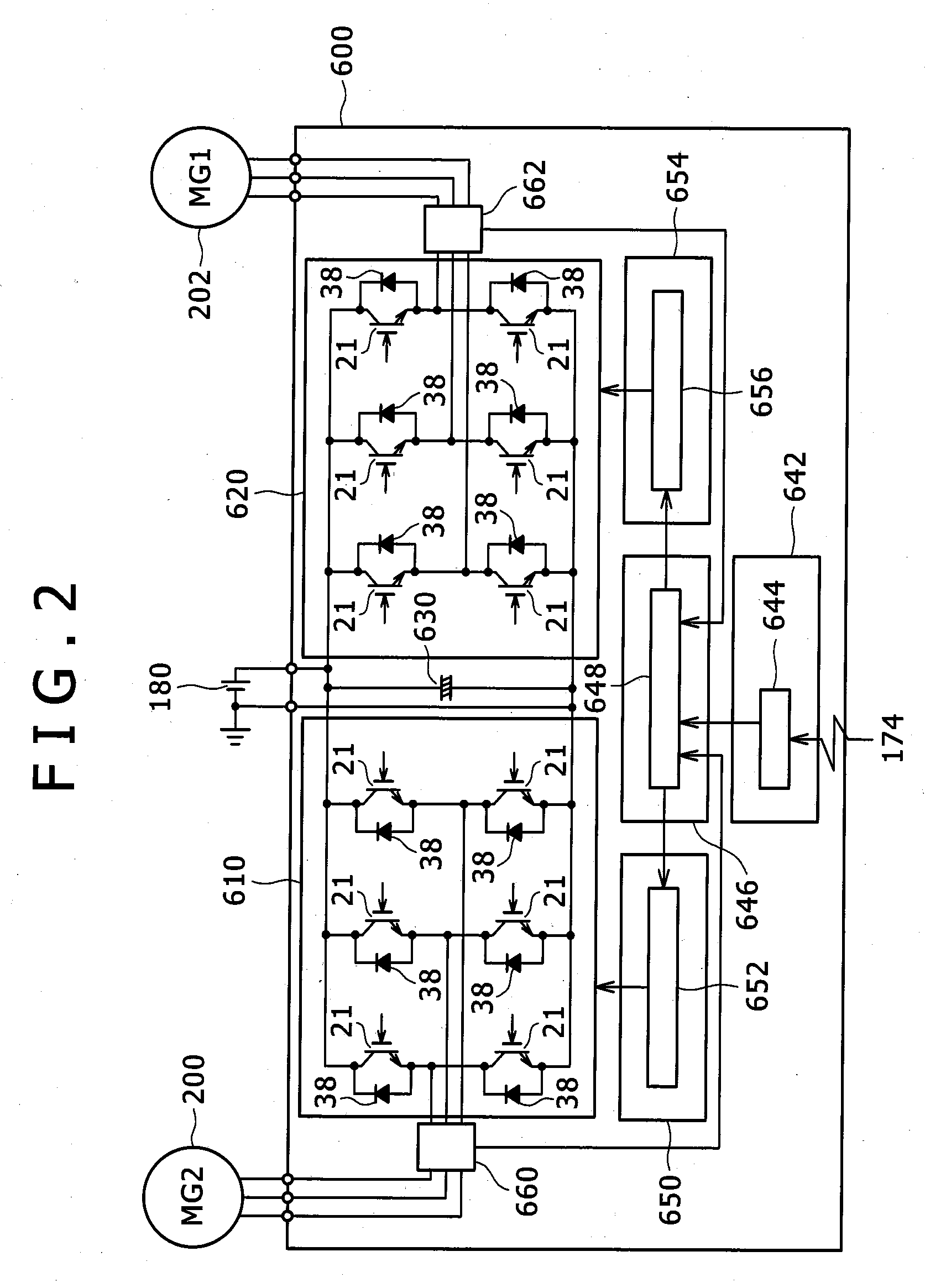
Patents
Literature
874results about "Magnetic circuit shape/form/construction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
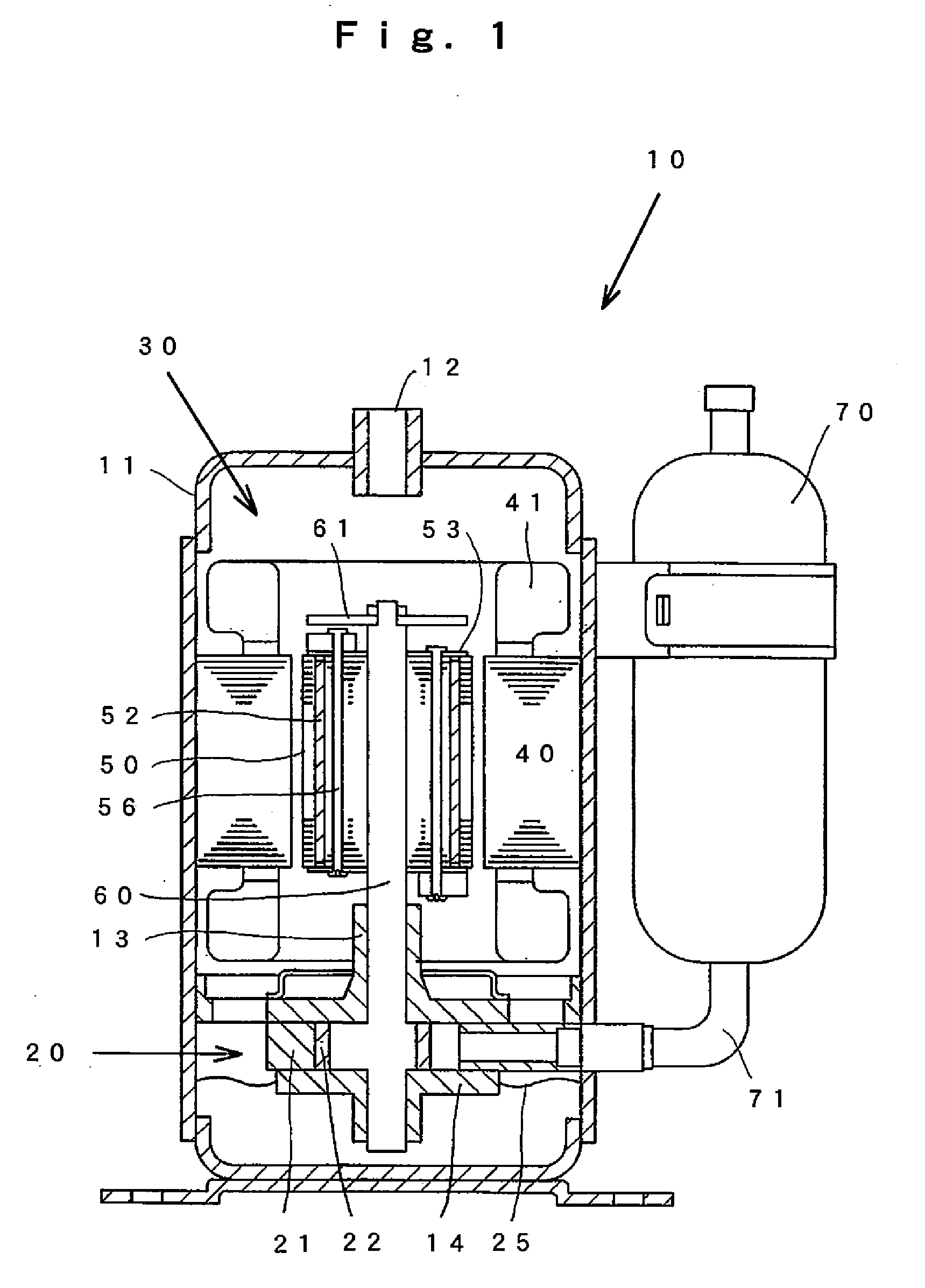
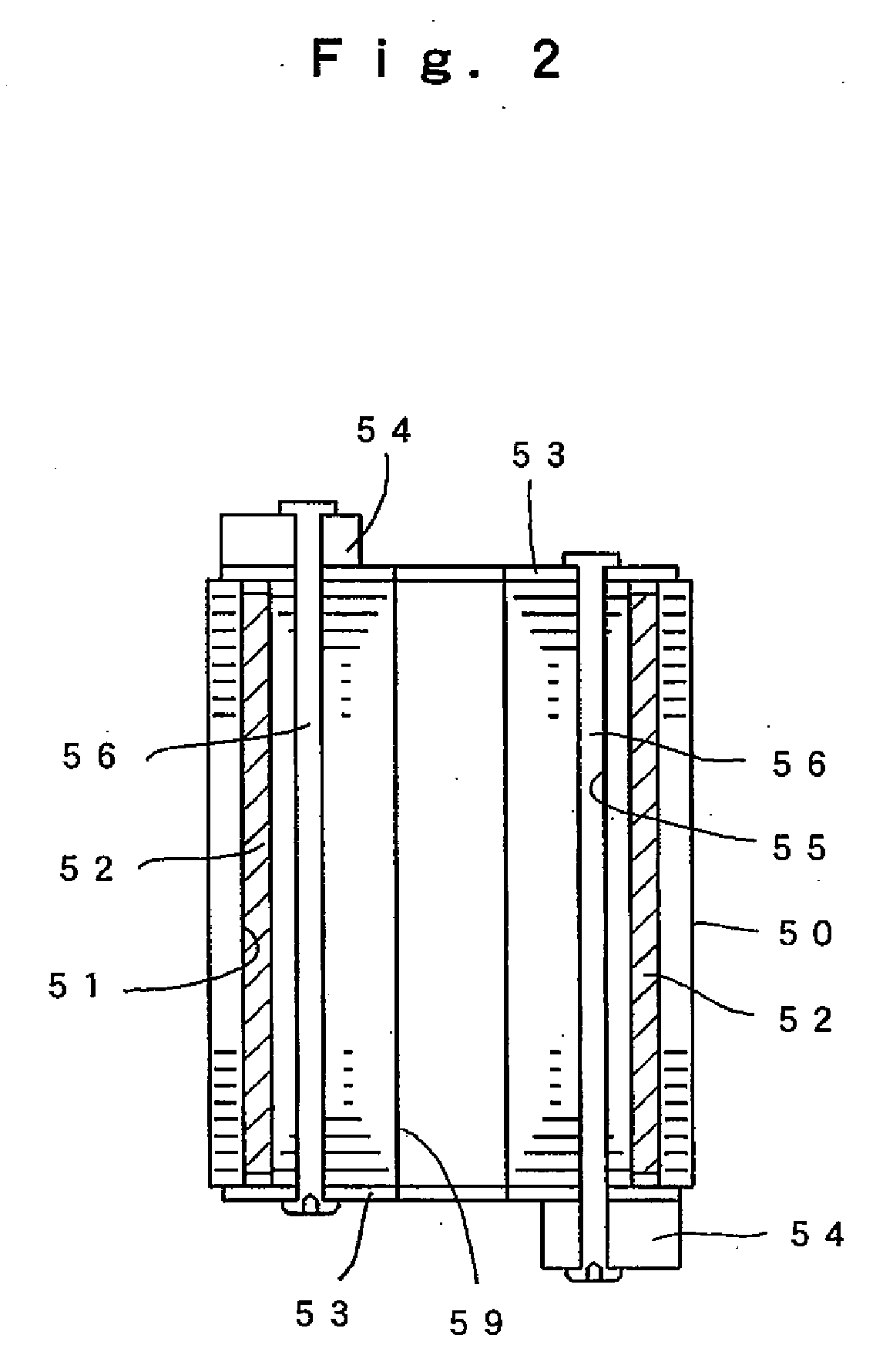
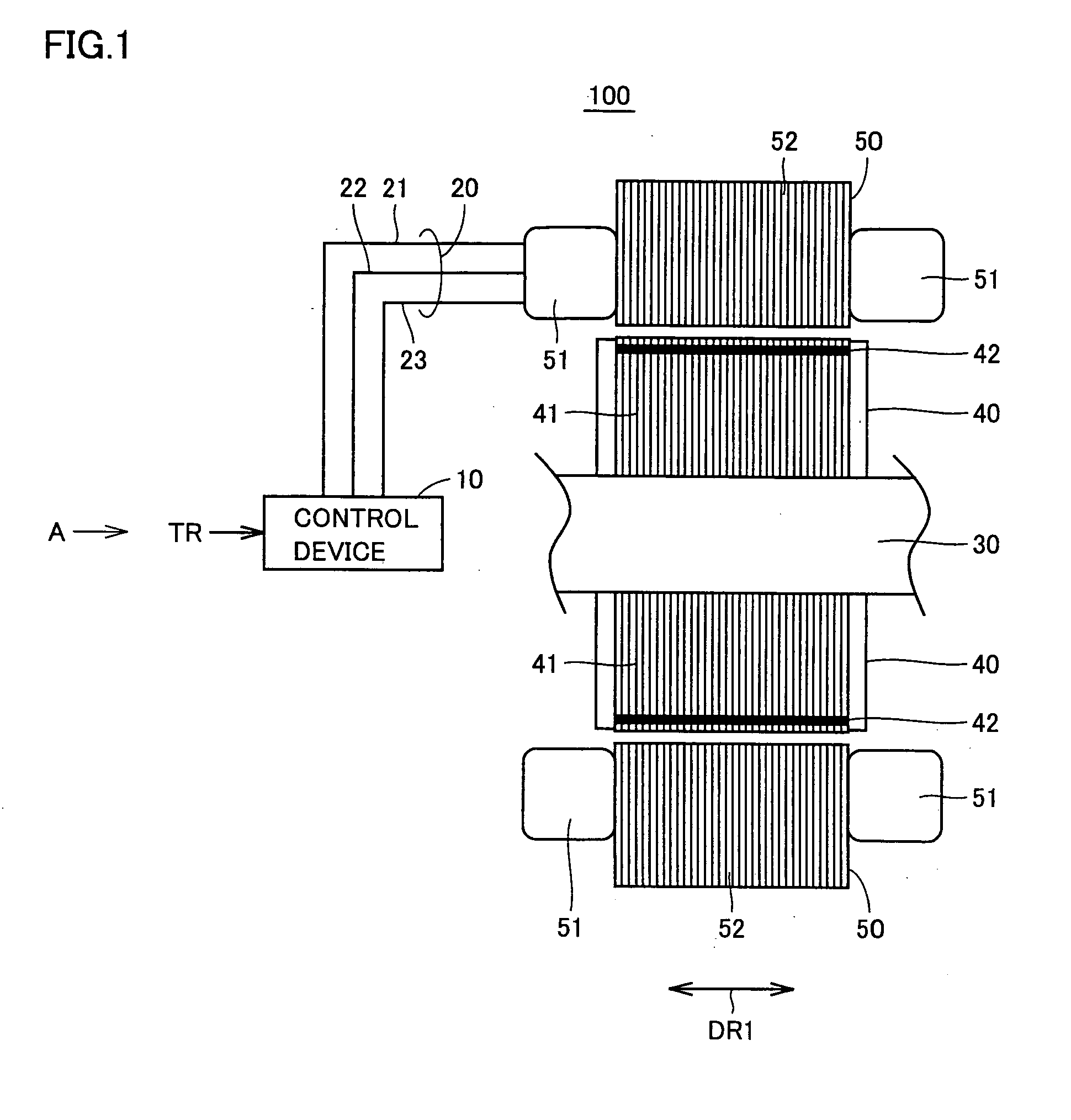
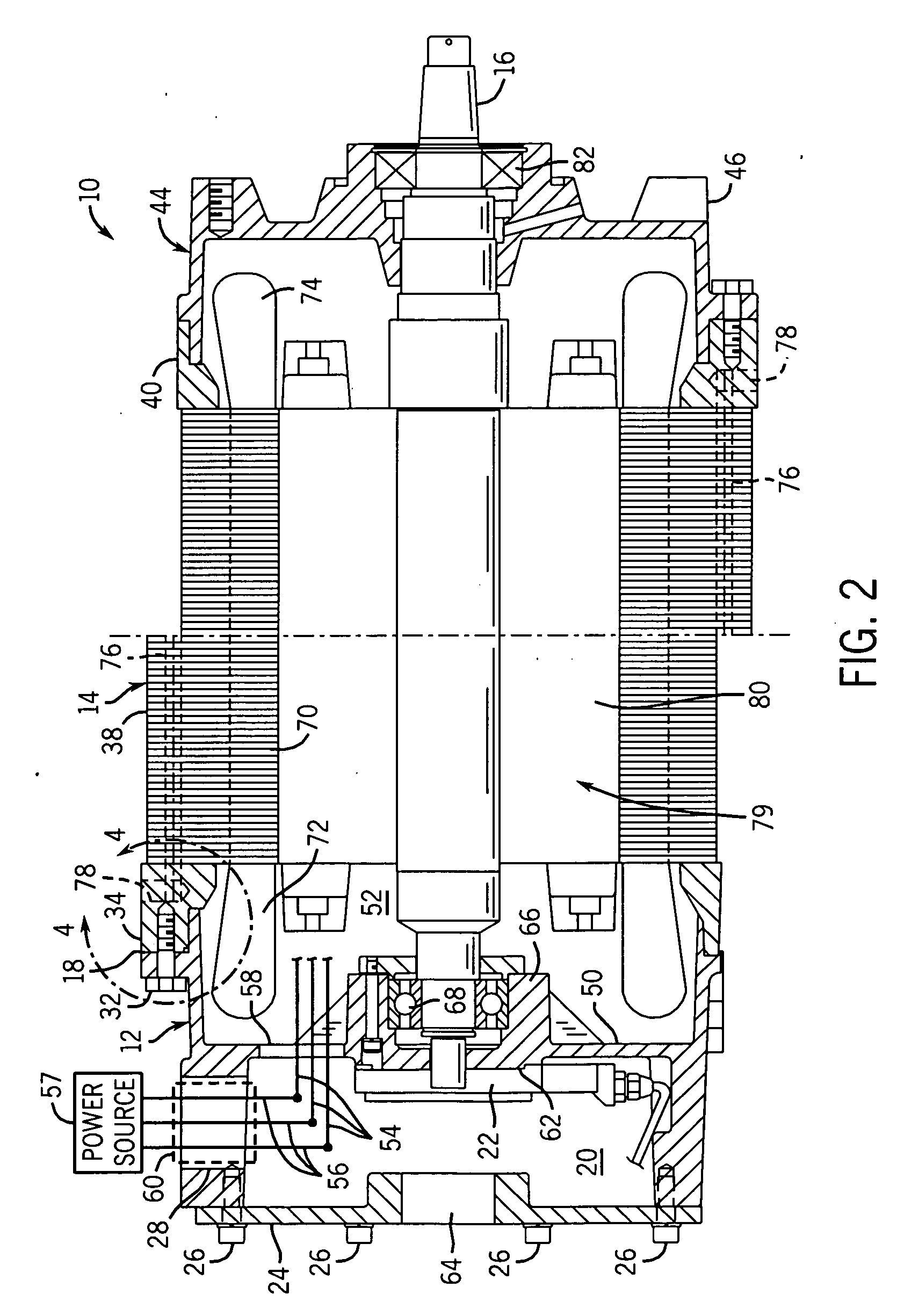
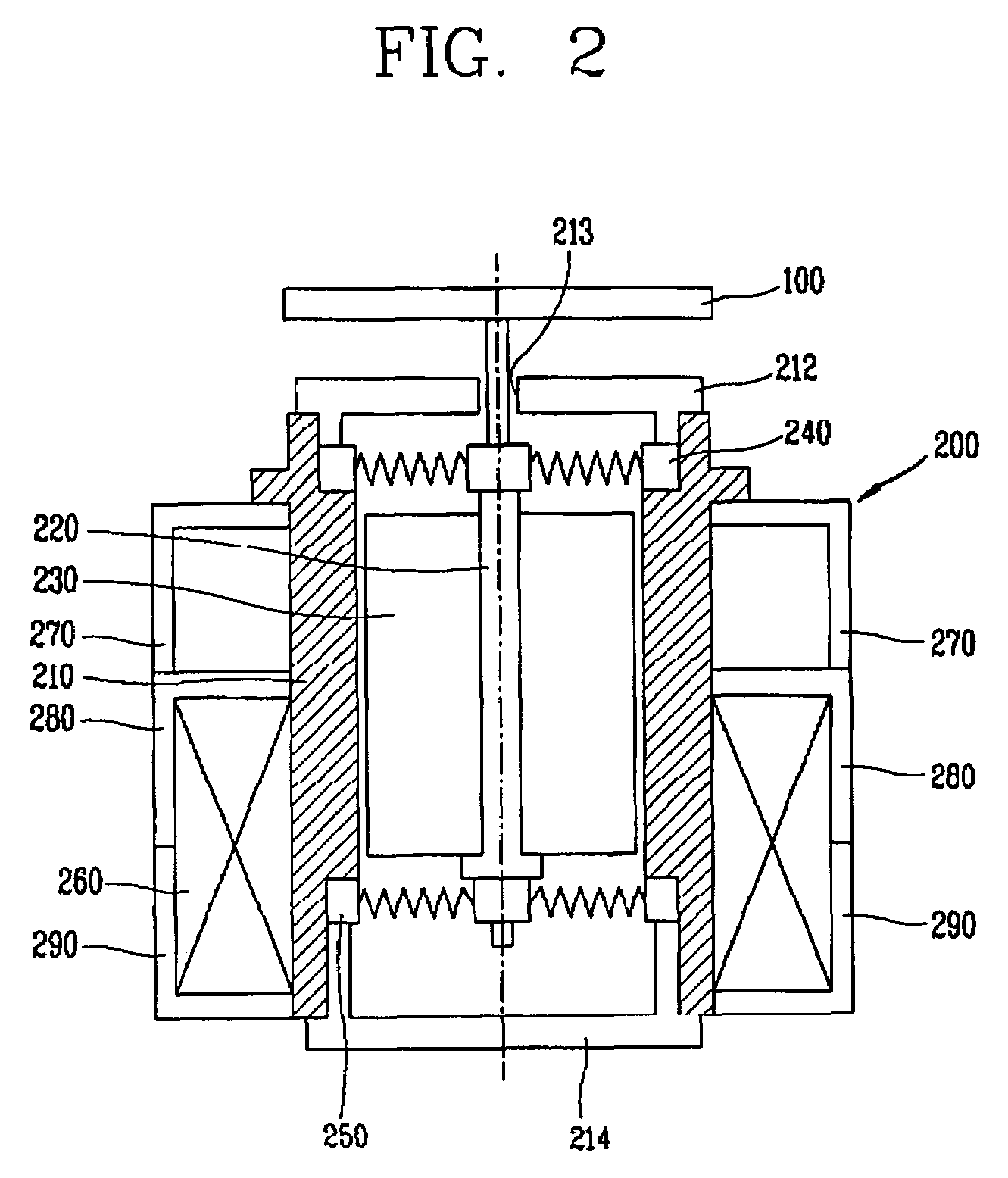
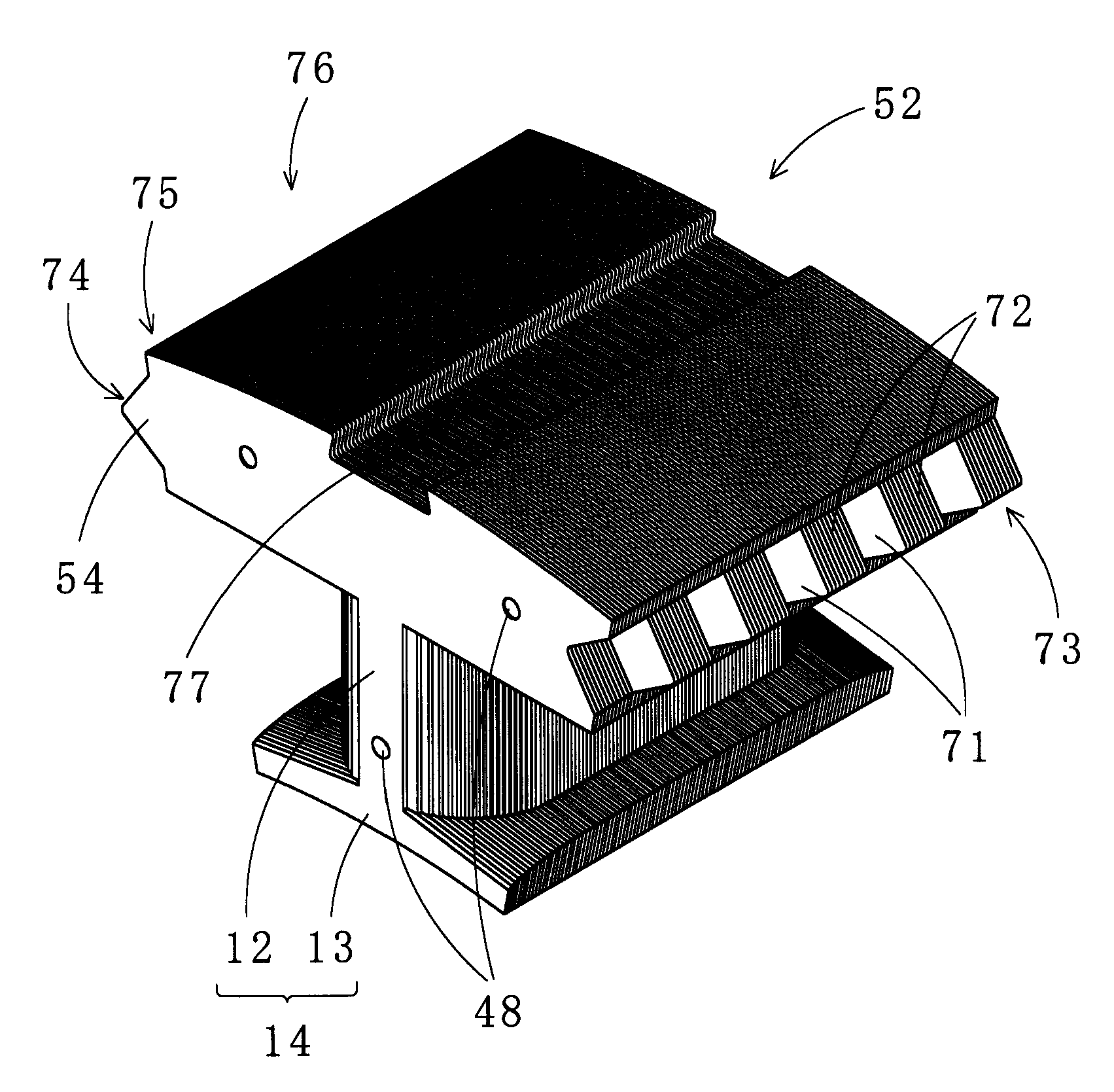
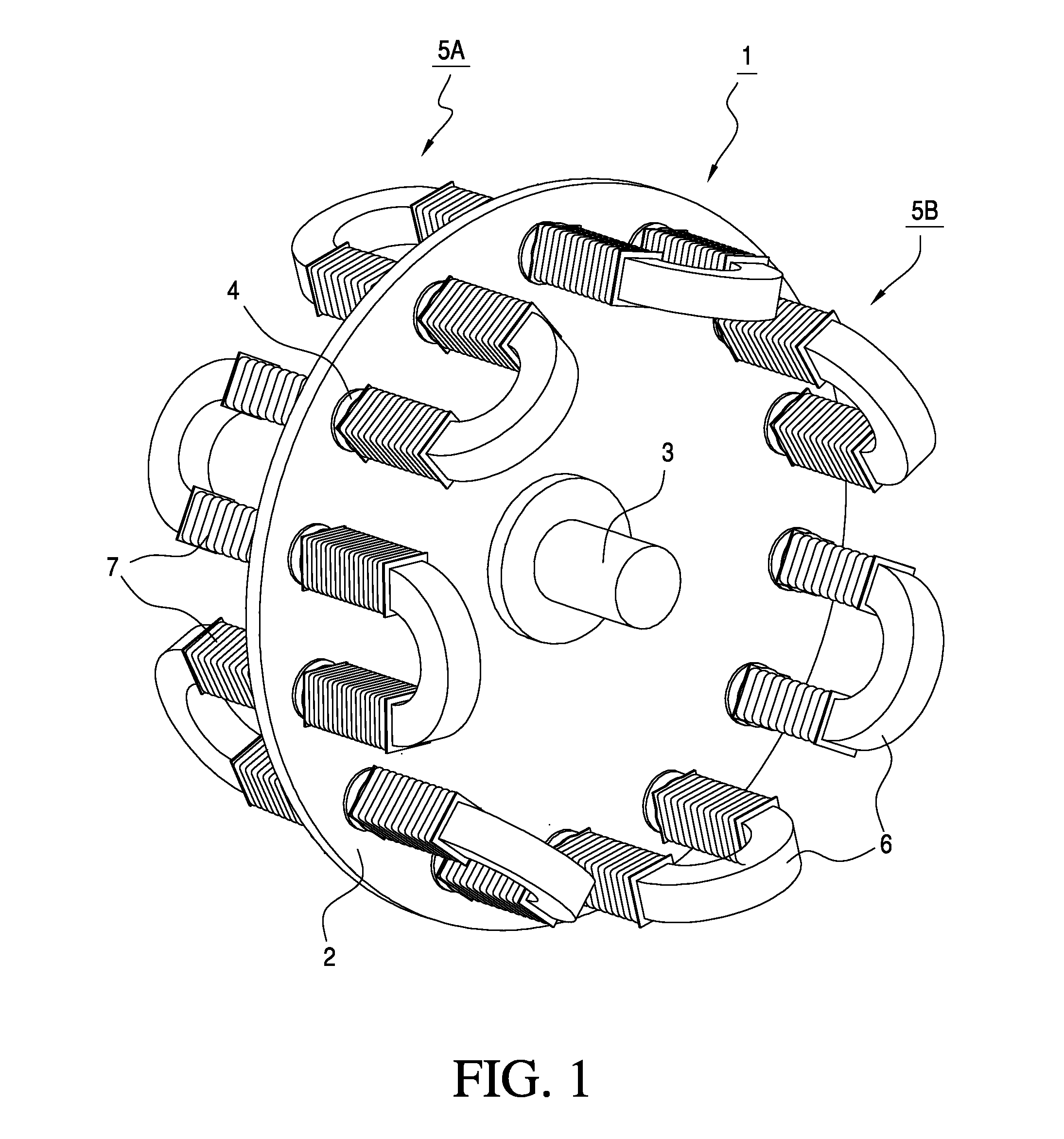
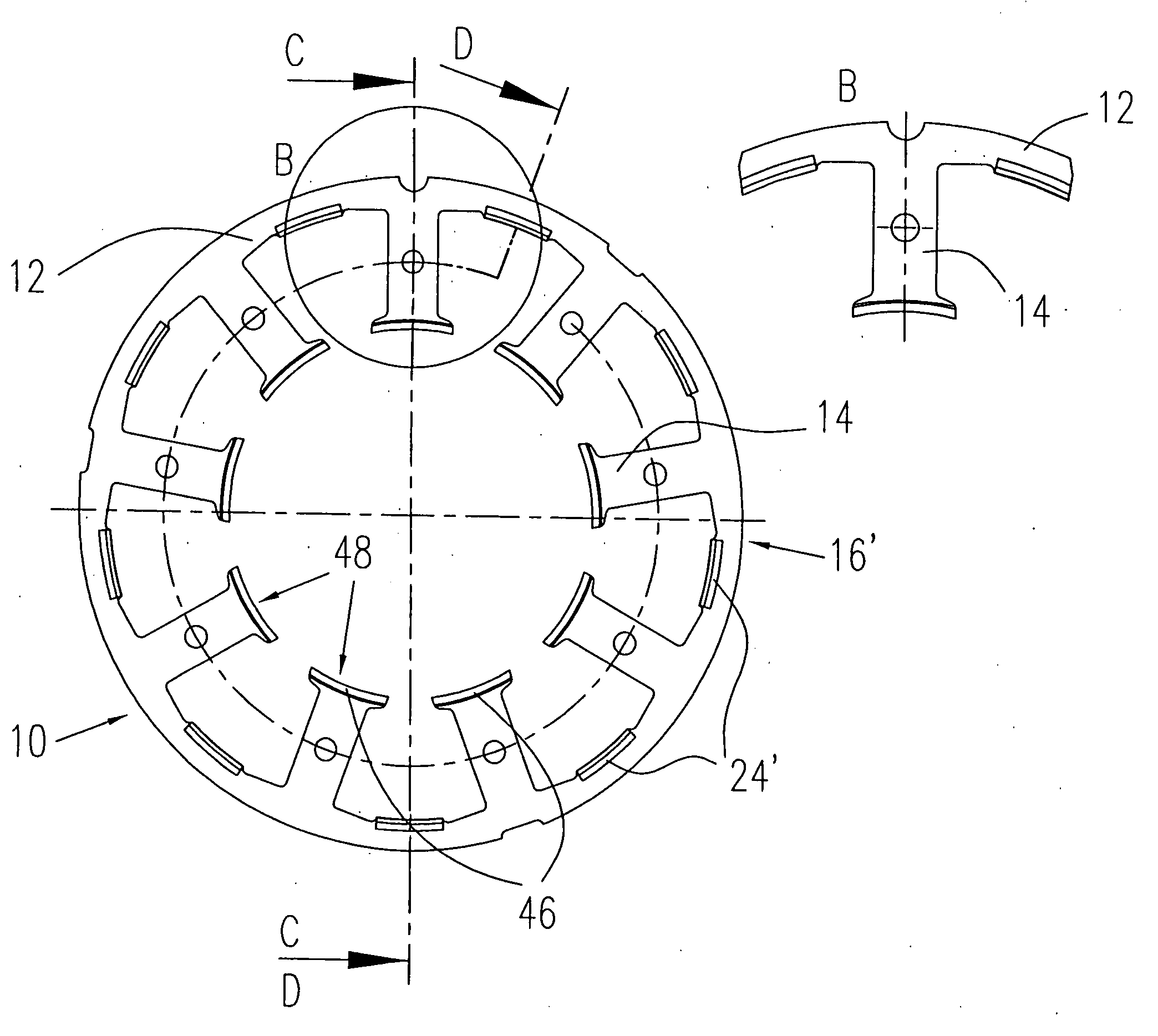
Linear oscillating actuator
InactiveUS6559563B1Without sacrificing oscillatory movementPrecise positioningMagnetic circuit shape/form/constructionMetal working apparatusActuatorDriven element
An improved linear oscillating actuator is capable of minimizing the undesired vibrations while moving first and second oscillators in parallel paths. The first and second oscillators carry first and second drive elements respectively for driving connection to individual reciprocating loads. The first and second drive elements project upwardly respectively from the first and second oscillators such that the first drive element is disposed immediately upwardly of the second oscillator and the second drive elements is disposed immediately upwardly of the first oscillator. With this reverse arrangement of the first and second drive elements relative to the first and second oscillators, the individual oscillating systems each including the oscillator, the drive element and the corresponding reciprocating load can have its mass center disposed in close proximity to a mass center of the actuator, thereby enabling to reduce undesired vibrations which would otherwise occur around the mass center of the actuator.
Owner:MATSUSHITA ELECTRIC WORKS LTD
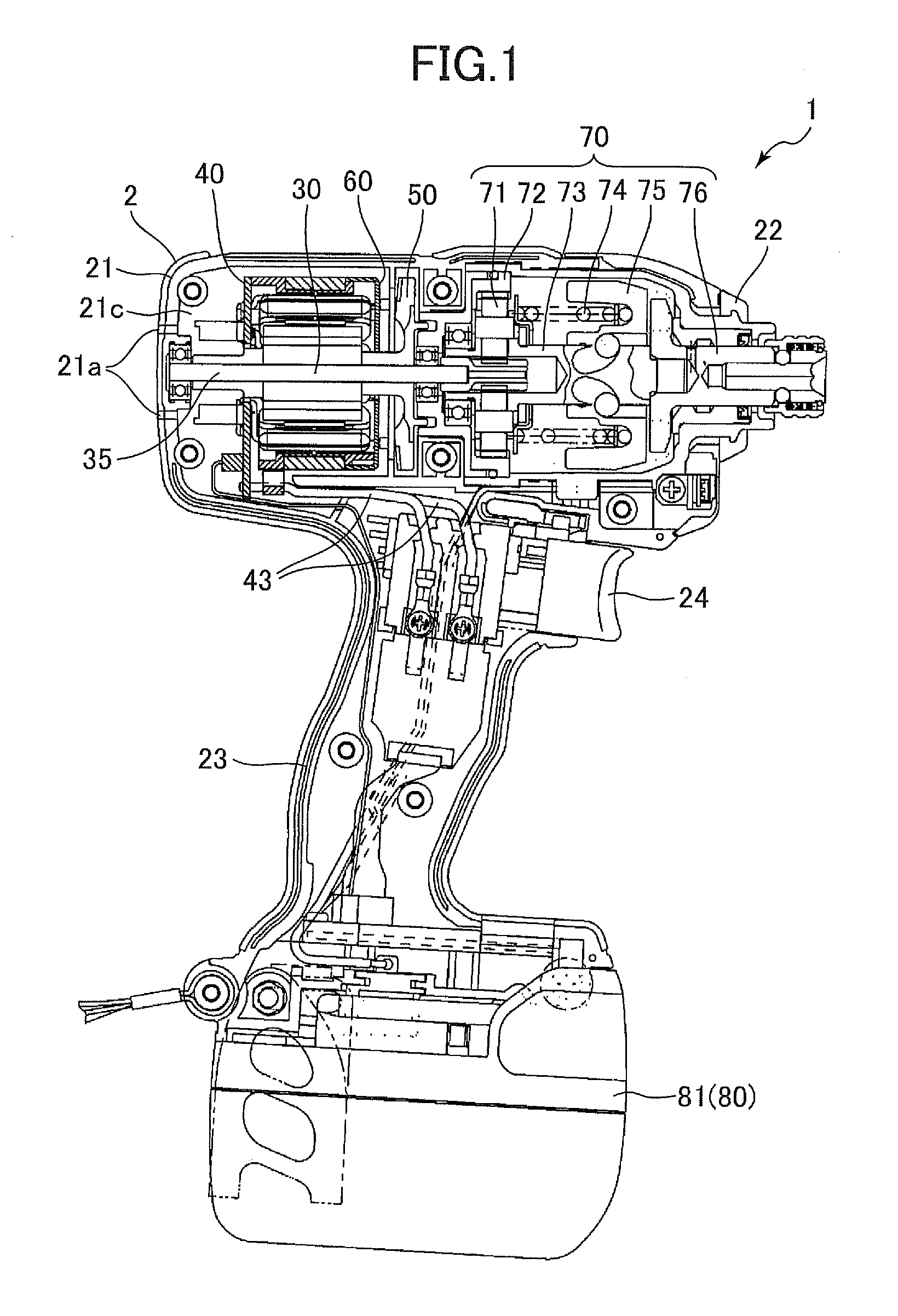
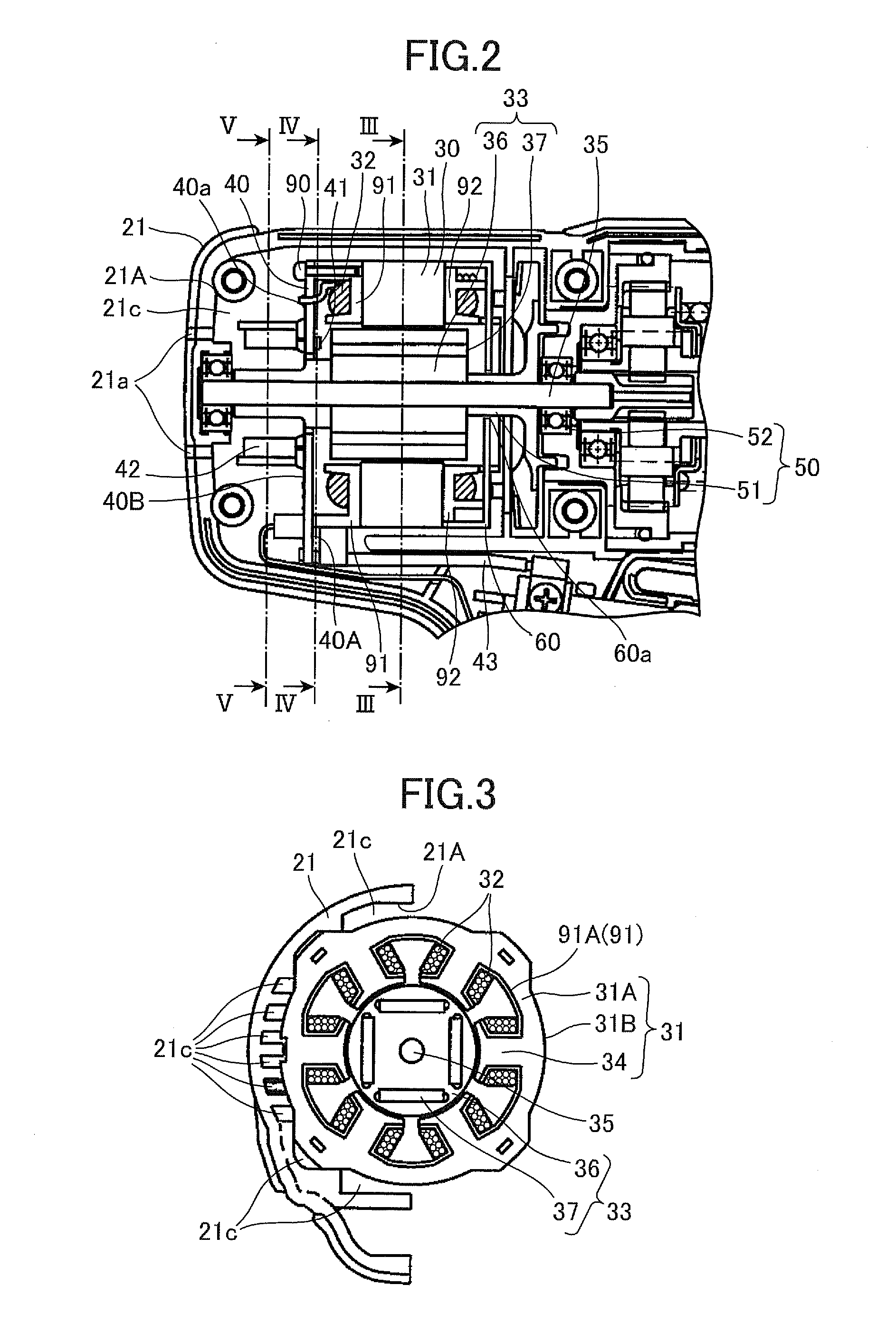
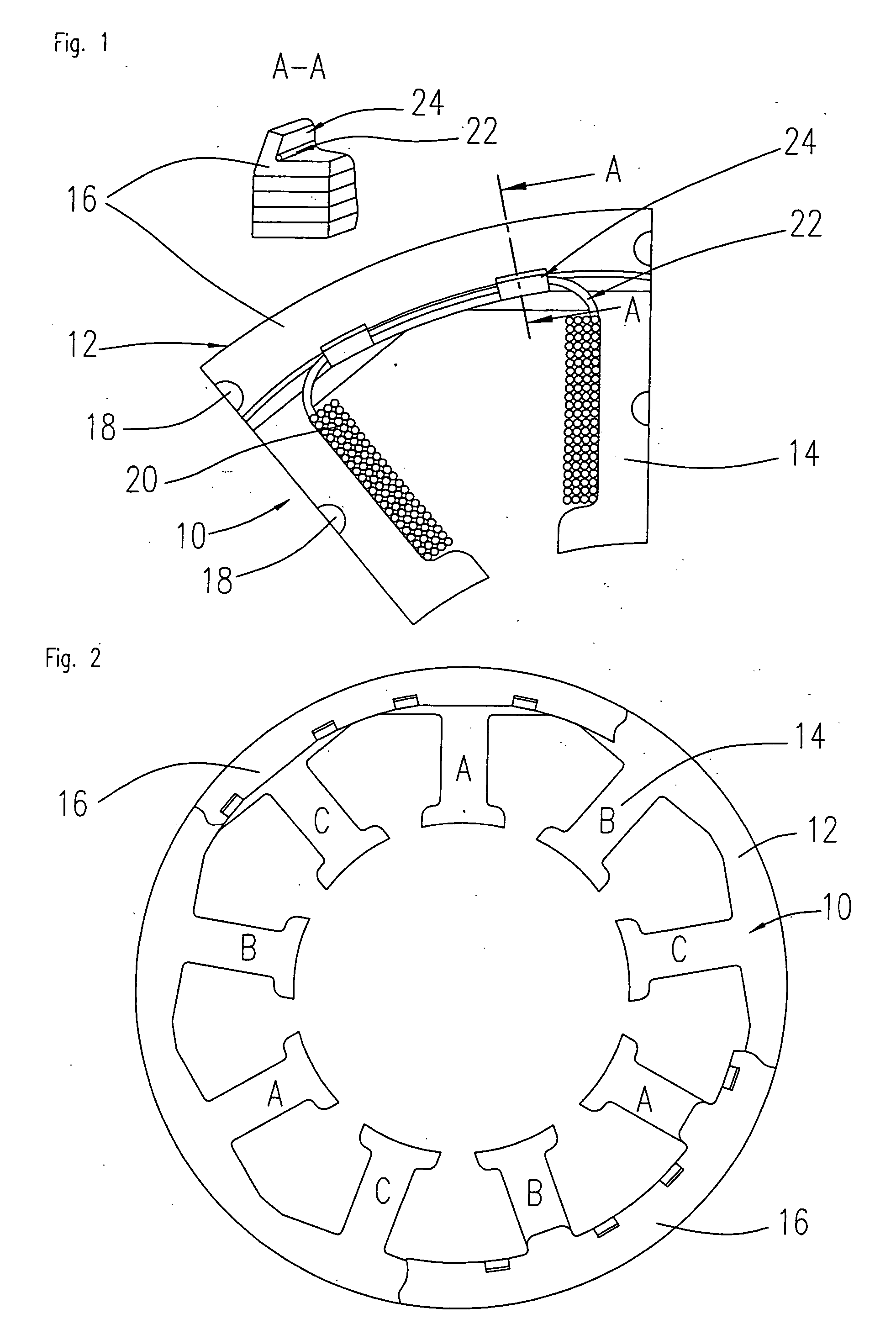
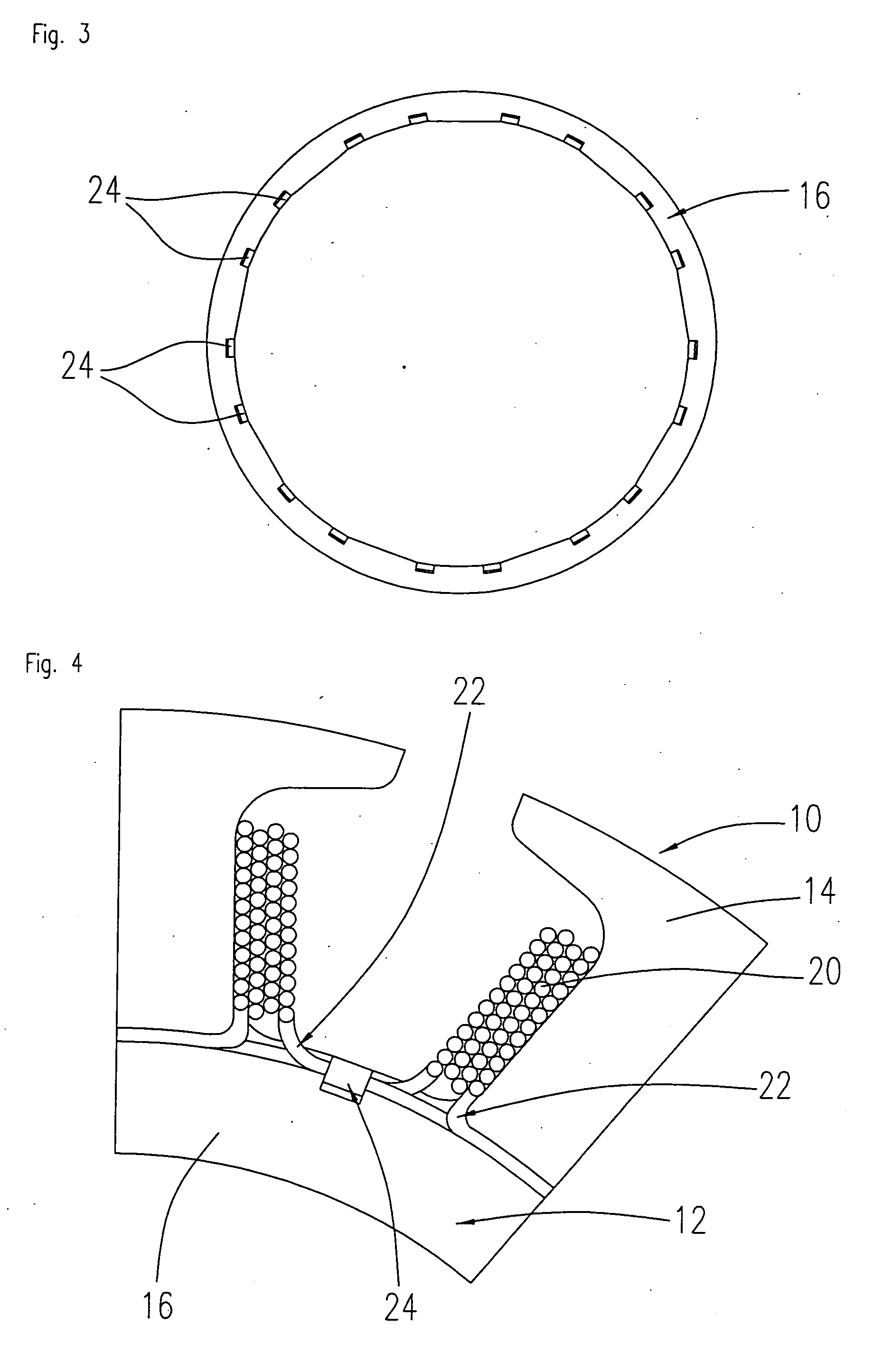
Power Tool
ActiveUS20080265695A1Portable power-driven toolsMagnetic circuit characterised by insulating materialsBrushless motorsEngineering
A power tool includes a housing, a brushless motor, and a cover member. The housing has an air intake hole and an air exhaust hole formed therein, the housing having an inner surface. The brushless motor has an outer surface disposed in the housing, a first endface near the air intake hole, and a second endface near the air exhaust hole. The cover member covers at least one of the first endface and the second endface for preventing dust from entering the brushless motor. The inner surface of the housing and outer surface of the brushless motor define a circulation path providing communication between the air intake hole and the air exhaust hole.
Owner:HITACHI KOKI CO LTD
Rotary electric machine and electric vehicle
ActiveUS20090224627A1Reduce pulsationSlow down drastic changesHybrid vehiclesPropulsion by batteries/cellsElectric machineEngineering
A rotary electric machine includes a stator having stator windings; and a rotor rotatably disposed in the stator, said rotor having a rotor core provided with a plurality of magnets and a plurality of magnetic auxiliary salient poles formed between poles of the magnets. In this rotary electric machine: a magnetic air gap is provided in an axial direction of the rotor in a position shifted in a circumferential direction from a q axis passing through a center of the magnetic auxiliary salient pole within the magnetic auxiliary salient pole; and an amount of shifting the magnetic air gap from the q axis in the circumferential direction differs according to a position of the magnetic air gap in the axial direction so as to cancel torque pulsation in energization caused due to the magnetic air gap.
Owner:HITACHI ASTEMO LTD
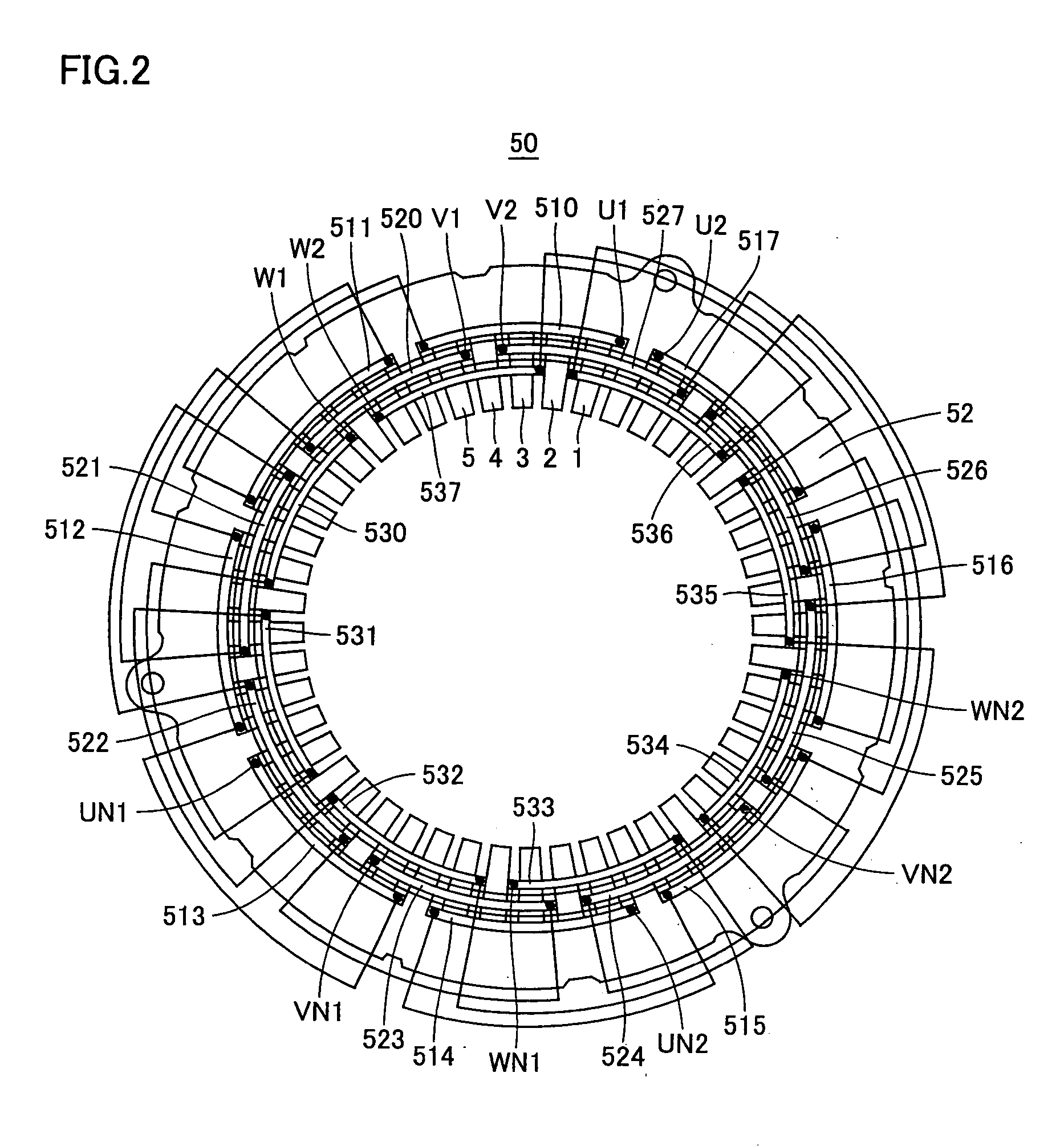
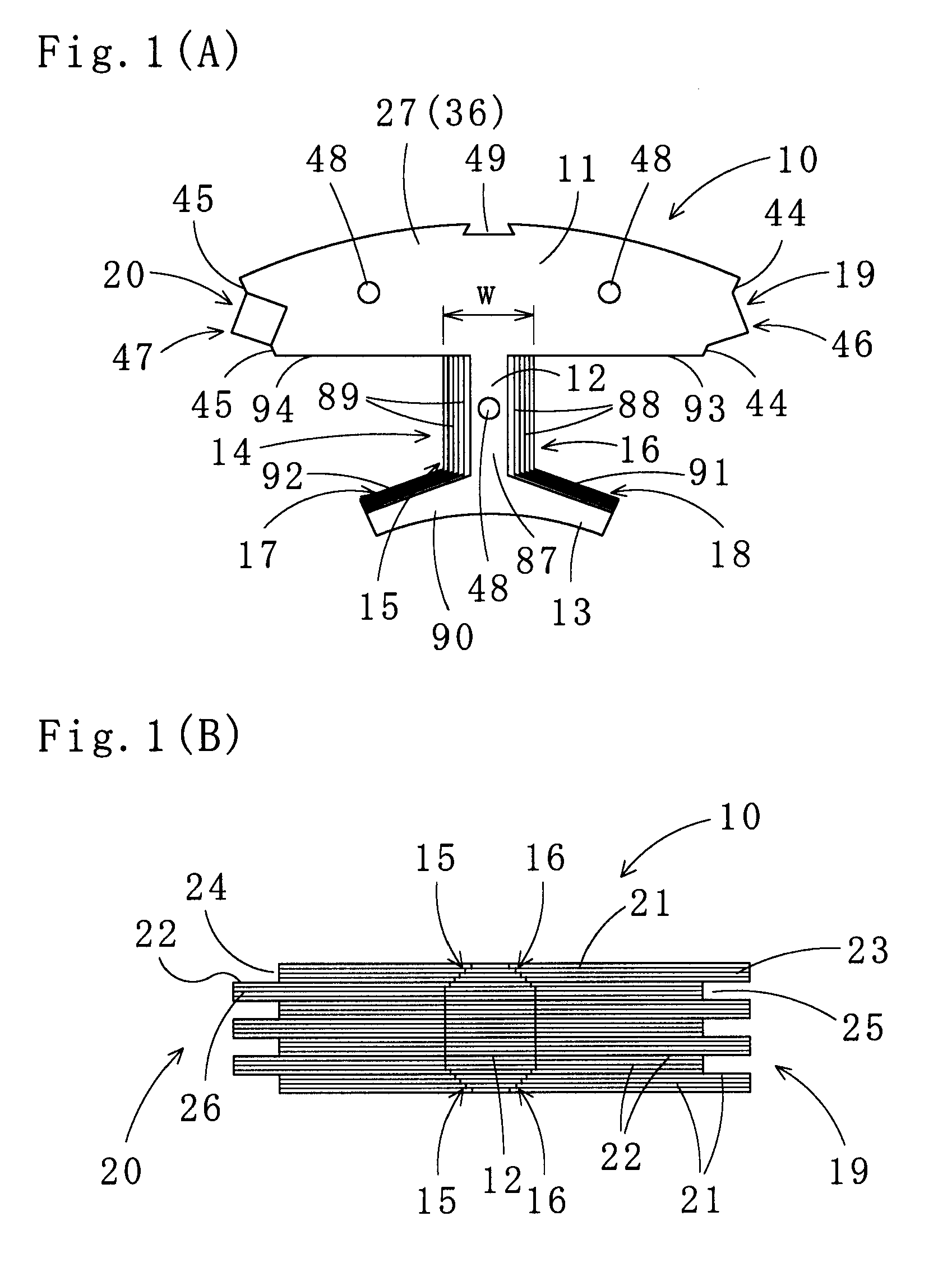
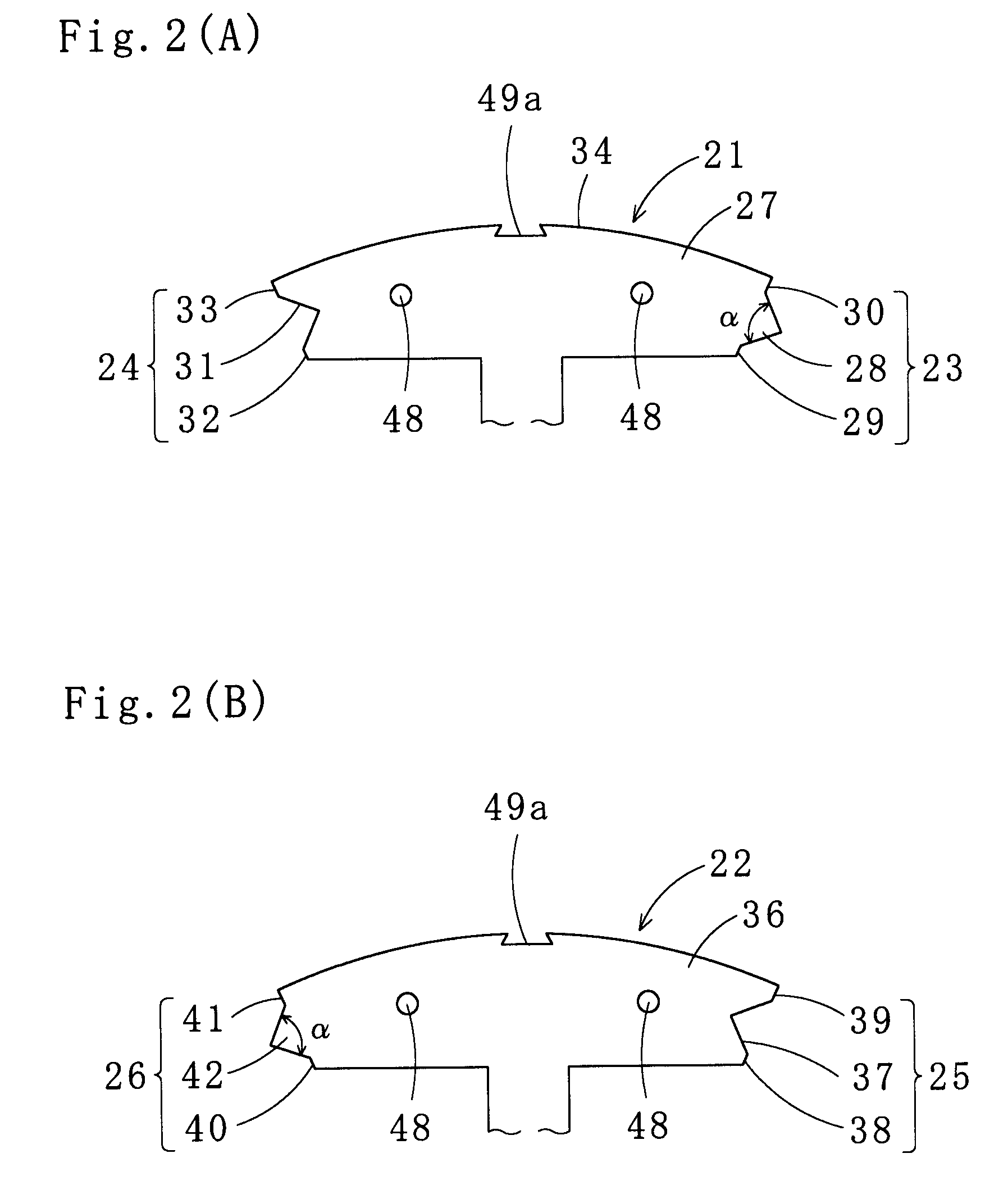
Stator and brushless motor
InactiveUS20060022544A1Remarkable effectSynchronous generatorsDC commutatorBrushless motorsThree-phase
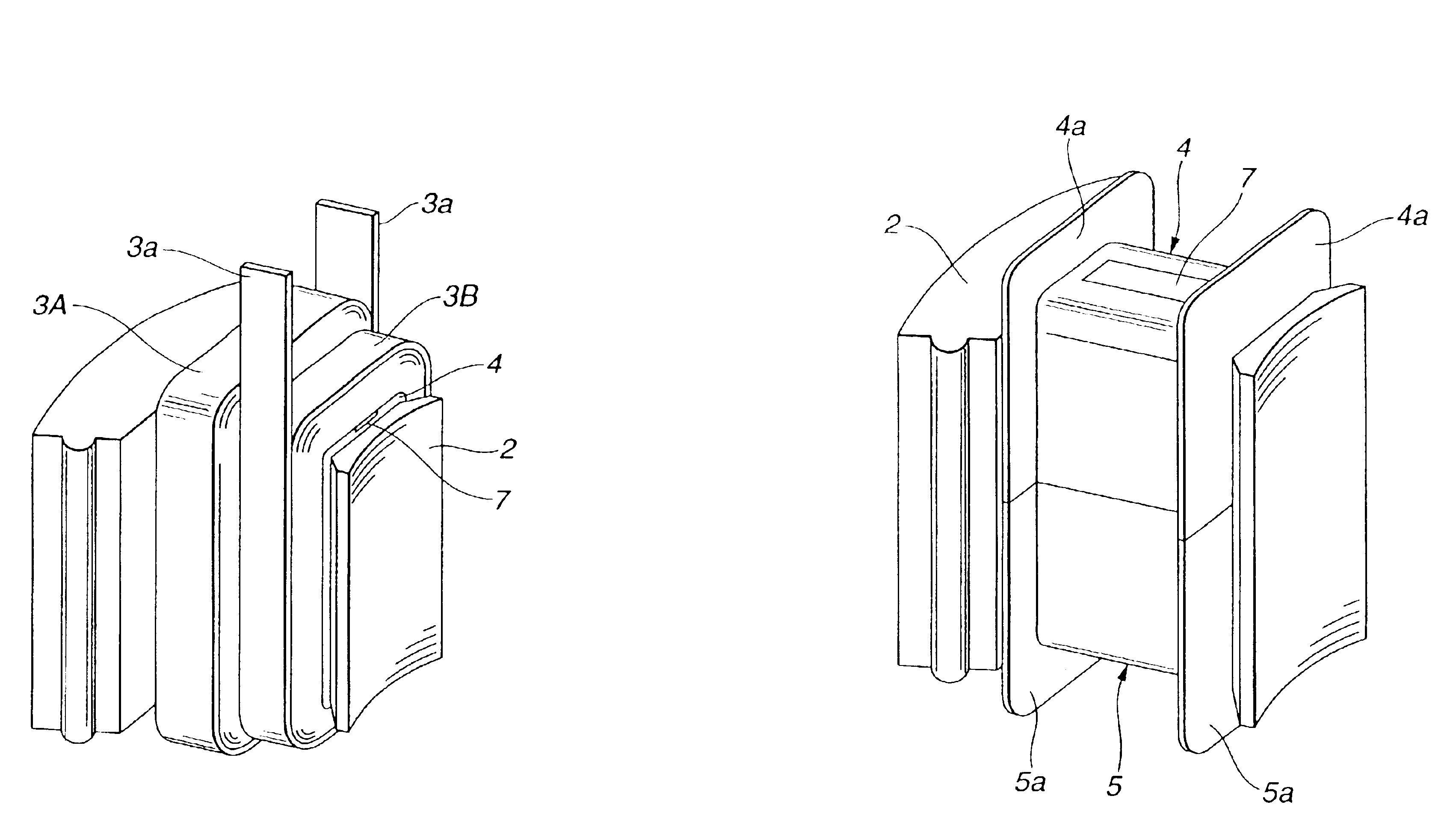
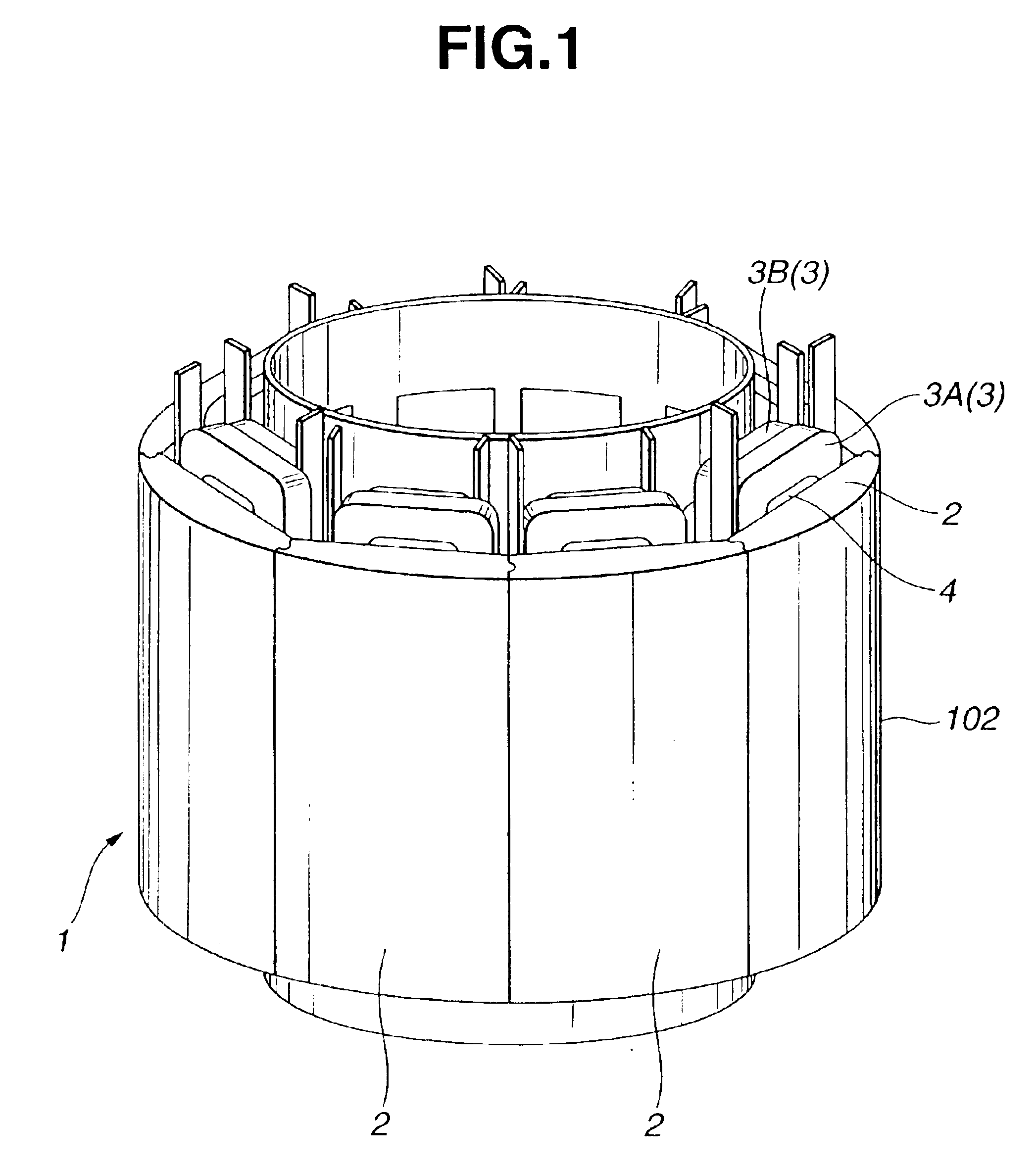
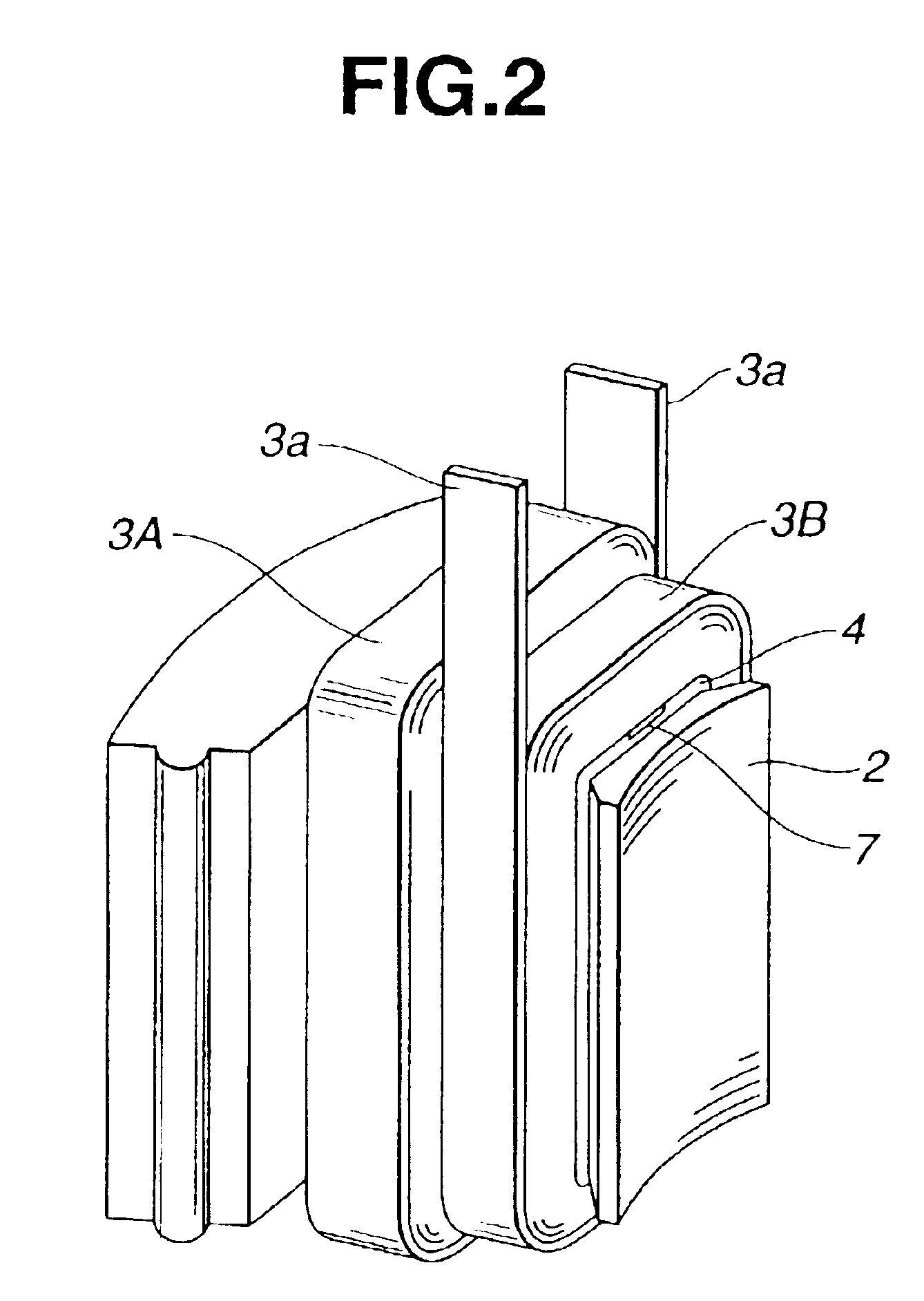
The invention provides a technique of facilitating a coil winding work by continuously winding coils in the same direction, in a stator in which a plurality of coils constituting a coil group of the same phase are respectively arranged so as to include positions at which phases of induction voltage are different, whereby coil groups of three phases are disposed in a ring shape. A stator (102) of the invention has a structure in that a pair of coils (21U1, 21U4) and coils (21U2, 21U3) in which phases of induction voltage are identical in a plurality of coils (21U1 to 21U4) constituting a U-phase coil group (21U) are set as different divided groups, the respective coils (21U1, 21U4) and coils (21U2, 21U3) in the divided group are continuously wound in the same winding direction while arranging crossovers (26U1, 26U3) respectively between the coils (21U1, 21U4) and between the coils (21U2, 21U3), the divided groups are connected in parallel, and a V phase and a W phase are executed in the same manner, whereby lead wires of three-phase coil groups (21U, 21V, 21W) are star connected.
Owner:ICHINOMIYA ELECTRIC
Stator for motor
InactiveUS6870292B2Overall small sizeUndesired shiftSynchronous generatorsDC commutatorEngineeringConductor Coil
A stator for a motor is a segmented type including a plurality of stator segments. Each stator segment includes a core segment forming a stator core, a stator winding including a first winding wound in one direction on the core segment, and a second winding wound in the opposite direction on the core segment, and an insulating member interposed between the core segment and the stator winding. A connecting member is formed integrally in the insulating member, and arranged to electrically connect inner ends of the first and second windings to form a single continuous winding.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
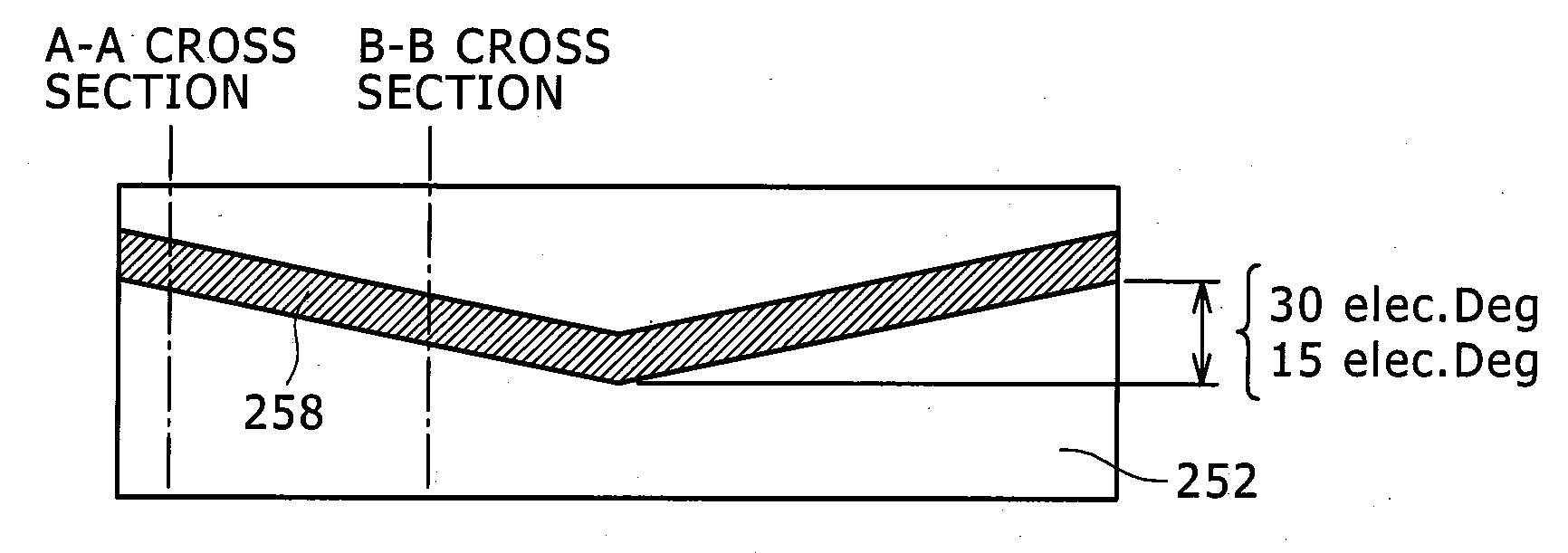
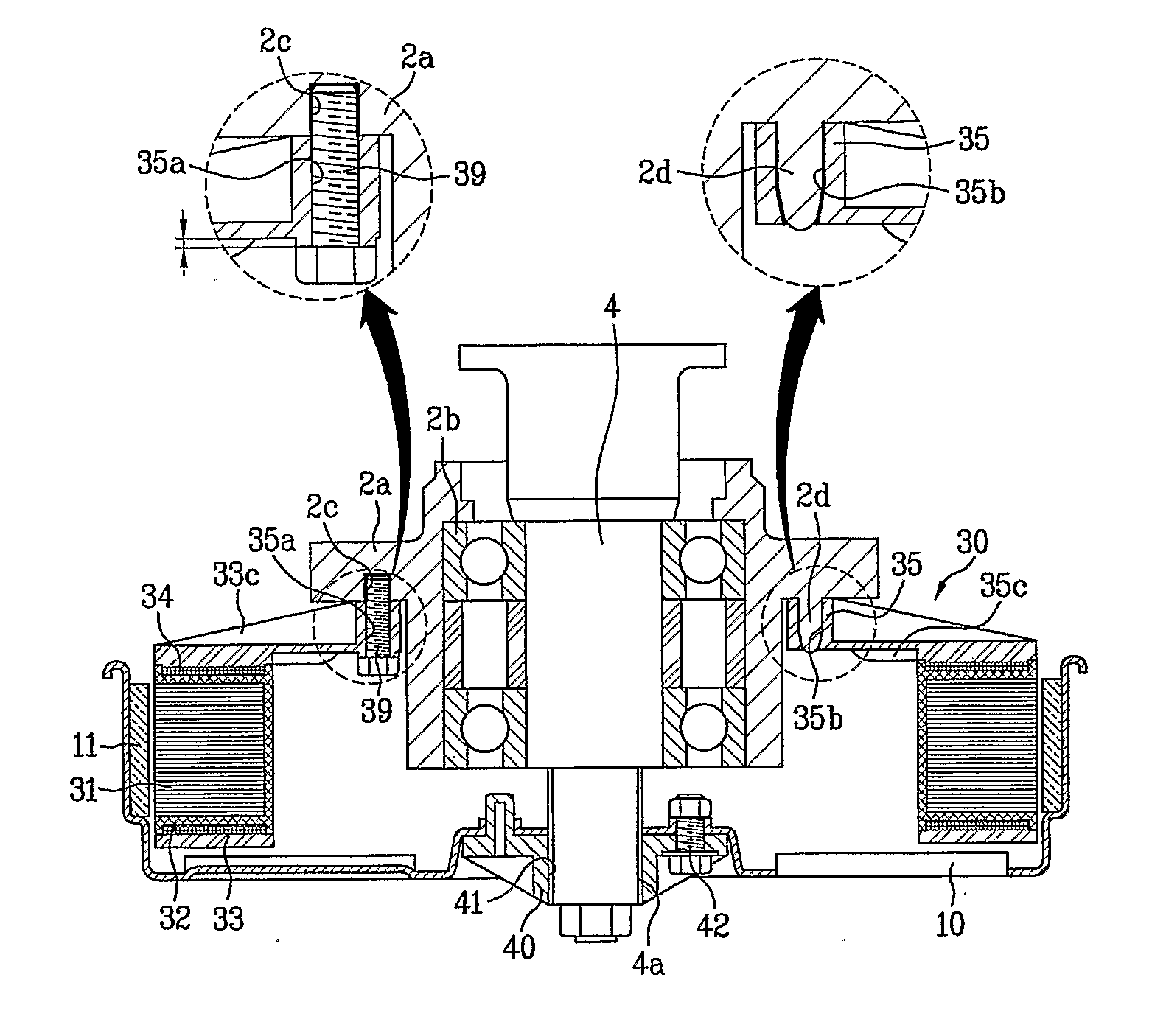
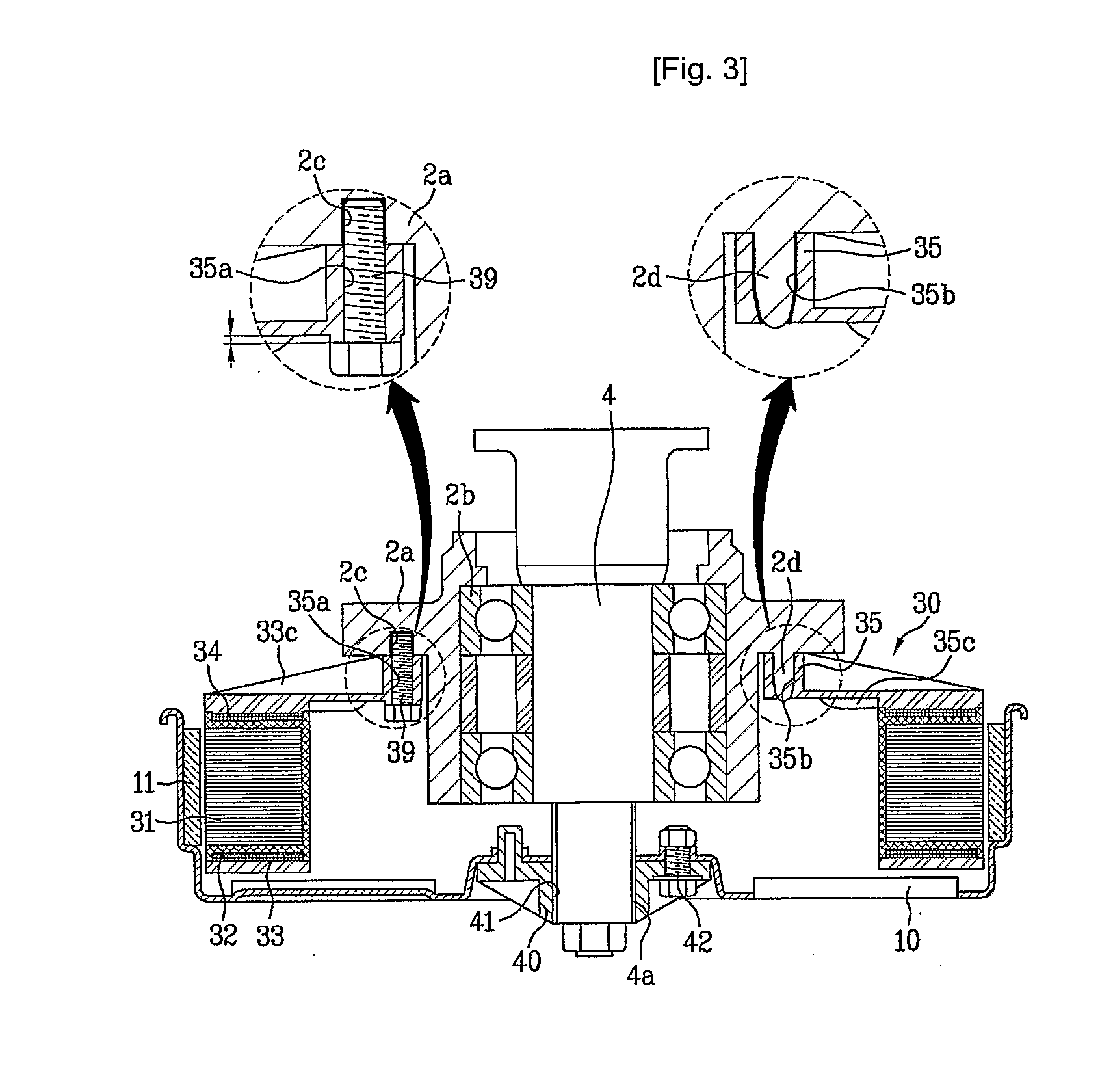
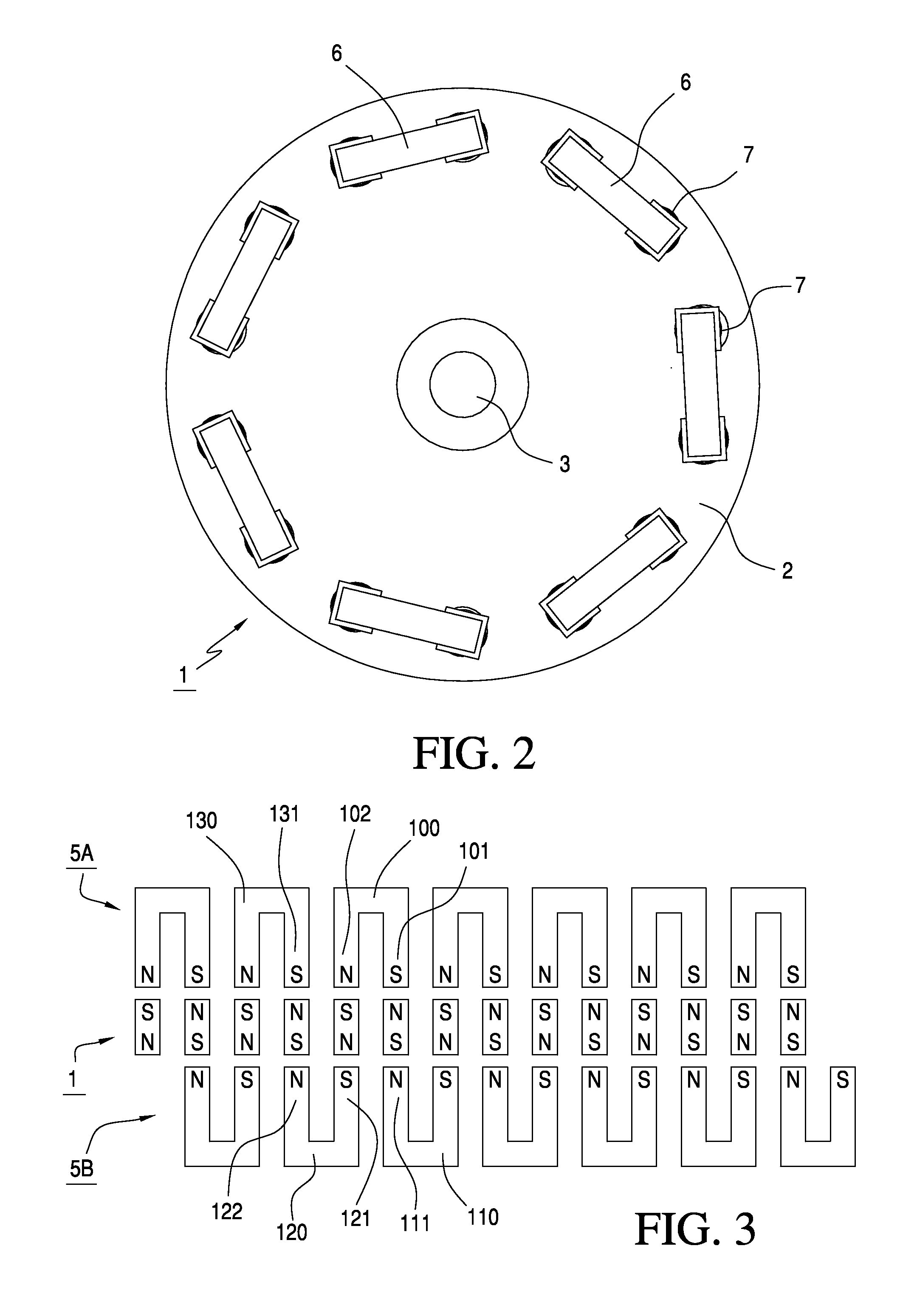
Permanent magnet rotating machine
ActiveUS20070126305A1Improve efficiencyReduce noiseMagnetic circuit shape/form/constructionSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsMagnetic polesEngineering
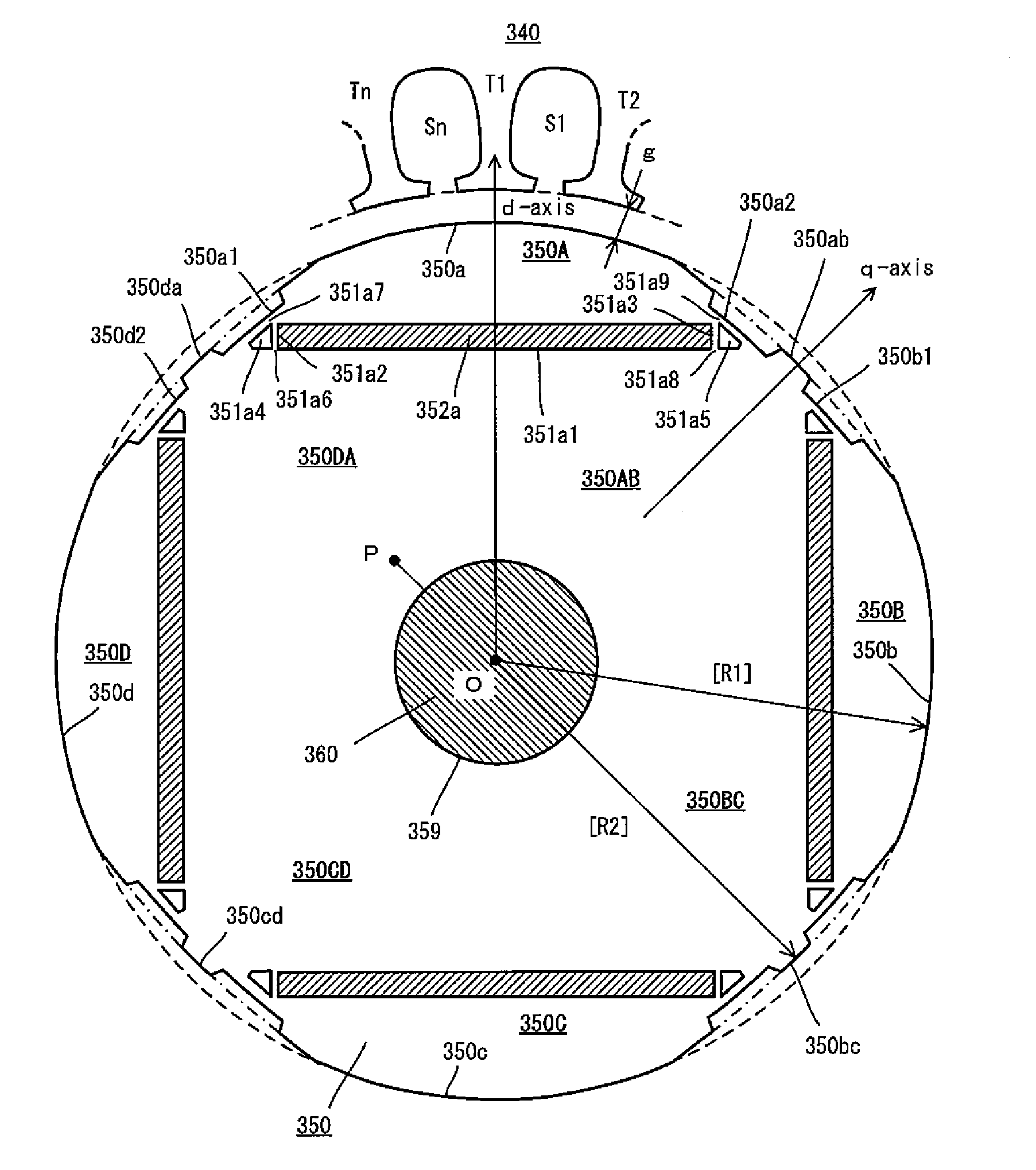
Permanent magnets 52a1, 52a2 are inserted into magnet insert holes 51a1, 51a4 formed in a main magnetic pole 50A of a rotor 50. An outer circumferential surface of the rotor includes a first outer circumferential surface portion 50a which intersects with a d-axis and second outer circumferential surface portions 50da, 50ab which intersect with a q-axis. A radius R2 of curvature of the second outer circumferential surface portions 50da, 50ab is larger than a radius of curvature of the first outer circumferential surface portions 50a. Recesses 50a1, 50a2 are formed in the second outer circumferential surface portions 50da, 50ab and in a position to face end walls 51a2, 51a5 of the magnet insert holes 51a1, 51a4 which are adjacent to the outer circumferential surface of the rotor. It is constructed such that [(74 / P)°≦θ≦(86 / P)°] and [(16 / P)°≦α≦(48 / P)°], where θ is a mechanical angle of the first outer circumferential surface portion 50a, P is the number of pairs of poles of the rotor 50, and α is a mechanical angle of the recesses 50a1, 50a2.
Owner:AICHI ELECTRIC
Transverse and/or commutated flux system stator concepts
Disclosed are transverse and / or commutated flux machines and components thereof, and methods of making and using the same. Certain exemplary stators for use in transverse and commutated flux machines may be configured with gaps therebetween, for example in order to counteract tolerance stackup. Other exemplary stators may be configured as partial stators having a limited number of magnets and / or flux concentrators thereon. Partial stators may facilitate ease of assembly and / or use with various rotors. Additionally, exemplary floating stators can allow a transverse and / or commutated flux machine to utilize an air gap independent of the diameter of a rotor. Via use of such exemplary stators, transverse and / or commutated flux machines can achieve improved performance, efficiency, and / or be sized or otherwise configured for various applications.
Owner:ELECTRIC TORQUE MASCH INC
Permanent magnet rotating machine
ActiveUS7605510B2Improve efficiencyReduce noiseMagnetic circuit shape/form/constructionSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsMagnetic polesEngineering
Owner:AICHI ELECTRIC
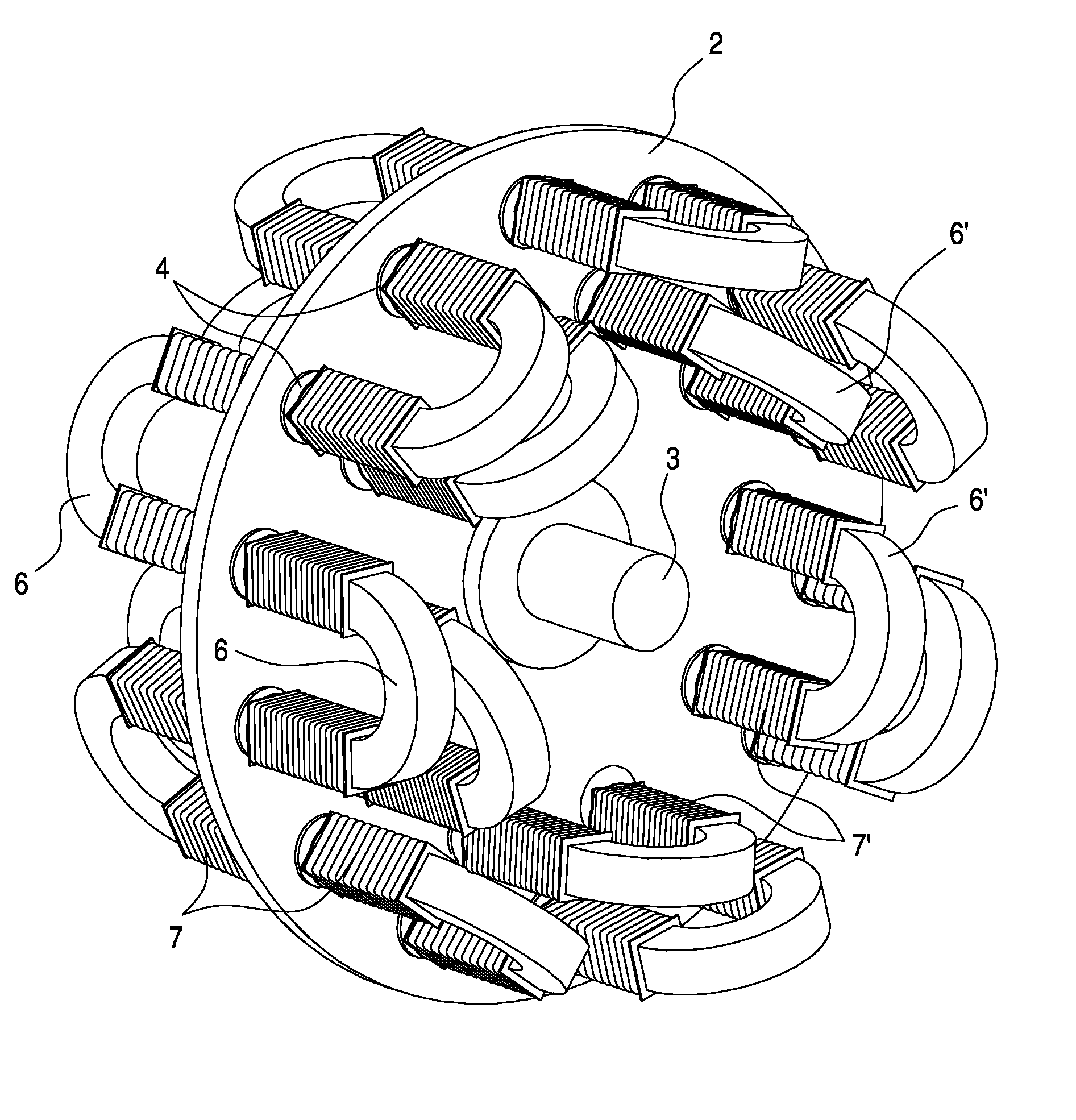
Permanent magnet excited transverse flux motor with outer rotor
ActiveUS20070152528A1Improve output power densityReduce noiseMagnetic circuit stationary partsManufacturing dynamo-electric machinesTransverse fluxConductor Coil
Disclosed herein is a permanent magnet-excited transverse flux motor with an outer rotor. The permanent magnet-excited transverse flux motor comprises: a stator including a stator powdered iron core formed by an extruded molding through a mold, a pair of stator laminated iron cores stacked respectively at an upper layer portion and a lower layer portion of an outer circumference of the stator powdered iron core in such fashion as to be spaced apart from each other by a certain interval, and a stator winding interposed between the upper layer portion and the lower layer portion in such fashion as to be wound around the stator powdered iron core to form a multiple coil through which current flows; and a rotor including a plurality of rotor permanent magnets and a plurality of rotor powdered iron cores disposed on the outer circumference of the stator in such a fashion as to be are alternately arranged adjacent to one another.
Owner:KOREA ELECTROTECH RES INST
Rotor and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20060186752A1Promote disseminationHigh strengthSpeed controllerElectric devicesEngineeringMagnet
A rotor includes a rotor core fixedly provided on a shaft and having a hole, a magnet inserted into the hole, and a resin portion injected between the side surface of the hole and the side surface of the magnet and, the side surface of the magnet has a groove formed therein as a spread-promoting portion that promotes spread of the injected resin portion.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
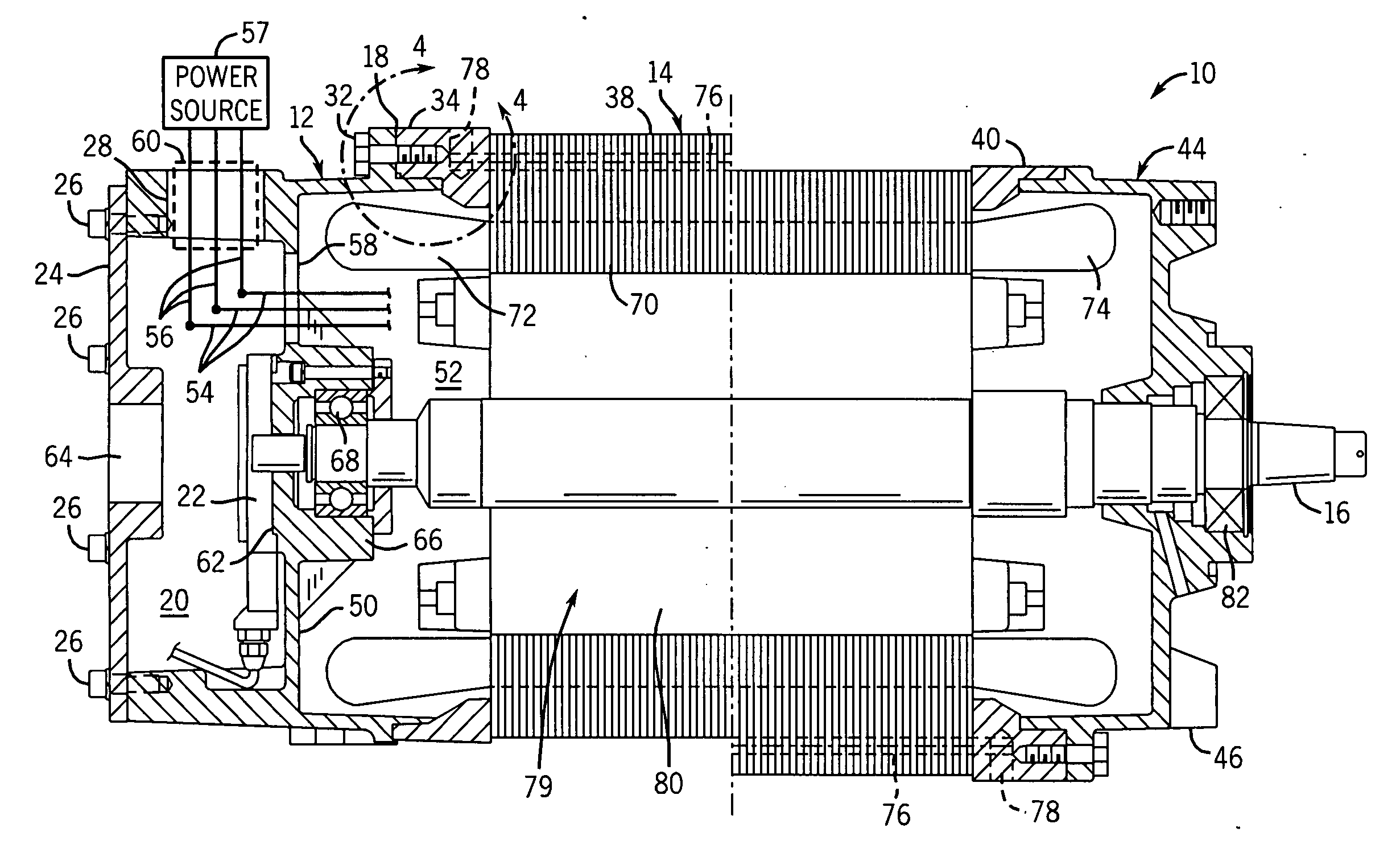
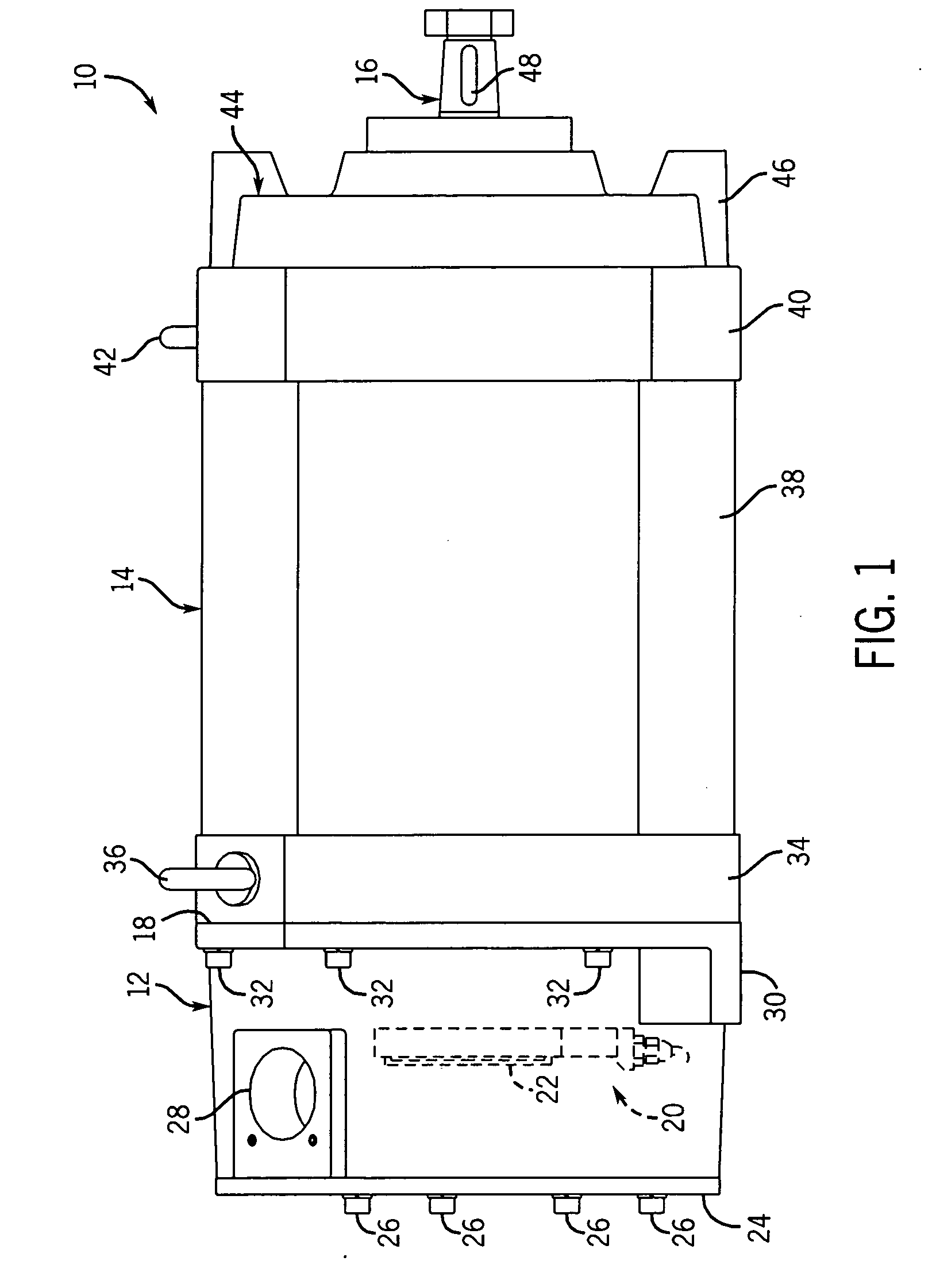
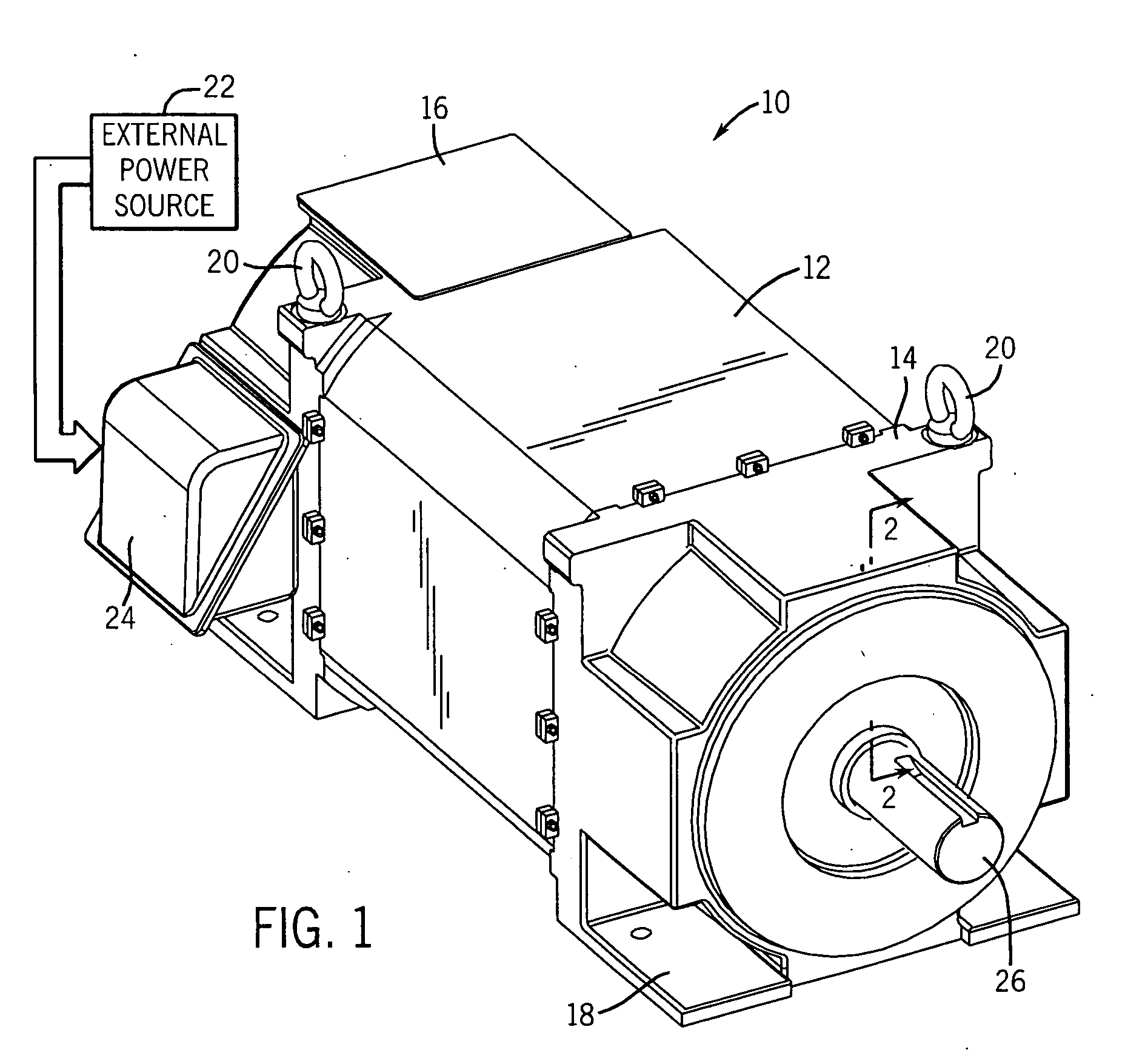
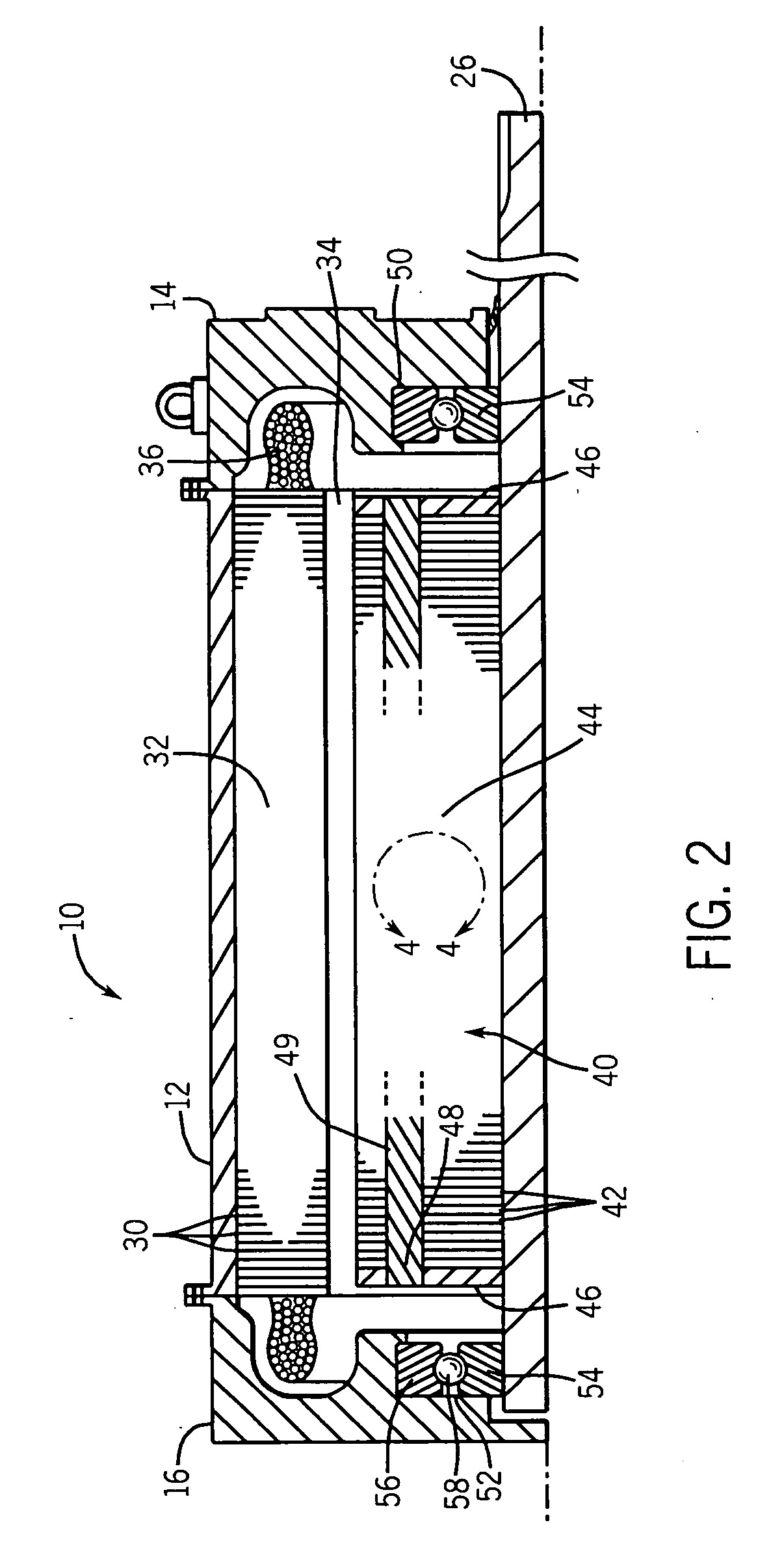
Explosion-proof motor with integrated sensor/lead housing
InactiveUS20070159017A1Reduce in quantityStructural associationMagnetic circuit shape/form/constructionStator coilEngineering
A novel explosion-proof motor, which includes an integrated explosion-proof housing. In some embodiments, the integrated explosion-proof housing contains various electronic components that support the operation of the explosion-proof motor. To this end, embodiments of the explosion-proof motor may include a stator having an end ring, a plurality of stator coils extending from a core, and an end bracket fitted to the stator end ring to form a generally circumferential flame path. The end bracket may include an inner volume on one side thereof for receiving the stator coils, and an integrated explosion-proof housing on the other side. To reduce the number of explosion-proof seals, the inner volume and integrated explosion-proof housing may share the circumferential flame path to enclose their respective volumes.
Owner:RELIANCE ELECTRIC TECH
Motor
InactiveUS20080122300A1Waterproofness can be improvedSimple structureWindings insulation shape/form/constructionManufacturing dynamo-electric machinesEngineeringMagnet
A motor adapted to rotate an element of an appliance, for example, a drum of a washing machine, is disclosed. The motor includes a rotating shaft which is rotatably mounted to a motor mounting member of an appliance, a rotor which includes magnets circumferentially arranged at a position radially spaced apart from a center of the rotating shaft by a predetermined distance such that N and S poles are alternately arranged, and a stator which includes a core made of metal, an insulator enclosing the core while allowing a surface of the core facing the magnets of the rotor to be outwardly exposed, the insulator being made of an insulating resin material, coils wound on the insulator, and a circular molded member formed in accordance with an insert molding method to enclose the insulator and the coils while allowing the surface of the core outwardly exposed through the insulator to be outwardly exposed.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
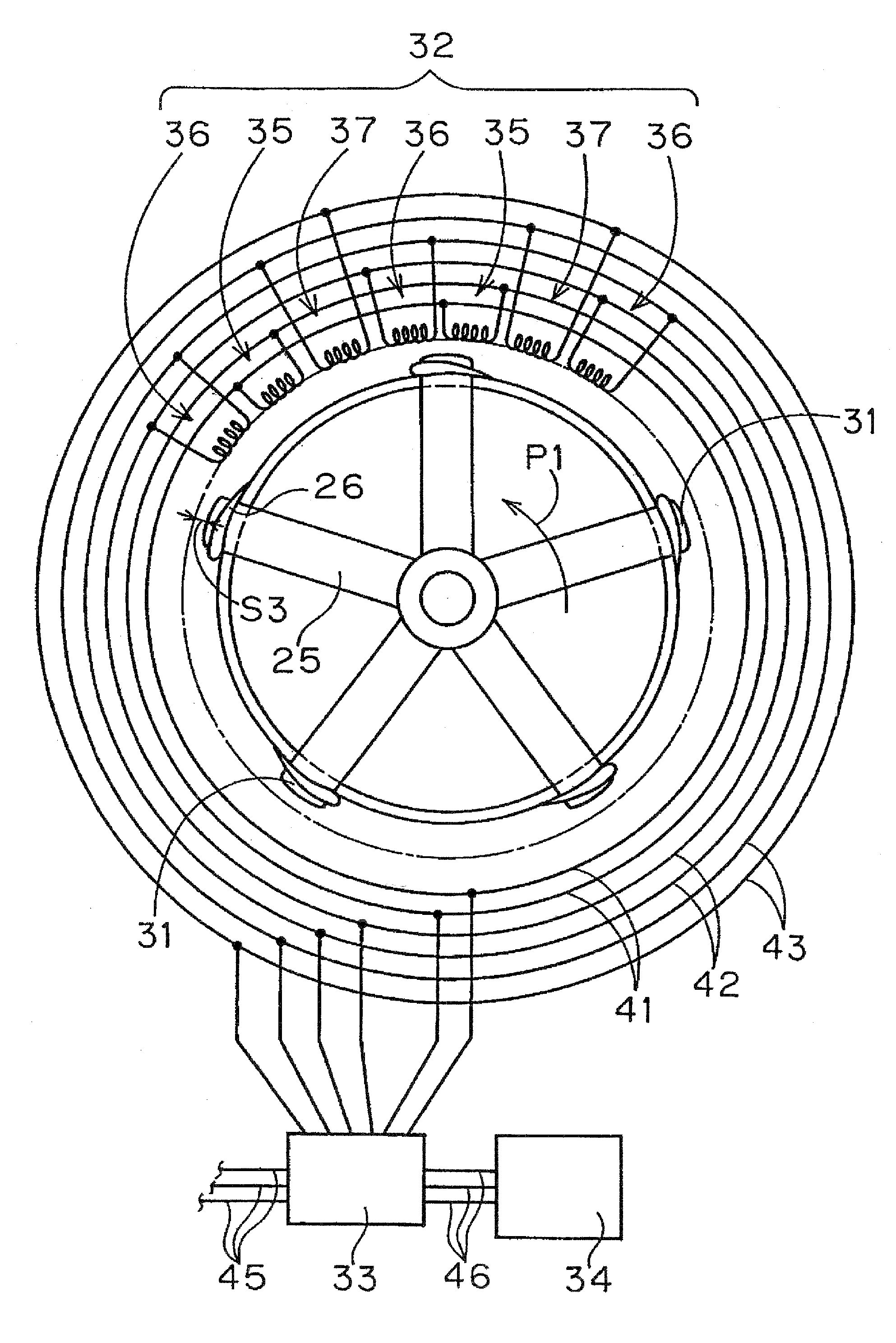
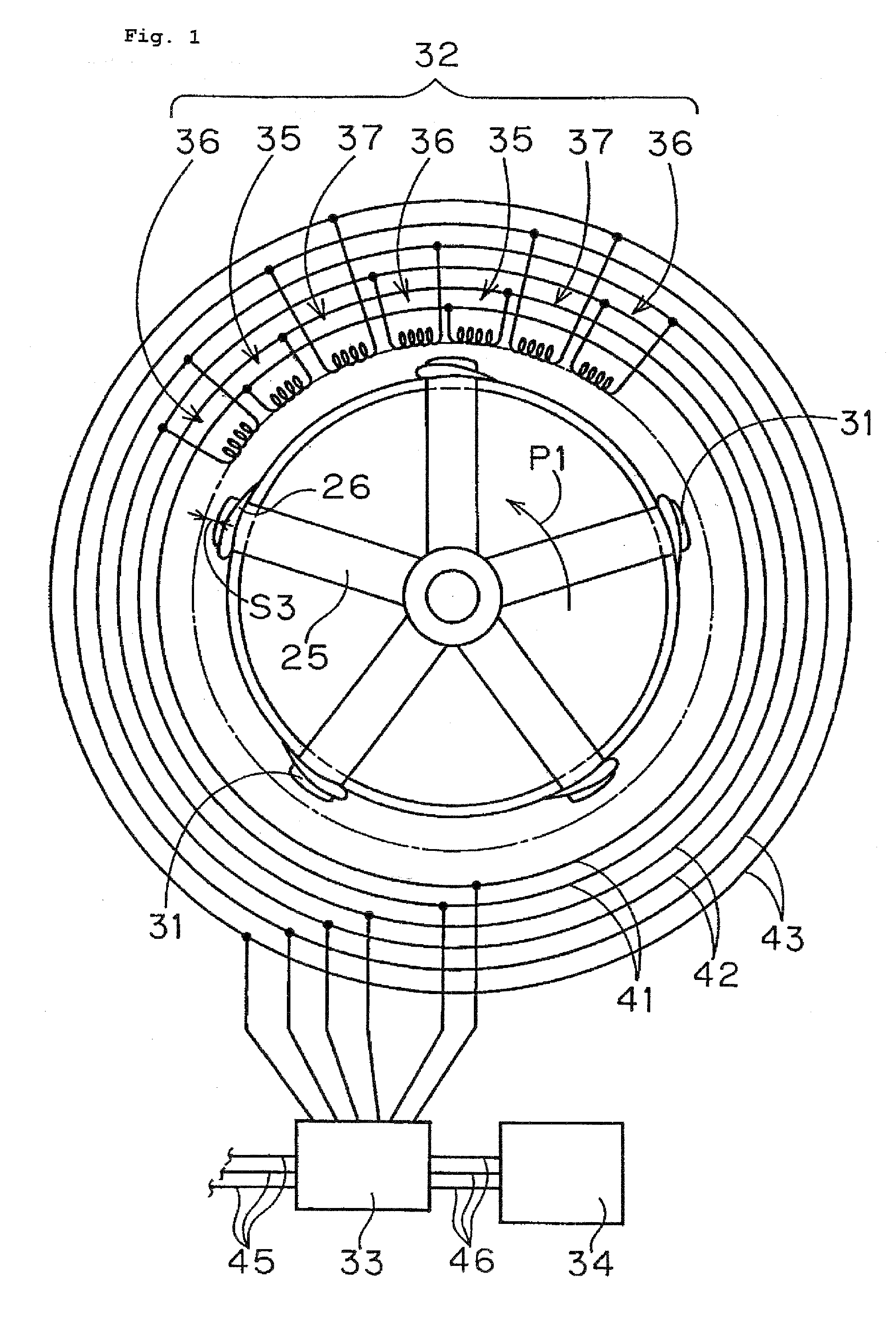
Wind power generation system, arrangement of permanent magnets, and electrical power-mechanical force converter
InactiveUS20080315709A1Reduce weightSmooth rotationWind motor supports/mountsAsynchronous induction motorsImpellerRelative motion
A wind power generation system 10 comprising a frame, an impeller 12 rotatably supported by the frame, plural permanent magnets 31 aligned at equal intervals from the rotation center, and coils 32 aligned annularly on the frame. The relative motion of the permanent magnets 31 and the coils 32 in close vicinity generates electric powers by the inverse action of a linear motor. The coils 32 are mounted on the ring provided on the frame, and the permanent magnets 31 are provided on the lower end of the longitudinal blades 26 of the impeller.
Owner:COSMO PLANT
Brushless DC motor with molded resin housing
InactiveUS20060220474A1Avoid flowAssociation with grounding devicesMagnetic circuit characterised by insulating materialsEngineeringElectric current flow
An invention is provided wherein the bearings of a molded motor do not become electro-eroded. An inner rotor type, brushless DC motor 10 is provided having a stator 22 which has a stator core 12 wound with a coil 16, a housing 26 formed by covering the outside surfaces of the motor 10 with an unsaturated polyester, molding resin having electrical insulating properties, and an earth electrode 40 made of metal, installed to go through a metal bracket 38 and the housing 26 to reach the stator core 12, such that electric current flows from the stator core 12 and the bracket 38 to the exterior, preventing electro-erosion and resulting deterioration of bearings 30, 32.
Owner:NIDEC SHIBAURA CORP
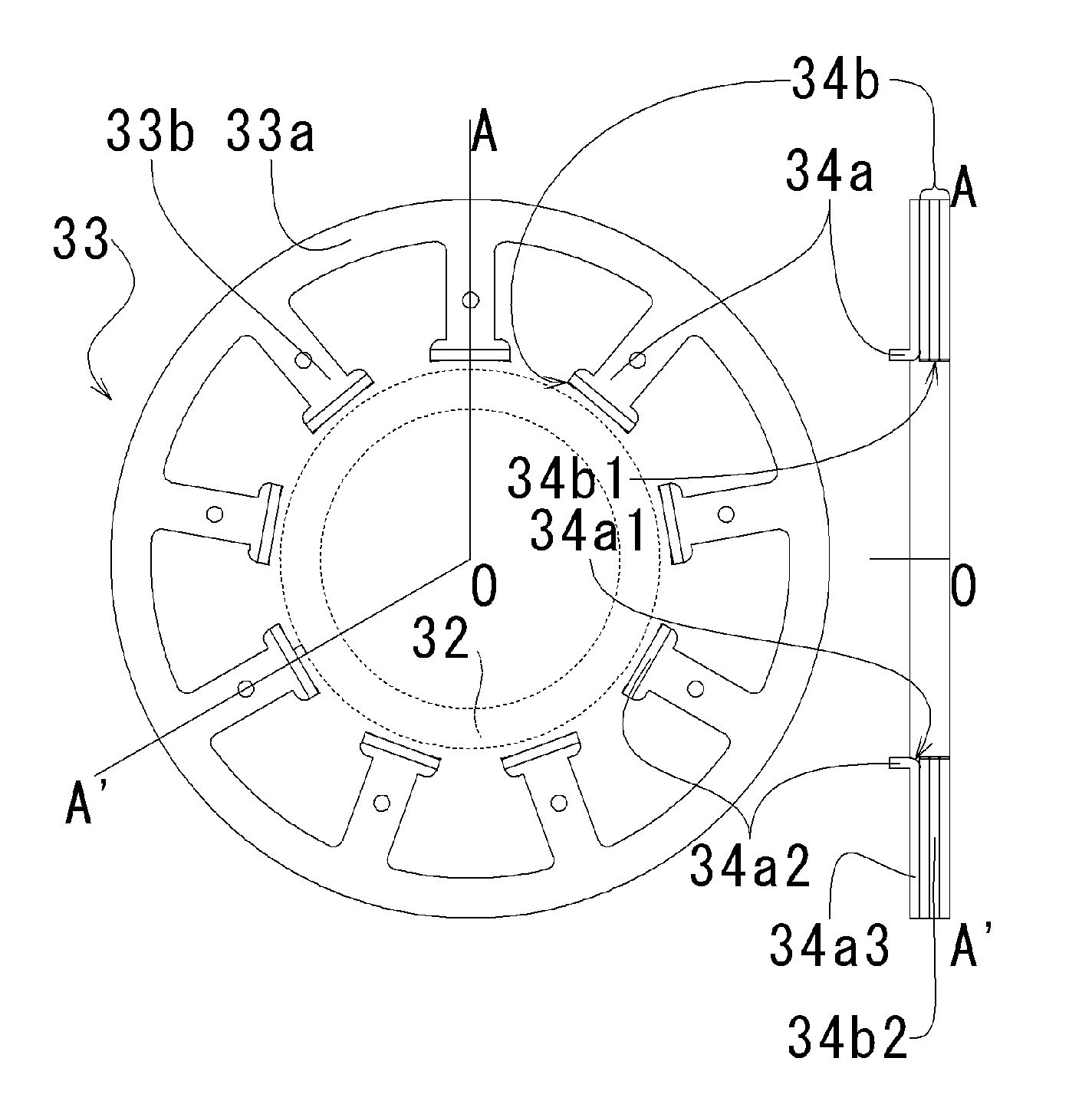
Motor and Recording Disk Drive Device Provided with the Same
InactiveUS20060197402A1Easy to adjustCombined cogging waveform can be reducedMagnetic circuit shape/form/constructionSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsRotor magnetsEngineering
In a spindle motor, a core (33) includes a plurality of core plates (34), which are laminated one on another. The core (33) is constituted by laminating two cores, that is, a first core (34a) and a second core (34b), which are different from each other in shape of a surface facing to a rotor magnet (32). At least a part of a cogging torque generated at the second core (34b) can be cancelled by a cogging torque generated at the first core (34a).
Owner:NIPPON DENSAN CORP
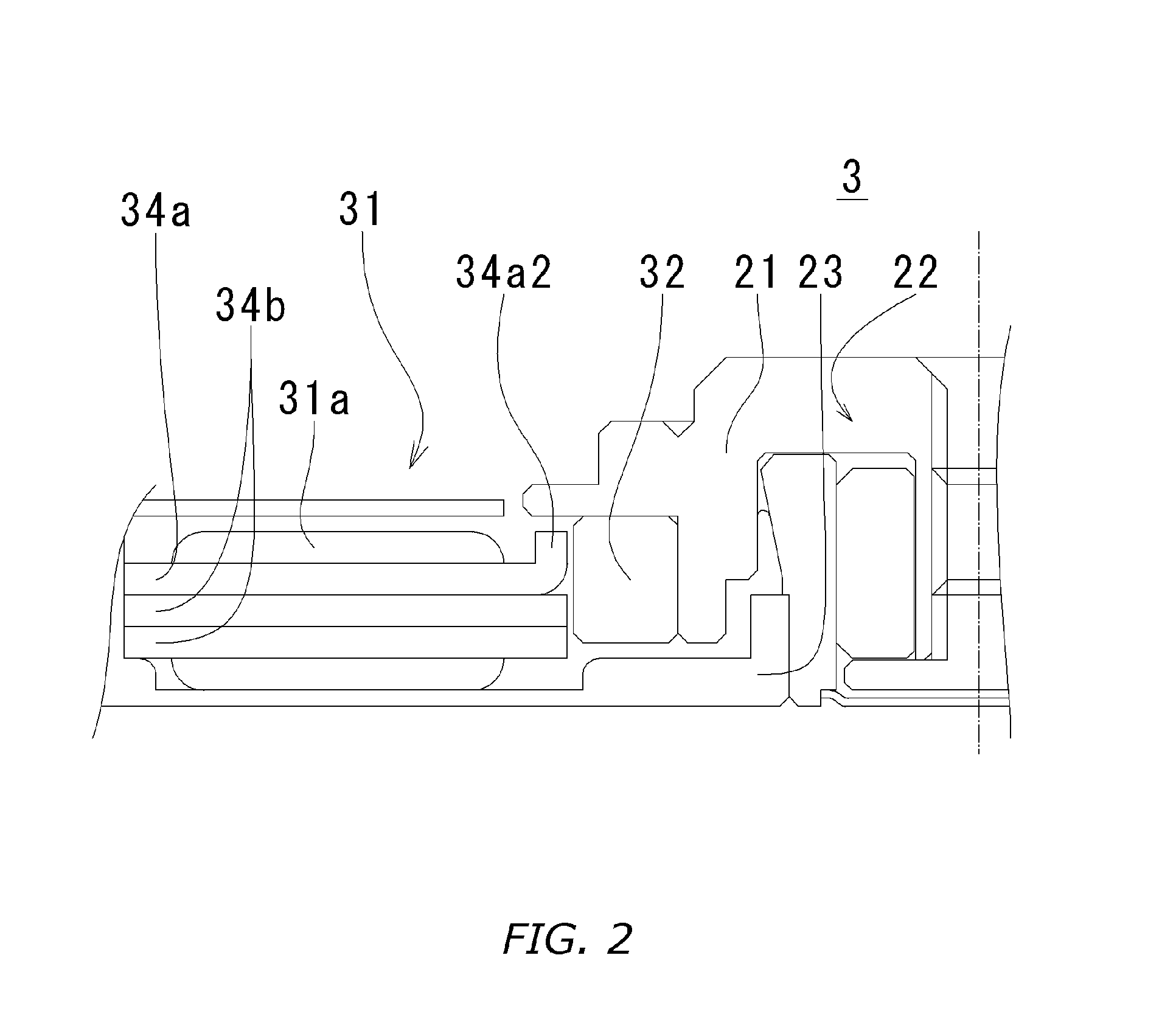
Spindle motor
ActiveUS20070013255A1Thin thicknessMaximize number of turnMechanical energy handlingStructural associationRotor magnetsConductor Coil
In a spindle motor in which teeth portions of a stator core formed by laminating magnetic plates are bent in order to increase the number of turns of the stator windings, a gap in the teeth portions between the magnetic plates is avoided and a precise attractive force adjustment becomes possible. The stator core is bent such that its teeth portions faces a surface of a rotor magnet at right angles, and the teeth portions and salient pole arm portions around which windings are wound are substantially parallel to each other. The salient pole arm portions locate approximately halfway between a lower surface of a hub and an upper surface of a base. Further, a thickness of a magnetic plate is set to be 0.5 to 0.9 times that of other portions.
Owner:PHC HLDG CORP
Fan and motor used thereto
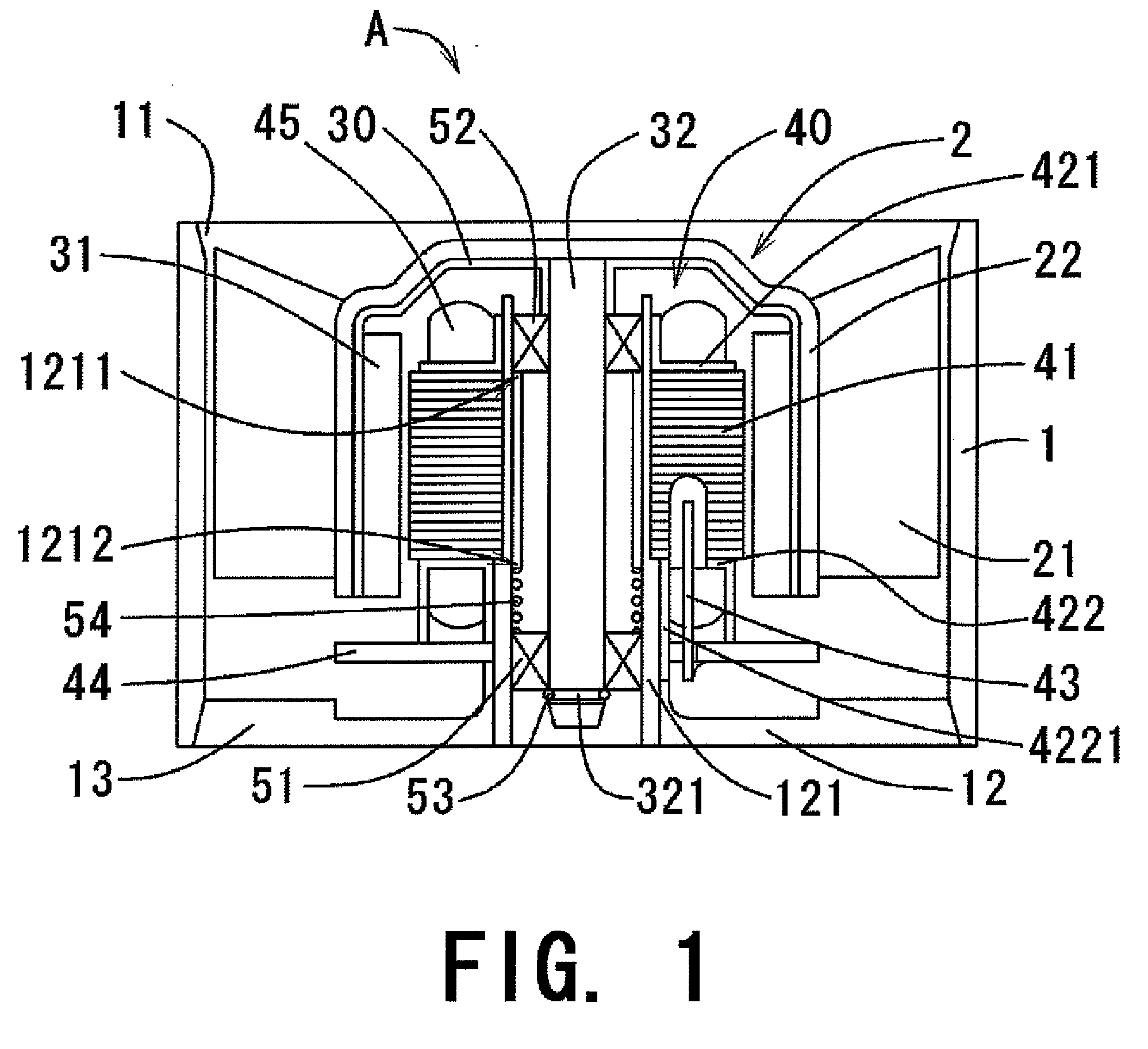
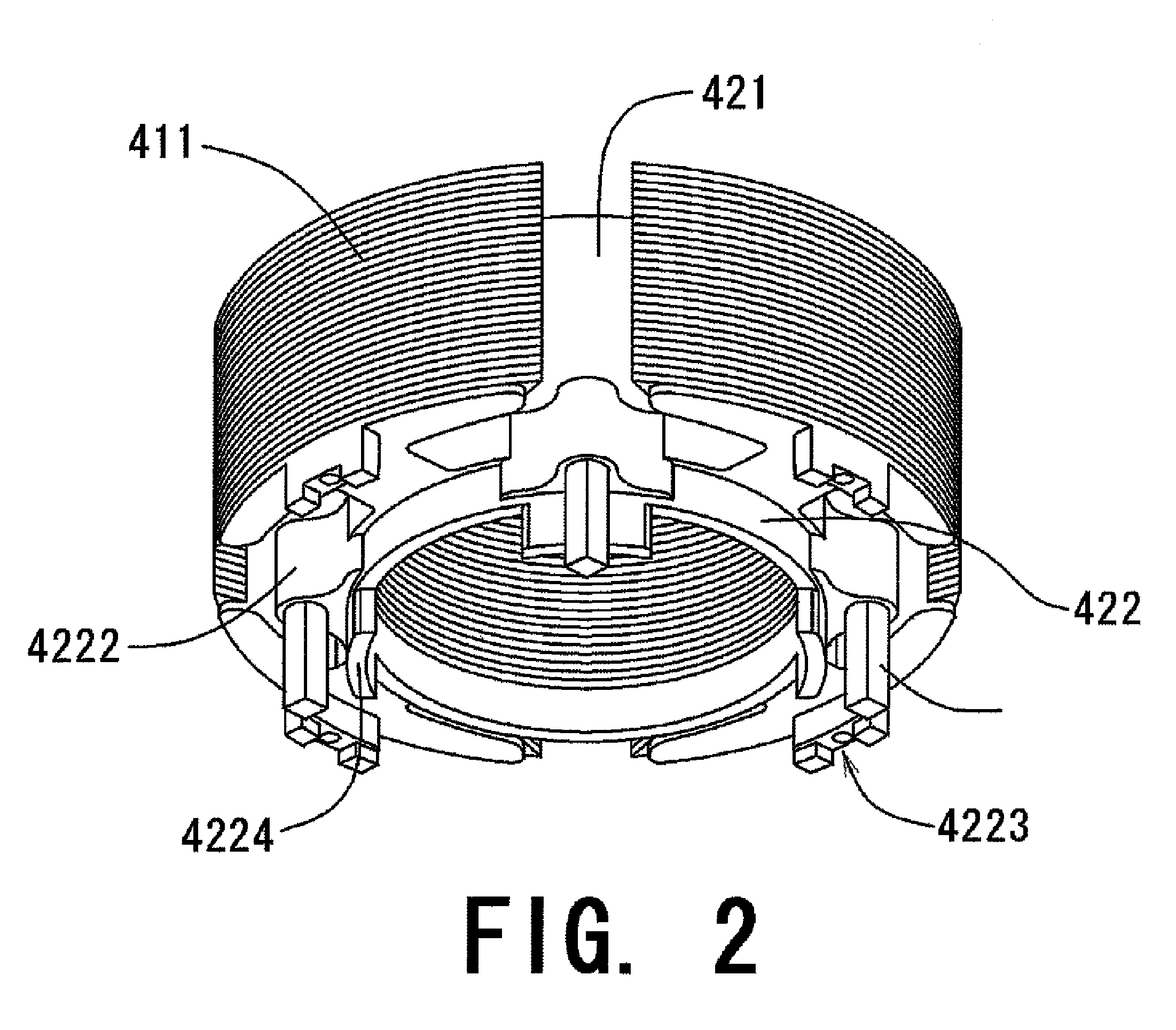
ActiveUS20080054735A1WindingsMagnetic circuit characterised by insulating materialsElectrical conductorEngineering
Axially upper and lower end surfaces of the stator core 41 are substantially covered by the first insulator 421 and the second insulators 422, both of which are made of resin. A boss 4222 is arranged circumferentially between the two neighboring teeth 411. In the preferred embodiment of the present invention, three bosses 4222 are arranged at three out of four positions defined between any two neighboring teeth 411. A conductor pin 43 is inserted into each boss 4222 along the axial direction. The boss 4222 includes a hole extending axially upward from the axially lower end thereof, in which a conductor pin 43 is fitted. An axially lower position of the conductor pin 43 axially downwardly protrudes from the boss 4222. Into each of the notched portions 441 arranged to the circuit board 44, the conductor pin 43 is inserted and is soldered with the circuit board 44 such that the conductor pin 43 and the circuit board are electrically connected.
Owner:NIPPON DENSAN CORP
Device for reducing deterioration of image quality in display using laser
InactiveUS7116017B2Reduce deteriorationTelevision system detailsMirrorsImaging qualityDisplay device
Disclosed is a device for reducing deterioration of image quality which can get rid of speckle by equalizing a laser from a light source on a screen by vibrating a reflective mirror installed between the light source and the screen at a predetermined amplitude. The device for reducing deterioration of image quality in a display system using a laser as a light source includes: a reflective mirror formed at the path of light positioned between the light source and a screen, for reflecting the laser; and a driving unit connected to the reflective mirror and vibrating the reflective mirror at a predetermined amplitude by using an electromagnetic force.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Electric motor
InactiveUS7795830B2Improve motor efficiencyEfficient captureAssociation with control/drive circuitsMotor/generator/converter stoppersConductor CoilElectric motor
An electric motor (10) which includes an armature (11) with at least two armature phase pair windings (12) and salient pole rotor arrangement (15) having field windings (17) terminating in a selective electrical switch which determines the electrical continuity of said field windings (17). Also included is control means which is configured to regulate the magnetizing of the field winding (17) so that, at any given moment, one armature phase pair is usable for magnetizing the field winding while the other pair is responsible for torque production.
Owner:ELCKON
Wheel driving apparatus and electric vehicle including the same
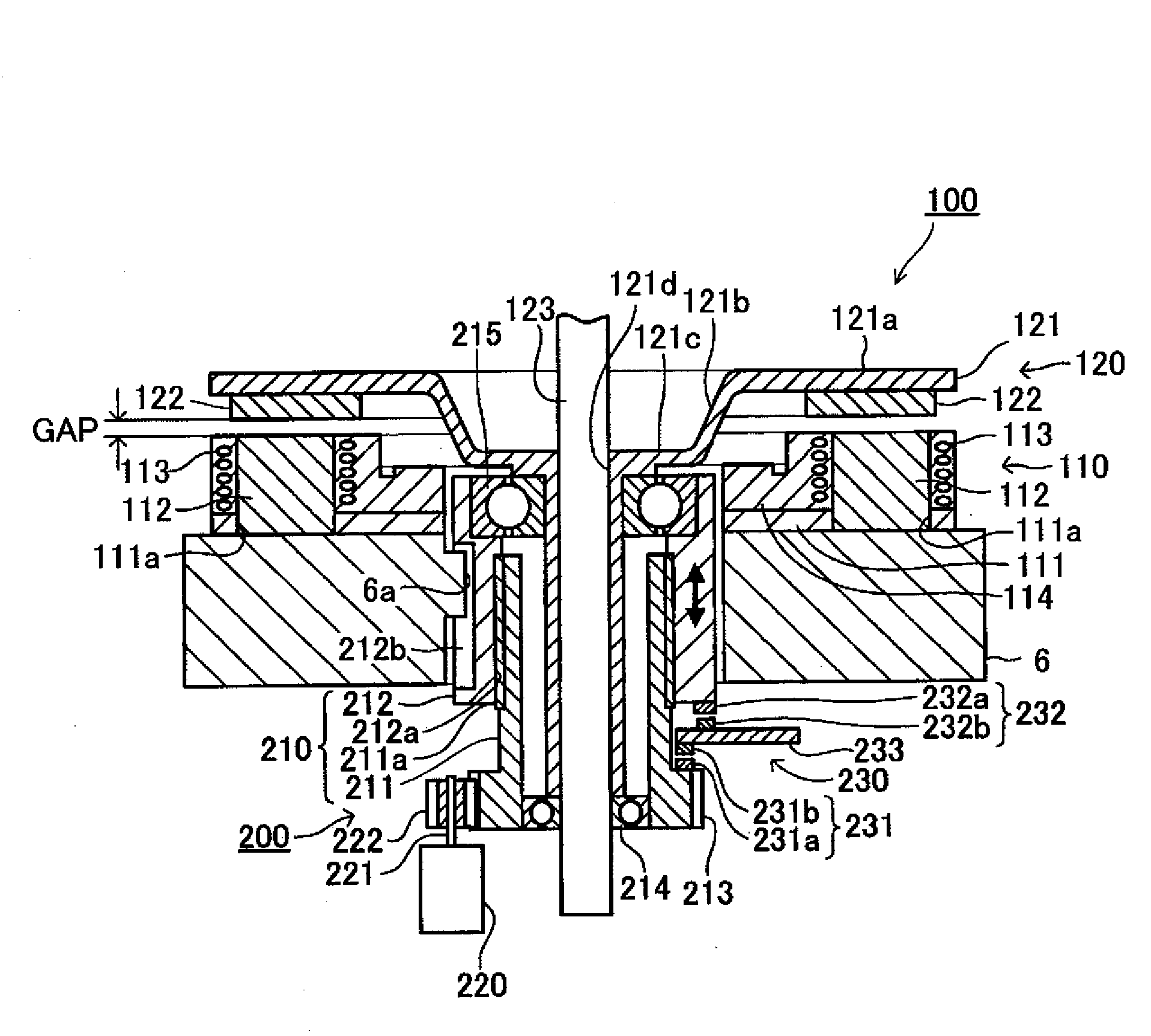
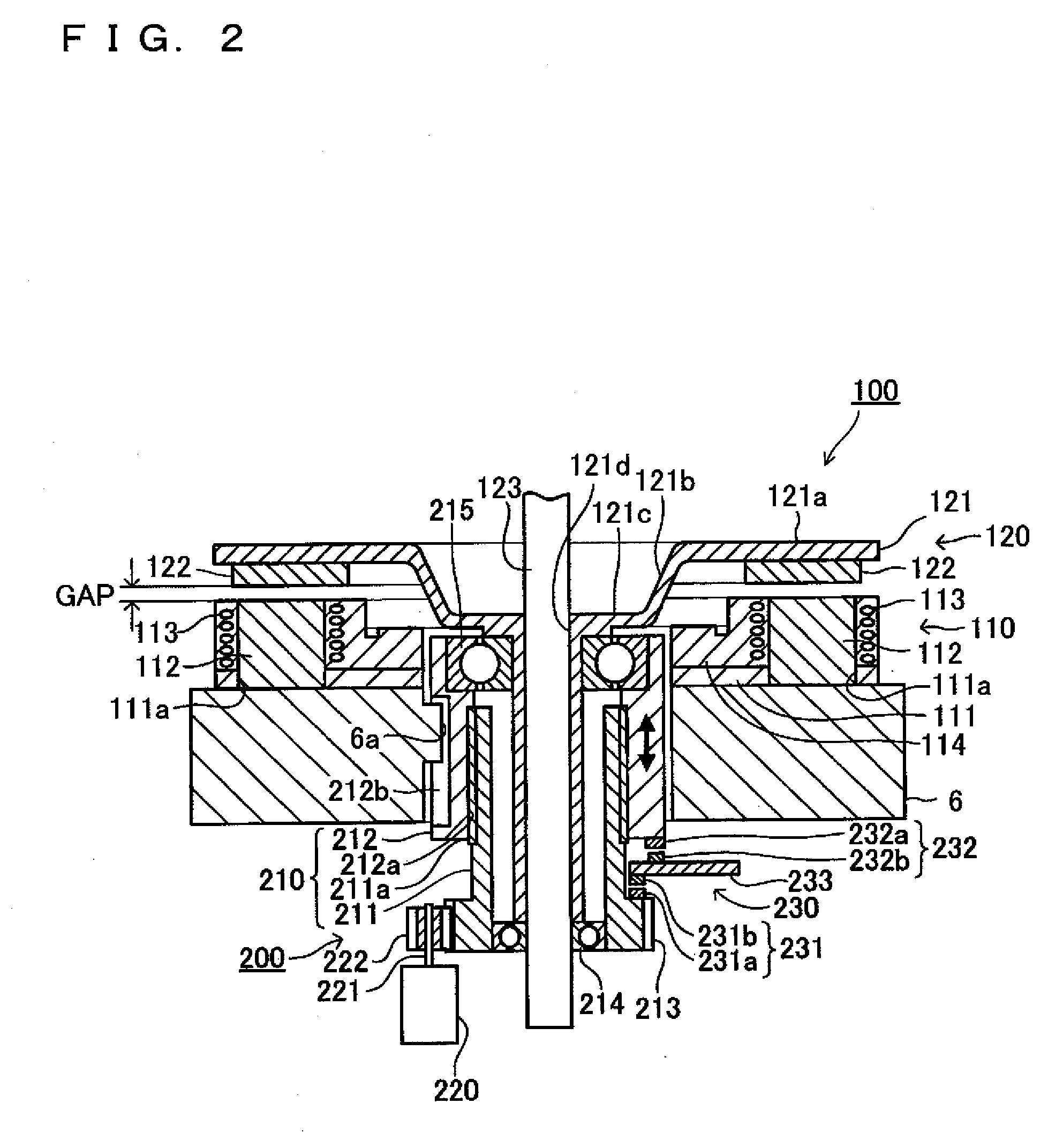
InactiveUS20090212728A1Good vehicle characteristicEfficient driveDC motor speed/torque controlMagnetic circuitLow speedEngineering
An electric bike includes a wheel driving apparatus. The wheel driving apparatus includes an electric wheel drive motor which drives a wheel, a gap changer which changes a gap length in the wheel drive motor, and a motor control unit which controls the wheel drive motor and the gap changer. The motor control unit calculates a target gap length for the gap changing motor in the gap changer based on an accelerator opening-degree signal, a rotation speed, a q-axis electric-current command value, a power source voltage, and a voltage utilization rate. Then, a feedback control is provided to the gap changer based on a difference value between the target gap length and the actual gap-length. A good vehicle characteristic is obtained without being affected by individual variability or operating environment of the electric motor through efficient drive of the electric motor from a low-speed range through a high-speed range.
Owner:YAMAHA MOTOR CO LTD
Motor and electric apparatus equipped with same
ActiveUS20060186746A1Reduce voltageAvoiding the electrolytic corrosionAssociation with grounding devicesMagnetic circuit characterised by insulating materialsEngineeringElectric motor
A motor comprises a stator having a stator core and a stator winding wound on the stator core and integrally molded with insulation resin, a rotor provided with a shaft, a first bearing and a second bearing for supporting the shaft, a bracket connected to the stator and retaining at least one of the first bearing and the second bearing, and a conductive member short-circuiting between the stator core and the bracket.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Permanent magnet dynamo electric machine, and permanent magnet synchronous generator for wind power generation
A dynamo electric machine includes a rotor having magnetic poles with permanent magnets and a stator having armature windings concentratedly wound around teeth. When the number of pole pairs of the magnetic poles of the rotor is P, diameter of the rotor is D (meters), and a spatial harmonic order of a predetermined harmonic component of an armature magnetomotive force of the rotor is N ((N=P to the 1.5th power)×(N to the minus 4-th power)×(the square of P)×D<0.6 (in meters).
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
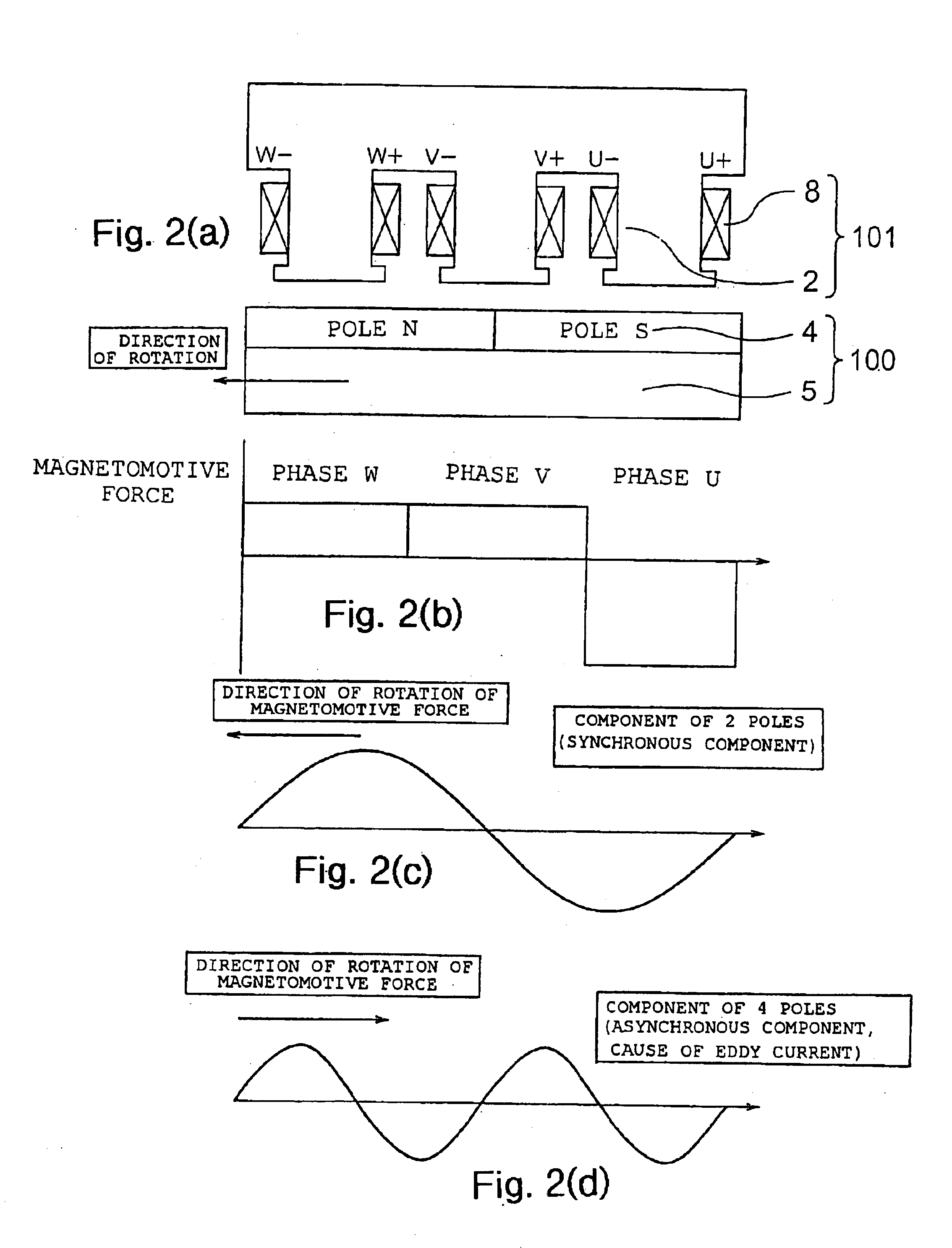
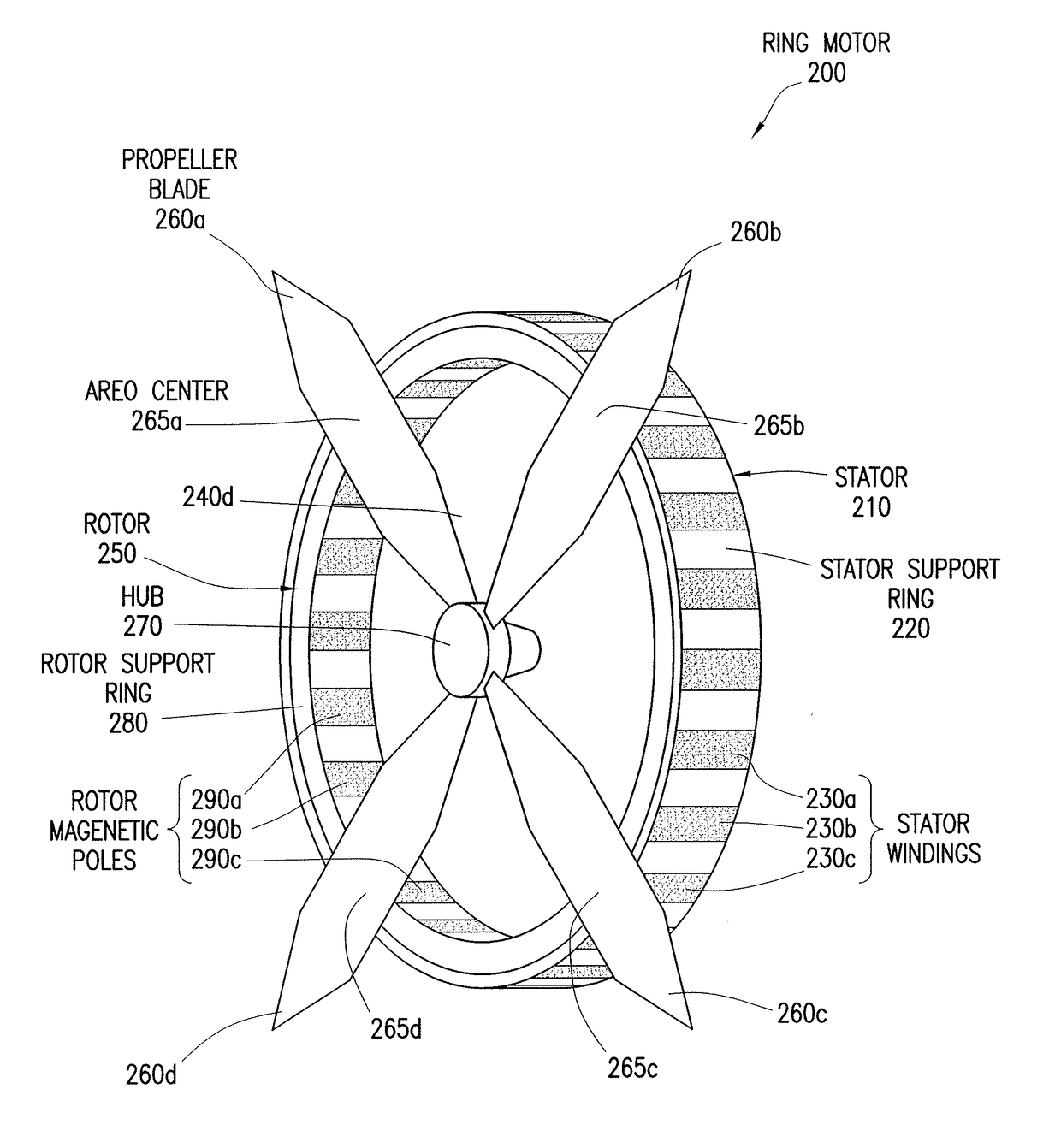
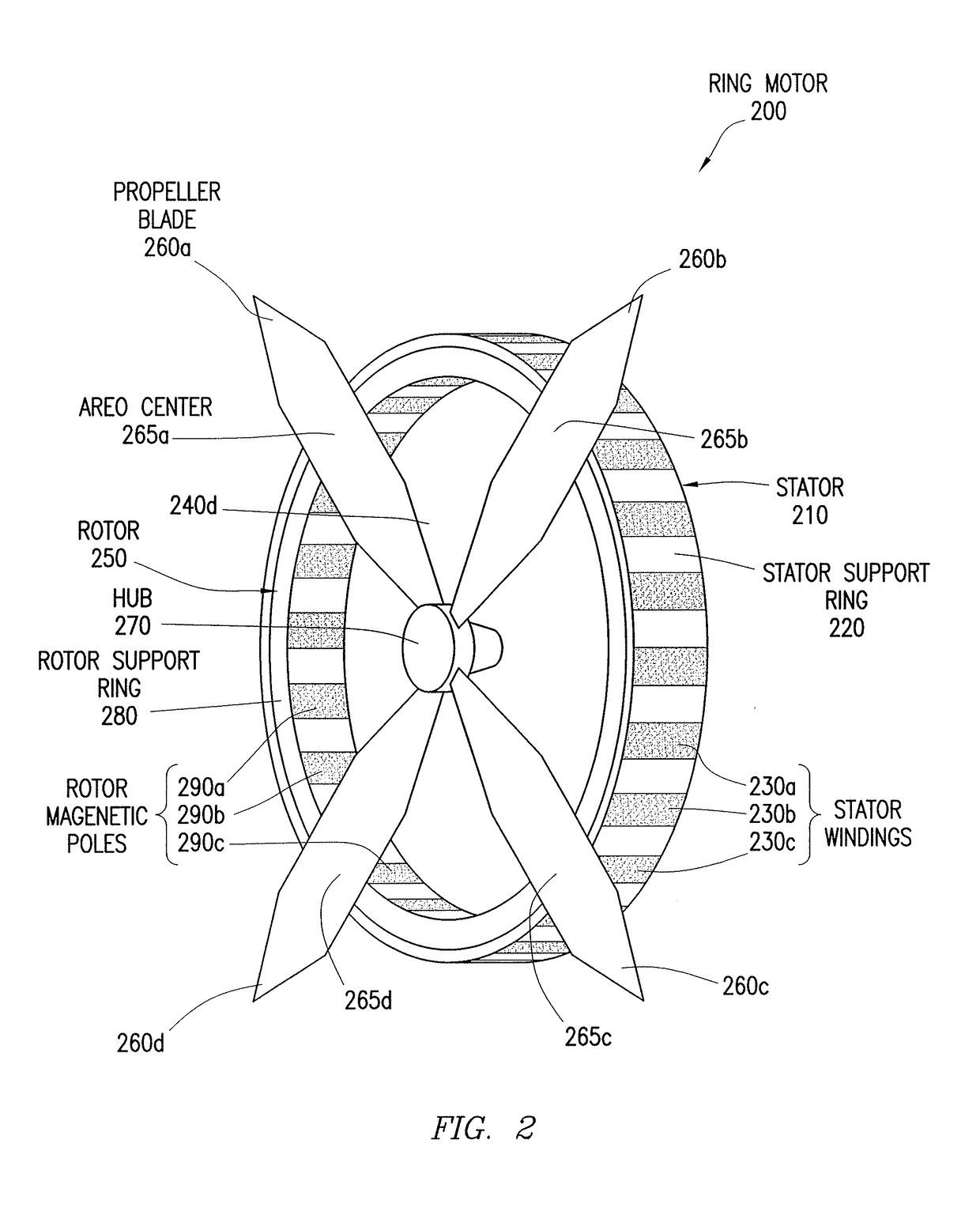
Reduced Complexity Ring Motor Design for Propeller Driven Vehicles
InactiveUS20170104385A1Extended operating timeImprove engine efficiencyPropellersRotary propellersPropellerMagnetic poles
A motor includes a stator and a rotor coupled via the center hub of the rotor. The stator includes a support ring, the support ring comprising a plurality of windings arranged circumferentially. The rotor is configured to operate as a rotating propeller and includes a center hub, a rotor support ring, and a plurality of blades. The rotor support ring comprises a plurality of magnetic poles arranged circumferentially. Each particular blade is individually coupled to the rotor support ring.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Laminated core and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS7667367B2Avoid vertical movementManufacturing dynamo-electric machinesMagnetic circuit shape/form/constructionMagnetic polesEngineering
Owner:MITSUI HIGH TEC INC
High efficiency magnetic core electrical machine
InactiveUS20110109185A1Reduced torque outputReduce voltage outputMotor/generator/converter stoppersSynchronous motors startersLow speedElectric machine
A magnetic core electrical machine includes a plurality of “U”-shaped stator yokes arranged circumferentially with respect to a rotor and either staggered to form a continuous flux return path or displaced relative to permanent magnets of the rotor in order to reduce cogging. Various mechanisms and / or circuits are provided to limit an output of the electrical machine at high speeds, and boost the voltage output at low speeds.
Owner:SULLIVAN JOHN T
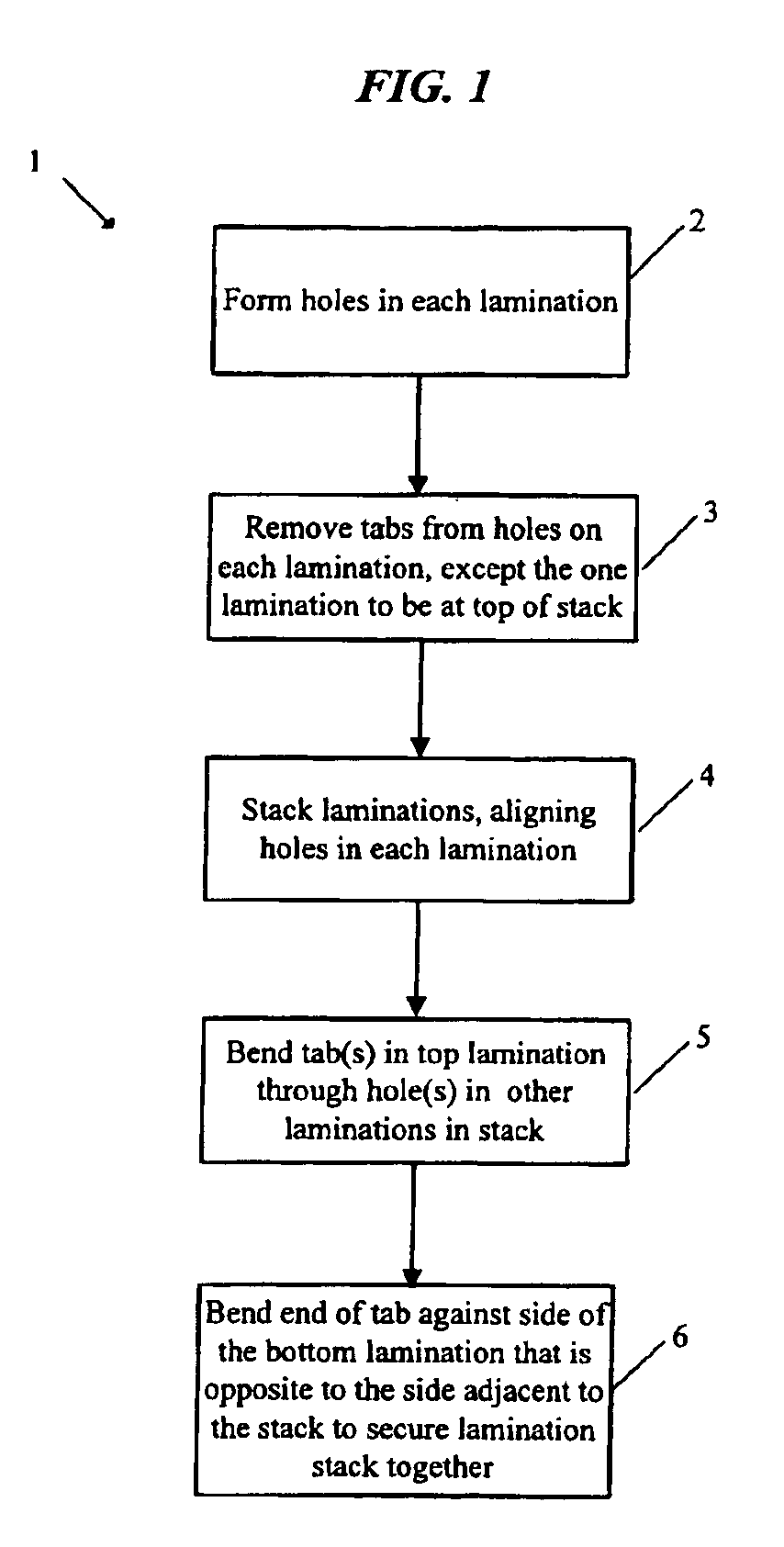
Interlock tabs for laminations
InactiveUS6847285B2Eliminate needTransformers/inductances magnetic coresMagnetic circuit shape/form/constructionEngineeringMechanical engineering
A laminated plate assembly in which the laminations in a stack are secured together by means of one or more interlocks or tabs that project from the uppermost lamination in the assembly through holes or slots in all the other laminations in the assembly, or around the periphery of the other laminations in the assembly, with each tab being bent or pressed against the underside of the bottom lamination in the assembly. This secures all the laminations in the stack together, much like a staple secures papers in a stack together, allowing for additional handling and processing of the laminated plate assembly without concern that the laminated plates in the stack will become misaligned or even become removed from the stack.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
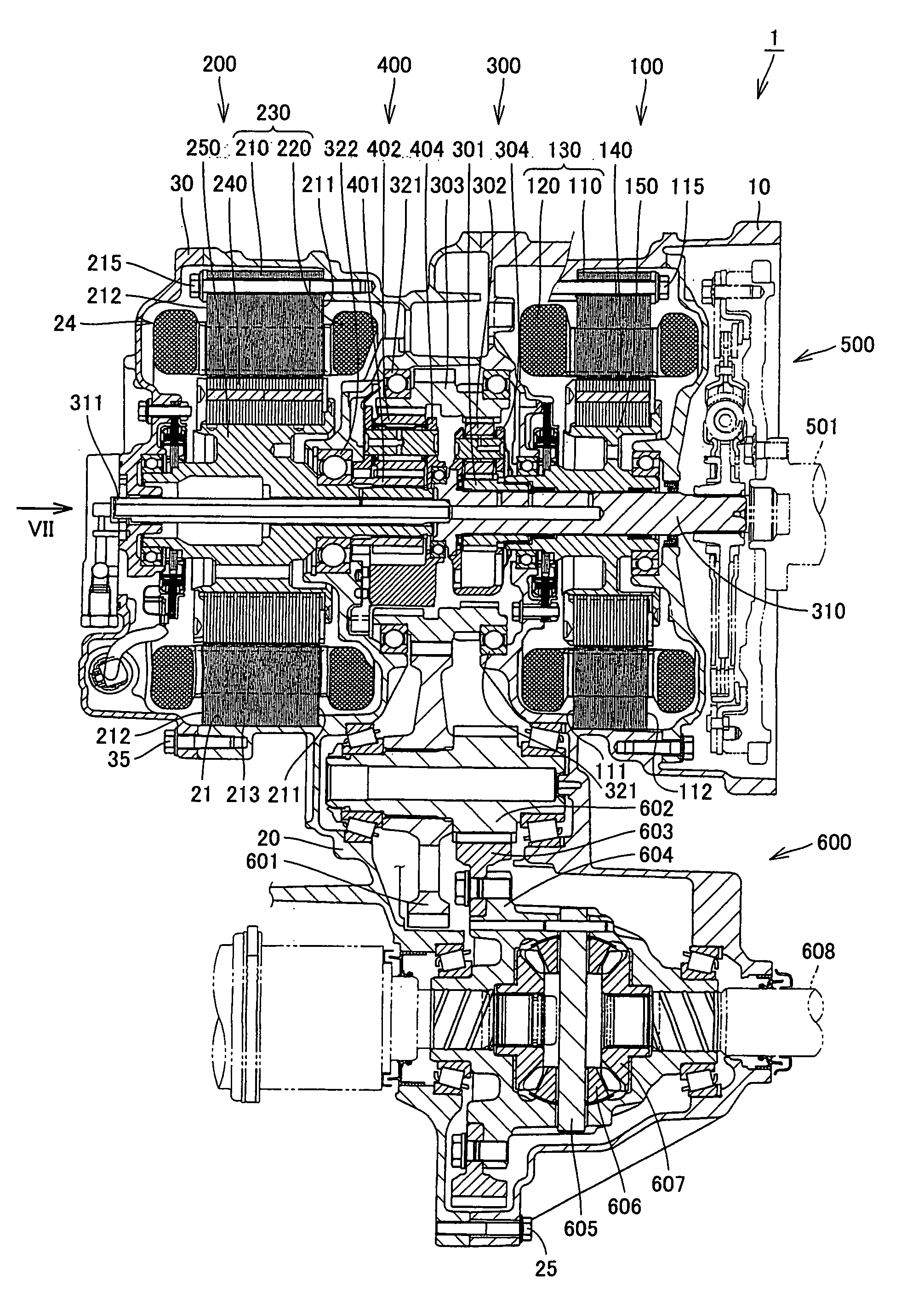
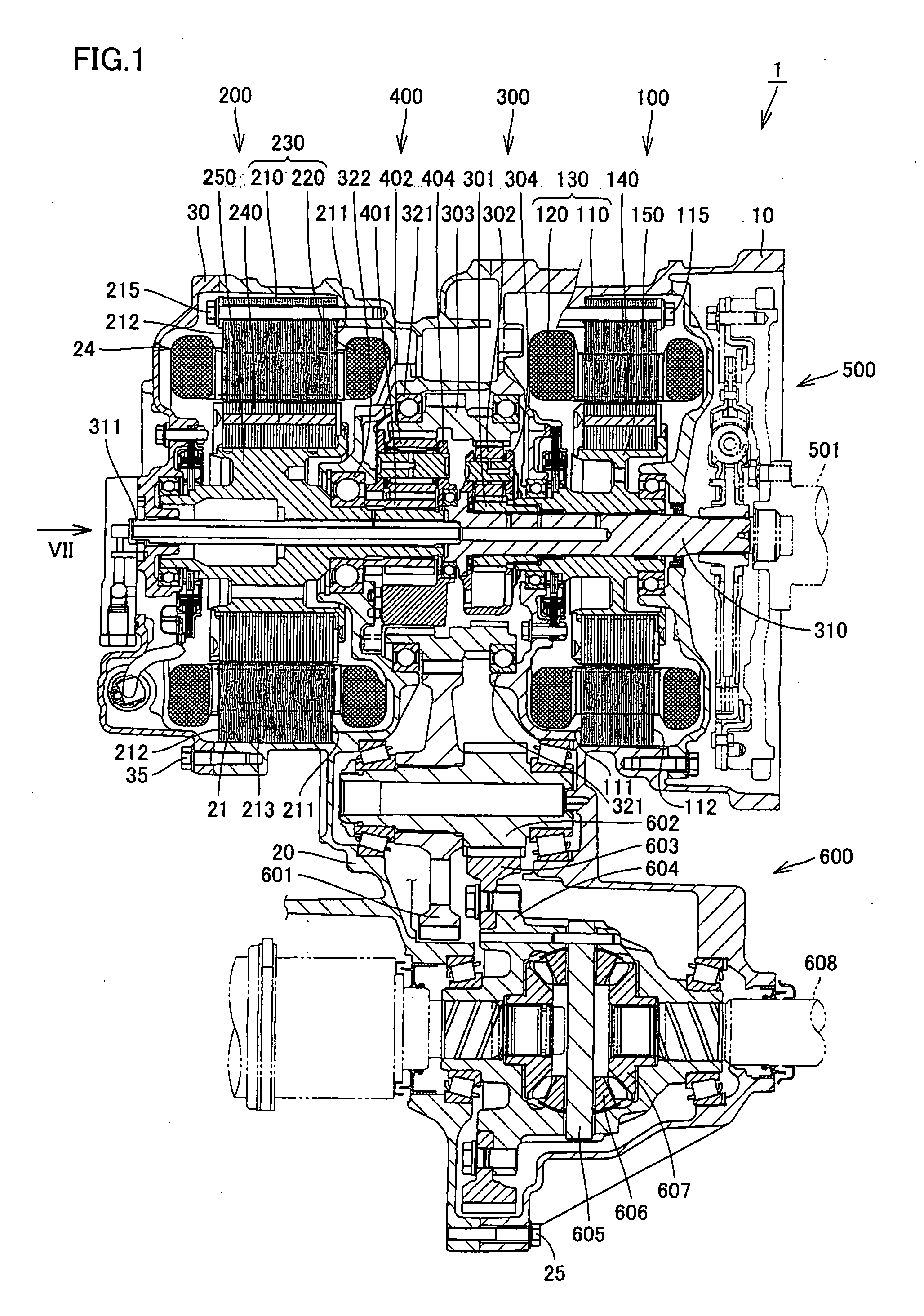
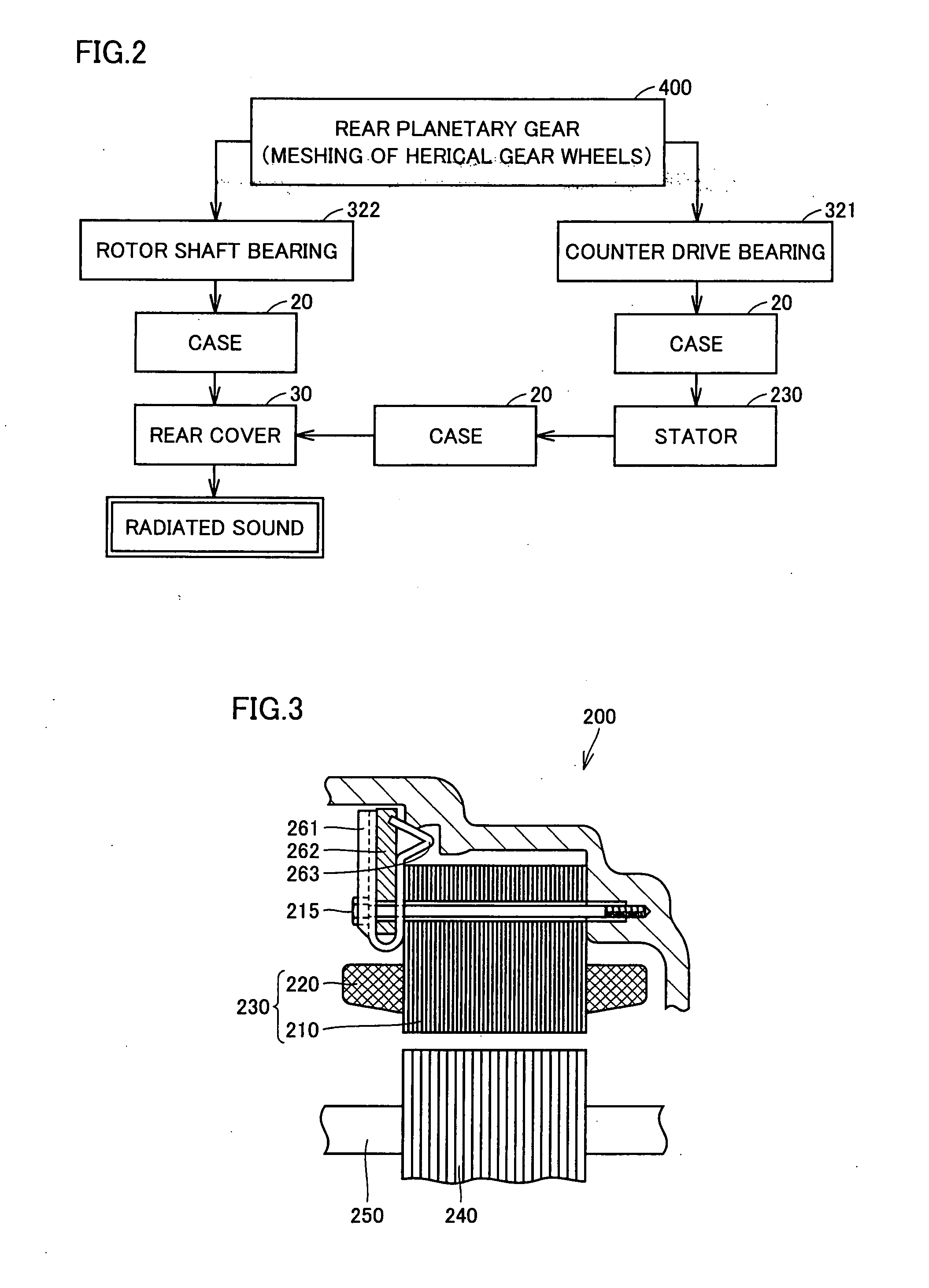
Driving Device With Rotating Electric Machine
InactiveUS20080106163A1Improve appearance qualityAvoid vibrationHybrid vehiclesGear vibration/noise dampingElectric machineGear wheel
A transaxle includes a case having an opening, a second rotating electric machine stored in the opening of the case and having a stators, a rear planetary gear stored in the transaxle case and connected to the second rotating electric machine, a transaxle rear cover sealing the opening and a bolt fixing the second rotating electric machine to the transaxle case. The stator has first and second thrust end faces defining an axial length thereof. The first thrust end face is pressed against an inner surface of the case.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Stator arrangement for an electric machine and a method for manufacturing the stator arrangement
InactiveUS20070040467A1Increase surface areaMagnetic saturation can be reduced and avoidedWindingsMagnetic circuit shape/form/constructionConductor CoilMechanical engineering
A stator arrangement for an electric machine having a stator body which has a back yoke ring and a number of stator teeth that project in a radial direction from the back yoke ring, wherein at least one additional ferromagnetic stator end lamination is mounted on at least one end face of the back yoke ring, the additional ferromagnetic stator end lamination being substantially flush with the back yoke ring, wherein projections are formed at the inner or outer circumference of the additional stator end lamination, the projections projecting axially from the outer end face of the stator end lamination and forming a guide for the winding wire.
Owner:MINEBEA CO LTD
Bonded rotor laminations
InactiveUS20060066168A1Increase stiffnessEasy to operateSynchronous motorsAsynchronous induction motorsEngineeringMechanical engineering
In accordance with an exemplary embodiment, the present technique provides a rotor assembly formed of a plurality of rotor laminations that are bonded to one another. Specifically, the rotor laminations are bonded to one another via a bonding agent disposed between end surfaces of adjacent rotor laminations. Advantageously, the bonding of the rotor laminations increases the overall stiffness of the rotor assembly, thereby facilitating high-speed operation. Moreover, the bonding of the rotor laminations increases the consistency in construction of the rotor assembly, thereby facilitating more accurate modeling of the rotor assembly.
Owner:RELIANCE ELECTRIC TECH
PMBDCM and two phase SRM motor, two phase SRM rotor and stator, and coil wrap for PMBDCM and SRM motors
InactiveUS20050156475A1Reduce noiseReduce vibrationSynchronous generatorsWindingsMagnetic reluctanceMechanical engineering
A two-phase switched reluctance motor in an embodiment includes a plurality of salient rotor poles that each have asymmetric reluctances about a central radial axis of the respective rotor pole. Each of the rotor poles has the same width, and the rotor poles are operable to provide preferential torque generation in one direction of rotation for all rotor positions. Such preferential torque generation occurs under the influence of an electromagnetic flux, which is provided by a plurality of salient stator poles having substantially the same width as the rotor poles.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com