Molecular marker of main active gene BLS1 of paddy rice resisting bacterial streak and application of molecular marker
A major gene and molecular marker technology, applied in the field of molecular biology, can solve the problems of less research on molecular genetic mechanism and lack of in-depth molecular basic research, and achieve the effect of clear location, convenient identification and cost saving.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0050] 1. The origin of the main gene BLS1:
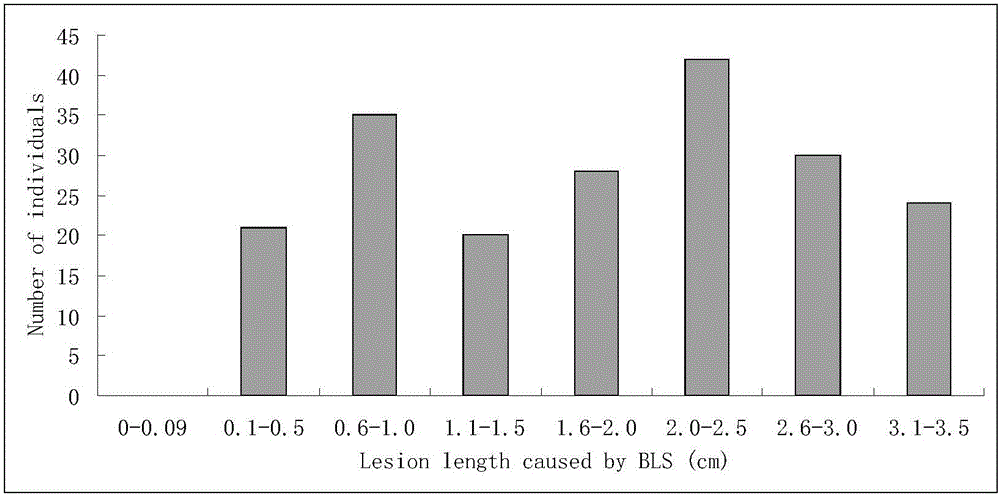
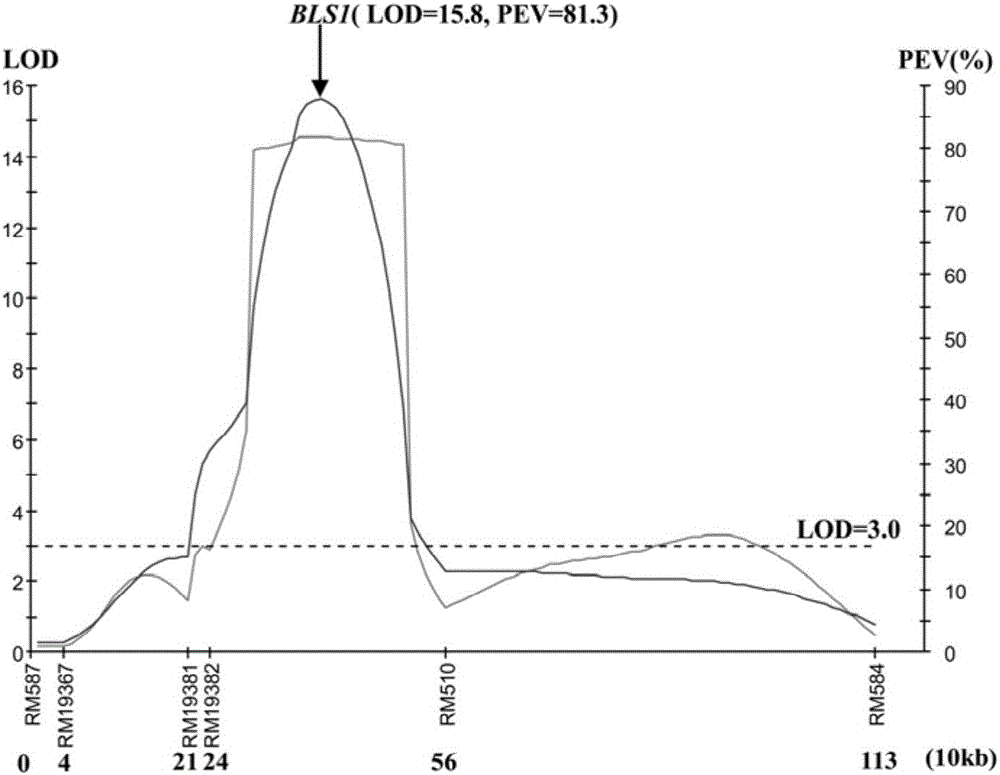
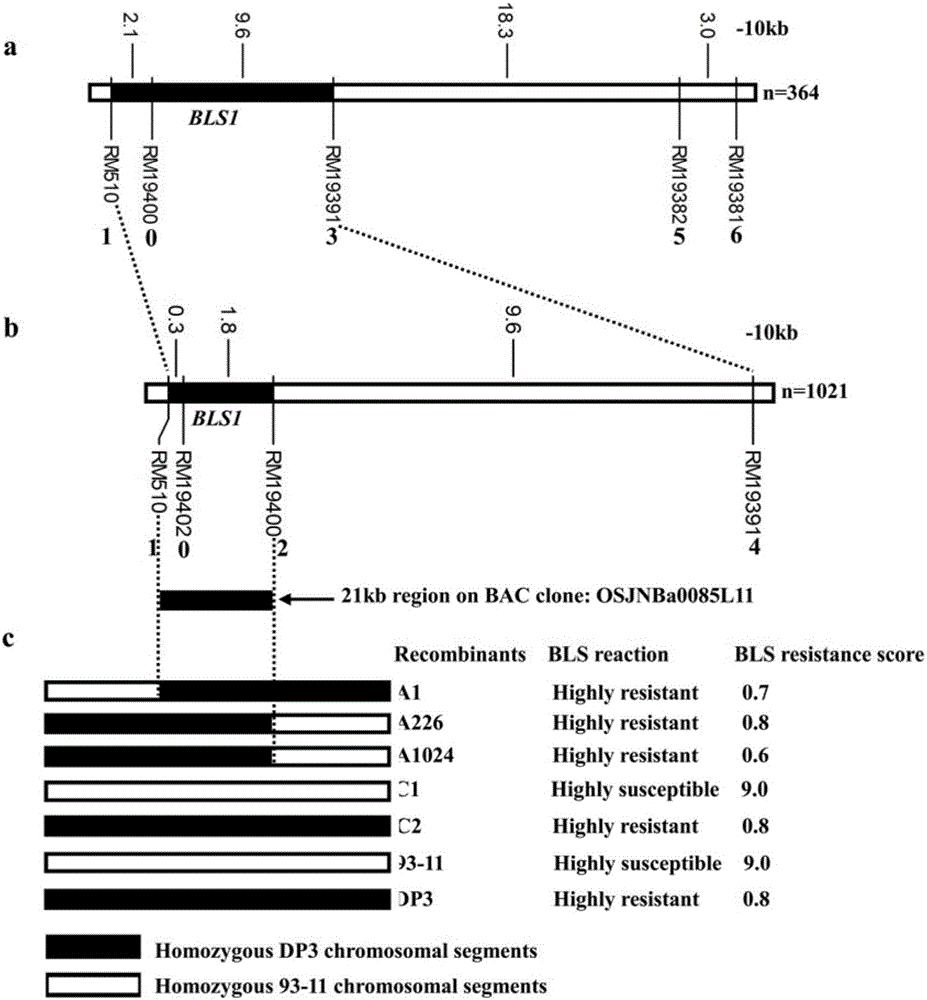
[0051] Huang Dahui et al. (2008) first found that common wild rice DP3 is resistant to bacterial streak type III by using resistance identification screening (Huang Dahui, Cen Zhenlu, Liu Chi, He Wenai, Chen Yingzhi, Ma Zengfeng, Yang Lang, Wei Shaoli, Liu Yali, Huang Siliang, Yang Xinqing, Li Rongbai. Screening and genetic analysis of wild rice bacterial streak resistance resources. Journal of Plant Genetic Resources, 2008, 9(1):11-14). He et al. (2012) showed through genetic analysis that DP3 carries a pair of recessive bacterial stripe disease resistance genes and tentatively named it bls1, and located the gene in the 4.0-cM region between RM587 and RM510 (He W A, Huang D H*,Li R B,Qiu Y F,Song J D,Yang H N,Zheng J X,Huang Y Y,Li X Q,Liu C,ZhangY X,Ma Z F and Yan Y. Identification of a resistance gene bls1to bacterial leaf streak in wild rice Oryza rufipogon Griff . Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 11(6):962-969). This gene...
Embodiment 2
[0067] Example 2: Verification of Molecular Markers
[0068] 1. Materials and methods
[0069] 1.1 Materials
[0070] Negative varieties: 10 copies, 8 copies of non-insect-resistant materials in the breeding combination of susceptible variety 93-11, resistant parent DP3, and DP3X 93-11.
[0071] Positive varieties: 9 insect-resistant materials in the breeding combination of insect-resistant varieties DP3 and 93-11X DP3.
[0072] Molecular marker primers: RM19382, RM 19391, RM19400, RM 19402, RM510.
[0073] 1.2 Method
[0074] Genomic DNA of rice sample was extracted by CTAB extraction method (method is the same as in Example 1). Sample DNA was amplified with primers RM19382, RM19391, RM19400, RM19402 and RM510, respectively. The reaction system included 0.10 μM primers, 250 μM dNTPs, 1× PCR reaction buffer (50 mM KCl, 10 mM Tris-HCl pH8.3, 1.5 mM MgCl 2 ), 100ng of DNA template, 1UTaq enzyme. The reaction program was: pre-denaturation at 94°C for 5 minutes, cycle (94°C...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com