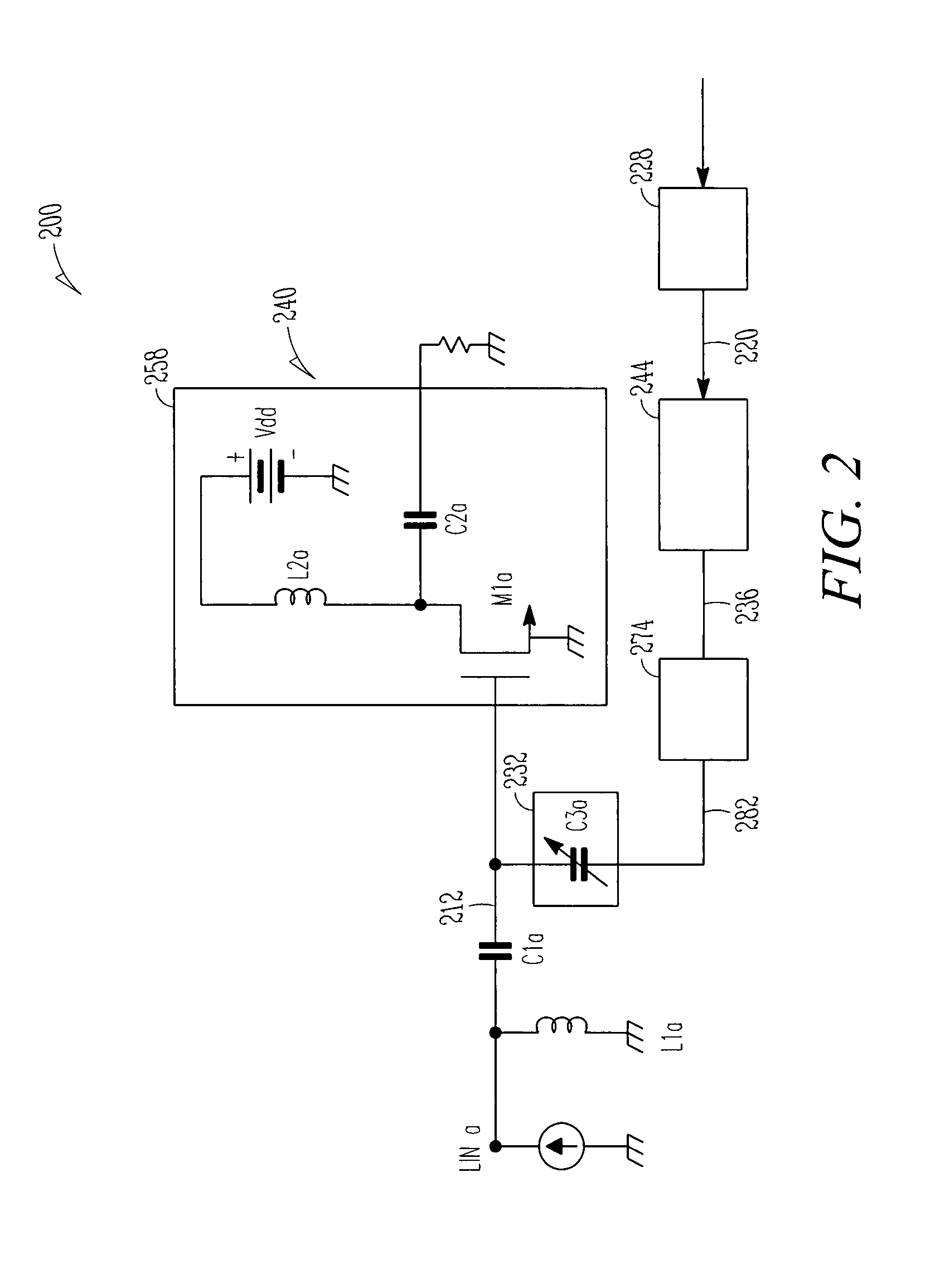
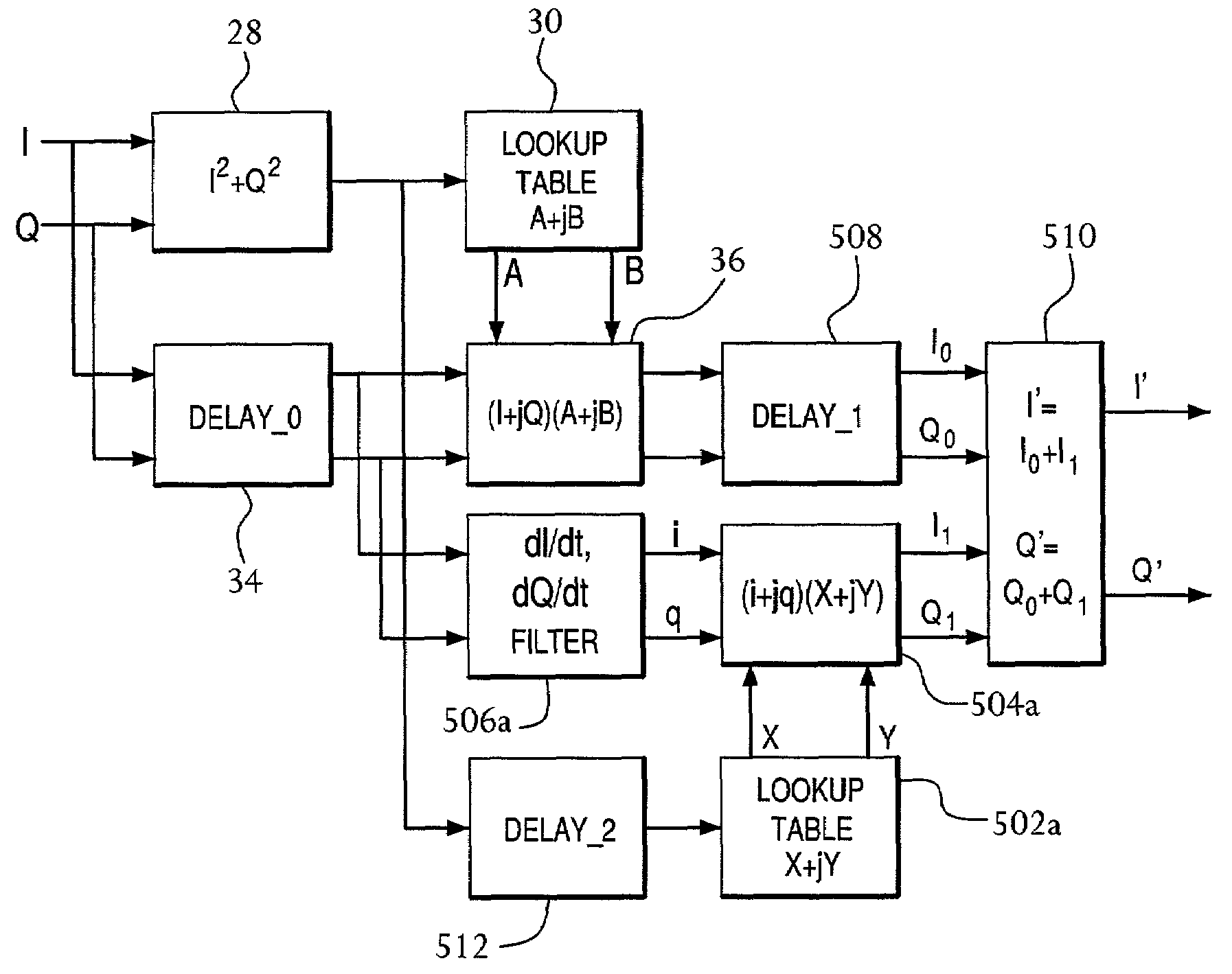
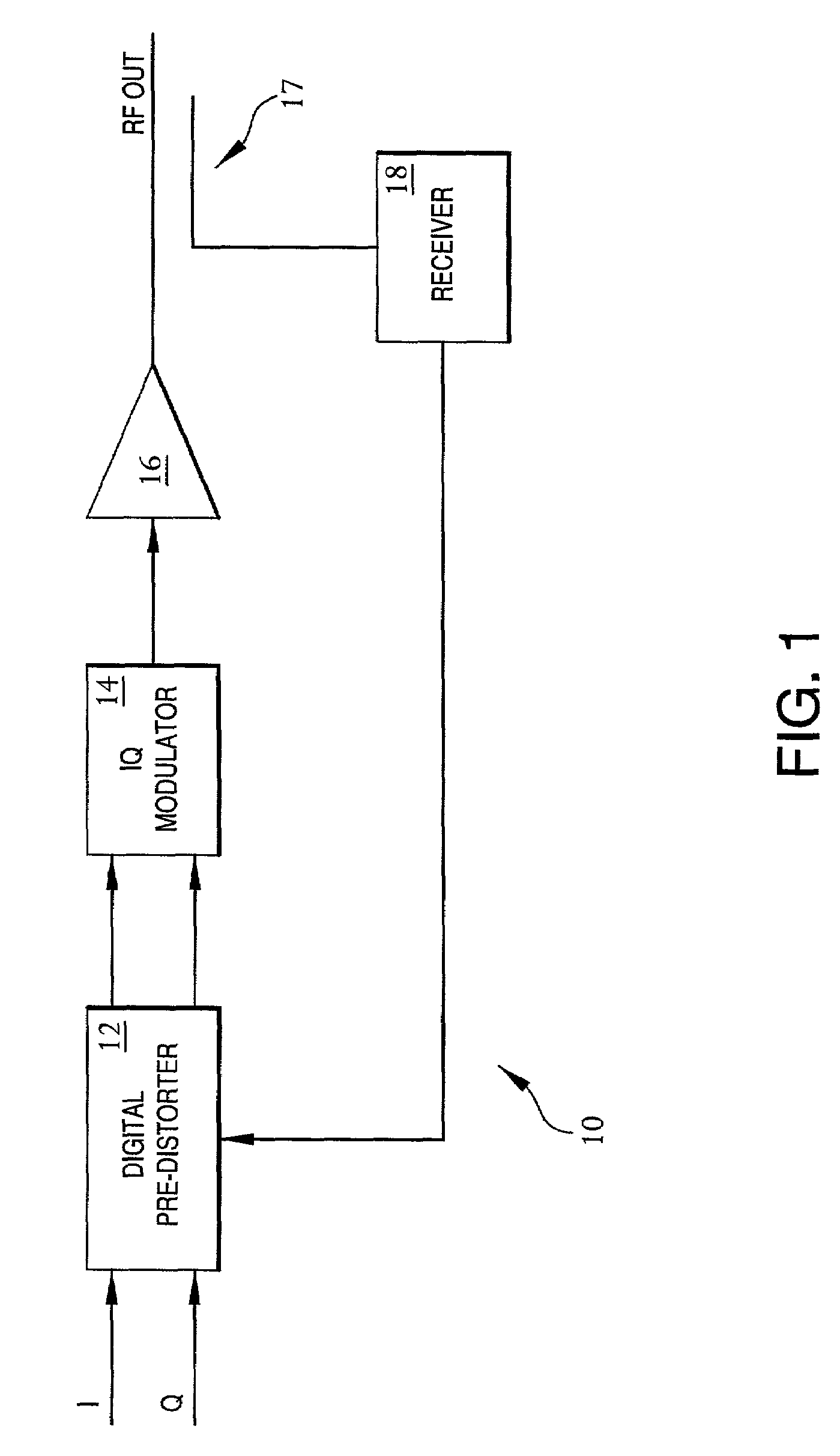
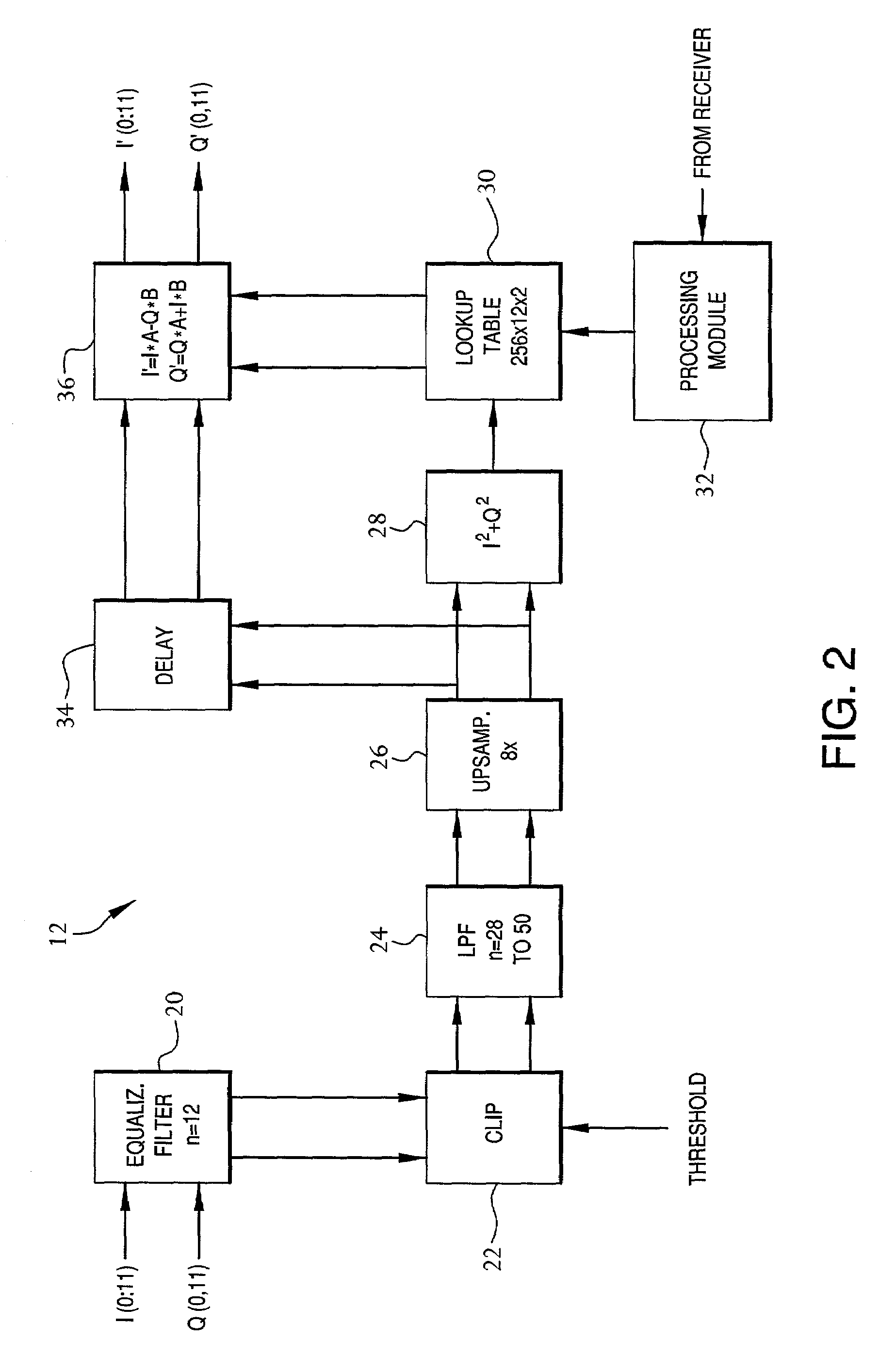
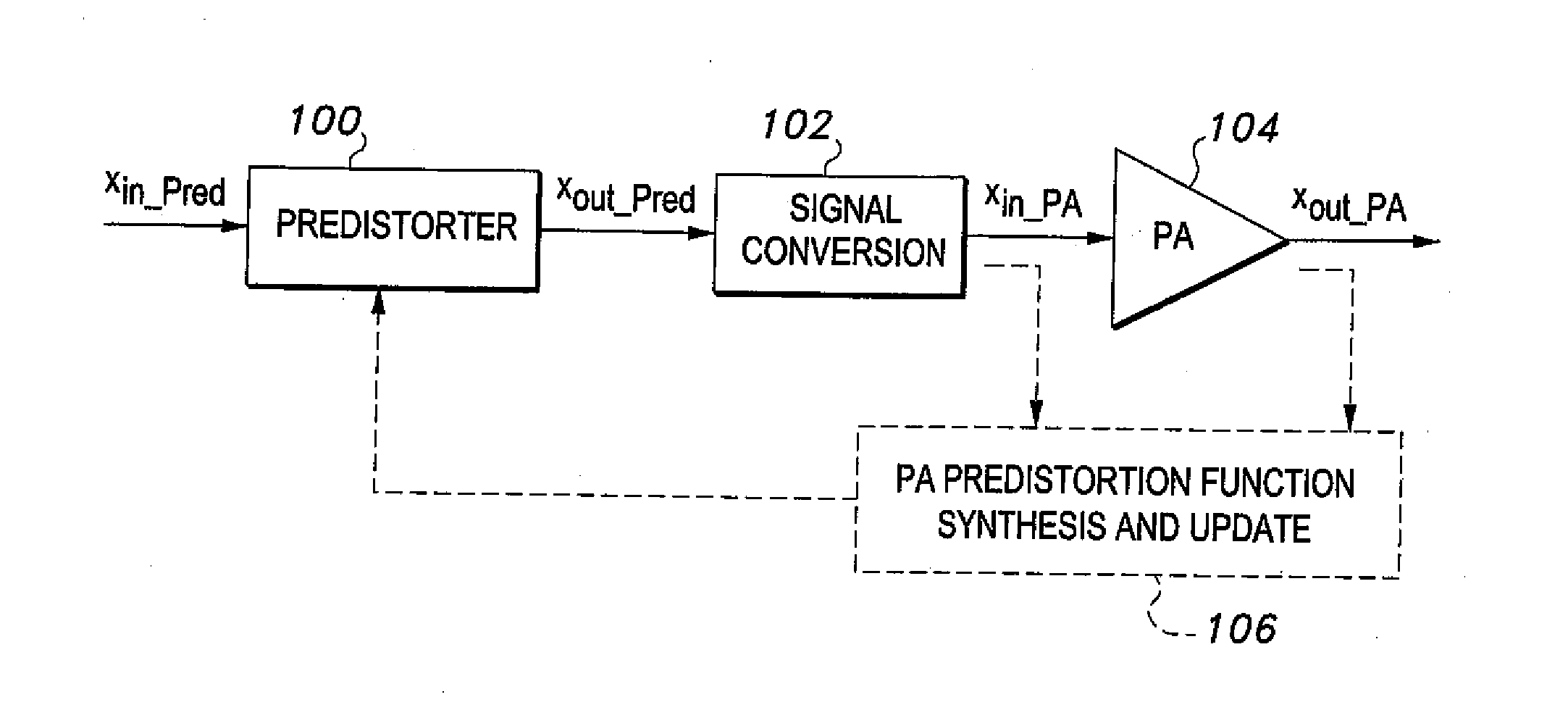
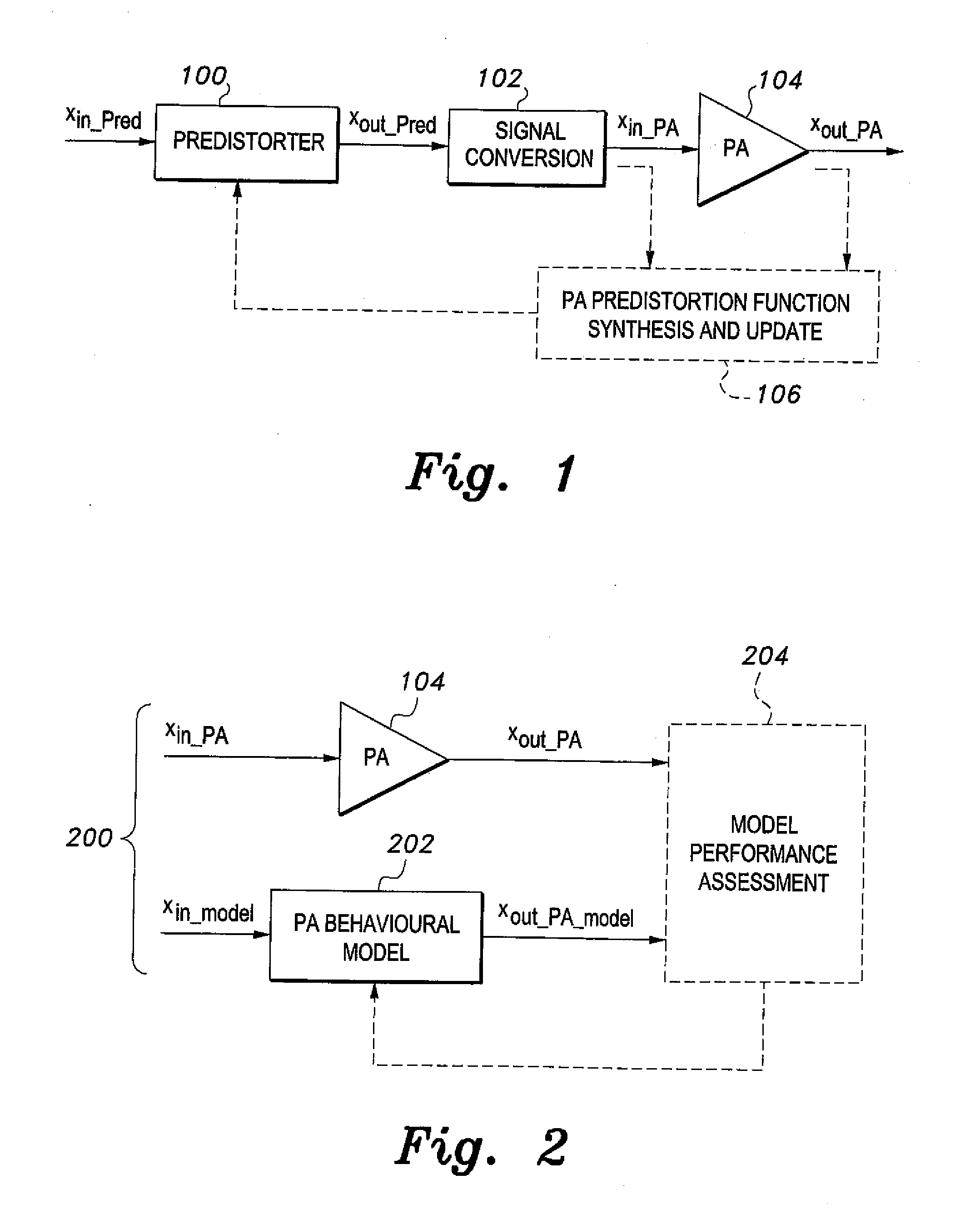
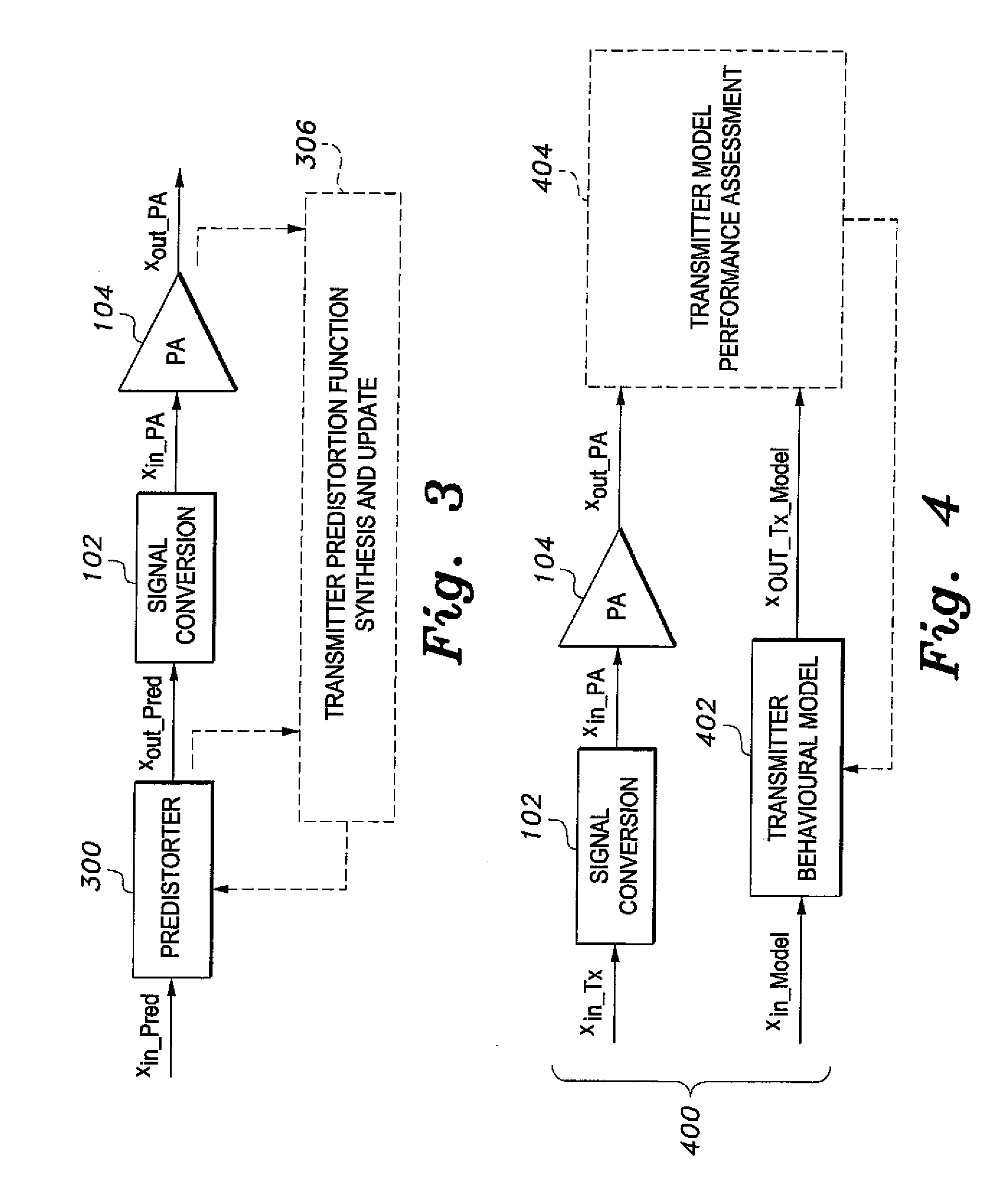
Patents
Literature
63 results about "Amplifier distortion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
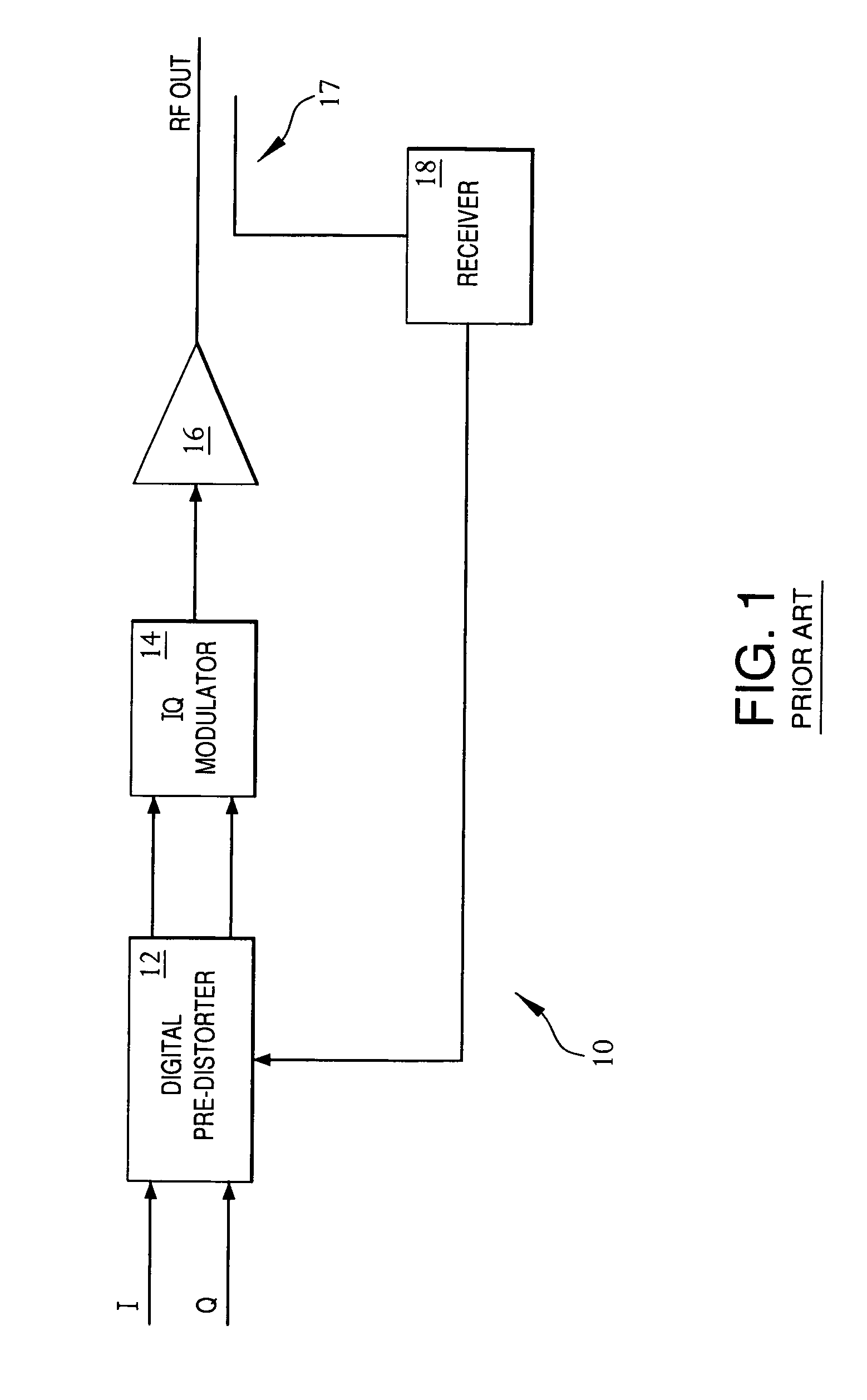
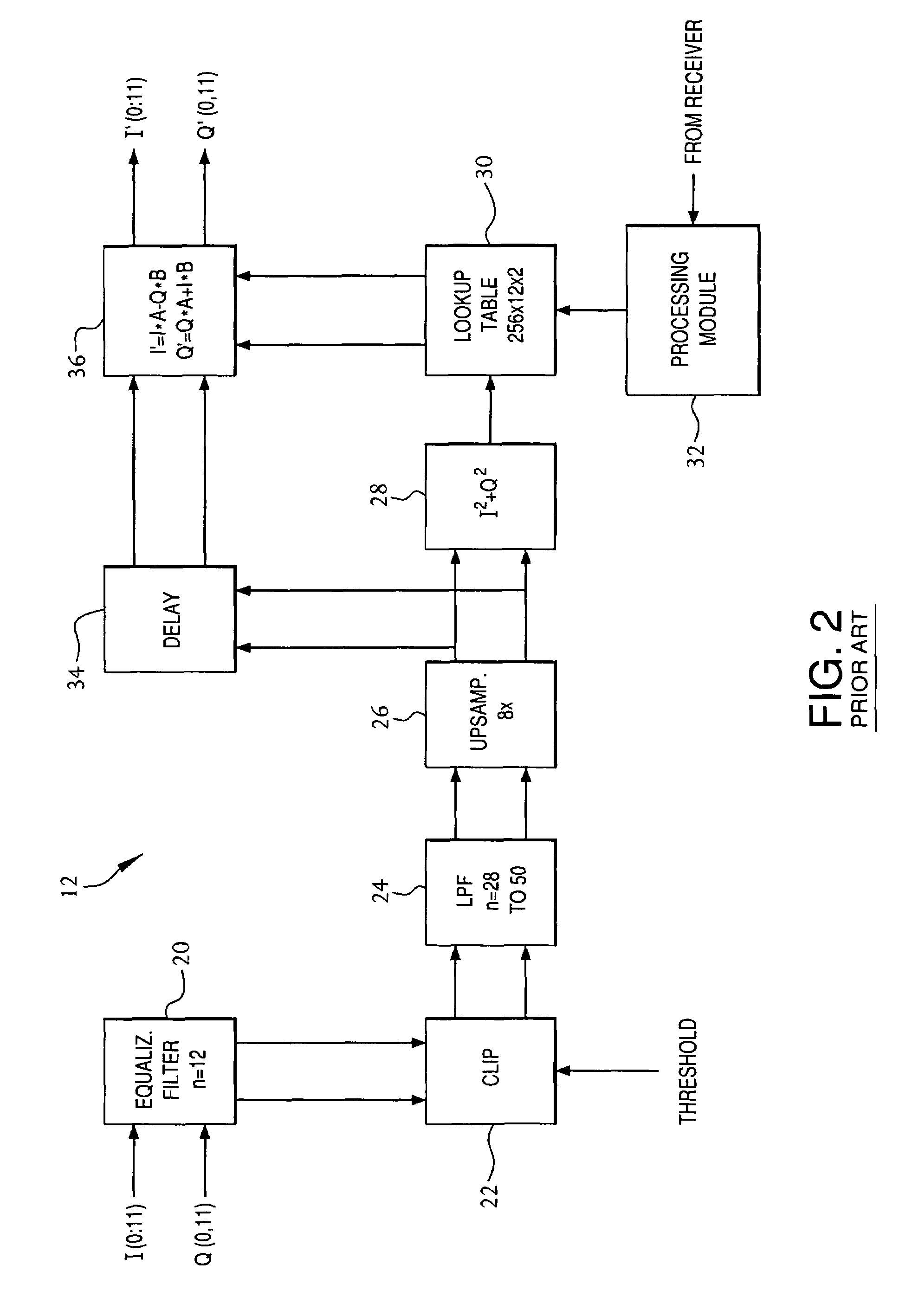
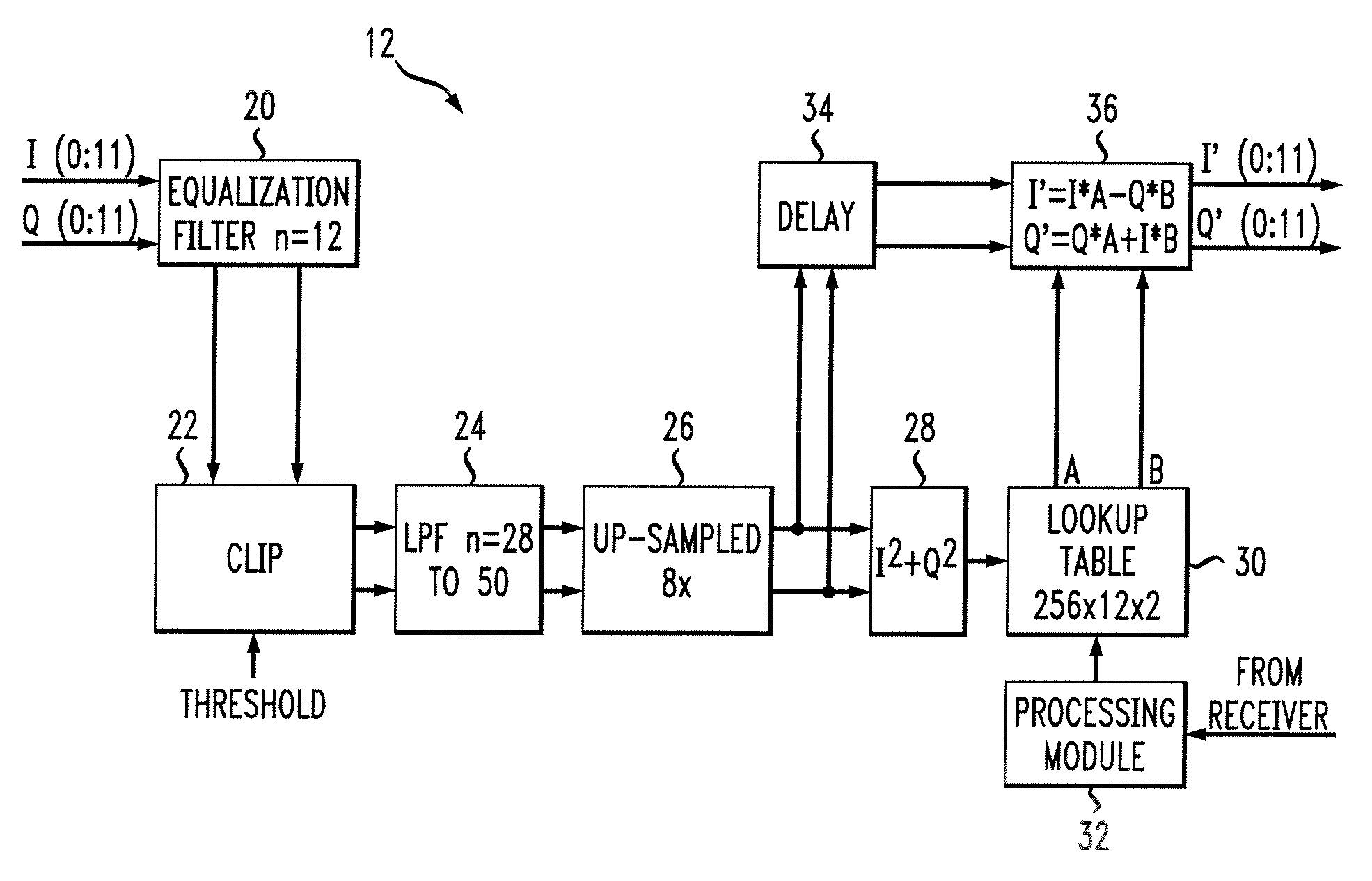
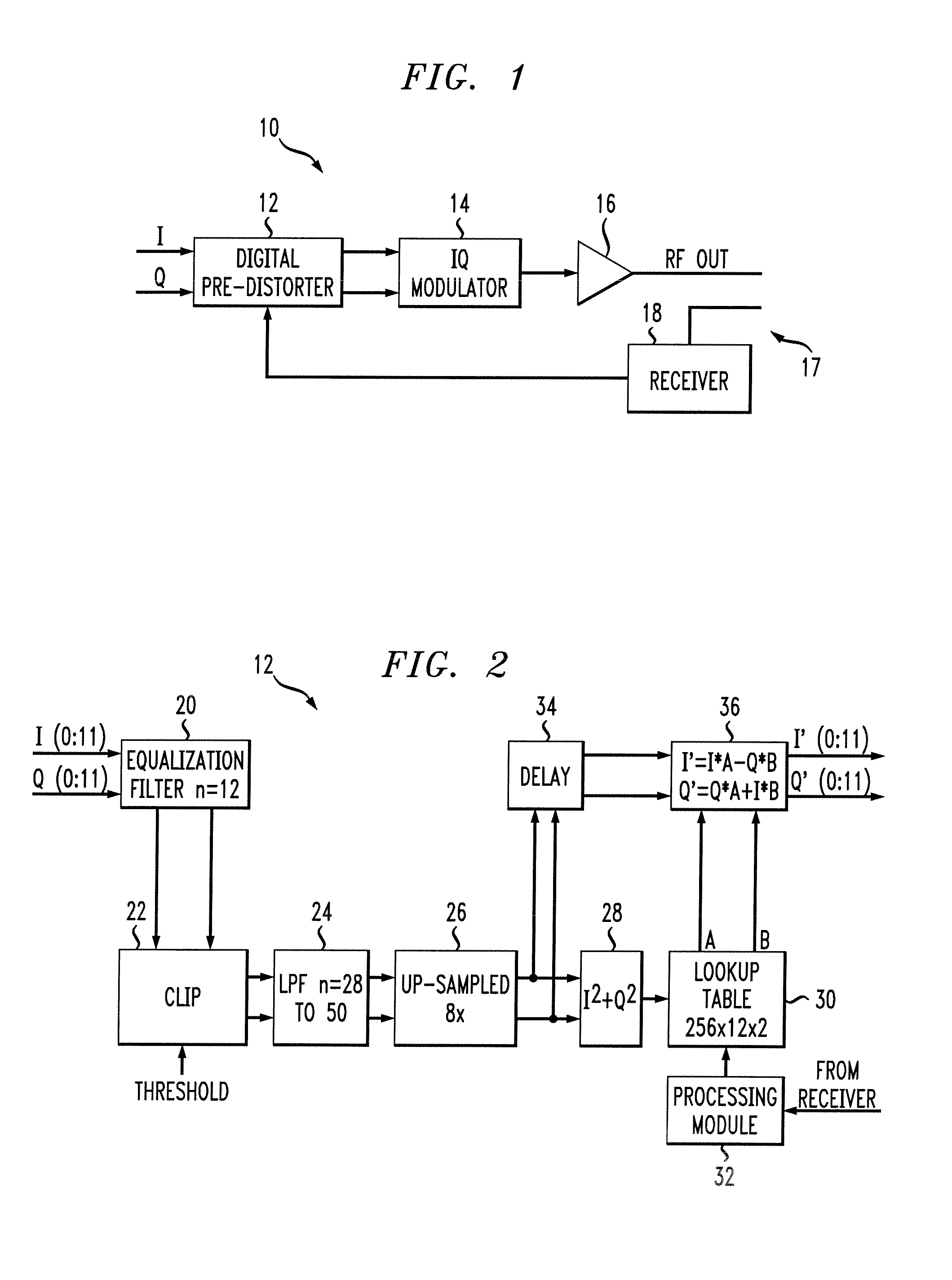
Amplifier predistortion and autocalibration method and apparatus
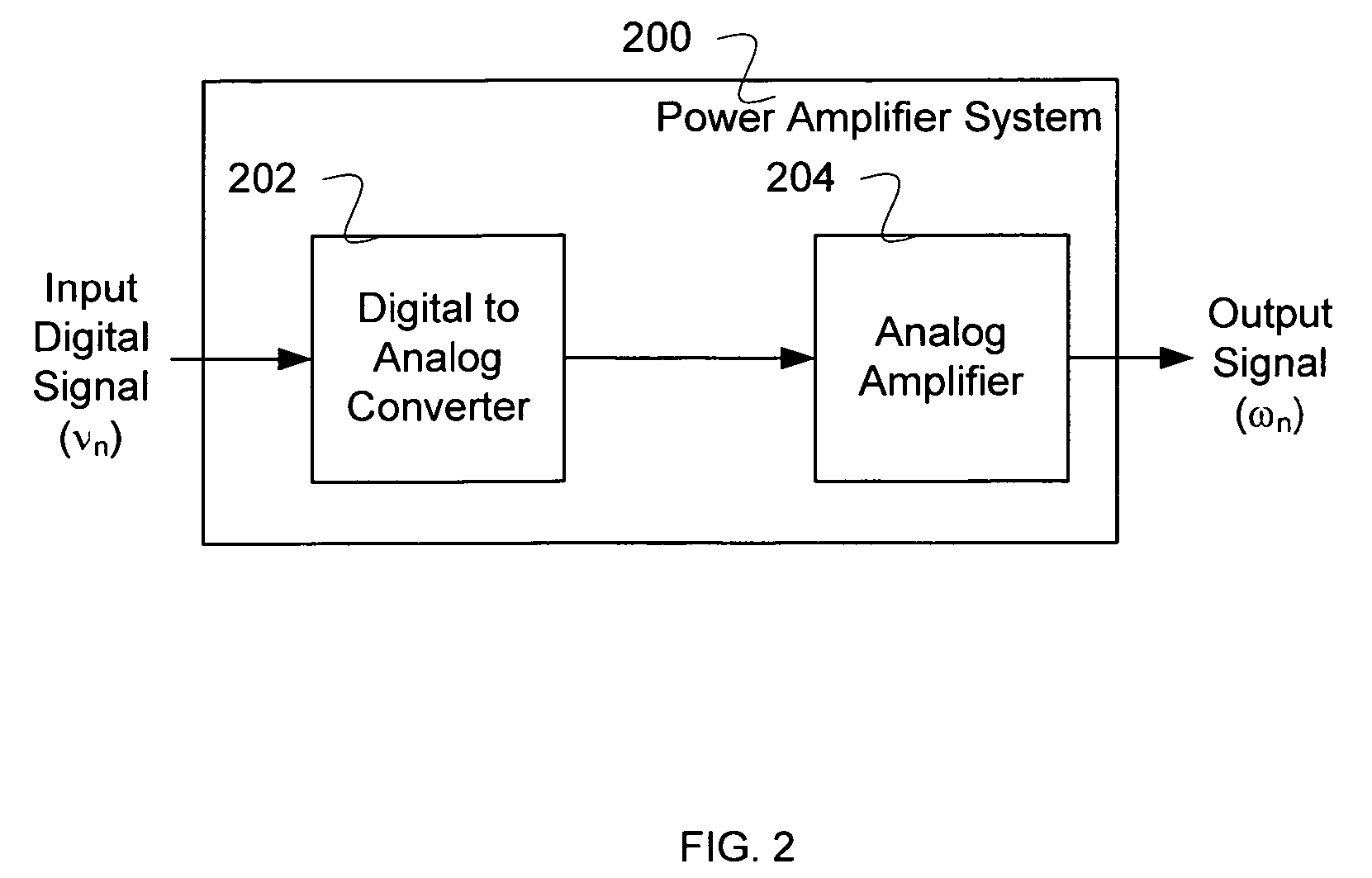
ActiveUS20050156662A1Improve performanceReduce the amount of distortionAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAudio power amplifierPhysics
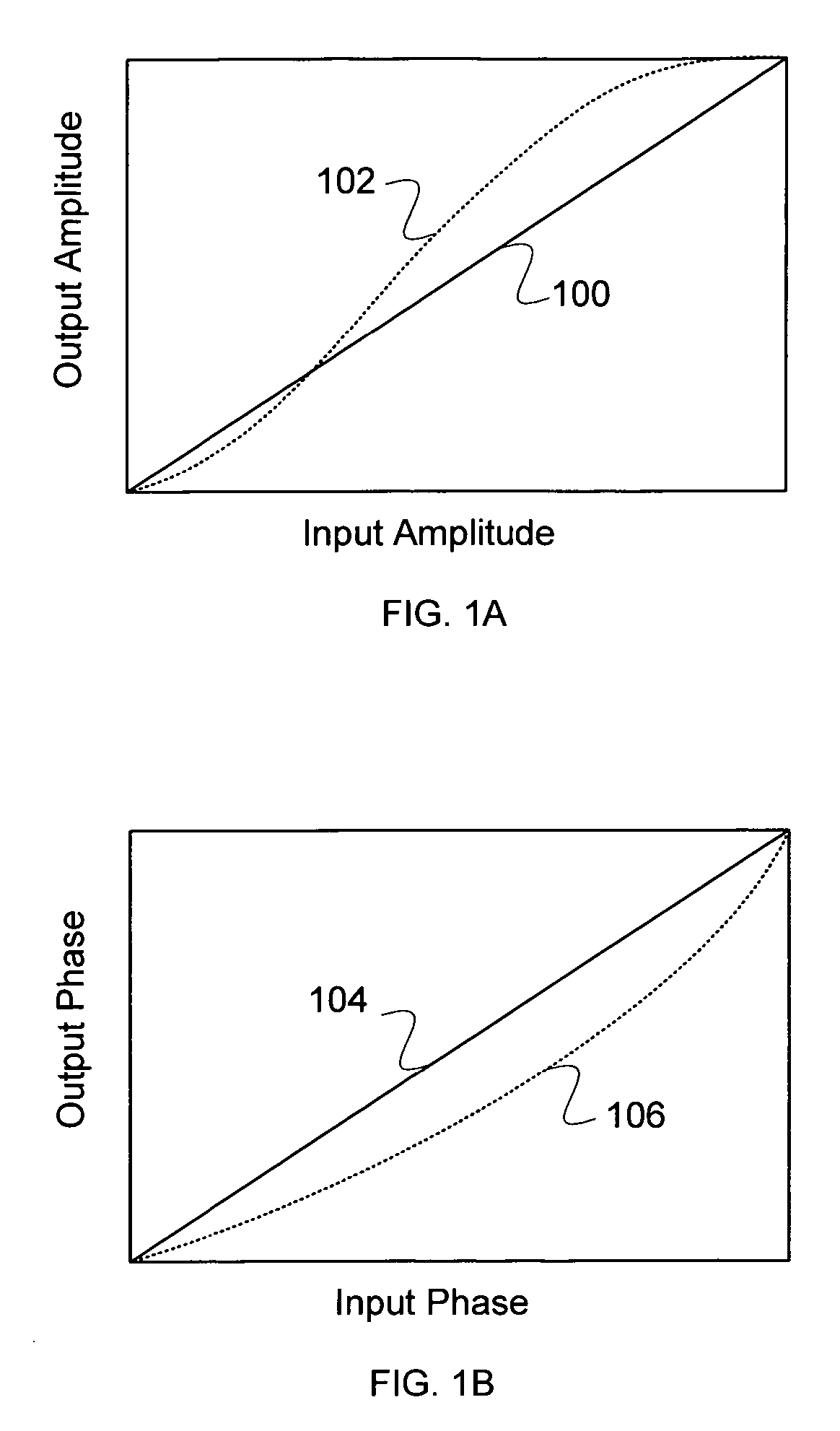
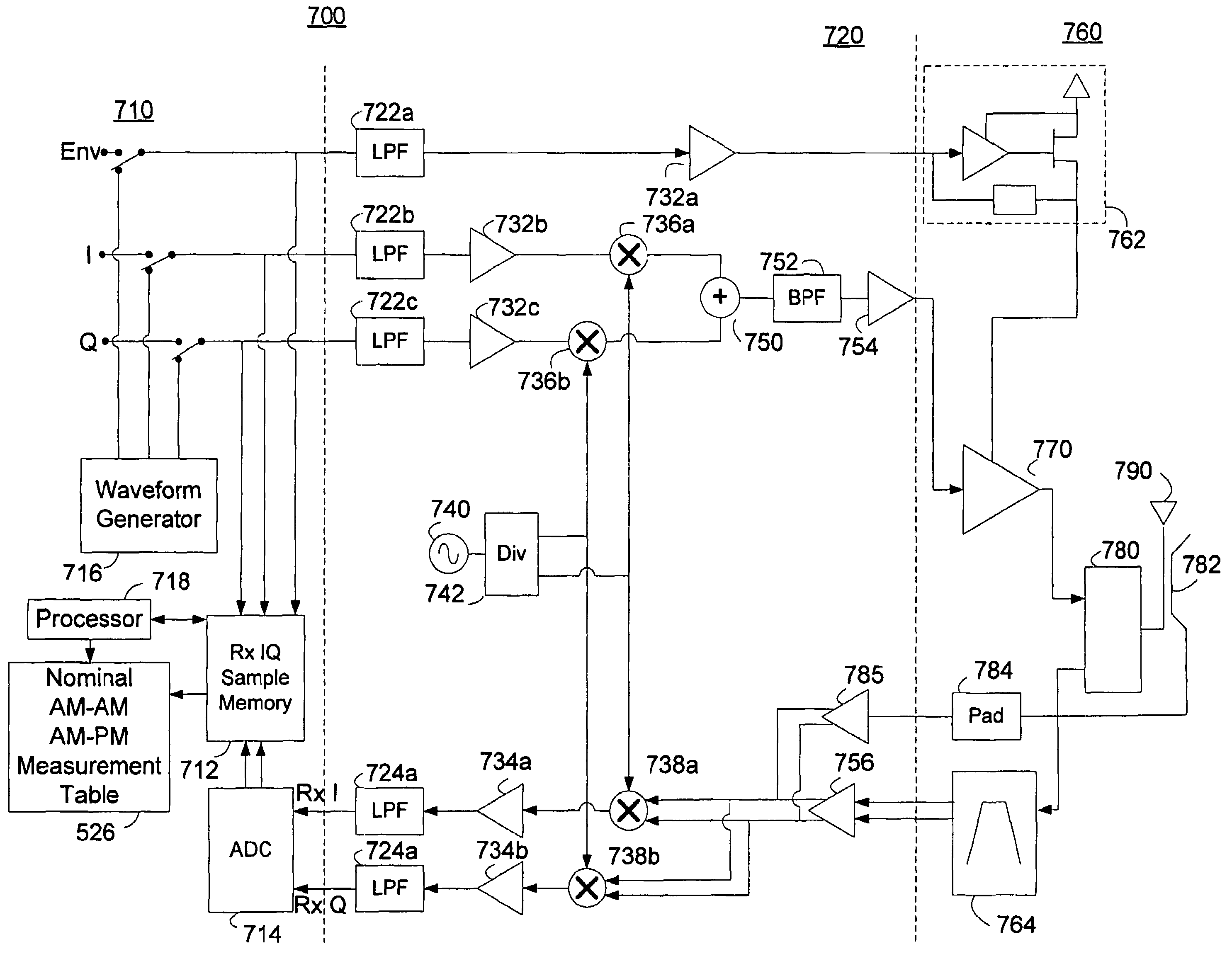
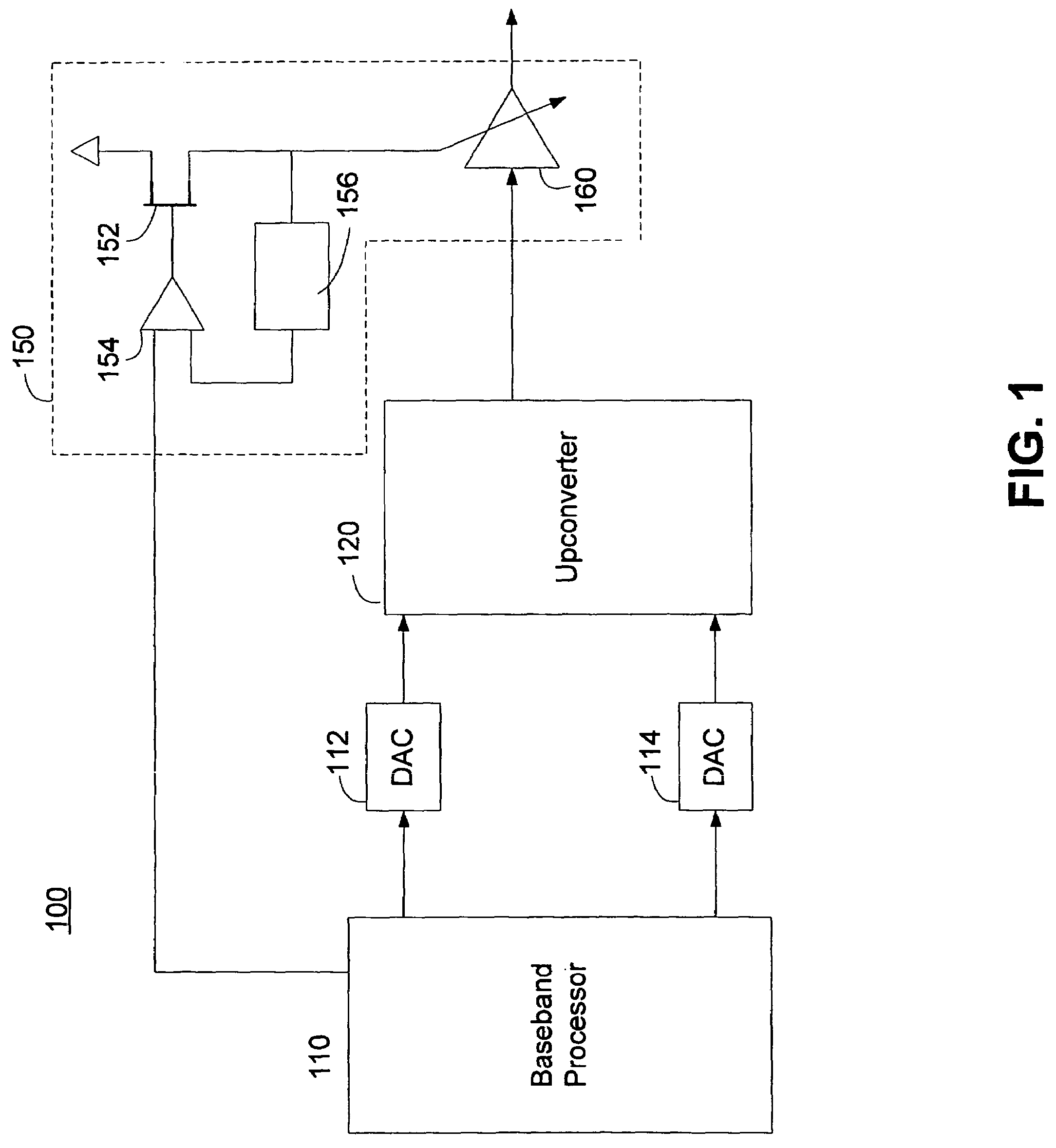
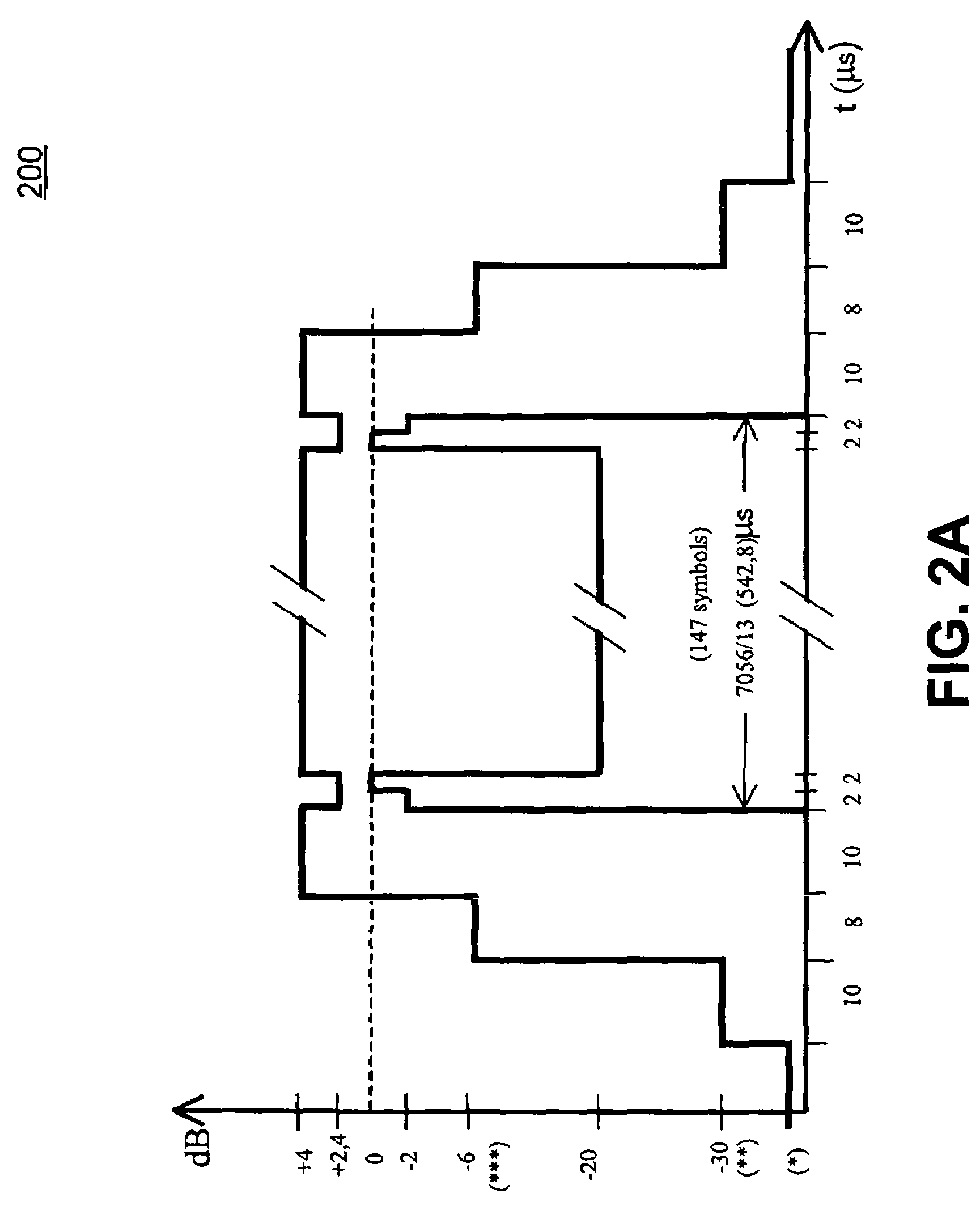
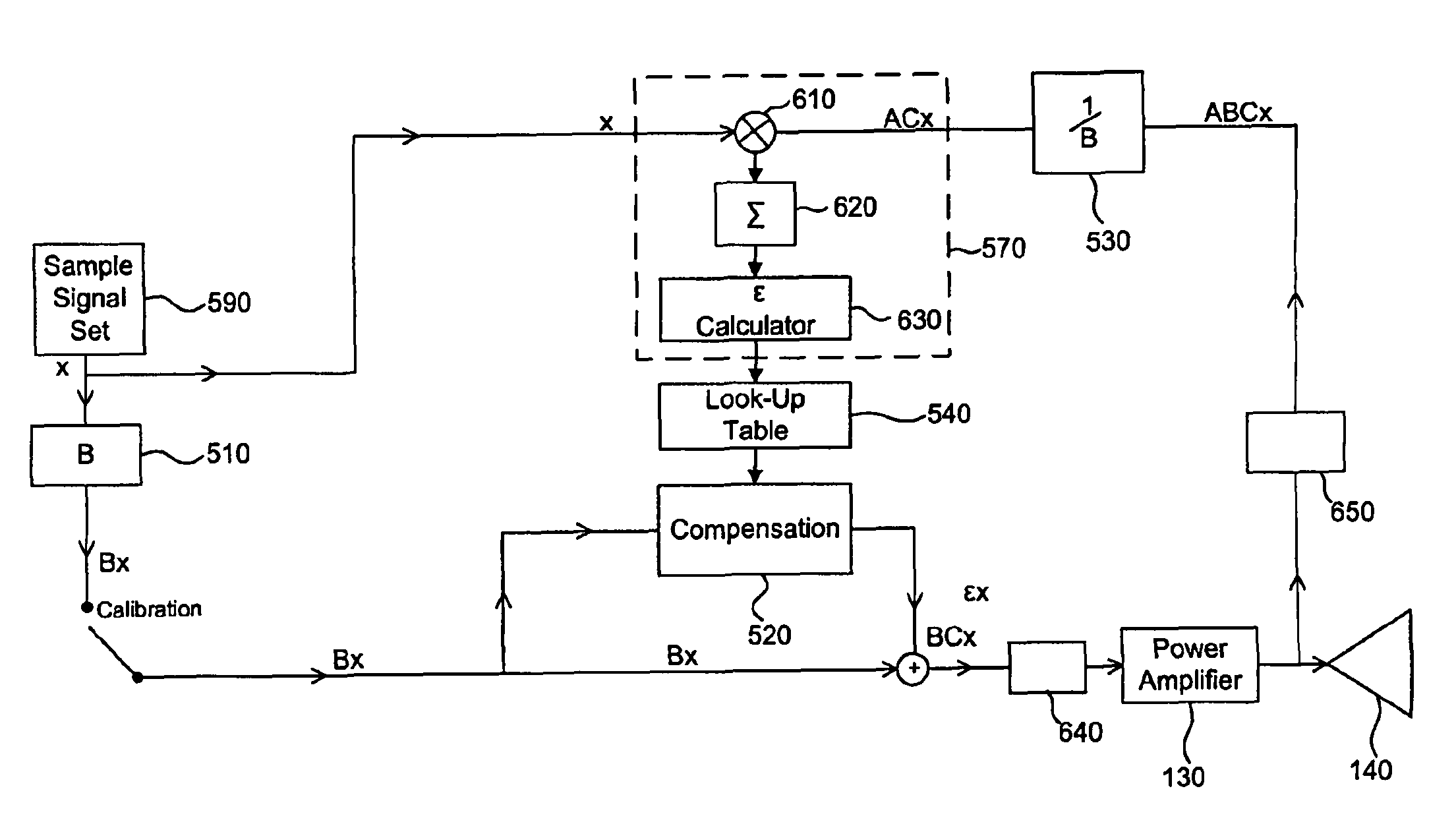
Methods and apparatus for amplifier AM and PM predistortion and autocalibration. AM and PM amplifier distortion can be corrected using predistortion. The AM and PM distortion characteristics of the amplifier are determined using an autocalibration technique. The amplifier characteristics can be stored in distinct look up tables. Alternatively, the inverse of the amplifier characteristics can be stored in distinct look up tables. Signals that are to be amplified are characterized in polar format having a phase component with a normalized magnitude and a magnitude component. The phase component can be predistorted by applying the inverse of the PM distortion characteristics to the signal. Similarly, the magnitude component can be predistorted by applying the inverse of the AM distortion characteristics to the signal. The predistorted phase component can be amplified using the previously characterized amplifier. The predistorted magnitude component can be used to set the gain of the previously characterized amplifier.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
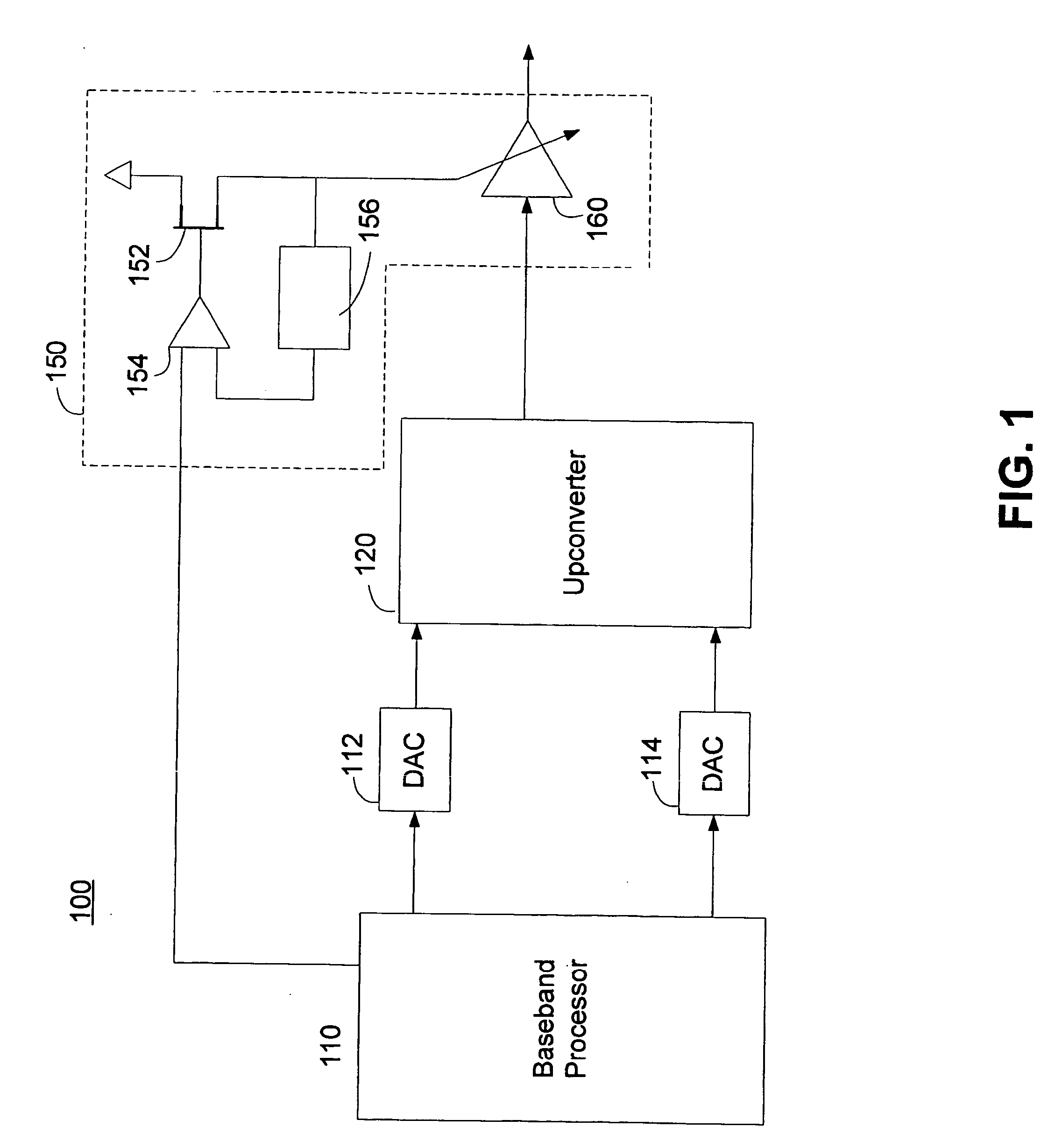
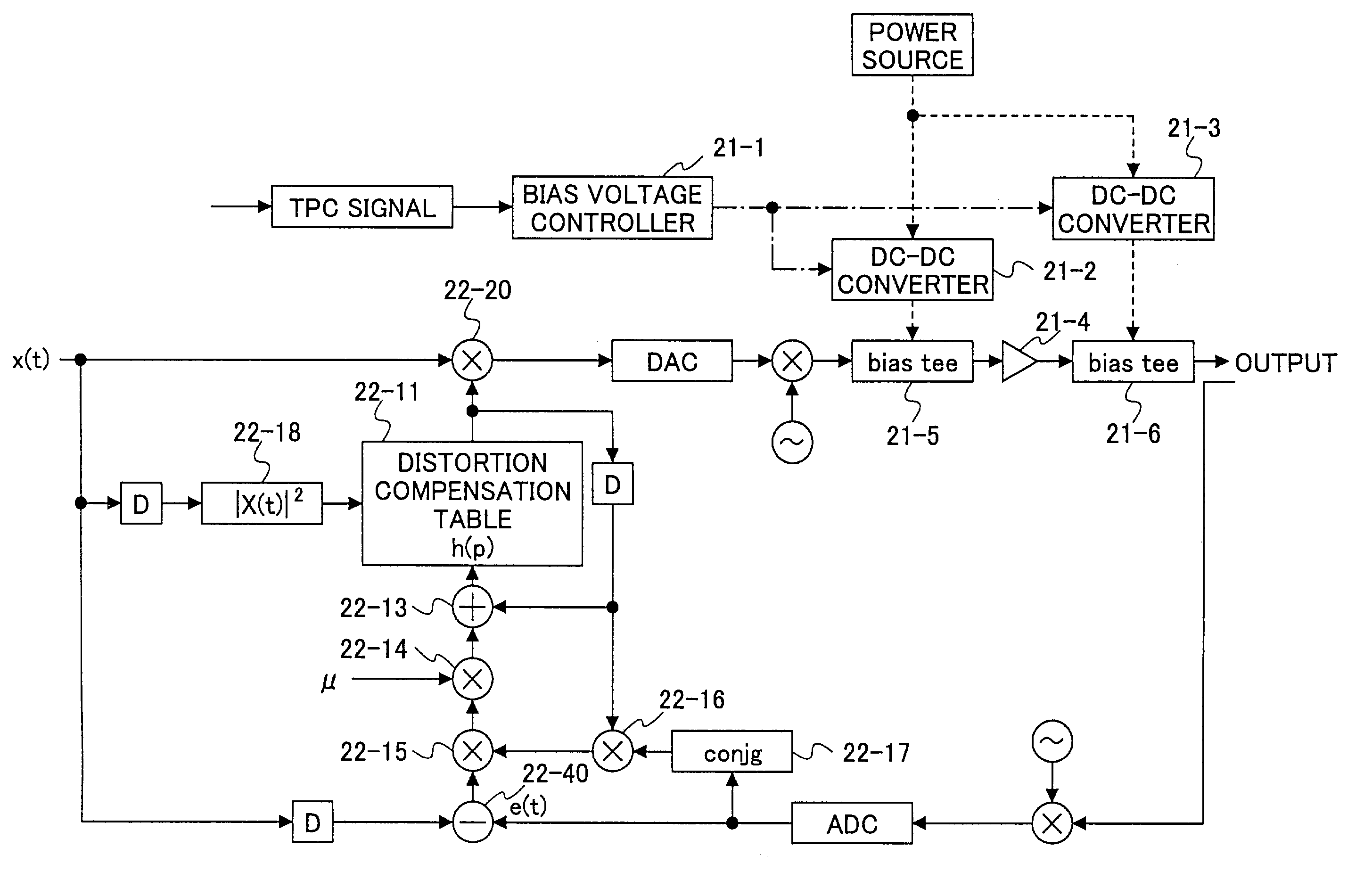
Radio with a distortion compensation capability
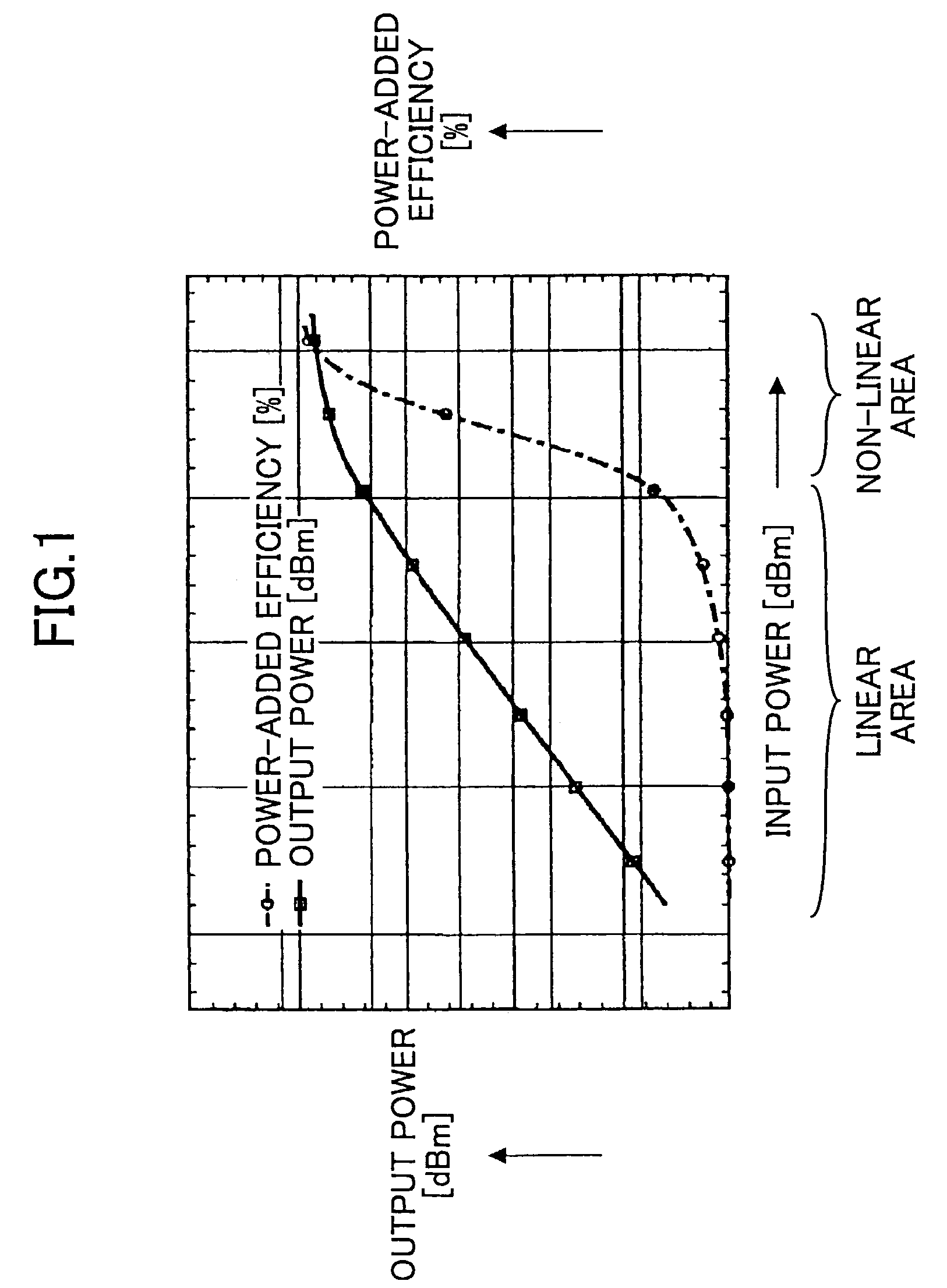
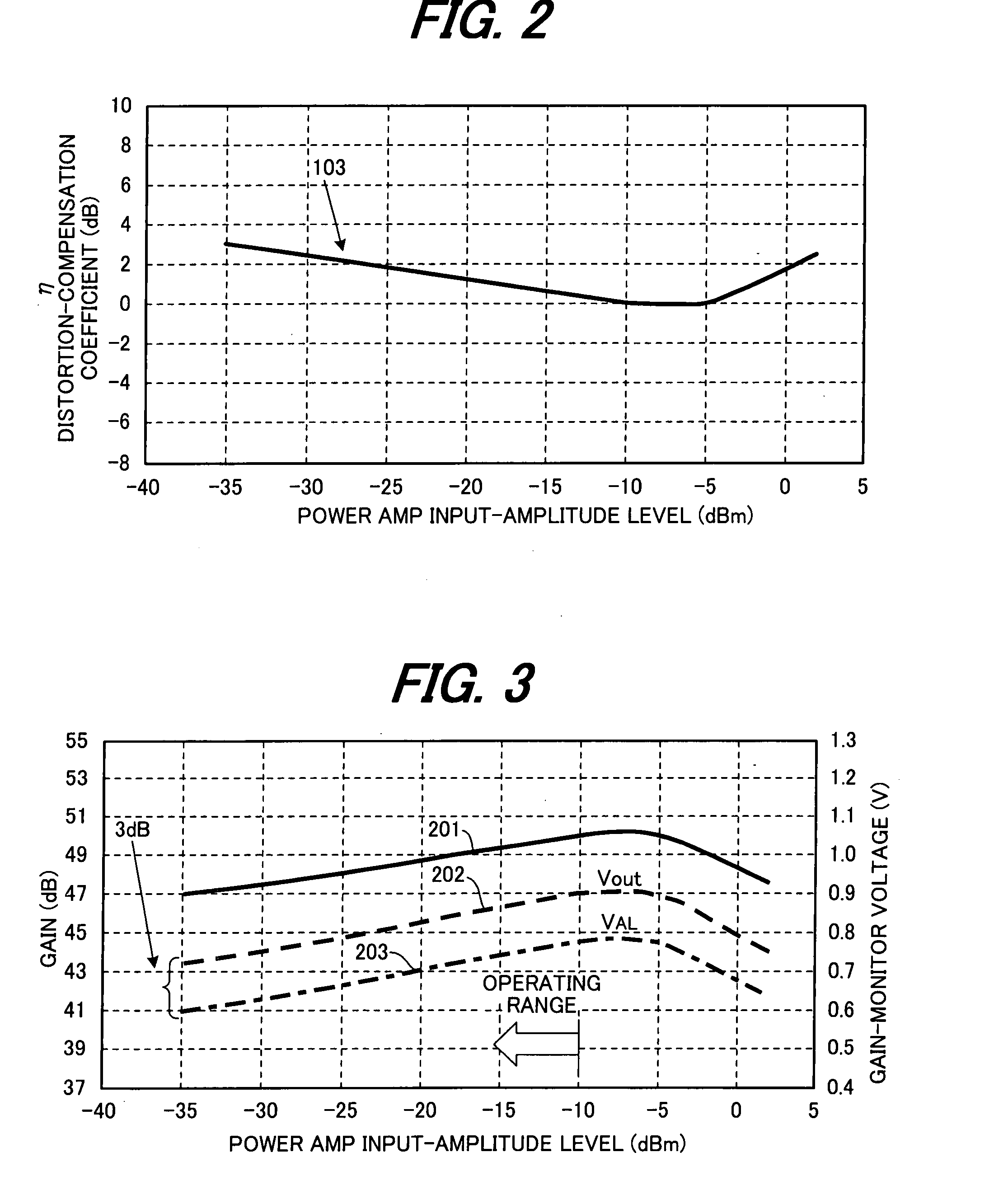
InactiveUS7197286B2Improve power added efficiencyBest power-added efficiencyEnergy efficient ICTAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionDistortionAmplifier distortion
A radio comprises a power amplifier for amplifying a signal to be transmitted; a distortion compensation table storing distortion compensation coefficients for compensating a distortion of the power amplifier; a computing unit for updating the distortion compensation coefficient based on a difference between a transmission input signal and a transmission output signal; a bias voltage controller for applying a bias voltage to the power amplifier, said bias voltage determined based on a transmit control signal so as to maximize a power efficiency of the power amplifier.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Amplifier distortion management apparatus, systems, and methods
ActiveUS7250815B2Negative-feedback-circuit arrangementsAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAudio power amplifierAmplifier distortion
Owner:APPLE INC
Frequency-dependent magnitude pre-distortion for reducing spurious emissions in communication networks
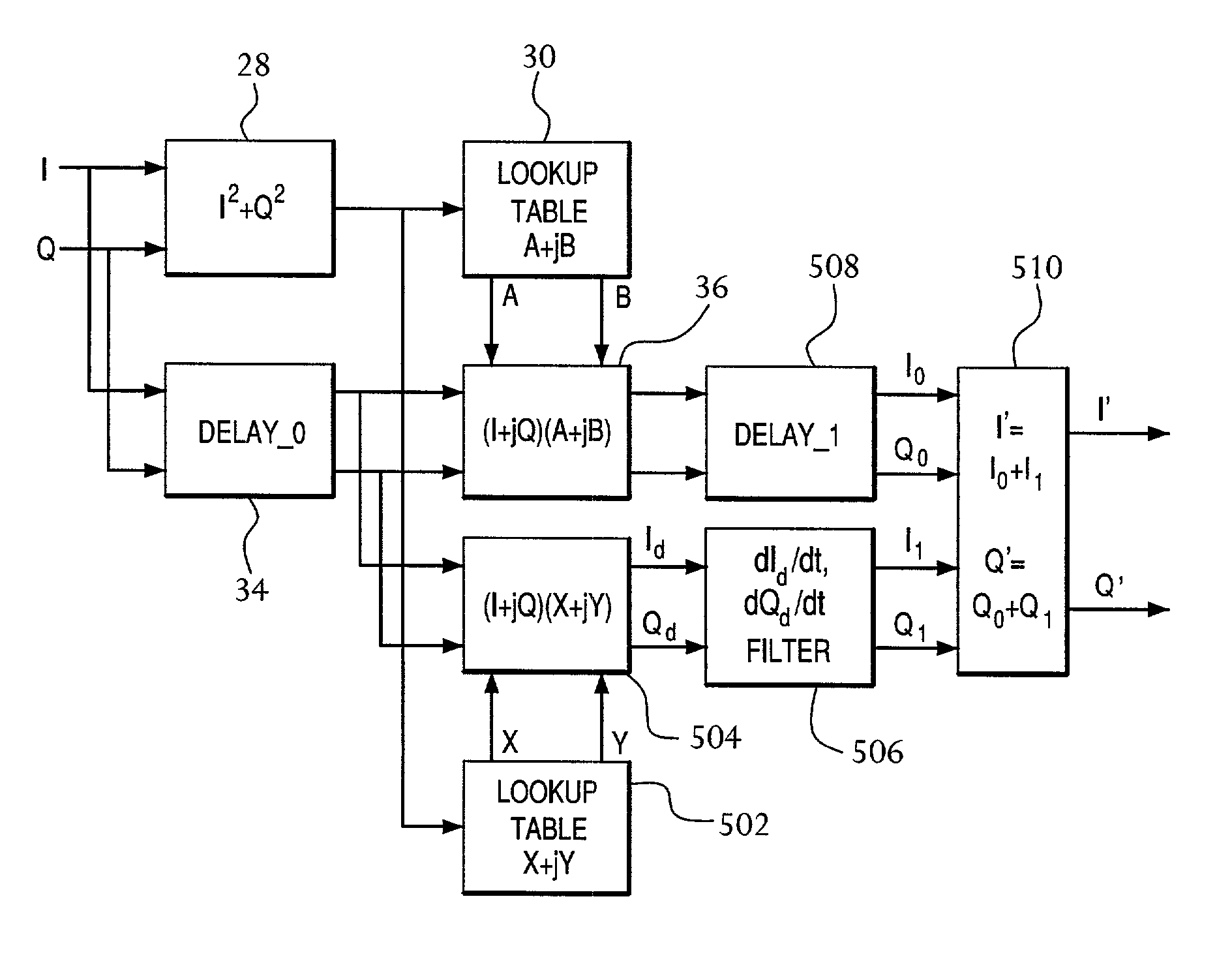
ActiveUS7197085B1Spurious emission can be reducedEmission reductionAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionSecret communicationDifferentiatorAudio power amplifier
Pre-distortion, whose magnitude—and preferably phase—are frequency-dependent, is applied to an input signal in order to reduce spurious emissions resulting from subsequent amplification of the signal. In preferred embodiments, the pre-distortion technique of the present invention is implemented in combination with the (frequency-independent) magnitude and phase pre-distortion technique described in U.S. patent application Ser. No. 09 / 395,490 (“the '490 application”), where the frequency-dependent pre-distortion corresponds to amplifier distortion that has a magnitude that is proportional to the frequency offset from the carrier frequency and a phase shift of ±90° on either side of the carrier frequency. Since these characteristics match those of a differentiator, a thorough correction of this part of the amplifier's distortion can be achieved using a differentiating filter. Embodiments of the present invention may be implemented in the baseband domain. Implementations may also be based on look-up tables that are adaptively updated to ensure optimal performance over time.
Owner:COMMSCOPE TECH LLC
Method and apparatus for generating a radio frequency signal
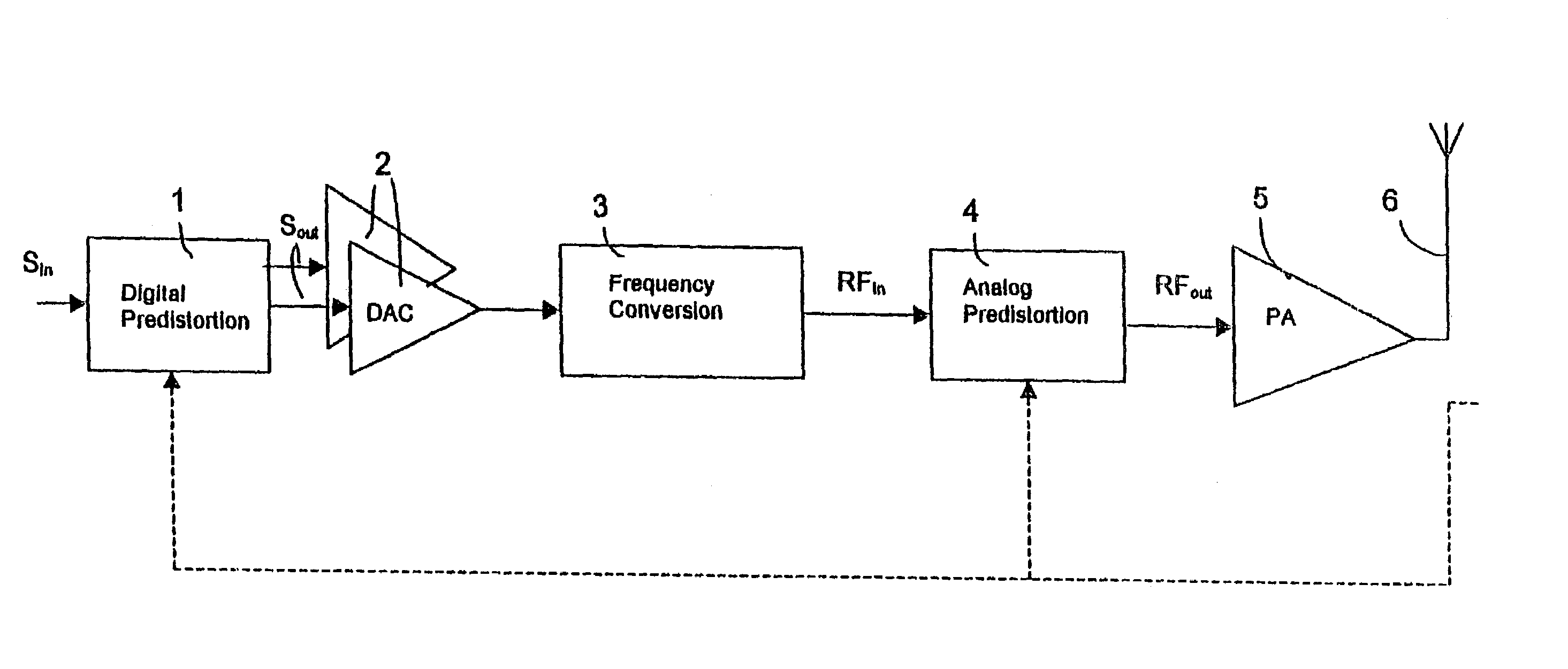
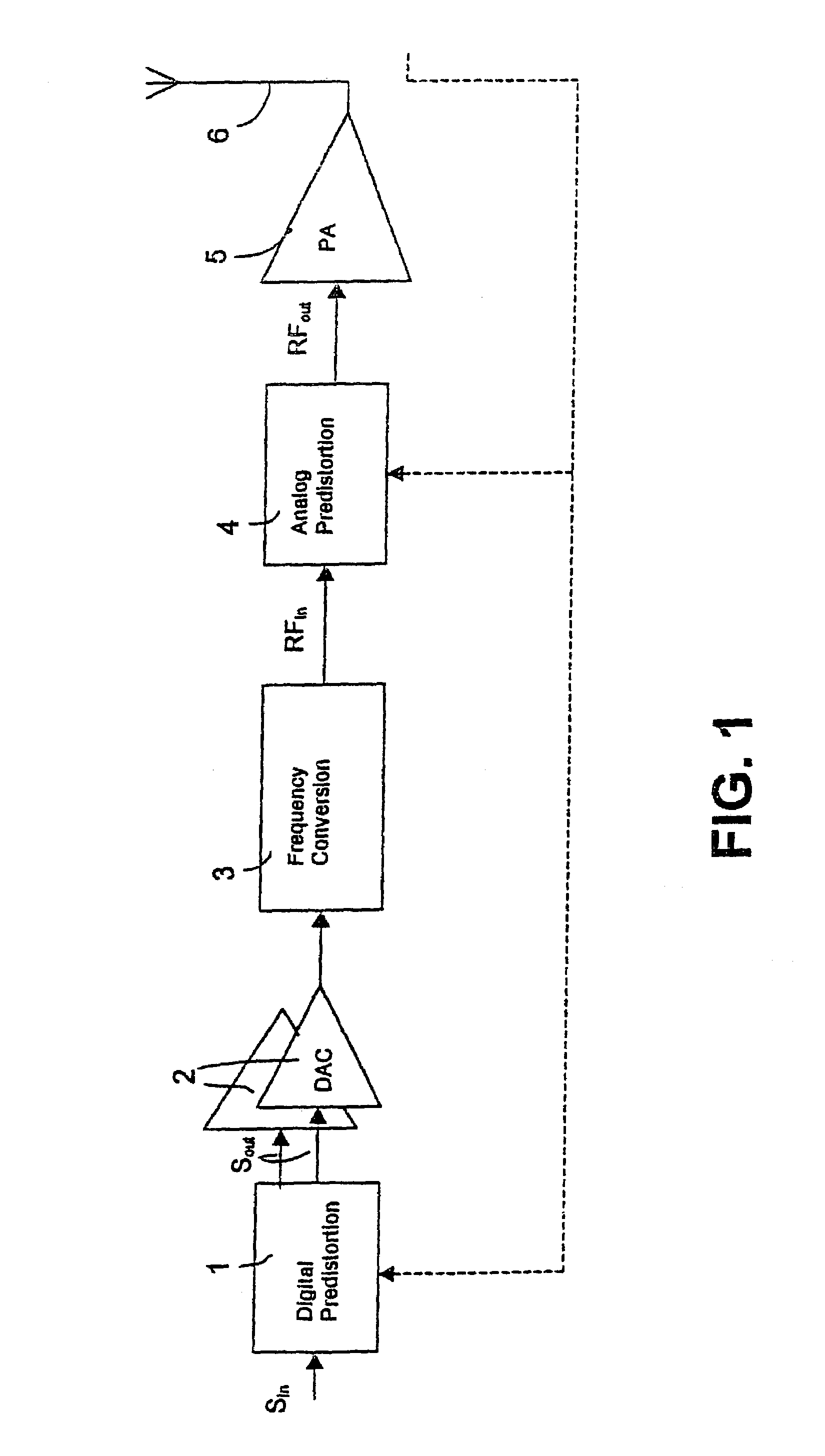
InactiveUS6947711B1Improve linearizationOvercome problemsAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionTransmission control/equalisingAudio power amplifierFrequency conversion
The invention relates to linearization of a radio frequency (RF) power amplifier (5) by predistortion. Digital predistortion is performed (1) on received digitized base-band input signals to compensate for amplifier distortion. The resulting signal is converted to an analog signal via two D / A converters (2), after which analog frequency conversion is performed (3) on the analog signal to achieve a radio frequency (RF) signal. This radio frequency signal is exposed to analog predistortion (4) and thereafter amplified by the power amplifier.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
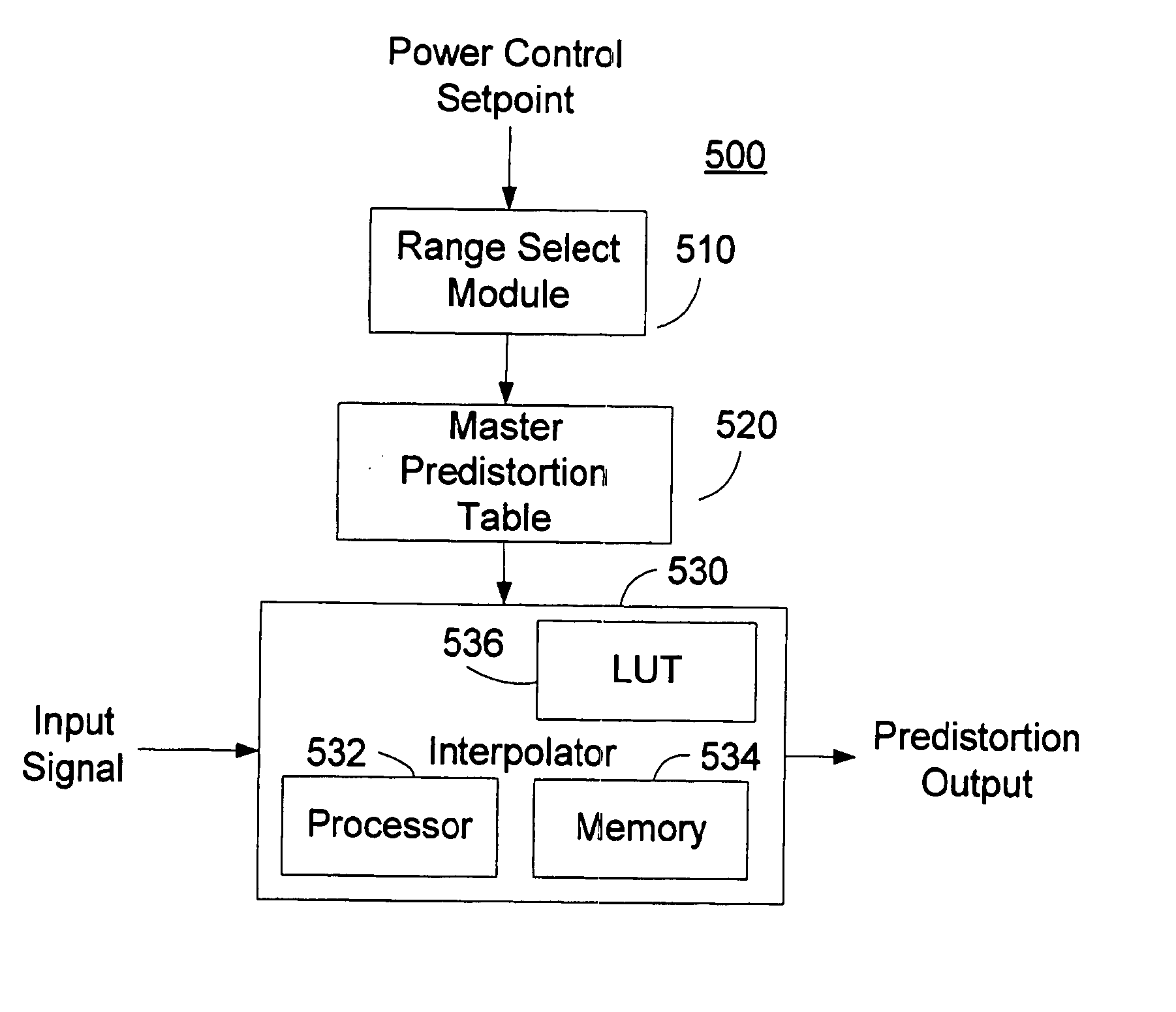
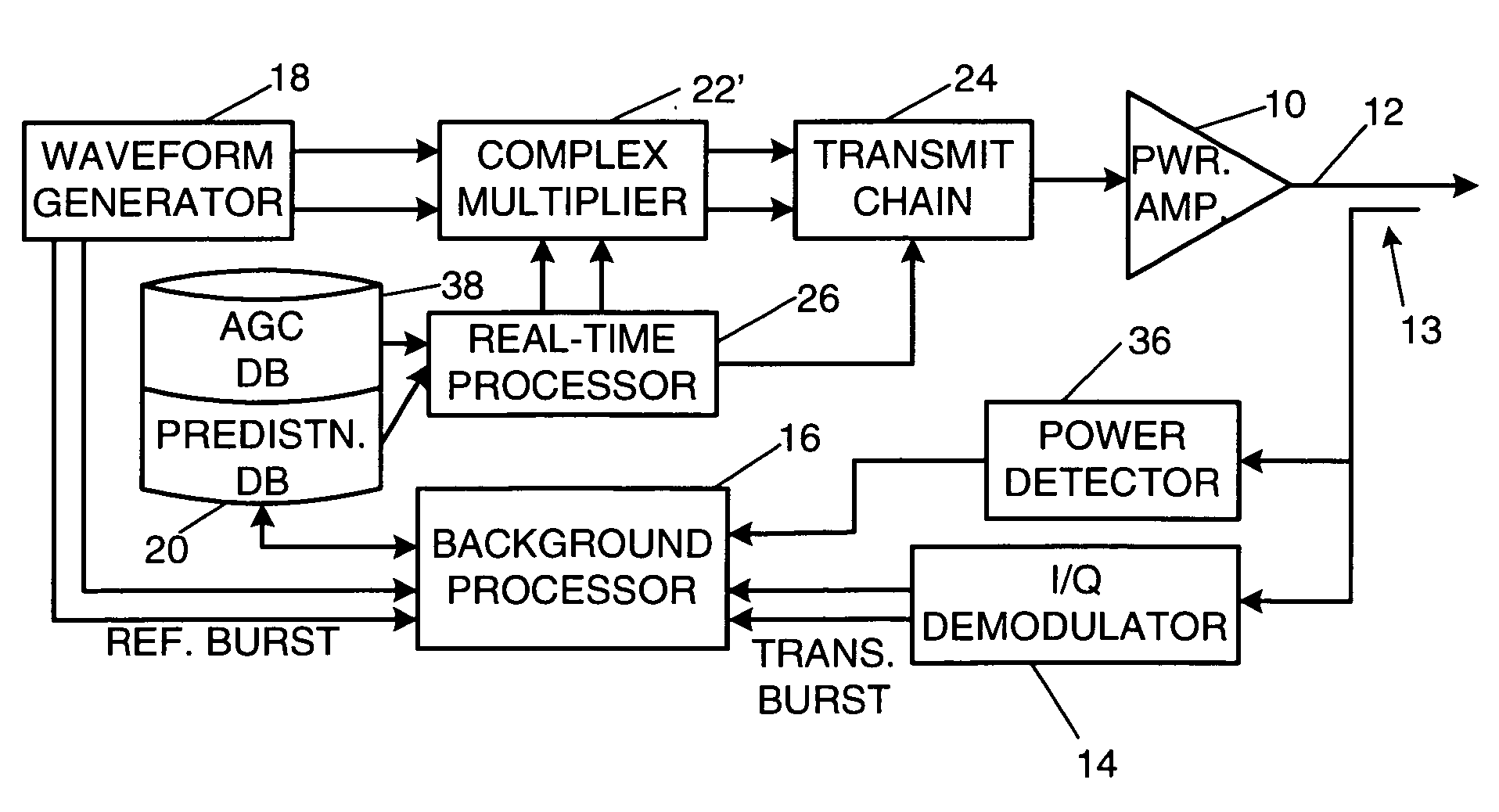
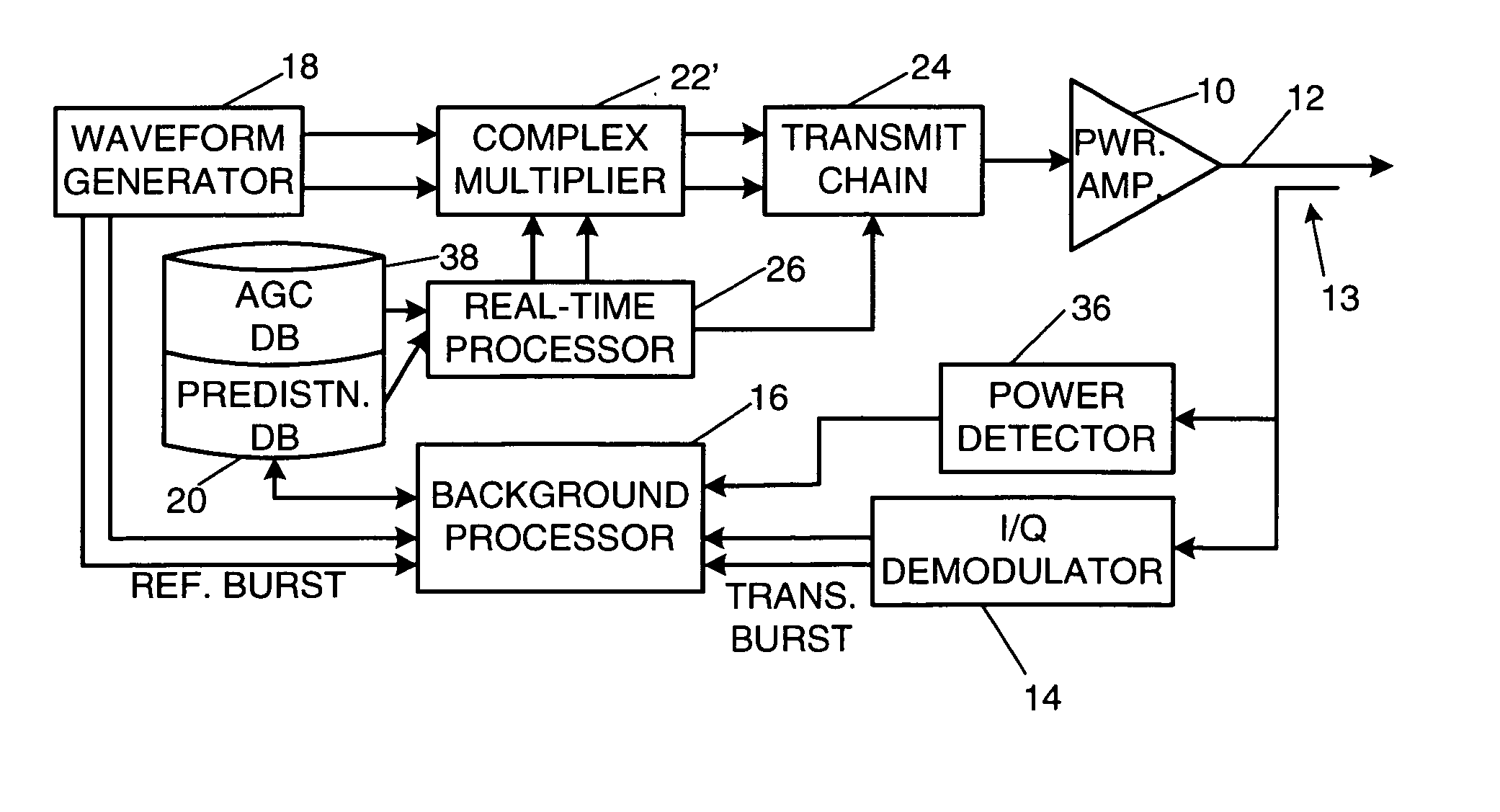
Efficient method and means for integration of power control and predistortion in a transmitter
ActiveUS7102430B2Linearization of amplifier performanceAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAmplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationRadio frequencyAutomatic gain control
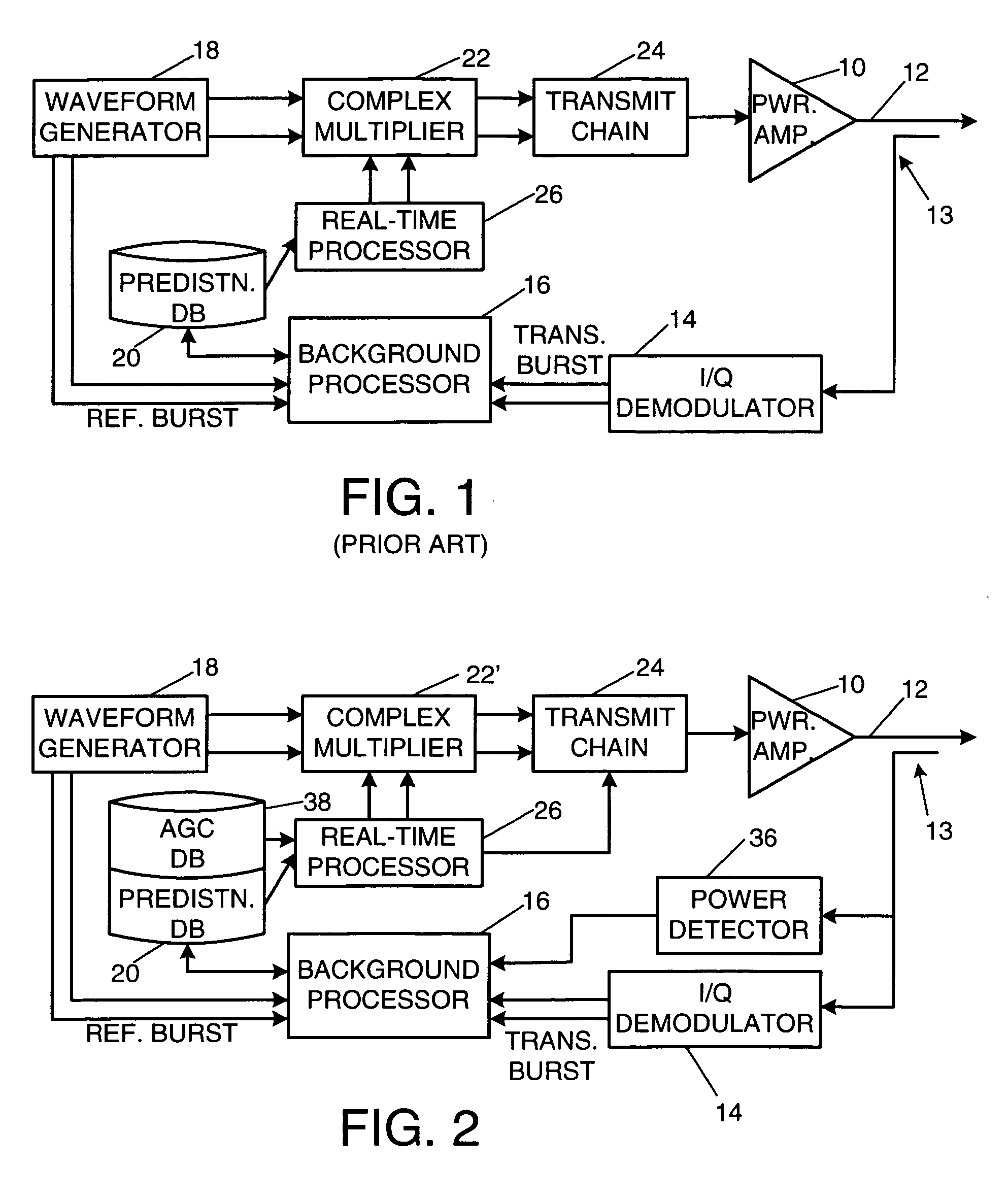
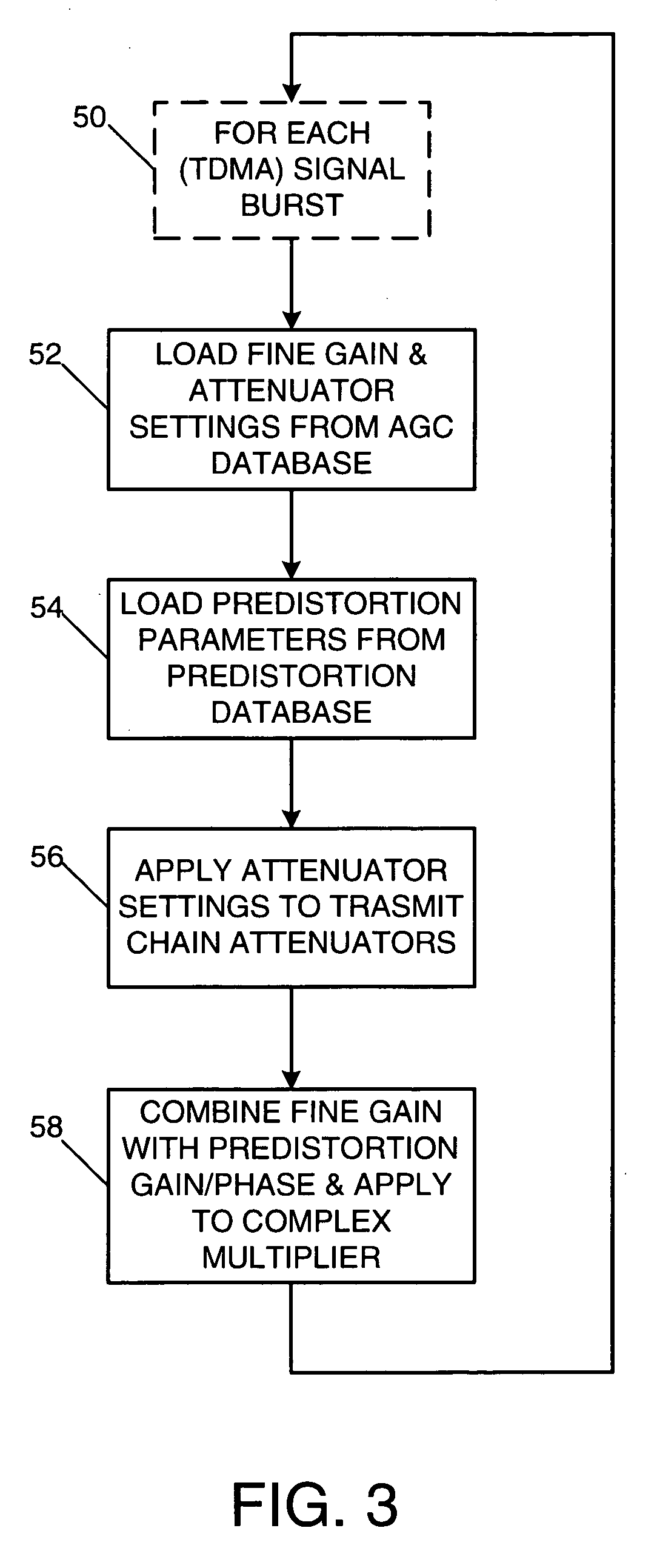
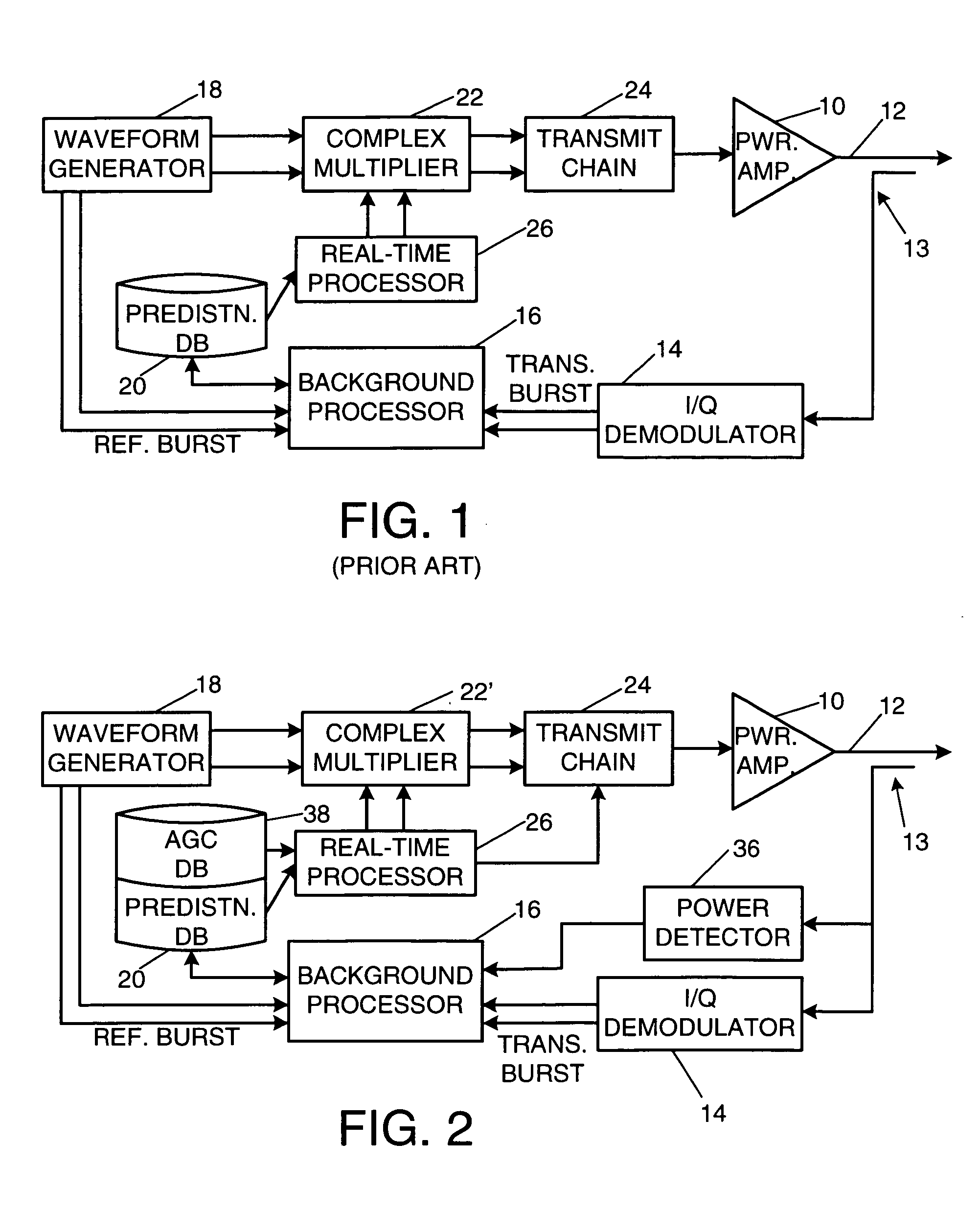
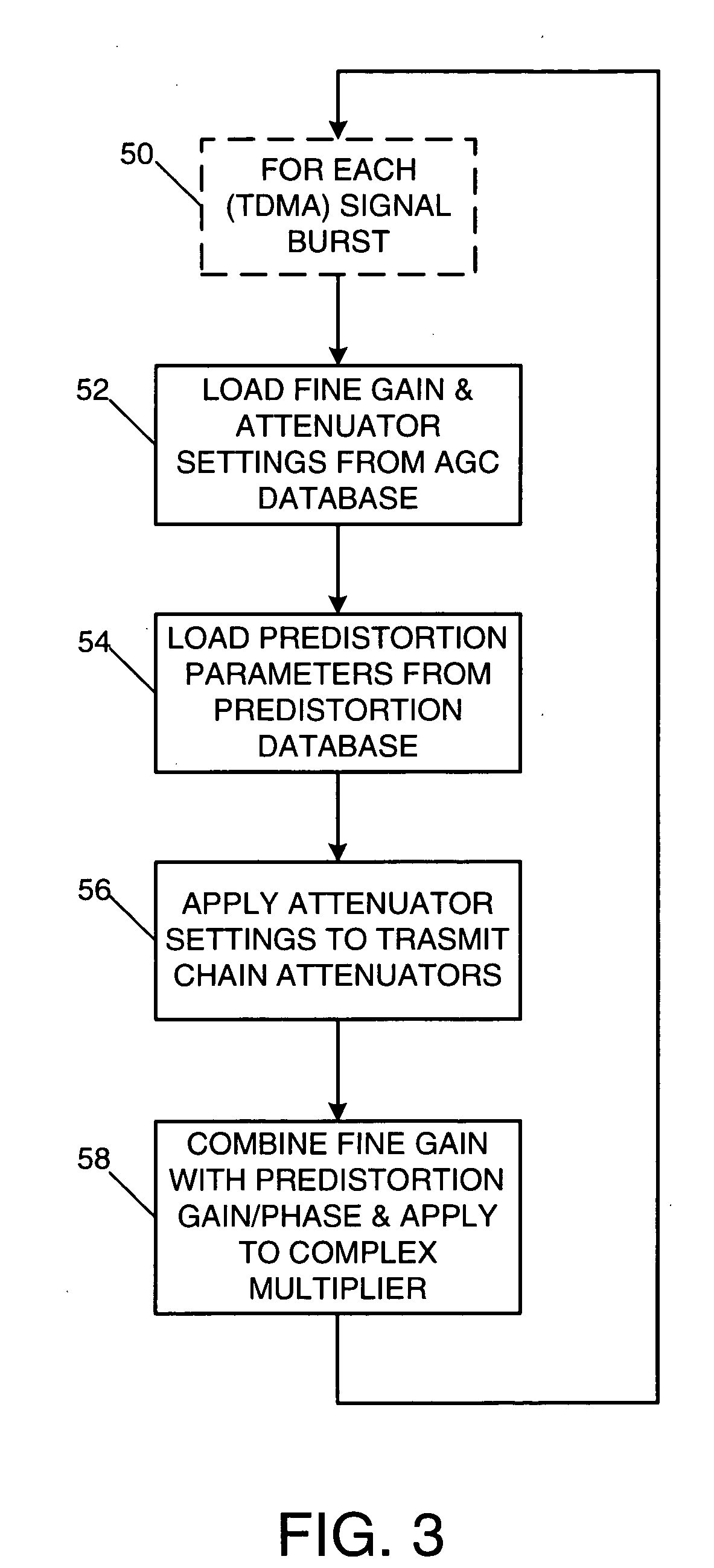
A radio-frequency (RF) transmitter power amplifier circuit provides for practically linear performance by predistorting the amplifier input signals to compensate for amplifier distortion at high power levels, and provides a fine degree of control of amplifier power needed to handle complex modulation schemes with widely and rapidly varying power requirements. A predistortion database (20) contains gain and phase corrections for various transmission types and a separate automatic gain control database (38) contains fine amplifier gain corrections. A real-time processor (26) combines the two types of corrections and applies them to the amplifier input signals, and a background processor (16) continually updates both databases in accordance with a programmable priority scheme. Integration of predistortion and amplifier power control is achieved in a manner that minimizes adverse effects of one type of control on the other. One feature of the invention provides for rapid convergence of the predistortion correction.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
Model based distortion reduction for power amplifiers
InactiveUS20050212596A1Amplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAudio power amplifierDistortion reduction
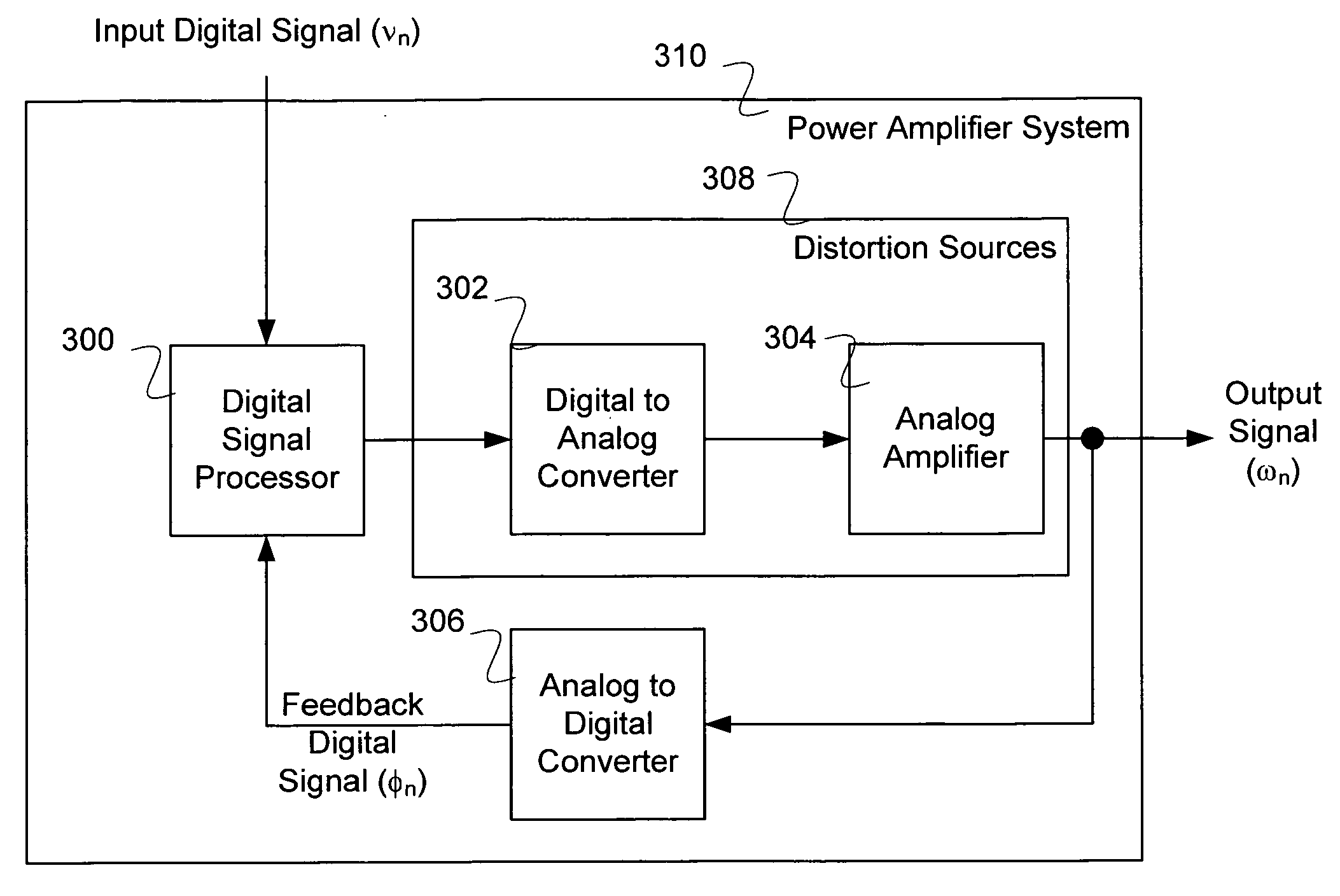
A method of processing a signal is disclosed. The method comprises generating a digital signal, converting the digital signal to an analog signal, and generating an amplified analog signal having distortions. The method further comprises converting the amplified analog signal to a feedback digital signal at a sample rate and updating a model of the distortions based on the feedback digital signal.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
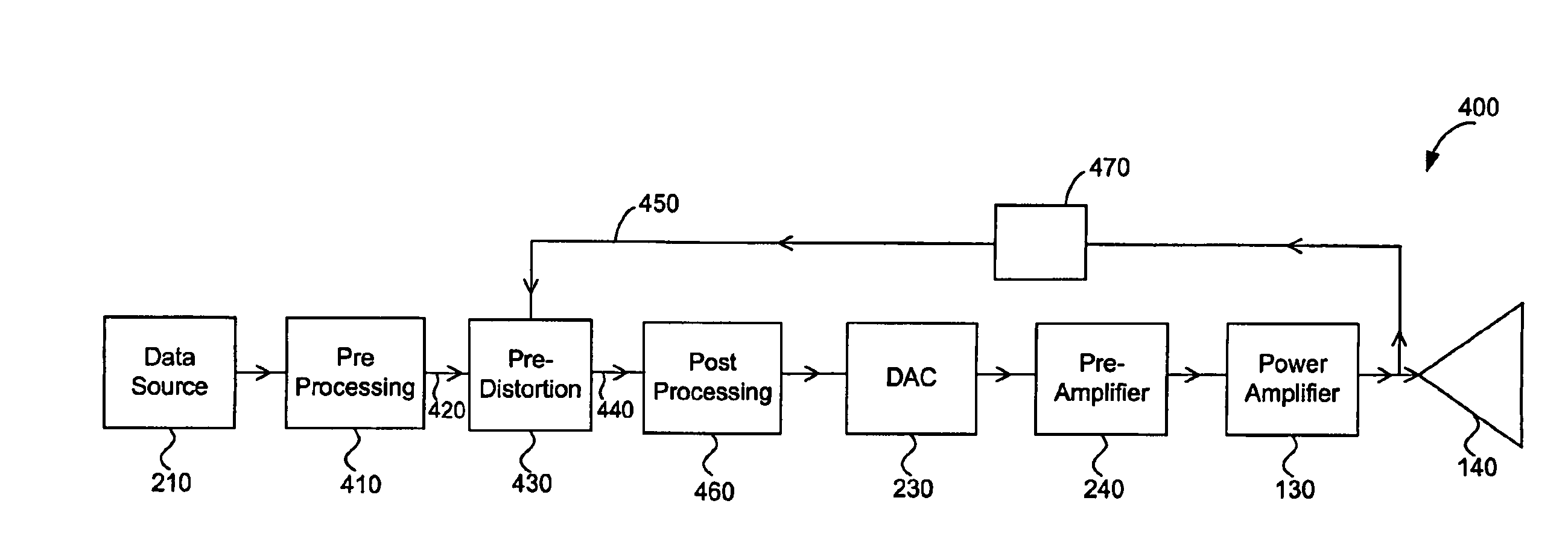
Power Amplifier Pre-Distortion
ActiveUS20080309405A1Reduce the required powerPower amplifiersFrequency analysisAudio power amplifierPre distortion
The present invention is directed to systems and methods for reducing the distortion of power amplifiers. In particular, methods and systems are described that enable a determination of a pre-distortion correction signal to be determined, which when added to the nominal signal, a reduction in the distortion of the power amplifier results. In addition, methods and systems are described that enable calibration of individual power amplifiers to be accomplished for use with the above described approach. More specifically, the methods and systems are described for use in a MIMO application. These approaches may be applied to on-chip power amplifiers, off-chip power amplifiers, or any combination thereof.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
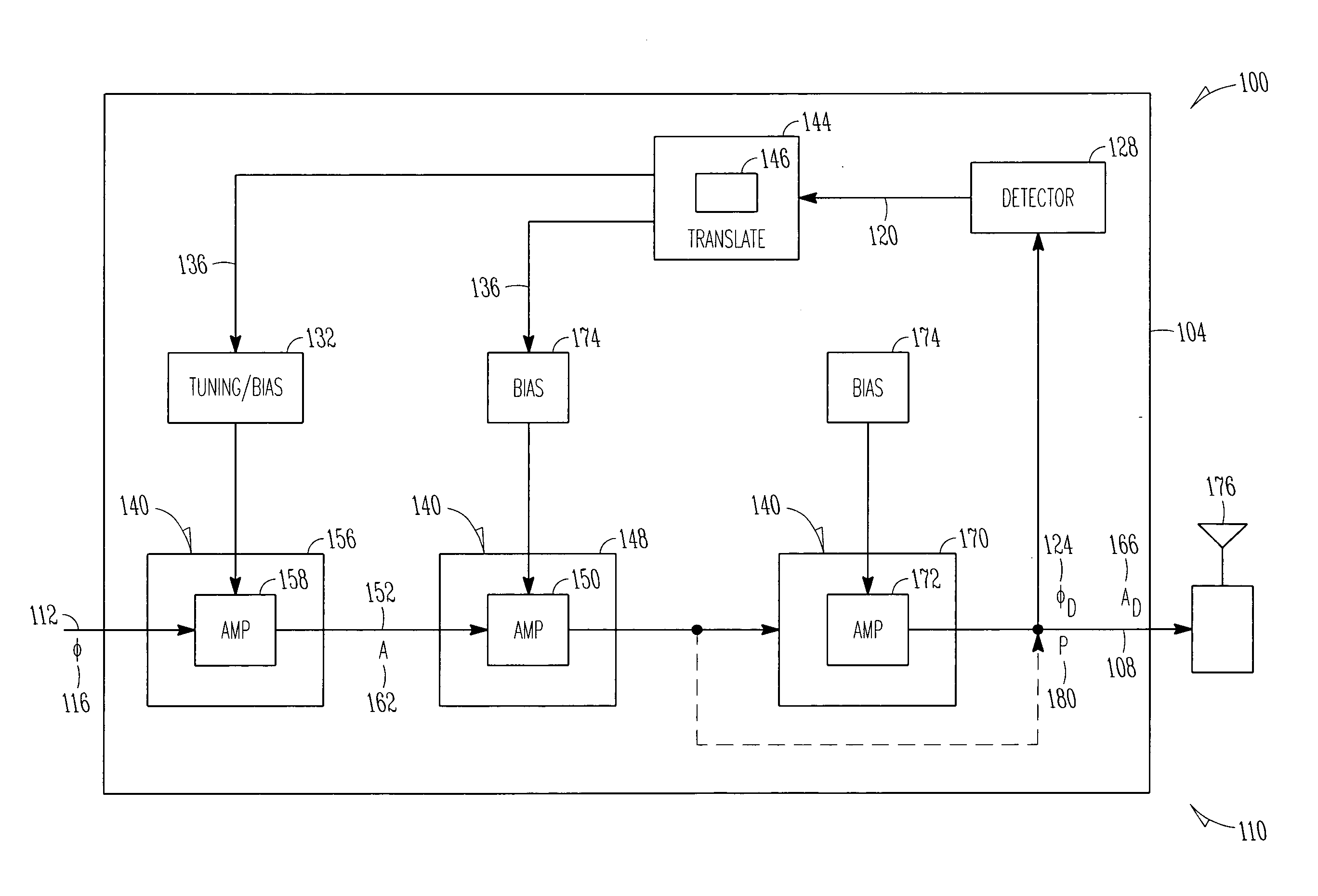
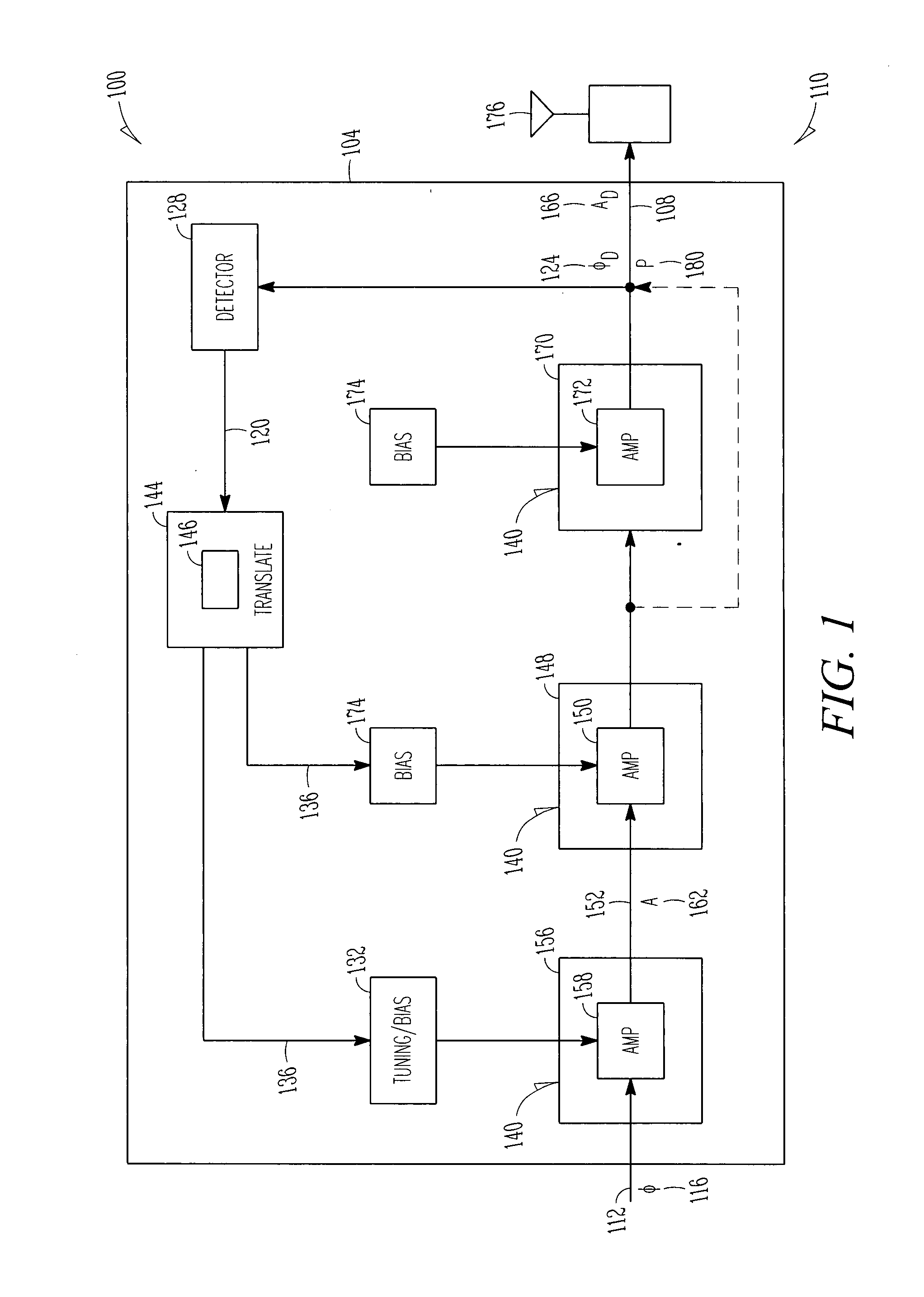
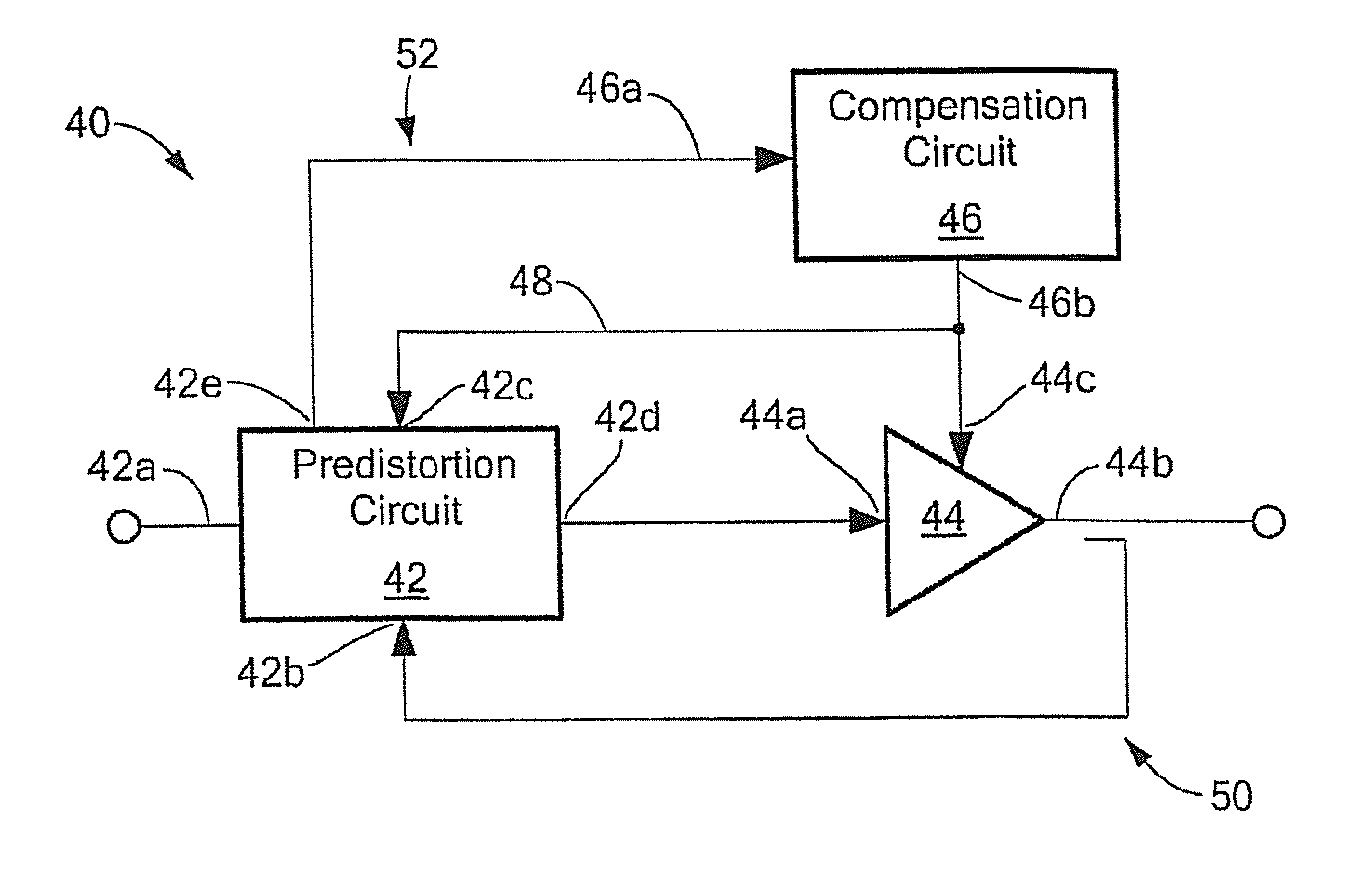
Radio frequency (RF) amplifier utilizing a predistortion circuit and related techniques
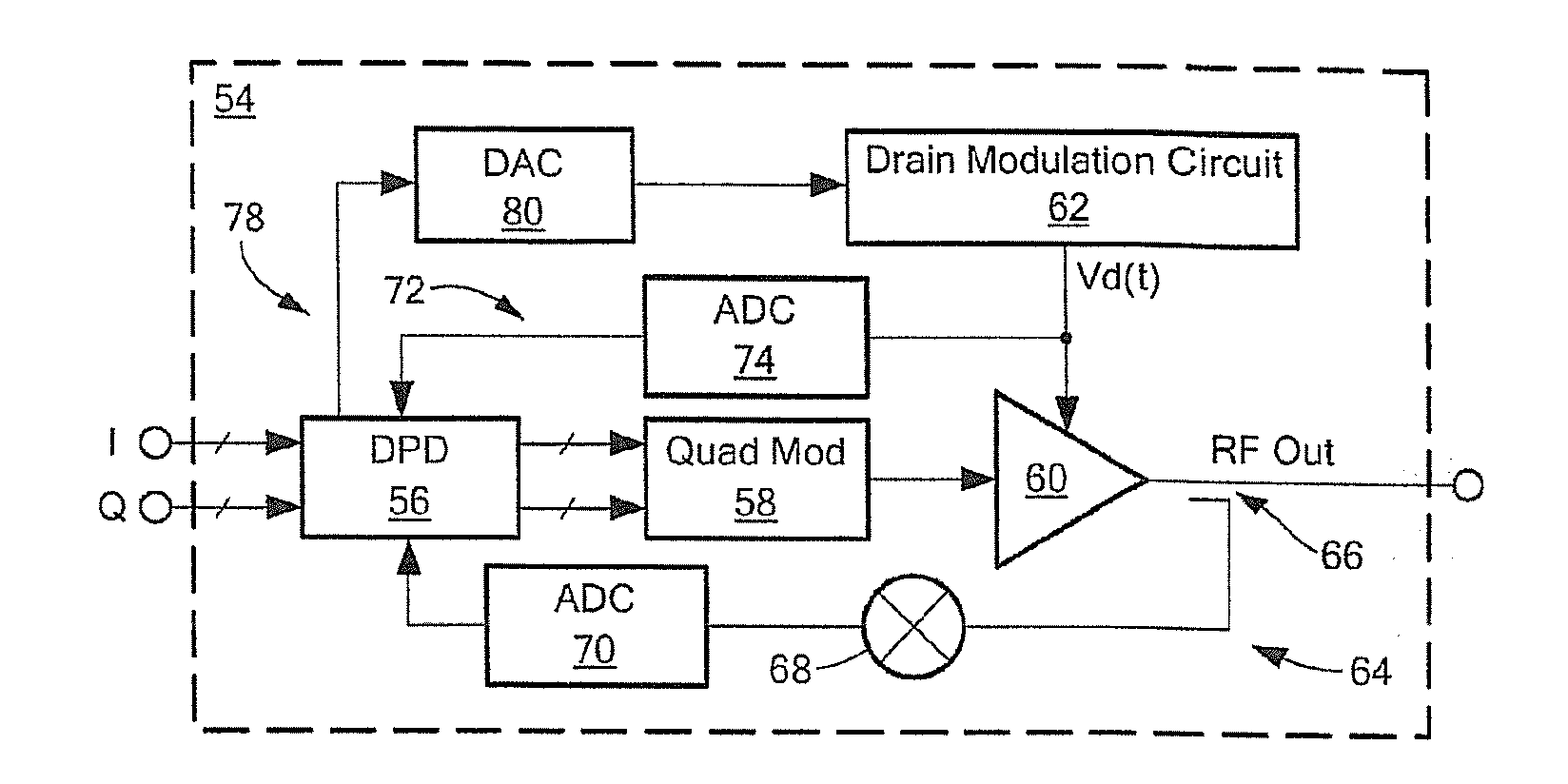
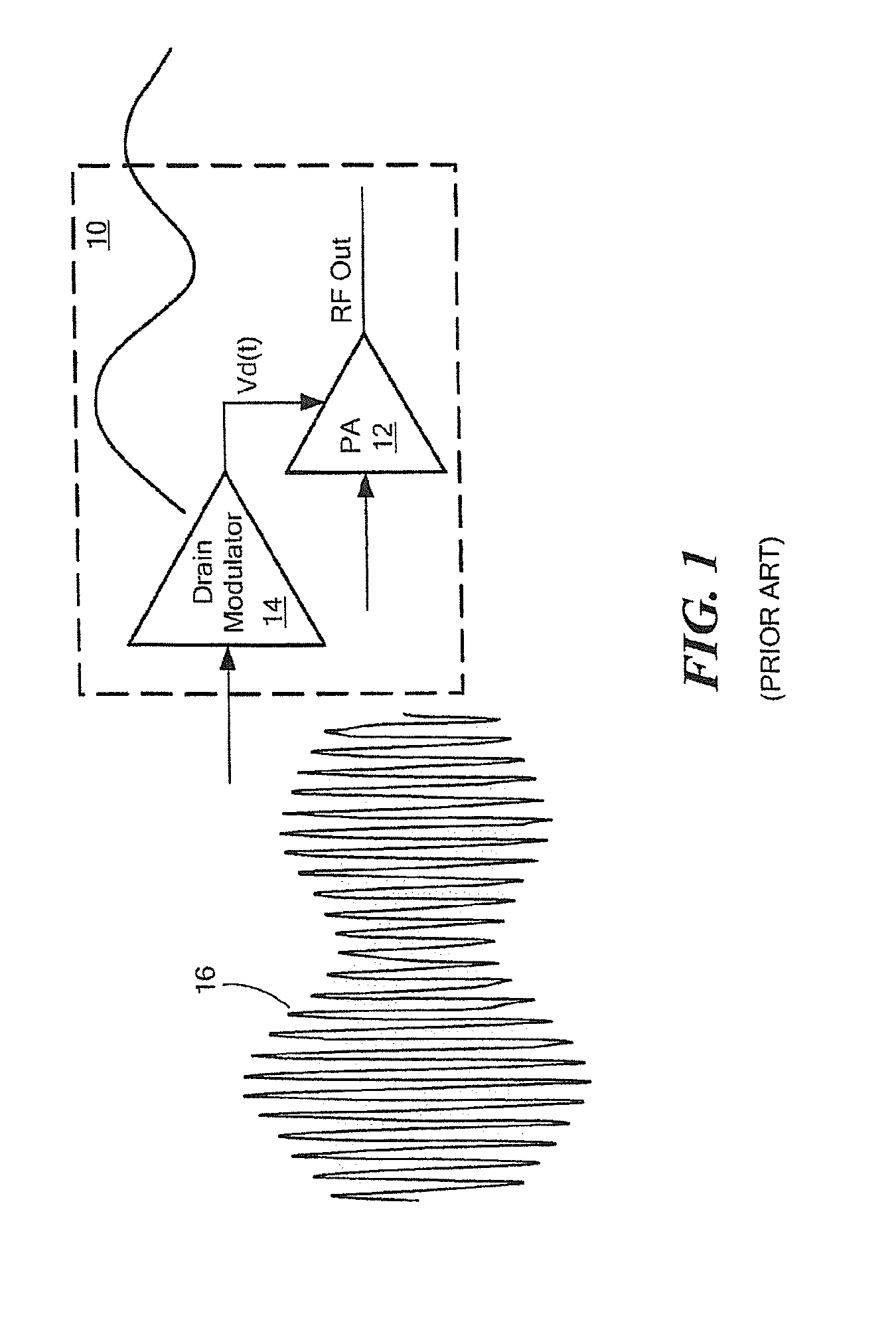
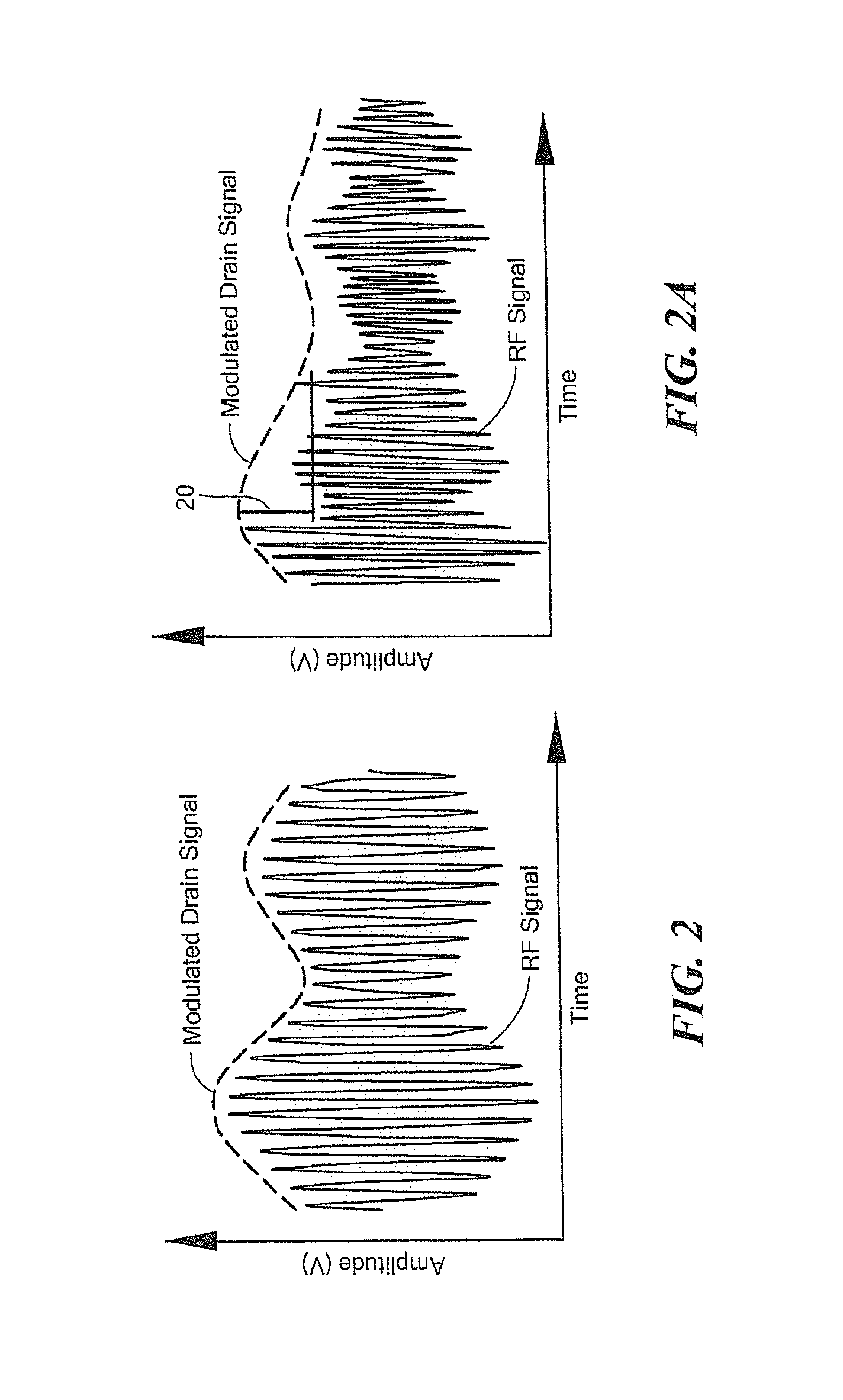
InactiveUS20120256686A1Improve RF bandwidthEliminate Bandwidth LimitationsAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAmplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationEngineeringRadio frequency
An apparatus and technique for operating an RF amplifier having a pre-distortion processor and a drain modulation circuit includes generating a compensating drain bias signal having a value which is a function of an RF input signal, a sampled RF output signal and a sampled drain bias signal. The compensating drain bias signal is applied to the RF amplifier. By sampling both the drain bias signal and the RF output signal and providing drain feedback and RF output feedback signals to a pre-distortion processor, RF amplifier distortions can be linearized enabling the RF amplifier to operate over a bandwidth which exceeds the bandwidth of the drain modulation circuit (i.e., the RF bandwidth can exceed the bandwidth of the drain modulator).
Owner:AURIGA MEASUREMENT SYST
Digital pre-distortion for the linearization of power amplifiers with asymmetrical characteristics
InactiveUS7251293B2Amplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influencePower amplifier linearizationEngineering
An input signal is pre-distorted to reduce spurious emissions resulting from subsequent signal amplification. Frequency-dependent pre-distortion is preferably implemented in combination with frequency-independent pre-distortion, where the frequency-dependent pre-distortion corresponds to amplifier distortion that has a magnitude that is proportional to the frequency offset from the carrier frequency and a ±90° phase shift on either side of the carrier frequency. The frequency-dependent pre-distortion is generated by differentiating waveforms corresponding to two different sets of pre-distortion parameters with respect to time. In one embodiment, one of the differentiated waveforms is applied to a positive-frequency filter and the other to a negative-frequency filter to generate positive- and negative-frequency pre-distortion signals, respectively, to account for asymmetries in the amplifier characteristics. In another embodiment, only one of the differentiated waveforms is applied to an asymmetric filter (i.e., either a positive-frequency filter or a negative-frequency filter).
Owner:COMMSCOPE TECH LLC
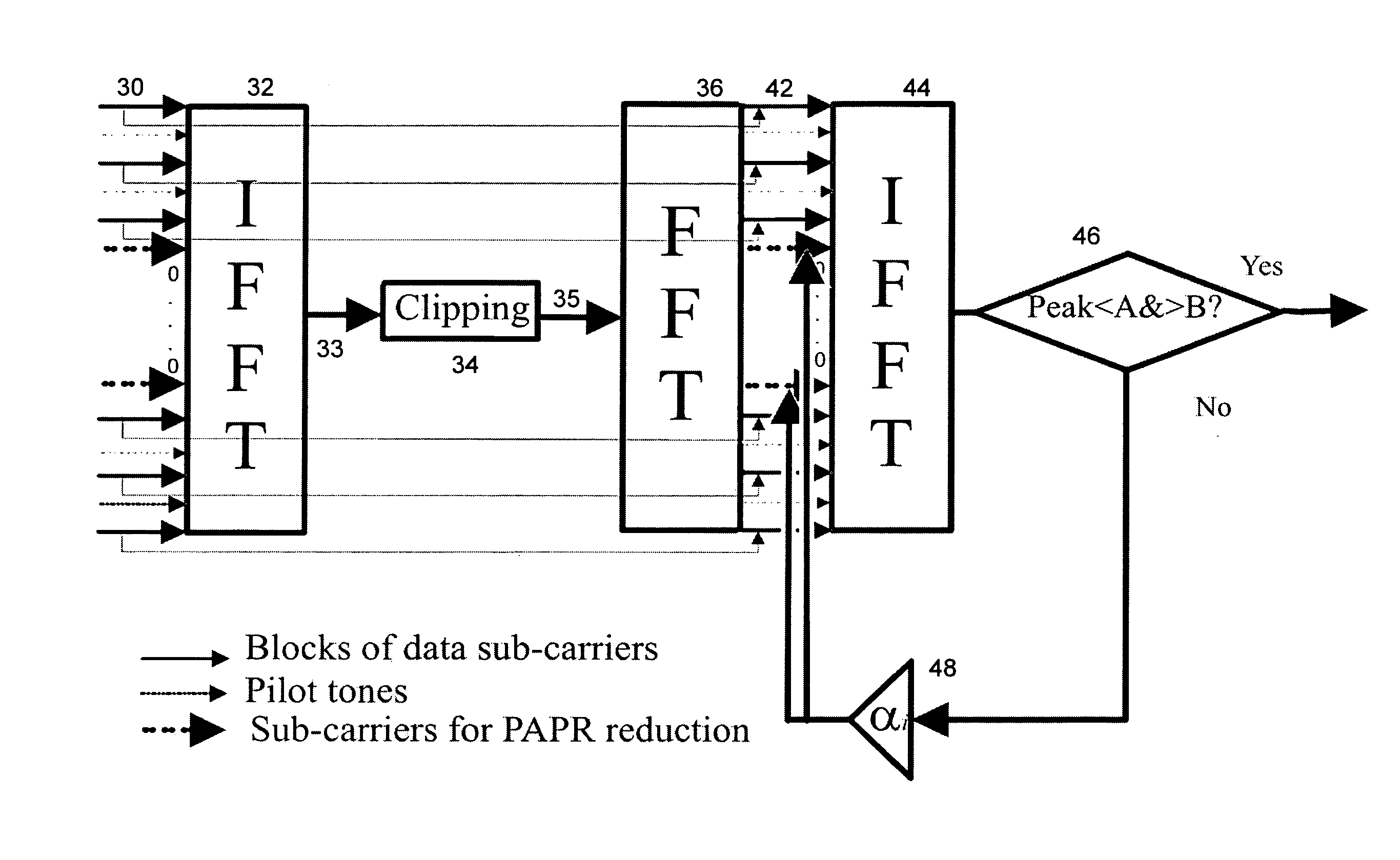
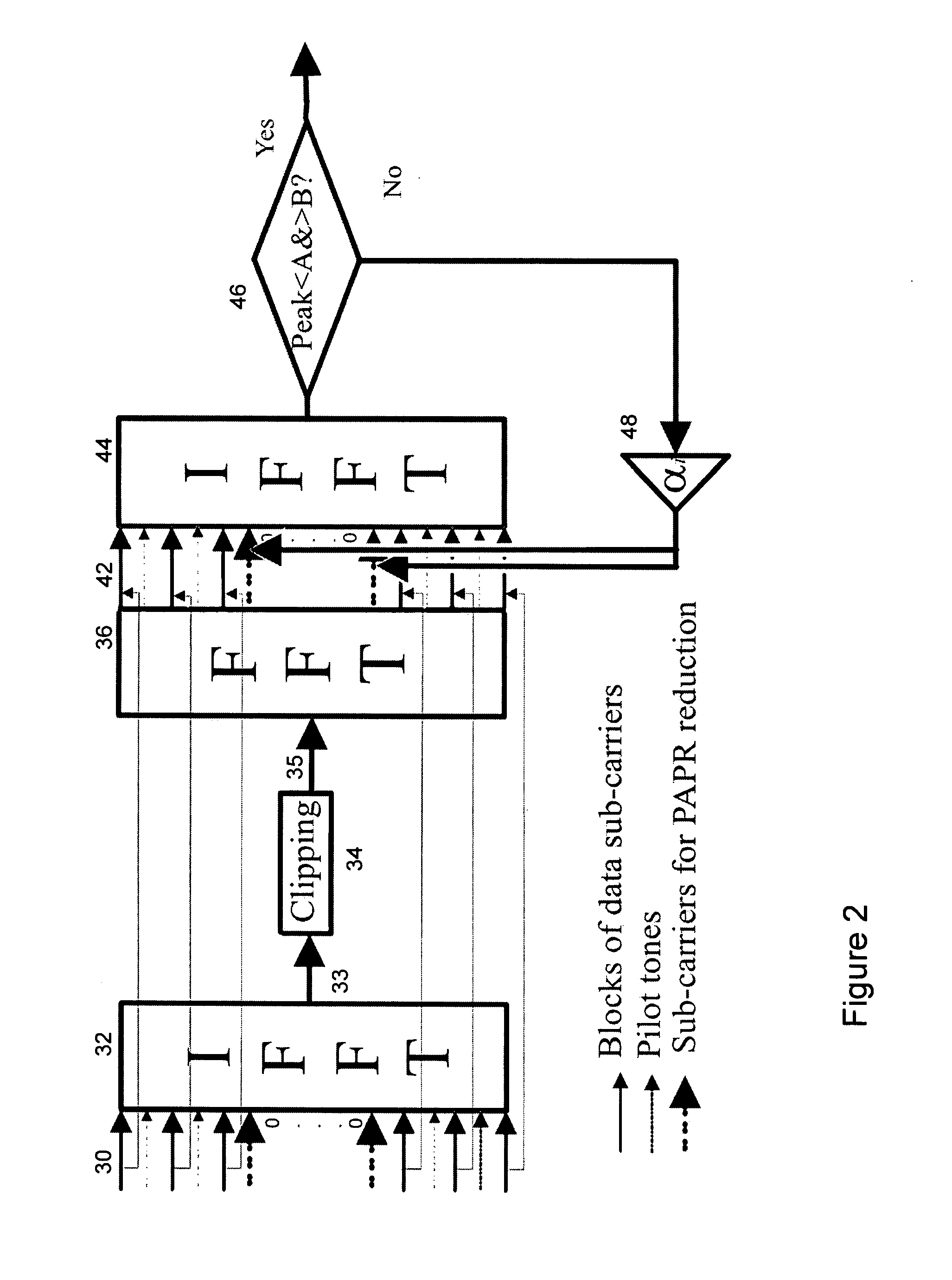
Peak-to-average-power reduction of OFDM signals
InactiveUS20080112496A1Improvement in Peak-to-Average-Power ratioEffect of clipping is minimisedAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionPower amplifiersTime domainAudio power amplifier
A method of processing an Orthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplex (OFDM) signal having a plurality of data carriers and a plurality of unused carriers is disclosed. The method comprises transforming an original frequency-domain OFDM signal into a time domain signal and simulating the effect of a non-linear amplifier on the time-domain signal to provide a potentially distorted time domain signal. The potentially distorted time domain signal is transformed into a potentially distorted frequency domain signal and at least some of any values of the data carriers in the potentially distorted frequency domain signal are restored with corresponding values from the original frequency domain signal. At least some of the unused carriers in the at least partially restored frequency domain signal are scaled with a scaling factor. The scaled frequency domain signal is transformed into a temporary time domain signal and the temporary time domain signal is analysed for the presence of a peak or near zero amplitude value that would lead to distortion by said amplifier. If the signal includes such a peak or near zero value, the scaling, transforming and analysing are repeated with an increased scaling factor.
Owner:UNIV COLLEGE DUBLIN NAT UNIV OF IRELAND DUBLIN
Radio frequency (RF) amplifier utilizing a predistortion circuit and related techniques
InactiveUS8610499B2Eliminate Bandwidth LimitationsReduce and even eliminate bandwidth limitAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAmplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationEngineeringRadio frequency
An apparatus and technique for operating an RF amplifier having a pre-distortion processor and a drain modulation circuit includes generating a compensating drain bias signal having a value which is a function of an RF input signal, a sampled RF output signal and a sampled drain bias signal. The compensating drain bias signal is applied to the RF amplifier. By sampling both the drain bias signal and the RF output signal and providing drain feedback and RF output feedback signals to a pre-distortion processor, RF amplifier distortions can be linearized enabling the RF amplifier to operate over a bandwidth which exceeds the bandwidth of the drain modulation circuit (i.e., the RF bandwidth can exceed the bandwidth of the drain modulator).
Owner:AURIGA MEASUREMENT SYST
Augmented twin nonlinear two-box modeling and predistortion method for power amplifiers and transmitters
ActiveUS20150162881A1Improve accuracyReduce complexityAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifiers with memory effect compensationAudio power amplifierBox modeling
The augmented twin nonlinear two-box modeling and predistortion method for power amplifiers and transmitters provides power amplifier distortion modeling and predistortion linearization. A memoryless nonlinearity is combined with a memory polynomial function that includes cross-terms. The method can utilize an augmented forward twin-nonlinear two-box model, an augmented reverse twin-nonlinear two-box model, or alternatively, an augmented parallel twin-nonlinear two-box model. The present two-box models are validated in modeling and predistortion applications. Measurement results demonstrate the superiority of the present two-box models with respect to conventional state of the art models. The present two-box models lead to better accuracy with reduced complexity.
Owner:KING FAHD UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM AND MINERALS
Efficient method and means for integration of power control and predistortion in a transmitter
ActiveUS20060158254A1Efficient integrationLinearization of amplifier performanceAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAmplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationEngineeringRadio frequency
A radio-frequency (RF) transmitter power amplifier circuit provides for practically linear performance by predistorting the amplifier input signals to compensate for amplifier distortion at high power levels, and provides a fine degree of control of amplifier power needed to handle complex modulation schemes with widely and rapidly varying power requirements. A predistortion database (20) contains gain and phase corrections for various transmission types and a separate automatic gain control database (38) contains fine amplifier gain corrections. A real-time processor (26) combines the two types of corrections and applies them to the amplifier input signals, and a background processor (16) continually updates both databases in accordance with a programmable priority scheme. Integration of predistortion and amplifier power control is achieved in a manner that minimizes adverse effects of one type of control on the other. One feature of the invention provides for rapid convergence of the predistortion correction.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
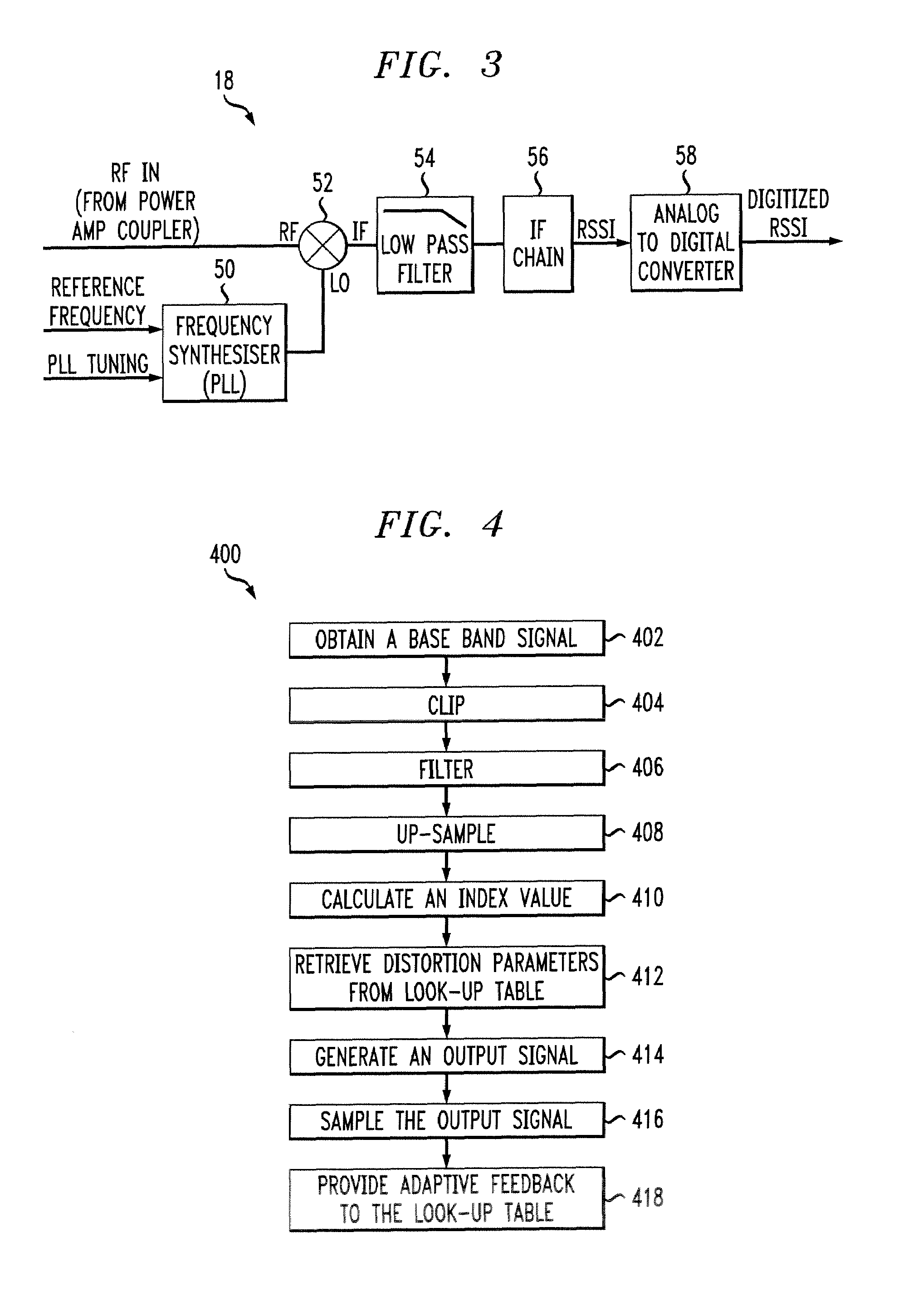
Amplifier failure detection apparatus
InactiveUS20080068191A1Accurate fault detectionSure easyEmergency protective circuit arrangementsLookup table adaptive predistortionAudio power amplifierEngineering
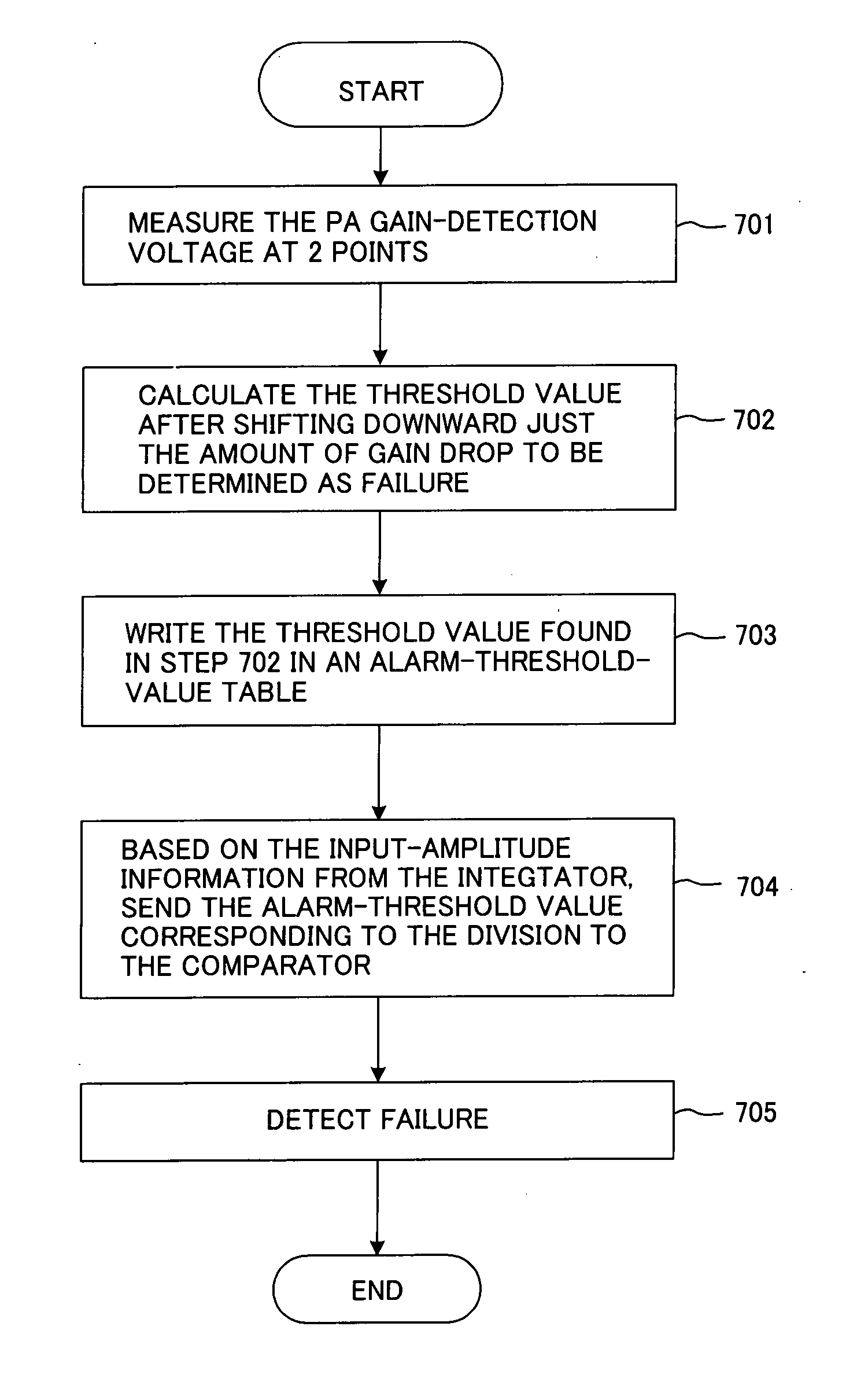
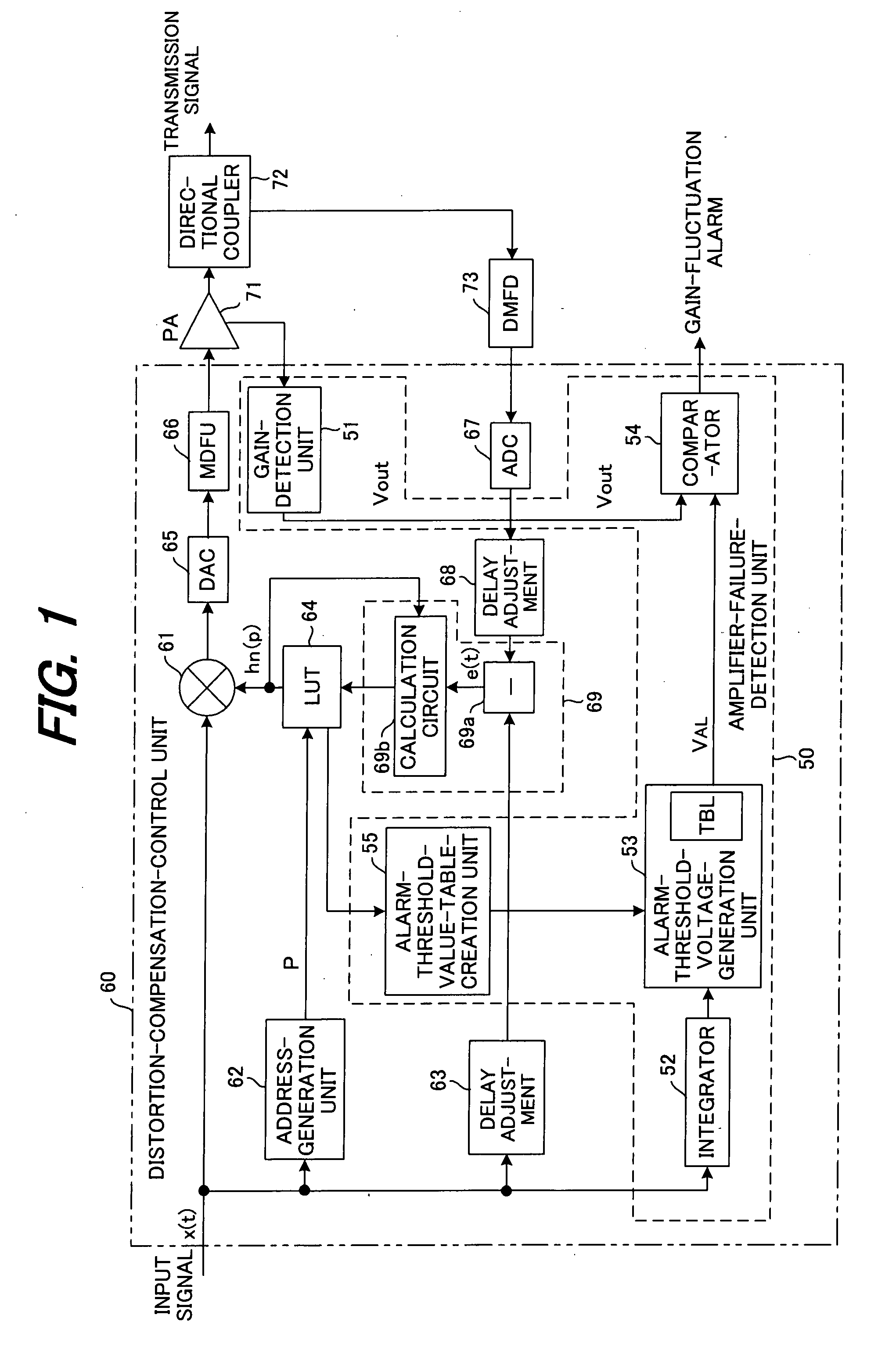
An amplifier failure detection apparatus for a radio transmitter that has a function for compensating for amplifier distortion of the radio transmitter and a function for determining amplifier failure has occurred by detecting that the gain of an amplifier has dropped a set level or more, in which: a gain-detection unit detects the gain of the amplifier; an alarm-detection-level-generation unit, which has a table for storing alarm-detection levels that correspond to input-amplitude levels, generates an alarm-detection level that corresponds to an input-amplitude level; and a comparison unit compares the gain detected by the gain-detection unit with the alarm-detection level, and generates an alarm based on the comparison results.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
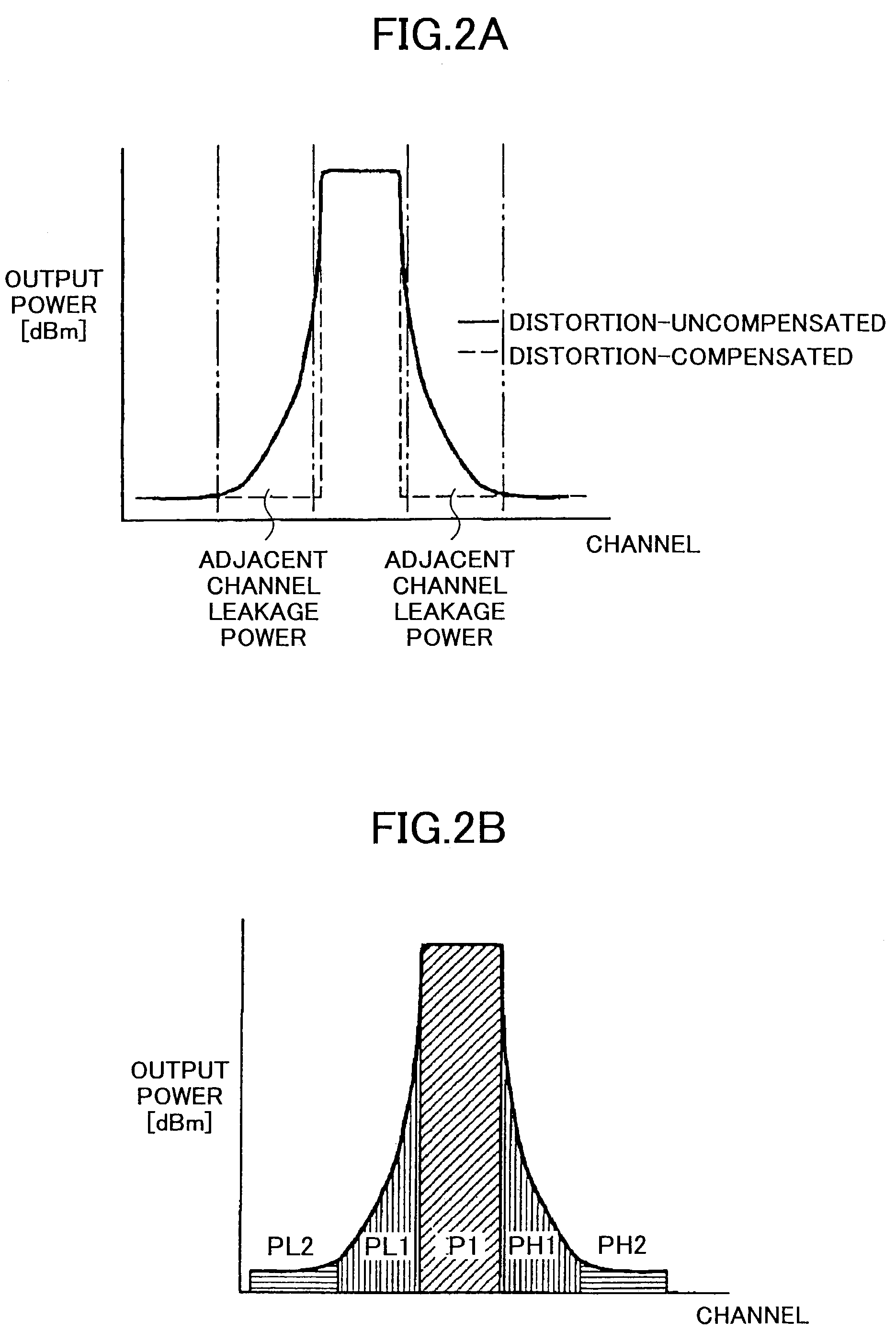
Method and apparatus for reducing adjacent channel power in wireless communication systems
InactiveUS7409007B1Reduce adjacent channel powerEfficient and reliableEnergy efficient ICTSecret communicationAudio power amplifierCommunications system
This invention relates to a method and apparatus for reducing adjacent channel power in wireless communication systems. More particularly, the present invention is directed to a system for digitally and adaptively pre-distorting a signal that includes applying a correction to the signal before it is applied to the input of an amplifier such that the correction is equal and opposite to anticipated distortion produced by the amplifier. Thus, the correction and the amplifier distortion cancel one another resulting in a system with an overall linear transfer characteristic. In these circumstances, the adjacent channel power is desirably reduced.
Owner:RPX CORP +1
Amplifier predistortion and autocalibration method and apparatus
ActiveUS7915954B2Improve performanceReduce the amount of distortionAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAudio power amplifierPhysics
Methods and apparatus for amplifier AM and PM predistortion and autocalibration. AM and PM amplifier distortion can be corrected using predistortion. The AM and PM distortion characteristics of the amplifier are determined using an autocalibration technique. The amplifier characteristics can be stored in distinct look up tables. Alternatively, the inverse of the amplifier characteristics can be stored in distinct look up tables. Signals that are to be amplified are characterized in polar format having a phase component with a normalized magnitude and a magnitude component. The phase component can be predistorted by applying the inverse of the PM distortion characteristics to the signal. Similarly, the magnitude component can be predistorted by applying the inverse of the AM distortion characteristics to the signal. The predistorted phase component can be amplified using the previously characterized amplifier. The predistorted magnitude component can be used to set the gain of the previously characterized amplifier.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Power amplifier pre-distortion
The present invention is directed to systems and methods for reducing the distortion of power amplifiers. In particular, methods and systems are described that enable a determination of a pre-distortion correction signal to be determined, which when added to the nominal signal, a reduction in the distortion of the power amplifier results. In addition, methods and systems are described that enable calibration of individual power amplifiers to be accomplished for use with the above described approach. More specifically, the methods and systems are described for use in a MIMO application. These approaches may be applied to on-chip power amplifiers, off-chip power amplifiers, or any combination thereof.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Frequency-dependent magnitude pre-distortion on non-baseband input signals for reducing spurious emissions in communication networks
InactiveUS7266159B2Spurious emission can be reducedEmission reductionAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDifferentiatorAudio power amplifier
Pre-distortion, whose magnitude—and preferably phase—are frequency-dependent, is applied to a non-baseband input signal in order to reduce spurious emissions resulting from subsequent amplification of the signal. In preferred embodiments, the pre-distortion technique of the present invention is implemented in combination with the (frequency-independent) magnitude and phase pre-distortion technique described in U.S. patent application Ser. No. 09 / 395,490 (“the '490 application”), where the frequency-dependent pre-distortion corresponds to amplifier distortion that has a magnitude that is proportional to the frequency offset from the carrier frequency and a phase shift of ±90° on either side of the carrier frequency. Since these characteristics match those of a differentiator, a thorough correction of this part of the amplifier's distortion can be achieved using a differentiating circuit. Embodiments of the present invention may be implemented in the RF domain. Implementations may also be based on look-up tables that are adaptively updated to ensure optimal performance over time.
Owner:COMMSCOPE TECH LLC
Optimized digital correction for power amplifier distortion and quadrature error
InactiveUS20100111221A1Excessive distortionReduce distortion problemsModulated-carrier systemsSecret communicationNonlinear distortionAudio power amplifier
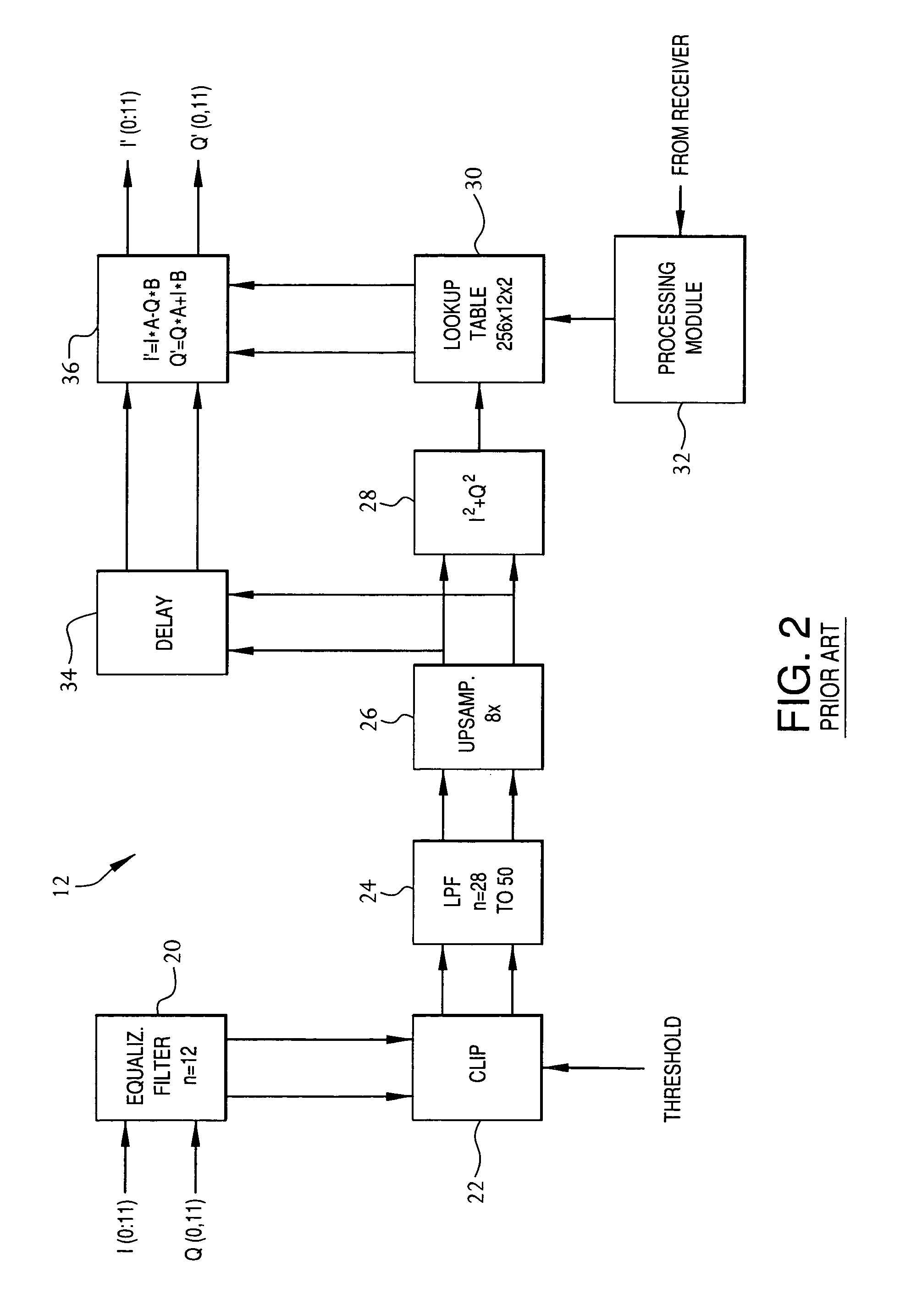
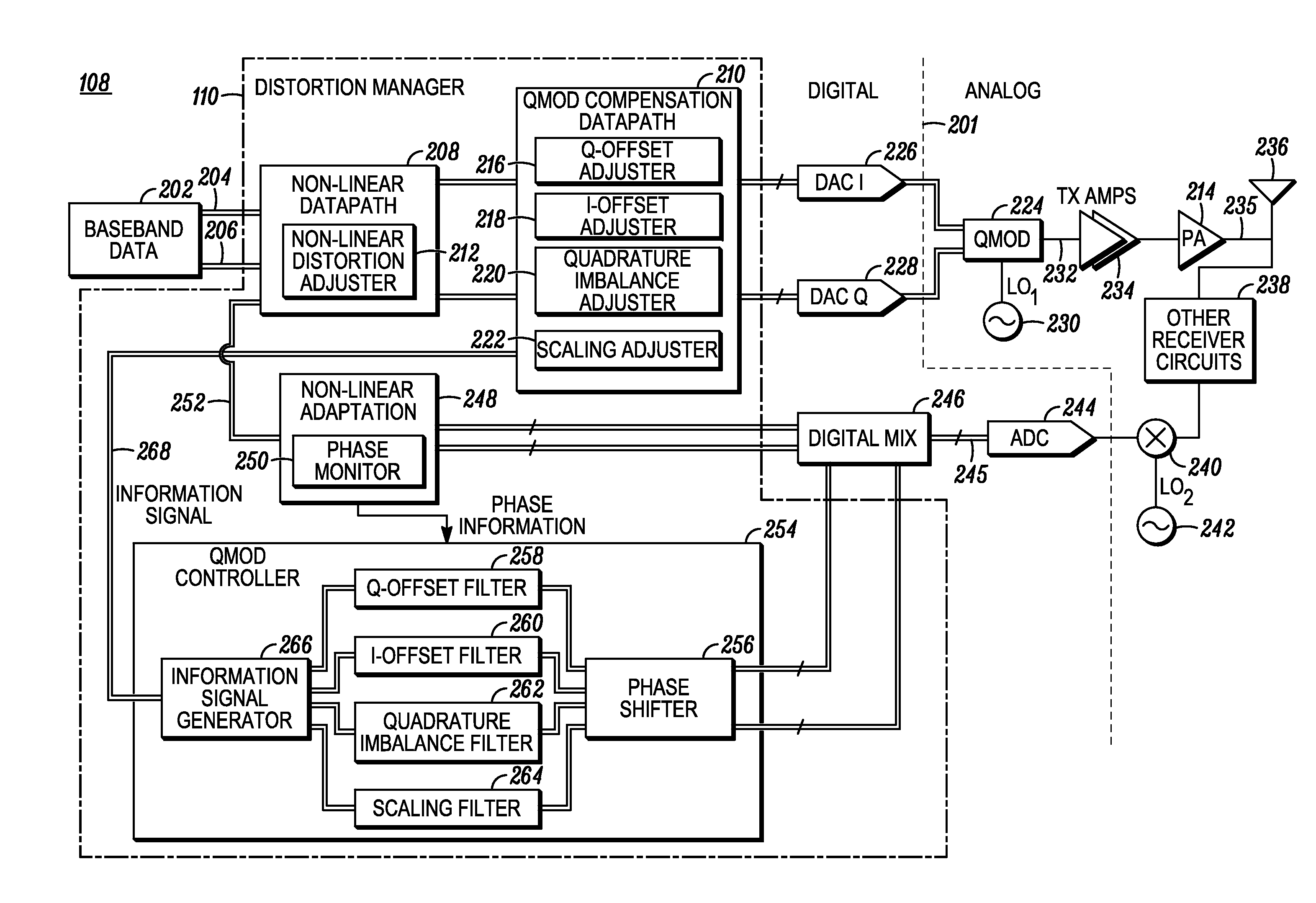
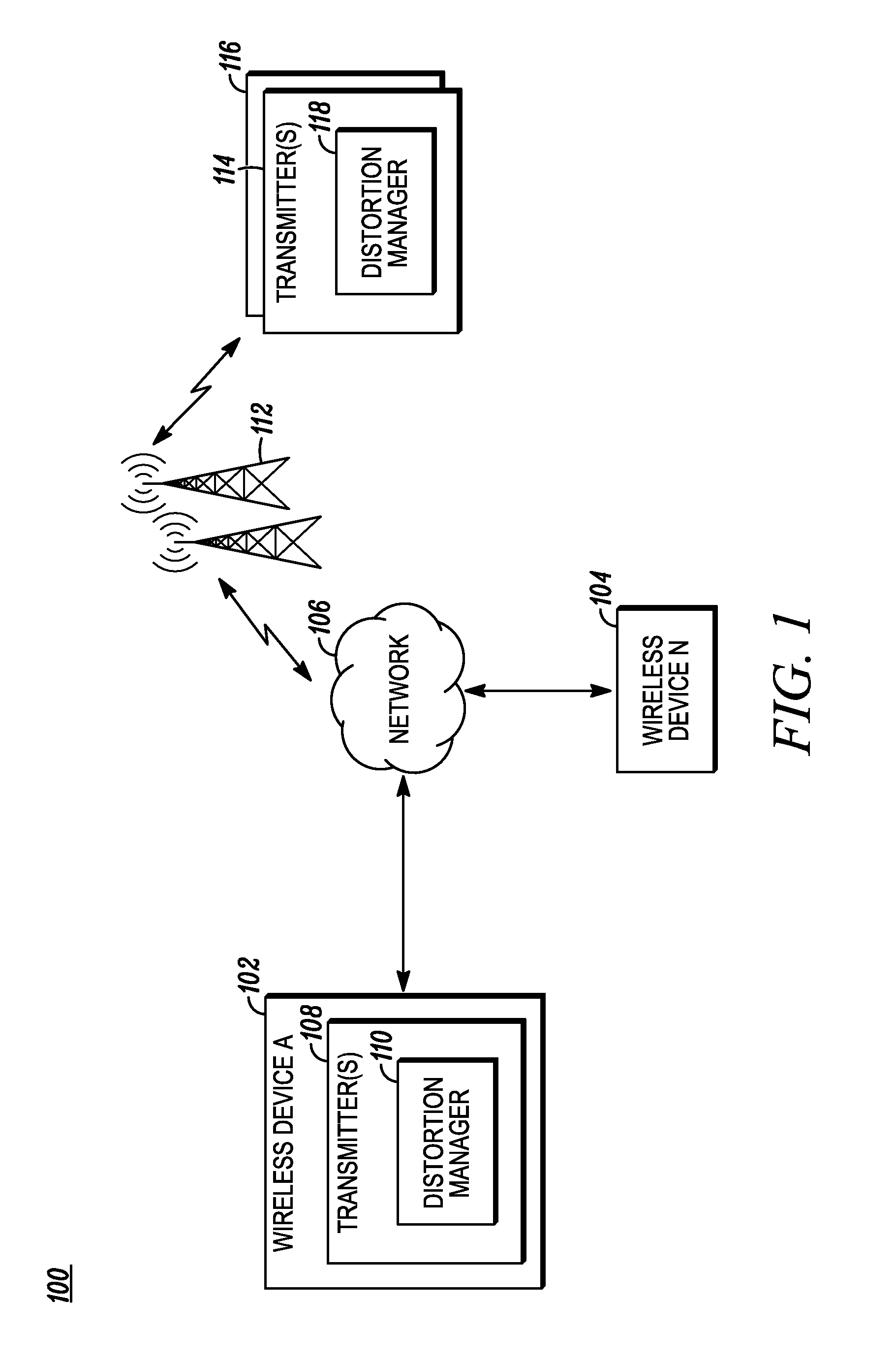
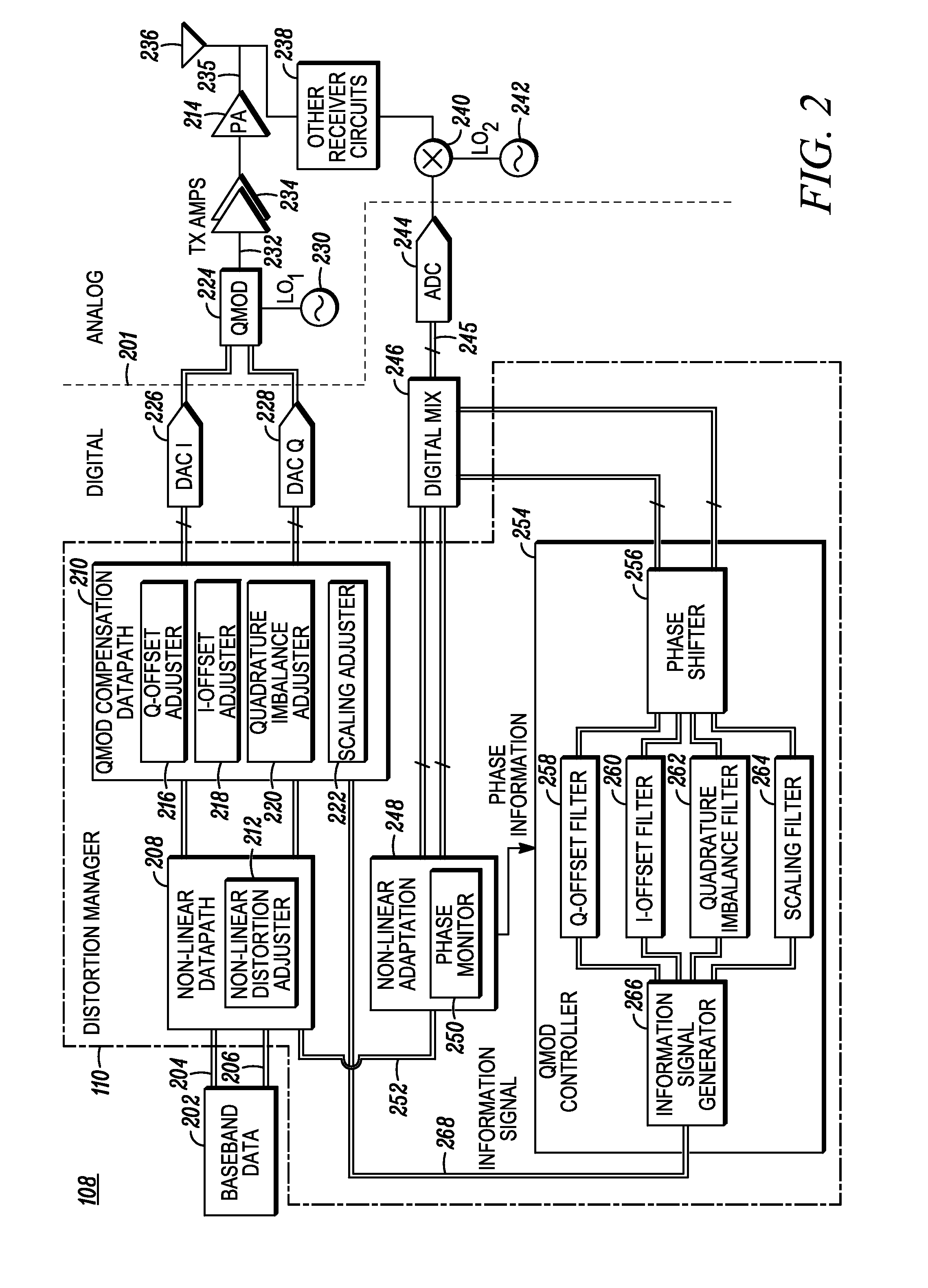
A method, wireless device, and wireless communication system manage quadrature and non-linear distortions in a transmitter system (100). A transmit data signal (235) is generated from a baseband data signal (202). The transmit data signal (235) can include one or more non-linear and / or quadrature distortions. An RF receiver circuit (238) receives the transmit data signal (235). A received signal, from the RF receiver circuit (238), includes a digital representation of the received transmit data signal (235). The received signal is statistically analyzed (404). A representation of each distortion of the one or more distortions is identified in the transmit data signal (235). At least one information signal (268) including an information set of distortion adjustments is generated. Distortion of the transmit data signal (235) is adjusted (410) based on the information set to reduce the one or more distortions in the transmit data signal (235).
Owner:MOTOROLA MOBILITY LLC
Digital predistortion for power amplifier
InactiveUS6882221B2Amplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAudio power amplifierGain compression
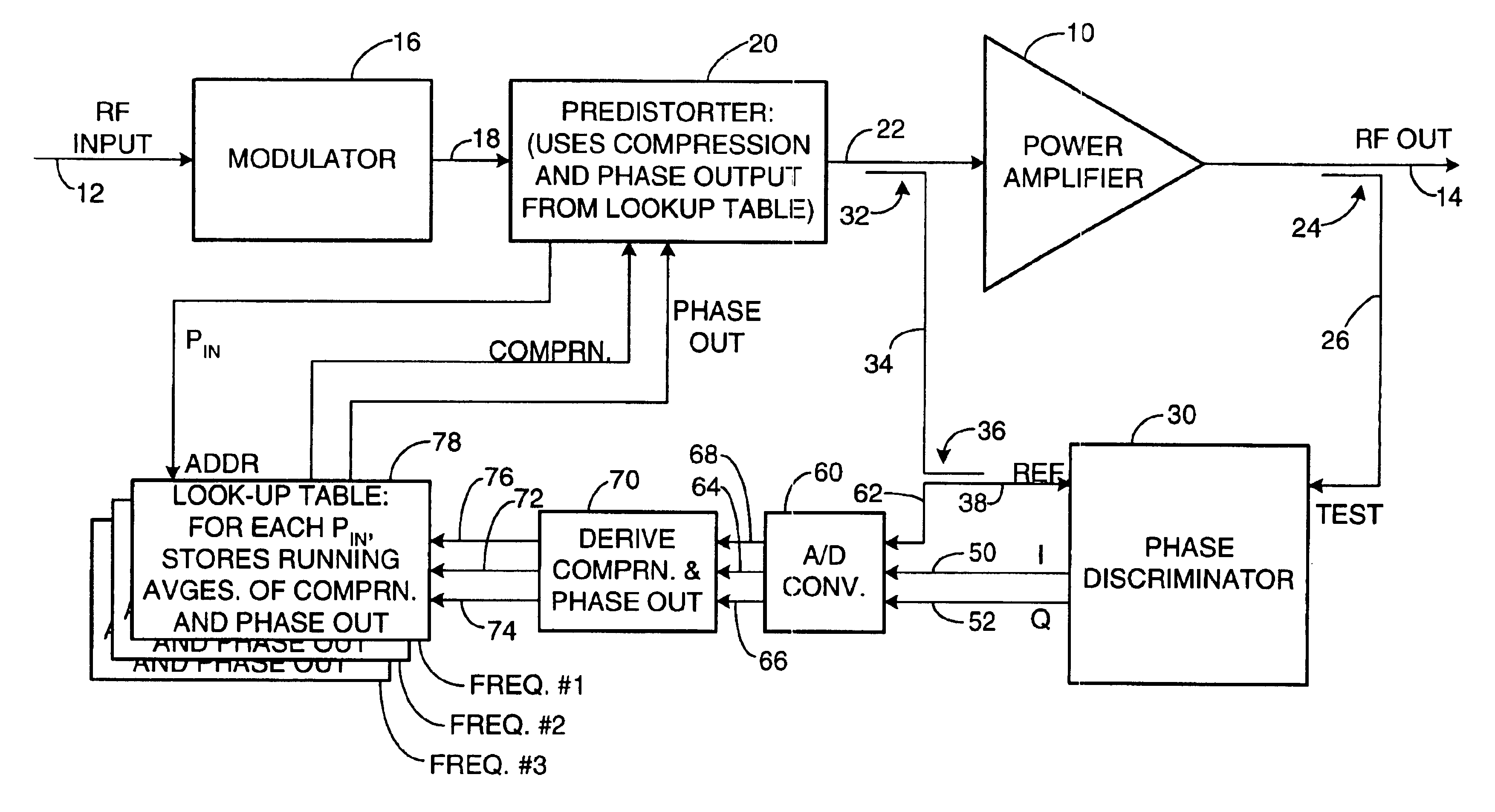
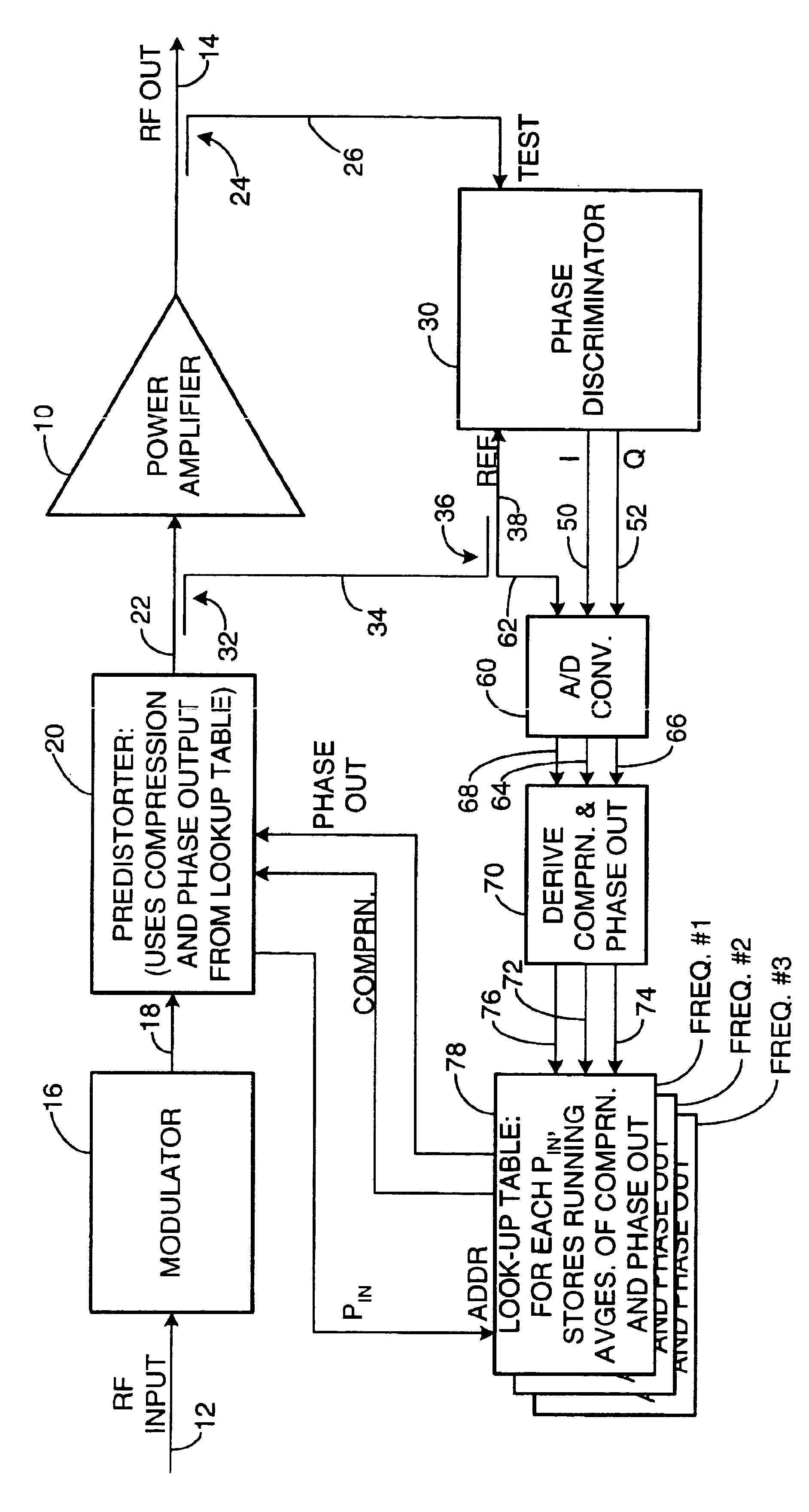
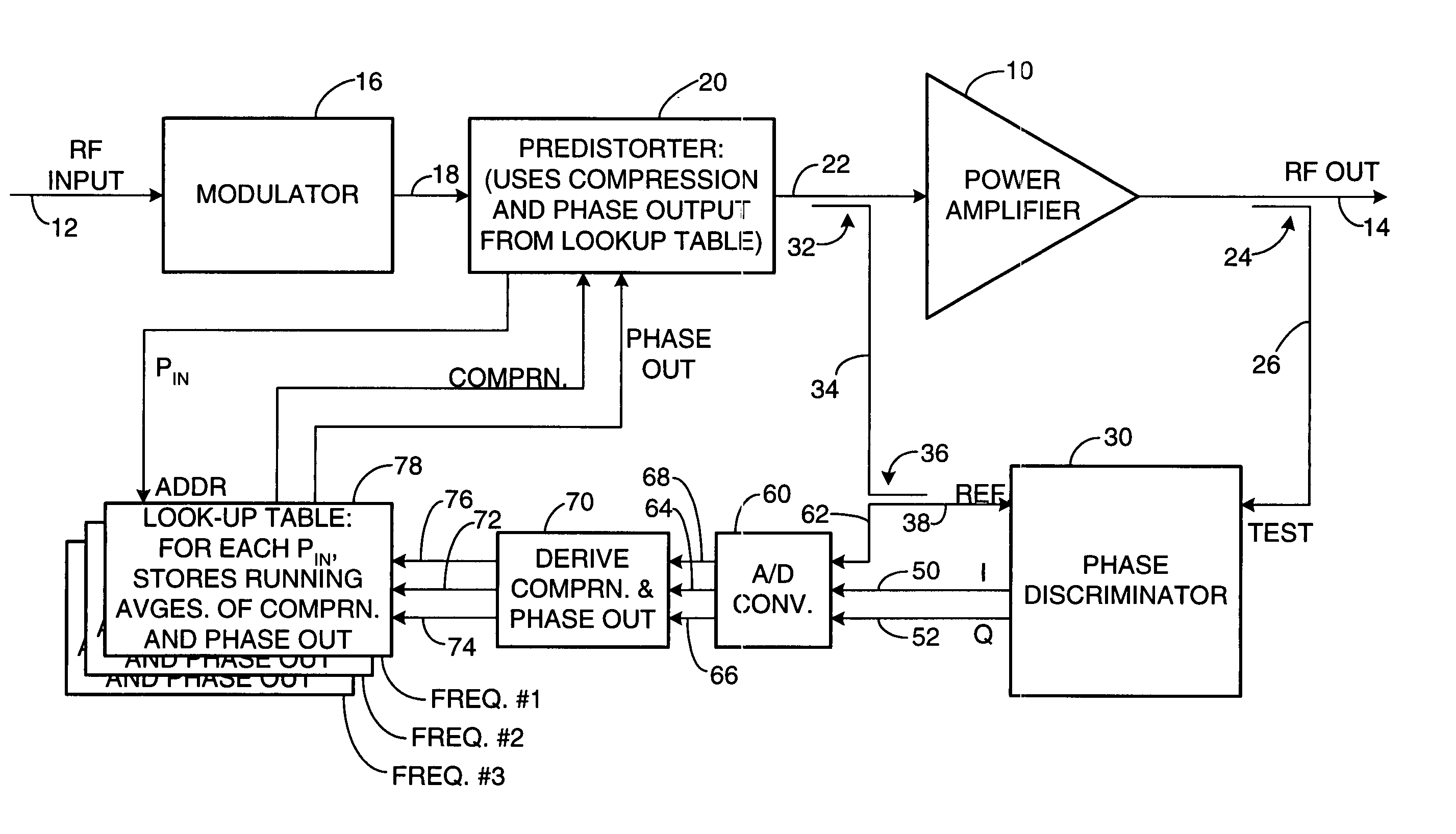
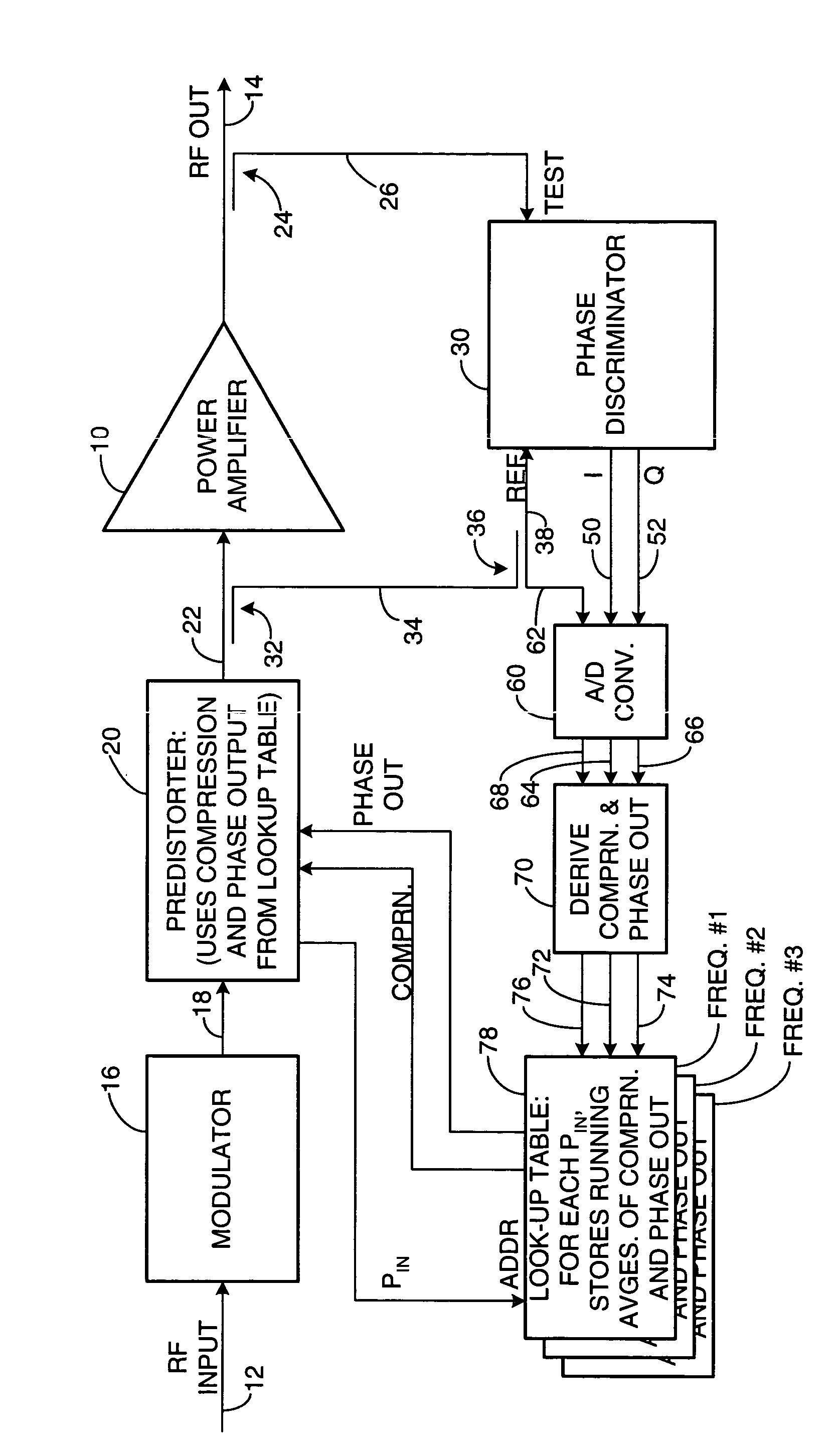
Apparatus and a corresponding method for predistorting an input signal applied to a radio frequency (RF) power amplifier, to compensate for amplifier distortion at high powers. The RF amplifier input and output signals are continuously monitored and difference signals are generated in an RF phase discriminator. The difference signals are converted to digital form and stored in a lookup table in the form of running averages of an RF amplifier gain compression value and an RF amplifier output phase value for each observed RF input power value. A predistorter module retrieves these values and predistorts the RF amplifier input by way of compensation.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
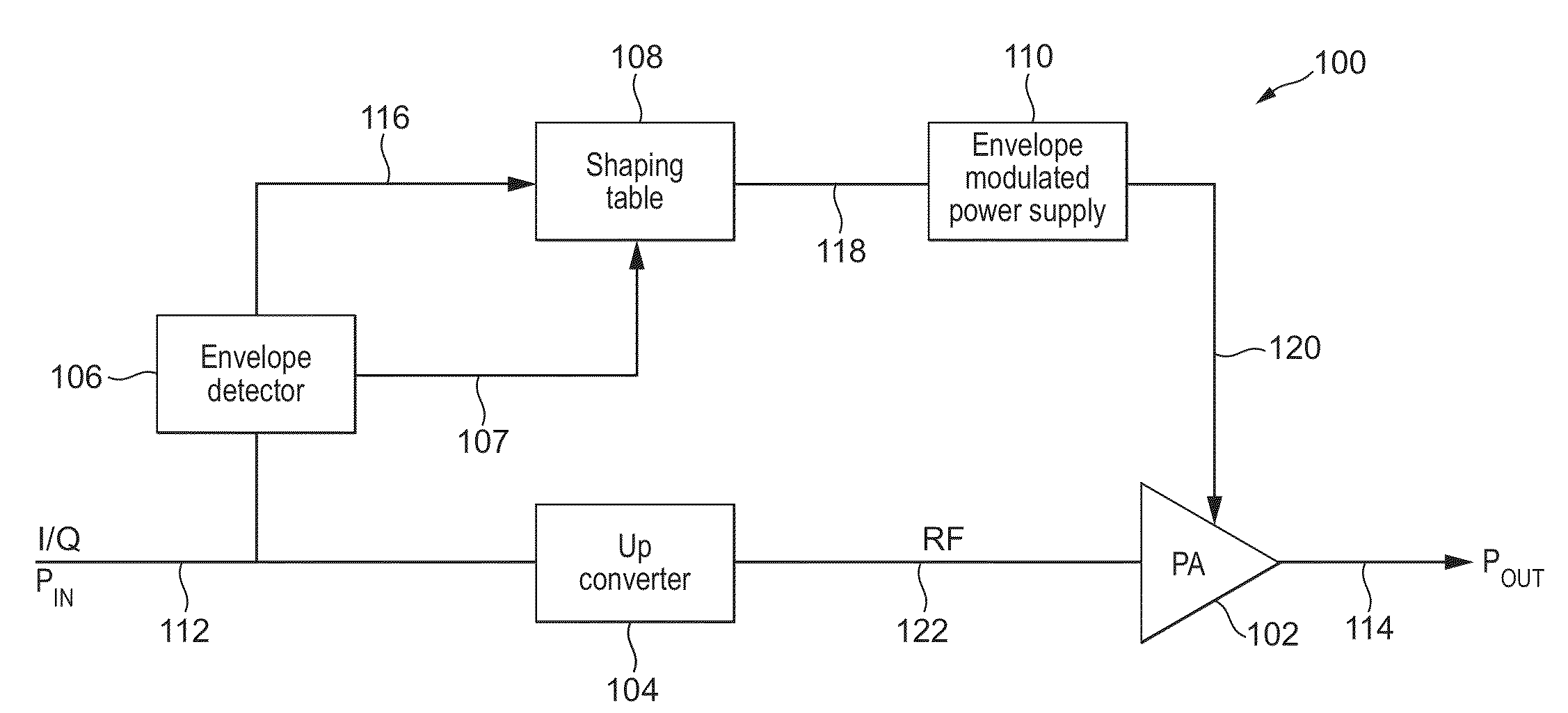
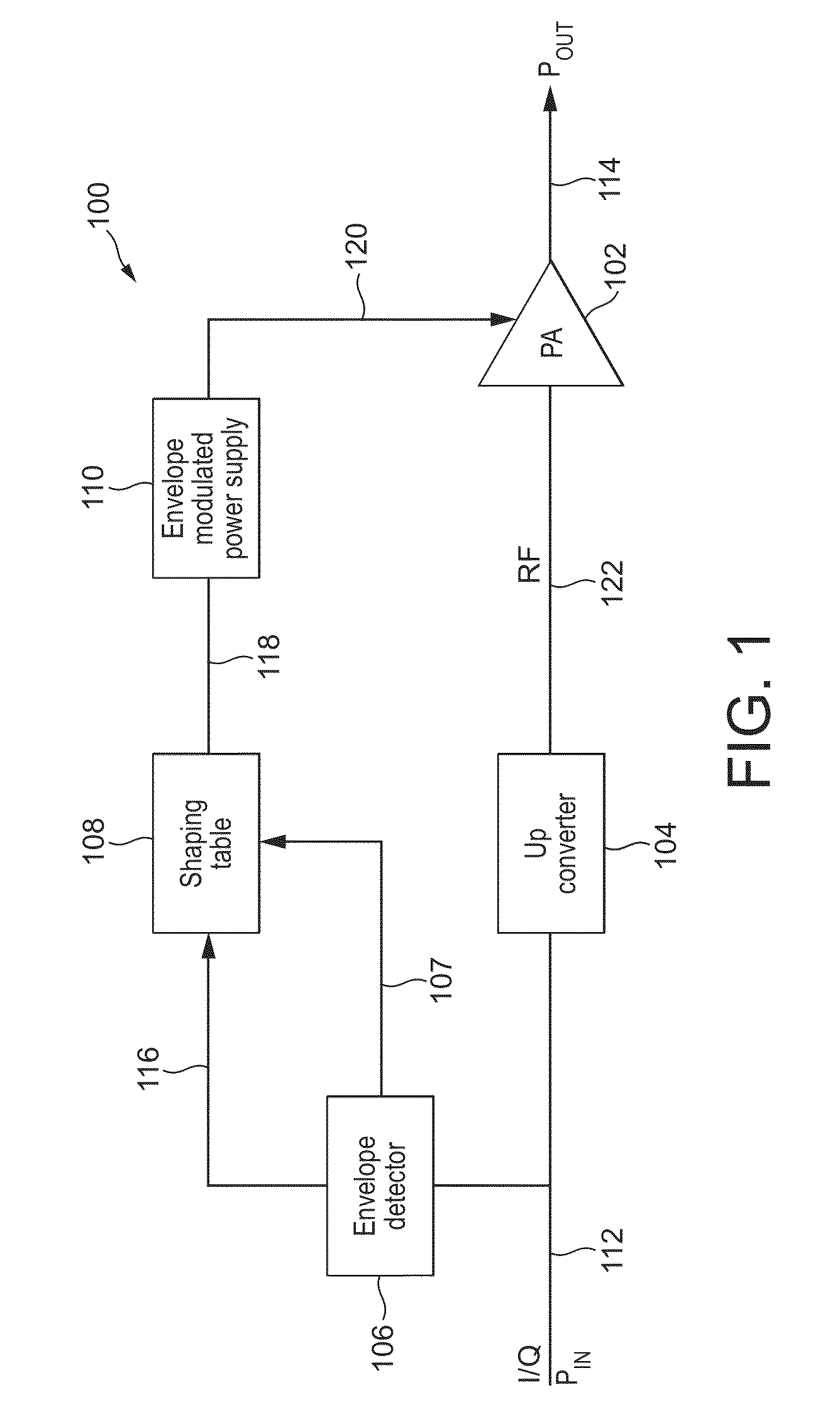
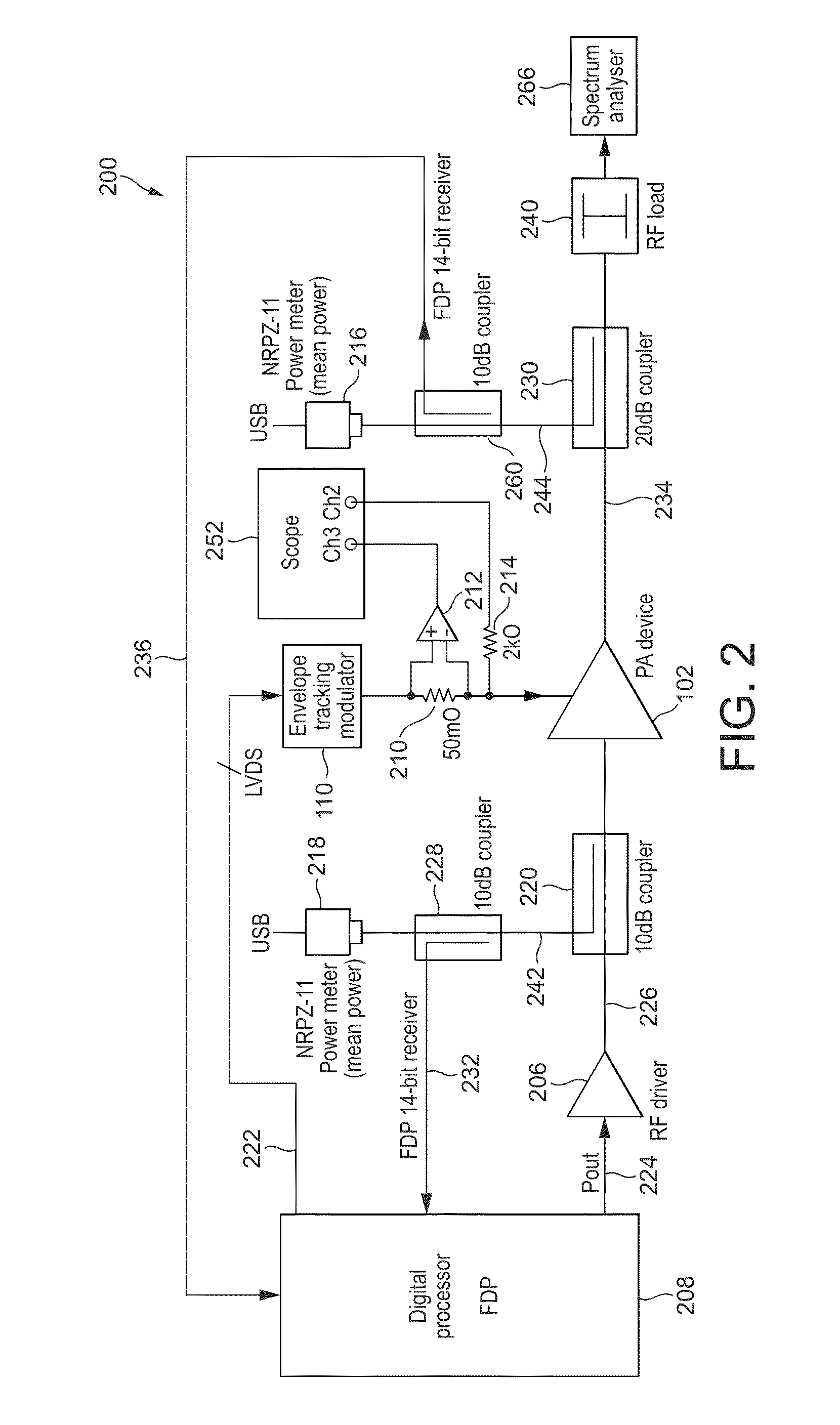
Systems and Methods for Adaptive Power Amplifier Linearization
ActiveUS20130082775A1Reduce distortion problemsAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAudio power amplifierControl signal
An exemplary system comprises a linearizer, a power amplifier, and a feedback block. The linearizer may be configured to use a predistortion control signal to add predistortion to a receive signal to generate a predistorted signal. The power amplifier may be configured to amplify power of the predistorted signal to generate a first amplified signal. The power amplifier may also add high side and low side amplifier distortion to the predistorted signal. The high side and low side amplifier distortion may cancel at least a portion of the predistortion. The feedback block may be configured to capture a feedback signal based on a previous amplified signal from the power amplifier, to determine high side and low side distortion of the captured feedback signal, and to generate the predistortion control signal based on the determined high side and low side distortion.
Owner:AVIAT U S
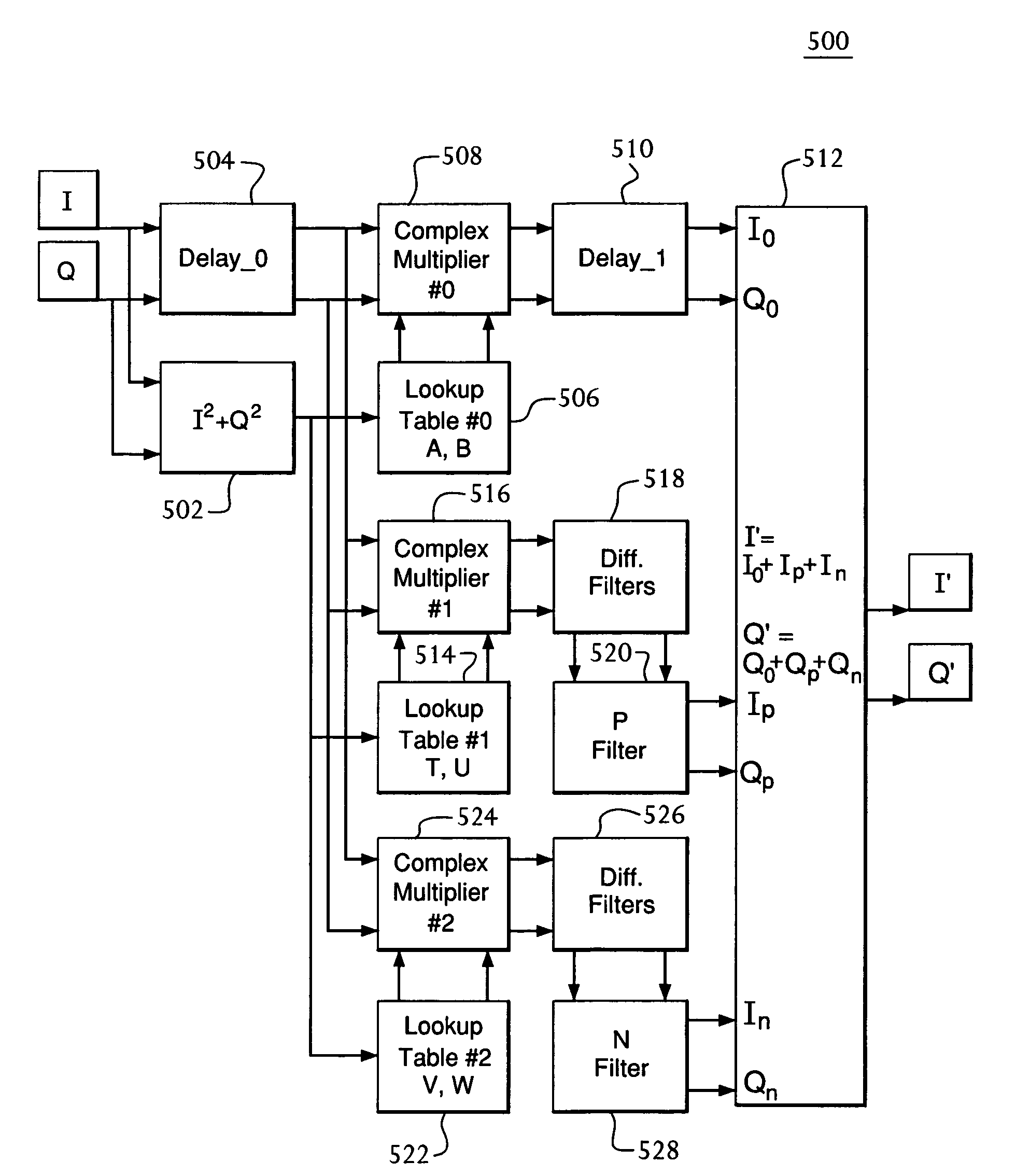
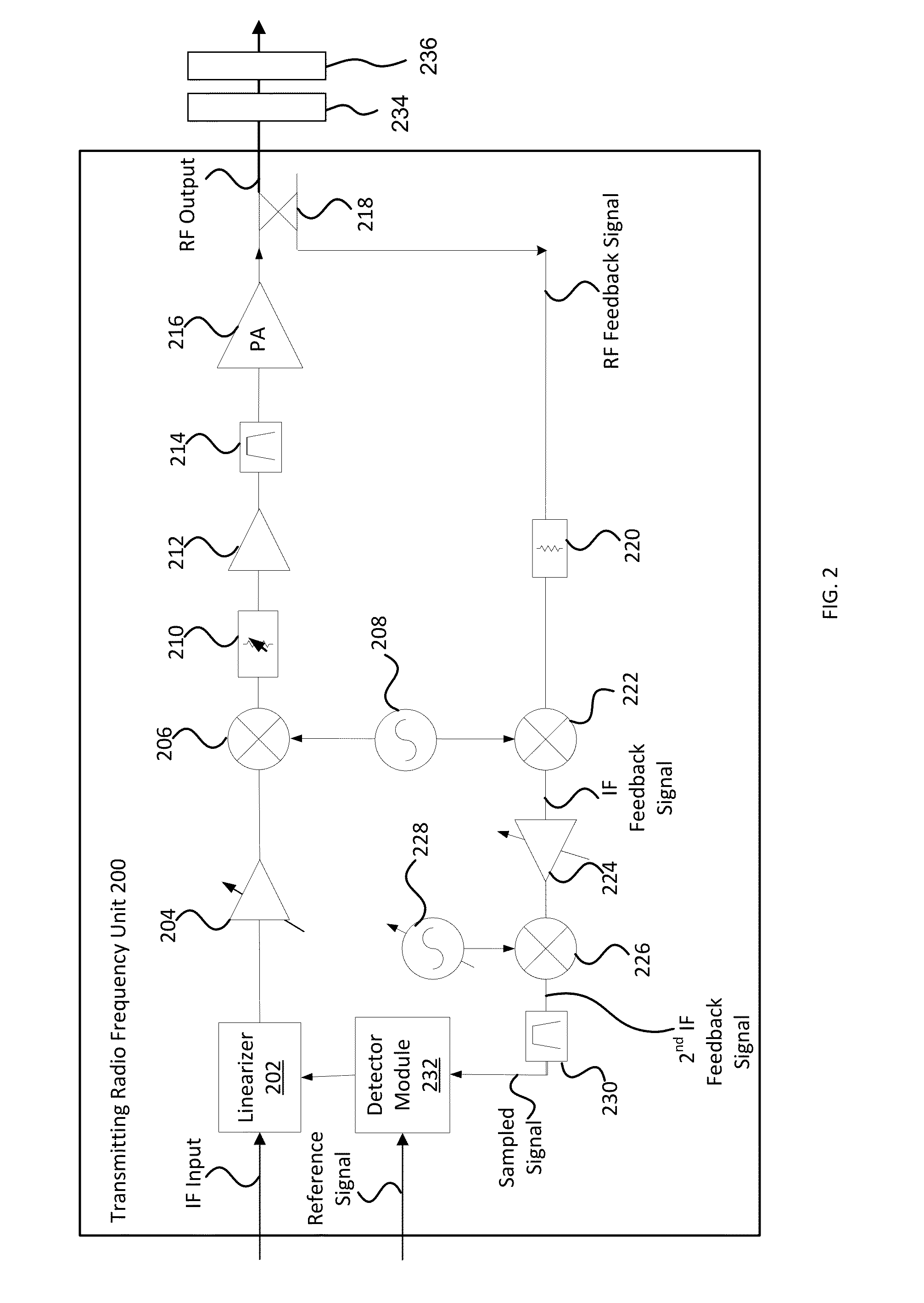
Dynamic characterisation of amplifier AM-PM distortion
ActiveUS9116183B2Spectral/fourier analysisAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAudio power amplifierReference Period
Owner:SNAPTRACK
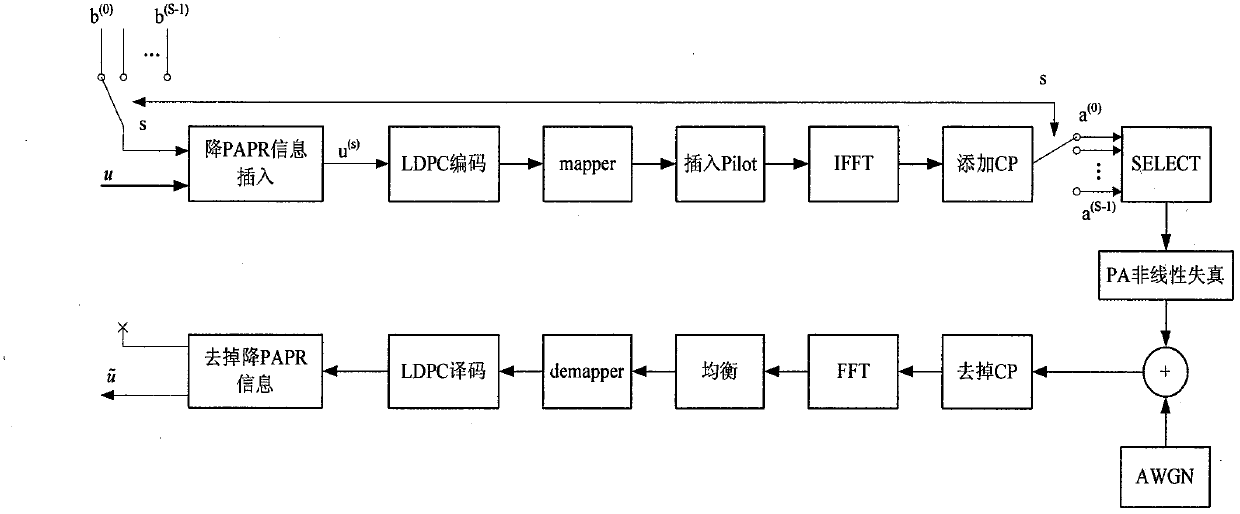
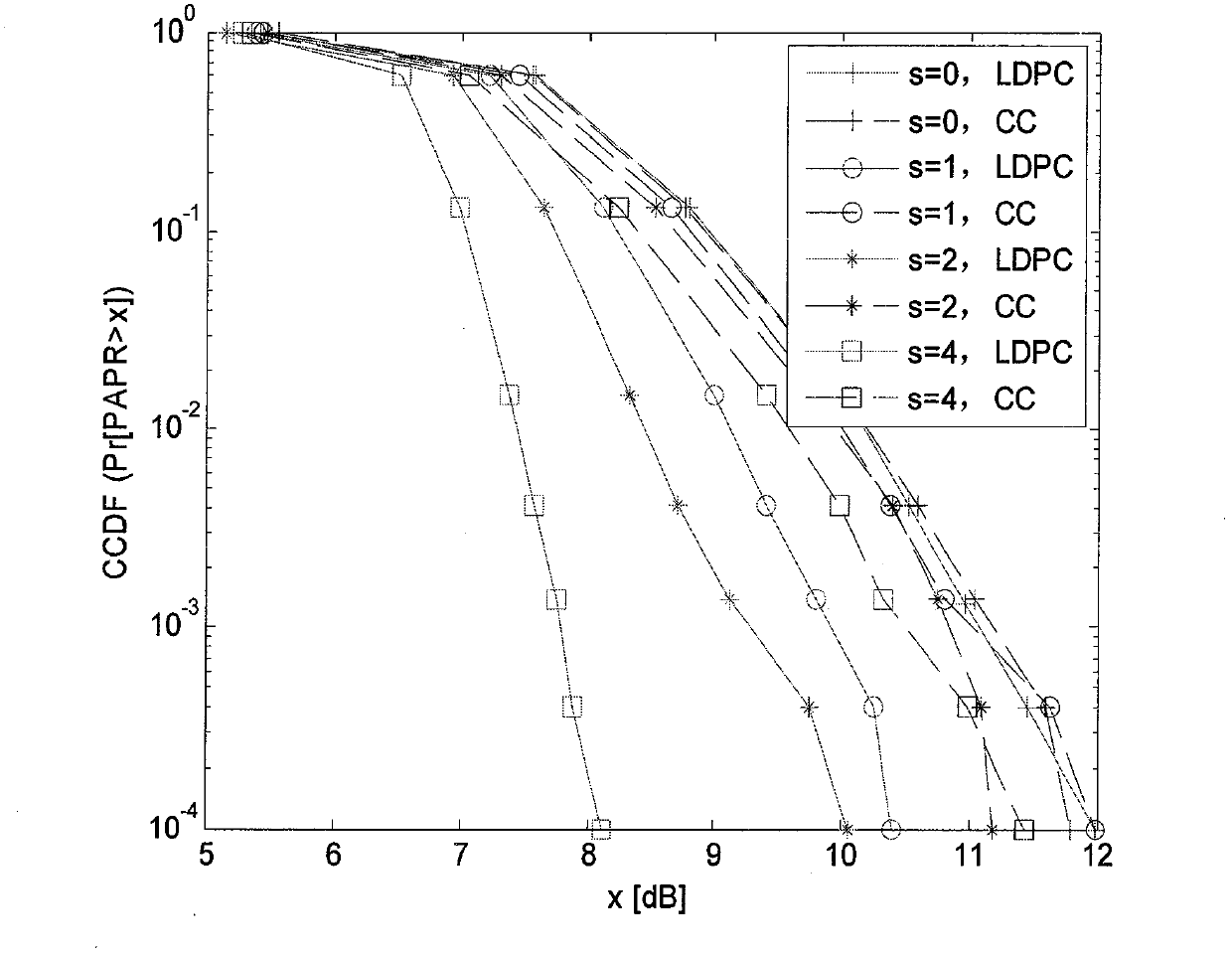
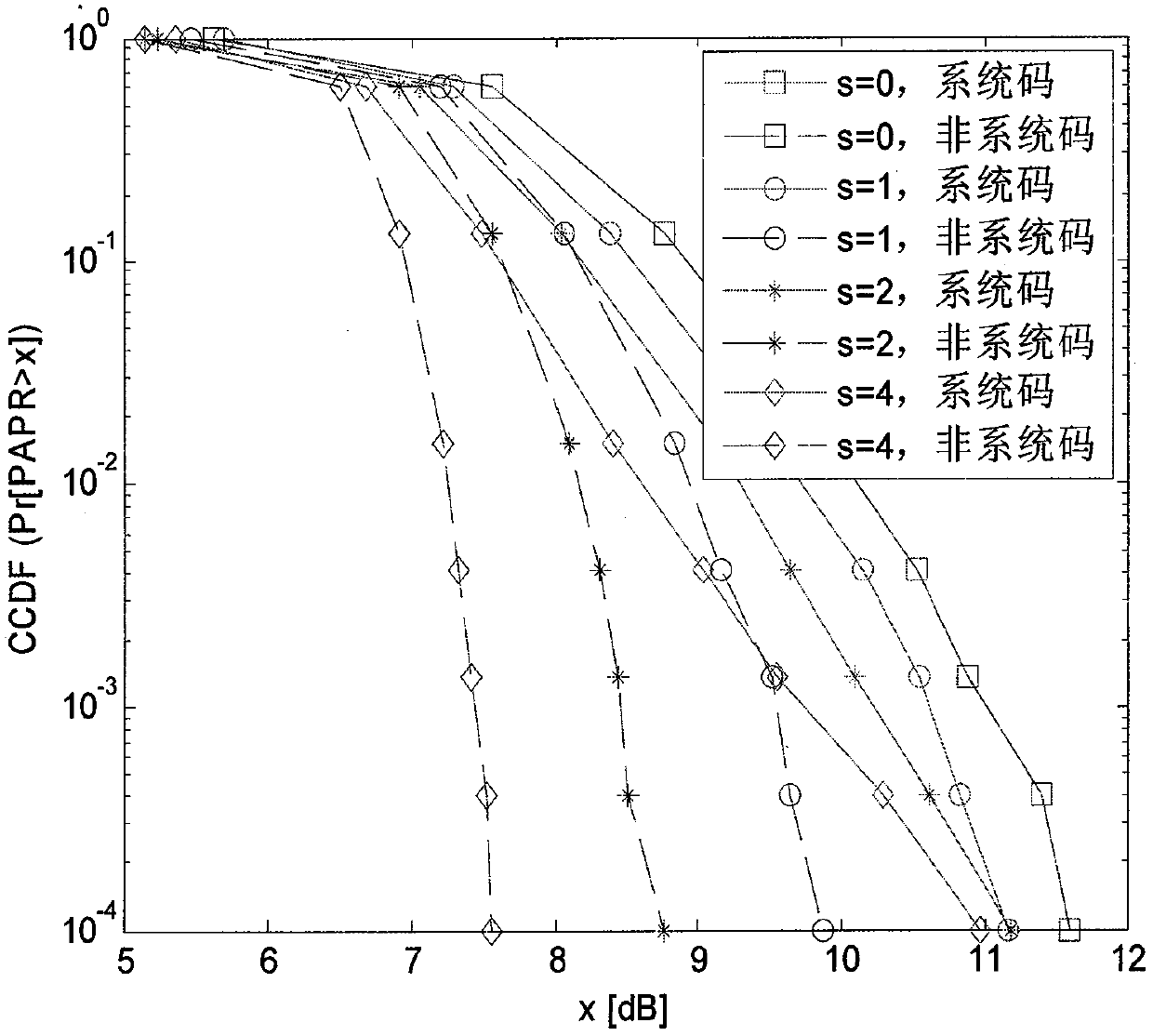
Method and device of lowering PAPR (peak to average power ratio) of 60 GHz communication system based on LDPC (low density parity check) coding mechanism
InactiveCN103124251AReduce complexityWide applicabilityError preventionMulti-frequency code systemsMillimeter wave communication systemsHigh density
The invention is specific to the problem of PAPR (peak to average power ratio) presented by OFDM (orthogonal frequency division multiplexing) modulation of 60 GHz millimeter wave communication system, and provides a method of lowering OFDM signal PAPR by using selectivity mapping combined with LDPC (low density parity check) to generate matrix high density character. By adding a little bit information, PAPR of the millimeter wave OFDM transmission signal is effectively lowered. In a big rate situation, a construction plan of improving an LDPC non-systematic code is provided, which can remarkably lower PAPR and effectively improve the transmission performance in the case of nonlinearity power amplifier distortion of 60 GHz millimeter waves system. Compared with the traditional coding scheme, the invention can remarkably lower PAPR, improve the transmission performance of millimeter wave signal in the presence of device nonlinearity and excels other coding scheme in aspect of anti-power amplifier PA nonlinearity. At the same time, the non-systematic code which is designed and constructed in the method and device can still have a fine performance when the coding rate is big. The arithmetic implementation of the non-systematic code is simple, and parallel computation can be used by the non-systematic code, so that the method and the device of lowering 60 GHz communication system PAPR (peak to average power ratio) based on LDPC (low density parity check) coding mechanism has great practical value in high-speed millimeter waves OFDM system.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
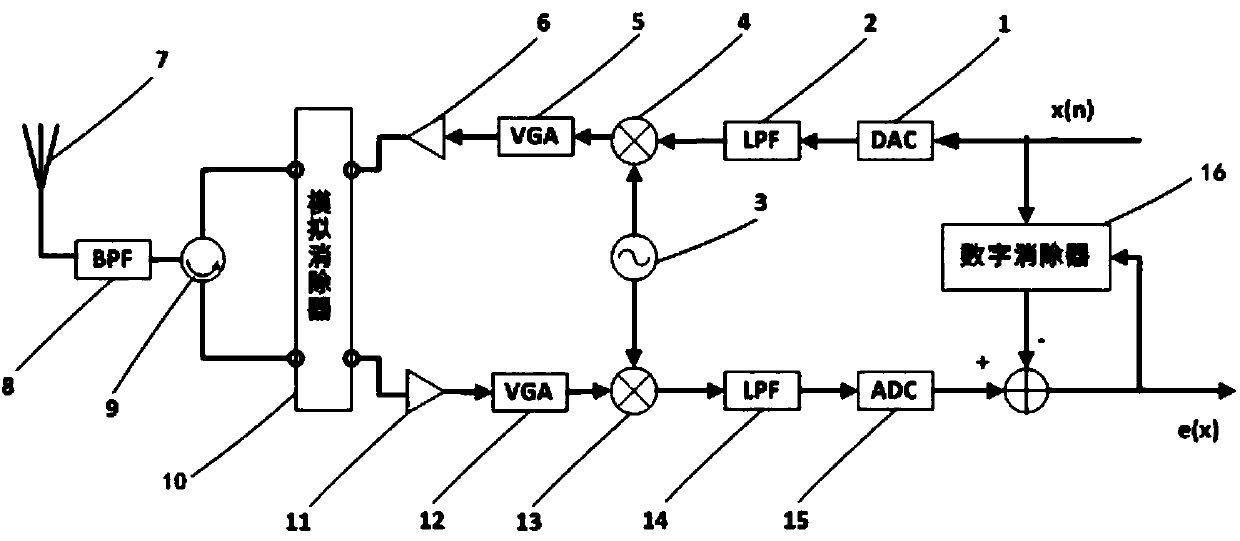
Digital self-interference eliminating method of zero-medium-frequency full-duplex transceiver
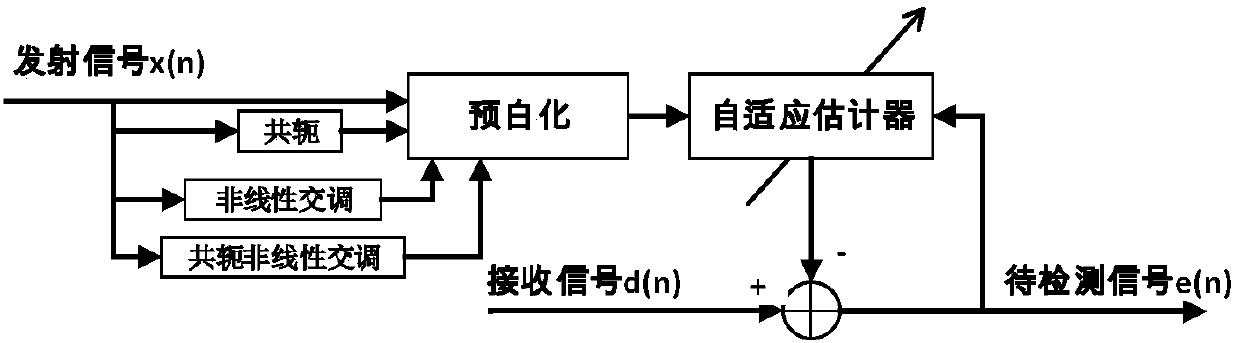
The invention discloses a digital self-interference eliminating method of a zero-medium-frequency full-duplex transceiver. The method is mainly applied to a digital self-interference eliminator, and the self-interference in the signal transmission link of the transceiver is estimated according to the digital signal obtained after sampling of the receiving end and known digital waveforms of the transmitting end. The method can eliminate self-interference generated by a transmitter under ideal components, the image self-interference generated by IQ imbalance of a transmitting chain up-conversionmodulator and a receiving chain down-conversion demodulator nonlinear self-interference generated by transmission chain power amplifier distortion, and image nonlinear self-interference caused by combination of IQ imbalance and power amplifier distortion. The method, compared with a traditional augmented complex LMS algorithm, can obtain an ideal self-interference eliminating effect and a relatively high convergence speed when the power of the transmitting signals is large, and the method is good in practicability.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
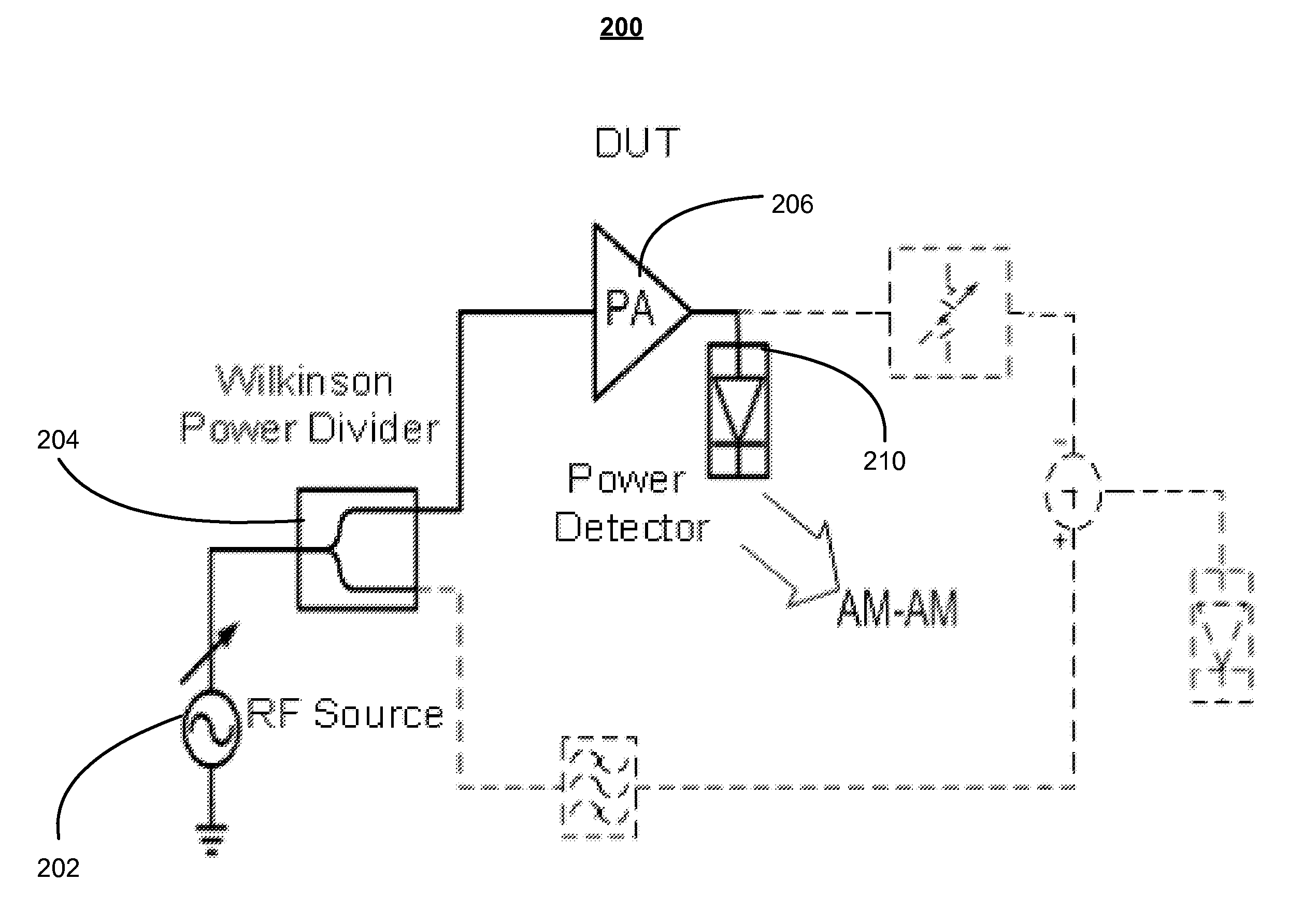
Systems and methods for distortion measurement using distortion-to-amplitude transformations
InactiveUS20110102080A1Accurately measure distortion effectReduce testing costsElectric devicesAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAudio power amplifierAmplitude response
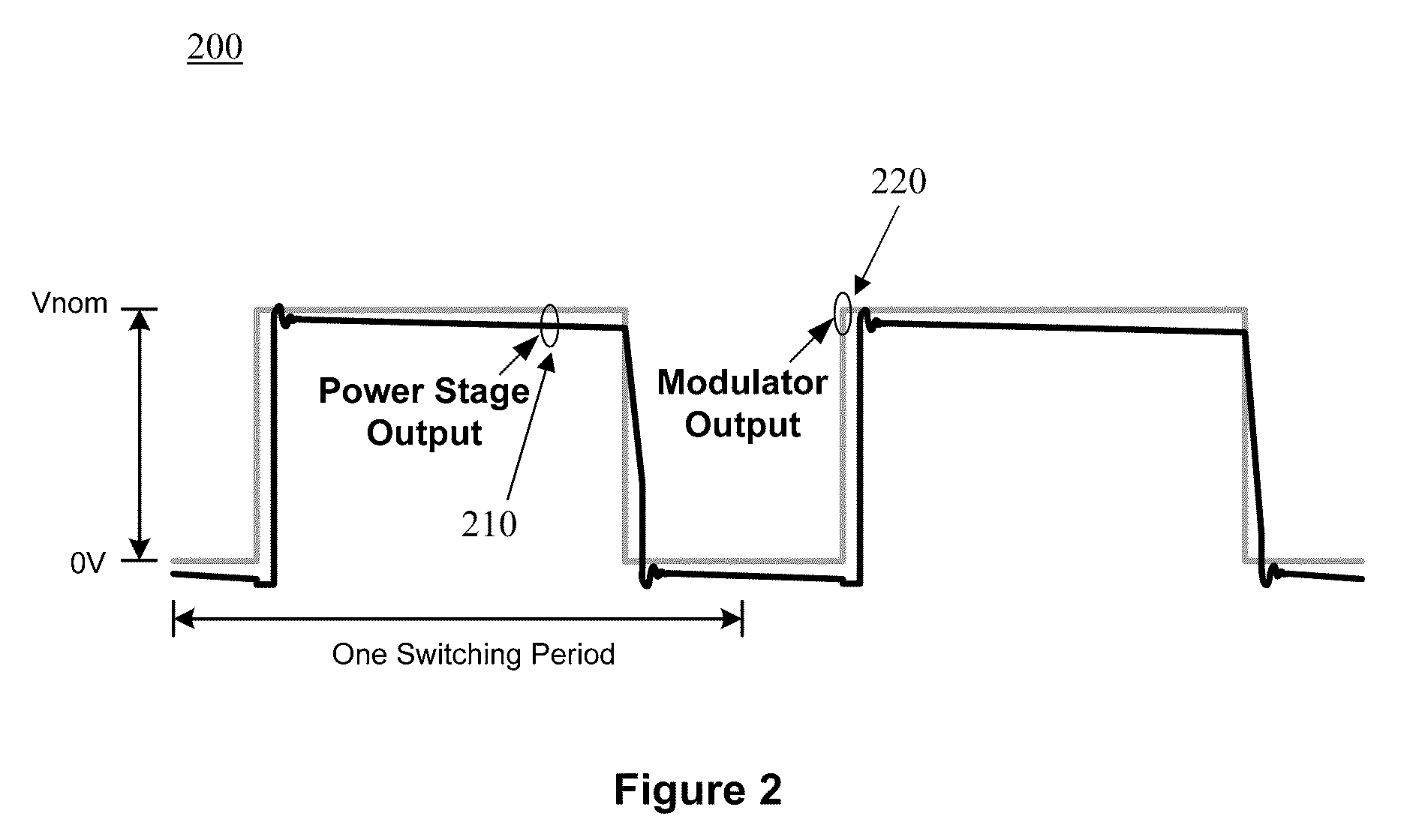
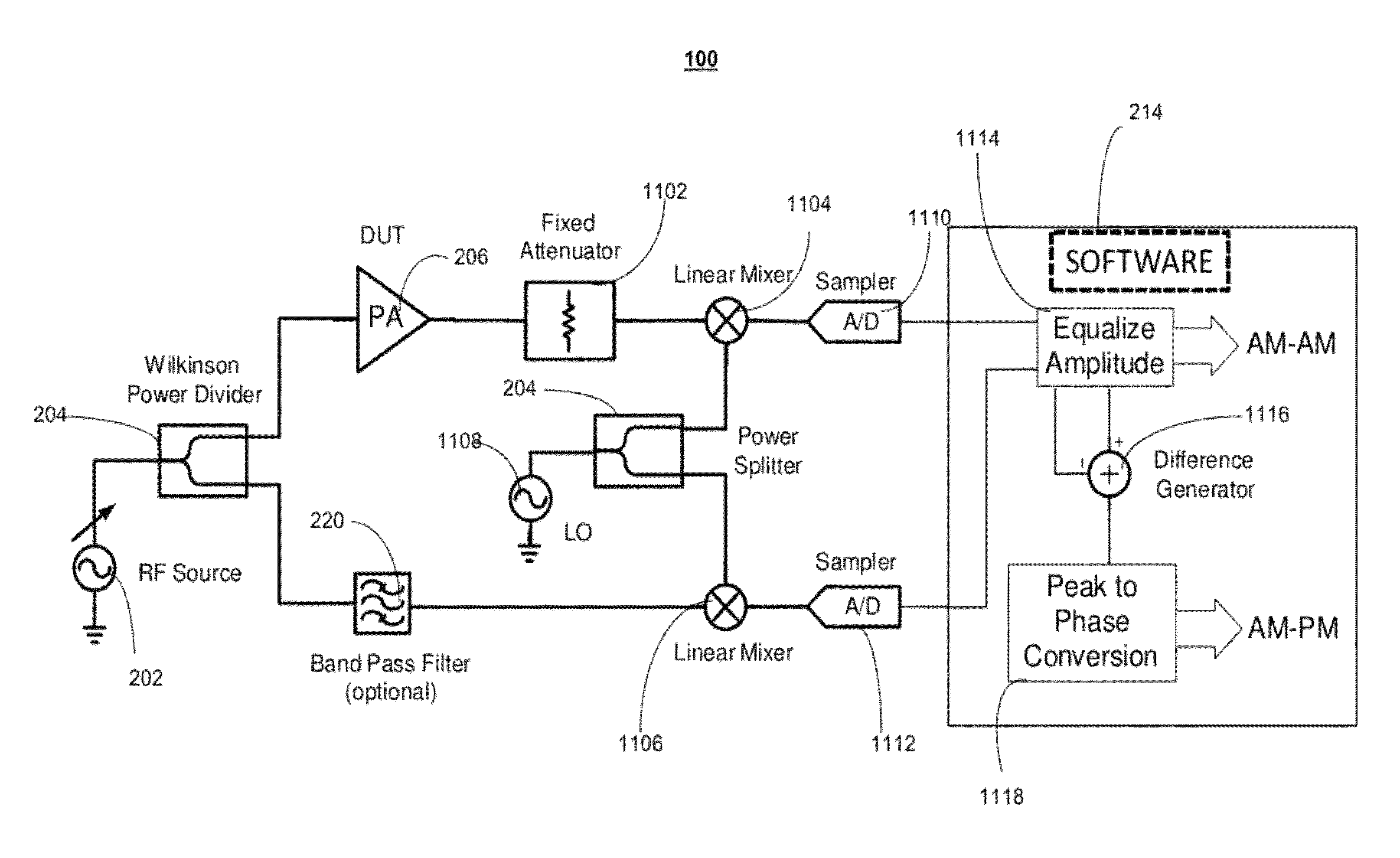
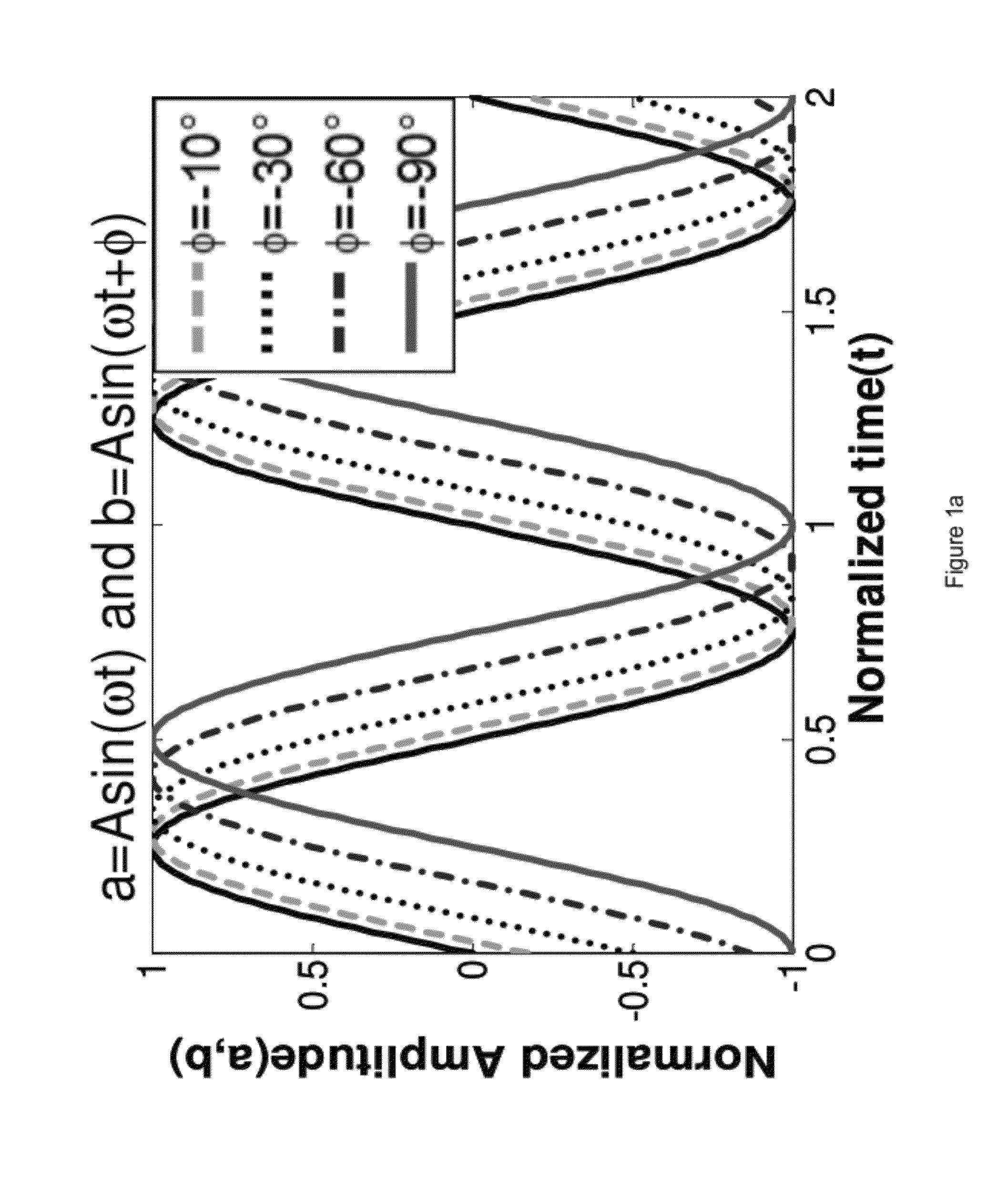
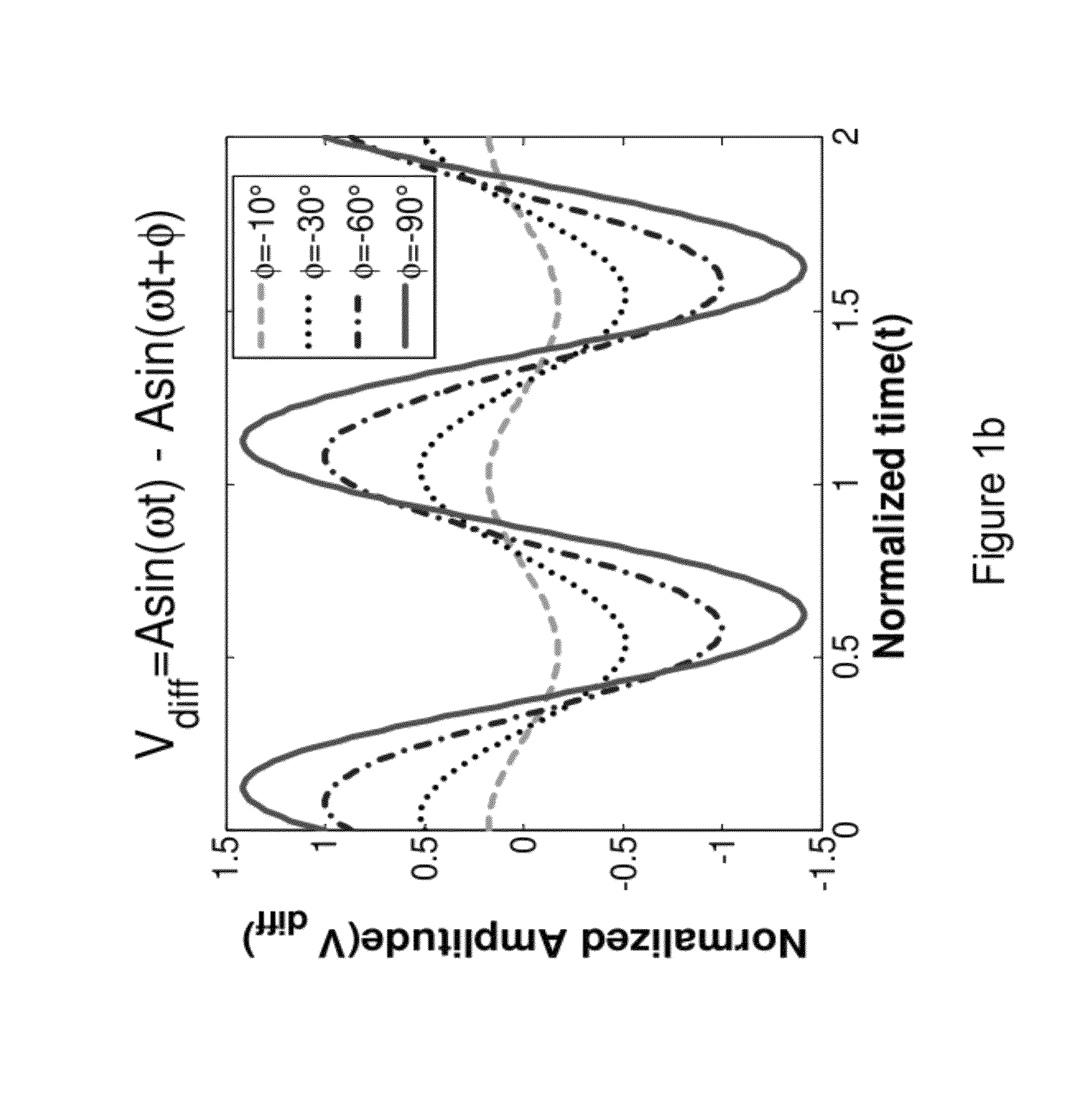
The presently invention is directed to ways to measure distortion effects while allowing for the possibility of significant reduction in test cost. An exemplary embodiment of the present invention provides a method for amplifier distortion measurement including comparing a first amplitude response of an output signal from a power amplifier to a second amplitude response of a reference input signal to determine a set of Amplitude-to-Amplitude (“AM-AM”) distortion values. Additionally, the method for amplifier distortion measurement includes equalizing the first amplitude response of the output signal to match the second amplitude response of the reference input signal based on the set of AM-AM distortion values and creating a difference signal based on a comparison of the equalized output signal to the reference input signal. Furthermore, the method for amplifier distortion measurement includes calculating a set of Amplitude-to-Phase (“AM-PM”) distortion values based on a third amplitude response of the difference signal.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
Feedforward amplifier with dual loop
InactiveUS6838934B2Easy balance controlAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAudio power amplifierFeedforward amplifiers
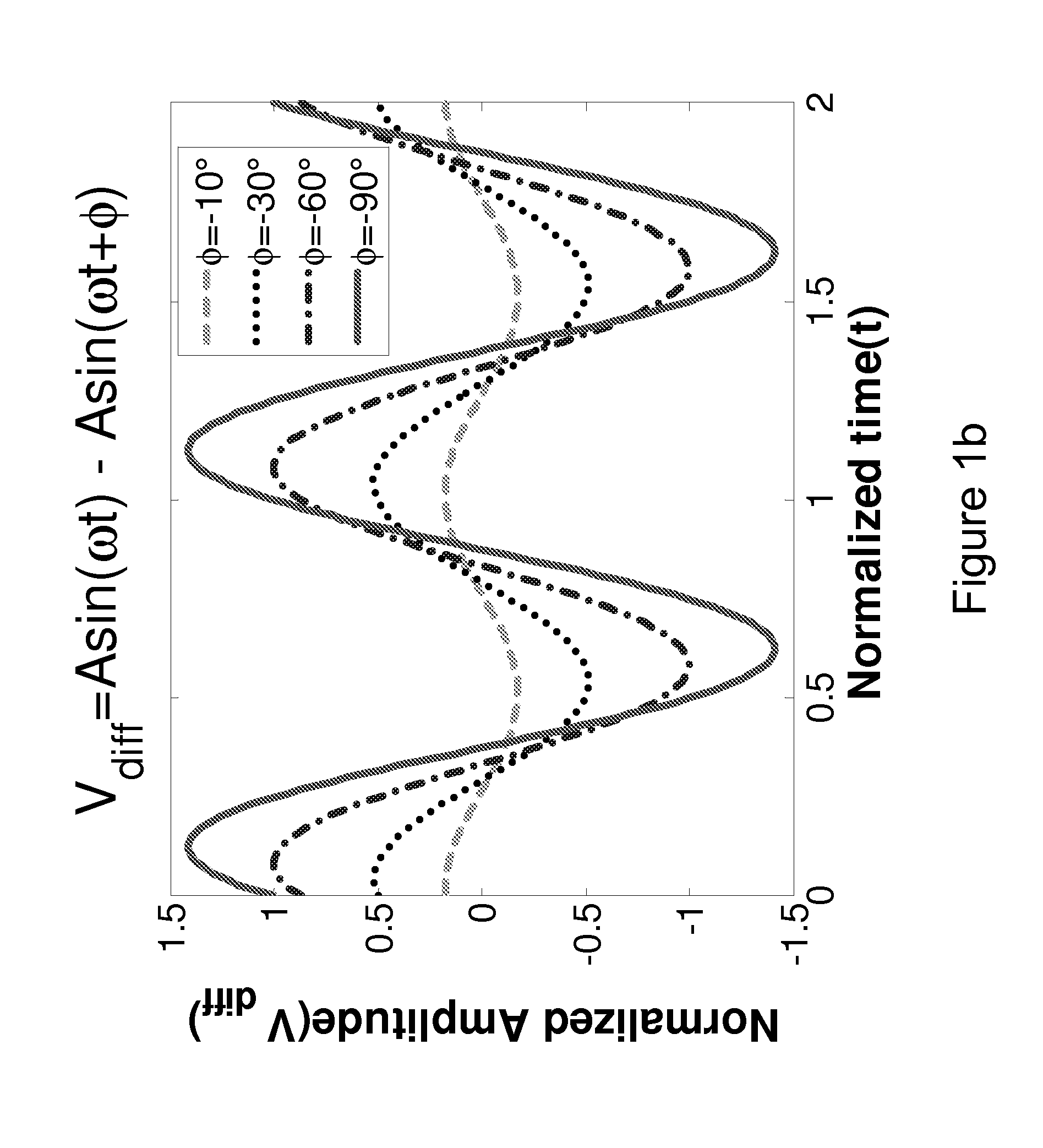
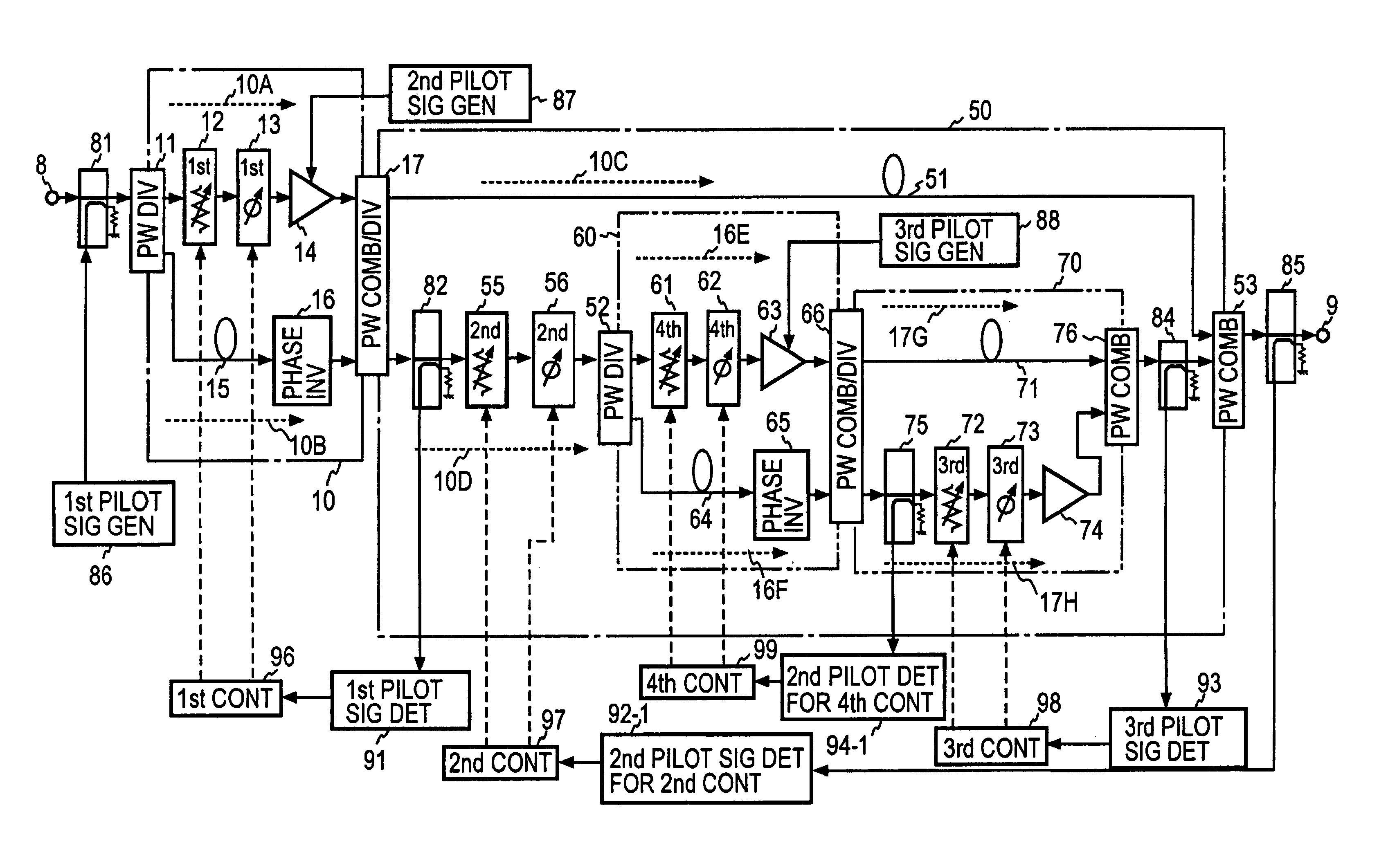
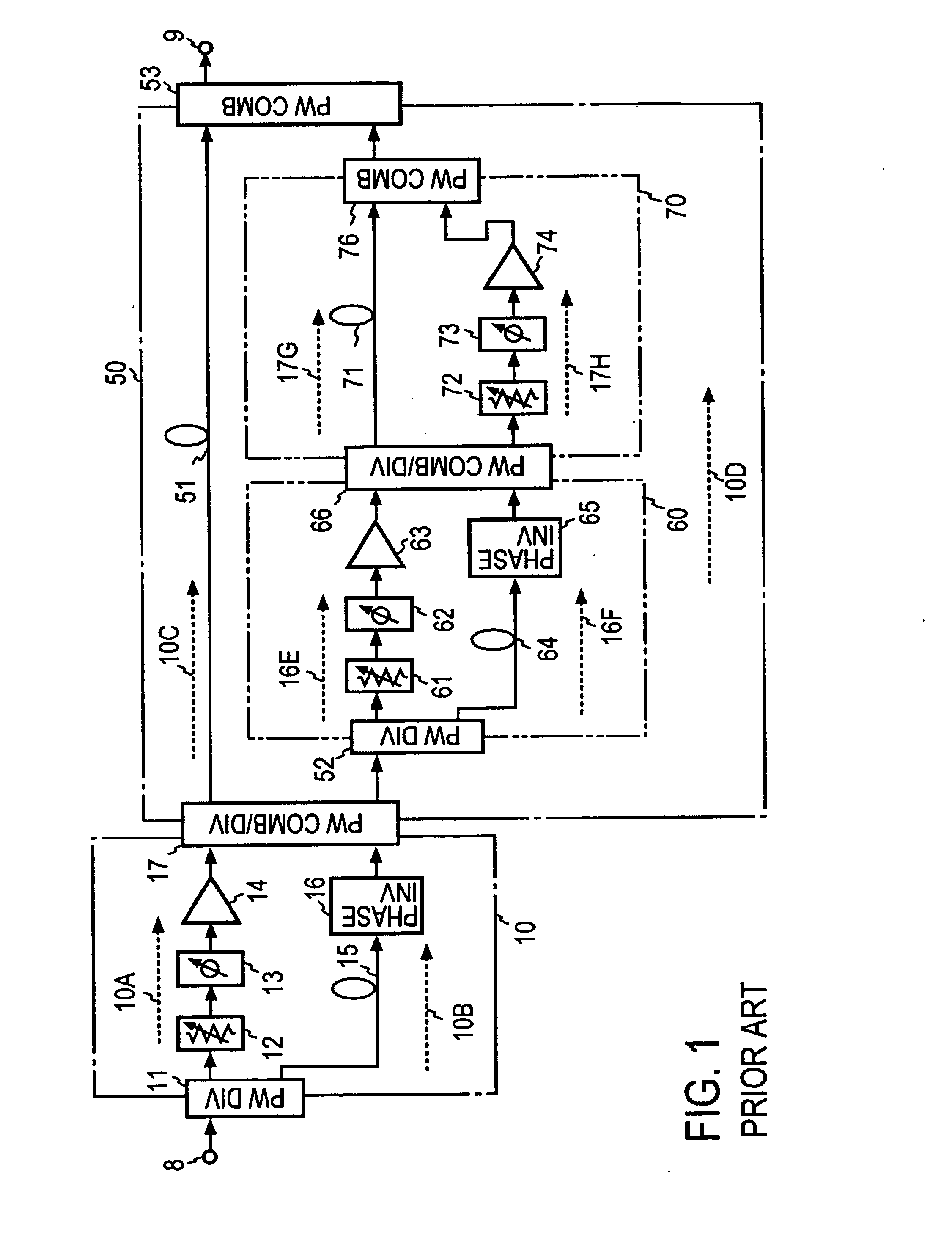
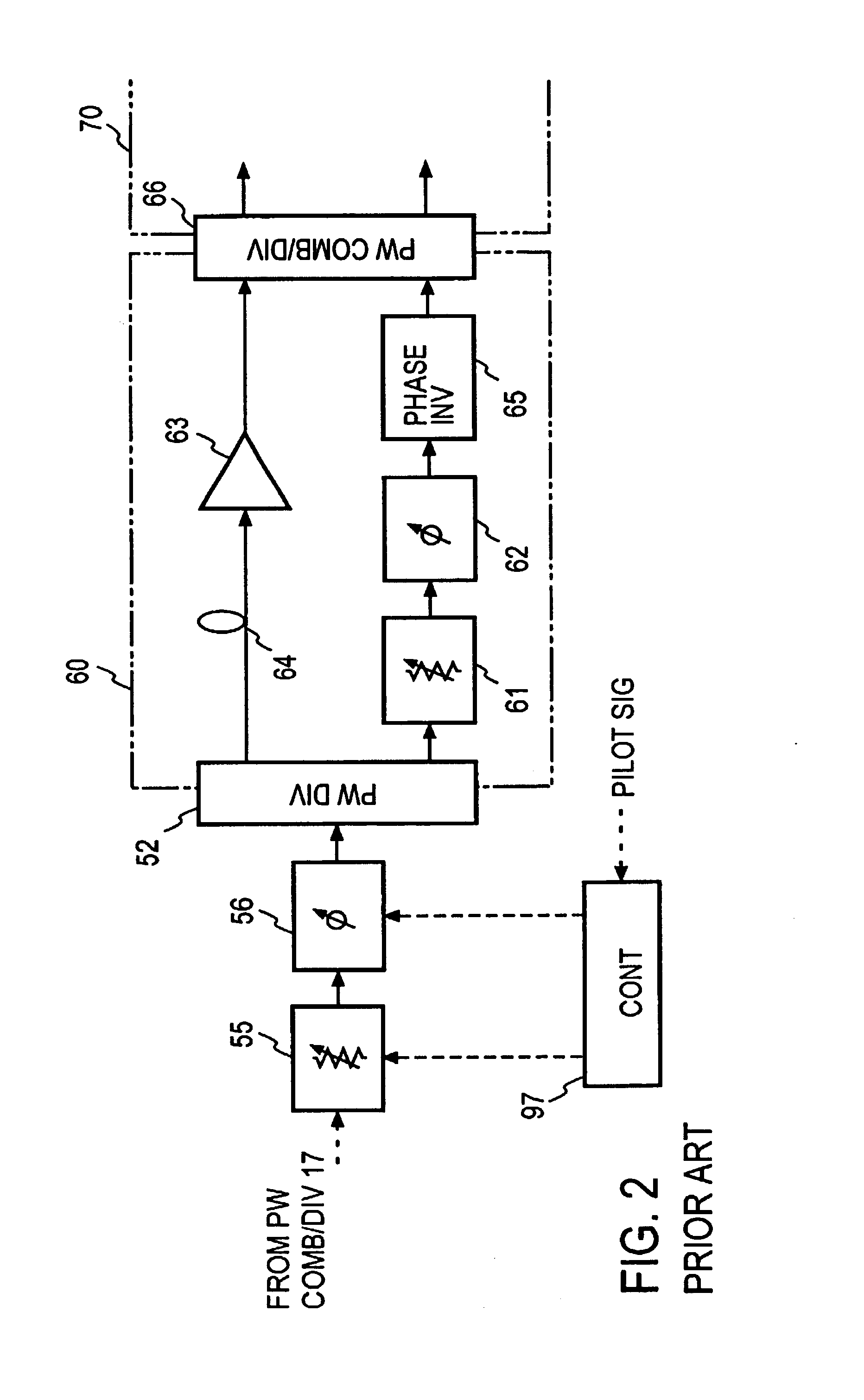
In a feedforward amplifier with a dual loop in which a distortion injection path of a distortion elimination circuit 50 is provided as a feedforward configuration composed of a first auxiliary amplifier distortion elimination circuit 60 and a first auxiliary amplifier distortion elimination circuit, a second variable attenuator 55 and a second variable phase shifter 56 are provided preceding the distortion detection circuit 60, a second pilot signal injected between stages of a main amplifier 14 is detected by a directional coupler 85, and the second variable attenuator 55 and the second variable phase shifter 56 are controlled by a second controller 97 to minimize the level of the detected second pilot signal, thereby bringing the distortion elimination circuit and the first auxiliary distortion detection circuit into balance at the same time.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
Digital predistortion for power amplifier
ActiveUS20050062531A1Compensation for amplifier distortionEasy to implementAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAudio power amplifierGain compression
Apparatus and a corresponding method for predistorting an input signal applied to a radio frequency (RF) power amplifier, to compensate for amplifier distortion at high powers. The RF amplifier input and output signals are continuously monitored and difference signals are generated in an RF phase discriminator. The difference signals are converted to digital form and stored in a lookup table in the form of running averages of an RF amplifier gain compression value and an RF amplifier output phase value for each observed RF input power value. A predistorter module retrieves these values and predistorts the RF amplifier input by way of compensation.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
Distortion suppression circuit for digital class-d audio amplifier
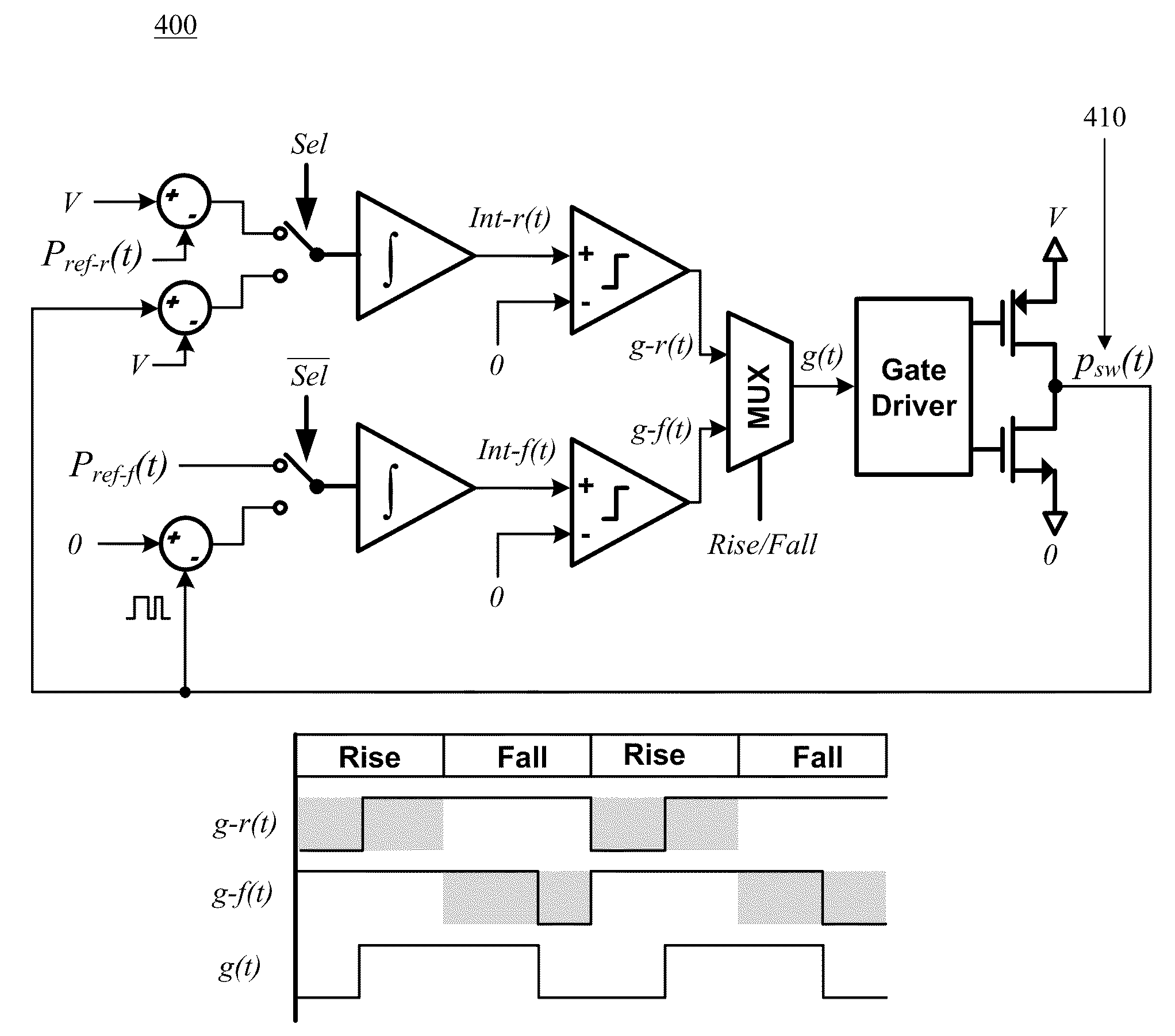
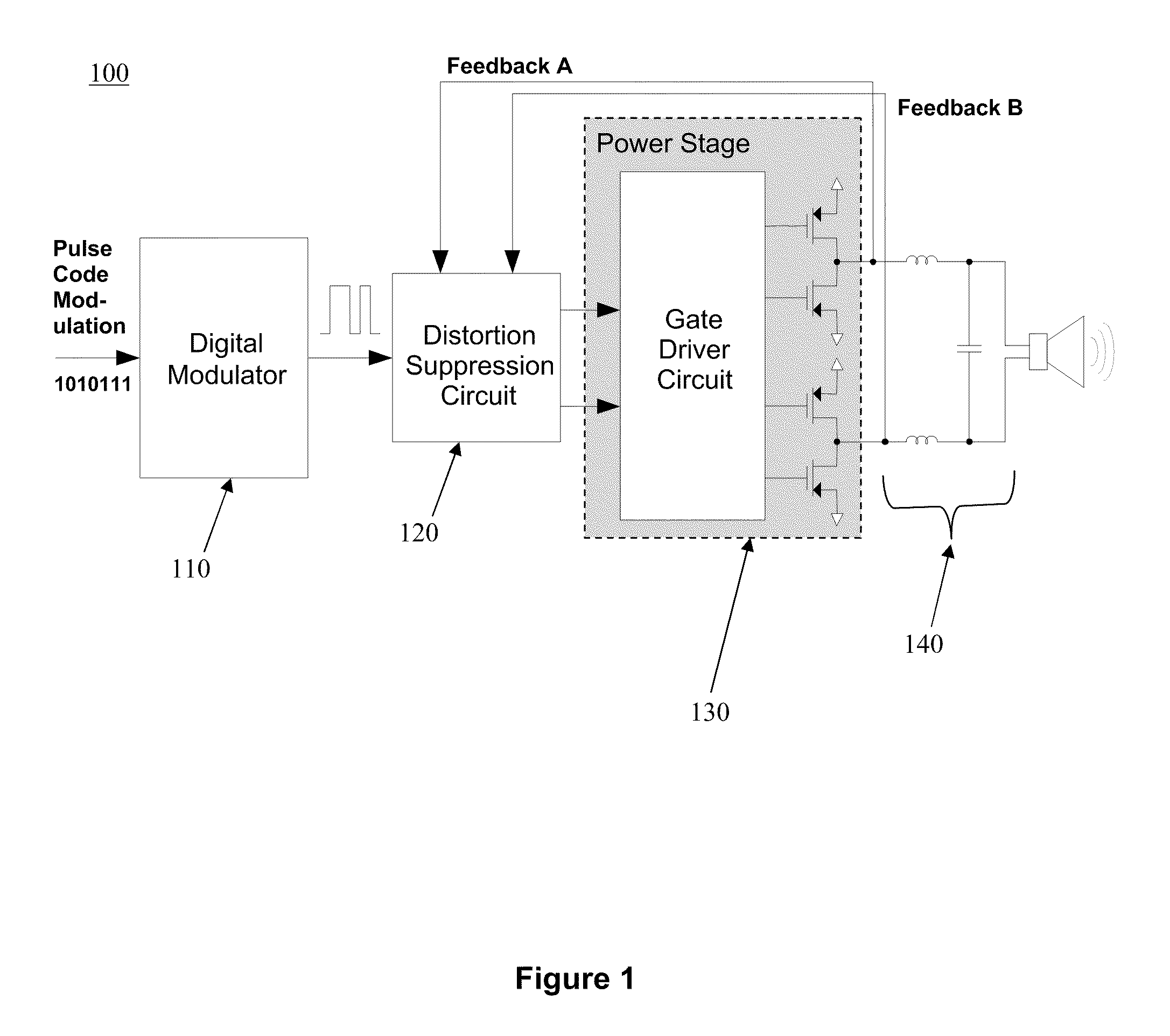
ActiveUS20090160553A1Improve efficiencyImprove audio performanceAmplifier detailsDc amplifiers with modulator-demodulatorClass-D amplifierEngineering
A digital Class-D amplifier distortion suppression circuit design is disclosed. A distortion suppression feedback loop is described to improve audio performance by suppressing output stage non-linearity and improving power supply noise rejection achieving reduced THD+N. The feedback loop is placed around the power stage. It forces tracking between the audio band signals at the input and output of the power stage by automatically adjusting the gating signal timing based on sensed effective duty ratio error. Error sensing and compensation are performed using techniques that lend to simple circuit implementation.
Owner:ASAHI KASEI ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Systems and methods for distortion measurement using distortion-to-amplitude transformations
InactiveUS8358169B2Electric devicesAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAudio power amplifierAmplitude response
The presently invention is directed to ways to measure distortion effects while allowing for the possibility of significant reduction in test cost. An exemplary embodiment of the present invention provides a method for amplifier distortion measurement including comparing a first amplitude response of an output signal from a power amplifier to a second amplitude response of a reference input signal to determine a set of Amplitude-to-Amplitude (“AM-AM”) distortion values. Additionally, the method for amplifier distortion measurement includes equalizing the first amplitude response of the output signal to match the second amplitude response of the reference input signal based on the set of AM-AM distortion values and creating a difference signal based on a comparison of the equalized output signal to the reference input signal. Furthermore, the method for amplifier distortion measurement includes calculating a set of Amplitude-to-Phase (“AM-PM”) distortion values based on a third amplitude response of the difference signal.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com