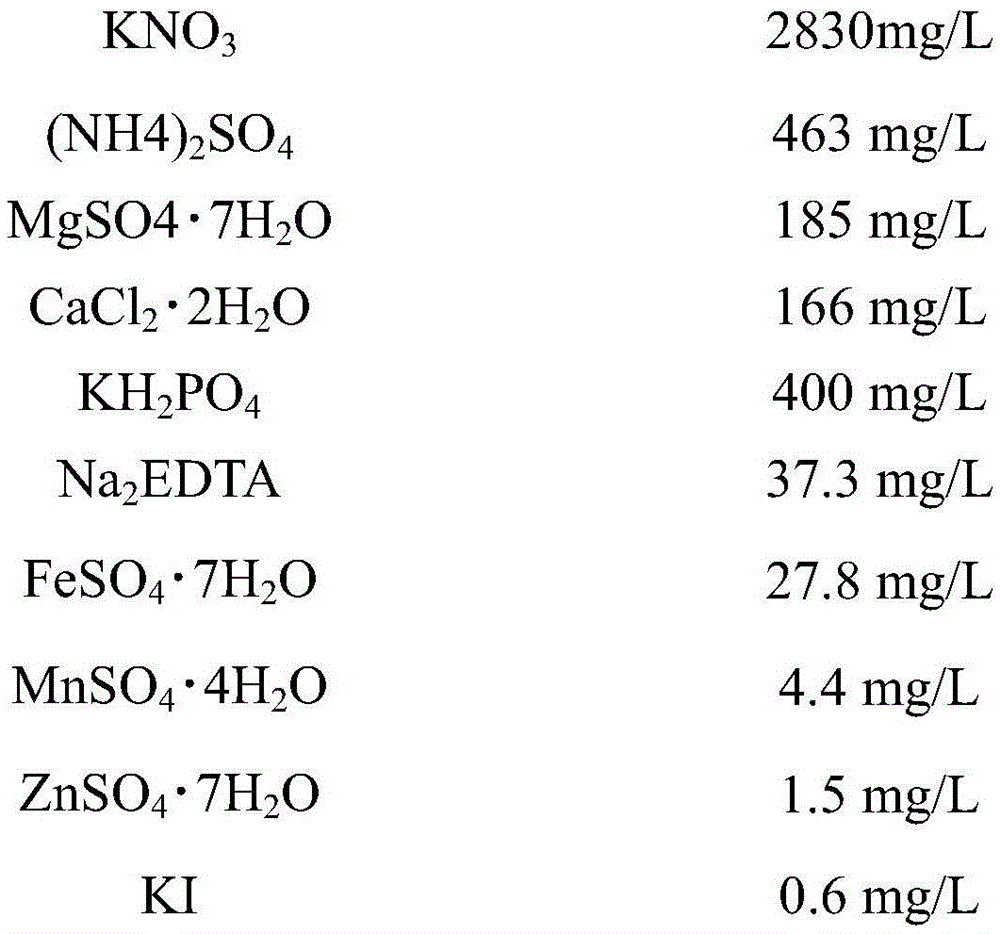
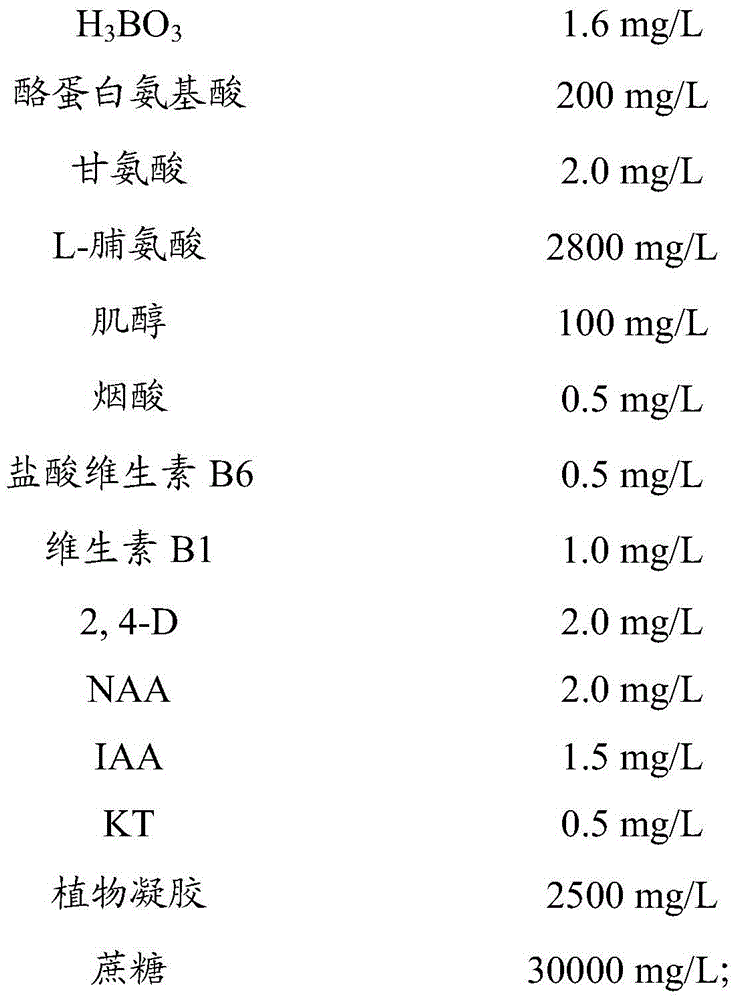
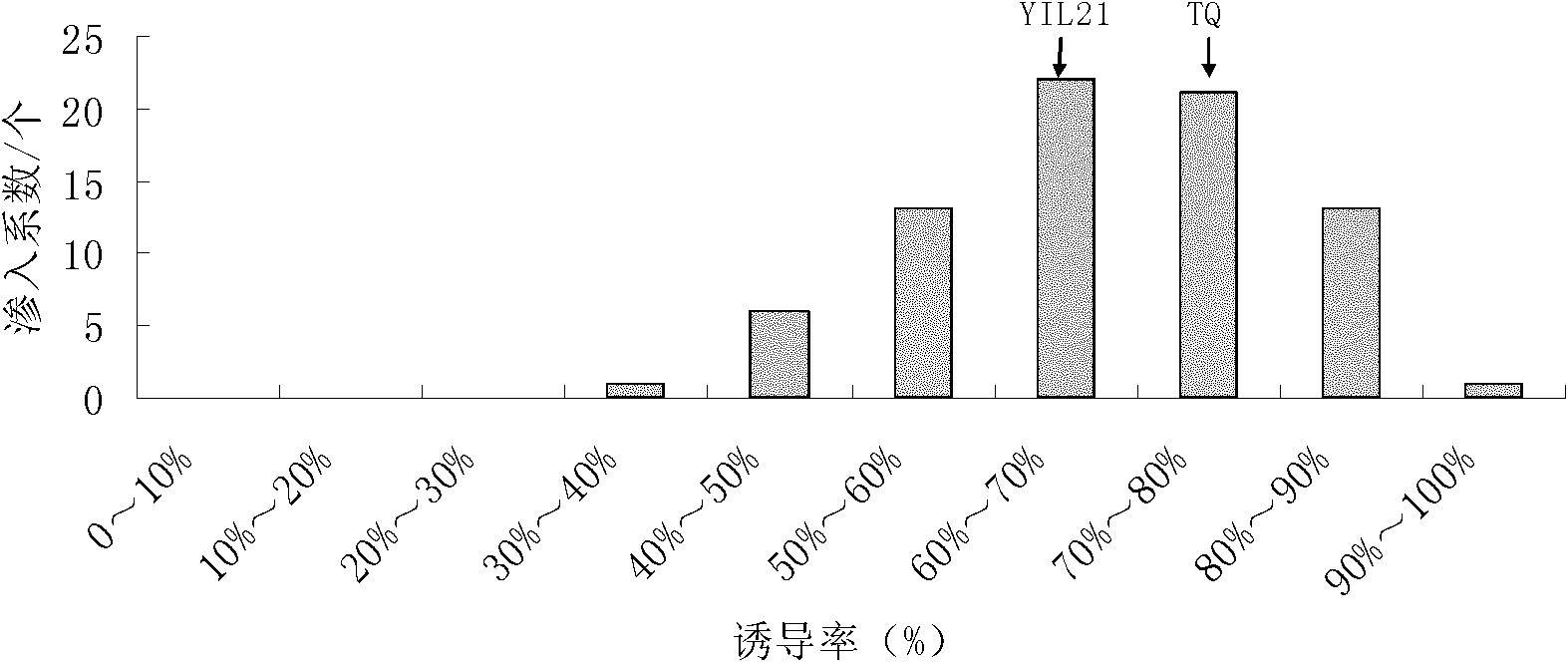Patents
Literature
47 results about "Common wild rice" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method for improving culture efficiency of anther of filial generation of Oryza rufipogon
InactiveCN104542299AImprove breeding efficiencySpeed up the breeding processPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsBiologySkin callus
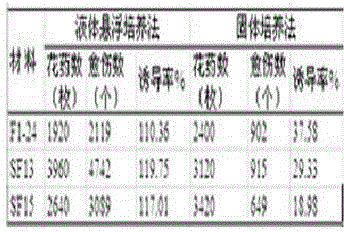
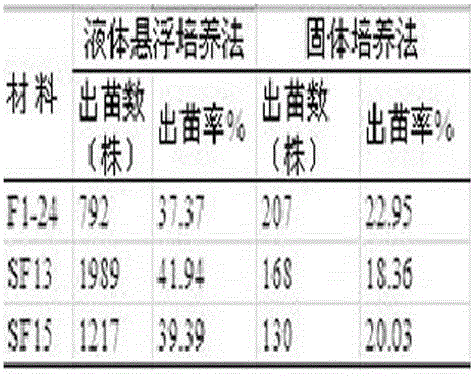
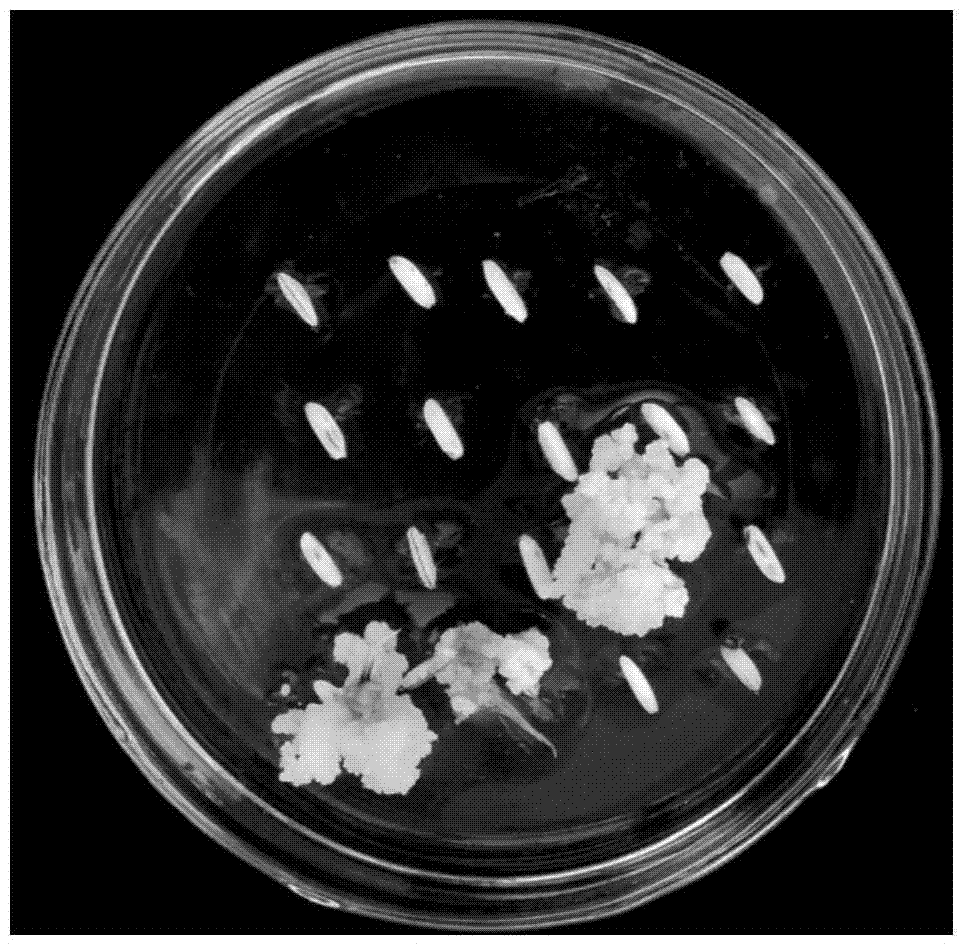
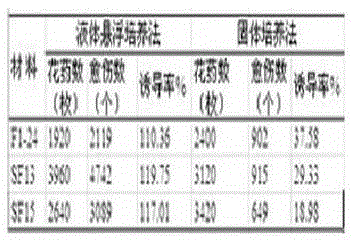
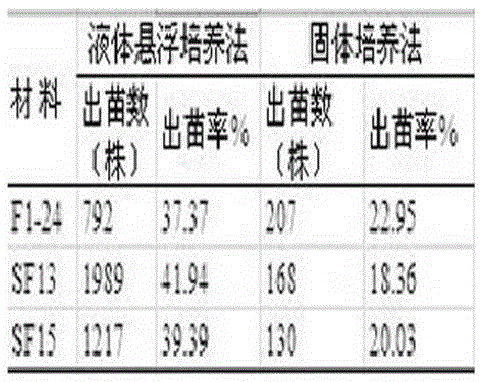
The invention relates to a method for improving the culture efficiency of the anther of the filial generation of Oryza rufipogon, and belongs to the field of a plant tissue culture technology. The method for improving the culture efficiency of the anther of the filial generation of the Oryza rufipogon comprises the following steps: selecting an explant, sterilizing the explant, inducing an anther derived callus by use of fluid suspension, performing multiplication culture on the anther derived callus, performing differentiation culture on the anther derived callus, performing rooting culture on a differentiated seedling (anther cultured seedling), hardening the seedling and transplanting. According to the method, the anther is inoculated in a fluid nutrient medium to be subjected to suspension culture, the callus induction rate is improved, the callus is transferred onto a multiplying medium to be subjected to the multiplication culture, the quality of the callus is improved and the quantity of the callus is increased. The method has the advantages that the callus induction rate and the seedling survival rate in the anther culture of the filial generation of the Oryza rufipogon are improved greatly, the rice breeding process is accelerated, the breeding efficiency of the good rice variety is improved, and the method can provide a powerful technical support for acceleration of breeding of rice varieties by use of good genes of the Oryza rufipogon.
Owner:云南省农业科学院生物技术与种质资源研究所
q srbsdv6 (southern rice black-streaked dwarf virus 6) and molecular marker method thereof
ActiveCN104450694APredicted resistance levelImprove selection efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceSelfing
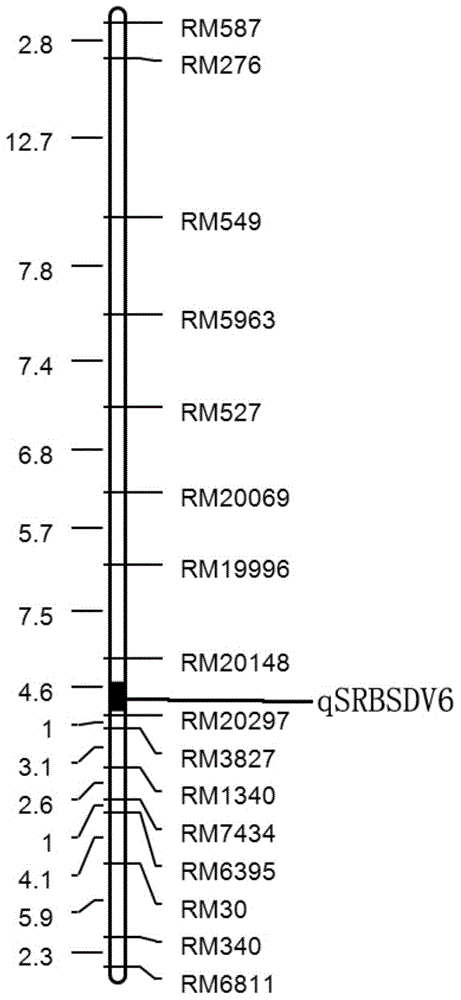
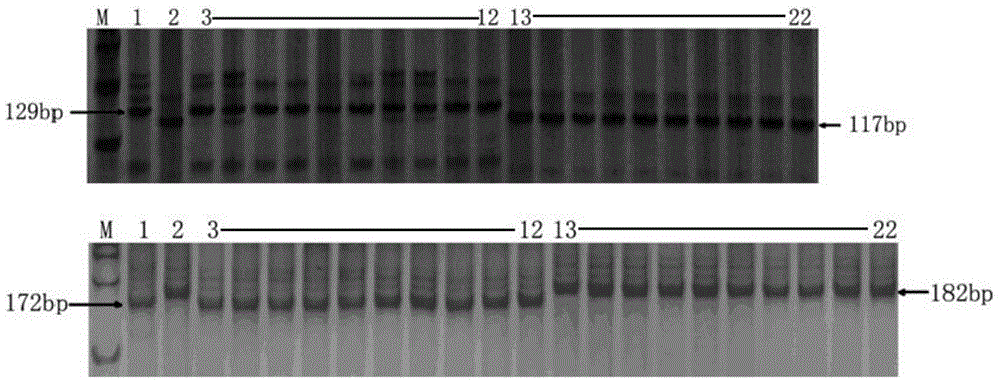
The invention provides a q SRBSDV6 (Southern rice black-streaked dwarf virus 6) and a molecular marker method thereof. BC3F7 is obtained through hybridization, backcross and selfing of Guangxi common wild rice material y11 and the susceptible variety Guanghui 998 and then is subjected to association analysis and genetic linkage analysis to obtain the q SRBSDV6, and the q SRBSDV6 is positioned between RM20148 and RM 20297; when the molecular marker RM20148 primer has q SRBSDV6, the amplification band is 129 bp band; when the molecular marker RM 20297 primer has q SRBSDV6, the amplification band is 172 bp band. According to the invention, the molecular markers of q SRBSDV6 genes can be adopted to detect whether the resistant material y11 and the derived varieties (series) contain the q SRBSDV6, the resistance level of the SRBSDV6 can be predicted, and the selective efficiency of the q SRBSDV6 rice can be greatly improved.
Owner:广西壮族自治区农业科学院水稻研究所
Molecule marker of red peel gene of weedy rice
InactiveCN101338338ANot affectedEasy to identifyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationOryzaAgricultural science
The invention relates to a molecule marking method for a red peel gene of weed rice and belongs to the field of molecular genetics. A rice type of 02428(white peel) is utilized to be hybridized with Yangzhong weed rice (red peel) to confirm that the red peel gene of the Yangzhong weed rice is a dominance single gene which is decided by a maternal gene; a reciprocal cross result shows to have no cytoplasm effects. An InDel marker RID14 is designed according to the gene structure of the red peel gene Rc of the cloned common wild rice; the InDel marker is co-separated with the red peel gene of the weed rice. The marker can be utilized to accurately and effectively identify the red weed rice and the derived line thereof from the cultivated rice and can provide a molecule basis for the identifying of the weed rice.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Method for constructing suppression subtractive hybridization (SSH) library of oryza rufipogon threatened by bacterial blight germs
InactiveCN102660777AHigh sensitivitySuppression Subtraction Libraries GoodBacteriaMicroorganism based processesTotal rnaPolarization mode dispersion
The invention discloses a method for constructing a suppression subtractive hybridization (SSH) library of oryza rufipogon threatened by bacterial blight germs. The method includes steps of: sample processing, total ribonucleic acid (RNA) extraction, mRNA purification, suppression subtractive hybridization and polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification of testing parts and driven elements, PCR products and polarization mode dispersion 18-T (pMD18-T) carrier connection restraining, connection product conversion, monoclonal storing and the like. The SSH library of oryza rufipogon threatened by bacterial blight germs constructed by the method is high in sensitivity, even length of insertion elements of the library is 450bp, a large number of difference expressed sequence tags (ESTs) of the oryza rufipogon threatened by the bacterial blight germs can be obtained fast in one step, partial sequence information is provided for separating overall-length cDNA sequence of clone bacterial blight resisting related genes, simultaneously important theoretical basis for improvement of biology is provided and new bacterial blight resisting related genes can be obtained.
Owner:云南省农业科学院生物技术与种质资源研究所
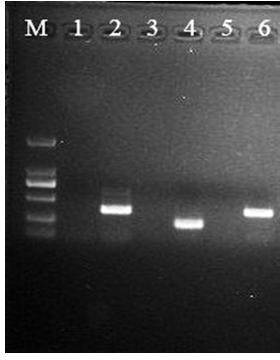
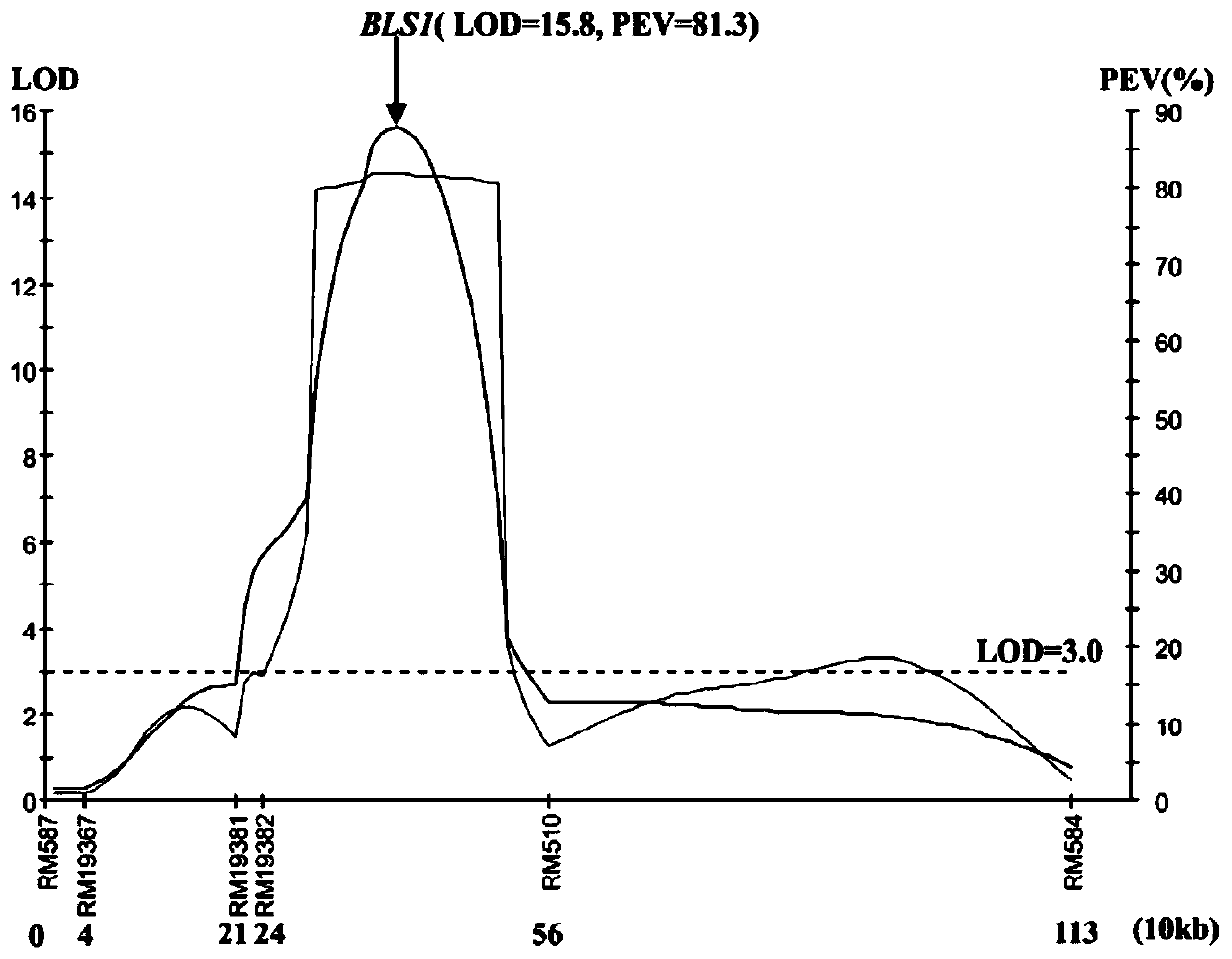
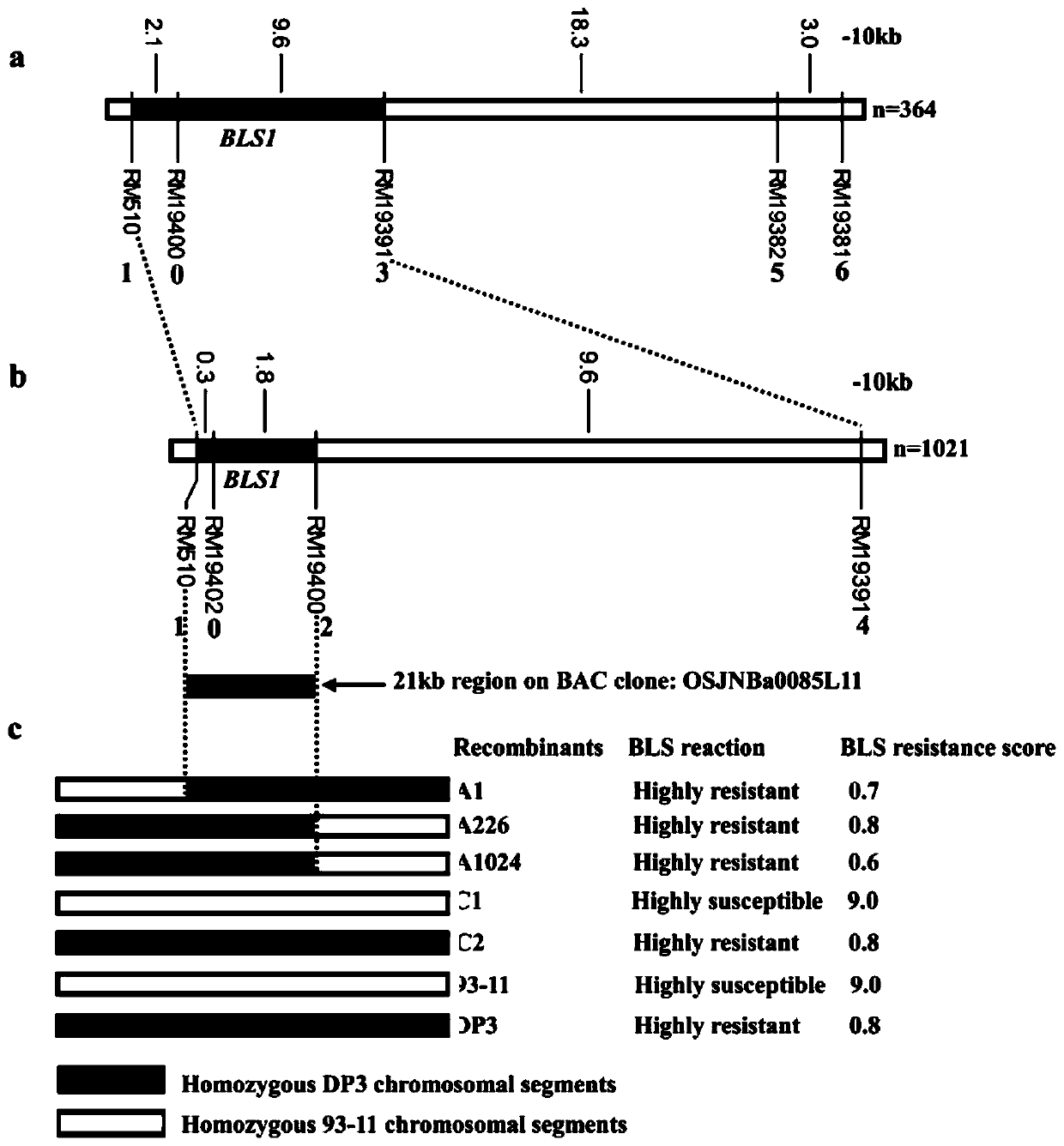
Molecular marker of main active gene BLS1 of paddy rice resisting bacterial streak and application of molecular marker
ActiveCN106244678AImprove selection efficiencyNot affectedMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceOffspring F1
The invention discloses a molecular marker of a main active gene BLS1 of paddy rice resisting bacterial streak and an application of the molecular marker. A bacterial streak resistant backcross inbred line obtained from deriving an ordinary wild paddy rice resistant source DP3 is crossed with a bacterial streak-infected nonglutinous rice variety 93-11 to obtain an offspring F1 hybrid and then the hybrid is self-fertilized to obtain F2 generation, genetic linkage analysis is performed for a gene type and corresponding resistant phenotype of each family of F2, and the bacterial streak-resistant main active gene BLS1 sourced from the ordinary wild paddy rice DP3 is detected. Molecular markers capable of being used for breeding such as RM19382, RM19391, RM19400, RM19402 and RM510 are obtained. The molecular markers can effectively detect whether the bacterial streak-resistant ordinary wild paddy rice DP3 and erivative varieties (lines) thereof contain a main active gene site, thereby greatly improving the selection efficiency of the bacterial streak resistant paddy rice, and obtaining the bacterial streak resistant paddy rice variety containing the BLS1 gene.
Owner:广西壮族自治区农业科学院水稻研究所
Rapid propagation method of Oryzarufipogon Griff by tissue culture
ActiveCN107333653AIncrease the multiplication factorImprove seedling qualityHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureWheat germSeaweed extract
The invention relates to the technical field of rapid propagation of plants, in particular to a rapid propagation method of Oryzarufipogon Griff by tissue culture. The method comprises the steps as follows: selecting and disinfecting rice seeds; inoculating the seeds into a culture medium containing seaweed extracts to obtain sterile test tube seedlings; inoculating the test tube seedlings into a medium containing aloe extracts to obtain cluster buds; inoculating the cluster buds into a medium containing wheat germ extracts to obtain robust plants; transplanting the robust plants into a medium containing chlorella extracts for culture to obtain complete plants with roots. Compared with a traditional method, the method has the advantages that by optimizing the medium at each stage of rapid propagation, the germination rate of the wild rice seeds is further increased, propagation and differentiation of the cluster buds are promoted, rooting capacity of new plants is enhanced, obtained new seedlings grow well and are robust, and the success rate of rapid propagation of tissue culture of wild rice is significantly increased.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
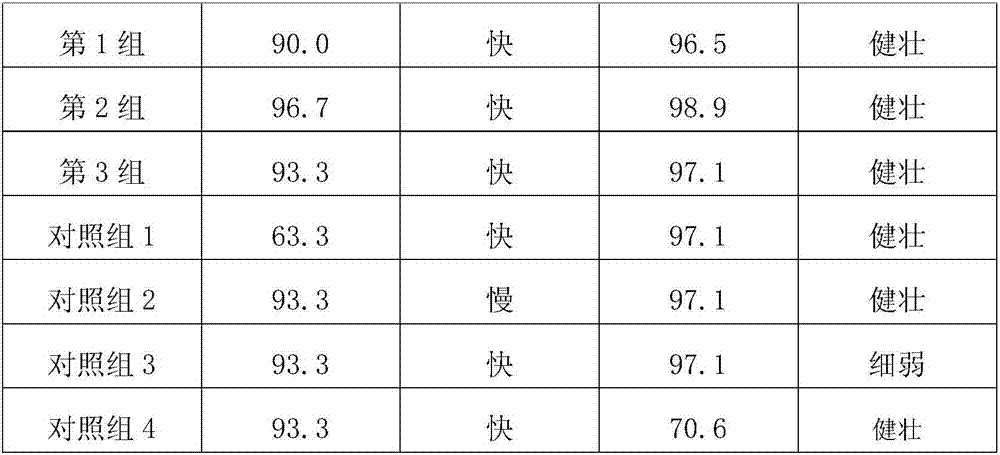
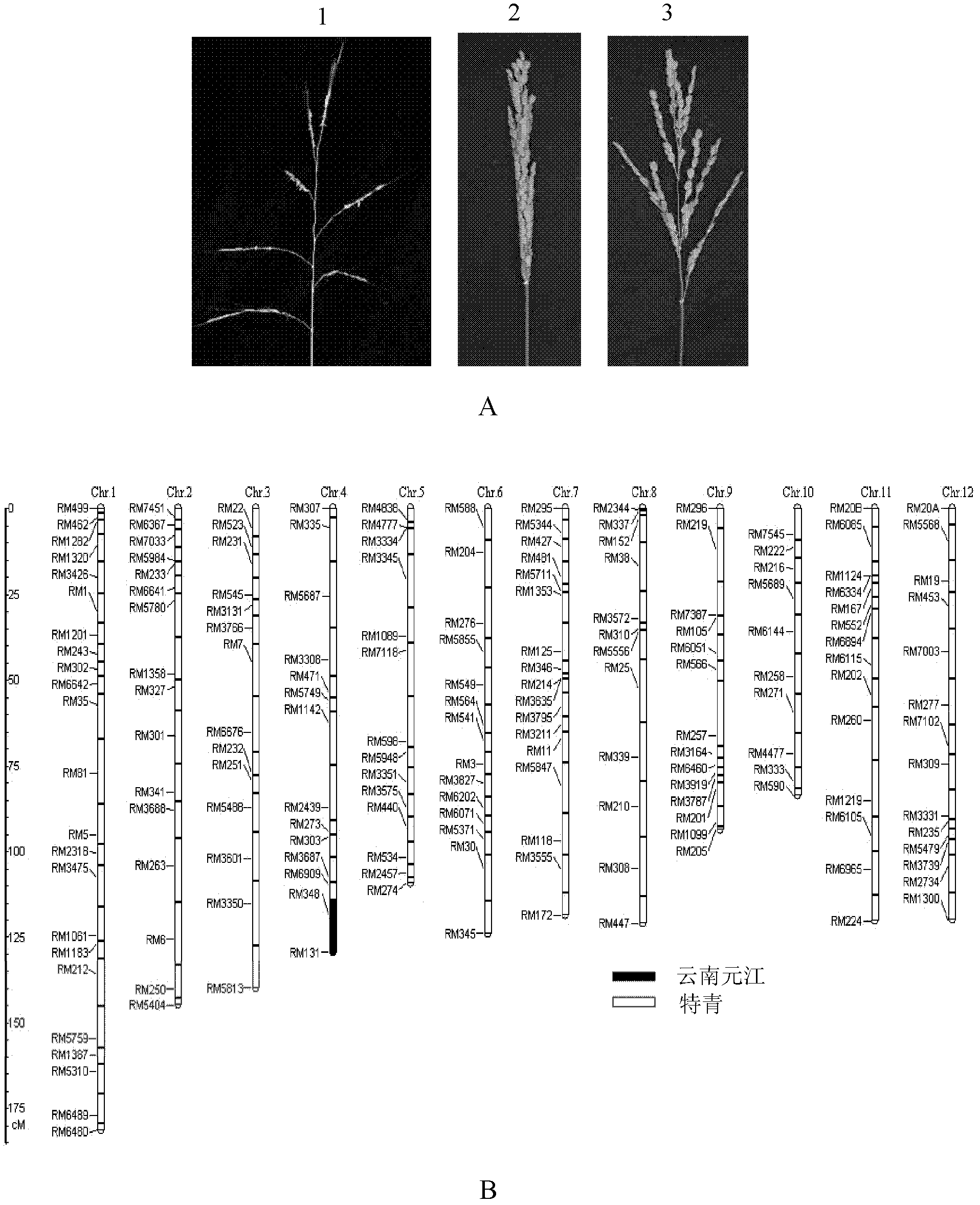
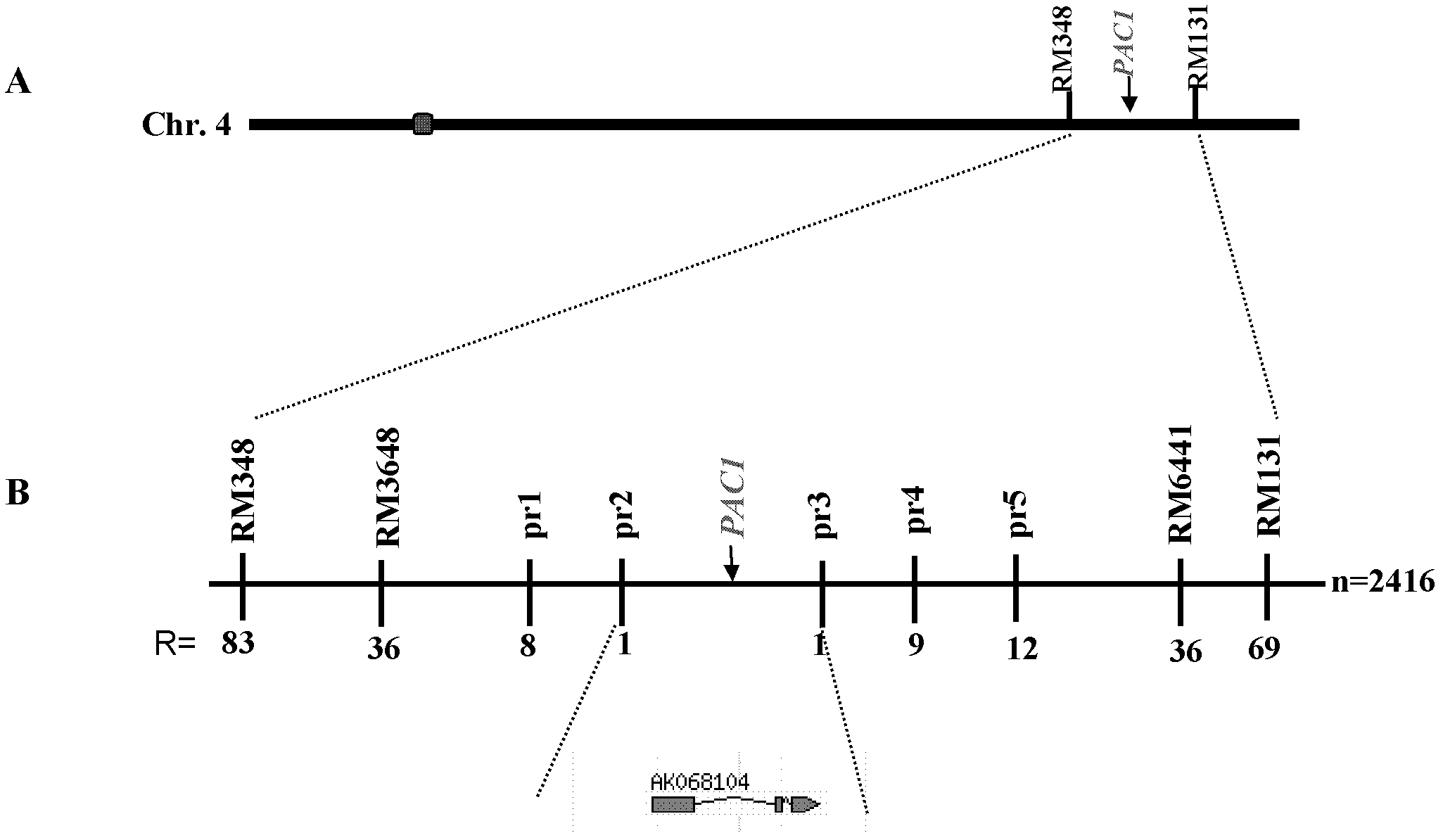
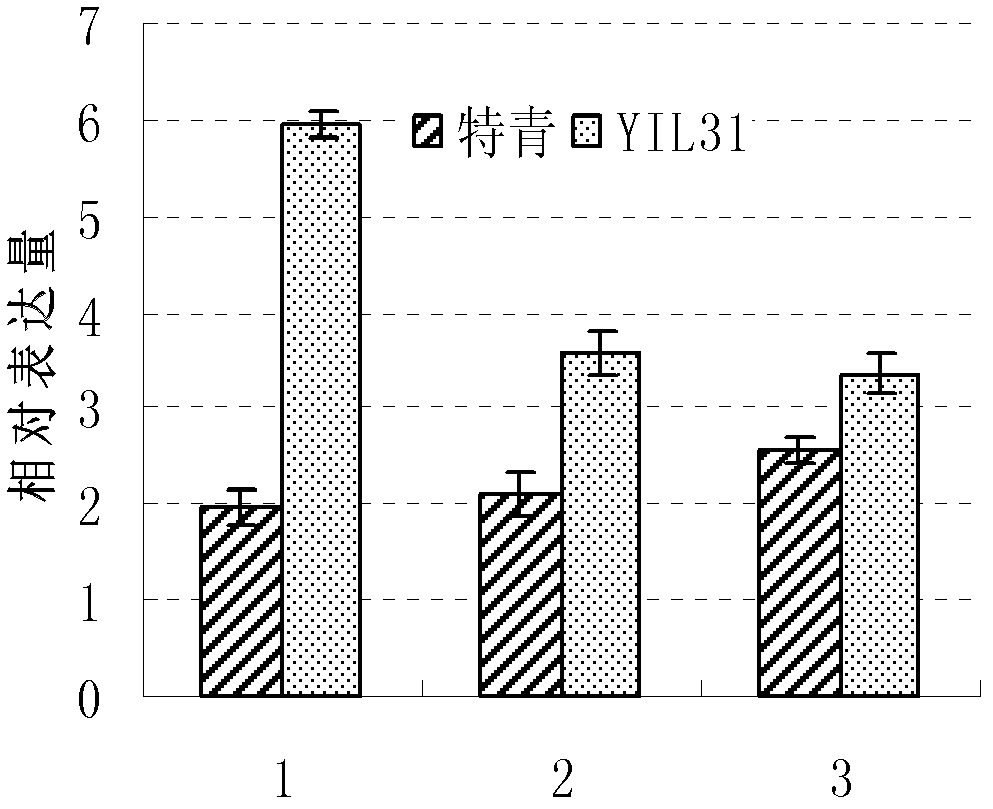
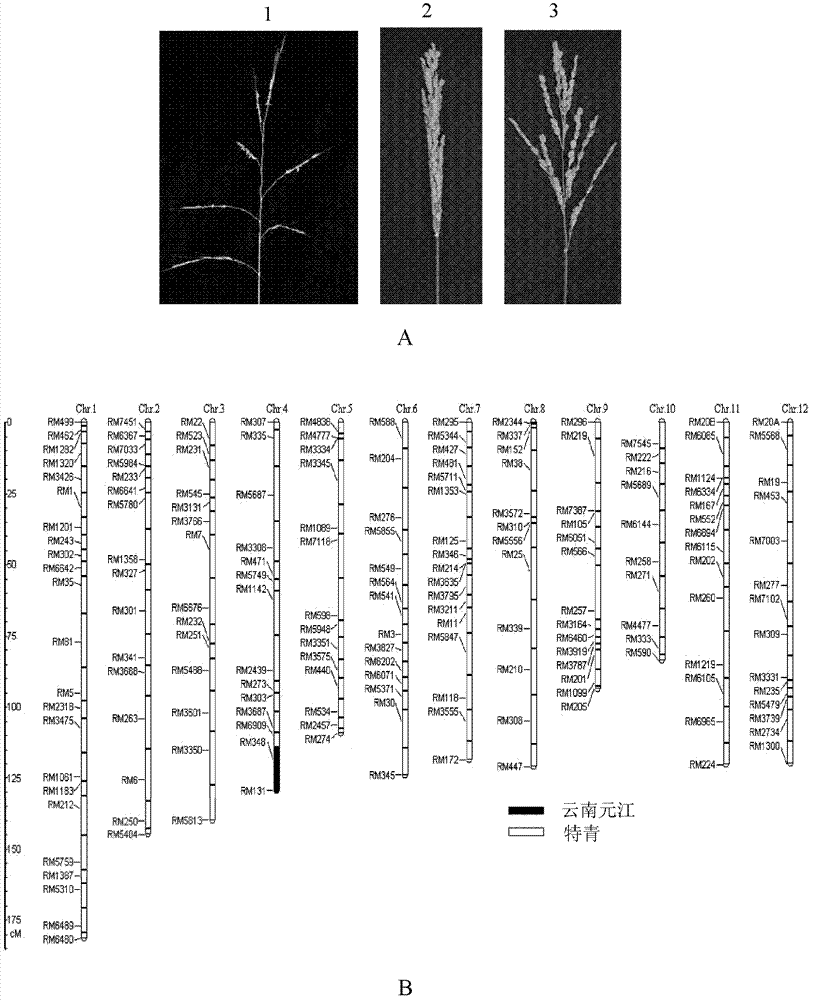
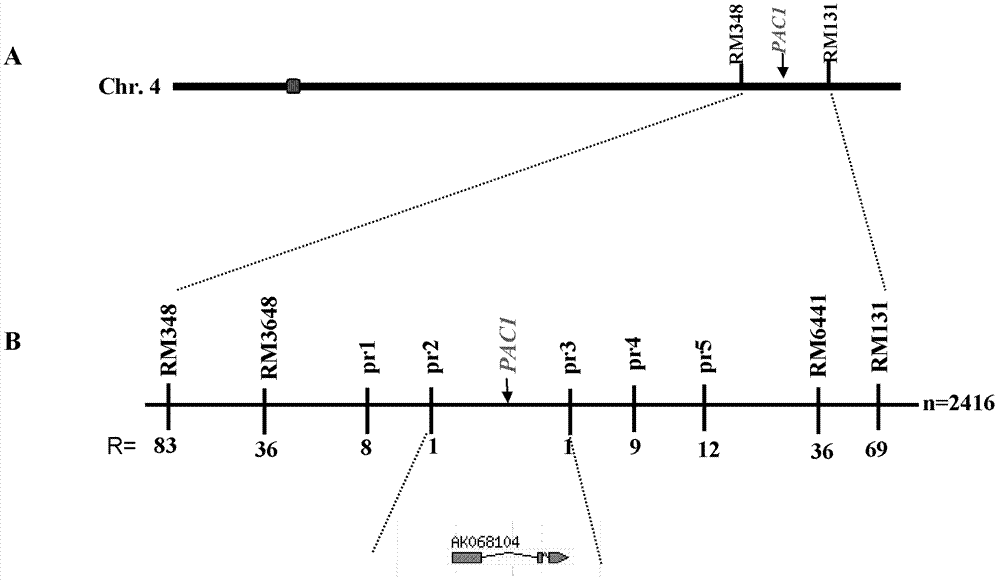
Gene PAC1 for controlling rice panicle and application
InactiveCN103215303AIncrease productionHigh rate of outcrossingPlant peptidesFermentationGenetically modified riceAgricultural science
The invention discloses a gene PAC1 for regulation and control of rice panicle from common wild rice and its protein, and an application of the gene PAC1 and the protein in regulation and control of rice panicle. The application provided by the invention is the application of protein composed by an amino acid sequence shown in a sequence 2 in a sequence table in regulation and control of rice panicle property. The invention also relates to a method for culturing the transgenic rice having panicle ears property, which comprises the following steps: encoding gene composed of the amino acid sequence shown in the sequence 2 in the sequence table is introduced into target paddy rice to obtain the transgenic rice through overexpression of the encoding gene, compared with the target paddy rice, the panicle ears of the transgenic rice are loosening. The experiment proves that the protein composed of the amino acid sequence shown in the sequence 2 in the sequence table enables the rice panicle to turn loose, and is in favor of increasing outcrossing rate and increasing the seed production output of hybrid rice.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
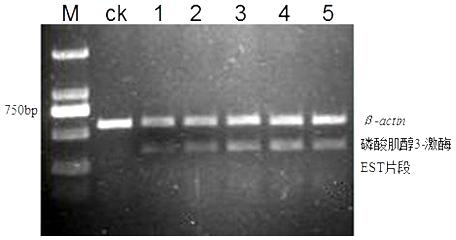
Phosphoinositide 3-kinase EST segment in common wild rice expressed by bacterial blight stress
The invention discloses a phosphoinositide 3-kinase EST segment in common wild rice expressed by bacterial blight stress. The nucleotide sequence of the EST segment is disclosed as SEQ ID NO:1. The invention provides the EST segment for the first time, and the EST directly participates in the anti-disease response process of common wild rice and is a gene directly related to bacterial blight resistance. The EST segment provides partial sequence information for separating and cloning the gene full-length cDNA sequence, and provides theoretical references for researching bacterial blight resistance mechanism of the phosphoinositide 3-kinase in common wild rice. The primer designed by using the EST segment can detection the expression condition of the EST segment by bacterial blight stress in common wild rice leaves, thereby obtaining the expression spectrum of the gene after expression by bacterial blight stress in common wild rice, and laying the foundation for recognizing the functions of the gene and deeply researching the bacterial blight resistance mechanism of the gene in common wild rice.
Owner:云南省农业科学院生物技术与种质资源研究所
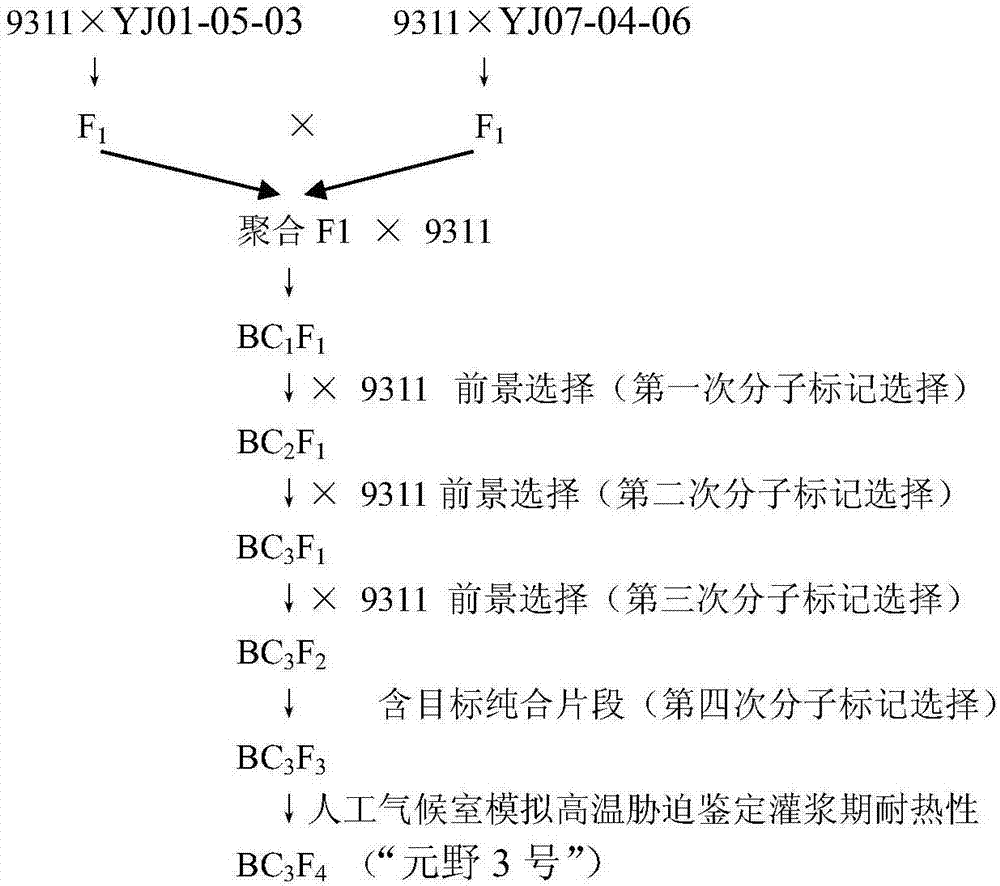
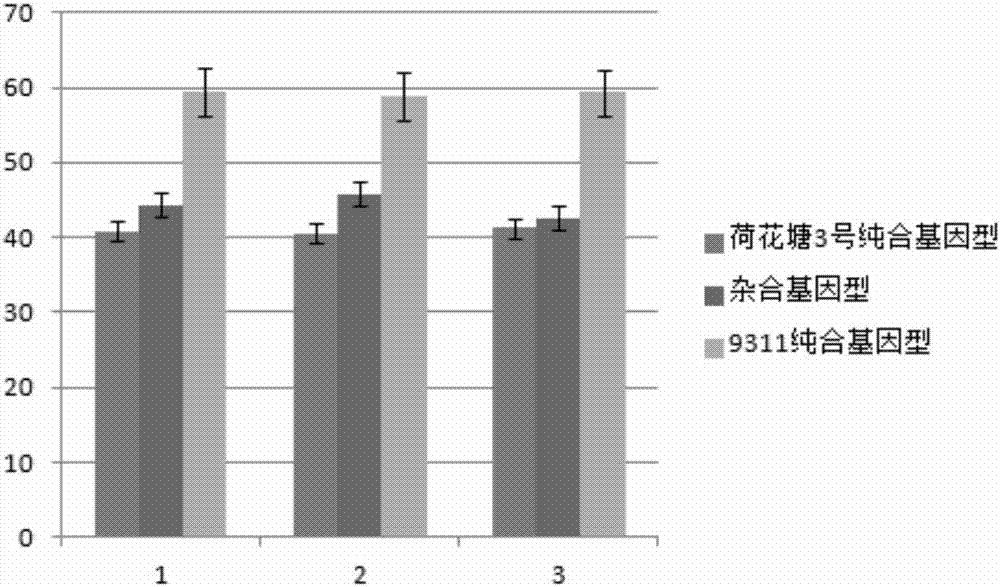
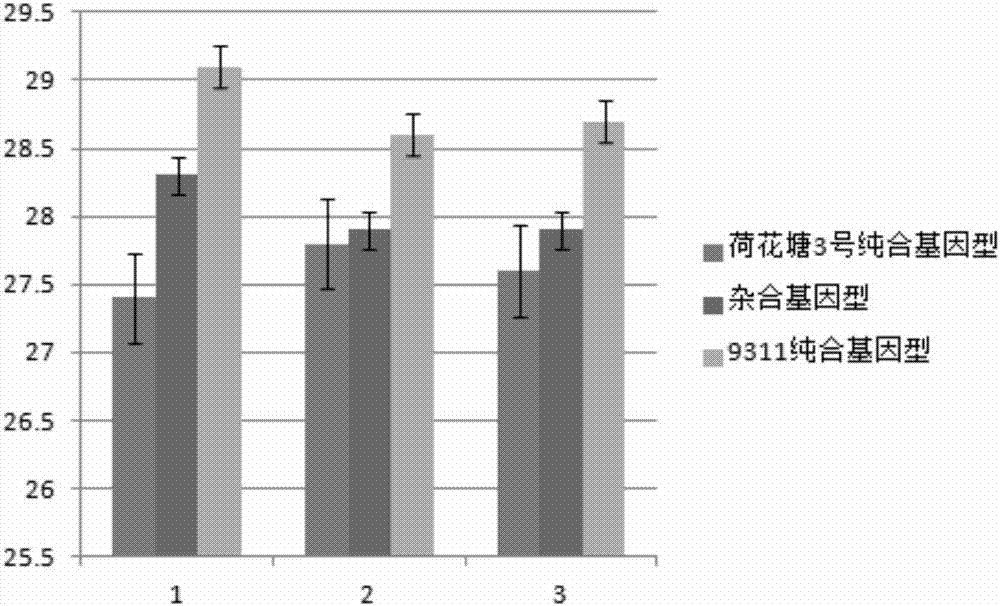
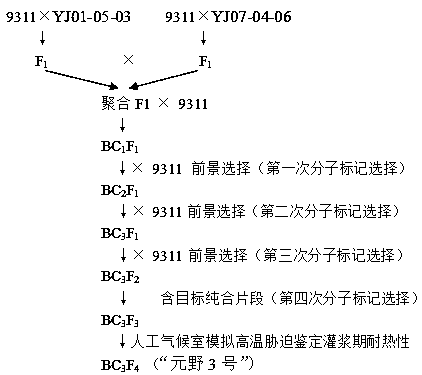
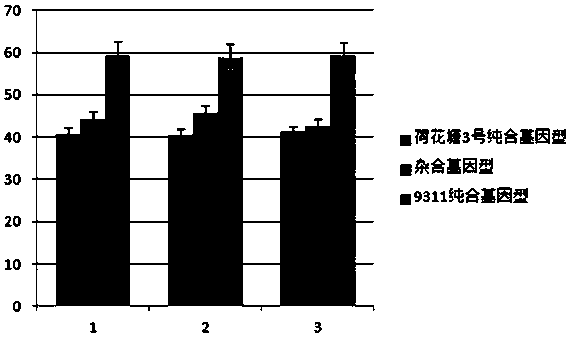
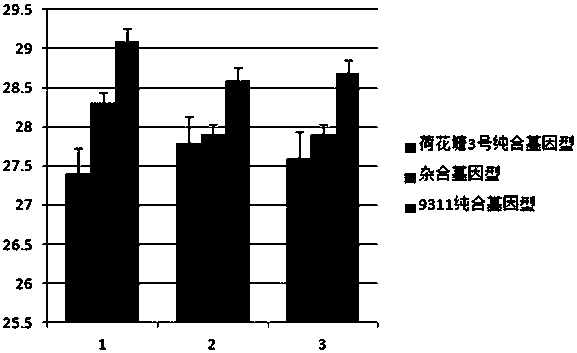
Molecular seed breeding method by using single-fragment substitution line for pyramid-improving heat resistance during heading and flowering stage and filling stage of paddy rice
InactiveCN106947802AIncreased heat resistance at the heading and flowering stageMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant genotype modificationTemperature stressAgricultural science
The invention belongs to molecular seed breeding and relates to a molecular seed breeding method for breeding a new paddy rice variety which has heat resistance during heading and flowering stage and filling stage. The method includes the steps of: 1) with a mid-indica two-line elite restorer line 9311, which is assigned the accession number of CGMCC No.12532, as a female parent, and an F1 generation, which is obtained by hybridizing Yuanjiang common wild rice single-fragment substitution lines YJ07-04-06 and YJ01-05-03 assigned the accession numbers of CGMCC No.12534 and CGMCC No.12535, as a male parent, performing intercross for 1 generation, performing backcross for 3 generations with a recurrent parent, and then performing selfing for 3 generations to obtain a stable homozygous plant strain BC3F4, wherein each generation is harvested in a single spike manner; and 2) identifying and selecting a new paddy rice variety by means of molecule marker assisted selection with combination of phytotron for simulating high temperature stress. By means of the method, a new paddy rice variety "Yuanye No.3" having heat resistance during the heading and flowering stage and filling stage has been cultured. Target characters are selected through molecule marker assistance, so that a restorer line having heat resistance during the heading and flowering stage and filling stage can be cultured within 3-4 years quickly and high-effectively.
Owner:JIANGXI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
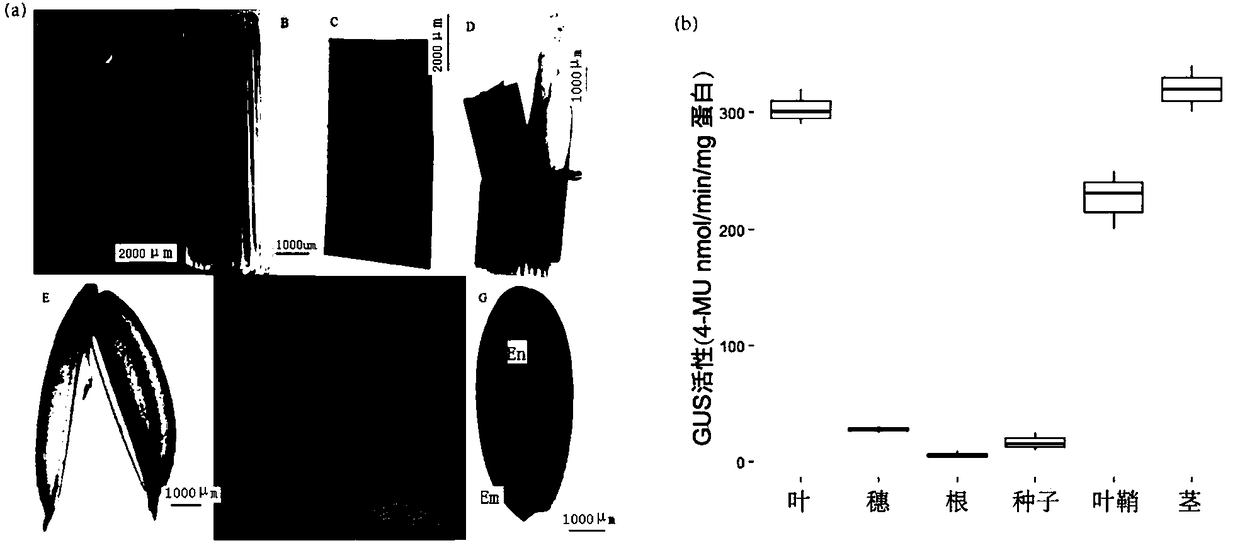
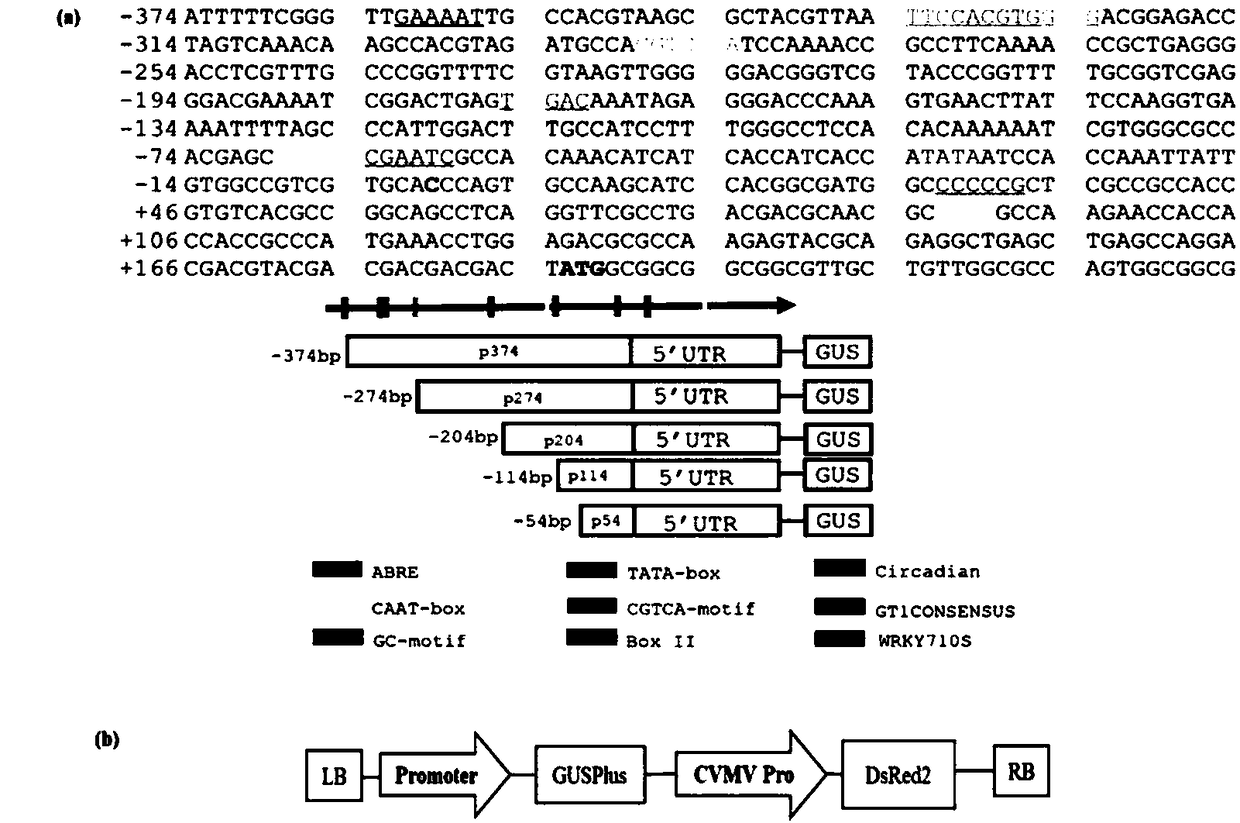
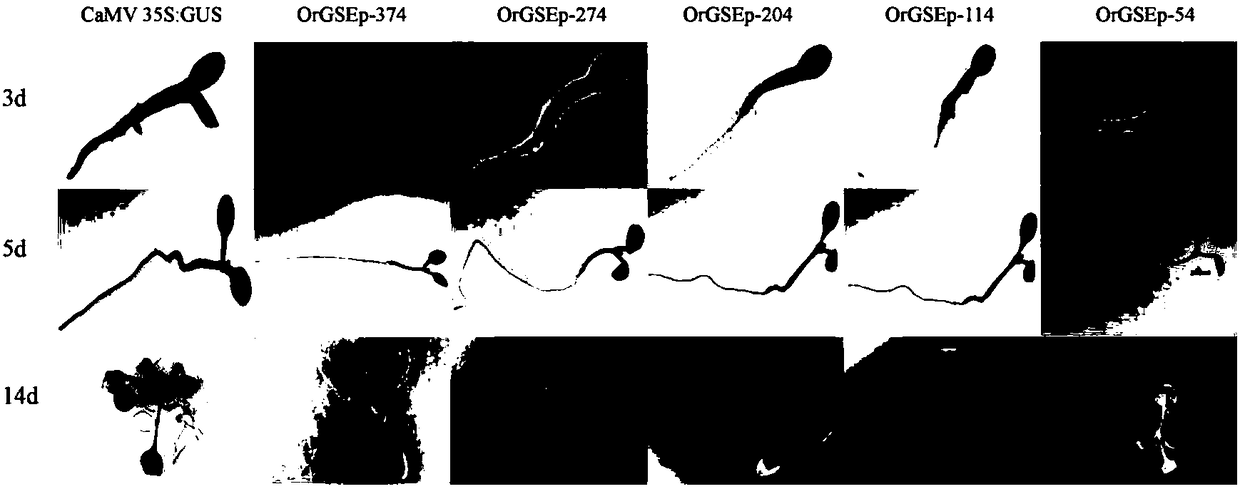
Common wild rice green tissue specific expression gene promoter and application thereof
ActiveCN108588080APlant peptidesVector-based foreign material introductionAgricultural scienceExpression gene
The invention discloses a common wild rice green tissue specific expression gene promoter and application thereof. The invention provides a DNA molecule which is a DNA molecule as follows: 1) a DNA molecule of which an encoding zone is shown in sequence 1 in a sequence table; 2) a DNA molecule of which an encoding zone is shown in sequence 2 in the sequence table; 3) a DNA molecule of which an encoding zone is shown in sequence 3 in the sequence table; 4) a DNA molecule of which an encoding zone is shown in sequence 4 in the sequence table; 5) a DNA molecule which is hybridized with any defined DNA sequence of 1)-4) under a strict condition and has functions same as those of the DNA sequences. The invention finds a novel green tissue specific promoter, and novel regulation and control elements are provided for genetic engineering breeding of rice.
Owner:THE INST OF BIOTECHNOLOGY OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
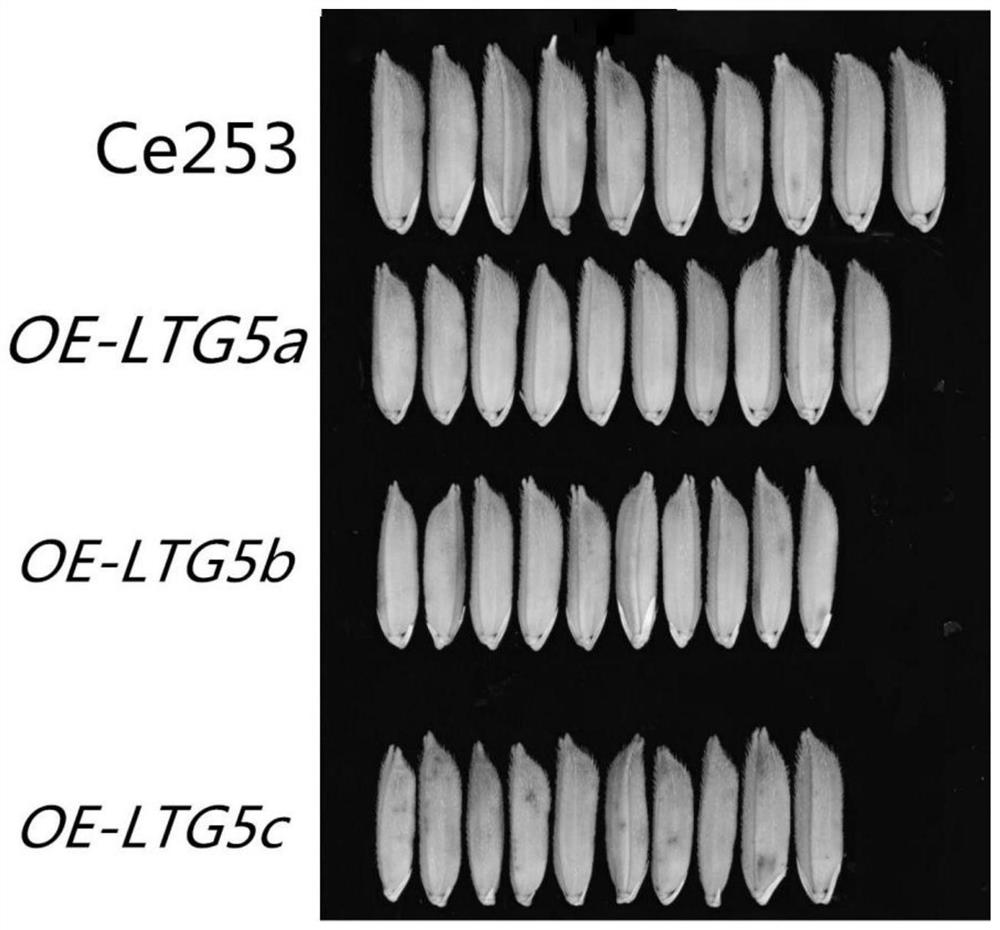
Grain type related coding gene of common wild rice and application thereof
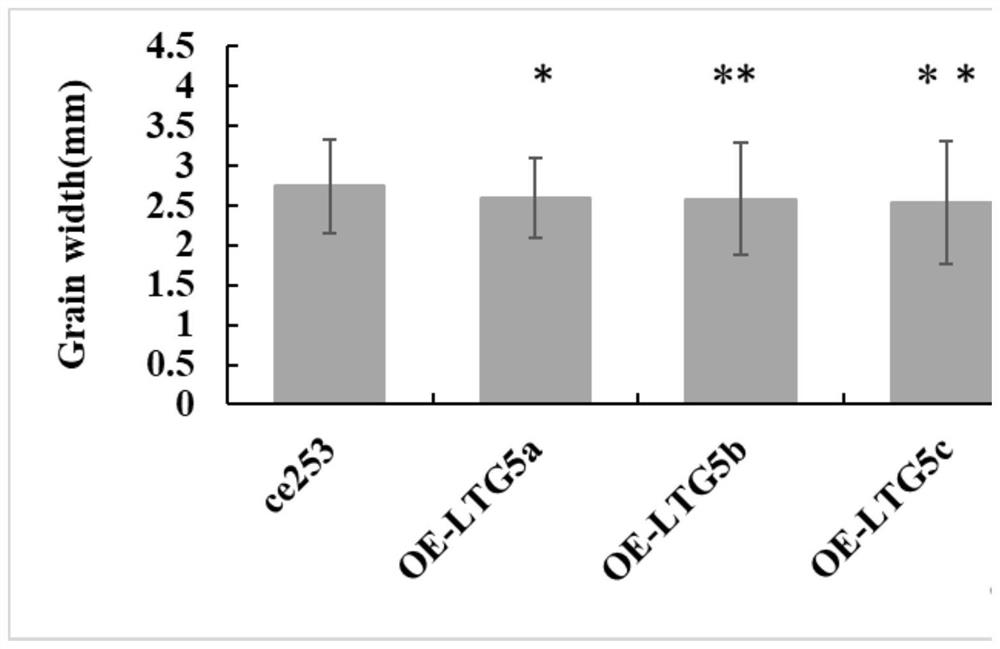
The invention discloses an application of a grain type related coding gene LTG5 of common wild rice in regulating rice grain type. The grain type related coding gene LTG5 of common wild rice is derived from a DNA sequence of Y12 strain of oryza common wild rice (Oryzarufipogon Griff.). The regulation of the rice grain type refers to the regulation of the rice grain type to be shortened and narrowed. The grain type related gene LTG5 of common wild rice is identified for the first time, a wild rice with common grain type can be obtained under the condition of enhanced function or increased expression level of the common wild rice grain type related gene LTG5, and it is proved that common wild rice grain type related gene protein or its protein plays an important role in controlling the common wild rice grain type. The transgenic rice with increased expression of LTG5 gene obtained by the invention is used as a new rice germplasm material, and can be used for studying the grain type ricemechanism and discovering more genes for regulating the grain type development of common wild rice.
Owner:GUANGXI ZHUANG AUTONOMOUS REGION ACAD OF AGRI SCI
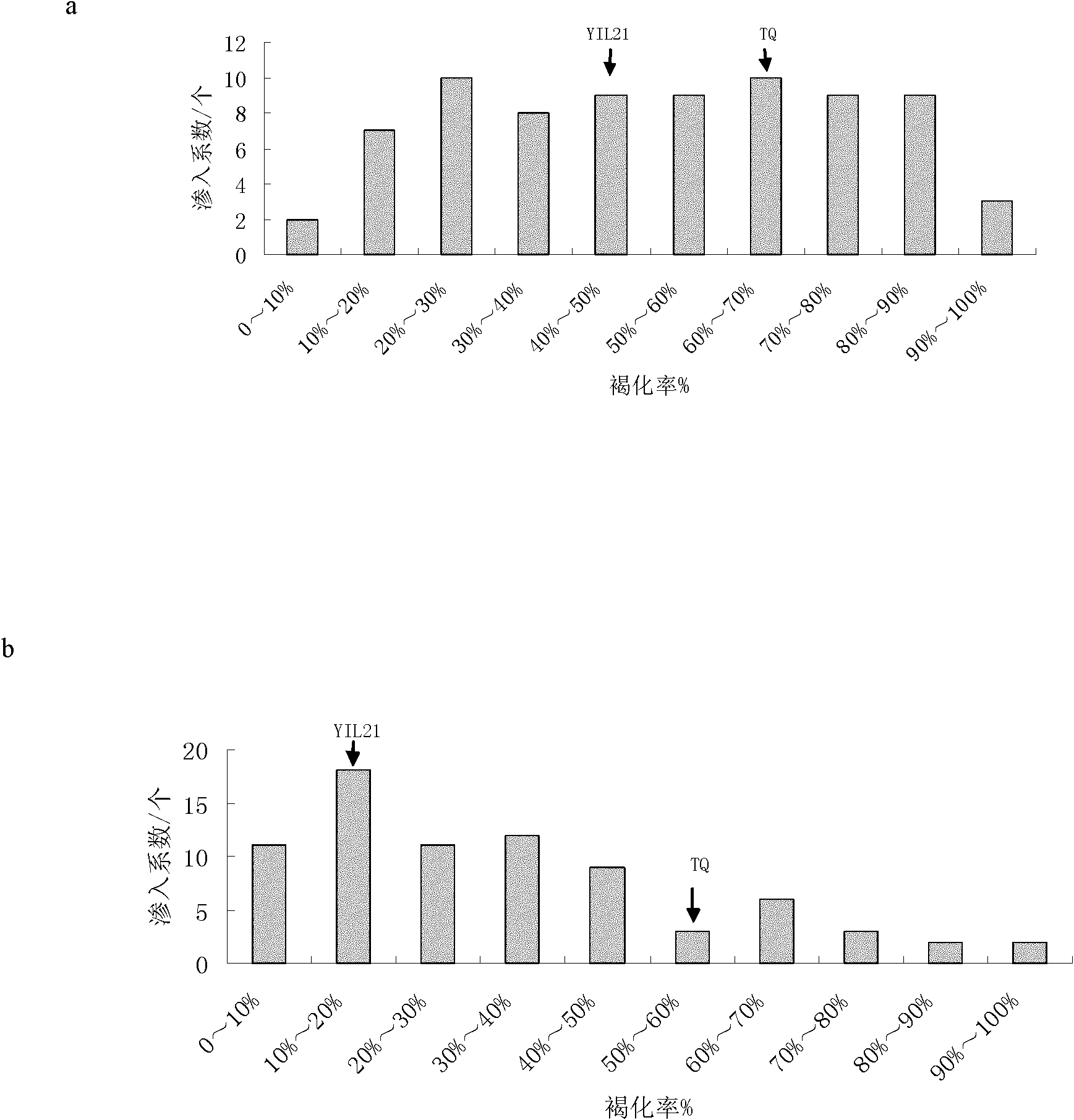
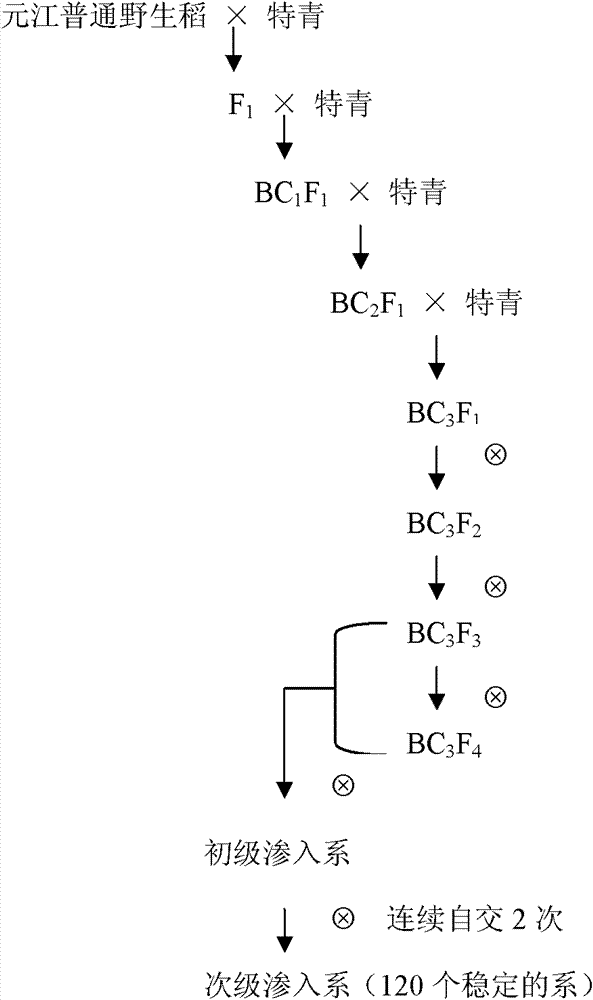
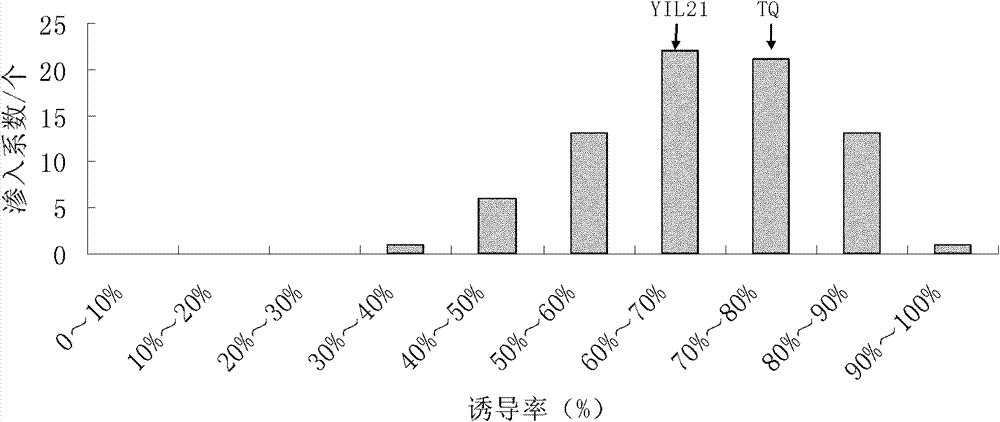
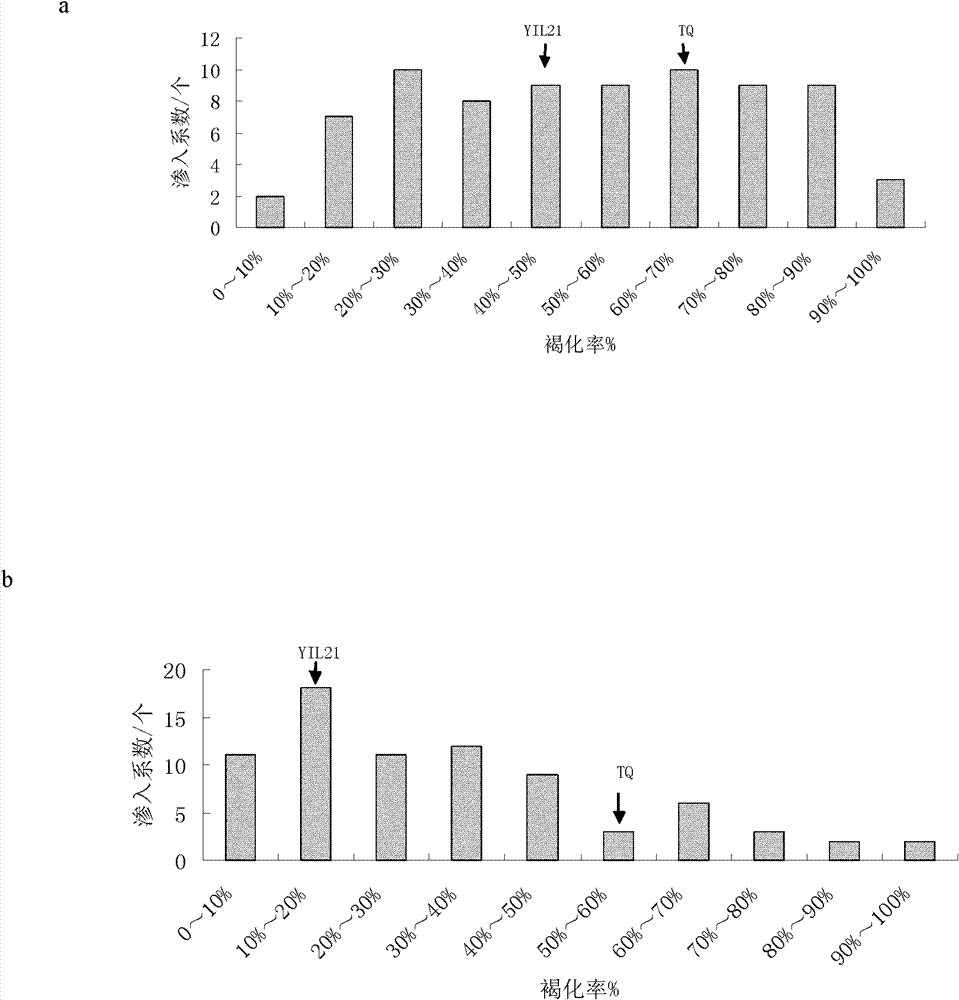
Method for identifying plant introgression line with high tissue culture ability
The invention discloses a method for screening a Yuanjiang common wild rice introgression line material with high tissue culture ability. The method comprises the following steps of: 1) performing inducing culture on seeds of plant introgression lines to be identified to obtain calluses, and counting the inductivity; 2) sequentially subculturing the calluses obtained in step 1) twice to obtain first subcultured calluses and second subcultured calluses respectively, and counting the browning rate of the first subcultured calluses and the browning rate of the second subcultured calluses respectively; and 3) differentiating the calluses obtained in step 2), and counting the differentiation rate. The experiment proves that: Yuanjiang common wild rice and Teqing are utilized to construct an introgression line population, mature embryos of 80 introgression lines are cultured, and phenotype data of characters related to culture abilities of the introgression lines are investigated to screen the line with high culture ability by using the Teqing as control, so that a transgenic receptor with high culture ability can be provided for genetic improvement and functional genome research of rice.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Hybrid rice anther culture method
PendingCN112385544AHigh induction rateImprove germination ratePlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsOryzaSeedling
The invention discloses a hybrid rice anther culture method. The hybrid rice anther culture method comprises the steps of anther collection and pretreatment, anther disinfection and sterilization, anther callus culture, anther differentiation seedling rooting culture, anther seedling hardening and transplantation. According to the hybrid rice anther culture method, the rice anther is pretreated, and resistant callus induction culture and improved culture medium proliferation culture methods are adopted, so that the inductivity and the emergence rate are improved and the resistance of seedlingsis increased during rice anther culture, and the main problems of low anther callus inductivity, low seedling resistance and low emergence rate of conventional rice anther culture are solved. The application of an anther culture technology to crossbreeding practice of common wild rice and cultivated rice is greatly promoted.
Owner:黑龙江省农业科学院绥化分院
A culture medium for inducing embryogenic callus of inbred line of common wild rice in Southeast Asia
ActiveCN105613290BImprove recovery rateImprove the quality of healingHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureSoutheast asiaBiology
The invention provides an induction medium of a selfing line embryonic callus of Southeast Asia common wild rice. The induction medium is obtained by adding specific hormone of specific concentration to the base of a N6D culture medium, and by performing induction culture on the culture medium, a callus rate is improved, a callus diameter is increased and a callus quality is improved.
Owner:广西壮族自治区农业科学院水稻研究所
Potting preservation method for common wild rice seed stems
ActiveCN113455365ASuitable for cultivationBalanced nutritionGrowth substratesCulture mediaAxillary budOryza
The invention provides a potting preservation method for common wild rice seed stems, and relates to the technical field of rice planting. The preservation method comprises the following steps: cutting green stems with white new roots and axillary buds on bases of wild rice seedlings as seed stems; and cultivating and planting the seed stems in pots filled with nutrient soil, and then carrying out daily maintenance and preservation, wherein the nutrient soil comprises the following components in parts by volume: 30-40 parts of moss peat, 15-25 parts of wood fiber, 20-30 parts of coco coir and 10-30 parts of coconut blocks. The preservation method effectively solves the problems of high management difficulty, mechanical mixing, soil hardening, weak plant growth vigor and the like of common wild rice.
Owner:江西省超级水稻研究发展中心
Induction medium of selfing line embryonic callus of Southeast Asia common wild rice
ActiveCN105613290AImprove recovery rateImprove the quality of healingHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureSoutheast asiaSelfing
The invention provides an induction medium of a selfing line embryonic callus of Southeast Asia common wild rice. The induction medium is obtained by adding specific hormone of specific concentration to the base of a N6D culture medium, and by performing induction culture on the culture medium, a callus rate is improved, a callus diameter is increased and a callus quality is improved.
Owner:广西壮族自治区农业科学院水稻研究所
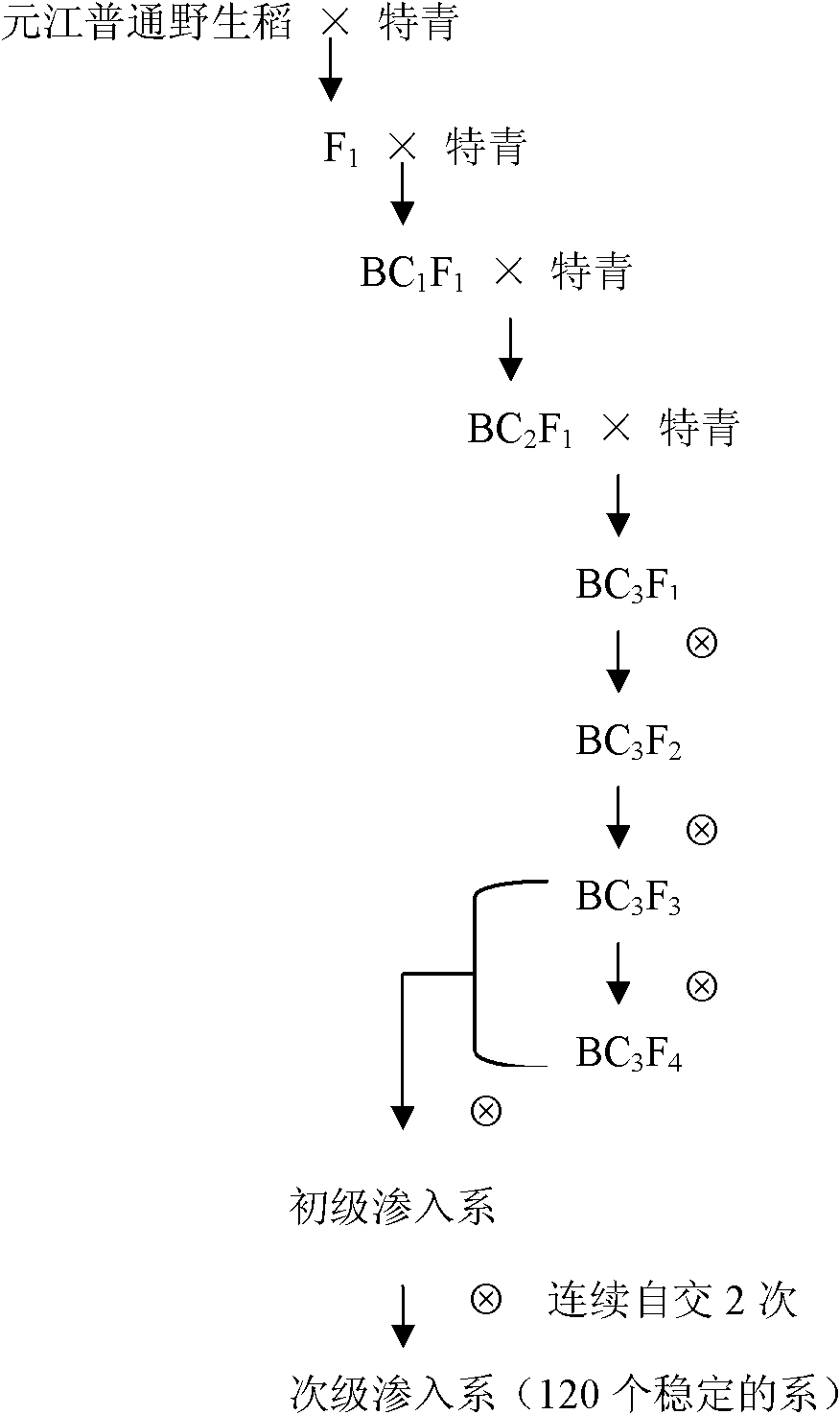
A Molecular Marker and Special Primers Used to Identify the Restorer Line of Cytoplasmic Male Sterile Line of Common Wild Rice in Yuanjiang, Yunnan
InactiveCN103882096BShorten the breeding cycleShort cycleMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceGermplasm
The invention discloses a molecular marker and special primers used for identifying a restorer line of a cytoplasmic male sterile line of common wild rice in Yuanjiang Yunnan. The nucleotide sequence of one of the special primers used for assisting identification of the restorer line of the cytoplasmic male sterile line of the common wild rice in Yuanjiang Yunnan is shown as the sequence 1 in the sequence table, and the nucleotide sequence of the other special primer is shown as the sequence 2 in the sequence table. The molecular marker and the special primers can be used for breeding the restorer line of the cytoplasmic male sterile line of the common wild rice in Yuanjiang Yunnan, shortening the breeding period of three-line hybrid rice containing high-quality genetic resources of the common wild rice in Yuanjiang Yunnan, accelerating the breeding speed, and reducing the breeding cost. The primers and the molecular marker have advantages of simple operation, low cost, and short period, are suitable for popularization and application, and provide a rapid selection method for the restorer line having the genetic background of the common wild rice in Yuanjiang Yunnan.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Molecular marker for identifying fertility of hybrid progeny of common wild rice and cultivated rice and application of molecular marker
The invention discloses a molecular marker for identifying fertility of hybrid progeny of common wild rice and cultivated rice and an application of the molecular marker. The rice molecular marker isnucleotide, corresponding to the 2099th position in sequence 1 of a sequence table, in a rice genome, namely, T or C. Experiments prove that the rice molecular marker is related to fertility of distant hybrid progeny of rice, especially fertility of female gametes; in the hybrid progeny of the common wild rice and the cultivated rice, fertility of TT genotype rice with the rice fertility molecularmarkers in two chromosomes being both T and fertility of TC genotype rice with the rice fertility molecular markers being T in one chromosome and C in the other chromosome are lower than the fertility of CC genotype rice with the rice fertility molecular markers in two chromosomes being both C; the female gametes of the TT genotype rice and the TC genotype rice develop abnormally, while female gametes and male gametes of the CC genotype rice develop normally. Therefore, the molecular marker can be used for detecting the fertility of the distance hybrid progeny of the rice, especially the fertility of the female gametes.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
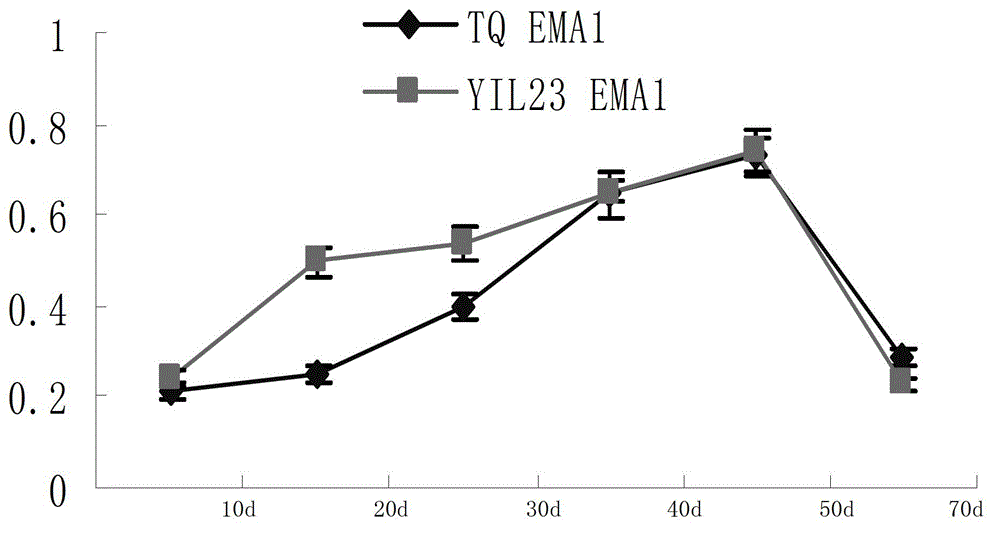
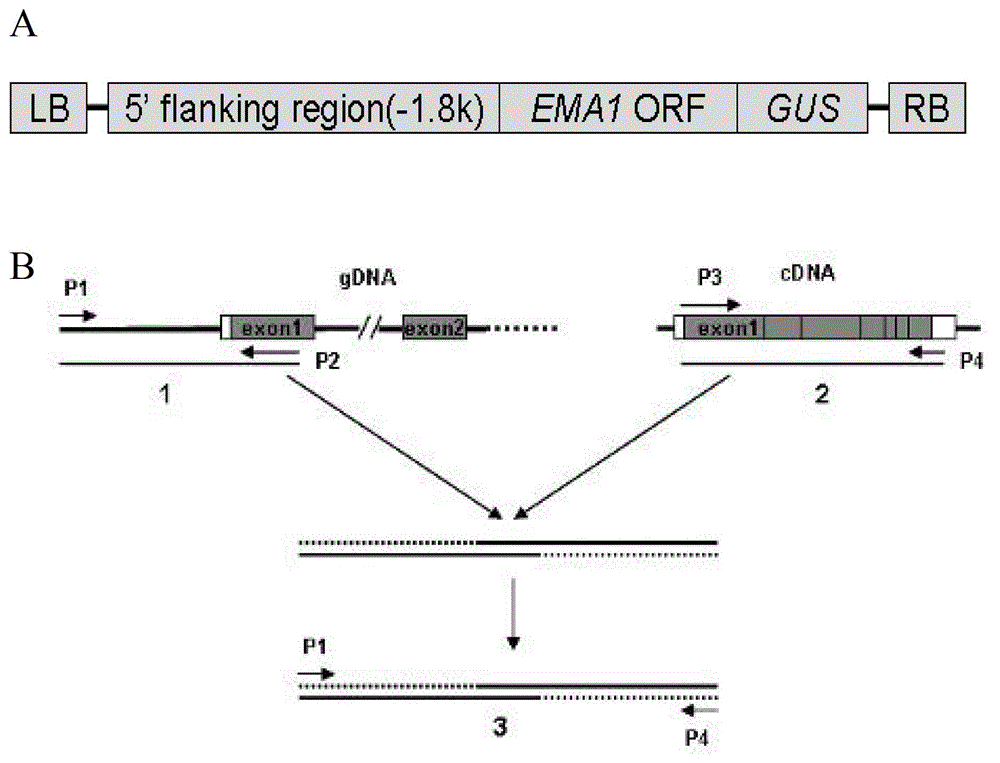
Newborn tissue-specific promoter p-ema1 in rice and its application
The present invention discloses a rice newly-growing tissue specific promoter p-EMA1 and an application thereof. According to the present invention, the promoter is derived from O.rufipogon Griff., and can be the following 1) or 2) or 3) or 4): 1) DNA molecule represented by the 5' terminal nucleotide from site 1 to site 1841 in the sequence 1, 2) DNA molecule represented by the sequence 1, 3) DNA molecule capable of being subjected to hybridization with the DNA sequence limited by the sequence 1 or the sequence 2 and having a promoter function, and 4) DNA molecule having more than 90% homology with the DNA sequence limited by the sequence 1 or the sequence 2 and having a promoter function; important theoretical and practical significance is provided for research on the rice pre-maturing molecular mechanism and breeding of the rice pre-maturing variety; important theoretical and practical significance is provided for research on the molecular mechanism of special rice newly-growing tissue expression and breeding of the special rice newly-growing tissue expression characteristic molecule; and broad application and market prospects are provided in the agriculture field.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
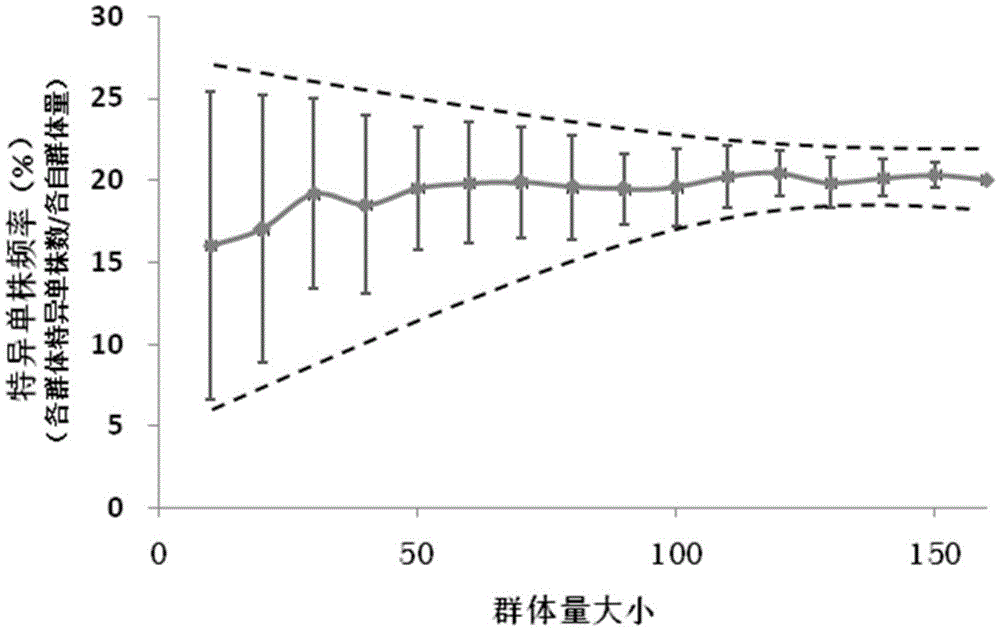
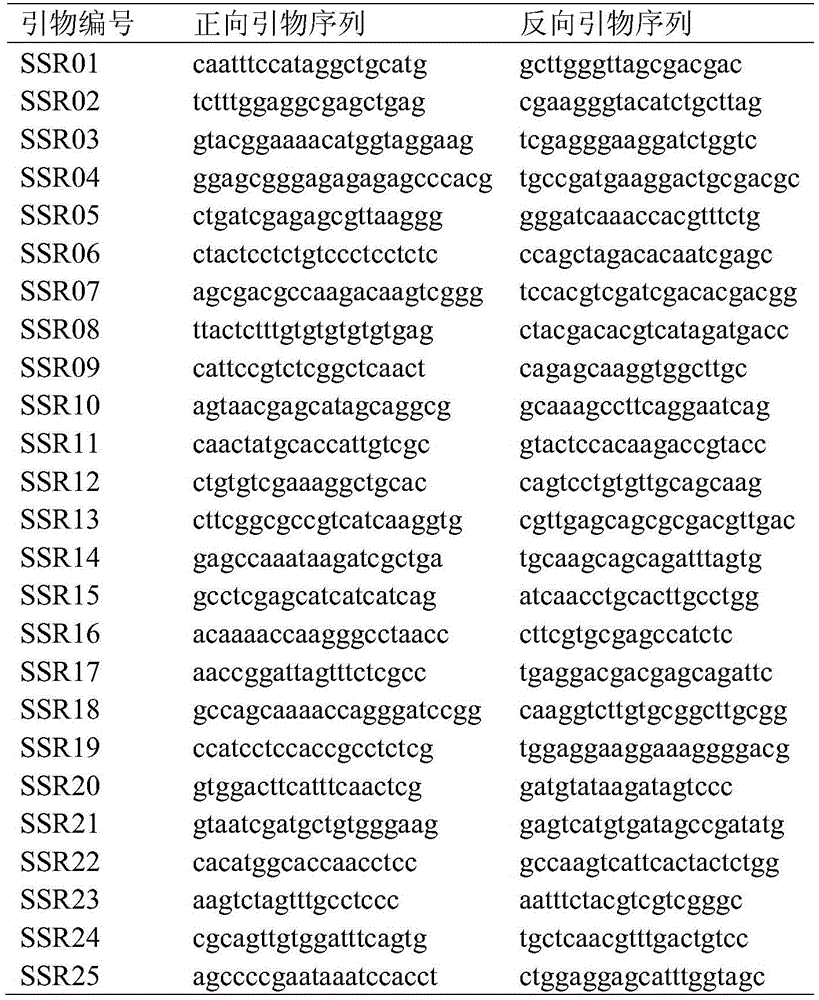
Primer combination for genetic integrity analysis of common wild rice and application of primer combination
The invention relates to genetic integrity analysis primers, and particularly discloses SSR molecular marker core primers for genetic integrity analysis of common wild rice and application of the core primers. A batch of the SSR core primers used for the genetic integrity analysis of the common wild rice are screened out by taking the common wild rice in Jiangxi province as a material through a large number of experimental studies, a primer combination for the genetic integrity analysis of the common wild rice is built, and an analyzing method is built on the basis of the primer combination. The analyzing method is suitable for analyzing the genetic integrity analysis of the common wild rice. Through the group quantity of the screened primer combination and at least 90 single plants, a standard method is supplied to accurate analysis of genetic integrity detection in the germplasm preservation and reproduction updating process of the common wild rice.
Owner:江西省农业科学院水稻研究所 +1
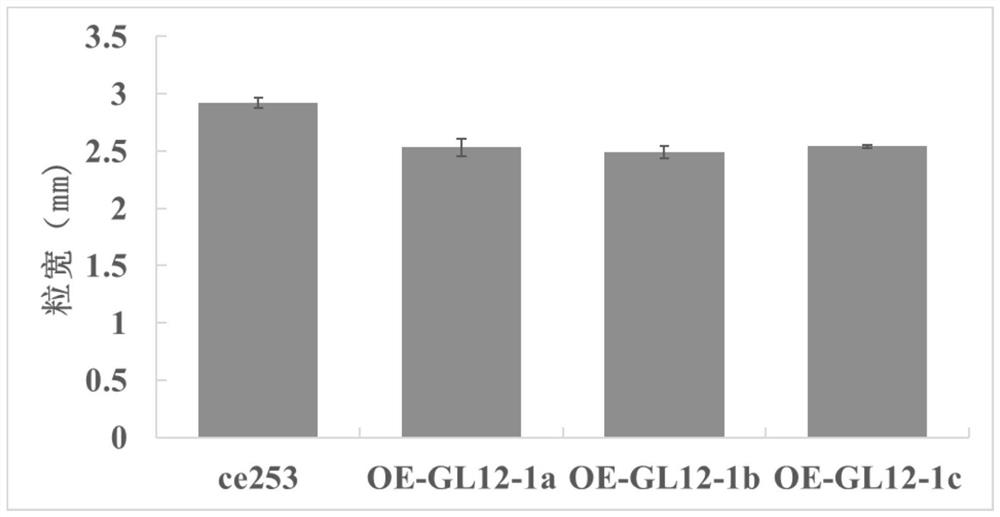
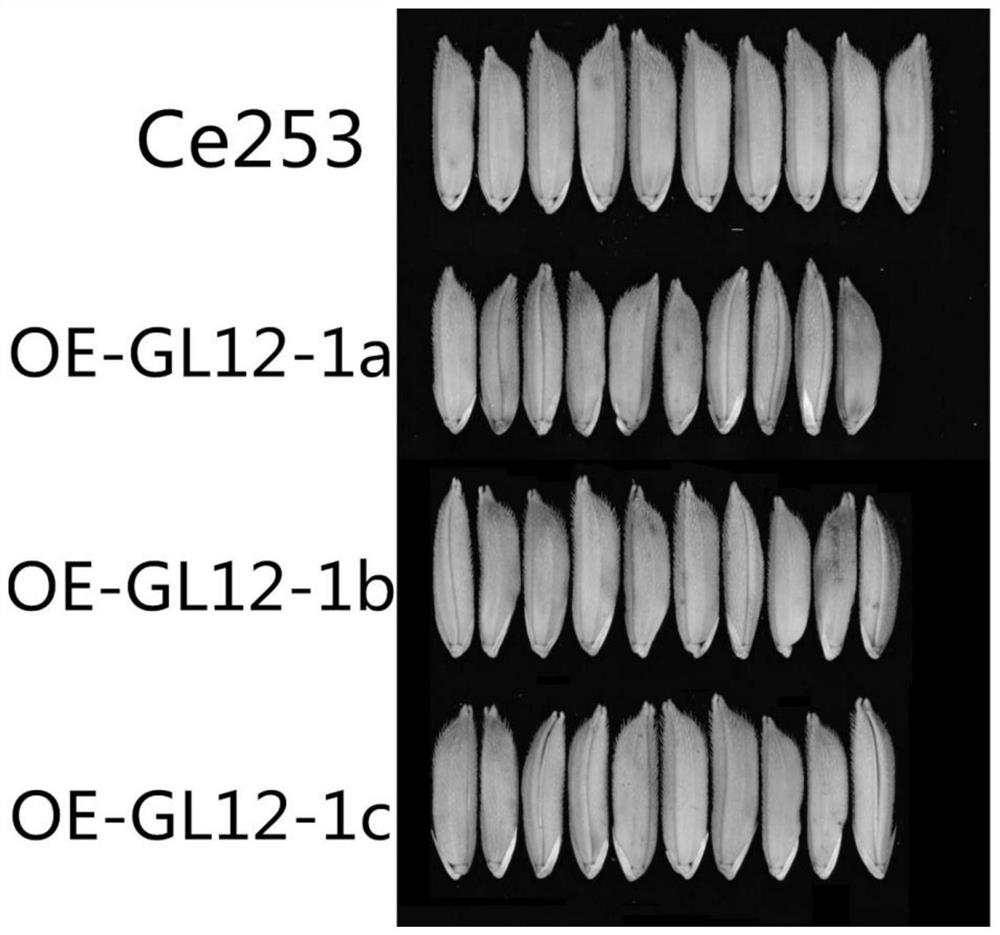
Common wild rice grain shape related coding gene and application thereof
ActiveCN112501147AHydrolasesVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyGenetically modified rice
The invention discloses an application of a common wild rice grain shape related coding gene GL12-1 in regulation and control of a rice grain shape. The common wild rice grain shape related coding gene GL12-1 is derived from a DNA sequence of a Y12 strain of oryza common wild rice (Oryzarufipogon Griff.), and the regulation and control of the rice grain shape refers to the regulation and control of the rice grain shape to be shortened and narrowed. According to the coding gene, the common wild rice grain shape related gene GL12-1 is identified for the first time, and the grain shape related common wild rice can be obtained by the GL12-1 under the condition of function enhancement or expression quantity increase, so that the common wild rice grain shape related gene protein or the protein thereof is proved to play an important role in controlling the common wild rice grain shape; the transgenic rice with increased GL12-1 gene expression obtained by the invention is used as a new rice germplasm material, and can be used for researching the grain shape rice mechanism and discovering more genes for regulating and controlling the grain shape development of common wild rice.
Owner:GUANGXI ZHUANG AUTONOMOUS REGION ACAD OF AGRI SCI
A kind of common wild rice tissue culture rapid propagation method
ActiveCN107333653BIncrease the multiplication factorImprove seedling qualityHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureAloe arborescensWheat germ
The invention relates to the technical field of rapid propagation of plants, in particular to a rapid propagation method of Oryzarufipogon Griff by tissue culture. The method comprises the steps as follows: selecting and disinfecting rice seeds; inoculating the seeds into a culture medium containing seaweed extracts to obtain sterile test tube seedlings; inoculating the test tube seedlings into a medium containing aloe extracts to obtain cluster buds; inoculating the cluster buds into a medium containing wheat germ extracts to obtain robust plants; transplanting the robust plants into a medium containing chlorella extracts for culture to obtain complete plants with roots. Compared with a traditional method, the method has the advantages that by optimizing the medium at each stage of rapid propagation, the germination rate of the wild rice seeds is further increased, propagation and differentiation of the cluster buds are promoted, rooting capacity of new plants is enhanced, obtained new seedlings grow well and are robust, and the success rate of rapid propagation of tissue culture of wild rice is significantly increased.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Gene PAC1 for controlling rice panicle and application
InactiveCN103215303BIncrease productionHigh rate of outcrossingPlant peptidesFermentationGenetically modified riceAgricultural science
The invention discloses a gene PAC1 for regulation and control of rice panicle from common wild rice and its protein, and an application of the gene PAC1 and the protein in regulation and control of rice panicle. The application provided by the invention is the application of protein composed by an amino acid sequence shown in a sequence 2 in a sequence table in regulation and control of rice panicle property. The invention also relates to a method for culturing the transgenic rice having panicle ears property, which comprises the following steps: encoding gene composed of the amino acid sequence shown in the sequence 2 in the sequence table is introduced into target paddy rice to obtain the transgenic rice through overexpression of the encoding gene, compared with the target paddy rice, the panicle ears of the transgenic rice are loosening. The experiment proves that the protein composed of the amino acid sequence shown in the sequence 2 in the sequence table enables the rice panicle to turn loose, and is in favor of increasing outcrossing rate and increasing the seed production output of hybrid rice.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
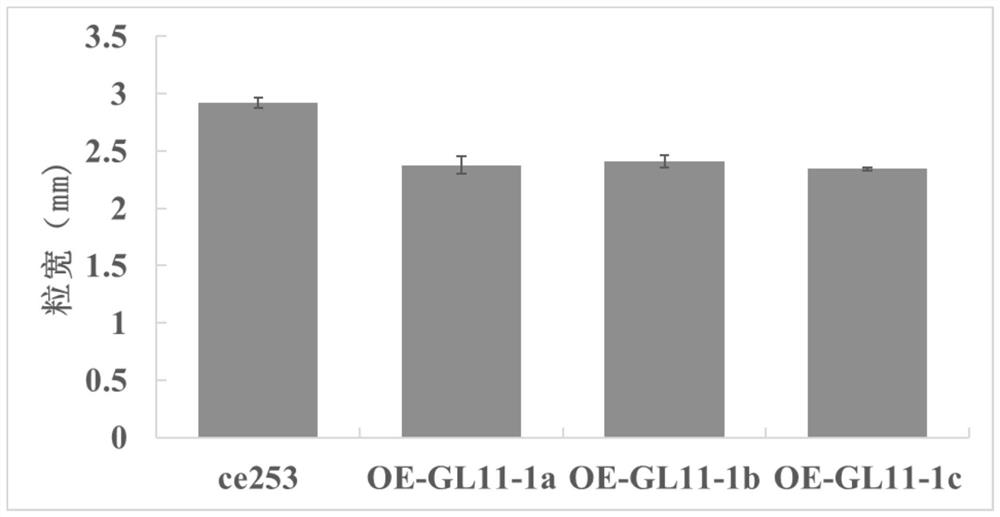
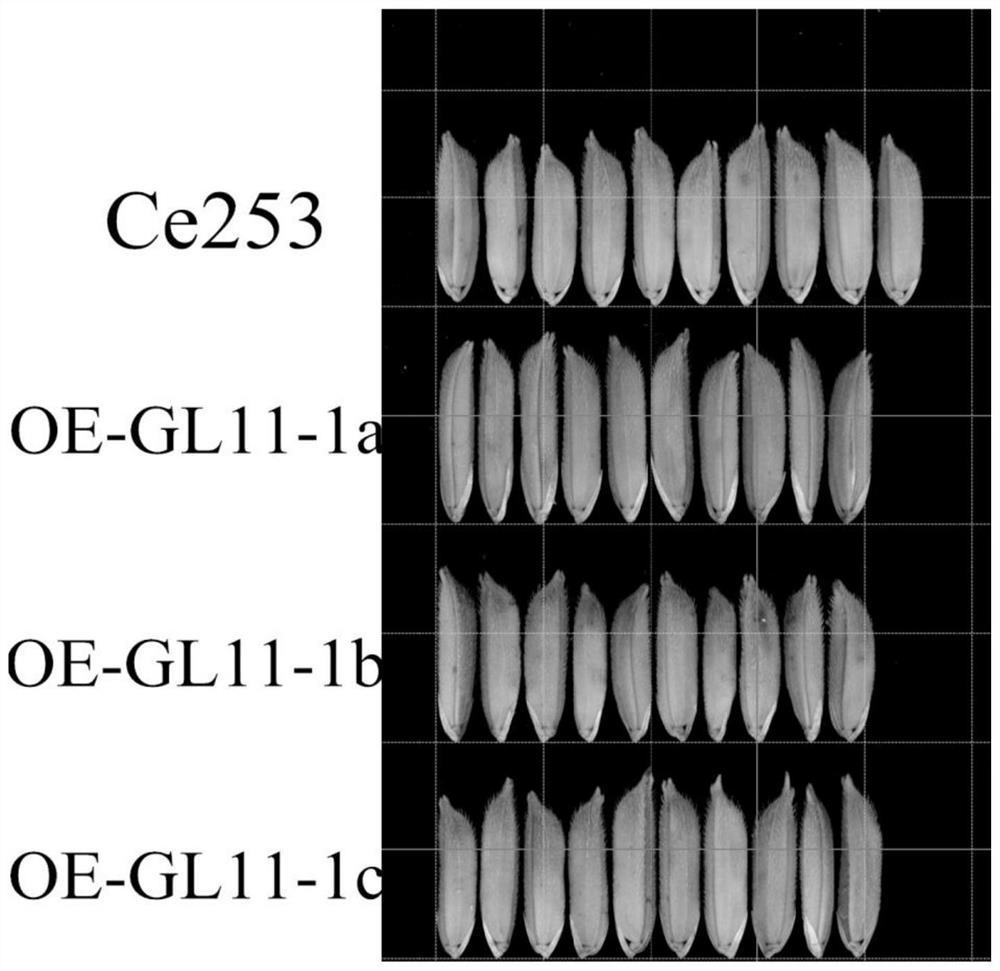
Encoding gene related to grain shape of common wild rice and application thereof
The invention discloses an application of an encoding gene GL11-1 related to a grain shape of common wild rice in regulation and control of grain shape of rice. The encoding gene GL11-1 is derived from a DNA sequence of a Y12 strain of Oryzarufipogon Griff.; and the regulation and control of the rice grain shape refers to regulation and control of rice grain shape to be shortened and narrowed. The gene GL11-1 related to grain shape of common wild rice is identified for the first time, under conditions of enhanced function or increased expression of gene GL11-1, common wild rice with shorter and narrower grain shape can be obtained, and it is proved that common wild rice grain type related gene protein or the protein thereof plays an important role in controlling grain shape of common wild rice.
Owner:GUANGXI ZHUANG AUTONOMOUS REGION ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for identifying plant introgression line with high tissue culture ability
The invention discloses a method for screening a Yuanjiang common wild rice introgression line material with high tissue culture ability. The method comprises the following steps of: 1) performing inducing culture on seeds of plant introgression lines to be identified to obtain calluses, and counting the inductivity; 2) sequentially subculturing the calluses obtained in step 1) twice to obtain first subcultured calluses and second subcultured calluses respectively, and counting the browning rate of the first subcultured calluses and the browning rate of the second subcultured calluses respectively; and 3) differentiating the calluses obtained in step 2), and counting the differentiation rate. The experiment proves that: Yuanjiang common wild rice and Teqing are utilized to construct an introgression line population, mature embryos of 80 introgression lines are cultured, and phenotype data of characters related to culture abilities of the introgression lines are investigated to screen the line with high culture ability by using the Teqing as control, so that a transgenic receptor with high culture ability can be provided for genetic improvement and functional genome research of rice.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
A molecular marker and special primers used for identifying a restorer line of a cytoplasmic male sterile line of common wild rice in Yuanjiang Yunnan
InactiveCN103882096AShorten the breeding cycleShort cycleMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceGermplasm
The invention discloses a molecular marker and special primers used for identifying a restorer line of a cytoplasmic male sterile line of common wild rice in Yuanjiang Yunnan. The nucleotide sequence of one of the special primers used for assisting identification of the restorer line of the cytoplasmic male sterile line of the common wild rice in Yuanjiang Yunnan is shown as the sequence 1 in the sequence table, and the nucleotide sequence of the other special primer is shown as the sequence 2 in the sequence table. The molecular marker and the special primers can be used for breeding the restorer line of the cytoplasmic male sterile line of the common wild rice in Yuanjiang Yunnan, shortening the breeding period of three-line hybrid rice containing high-quality genetic resources of the common wild rice in Yuanjiang Yunnan, accelerating the breeding speed, and reducing the breeding cost. The primers and the molecular marker have advantages of simple operation, low cost, and short period, are suitable for popularization and application, and provide a rapid selection method for the restorer line having the genetic background of the common wild rice in Yuanjiang Yunnan.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
A method for improving the anther culture efficiency of common wild rice hybrid progeny
InactiveCN104542299BImprove breeding efficiencySpeed up the breeding processPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsBiologyObserved Survival
The invention relates to a method for improving the culture efficiency of the anther of the filial generation of Oryza rufipogon, and belongs to the field of a plant tissue culture technology. The method for improving the culture efficiency of the anther of the filial generation of the Oryza rufipogon comprises the following steps: selecting an explant, sterilizing the explant, inducing an anther derived callus by use of fluid suspension, performing multiplication culture on the anther derived callus, performing differentiation culture on the anther derived callus, performing rooting culture on a differentiated seedling (anther cultured seedling), hardening the seedling and transplanting. According to the method, the anther is inoculated in a fluid nutrient medium to be subjected to suspension culture, the callus induction rate is improved, the callus is transferred onto a multiplying medium to be subjected to the multiplication culture, the quality of the callus is improved and the quantity of the callus is increased. The method has the advantages that the callus induction rate and the seedling survival rate in the anther culture of the filial generation of the Oryza rufipogon are improved greatly, the rice breeding process is accelerated, the breeding efficiency of the good rice variety is improved, and the method can provide a powerful technical support for acceleration of breeding of rice varieties by use of good genes of the Oryza rufipogon.
Owner:云南省农业科学院生物技术与种质资源研究所
A molecule breeding method for improving heat resistance of rice heading and flowering stage and filling stage by utilizing single-segment substitution line polymerization
InactiveCN108703063AIncreased heat resistance at the heading and flowering stageMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant genotype modificationTemperature stressAgricultural science
The invention belongs to the field of molecule breeding and relates to a molecule breeding method for cultivating rice with heat resistance which is increased heading and flowering stage and grain filling stage. The method includes the following steps: a middle indica rice two-line elite restorer lines restorer 9311 with the accession number CGMCC No.12532 is served as female parent, single-segment substitution lines, YJ-07-04-06 and YJ01-05-03, of Yuanjiang common wild rice are hybridized to obtain a F1 as parent, the female parent and the parent are intercrossed for one generation, backcrossed is performed for three generations with the recurrent parent, and then self-cross is performed for three generations to obtain the stable homozygous plant line BC3F4, and each generation is harvested with single spike; and the new rice line is identified and obtained by the molecule mark auxiliary selection combined with the phytotron simulation high temperature stress. Yuan ye no.3 with substantial heat resistance of the rice heading flowering stage and grain filling stage is cultivated by utilizing the method. The character of the target is selected through the molecule mark auxiliary, and the heat resistance restorer of the heading and flowering stage and grain filling stage can be rapidly and efficiently cultivated in 3-4 years.
Owner:JIANGXI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
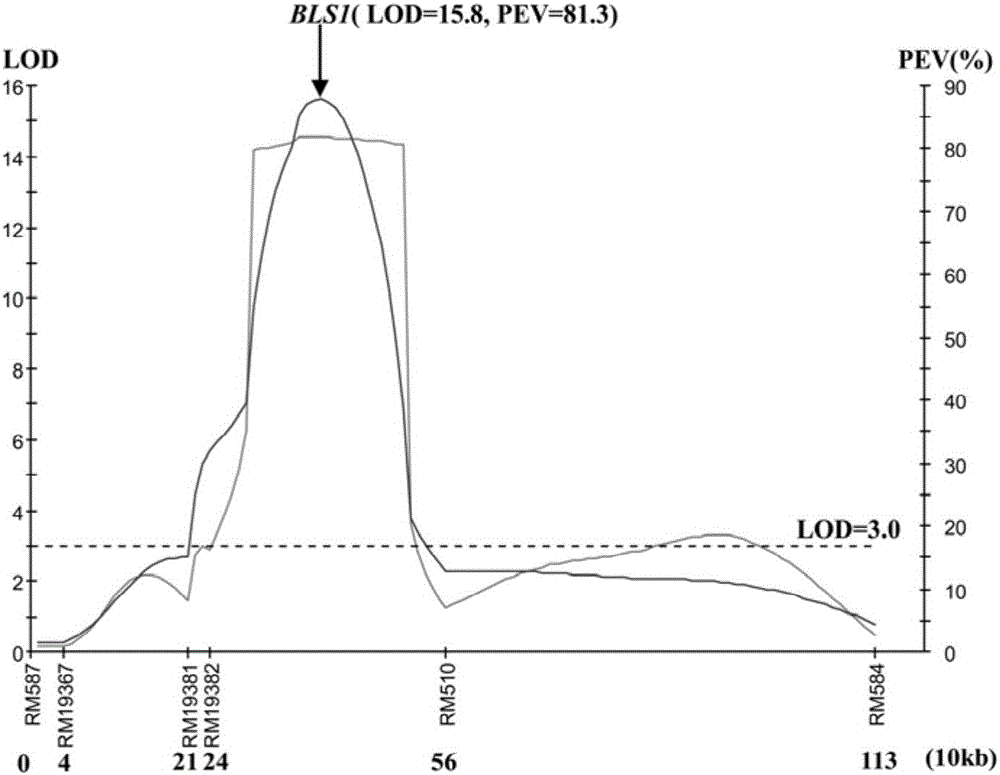
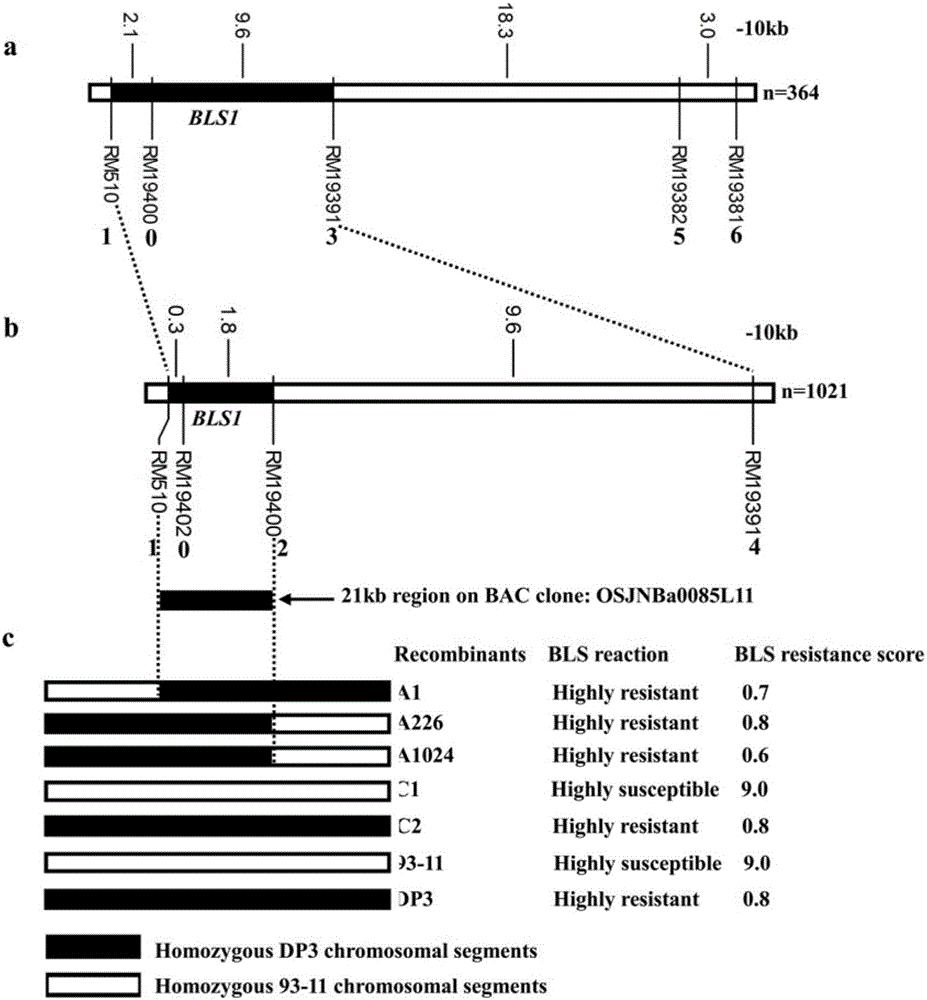
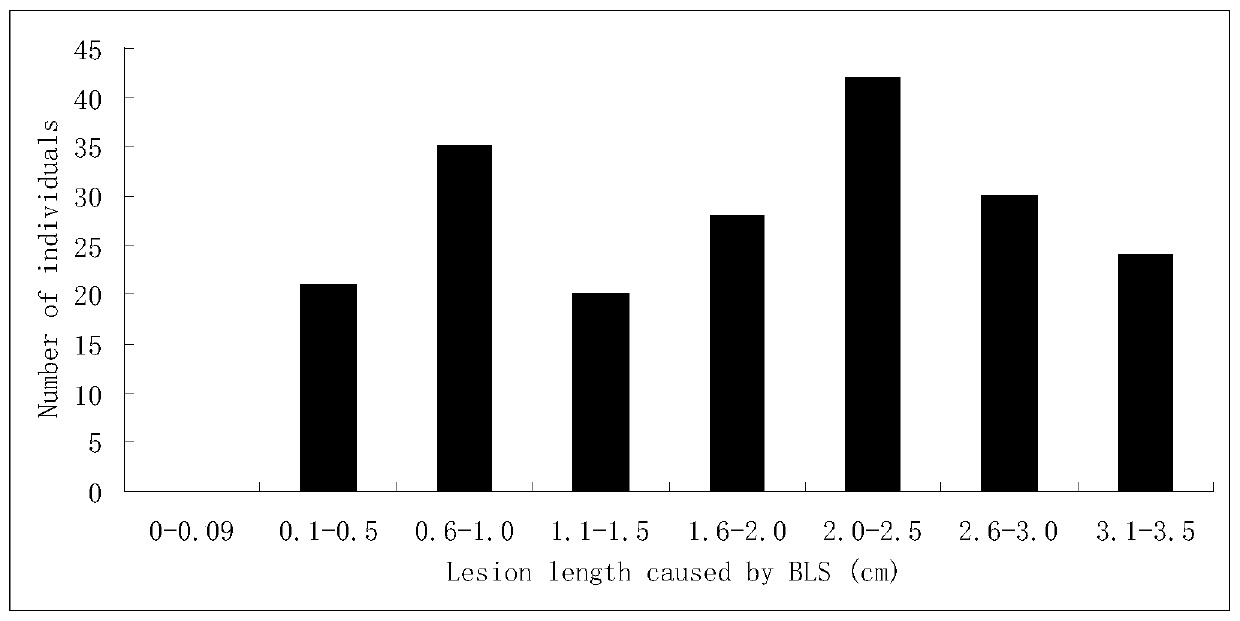
Molecular Marker and Application of Rice Bacterial Spot Resistance Main Gene bls1 Locus
ActiveCN106011287BShorten the breeding cycleLow reliabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyOryza
The invention discloses a molecular marker for a bacterial stripe resisting major gene BLS1 locus of rice and an application of the molecular marker. Specific steps for screening are as follows: (1) constructing a positioned segregation population, so as to obtain an approximate isogenic line F2 of the positioned segregation population; (2) extracting genomic DNA of rice leaves of each single strain of parents and a F2 population by adopting a CTAB method so as to carry out SSR molecular marker analysis; (3) preliminarily positioning a gene BLS1 in a region between RM19382 and RM510; (4) carrying out BLS1 close-linkage marking: carrying out detection and analysis after carrying out molecular marking by several kinds of marking primers, so as to position the BLS1 in a physical range, i.e., 21-kb between RM19400 and RM510. The molecular marker is applied to the selective breeding of bacterial stripe resisting rice varieties or the screening of resistant genetic resources. The molecular marker disclosed by the invention can be used for effectively detecting whether ordinary bacterial stripe resisting wild rice DP3 and derived varieties (lines) thereof contain the major gene locus or not, the efficiency of selection of bacterial stripe resisting rice is increased, and the bacterial stripe resisting rice varieties containing the gene BLS1 are obtained.
Owner:广西壮族自治区农业科学院水稻研究所
Common wild rice root-specific promoter orrsgp and its application
The invention discloses a common wild rice root specific promoter OrRSGp and application thereof. The invention provides a DNA molecule which is any one of NDA molecules of 1)-3) as follows: 1) a DNAmolecule of which an encoding zone is shown in sequence 1 in a sequence table; 2) a DNA molecule which is hybridized with a DNA sequence defined by 1) under a strict condition and has functions same as those of the DNA sequence; 3) a DNA molecule which has at least 70%, 75%, 80%, 85%, 90%, 95%, 96%, 97%, 98% or 99% of homology with the DNA sequence defined by 1) and has functions same as those ofthe DNA sequence. According to the common wild rice root specific promoter OrRSGp, one root specific promoter is obtained from a common wild rice genome through separation, and transgenosis GUS analysis shows that a segment of the promoter has a root-specific activity.
Owner:THE INST OF BIOTECHNOLOGY OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com