Method for constructing suppression subtractive hybridization (SSH) library of oryza rufipogon threatened by bacterial blight germs
A bacterial blight bacteria and library construction technology, applied in the direction of microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, chemical libraries, etc., can solve the problems of no patents and achieve high sensitivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0047] Example 1 A method for constructing a common wild rice SSH library under bacterial blight stress, comprising the following steps:
[0048] (1) Inoculation treatment of common wild rice leaf material
[0049] ① Streak the strains C1 and Y8 of bacterial blight on the NA medium plate, and incubate at 28°C for 2-3 days for activation. Turbidimetric method prepared to 6 × 10 8 ·ml -1 the bacterial liquid;
[0050] ② After 15:00 in the afternoon, use the scissors dipped in the bacterial solution to subtract 2-3 cm from the tip of the leaf to inoculate the leaves of common wild rice with bacterial blight in the greenhouse, and each strain is inoculated with 3 pier , 30 leaves, the control is to inoculate common wild rice leaves with sterile water instead of bacterial solution, and inoculate with sterile water as a control;
[0051] ③Samples were taken every 24 hours after inoculation, that is, at 24 hours, 48 hours, 72 hours, 96 hours, 120 hours, and 144 hours. Quick-fr...
Embodiment 2
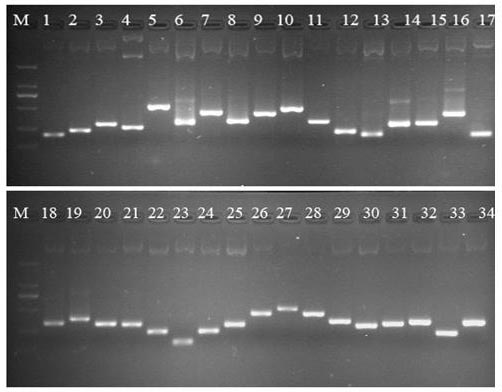
[0081] Example 2 Detection of the size of the inserted cDNA fragment in the common wild rice SSH library under bacterial blight stress constructed by the present invention
[0082] (1) 34 positive clones were randomly selected from the constructed Oryza sativa SSH library, inoculated in LB liquid medium containing AMP antibiotics, and cultured overnight at 28°C with shaking at 180 rpm;
[0083] (2) Extract plasmids from 34 positive clones by alkaline lysis;
[0084] (3) Use the plasmid extracted in step (2) as a template to establish a PCR reaction system: 5.0 μl of 10×PCR buffer, MgCl 2 3 μl, dNTP 4 μl, Nested PCR primer F 1 μl, Nested PCR primer R 1 μl, Taq polymerase 0.5 μl, plasmid template 1 μl, sterile water to make up the reaction volume of 50 μl;
[0085] (4) PCR reaction program: pre-denaturation at 94°C for 5 min, followed by denaturation at 94°C for 35 s, annealing at 55°C for 30 s, extension at 72°C for 1 min, a total of 35 cycles, and a final extension at 72°C f...
Embodiment 3
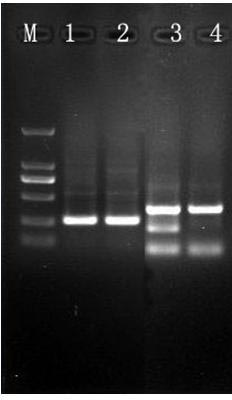
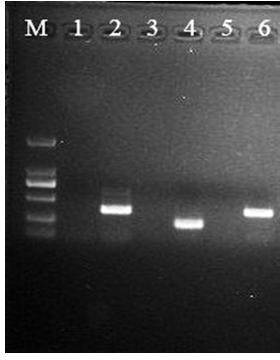
[0088] Example 3 Application of the common wild rice SSH library constructed in Example 1 under bacterial blight stress
[0089] The steps are as follows:
[0090] (1) Inoculate all the single clones from the SSH library constructed in Example 1 in LB liquid medium containing AMP antibiotics, culture overnight at 28°C with shaking at 180 rpm;
[0091] (2) Send the bacterial liquid to Huada Gene Company for sequencing. The DNAStar software is used to remove the carrier of the sequencing results, and the ContigExpress software is used for sequence splicing to remove repetitive sequences;
[0092] (3) Compare and analyze the non-redundant sequences in the protein database and nucleic acid database in NCBI (http: / / www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov), the National Center for Biological Information of the United States, respectively, and the judgment standards refer to rice, In the EST research of Arabidopsis, the consistency of blastx results is greater than 40%, and the score is greater than 8...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com