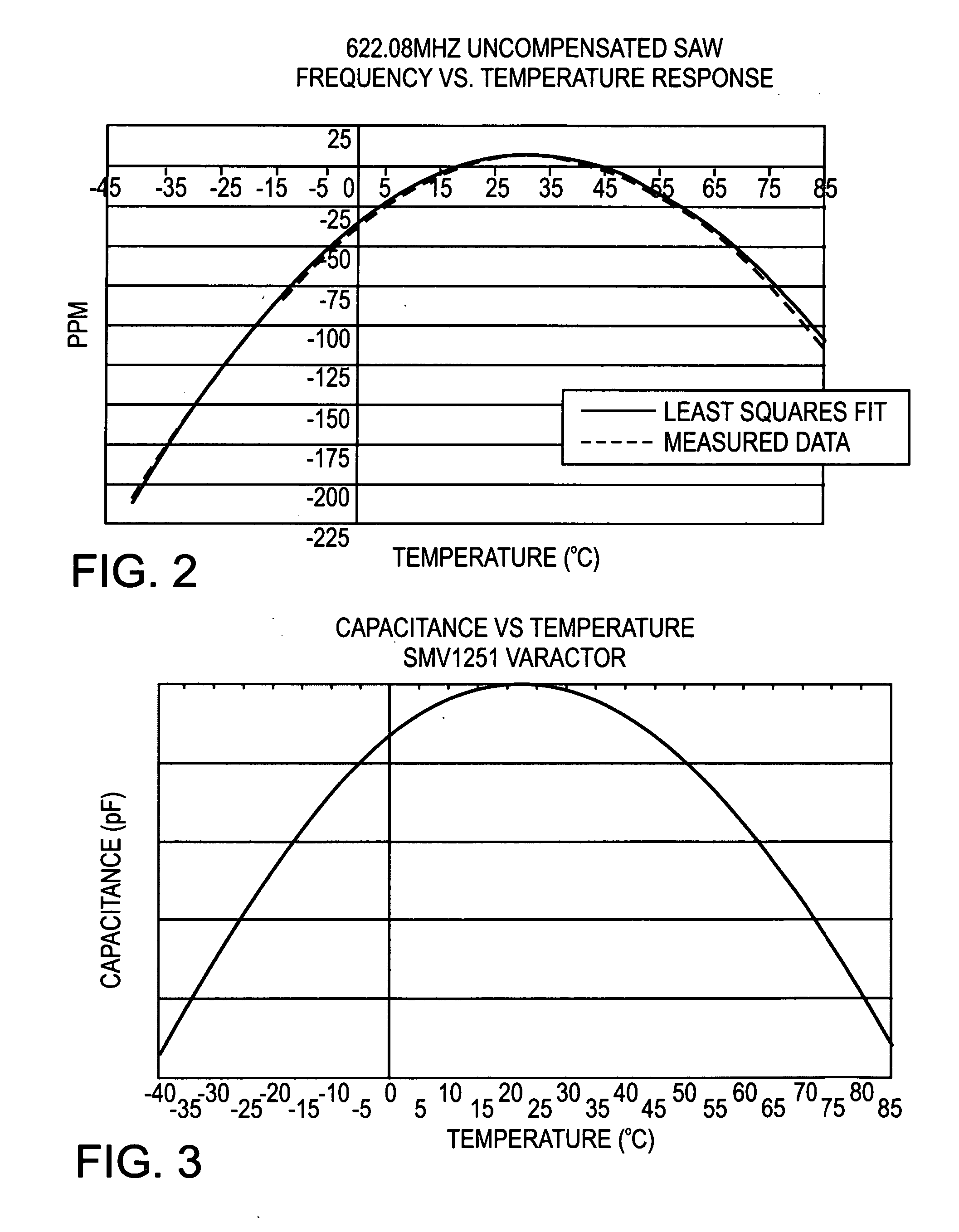
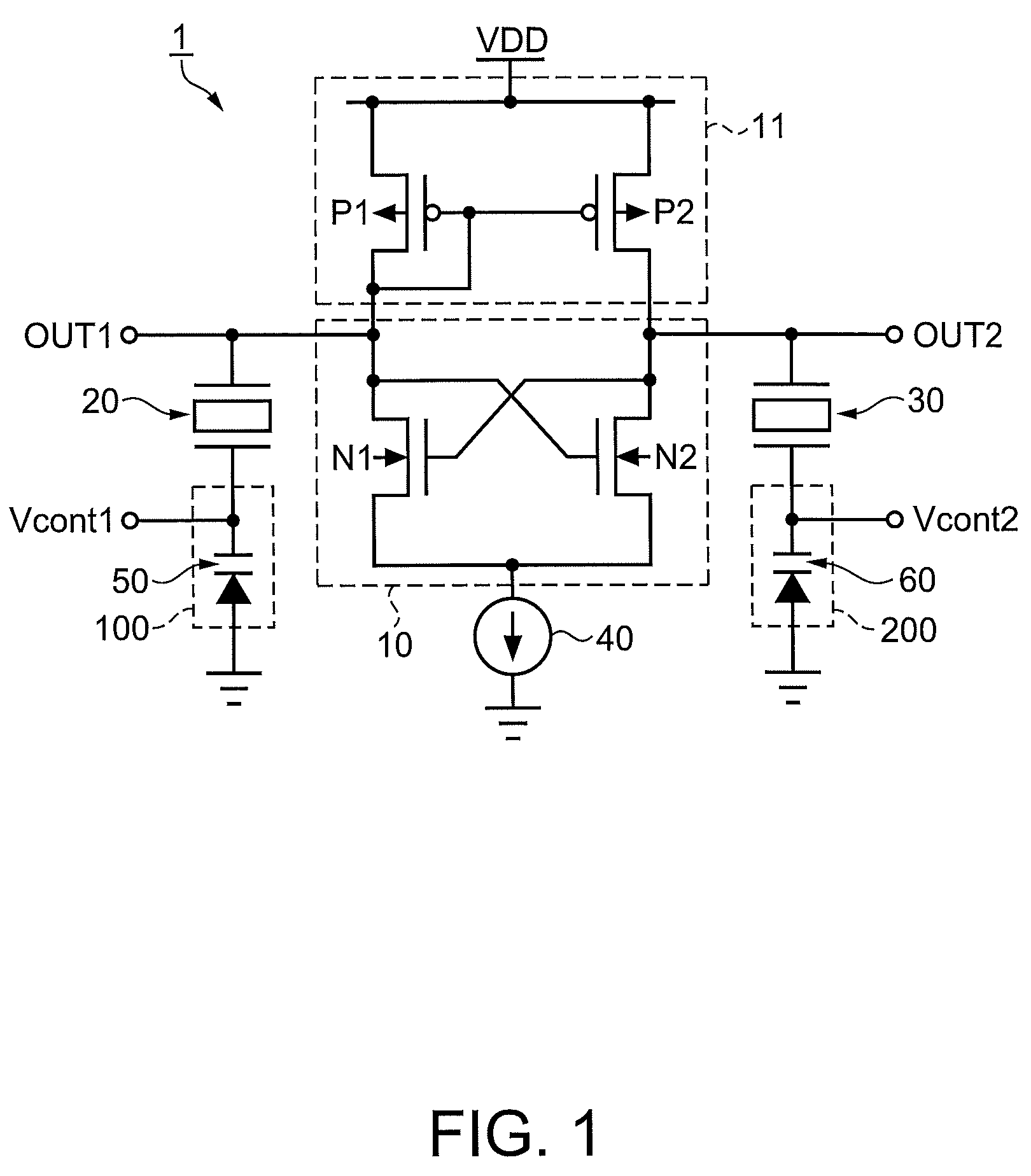
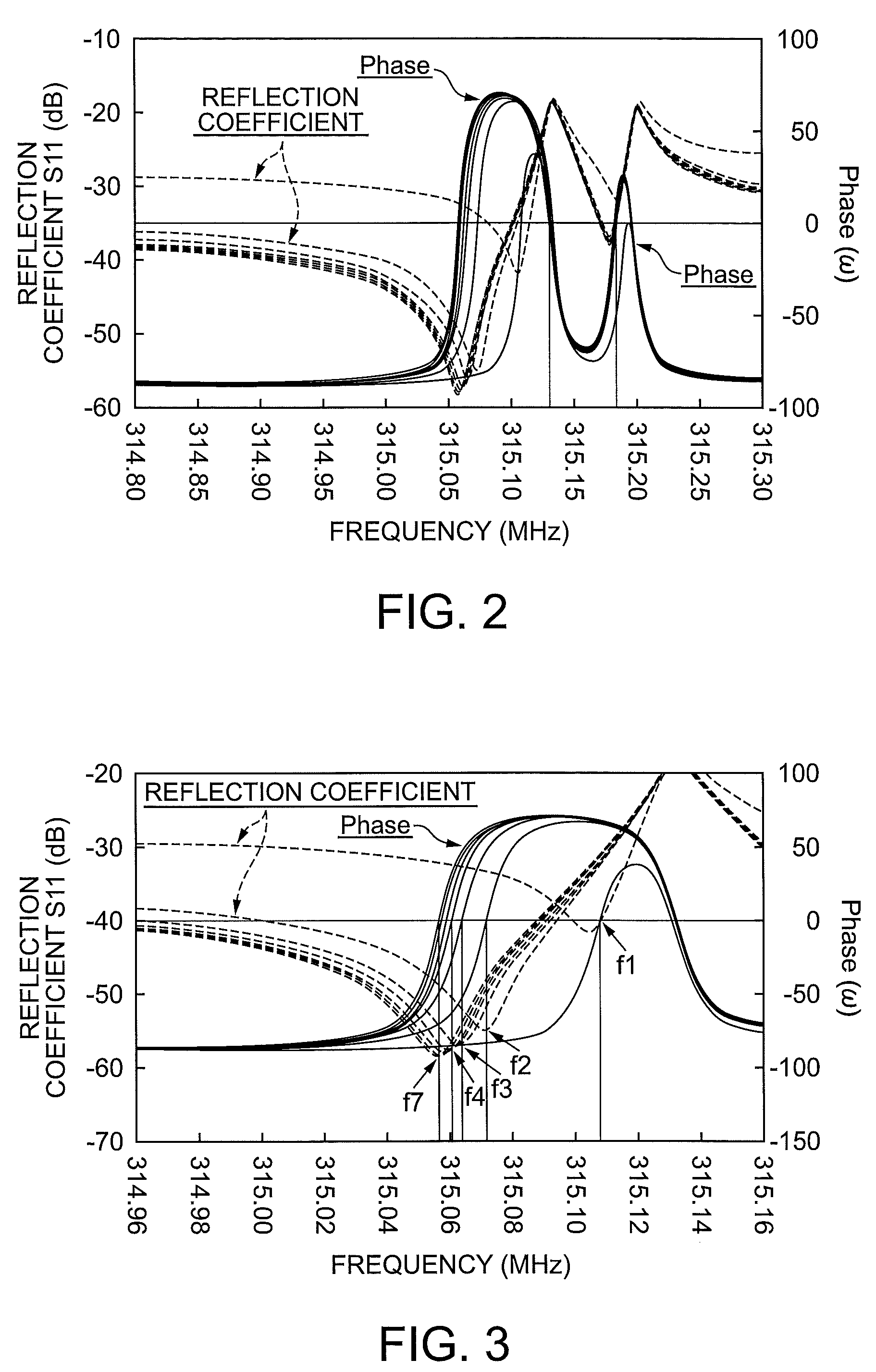
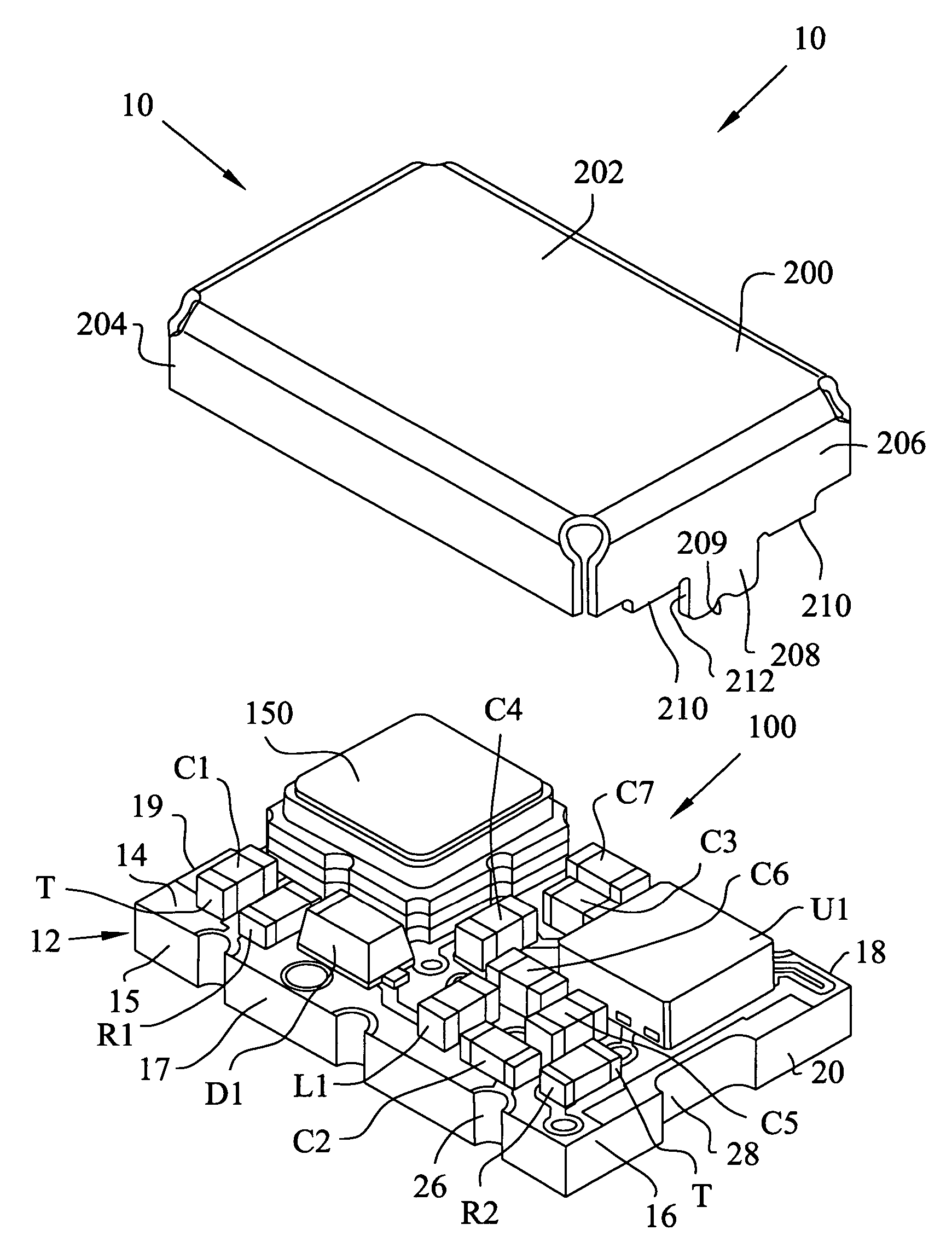
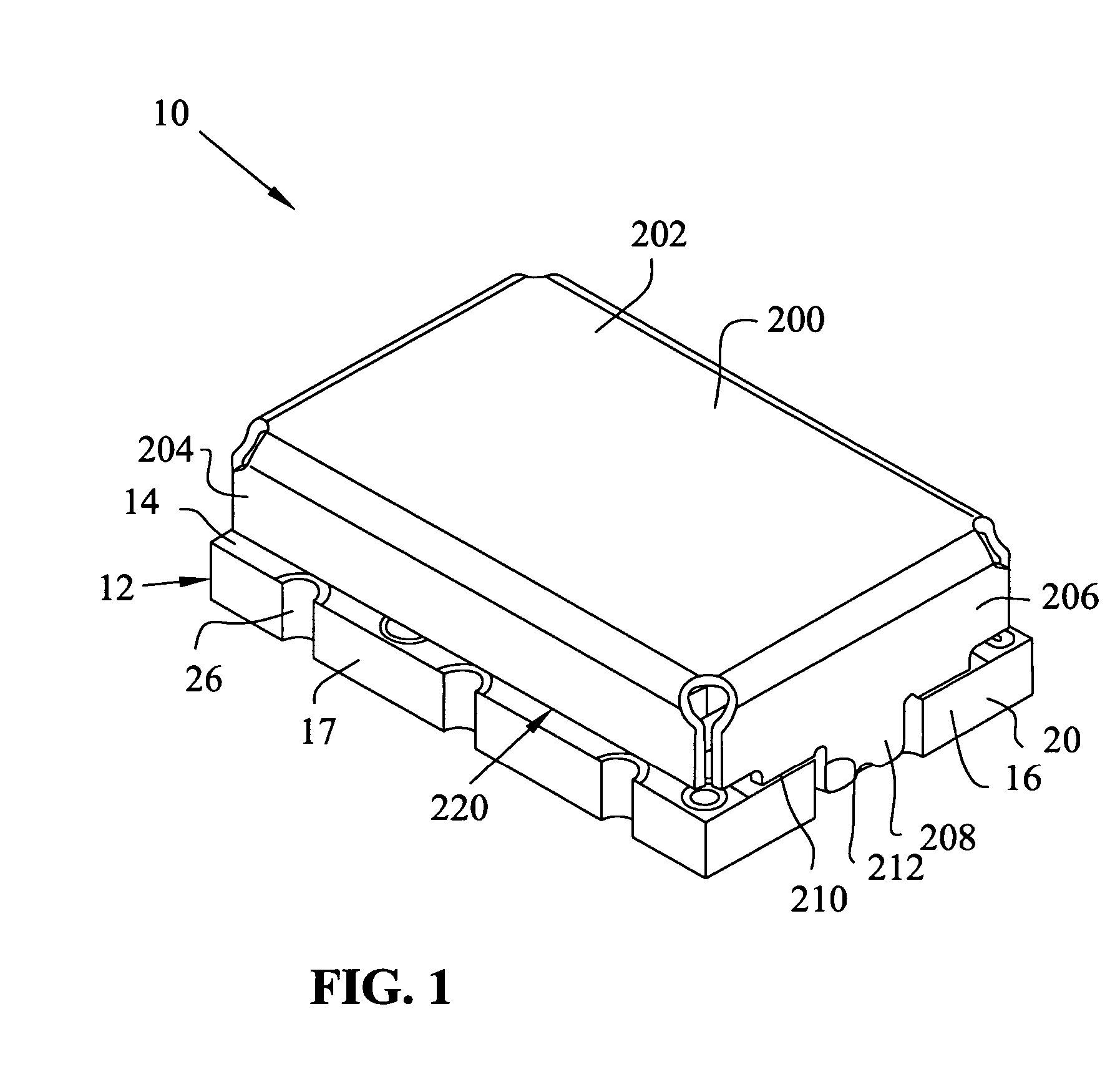
Patents
Literature
50 results about "Surface acoustic wave oscillators" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
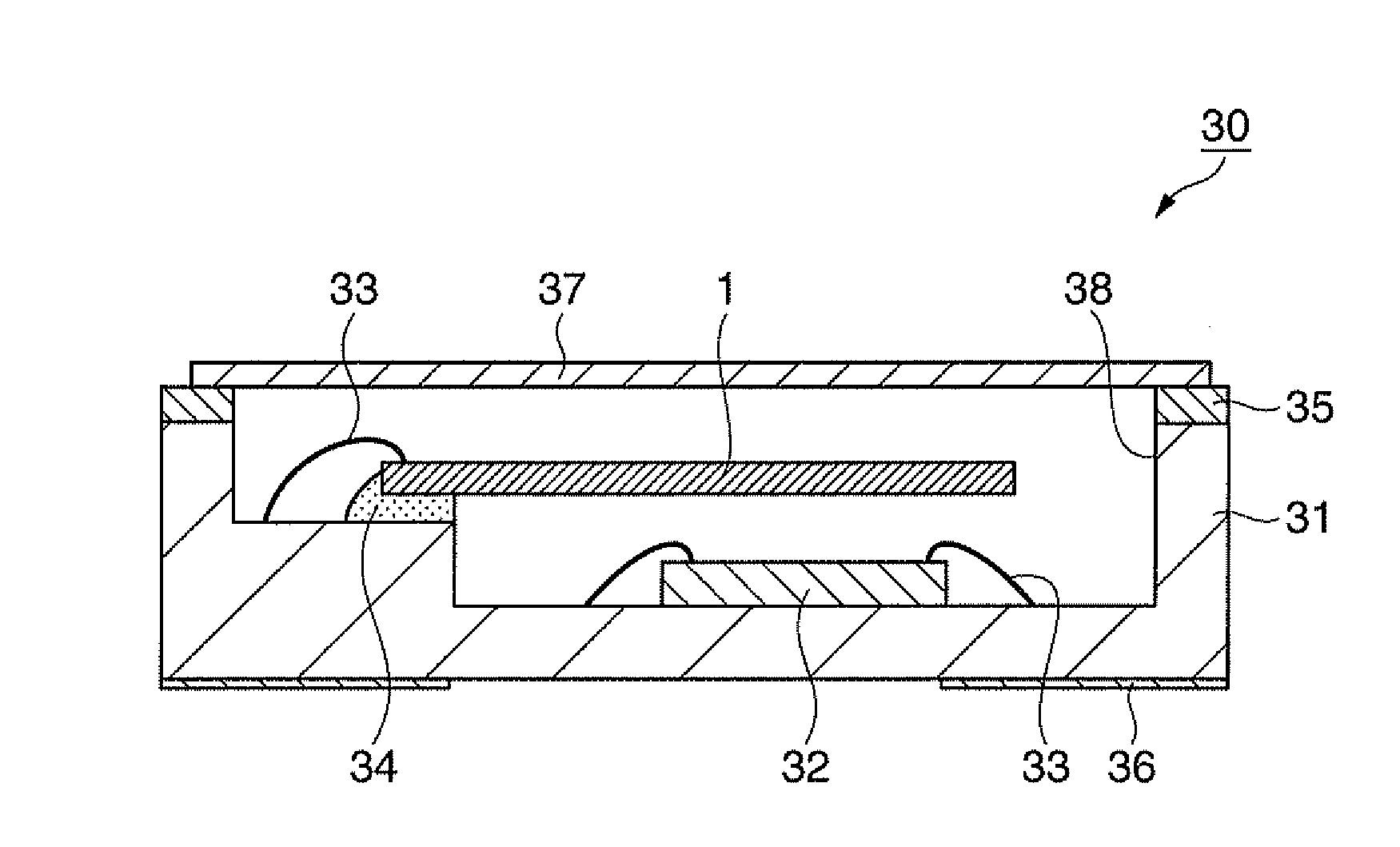
Surface acoustic wave resonator, surface acoustic wave oscillator, and surface acoustic wave module unit
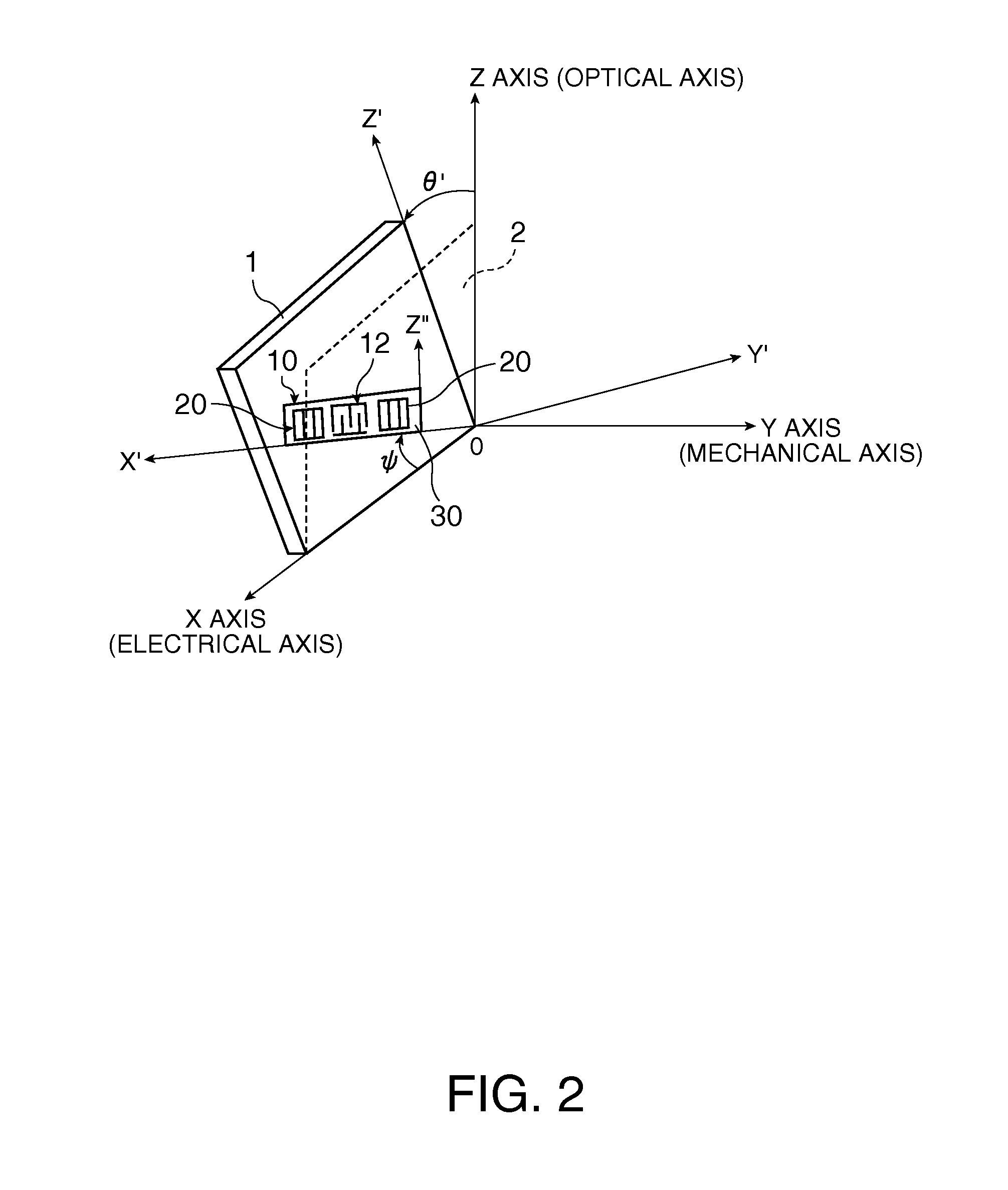
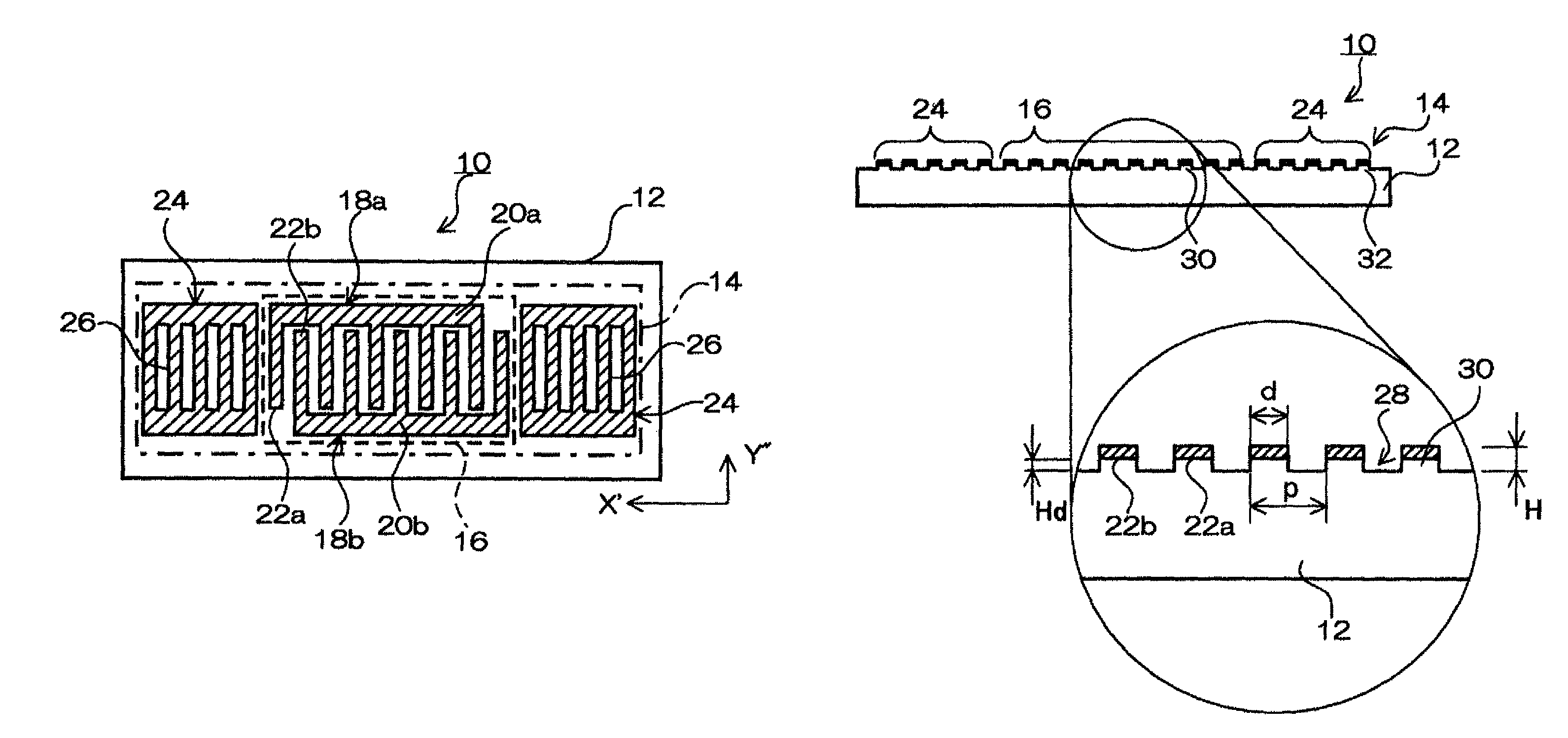
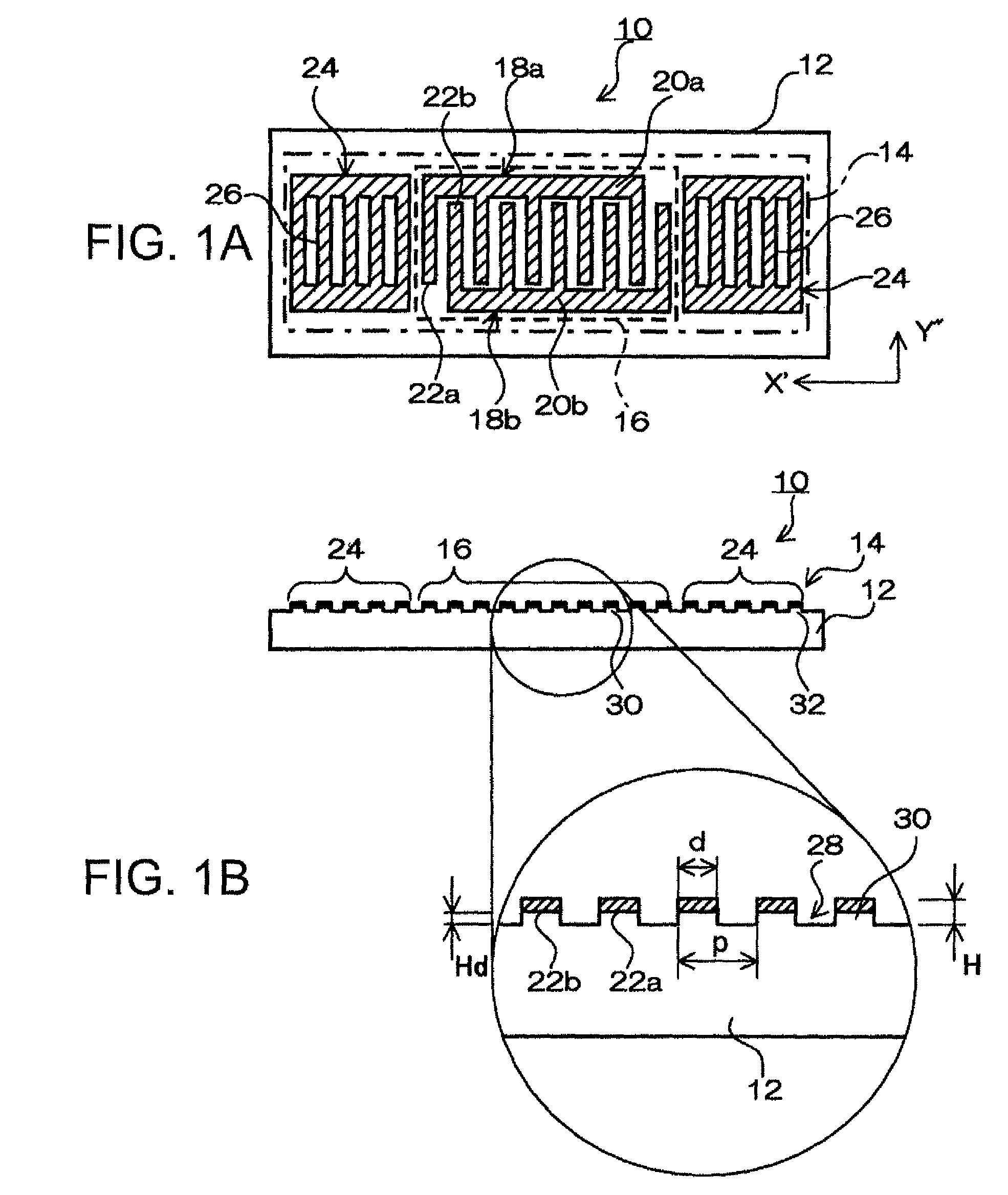
ActiveUS8344815B2Improve confinementExcellent CIPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesImpedence networksElectromechanical coupling coefficientSurface acoustic wave oscillators
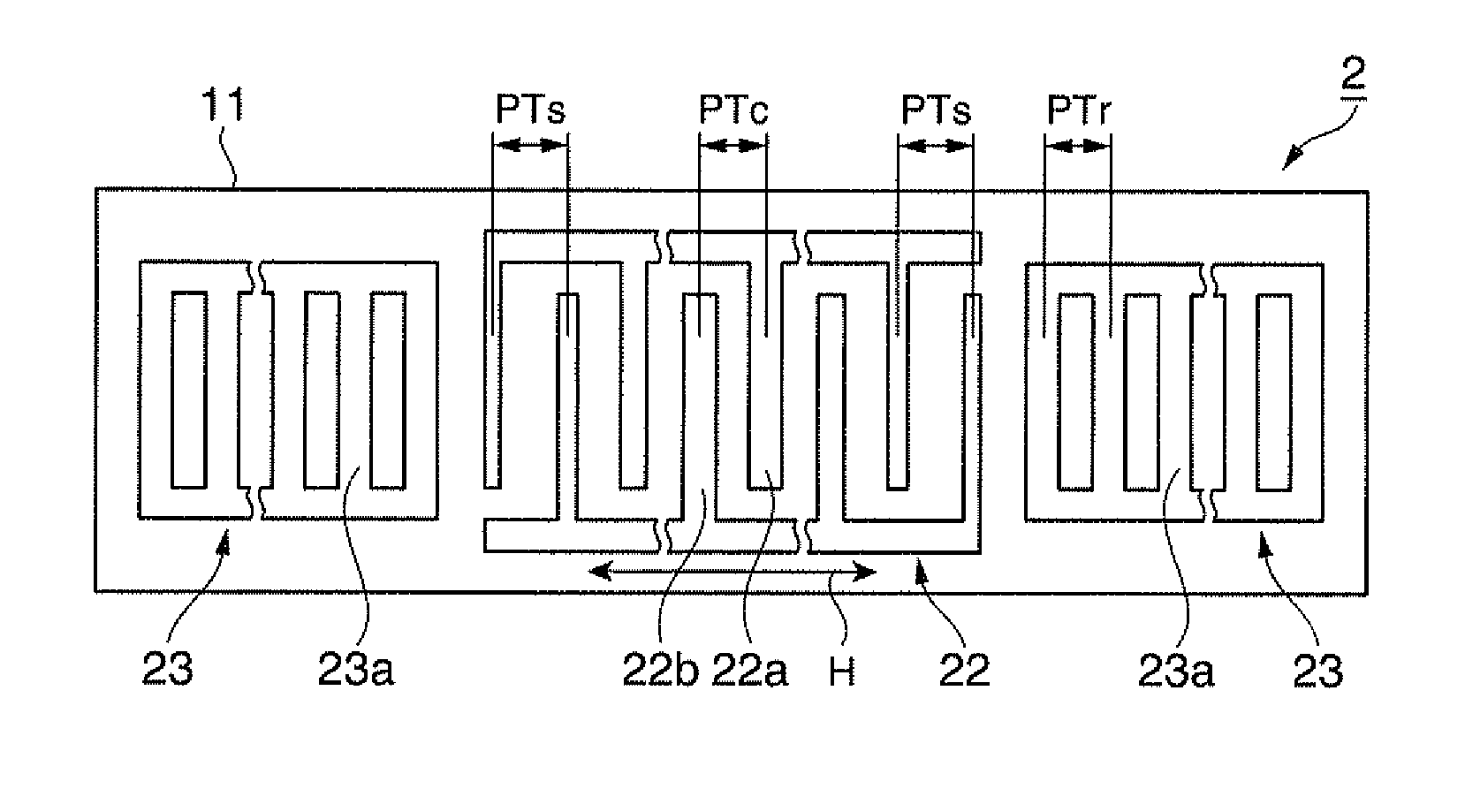
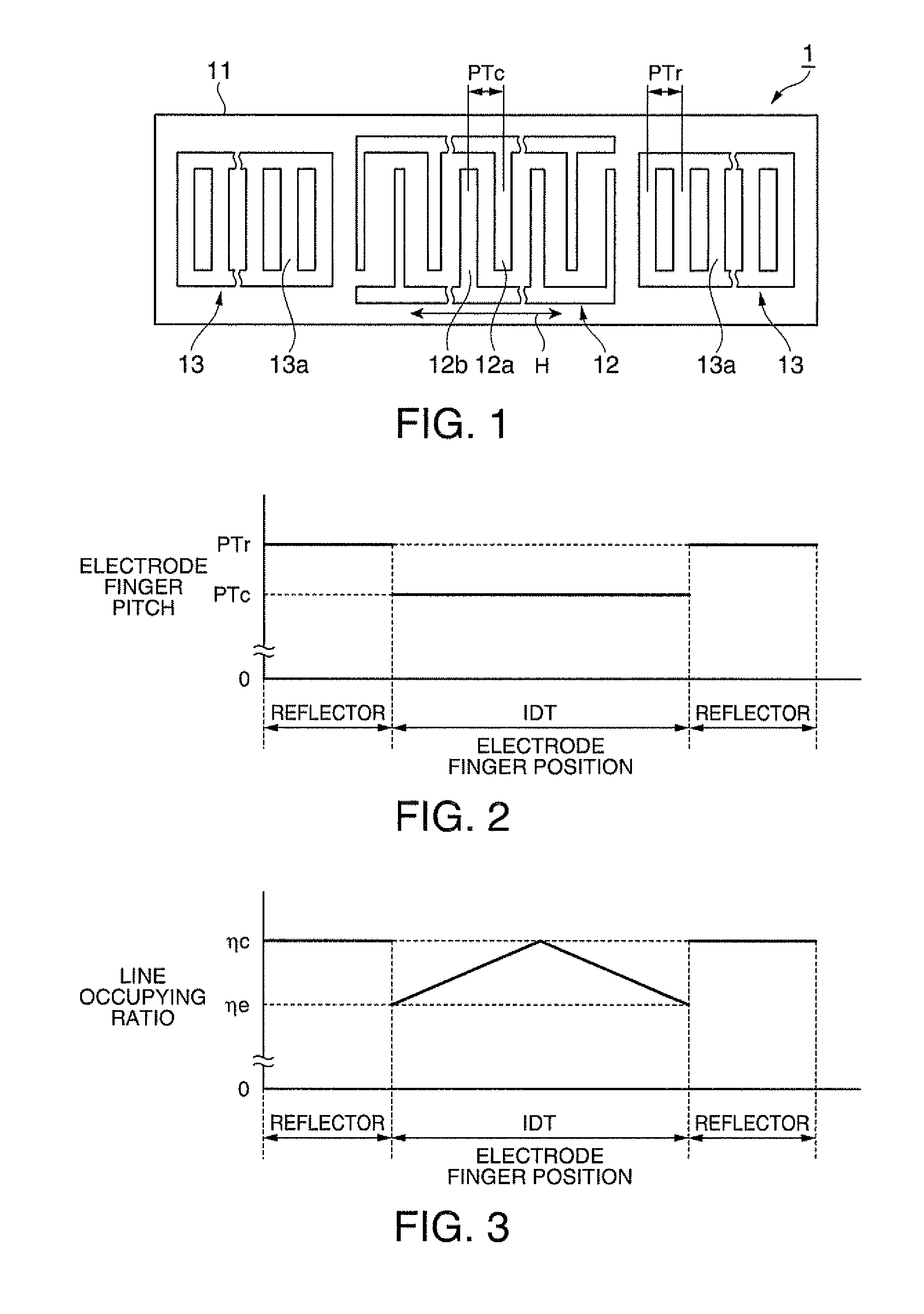
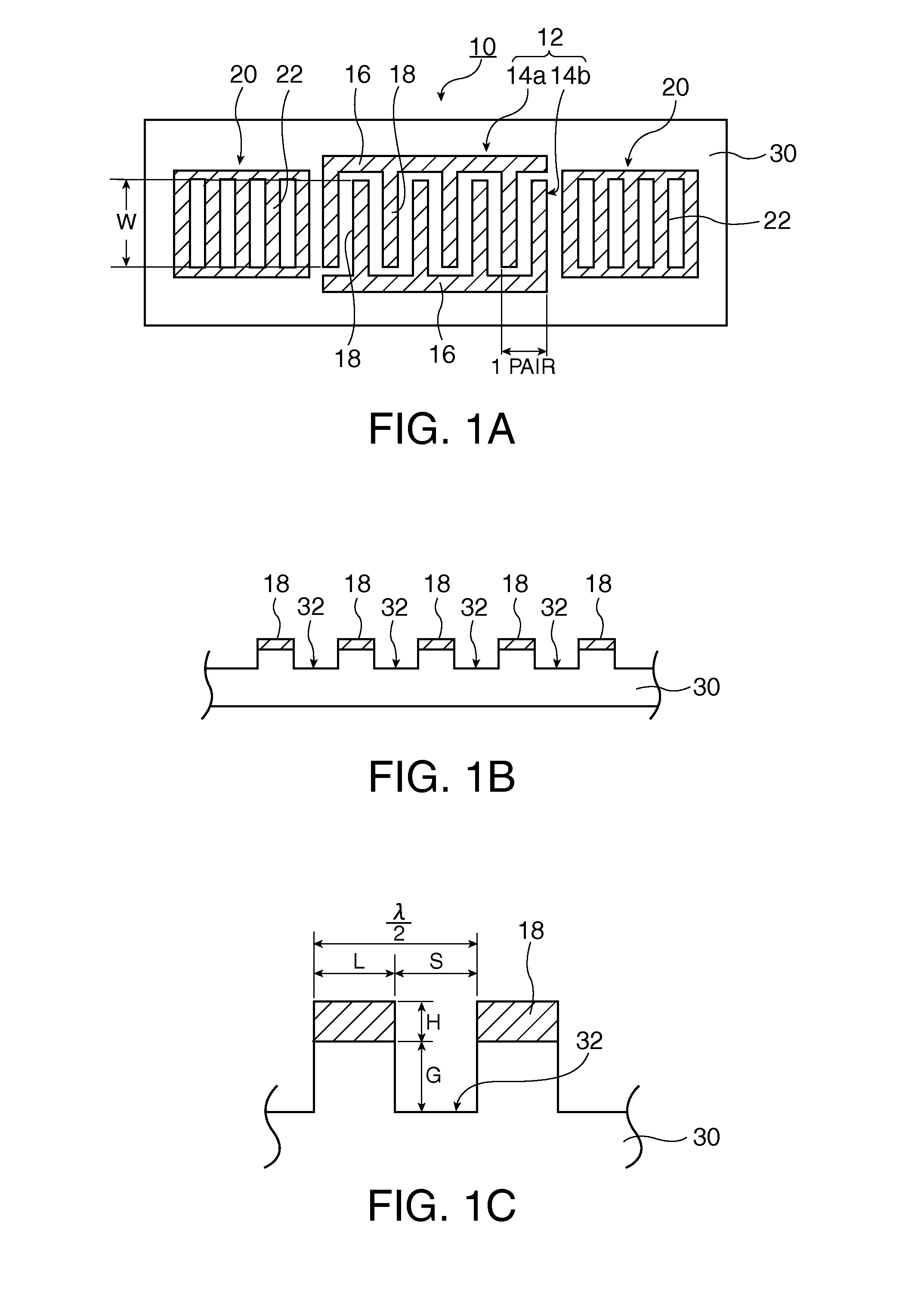
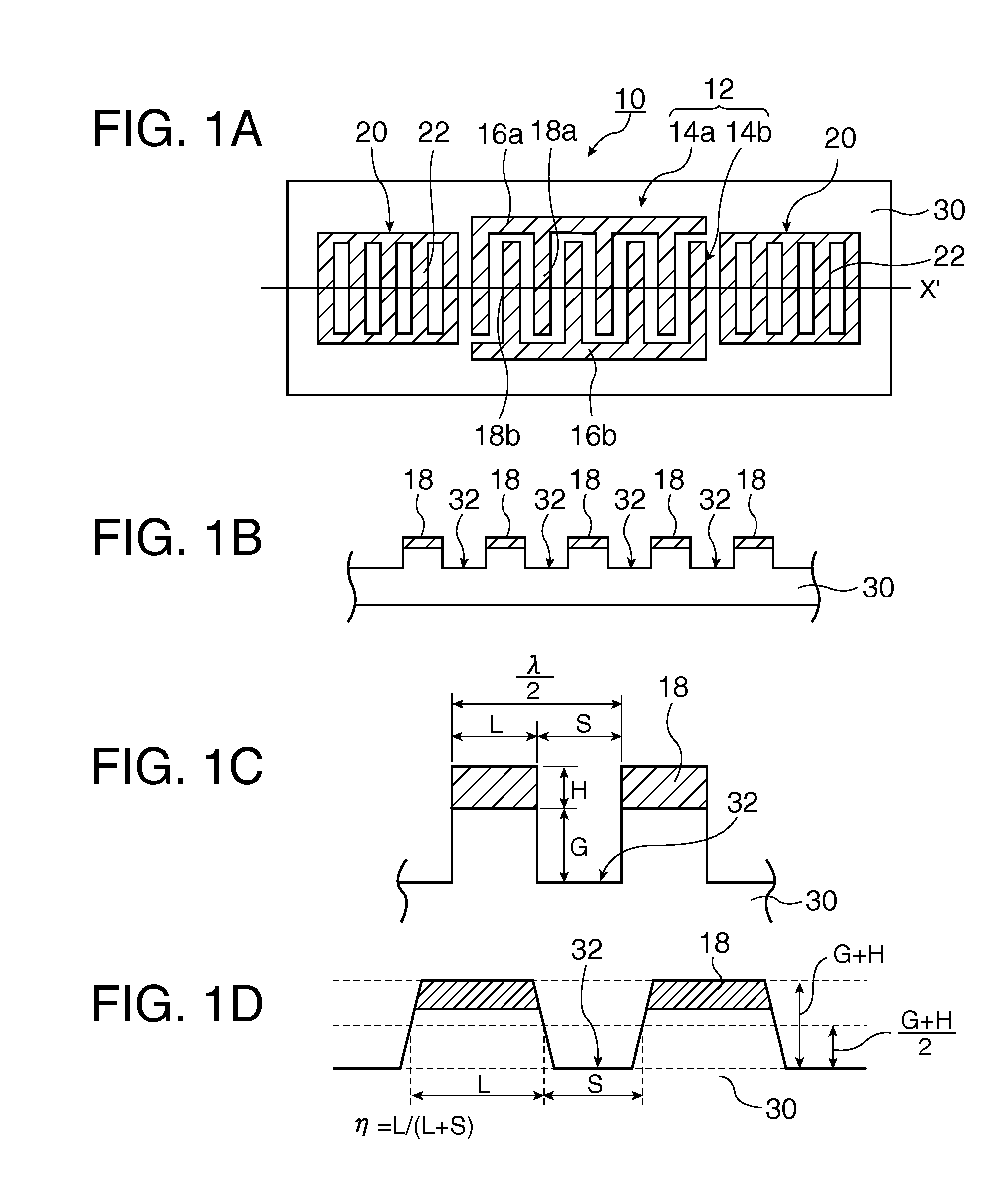
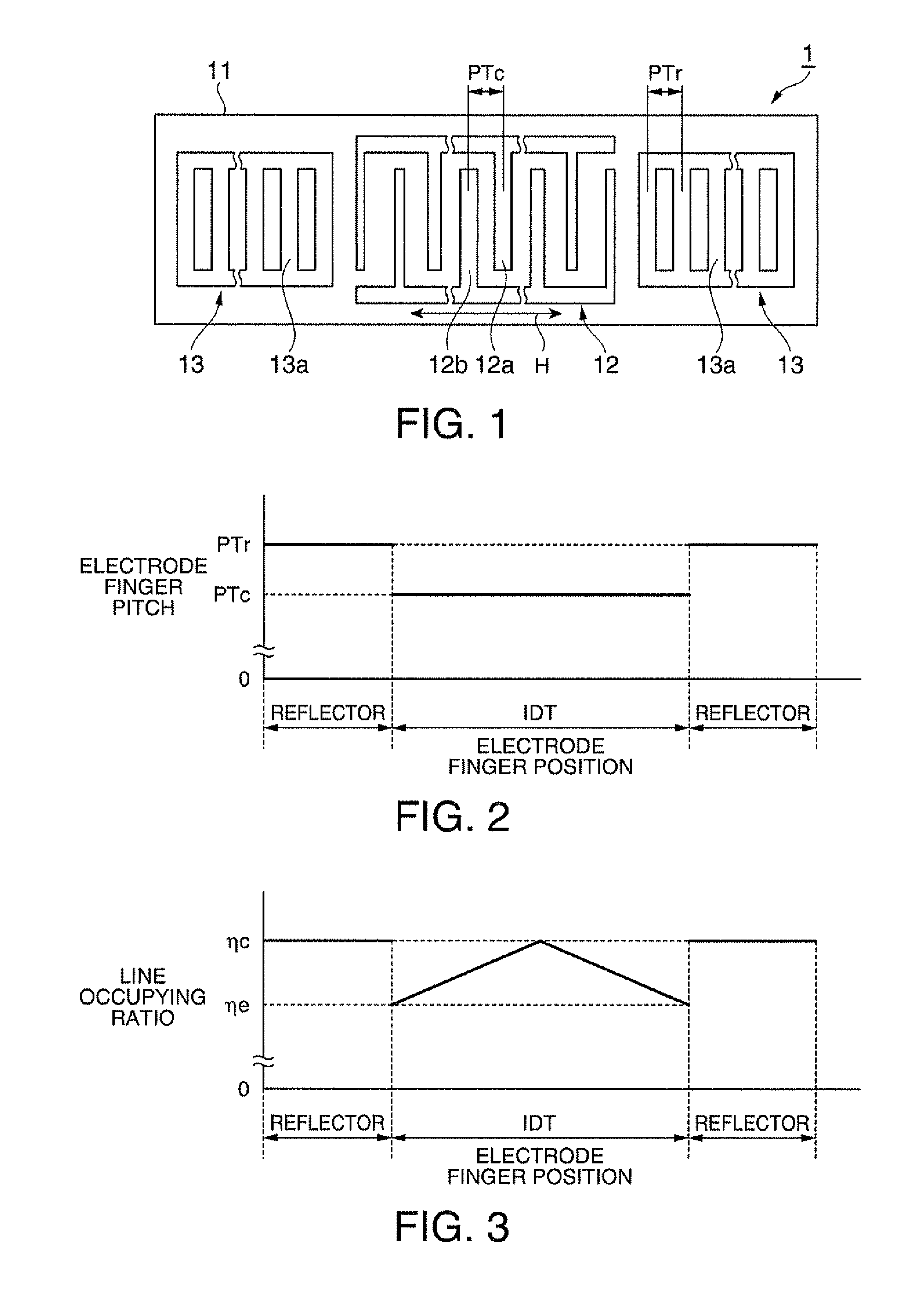
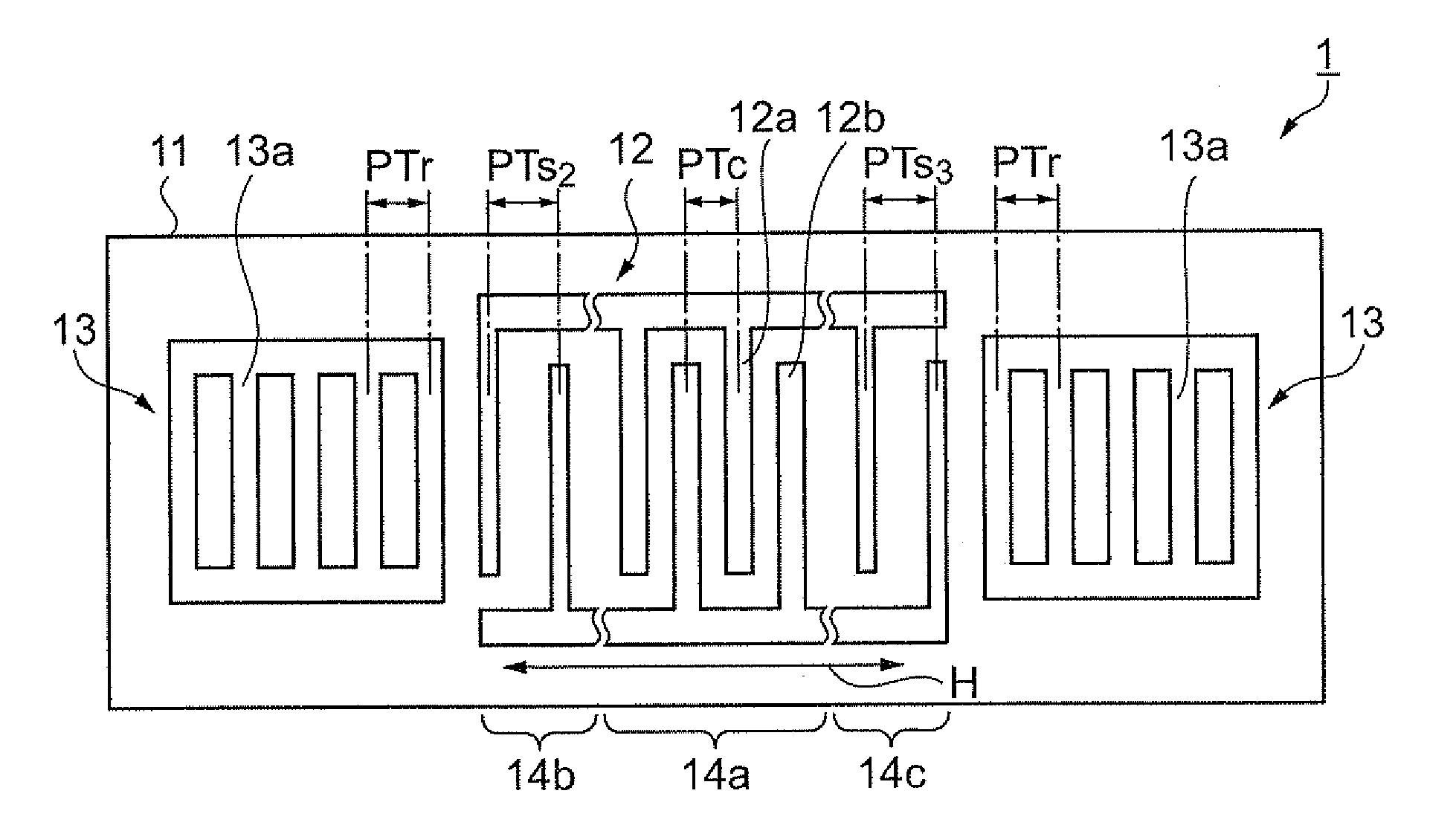
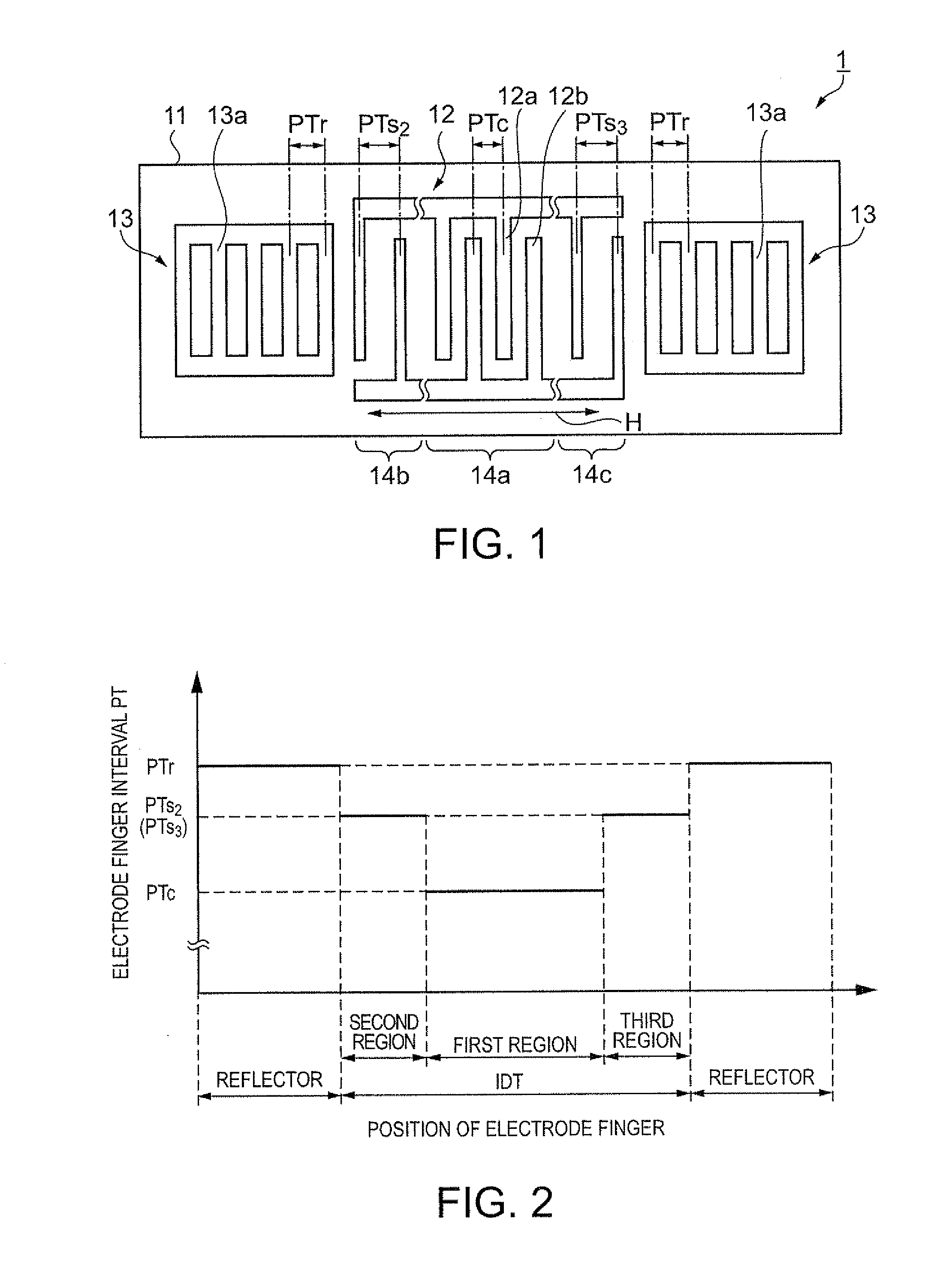
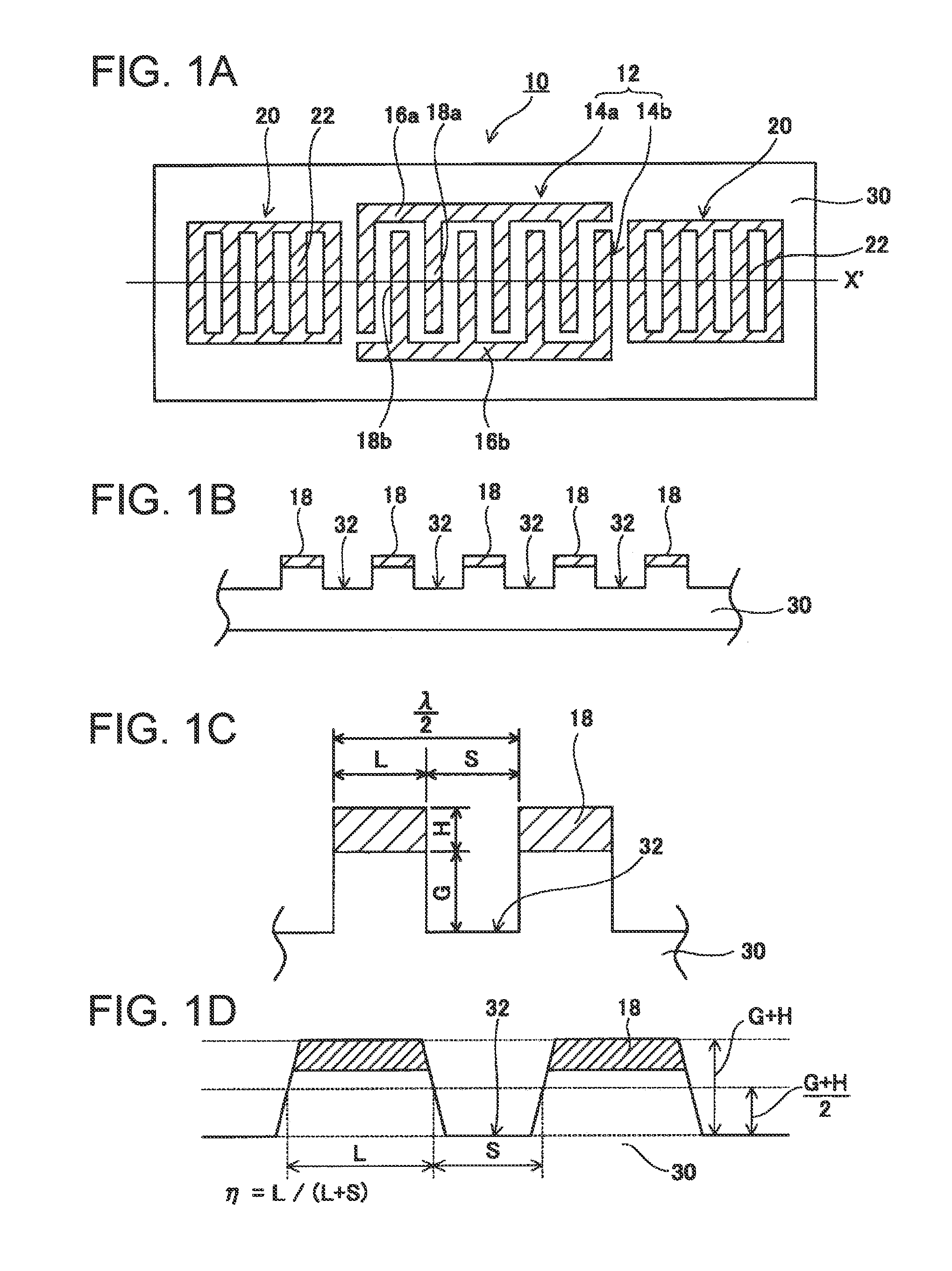
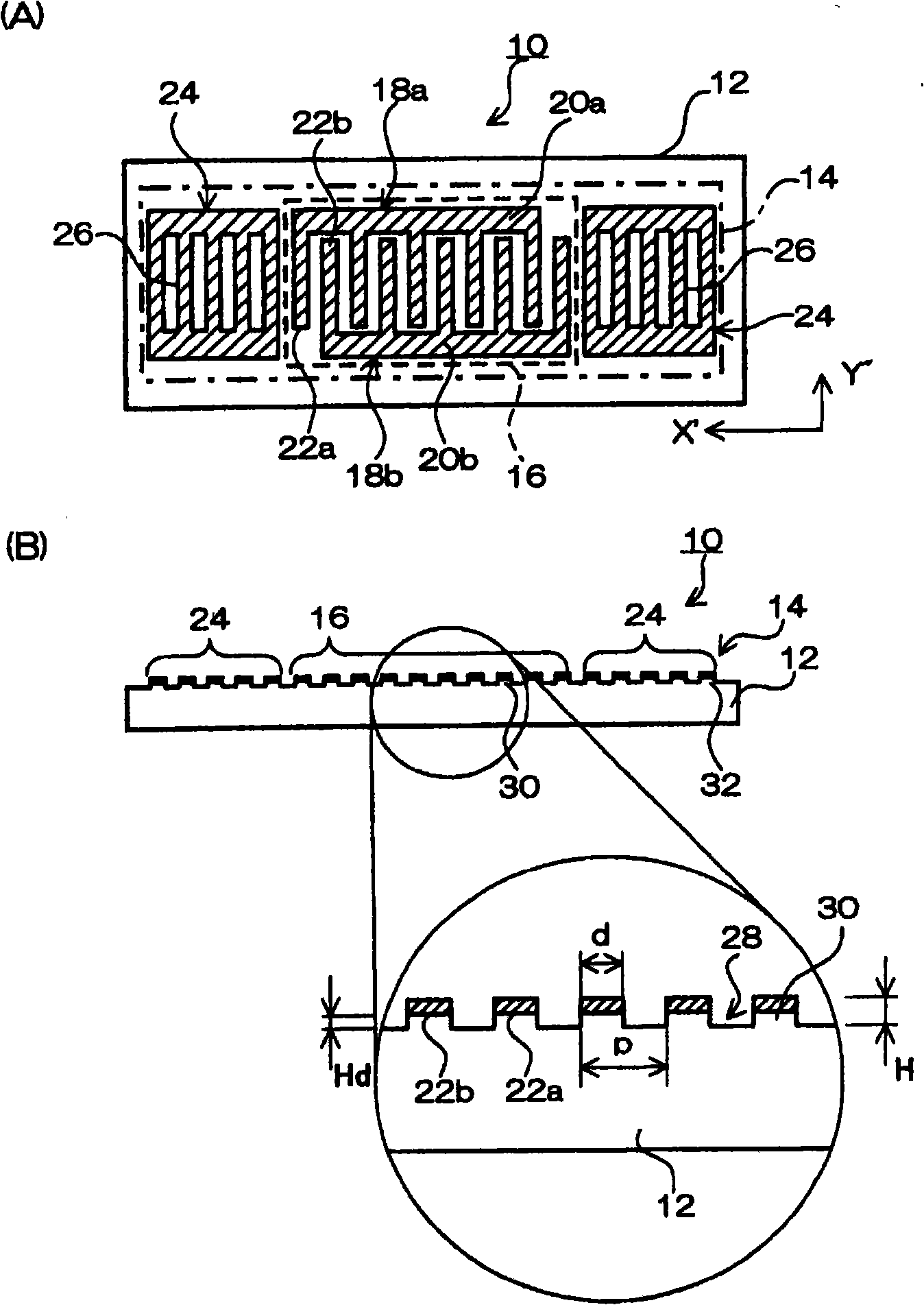
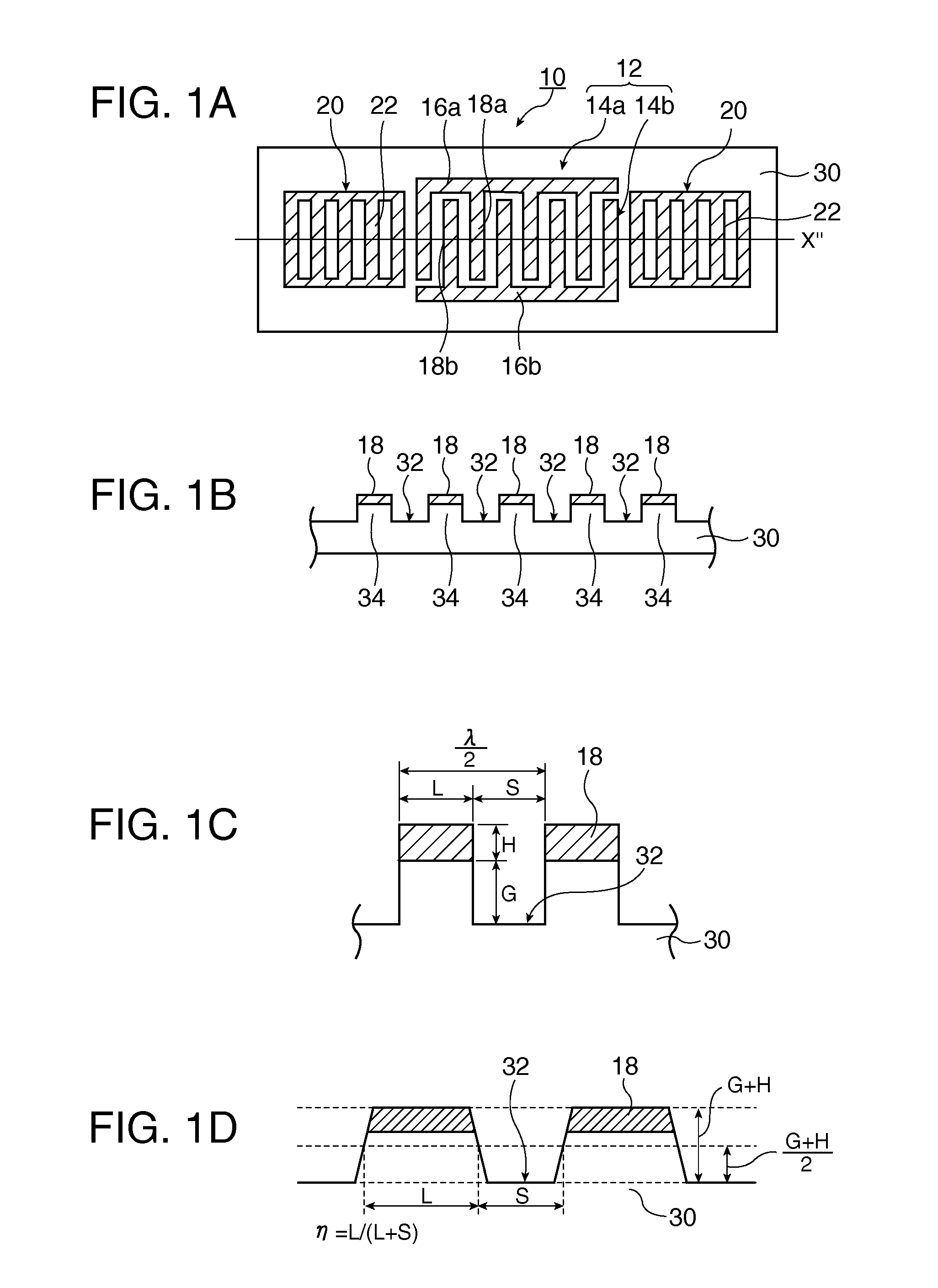
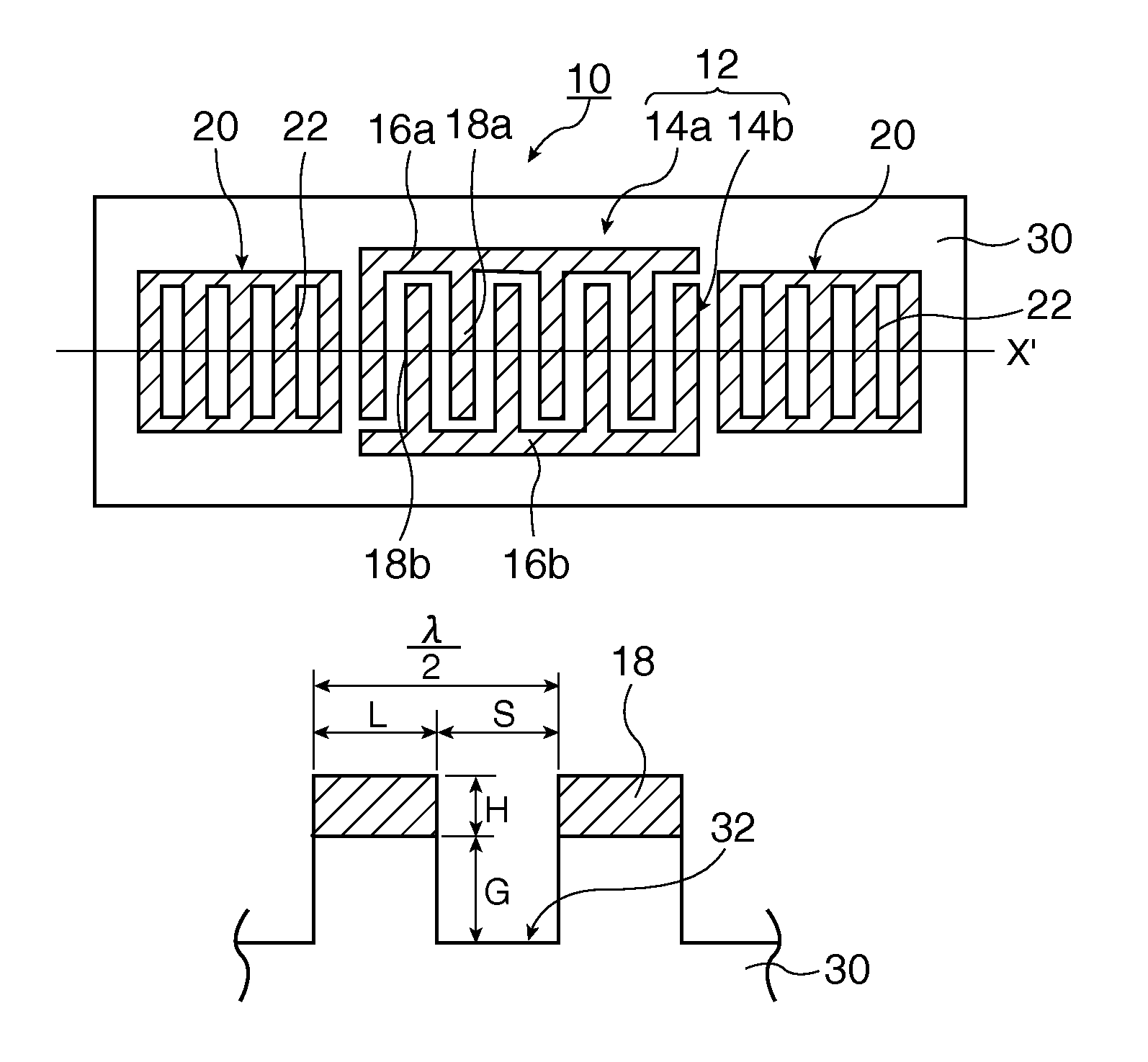
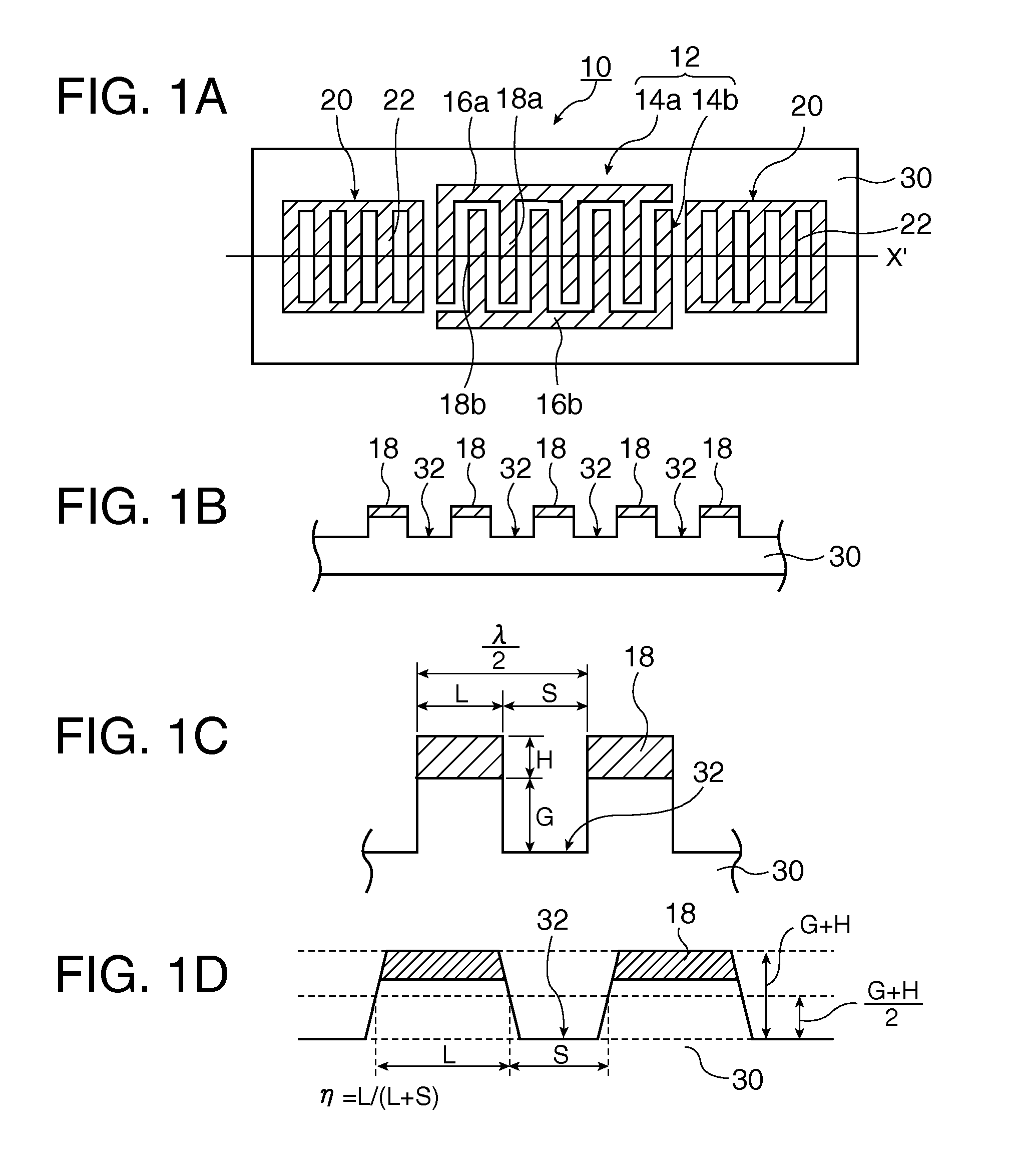
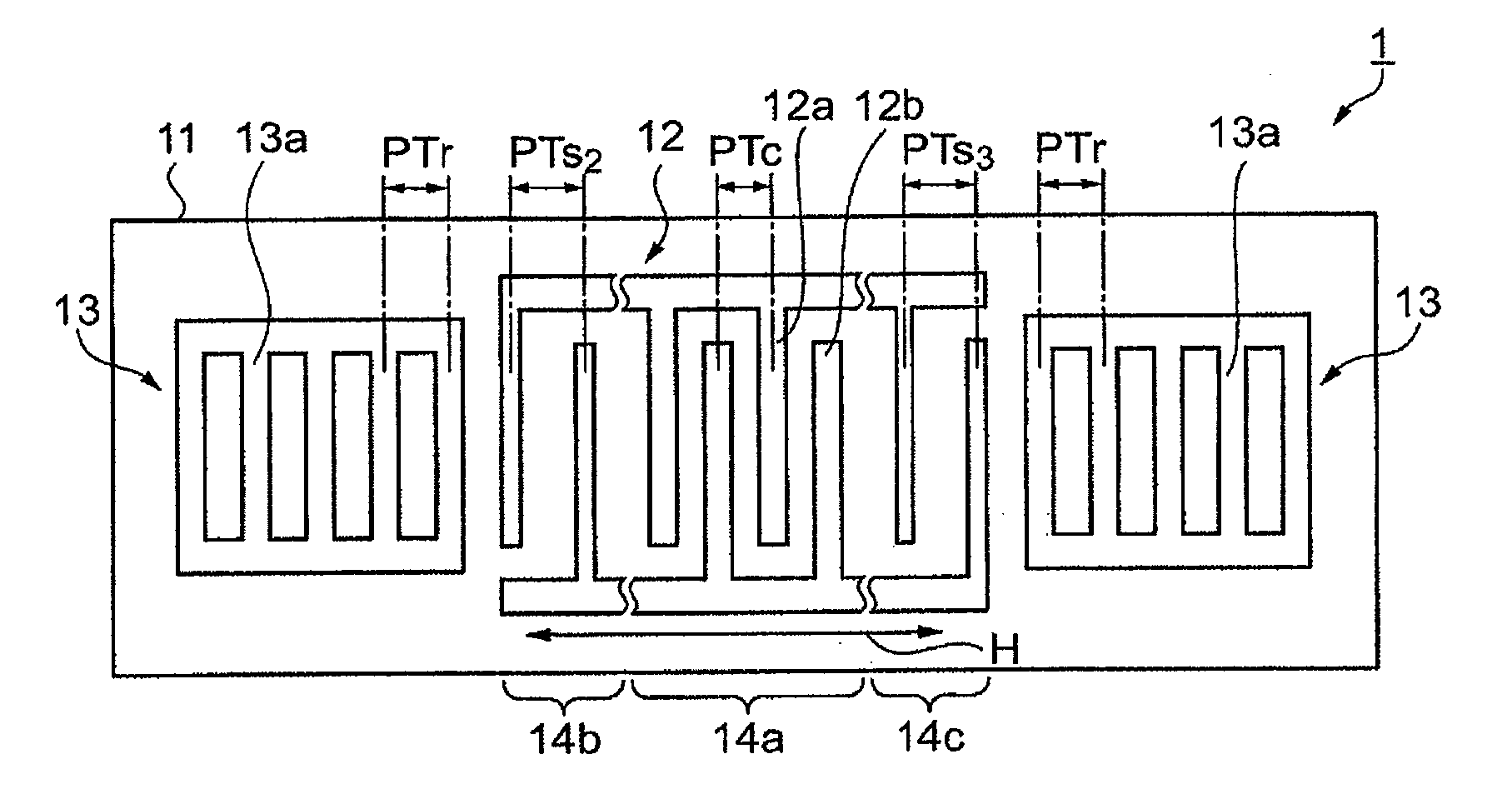
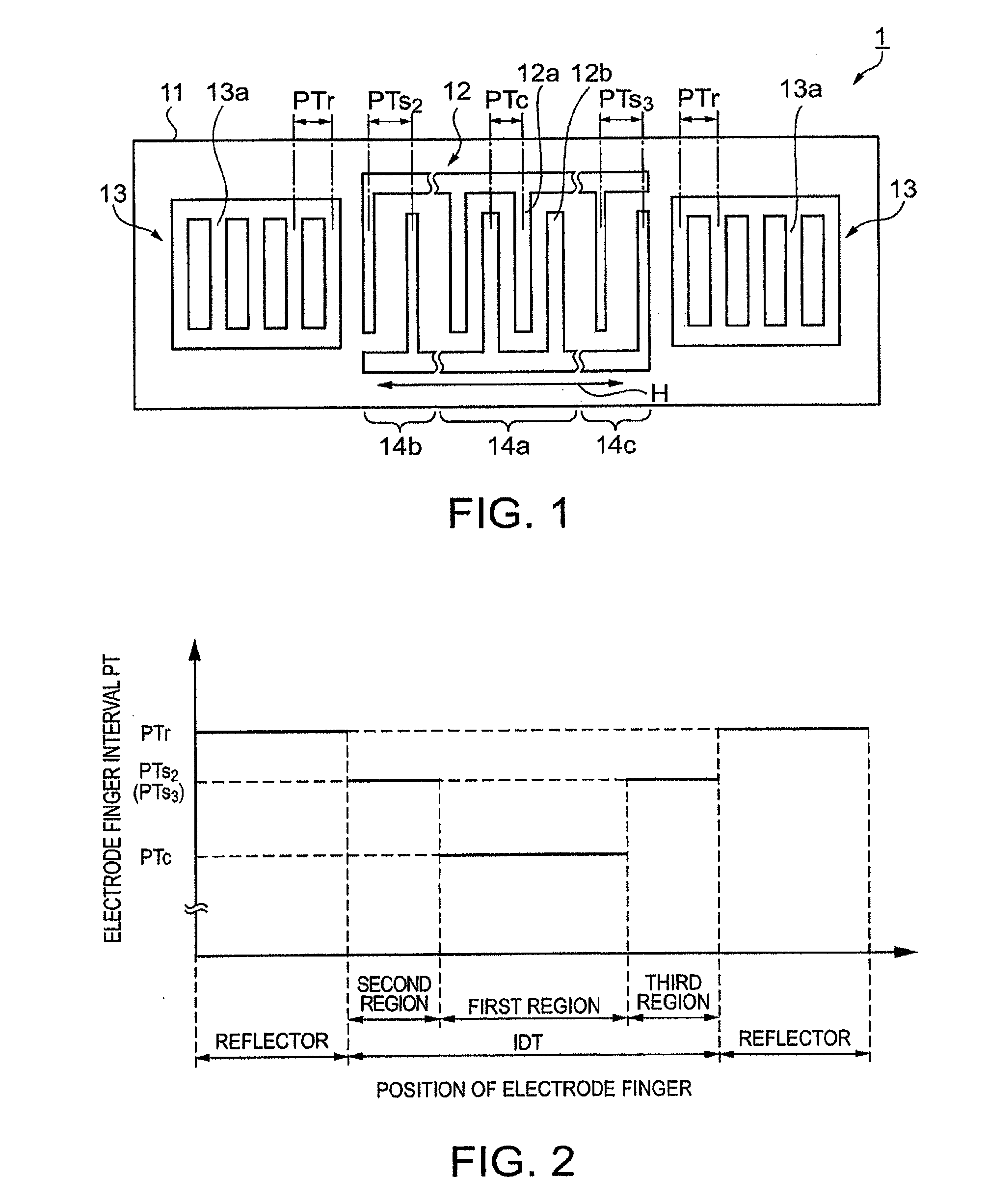
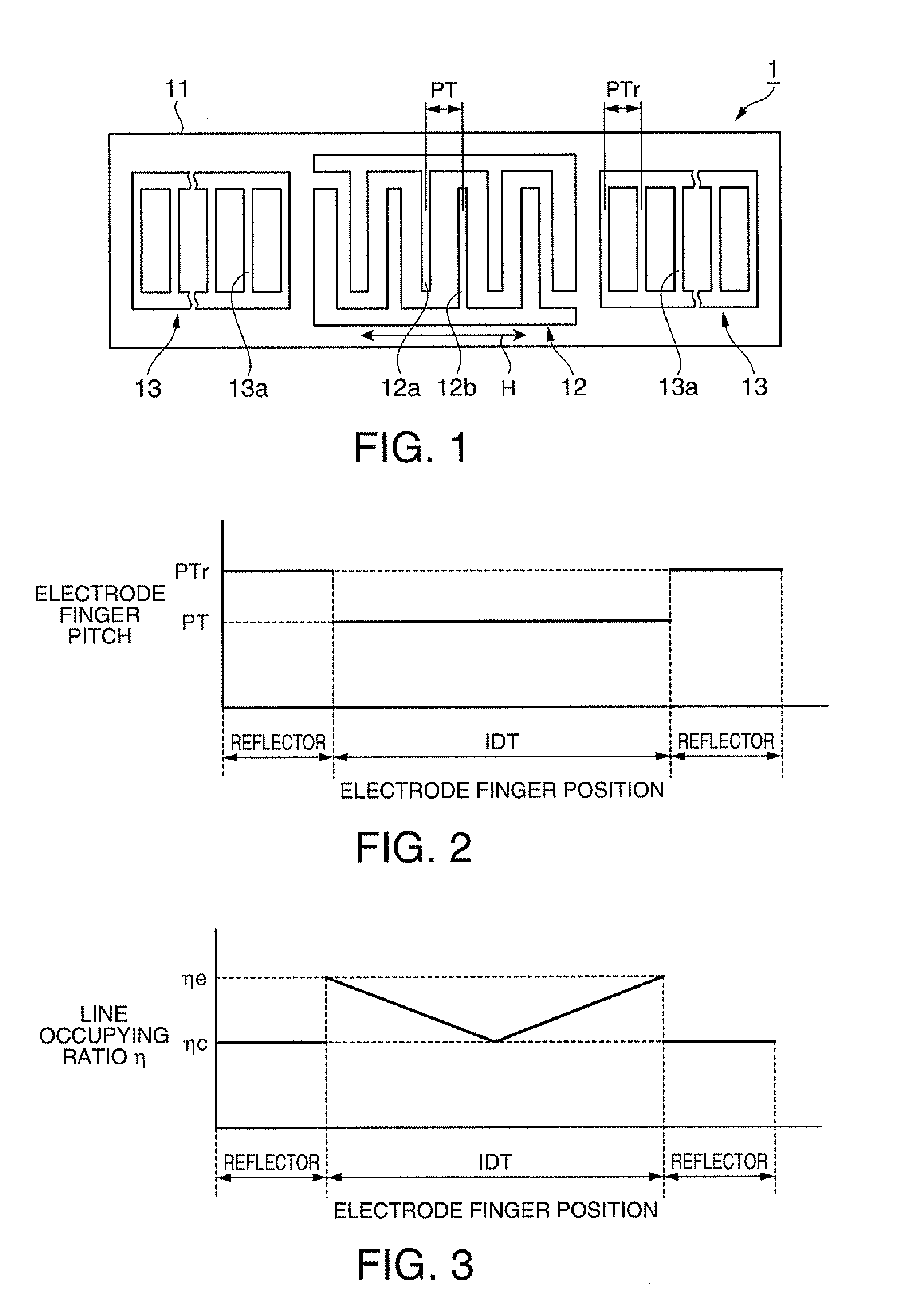
In a surface acoustic wave resonator in which an IDT having electrode fingers for exciting surface acoustic waves is formed on a crystal substrate, the line occupying ratio causing the maximum electromechanical coupling coefficient and the line occupying ratio causing the maximum reflection of the surface acoustic waves in the IDT are different from each other, the center of the IDT has the line occupying ratio causing an increase in electromechanical coupling coefficient in comparison with the edges of the IDT, and the edges of the IDT have the line occupying ratio causing an increase in reflection of the surface acoustic waves in comparison with the center of the IDT.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
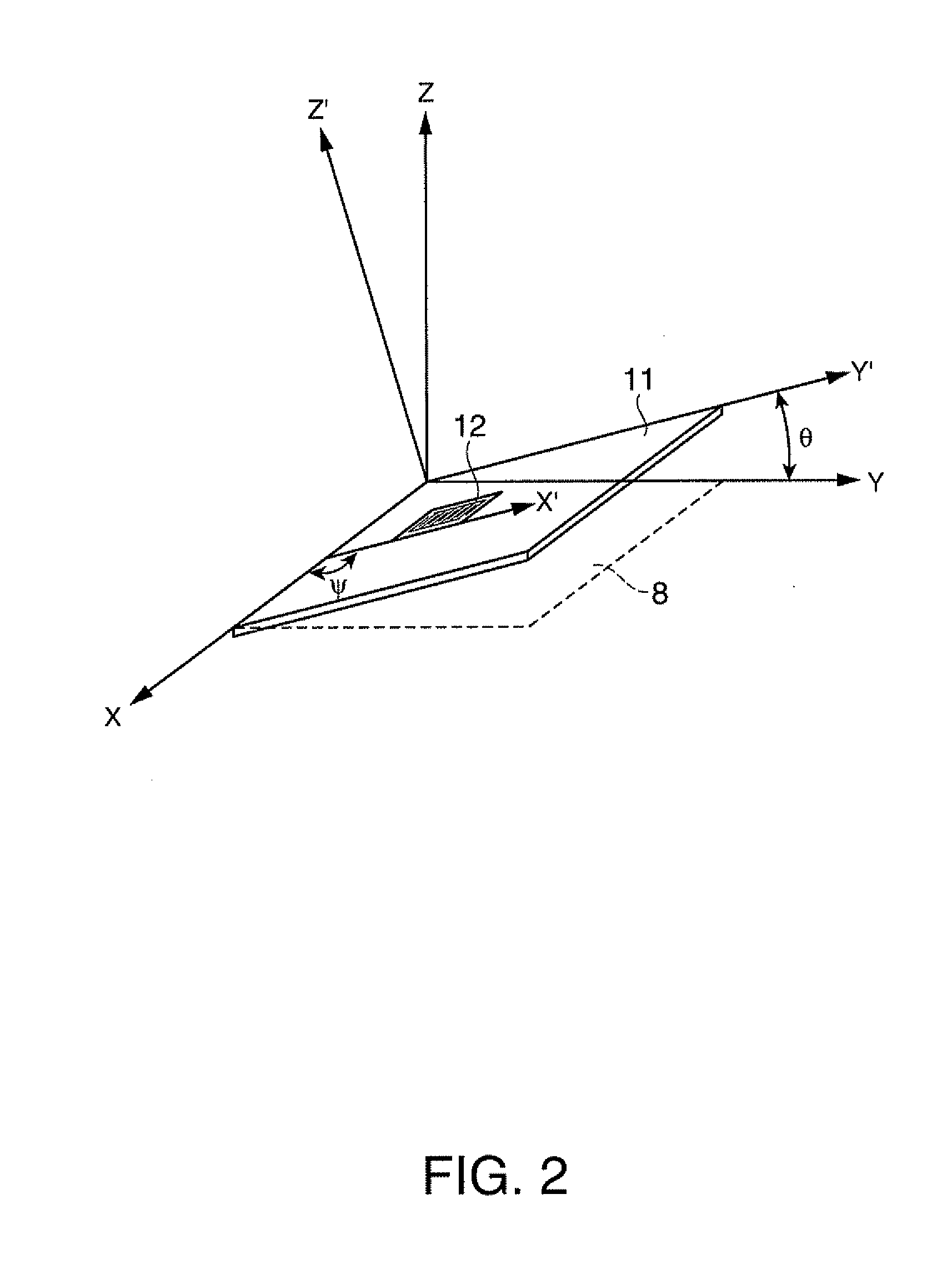
Surface acoustic wave resonator, surface acoustic wave oscillator, and electronic apparatus
InactiveUS20120049979A1Excellent frequency temperature characteristicsImprove environmental resistanceImpedence networksOscillations generatorsSurface acoustic wave oscillatorsAlloy
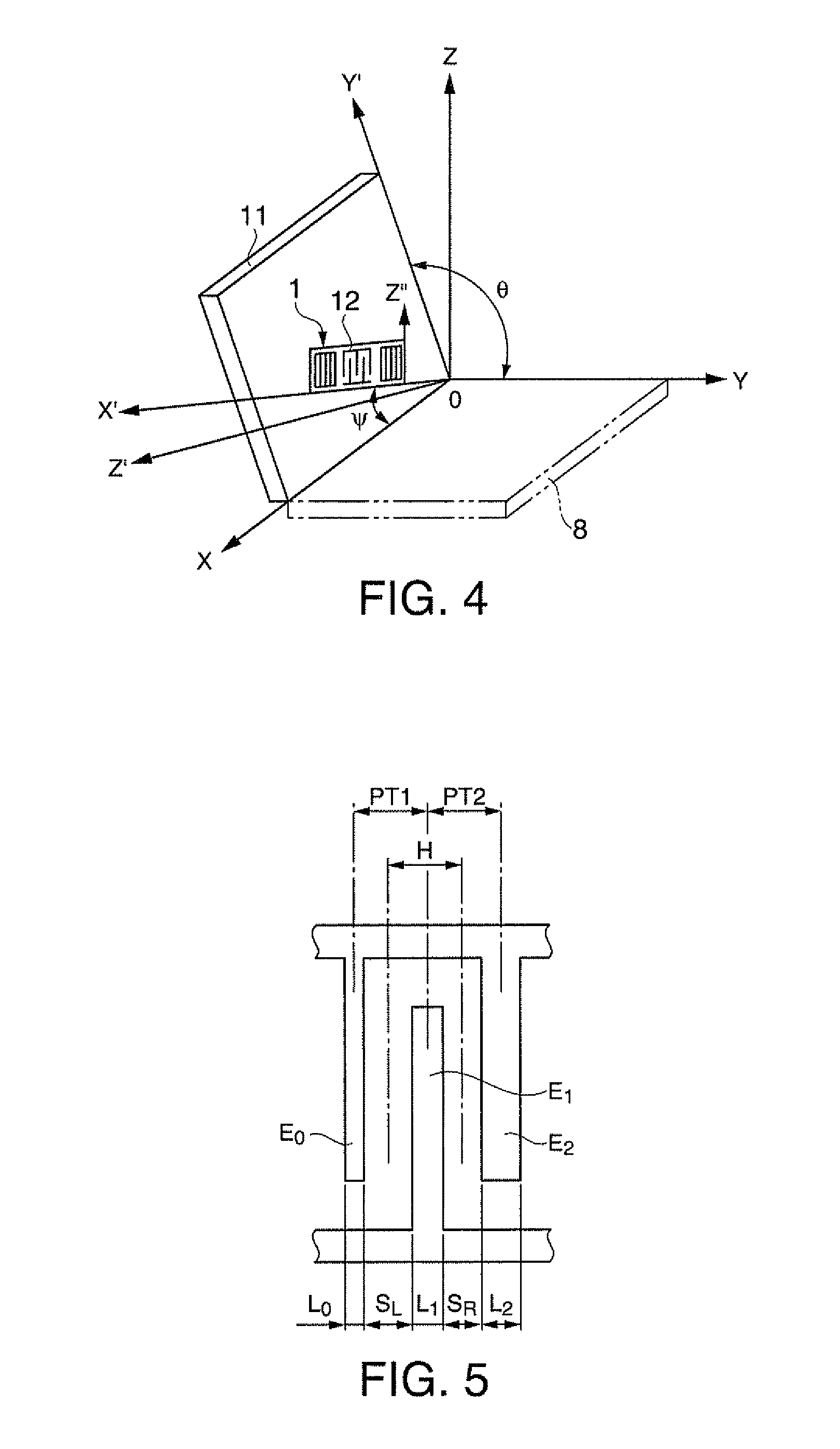
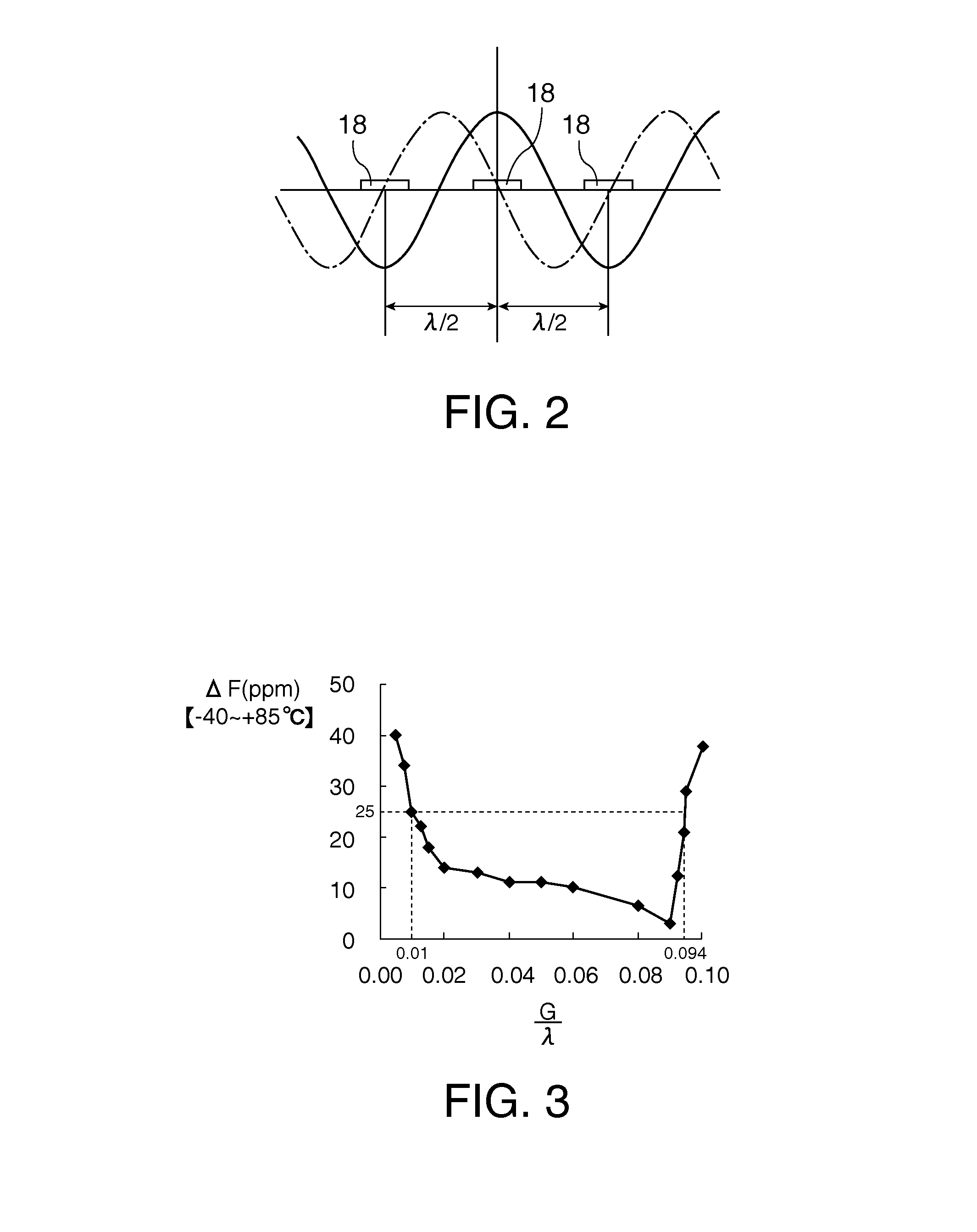
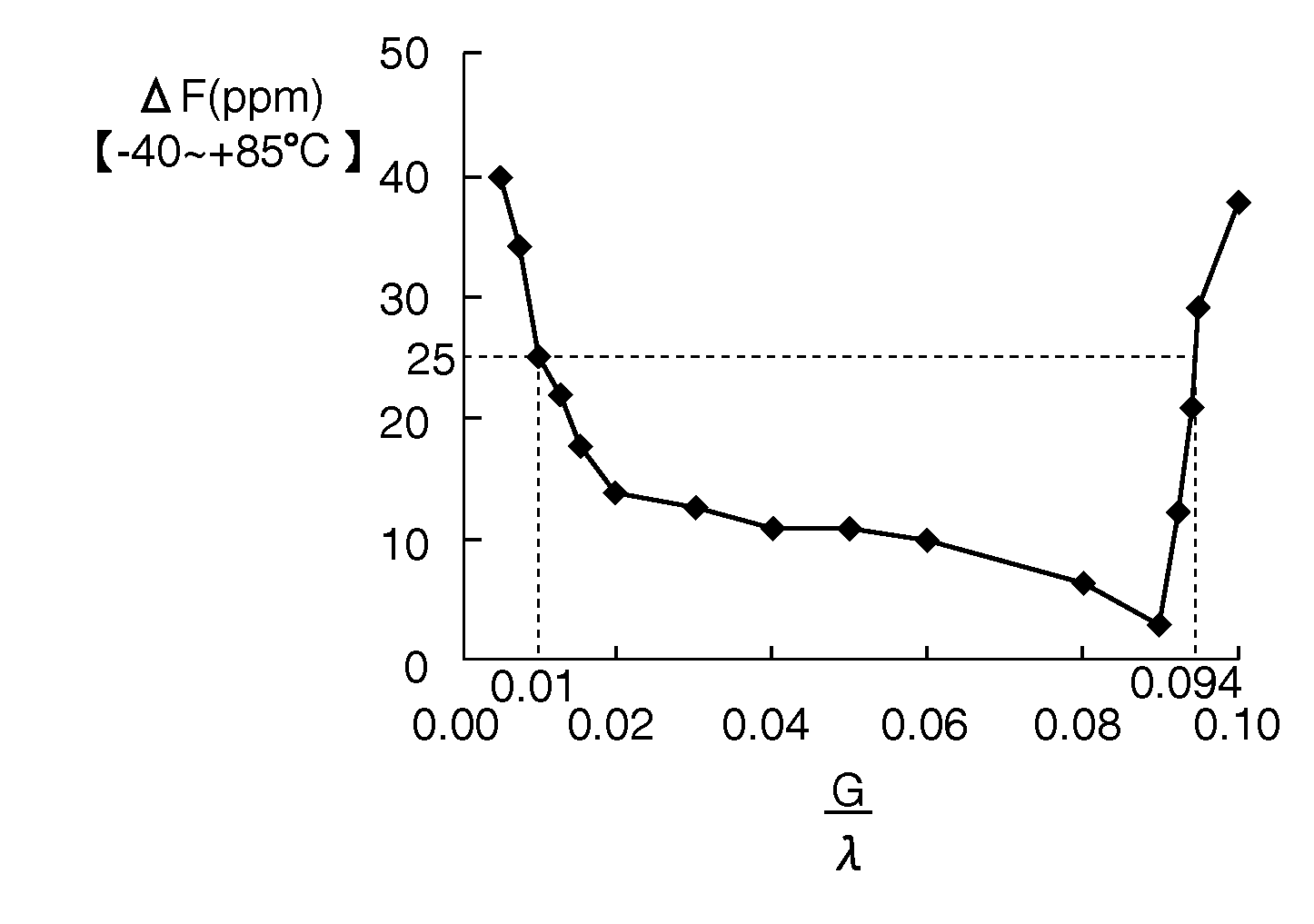
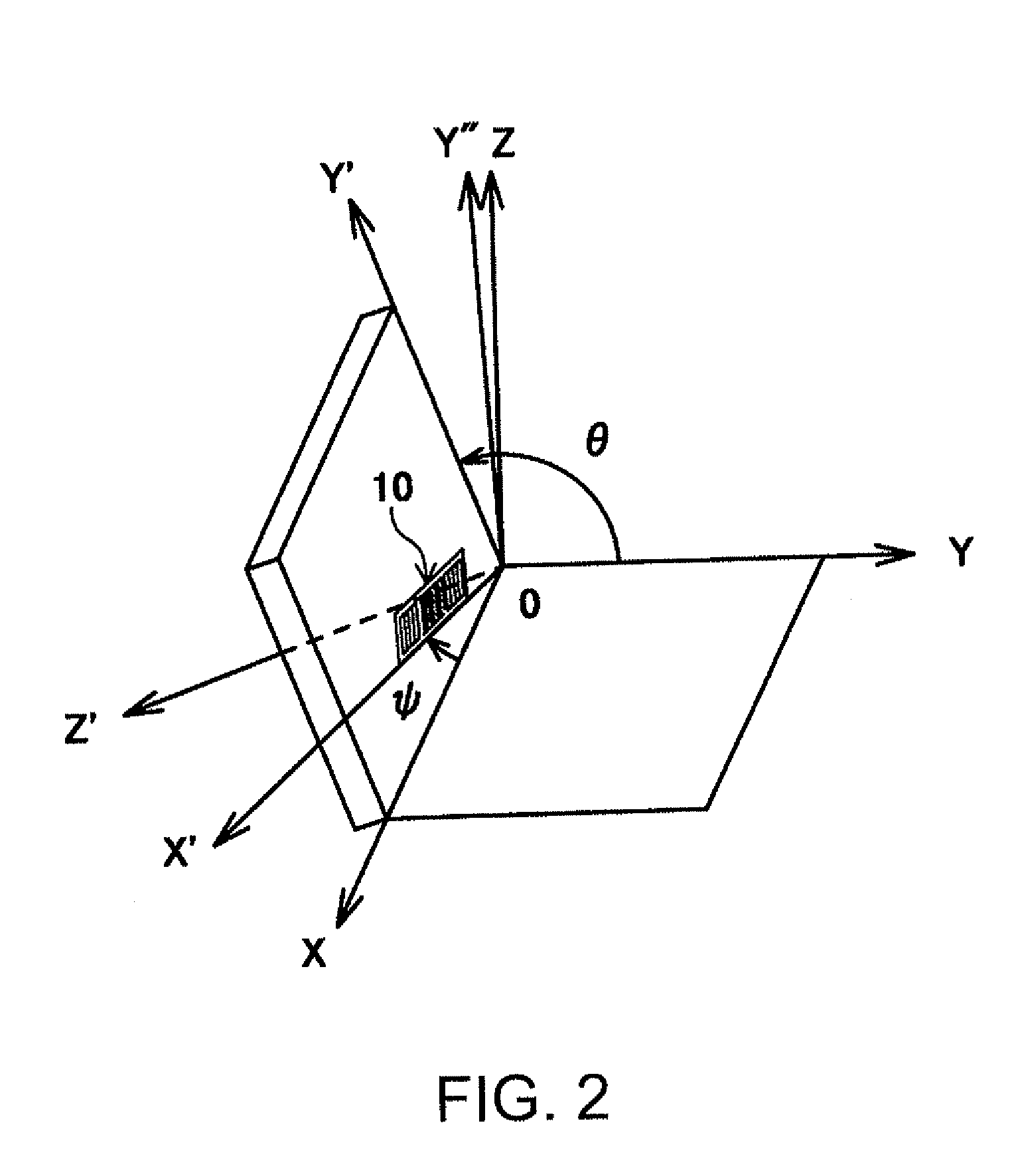
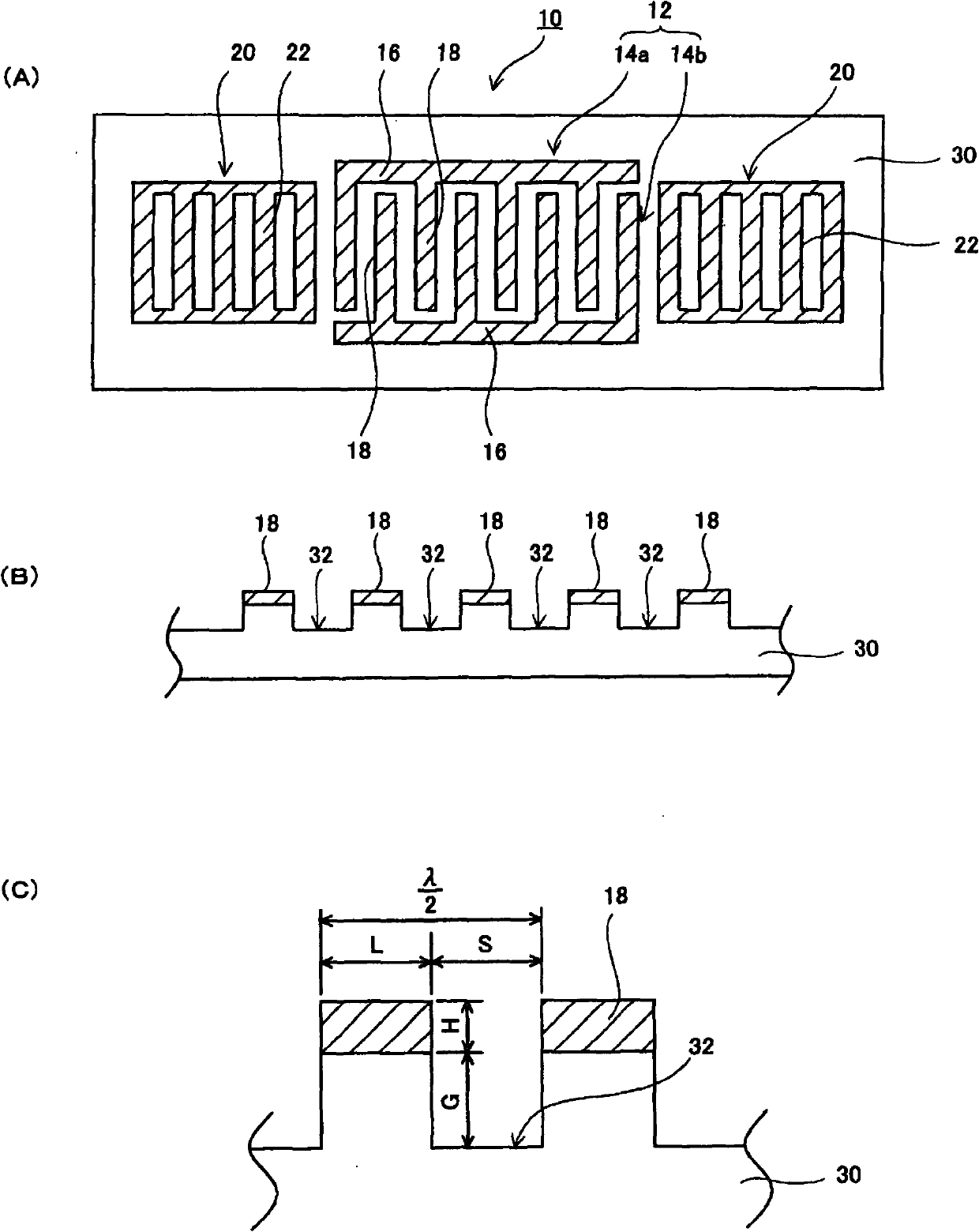
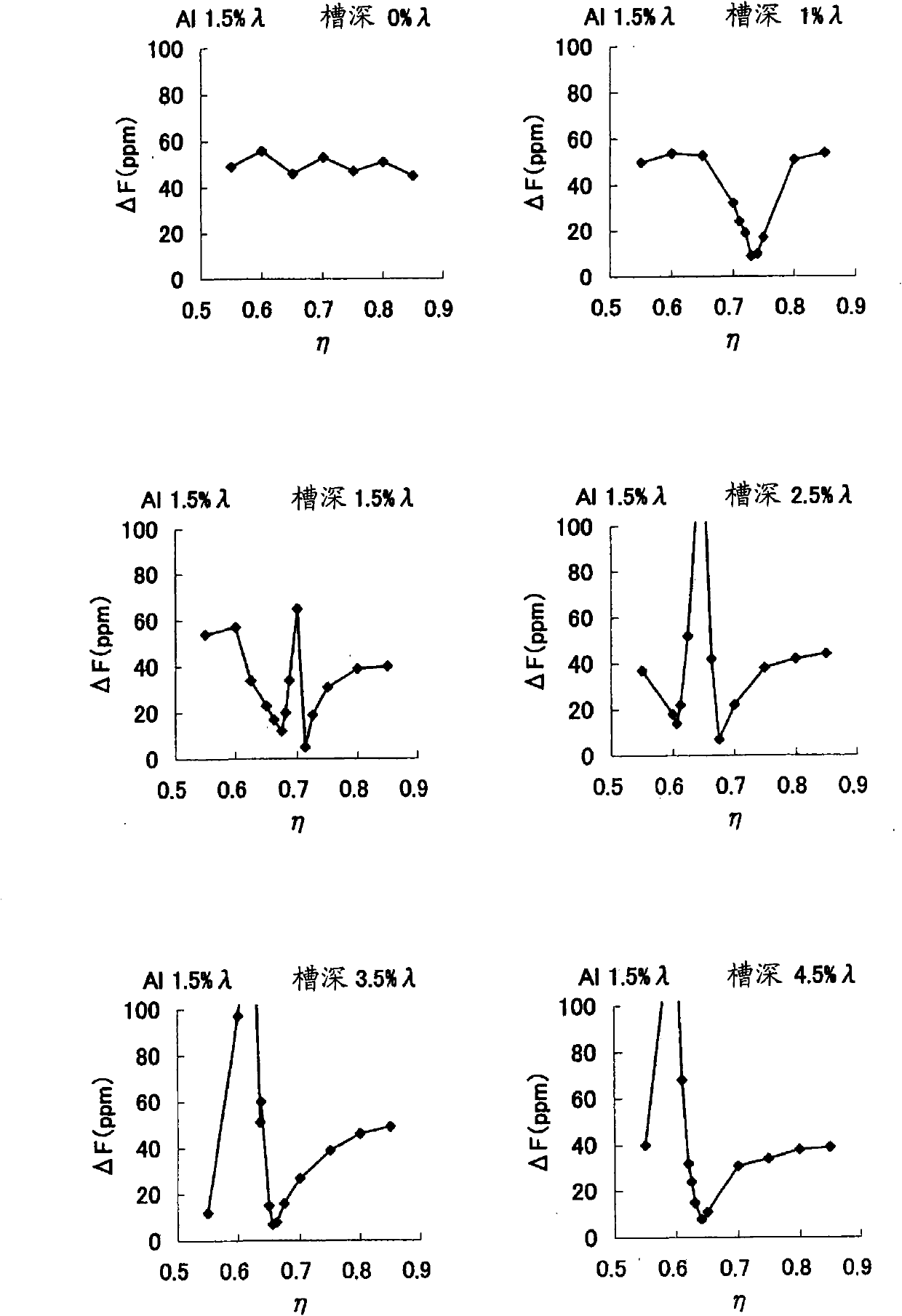
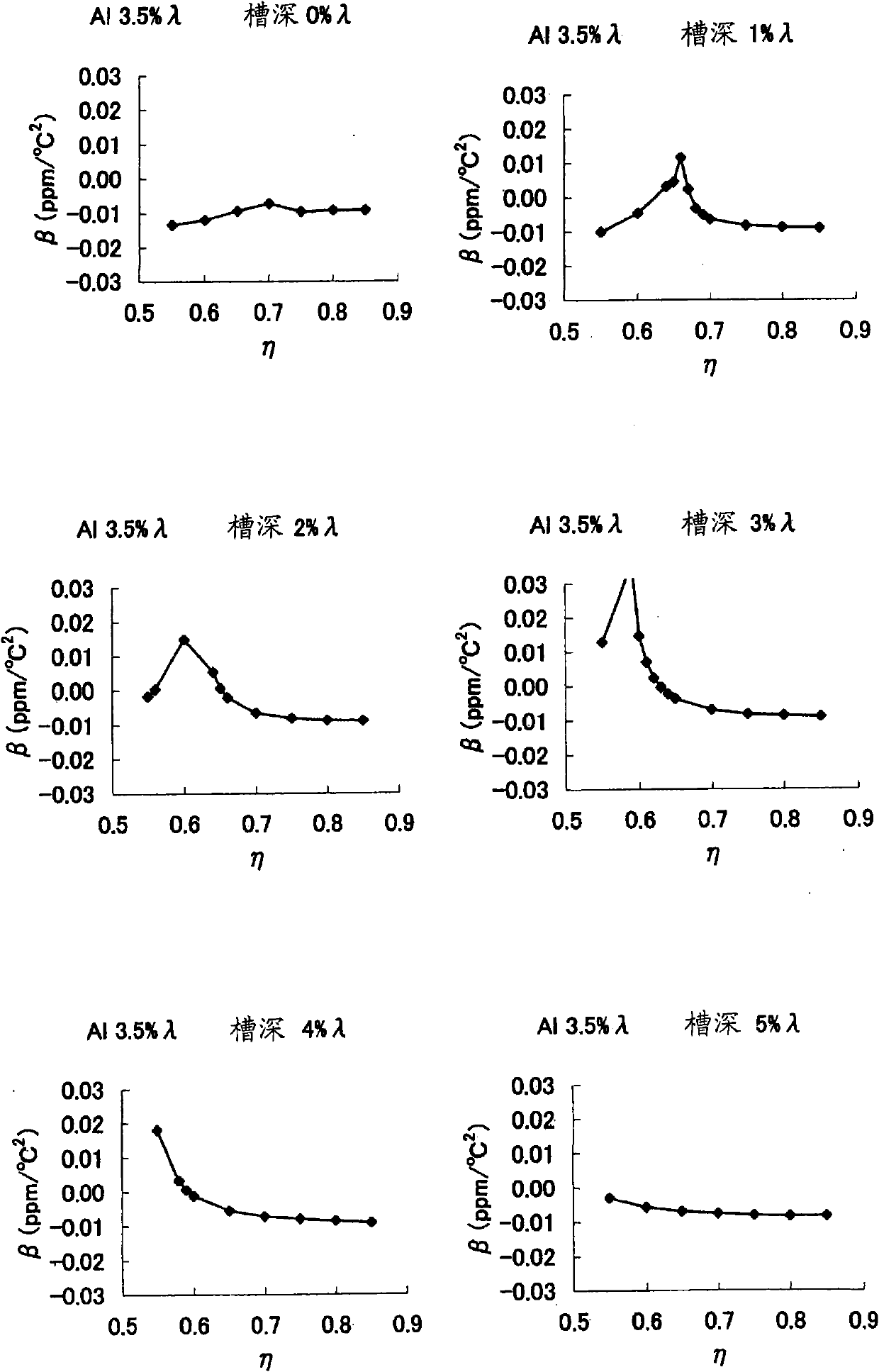
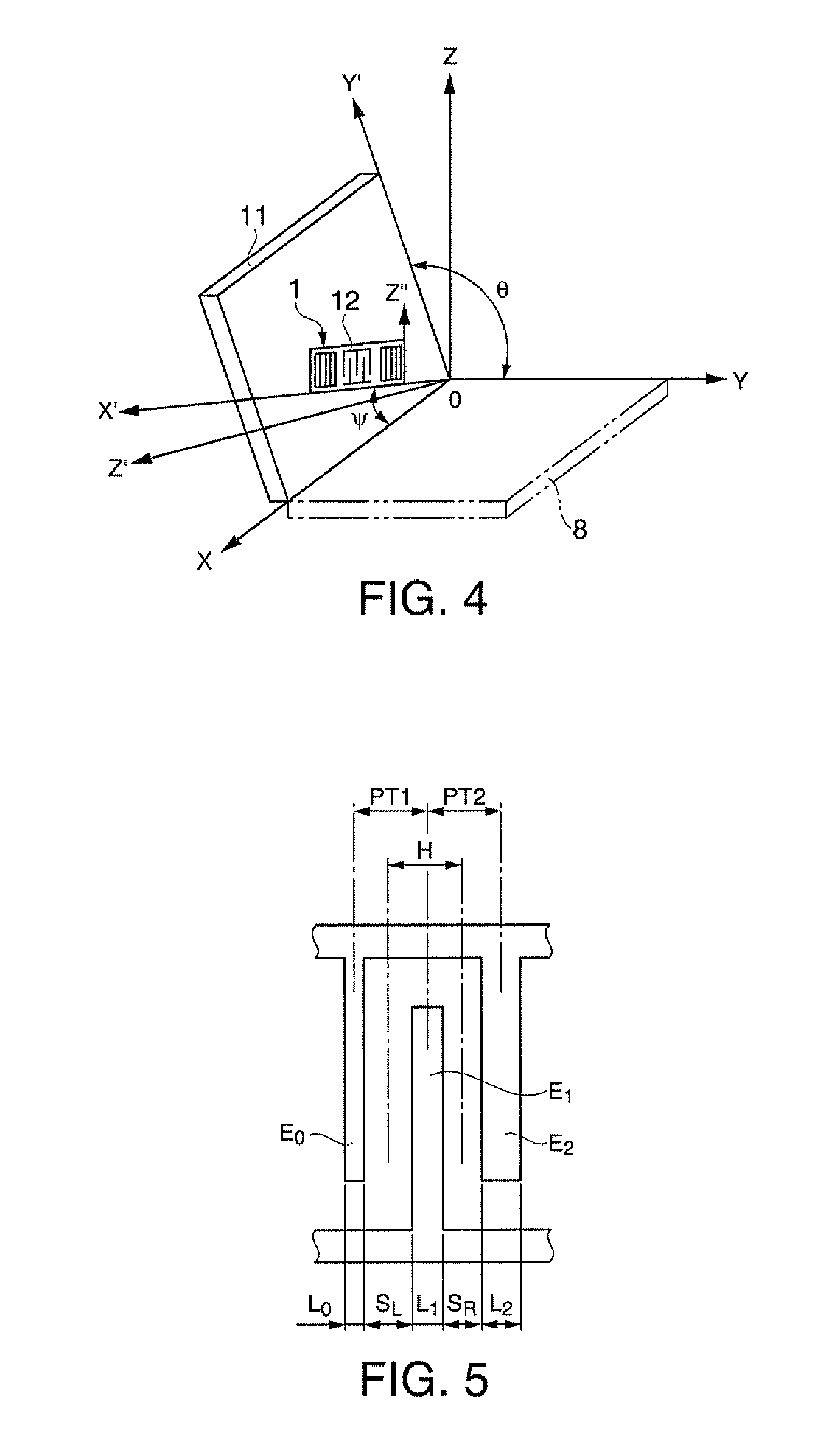
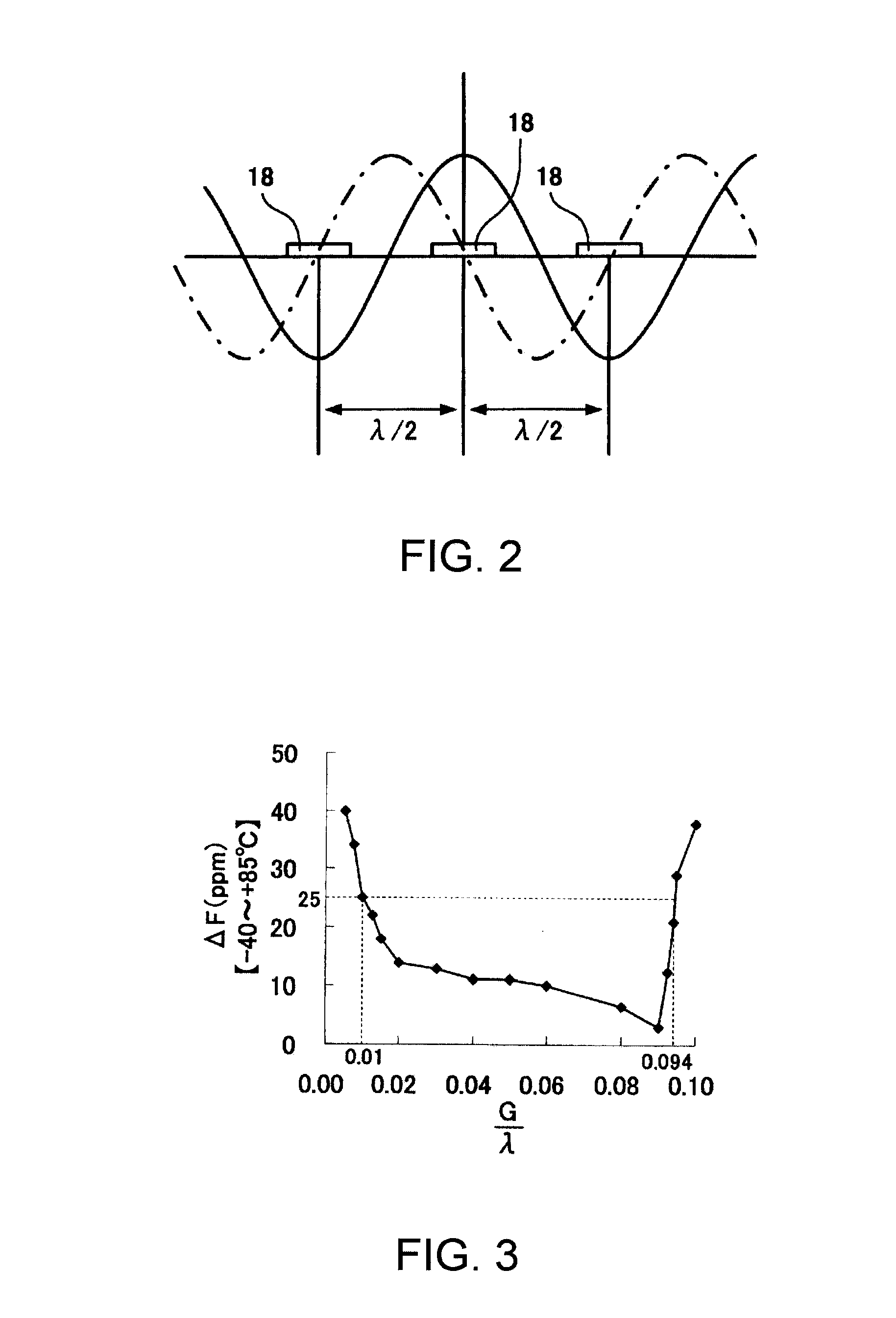
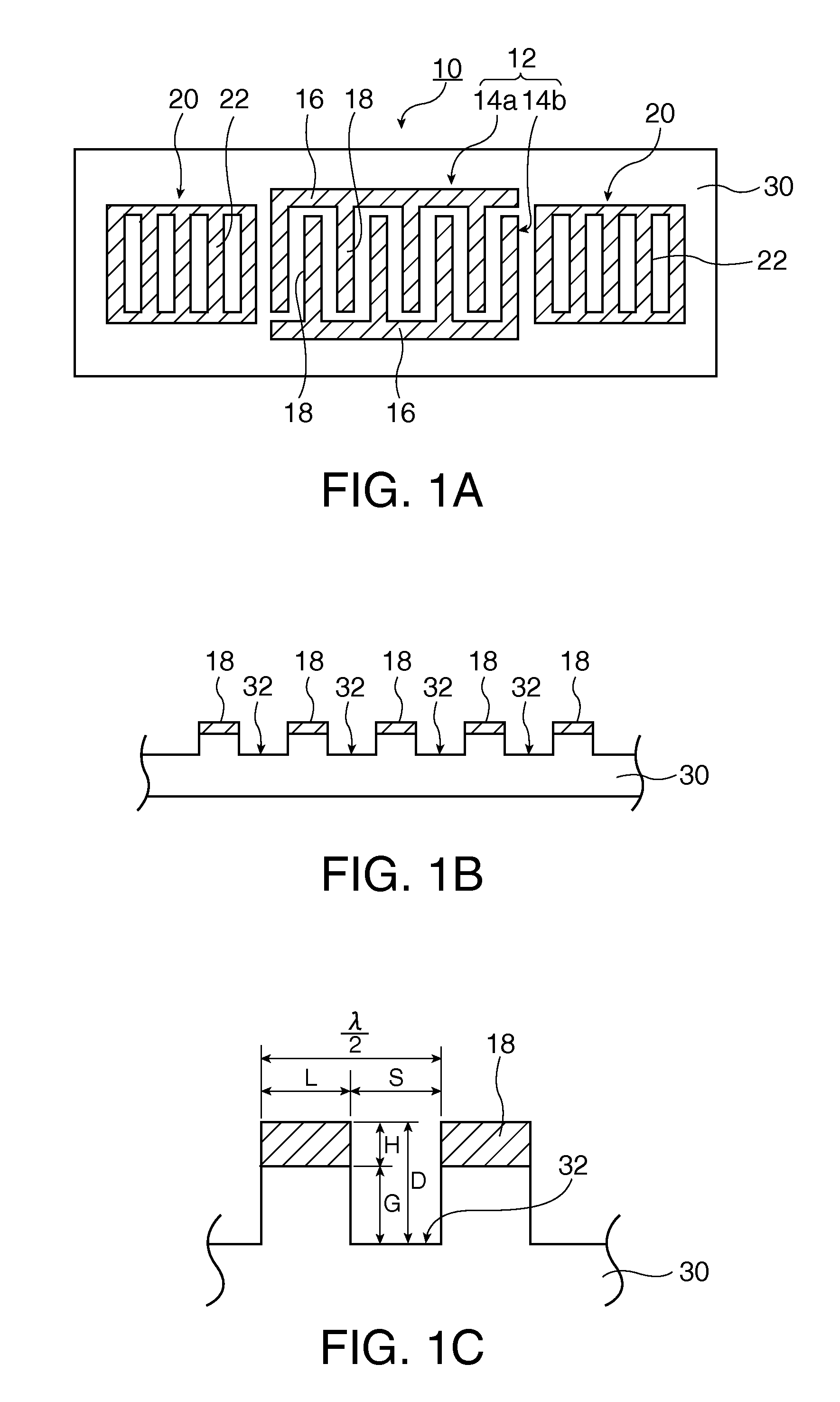
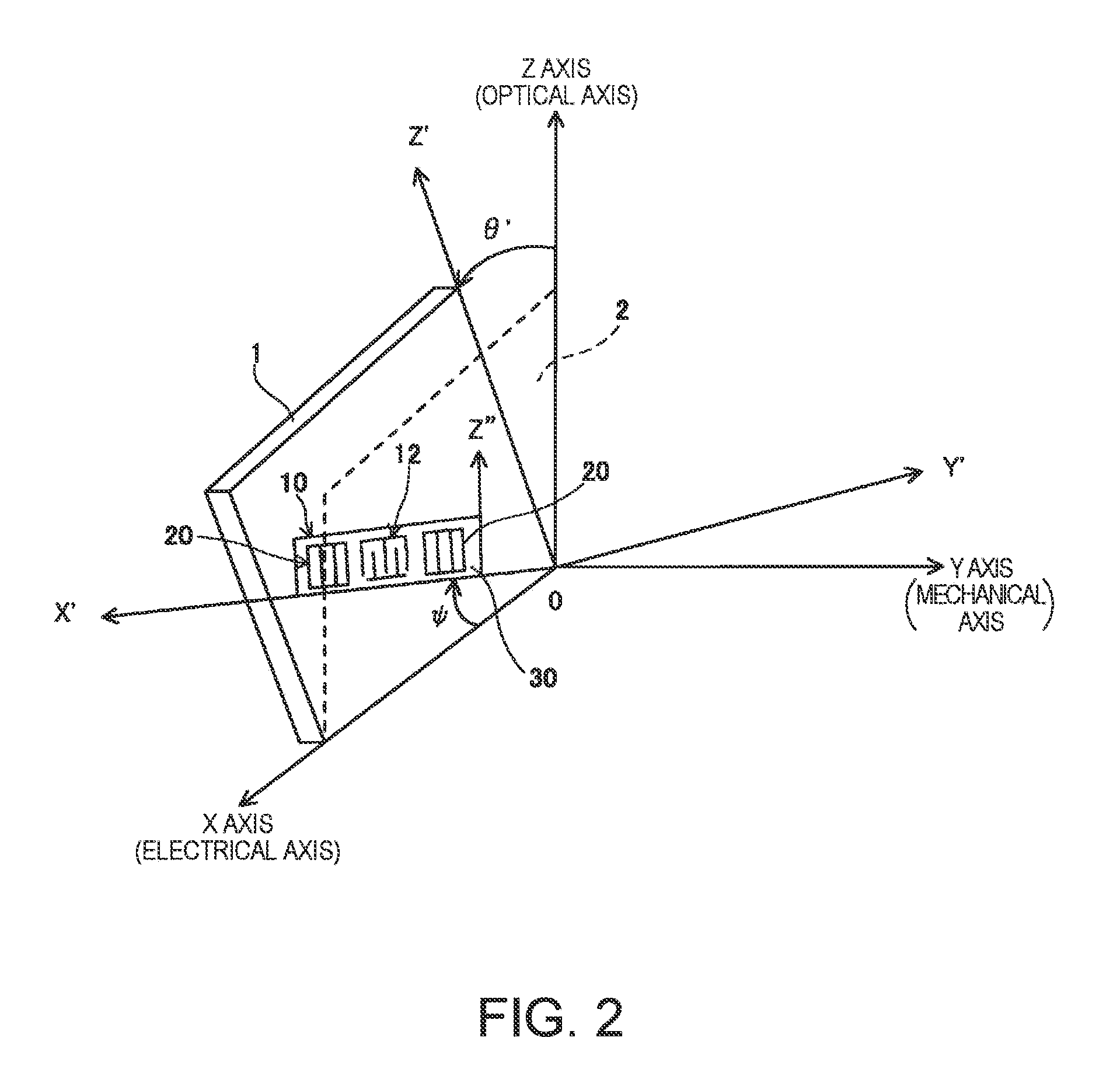
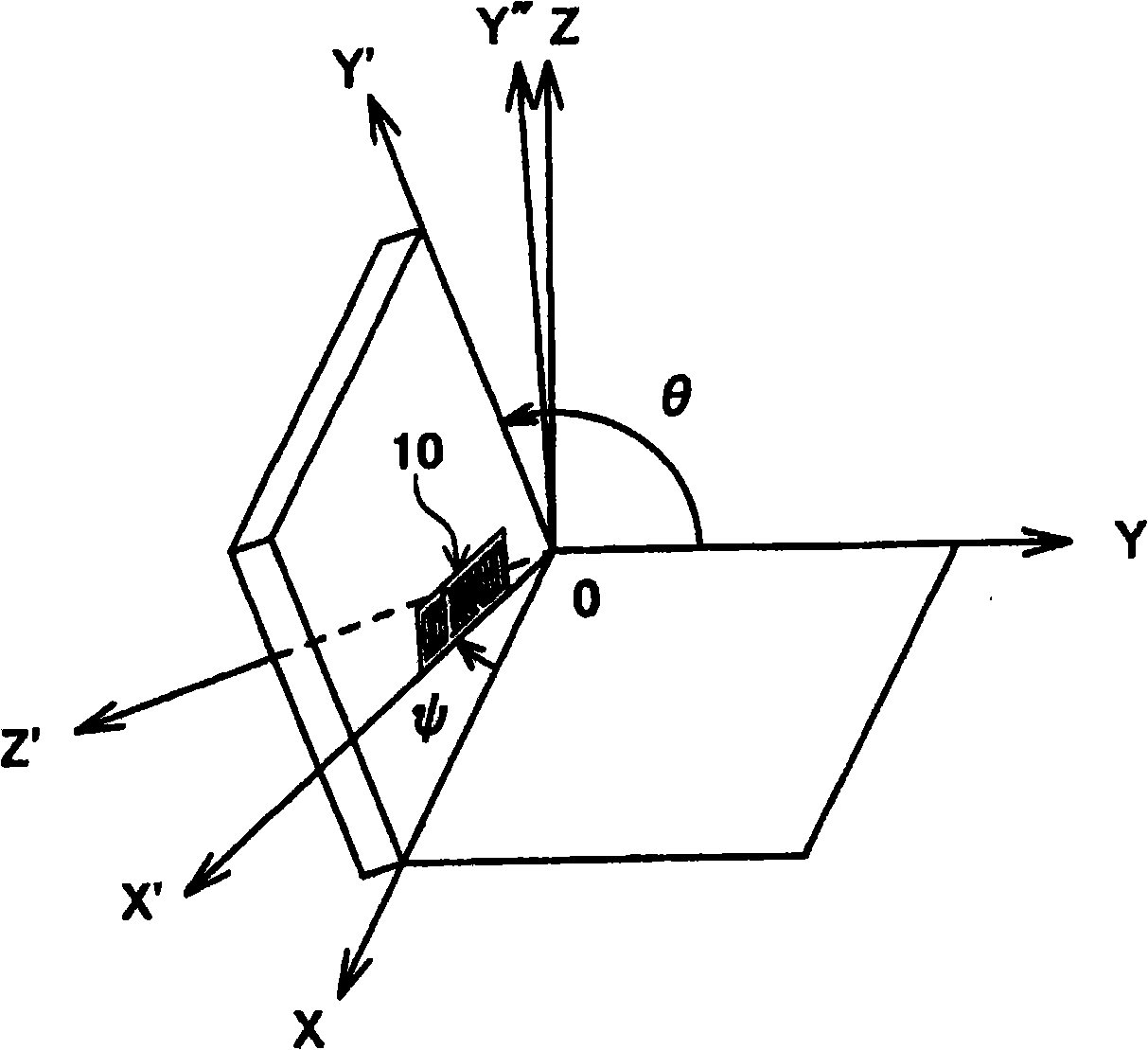
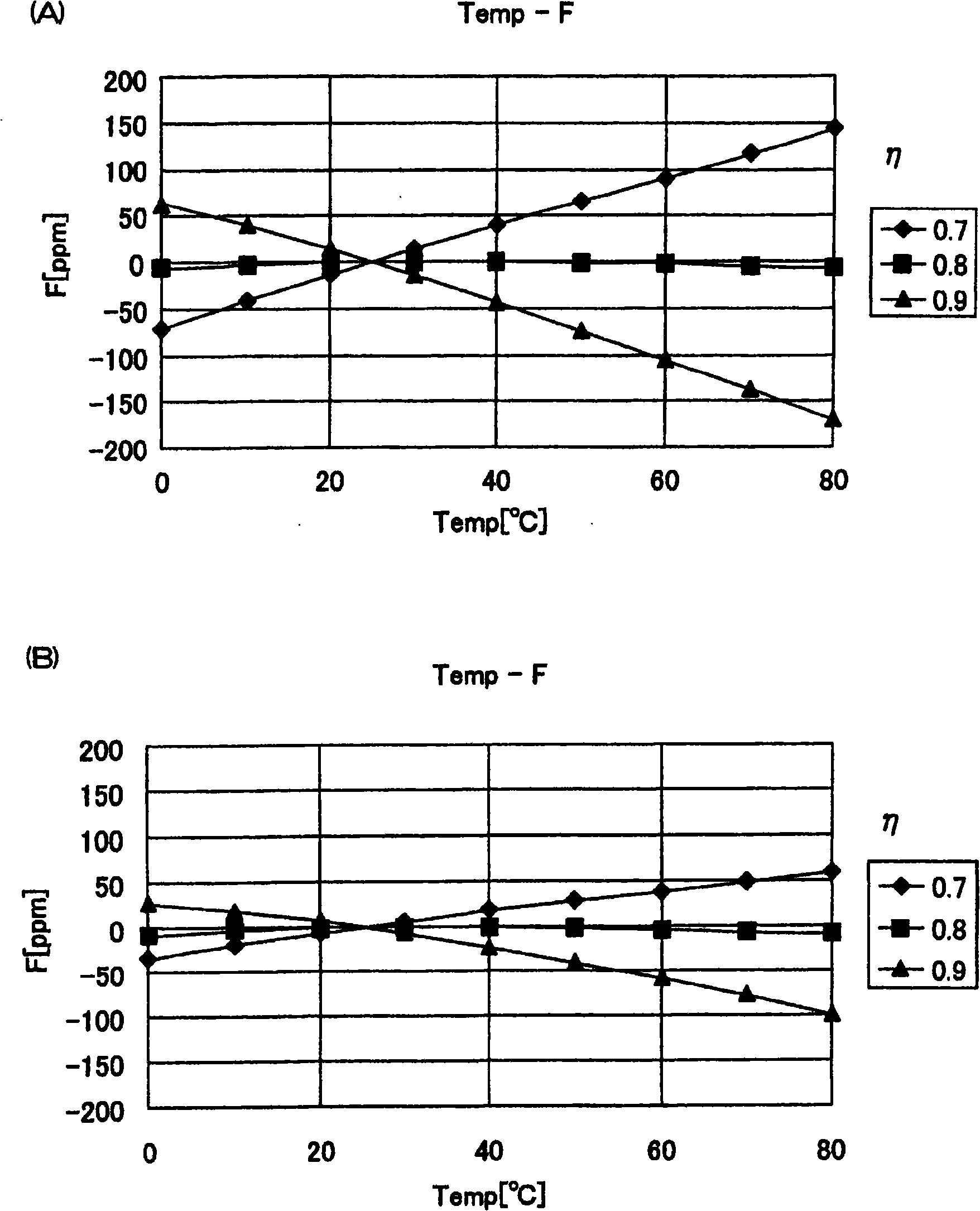
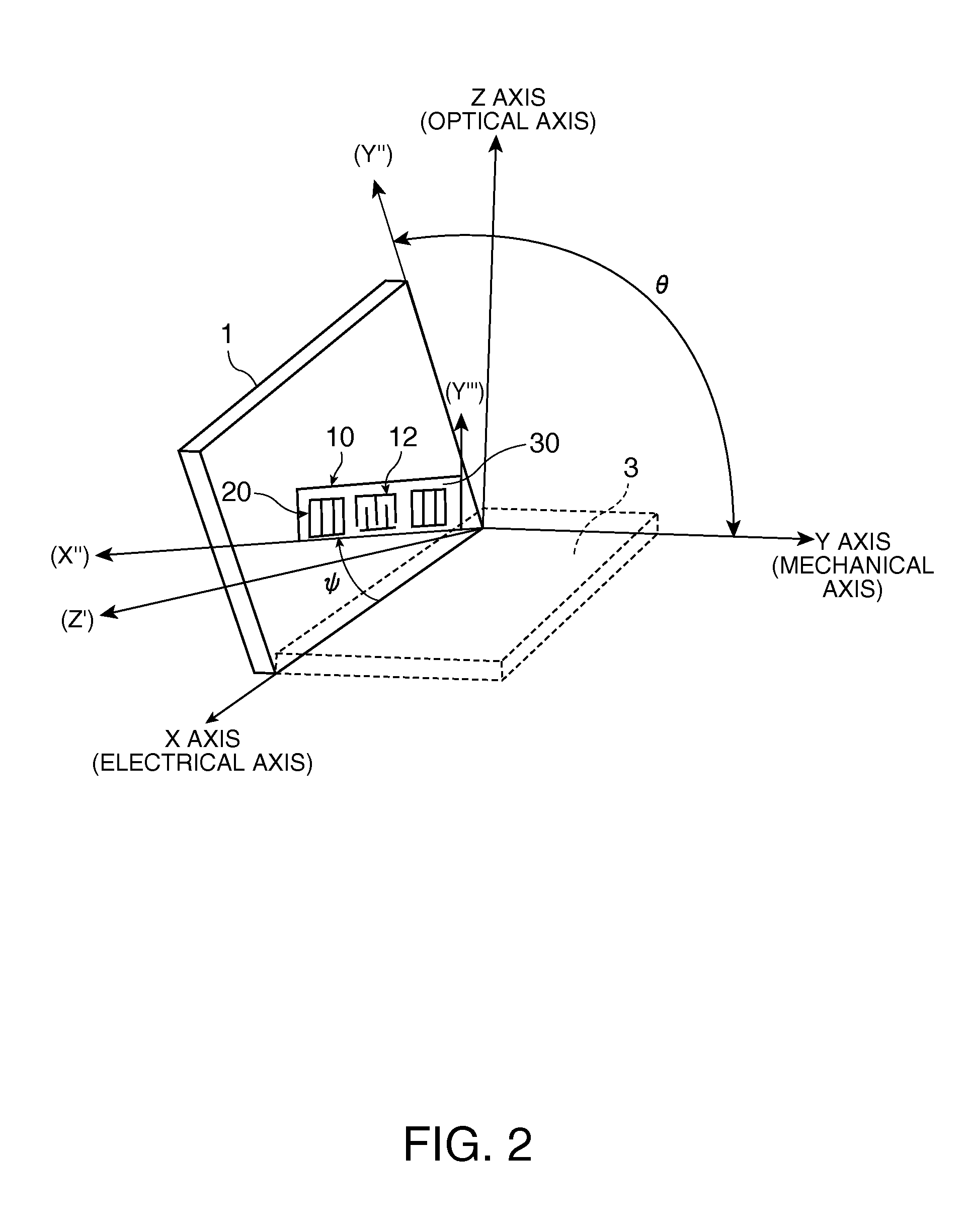
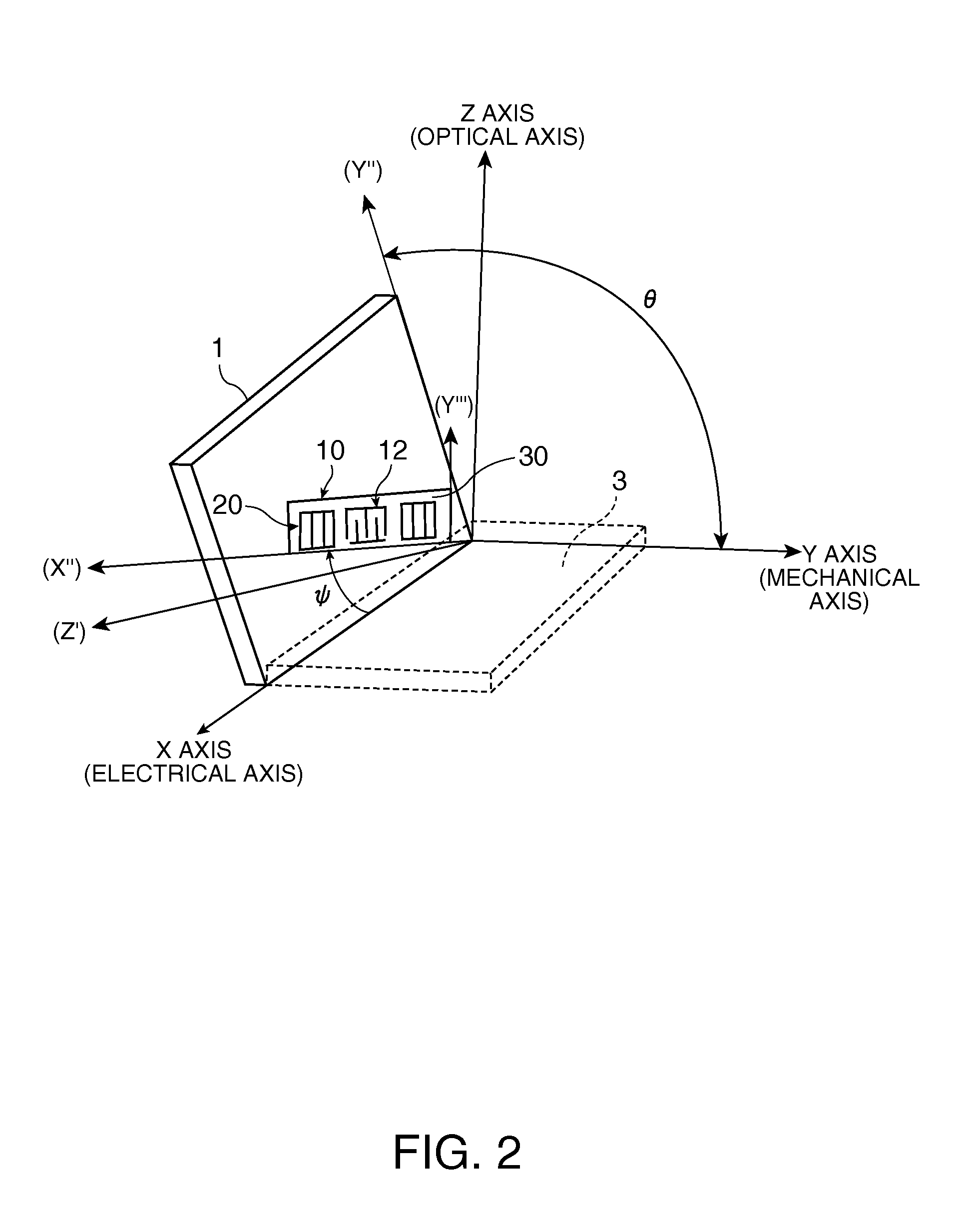
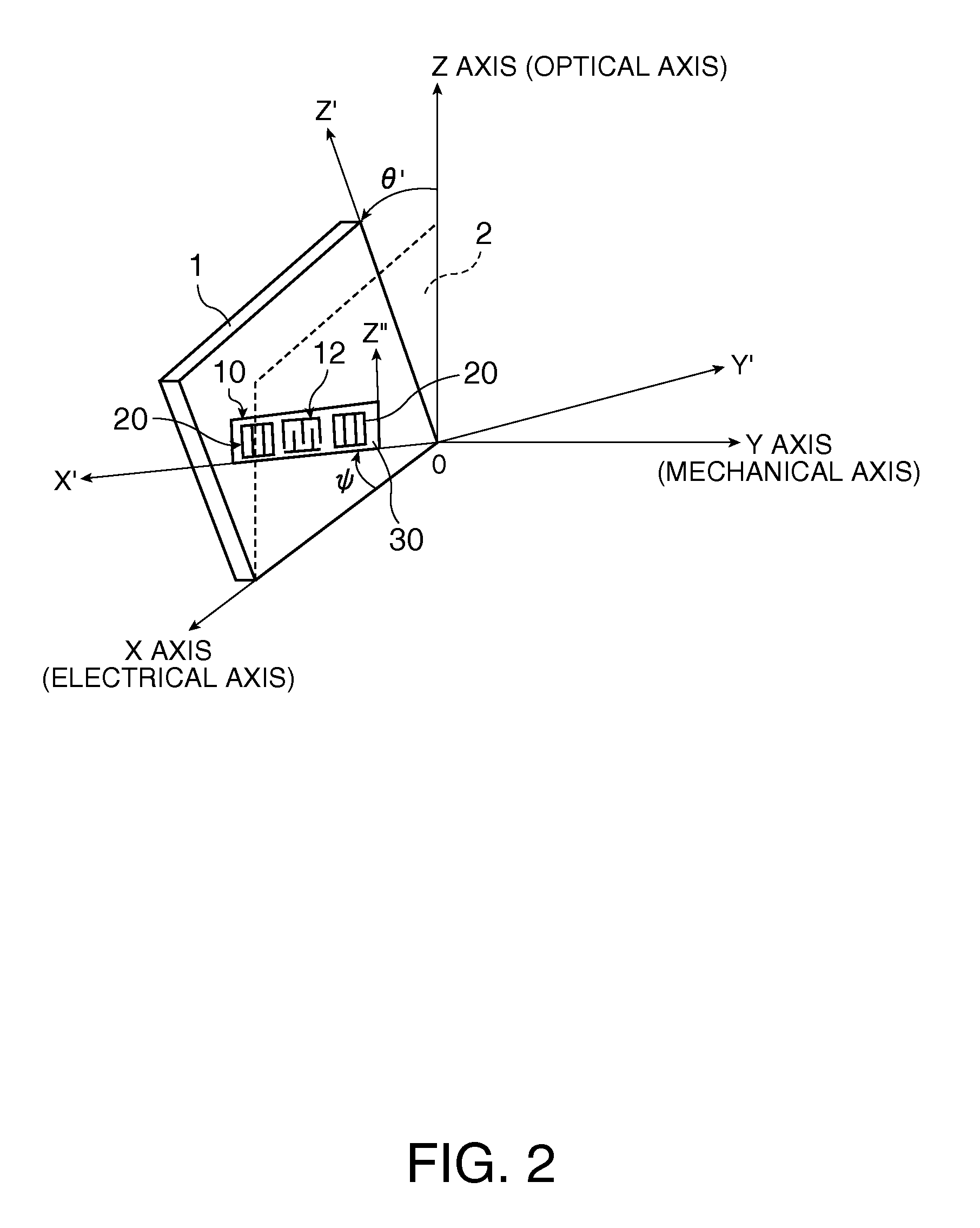
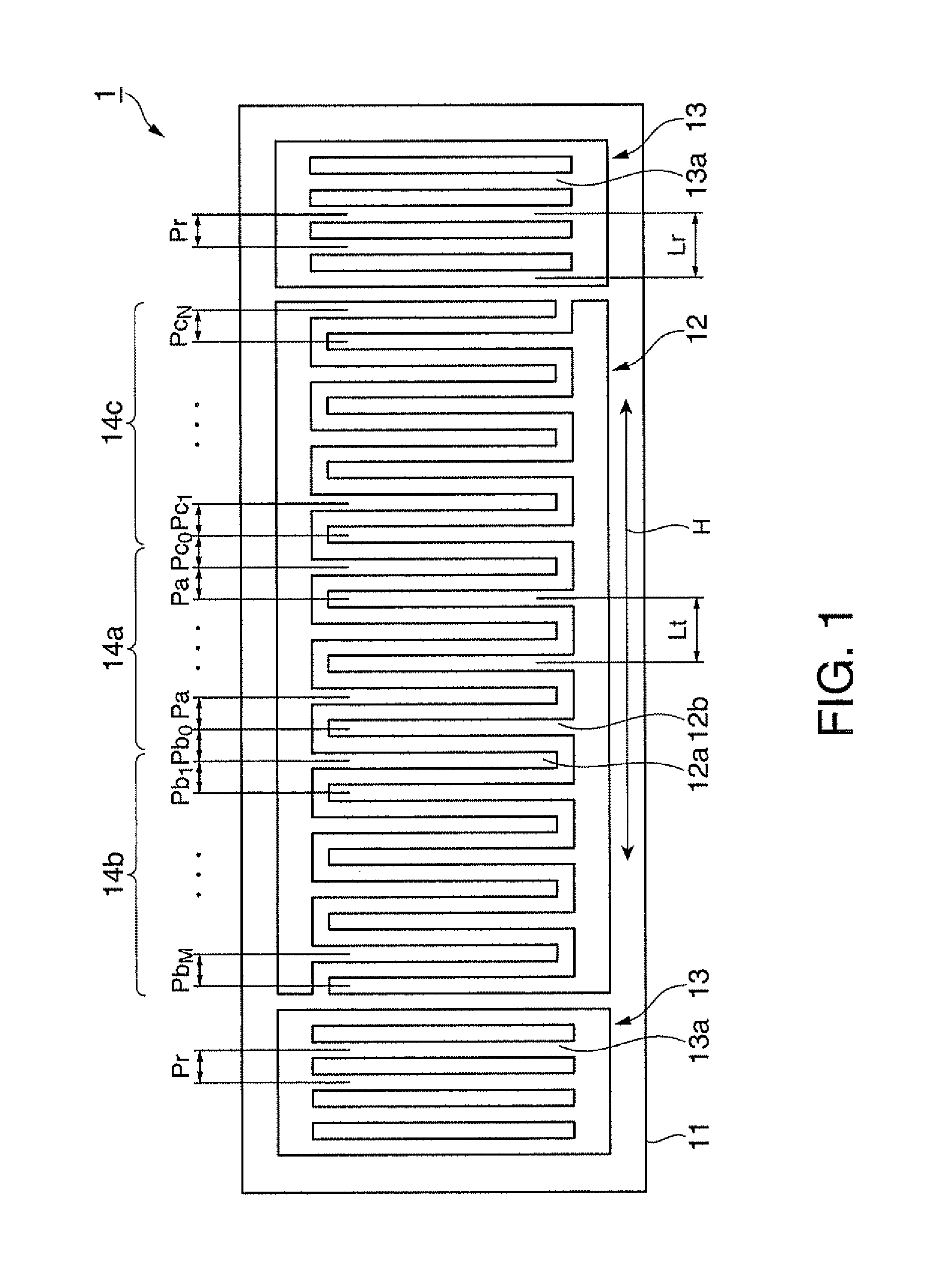
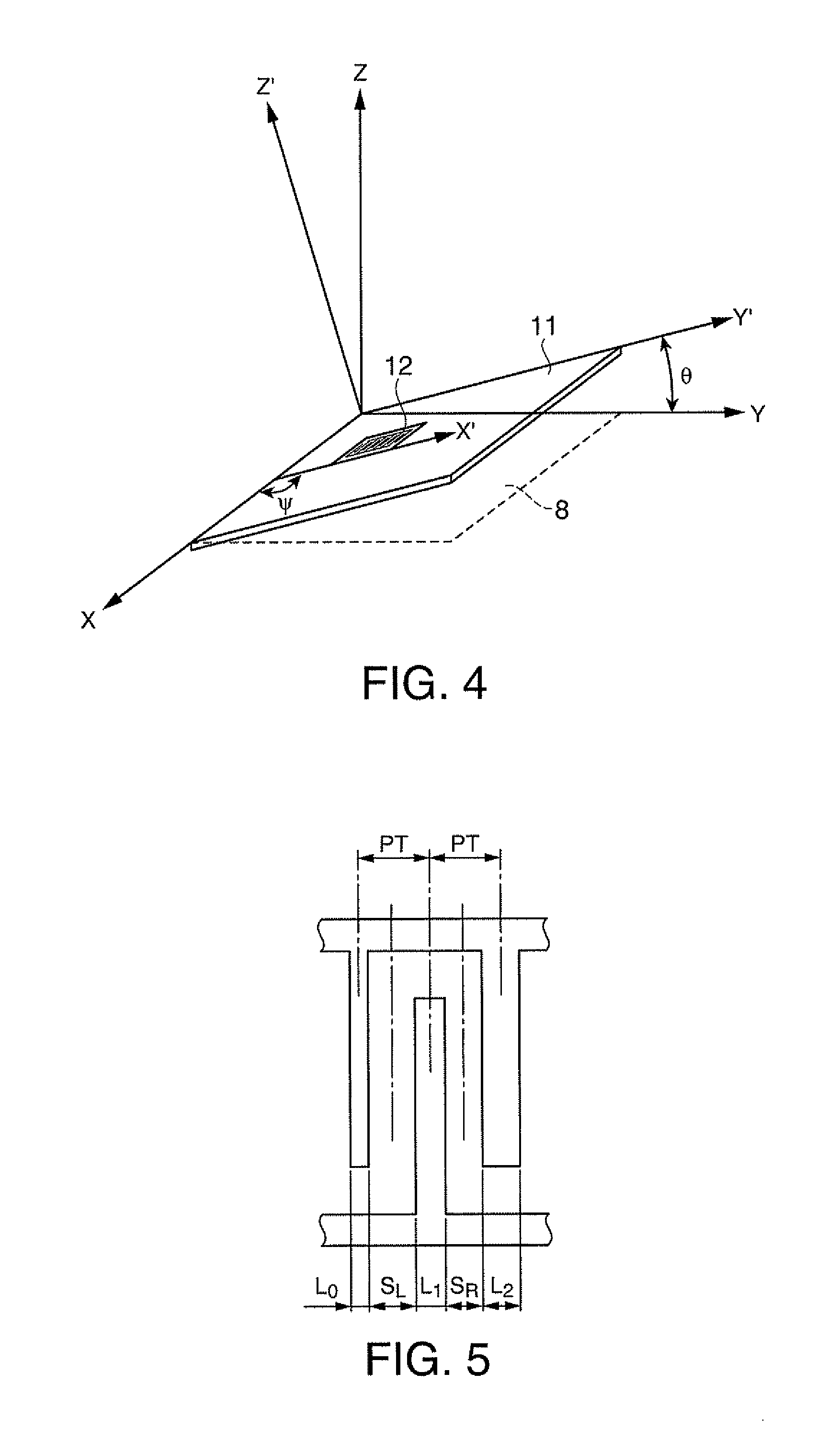
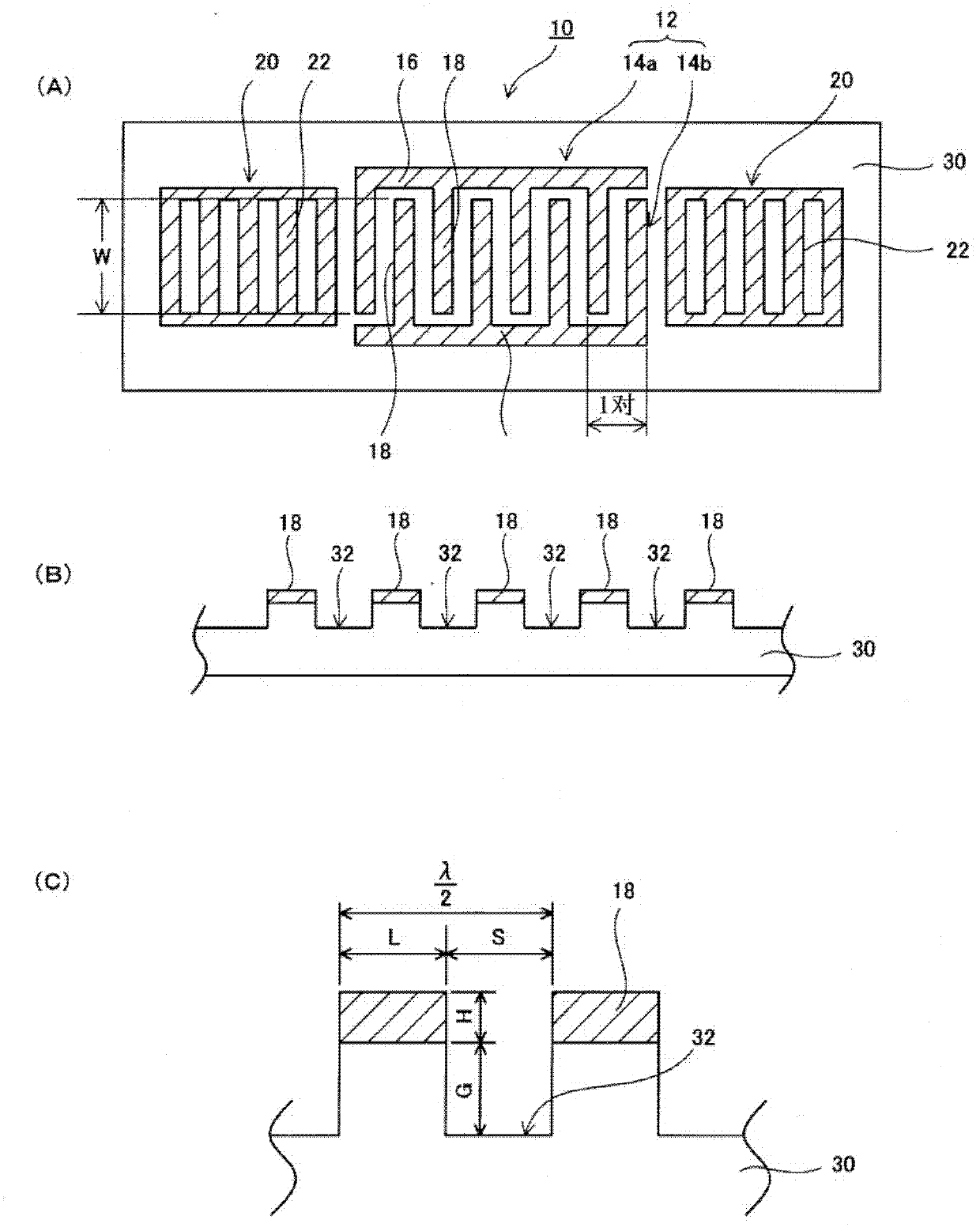
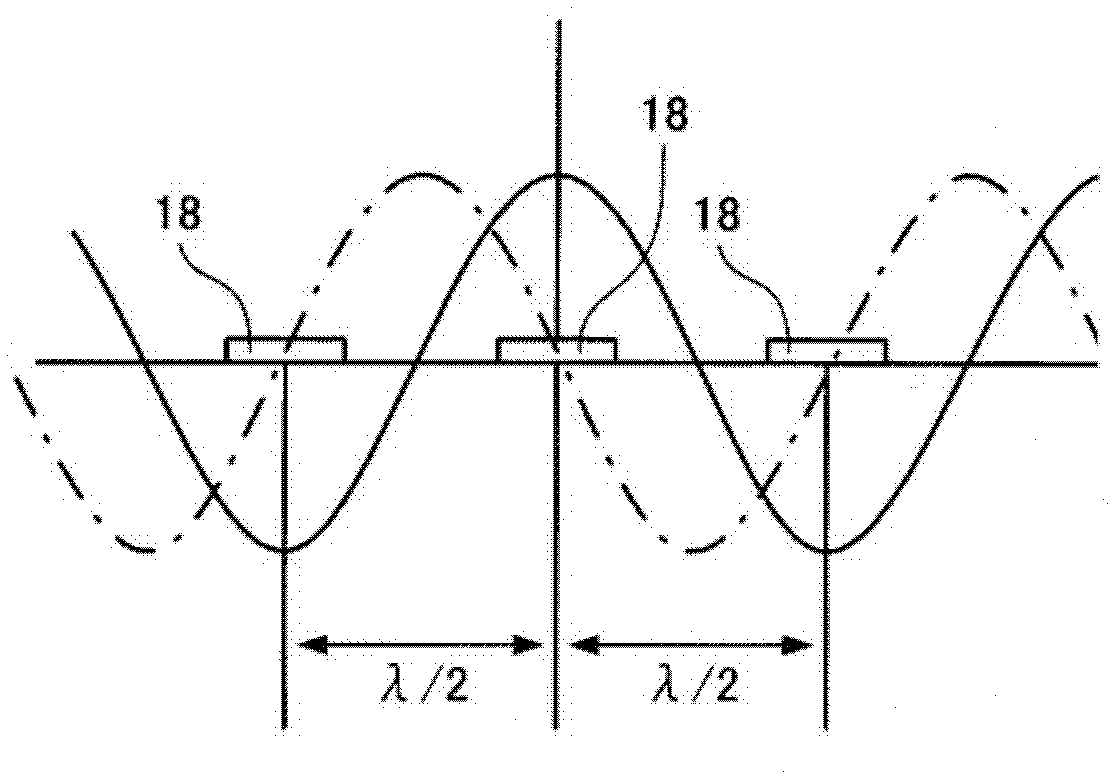
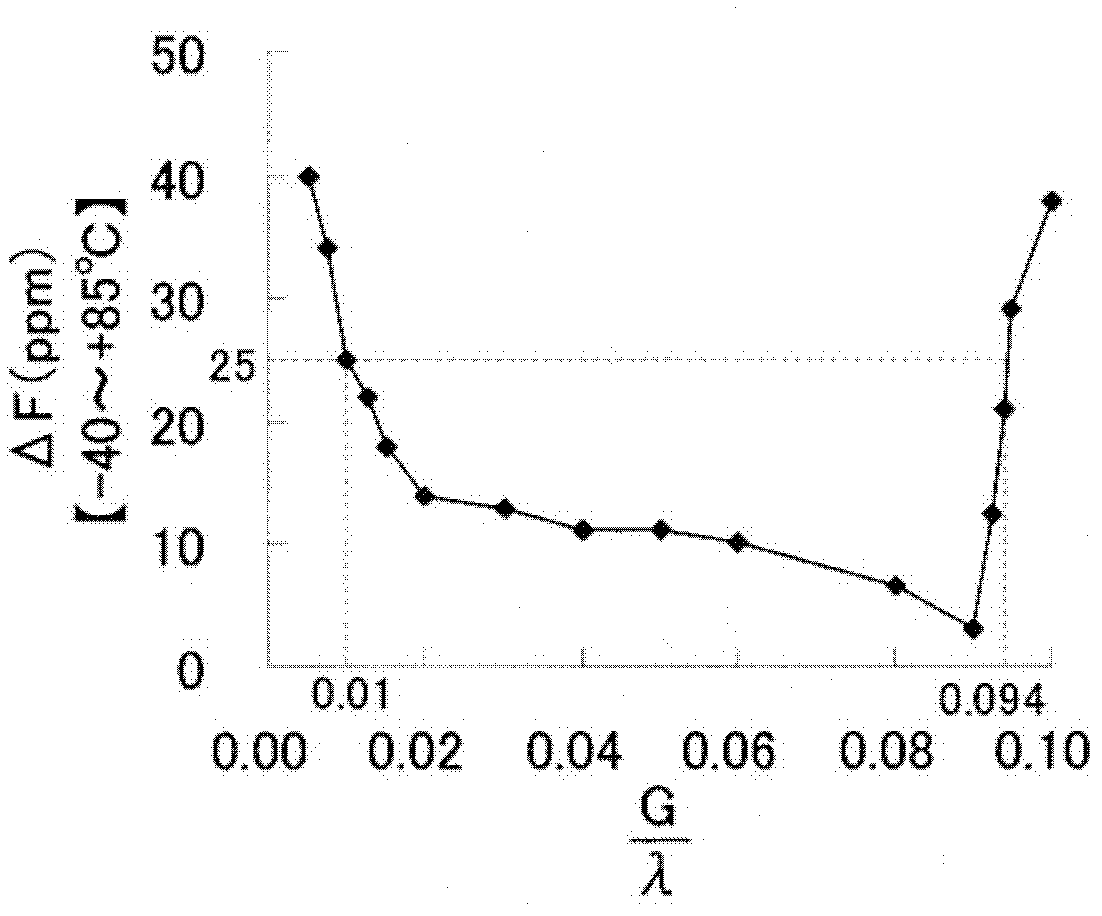
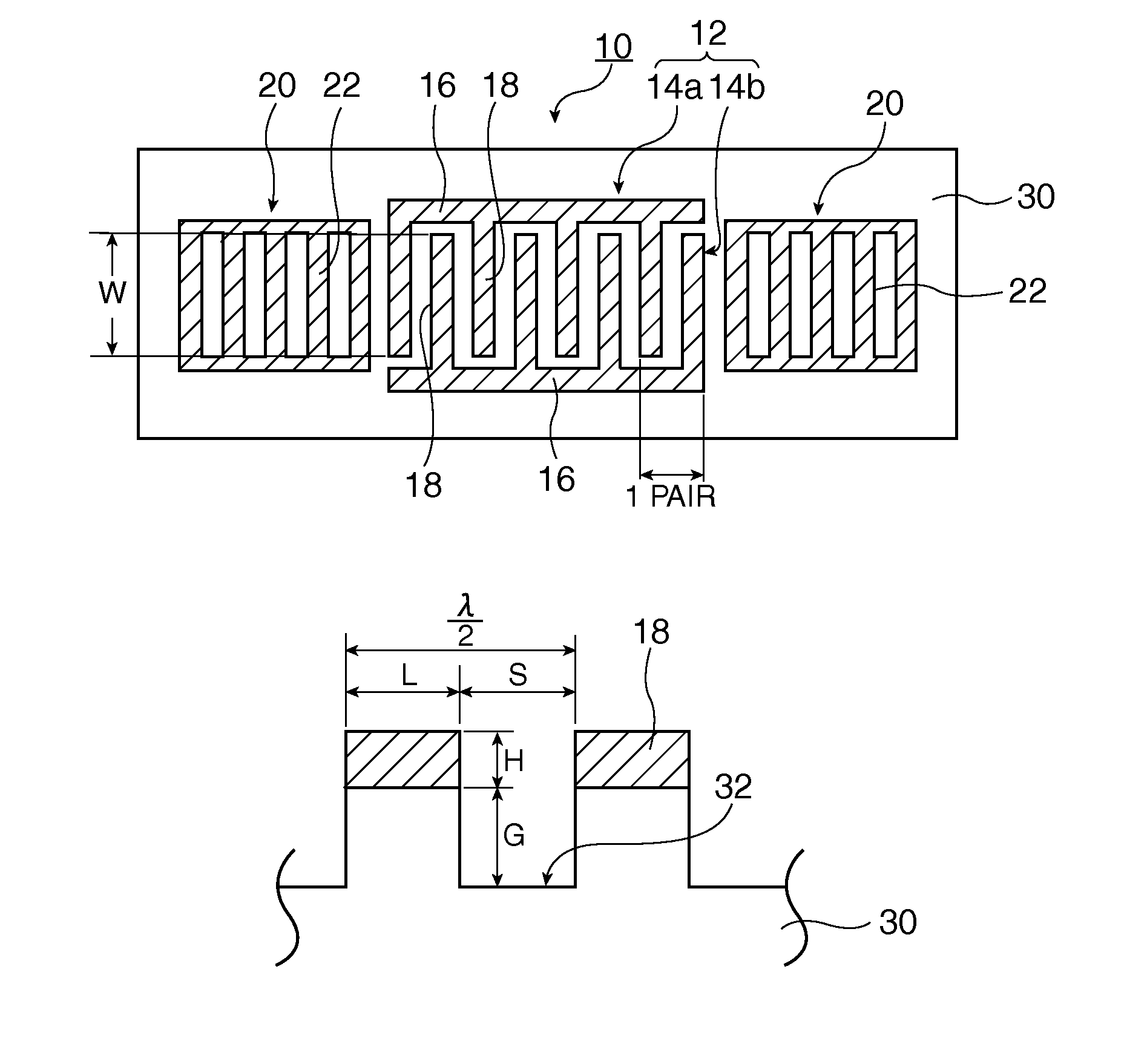
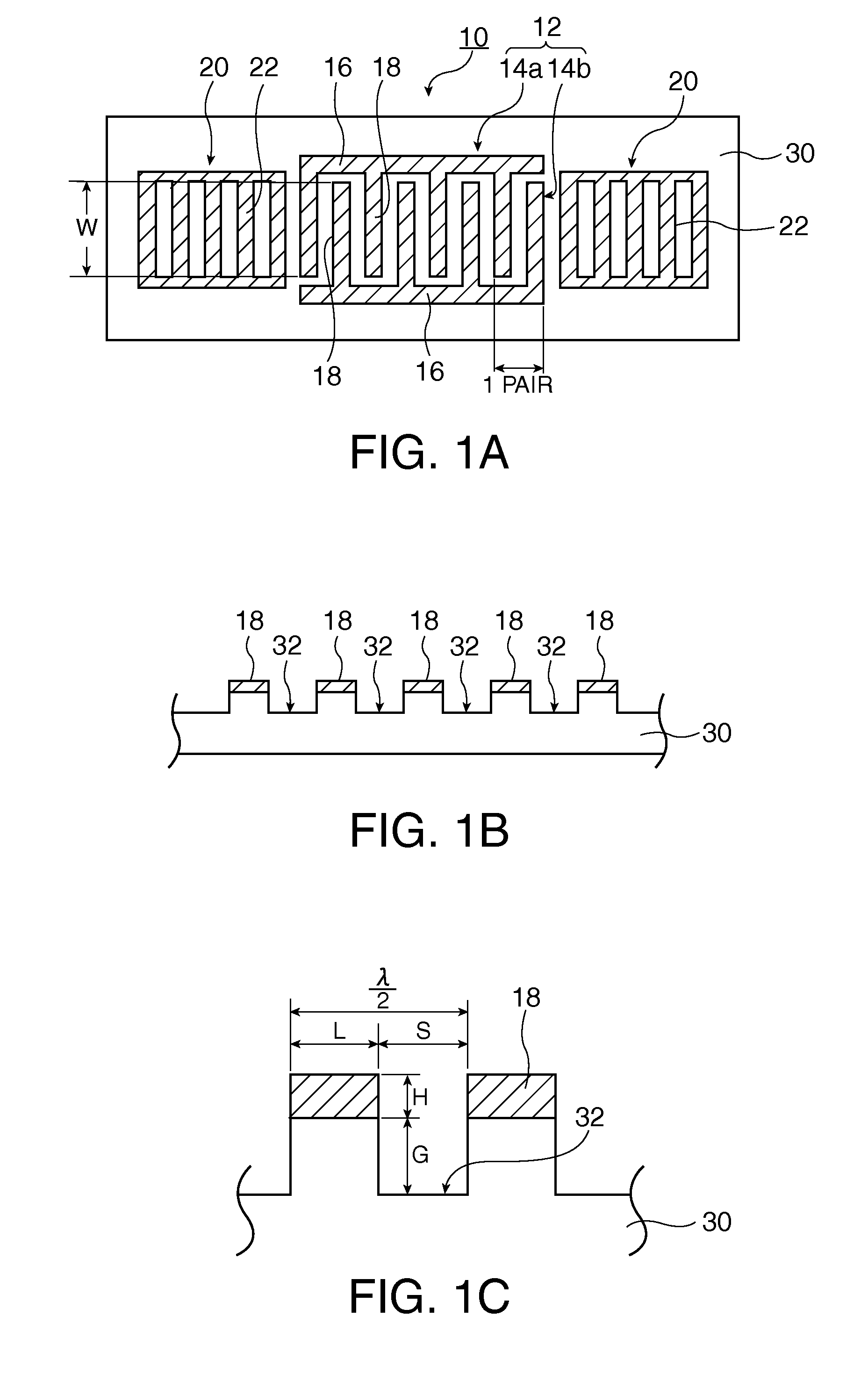
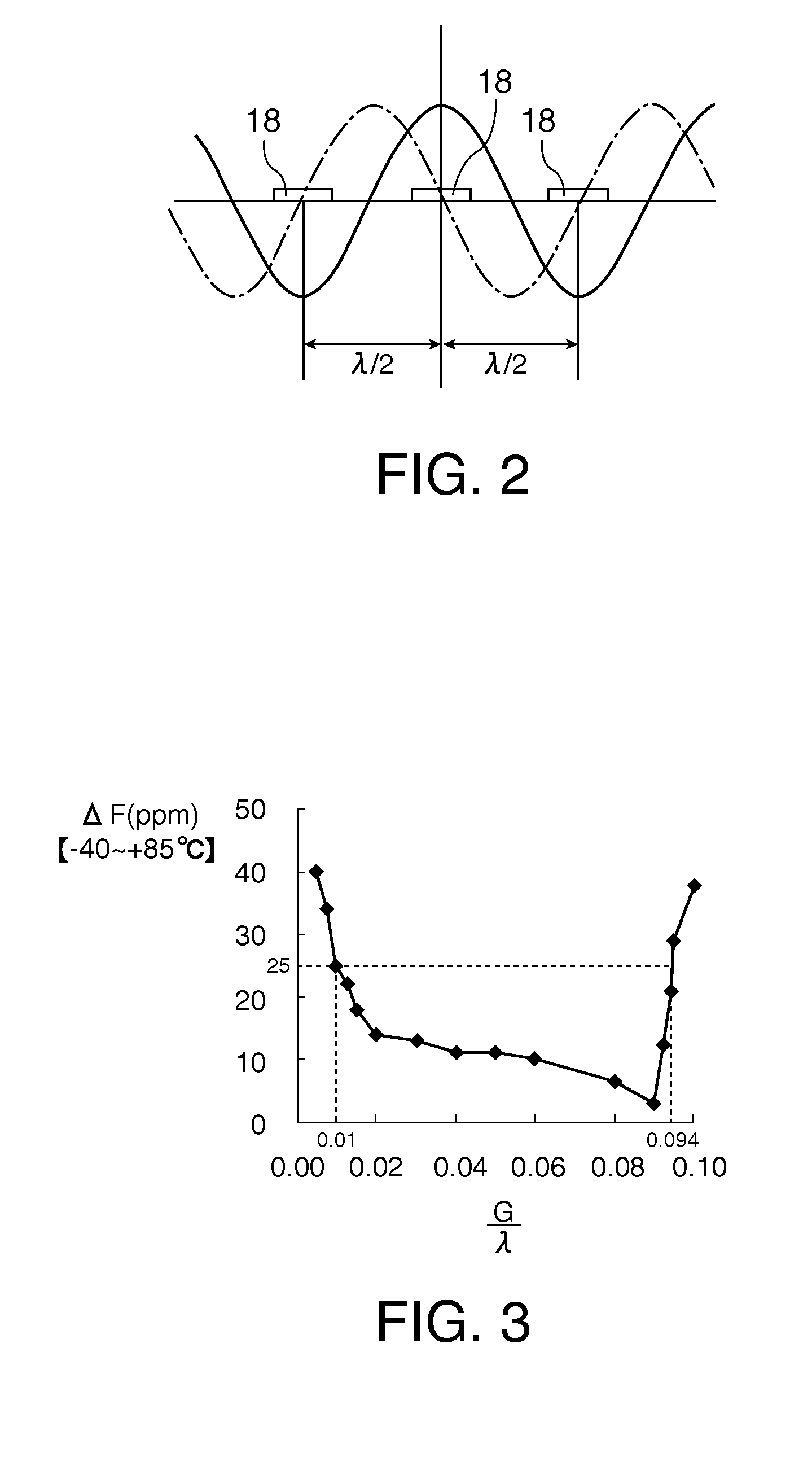
A surface acoustic wave resonator includes: an IDT which is disposed on a quartz substrate with Euler angles of (−1°≦φ≦1°, 117°≦θ≦142°, 42.79°≦|ψ|≦49.57°, which is made of Al or alloy including Al as a main component and which excites a surface acoustic wave in an upper mode of a stop band; and an inter-electrode-finger groove which is formed by recessing the quartz substrate between electrode fingers which form the IDT. Here, the following expression is satisfied:0.01λ≦G (1),where λ represents a wavelength of the surface acoustic wave and G represents a depth of the inter-electrode-finger groove. The depth G of the inter-electrode-finger groove and a line occupancy η of the IDT satisfy the following expression:-2.5×Gλ+0.675≦η≦-2.5×Gλ+0.775(5)and a number of pairs N of the electrode fingers in the IDT is in the range of the following expression:160≦N≦220 (19).
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Surface acoustic wave resonator, surface acoustic wave oscillator, and electronic apparatus
InactiveUS20110309897A1Improve reliabilityImpedence networksOscillations generatorsSurface acoustic wave oscillatorsAcoustic wave
A surface acoustic wave (SAW) resonator and a SAW oscillator and an electronic apparatus including the resonator are to be provided. A SAW resonator includes: an IDT exciting a SAW using a quartz crystal substrate of Euler angles (−1.5°≦φ≦1 / 5°, 117°≦θ≦142°, 42.79°≦|ψ|≦49.57°; one pair of reflection units arranged so as allow the IDT to be disposed therebetween; and grooves acquired by depressing the quartz crystal substrate located between electrode fingers. When a wavelength of the SAW is λ, and a depth of the grooves is G, “0.01λ≦G” is satisfied.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
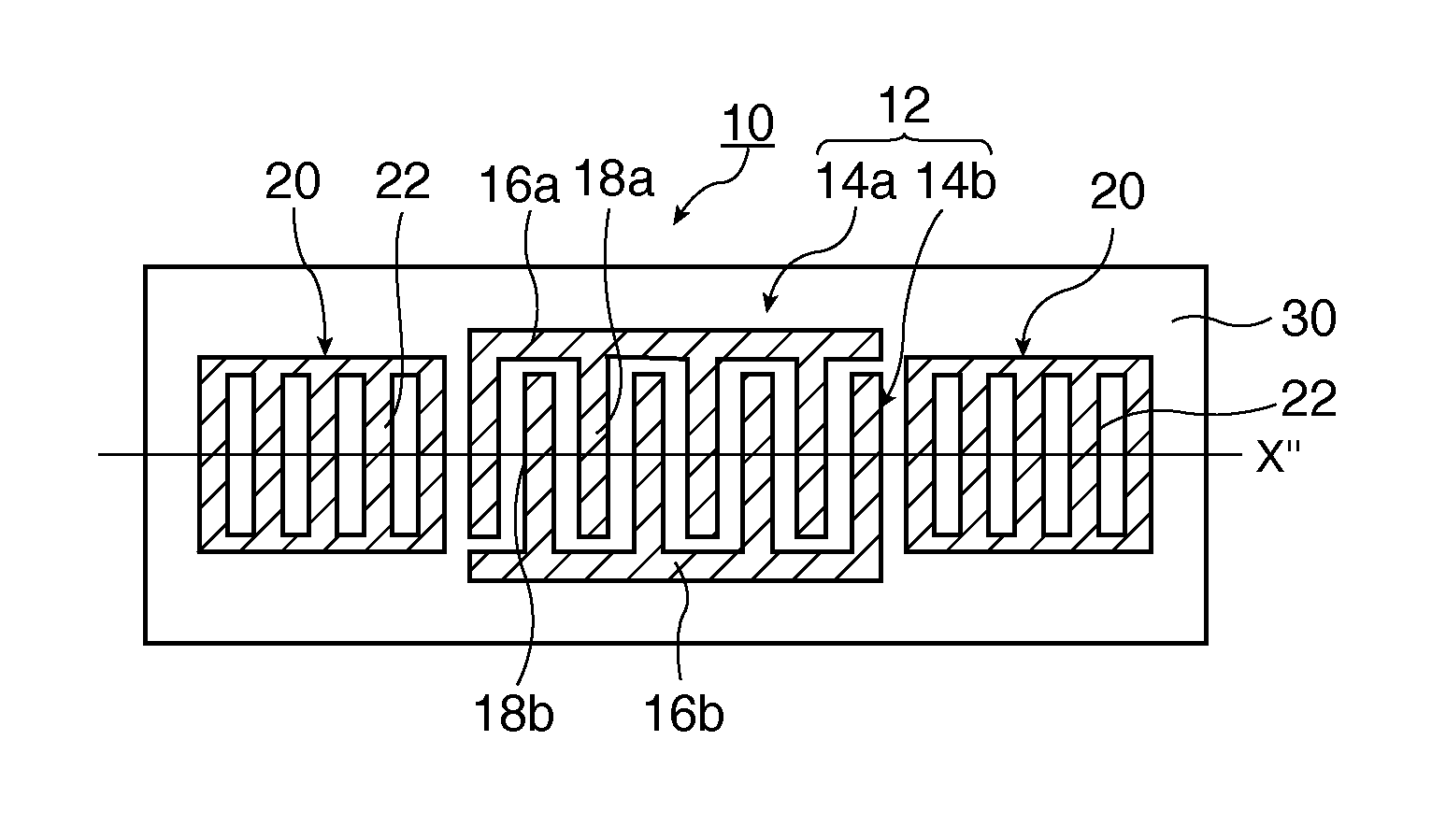
Surface acoustic wave device and surface acoustic wave oscillator
InactiveUS8063534B2Reduce disagreementReduce frequency differenceImpedence networksPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesSurface acoustic wave oscillatorsQuartz substrate
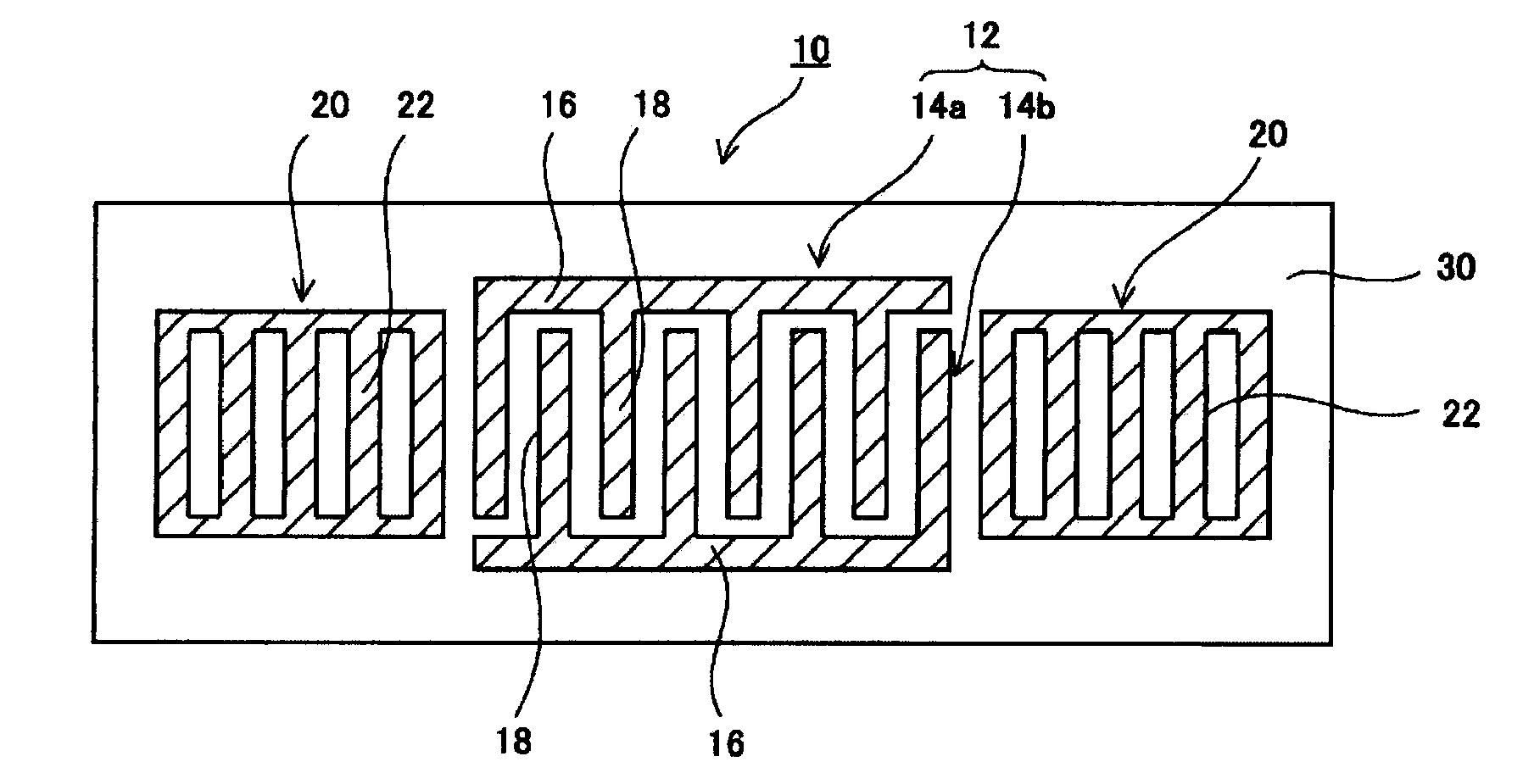
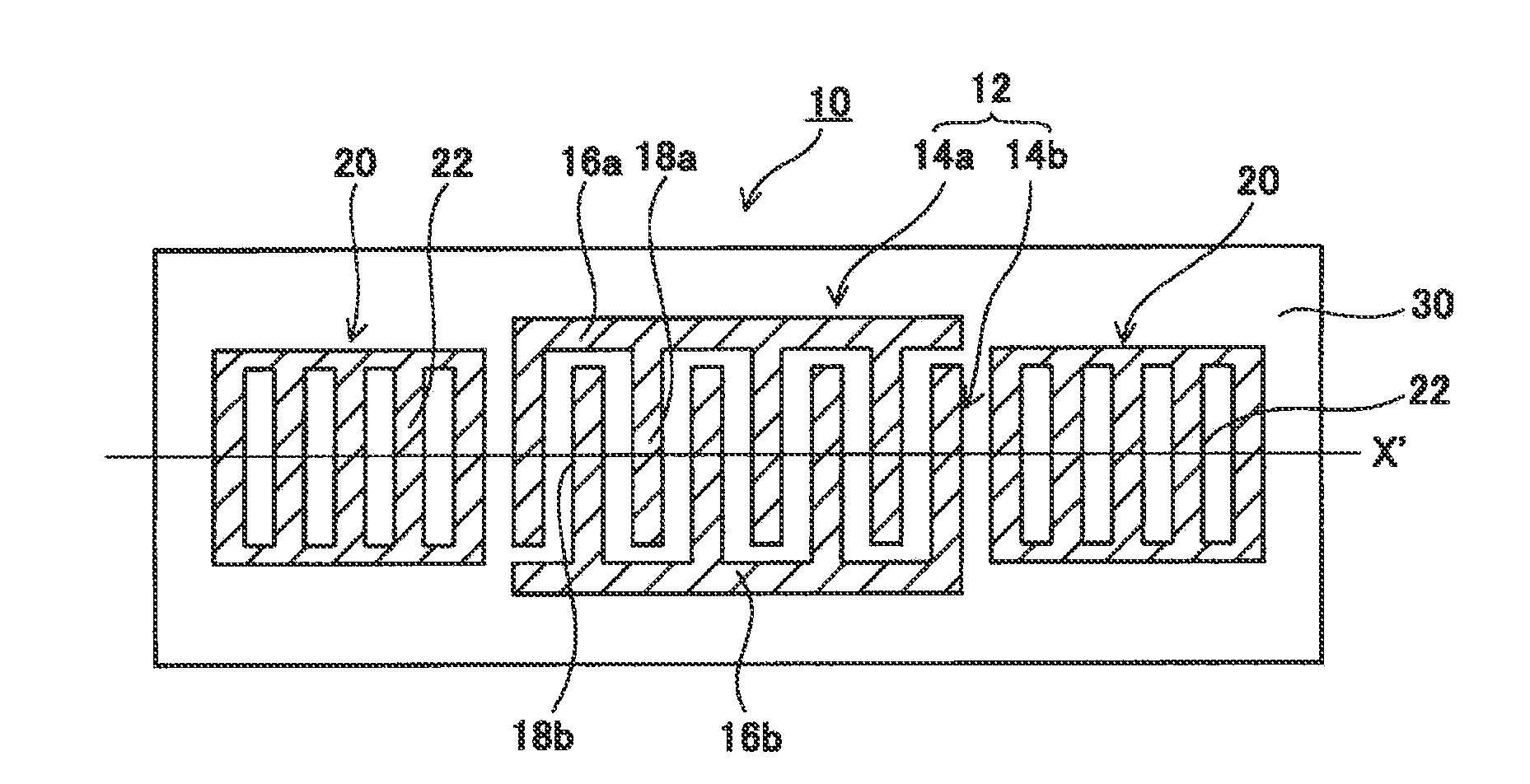
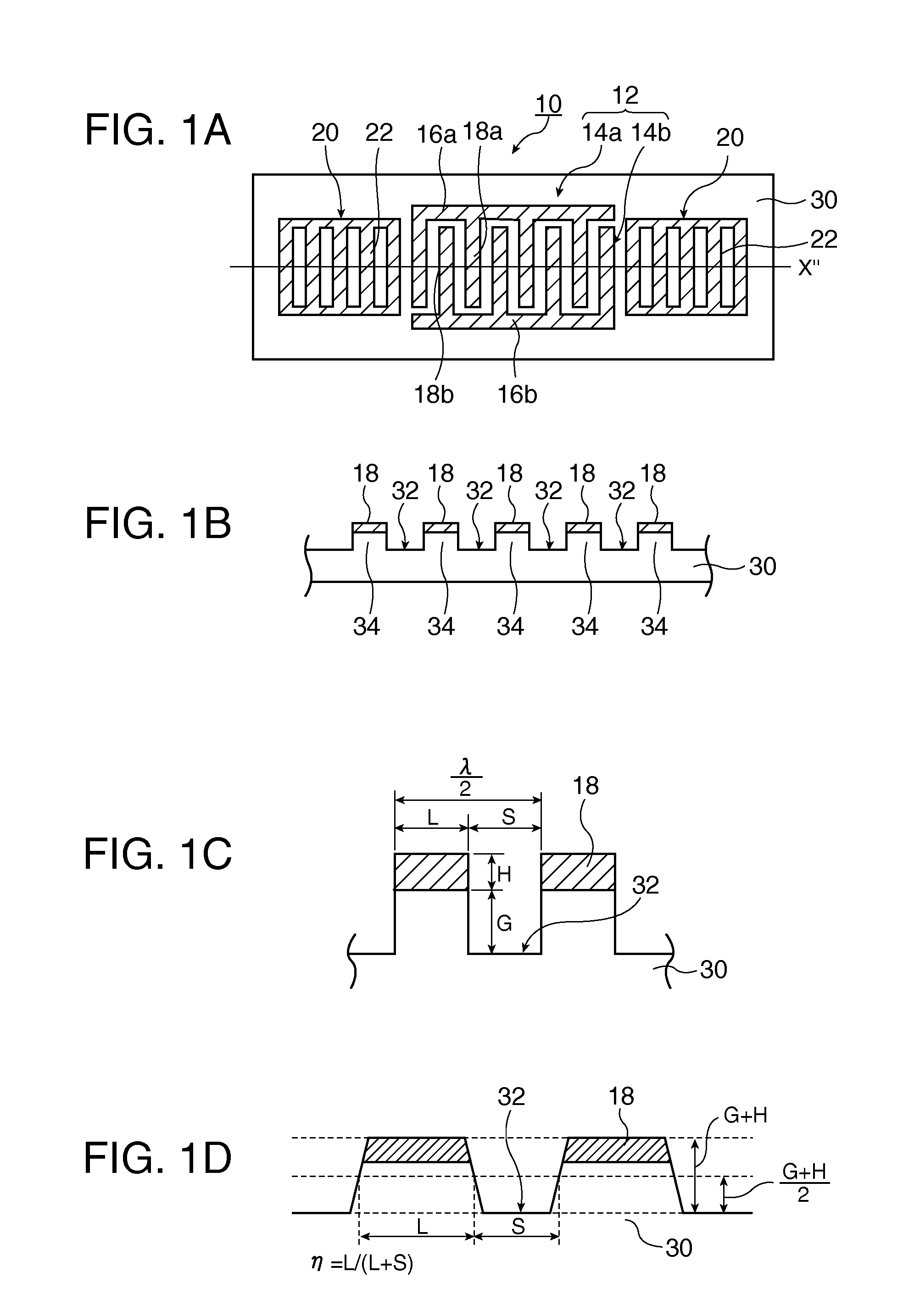
A surface acoustic wave device, includes: an interdigital transducer serving as an electrode pattern to excite a Rayleigh surface acoustic wave, the interdigital transducer including a comb-tooth-shaped electrode having a plurality of electrode fingers; a piezoelectric substrate on which the interdigital transducer is formed, the piezoelectric substrate being made of a quartz substrate that is cut out at a cut angle represented by an Euler angle representation (φ, θ, Ψ) of (0°, 95°≦θ≦155°, 33°≦|Ψ|≦46°); electrode finger grooves formed between the electrode fingers of the comb-tooth-shaped electrode; and electrode finger bases being quartz portions sandwiched between the electrode finger grooves and having upper surfaces on which the electrode fingers are positioned. The surface acoustic wave device provides an excitation in an upper limit mode of a stop band of the surface acoustic wave.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Surface acoustic wave resonator and surface acoustic wave oscillator
ActiveCN101820265AImpedence networksPiezoelectric/electrostrictive devicesSurface acoustic wave oscillatorsAcoustic wave
The invention provides a surface acoustic wave resonator and a surface acoustic wave oscillator with a good frequency temperature characteristic. A SAW resonator (10) which, using a quartz crystal substrate (30) with Euler angles (117 DEG<=theta<=142 DEG, and 42.79 DEG<=Psi<=49.57 DEG, includes an IDT (10) which excites a stop band upper end mode SAW, and grooves (32) hollowed out of the substrate positioned between electrode fingers (18) configuring the IDT, wherein, when the wavelength of the SAW is [lambda] and the depth of the inter-electrode finger grooves is G, [lambda] and G satisfy the relationship of 0.01[lambda]<=G and wherein, when the line occupation rate of the IDT is [eta], the groove (32) depth G and line occupation rate [eta] satisfy the relationships of - 2.5xG / Lambda+0.675<=-2.5xG / Lambda+0.775.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Surface acoustic wave resonator, surface acoustic wave oscillator, and surface acoustic wave module unit
ActiveUS20110199163A1Improve confinementExcellent CIImpedence networksPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesElectromechanical coupling coefficientSurface acoustic wave oscillators
In a surface acoustic wave resonator in which an IDT having electrode fingers for exciting surface acoustic waves is formed on a crystal substrate, the line occupying ratio causing the maximum electromechanical coupling coefficient and the line occupying ratio causing the maximum reflection of the surface acoustic waves in the IDT are different from each other, the center of the IDT has the line occupying ratio causing an increase in electromechanical coupling coefficient in comparison with the edges of the IDT, and the edges of the IDT have the line occupying ratio causing an increase in reflection of the surface acoustic waves in comparison with the center of the IDT.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Surface acoustic wave resonator and surface acoustic wave oscillator
ActiveUS20130027147A1Improve featuresImprove environmental resistanceImpedence networksPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesSurface acoustic wave oscillatorsAcoustic wave
A surface acoustic wave resonator includes: an IDT which is disposed on a quartz crystal substrate with an Euler angle of (−1.5°≦φ≦1.5°, 117°≦θ≦142°, 41.9°≦|ψ|≦49.57°) and which excites a surface acoustic wave in an upper mode of a stop band; and an inter-electrode-finger groove formed by recessing the quartz crystal substrate between electrode fingers of the IDT, wherein the following expression:0.01λ≦G where λ represents a wavelength of the surface acoustic wave and G represents a depth of the inter-electrode-finger groove, is satisfied and when a line occupancy of the IDT is η, the depth of the inter-electrode-finger groove G and the line occupancy η are set to satisfy the following expression:−2.5×G / λ+0.675≦η≦−2.5×G / λ+0.775.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Surface acoustic wave resonator, surface acoustic wave oscillator, and electronic device
InactiveUS20120049969A1Reduce frequencyReduce strainImpedence networksPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesSurface acoustic wave oscillatorsAcoustic wave
A surface acoustic wave resonator has a quartz crystal substrate having Euler angles of (φ=0°, 110°≦θ≦150°, 88°≦ψ≦92°) and an IDT having a plurality of electrode fingers disposed on the quartz crystal substrate, and using a surface acoustic wave as an excitation wave, a plurality of grooves arranged in a propagation direction of the surface acoustic wave to form stripes is disposed on the quartz crystal substrate, and the electrode fingers are disposed one of between the grooves and inside the grooves.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Surface acoustic wave resonator, surface acoustic wave oscillator, and surface acoustic wave module device
ActiveUS20100102669A1Reduce power consumptionGrowth inhibitionPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesImpedence networksElectromechanical coupling coefficientSurface acoustic wave oscillators
A surface acoustic wave resonator includes a piezoelectric substrate and an interdigital transducer (IDT) that includes electrode fingers exciting a surface acoustic wave on the piezoelectric substrate, a first region at a center of the IDT, and a second region and a third region at opposite sides of the IDT. In the IDT, a line occupation rate at which an electromechanical coupling coefficient becomes a maximum is different from the line occupation rate at which reflection of the surface acoustic wave becomes a maximum.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Surface acoustic wave resonator, surface acoustic wave oscillator, and electronic instrument
ActiveUS20120212301A1Suppress deterioration of environmental resistance characteristicImprove featuresImpedence networksPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesSurface acoustic wave oscillatorsElectronic instrument
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Frequency adjustable surface acoustic wave oscillator
InactiveUS7932789B2Wide tunable frequency rangeReduce phase noiseImpedence networksPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesSurface acoustic wave oscillatorsPhase relationship
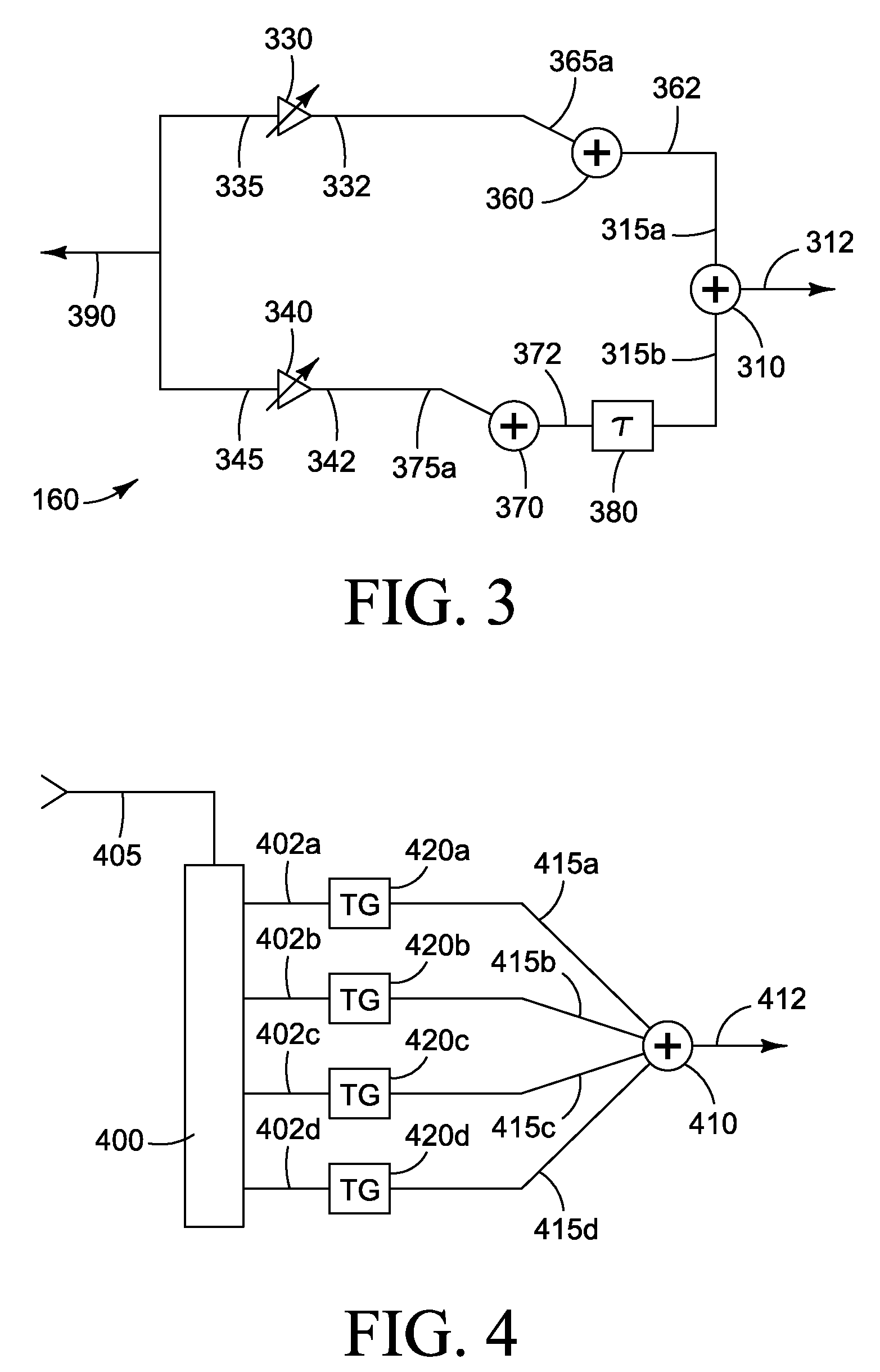
A frequency adjustable surface acoustic wave oscillator uses circuitry in which the phase relationship between the corresponding input and output signals and the voltage applied to or received by transducer fingers is controlled in such a manner that the frequency of the surface acoustic wave oscillator is arbitrarily controlled over a wide range by digital means. This provides an oscillator that exhibits a wide tunable frequency range while providing low phase noise.
Owner:HAY ROBERT
Surface acoustic wave device and surface acoustic wave oscillator
ActiveCN101515792AReduce the difference in the amount of frequency variationSuitable for mass productionImpedence networksSurface acoustic wave oscillatorsQuartz substrate
The surface acoustic wave device (10) includes at least an IDT (16) serving as an electrode pattern (14) to excite a Rayleigh surface acoustic wave, to excite the upper limit mode of the surface acoustic wave stop band. The surface acoustic wave device is characterized in: the piezoelectric substrate (12) for fabricating IDT (16) is made of a quartz substrate that is cut out at a cut angle represented by an Euler angle representation (phi, theta, Psi) of (0 DEG , 95 DEG <=theta<=155 DEG , 33 DEG <=|Psi|<=46 DEG ); electrode finger grooves are formed between the electrode fingers of the comb-tooth-shaped electrode (18 (18a, 18b)) which compose the IDT (16); and electrode finger bases is the quartz portions sandwiched between the electrode finger grooves and has upper surfaces on which the electrode fingers are positioned.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Surface acoustic wave resonator, surface acoustic wave oscillator, and surface acoustic wave module unit
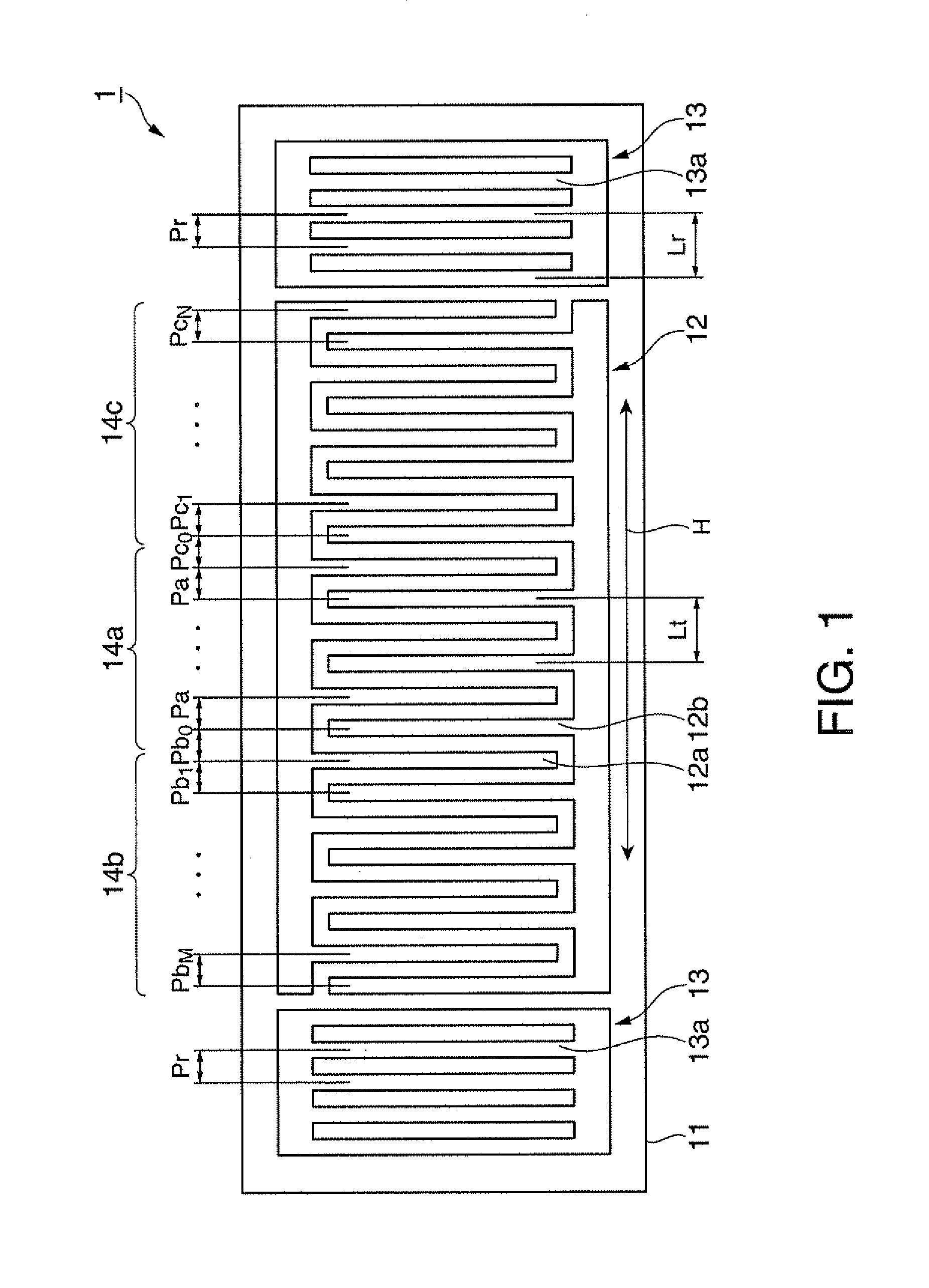
ActiveUS20110199160A1Improve Q valueSmall sizePiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesImpedence networksAcoustic waveSurface acoustic wave oscillators
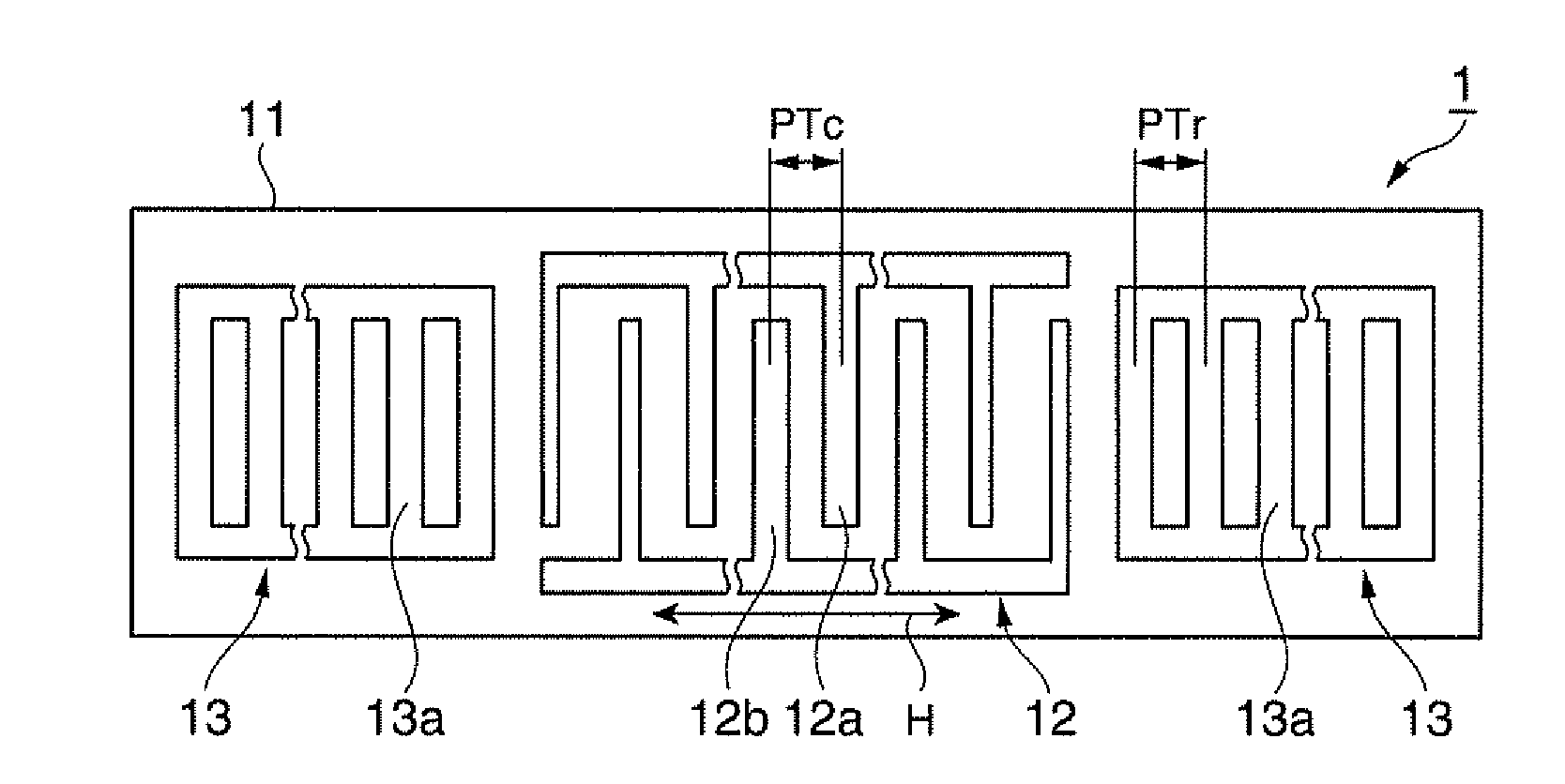
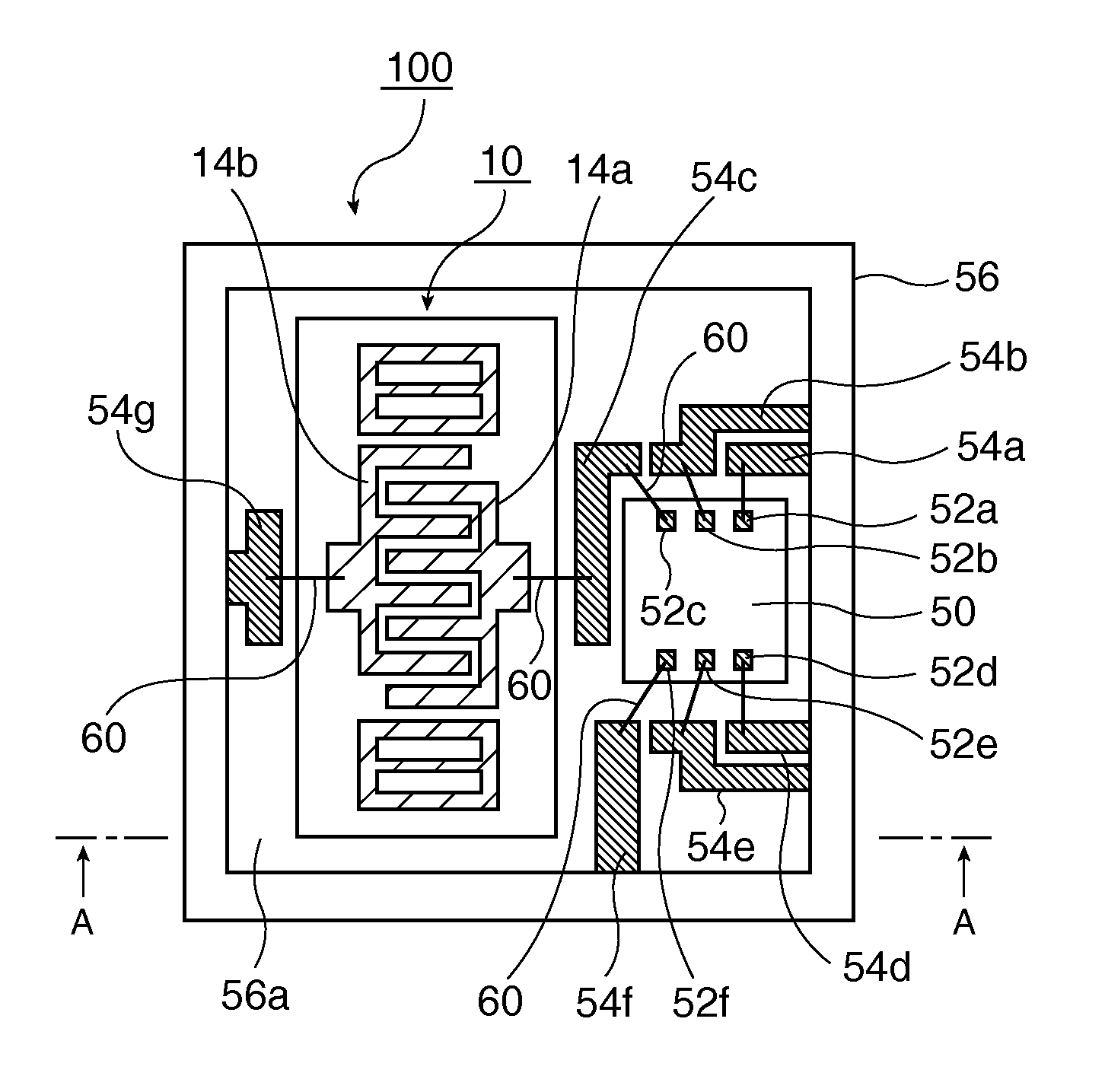
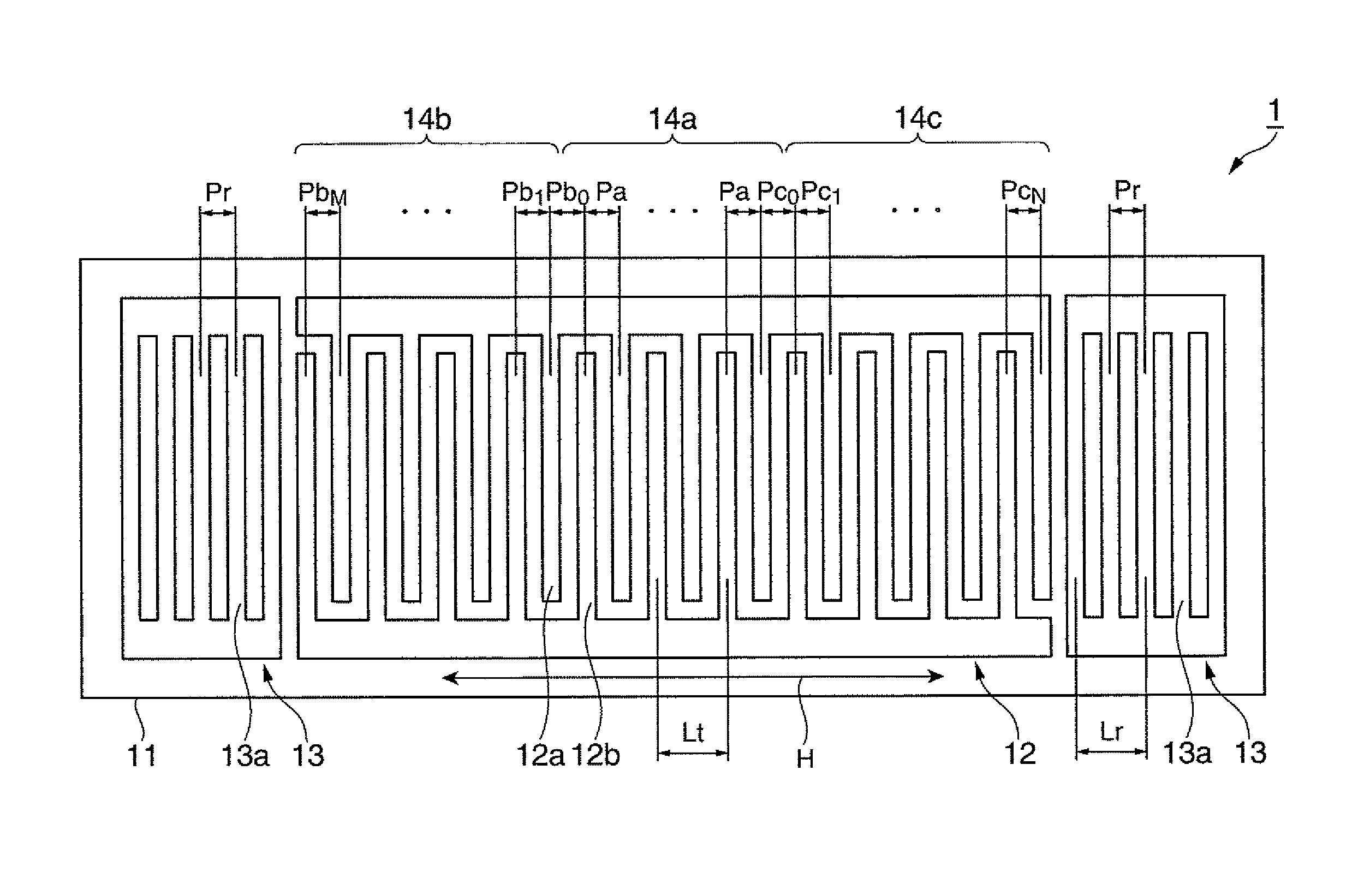
It is possible to reduce the size of a surface acoustic wave (SAW) resonator by enhancing a Q value. In a SAW resonator in which an IDT having electrode fingers for exciting SAW is disposed on a crystal substrate, the IDT includes a first region disposed at the center of the IDT and a second region and a third region disposed on both sides of the first region. A frequency is fixed in the first region and a portion in which a frequency gradually decreases as it approaches an edge of the IDT is disposed in the second region and the third region. When the frequency of the first region is Fa, the frequency at an edge of the second region is FbM, and the frequency at an edge of the third region is FcN, the variations in frequency are in the ranges of 0.9815<FbM / Fa<0.9953 and 0.9815<FcN / Fa<0.9953, respectively.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP +1
Surface acoustic wave resonator, surface acoustic wave oscillator, and electronic apparatus
ActiveUS20140055207A1Reduce lossesSuppress fluctuationsImpedence networksPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesSurface acoustic wave oscillatorsAcoustic wave
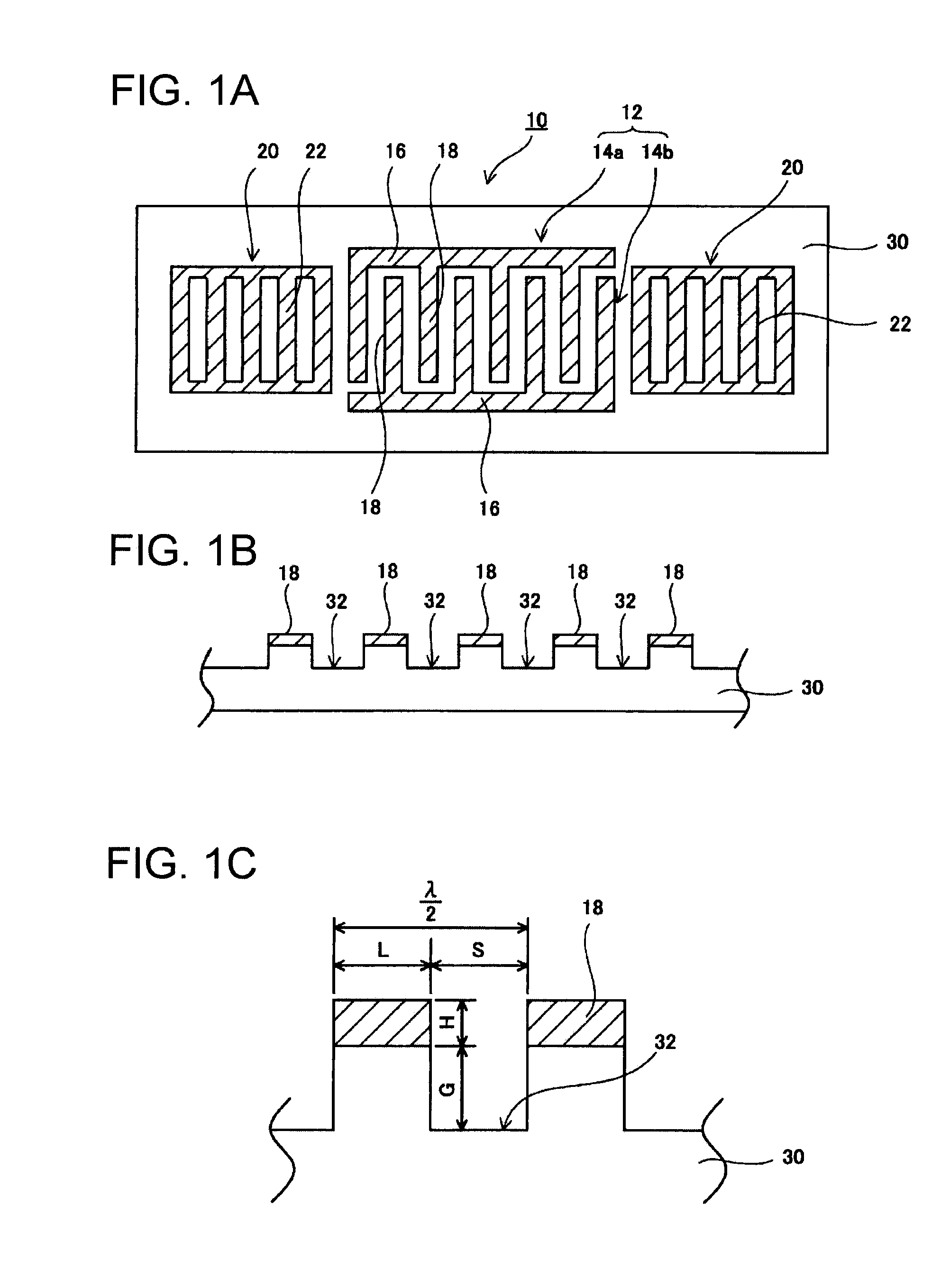
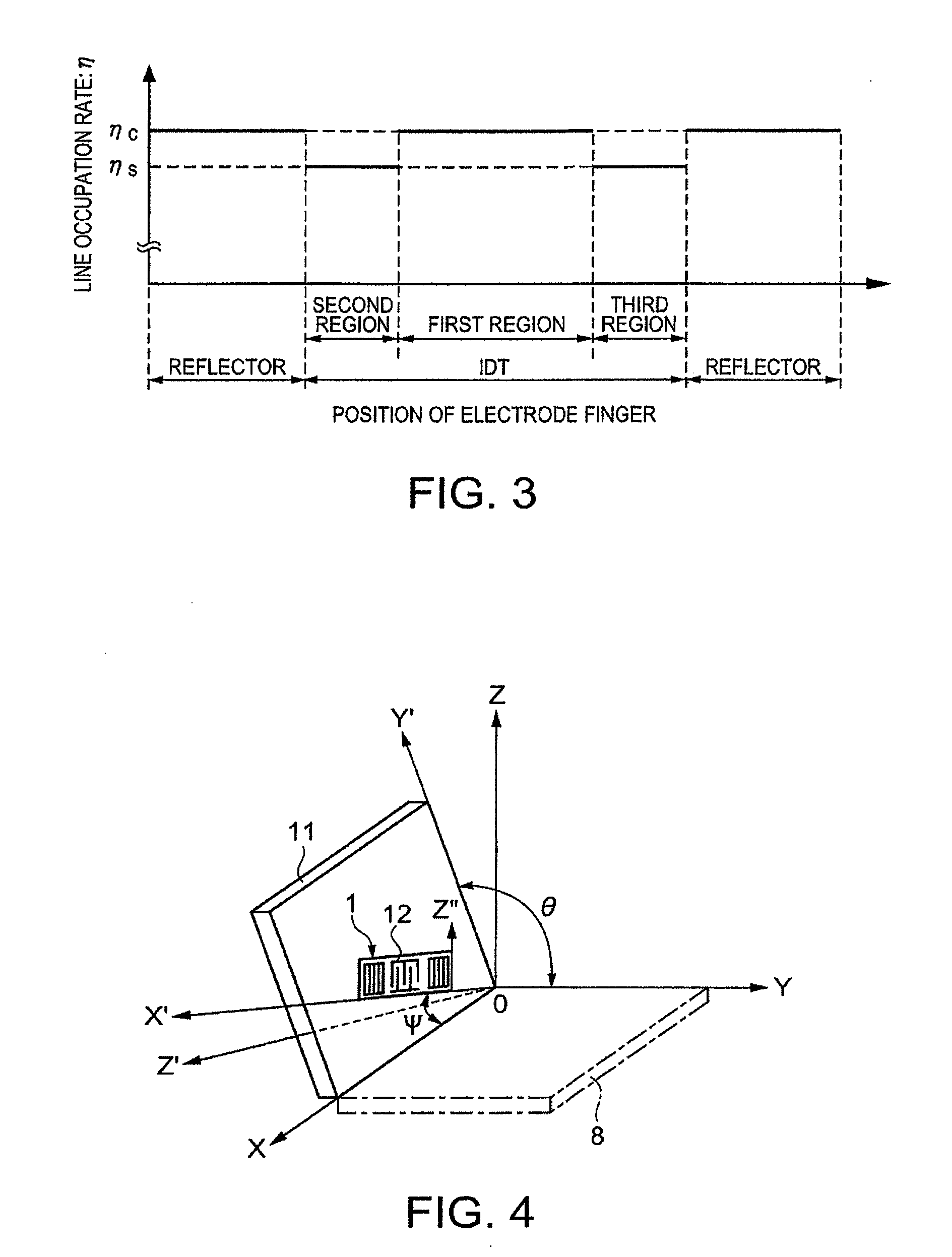
A surface acoustic wave resonator includes a quartz crystal substrate with preselected Euler angles, and an IDT that is provided on the quartz crystal substrate, that includes a plurality of electrode fingers, and that excites a stop band upper end mode surface acoustic wave. Inter-electrode finger grooves are provided in the quartz crystal substrate between the electrode fingers in a plan view. When a wavelength of the surface acoustic wave is λ, a first film thickness of the electrode finger is H, and a first depth of the inter-electrode finger groove is G, and when a line occupation rate of convex portions of the quartz crystal substrate disposed between the inter-electrode finger grooves is ηg, and a line occupation rate of the electrode fingers disposed on the convex portions is ηe, the following relationships are satisfied 0.0407λ≦G+H; and ηg>ηe.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
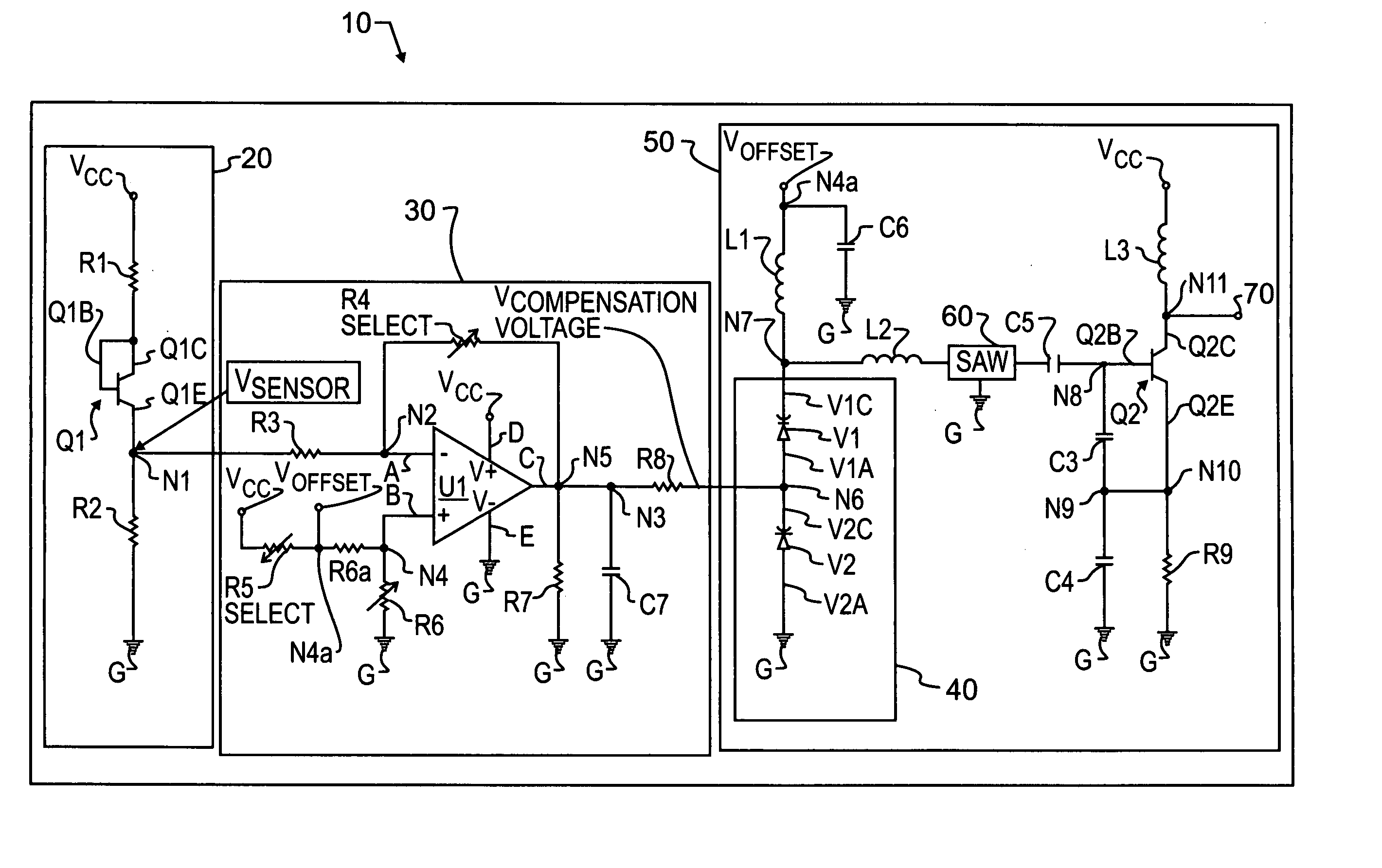
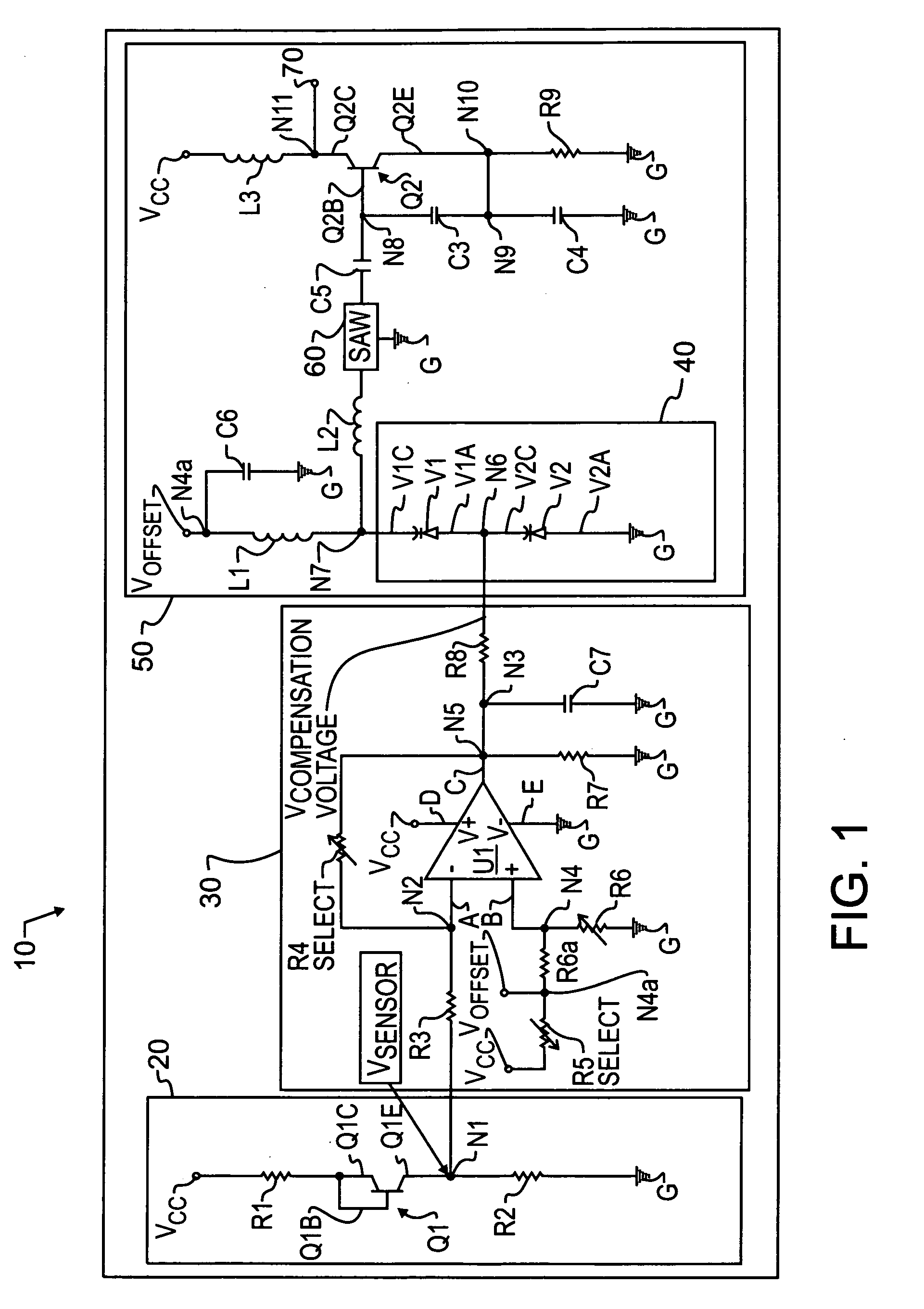
Temperature compensation circuit for a surface acoustic wave oscillator
A surface acoustic wave oscillator includes a temperature sensor adapted to generate a temperature sensor signal. A temperature signal conditioner is coupled to the temperature sensor. The temperature signal conditioner receives the temperature sensor signal and generates a conditioned temperature sensor signal. A reactance generator is coupled to the temperature signal conditioner. The reactance generator receives the conditioned temperature sensor signal and generates a compensation signal. A surface acoustic wave device is coupled to the reactance generator. An oscillator circuit is coupled to the surface acoustic wave device.
Owner:CTS CORP ELKHART
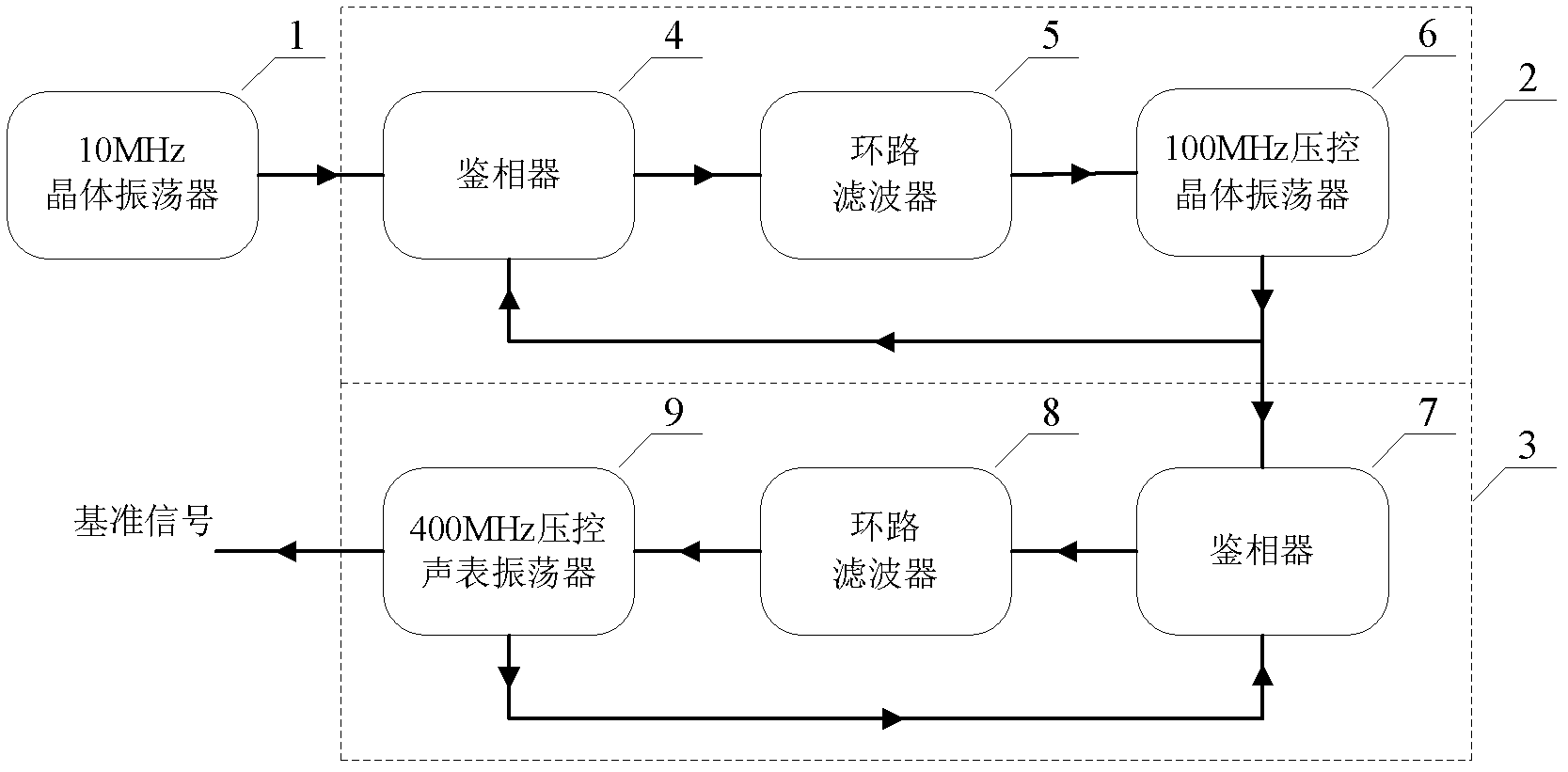
Ultralow phase noise reference signal generating device for frequency synthesizer
InactiveCN102611441AImprove phase noiseTake full advantage of phase noise characteristicsPulse automatic controlDiscriminatorPhase detector
The invention relates to an ultralow phase noise reference signal generating device for a frequency synthesizer. The reference signal generating device comprises a crystal oscillator, a first phase locked loop and a second phase locked loop which are in sequential connection. The first phase locked loop comprises a first phase discriminator, a first loop filter and a voltage-controlled crystal oscillator which are in sequential connection, wherein the voltage-controlled crystal oscillator is connected with a feedback input end of the first phase discriminator. The second phase locked loop comprises a second phase discriminator, a second loop filter and a voltage-controlled surface acoustic wave oscillator which are in sequential connection, wherein the voltage-controlled surface acoustic wave oscillator is connected with a feedback input end of the second phase discriminator. Phase noises of reference signals generated by the ultralow phase noise reference signal generating device are optimal values at different frequency deviation positions of each oscillator, and the reference signal at each frequency deviation position can acquire the optimal phase noise.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF RADIO METROLOGY & MEASUREMENT
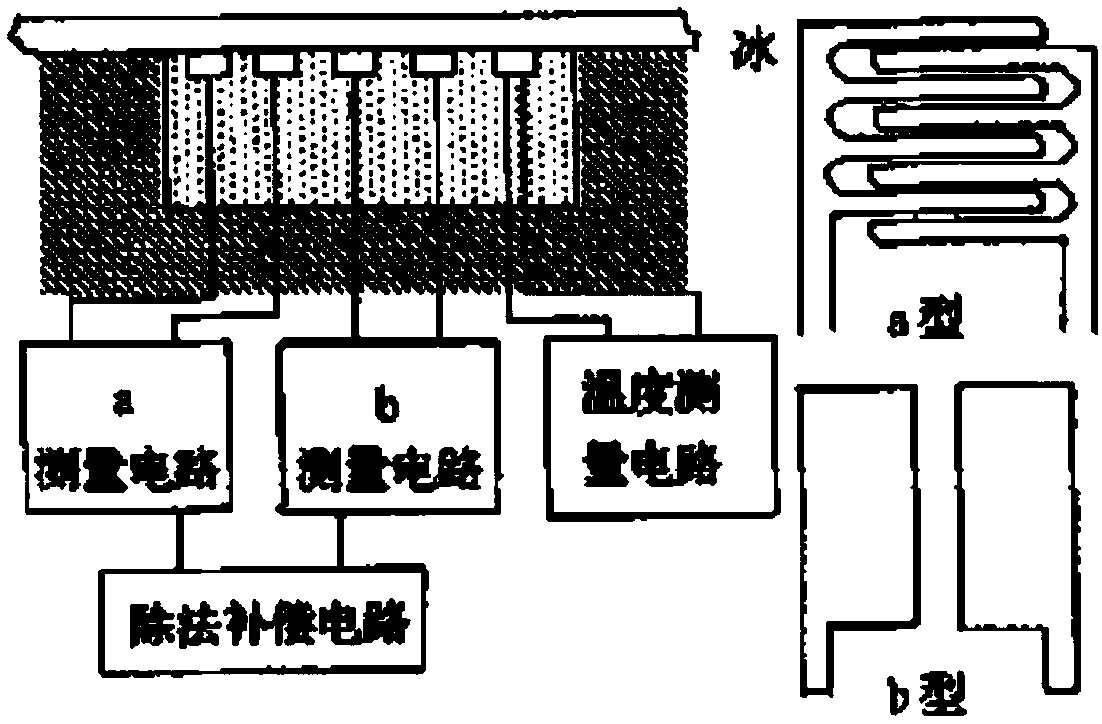
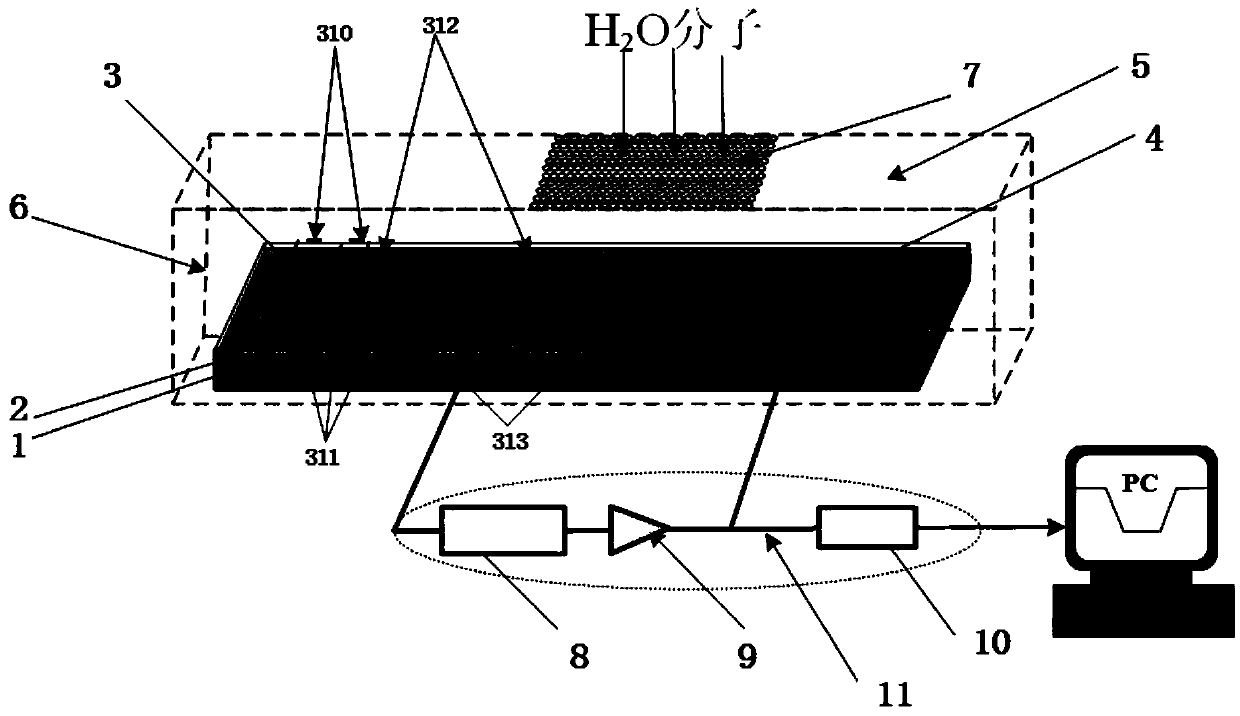
Icing sensor based on surface acoustic wave oscillator
ActiveCN111366932AHigh detection sensitivityImprove temperature stabilityICT adaptationAcoustic wave reradiationSurface acoustic wave oscillatorsSurface acoustic wave
The invention relates to an icing sensor based on a surface acoustic wave oscillator. The icing sensor comprises a surface acoustic wave device and an oscillation circuit (11), and further comprises apackaging tube shell (6) and a water permeable film (7), wherein the exterior of the surface acoustic wave device is packaged by the packaging tube shell (6), the water permeable film (7) is arrangedat an opening of the packaging tube shell (6), a surface of the surface acoustic wave oscillator is covered with a SiO2 protective thin layer (2), the surface acoustic wave device outputs an electricsignal with the changed oscillation frequency to the oscillation circuit (11), and the oscillation circuit (11) detects abrupt change of the oscillation frequency of the electric signal and outputs the oscillation frequency to realize icing early warning and monitoring. The icing sensor is advantaged in that the icing sensor has high detection sensitivity and good temperature stability, and can timely warn freezing, so the surface acoustic wave technology is easy to implement.
Owner:INST OF ACOUSTICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Frequency Adjustable Surface Acoustic Wave Oscillator
InactiveUS20090273404A1Reduce phase noiseWide frequency rangePiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesImpedence networksSurface acoustic wave oscillatorsPhase relationship
A frequency adjustable surface acoustic wave oscillator uses circuitry in which the phase relationship between the corresponding input and output signals and the voltage applied to or received by transducer fingers is controlled in such a manner that the frequency of the surface acoustic wave oscillator is arbitrarily controlled over a wide range by digital means. This provides an oscillator that exhibits a wide tunable frequency range while providing low phase noise.
Owner:HAY ROBERT
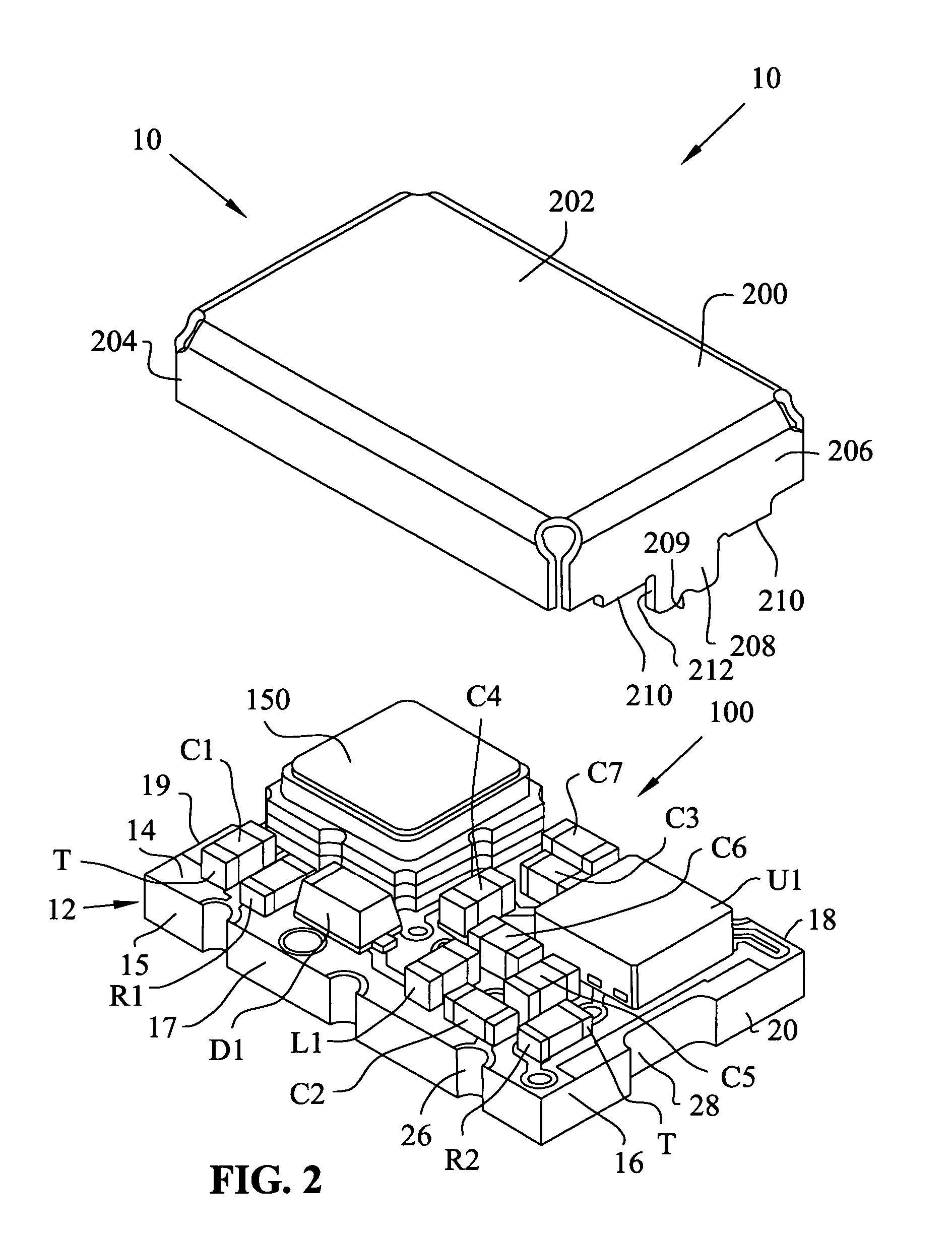
Voltage controlled surface acoustic wave oscillator module
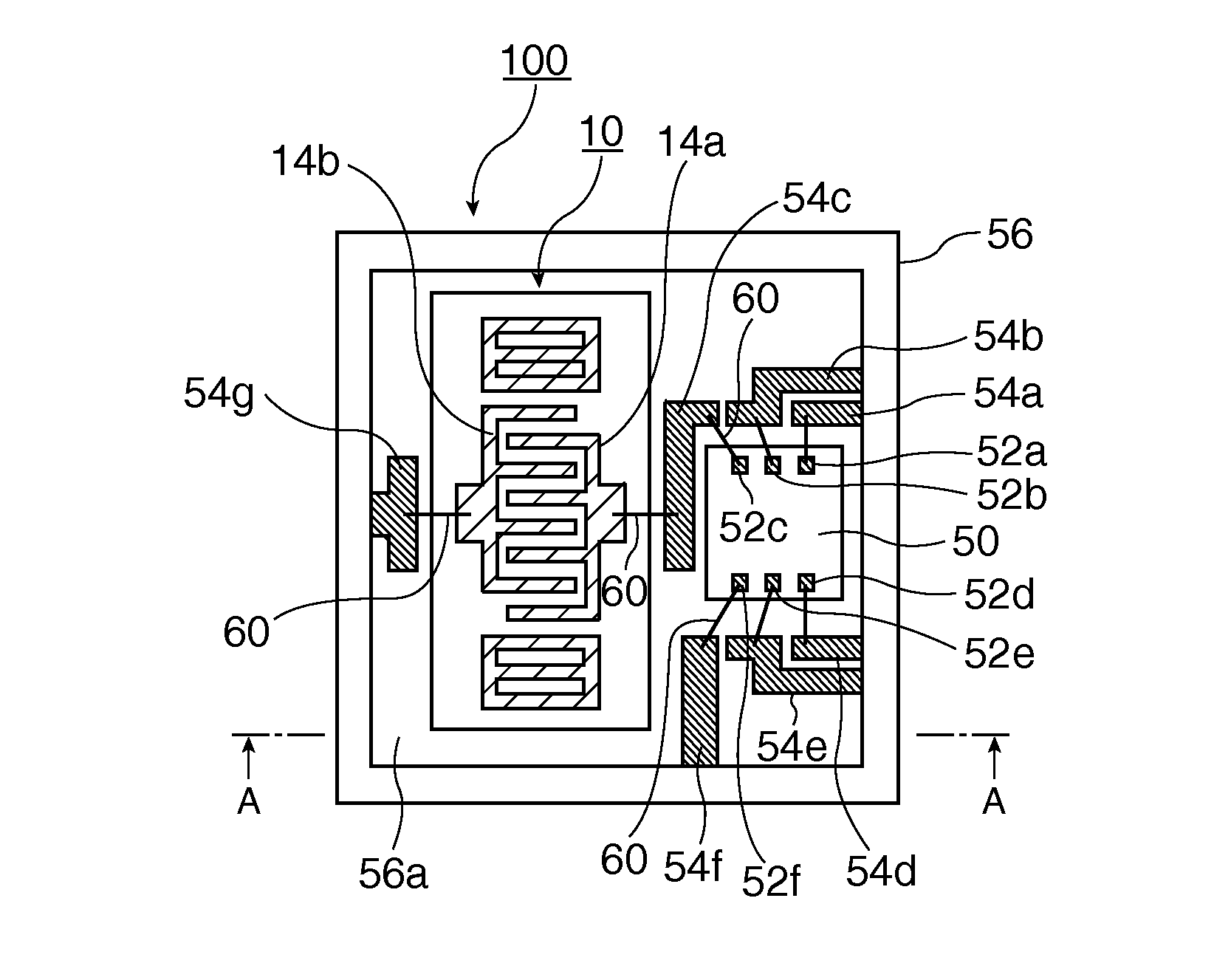
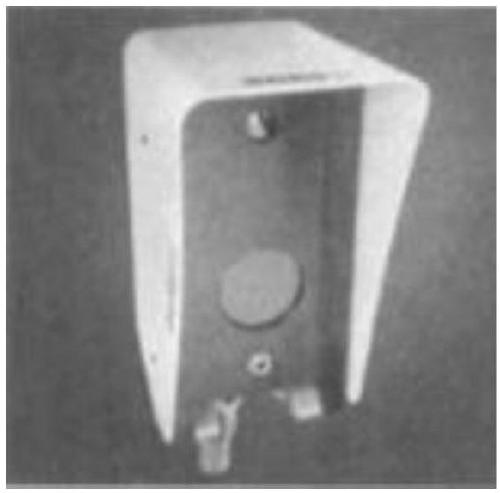
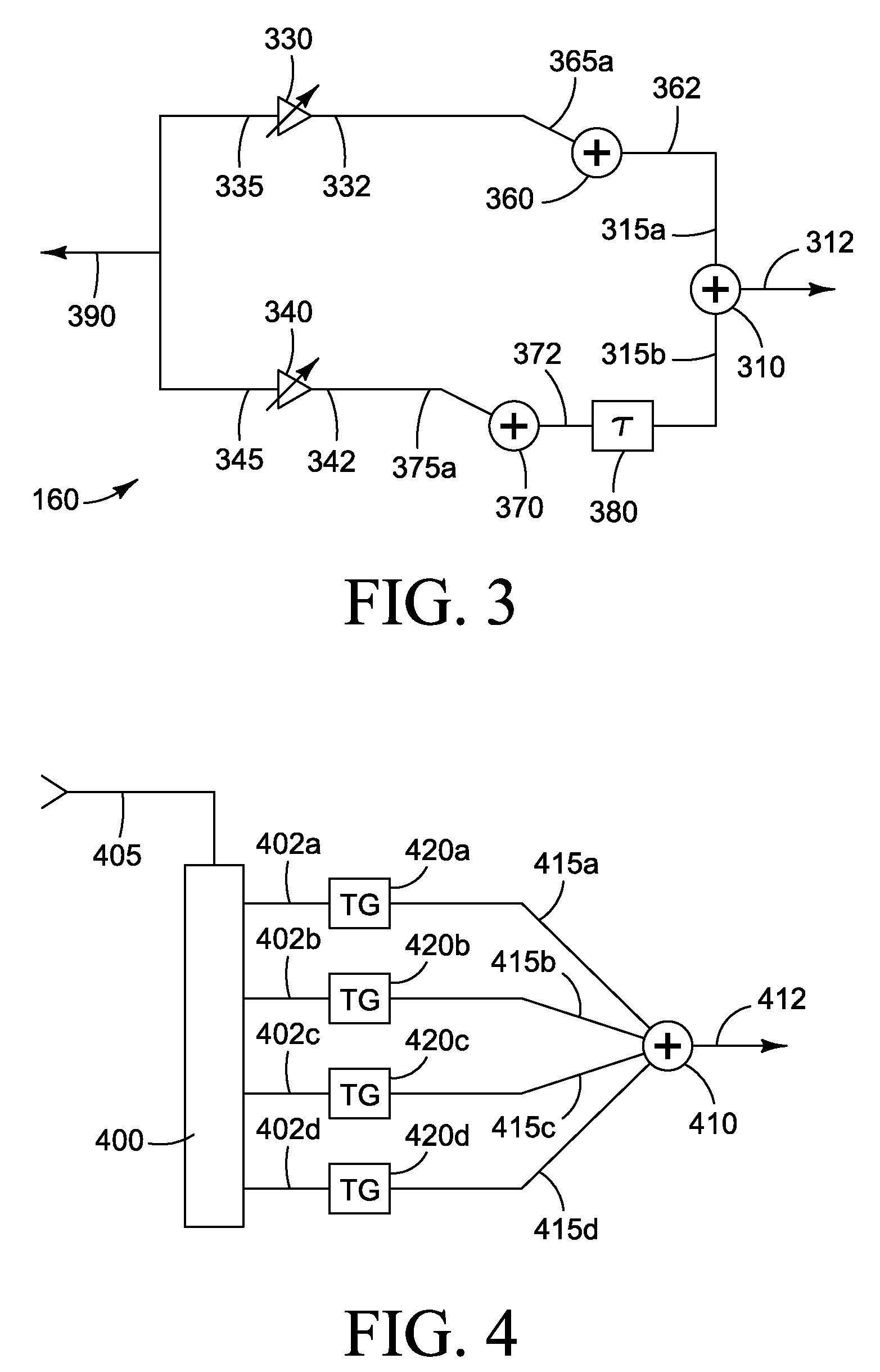
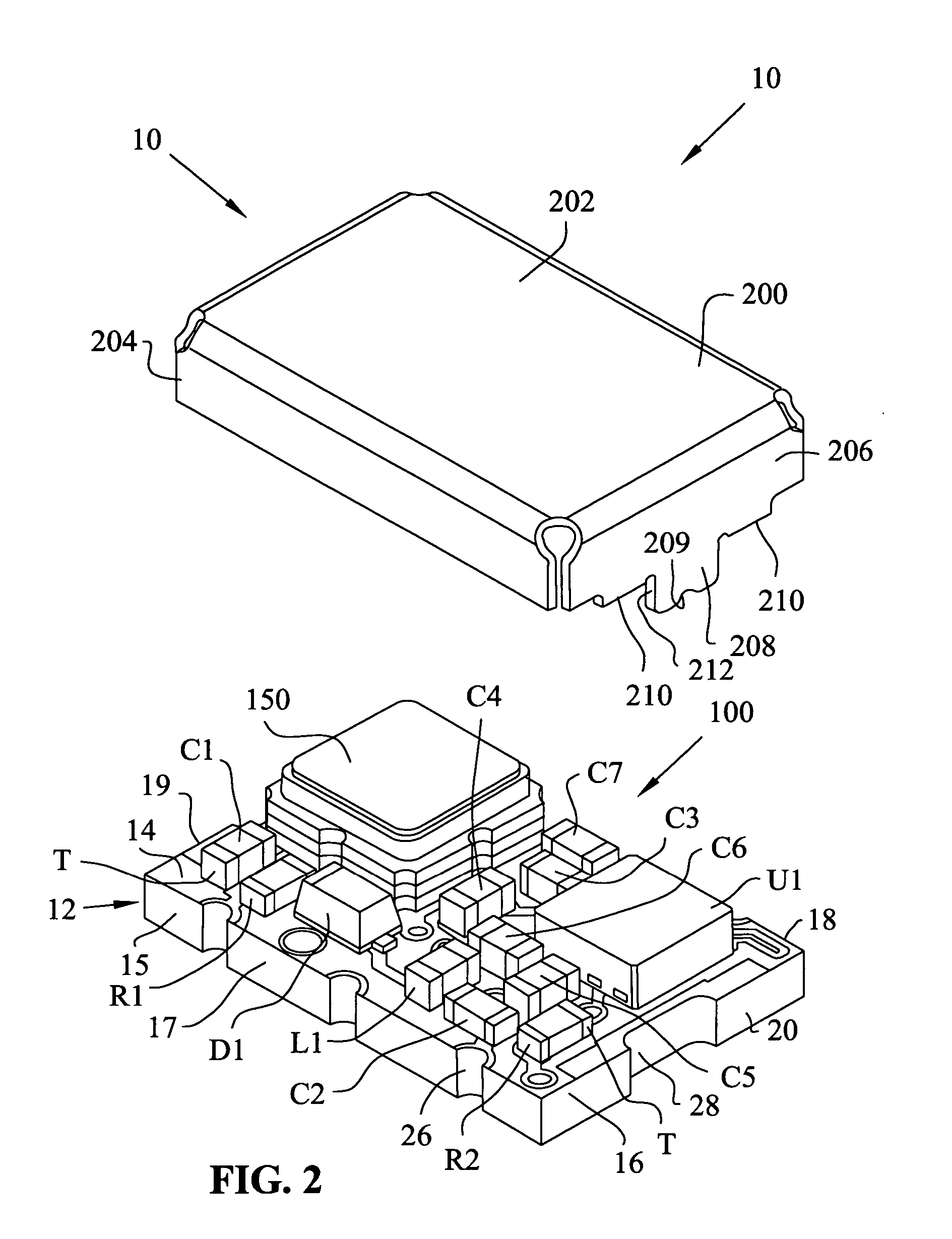
ActiveUS20060279367A1Impedence networksPrinted circuit aspectsSurface acoustic wave oscillatorsElectrical connection
A module for a surface acoustic wave oscillator includes a substrate having a top surface, a bottom surface and peripheral side faces. Several castellations are located about the outer peripheral side faces thereof. The castellations form an electrical connection between the top and bottom surfaces of the substrate. Connection pads are mounted on the top surface and are adapted for connection to the castellations. An oscillator circuit and a surface acoustic wave device are mounted on the top surface and connected to the connection pads. A cover is mounted over the substrate and has at least one tab adapted to be fitted within a respective one of the castellations. The overall module with the cover has a dimension of approximately 5 mm in width, 7 mm in length, and 2.7 mm in height.
Owner:CTS CORP ELKHART
Surface acoustic wave resonator, surface acoustic wave oscillator, and electronic apparatus
InactiveUS20120139653A1Reduce lossesSuppress fluctuationsImpedence networksOscillations generatorsSurface acoustic wave oscillatorsSurface acoustic wave resonators
A surface acoustic wave resonator which can realize favorable frequency-temperature characteristics and suppress frequency variations is provided. The surface acoustic wave resonator includes a quartz crystal substrate with Euler angles (−1.5°≦̸&phgr;≦̸1.5°, 117°≦̸&thetas;≦̸142°, and 42.79°≦̸|Ψ|≦̸49.57°), and an IDT that is provided on the quartz crystal substrate, includes a plurality of electrode fingers, and excites a stop band upper end mode surface acoustic wave, wherein inter-electrode finger grooves are provided between the electrode fingers in a plan view, and wherein if a line occupation rate of convex portions of the quartz crystal substrate disposed between the inter-electrode finger grooves is &eegr;g, and a line occupation rate of the electrode fingers disposed on the convex portions is &eegr;e, &eegr;g>&eegr;e and 0.59<&eegr;eff<0.73 are satisfied in a case where an effective line occupation rate &eegr;eff of the IDT is an arithmetic mean of the line occupation rate &eegr;g and the line occupation rate &eegr;e.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Application circuit of surface acoustic wave transducer
InactiveCN103873013AEffective filteringHigh harmonic impedance is smallImpedence networksCapacitanceNegative feedback
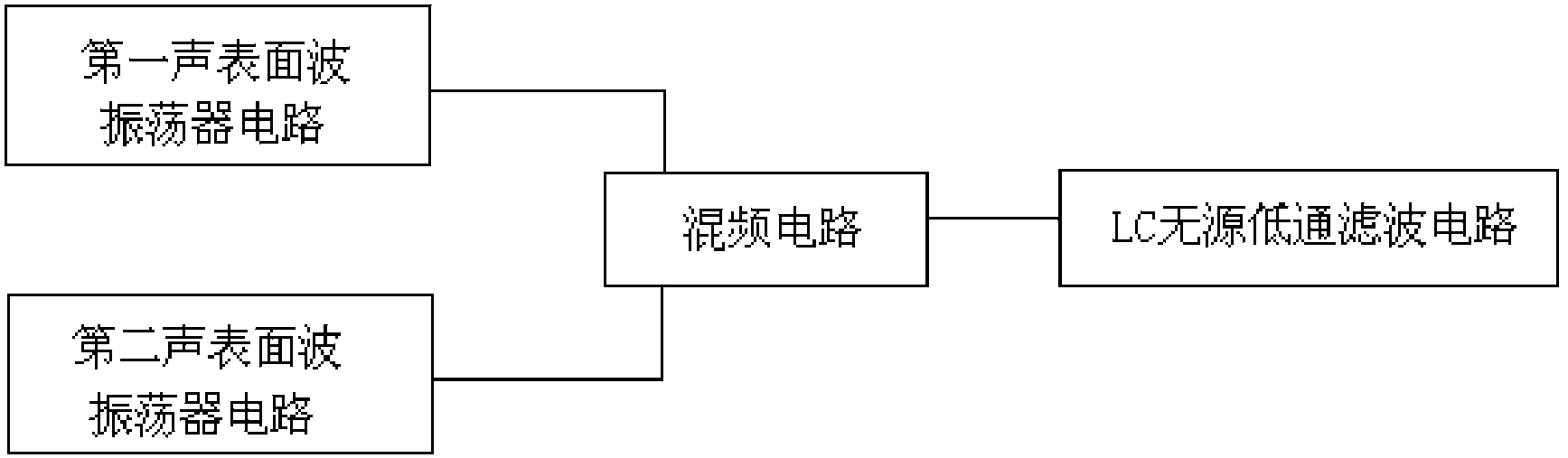
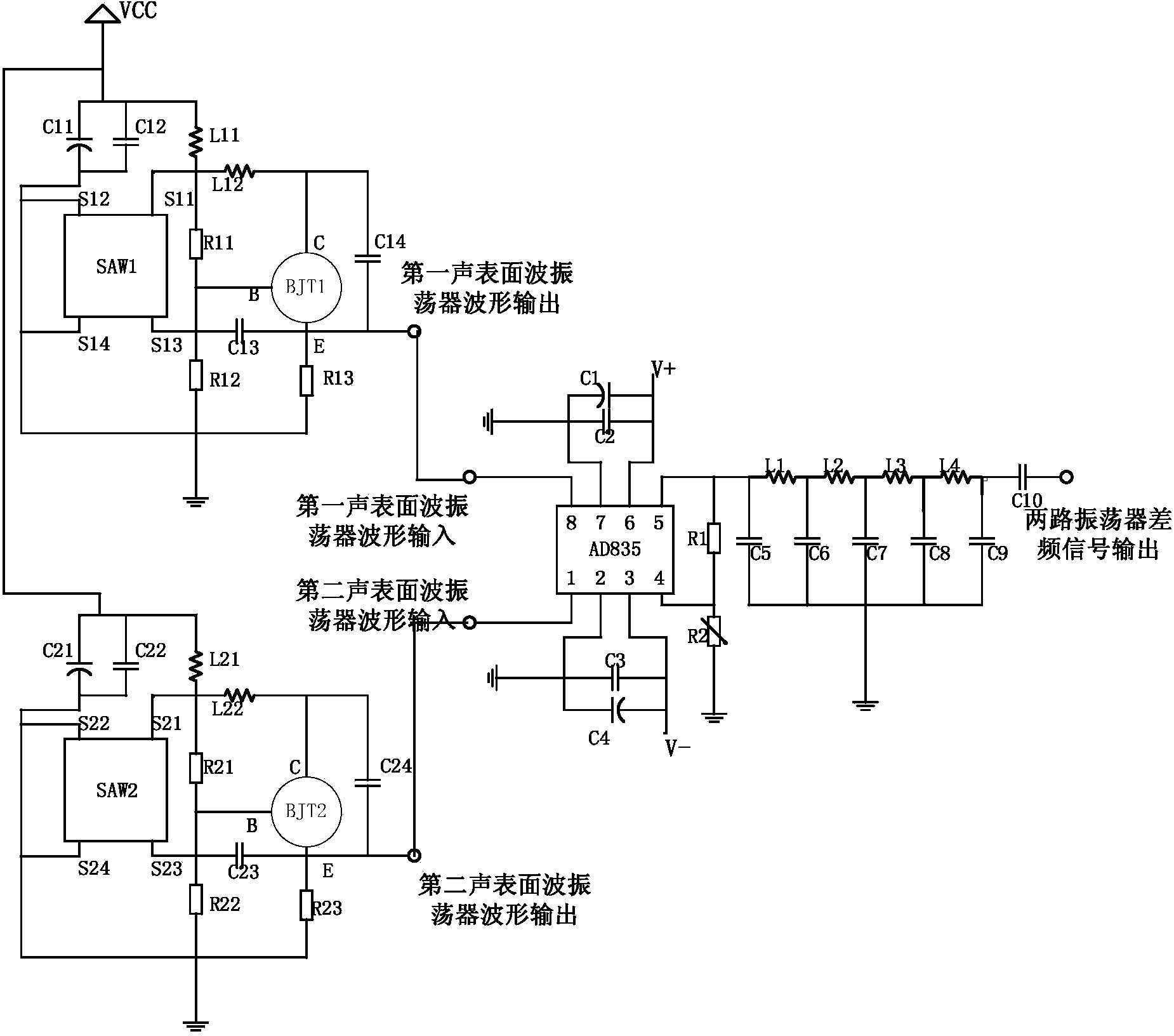
The invention discloses an application circuit of a surface acoustic wave transducer. The application circuit comprises a first surface acoustic wave oscillator circuit, a second surface acoustic wave oscillator circuit, a mixer circuit and an LC passive low-pass filter circuit, wherein the output end of the first surface acoustic wave oscillator circuit and the output end of the second surface acoustic wave oscillator circuit are connected with the input end of the mixer circuit respectively, and the output end of the mixer circuit is connected with the input end of the LC passive low-pass filter circuit. According to the application circuit, a three-point capacitive negative feedback element is adopted as a frequency selection and feedback network, the feedback voltage of the capacitive negative feedback element is tapped from the two ends of a capacitor, higher harmonics can be effectively filtered out with small impedance, and stable waveform output is achieved; a high-frequency low-power tube amplifying circuit is a bias-emitter common-collector amplifying circuit, persistent oscillation is achieved, and therefore oscillation signals are more stable; two surface acoustic wave oscillators form a two-channel structure, interference caused by the external environment is avoided, and high-precision measurement of physical quantities to be measured is achieved.
Owner:CHANGAN UNIV
Surface acoustic wave resonator, surface acoustic wave oscillator, and electronic apparatus
ActiveUS9537464B2Improve reliabilityImpedence networksOscillations generatorsSurface acoustic wave oscillatorsAcoustic wave
A surface acoustic wave resonator includes an IDT that is disposed on a quartz crystal substrate of Euler angles (−1.5°≦φ≦1.5°, 117°≦θ≦142°, ψ) and excites a surface acoustic wave resonant in an upper part of a stop-band of the IDT, and inter-electrode finger grooves that are acquired by depressing the substrate located between electrode fingers configuring the IDT. The wavelength of the surface acoustic wave, the depth of the inter-electrode finger grooves, the line occupancy ratio of the IDT, and the film thickness of the electrode fingers of the IDT are set in correspondence with one another.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Surface acoustic wave resonator, surface acoustic wave oscillator, and surface acoustic wave module unit
ActiveUS8358177B2Improve vibrationIncrease vibrational energyPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesImpedence networksSurface acoustic wave oscillatorsAcoustic wave
It is possible to reduce the size of a surface acoustic wave (SAW) resonator by enhancing a Q value. In a SAW resonator in which an IDT having electrode fingers for exciting SAW is disposed on a crystal substrate, the IDT includes a first region disposed at the center of the IDT and a second region and a third region disposed on both sides of the first region. A frequency is fixed in the first region and a portion in which a frequency gradually decreases as it approaches an edge of the IDT is disposed in the second region and the third region. When the frequency of the first region is Fa, the frequency at an edge of the second region is FbM, and the frequency at an edge of the third region is FcN, the variations in frequency are in the ranges of 0.9815<FbM / Fa<0.9953 and 0.9815<FcN / Fa<0.9953, respectively.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP +1
Surface acoustic wave resonator, surface acoustic wave oscillator, and surface acoustic wave module device
InactiveUS20120105165A1Growth inhibitionExcellent CIImpedence networksPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesElectromechanical coupling coefficientSurface acoustic wave oscillators
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Surface acoustic wave resonator, surface acoustic wave oscillator, and surface acoustic wave module unit
ActiveUS20110204984A1Reduce power consumptionImprove confinementImpedence networksOscillations generatorsSurface acoustic wave oscillatorsSurface acoustic wave resonators
It is possible to reduce the size of a surface acoustic wave resonator by enhancing the Q value. In a surface acoustic wave resonator in which an IDT having electrode fingers for exciting surface acoustic waves is formed on a crystal substrate, a line occupying ratio is defined as a value obtained by dividing the width of one electrode finger by the distance between the center lines of the gaps between one electrode finger and the electrode fingers adjacent to both sides thereof, and the IDT includes a region formed by gradually changing the line occupying ratio from the center to both edges so that the frequency gradually becomes lower from the center to both edges than the frequency at the center of the IDT.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
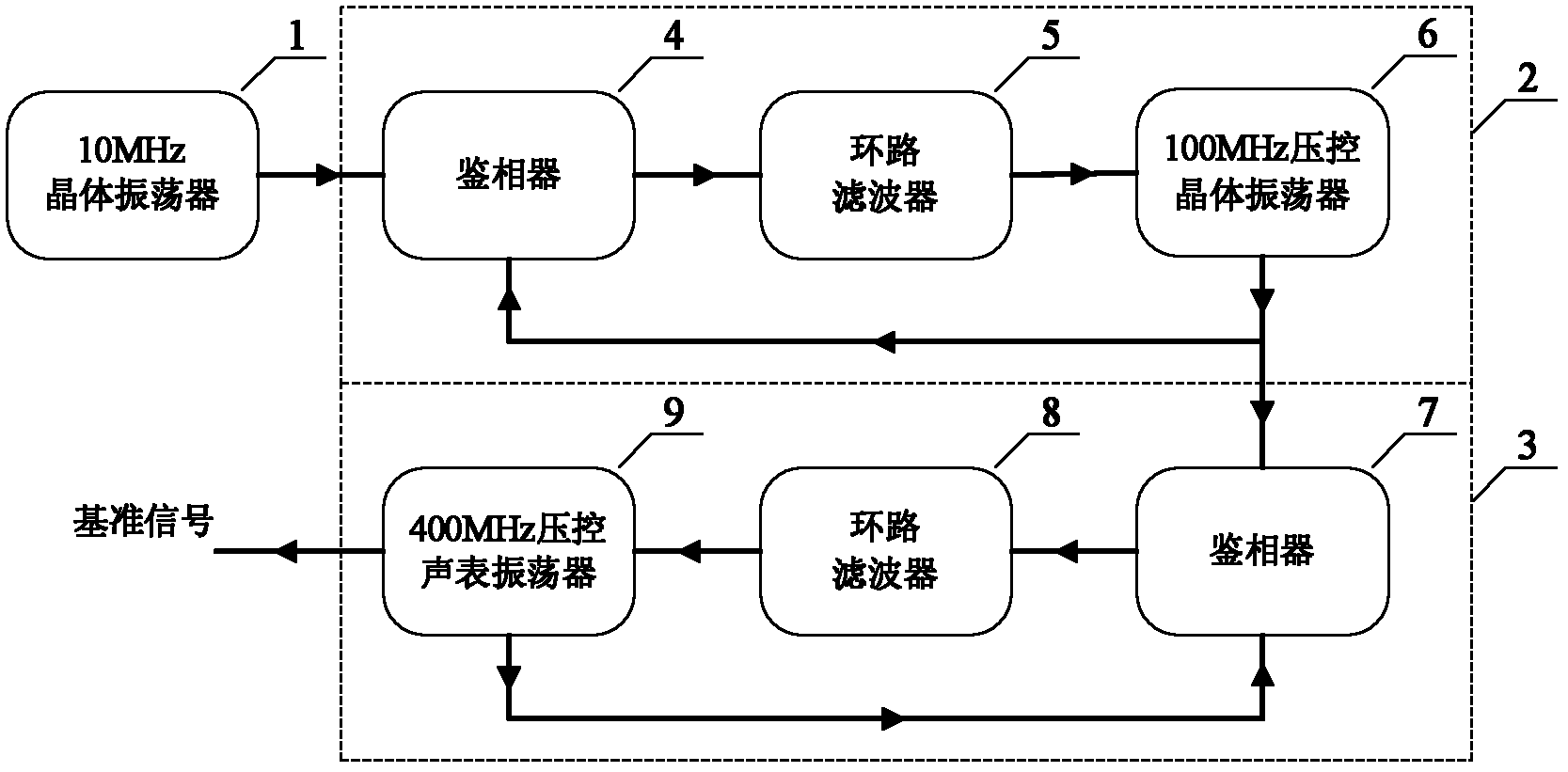
Low-phase noise reference source
InactiveCN105553468AImprove phase noisePhase Noise Index ImprovementPulse automatic controlLoop filterSurface acoustic wave oscillators
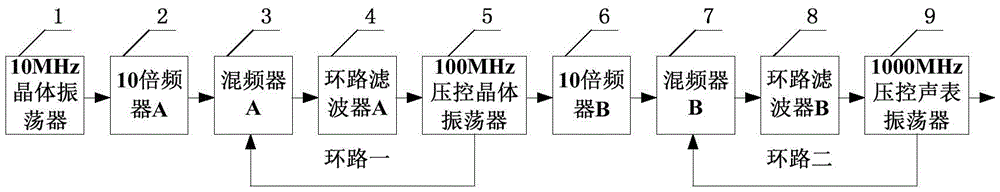
The invention discloses a low-phase noise reference source. The low-phase noise reference source includes a phase-locked 100MHz signal source, a first frequency multiplier, a first mixer, a first loop filter and an ultra-high frequency voltage controlled surface acoustic wave oscillator; the first frequency multiplier performs frequency multiplication on stable 100MHz signals generated by the phase-locked 100MHz signal source so as to generate ultra-high frequency signals the frequency of which is same with the that of the output signals of the ultra-high frequency voltage controlled surface acoustic wave oscillator; the first mixer performs phase discrimination on the ultra-high frequency signals generated by the first frequency multiplier and signals outputted by the auxiliary path signal output end of the ultra-high frequency voltage controlled surface acoustic wave oscillator so as to generate first phase discrimination voltage; the first loop filter filters the first phase discrimination voltage so as to generate first voltage controlled voltage; and the ultra-high frequency voltage controlled surface acoustic wave oscillator outputs stable ultra-high frequency signals through a main path signal output end according to the control of the first voltage controlled voltage, wherein the stable ultra-high frequency signals are adopted as the output signals of the low-phase noise reference source. According to the low-phase noise reference source of the invention, the phase noise index of the reference source on higher frequencies can be improved.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF RADIO METROLOGY & MEASUREMENT
Surface acoustic wave oscillator and method of varying frequency thereof
InactiveUS7642871B2Wide bandwidthContinuous changeImpedence networksElectric windingCapacitanceResonance
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Voltage controlled surface acoustic wave oscillator module
ActiveUS7466210B2Printed circuit aspectsHigh frequency circuit adaptationsSurface acoustic wave oscillatorsElectrical connection
A module for a surface acoustic wave oscillator includes a substrate having a top surface, a bottom surface and peripheral side faces. Several castellations are located about the outer peripheral side faces thereof. The castellations form an electrical connection between the top and bottom surfaces of the substrate. Connection pads are mounted on the top surface and are adapted for connection to the castellations. An oscillator circuit and a surface acoustic wave device are mounted on the top surface and connected to the connection pads. A cover is mounted over the substrate and has at least one tab adapted to be fitted within a respective one of the castellations. The overall module with the cover has a dimension of approximately 5 mm in width, 7 mm in length, and 2.7 mm in height.
Owner:CTS CORP ELKHART
Surface acoustic wave resonator, surface acoustic wave oscillator, and electronic apparatus
InactiveCN102386879AImpedence networksOscillations generatorsSurface acoustic wave oscillatorsAcoustic wave
The invention provides a surface acoustic wave resonator, a surface acoustic wave oscillator, and an electronic apparatus, capable of realizing excellent frenquency temperature characteristics. The surface acoustic wave resonator (10) includes: an IDT (12) which is disposed on a quartz substrate (30) with Euler angles of (-1 DEG <=[phi]<=1 DEG , 117 DEG<=[theta]<=142 DEG , 42.79 DEG <=|[psi]|<=49.57 DEG , which excites a surface acoustic wave in an upper mode of a stop band; and a groove 32 which is formed by recessing the quartz substrate between electrode fingers (18) which form the IDT (12). Here, the following expression is satisfied: 0.01[lambda]<=G, where [lambda] represents a wavelength of the surface acoustic wave and G represents a depth of the groove (13). The depth G of the groove (32) and a line occupancy [eta] of the IDT satisfy the following expression: - 2.5 G [lambda] + 0.675 <= [eta] <= - 2.5 G [lambda] + 0.775 and a number of pairs N of the electrode fingers in the IDT is in the range of the following expression: 160<=N<=220.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Surface acoustic wave resonator, surface acoustic wave oscillator, and electronic apparatus
InactiveUS8928432B2Excellent frequency temperature characteristicsInhibit deteriorationPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesImpedence networksSurface acoustic wave oscillatorsAlloy
A surface acoustic wave resonator includes: an IDT which is disposed on a quartz substrate with Euler angles of (−1°≦φ≦1°, 117°≦θ≦142°, 42.79°≦|ψ|≦49.57°), which is made of Al or alloy including Al as a main component and which excites a surface acoustic wave in an upper mode of a stop band; and an inter-electrode-finger groove which is formed by recessing the quartz substrate between electrode fingers which form the IDT. Here, the following expression is satisfied:0.01λ≦G (1),where λ represents a wavelength of the surface acoustic wave and G represents a depth of the inter-electrode-finger groove. The depth G of the inter-electrode-finger groove and a line occupancy η of the IDT satisfy the following expression:-2.5×Gλ+0.675≦η≦-2.5×Gλ+0.775(5)and a number of pairs N of the electrode fingers in the IDT is in the range of the following expression:160≦N≦220 (19).
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com