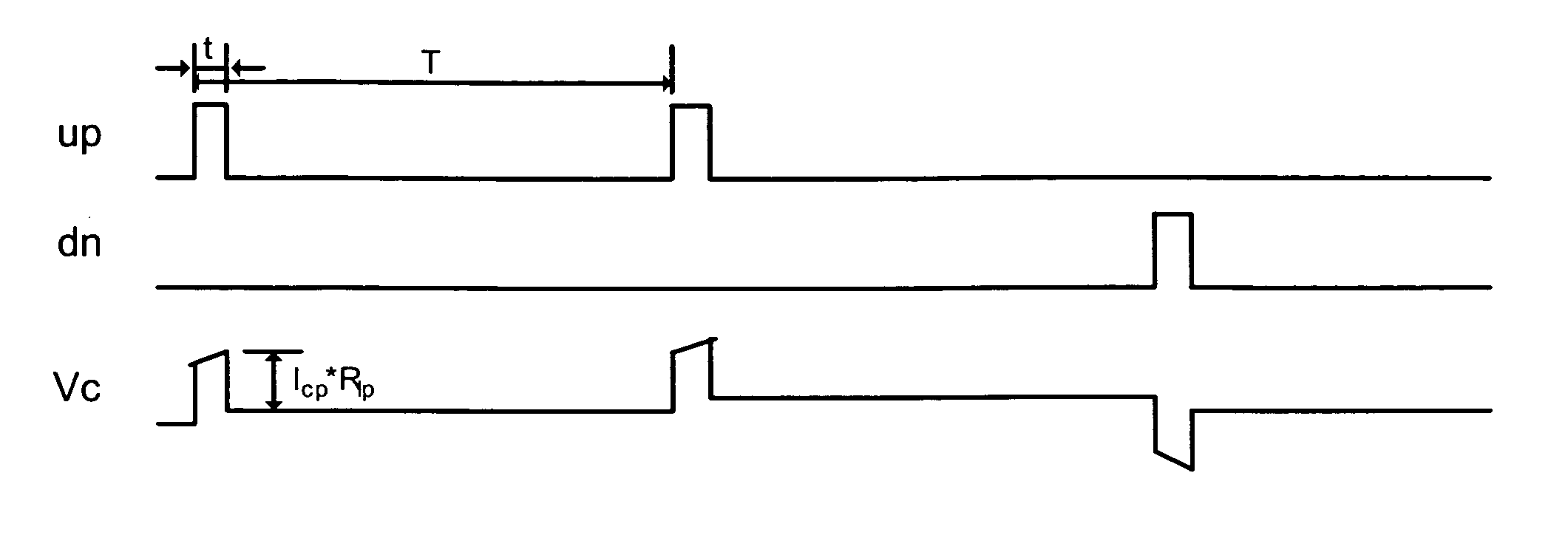
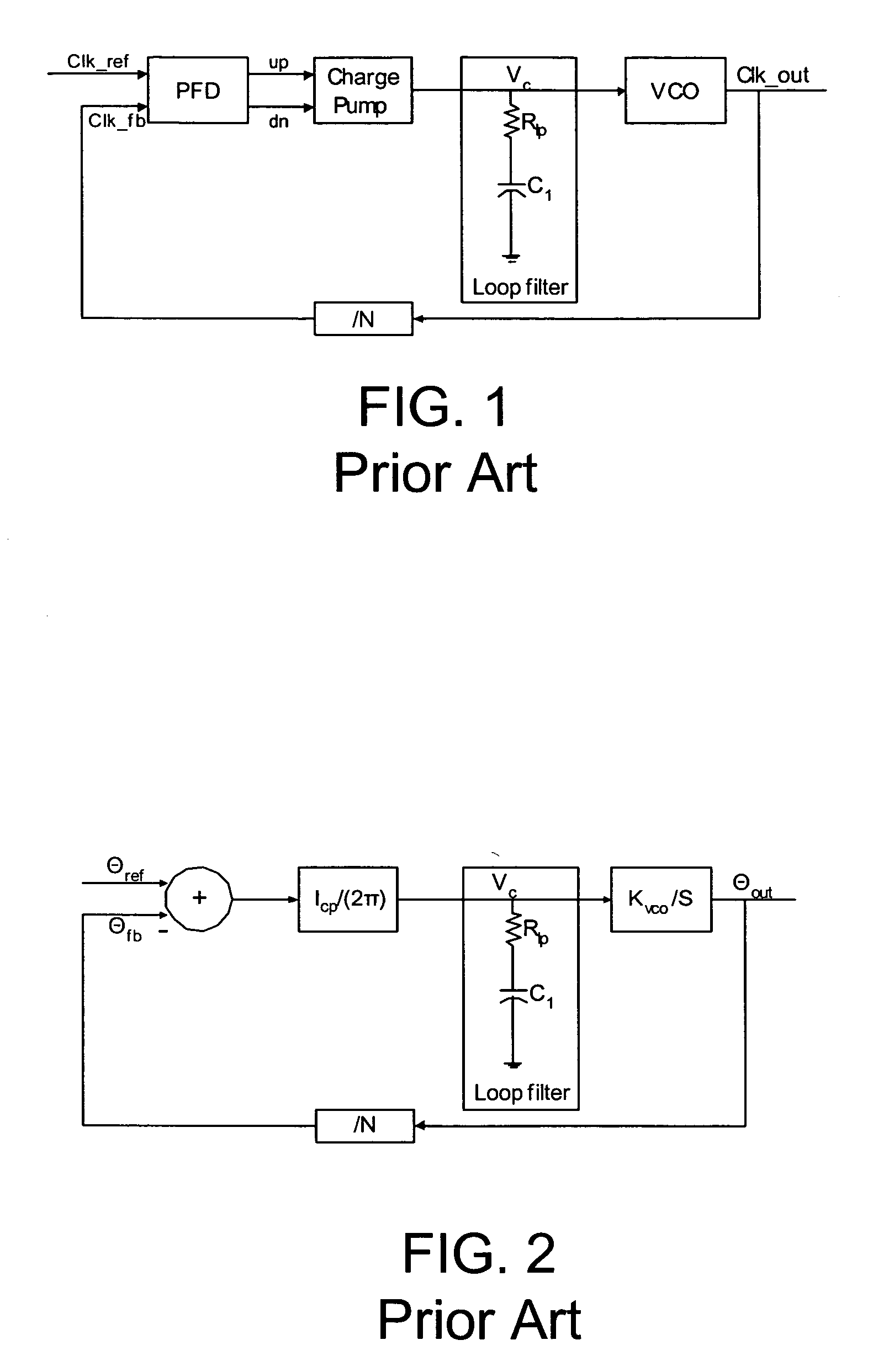
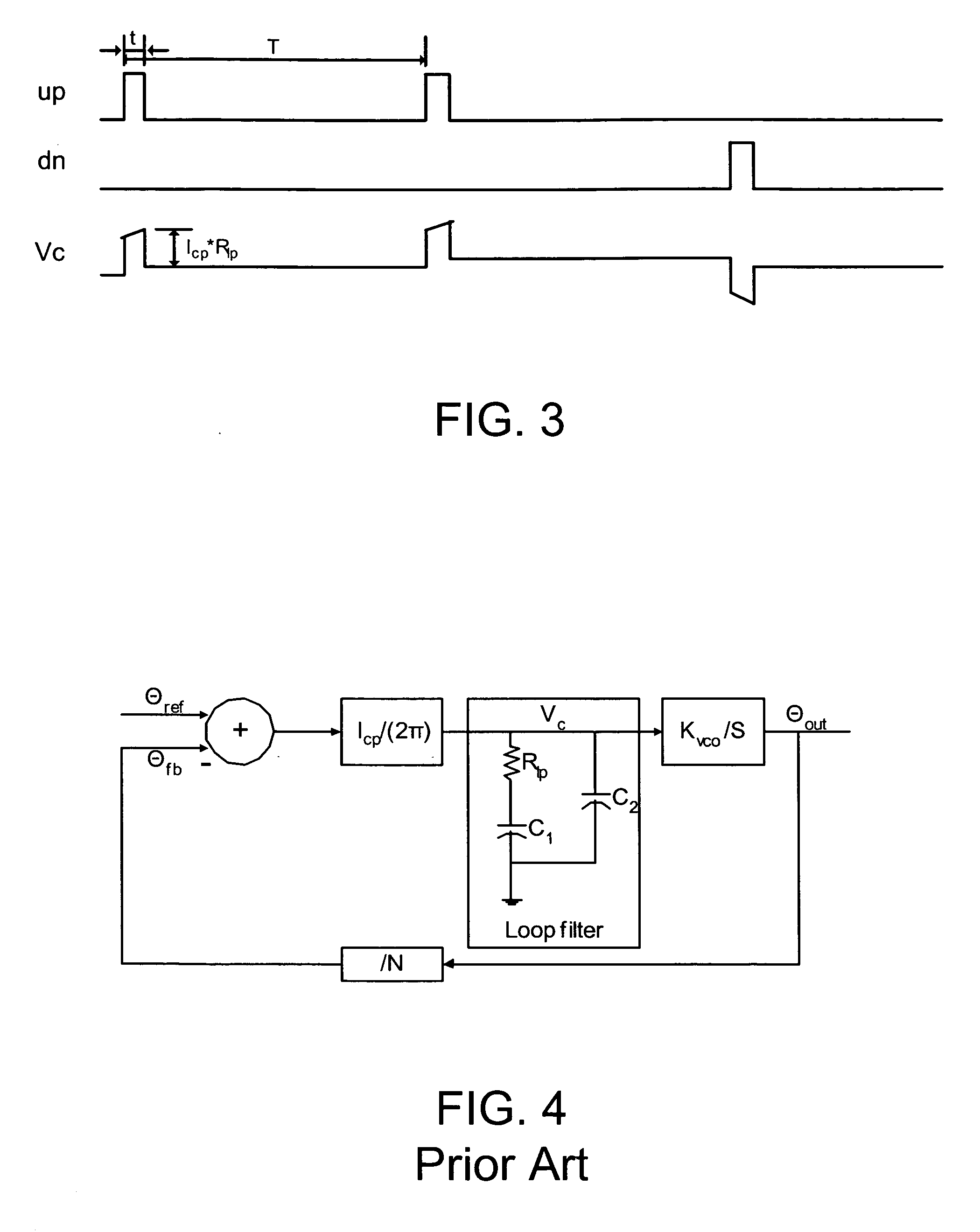
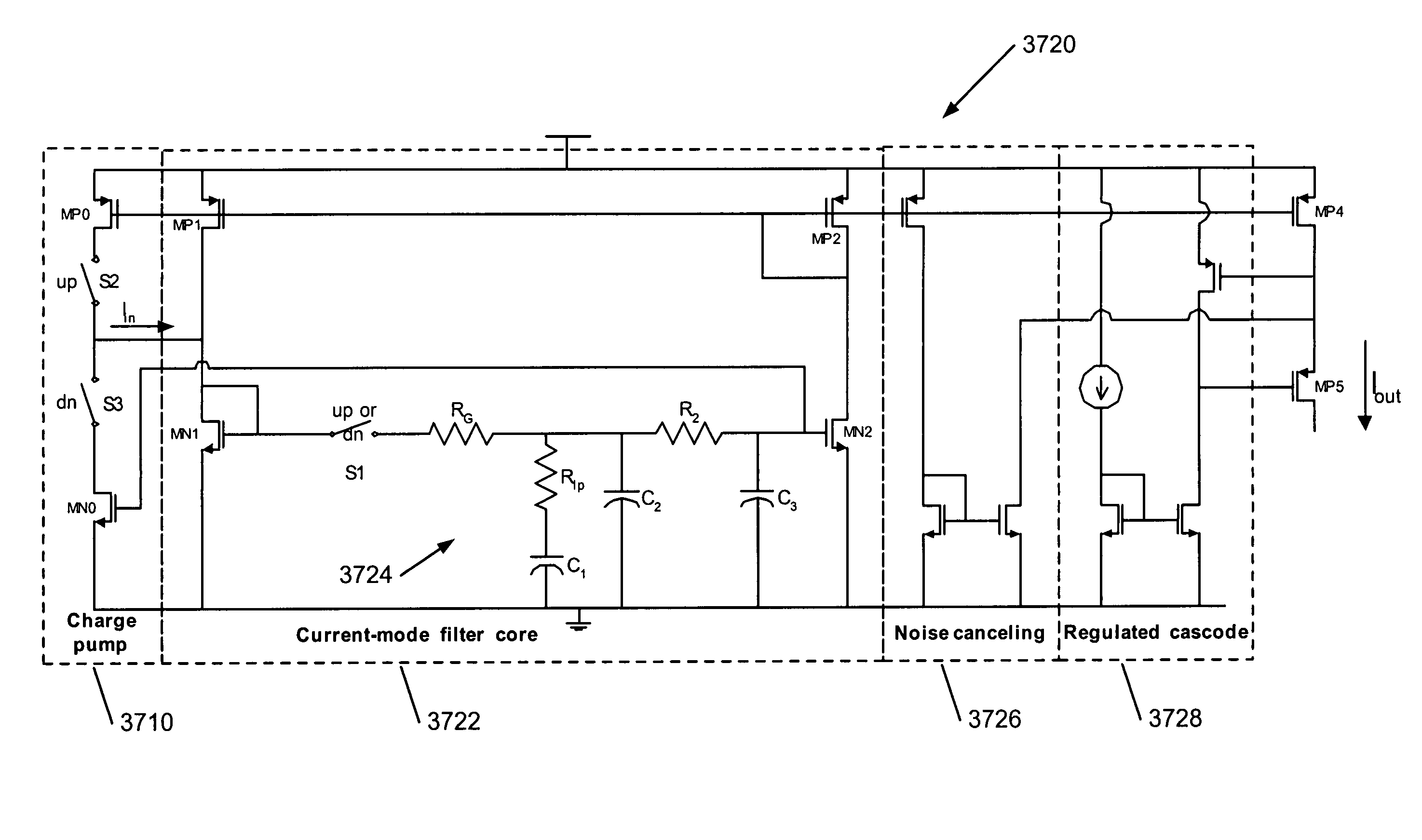
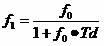Patents
Literature
144 results about "Current controlled oscillator" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
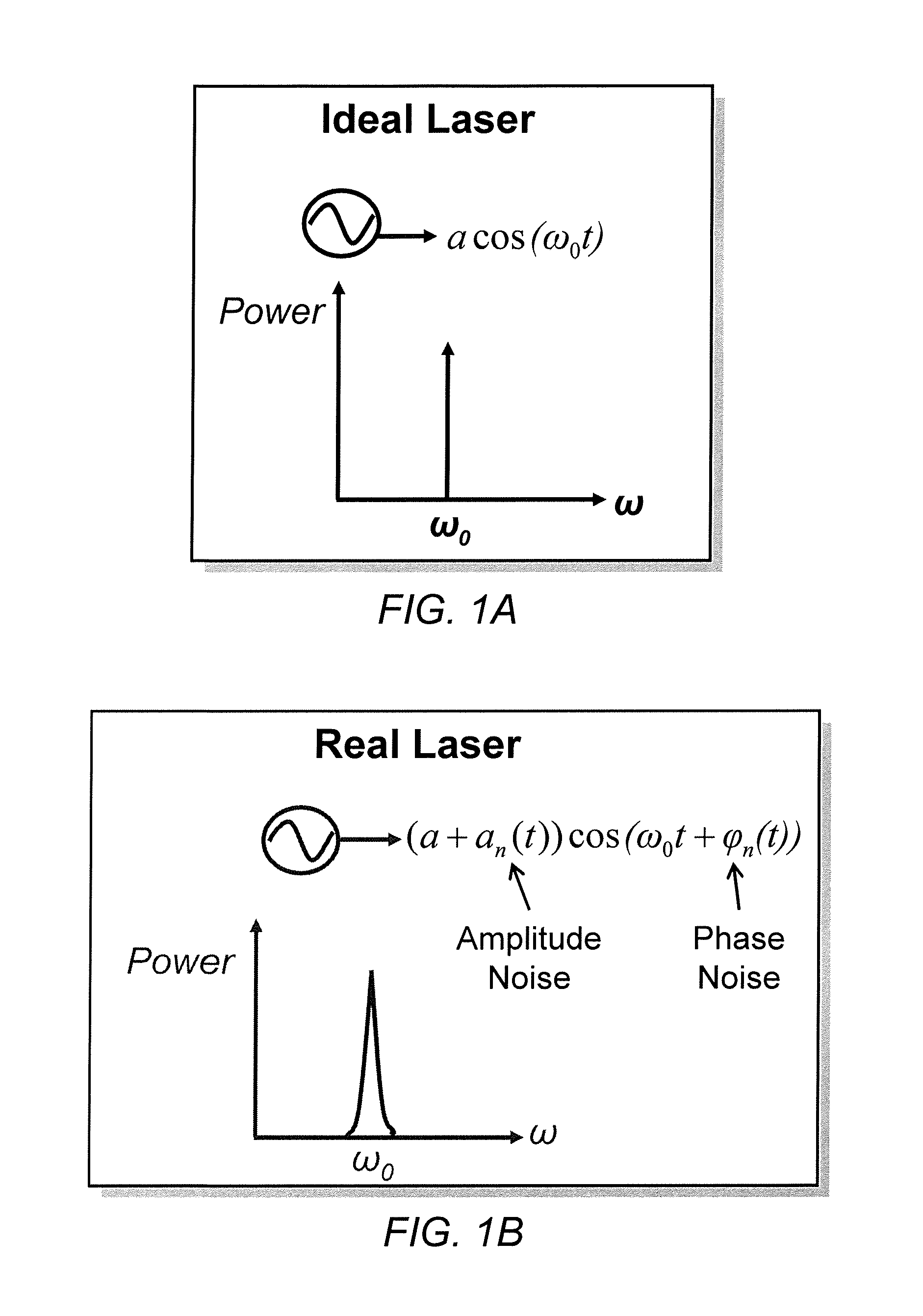
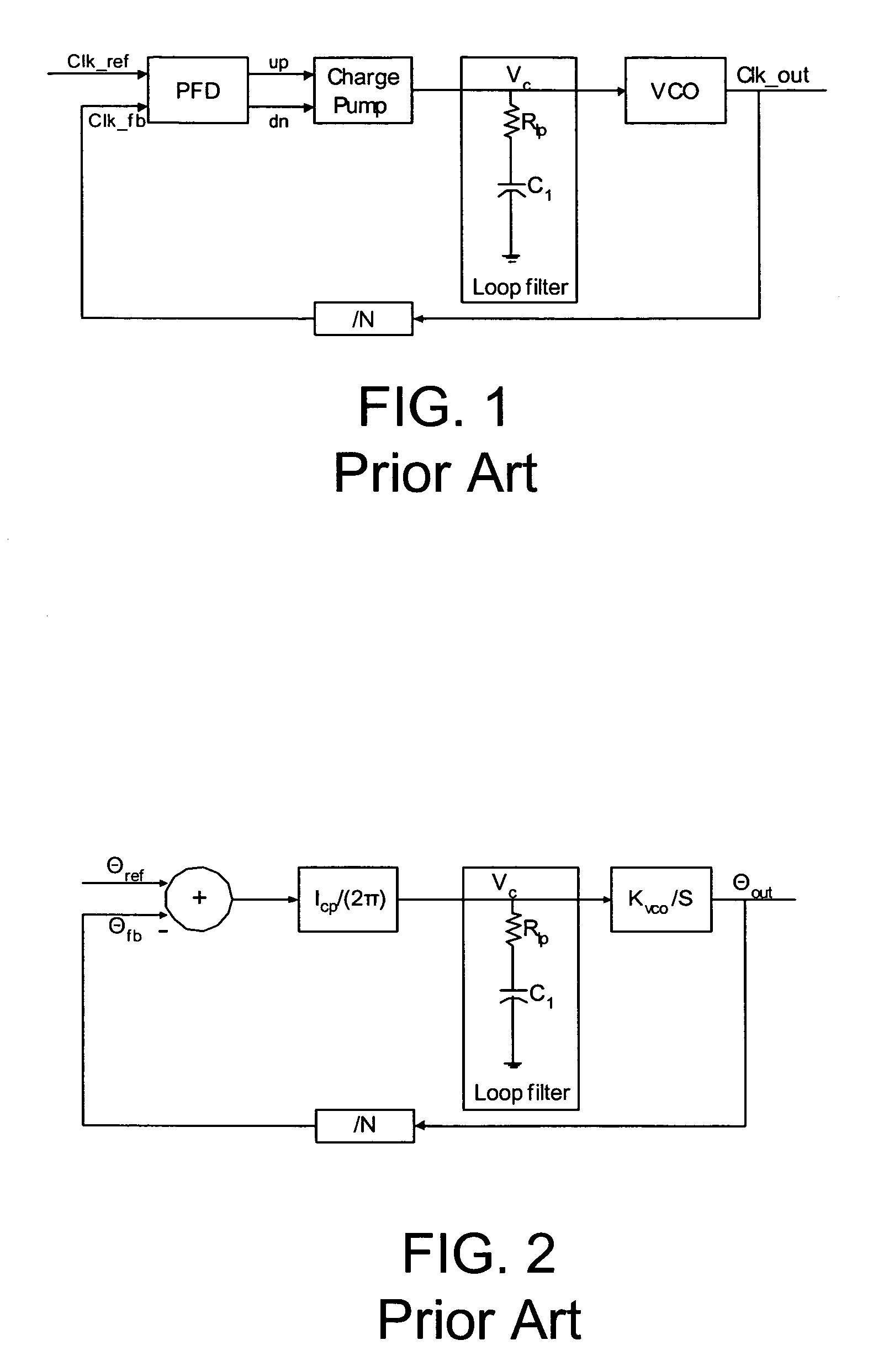
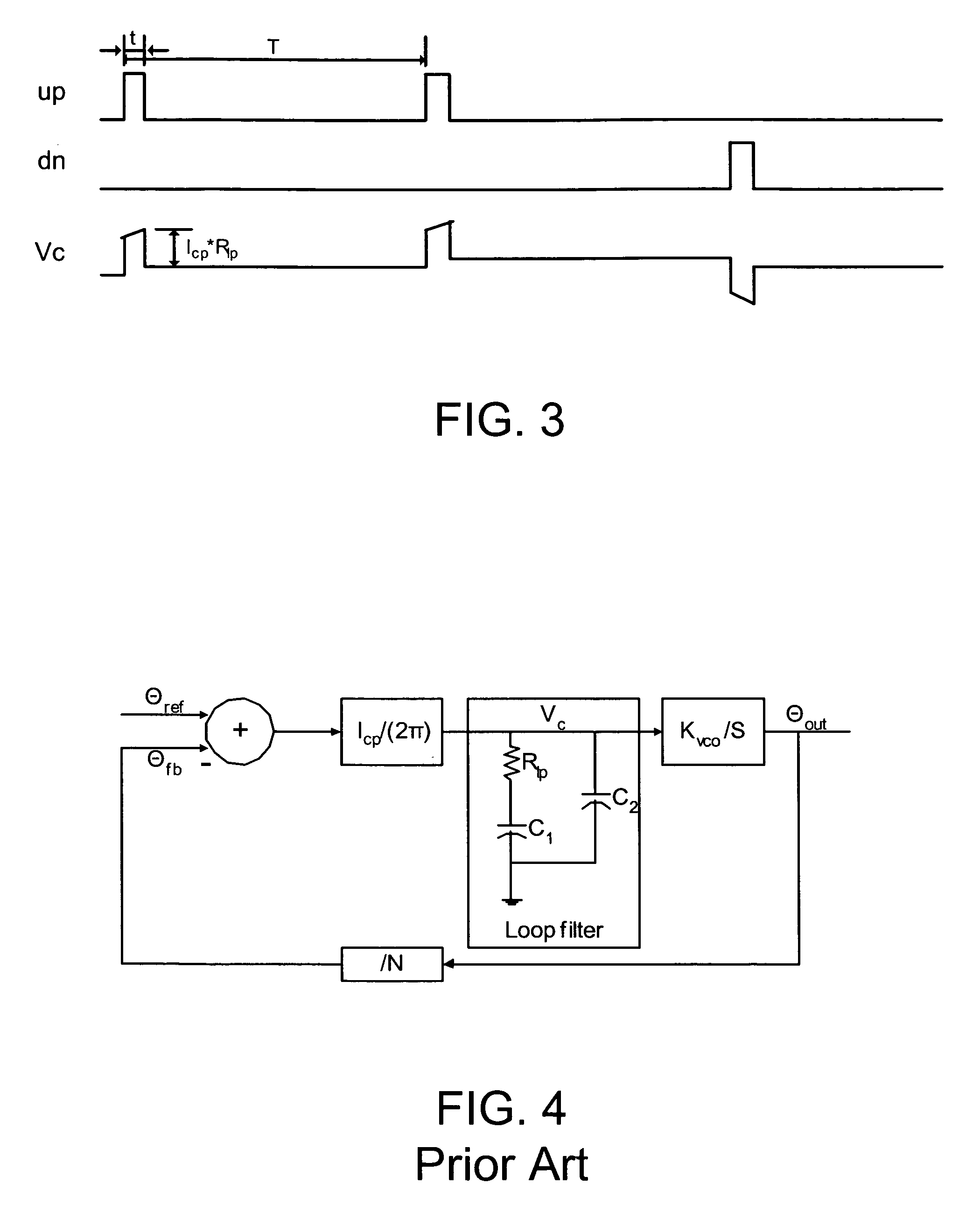
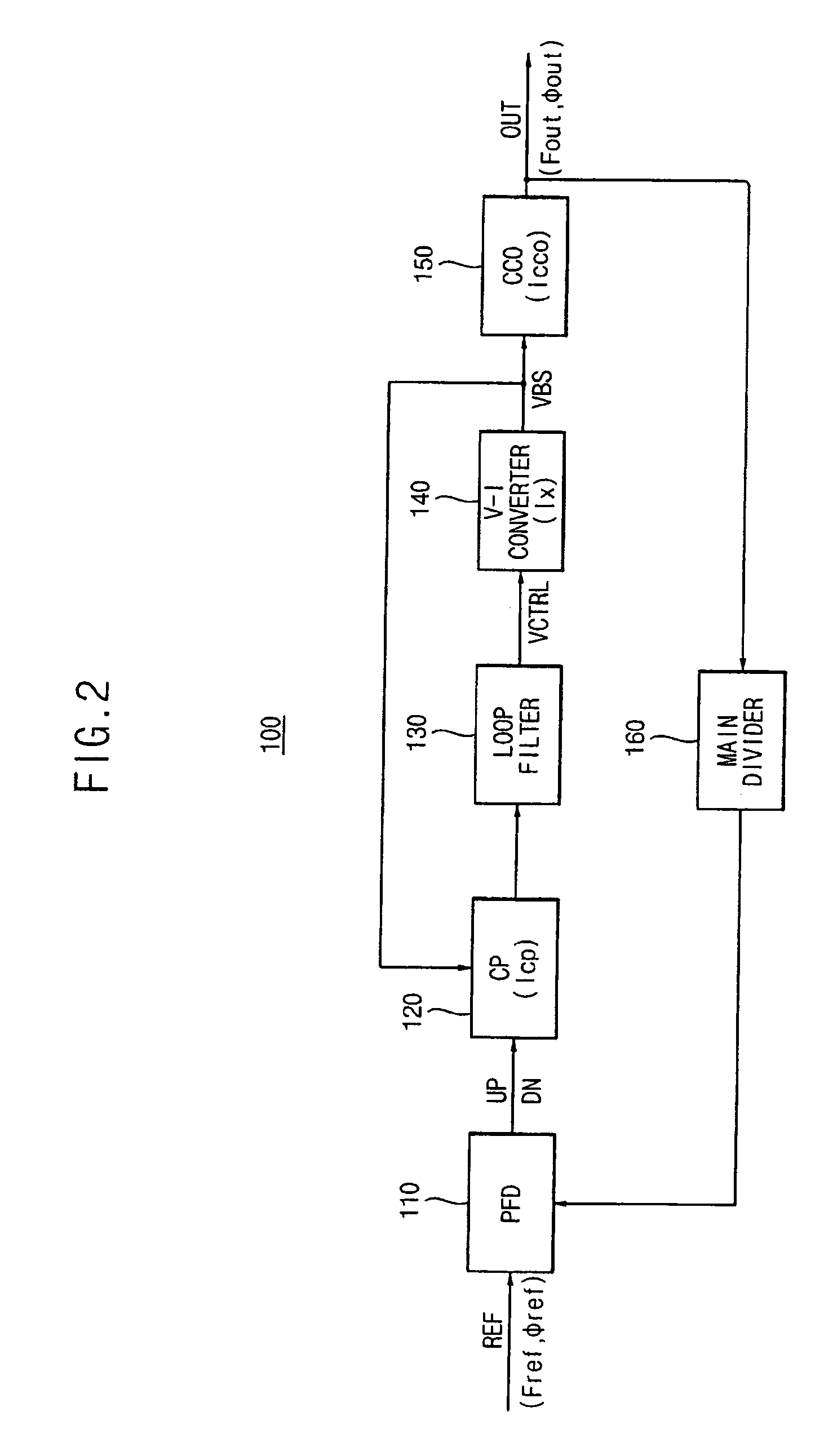
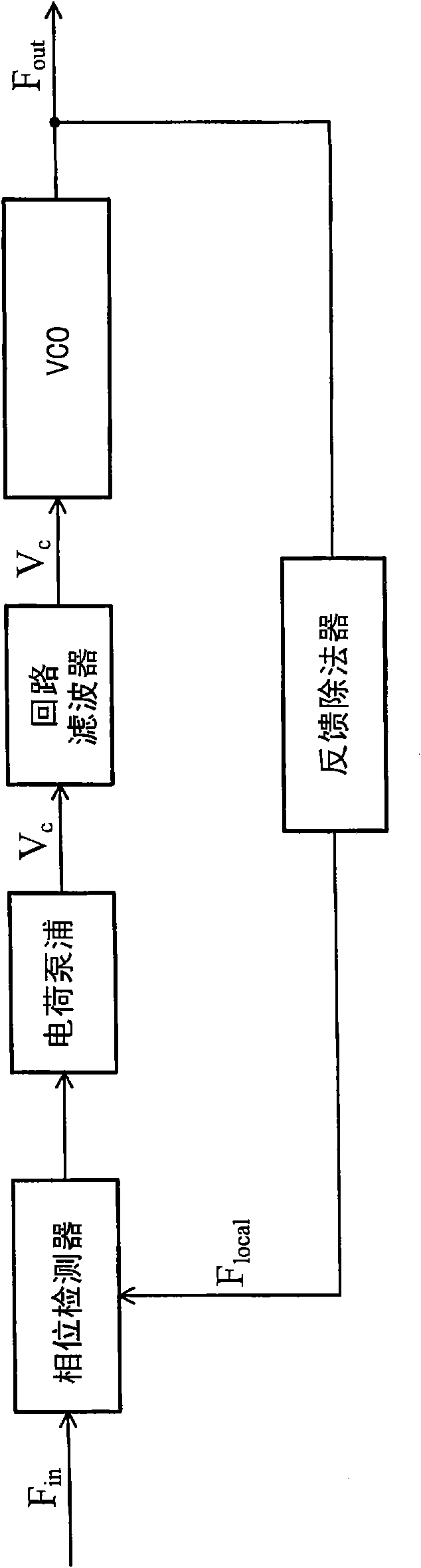
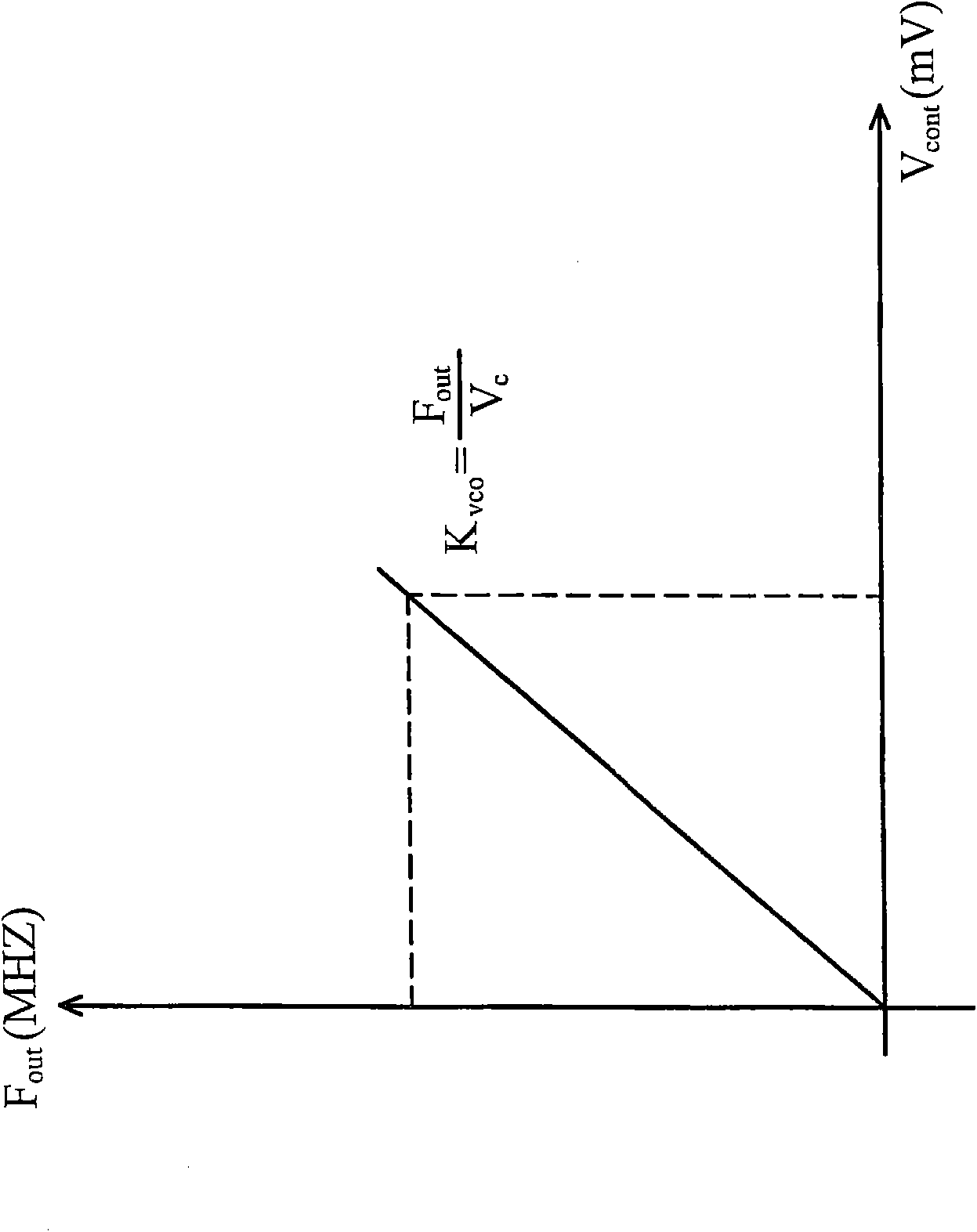
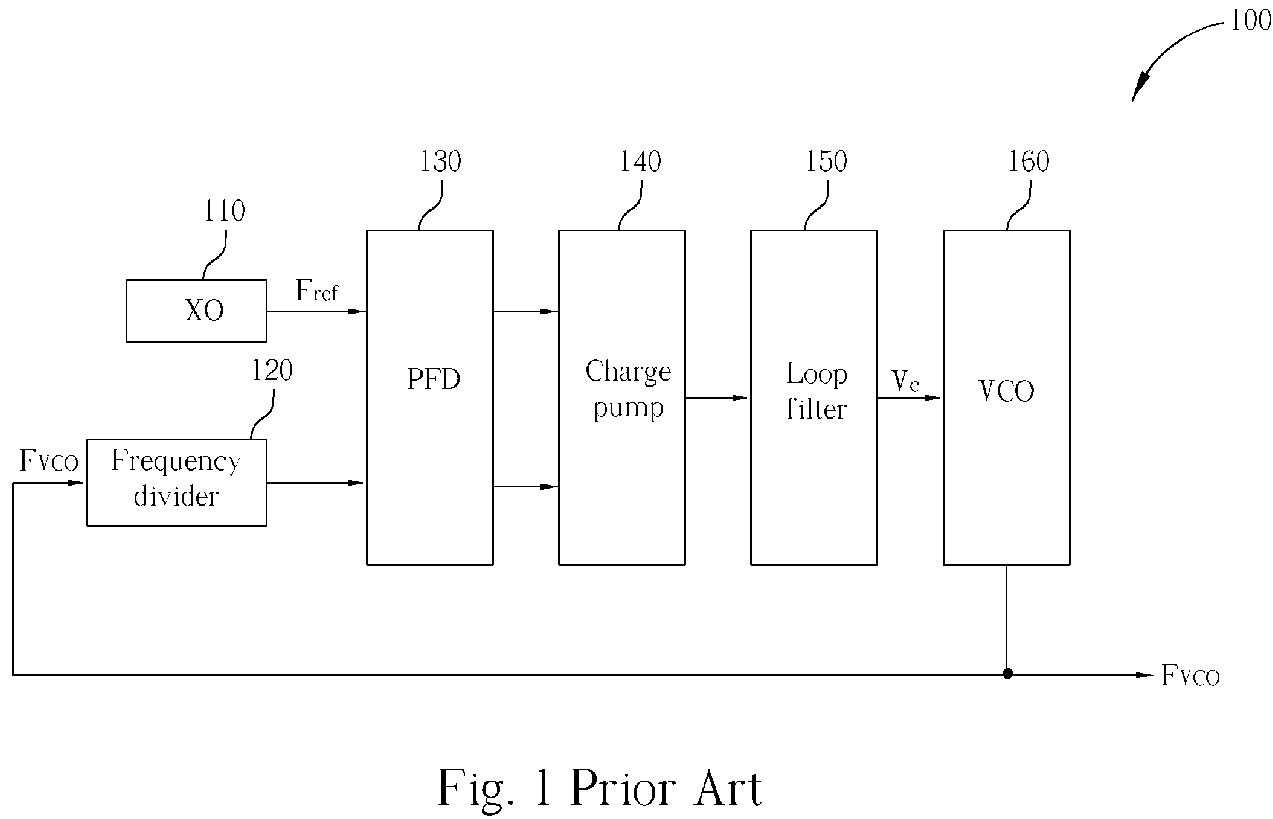
A current controlled oscillator (CCO) is a circuit that generates a signal whose frequency depends on a current source. It is a basic building block in many communication and data processing circuits such as phase locked loop (PLL) [1,2], spread spectrum clock oscillator [3] and etc.
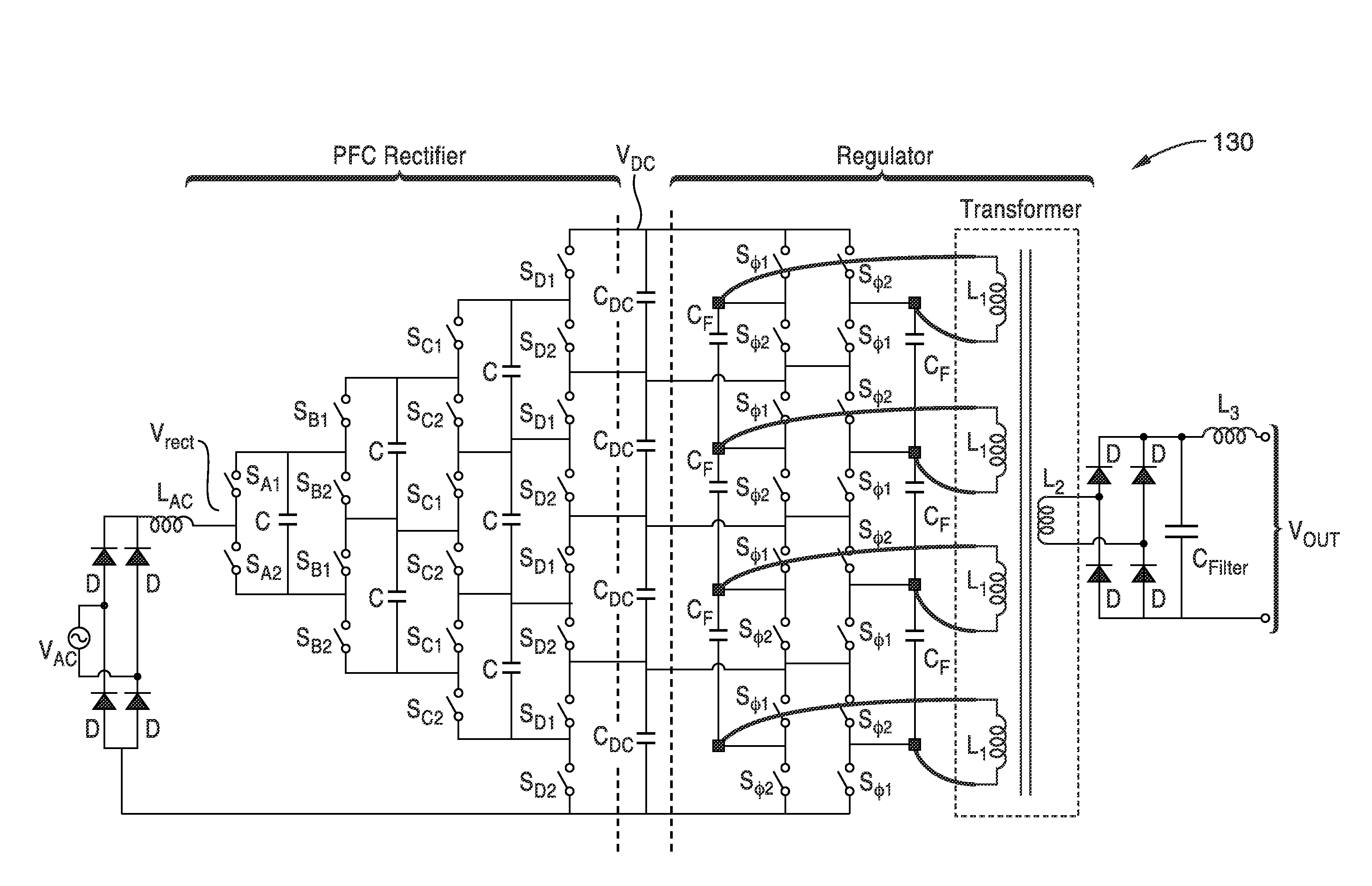
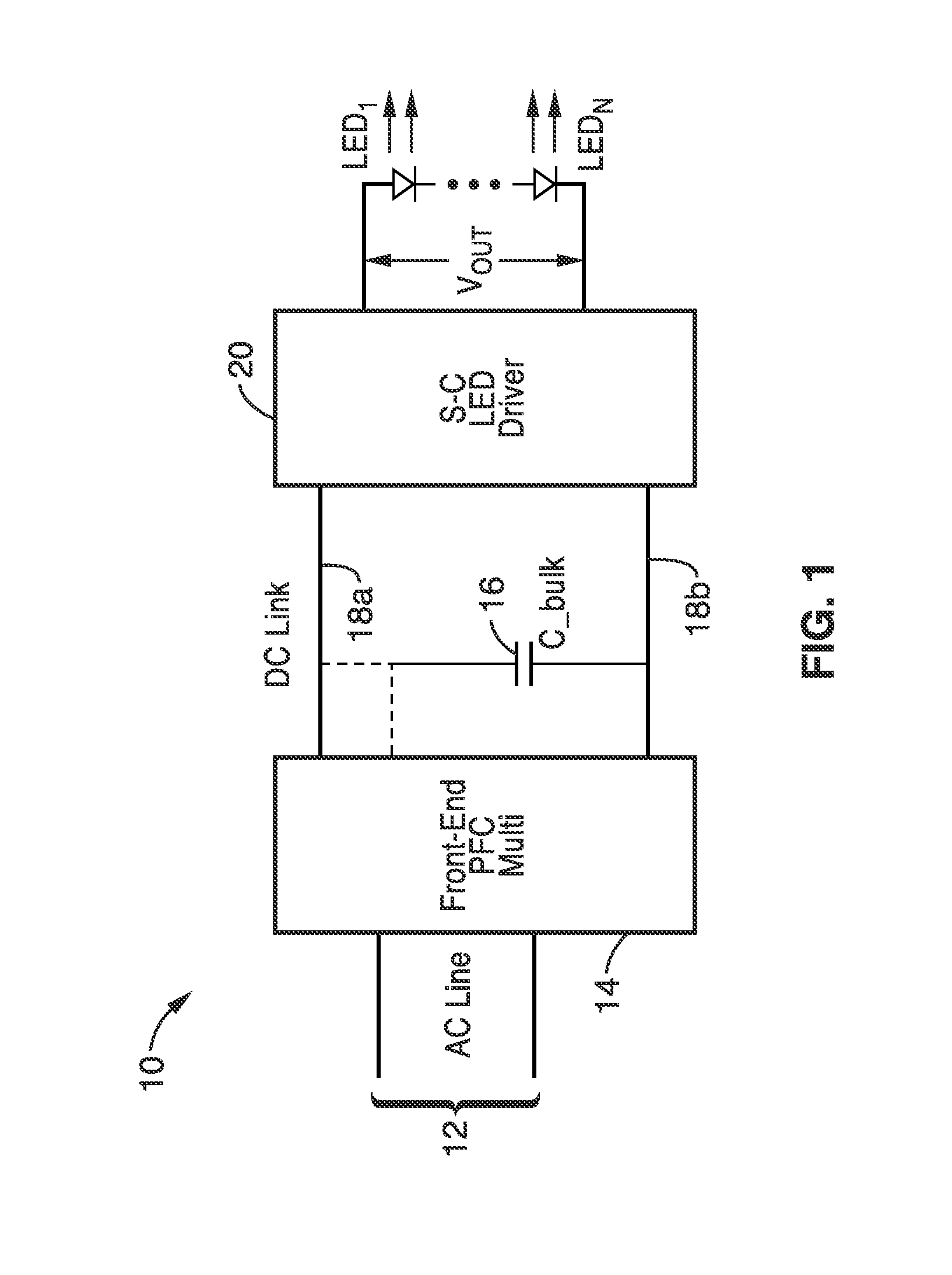
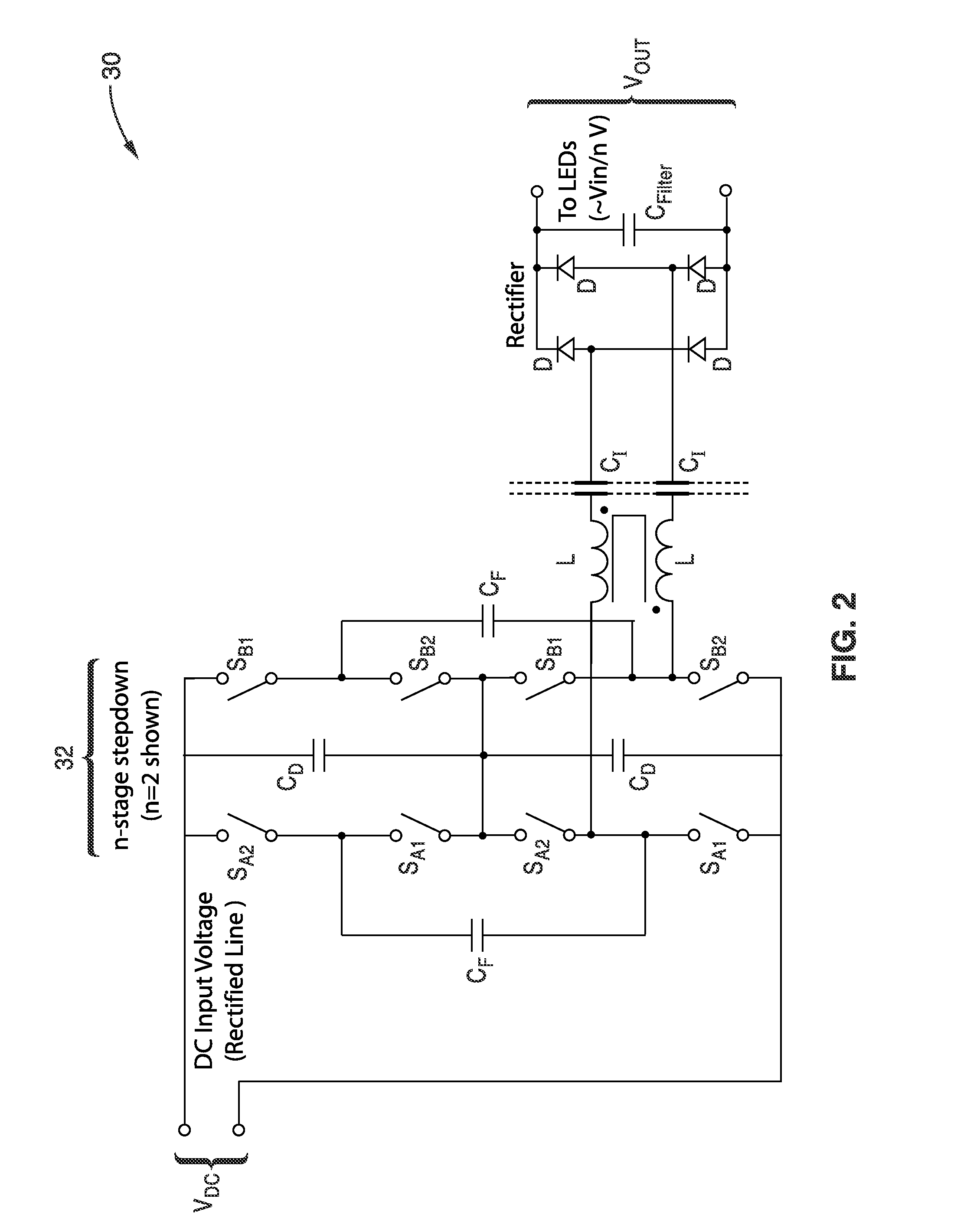
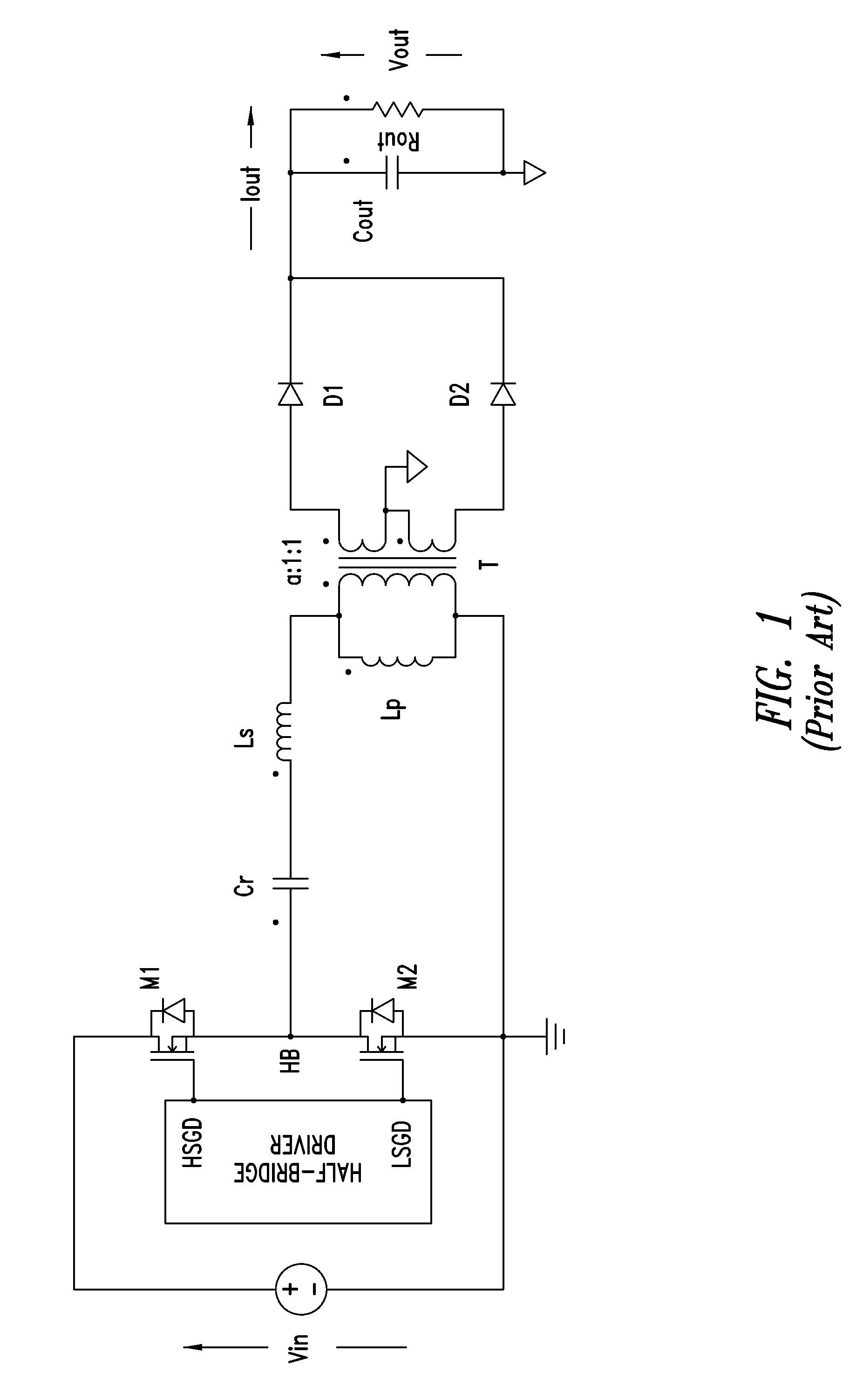
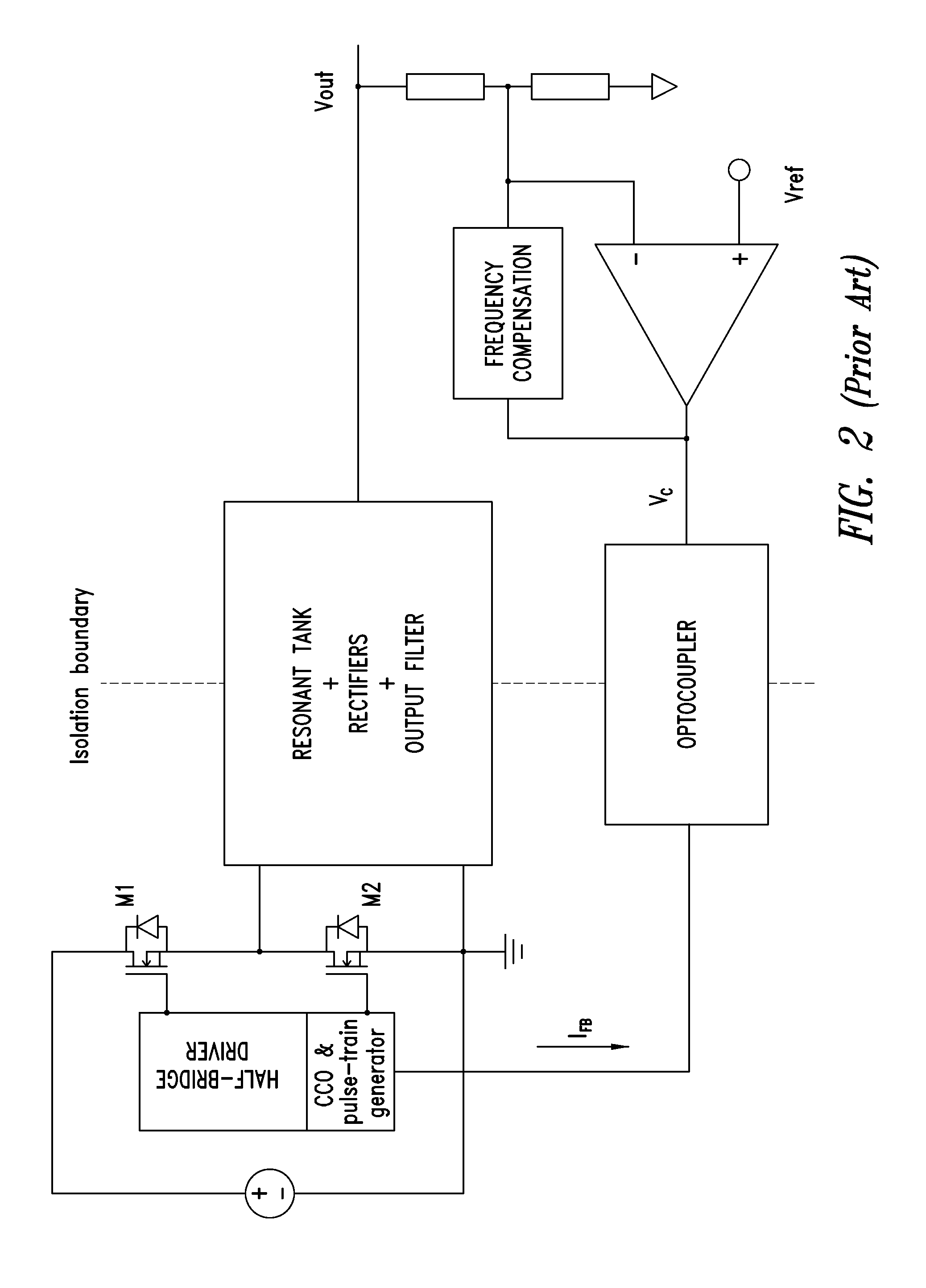
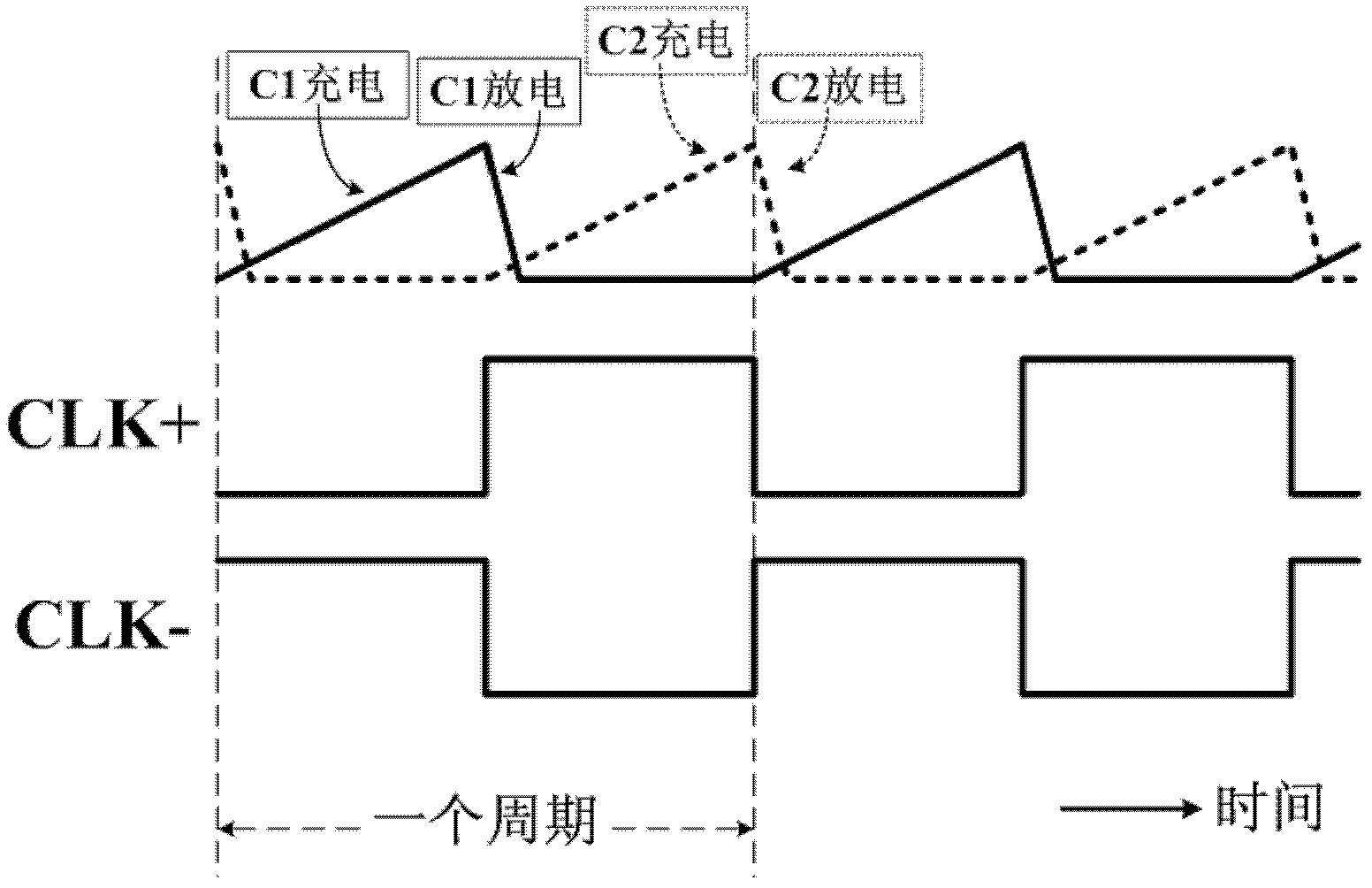
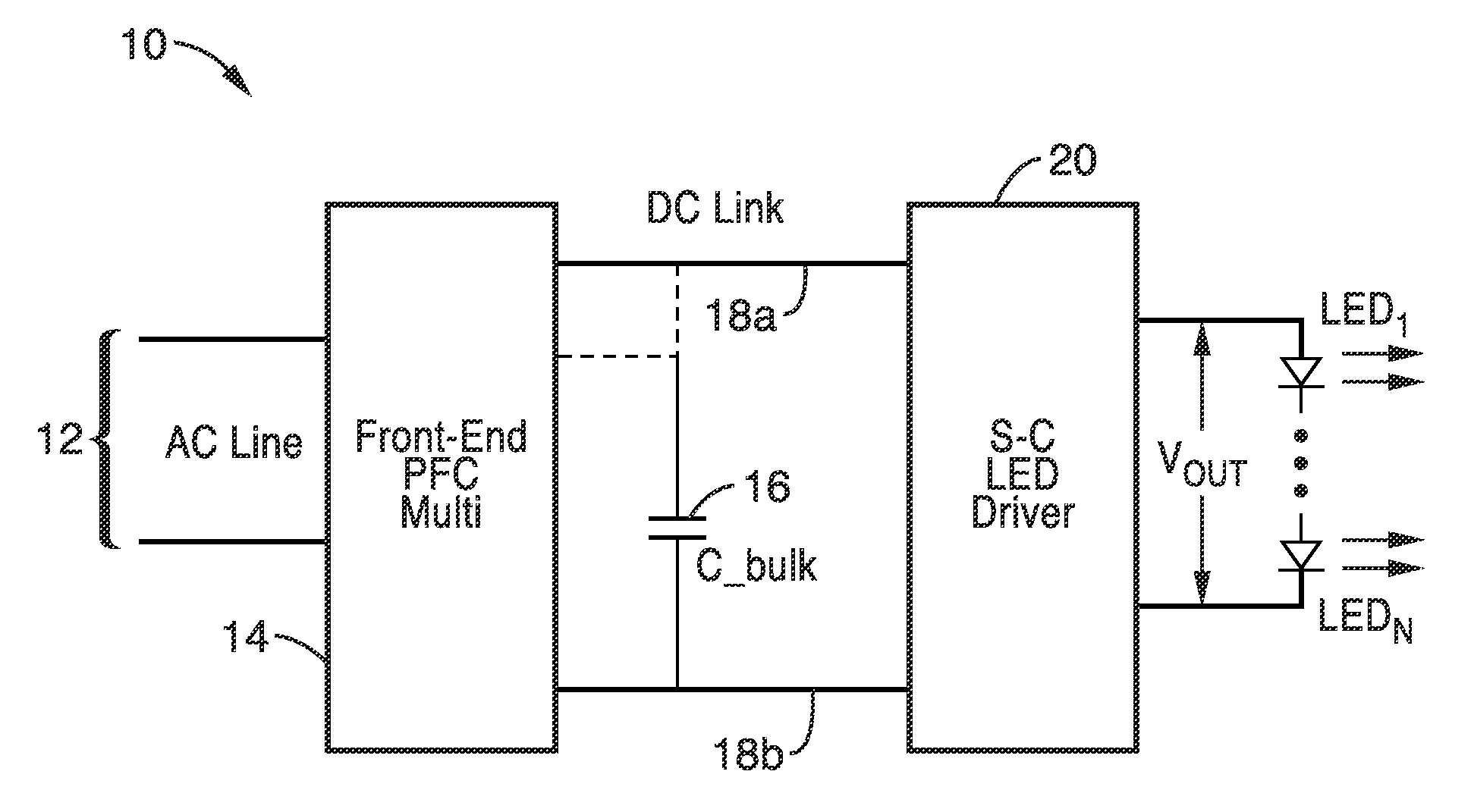
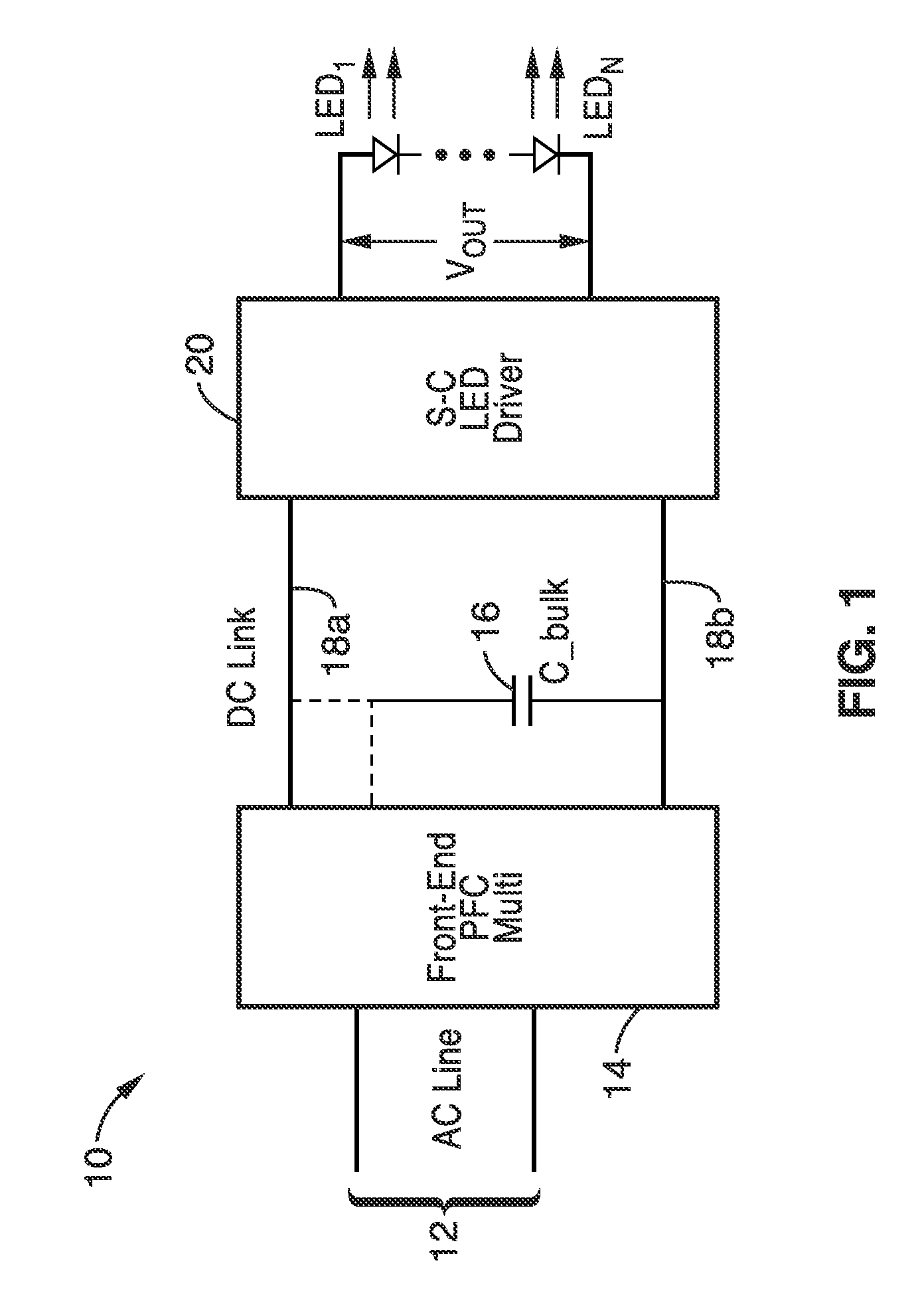
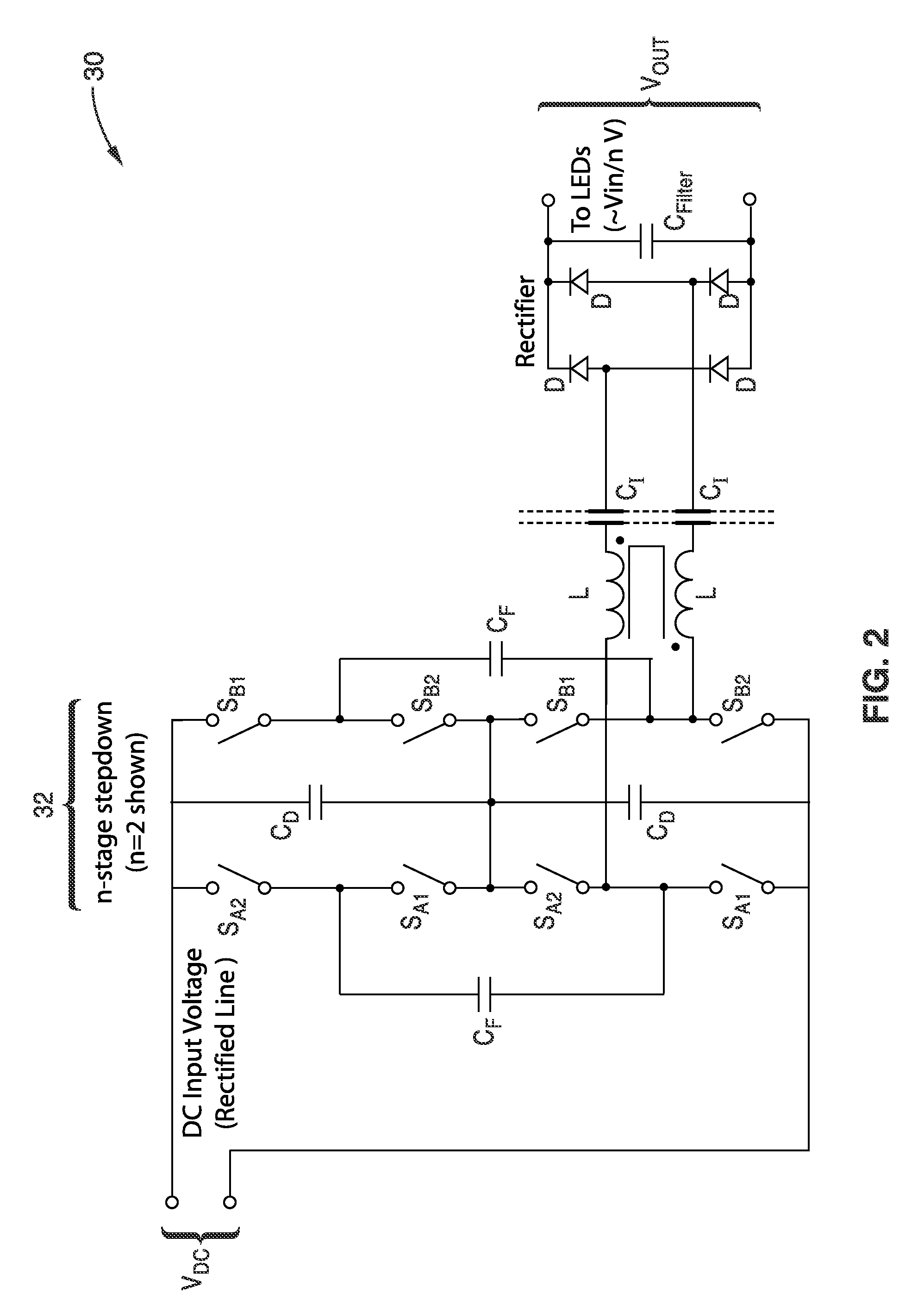
Switched-capacitor isolated LED driver
ActiveUS20140346962A1Improve cooling effectElectroluminescent light sourcesDc-dc conversionCapacitanceLc resonant circuit
A switched-capacitor voltage converter which is particularly well-suited for receiving a line voltage from which to drive current through a series of light emitting diodes (LEDs). Input voltage is rectified in a multi-level rectifier network having switched capacitors in an ascending-bank configuration for passing voltages in uniform steps between zero volts up to full received voltage VDC. A regulator section, operating on VDC, comprises switched-capacitor stages of H-bridge switching and flying capacitors. A current controlled oscillator drives the states of the switched-capacitor stages and changes its frequency to maintain a constant current to the load. Embodiments are described for isolating the load from the mains, utilizing an LC tank circuit or a multi-primary-winding transformer.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
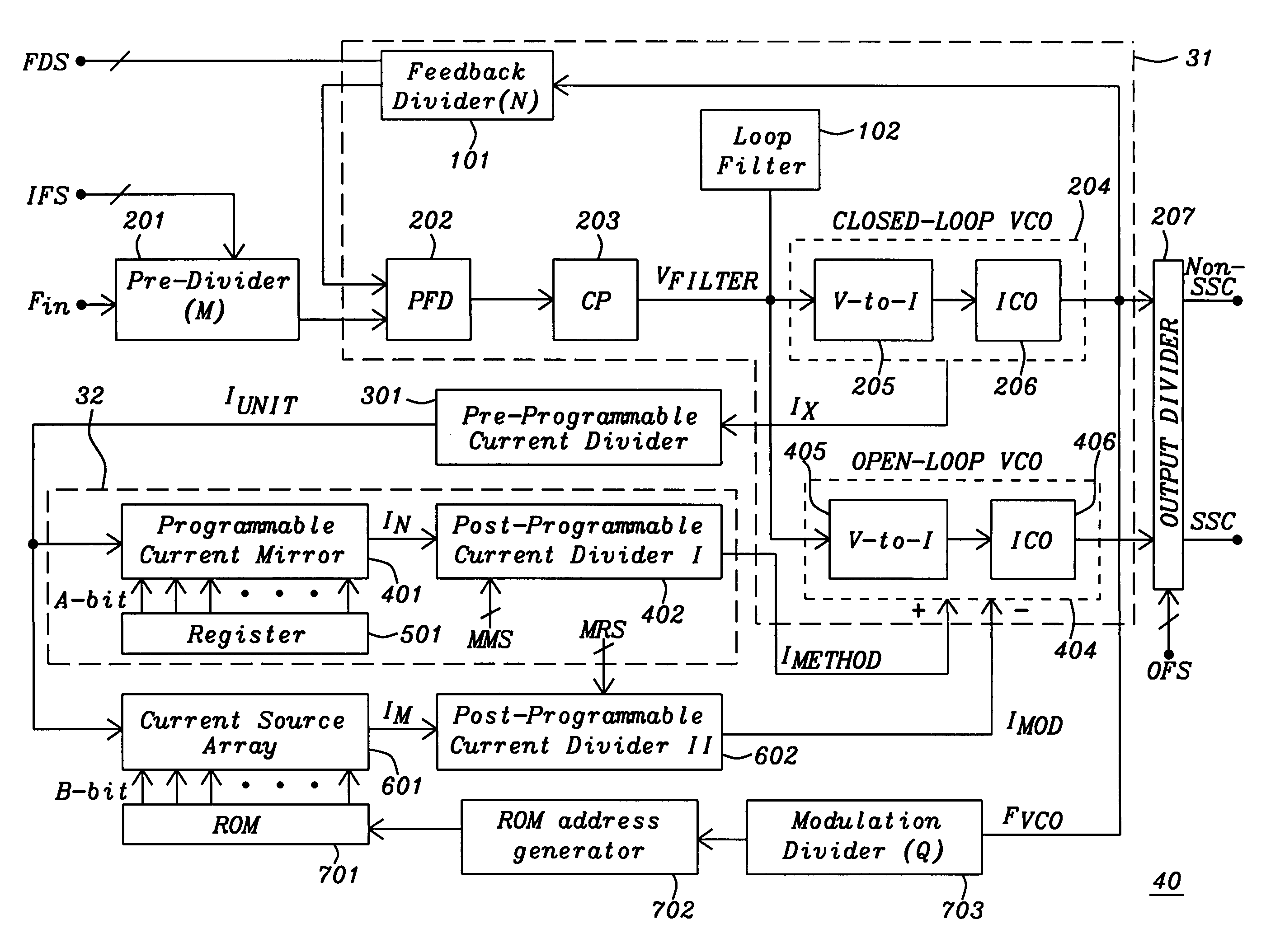
Spread spectrum clock generator
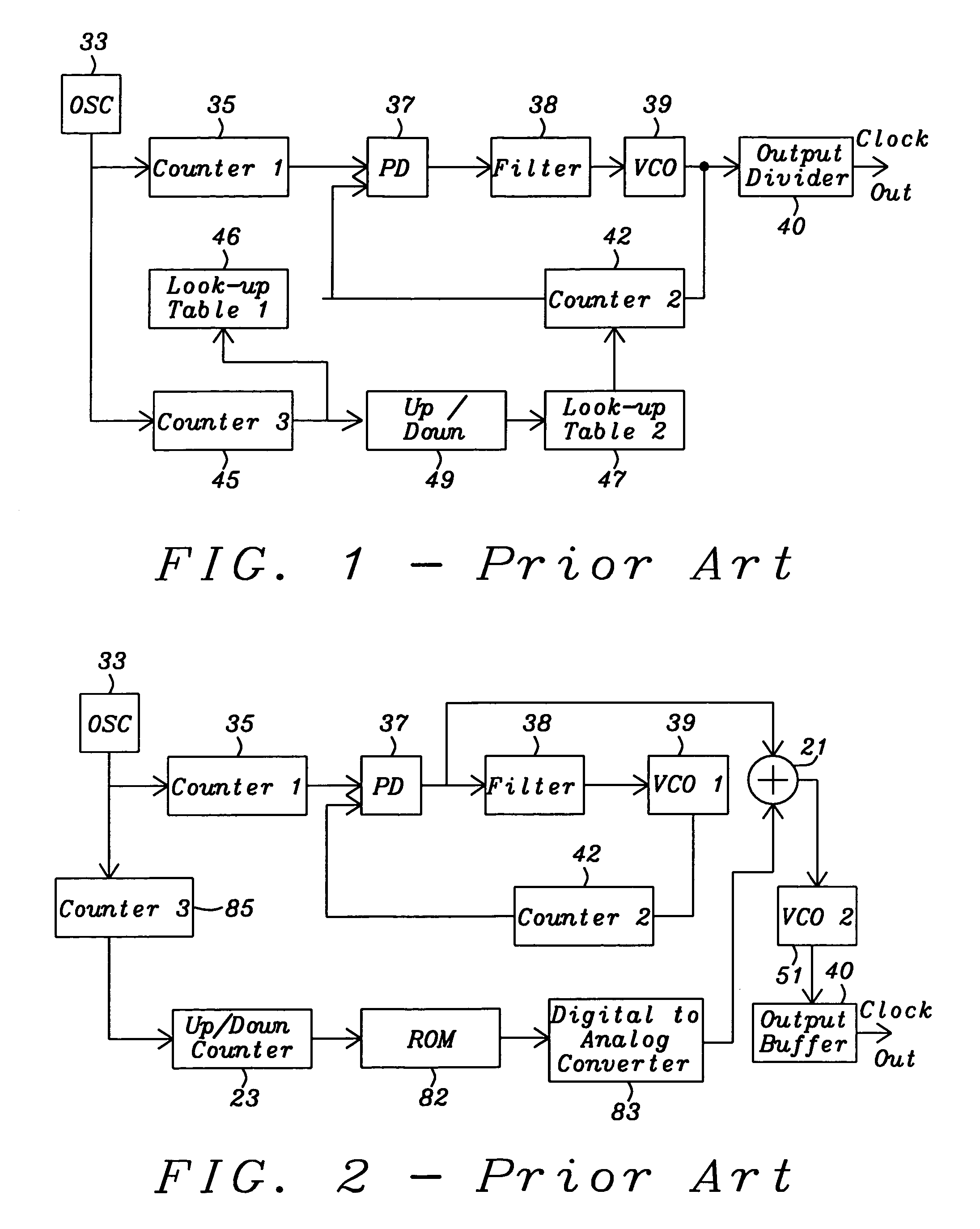
InactiveUS20060056491A1Robust architectureLess susceptible to noisePulse automatic controlElectrical apparatus interference reductionClosed loopCurrent controlled oscillator
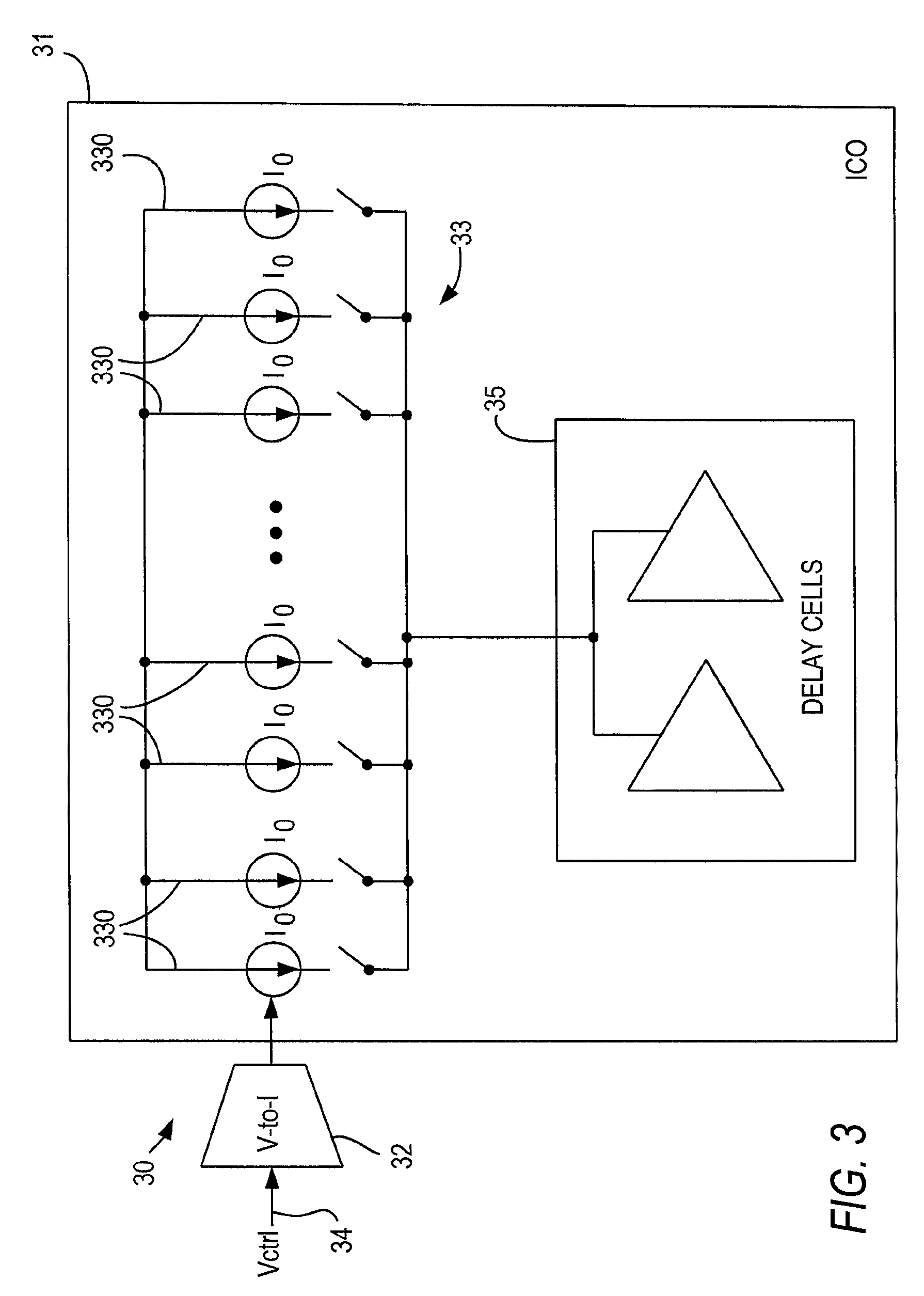
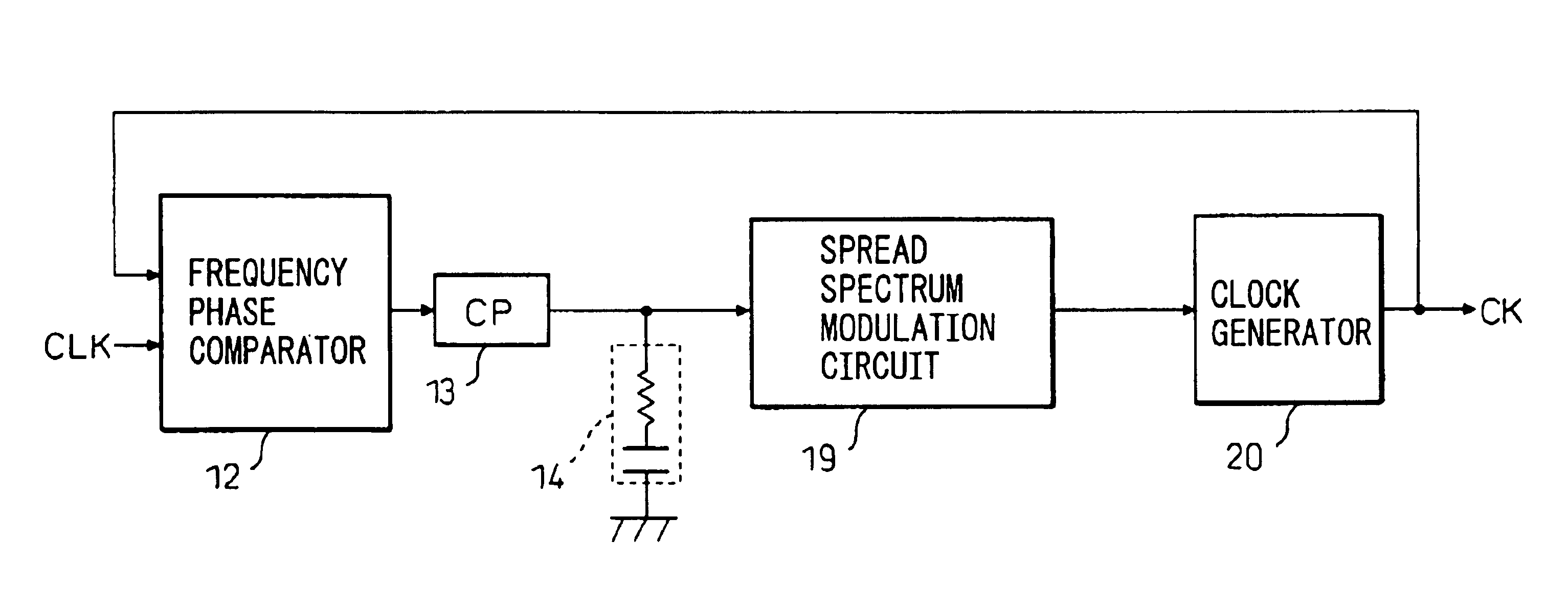
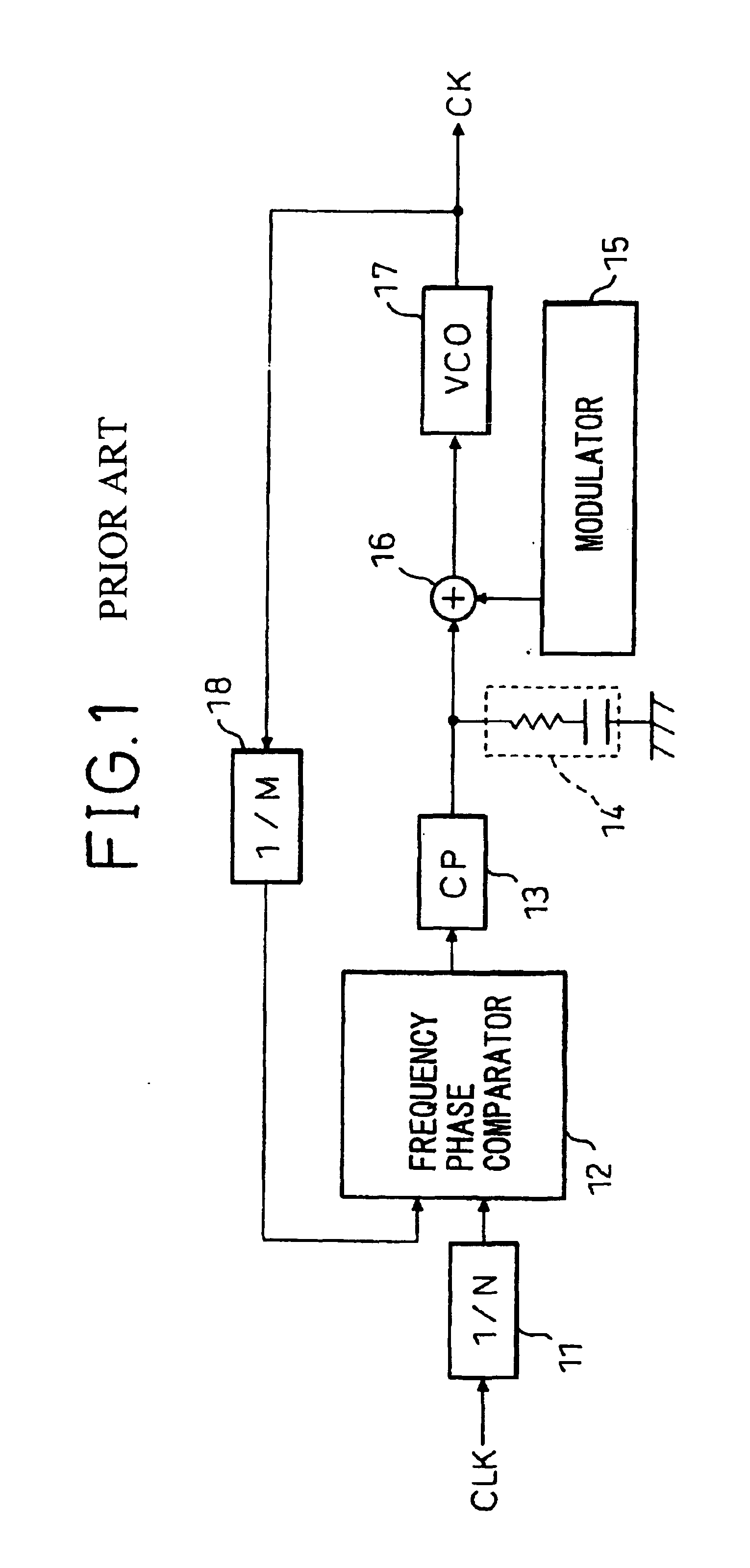
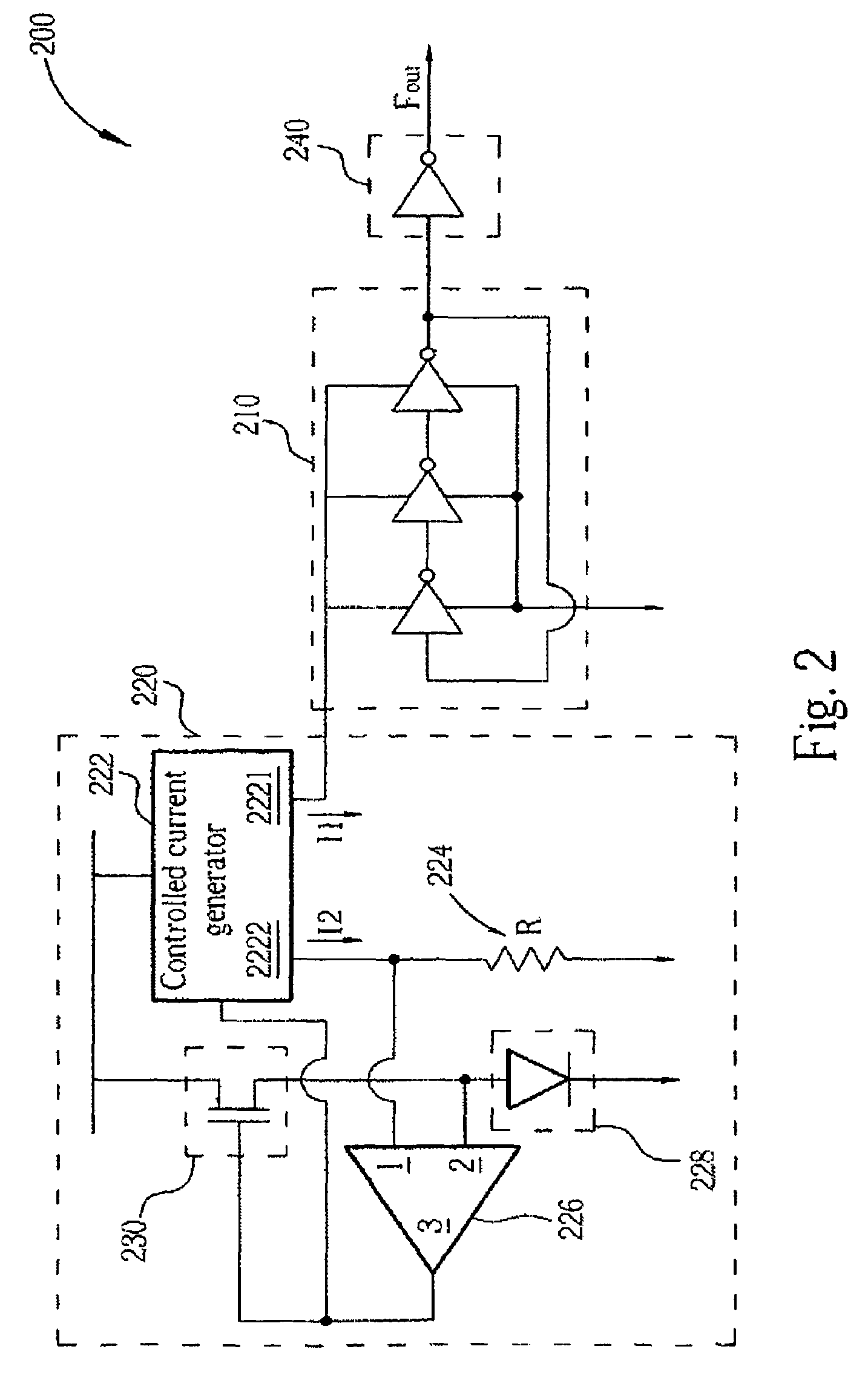
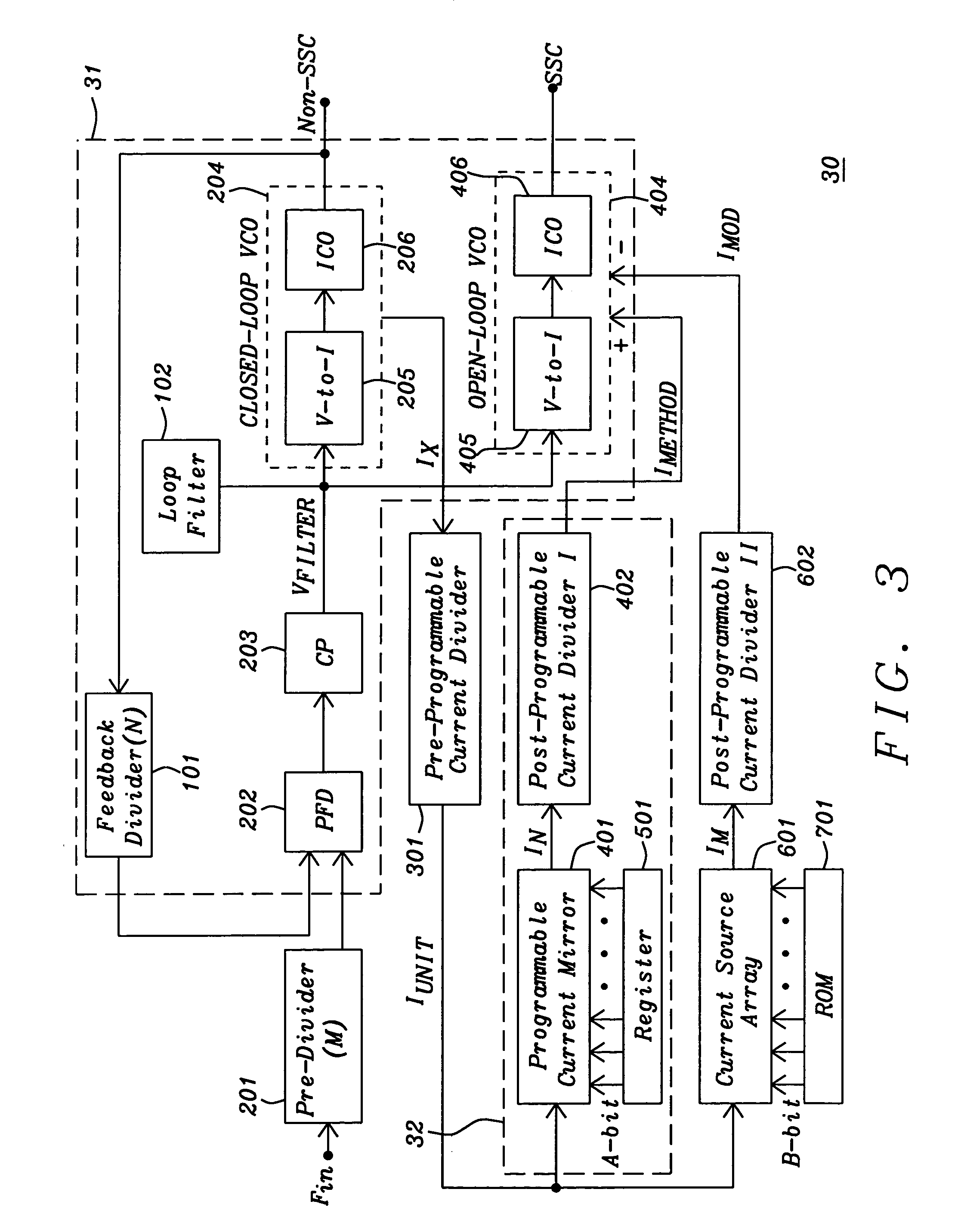
A spread spectrum clock generator comprises a conventional closed-loop VCO and an open-loop VCO where both are coupled to the same point of the PLL. Both VCOs comprise a V-to-I converter followed by a current-controlled oscillator and are identical in design but only the open-loop VCO receives the modulation current to generate the spread spectrum clock signal. The open-loop ICO is part of the spread spectrum generator and in one embodiment of the invention receives feedback current signals representing the modulation method and modulation ratio. This ensures that the modulated clock output tracks the PLL output frequency. In a second embodiment the closed-loop VCO receives from the spread spectrum generator the feedback current signal representing the modulation method (center / down spread) while the open-loop VCO receives the feedback signal representing the modulation ratio.
Owner:KARMIC DESIGN USA
High-frequency low-gain ring VCO for clock-data recovery in high-speed serial interface of a programmable logic device
ActiveUS7956695B1Angle modulation by variable impedencePulse automatic controlControl signalProgrammable logic device
A voltage-controlled oscillator operates at high frequency without high gain by dividing the frequency range into a plurality of subranges, which preferably are substantially equal in size. Within any subrange, the full extent of variation in the control signal changes the frequency only by the extent of the subrange. The gain is thus substantially equal to the gain one would expect for the full frequency range, divided by the number of subranges. The subrange may be selected manually, or by an initial calibration process. In one embodiment, the oscillator includes a voltage-to-current converter and a current-controlled oscillator, with a current mirror arrangement. In that embodiment, selection of the subrange may be controlled by turning on the correct number of current legs.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
Burst-mode control method for low input power consumption in resonant converters and related control device
ActiveUS20140016362A1Improve efficiencySuppression of shortcomingsEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionMicrocontrollerMode control
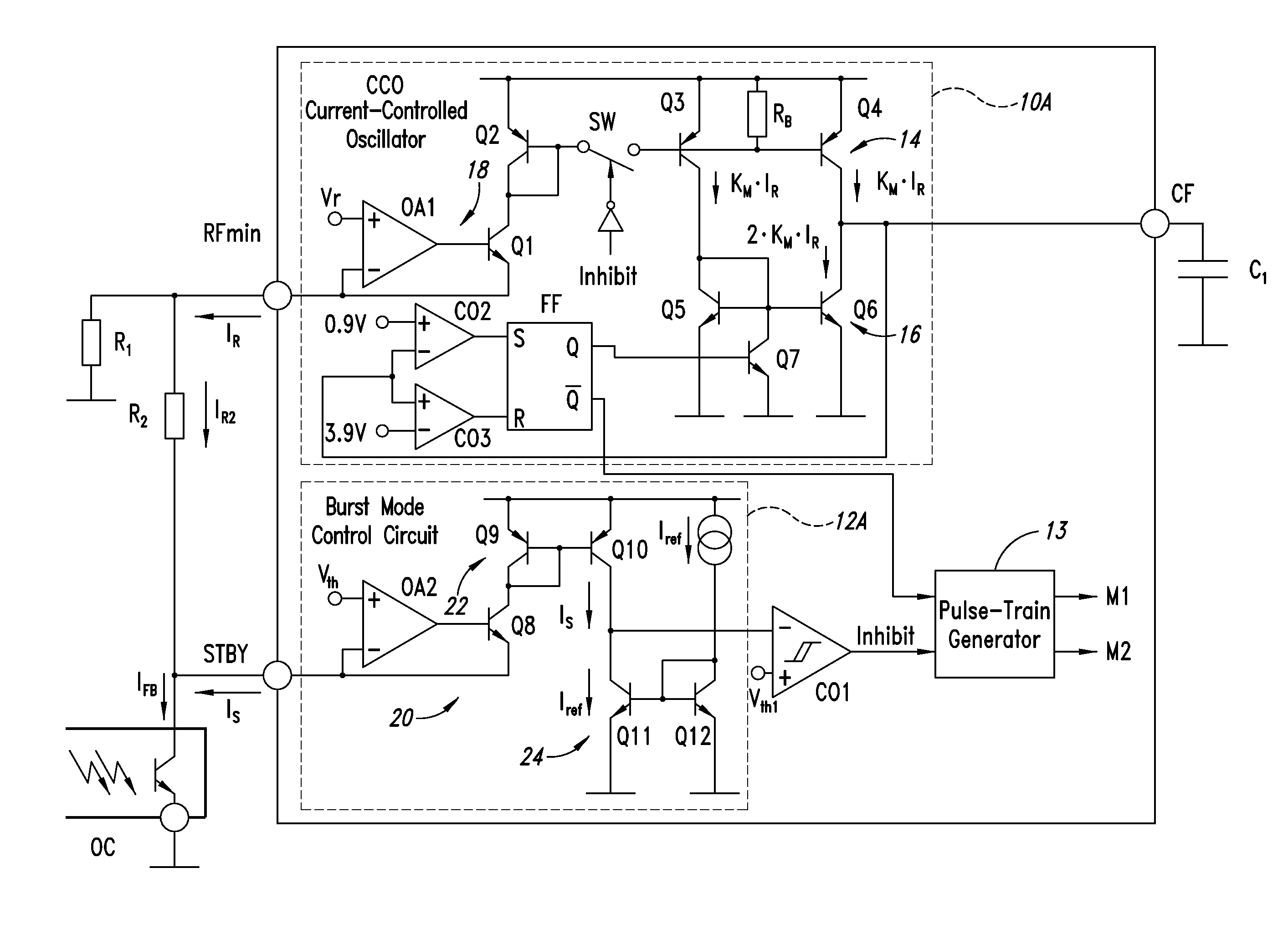
An effective method enhances energy saving at low load in a resonant converter with a hysteretic control scheme for implementing burst-mode at light load. The method causes a current controlled oscillator of the converter to stop oscillating when a feedback control current of the output voltage of the converter reaches a first threshold value, and introduces a nonlinearity in the functional relation between the frequency of oscillation and said feedback control current or in a derivative of the functional relation, while the control current is between a lower, second threshold value and the first threshold value, such that the frequency of oscillation remains equal or smaller than the frequency of oscillation when the control current is equal to the second threshold value. Several circuital implementations are illustrated, all of simple realization without requiring any costly microcontroller.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS INT NV
Wideband tunable laser line-width reduction
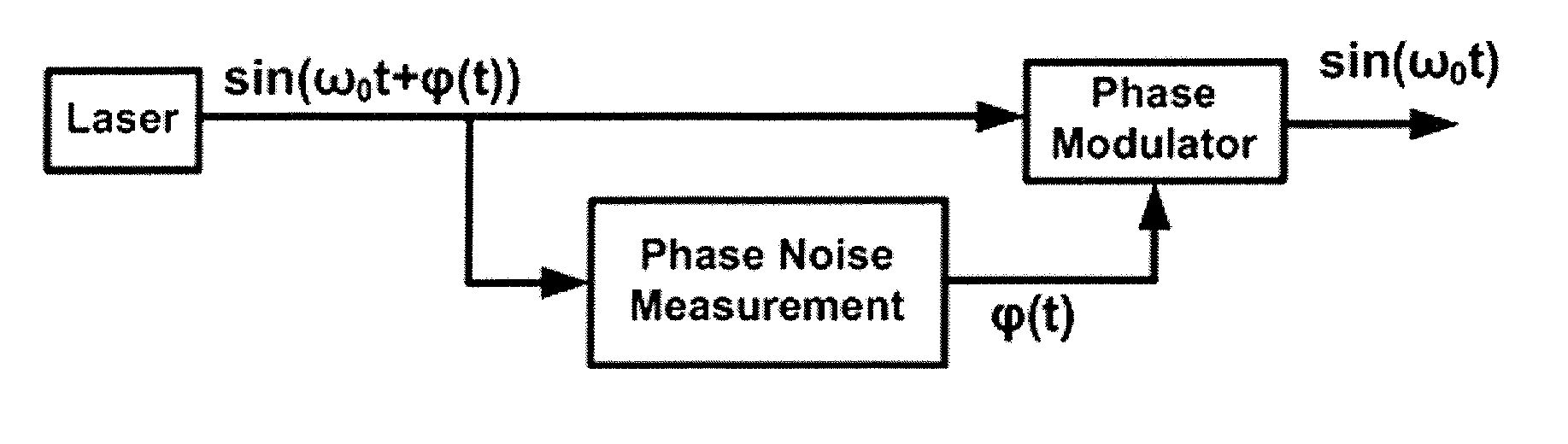
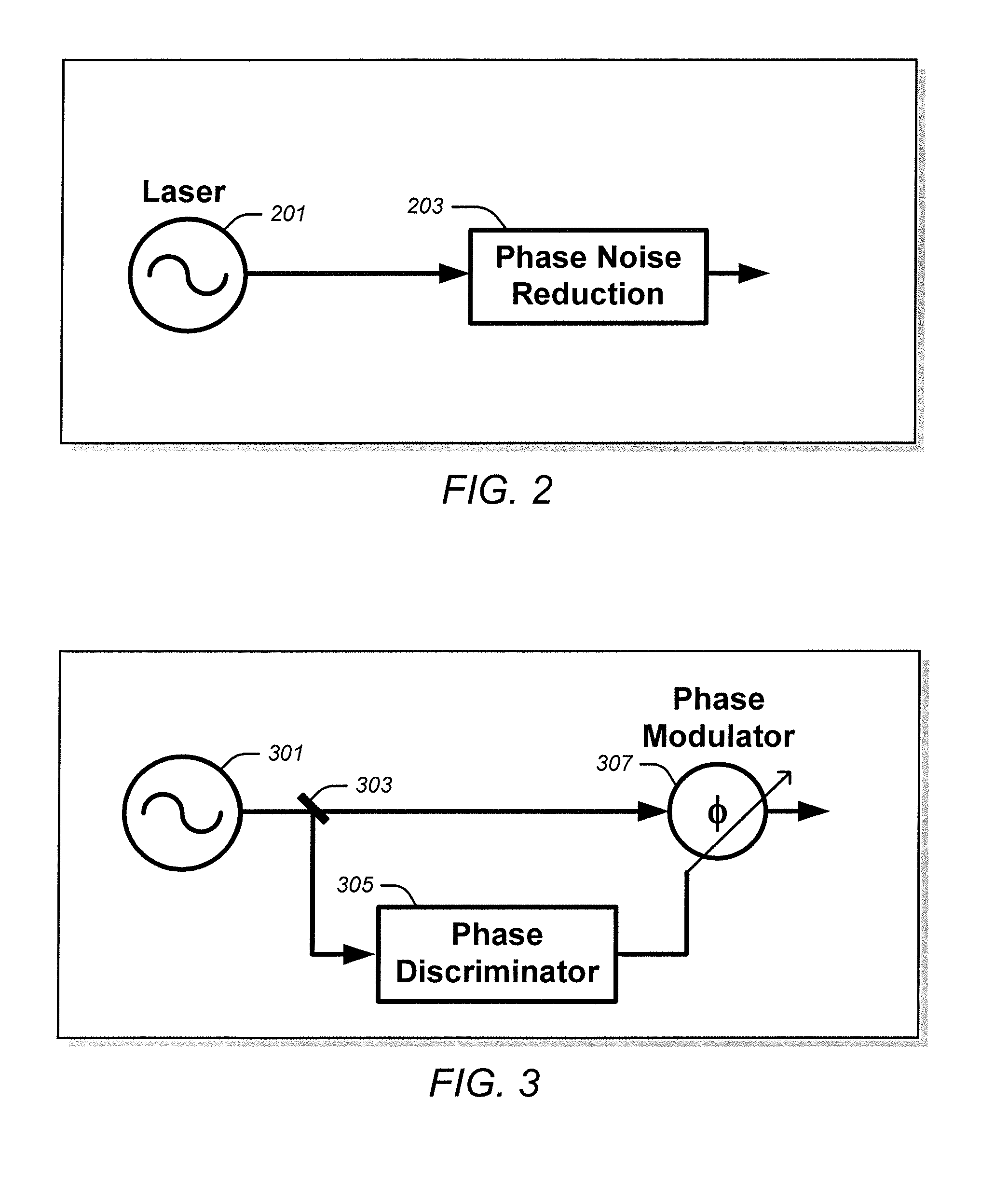
InactiveUS20130215919A1Reduce phase noiseLaser detailsWave based measurement systemsDiscriminatorPhase noise
Various examples of feed-forward systems that reduce phase noise in a laser field generated by a laser. These include feed-forward systems that utilize phase and / or frequency discriminators, filters, integrators, voltage controlled oscillators (VCOs), current controlled oscillators (CCOs), phase modulators, and / or amplitude modulators. It also includes systems that use both feed-forward and feedback phase noise reduction systems, tunable semiconductor lasers, and multiple, sequential feed-forward systems.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
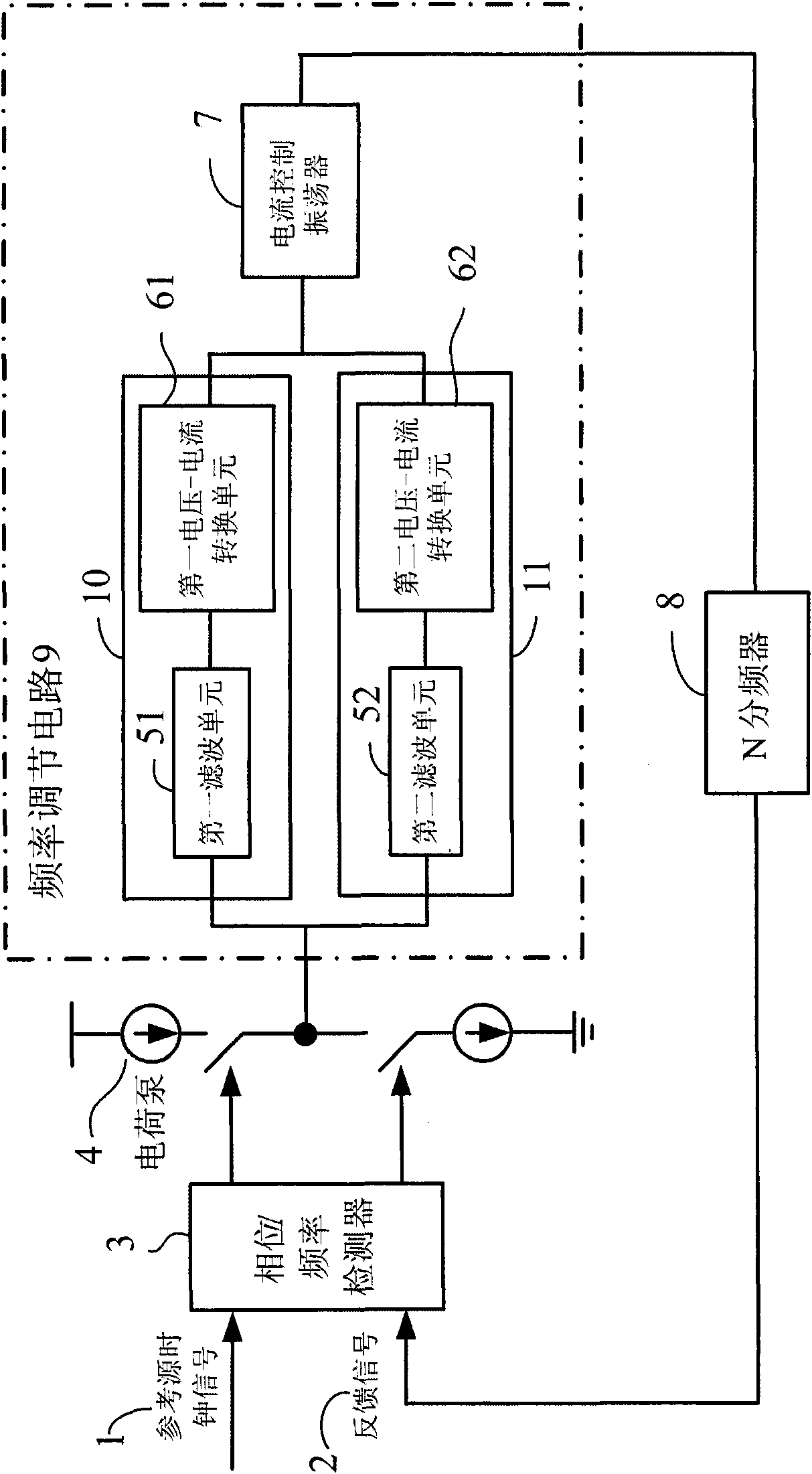
Double-phase-locked loop circuit and control method thereof
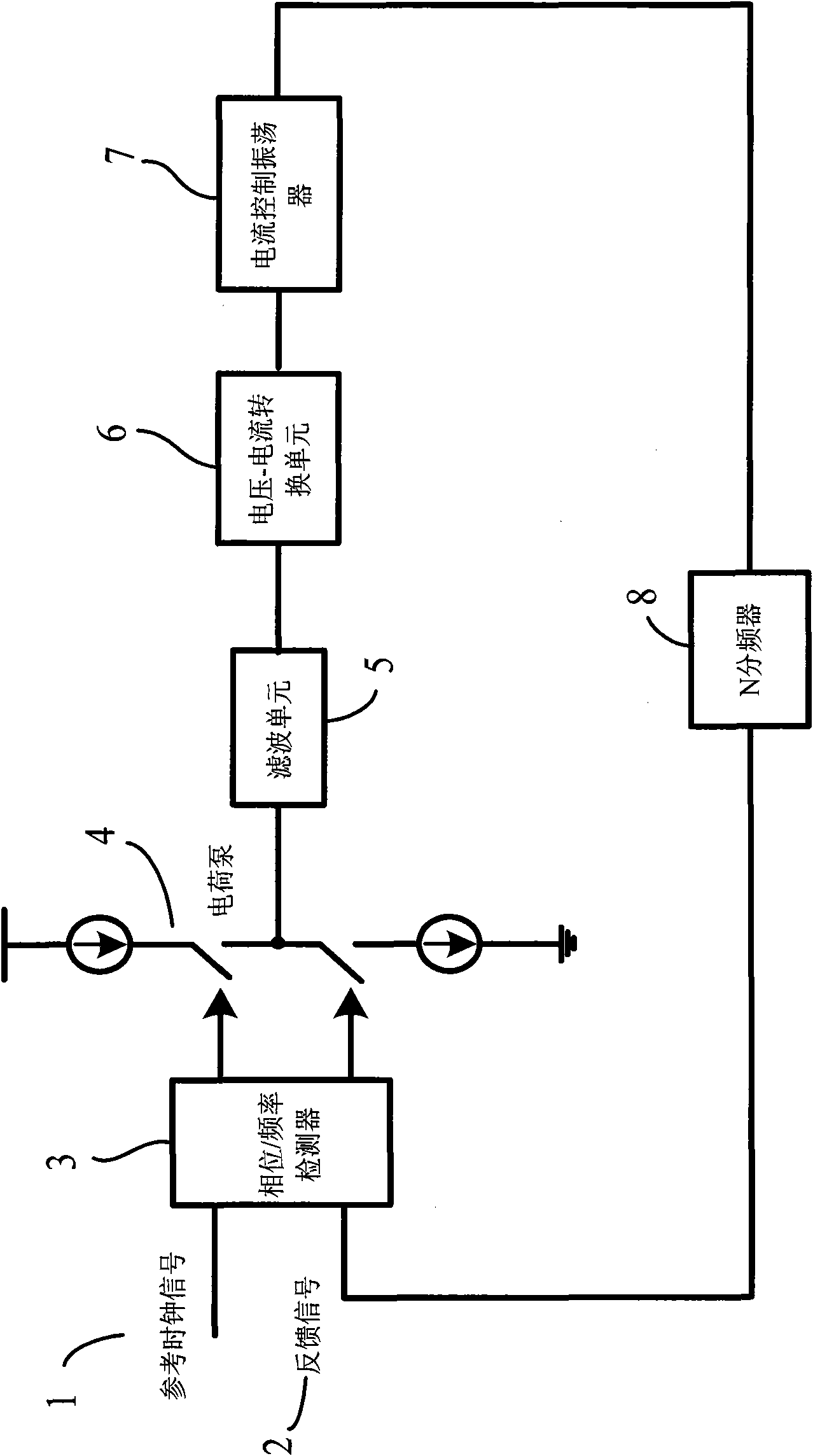
ActiveCN101944910AReduce Design ComplexityImprove performancePulse automatic controlPhase locked loop circuitDouble phase
The invention discloses a double-phase-locked loop circuit and a control method thereof. The double-phase-locked loop circuit comprises a phase / frequency detector, a charge pump, a frequency adjustment circuit and an N frequency divider. The frequency adjustment circuit comprises a coarse adjustment circuit, a fine adjustment circuit and a current-controlled oscillator, wherein the coarse adjustment circuit is used for coarse adjustment of frequency of output signals of phase-locked loops till approaching a target frequency; the fine adjustment circuit is used for fine adjustment of the frequency of the output signals of the phase-locked loops till the target frequency; and the current-controlled oscillator is coupled with the coarse adjustment circuit and the fine adjustment circuit and used for producing the output signals of the phase-locked loops, wherein the frequency of the output signals is the target frequency. The double-phase-locked loop circuit can effectively achieve the purpose of expanding the frequency adjustment range under the situation of keeping the loop bandwidth of the phase-locked loops smaller, realize the on-chip integration and further reduce the cost and the design complexity of the circuit.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
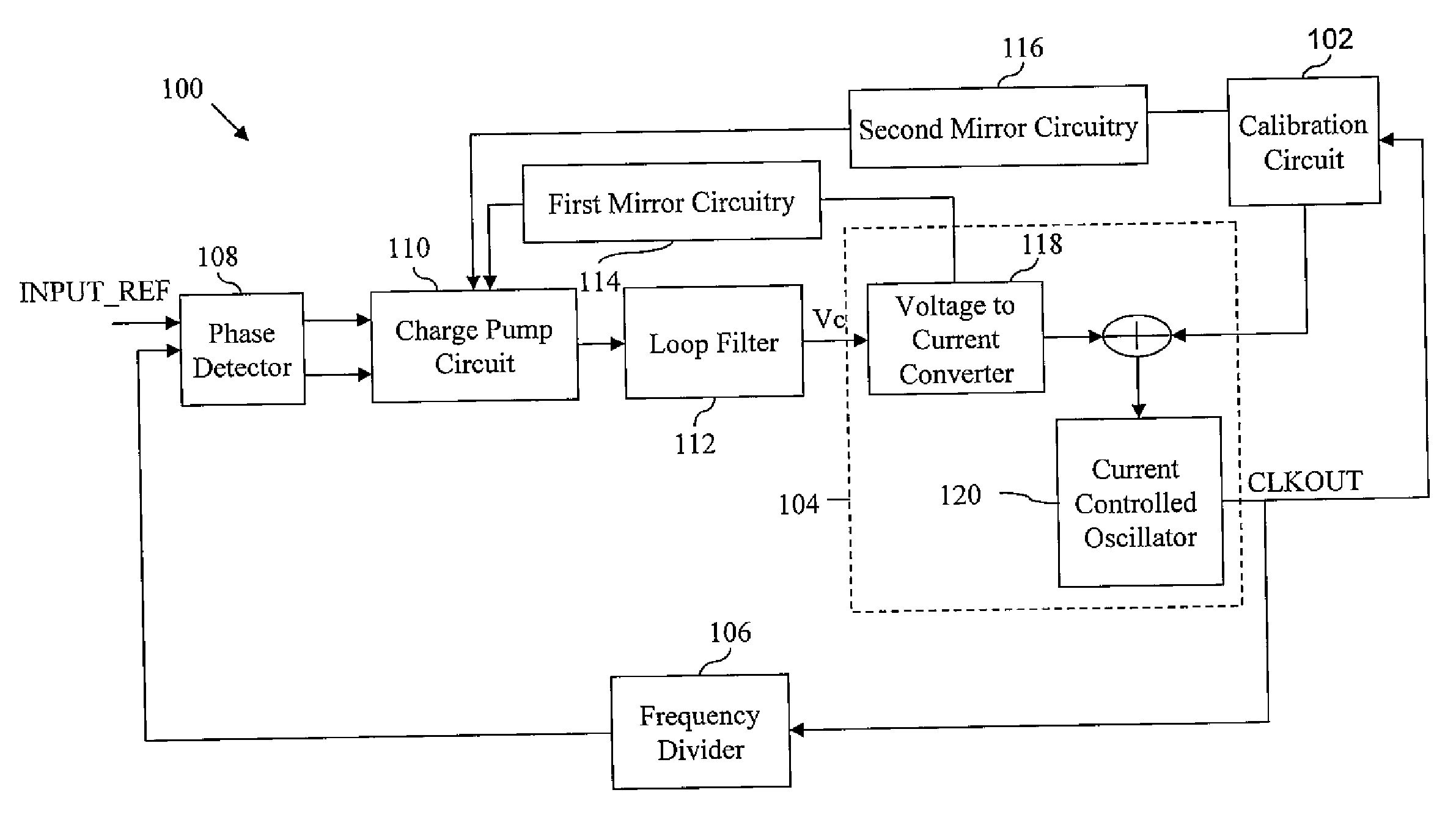
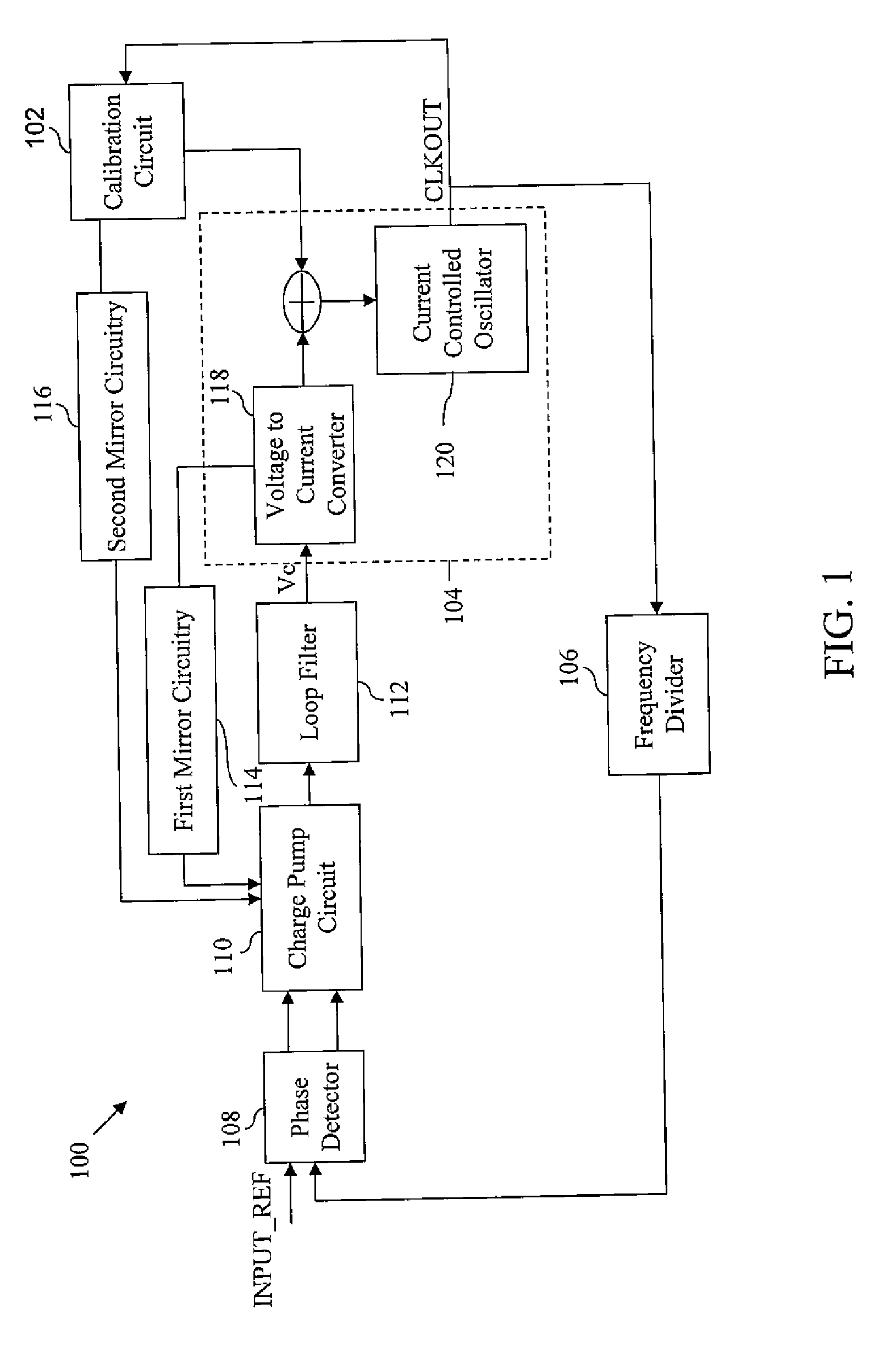
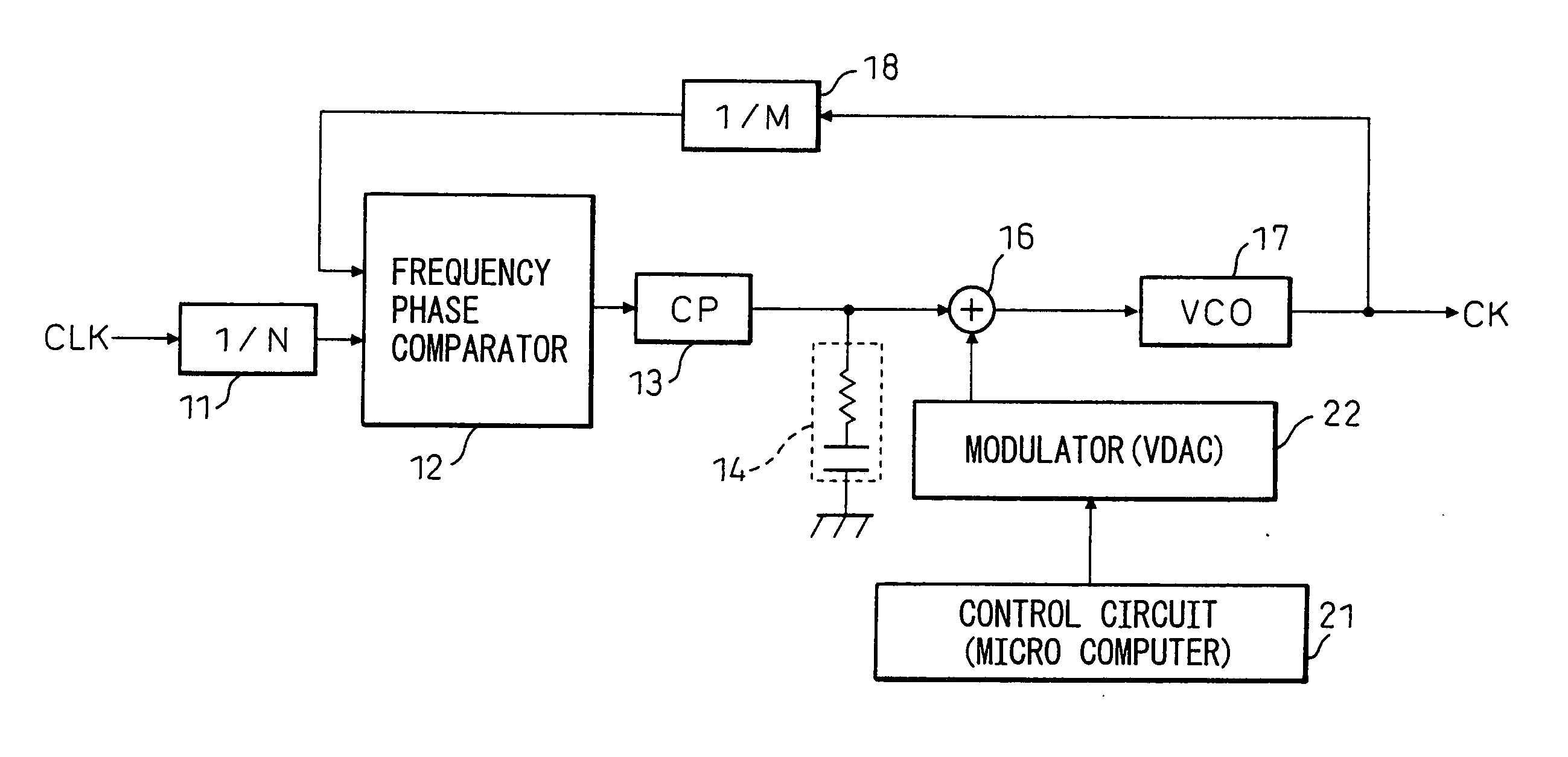
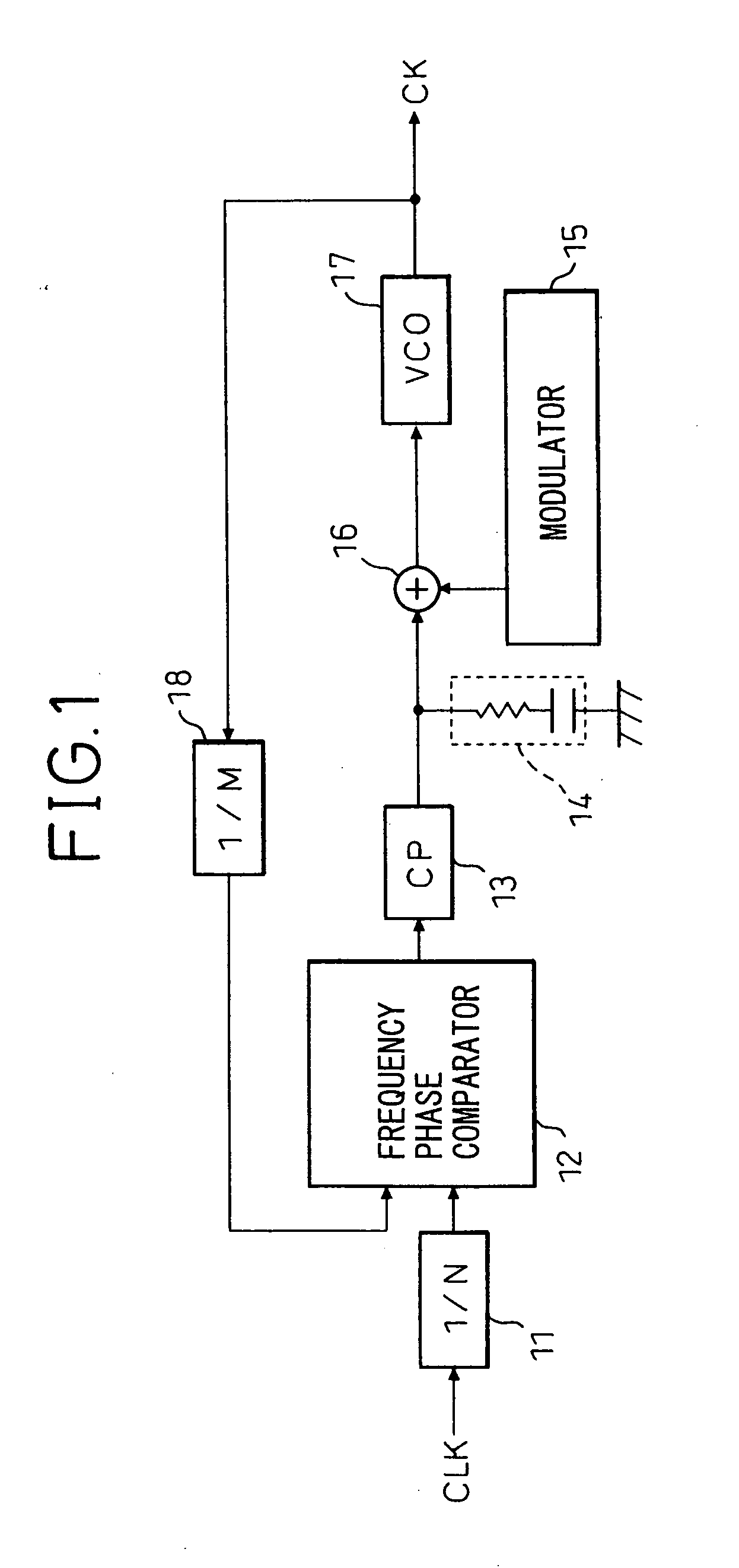
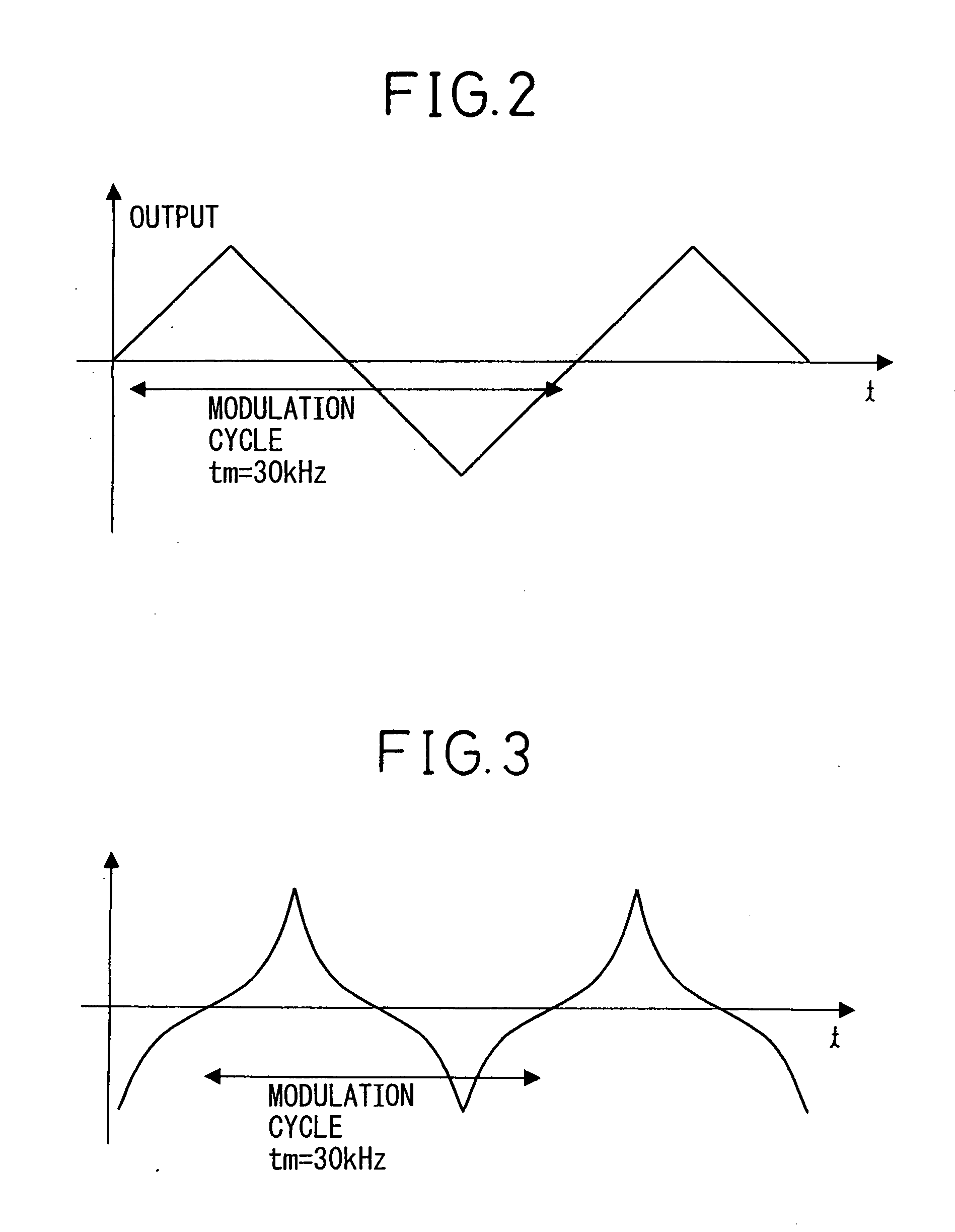
Phase-locked loop and method for operating the same
ActiveUS20100271138A1Pulse automatic controlFrequency analysisPhase detectorCurrent controlled oscillator
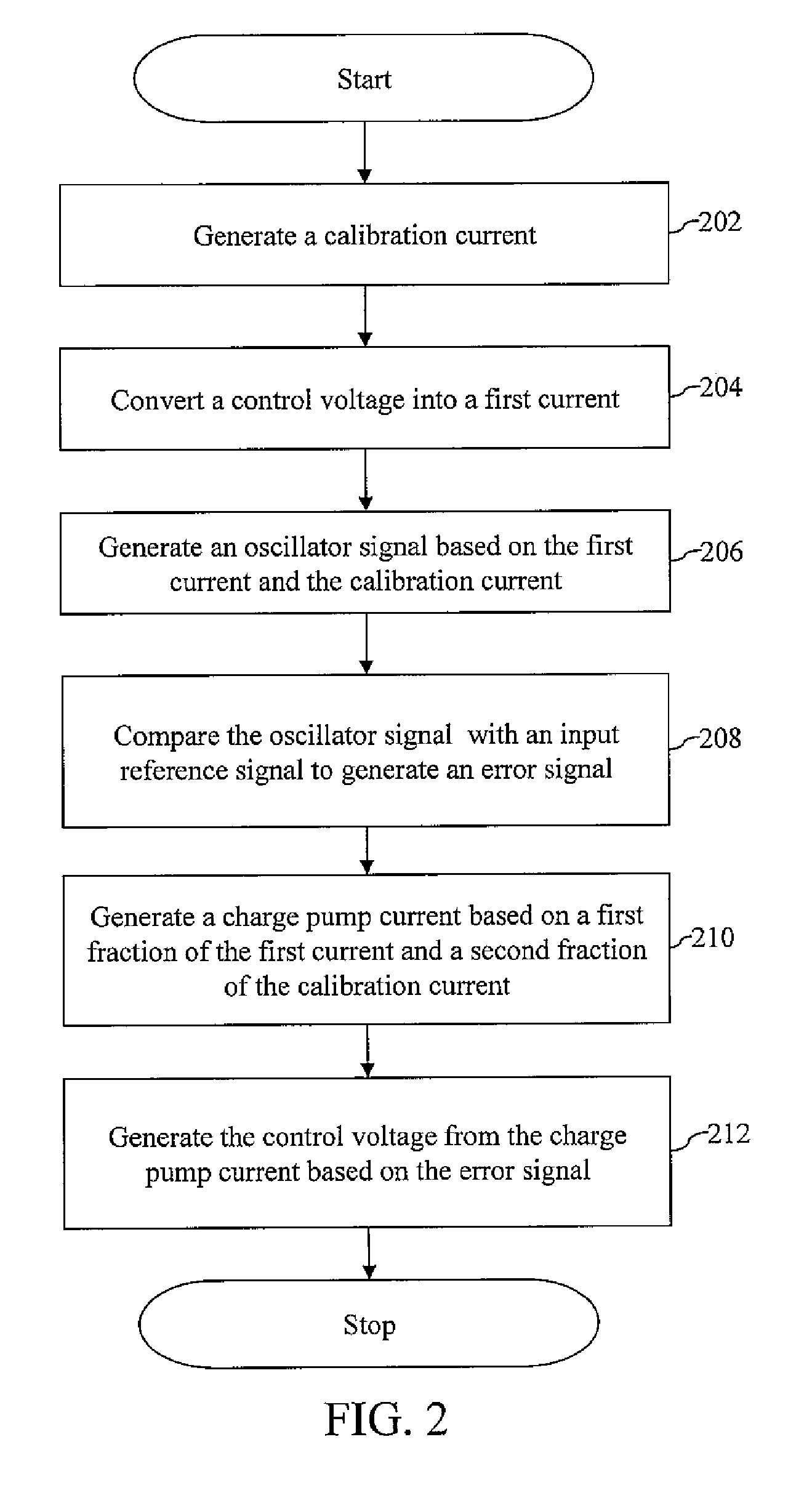
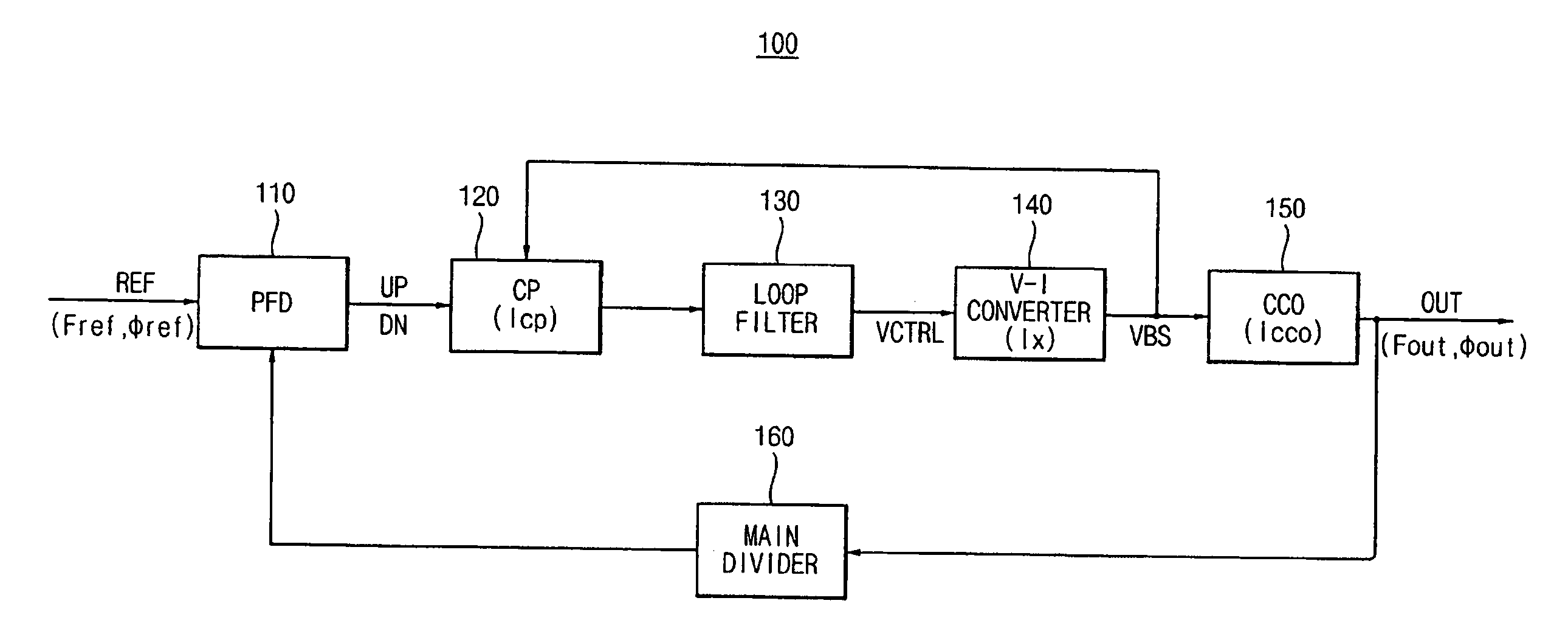
A phase-locked loop (PLL) system generates an oscillator signal based on an input reference signal. A calibration circuit generates a calibration current, and a voltage-to-current converter converts a control voltage into a first current. A current-controlled oscillator generates the oscillator signal based on the first current and the calibration current. A charge pump circuit, which is connected to a phase detector, the voltage-to-current converter, and the calibration circuit, generates a charge pump current based on the first current and the calibration current. The charge pump current is used to generate the control voltage based on an error signal.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Spread spectrum clock generation circuit, jitter generation circuit and semiconductor device
ActiveUS6975148B2Reduce radiated noiseIncrease circuit speedElectric signal transmission systemsPulse automatic controlDevice materialCurrent controlled oscillator
A spread spectrum clock generation circuit capable of further reducing the electromagnetic wave radiation with a simple configuration has been disclosed and, particularly in a spread spectrum clock generation circuit using a current control oscillator (ICO), a differential signal to which a spread spectrum modulation signal, the period or amplitude of which changes, is added is generated, and the differential signal is applied to the ICO and a clock is generated.
Owner:MONTEREY RES LLC
Phase-locked loop circuit
InactiveUS20100052798A1Accurately knowSwitch accuratelyPulse automatic controlPulse generation by logic circuitsPhase locked loop circuitPhase difference
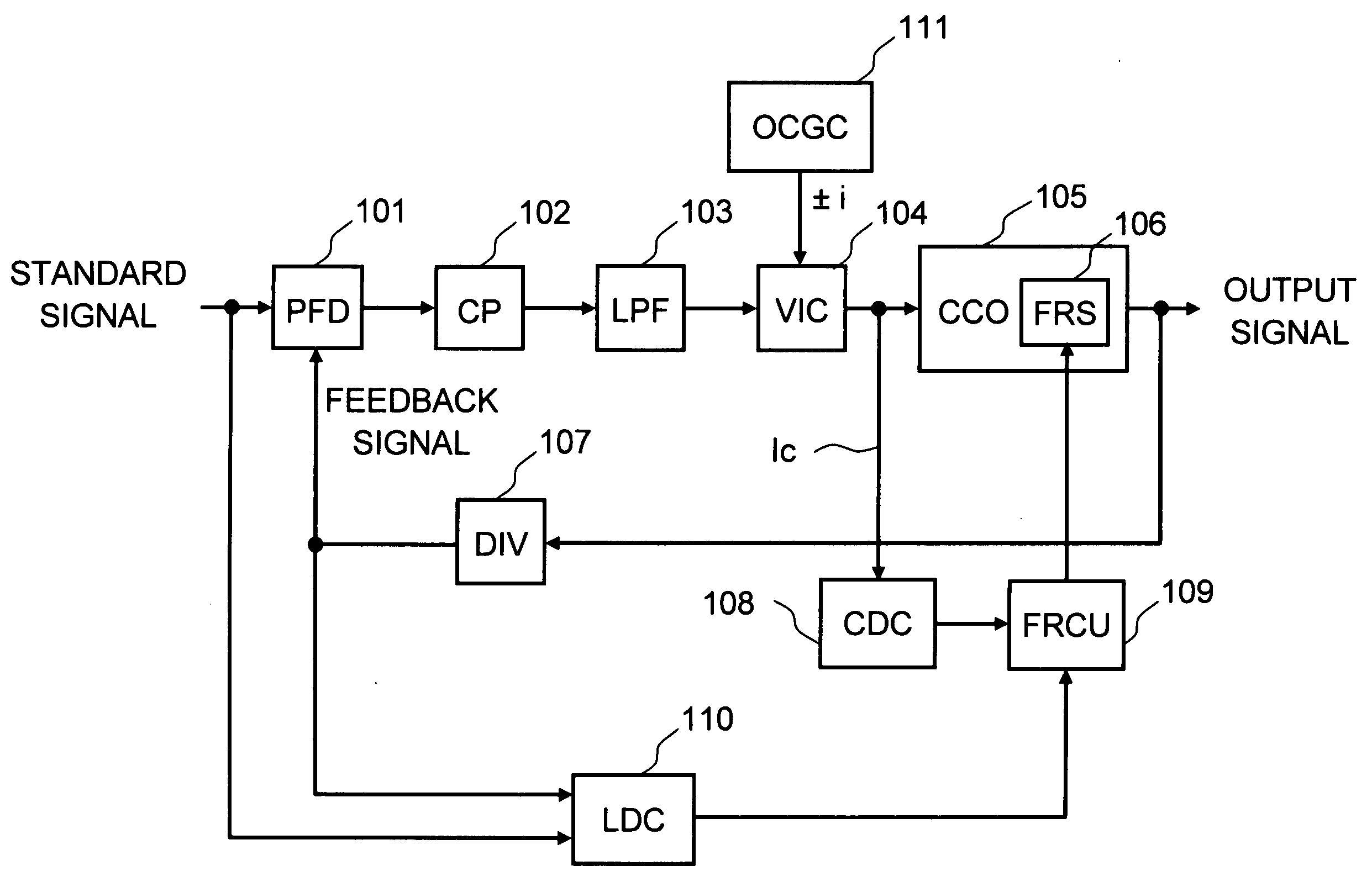
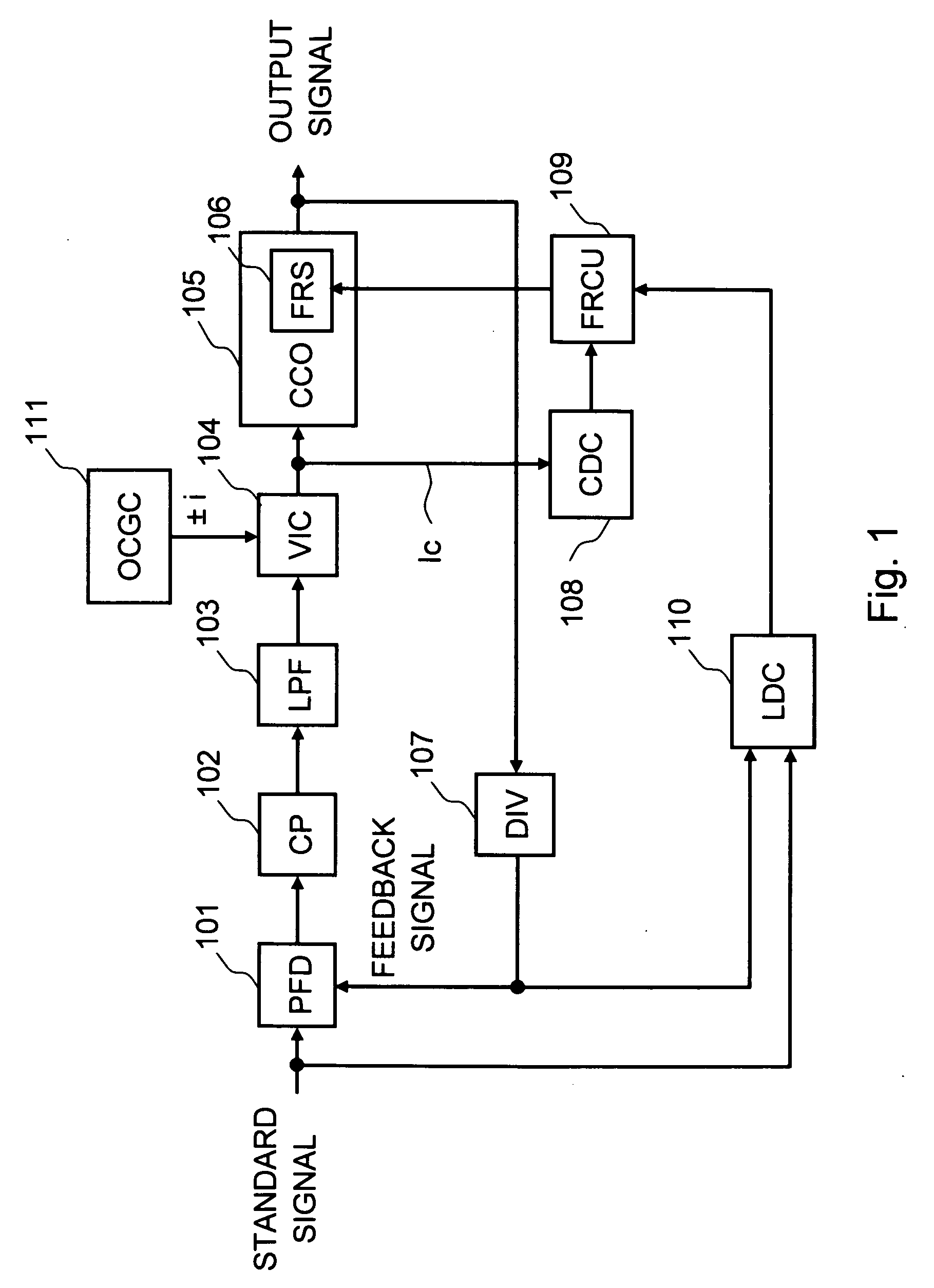
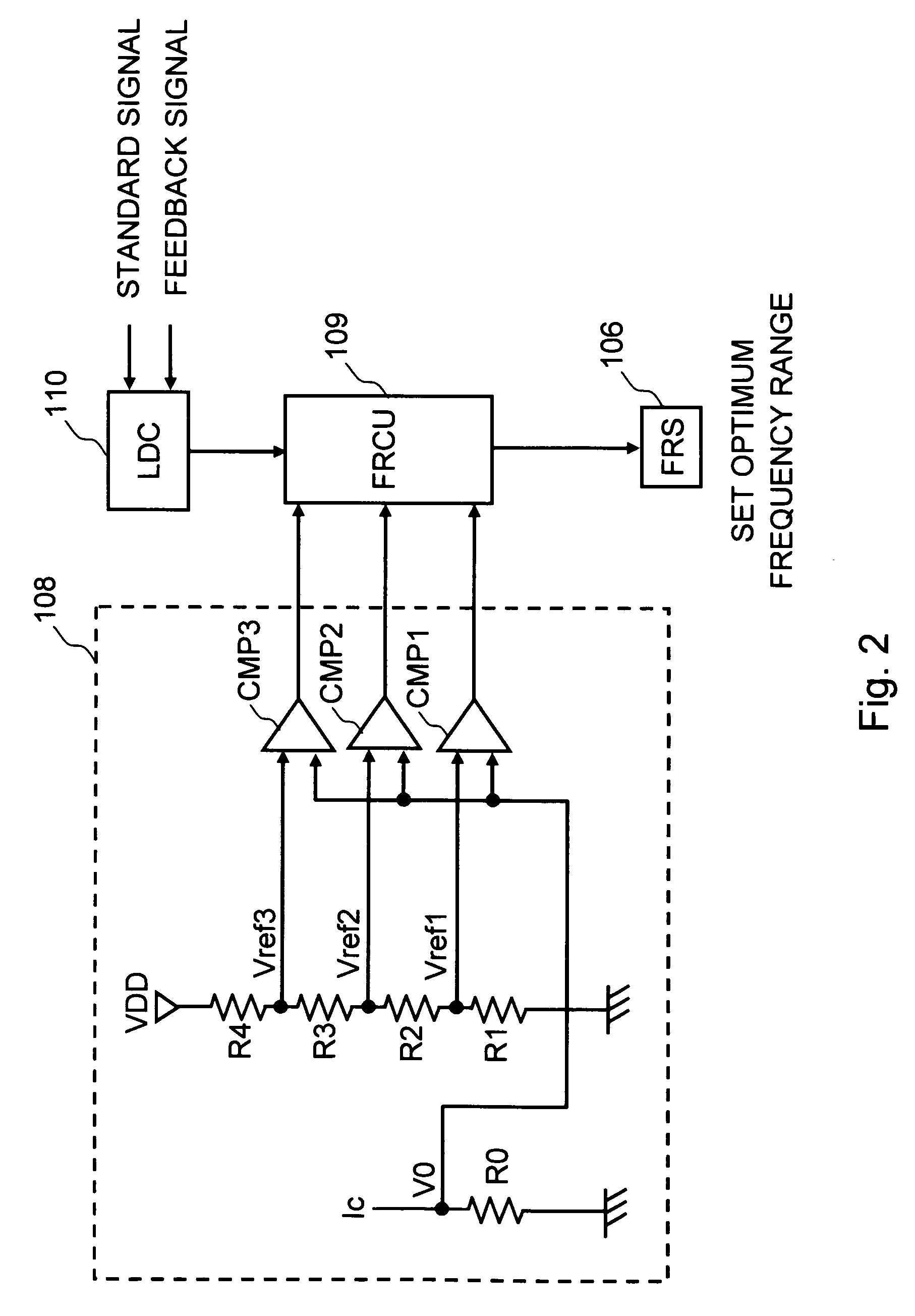
A first exemplary aspect of an embodiment of the present invention is a phase-locked loop circuit including: a voltage-current converter that converts a control voltage into a control current, the control voltage generated according to a phase difference between an input pulse signal and a feedback pulse signal fed back from an output side of a current controlled oscillator; the current controlled oscillator that generates an output pulse signal having a frequency according to the control current; a current detection unit that detects the control current; and a frequency range switch that switches a frequency range of the output pulse signal according to the detected control current.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
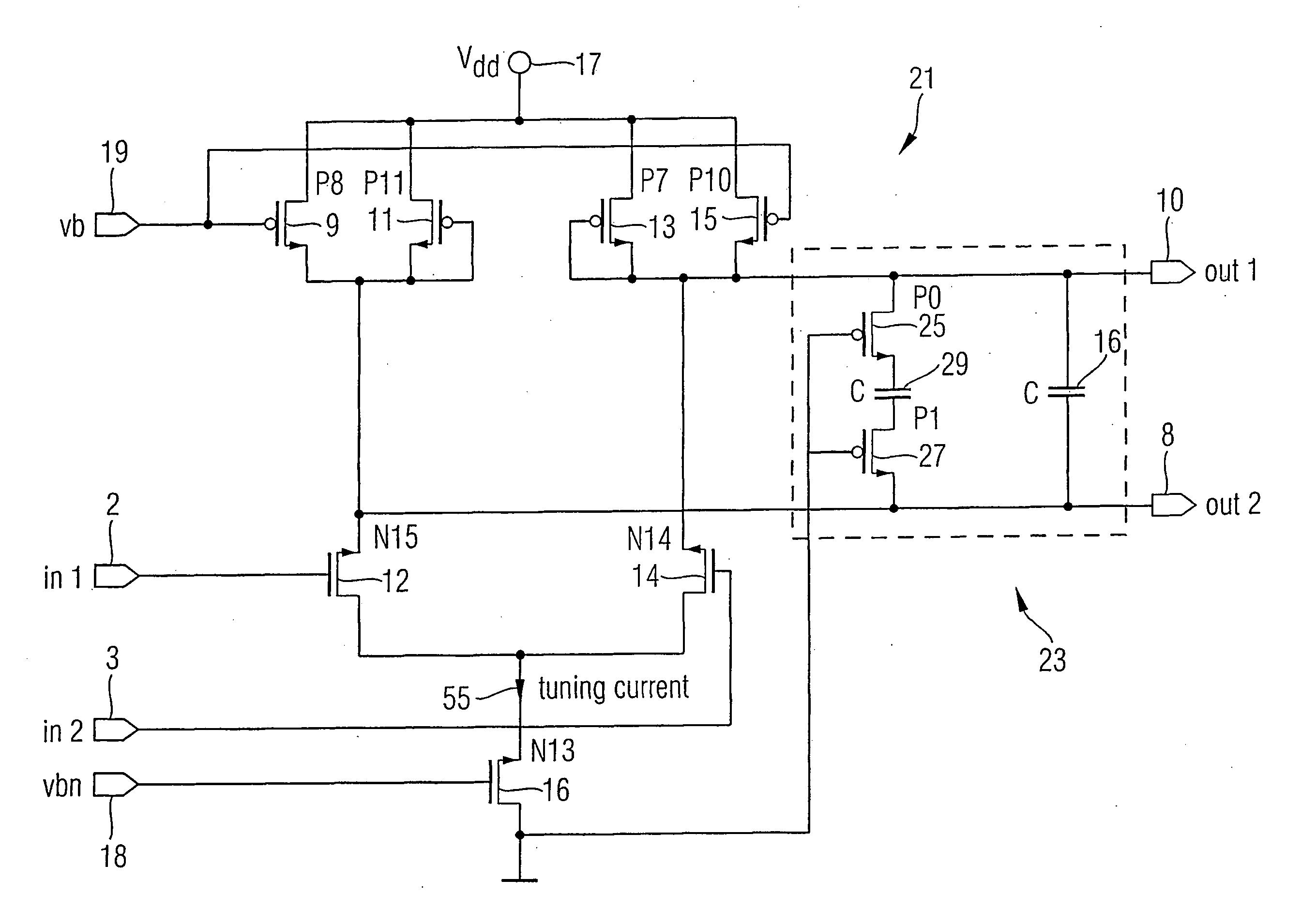
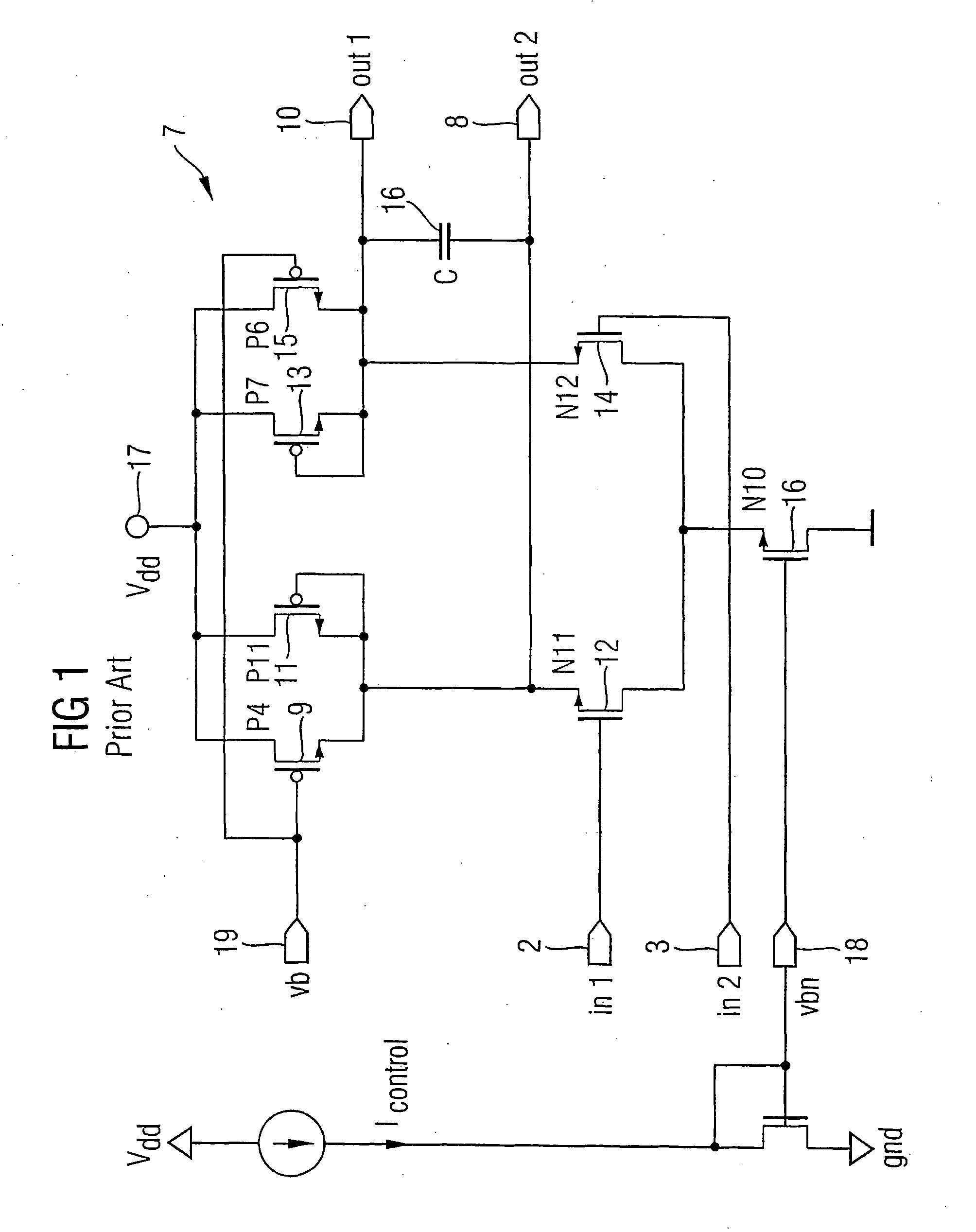
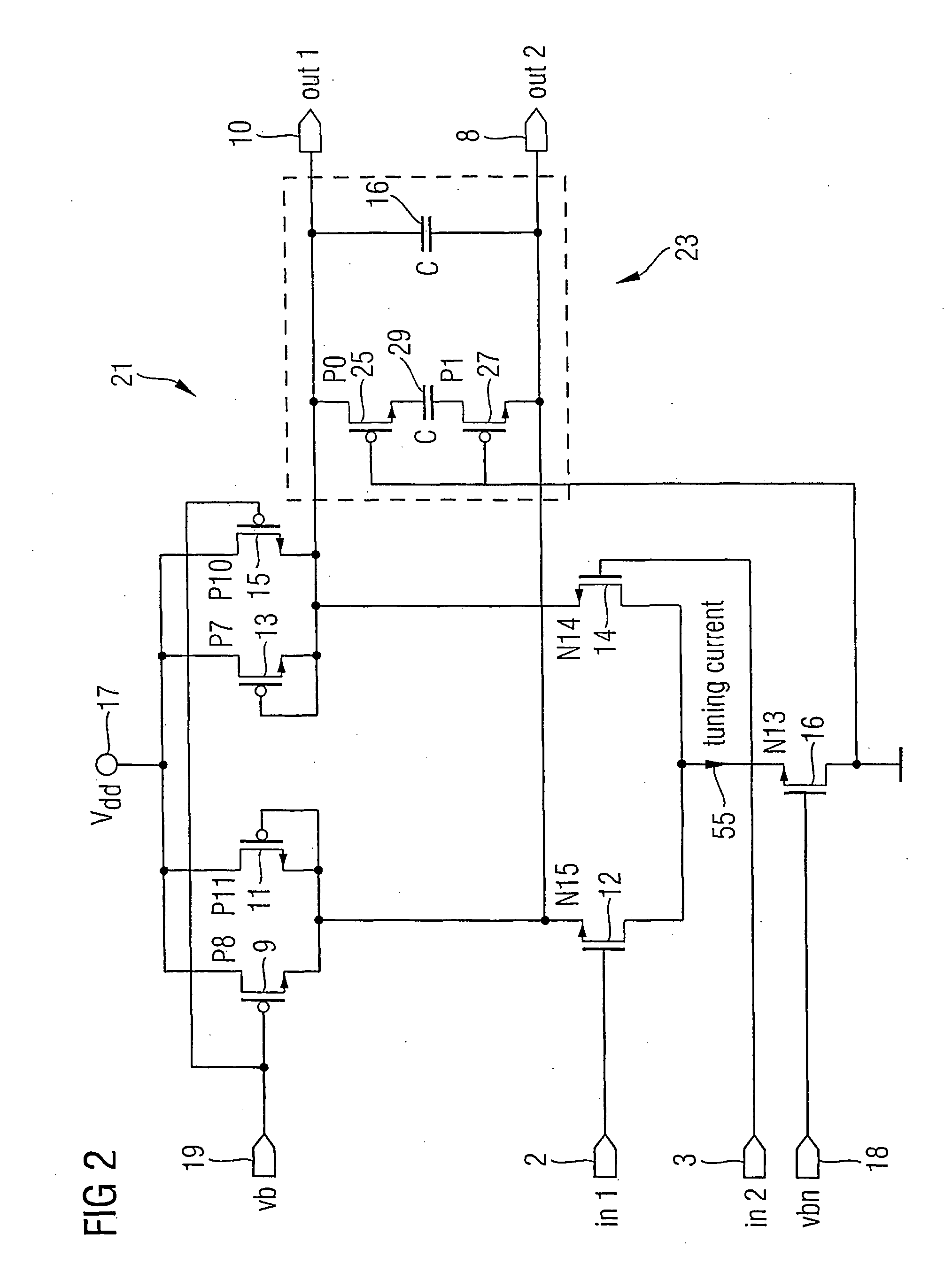
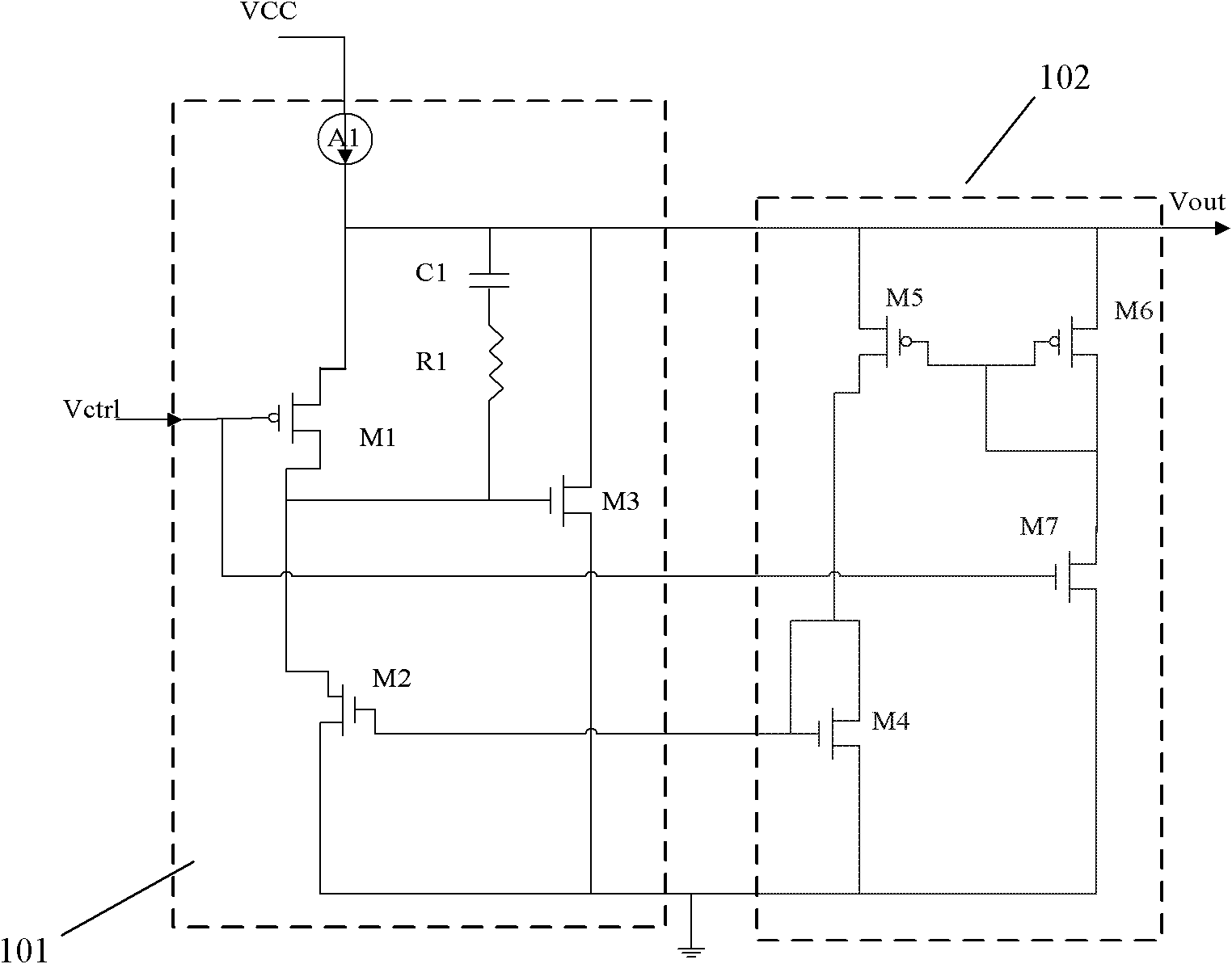
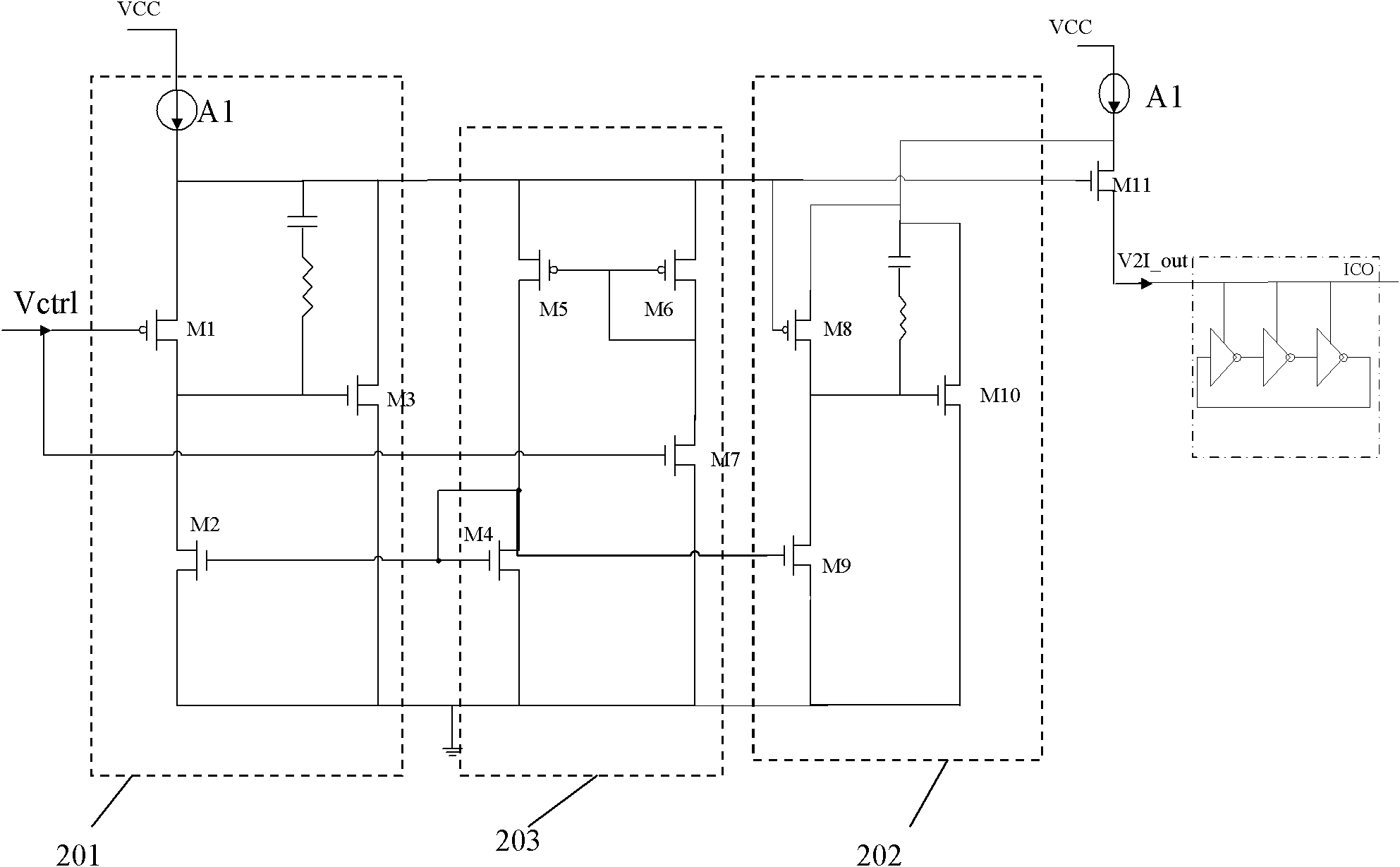
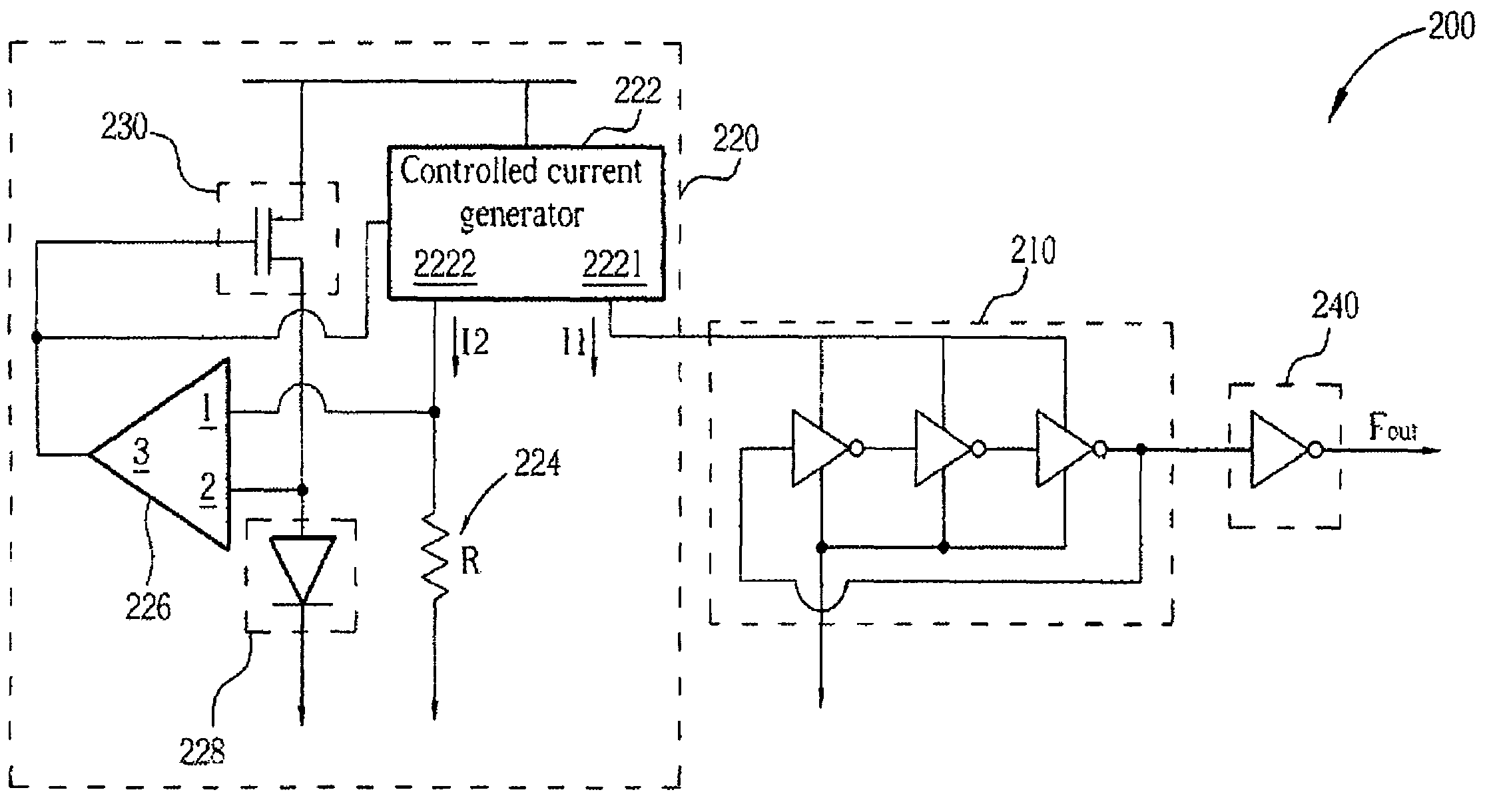
Current controlled oscillator
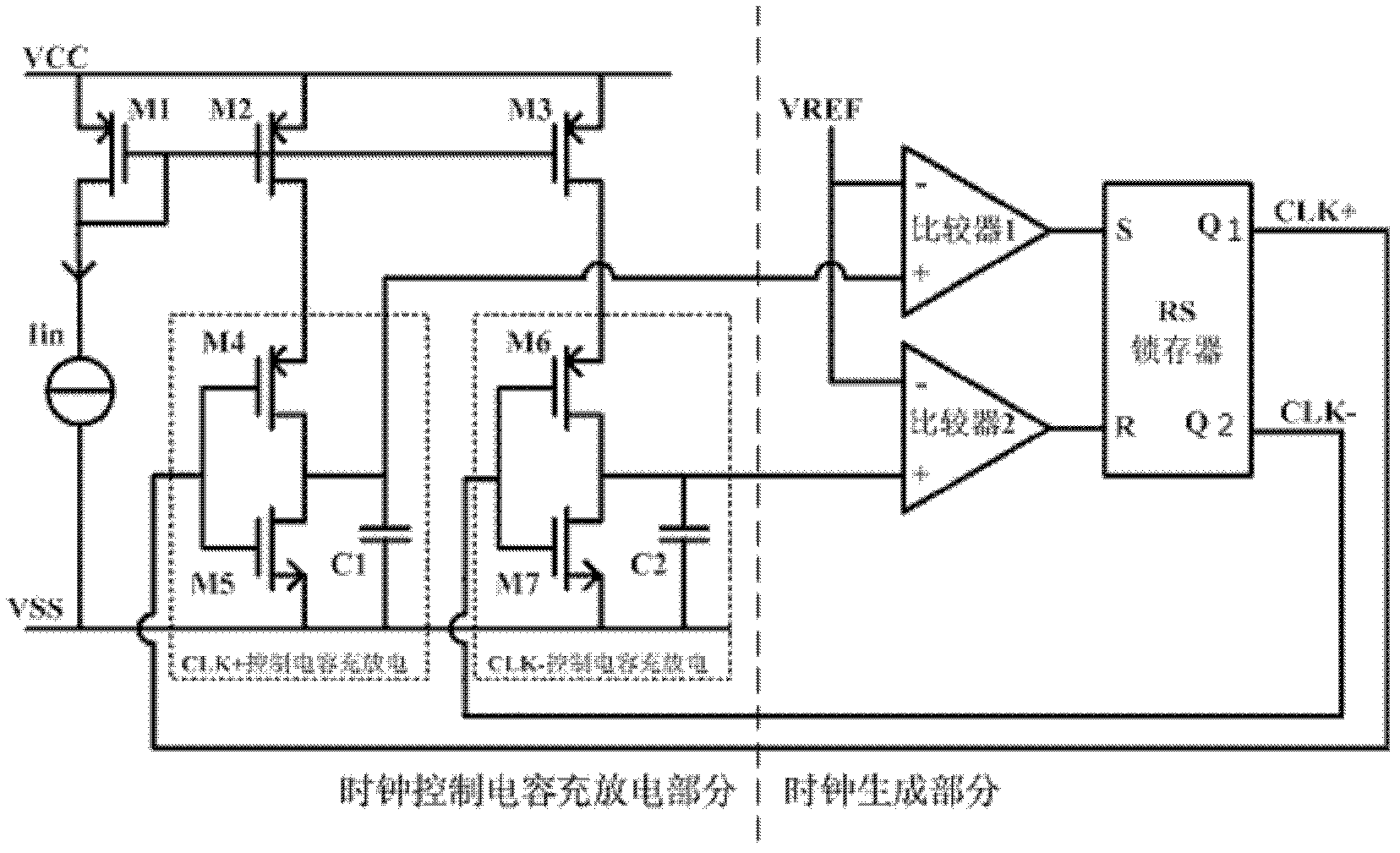
InactiveCN102324912AReduce power consumptionImprove stabilityElectric pulse generatorCapacitanceEngineering
The invention discloses a current controlled oscillator which comprises a clock control capacitor charge and discharge part and a clock generation part, wherein, the clock control capacitor charge and discharge part is composed of input current Iin, a current mirror and a charge and discharge capacitor of clock control, the clock generation part is composed of a comparator 1, a comparator 2, reference voltage VREF and an RS latch register; under the control of a clock signal outputted by the clock generation part finally, the clock control capacitor charge and discharge part carries out charge and discharge on a capacitor, a result of comparing polar plate voltage and reference voltage on the capacitor is used for determining setting or reset of the RS latch register, thereby clock signal output of certain frequency is realized. The current controlled oscillator has the following advantages: stability of output frequency is raised; output waveform of a 50% duty ratio can be obtained; circuit power consumption is saved.
Owner:CHINA KEY SYST & INTEGRATED CIRCUIT
Switched-capacitor isolated LED driver
A switched-capacitor voltage converter which is particularly well-suited for receiving a line voltage from which to drive current through a series of light emitting diodes (LEDs). Input voltage is rectified in a multi-level rectifier network having switched capacitors in an ascending-bank configuration for passing voltages in uniform steps between zero volts up to full received voltage VDC. A regulator section, operating on VDC, comprises switched-capacitor stages of H-bridge switching and flying capacitors. A current controlled oscillator drives the states of the switched-capacitor stages and changes its frequency to maintain a constant current to the load. Embodiments are described for isolating the load from the mains, utilizing an LC tank circuit or a multi-primary-winding transformer.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Integrated circuit capacitors for analog microcircuits
ActiveUS20150270393A1Reduce unstable oscillationImprove circuit performanceTransistorPulse automatic controlCapacitanceDielectric
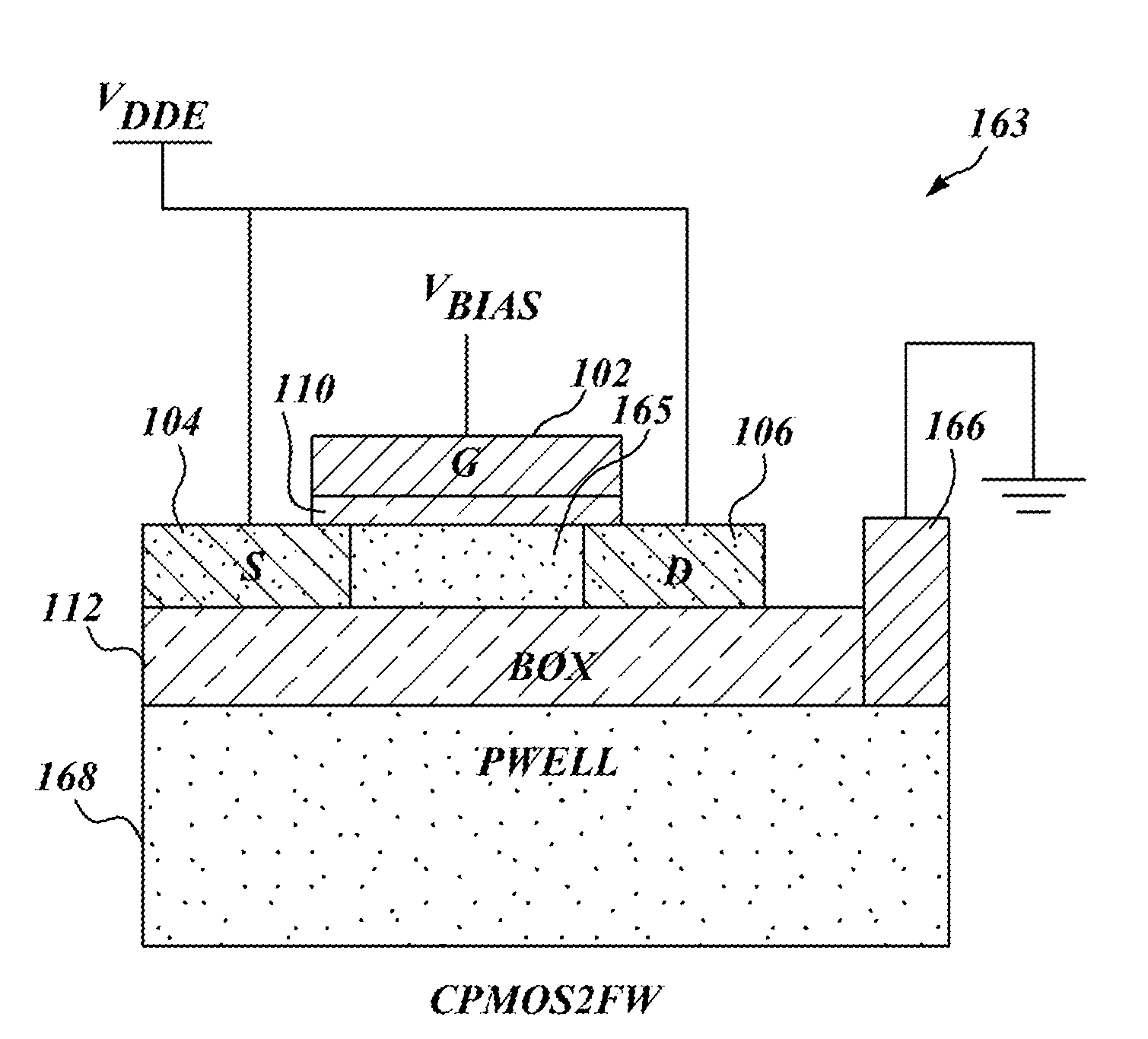
Dual gate FD-SOI transistors are used as MOSFET capacitors to replace passive well capacitors in analog microcircuits. Use of the dual gate FD-SOI devices helps to reduce unstable oscillations and improve circuit performance. A thick buried oxide layer within the substrate of an FD-SOI transistor forms a capacitive dielectric that can sustain high operating voltages in the range of 1.2 V-3.3 V, above the transistor threshold voltage. A secondary gate in the FD-SOI transistor is used to create a channel from the back side so that even when the bias voltage on the first gate is small, the effective capacitance remains higher. The capacitance of the buried oxide layer is further utilized as a decoupling capacitor between supply and ground. In one example, a dual gate PMOS FD-SOI transistor is coupled to an operational amplifier and a high voltage output driver to produce a precision-controlled voltage reference generator. In another example, two dual gate PMOS and one dual gate NMOS FD-SOI transistor are coupled to a charge pump, a phase frequency detector, and a current-controlled oscillator to produce a high-performance phase locked loop circuit in which the decoupling capacitor footprint is smaller, in comparison to the conventional usage of passive well capacitance.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS INT NV
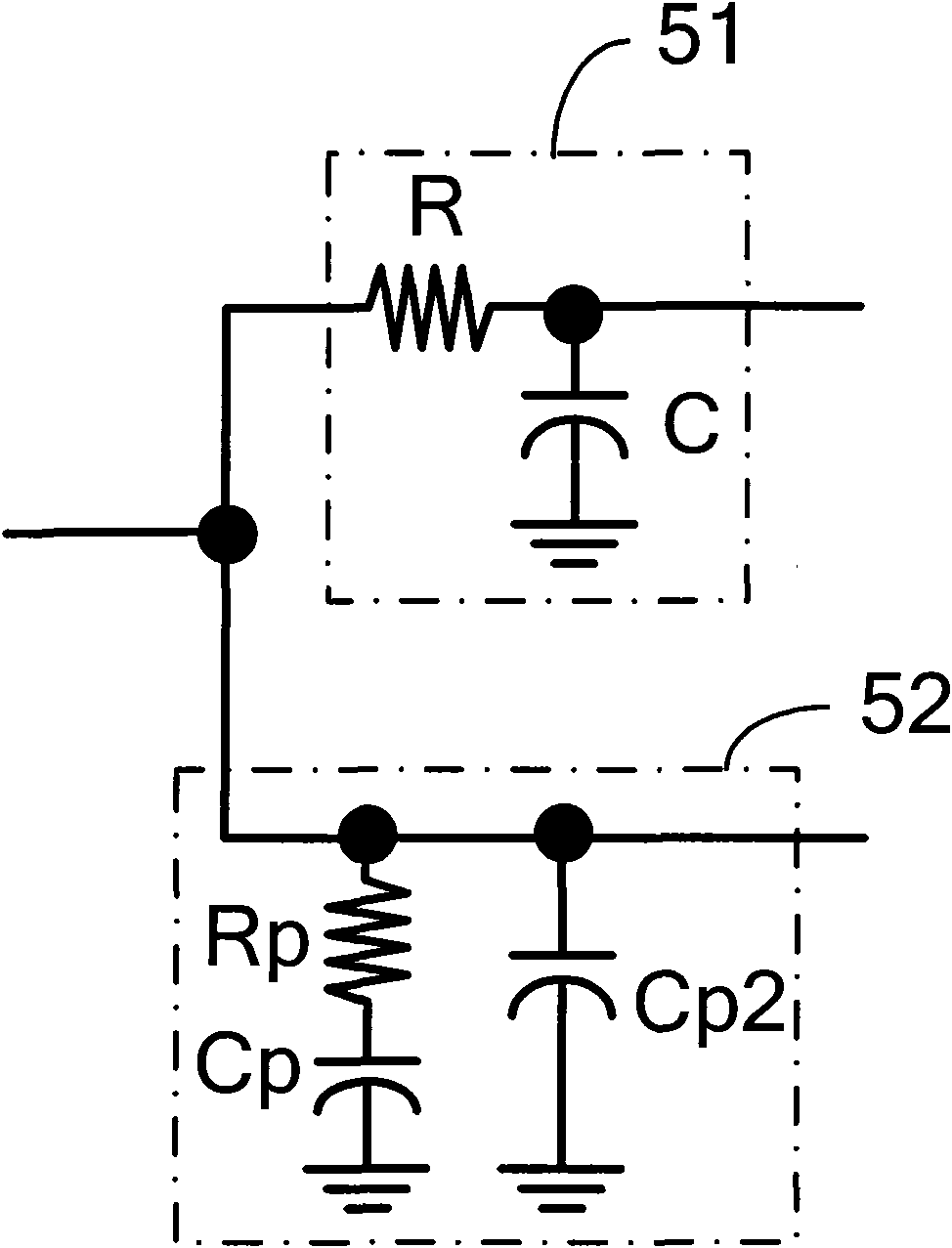
Phase-locked loop circuits with current mode loop filters
ActiveUS20060197611A1Pulse automatic controlActive element networkLoop filterPhase locked loop circuit
A phase-locked loop (PLL) includes a phase-frequency detector circuit configured to detect an error of an output clock signal in relation to a reference clock signal and to generate a charge pump control signal therefrom and a charge pump circuit configured to charge and discharge an output node thereof responsive to the charge pump control signal. The PLL further includes a current-mode loop filter circuit coupled to the output node of the charge pump circuit and configured to generate a filtered current from the current at the output node of the charge pump circuit, and a current-controlled oscillator configured to generate the output clock signal responsive to the filtered current. The current-mode loop filter circuit may be self-biased. For example, the current-mode loop filter circuit and the charge pump may be biased responsive to a common bias control signal generated by the current-mode loop filter circuit.
Owner:INTEGRATED DEVICE TECH INC
Phase-locked loop circuits with current mode loop filters
Owner:INTEGRATED DEVICE TECH INC
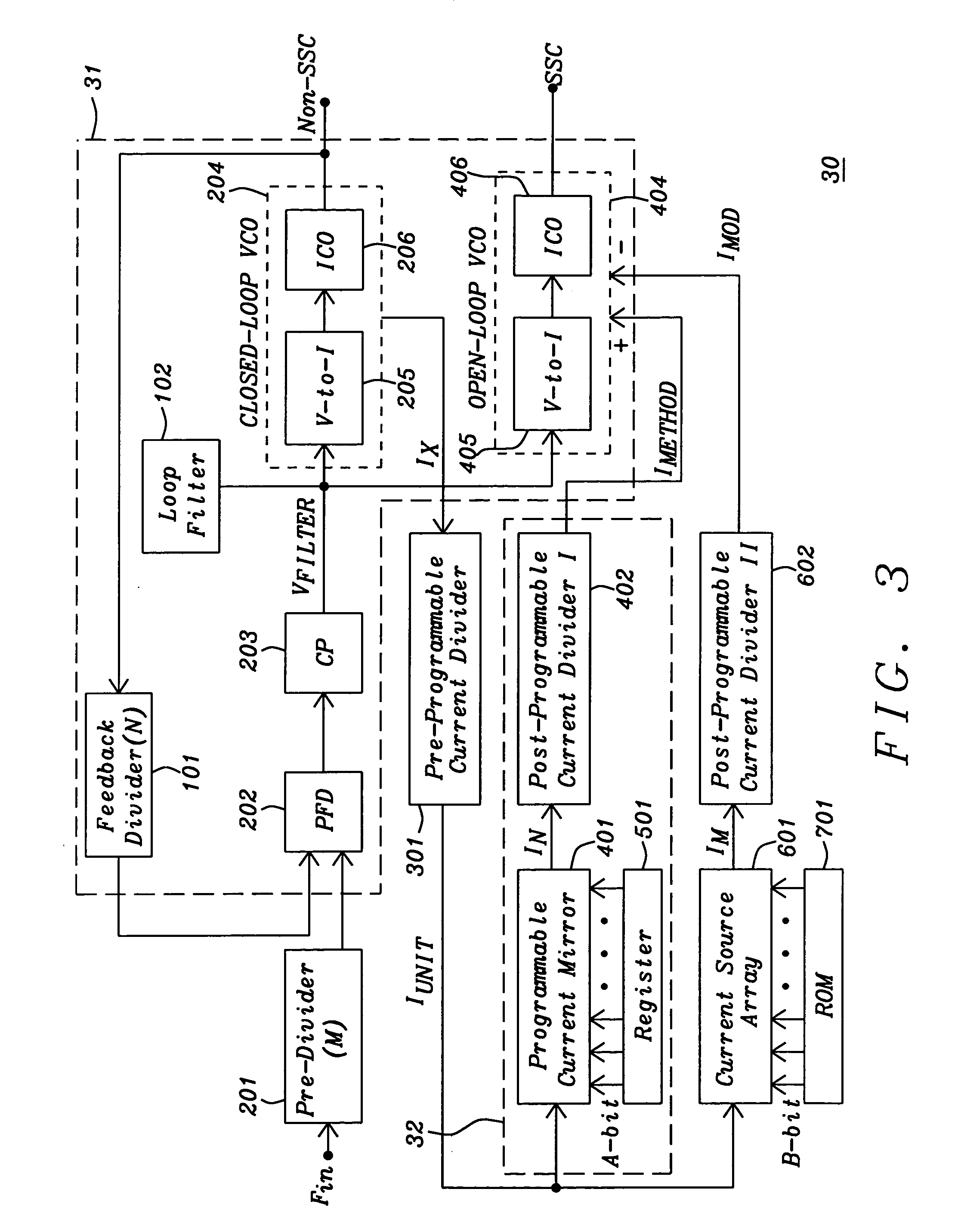
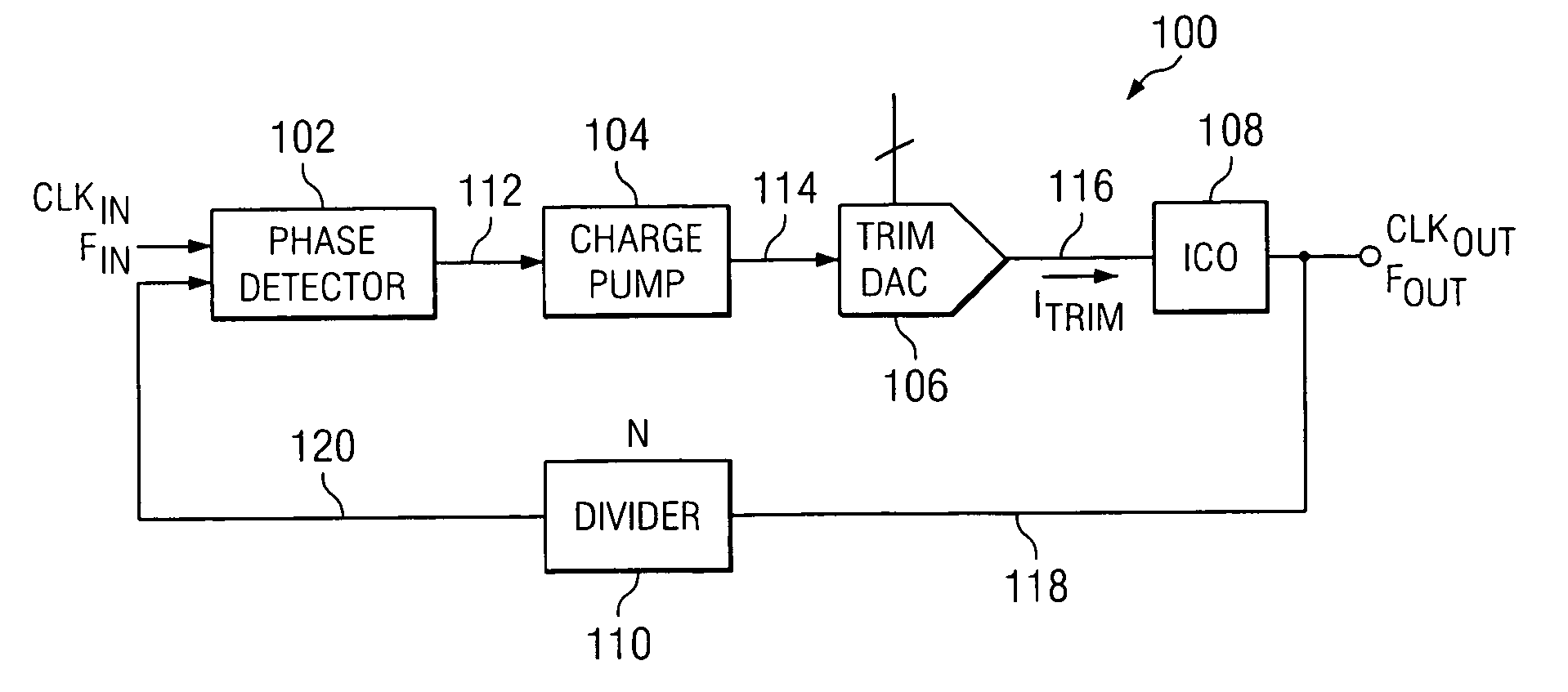
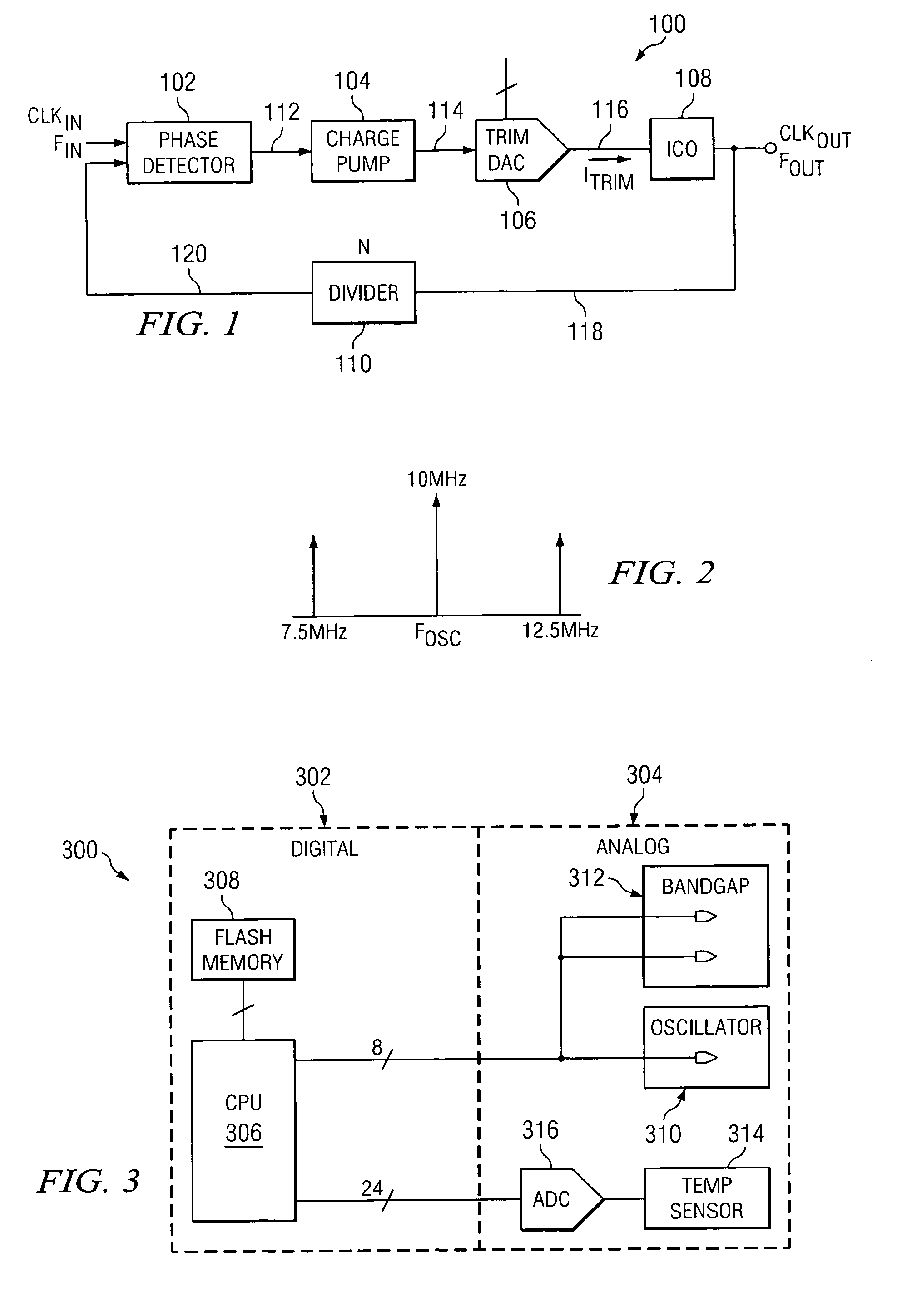
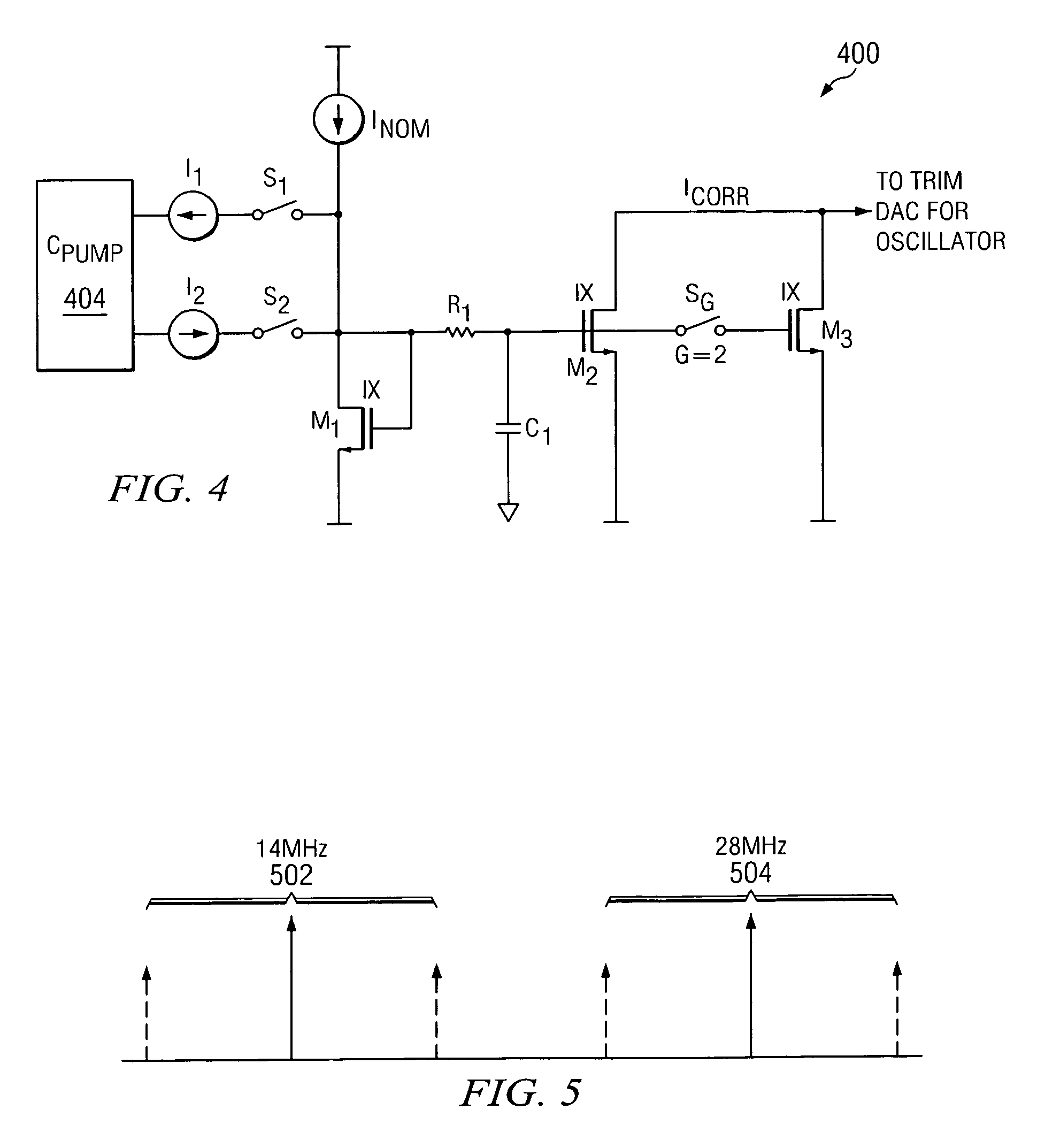
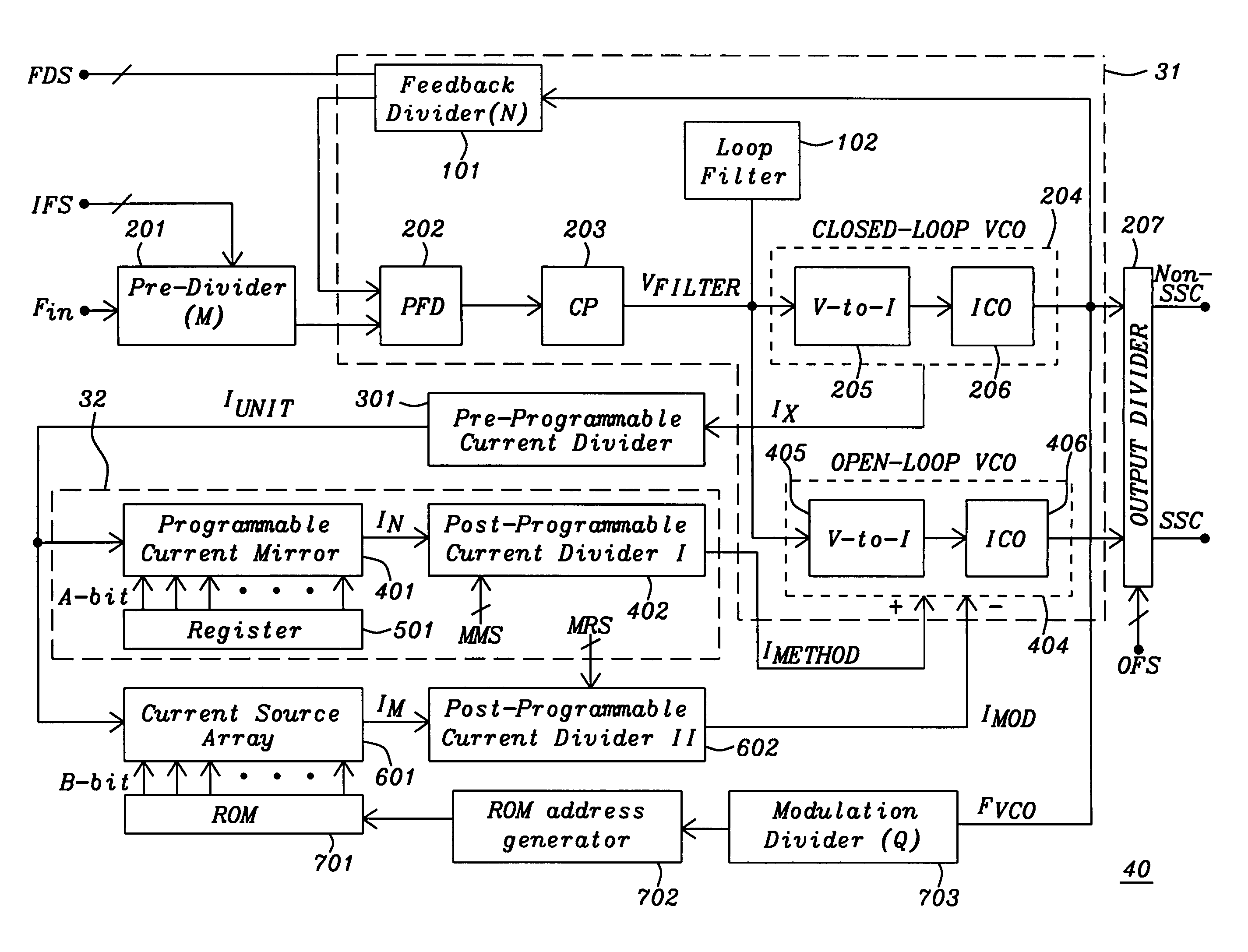
Method and circuit for frequency synthesis using a low drift current controlled oscillator with wide output frequency range
ActiveUS20060164174A1Control center frequencyGood low temperaturePulse automatic controlGenerator stabilizationPhase detectorPhase locked loop circuit
A method and circuit for frequency synthesis using a low drift current controlled oscillator configured to provide a wide output frequency and high accuracy are provided. An exemplary frequency synthesis circuit is configured for programmable control of a center frequency of the current controlled oscillator to provide a wide range of output frequencies with high accuracy. In accordance with an exemplary embodiment of the present invention, an exemplary circuit comprises a phase-locked loop (PLL) circuit comprising a phase detector, a charge pump, a current controlled oscillator and a divider circuit. For programmable control of the current controlled oscillator, the PLL circuit further comprises a trim digital-to-analog converter (DAC) configured to provide a trimmed current signal for control of the current controlled oscillator. In accordance with an exemplary embodiment of the present invention, trim values for operation of the trim DAC can be suitably located within a trim register of flash memory, such as programmable flash memory within any mixed-signal device or system.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Spread spectrum clock generation circuit, jitter generation circuit and semiconductor device
ActiveUS20050285641A1Low costLarge scaleElectric signal transmission systemsPulse automatic controlDevice materialCurrent controlled oscillator
Owner:MONTEREY RES LLC
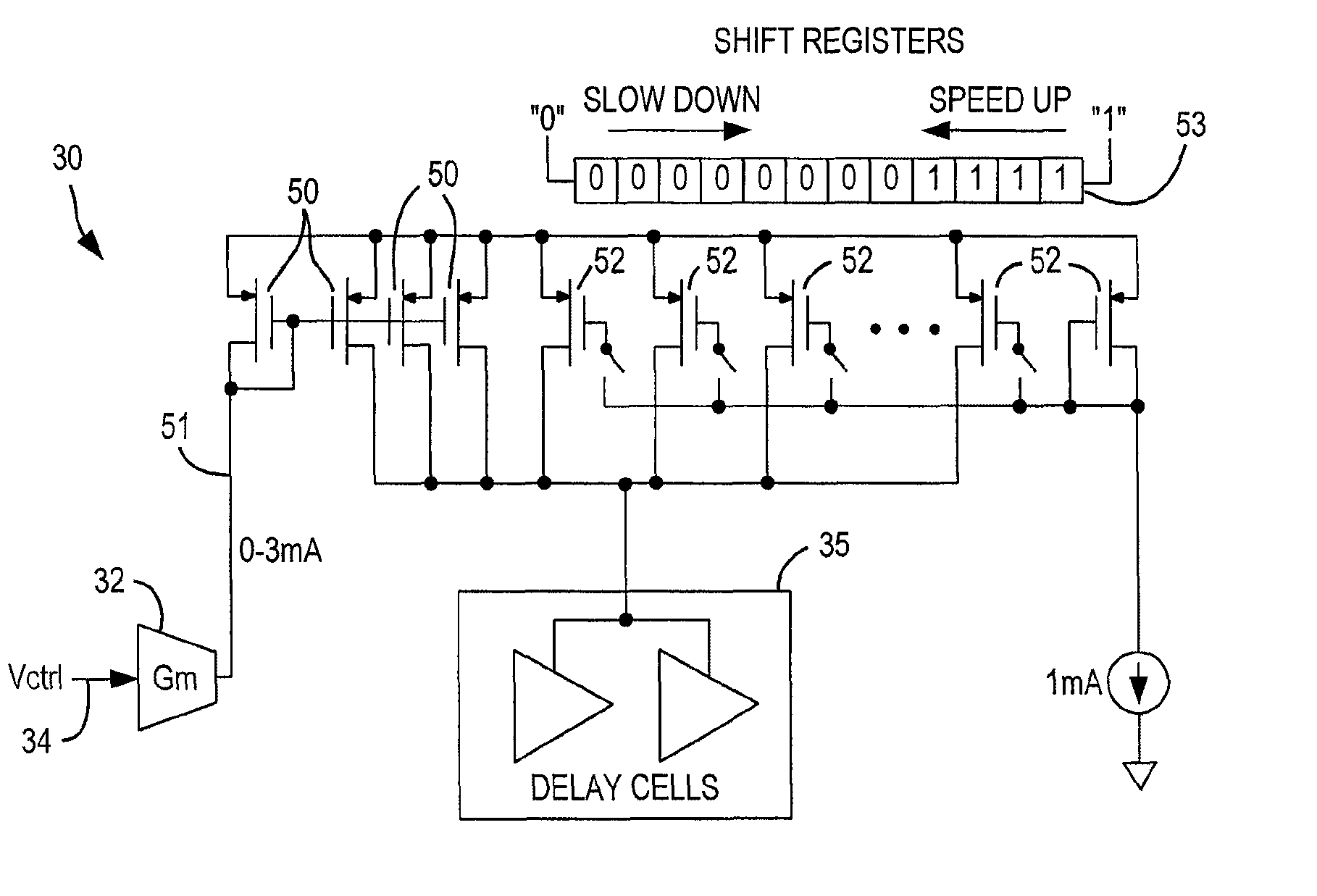
Current-controlled oscillator
InactiveUS20060022760A1Extended linear gainImprove stabilityGenerator stabilizationPulse generation by logic circuitsElectrical resistance and conductanceElectricity
The present invention provides a current controlled oscillator comprising a first section providing a first differential output and a second section providing a second differential output. A loading structure comprised of resistive and reactive elements electrically connects the first differential output with the second differential output. The resistive and reactive elements have values chosen such that the resistive elements substantially extend the linear operating frequency range of the current controlled oscillator. Transistors of the loading structure have which are tied to a power supply rejection ratio compensation section for compensating for variations in power supply voltage.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
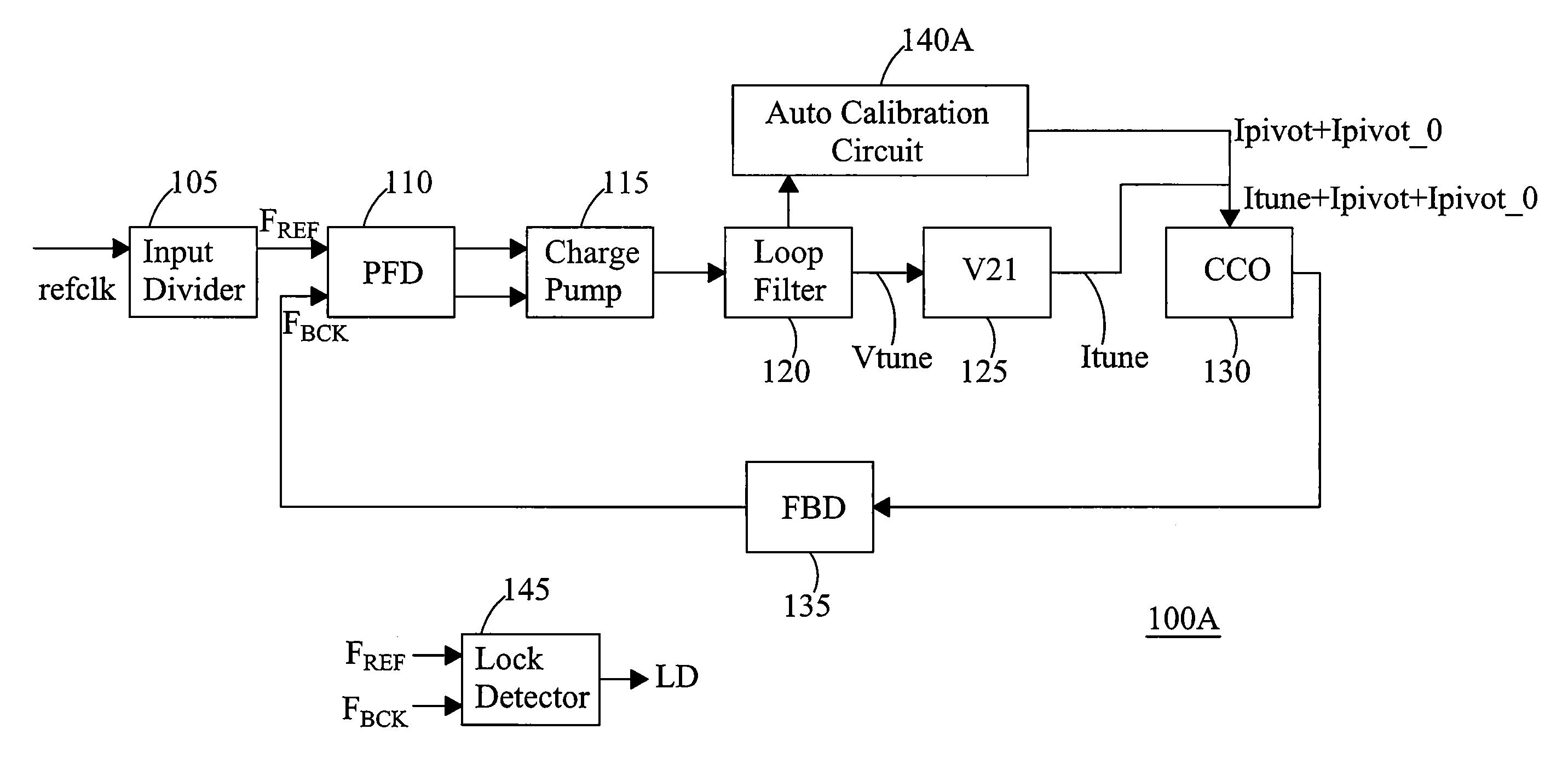
Current-controlled oscillator (CCO) based PLL
ActiveUS8432204B1Minimizing noise transferredSignificant changePulse automatic controlLoop filterPhase frequency detector
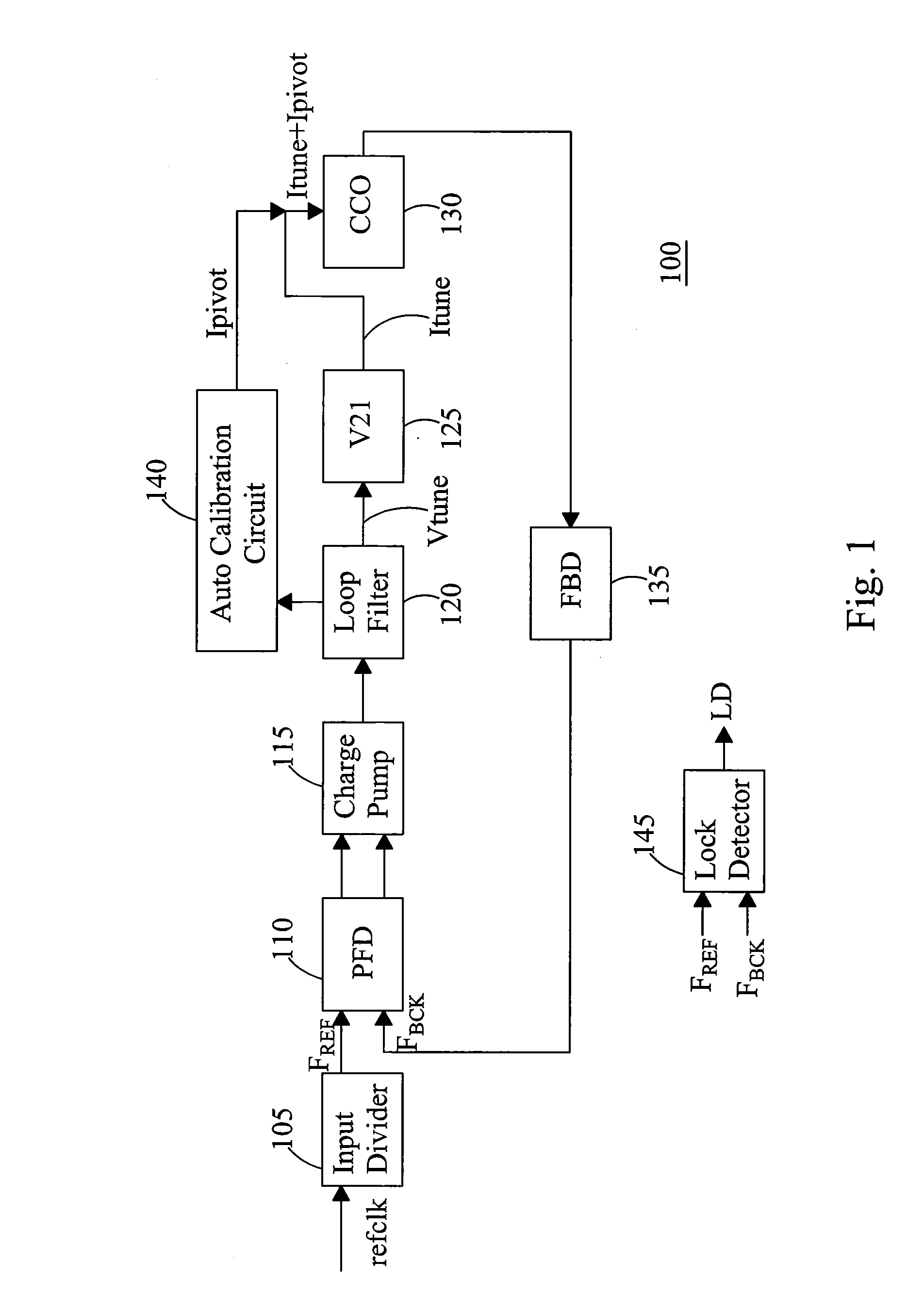
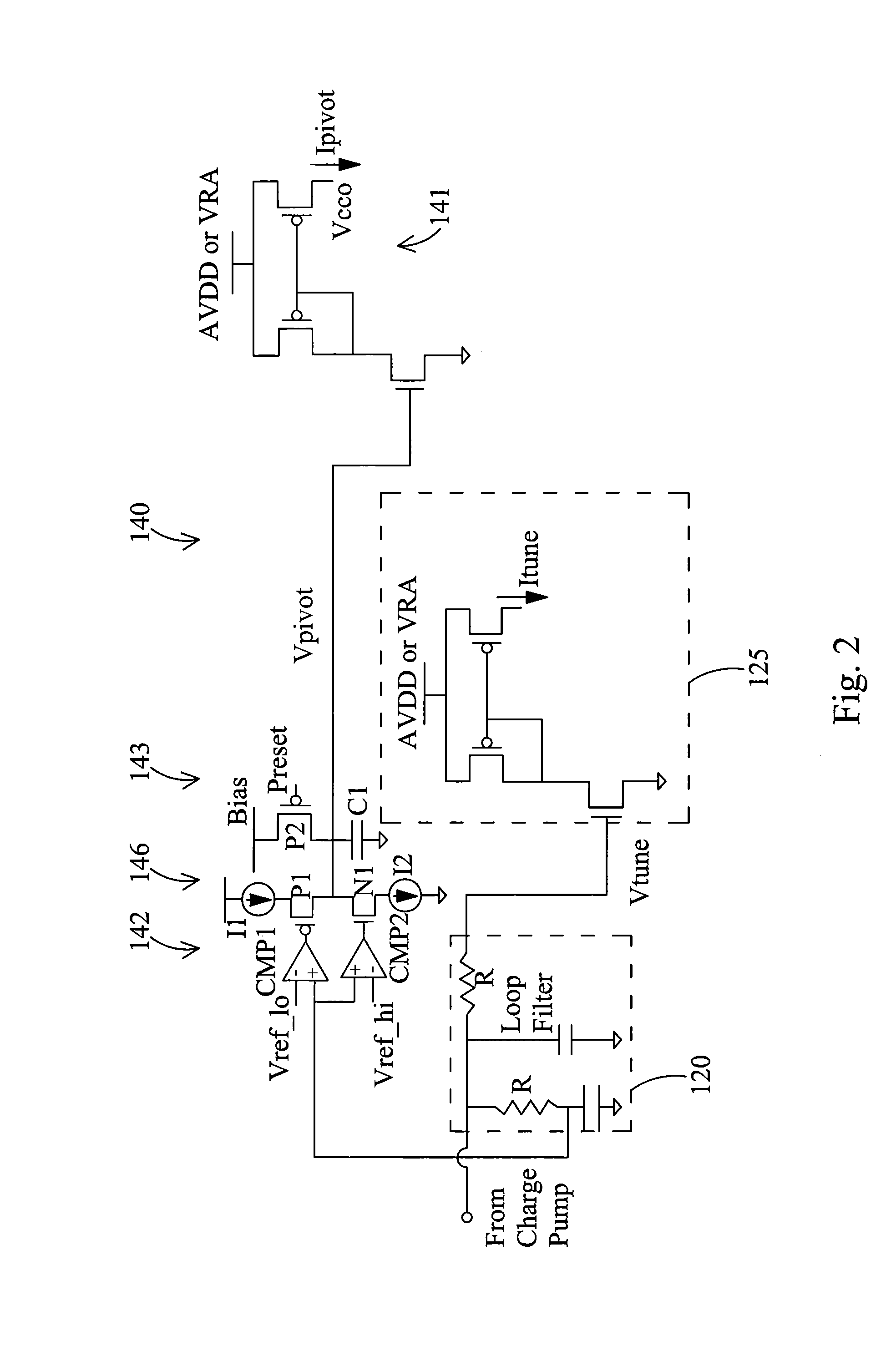
A PLL circuit includes a phase frequency detector; a programmable charge pump coupled to an output of the phase frequency detector; a loop filter coupled to an output of the charge pump, the loop filter providing a fine tuning voltage; a first voltage-to-current converter, the first voltage-to-current converter providing a fine tuning current corresponding to the fine tuning voltage; a current-controlled oscillator (CCO); a feedback divider coupled to an output of the CCO and an input of the phase frequency detector; and an analog calibration circuit. The analog calibration circuit provides a coarse adjustment current for coarse adjustments to a frequency pivot point for an oscillator frequency of the CCO, wherein the CCO generates a frequency signal at an output responsive to a summed coarse adjustment and fine tuning current, wherein the frequency pivot point is continuously adjustable.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Phase locked loop and phase locking method
ActiveUS20080186066A1Small sizeReduce voltagePulse automatic controlPhase differenceCurrent controlled oscillator
A phase locked loop includes a charge pump, a voltage-current converter, and a current controlled oscillator. The charge pump generates a pump current based on a bias voltage and a phase difference detection signal, in which the pump current is for adjusting a control voltage. The voltage-current converter is self-biased, generates the bias voltage, and converts the control voltage to a converter current. The current controlled oscillator generates an oscillator current based on the bias voltage, and generates an output signal that has a frequency corresponding to the oscillator current. The phase locked loop is insensitive to a division ratio and PVT variations.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Clock data restorer
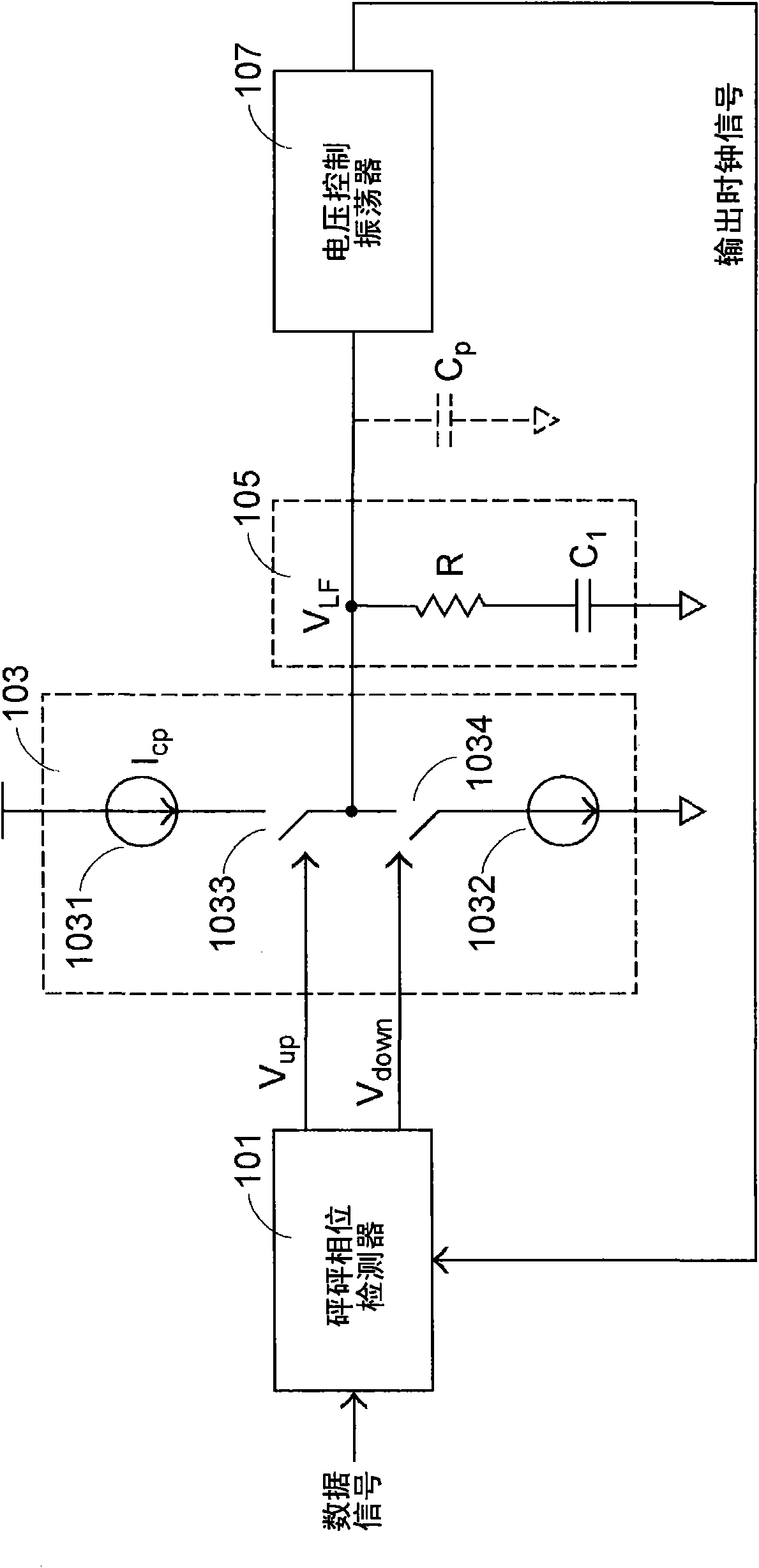
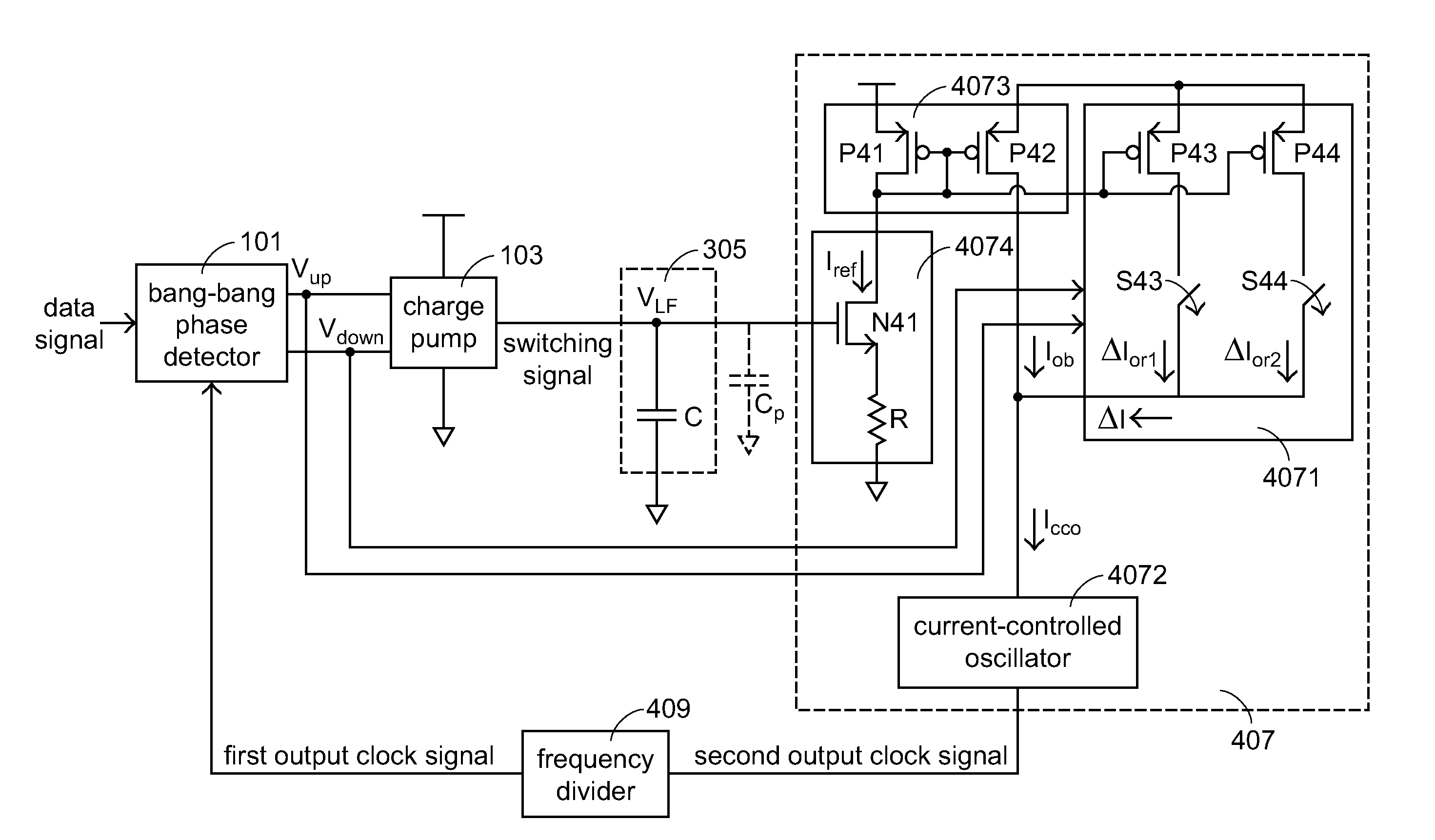
The invention discloses a clock data restorer, which comprises a phase detector, an electric charge charging pump, a loop filter, a voltage control oscillator, a current adjusting module, a current control oscillator and a frequency eliminator, wherein the phase detector compares a data signal with a first output clock signal and then generates a judgment signal; the electric charge charging pump converts the judgment signal into a switching signal; the loop filter converts the switching signal into a control voltage; the voltage control oscillator adjusts a generated second output clock signal according to the control voltage, and comprises a current mirror which is provided with a current control path and a current output path between which currents are in a proportional relation, and a control circuit which changes the current of the current control path according to the control voltage; the current adjusting module outputs difference current according to the judgment signal; the current control oscillator adjusts the phase of the second output clock signal according to the sum of the difference current and the current of the current output path; and the frequency eliminator converts the second output clock signal into the first output clock signal. The clock data restorer of the invention does not become a three-order system due to the influence of a parasitic capacitor or a decoupling capacitor.
Owner:FARADAY TECH CORP
Low-power-consumption charge pump for field effect power tube grid drive
InactiveCN103199696AEfficient power electronics conversionApparatus without intermediate ac conversionWave shapeSwitching frequency
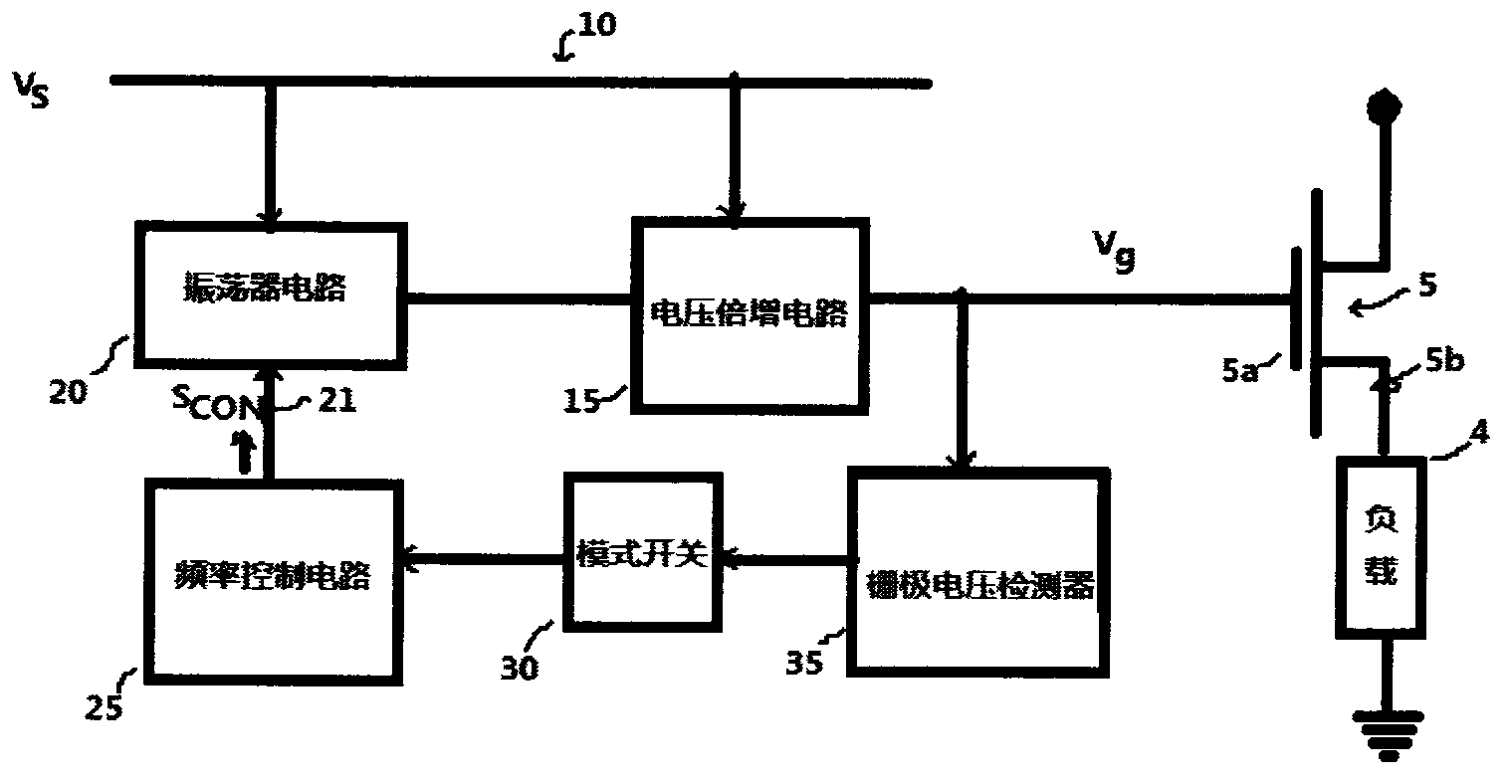
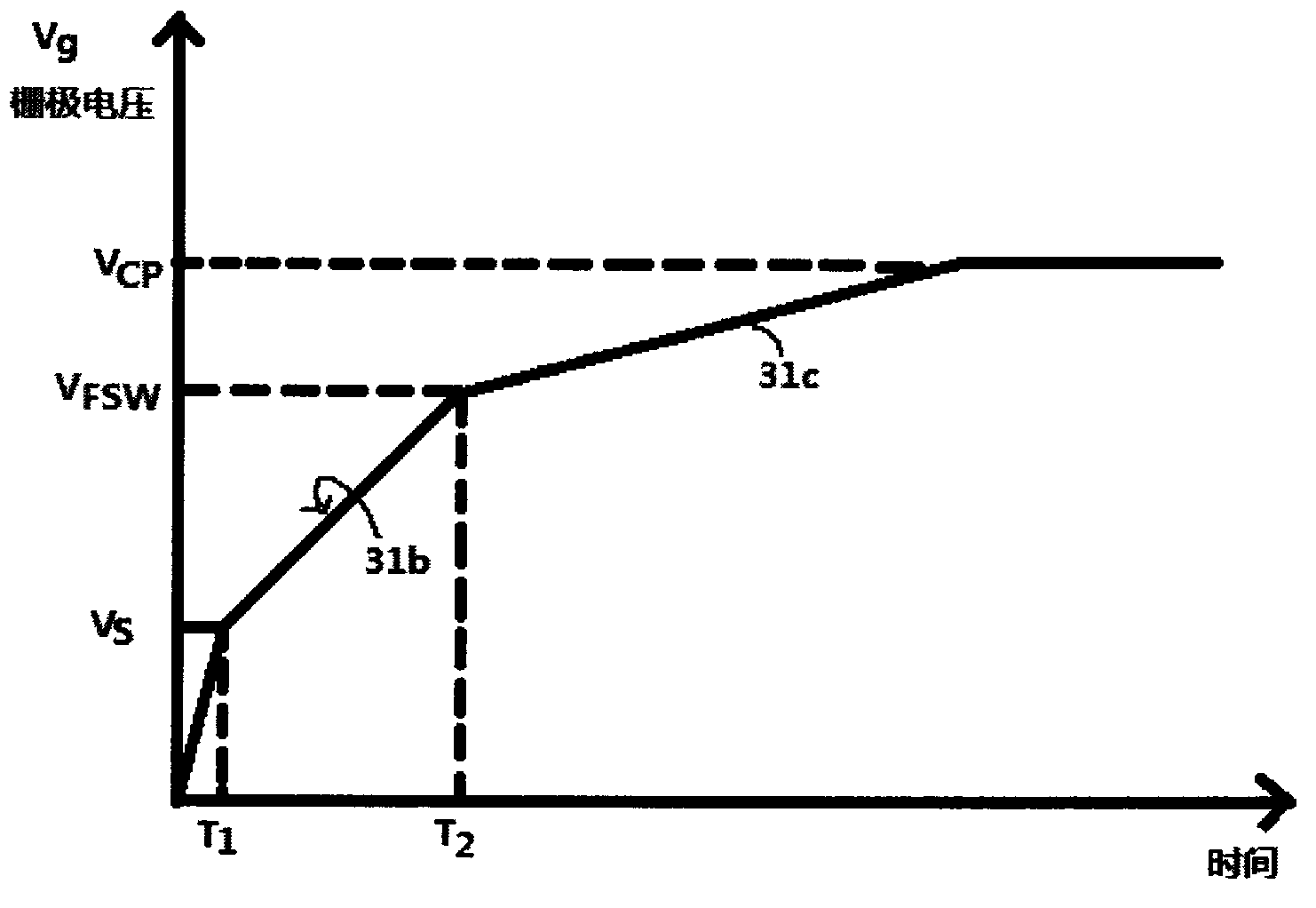
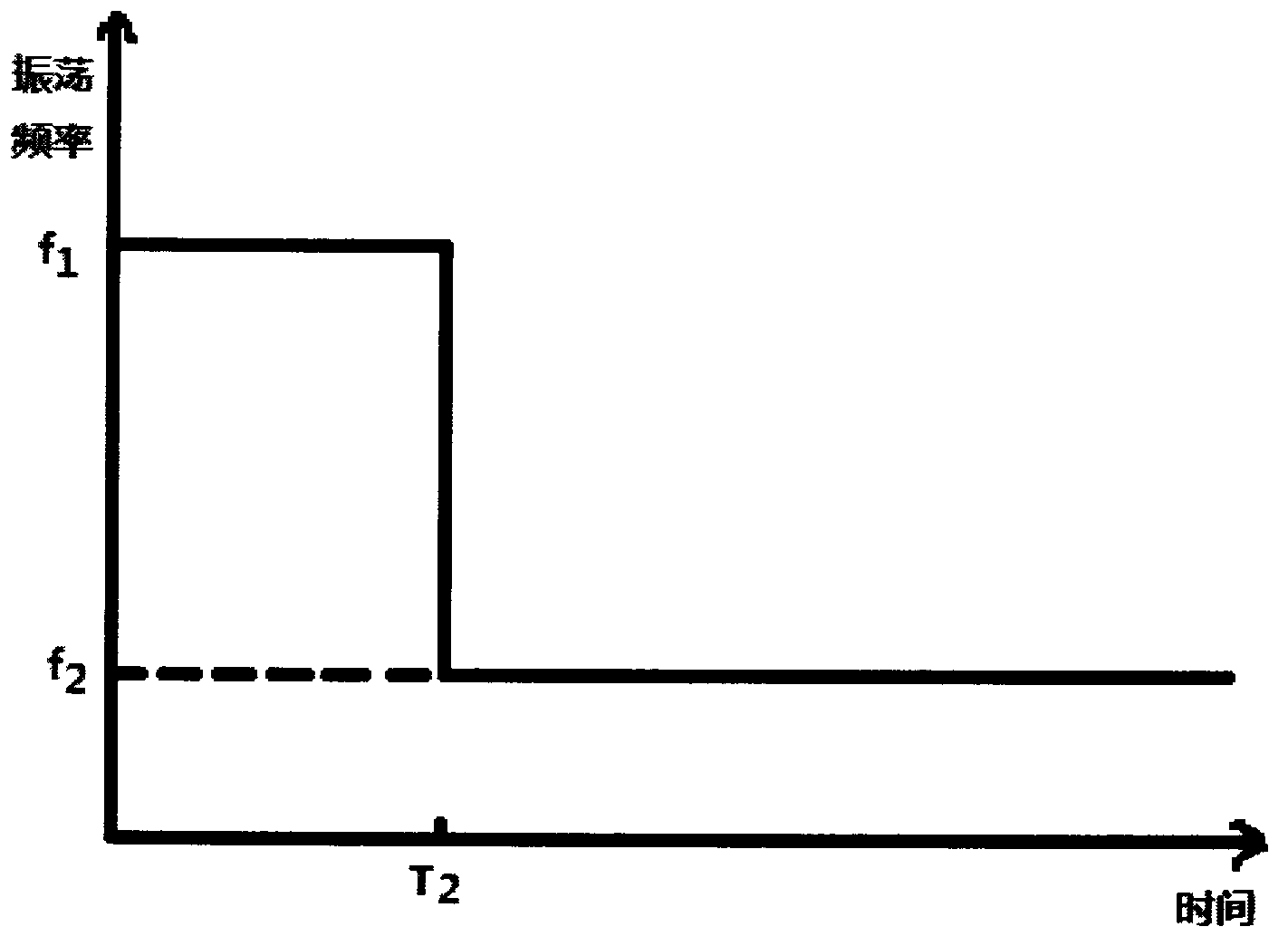
The invention discloses a low-power-consumption charge pump for field effect power tube grid drive. A low-power-consumption circuit capable of charging the grid of a transistor switch to a charge pump voltage (higher than a supply voltage) provided by the invention comprises a current control oscillator which can generate an oscillation waveform to drive a capacitive type charge pump circuit. The circuit can be used for monitoring the grid voltage of the transistor switch and reducing the frequency of oscillation waveform, thus reducing the power consumption. When the grid voltage exceeds the switch frequency, the fact that the transistor switch can sufficiently make the circuit in a micro-power consumption mode is revealed.
Owner:苏州硅智源微电子有限公司
Phase lock loop (pll) with gain control
ActiveCN101594142AReduce frequency gainPulse automatic controlReference currentCurrent controlled oscillator
A Phase Lock Loop (PLL) with gain control is provided. The PLL has a dual-path configuration, where a first and a second VCO control voltage are generated in response to a phase or frequency difference between a PLL input signal and an output signal. The PLL comprises a dynamic voltage gain control (DVGC) unit and a voltage-to-current (V2I) unit, where the DVGC creates a baseline reference current in response to the first VCO control voltage and the V2I provides a substantially linear current in response to the second VCO control voltage. The currents from the DVGC and V2I are combined and fed into a current-controlled oscillator, which generates a PLL output frequency signal. Frequency gain of the VCO is substantially reduced, thus providing a PLL with improved tuning precision.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
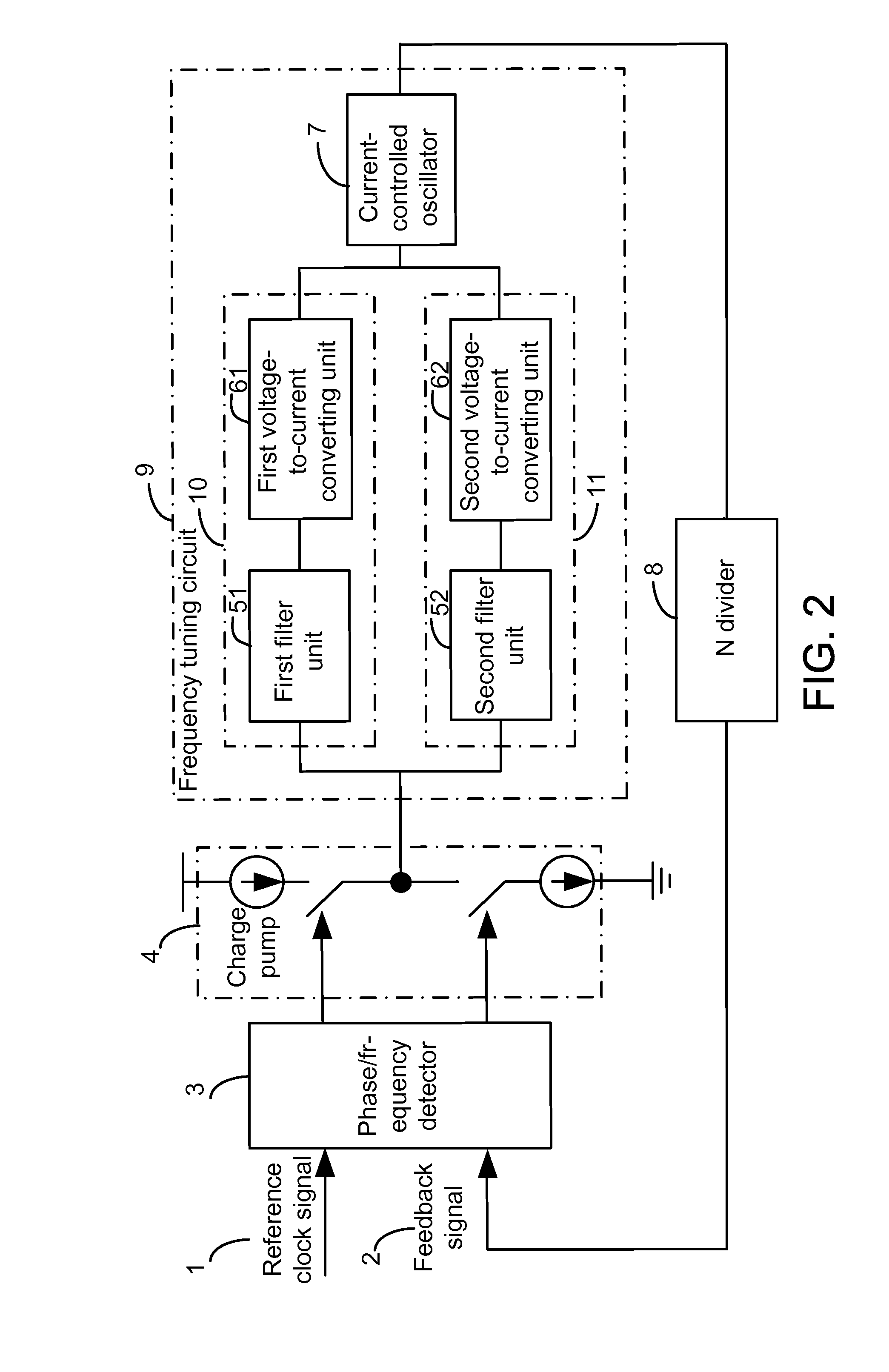
Dual Phase-Locked Loop Circuit and Method for Controlling the Same
ActiveUS20110006820A1Increased frequency rangeSmall loop bandwidthPulse automatic controlAngle demodulation by phase difference detectionPower flowPhase locked loop circuit
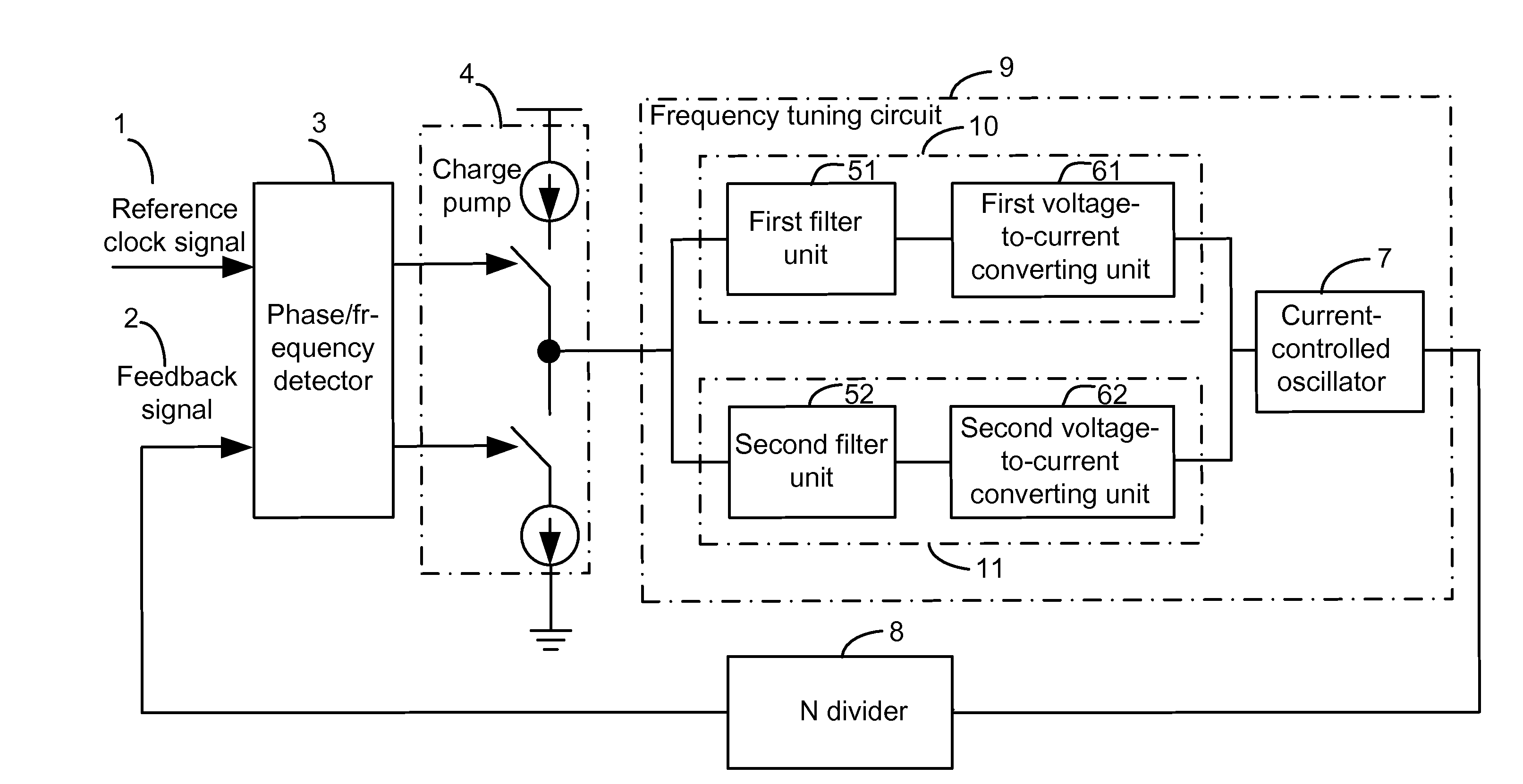
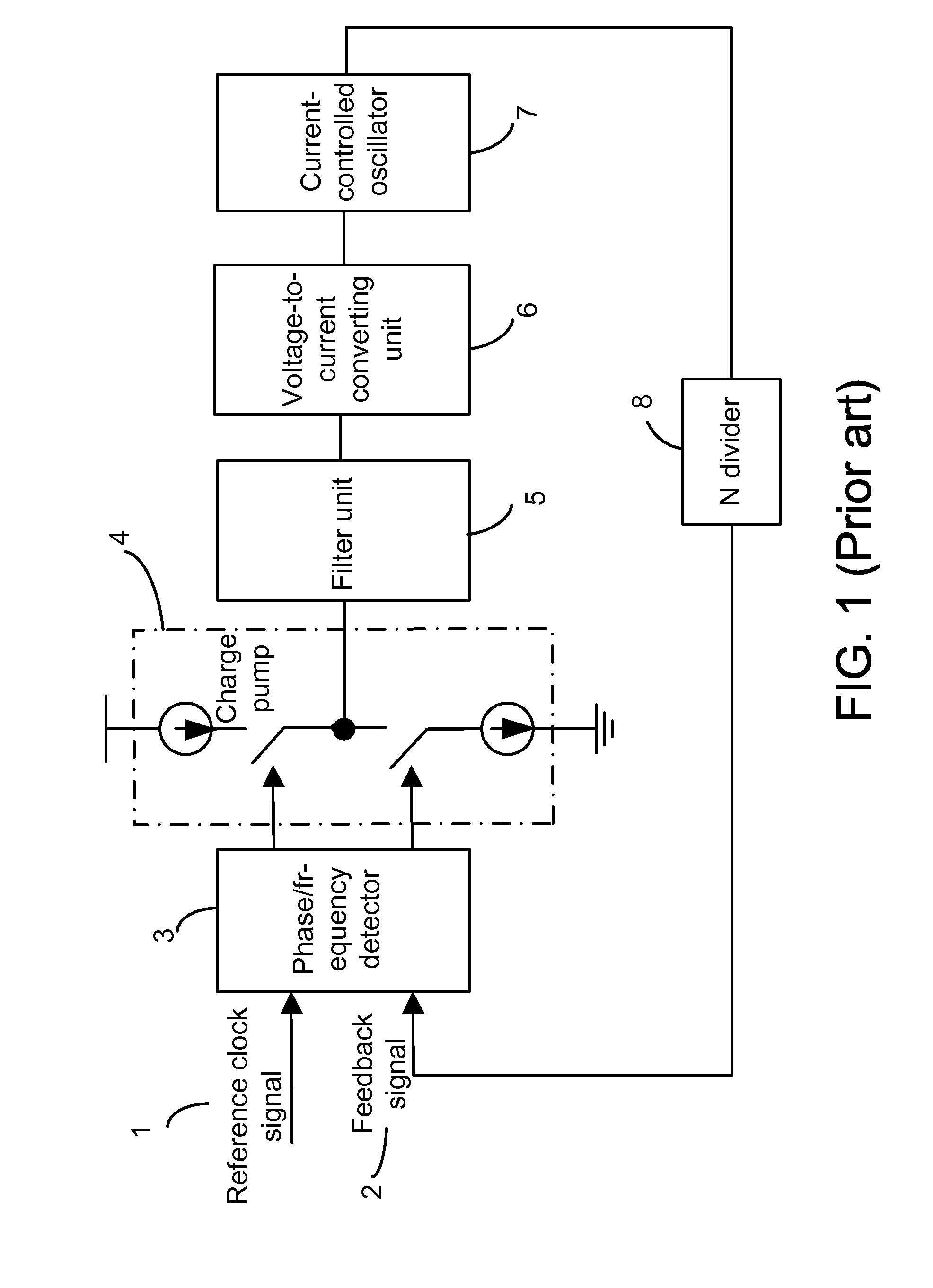
A dual phase-locked loop (PLL) circuit includes a phase / frequency detector, a charge pump, a frequency tuning circuit and an N divider. The frequency tuning circuit includes a coarse-tuning circuit, for coarse-tuning an output frequency of the dual PLL circuit to approximate a target frequency; a fine-tuning circuit, for fine-tuning the output frequency of the dual PLL circuit to the target frequency; and a current control oscillator (CCO), for generating an output signal of the dual PLL circuit. The output frequency of the output signal is equal to the target frequency.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
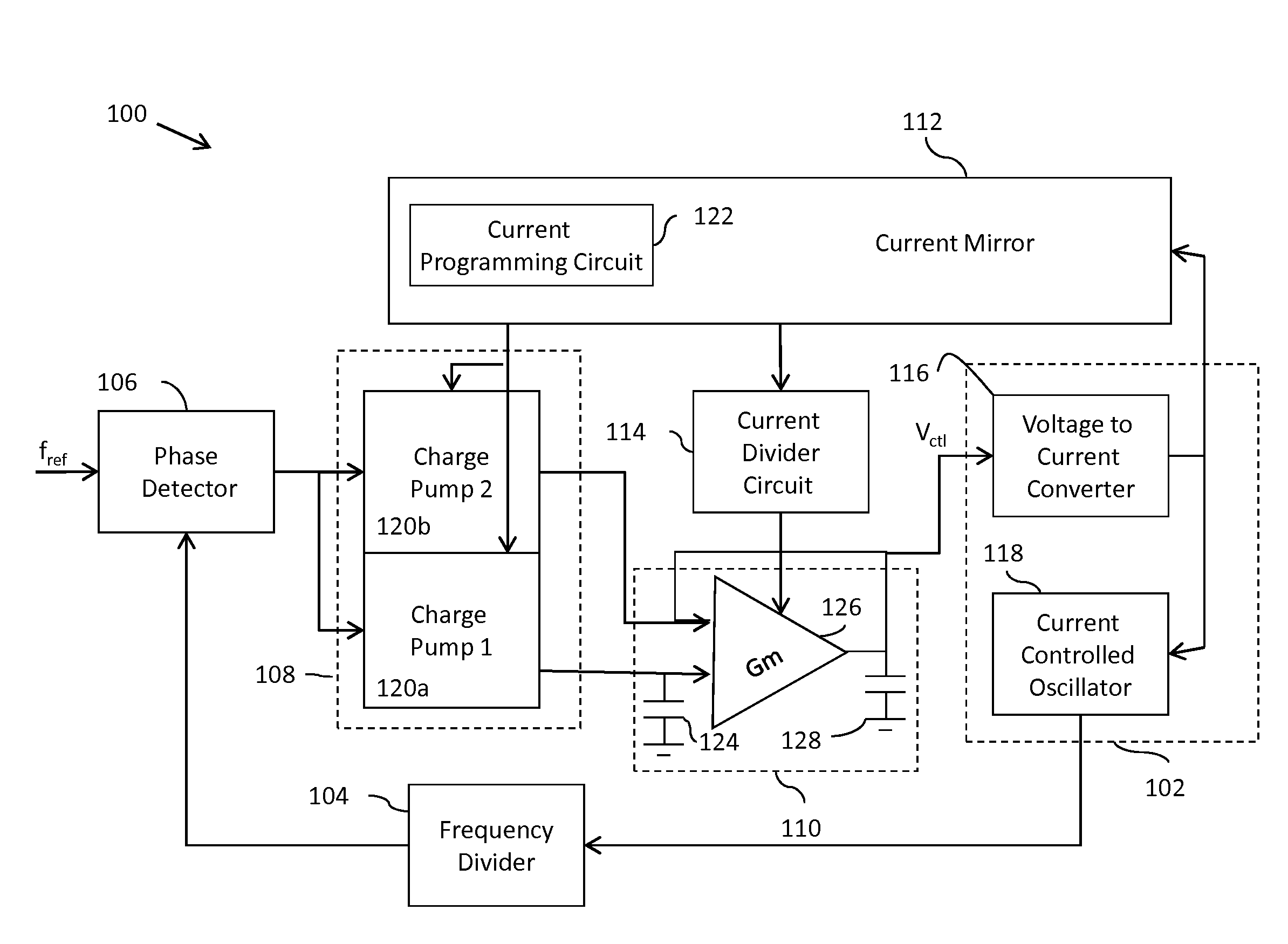
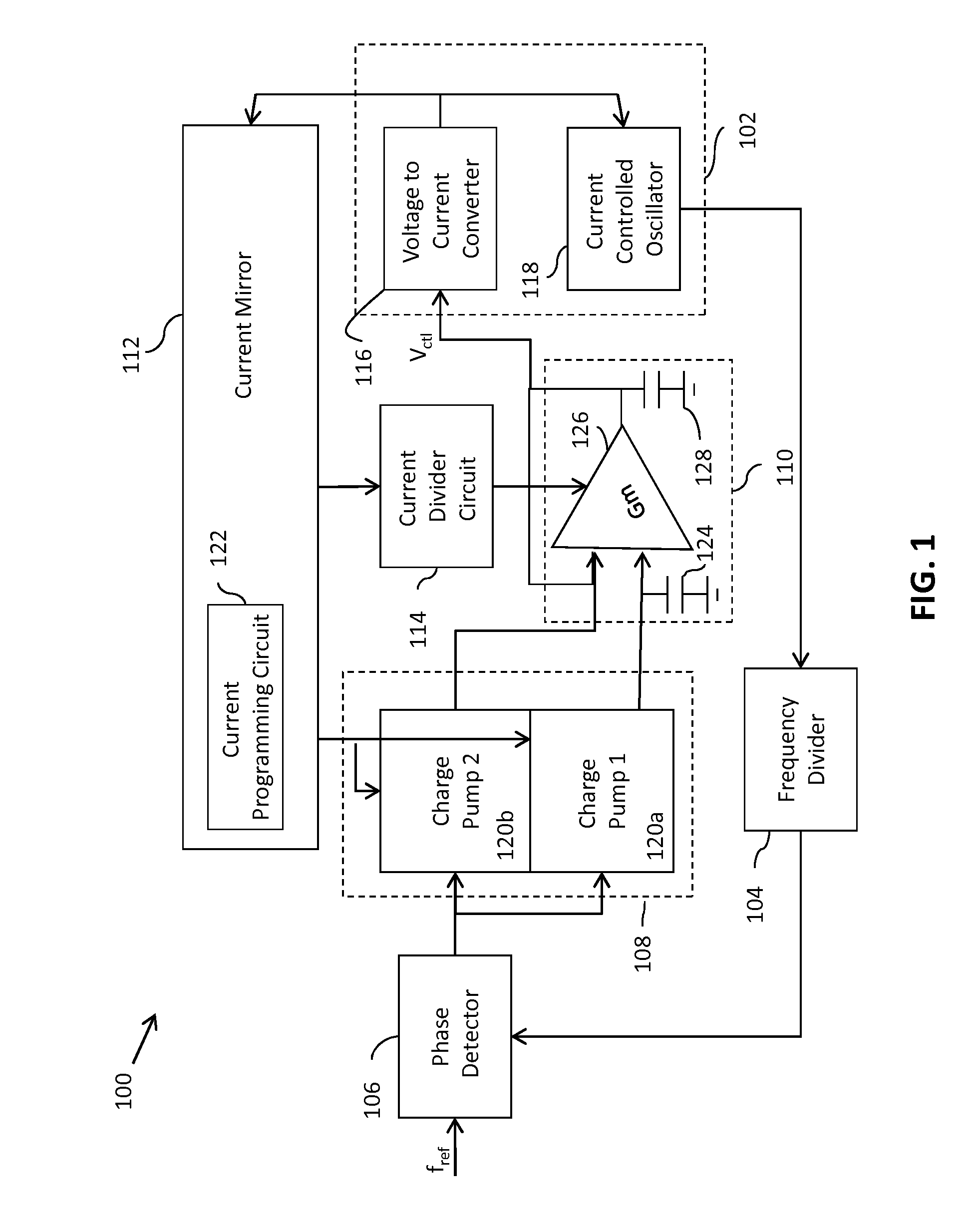
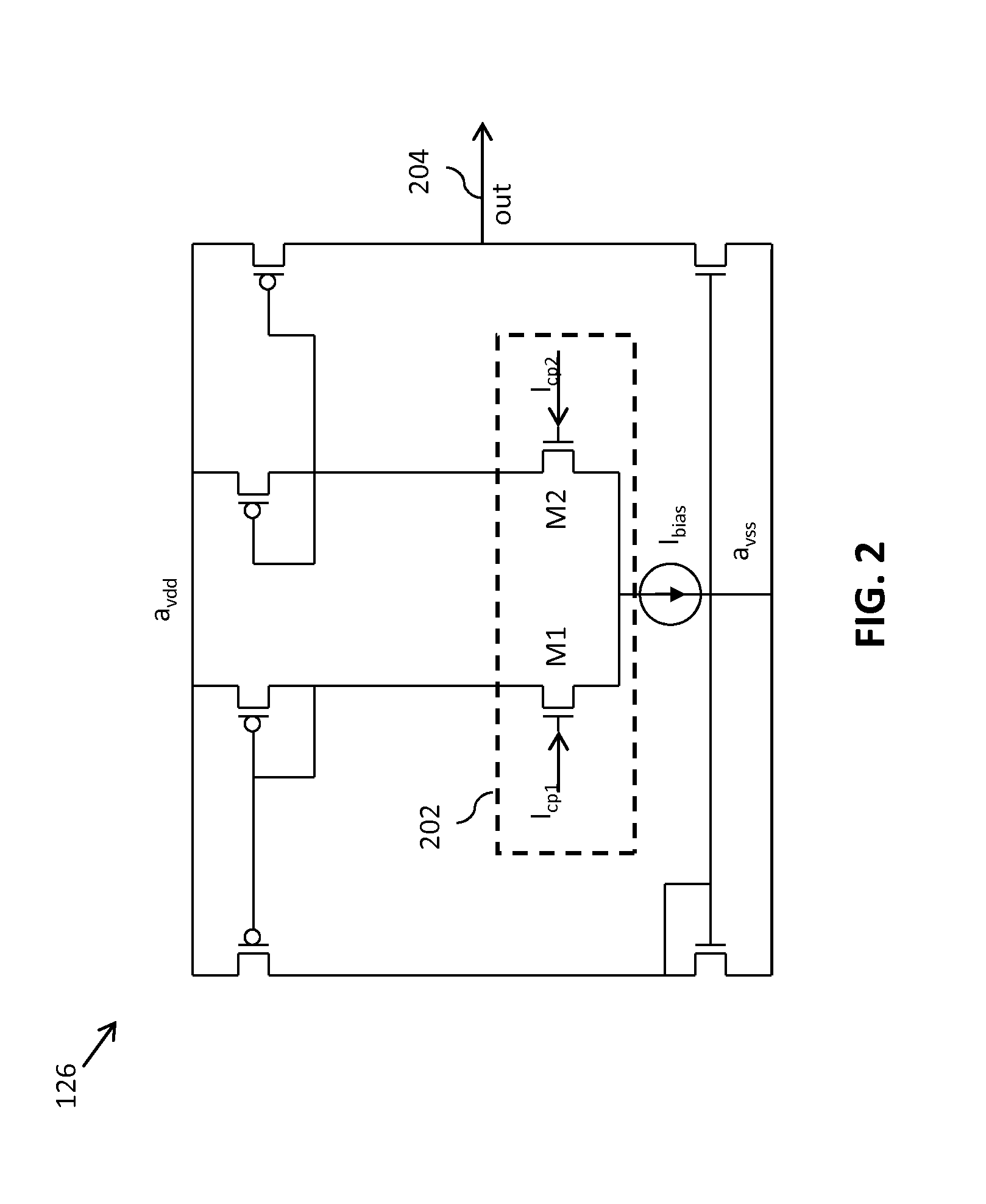
Adaptive bandwidth phase-locked loop
A phase-locked loop (PLL) generates an oscillator signal based on an input reference signal. A voltage-to-current converter converts a control voltage to a first current. A current-controlled oscillator generates the oscillator signal based on the first current. A dual charge pump circuit generates first and second charge pump currents having a predetermined ratio, based on a second current generated by a current mirror circuit and an error (feedback) signal. An active loop filter generates the control voltage based on the first and second charge pump currents. The active loop filter includes an input capacitance that varies with a variation in the predetermined ratio of the charge pump currents. The active loop filter also includes a transconductance stage having a transconductance that varies based on a third current generated by a current mirror circuit. The PLL bandwidth is independent of PVT variations and dependent only on the frequency of the input reference signal. In addition, the size of the input capacitor is relatively small so that the circuit requires very little space.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Method and system for controlling a tuning voltage of a phase-locked loop circuit to an optimal value
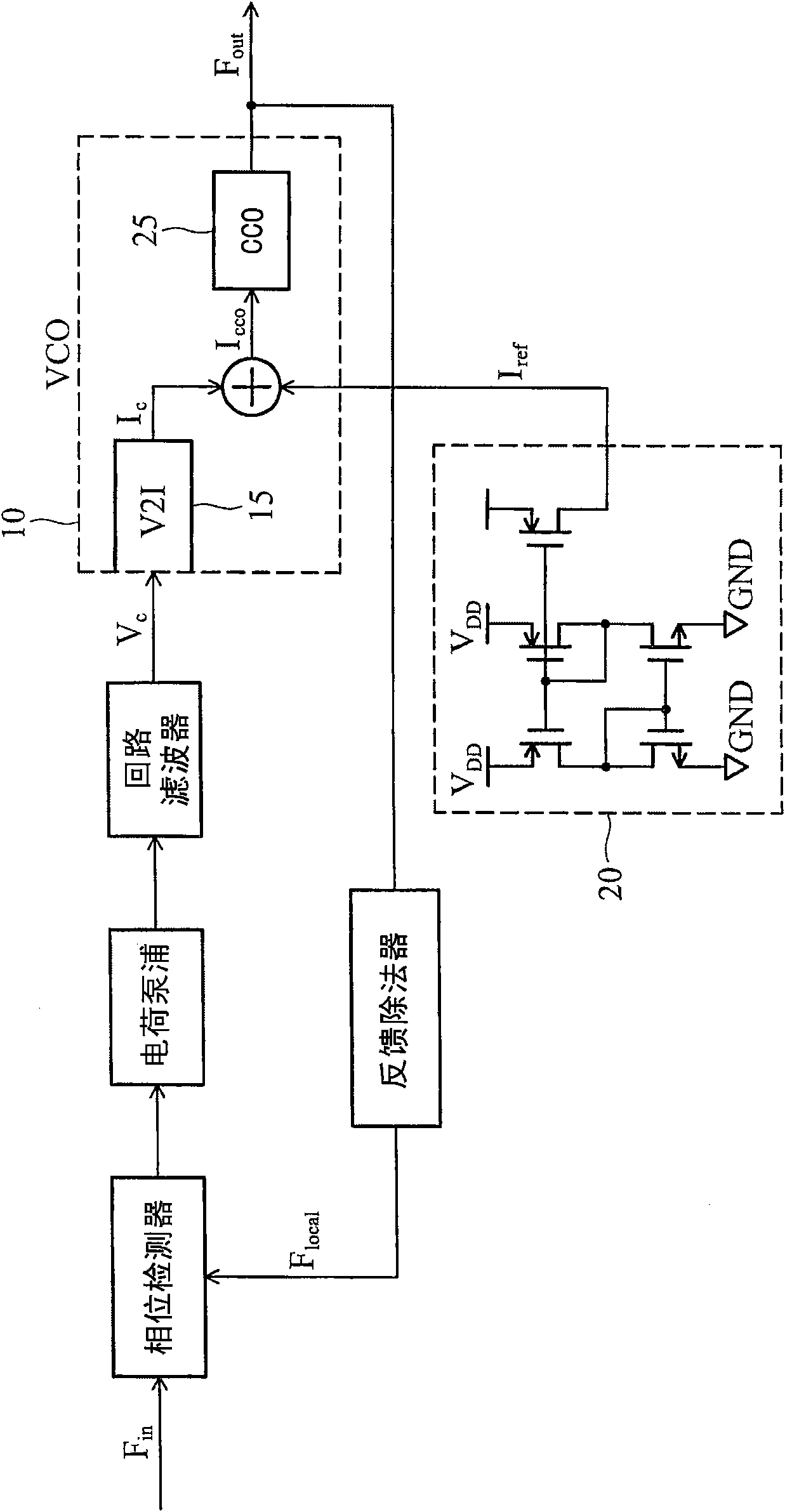
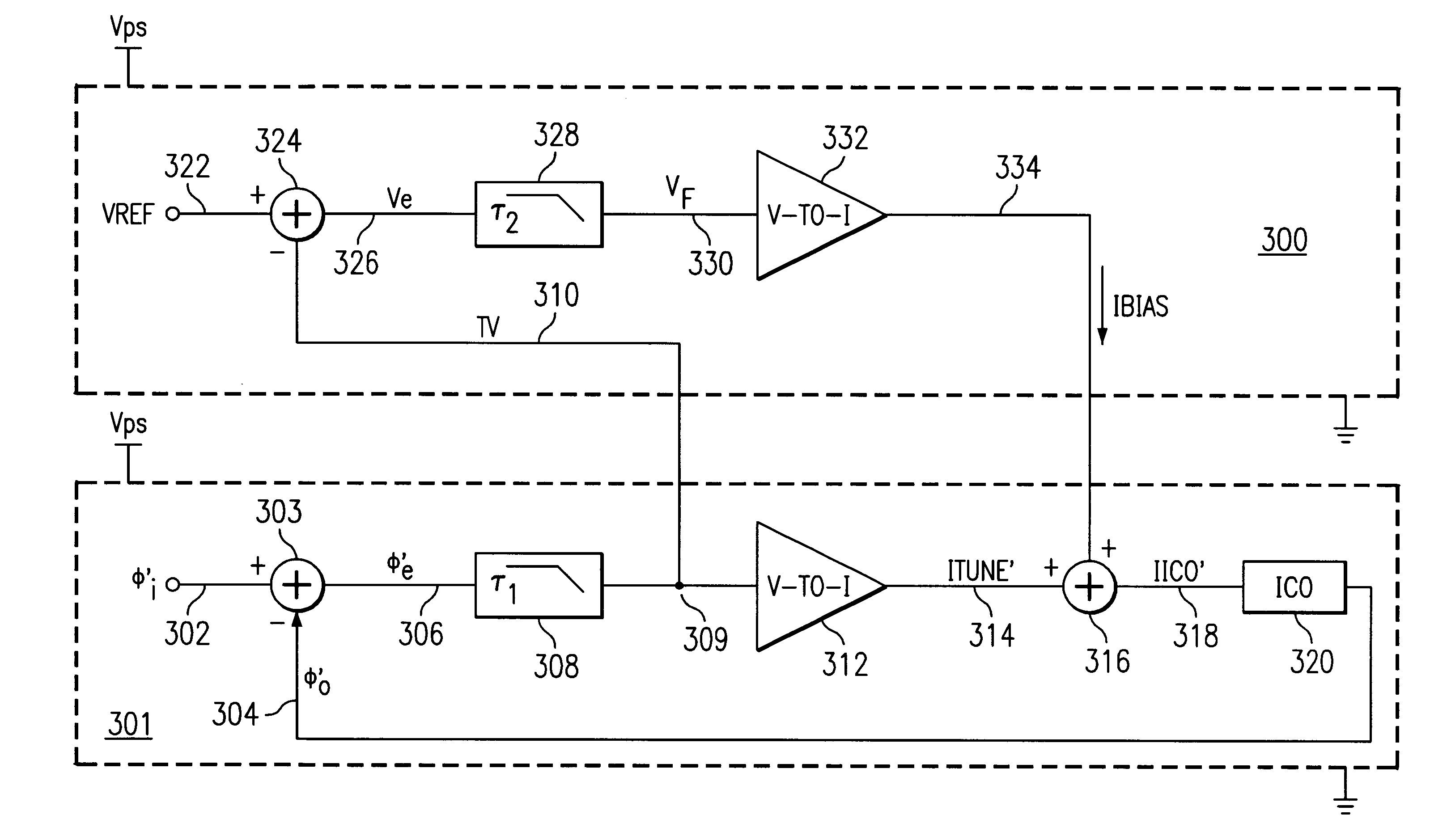
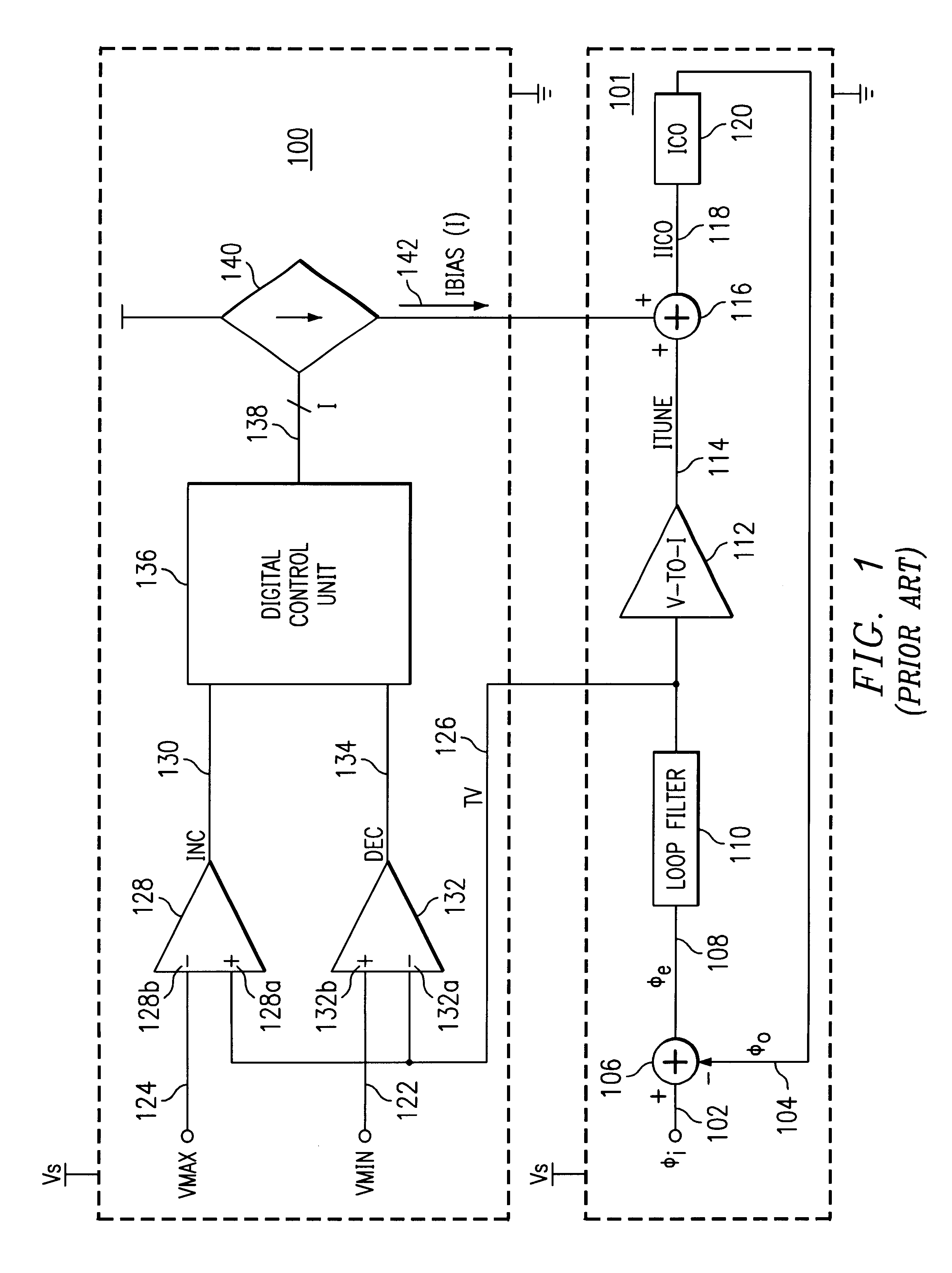
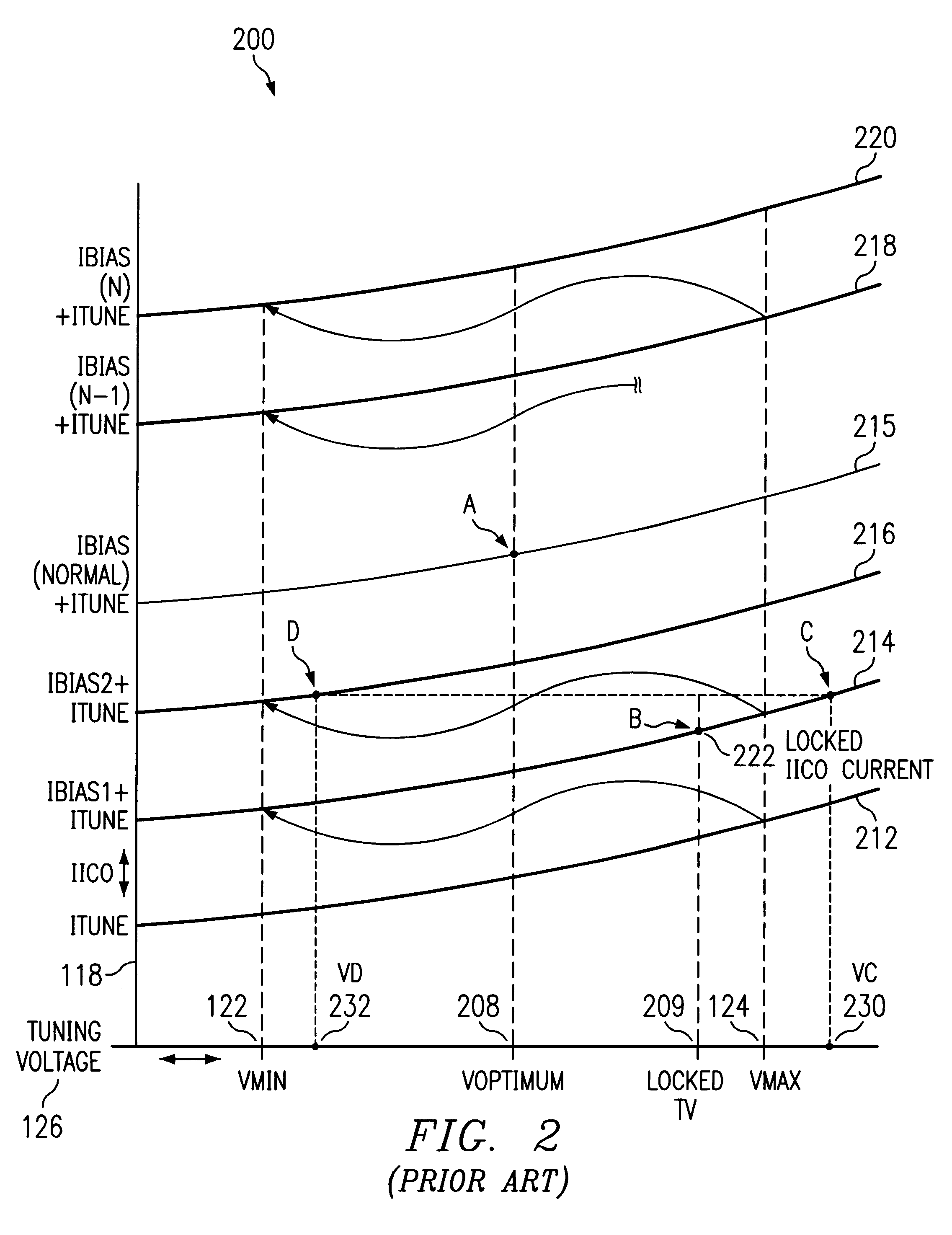
A method and system for controlling a tuning voltage of a phase-locked loop circuit to an optimal value are disclosed. Minimum and maximum bias current values are defined for a bias current from the linear control loop circuit. The linear control loop circuit is coupled to the phase-locked loop circuit. The linear control loop circuit infinitely varies a current value for a current-controlled oscillator of the phase-locked loop circuit. The current value is based on a tuning current of the phase-locked loop circuit and the bias current. The bias current infinitely varies in value between the minimum bias current value and the maximum bias current value to direct the tuning voltage to an optimal value. The phase-locked loop circuit includes a phase detector, a filter, a voltage-to-current converter, a current adder, and the current-controlled oscillator coupled together in series. The linear control loop circuit is an analog, voltage control loop that has a voltage summer, another filter, and another voltage-to-current converter coupled together in series. A reference voltage and the tuning voltage are inputted into the voltage summer, and a bias current is outputted and injected from the other voltage-to-current converter into the tuning current. The other voltage-to-current converter has a sufficient gain to provide the bias current between the minimum bias current value and the maximum bias current value. The linear control loop circuit is designed with a time constant characteristic that is slower than another time constant characteristic of the phase-locked loop circuit.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
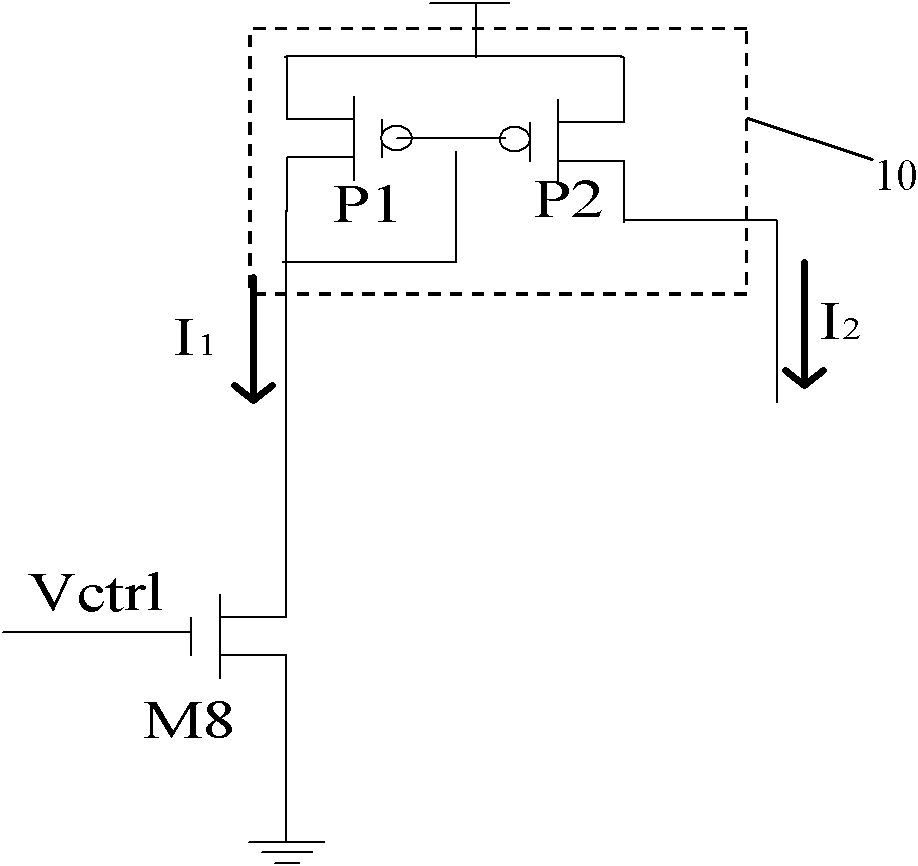
Voltage-to-current converter
The invention discloses a voltage-to-current converter. The voltage-to-current converter comprises a first super source follower, a second super source follower and a current mirror image circuit. In the converter, output resistance is reduced by combining the two super source followers with the current mirror image circuit, and current is fed back to the super source followers to stabilize the super source followers through the current mirror image circuit to realize low impedance of an output end of the voltage-to-current converter; thus extremely high power supply rejection ratio can be obtained and good suppression effect on power noise can be achieved. The two super source followers are adopted to reduce the output voltage of the voltage-to-current converter and keep the output voltage close to input control voltage, so output of the converter can act on a current controlled oscillator of a metallic oxide semiconductor field effect transistor (MOSFET) device using low working voltage to improve the frequency of a voltage controlled oscillator.
Owner:SHANGHAI INTEGRATED CIRCUIT RES & DEV CENT
Clock generator and related biasing circuit
ActiveUS7154352B2Reduce jitterLow costPulse automatic controlGenerator stabilizationEngineeringCurrent controlled oscillator
A clock generator capable of providing reduced low-frequency jitter clock signals without utilization of a crystal oscillator is introduced. The present invention clock generator utilizes a diode in related biasing circuit such that the generated control current to a current control oscillator is stable and clear due to the low flicker noise and low thermal noise of the voltage across the diode. The cost of PLL systems utilizing the present invention clock generator instead of a crystal oscillator is decreased. The adopted biasing circuit is introduced as well.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
Spread spectrum clock generator
InactiveUS7161970B2Robust architectureLess susceptible to noisePulse automatic controlElectrical apparatus interference reductionClosed loopEngineering
A spread spectrum clock generator comprises a conventional closed-loop VCO and an open-loop VCO where both are coupled to the same point of the PLL. Both VCOs comprise a V-to-I converter followed by a current-controlled oscillator and are identical in design but only the open-loop VCO receives the modulation current to generate the spread spectrum clock signal. The open-loop ICO is part of the spread spectrum generator and in one embodiment of the invention receives feedback current signals representing the modulation method and modulation ratio. This ensures that the modulated clock output tracks the PLL output frequency. In a second embodiment the closed-loop VCO receives from the spread spectrum generator the feedback current signal representing the modulation method (center / down spread) while the open-loop VCO receives the feedback signal representing the modulation ratio.
Owner:KARMIC DESIGN USA
Clock and data recovery circuit with proportional path
A clock and data recovery circuit includes a phase detector, a charge pump, a loop filter, a voltage-controlled oscillator and a frequency divider. The voltage-controlled oscillator includes a current mirror, a control circuit, a current modulation module and a current-controlled oscillator. The current mirror has a current-controlling path and a current-outputting path. The current-controlling path and the current-outputting path are in a proportional relationship. The control circuit is used for adjusting the current flowing through the current-controlling path according to the control voltage. The current modulation module is used for generating a differential current according to the judging signal. The current-controlled oscillator is used for adjusting the phase of the second output clock signal according to the sum of the differential current and the current flowing through the current-outputting path.
Owner:FARADAY TECH CORP
Ling intensity detection method and light intensity detection circuit
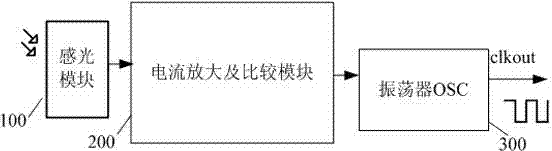
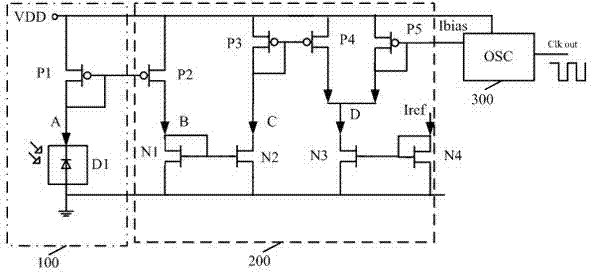
ActiveCN102331297ASimple structureReduce chip areaPhotometry using reference valueCurrent controlled oscillatorUltimate tensile strength
The invention relates to a light intensity detection method and a light intensity detection circuit. According to the method, photo-generated current generated by a photographic module is amplified and is used for controlling the frequency of an oscillator, thereby the change of the photo-generated current is converted into change of the output frequency of the oscillator; and the strength of light can be detected by only detecting the output frequency of the oscillator, so that the light intensity can be detected more simply and conveniently. In addition, the light intensity detection circuit adopting the light intensity detection method comprises the photo-generated module, a current amplifying and comparing module and the oscillator; and the circuit has the advantages of more simplified structure, reduced power consumption and reduced chip area occupied by the circuit.
Owner:NATIONZ TECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com