Multivalent transgenic insect-resistant rice genotype identification primer pair and method
A genotype and gene technology, applied in the field of primer pairs for identifying genotypes of multivalent transgenic insect-resistant rice, can solve the problems of inability to distinguish monovalent and multivalent in insect-resistant phenotype identification, and speed up the breeding process of insect-resistant transgenic rice, etc. Achieve the effect of obvious band size distinction, clear band, and good amplification results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0054] [Example 1] Material preparation
[0055] Transgenic Bt gene homozygous lines TT51(cry1Ab / 1Ac), T2A-1(cry2A), T1C-19(cry1C) were provided by the State Key Laboratory of Crop Genetic Improvement / National Plant Gene Research Center (Wuhan), Huazhong Agricultural University. Non-transgenic rice 9311, R988, and Chaotai B are preserved by the State Key Laboratory of Hybrid Rice (Wuhan University).
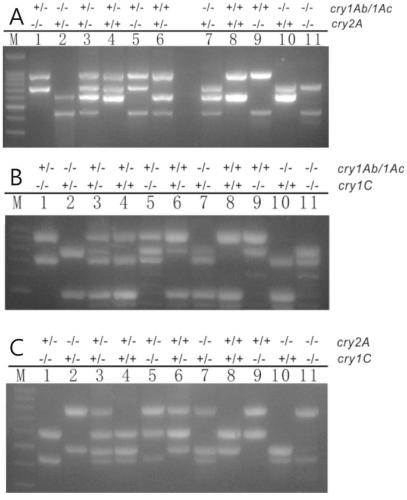
[0056] 9311 was crossed with TT51, R988 with T2A-1, Chaotai B with T1C-19, and the F1 obtained was self-crossed to obtain F2 for screening different genotype plants of the monovalent Bt transgene; Hybridization, screening for different genotypes of the bivalent Bt transgene in the F2 offspring of the cross; screening out the bivalent homozygous cry1Ab / 1Ac(+ / +)cry2A(+ / +) genotype rice single plant was crossed with T1C-19 (cry1C), and different genotypes of the trivalent Bt transgene were screened in the hybrid F2 progeny.
Embodiment 2
[0057] [Example 2] Primer Design
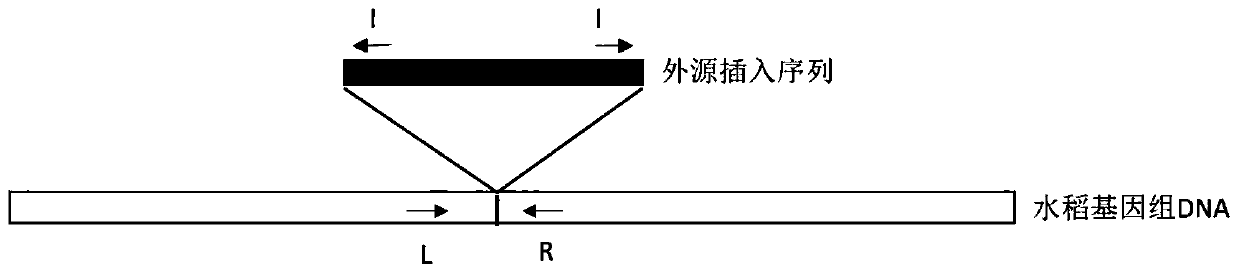
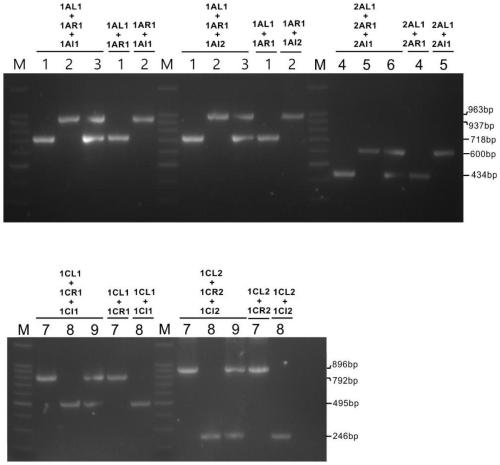
[0058] The foreign fragment insertion sequence of TT51 (Genebank: EU880444.1) and the rice genome sequence on both sides of the insertion site, part of the foreign fragment sequence and insertion site of T2A-1 (Genbank: HQ161063.1) were obtained from the NCBI database The rice genome sequence on the left, the partial exogenous fragment sequence of T1C-19 (Genbank: HQ161062.1) and the rice genome sequence on the left of the insertion site. Such as figure 1 As shown, L+R and I+R combinations were designed according to the TT51 insertion sequence and the genome sequences on both sides to detect genomic fragments and insertion events, respectively. According to the T2A-1 and T1C-19 insertion sequence and the left genome sequence, L+I primer combination was designed to detect the insertion event, and R primers were designed by selecting a genome fragment of about 1 kb on the right side of the insertion site, and the genome fragment was detected w...
Embodiment 3
[0062] [Example 3] DNA extraction
[0063] Cut rice leaves about 1-2 cm long and put them in a 2 mL round-bottomed centrifuge tube, and add steel balls and 40 μL 0.25 mol / L NaOH solution, put them in a QIAGEN Tissuelyser sample maker to grind and homogenate, and then add 160 μL 0.25 mol / L NaOH solution. 05 mol / L (pH=8.0) Tris-HCl, vortexed to mix and shake well, centrifuged at 12000r / min, and took the supernatant.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com