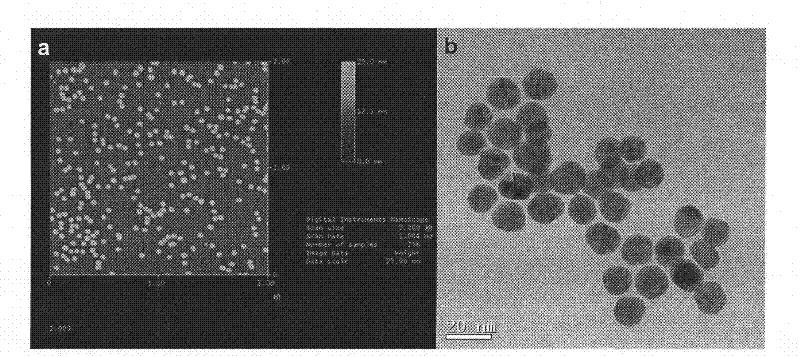
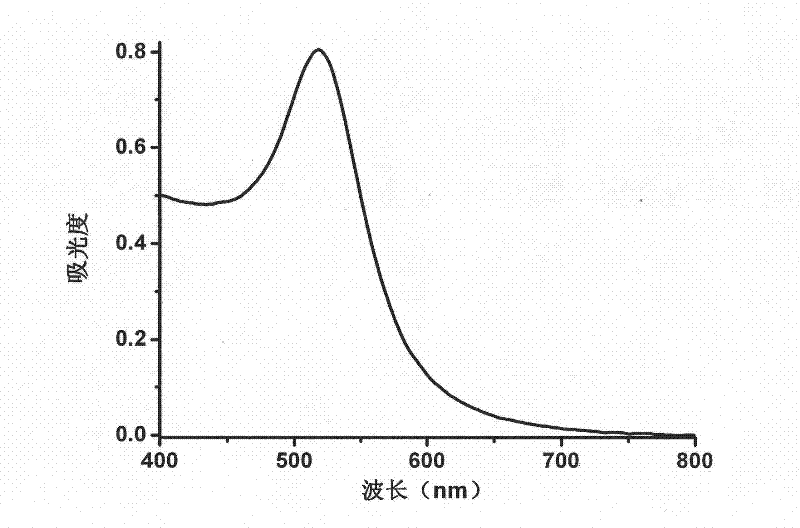
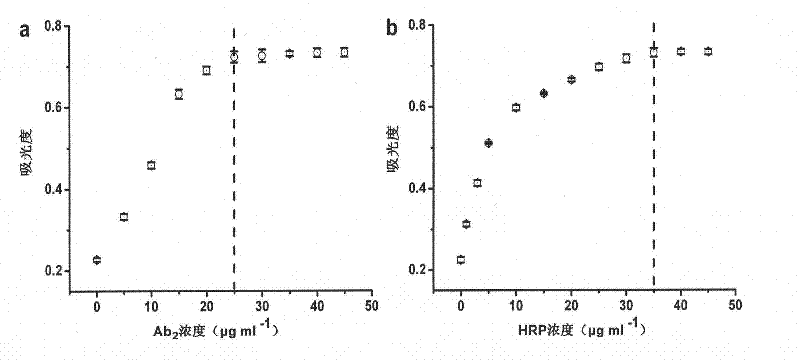
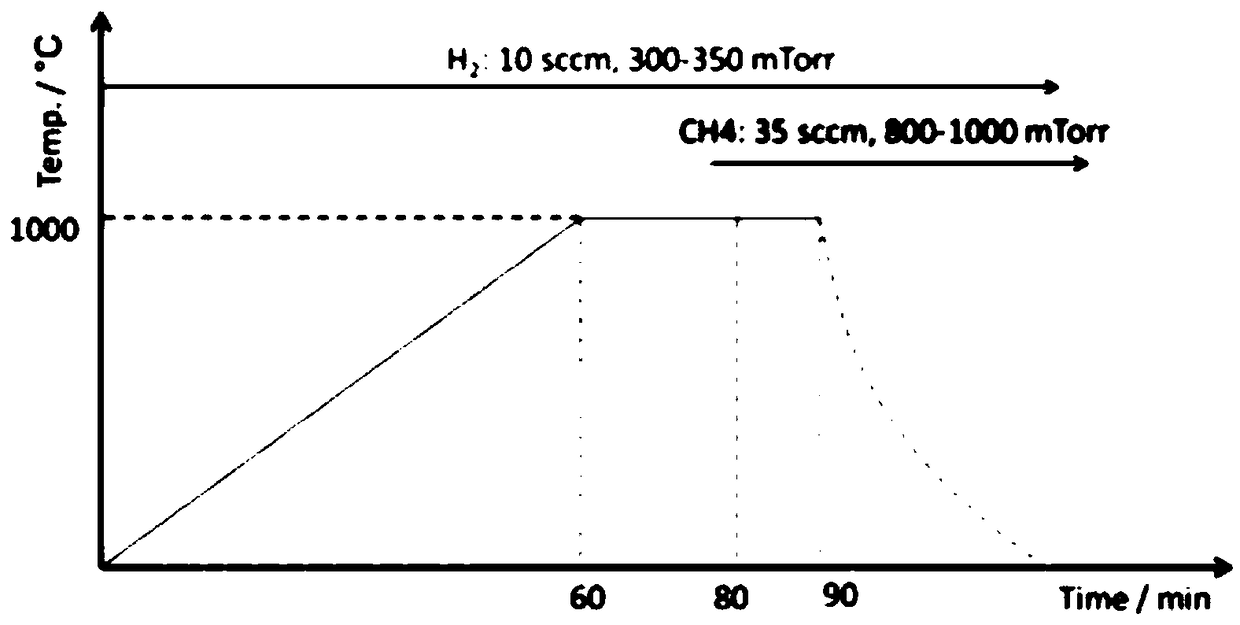
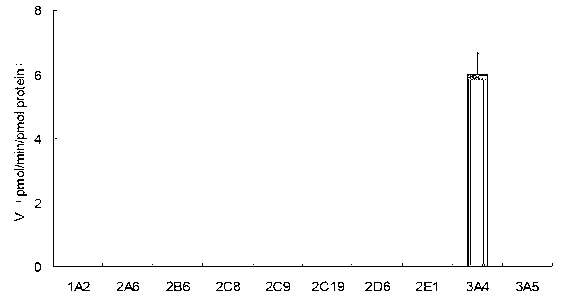Patents
Literature
136 results about "Specific substrate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Substrate specificity. In an enzyme activity, the substrate must bind with the enzyme to become a catalyst of a chemical reaction. And most enzymes are highly specific particularly to the nature of the substrate they bind to. Substrate specificity is one of the most essential distinctive features of enzymes.
Enzyme substrate comprising a functional dye and associated technology and methods
ActiveUS8092784B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMicrobiological testing/measurementMoietyFluorochrome Dye
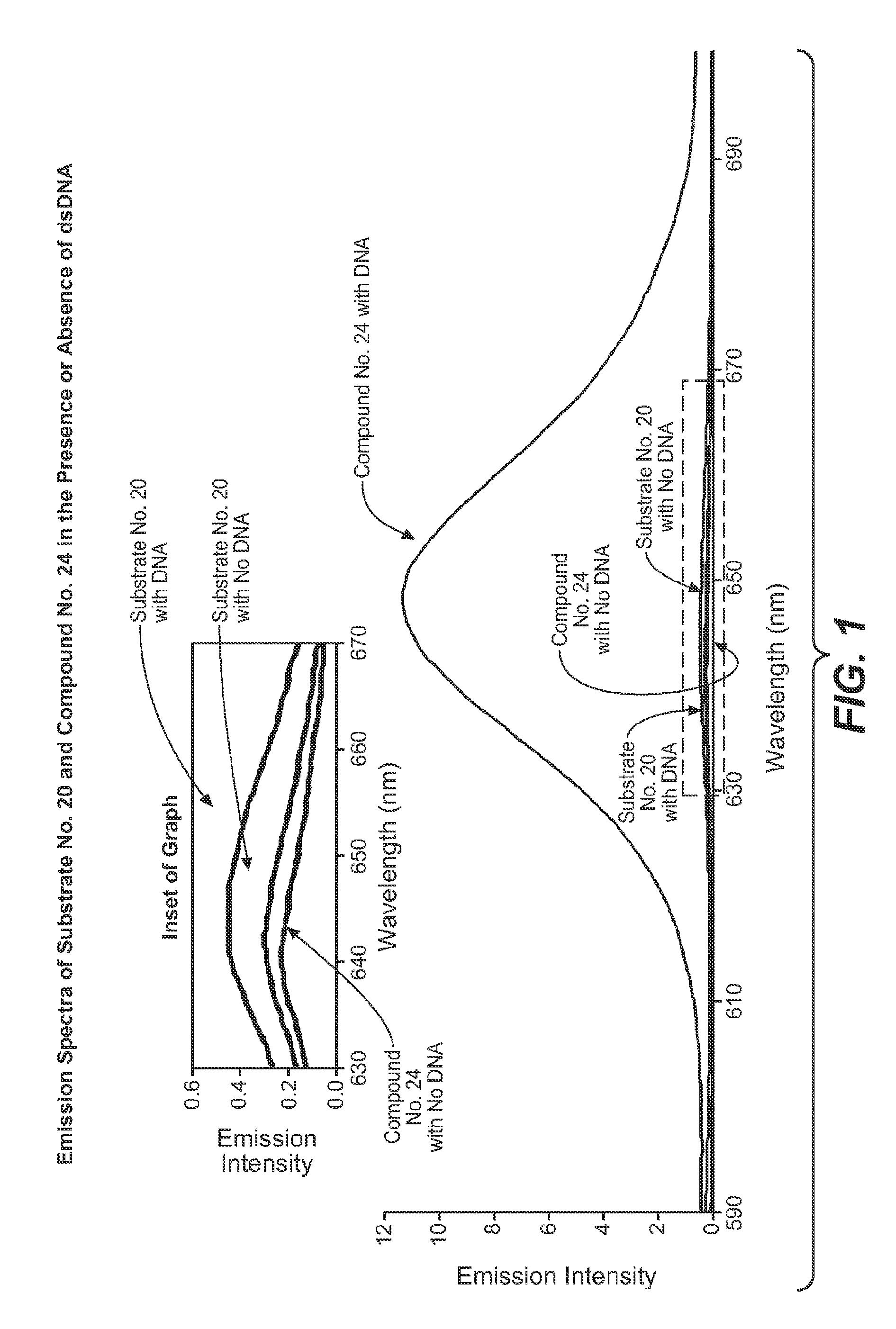
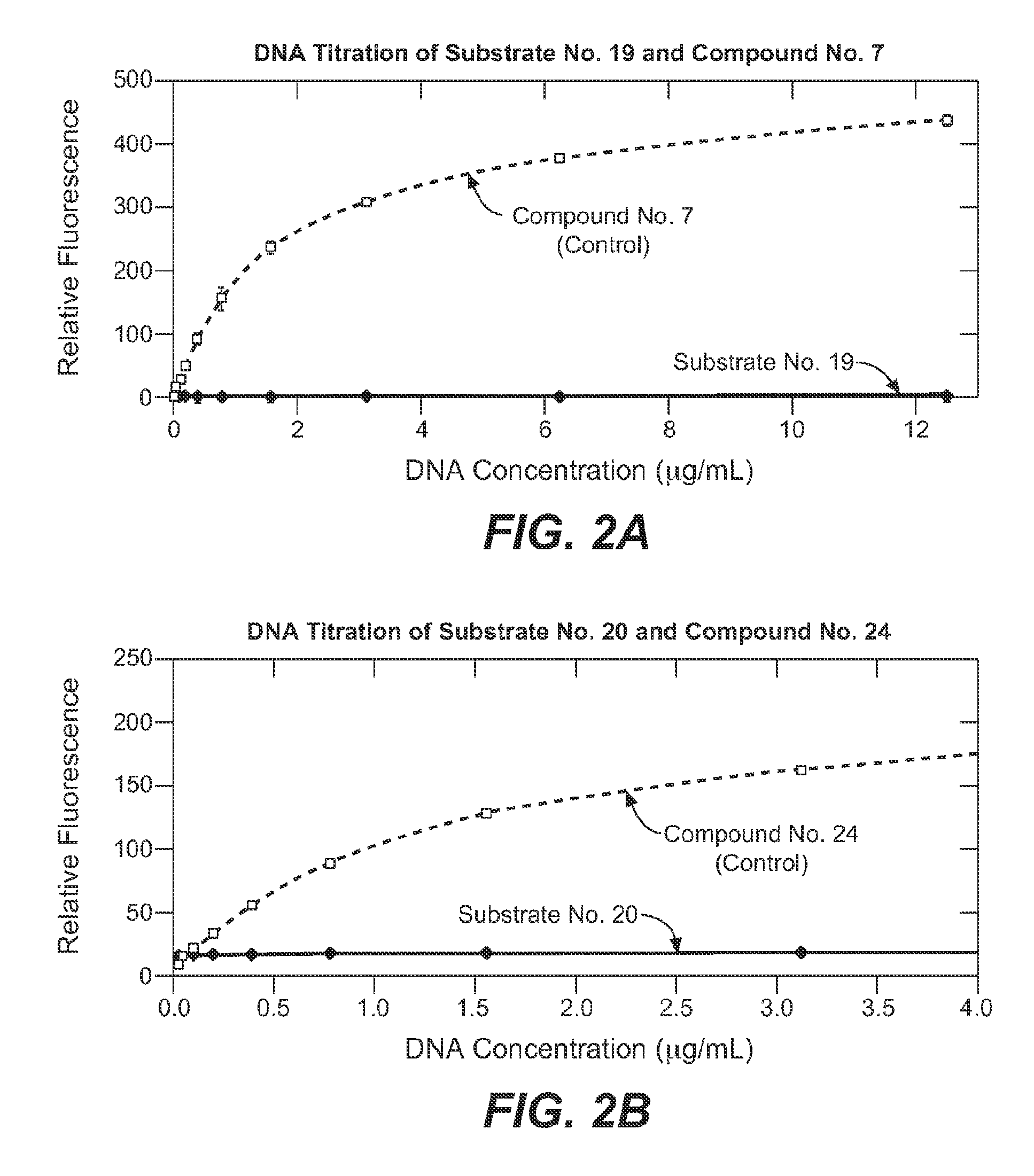
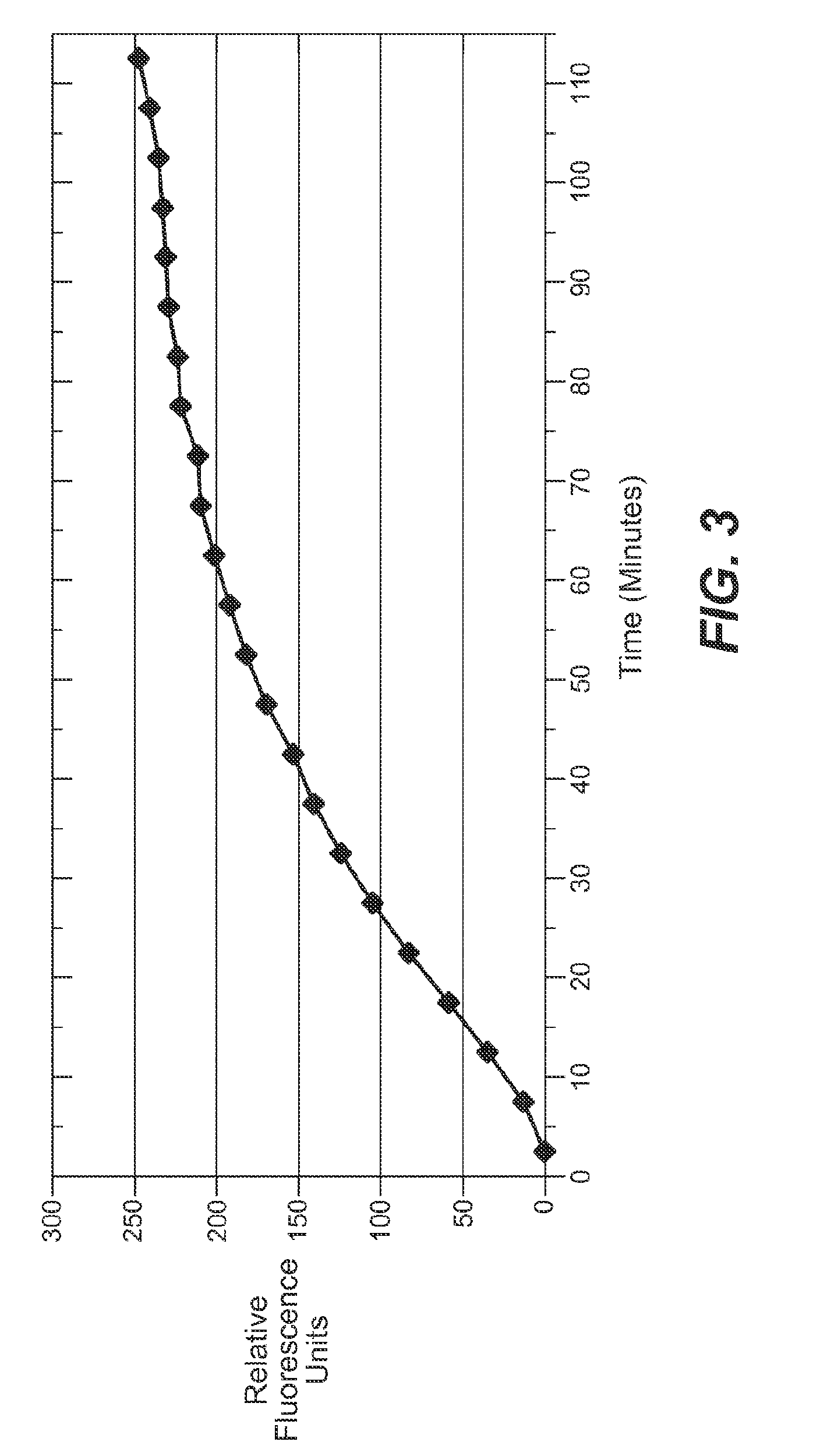
Enzyme substrates and associated technology of the present invention are provided. An enzyme substrate of the invention may comprise a biologically functional fluorescent dye and an enzyme-specific substrate moiety attached in such a way that the functionality of the functional dye is diminished. An enzymatic reaction may cleave at least a portion of the substrate moiety from the enzyme substrate to provide a more functional product dye. This product dye may be nonfluorescent or weakly fluorescent, in general, and relatively fluorescent, in a particular condition, such as when bound to a partner biological molecule or an assembly of partner biological molecules. An enzyme substrate of the present invention may thus be useful in fluorescence detection, and / or in any of a variety of useful applications, such as the detection of enzymatic activity in a cell-free system or in a living cell, the screening of drugs, or the diagnosis of disease.
Owner:BIOTIUM INC
Flexible pressure sensor and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106197772AHigh sensitivityImprove reliabilityForce measurement using piezo-resistive materialsElectrical resistance and conductanceIsolation layer
The invention discloses a flexible pressure sensor which comprises an induction layer, a substrate layer, an isolation layer and electrodes. The isolation layer is positioned between the induction layer and the substrate layer and bonded to the induction layer and the substrate layer, and enables electric contact between the induction layer and the substrate layer to be isolated discontinuously; the surface of the induction layer is provided with a first conductive layer, the surface of the substrate layer is provided with a second conductive layer, and the first and second conductive layers are bonded to the isolation layer in opposite directions; and the electrodes are led out of the first or second conductive layer and connected with an external circuit. The flexible pressure sensor is used to detect the size and fluctuation of pressure, a flexible conductive material on the specific substrate is bonded to other conductive substrate, the electrodes are led out, change of resistance between the electrodes is measured, and the size and fluctuation of the pressure is detected in directly. The pressure sensor of high flexibility and high reliability can be applied to a flexible bearing body, technology is simple, and the sensor can be compatible with a present processing technology of a resistant screen to realize scaled production and application.
Owner:常州第六元素半导体有限公司
Vivo use of glutathione s-transferase activated nitric oxide donors
ActiveUS20050171066A1Increase delayReduce tumor volumeBiocideOrganic active ingredientsApoptosisNitric oxide
The present invention provides for a method of simultaneously treating both cancer and the Multidrug Resistance Phenotype via inhibition of cellular thiols, such as Glutathione S-Transferase (GST). This enzyme is overproduced in leukemia and solid tumor cells and is one of the main pathways involved in the Multidrug Resistance phenotype. The treatment provides for the administration of a chemically inert pro-drug, designed to be a specific substrate for the GST enzyme that, once cleaved, liberates the bioactive toxin Nitric Oxide (NO) intracellularly at the site of a malignant growth. NO then acts to inhibit the growth of the malignant cells and to induce cellular differentiation and apoptosis therein, effectively treating an existing cancerous condition. Additionally, once NO is liberated from the pro-drug, the remaining structure acts to inhibit further GST activity, providing a treatment for the Multidrug Resistant phenotype.
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND
Substrates specific to von willebrand factor cleaving protease and method of assaying the activity
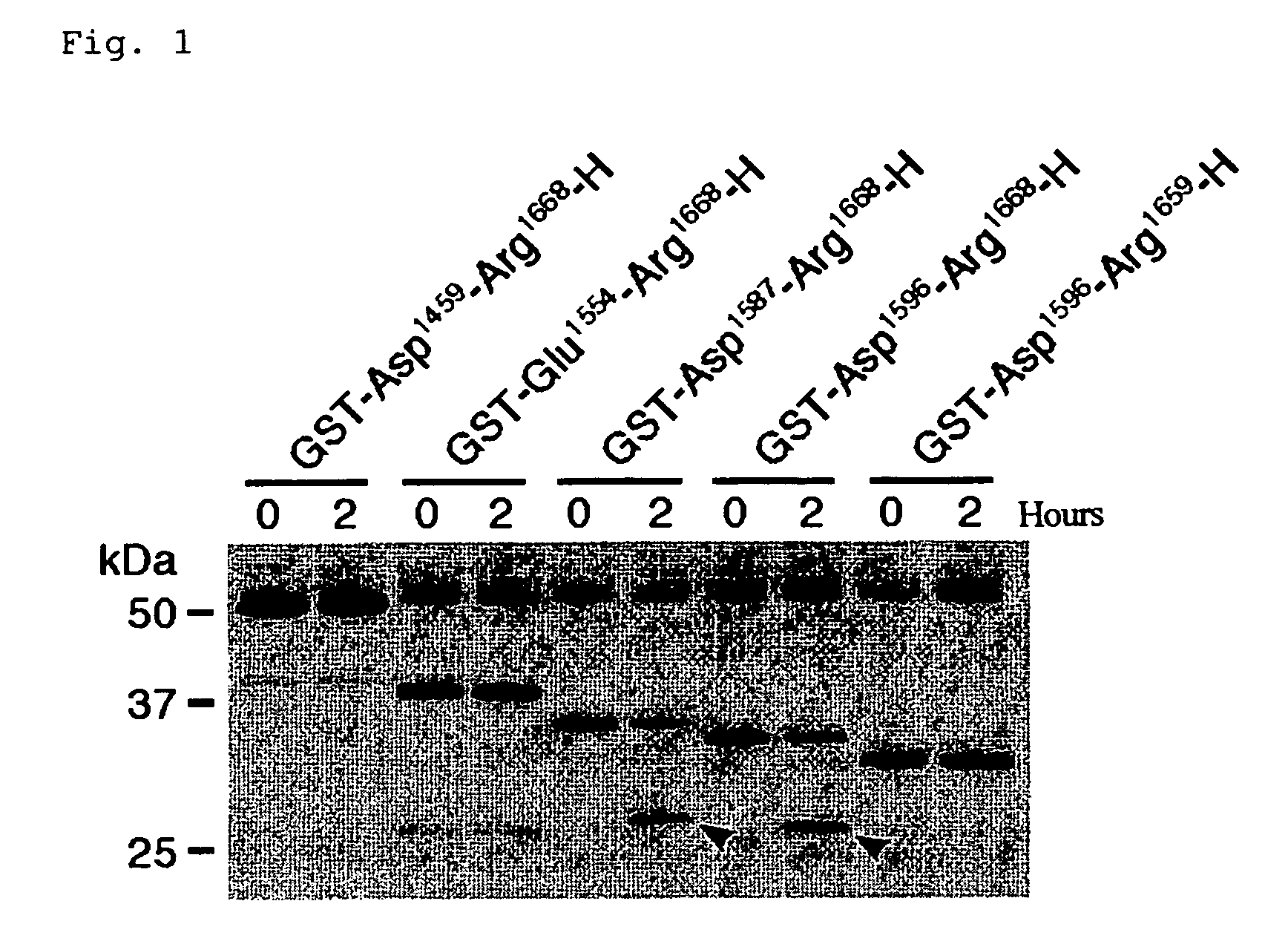
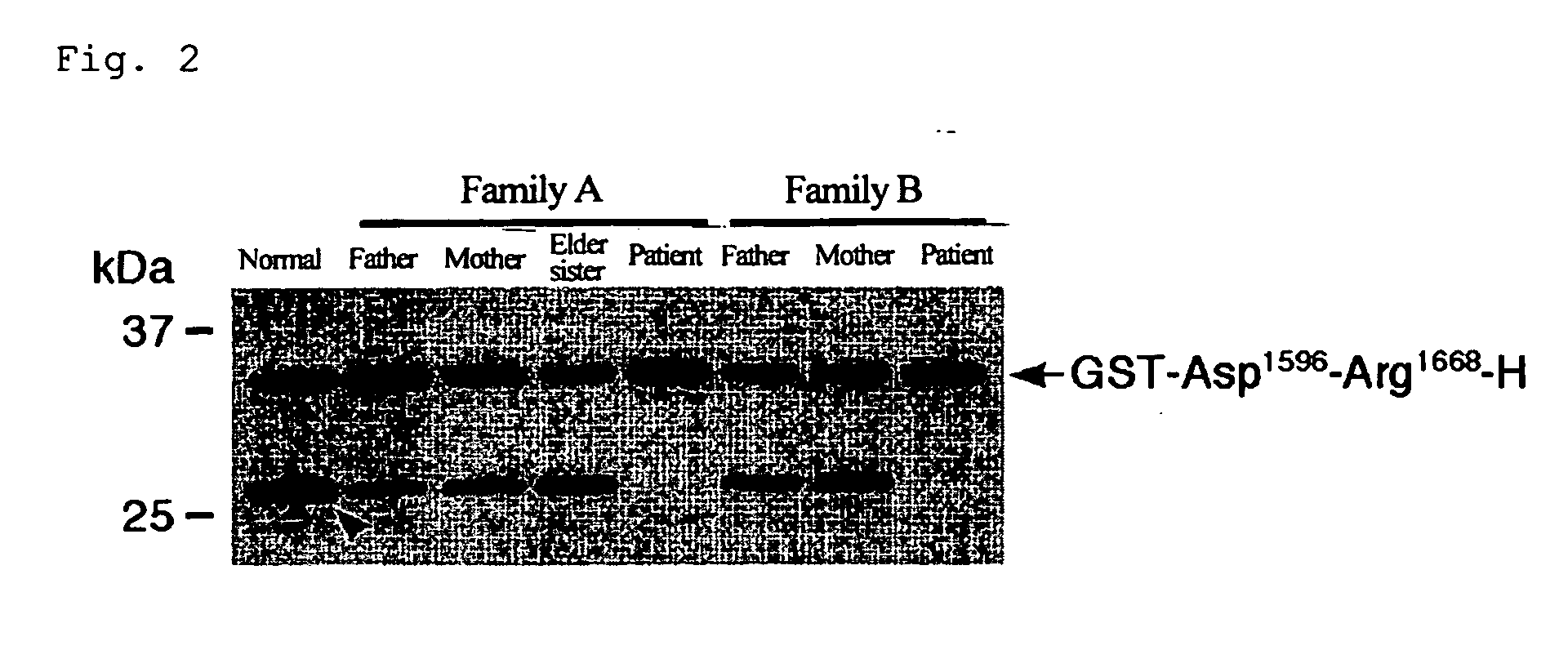
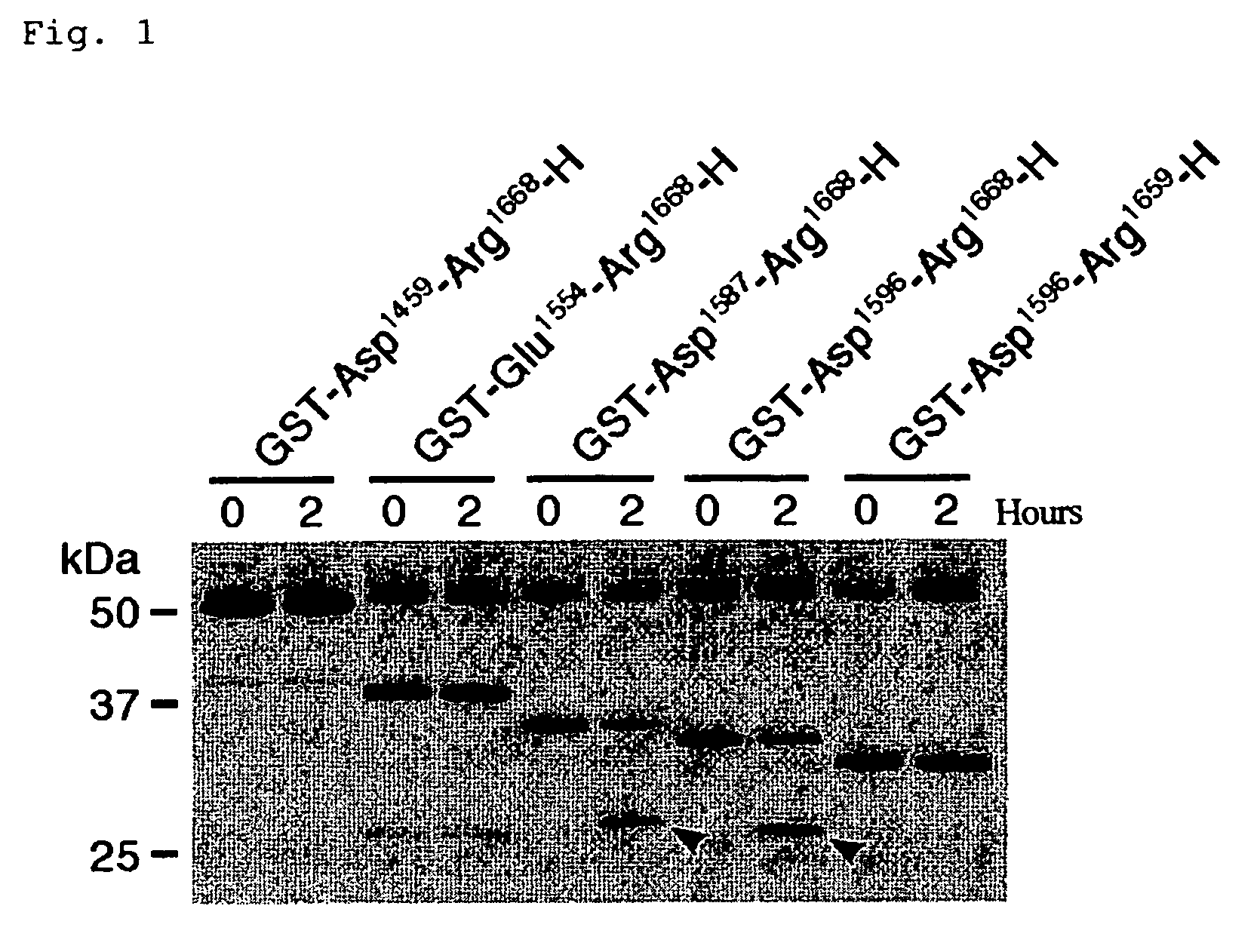
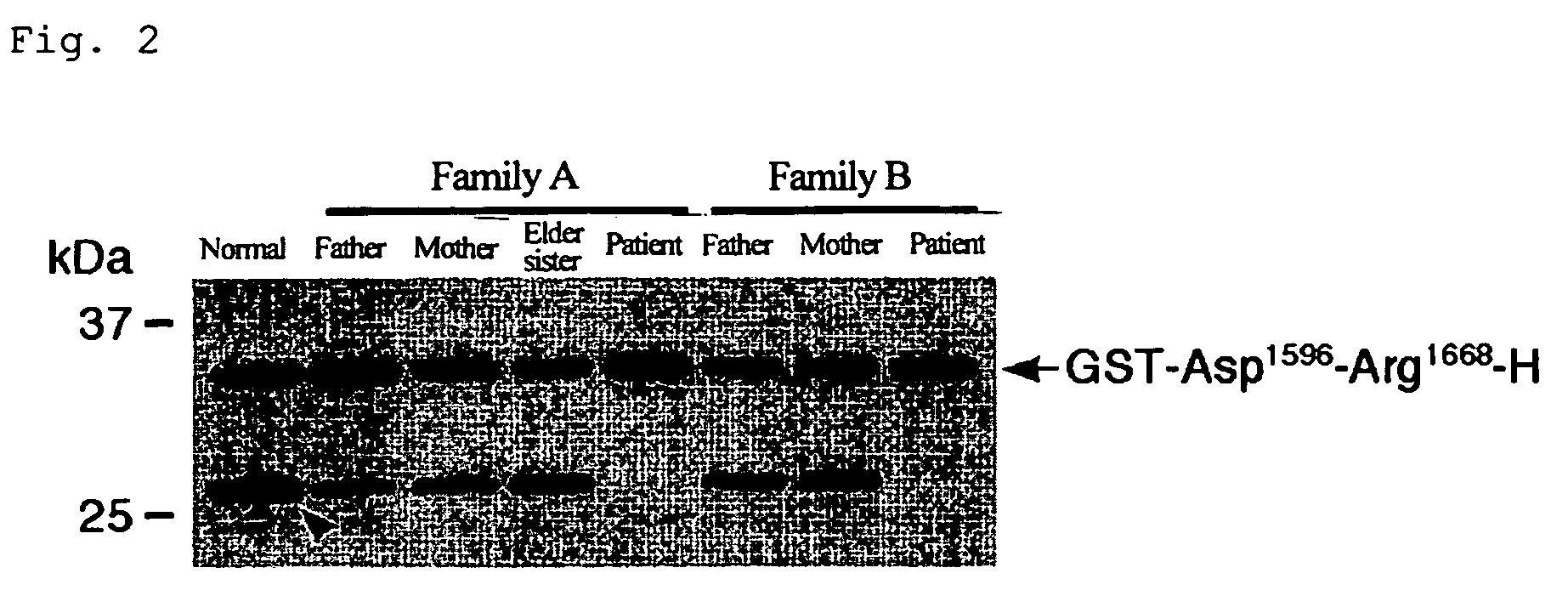
The present invention relates to specific substrates for a von Willebrand factor cleaving enzyme, ADAMTS-13, as well as to diagnosis of ADAMTS-13 deficient patients, diagnostic compositions, and kits employing the substrates. Particularly preferable substrate polypeptides for ADAMTS-13 are the polypeptide which begins at amino acid 1587 and ends at amino acid 1668 of SEQ ID NO: 1 in the Sequence Listing, and the polypeptide which begins at amino acid 1596 and ends at amino acid 1668 of SEQ ID NO: 1 in the Sequence Listing. These substrate polypeptides for ADAMTS-13 have high substrate specificity and also superior quantitativeness, and a suitable size for production by recombinant methods.
Owner:NAT CEREBRAL & CARDIOVASCULAR CENT
Electrochromic device
InactiveCN102736342AChange colorPhotovoltaicsTenebresent compositionsOptoelectronicsConductive materials
The invention discloses an electrochromic device, and in particular discloses a multi-layer structure of which a main body is transparent glass. A porous aerogel layer is packaged, conductive materials are coated on a specific substrate, and an electrochromic material is packaged among the conductive materials; voltage is applied to the conductive material layer, so that the characteristics of the electrochromic material can be changed; and moreover, photocatalyst materials can be coated on the outer side of the substrate, and a solar power supply layer is arranged, so that power can be supplied to the electrochromic device or the power can be supplied to other devices. According to another embodiment, an electrochromic composite material layer can be packaged between two adjacent substrates in the electrochromic device and has a composite structure consisting of aerogel and the electrochromic material.
Owner:J TOUCH CORPORATION
Semiconductor light emitting element, group iii nitride semiconductor substrate and method for manufacturing such group iii nitride semiconductor substrate
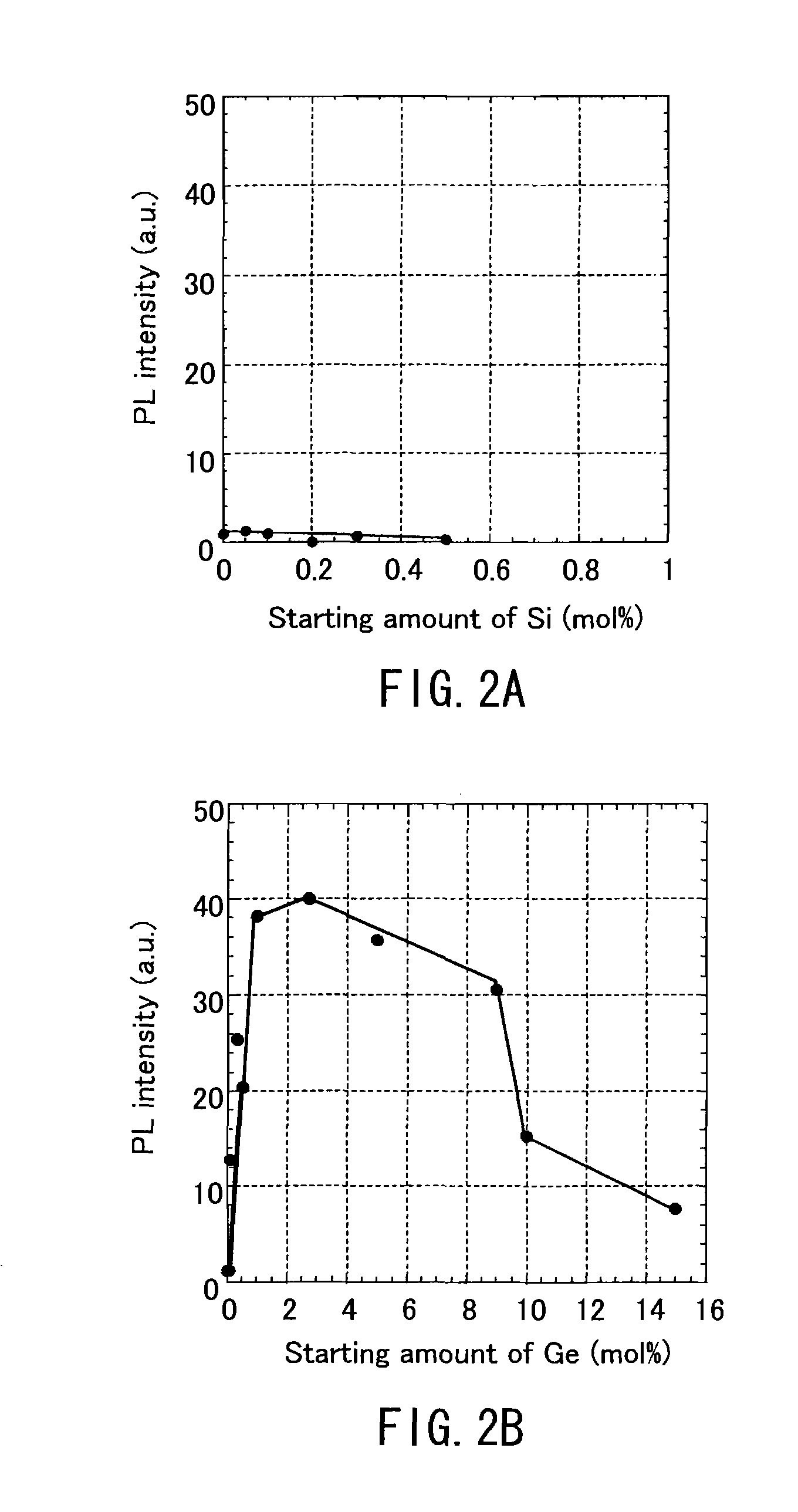
InactiveUS20100230713A1Excellent light extraction propertyDopant concentration is therefore limitedOptical wave guidancePolycrystalline material growthDopantAlkaline earth metal
An object of the present invention is to obtain, with respect to a semiconductor light-emitting element using a group III nitride semiconductor substrate, a semiconductor light-emitting element having an excellent light extraction property by selecting a specific substrate dopant and controlling the concentration thereof. The semiconductor light-emitting element comprises a substrate composed of a group III nitride semiconductor comprising germanium (Ge) as a dopant, an n-type semiconductor layer composed of a group III nitride semiconductor formed on the substrate, an active layer composed of a group III nitride semiconductor formed on the n-type semiconductor layer, and a p-type semiconductor layer composed of a group III nitride semiconductor formed on the active layer in which the substrate has a germanium (Ge) concentration of 2×1017 to 2×1019 cm−3. The substrate is produced in a nitrogen-containing atmosphere using a melt comprising at least a group III element, an alkali or alkaline earth metal, and germanium (Ge) and nitrogen.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Silicon wafer and process for the heat treatment of a silicon wafer
ActiveUS20060213424A1Reduce defect densityIncrease productionFrom gel stateFrom solid stateNitrogenOxygen
A silicon wafer having no epitaxially deposited layer or layer produced by joining to the silicon wafer, with a nitrogen concentration of 1·1013-8·1014 atoms / cm3, an oxygen concentration of 5.2·1017-7.5·1017 atoms / cm3, a central thickness BMD density of 3·108-2·1010 cm−3, a cumulative length of linear slippages ≦3 cm and a cumulative area of areal slippage regions ≦7 cm2, the front surface having <45 nitrogen-induced defects of >0.13 μm LSE in the DNN channel, a layer at least 5 μm thick, in which ≦1·104 COPs / cm3 with a size of ≧0.09 μm occur, and a BMD-free layer ≧5 μm thick. Such wafers may be produced by heat treating the silicon wafer, resting on a substrate holder, a specific substrate holder used depending on the wafer doping. For each holder, maximum heating rates are selected to avoid formation of slippages.
Owner:SILTRONIC AG
Fluorescent probe for detecting glutathione in blood, and synthesis method and application thereof
ActiveCN106866689AHigh selectivitySpecific recognition abilityOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescenceSynthesis methods
The invention discloses a fluorescent probe for detecting the content of glutathione (GSH) in blood, and a synthesis method and an application thereof. The synthesis steps of the probe are simple, and the light stability is good. In the detection process, the fluorescent probe firstly as a substrate is combined with glutathione S-transferase (GST), and undergoes a reaction with another specific substrate GSH of the GST to produce fluorescence, the fluorescence is enhanced by about 35 times, and the maximum emission wavelength is at the near infrared region (beyond 700 nm). Compared with conventional GSH fluorescent probes, the probe can specifically detect the content of the GSH in a complex system, and has the advantages of wide dynamic response window, high efficiency and the like. The probe realizes the specific and high-efficiency identification on the GSH in the complex environment, and has extremely important application value in the biological and medical fields.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Micro-nano machining method based on electrochemical micro-nano system for functional material and device thereof
InactiveCN102887478AEfficient processingDecorative surface effectsChemical vapor deposition coatingAll solid stateInformation processing
The invention provides a micro-nano machining method based on an electrochemical micro-nano system for a functional material and a device thereof. According to the method and the device, a functional material of a micro-nano scale can be synthesized in situ on a specific substrate or a micro-nano chip for constructing an all-solid-state micro-nano device. The method comprises the following steps of: constructing an electrochemical reactor of a micro-nano scale to limit a physical-chemical process for synthesizing the functional material in a space of a micro-nano scale; and regulating and controlling a micro-area physical-chemical environment on a conducting substrate or a chip to be processed to synthesize the functional material of the micro-nano scale in situ on the conducting substrate or the micro-nano chip. The device comprises an electrochemical reactor of a micro-nano scale, an electrochemical workstation, a three-dimensional inching system of micro-nano accuracy, a video monitor and an information processing computer.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Vegetable seedling substrate
InactiveCN105393835AIncrease productionRapid and neat germinationGrowth substratesCulture mediaPlant growthFermentation
The invention discloses a vegetable seedling substrate. A substrate raw material comprises, by weight, waste fungi bags, perlite, remote mountain humus soil, puffed cow dung, pine tree barks, and a Chinese medicine residue; the Chinese medicine residue is a mixture including pine needles, Radix stemonae, Eupatorium adenophora, Dendrobiumnobile, liquorices, and Codonopsispilosula, wherein the mixture is obtained through high-temperature aerobic fermentation processing. The three-phase equilibrium (solids, liquid, and air) optimum environment which can ensure growth and development of plant roots and is required by vegetables, can be established through the specific substrate raw material which has good physical and chemical properties by means of the optimum proportion; the soil is fertile and the cost is low by adoption of the remote mountain humus soil; the Chinese medicine residue including ample organic matters and ample inorganic matters, and nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium which are required by plant growth, can improve the fertilizer efficiency of the seedling substrate and can kill bacteria; vermiculite and the perlite can change the permeability and the volume-weight of the seedling substrate, can absorb effective constituents of the Chinese medicine residue, and can play the effect of sustained release.
Owner:WULONG DENGFENG SEEDLING CO LTD
Process and apparatus for making oriented crystal layers
Thin films of single crystal-like materials are made by using flow-through ion beam deposition during specific substrate rotation around an axis in a clocking action. The substrate is quickly rotated to a selected deposition position, paused in the deposition position for ionized material to be deposited, then quickly rotated to the next selected deposition position. The clocking motion can be achieved by use of a lobed cam on the spindle with which the substrate is rotated or by stopping and starting a stepper motor at long and short intervals. Other symmetries can be programmed into the process, allowing virtually any oriented inorganic crystal to be grown on the substrate surface.
Owner:LOS ALAMOS NATIONAL SECURITY
Preparation method of metal probe applicable to AFM (Atomic Force Microscope)
InactiveCN104071746AImprove conductivitySharp endNanostructure manufactureScanning probe microscopyMulti materialElectrostatic force microscope
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
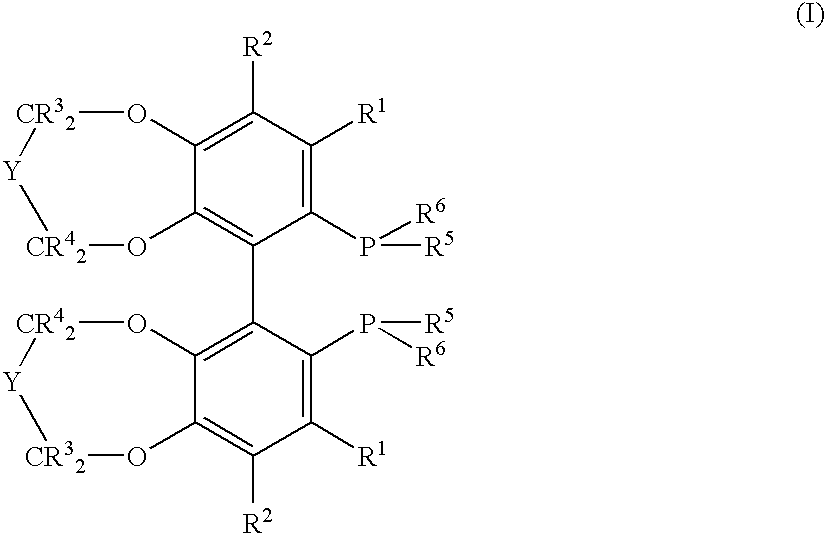
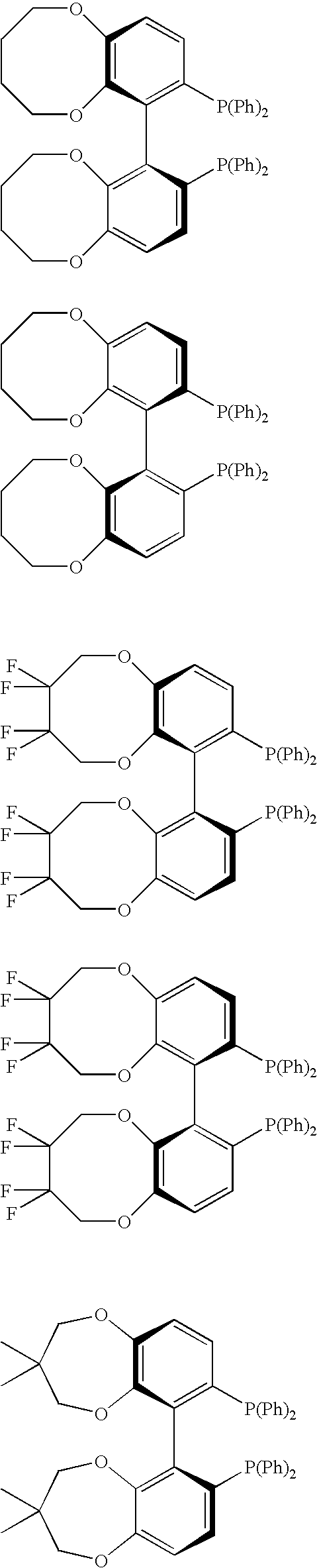
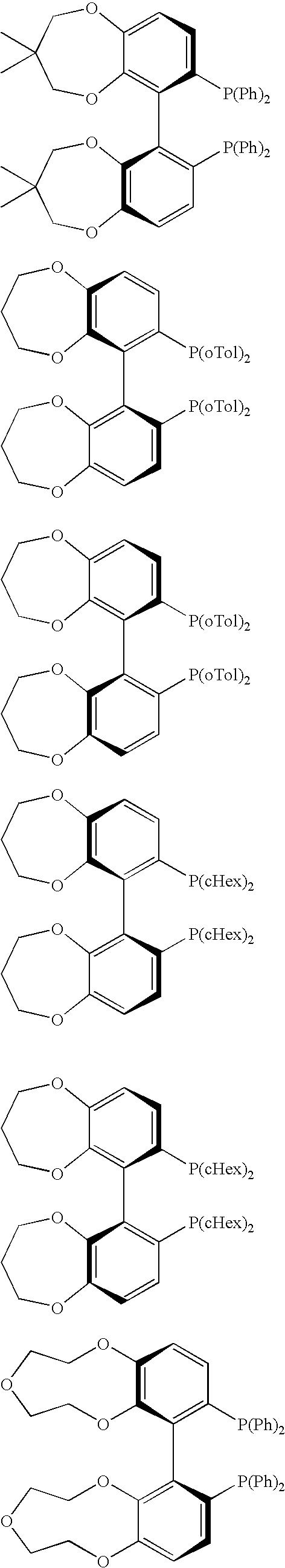
Chiral C2-symmetric biphenyls, their preparation and also metal complexes in which these ligands are present and their use as catalysts in chirogenic syntheses
InactiveUS20050250951A1Wide range of applicationsMeet the requirementsRuthenium organic compoundsOrganic compound preparationOrganic synthesisMetal
A new class of C2-symmetric biaryldiphosphines comprising a fused ring system (dioxacycle) which has at least seven ring atoms and can be varied synthetically. The biaryldiphosphines can be used as ligands for preparing metal complexes useful as catalysts in organic synthesis, and the dioxacycles can be varied to optimize reaction with specific substrates.
Owner:WACKER CHEM GMBH
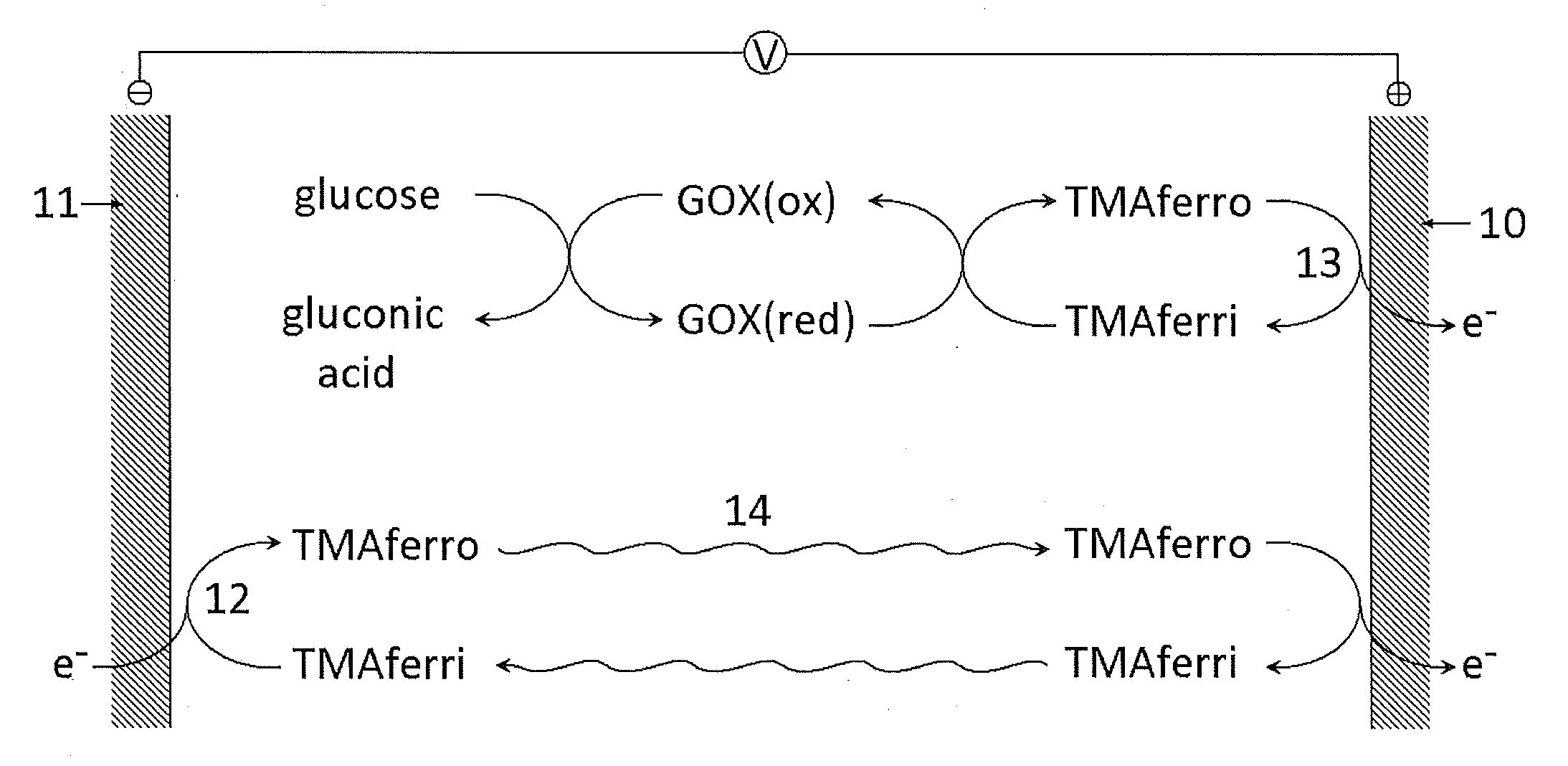
Reagents for Electrochemical Test Strips
ActiveUS20130026050A1Extended shelf lifeWithout impairing qualityImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsRedox enzymesSolubility
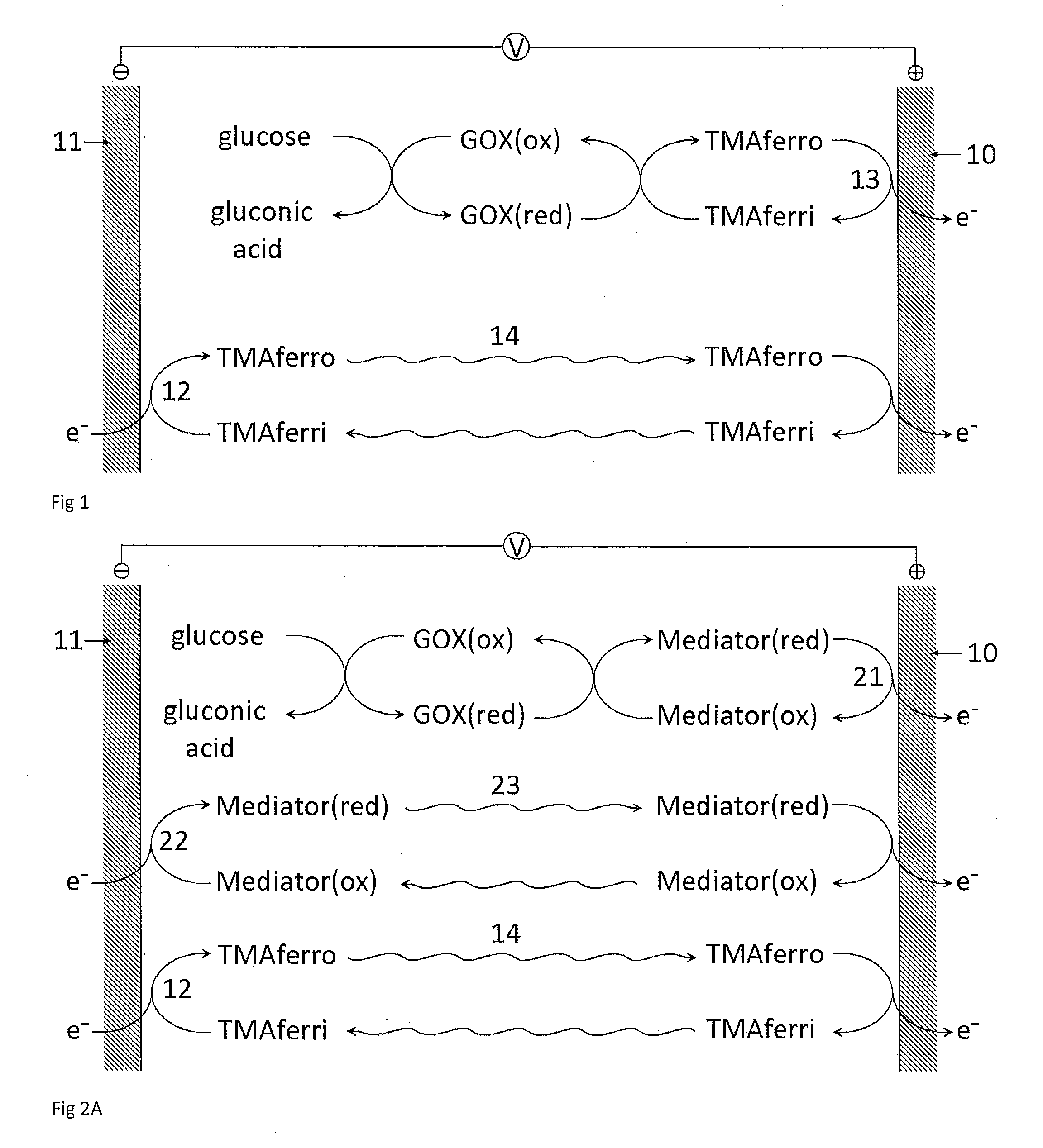
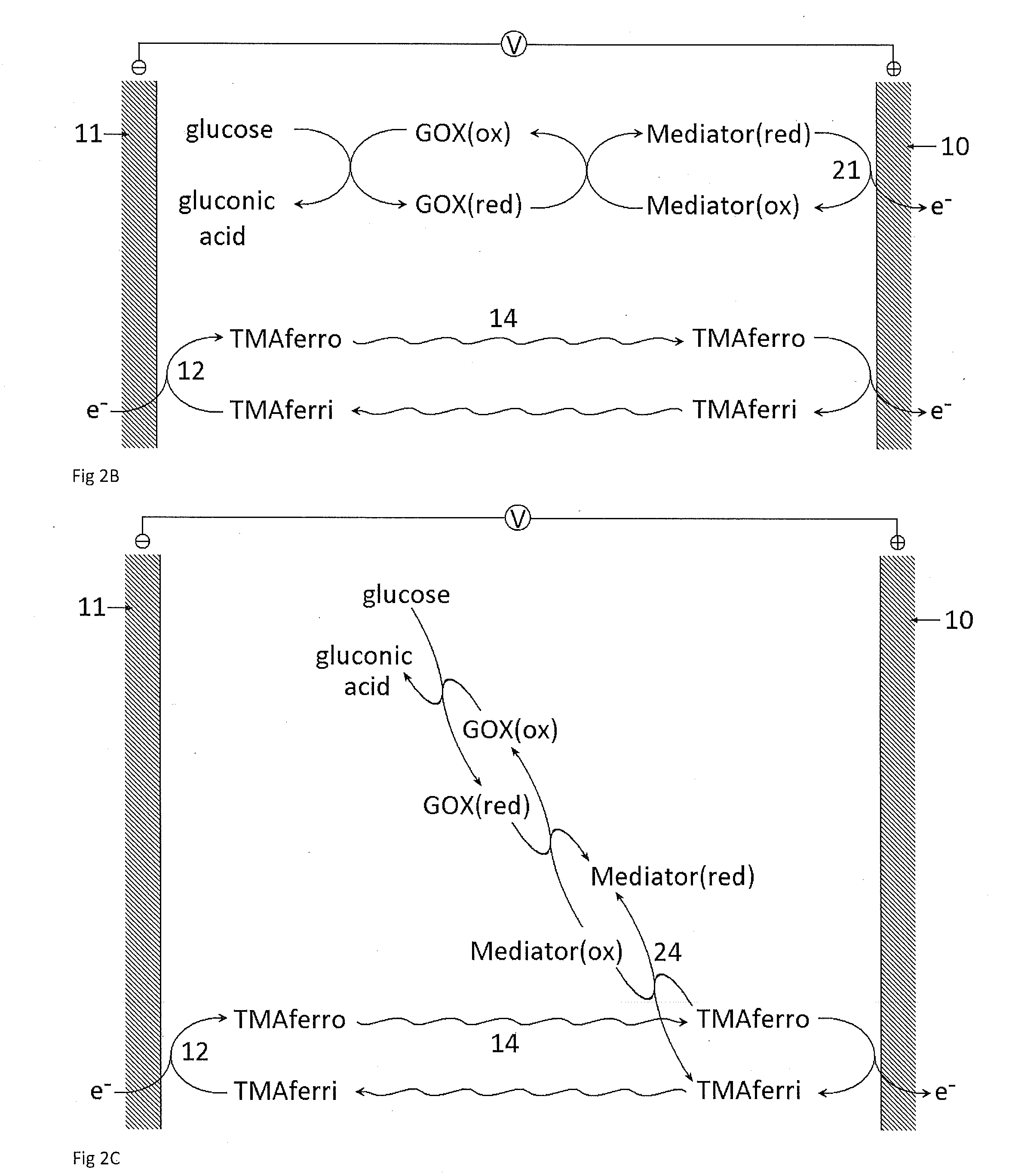
A dry reagent composition that includes an active redox enzyme that oxidizes an analyte as a specific substrate to produce an inactive reduced form of the enzyme; and a salt of ferricyanide provides improved performance in electrochemical test strips such as those used for detection of glucose. The salt of ferricyanide consists of ferricyanide and positively-charged counter ions, and the positively charged counter ions are selected such that the salt of ferricyanide is soluble in water, and such that the salt of ferricyanide or the crystalline phase of the salt of ferricyanide has a solubility in water and / or a lower E0eff at a concentration of 100 mM than potassium ferricyanide. For example, the salt of ferricyanide may be tetramethylammonium ferricyanide.
Owner:AGAMATRIX INC
Method for preparing perylenequinone pigment under catalysis of Shiraia bambusicola
InactiveCN101603062AImprove conversion rateLow costMicroorganism based processesFermentationNaphthoquinoneMicrobiology
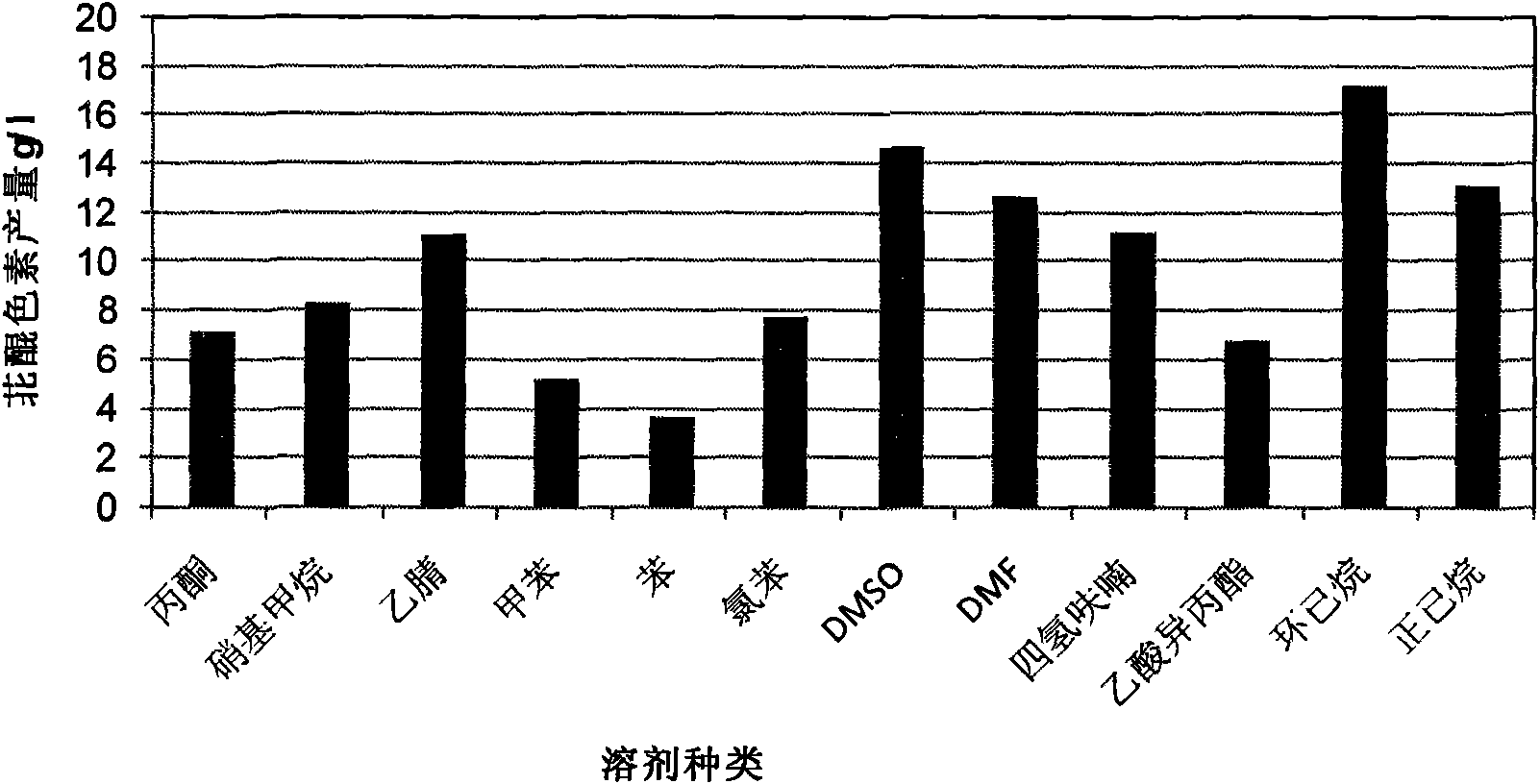
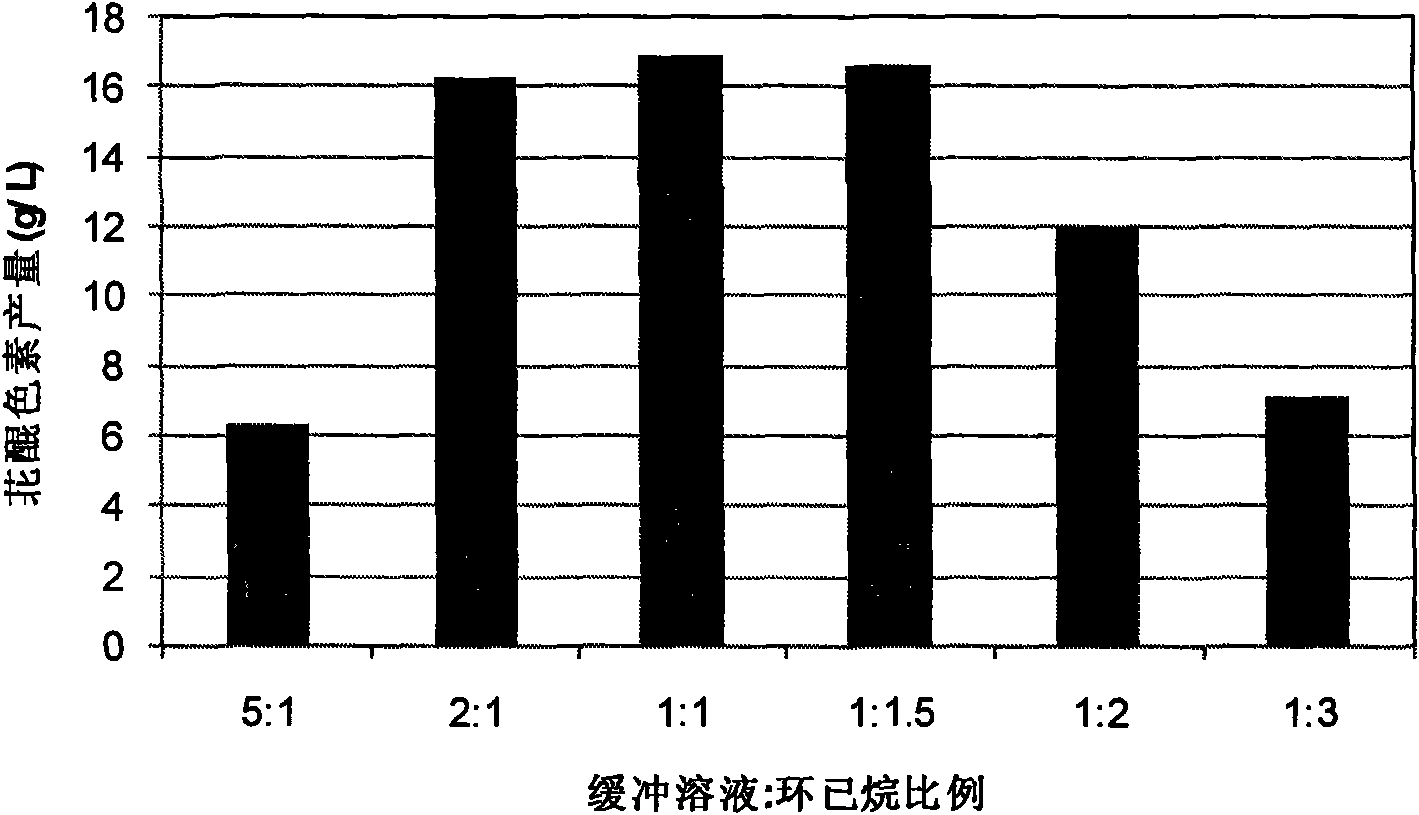
The invention discloses a method for preparing a perylenequinone pigment under the catalysis of Shiraia bambusicola and belongs to the technical field of bioengineering. In the method, naphthoquinone, cinnamic acid and the like which form a substrate are used to prepare the perylenequinone pigment under the catalysis of the Shiraia bambusicola. The catalytic process is implemented by: A), adding the substrate into culture system in a cell liquid culture process, wherein the perylenequinone pigment yield is up to 2.9g / L and the transformation rate is up to 9.7 percent; or B), placing cells obtained by liquid fermentation culture in a reaction system having the substrate, wherein the perylenequinone pigment yield is up to 35.3g / L and the transformation rate is up to 39.7 percent; or C), adding the substrate into a culture system in a cell solid culture process, wherein the perylenequinone pigment yield is up to 1.5g / 100g and the transformation rate is up to 46 percent. The method adopts a perylenequinone pigment-producing Shiraia bambusicola strain and specific substrate transformation to produce hypocrellin, is high in transformation rate, low in cost, less in step and applicable to industrial production and has excellent industrial application prospect.
Owner:江苏竹红生物科技有限公司
Modified wound dressings
InactiveUS20190307904A1Maximize efficiencyMaximize accuracyOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsWound dressingChronic wound
Owner:CONVATEC TECH INC
Silicon wafer and process for the heat treatment of a silicon wafer
ActiveUS7828893B2Reduce defect densityIncrease productionFrom gel stateFrom solid stateNitrogenNitrogen gas
A silicon wafer having no epitaxially deposited layer or layer produced by joining to the silicon wafer, with a nitrogen concentration of 1·1013-8·1014 atoms / cm3, an oxygen concentration of 5.2·1017-7.5·1017 atoms / cm3, a central thickness BMD density of 3·108-2·1010 cm−3, a cumulative length of linear slippages ≦3 cm and a cumulative area of areal slippage regions ≦7 cm2, the front surface having <45 nitrogen-induced defects of >0.13 μm LSE in the DNN channel, a layer at least 5 μm thick, in which ≦1·104 COPs / cm3 with a size of ≧0.09 μm occur, and a BMD-free layer ≧5 μm thick. Such wafers may be produced by heat treating the silicon wafer, resting on a substrate holder, a specific substrate holder used depending on the wafer doping. For each holder, maximum heating rates are selected to avoid formation of slippages.
Owner:SILTRONIC AG
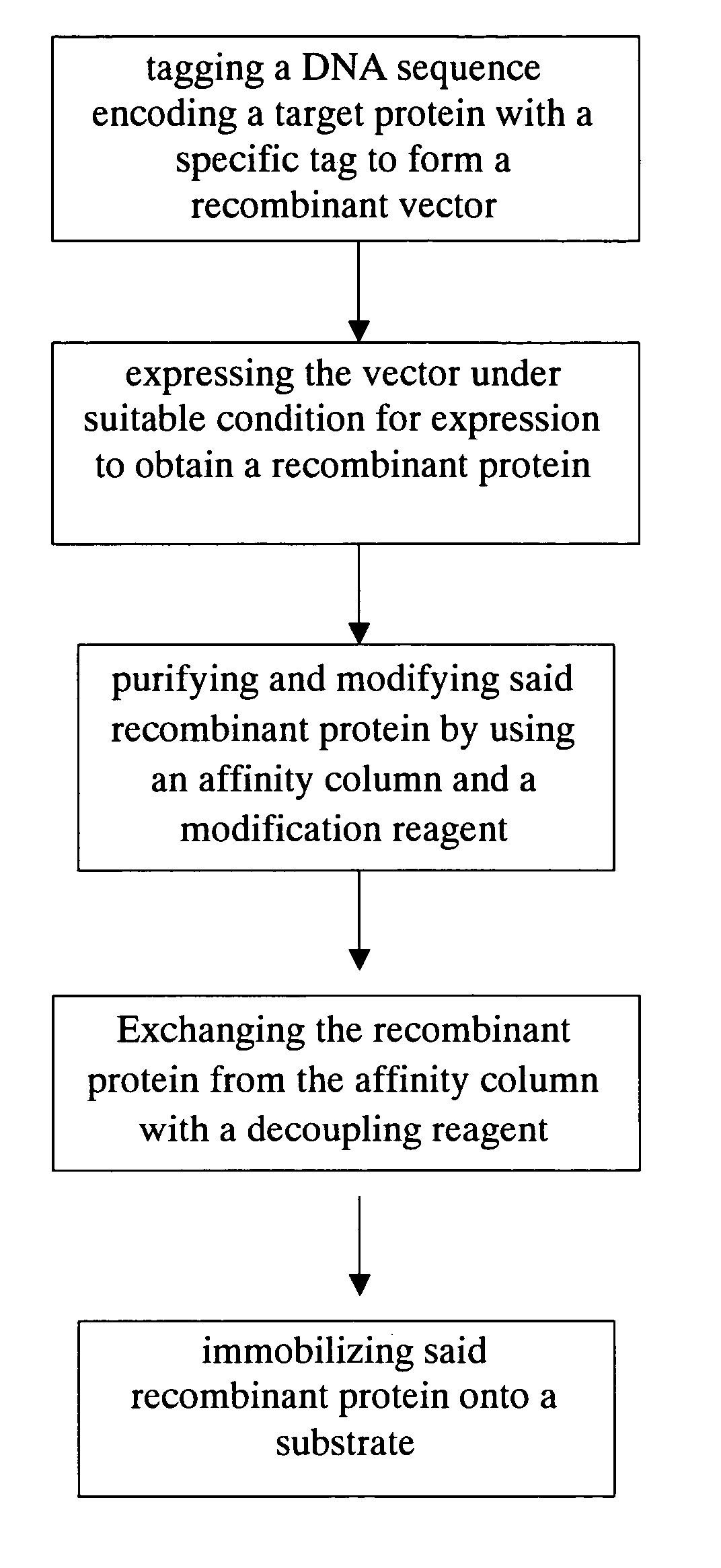
Method for purification, modification and immobilization of recombinant protein
InactiveUS20050112603A1Easy to limitBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMolecular sieveProtein target
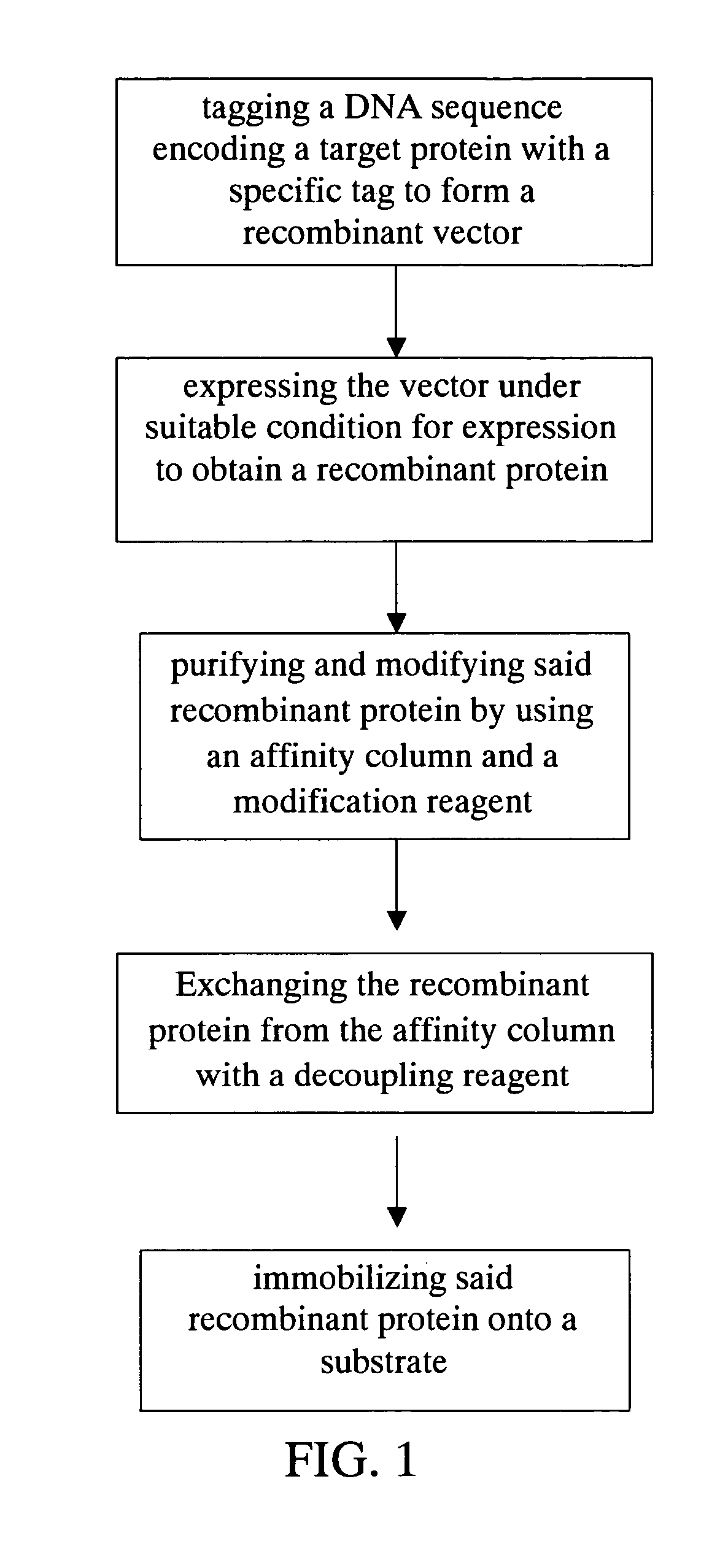
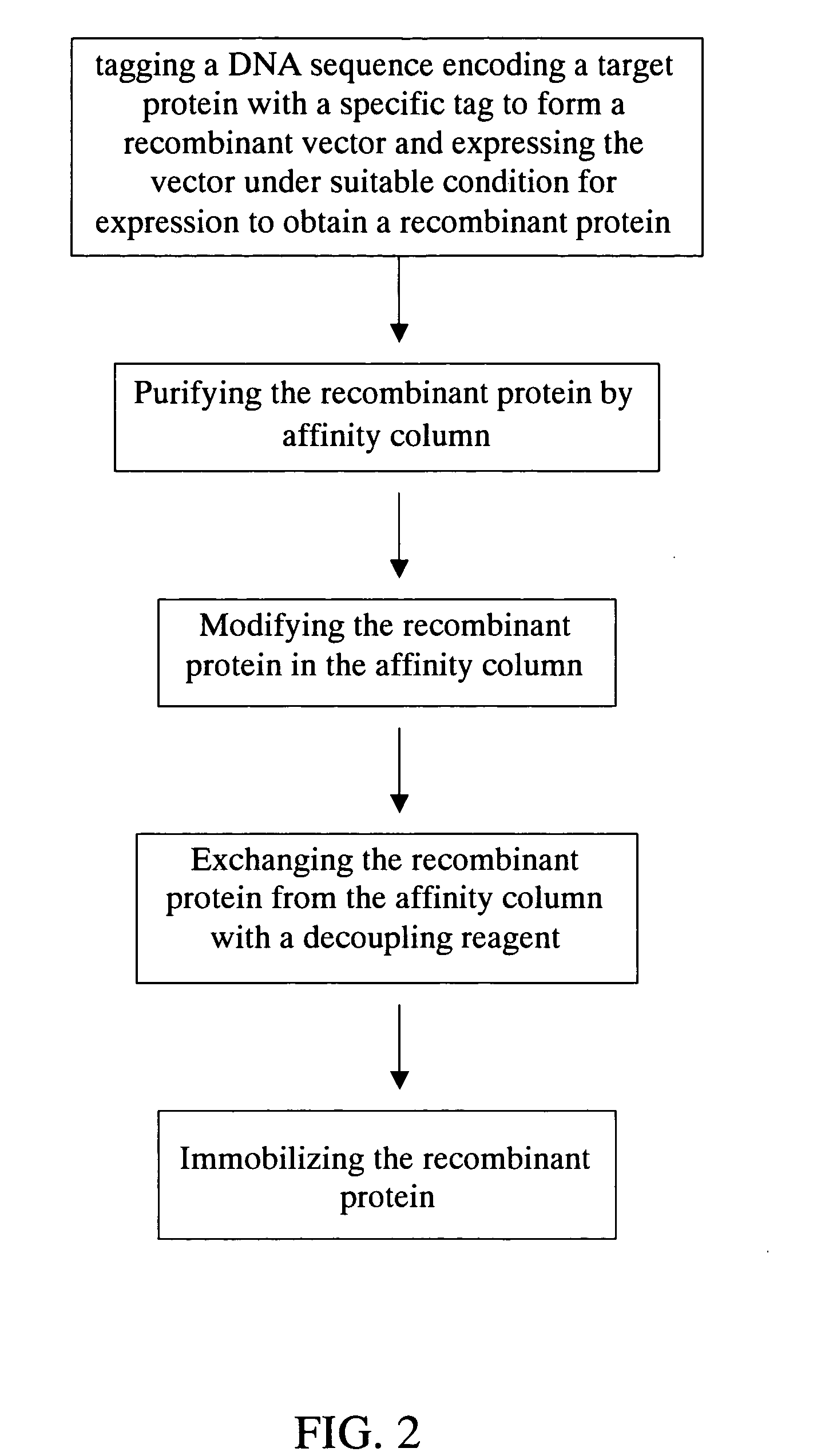
The present invention relates to a method for purifying, modifying and immobilizing recombinant protein. The method utilizes genetic engineering to tag a DNA sequence encoding a target protein with a specific tag and express the vector to obtain a recombinant protein. The recombinant protein is then purified and modified by an affinity column and modification reagent. After exchanging the recombinant protein with a decoupling reagent, the recombinant protein is immobilized onto a specific substrate. The method, combining steps of purification, modification and immobilization, provides convenience to using recombinant protein. The omission of the use of dialysis or molecular sieve leads to a shorter period dedicating for removing excessive reagents and the increase of efficiency of recombinant protein recovery.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Production of flavonoids by recombinant microorganisms
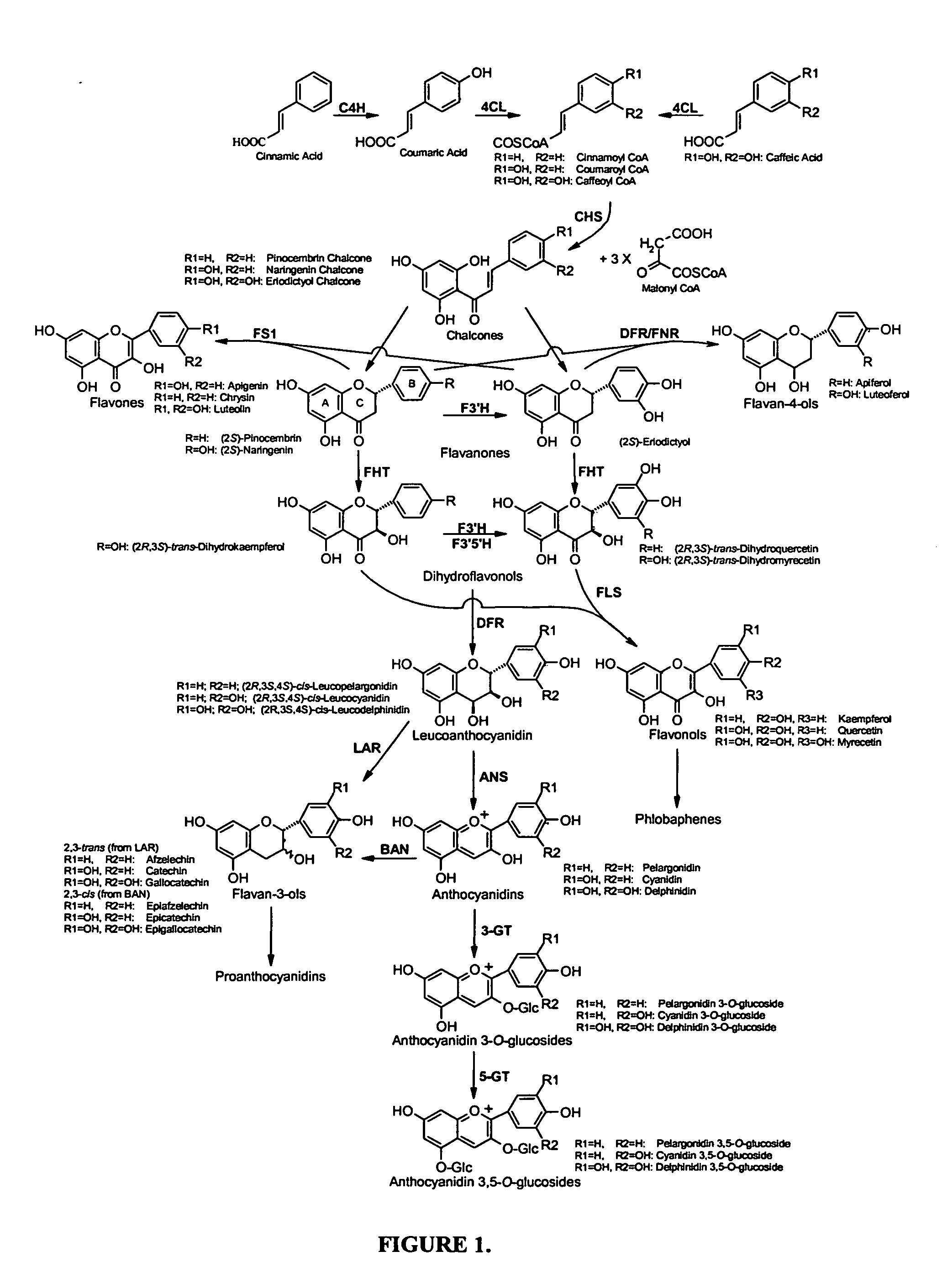
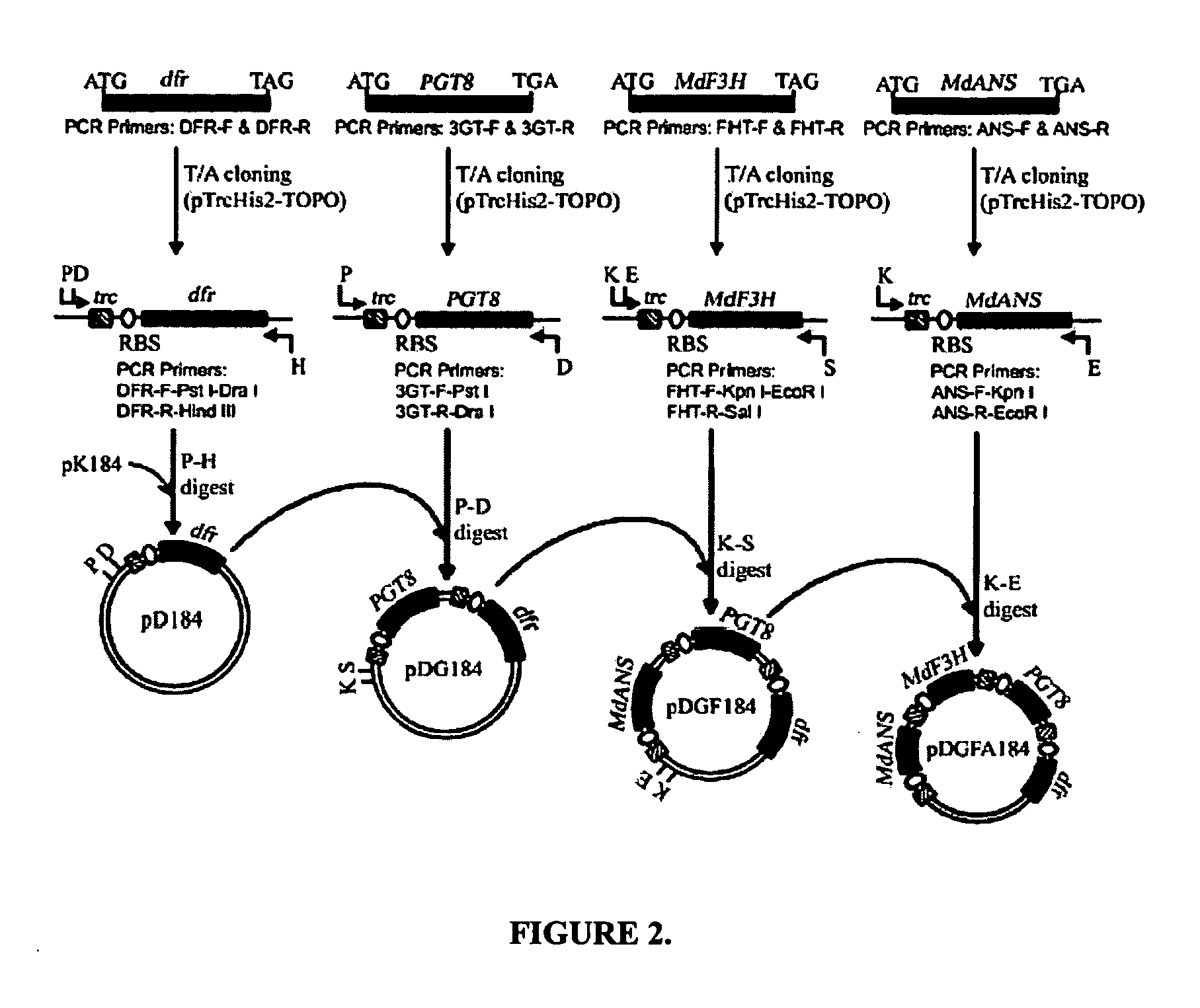
Methods and compositions are provided for production of flavonoids in microbial hosts. The compositions comprises a set of genes which encode for enzymes involved in one or more steps in the biosymthetic pathway for the conversion of phenylpropanoids to various flavonoids. The method comprises the steps of introducing the set of genes into a heterologous host cell, allowing growth of the cells in a suitable medium such that the expression of the genes results in production of enzymes. When specific substrate(s) is / are provided to the transformed cell, the enzymes act on the substrate(s) to produce the desired flavonoids.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Spinner apparatus with chemical supply nozzle and methods of forming patterns and performing etching using the same
InactiveUS6566275B1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotosensitive material processingResistCompound (substance)
A spinner apparatus for manufacturing a photomask, performing a developing process for forming a resist pattern on a specific substrate, and performing an etching process in which a resist pattern is used as an etching mask are provided. A plurality of supply nozzles for supplying a developing solution or an etching solution are provided above the substrate on which processes will be performed and processing conditions such as the temperature and flux of the chemicals supplied from each supply nozzle are independently controlled. Accordingly, it is possible to control the deviation of the critical dimensions of the device.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Nano/ALISA method and kit used for rapid detection of Salmonella
InactiveCN102565389ALow costEasy to operateColor/spectral properties measurementsPositive controlSorbent
The invention relates to a novel method used for rapid detection of Salmonella based on nano / aptamer-linked immobilized sorbent assay (Nano / ALISA) and a kit used for rapid detection of Salmonella, and the method is established by using an aptamer to substitute an antibody for capture of Salmonella and using gold nanoparticle couplet as a signal reporting group. The method comprises the following steps: (1) modifying the surface of magnetic particles with a specific aptamer of Salmonella; (2) adding a specimen for a reaction; (3) adding a specific primary antibody of Salmonella for reaction; (4) adding the couplet of secondary antibody-gold nanoparticle-reporting group for reaction; and (5) adding a specific substrate for reaction or directly recording light signals at the time. The kit comprises (1) the magnetic particles modified by the specific aptamer, (2) the specific primary antibody of Salmonella, (3) the couplet of secondary antibody-gold nanoparticle-reporting group, (4) confining liquid, (5) rinsing liquid, (6) the substrate, (7) positive control bacteria liquid and negative control bacteria liquid, etc.
Owner:WENZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
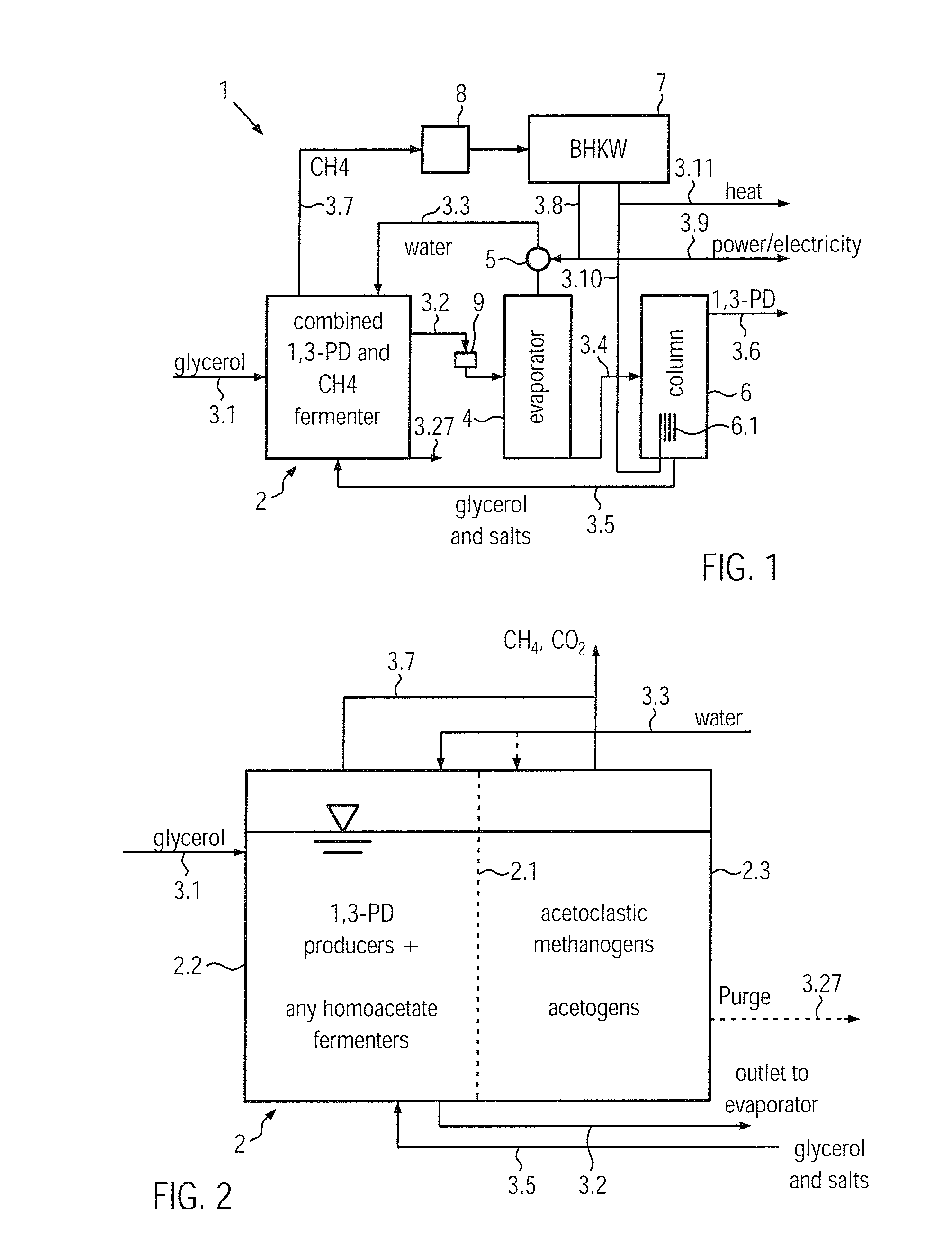
Process And Apparatus For The Microbial Production Of A Specific Product And Methane
InactiveUS20100285548A1High yieldImprove energy efficiencyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicroorganismHydrogen
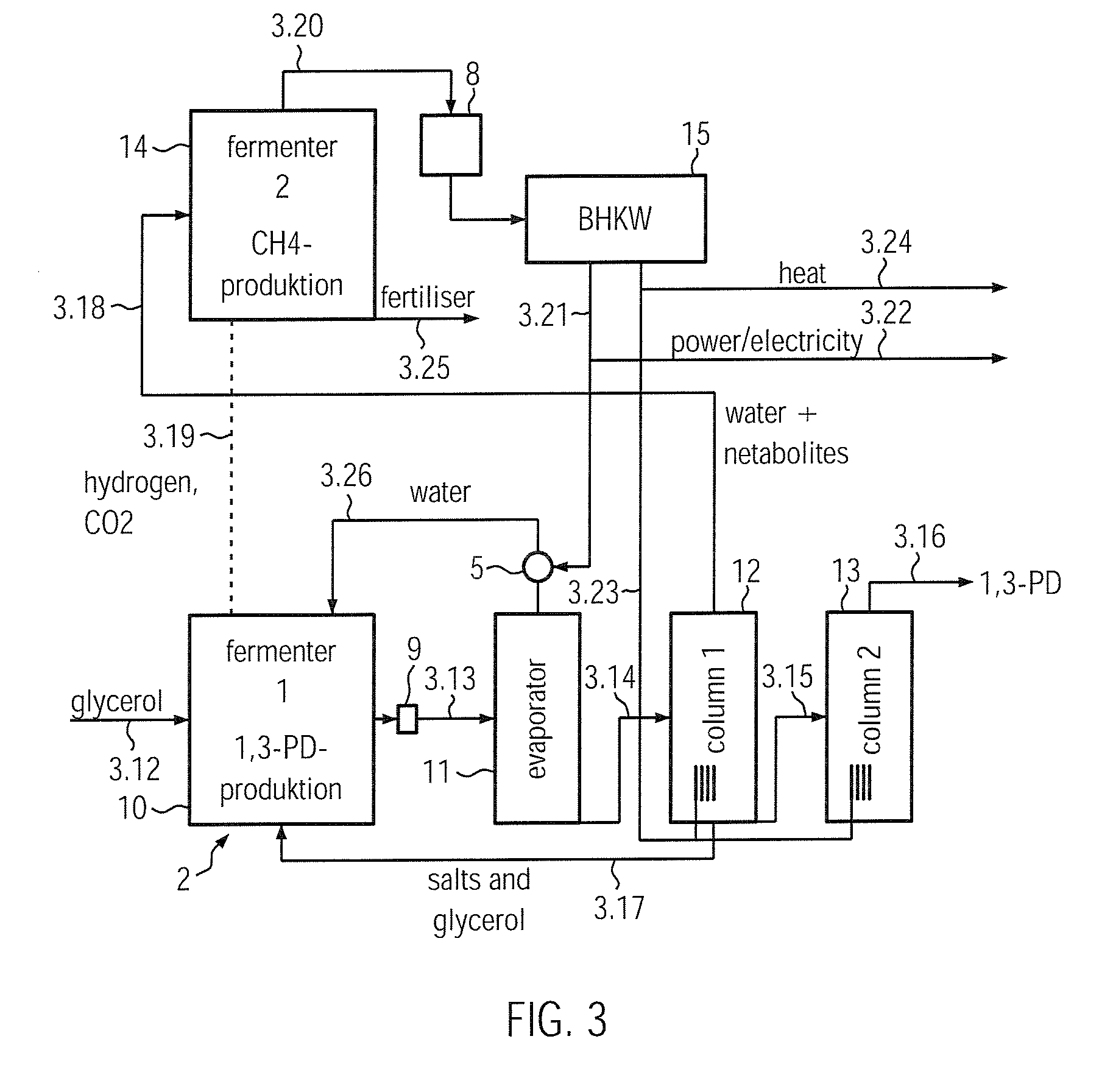
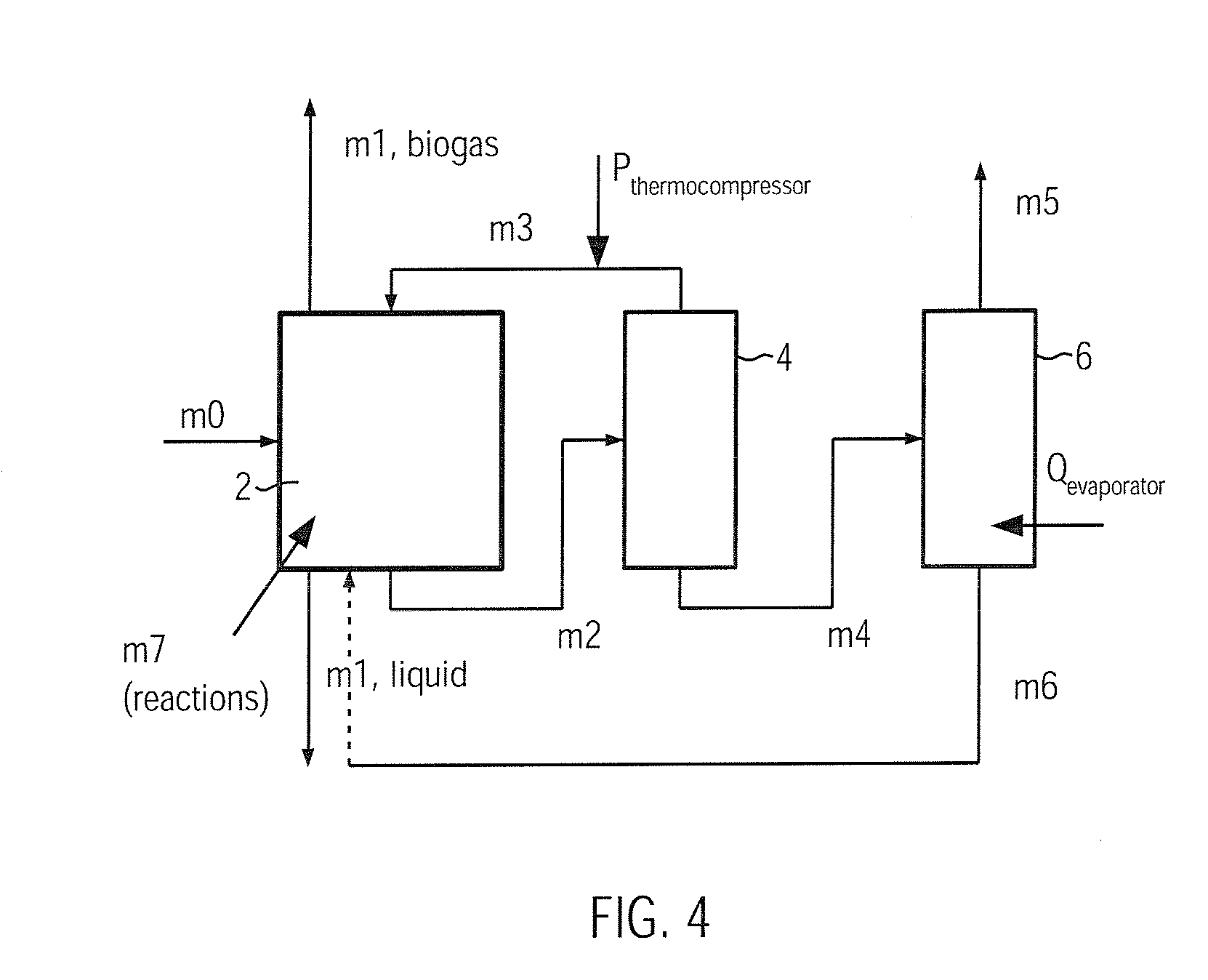
The process according to the invention for the microbial production of a specific product and methane comprises the following steps: a) the production in a bioreactor (2, 10) of a specific product from a specific substrate using a specific organism, the producer, wherein during the production of this product metabolites such as e.g. low-molecular alcohols, aldehydes and acids, hydrogen and CO2, which may inhibit the production of the product, are obtained; and b) the production of methane by means of a methanogen, wherein in the production of the methane at least one metabolite is decomposed and by this means removed from the bioreactor (2, 10) and its energy is made usable.
Owner:AGRAFERM TECH +2
Method for cleanly transferring single layer graphene by using PMMA
The invention discloses a method for cleanly transferring single layer graphene by using PMMA, and relates to a method for transferring the single layer graphene, aiming to solve the problems of an existing graphene transferring method that existing graphene grows unstably on a specific substrate such as a silicon wafer and the transferring is incomplete and curling easily occurs. The method disclosed by the invention is as follows: first, single layer graphene is grown on a copper foil substrate; second, then the copper foil substrate is coated with a PMMA glue in a suspending way, and then placed on a heating plate, heated, solidified, and trimmed; third, the copper foil is floated on the liquid-level of corrosive liquid, and fished out until the copper foil becomes transparent; fourth,standing in water is performed; fifth, the operation of the fourth step is repeated; sixth, the target substrate is picked up, blow-dried with nitrogen, and baked in an oven until the surface turns purple; seventh, PMMA is added dropwise, and standing is performed; and eighth, soaking in acetone, heating and washing are performed to complete the transfer of the single layer graphene. The method disclosed by the invention has broad prospects in the fields of optoelectronic devices and the like.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
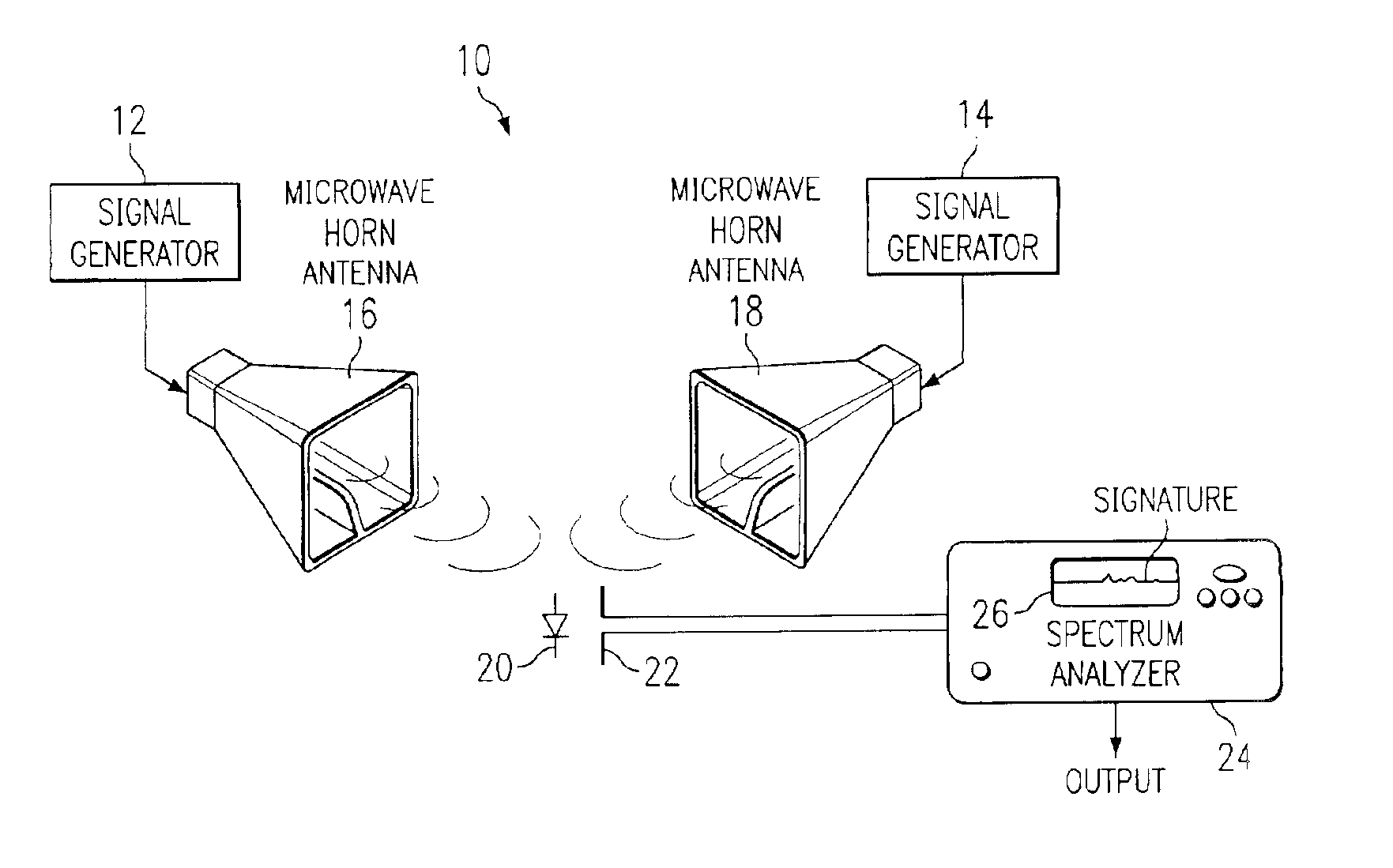
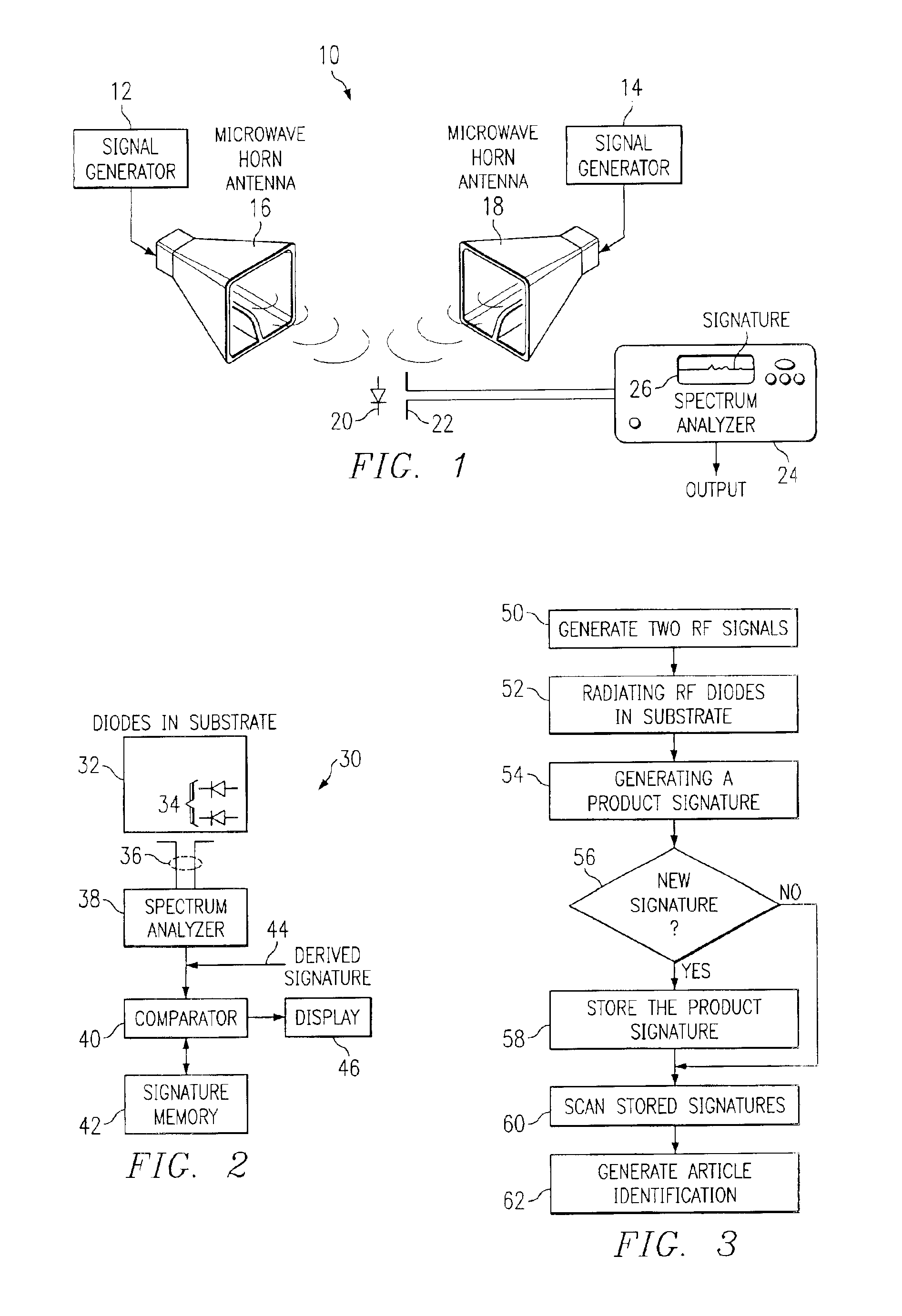
Semiconductor article harmonic identification
InactiveUS6856275B1Low costOpportunity for identificationSubscribers indirect connectionTransmissionSpectrum analyzerHarmonic
An harmonic intermodulation article identification system comprises a scanning dipole antenna response to an RF intermodulation harmonic product radiated from RF diodes carried by or embedded in a substrate. The product signature is applied to a spectrum analyzer that outputs a signature identification to a comparator. In response to receiving a signature identification, the comparator scans previously stored signature identifications for a match. A match indicates the received product identification from the analyzer defined a specific substrate such as a document or product tag. A match by the comparator outputs a signal to a display that indicates the identification of a substrate carrying RF diodes generating the compared product identification.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Method for preparing diamond-graphene composite film
InactiveCN102367570ASimple methodEasy to implementChemical vapor deposition coatingPlasma jetComposite film
The invention discloses a method for preparing a diamond-graphene composite film and relates to a method for preparing a diamond-graphene composite film by adopting a chemical vapor deposition method, belonging to the technical field of novel inorganic functional material preparation. The method comprises the following steps: 1) carrying out special treatment on the surface of a heterogeneous substrate to obtain specific substrate surface micro-pit having high surface energy and high density so as to induce graphene to grow; 2) placing the substrate on the substrate in a vacuum deposition chamber of a direct current plasma jetting growth system to grow a single-layer or minority-layer graphene film; 3) and controlling growth parameter conditions to achieve the self-coordination of a carbon bond atom structure of graphene on the surface layer, thus a diamond microstructure is evolved for growing a diamond film and the diamond-graphene composite film is prepared. The preparation method has simple and reliable process, high efficiency and no pollution, is beneficial to environmental protection and is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:NANCHANG HANGKONG UNIVERSITY
Method for quickly detecting heavy metal in water quality based on ultra-infiltration microchip
ActiveCN108132214ALow costSolve the cumbersome operationMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorTesting waterWater qualityHydrophobic silica
The invention discloses a method for quickly detecting heavy metal in water quality based on an ultra-infiltration microchip and belongs to the fields of material preparation and chemical examinationand analysis. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, reacting hydrophobic silica particles with fluorosilane in an ethanol solution to obtain superhydrophobic silica suspension; secondly,coating one side of a double-sided adhesive tape with the suspension to obtain superhydrophobic surface; finally, carrying out plasma etching in a designated area to obtain superhydrophilic microporesand an ultra-infiltration chip; pasting the ultra-infiltration chip on a specific substrate instrument by using the stickiness of the adhesive tape. By use of the ultra-infiltration chip, a color-producing reagent can be concentrated and enriched on the superhydrophilic micropores; the prepared ultra-infiltration chip can fix a detected solution on superhydrophilic sites by simple dipping operation, and colorimetric detection is realized by using a detection reagent on the hydrophilic sites. According to the method, the problems of high cost of a traditional apparatus analysis method and troublesome operation of a chemical analysis method are solved; the method is suitable for quick field detection of an aqueous solution.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
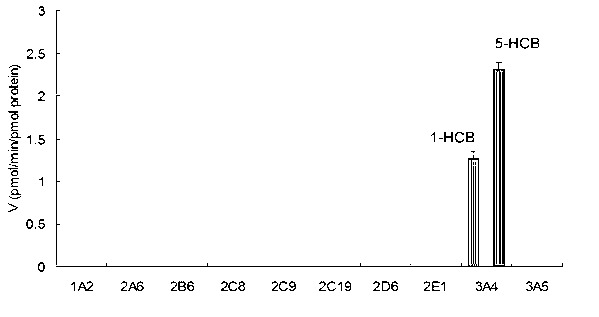
Specific probe substrate for cytochrome P450 3A4 enzyme and application of substrate
ActiveCN102993263AAdvantages of in vitro activityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementSteroidsQuantitative determinationHistiocyte
The invention provides a specific probe substrate for a cytochrome P450 3A4 enzyme and an application of the substrate in CYP3A4 enzyme activity measurement. The specific operation flow of the enzyme activity measurement comprises the following steps: carrying out the CYP catalytic reaction of the specific substrate by virtue of a CYP in-vitro incubation system by selecting any monomer in toad steroid series of compounds as a high-specificity probe substrate; and measuring the activity of the CYP3A4 enzyme in each biological sample and each cell by quantitatively detecting a product generated quantity or a substrate eliminated quantity in a unit time. The specific probe substrate provided by the invention can be used for quantitative evaluation of CYP3A4 enzyme activity in biological samples belonging to different species and deriving from different individual sources, and quantitative measurement of CYP3A4 enzyme activity in animal tissue cell culture fluids and cell products deriving from different sources.
Owner:ZHANGJIAGANG IND TECH RES INST CO LTD DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Method for preparing duck oil diglyceride
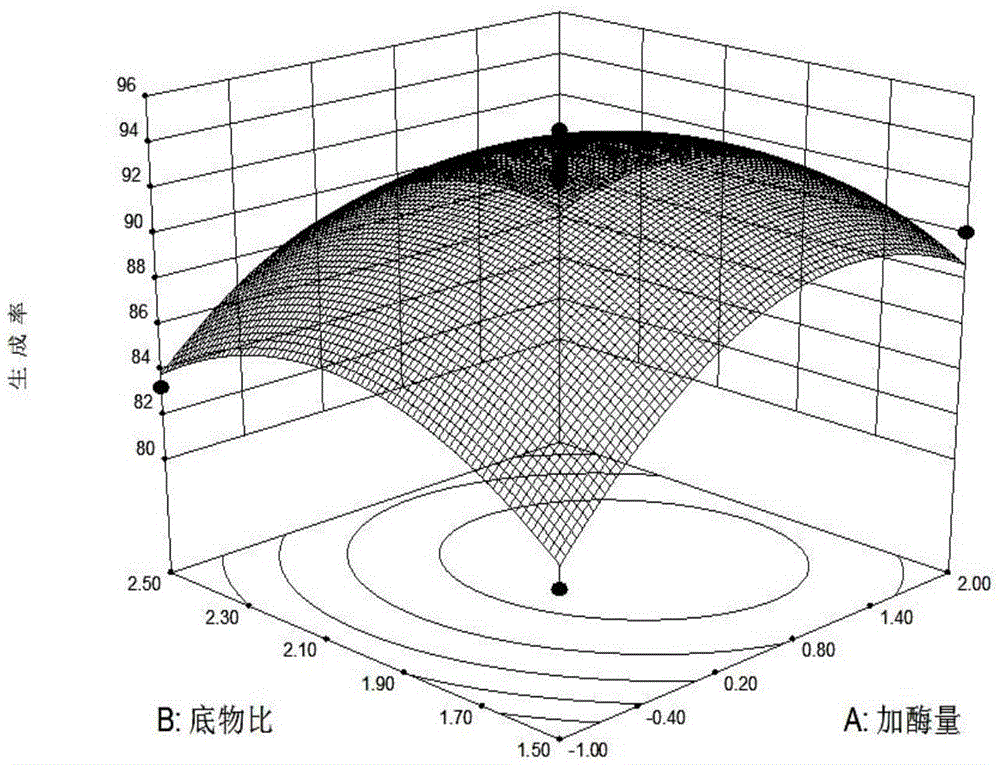
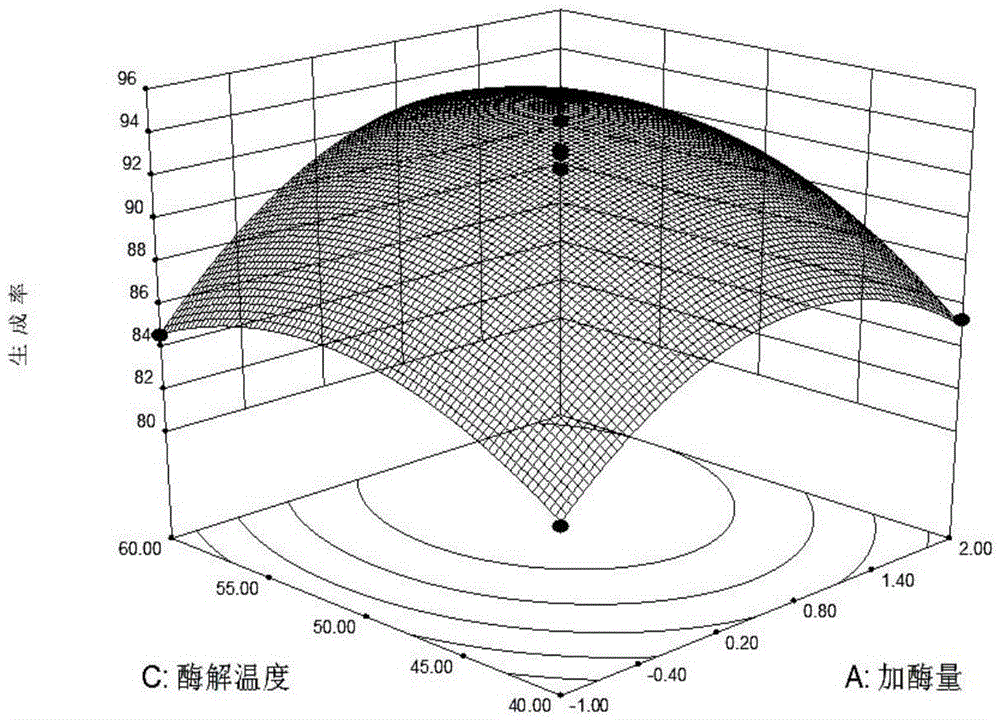
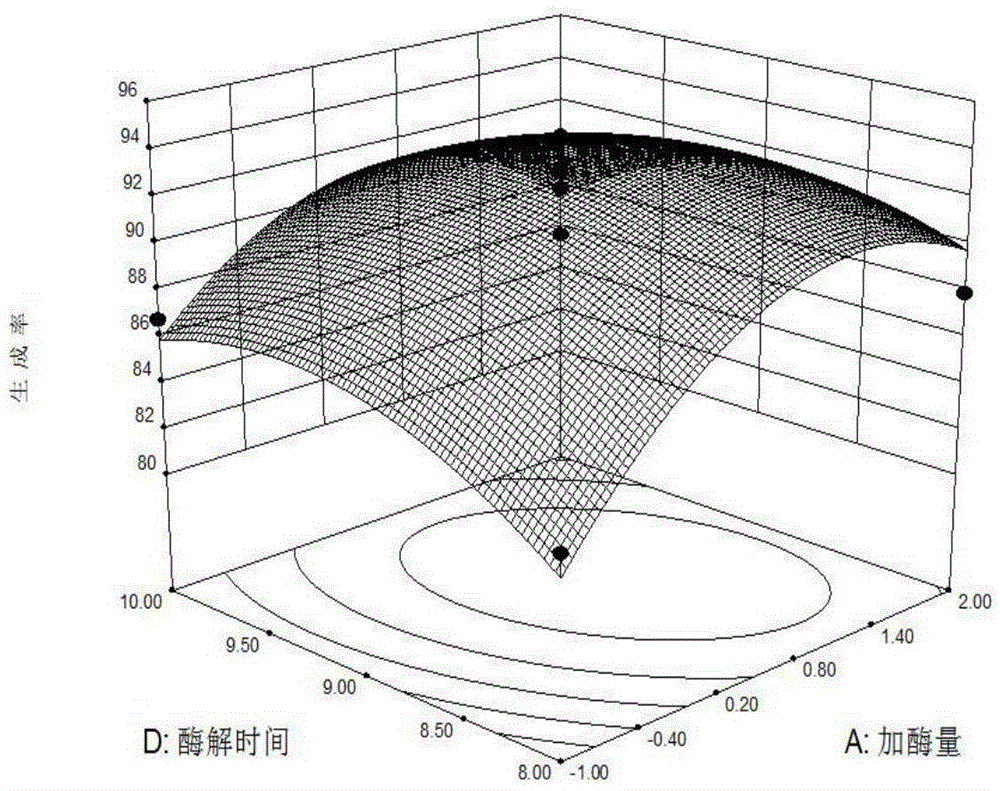
The invention relates to a method for preparing duck oil diglyceride through catalysis of immobilized lipase. The method for preparing the duck oil diglyceride through the catalysis of the immobilized lipase comprises the following steps: firstly utilizing an alkali hydrolysis method to prepare fatty acid mixture, mixing the fatty acid mixture with glycerinum, and generating a catalytic reaction by utilizing the immobilized lipase; by utilizing an experiment of four single factors, including enzyme dosage, specific substrate, enzymolysis temperature and enzymolysis time, and response surface analysis method, optimal conditions for preparing the duck oil diglyceride from the immobilized lipase are obtained. When the duck oil diglyceride is prepared from the immobilized lipase, enzyme and product diglyceride can be completely separated, so that no enzyme residue exists in the product, the purity of the product is high, and the safety of foods is guaranteed. Furthermore, the selected immobilized lipase can be recycled and reutilized, so that the production costs are reduced, and environmental pollution is reduced. The method for preparing the duck oil diglyceride, which is provided by the invention, creates a new way for comprehensive utilization of duck oil side-products, the additional value of the duck oil can be largely increased, and the method is a green creative project with the important development value.
Owner:QINGDAO RICHEN FOODS
Substrate polyeptides for von Willebrand factor cleaving protease ADAMTS-13
The present invention relates to specific substrates for a von Willebrand factor cleaving enzyme, ADAMTS-13, as well as to diagnosis of ADAMTS-13 deficient patients, diagnostic compositions, and kits employing the substrates. Particularly preferable substrate polypeptides for ADAMTS-13 are the polypeptide which begins at amino acid 1587 and ends at amino acid 1668 of SEQ ID NO: 1 in the Sequence Listing, and the polypeptide which begins at amino acid 1596 and ends at amino acid 1668 of SEQ ID NO: 1 in the Sequence Listing. These substrate polypeptides for ADAMTS-13 have high substrate specificity and also superior quantitativeness, and a suitable size for production by recombinant methods.
Owner:NAT CEREBRAL & CARDIOVASCULAR CENT
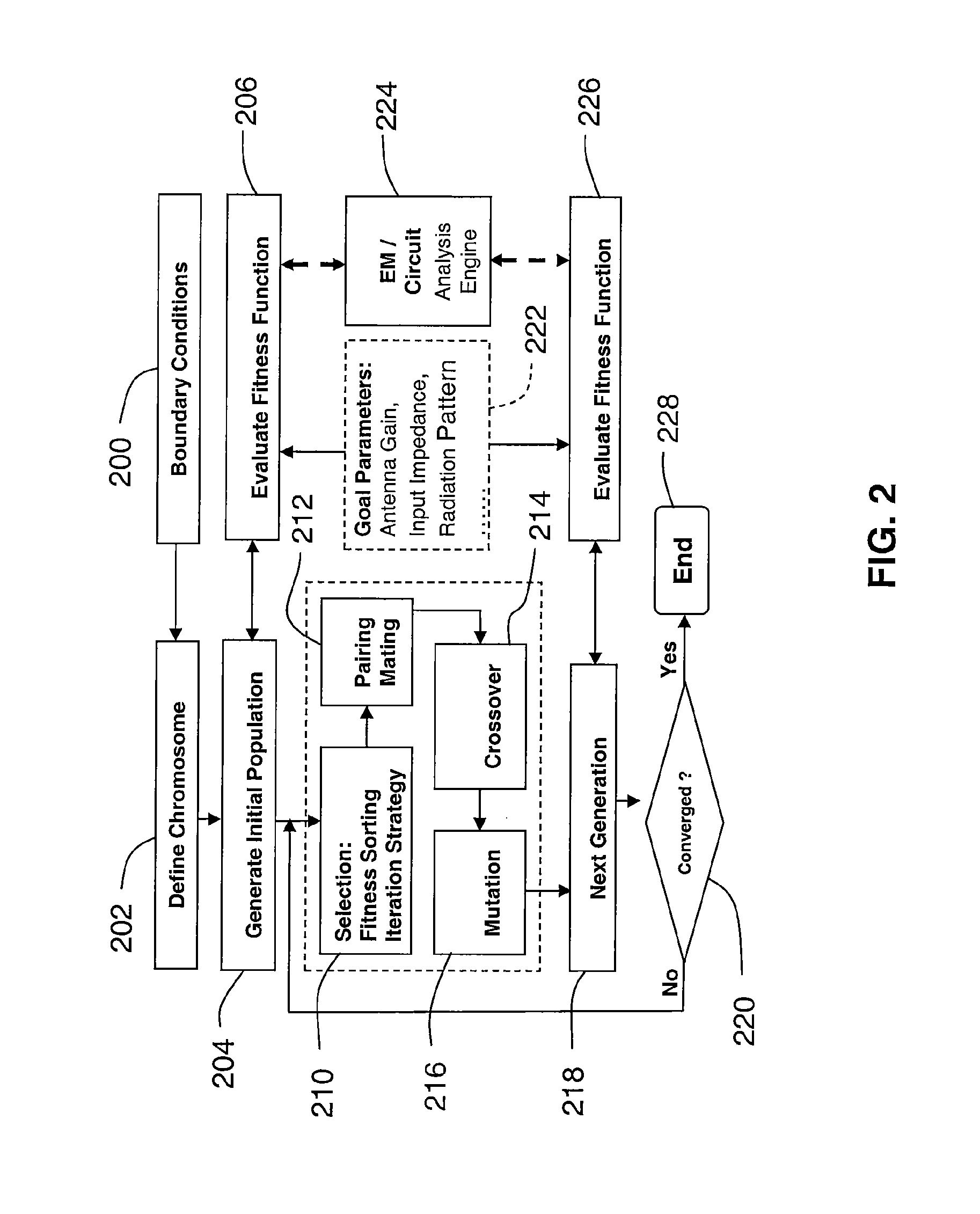
Optimization of unique antenna and RF systems for specific substrates
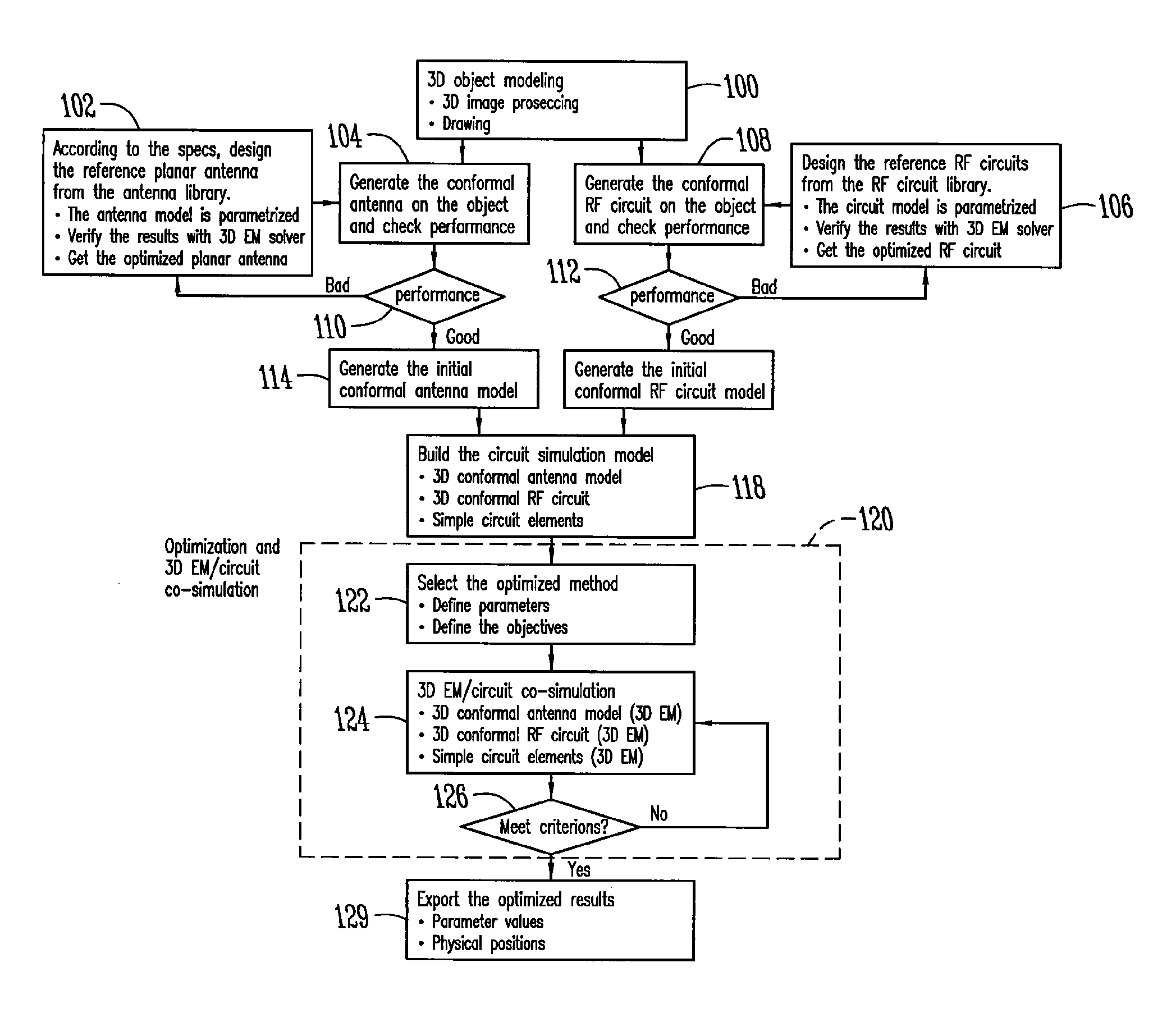
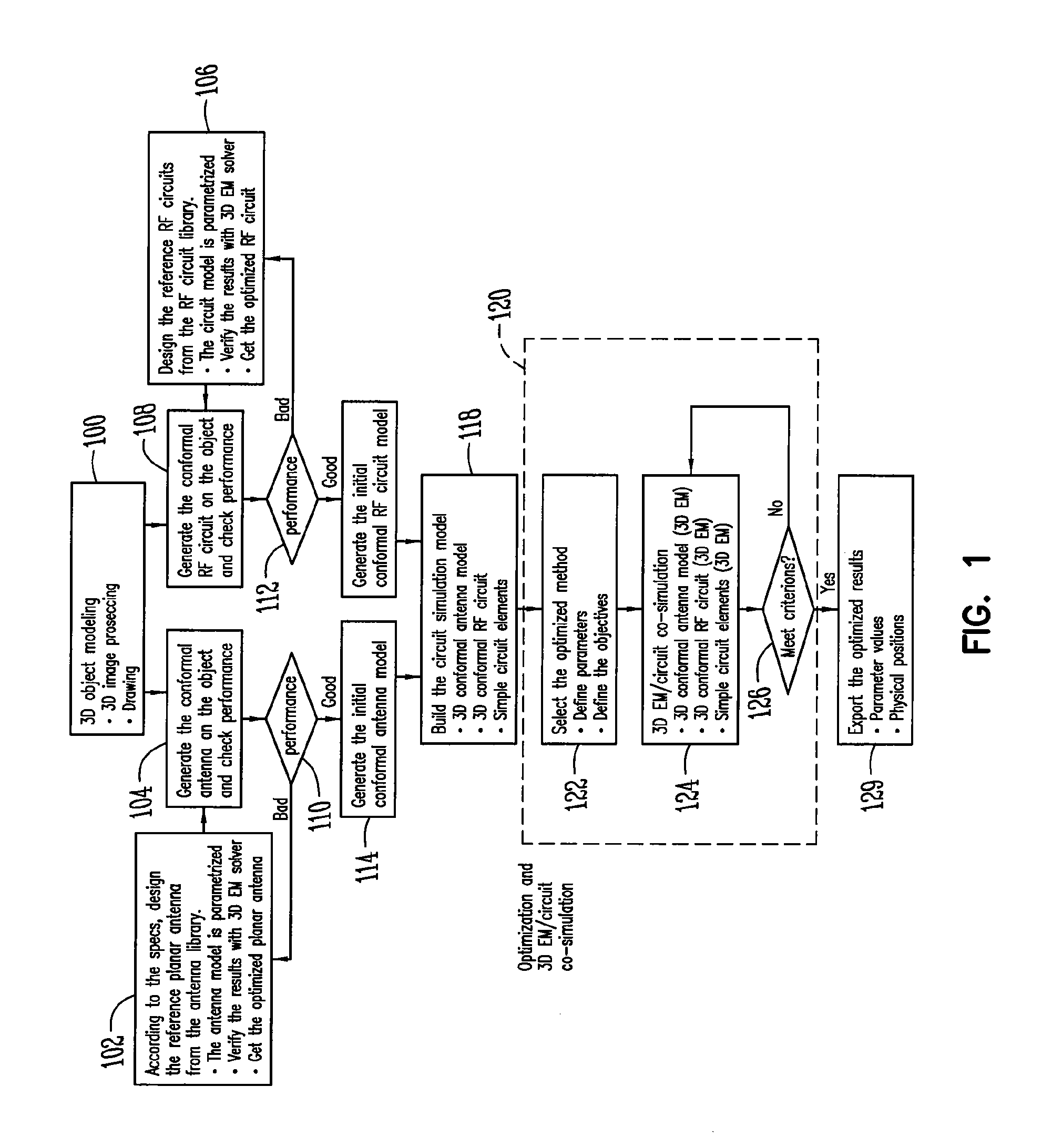
ActiveUS9395718B1Improved antenna designSimple designProgramme controlComputer controlThree dimensional shapeEngineering
A method incorporating an antenna and RF circuitry into the object acting as a substrate includes modeling the object as a three-dimensional object, and designing the antenna and RF circuitry for direct placement on the surface of the object. The step of designing is at least partially based on the size, three-dimensional shape, and material properties of the surface of the object acting as the substrate. The step of designing is preferably performed through use of an evolutionary optimizer implemented using parallel computing devices.
Owner:SCIPERIO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com