Patents
Literature
97results about How to "Improve power added efficiency" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
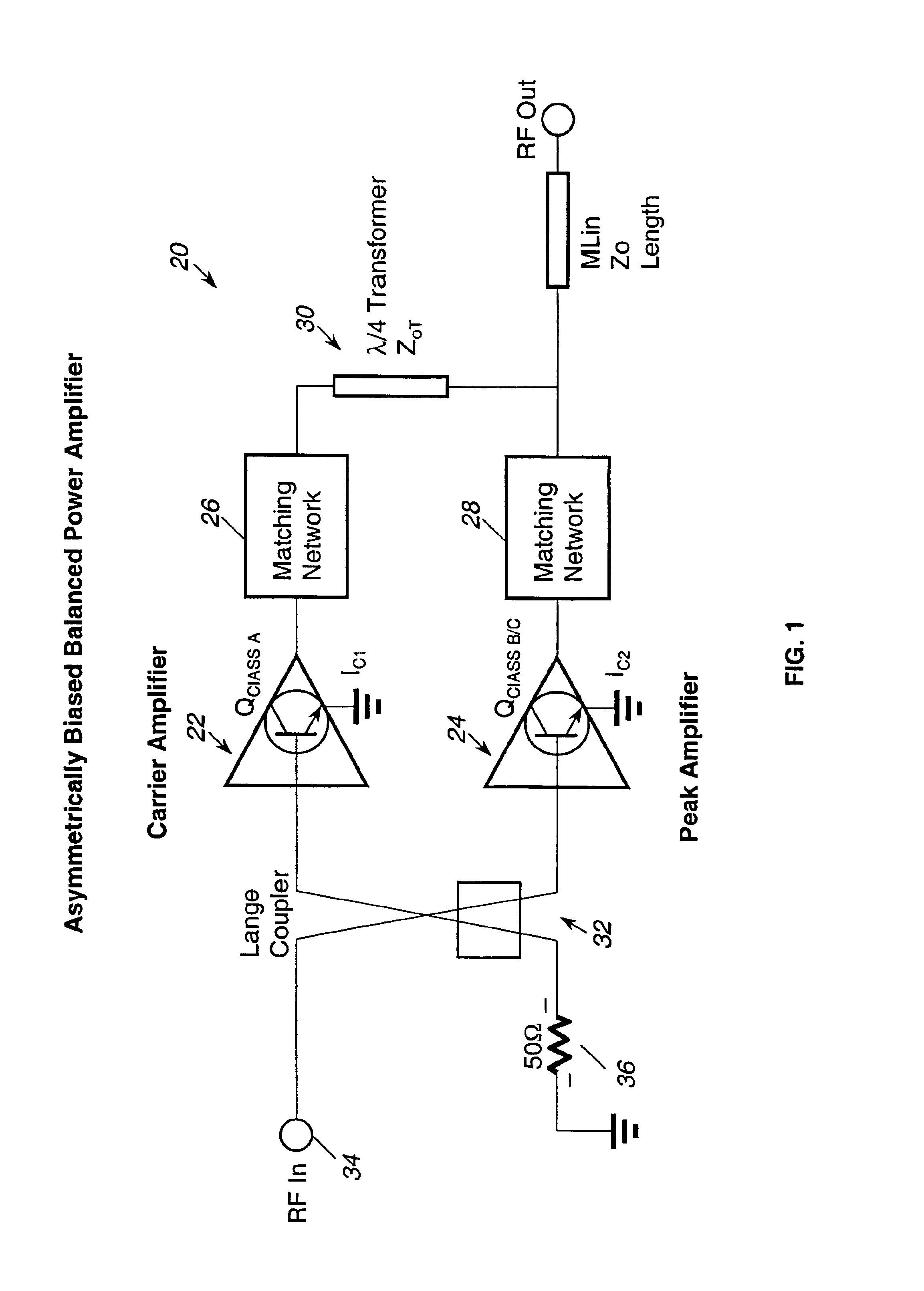
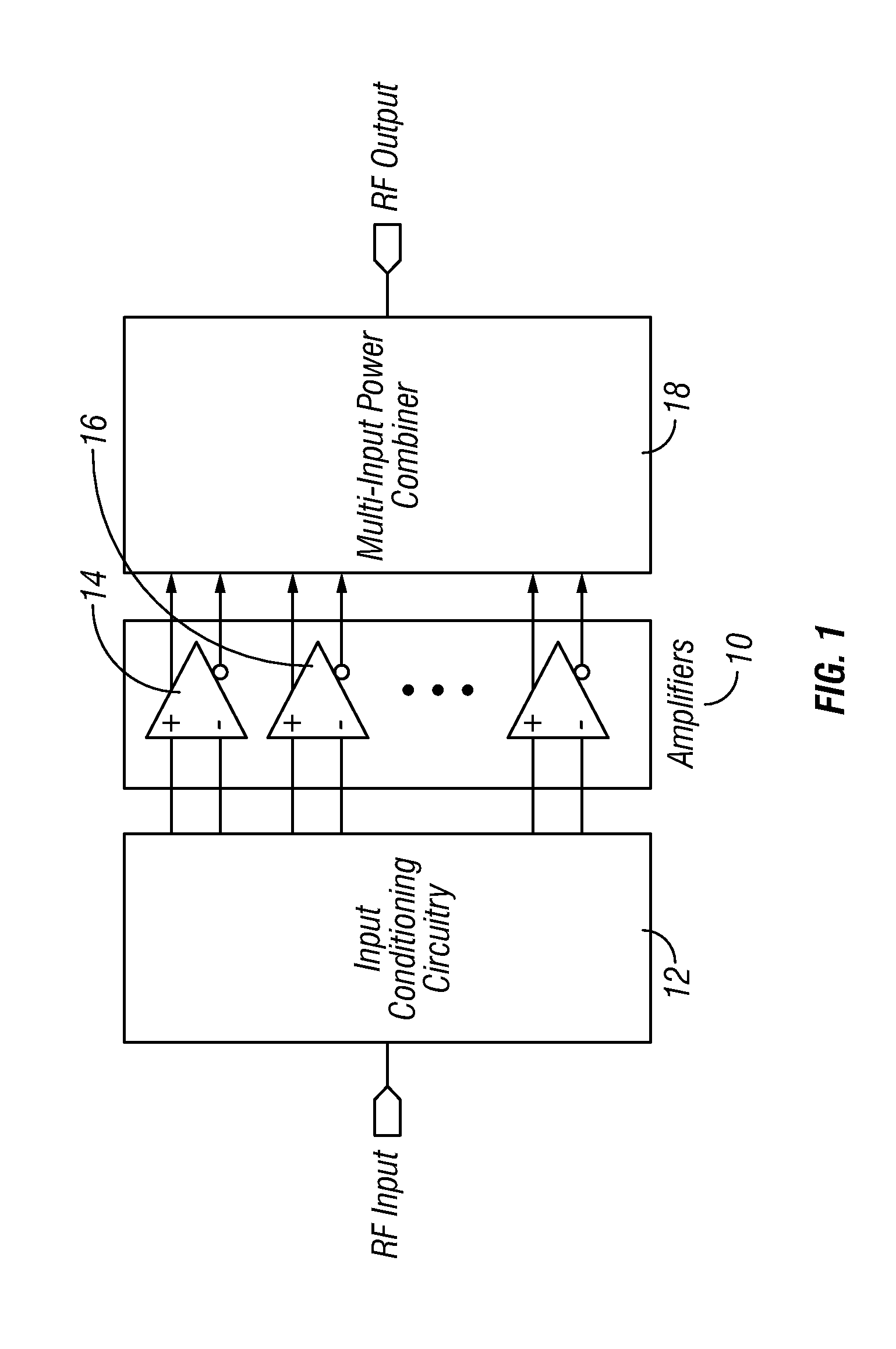
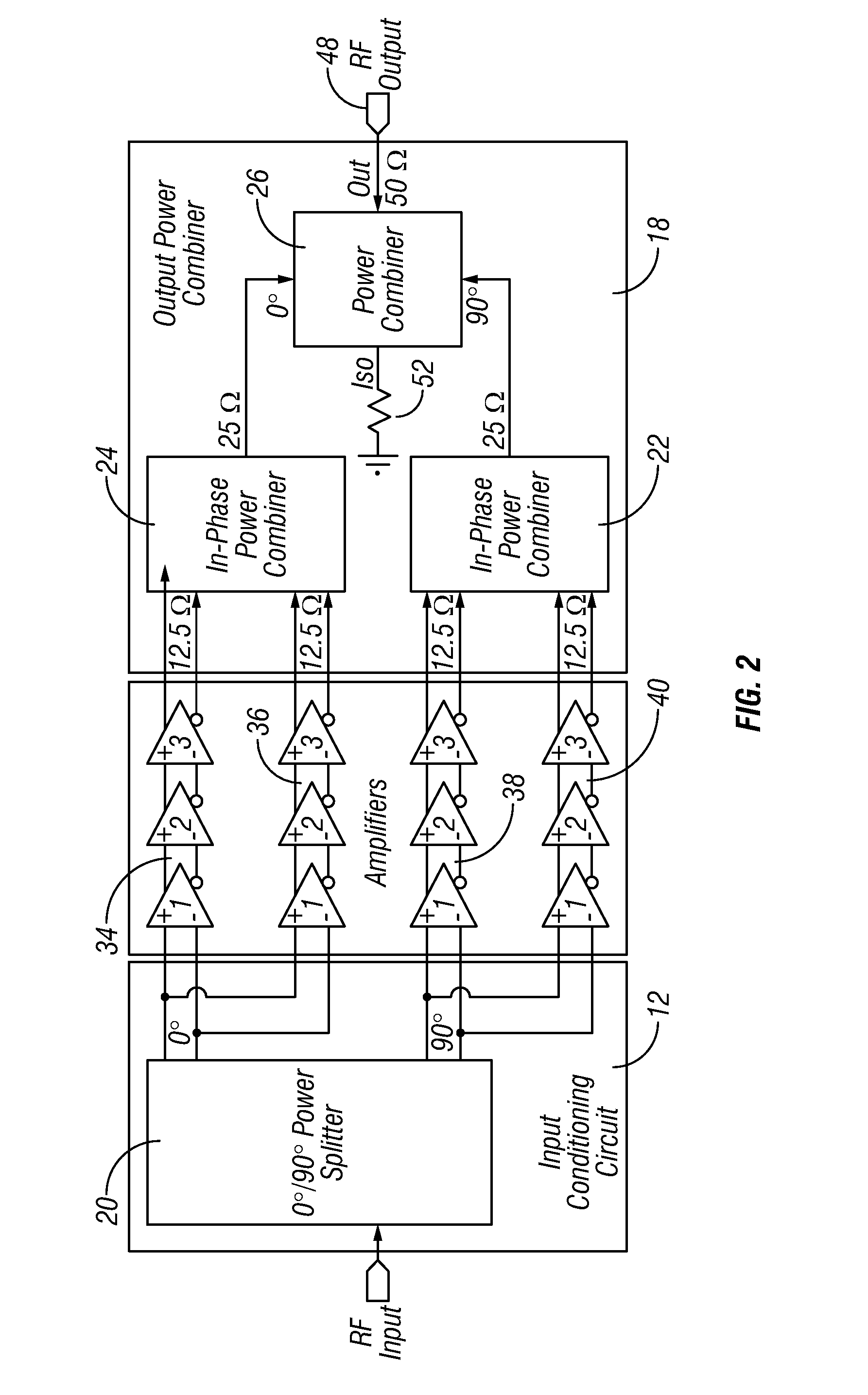
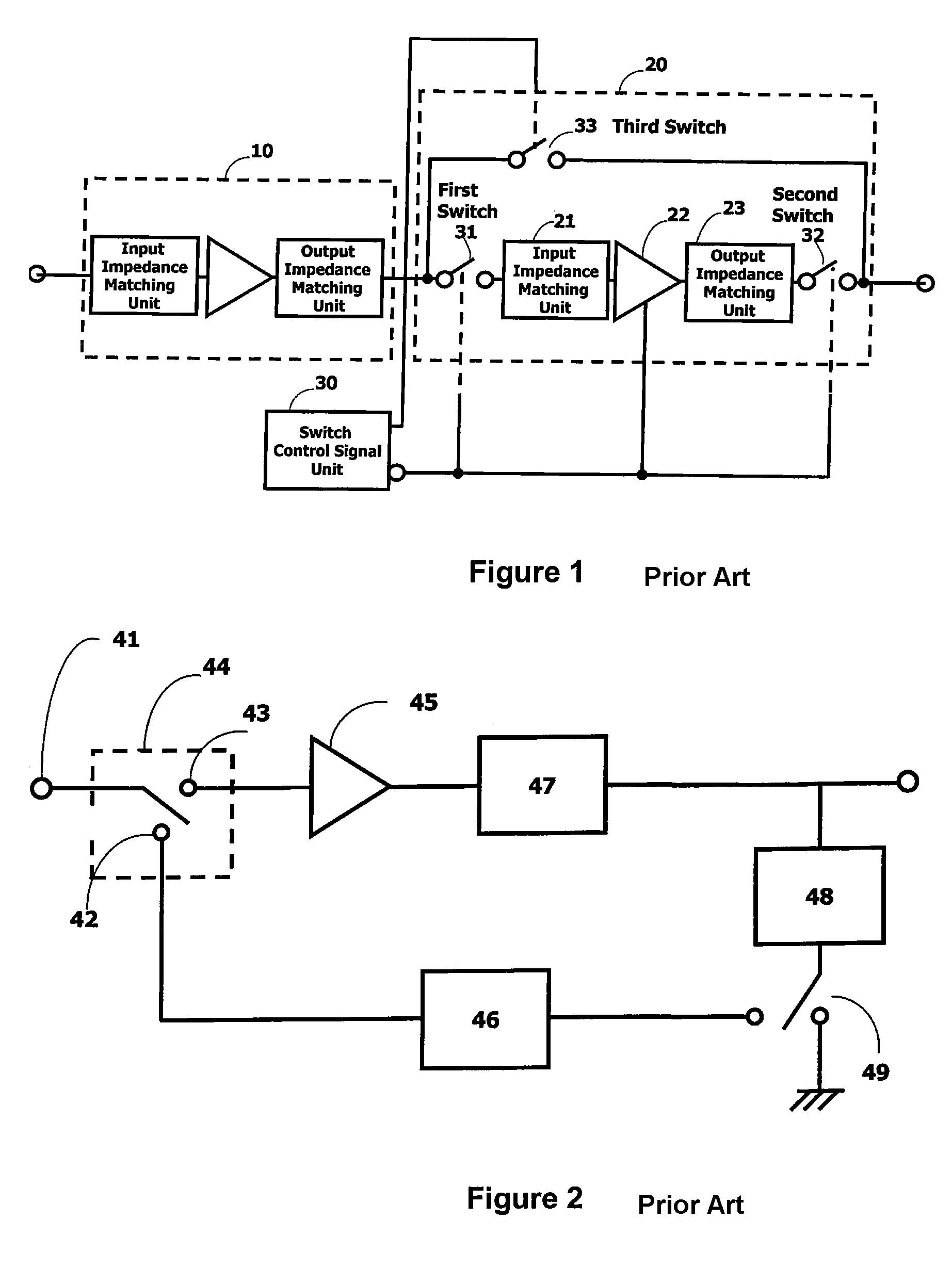
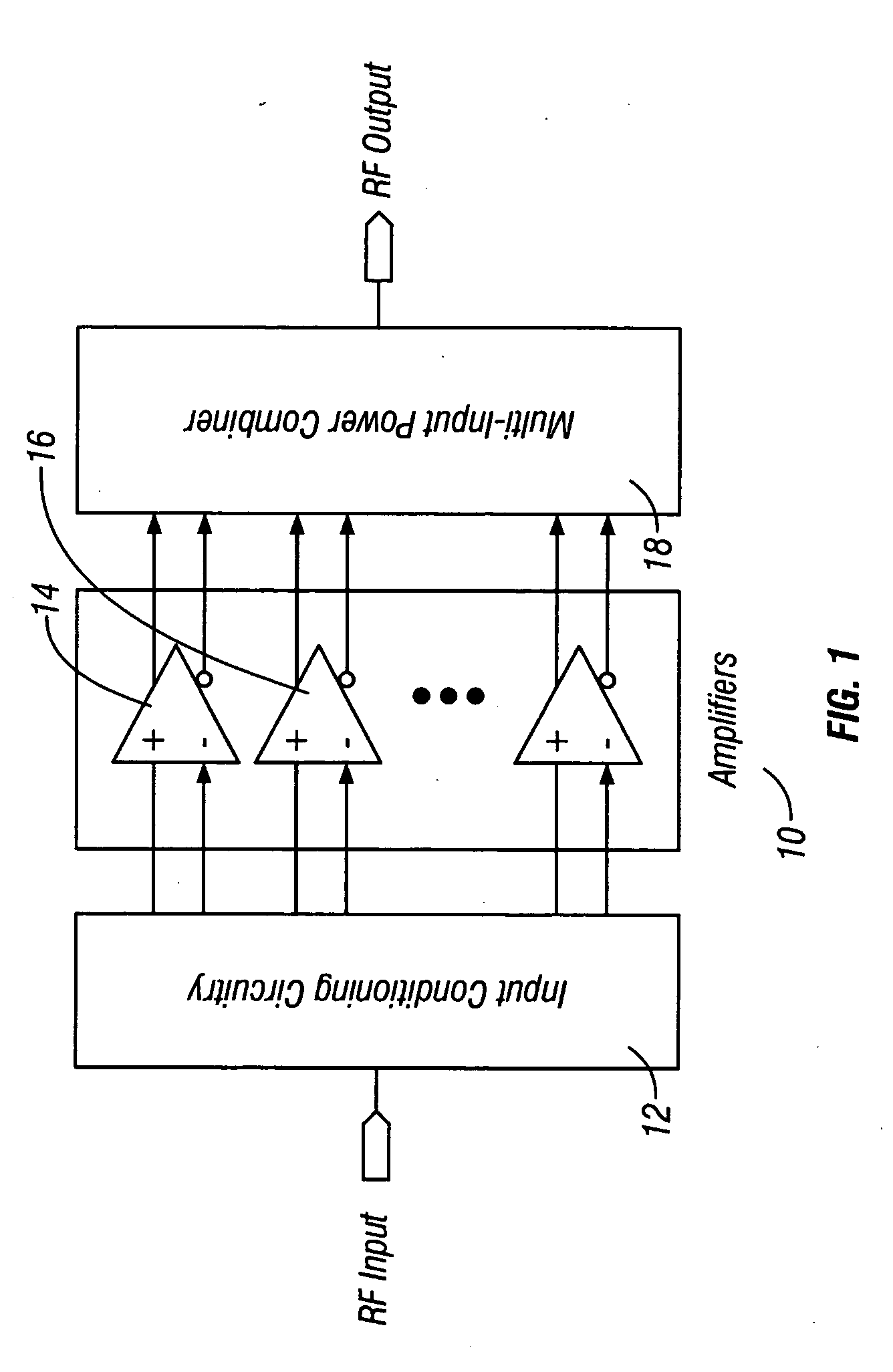
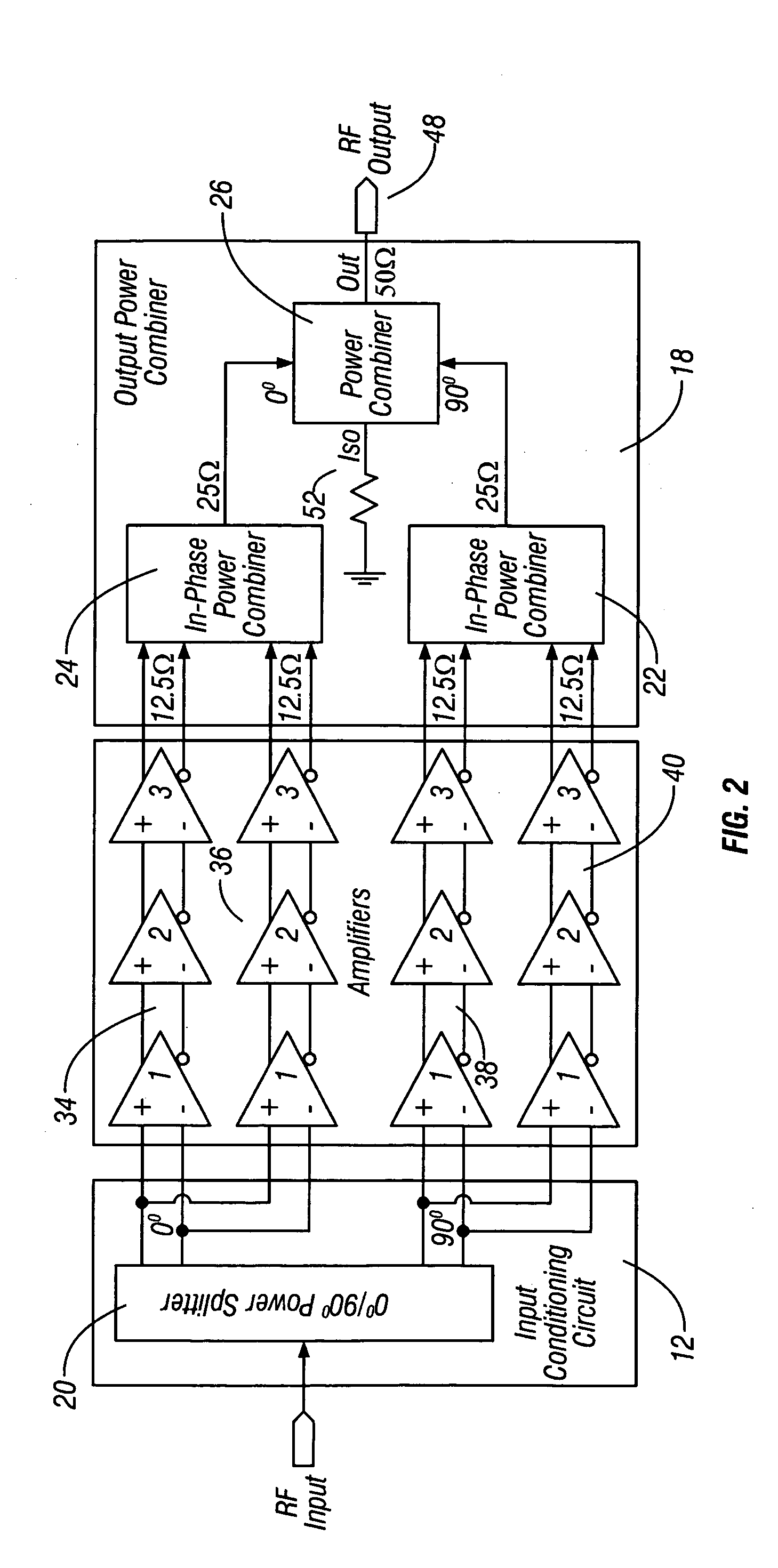
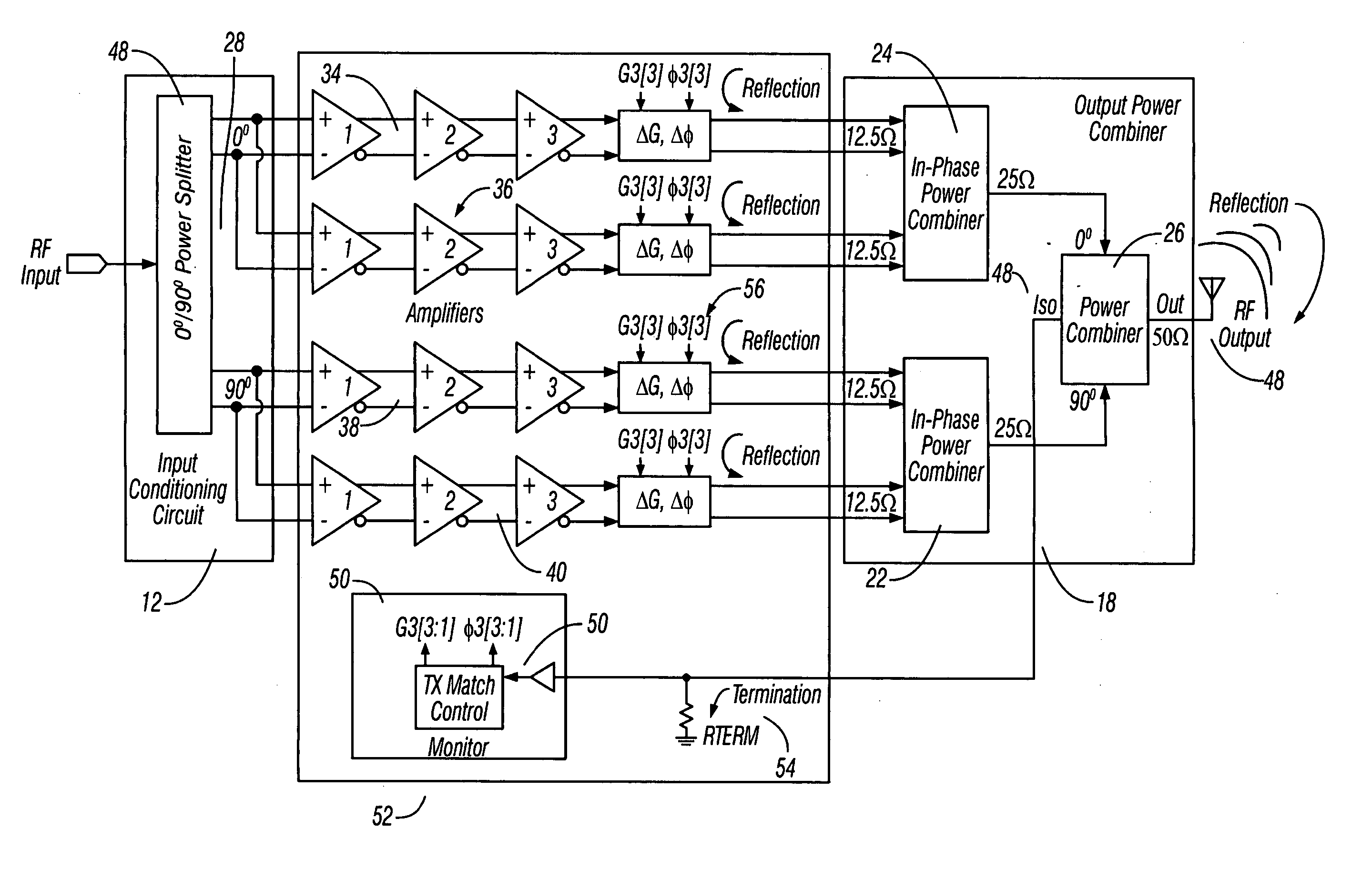
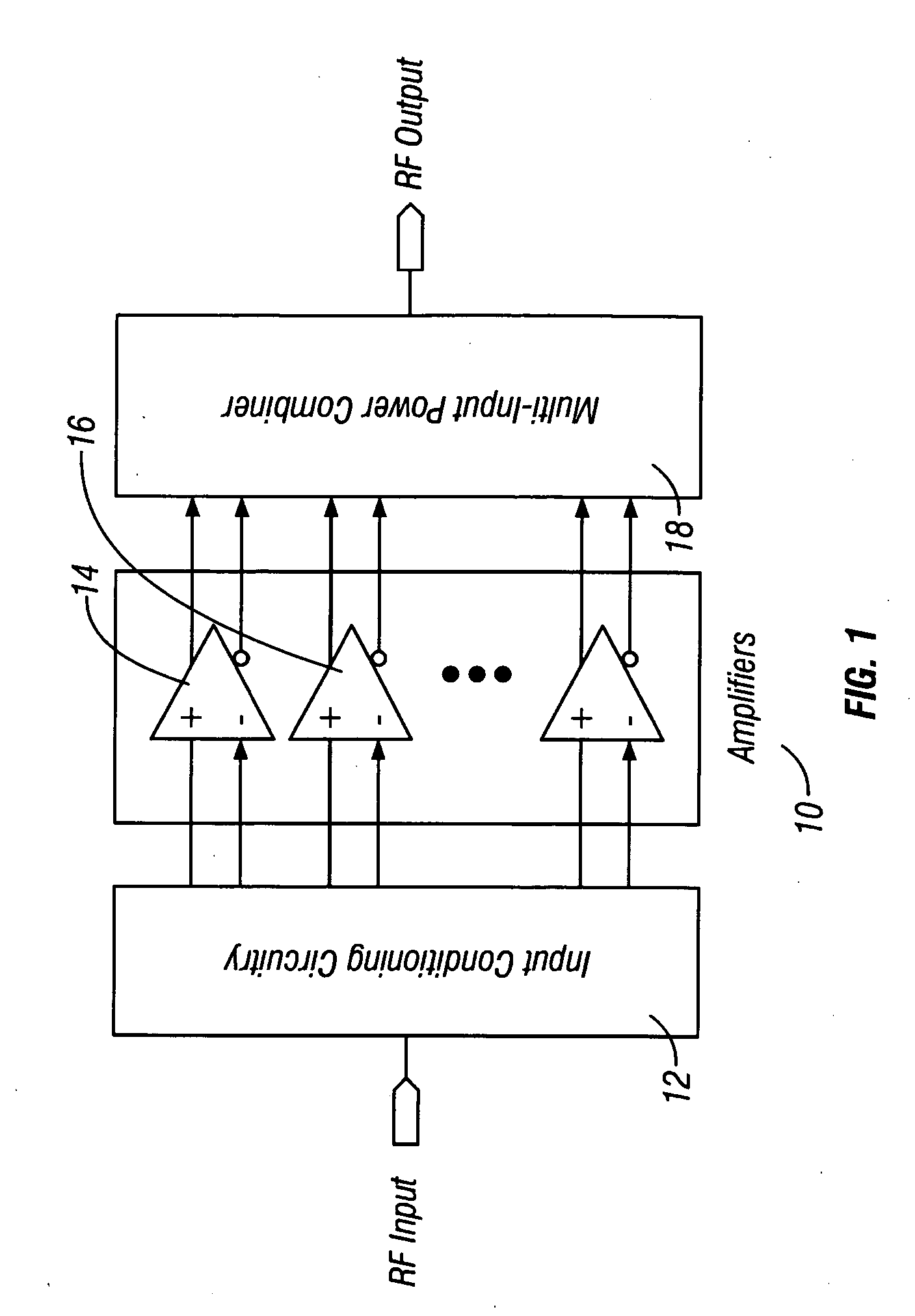
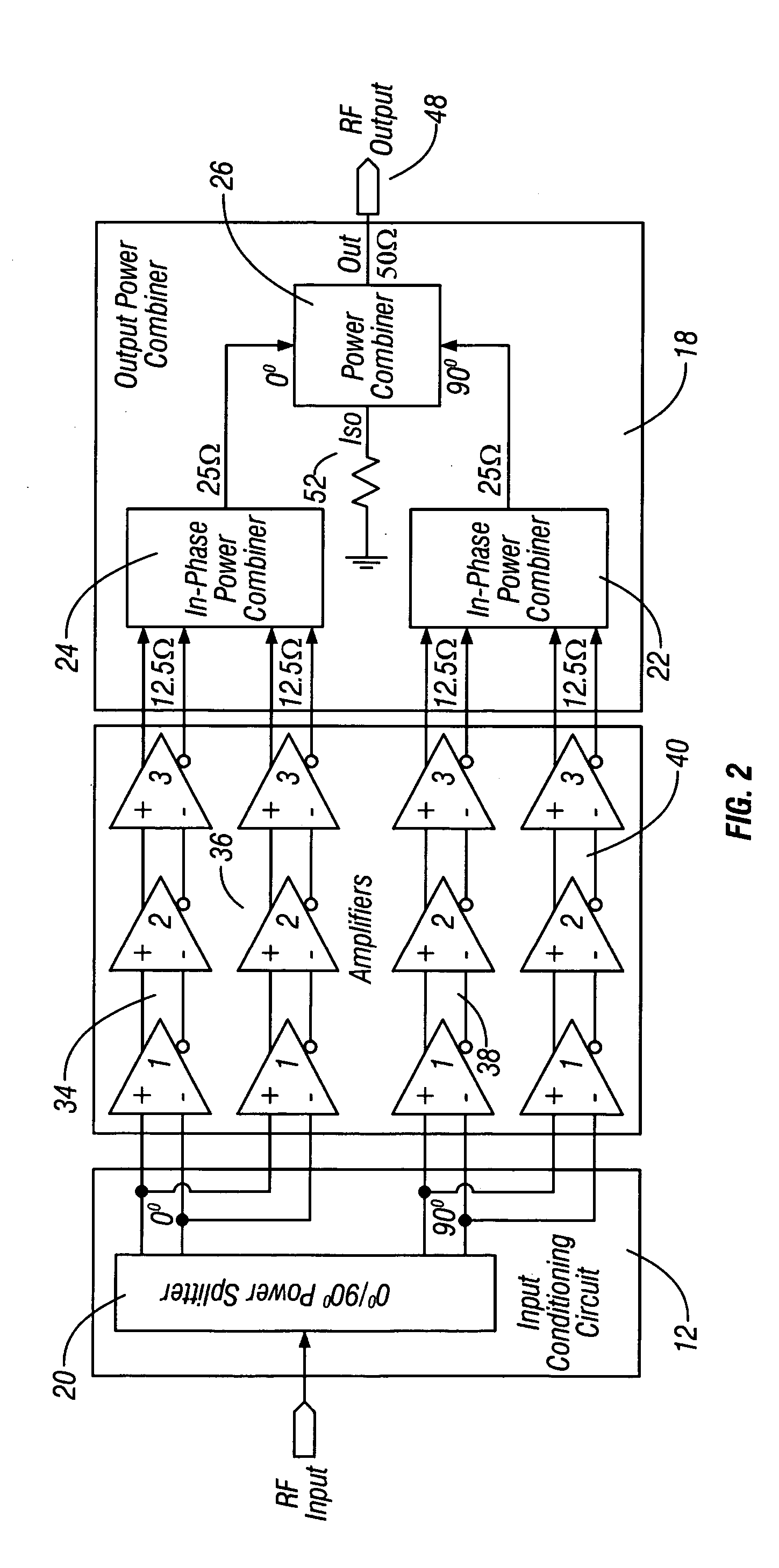
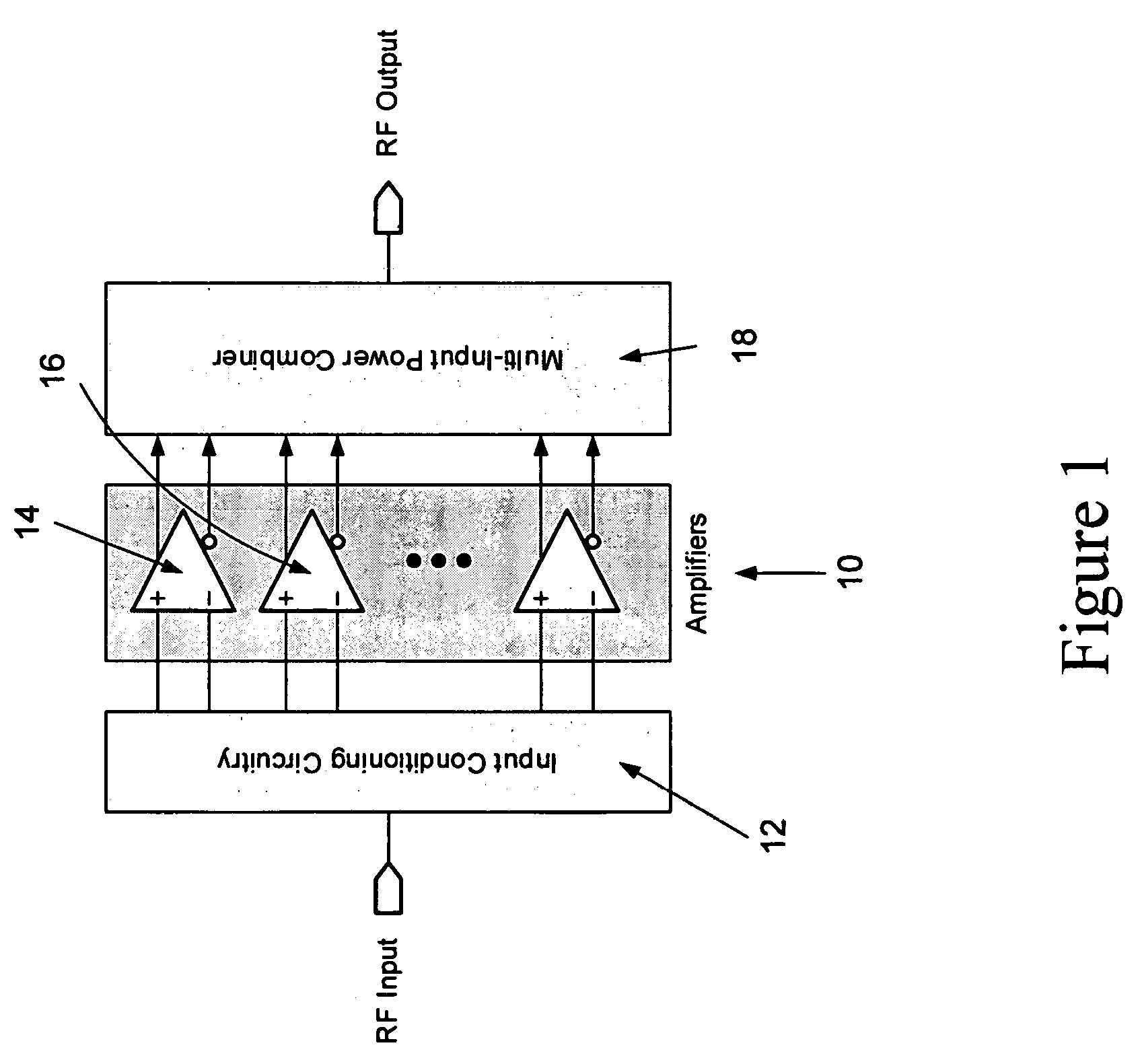
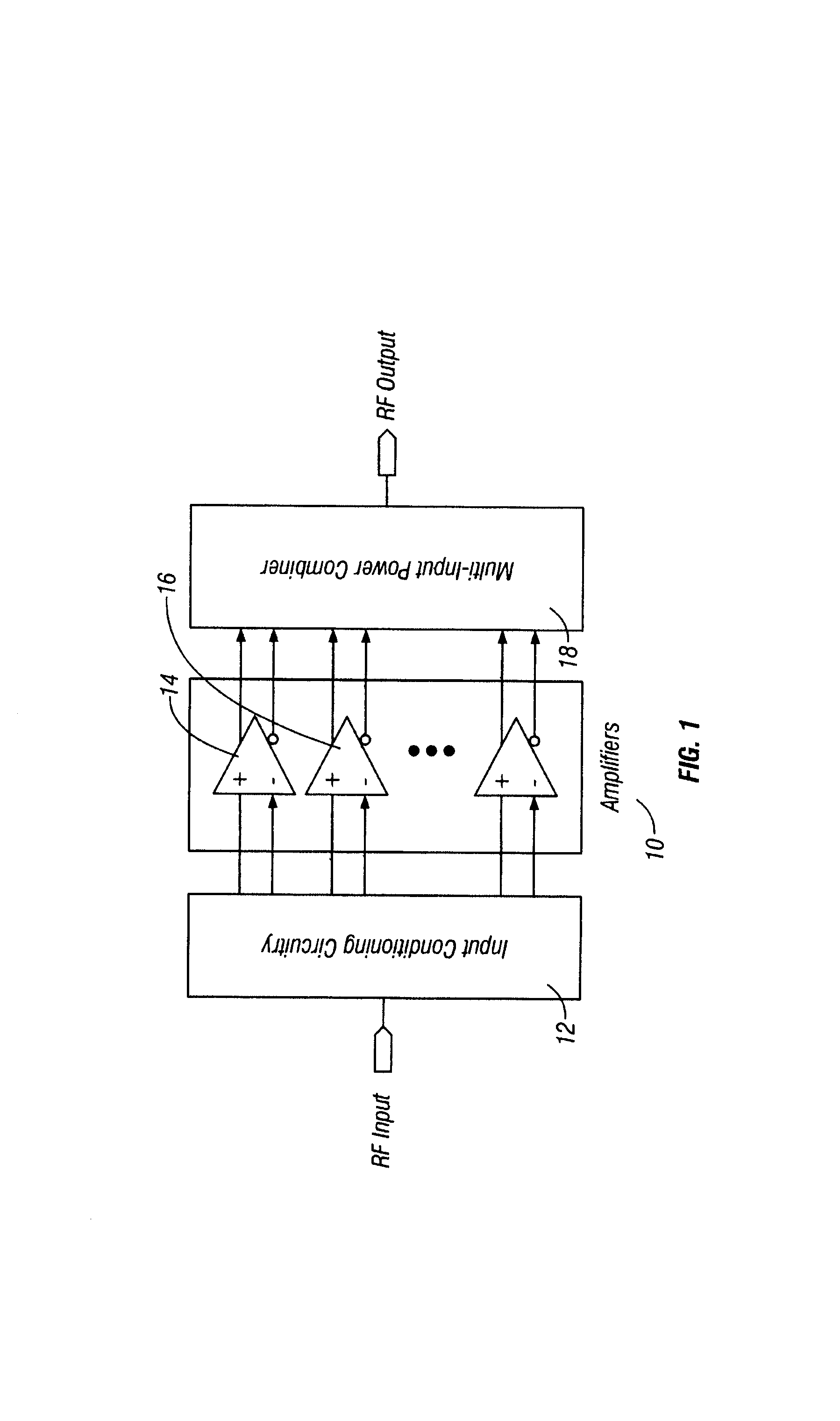
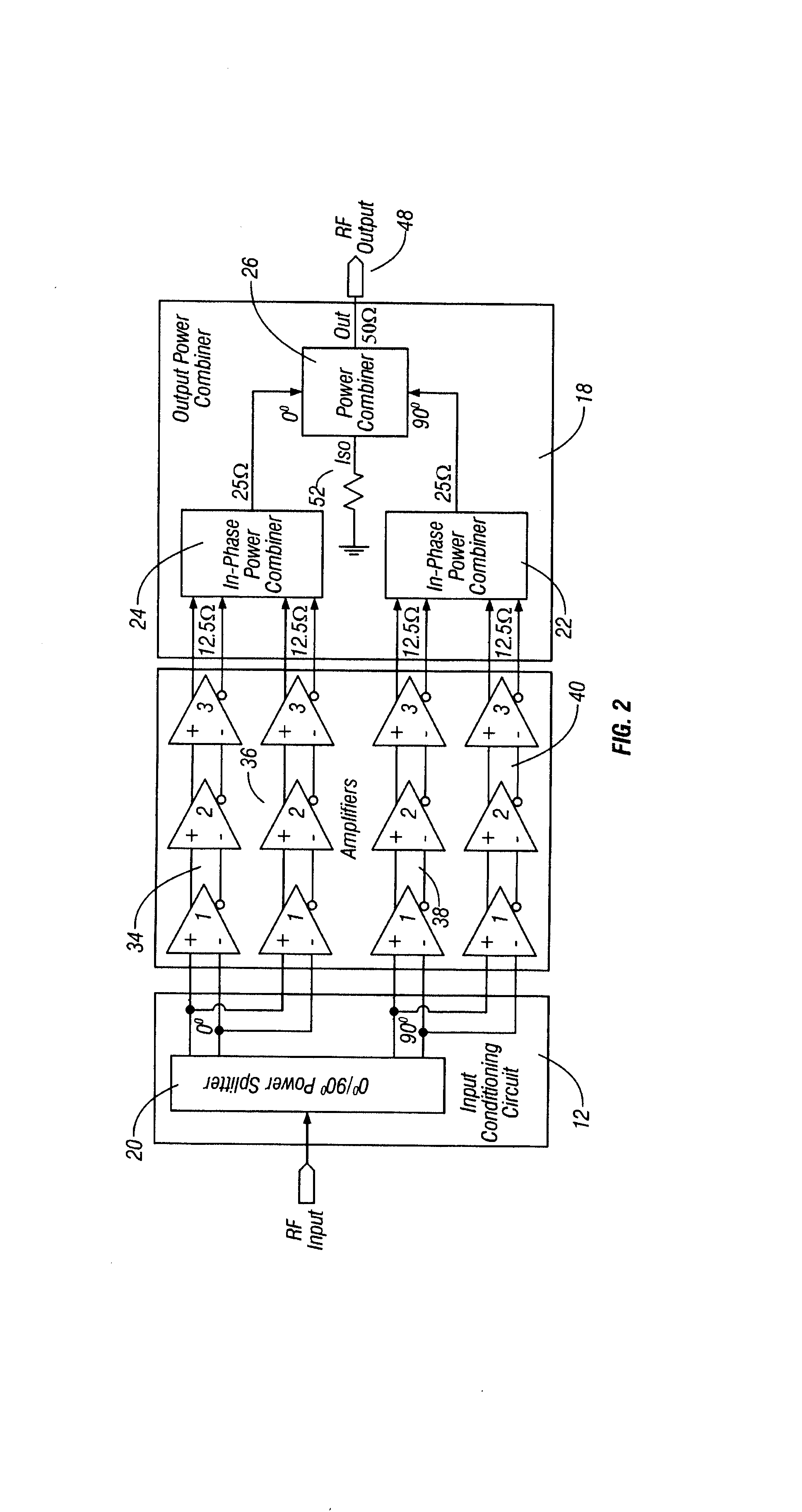
Method and apparatus for an improved power amplifier
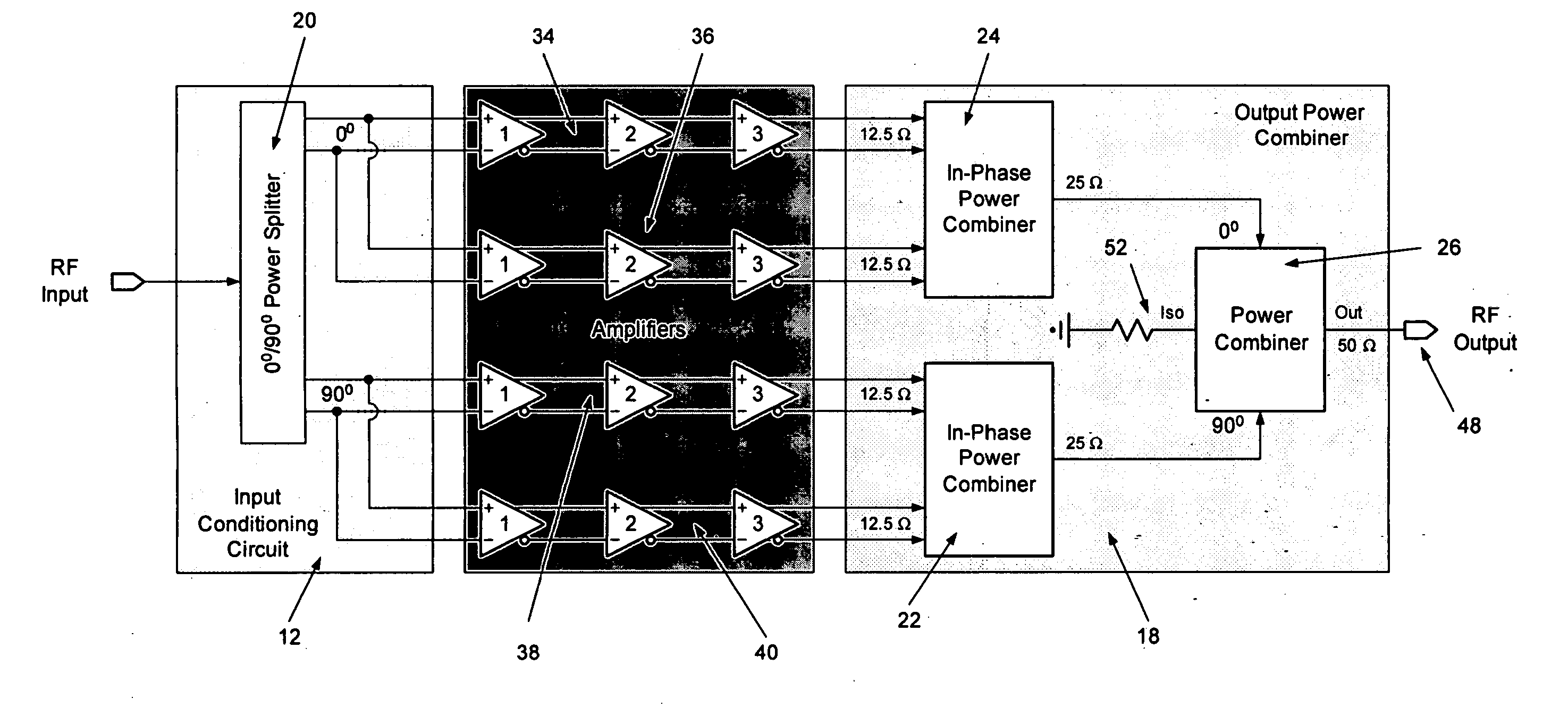
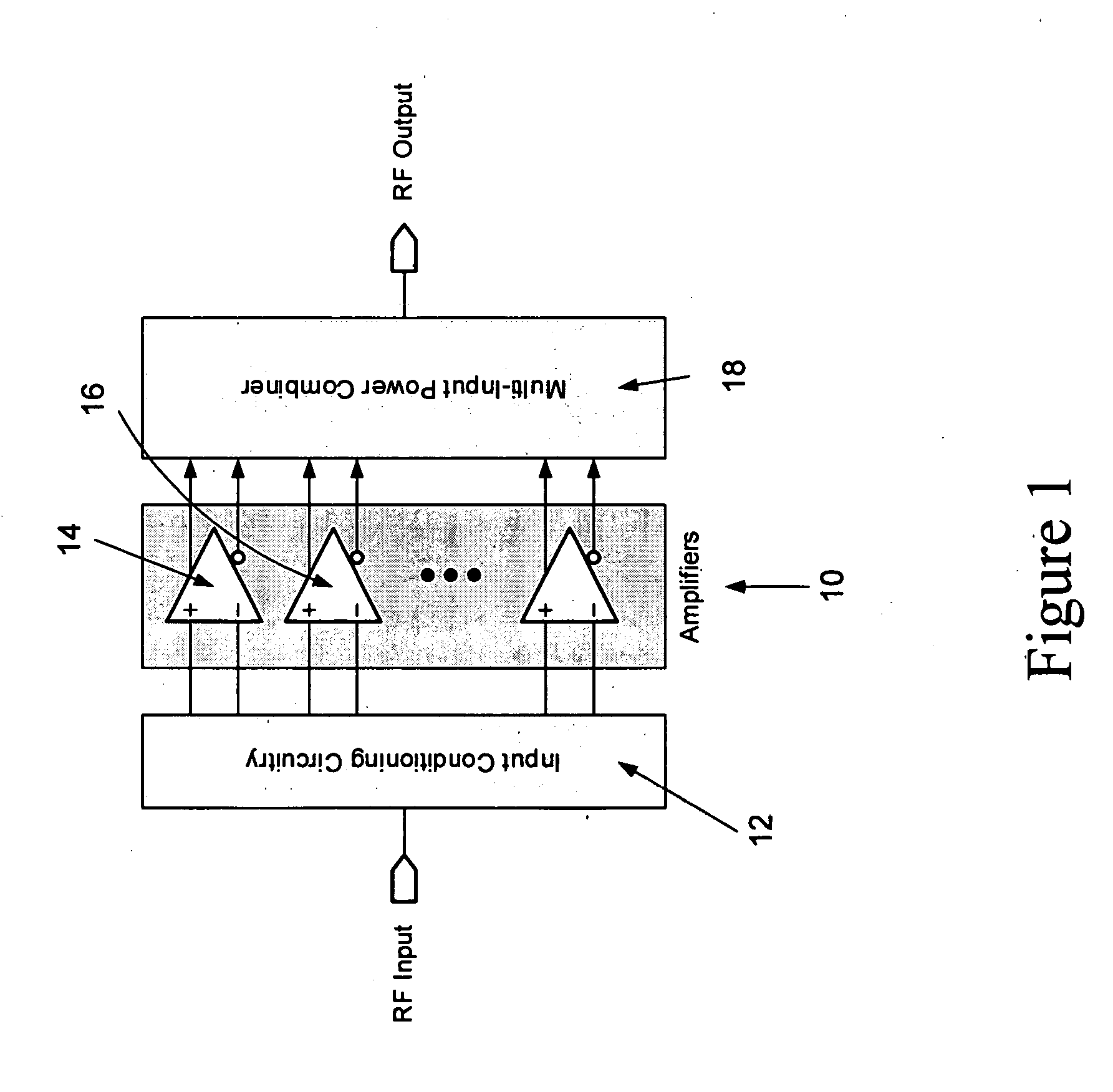
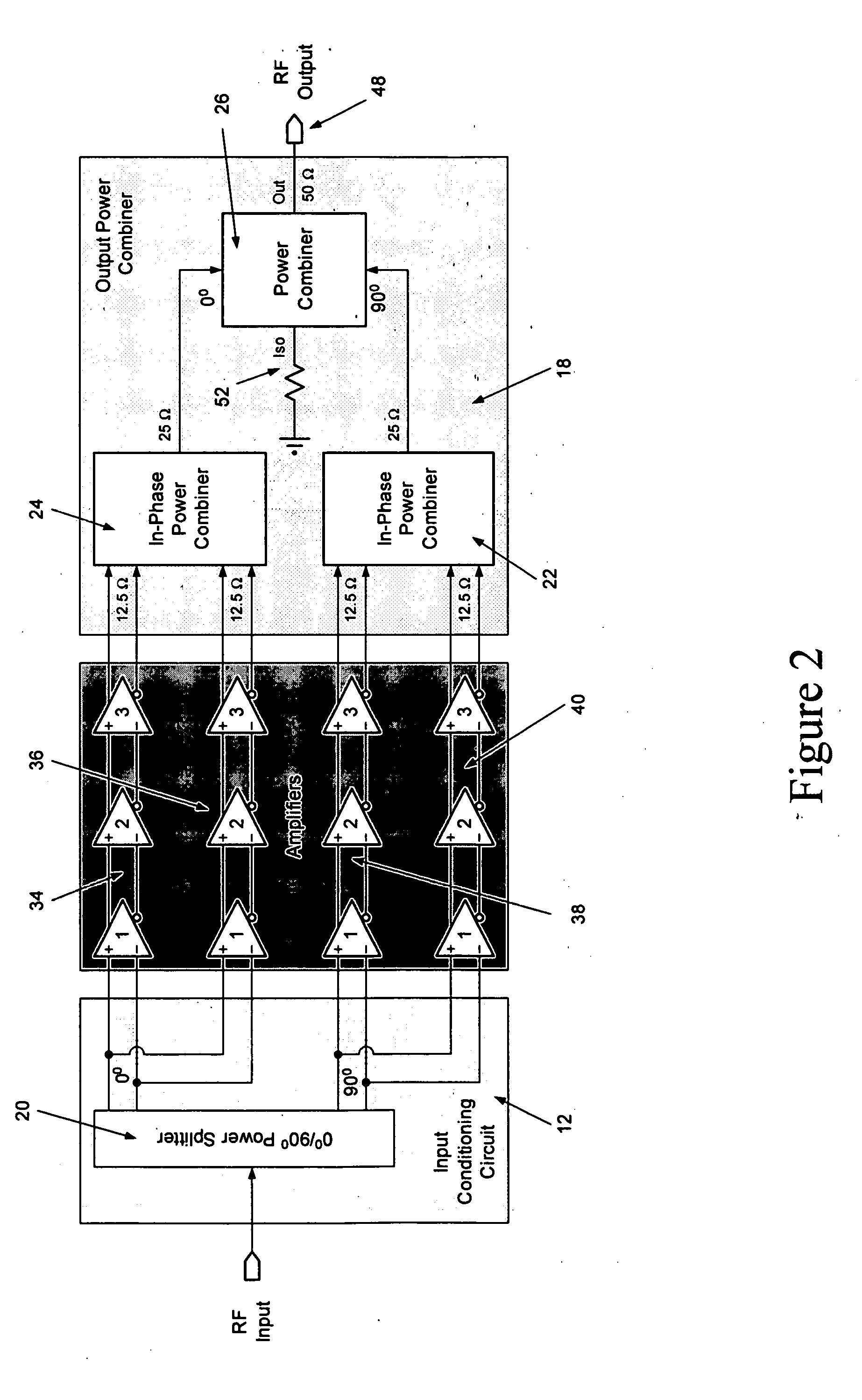
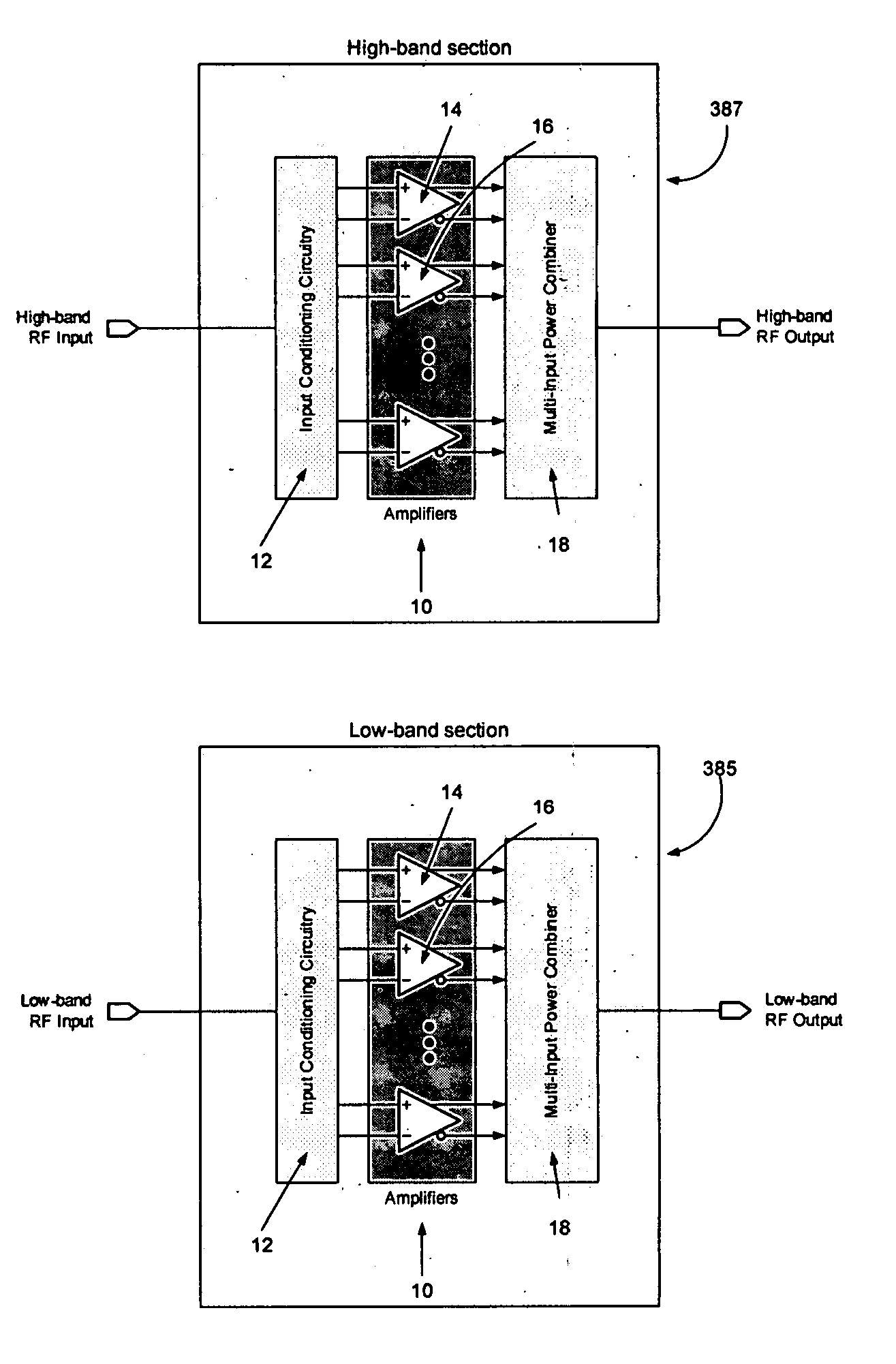
ActiveUS20060006946A1Increase output powerImprove power added efficiencyAmplifier combinationsMulti inputAudio power amplifier
A power amplifier assembly has a first power amplifier with a first input conditioning circuit. At least first and second amplifiers are in parallel with each other and having inputs and outputs. An input signal is coupled to the inputs of the first and second amplifiers. A first multi-input power combiner is provided. The outputs of the at least first and second parallel amplifiers are combined by the first multi-input power combiner to add signals of the outputs constructively. A second power amplifier has a first input conditioning circuit. At least first and second amplifiers are in parallel with each other and having inputs and outputs. An input signal is coupled to the inputs of the first and second amplifiers. A second multi-input power combiner is provided. The outputs of the at least first and second parallel amplifiers are combined by the second multi-input power combiner to add signals of the outputs constructively.
Owner:QORVO INT PTE LTD
Application of the doherty amplifier as a predistortion circuit for linearizing microwave amplifiers
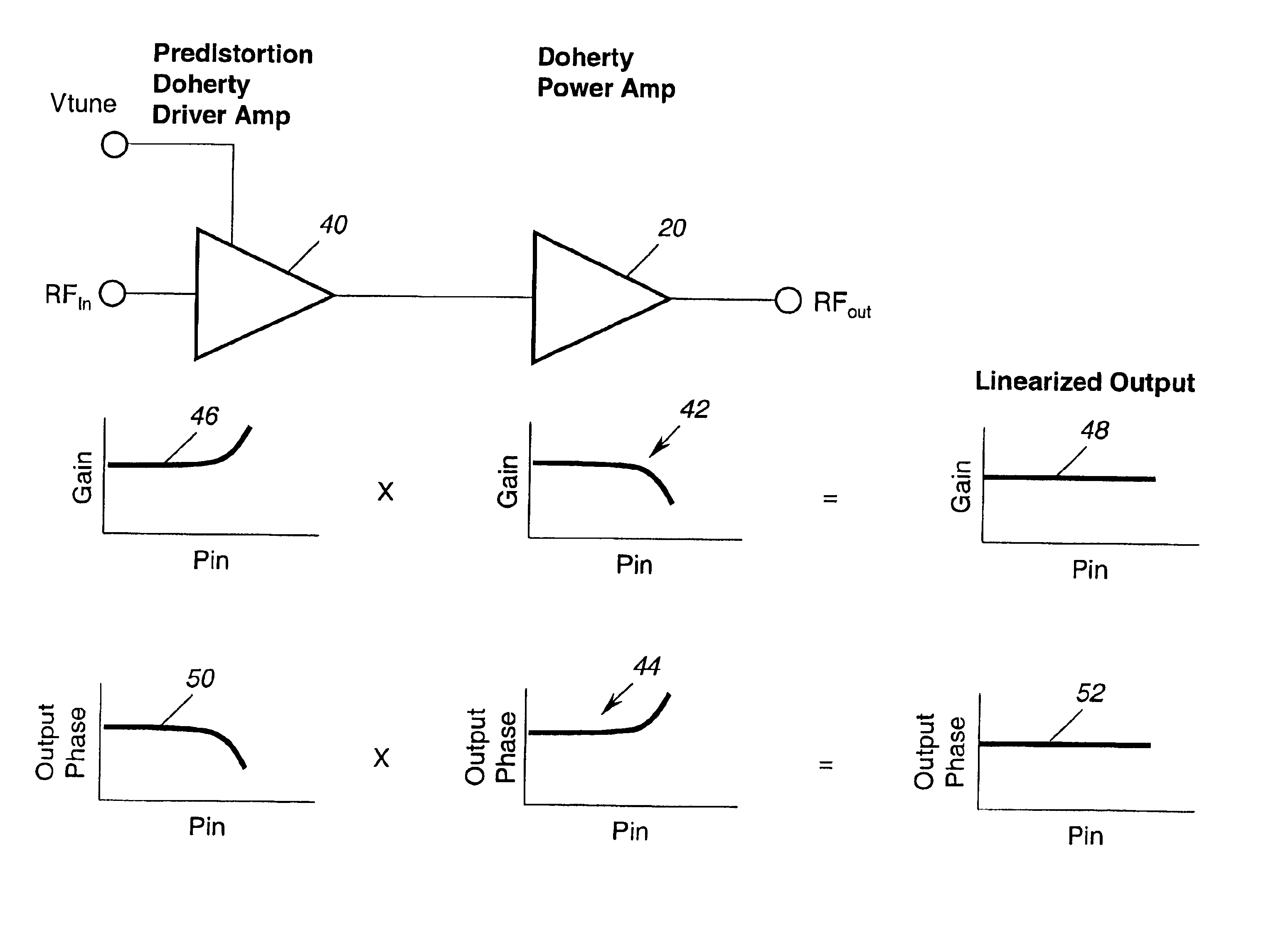
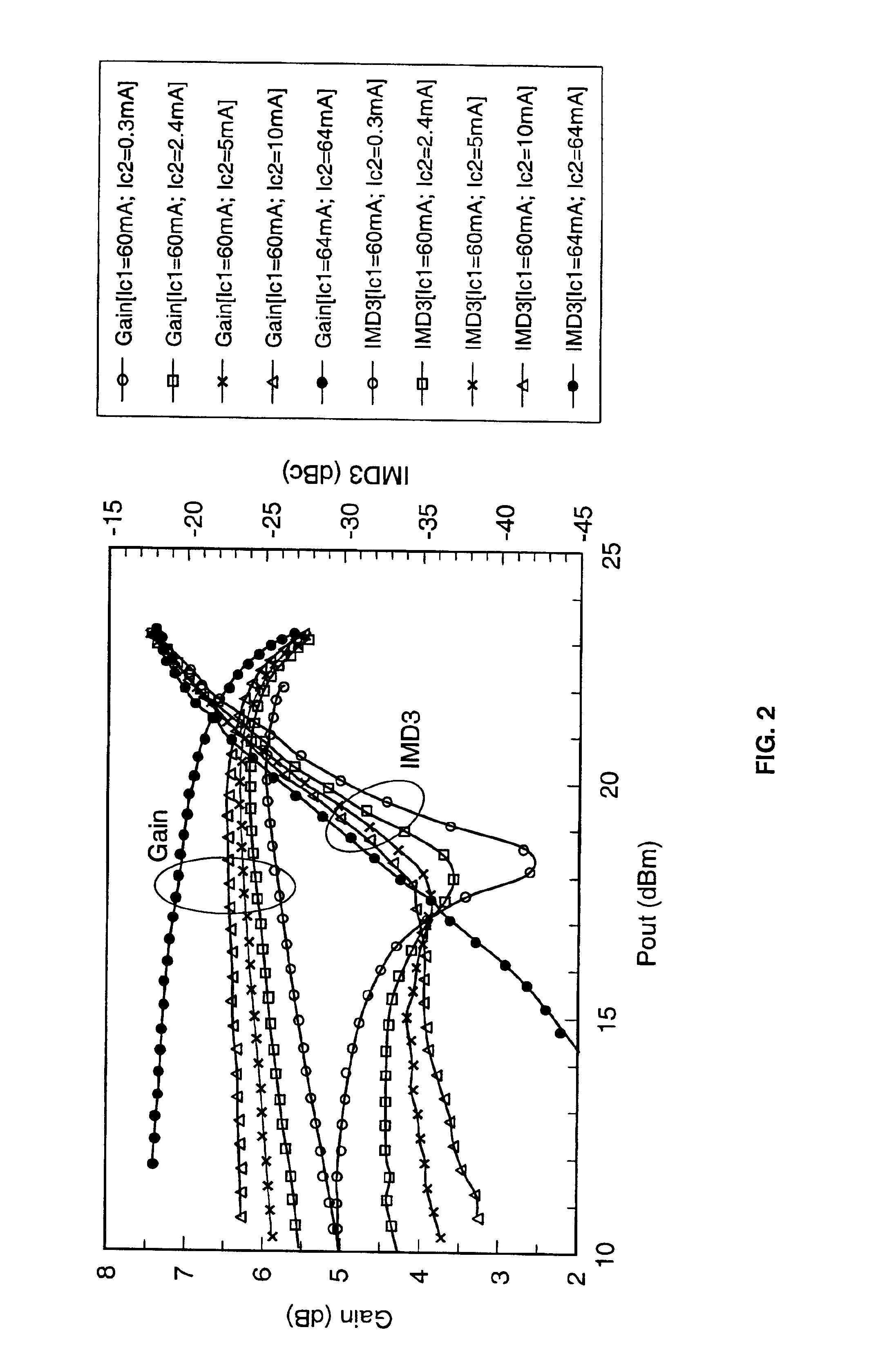
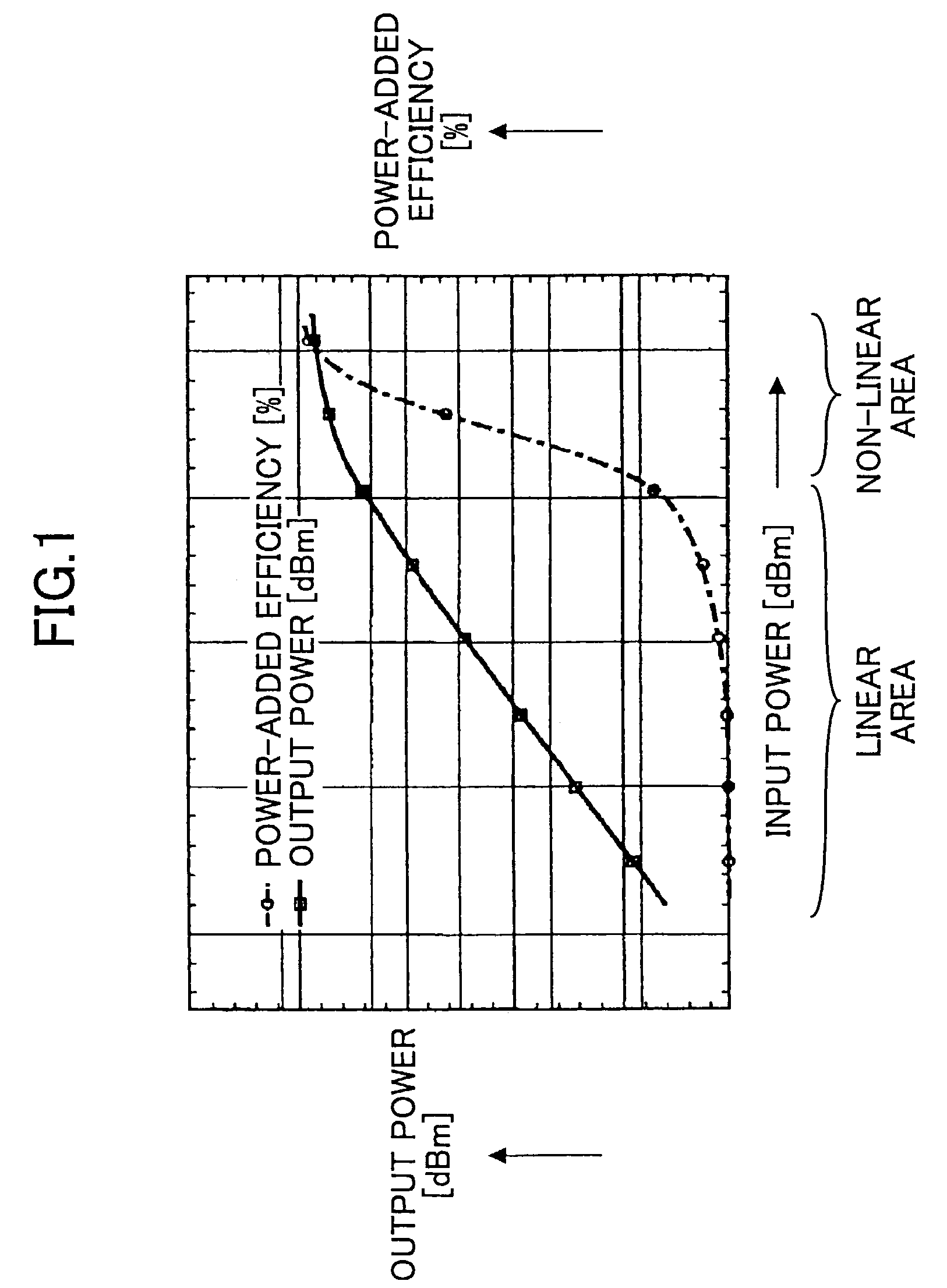
InactiveUS6864742B2Reducing intermodulation (IM) distortionImprove power added efficiencyAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influencePower-added efficiencyAudio power amplifier
A predistortion circuit for a microwave amplifier and more particularly to predistortion circuit configured as a Doherty amplifier. The predistortion circuit is adapted to be coupled to a downstream Doherty amplifier to precompensate for the gain compression and phase expansion of the downstream Doherty amplifier as the input power level is increased while simultaneously reducing the intermodulation (IM) distortion. In order to provide precompensation, the precompensation circuit is operated at bias level to provide gain expansion and phase compression to cancel out the gain compression and phase expansion of the downstream Doherty amplifier to provide a higher overall linear power added efficiency (PAE).
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
Method and apparatus for an improved power amplifier
ActiveUS7242245B2Increase output powerImprove power added efficiencyAmplifier combinationsRF amplifierAudio power amplifierEngineering
Owner:QORVO INT PTE LTD
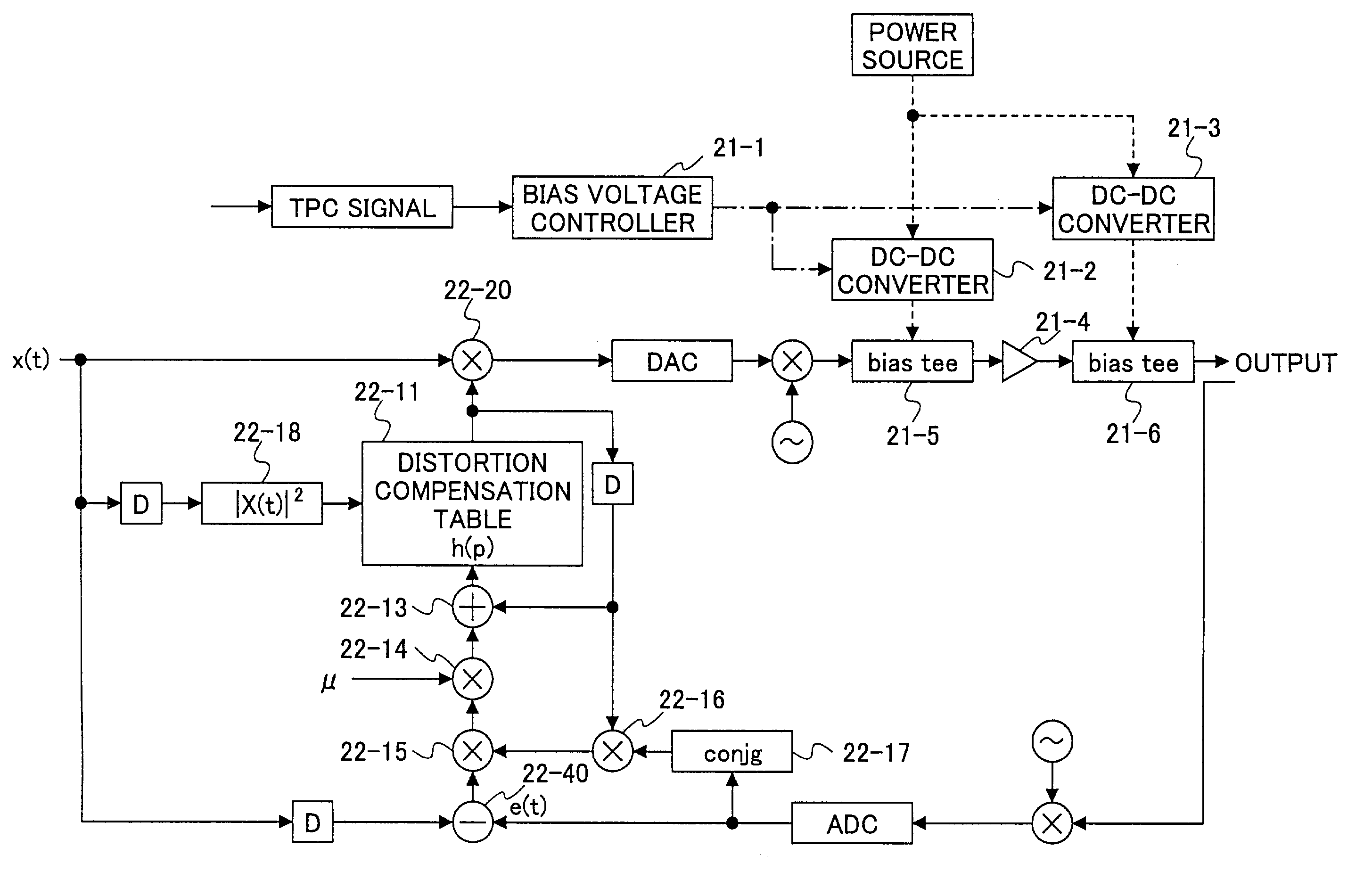
Radio with a distortion compensation capability
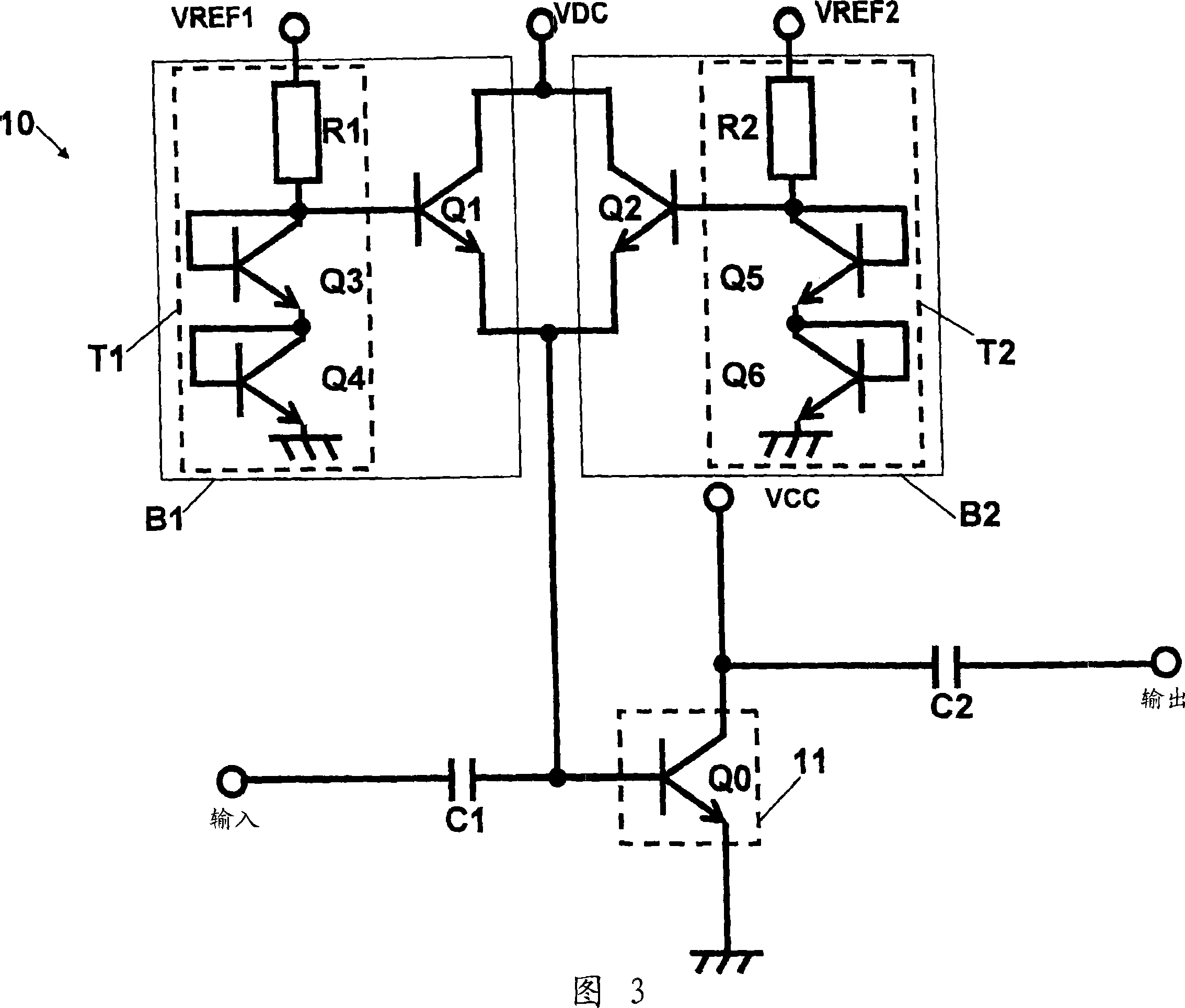
InactiveUS7197286B2Improve power added efficiencyBest power-added efficiencyEnergy efficient ICTAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionDistortionAmplifier distortion
A radio comprises a power amplifier for amplifying a signal to be transmitted; a distortion compensation table storing distortion compensation coefficients for compensating a distortion of the power amplifier; a computing unit for updating the distortion compensation coefficient based on a difference between a transmission input signal and a transmission output signal; a bias voltage controller for applying a bias voltage to the power amplifier, said bias voltage determined based on a transmit control signal so as to maximize a power efficiency of the power amplifier.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
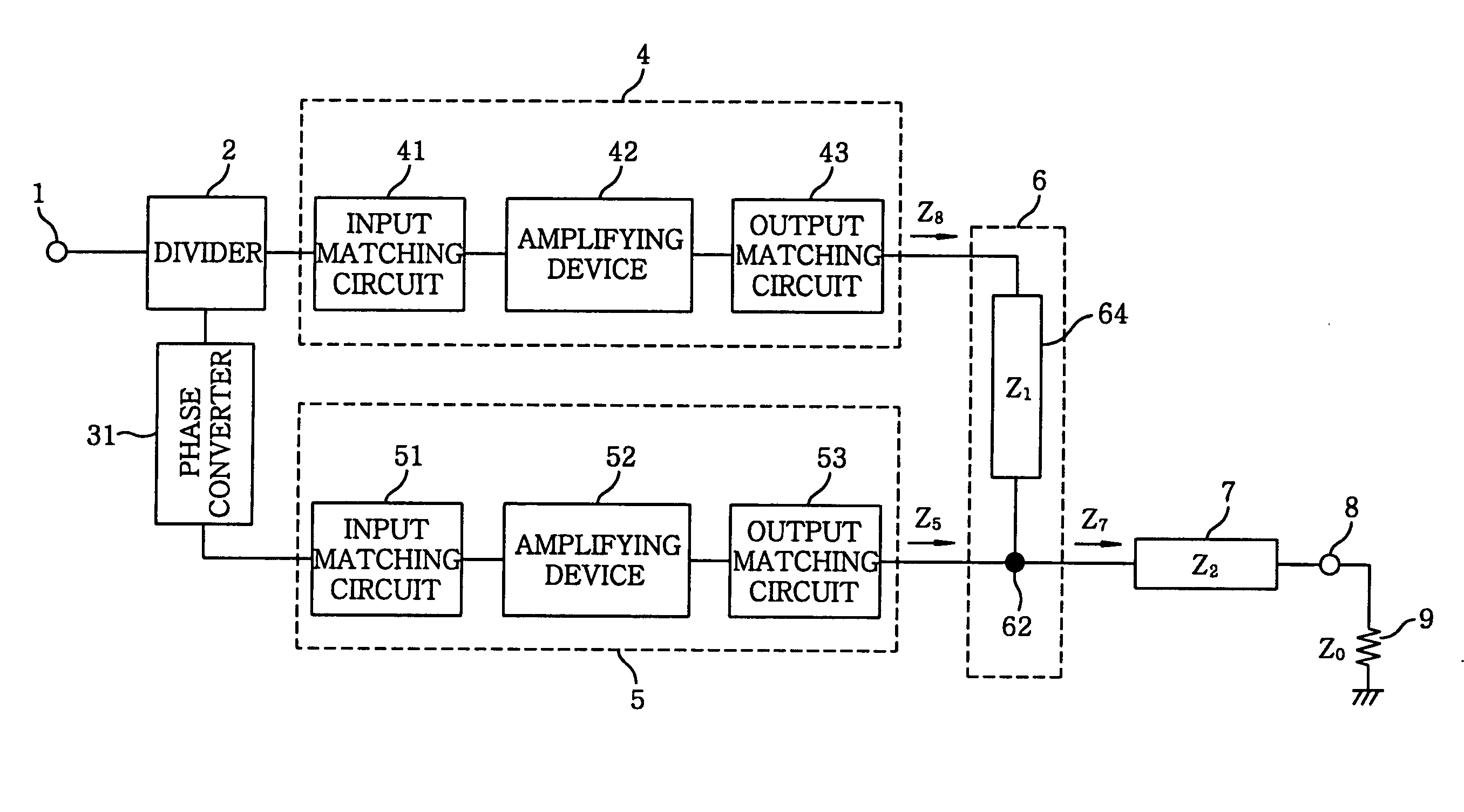
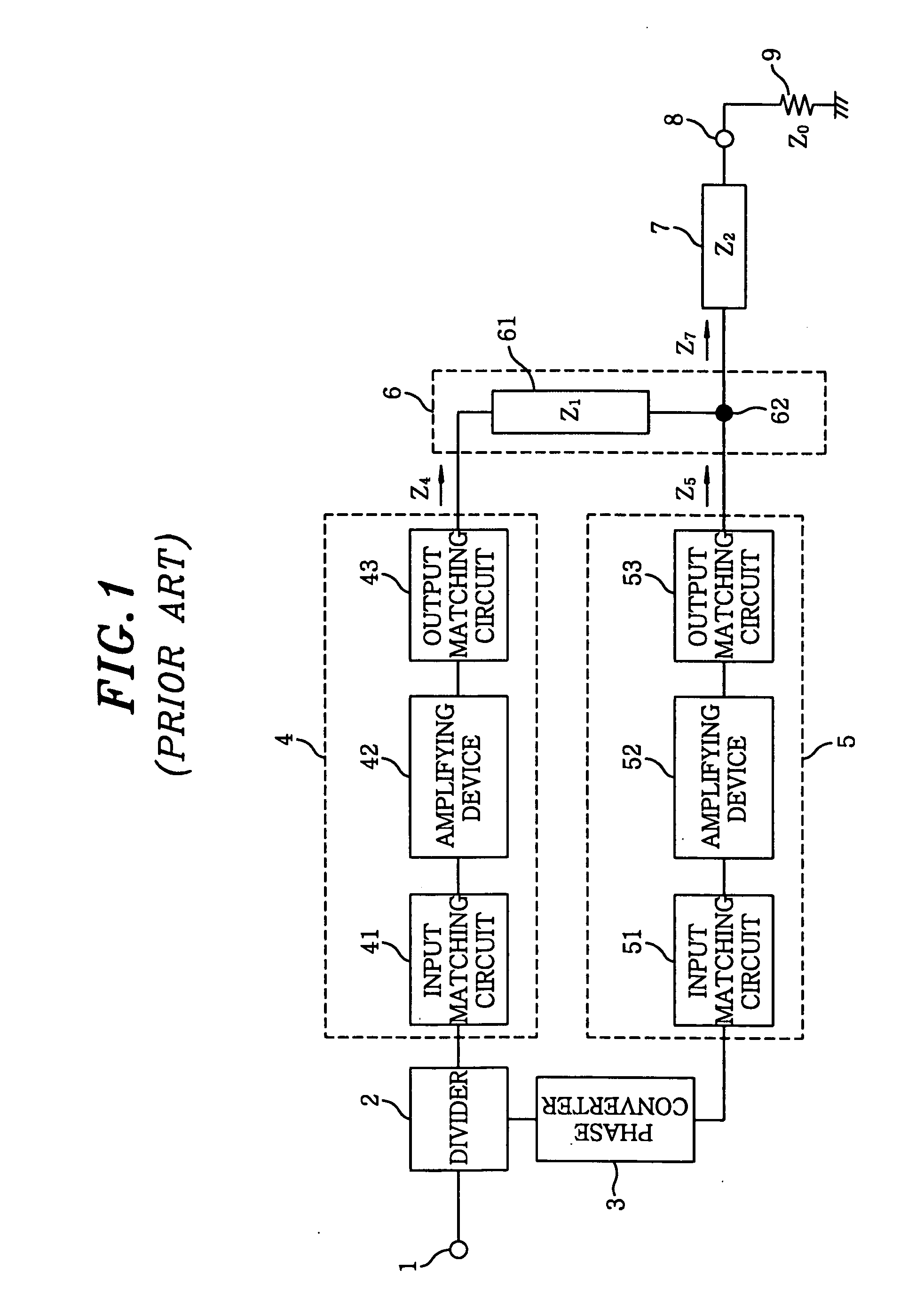
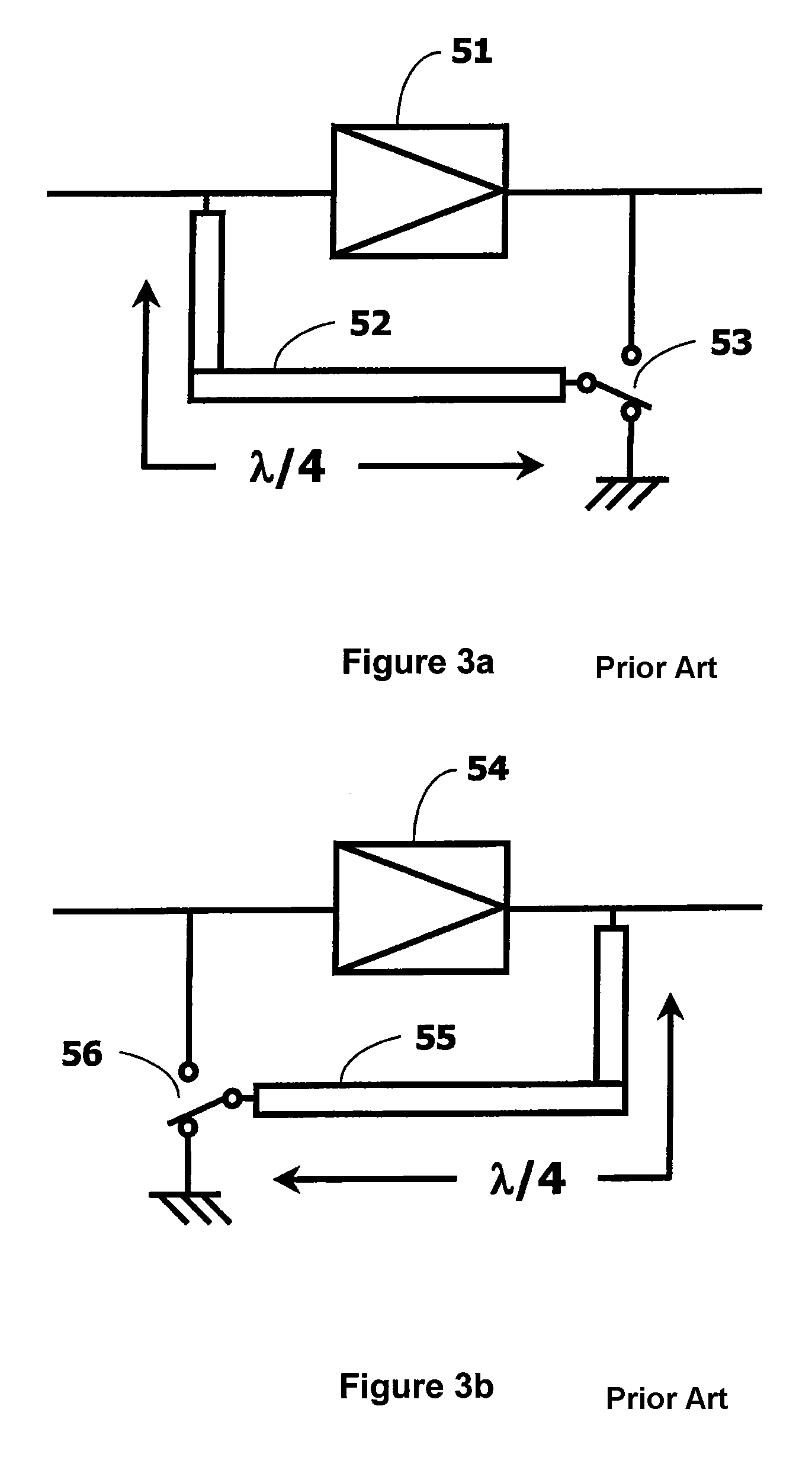
Amplifier
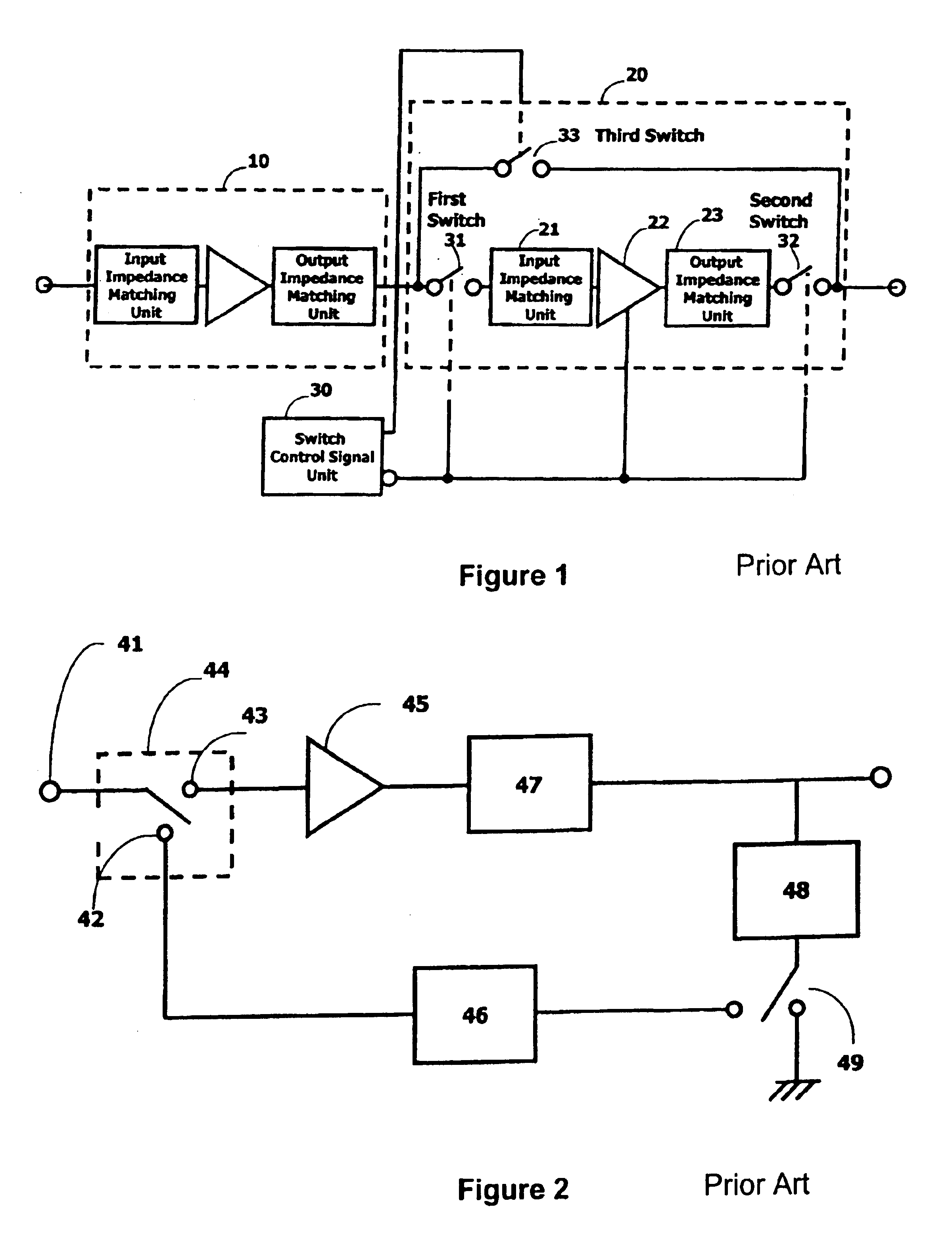
InactiveUS20060097783A1Improve performanceGain is largeNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsAmplifier combinationsAudio power amplifierImpedance transformer
There is provided an amplifier for combining outputs of a plurality of amplifying circuits to generate an amplifier output. The amplifier includes a first amplifying circuit for operating a first amplifying device in class-AB, wherein the first amplifying circuit is one among the plurality of the amplifying circuits; a second amplifying circuit for operating a second amplifying device in class-B or class-C, wherein the second amplifying circuit is one among the plurality of the amplifying circuits; and a summing node at which an output of the first amplifying circuit is combined with an output of the second amplifying circuit via a first impedance transformer containing a transmission line of an electrical length other than λ / 4. The second amplifying device is connected to the summing node via an output matching circuit and a second impedance transformer containing a transmission line.
Owner:KOKUSA ELECTRIC CO LTD
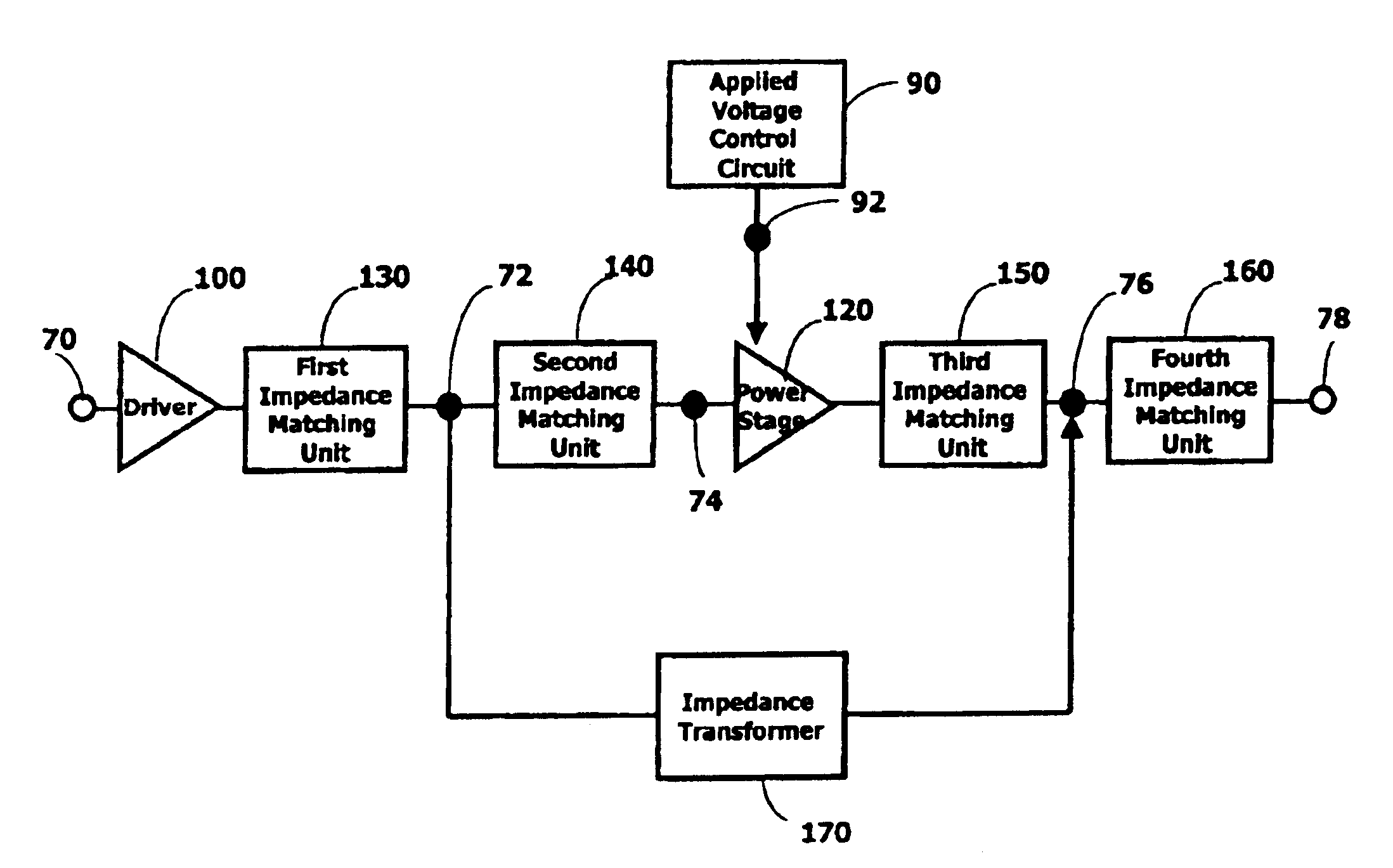
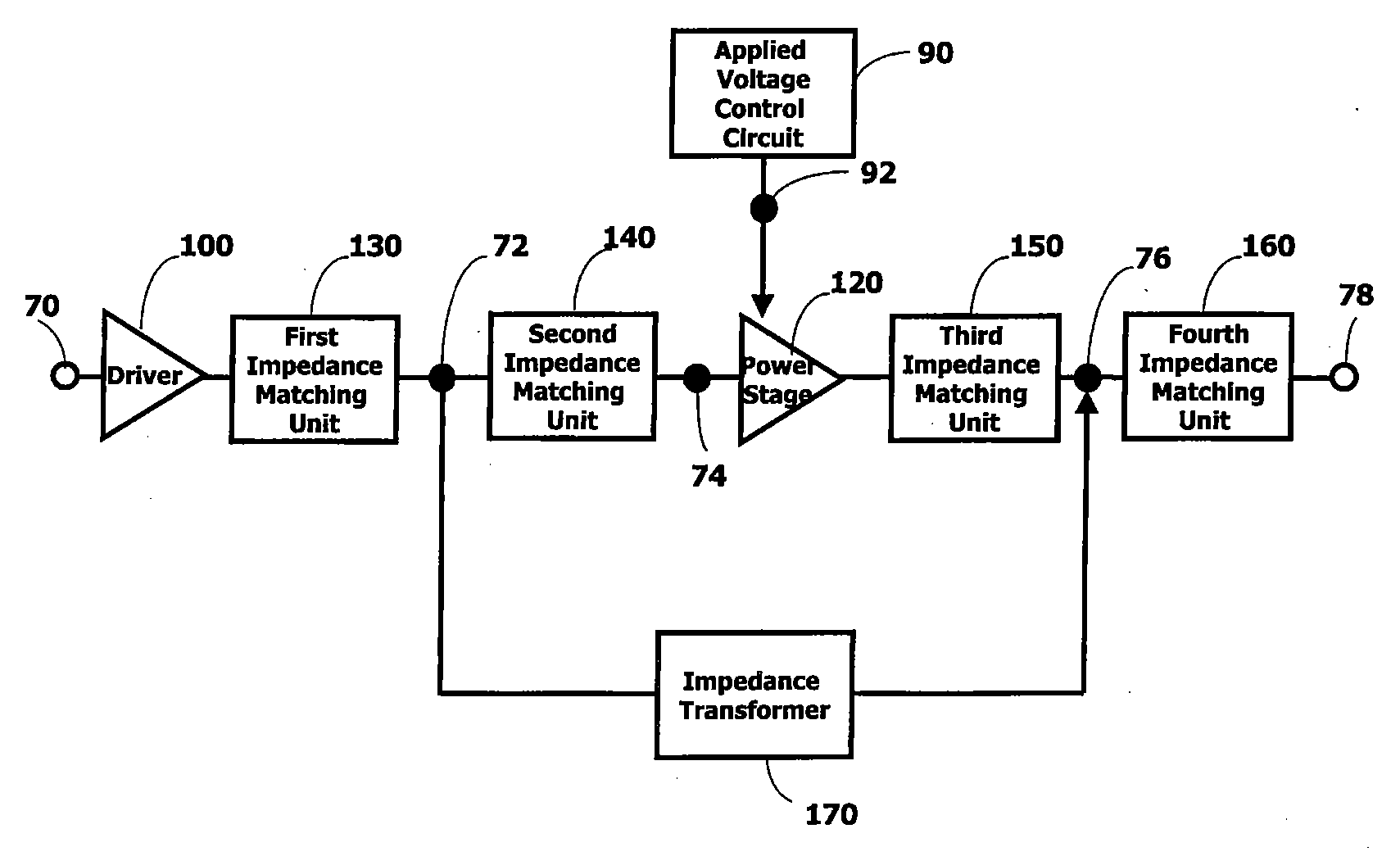
High efficiency power amplifier with multiple power modes
InactiveUS6900692B2Reduced DC power consumptionIncrease in sizeSpecial service provision for substationGated amplifiersPower modeAudio power amplifier
A multiple power mode amplifier provides a low and a high power mode without using switches. This amplifier may be used in RF applications such as mobile telephones. In the low power mode, the power consumption of the amplifier is reduced, which will increase operation time, especially important for battery-operated devices. In one implementation, the amplifier includes a number of impedance matching network units (130, 140, 150, and 160), impedance transformer (170), and a power stage (120).
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
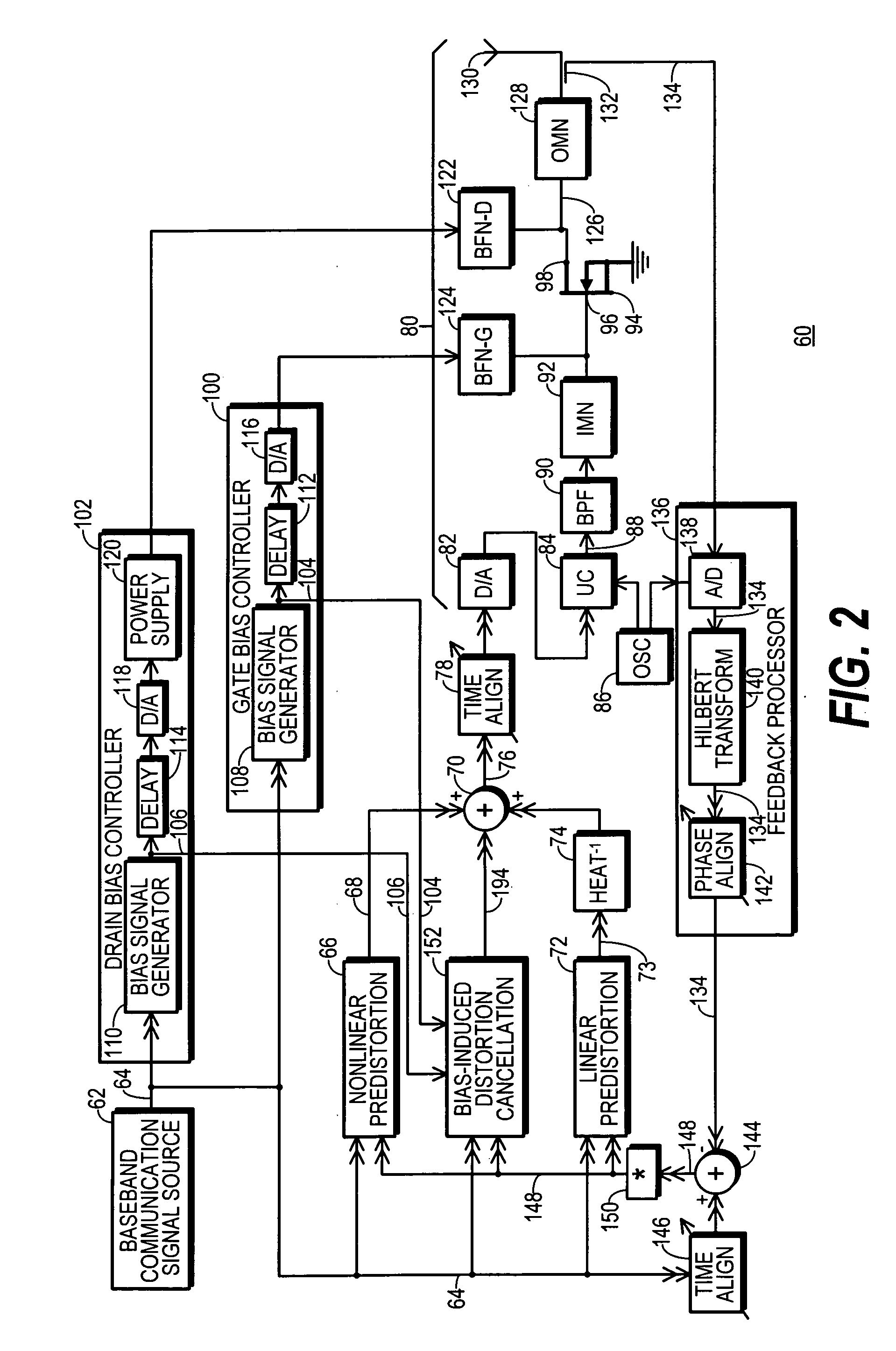
RF Transmitter with Bias-Signal-Induced Distortion Compensation and Method Therefor
InactiveUS20090227215A1Improve power added efficiencyImprove linearizationNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsPower amplifiersPower-added efficiencyEngineering
An RF transmitter (60) generates non-DC bias signals (104, 106) configured to improved power-added efficiency (PAE) in the operation of an RF amplifier (94). The RF amplifier (94) generates an amplified RF signal (126) which, due to the addition of the bias signals (104, 106), includes bias-signal-induced RF distortion (48, 50). The bias signals (104, 106) drive a bias-induced distortion cancellation circuit (152) that adjusts the bias signals to compensate for the influence of impedances experienced by the bias signals (104, 106) before being applied to the RF amplifier (94). After mixing with a baseband communication signal (64), adjusted bias signals (186, 188) are combined into a composite baseband signal (76), upconverted to RF in an upconversion section 84, and applied to the RF amplifier (94) where they cancel at least a portion of the bias-signal-induced RF distortion (48, 50).
Owner:CRESTCOM INC
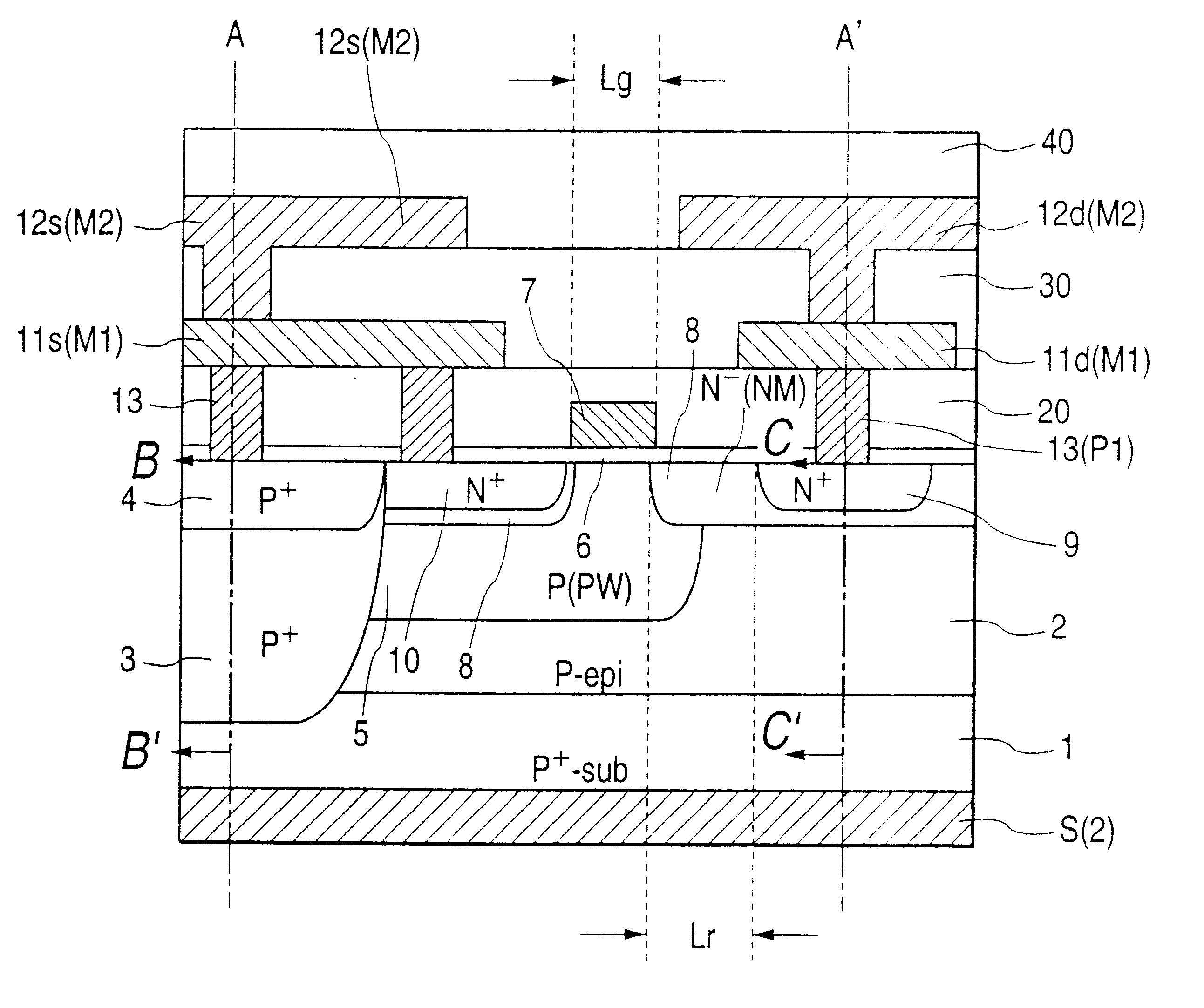
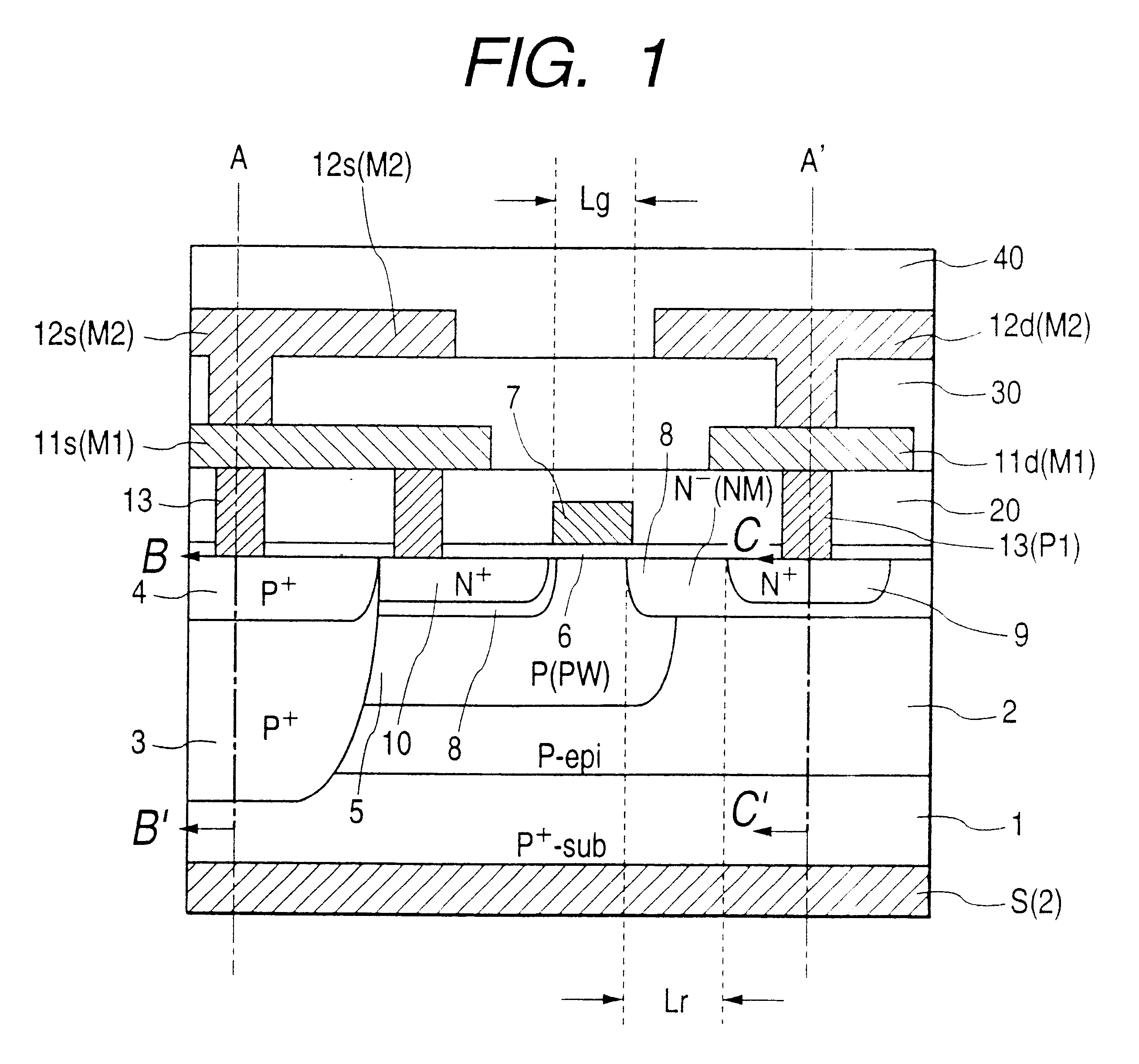
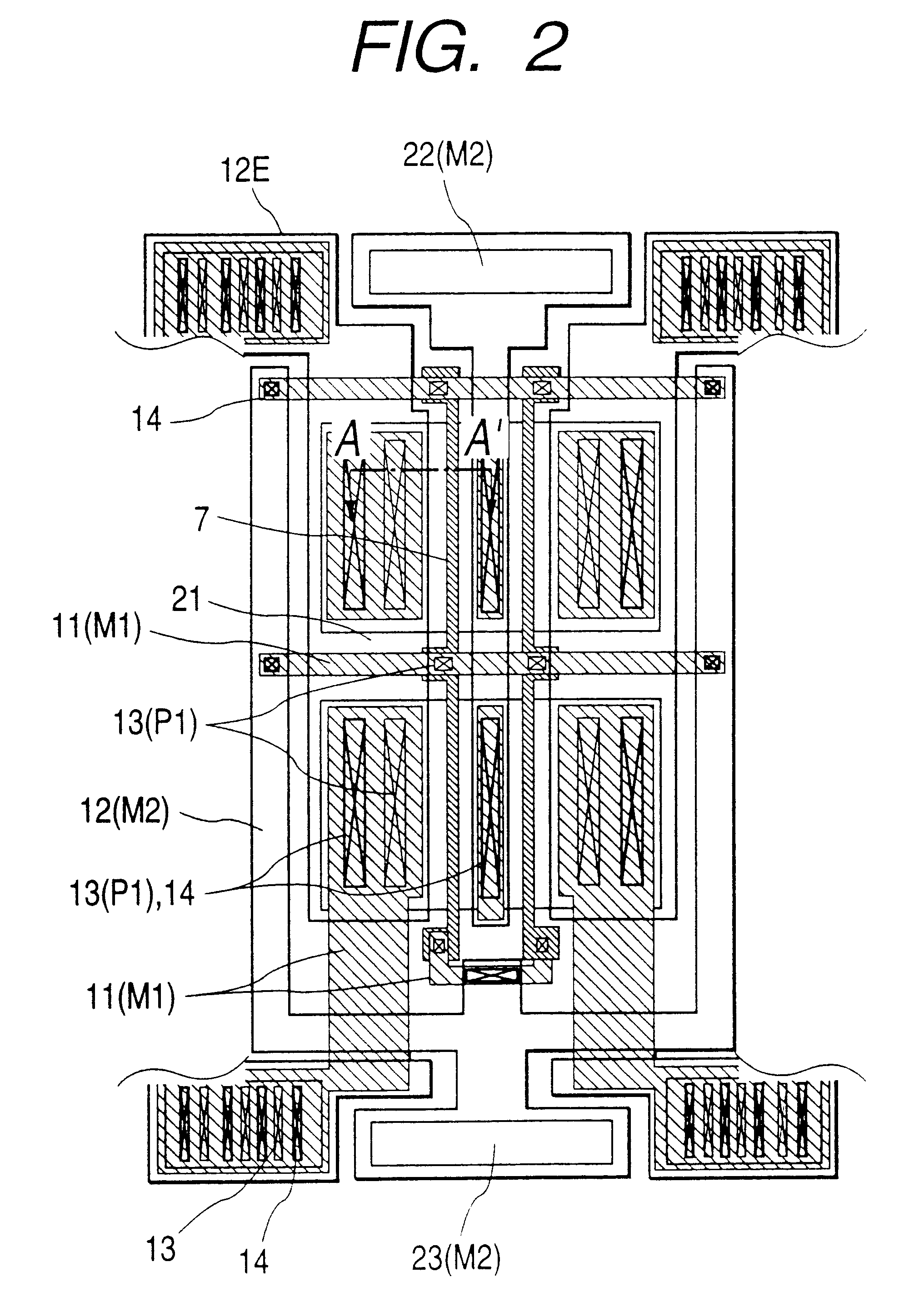
Semiconductor device and a method of manufacturing the same
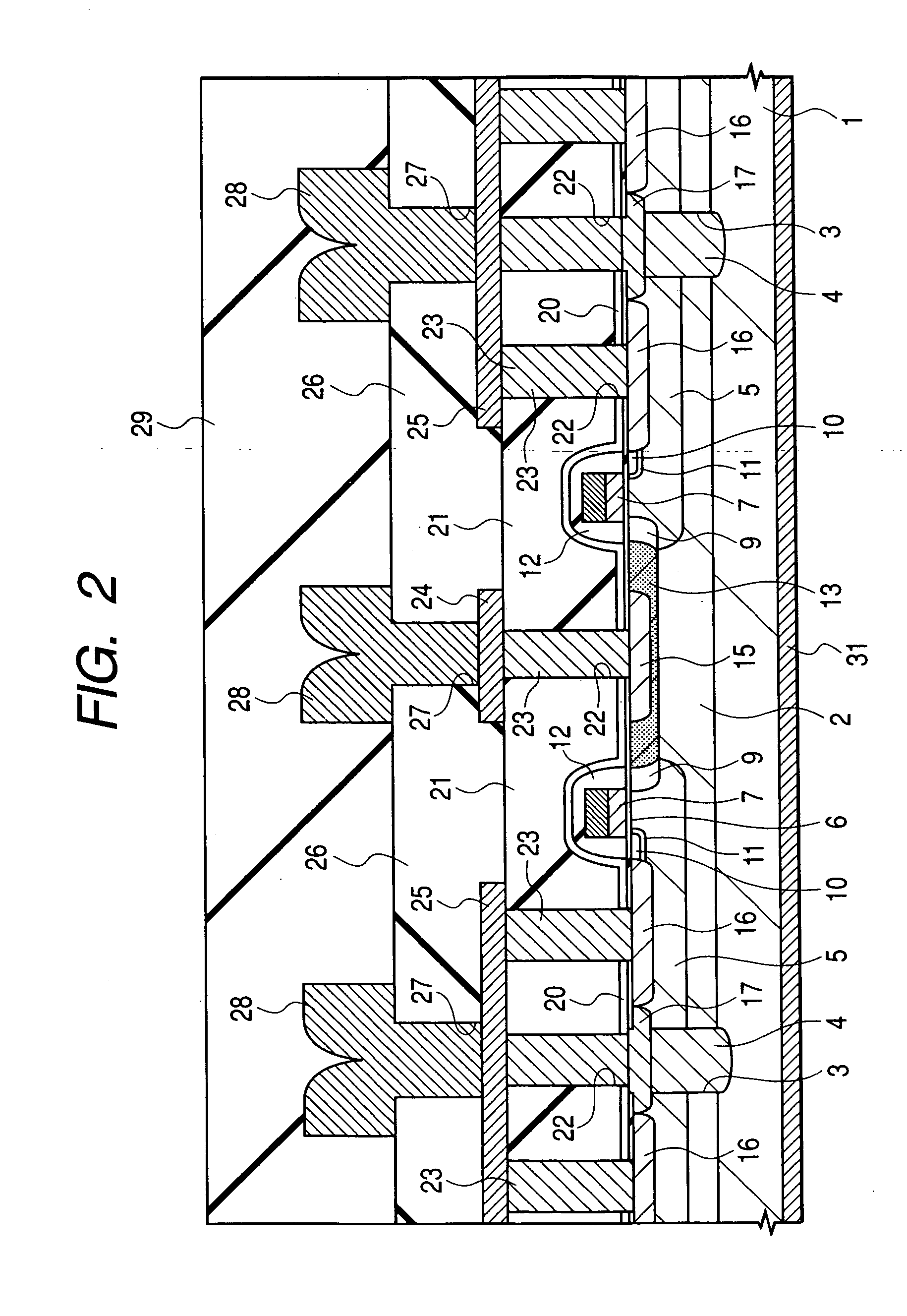
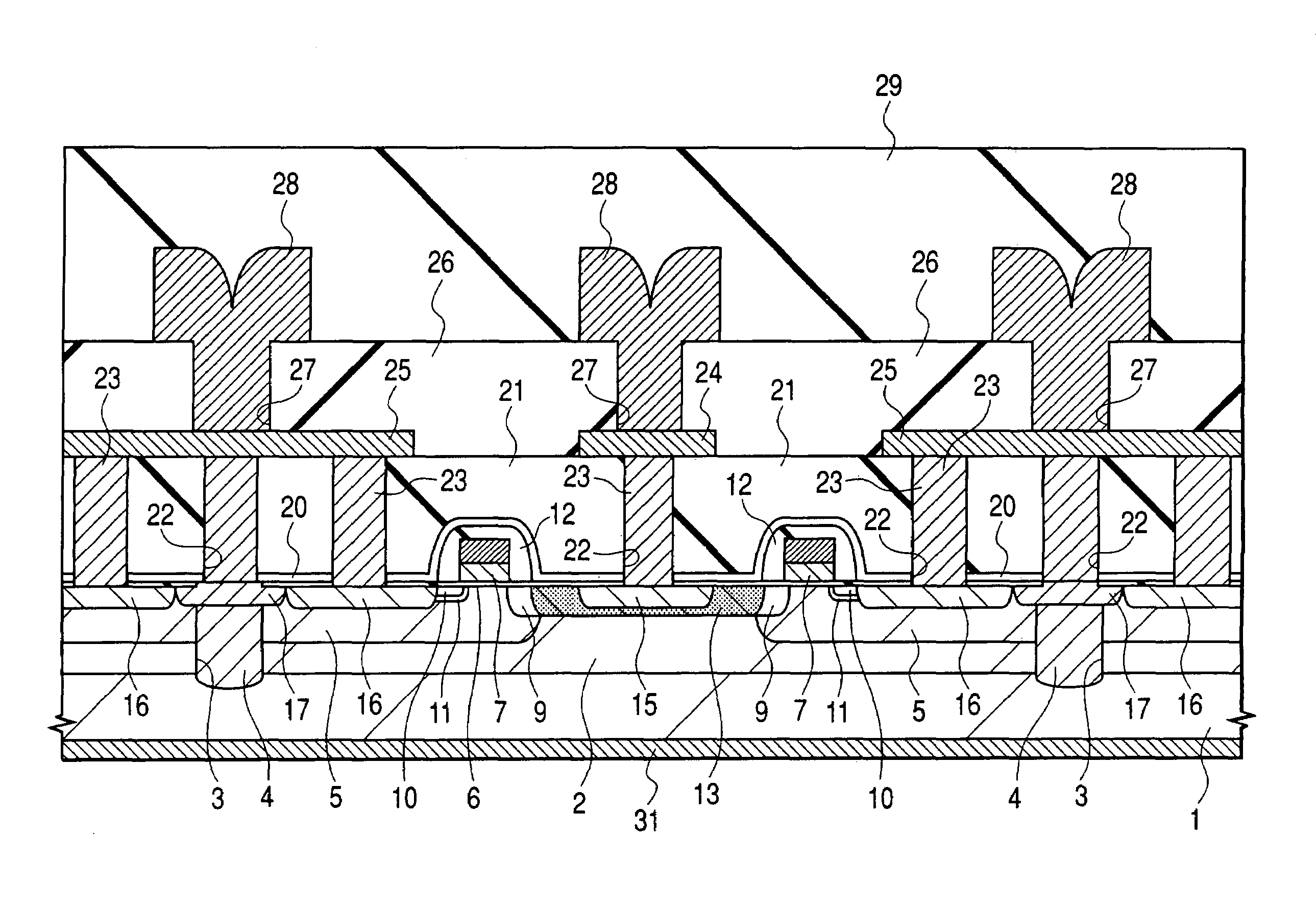
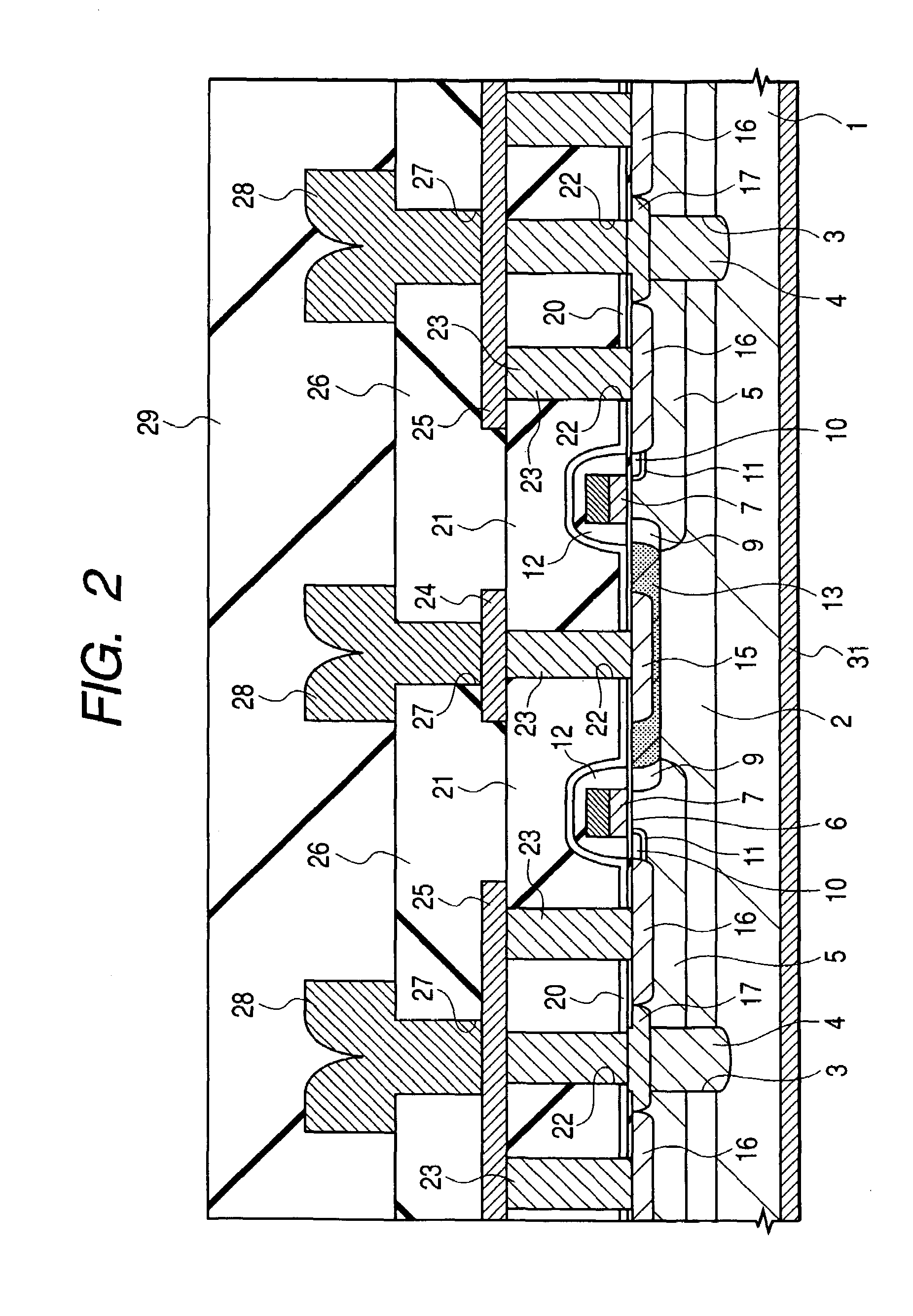
InactiveUS6528848B1Lower on-resistanceEffectively decrease the resistance in the P type gate deviceTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsMOSFETSecondary layer
In a high frequency amplifying MOSFET having a drain offset region, the size is reduced and the on-resistance is decreased by providing conductor plugs 13 (P1) for leading out electrodes on a source region 10, a drain region 9 and leach-through layers 3 (4), to which a first layer wirings 11a, 11d (M1) are connected and, further, backing second layer wirings 12a to 12d are connected on the conductor plugs 13 (P1) to the first layer wirings 11s, 11d (M1).
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
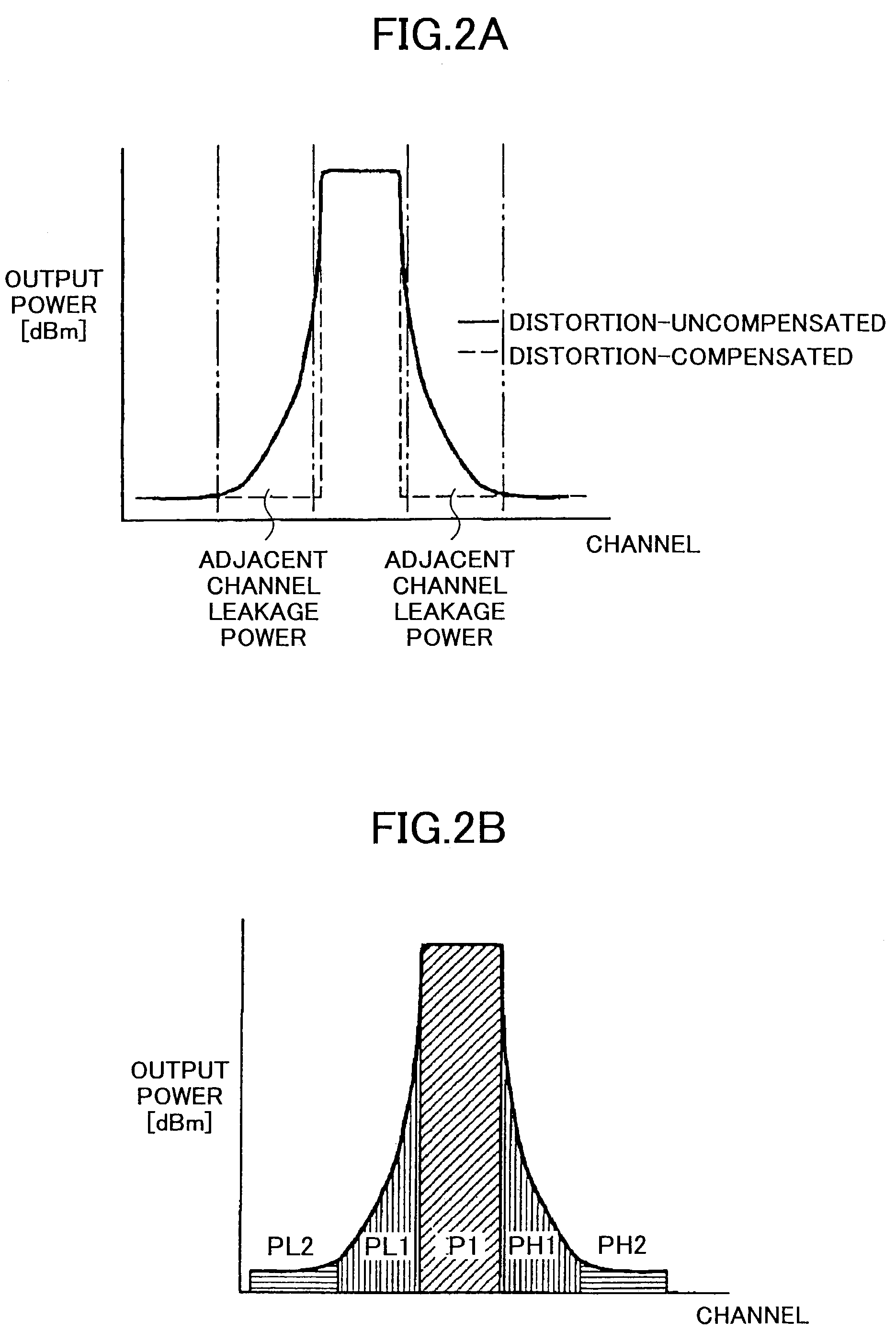
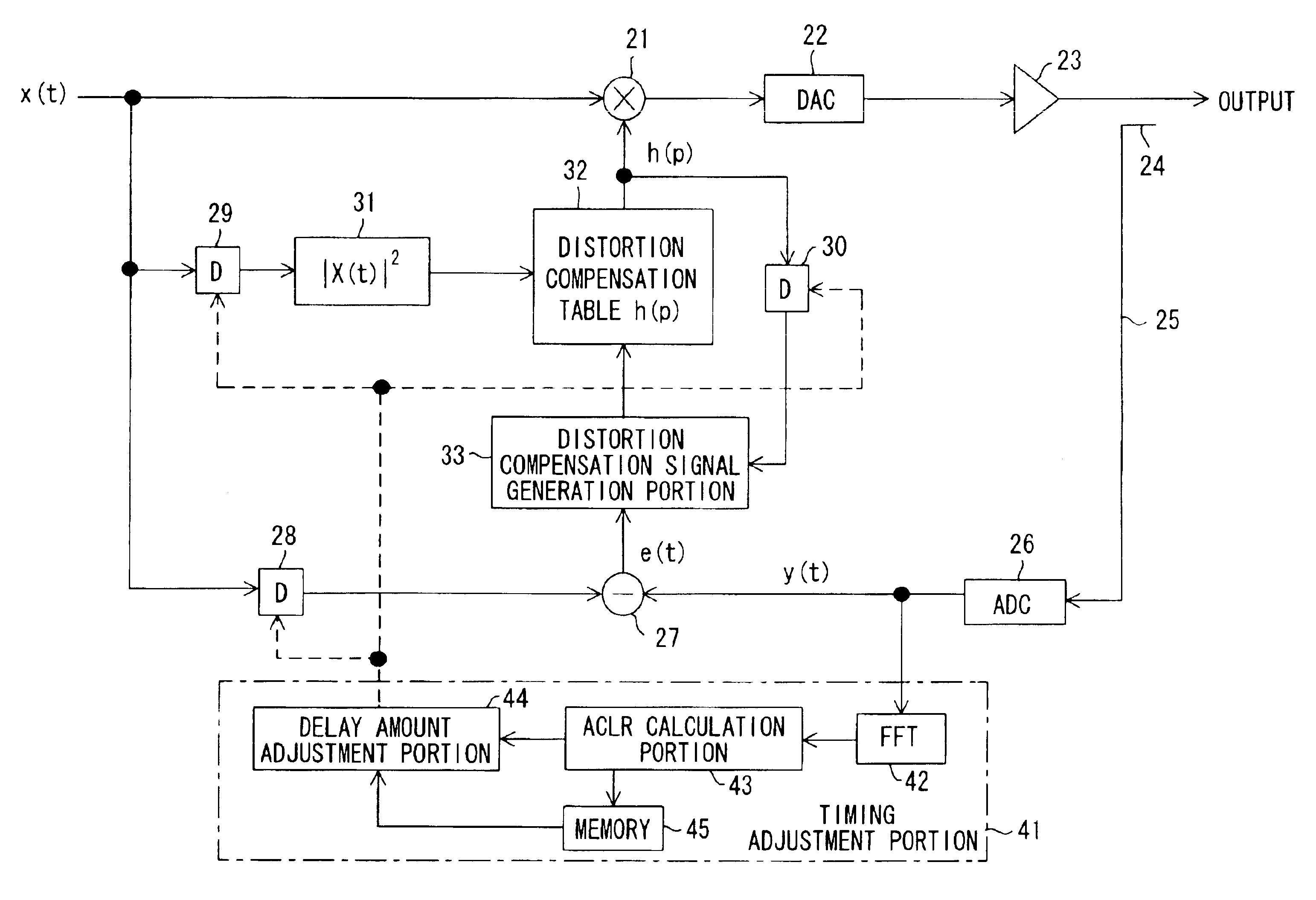
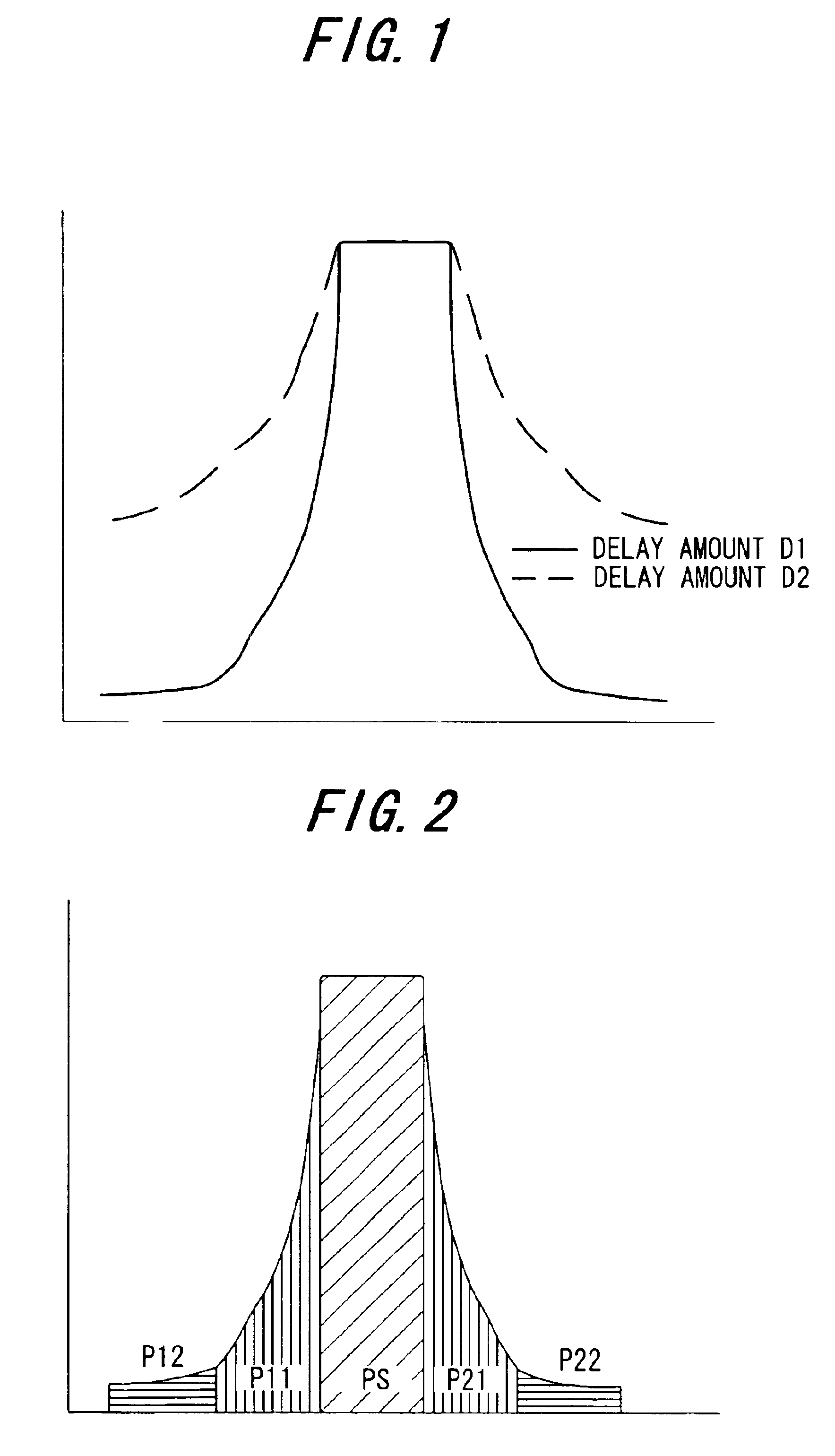
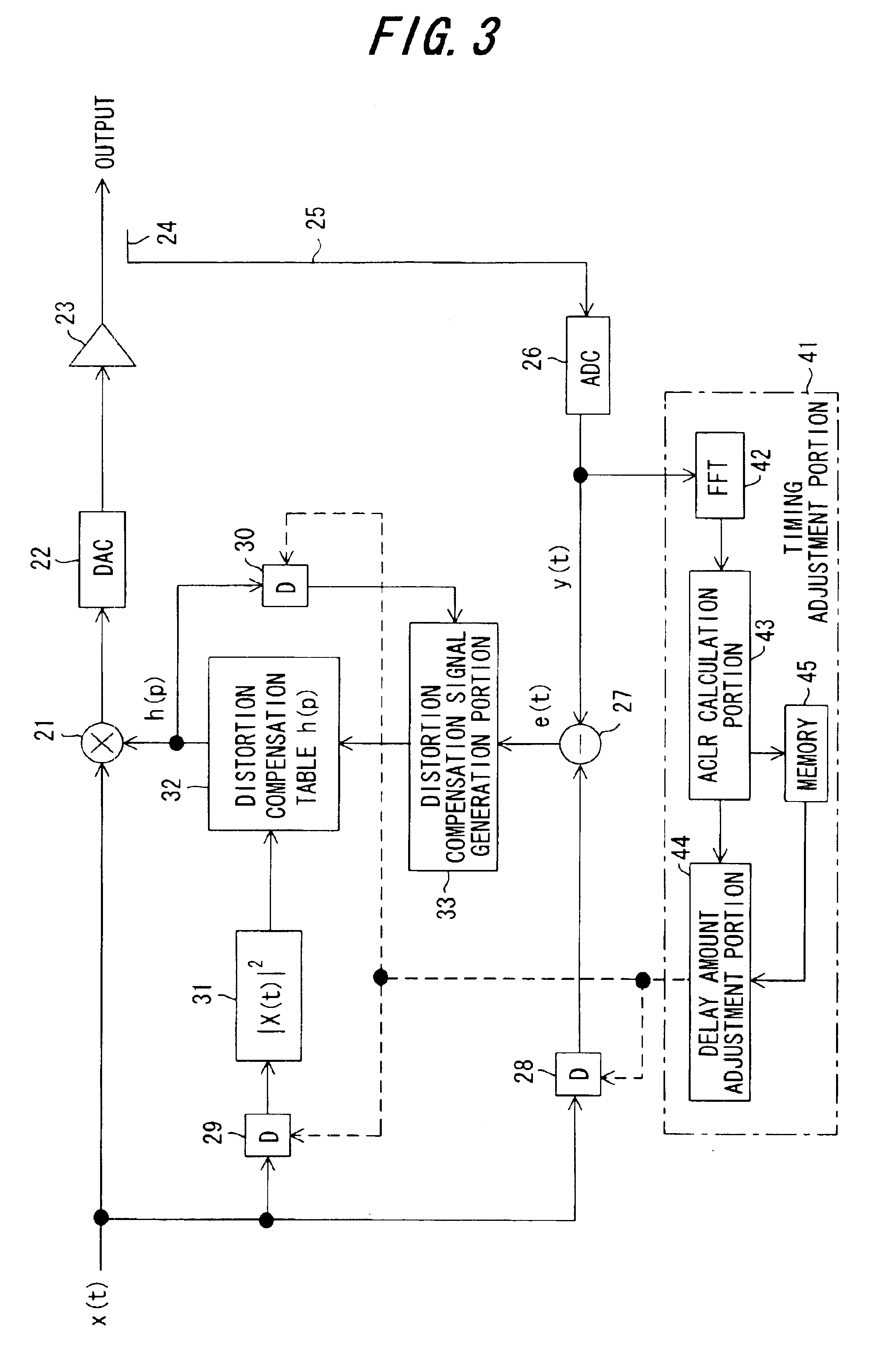
Distortion compensation device
InactiveUS6864745B2Guaranteed uptimeHigh precisionAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceFast Fourier transformSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
In a distortion compensation device which uses distortion compensation coefficients to subject distortion compensation processing to an input signal and supply the result of the distortion compensation processing to a distorting device, calculates the distortion compensation coefficients based on the input signal before distortion compensation and the feedback signal fed back from the output side of the distorting device, and stores the calculated distortion compensation coefficients in association with the input signal, (1) the feedback signal is AD-converted; (2) the AD-converted output is subjected to fast Fourier transform (FFT) processing; (3) the FFT calculation result is used to calculate the value of either the signal-to-noise ratio SNR, or the adjacent channel leakage power ratio ACLR, or the noise level; (4) the delay time occurring in the distorting device and feedback loop is adjusted such that the difference between the above calculated value at the current time and the above calculated value at the immediately preceding time is either zero, or is equal to or less than a threshold value; and, (5) this adjustment processing is repeated to determine the accurate delay time, and based on this delay time the timing of each of the portions of the distortion compensation device is adjusted.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Wireless communication apparatus
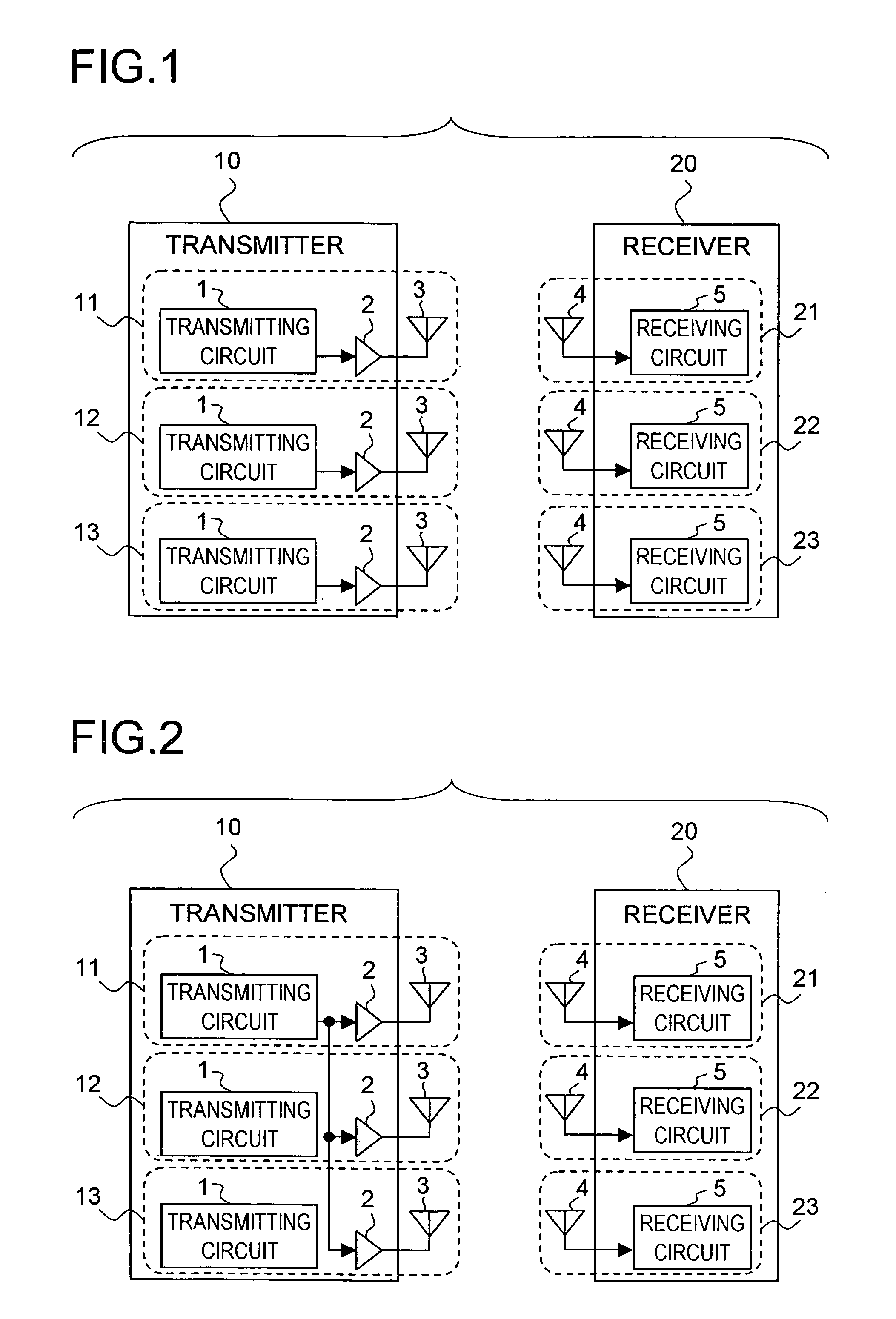
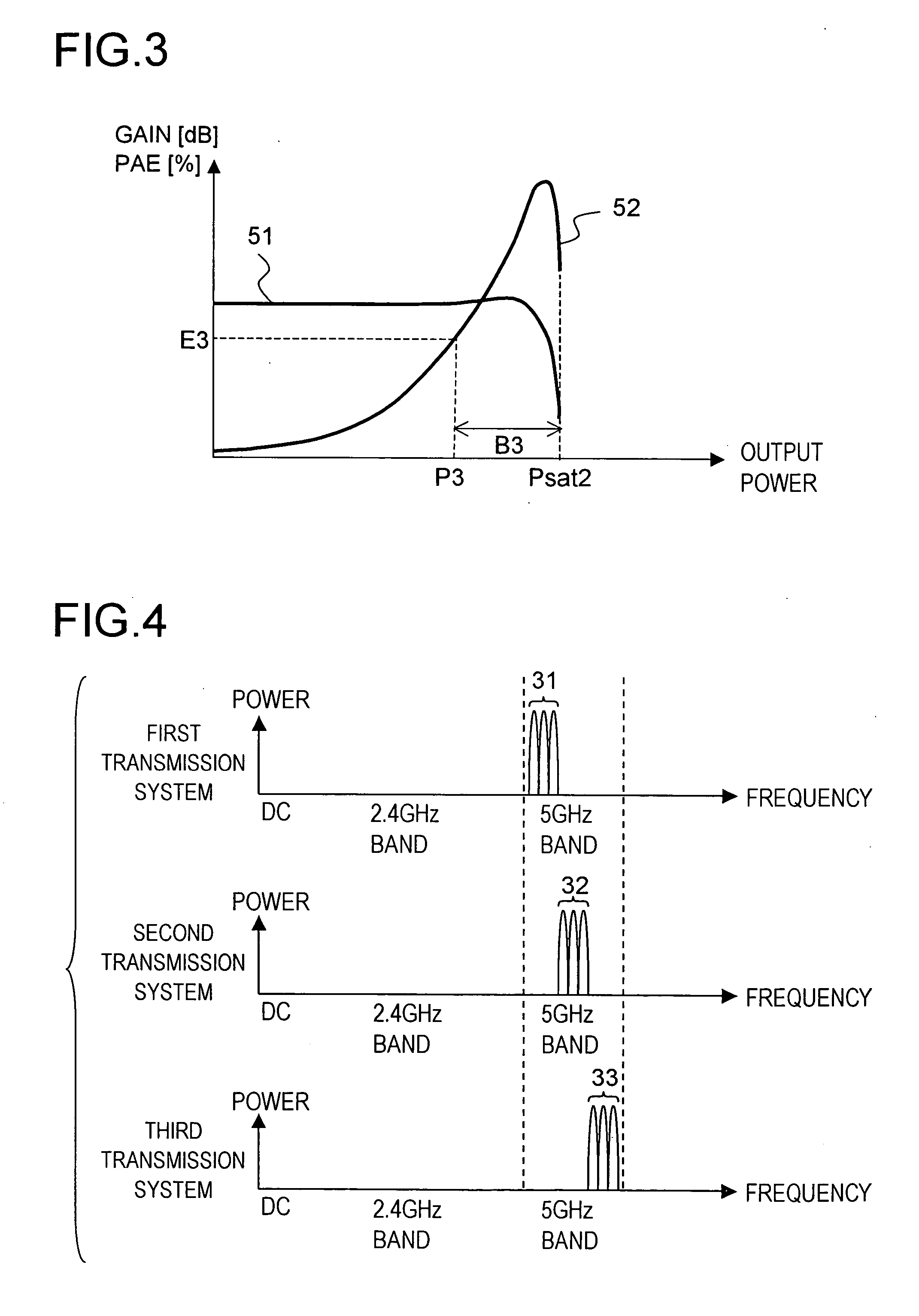
InactiveUS20050272382A1Improve power added efficiencyImprove efficiencySpatial transmit diversityMultiplex communicationAudio power amplifierTransfer system
In a wireless communication apparatus which is provided with three transmission systems each including therein a transmission power amplifier for amplifying a signal received and a transmitting antenna for transmitting the amplified signal and which is applicable to an MIMO transmission method for simultaneously transmitting three units of data having mutually different contents, in transmitting single unit of data without use of the MIMO transmission method, power of a transmission signal is dispersed for the transmission by simultaneously transmitting same signals from the transmitting antennas corresponding to the transmission power amplifiers by use of the three transmission power amplifiers included in the three transmission systems.
Owner:SHARP KK
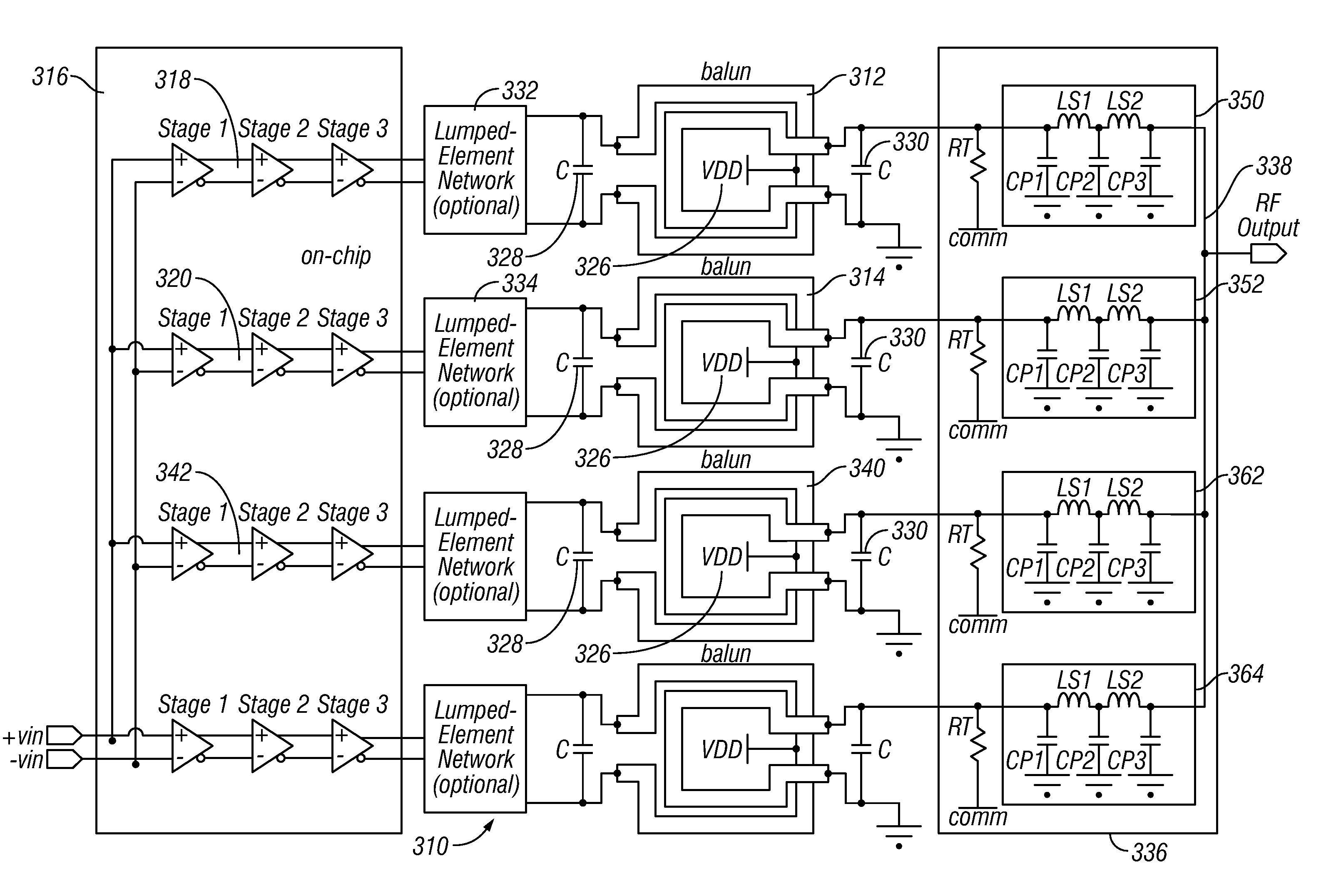
Method and apparatus for an improved power amplifier
ActiveUS20060006949A1Improve power added efficiencyIncrease output powerAmplifier combinationsRF amplifierAudio power amplifierEngineering
An amplifier system is provided that includes a first balun with an input and an output. A second balun has an input and an output. An amplifier assembly is provided and has at least a first amplifier in parallel to a second amplifier. The first amplifier provides the input to the first balun and the second amplifier provides the input to the second balun. A power combining circuit is provided. The first and second baluns are coupled to a common node of the power combining circuit. A first lumped element circuit is coupled between the output of the first balun and the power combining circuit. A second lumped element circuit is coupled between the output of the second balun and the power combing circuit. The outputs are coupled to the common node.
Owner:QORVO INT PTE LTD
Semiconductor device
InactiveUS20060220165A1Easy to controlReduces size and costSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesLow distortionDevice material
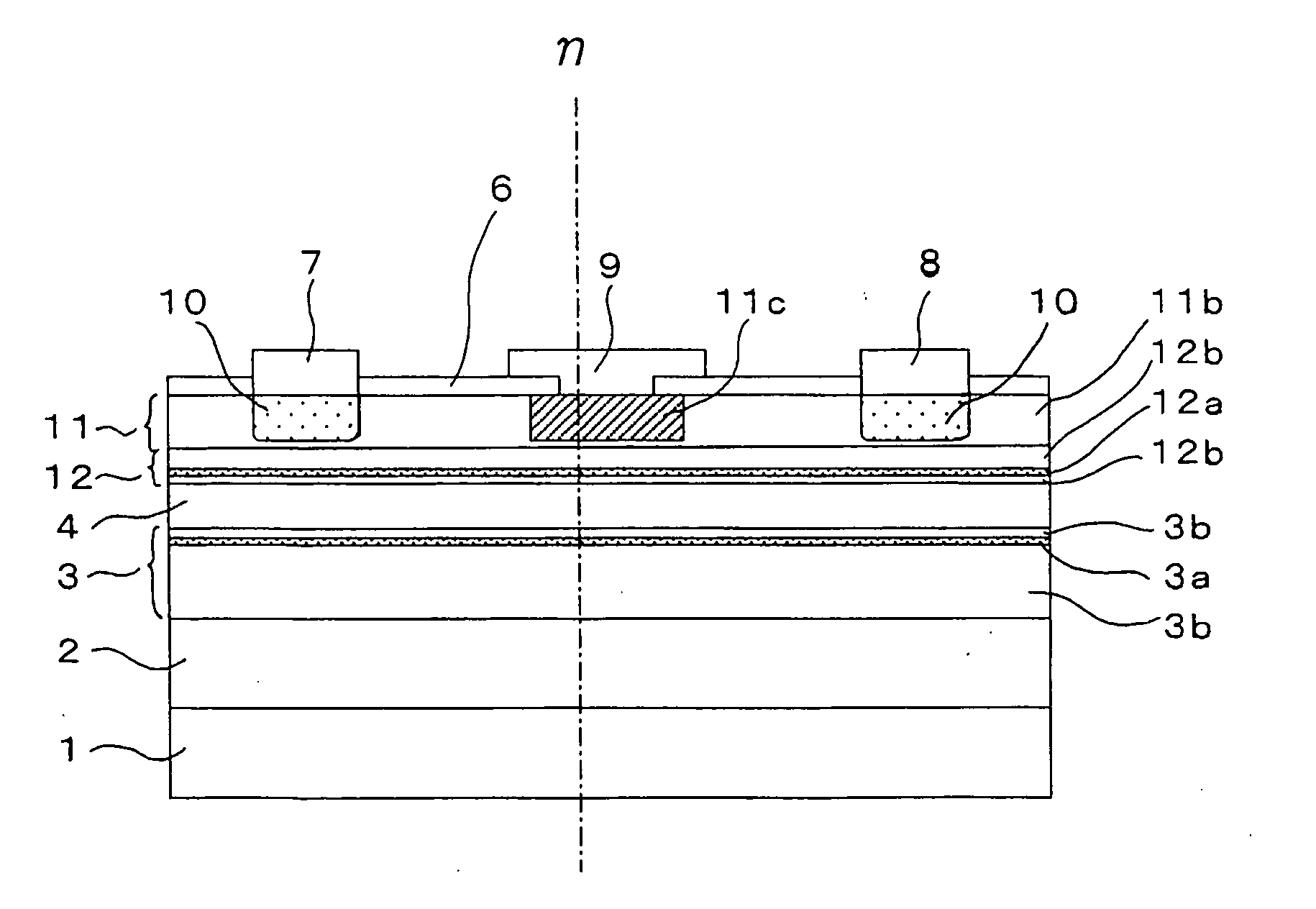
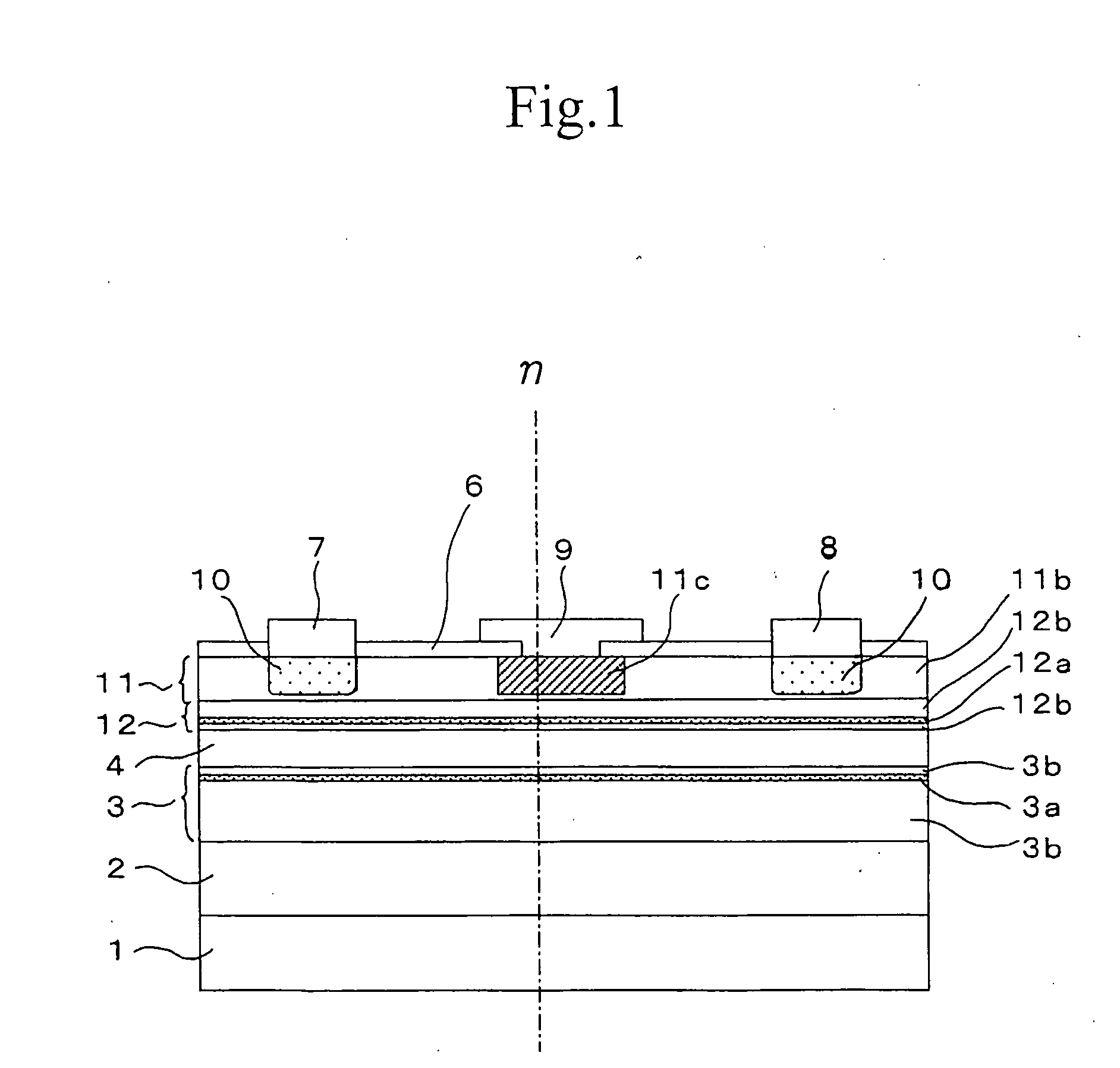
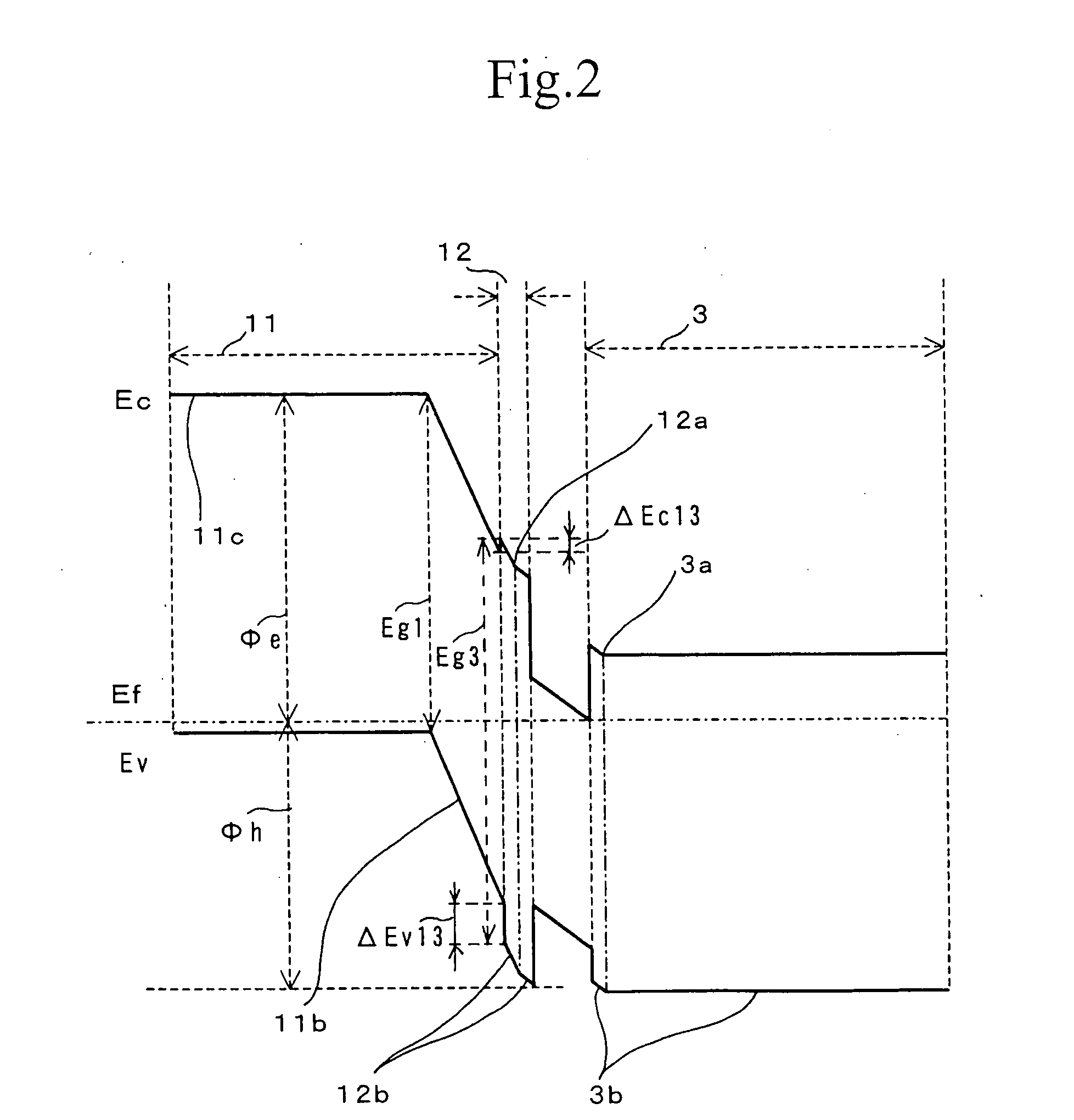
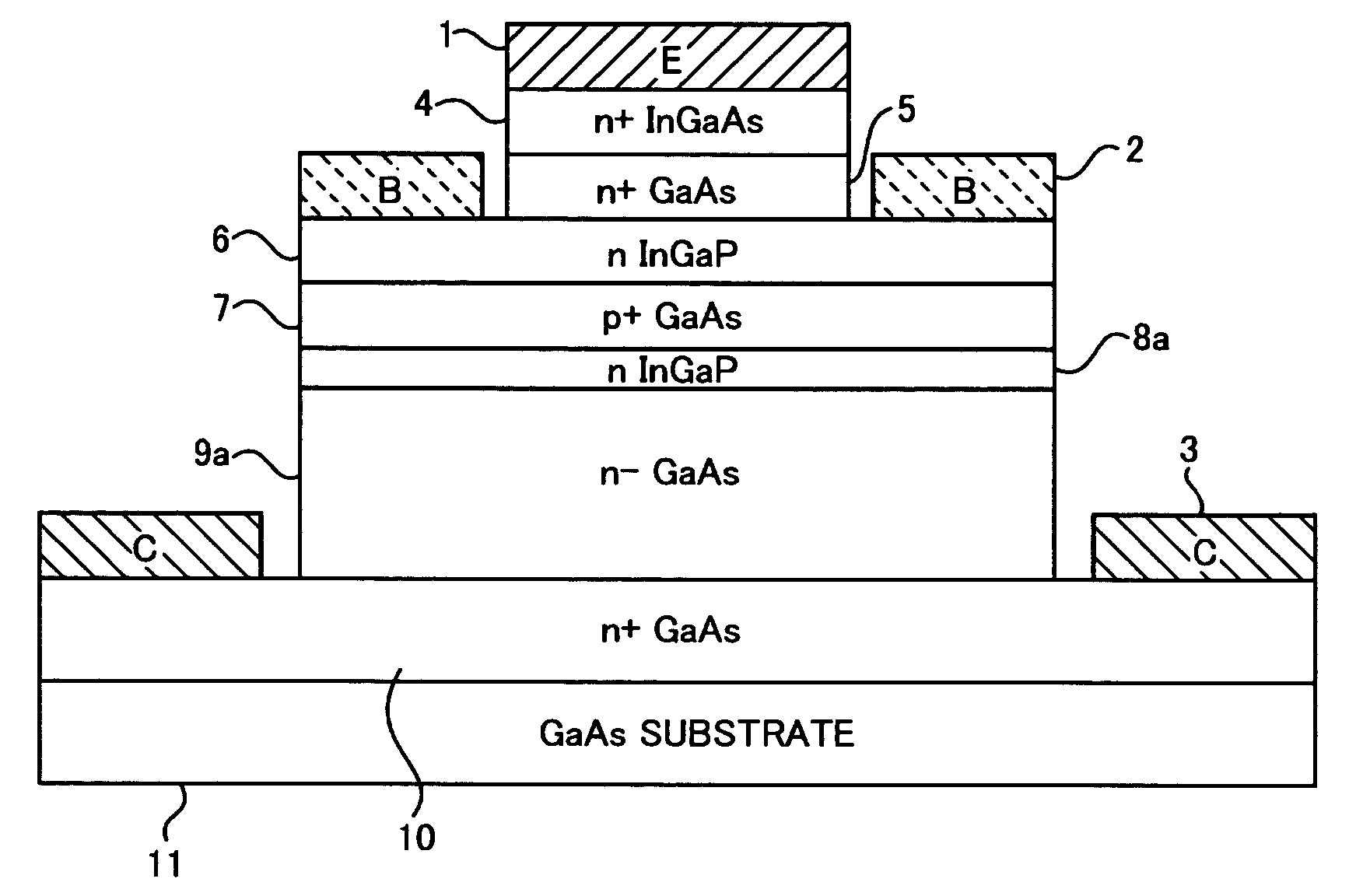
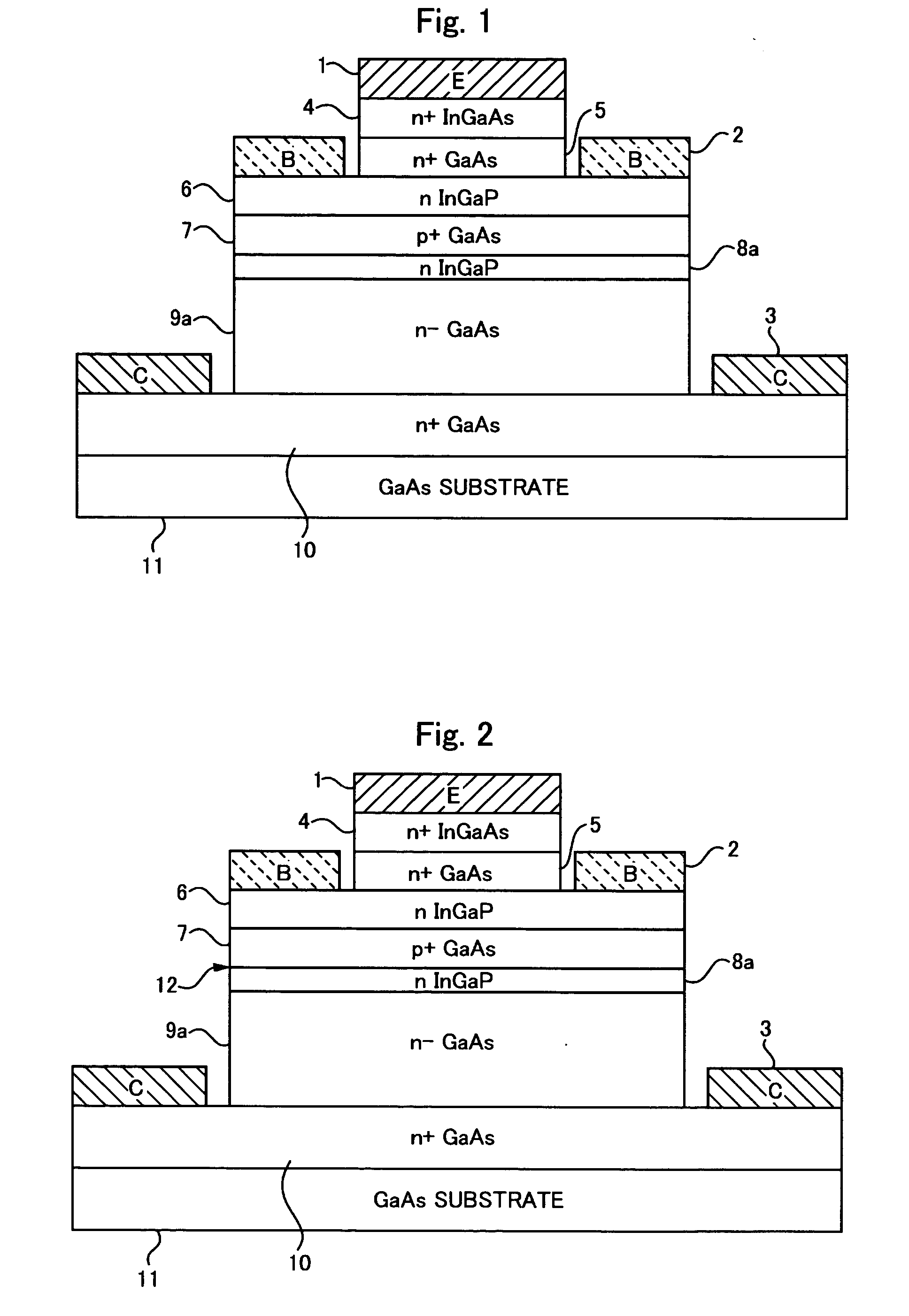
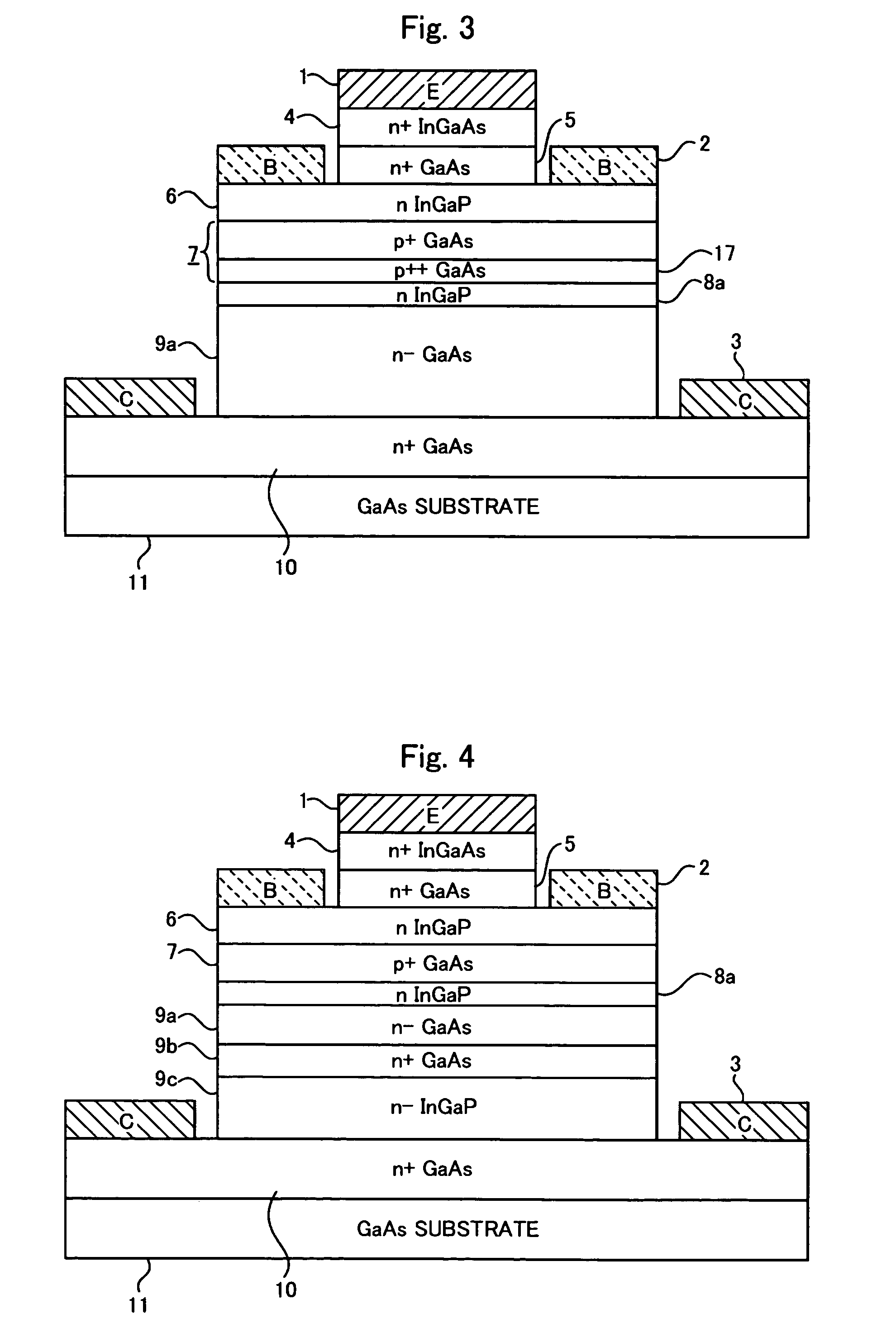
There is provided a semiconductor device capable of ensuring a complete enhancement-mode operation and realizing a power transistor excellent in the low-distortion, high-efficiency performance. On a surface of a substrate (1) composed of single crystal GaAs, a second barrier layer (3) composed of AlGaAs, a channel layer (4) composed of InGaAs, a third barrier layer (12) composed of InGaP and a first barrier layer (11) composed of AlGaAs are stacked in this order, while placing in between a buffer layer (2). Relation of χ1−χ3≦0.5*(Eg3-Eg1), where χ1 is electron affinity of the first barrier layer (11), Eg1 is a band gap of the same, χ3 is electron affinity of the third barrier layer (12), and Eg3 is a band gap of the same, is satisfied between the first barrier layer (11) and the third barrier layer (12).
Owner:SONY CORP
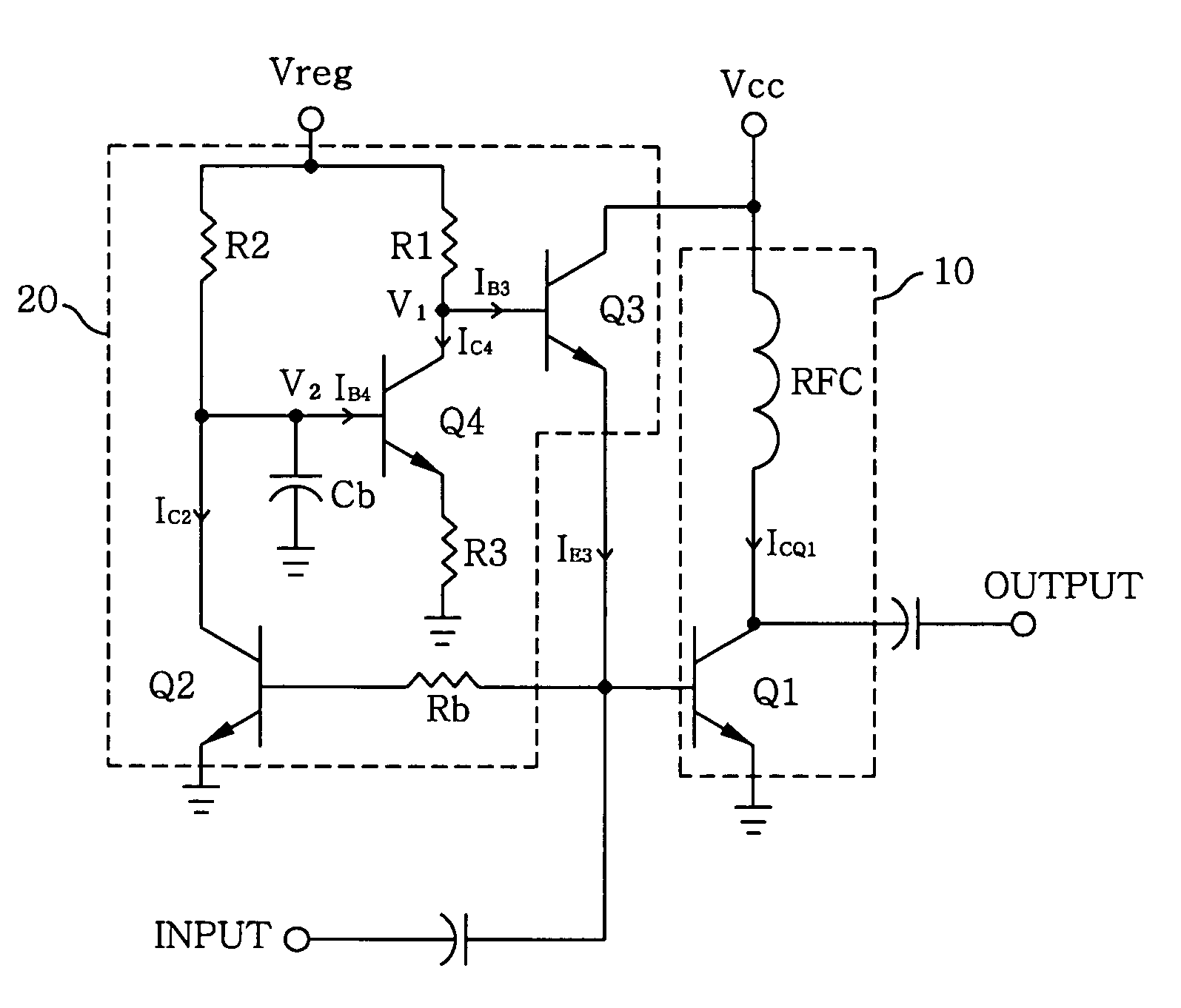
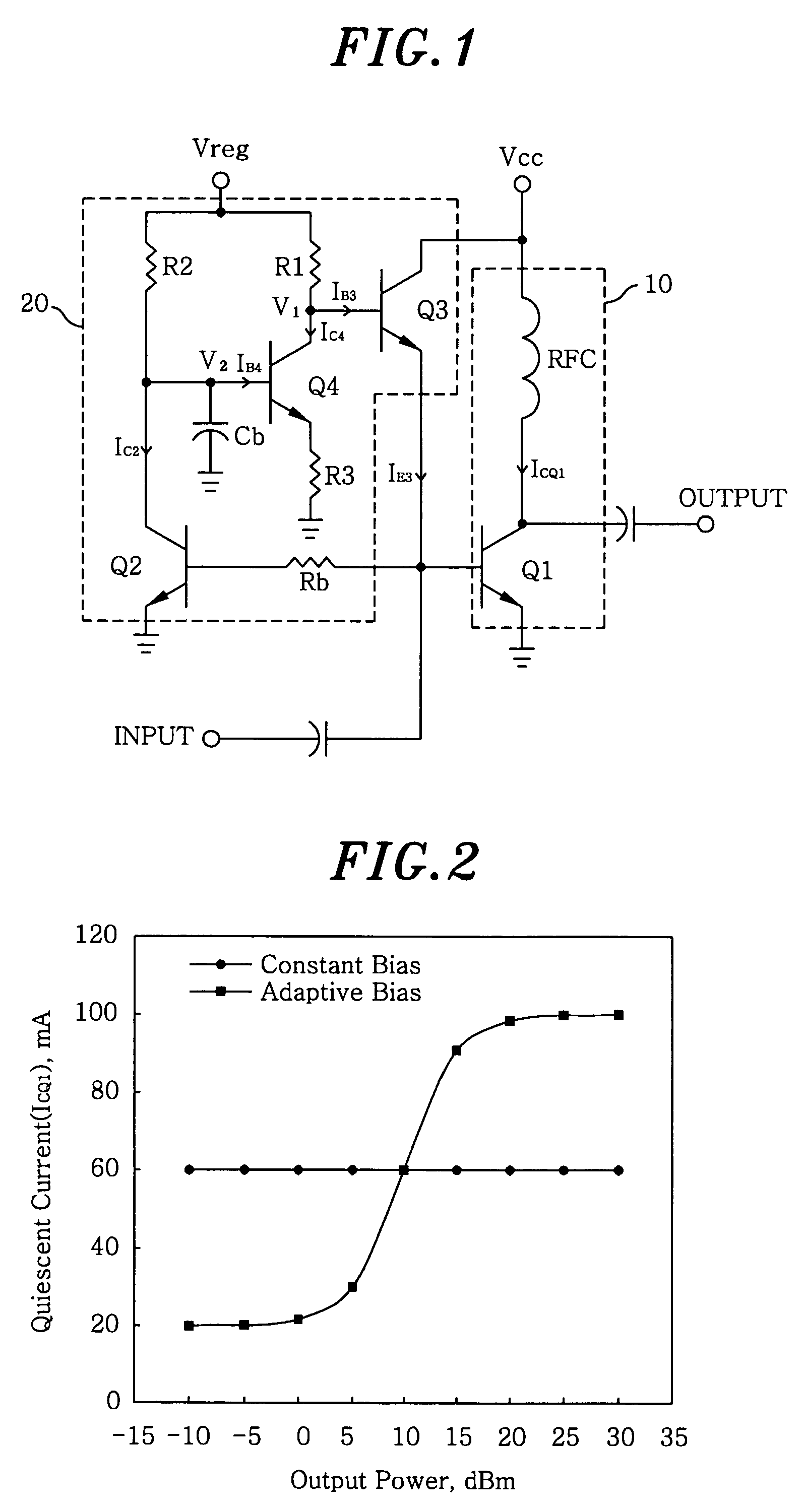
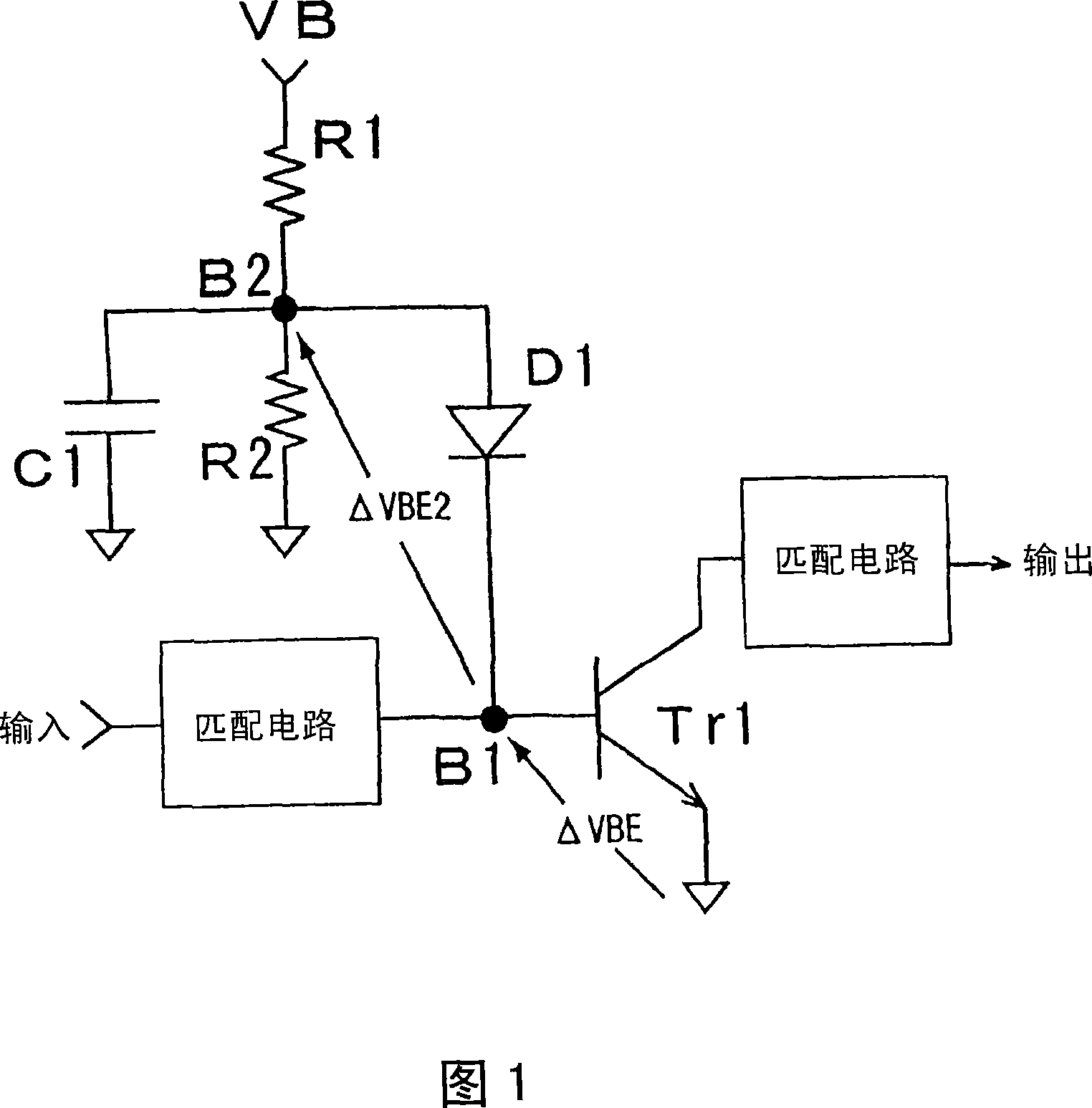
Adaptive bias circuit for a power amplifier
InactiveUS7005923B2Effective controlImprove power added efficiencyAmplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationGain controlAdaptive biasDriving current
An adaptive bias circuit is provided for an amplifier module including a RF power amplifier for amplifying an input signal to generate an output signal, wherein the bias circuit receives the input signal to adjust a driving current to control a quiescent current of the RF power amplifier. The adaptive bias circuit includes means for providing the driving current to the bias circuit and means for drawing a bypass current from the providing means to reduce the driving current in response to the input signal, wherein the quiescent current is reduced when the driving current is reduced and the bypass current increases when the input signal is reduced.
Owner:INFORMATION & COMM UNIV EDUCATIONAL FOUND
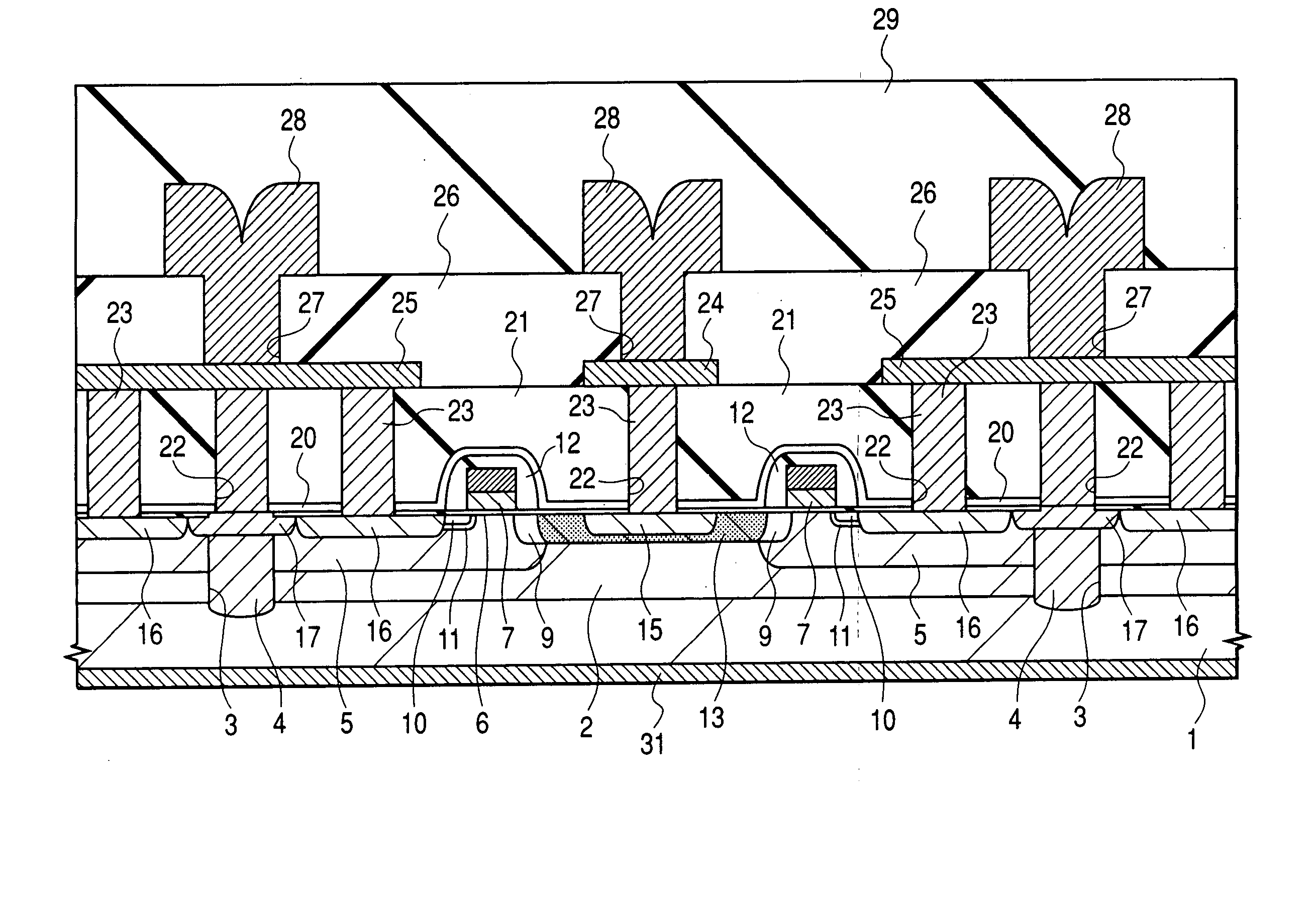
Semiconductor device and a method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20050051814A1Easy to controlImprove batch productivityTransistorEnergy efficient ICTCapacitanceDevice material
To reduce the size and improve the power added efficiency of an RF power module having an amplifier element composed of a silicon power MOSFET, the on resistance and feedback capacitance, which were conventionally in a trade-off relationship, are reduced simultaneously by forming the structure of an offset drain region existing between a gate electrode and an n+ type drain region of the power MOSFET into a double offset one. More specifically, this is accomplished by adjusting the impurity concentration of an n− type offset drain region, which is closest to the gate electrode, to be relatively low and adjusting the impurity concentration of an n type offset drain region, which is distant from the gate electrode, to be relatively high.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Semiconductor device and a method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS7176520B2Easy to controlImprove batch productivityTransistorEnergy efficient ICTCapacitanceFeedback capacitance
To reduce the size and improve the power added efficiency of an RF power module having an amplifier element composed of a silicon power MOSFET, the on resistance and feedback capacitance, which were conventionally in a trade-off relationship, are reduced simultaneously by forming the structure of an offset drain region existing between a gate electrode and an n+ type drain region of the power MOSFET into a double offset one. More specifically, this is accomplished by adjusting the impurity concentration of an n− type offset drain region, which is closest to the gate electrode, to be relatively low and adjusting the impurity concentration of an n type offset drain region, which is distant from the gate electrode, to be relatively high.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Push-pull radio-frequency power amplifier with improved linearity and efficiency
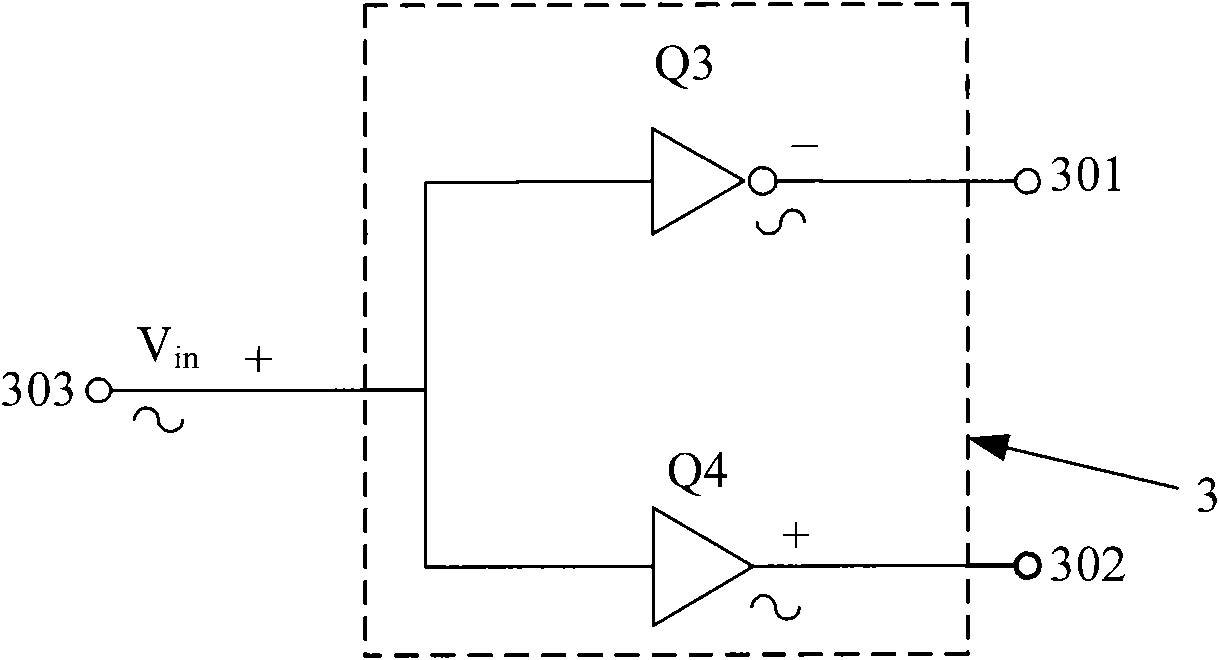
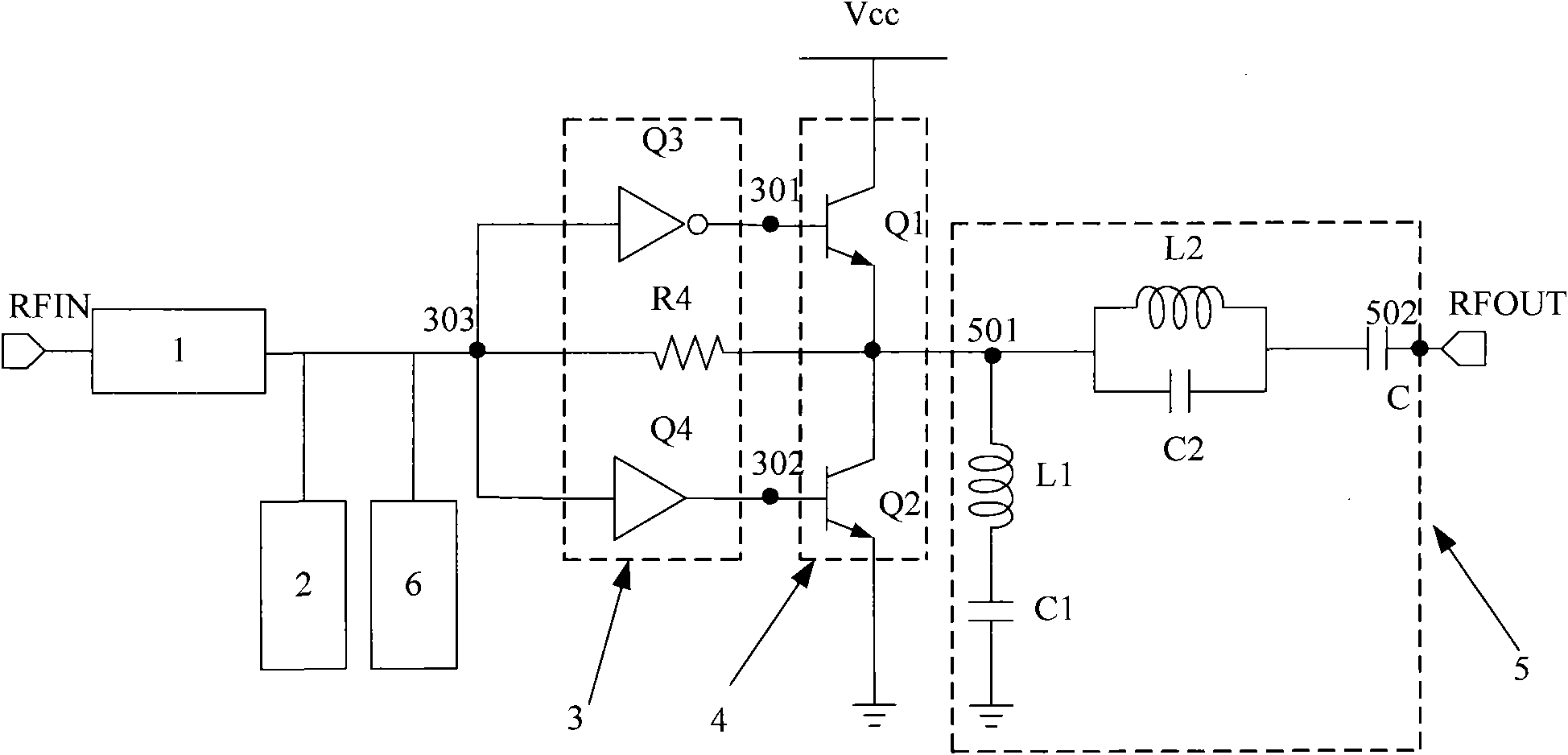
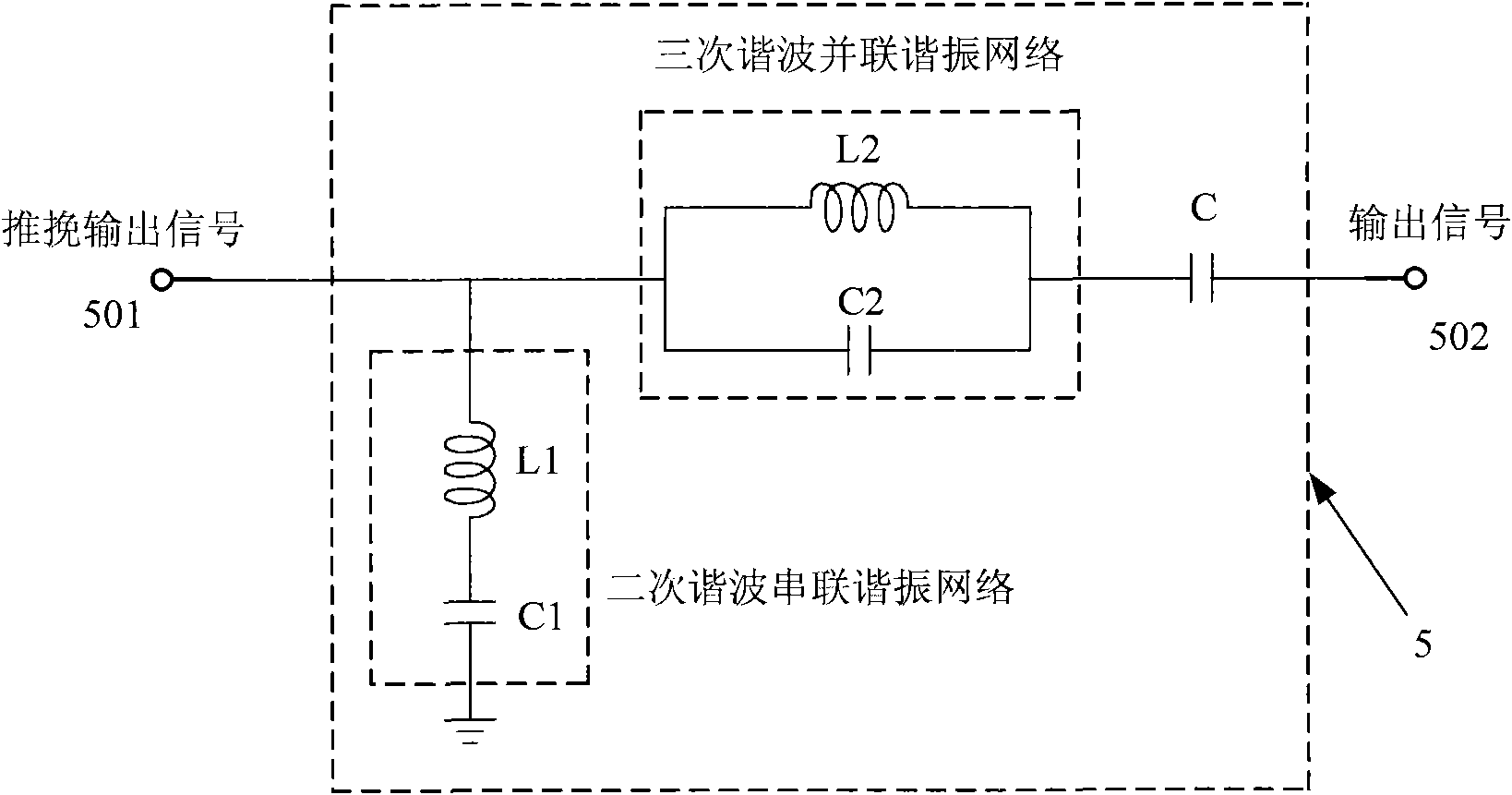
InactiveCN101888213ARealize the structureImprove power added efficiencyAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionHigh frequency amplifiersCapacitanceCommon emitter
The invention discloses a push-pull radio-frequency power amplifier with improved linearity and efficiency, comprising an input matching network, an output matching network and a power amplification circuit, wherein the power amplification circuit comprises a first-stage amplification circuit and a second-stage amplification circuit, the first-stage amplification circuit is connected with the input matching network, the second-stage amplification circuit is connected between the first-stage amplification circuit and the output matching network, and the second-stage amplification circuit is an NPN-NPN push-pull amplification circuit composed of a second common collector amplifying tube and a second common-emitter amplifying tube. The output matching network is an output filter matching network which comprises a secondary harmonic series resonance network, a third harmonic series resonance network and a stopping condenser, wherein the secondary harmonic series resonance network is connected between the output end of the second-stage amplification circuit and the ground, the third harmonic series resonance network is connected between the output end of the secondary harmonic series resonance network and the stopping condenser, and the stopping condenser is connected between the third harmonic series resonance network and the power amplifier. The invention improves the additional efficiency of the radio-frequency power amplifier and improves the linearity of the radio-frequency power amplifier.
Owner:SUZHOU INNOTION TECH
High Efficiency Power Amplifier
InactiveUS20050099227A1Reduced DC power consumptionIncrease in sizeGated amplifiersAmplification control detailsPower modeWork period
A multiple power mode amplifier provides a low and a high power mode without using switches. This amplifier may be used in RF applications such as mobile telephones. In the low power mode, the power consumption of the amplifier is reduced, which will increase operation time, especially important for battery-operated devices. In one implementation, the amplifier includes a number of impedance matching network units, impedance transformer, and a power stage.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
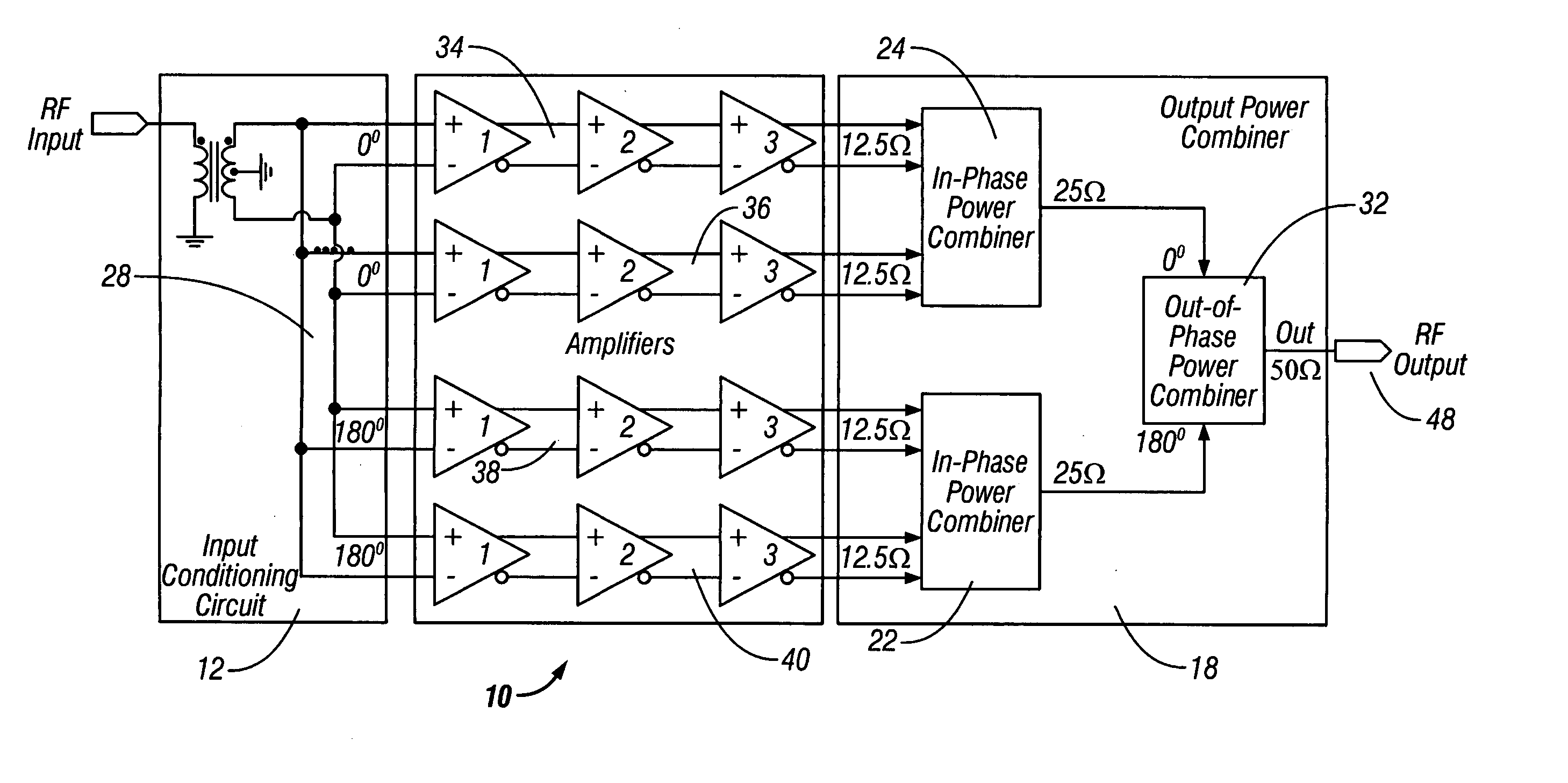
Method and apparatus for an improved power amplifier
ActiveUS20060006939A1Improve power added efficiencyIncrease output powerPrinted electric component incorporationHigh frequency circuit adaptationsAudio power amplifierBalun
An amplifier system is provided,with a first balun that has an input and an output. A second balun has an input and an output. An amplifier assembly is provided with at least a first amplifier in parallel to a second amplifier. The first amplifier provides the input to the first balun, and the second amplifier provides the input to the second balun. The outputs of the first and second baluns add constructively and substantially in series.
Method and apparatus for an improved power amplifier
InactiveUS20060006934A1Improve power added efficiencyIncrease output powerPower amplifiersAmplifier detailsEngineeringBalun
An amplifier system is provided that has a first balun with an input and an output, and a second balun with an input and an output. A first set of amplifiers is coupled in series and to the output of the first balun. A second set of amplifiers is coupled in series and to the output of the second balun. The first and second sets of amplifiers are in series or parallel. A load impedance of the first and second sets of amplifiers does not substantially change at an output of any amplifier that is switched on when another amplifier is switched off.
Owner:QORVO INT PTE LTD
Semiconductor device
InactiveUS20050104088A1Lower turn-on resistanceImprove power added efficiencySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSemiconductor materialsDevice material
A heterojunction bipolar transistor, having a structure in which a subcollector layer of a first conductive type having a higher doping concentration than a collector layer, a collector layer of the first conductive type, a base layer of the second conductive type, and an emitter layer of the first conductive type are deposited, in order, on a semi-insulating semiconductor substrate, and in which a hole barrier layer of semiconductor material with a band gap wider than that of the base layer is inserted between the base layer and the collector layer, so as to be in direct contact with the base layer.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Amplifier
InactiveCN1926759AImprove power added efficiencyAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationEngineeringMultistage amplifier
The present invention provides an apparatus for compensating distortion of a multi-stage amplifier having gain extension characteristics. The present invention also provides a method for biasing the amplification stages closer to a Class B regime exhibiting higher power added efficiency at low output, so as to have gain extension characteristics in all stages of a multistage amplifier. The amplifier of the present invention has the characteristic of gain expansion, and it shows that the gain increases with the increase of the input power or output power within a certain range of input power or output power. The amplifier is characterized in that the emitter-grounded amplifier circuit comprising a first bipolar transistor has a base terminal which passes through a first impedance element which does not block direct current and an input matching circuit and a first diode which provides a bias voltage. The cathode is connected, while the first diode has an anode connected to a reference power supply that presents a very low impedance at high frequencies.
Owner:NEC CORP
High-frequency power amplifier
InactiveCN101043202AImprove power added efficiencyStable output power characteristicsHigh frequency amplifiersAmplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationAudio power amplifierHigh frequency power
A high-frequency power amplifier with a temperature compensation function for power amplifying a high-frequency signal, includes: a power amplifying transistor having an emitter grounded; a high power output bias circuit that supplies a high power output current corresponding to a high power output of the high-frequency power amplifier to the power amplifying transistor; and a low power output bias circuit that supplies a low power output current corresponding to a low power output of the high-frequency power amplifier to the power amplifying transistor.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Radio communication system
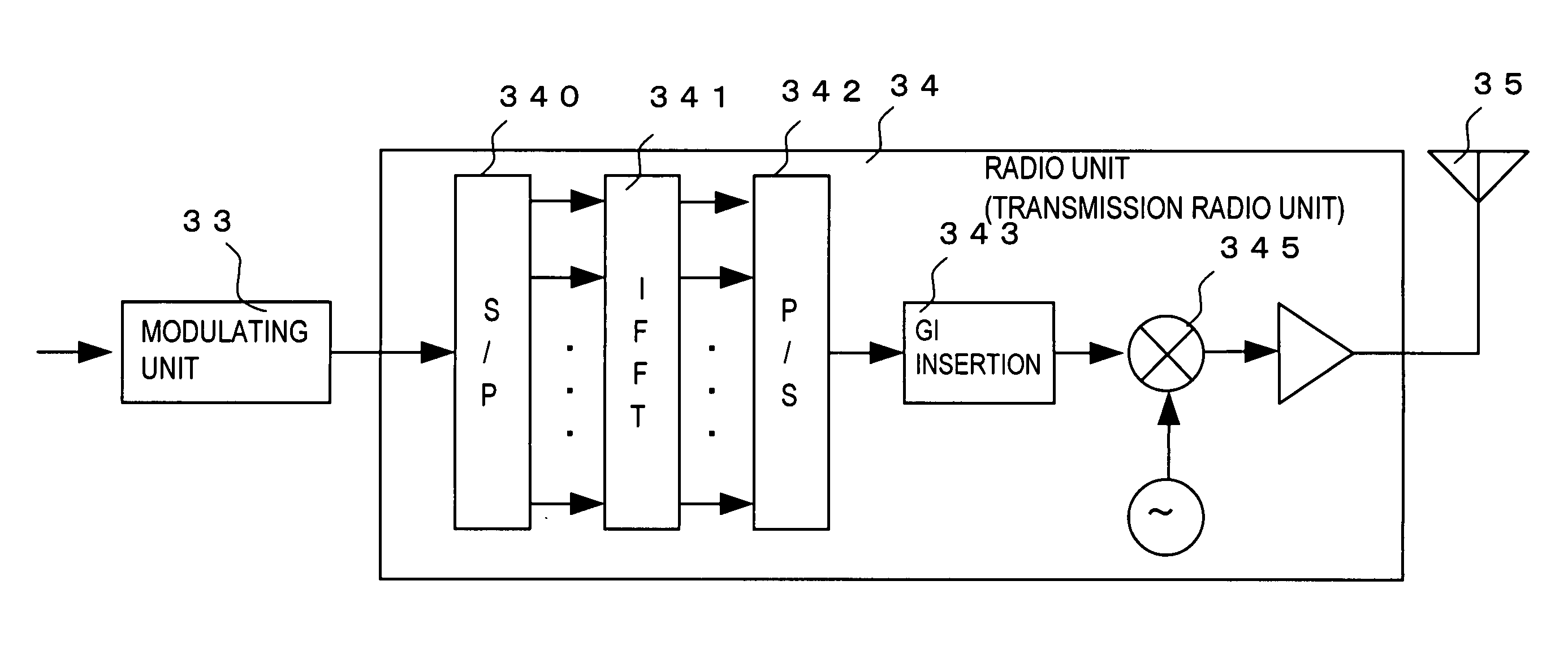
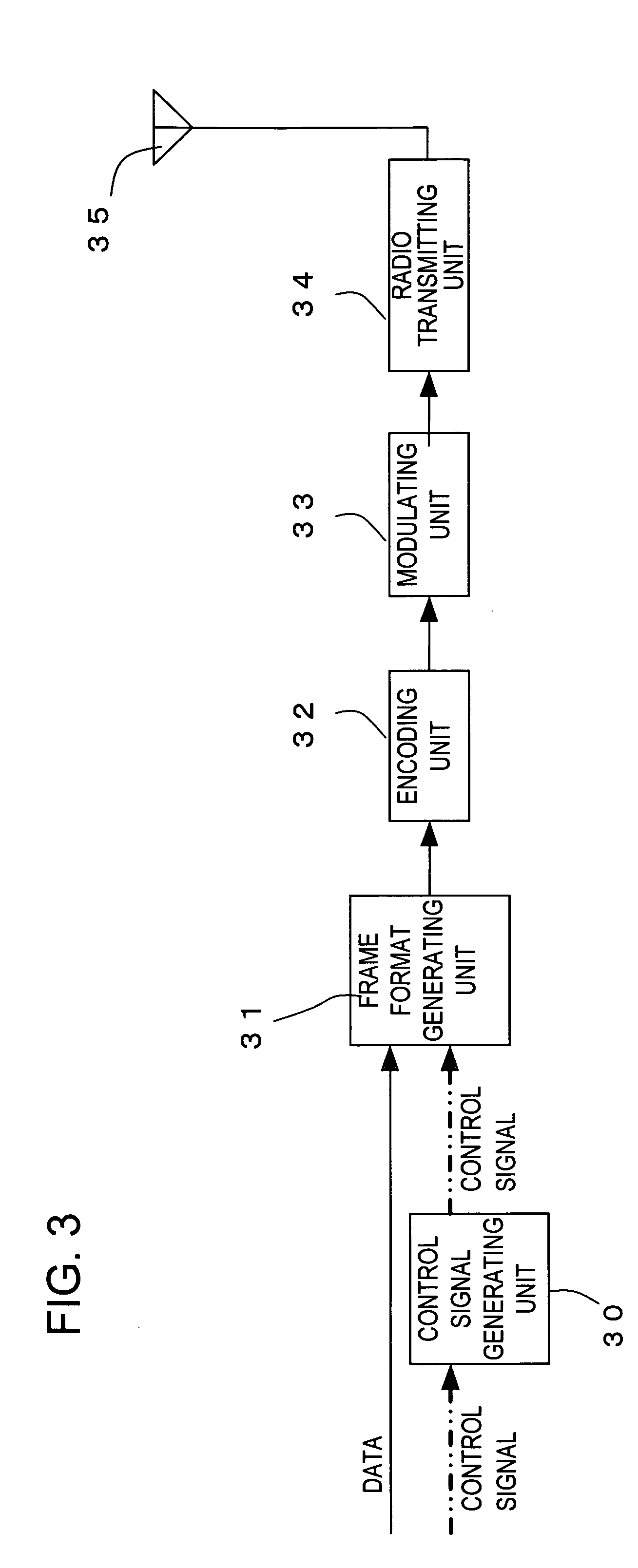
ActiveUS20070178928A1Reduce transmit powerPAPR can also be reducedPower managementEnergy efficient ICTCommunications systemControl signal
A frame format is generated which can constrain the PAPR at a lower level without limitation in code selections in a radio communication system. The radio communication system with each radio channel constituted by a control channel and a data channel divides a plurality of the radio channels in a frequency direction for mapping to a radio frame format. A control signal position on the control channel is controlled in the radio frame format for each user or service to reduce peak transmission power or a peak-to-average power ratio of a radio communication apparatus.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
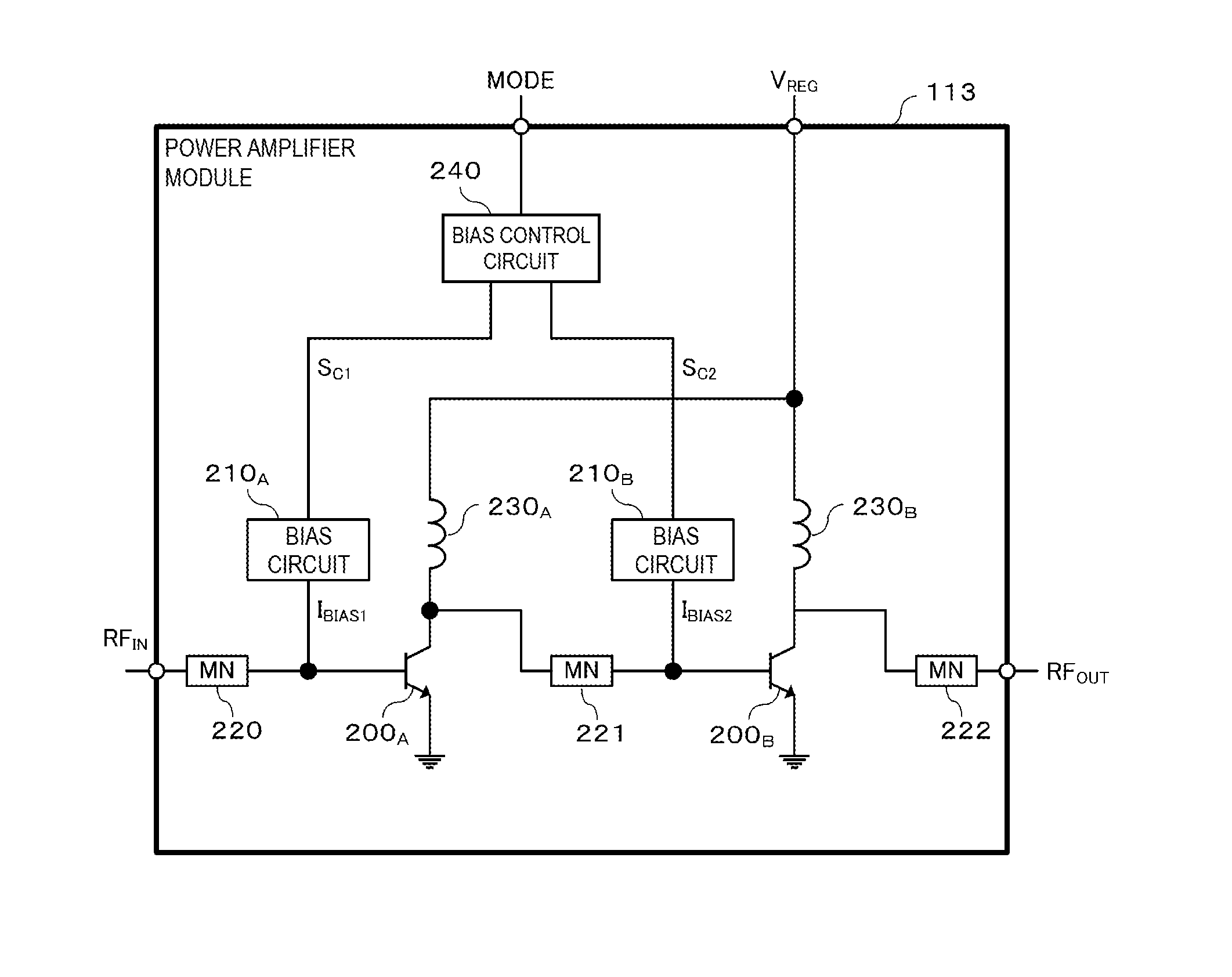
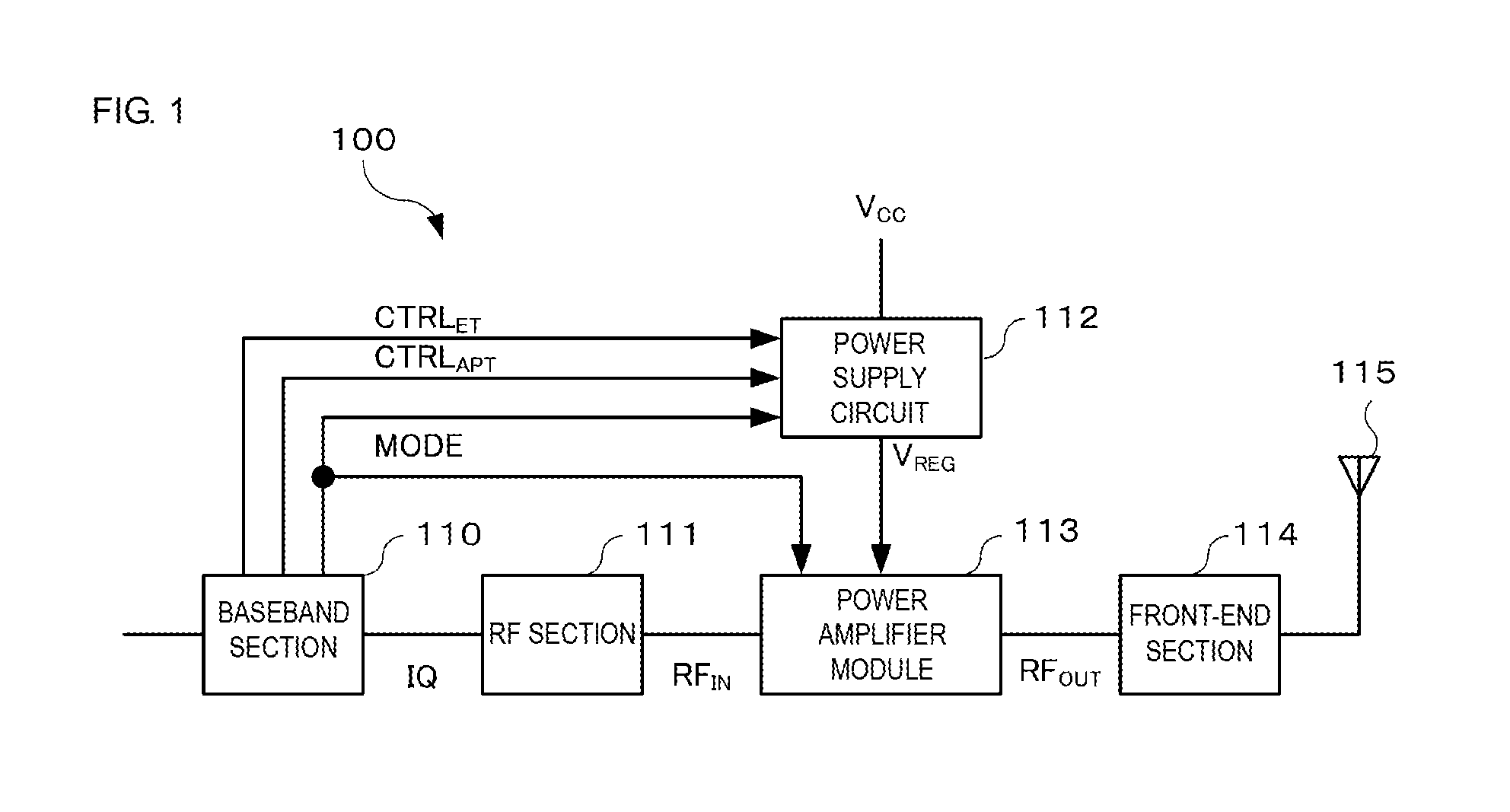
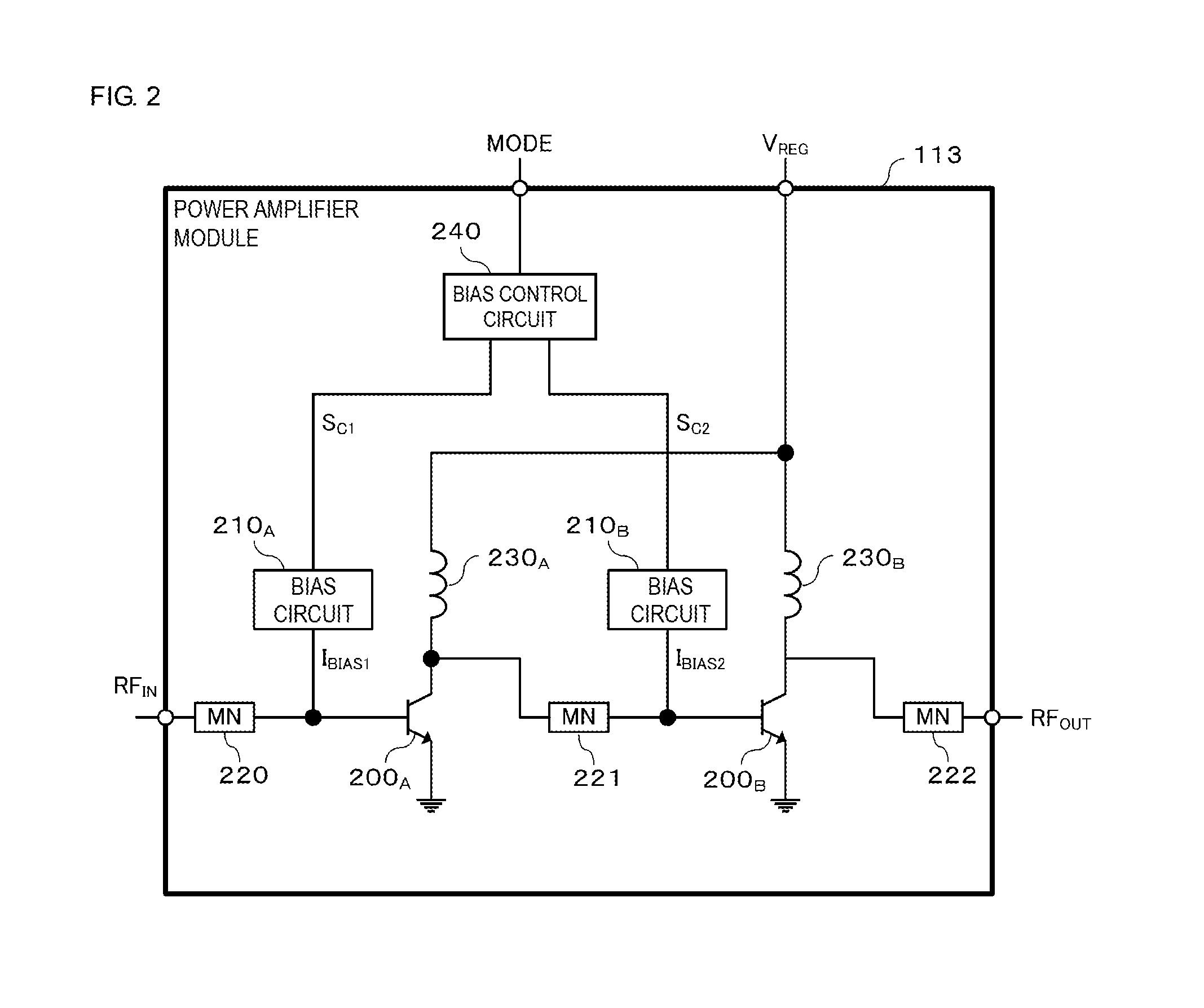
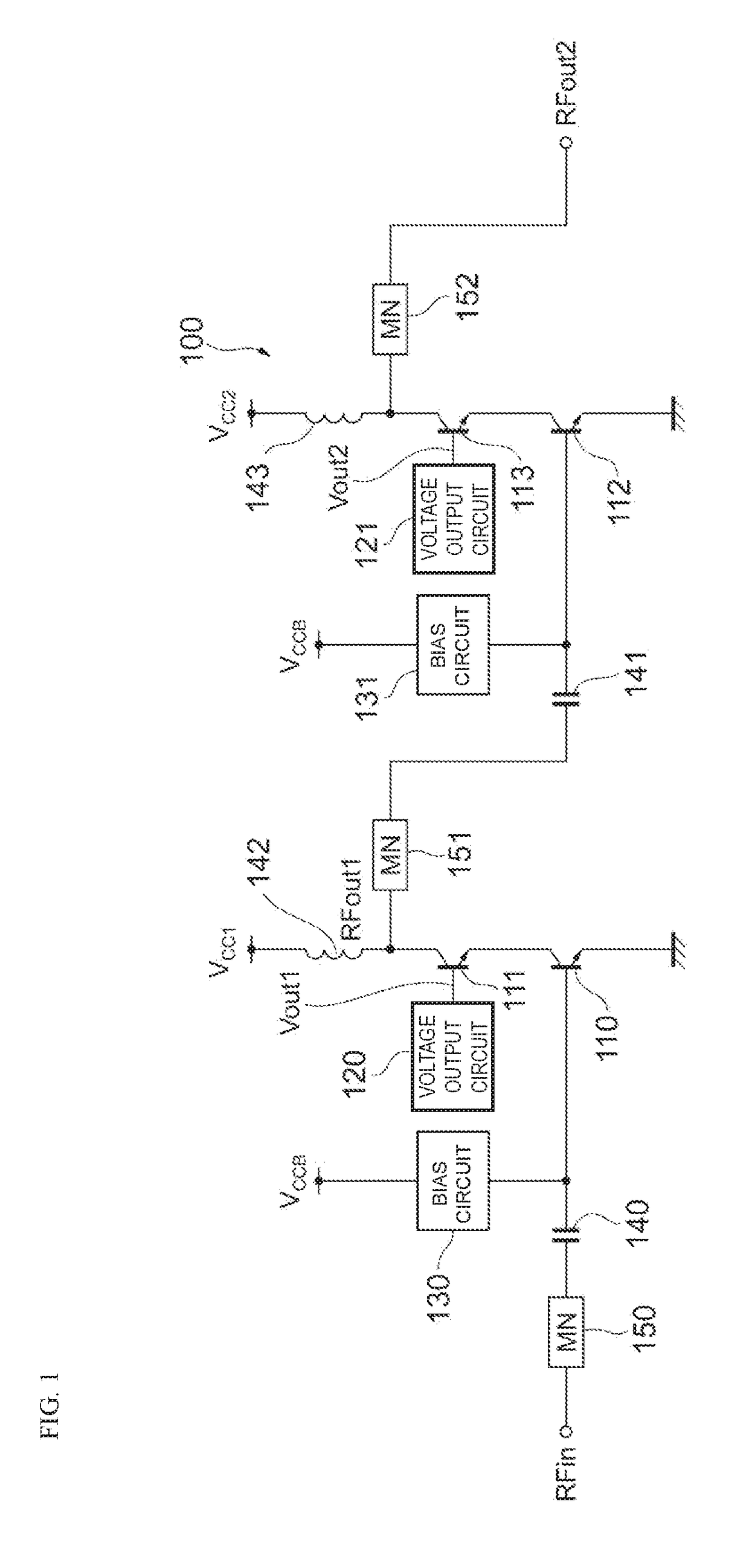
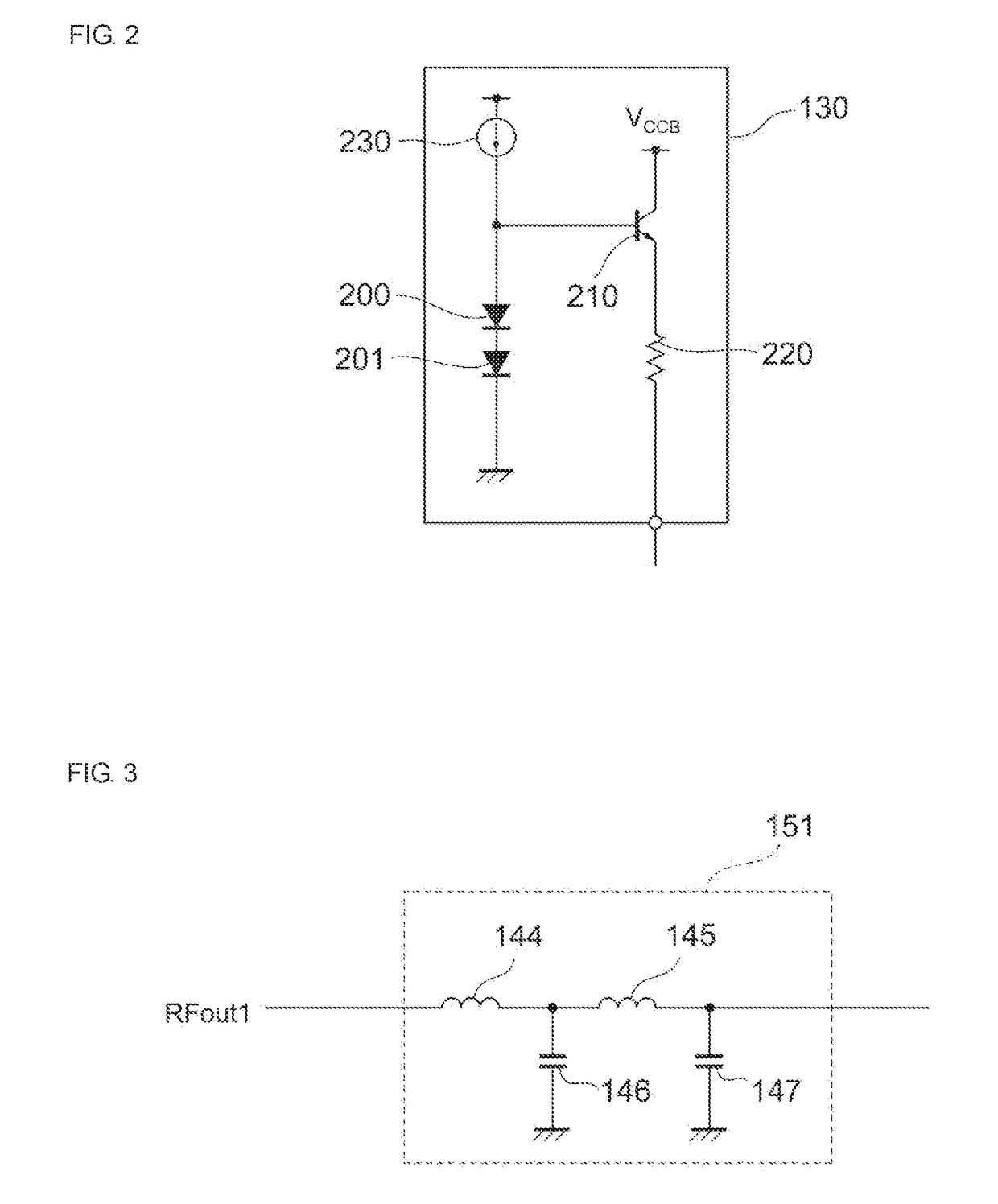
Power amplifier module
ActiveUS20160294328A1Improve linearityImprove power added efficiencyHigh frequency amplifiersPower amplifiersAudio power amplifierEngineering
A power amplifier module includes an amplifier transistor and a bias circuit. A first power supply voltage based on a first operation mode or a second power supply voltage based on a second operation mode is supplied to the amplifier transistor. The amplifier transistor receives a first signal and outputs a second signal obtained by amplifying the first signal. The bias circuit supplies a bias current to the amplifier transistor. The bias circuit includes first and second resistors and first and second transistors. The first transistor is connected in series with the first resistor and is turned ON by a first bias control voltage which is supplied when the first operation mode is used. The second transistor is connected in series with the second resistor and is turned ON by a second bias control voltage which is supplied when the second operation mode is used.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
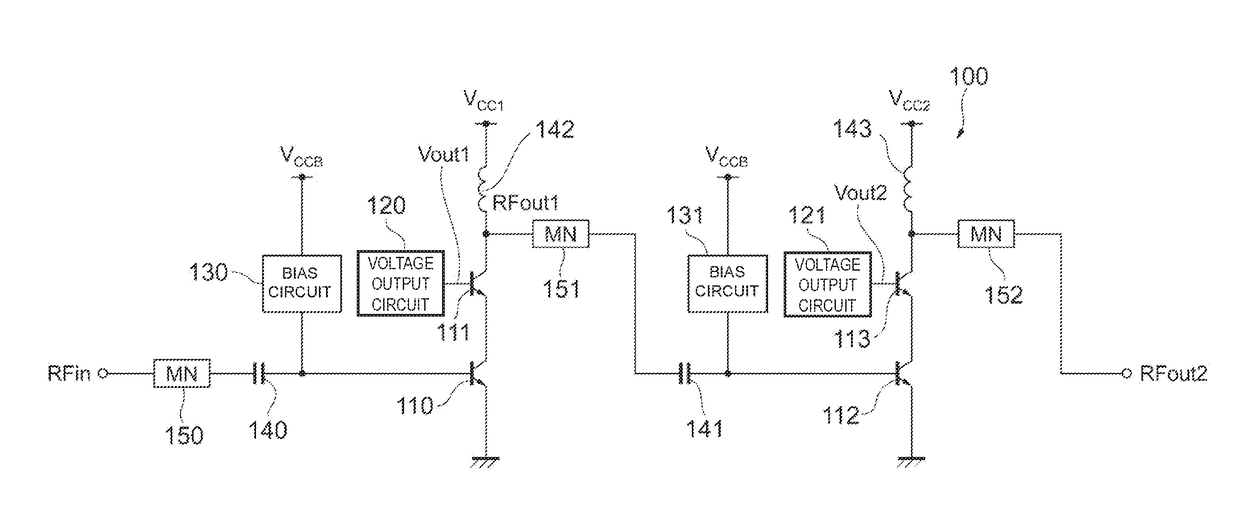
Power amplifier circuit
ActiveUS20170359038A1Reduce lossesIncrease load impedanceTransmission path divisionPower amplifiersAudio power amplifierRadio frequency signal
A power amplifier circuit includes first and second transistors and a first voltage output circuit. A radio frequency signal is input into a base of the first transistor. The first voltage output circuit outputs a first voltage in accordance with a power supply voltage. The first voltage is supplied to a base or a gate of the second transistor. An emitter or a source of the second transistor is connected to a collector of the first transistor. A first amplified signal generated by amplifying the radio frequency signal is output from a collector or a drain of the second transistor.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
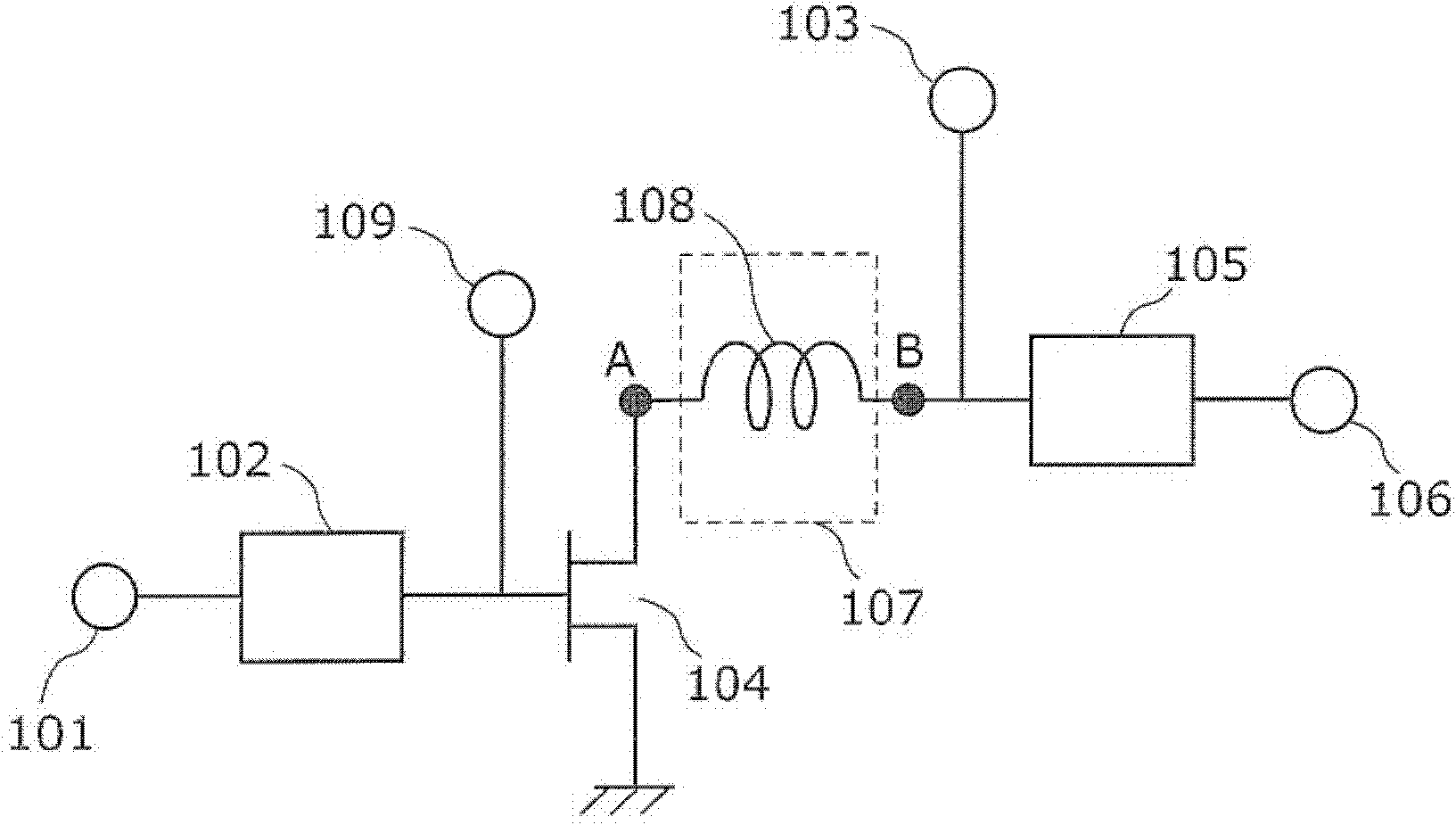
High- frequency power amplifier
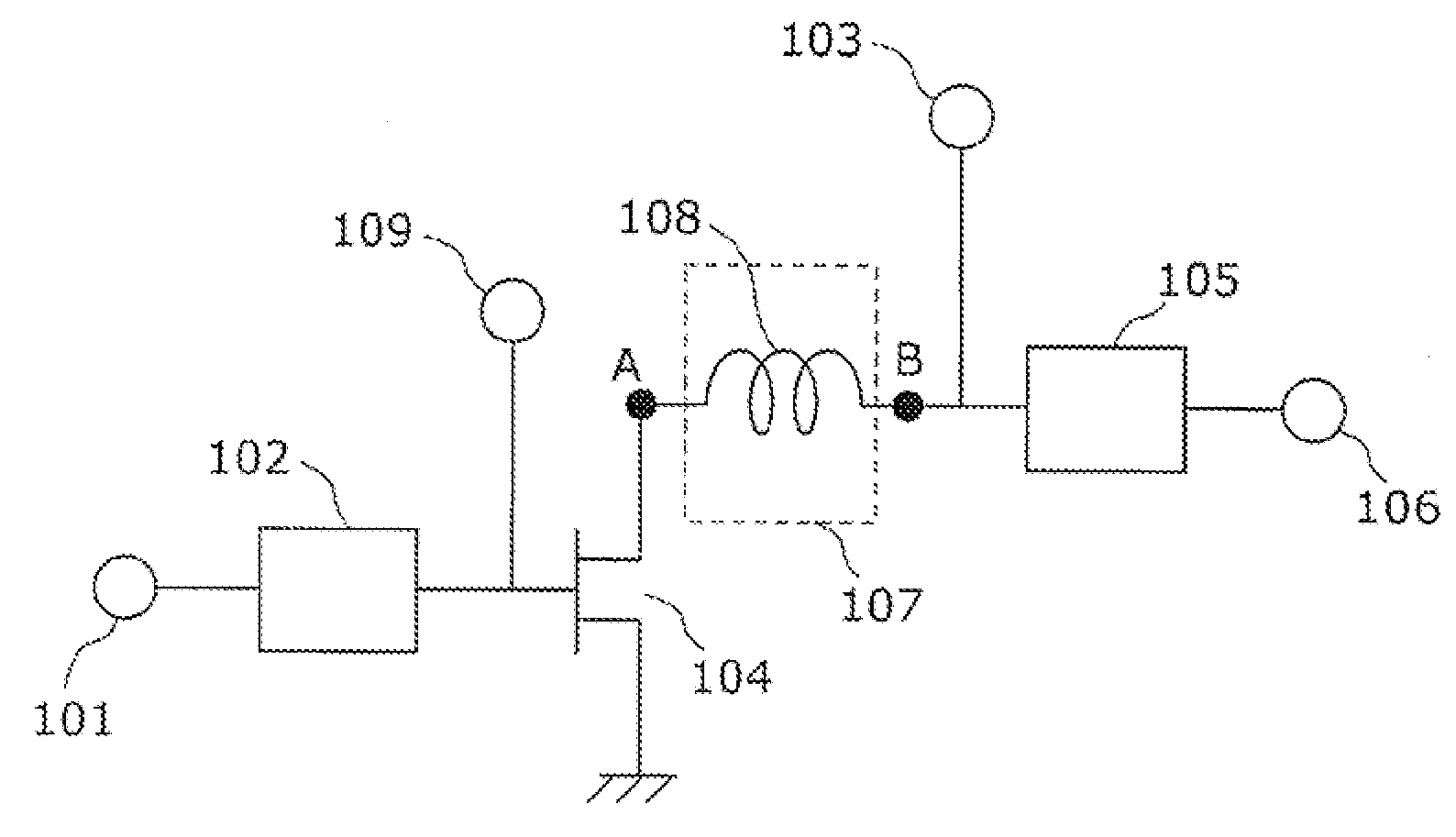
InactiveCN102474228AReduce distortionReduce power consumptionAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionHigh frequency amplifiersHigh frequency powerAudio power amplifier
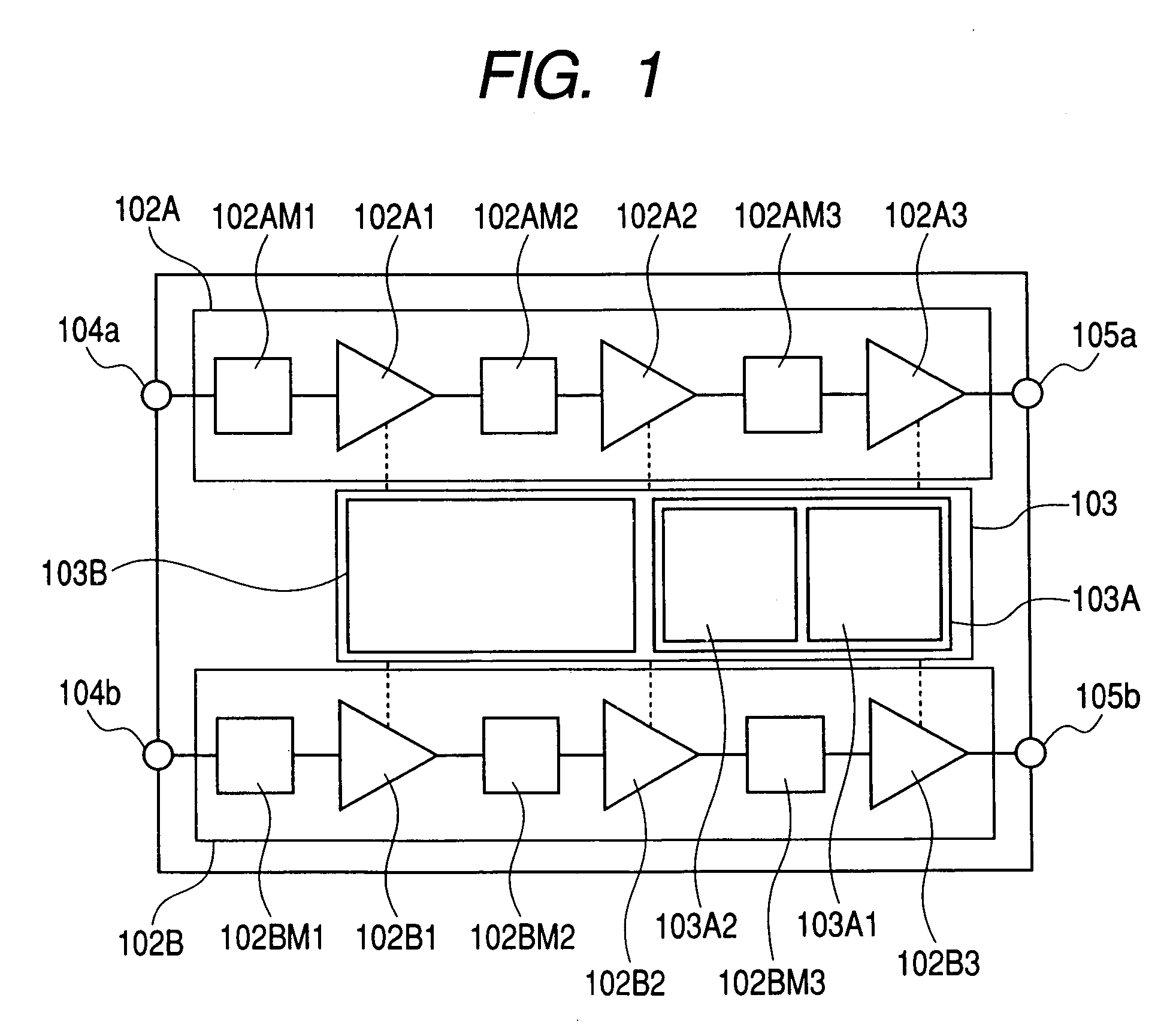
A radio frequency power amplifier having a transistor 104 that amplifies a radio frequency signal of a first frequency; an input matching circuit 102 connected to an input terminal of the transistor 104; an output matching circuit 105 connected to an output terminal of the transistor 104; and a reactance control circuit 107 with one end connected to the output terminal of the transistor 104, and the other end connected to an input terminal of an output matching circuit 105 and a bias terminal 103. The reactance control circuit 107 has a reactance which resonates at a second frequency with a parasitic capacitance of the transistor 104 at the output terminal of the transistor 104. The second frequency is identical or close to the first frequency.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Method and apparatus for an improved power amplifier
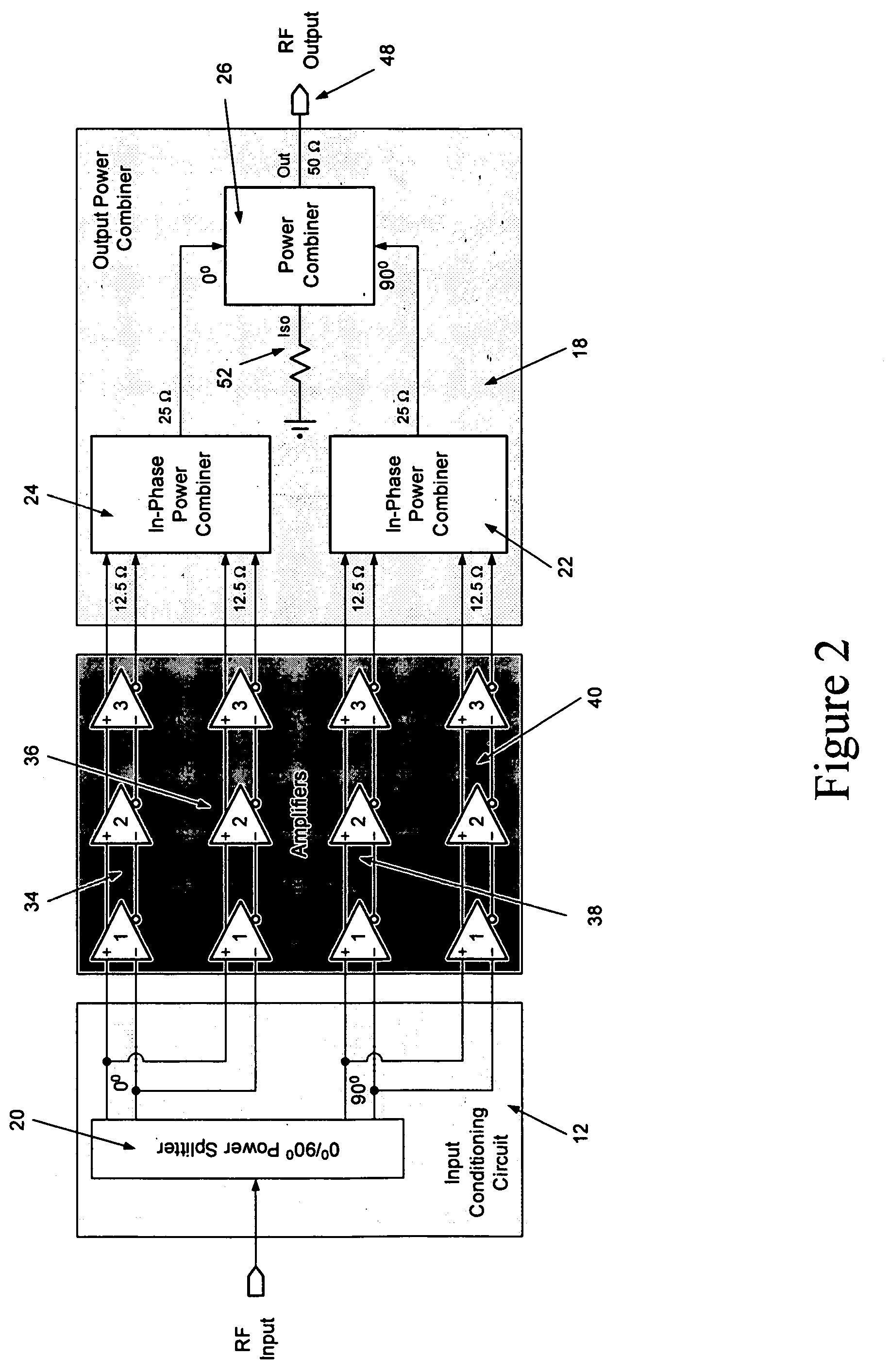
ActiveUS7358806B2Increase output powerImprove power added efficiencyAmplifier combinationsMulti inputAudio power amplifier
A power amplifier assembly has a first power amplifier with a first input conditioning circuit. At least first and second amplifiers are in parallel with each other and having inputs and outputs. An input signal is coupled to the inputs of the first and second amplifiers. A first multi-input power combiner is provided. The outputs of the at least first and second parallel amplifiers are combined by the first multi-input power combiner to add signals of the outputs constructively. A second power amplifier has a first input conditioning circuit. At least first and second amplifiers are in parallel with each other and having inputs and outputs. An input signal is coupled to the inputs of the first and second amplifiers. A second multi-input power combiner is provided. The outputs of the at least first and second parallel amplifiers are combined by the second multi-input power combiner to add signals of the outputs constructively.
Owner:QORVO INT PTE LTD
High- frequency power amplifier
ActiveUS20120098598A1Reduce power consumptionHigh output powerAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionHigh frequency amplifiersElectrical reactanceHigh frequency
A radio frequency power amplifier having a transistor 104 that amplifies a radio frequency signal of a first frequency; an input matching circuit 102 connected to an input terminal of the transistor 104; an output matching circuit 105 connected to an output terminal of the transistor 104; and a reactance control circuit 107 with one end connected to the output terminal of the transistor 104, and the other end connected to an input terminal of an output matching circuit 105 and a bias terminal 103. The reactance control circuit 107 has a reactance which resonates at a second frequency with a parasitic capacitance of the transistor 104 at the output terminal of the transistor 104. The second frequency is identical or close to the first frequency.
Owner:PANASONIC SEMICON SOLUTIONS CO LTD
High electron mobility transistor and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS6908799B2High electron mobilityPrevent kinkingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesPower-added efficiencyImpact ionization
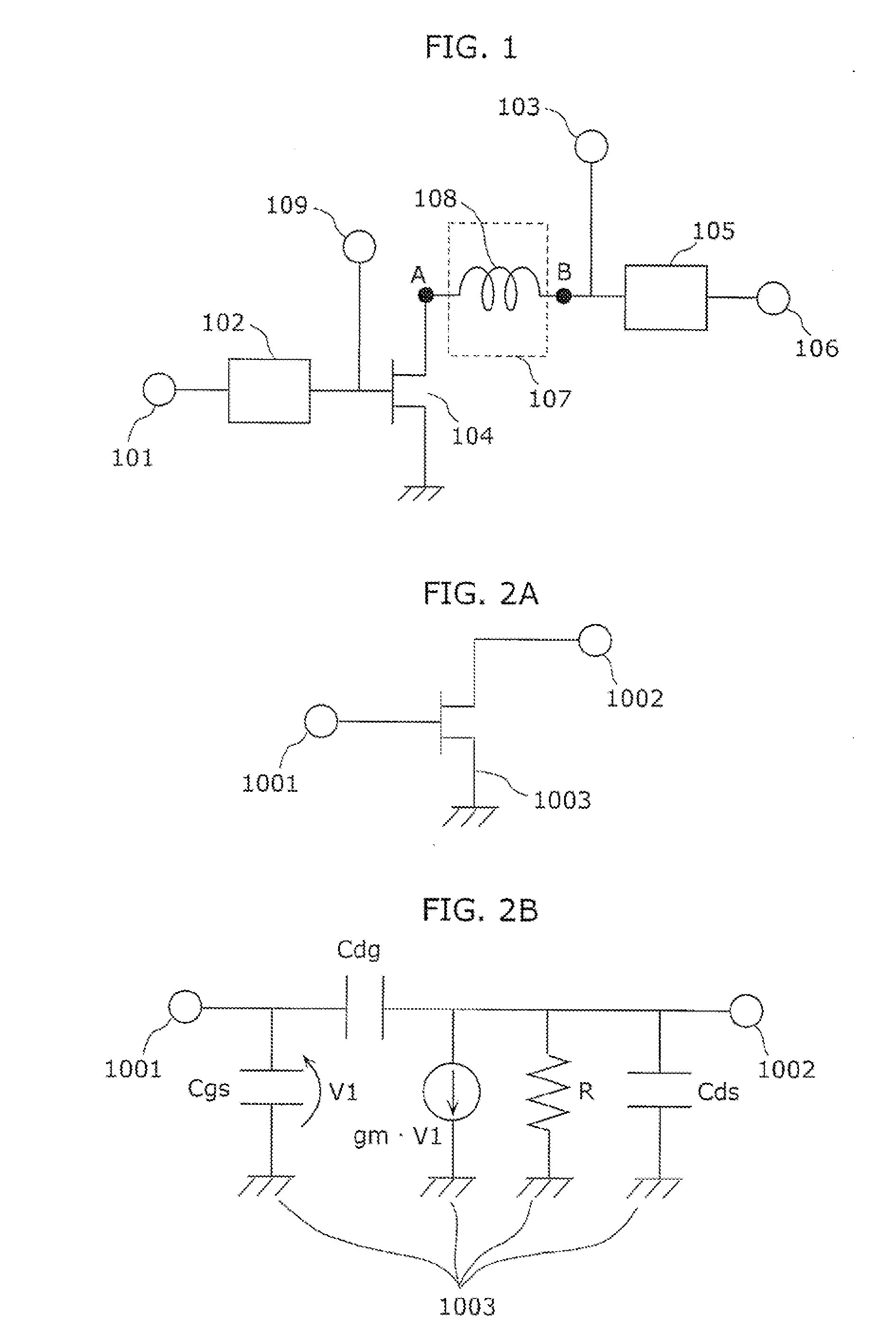
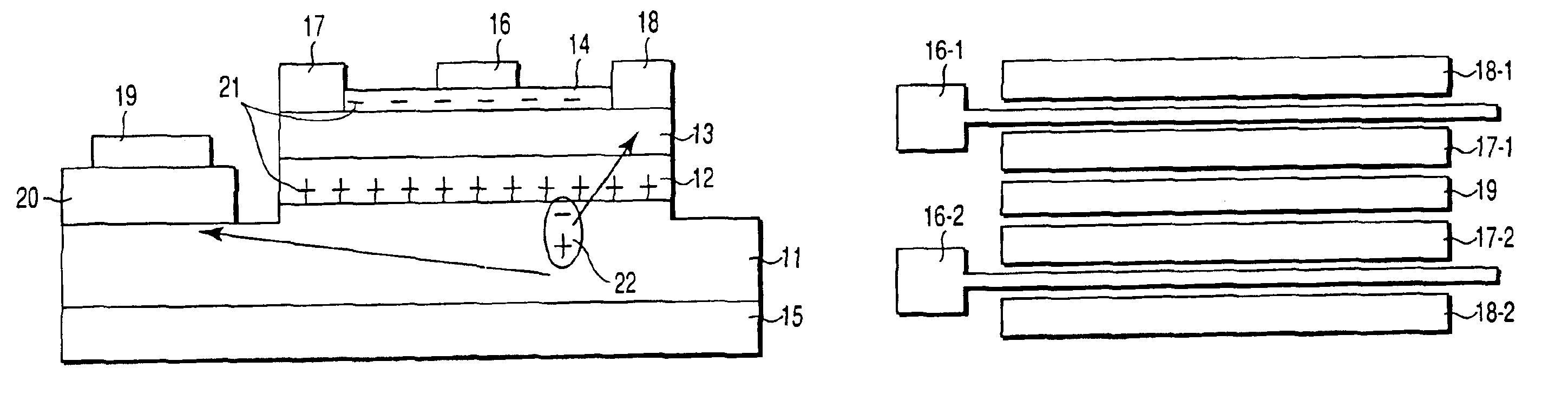
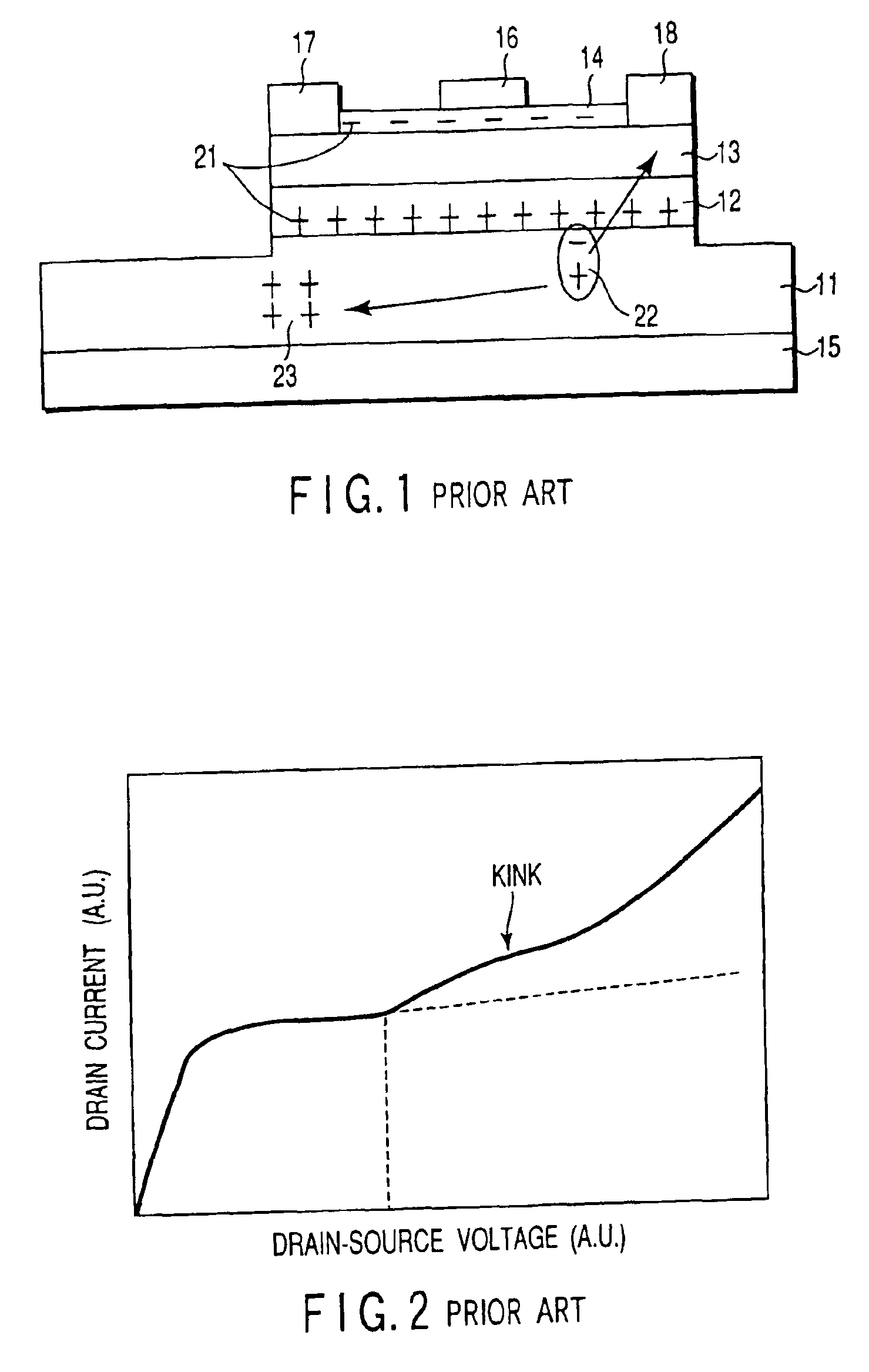
A high electron mobility transistor comprises a GaN-based electron accumulation layer formed on a substrate, an electron supply layer formed on the electron accumulation layer, a source electrode and a drain electrode formed on the electron supply layer and spaced from each other, a gate electrode formed on the electron supply layer between the source and drain electrodes, and a hole absorption electrode formed on the electron accumulation layer so as to be substantially spaced from the electron supply layer. Since the hole absorption electrode is formed on the electron absorption layer in order to prevent holes generated by impact ionization from being accumulated on the electron accumulation layer, a kink phenomenon is prevented. Good drain-current / voltage characteristics are therefore obtained. A high power / high electron mobility transistor is provided with a high power-added efficiency and good linearity.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Method and apparatus for an improved power amplifier
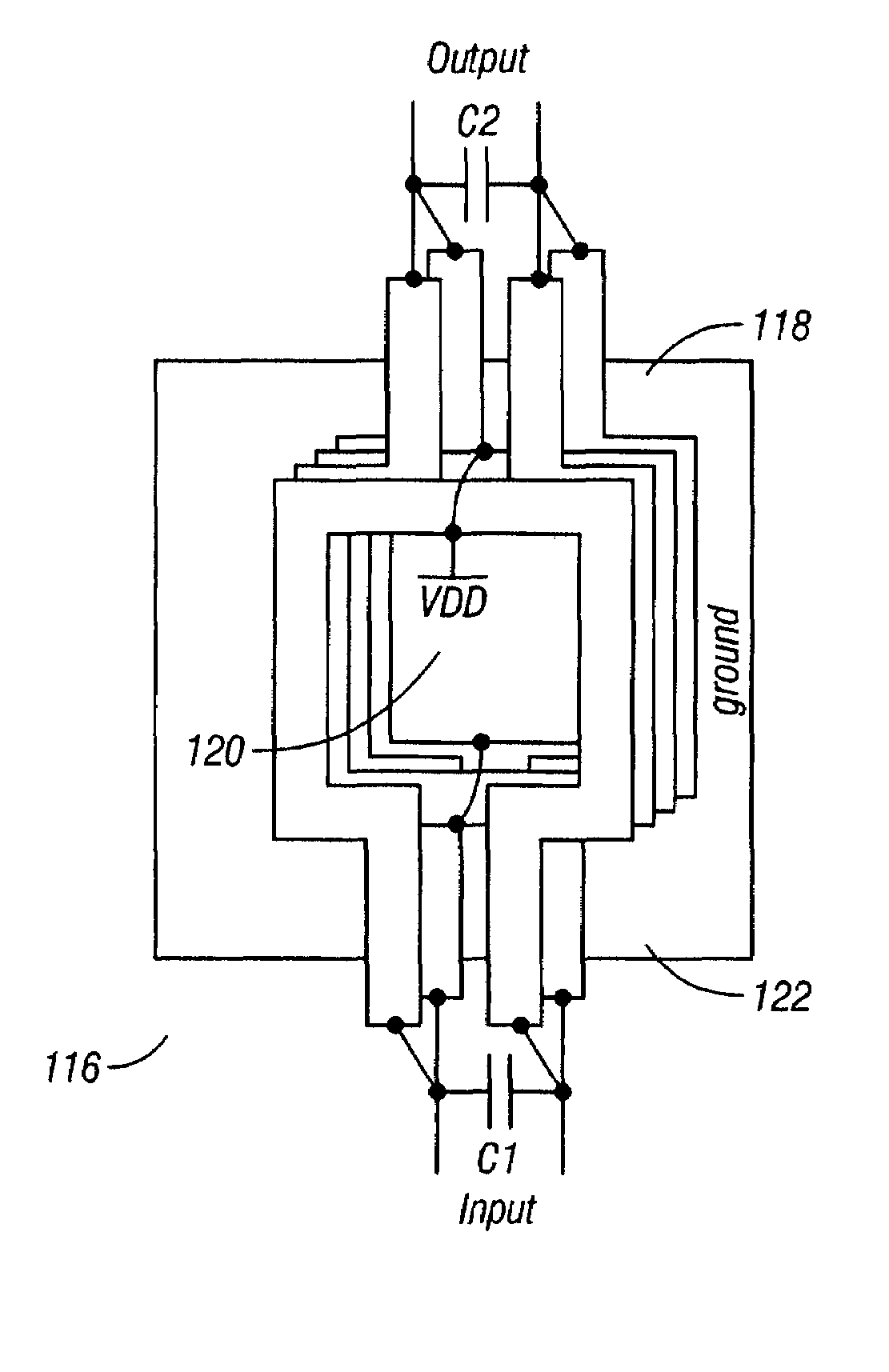
InactiveUS7268616B2Increase output powerImprove power added efficiencyPrinted electric component incorporationHigh frequency circuit adaptationsMulti inputPower combiner
A multi-input power combiner includes a balun with a plurality of layers. A plurality of transmission lines are associated with the plurality of layers. The balun has a largest dimension that is less than half of a ¼ wavelength in a selected material.
Owner:QORVO INT PTE LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com