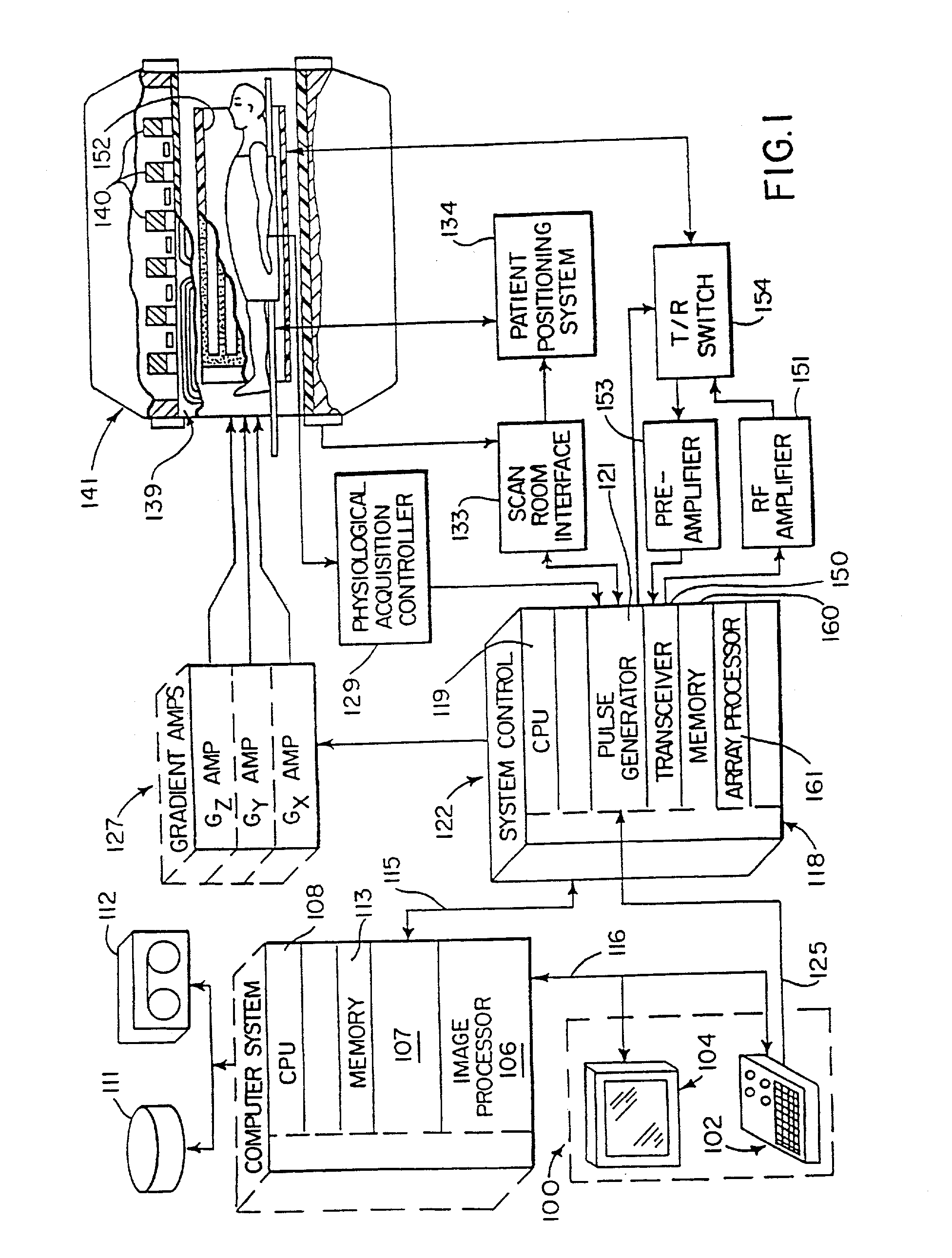
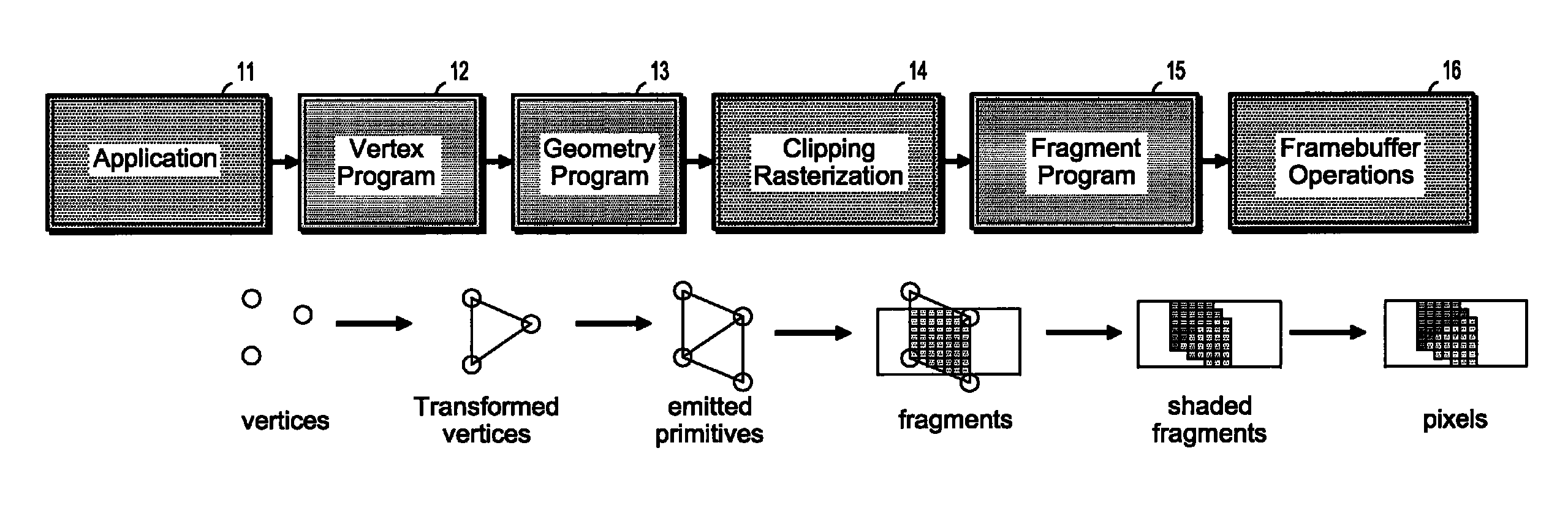
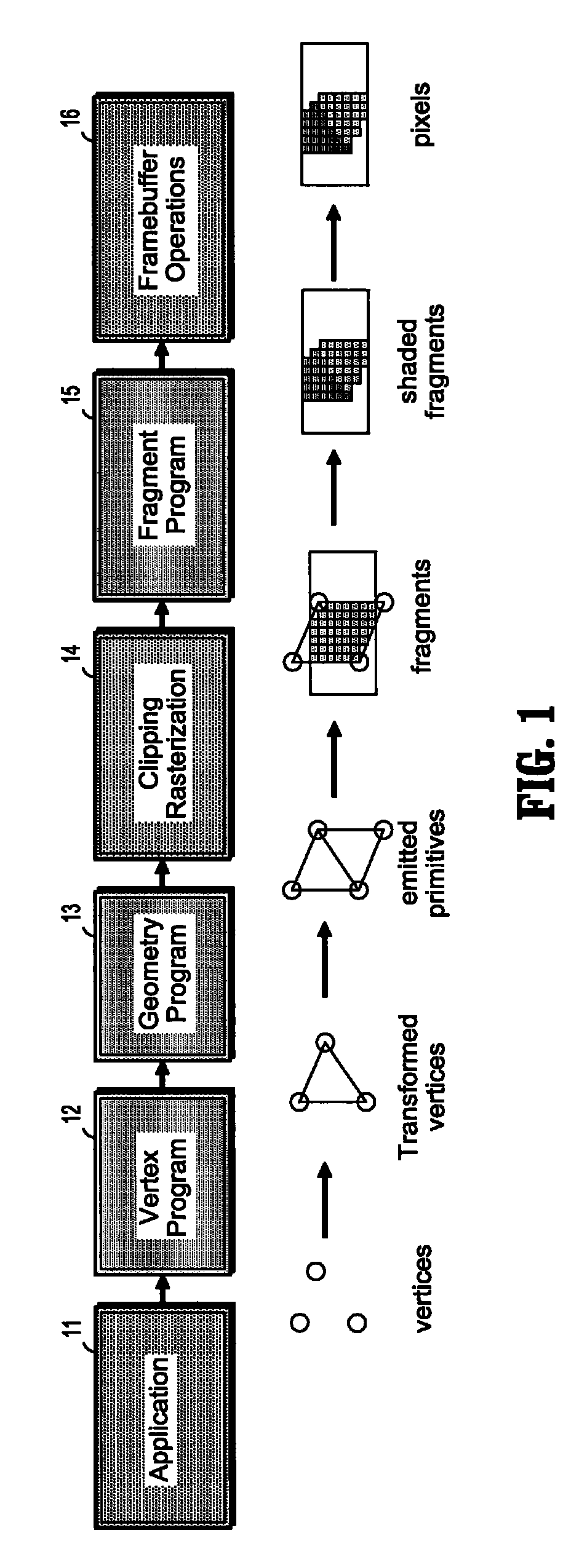
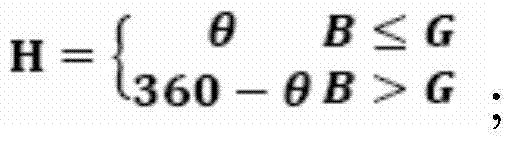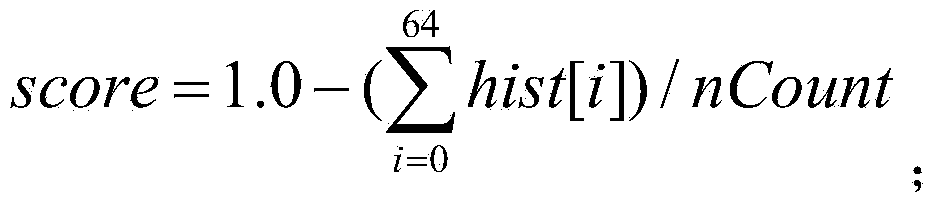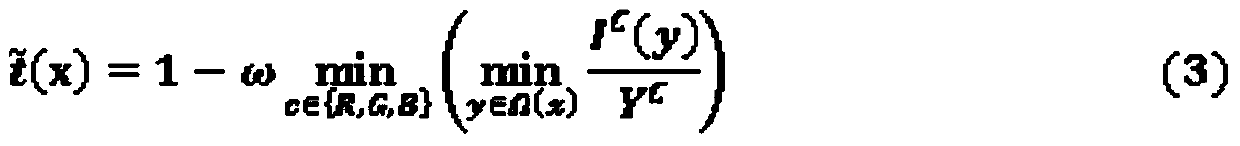Patents
Literature
52 results about "Intensity histogram" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
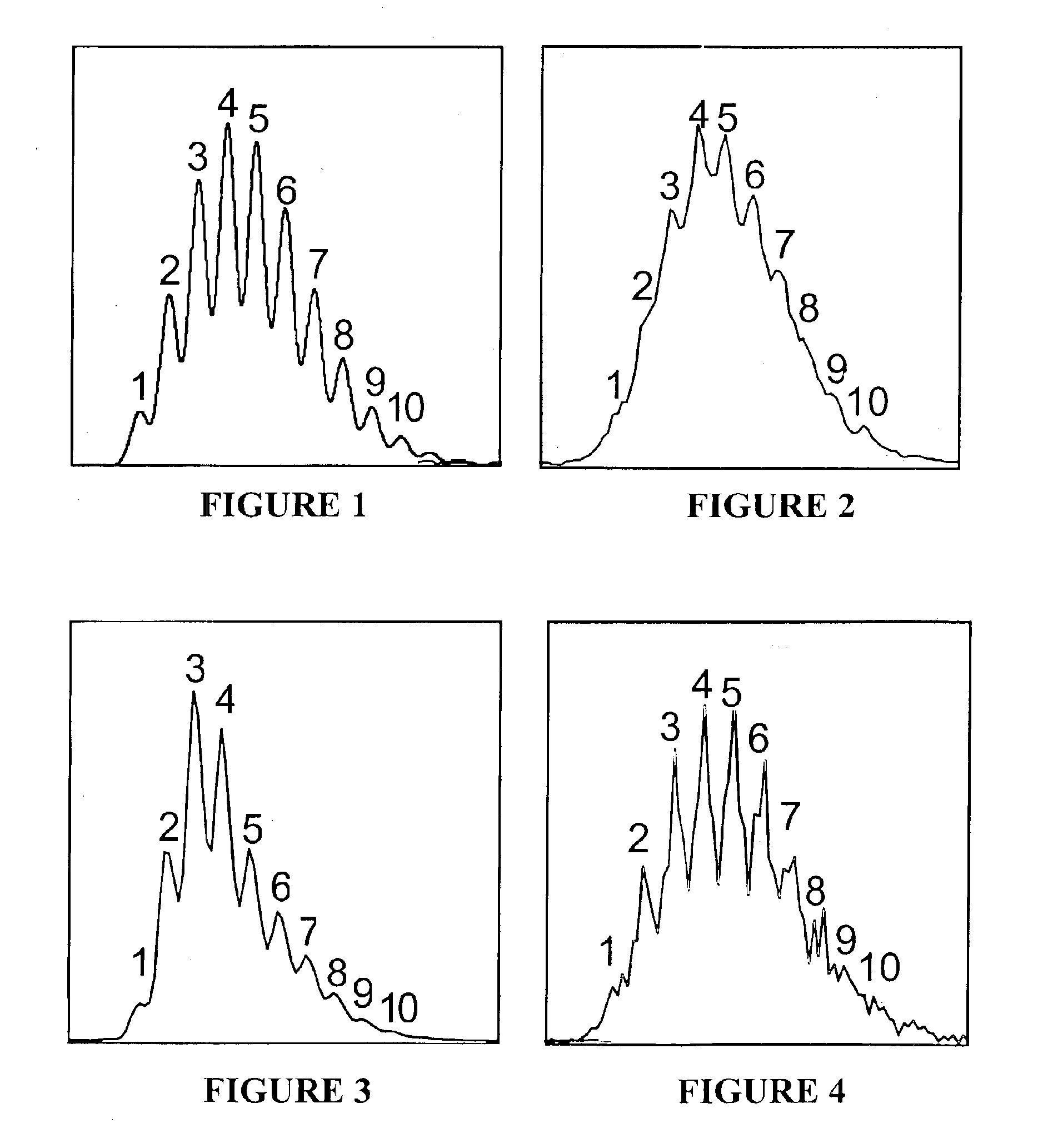
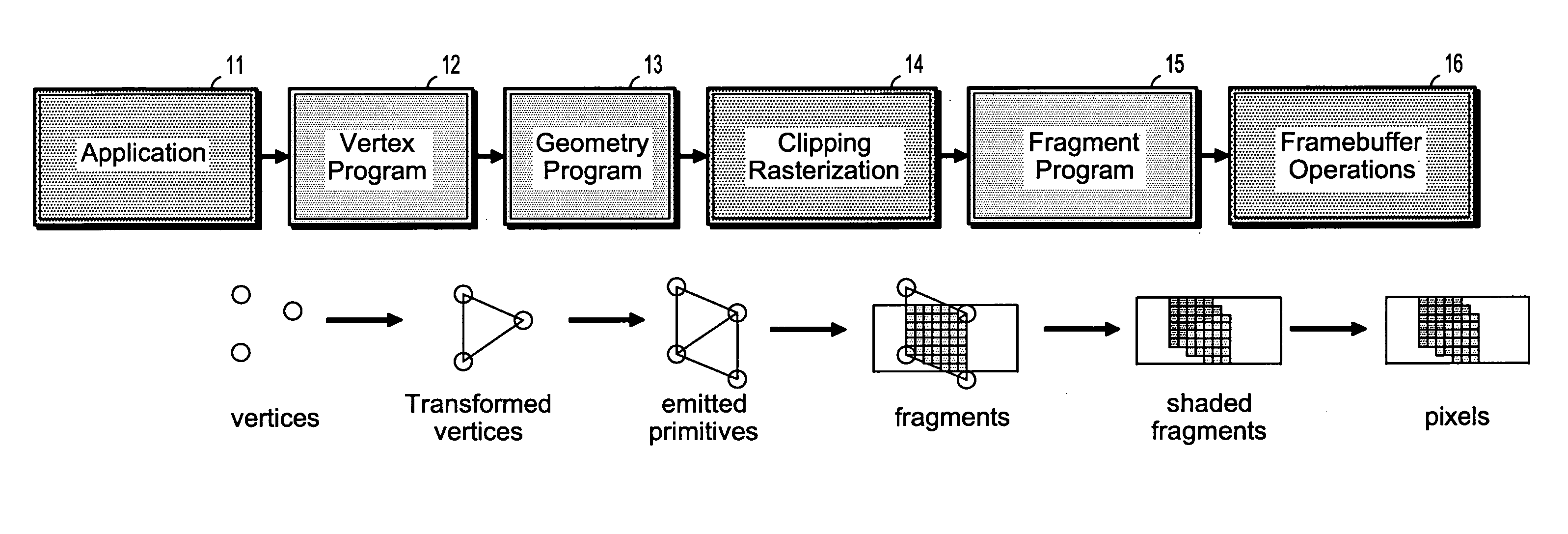
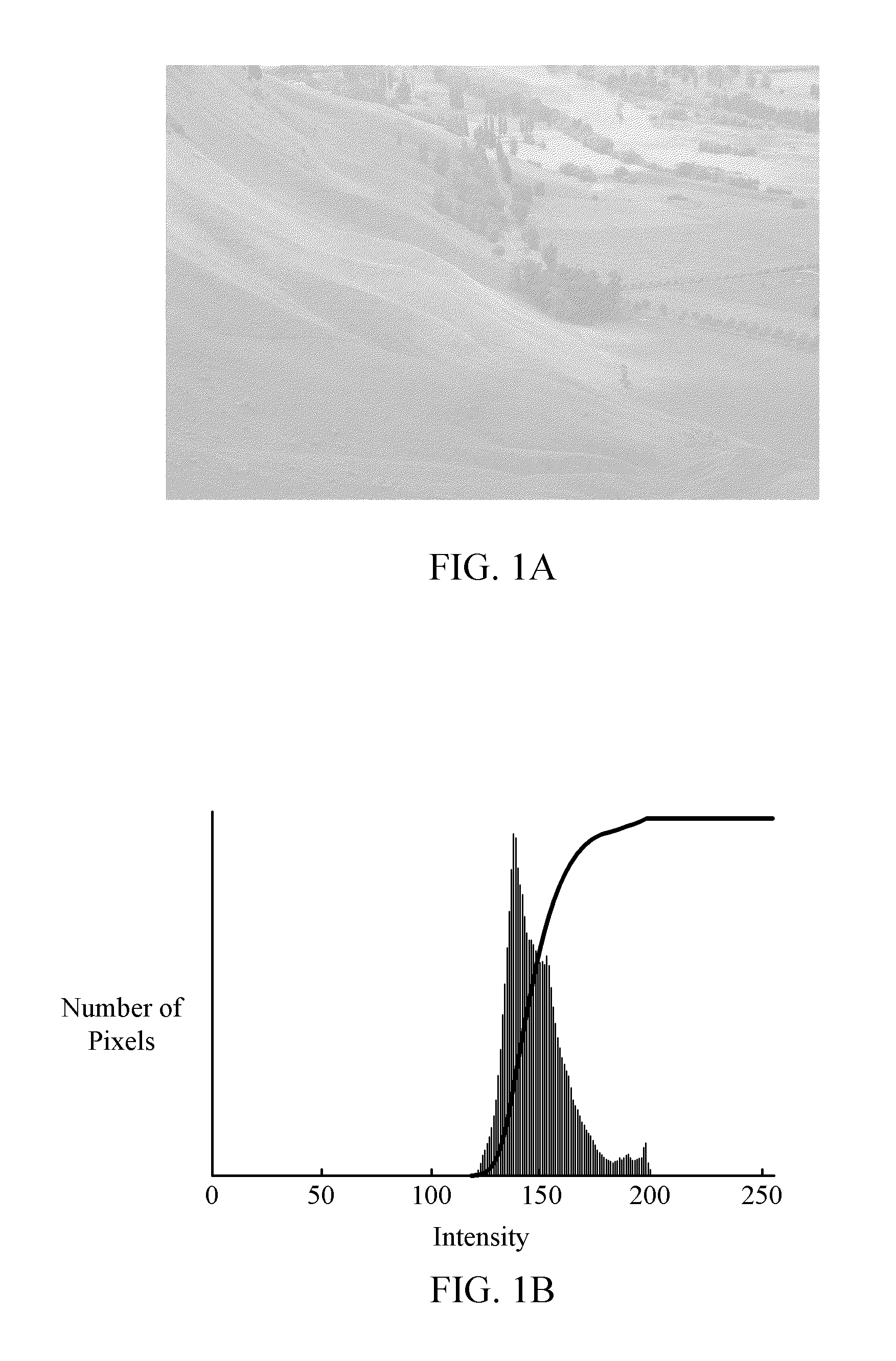
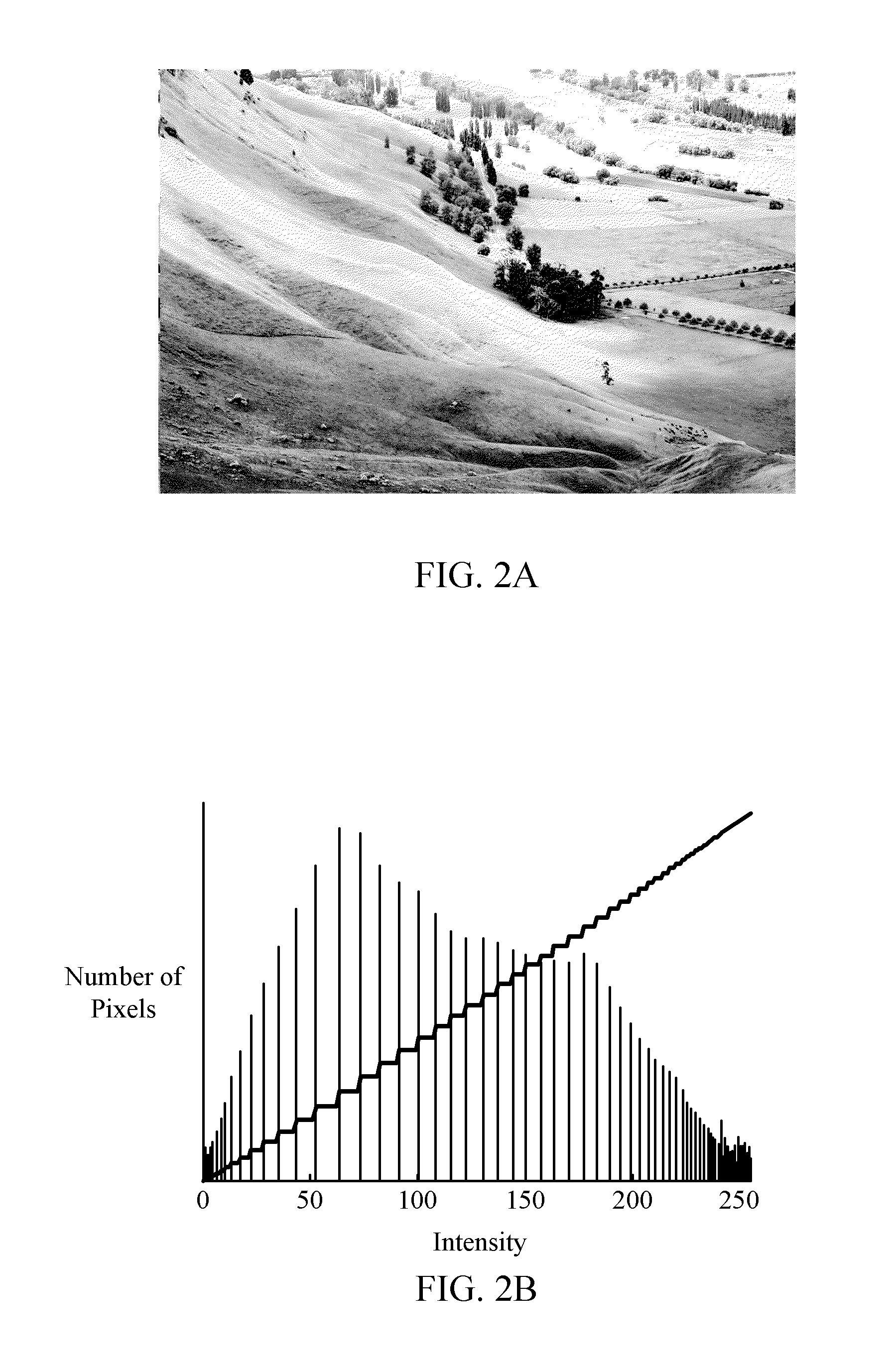
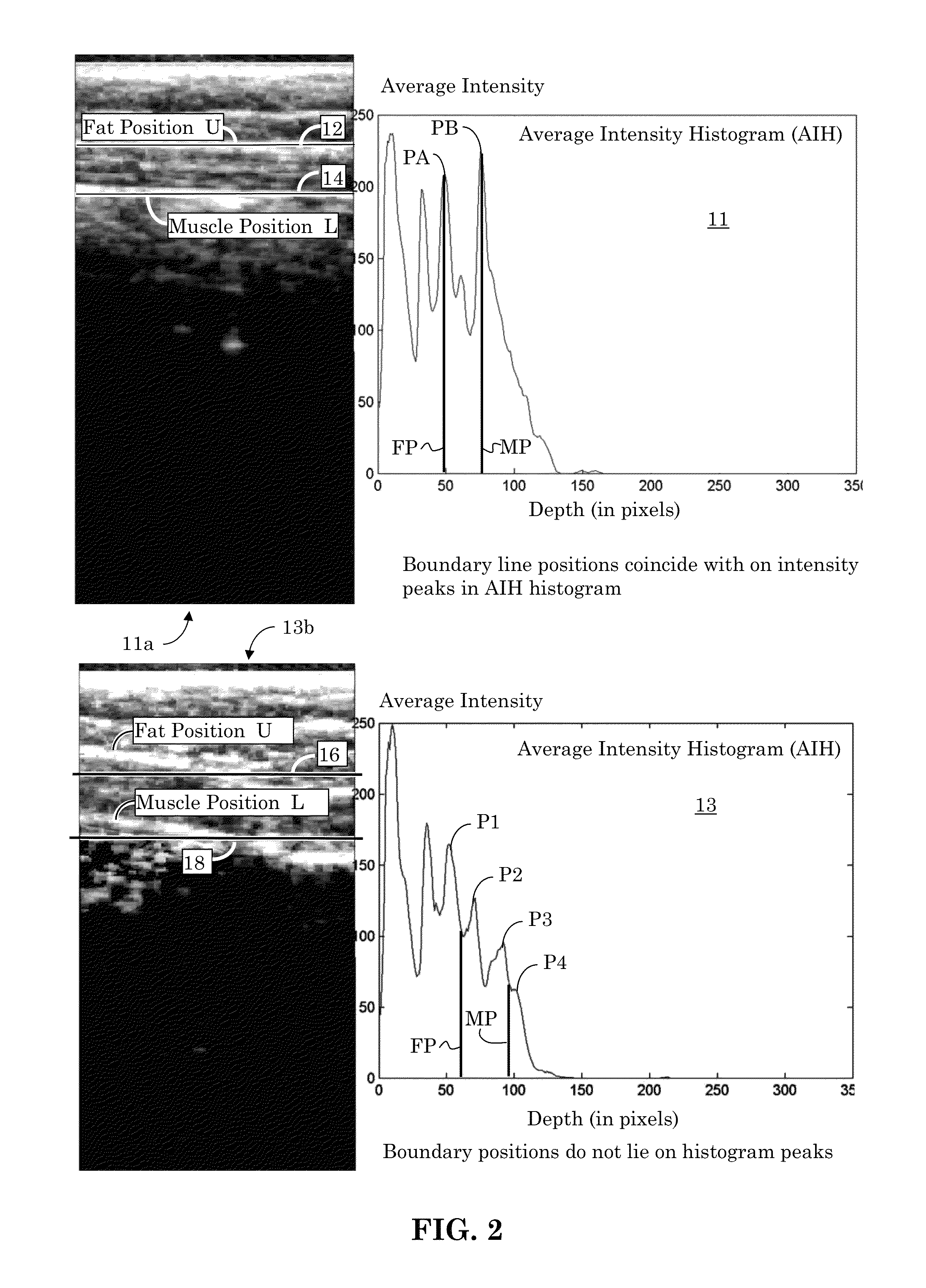
In an image processing context, the histogram of an image normally refers to a histogram of the pixel intensity values. This histogram is a graph showing the number of pixels in an image at each different intensity value found in that image.
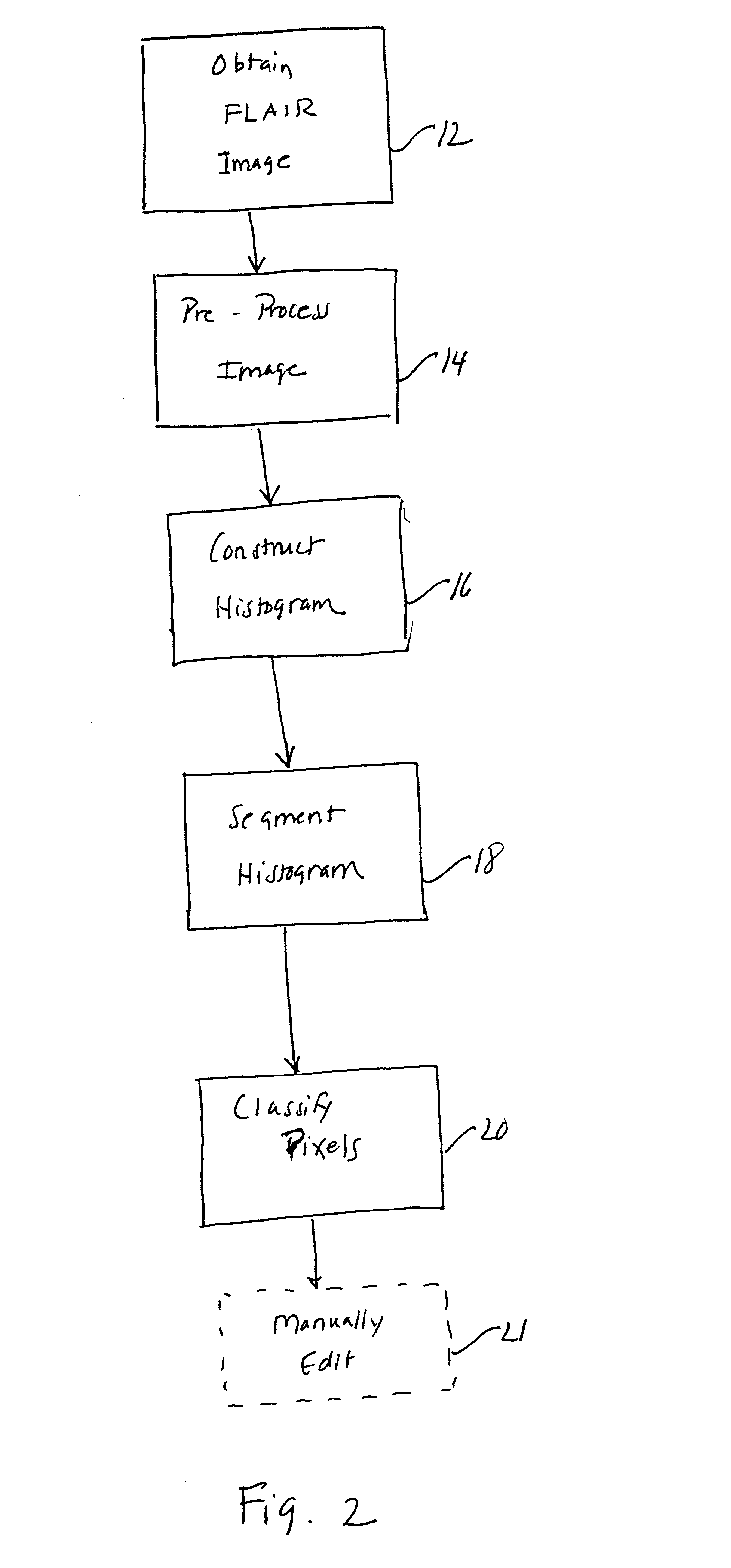
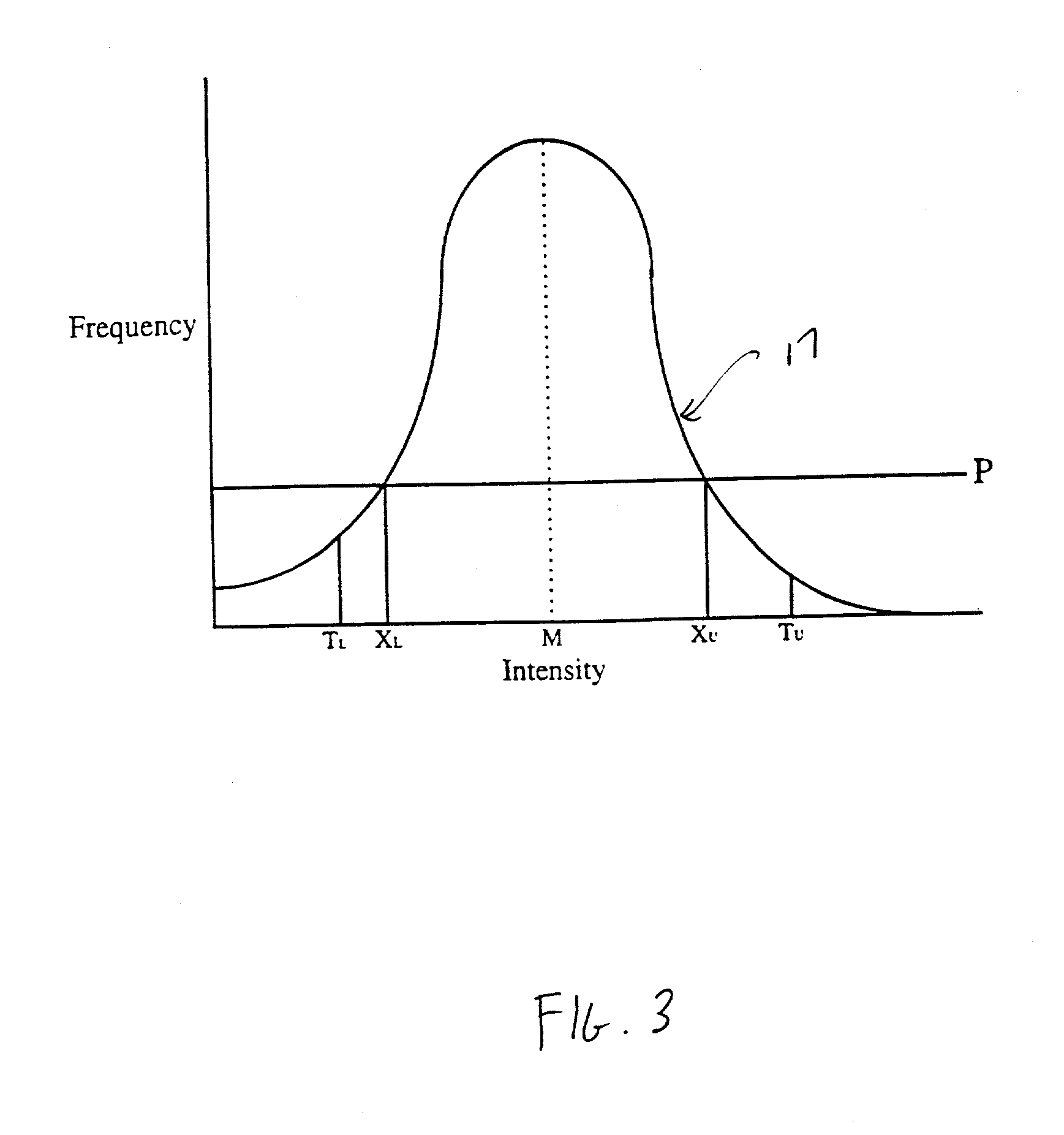
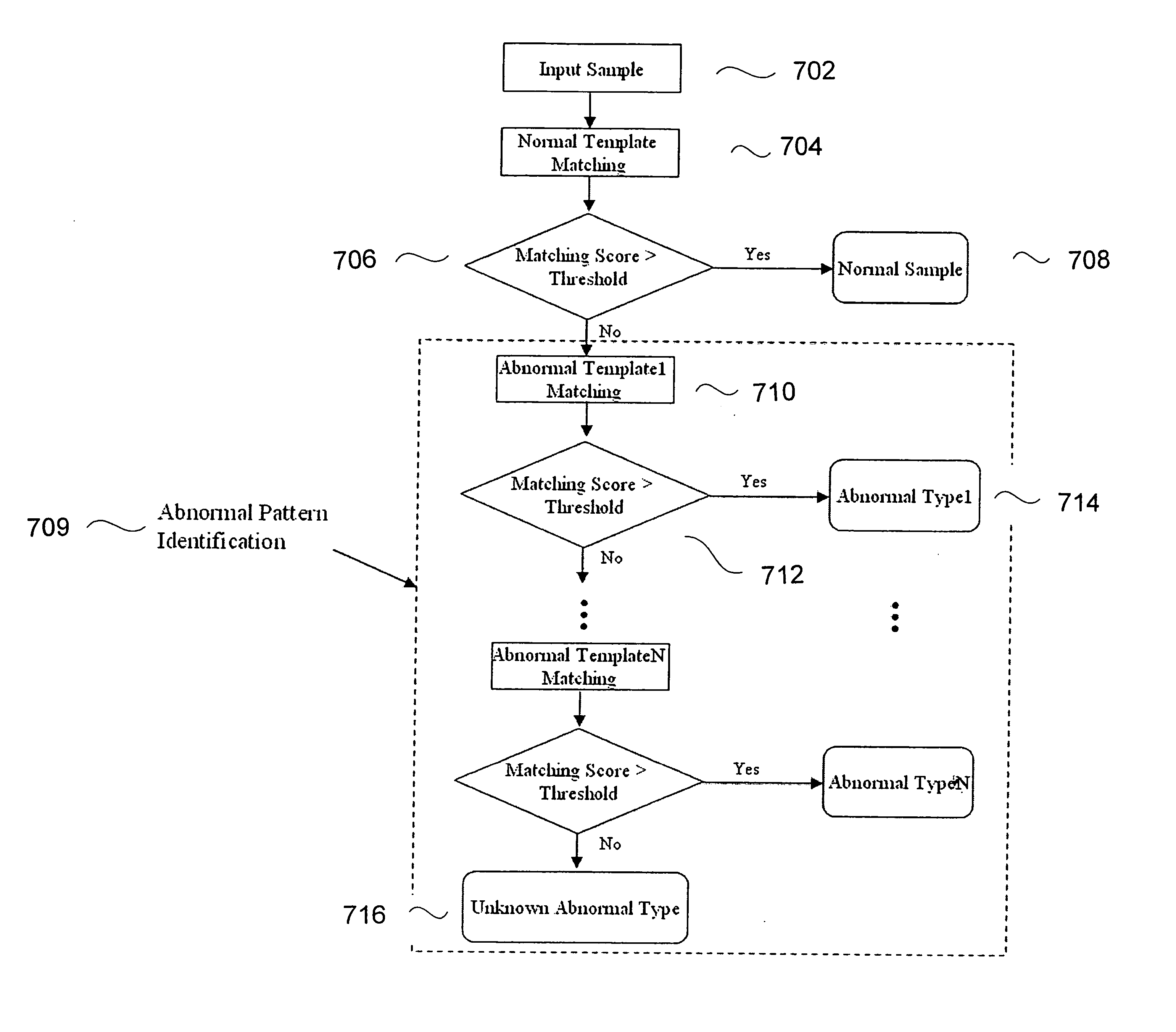
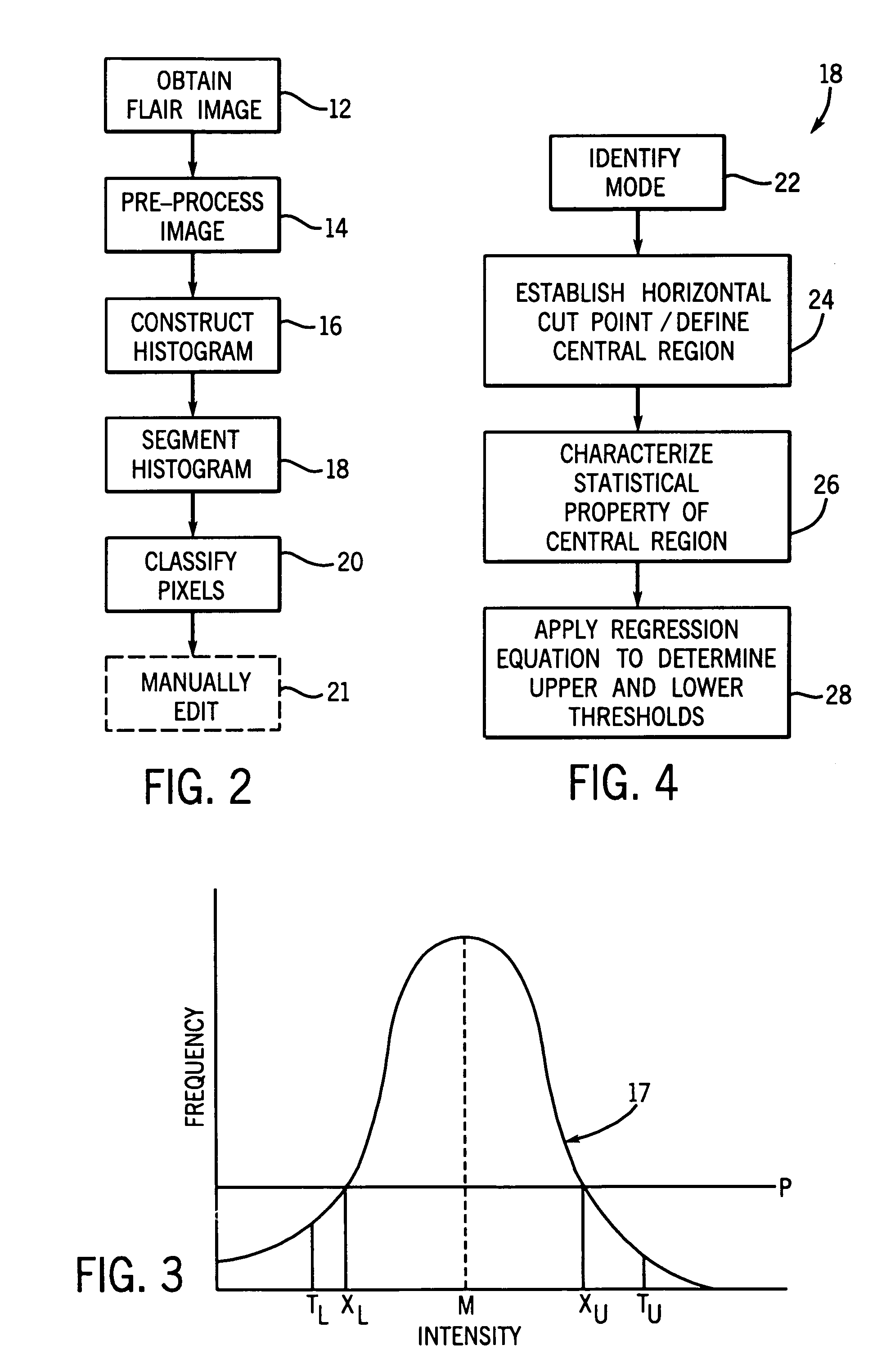
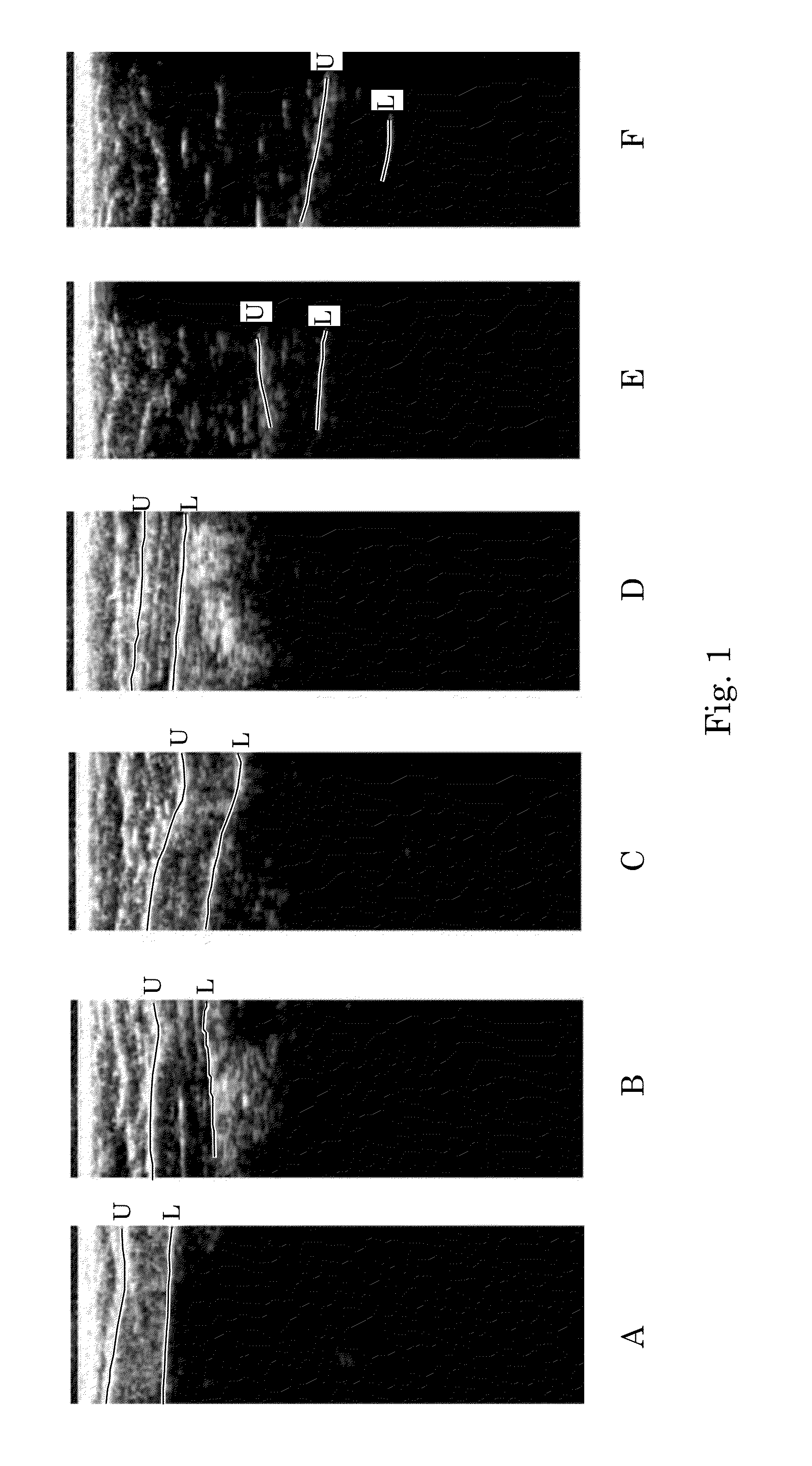
Histogram segmentation of FLAIR images
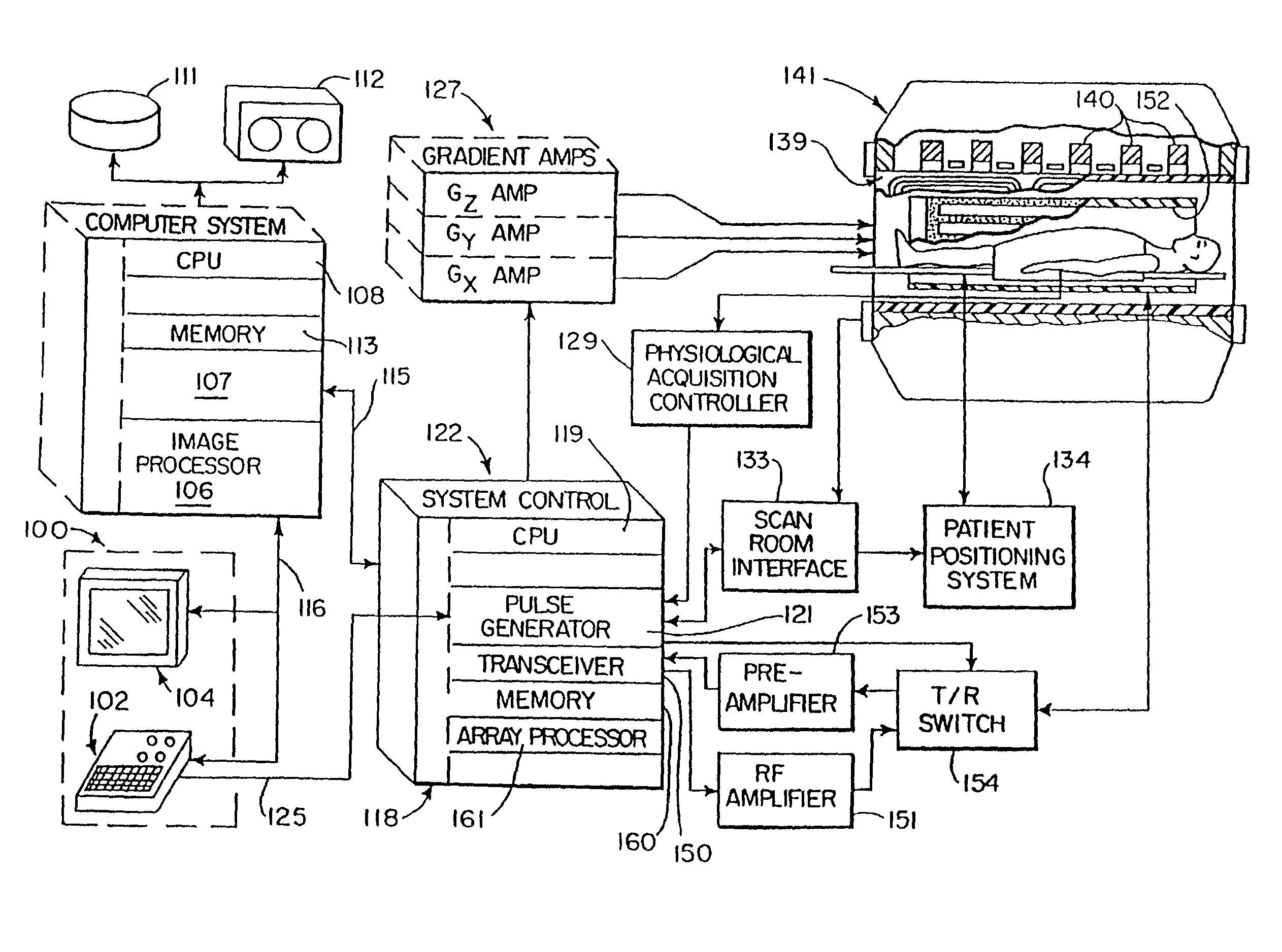
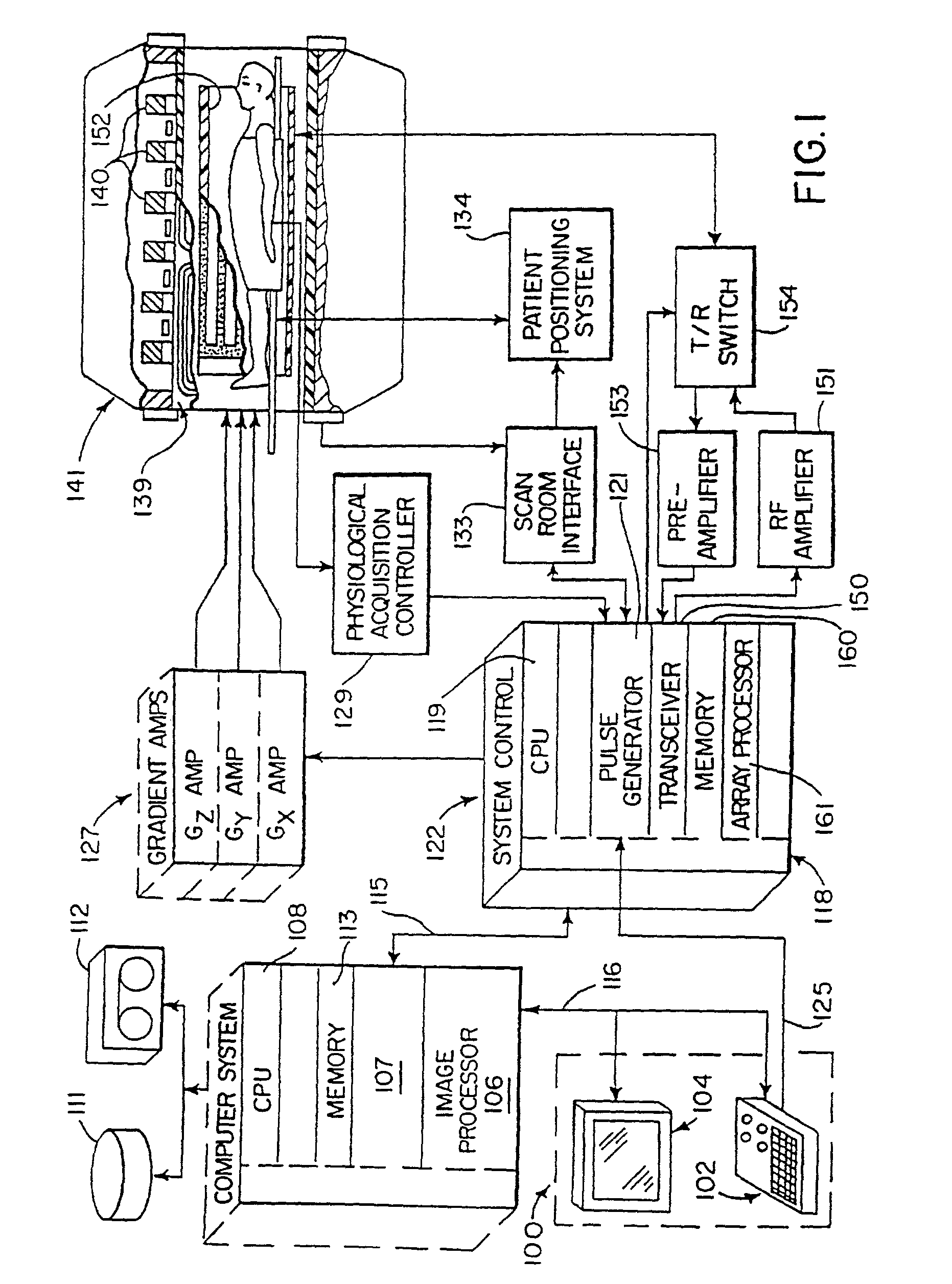
ActiveUS20030009098A1Automatically measuring the volume of tissueThe classification result is accurateImage enhancementImage analysisFluid-attenuated inversion recoveryLeukoaraiosis
A method for classifying tissue in a magnetic resonance image. and particularly for measuring a volume of pathological tissue such as white tissue hyperintensity (leukoaraiosis) in the brain based on the segmentation of the intensity histogram of fluid attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) images is described. A magnetic resonance image of the brain of a subject is acquired, and a pixel intensity histogram is constructed from the image. A statistically-based regression analysis is applied to the histogram to determine upper and lower threshold values, which define different types of brain tissue, particularly normal brain, cerebral spinal fluid (CSF), or lesion.
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES
High resolution detection for time-of-flight mass spectrometers
InactiveUS6870156B2High resolutionInhibit transferSpectrometer detectorsTime-of-flight spectrometersEngineeringMass analyzer
The invention covers a method for detecting ions in high resolution time-of-flight mass spectrometers which operate with secondary electron multiplier multichannel plates and in which many single spectra are acquired and added to produce a sum spectrum. The invention involves (a) using an analog digital converter (ADC) for converting electron currents from secondary electron multipliers, instead of a time-to-digital converter (TDC) which was previously used for highest possible signal resolution, (b) performing a separate rapid peak recognition procedure for the ion signals of each spectrum by a fast calculation method, thereby collecting flight time and intensity value pairs for the ion peaks, and (c) constructing a time-of-flight / intensity histogram, which is further processed as a composite time-of-flight spectrum. The invention retains the significantly higher measurement dynamics of an ADC and achieves the improved resolution capability of a TDC, but without showing the latter's known signal distortion due to dead times.
Owner:BRUKER DALTONIK GMBH & CO KG
System and method for global-to-local shape matching for automatic liver segmentation in medical imaging
ActiveUS20090052756A1Improve robustnessPreserve topologyImage enhancementImage analysisIntensity histogramMedical imaging
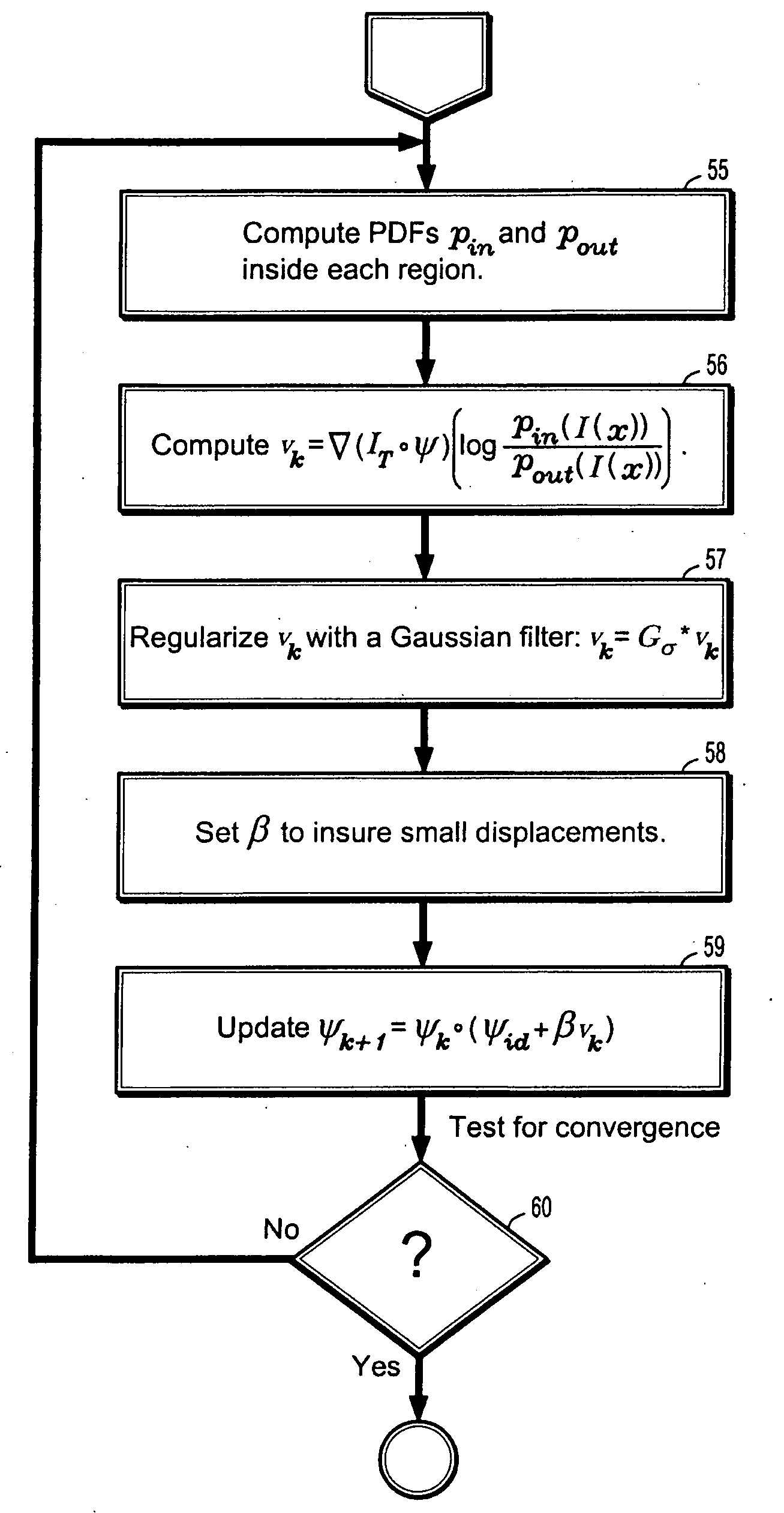
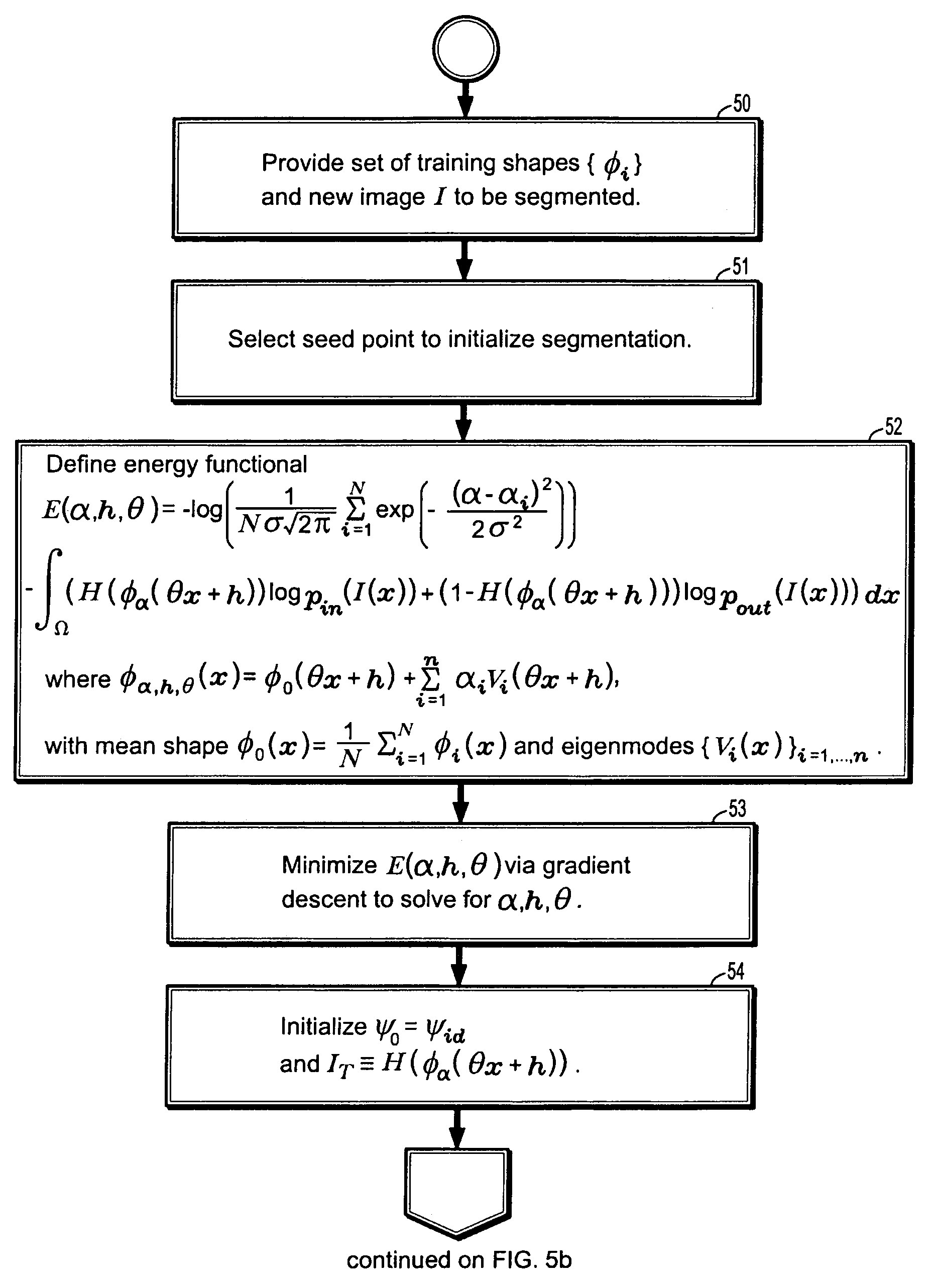
A method for automatically segmenting a liver in digital medical images includes providing a 3-dimensional (3D) digital image I and a set of N training shapes {φi}i=1, . . . , N for a liver trained from a set of manually segmented images, selecting a seed point to initialize the segmentation, representing a level set function φα(θx+h) of a liver boundary Γ in the image asφα(x)=φ0+∑i=1nαiVi(x),whereφ0(x)=1N∑i=1Nφi(x)is a mean shape, {Vi(x)}i=1, . . . , n are eigenmodes where n<N, αi are shape parameters, and h ε R3 and θε [0,2π]3 are translation and rotation parameters that align the training shapes, minimizing a first energy functional to determine the shape, translation, and rotation parameters to determine a shape template for the liver segmentation, defining a second energy functional of the shape template and a registration mapping weighted by image intensity histogram functions inside and outside the boundary, and minimizing the second energy functional to determine the registration mapping, where the registration mapping recovers local deformations of the liver.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Methods and Apparatus for Analysing Ultrasound Images
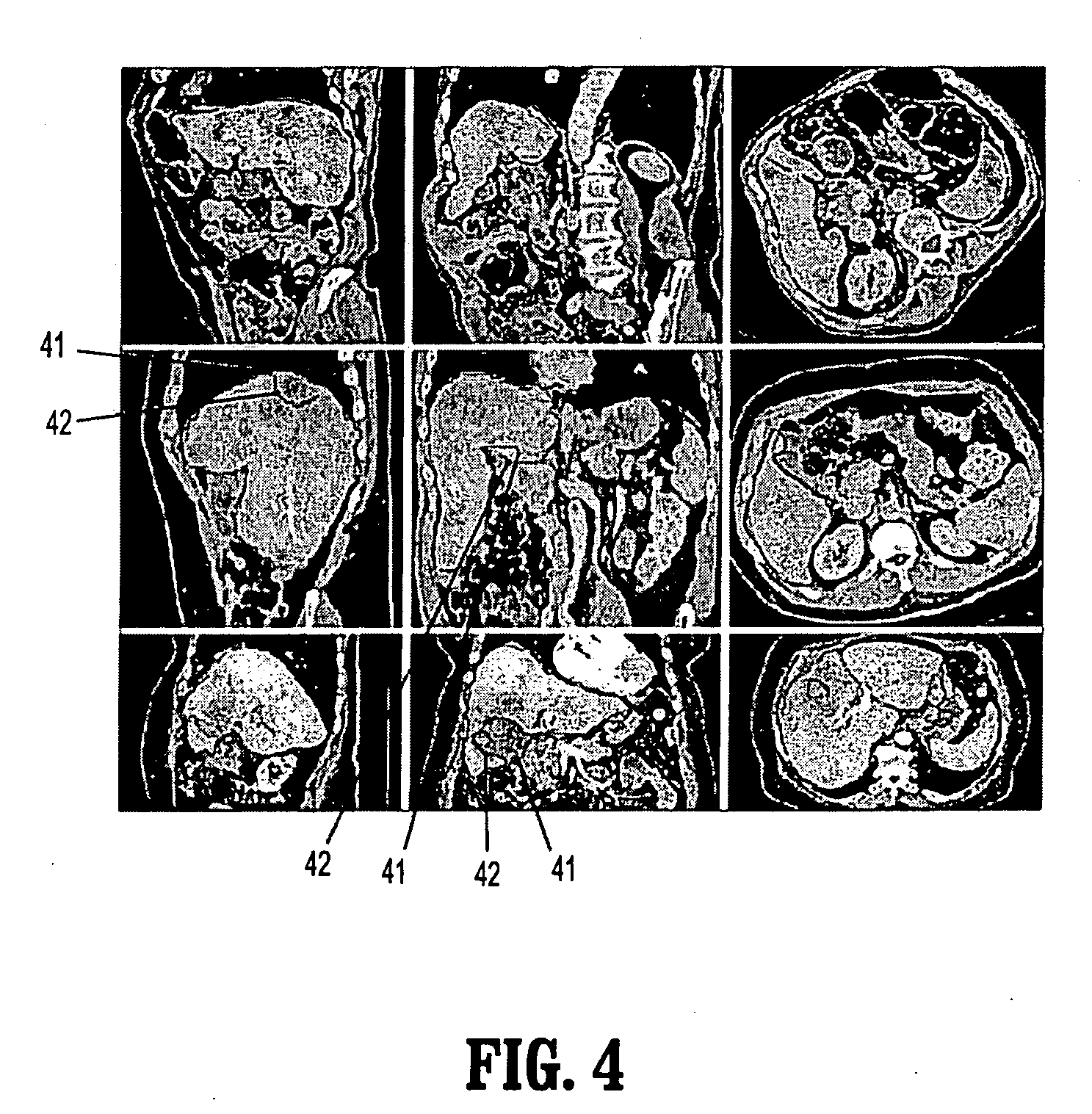
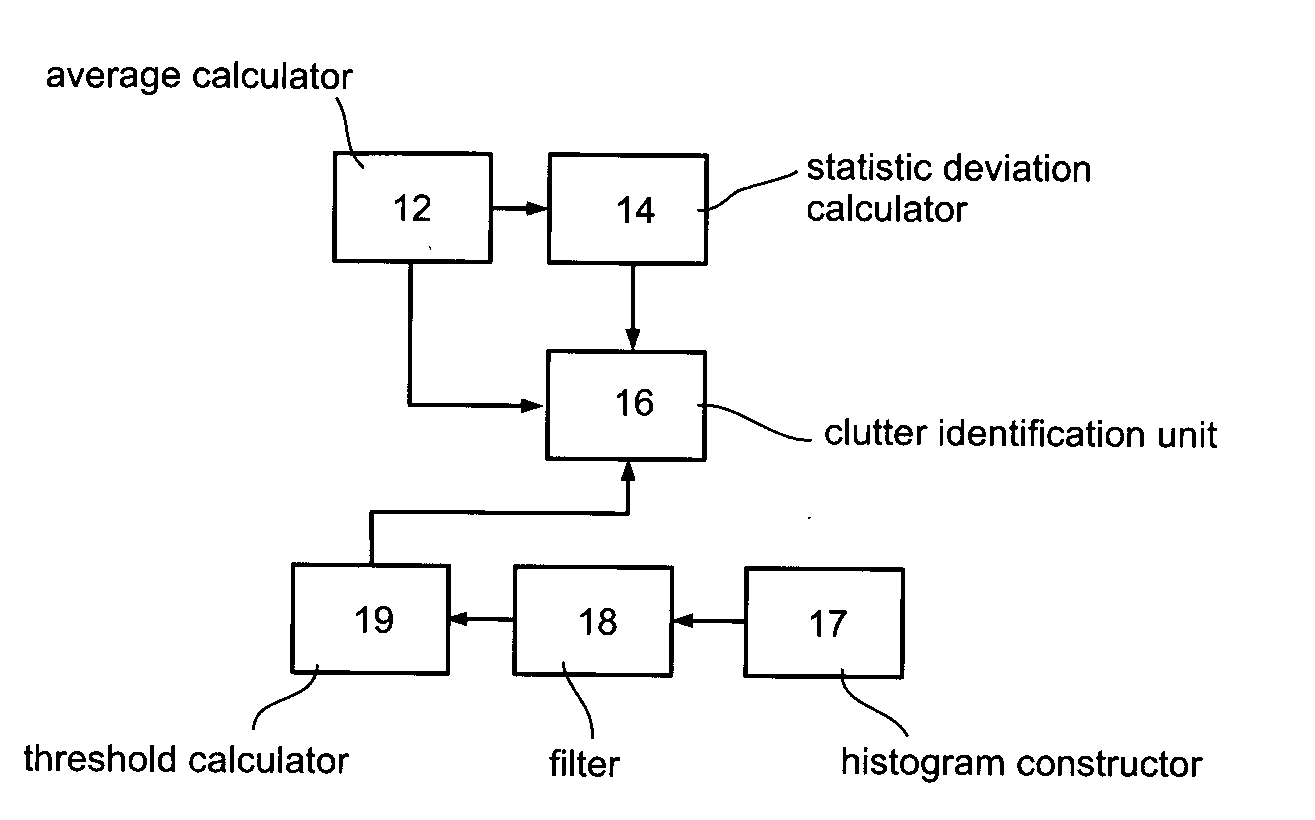
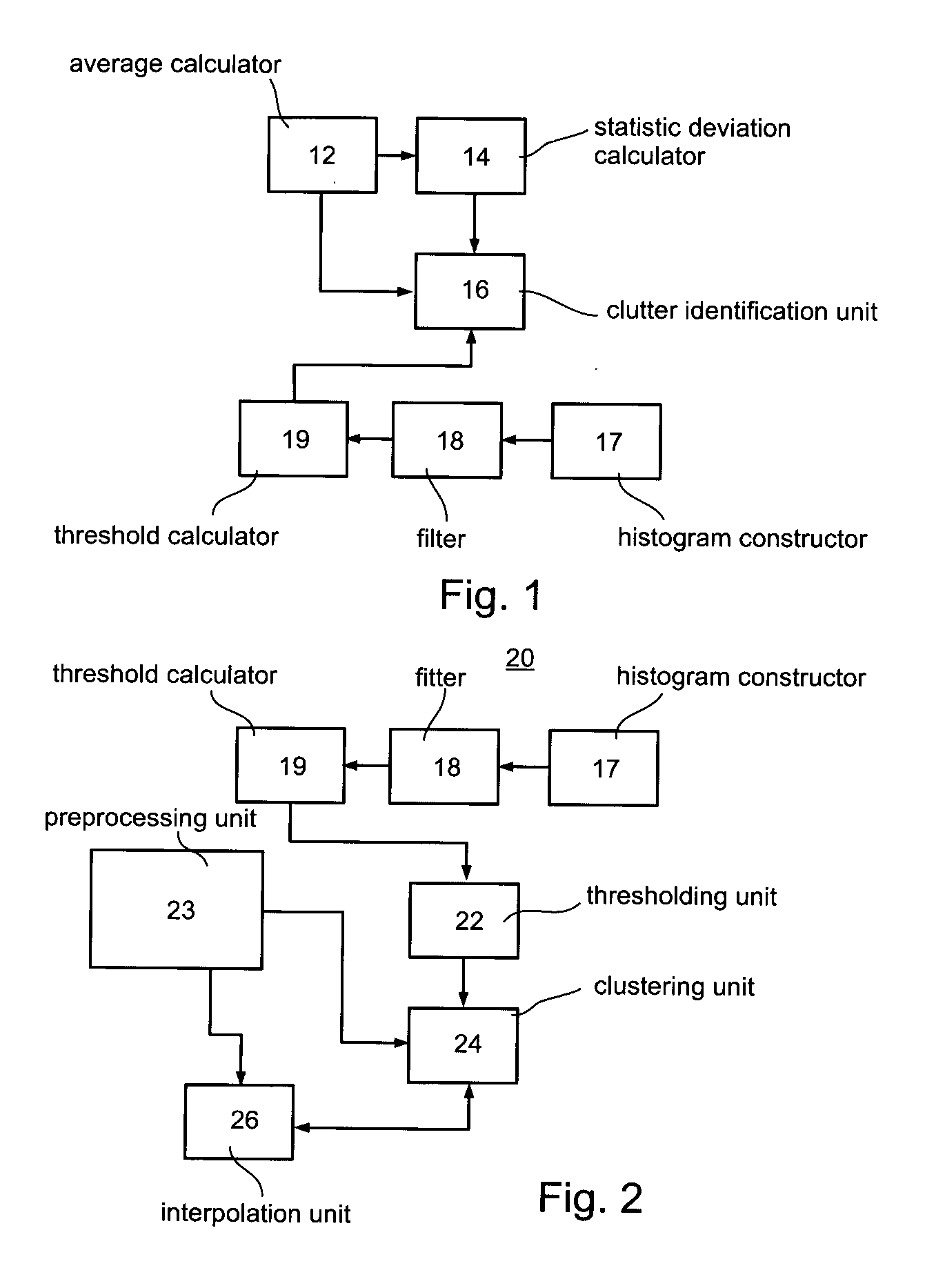
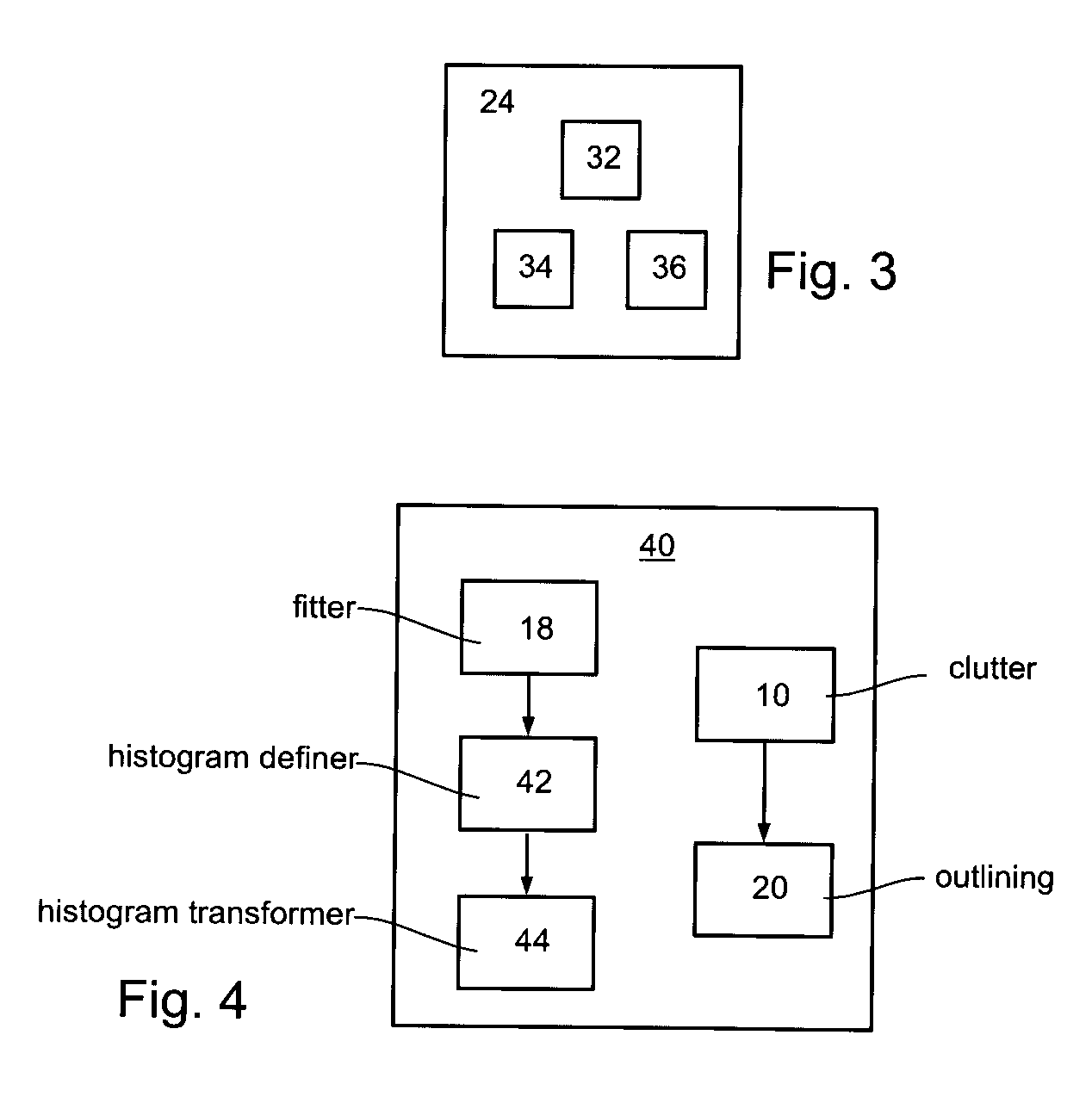
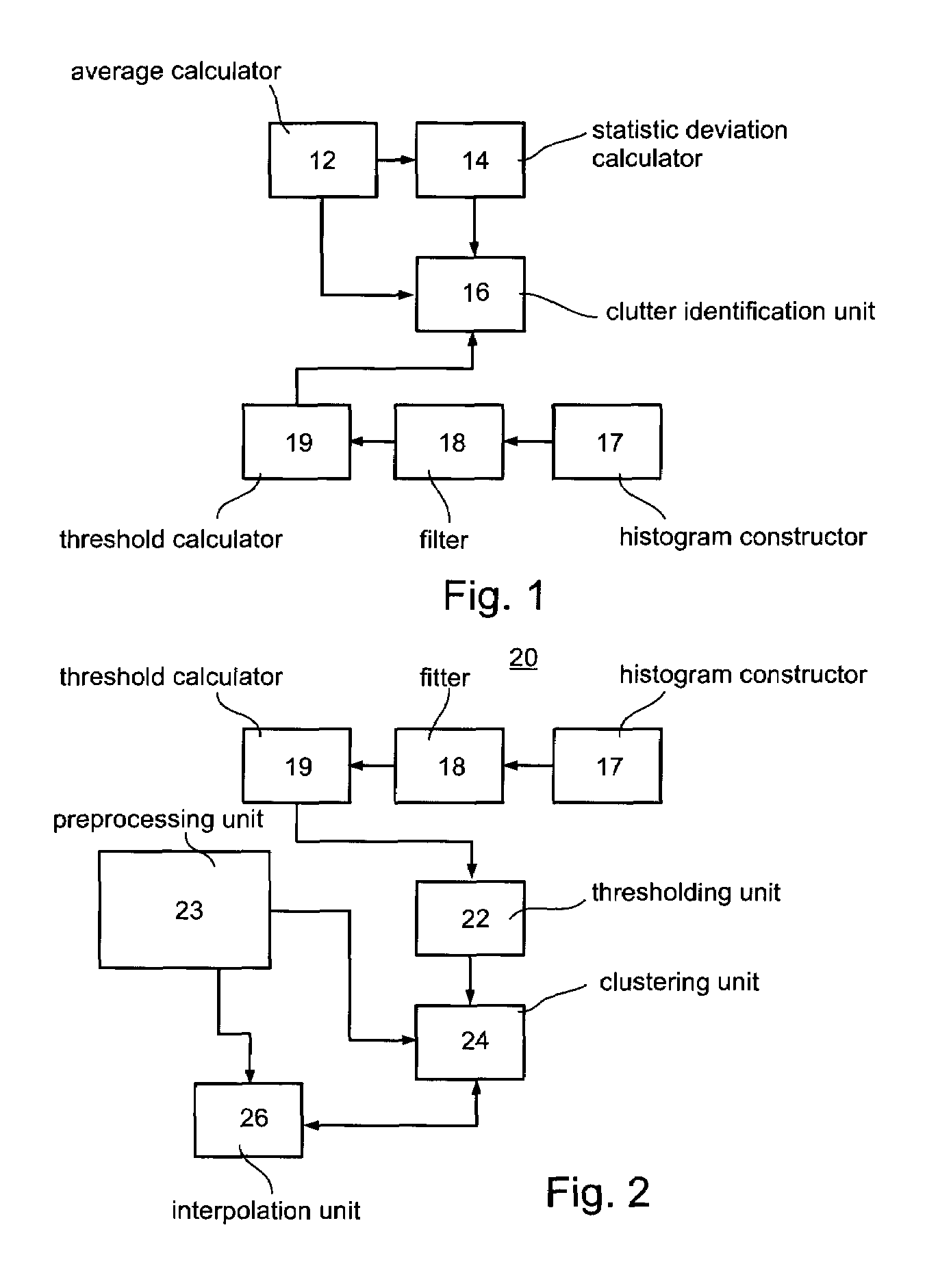
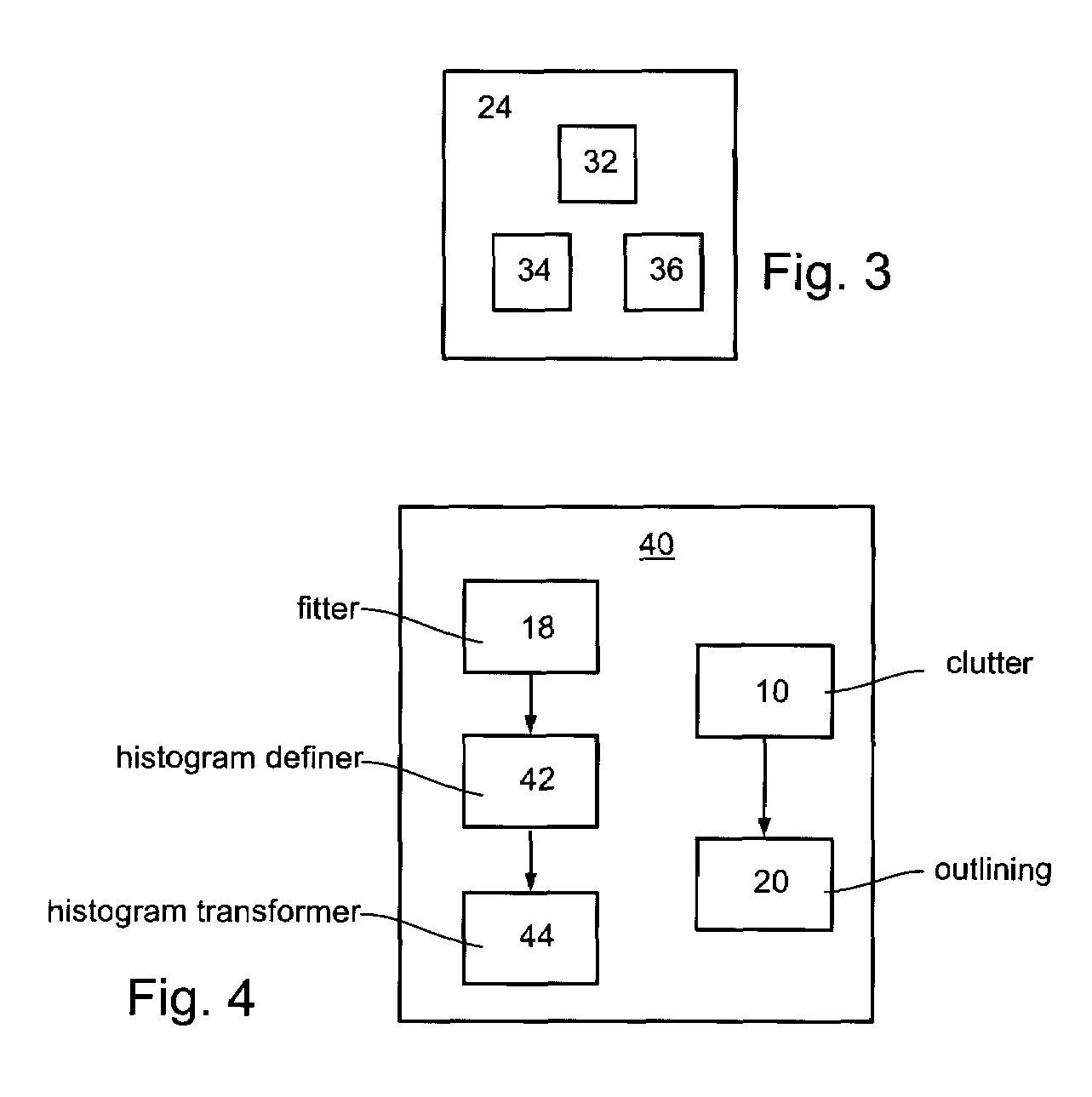
A method of improving an image or a set of images, by transforming an intensity histogram thereof is disclosed. The method comprises: (a) fitting the intensity histogram to a sum of a plurality of localized functions; (b) using the plurality of localized functions to define a plurality of localized intensity histograms; (c) for each localized intensity histogram, performing at least one image enhancement procedure, thereby providing a plurality of improved localized intensity histograms; and (d) combining the plurality of improved localized intensity histograms, thereby transforming the intensity histogram of the image. In various exemplary embodiments, the method further comprises detecting clutter and / or an outline of at least one region in the image or set of images.
Owner:RAMOT AT TEL AVIV UNIV LTD
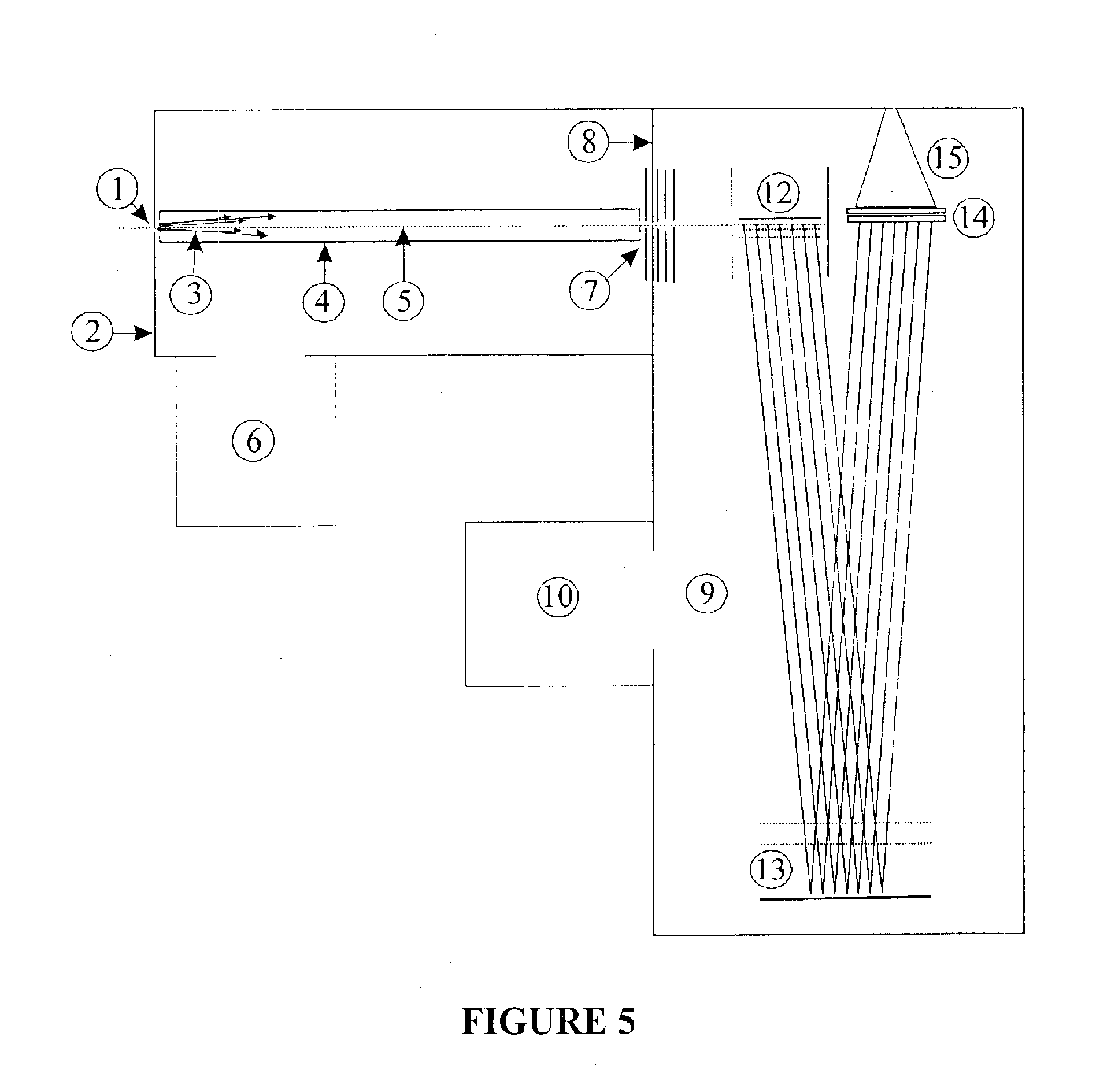
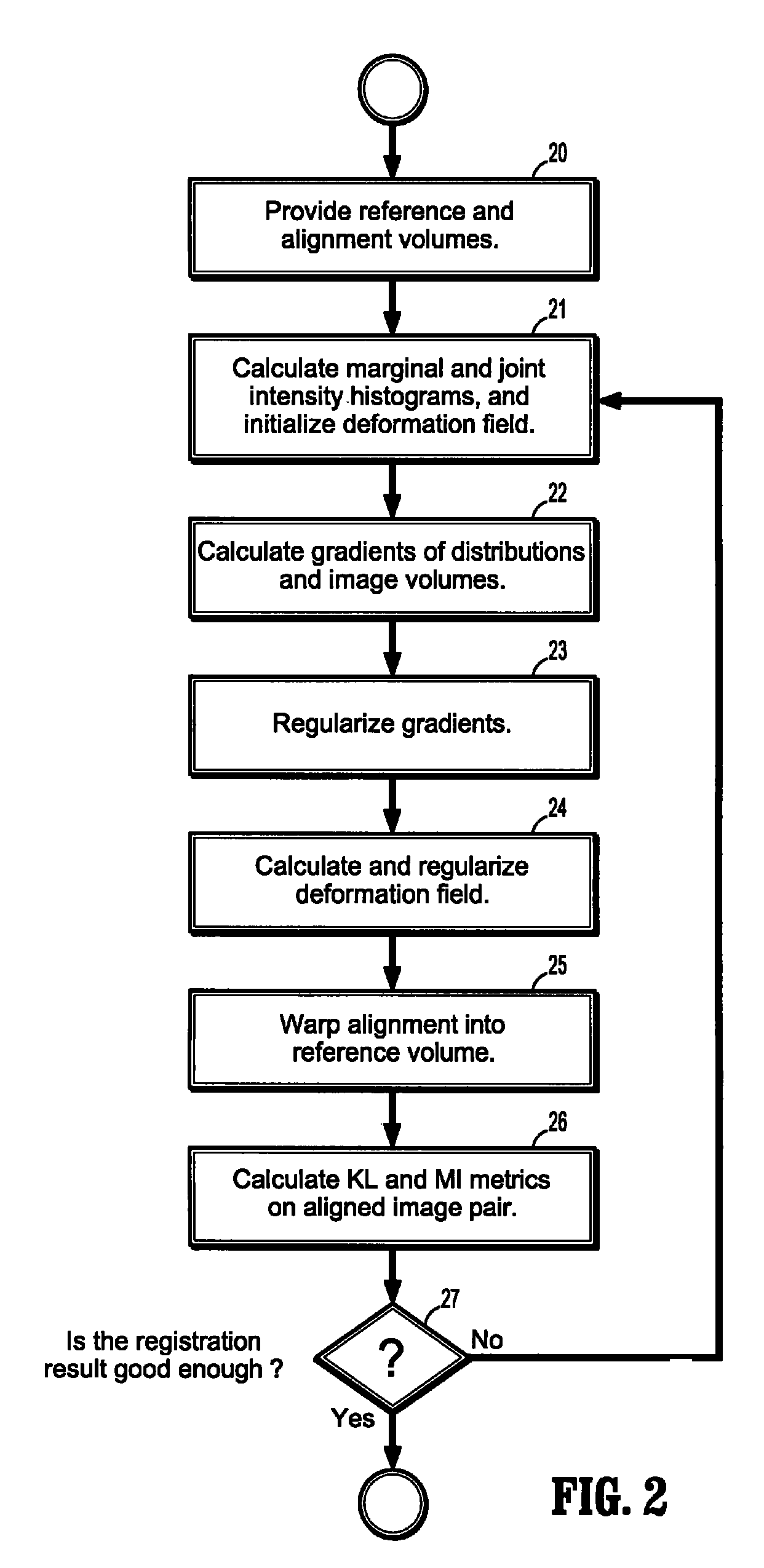
System and method for non-rigid multi-modal registration on the GPU
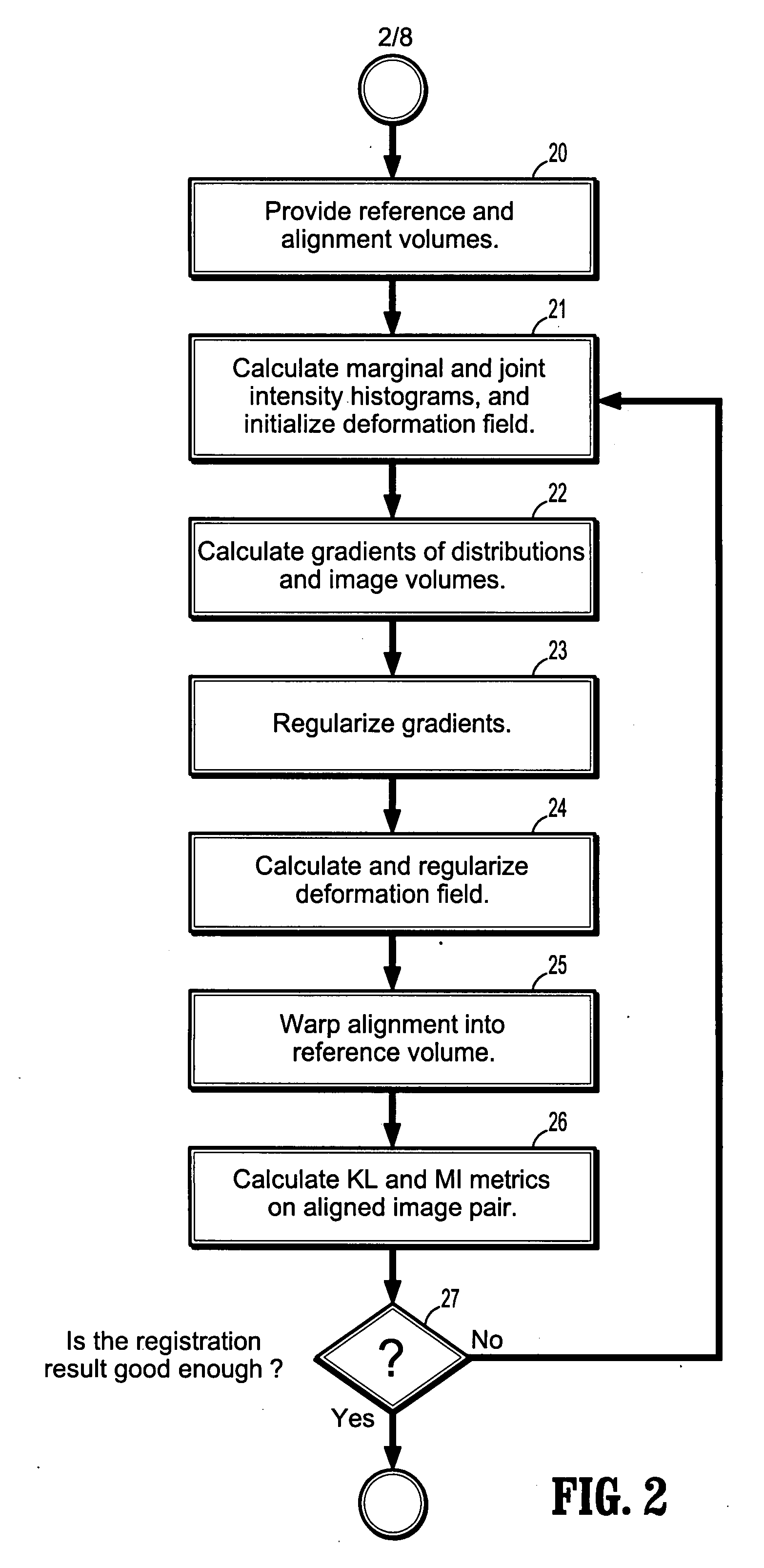
A method for non-rigid multi-modal registration of digitized images includes providing a reference image and an alignment images acquired from different imaging modalities to a graphics processing unit (GPU), initializing a deformation field for registering said reference image and said alignment image, computing marginal and joint intensity histograms of the reference image and the alignment image as registered by said deformation field, computing gradients of the reference and registered alignment images and of their respective marginal and joint intensity histograms, smoothing said histograms and gradients using Gaussian filters, calculating a new deformation field using said smoothed gradients, and registering said alignment image to said reference image using said deformation field.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Method for determining noise floor level and radar using the same
ActiveCN101271158AAccurately determine interferenceRadio wave reradiation/reflectionIntensity histogramElectric signal
Owner:DENSO CORP
System and method for global-to-local shape matching for automatic liver segmentation in medical imaging
ActiveUS8131038B2Improve robustnessPreserve topologyImage enhancementImage analysisIntensity histogramMedical imaging
A method for automatically segmenting a liver in digital medical images includes providing a 3-dimensional (3D) digital image I and a set of N training shapes {φi}i=1, . . . , N for a liver trained from a set of manually segmented images, selecting a seed point to initialize the segmentation, representing a level set function φα(θx+h) of a liver boundary Γ in the image asϕα(x)=ϕ0+∑i=1nαiVi(x),whereϕ0(x)=1N∑i=1Nϕi(x)is a mean shape, {Vi(x)}i=1, . . . , n are eigenmodes where n<N, αi are shape parameters, and h ε R3 and θε [0,2π]3 are translation and rotation parameters that align the training shapes, minimizing a first energy functional to determine the shape, translation, and rotation parameters to determine a shape template for the liver segmentation, defining a second energy functional of the shape template and a registration mapping weighted by image intensity histogram functions inside and outside the boundary, and minimizing the second energy functional to determine the registration mapping, where the registration mapping recovers local deformations of the liver.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
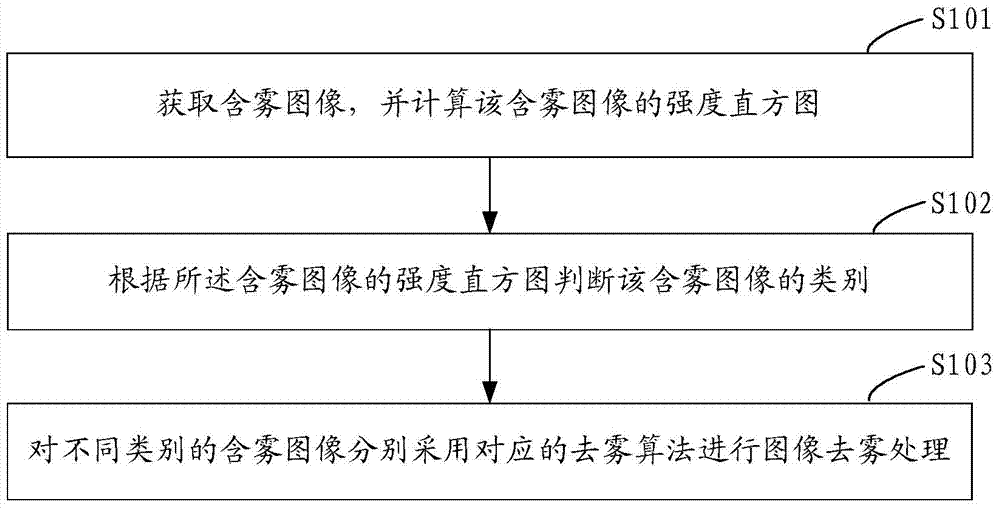
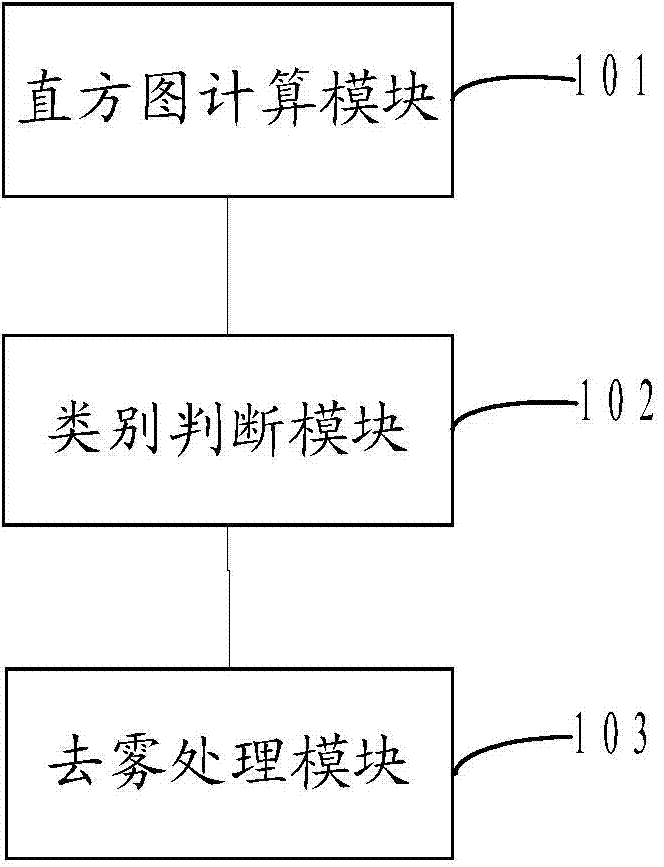
Image defogging method and device
InactiveCN103700079AQuality improvementStrong targetingImage enhancementIntensity histogramImage quality
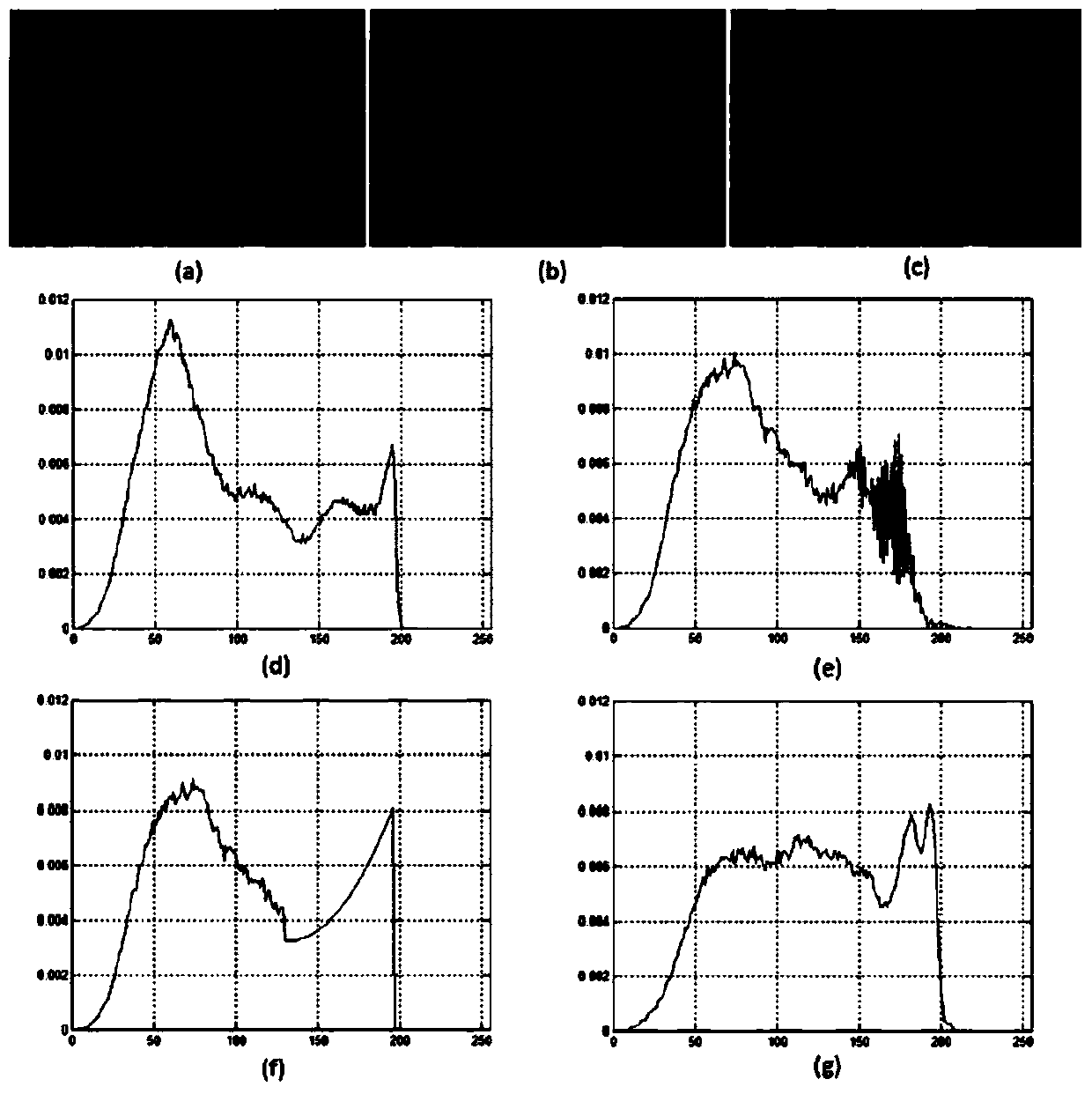
The invention provides an image defogging method and device. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring a fog-containing image, and calculating an intensity histogram of the fog-containing image; judging the type of the fog-containing image according to the intensity histogram of the fog-containing image; defogging different types of fog-containing images by adopting corresponding defogging algorithms respectively. According to the image defogging method and device provided by the invention, different defogging algorithms are adopted specific to different fog-containing images in a highly-specific way, so that a better defogging effect is achieved, the quality of an obtained defogged image is high, and the defogged image is closer to a real fog-free image.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
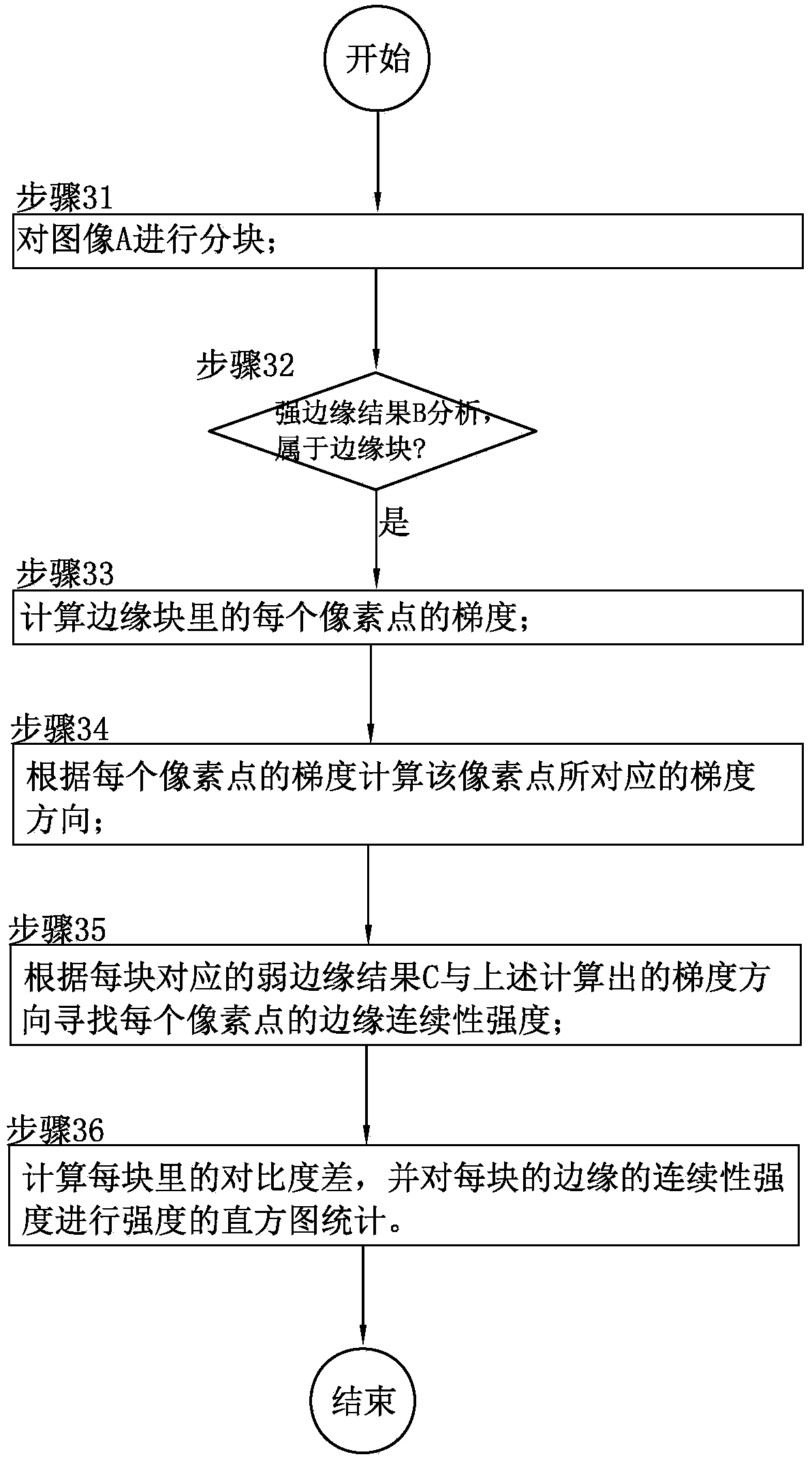
Edge-based fuzzy detection method
The invention discloses an edge-based fuzzy detection method. The edge-based fuzzy detection method comprises the following steps that an image is received and is processed in a graying mode to obtain an image A; strong edge detection and weak edge detection are respectively conducted on the image A, and a strong edge result B and a weak edge result C are respectively obtained; the image A is partitioned, and statistics are conducted on blocks, the strong edge result and the weak edge result to obtain strength histogram statistics, wherein the strong edge result and the weak edge result correspond to the blocks respectively; the fuzzy image probability of the image A is worked out through results of the strength histogram statistics. Due to the adoption of the scheme, no matter where an object focused on by people appears in the image, people can carry out fuzzy detection and processing on the image, and universality and accuracy of the detection method are achieved.
Owner:MEITU
System for creating a capsule representation of an instructional video
InactiveCN102612707AImage analysisElectronic editing analogue information signalsObjective qualityHide markov model
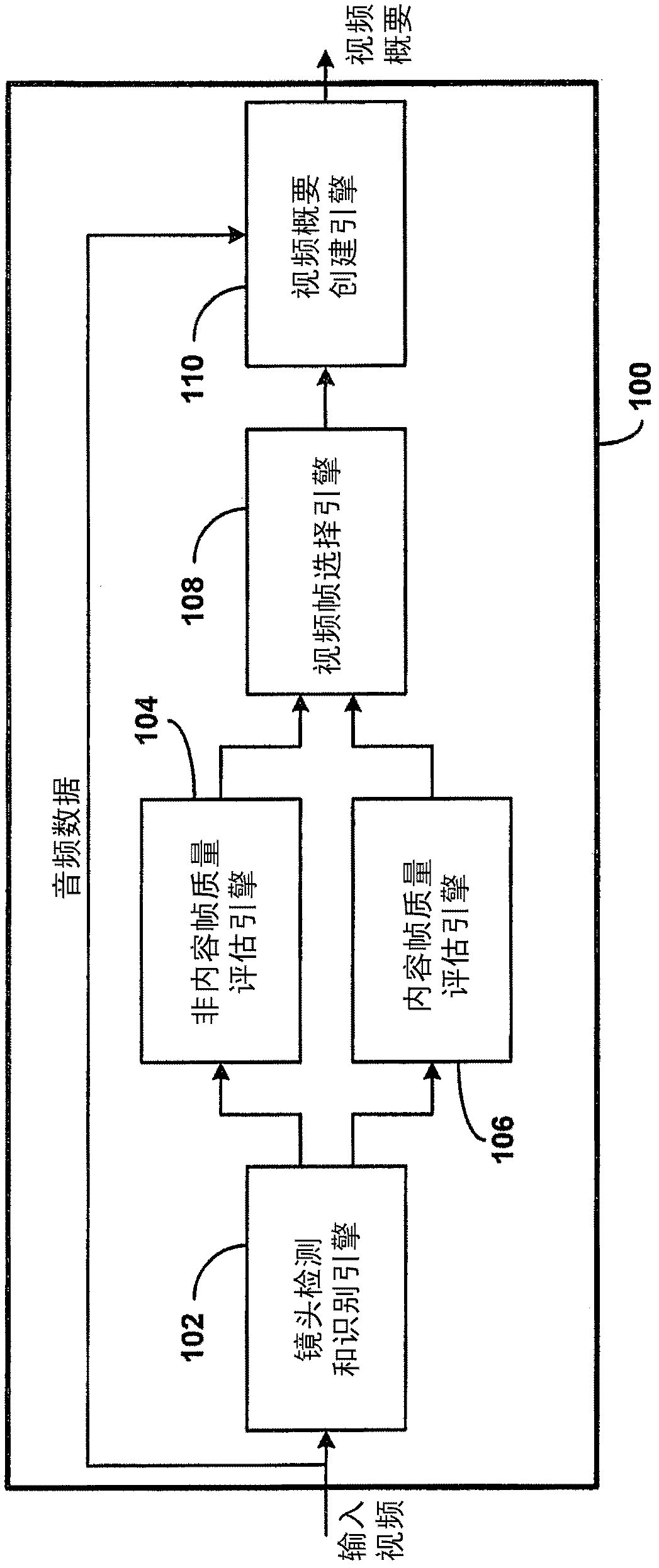
A method is provided that creates a lecture video capsule containing highlights of an original instructional video based on visual quality and content. The method includes segmenting and recognizing activities in the video using a hidden Markov model (HMM). The activities are classified into three categories: talking head, writing hand and slideshow. The talking head frames are classified as non- content frames, while the writing hand and slideshows are classified as content frames. A non-reference based objective quality assessment of the non-content frames is performed to detect high quality frames. Statistical parameters of an intensity histogram and a horizontal projection profile (HPP) of the content frames is used to derive an objective quality measure of the content frames that is used to extract high quality content frames. The selected high quality non-content and content frames form a video clip or capsule, which is a temporally compressed representation of the video.
Owner:INDIAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY BOMBAY
Method for tracing human body movement based on maximum geometric flow histogram
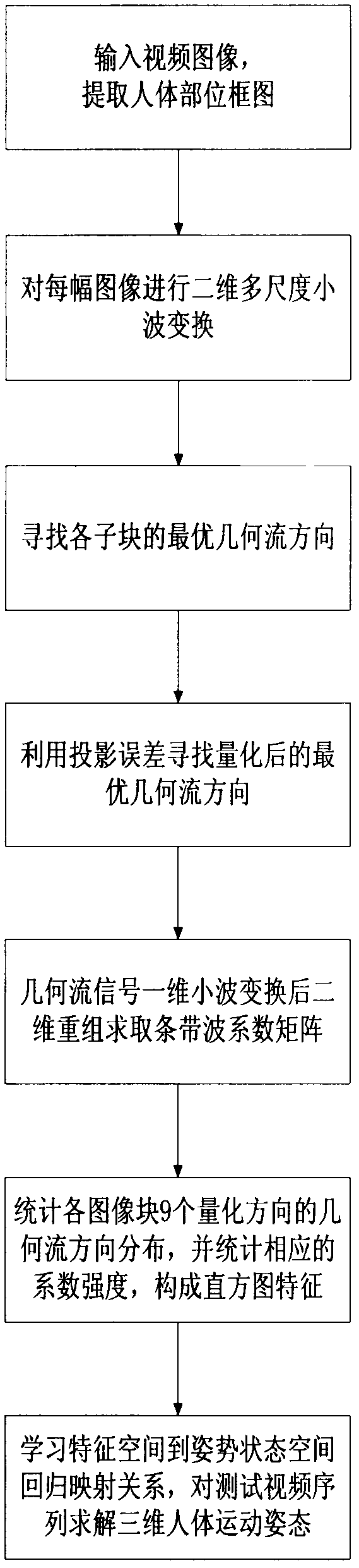
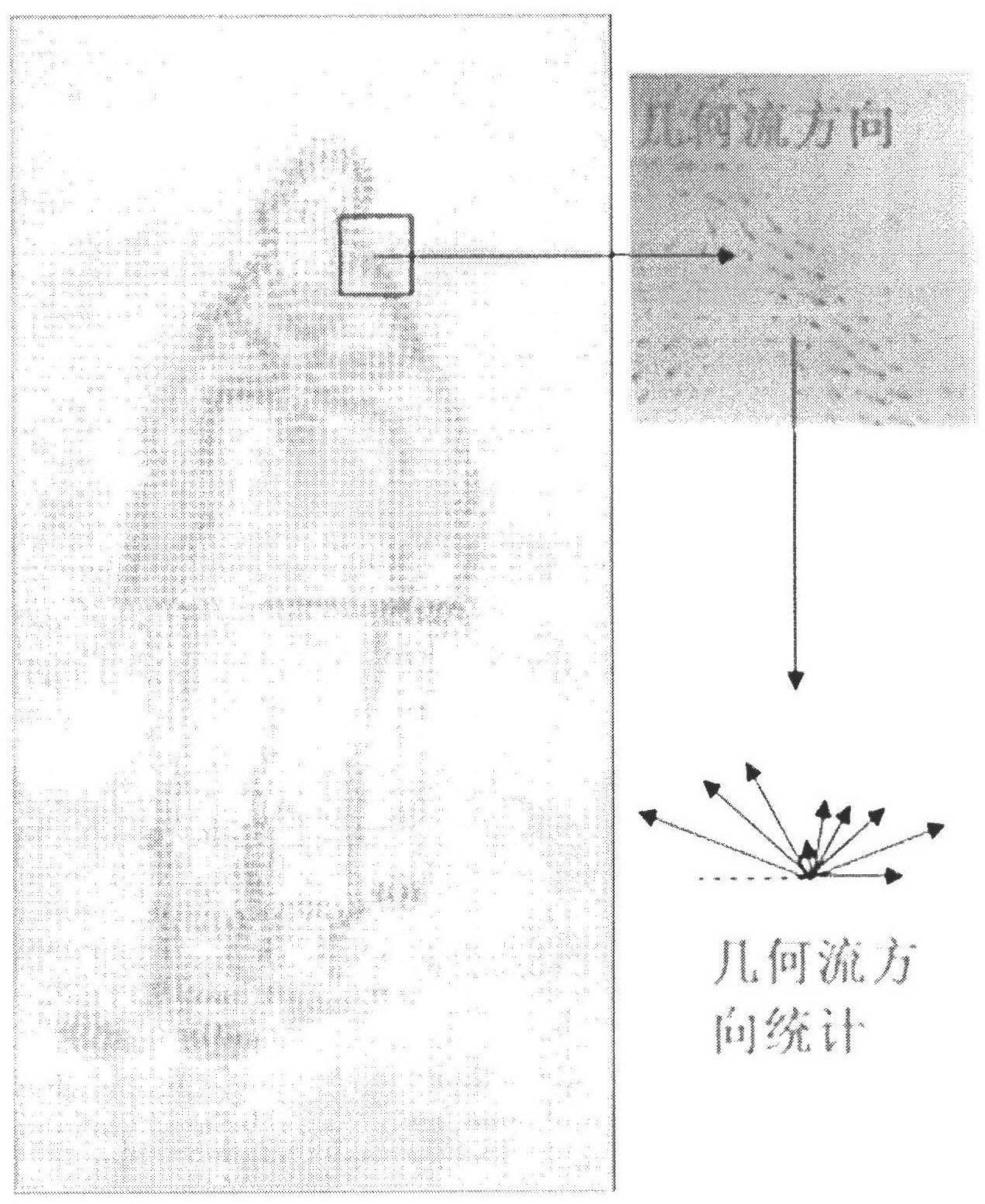
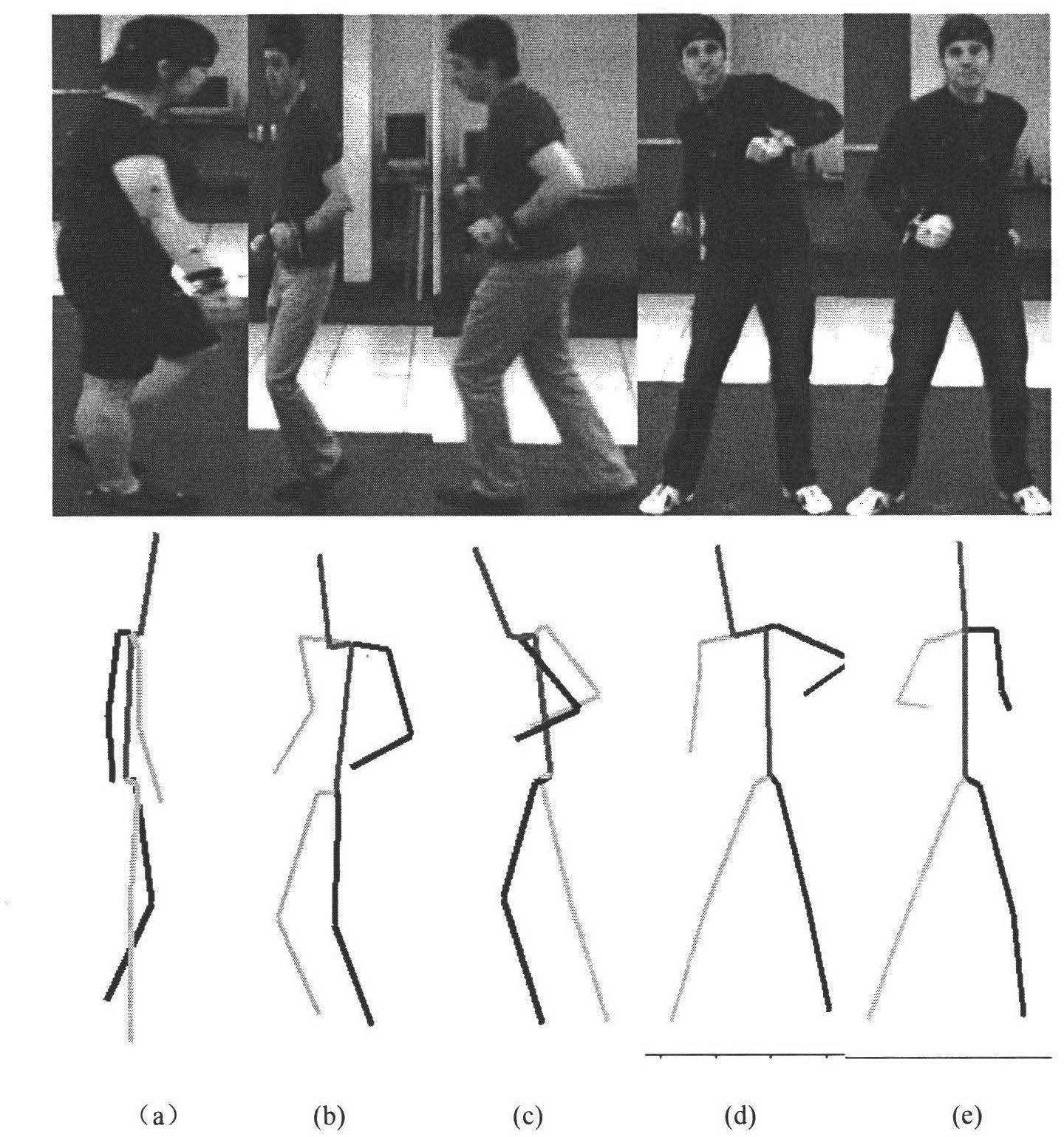
InactiveCN102663449ASave resourcesReduce dimensionalityCharacter and pattern recognitionHuman bodyFeature extraction
The present invention discloses a method for tracing human body movement based on a maximum geometric flow histogram, and mainly solves defaults such as fuzziness of human contour and edge descriptions, and failure to reflect characteristic internal geometric structure and texture mode in existing characteristic extraction method. Realization processes are: inputting video images to be treated and extracting a block diagram of a major human body part; performing a two-dimensional multi-scale wavelet transform to the image; searching for an optimal geometric flow direction by using quadtree division and bottom-up fusion principles; performing a one-dimensional wavelet transform to the quantized optimal geometric flow direction signals which are then reconstructed to a two-dimensional form and obtain a coefficient matrix; counting geometric flow coefficient strength histogram of 9 directions of each area as a final image characteristic expression; and through a regression progress, learning mapping relations from image characteristics to three-dimensional movement data, and predicting and recovering three-dimensional postures of the new training video images. The method for tracing human body movement based on the maximum geometric flow histogram, which is of fast computing speed and accurate results, reinforces image characteristic robustness, and can be applied to human body target identification, detection, and posture reconstruction.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Systems and methods for localized contrast enhancement
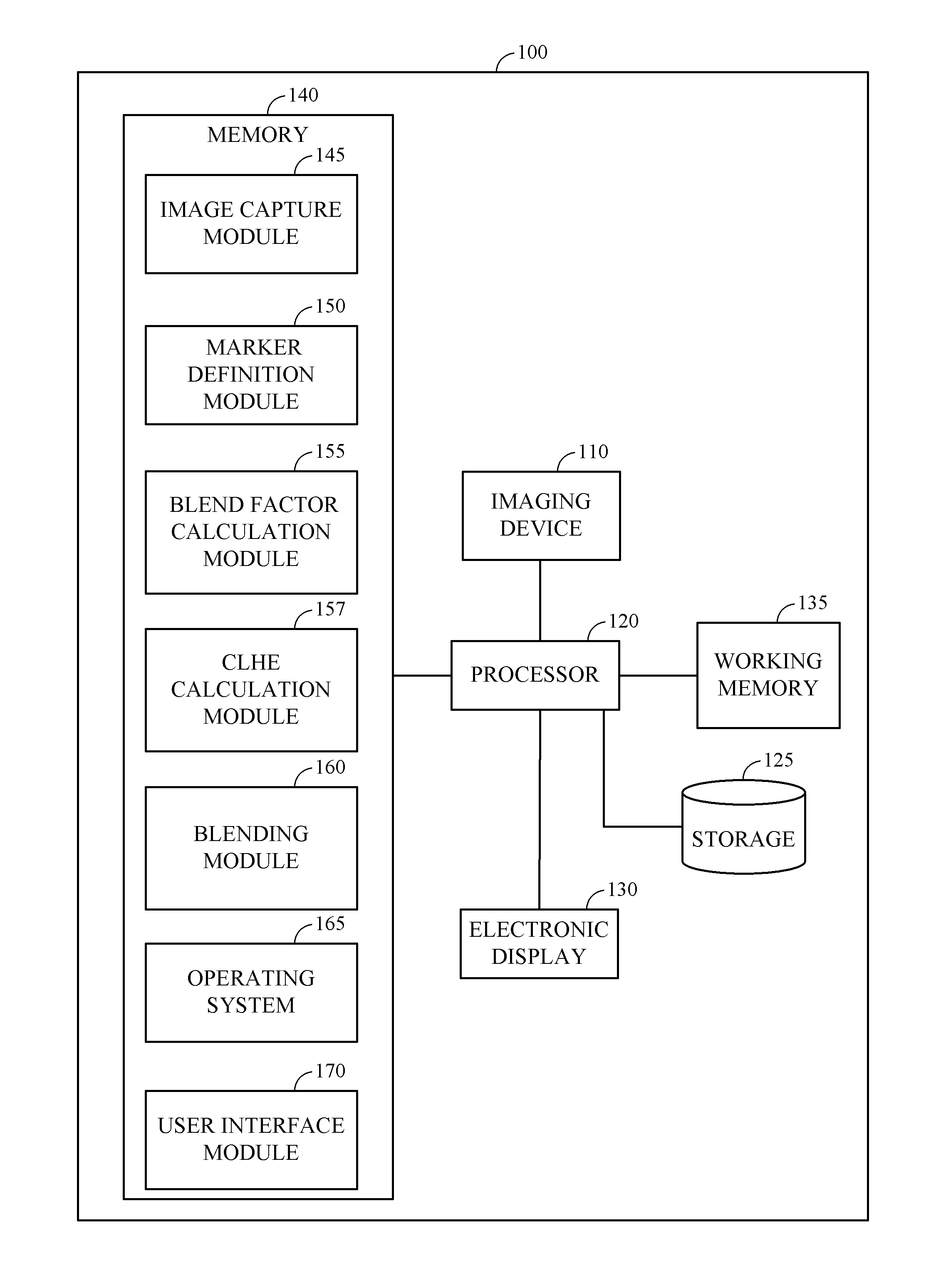
ActiveUS9165210B1Increase speedImprove efficiencyImage enhancementImage analysisIntensity histogramContrast enhancement
Systems and methods for improving the contrast of image frames are disclosed. In one embodiment, a system for improving the contrast of image frames includes a control module configured to create an intensity histogram for an image frame, define a set of markers on an intensity range of the histogram, assign a blend factor to each marker, calculate a blend factor for each original pixel of the image, obtain a first equalized pixel output value, calculate a final equalized pixel output value using the blend factor, the first equalized pixel output value, and an original pixel value, and output new pixel values that constitute the output image.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
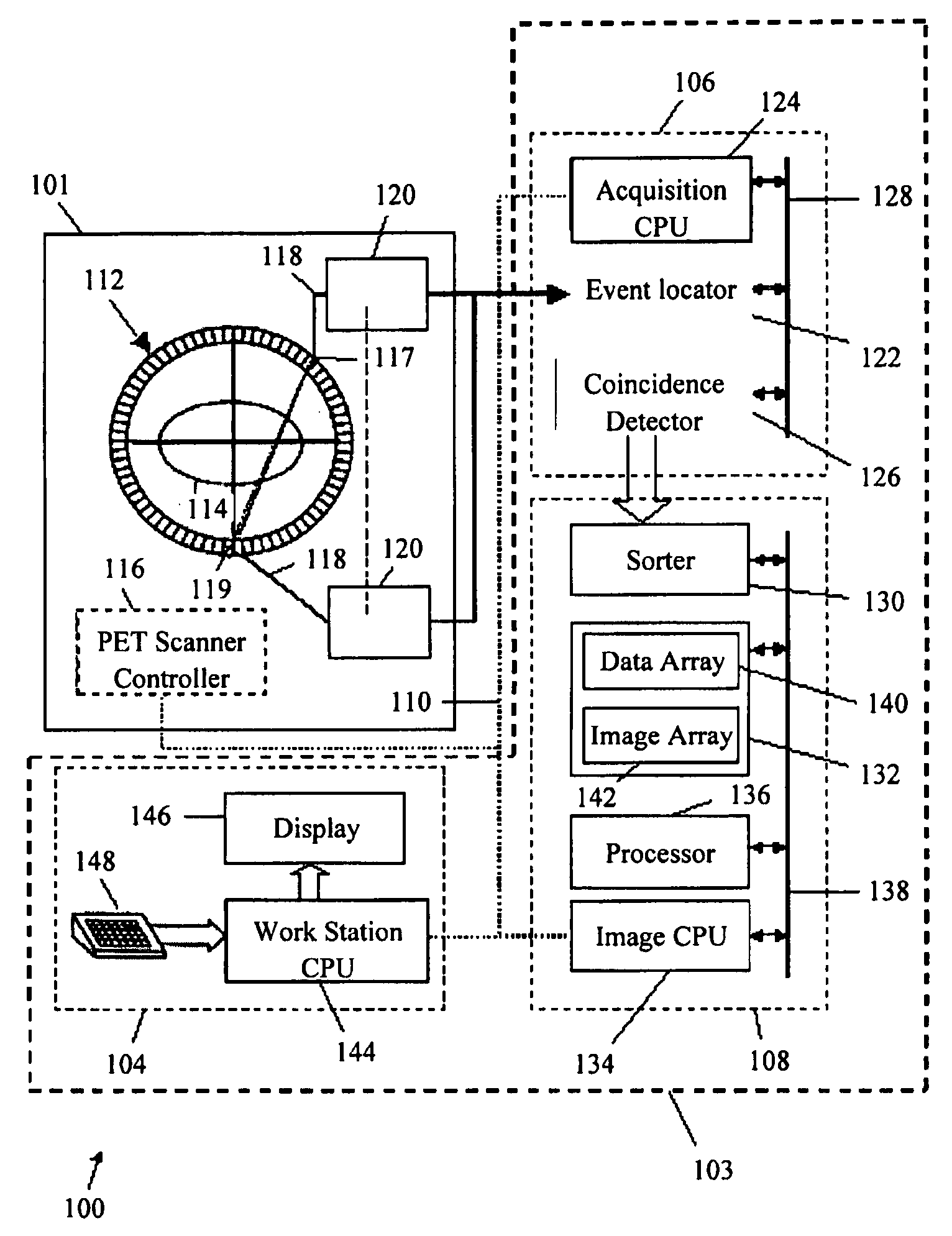
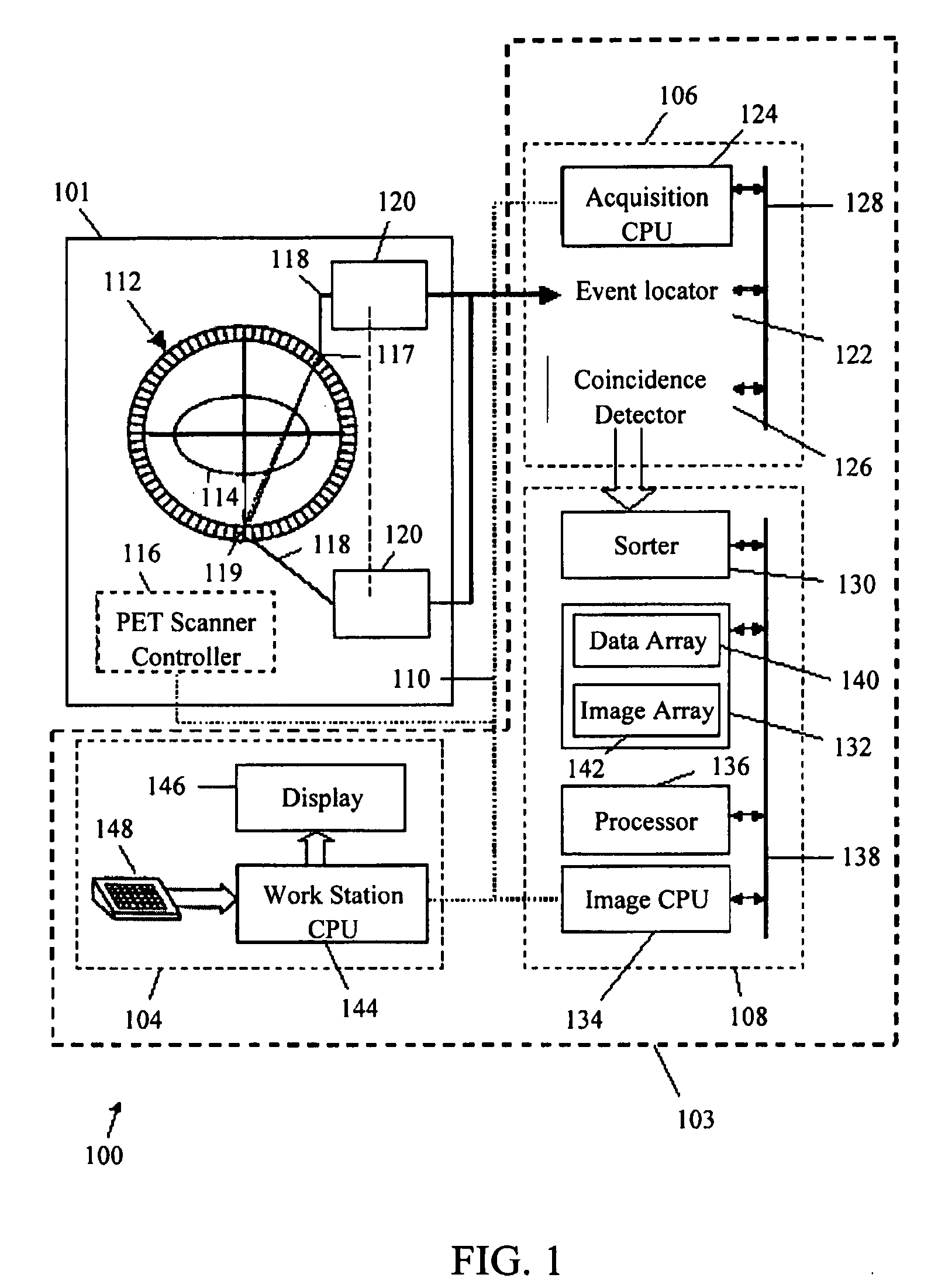
Method and system for calibrating a time of flight positron emission tomography system
InactiveUS20070205368A1Material analysis by optical meansCalibration apparatusIntensity histogramCompanion animal
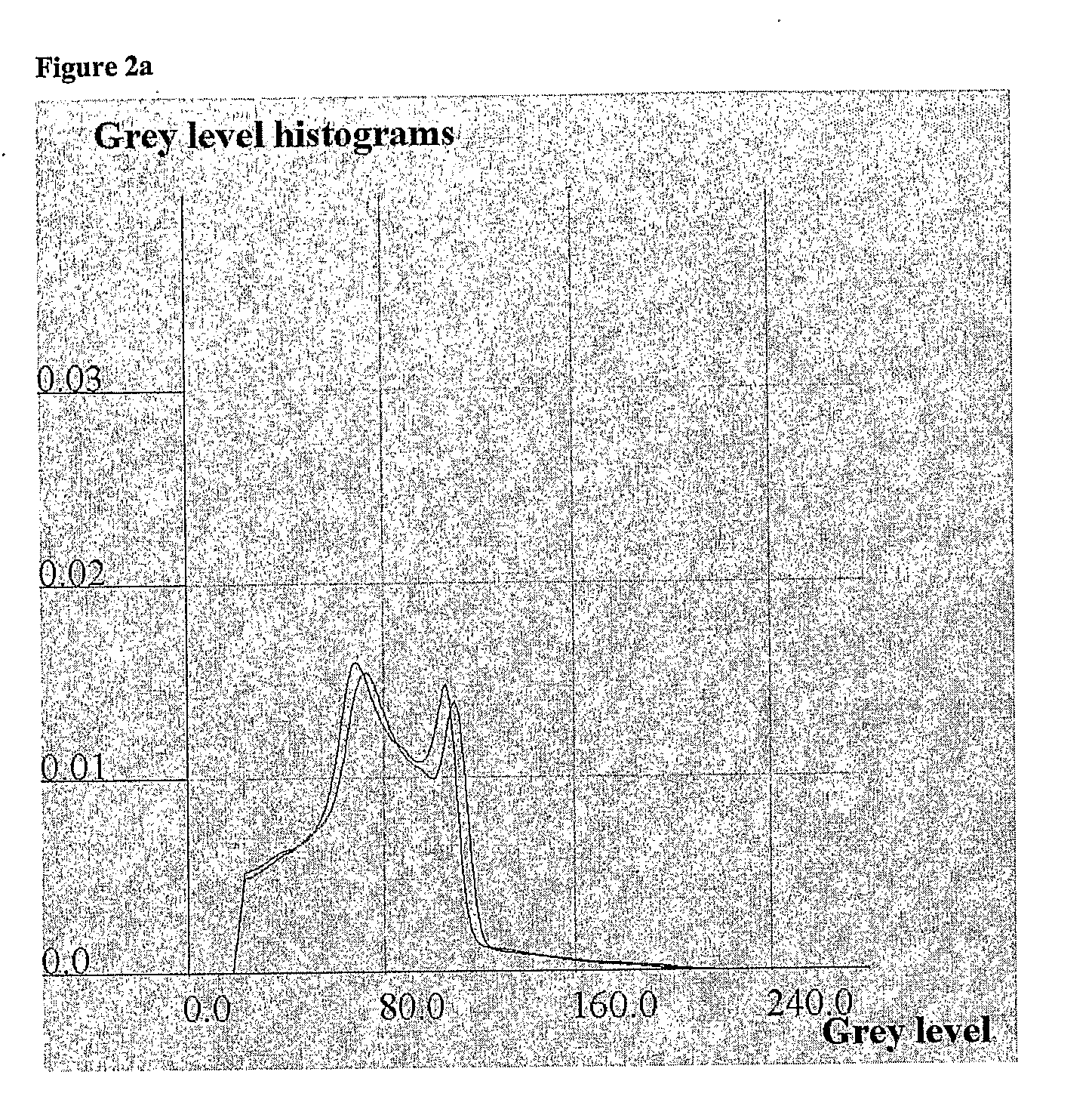
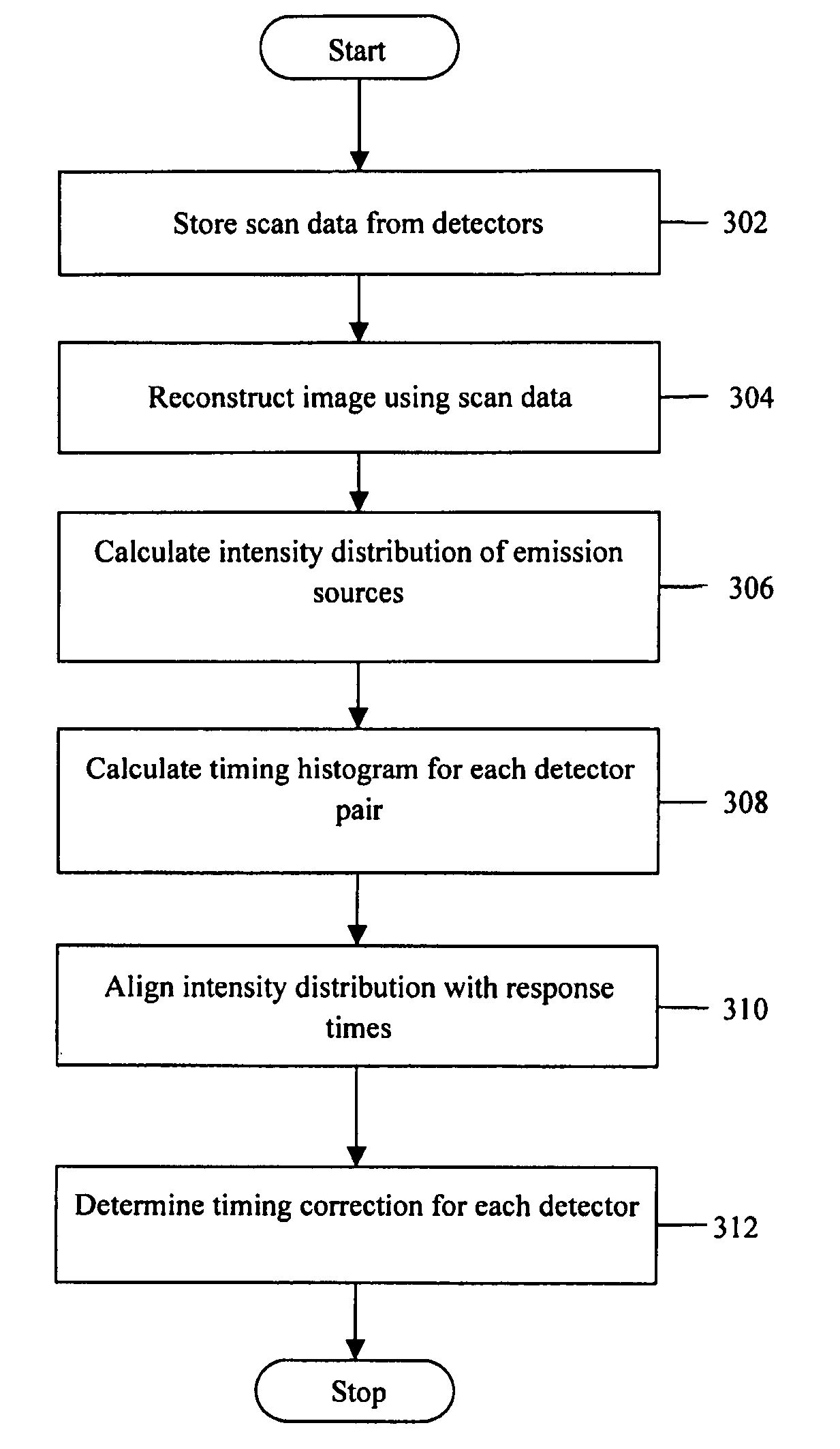
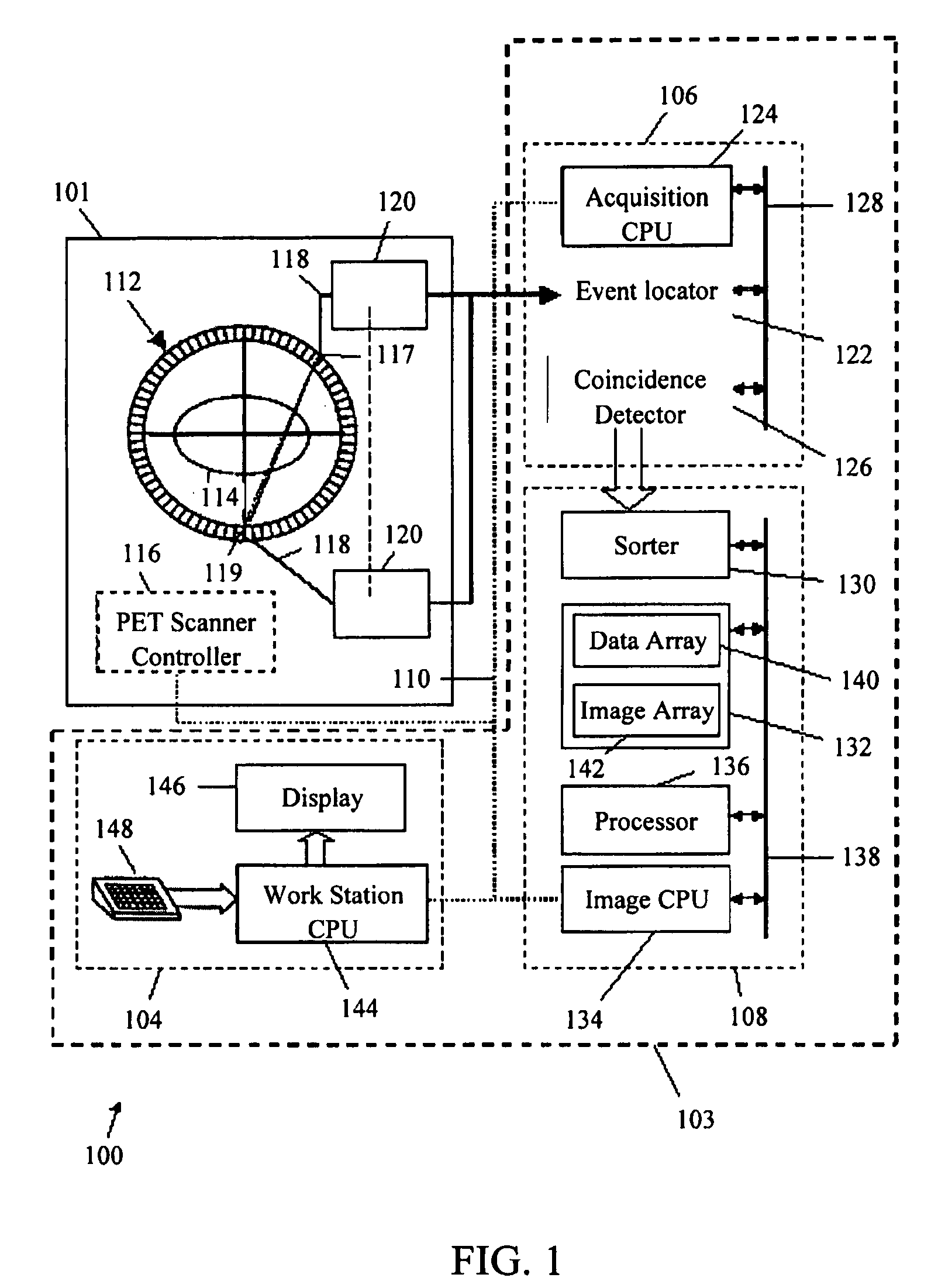
A method and system for calibrating a time of flight (TOF) positron emission tomography (PET) scanner are provided. The method stores acquired scan data from detector pairs including data and timing information. The method further calculates an intensity distribution of emission sources based on the scan data and defines a timing pivot point based on a median of an intensity histogram. The method determines a timing correction for each detector based on the location of the timing pivot point. The positron emission tomography (PET) system further provides a plurality of detectors, used in performing imaging scans, and a processor. The processor is configured to determine a timing correction for each detector.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Defogging method for image with few backgrounds containing fog
ActiveCN103700078AAvoid difficult fine-tuningQuality improvementImage enhancementIntensity histogramPeak value
The invention discloses a defogging method for an image with few backgrounds containing fog. The defogging method comprises the steps of S1, obtaining an intensity histogram A of a fog-containing image, judging whether the condition of containing little background light is met or not, and determining the coordinates of a termination point of a right boundary; S2, defogging the fog-containing image by utilizing a dark passage apriori algorithm; S3, judging the defogging degree, if the fog is not completely removed, changing parameters and executing the step S2 again; S4, if the fog is completely removed, determining a histogram B of the defogged image, marking the coordinates of a starting point of the right boundary of a peak value, and marking the coordinates of a termination point of the right boundary; S5, stretching the histogram; S6, performing histogram specification on the reconstructed histogram B' and the defogged image. The method is used for performing post-processing on the dark passage apriori algorithm through the histogram, the operation is simple and flexible, and different parameters can be set according to different specific images, so that the condition that a dark passage apriori processing result has difficulty in fine adjustment is avoided; the efficiency of the algorithm is high, and the obtained defogged image is relatively high in quality, and is similar to a real fog-free picture.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Systems and methods for displaying a cellular abnormality
In accordance with the principles of the invention, methods, systems, and computer-readable mediums are provided for processing image data representing cellular analysis result data including accessing image data; generating an intensity histogram based on the image data; transforming the intensity histogram into a stepped image; performing normalized cross-correlation between the stepped image and a reference image to measure similarity; and determining an abnormality based on the measured similarity.
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC
Method and apparatus for analysing ultrasound images
A method of improving an image or a set of images, by transforming an intensity histogram thereof is disclosed. The method comprises: (a) fitting the intensity histogram to a sum of a plurality of localized functions; (b) using the plurality of localized functions to define a plurality of localized intensity histograms; (c) for each localized intensity histogram, performing at least one image enhancement procedure, thereby providing a plurality of improved localized intensity histograms; and (d) combining the plurality of improved localized intensity histograms, thereby transforming the intensity histogram of the image. In various exemplary embodiments, the method further comprises detecting clutter and / or an outline of at least one region in the image or set of images.
Owner:RAMOT AT TEL AVIV UNIV LTD
Method and apparatus for detecting targets through temporal scene changes
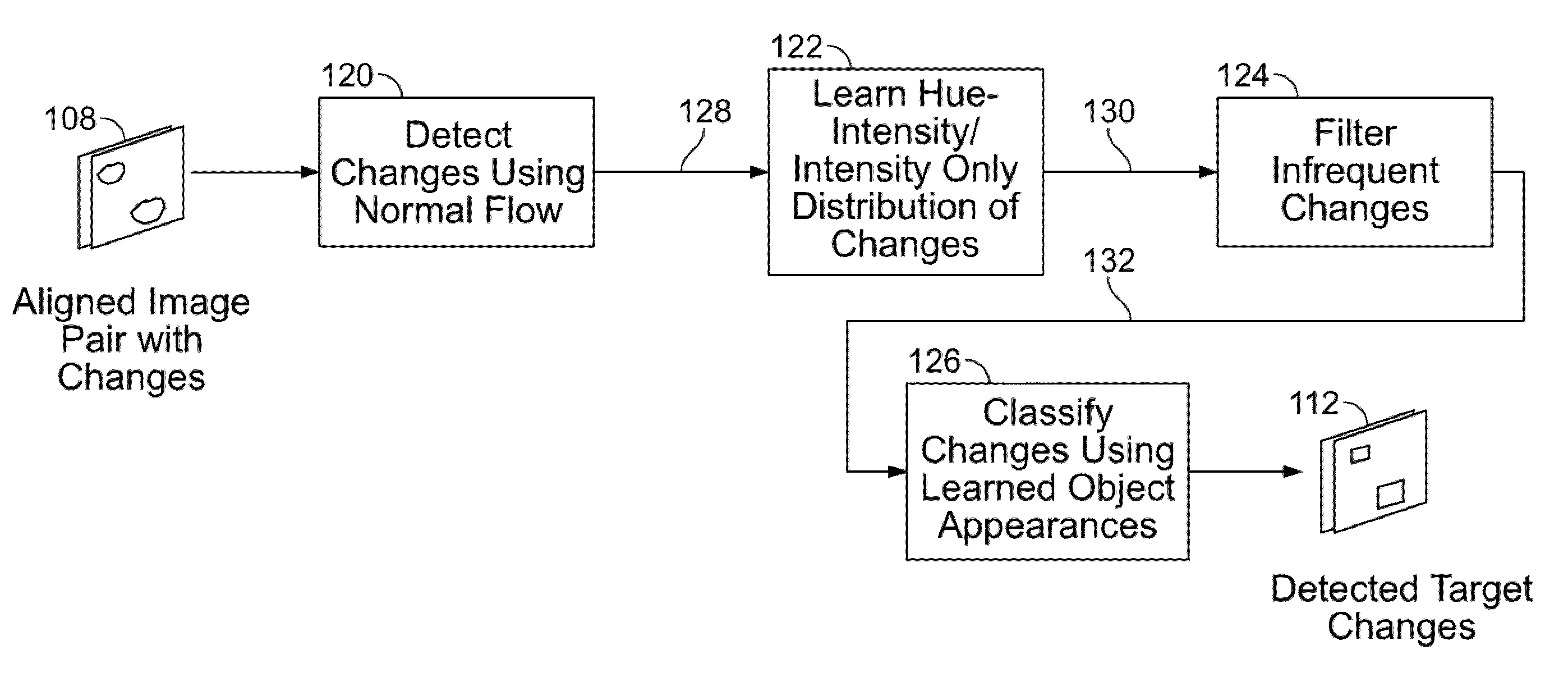
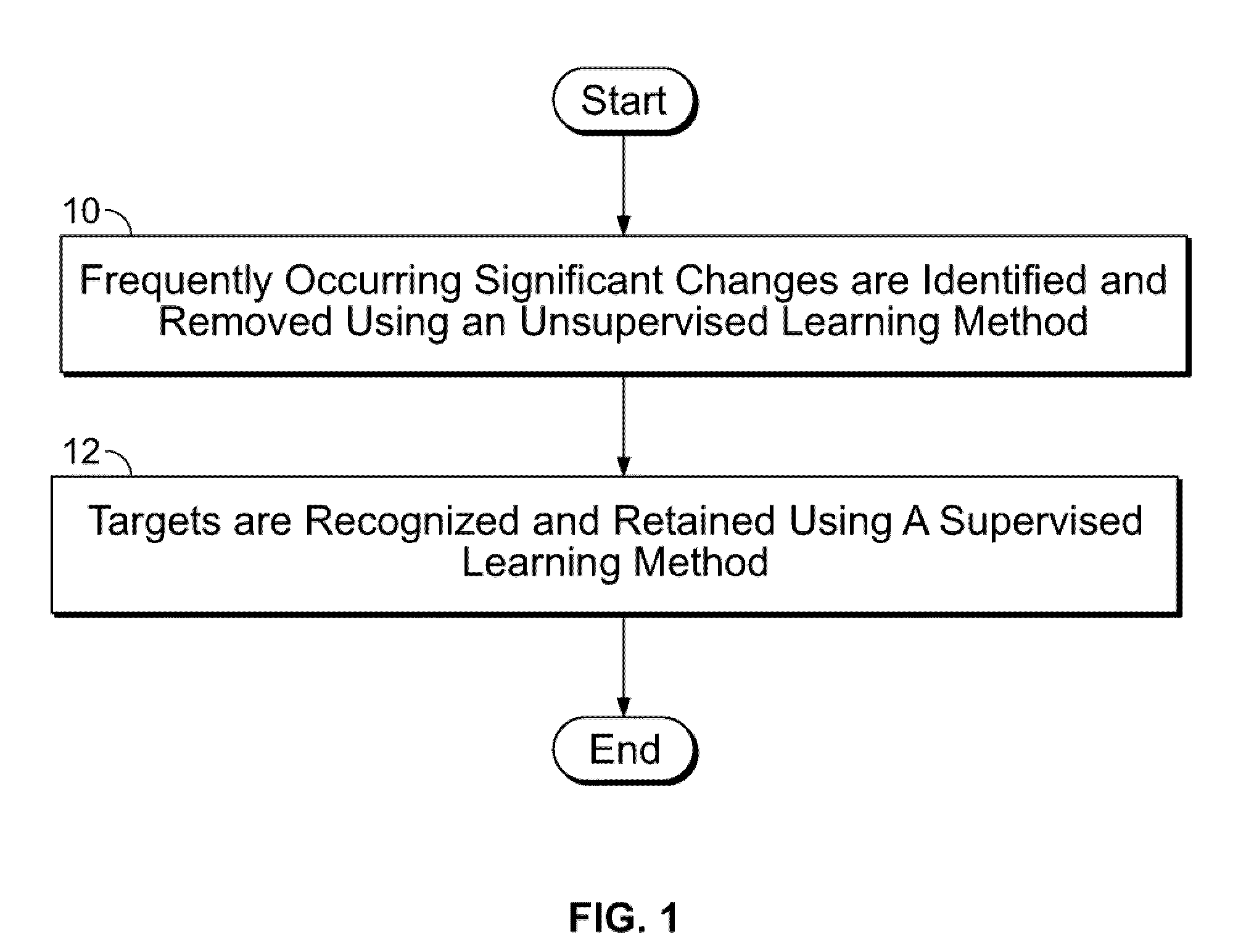
A system and method for detecting a target in imagery is disclosed. At least one image region exhibiting changes in at least intensity is detected from among at least a pair of aligned images. A distribution of changes in at least intensity inside the at least one image region is determined using an unsupervised learning method. The distribution of changes in at least intensity is used to identify pixels experiencing changes of interest. At least one target from the identified pixels is identified using a supervised learning method. The distribution of changes in at least intensity is a joint hue and intensity histogram when the pair of images pertain to color imagery. The distribution of changes in at least intensity is an intensity histogram when the pair of images pertain to grey-level imagery.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
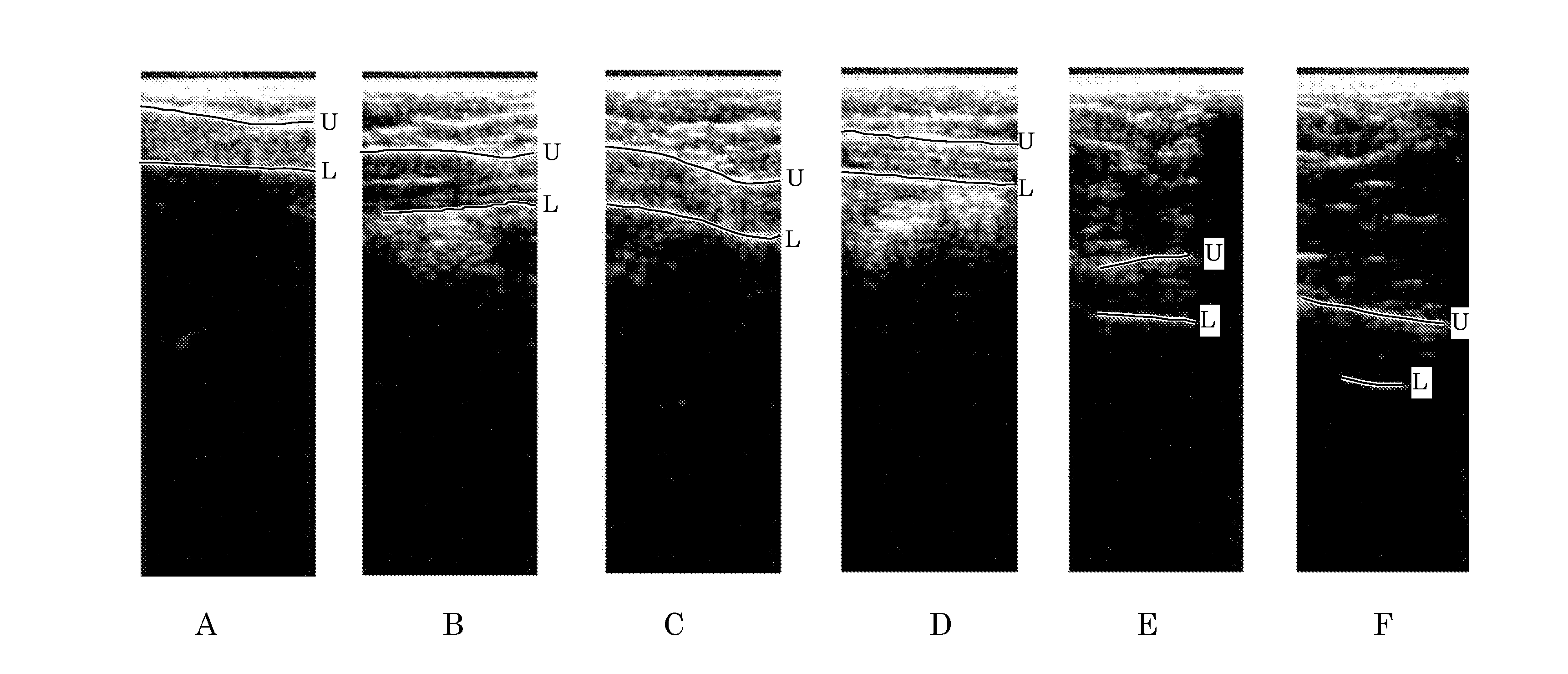
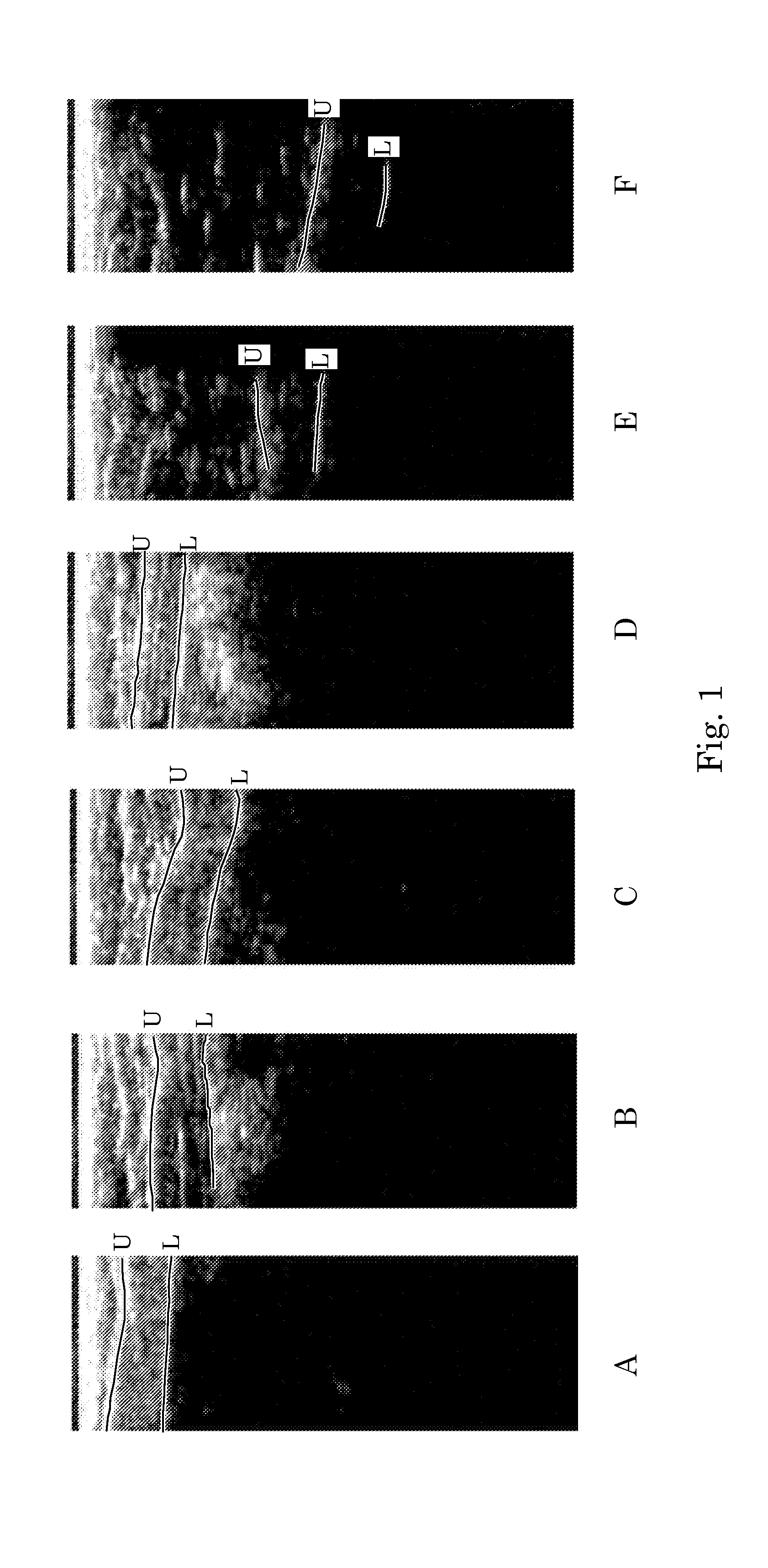
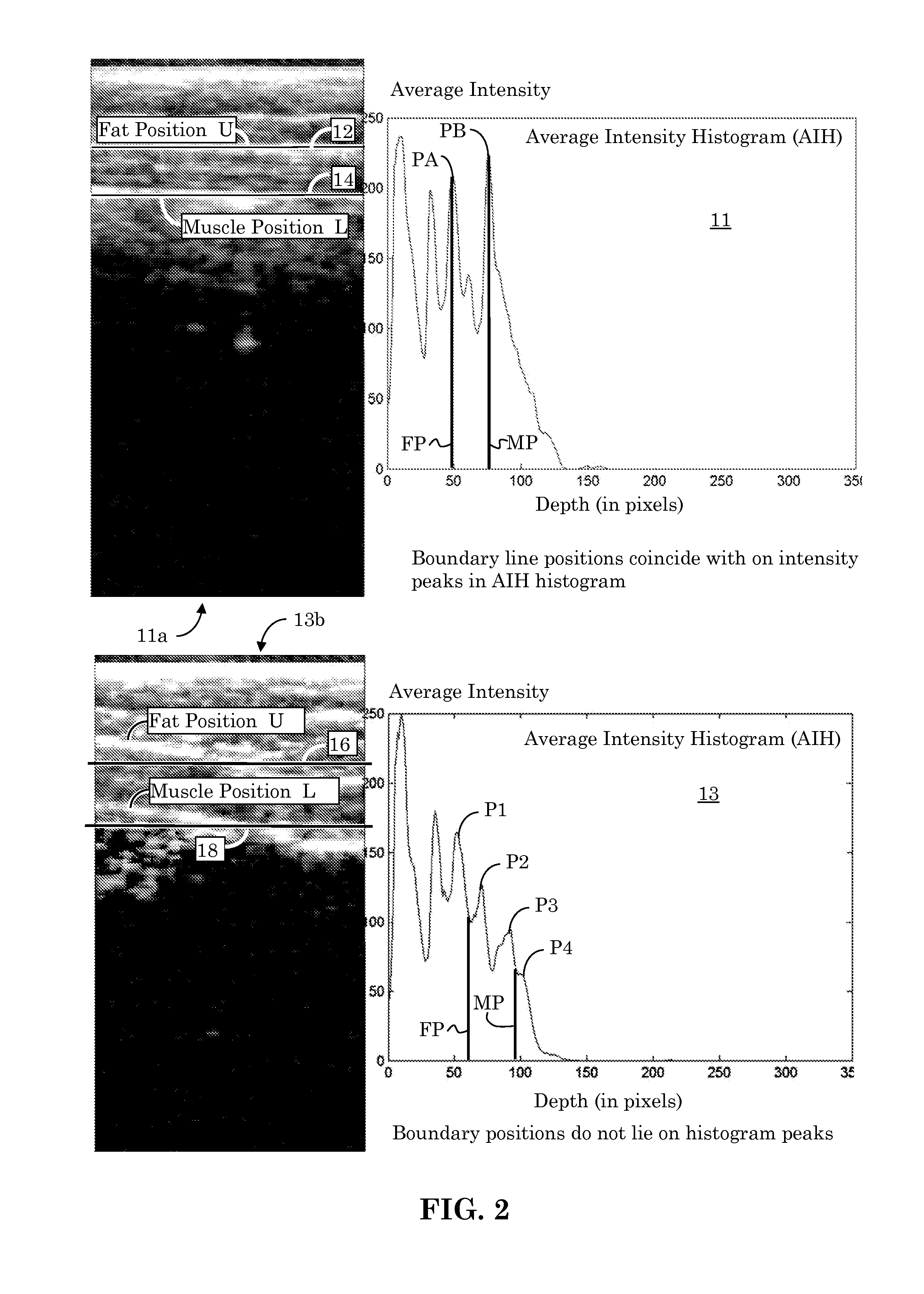
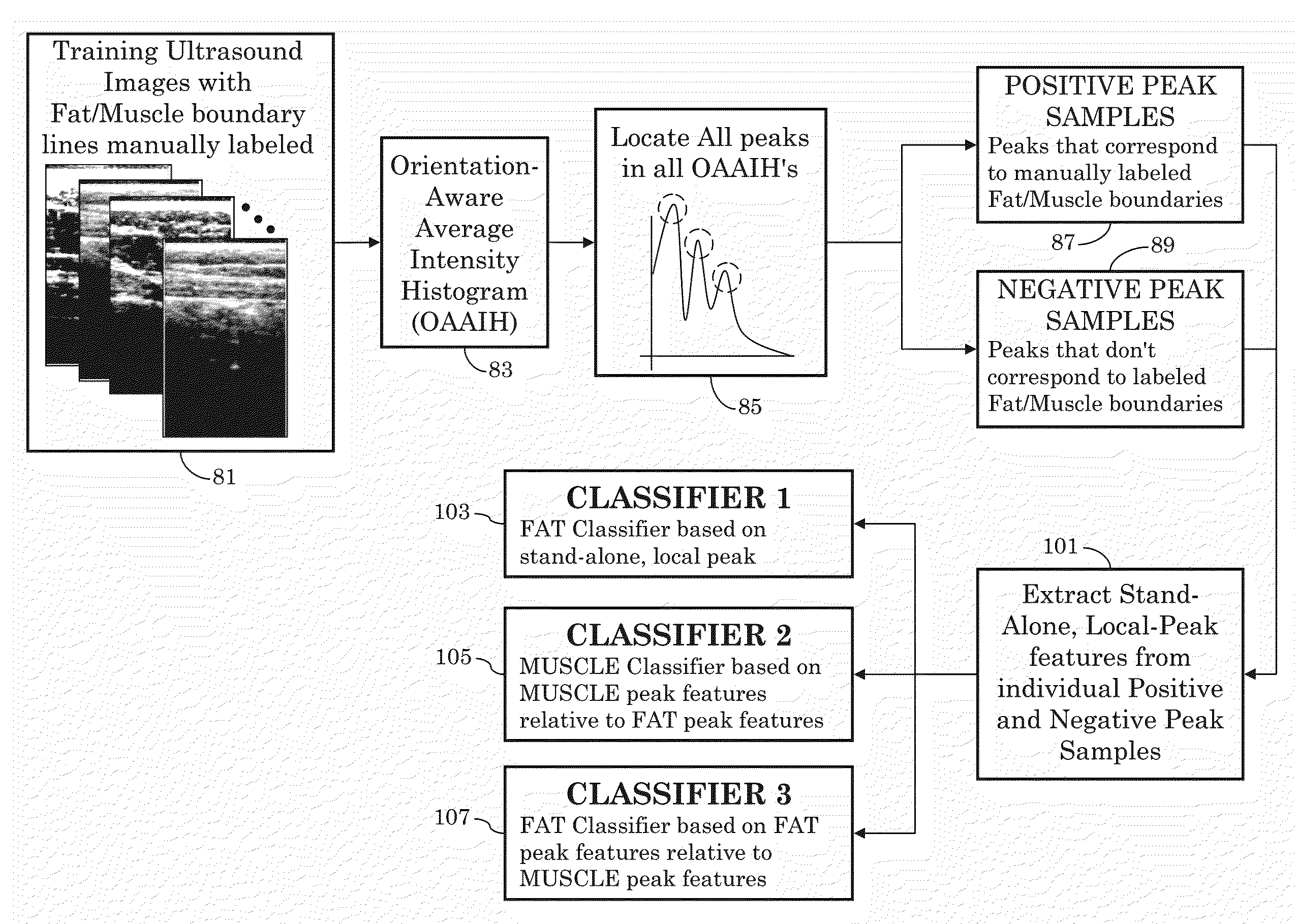
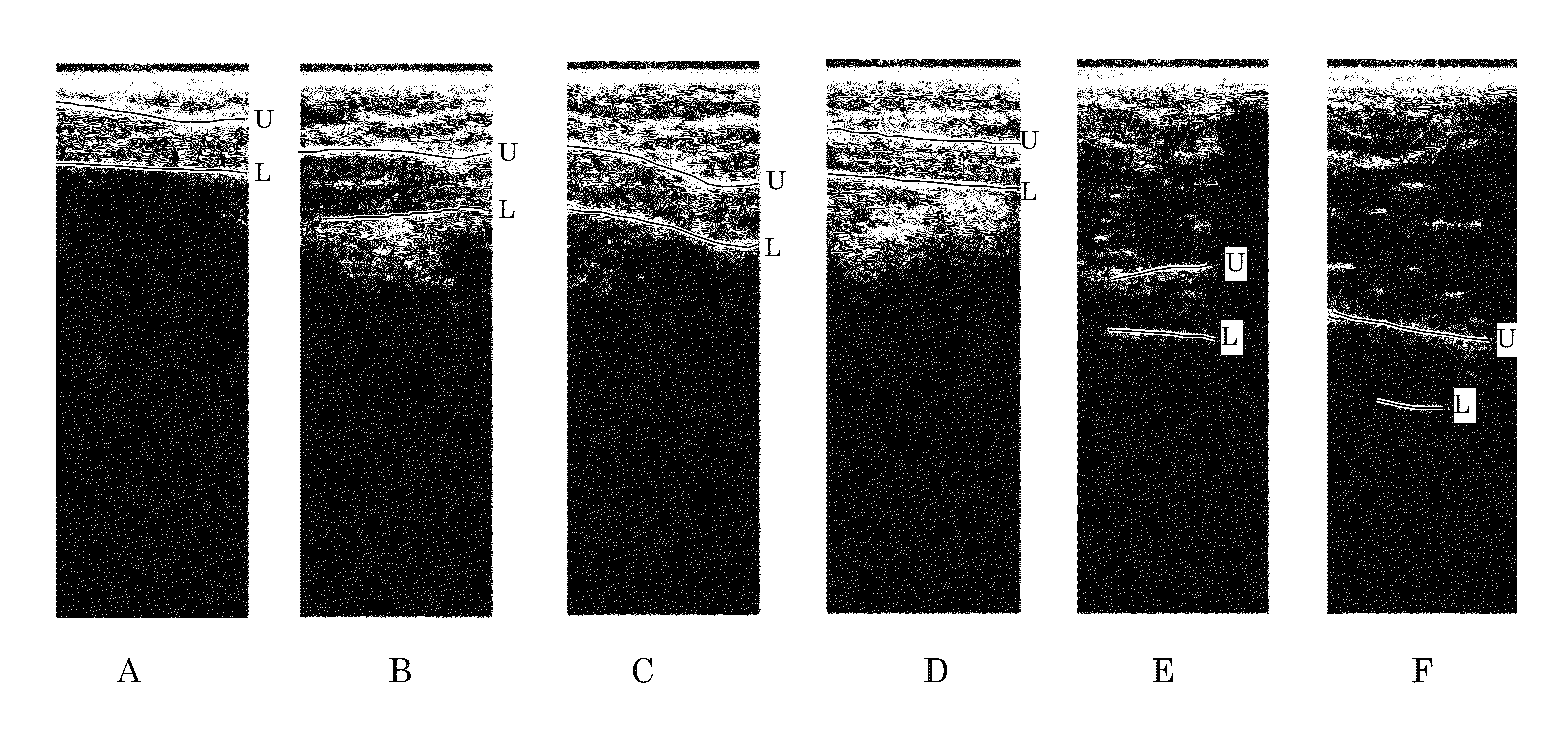
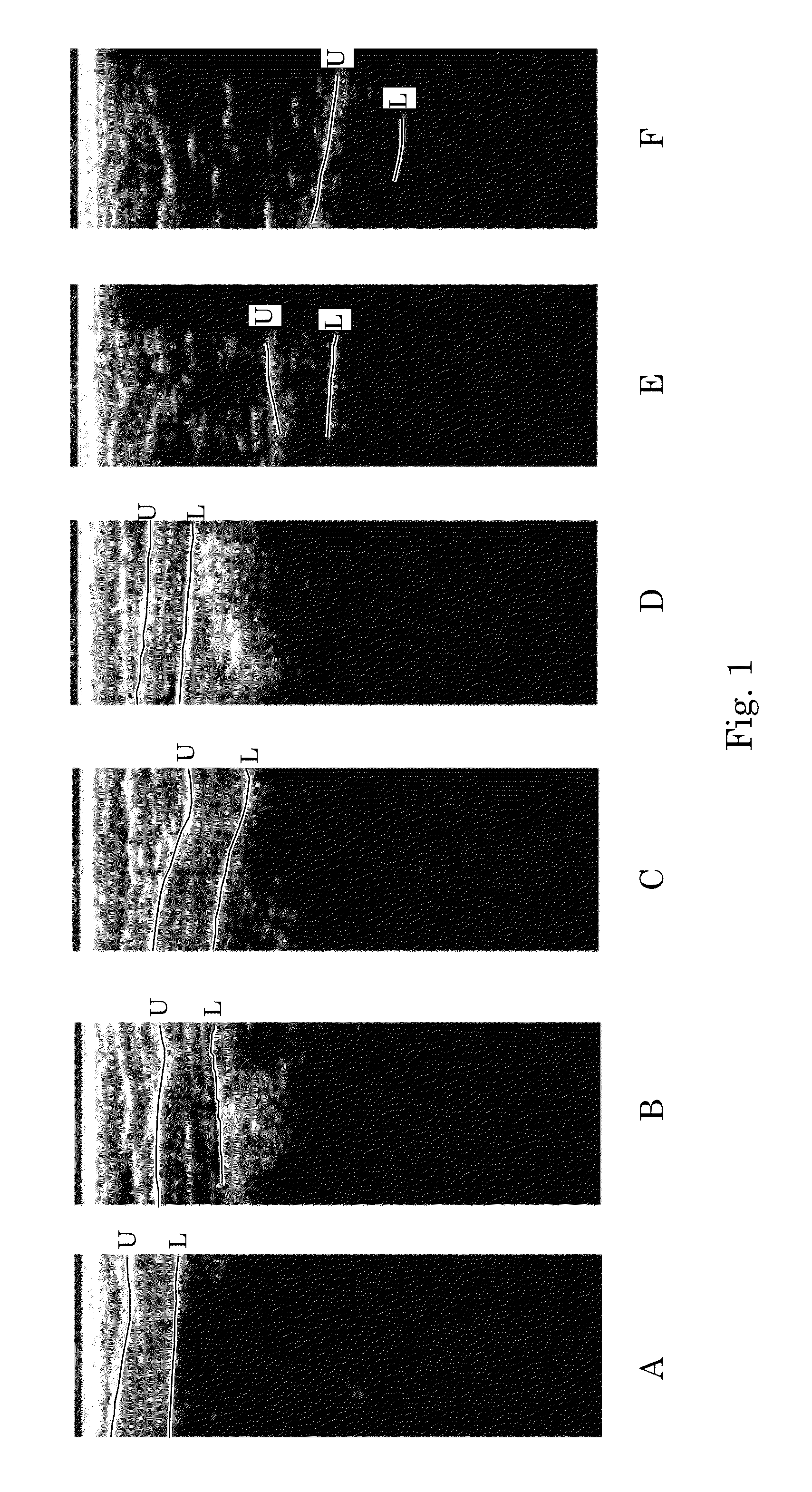
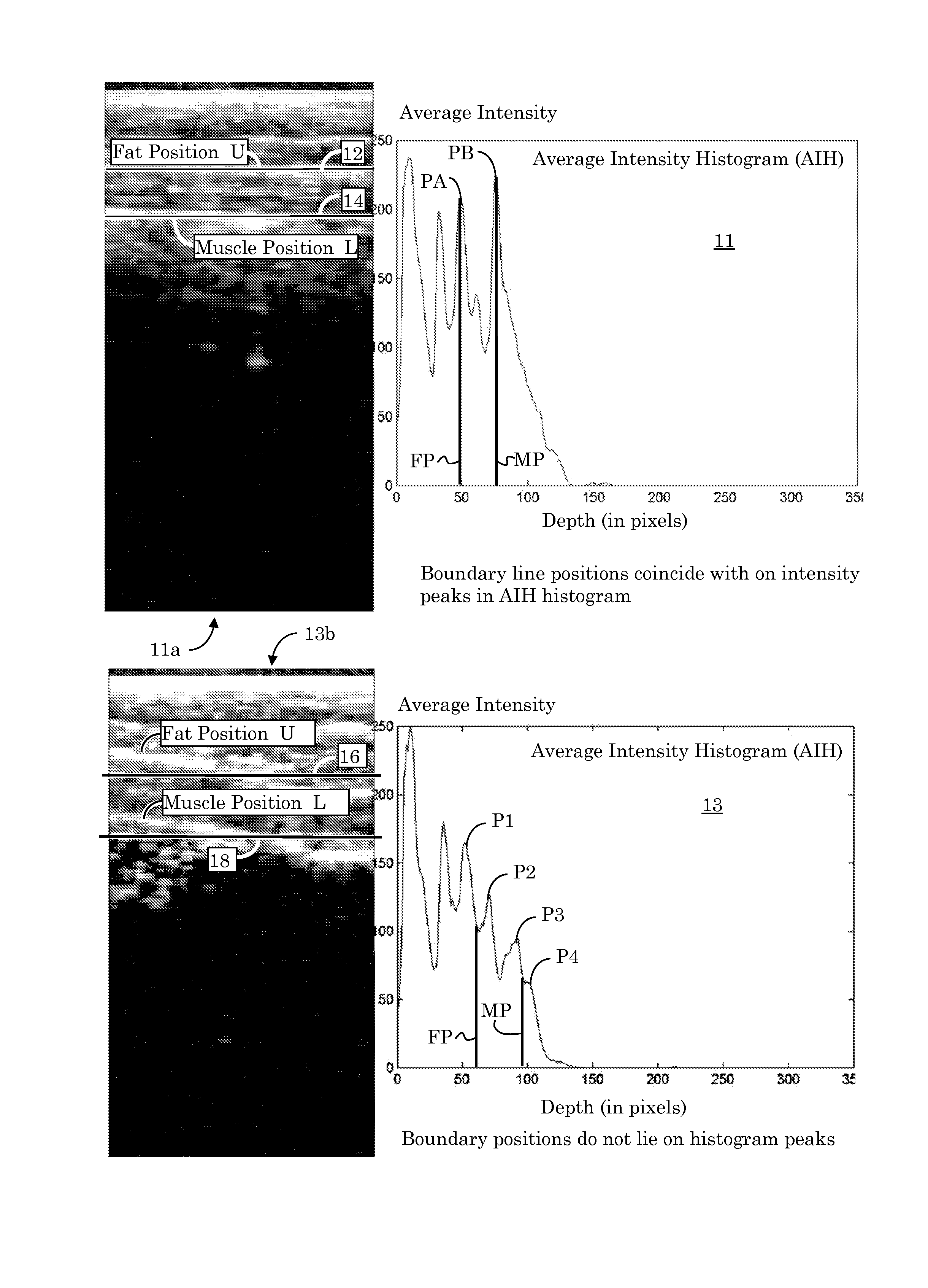
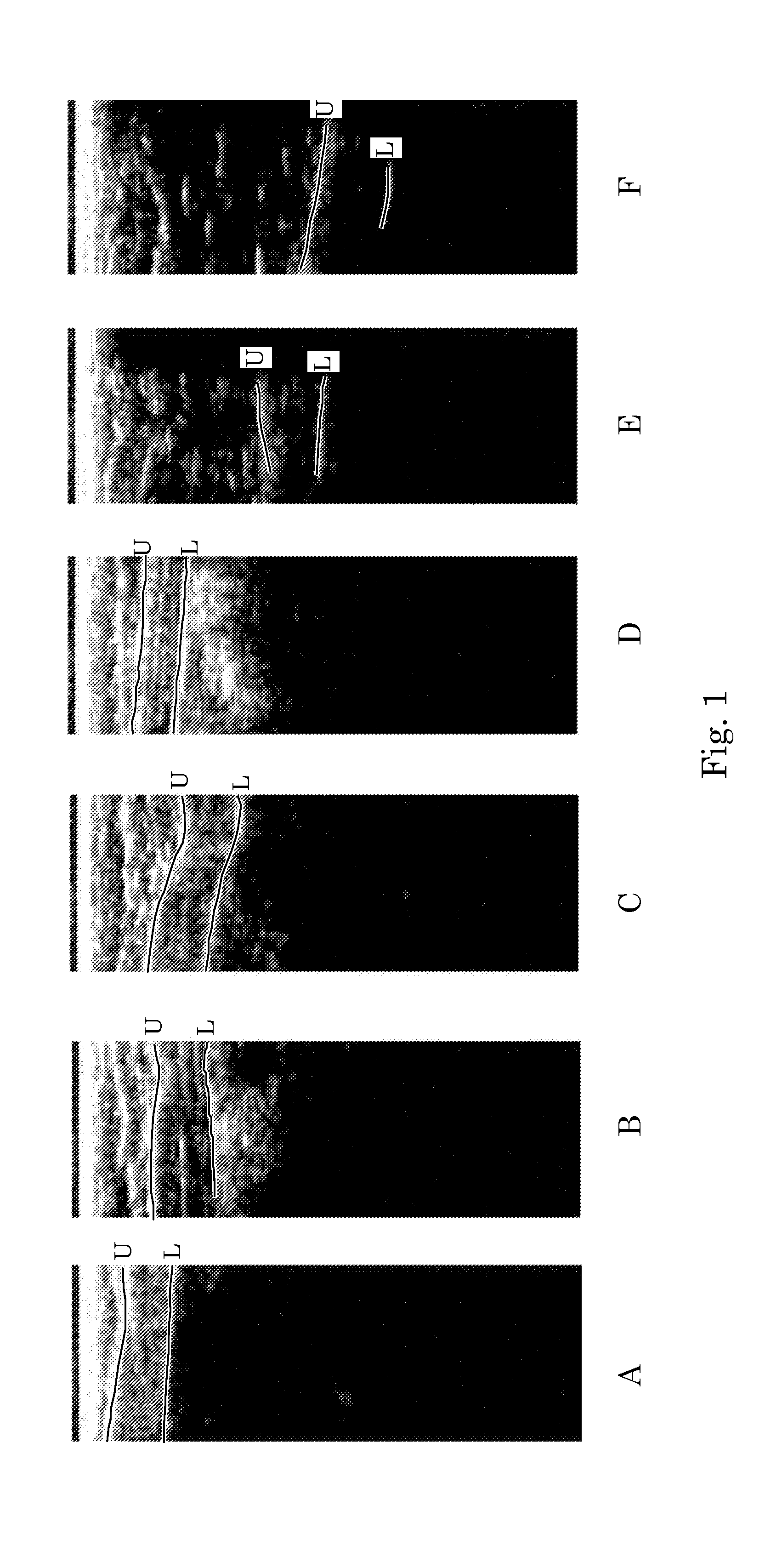
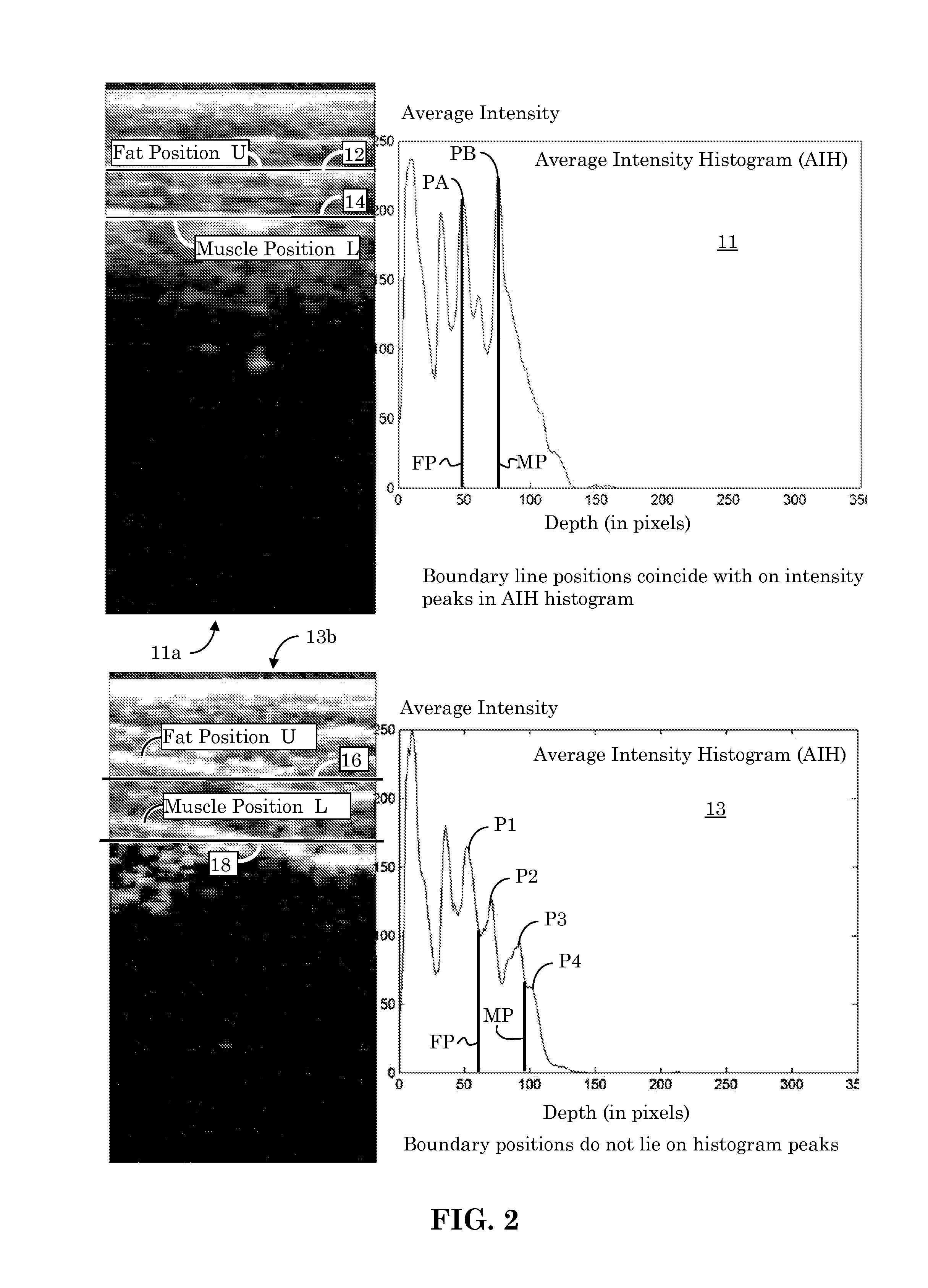
Orientation-Aware Average Intensity Histogram to Indicate Object Boundary Depth in Ultrasound Images
ActiveUS20150055841A1Reduce in quantityImage enhancementImage analysisSonificationIntensity histogram
Linear candidate lines at different angles are used to determine an average intensity for each pixel level of an ultrasound image. The resultant average intensities are collected into a histogram, and the histogram is used to determine the depth positions of tissue boundary lines within an ultrasound image.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Histogram segmentation of FLAIR images
ActiveUS7995825B2Image enhancementImage analysisRegression analysisFluid-attenuated inversion recovery
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES
Ultrasound image object boundary localization by intensity histogram classification using relationships among boundaries
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
System and method for non-rigid multi-modal registration on the GPU
ActiveUS7813592B2Character and pattern recognitionCathode-ray tube indicatorsGraphicsImaging modalities
A method for non-rigid multi-modal registration of digitized images includes providing a reference image and an alignment images acquired from different imaging modalities to a graphics processing unit (GPU), initializing a deformation field for registering said reference image and said alignment image, computing marginal and joint intensity histograms of the reference image and the alignment image as registered by said deformation field, computing gradients of the reference and registered alignment images and of their respective marginal and joint intensity histograms, smoothing said histograms and gradients using Gaussian filters, calculating a new deformation field using said smoothed gradients, and registering said alignment image to said reference image using said deformation field.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
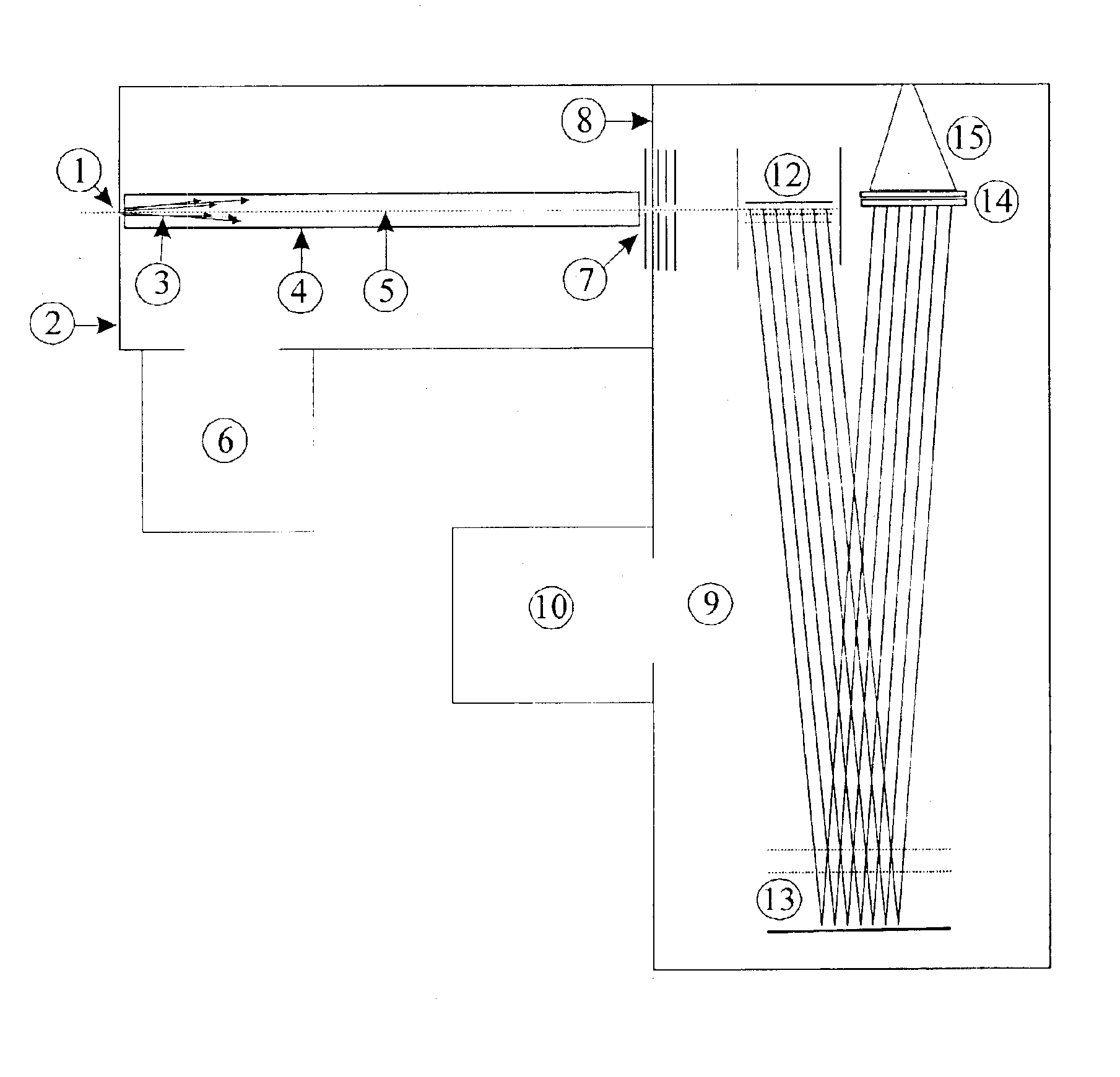
Contact area measurement device and method for measuring contact area
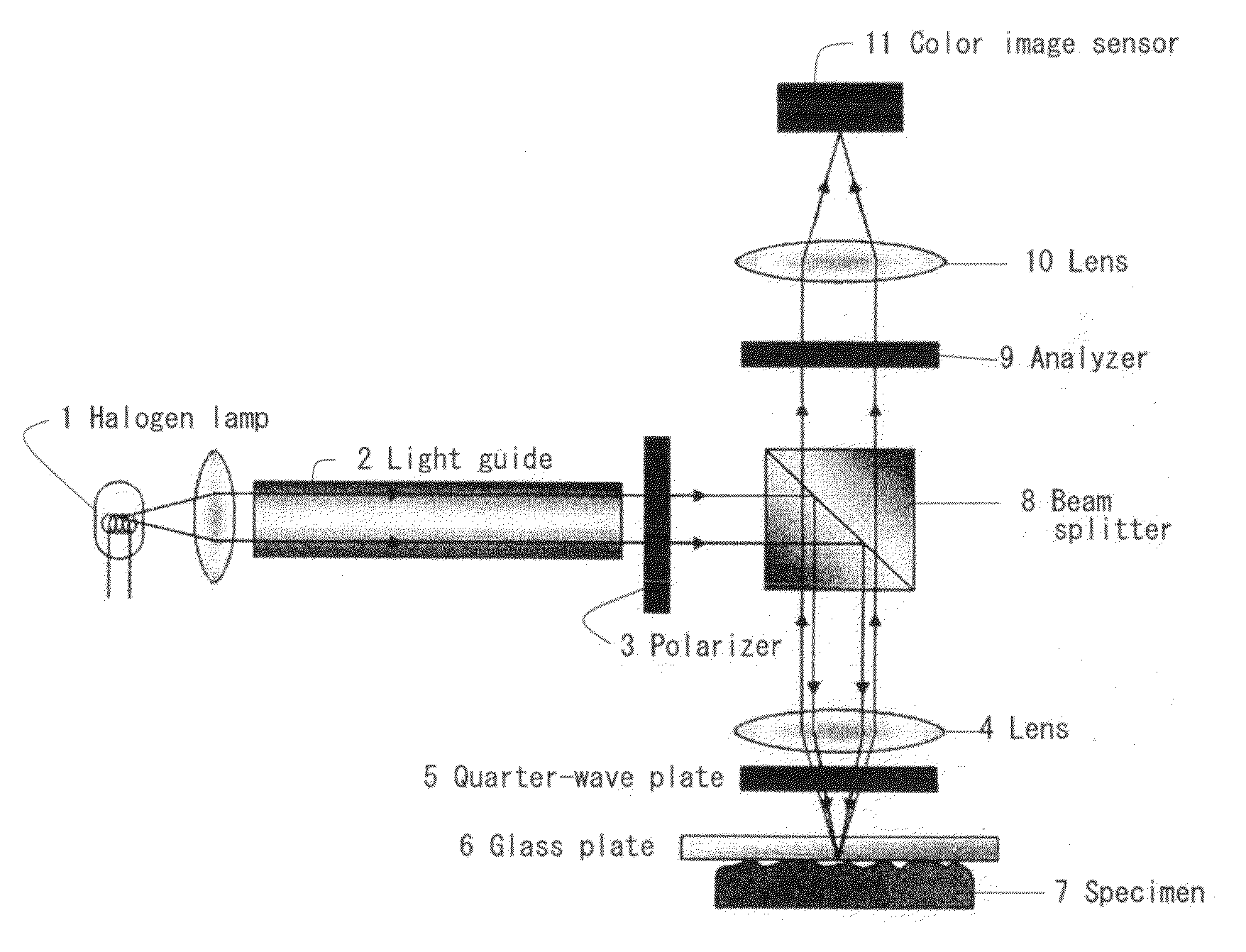
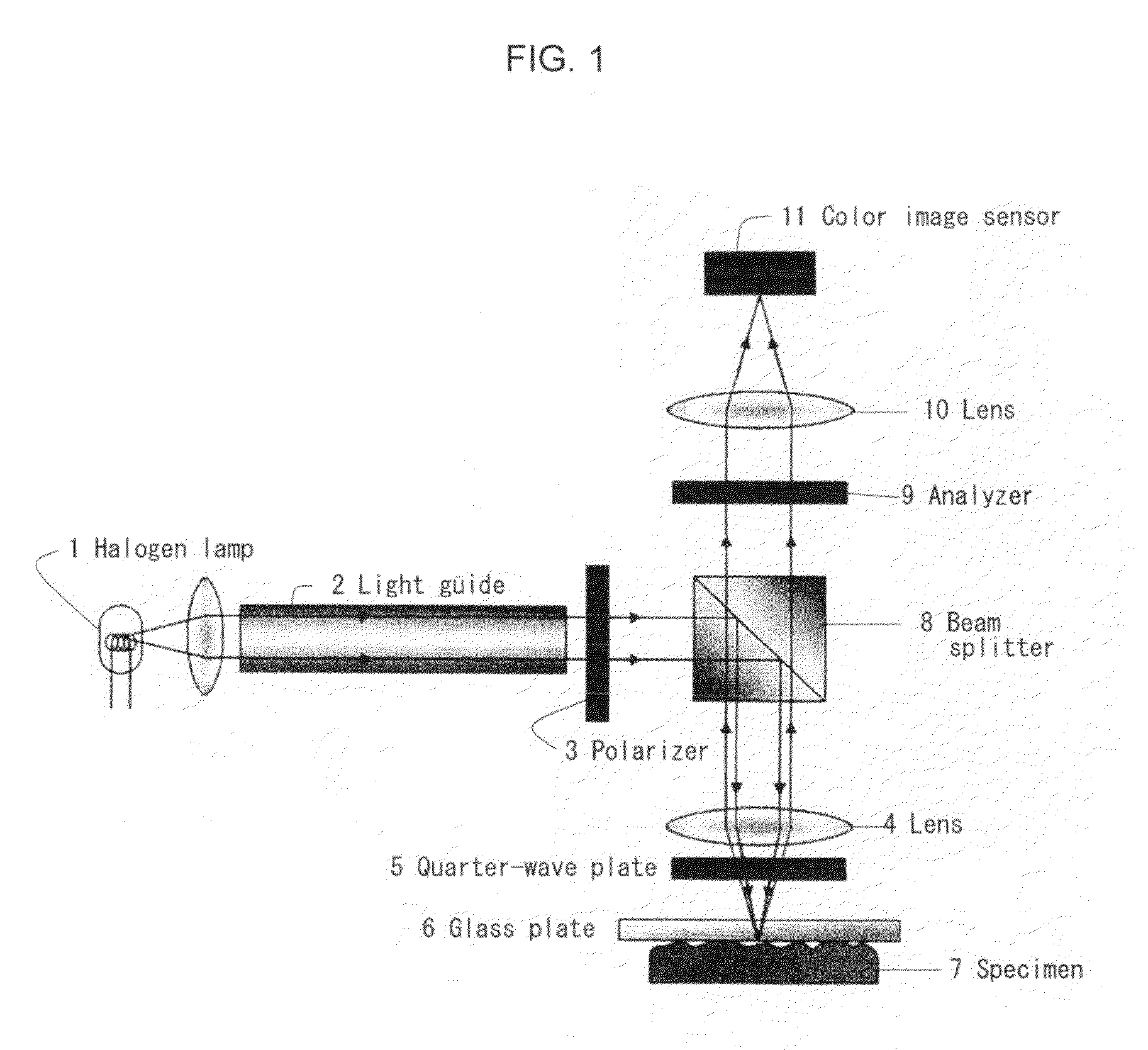
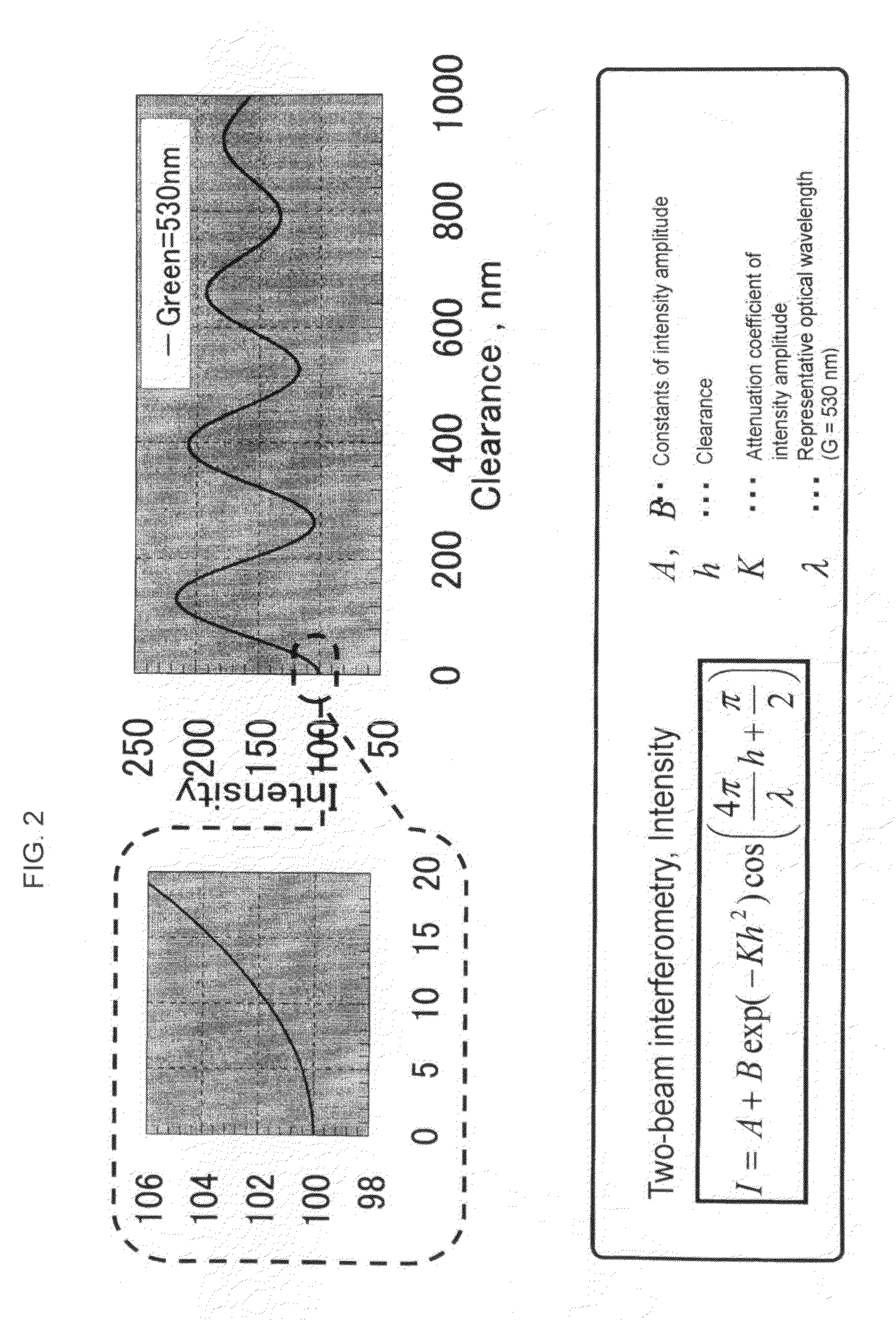
ActiveUS20110013835A1Phase-affecting property measurementsCharacter and pattern recognitionComplex normal distributionMeasurement device
A novel contact area measuring apparatus is provided. The contact area measuring apparatus includes a light transmissive substrate 6 in contact with a specimen 7, illumination means for illuminating the light transmissive substrate 6 with white light from the opposite side of the light transmissive substrate 6 to the specimen 7, interference image acquisition means 11 for acquiring an interference image produced by the light reflected off the specimen 7 and the light reflected off the light transmissive substrate 6, intensity histogram creation means for creating an intensity histogram from information on the intensity of the interference image, and contact area computation means for calculating a contact area from the intensity histogram. The interference image acquisition means 11 acquires an interference image and information on the intensity of the interference image. The intensity histogram creation means forms separate RGB intensity information from the information on the intensity of the interference image and creates a G-intensity histogram. The contact area computation means separates the intensity histogram into a plurality of normal distributions by using optimized approximation of complex normal distribution and calculates the contact area from the lowest-intensity normal distribution.
Owner:NSK WARNER +1
A method, a system and a computer program for determining a threshold in an image comprising image values
The invention relates to a method (1) for determining a threshold in an image comprising image values, said method comprising the steps of: analyzing (3) the image values for determining edge points and associated gradients; classifying (5) image values into classes with respect to the edge points; obtaining (7) image threshold by combining data from the intensity histograms calculated for each class with statistical analysis of the said histograms. The invention further relates to a method of image segmentation, an image processing system and a computer program.
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Method and Apparatus for Determining Asymmetry in an Image
InactiveUS20080095419A1The process is fast and accurateFast and accurate techniqueImage enhancementImage analysisVoxelIntensity histogram
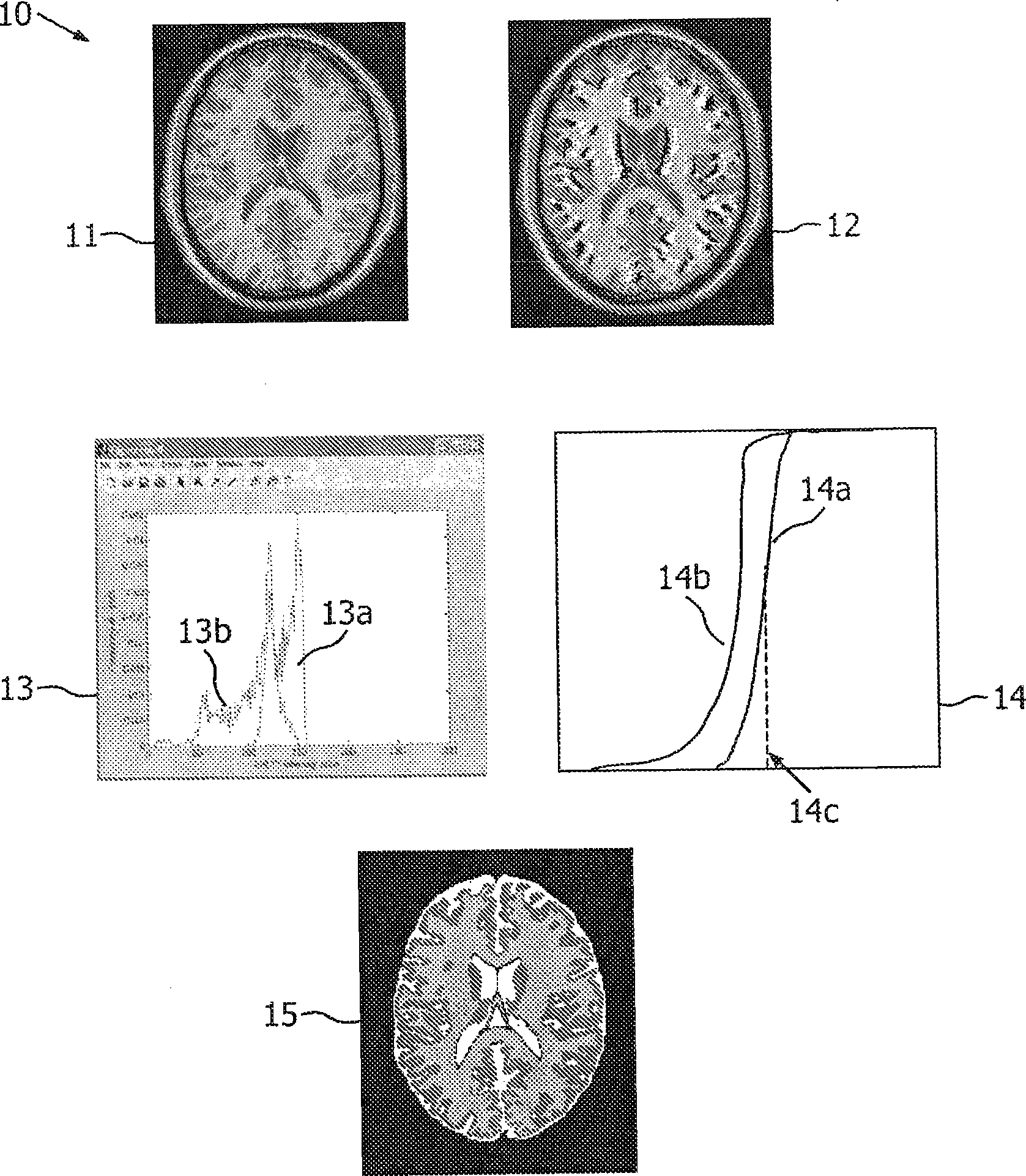
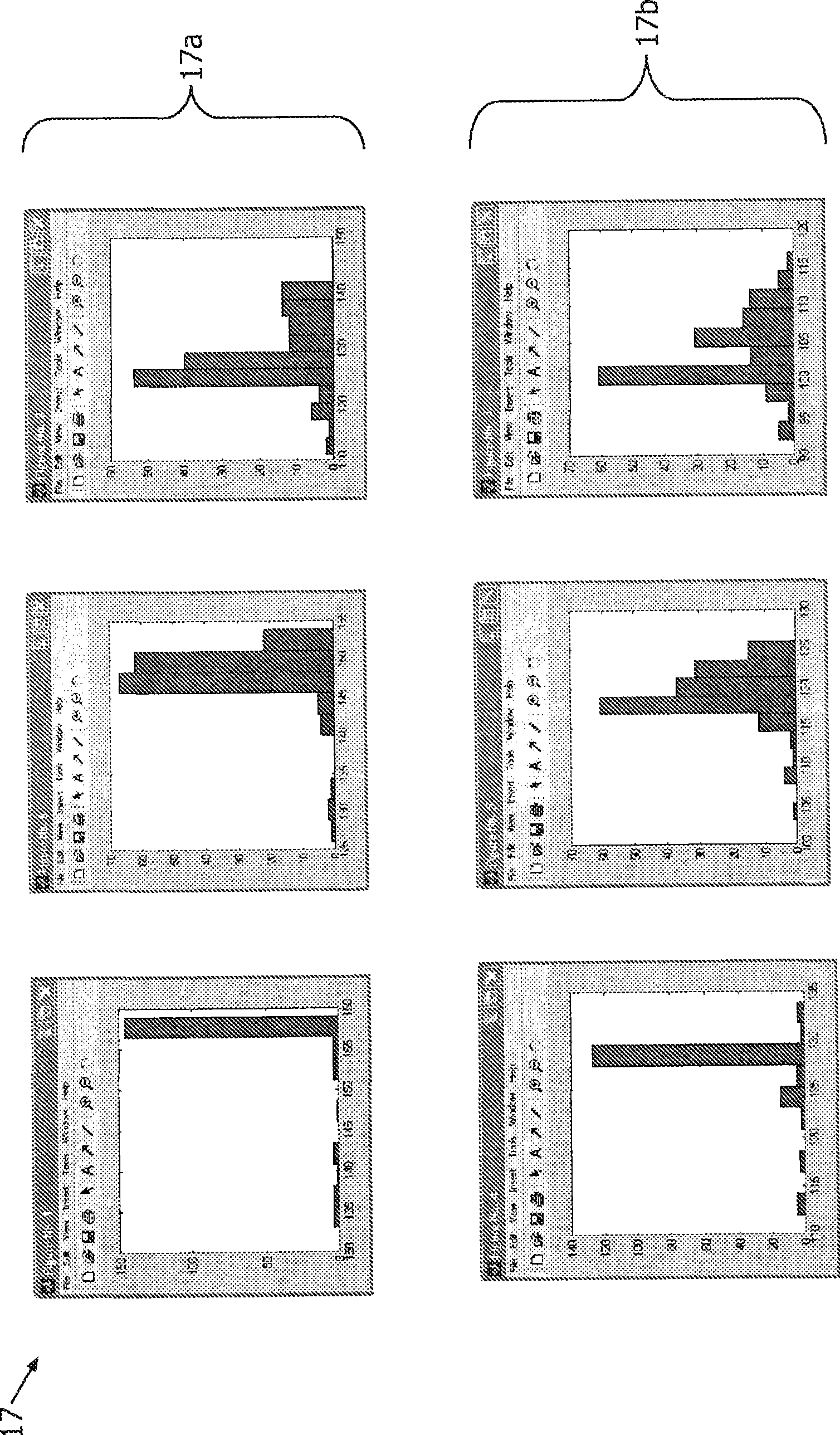
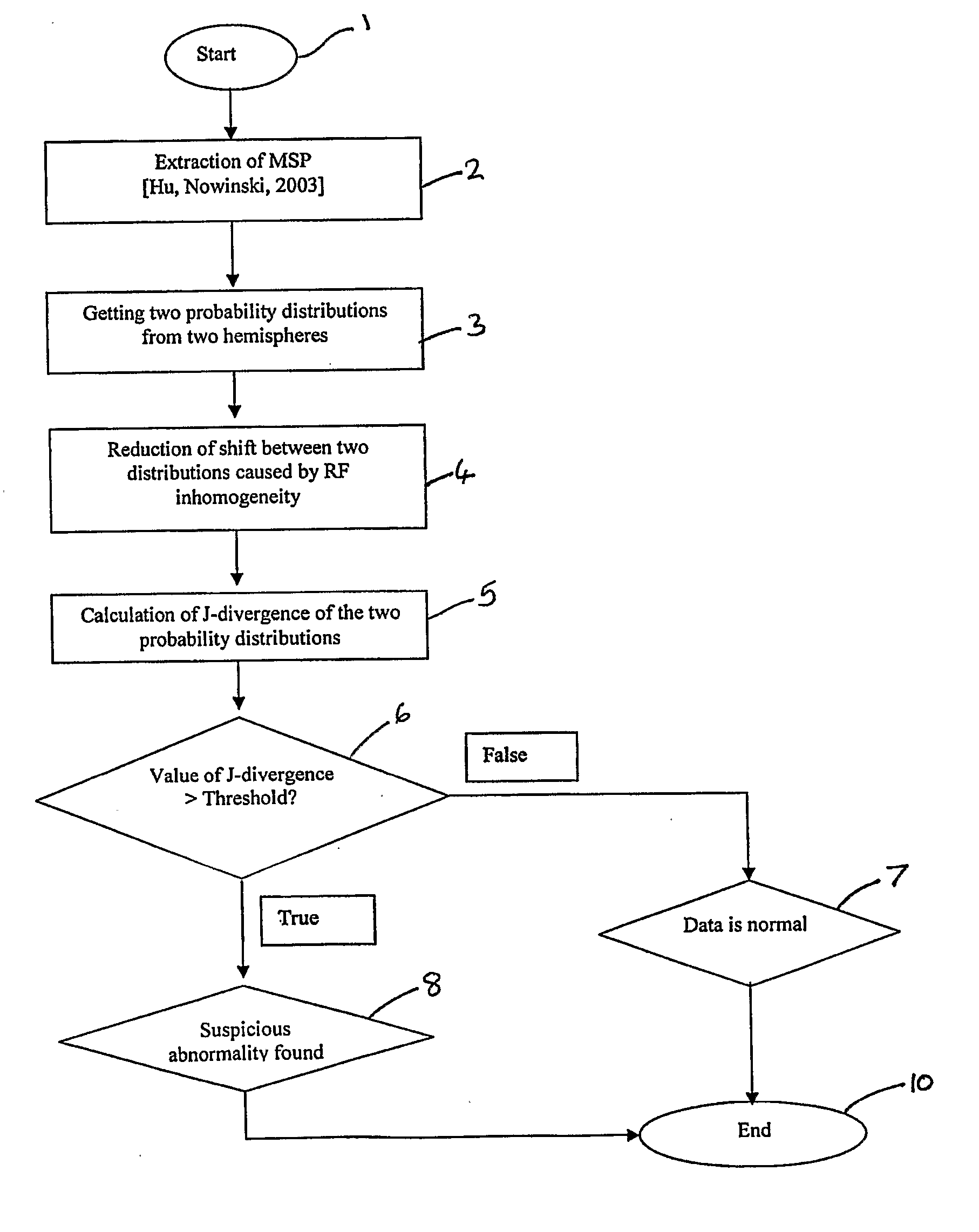
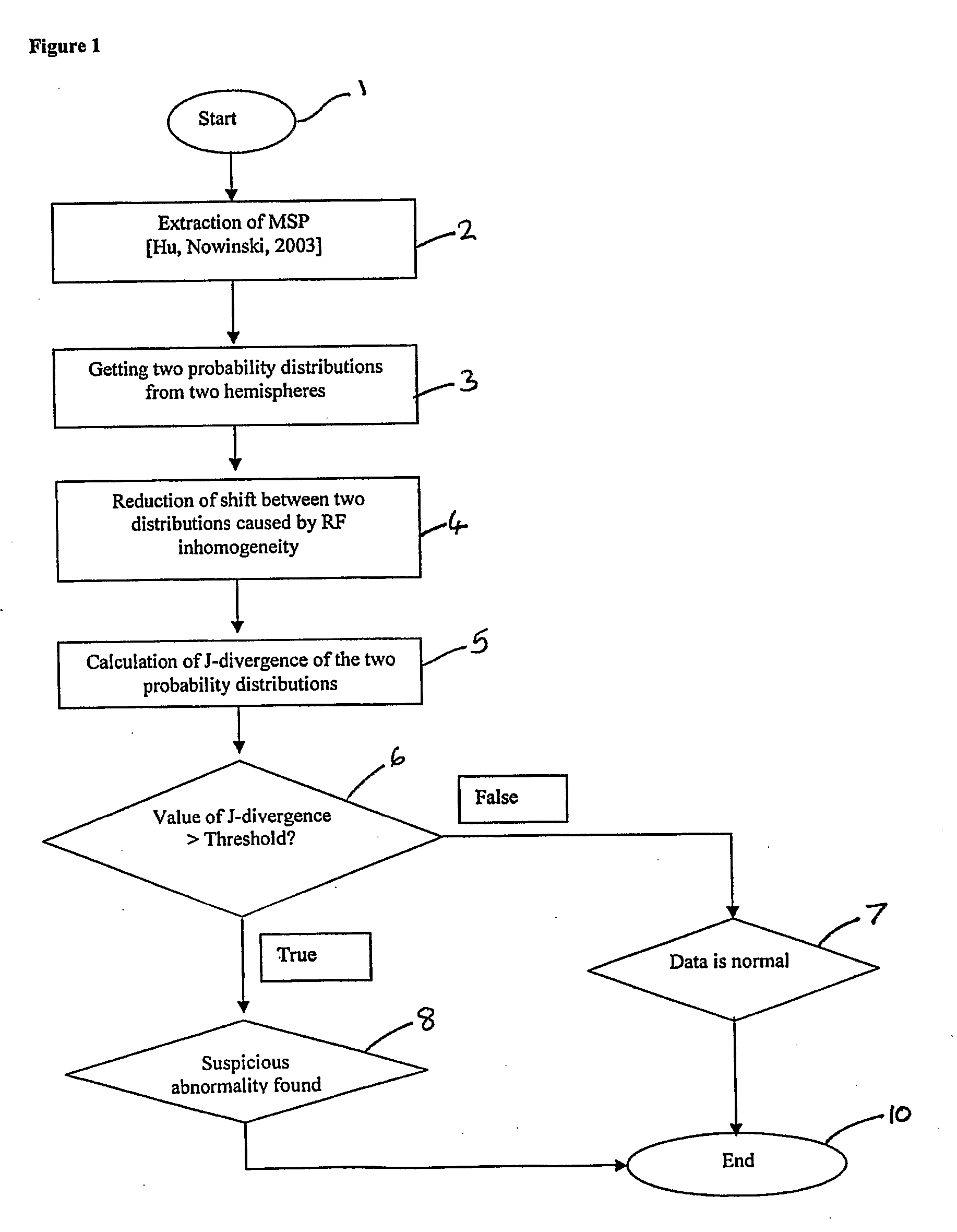
A method for determining asymmetry in an image such as an MR image of a brain comprises determining a symmetry plane to divide the image into a first part and a second part representative of, for example, the hemispheres of the brain. The probability distributions of voxels against intensities are determined for the first and second parts and histograms of intensities representative of the parts are generated. Compensation is made for any relative shift along a predetermined axis between the histograms. A divergence value based on a distance between the first and second histograms is then calculated and it is determined if the calculated divergence value is greater than a predetermined threshold. A divergence of greater than the predetermined threshold is indicative of asymmetry in the image that may be considered as suspicious for abnormality. There is also disclosed an apparatus for determining asymmetry in an image.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
Method and system for calibrating a time of flight positron emission tomography system
InactiveUS7345281B2Material analysis by optical meansCalibration apparatusIntensity histogramCompanion animal
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Orientation-aware average intensity histogram to indicate object boundary depth in ultrasound images
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Haze removing method for large-area background light haze-containing image
InactiveCN103745438AAvoid difficult fine-tuningQuality improvementImage enhancementIntensity histogramPeak value
The invention discloses a haze removing method for a large-area background light haze-containing image. The haze removing method comprises the steps of 1) obtaining an intensity histogram A of a haze-containing image, judging whether the histogram A meets the requirement of having large-area background light or not and calculating the horizontal coordinate xA of partial peak values of the background light; 2) haze removing the image by using a dark channel prior algorithm, calculating a histogram B of a haze-removed picture and determining the coordinate (xB, hB) on which burr occurs; 3) reestablishing the histogram B: reserving the part with intensity which is smaller than xB, reestablishing the part with intensity which is larger than xB and performing reestablishment by adopting a monotonic increasing convex function; 4) performing histogram specification to the reestablished histogram and the haze-removed picture to obtain an improved haze-removed picture. The haze removing method for the large-area background light haze-containing image has the advantages that since the dark channel prior algorithm is post-processed through the histogram, the method is simple and flexible to operate; since different parameters are set according to different specific images, the situation that the result of dark channel prior processing is difficult to fine tune is avoided; the algorithm efficiency is higher, the quality of the obtained haze-removed picture is higher and the picture is more close to an actual haze-free picture.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
3D segmentation by voxel classification based on intensity histogram thresholding intialised by K-means clustering
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Electronic camera
InactiveUS7151566B2Improve accuracyIncrease speedTelevision system detailsColor television detailsIntensity histogramComputer science
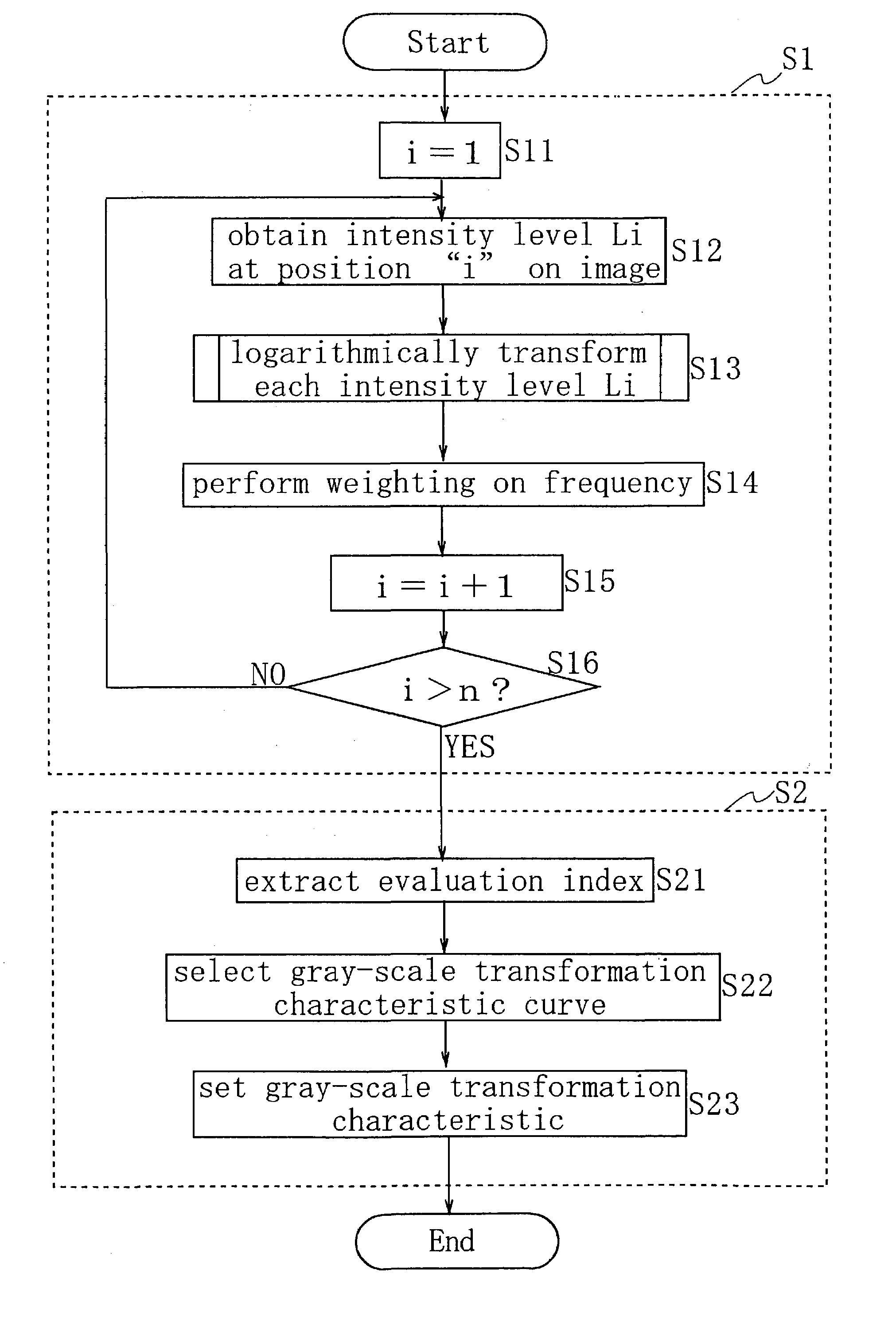
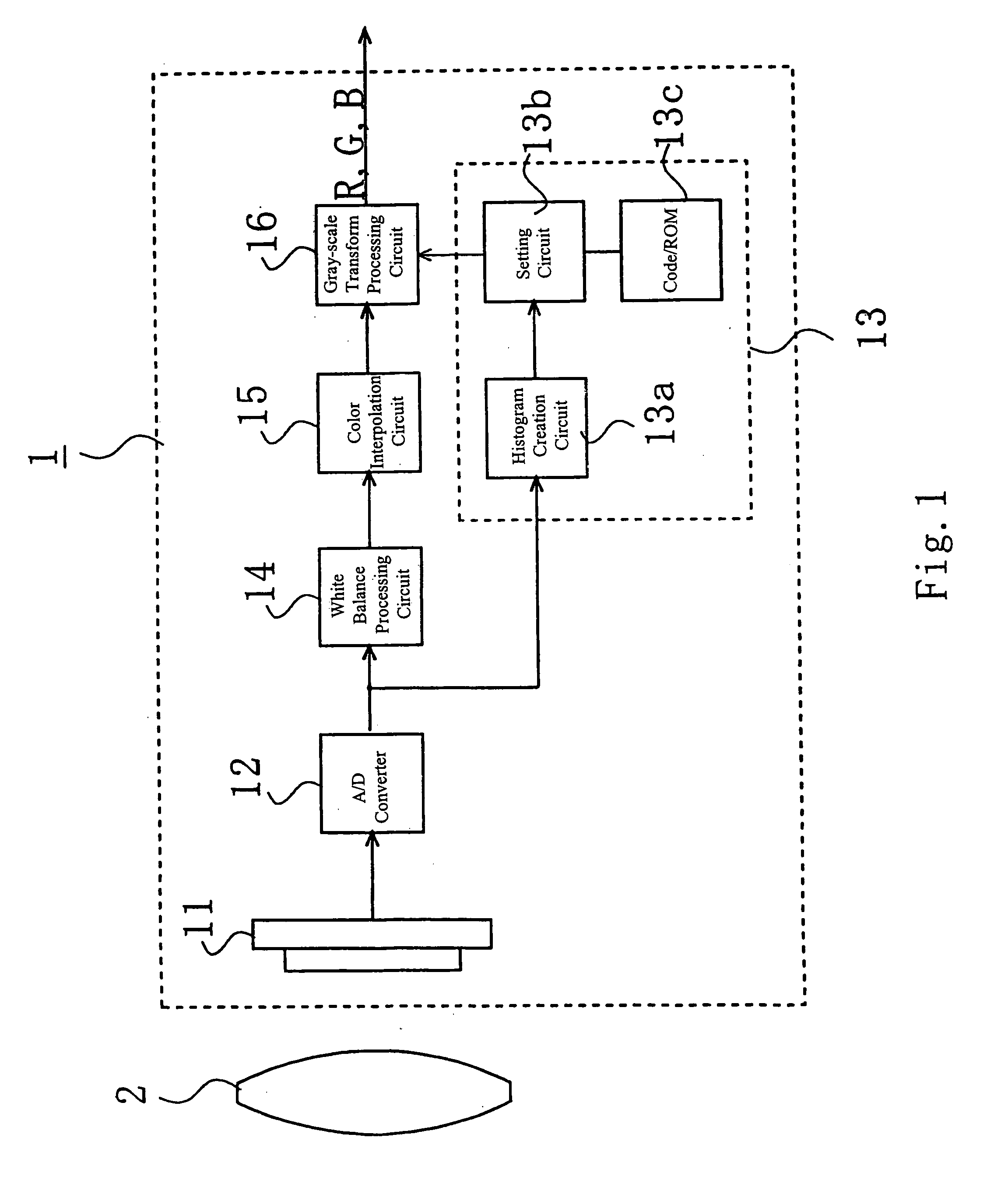
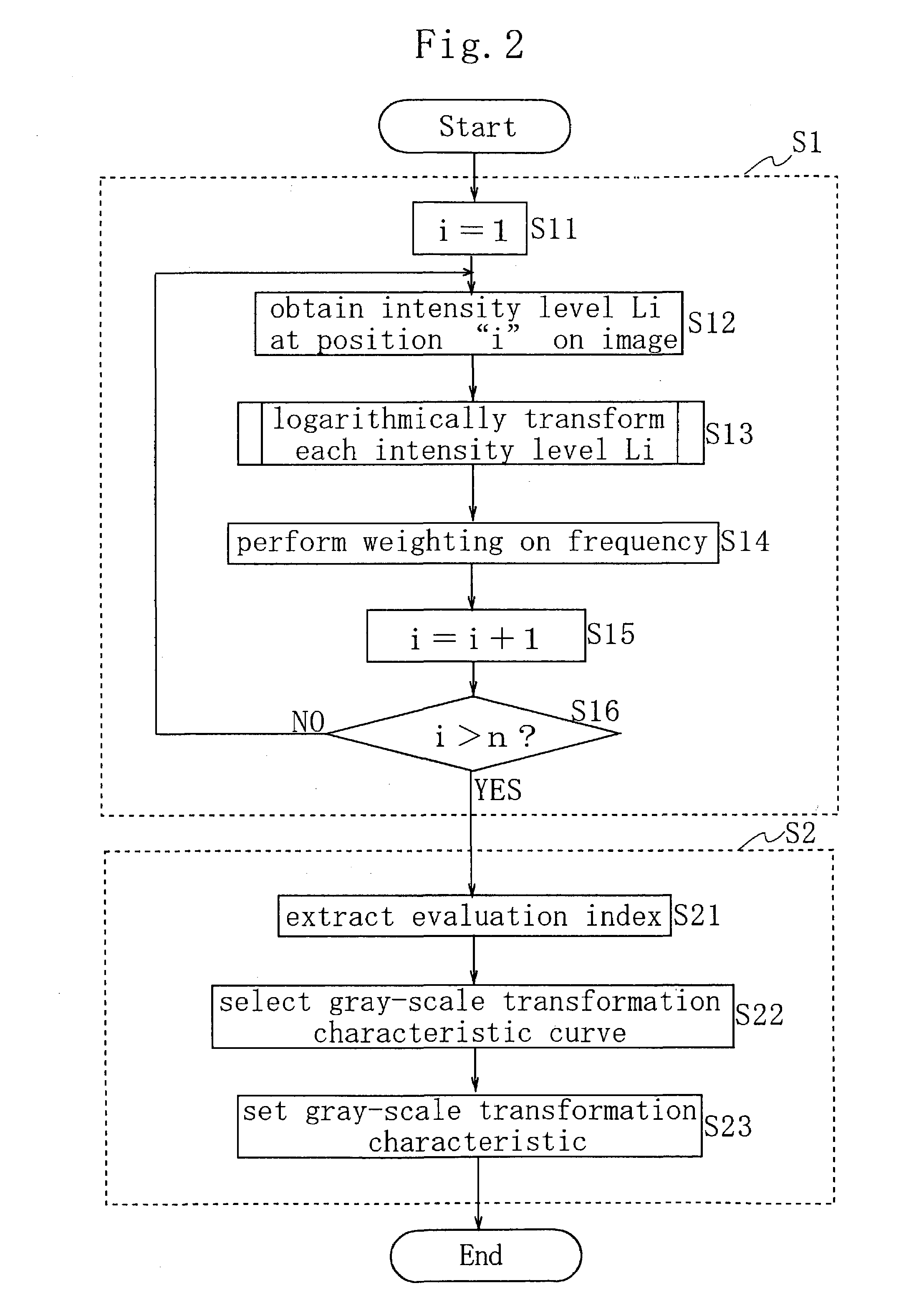
The objects of the present invention are to provide an electronic camera which is able to precisely evaluate the type of a subject and perform an optimal gray-scale transformation on the image of the subject. The electronic camera comprises: an histogram creation unit for creating an intensity histogram of an image obtained with an image sensor; and a setting unit for setting a gray-scale transformation characteristic to be applied to the image according to the created intensity histogram. Using the created histogram makes it possible to precisely evaluate the type of the subject and set an optimal gray-scale transformation characteristic.
Owner:NIKON CORP
Ultrasound Image Object Boundary Localization by Intensity Histogram Classification Using Relationships Among Boundaries
Fatty tissue boundary depths and muscle tissue boundary depths are identified in an ultrasound image by first creating an average intensity histogram of the ultrasound image. The histogram has a plurality of peaks, but has the characteristic that one of its peaks corresponds to a fat boundary depth, and a second of its peaks corresponds to a muscle boundary depth. A first classifier based solely on the local-characteristics of individual peaks is used to identify a first fat tissue depth. A second classifier trained to find a muscle depth given a fat depth, receives the output from the first classifier and identifies an output muscle tissue depth relative to the first fat tissue depth. A third classifier trained to find a fat boundary depth given a muscle boundary depth, receives the output muscle tissue depth and outputs a second fat boundary depth.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com