Patents
Literature
101 results about "Common collector" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In electronics, a common collector amplifier (also known as an emitter follower) is one of three basic single-stage bipolar junction transistor (BJT) amplifier topologies, typically used as a voltage buffer.
Resistor triggered electrostatic discharge protection
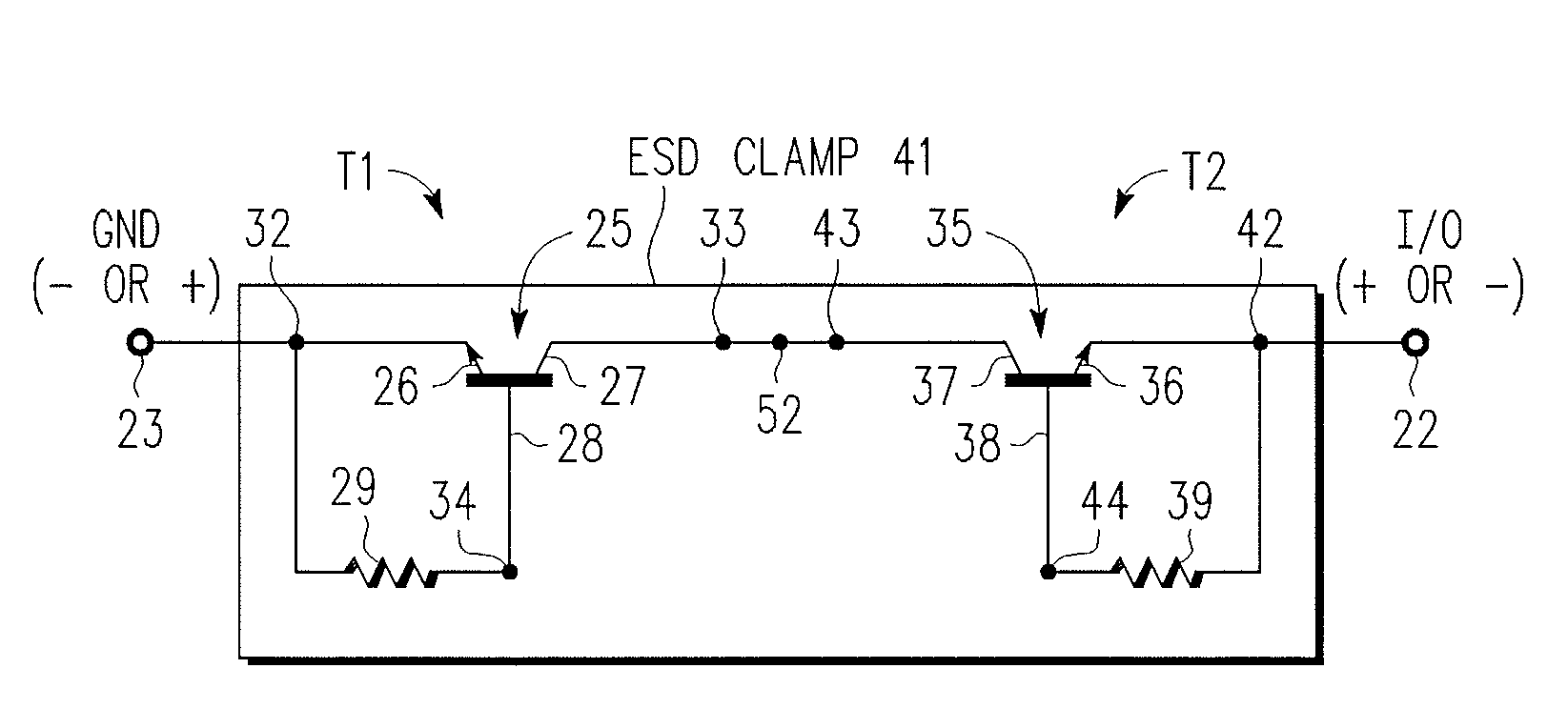
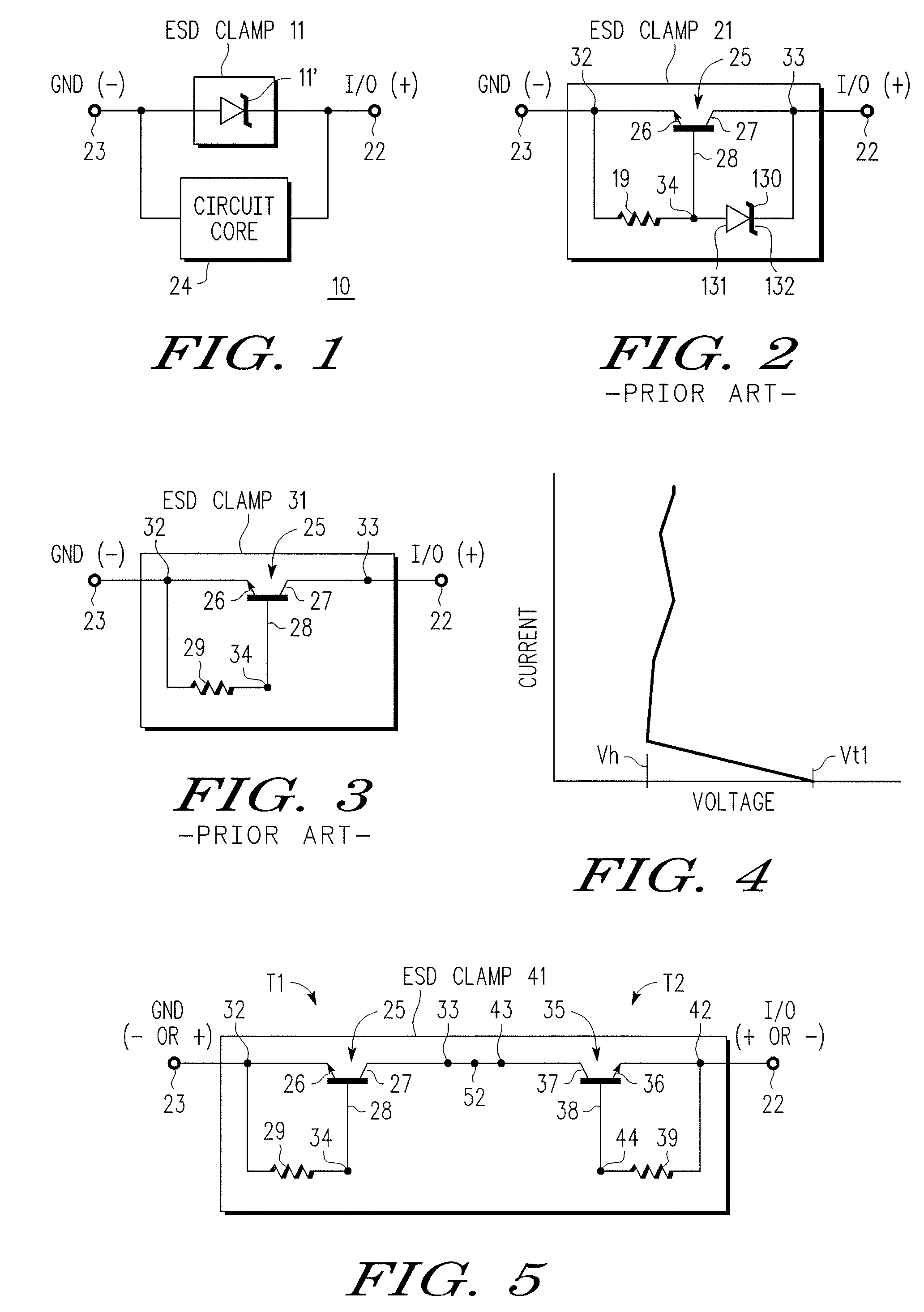
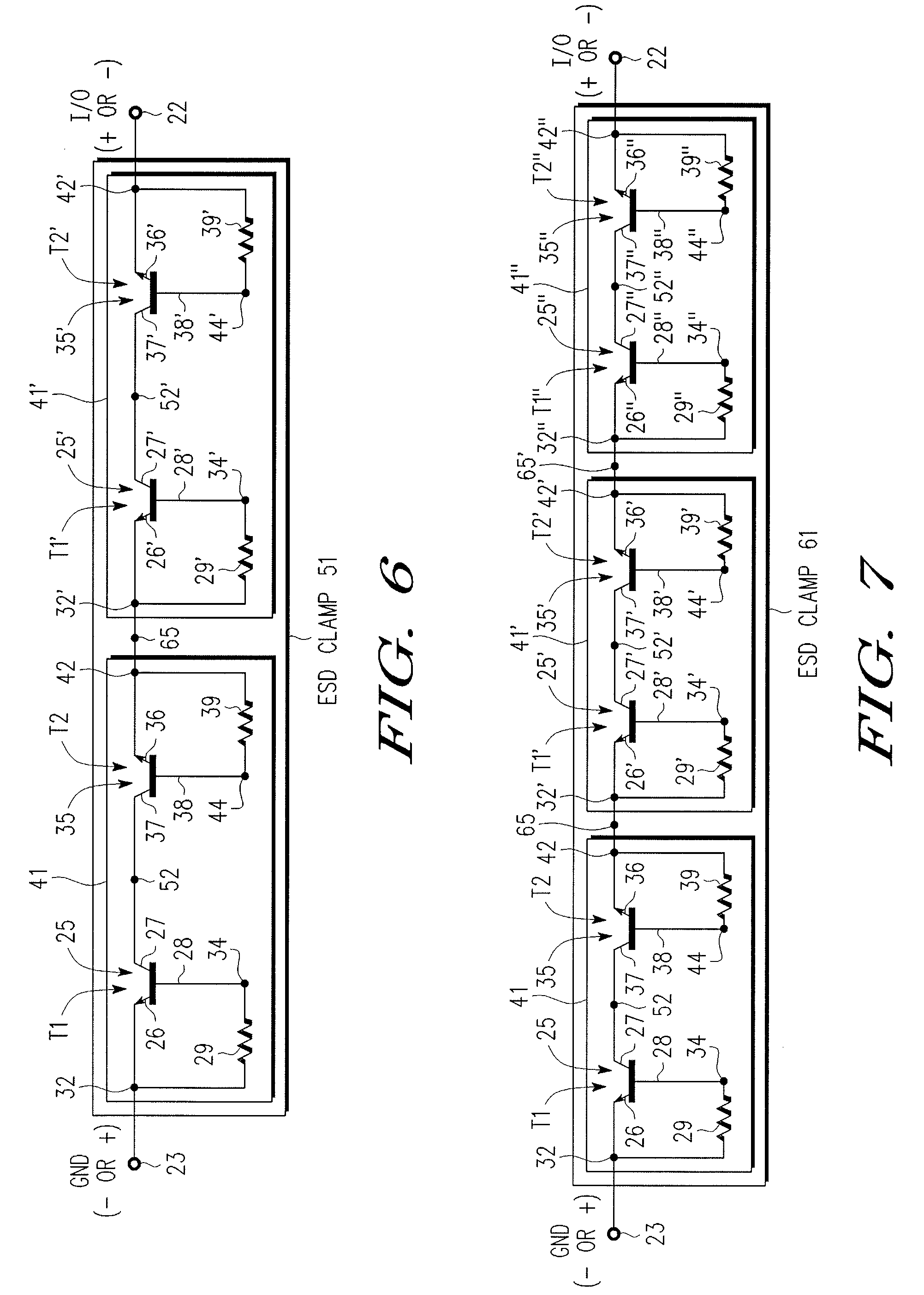
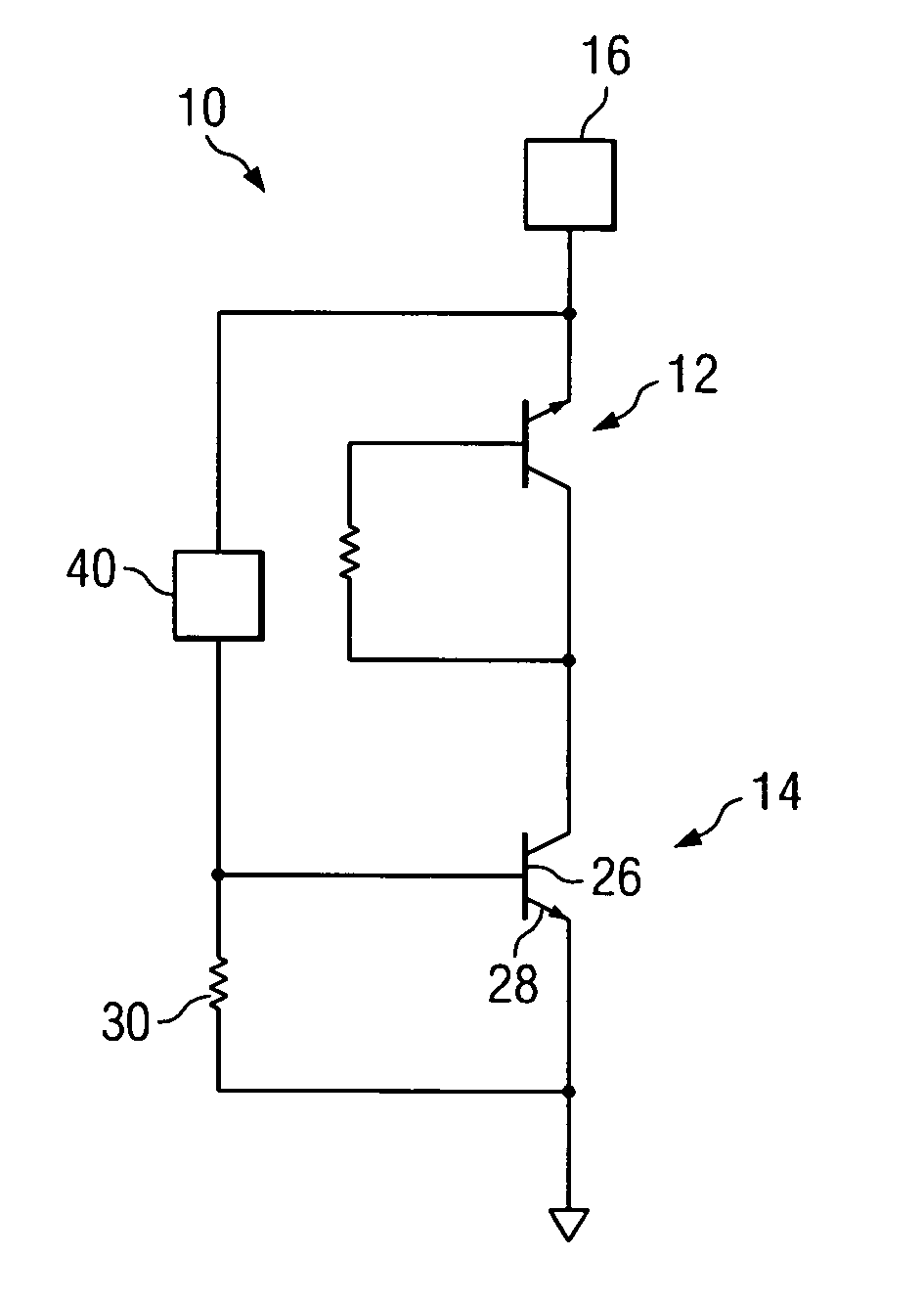
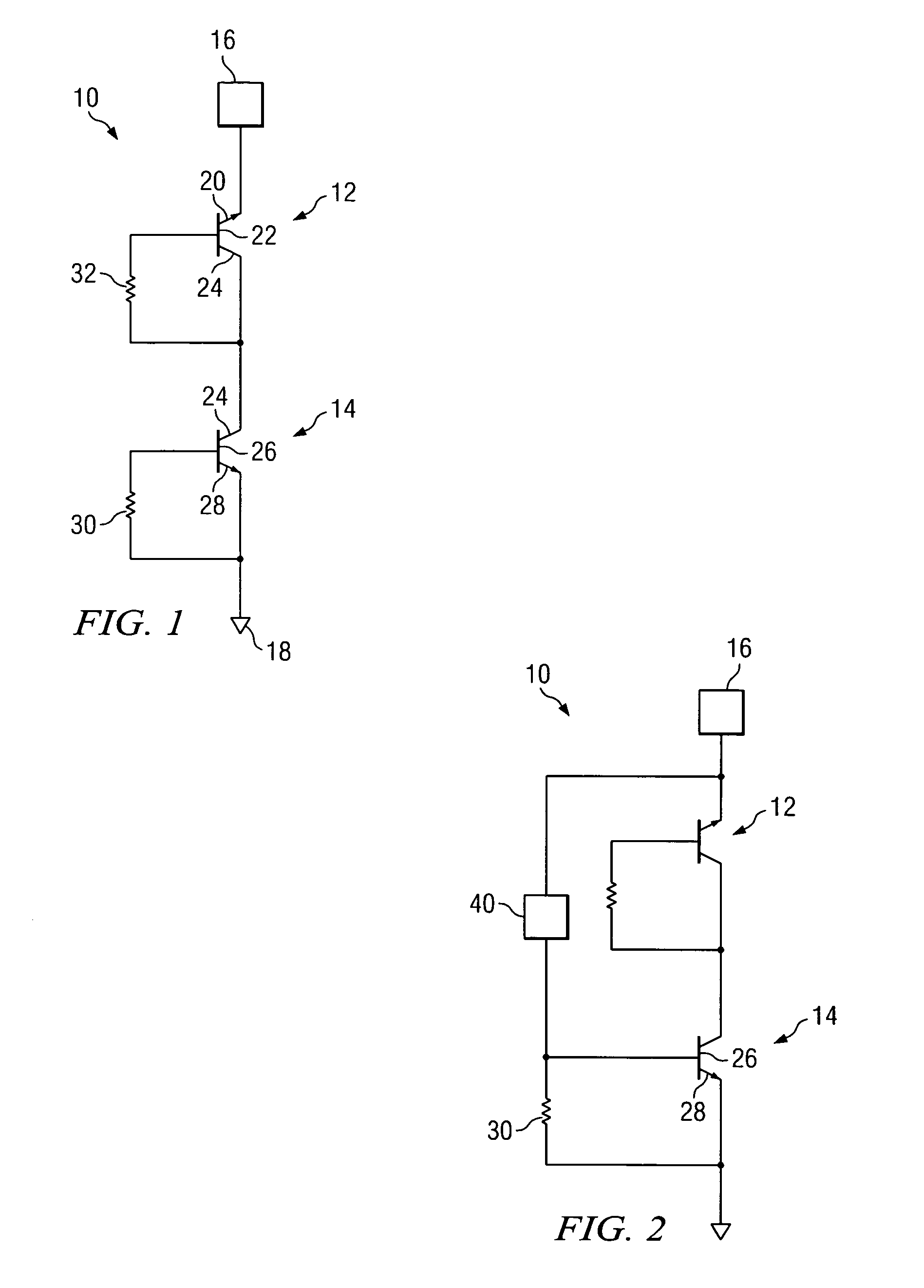
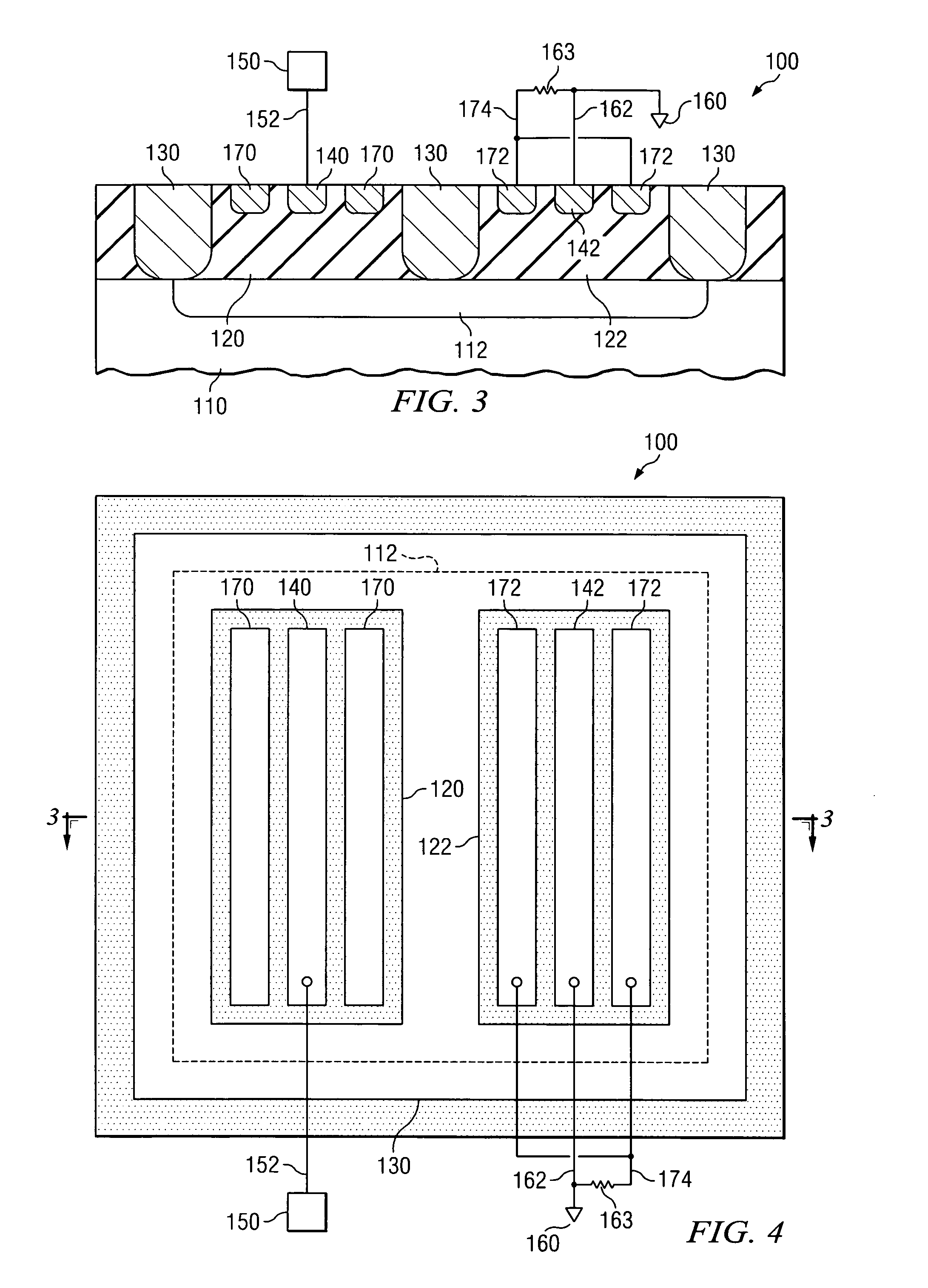
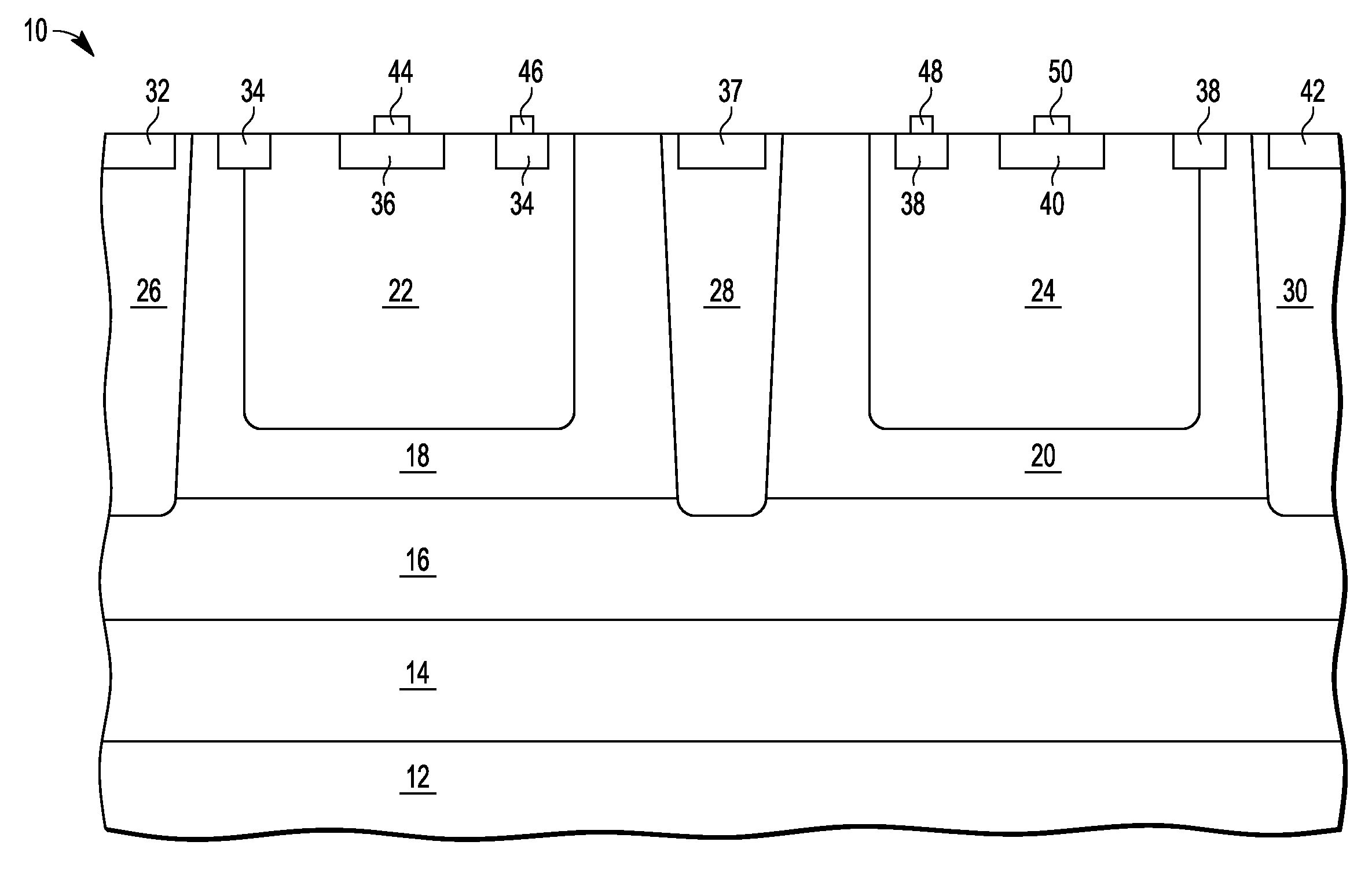
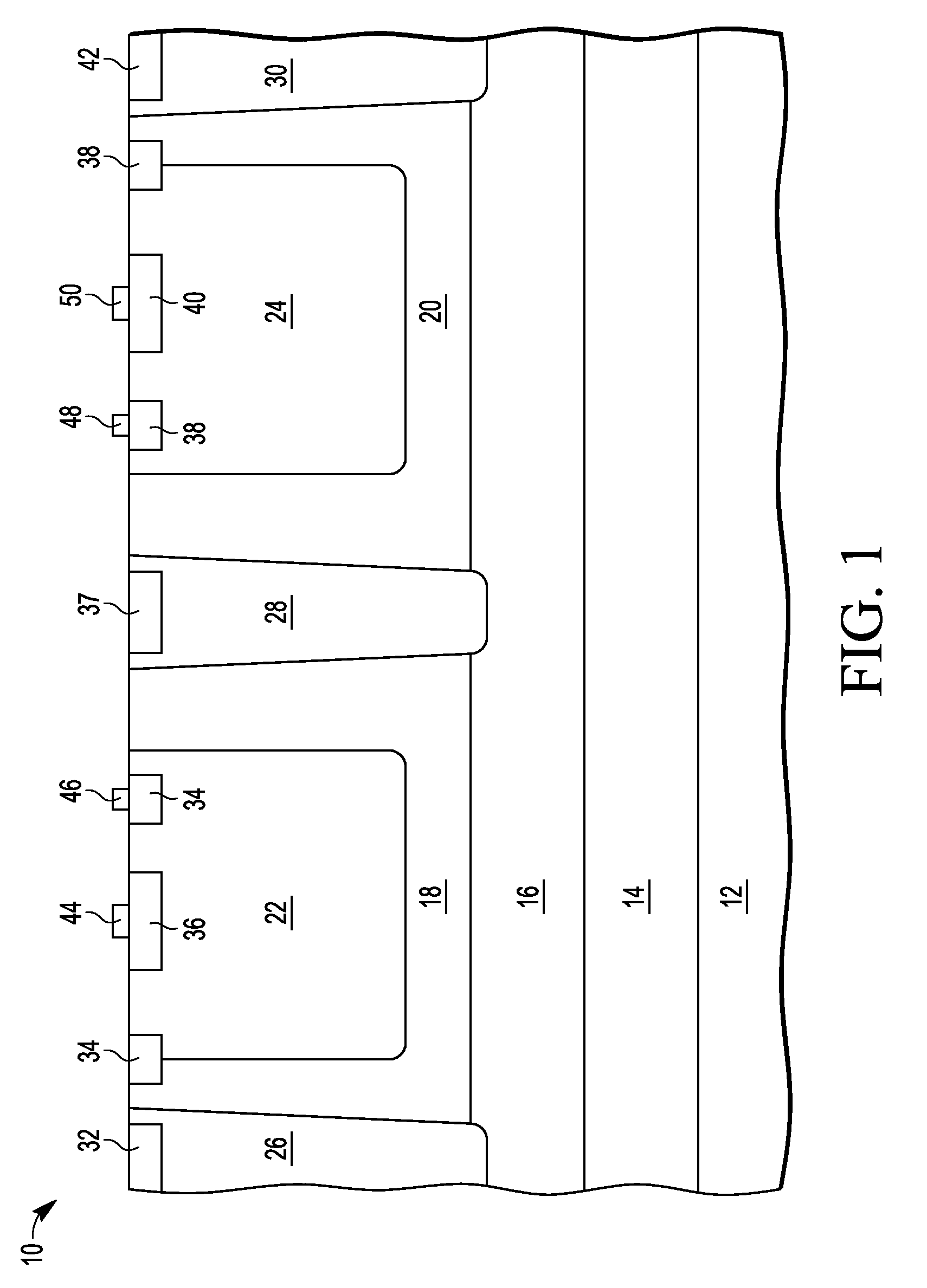
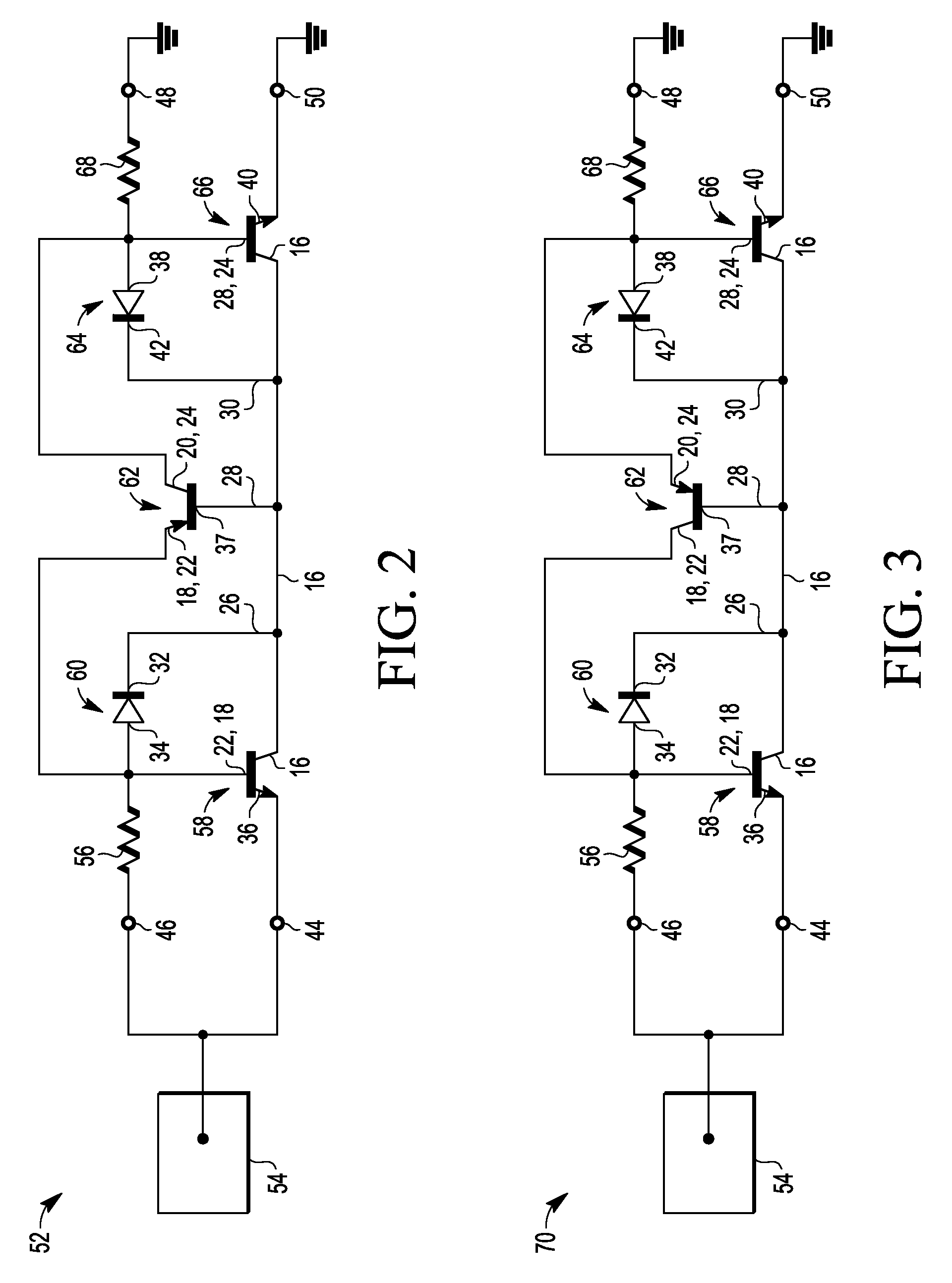
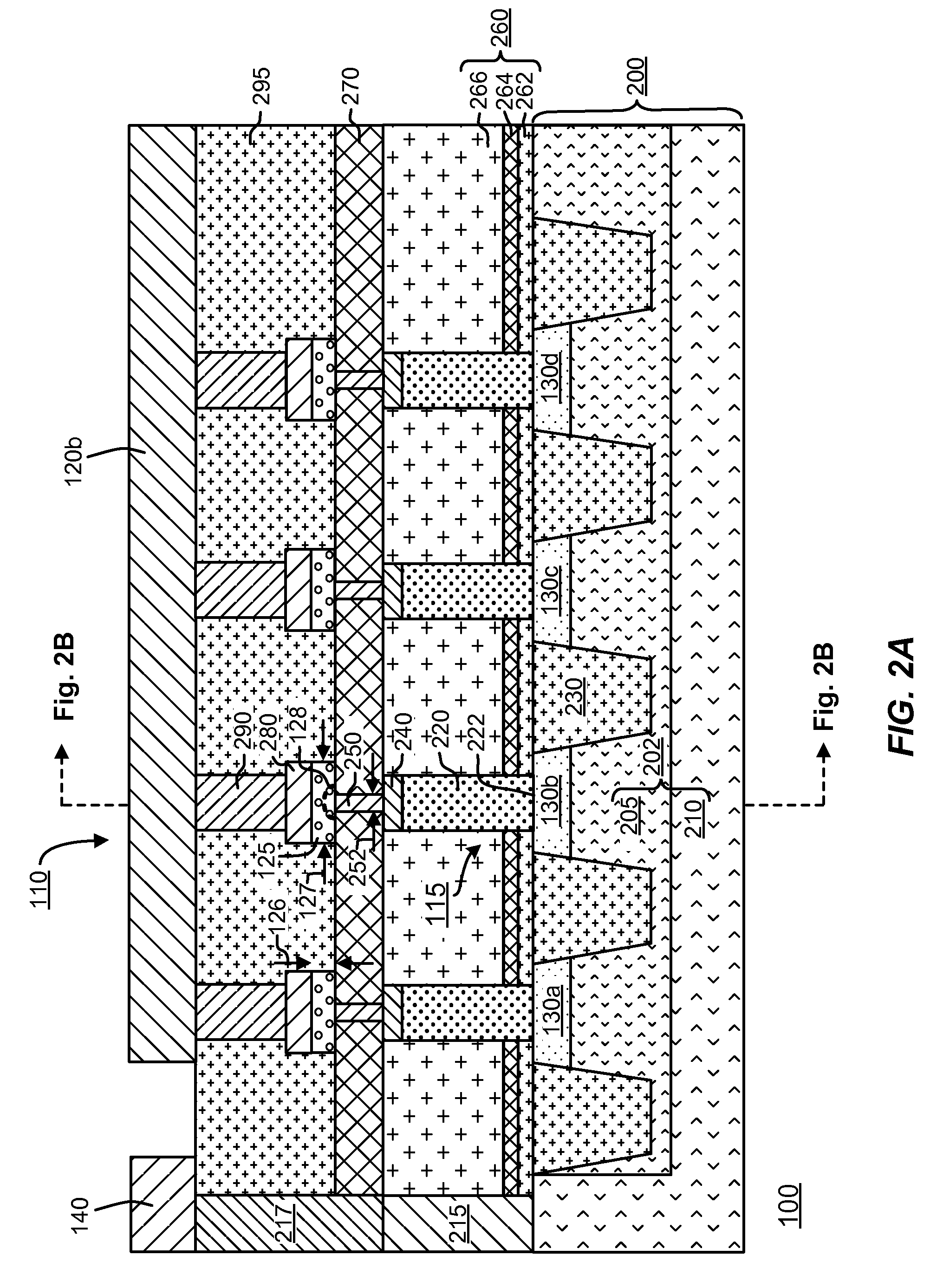
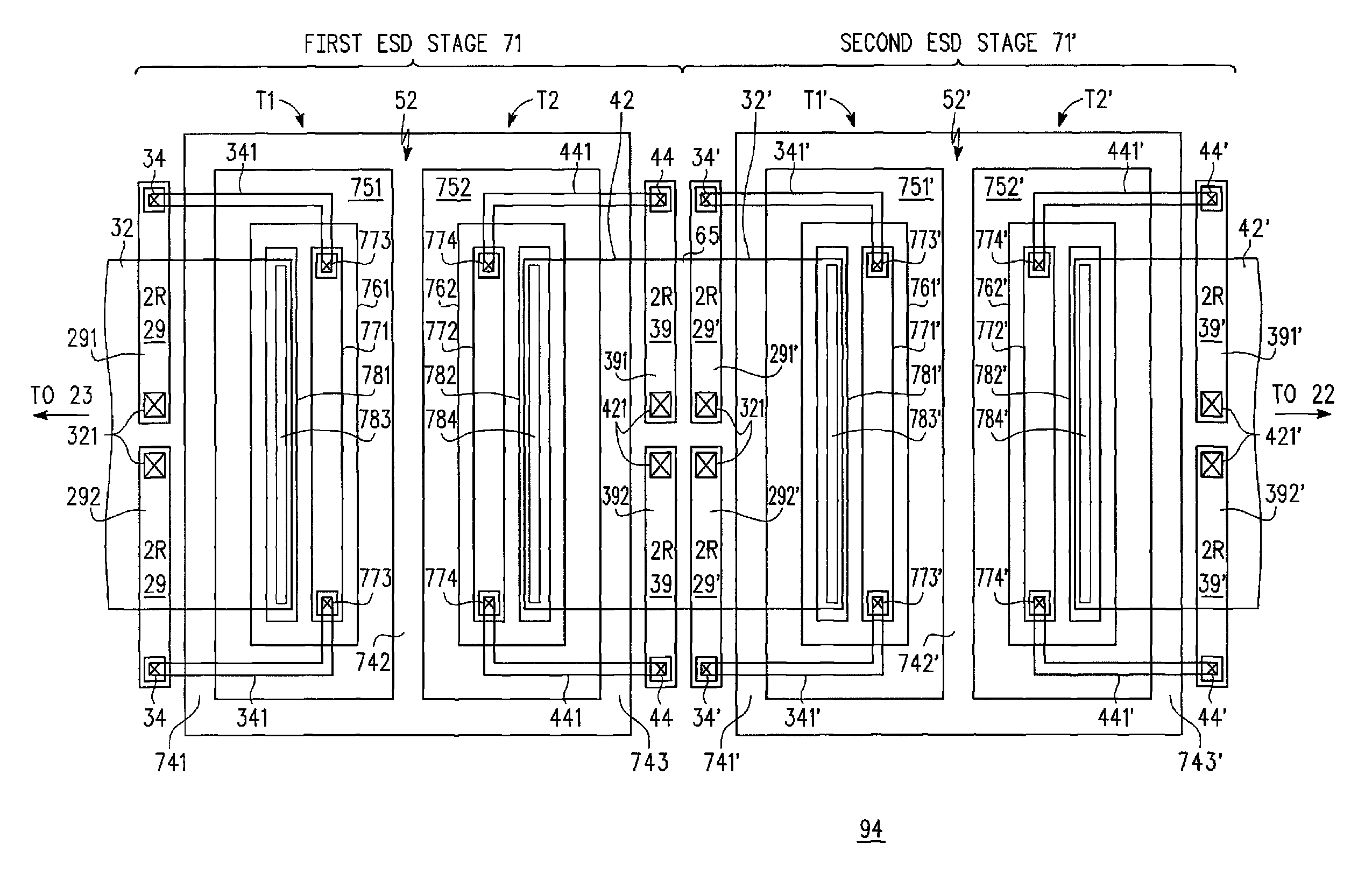
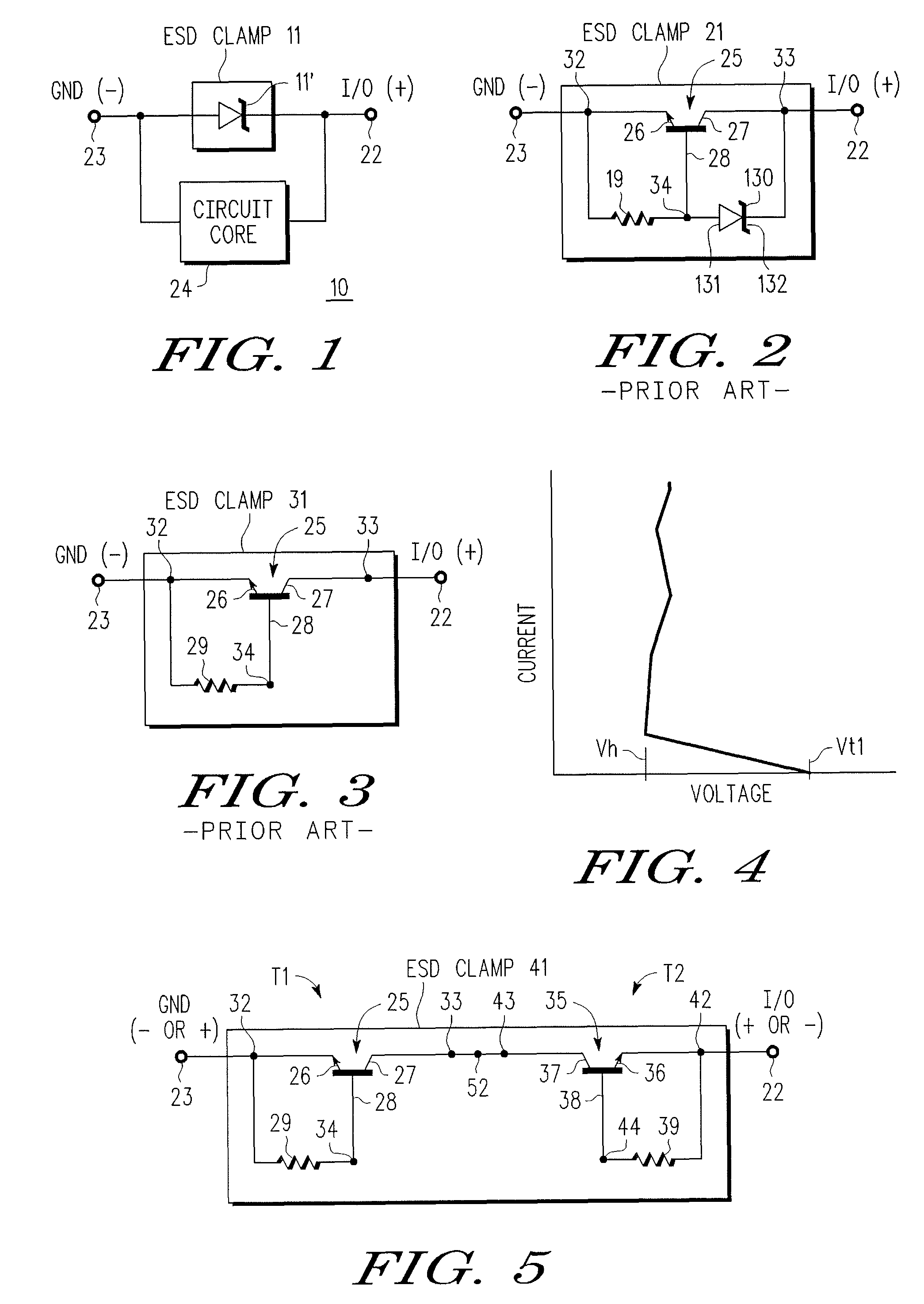
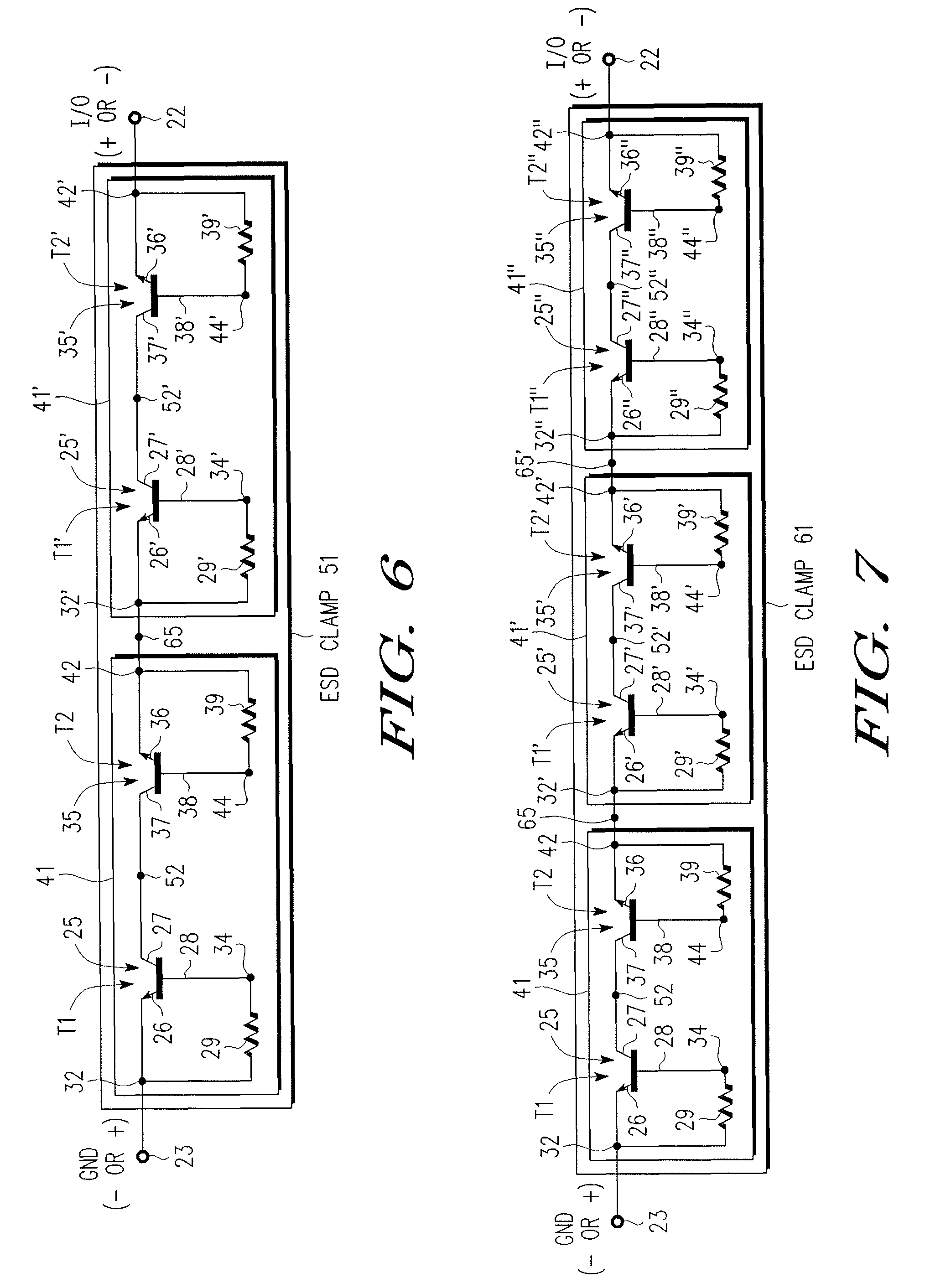
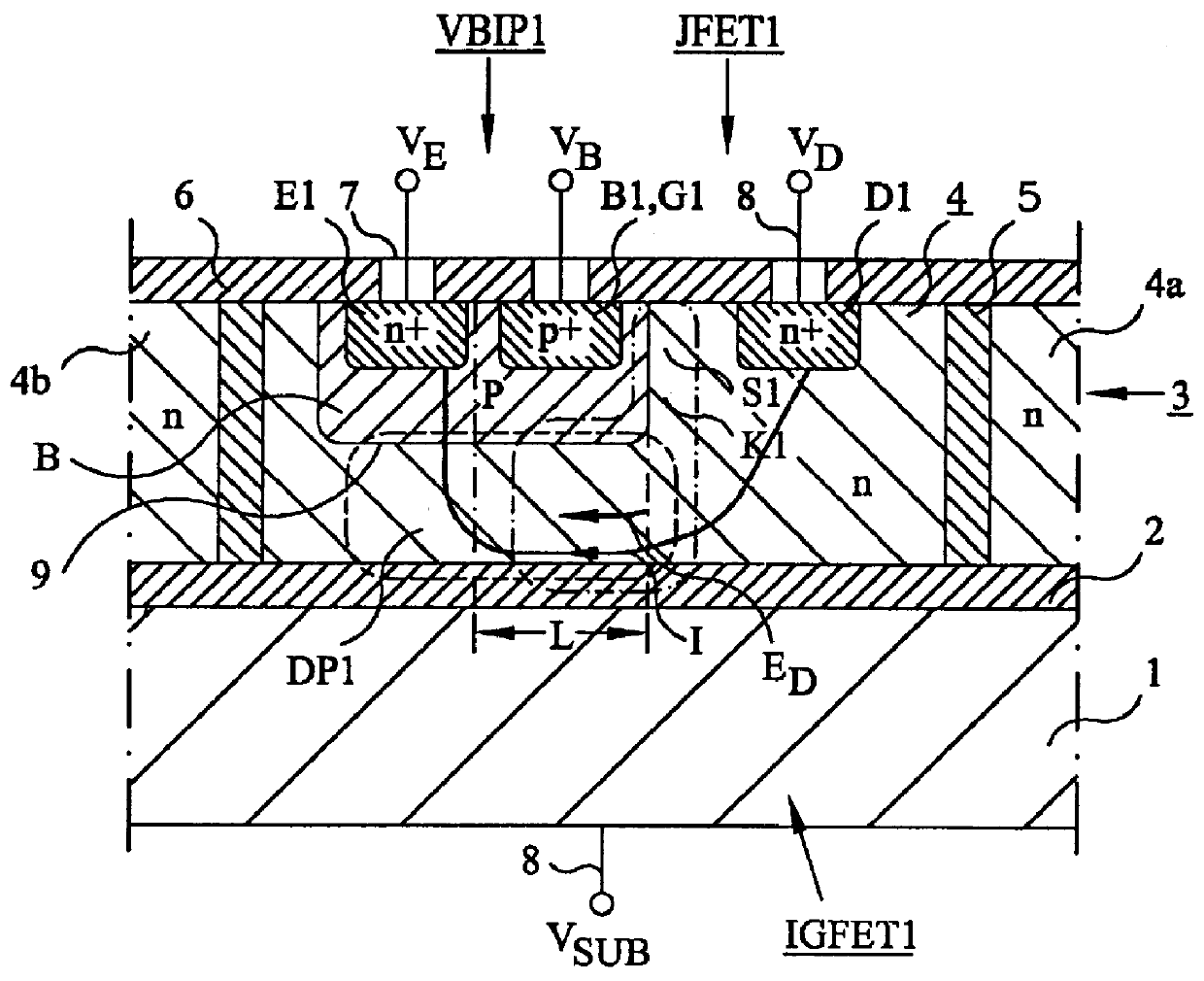
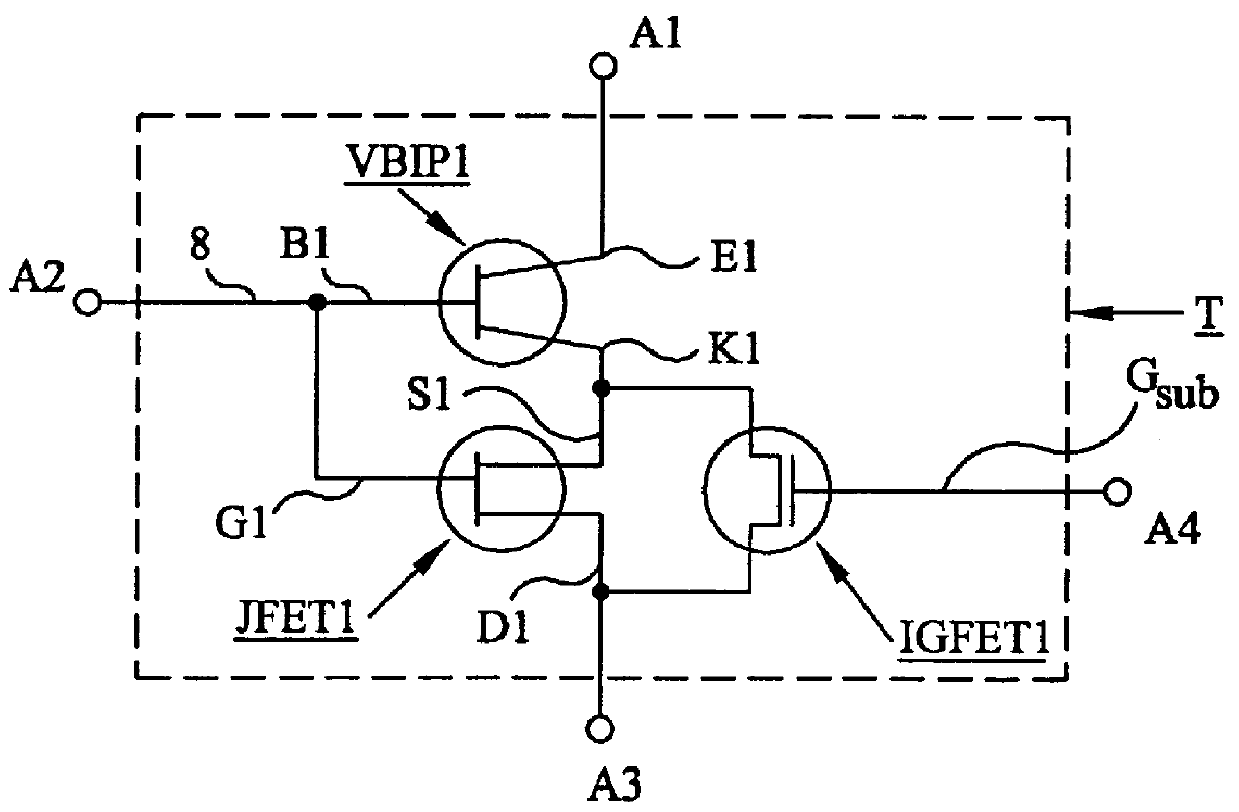
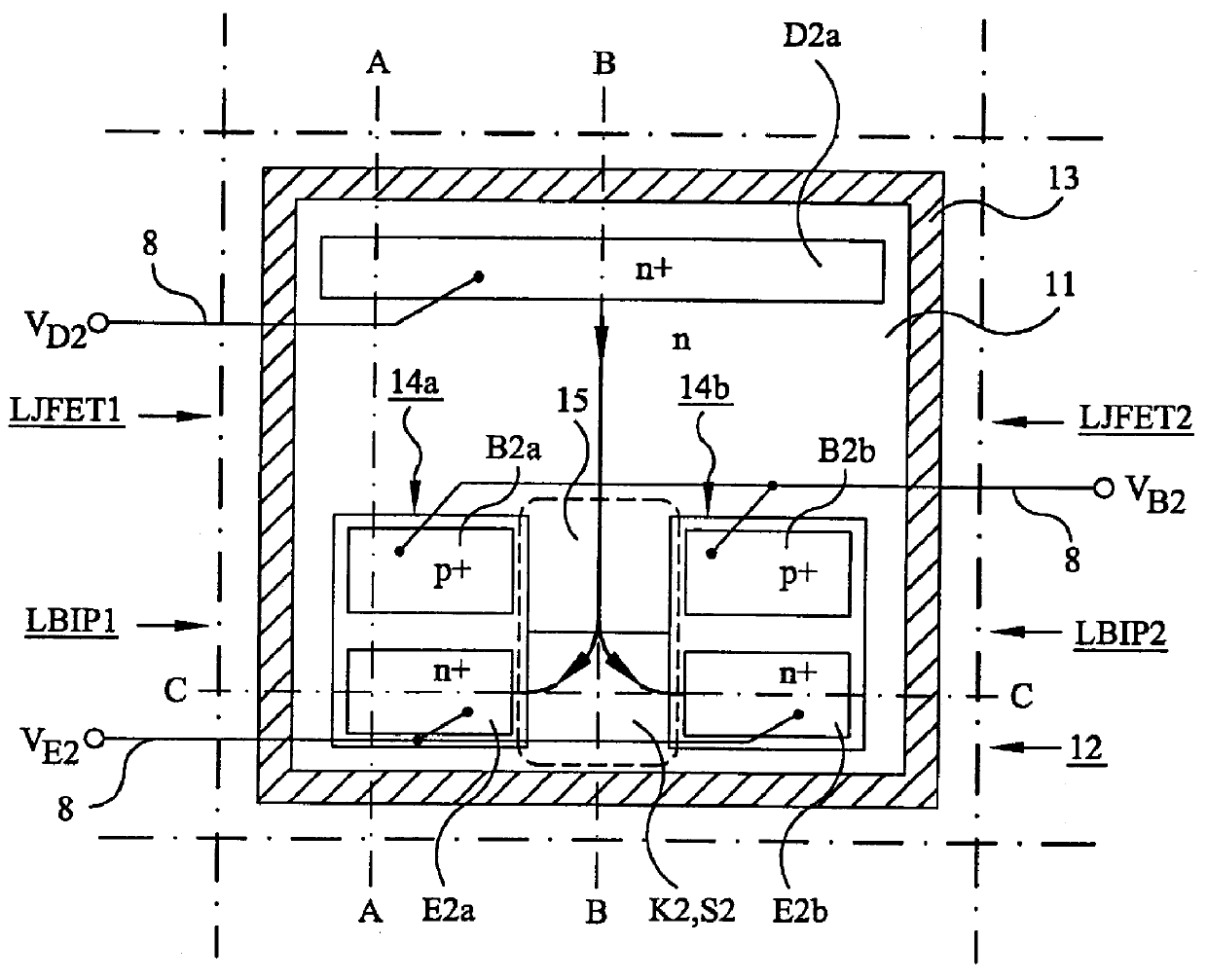
An electrostatic discharge (ESD) protection device (41, 51, 61, 71, 81) coupled across input-output (I / O) (22) and common (23) terminals of a core circuit (24) that it is intended to protect from ESD events, comprises, one or more serially coupled resistor triggered ESD clamp stages (41, 41′, 41″; 71, 71′, 71″), each stage (41, 41+, 41″; 71, 71′, 71″) comprising first (T1, T1′, T1″, etc.) and second transistors (T2, T2′, T2′″ etc.) having a common collector (52, 52′, 52″) and first (26, 26′, 26″) and second (36, 36′, 36″) emitters providing terminals (32, 42; 32′, 42′; 32″, 42″) of each clamp stage (41, 41′, 41″; 71, 71′, 71. A first emitter (25) of the first stage (41, 71) couples to the common terminal (23) and a second emitter (42″) of the last stage (41″, 71′) couples to the I / O terminals (22). Zener diode triggers are not used. Integrated external ESD trigger resistors (29, 29′, 29″; 39, 39′, 39″) (e.g., of poly SC) are coupled between the base (28, 28′, 28″; 38, 38′, 38″) and emitter (26, 26′, 26″; 36, 36′, 36″) of each transistor (T1, T1′, T1″; T2, T2′, T2″). Different resistor values (e.g., ˜0.5 k to 150 k Ohms) give different ESD trigger voltages. Cascading the clamp stages (41, 41′, 41″; 71, 71′) gives even higher trigger voltages. The ESD trigger resistances (29, 29′, 29″; 39, 39′, 39″) are desirably located outside the common collector-isolation wall (741, 742, 743; 741′, 742′, 743″) surrounding the transistors (T1, T1′, T1″; T2, T2′, T2″).
Owner:NXP USA INC
ESD protection for integrated circuits
An ESD protection device includes two bipolar npn transistors that are coupled in series for use in clamping applications. The emitter of the first bipolar transistor can be coupled to a protected node and the emitter of the second bipolar transistor can be coupled to a grounded node. The first bipolar transistor and the second bipolar transistor can share a common collector.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
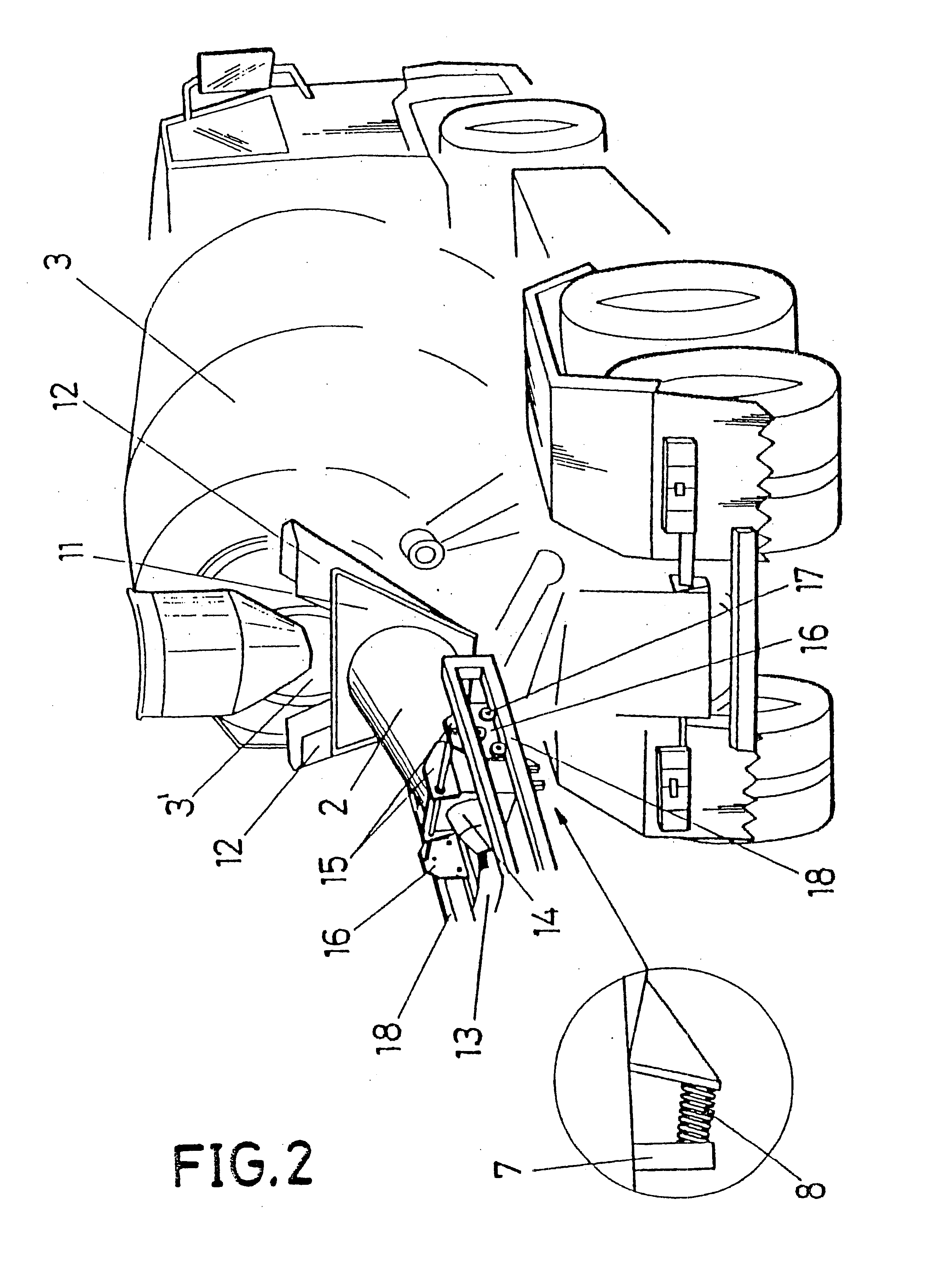
Device for capturing dust in the loading of concrete mixer trucks
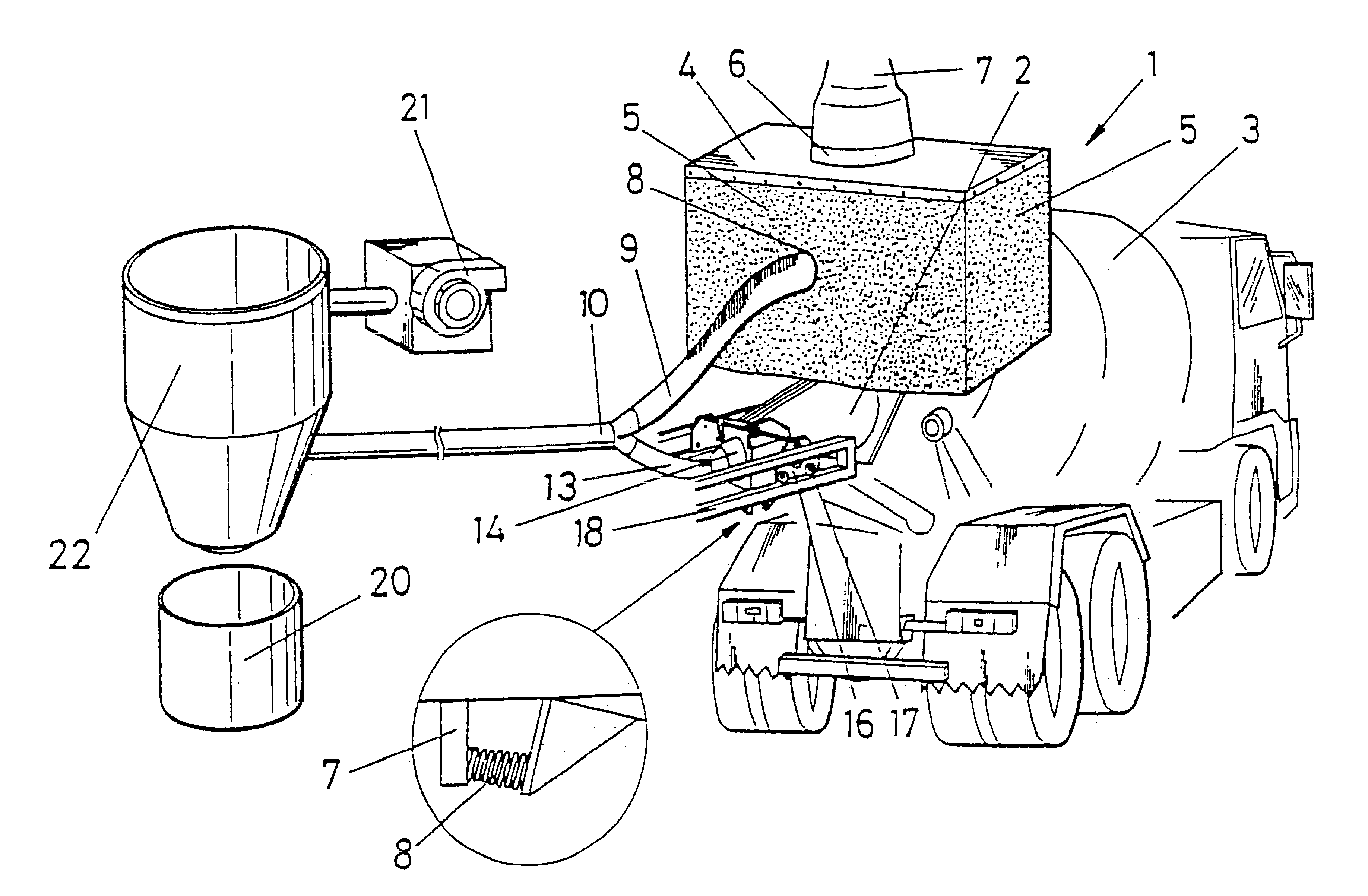
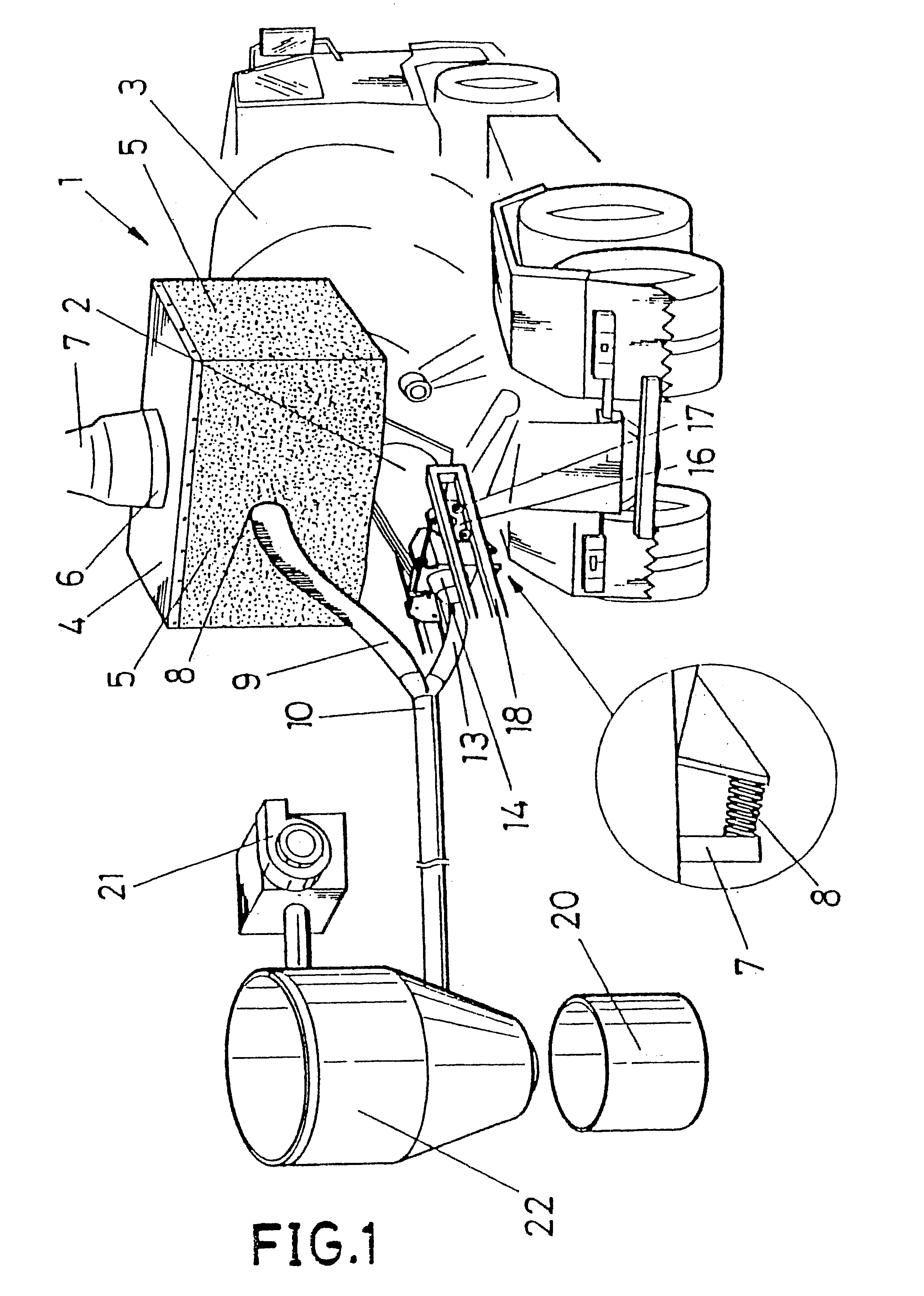
The device comprises a container (1) with a mouth (4') to which the end of the conduit through which cement falls into the drum (3) of a concrete mixer truck is coupled, said container being fixed and having a trap door (6) for adapting the back part of said drum (3) so that the dust originating from the fall of the cement remains inside sad container (1). Part of the dust goes out through the conduit (9) to a common collector (10) while the other part is suctioned in through a suctioning head (2) formed by a truncated cone-shaped body, the biggest base thereof being coupled to the mouth (3') for loading the drum (3) and the smallest base leading to a conduit (13) that ends in the common collector (10). The dust is suctioned in from said collector and passed through a container or hopper (22) with filters with the purpose of cleaning and final reception in a tank or common collector (20).
Owner:ESPINA FRUTOS JUAN JOSE
Negative plate for lithium slurry battery
ActiveCN107681115AReduces the possibility of short circuitsIncrease energy densitySecondary cellsNegative electrodesHigh rateSlurry
The invention provides a negative plate for a lithium slurry battery. The negative plate comprises an insulated sealing frame, a lithium-containing metal body and an intercalated lithium collector structure layer, wherein the intercalated lithium collector structure layer, the lithium-containing metal body and another intercalated lithium collector structure layer form a sandwich composite structure; the insulated sealing frame seals the surrounding margins of the sandwich composite structure; and the material of the intercalated lithium collector structure layer contains the lithium intercalated material which can intercalate lithium in the charge and discharge process of the lithium slurry battery. The intercalated lithium collector structure layer in the negative plate can play the roleof intercalating lithium during charging, and avoid the deposition of lithium on the surface of the lithium-containing metal body to form lithium dendrites, thereby improving the safety of the battery. Besides, the lithium-containing metal body can also be used as a lithium source to effectively supplement the consumption on positive electrode lithium of the side reaction in the process of negative SEI membrane formation and battery cycle. In addition, a common collector of the lithium-containing metal body and the intercalated lithium collector structure layer makes the current collection effect uniform, and avoids the occurrence of heating and so on caused by high-rate charge and discharge.
Owner:南京竞予能源有限公司
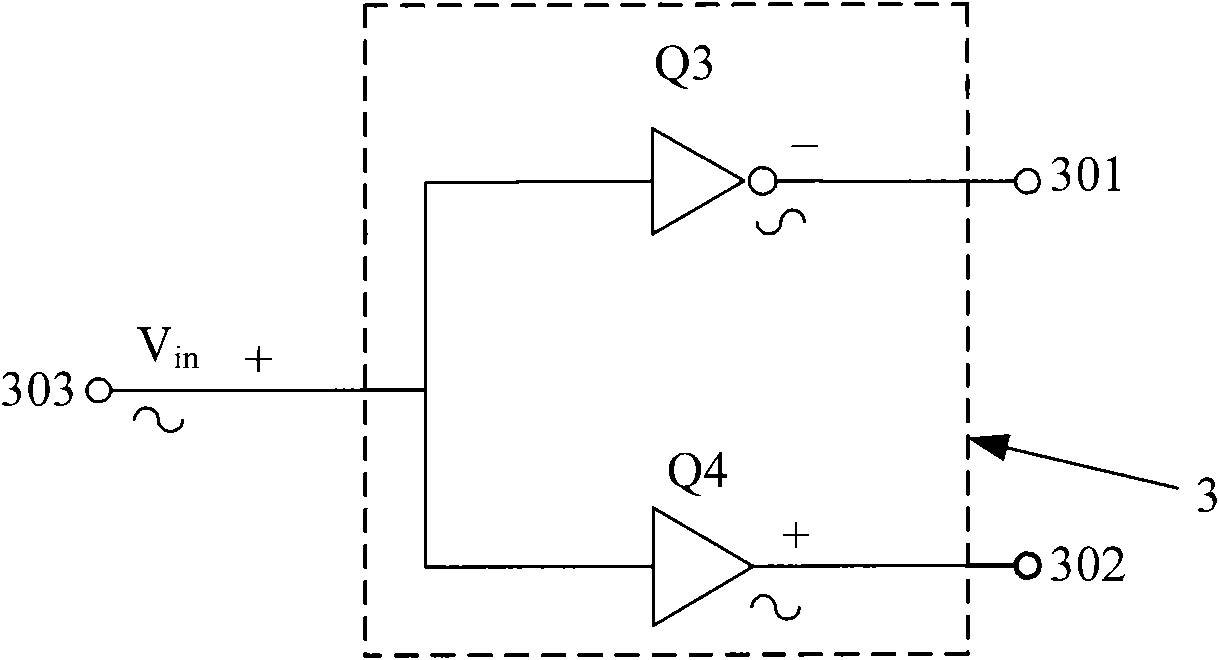
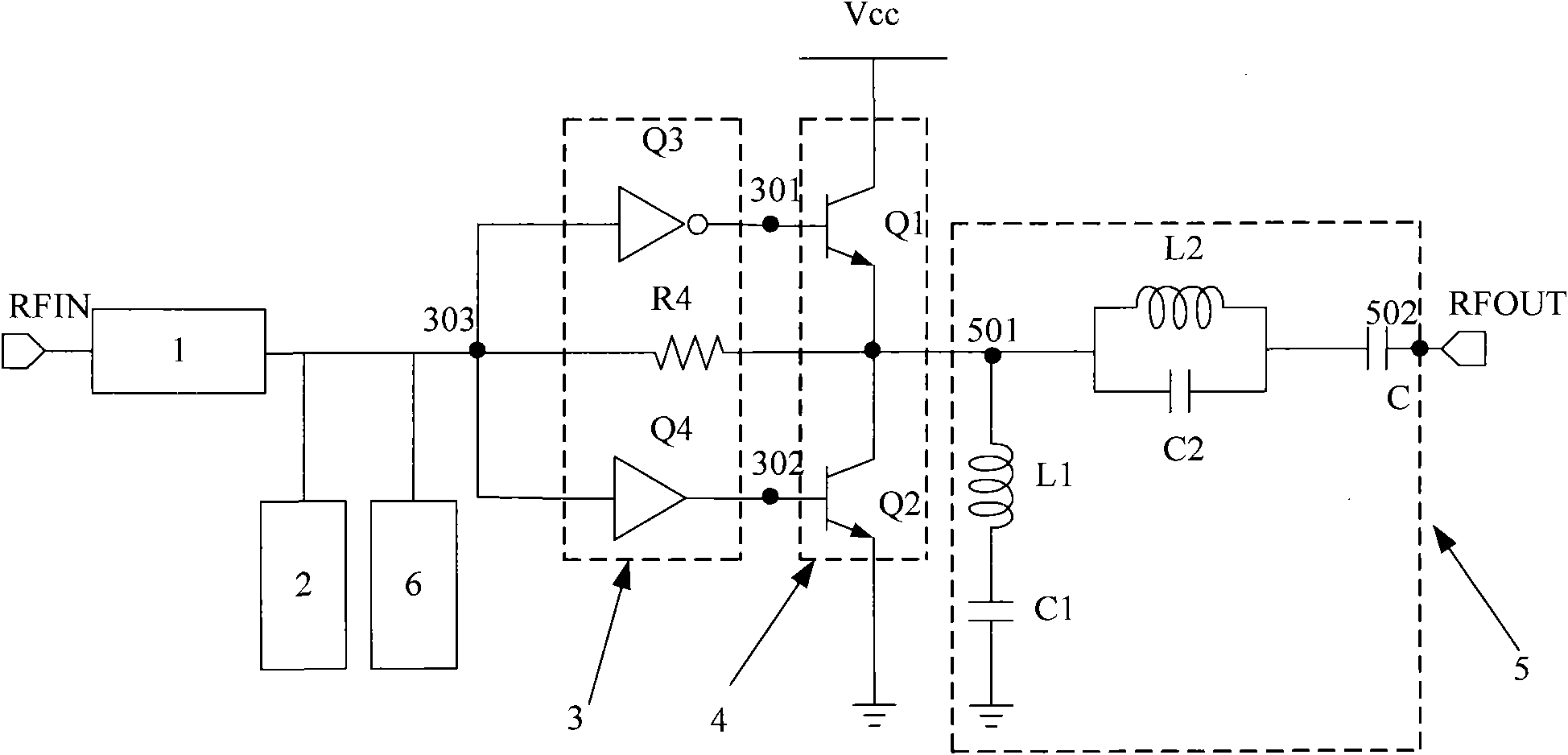
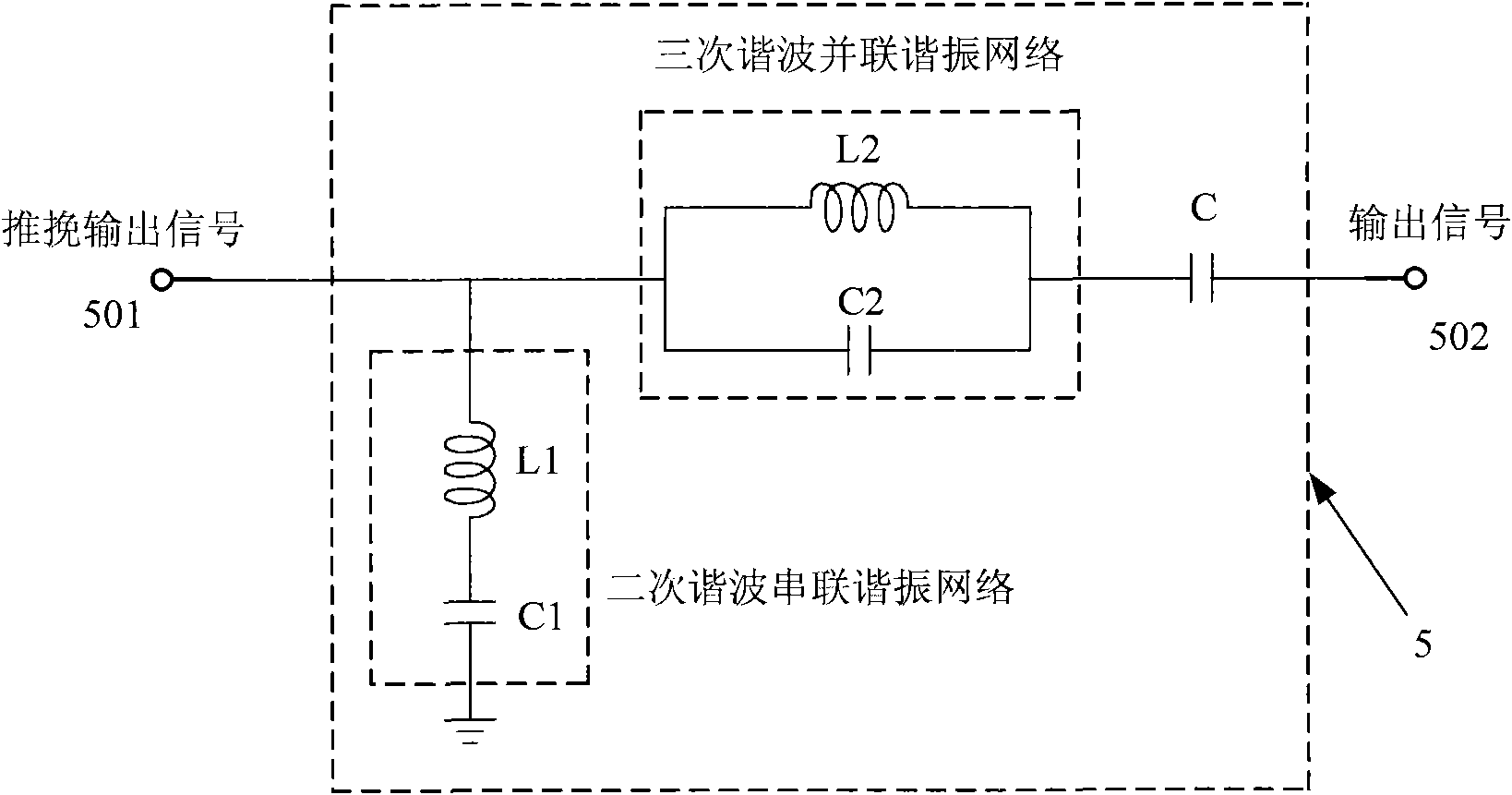
Push-pull radio-frequency power amplifier with improved linearity and efficiency
InactiveCN101888213ARealize the structureImprove power added efficiencyAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionHigh frequency amplifiersCapacitanceCommon emitter
The invention discloses a push-pull radio-frequency power amplifier with improved linearity and efficiency, comprising an input matching network, an output matching network and a power amplification circuit, wherein the power amplification circuit comprises a first-stage amplification circuit and a second-stage amplification circuit, the first-stage amplification circuit is connected with the input matching network, the second-stage amplification circuit is connected between the first-stage amplification circuit and the output matching network, and the second-stage amplification circuit is an NPN-NPN push-pull amplification circuit composed of a second common collector amplifying tube and a second common-emitter amplifying tube. The output matching network is an output filter matching network which comprises a secondary harmonic series resonance network, a third harmonic series resonance network and a stopping condenser, wherein the secondary harmonic series resonance network is connected between the output end of the second-stage amplification circuit and the ground, the third harmonic series resonance network is connected between the output end of the secondary harmonic series resonance network and the stopping condenser, and the stopping condenser is connected between the third harmonic series resonance network and the power amplifier. The invention improves the additional efficiency of the radio-frequency power amplifier and improves the linearity of the radio-frequency power amplifier.
Owner:SUZHOU INNOTION TECH
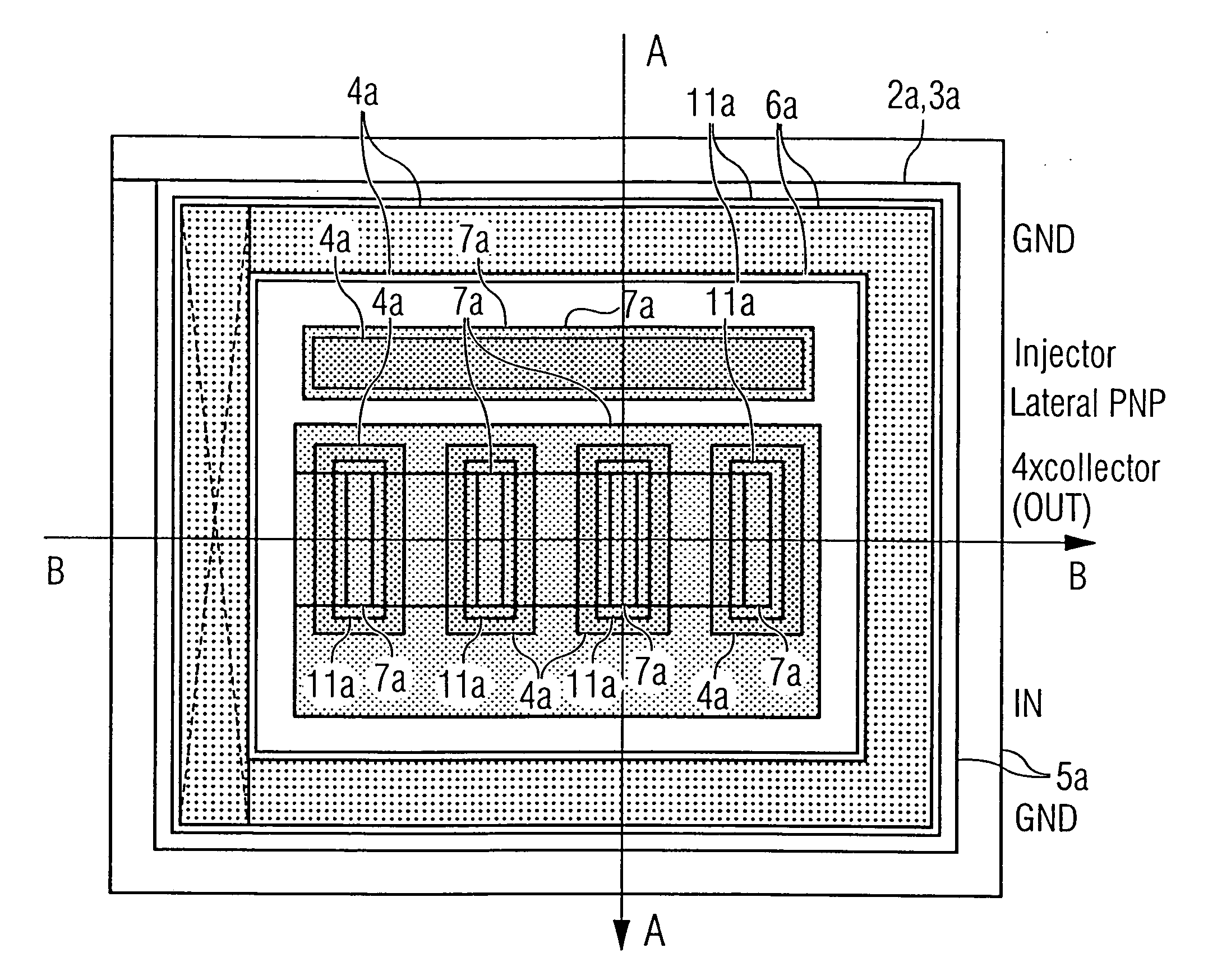
Method in the fabrication of an integrated injection logic circuit
InactiveUS20060105517A1High complexityExtend cycle timeSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCommon baseHemt circuits
A method in the fabrication of an I2L circuit comprises (i) forming a common base of a lateral bipolar transistor and emitter of a vertical bipolar multicollector transistor, a common collector of the lateral transistor and base of the vertical multicollector transistor, and an emitter of the lateral transistor in a substrate; (ii) forming, from a first deposited polycrystalline layer, a contact region for the common collector / base and a contact region for the emitter of the lateral transistor; (iii) forming an isolation structure for electric isolation of the polycrystalline contact region for the common collector / base; and (iv) forming, from a second deposited polycrystalline layer, a contact region for the common base / emitter and multiple collectors of the vertical multicollector transistor.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
IGBT module
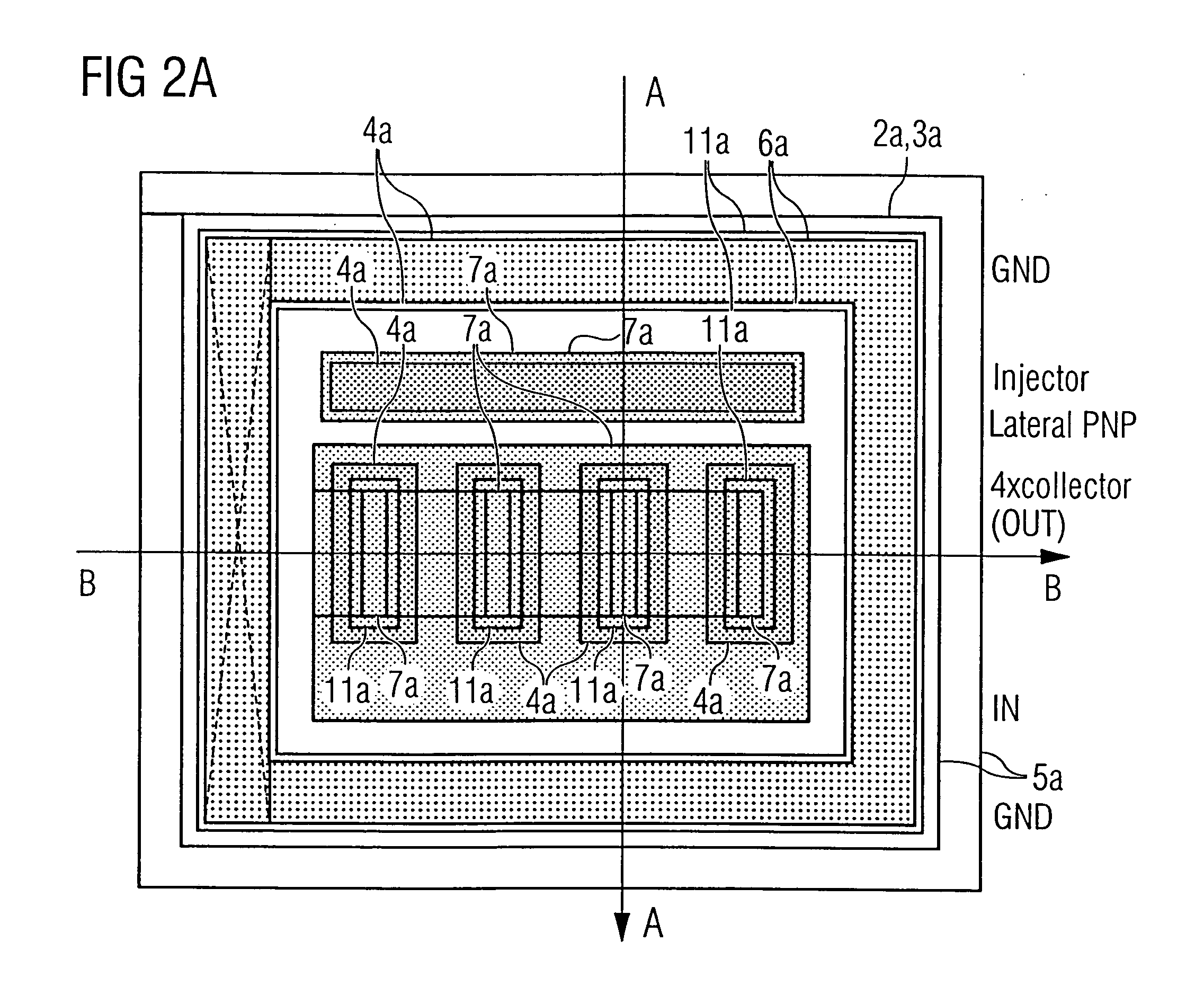
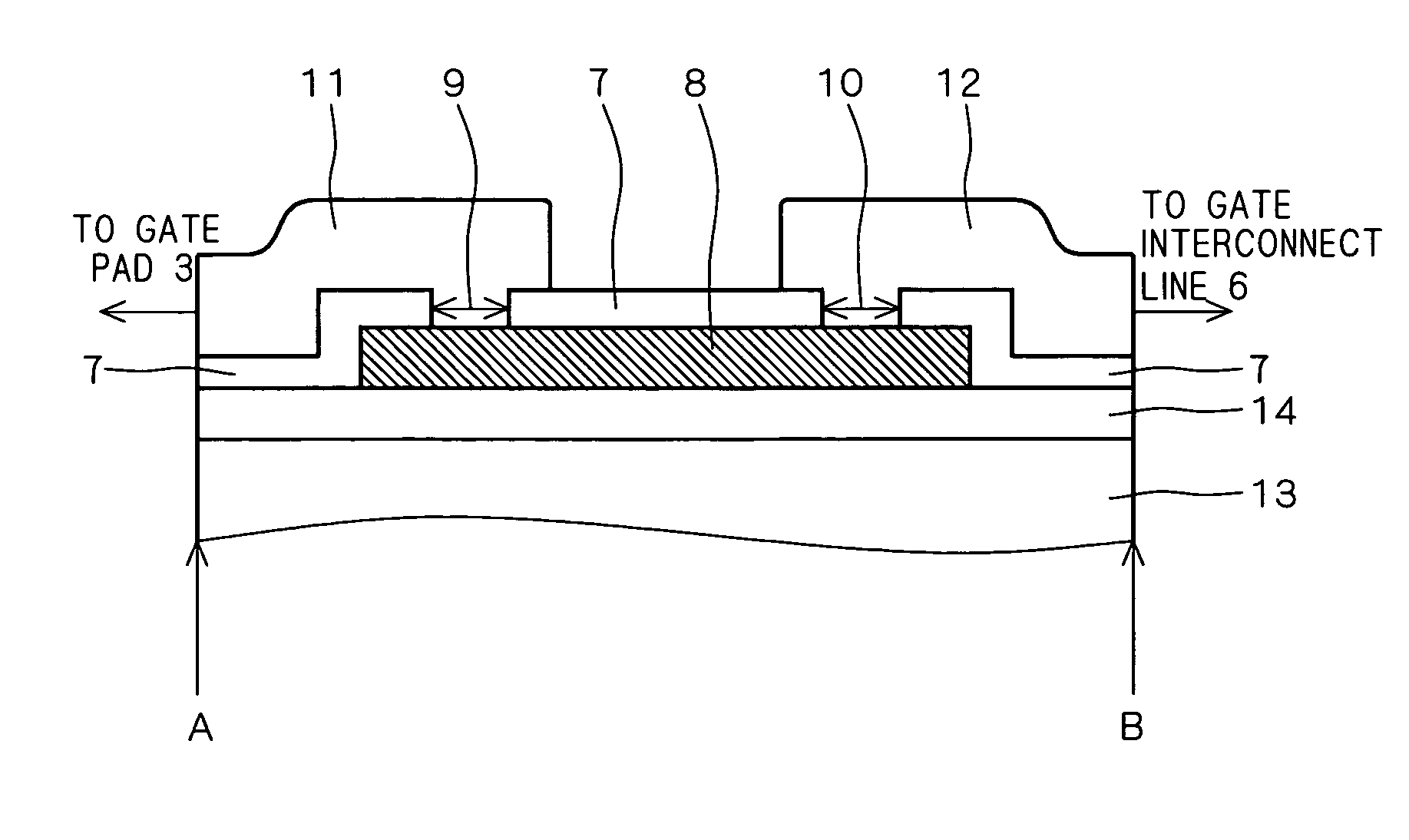
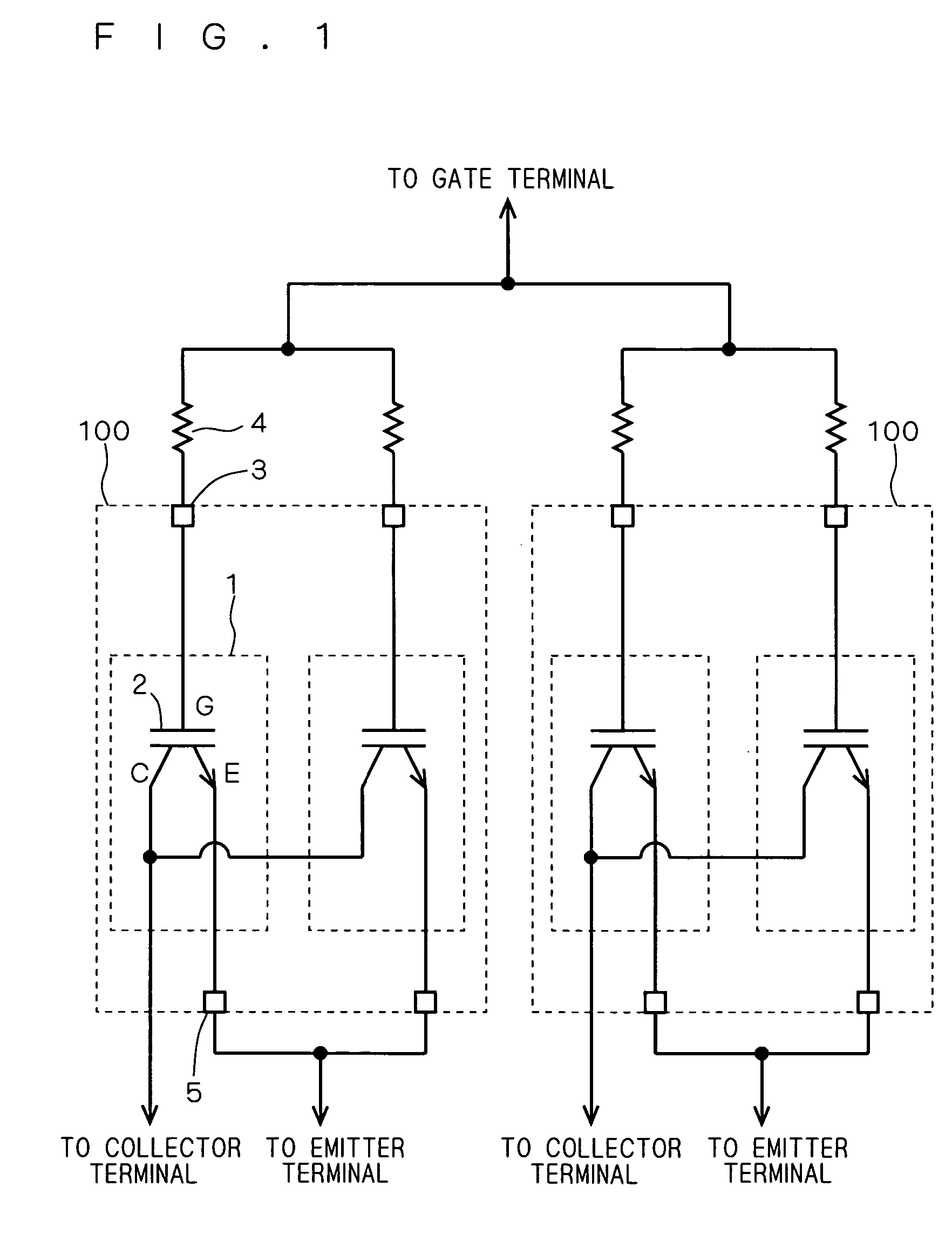
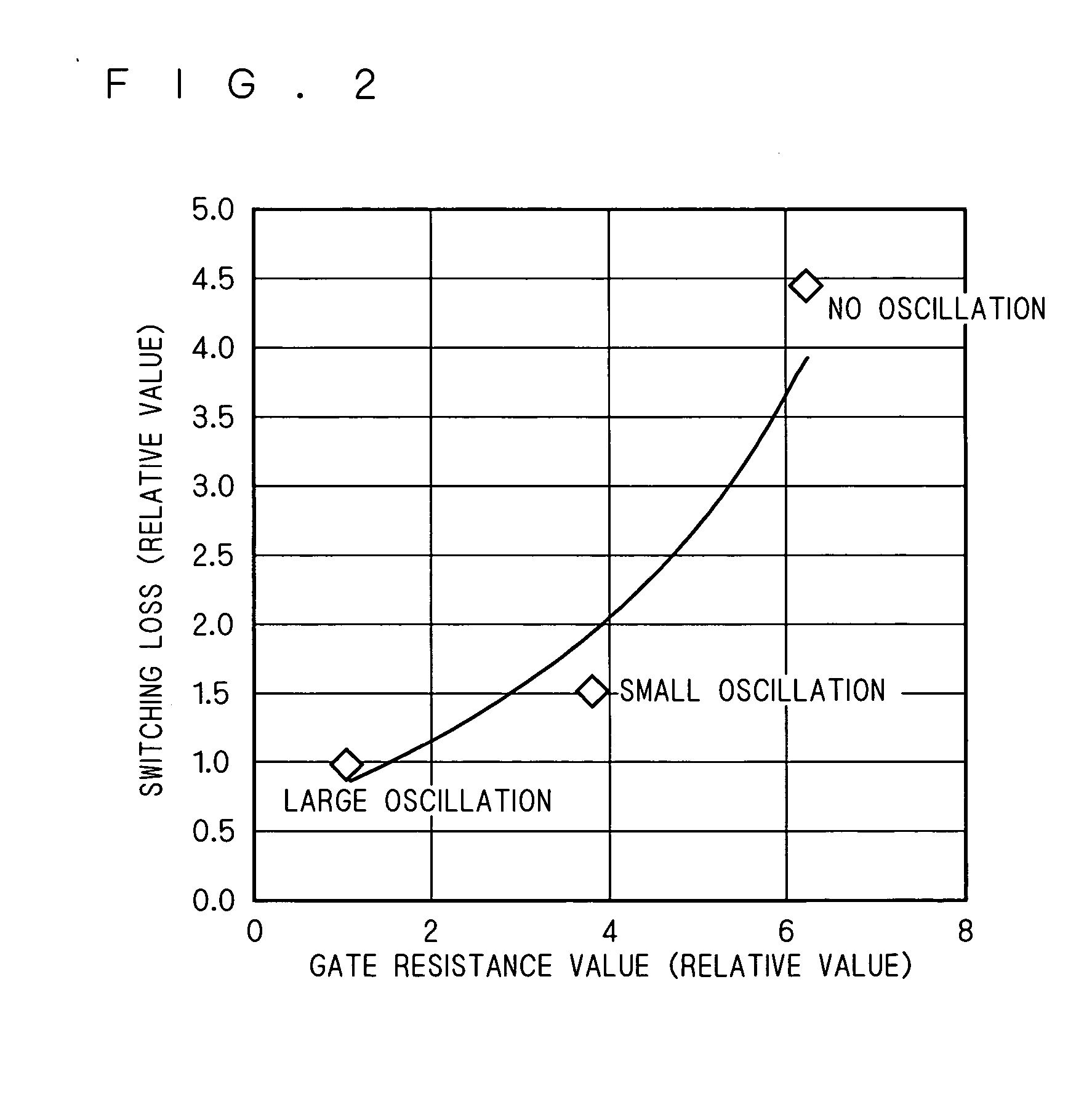
InactiveUS20050194660A1Suppressing gate voltage oscillationIncreased switching lossesTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsCommon emitterCommon collector
An IGBT module is configured with a plurality of IGBT cells connected to each other. The IGBT chips are each configured a plurality of unit cells connected to each other. The unit cells each include one IGBT element. Gate voltage is applied to the gate of the IGBT element from a common gate terminal through a gate pad and a gate resistor. Emitter voltage is applied to the emitter of the IGBT element from a common emitter terminal through an emitter pad. Collector voltage is applied to the collector of the IGBT element from a common collector terminal. The gate pad, gate transistor and emitter pad are provided for each of the unit cells. Thus obtained is an IGBT module capable of suppressing gate voltage oscillation without significantly increasing switching loss.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
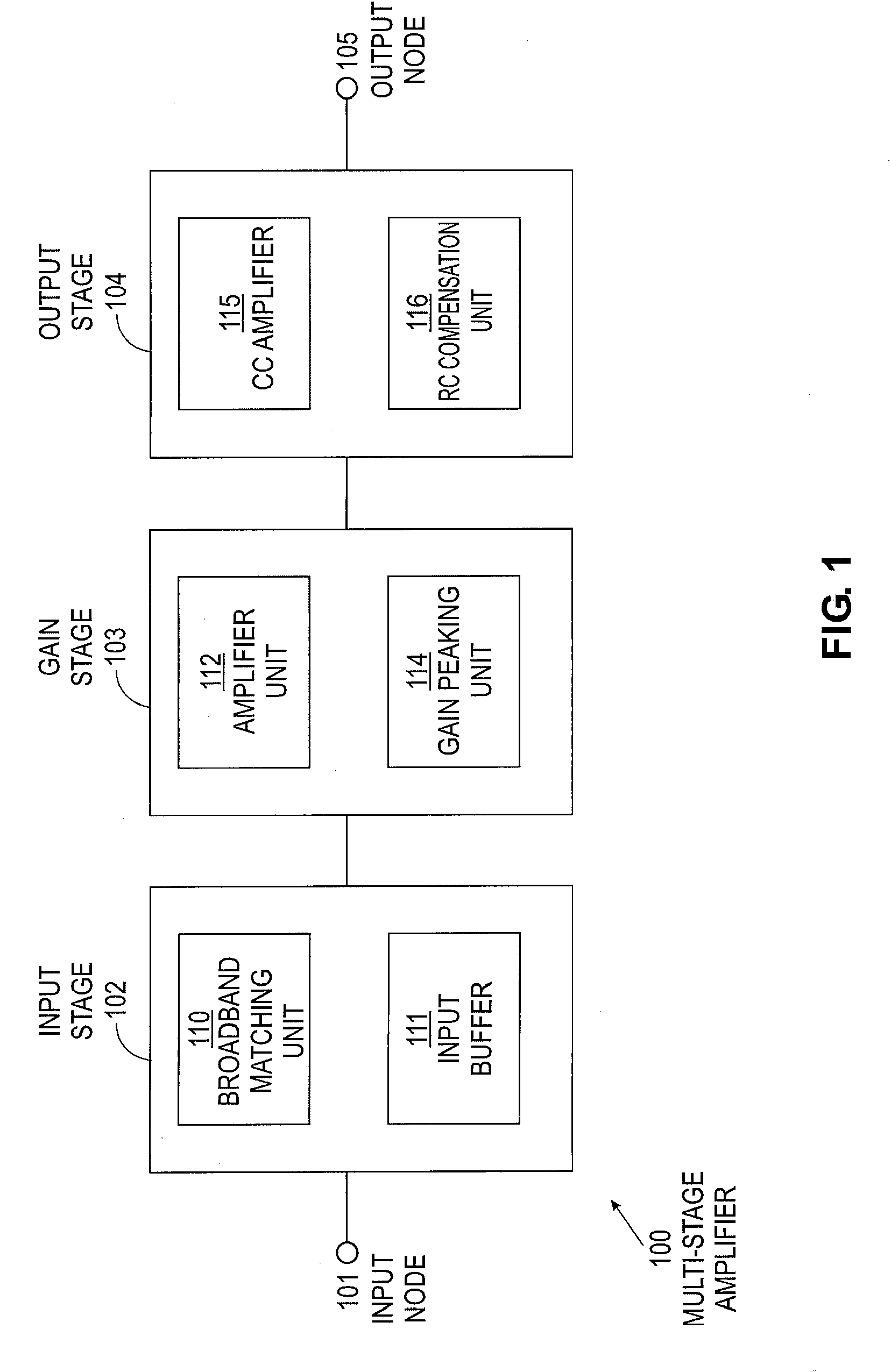
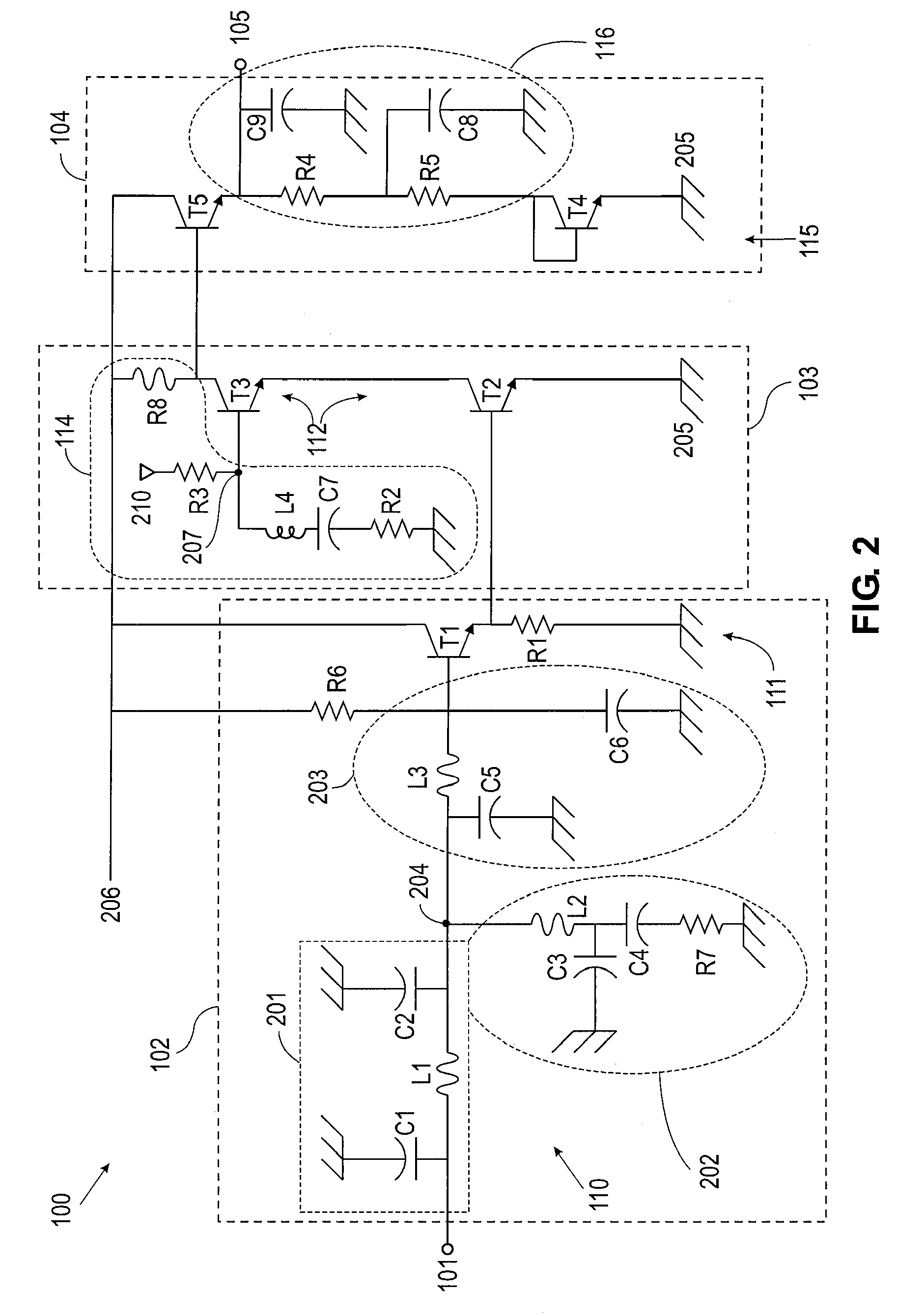
Multi-stage broadband amplifiers
ActiveUS20070096831A1High frequency amplifiersAmplifier combinationsAudio power amplifierBroadband amplifiers
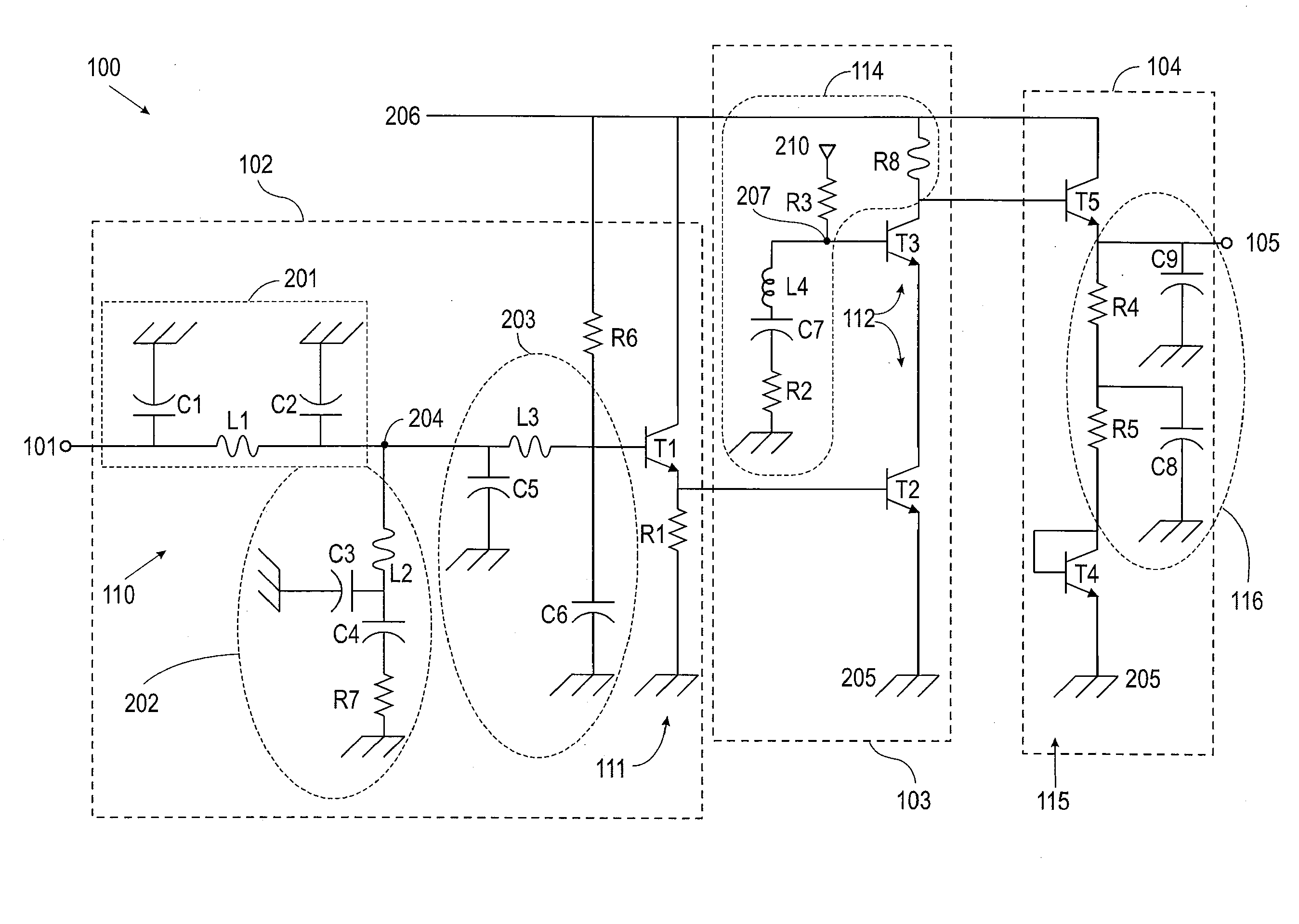
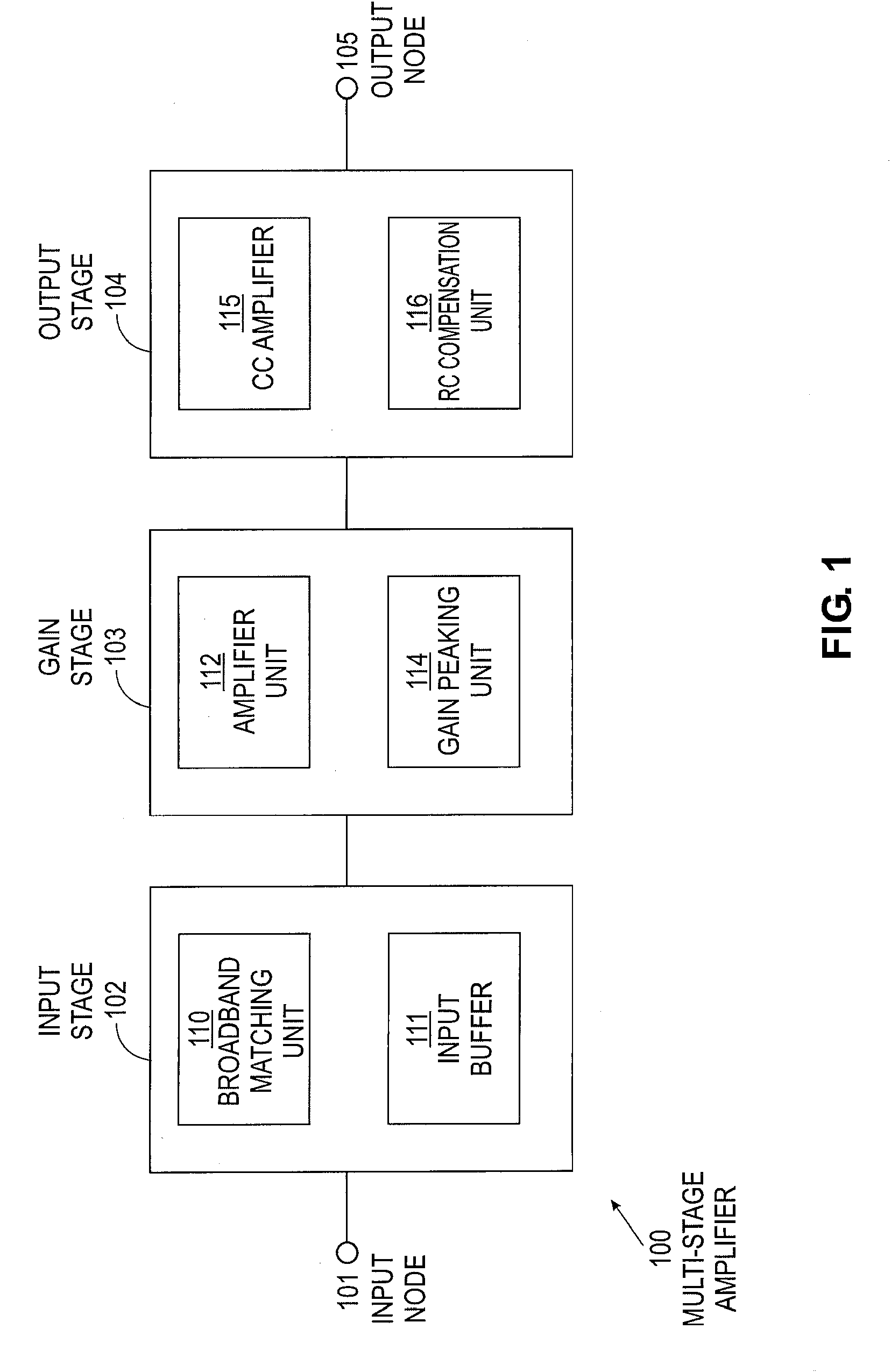
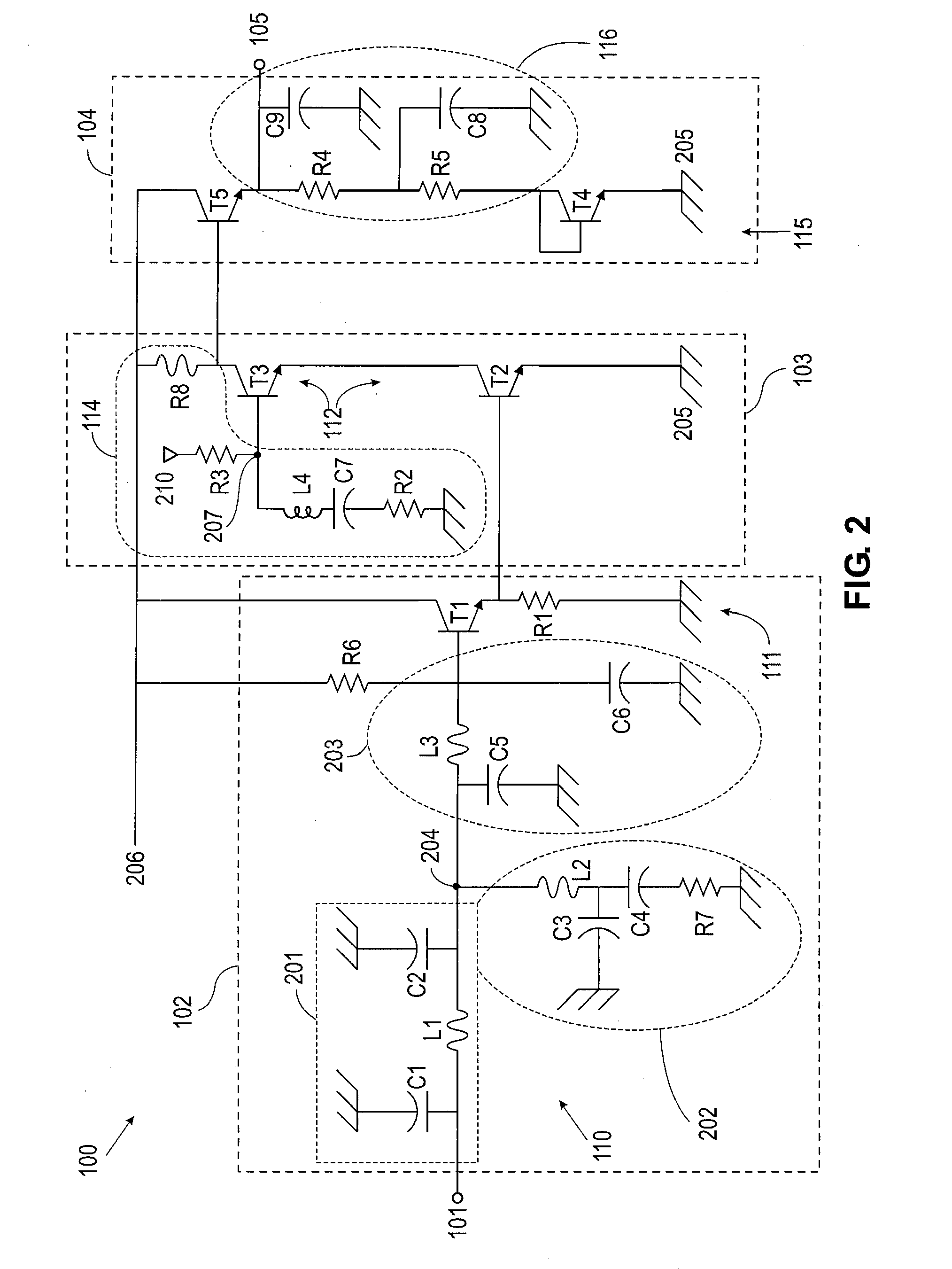
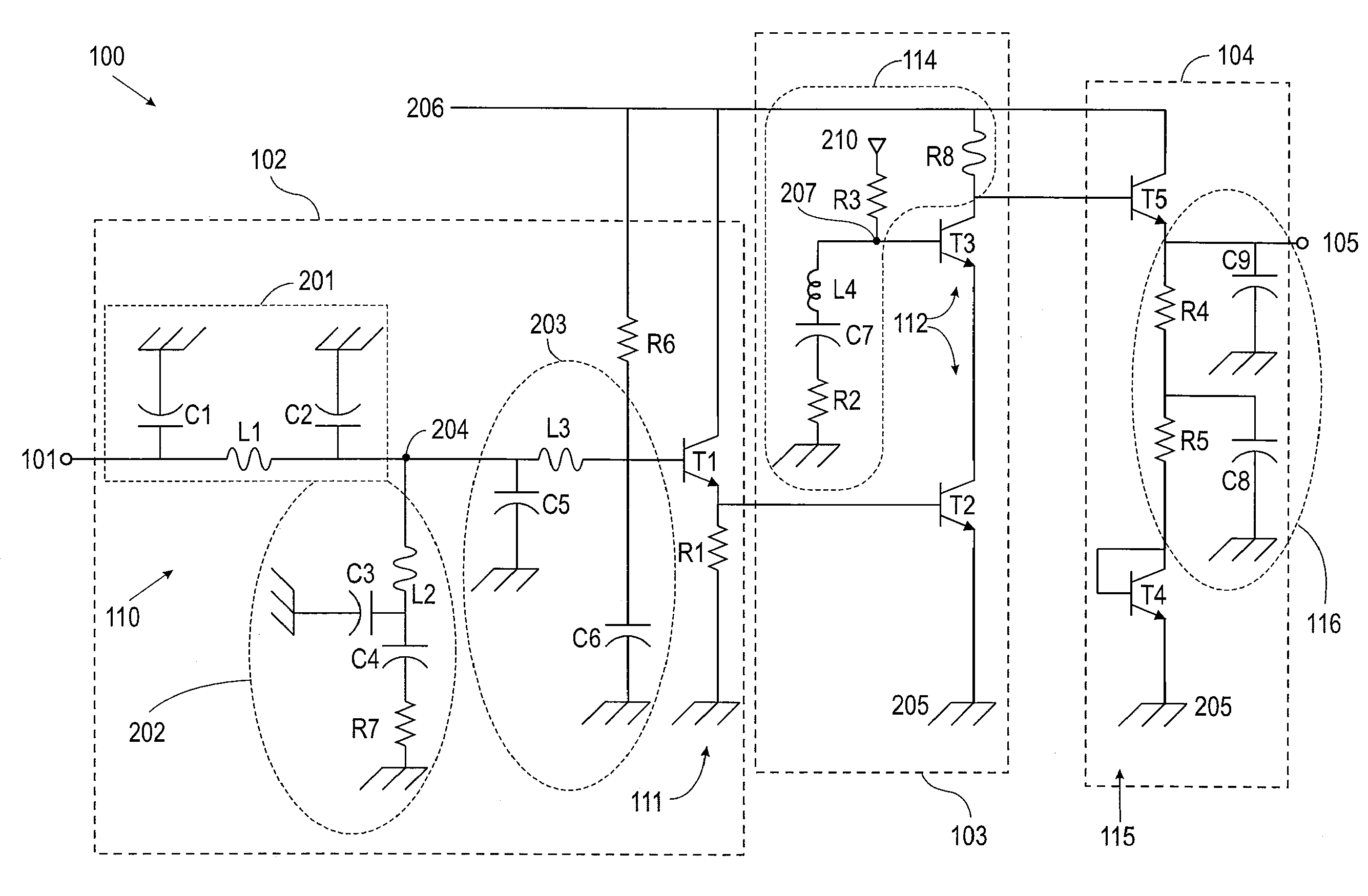
Provided herein are multi-stage broadband amplifier configured to achieve a high gain-bandwidth product in a non-distributed architecture and methods for designing the same. The broadband amplifier can include an input stage having a broadband matching unit and an input buffer unit, a gain stage having an RLC network and a amplifier unit and an output stage having a common collector amplifier and an RC compensation unit.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
ESD protection structure
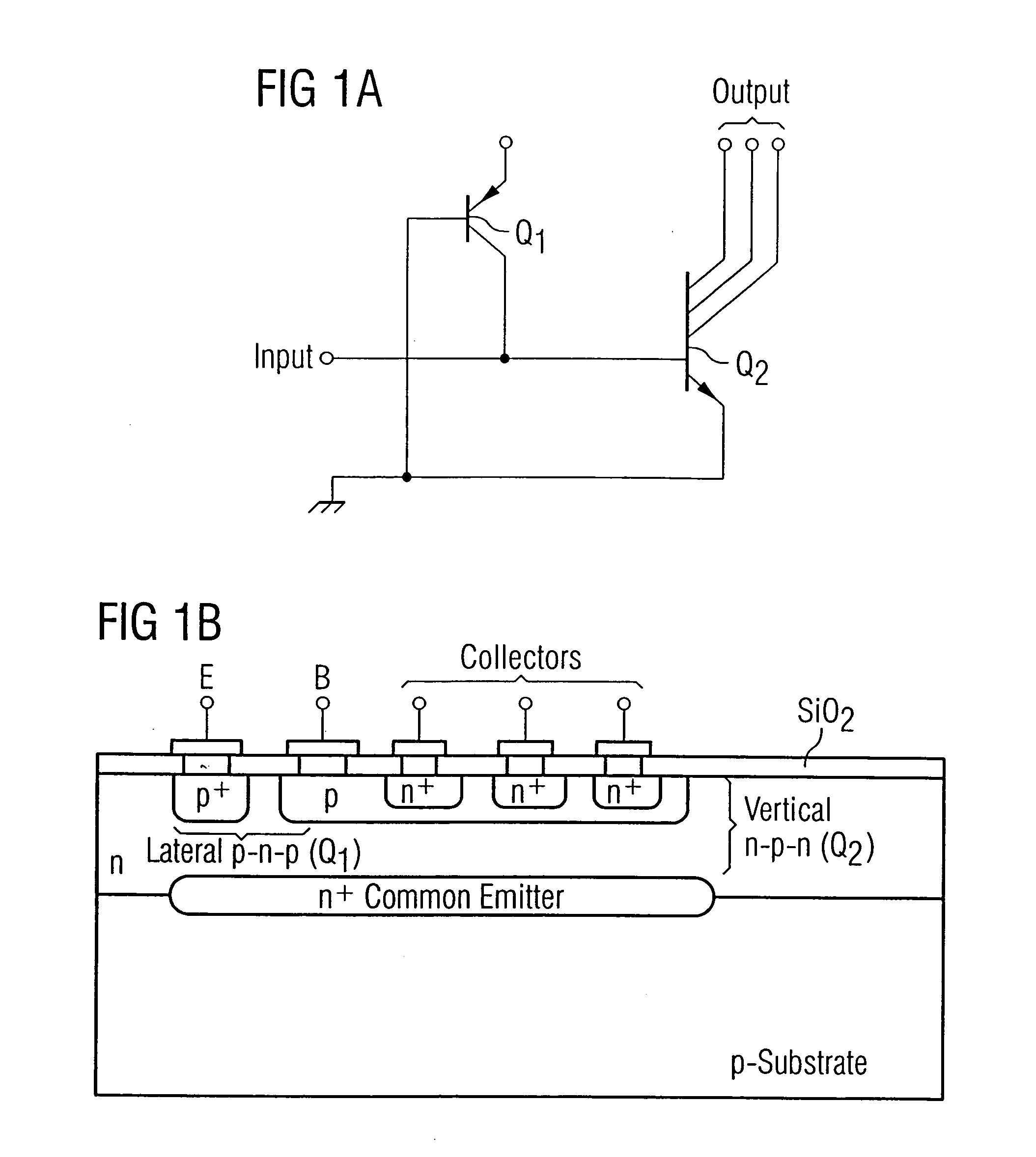
InactiveUS20100301389A1TransistorEmergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentAvalanche diodeCommon collector
An electrostatic discharge protection structure includes a first vertical bipolar junction transistor; a second vertical bipolar junction transistor, wherein the second vertical bipolar junction transistor has a common collector with the first vertical bipolar junction transistor, and the common collector has a first conductivity; a horizontal bipolar junction transistor wherein the collector of the horizontal bipolar junction transistor has a second conductivity that is a different conductivity than the first conductivity, and the base of the horizontal bipolar junction transistor is electrically coupled to the common collector of the first vertical bipolar junction transistor and the second vertical bipolar junction transistor; a first avalanche diode electrically coupled to the base and the collector of the first vertical bipolar junction transistor; and a second avalanche diode electrically coupled to the base and the collector of the second vertical bipolar junction transistor.
Owner:FREESCALE SEMICON INC
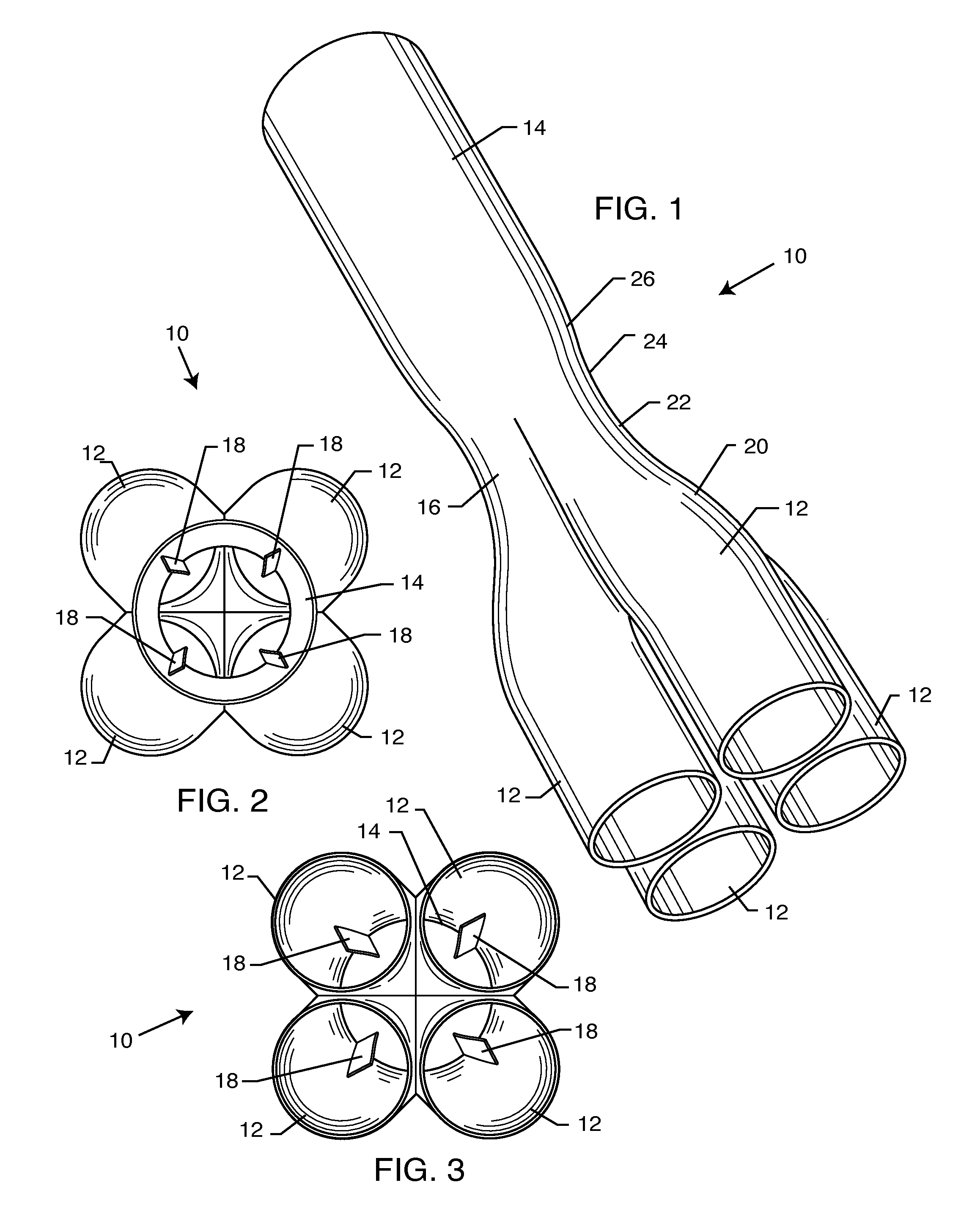
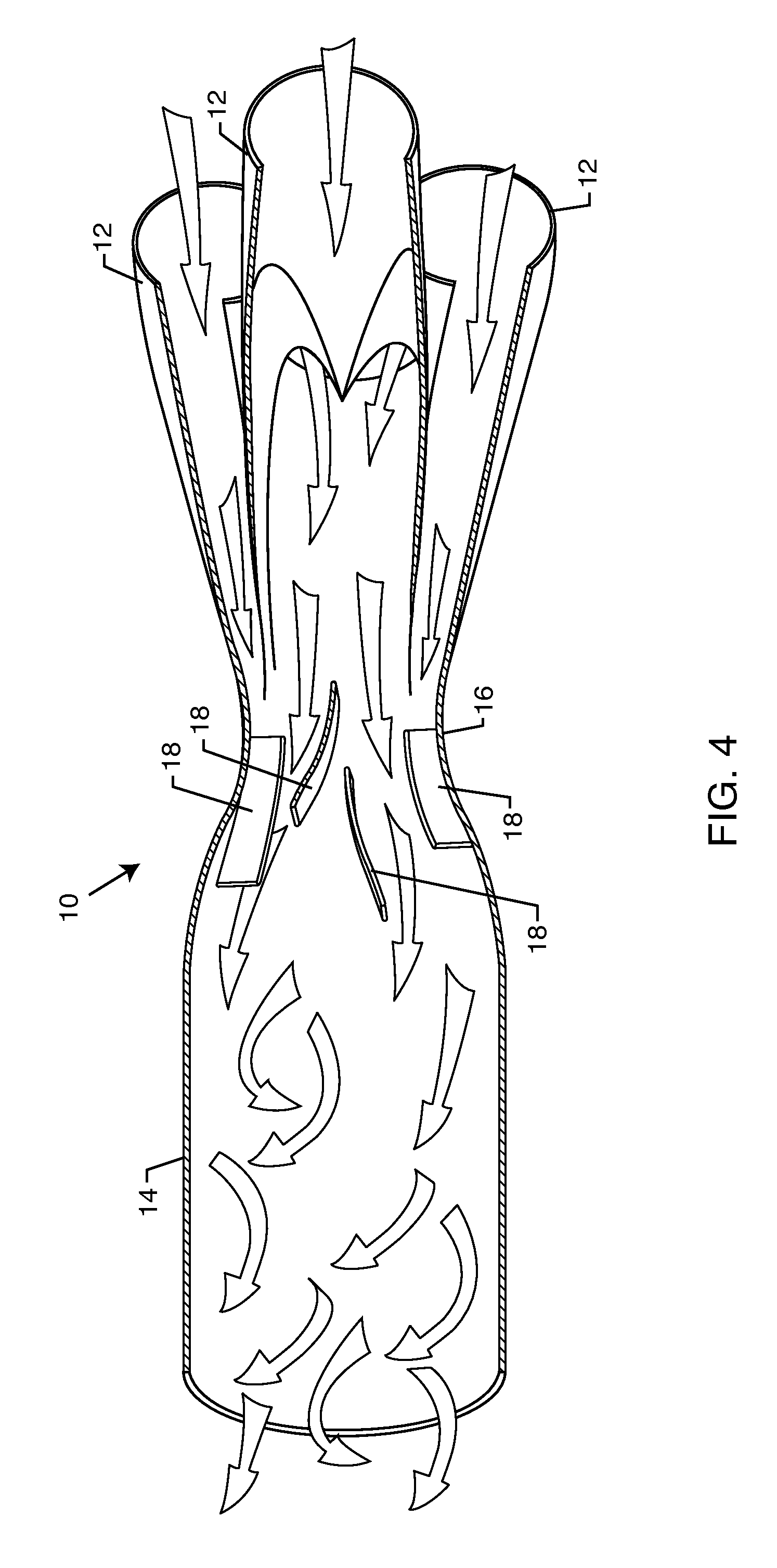
Automotive exhaust system
InactiveUS20100146956A1Quickly and efficiently expelSilencing apparatusMachines/enginesExhaust fumesCommon collector
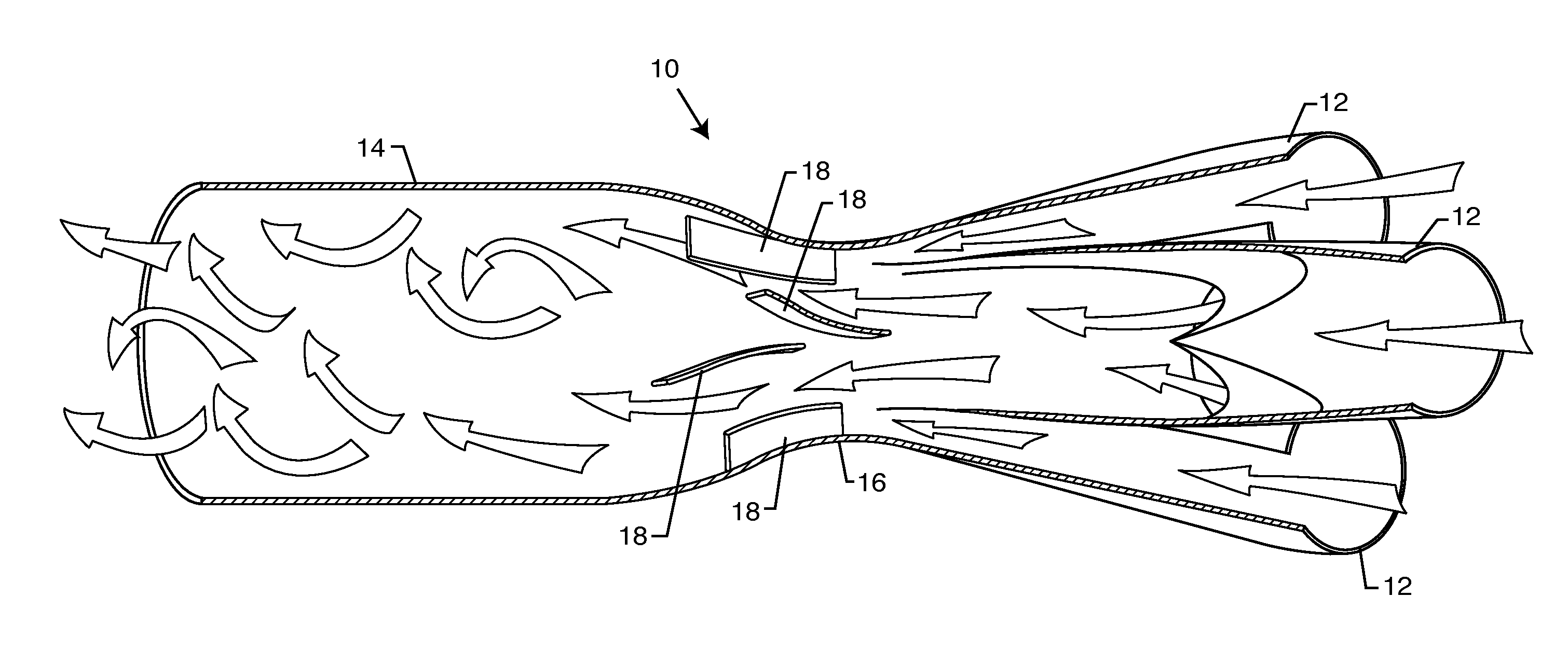
The automotive exhaust system includes a plurality of exhaust pipes that feed into a common collector. The collector includes a venturi at the point where the exhaust gases enter the collector from the multiple exhaust pipes. The exhaust gases accelerate through the venturi by virtue that the venturi has a cross-sectional area smaller than that of the exhaust pipes and the collector. A plurality of vanes located in the venturi further accelerate the exhaust gases into a spinning vortex along the interior surface of the main body of the collector to efficiently and quickly expel the exhaust gases out from within the automotive exhaust system. The diameter of the venturi relative to the collector is specific to each diameter of tubing as matched with the corresponding vehicle specifications.
Owner:GRUDYNSKI III JOHN M
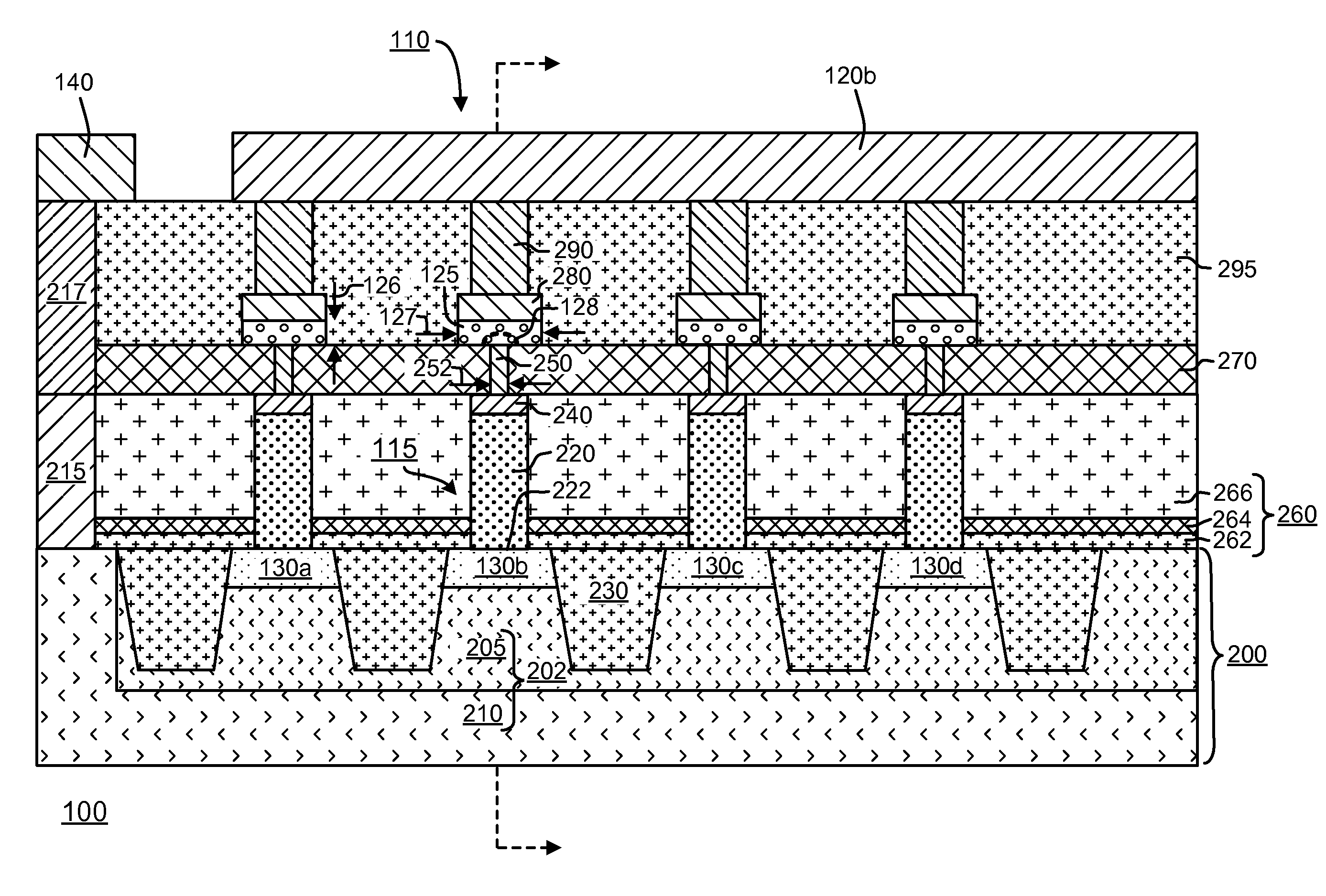
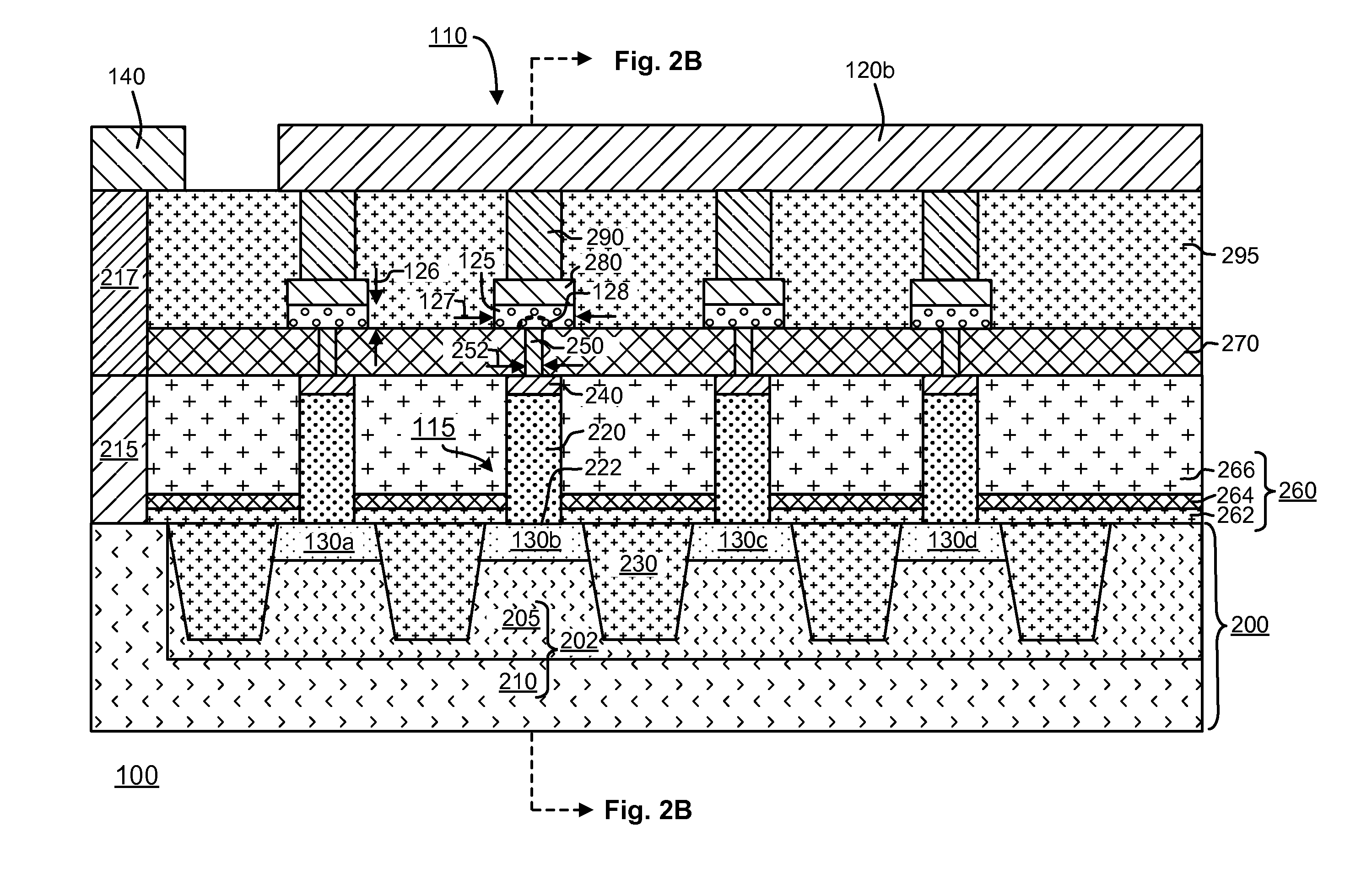
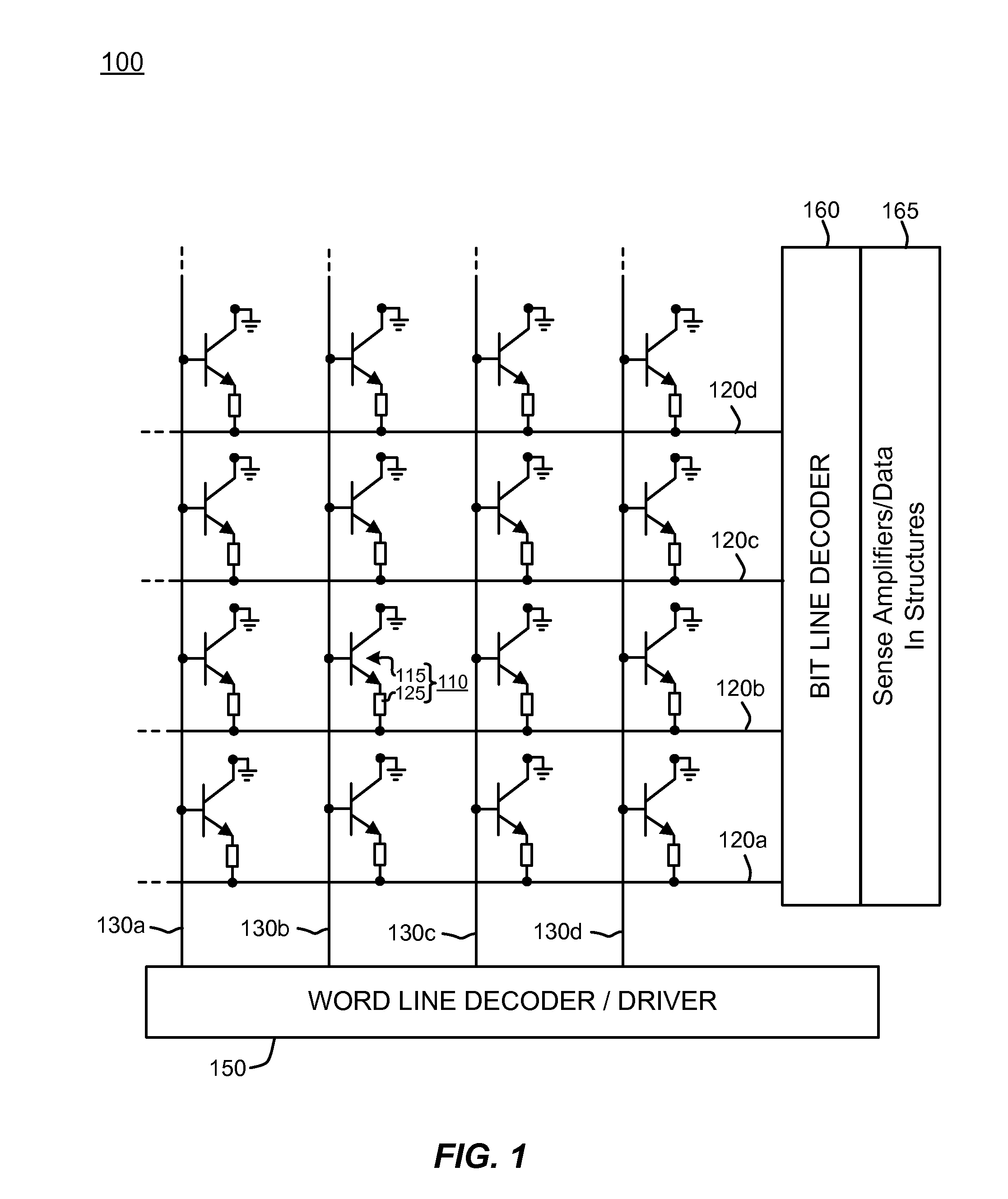
Polysilicon plug bipolar transistor for phase change memory
Memory devices and methods for manufacturing are described herein. A memory device described herein includes a plurality of memory cells. Memory cells in the plurality of memory cells comprise respective bipolar junction transistors and memory elements. The bipolar junction transistors are arranged in a common collector configuration and include an emitter comprising doped polysilicon having a first conductivity type, the emitter contacting a corresponding word line in a plurality of word lines to define a pn junction. The bipolar junction transistors include a portion of the corresponding word line underlying the emitter acting as a base, and a collector comprising a portion of the single-crystalline substrate underlying the base.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD +1
Resistor triggered electrostatic discharge protection
An electrostatic discharge (ESD) protection device (41, 51, 61, 71, 81) coupled across input-output (I / O) (22) and common (23) terminals of a core circuit (24) that it is intended to protect from ESD events, comprises, one or more serially coupled resistor triggered ESD clamp stages (41, 41′, 41″; 71, 71′, 71″), each stage (41, 41′, 41″; 71, 71′, 71″) comprising first (T1, T1′, T1″, etc.) and second transistors (T2, T2′, T2′″ etc.) having a common collector (52, 52′, 52″) and first (26, 26′, 26″) and second (36, 36′, 36″) emitters providing terminals (32, 42; 32′, 42′; 32″, 42″) of each clamp stage (41, 41′, 41″; 71, 71′, 71. A first emitter (25) of the first stage (41, 71) couples to the common terminal (23) and a second emitter (42″) of the last stage (41″, 71′) couples to the I / O terminals (22). Zener diode triggers are not used. Integrated external ESD trigger resistors (29, 29′, 29″; 39, 39′, 39″) (e.g., of poly SC) are coupled between the base (28, 28′, 28″; 38, 38′, 38″) and emitter (26, 26′, 26″; 36, 36′, 36″) of each transistor (T1, T1′, T1″; T2, T2′, T2″). Different resistor values (e.g., ˜0.5 k to 150 k Ohms) give different ESD trigger voltages. Cascading the clamp stages (41, 41′, 41″; 71, 71′) gives even higher trigger voltages. The ESD trigger resistances (29, 29′, 29″; 39, 39′, 39″) are desirably located outside the common collector-isolation wall (741, 742, 743; 741′, 742′, 743″) surrounding the transistors (T1, T1′, T1″; T2, T2′, T2″).
Owner:NXP USA INC
Lateral bipolar field effect mode hybrid transistor and method for operating the same
InactiveUS6015982AHigh gainEasy to implementTransistorSolid-state devicesLateral extensionEngineering
The invention relates to a semiconductor device and a method in this device, wherein the semiconductor device operates completely or partly in lateral extension. The semiconductor device comprises at least two high-voltage lateral bipolar transistors with at least two mutually opposite emitter / base regions, which are placed at the surface of the epi-taxial layer at a mutual distance such that an intermediate common collector region is formed. The common collector region can be completely depleted when the device has a voltage applied and by using a lateral depletion of said collector region, the voltage durability of the semiconductor device can be determined lithographically by the distance between the doped regions comprised in the device. Furthermore, undesired parasitic components, which are dependent on the quality of the active layer of the device, resistivity and substrate potential, can be eliminated or suppressed.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
Multi-stage broadband amplifiers
ActiveUS7652539B2High frequency amplifiersAmplifier combinationsAudio power amplifierBroadband amplifiers
Provided herein are multi-stage broadband amplifier configured to achieve a high gain-bandwidth product in a non-distributed architecture and methods for designing the same. The broadband amplifier can include an input stage having a broadband matching unit and an input buffer unit, a gain stage having an RLC network and a amplifier unit and an output stage having a common collector amplifier and an RC compensation unit.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Semiconductor device having an improved voltage controlled oscillator
ActiveUS7323763B2Resistance component in the horizontal direction between respective base layers is decreasedReduce resistanceTransistorAngle modulation by variable impedenceCapacitanceEngineering
A semiconductor device having an improved voltage control oscillator circuit is provided. The voltage control oscillator circuit includes, in combination, a variable-capacitance element and at least one bipolar transistor on a single semiconductor substrate. The variable-capacitance element includes reversely serially connected PN junctions, and junctions are formed by a single common collector layer and separated base layers on the common collector layer. The capacitance of the variable-capacitance element is generated between respective base layers of the PN junctions with the common collector layer, and varies in correspondence with the voltage applied to the common collector layer.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Oscillator and an integrated circuit
ActiveUS20060049883A1Readily biasedExcellent frequency shift performanceOscillations generatorsCommon baseInterconnection
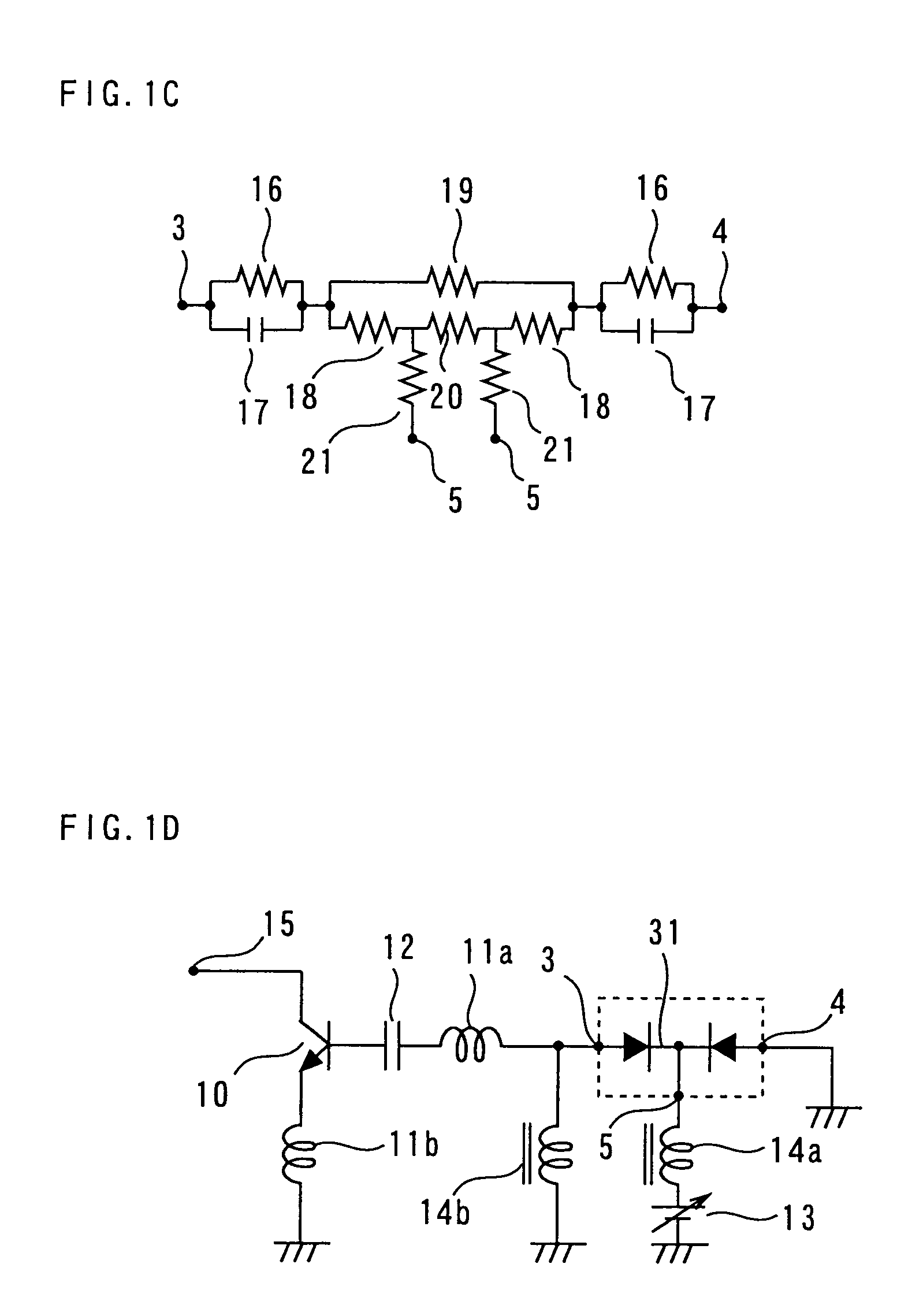
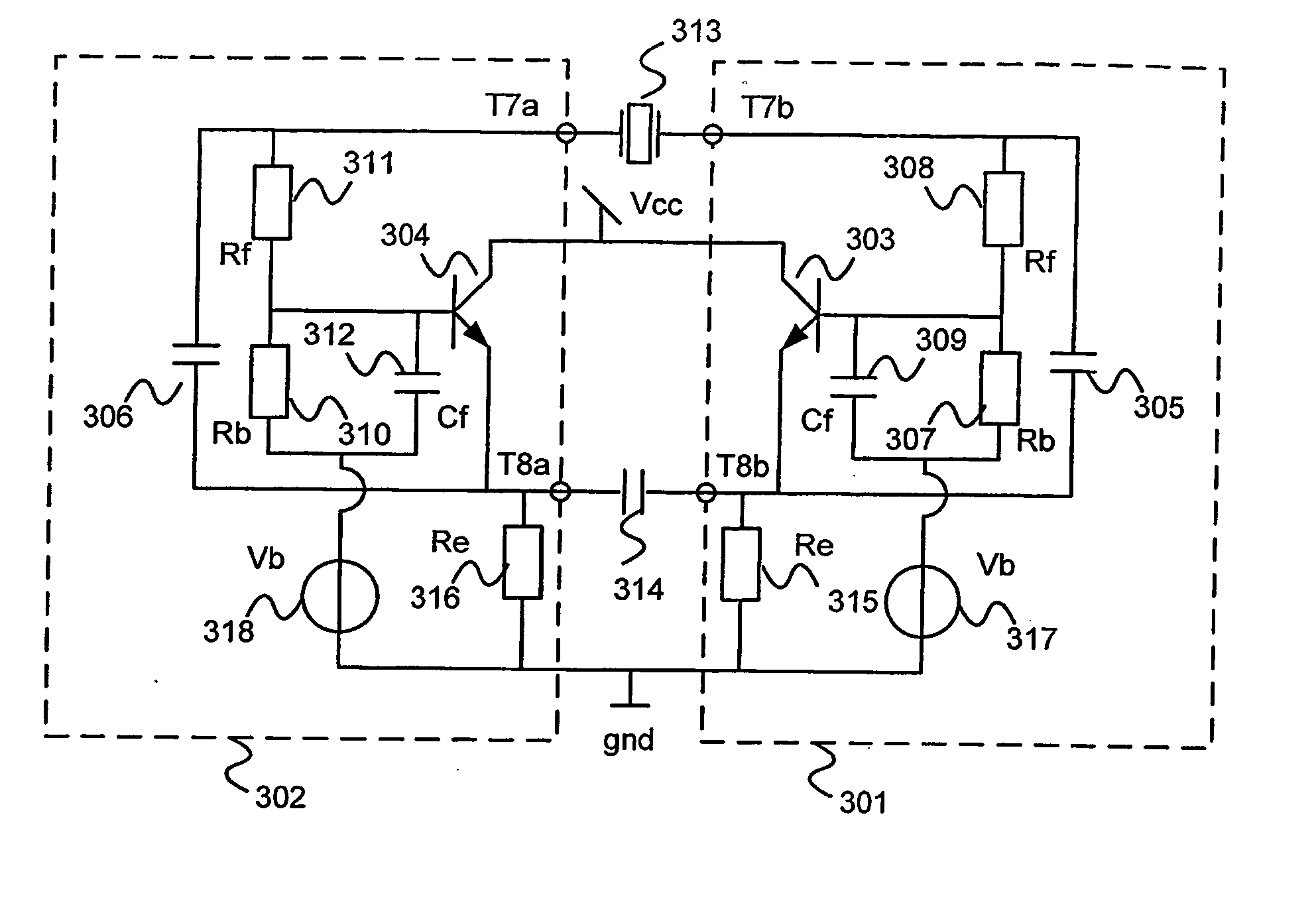
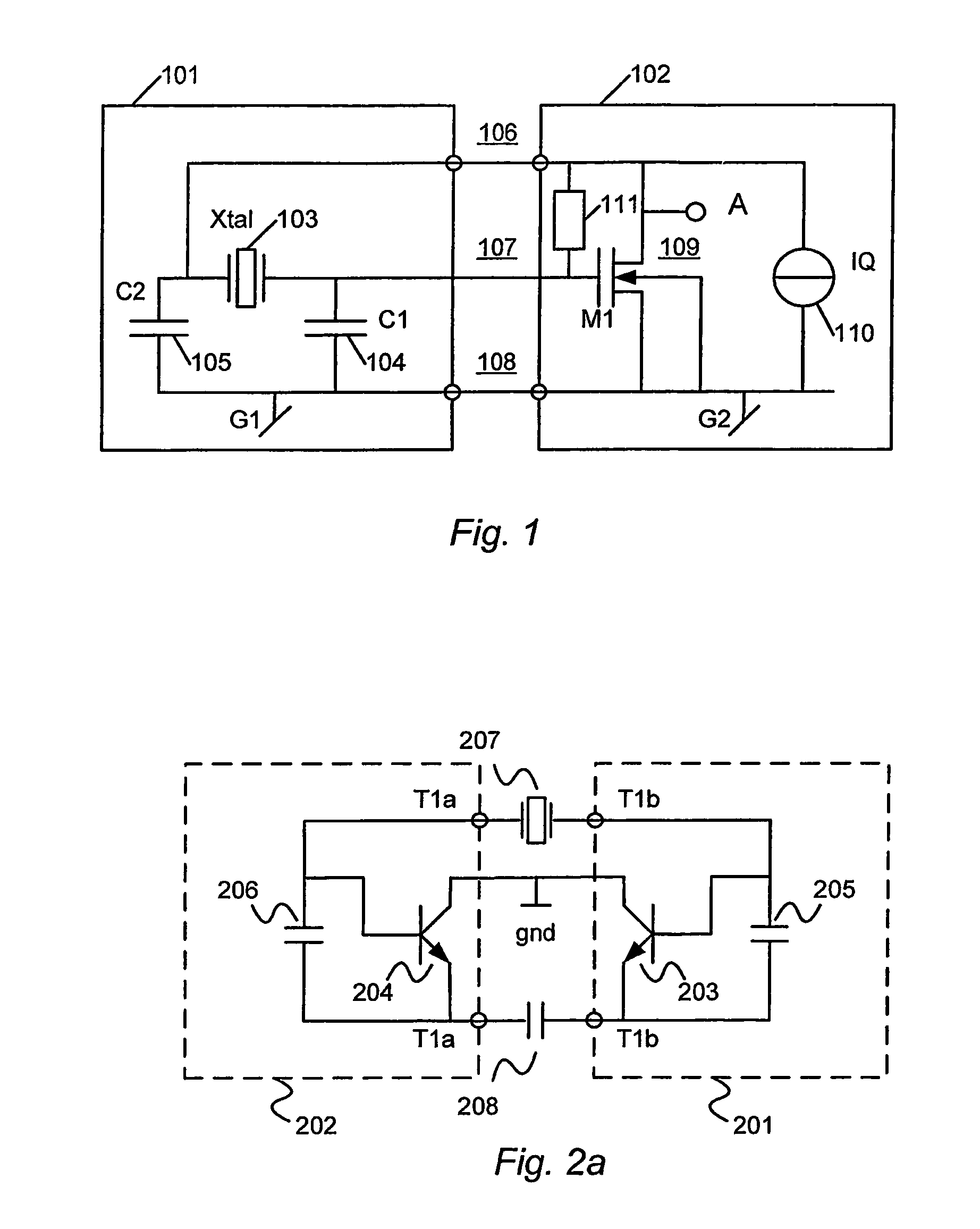
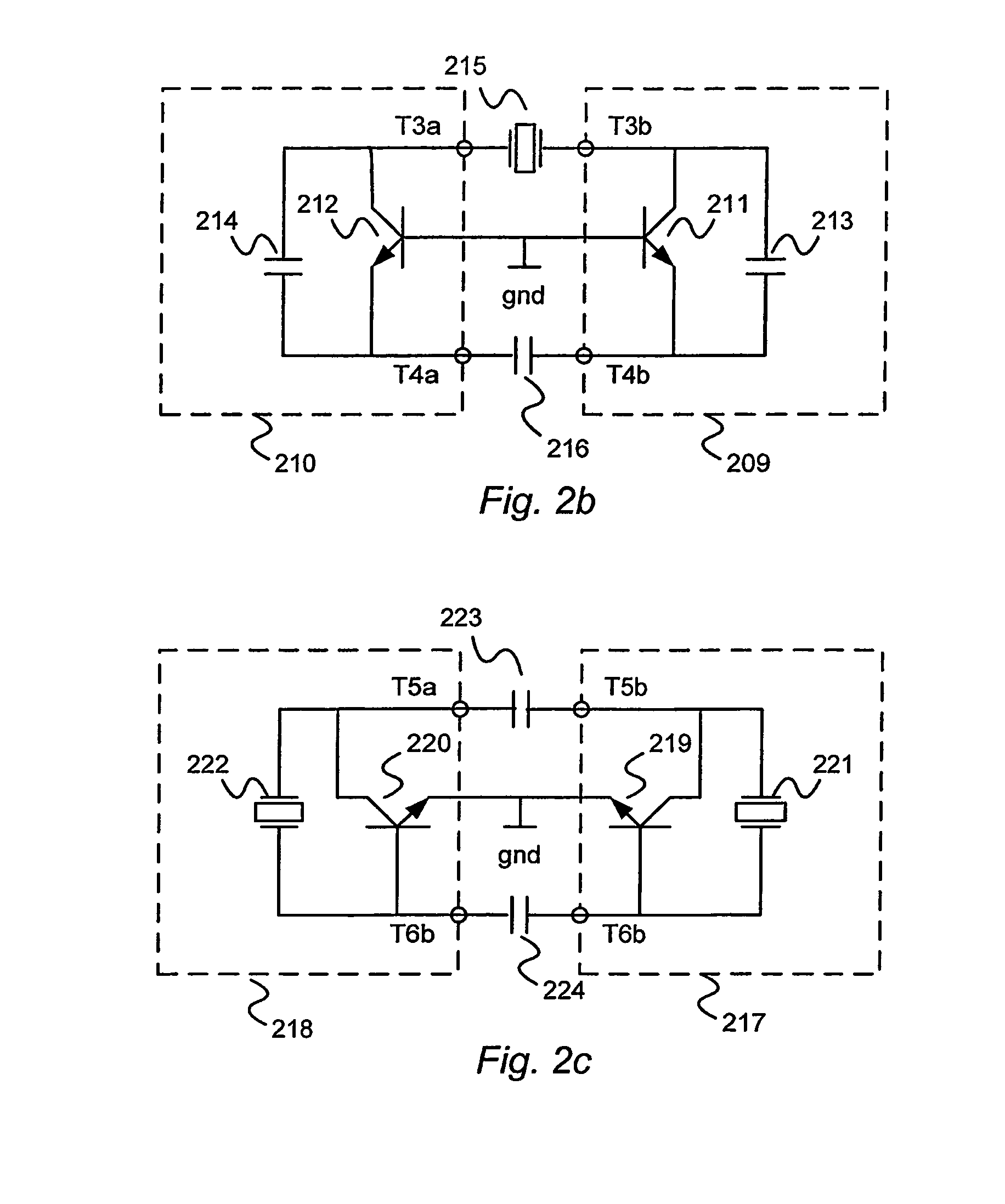
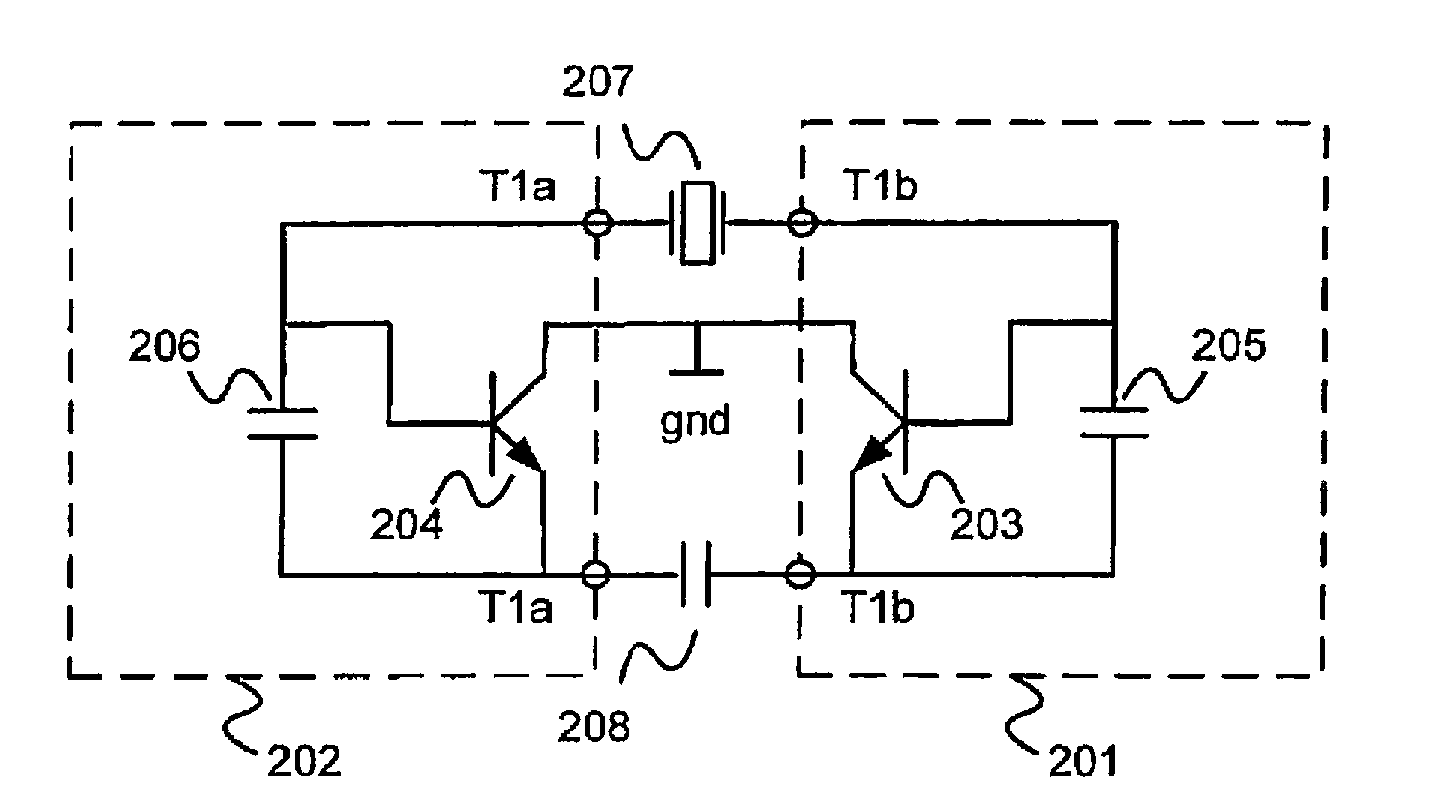
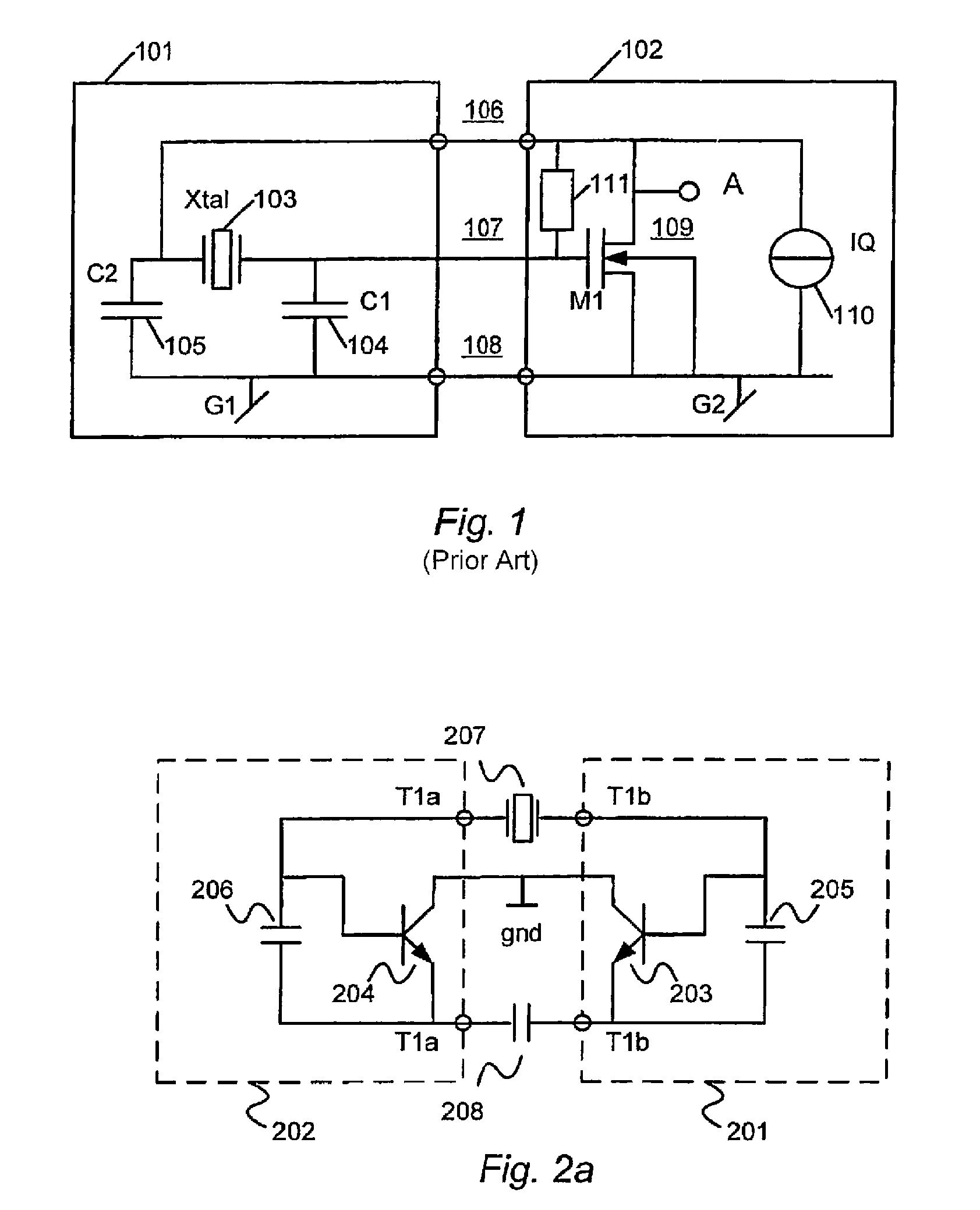
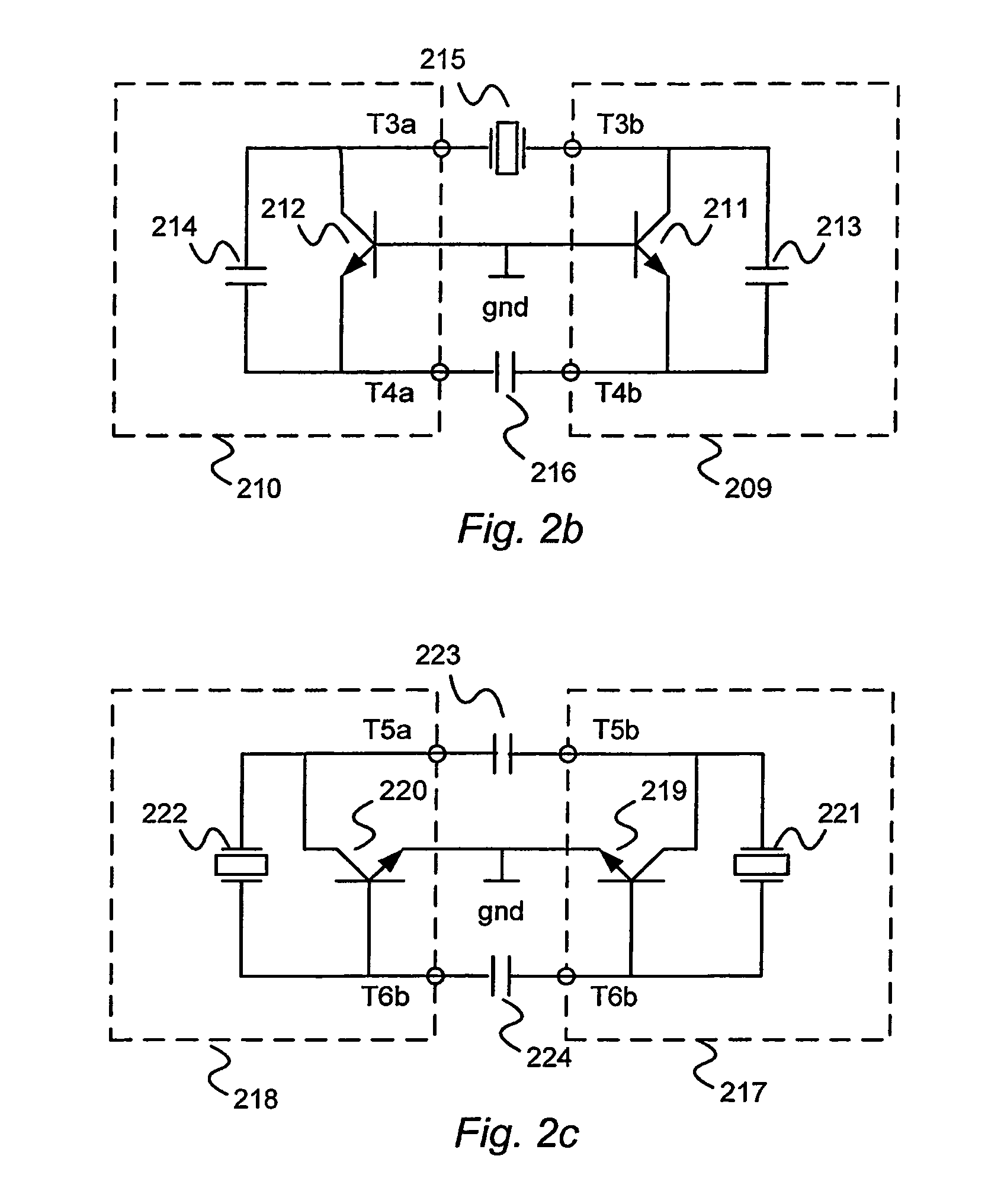
A balanced crystal oscillator circuit comprising: a piezoelectric element Xtal (207; 215; 222,221; 313); a first oscillator subcircuit (202; 210; 218; 302) incorporating a transistor (204;212;220;304); and a second oscillator subcircuit (201;209;217;301) incorporating a transistor (203; 211; 219; 303); wherein the transistors each have different types of transistor terminals (C,B,E; D;G;S), and wherein the oscillator subcircuits are configured with at least three interconnections. Each interconnection comprise a pair of like type of transistor terminals; wherein a first of said interconnections constitutes a connection to a ground reference (gnd); a second of said interconnections is via a first resonator element (207;215;223;313); and a third of said interconnections is via a second resonator element (208;216;224;314); said first and second circuits are arranged to interact by means of said first and second resonator elements to form a balanced oscillator signal. A dual common base or a dual common collector configuration is preferred.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
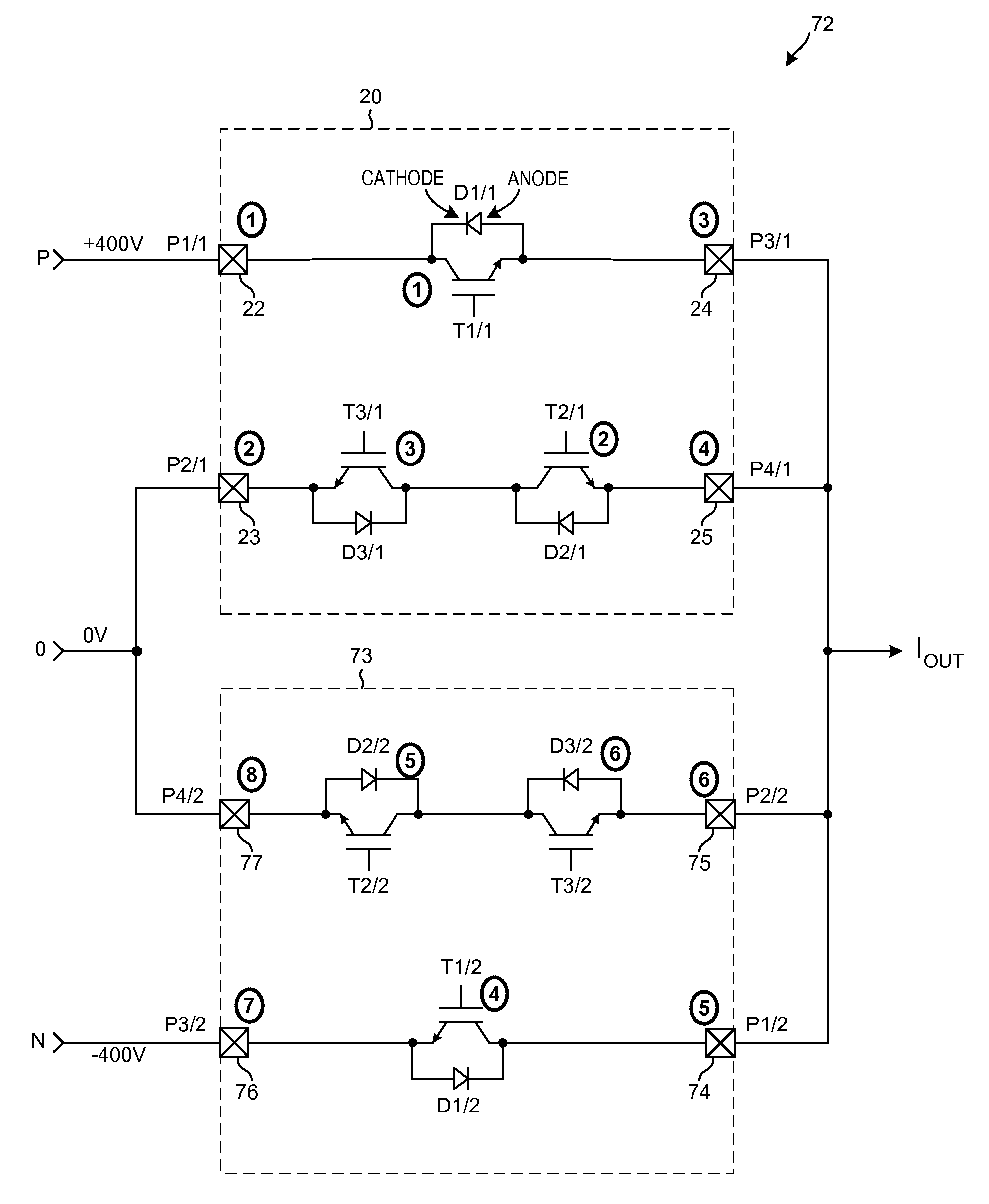
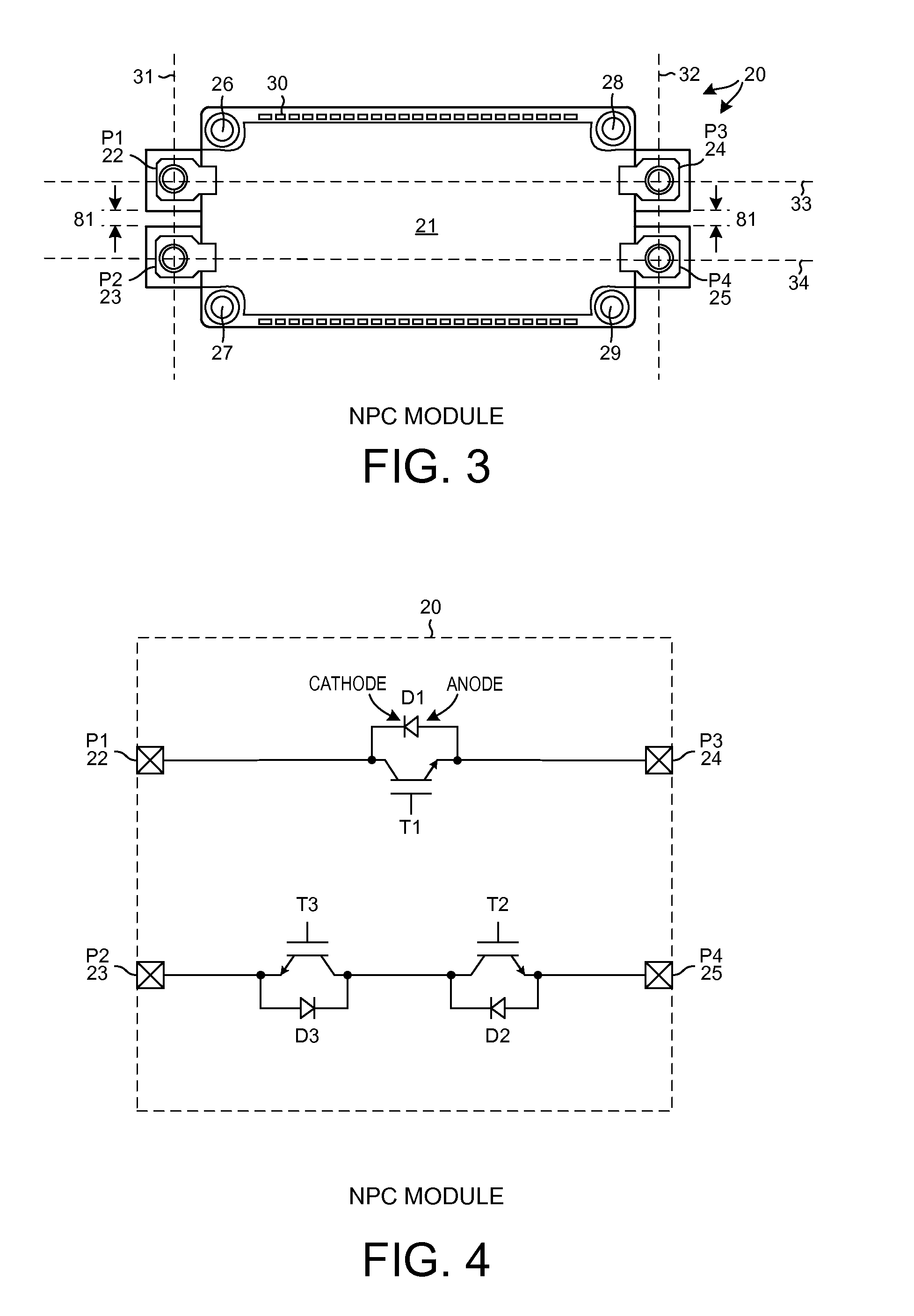
Module and assembly with dual DC-links for three-level NPC applications
InactiveUS8847328B1Reduce module unit manufacturing costHigher manufacturing quantityTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsThree levelStray inductance
Owner:LITTELFUSE INC
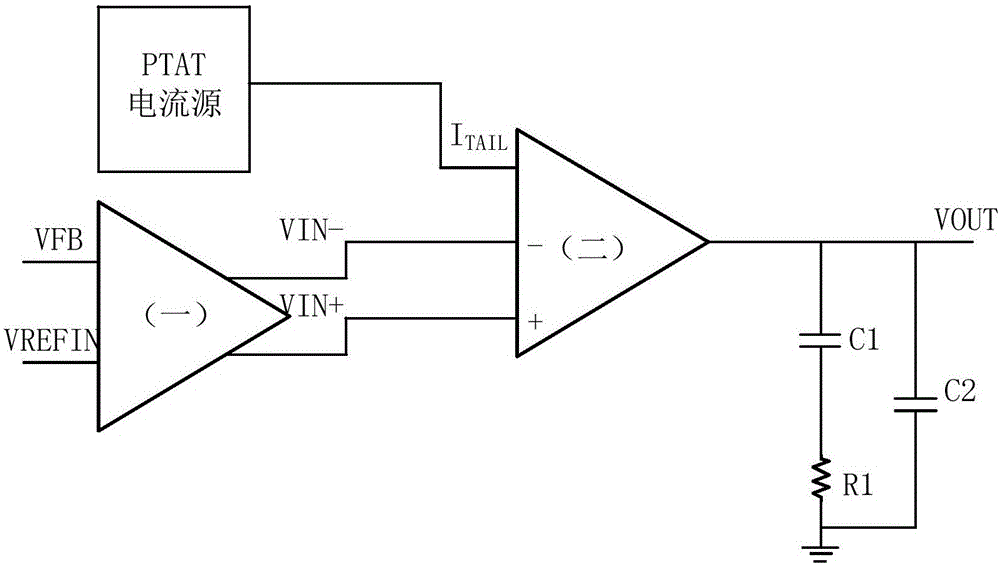
Linear error amplifier with temperature compensation
InactiveCN106788284AHigh inhibition ratioImprove input dynamic rangeAmplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationDifferential amplifiersLow voltageInstability
The invention belongs to the technical field of analog integrated circuitry and particularly provides a linear error amplifier with temperature compensation, comprising a PTAT (proportional to absolute temperature) current source, a common collector level shift circuit, a transconductance amplifier composed of an imbalance differential pair, and a frequency compensation network composed of C1, C2 and R1. The common collector level shift circuit raises low voltage to a higher one which is input to a secondary transconductance amplifier; the secondary transconductance amplifier is composed of an imbalance differential pair according to poly-hyperbolic tangent principle, with effective input voltage range widened and linearity improved; the PTAT current source provides tail current for the differential pair to compensate amplifier transconductance instability due to temperature changes; the frequency compensating network generates a suitable zero polar point so that the phase margin of the transconductance amplifiers reaches 60 degrees. The linear error amplifier disclosed herein has a wide dynamic voltage input range and low temperature sensitivity, and is suitable particularly for error amplifiers of DC-DC converters.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Oscillator and an integrated circuit
InactiveUS7362193B2Excellent frequency shift performanceReduce variationOscillations generatorsCommon baseInterconnection
A balanced crystal oscillator circuit comprising: a piezoelectric element Xtal (207; 215; 222,221; 313); a first oscillator subcircuit (202; 210; 218; 302) incorporating a transistor (204;212;220;304); and a second oscillator subcircuit (201;209;217; 301) incorporating a transistor (203; 211; 219; 303); wherein the transistors each have different types of transistor terminals (C,B,E; D;G;S), and wherein the oscillator subcircuits are configured with at least three interconnections. Each interconnection comprise a pair of like type of transistor terminals; wherein a first of said interconnections constitutes a connection to a ground reference (gnd); a second of said interconnections is via a first resonator element (207;215;223;313); and a third of said interconnections is via a second resonator element (208;216;224;314); said first and second circuits are arranged to interact by means of said first and second resonator elements to form a balanced oscillator signal. A dual common base or a dual common collector configuration is preferred.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Method, system and computer program for collecting inventory information through a data mover
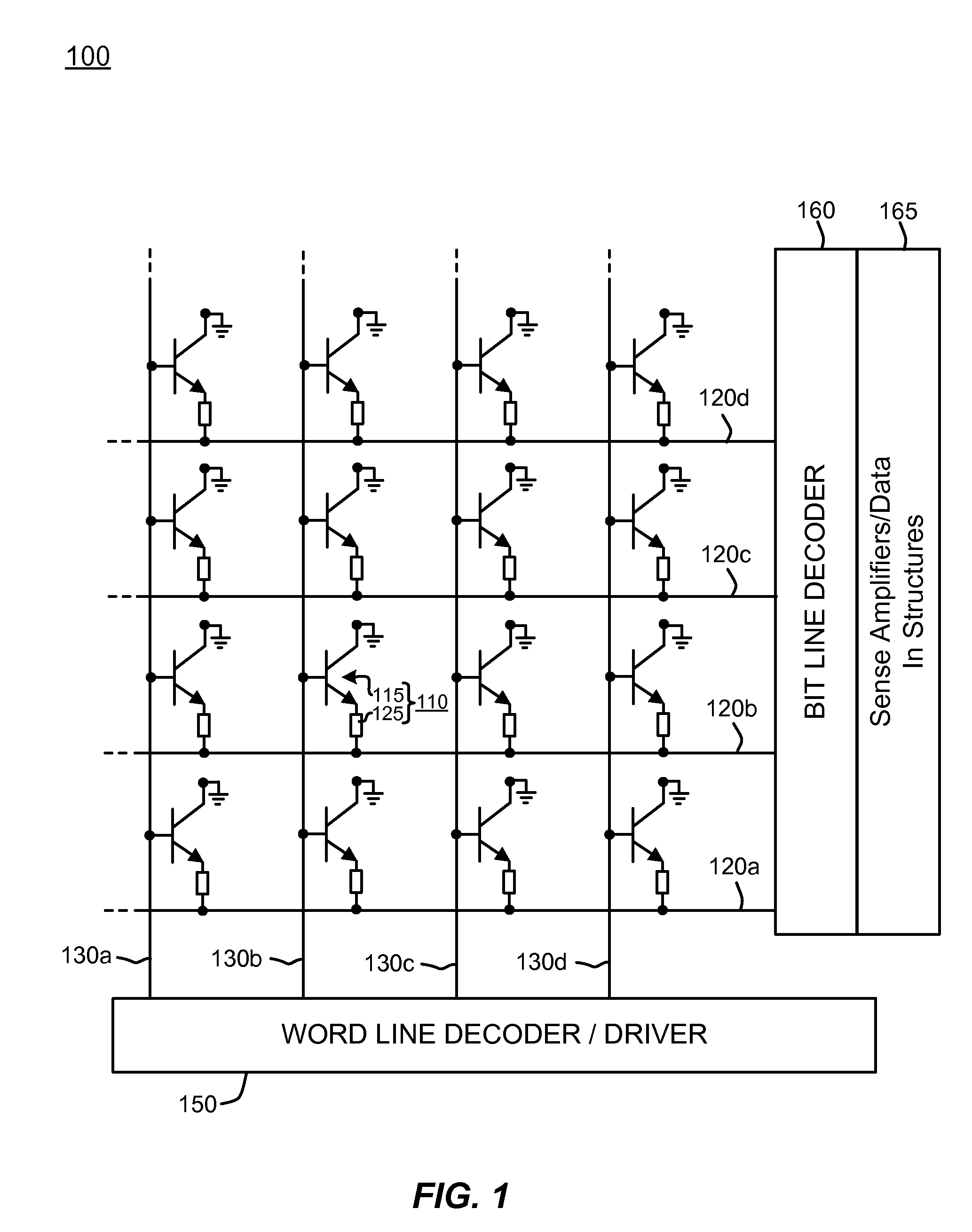
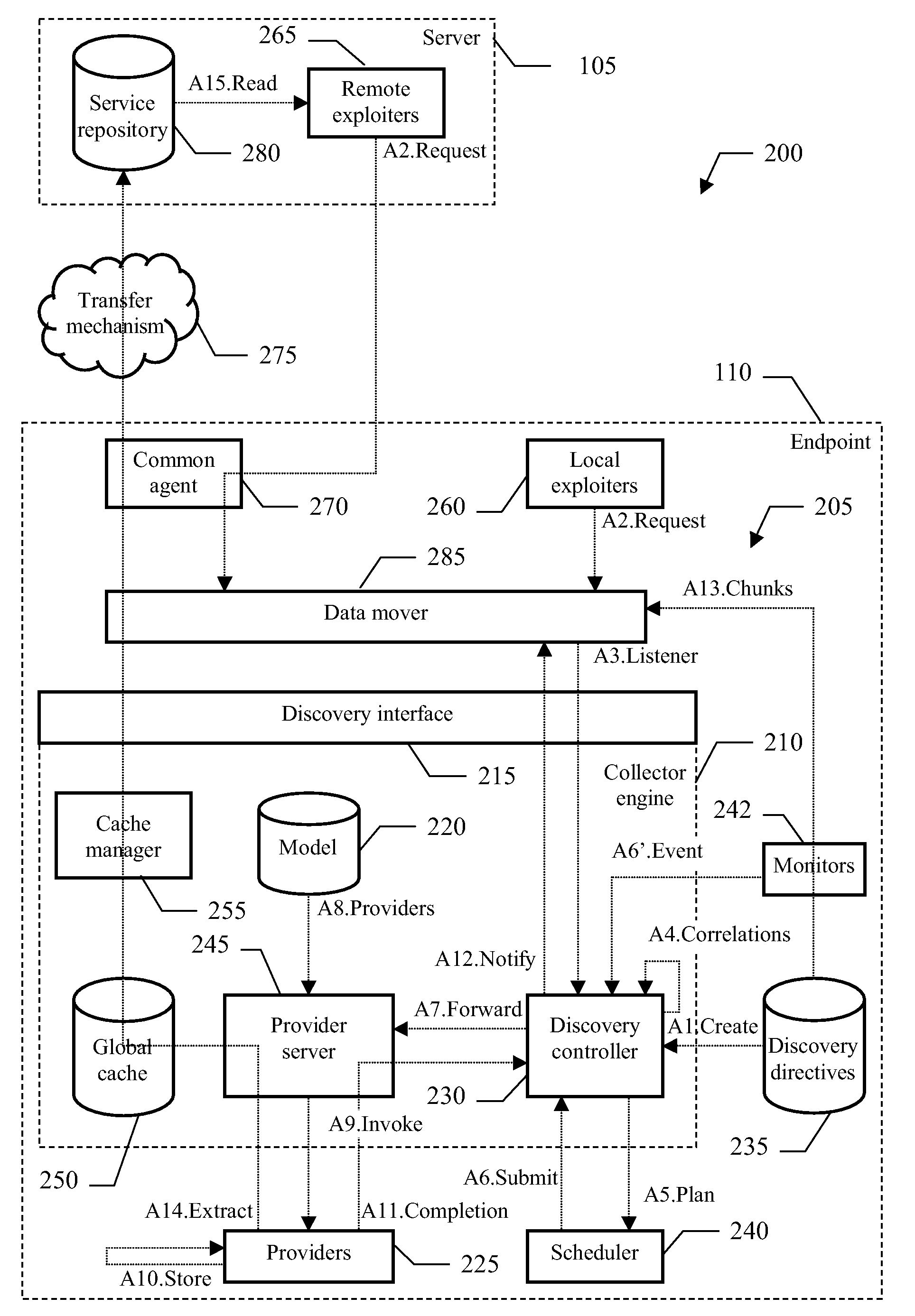
InactiveUS20070245314A1Specific program execution arrangementsMemory systemsProgram planningCommon collector
A solution (200) for collecting inventory information relating to complex resources is proposed. For this purpose, a data mover (285) interfaces with a common collector engine (210). The data mover registers (A3) itself as a listener for a selected resource class on behalf of every exploiter (265). The collector engine solves (A4) the correlations involving the selected resource class, as indicated in predefined discovery directories (235). Providers (225) adapted to discover inventory information about the correlated resource classes are periodically invoked (A5-A9), according to a scheduling plan defined in the same discovery directives. As soon as the providers for all the correlated resource classes have completed the discovery of the corresponding information (A10), the data mover is notified accordingly (A11). In response thereto, the data mover transfers (A13-A15) the discovered (delta) inventory information to the exploiter.
Owner:IBM CORP
Transistor and electronic device
InactiveUS7109534B2Large outputIncrease speedTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsCommon baseCommon emitter
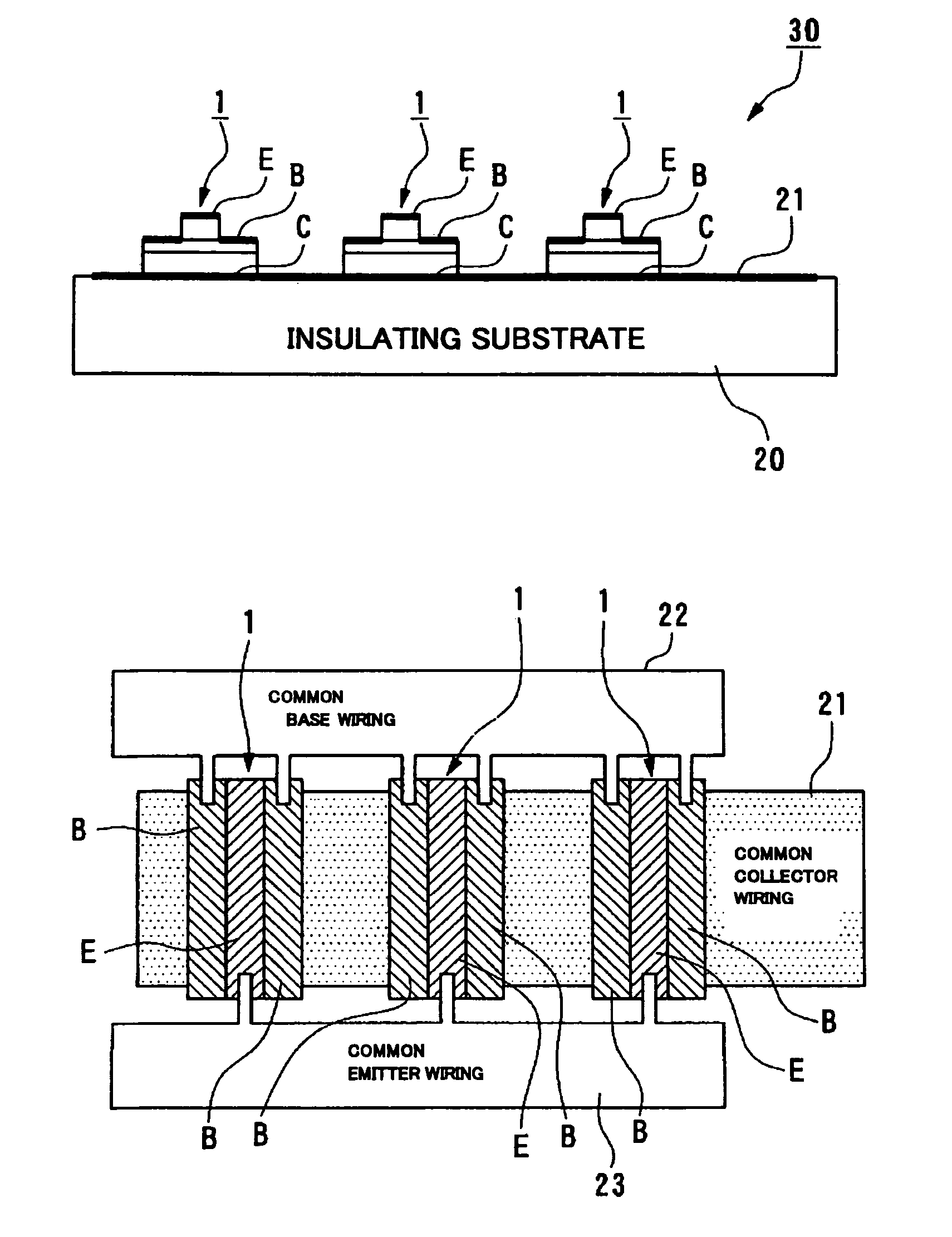
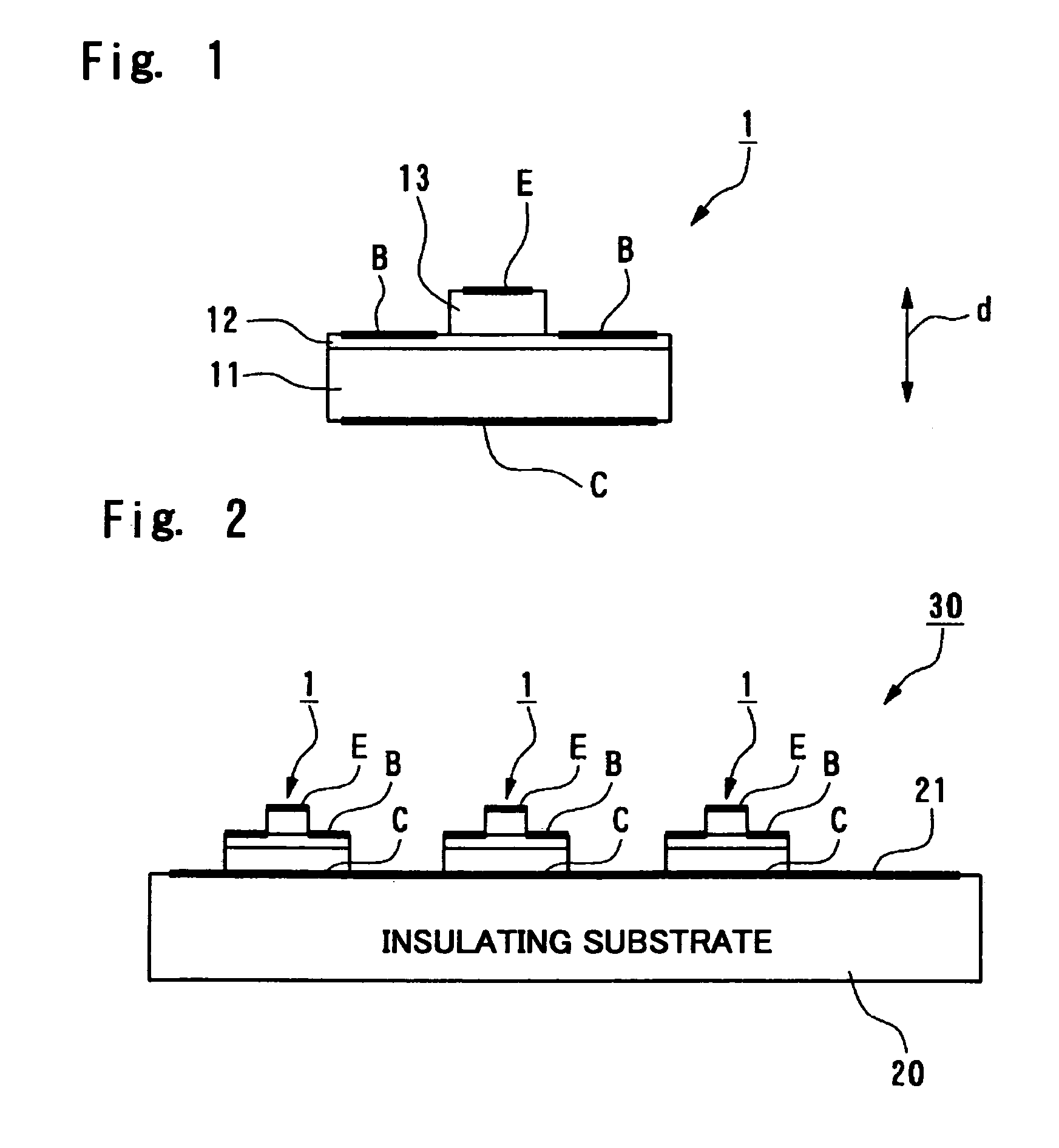
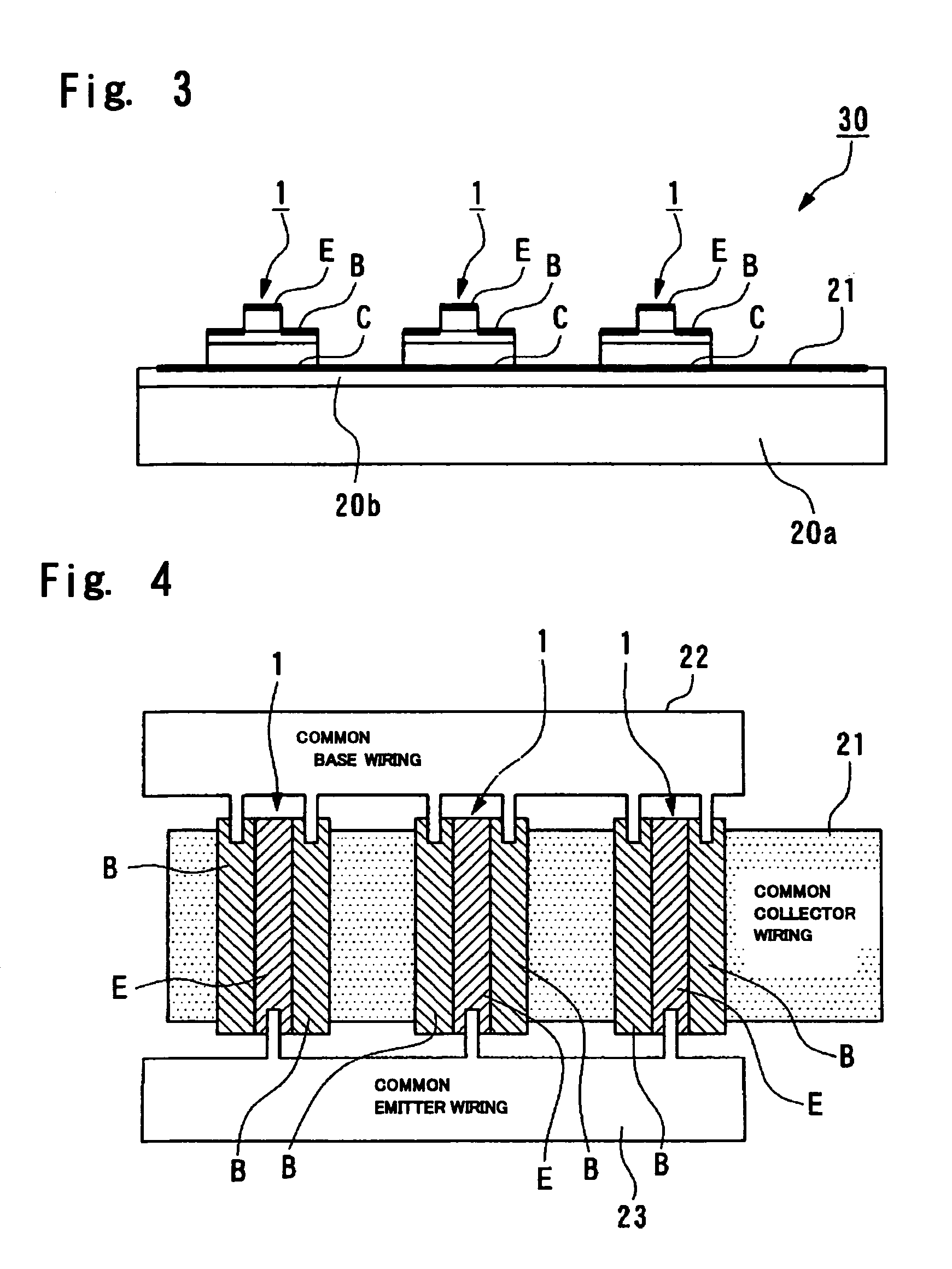
The invention provides a transistor capable of achieving a higher speed although its construction is easy to manufacture without requiring wiring to intersect three-dimensionally even if unit elements of transistors are connected in parallel, and to provide an electronic device. The transistor can include common collector wiring provided on an insulating substrate, a first layer, which is provided on the common collector wiring which is made of an N-type semiconductor, a second layer, made of a P-type semiconductor, provided on the first layer low, a third layer, which is provided on the second layer and which is made of an N-type semiconductor, common base wiring, which is provided on the insulating substrate and which is connected to the second layer, and common emitter wiring, which is provided on the insulating substrate and which is connected to the third layer.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Starting circuit of reference voltage source
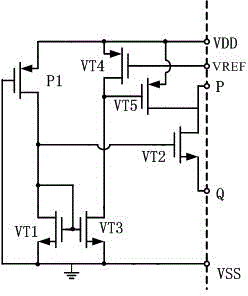
ActiveCN104615185AEliminate power-up spikesFast startupElectric variable regulationNegative feedbackElectricity
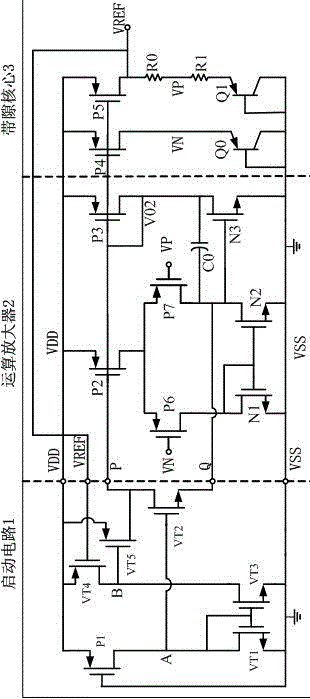
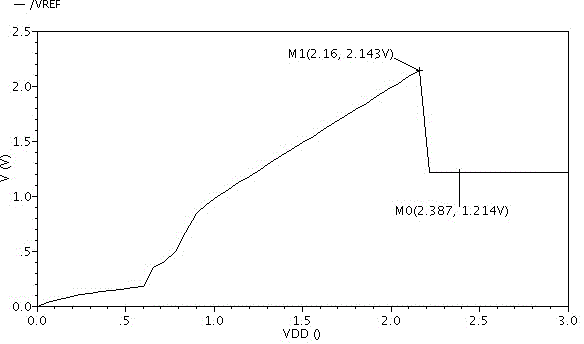
The invention discloses a starting circuit of a reference voltage source. The starting circuit of the reference voltage source comprises a first transistor VT1, a second transistor VT2, a third transistor VT3, a fourth transistor VT4 and a fifth transistor VT5. The third transistor VT3 and the fourth transistor VT4 constitute a common collector amplification circuit, the output voltage VERF of the reference voltage source is connected into the base electrode of the fourth transistor VT4 to be used as the input of the common collector amplification circuit, the output end of the common collector amplification circuit controls the fifth transistor VT5 to charge and discharge internal nodes of the reference voltage source, and therefore a negative feedback circuit for the output voltage VERF of the reference voltage source is formed. By means of the starting circuit of the reference voltage source, the output voltage overshoot peak happening to a power source circuit in the electrical starting process can be eliminated, the output voltage can rise smoothly and steadily, the quiescent operating point of the reference voltage source is stabilized, the starting speed is increased, and the improved effect is obvious especially on a low power consumption band-gap reference voltage source. The structure is simple, implementation is easy, and the cost is low.
Owner:惠州市德赛精密部件有限公司
Cultural relic identification method and device based on artificial intelligence, equipment and storage medium
InactiveCN109948539ASolve the problem of weak identification abilityCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesState of artPattern recognition
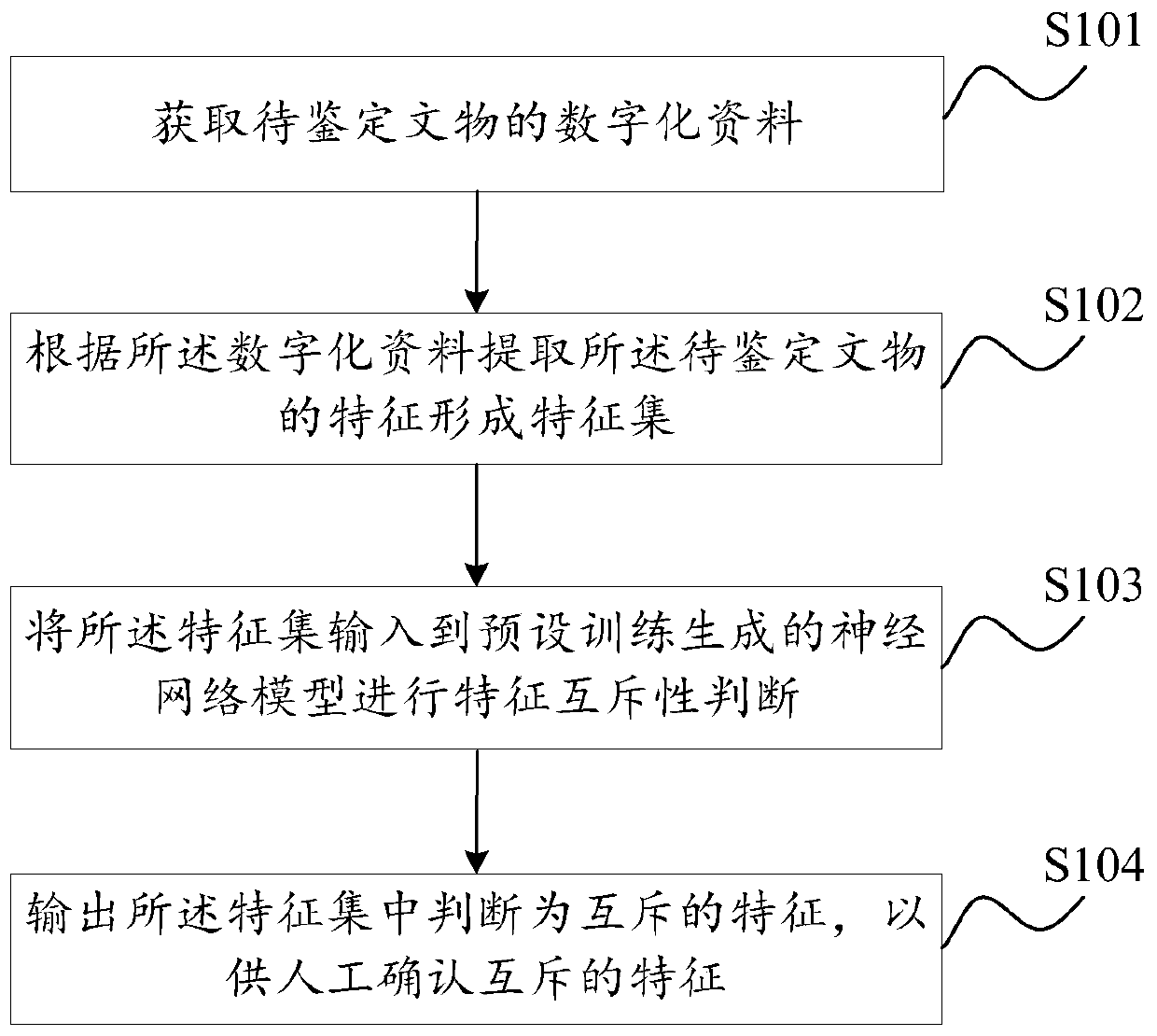
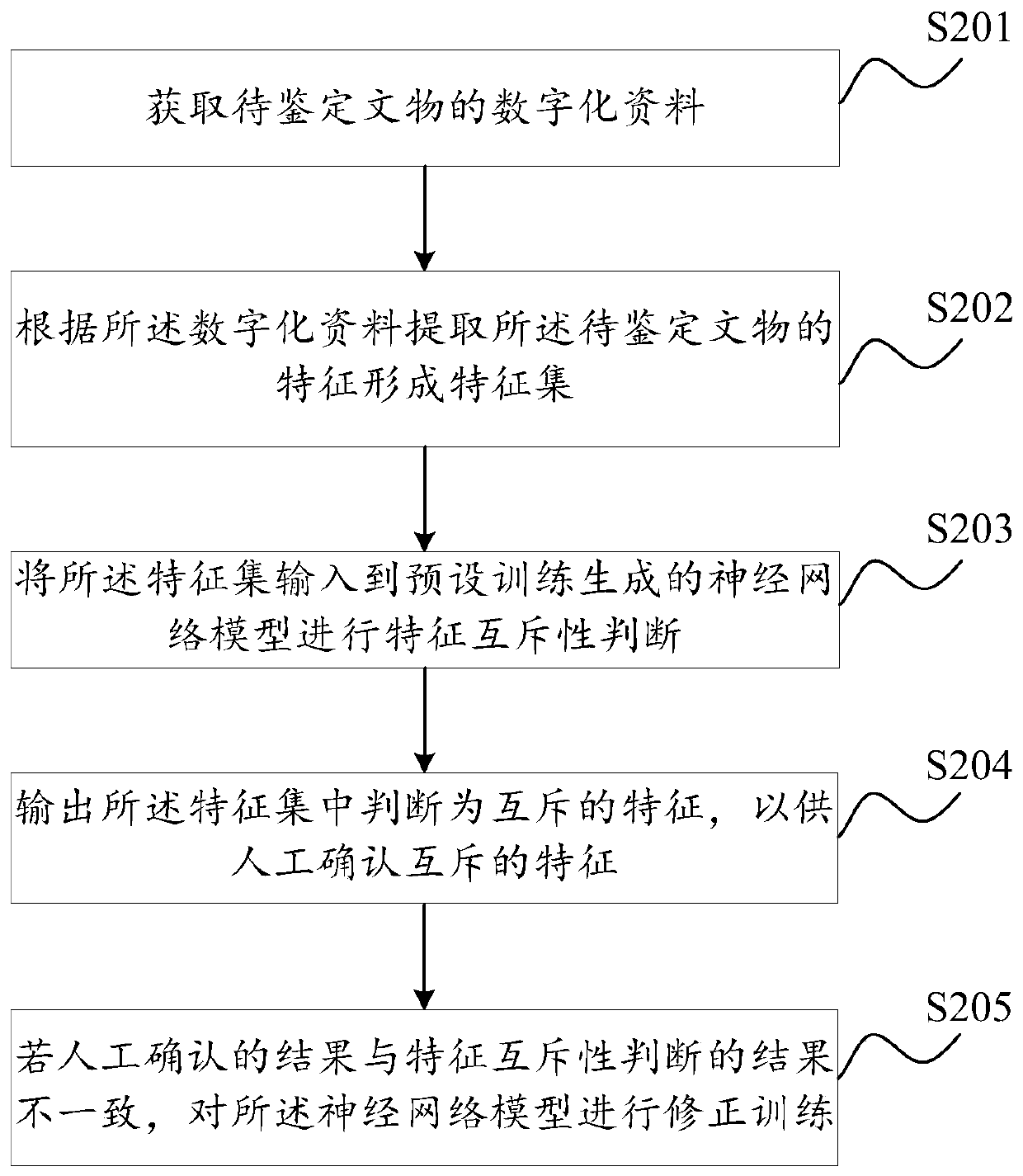
The embodiment of the invention discloses a cultural relic identification method and device based on artificial intelligence, equipment and a storage medium, and the method comprises the steps: obtaining digital data of a to-be-identified cultural relic, the digital data comprising at least one of image data and instrument detection data; extracting features of the to-be-identified cultural relicsaccording to the digital data to form a feature set; inputting the feature set into a neural network model generated by preset training for feature mutex judgment, wherein the neural network model isobtained by training from a historical database; and outputting the mutually exclusive features judged in the feature set so as to manually confirm the mutually exclusive features, preliminarily solving the problem that in the prior art, common collectors and investors have relatively weak identification capability on cultural relics through artificial intelligence-based identification.
Owner:广州欧科信息技术股份有限公司
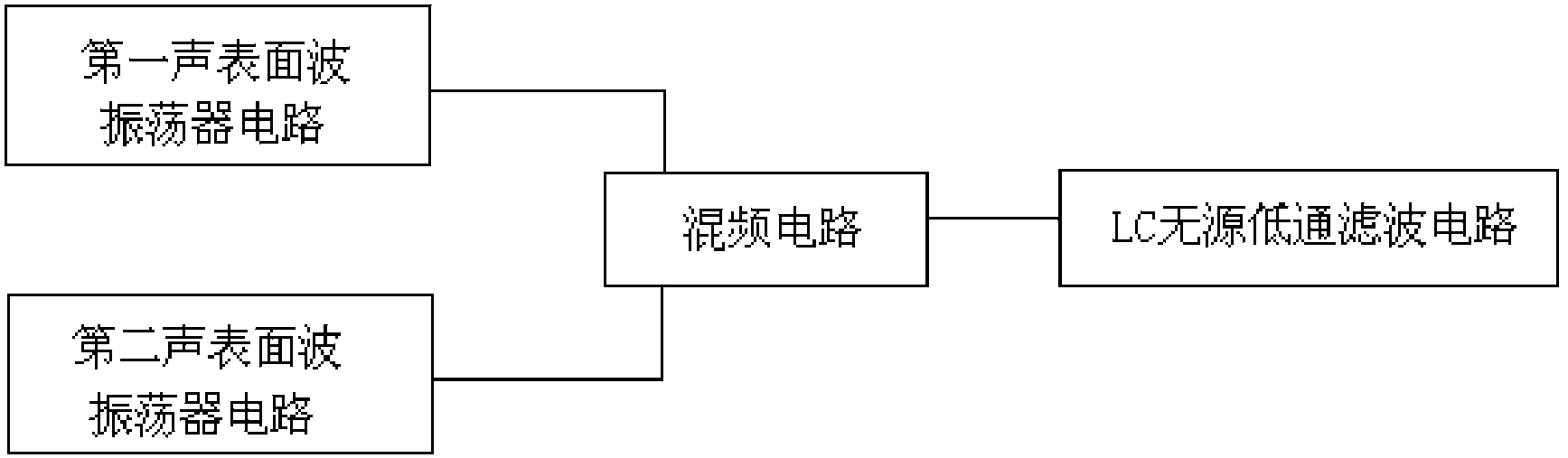
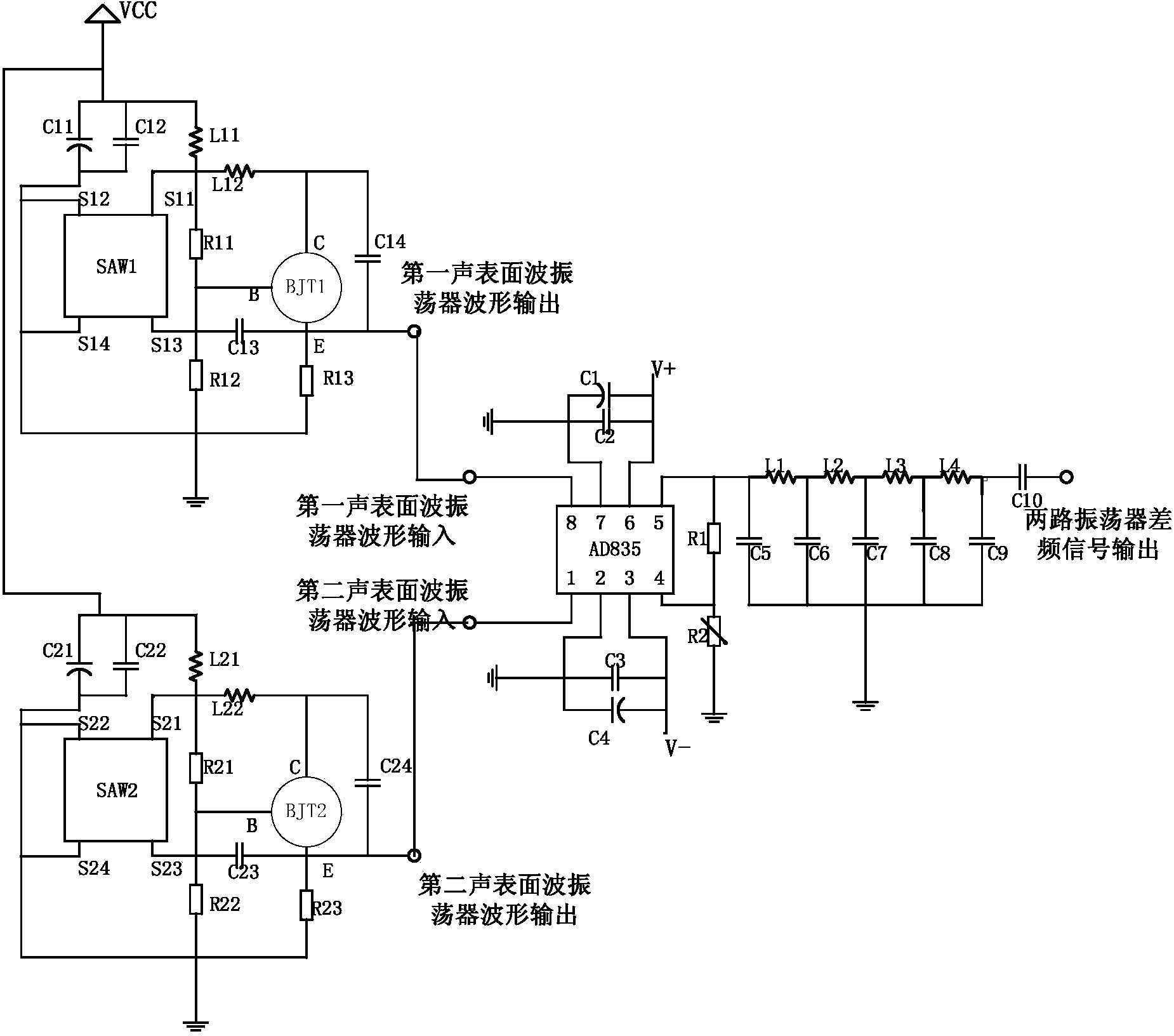
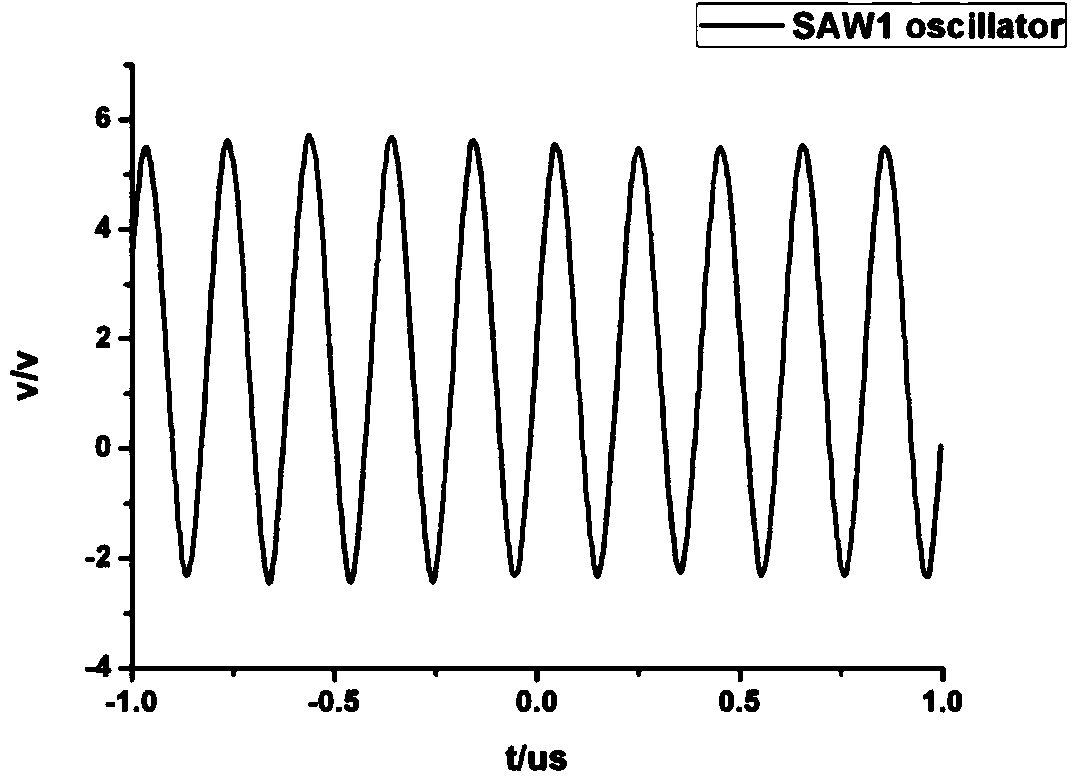
Application circuit of surface acoustic wave transducer
InactiveCN103873013AEffective filteringHigh harmonic impedance is smallImpedence networksCapacitanceNegative feedback
The invention discloses an application circuit of a surface acoustic wave transducer. The application circuit comprises a first surface acoustic wave oscillator circuit, a second surface acoustic wave oscillator circuit, a mixer circuit and an LC passive low-pass filter circuit, wherein the output end of the first surface acoustic wave oscillator circuit and the output end of the second surface acoustic wave oscillator circuit are connected with the input end of the mixer circuit respectively, and the output end of the mixer circuit is connected with the input end of the LC passive low-pass filter circuit. According to the application circuit, a three-point capacitive negative feedback element is adopted as a frequency selection and feedback network, the feedback voltage of the capacitive negative feedback element is tapped from the two ends of a capacitor, higher harmonics can be effectively filtered out with small impedance, and stable waveform output is achieved; a high-frequency low-power tube amplifying circuit is a bias-emitter common-collector amplifying circuit, persistent oscillation is achieved, and therefore oscillation signals are more stable; two surface acoustic wave oscillators form a two-channel structure, interference caused by the external environment is avoided, and high-precision measurement of physical quantities to be measured is achieved.
Owner:CHANGAN UNIV
Puf method using and circuit having an array of bipolar transistors
ActiveUS20150028847A1Easy to implementHarderElectronic circuit testingInternal/peripheral component protectionCommon emitterCommon base
A method of identifying a component by a response to a challenge is disclosed, the component comprising an array of bipolar transistors connectable in parallel so as to have a common collector contact, a common emitter contact and a common base contact, the challenge comprising a value representative of a total collector current value, the method comprising: receiving the challenge; supplying the total collector current to the common collector contact; detecting instability in each of a group of the transistors; and determining the response in dependence on the group. A circuit configured to operate such a method is also disclosed.
Owner:NXP BV
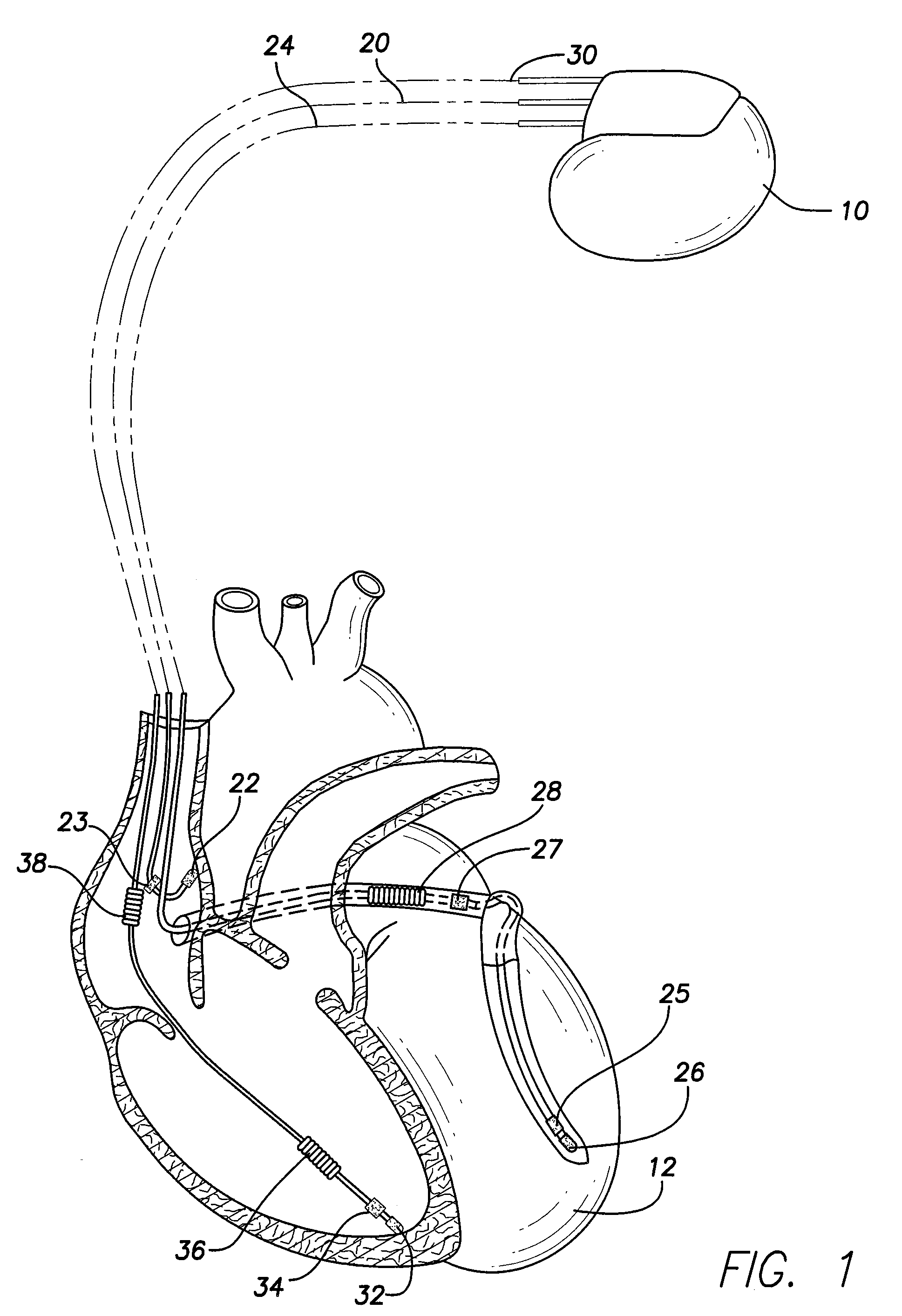
Methods and systems for implementing an SCR topology in a high voltage switching circuit
In accordance with an embodiment, a high voltage switching and control circuit for an implantable medical device (IMD) is provided that comprises a high voltage positive (HVP) node configured to receive a positive high voltage signal from a high energy storage source; and a high voltage negative (HVN) node configured to receive a negative high voltage signal from a high energy storage source. First and second output terminals are configured to be connected to electrodes for delivering high voltage energy. First and second Silicon Controlled Rectifiers (SCR) switches are connected to the HVP node, the first and second SCR switches connected to the first and second output terminals respectively, wherein the first and second SCR switches each include a Darlington transistor pair having a first transistor stage joined to a second stage transistor at a common collector node.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Polysilicon Plug Bipolar Transistor For Phase Change Memory
Memory devices and methods for manufacturing are described herein. A memory device described herein includes a plurality of memory cells. Memory cells in the plurality of memory cells comprise respective bipolar junction transistors and memory elements. The bipolar junction transistors are arranged in a common collector configuration and include an emitter comprising doped polysilicon having a first conductivity type, the emitter contacting a corresponding word line in a plurality of word lines to define a pn junction. The bipolar junction transistors include a portion of the corresponding word line underlying the emitter acting as a base, and a collector comprising a portion of the single-crystalline substrate underlying the base.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
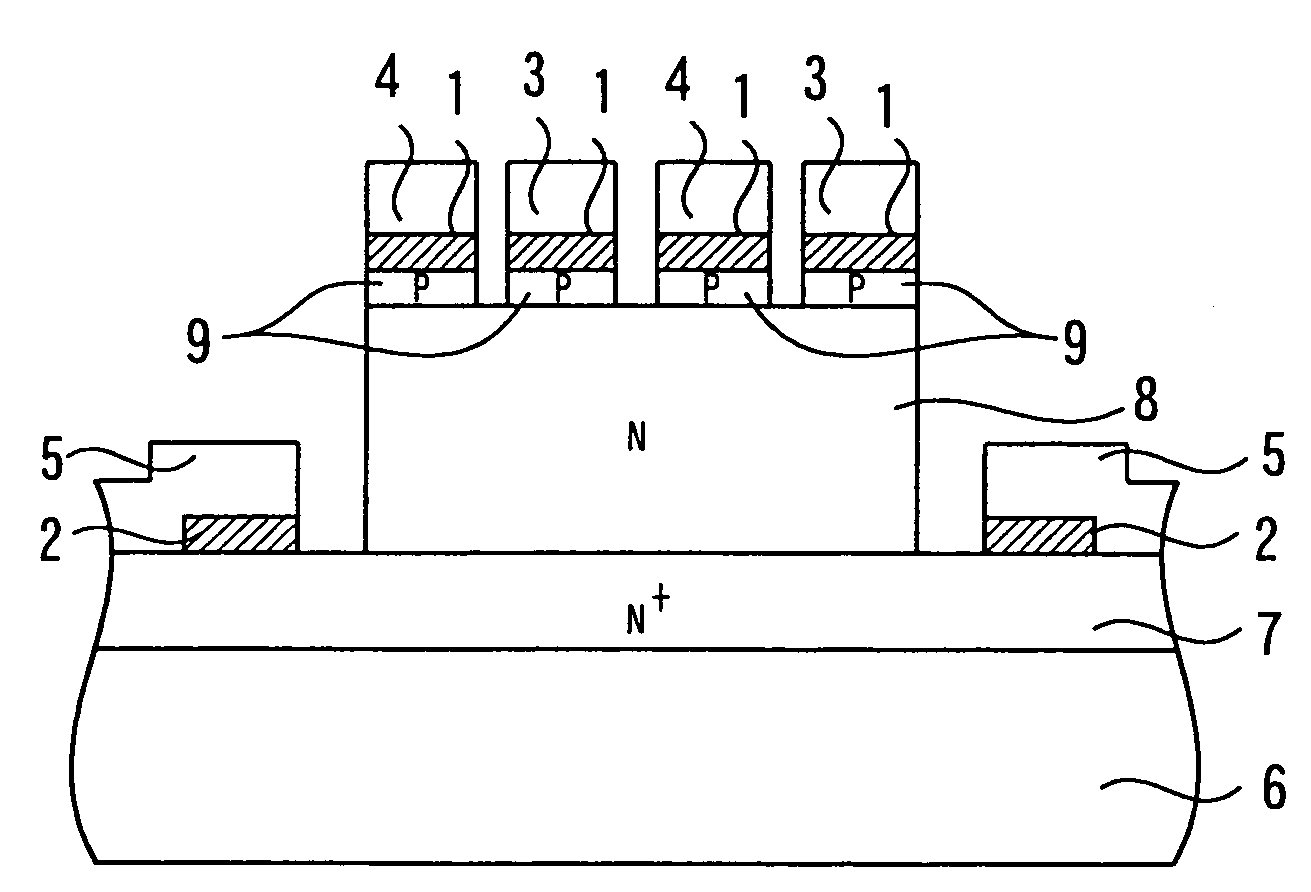
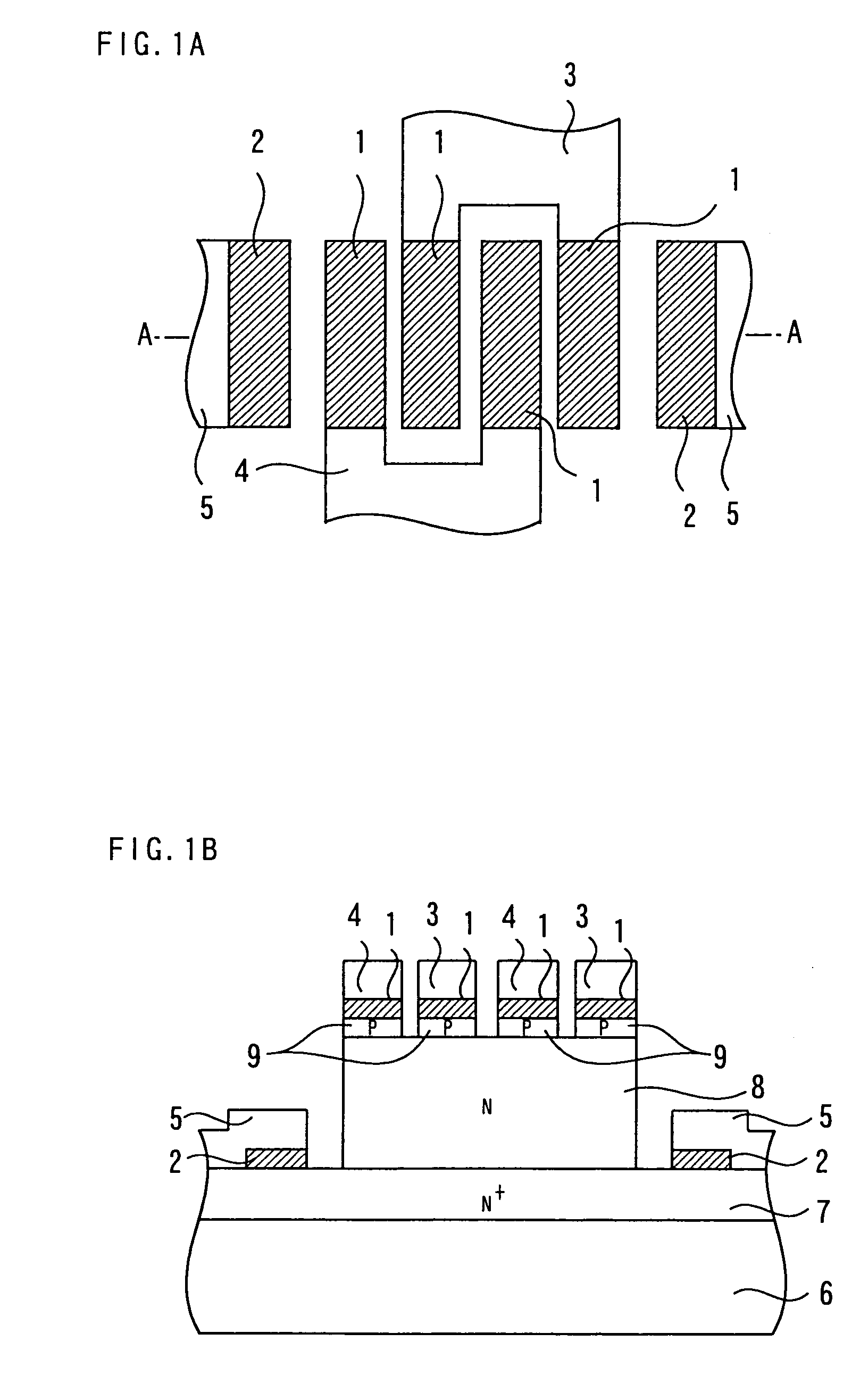
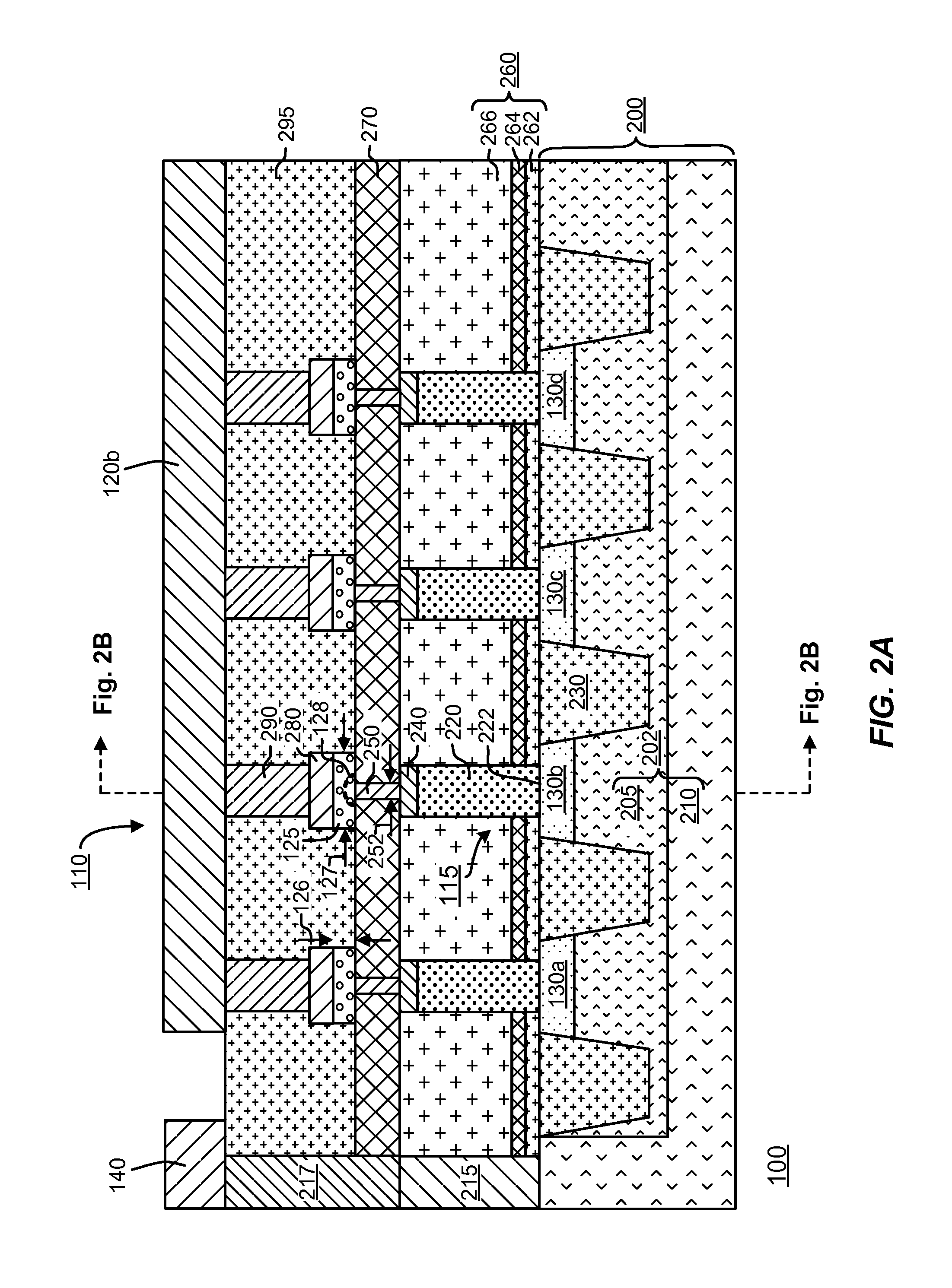
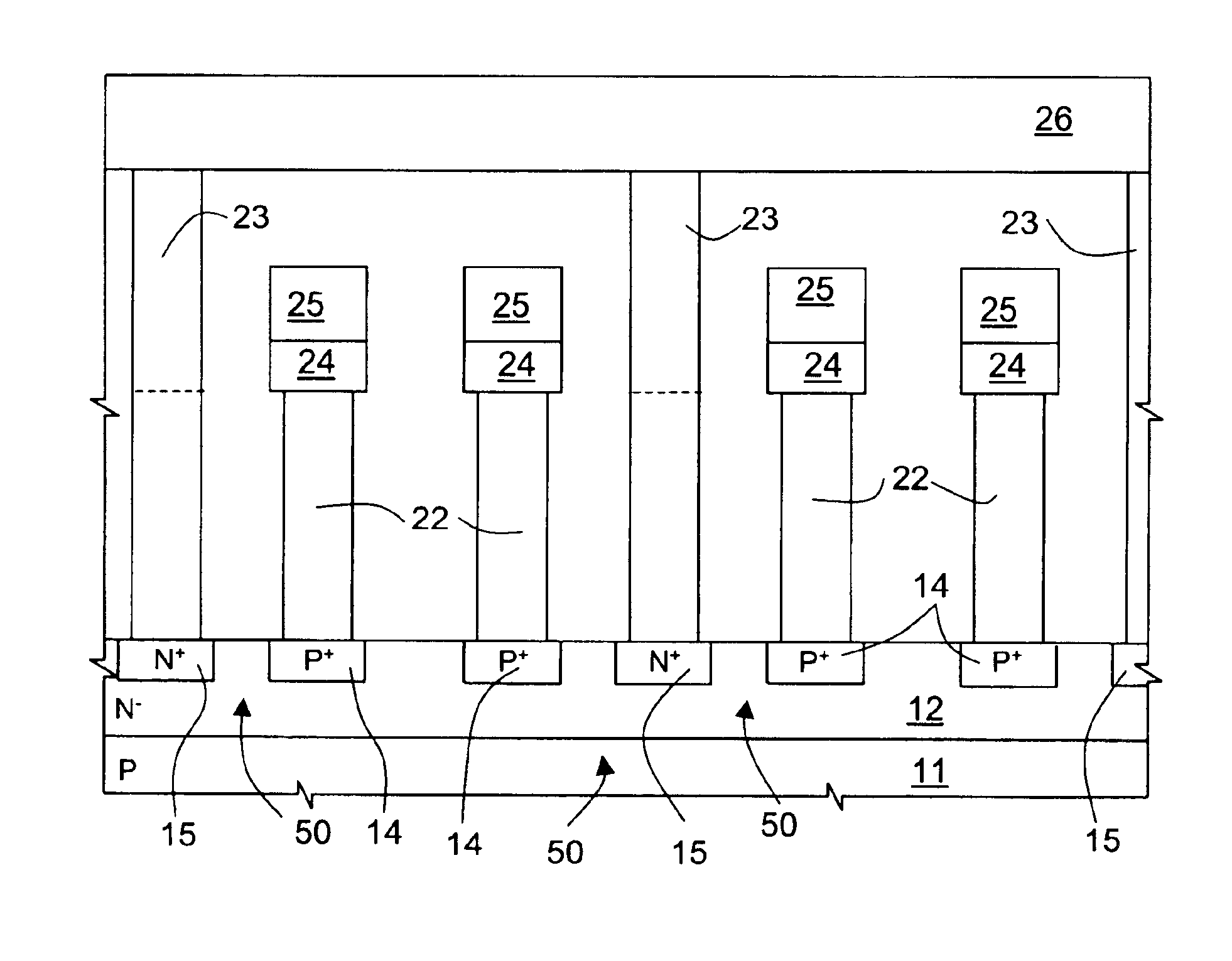
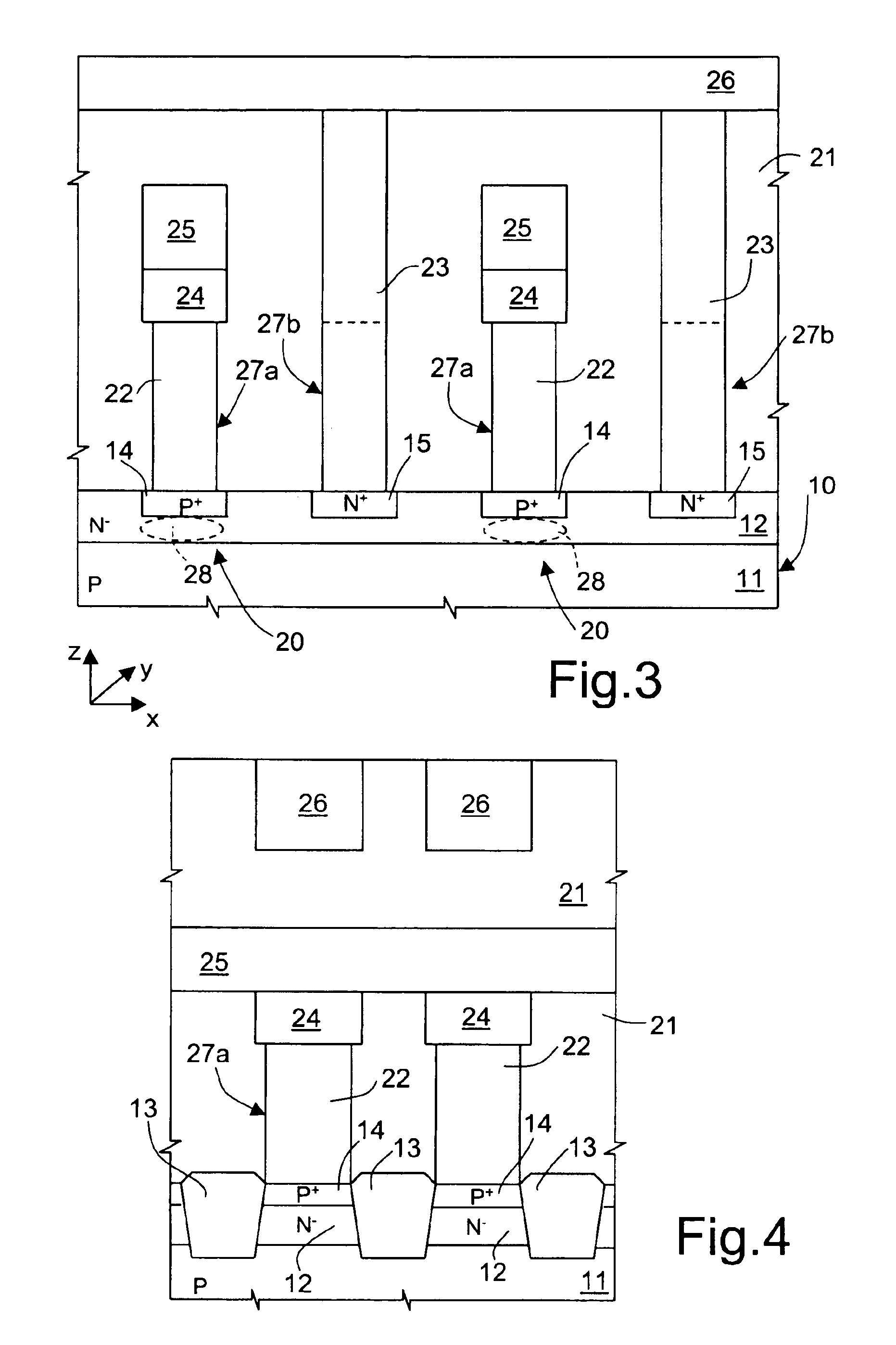
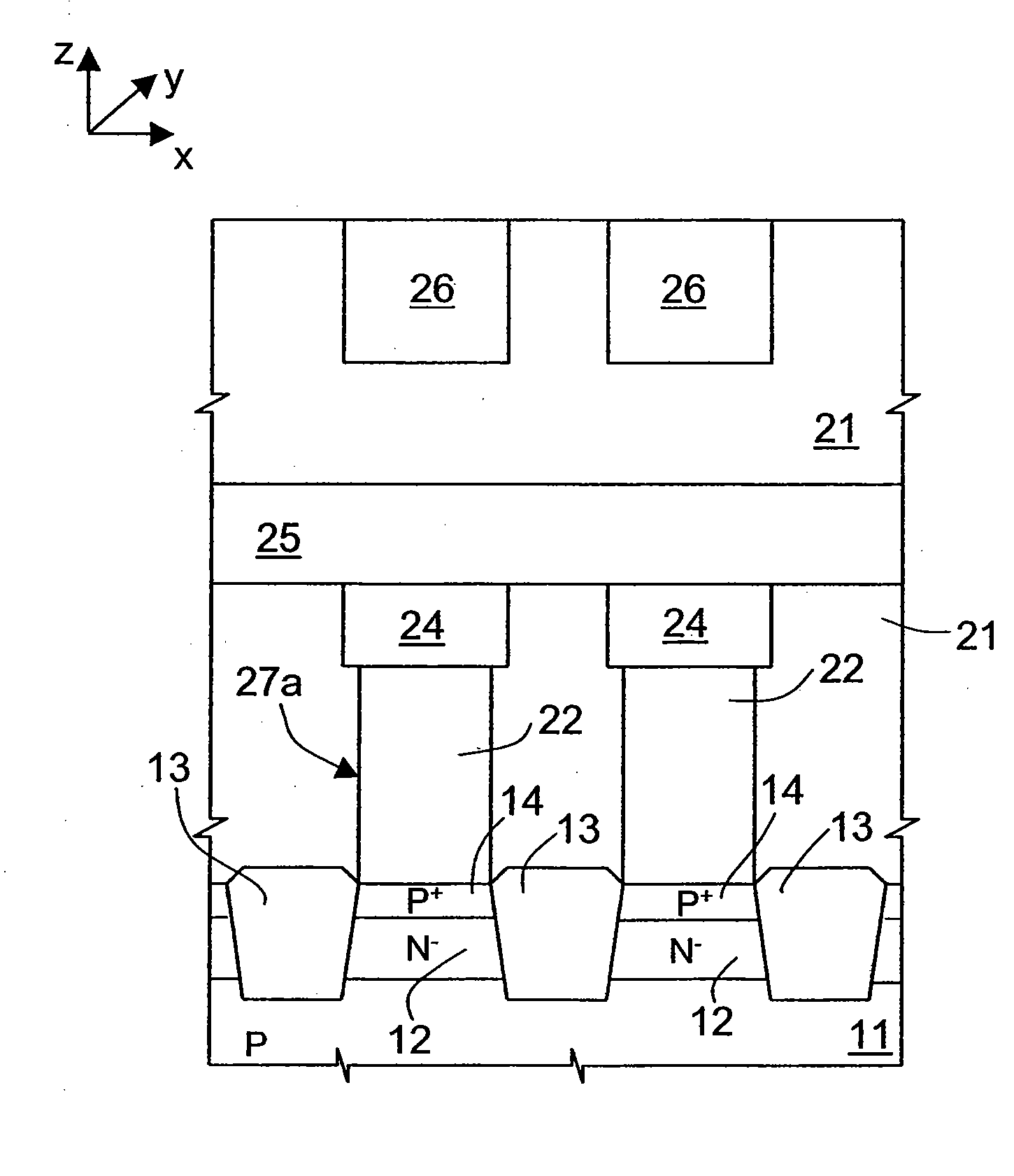
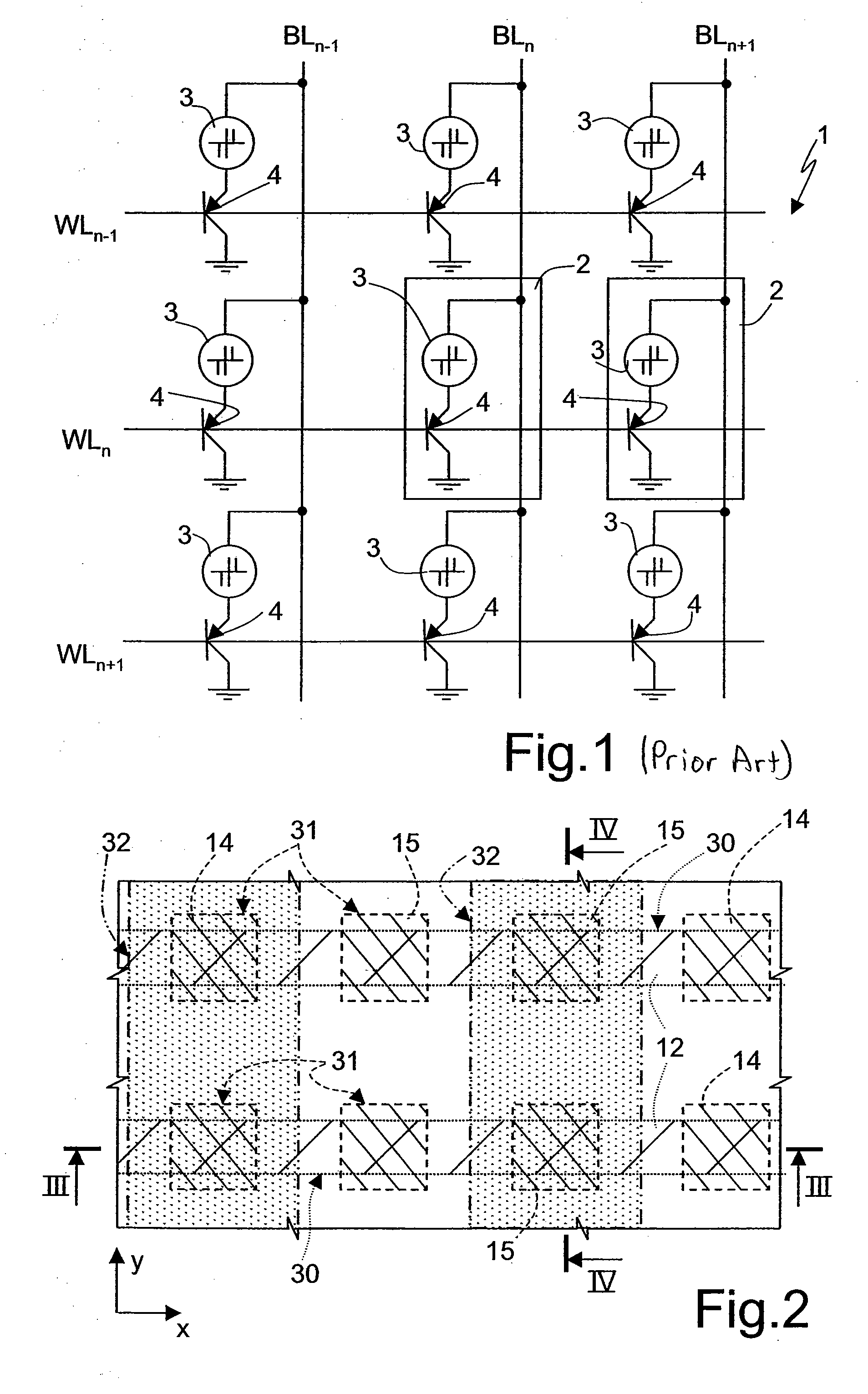
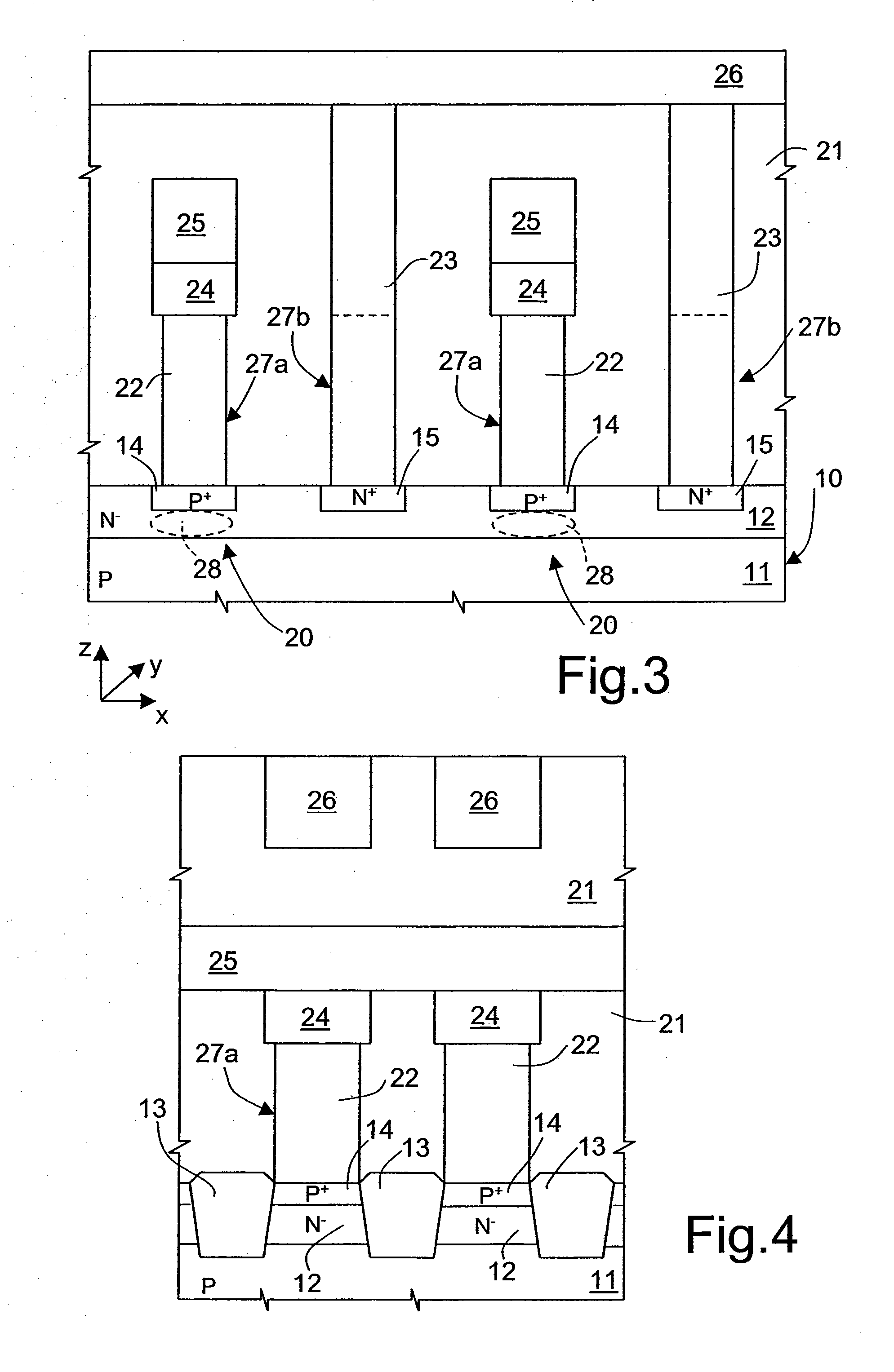
Array of cells including a selection bipolar transistor and fabrication method thereof
A cell array is formed by a plurality of cells each including a selection bipolar transistor and a storage component. The cell array is formed in a body including a common collector region of P type; a plurality of base regions of N type, overlying the common collector region; a plurality of emitter regions of P type formed in the base regions; and a plurality of base contact regions of N type and a higher doping level than the base regions, formed in the base regions, wherein each base region is shared by at least two adjacent bipolar transistors.
Owner:OVONYX MEMORY TECH LLC
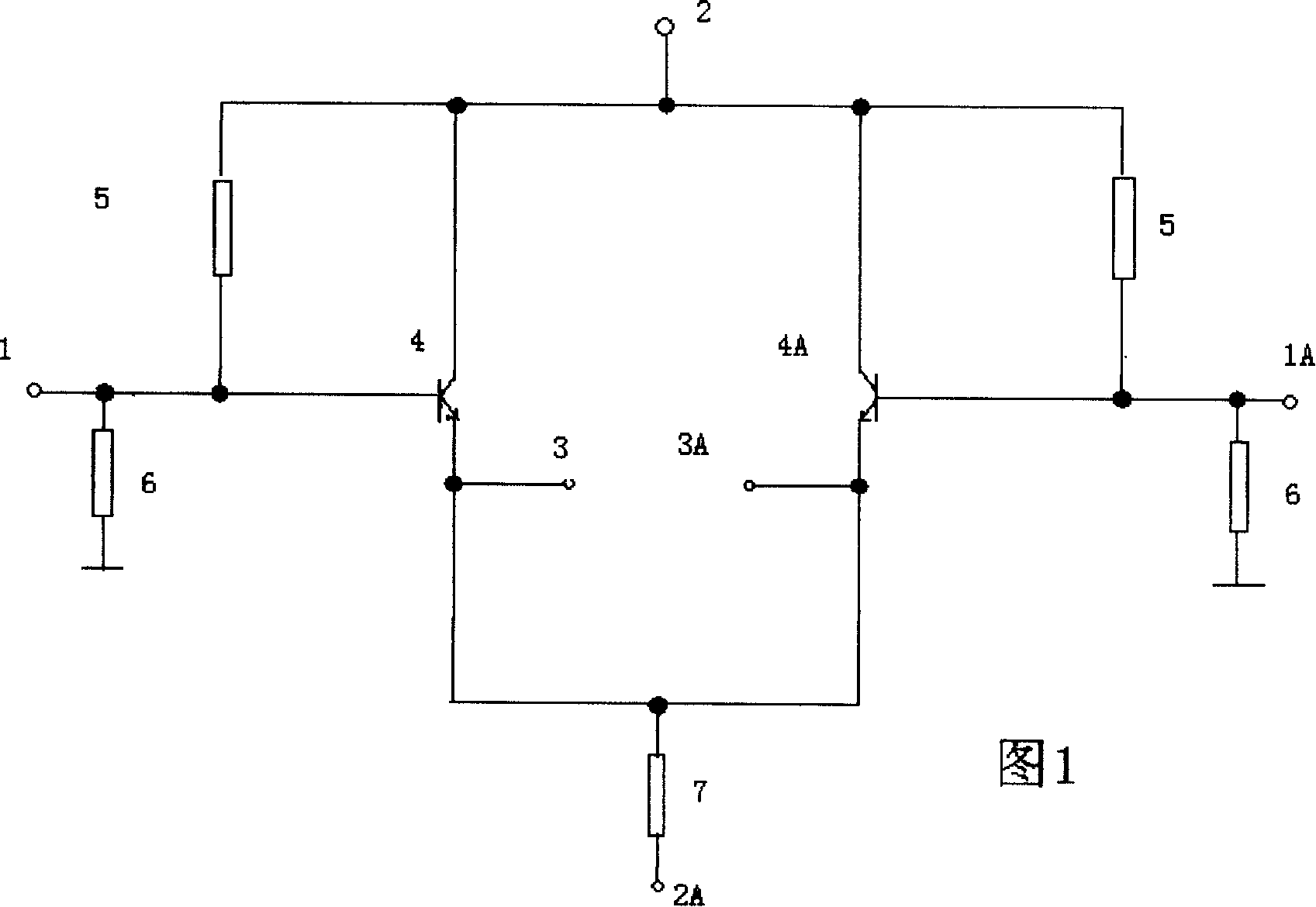
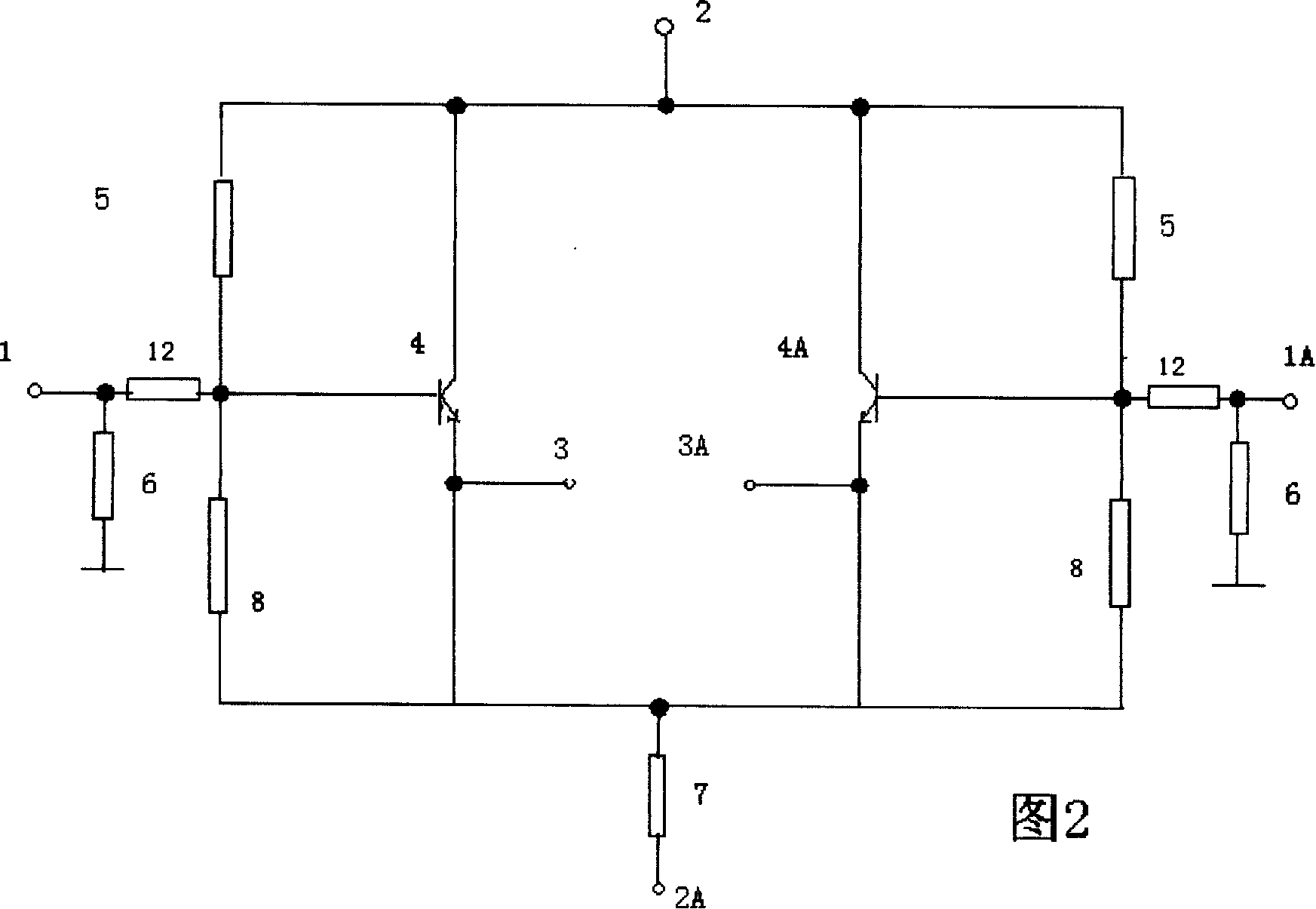
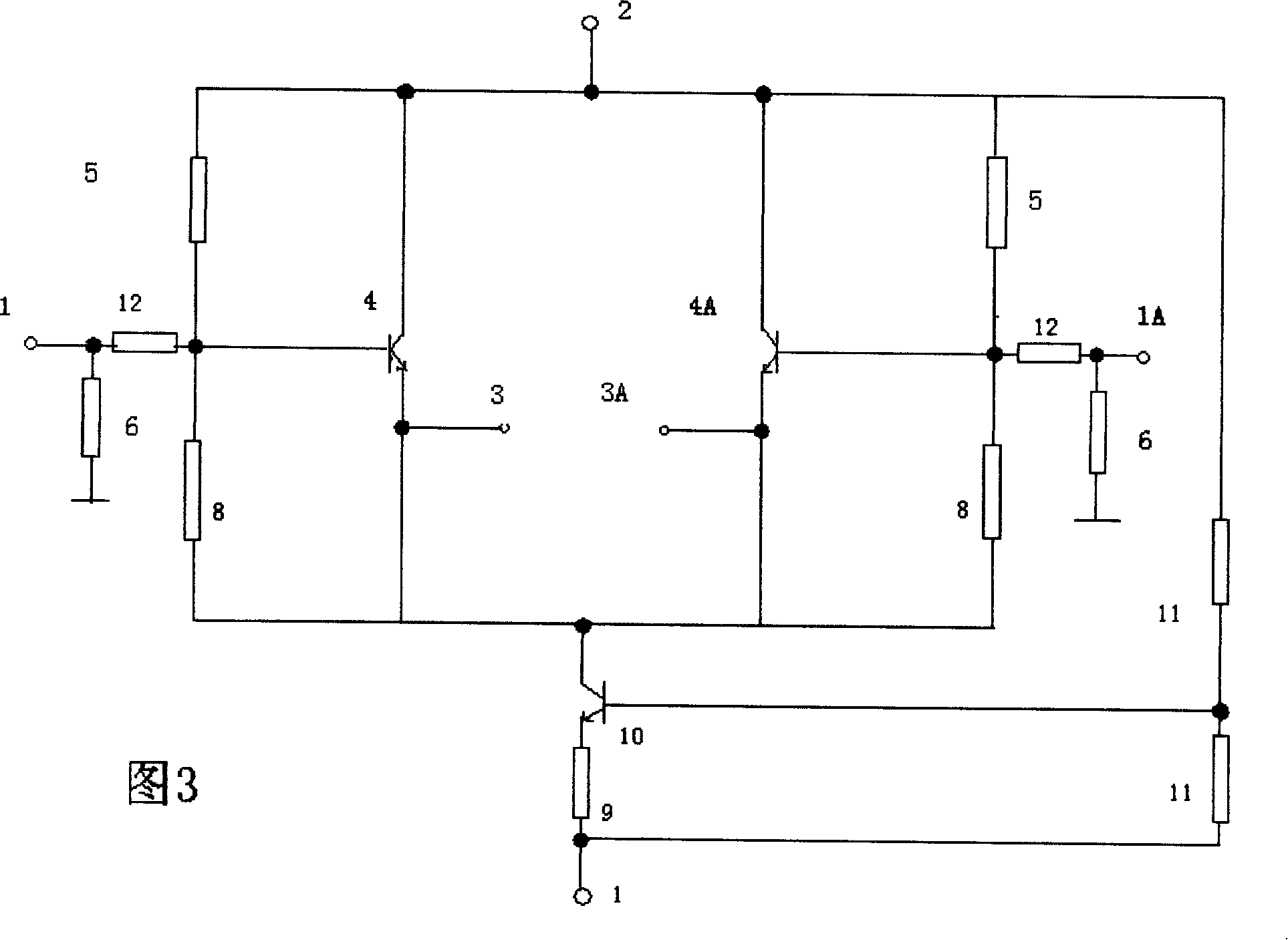
Differential common collector amplifying circuit
InactiveCN101232273AStrong interference abilityHigh input resistanceAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionPower amplifiersCommon collectorLow input
The invention relates to a difference common collector amplifying circuit which is a device of an amplifying signal current for decreasing the distortion factor of a power amplification circuit. At present, a well-known current amplifying circuit of a station amplifier generally adopts an OCL circuit, in which the utility ratio of a power supply is higher, the direct coupling is realized, the circuit is simple and the power is big, but the performance of common-mode interference resistance of the circuit is reduced because non-equilibrium design is adopted, and the distortion is larger. Based on a traditional monotube common collector amplifying circuit, the difference common collector amplifying circuit introduces a difference structure, and a fully symmetrical and balanceable circuit structure is used for resisting the common-mode interference. The invention can be mainly used in the fields of low-frequency signal current amplification, aural signal current amplification, amplifier impedance match, an amplifier high input impedance input circuit, an amplifier low input impedance output circuit, single end-balanced signal transformation, etc.
Owner:黄骐
Array of cells including a selection bipolar transistor and fabrication method thereof
ActiveUS20070099347A1Improve compactnessSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringCommon collector
A cell array is formed by a plurality of cells each including a selection bipolar transistor and a storage component. The cell array is formed in a body including a common collector region of P type; a plurality of base regions of N type, overlying the common collector region; a plurality of emitter regions of P type formed in the base regions; and a plurality of base contact regions of N type and a higher doping level than the base regions, formed in the base regions, wherein each base region is shared by at least two adjacent bipolar transistors.
Owner:OVONYX MEMORY TECH LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com