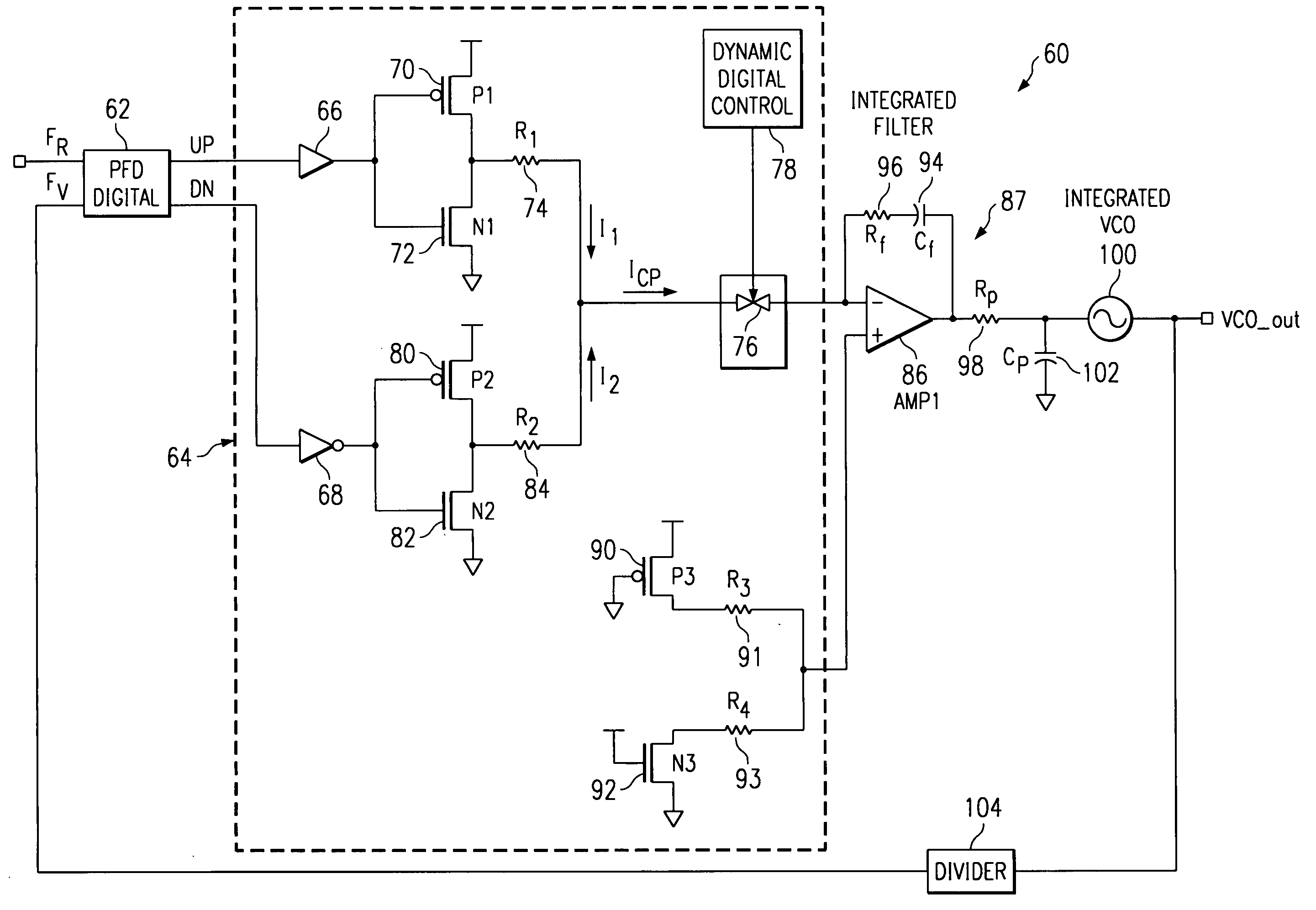
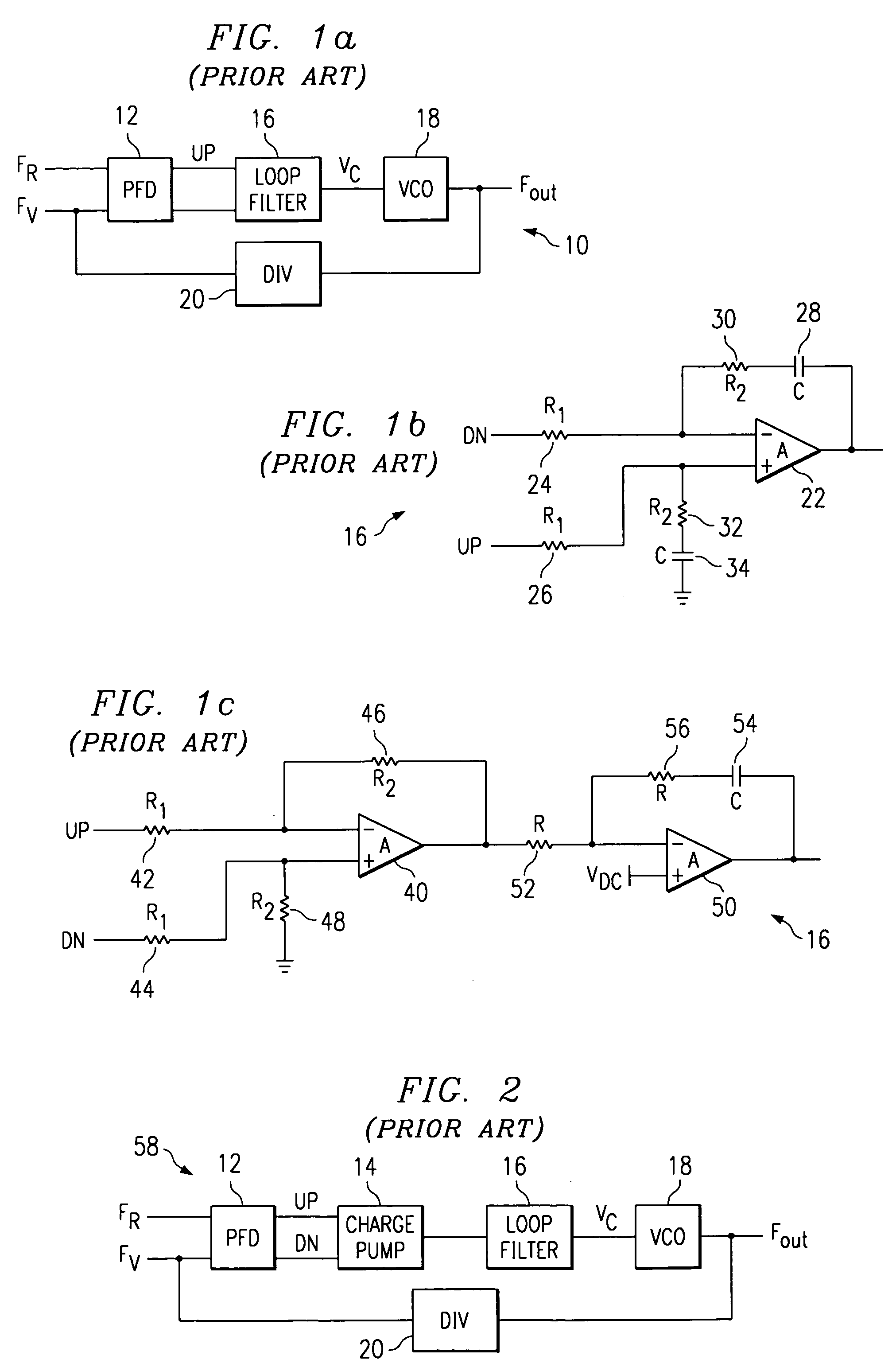
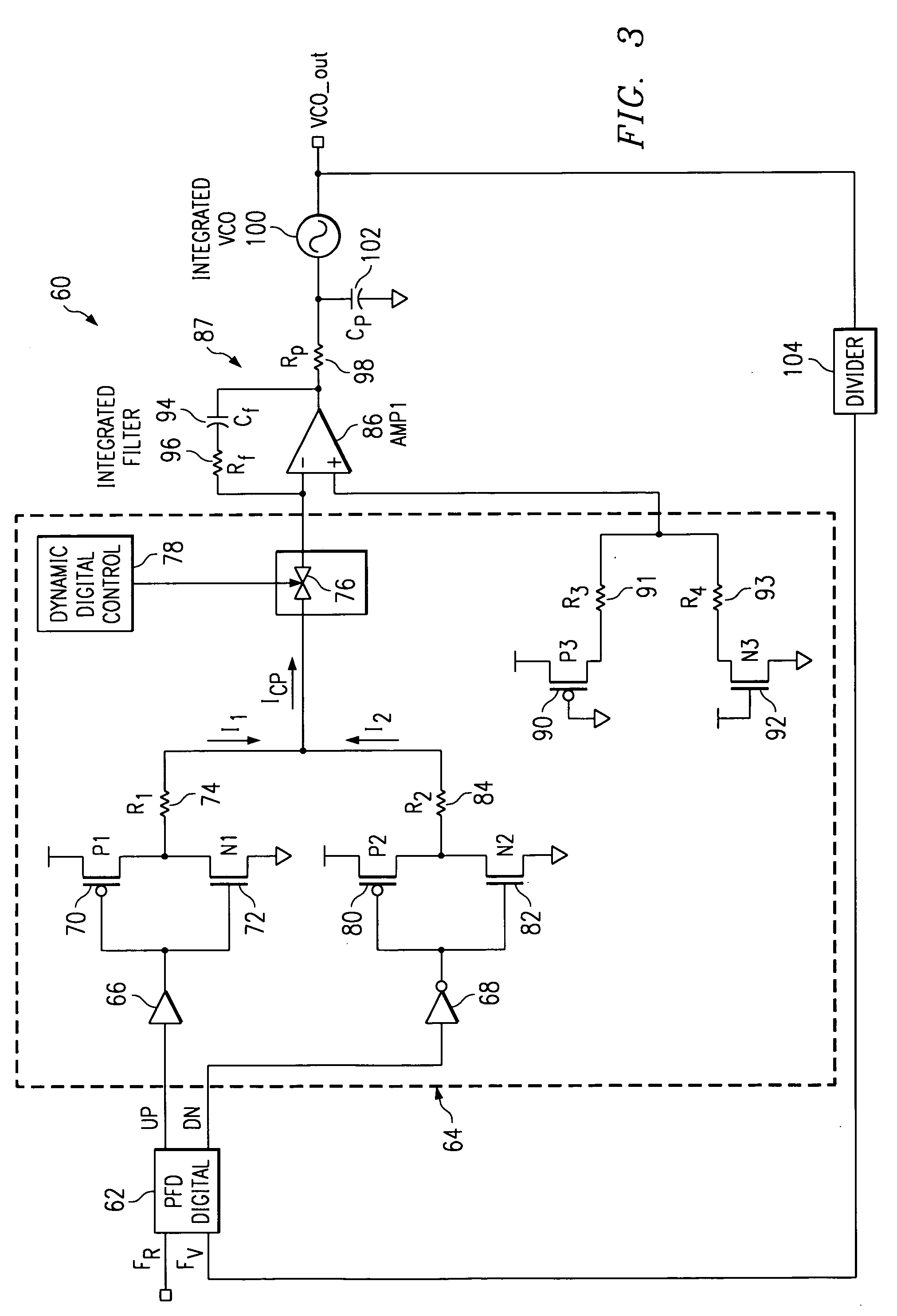
Charge pump phase locked loop with improved power supply rejection
ActiveUS6963233B2Improve power supply rejection ratioVoltage variationPulse automatic controlElectric variable regulationPhase detectorElectricity
A phase lock loop circuit (60) has a phase frequency detector (62), a charge pump (64), an active filter (87) and a voltage-controlled oscillator (100). The phase detector generates signals responsive to reference signal FR and VCO output signal FV. A charge pump generates a voltage at the input of a first transmission gate (76) according to the values of the phase detector signals. A predetermined voltage is generated at the input of a second transmission gate (112). When the transmission gates (76, 110) are closed (low impedance) the charge pump may sink or source current to the inverting input of the operational amplifier (86) of the active filter 86 and the predetermined voltage is applied to the non-inverting input. When the transmission gates are open (high impedance state) the inverting input is electrically isolated from the node and the non-inverting output is isolated from the power supply.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Amplifier circuit
InactiveUS7068095B2Improve power supply rejection ratioNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyAudio power amplifierAmplitude control
The invention is directed to an amplifier circuit based on the principle of a class D amplifier. To avoid unwanted convolution effects and to improve the power supply rejection ratio, provision is made for the amplitude of the ramp signal used for pulse width modulation to track proportionally the supply voltage for the amplifier circuit. For this purpose, the ramp signal generator has an amplitude control input suitably connected to supply and reference potentials. This ensures a constant duty ratio which is independent of the supply voltage. The present circuit may be used, for example, as a DC / DC converter or as an audio amplifier.
Owner:INTEL MOBILE COMM GMBH
Band-gap reference circuit
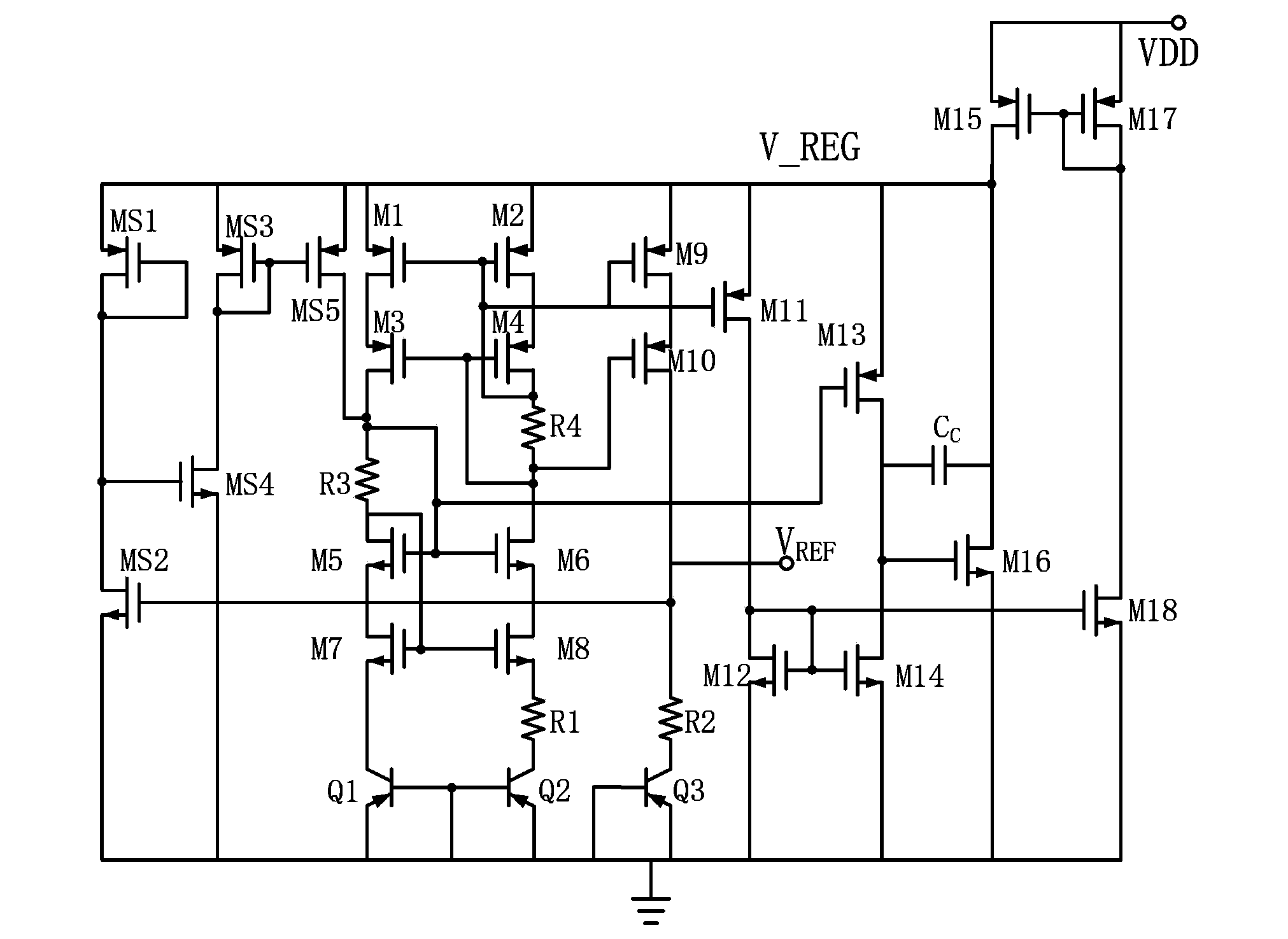
ActiveCN104122918AImprove power supply rejection ratioSave area and powerElectric variable regulationPower supply rejection ratioEngineering
The invention relates to a band-gap reference circuit. The band-gap reference circuit comprises a reference voltage source VREF, a band-gap core circuit, a negative feedback circuit and a starting circuit, wherein gate voltage V_REG is stretched by the reference voltage source VREF so that internal voltage pre-stabilization can be achieved, an internal voltage pre-stabilizing circuit is formed, the band-gap core circuit is provided with an automatic biasing cascode amplifying circuit used for increasing a power supply rejection ratio, the negative feedback circuit provides the supply voltage VDD, processed through voltage stabilization, for the band-gap core circuit, and the starting circuit stretches the reference voltage source VREF when work begins so that the automatic biasing cascode amplifying circuit can work normally. According to the band-gap reference circuit, due to the facts that the supply voltage VDD processed through voltage stabilization is provided for the band-gap core circuit through the negative feedback circuit, and the automatic biasing cascode amplifying circuit is adopted inside for increasing the power supply rejection ratio, area and power consumption are saved.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Reference voltage generator
InactiveUS20140091780A1Improve power supply rejection ratioReduce voltageElectric variable regulationVoltage generatorEngineering
A reference voltage generator including a reference voltage generating unit is provided. The reference voltage generating unit receives a first bias voltage current and a first mirror current and generates a reference voltage. The reference voltage generating unit includes a first metal-oxide-semiconductor (MOS) transistor, a second MOS transistor, a first impedance providing element and a second impedance providing element. The first and the second MOS transistors operate in a sub-threshold region so as to generate a first gate-source voltage and a second gate-source voltage having a negative temperature coefficient. The first impedance providing element is configured to generate a first current having a positive temperature coefficient. The second impedance providing element is configured to generate a first voltage having a negative temperature coefficient at its first terminal. The reference voltage is equal to a sum of the second gate-source voltage and the first voltage.
Owner:NOVATEK MICROELECTRONICS CORP
Bandgap reference voltage source
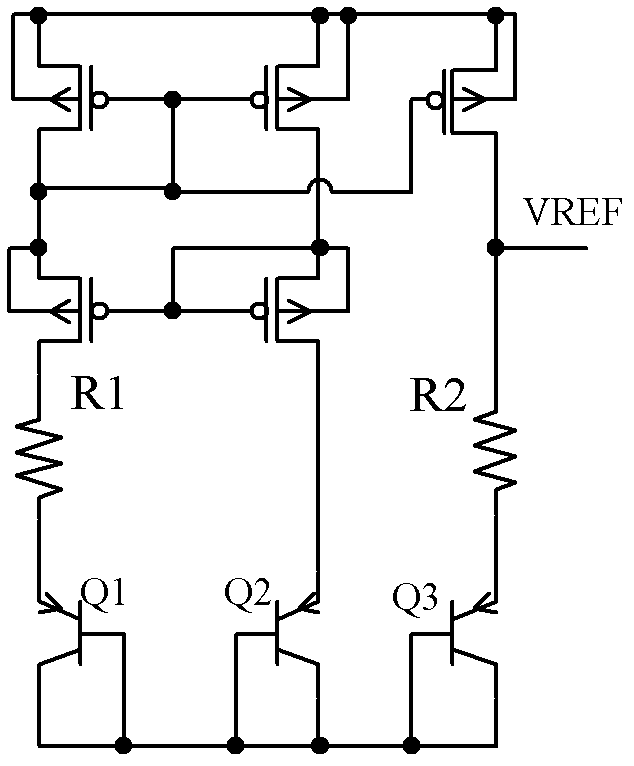
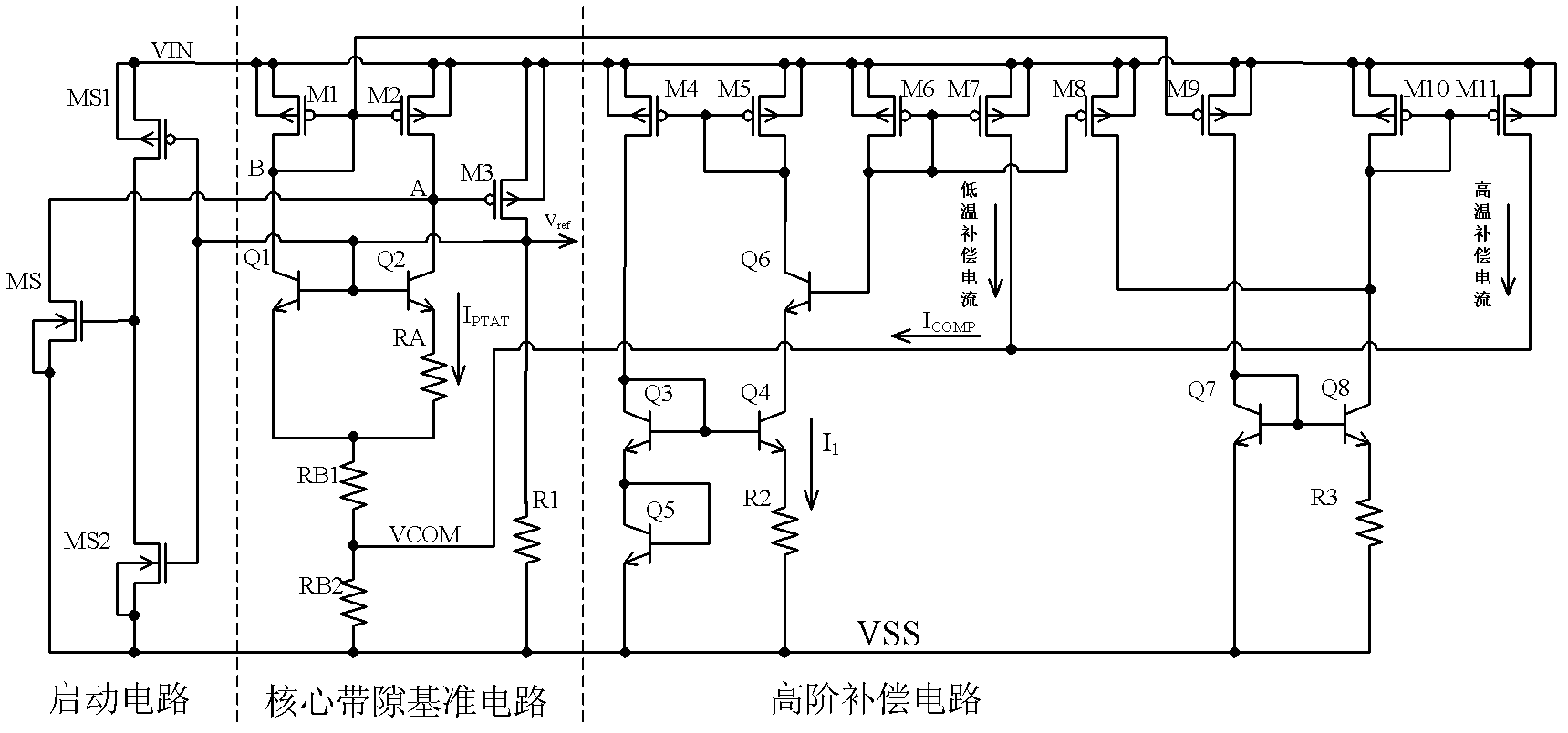
ActiveCN102591394ASmall temperature coefficientImprove power supply rejection ratioElectric variable regulationEngineeringVoltage source
The invention discloses a bandgap reference voltage source which comprises a starting circuit, a core bandgap reference circuit and a high-order compensation circuit. The core bandgap reference circuit comprises PMOS tubes M1, M2 and M3, NPN triodes Q1 and Q2 and resistance units R1, RB1, RB2 and RA; and the high-order compensation circuit comprises PMOS tubes M4, M5, M6, M7, M8, M9, M10 and M11, NPN triodes Q3, Q4, Q5, Q6, Q7 and Q8 and resistance units R2 and R3. The bandgap reference voltage source disclosed by the invention adopts the high-order compensation circuit, thereby the temperature coefficient is reduced greatly; the circuits adopt the resistance ratio, thus the circuits can not be affected by the absolute value of the resistance, and the influence of the temperature coefficient of the resistance to the output quantity can be reduced. The bandgap reference voltage source has high power supply rejection ratio and can ensure that the circuits can resist the interference of a power supply.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
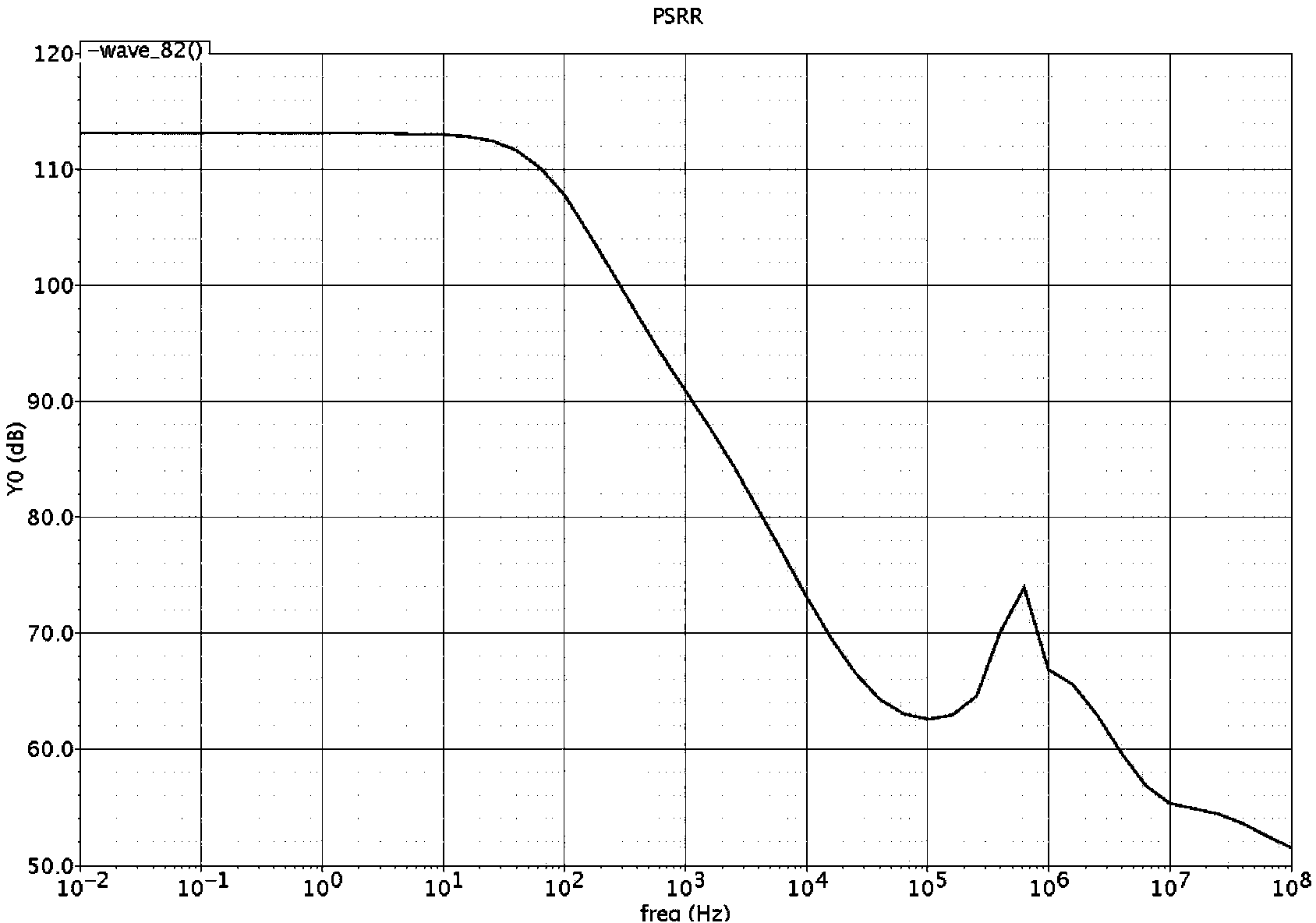
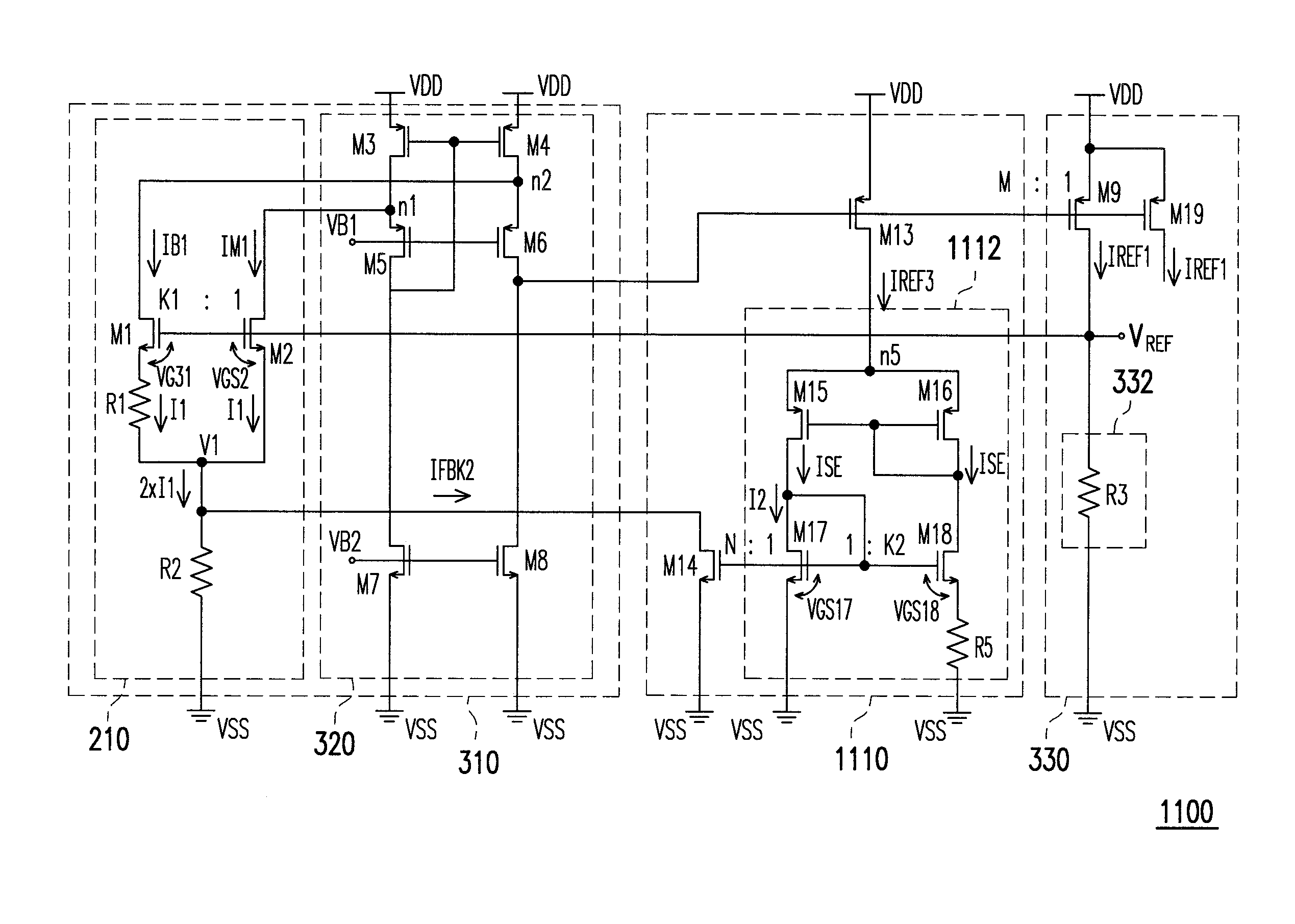
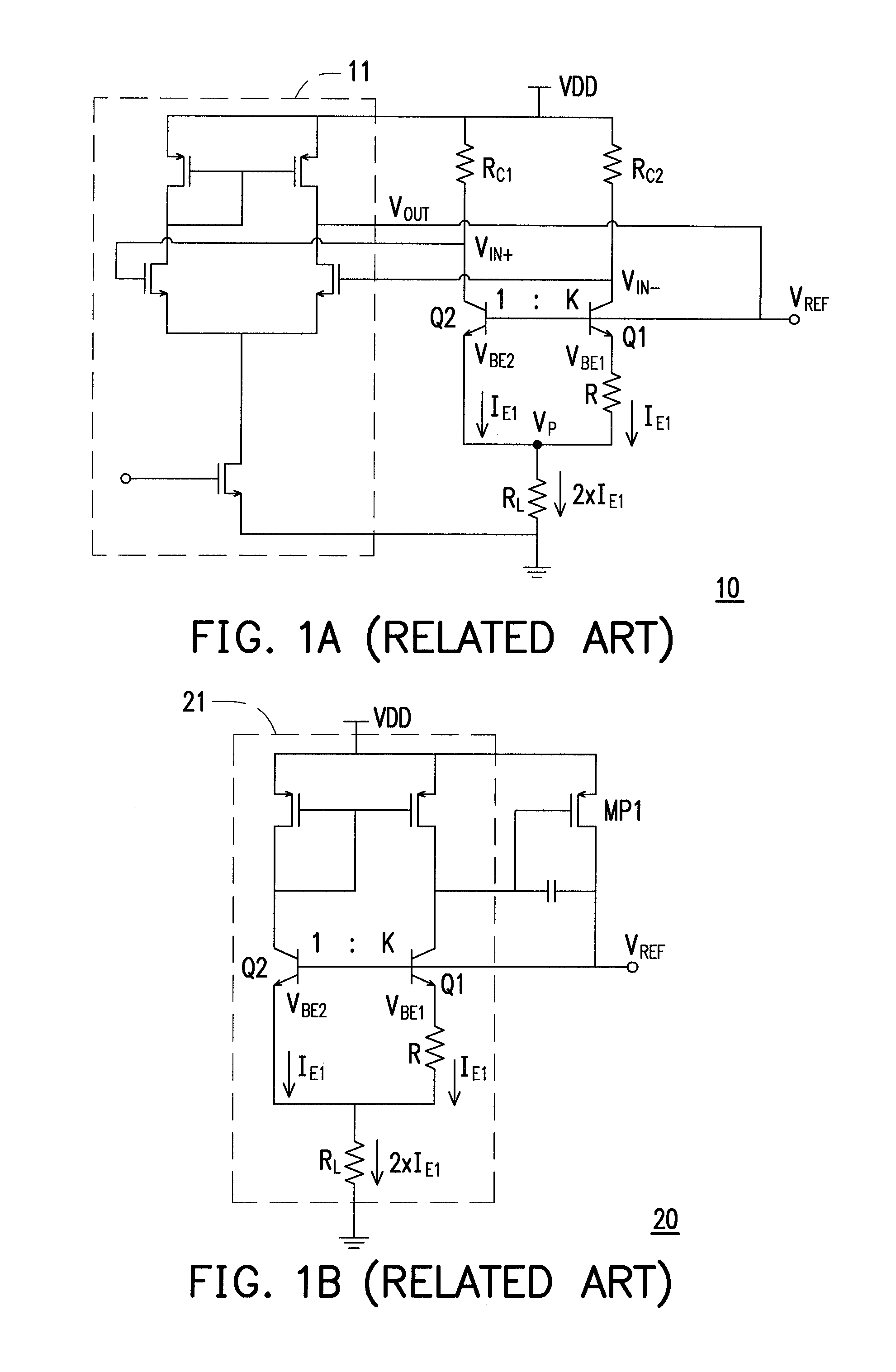
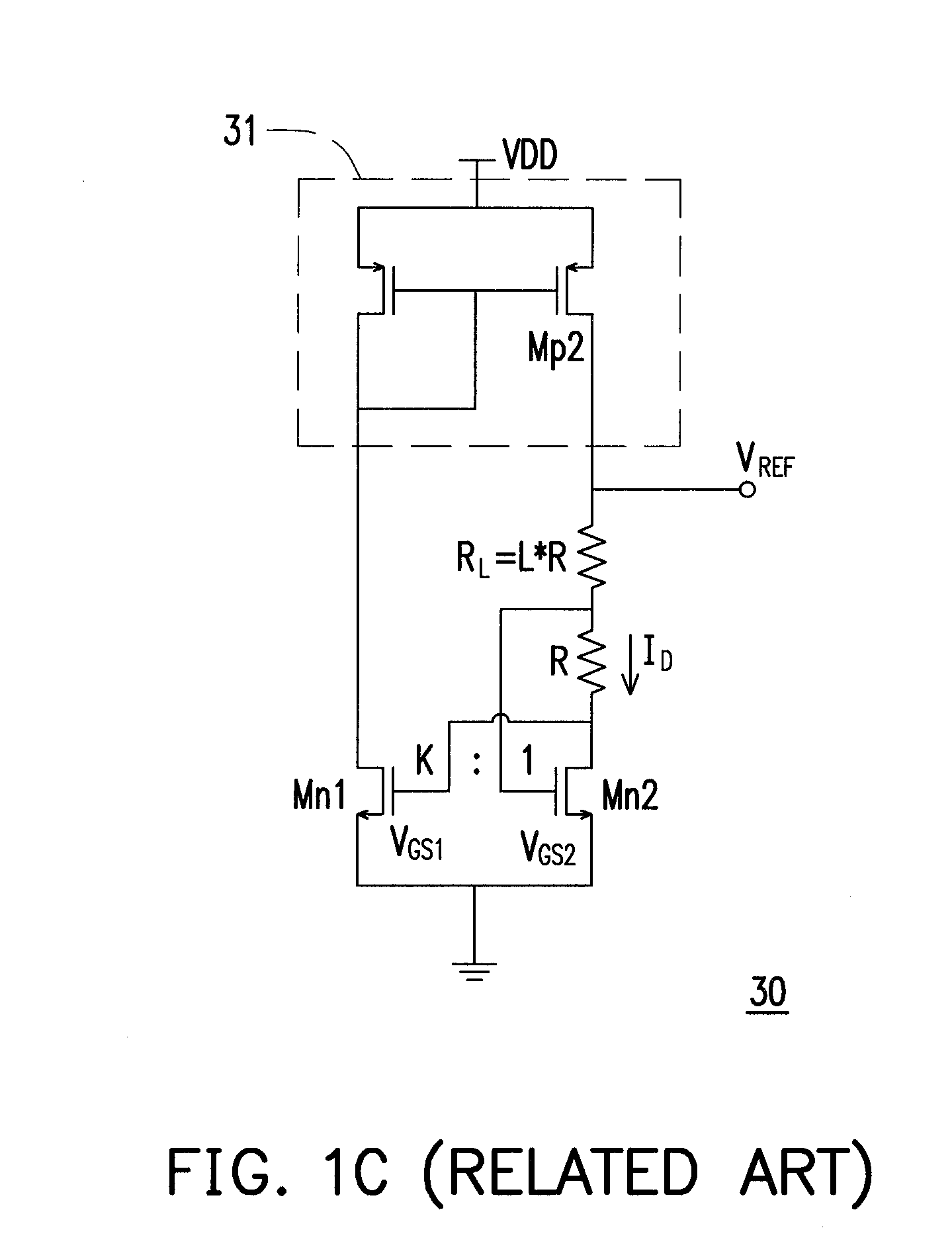
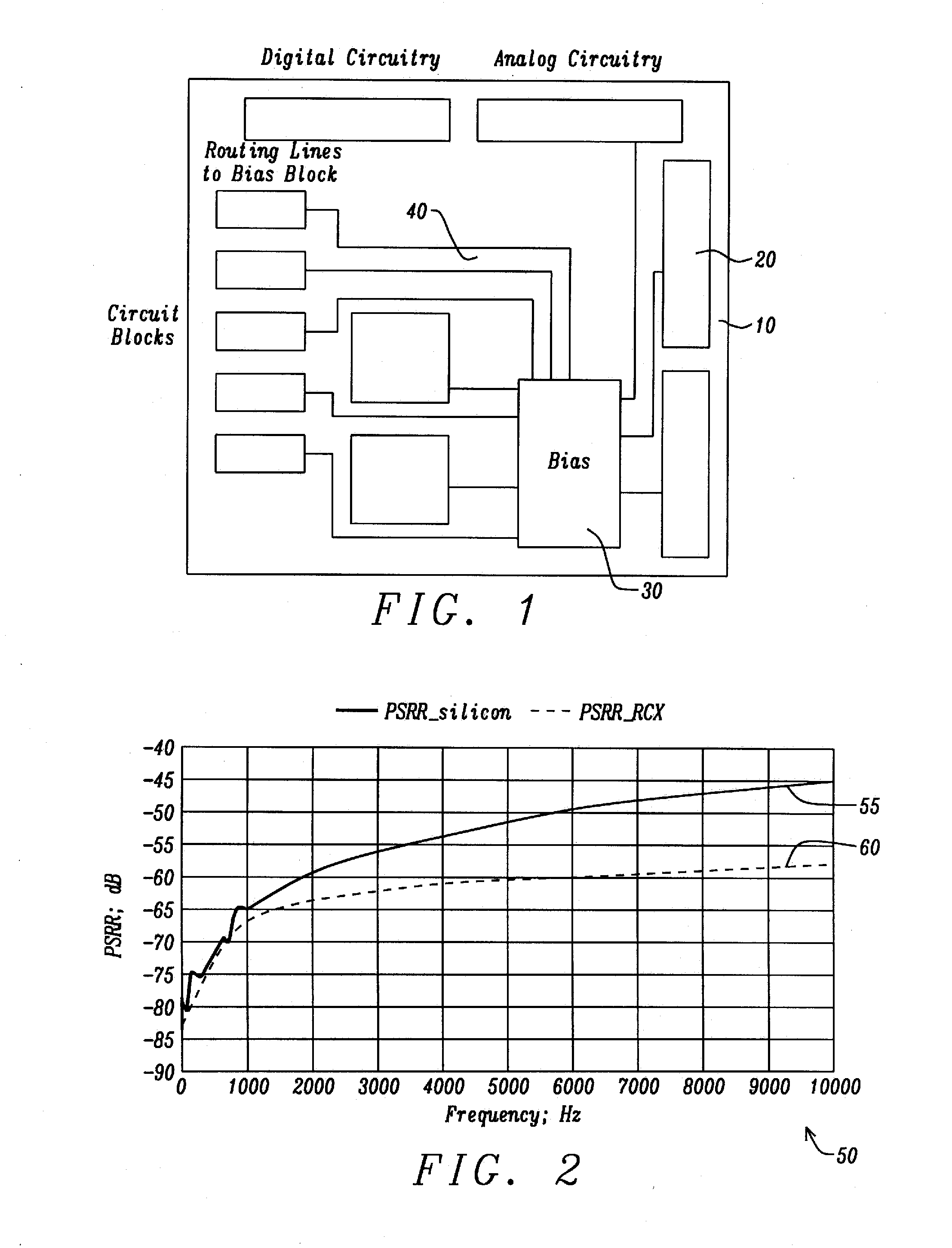
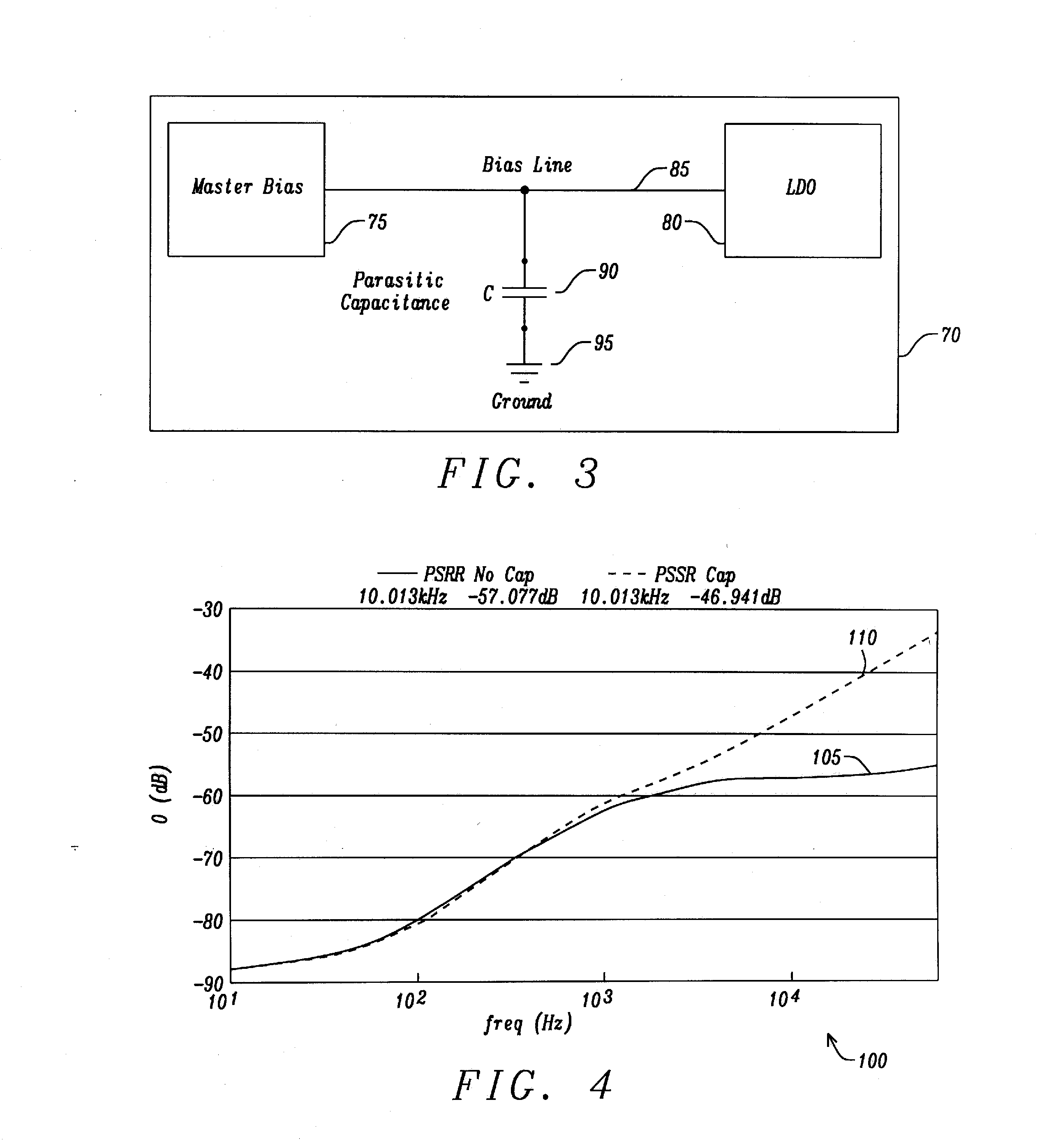
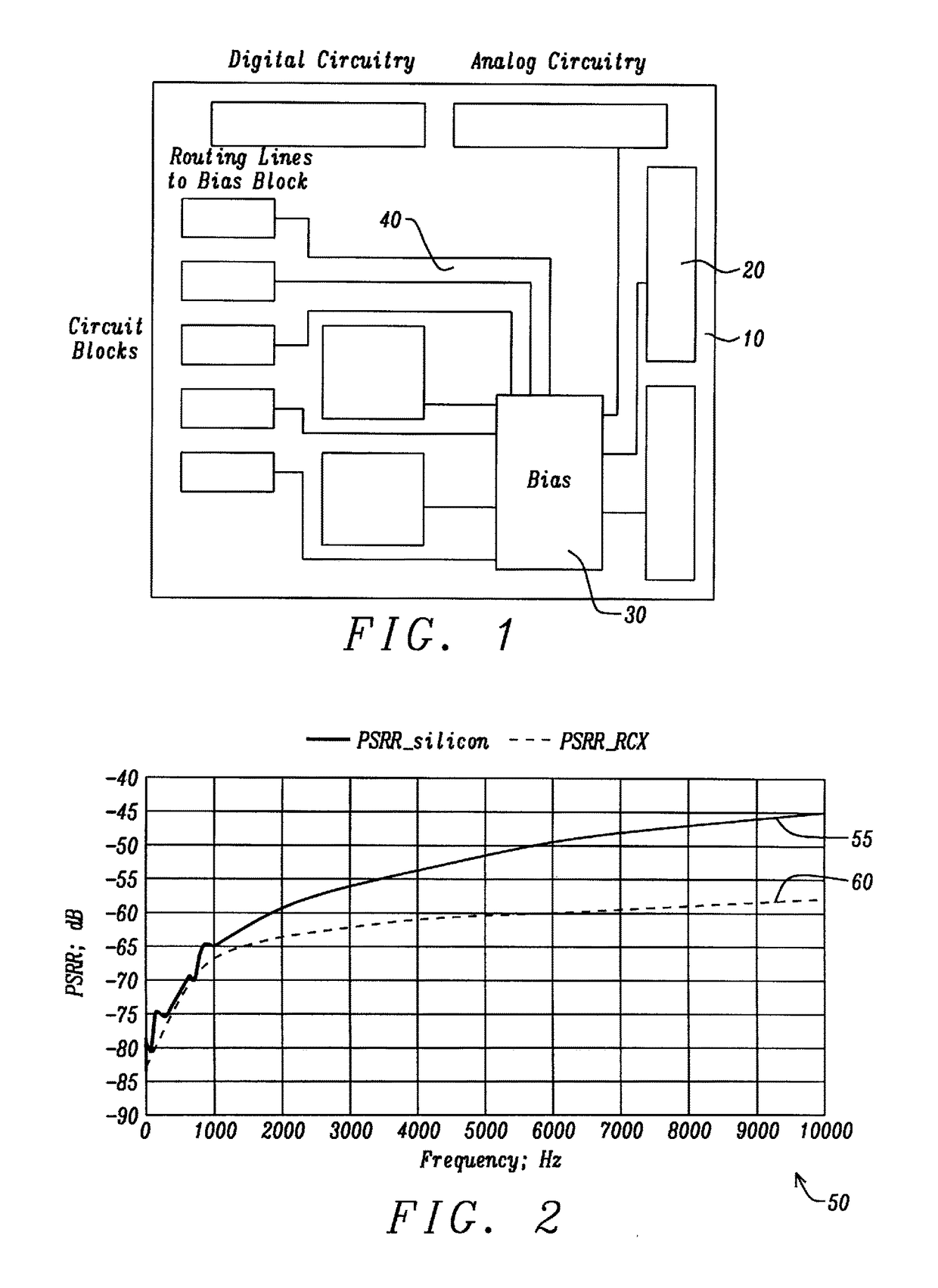
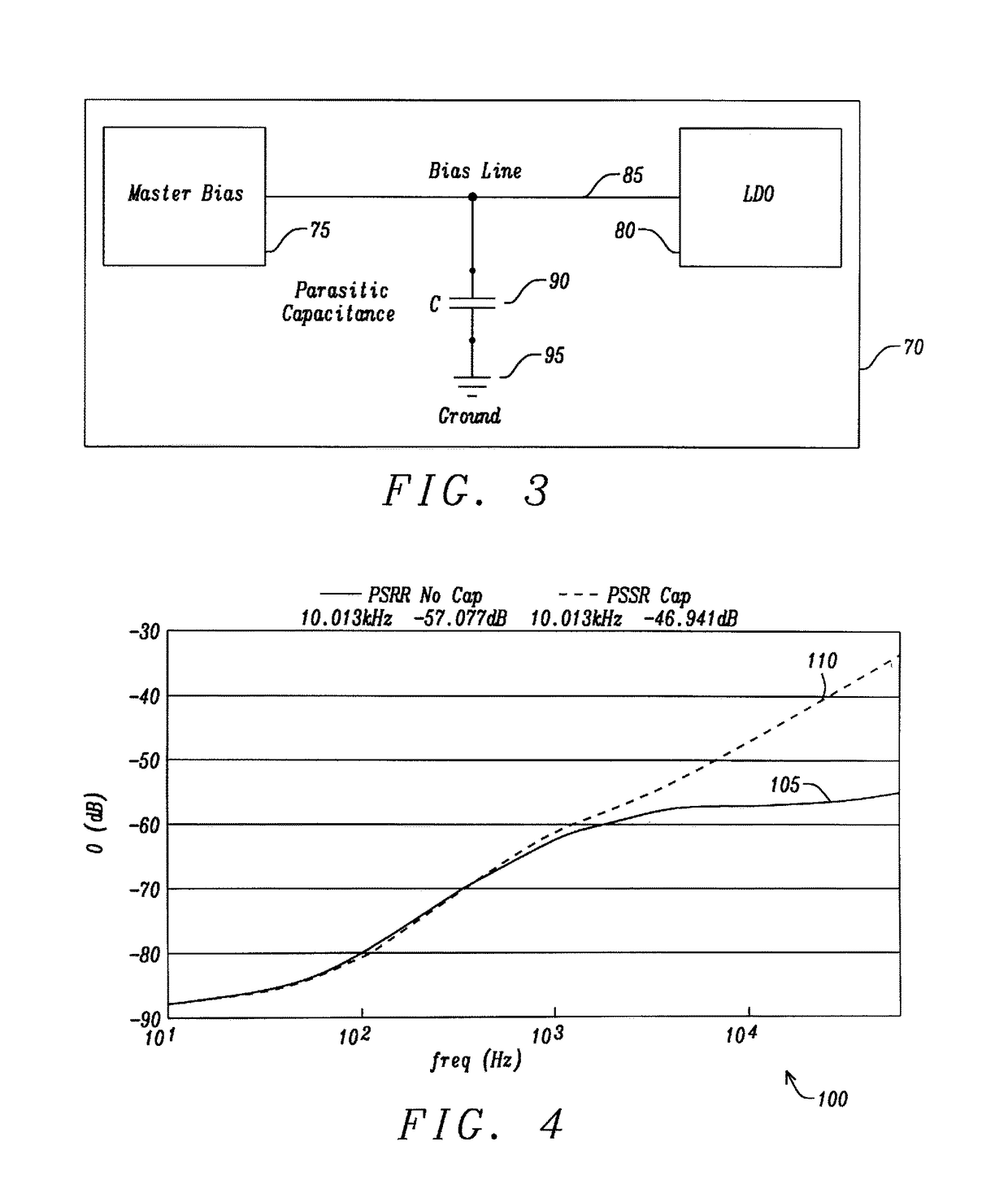
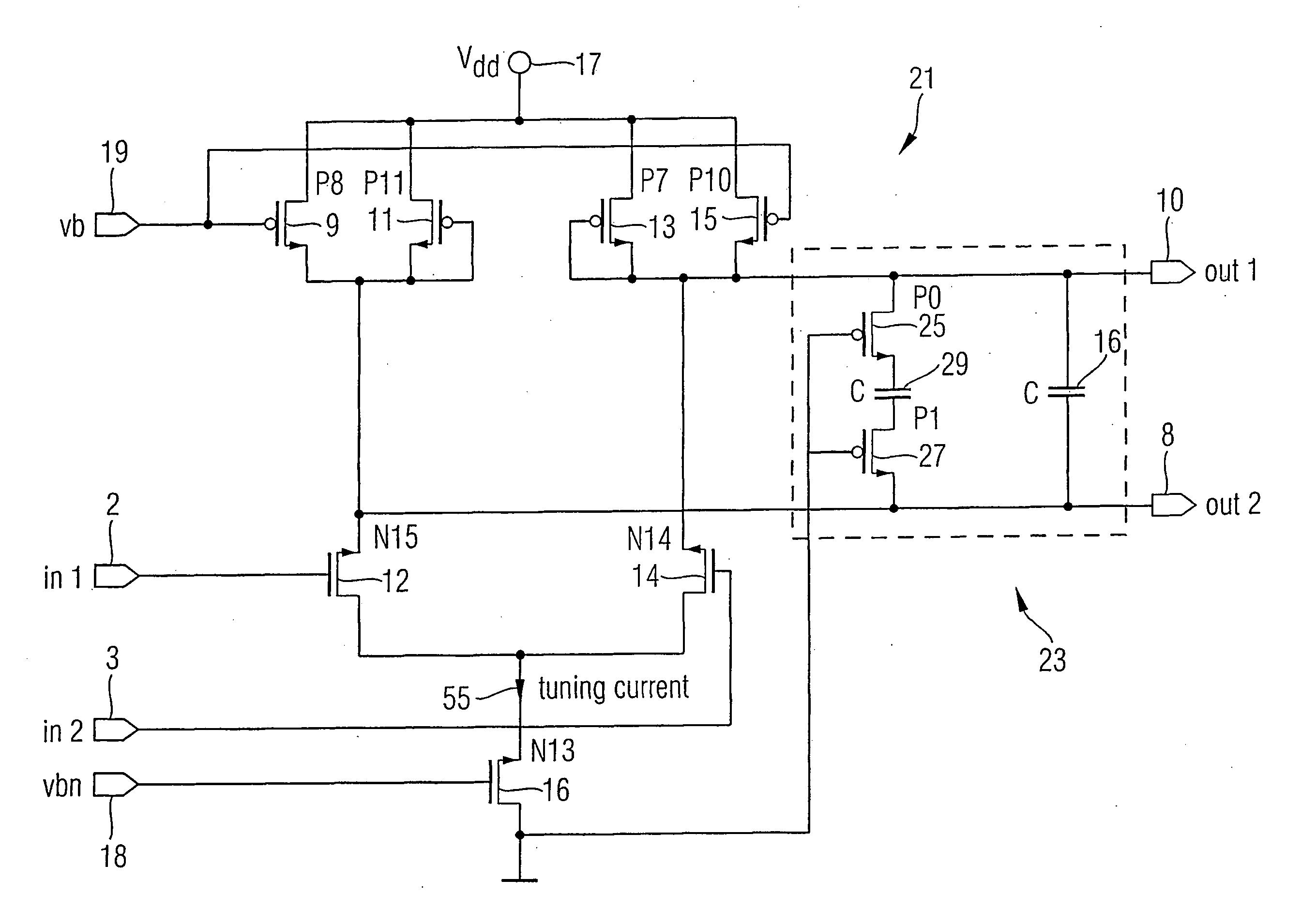
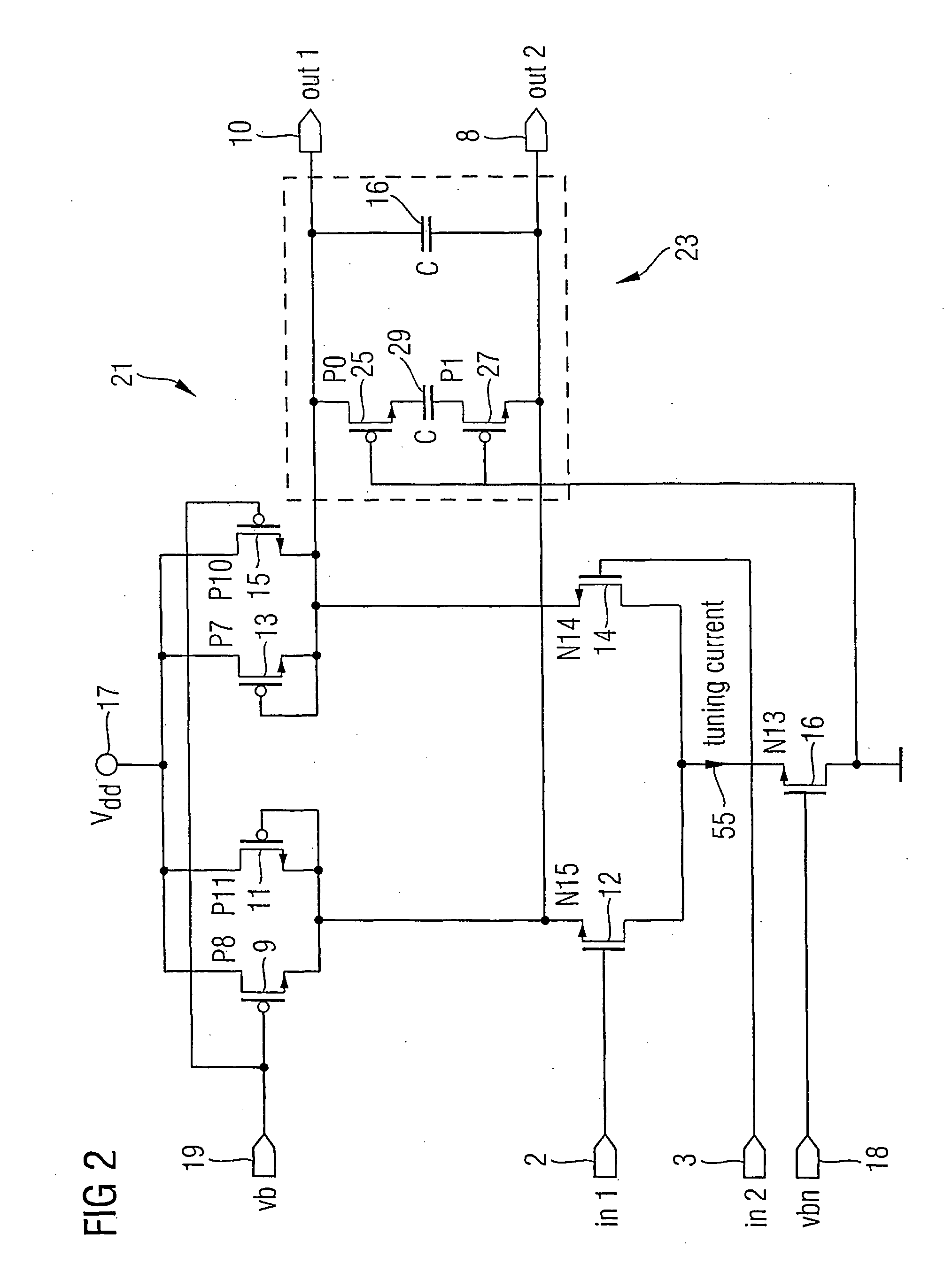
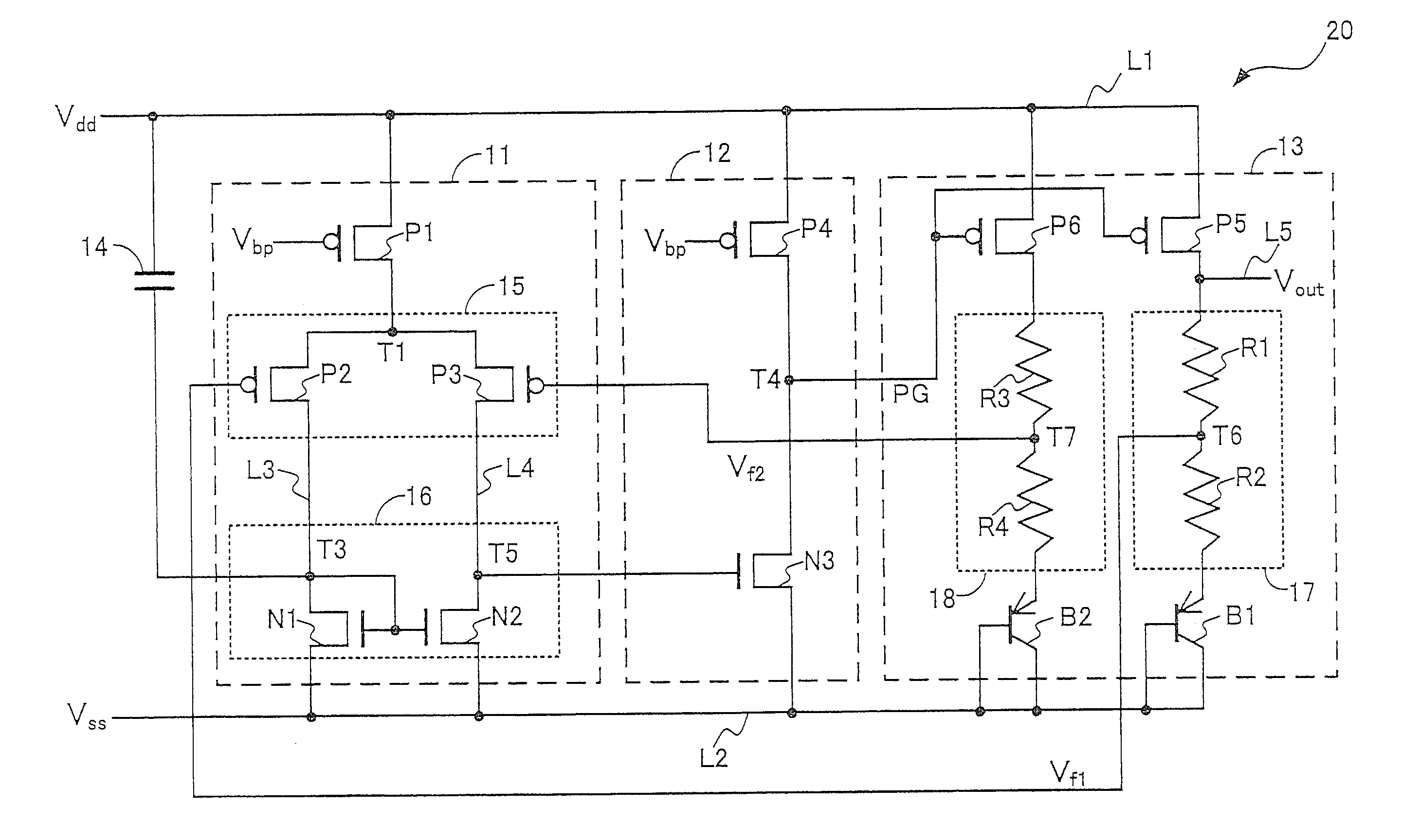
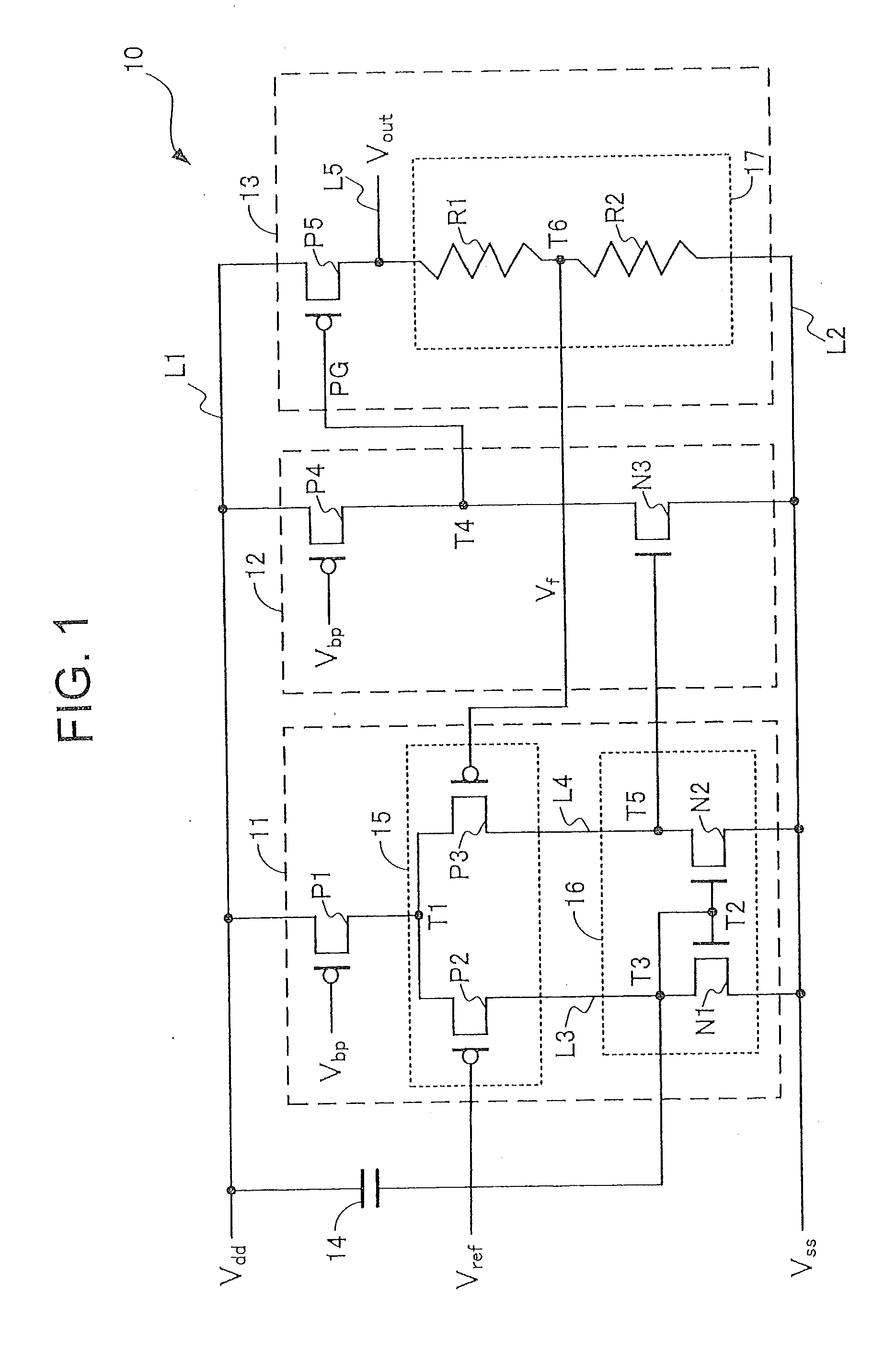
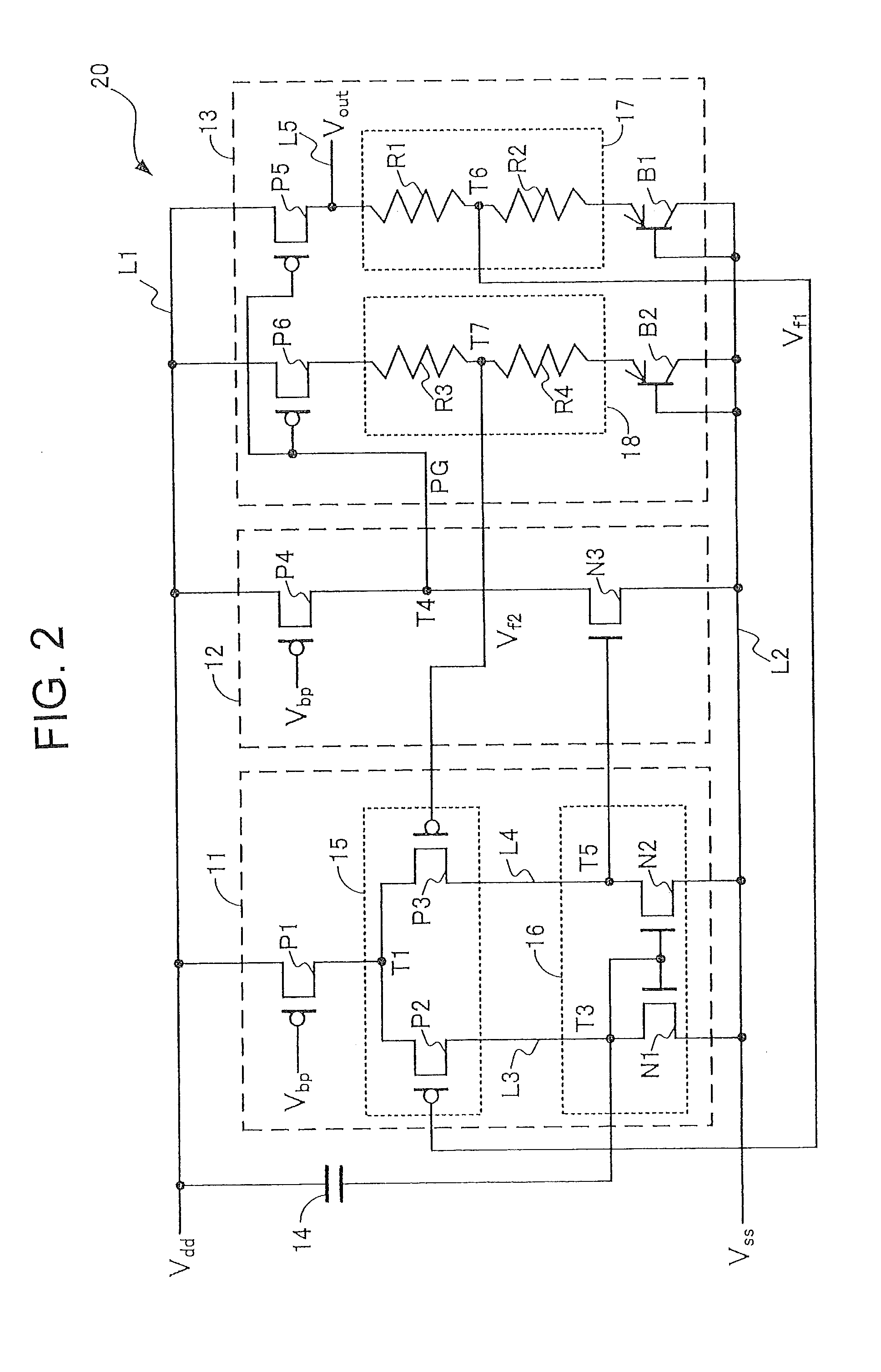
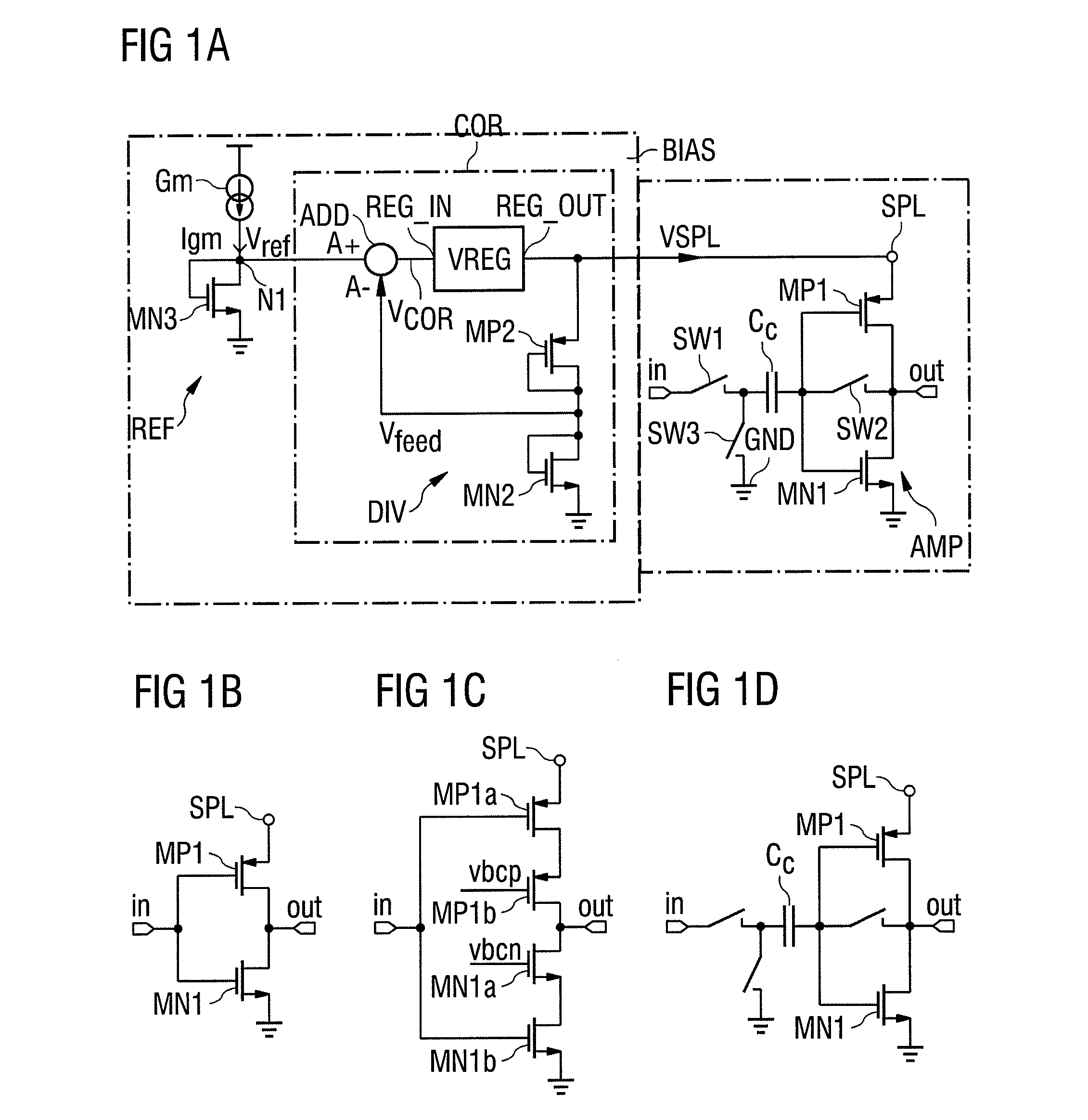
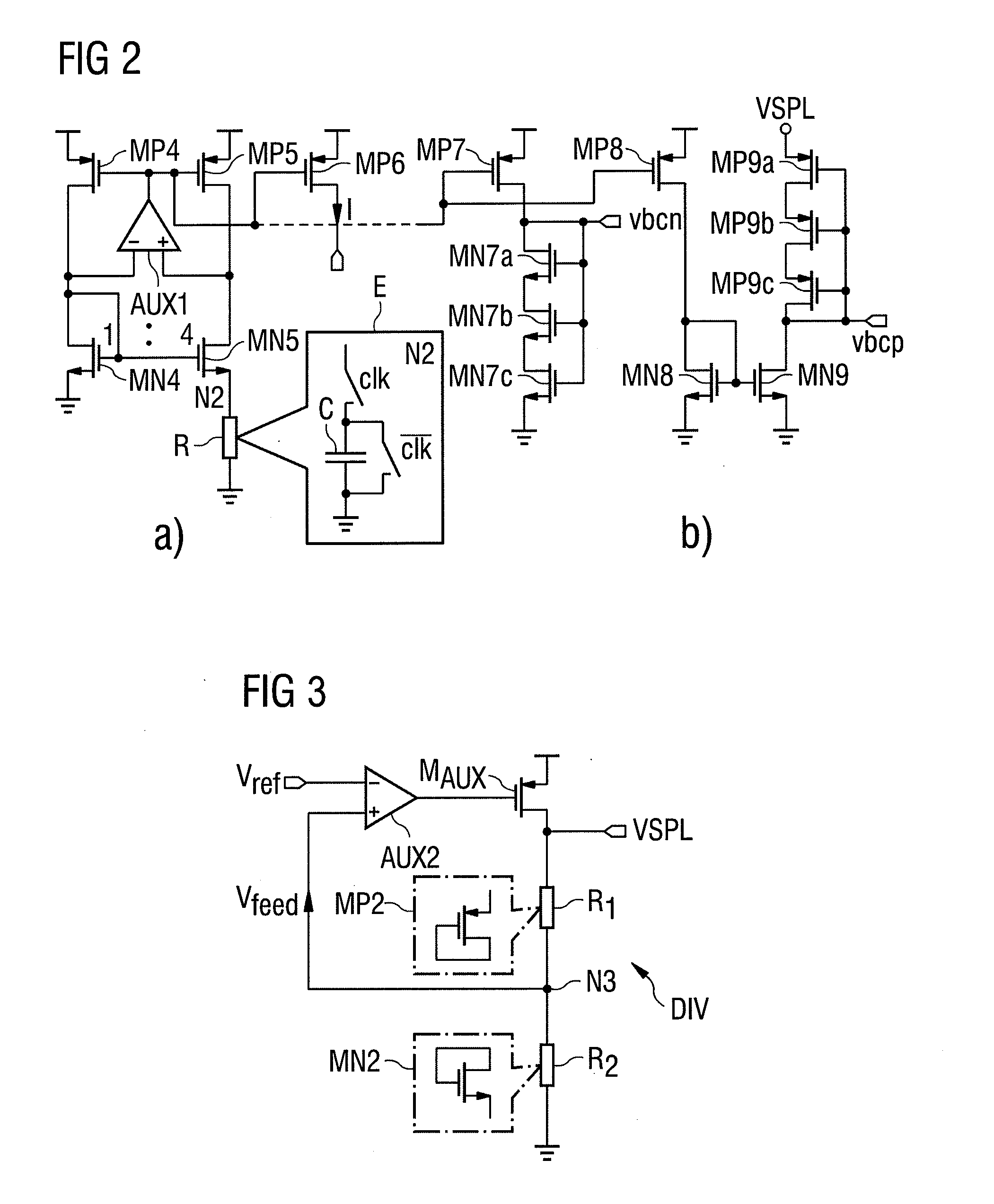
Apparatus and Method for a Voltage Regulator with Improved Power Supply Reduction Ratio (PSRR) with Reduced Parasitic Capacitance on Bias Signal Lines
ActiveUS20150123628A1Reduce the impactReduce impactElectric variable regulationMOSFETReduction ratio
An apparatus and method for a system with improved power supply rejection ratio (PSRR) over a wide frequency range. The improved PSRR is achieved by negating the influence of the parasitic capacitance associated with the bias lines and the introduction of a regulated power supply with embodiments associated with providing a ripple free and regulated supply. With reduction of parasitic capacitance, and providing an ENABLE switch by a pre-regulated supply, the degradation of the PSRR is achieved. The embodiments include both n-channel and p-channel MOSFETs implementations, and a positive and negative regulated power supply voltage. With the combined influence of the utilization of the VREG supply, and the lowering of battery-to-bias line capacitance using design layout and improved floor planning an improved PSRR over a wide frequency distribution is achieved.
Owner:DIALOG SEMICONDUCTOR GMBH
Difference amplifier for regulating voltage
ActiveUS7126316B1Avoid impedanceImprove performancePower supply linesElectric variable regulationCurrent loadDriver circuit
A voltage regulation circuit. The voltage regulator includes an input stage, a reference voltage circuit, a gain stage, and an output stage. The reference voltage circuit is coupled to one input of the input stage, and the output stage is coupled to another input of the input stage. The gain stage includes a buffer device coupled to the output of the input stage and a drive circuit coupled to the output stage. The buffer device is operable to provide isolation between the input stage and the drive circuit. The drive circuit may include a first transistor coupled to the output stage, a base current translation circuit, and a current divide circuit coupled to the first transistor and to said base current translation circuit. The input stage may be biased with a substantially constant bias current, such that output dependent current loading effects are avoided.
Owner:NAT SEMICON CORP
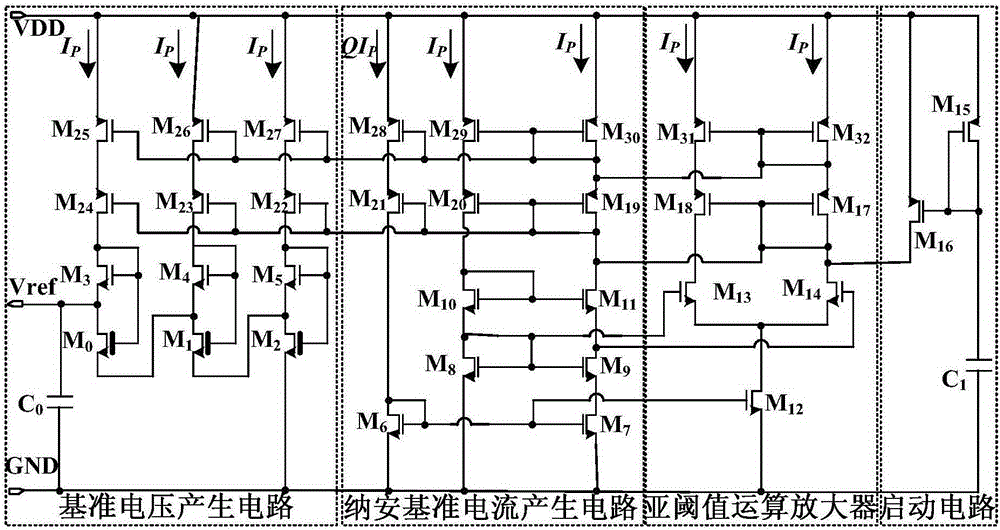
Sub-threshold full CMOS reference voltage source
ActiveCN105278606AHigh rejection ratioReduce layout areaElectric variable regulationReference currentEngineering
The invention discloses a sub-threshold full CMOS reference voltage source. A start-up circuit helps a reference voltage source from getting rid of a degeneration bias point to enter the normal working state. A sub-threshold operation amplifier is ensured to run at low power consumption while being larger in gain at the same time. In this way, the voltage rejection ratio of the power supply is increased. An Nano-ampere reference current generating circuit generates a Nano-ampere-level reference current and suppresses the generation of the noise of the power supply so as to provide a current bias for a reference voltage generating circuit. The reference voltage generating circuit is composed of two MOS tube gate voltage differences of different standard voltages, wherein a reference voltage independent of the temperature is obtained through the coadjustment process. According to the invention, no passive resistor, diode or triode is adopted, and the sub-threshold full CMOS reference voltage source is compatible with the standard CMOS process. Therefore, the layout area is greatly reduced, and the production cost is lowered. The sub-threshold full CMOS reference voltage source is small in power consumption, high in power supply rejection ratio, low in temperature drift coefficient and low in power supply voltage regulation rate.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
Reference voltage generator having a two transistor design
ActiveUS20100327842A1Reduce power consumptionImprove performanceElectric variable regulationVoltage generatorVoltage reference
An improved voltage reference generator is provided. The voltage reference generator comprises: a first transistor having a gate electrode biased to place the first transistor in a weak inversion mode; and a second transistor connected in series with said first transistor and having a gate electrode biased to place the second transistor in a weak inversion mode, where the threshold voltage of the first transistor is smaller than the threshold voltage of the second transistor and the gate electrode of the second transistor is electrically coupled to a drain electrode of the second transistor and the source electrode of the first transistor to form an output for a reference voltage.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Apparatus and method for a voltage regulator with improved power supply reduction ratio (PSRR) with reduced parasitic capacitance on bias signal lines
An apparatus and method for a system with improved power supply rejection ratio (PSRR) over a wide frequency range. The improved PSRR is achieved by negating the influence of the parasitic capacitance associated with the bias lines and the introduction of a regulated power supply with embodiments associated with providing a ripple free and regulated supply. With reduction of parasitic capacitance, and providing an ENABLE switch by a pre-regulated supply, the degradation of the PSRR is achieved. The embodiments include both n-channel and p-channel MOSFETs implementations, and a positive and negative regulated power supply voltage. With the combined influence of the utilization of the VREG supply, and the lowering of battery-to-bias line capacitance using design layout and improved floor planning an improved PSRR over a wide frequency distribution is achieved.
Owner:DIALOG SEMICONDUCTOR GMBH
Low-temperature drift detuning self-calibration operational amplifier circuit and design method thereof
ActiveCN103178789AHigh voltage gainImprove power supply rejection ratioAmplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationDifferential amplifiersPower supply rejection ratioOxide semiconductor
The invention relates to a low-temperature drift detuning self-calibration operational amplifier circuit and a design method of the low-temperature drift detuning self-calibration operational amplifier circuit. The low-temperature drift detuning self-calibration operational amplifier circuit comprises two gain units, a biased module, three capacitors, a current source, six switches, four P-type metal oxide semiconductor (MOS) pipes and five N-type MOS pipes, wherein each gain unit comprises a capacitor, two resistors, a switch, ten P-type MOS pipes and four N-type MOS pipes. A folded cascade structure is adopted to be used as a gain stage of an amplifier so that high voltage gain and a high power supply rejection ratio can be obtained. Due to the fact that the MOS capacitor is adopted to store, operate and amplify detuning information caused by technology variation, and the detuning information is successively and automatically calibrated when a closed loop is used, low direct current detuning is achieved. A lower temperature coefficient is achieved by adoption of a temperature compensation technology. A high drive capability is obtained by adoption of push-pull output of an AB class.
Owner:西安航天民芯科技有限公司
Low-dropout linear regulator circuit with high power supply rejection ratio
InactiveCN109683651AImprove power supply rejection ratioSimple structureElectric variable regulationLinear regulatorCapacitance
The invention provides a low-dropout linear regulator circuit with a high power supply rejection ratio, and belongs to the field of analog circuit integration. The low-dropout linear regulator circuitcomprises a bias module, an error amplifier, a buffer and an output stage, wherein the bias module provides bias voltage; a positive input end of the error amplifier is connected to reference voltage, a negative input end of the error amplifier is connected to feedback voltage, and an output end of the error amplifier passes through the buffer and the output stage to be connected to an output endof an LDO; the buffer comprises an amplification stage, a high-pass filter and a current source, and the amplification stage is connected between an input end and output end of the buffer; the current source is connected between power supply voltage and the output end of the buffer; the high-pass filter comprises a first NMOS transistor, a first PMOS transistor, a second PMOS transistor and a first capacitor, a grid electrode of the first PMOS transistor is connected with the bias voltage, a source electrode of the first PMOS transistor is connected with power supply voltage and is connectedto a drain electrode of the first PMOS transistor, a grid electrode of the second PMOS transistor and a grid electrode and drain electrode of the first NMOS transistor after passing through the firstcapacitor; a source electrode of the second PMOS transistor is connected with the output end of the buffer, and a drain electrode of the second PMOS transistor is connected with a source electrode ofthe first NMOS transistor and is grounded. The low-dropout linear regulator circuit with the high power supply rejection ratio improves the power supply rejection ratio.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Voltage level shift circuit and semiconductor integrated circuit
ActiveUS7564289B2Improve power supply rejection ratioPulse automatic controlElectric pulse generatorCascodeEngineering
Provided is a voltage level shift circuit including: a first voltage level shift circuit formed of a P-channel enhancement type transistor (M1) and an N-channel depletion type MOS transistor (M3); and a second voltage level shift circuit formed of a P-channel enhancement type transistor (M2) and an N-channel depletion type MOS transistor (M4). In the voltage lever shift circuit, a cascode circuit using an N-channel depletion type transistor (M5) is serially connected to the first voltage level shift circuit, a cascode circuit using an N-channel depletion type transistor (M6) is serially connected to the second voltage level shift circuit, and a unit for complementarily controlling bias voltages of the respective cascode circuits. As a result, an output signal of the voltage level shift circuit connected to an input of a differential amplifier circuit, for expanding an input voltage range of a signal, is not affected by fluctuations in power supply voltage.
Owner:ABLIC INC
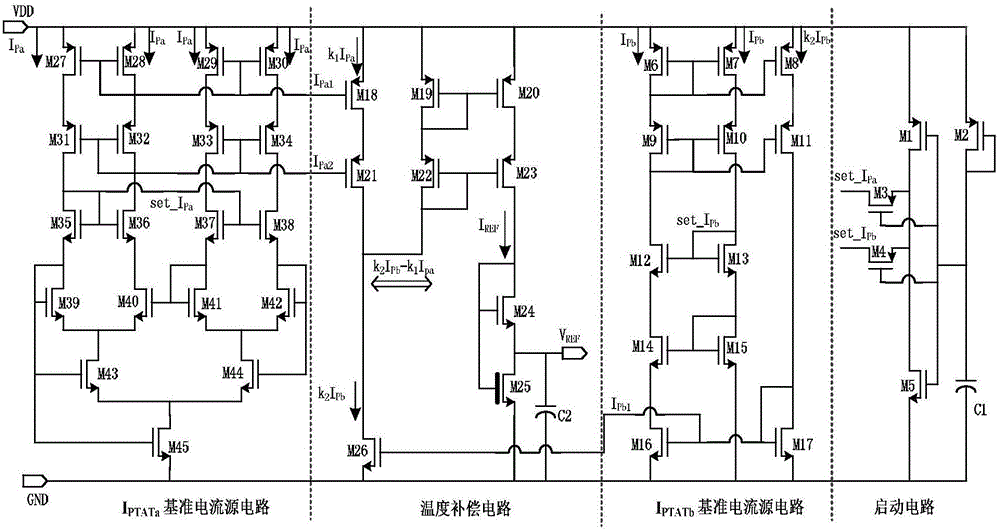
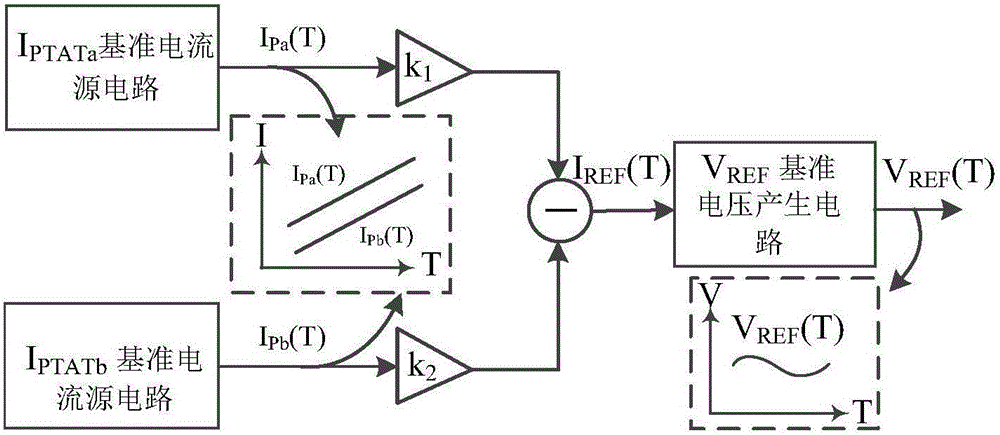
Low-voltage nanowatt-scale full CMOS current mode reference voltage source
ActiveCN106527559AReduce power consumptionReduce layout areaElectric variable regulationReference currentLow voltage
The invention discloses a low-voltage nanowatt-scale full CMOS current mode reference voltage source. The reference voltage source is characterized by comprising a starting circuit, an IPTATa reference current source circuit, an IPTATb reference current source circuit and a temperature compensating circuit, wherein the starting circuit is connected to the IPTATa reference current source circuit and the IPTATb reference current source circuit and is used for supplying current when the reference voltage source is started so as to deviate the reference voltage source from a degeneration bias point; the IPTATa reference current source circuit and the IPTATb reference current source circuit respectively generate a bias current to supply current bias to the temperature compensating circuit; and the temperature compensating circuit is used for making difference on the two bias currents in different multiples to obtain a temperature-irrelevant reference current and driving an MOS pipe in the temperature compensating circuit to obtain an output voltage which is not influenced by the supply voltage and the temperature change. The reference voltage source has the characteristics that the power consumption is low, the layout area is small, devices are matched with a standard CMOS process, the temperature coefficient is low, and the suppression ratio of the supply voltage is high.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
Current-controlled oscillator
InactiveUS20060022760A1Extended linear gainImprove stabilityGenerator stabilizationPulse generation by logic circuitsElectrical resistance and conductanceElectricity
The present invention provides a current controlled oscillator comprising a first section providing a first differential output and a second section providing a second differential output. A loading structure comprised of resistive and reactive elements electrically connects the first differential output with the second differential output. The resistive and reactive elements have values chosen such that the resistive elements substantially extend the linear operating frequency range of the current controlled oscillator. Transistors of the loading structure have which are tied to a power supply rejection ratio compensation section for compensating for variations in power supply voltage.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
High order temperature supplementary band gap reference circuit
InactiveCN101604175ASmall temperature coefficientImprove power supply rejection ratioElectric variable regulationTemperature coefficientPower supply rejection ratio
The invention discloses a high order temperature supplementary band gap reference circuit, comprising a band gap reference main circuit, a feedback control loop and an output circuit, wherein the band gap reference main circuit consists of six PMOS tubes, two NMOS tubes, three resistances and two PNP triodes, the feedback control loop consists of two PMOS tubes, two NMOS tubes and two PNP triodes, and the output circuit consists of two PMOS tubes and four resistances. The circuit of the invention has lower temperature coefficient, higher power supply rejection rate as well as higher process stability.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
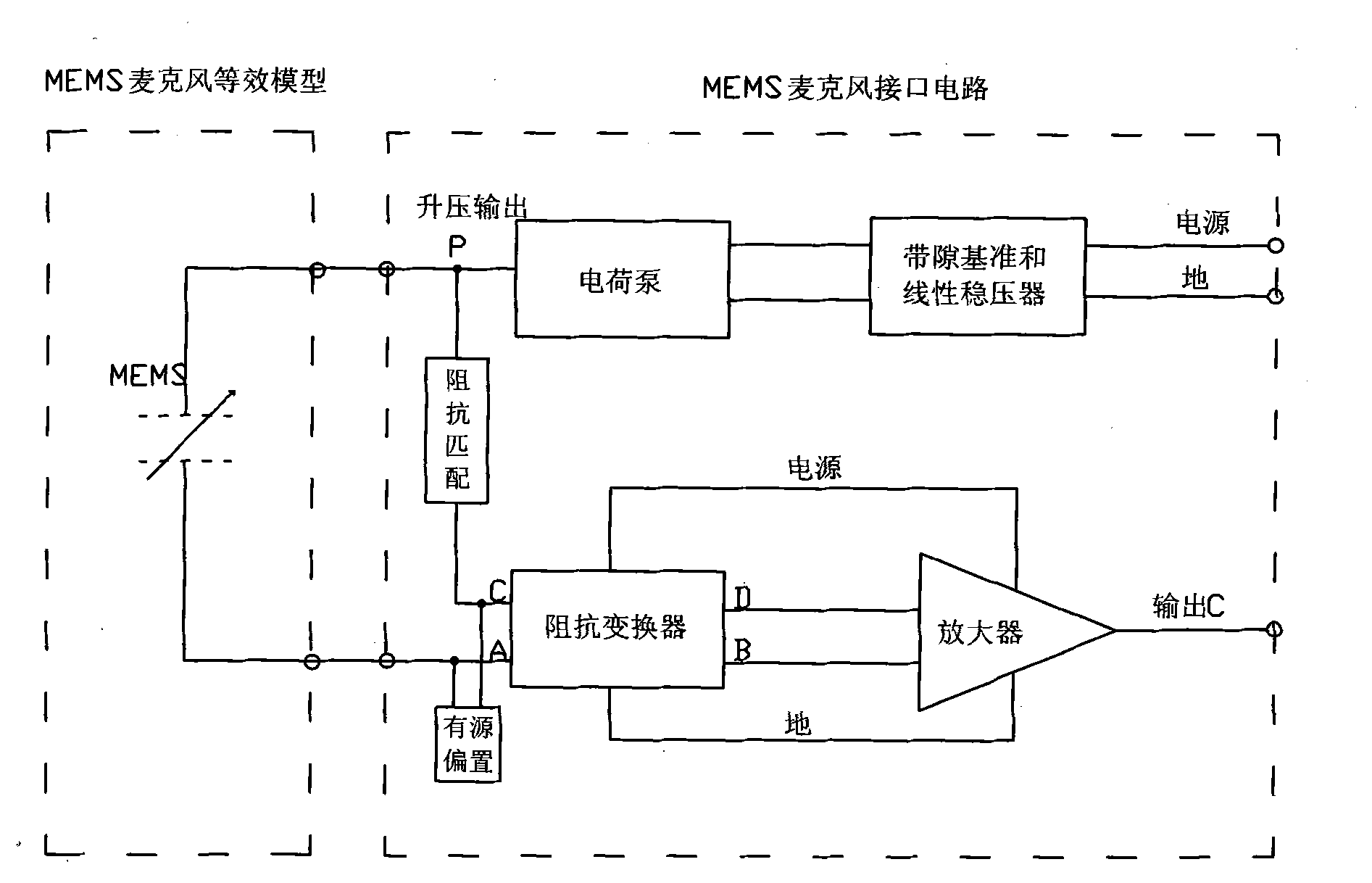
Microphone interface circuit
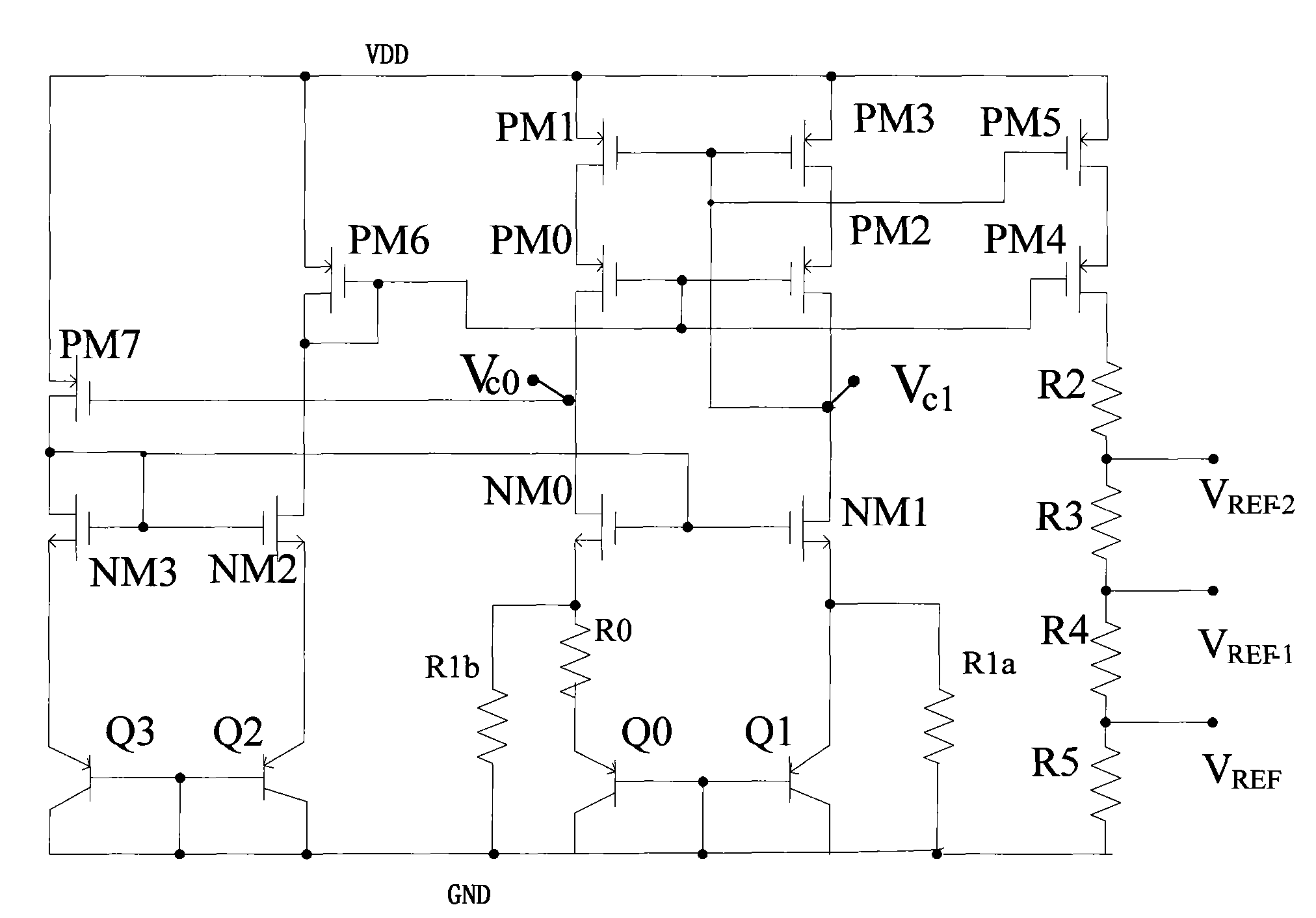
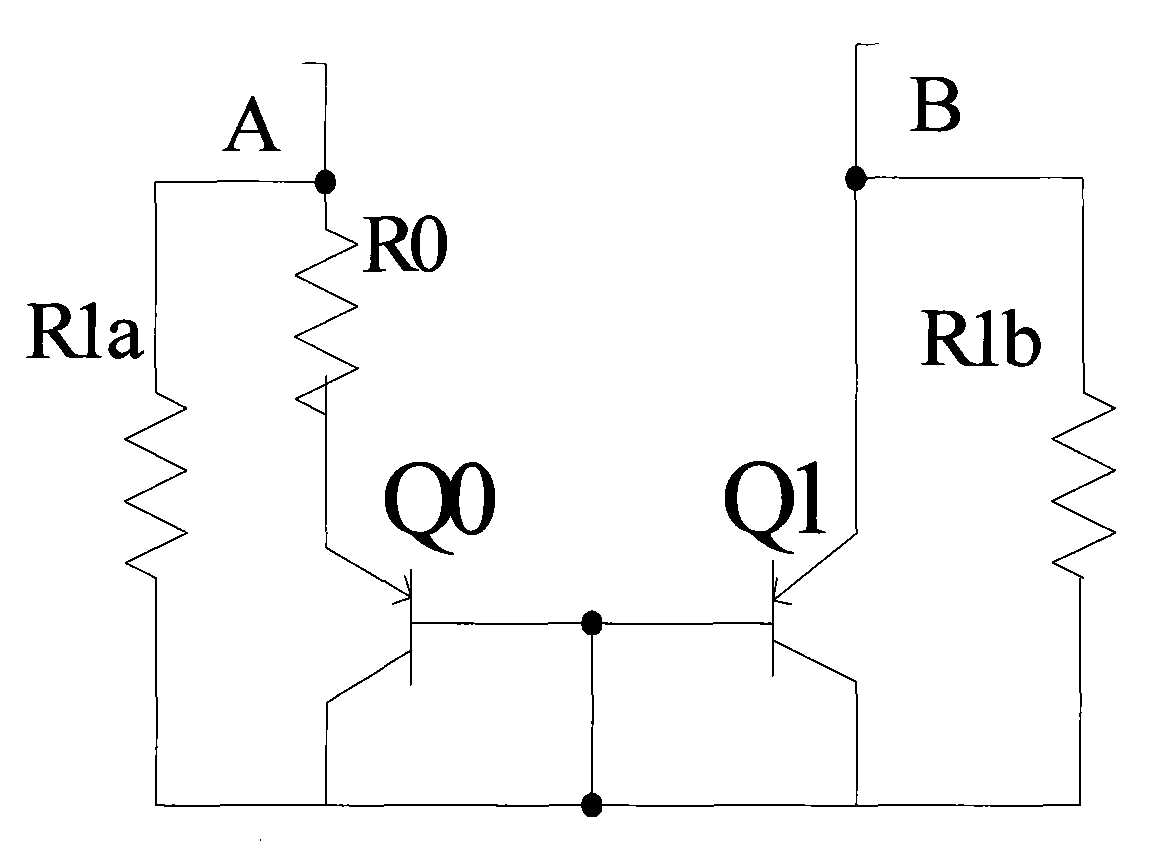
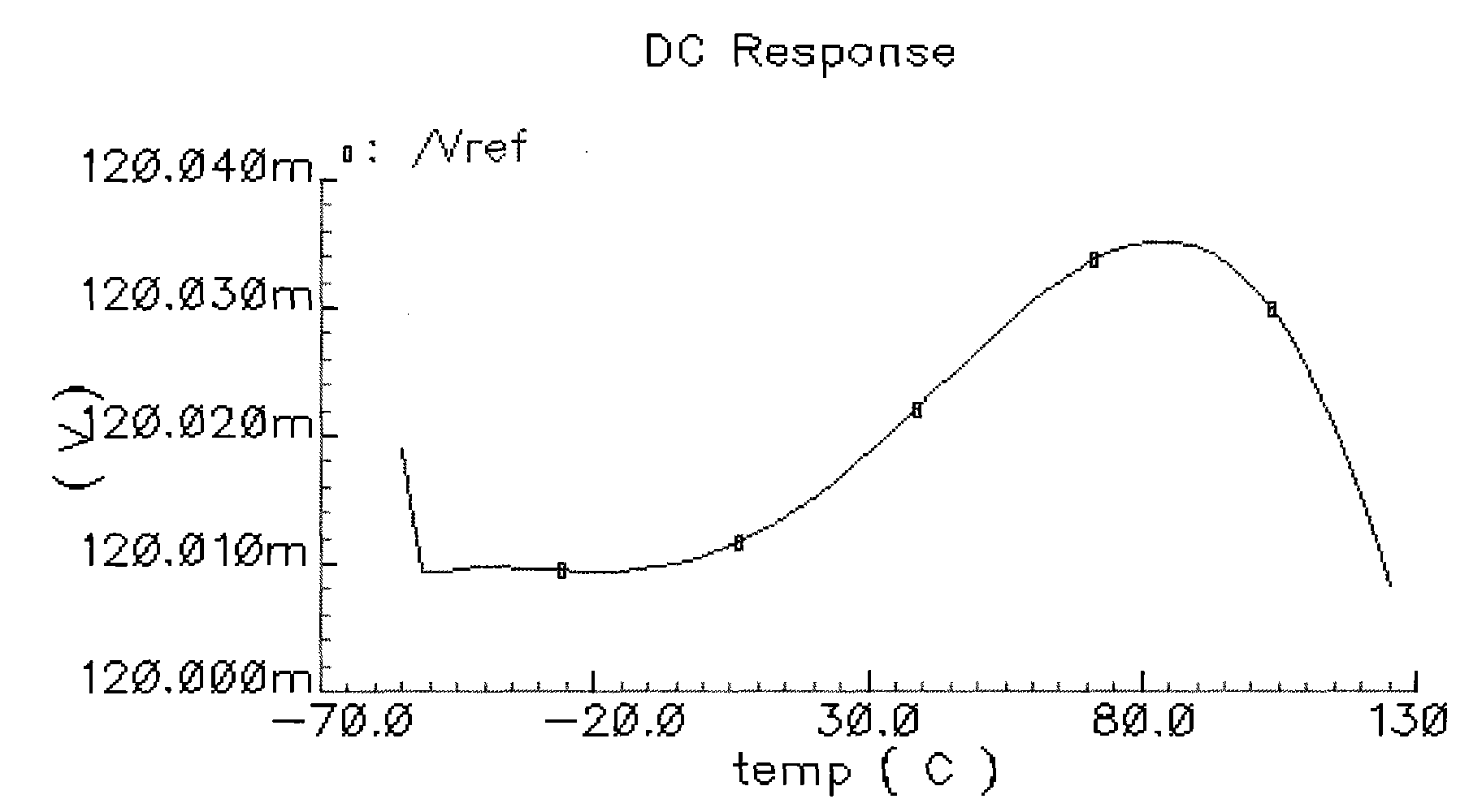
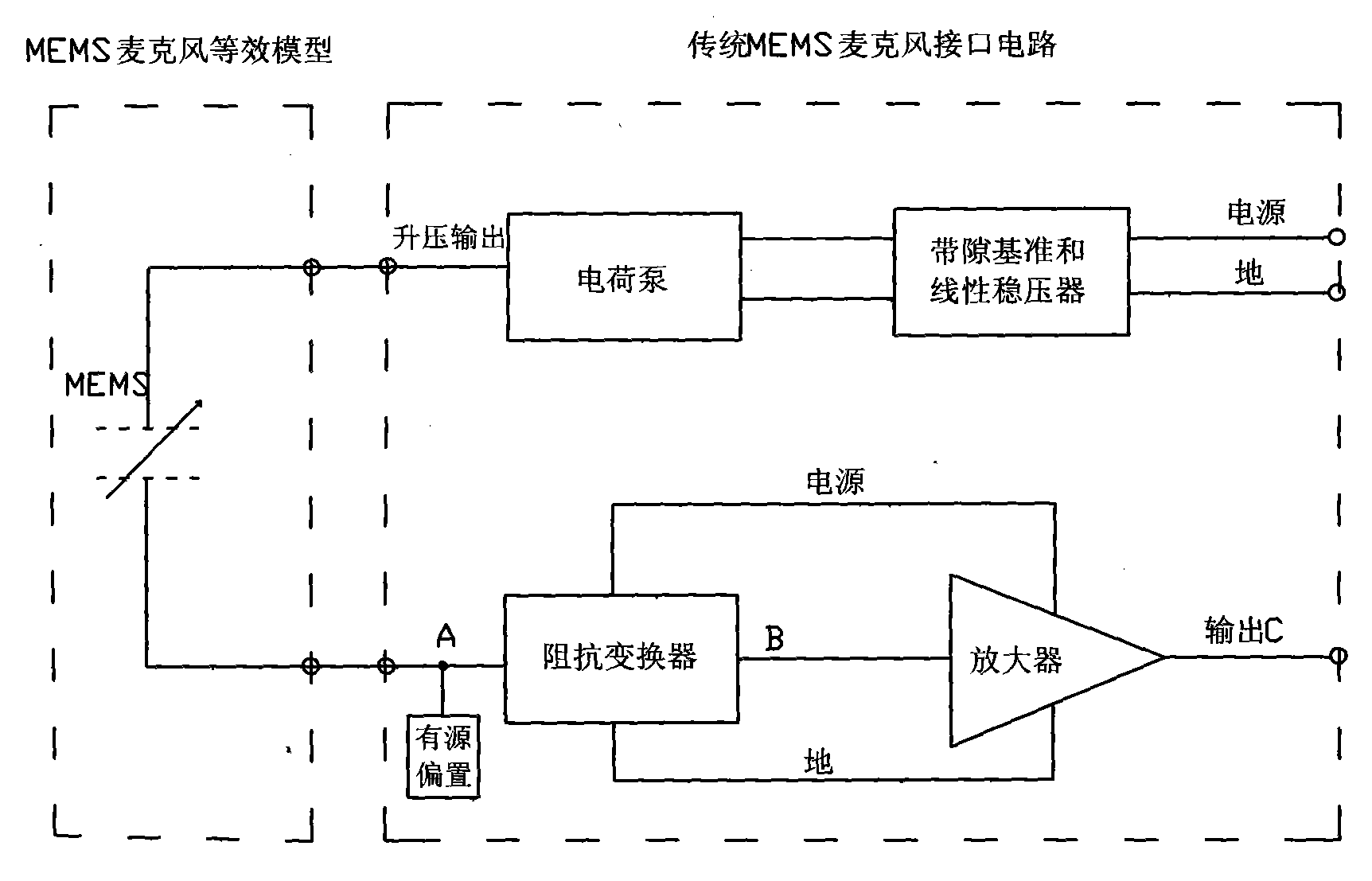
ActiveCN101902673ACancel noiseImprove power supply rejection ratioTransducer circuitsImpedance transformerPower supply rejection ratio
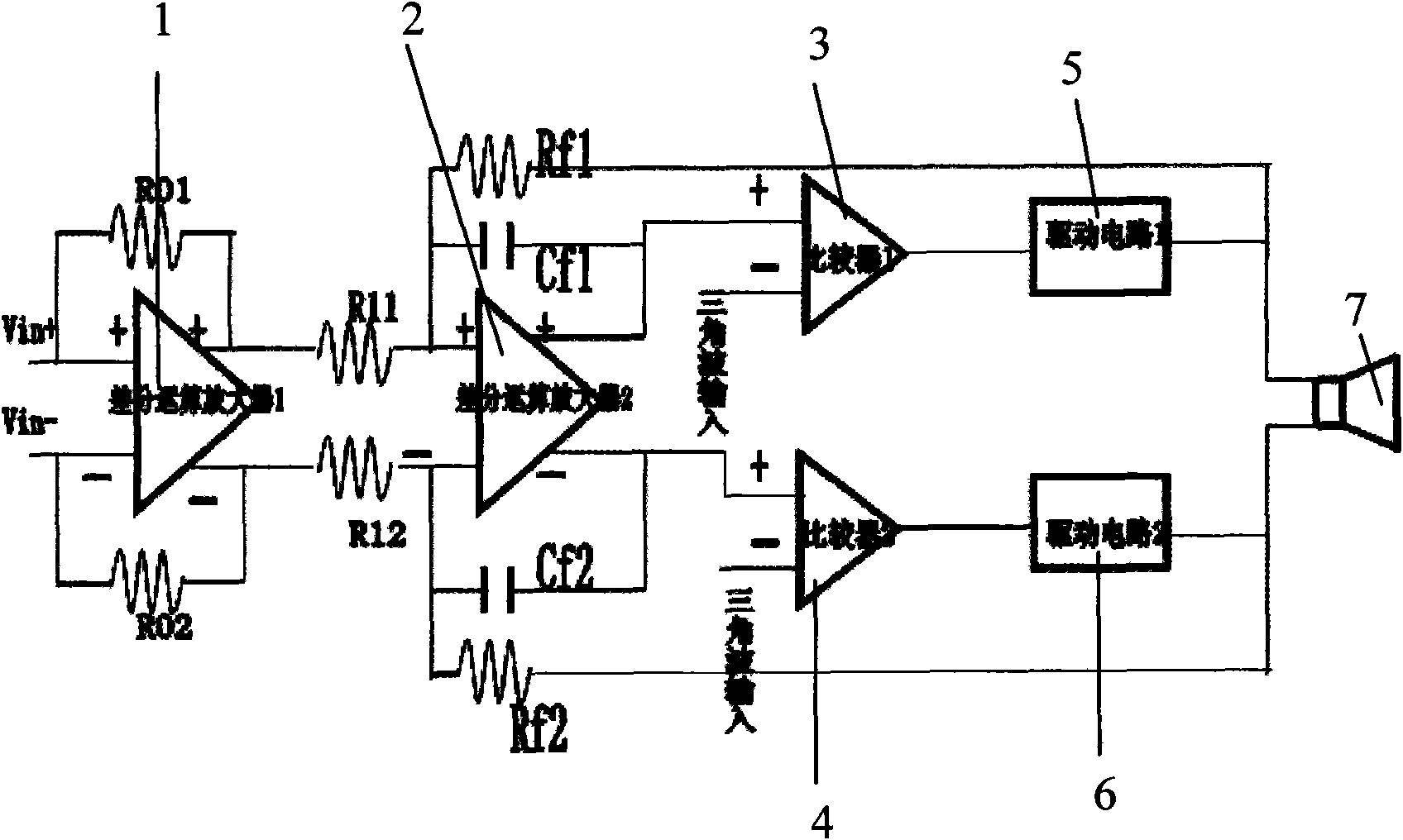
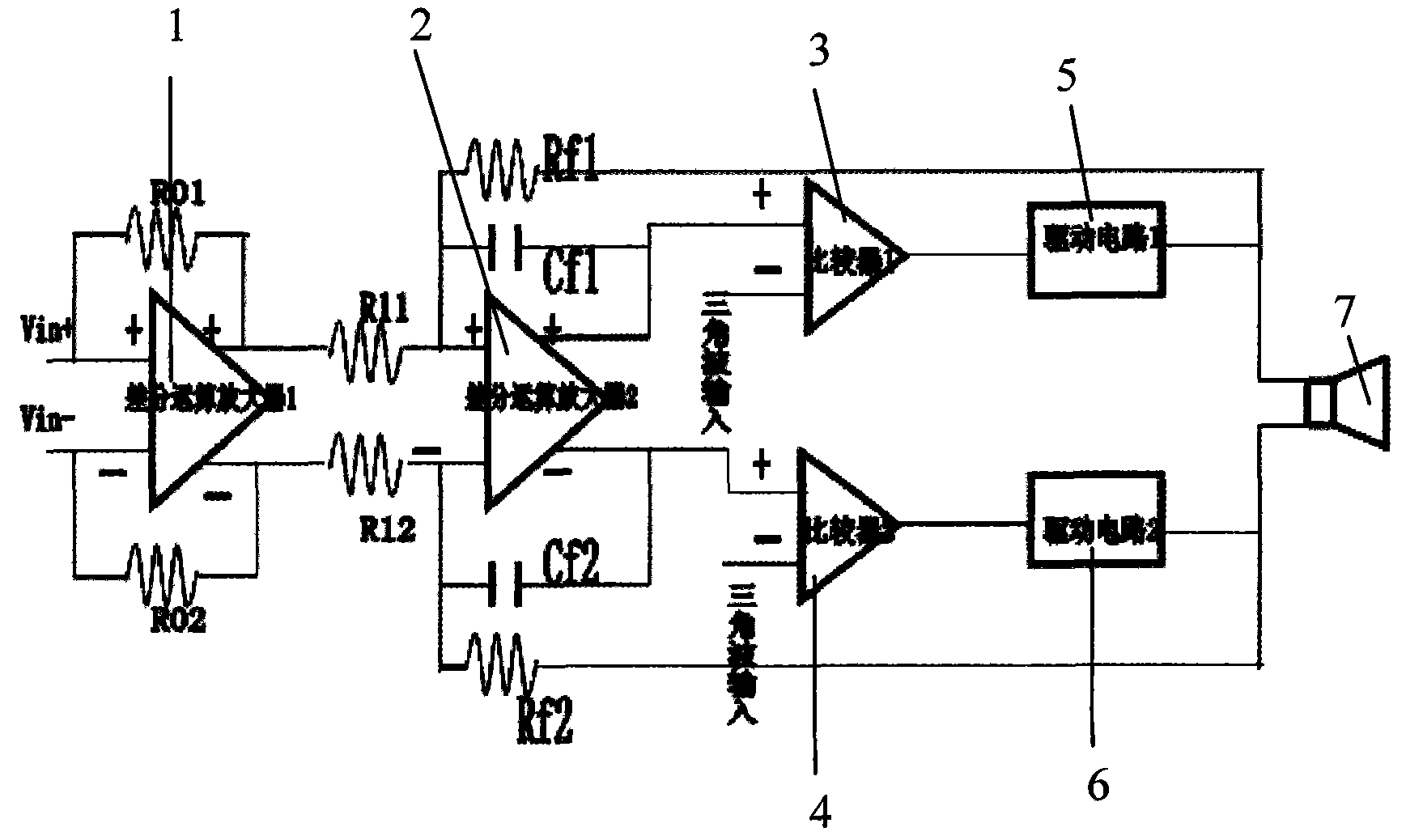
The invention provides a microphone interface circuit, comprising a power supply module, a resistance convertor and an amplifier, wherein the power supply module provides working voltage for a microphone via a first node; the impedance transformer is provided with a first input end and a second input end, receives an output signal of the microphone; the amplifier is coupled between the impedance transformer and the output end of the microphone interface circuit; and a impedance matcher is coupled between the first node and the second input end of the resistance convertor. The invention can well improve rejection ratio of the power supply, effectively eliminate noise signals and enhance the tone quality of the microphone.
Owner:AAC ACOUSTIC TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
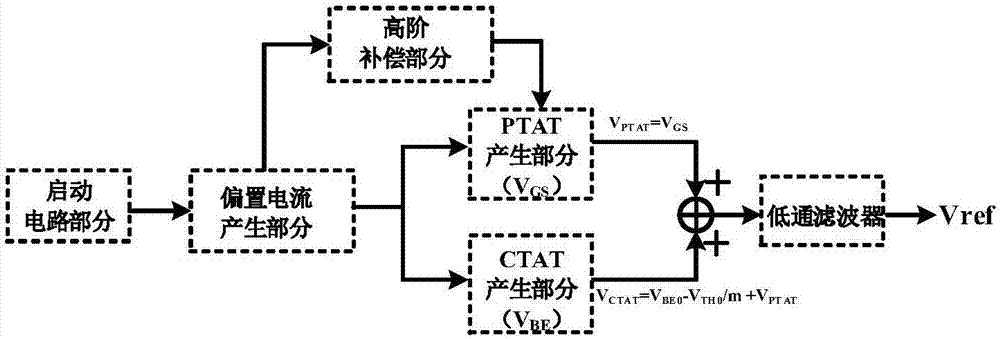
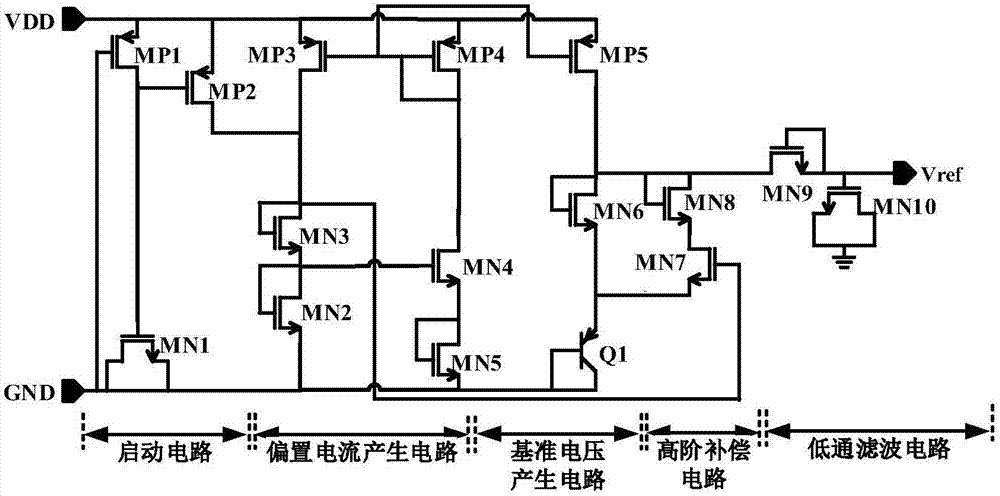
No-resistor-type high-precision low-power-consumption reference source
ActiveCN107340796AGood temperature characteristicsImprove power supply rejection ratioElectric variable regulationElectrical resistance and conductanceNegative temperature
The invention provides a no-resistor-type high-precision low-power-consumption reference source, and belongs to the technical field of power management. A starting circuit enables a reference circuit to work normally during the circuit initialization phase, and reference current generated by a bias current generating circuit is used as the bias current of a reference voltage generating circuit, and meanwhile used as the bias current of a high order compensation circuit; the generated bias current can achieve high order compensation and meet self-bias demands; in the reference voltage generating circuit, the negative temperature coefficient voltage generating part uses the bias current as the collector current of a BJT, and compared with the traditional VBE, an obtained negative temperature coefficient voltage VCTAT greatly reduces the negative temperature characteristics of the VBE; a positive temperature coefficient voltage VPTAT and the negative temperature coefficient voltage VCTAT are superposed to obtain the reference voltage. In addition, the high order compensation circuit is introduced to obtain the reference voltage with better temperature characteristics, and the output part is added with a low-pass filter circuit to improve the power supply rejection ratio PSRR of the reference circuit. The reference source can achieve nanowatt-level power dissipation, and no resistance is arranged, which reduces the chip area.
Owner:天津应大科讯电气设备有限公司
High power supply rejection ratio (PSRR) reference source circuit with adjustable output
InactiveCN101598953AImprove power supply rejection ratioElectric variable regulationPower supply rejection ratioEngineering
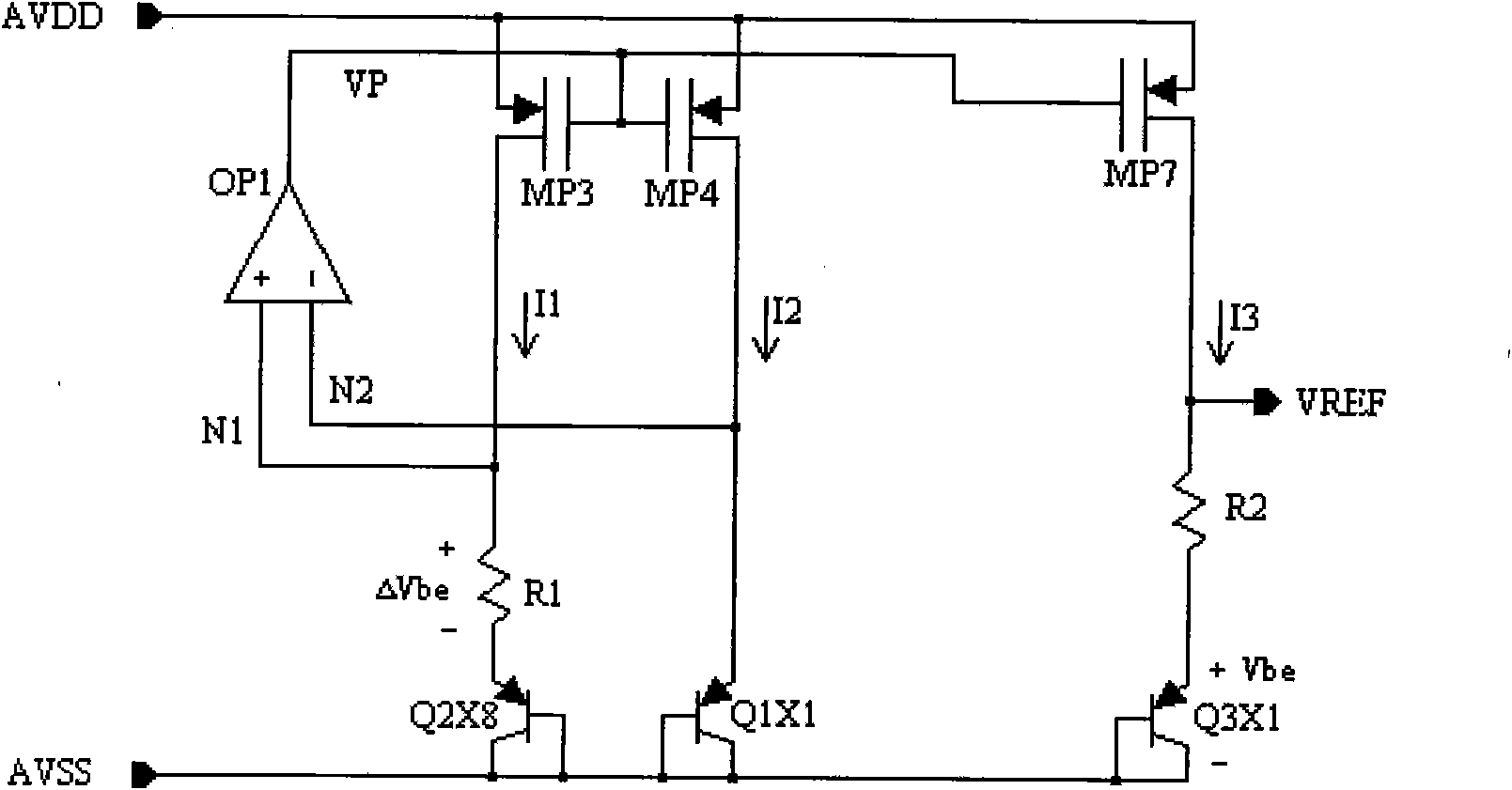
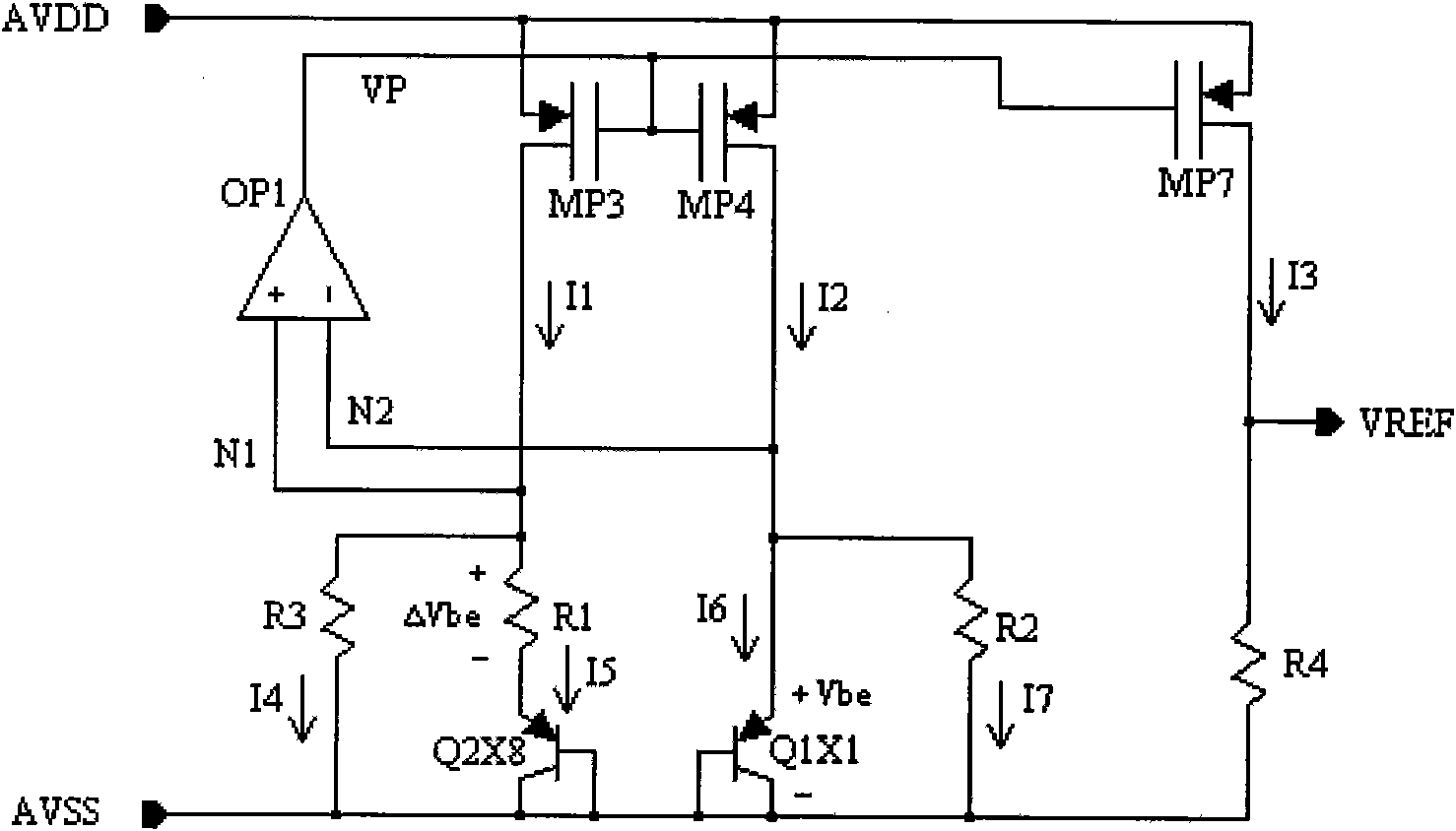
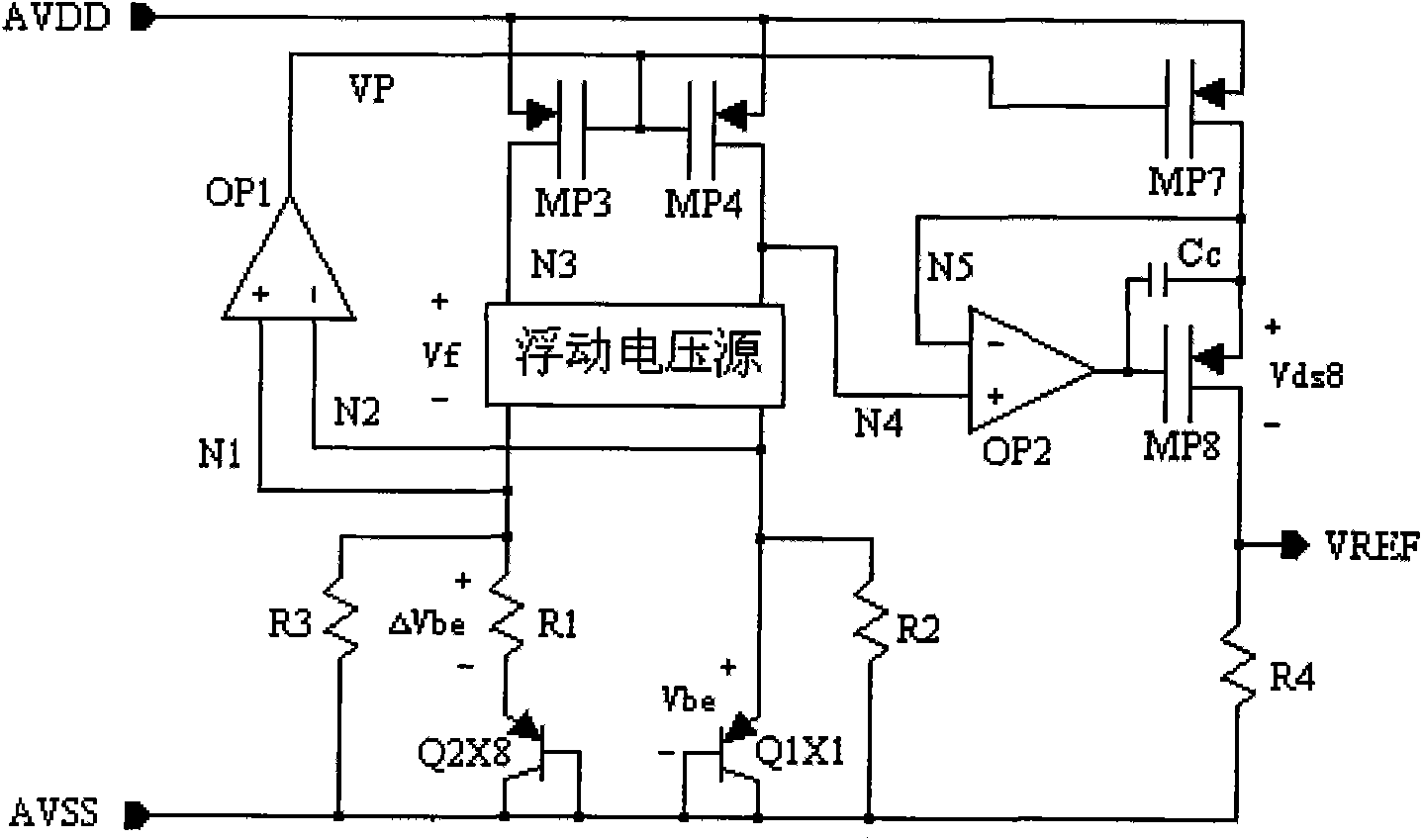
The invention discloses a high PSRR reference source circuit with adjustable output, comprising a generating circuit of a reference source circuit and a first grade circuit for PSRR increase. The circuit is characterized in that a floating voltage source is arranged in the generating circuit of the reference source circuit, a gain increase grade is arranged on a reference voltage output circuit, and the floating voltage source provides proper bias voltage for the gain increase grade so that the gain increase grade can competely work in a saturation region and the reference source circuit can have high PSRR in the entire VREF output region; and the floating voltage source and the gain increase grade guarantee that the reference source circuit can always have high PSRR during the output of wide range of VREF (higher than 1.2V).
Owner:IPGOAL MICROELECTRONICS (SICHUAN) CO LTD
Fast transient response bandgap reference circuit with high power supply rejection ratio
InactiveCN107656568AOptimizing Load RegulationImprove power supply rejection ratioElectric variable regulationLoop controlLoad regulation
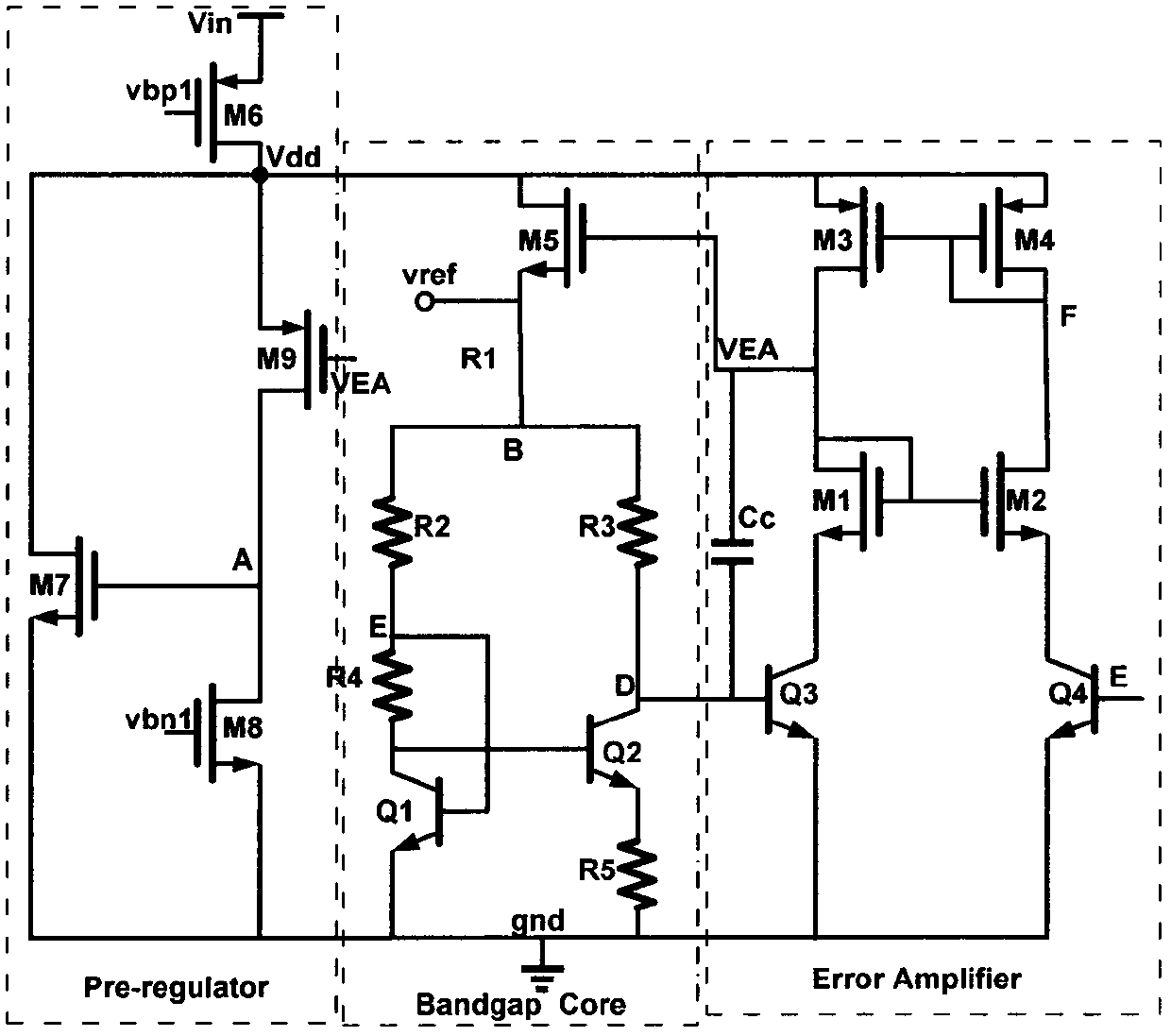
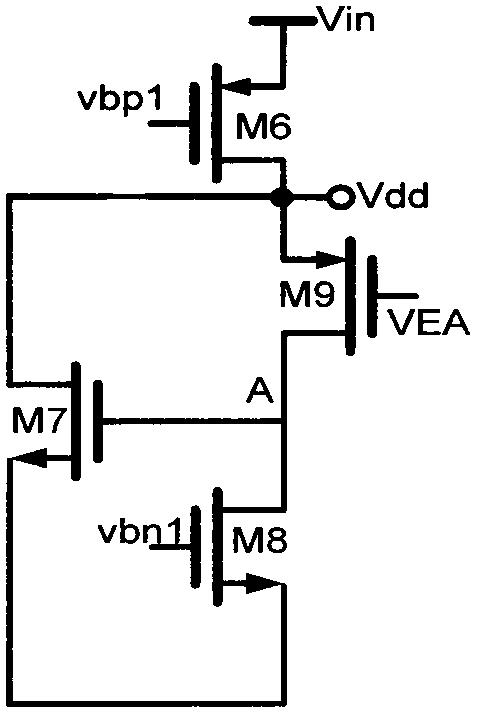
The invention belongs to the technical field of analog integrated circuits, and relates to a bandgap reference circuit with fast transient response and high power supply rejection ratio, including a bandgap reference core circuit (Bandgap Core), an error amplifier (Error Amplifier), a voltage pre-adjustment circuit ( Pre-regulator). Technically, the dual-loop control strategy combining the Widlar reference and the Kuijk reference is mainly used to improve the load regulation rate and transient response speed; in addition, the present invention also introduces the voltage pre-adjustment technology, which effectively realizes the traditional bandgap Improvement of reference circuit power supply rejection ratio.
Owner:刘阳
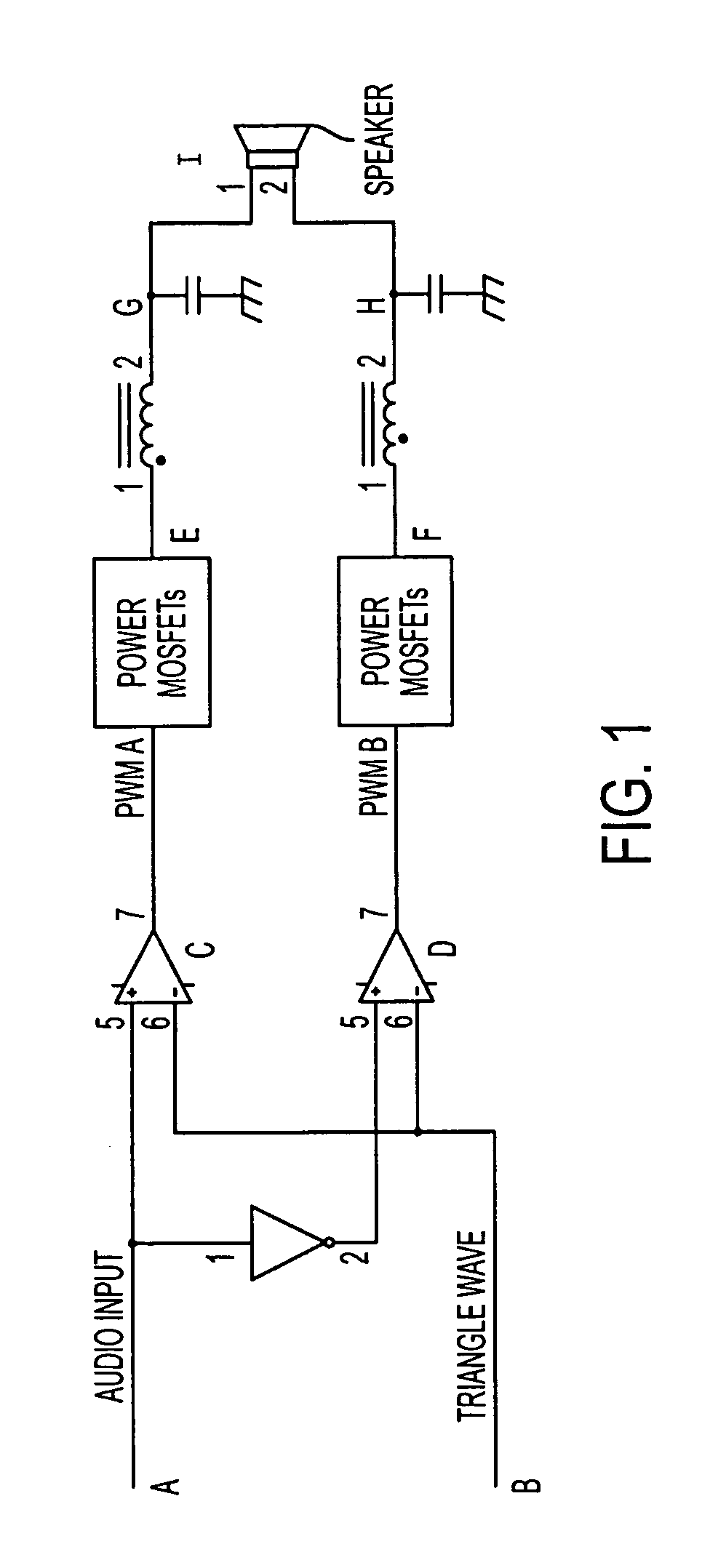
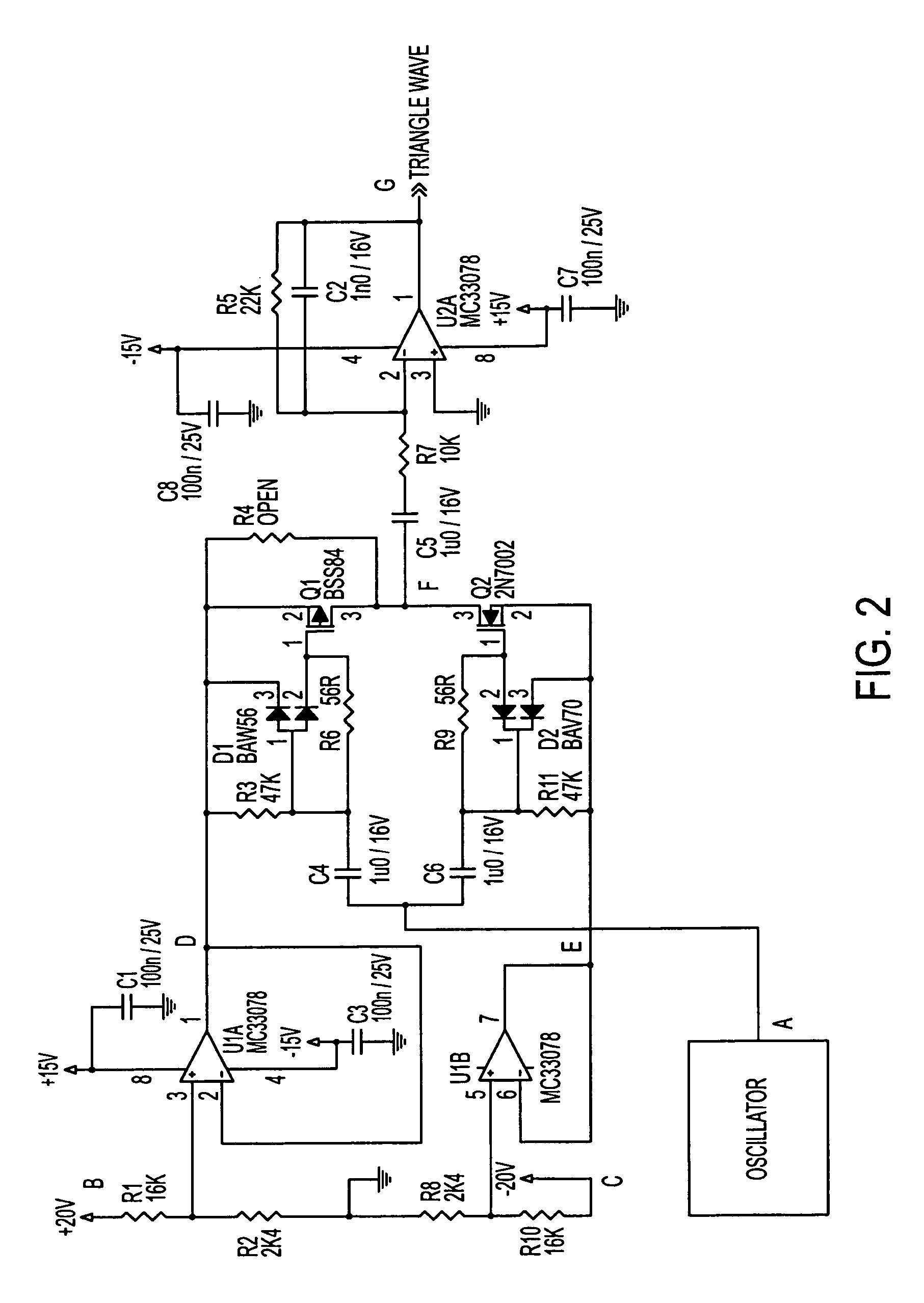
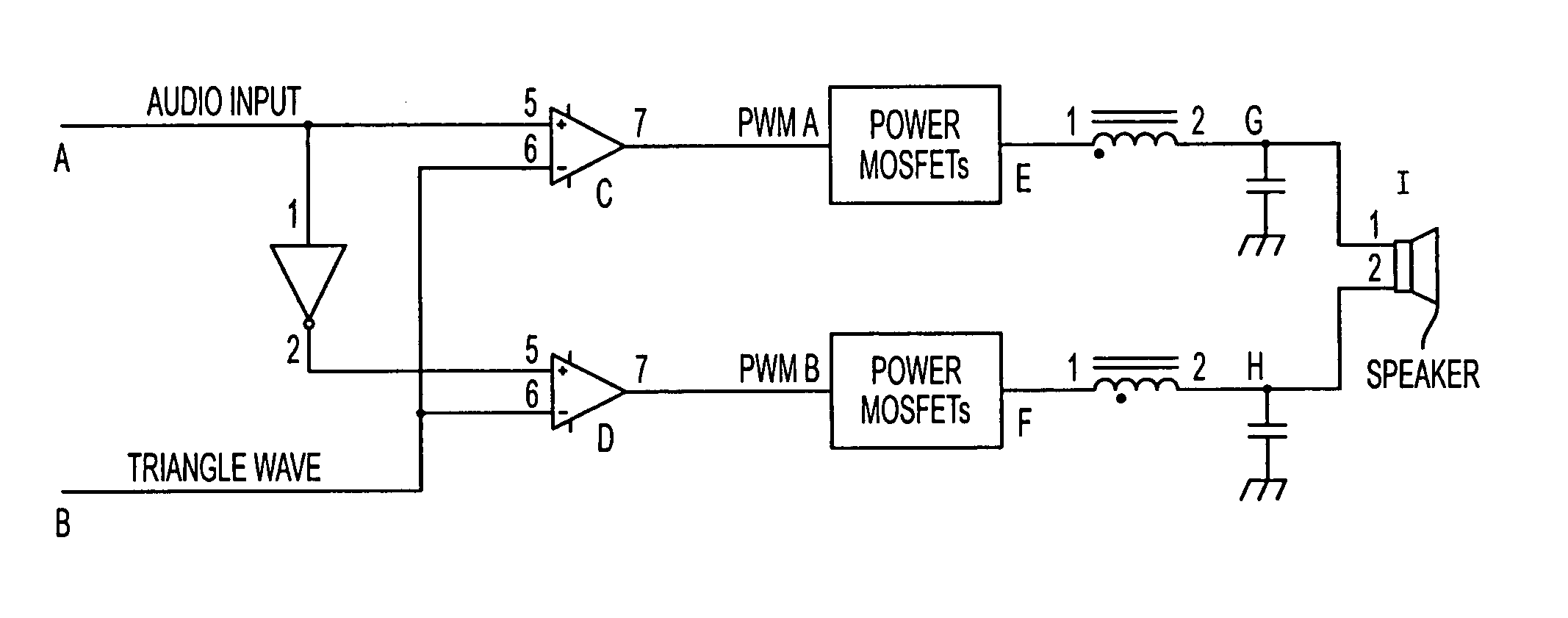
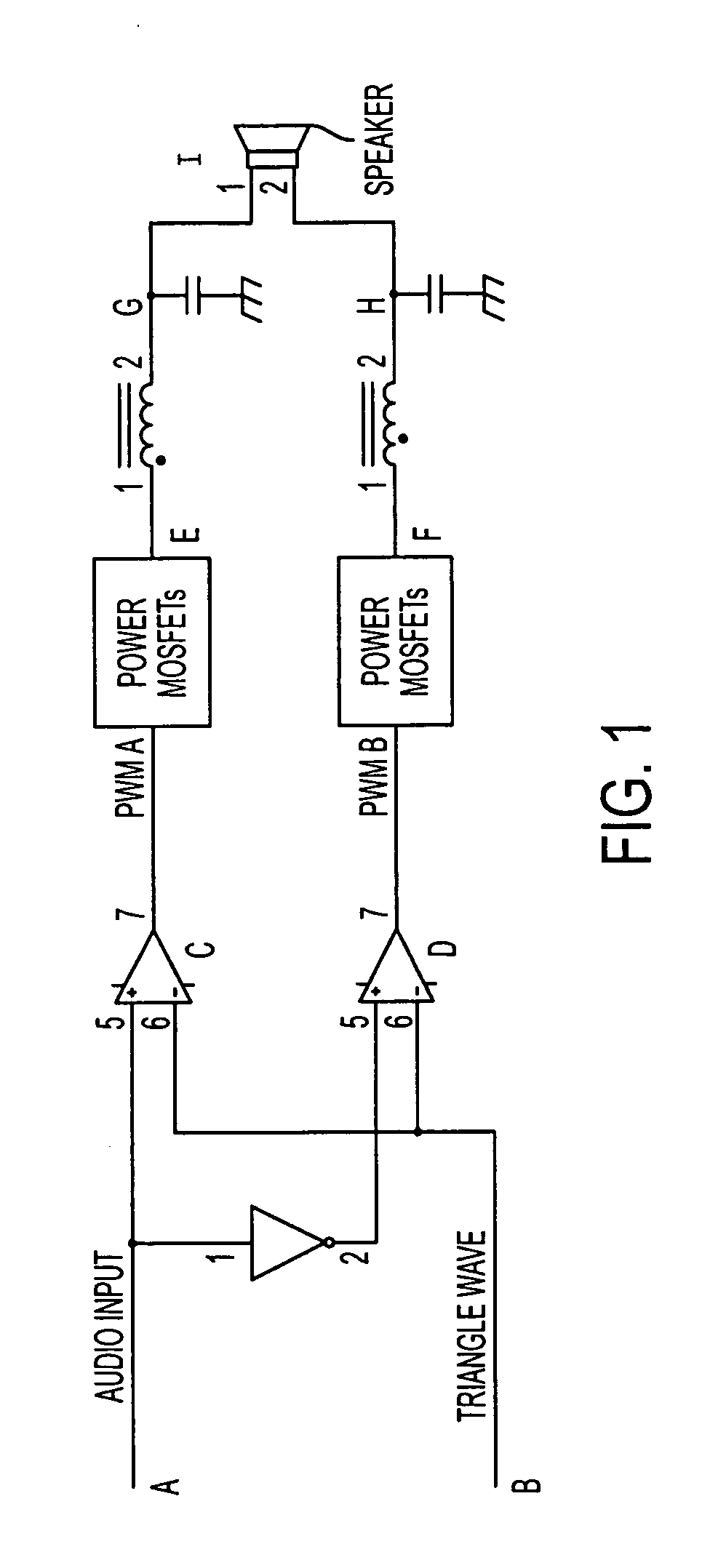
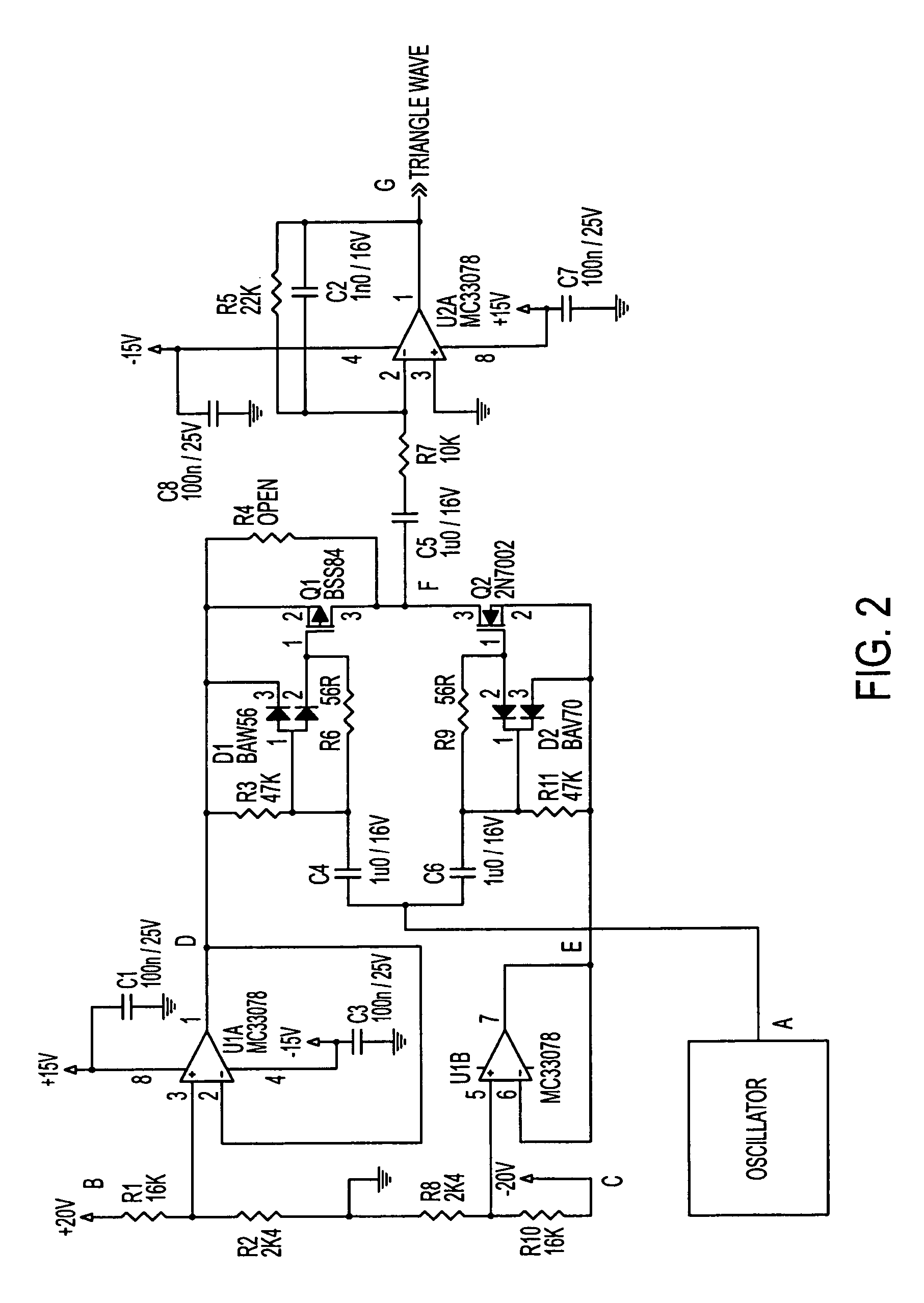
Power supply rejection for pulse width modulated amplifiers and automatic gain control
InactiveUS7135922B2Improve power supply rejection ratioImproved power supply rejectionAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsAutomatic controlClass-D amplifier
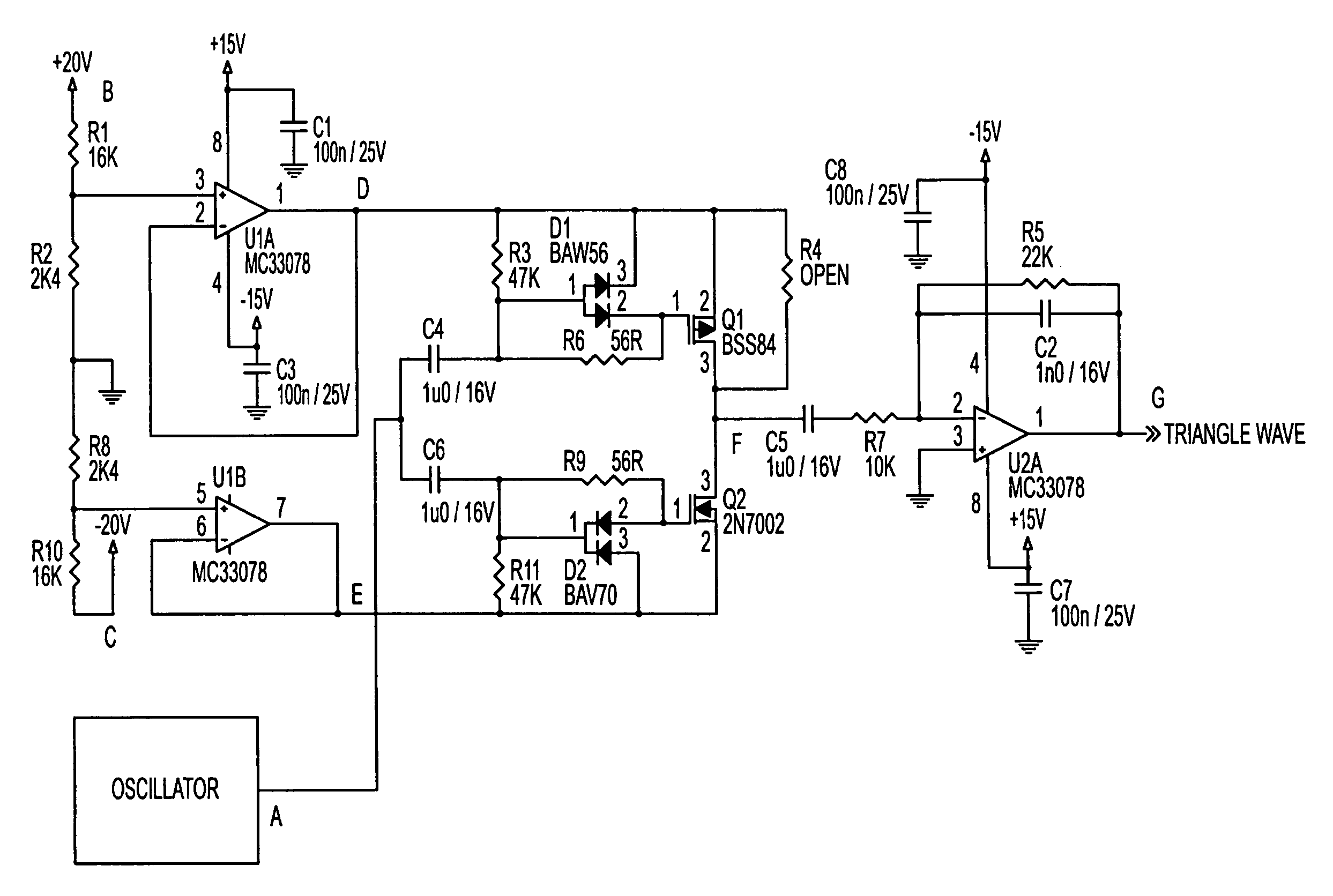
A circuit according to the present invention improves the power supply rejection ratio for a pulse width modulated digital amplifier and can be used as a compressor and / or limiter. The circuit preferably operates by using voltage level translation to vary the amplitude of a triangle wave in response to changes in power supply voltage prior to input of the wave into a comparator of the PWM device. Because the circuit operates to improve power supply rejection, little or no distortion is introduced into the signal when used as a compressor and / or limiter. Additionally, the circuit is optionally implemented in a Class D amplifier, and provides a lower cost of implementation than conventional designs in such implementations.
Owner:ALTEC LANSING LLC
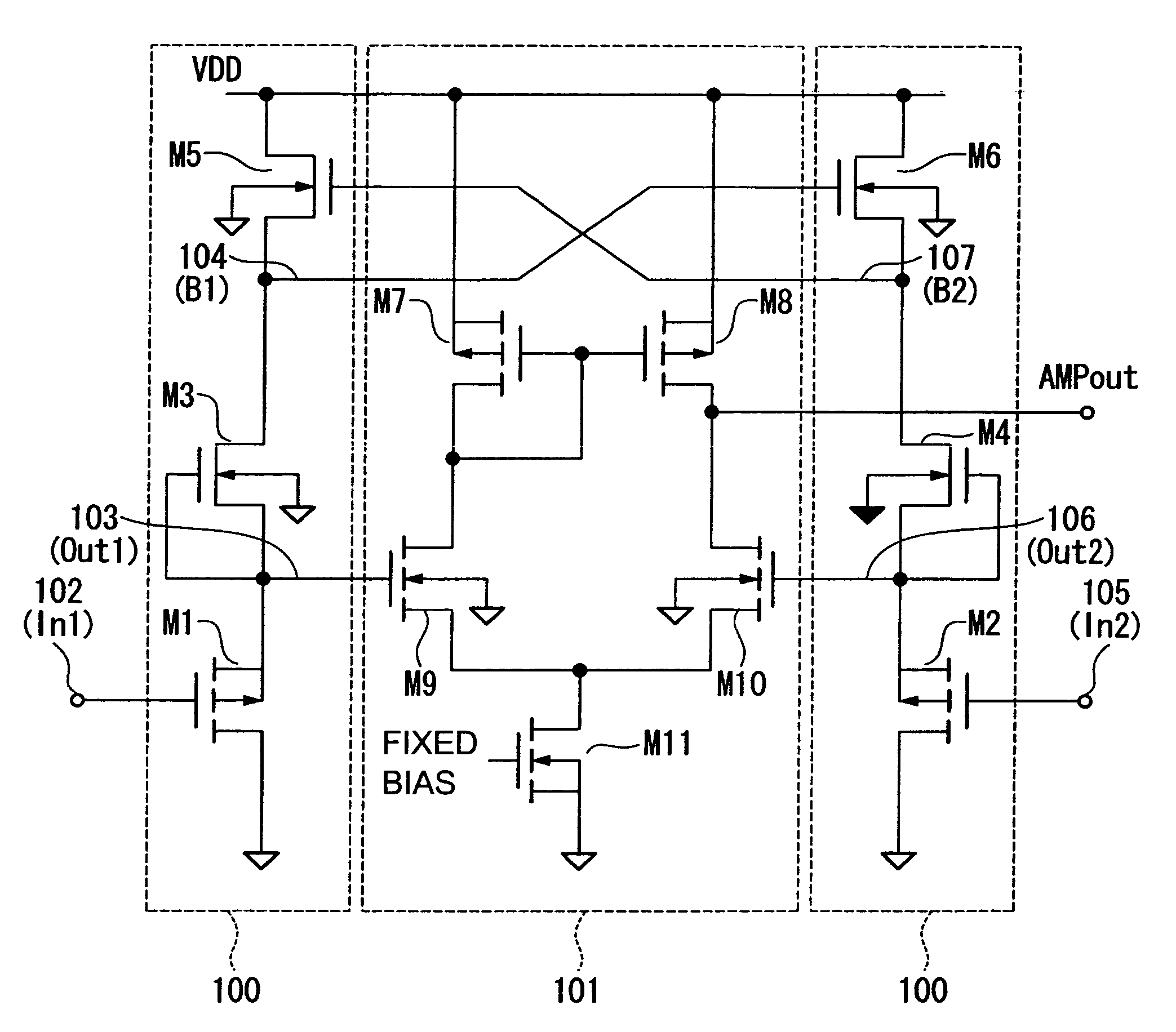
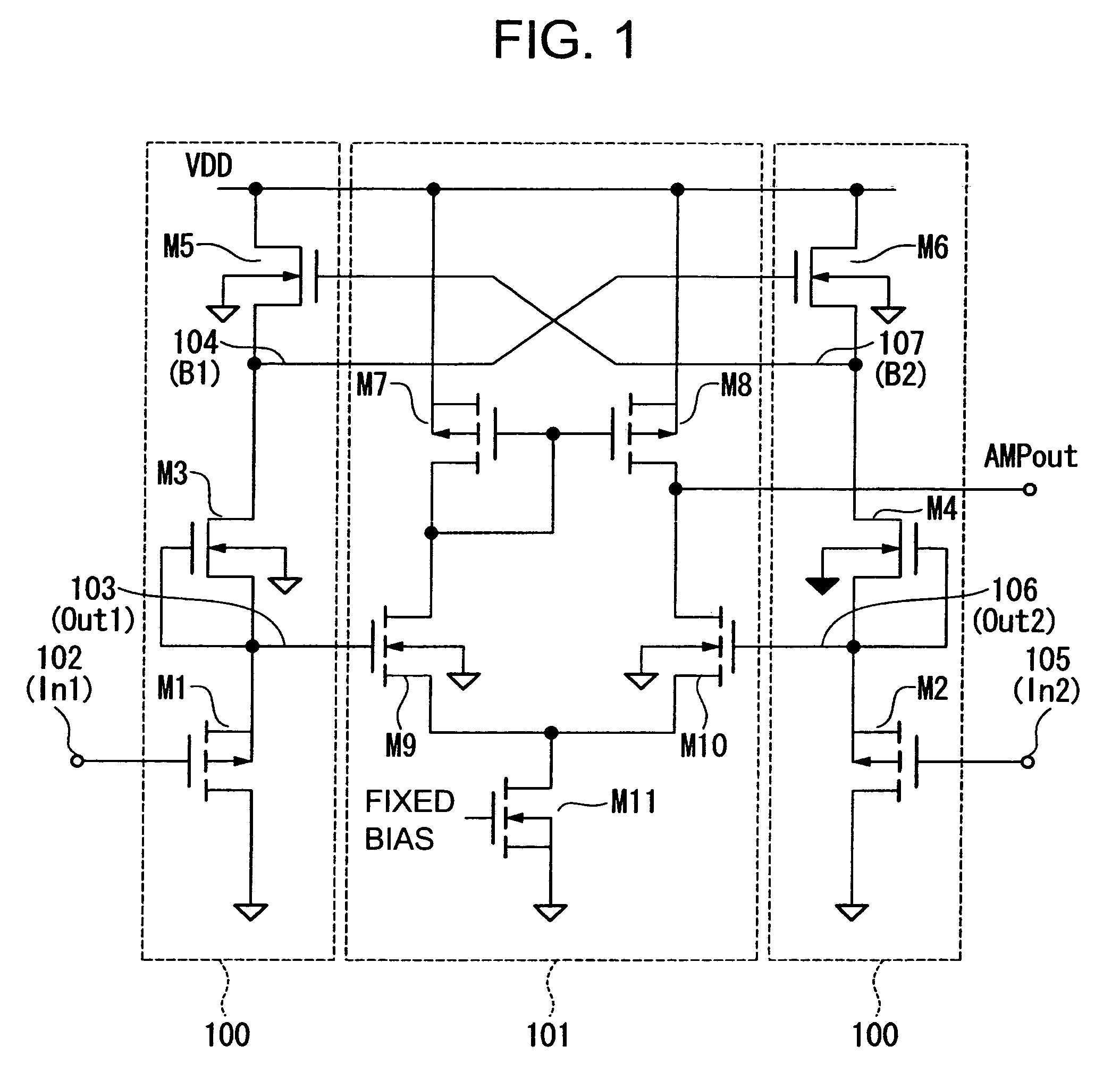
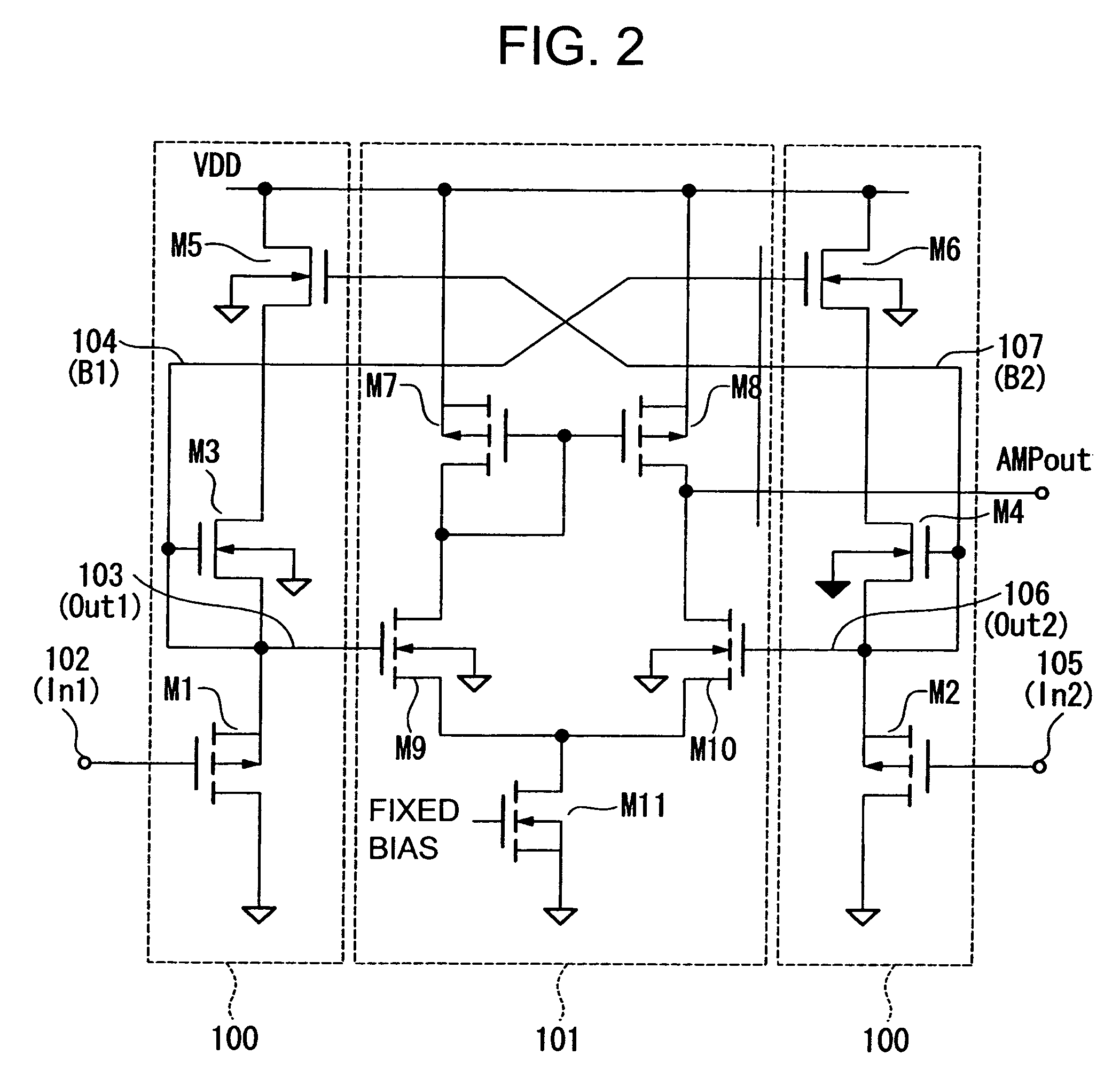
Differential amplifier circuit
ActiveUS20120025912A1Small capacitanceLow costDifferential amplifiersDc-amplifiers with dc-coupled stagesHemt circuitsComputer science
A differential amplifier circuit can reduce consumption current and the circuit size while improving a power supply rejection ratio. The differential amplifier circuit includes a power supply line and an input part that includes an input circuit and an active load. The input circuit includes two differential input elements, and the active load includes two transistors connected to the two differential input elements. The input part generates a differential signal in response to an input signal given to the two differential input elements. The differential amplifier circuit also includes an amplifying part for generating an output voltage generating signal by amplifying the differential signal. The differential amplifier circuit also includes an output part for generating an output voltage based on the output voltage generating signal and a power supply voltage. The differential amplifier circuit includes a noise permitting part located between control terminals of the two transistors and the power supply line.
Owner:LAPIS SEMICON CO LTD
Power supply rejection for pulse width modulated amplifiers and automatic gain control
InactiveUS20050179489A1Improve power supply rejection ratioImprove power supply rejectionAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationAutomatic Generation ControlAutomatic control
A circuit according to the present invention improves the power supply rejection ratio for a pulse width modulated digital amplifier and can be used as a compressor and / or limiter. The circuit preferably operates by using voltage level translation to vary the amplitude of a triangle wave in response to changes in power supply voltage prior to input of the wave into a comparator of the PWM device. Because the circuit operates to improve power supply rejection, little or no distortion is introduced into the signal when used as a compressor and / or limiter. Additionally, the circuit is optionally implemented in a Class D amplifier, and provides a lower cost of implementation than conventional designs in such implementations.
Owner:ALTEC LANSING TECH
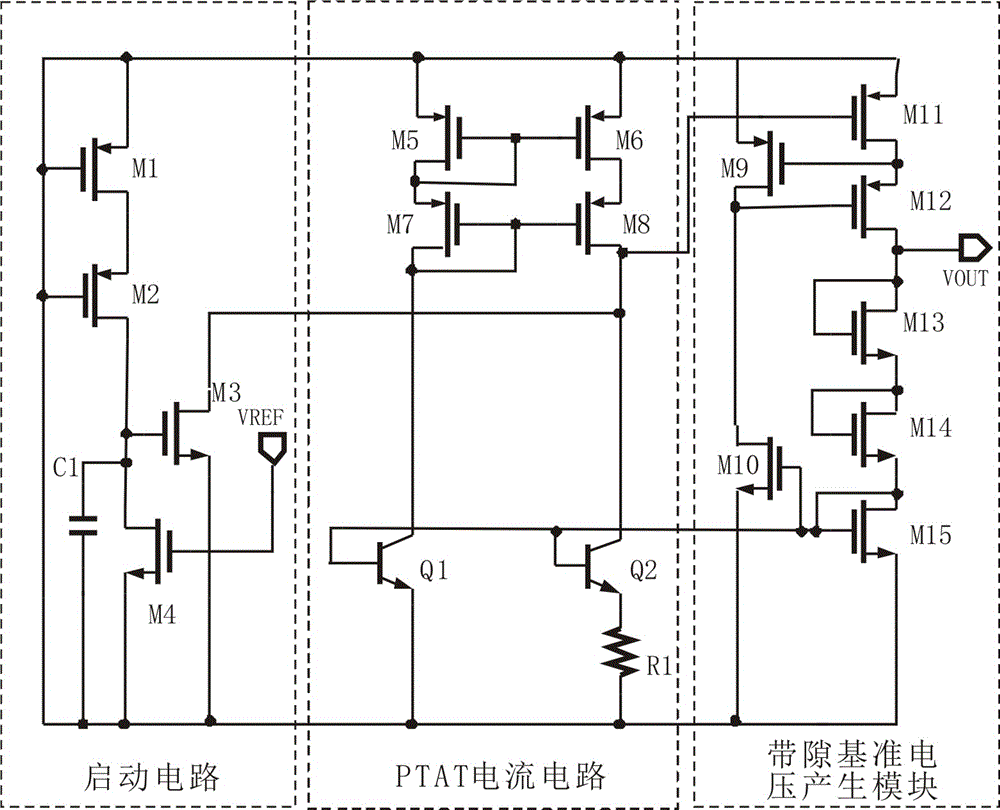
Pre-regulator circuit capable of increasing band-gap reference power supply rejection ratio
InactiveCN105786075AHigh impedanceImprove power supply rejection ratioElectric variable regulationPhysicsPower supply rejection ratio
The invention discloses a pre-regulator circuit capable of increasing band-gap reference power supply rejection ratio. The pre-regulator circuit comprises a starting circuit, a PTAT current circuit and a band-gap referent voltage generating module, wherein the PTAT current circuit comprises a PMOS transistor M5, a PMOS transistor M6, a PMOS transistor M7, a PMOS transistor M8, a transistor Q1, a transistor Q2 and a resistor R1; the band-gap reference voltage generating module comprises a PMOS transistor M9, an NMOS transistor M10, a PMOS transistor M11, a PMOS transistor M12, an NMOS transistor M13, an NMOS transistor M14 and an NMOS transistor M15. The pre-regulator circuit has the advantages that part of the noise fluctuation of power supply voltage is removed through the pre-regulator technology, the pre-regulated voltage is used as the band-gap reference power supply voltage to increase the power supply rejection ratio of the circuit, a negative feedback method is used to increase the impedance from VOUT to power supply voltage in the pre-regulator technology, and the power supply rejection ratio is further increased.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Class-D audio power amplifier circuit
InactiveCN101958690AImprove power supply rejection ratioSuppress high frequency componentsAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesTransducer circuitsCapacitanceTotal harmonic distortion
The invention relates to a class-D audio power amplifier circuit. Two input ends of a first-stage amplifier are connected with audio signals, two output ends of the first-stage amplifier are connected with two input ends of a second-stage amplifier after being connected with an input resistor in series, and two feedback resistors are connected with the two pairs of input ends and output ends of the first-stage amplifier; one output end of the second-stage amplifier is connected with a first comparator in series, a first drive circuit is connected with one input end of a loudspeaker, another output end of the second-stage amplifier is connected with a second comparator in series, and a second drive circuit is connected with another input end of the loudspeaker; and two feedback capacitors are connected with the two pairs of input ends and output ends of the second-stage amplifier, and two feedback resistors are connected with the input ends of the second-stage amplifier and the input ends of the loudspeaker. The dominant pole of the circuit is controlled by using the second-stage feedback resistors and feedback capacitors to ensure that the audio signals can be amplified and other high-frequency components can be inhibited. Meanwhile, two loops can effectively increase the power supply rejection ratio of the circuit and reduce total harmonic distortion.
Owner:SHANGHAI SANDHILL MICROELECTRONICS
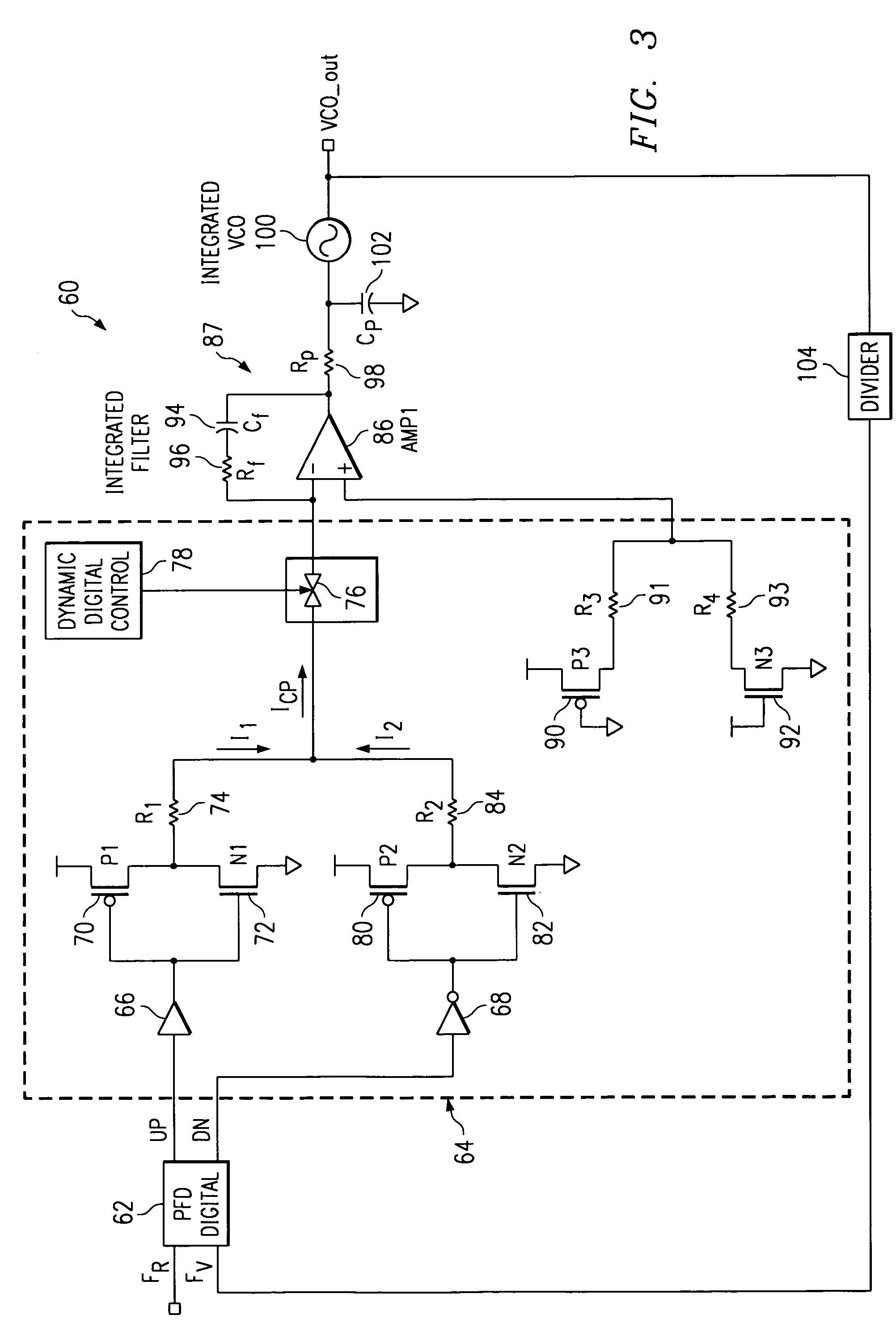
Charge pump phase locked loop with improved power supply rejection
ActiveUS20050195002A1Improve power supply rejection ratioVoltage variationPulse automatic controlElectric variable regulationTransmission gateActive filter
A phase lock loop circuit (60) has a phase frequency detector (62), a charge pump (64), an active filter (87) and a voltage-controlled oscillator (100). The phase detector generates signals responsive to reference signal FR and VCO output signal FV. A charge pump generates a voltage at the input of a first transmission gate (76) according to the values of the phase detector signals. A predetermined voltage is generated at the input of a second transmission gate (112). When the transmission gates (76, 110) are closed (low impedance) the charge pump may sink or source current to the inverting input of the operational amplifier (86) of the active filter 86 and the predetermined voltage is applied to the non-inverting input. When the transmission gates are open (high impedance state) the inverting input is electrically isolated from the node and the non-inverting output is isolated from the power supply.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
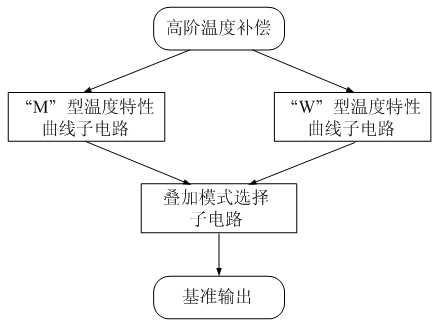
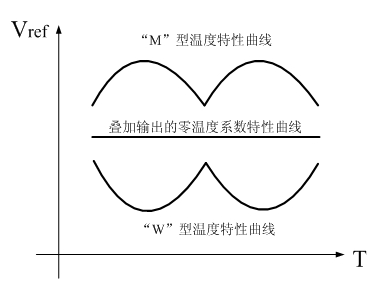
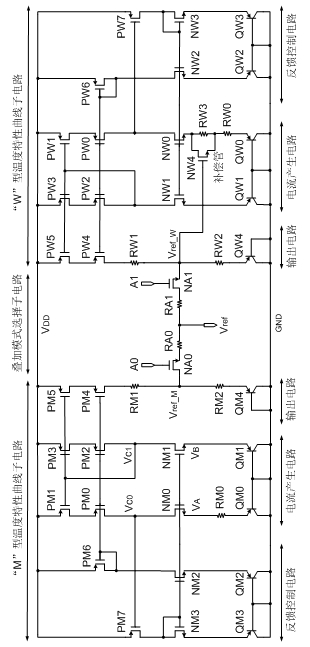
High-order temperature compensation complementary superposition-based high-precision band-gap reference circuit
InactiveCN102073334AImprove power supply rejection ratioElectric variable regulationEngineeringFeedback control
The invention discloses a high-order temperature compensation complementary superposition-based high-precision band-gap reference circuit. The circuit comprises an M-type temperature characteristic curve sub-circuit, a W-type temperature characteristic curve sub-circuit and a superposition mode selection sub-circuit, wherein the M-type temperature characteristic curve sub-circuit and the W-type temperature characteristic curve sub-circuit are arranged complementarily and symmetrically; both the M-type temperature characteristic curve sub-circuit and the W-type temperature characteristic curve sub-circuit comprise a feedback control circuit, a current generating circuit and an output circuit, wherein the current generating circuit is connected with the input end of the superposition mode selecting sub-circuit after being connected with an output circuit in series; and the output end of the output circuit is connected with the input end of the current generating circuit after being connected with the feedback control circuit in series. The circuit reduces a temperature coefficient of an output reference voltage to the maximum by using a nonlinear temperature compensation structure and a nonlinear temperature compensation method, thereby meeting the application of a high-precision system.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Regulator with load tracking bias
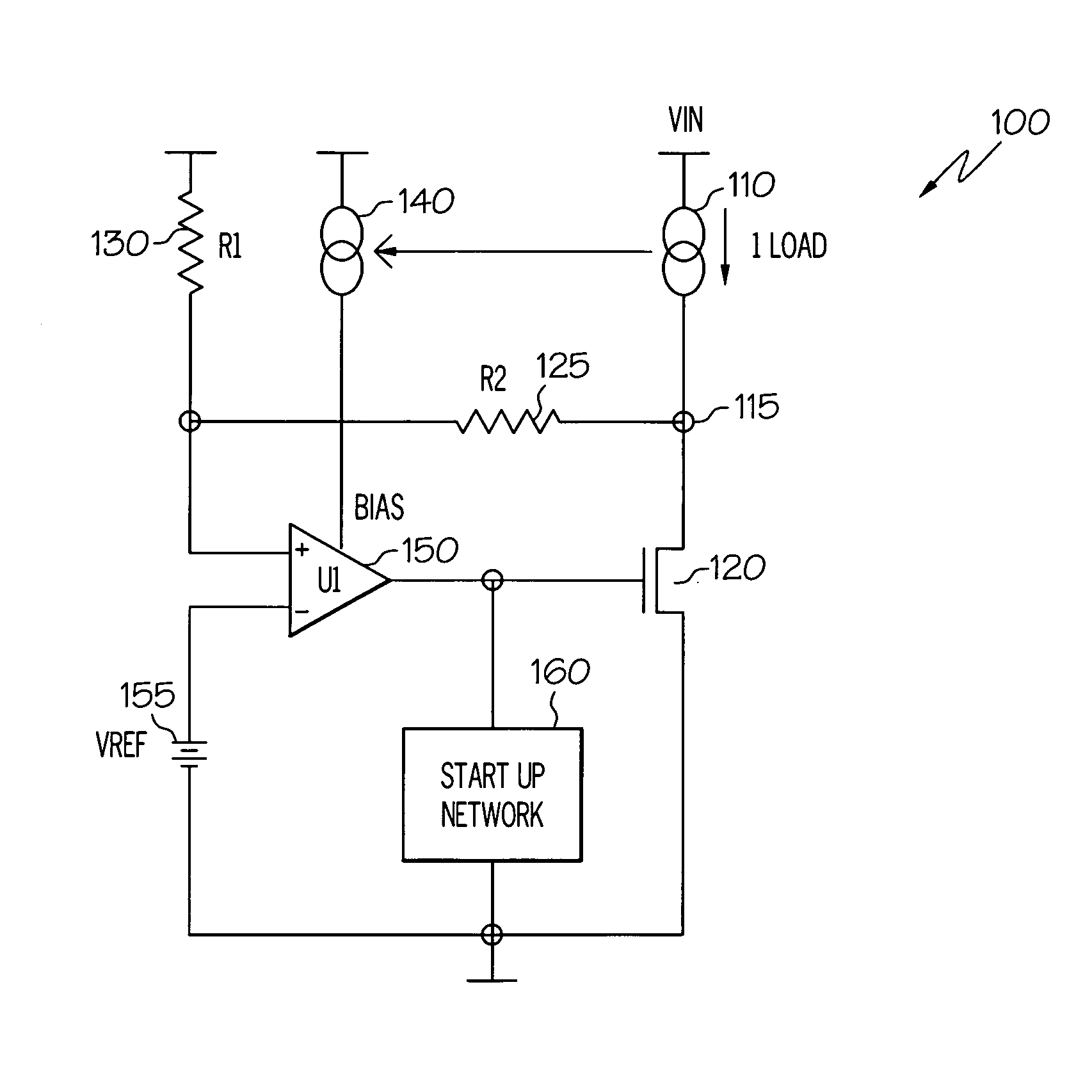
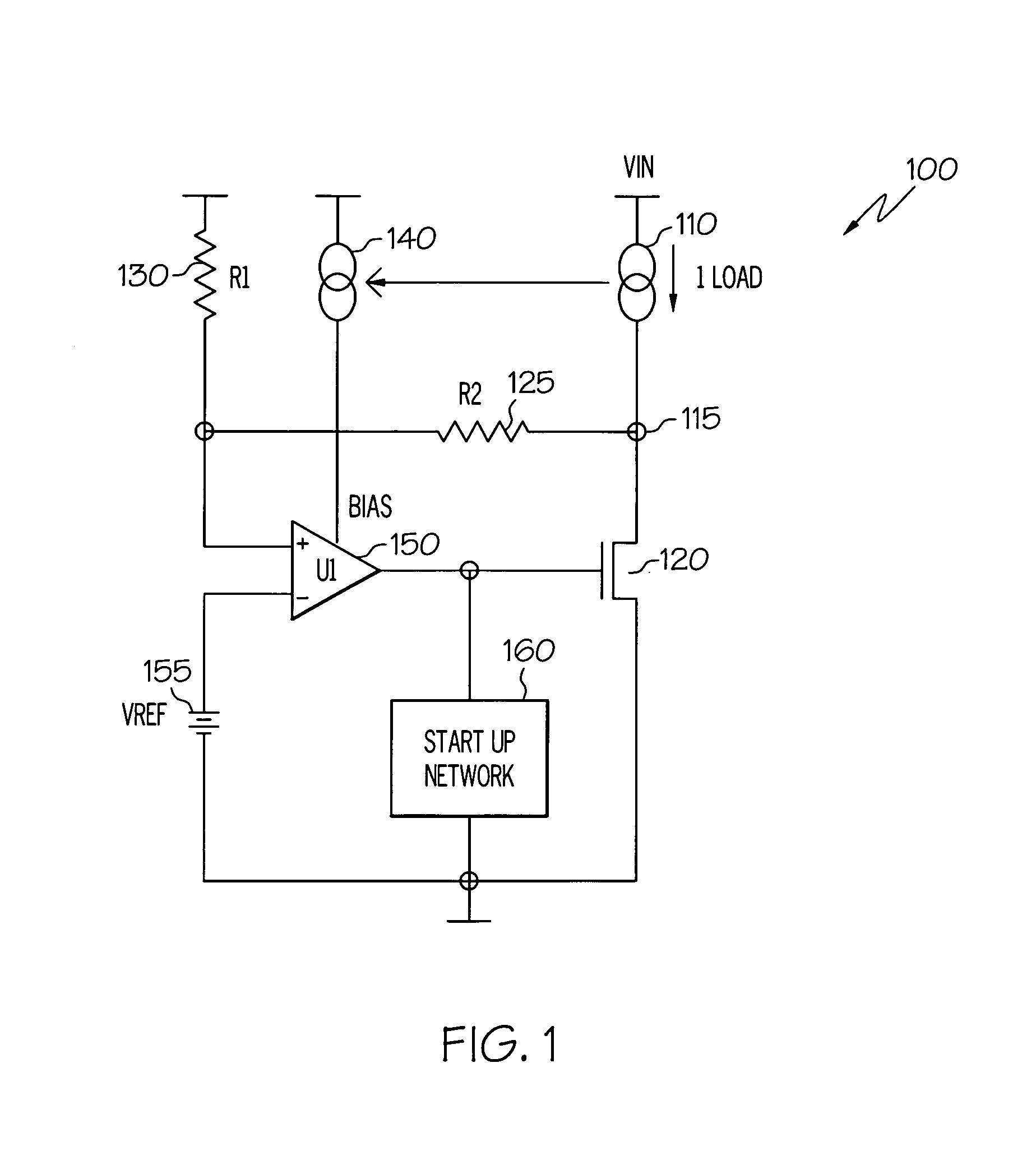
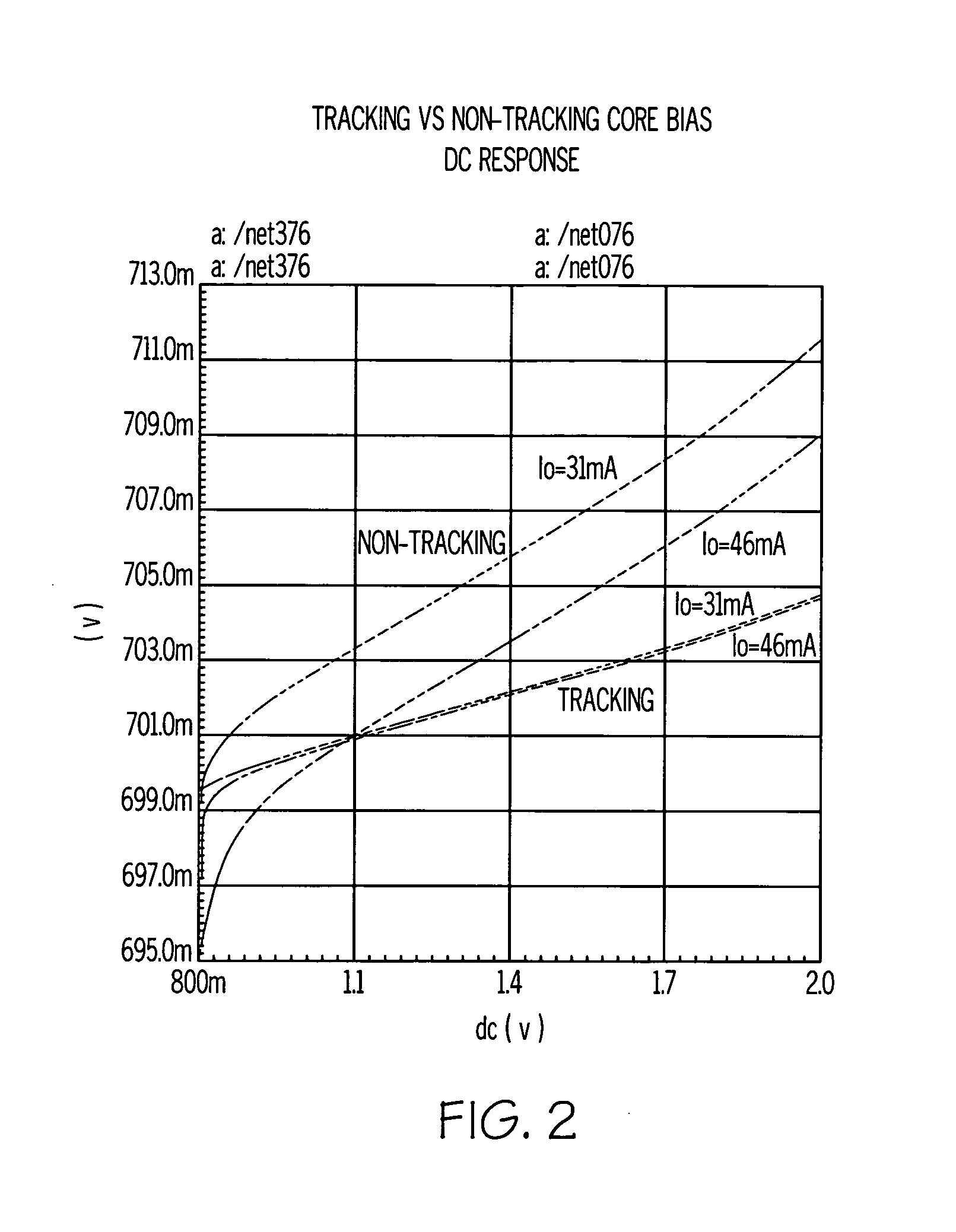
InactiveUS20070096702A1Improve power supply rejection ratioThe output voltage is accuratePower supply linesElectric variable regulationAudio power amplifierVoltage regulation
An electrical circuit that provides accurate, regulated output voltage over a wide range of input voltages, while exhibiting each of three desired characteristics: accuracy across different supply / process / temperature; stability and linearity yielding phase / gain margins; and high (good) power supply rejection ratio (PSRR). The circuit comprises an output node having a load current and an amplifier having a first input coupled to a reference voltage and receiving a bias input current that is a pre-established proportionate size of the load current across the output node, such that a change in the load current results in a proportionate change in the bias input current. The electrical circuit represents a voltage regulator that provides accurate, linear output voltage that is a predictable portion of the reference voltage.
Owner:IBM CORP
Amplifier Arrangement and Method for Operating an Amplifier Arrangement
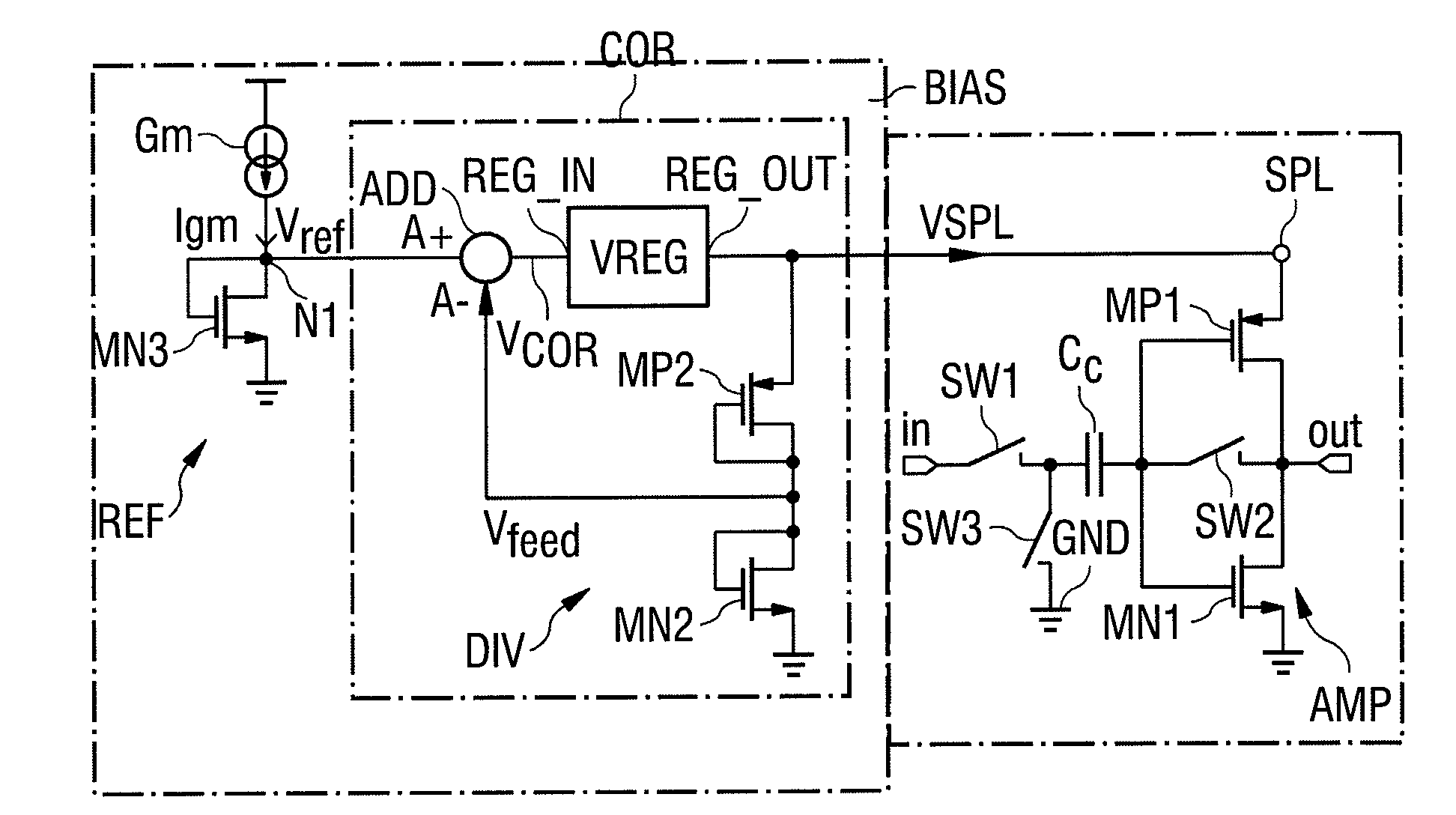
ActiveUS20120268212A1Precise adjustmentEasy to adjustAmplifiers using switched capacitorsPositive-feedback-circuit arrangementsEngineeringOperating point
Owner:AMS AG
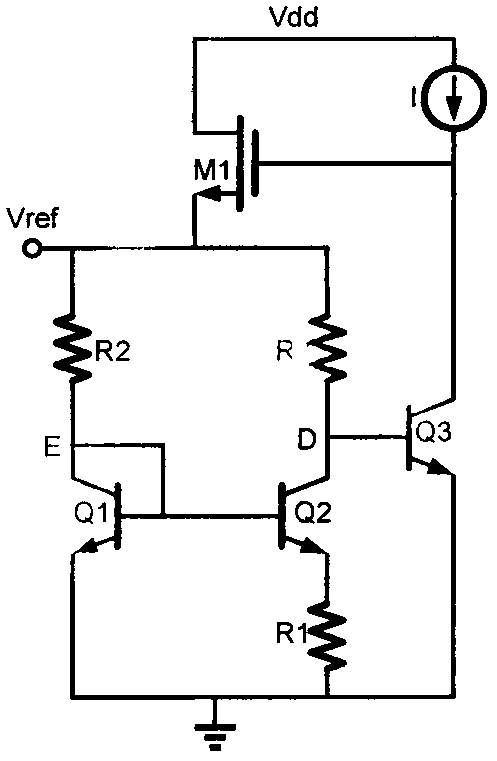
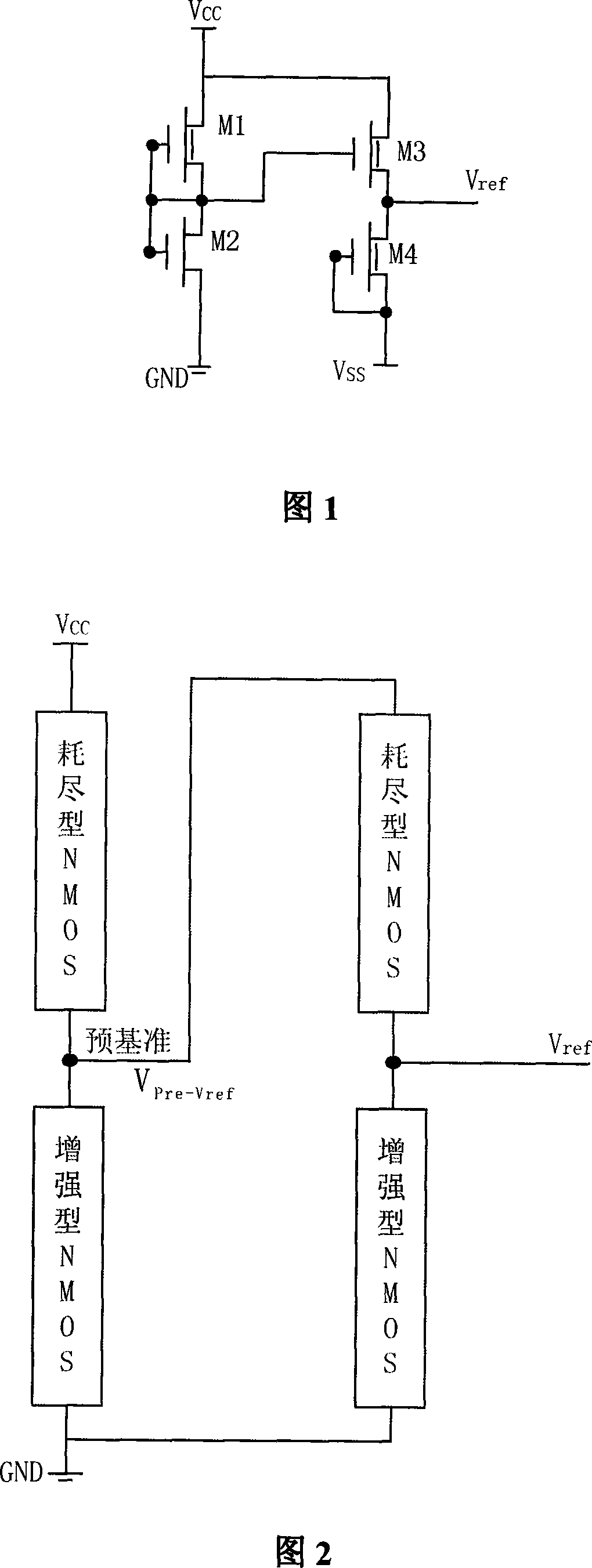
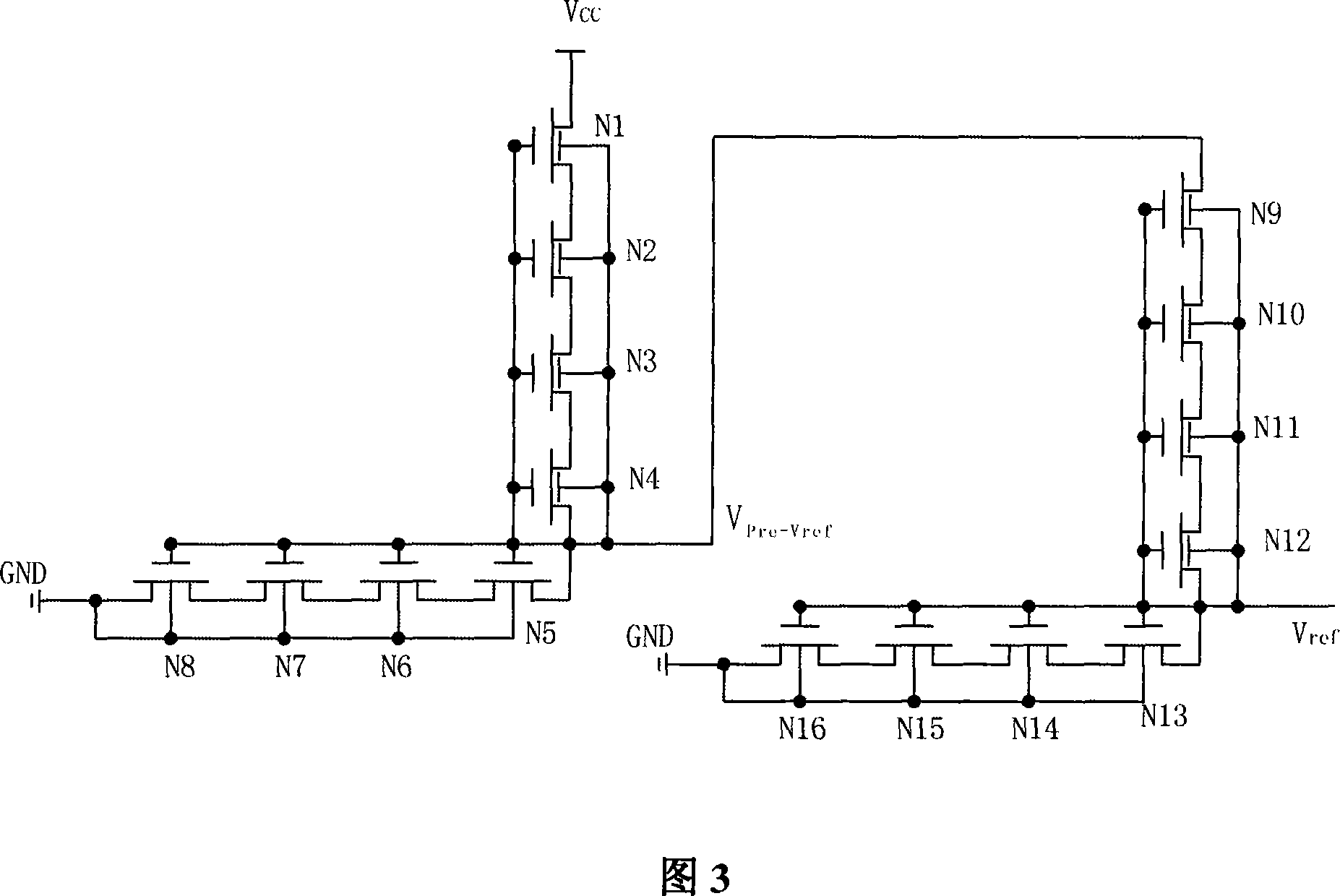
E/D NMOS reference voltage source with high electric power rejection ratio
InactiveCN101135918ASimple structureSimple processElectric variable regulationCapacitanceEngineering
Owner:NO 24 RES INST OF CETC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com