Amplifier
一种放大器、多级放大器的技术,应用在放大器、改进放大器以提高效率、改进放大器以减少非线性失真等方向,能够解决不能采用放大级、信号畸变等问题,达到高功率附加效率的效果
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
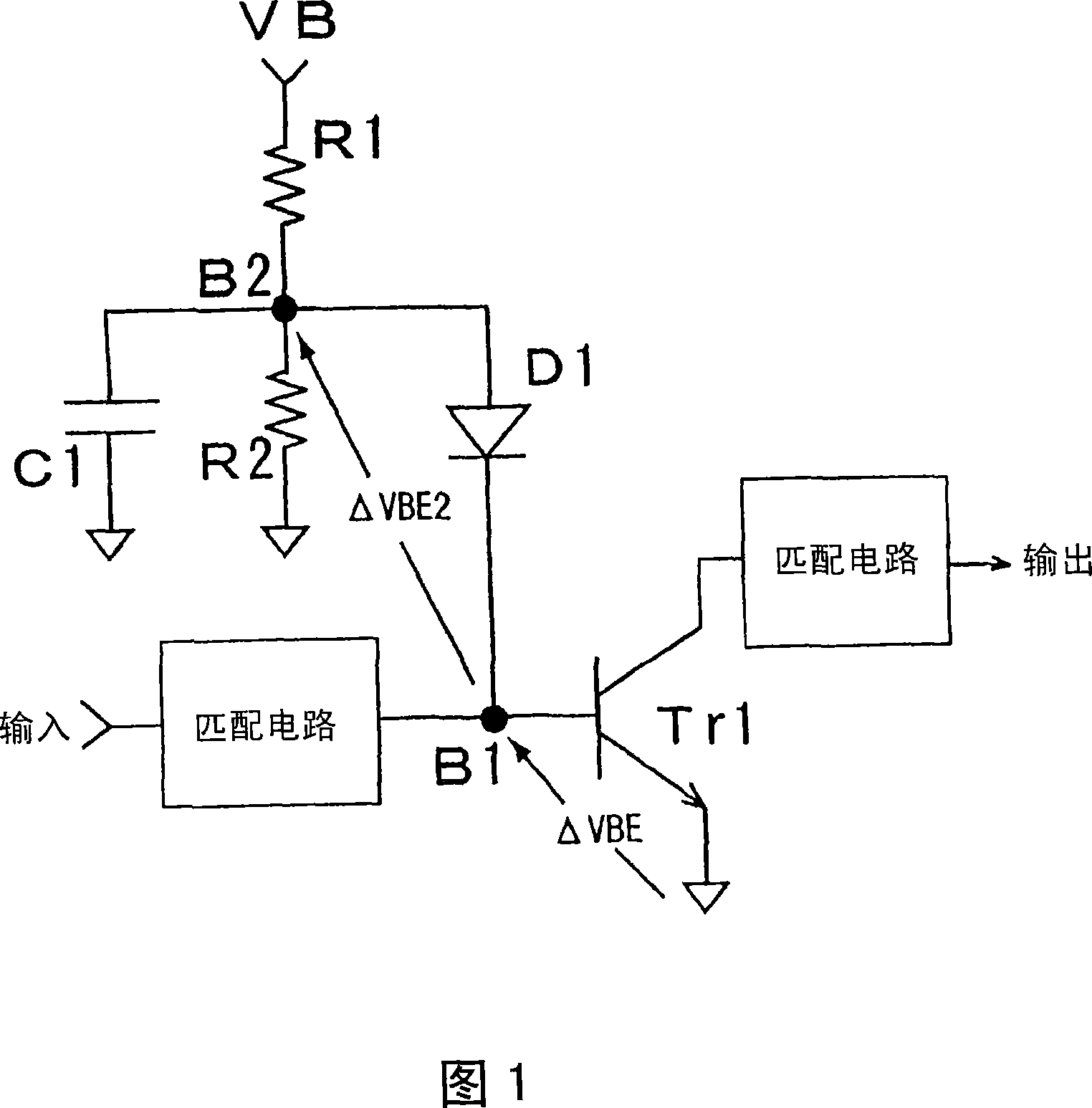
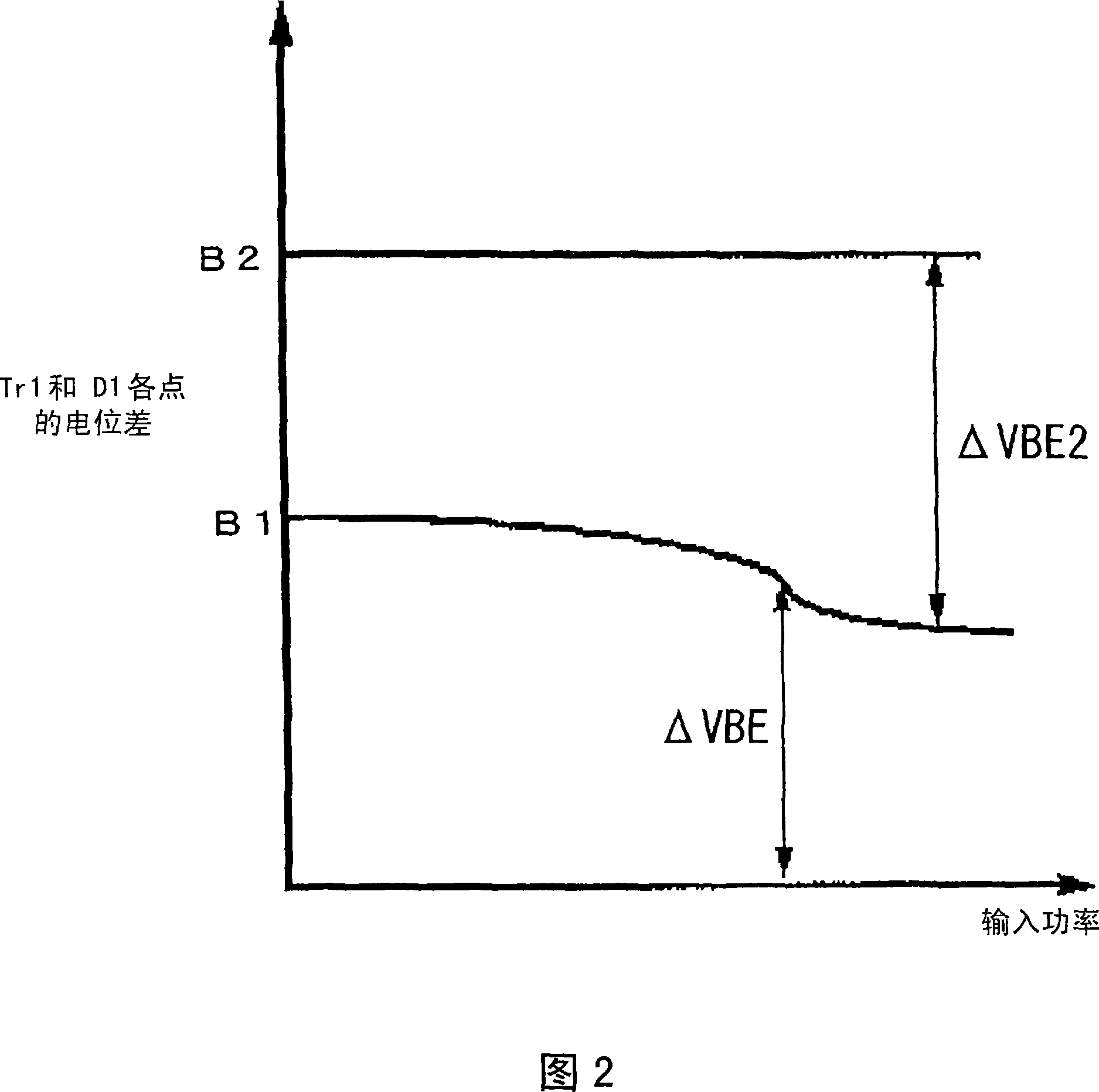
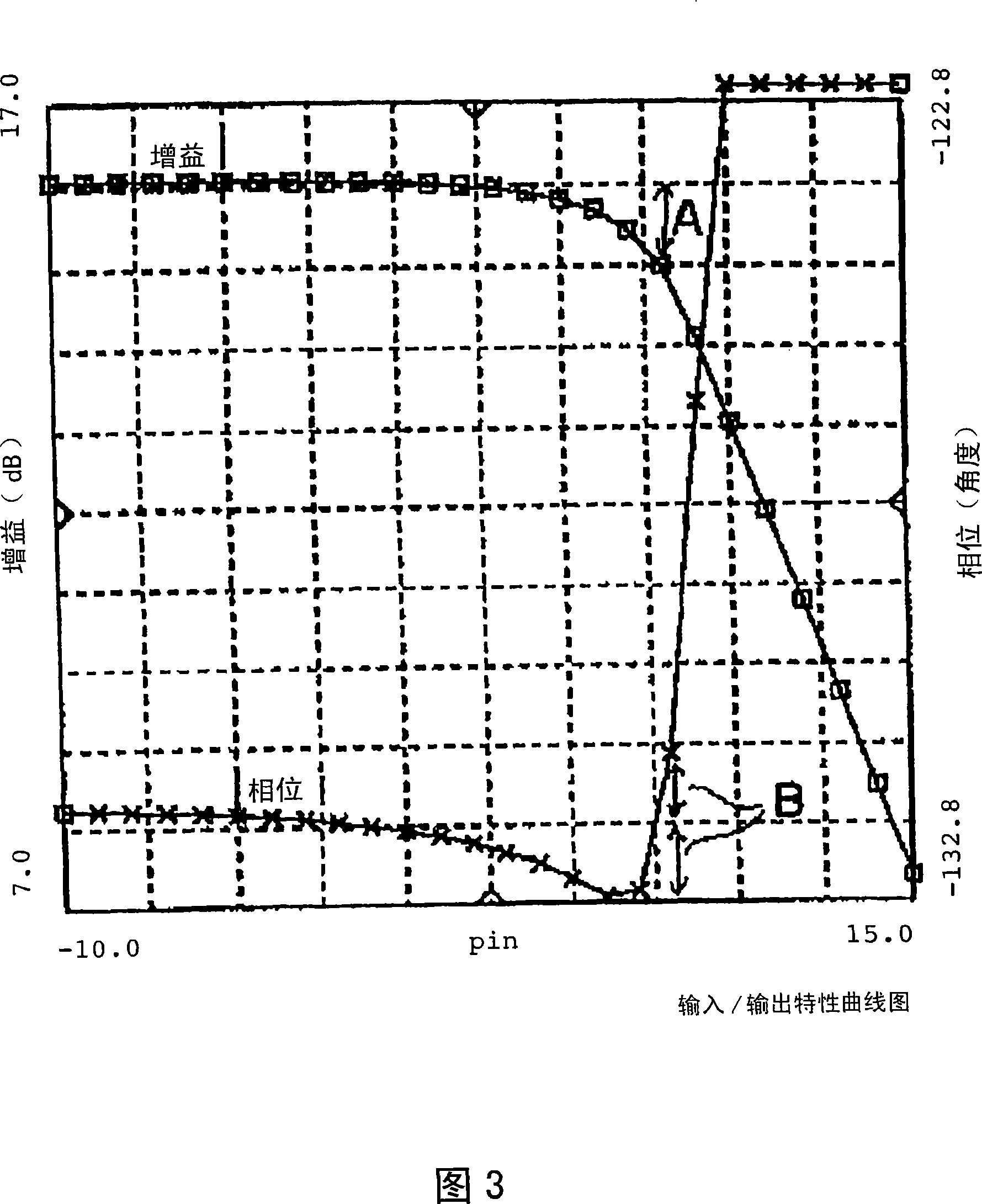
[0146] FIG. 24 is an amplifier diagram illustrating the phase conversion of IM3 with respect to the fundamental wave according to the first embodiment of the present invention. The amplifier transistor 1 constitutes an amplifier circuit whose emitter is grounded, wherein the base of the transistor 1 is connected to an input matching circuit 3 and a cathode of a bias supply diode 4 via an impedance element 2 . The anode of the bias providing diode 4 is connected to a reference power supply 5 which presents a very low impedance at high frequencies. The collector of the transistor 1 is connected to the collector power source 7 through the load 6 and connected to the output terminal 9 through the output matching circuit 8 .
[0147] Fig. 24 illustrating this embodiment corresponds to Fig. 1 illustrating the first conventional example. Comparing the first embodiment illustrated in FIG. 24 with the first conventional example of FIG. 1, in the prior art, the bias supply diode D1 cat...
no. 2 example
[0149] FIG. 27 is a diagram illustrating an amplifier that converts the phase of IM3 with respect to the fundamental wave according to the second embodiment, and corresponds to FIG. 4 of the second conventional example. This embodiment utilizes the base-emitter of bias providing transistor 11 in place of diode 4 in the first embodiment. Therefore, its effects and operations are the same as those of the first embodiment. When the reference power supply 5 is realized by a resistor, the resistor causes a voltage drop, so this embodiment alleviates the second problem mentioned above. In this embodiment, since the bias voltage is also supplied to the amplifying transistor 1 via the impedance element 21, this impedance element 21 does not block any DC current. Since this embodiment is substantially the same in effect and operation as the first embodiment described above, they will be described together below.
[0150] Fig. 25 is a diagram for describing a second embodiment of the ...
no. 3 example
[0158] FIG. 30 is a diagram illustrating an amplifier that converts the phase of IM3 with respect to the fundamental wave according to a third embodiment of the present invention. The amplifier transistor 1 constitutes an amplifier circuit whose emitter is grounded, wherein the base of the transistor 1 is biased by a bias supply diode 23 . Also, the base of the same transistor 1 is connected to the input matching circuit 3 and the bias supply diode 24 through the impedance element 25 . The anodes of the bias supply diodes 23 and 24 are both connected to the reference power supply 5 . The collector of the transistor 1 is connected to the collector power supply 7 through the load 6 and also connected to the output terminal 9 through the output matching circuit 8 .
[0159] Since this embodiment is the same in effect and operation as the sixth embodiment, it will be described together in the sixth embodiment later.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com