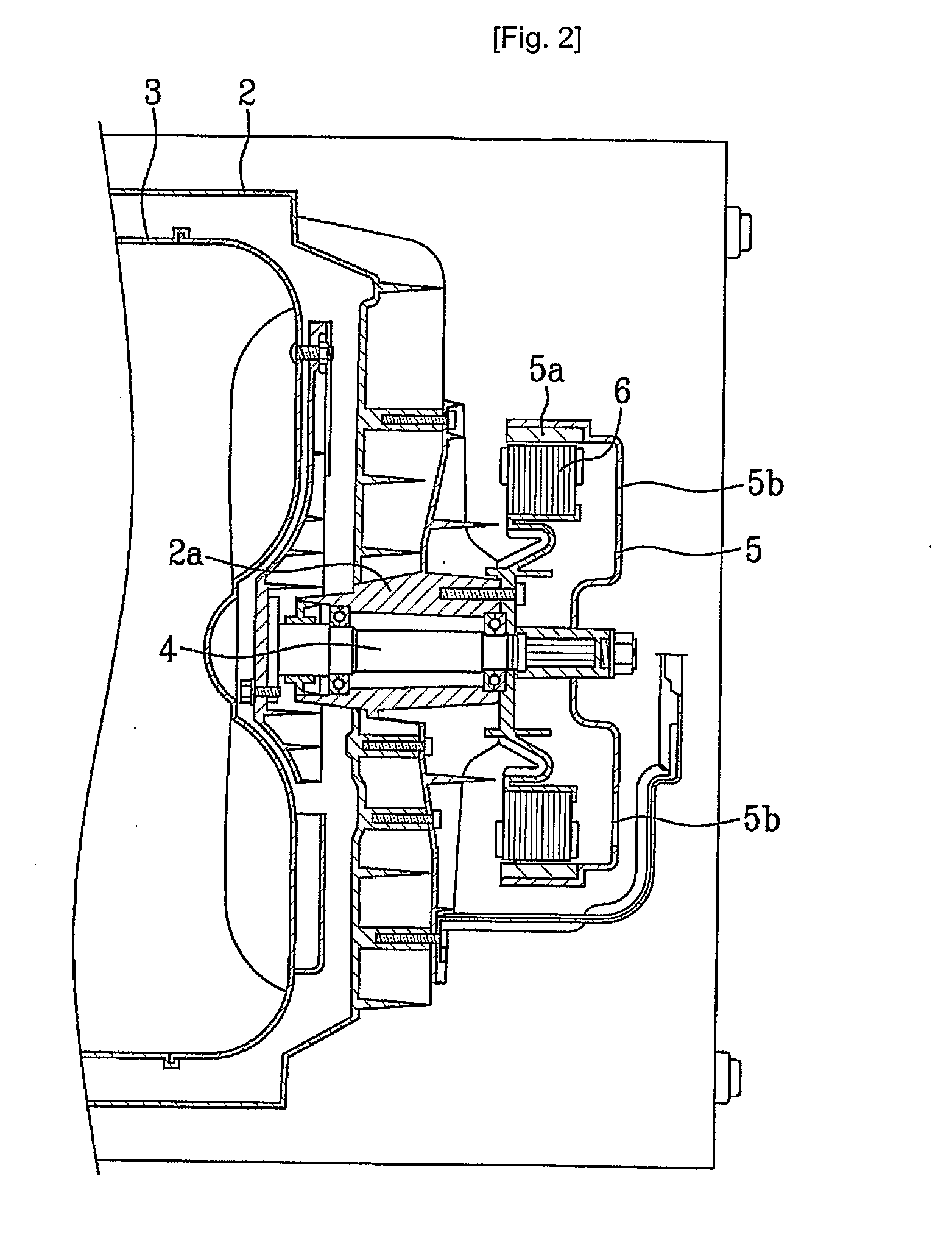
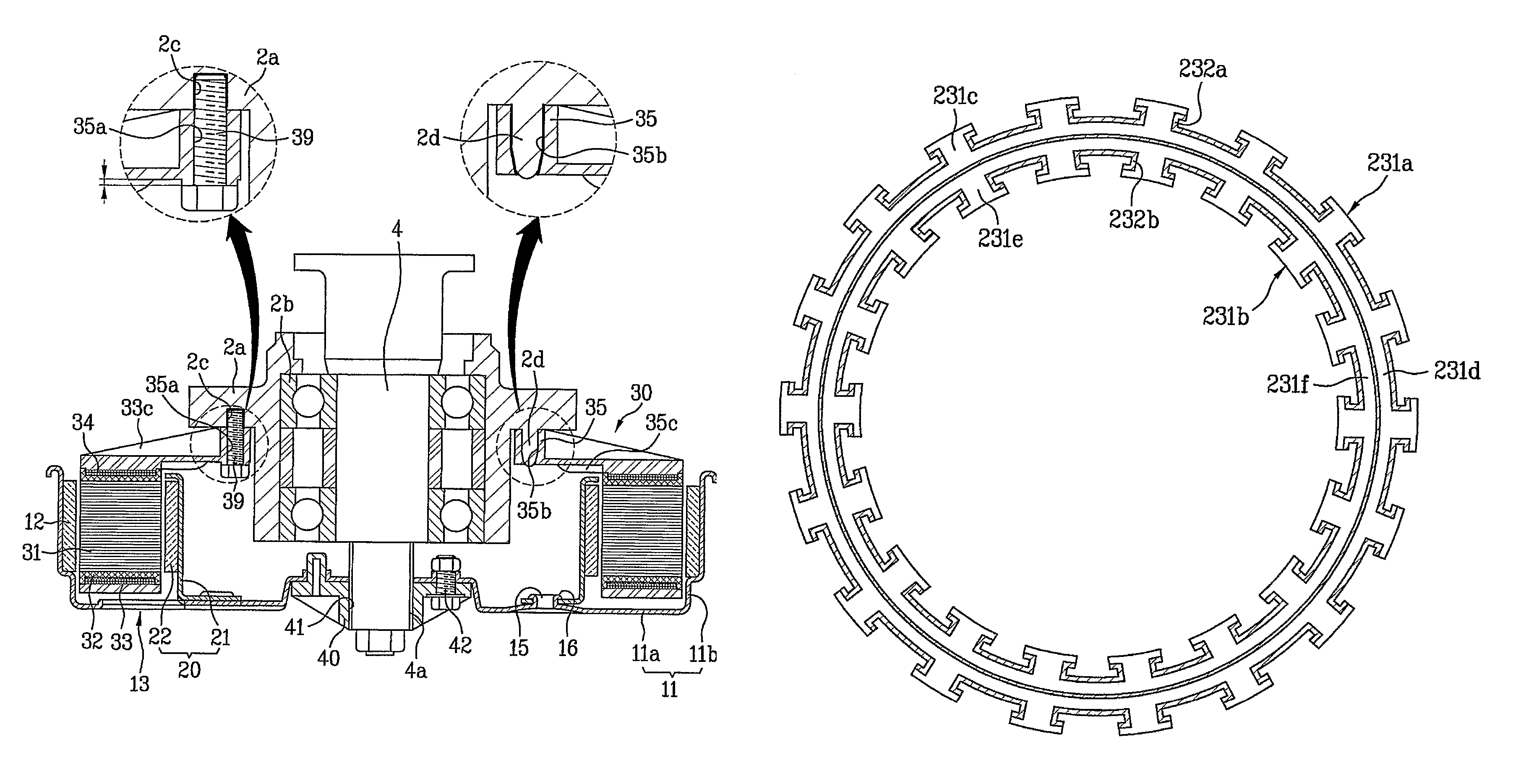
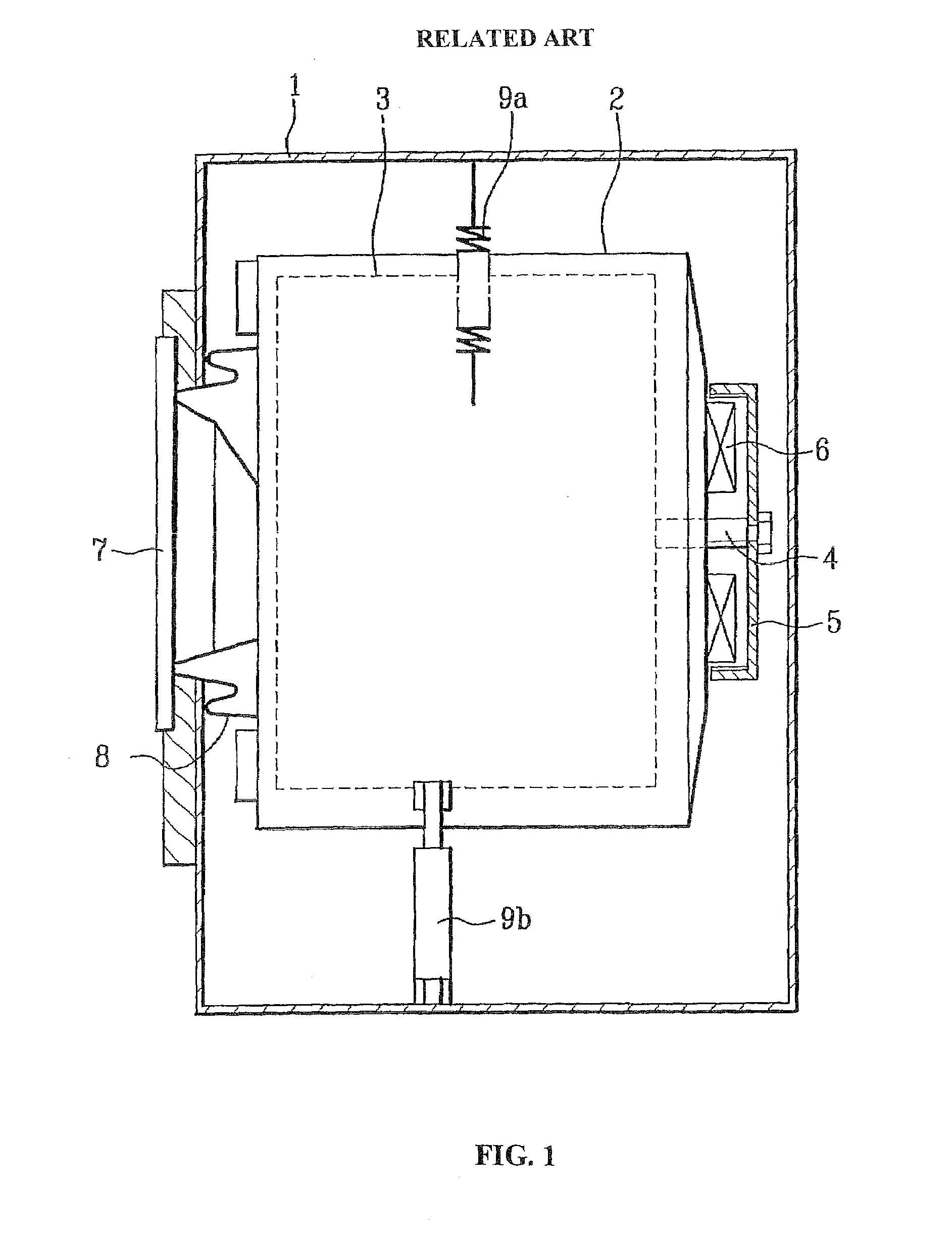
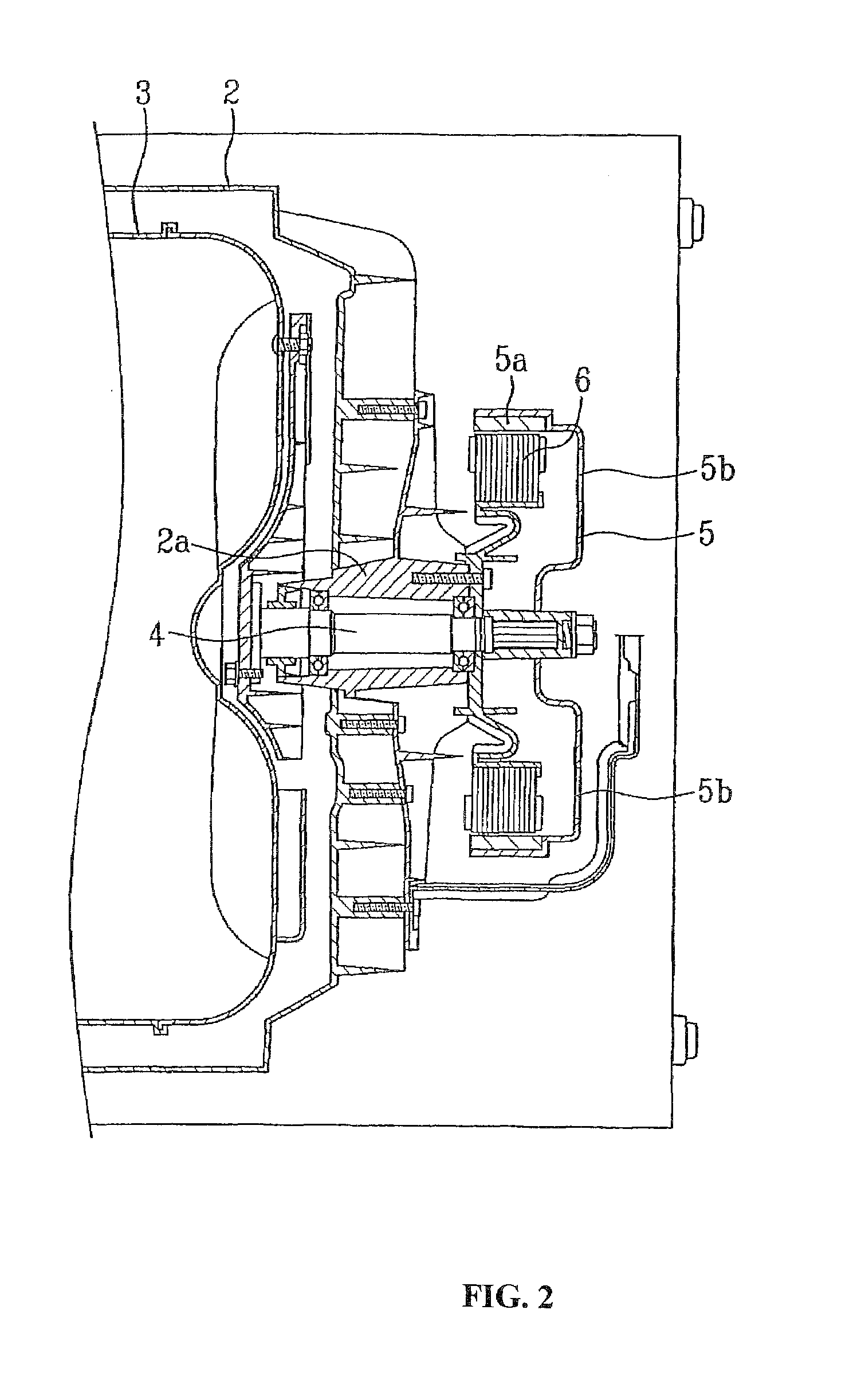
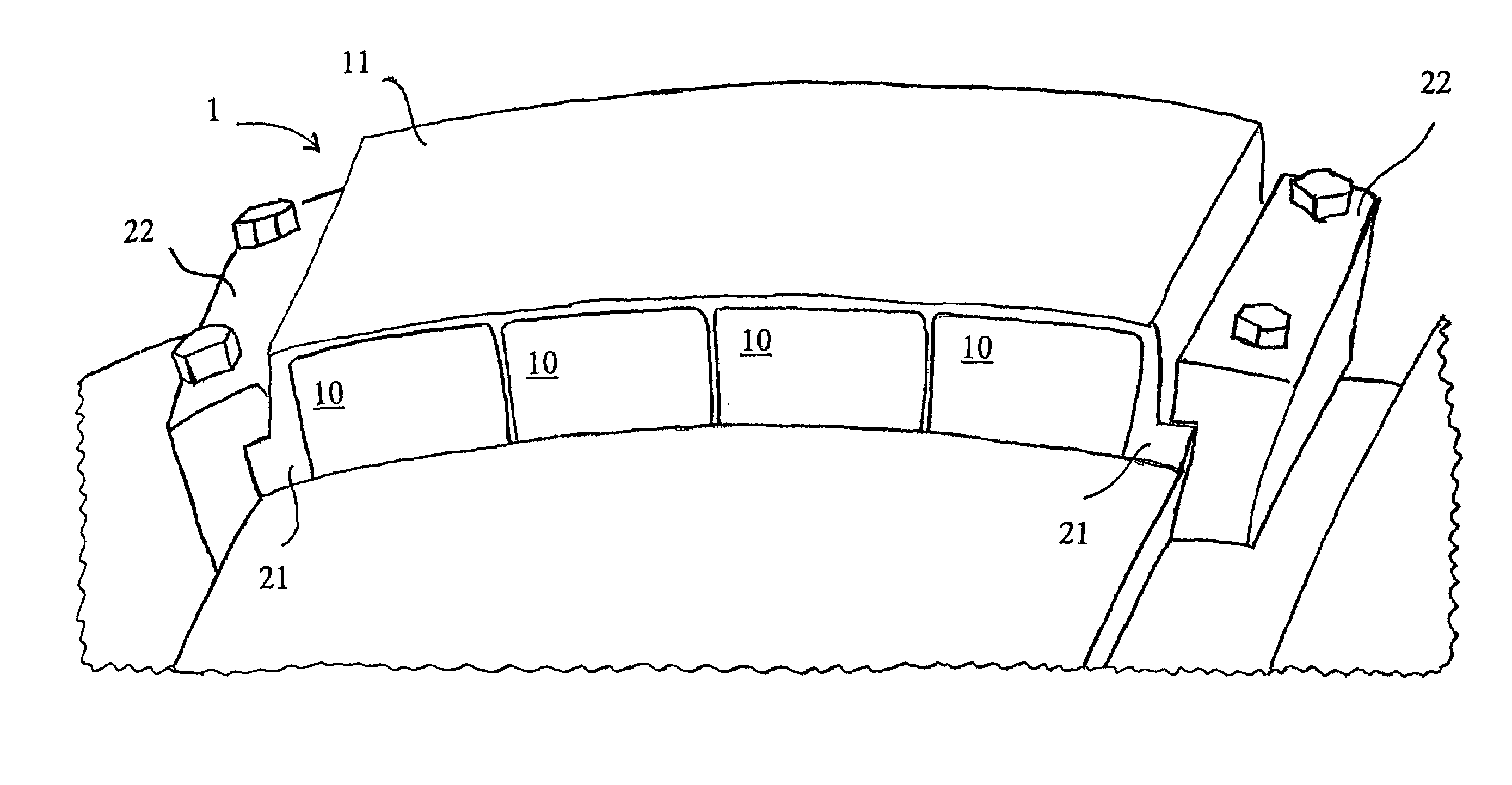
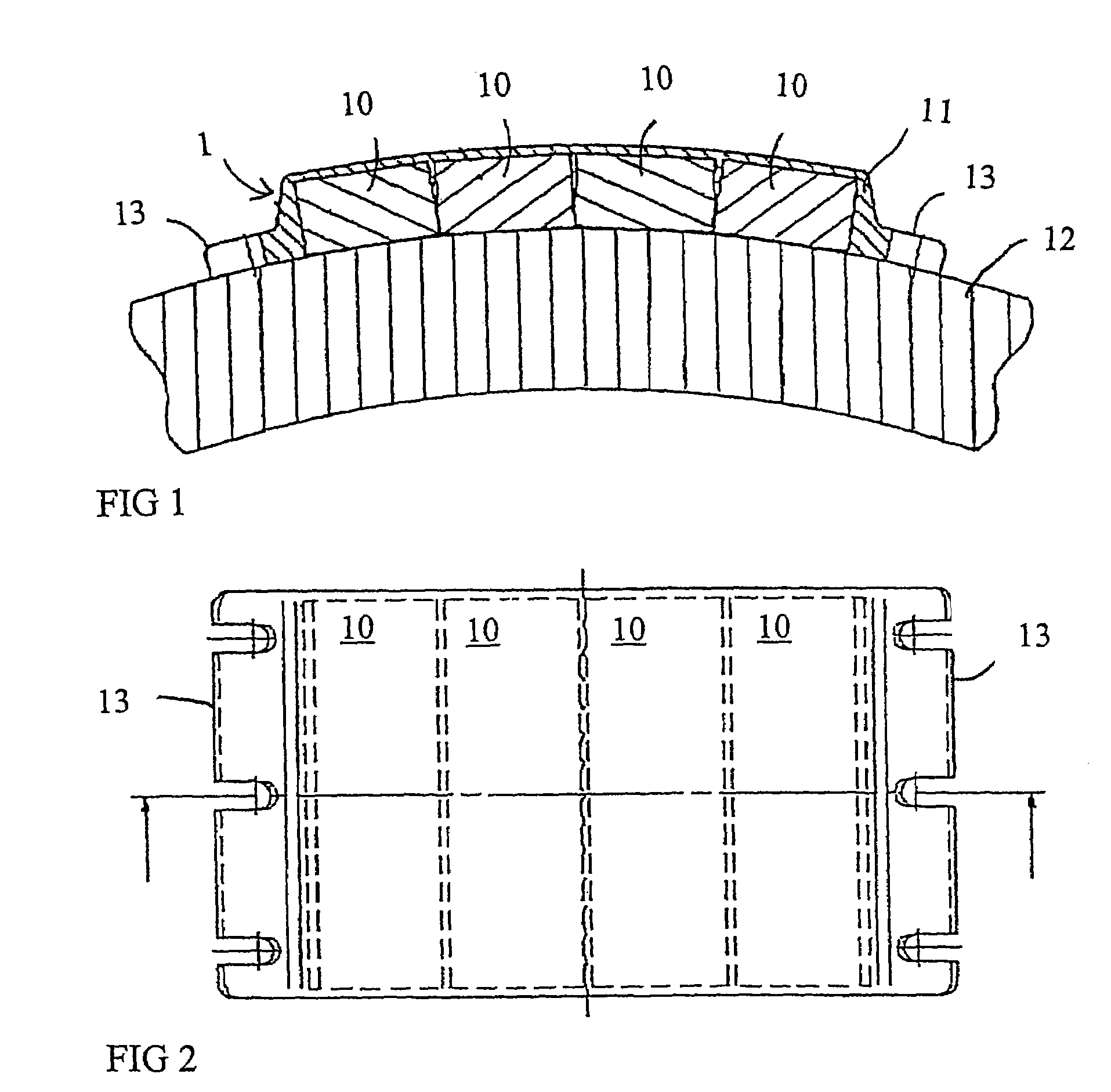
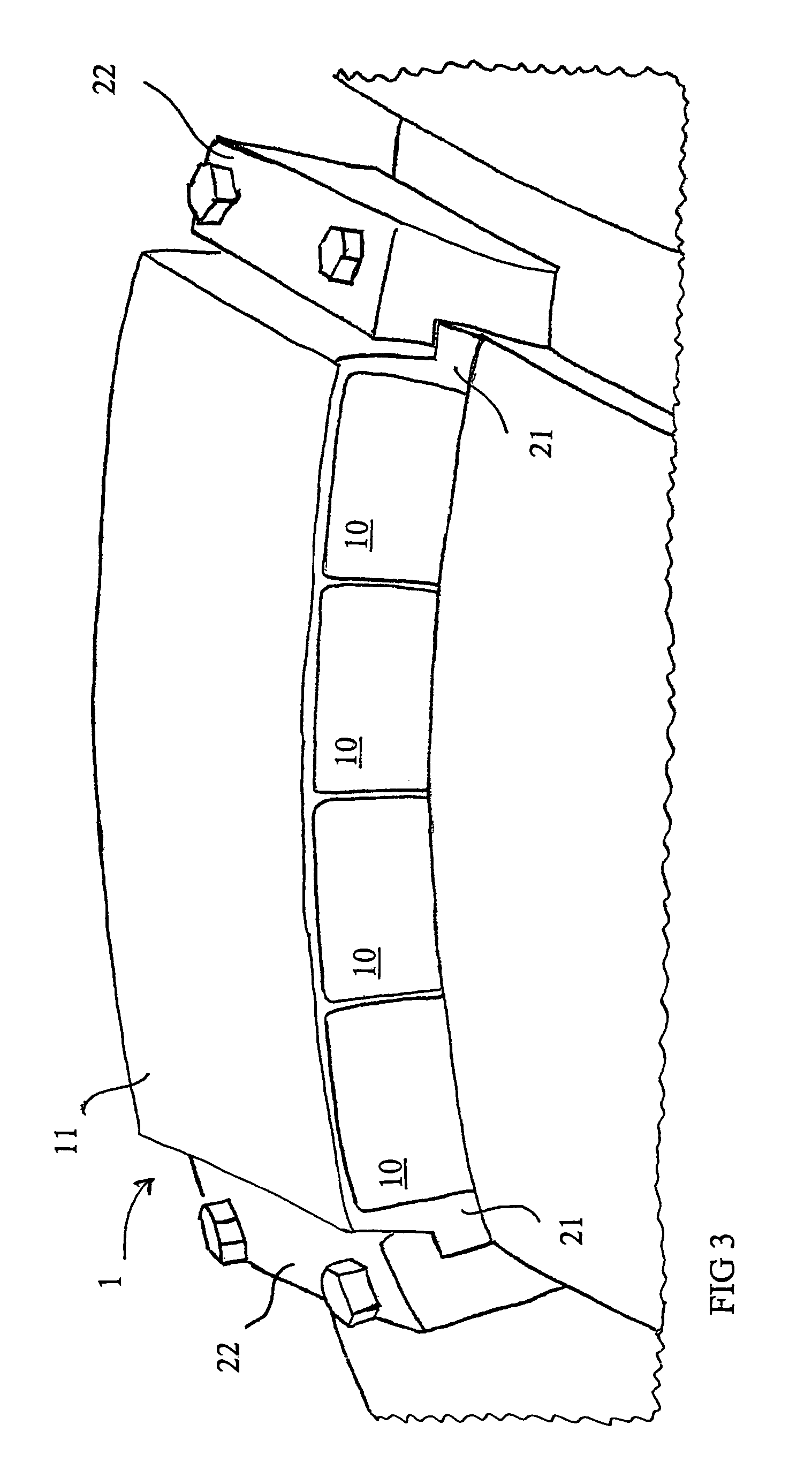
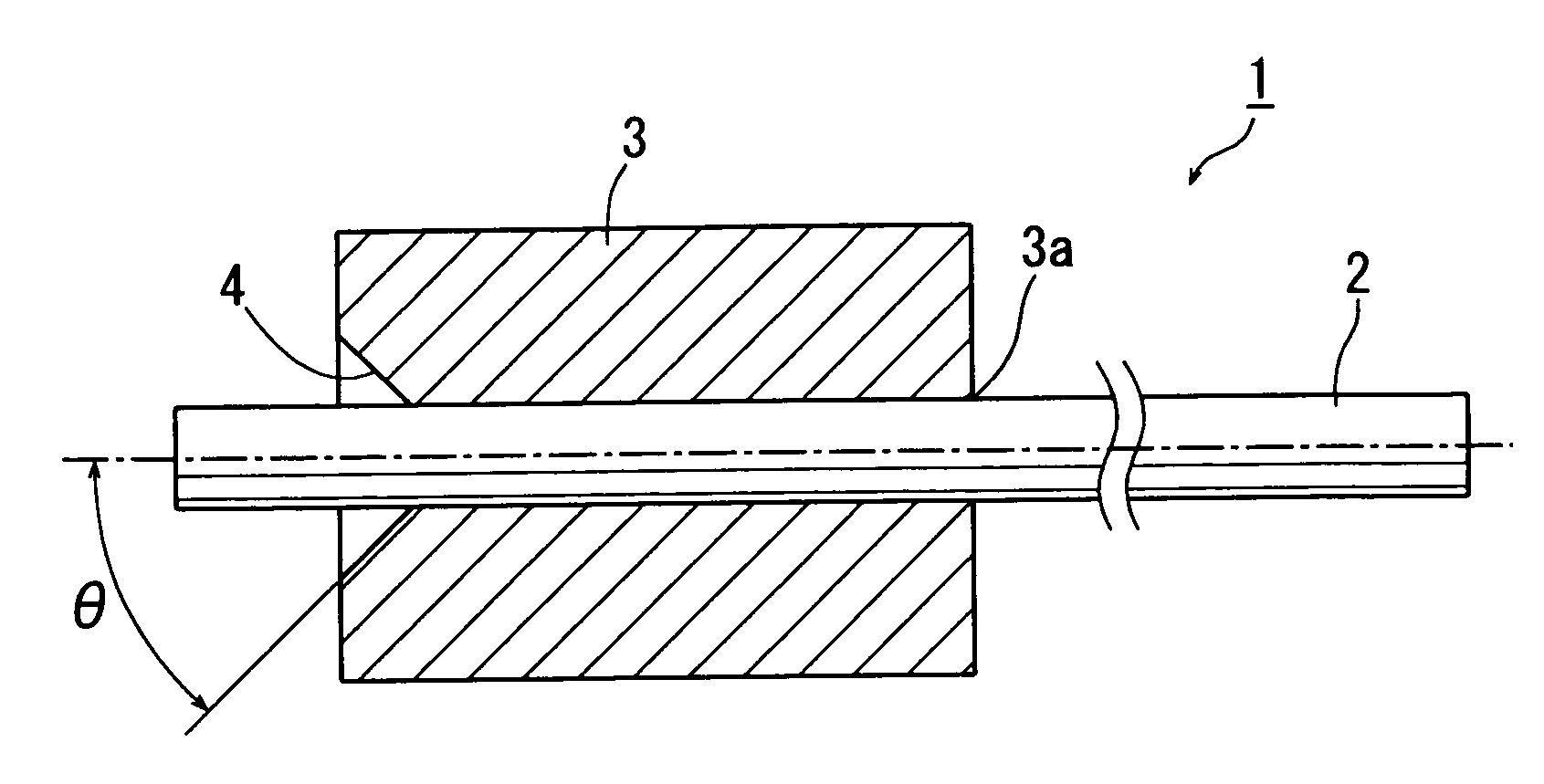
Patents
Literature
544results about "Synchronous machines with rotating armatures and stationary magnets" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Apparatus and method for controlling hybrid motor
ActiveUS8228020B2Reduce capacityReduce electricity loadSingle-phase induction motor startersWindingsDriver circuitPower switching
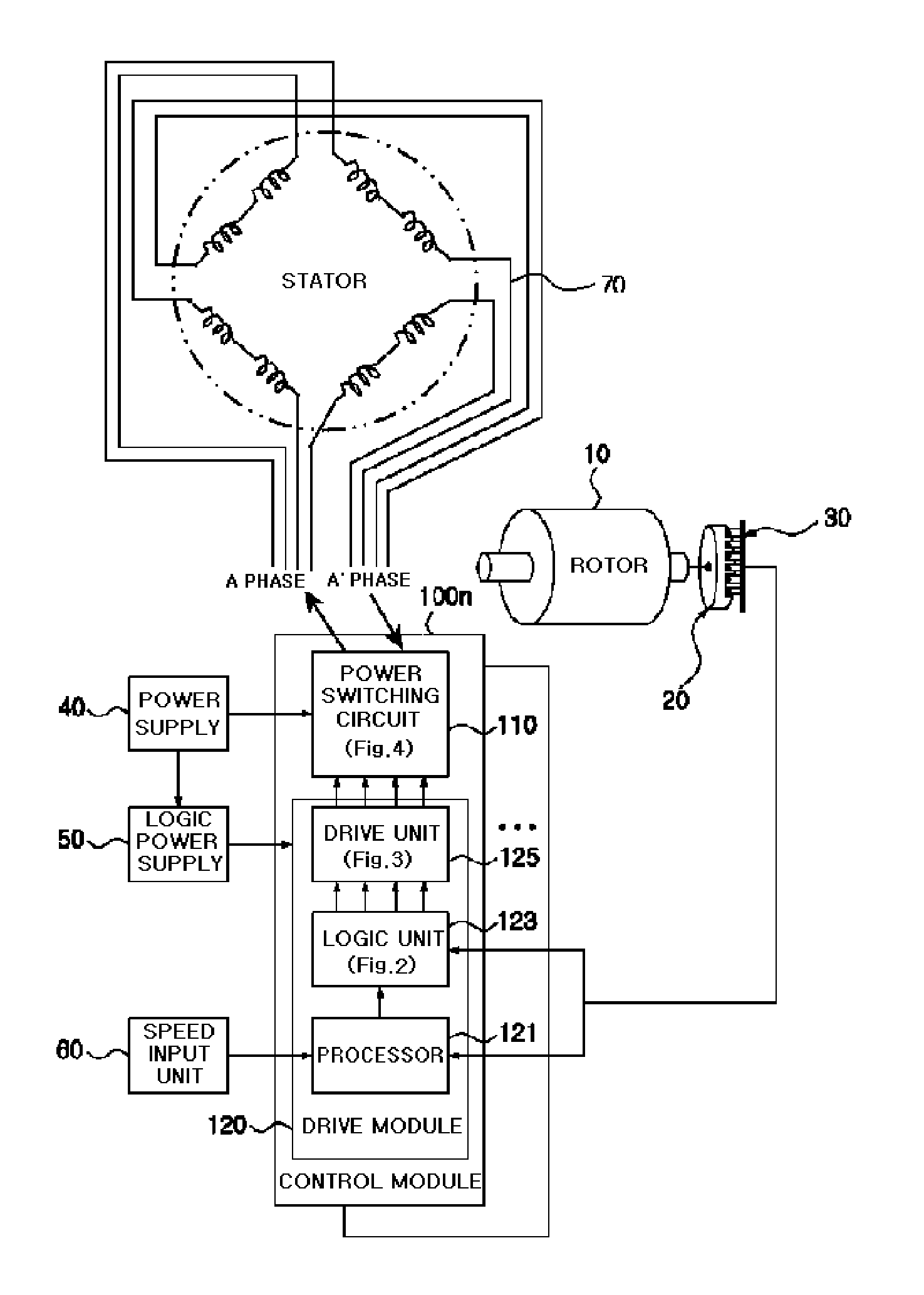
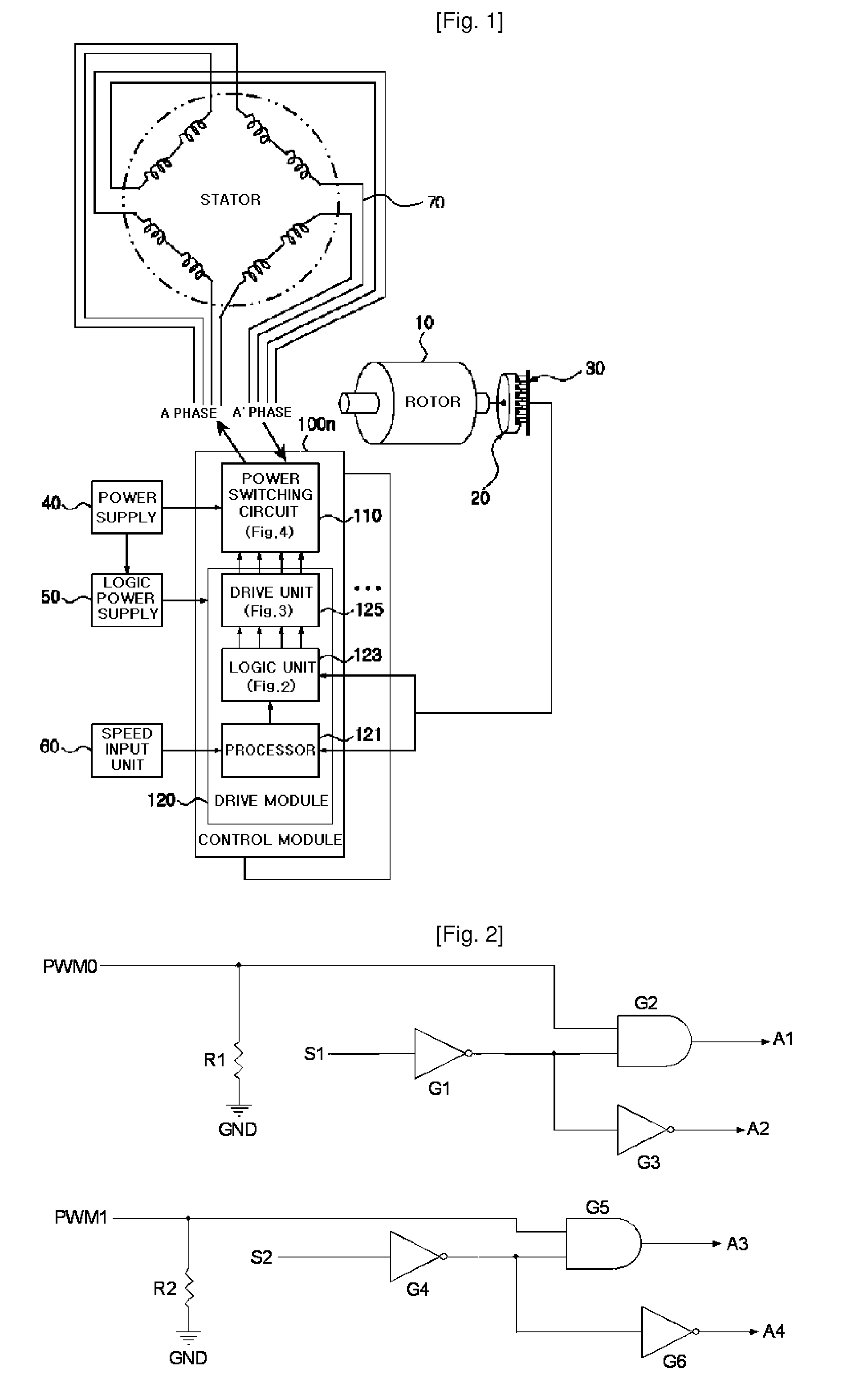
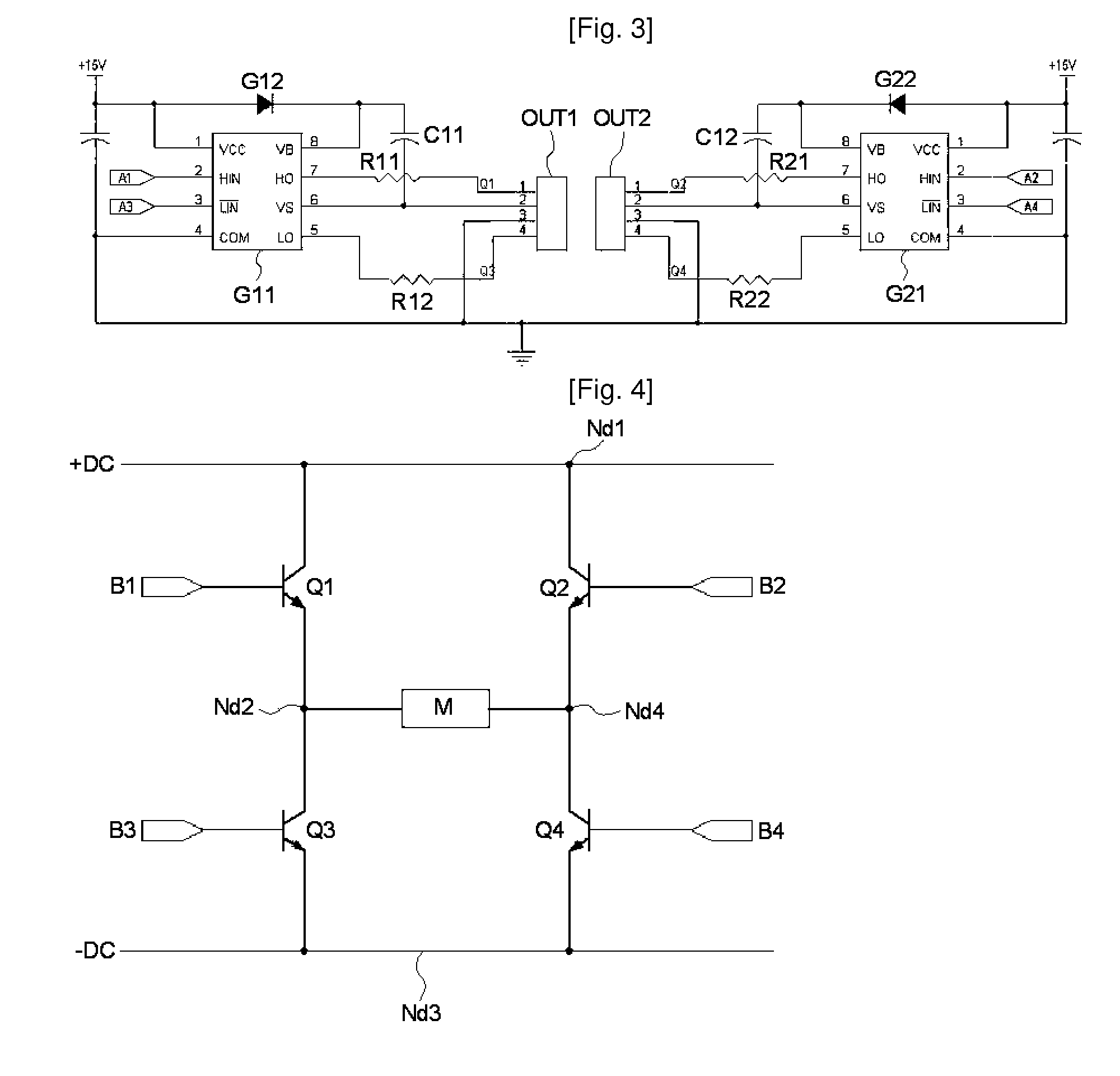
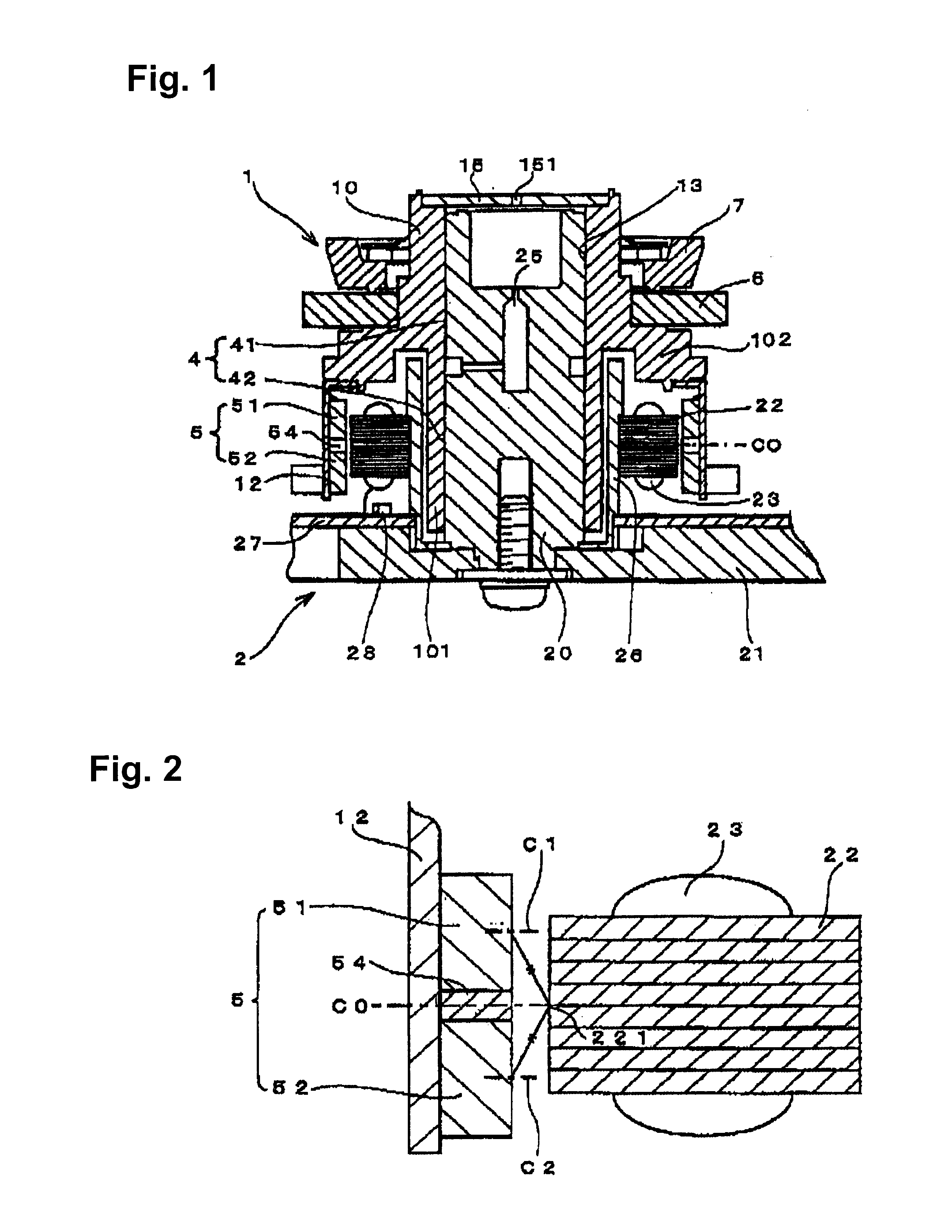
An apparatus and method for controlling a hybrid motor, The hybrid motor, uses a permanent magnet instead of a field coil for a rotor, winds a coil round a stator in a multi-phase independent parallel manner, fixes a rectifying type encoder to the rotor and connects a sensor to a driving circuit. The apparatus comprises: an encoder attached to a rotor in cooperation with a pole sensor a speed input unit for generating a speed instruction signal a power switching circuit to generate motor driving signals; a drive module receiving the speed instruction signal and the sensor signal and outputting the speed instruction signal synchronized with the sensor signal as a driving motor signal; a power supply for applying a DC voltage to the power switching circuit; A logic power supply for converting the DC voltage into a logic voltage, and applying logic voltage to the drive module. The motor has n phases, n power switching circuits and n drive modules.
Owner:NAMYANG NEXMO CO LTD
Driving apparatus for a ceiling fan
InactiveUS7664377B2Reduce the amount presentReduce in quantityPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesElectric testing/monitoringBrushless motorsCeiling fan
A driving apparatus for a DC brushless motor of a ceiling fan is provided. By setting at least one coder and one sensor outside the DC brushless motor, the driving apparatus can sense the position of magnetic poles of the motor for driving the motor. Meanwhile, a controller set with the motor stores the rotation speed of the motor before being turned off by detecting the turn-off time of a turn-on / off signal.
Owner:RHINE ELECTRONICS
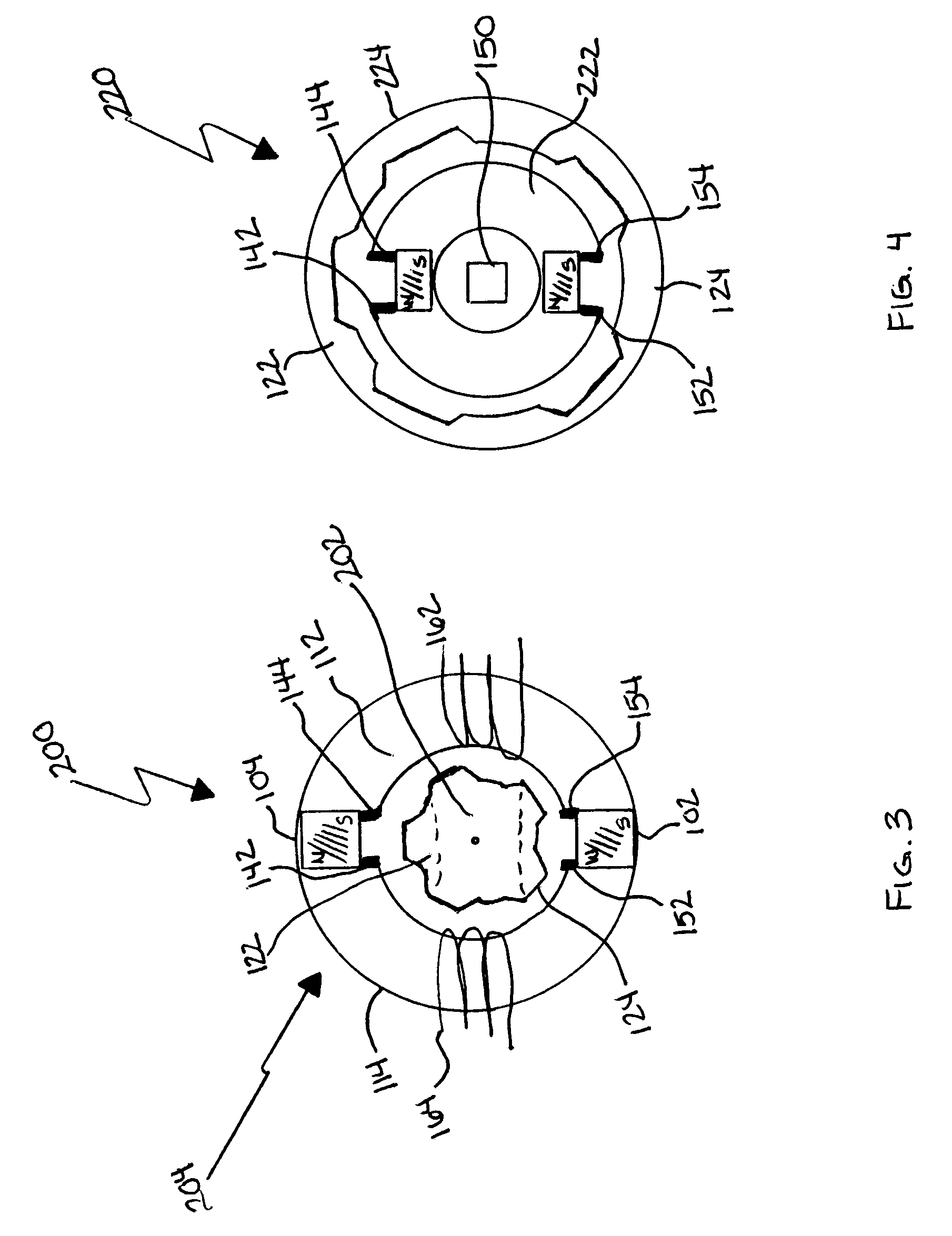
Permanent magnet electro-mechanical device providing motor/generator functions
InactiveUS20080272664A1DC commutatorSynchronous machines with rotating armatures and stationary magnetsMagnetic reluctanceCooling temperature
Owner:QM POWER
Thin hybrid magnetization type ring magnet, yoke-equipped thin hybrid magnetization type ring magnet, and brush-less motor
ActiveUS20060113857A1Decrease in cogging torqueIncrease in torque per unit volume of magnetMagnetic circuit rotating partsPermanent magnetsBrushless motorsMagnetization
The present invention provides miniaturization of brushless motors and brush motors used in electric devices, a ring magnet which simultaneously achieves both high torque and a reduction in cogging torque, a ring magnet with yoke, and a brushless motor. The thin hybrid magnetized ring magnet of the present invention is structured of, in a ring magnet comprised of a plurality of magnetic poles, a radially magnetized main pole and an interface for which the interface of the adjoining main pole is polar anisotropic. When the thin hybrid magnetized ring magnet structured in this manner is applied to a brushless motor, in the case of radial magnetizing, the abrupt change in magnetic flux of the interface between the magnetic poles becomes smooth and cogging torque is greatly reduced due to polar anisotropic magnetization of the interface. At the same time, by polar anisotropically magnetizing the interface between the magnetic poles, magnetic flux is concentrated on the radially magnetized main pole, and in comparison to only radial magnetization, maximum surface magnetic flux improves and it is possible to attain high torque.
Owner:AICHI STEEL
Internal rotor motor
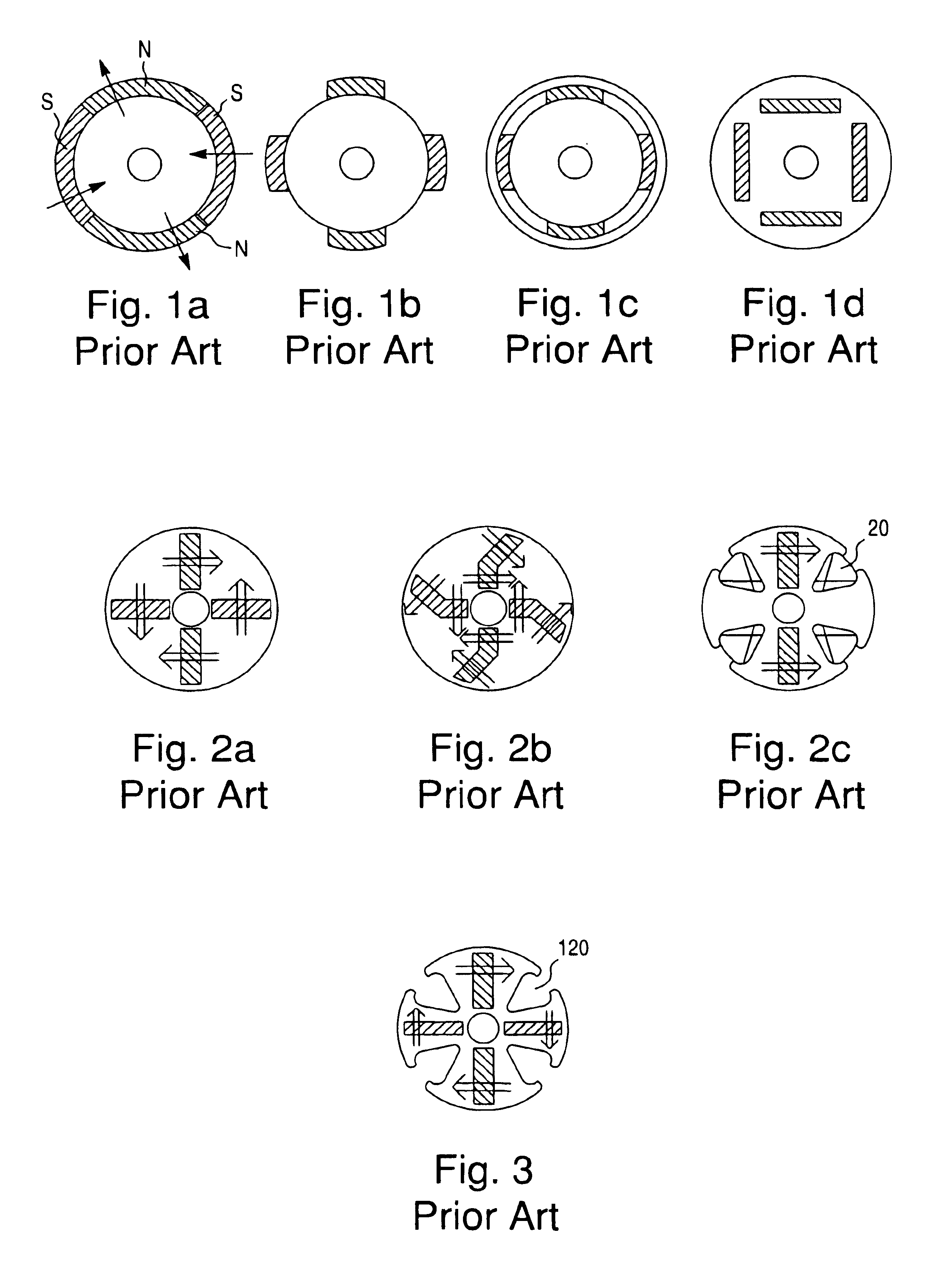
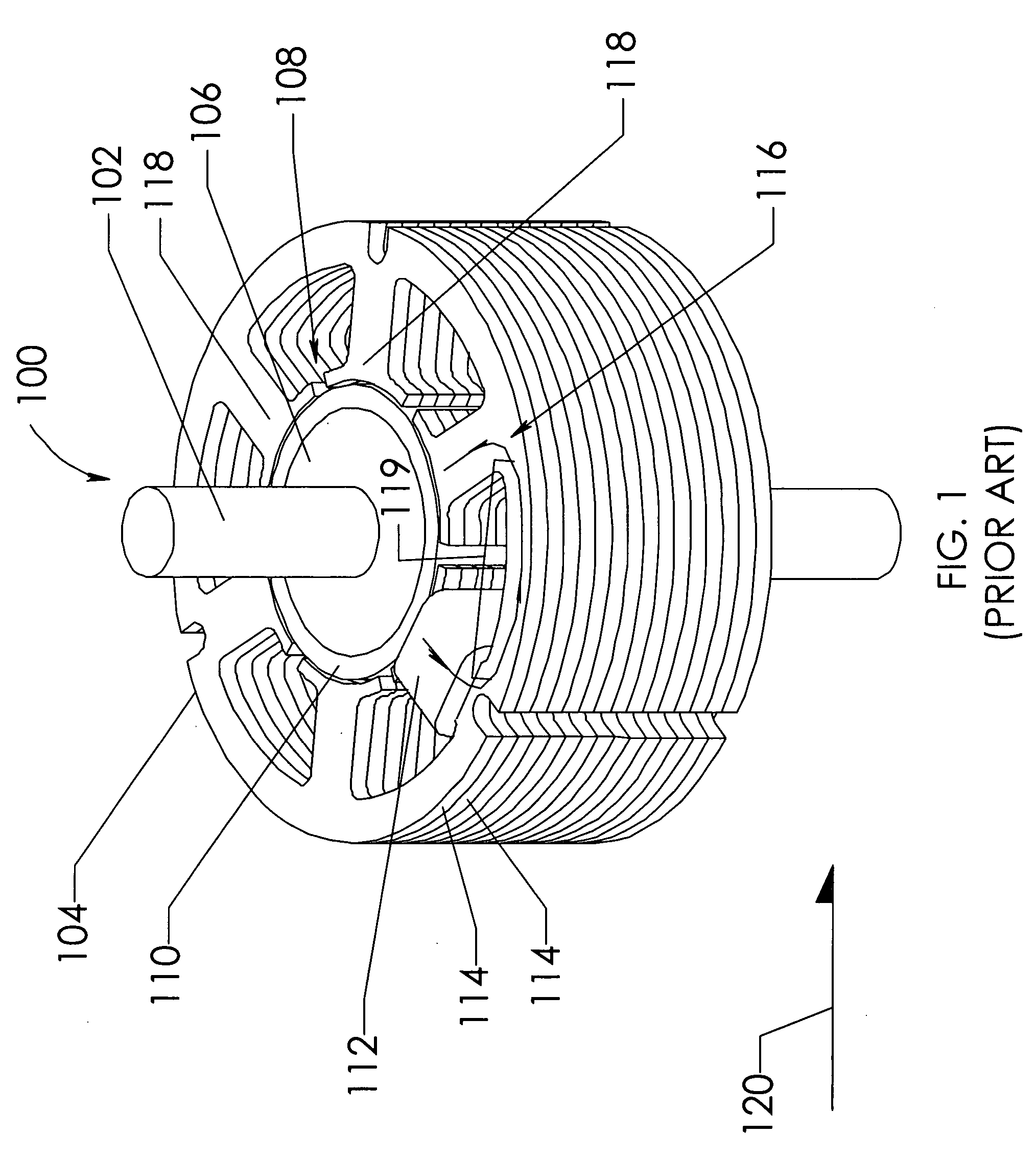
InactiveUS6919663B2Minimized cogging torqueImprove featuresMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsRotor magnetsElectric machine
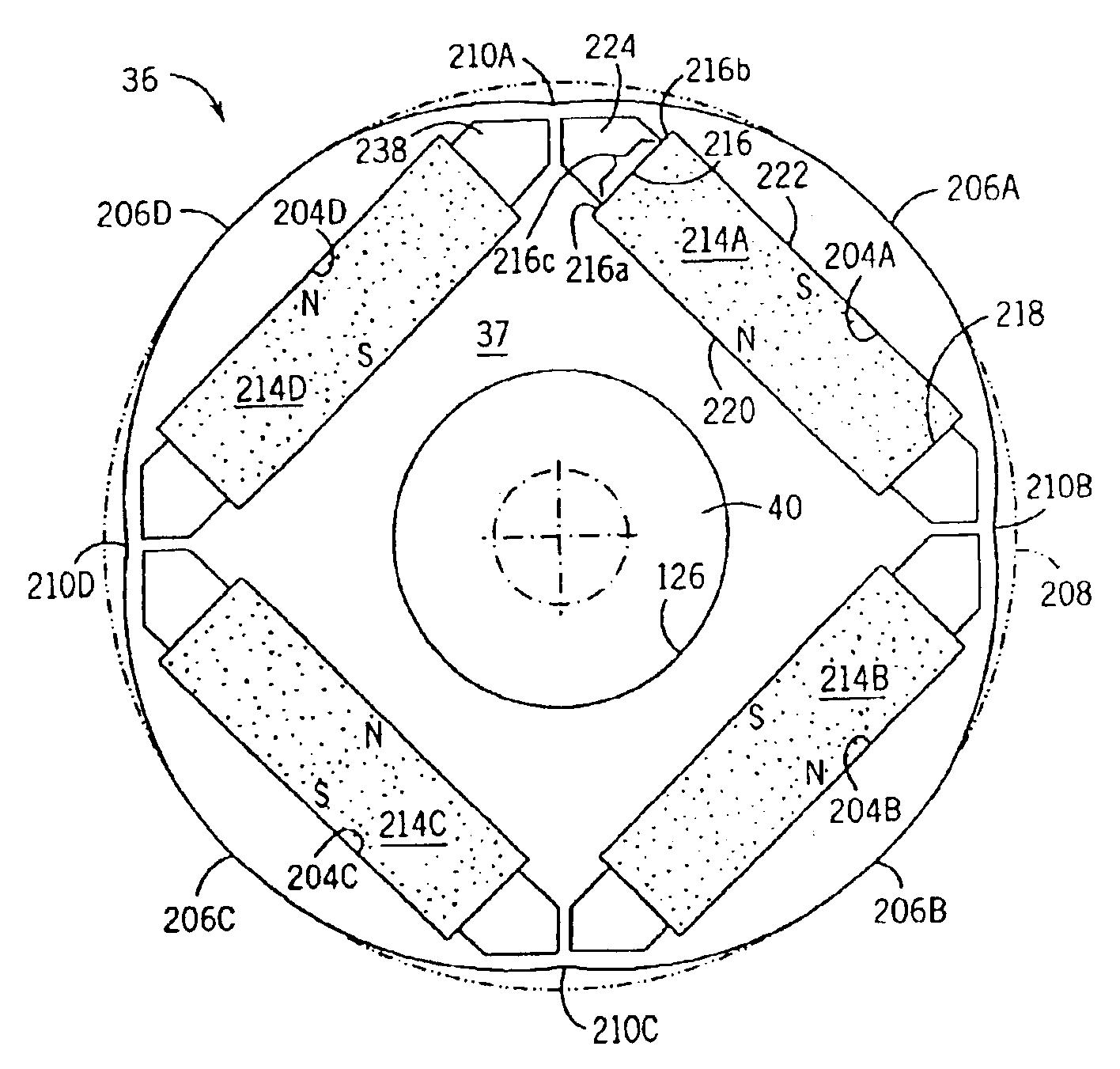
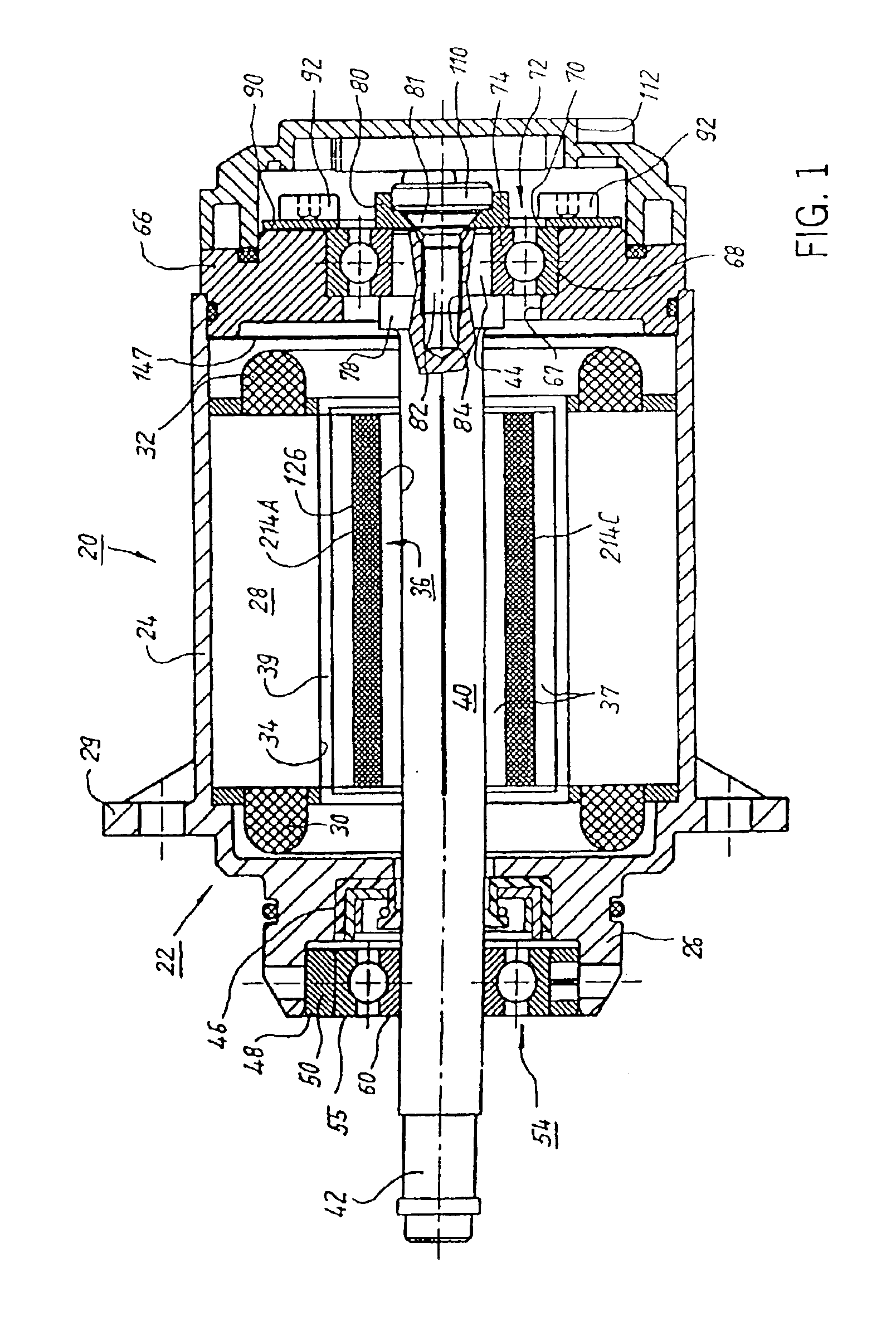
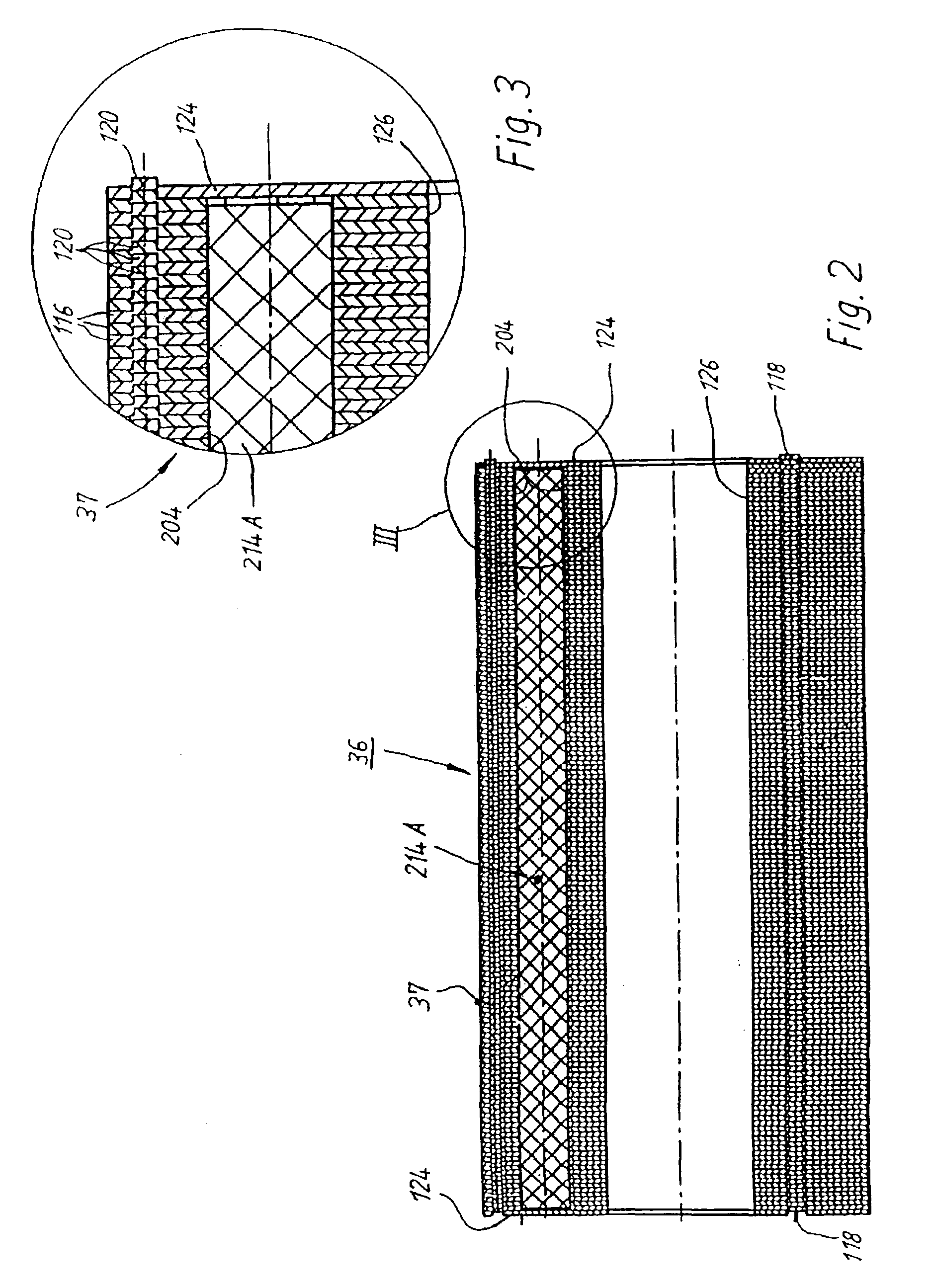
A low-ripple multi-phase internal rotor motor has a slotted stator (28) separated by an air gap (39) from a central rotor (36). The rotor has a plurality of permanent magnets (214), preferably neodymium-boron, arranged in pockets (204) formed in a lamination stack (37), thereby defining a plurality of poles (206) separated by respective gaps (210). In a preferred embodiment, the motor is three-phase, with four rotor poles and six stator poles. As a result, when the first and third rotor poles are so aligned, with respect to their opposing stator poles, as to generate a reluctance torque, the second and fourth rotor poles are aligned to generate oppositely phased reluctance torques, so that these torques cancel each other, and essentially no net reluctance torque is exerted on the rotor. In order to magnetically separate the rotor magnets from each other, a hollow space (224, 238) is formed at the interpolar-gap-adjacent end face (216, 218) of each rotor magnet. A control circuit (147) provides electronic commutation and current control, based on rotor position signals generated with the aid of a control magnet (110) on the rotor shaft (40).
Owner:EBM PAPST ST GEORGEN & -
Permanent magnet motor
A motor providing unidirectional rotational motive power is provided. The motor has a generally circular stator with a stator axis, an outer surface, and a circumferential line of demarcation at about a midpoint of the outer surface. The motor also includes one or more stator magnets attached to the outer surface of the stator. The stator magnets are arranged in a generally circular arrangement about the stator axis and generate a first magnetic field. An armature is attached to the stator for rotation therewith, the armature having an axis parallel to the stator axis. One or more rotors, are spaced from the armature and coupled thereto by an axle for rotation about an axis of each rotor, each rotor rotating in a plane generally aligned with the armature axis. Each rotor includes one or more rotor magnets, with each rotor magnet generating a second magnetic field. The second magnetic field generated by each rotor magnet interacts with the first magnetic field to cause each rotor to rotate about the rotor axis. A linkage assembly drivingly connects each rotor to the stator to cause the armature to rotate about the armature axis thereby providing the unidirectional rotational motive power of the motor.
Owner:FECERA FR J
System and method for utilizing magnetic energy
InactiveUS7453341B1Improve energy efficiencyIncrease the magnetic fieldSynchronous generatorsWindingsEngineeringMagnetic energy
The present invention is a system and method for utilizing magnetic energy. The basic principles of the present invention may be implemented in a variety of systems and methods. A magnet may be rotated or an electromagnet may be controlled in order to control a magnetic field generated by a set of magnets. As a result, numerous, substantial benefits may be achieved by providing at least one set of multiple magnets. For example, the present invention may be used in systems and methods to perform a variety of functions including, but not limited to: (1) to control, manipulate, hold, and / or release a load; (2) to open and / or close a pathway; (3) to open and / or close a circuit; (4) to apply a magnetic field to a load and / or to remove a magnetic field from a load; (5) to intermittently apply and remove a magnetic field; (6) to increase the magnetic field that may be applied to a load; (7) to induce a load into motion; (8) to create energy; and (9) to improve the energy efficiency of a device or system.
Owner:HILDENBRAND JACK W
Center housing design for electric assisted turbocharger
InactiveUS6845617B1Shorten the axial lengthInhibit migrationInternal combustion piston enginesGas turbine plantsTurbochargerDynamic balance
An electric assisted turbocharger has an electric motor with a stator and a rotor that is coupled to a turbocharger shaft carried by a bearing assembly. The stator has a left-hand winding and a right hand-winding each projecting axially outwardly therefrom. The winds each extend a different distance radially along the motor (and are thus asymmetrical with respect to one another), thereby forming a radial gap along an axial end of the stator. The so-formed stator is disposed within a motor housing and together, the stator and motor housing, facilitate placement center housing axial end therein to minimize turbocharger axial length. The rotor is configured to prevent migration of oil into the motor housing, to improve dynamic balance, and comprises an integral thrust washer for placement against the bearing assembly.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Transverse and/or commutated flux system stator concepts
Disclosed are transverse and / or commutated flux machines and components thereof, and methods of making and using the same. Certain exemplary stators for use in transverse and commutated flux machines may be configured with gaps therebetween, for example in order to counteract tolerance stackup. Other exemplary stators may be configured as partial stators having a limited number of magnets and / or flux concentrators thereon. Partial stators may facilitate ease of assembly and / or use with various rotors. Additionally, exemplary floating stators can allow a transverse and / or commutated flux machine to utilize an air gap independent of the diameter of a rotor. Via use of such exemplary stators, transverse and / or commutated flux machines can achieve improved performance, efficiency, and / or be sized or otherwise configured for various applications.
Owner:ELECTRIC TORQUE MASCH INC
Rotary electrical machine having magnet arrangements with magnets of different compositions
InactiveUS6847143B1Improve concentrationImprove machine performanceMagnetic circuit rotating partsDC commutatorAlternatorElectric machine
A rotary electrical machine, especially an alternator or an alternator-starter for a motor vehicle, comprises a stator (S), a rotor (R) and permanent magnets incorporated in the rotor and / or the stator, in which the said magnets are formed into at least two groups each of which is defined by a specific type of composition, with each sub-assembly being a combination of a magnet containing rare earths with a ferrite magnet, at least one of the magnets being arranged radially so as to generate an orthoradial magnetic flux.
Owner:VALEO EQUIP ELECTRIC MOTEUR
Stator assembly with an overmolding that secures magnets to a flux ring and the flux ring to a stator housing
InactiveUS6903475B2Prevent crashMagnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetic circuit stationary partsMagnetic polesInjection moulding
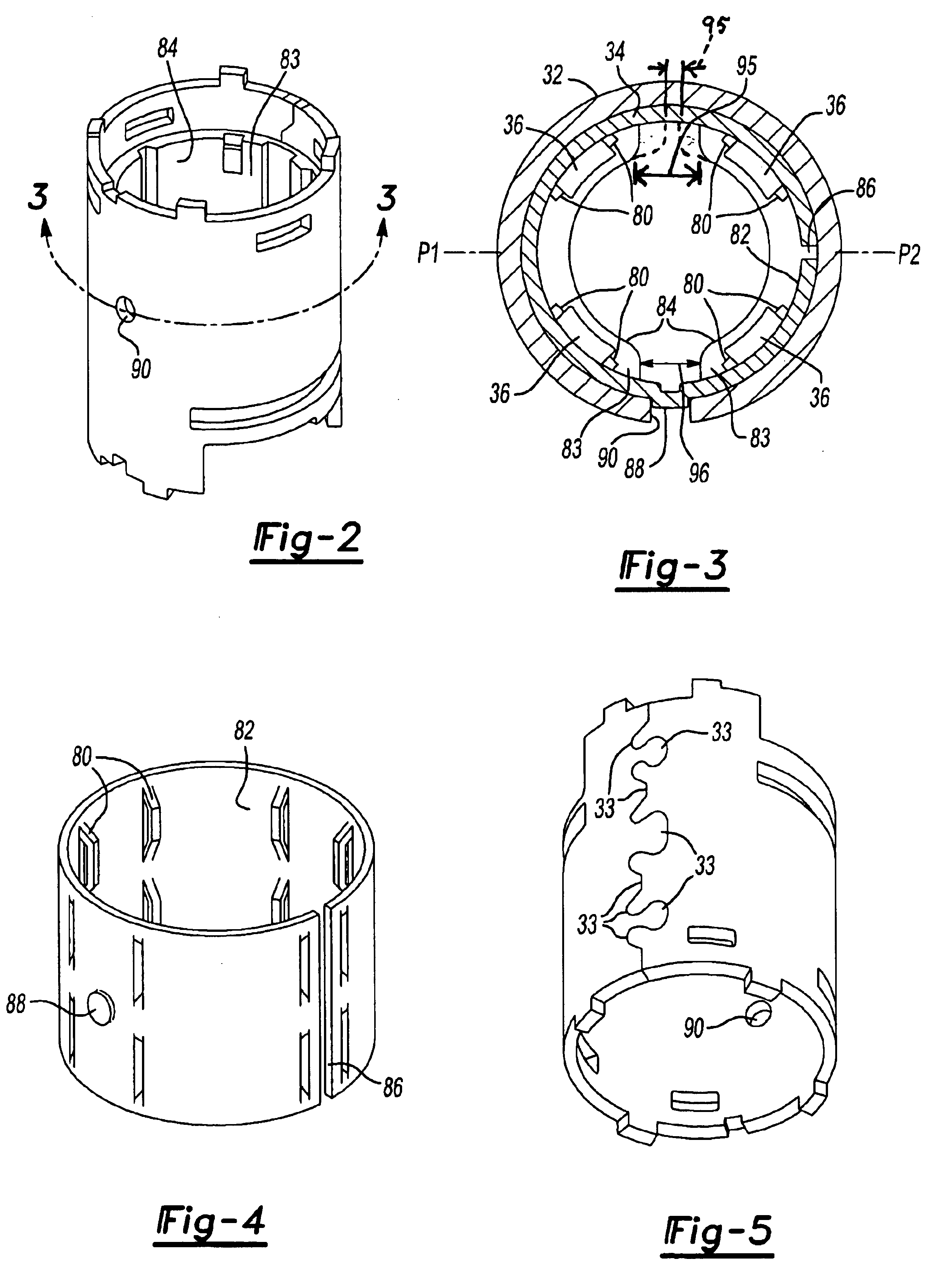
A stator assembly for an electric motor includes a stator housing, an expandable flux ring inserted into the stator housing and a plurality of magnets on an inner surface of the flux ring. Overmold material is molded around the magnets in the flux ring, such as by injection molding. The pressure of the overmold material as it is being molded expands the flux ring pressing the flux ring into engagement with the stator housing. The overmold material secures the magnets to the flux ring and the flux ring to the housing. One of the flux ring and stator housing has a dimple that engages a hole in the other of the flux ring and stator housing to align the flux ring and stator housing. In an aspect, the overmold material is molded to form at least one of a commutator end or rear bearing support, front bearing support and fan baffle. In an aspect, the overmold material is molded to form a keying feature. The keying feature can be slots of different widths between magnetic poles of the stator assembly. In an aspect, the flux ring and housing are preformed as a unit by stamping them from blanks and rolling them together. In a variation, the flux ring blank is rolled first to form the flux ring and the housing blank rolled around the flux ring with the flux ring acting as a rolling arbor.
Owner:BLACK & DECKER INC
Field assembly for a motor and method of making same
InactiveUS7038343B2Prevent movementGood for scrollingMagnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetic circuit stationary partsPower toolRadial surface
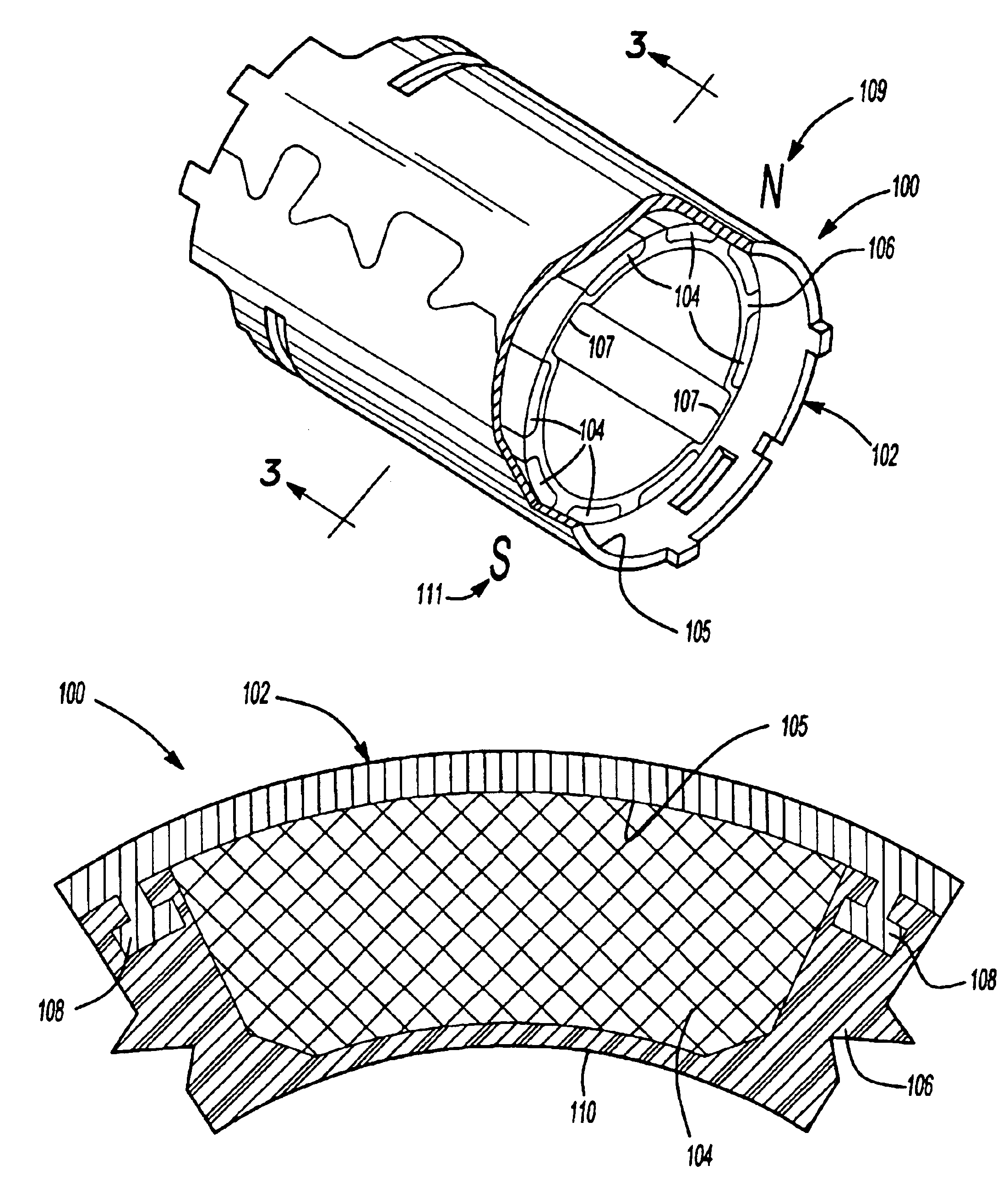
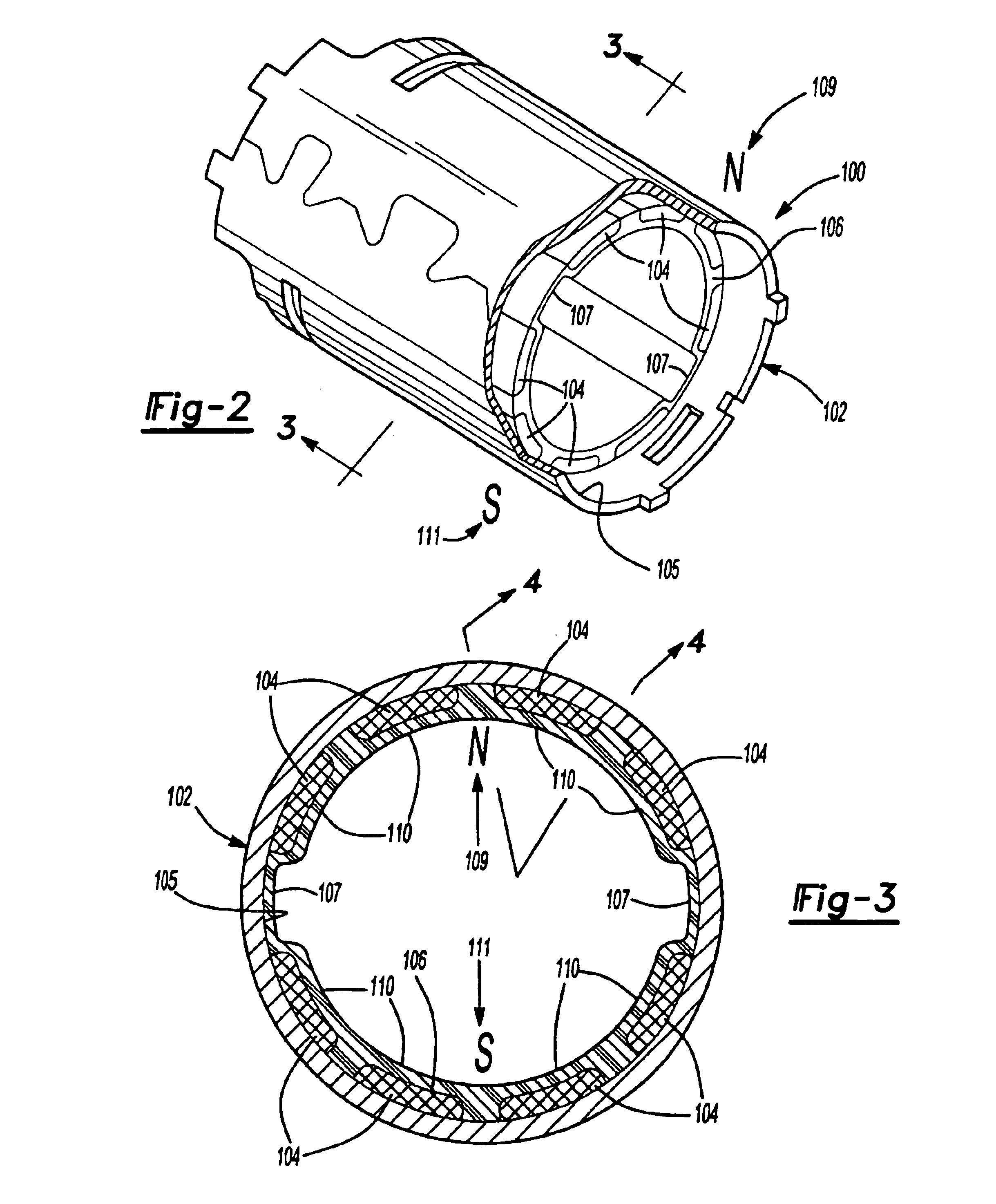
A cylindrical magnet ring assembly having a cylinder magnet flux ring (102) formed with a plurality of inwardly projecting anchors (108); a plurality of permanent magnets (104), wherein the magnet can be formed with step portions (112) in the inner radial surface; a molded plastic member (106) being molded around the magnets and anchors to secure the magnets to a surface of the cylinder flux ring. There are several variations of the embodiments of the invention. Few embodiments are the following: in one aspect of the invention, magnets are inserted into magnet molded around an assembly ring (806) and the molded plastic secures the assembly ring to the flux ring; in another aspect, there are two assembly rings, a first assembly ring (is inserted into the one side of the cylinder flux ring then the second assembly ring is inserted into the other side of the cylinder flux ring and mated to the first assembly ring, after that the molded plastic secures the two assembly rings. The foregoing cylindrical magnet ring assembly is used in a stator of a motor which is used in a power tool.
Owner:BLACK & DECKER INC
End cap for segmented stator
ActiveUS20050212377A1Easy windingSynchronous generatorsWindings insulation shape/form/constructionInterference fitCoupling
A stator for an electromagnetic machine includes a plurality of discrete and individually wound stator segments having end caps positioned on the segments. The end caps have legs for positioning the end cap on the segments with an interference fit. The end caps have angled surfaces to facilitate winding of wire on the segments. The end caps have male and female couplings that mate together to couple adjacent segments together. The end caps have fingers and slots for aligning the segments on substantially the same plane. The end caps have wire isolation features, including hooks, shelves and ledges, for separating the interconnect wires routed on the stator to electrically interconnect the segments. The segments include scalloped contours on their outer edges for draining oil, and the end caps have passages for draining oil.
Owner:HERMETIC MOTORS LP
Polyphase transverse and/or commutated flux systems
Disclosed are single- and poly-phase transverse and / or commutated flux machines and components thereof, and methods of making and using the same. Exemplary devices, including polyphase devices, may variously be configured with an interior rotor and / or an interior stator. Other exemplary devices, including polyphase devices, may be configured in a slim, stacked, and / or nested configuration. Via use of such polyphase configurations, transverse and / or commutated flux machines can achieve improved performance, efficiency, and / or be sized or otherwise configured for various applications.
Owner:ELECTRIC TORQUE MASCH INC
Dual Rotor Type Motor
ActiveUS20070205682A1Enlarging sizeEnlarging weightMagnetic circuit rotating partsOther washing machinesEngineeringDistance space
Abstract: A dual rotor type motor of the present invention is disclosed. The dual rotor type motor according to the present invention includes a shaft rotatably provided in a motor securing part; a rotor assembly rotated with a center thereof fastened to the shaft, the rotor assembly comprising an outer rotor spaced apart at a predetermined distance from the center of the shaft with magnets secured along a circumferential direction, and an inner rotor provided in an inside of the outer rotor at a predetermined distance spaced apart with magnets secured along a circumferential direction; and a stator comprising a core made of metal, an insulator of an insulating material for surrounding the core so as to have a first and second surface of the core facing each other to be exposed outside, a coil wound on the outer surface of the insulator, a molding part of insulating material for surrounding the insulator and the coil by insert molding as one body to expose the first and second surface of the core in a state of the insulator being provided in a circular shape and a fixing part for securing the molding part to the motor securing part, and the stator provided between the outer rotor and the inner rotor for having the exposed first and second surface of the core to face each other at a predetermined distance with the magnet of the outer and inner rotor.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Dual rotor type motor
ActiveUS7557486B2Enlarging size and weightHigh outputMagnetic circuit rotating partsOther washing machinesEngineeringMagnet
A dual rotor-type motor includes a stator located between inner and outer rotors. The stator includes a core having first and second surfaces that face magnets on respective circumferential surfaces of the rotors. The surfaces of the core are spaced predetermined distances from the magnets on thr rotors and an insulating material can be included around the core.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Axial gap type dynamo-electric machine
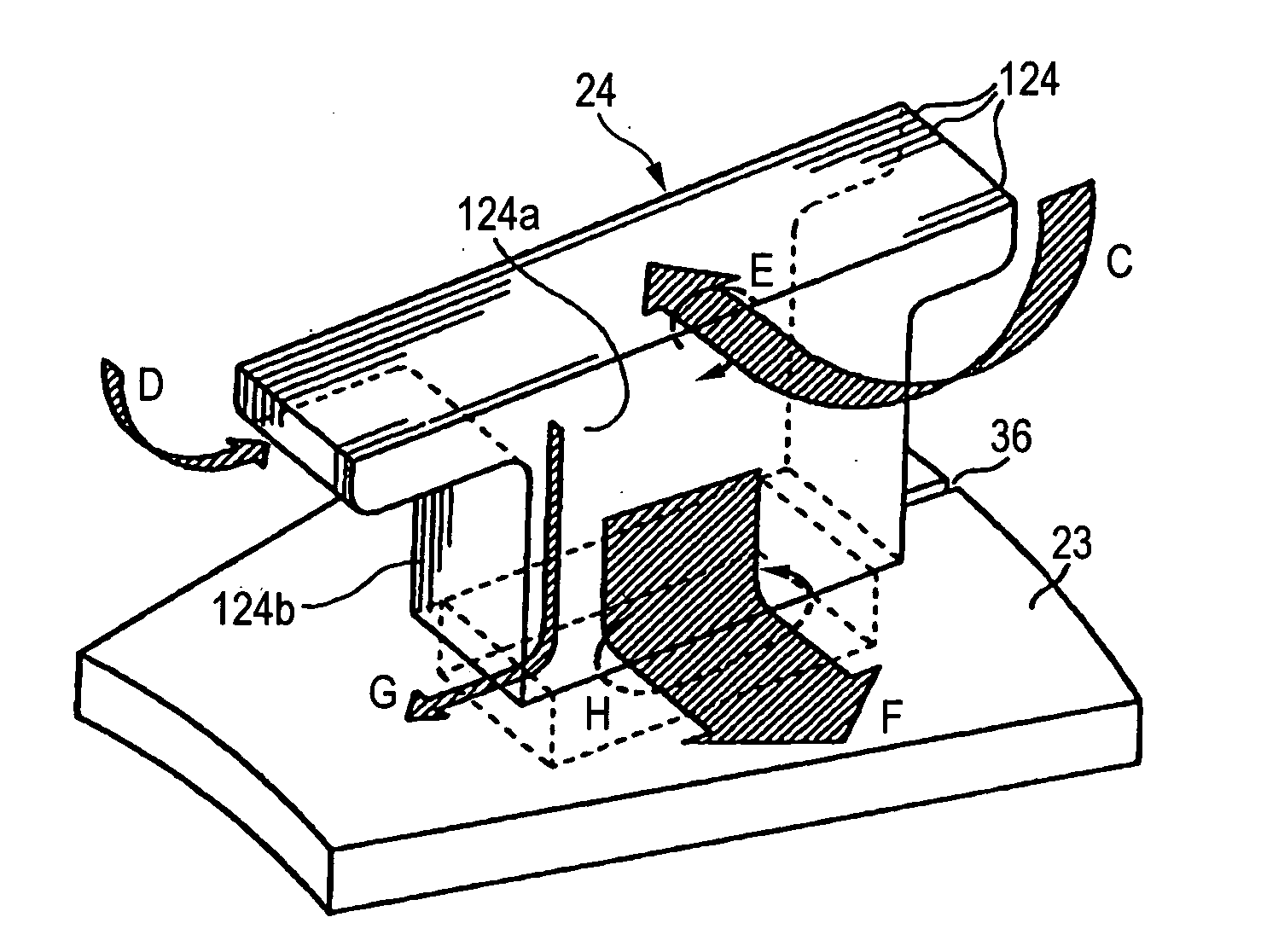
InactiveUS20050073213A1Total current dropImprove electrical resistanceSuspensionsMagnetic circuit rotating partsElectric machineHigh torque
There is provided an axial gap type rotating electric machine which is small-sized and achieves a high motor efficiency as a drive source having a high torque using, for example, a strong magnet by reducing an energy loss by an induced current. An axial gap type rotating electric machine having a yoke on a side of a rotor in a circular plate shape fixed to a rotating shaft, a yoke 23 on a side of a stator in a circular plate shape opposed to the yoke on the side of the rotor, a magnet fixed to a side of an opposed face of either one of the yokes on the side of the rotor or the side of the stator, a plurality of teeth 24 arranged on a side of an opposed face of other yoke on the side of the rotor or the side of the stator radially and opposedly to the magnet and fixed to the yoke 23, and a coil wound around each of the plurality of teeth, in which the teeth 24 has a laminated member of plate members 124 for the teeth and faces 124a to be superposed of the plate members 124 for the teeth are arranged in a circumferential direction.
Owner:YAMAHA MOTOR CO LTD
Electricity generating assembly
InactiveUS7816802B2Increase the number of revolutionsEasy to spreadWind motor controlPV power plantsElectricityEngineering
A electricity generating assembly includes a plurality of rotatable fan blades. A generator is connected to the plurality of fan blades to convert rotation of the fan blades into electricity. A plurality of shutters surround the plurality of fan blades. The plurality of shutters are movable between a first position in which said plurality of shutters are open to allow access to the plurality of fan blades and a second position in which the plurality of shutters are closed to prevent access to the plurality of fan blades. A motor is connected to the plurality of shutters to move the plurality of shutters between the first and second positions.
Owner:GREEN WILLIAM M
Structure for linear and rotary electric machines
ActiveUS20100259112A1Reduce material costsSmall sizeMagnetic circuit stationary partsMaster clocksLow speedElectric machine
Disclosed herein is a structure for linear and rotary electric machines. The present invention provides a modular mover structure which includes coils that have an electrical phase difference of 180°, so that the path of magnetic flux is shortened, thus reducing the size of the machine and mitigating the back-EMF unbalance. Furthermore, the modular mover structure can be modified into various shapes. For example, when a skew structure is applied to a mover or stator iron core, the force ripples in an electric machine can be reduced. In addition, when a hinge structure is applied to a modular mover iron core, the mover can move in a linear and curved manner. Moreover, the structure of the present invention can be applied to a rotary electric machine. In this case, because the number of poles can be easily increased, a low speed high torque direct drive type rotary electric machine can be realized.
Owner:KOREA ELECTROTECH RES INST
Direct-current motor and manufacturing method for the direct-current motor
InactiveUS20080122303A1Reduce vibrationRotary current collectorMagnetic circuit stationary partsEngineeringSliding contact
A direct-current motor includes a stator having a magnetic field system, a rotor disposed around the stator, a commutator which rotates together with the rotor, and power supply brushes which are urged in the axial direction by urging members so as to come into contact with the sliding contact surfaces. The rotor includes an armature core around which armature coils are wound, and a rotary shaft which rotates together with the armature core. The commutator has segments extending radially. The segments have sliding contact surfaces orthogonal to an axial line of the rotary shaft. At least a part of each power supply brush comes into contact with the sliding contact surface at a position further radially outward than the armature coil.
Owner:ASMO CO LTD
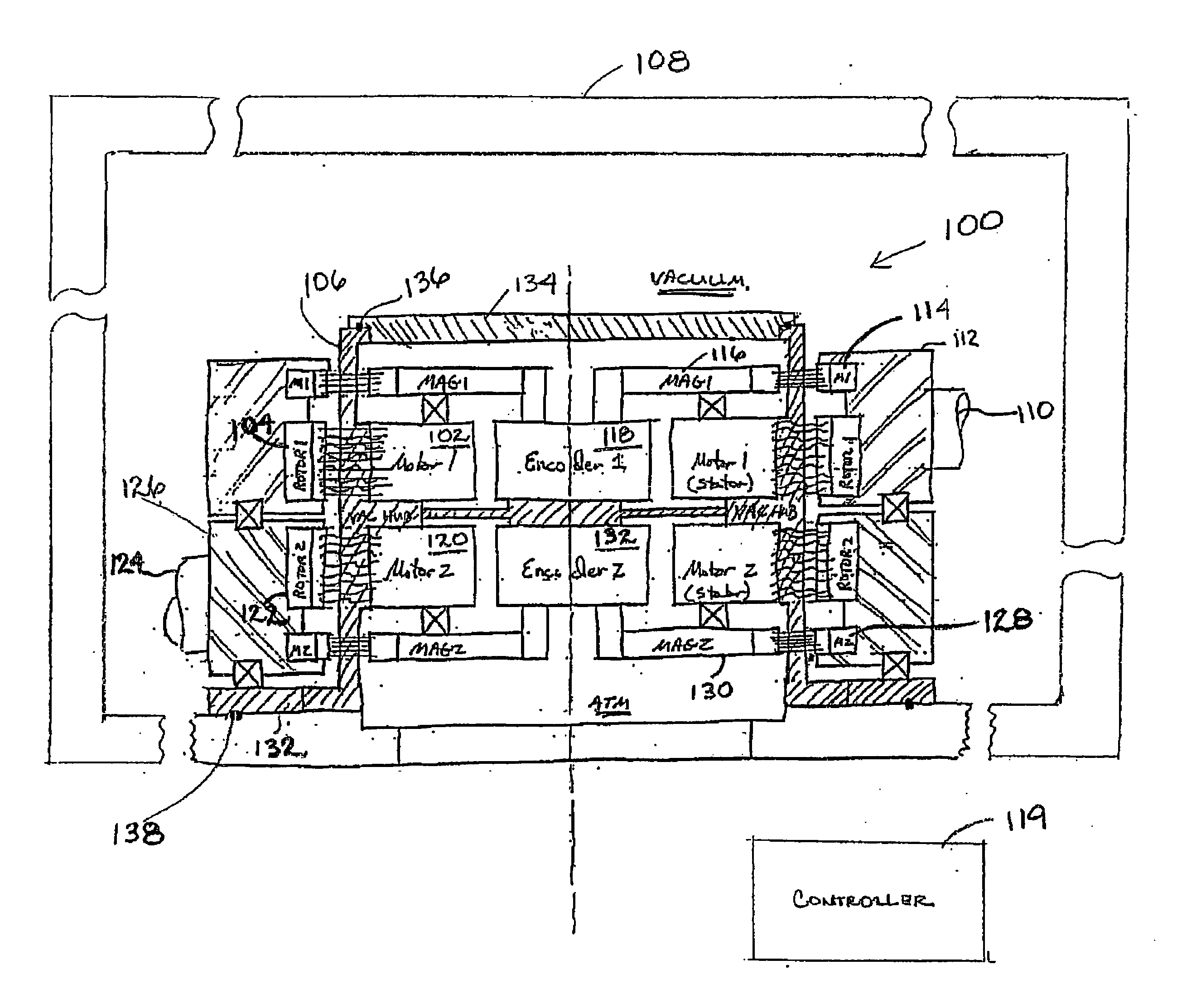
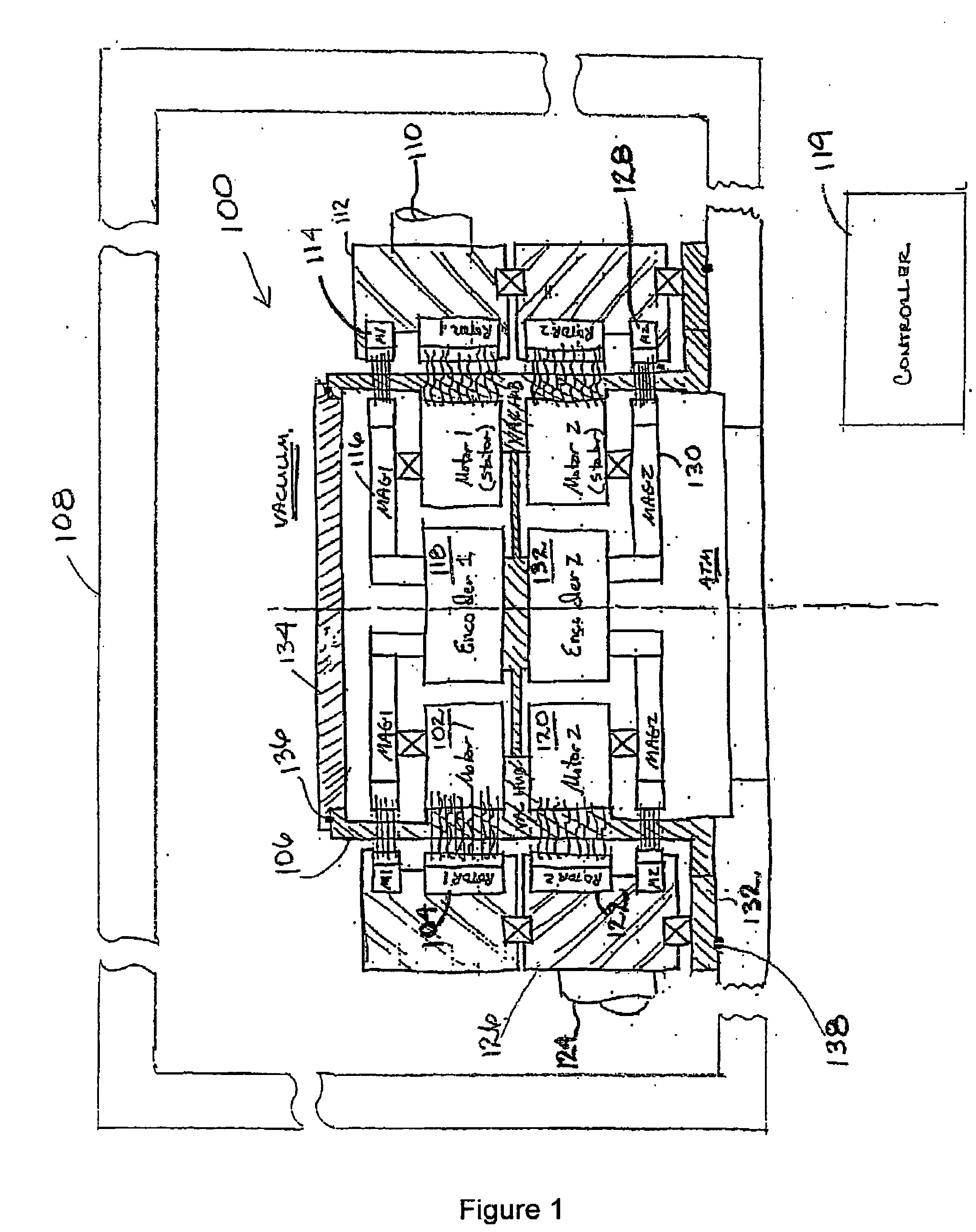
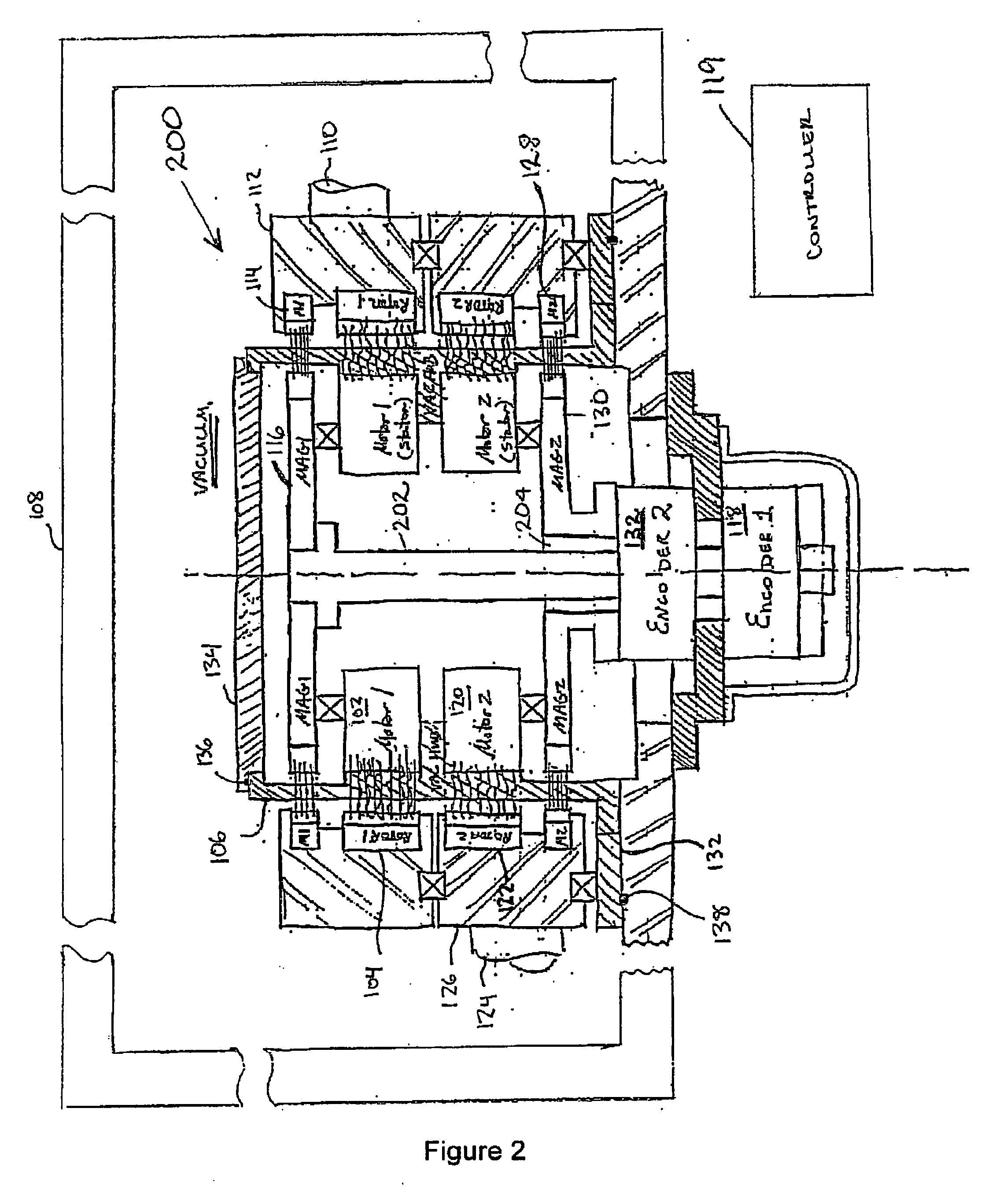
Multi-axis vacuum motor assembly
InactiveUS20060245905A1Programme-controlled manipulatorDC motor speed/torque controlElectric machineryMulti axis
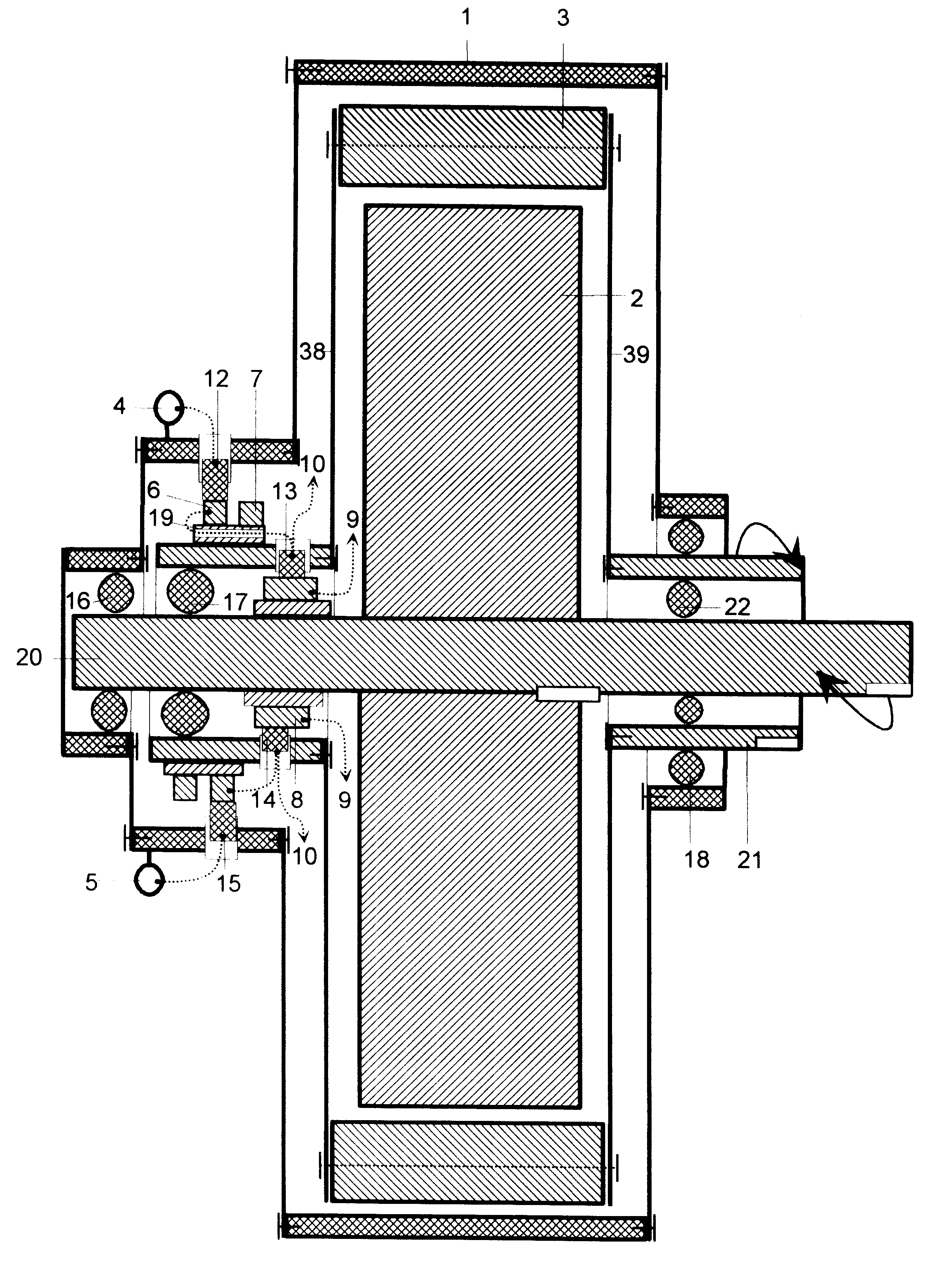
In at least one aspect, a second multi-axis vacuum motor assembly is provided. The second multi-axis vacuum motor assembly includes (1) a first rotor; (2) a first stator adapted to commutate so as to rotate the first rotor across a vacuum barrier and control rotation of a first axis of a robot arm within a vacuum chamber; (3) a second rotor below the first rotor; (4) a second stator below the first stator and adapted to commutate so as to rotate the second rotor across the vacuum barrier and control rotation of a second axis of the robot arm within the vacuum chamber; (5) a first feedback device adapted to monitor rotation of the first axis of the robot arm; and (6) a second feedback device adapted to monitor rotation of the second axis of the robot arm. Numerous other aspects are provided.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Circumferential confronting type motor
InactiveUS6580190B2Low costAddress rising pricesMagnetic circuit rotating partsRecord information storageMagnetElectric motor
A circumferential confronting type motor includes an armature core that has drive coils wound around its plurality of poles, and a drive magnet positioned opposite to the armature core in the radial direction. The drive magnet has a plurality of divided magnetized sections, each with a magnetic center, formed separated from each other in the axial direction by a non-magnetized section. The magnetic centers of the respective plurality of divided magnetized sections are provided in symmetrical positions with respect to a magnetic center in the axial direction of the armature core. Further, electromagnetic action between the drive magnet and the armature core causes the two to rotate relatively, while magnetic action between the plurality of divided magnetized sections and the armature core regulates their relative movements in the axial direction.
Owner:SANKYO SEIKI MFG CO LTD
Rotor-stator structure for electrodynamic machines
ActiveUS7294948B2Reduce wasteTotal current dropMagnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetic circuit stationary partsManufacturing cost reductionPath length
A rotor-stator structure for electrodynamic machinery is disclosed to, among other things, minimize magnetic flux path lengths and to eliminate back-iron for increasing torque and / or efficiency per unit size (or unit weight) and for reducing manufacturing costs. In one embodiment, an exemplary rotor-stator structure can comprise a shaft defining an axis of rotation, and a rotor on which at least two magnets are mounted on the shaft. The two magnets can be cylindrical or conical magnets having magnetic surfaces that confront air gaps. In some embodiments, substantially straight field pole members can be arranged coaxially and have flux interaction surfaces formed at both ends of those field poles. Those surfaces are located adjacent to the confronting magnetic surfaces to define functioning air gaps, which are generally curved in shape.
Owner:REGAL BELOIT AMERICA
Automatic power generation light-image fan device
An automatic power-generation light-image fan device is described. It has a fan motor, a vane set, a circuit board, a programmable chip, an automatic power-generation component, a rectifier filter circuit, a magnetic sensor and a positioning magnet. In this device, the circuit board is mounted on the vanes of the vane set and also has plural light-emitting elements, which are respectively connected to I / O terminals of the programmable chip, and an accommodating room is mounted on an inner surface of the vane set, in which an inner circular surface of the accommodating room is circularly mounted by an inductance coil whose ends are connected to an input terminal of the rectifier filter circuit. Thereby, the light-emitting elements mounted on the fan can be controlled to generate various different twinkling light-image variations and an effect of persistence of vision when the fan motor is rotating.
Owner:FANG YI FENG
Small DC motor
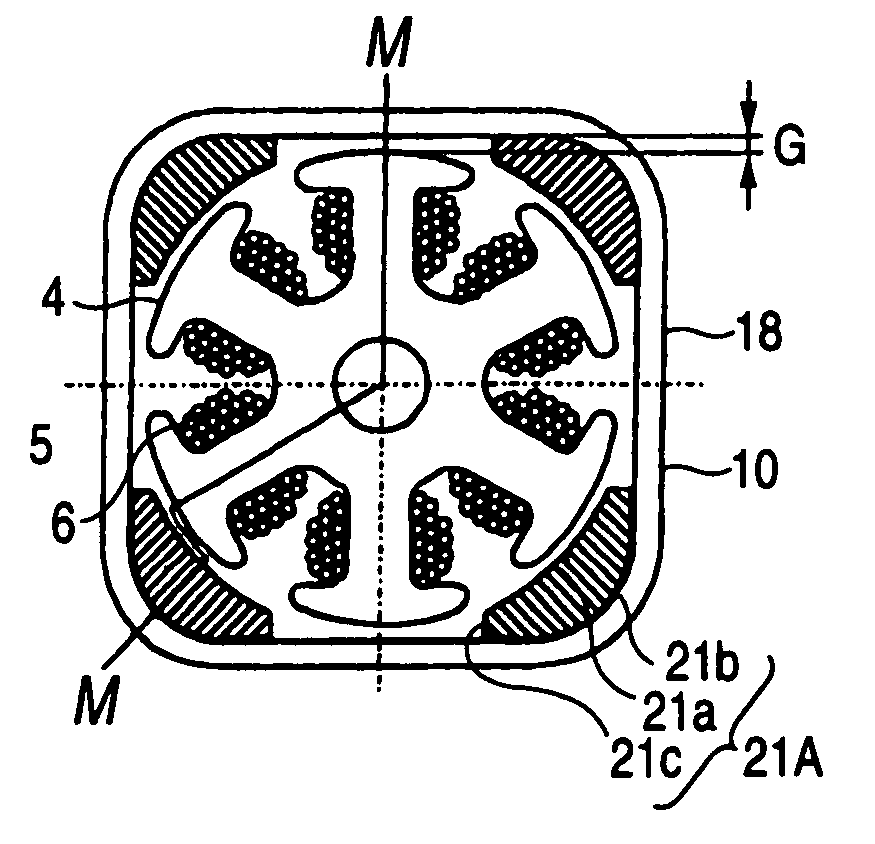
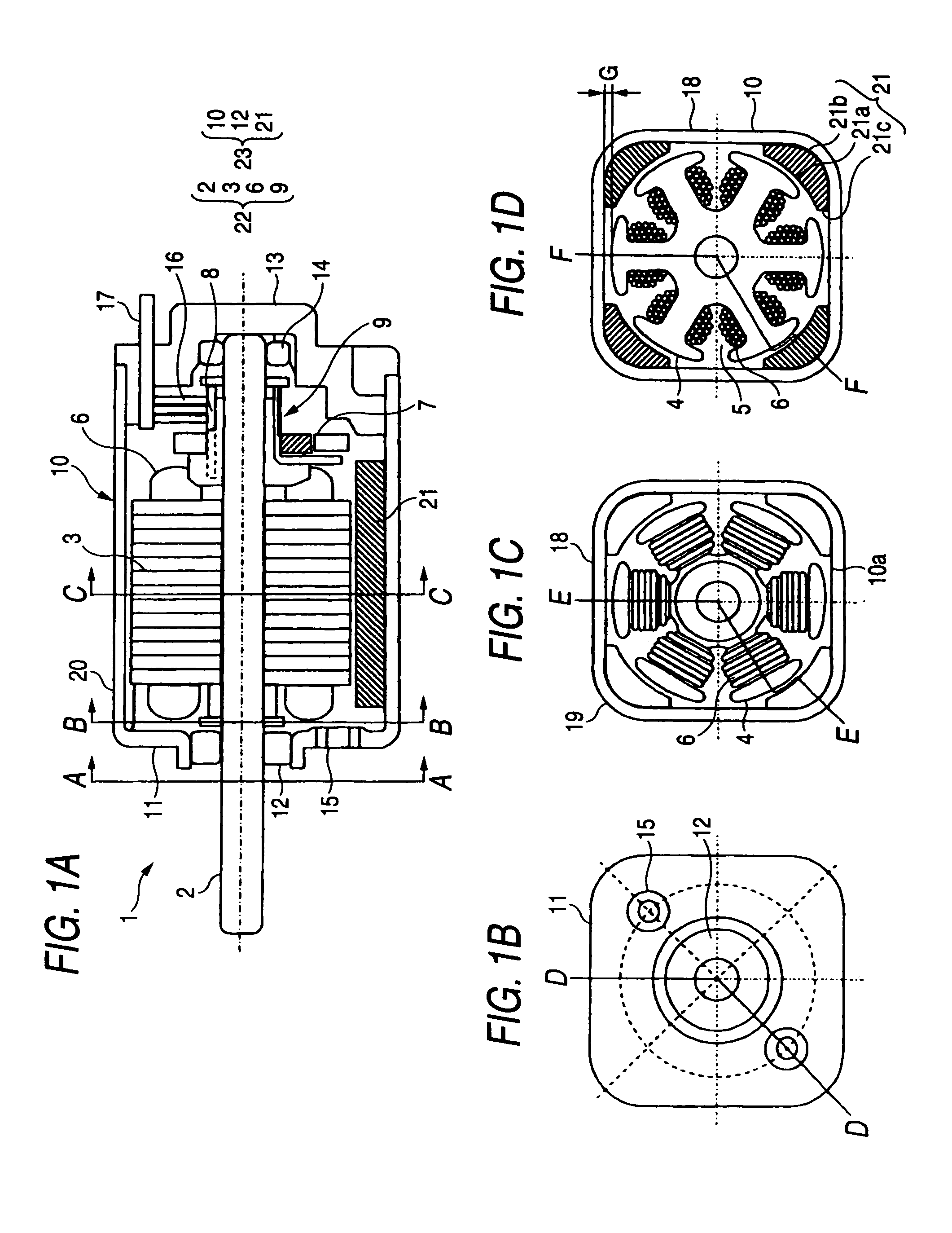
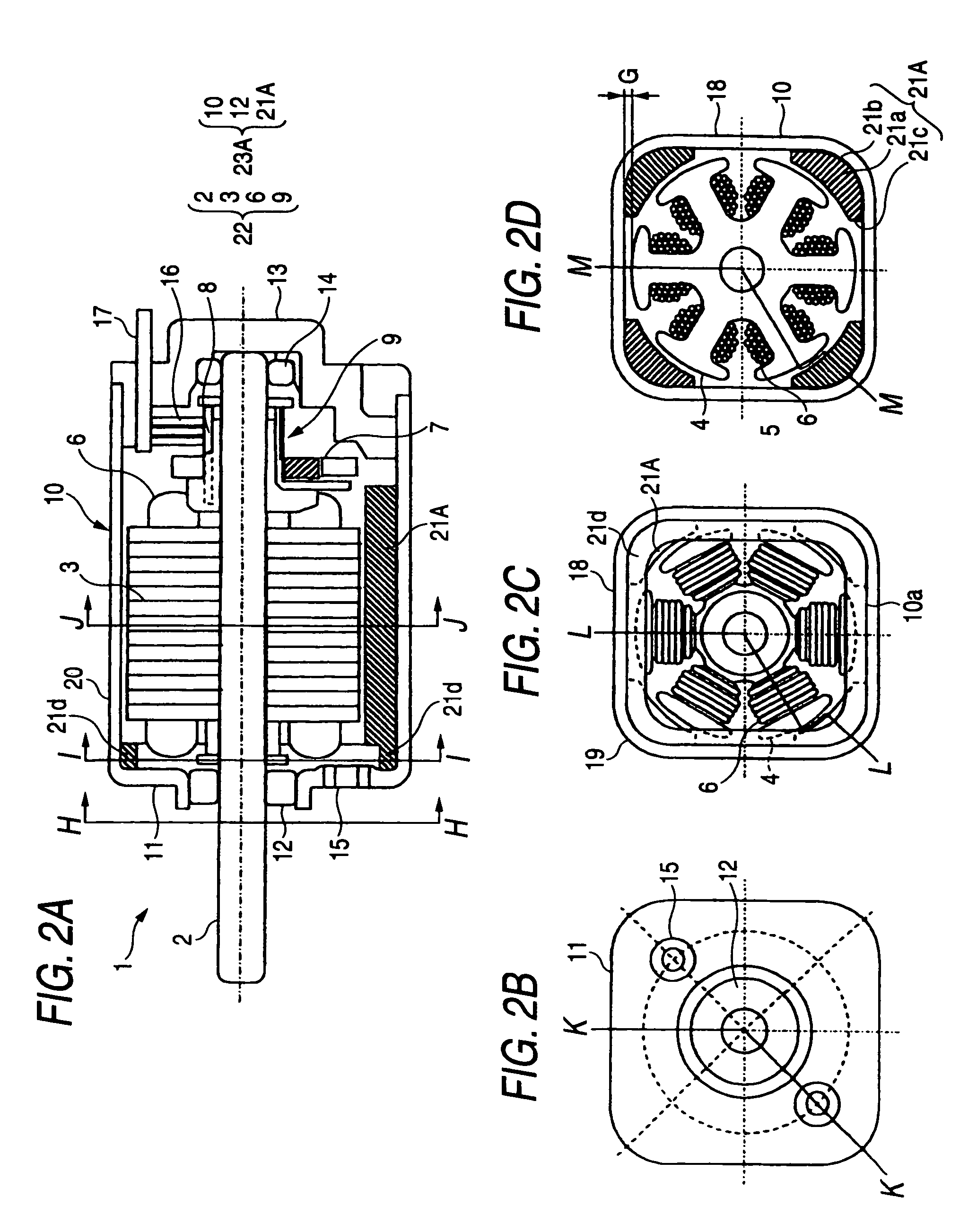
ActiveUS7498706B2Efficient assemblyTorque to be generated can be increasedElectrostatic generators/motorsDC commutatorEngineeringDC motor
A small DC motor includes: a motor frame including a cylindrical portion, the cylindrical portion having a constant thickness and having a cross section in a shape that includes four sides and connecting portions, each of the connecting portions connecting adjacent two of the four sides and being located inward from a corresponding corner in a quadrangle including the four sides; field magnets; and an armature assembly, wherein the field magnets are provided so as to be spaced apart from each other, and the small DC motor includes an air gap between each of the four sides and a radially outermost surface of the armature assembly, the air gap being a minimum size needed to rotate the armature assembly.
Owner:MINEBEA MOTOR MFG
Method and electric motor with rotational stator
An electric composite rotating machine haveing two rotors, capable of developing mechanical power and of runing on two rotational direction at selfadjutable speeds, of differential type, with 40% increase of output, doubling the torque at 30% reduction of used electrical energy.
Owner:CHERCIU TRAIAN
Method and apparatus for coil-less magnetoelectric magnetic flux switching for permanent magnets
InactiveUS6946938B1Improve magnetic flux characteristicSynchronous motorsPermanent magnetsMagnetic fluxMagnet
Methods and apparatus that employ a coil-less magnetoelectric flux switch arrangement to repeatedly switch magnetic flux from at least one permanent magnet for the purposes of generating motive force and / or electrical energy.
Owner:PEDERSEN BRAD D
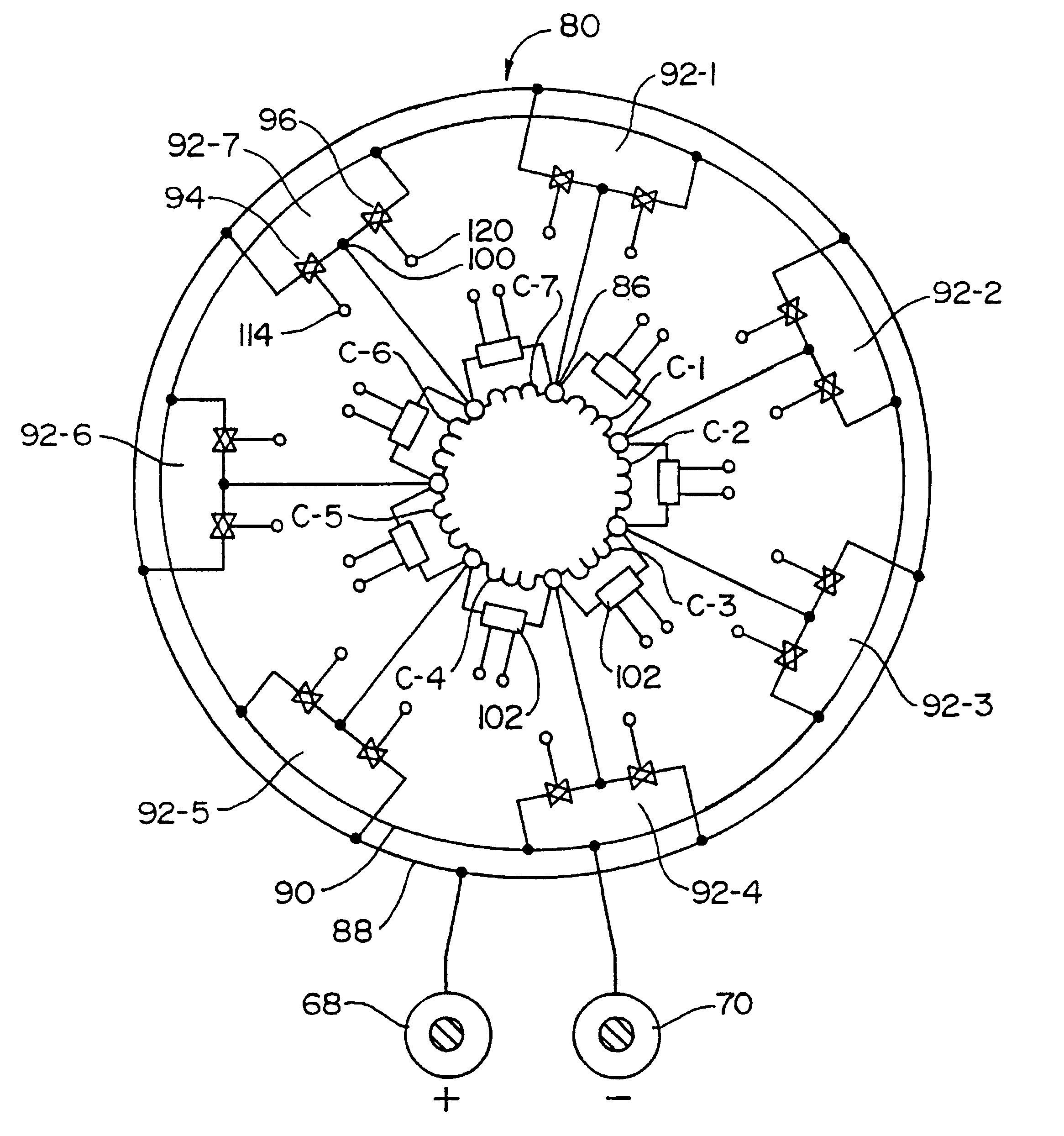
Dynamo-electric machines and control and operating system for the same
InactiveUS6222331B1Motor/generator/converter stoppersSynchronous motors startersElectric machineDc current
A dynamo-electric machine which can function as a motor or a generator. The machine comprising a stator and an armature, and switching of the armature coils is accomplished by means of a switching control assembly which is mounted to, and rotates with, the armature. In operation as a motor, direct current is supplied through brushes to slip rings that rotate with the armature, and the DC current supplied is first passed through switch means in the control assembly to deliver the current in properly timed relationship with respect to the rotation of the rotor. This provides greater versatility in the operation of the motor / generator and eliminates many of the problems related to the use of conventional brush commutation commonly used in present day DC motors and generators.
Owner:GRUND MOTORWERKS
Permanent magnet element and electric machine
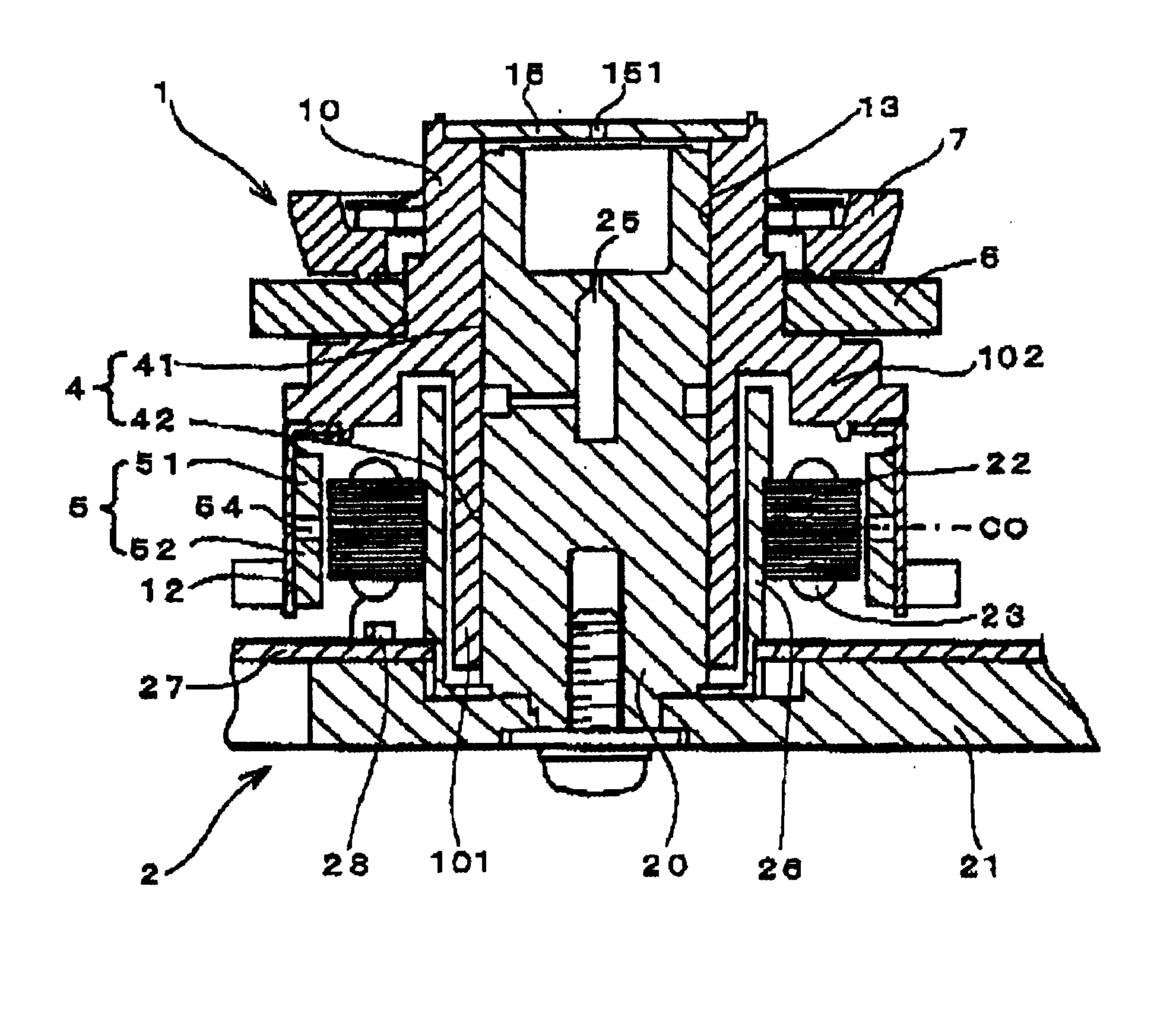
InactiveUS7030530B2Easy to installSimple and reliable processMagnetic circuit rotating partsPermanent magnetsElectric machineMagnet
A permanent magnet element intended especially for electrotechnical devices and an electric machine, the element (1) comprising at least one permanent magnet piece (10). The permanent magnet element (1) also comprises a protective cover (11) that is arranged to partly surround the permanent magnet pieces (10) arranged in the element, and the permanent magnet element (1) also comprises one or more fastening elements (13; 21).
Owner:ABB TECH AG
Rotor structure
ActiveUS20090001826A1Magnetic circuit rotating partsAsynchronous induction motorsMaximum diameterAdhesive
A rotor includes: a magnet having a circular cylinder shape and having a hole formed through its axial center, wherein the hole has in axial cross section a regular polygonal shape having flat portions and angle portions, and wherein a recess having a truncated cone shape is disposed at an axial end of the magnet such that the recess has its maximum diameter portion located at the axial end and has its minimum diameter portion communicating with the hole; and a shaft fitted in the hole of the magnet, wherein the outer circumference of the shaft makes contact with the flat portions of the hole of the magnet thereby forming a plurality of gaps between the outer circumference of the shaft and the angle portions of the hole of the magnet, and adhesive is filled in the gaps.
Owner:MINEBEAMITSUMI INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com