Patents
Literature
5098results about "Disposition/mounting of heads" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
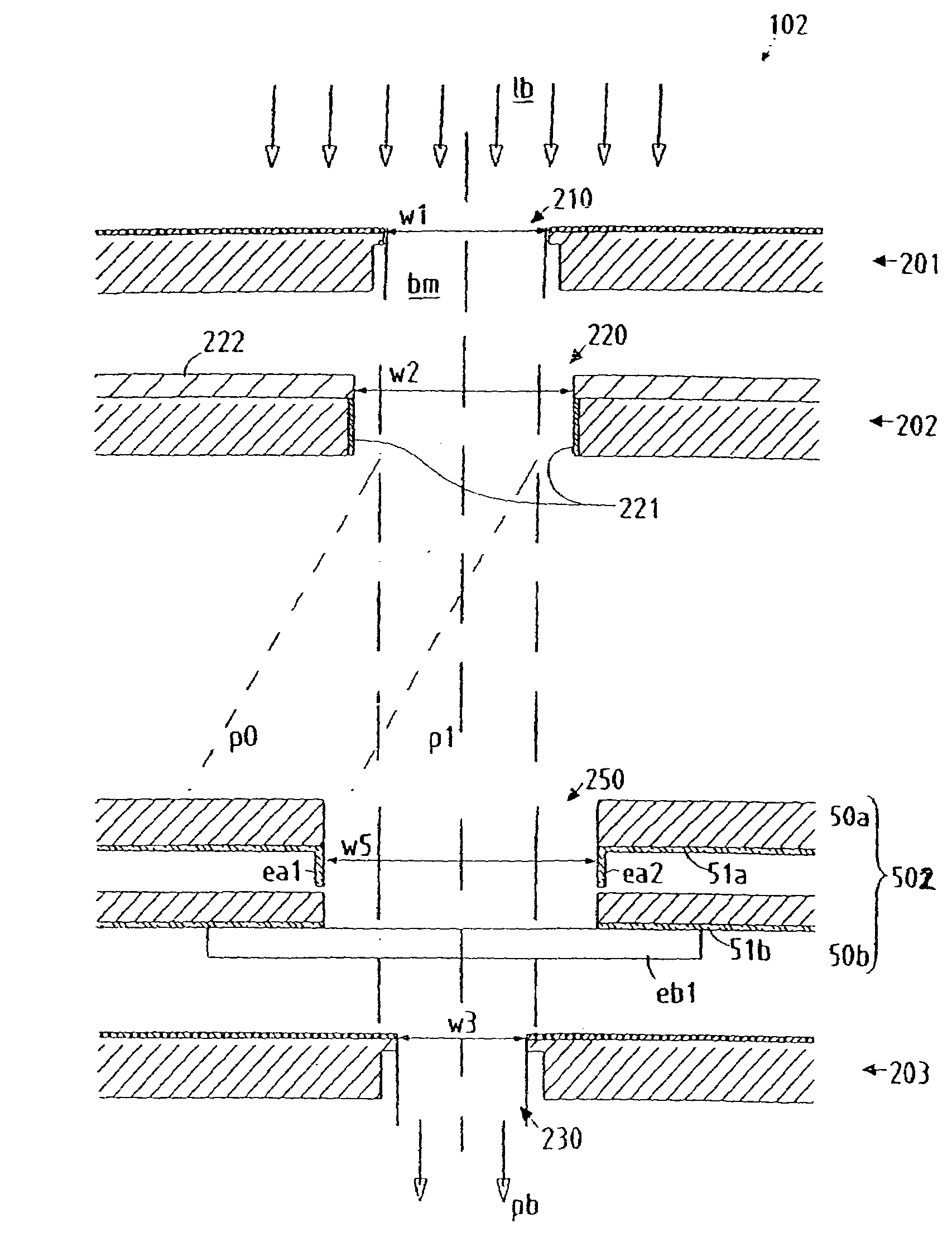
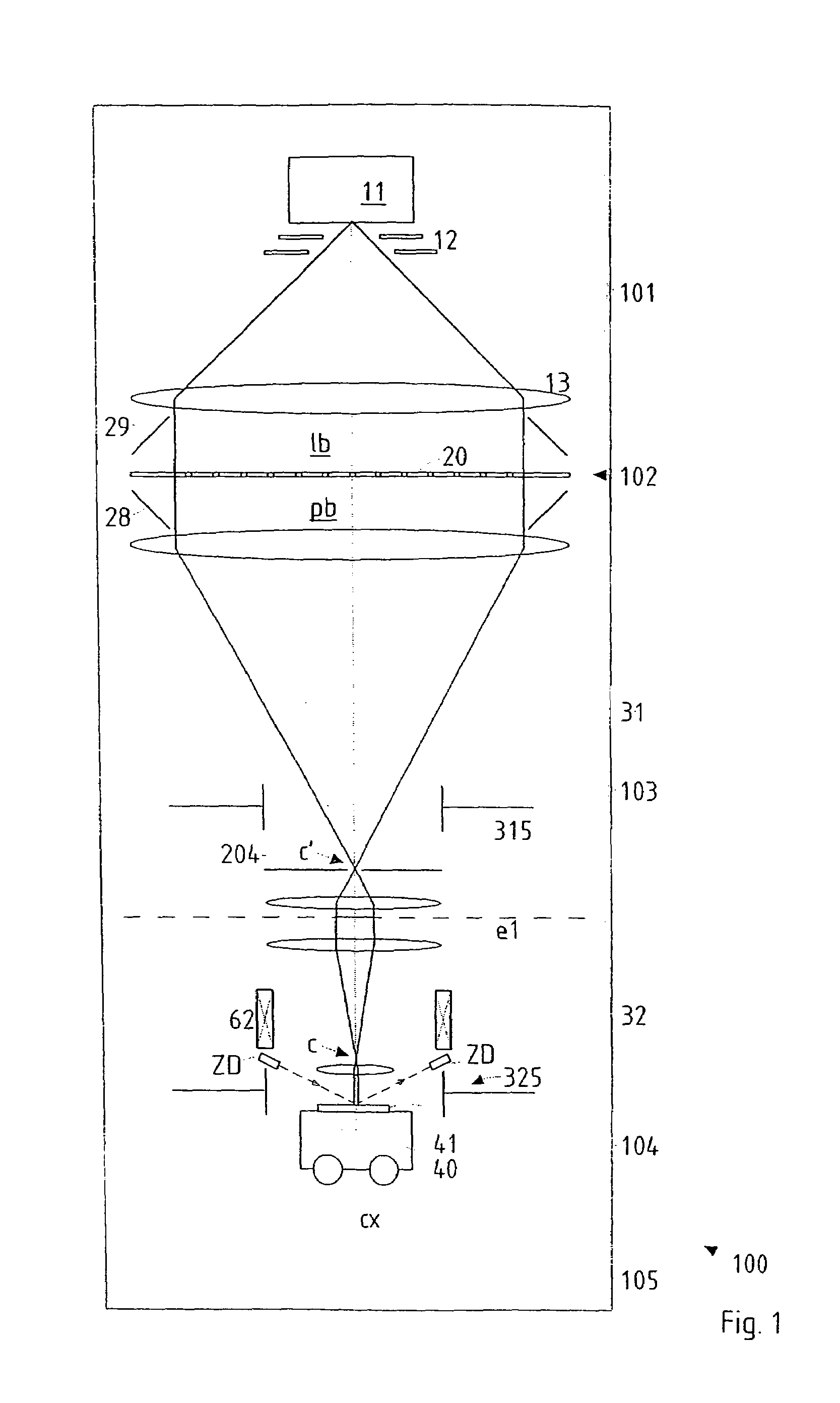
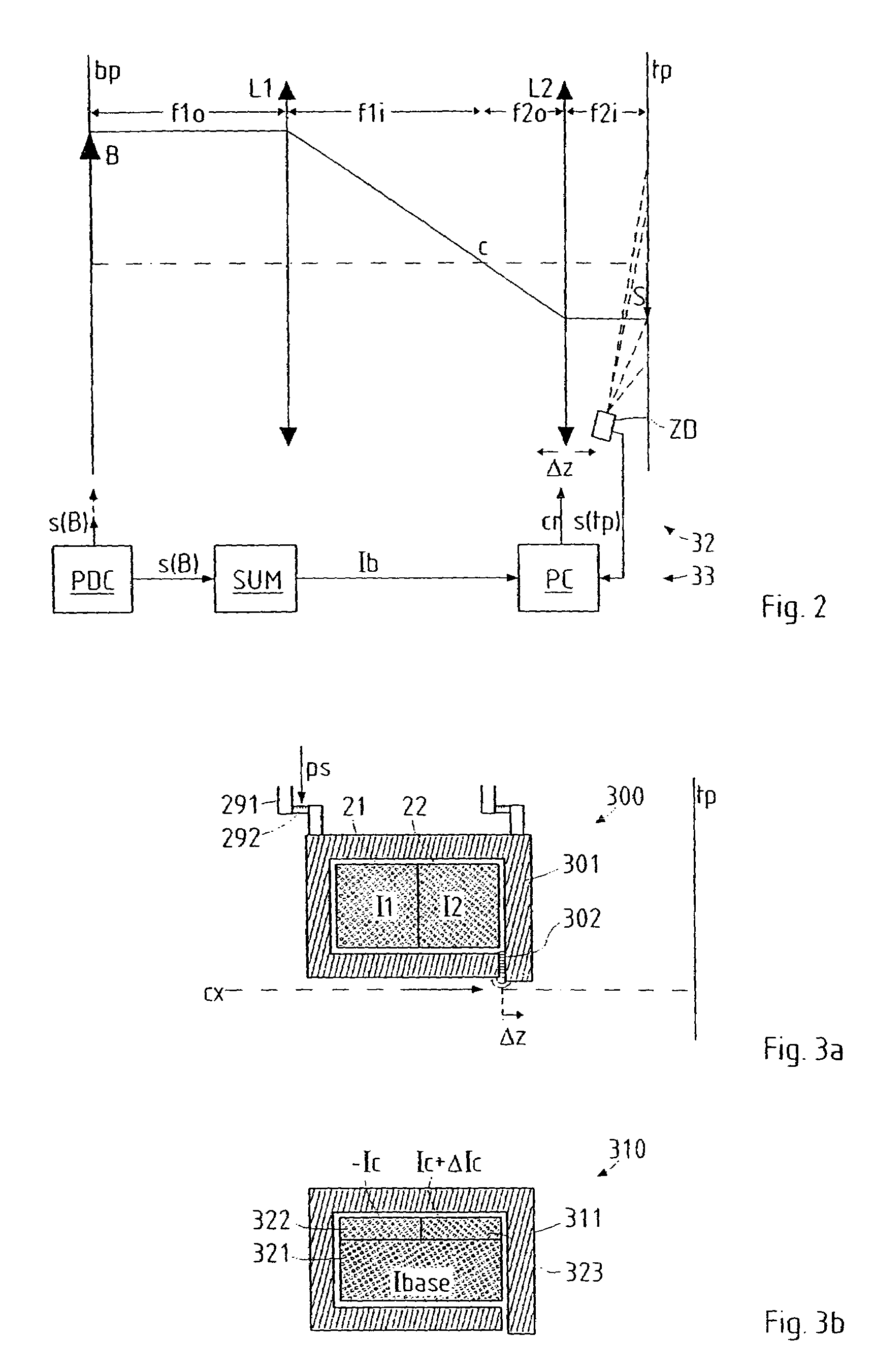
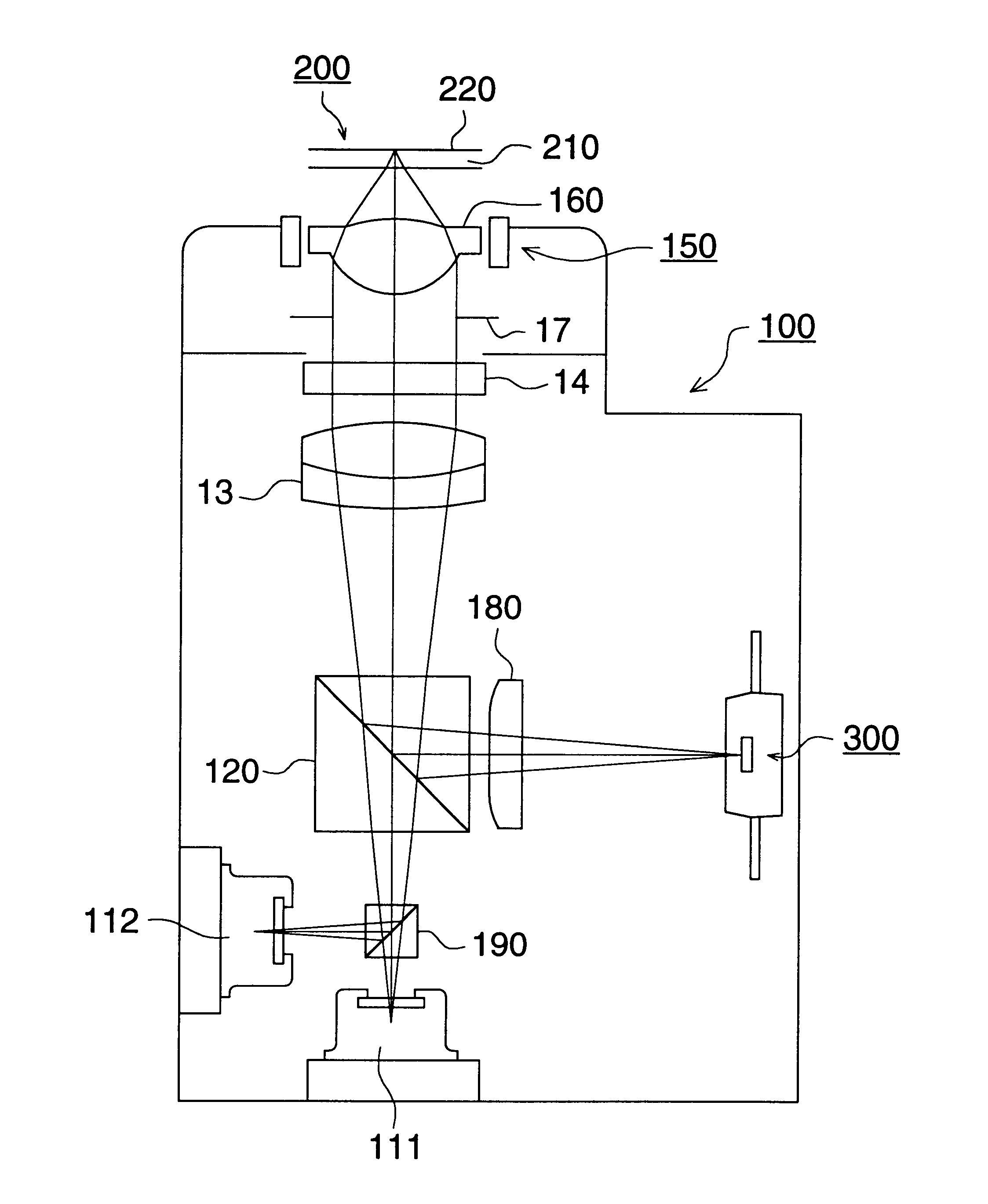
Particle-optical projection system
ActiveUS7388217B2Minimize distortionCompensation deviationElectric discharge tubesNanoinformaticsOptical axisProjection system
In a particle-optical projection system a pattern is imaged onto a target by means of energetic electrically charged particles. The pattern is represented in a patterned beam of said charged particles emerging from the object plane through at least one cross-over; it is imaged into an image with a given size and distortion. To compensate for the Z-deviation of the image position from the actual positioning of the target (Z denotes an axial coordinate substantially parallel to the optical axis), without changing the size of the image, the system includes a position detector for measuring the Z-position of several locations of the target, and a controller for calculating modifications of selected lens parameters of the final particle-optical lens and controlling said lens parameters according to said modifications.
Owner:IMS NANOFABTION
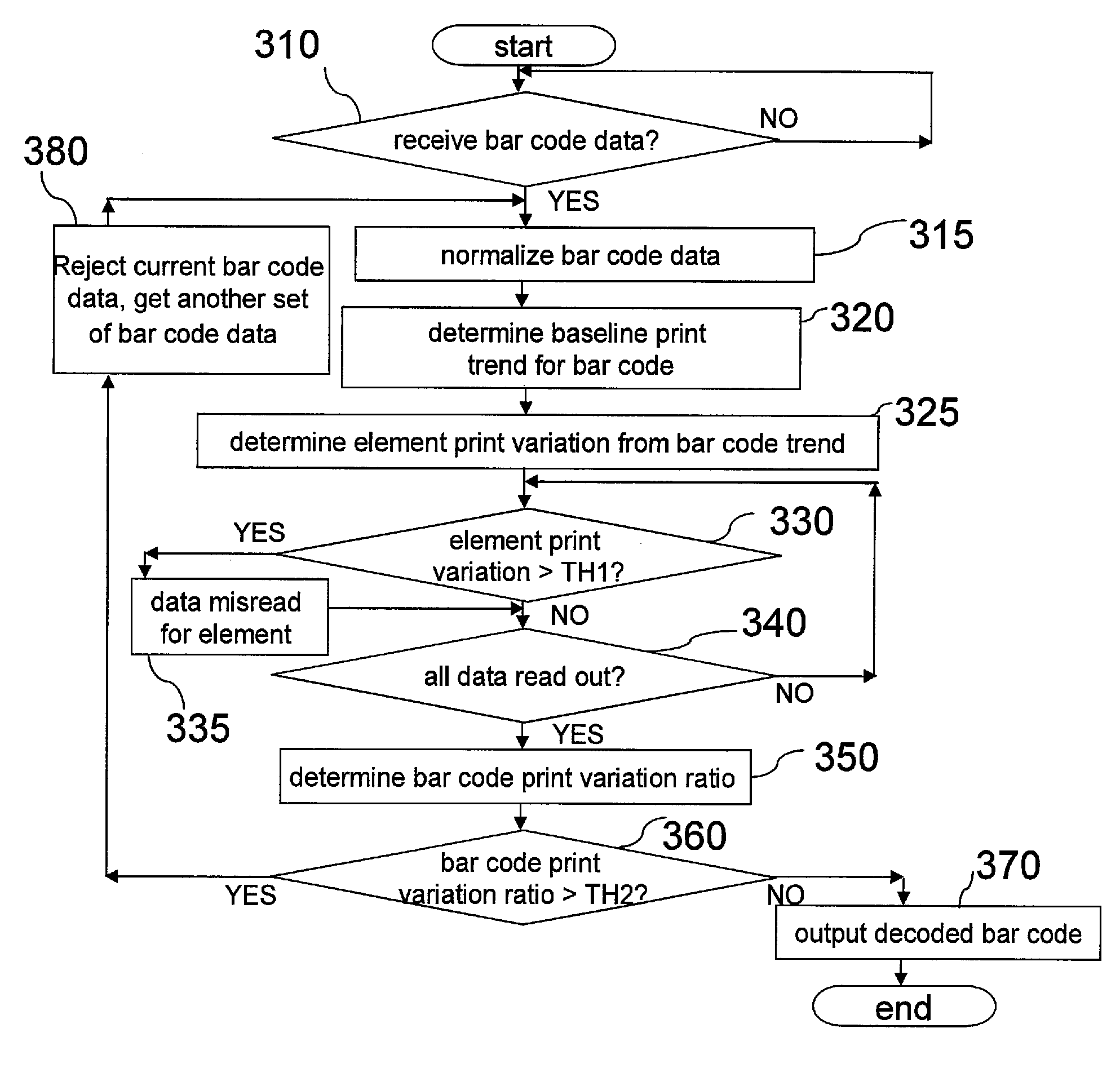
Bar code reader terminal and methods for operating the same having misread detection apparatus
ActiveUS8668149B2Increase read data rateRecord information storageCharacter and pattern recognitionError reductionBarcode
Owner:METROLOGIC INSTR INC
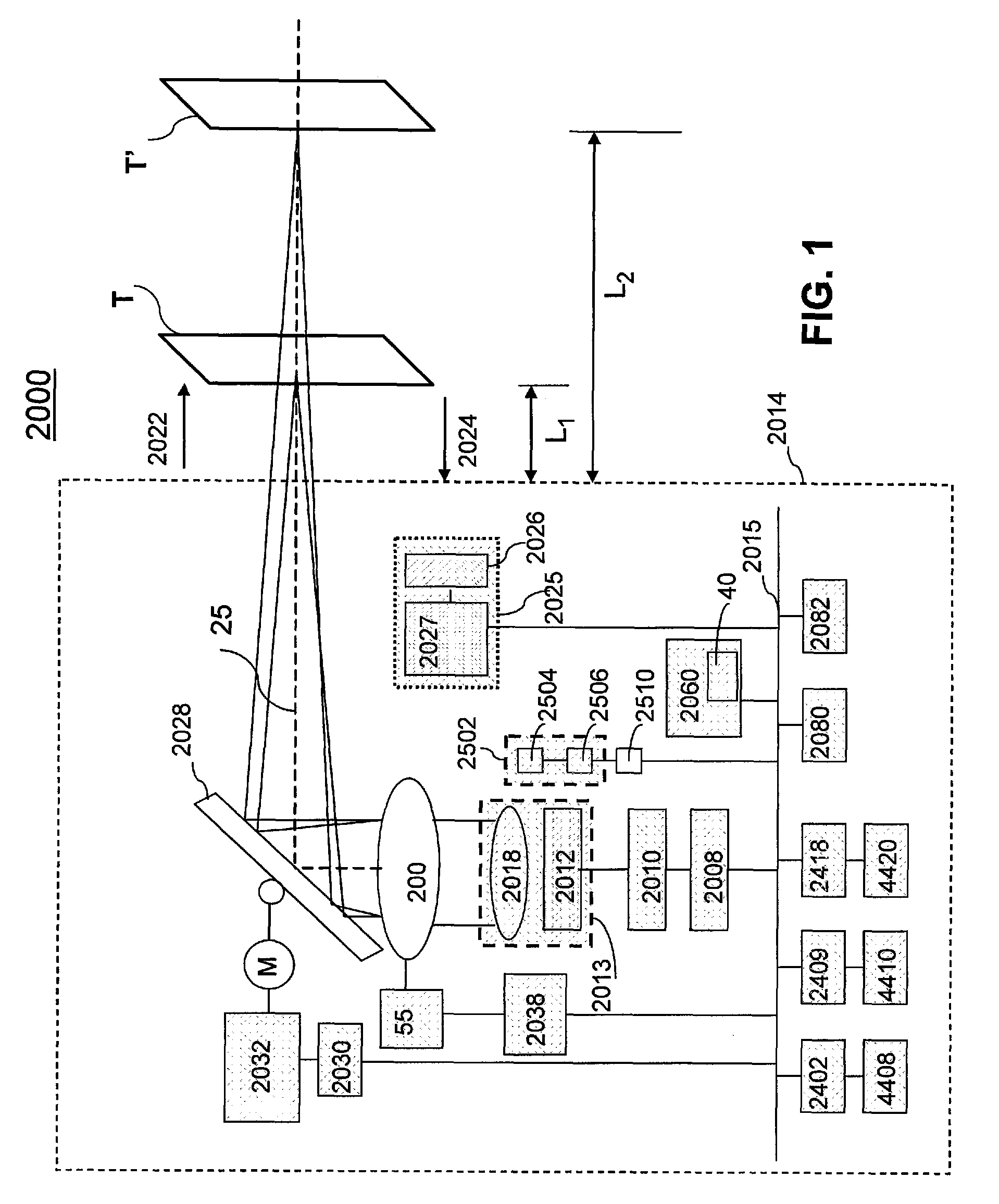
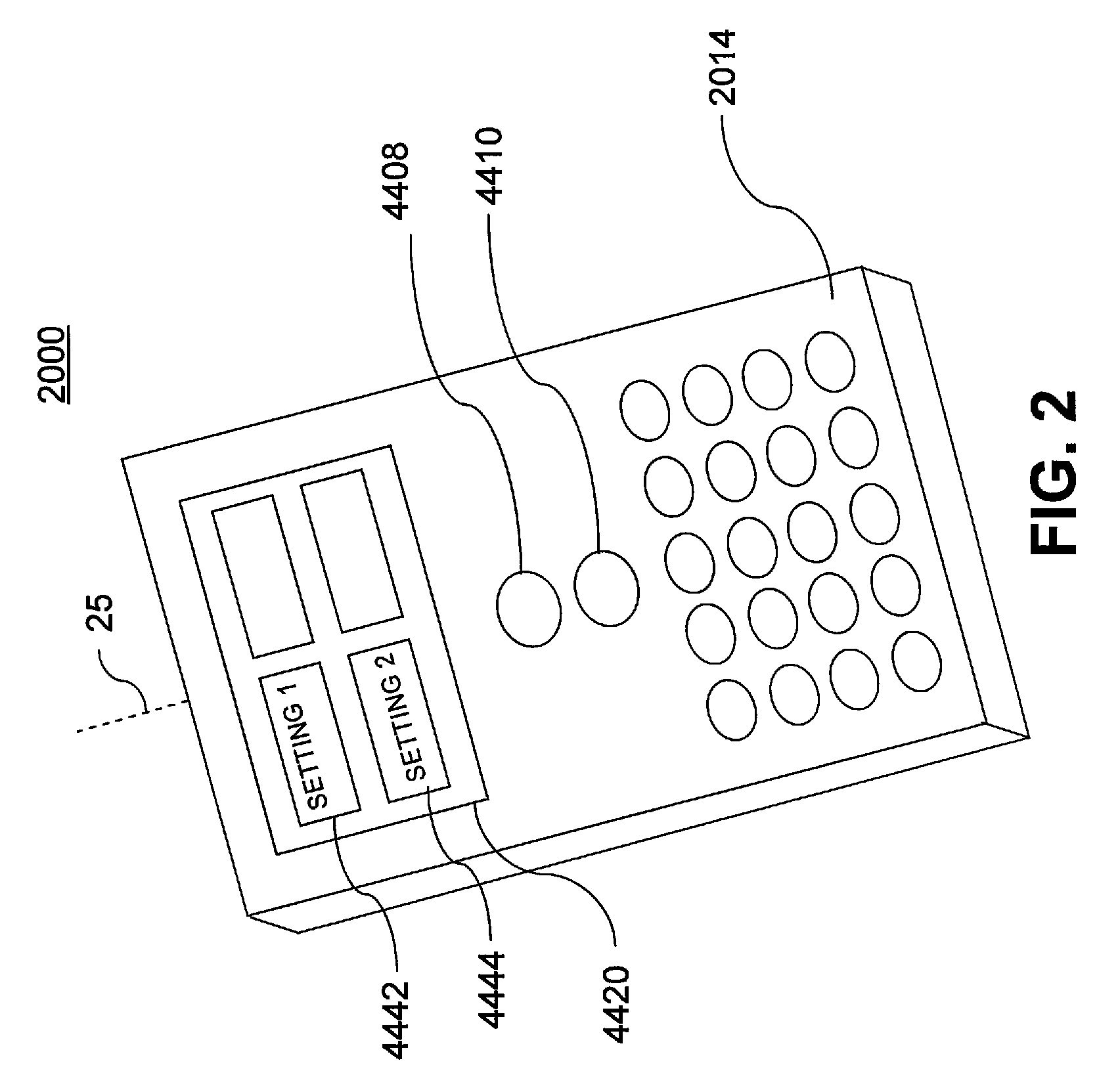
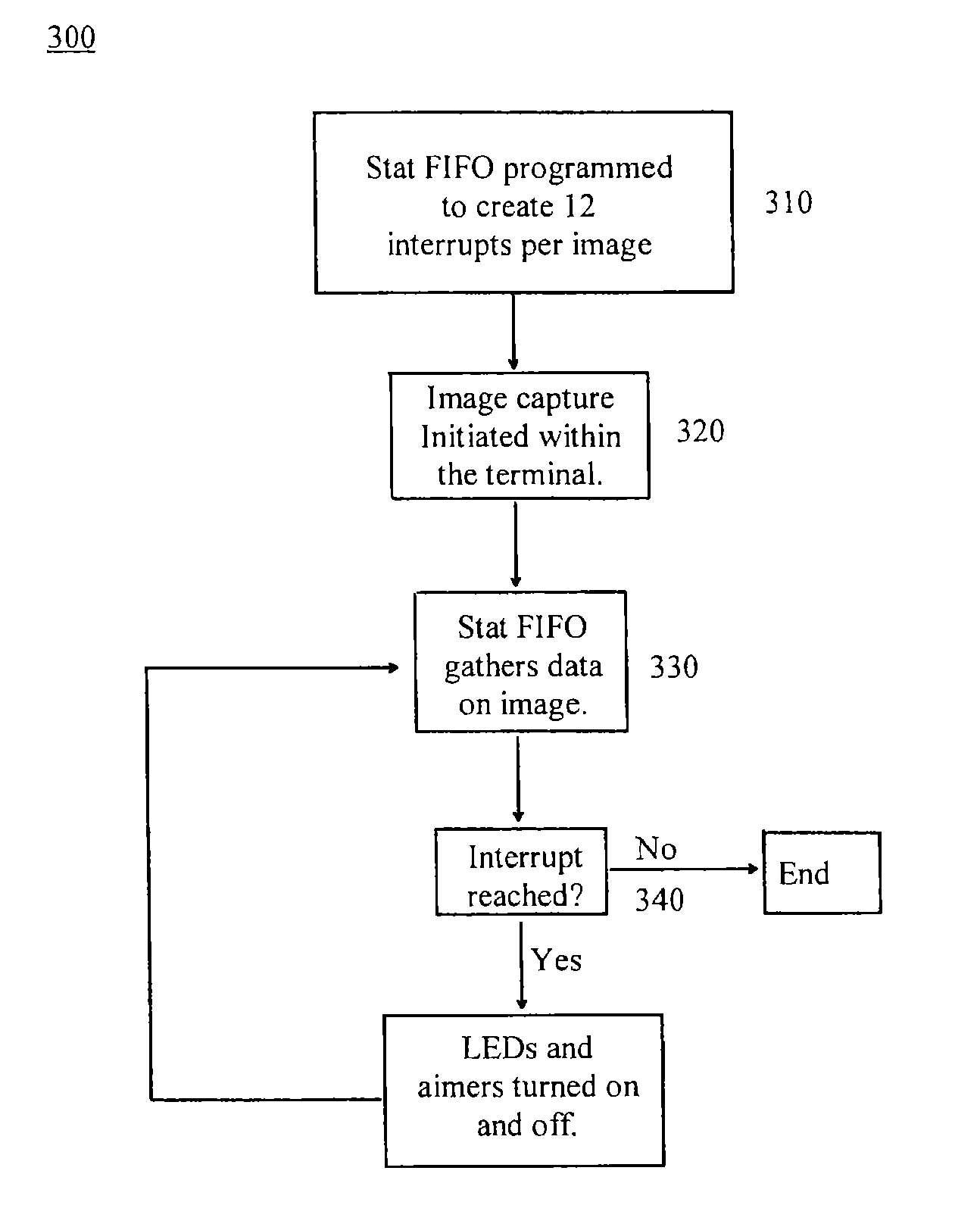
Cell phone reading mode using image timer
InactiveUS8777108B2Increase speed and efficiencyImprove compatibilityVisual representatino by photographic printingRecord information storageComputer graphics (images)Timer
An EIR terminal containing an image capture device configured to scan an image. The EIR terminal includes a lighting and exposure mechanism. The EIR terminal also includes a camera sensor interface with a stat FIFO. The stat FIFO is configured to receive data from the image capture device. When the stat FIFO, during image scanning, receives a pre-determined amount of image data, it fires an interrupt, which times the lighting and exposure mechanism in the EIR terminal.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Read/write head including displacement generating means that elongates and contracts by inverse piezoelectric effect of electrostrictive effect
A read / write head includes a slider provided with an electromagnetic transducer element (or an optical module), an actuator, and a suspension. The actuator includes a fixed part, a movable part, and at least two beam members for coupling them together. The beam members have a displacement generating means that elongates and contracts by inverse piezoelectric effect or electrostrictive effect. The fixed part is fixed to the suspension, and the movable part is fixed to the slider. Upon the elongation and contraction of the displacement generator, the displacement generator deflects and the movable part displaces linearly, circularly or rotationally with respect to the fixed part, and the electromagnetic transducer element displaces in a linear or circular orbit, so that the electromagnetic transducer element intersects recording tracks. In the actuator, the fixed part, movable part and beam members are formed as an integrated single piece by providing a hole and / or a cutout in a sheet-like member constructed of a piezoelectric or electrostrictive material. The actuator of the structure illustrated is used for the positioning of a direction intersecting recording tracks. In this case, the total sum of voltages applied on the displacement generating means is controlled in such a manner that it is constant at any time, thereby controlling position fluctuations of the electromagnetic transducer element in the direction vertical to the recording medium surface.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
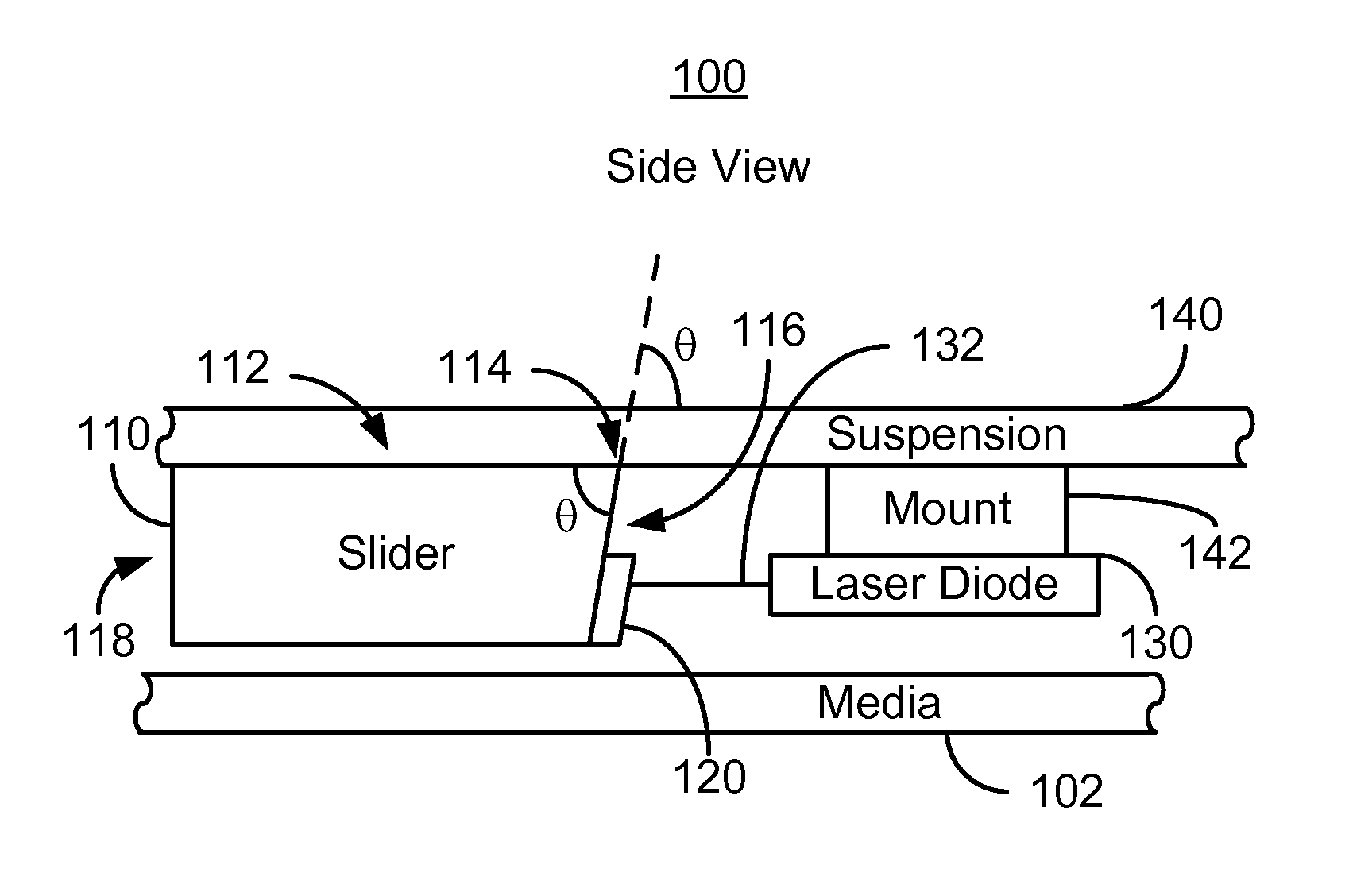
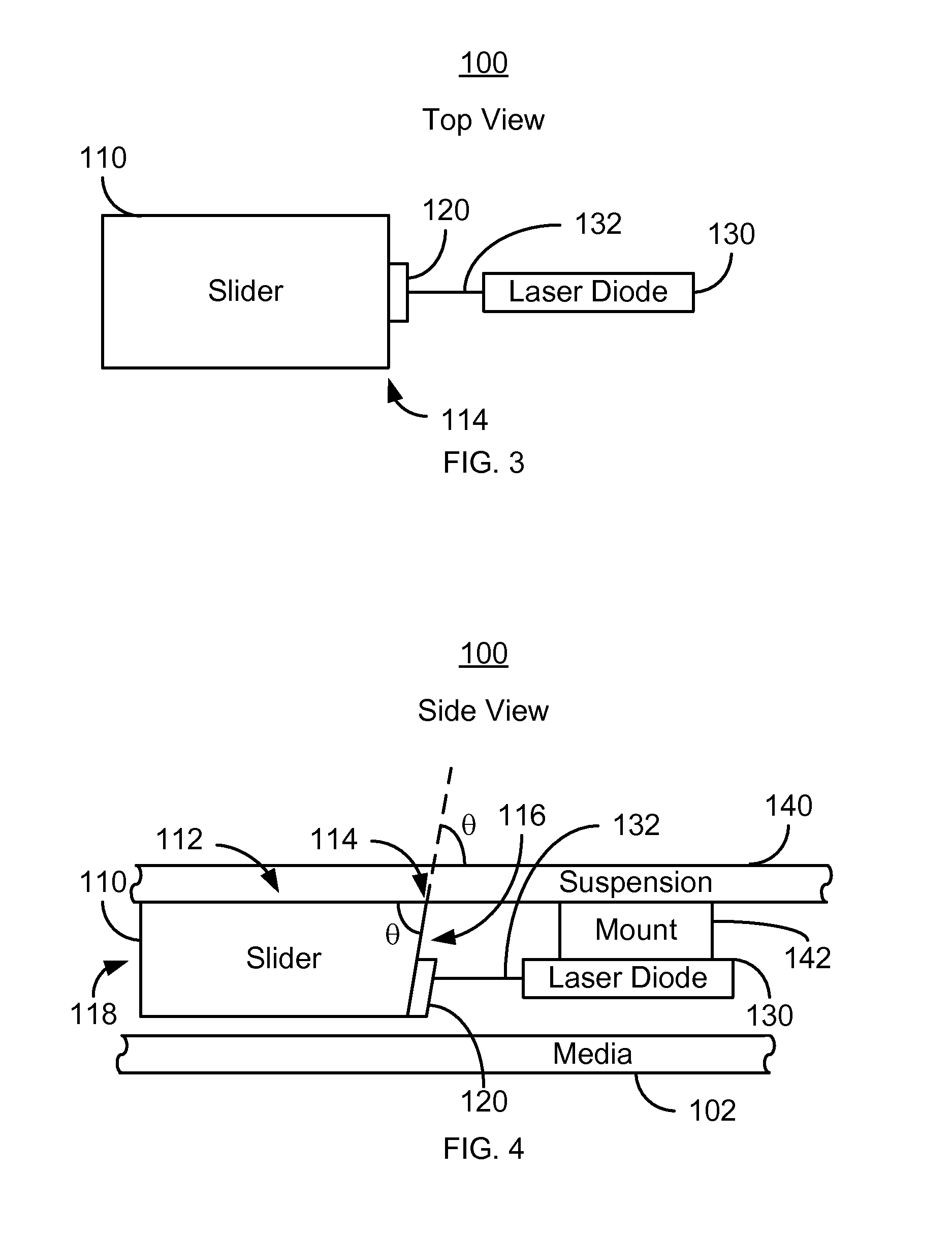
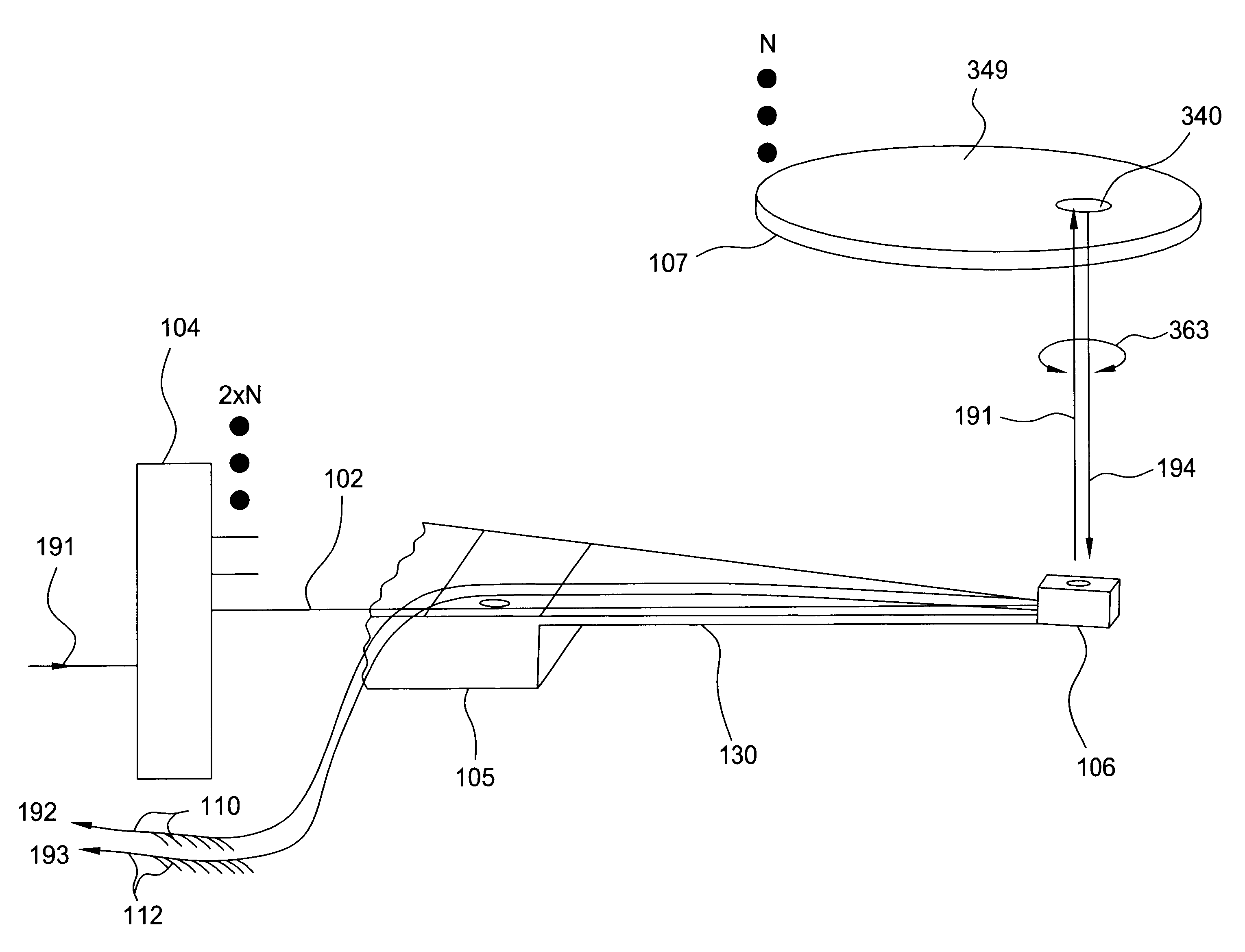
Method and system for coupling a laser with a slider in an energy assisted magnetic recording disk drive
A method and system for providing an energy assisted magnetic recording (EAMR) disk drive are described. The EAMR disk drive includes a slider, at least one EAMR transducer on the slider, and at least one laser coupled with the slider. The slider has a slider back side, a trailing face, and an intersection. The trailing face and the slider back side meet at the intersection. The trailing face makes an angle different from ninety degrees with the slider back side at the intersection. The laser(s) have an optical axis and are optically coupled with the trailing face of the slider. The optical axis is substantially perpendicular to the intersection and parallel to the slider back side.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Data storage system having an optical processing flying head
InactiveUS6781927B1Low costOptical flying-type headsOptical beam sourcesDigital dataData information
An optical data storage and retrieval system uses a flying head. The flying head is supported on a moving media having information stored in a plurality of stored data locations thereon. Information is stored in each of the plurality of media locations as physical structures capable of modulating the polarization state of incident light into one of two output polarization states. The flying head includes an optical processing assembly which directs an incident light beam having a source polarization state onto the moving media, accessing successive data locations. A reflected light beam having the source polarization state of the incident light beam modulated by a respective polarization modifying data location into one of the output polarization states is received by the flying head. The optical processing assembly optically transforms the modulated output polarization state of the reflected light beam into two return light beams having differentially modulated intensity related to the output polarization state of the reflected light beam. The two intensity modulated return light beams are optically coupled to a distal differential detector which outputs digital data representing the stored data information for the subject data location. A preferred embodiment includes optical fibers for coupling the incident and return light beams between the detector and the flying head. The optical assembly of a preferred embodiment includes an optical plate having pre-shaped and dimensioned recesses for automatically locating and aligning multiple optical components comprising the assembly. The flying head may also include a servo-controlled micro machined mirror for directing the incident and reflected light beams to and from the media.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL (FREMONT LLC)
Micro-positioning movement of holographic data storage system components
InactiveUS7116626B1Control positionRecord information storageRecording/reproducing/erasing using optical interference patternsSpatial light modulatorMicro actuator
According to one aspect, a holographic storage system including micro-actuators is presented. In one example of one aspect of the invention, the device includes a spatial light modulator, a detector, a storage medium, and at least one micro-actuator configured to move at least one of the spatial light modulator, the detector, and the storage medium. The micro-actuators may include a servomechanism or the like to control the positioning of a component based on feedback associated with a misalignment of a detected image. According to another aspect of the invention, various methods for determining component misalignments of a holographic storage system are presented.
Owner:AKONIA HOLOGRAPHICS
Virtual file system
ActiveUS20050114350A1Input/output to record carriersRecording by optical meansVirtual file systemProcessor node
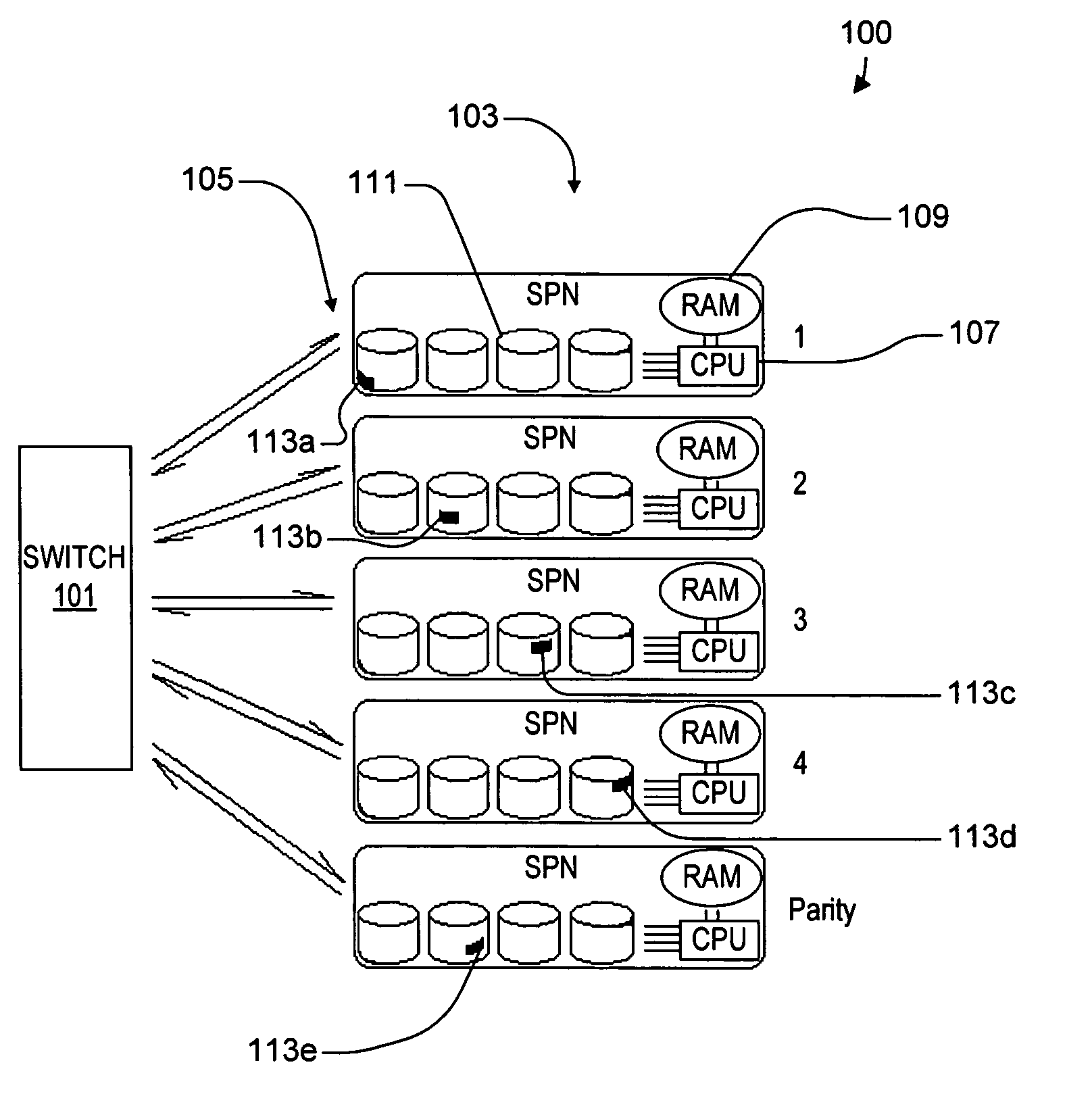
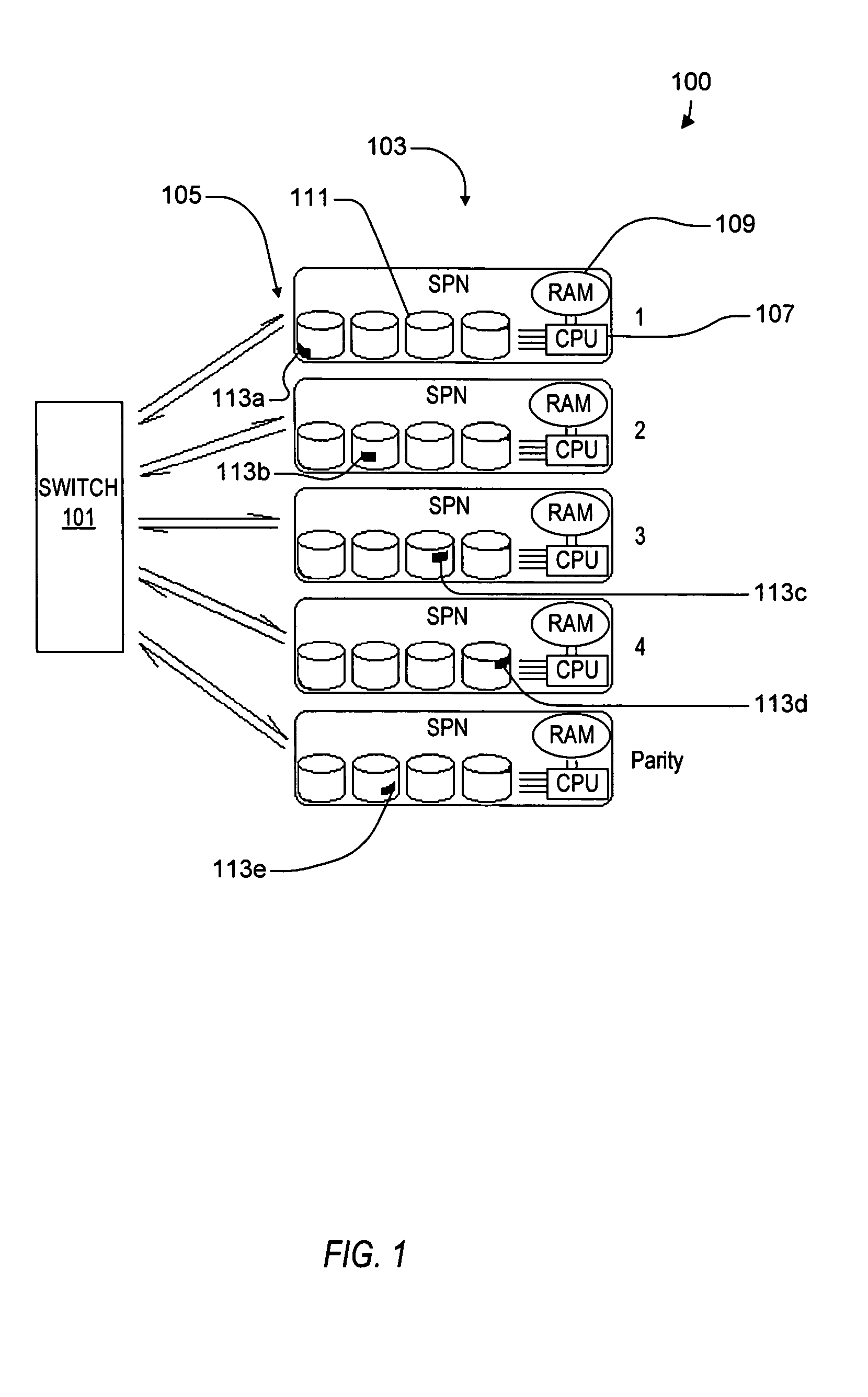
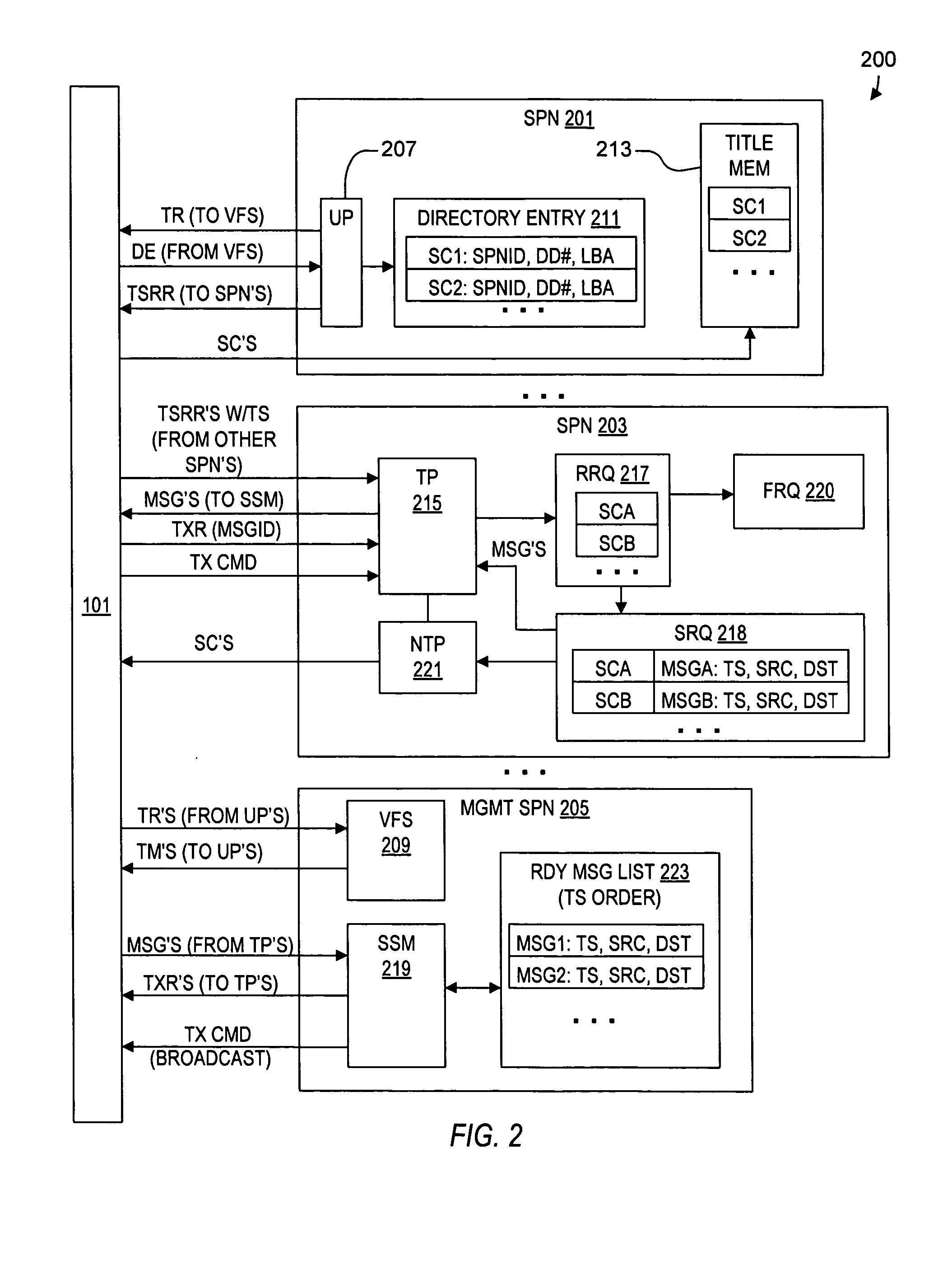
A virtual file system including multiple storage processor nodes including a management node, a backbone switch, a disk drive array, and a virtual file manager executing on the management node. The backbone switch enables communication between the storage processor nodes. The disk drive array is coupled to and distributed across the storage processor nodes and stores multiple titles. Each title is divided into data subchunks which are distributed across the disk drive array in which each subchunk is stored on a disk drive of the disk drive array. The virtual file manager manages storage and access of each subchunk, and manages multiple directory entries including a directory entry for each title. Each directory entry is a list of subchunk location entries in which each subchunk location entry includes a storage processor node identifier, a disk drive identifier, and a logical address for locating and accessing each subchunk of each title.
Owner:INTERACTIVE CONTENT ENGINES LLC
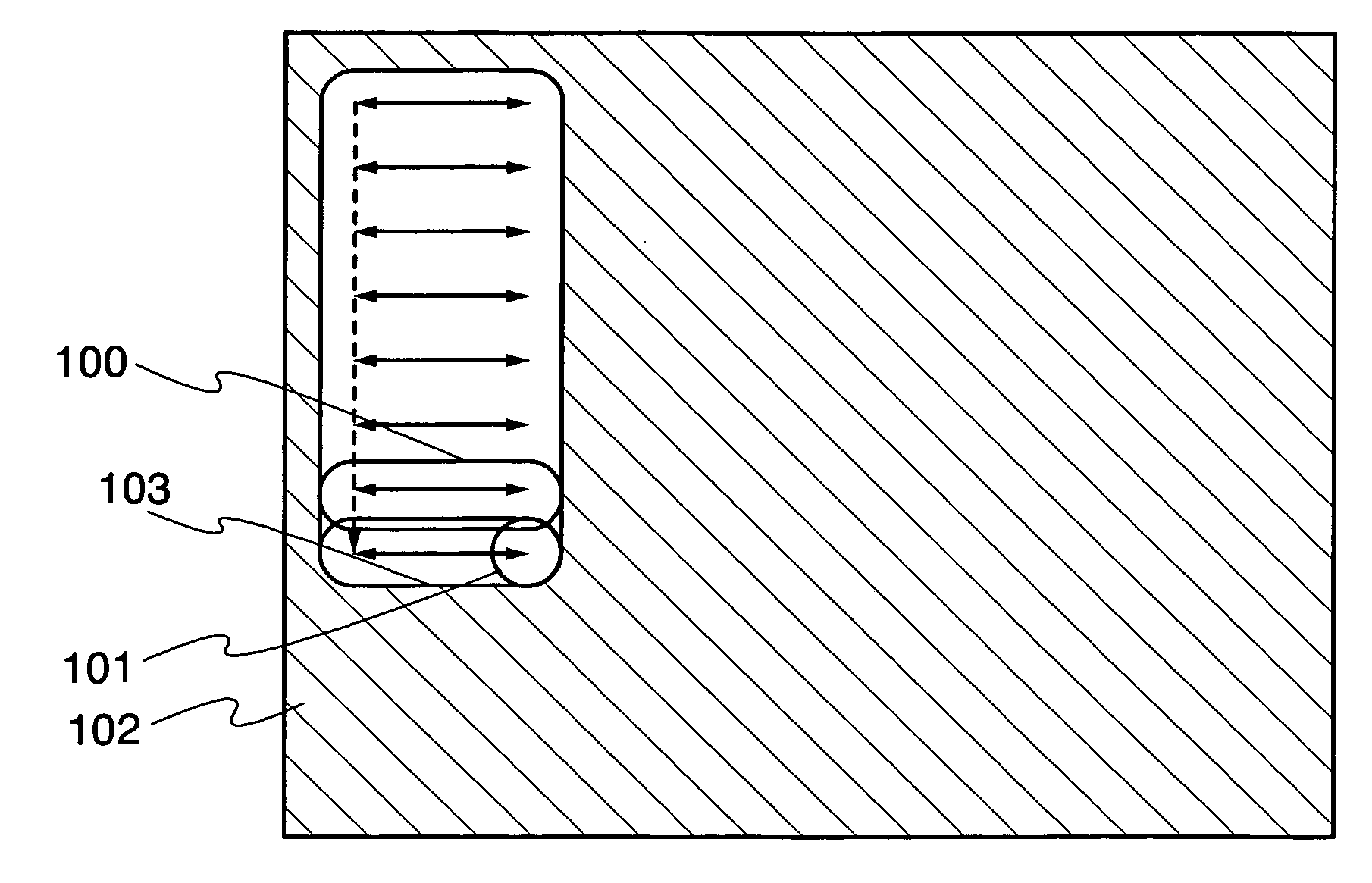
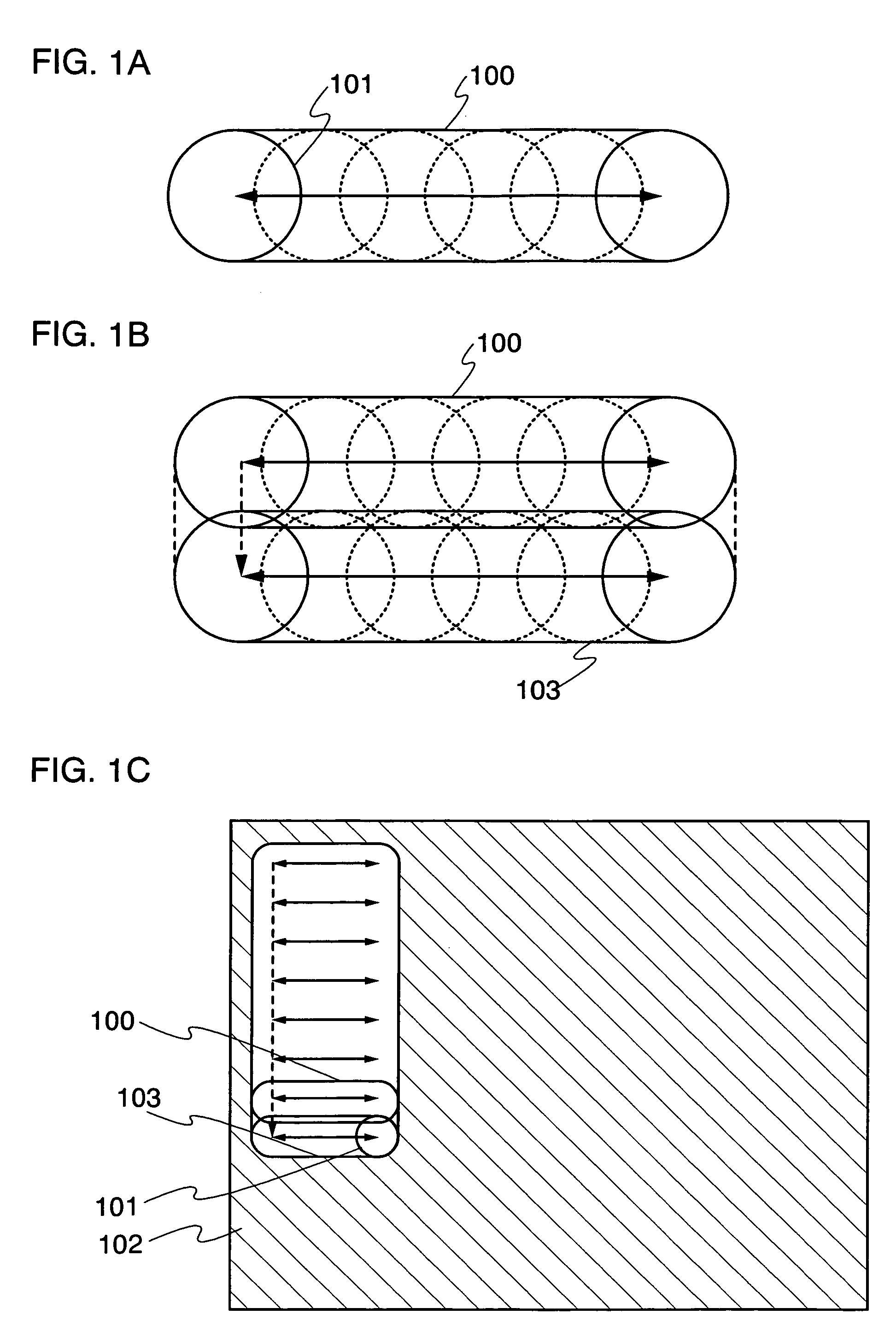
Recording disc and apparatus and method for reproducing recorded information
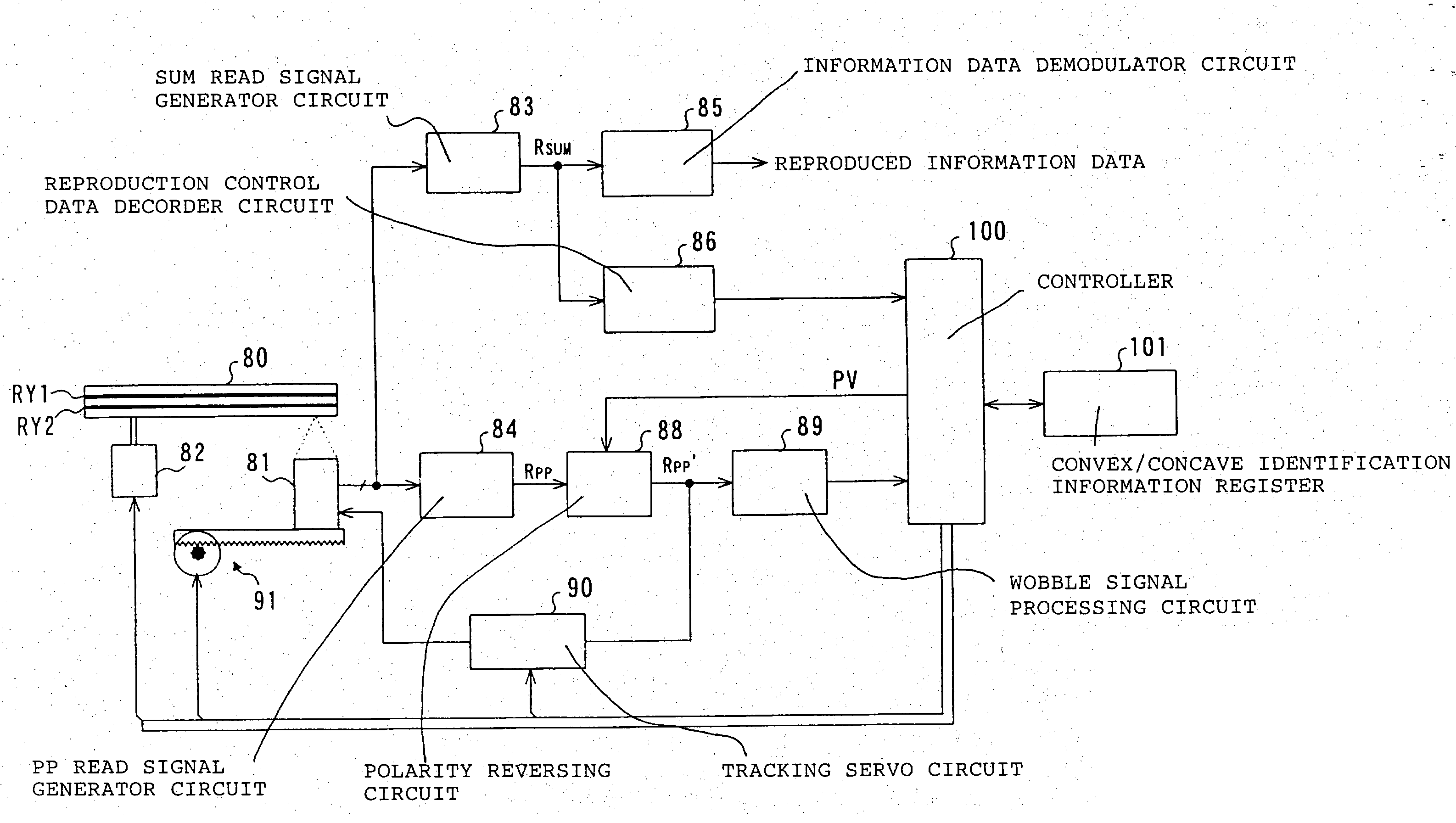
A recording disc and recorded information reproducing apparatus and method for immediately starting reproduction of information when a push-pull based tracking control is employed to reproduce recorded information from the recording disc. The recording disc comprises an information data area for recording recording marks which carry information data in columns, and a control data area for recording identification information indicative of a recording pattern of the recording marks in the information data area.
Owner:PIONEER CORP
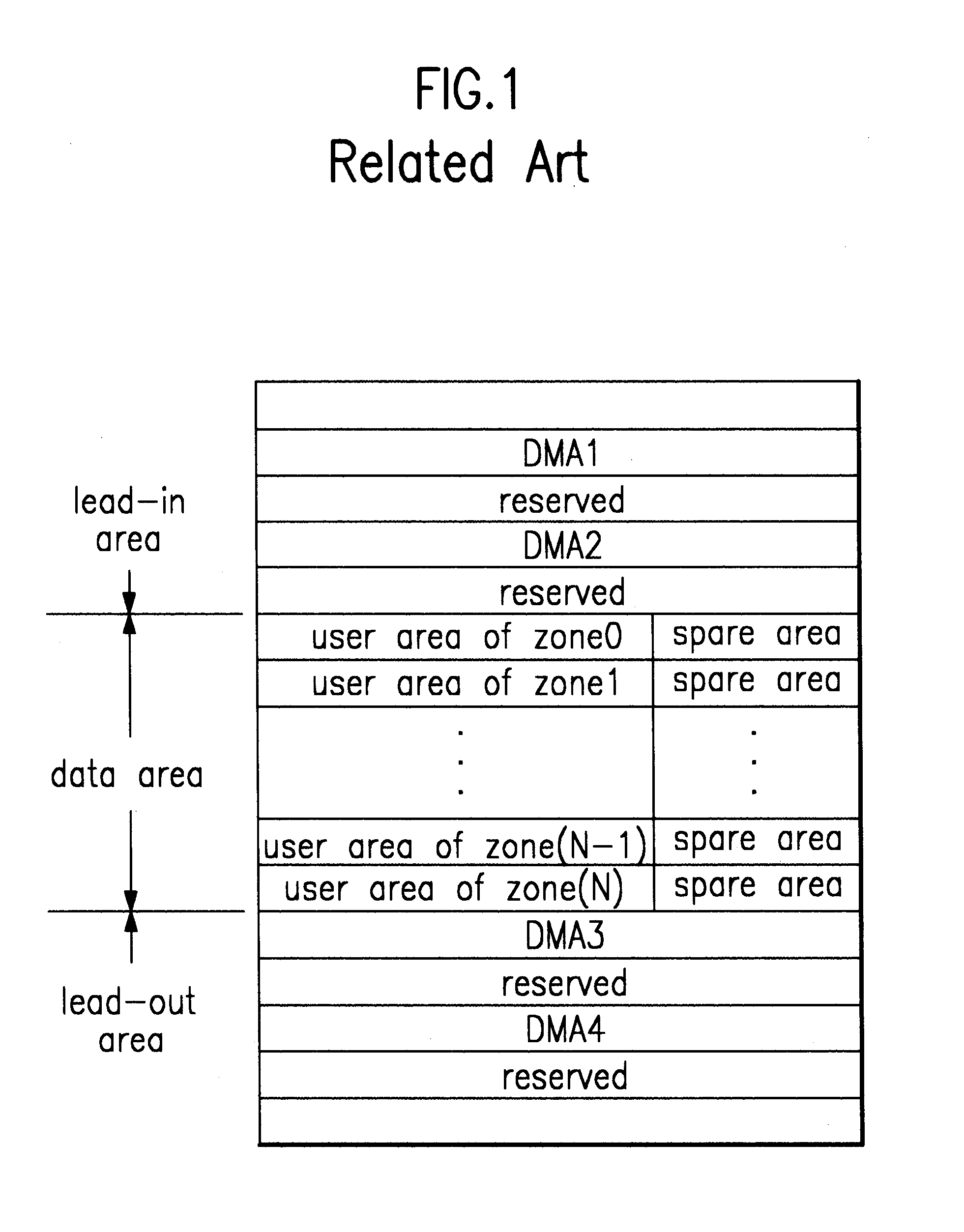
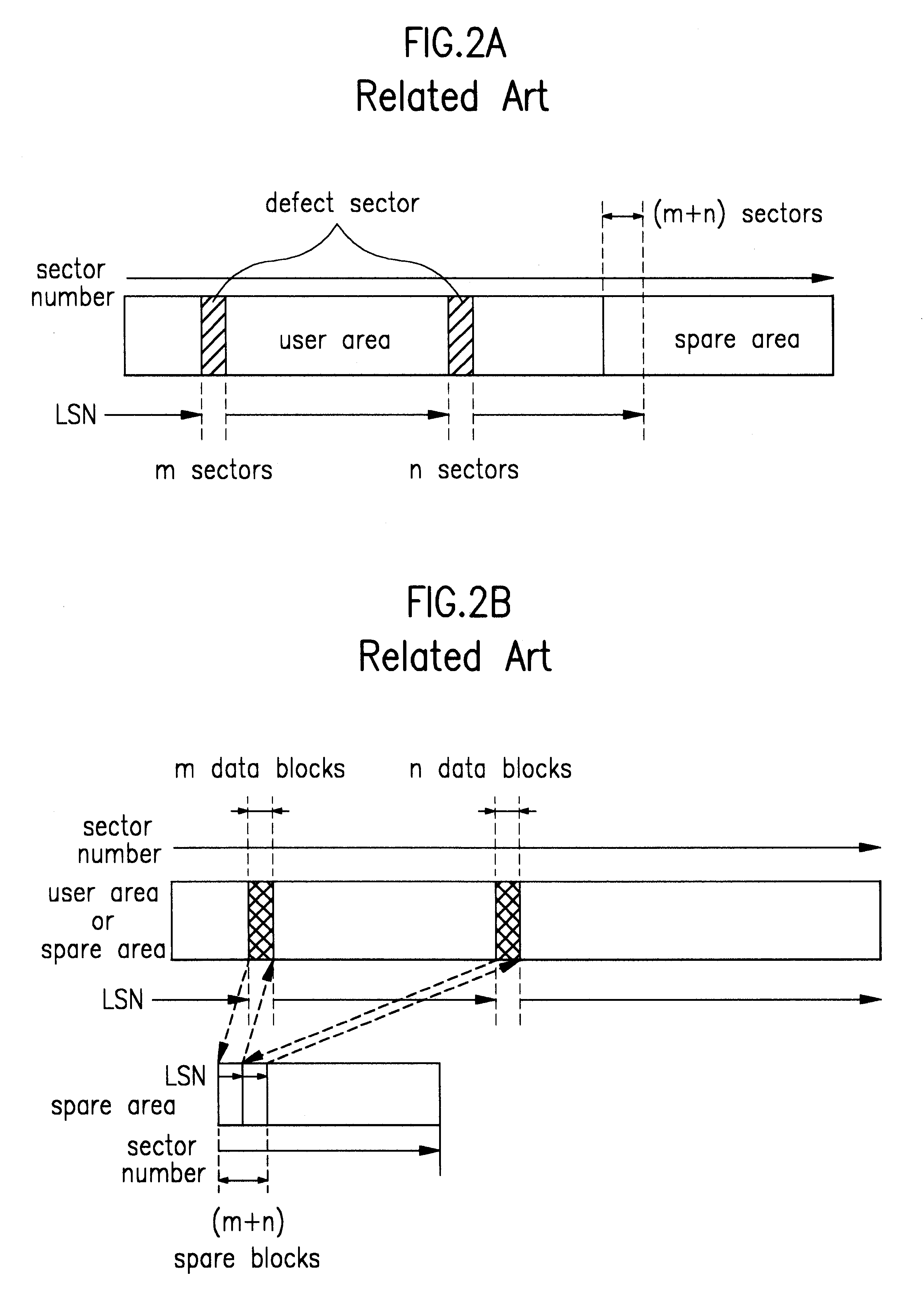
Optical recording medium and method of managing defect area of the optical recording medium
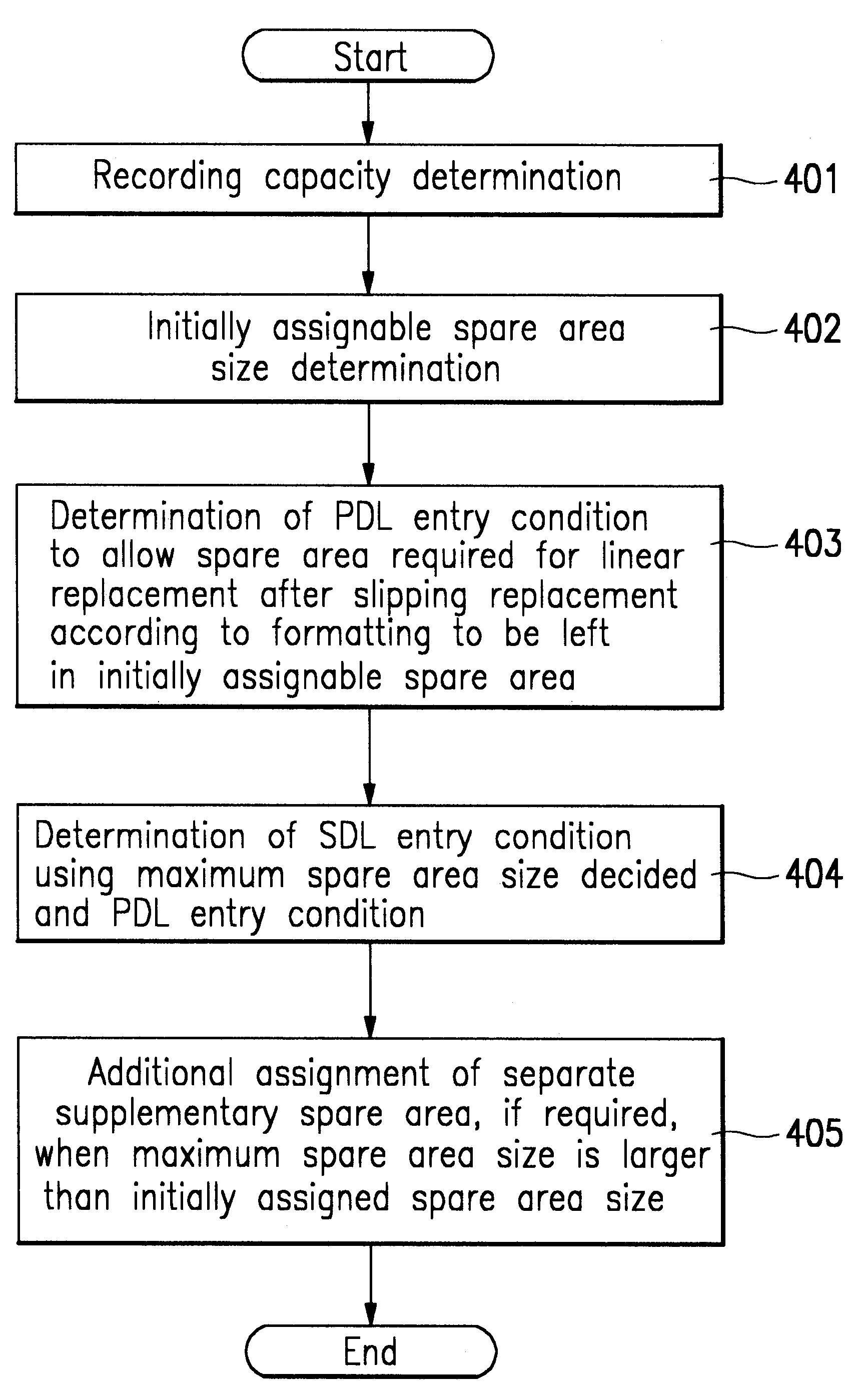
A rewritable optical medium and a method of managing its defect area is disclosed. The DMA condition or initially assignable spare area size in the present invention is determined based upon the interrelation between the spare area size and the DMA condition. Namely, the PDL entry condition among the DMA condition is determined to allow a minimum spare area for linear replacement in the initially assignable spare area after slipping replacement during formatting to facilitate management of the defect area of a rewritable optical medium. The present invention also discloses a method of controlling the recording / playback of optical media with the same format and different sizes, thereby improving the system performance.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Optical pickup apparatus, recording/reproducing apparatus provided with the optical pickup apparatus, optical element, and information recording/reproducing method
InactiveUS6870805B1Simple structureQuantity of light is lessOptical beam sourcesNon-mechanical controlsOptical pickupOptical axis
An optical pickup apparatus for reproducing information from an optical information recording medium or for recording information onto an optical information recording medium, is provided with a first light source for emitting first light flux having a first wavelength; a second light source for emitting second light flux having a second wavelength, the first wavelength being different from the second wavelength; a converging optical system having an optical axis and a diffractive portion, and a photo detector; wherein in case that the first light flux passes through the diffractive portion to generate at least one diffracted ray, an amount of n-th ordered diffracted ray of the first light flux is greater than that of any other ordered diffracted ray of the first light flux, and in case that the second light flux passes through the diffractive portion to generate at least one diffracted ray, an amount of n-th ordered diffracted ray of the second light flux is greater than that of any other ordered diffracted ray of the second light flux, where n stands for an integer other than zero.
Owner:KONICA CORP
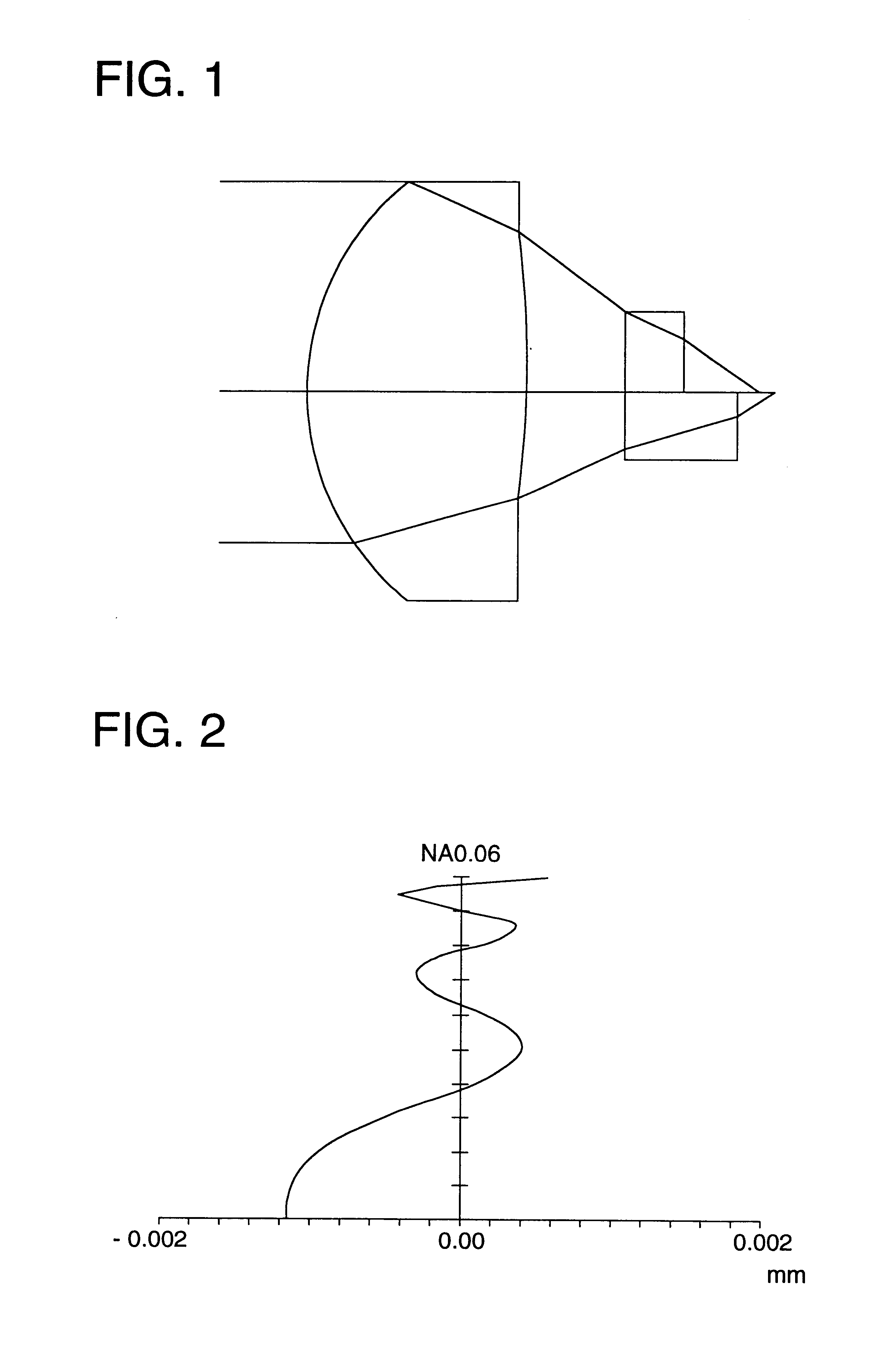
Objective lens, optical pick-up device, and optical disk device
InactiveUS20050007906A1Reduce thicknessSmall sizeOptical head protectionIntegrated optical head arrangementsOptical pickupMiniaturization
To provide an optical pickup device and optical disk device capable of realizing at least one of thickness reduction, size reduction and suppression against characteristic deterioration even where coping with various wavelengths of laser including a blue laser. An optical pickup device comprising light sources for respectively emitting a plurality of different wavelengths of light, unit structured for causing at least a part of the light emitted from the light sources to pass a same optical path; and focusing unit for focusing the light. The focusing unit includes at least first and second focusing parts, the first focusing part being to focus mainly a wavelength of light different from a wavelength of light to be mainly focused by the second focusing part.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Read write device for optical memory and method therefore
InactiveUS7480215B2Small-size and low-weight optical storage systemGuaranteed uptimePharmaceutical product form changeRecord information storageLight beamOptical storage
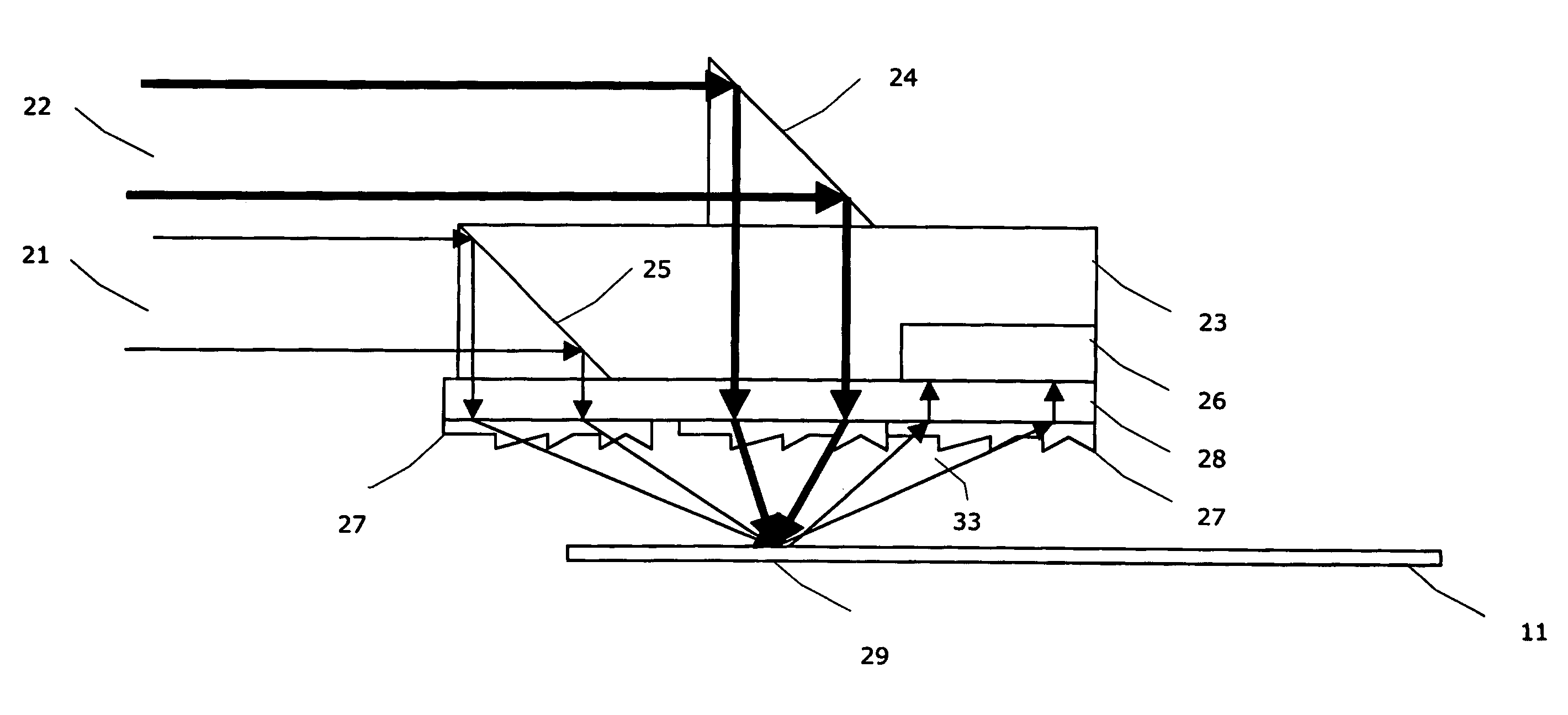
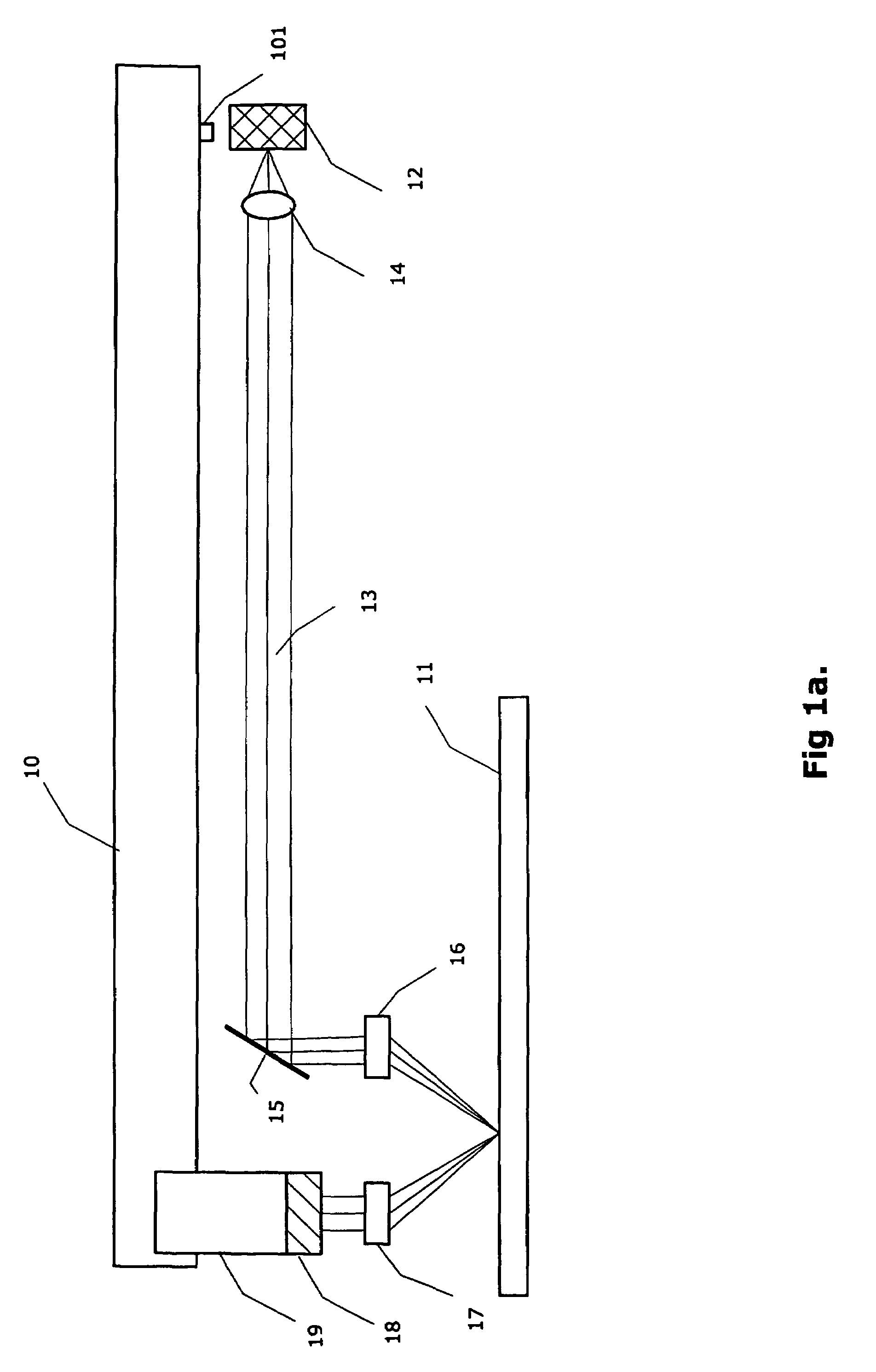
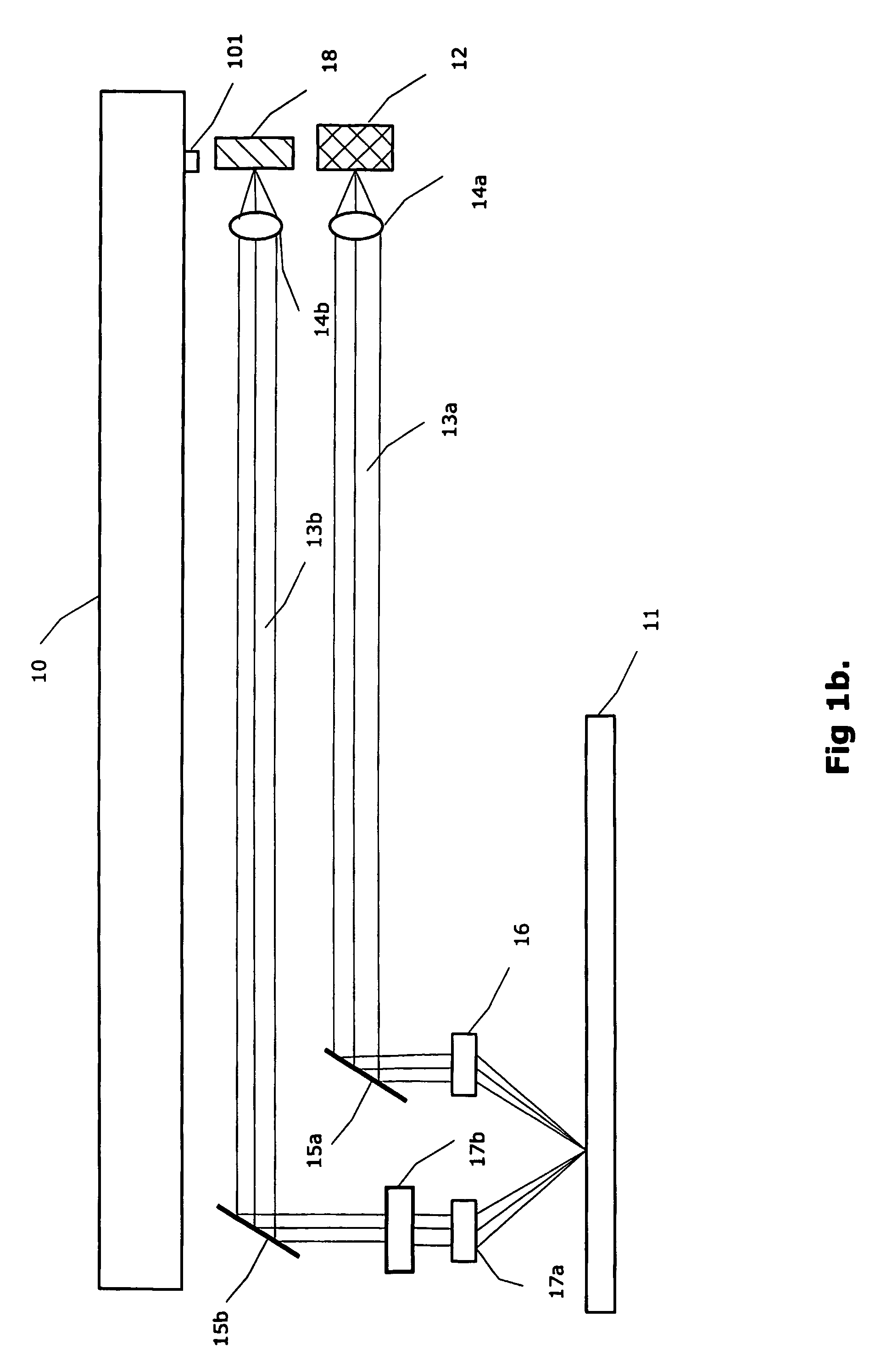
A method and miniaturizable device is described to read / write information to an optical storage medium (11). A device comprises one or more light sources (12) bounded up with an access unit (10) which is arranged to be controllable to a position, in which light beams (21, 22) are transmitted transversal towards an optical storage medium, and reflected light beams (33) are analysed by a detector element (18, 26) which further informs the access unit whether to move or stand still to keep light beams in focus and on track. A device according to the invention is possible to implement in a small size and low weight due to reduced component count and thin access unit geometries. A communication device (80) according to the invention may be implemented to fulfil a crucial need for ultraminiature range of communication devices.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Optical recording medium having pits that are formed with respect to a wobbled groove at substantially constant positions in each cycle of the groove having a pit
InactiveUS6075761AAccurate acquisitionHigh densityFilamentary/web record carriersRecord information storageHigh densityEngineering
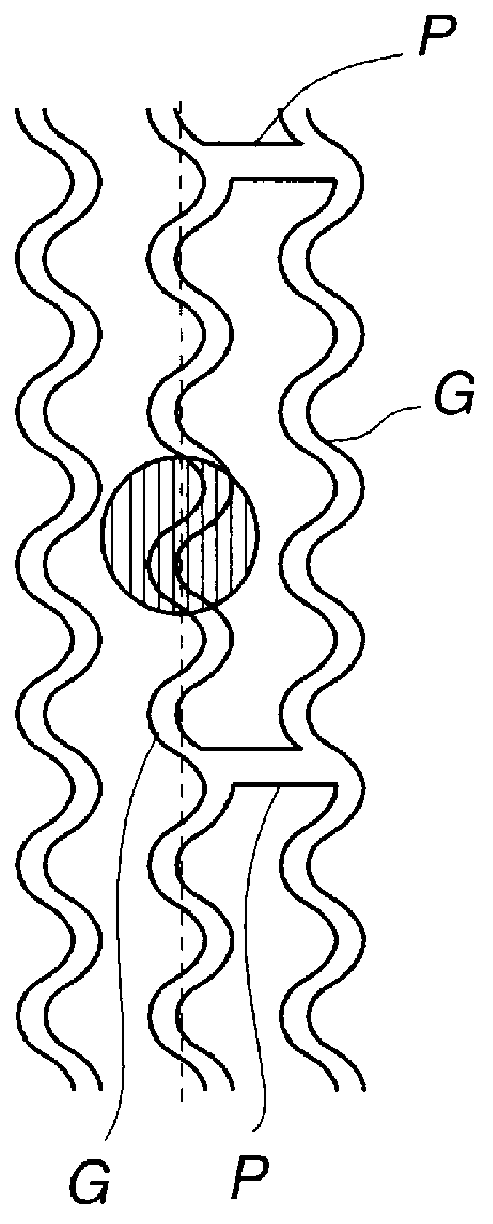
An optical recording medium for accurately deriving the address information or the disc rotation control information despite narrow track pitch and for recording signals to a high density, and a method and apparatus for recording and / or reproducing such optical recording medium. The optical recording medium has a wobbled groove and pits formed at a pre-set interval in an area between turns of the wobbled groove. The recording / reproducing method includes controlling rotation of the optical recording medium by a wobbled signal from the groove and detecting the position on the optical recording medium of a recording signal by pit signals detected from the pits. The recording / reproducing apparatus includes a detection device for detecting the wobbled signal from the groove and a detection device for detecting pit signals from the pits. The rotation of the optical recording medium is controlled by the wobbled signals detected from the groove and the position on the optical recording medium of the recording signal is detected by the pit signal detected from the pits.
Owner:SONY CORP +2
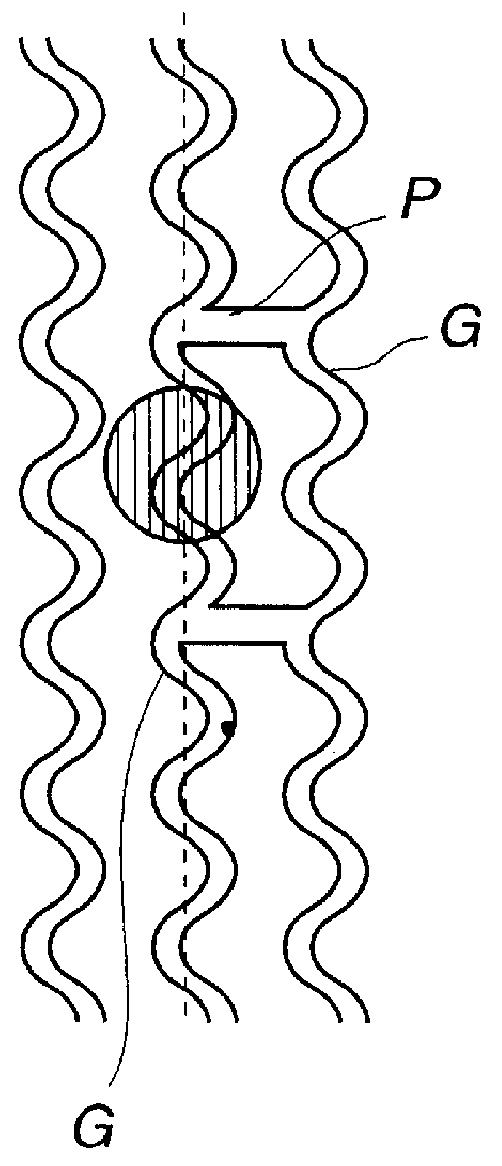
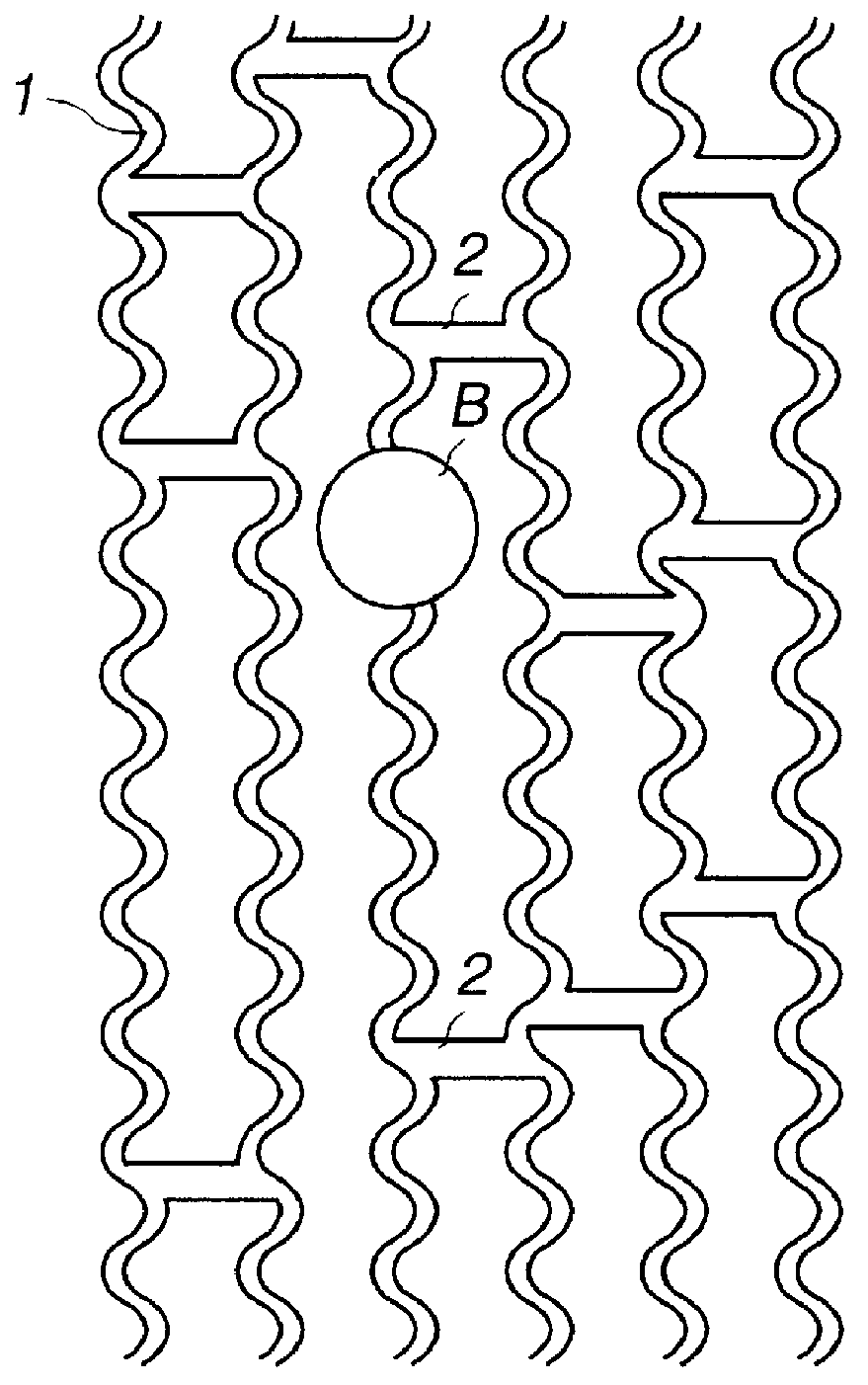
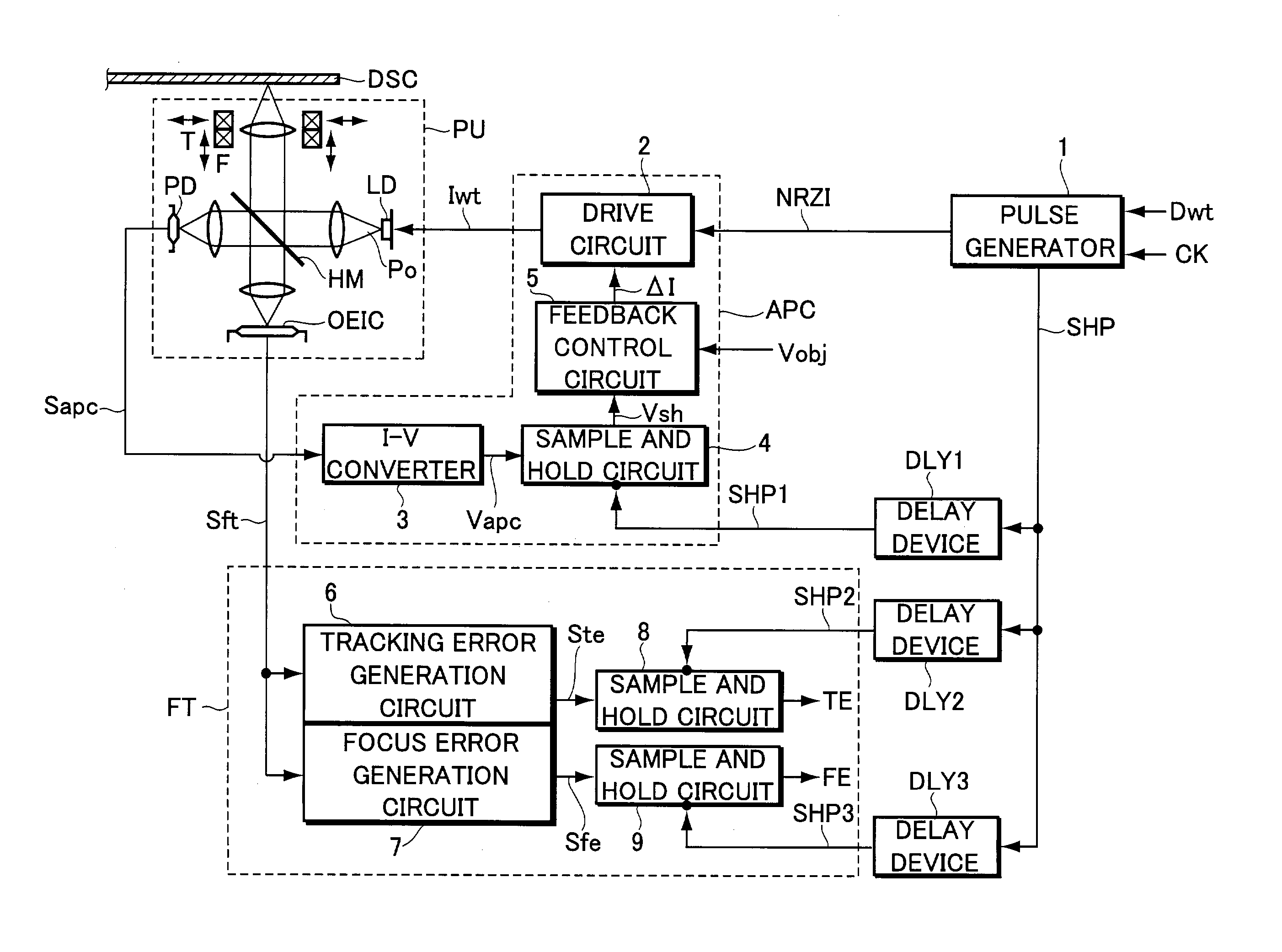
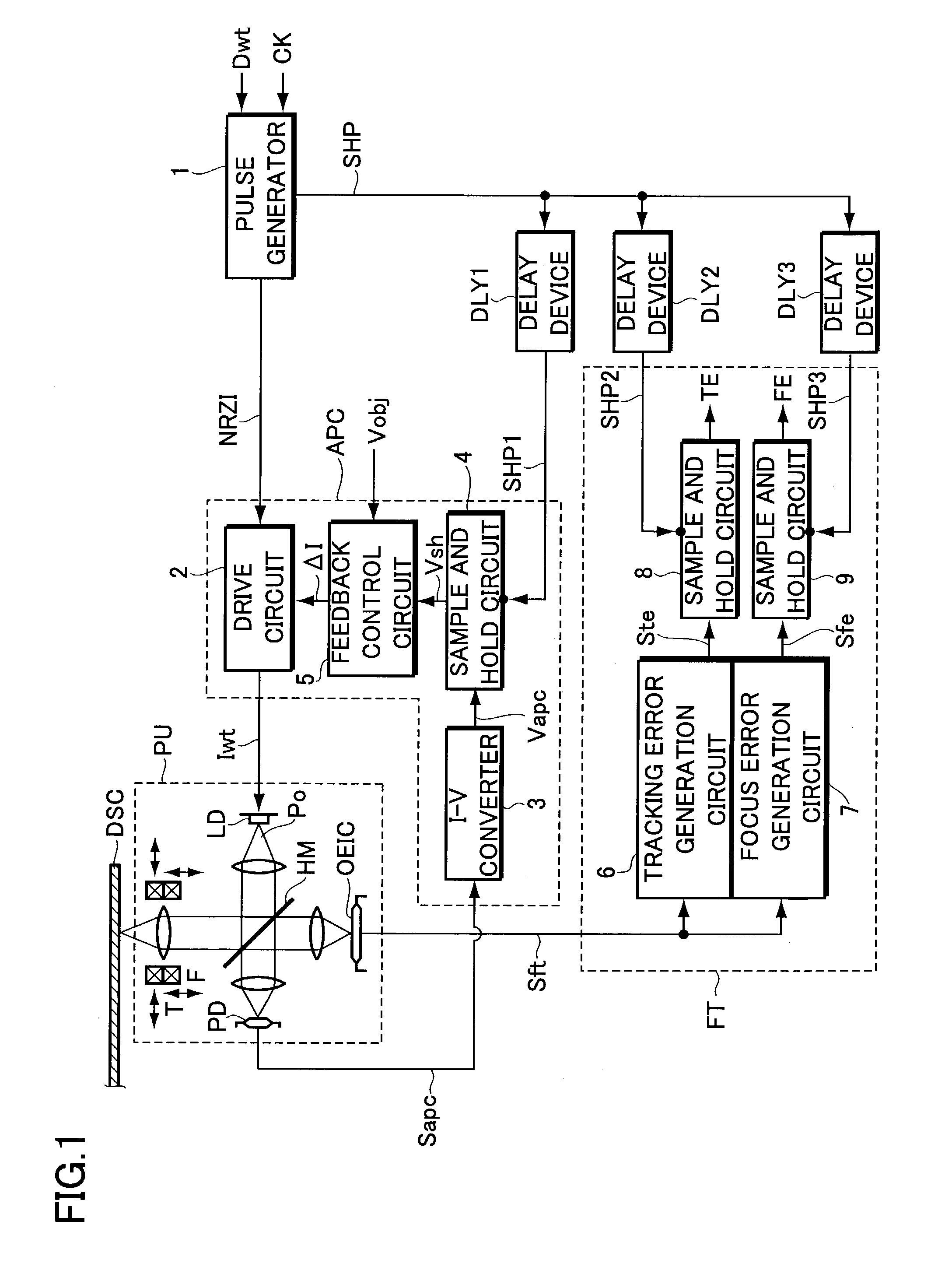
Information recording apparatus
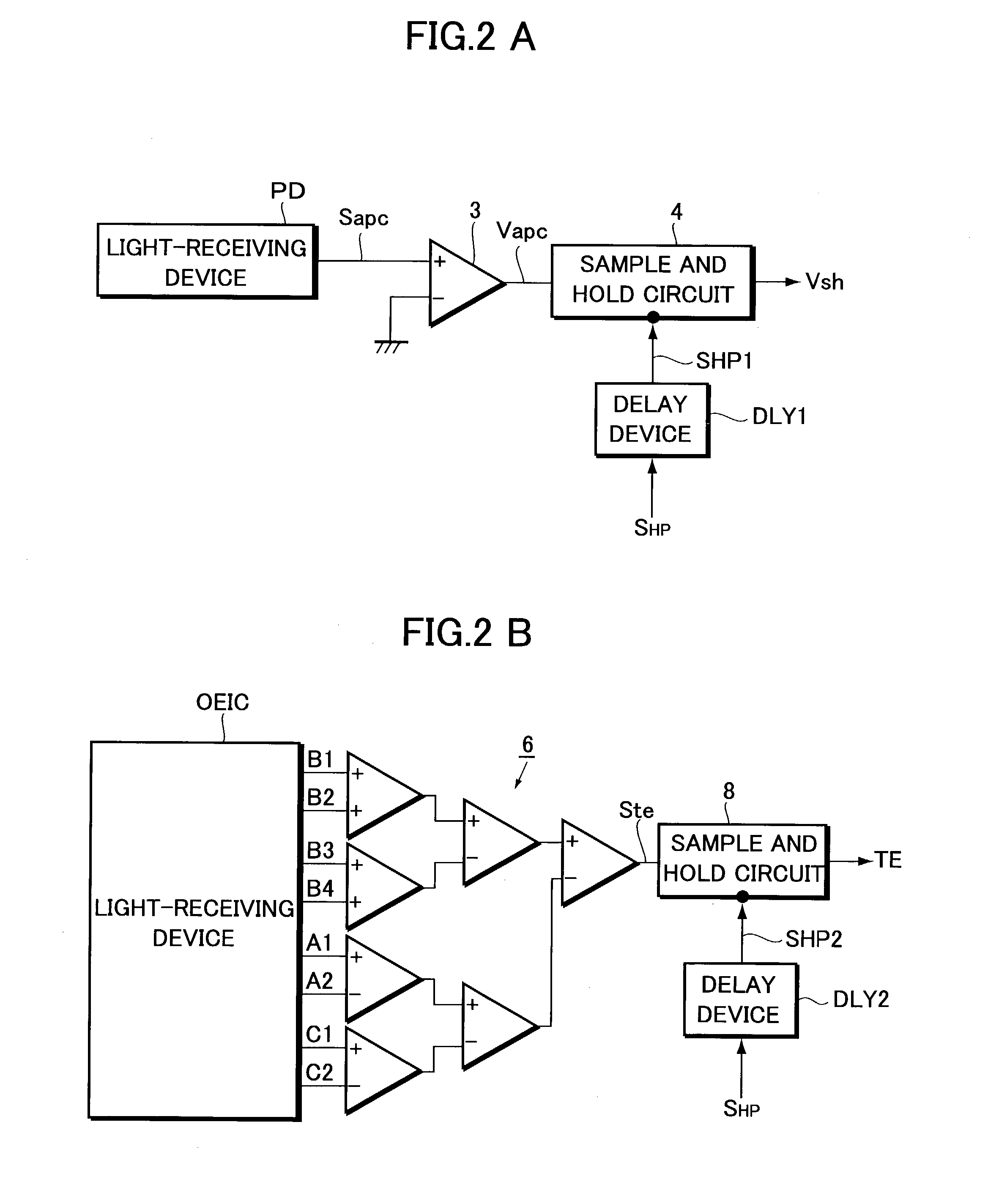
InactiveUS7164631B2Improve accuracyAccurate power adjustmentCombination recordingOptical beam sourcesTime delaysDelayed time
An information recording apparatus is provided, which can control over the power of light beams emitted from a light source and various types of servo control with higher accuracy. A laser beam is emitted from a semiconductor laser to write information onto an optical disc. A detection signal indicative of the power of the laser beam output from a light-receiving device is sampled and held with a sample and hold circuit via an I-V converter at a timing delayed by the time corresponding to the delay time of the I-V converter. A tracking error generation circuit and a focus error generation circuit generate a tracking error signal and a focus error signal, respectively, on the basis of a detection signal having information about tracking error and focus error and output from a light-receiving device. Sample and hold circuits sample and hold the tracking error signal and the focus error signal at a timing delayed by the time corresponding to the delay time of each of the generation circuits, respectively. Power control, tracking servo, and focus servo are performed using each of the signals held by the sample and hold circuits, respectively.
Owner:PIONEER CORP
Optical recording medium, manufacturing method thereof, method for recording data on optical recording medium, and data reproduction method
InactiveUS20070030795A1Excellent signal characteristicImprove featuresInformation arrangementMechanical record carriersRefractive indexPush pull
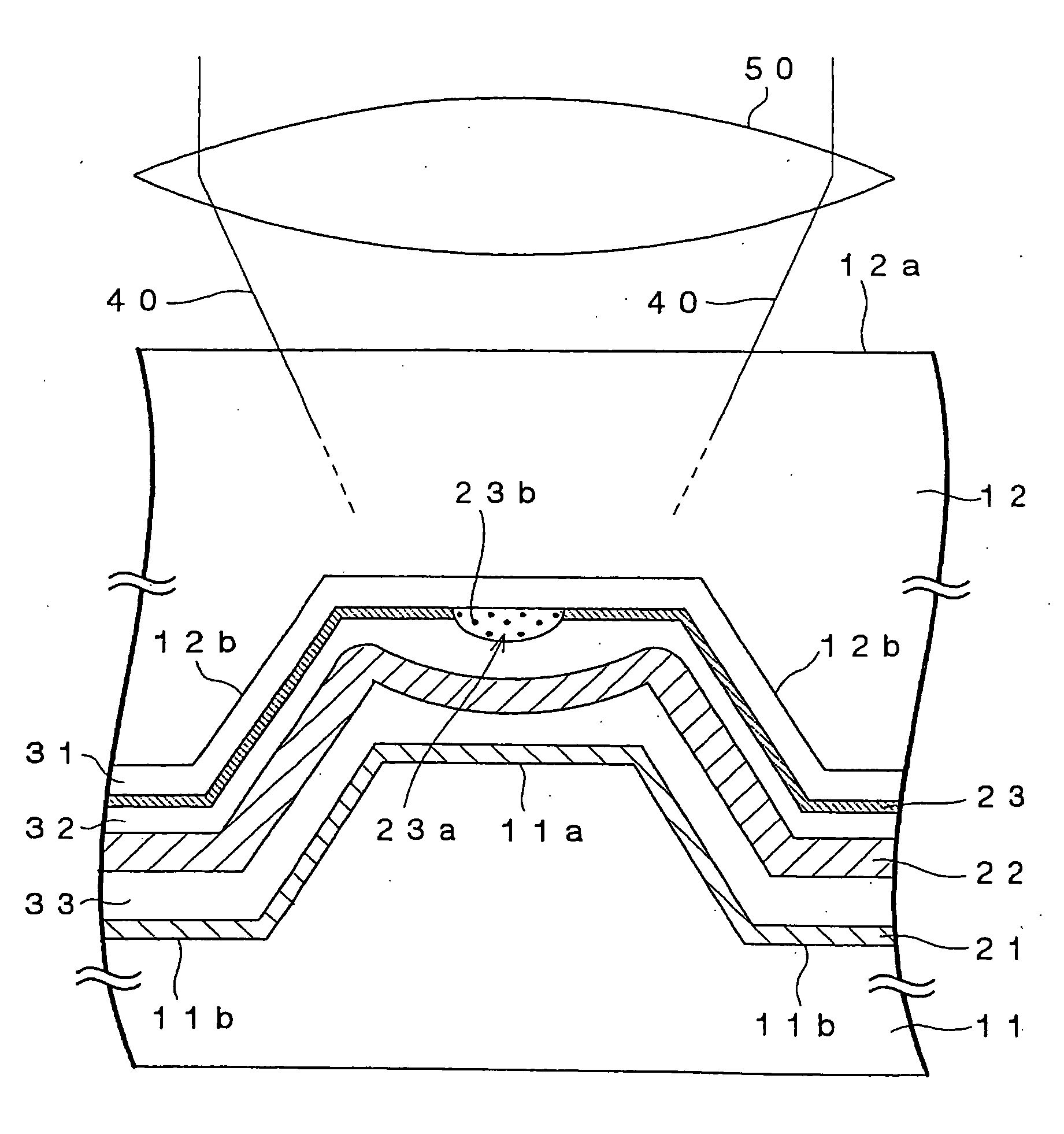
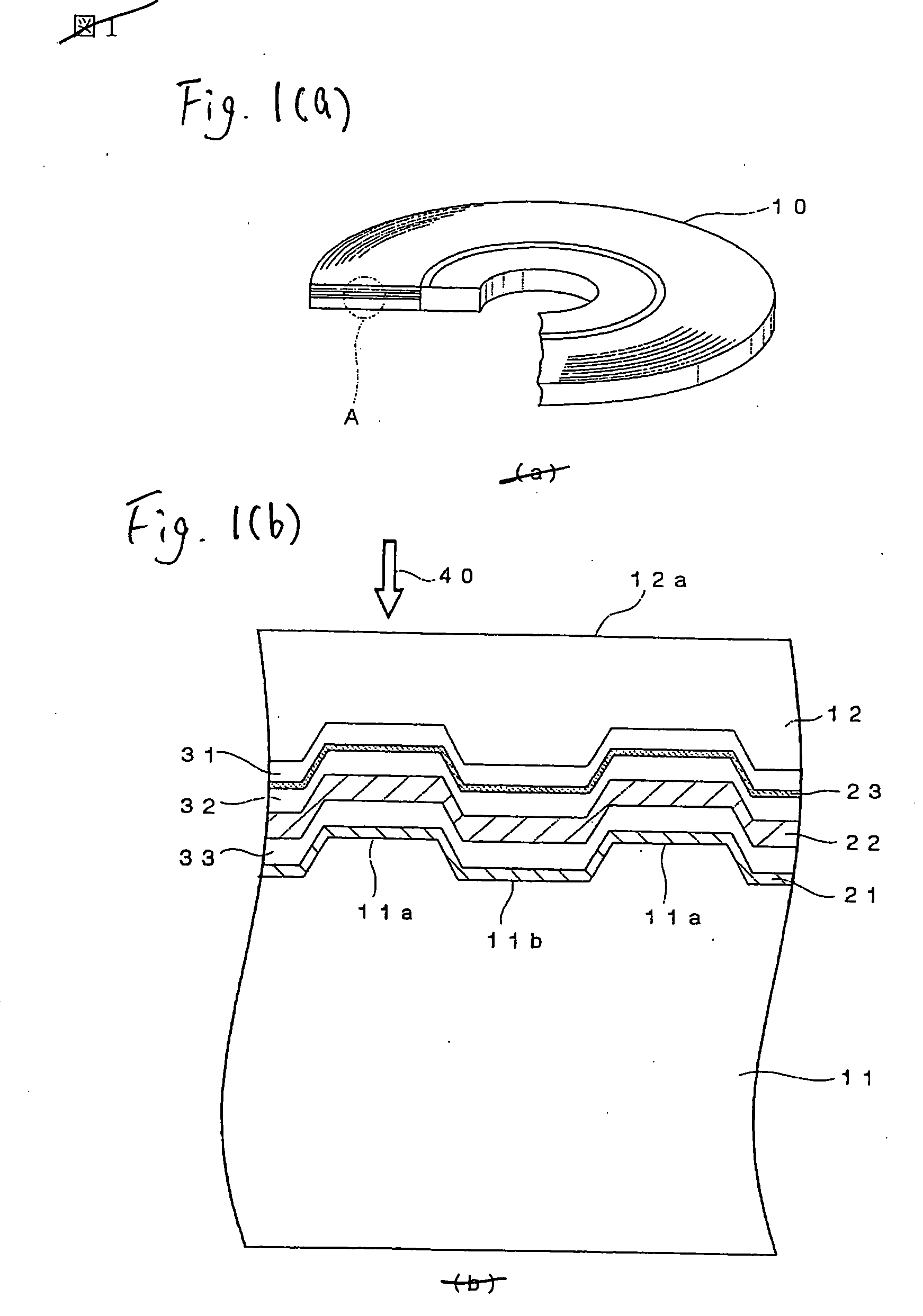
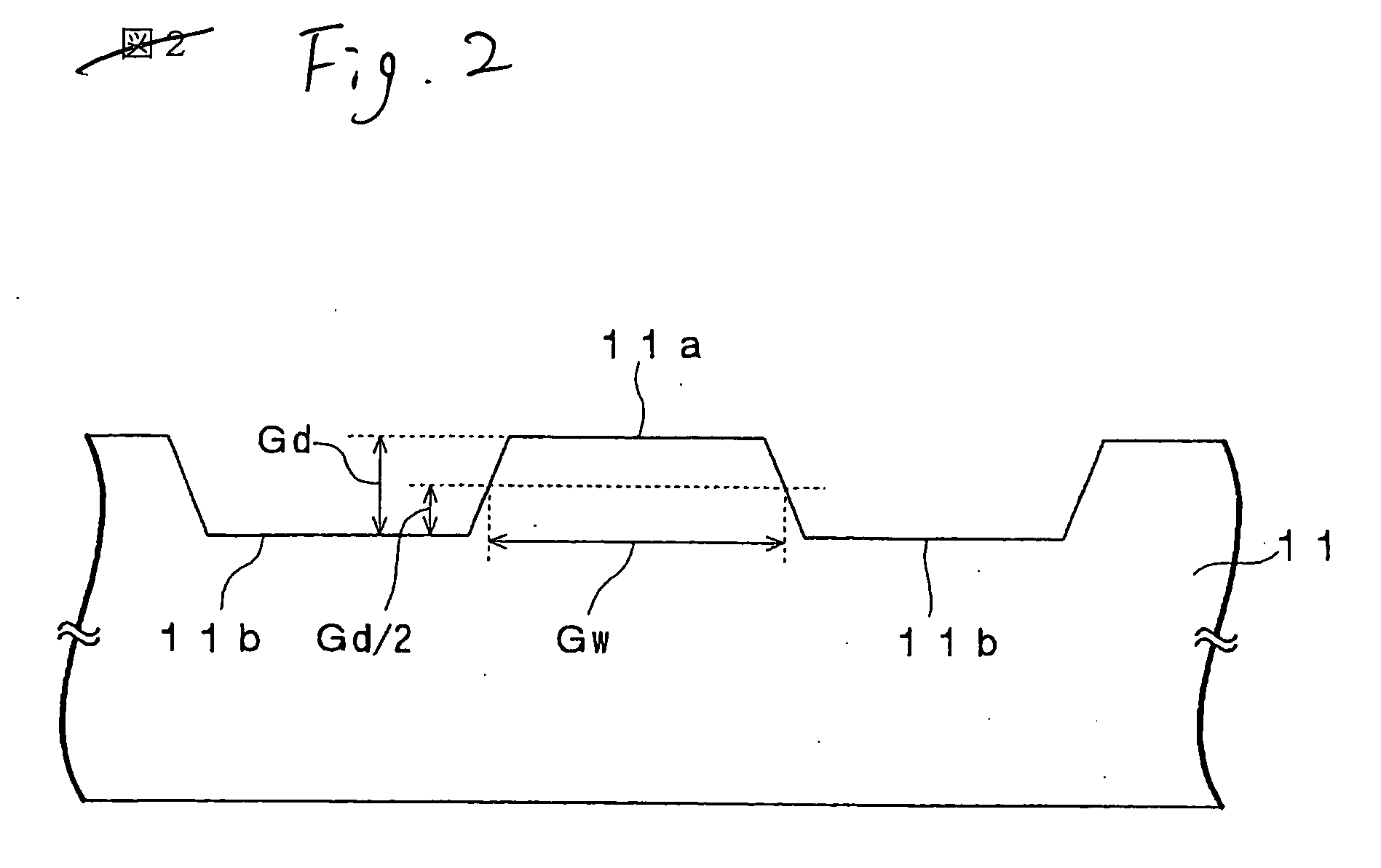
An optical recording medium 10 according to the present invention includes a supporting substrate 11 on which a groove 11a is formed, a light transmitting layer 12, a noble metal oxide layer 23 provided between the supporting substrate 11 and the light transmitting layer 12, wherein a depth of the groove 11a is set in excess of λ / 8 n but 60 nm or less, where n is a refractive index of the light transmitting layer 12 with respect to a light whose wavelength is λ. Thus, the good signal characteristics, especially a push-pull signal with an enough amplitude, can be obtained when the super-resolution recording and super-resolution reading are carried out by irradiating the laser beam onto the noble metal oxide layer 23. Also, since the depth of the groove is set to 60 nm or less, a grave difficulty never arises in producing a stamper used to manufacture the substrate.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Optical pick-up head, optical information apparatus, and optical information reproducing method
ActiveUS20050199778A1Improve reliabilityReduce signal amplitudeOptical detectorsMaterial analysis by optical meansBeam splitterPhotodetector
An optical information apparatus of the present invention includes: an optical pick-up head including: a light source; a diffraction unit; a condensing unit; a beam splitter; a photodetector; and a tracking error signal generator. An optical recording medium has tracks arranged substantially at a constant pitch. An average of a pitch is tp. When a main beam is placed on the track, a first sub-beam and a second sub-beam are placed between the tracks. The tracking error signal generator performs a differential arithmetic operation with respect to signals output from a light-receiving portion receiving the main beam to generate a first push-pull signal, performs a differential arithmetic operation with respect to signals output from the light-receiving portions receiving the first sub-beam and the second sub-beam to generate a second push-pull signal, and performs a differential arithmetic operation with respect to the first push-pull signal and the second push-pull signal to generate a tracking error signal, in a case where an amplitude of the first push-pull signal obtained at the pitch tp is fluctuated when the light beam is scanned in a direction orthogonal to the tracks of the optical recording medium.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Media drive with a luminescence detector and methods of detecting an authentic article
InactiveUS20060041898A1Paper-money testing devicesPhotomechanical apparatusComputer scienceLuminescent material
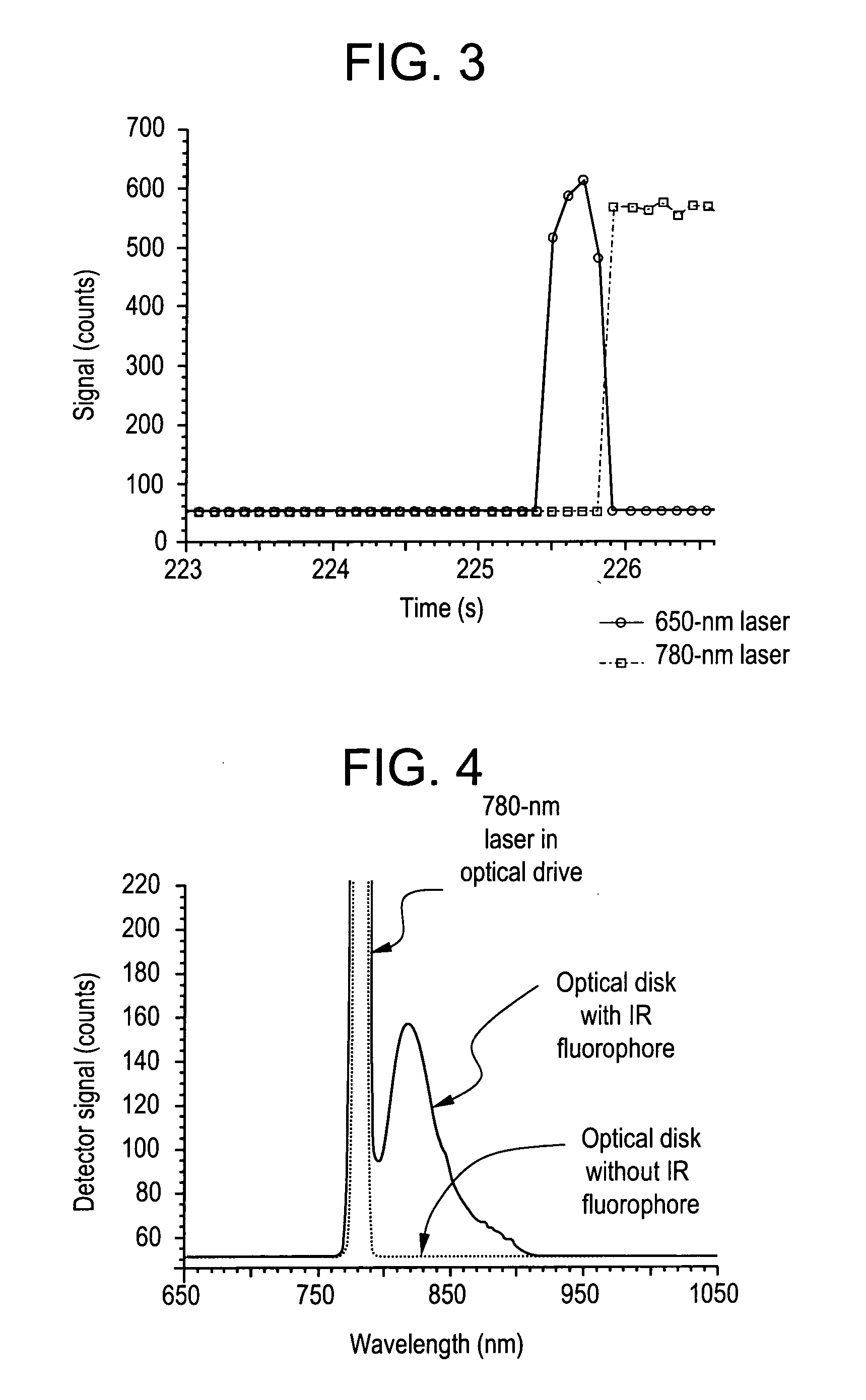
A media drive is disclosed. In one embodiment, a media drive can comprise: a disk holder, a drive laser, a disk reader, and a luminescence detector. The disk holder can be capable of applying a rotational force to a media disk. The drive laser is disposed so that light from the laser will be incident on the media disk when it is disposed in the disk holder. The disk reader is disposed to receive data from the media disk. A method for authenticating a media disk is also disclosed. The method can comprises: disposing the article in a reader, illuminating at least a portion of the article with the information reader, monitoring a luminescence emission of the illuminated article, and determining if the luminescence emission is consistent with an authentic article. If a luminescent material is present, the information reader excites the luminescent material to create a luminescence emission.
Owner:SABIC GLOBAL TECH BV
Multi-layer optical recording media and system for recording and reproducing information data
InactiveUS6498775B1Precise alignmentOptical beam sourcesRecord information storageEngineeringOptical recording
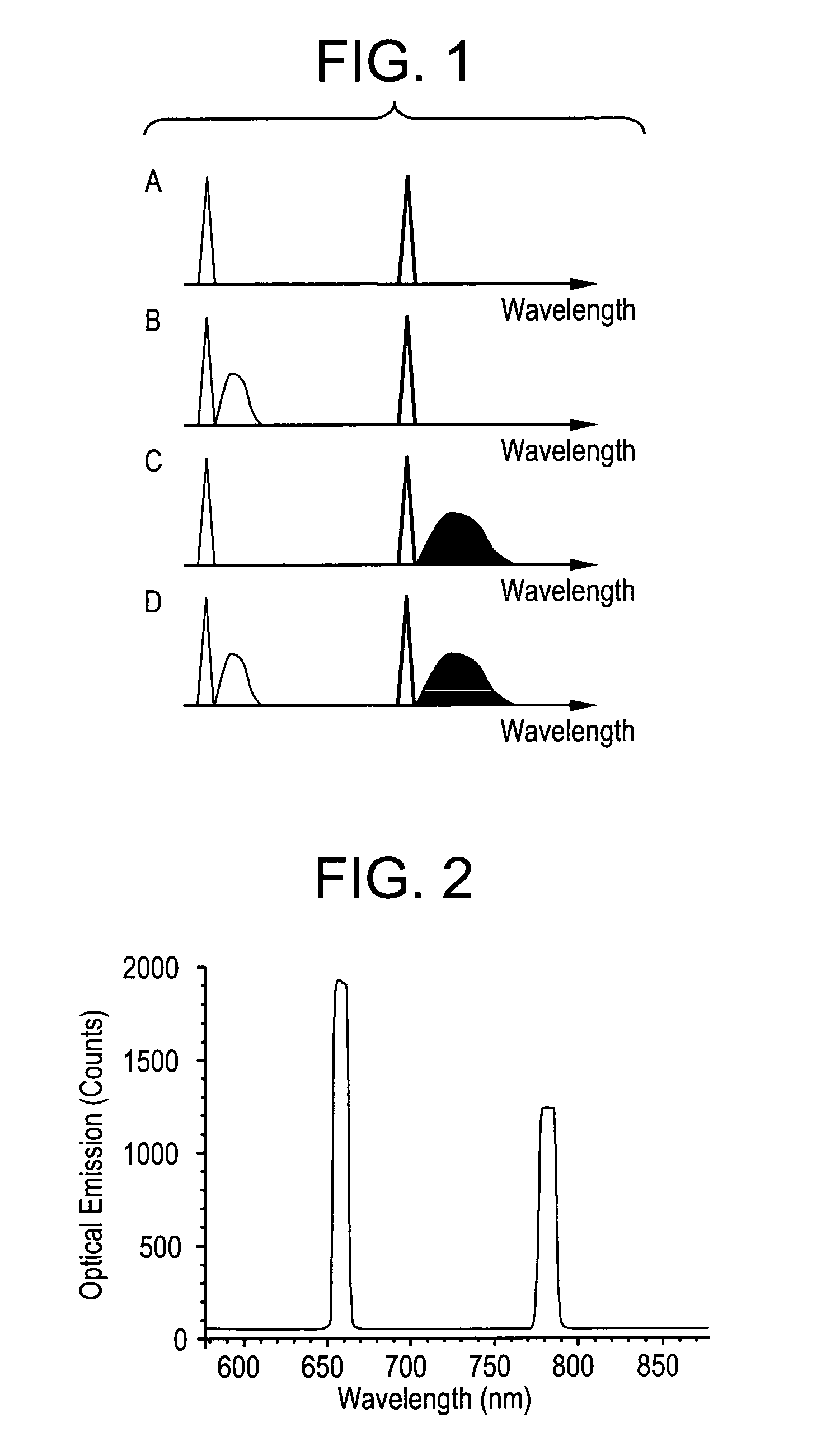
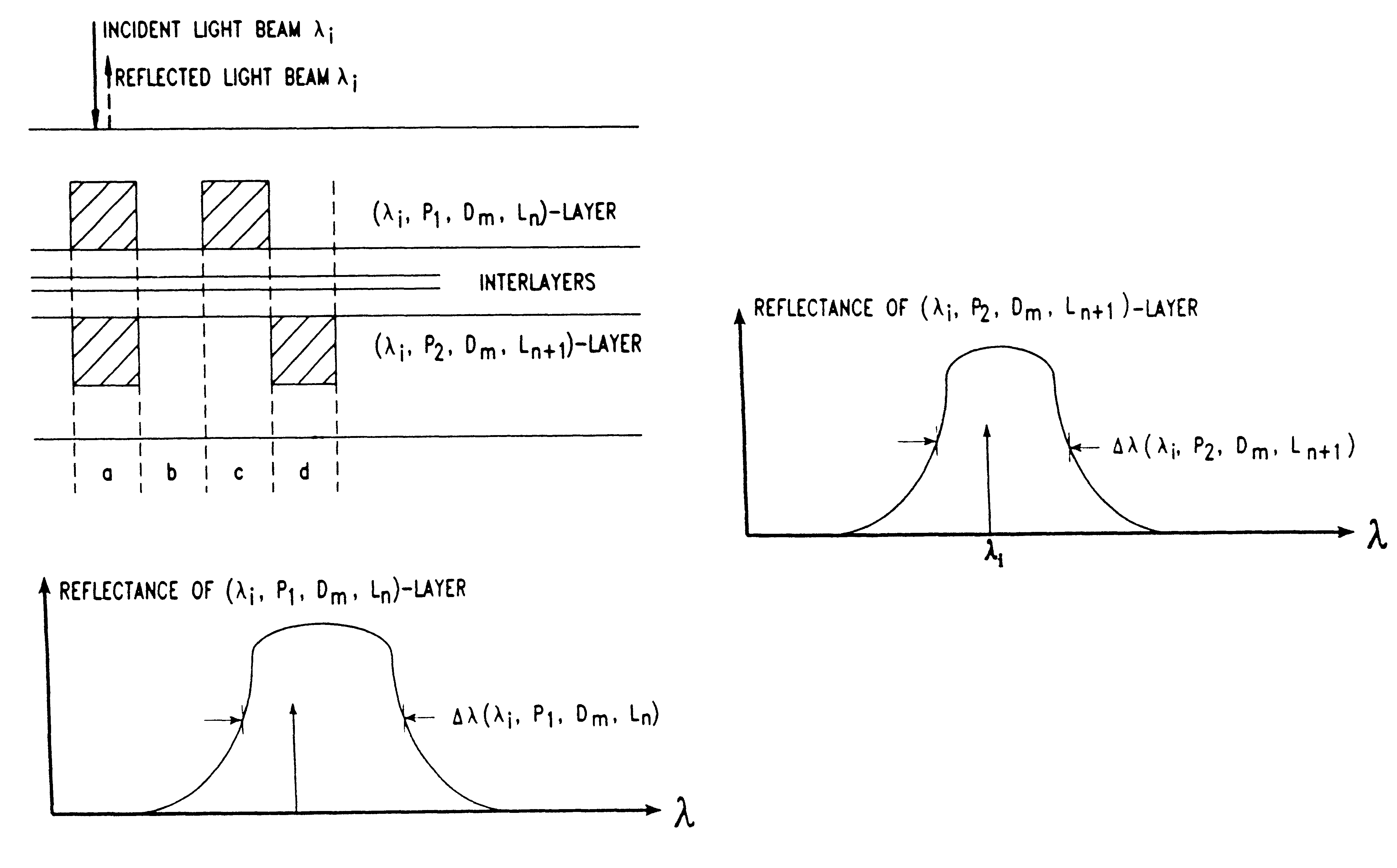
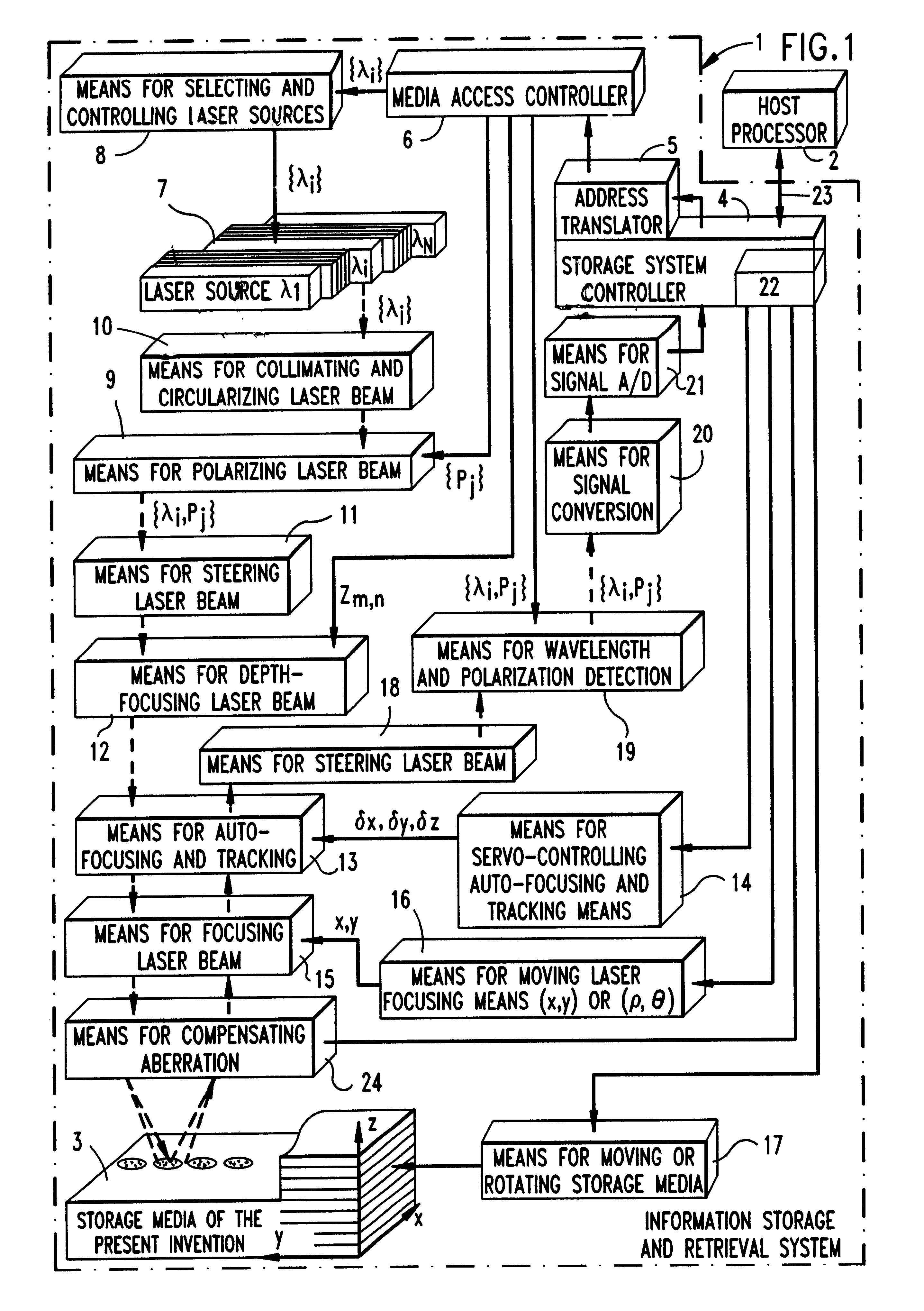
Disclosed is a novel multi-layered optical recording media and system for recording and reproducing information data. The multi-layered topical recording media has M information storage decks, and each information storage deck has N information storage layers, and each information storage layer has a pair of information storage structures. Each paired information storage structure has a characteristic wavelength and polarization state, and from which recorded information can be read by a laser beam having similar wavelength and polarization-state characteristics. In the illustrative embodiment, the multi-layered optical recording media of the present invention has MxNx2 information storage layers which can be read using only N laser lines (i.e. spectral components), thereby providing a 2M-fold increase in information storage capacity over prior art systems. The information storage and retrieval system of the present invention is completely backward compatible to allow for the reading of conventional CD-ROM devices.
Owner:REVEO
System and method for a high bandwidth servo system
InactiveUS20030043710A1Decrease servo overheadLonger gapInformation arrangementFilamentary/web record carriersHigh bandwidthControl theory
A storage medium is provided having a relatively large number of relatively small servo sectors. The storage medium includes a plurality of tracks. Each track includes a plurality of data sectors and a plurality of servo sectors. Each servo sector includes a plurality of servo marks and a synchronization gap. A plurality of first servo sectors includes a synchronization gap having a first length and a plurality of second servo sectors includes a synchronization gap having a second length. The first length is different from the second length, whereby, an unsynchronized reading device may recognize the longer synchronization gap and synchronize to the servo sector and a synchronized reading device may remain synchronized by recognizing the shorter synchronization gap.
Owner:EMC CORP
Laser irradiation apparatus and method for manufacturing semiconductor device
InactiveUS20050237895A1Improve throughputSimple processLaser detailsFilamentary/web record carriersOptoelectronicsIrradiation
It is an object of the present invention to provide a laser irradiation apparatus being able to irradiate the irradiation object with the laser beam having homogeneous energy density without complicating the optical system. The laser irradiation apparatus of the present invention comprises a laser oscillator, an optical system for scanning repeatedly a beam spot of the laser beam emitted from the laser oscillator in a uniaxial direction over the surface of the irradiation object, and a position controlling means for moving the position of the irradiation object relative to the laser beam in a direction perpendicular to the uniaxial direction.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
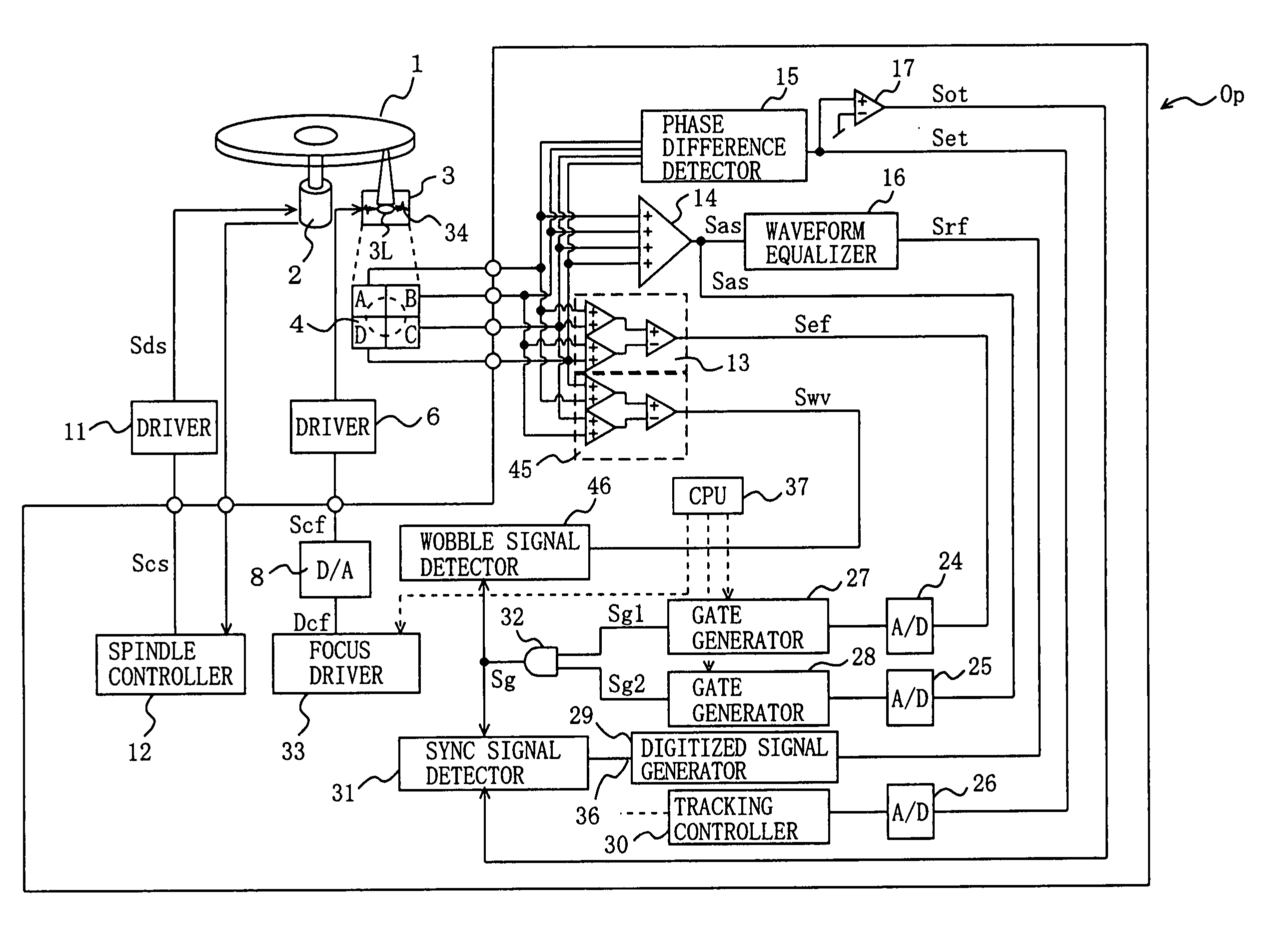
Optical disk identification device
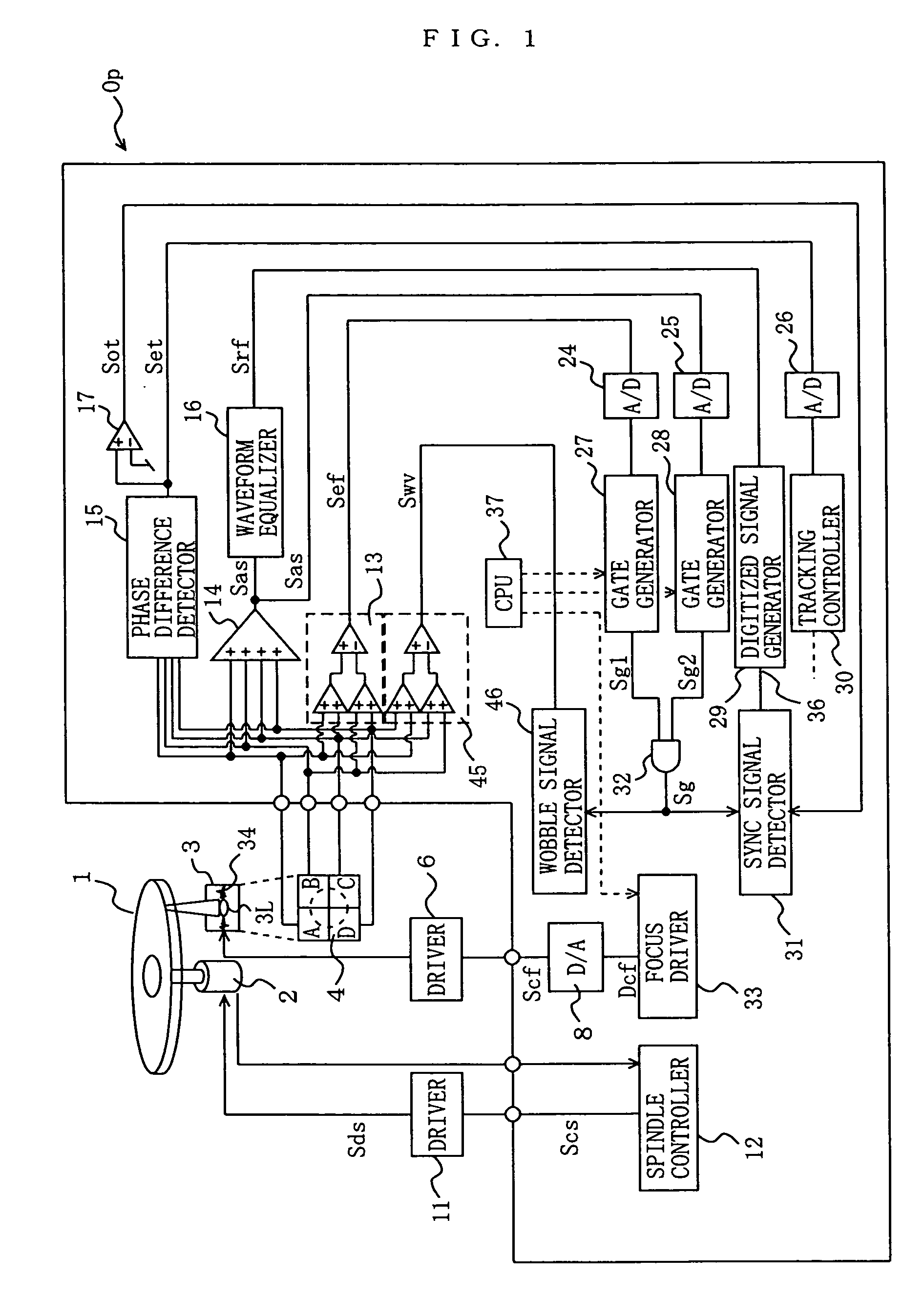
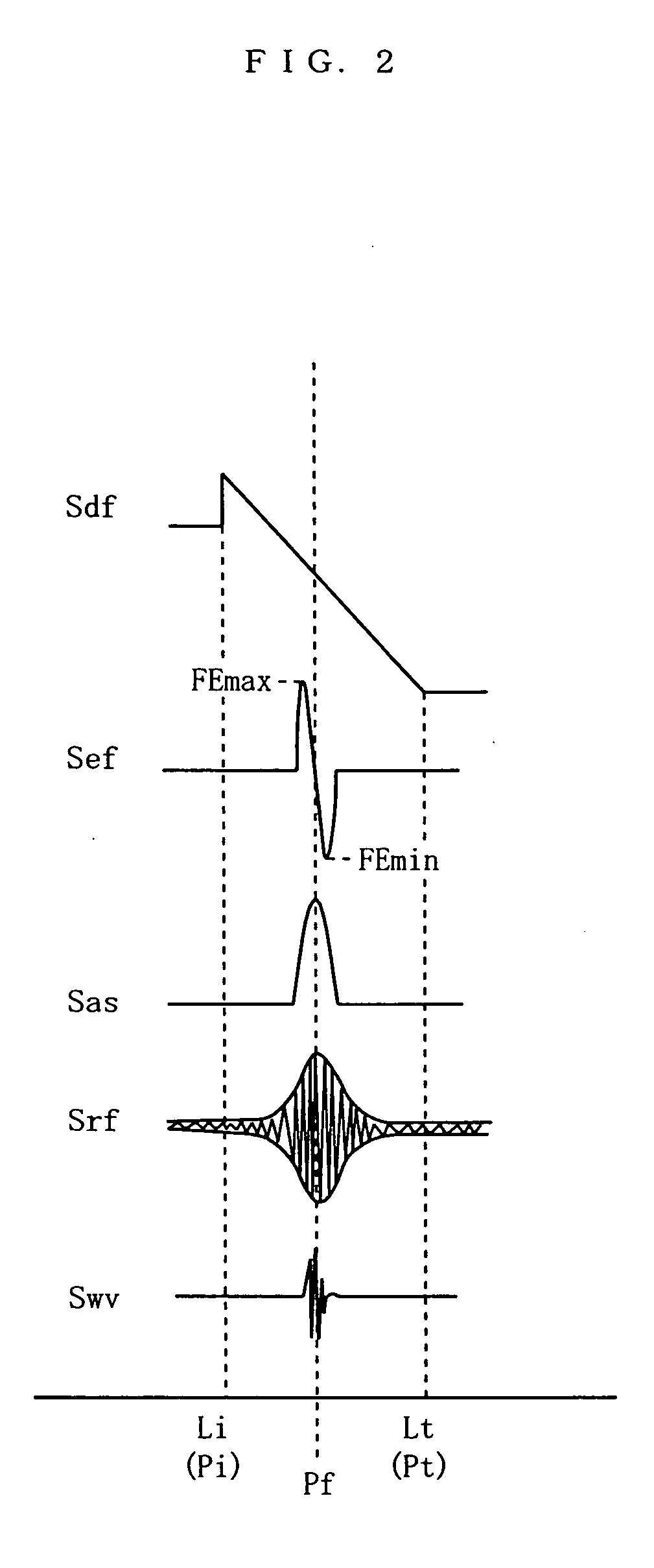
The present invention provides an optical disk identification device for use in an optical disk reproduction apparatus for reproducing a plurality of types of optical disks based on information recorded on the optical disks. Recorded information is reproduced from an optical disk 1 while an optical pickup 3 is fixed at a focal position Pf. A focal position detector 32 generates a focal position detection signal Sg that is either at a high level or at a low level at the focal position Pf based on reproduced signals Sa, Sb, Sc, Sd. An RF signal detector 20 detects an RF signal Srf from the reproduced signal based on the focal position detection signal Sg. A recording density identifier 31, S14, S20 identifies the recording density of the optical disk based on the RF signal. A format identifier S16 to S24 identifies the type of the optical disk based on the detected recording density.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Combination mastered and writeable medium and use in electronic internet appliance
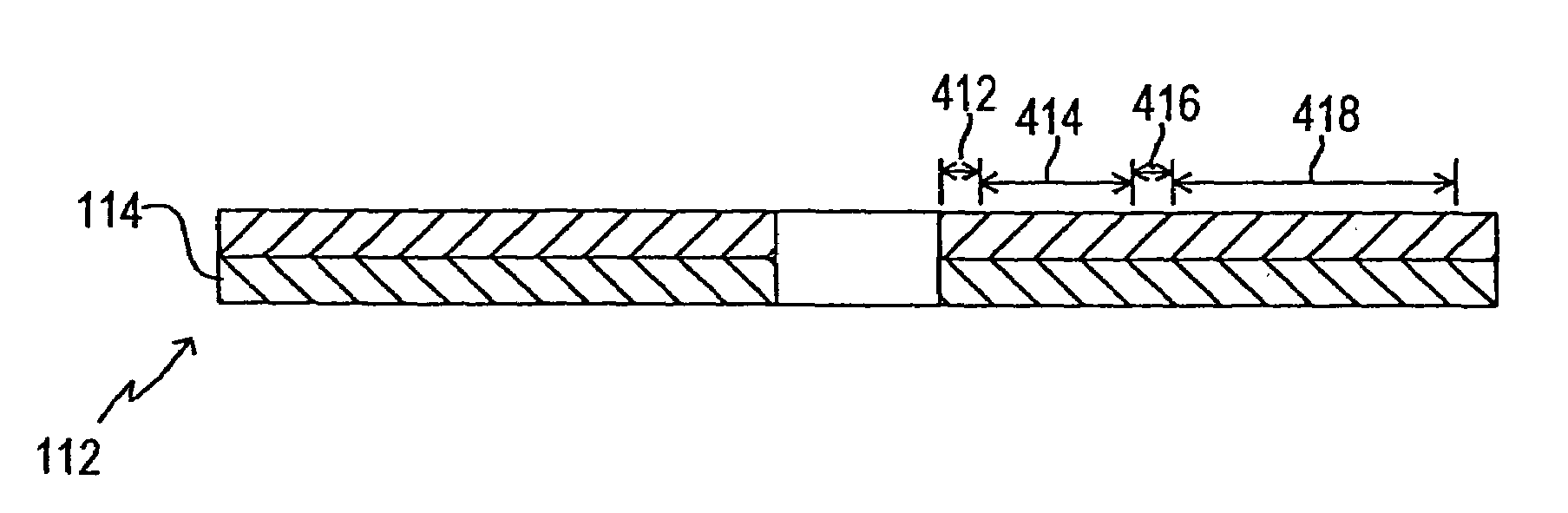
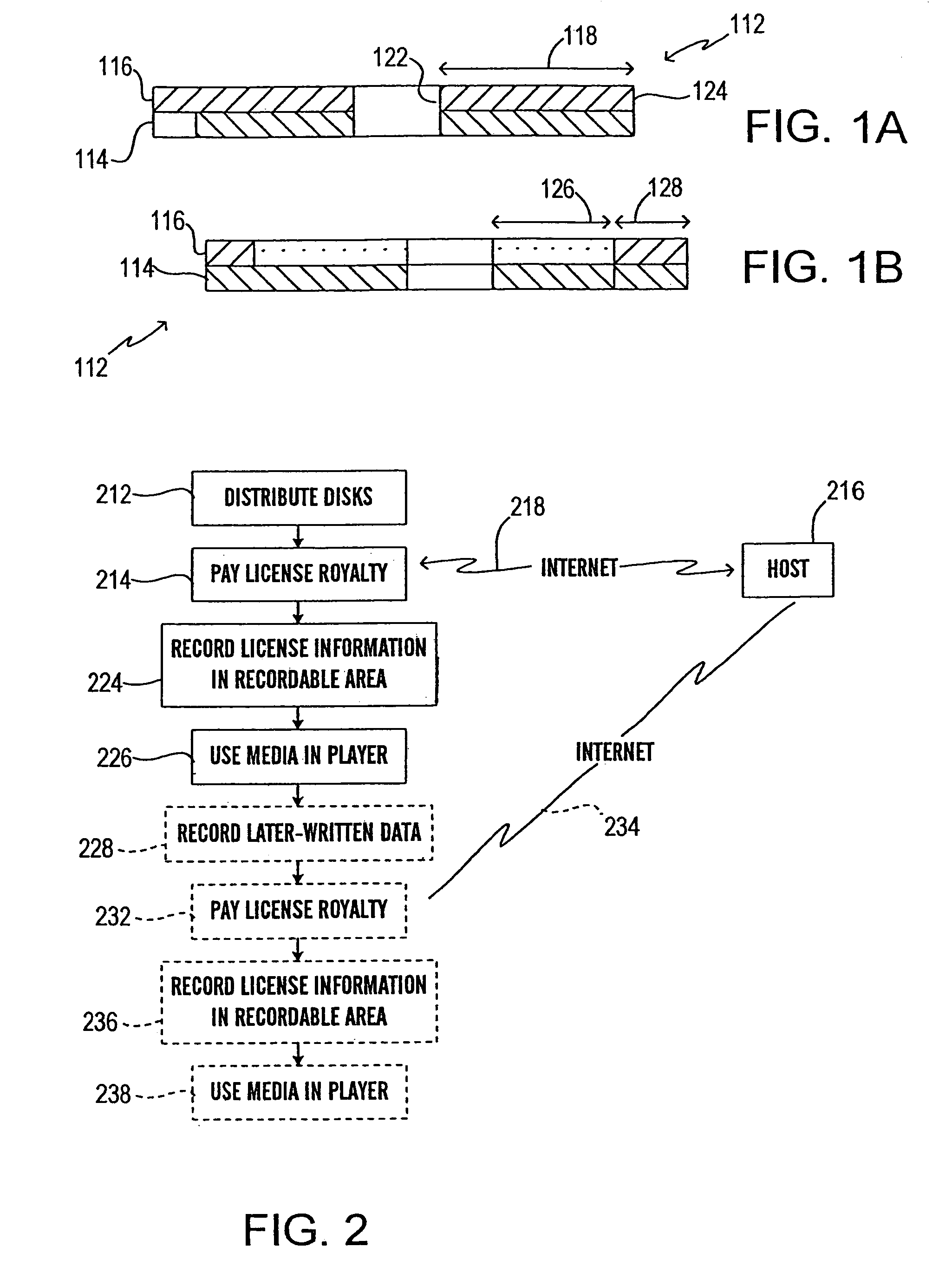
InactiveUS6980652B1Avoid viewingDisc-shaped record carriersAccessories for indicating/preventing prior/unwanted useHyperlinkIntellectual property
An optical medium uses a single structure or format (such as identical materials, layers and the like) for both a region for holding mastered data and a writeable area. In one aspect, a writeable region of a medium with mastered content is used in connection with paying, collecting or accounting for usage or royalties for proprietary intellectual property embodied in or associated with the content. In one embodiment, the (preferably write-once) writeable area can be used for storing later-written information such as annotations, highlighting, reordering, remixing, modifications, supplements, collections, additions, bookmarks, cross references, hypertext or hyperlinks and the like. Preferably, annotations and similar materials can be associated, by the user, with particular portions or content of the mastered data.
Owner:DATAPLAY
Hologram recording medium and method of hologram recording and reproduction
InactiveUS20050002311A1Good stability of tracking trackImprove formation efficiencyInformation arrangementRecord information storageLight beamOptoelectronics
A hologram recording medium has a transparent substrate having an incidence surface, on which a write beam and a reference beam are made incident, and a servo surface opposite to the incidence surface, the servo surface including a header section and a data section, a reflecting layer formed on the servo surface of the transparent substrate, and a hologram recording layer provided on the incidence surface of the transparent substrate, the servo surface having intermittent tracking grooves in the data section except for recording positions, and a width of the tracking grooves being set at a value to less than an e−2 diameter of the reference beam.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Focus jump device for reproducing information from a storage medium
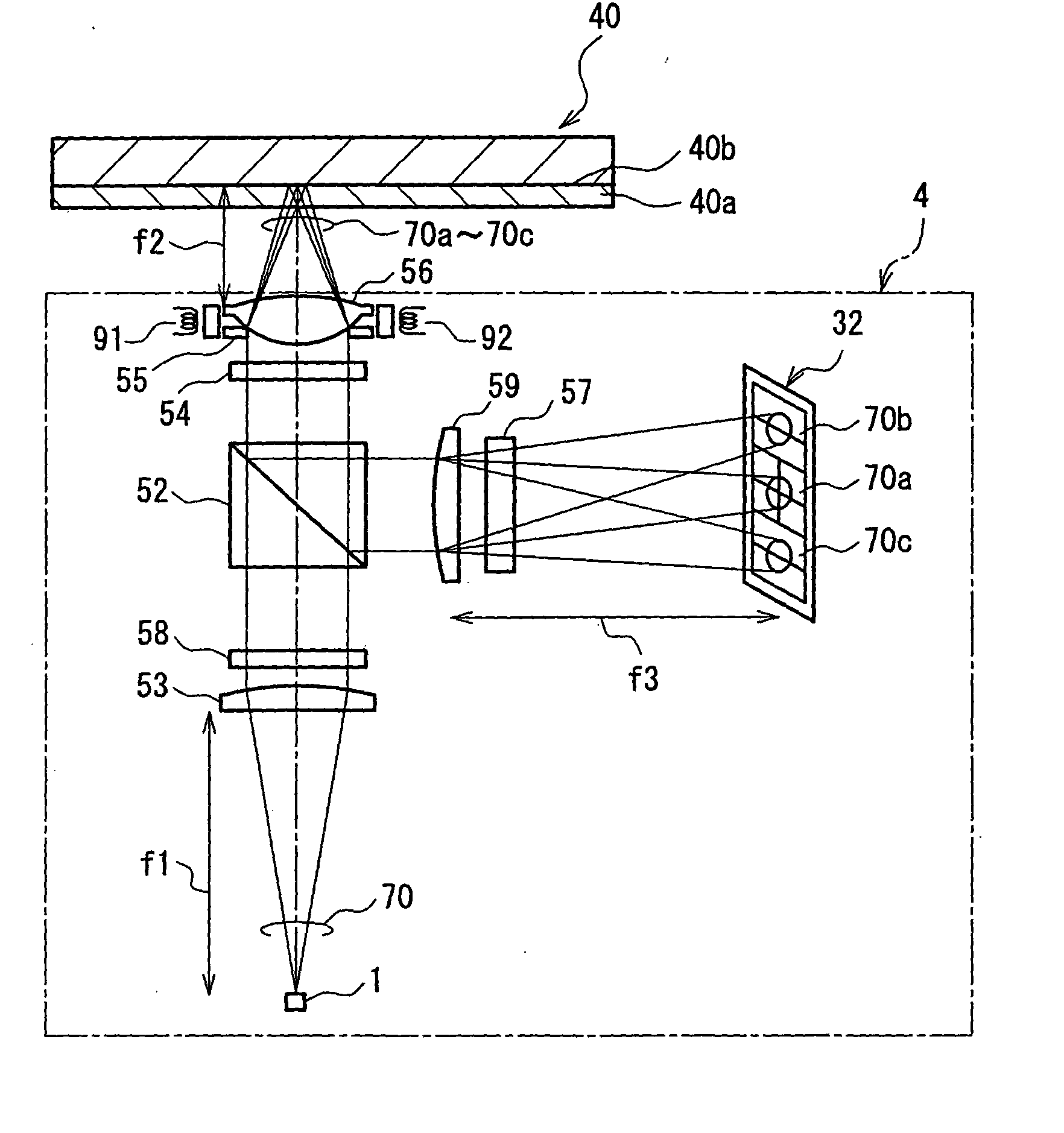
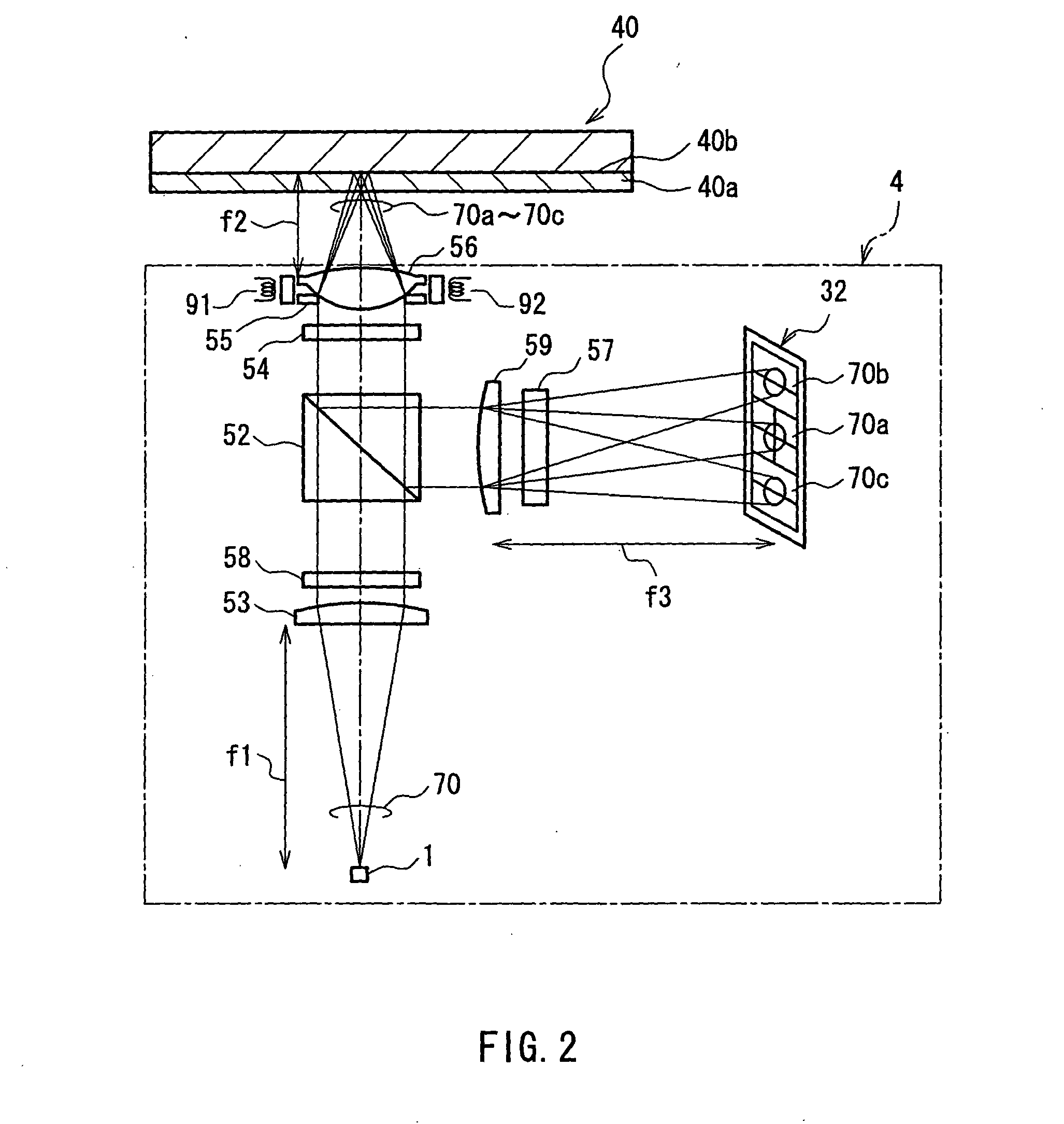
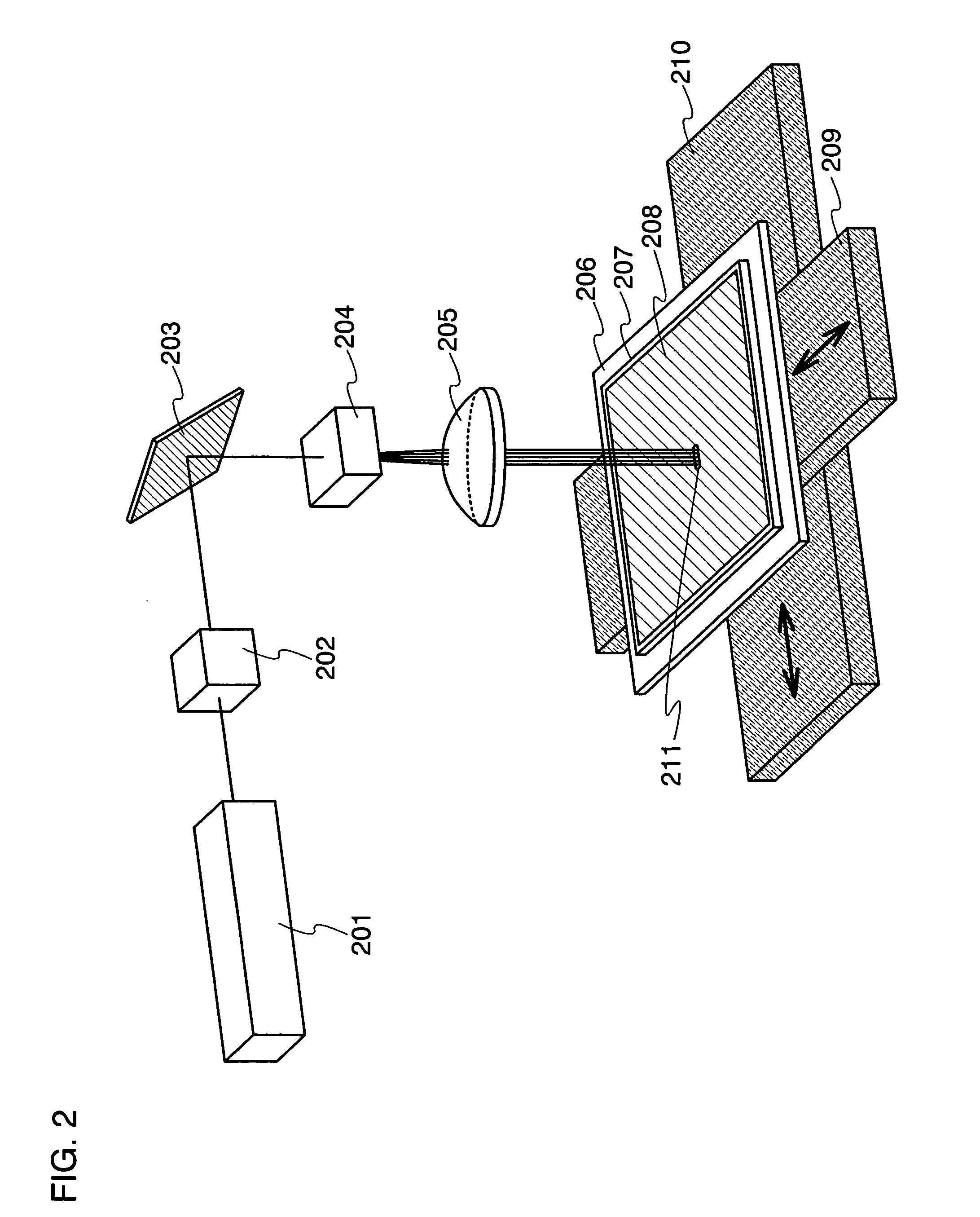
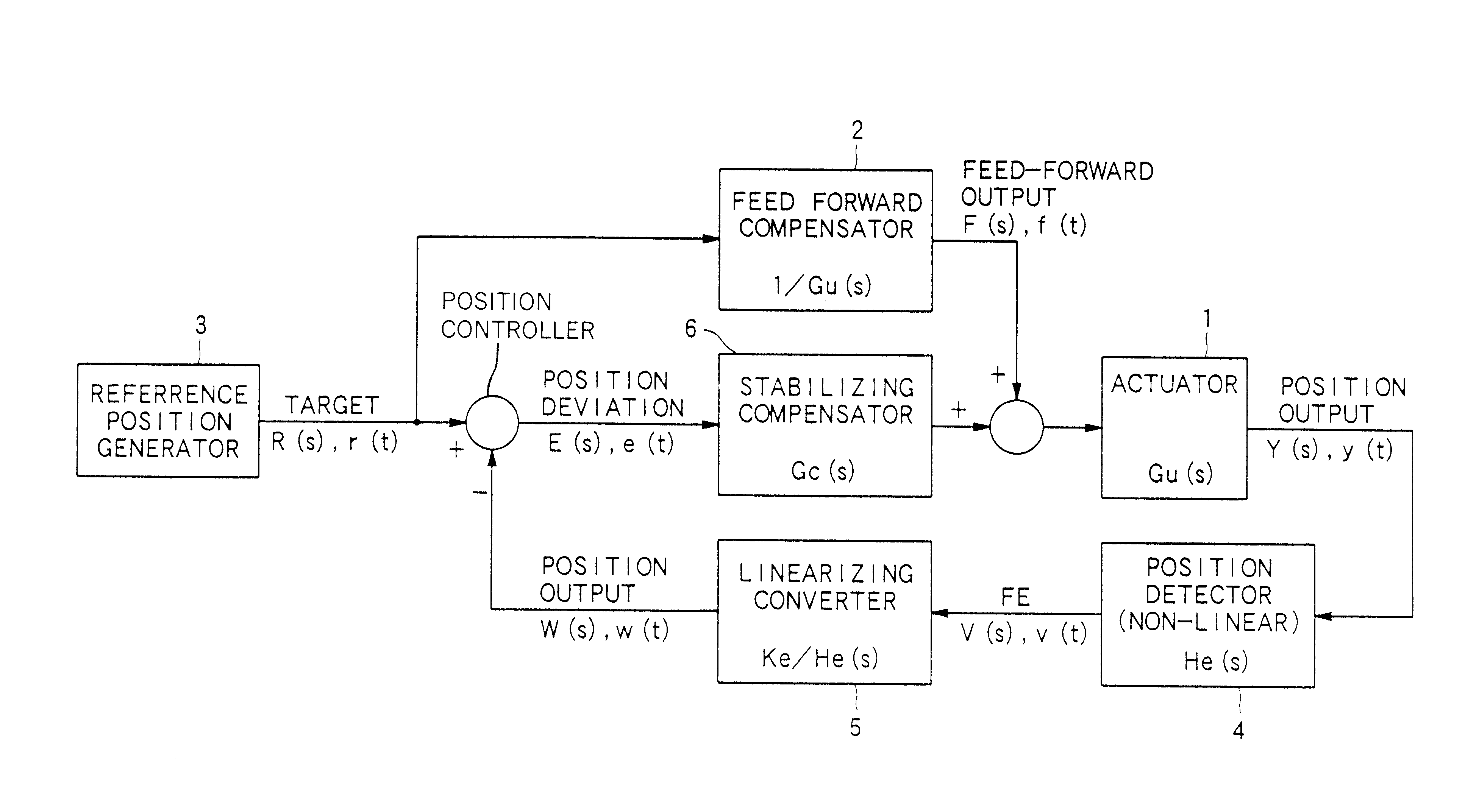
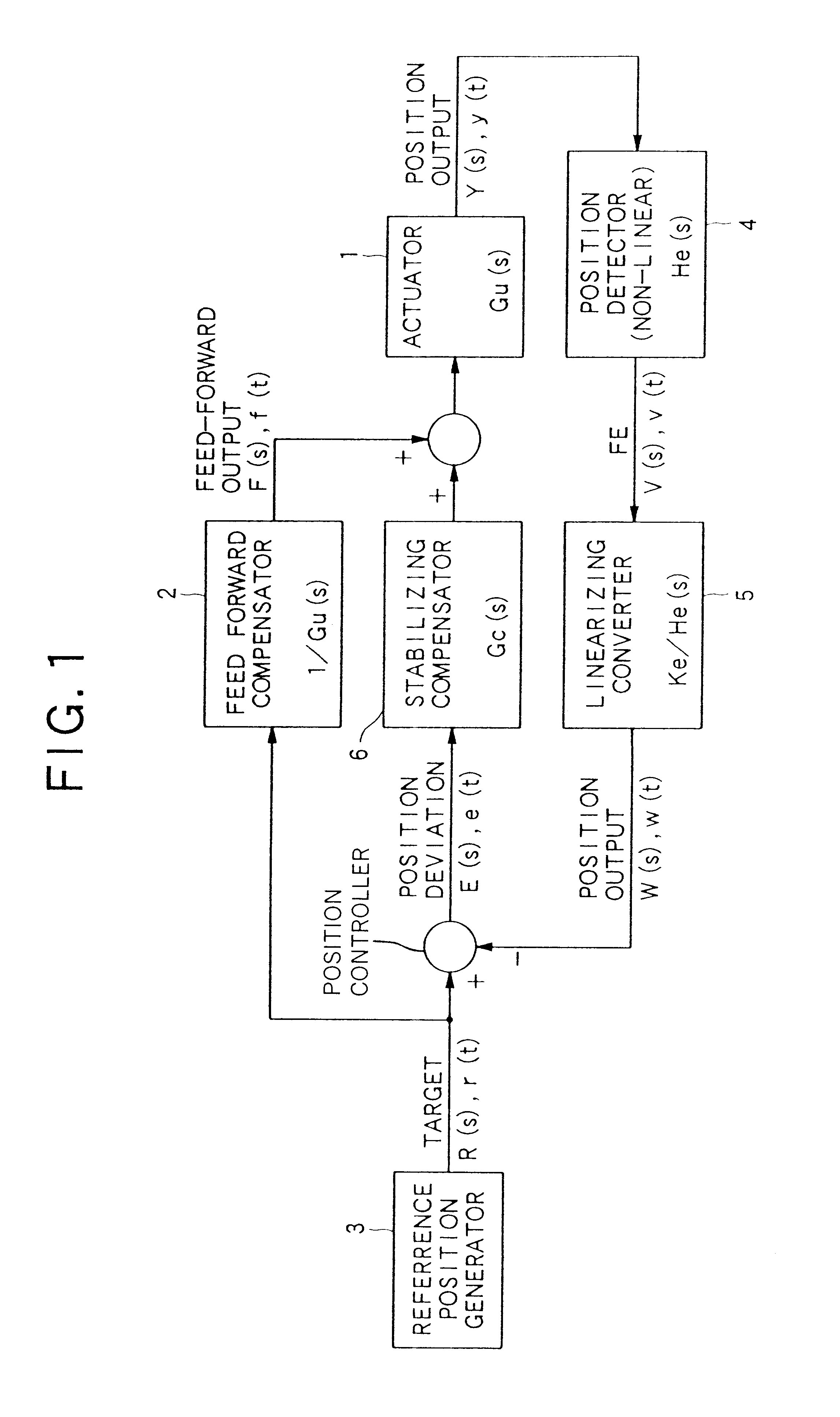
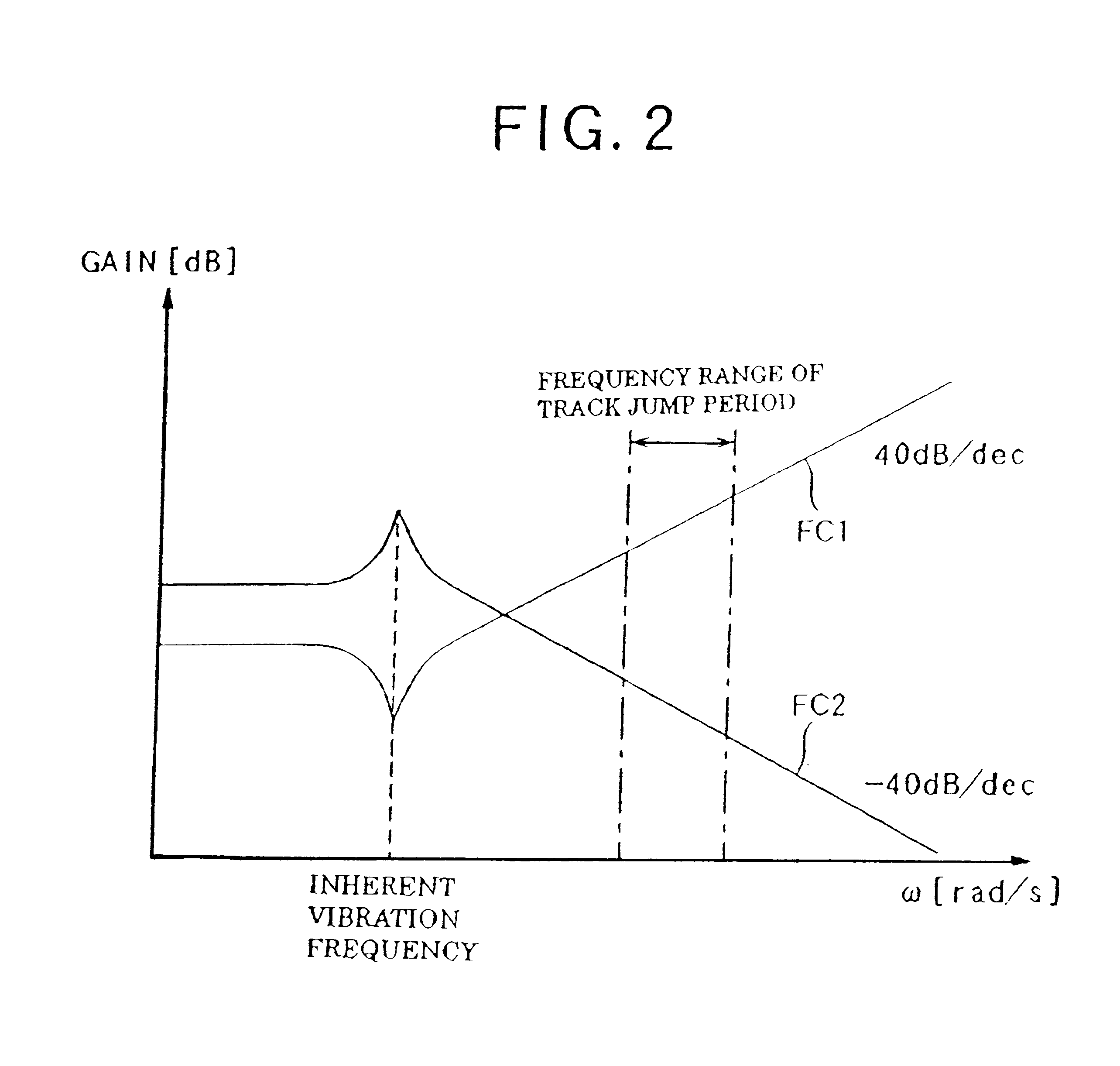
InactiveUS6584048B1Reduce errorsAccurate identificationRecord information storageDisposition/mounting of headsLight beamFocal position
A focus jump moves a focus position of a light beam in a direction perpendicular to the storage medium to the focus position corresponding to a target recording layer so that the light beam is irradiated on the target recording layer. The device includes: a focus position moving unit for moving the focus position of the light beam; a focus error signal detector for detecting a focus error signal based on a variation of a returning light from the storage medium; a feedforward controller for supplying a drive signal to the focus position moving unit to move the focus position of the light beam in an acceleration state in an acceleration control and to move the focus position of the light beam in a deceleration state in a deceleration control; and a position controller for comparing the focus error signal, detected the time of movement of the focus position of the light beam to the target recording layer, with a predetermined target value to generate an error, and for feeding back the drive signal to the focus position moving-unit to reduce the error thereby to control the focus position of the light beam.
Owner:PIONEER CORP
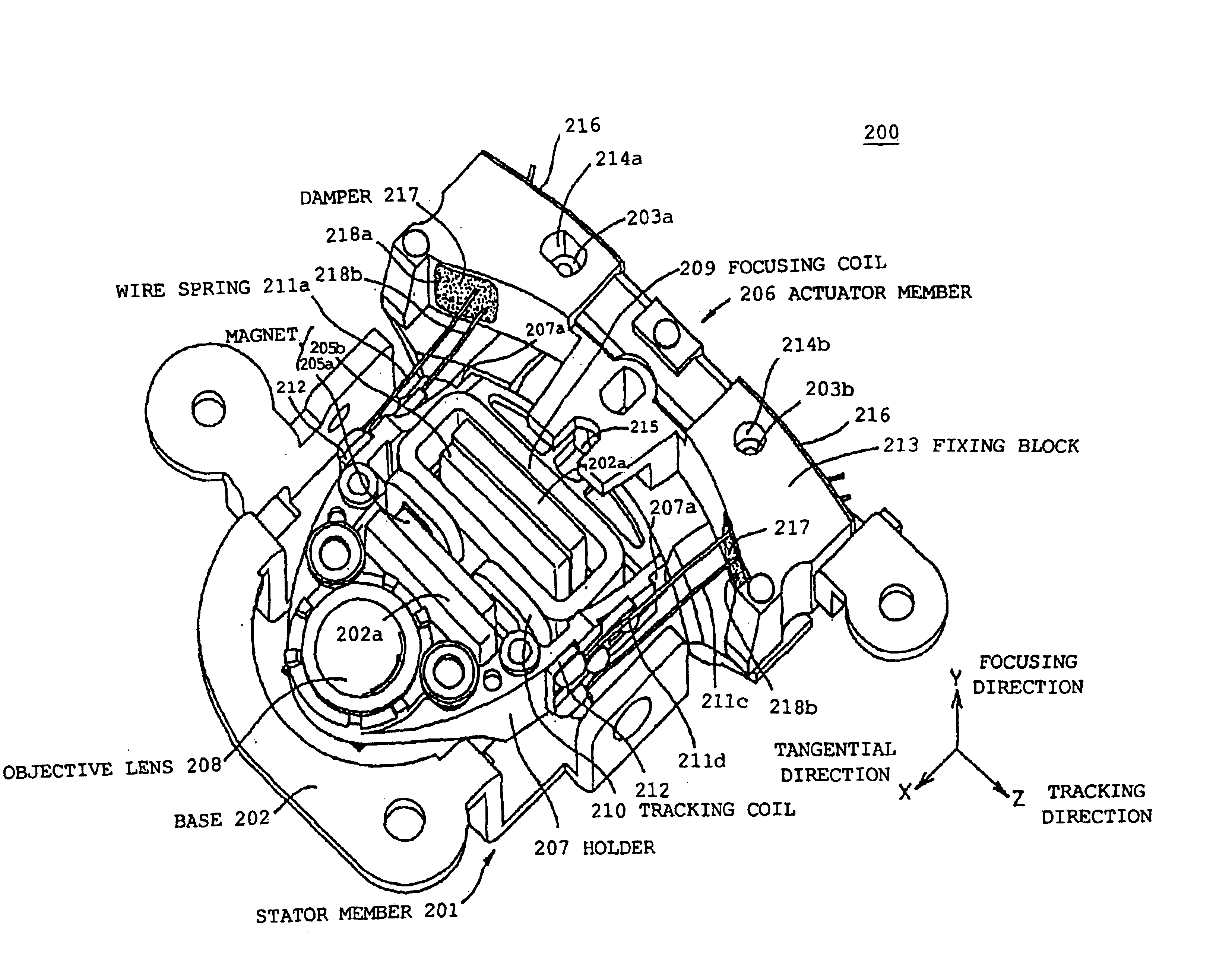
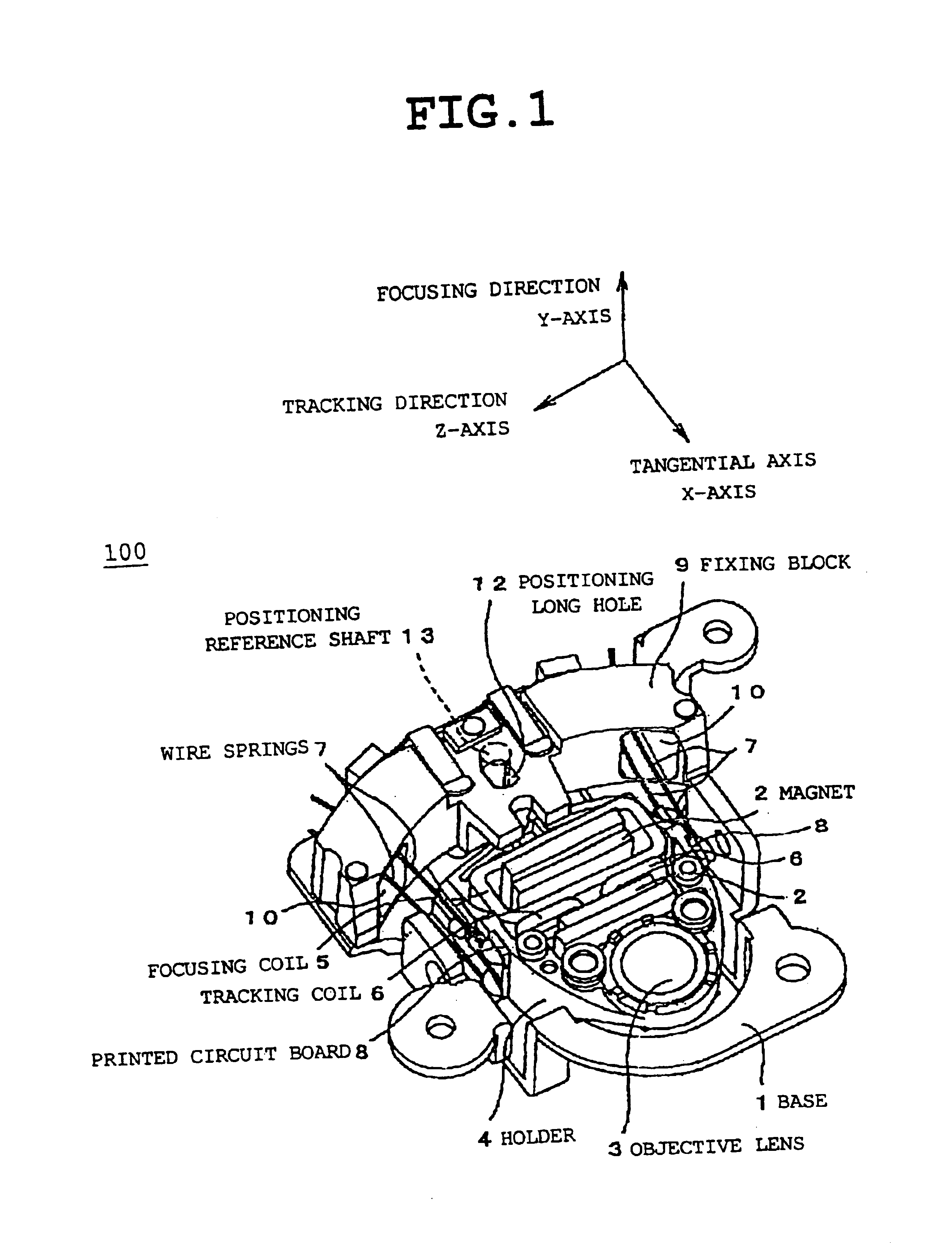
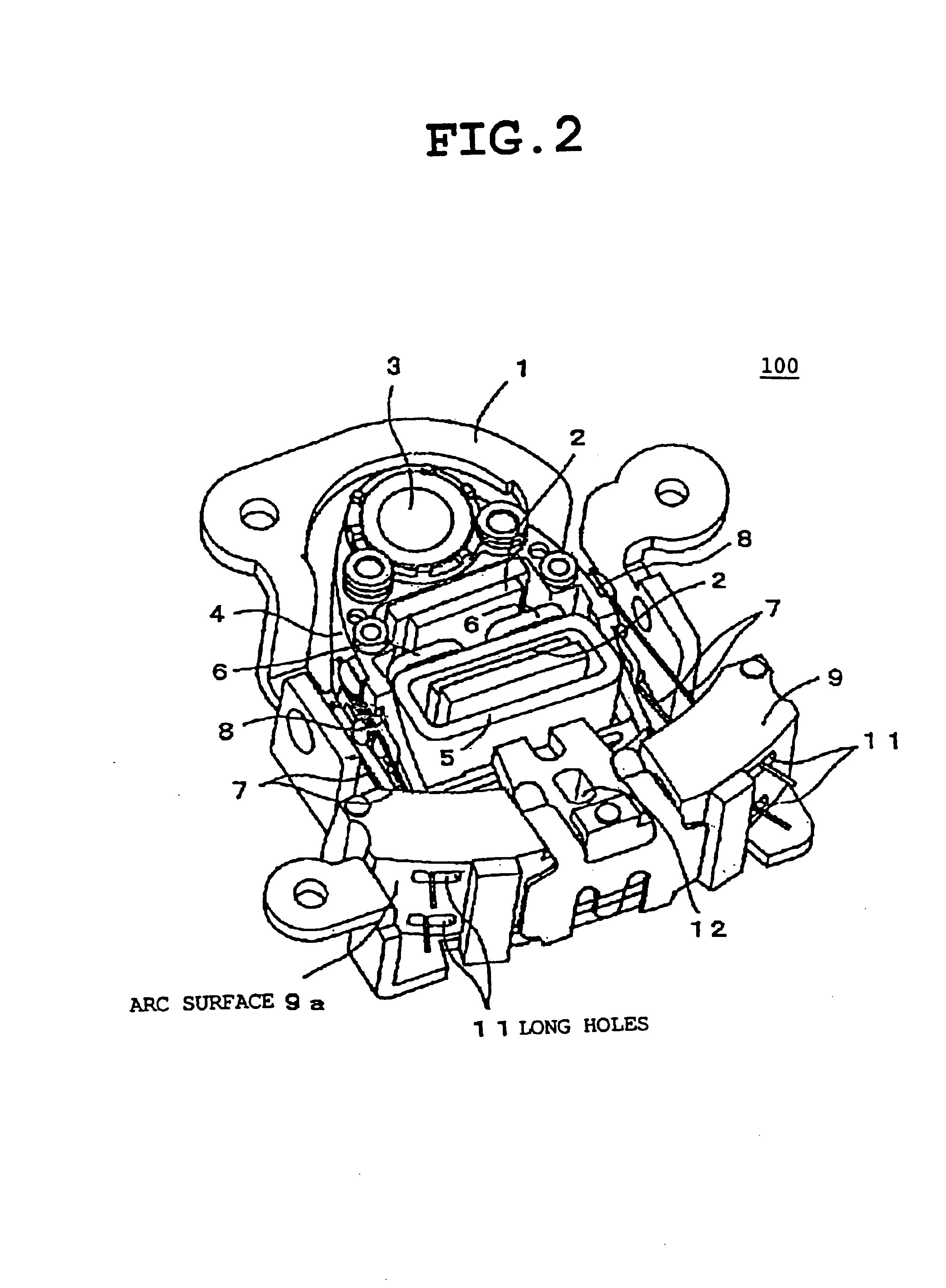
Lens actuator
InactiveUS6847595B2Prevent over attenuationReduce the impactRecord information storageMountingsCamera lensResonance
In a lens actuator for use with an optical recording and reproducing apparatus in accordance with a plurality of different multiplied response numeric values to record or reproduce to or from an optical recording medium, the lens actuator actuates an objective lens to control focusing and tracking and includes a fixed magnetic circuit including a magnet as a magnetic flux generating source and a back yoke, a support structure that is elastically displaceable depending on a thrust generated amount; and a movable part including a holder fixing the objective lens and a solenoid coil capable of generating a focusing thrust and a tracking thrust in accordance with current values, respectively. And in the lens actuator, a resonance frequency around a tangential axis is set to be different from spindle rotation frequencies corresponding to the plurality of multiplied response numeric values.
Owner:RICOH KK
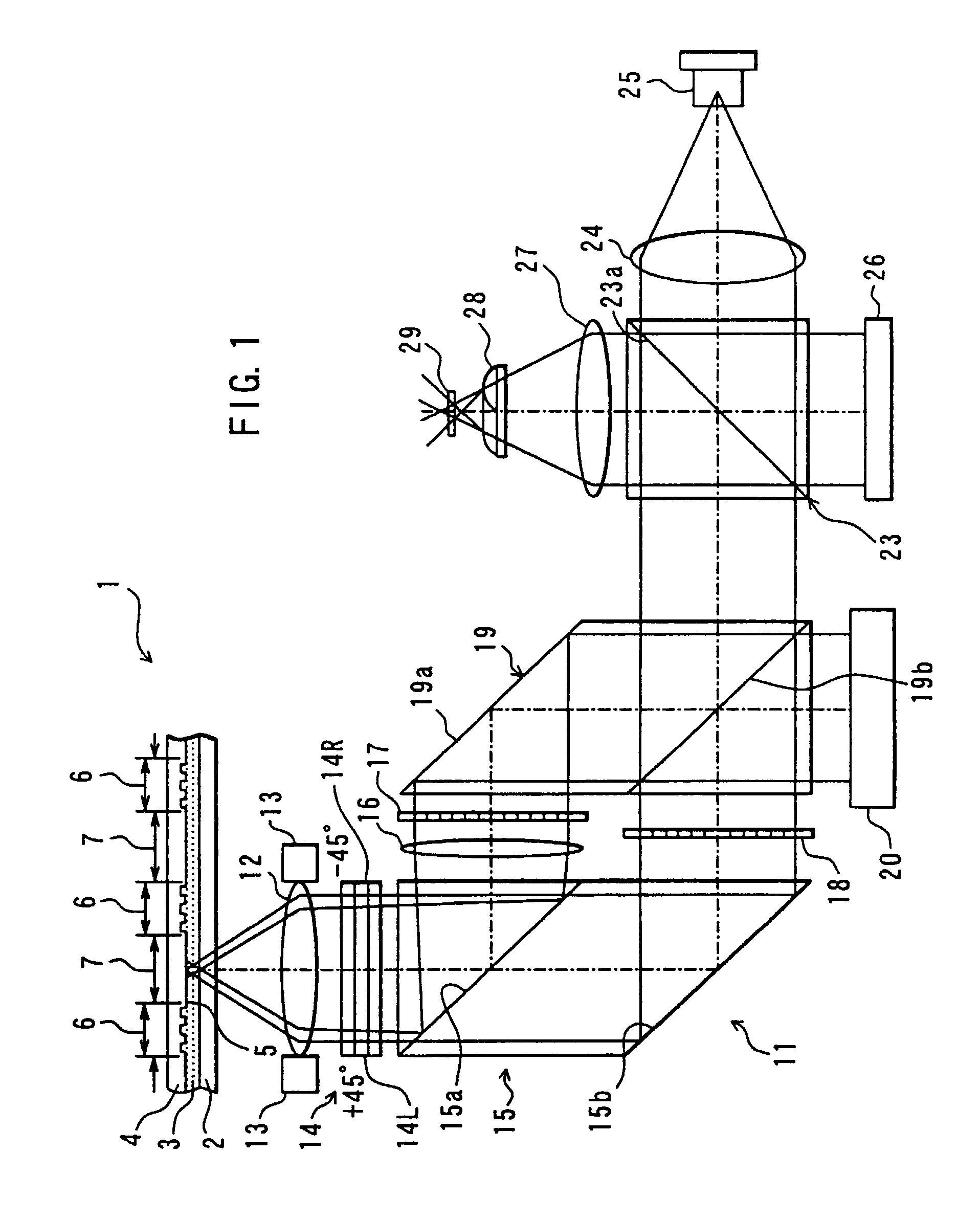
Apparatus for recording optical information
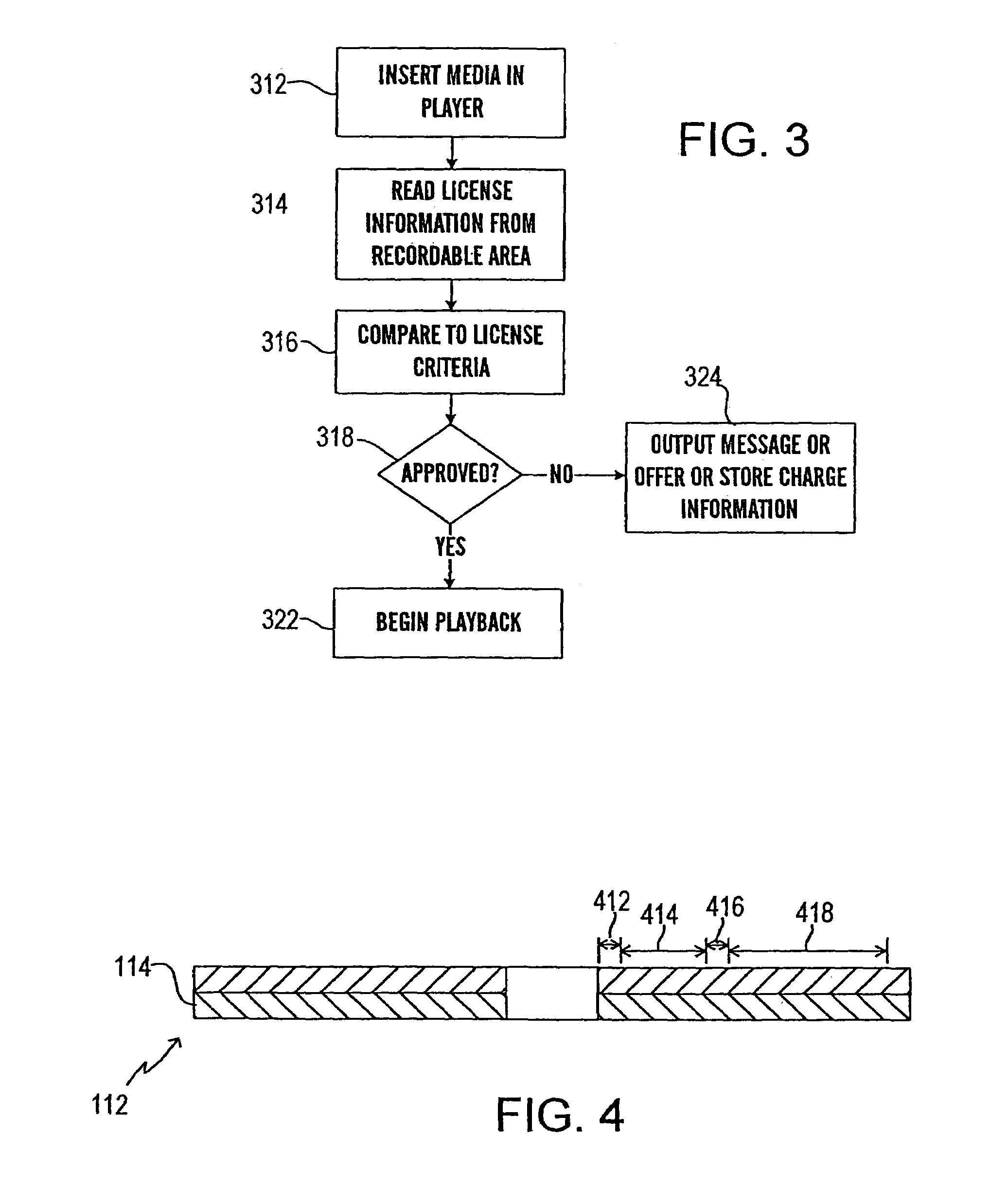
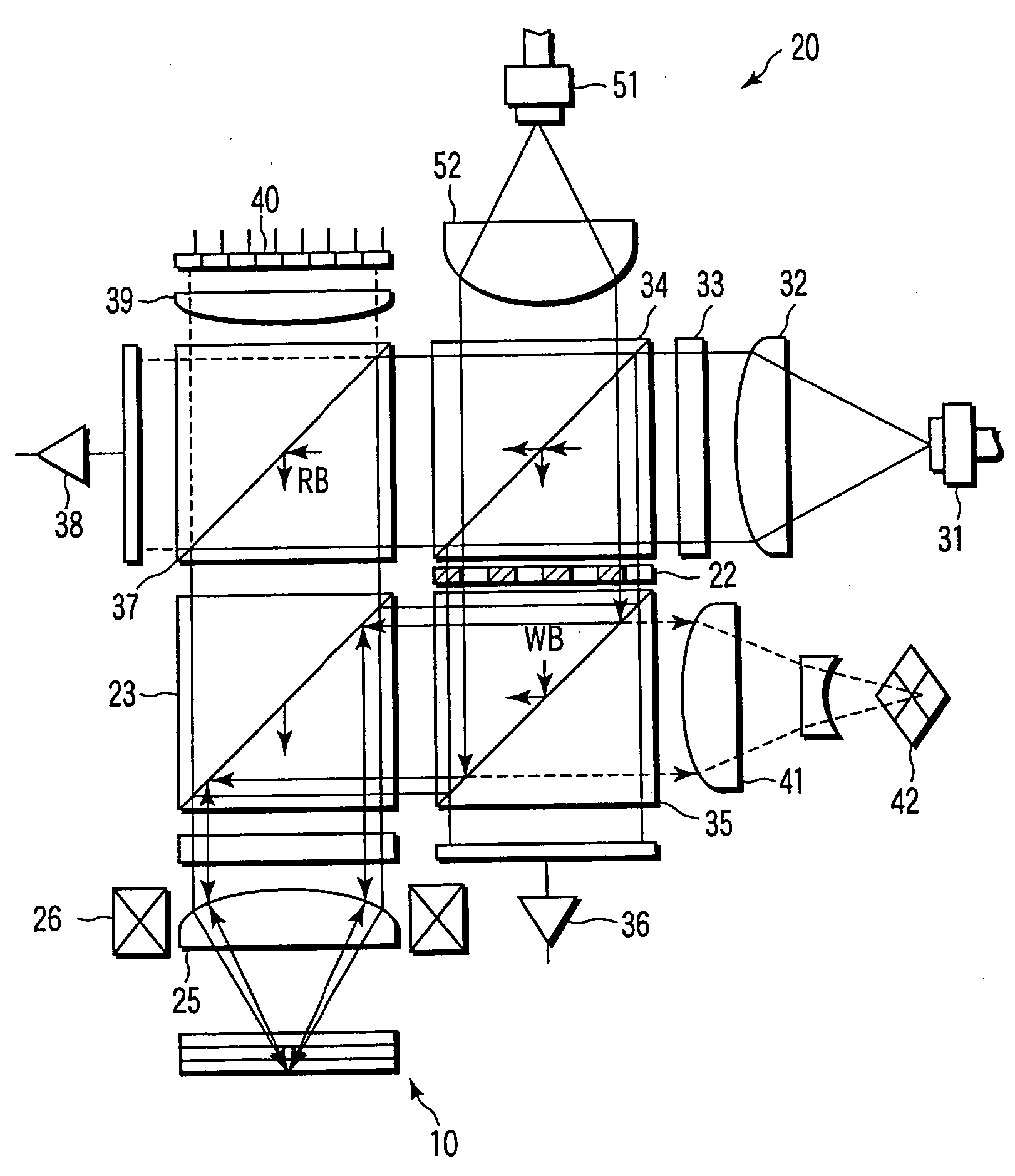
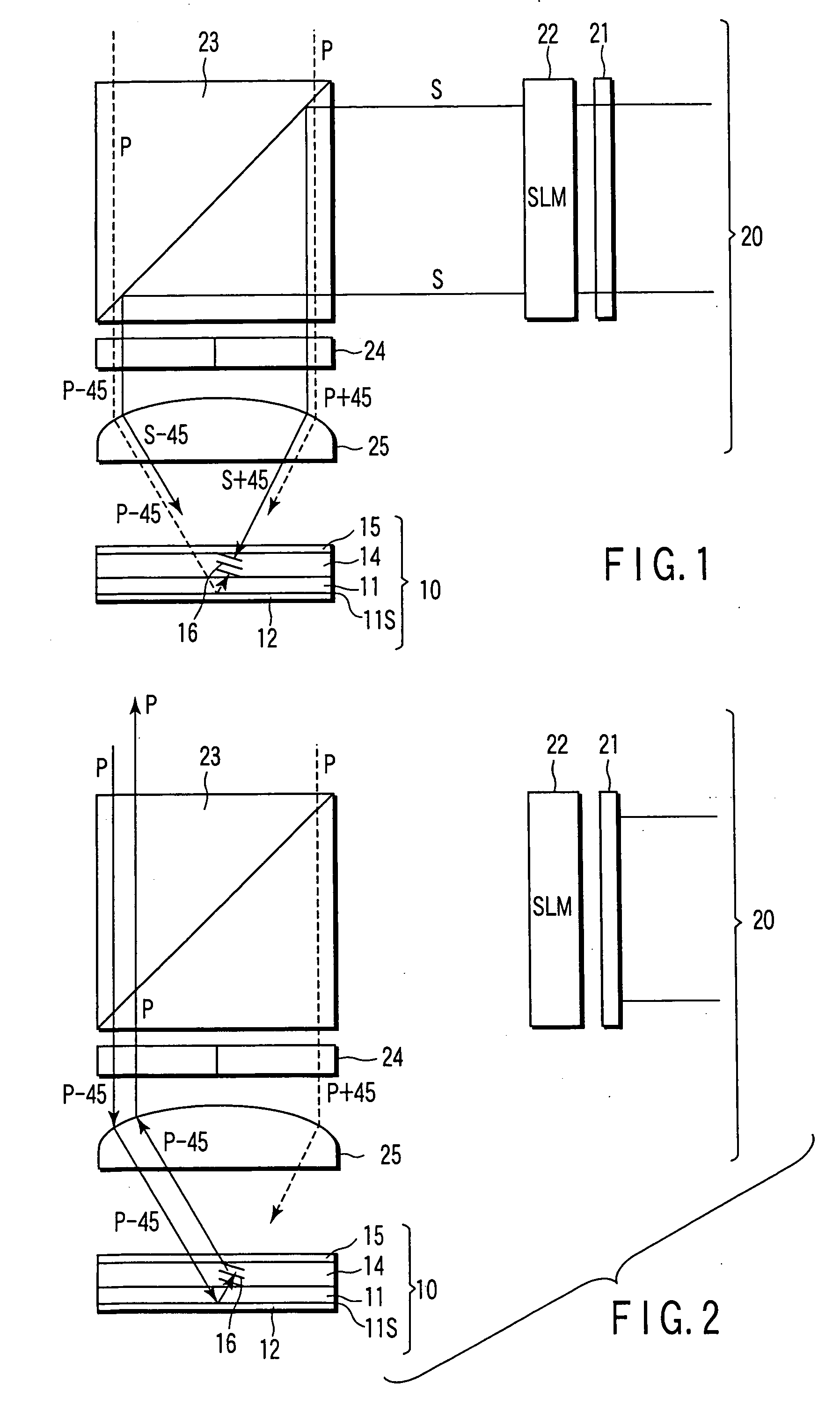
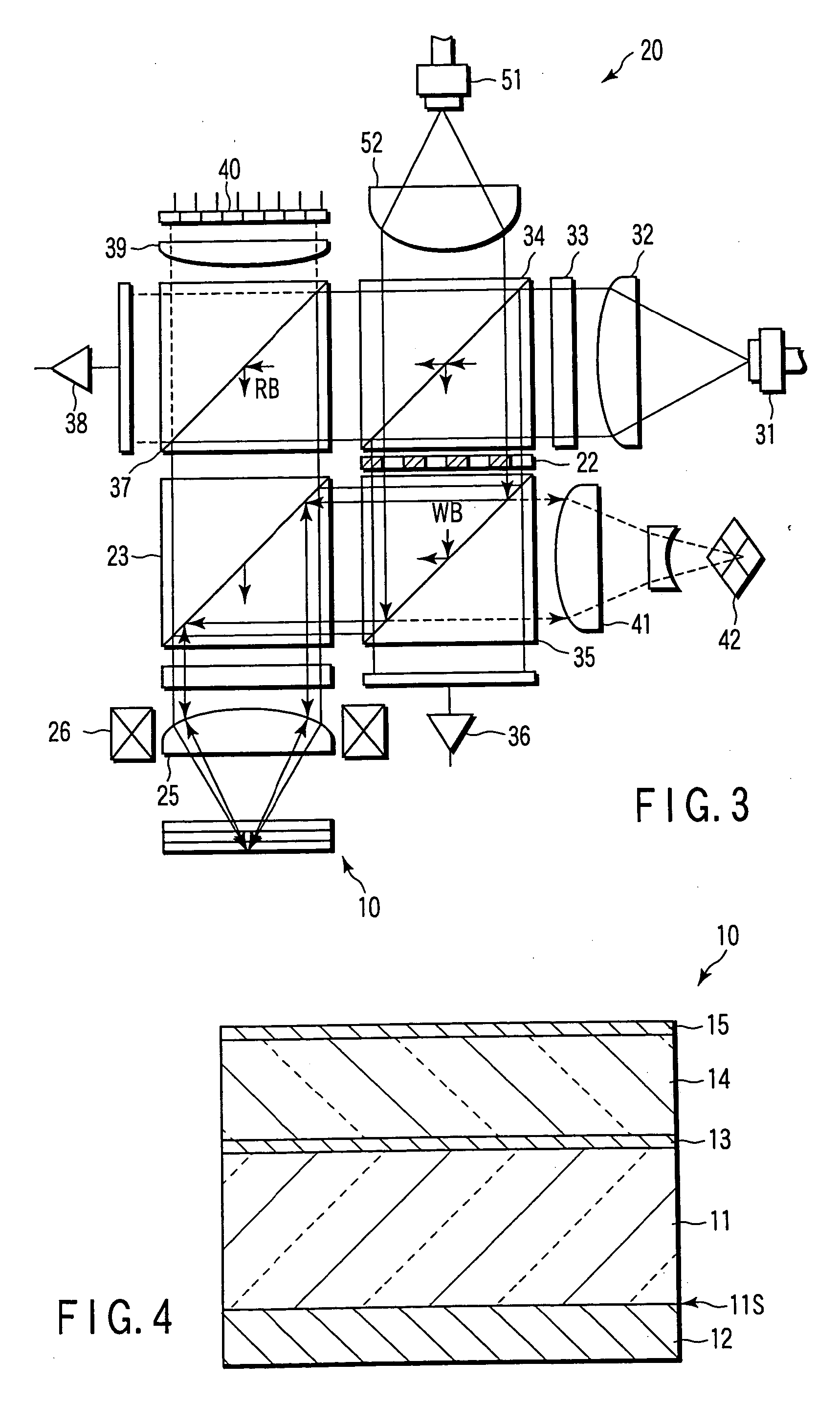
InactiveUS6995882B2Compact configurationPrecise positioningInformation arrangementOptical discsSpatial light modulatorLaser light
The present invention makes it possible to reduce the size of an optical system for multiplex recording or reproduction of information utilizing holography.A pick-up (11) of an optical information recording / reproducing apparatus generates information light by spatially modulating laser light emitted by a light source device (25) with a spatial light modulator (18) depending on the information to be recorded and generates reference light for recording having a spatially modulated phase by spatially modulating the phase of laser beam emitted by the light source device (25) with a phase-spatial light modulator (17). The information light and the reference light for recording are projected upon an optical information recording medium (1) such that they converge in different positions, and information is recorded in the hologram layer (3) in the form of an interference pattern as a result of interference between the information light reflected by a reflecting film (5) and the reference light for recording. The positioning of the information light and the reference light for recording is carried out based on information recorded in address servo areas (6).
Owner:OPTWARE
Optical pickup apparatus and optimal light spot focusing method
InactiveUS20020159378A1Minimized in sizeOptical beam sourcesOptical detectorsOptical pickupPhotodetector
An optical pickup apparatus includes a first light source to emit a first light beam having a predetermined wavelength, a first optical path changer to change a proceeding path of the first light beam, an objective lens to focus the first light beam on a recording medium, a diffraction member to divide the first light beam reflected by the recording medium into five light regions, the diffraction member having a first diffraction region having a wide width in a direction corresponding to a tangential direction of the recording medium and second through fifth diffraction regions sequentially arranged around the outside of the first diffraction region in a direction corresponding to a radial direction of the recording medium, and a first photodetector having first through fifth light receiving portions to receive the first light beam reflected by the recording medium.
Owner:TS OPTICS CORP
Optical information recording medium
Owner:RICOH KK
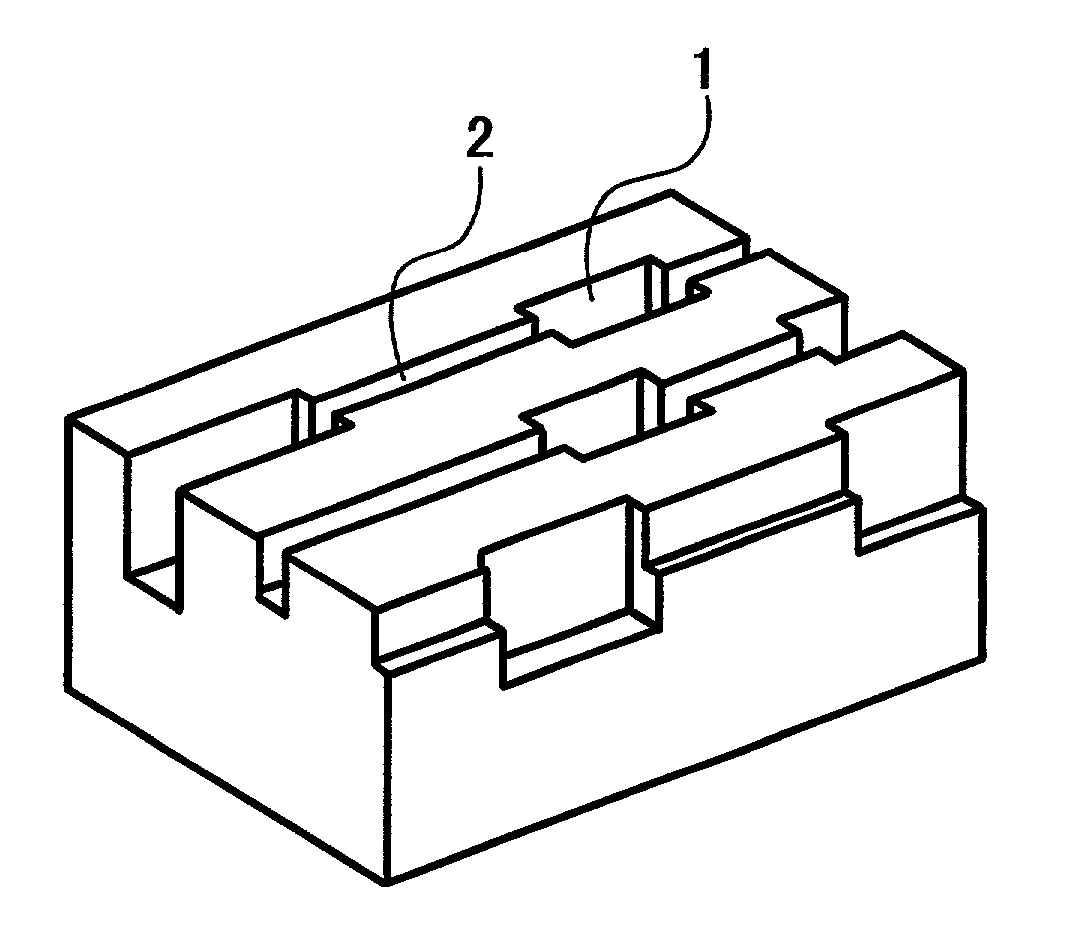
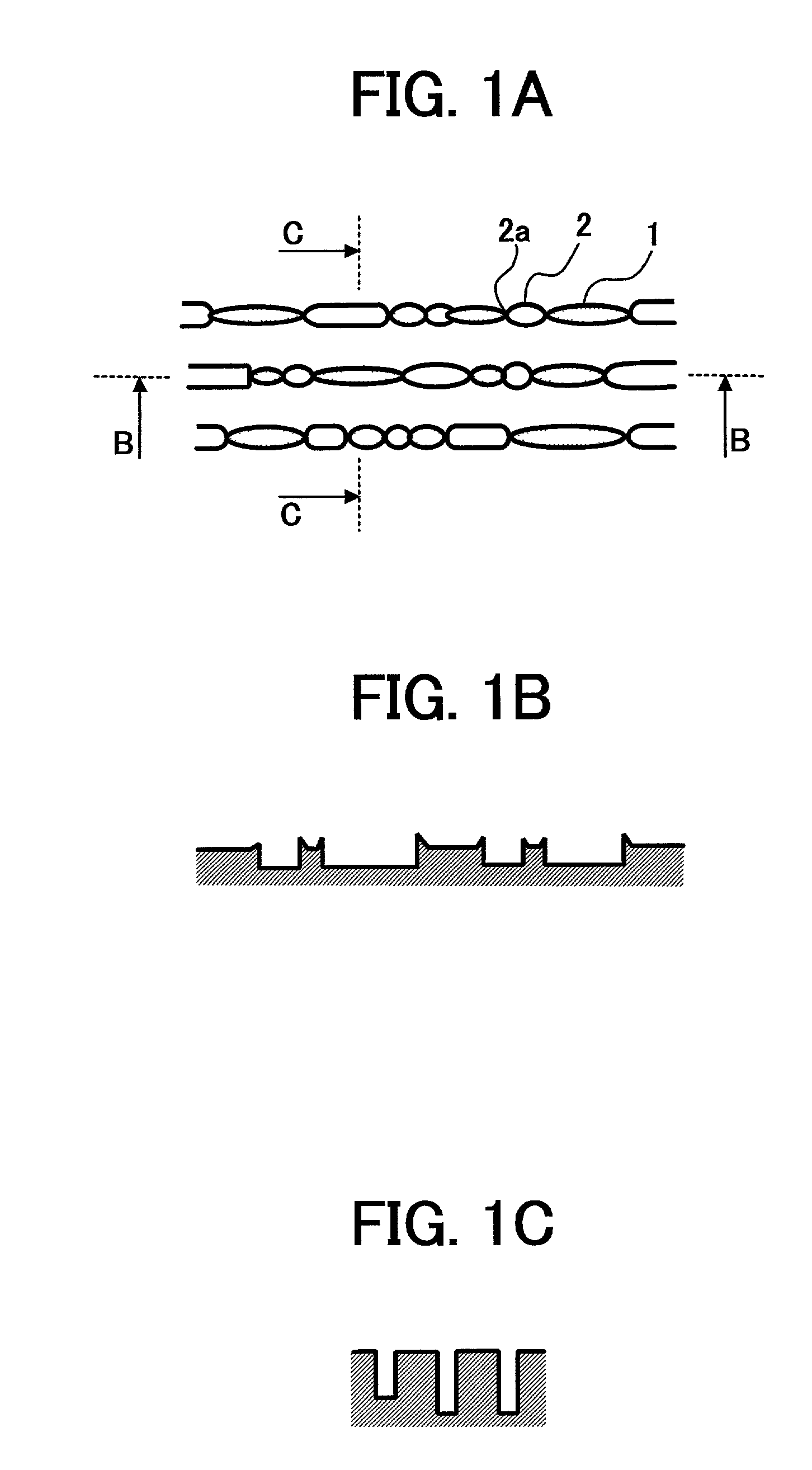
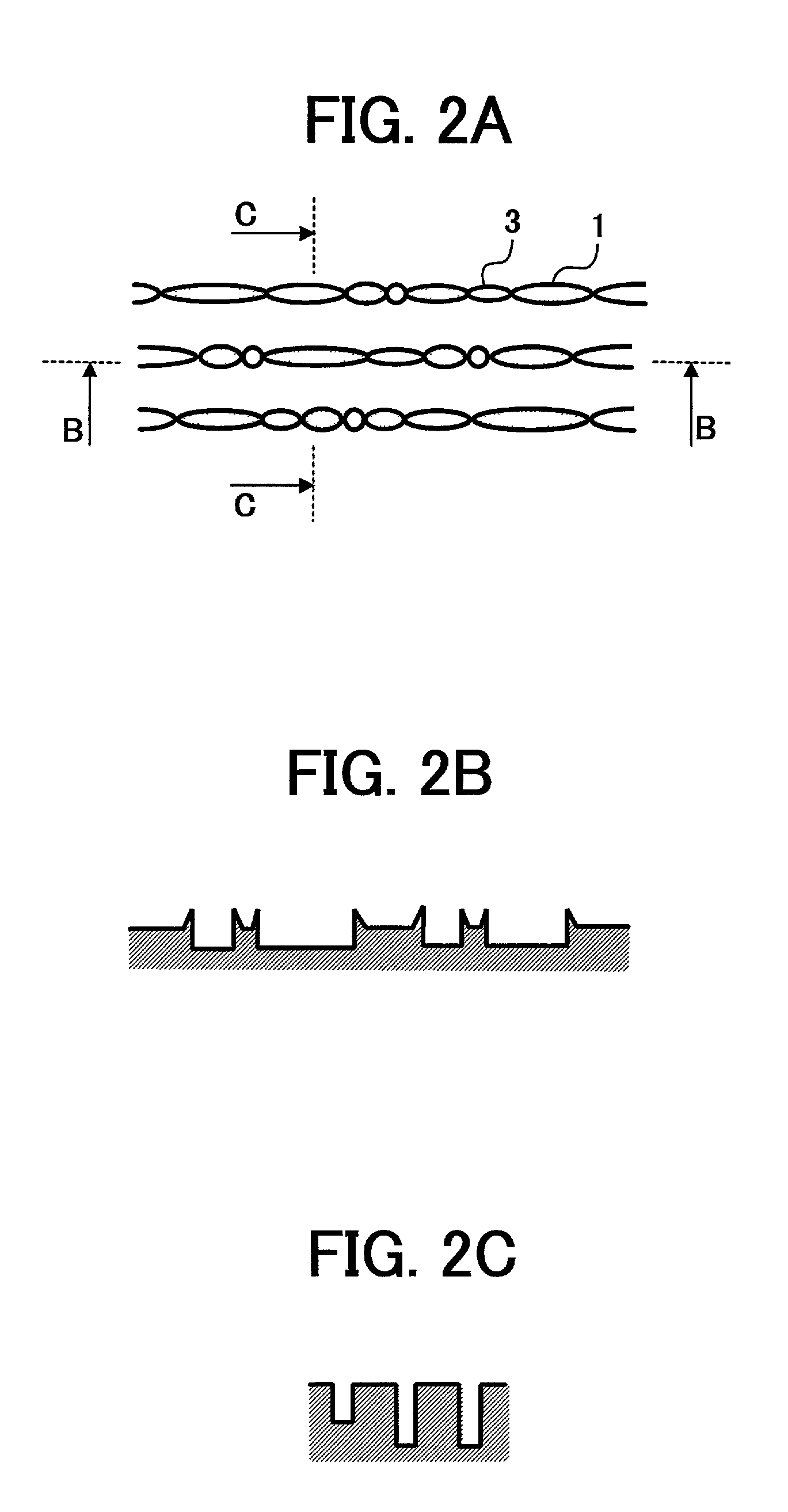
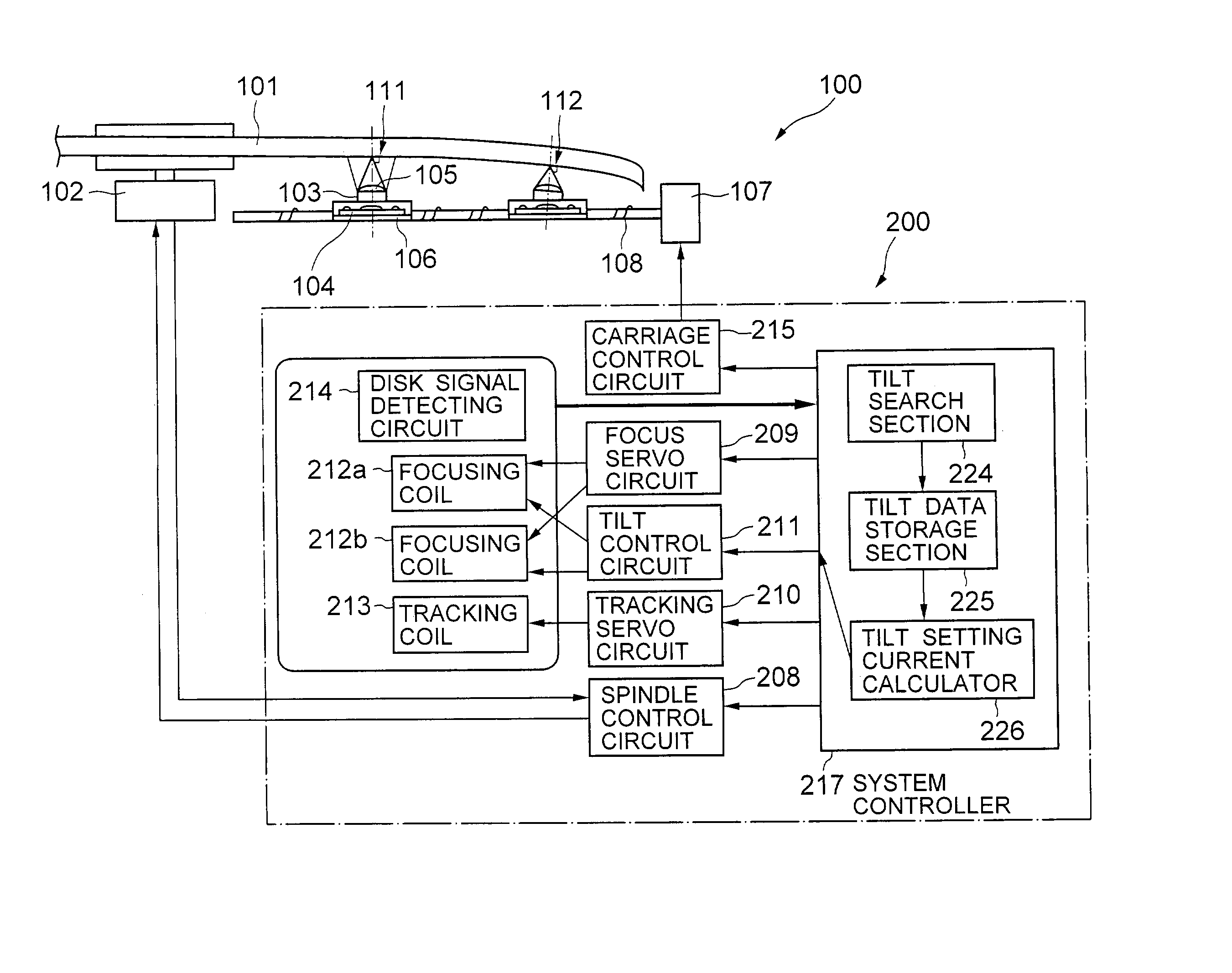
Optical disk drive having a tilt compensator
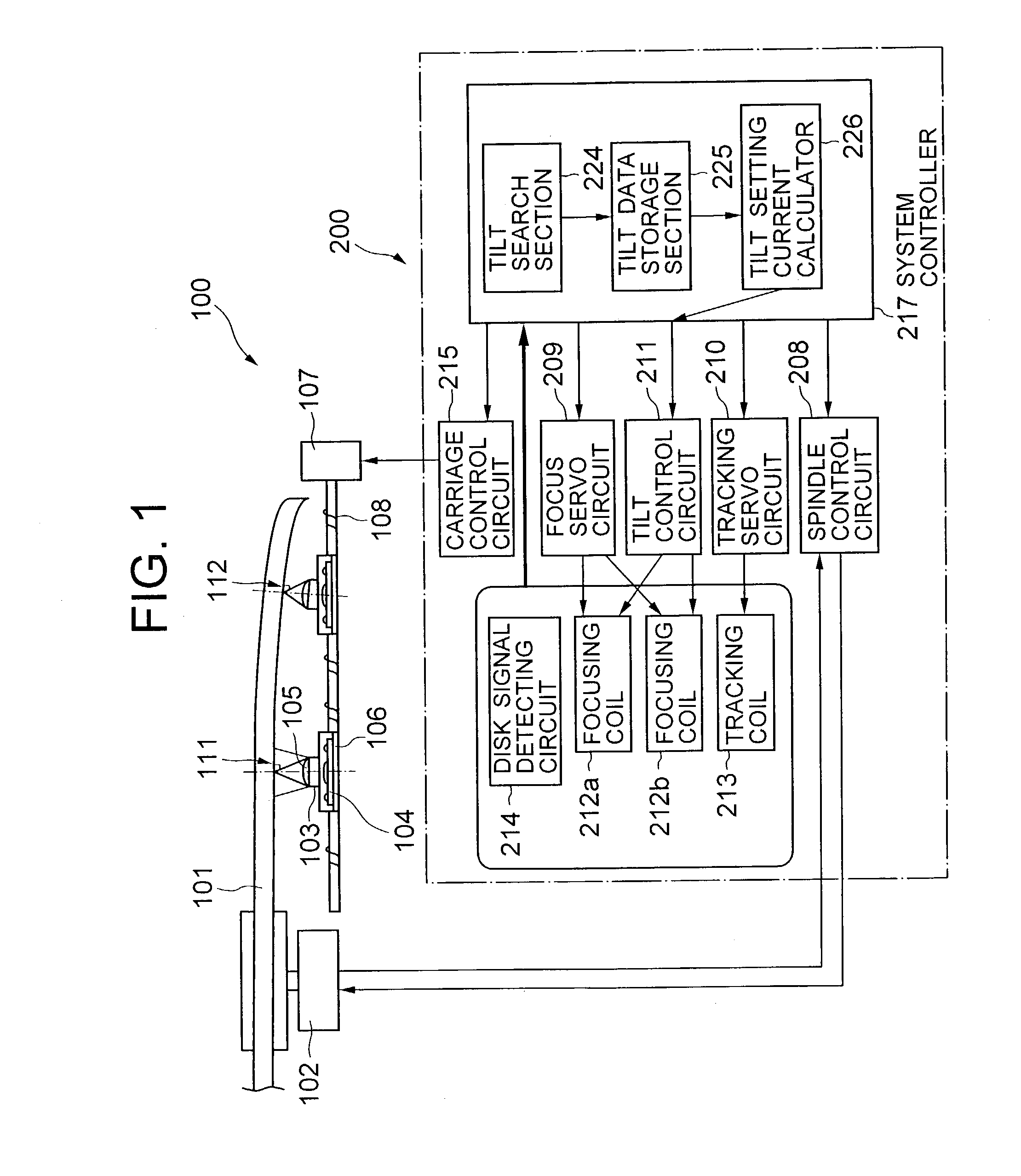
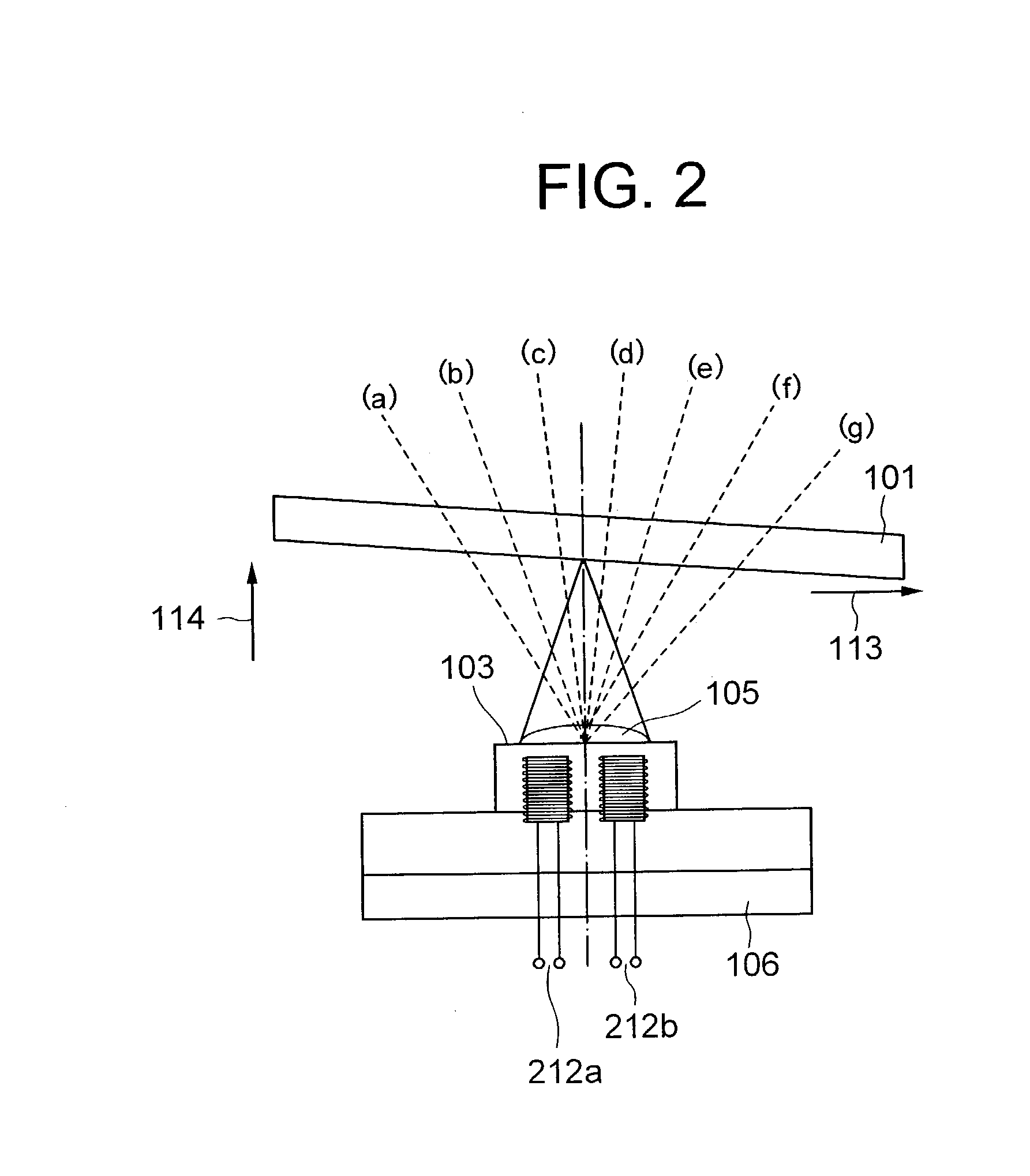
InactiveUS20030179665A1Accurate compensationCombination recordingRecord information storageRadial positionOptical disc drive
A tilt compensator in an optical disk drive detects an optimum tilt setting of the objective lens with respect to a reference plane of the optical head, which allows the optical head to obtain an optimum characteristic of a disk signal at a specified radial position of an optical disk. The optimum tilt setting is corrected at a desired track of the optical disk by using a difference between a first tilt angle of the reference plane with respect to the optical disk measured at the specified radial position and a second tilt angle of the reference plane measured at a desire track of the optical disk. The disk signal is a RF signal, a jitter of the encoded RF signal, a tracking error signal or a wobble signal.
Owner:NEC CORP
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com