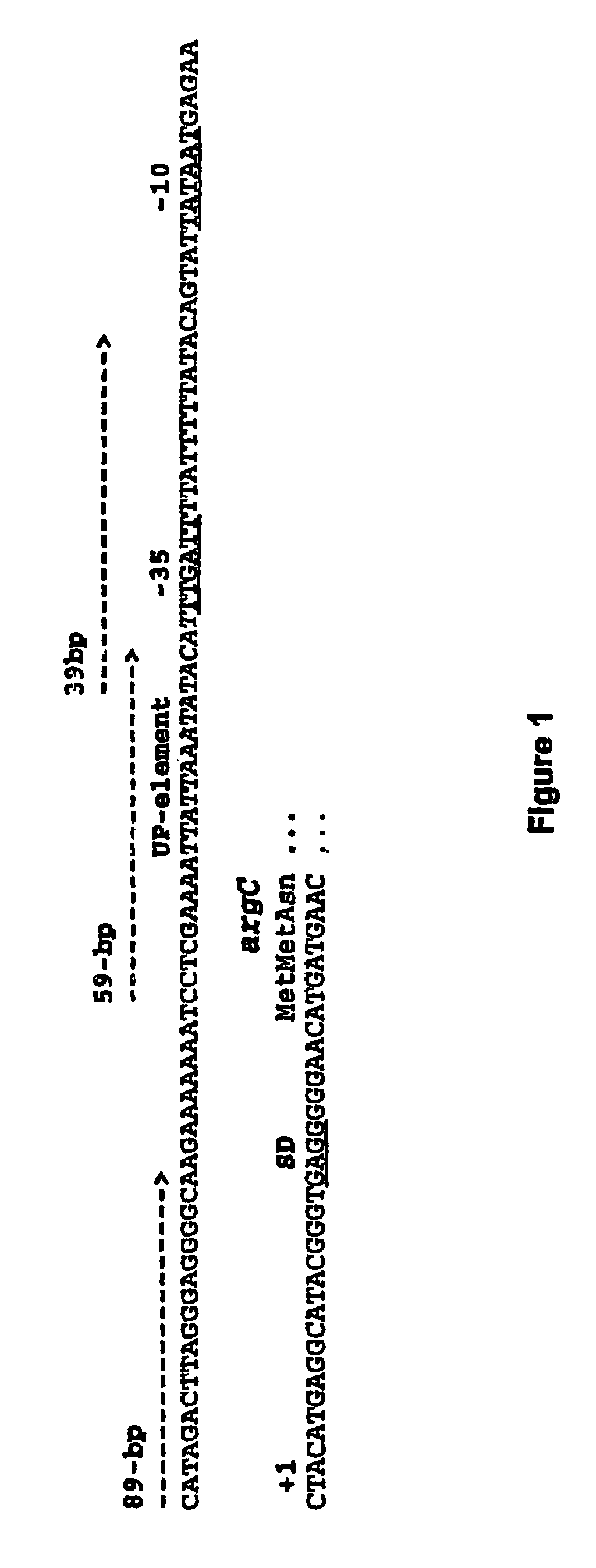
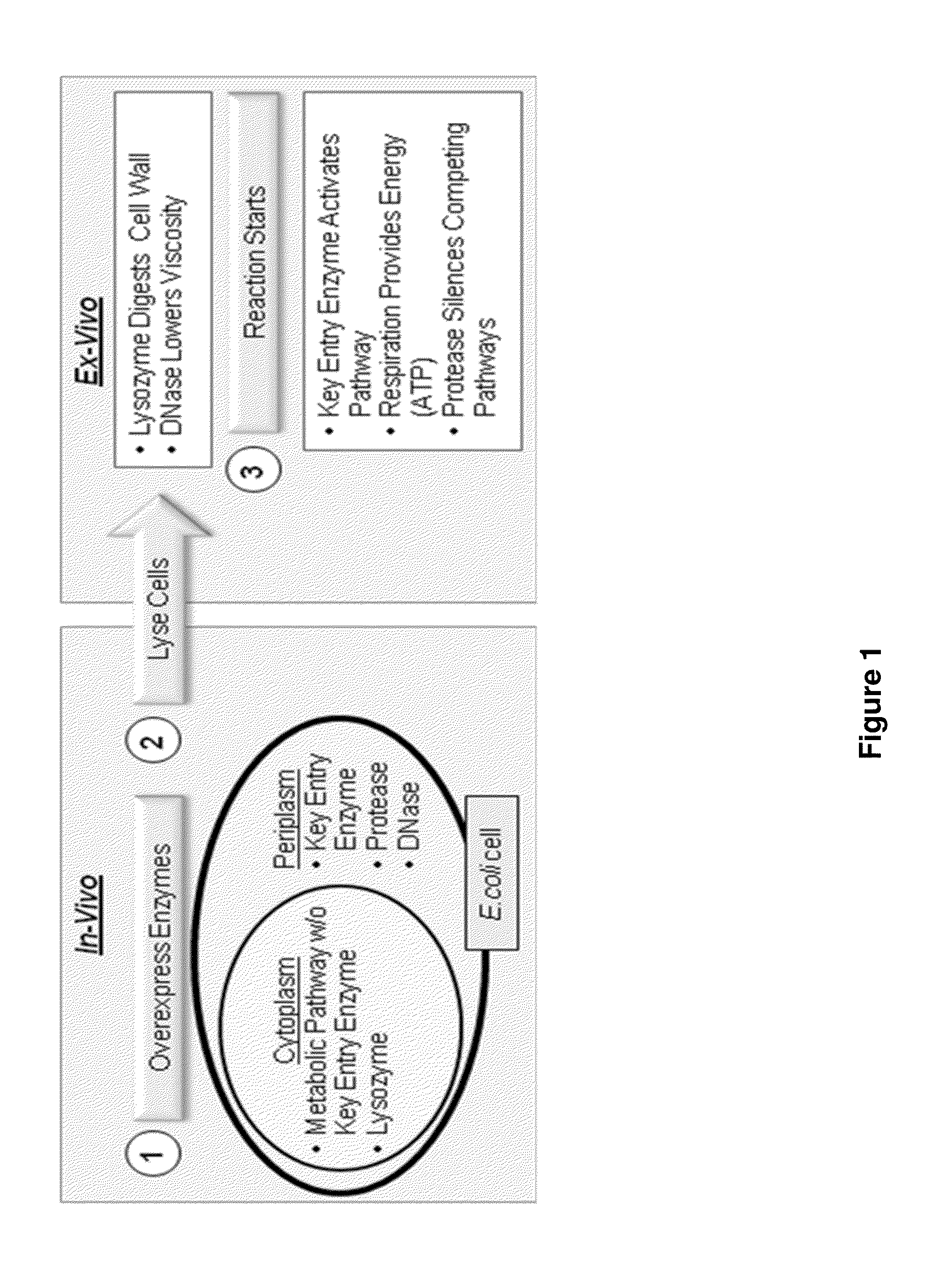
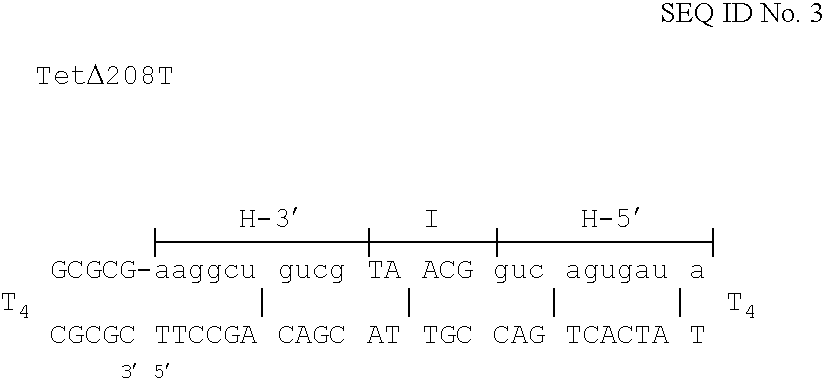Patents
Literature
84 results about "Cell-free system" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
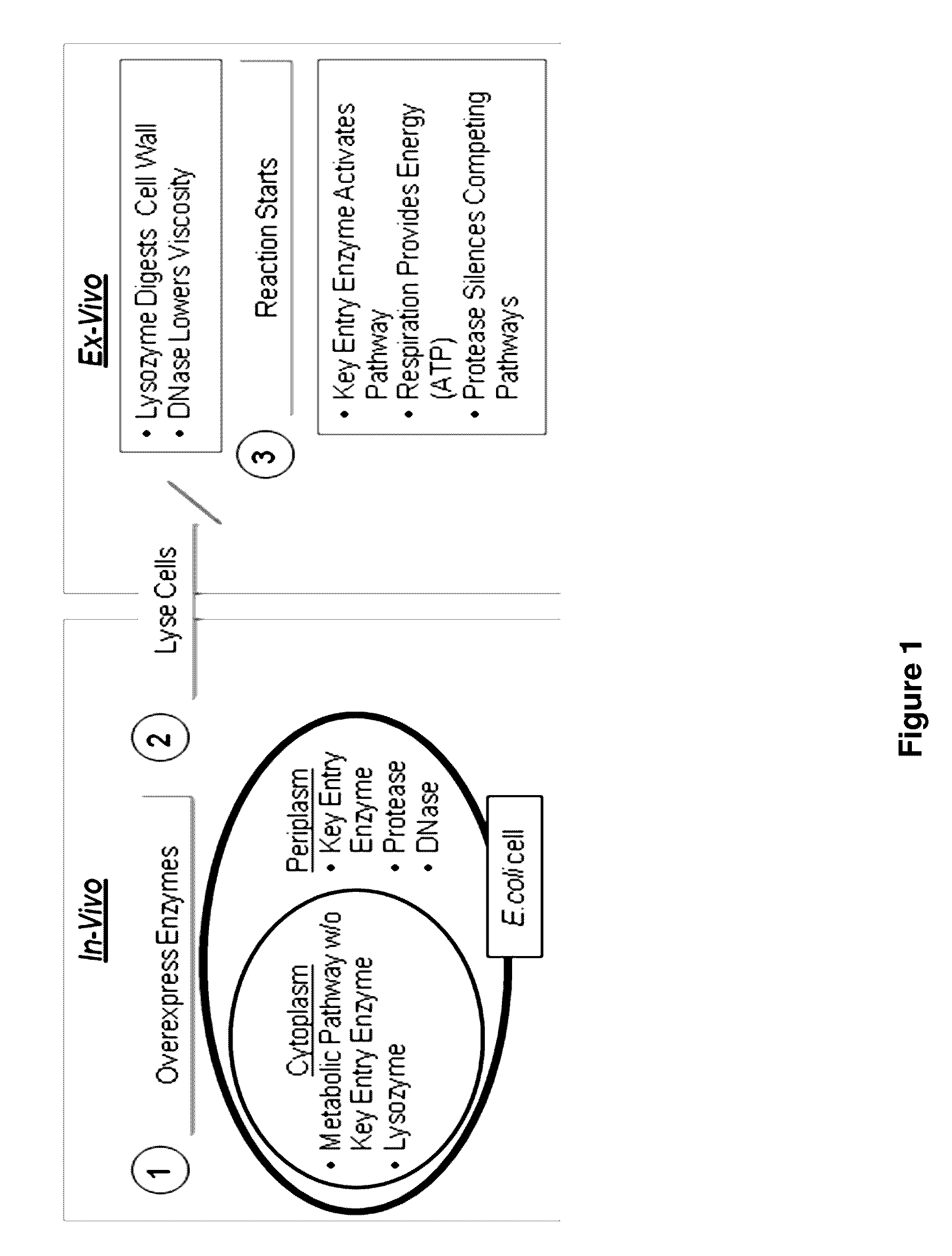
A cell-free system is an in vitro tool widely used to study biological reactions that happen within cells apart from a full cell system, thus reducing the complex interactions typically found when working in a whole cell. Subcellular fractions can be isolated by ultracentrifugation to provide molecular machinery that can be used in reactions in the absence of many of the other cellular components. Eukaryotic and prokaryotic cell internals have been used for creation of these simplified environments. These systems have enabled cell-free synthetic biology to emerge, providing control over what reaction is being examined, as well as its yield, and lessening the considerations otherwise invoked when working with more sensitive live cells.
Eukaryotic use of non-chimeric mutational vectors
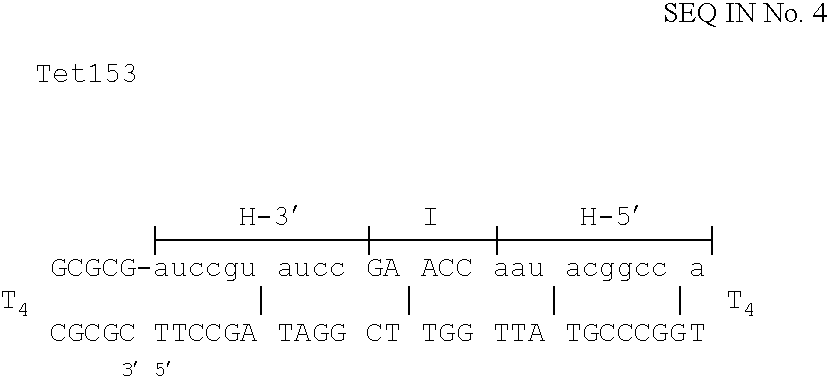
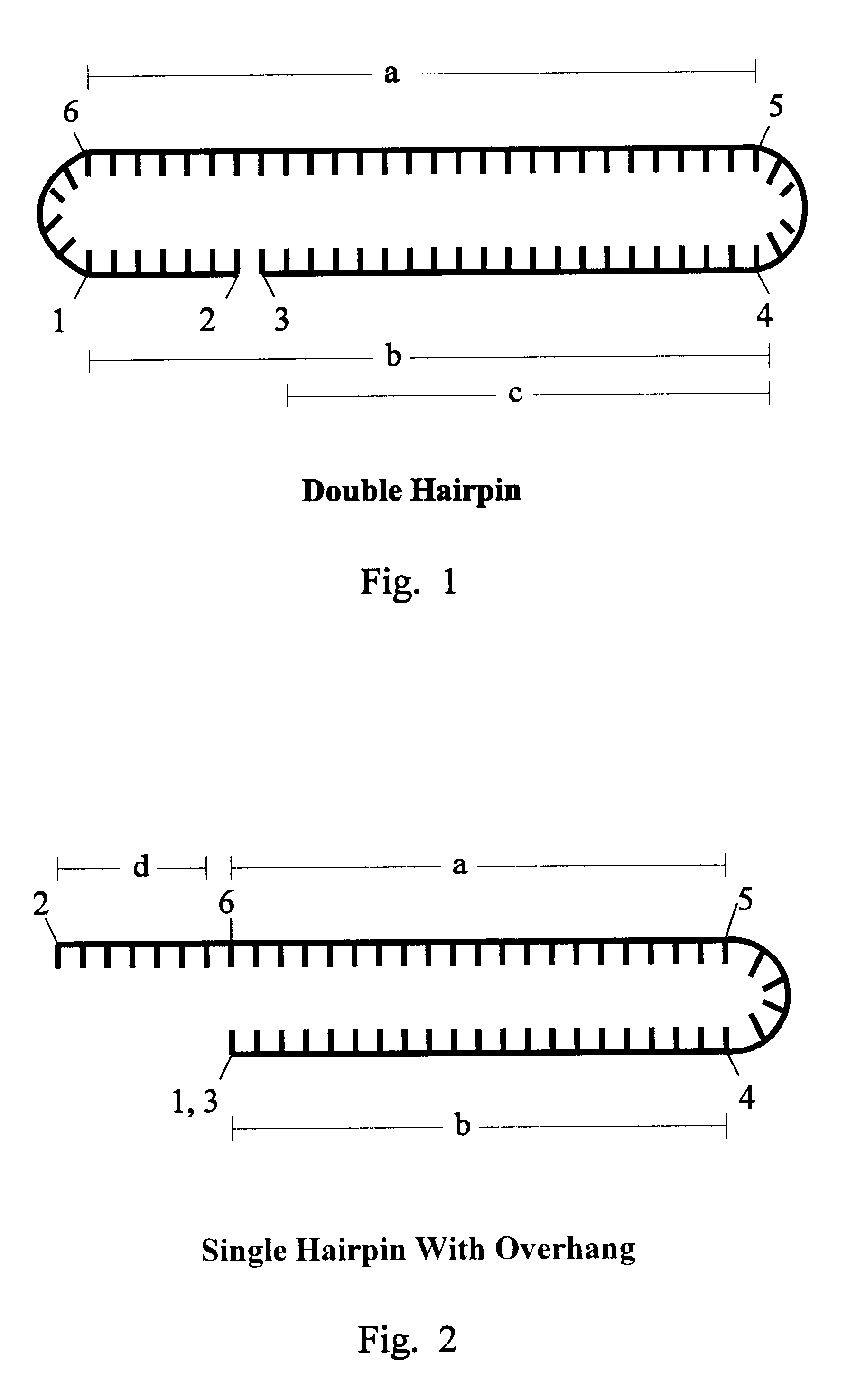
The invention is based on the reaction of Duplex Mutational Vector in a cell-free system containing a cytoplasmic cell extract and a test plasmid. The reaction specifically converts a mutant kanr gene to recover the resistant phenotype in transformed MutS, RecA deficient bacteria. Using this system a type of Duplex Mutational Vector termed a Non-Chimeric Mutational Vector, having no RNA:DNA hybrid-duplex is shown to be an effective substrate for eukaryotic enzymes. The invention concerns the use of Non-Chimeric Mutational Vectors protected from 3' exonuclease attack in eukaryotic cells. Such protection can be conferred by replacement of a tetrathymidine linker by a nuclease resistant oligonucleotide, such as tetra-2'-O-methyl-uridine, to link the two strands of the recombinagenic oligonucleobase.
Owner:VALIGEN US +1
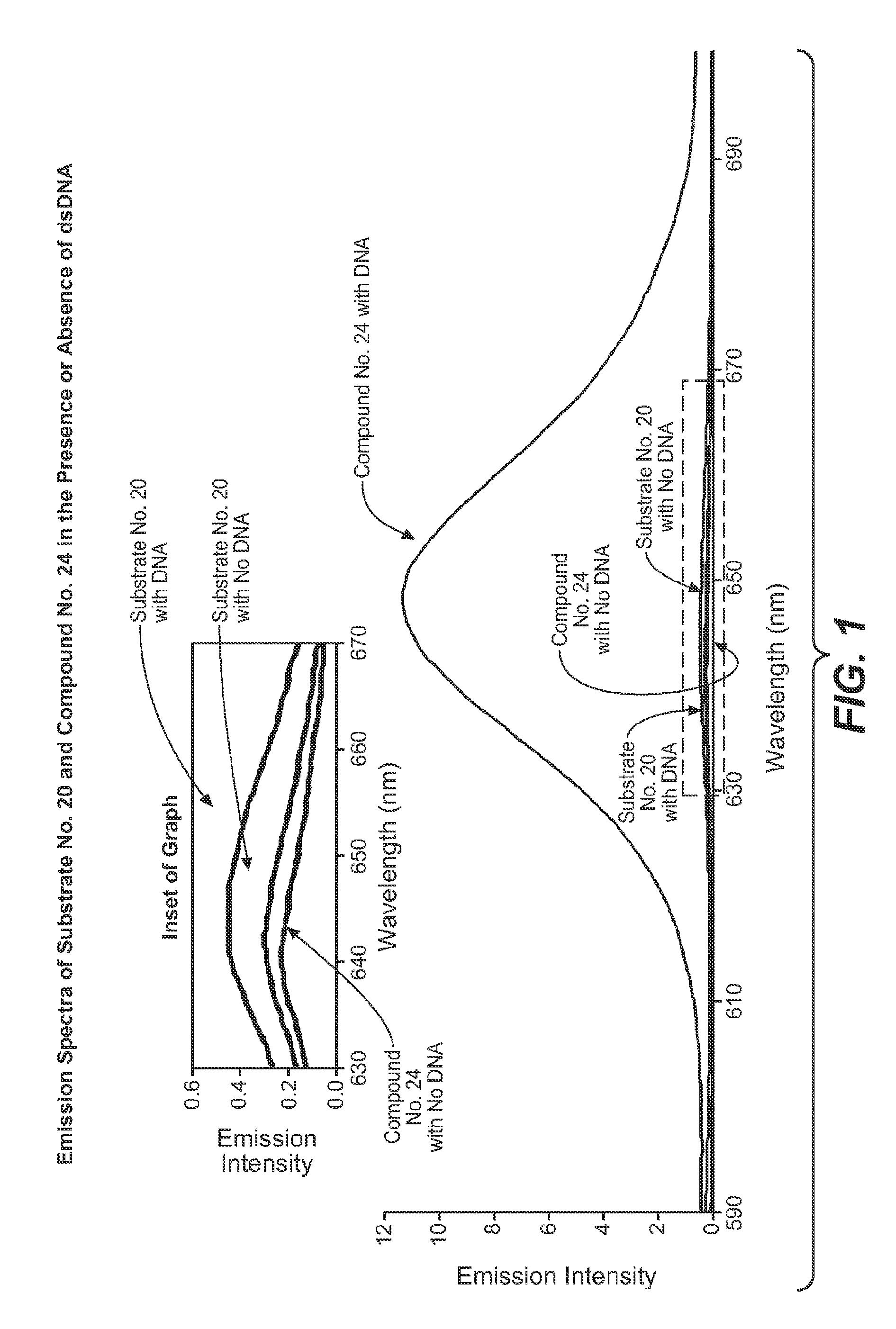
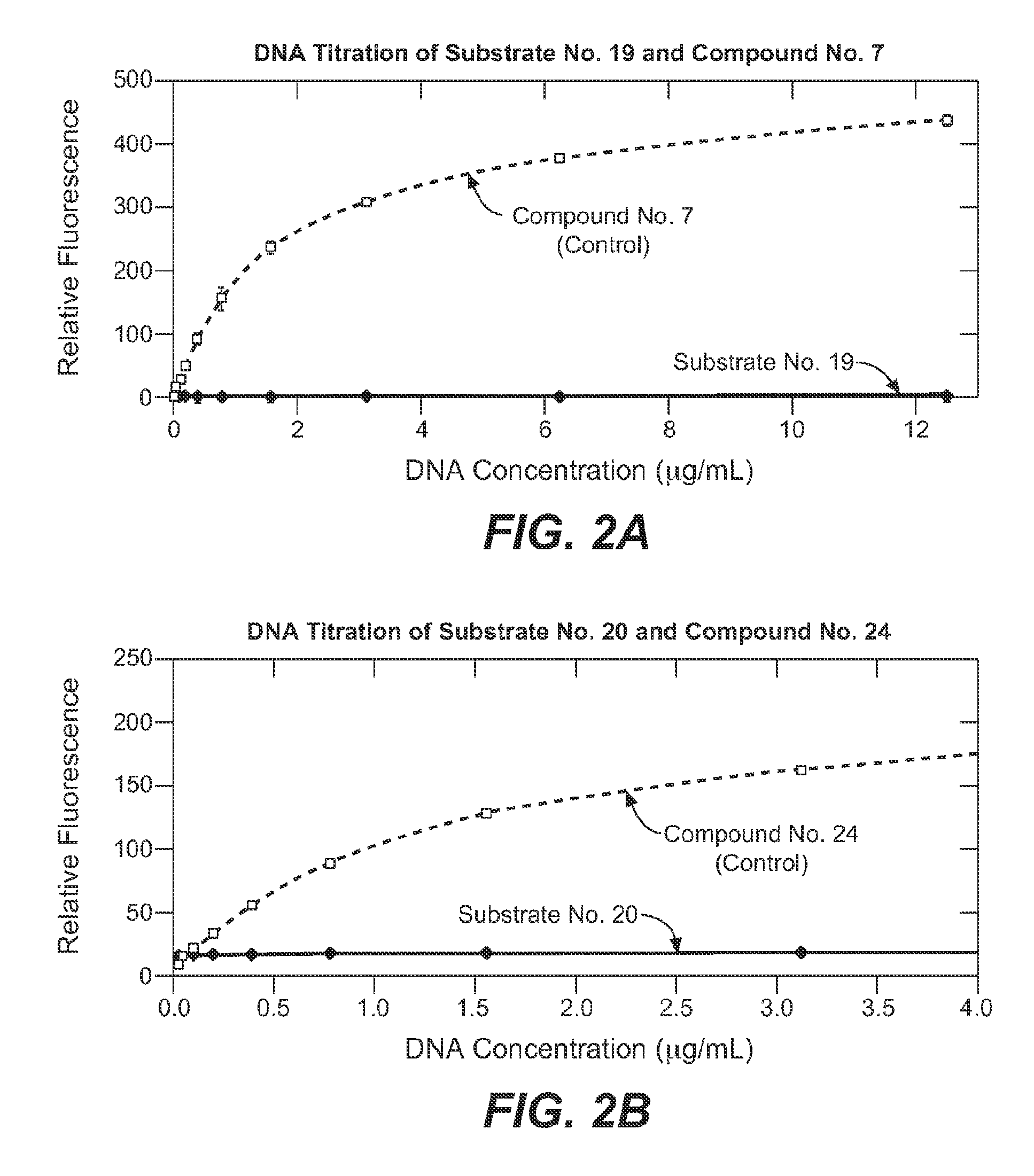
Enzyme substrate comprising a functional dye and associated technology and methods
ActiveUS8092784B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMicrobiological testing/measurementMoietyFluorochrome Dye
Enzyme substrates and associated technology of the present invention are provided. An enzyme substrate of the invention may comprise a biologically functional fluorescent dye and an enzyme-specific substrate moiety attached in such a way that the functionality of the functional dye is diminished. An enzymatic reaction may cleave at least a portion of the substrate moiety from the enzyme substrate to provide a more functional product dye. This product dye may be nonfluorescent or weakly fluorescent, in general, and relatively fluorescent, in a particular condition, such as when bound to a partner biological molecule or an assembly of partner biological molecules. An enzyme substrate of the present invention may thus be useful in fluorescence detection, and / or in any of a variety of useful applications, such as the detection of enzymatic activity in a cell-free system or in a living cell, the screening of drugs, or the diagnosis of disease.
Owner:BIOTIUM INC
Infrared thermography
InactiveUS6881584B1High expressionAbundantly expressDiagnostics using lightMaterial heat developmentCell freePresent method
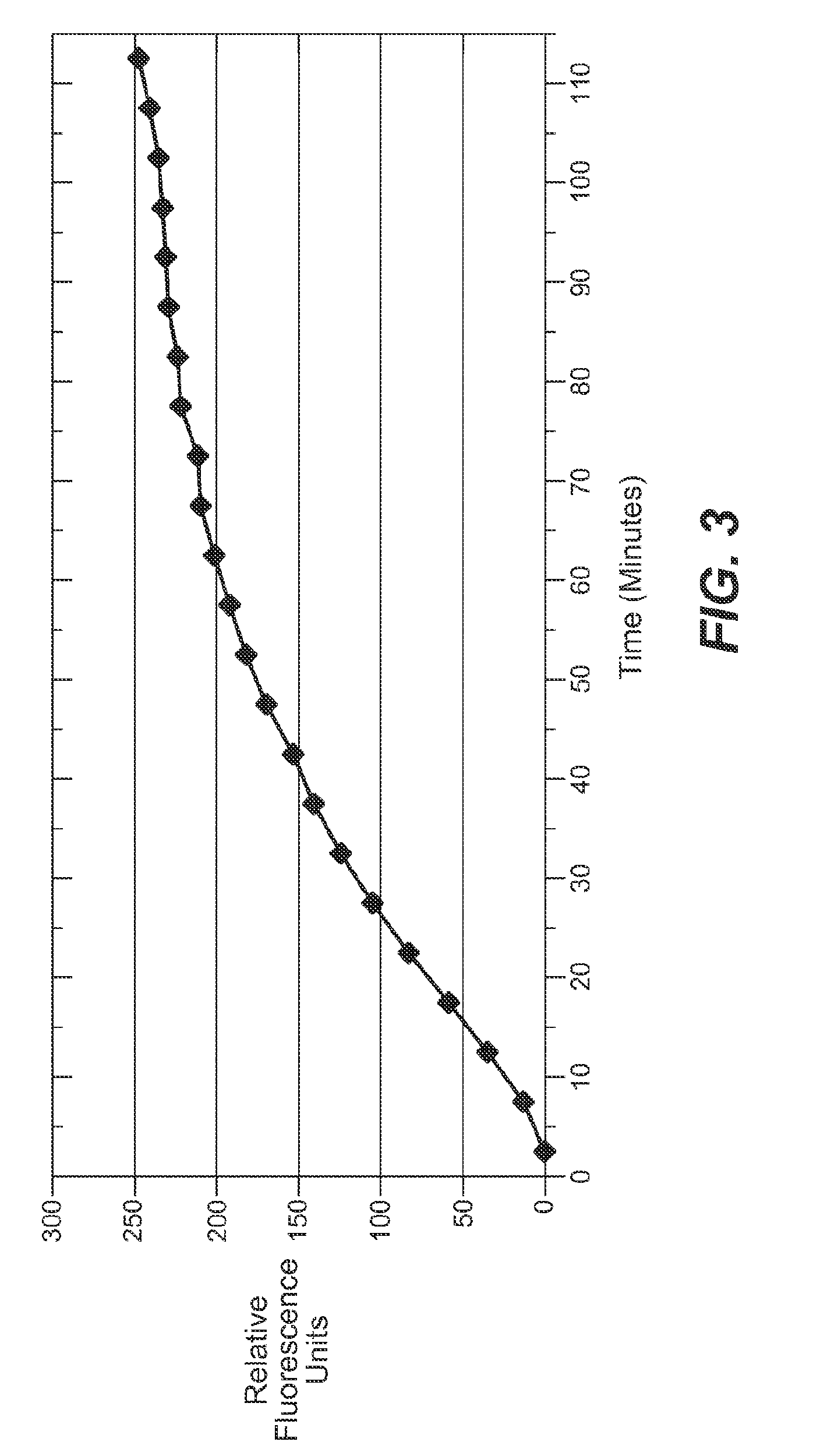
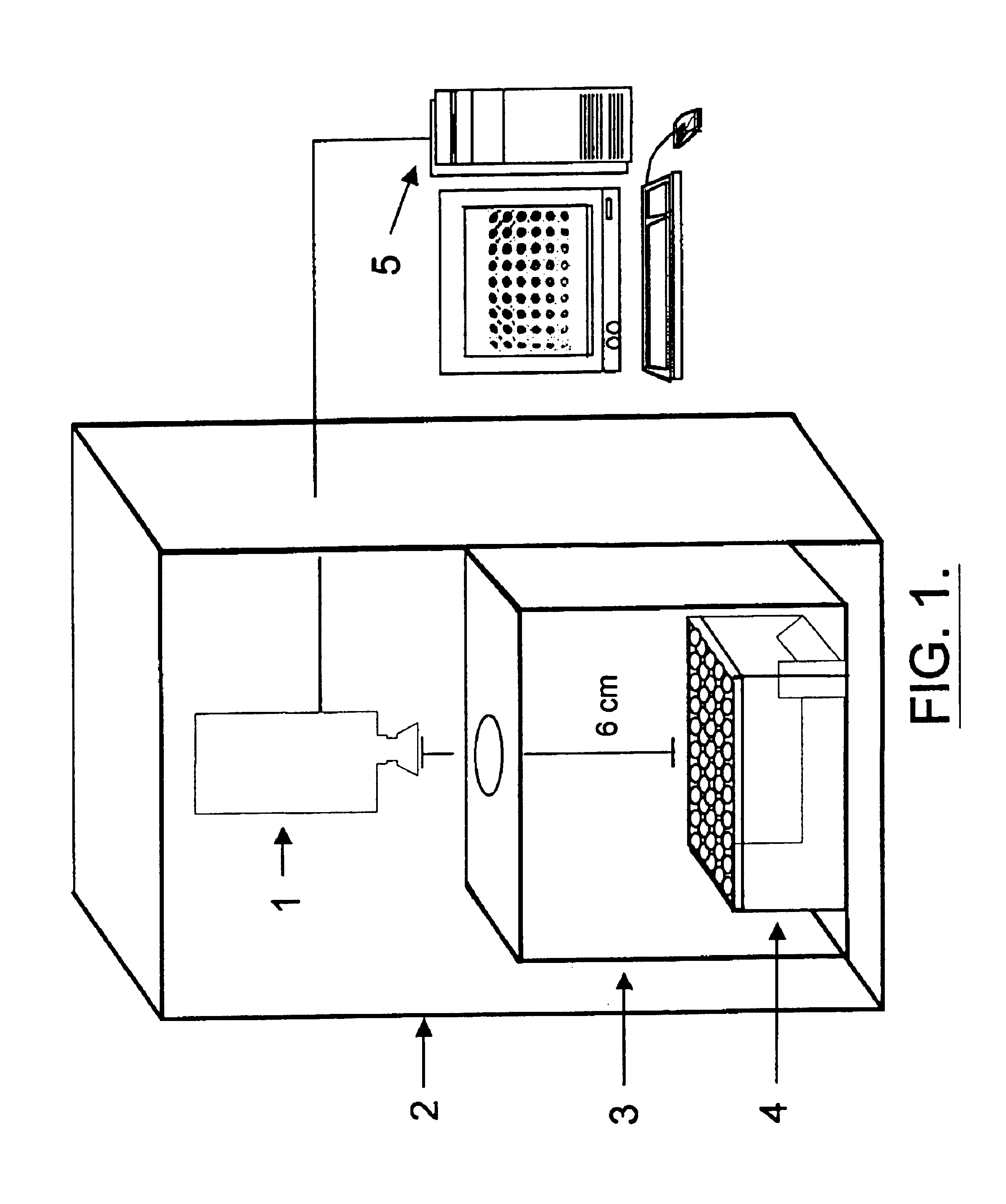
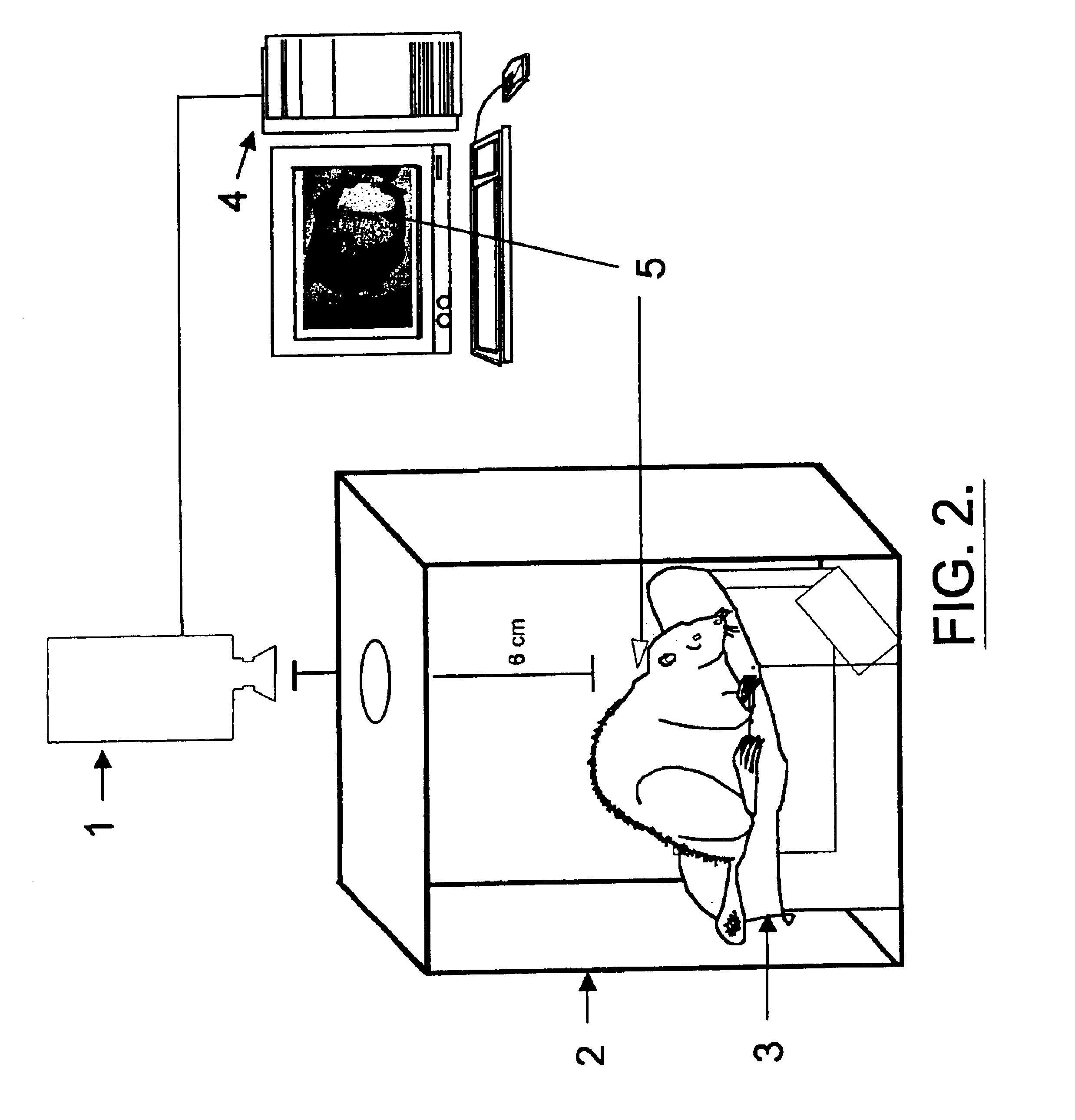
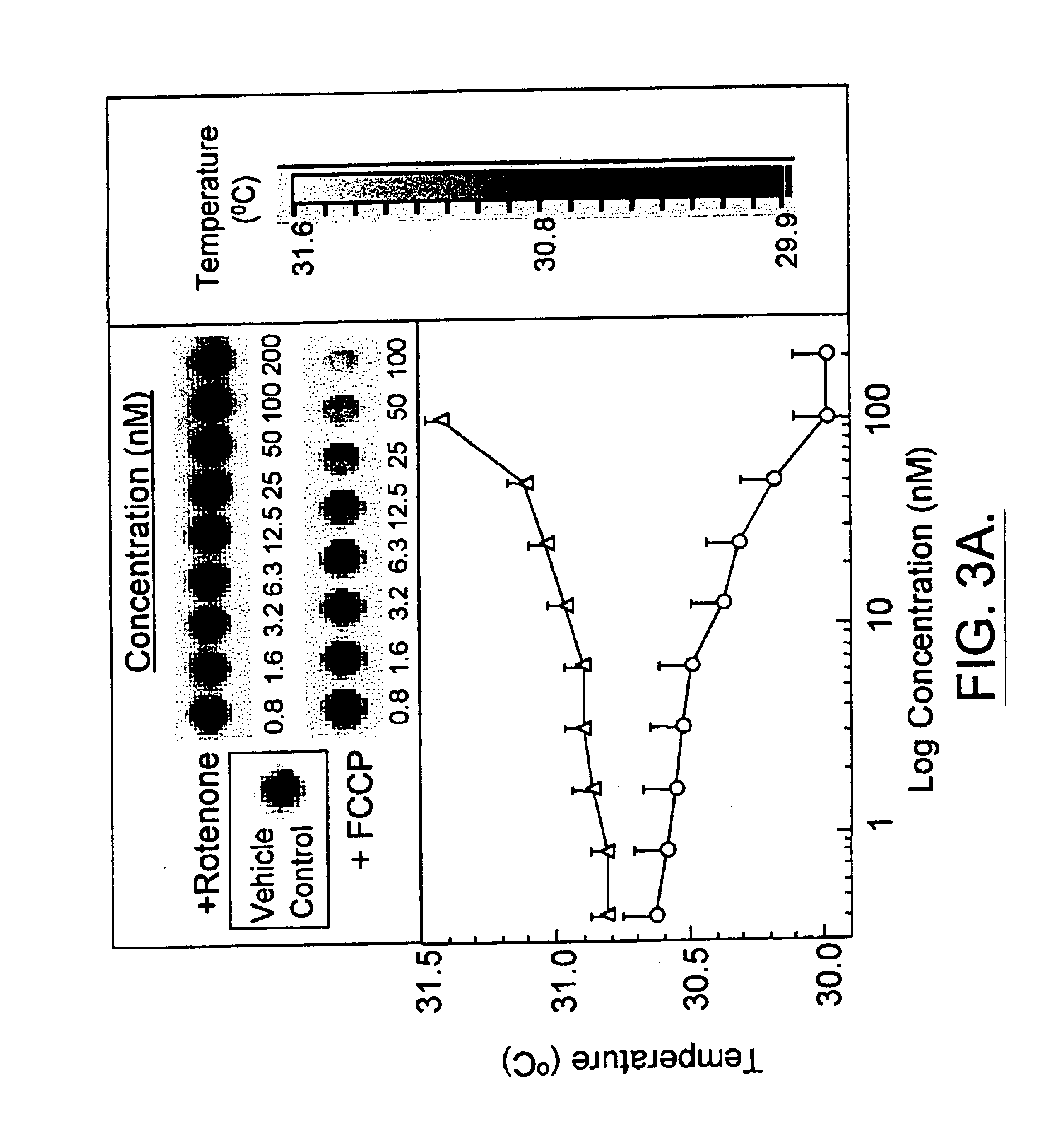
The present invention relates, in general, to thermography and, in particular, to a method of using infrared thermography to monitor physiological and molecular events that elicit a thermogenic response in animals (including humans), plants, tissues, cells and cell-free systems. The present method can be used for screening, identifying, and ranking drug candidates for multiple diseases, disorders and conditions.
Owner:SMITHKLINE BECKMAN CORP
Eukaryotic use of improved chimeric mutational vectors
The invention is based on the reaction of recombinagenic oligonucleotides in a cell-free system containing a cytoplasmic cell extract and a test duplex DNA on a plasmid. The reaction specifically converts a mutant kanr gene to recover the resistant phenotype in transformed MutS, RecA deficient bacteria and allows for the rapid and quantitative comparison of recombinagenic oligonucleobases. Using this system a type of Duplex Mutational Vector termed a Heteroduplex Mutational Vector, was shown to be more active in than the types of mutational vectors heretofore tested. Further improvements in activity were obtained by replacement of a tetrathymidine linker by a nuclease resistant oligonucleotide, such as tetra-2'-O-methyl-uridine, to link the two strands of the Duplex Mutational Vector and removal of the DNA-containing intervening segment. The claims concern Duplex Mutational Vectors that contain the above improvements. In an alternative embodiment the claims concern a reaction mixture containing a recombinagenic oligonucleobase, a cell-free enzyme mixture and a duplex DNA containing a target sequence. In yet an alternative embodiment, the invention concerns the use of such mixture to test improvements in recombinagenic oligonucleobases, as well as to test the effects of compounds on the activity of the cell-free enzyme mixture and also to make specific changes in the target DNA sequence.
Owner:CIBUS
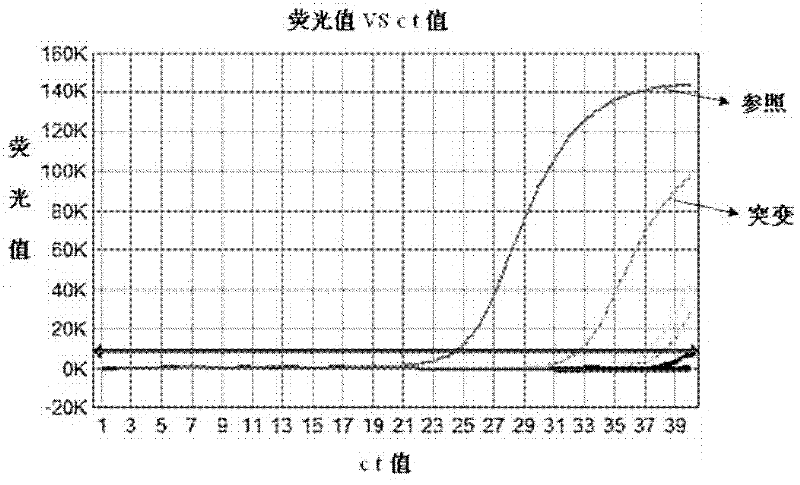
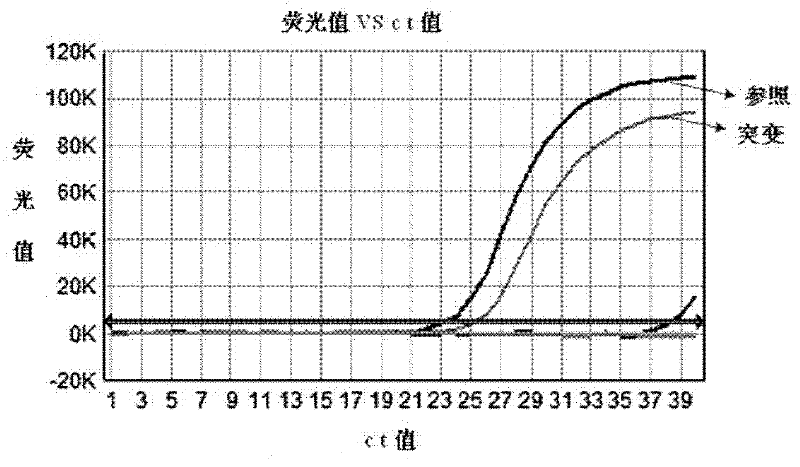
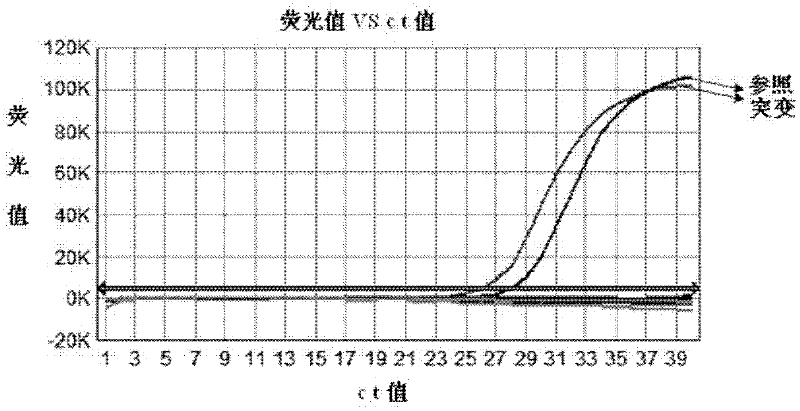
ARMS-qPCR (Allele Refractory Mutation System-quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction) detection kit for KRAS (Kirsten Rat Sarcoma Viral Oncogene Homolog) gene mutation subtype and detection method
InactiveCN102367478AIncreased sensitivityQuick checkMicrobiological testing/measurementViral OncogenePositive control
The invention relates to the field of molecular biology and aims to provide an ARMS-qPCR (Allele Refractory Mutation System-quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction) detection kit for KRAS (Kirsten Rat Sarcoma Viral Oncogene Homolog) gene mutation subtype and a detection method. The kit comprises a qPCR hybrid reaction solution, a locked nucleic acid retardant probe, a reference primer, an ARMS primer and a positive control sample, wherein the qPCR hybrid reaction solution comprises a PCR buffer solution, dNTPs (Deoxynucleotide Triphosphates), MgCl2, GoldStarbest Taq enzyme, a universal PCR reverse primer and a universal TaqMan probe. The kit provided by the invention can be used for rapidly and accurately detecting specific locus mutation of KRAS genes in various cancer tissues with high sensitivity, has high sensitivity, and can be used for detecting genome DNA with various tissue origins, specially free DNA segments adopting cell-free systems, such as blood serum and blood plasma, orother body fluid origins, wherein the genome DNA is derived from cell systems. Compared with direct sequencing and other mutation detection technologies, the kit and the detection method thereof havethe advantages of strong specificity, high sensitivity, simplicity and rapidness in operation, high throughput, safety, definiteness and objectivity in result identification and the like for detecting the KRAS gene mutation.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Infrared thermography
InactiveUS6983753B1Inhibit thermogenesisFacilitates production of heatSurgeryDiagnostic recording/measuringDiseasePresent method
The present invention relates, in general, to thermography and, in particular, to a method of using infrared thermography to monitor physiological and molecular events that elicit a thermogenic response in animals (including humans), plants, tissues, cells and cell-free systems. The present method can be used for screening, identifying, and ranking drug candidates for multiple diseases, disorders and conditions.
Owner:GLAXO WELLCOME INC
Methods for producing protein domains and analyzing three dimensional structures of proteins by using said domains
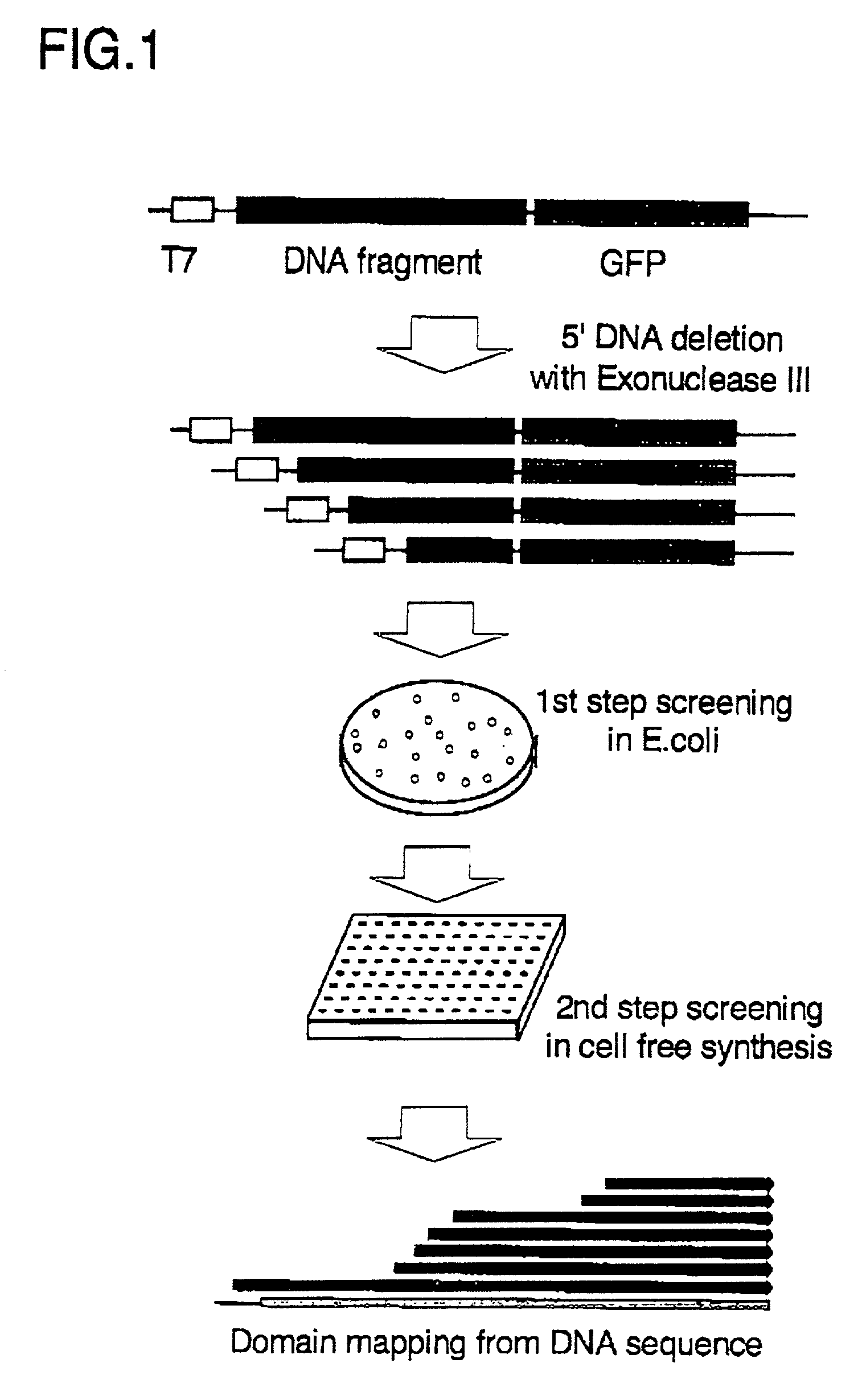
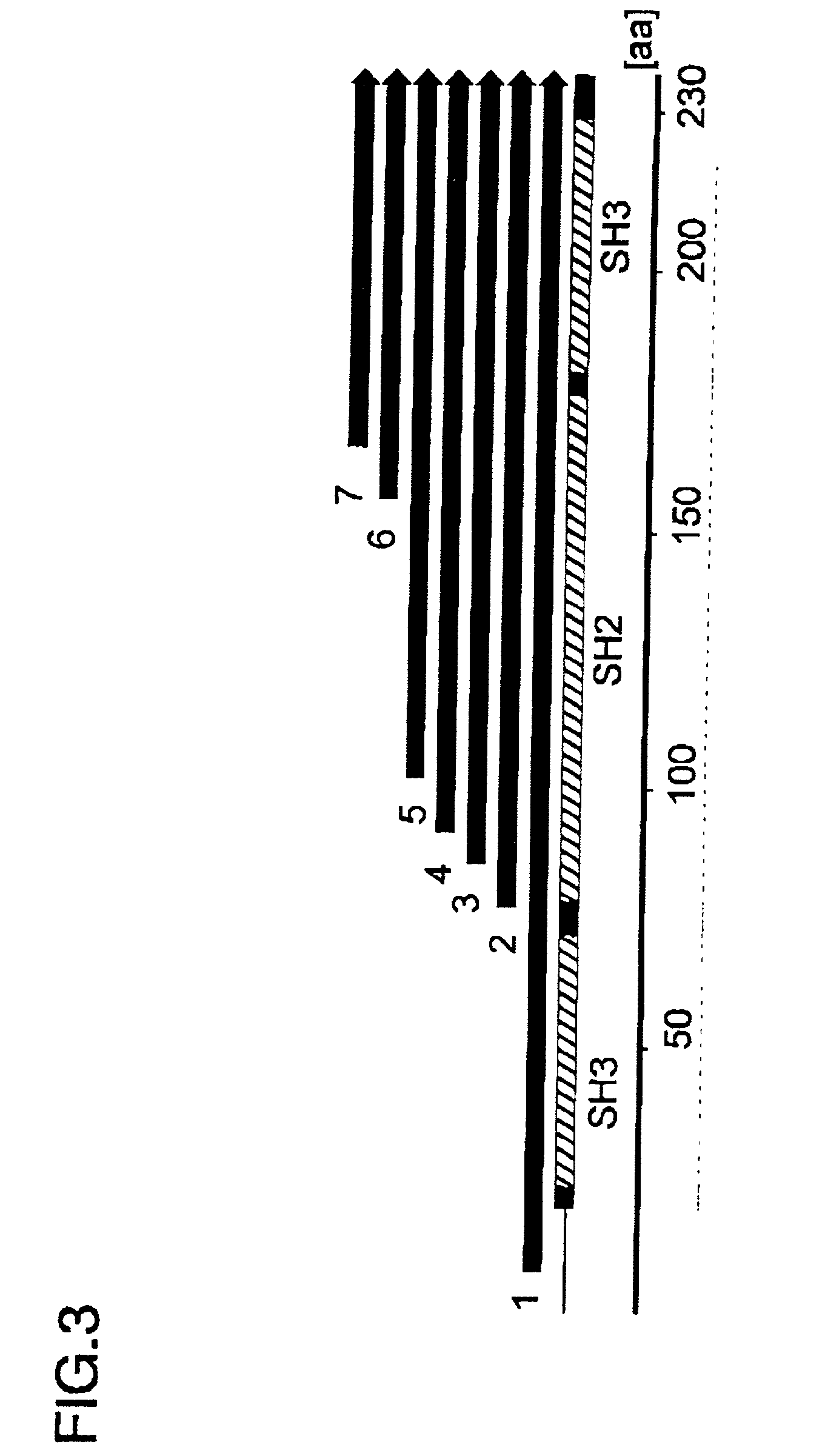
InactiveUS20020142387A1Easy and rapid methodEfficient preparationBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsDNA fragmentationA-DNA
There is provided a method for producing a soluble protein domain comprising: (a) preparing two or more DNA fragments by partially digesting a DNA coding for a protein; (b) expressing the protein which is coded on each of said DNA fragments, as a fusion protein with a functional protein; (c) selecting the fusion protein exhibiting said function among two or more fusion proteins synthesized in step (b); and, (d) synthesizing the soluble protein domain which is coded on said DNA fragment in a cell-free system, wherein said soluble protein domain is included in said fusion protein selected in step (c). By using this method, it can be easy and efficient to analyze the three dimensional structure of proteins of many clones.
Owner:RIKEN
Methods of RNA and protein synthesis
The present invention relates to methods for RNA and / or protein synthesis using in vitro or in vivo expression systems. More specifically, the present invention provides a method for RNA and / or protein synthesis characterized in that the concentration of alpha subunit of RNA polymerase, but not of other subunits, is increased in the cellular or cell-free system, comparing to its natural concentration existing in the cellular or cell-free system.
Owner:UNIV DE NANTES
Cell-free preparation of carbapenems
ActiveUS20130065878A1Improve propertiesGood water solubilityAntibacterial agentsBiocideCell freeChemical compound
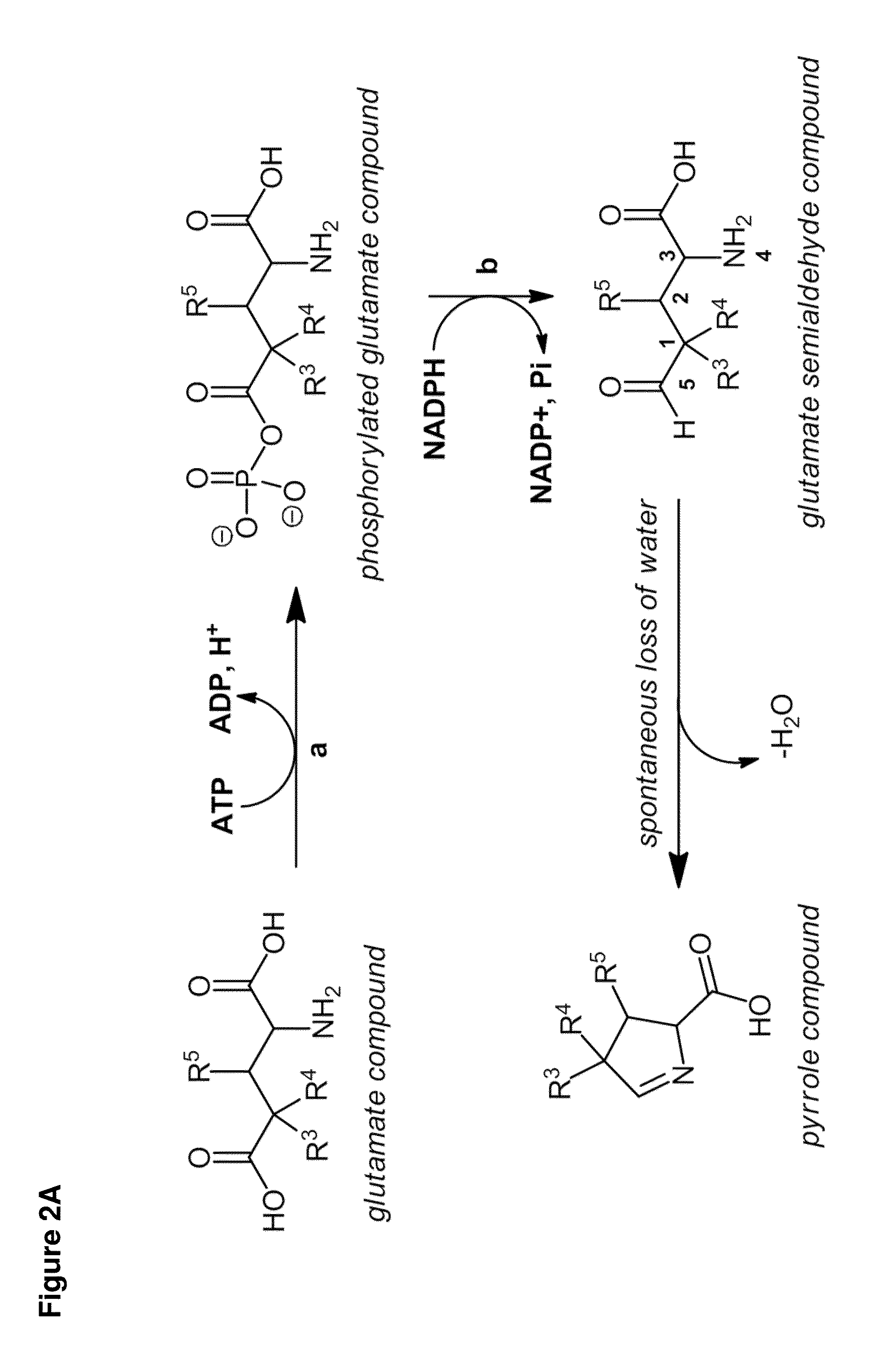
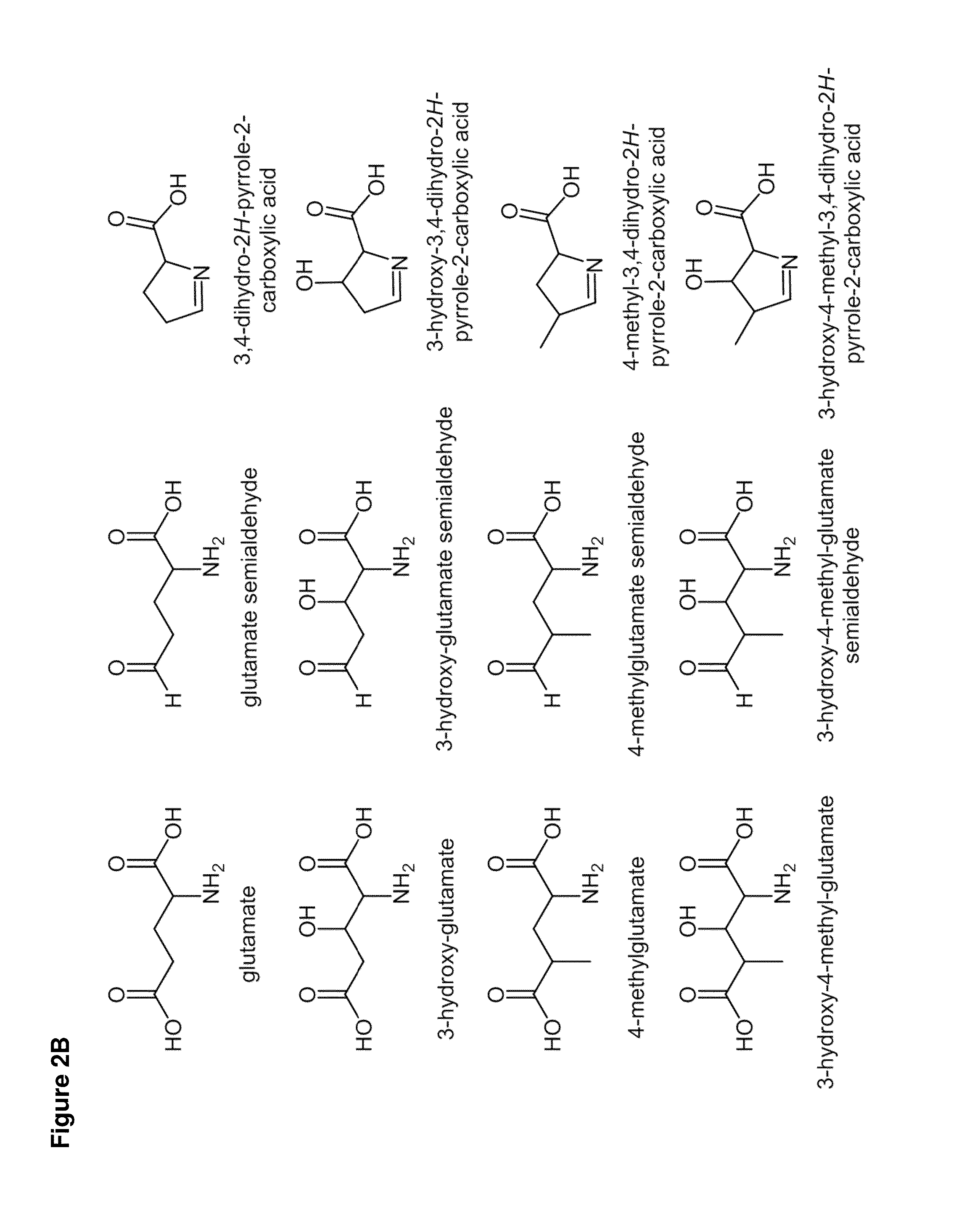
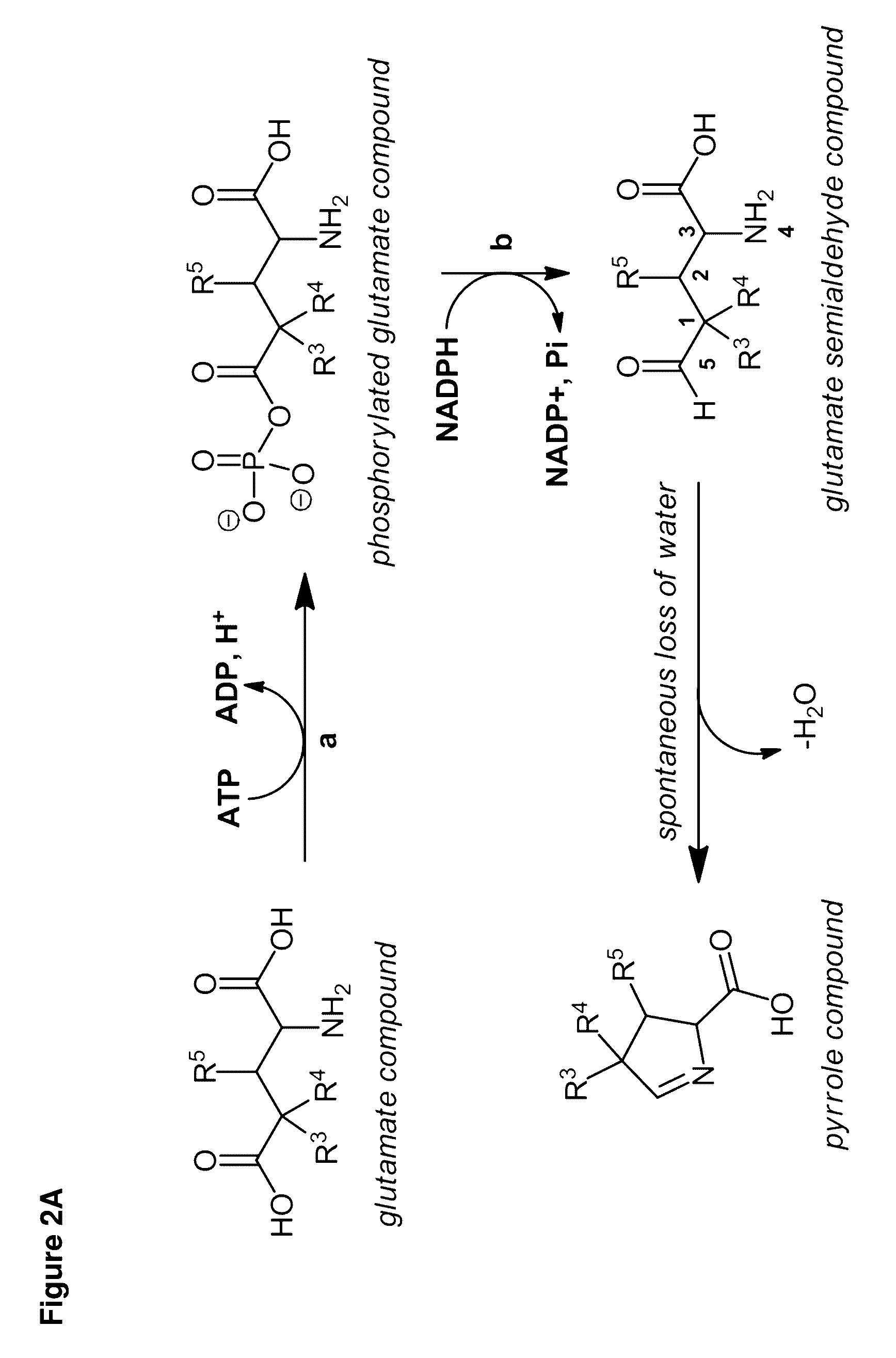
Provided herein are cell-free systems for generating carbapenems, e.g., a compound of the Formula (I):or salts thereof; wherein , R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, and R6 are defined herein. Also provided are pharmaceutical compositions comprising a compound generated by the inventive cell-free system, and use of these compounds and compositions for the treatment of bacterial infections.
Owner:GREENLIGHT BIOSCIENCES INC
Cell-free preparation of carbapenems
ActiveUS9469861B2Improve propertiesEnhance pharmaceuticallyAntibacterial agentsBiocideCell freePharmaceutical drug
Owner:GREENLIGHT BIOSCIENCES INC
Infrared thermography
The present invention relates, in general, to thermography and, in particular, to a method of using infrared thermography to monitor physiological and molecular events that elicit a thermogenic response in animals (including humans), plants, tissues, cells and cell-free systems. The present method can be used for screening, identifying, and ranking drug candidates for multiple diseases, disorders and conditions.
Owner:LENHARD JAMES +1
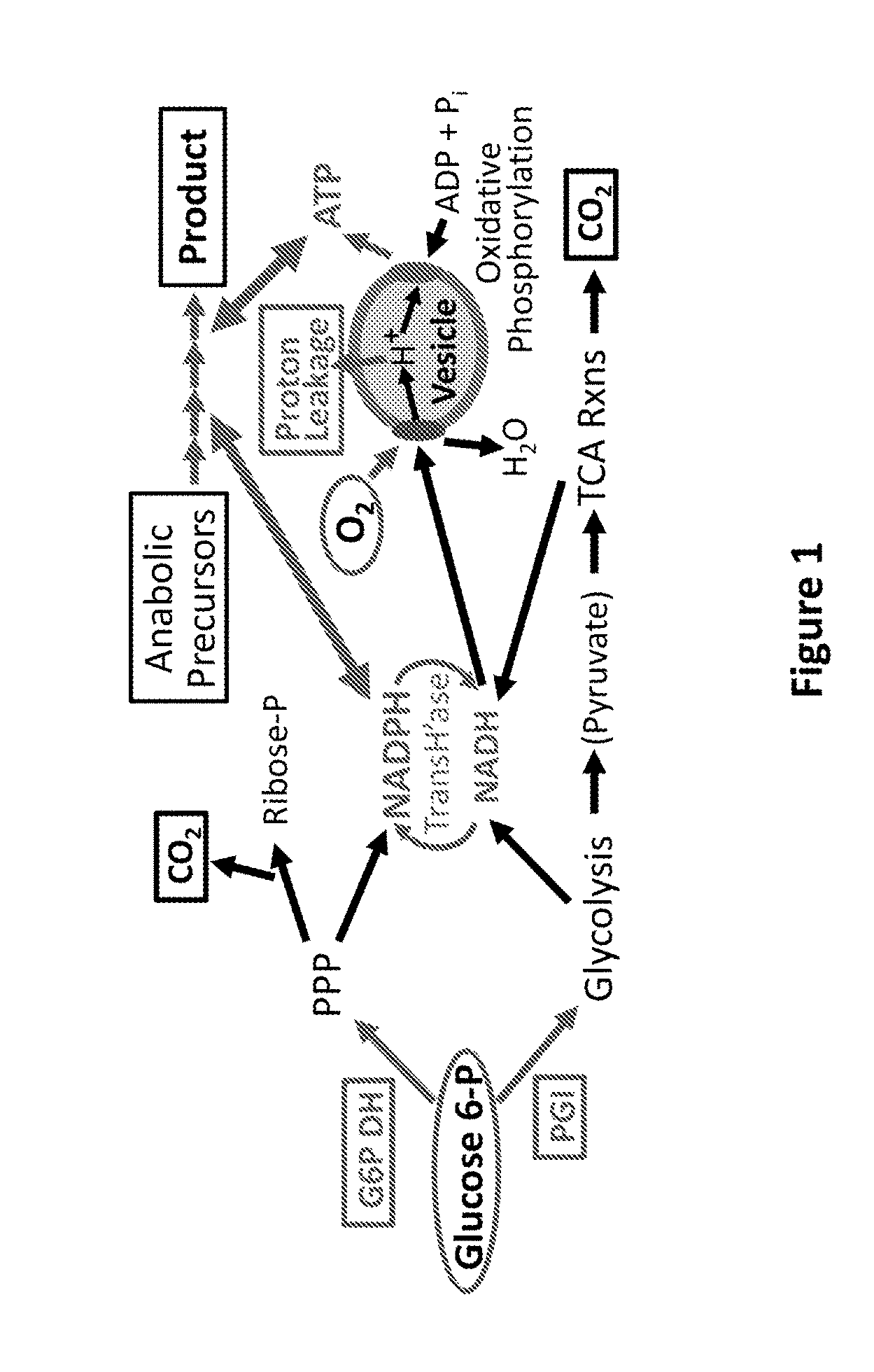
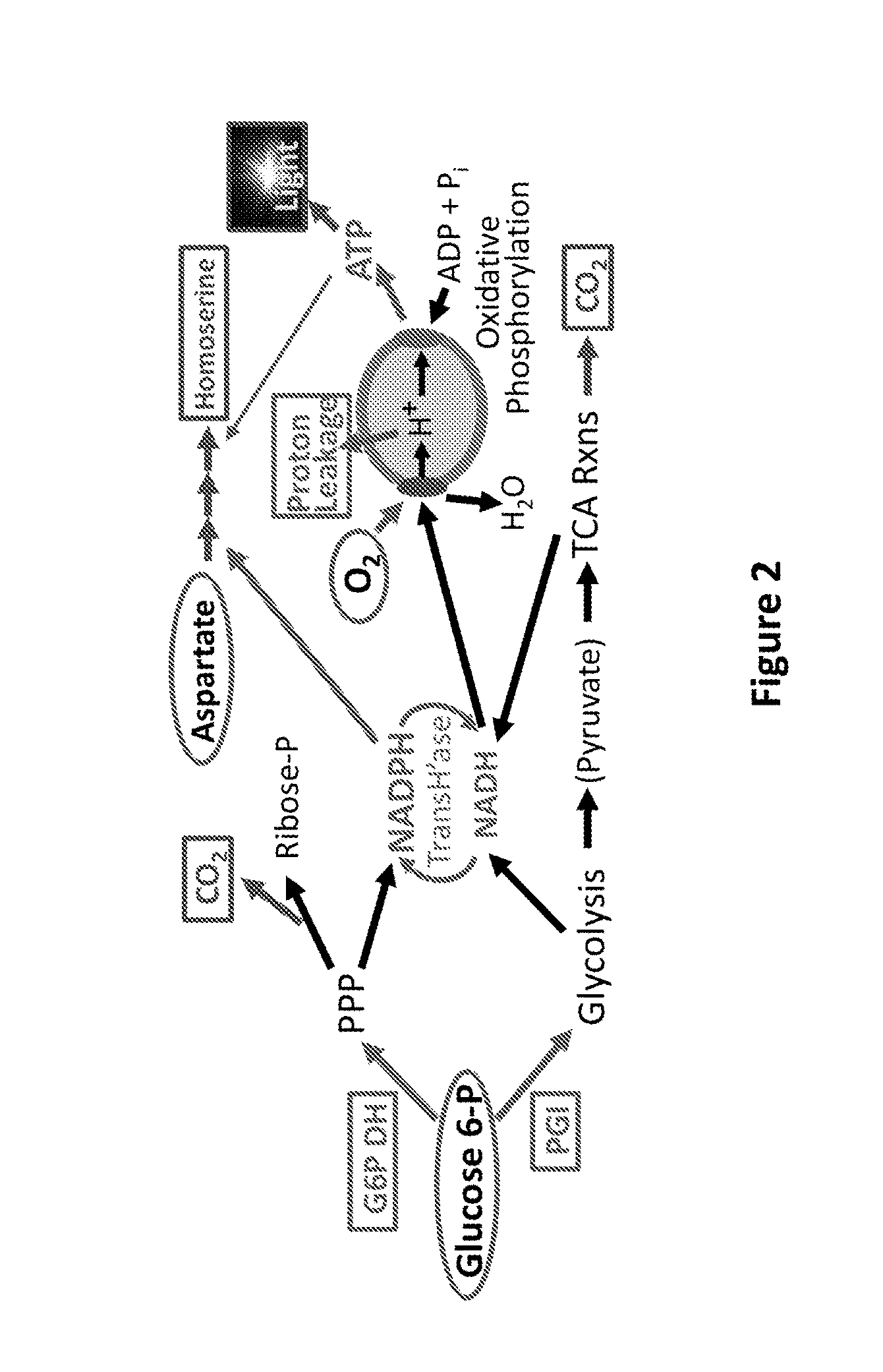
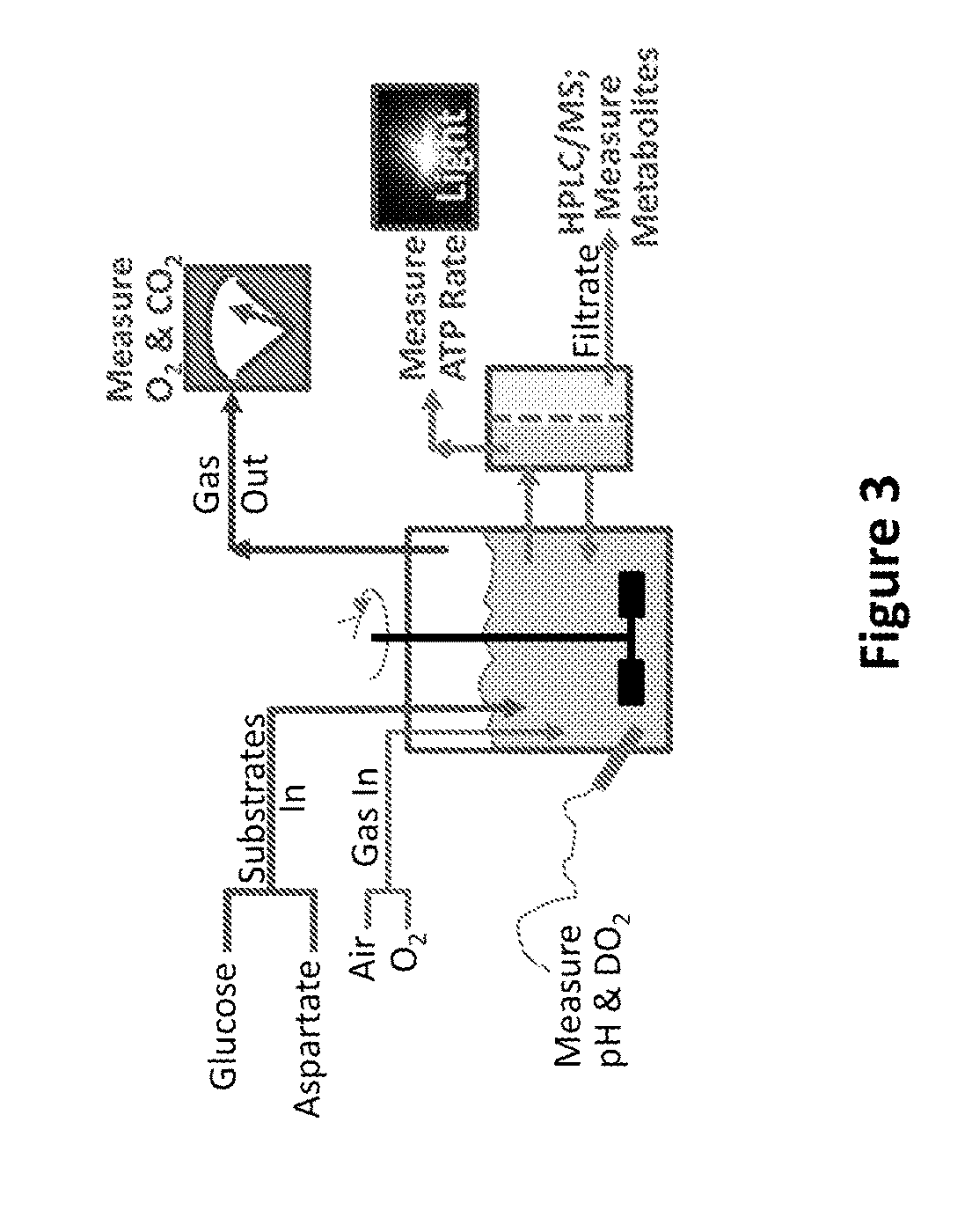
Control of metabolic flux in cell-free biosynthetic systems
InactiveUS20160115558A1Increase leakage of electronMicrobiological testing/measurementEnzymesBiotechnologyTransport system
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV +1
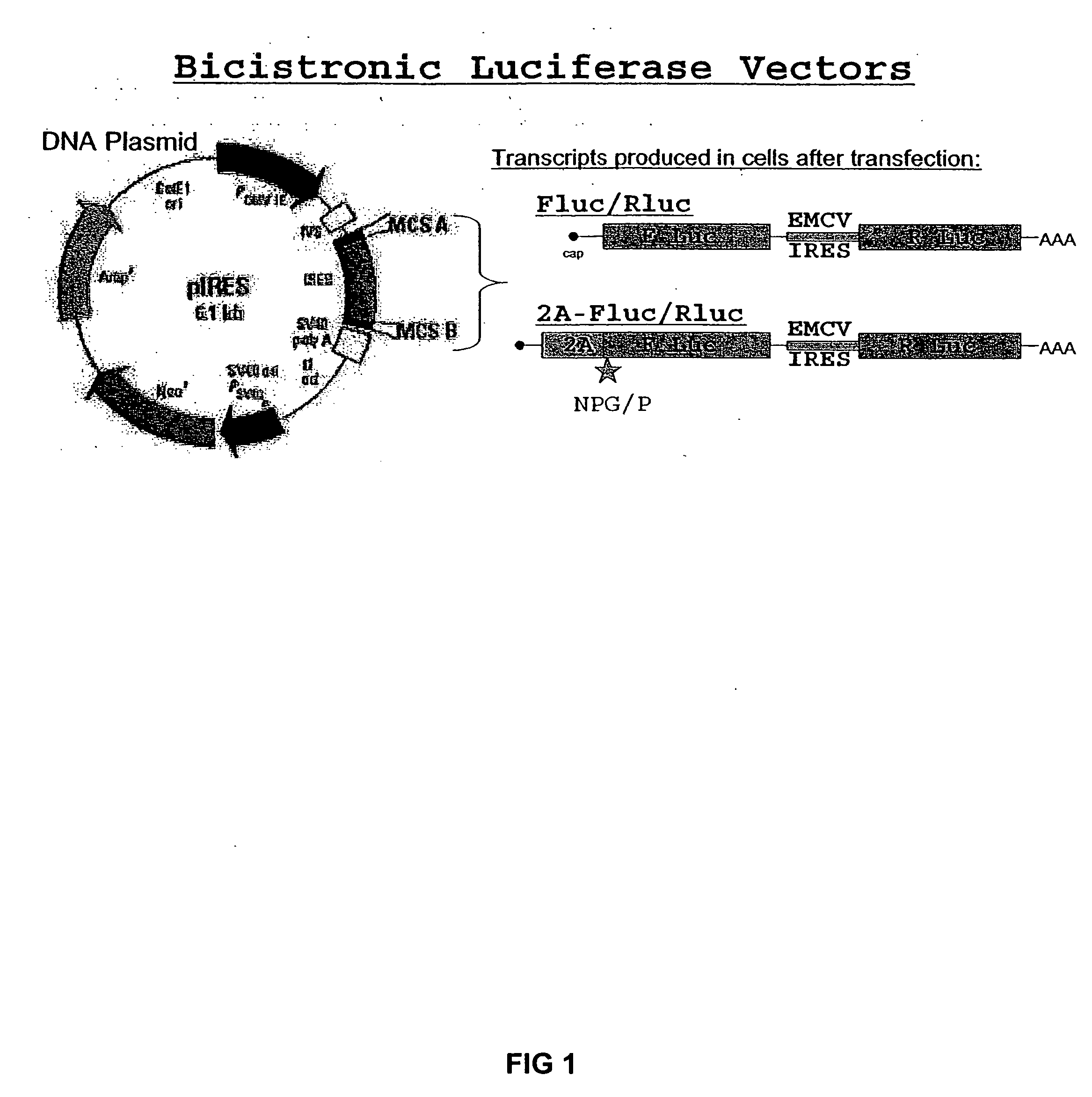
Compositions and methods for regulating mRNA transcription and translation
InactiveUS20050019808A1Significant changeSsRNA viruses positive-senseSugar derivativesCell freeInternal ribosome entry site
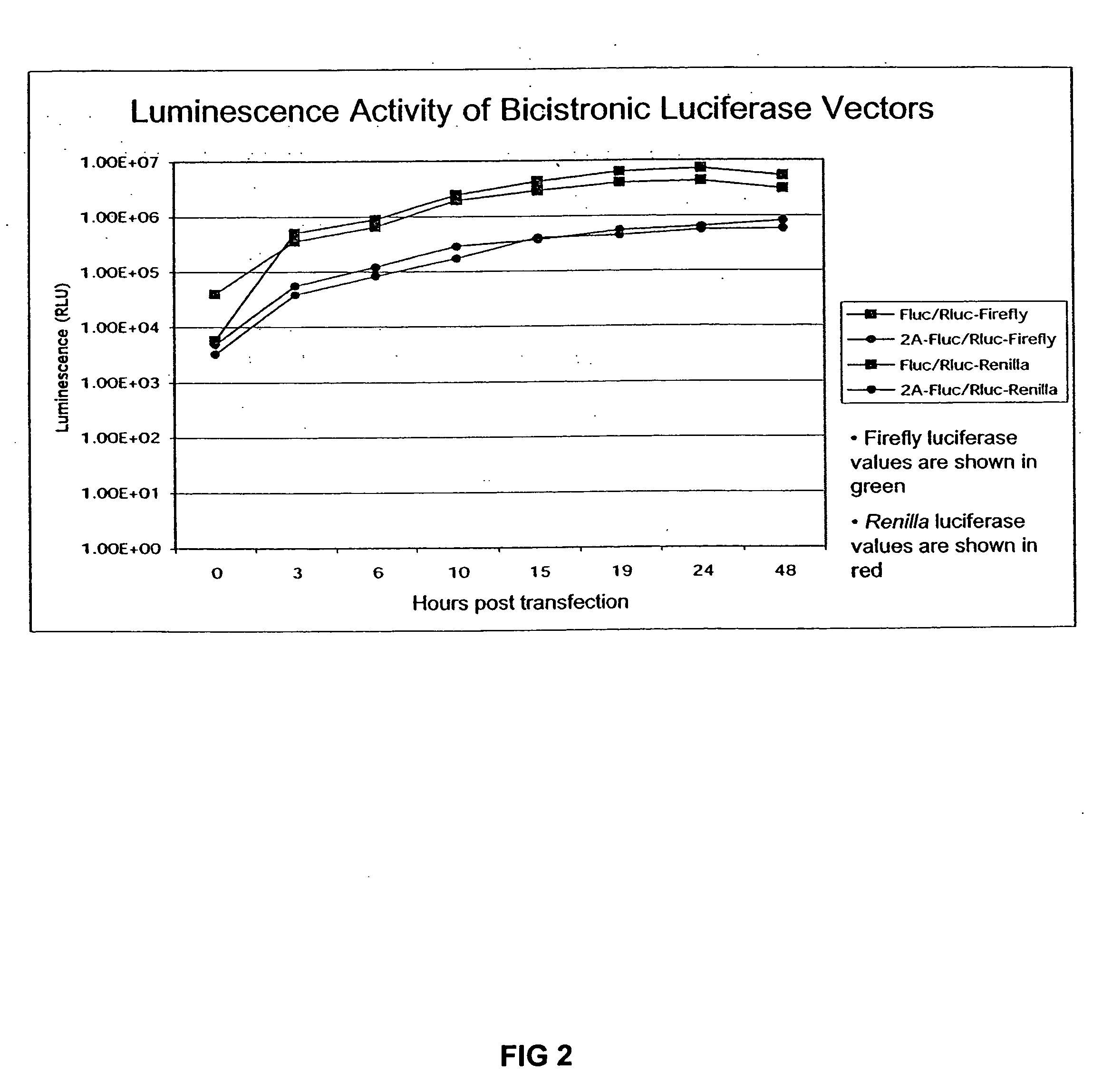
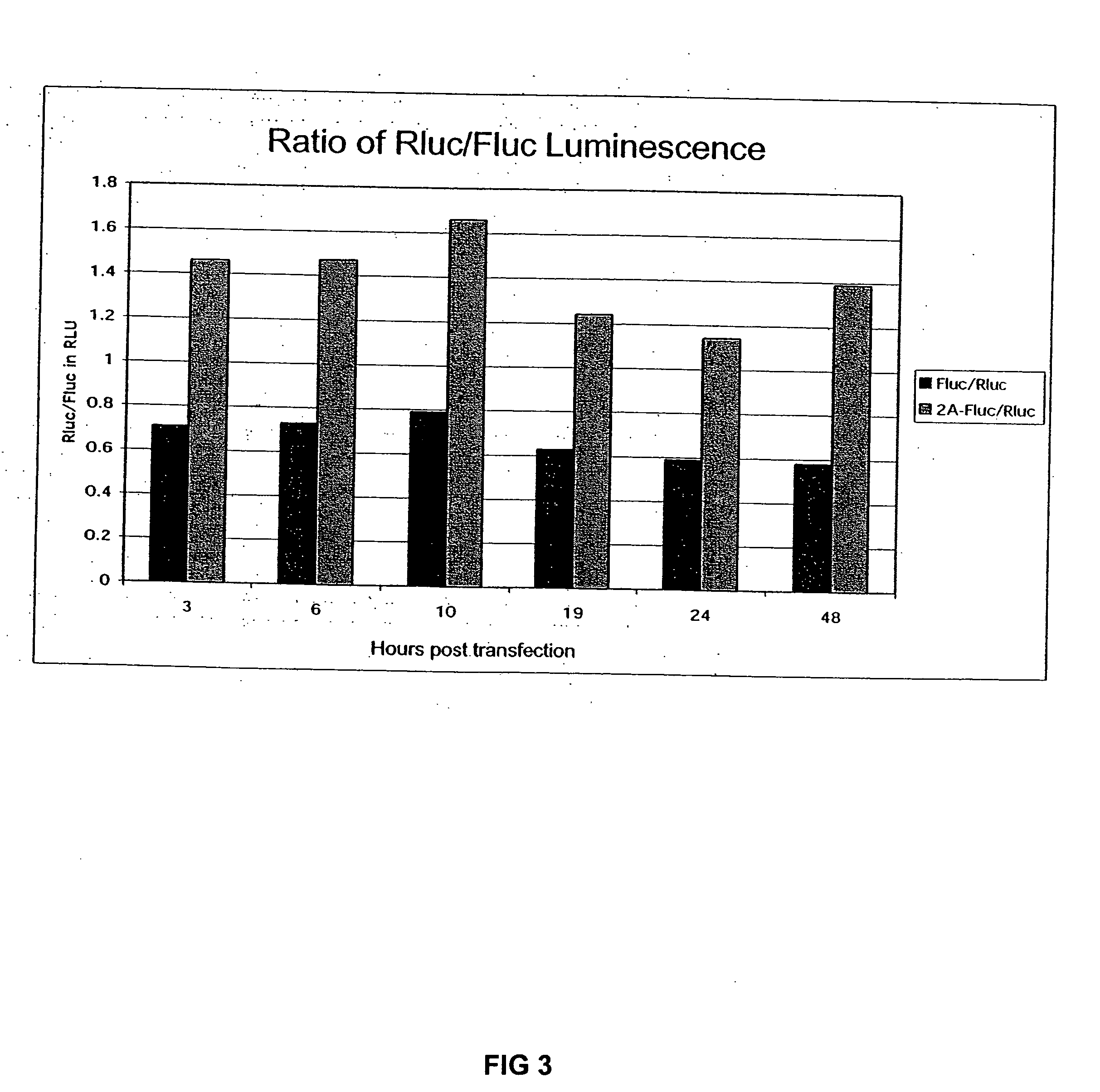
The invention relates to compositions, specifically novel nucleic acid constructs encoding a cardiovirus 2A polypeptide operably linked to suitable promoters. Also, disclosed are methods whereby the nucleic acid constructs are introduced into cells or cell free systems to regulate cellular mRNA transcription and cap-dependent or internal ribosomal entry site (IRES)-dependent mRNA translation.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Cell-free system for synthesis of proteins derived from cultured mammalian cells
InactiveUS20070281337A1High synthetic activityLow costVertebrate cellsPeptidesBiotechnologyInitiation factor
Prepared is an extract composition having an improved protein synthetic activity in a cell-free protein synthesis system using a mammalian cultured cell extract. An eukaryotic translation initiation factor and / or translational regulator are added to a cell-free protein synthesis system comprising an extract prepared from cultured mammalian cells and a template mRNA. These factors are one or more selected from the group consisting of eukaryotic translation initiation factors 4E (eIF4E), 2 (eIF2) and 2B (eIF2B), and eukaryotic translational regulator p97.
Owner:RIKEN
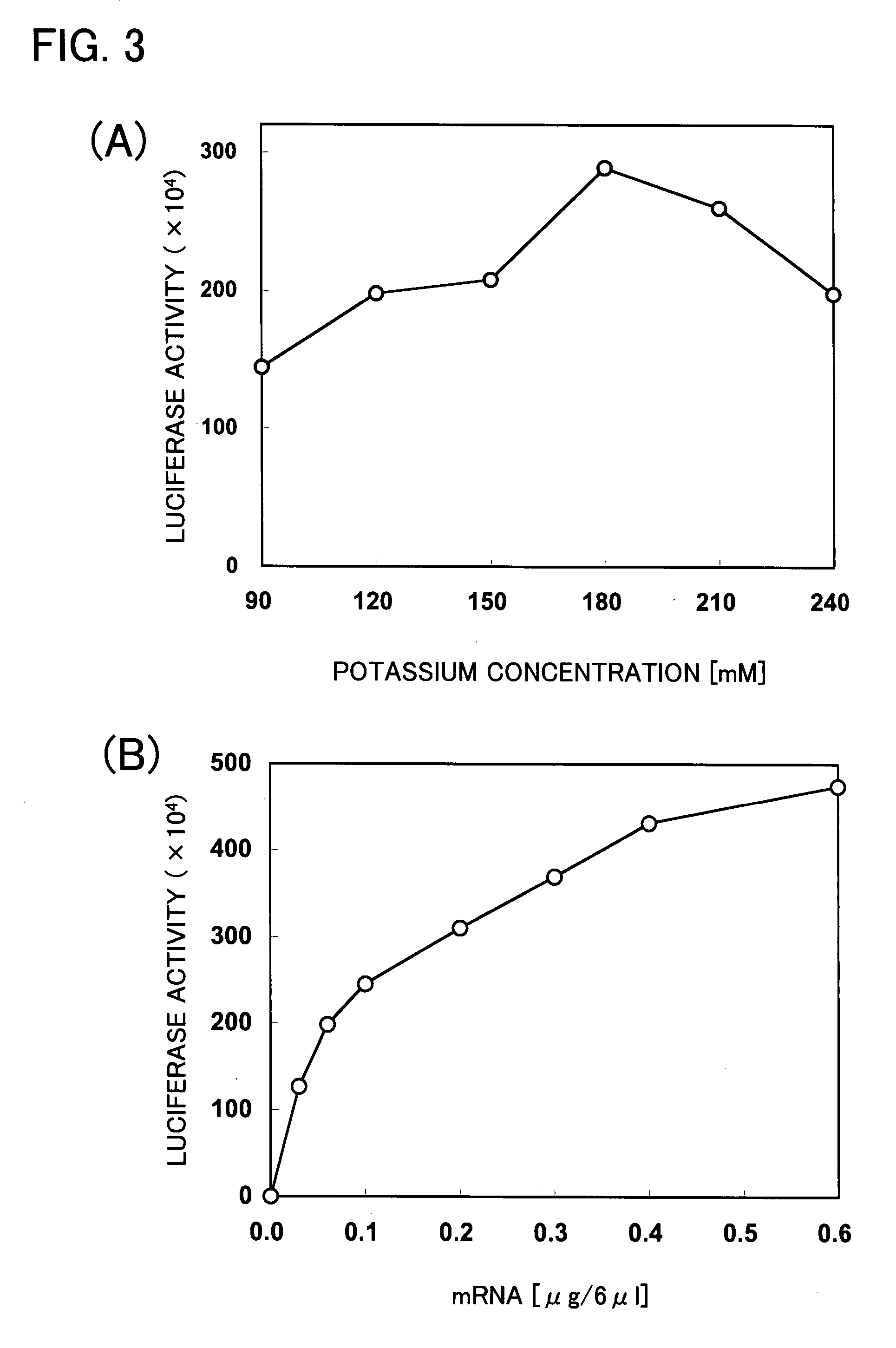
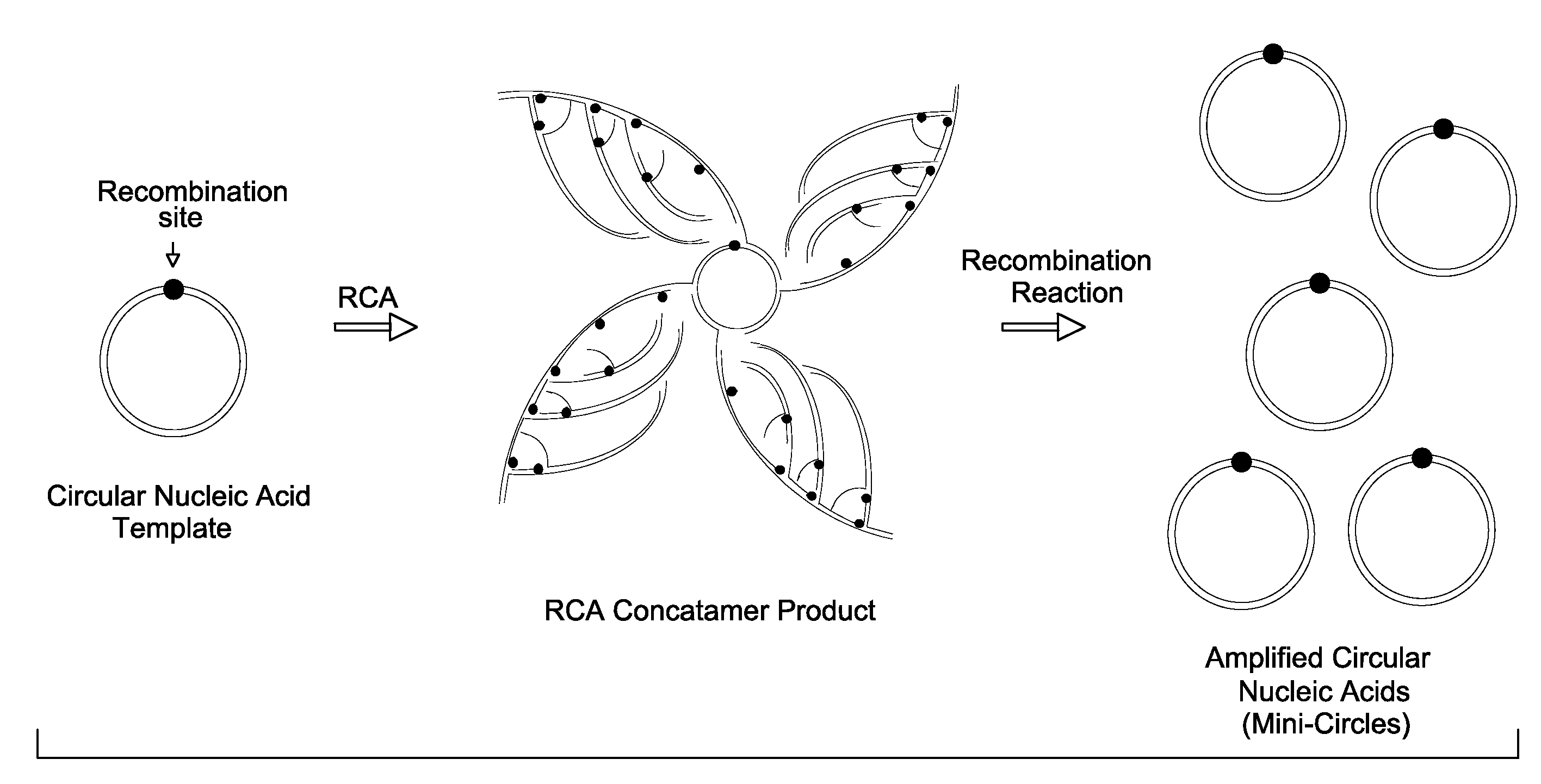
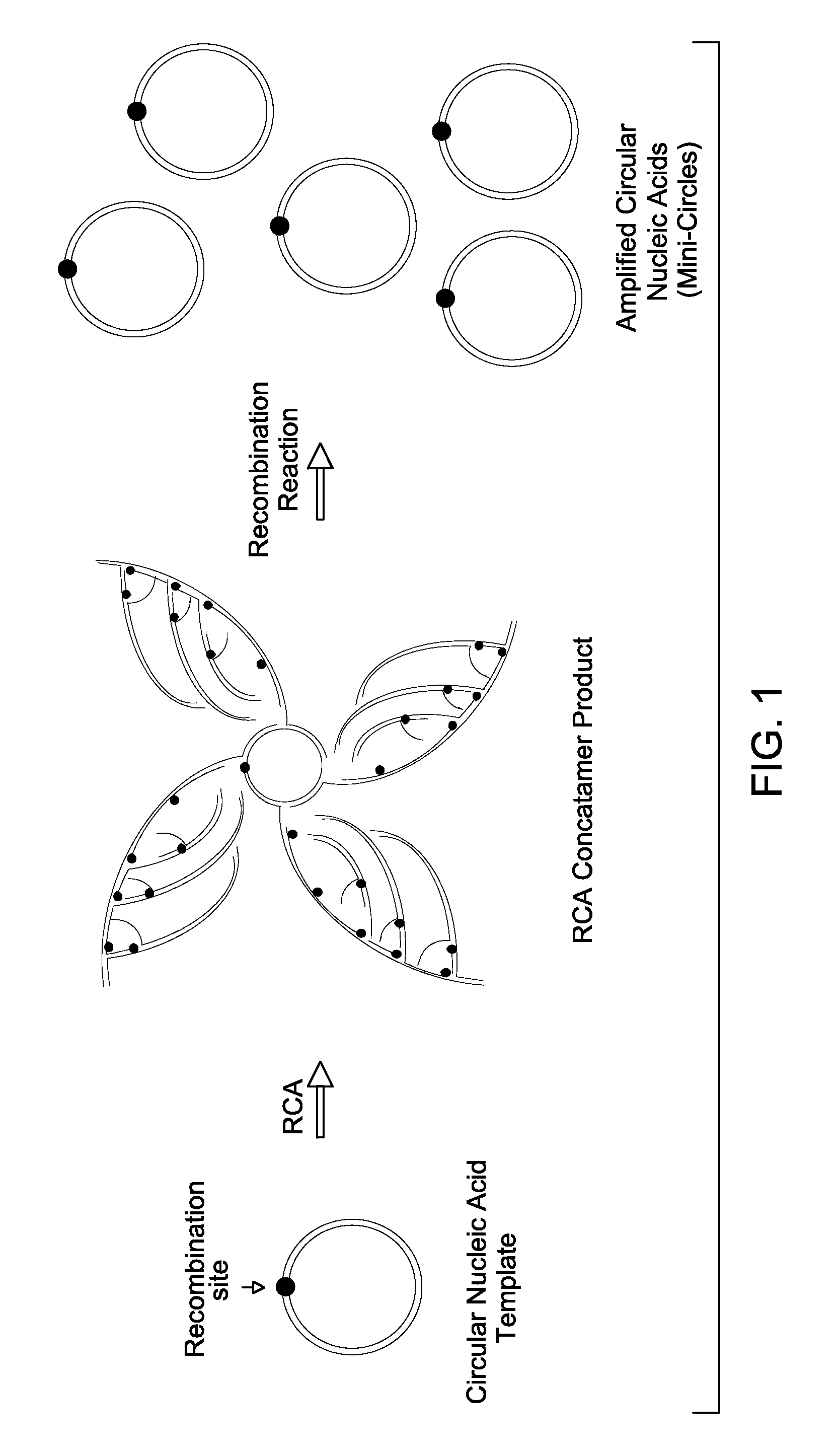
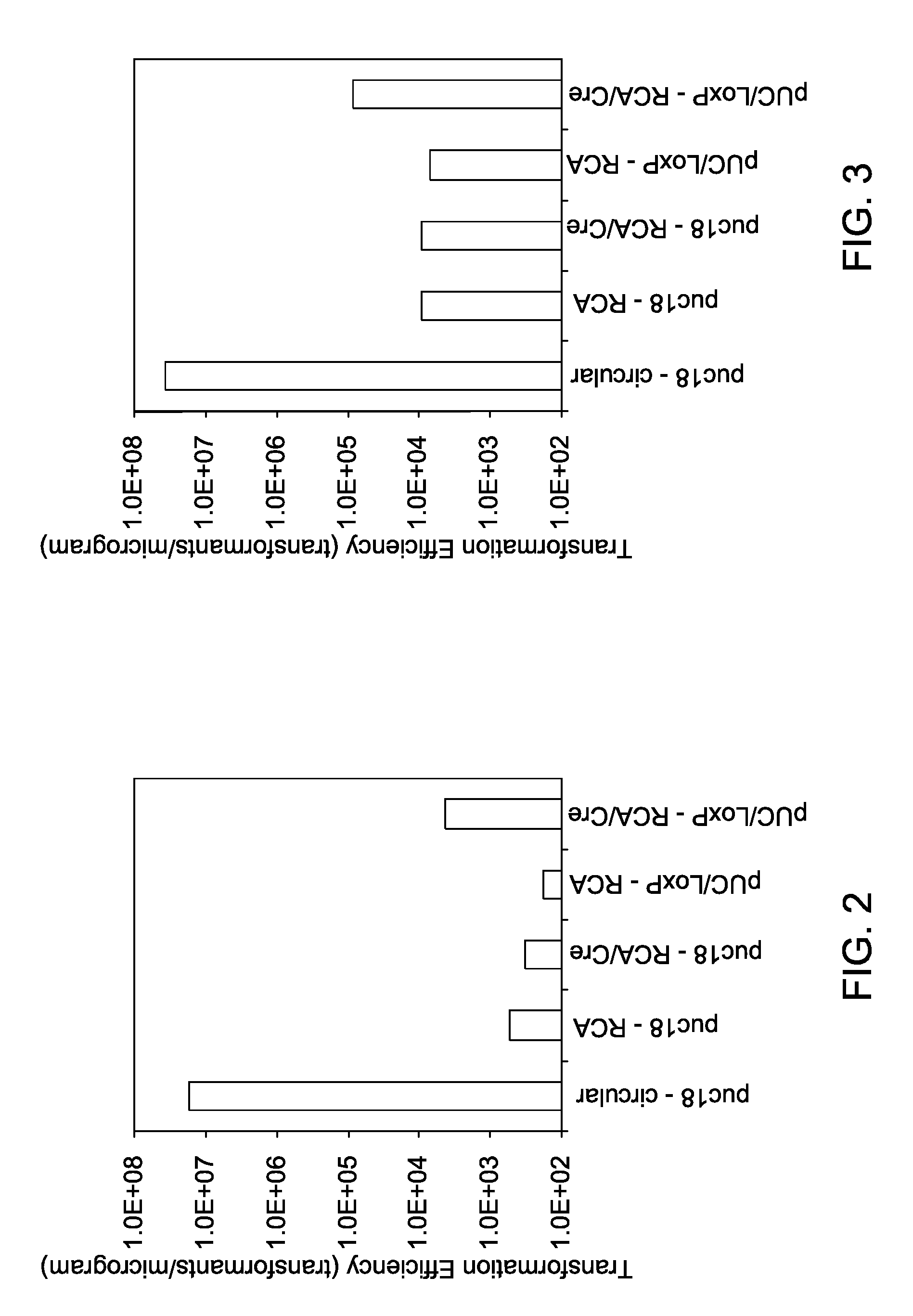
DNA mini-circles and uses thereof
ActiveUS20100055744A1Organic active ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsNucleic acid sequencingTandem repeat
Methods and kits for generating circular nucleic acids in a cell-free system, and uses for the generated circular nucleic acids are provided. The methods comprise in vitro amplification of a nucleic acid template comprising a recombination site to produce tandem repeat nucleic acid sequence, and employ a recombination protein to generate the circular nucleic acids from the tandem repeat nucleic acid sequence.
Owner:GLOBAL LIFE SCI SOLUTIONS OPERATIONS UK LTD
Enzymes, cells and methods for site specific recombination at asymmetric sites
InactiveUS20090217400A1Easy to removeEasy to reorganizeOrganic active ingredientsBiocideBiological bodySite-specific recombination
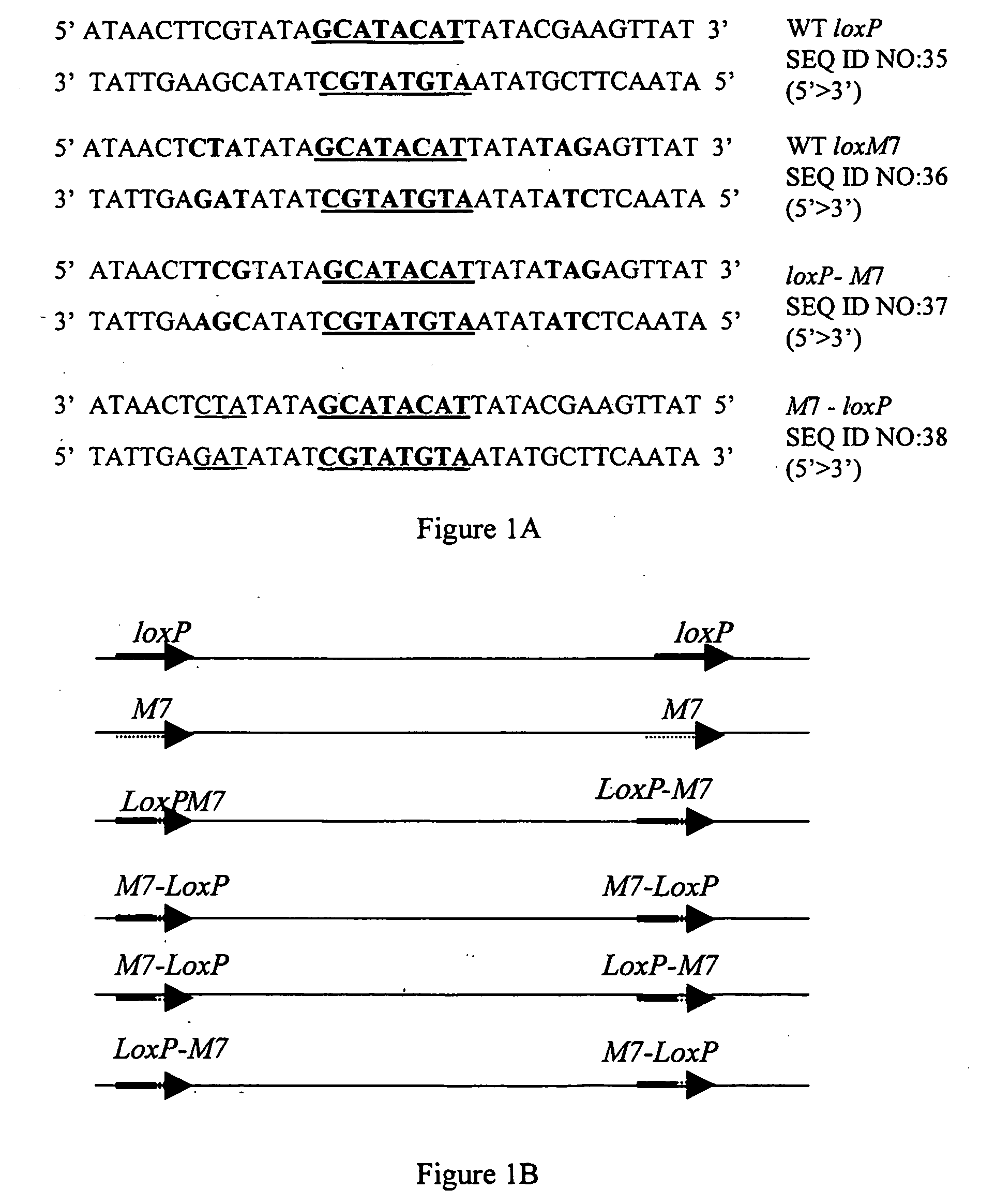
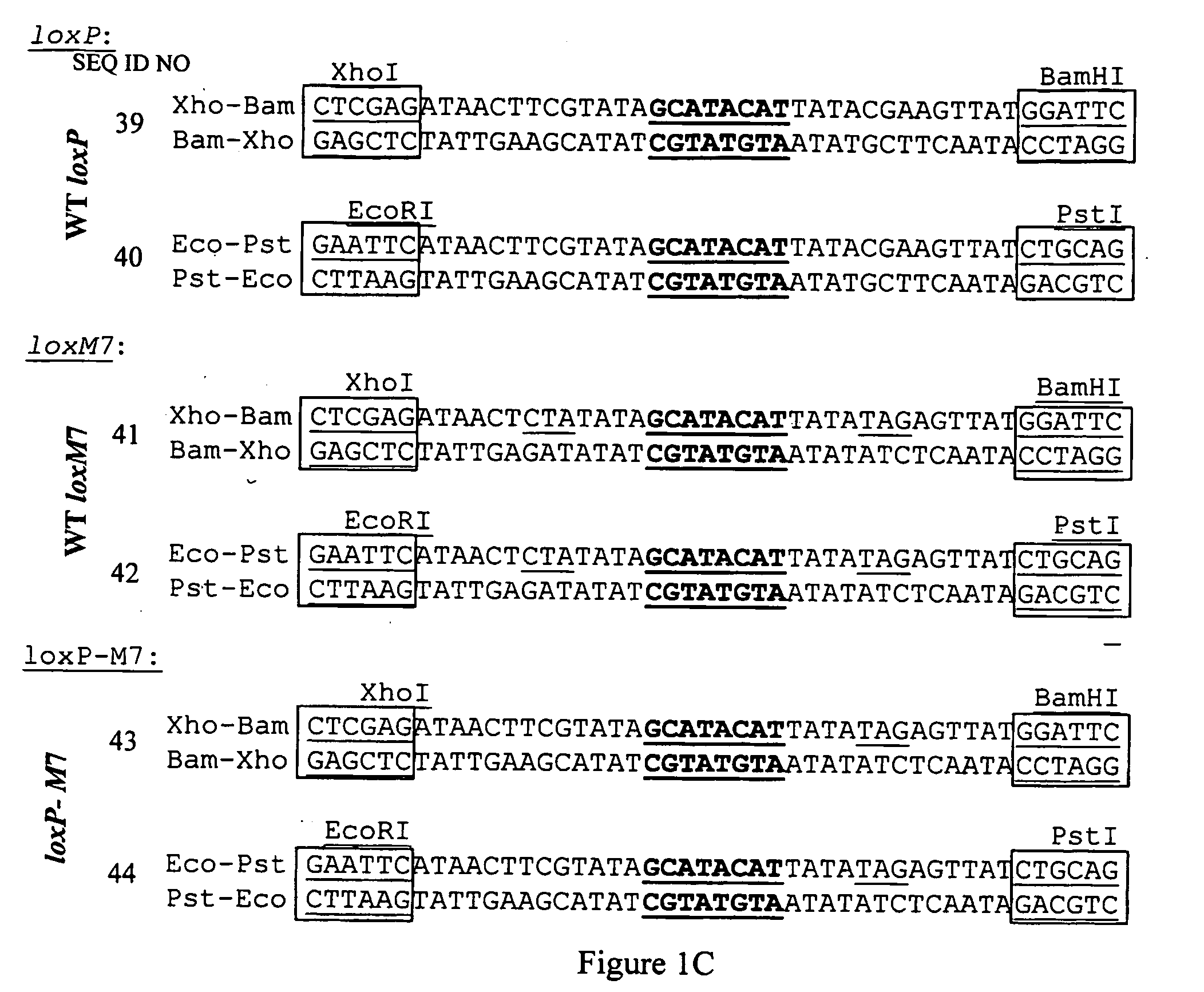
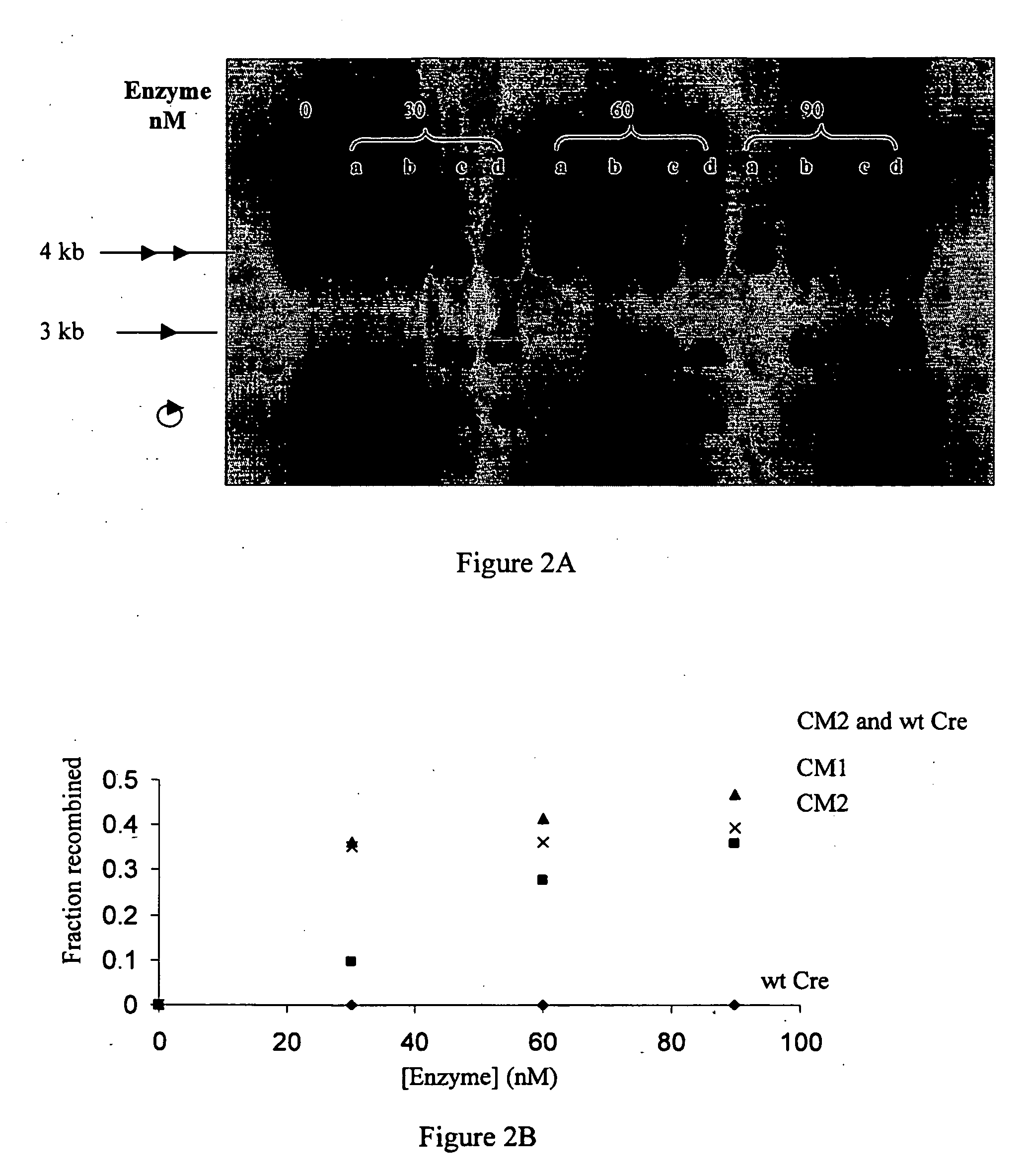
The present invention relates to enzymes, compositions and methods for catalyzing asymmetric recombination of non-palindromic recombination sites in a cell free system, in isolated cells or in living organisms. The enzymes and methods of the invention are suitable for mediating specific recombinations between DNA sequences comprising specific recombination sites without being limited to strict palindromic symmetry within each recombination site.
Owner:THE STATE OF ISRAEL MINIST OF AGRI & RURAL DEV AGRI RES ORG ARO VOLCANI CENT +1
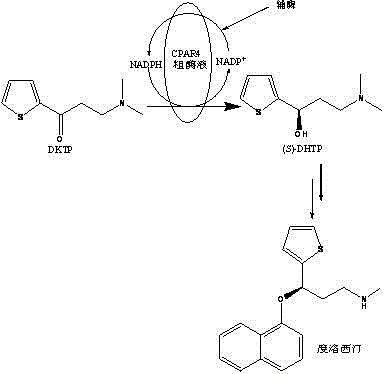
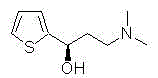
Method catalytically synthesizing (S)-N, N-dimethyl-3-hydroxy-(2-thiofuran)-1-propylamine((S)-DHTP) by aldehyde ketone reductase recombinant strain crude enzyme system
The invention discloses a method catalytically synthesizing (S)-N, N-dimethyl-3-hydroxy-(2-thiofuran)-1-propylamine((S)-DHTP) by aldehyde ketone reductase recombinant strain crude enzyme system, and belongs to the technical field of biological catalysis asymmetric conversion. An auxiliary substrate and original bulk coenzyme NADP<+> are added in the recombinant strain crude enzyme system to accelerate regeneration cycle of coenzyme NADPH in the system; the reaction substrate is N, N-dimethyl-3-ketone-(2-thiophene)-1-propylamine (DTKP); the recombinant strain is E. coliBL21(DE3)(pETCPAR4); aldehyde ketone reducing enzyme gene cpar4 comes from Candida parapsilosis; the gene coded aldehyde ketone reducing enzyme gene CPAR4 catalytically and asymmetrically reduces the DKTP into (S)-DHTP. The method utilizes the cell-free system to conduct catalytic reaction; coupling enzyme required by regeneration of the coenzyme is not extra added in the reaction system; direct acting efficiency of the enzyme and the substrate is improved; reaction time is shortened; the conversion effect is relatively good.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
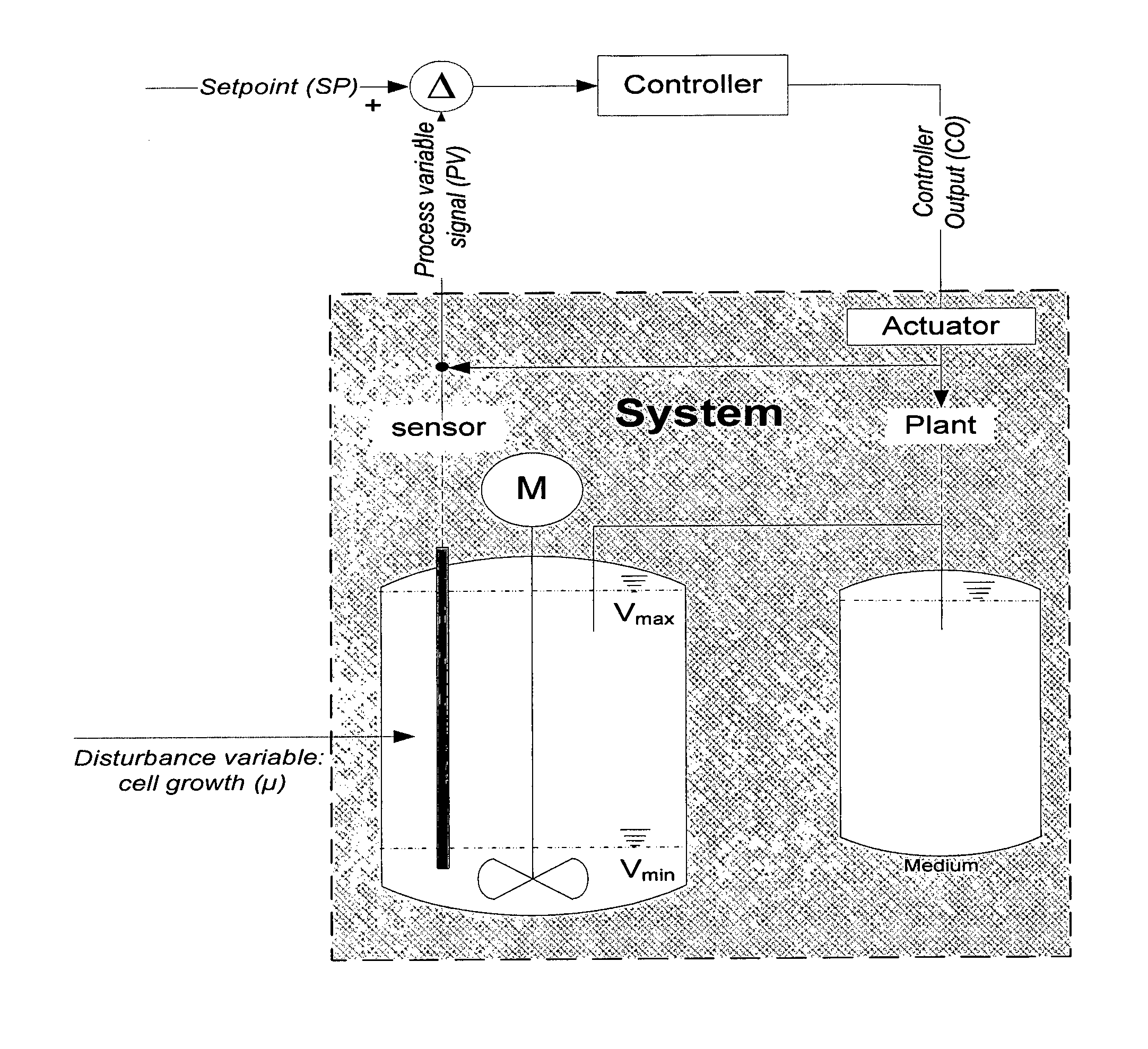
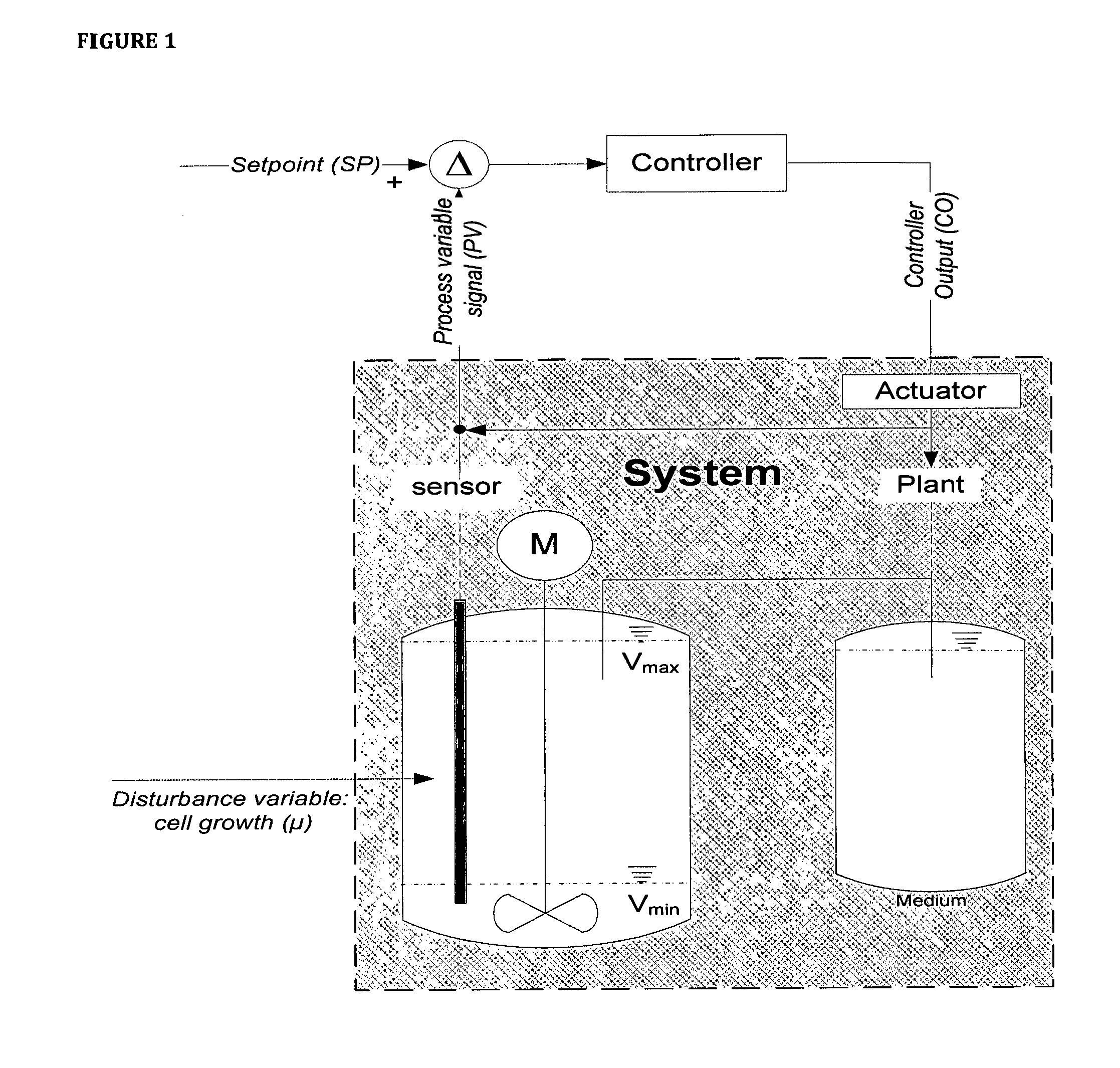
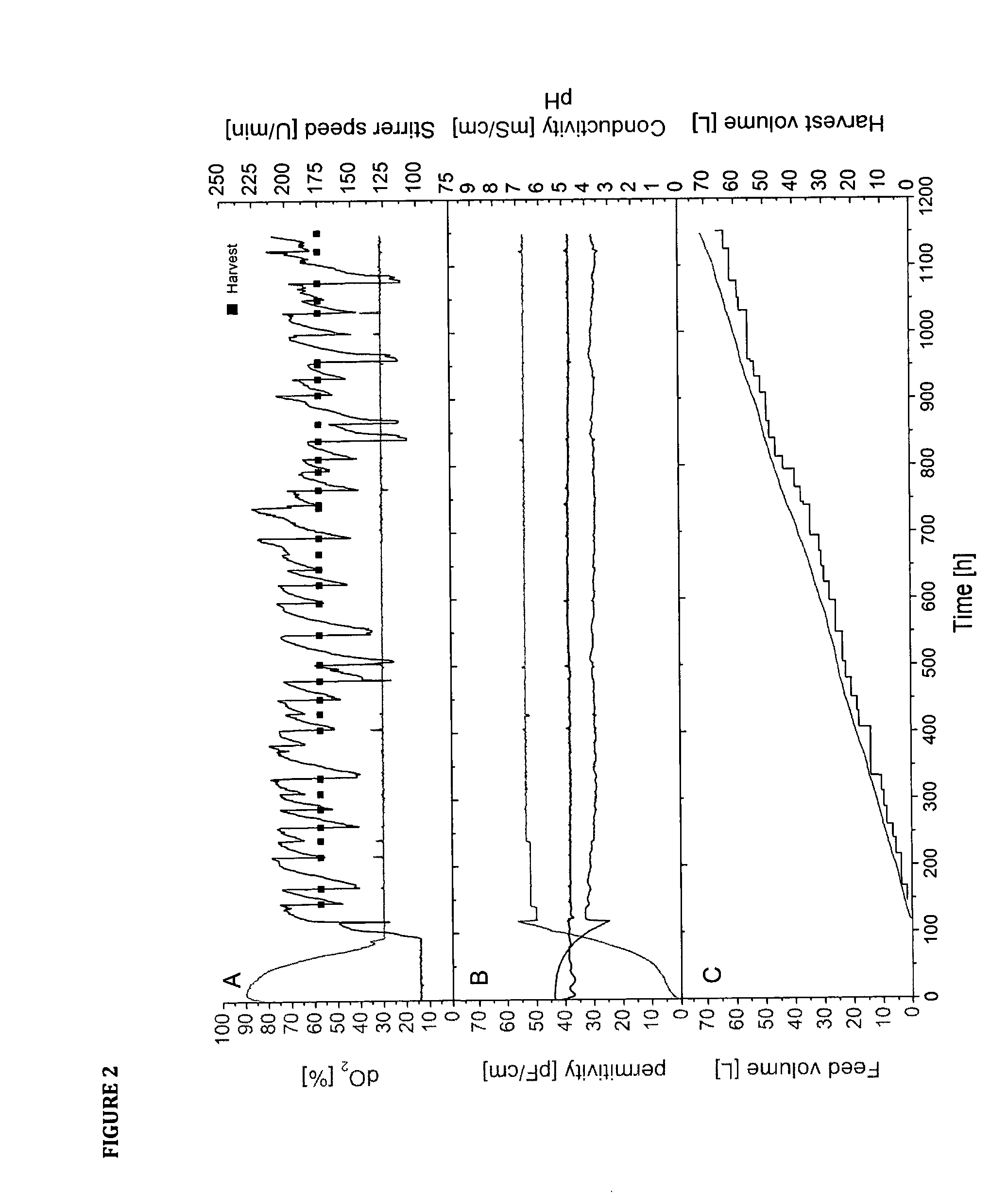
Fermentation systems
ActiveUS20170037421A1Efficient supplyIncreased space-time yieldVaccinesBiochemistry apparatusCell freeVirus
The present disclosure pertains to novel cell cultivation and cell and / or cell-derived product production processes that have advantages over currently existing fermentation strategies. The processes and methods according to the present disclosure may be used for an efficient supply of highly viable and metabolically active eukaryotic cells for transient production platforms, as an alternative production process with advantages over currently applied processes (batch, fed-batch or perfusion strategies) and for generating metabolically highly active biomass for subsequent use for transient expression systems or infection by a virus or pseudovirus or in cell-free systems.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
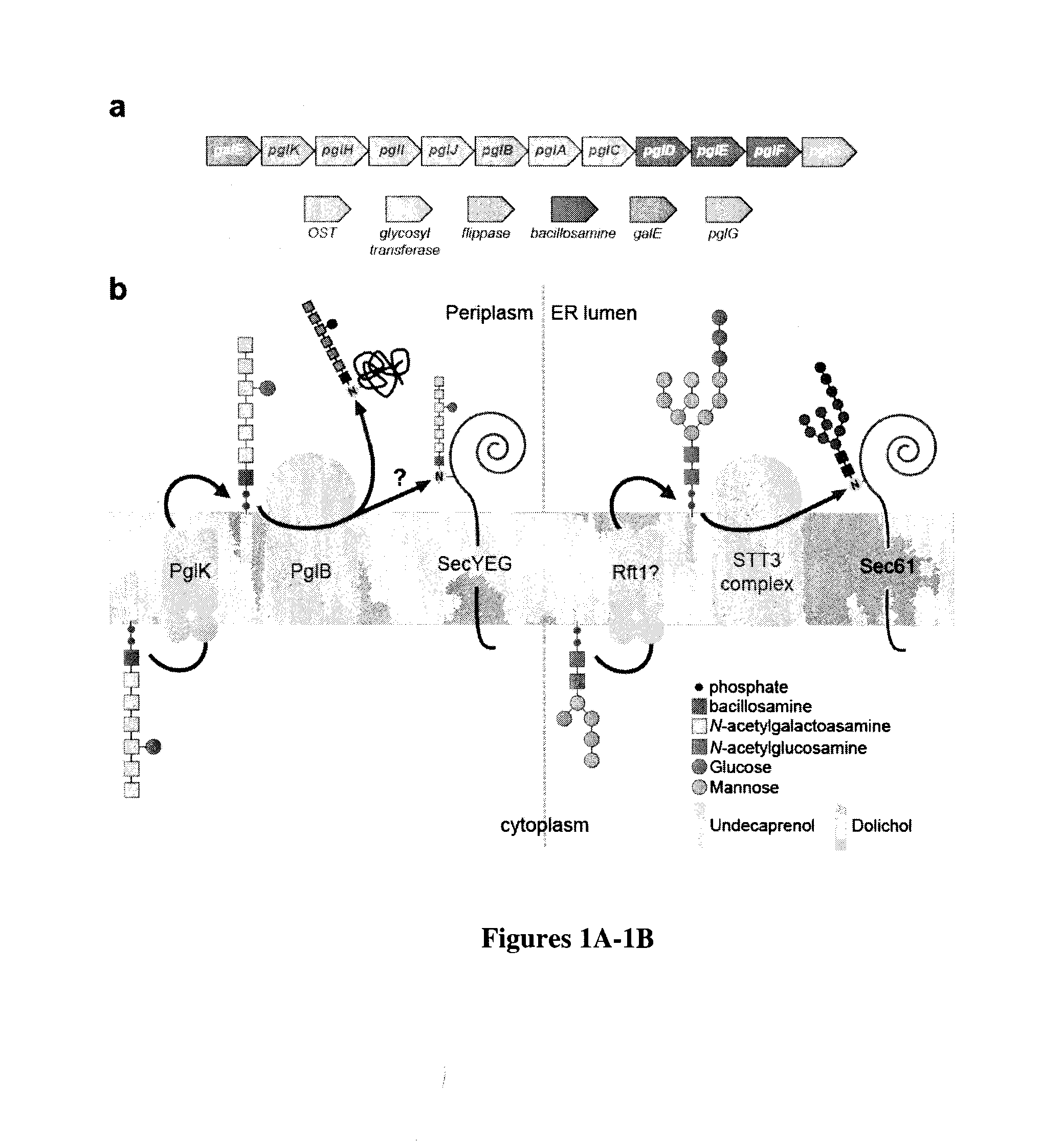
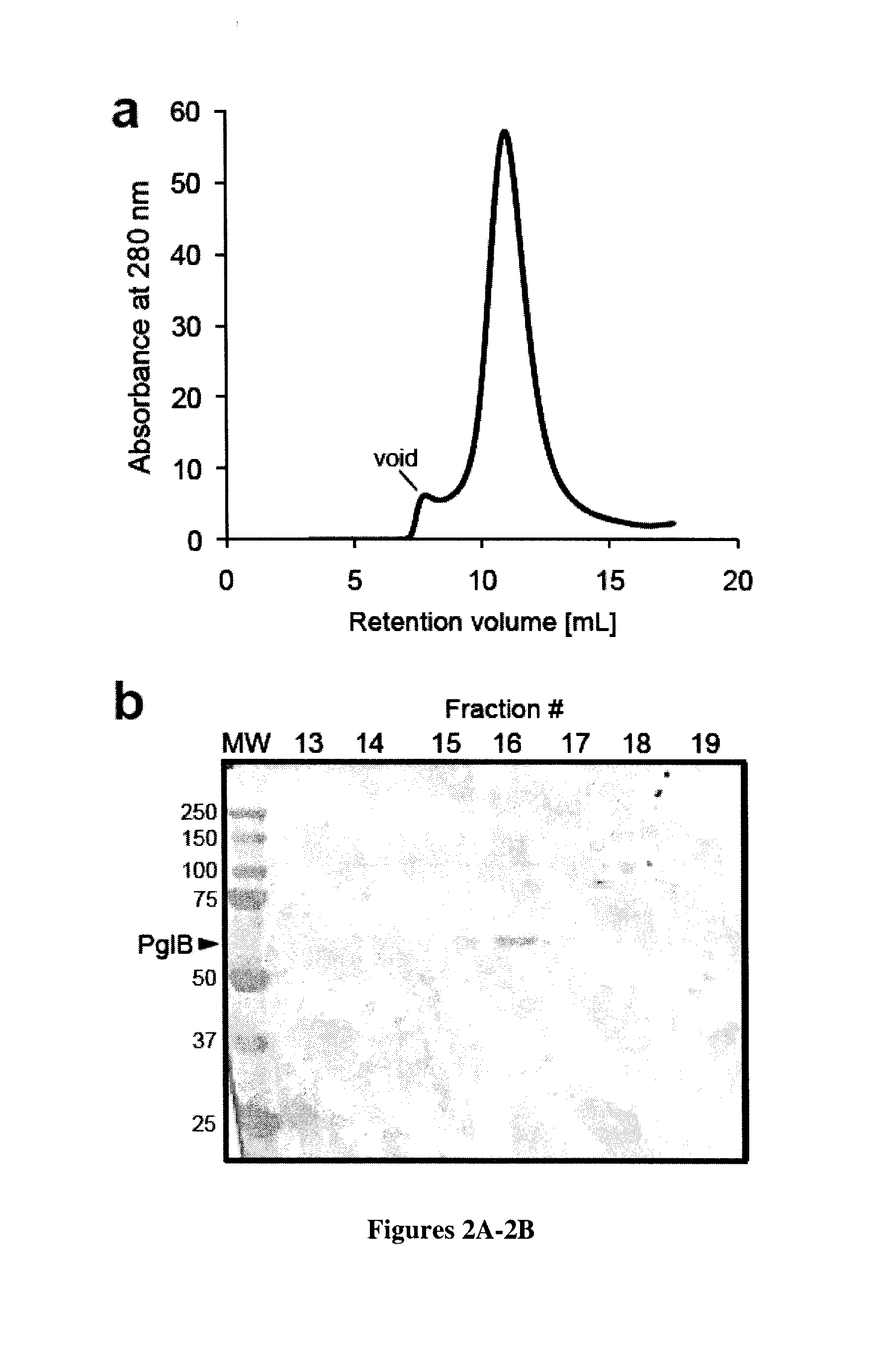
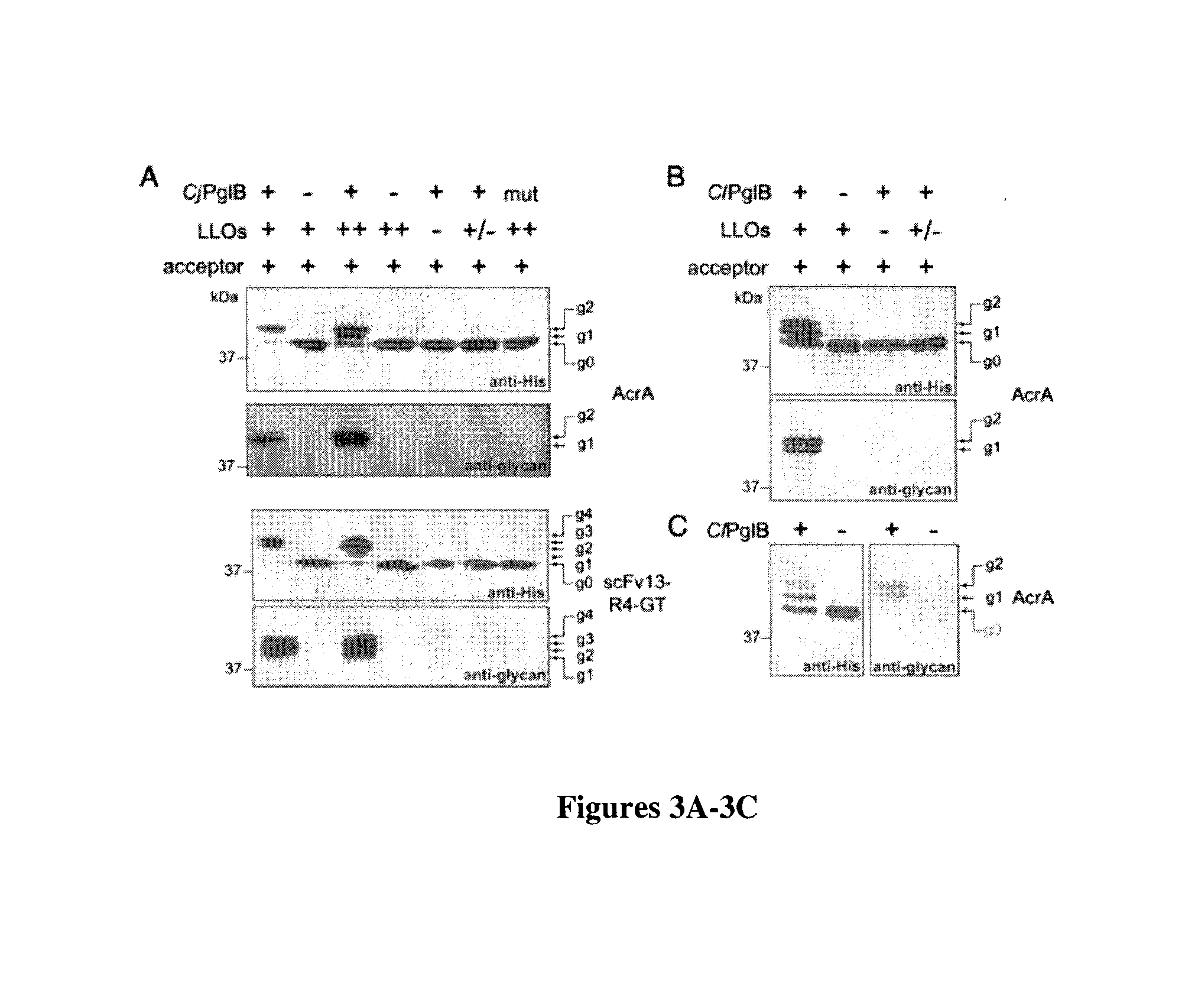
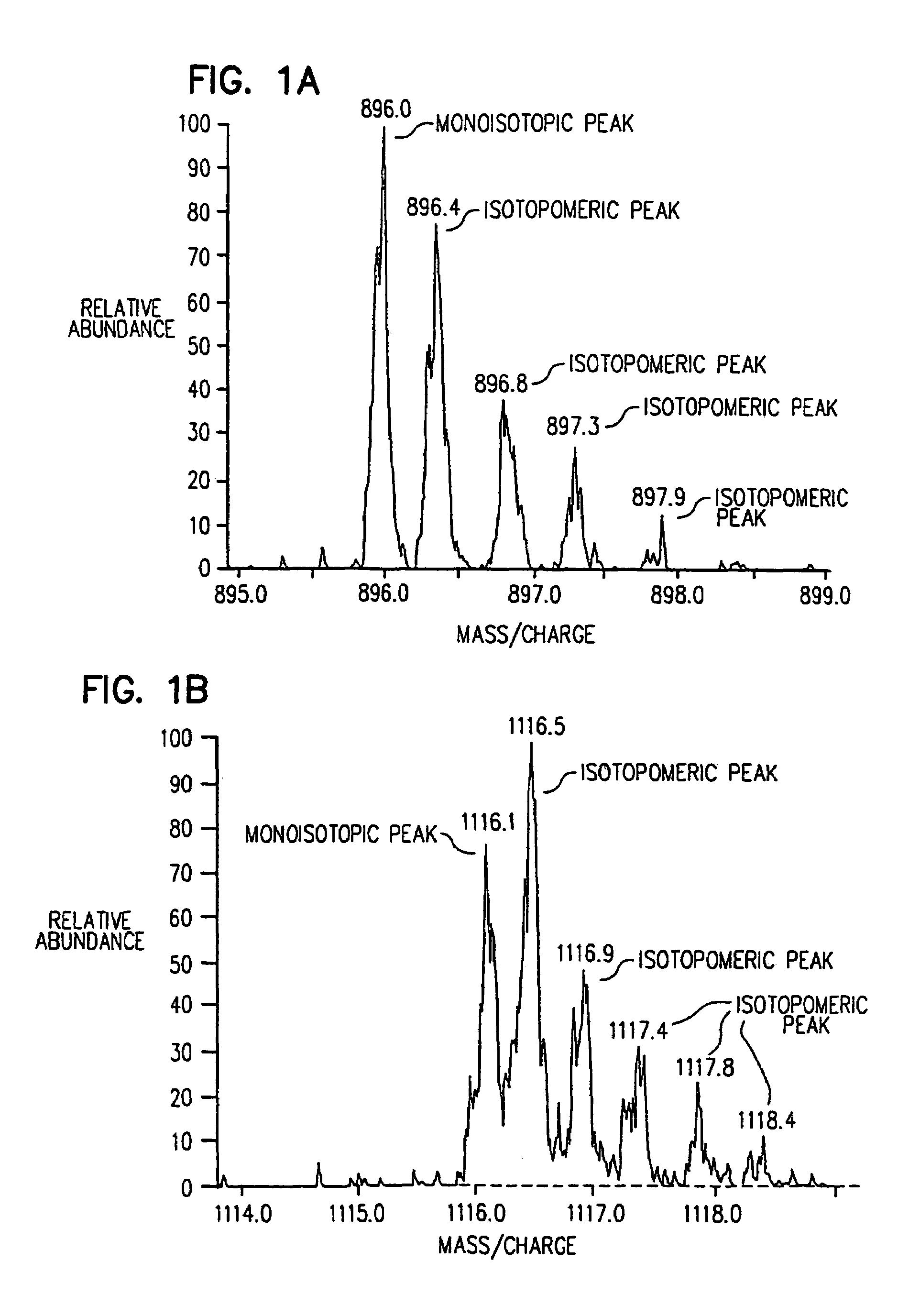
Prokaryote-based cell-free system for the synthesis of glycoproteins
ActiveUS20140255987A1Efficient and accurateEliminate pollutionFermentationGlycosyltransferasesGlycanGlycoprotein i
The present invention is directed to a cell-free system for producing a glycosylated protein. This system comprises an isolated oligosaccharyltransferase capable of transferring a glycan from a lipid carrier molecule to a glycoprotein target, one or more isolated glycans, where each glycan is linked to a lipid carrier molecule, and a glycoprotein target comprising one or more glycan acceptor amino acid residues or a nucleic acid molecule encoding said glycoprotein target. The present invention further relates to kits and methods for producing a glycosylated protein in this cell-free system.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
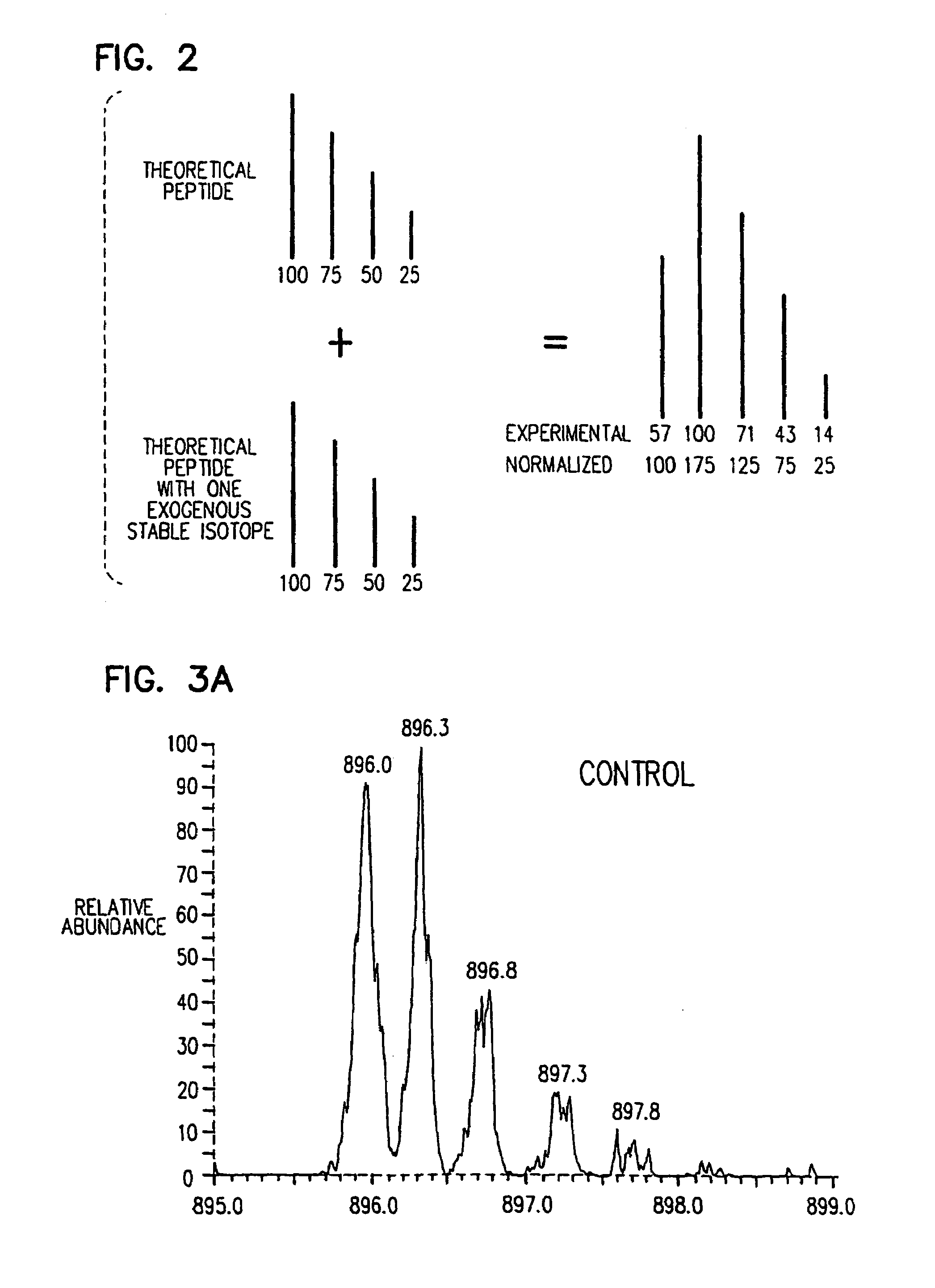
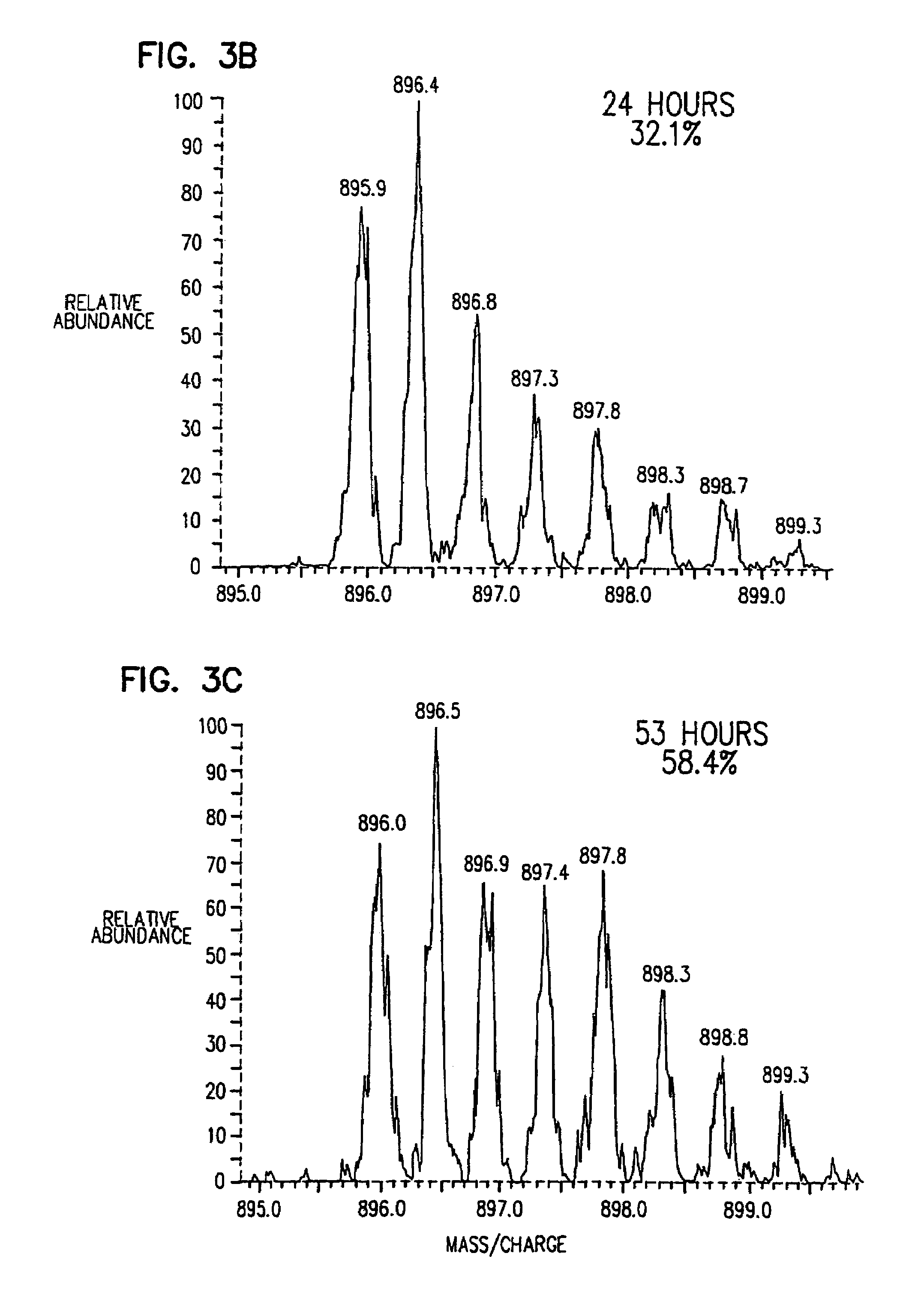
Stable isotope metabolic labeling for analysis of biopolymers
InactiveUS7588887B2Increase in sizeEasy to handleComponent separationMicrobiological testing/measurementStable Isotope LabelingCell free
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
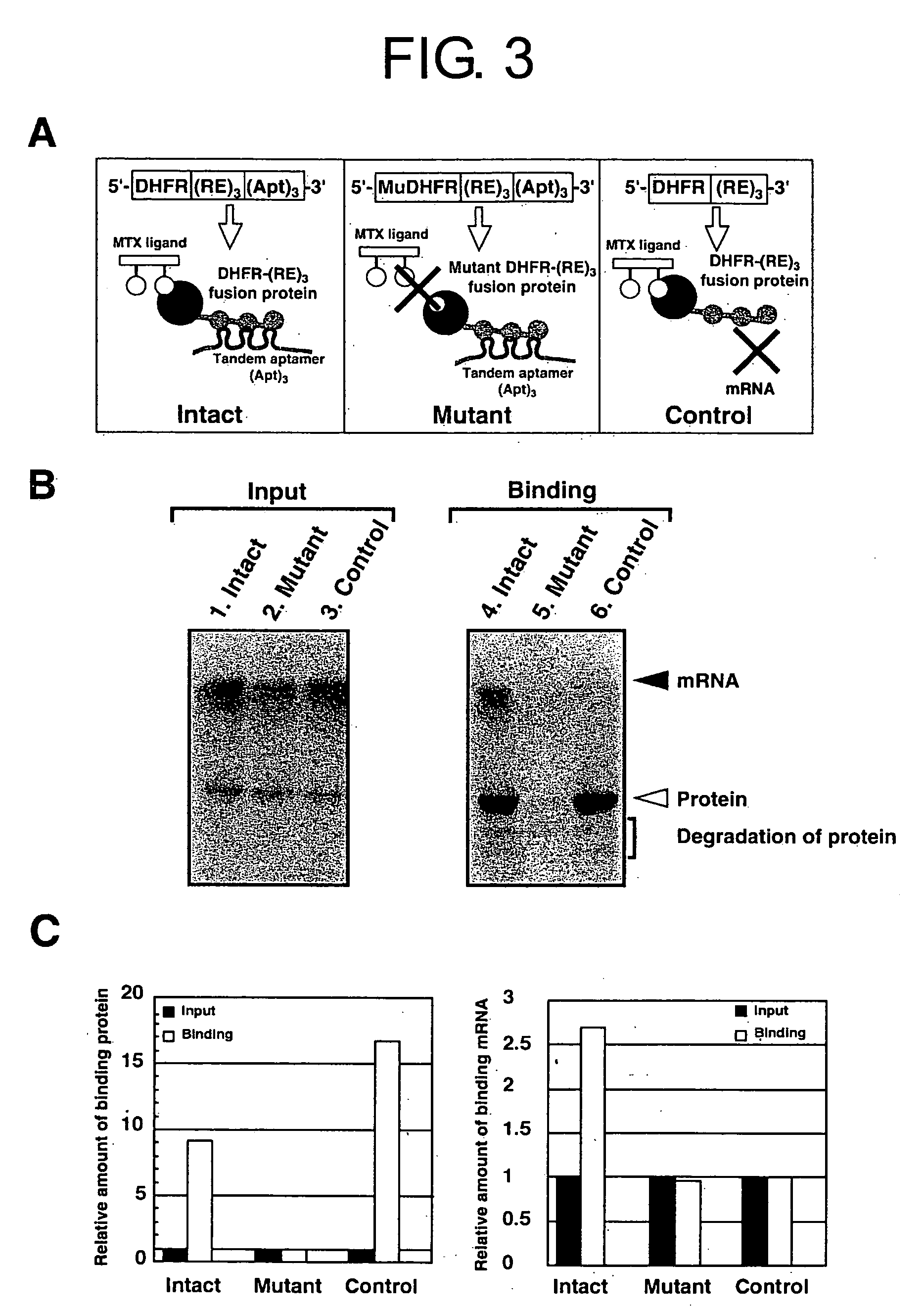
Method for forming a stable complex comprising a transcription product and translation product of a dna encoding a desired polypeptide, a nucleic acid construct used for the method, a complex formed by the method, and screening of a functional protein and mrna or dna encoding the protein using the method
InactiveUS20050191626A1Without reducing sequence varietyLinkage stabilitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGenotypeA-DNA
A stable linkage between a genotype and a phenotype in a cell-free system was successfully achieved by using interaction between a RNA-binding protein and RNA, between a DNA-binding protein and DNA, or by using a protein that inactivates a ribosome. Furthermore, it was found that functional proteins could be selected by using these stable linkages.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
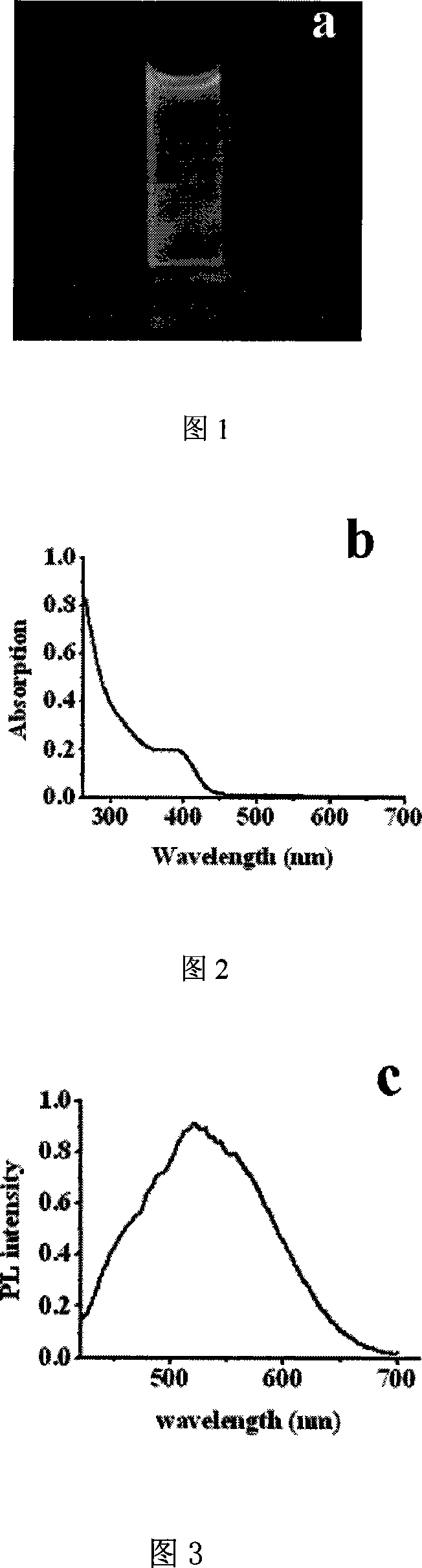
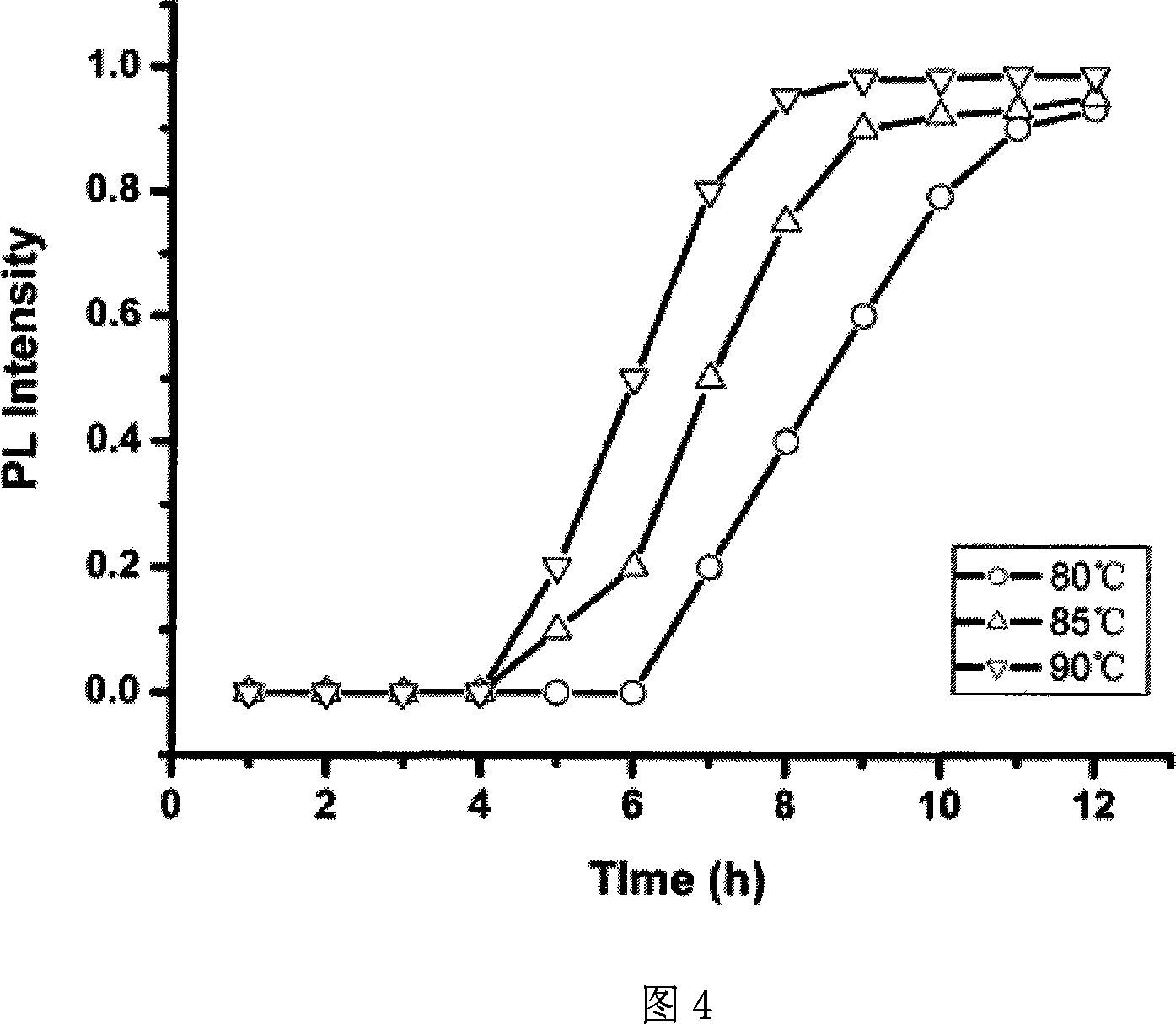
Method for synthesizing cadmium selenide quantum dots based on amino acid and polypeptide
InactiveCN101104807AEasy to separateImprove uniformityLuminescent compositionsCadmium selenideNanoparticle
The invention discloses a method of synthesizing CdSe quantum dots with Amino acid and polypeptide, comprising the following steps: A, preparing cell-free system of selenium-containing amino acid; B, preparing Cd-glutathione; C, synthesizing CdSe quantum dots. The invention is provided with a simple technology and mild reaction conditions. As no organometallic compounds are included in the preparation, the protection from the inert gas is not needed. The production is safe and low in cost, helpful to the industrial synthesis of the nano-particles (including quantum dots).
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Cell-free system for synthesis of proteins derived from cultured mammalian cells
InactiveUS20110300575A1High synthetic activityLow costHydrolasesPeptide/protein ingredientsInitiation factorFree protein
Prepared is an extract composition having an improved protein synthetic activity in a cell-free protein synthesis system using a mammalian cultured cell extract. An eukaryotic translation initiation factor and / or translational regulator are added to a cell-free protein synthesis system comprising an extract prepared from cultured mammalian cells and a template mRNA. These factors are one or more selected from the group consisting of eukaryotic translation initiation factors 4E (eIF4E), 2 (eIF2) and 2B (eIF2B), and eukaryotic translational regulator p97.
Owner:RIKEN
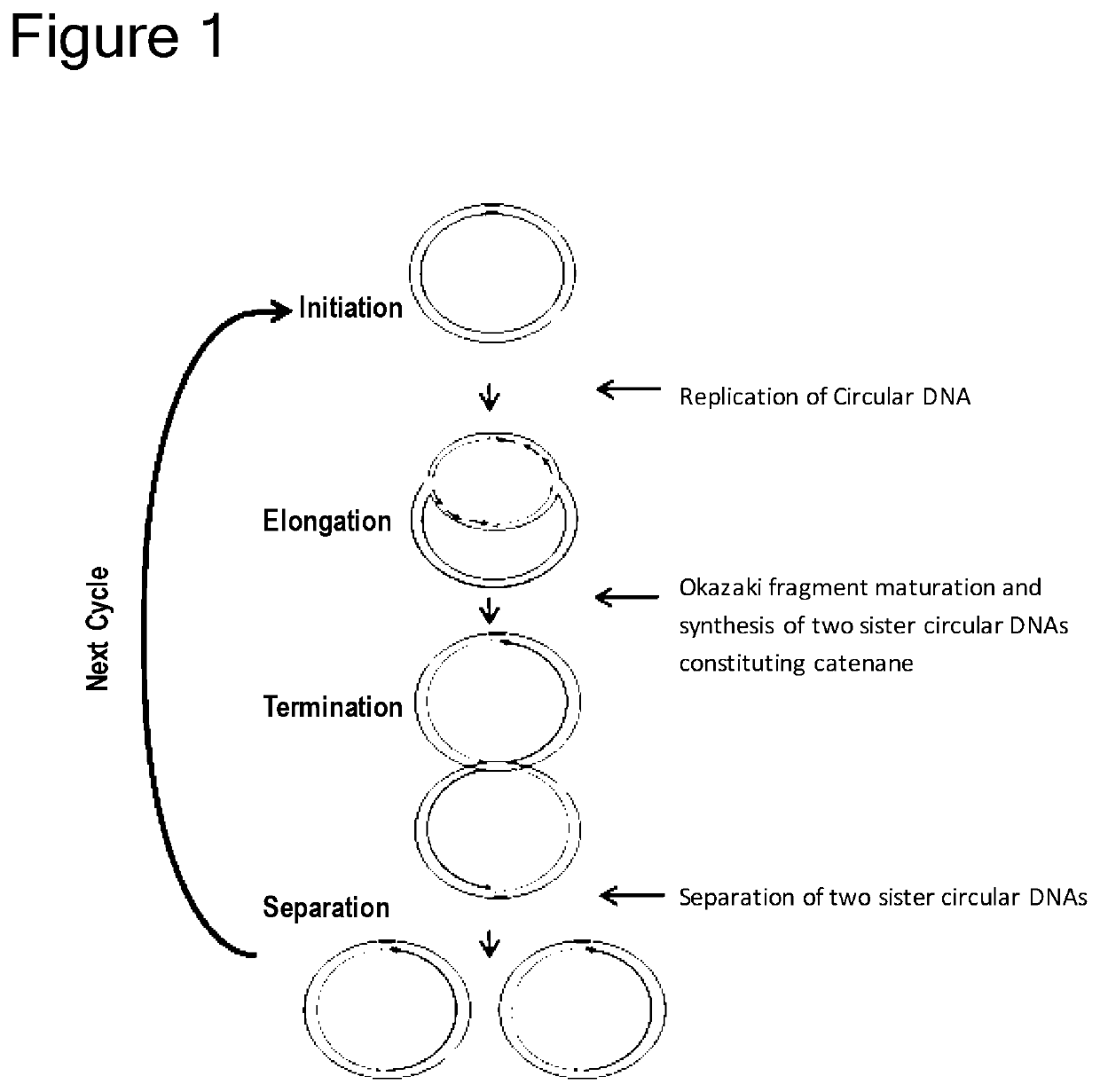
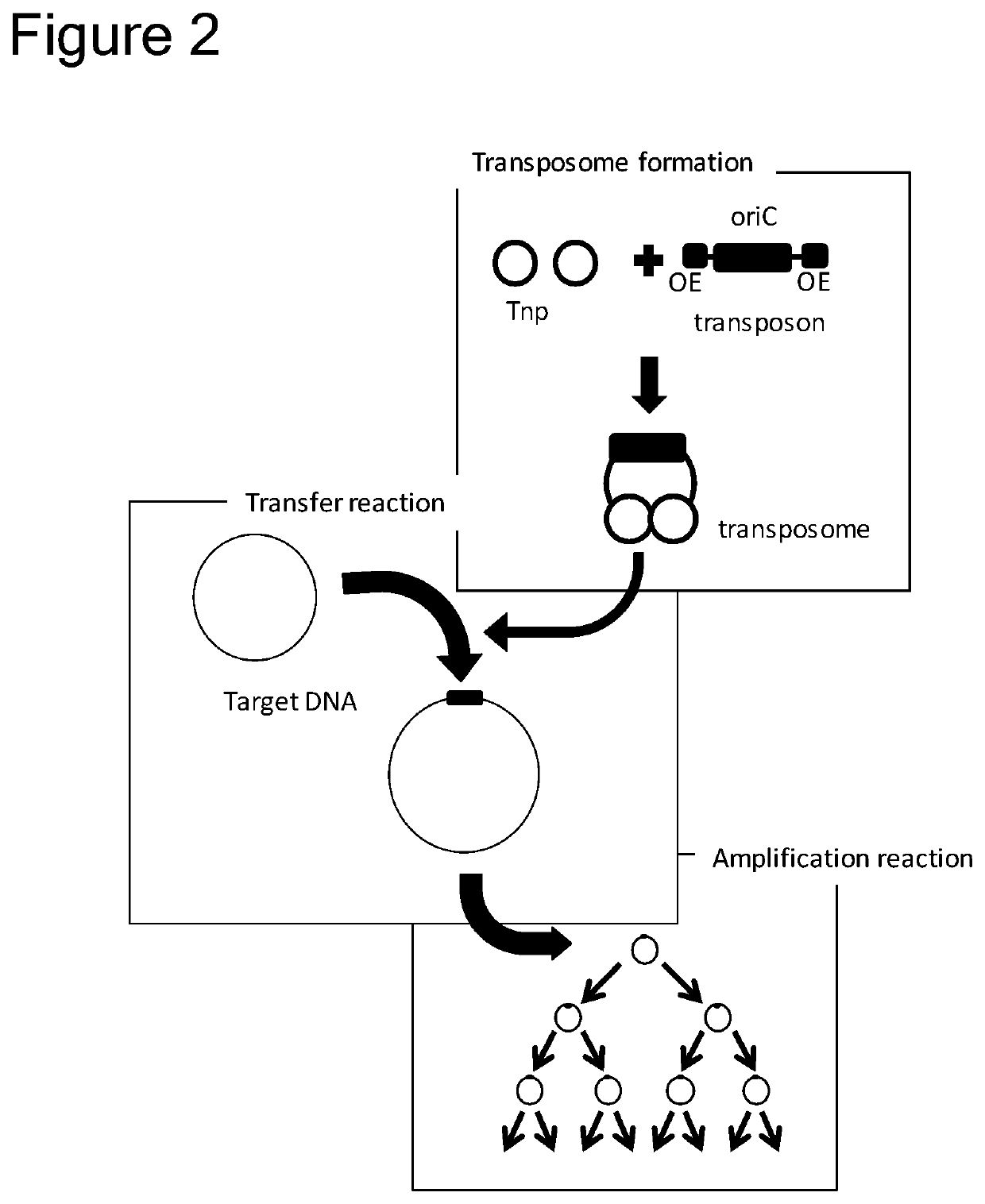
Method of replicating or amplifying circular DNA
ActiveUS20200115727A1Suppress generationReduce concentrationMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationOrigin of replicationA-DNA
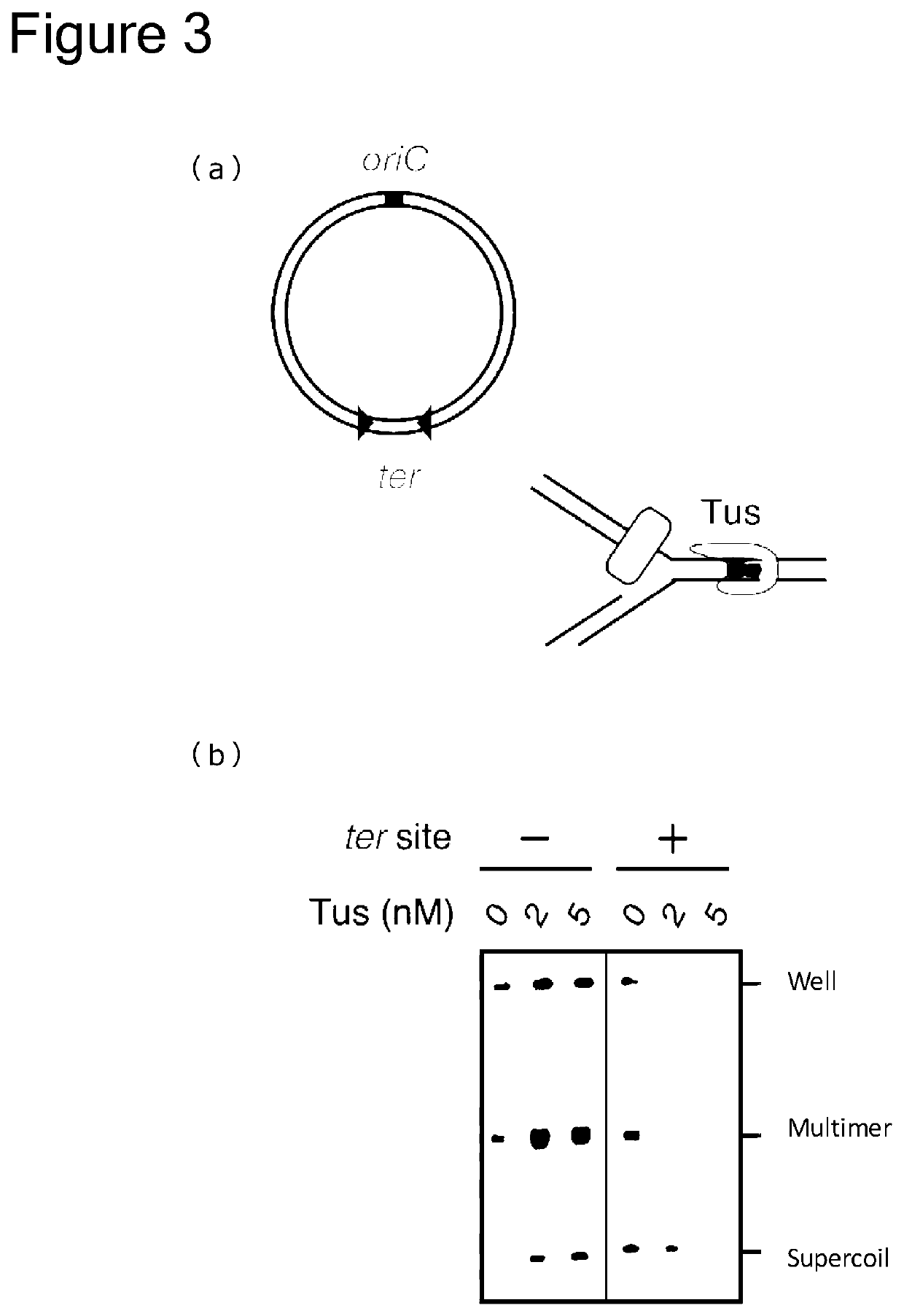
Provided is a method capable of replicating or amplifying circular DNA, and particularly, long-chain circular DNA, in a cell-free system. Specifically, provided is a method for suppressing generation of a DNA multimer as a by-product, when circular DNA having a replication origin sequence (origin of chromosome (oriC)) is replicated or amplified by using the following enzyme groups:(1) a first enzyme group that catalyzes replication of circular DNA;(2) a second enzyme group that catalyzes an Okazaki fragment maturation and synthesizes two sister circular DNAs constituting a catenane; and(3) a third enzyme group that catalyzes a separation of two sister circular DNAs.Moreover, also provided is a method comprising introducing oriC into circular DNA by using a transposon.
Owner:MODERNA ENZYMATICS CO LTD
Cell free translation system for compound screening and related uses
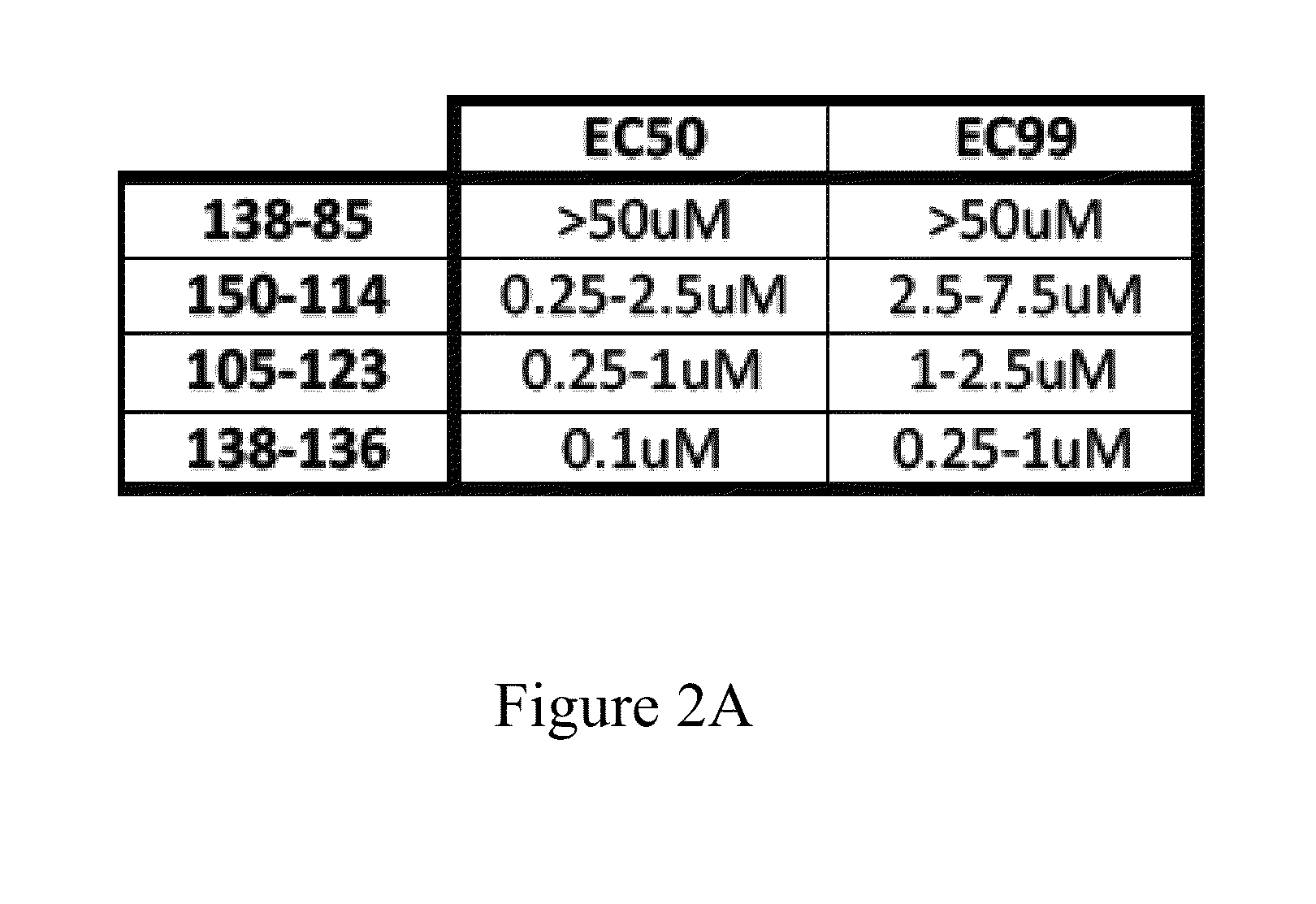
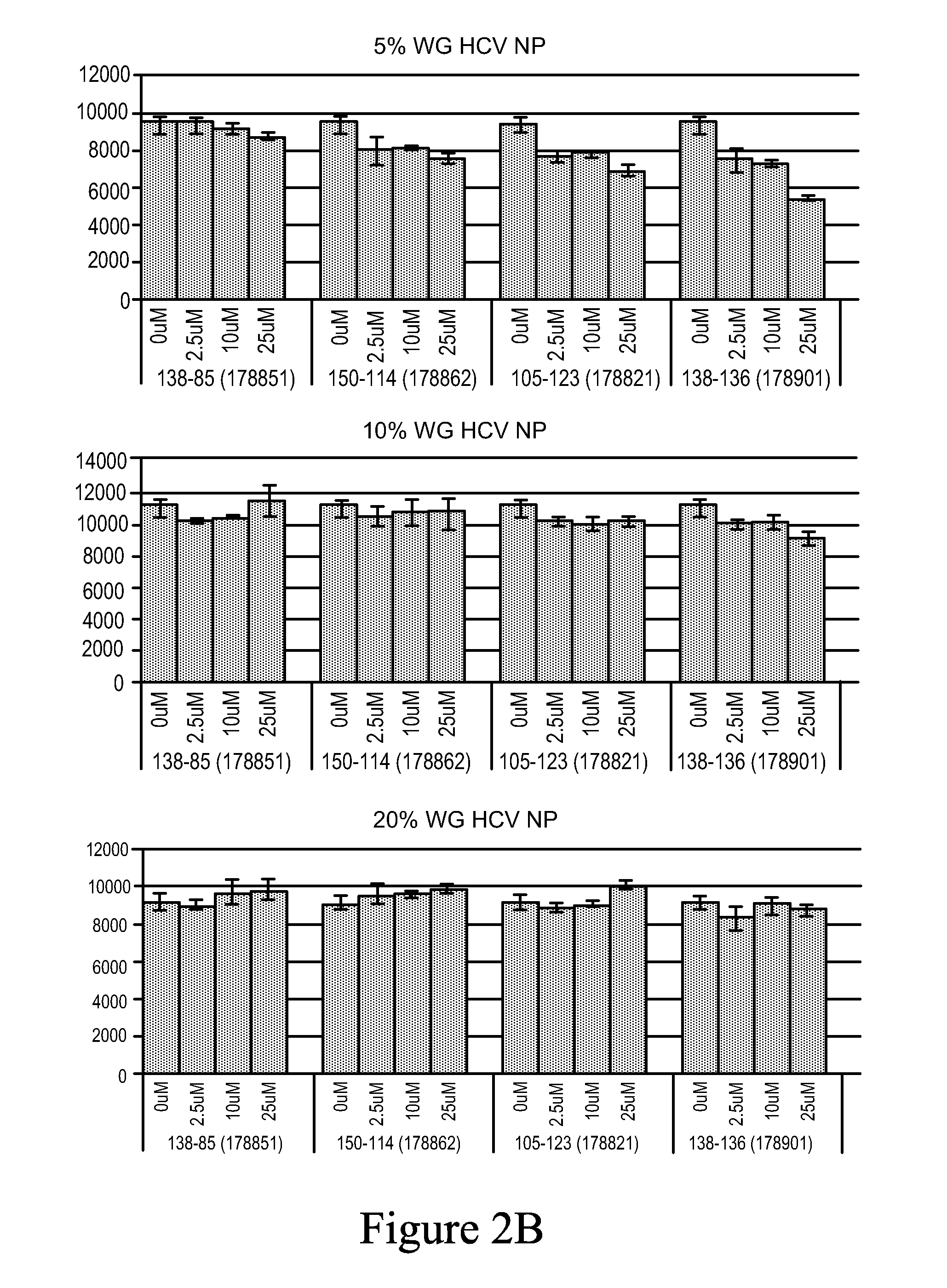
InactiveUS20130053267A1High sensitivitySlow-down in overall processingSsRNA viruses negative-senseCompound screeningCns diseaseWheat germ
Owner:PROSETTA ANTIVIRAL
Method for carrying out gene mutation detection on cell-free system by HRM technology
InactiveCN101955990AEasy to sampleEasy to monitor in real timeMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceDiseaseNucleotide
The invention discloses a method for carrying out gene mutation detection on a cell-free system by an HRM technology. The invention is characterized in that the method comprises the following steps: (1) designing and selecting a plurality of primer pairs containing continuous nucleotide sequences formed by at least 15 continuous nucleotides in the targeted region of a target gene; (2) extracting DNA from the cell-free system, and utilizing the plurality of primer pairs screened in advance to carry out specific amplification on the targeted sequence of the target gene; and (3) carrying out mutational site detection on the amplified gene sequence according to a high-resolution fusion curve method. The method provides more extensive selectable samples for the detection and the analysis on related diseases by the cell-free system application technical research and obviously reduces invasive harm of the diseases on patients.
Owner:JIANGSU MICRODIAG BIOMEDICINE TECH CO LTD
Methods and compositions that affect melanogenesis
The invention provides methods of screening for compounds that affect melanogenesis and the function of P protein in organisms, cells, or cell-free systems. The invention further relates to pharmacologic and cosmetic uses of methods of inhibiting melanogenesis, methods of activating melanogenesis, and compounds and pharmacologic compositions useful for the inhibition or activation of melanogenesis and, therefore, for lightening or darkening the pigmentation of cells and tissue, i.e., skin.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
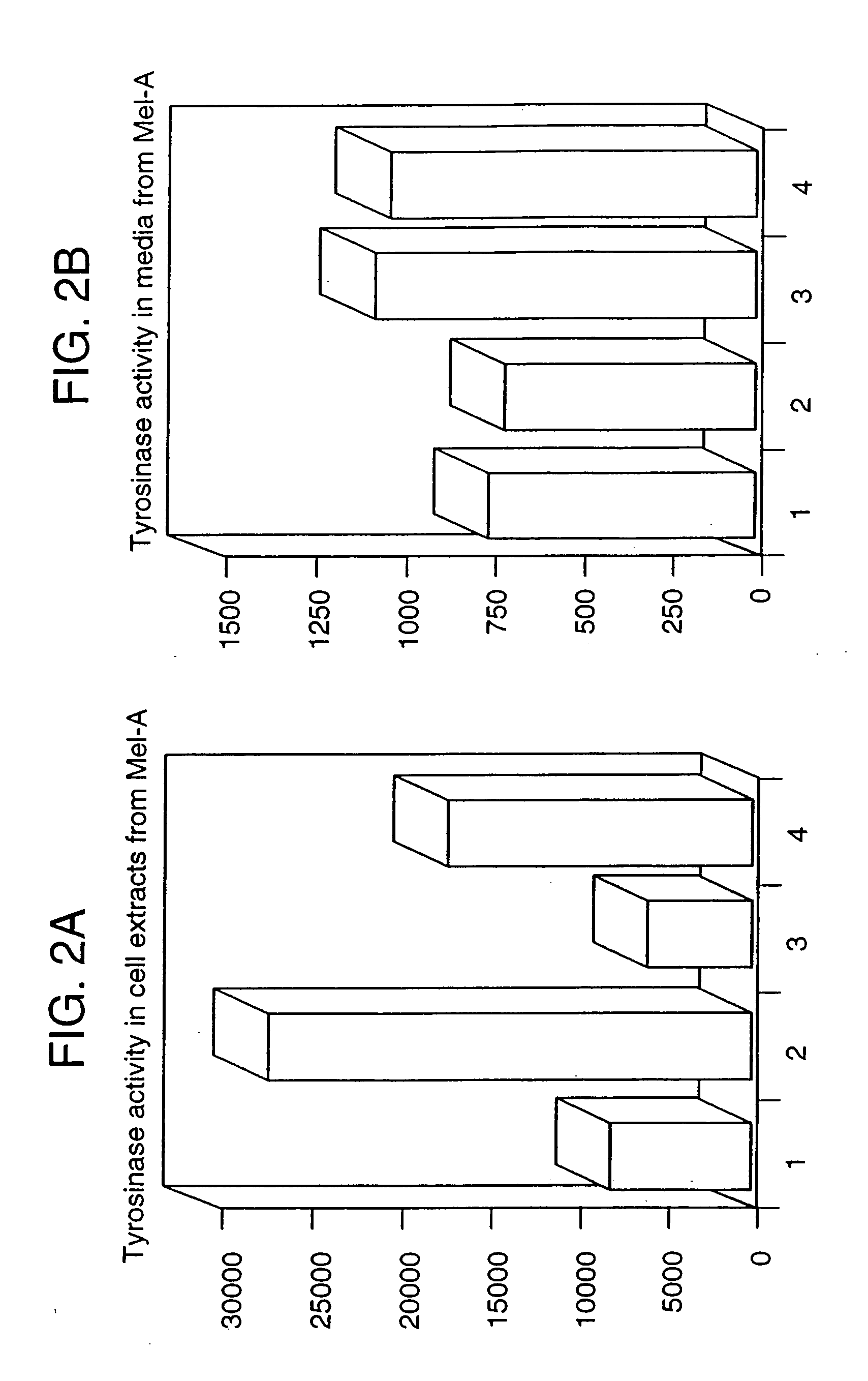
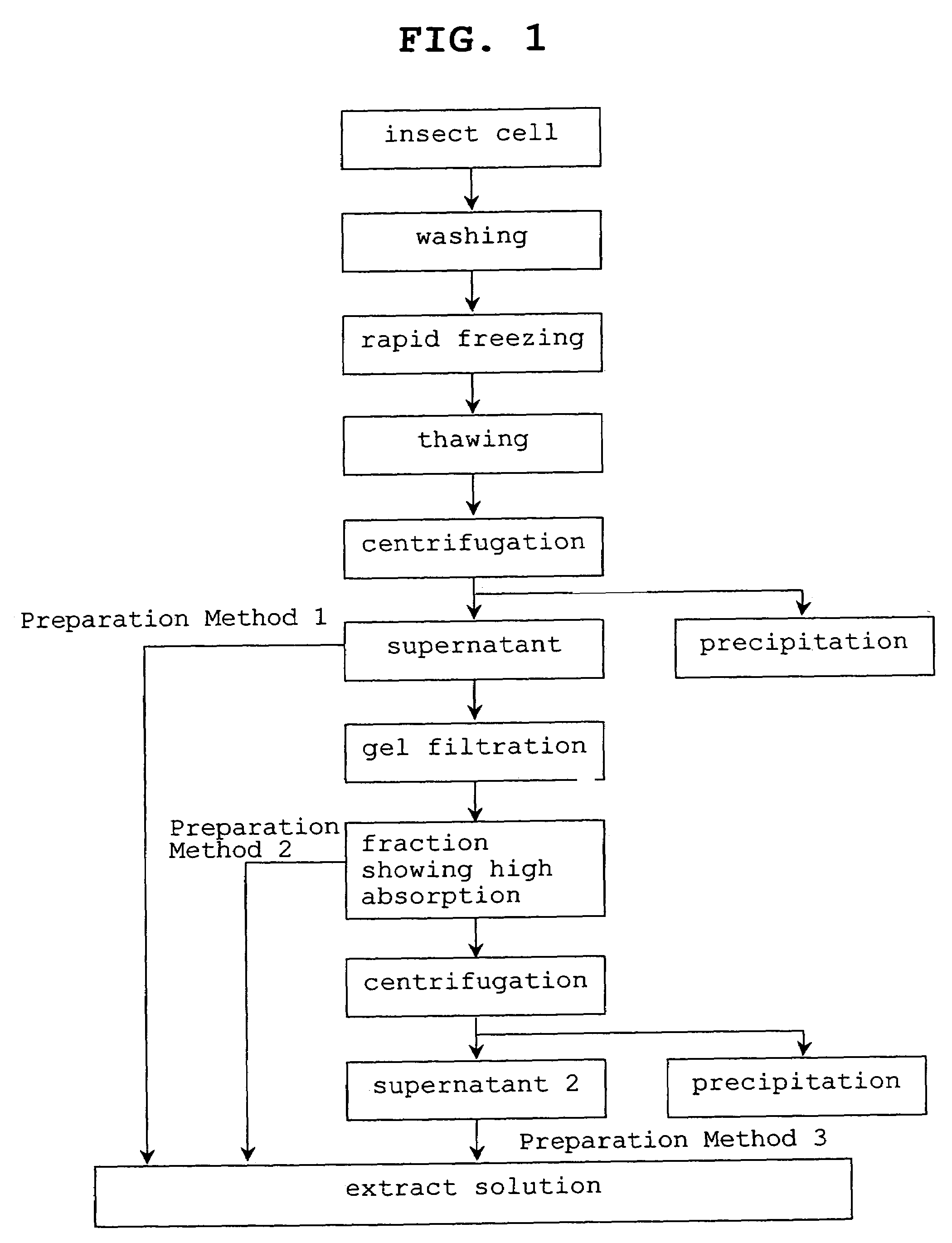
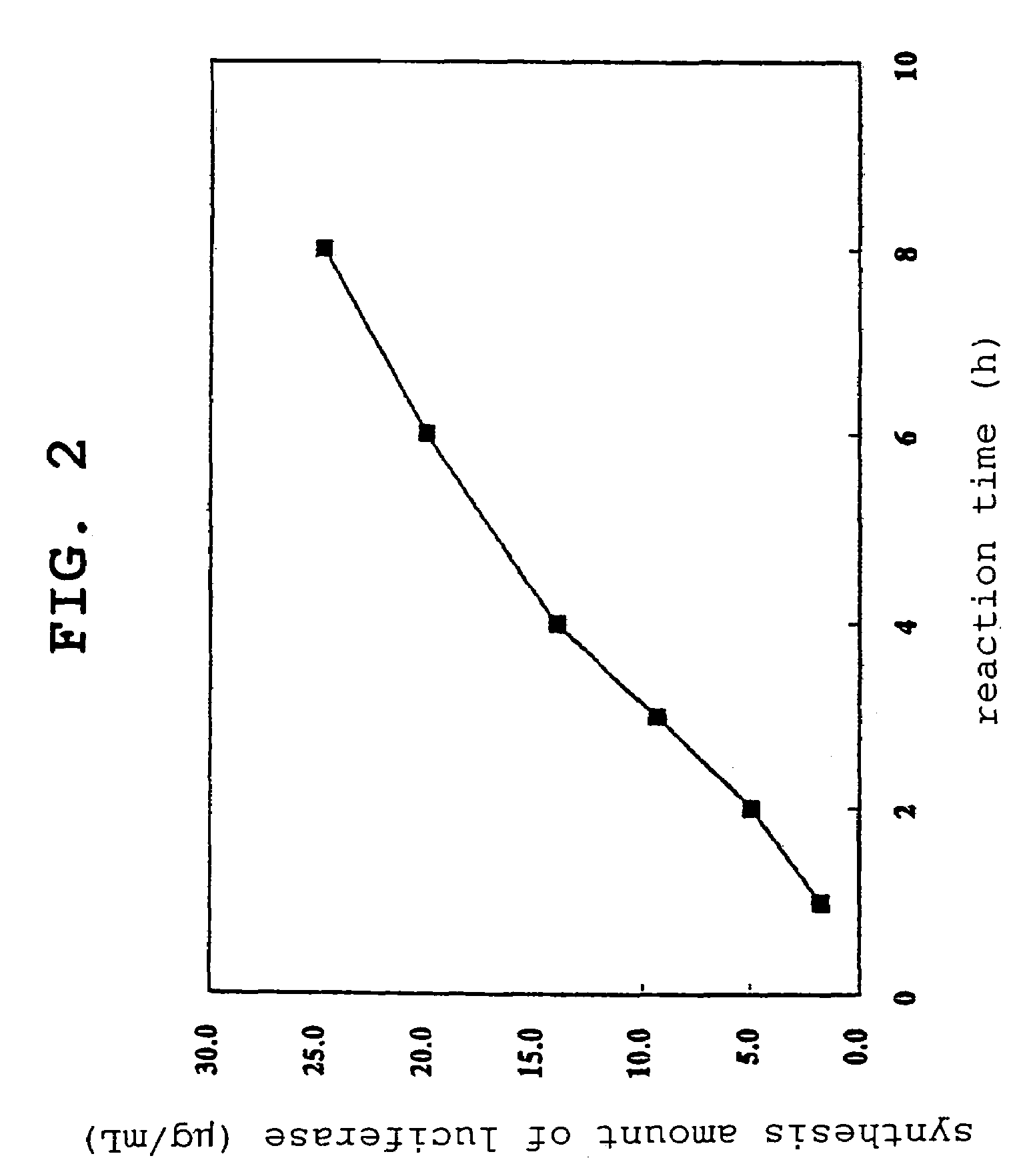
Preparation method of insect cell extract solution for cell-free protein synthesis, the insect cell extract solution and cell-free synthesis method of protein using the insect cell extract solution
The present invention provides a preparation method of an insect cell extract solution for cell-free protein synthesis, the insect cell extract solution, a protein synthesis method in a cell-free system, which uses the insect cell extract solution, and a kit for cell-free protein synthesis containing the insect cell extract solution. The extract solution is easily prepared by the method of the present invention and can synthesize a higher amount of protein than by extract solutions prepared by conventional methods.
Owner:SHIMADZU CORP
Methods and compositions for optimization of oxygen transport by cell-free systems
InactiveUS20050239686A1Limit on characteristicLow in DOOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsCell freePlasma expander
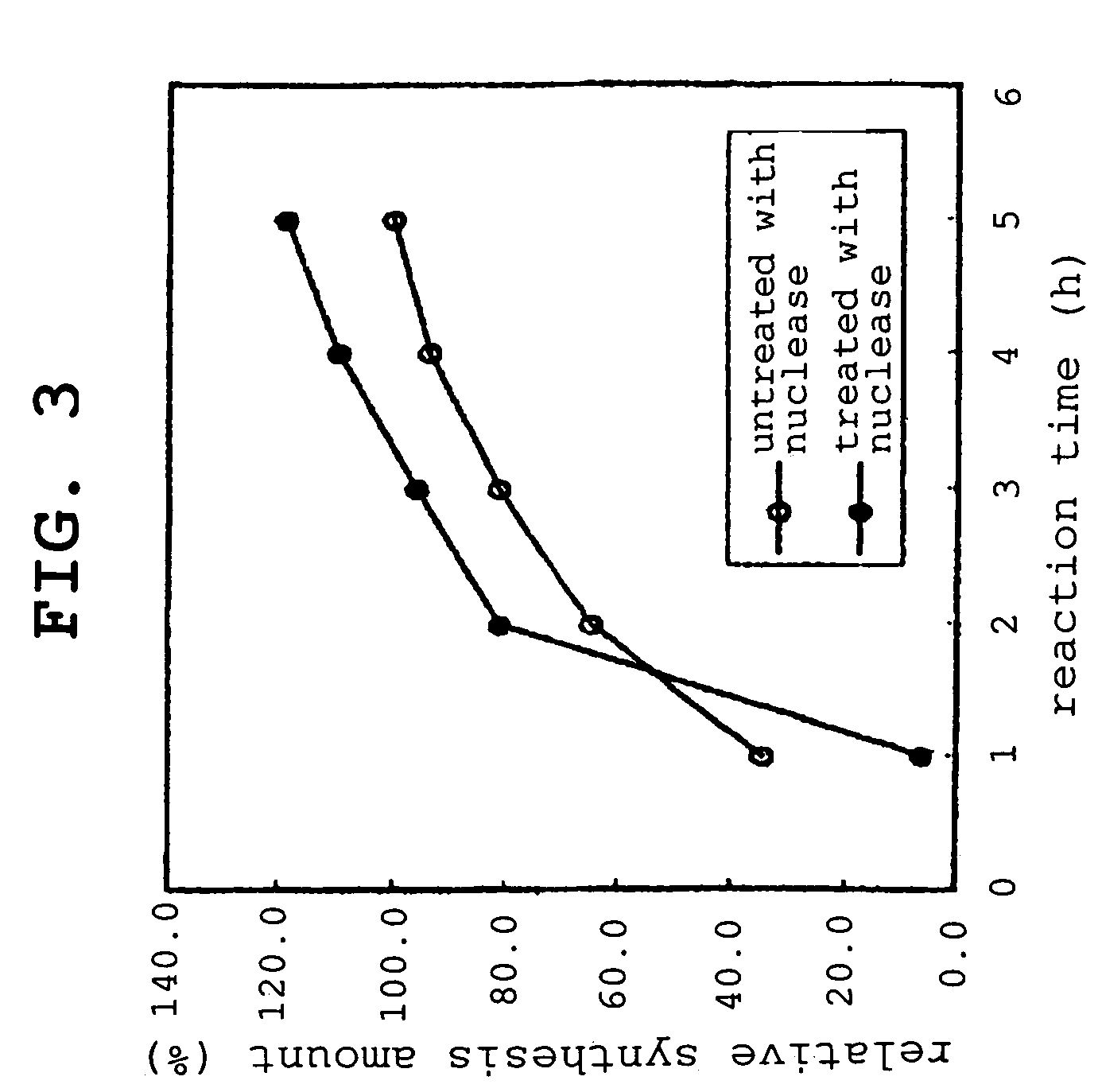
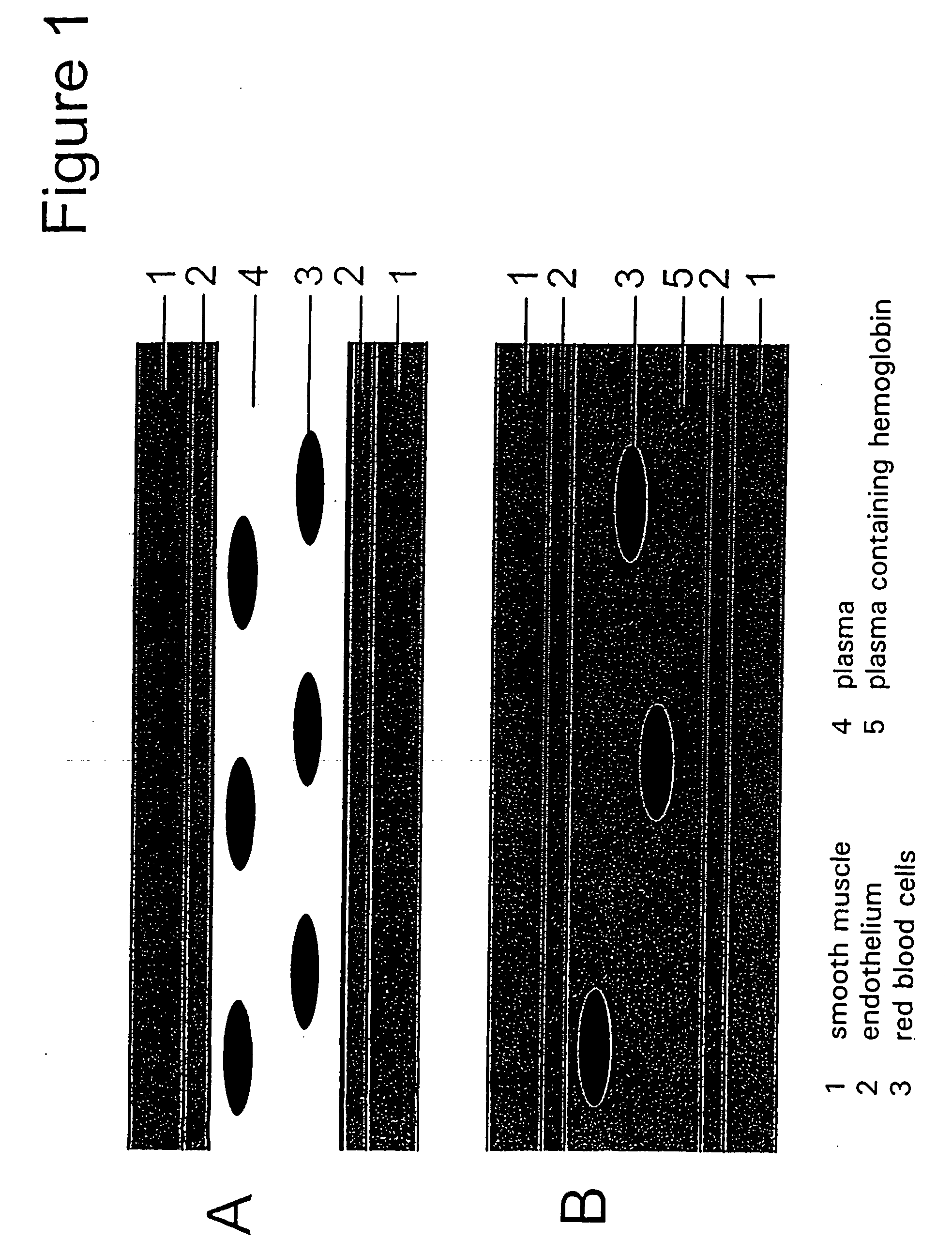
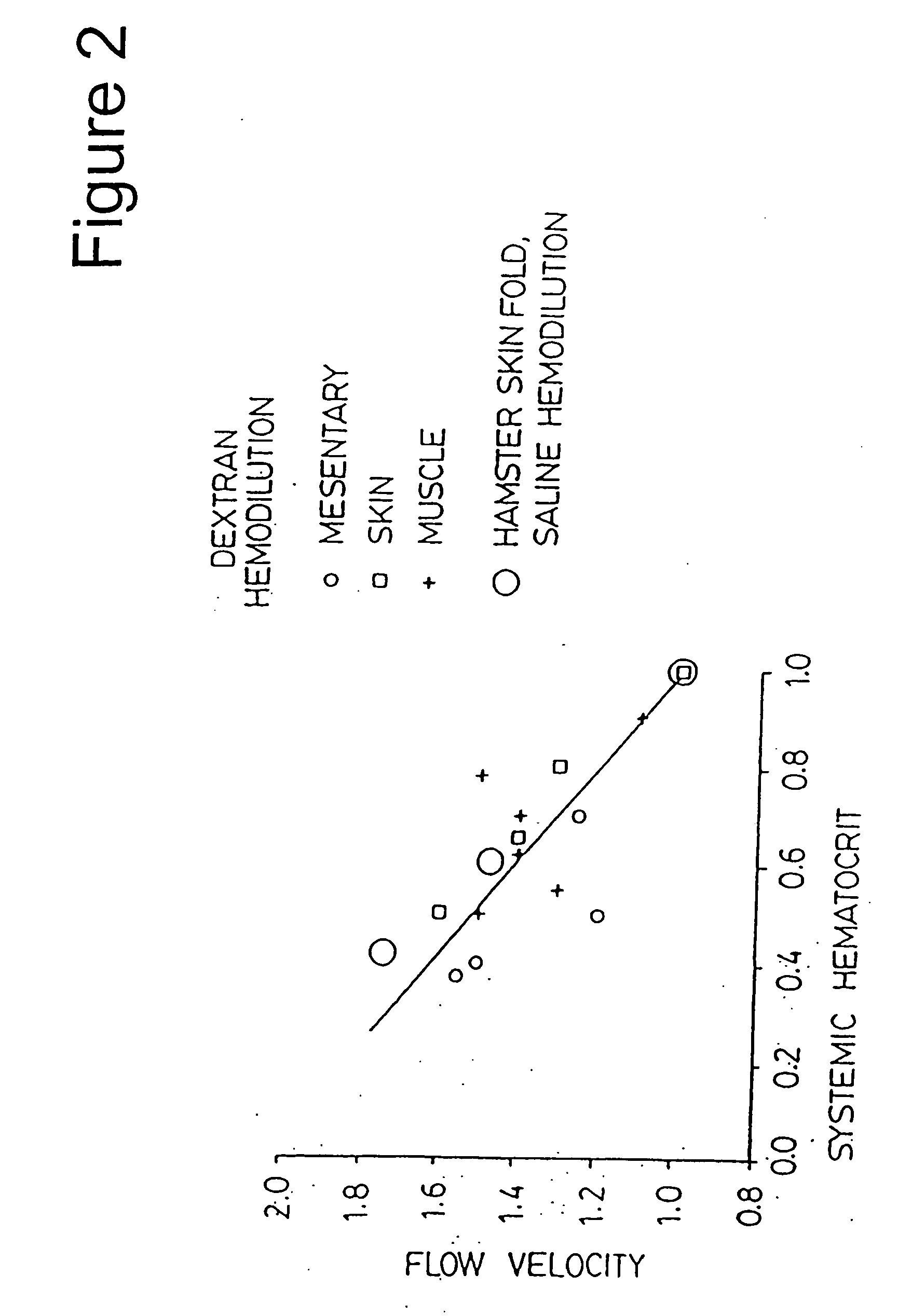
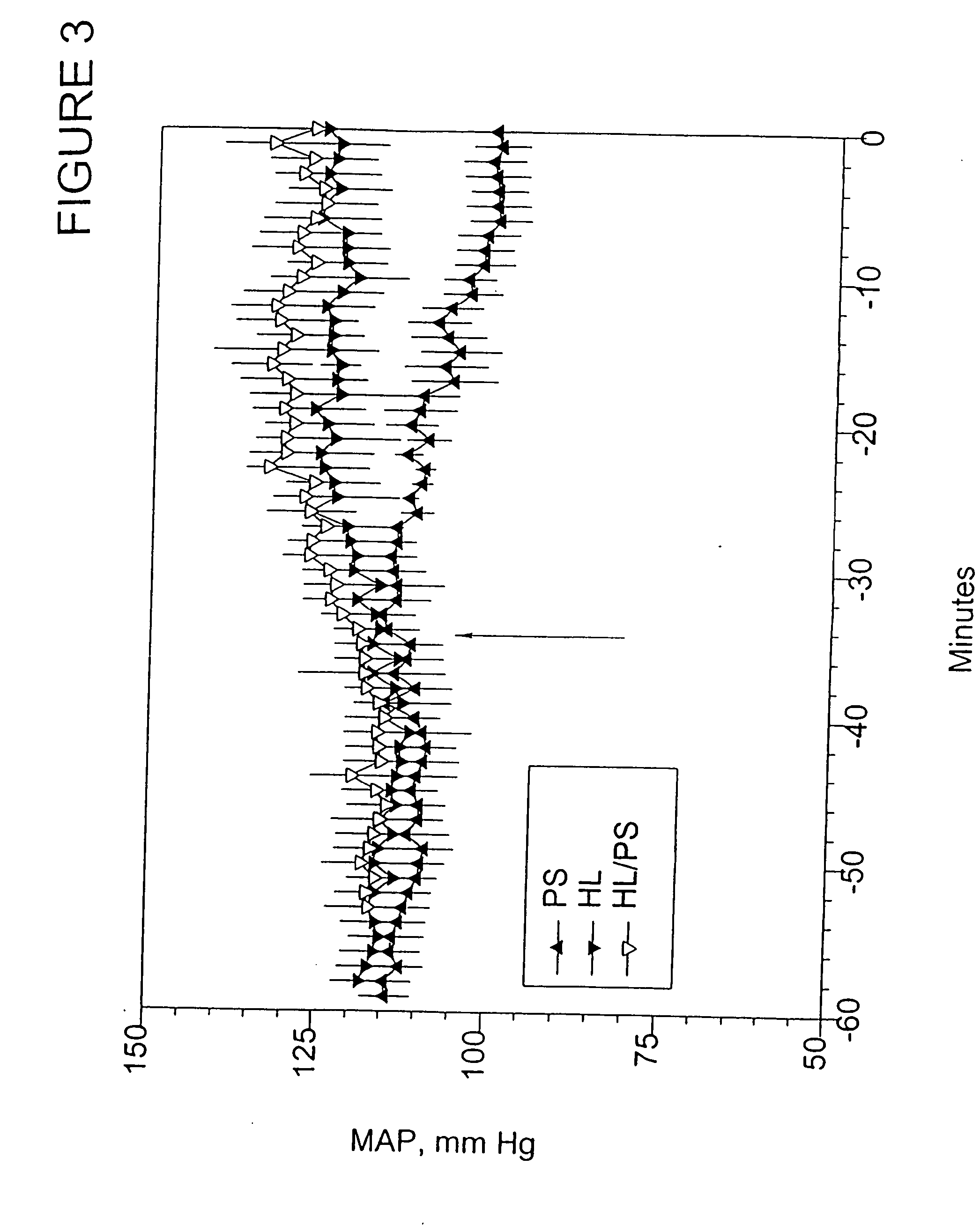
Compositions, and methods of use thereof, for use as blood substitute products comprise aqueous mixtures of oxygen-carrying and non-oxygen carrying plasma expanders and methods for the use thereof. The oxygen-carrying component may consist of any hemoglobin-based oxygen carrier, while the non-oxygen carrying plasma expander my consist of any suitable diluent.
Owner:WINSLOW ROBERT M
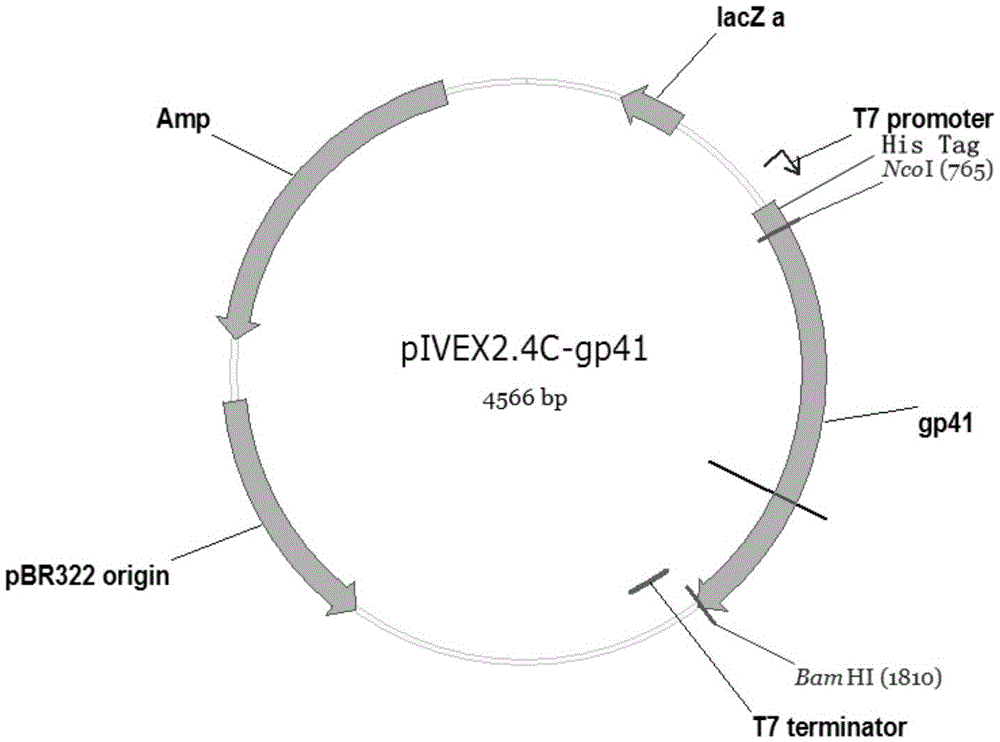
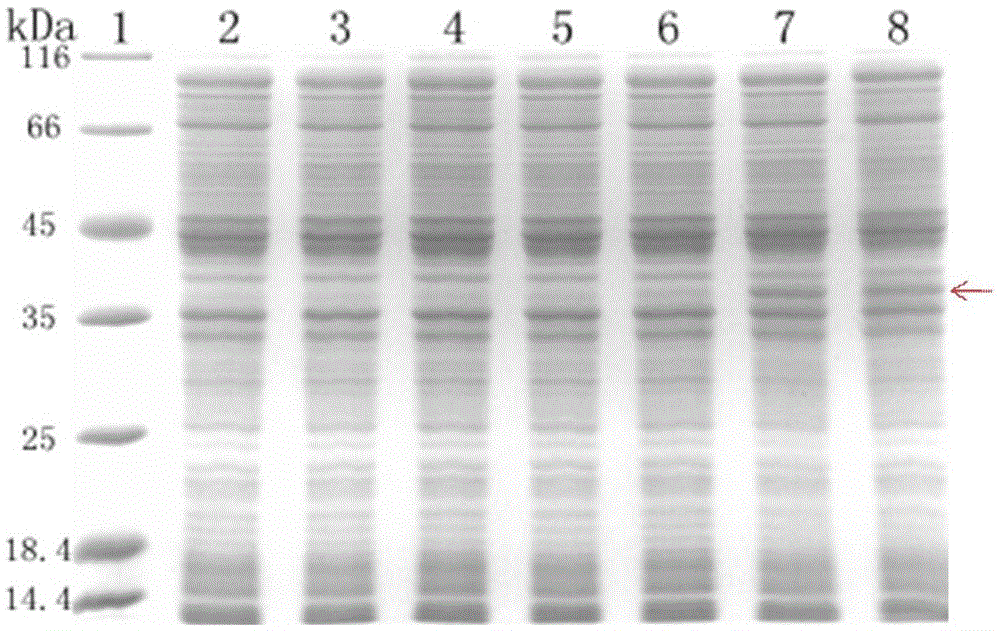
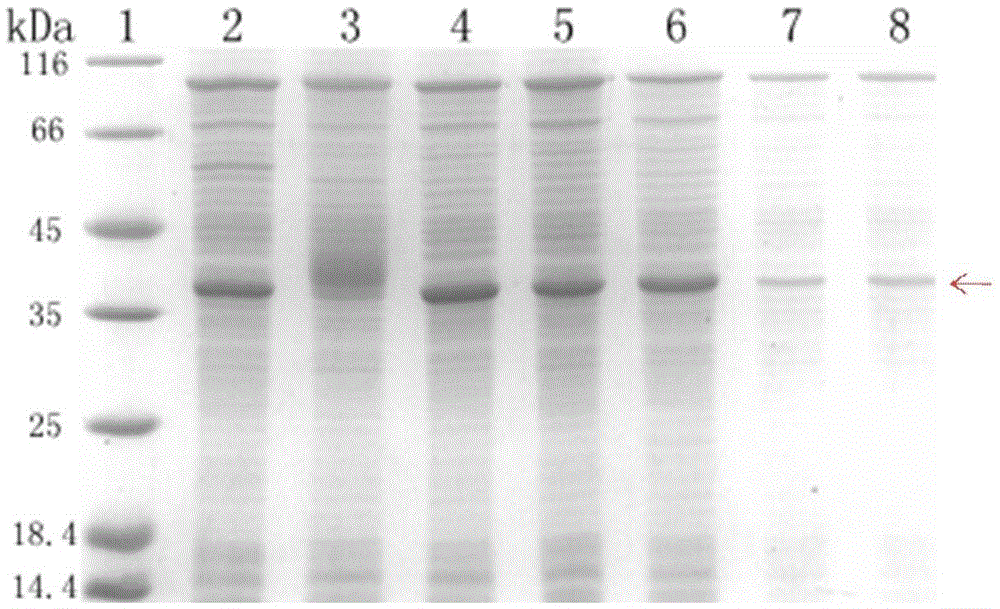
Method for producing HIV-1 gp41 recombinant antigen by means of Escherichia coli cell-free system
InactiveCN105039379AImprove soluble expression efficiencyAvoid damageVirus peptidesPeptide preparation methodsAntigenEscherichia coli
The invention discloses a method for producing an HIV-1 gp41 recombinant antigen by means of an Escherichia coli cell-free system. The method comprises the steps that an HIV-1 gp41 gene is cloned on a pIVEX2.4c plasmid to obtain a recombinant vector pIVEX2.4c-gp41; the recombinant vector pIVEX2.4c-gp41 is placed into the Escherichia coli cell-free system containing a decontamination agent for expression, and finally affinity chromatography purification is utilized for obtaining the HIV-1 gp41 protein. According to the HIV-1 gp41 protein produced through the HIV-1 gp41 protein, the decontamination agent is added into the reaction system to improve the solubility of the HIV-1 gp41, and the affinity chromatography purification is utilized for obtaining the target protein. The method can effectively improve the production capacity of the HIV-1 gp41 recombinant antigen and is of great significance in producing a series of HIV recombinant antigens by means of the Escherichia coli cell-free system.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com