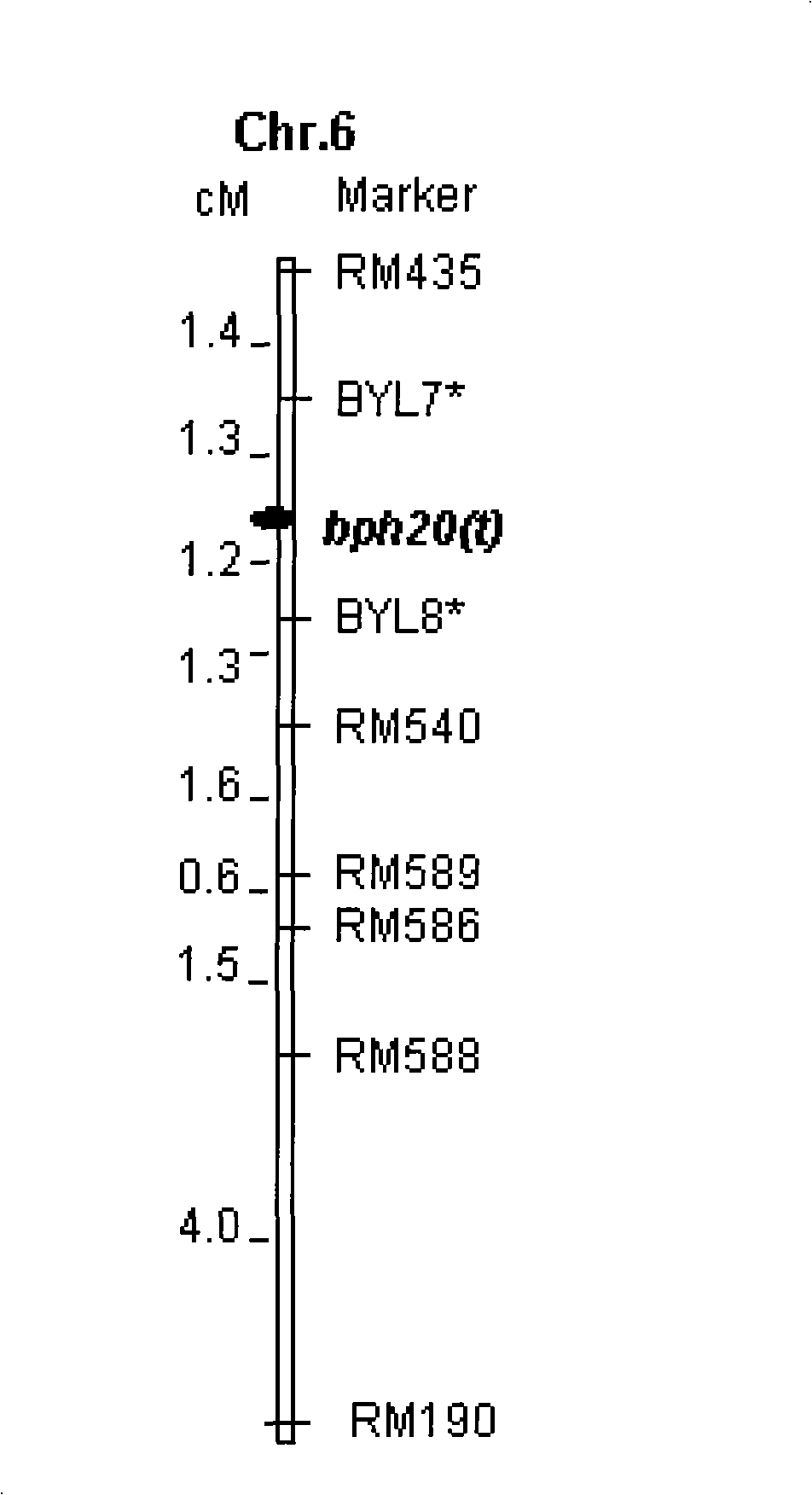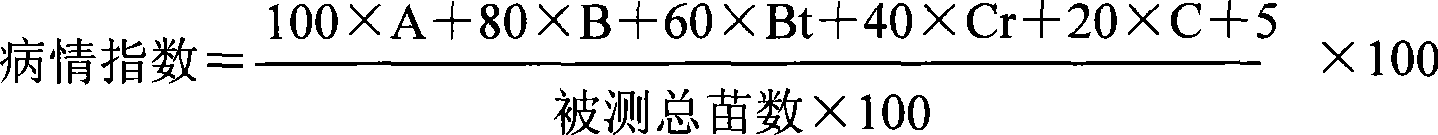Patents
Literature
59 results about "Genetic linkage analysis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Medical Definition of Linkage analysis. Linkage analysis: Study aimed at establishing linkage between genes. Today linkage analysis serves as a way of gene-hunting and genetic testing. Linkage is the tendency for genes and other genetic markers to be inherited together because of their location near one another on the same chromosome.
Molecular mark method for rice variety anti-brownspot gene site
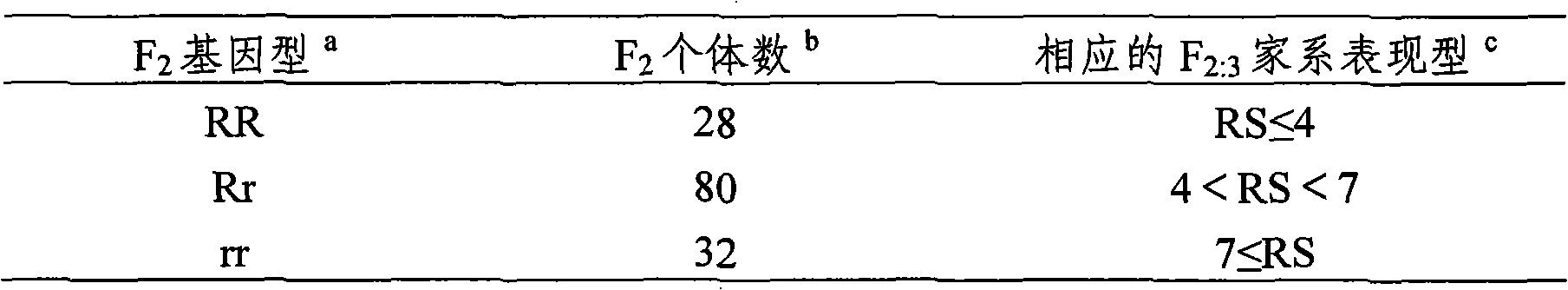
InactiveCN1896281AEasy to detectNot affectedMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBrown planthopperGenotype
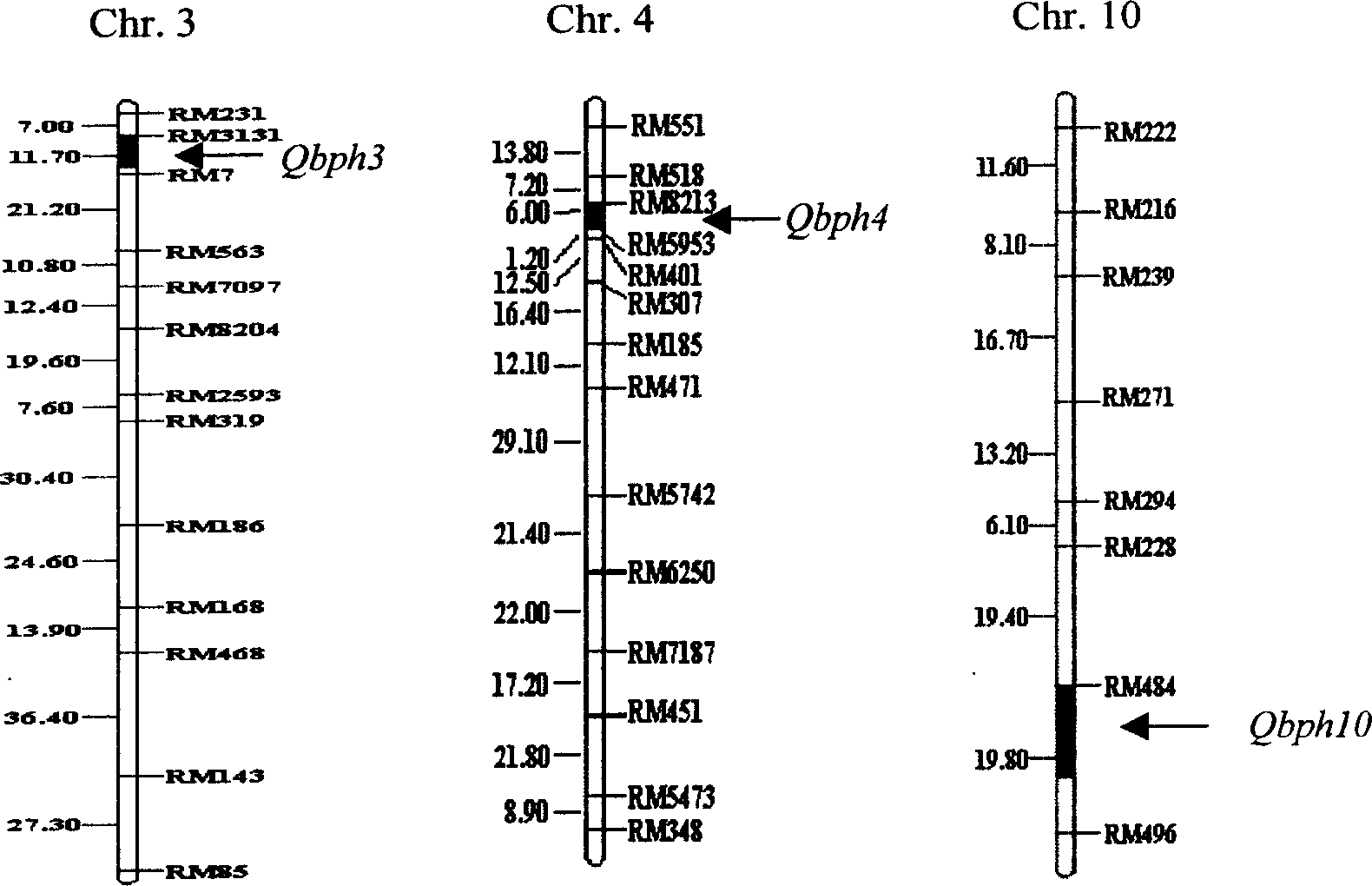
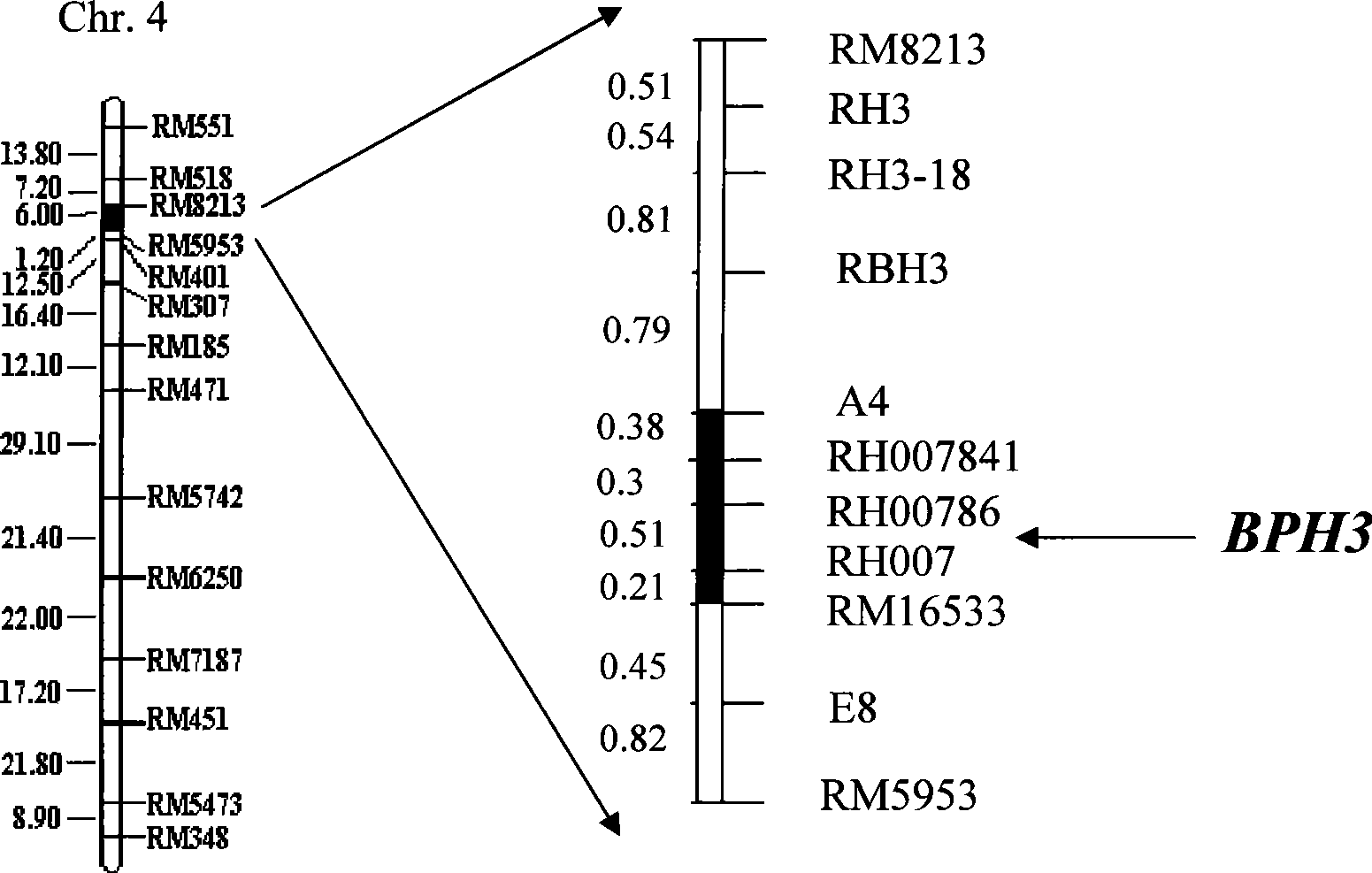
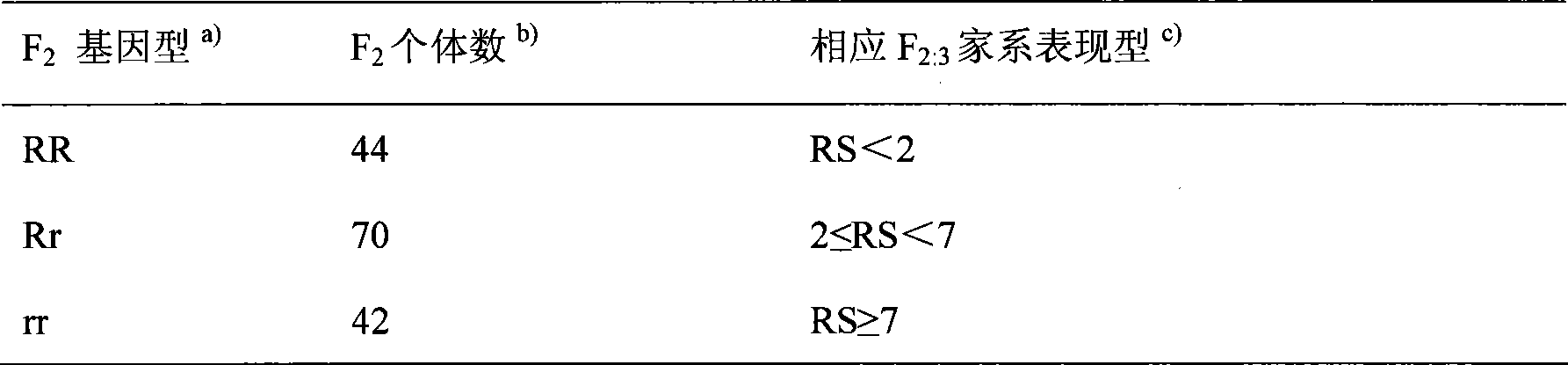
The present invention belongs to the molecular genetics field and relates to the molecular marker method of the major gene for brown planthopper resistance in the rice variety Rathu Heenati. Via genetic linkage analysis of the individual F2 plant genotype and the brown planthopper resistance level of each F2:3 family produced by hybridizing the insect-resistant variety Rathu Heenati with insect-susceptible variety 02428, the molecular markers RM8213 and RM5953 of the major gene loci Qbph4(Bph3) in the insect-resistant variety Rathu Heenati are obtained, the loci Qbph4(Bph3) is 3.6cM and 3.2cM distant from the markers RM8213 and RM5953 respectively. Detection of this major gene loci in Rathu Heenati and its derivatives via these molecular markers will increase the selection efficiency of brown plant hopper resistant rices.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Molecular marker method of rice variety brown planthopper resistance main gene Bph3
InactiveCN101418349AQuick checkQuick filterMicrobiological testing/measurementBrown planthopperGene type
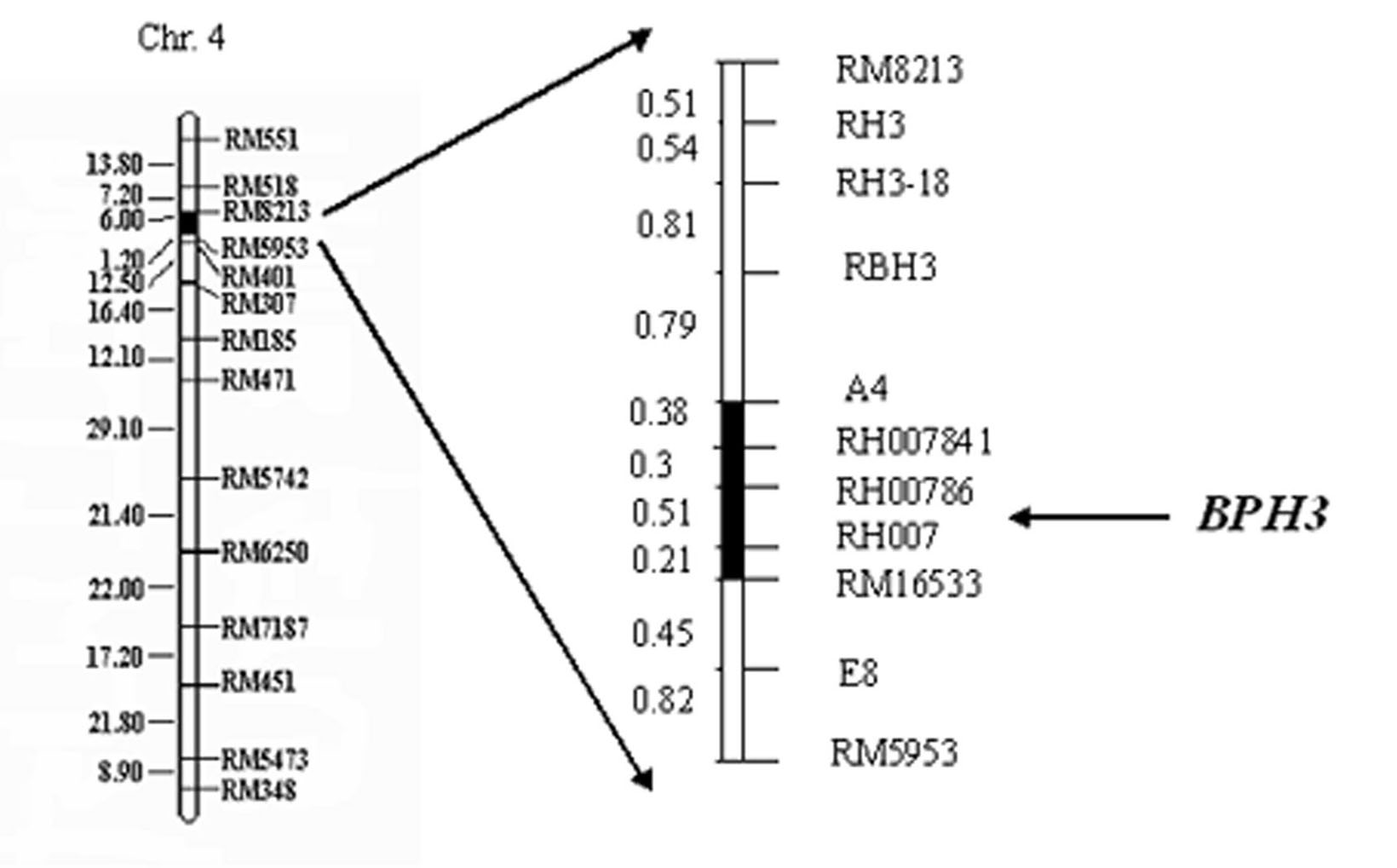
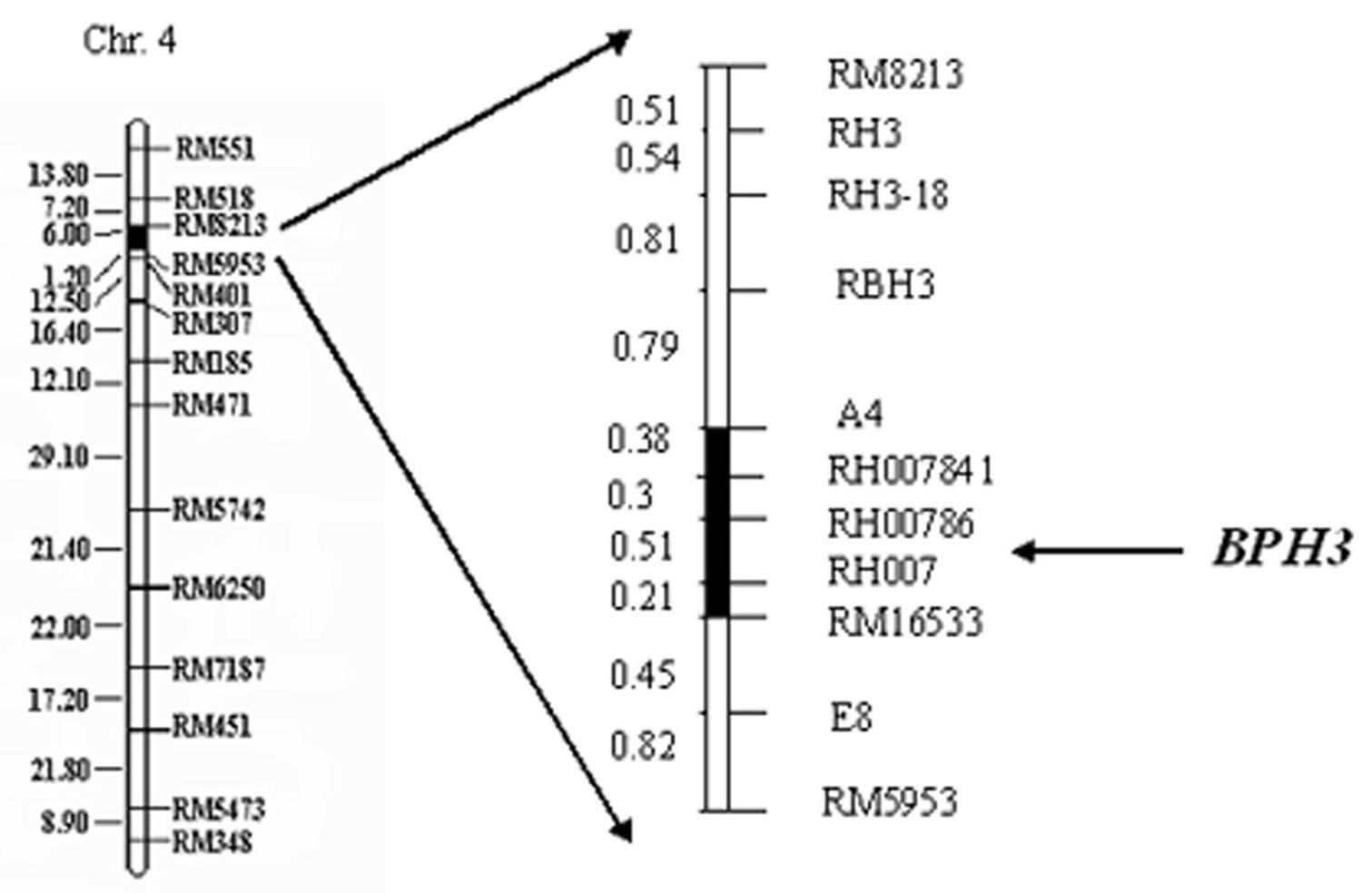
The invention relates to a molecule tagging method for a brown paddy plant hopper resistant master gene Bph3 of rice cultivars, which belongs to the technical field of genetic thremmatology. The brown paddy plant hopper resistant master gene Bph3 of an insect resistant variety Rathu Heenati is obtained by genetic linkage analysis of the brown paddy plant hopper resistant level of gene types of various single plants of F2 and various genealogies of F 2:3 obtained after hybridization of the insect resistant rice variety Rathu Heenati (female) and an insect susceptible variety 02428(male). The gene is positioned between a molecular marker A4 and a molecular marker RM16533, and the selection efficiency of three Indel indexes namely RH784, RH786 and RH007 of the interval is approximately 97 percent. Detection is made whether the insect resistant variety Rathu Heenati and derivative varieties (systems) of the insect resistant variety Rathu Heenati contain the master gene through the molecular markeres of the brown paddy plant hopper resistant master gene; the brown paddy plant hopper resistance level of the master gene can be predicted; and the selection efficiency of brown paddy plant hopper resistant rice can be greatly improved.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
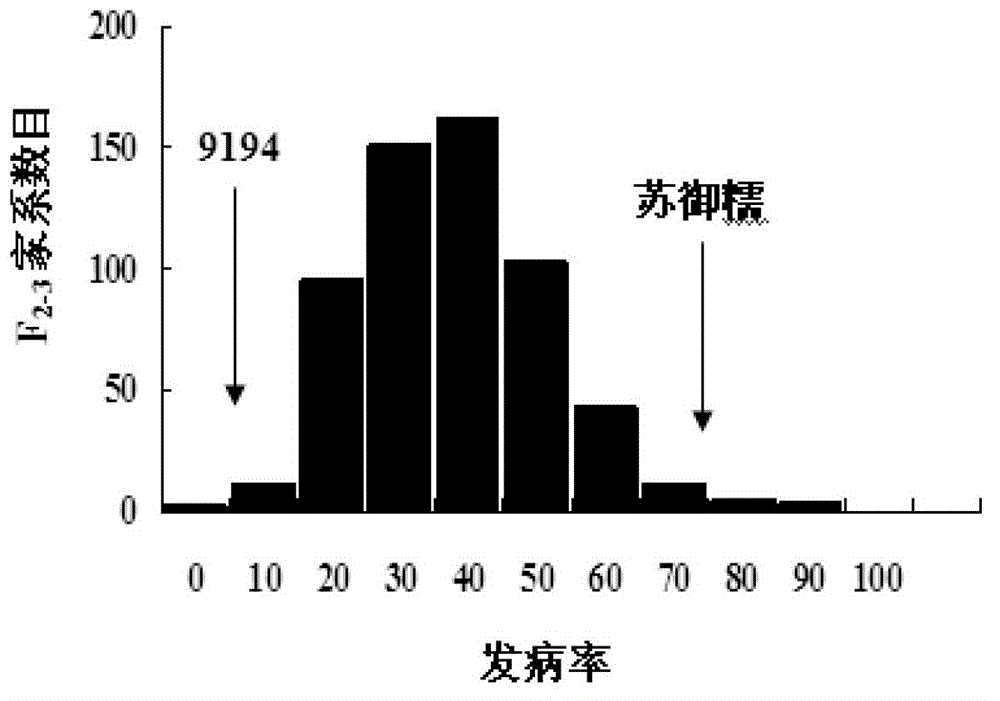
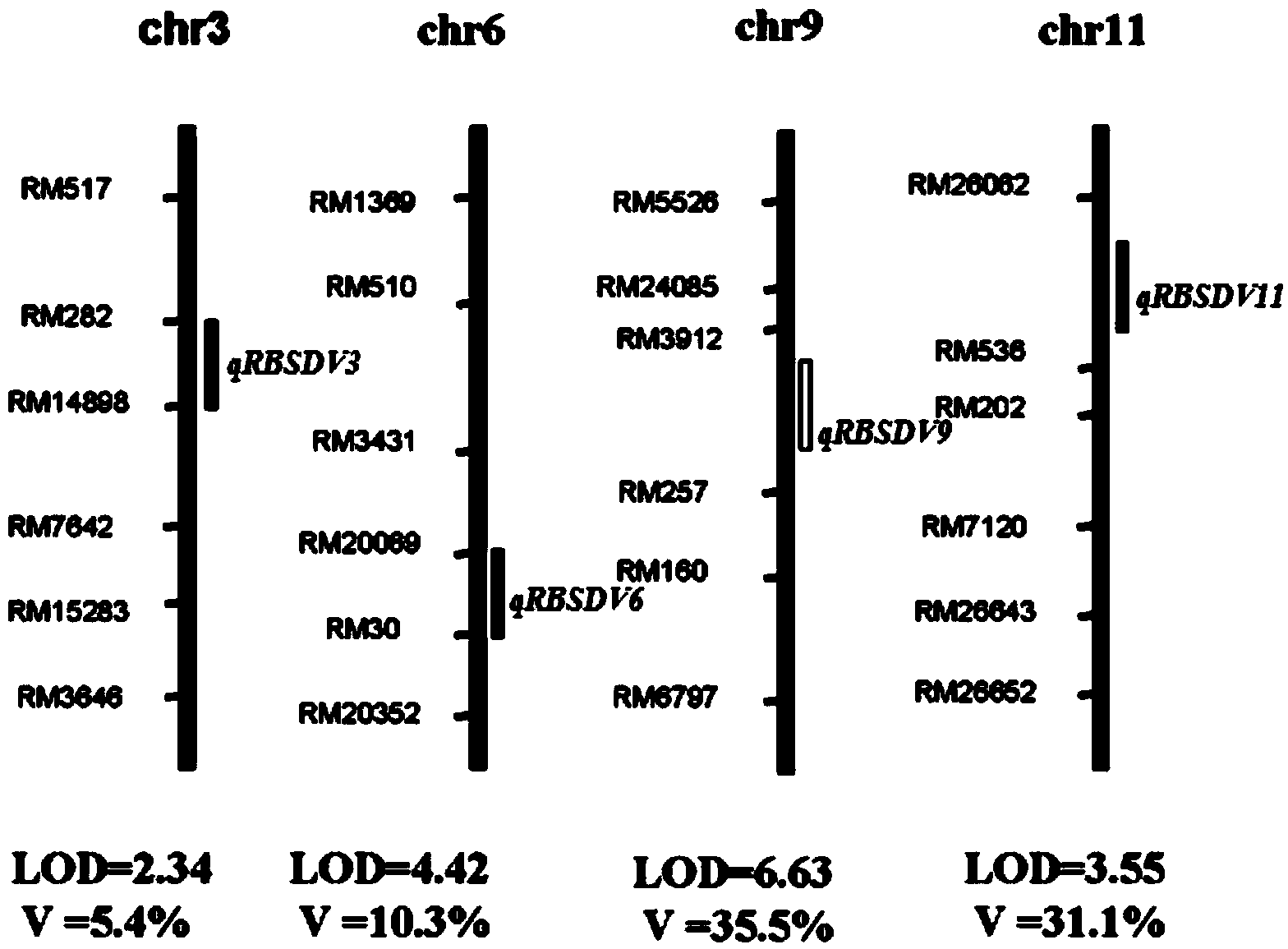
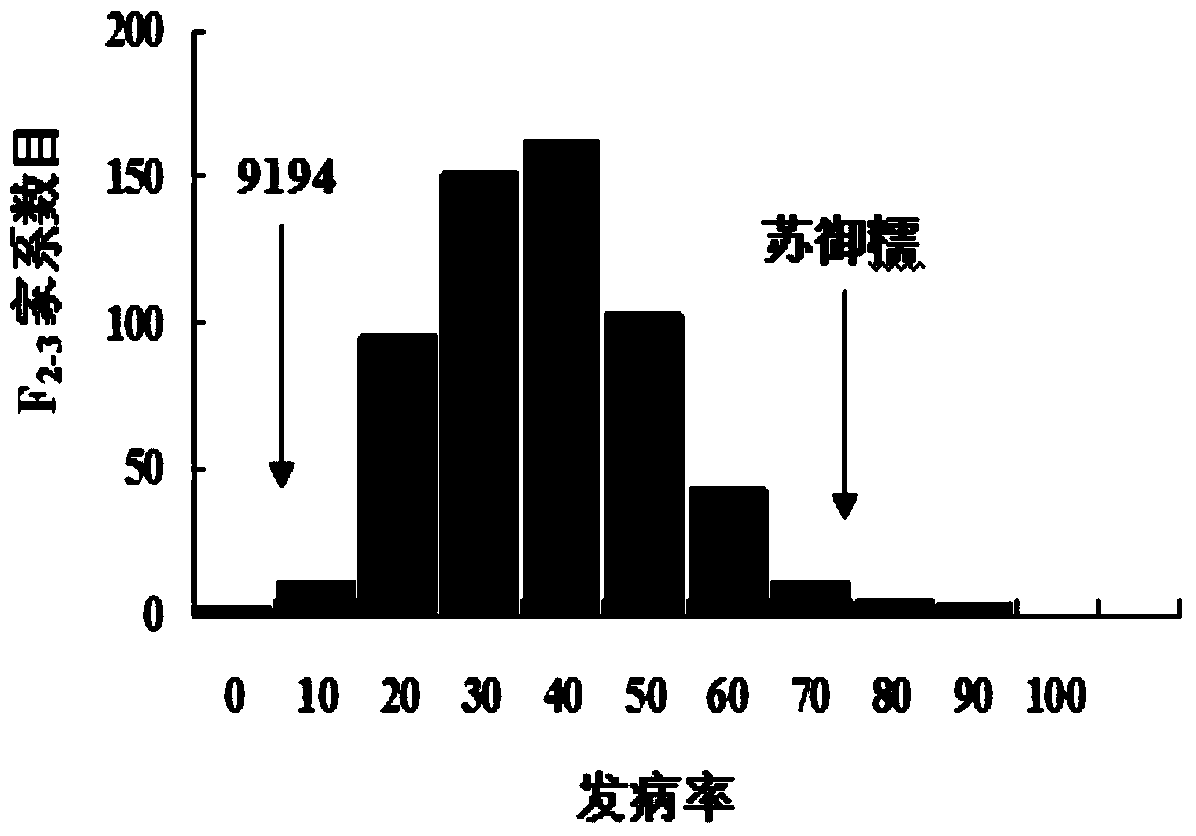
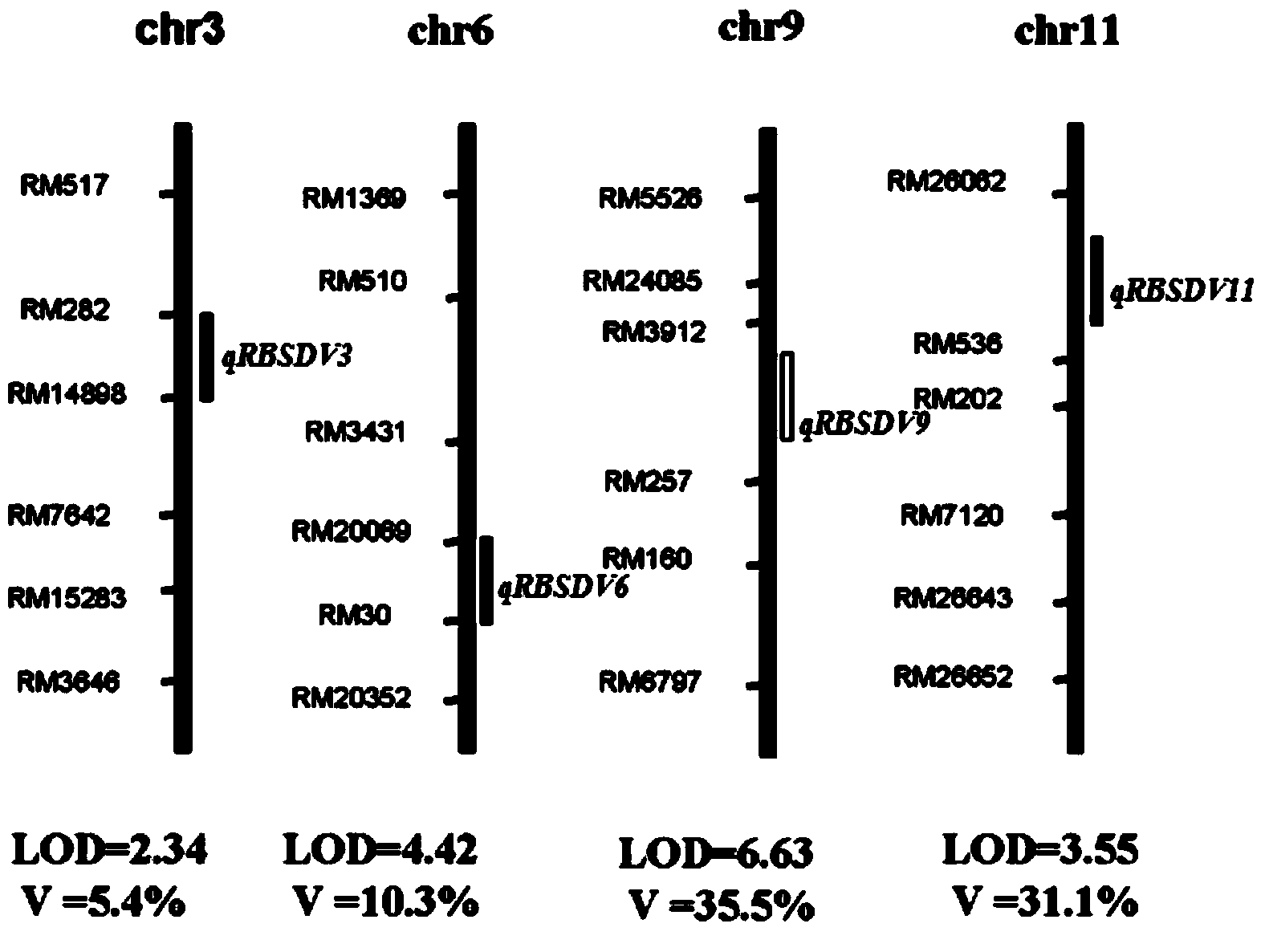
Rice variety 9194 black streaked dwarf restricting locus and molecular marking method thereof
ActiveCN103146700AEasy to detectQuick filterMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationResistant genesGenetics
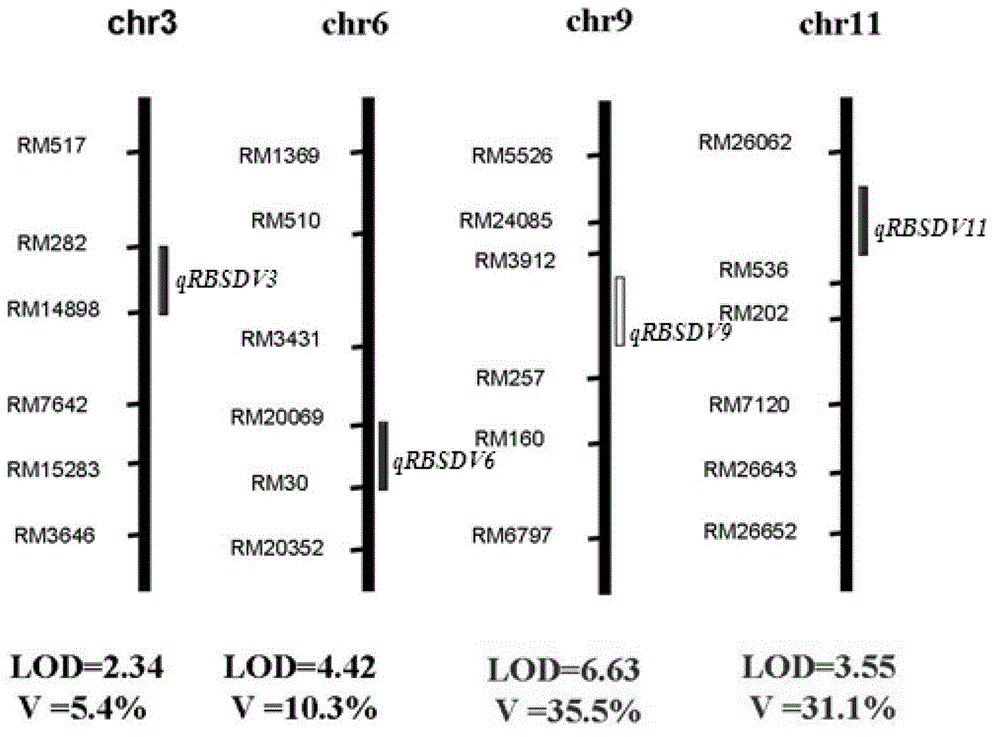
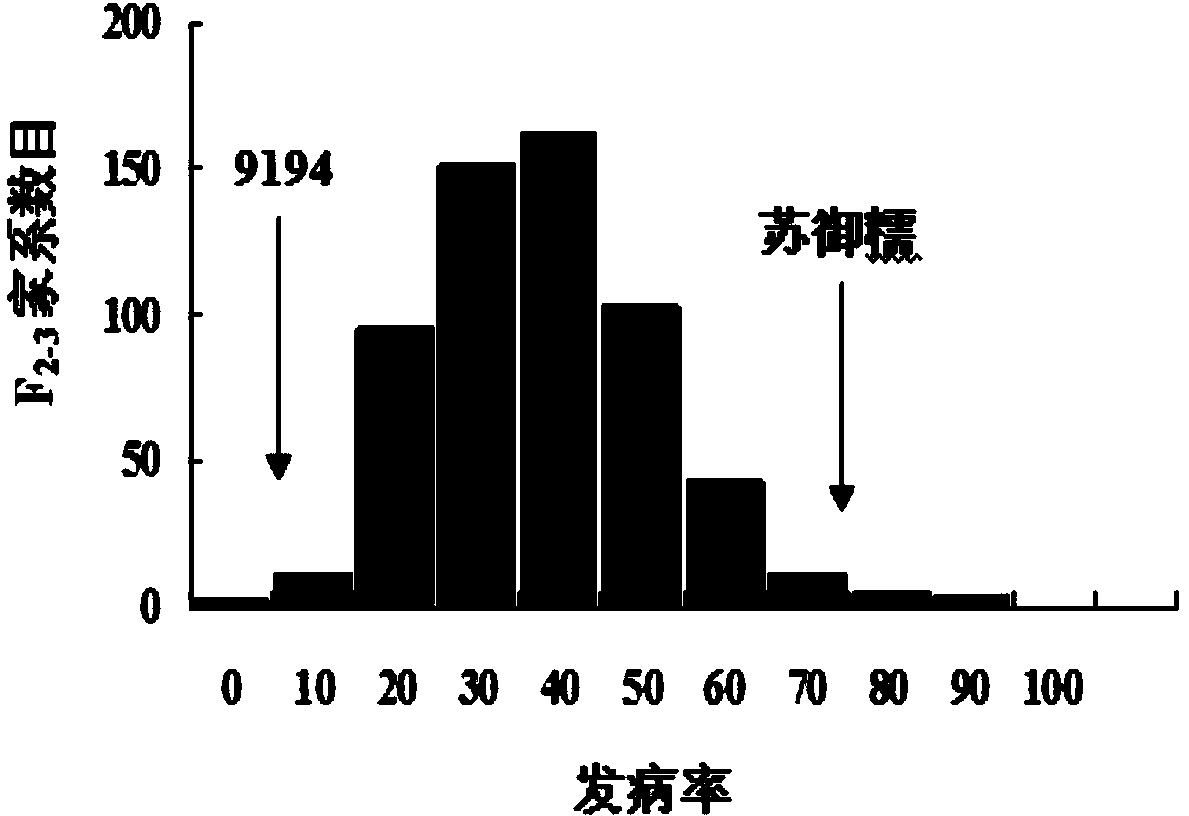
The invention relates to a rice variety 9194 black streaked dwarf restricting locus and a molecular marking method thereof. Four rice variety 9194 black streaked dwarf restricting locus are obtained by carrying out genetic linkage analysis on the black streaked dwarf resistance level of the genotype of an F2 single plant obtained from hybridization of the black streaked dwarf restricting rice variety 9194 and susceptible variety suyunuo and the corresponding F2:3 family, wherein qRBSDV3 is positioned between the markers RM282 and RM14898, qRBSDV6 is positioned between the markers RM20069 and RM30, qRBSDV9 is positioned between the markers RM3912 and RM257, and qRBSDV11 is positioned between the markers RM26062 and RM536. The molecular markers of the black streaked dwarf restricting gene are used for detecting whether the resistant variety 9194 and the derived varieties contain the black streaked dwarf restricting locus, so that the resistance level of the black streaked dwarf can be predicated, and the selecting efficiency of the black streaked dwarf restricting rice is greatly improved.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
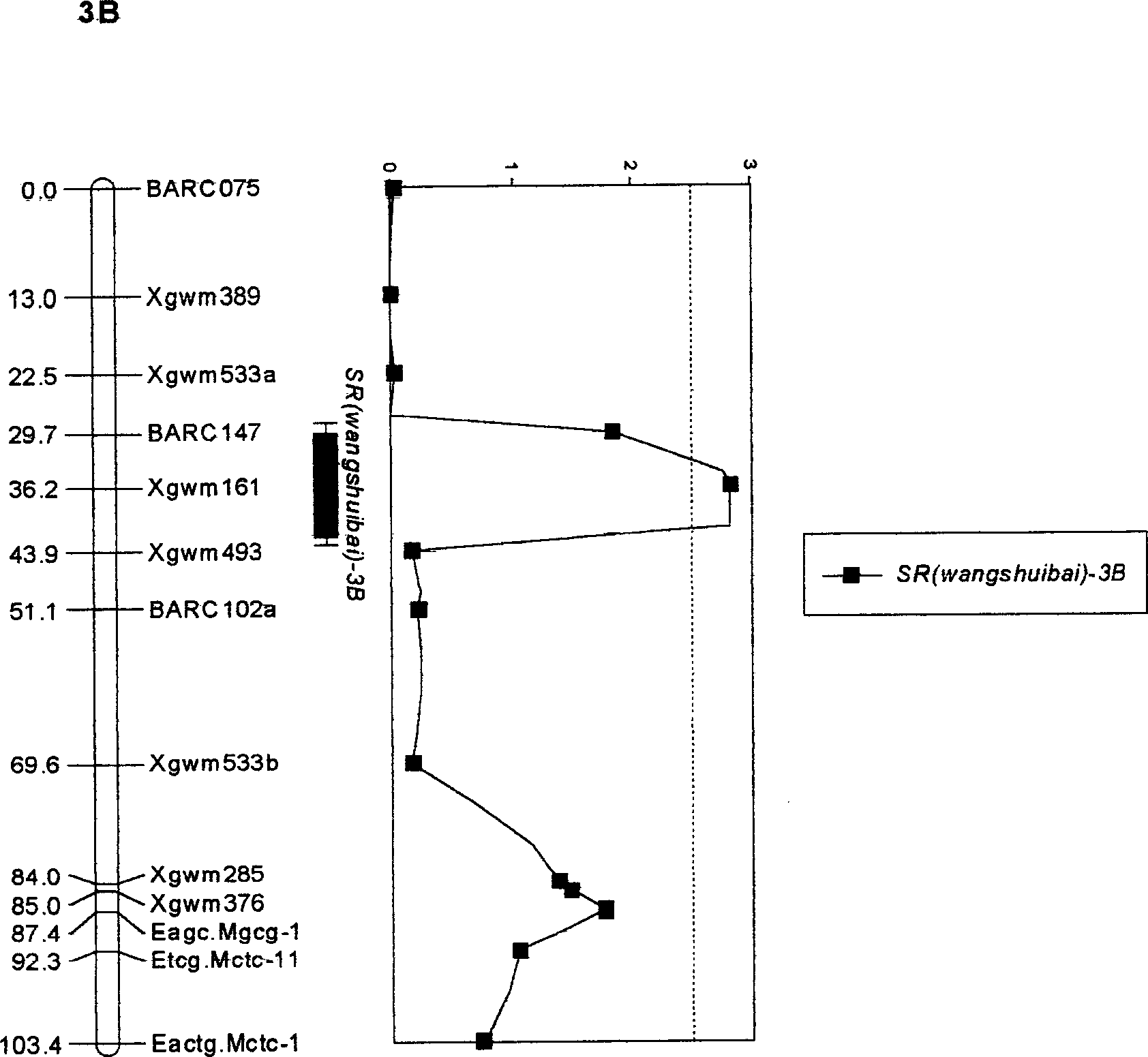
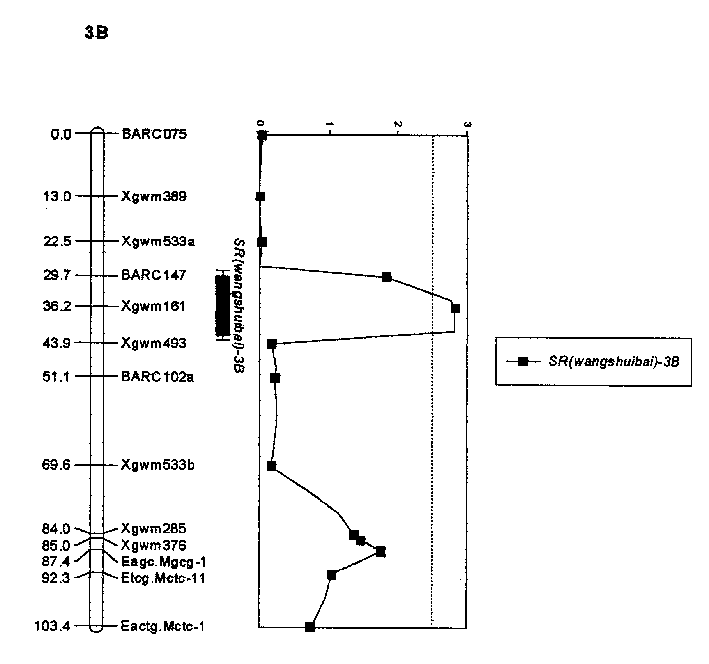
Molecular label closely linked with wheat gibberellin resistance main effect QTL and its application
InactiveCN1442039AReduce the waste of manpower and material resourcesImprove breeding efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationDiseaseAgricultural science
The molecular label closely linked with the active QTL of wheat fusarium blight resistance is prepared through hybridizing the disease-resistant wheat with the disease-sensitive wheat to obtain recombinant selfing line, and performing QTL and genetic linkage analysis to obtain the said molecular labels Xgwin 161, BARC 147 and Xgwin 493. They can be used to predict the level of the resistance to fusarium blight by detecting whether the DNA of wheat contains the said molecular labels or not.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
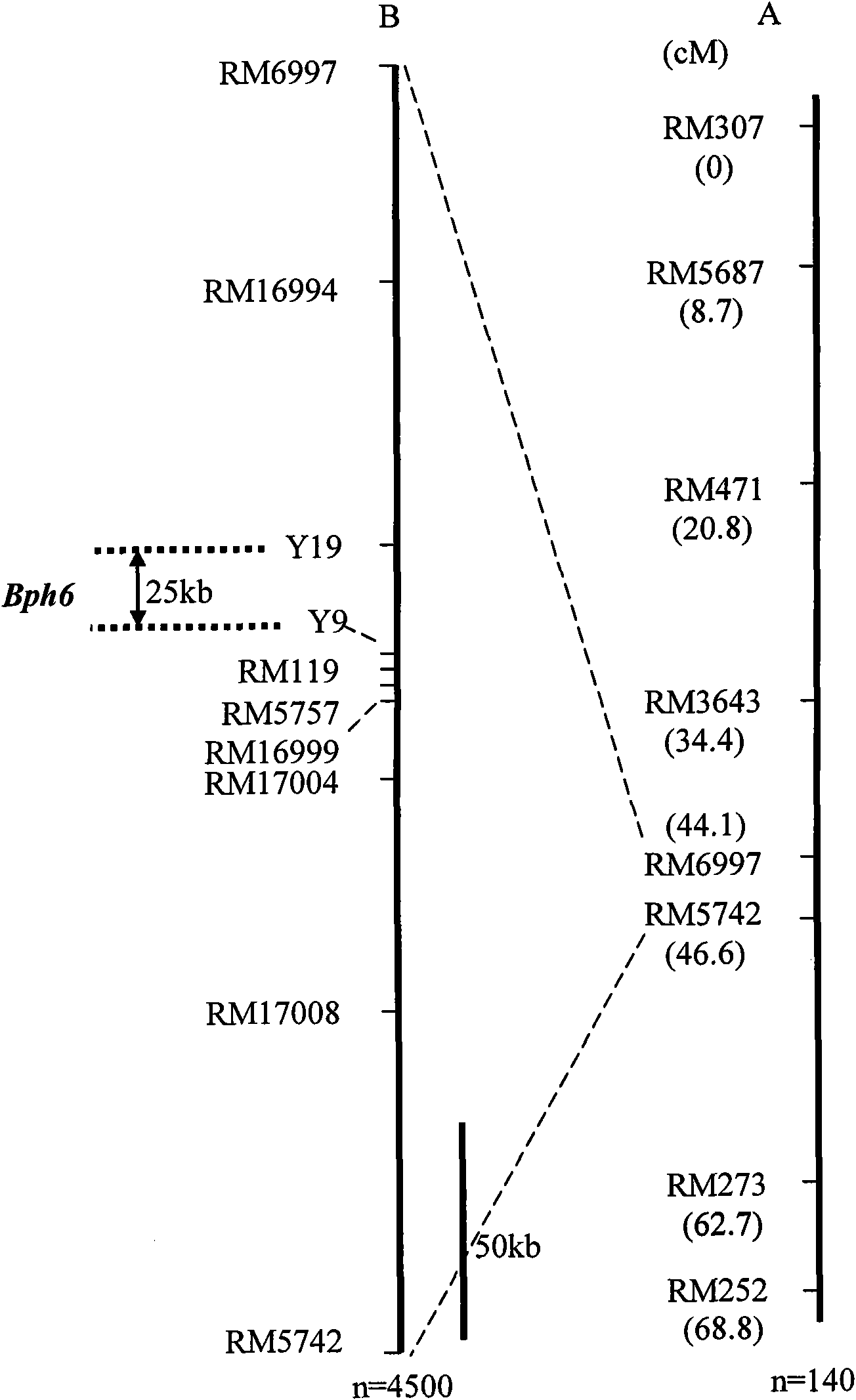
Molecular marker of major gene Bph6 resistant to brown planthopper and application thereof
InactiveCN101914531AQuick filterNot affectedMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyBrown planthopper
The invention provides a molecular marker of major gene Bph6 resistant to brown planthopper and an application thereof. The invention can obtain a pest-resistant cultivar Swarnalata resistance gene Bph6 and position the resistance gene between molecular marker Y1 and molecular marker Y9 by hybridizing a rice pest-resistant cultivar Swarnalata with 9311 (female) to obtain the genetype of each F2 plant and performing genetic linkage analysis by combining resistance levels resistant to brown planthopper of each family of F2:3. The molecular marker linked with the resistance gene is one of RM16994, Y19, Y9, RM119, RM5757, RM16999, RM17004 and RM17008. The molecular marker in the invention can effectively detect whether the major gene locus exists in the pest-resistant cultivar Swarnalata and derived varieties (strains) thereof, thus greatly improving the selection efficiency of rice resistant to brown planthopper and obtaining brown planthopper resistant rice varieties containing Bph6 gene.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Molecular marker of anti-nilaparvata-lugens major gene Bph3 of rice
InactiveCN101956019AQuick checkQuick filterMicrobiological testing/measurementBrown planthopperGenotype
The invention relates to a molecular marker of an anti-nilaparvata-lugens major gene Bph3 of rice and belongs to the technical field of genetic breeding. A genetic linkage analysis is preformed on a genotype of each single plant of F2 obtained by crossing an rice anti-insect variety RathuHeenati (female) with an insect-susceptible variety 02428 (male) as well as on an anti-nilaparvata-lugens level of each family of F2: 3, thereby obtaining the anti-nilaparvata-lugens major gene Bph3 of the anti-insect variety RathuHeenati. The gene is positioned between the molecular marker A4 and the molecular marker RM16533; the selection efficiencies of three Indel markers RH784, RH786 and RH007 in the interval are around 97%. The molecular marker of the anti-nilaparvata-lugens major gene is used for detecting whether the major gene is contained in the anti-insect variety RathuHeenati as well as derived varieties thereof (family), thereby forecasting the anti-nilaparvata-lugens level; therefore, the selection efficiency of the anti-nilaparvata-lugens rice is improved greatly.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Molecular marker for rice brown planthopper-resistance QBph3 and QBph4 genes
InactiveCN105087553AImprove reliabilityEasy to identifyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceGenotype
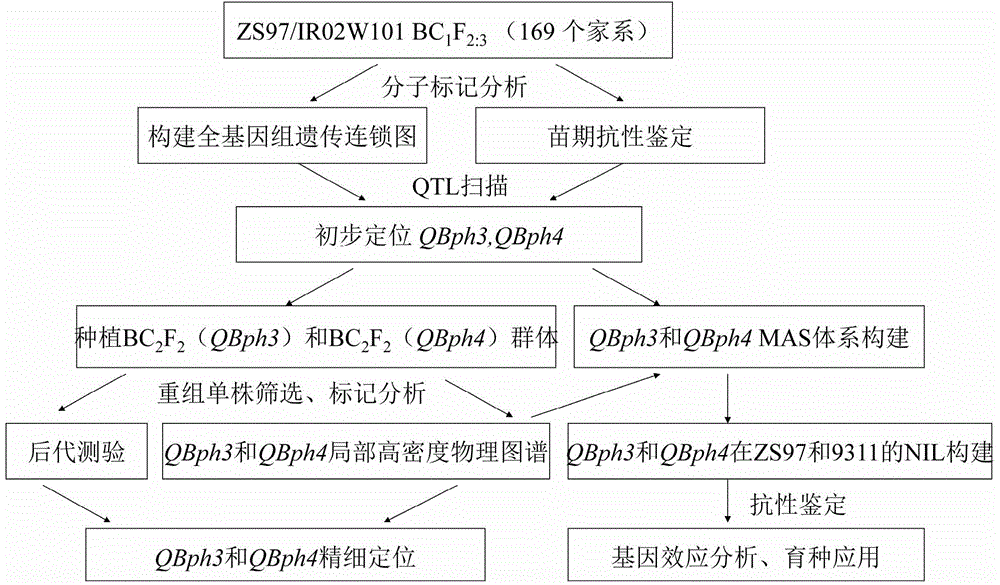
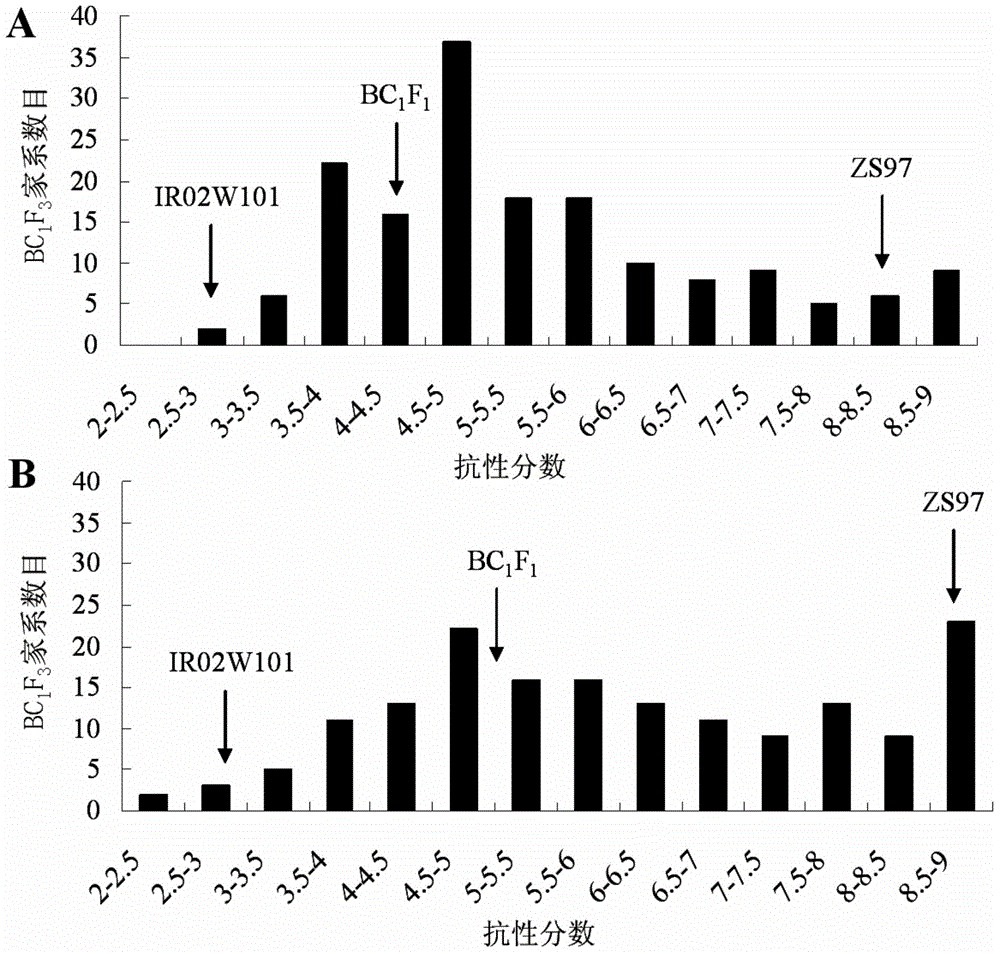
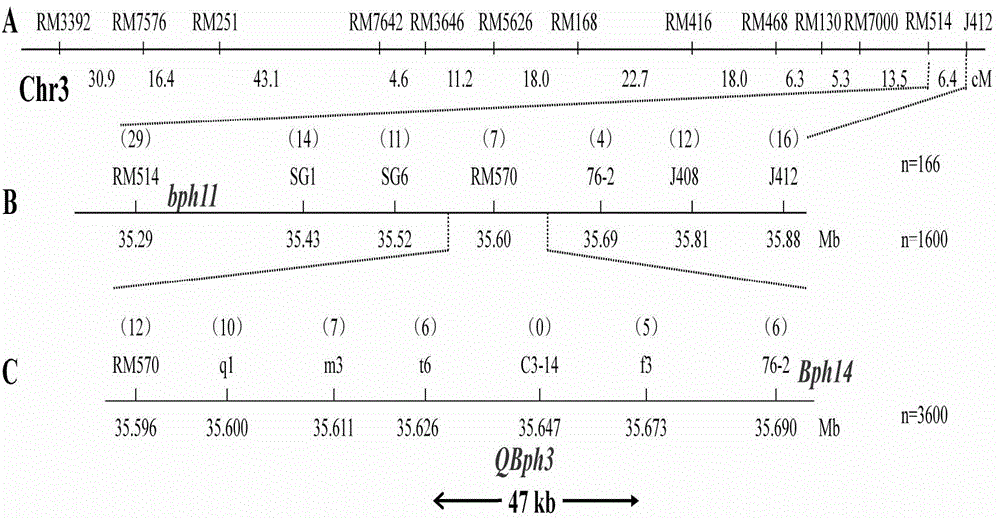
The invention belongs to the technical field of preparation of a rice molecular marker, and in particular relates to a molecular marker for two rice brown planthopper-resistance major genes QBph3 and QBph4 which are simultaneously derived from a pest-resistance introgression line IR02W101. The molecular marker comprises the following steps: carrying out crossing, self-crossing and backcrossing on Zhenshan97, which is an herbivore-susceptible variety, and IR02W101 so as to obtain genotypes of various BC1F2 single plants; carrying out genetic linkage analysis in accordance with brown planthopper-resistance grades of various F2: 3 lines during seedling stage; precisely locating a resistance gene QBph3 of the IR02W101 between long-arm markers t6 and f3 of the 3rd chromosome so as to obtain a co-segregative marker c3-14 as well as closely linked markers q1 and m3; and precisely locating QBph4 between short-arm markers p17 and xc4-27 of the 4th chromosome so as to obtain closely linked markers p6, p9, c4-5, xc4-7, HJ16, J417 and IN156. The molecular marker disclosed by the invention can be used for effectively detecting whether the pest-resistance introgression line IR02W101 and derived varieties thereof contain the major gene site or not.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
q srbsdv6 (southern rice black-streaked dwarf virus 6) and molecular marker method thereof
ActiveCN104450694APredicted resistance levelImprove selection efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceSelfing
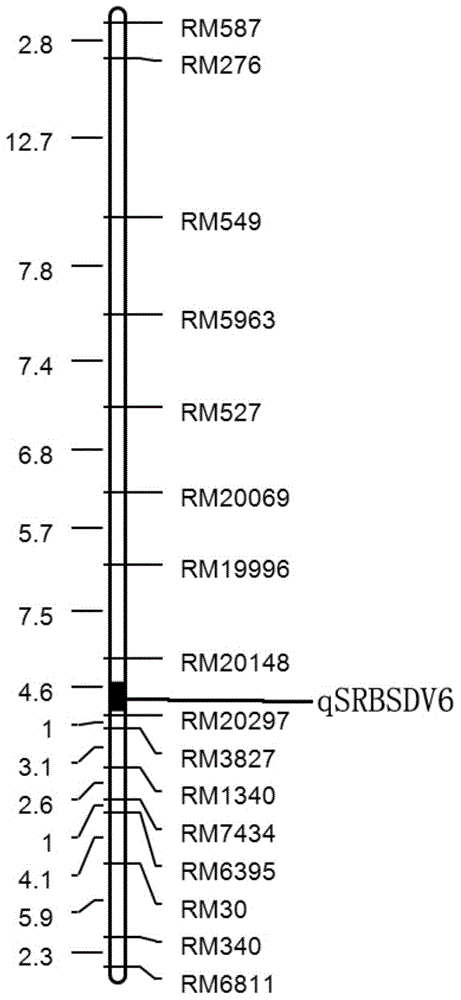
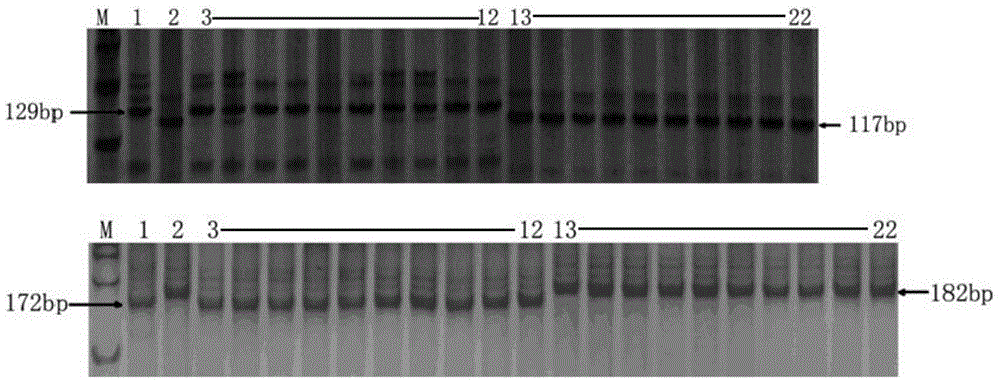
The invention provides a q SRBSDV6 (Southern rice black-streaked dwarf virus 6) and a molecular marker method thereof. BC3F7 is obtained through hybridization, backcross and selfing of Guangxi common wild rice material y11 and the susceptible variety Guanghui 998 and then is subjected to association analysis and genetic linkage analysis to obtain the q SRBSDV6, and the q SRBSDV6 is positioned between RM20148 and RM 20297; when the molecular marker RM20148 primer has q SRBSDV6, the amplification band is 129 bp band; when the molecular marker RM 20297 primer has q SRBSDV6, the amplification band is 172 bp band. According to the invention, the molecular markers of q SRBSDV6 genes can be adopted to detect whether the resistant material y11 and the derived varieties (series) contain the q SRBSDV6, the resistance level of the SRBSDV6 can be predicted, and the selective efficiency of the q SRBSDV6 rice can be greatly improved.
Owner:广西壮族自治区农业科学院水稻研究所
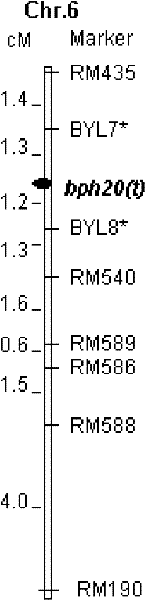
SSR marker BYL8 of brown planthopper resistant genetic locus bph20(t)
InactiveCN102199596AImprove breeding efficiencyReduce lossMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationResistant genesBrown planthopper
The invention provides a molecule marker of brown planthopper resistant gene. According to the present invention, through the hybridization and backcrossing of a resistant parent RBPH54 and a susceptible variety TN1, progenies are obtained. Through respective resistance identifications and molecule genetic linkage analysis of the progeny strains, a brown planthopper resistant major recessive genebph20(t) is obtained. Two nearest molecule markers linked beside bph20(t) are BYL7 and BYL8, which are self-developed SSR markers. The distances from the markers to bph20(t) are 1.3cM and 1.2 cM. With molecule markers linked to the brown planthopper resistant gene, the detection can be carried out to detect whether the pest resistant variety RBPH54 or the derivative varieties (systems) of RBPH54 contain the pest resistant genetic locus. Therefore, the selection of brown planthopper resistant paddy varieties or paddy qualities can be substantially improved in efficiency.
Owner:GUANGXI ZHUANG AUTONOMOUS REGION ACAD OF AGRI SCI
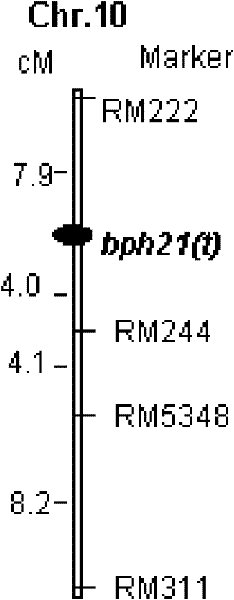
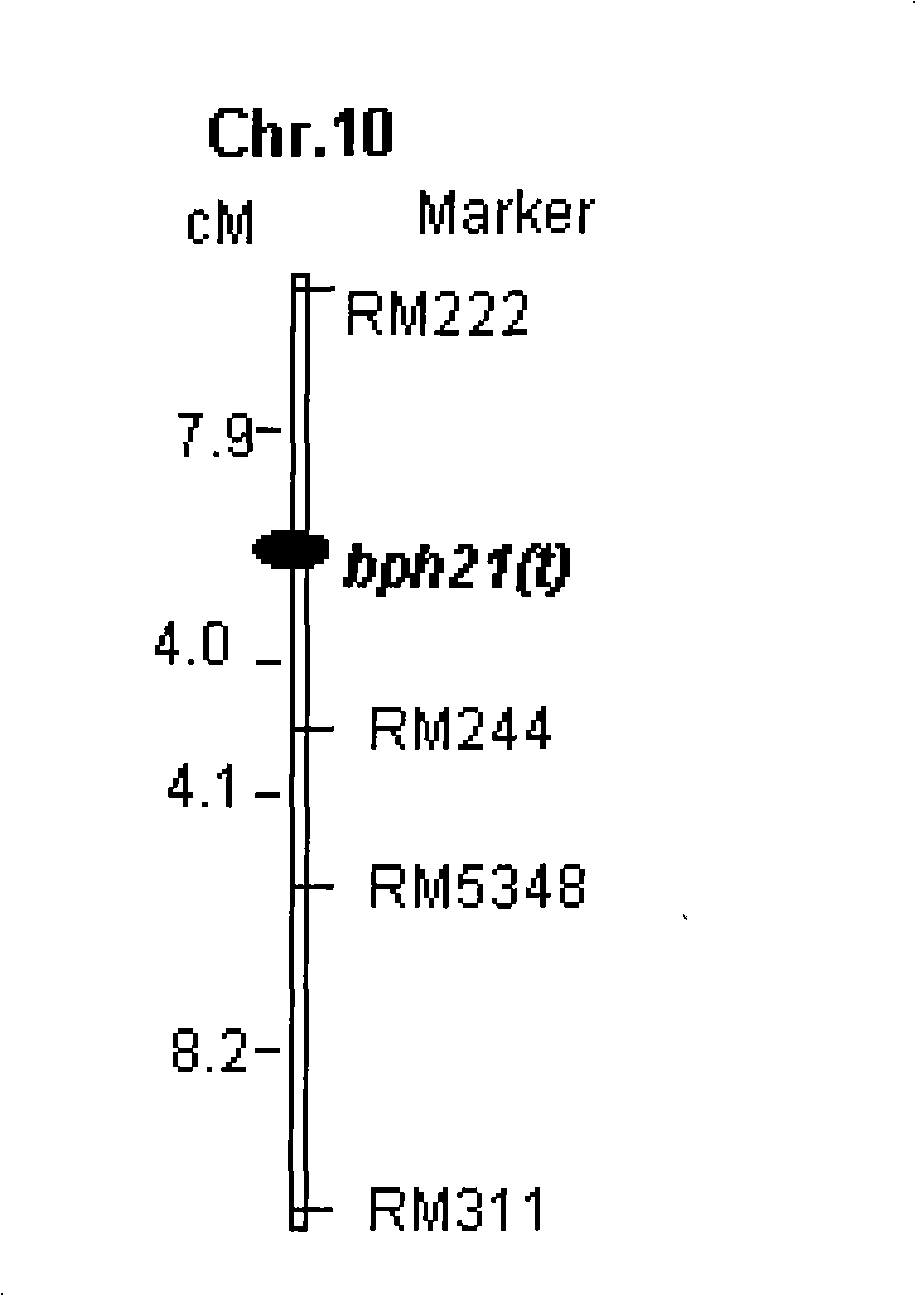
Anti-nilaparvata lugens major gene, numerator mark method and uses thereof
InactiveCN101403011AImprove breeding efficiencyReduce lossMicrobiological testing/measurementGenetic engineeringBiotechnologyResistant genes
The invention provides molecular markers of genes which resist brown plant-hoppers of rice. The invention is characterized in that each offspring is obtained by hybridizing and back crossing a resistant parent RBPH54 and a susceptible variety TN1, and resistance identification and molecular genetic linkage analysis are carried out to the strain of each offspring, thus obtaining brown plant-hoppers resistant major recessive genes, bph20(t) and bph21(t); nearest molecular markers on both sides and linked with the bph20(t) are SSR markers, BYL7 and BYL8, which are autonomously developed, and the distances between the SSR markers and the bph20(t) are 1.3cm and 1.2cm respectively; and nearest molecular markers on both sides and linked with the bph21(t) are RM222 and RM224 and the distances between the RM222 and the bph21(t) and between the RM224 and the bph21(t) are 7.9cm and 4.0cm respectively. Whether the locus of the pest-resistant genes is contained in a pest-resistant variety RBPH54 and a derived variety (species) thereof can be detected by the molecular markers linked with the genes resistant to the brown plant-hoppers, which can greatly improve the selection efficiency of the brown plant-hopper resistant rice.
Owner:GUANGXI ZHUANG AUTONOMOUS REGION ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Photoperiod-insensitivity Hd1 allele and molecular marker and application thereof
ActiveCN109055395AIncrease photosensitivityImprove adaptabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant peptidesGenotypeAllele
The invention discloses a photoperiod-insensitivity Hd1 allele and a molecular marker and application thereof. Zhengeng 2400 (female) of a photoperiod-insensitivity variety and Jiahe 218 (male) of a photoperiod-sensitivity variety are hybridized to obtain the genotype of an F2 single plant, and genetic linkage analysis is carried out to judge whether photoperiod-insensitivity phenotype separationof a corresponding F2:3 family is achieved or not; a heading period photoperiod-insensitivity gene of the Zhengeng 2400 is positioned at the sixth chromosome and located between a mark RM276 and a mark I6-5; the Zhengeng 2400 and the Jiahe 218 are subjected to WGS-variation point detection and gene sequencing analysis, and the analysis discovers that 123bp is inserted at the first exon 517bp of the Hd1 allele of the Zhengeng 2400; and the molecular marker H1 is developed according to the difference for detecting whether the Zhengeng 2400 and derivative varieties thereof contain the photoperiod-insensitivity gene or not. Thus, the photosensitivity of japonica rice varieties can be improved, and the regional adaptability and breeding efficiency of the japonica rice varieties are greatly improved.
Owner:ZHENJIANG AGRI SCI INST JIANGSU HILLY AREAS
Anti-southern rice black-streaked dwarf disease site qSRBSDV9 and molecular marking method thereof
ActiveCN108913795AImprove selection efficiencyEasy to detectMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceSelfing
The invention belongs to the field of plant molecular genetics and relates to an anti-southern rice black-streaked dwarf disease site qSRBSDV9 and a molecular marking method thereof. Through hybridization and selfing of a rice disease resistance line D4 and a susceptible variety Guanghui 998, a F2 group is obtained and is subjected to association analysis and genetic linkage analysis so that an anti-southern rice black-streaked dwarf disease site qSRBSDV9 is obtained and is located between molecular markers Indel32 and Indel35. Based on molecular marker Indel32 primers, when the qSRBSDV9 exists, the amplified band has 111 bp. Based on molecular marker Indel35 primers, when the qSRBSDV9 exists, the amplified band has 147 bp. Through the molecular markers of the anti-southern rice black-streaked dwarf disease gene, it is detected whether the resistant material D4 and its derivative varieties (lines) contain the anti-southern rice black-streaked dwarf disease site. The molecular marking method can predict the resistance level of the southern rice black-streaked dwarf disease and greatly improve the selection efficiency of rice against the southern rice black-streaked dwarf disease.
Owner:广西壮族自治区农业科学院水稻研究所 +2
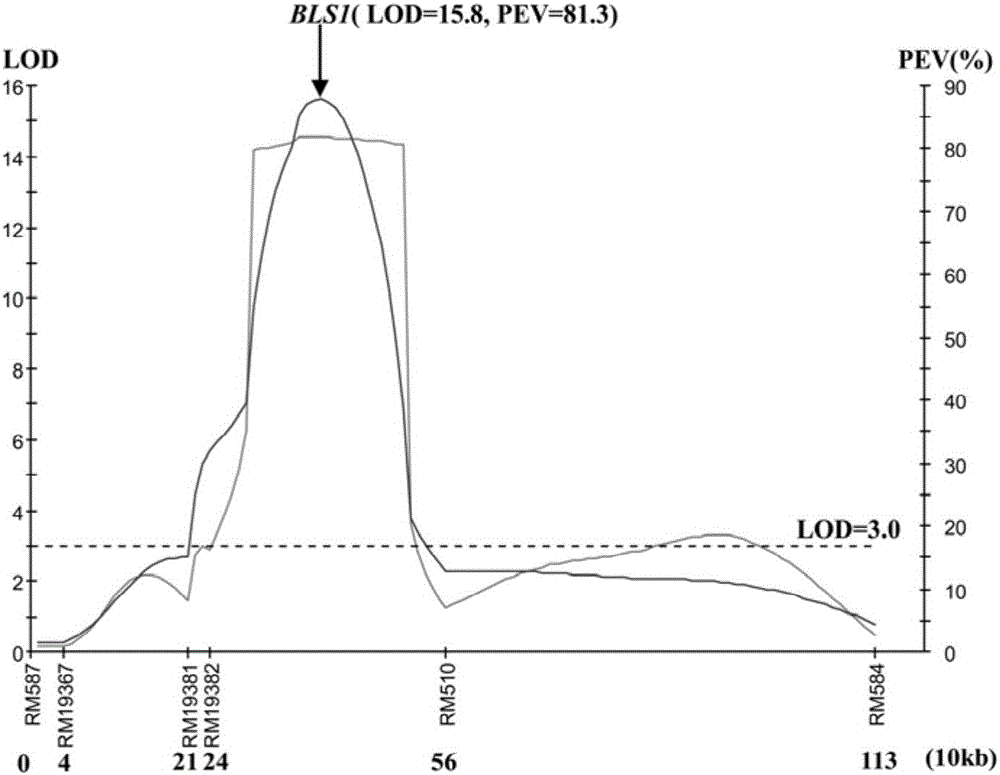
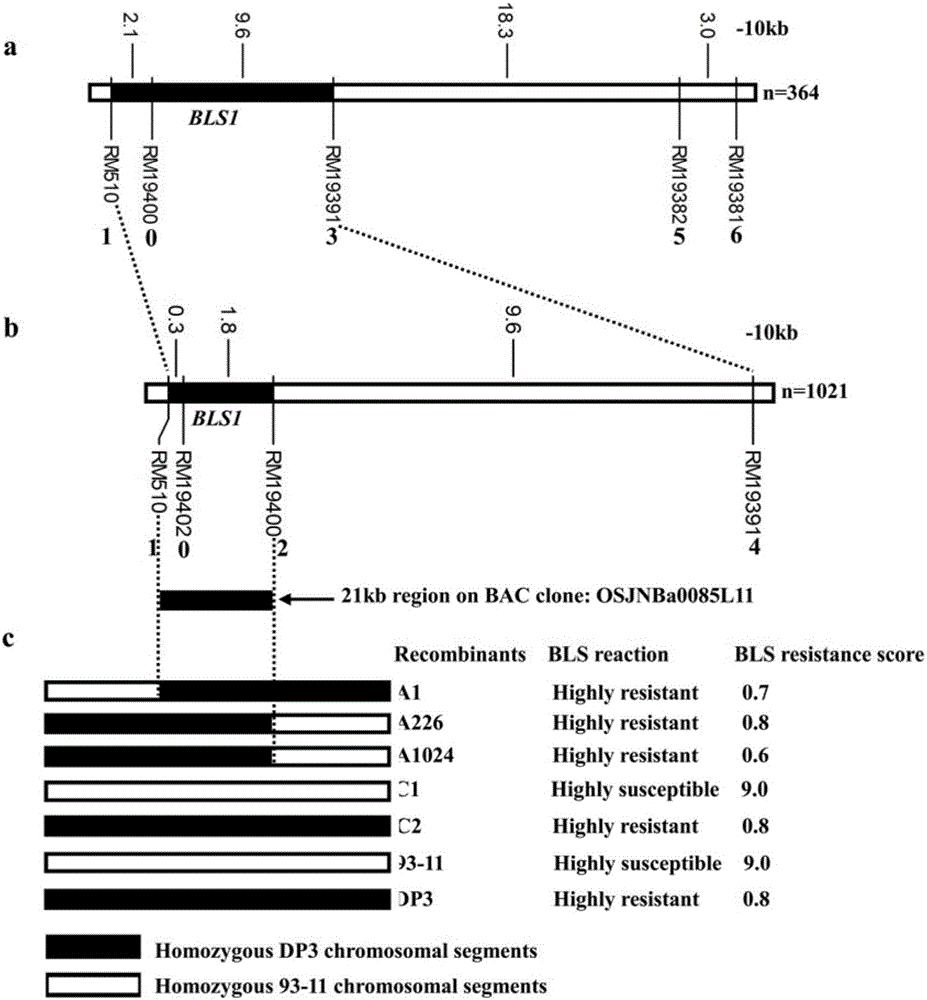
Molecular marker of main active gene BLS1 of paddy rice resisting bacterial streak and application of molecular marker
ActiveCN106244678AImprove selection efficiencyNot affectedMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceOffspring F1
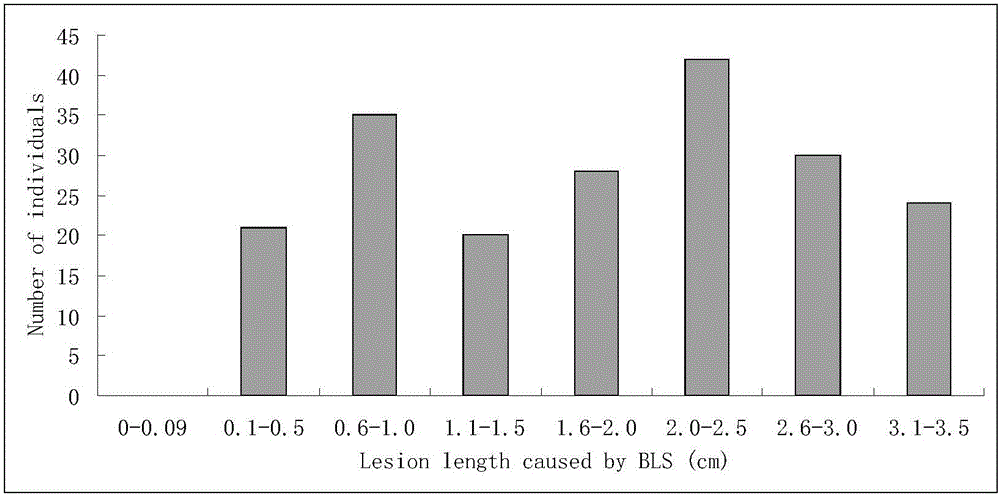
The invention discloses a molecular marker of a main active gene BLS1 of paddy rice resisting bacterial streak and an application of the molecular marker. A bacterial streak resistant backcross inbred line obtained from deriving an ordinary wild paddy rice resistant source DP3 is crossed with a bacterial streak-infected nonglutinous rice variety 93-11 to obtain an offspring F1 hybrid and then the hybrid is self-fertilized to obtain F2 generation, genetic linkage analysis is performed for a gene type and corresponding resistant phenotype of each family of F2, and the bacterial streak-resistant main active gene BLS1 sourced from the ordinary wild paddy rice DP3 is detected. Molecular markers capable of being used for breeding such as RM19382, RM19391, RM19400, RM19402 and RM510 are obtained. The molecular markers can effectively detect whether the bacterial streak-resistant ordinary wild paddy rice DP3 and erivative varieties (lines) thereof contain a main active gene site, thereby greatly improving the selection efficiency of the bacterial streak resistant paddy rice, and obtaining the bacterial streak resistant paddy rice variety containing the BLS1 gene.
Owner:广西壮族自治区农业科学院水稻研究所
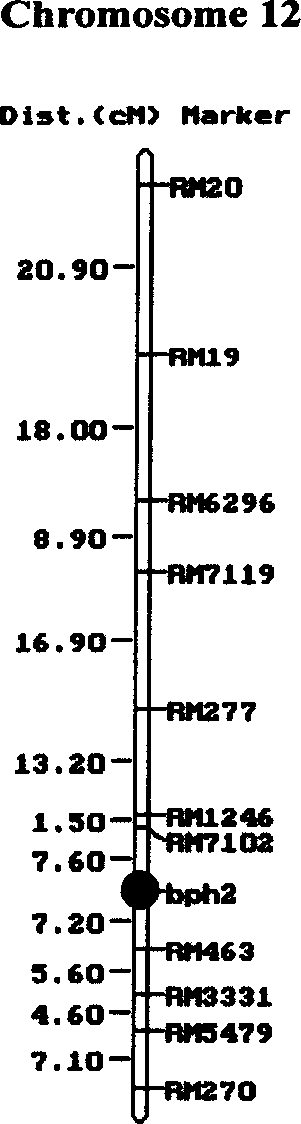
Main-gene bph2 molecular mark method for rice variety anti-brownspot gene site
InactiveCN1896282AQuick filterNot affectedMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBrown planthopperGenotype
The present invention belongs to the molecular genetics field and relates to the molecular marker method of the major gene bph2 for brown planthopper resistance in the rice variety ASD7. Via genetic linkage analysis of the individual F2 plant genotype and the brown planthopper resistance level of each F2:3 family produced by hybridizing the insect-resistant variety ASD7 with insect-susceptible variety C418, the molecular markers RM463 and RM7102 of the major gene loci bph2 in the insect-resistant variety ASD7 are obtained. In the ASD7 / C418BC1 population the correct rate of selection by either marker is 91.2%. In the BC2 population, the correct rate of selection by RM463 is 91.2%, the correct rate of selection by RM7102 is 89.9%. Detection of this major gene loci in ASD7 and its derivatives via these molecular markers will increase the selection efficiency of brown planthopper resistant rices.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
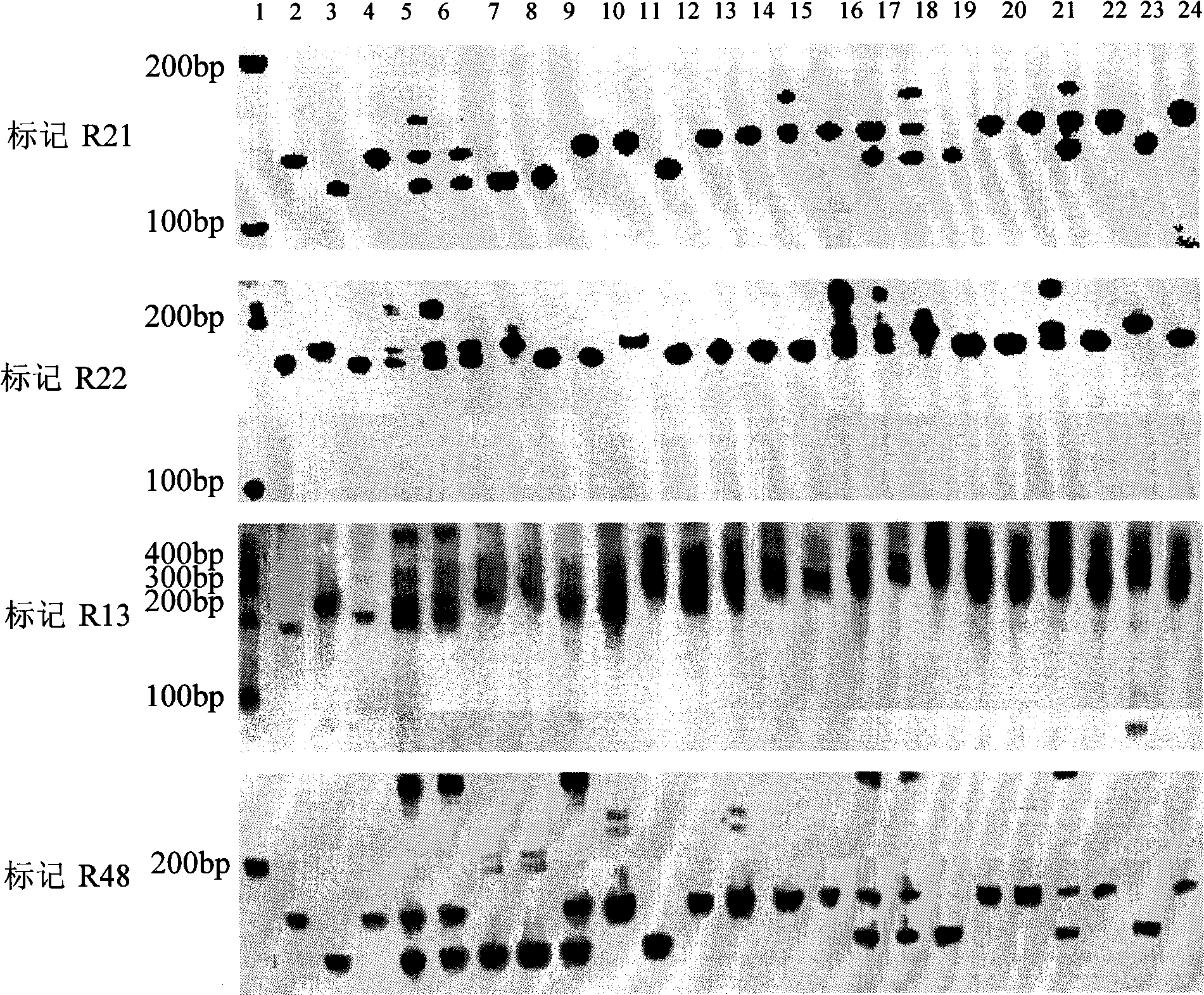
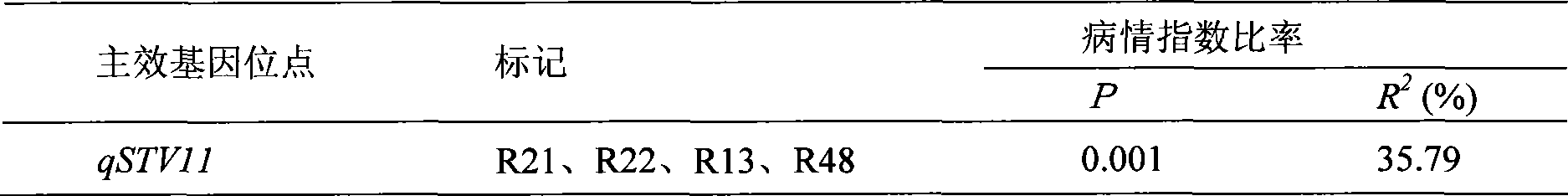
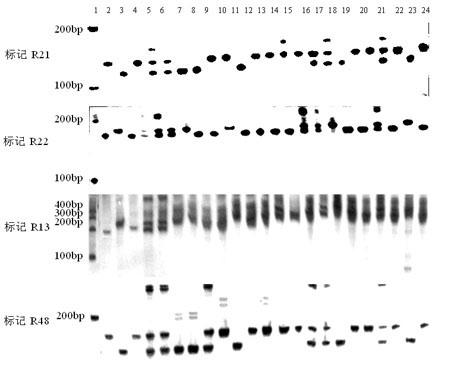
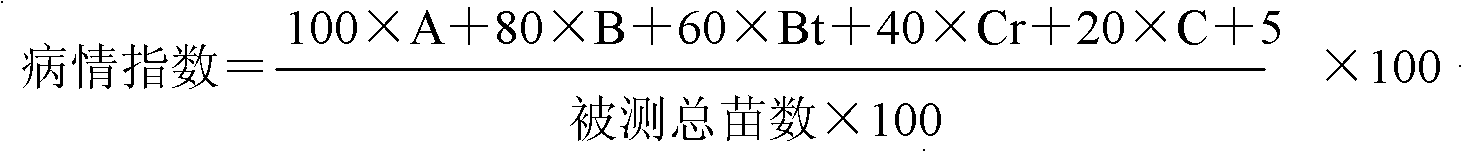
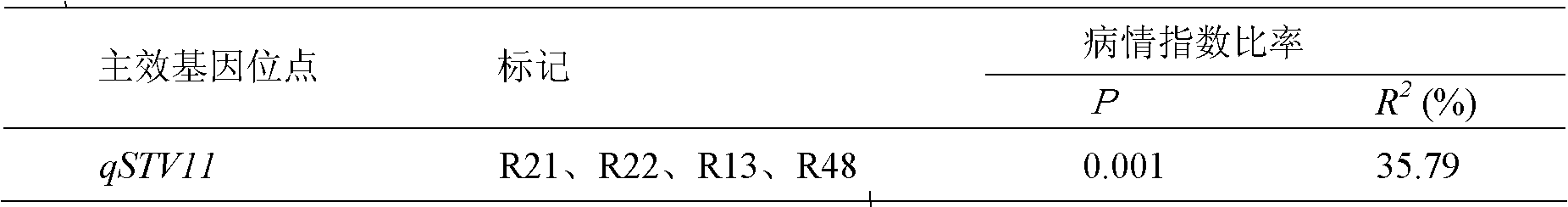
Molecular marker method for rice anti-rice stripe major gene loci qSTV11
InactiveCN101487050AImprove utilizationEasy to detectMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseBiotechnology
The invention relates to a molecular marking method of a major gene locus qSTV11 with rice stripe and leaf blight resistance and belongs to the field of molecular genetics. Hybridization with female plant of rice Nipponbare and male plant of Kasalath, backcross with Nipponbare and derivation are orderly realized, thus obtaining a backcross recombinant inbred system, genetic linkage analysis between genotypes and corresponding disease indexes and ratios in each family is realized, the resistant effects of the major gene locus qSTV11 with rice stripe and leaf blight resistance and allelic genes from Kasalath are detected, and molecular markers R21, R22, R13 and R48 that can be utilized in breeding are obtained through filtering. The four molecular markers are utilized for detecting whether Kasalath and derived varieties thereof contain the major gene locus, and consequently the rice stripe and leaf blight resistant level of the varieties can be predicted, and the selection efficiency of rice varieties with rice stripe and leaf blight resistance can be remarkably raised.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Molecular mark method for rice anti-leaf drop streak site
InactiveCN1896283AImprove utilizationEasy to detectMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationDiseaseAgricultural science
The present invention belongs to the molecular genetics field and relates to the the molecular marker method of the major gene loci conferring rice stripe disease resistance. The rice variety Nipponbare is hybridized with Kasalath and then backcrossed with Nipponbare. Via genetic linkage analysis of the genotype and disease index ratio of each family in aquired backcross inbred lines, the molecular marker BJ11-8 of the major rice stripe disease resistance gene loci qSTVll is obtained. Detection of this major gene locus in Kasalath and its derivatives via the molecular marker BJ11-8 will forecast the resistance level to the rice stripe disease and increase the selection efficiency of rice stripe disease resistant rices significantly.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
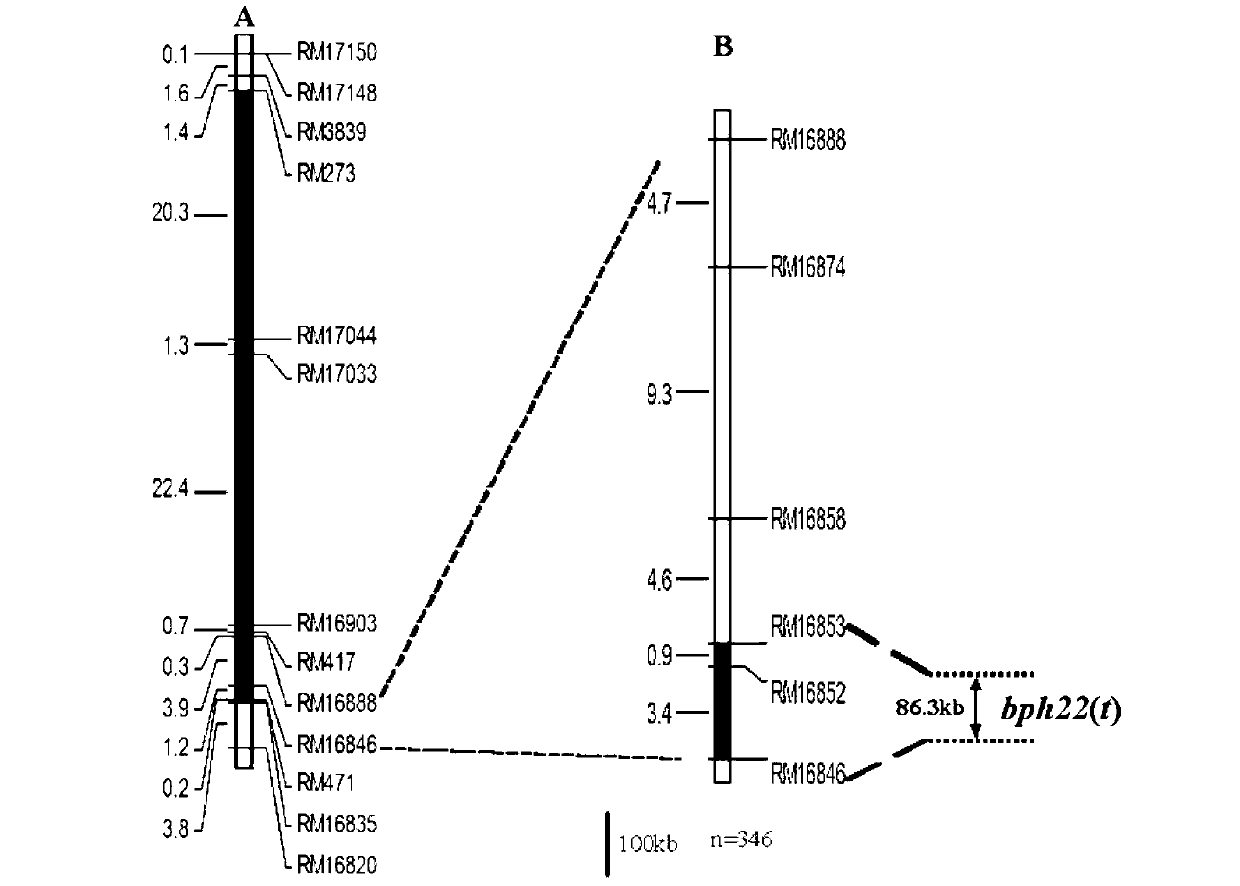
Molecular marker of rice major gene bph22 (t) resistant to brown planthoppers and application thereof
ActiveCN102766625AYears of delayed degradationProtection against new biotypes of brown planthopperMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceBrown planthopper
The invention provides a molecular marker of rice major gene bph22 (t) resistant to brown planthoppers and an application of the molecular marker of the rice major gene bph22 (t) resistant to the brown planthopper. The inspect-resistant strain W2183 of the rice and the susceptible variety white hair (white R54) (female) of the rice are hybridized and backcrossed to obtain different progenies; thelines of the different progenies are respectively subjected to identification of the character of the resistance to brown planthoppers and genetic linkage analysis to obtain the resistance gene bph22(t) carried by the inspect-resistant strain W2183 and locate the resistance gene between the molecular marker RM16846 and the molecular marker RM16888; and, the molecular marker tightly linked to the resistance gene also comprises one of RM16852, RM16853, RM16858 and RM16874. The molecular maker provided by the invention effectively detects whether the inspect-resistant strain W2183 and the derived varieties (strains) of the inspect-resistant strain W2183 contain the locus of the major gene; the selection efficiency of the rice resistant to the brown planthoppers is greatly enhanced; and, the gene bph22(t)-containing varieties of the rice resistant to the brown planthoppers are obtained.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Rice brown planthopper resistant major gene Bph30 molecular marker and application thereof
ActiveCN107201395AQuick filterNot affectedMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBrown planthopperGenetics
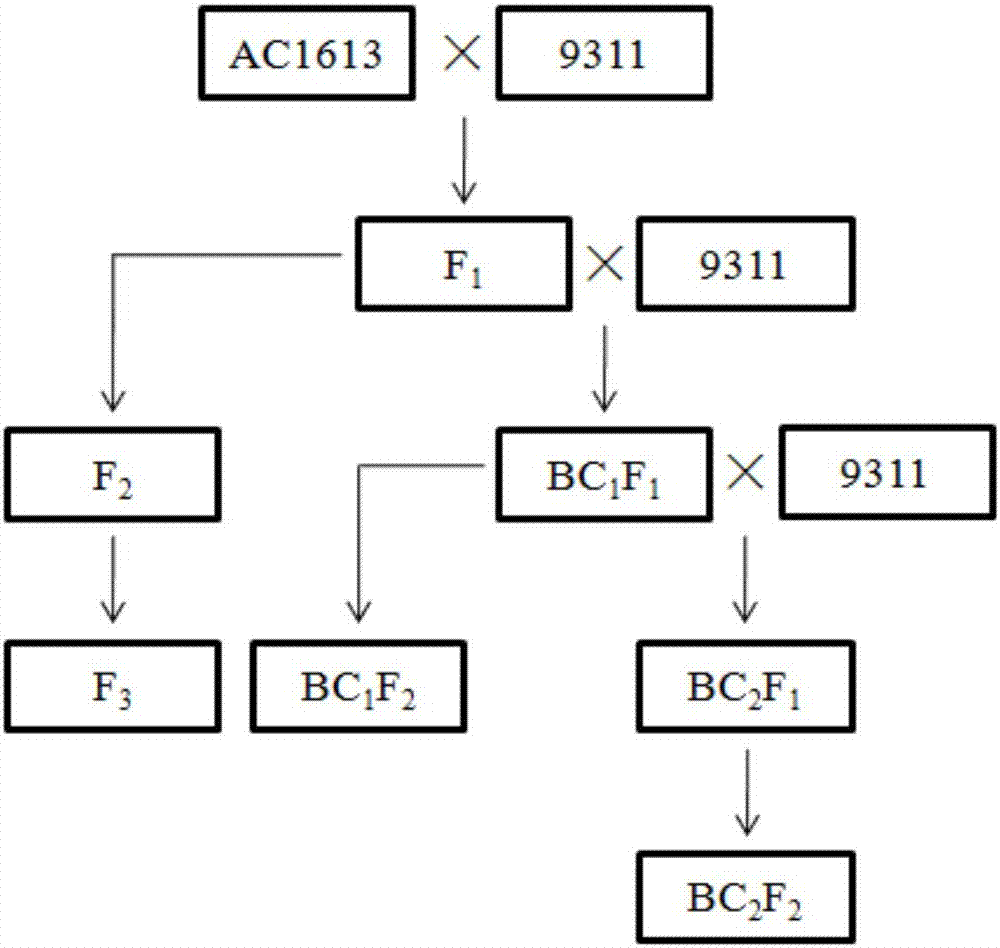
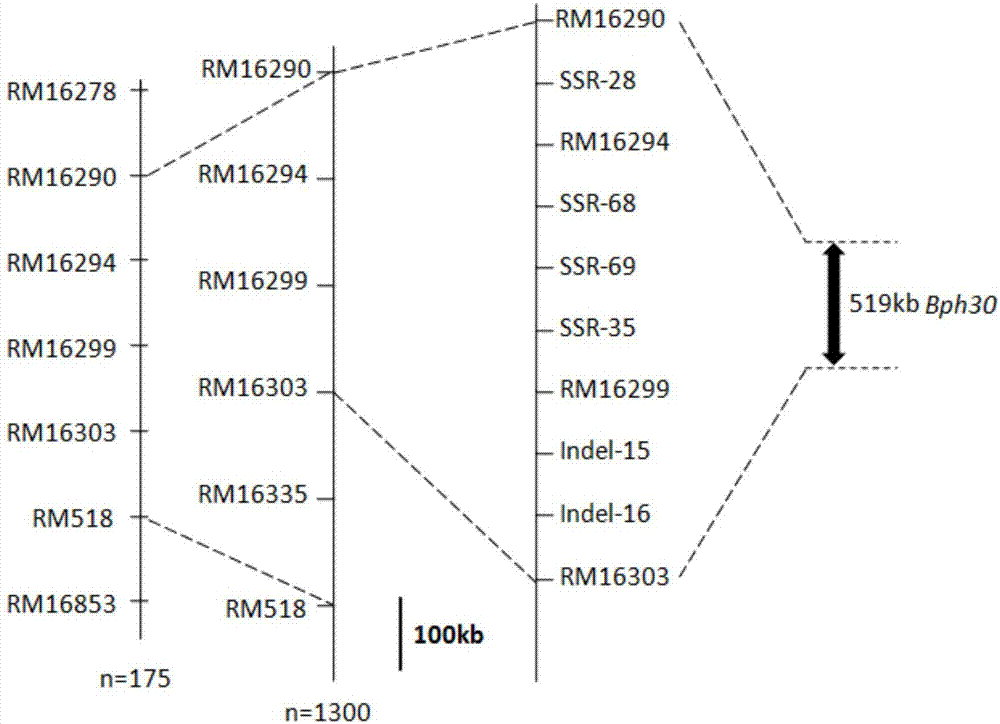
The invention provides a rice brown planthopper resistant major gene Bph30 molecular marker and application thereof. A genotype of each F2 single plant obtained by hybridization of a rice insect-resistant variety AC1613 (male parent ) and a susceptible variety 9311 (female parent ) and a brown planthopper resistant phenotype of each F2 single plant is combined for genetic linkage analysis to obtain an insect-resistant variety AC1613 resistance gene Bph30 positioned between molecular markers RM16290 and RM16303, and molecular markers in linkage with the gene also include SSR-28, RM16294, SSR-68, SSR-69, RM16299, Indel-15, Indel-16 and SSR-35. By the molecular marker, whether a locus of the major gene exists in rice or not can be effectively detected, and accordingly brown planthopper resistant rice selection efficiency is greatly improved, and brown planthopper resistant rice varieties with the gene Bph30 can be obtained.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Rice black-streaked dwarf virus (RBSDV) resistant locus qRBSDV9 of rice variety 9194 and molecular marker method thereof
ActiveCN104046693AHigh black-streaked dwarf resistanceImprove selection efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementResistant genesGenotype
The invention relates to a rice black-streaked dwarf virus (RBSDV) resistant locus qRBSDV9 of a rice variety 9194 and a molecular marker method thereof. Four RBSDV resistant genetic loci of the RBSDV resistant variety 9194 are obtained by carrying out genetic linkage analysis on the genotype of a single plant F2 obtained by hybridizing the RBSDV resistant rice variety 9194 (male) with a susceptible variety Suyunuo (female) and the RBSDV resistance grade of a corresponding F2:3 family, wherein qRBSDV9 is between a marker RM3912 and a marker RM257. The RBSDV resistance levels of the resistant variety 9194 and derived varieties (lines) thereof can be predicated and the selection efficiency of the RBSDV resistant rice can be greatly improved by detecting whether the resistant variety 9194 and the derived varieties (lines) thereof contain the RBSDV resistance genetic loci via the molecular markers of the RBSDV resistant genes.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Rice black-streaked dwarf virus (RBSDV) resistant locus qRBSDV11 of rice variety 9194 and molecular marker method thereof
InactiveCN104046692AEasy to detectQuick filterMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationRice black-streaked dwarf virusResistant genes
The invention relates to a rice black-streaked dwarf virus (RBSDV) resistant locus qRBSDV11 of a rice variety 9194 and a molecular marker method thereof. Four RBSDV resistant genetic loci of the RBSDV resistant variety 9194 are obtained by carrying out genetic linkage analysis on the genotype of a single plant F2 obtained by hybridizing the RBSDV resistant rice variety 9194 (male) with a susceptible variety Suyunuo (female) and the RBSDV resistance grade of a corresponding F2:3 family, wherein qRBSDV11 is between a marker RM26062 and a marker RM536. The RBSDV resistance levels of the resistant variety 9194 and derived varieties (lines) thereof can be predicated, and the selection efficiency of the RBSDV resistant rice can be greatly improved by detecting whether the resistant variety 9194 and the derived varieties (lines) thereof contain the RBSDV resistance genetic loci via the molecular markers of the RBSDV resistant genes.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
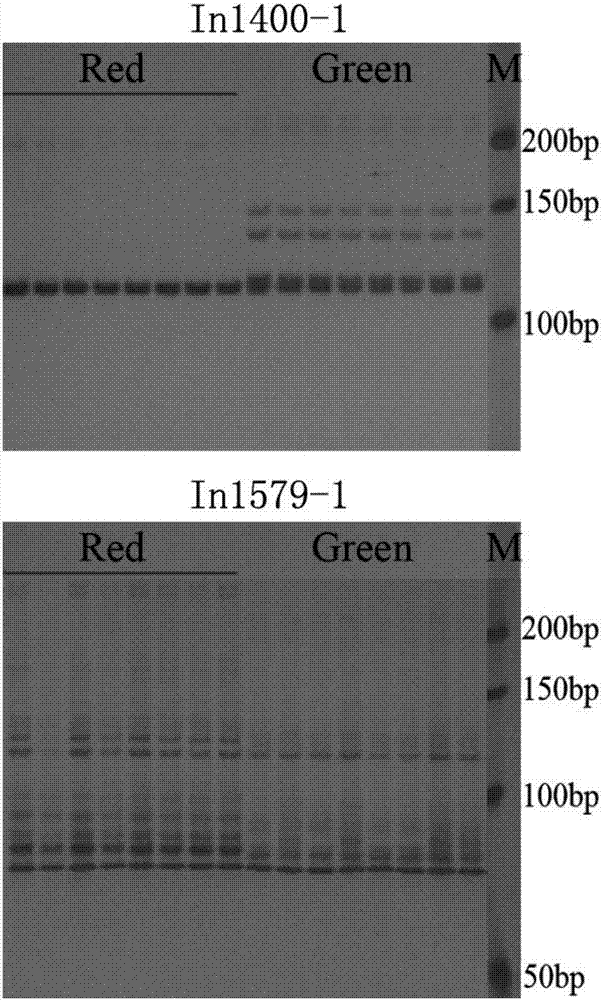
Molecular markers of pear peel all-red bud mutation trait locus, primers and application thereof
InactiveCN106929594AImprove selection efficiencyReduce cost inputMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceGenotype
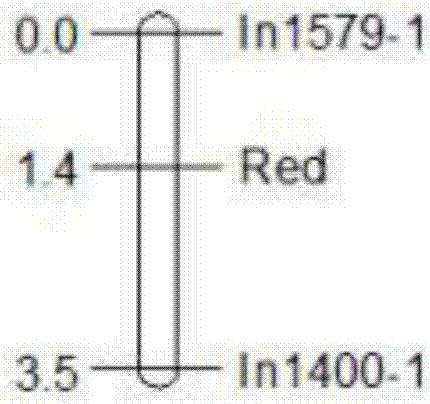
The invention discloses InDel molecular markers of a pear peel all-red bud mutation trait locus Red and application thereof. Genetic linkage analysis is carried out on a hybrid F1 population genotype of a non-all red bud mutation material 'T109' and a 'red Zaosu' pear all-red bud mutation variety 'red Zaosu' and the trait phenotype of each single plant to acquire molecular markers linked to the bud mutation trait locus. The pear peel all-red bud mutation trait locus Red is located on a chromosome 4 of pear. The InDel molecular markers linked to the pear peel all-red bud mutation trait locus Red are In1579-1 and In1400-1 respectively, and the genetic distances to the pear peel all-red bud mutation trait locus Red are 1.4cM and 2.1cM respectively. The markers are utilized to detect the filial generations of pear peel all-red bud mutation varieties, the peel color can be predicted in advance, the selection efficiency of red-peel pear breeding is greatly improved, and the cost is saved, therefore the molecular markers have good social and economic benefits.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU FRUIT RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI +1
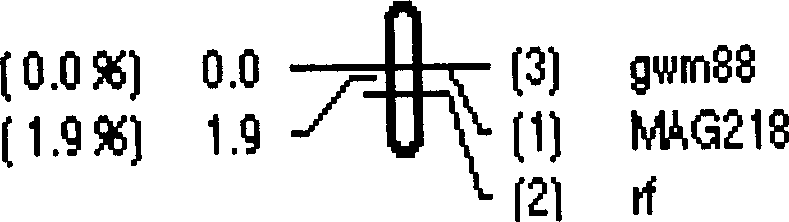
Wheat fertile activity recovery gene RF6 molecular mark and its obtaining method
InactiveCN1570103AQuick and accurate transferAvoid influenceSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementAgricultural scienceTriticeae
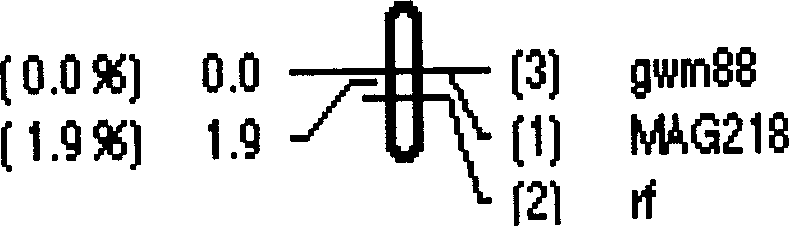
The invention relates to wheat fertility recovery gene Rf6 molecular tag and its obtaining method and belongs to crop breeding and production fields. F2 population arising from wheat T.um-bellulatum translocation line N2114 with susan is analysed in individual genotype and its fertility. Codominant SSR mark MAG218 and dominant mark gwm88 is obtained, which are closely linked to T cell cytoplasm sterility fertility recovery gene Rf6, and can determine the existence of Rf6 and forecast the wheat plant fertility, so can screening the Rf6 plant rapidly.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Wheat fertility recovery gene molecular mark and its obtaining method
InactiveCN1769448AQuick and accurate transferEasy to identifySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementAgricultural scienceGenotype
The invention relates to a molecular labeling of wheat fertility restorer genes Rf6 genes and its acquisition method, belonging to crop breeding and producing fields. Analyze the inheritance link of every single strain's gene-type and fertility thereof of the F2 generation group acquired by crossing wheat umbrella goatstraw transposition system N2114(íÔ) and perilla fruit (íß) to gain codominant SSR labeling MAG218 labeling and dominant labeling gwm88 labeling which are linked most tightly to T-type cytoplasm infertility restorer system Rf6. It could be used to make sure the existence of Rf6 and its existing state, and esmimate the fertility of wheat strains and futher screening check strains with Rf6 quickly to avoid the effection of environment to varieties which could increase the breeding velocity and identification efficiency of T-type cytoplasm infertility restorer system.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
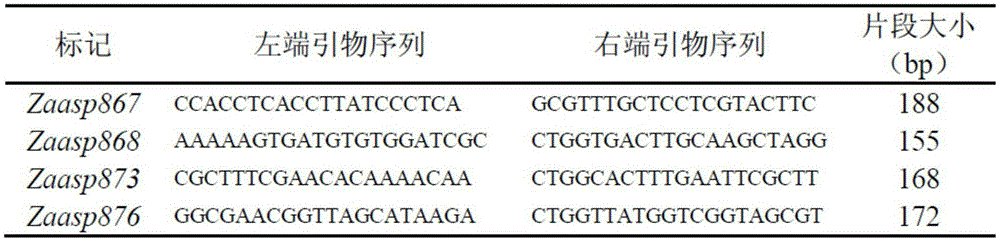
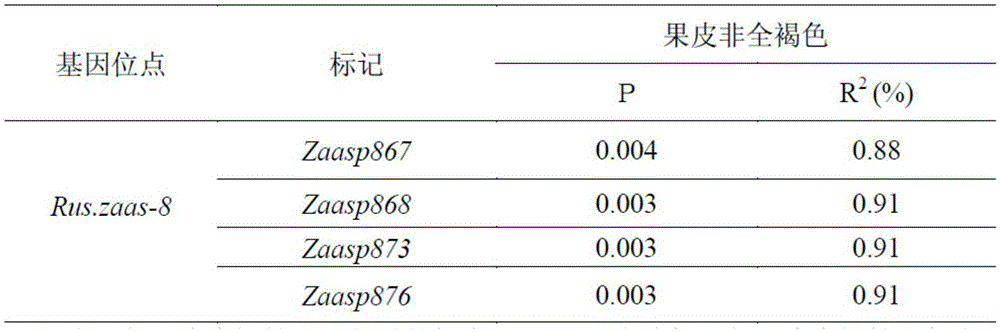
Molecular marker of peel full-brown trait gene locus of Chinese 'Qingxiang'-variety pears and screening method of molecular marker
ActiveCN105296472ASpeed up the selection processQuick checkMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationPEARPhenotypic trait
The invention relates to the field of molecular genetics and discloses a molecular marker of a peel full-brown trait gene locus of Chinese 'Qingxiang'-variety pears and a screening method of the molecular marker of the peel full-brown trait gene locus of the Chinese 'Qingxiang'-variety pears. A peel full-brown trait and a genotype of each F1 individual plant obtained by hybridization of Chinese 'Qingxiang'-variety pears and Chinese 'Guancui'-variety pears are subjected to genetic linkage analysis to obtain the molecular marker of the peel full-brown trait gene locus Rus.zaas-8 of the Chinese 'Qingxiang'-variety pears. Whether the gene locus is contained in the 'Qingxiang' variety or other derived varieties (strains) or not is detected by means of the molecular marker of the peel full-brown trait gene locus, peel colors of fruits can be predicated, and accordingly selecting efficiency of fruit peel colors of Chinese pears can be greatly improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE SCIENCES
Molecular markers of rice stripe virus disease-resistant major gene locus qSTV11
InactiveCN102021244AEasy to detectQuick filterMicrobiological testing/measurementAgricultural scienceGenotype
The invention relates to molecular markers of a rice stripe virus disease-resistant major gene locus qSTV11, which belongs to the field of molecular genetics. The molecular markers are obtained by the following steps of: hybridizing a rice variety Nipponbare serving as a female parent with kasalath serving as a male parent; performing back crossing on a hybrid product and the Nipponbare; deriving to obtain a back crossing recombinant inbred line; performing genetic linkage analysis on the genotype of each family and corresponding disease index ratio; detecting the stripe virus disease-resistant major gene locus qSTV11, wherein alleles from kasalath have resistance effects; and screening to obtain molecular markers R21, R22, R13 and R48 which can be bred and utilized. The four molecular markers are used for detecting whether the kasalath and a derivative variety (line) contain the major gene locus or not, so that the rice stripe virus disease resistance level can be predicted and the selection efficiency of a stripe virus disease-resistant rice variety is improved remarkably.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
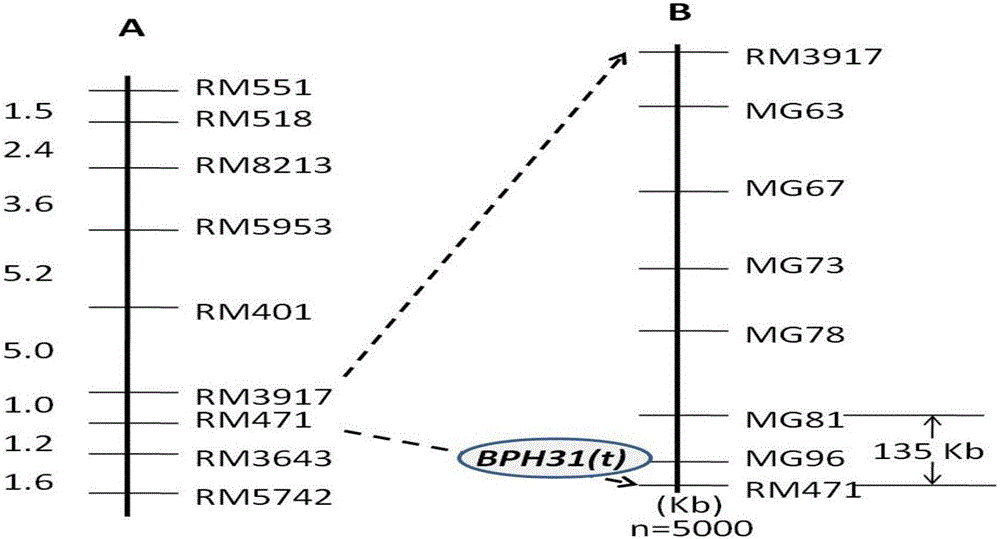
Molecular marker of rice brown-plant-hopper-resistant gene Bph31 (t) and application of molecular marker
InactiveCN106434948AIncrease resistance levelTimely crossbreedingMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceResistant genes
The invention discloses a molecular marker of a rice brown-plant-hopper-resistant gene Bph31 (t) and application of the molecular marker. Varieties K41 with high brown-plant-hopper resistance and varieties Gui1025 with high brown-plant-hopper sensitivity are hybridized to obtain F2:3 family population and recombinant selfing line population by the aid of heredity linkage analysis, the rice brown-plant-hopper-resistant gene Bph31 (t) on a fourth chromosome of rice is precisely positioned and is positioned in an interval between molecular markers MG81 and RM471, and the individual resistant plant selection efficiency of a single molecular marker MG96 in the interval is 97% approximately. The molecular marker which is in linkage with the gene further comprises the molecular markers MG81 and RM471. The molecular marker and the application have the advantages that the molecular marker can be used for detecting the insect-resistant varieties K41 and derived varieties (lines) of the insect-resistant varieties K41 to determine whether the insect-resistant varieties K41 and the derived varieties (lines) contain the gene or not, and accordingly brown-plant-hopper-resistant rice varieties with the brown-plant-hopper-resistant gene Bph31 (t) can be screened.
Owner:南宁维尔凯生物科技有限公司
Molecular marker tightly linked with rice large-grain gene GS12 and application
InactiveCN106636127AIncrease grain weightIncrease in grain widthMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant peptidesAgricultural scienceGenotype
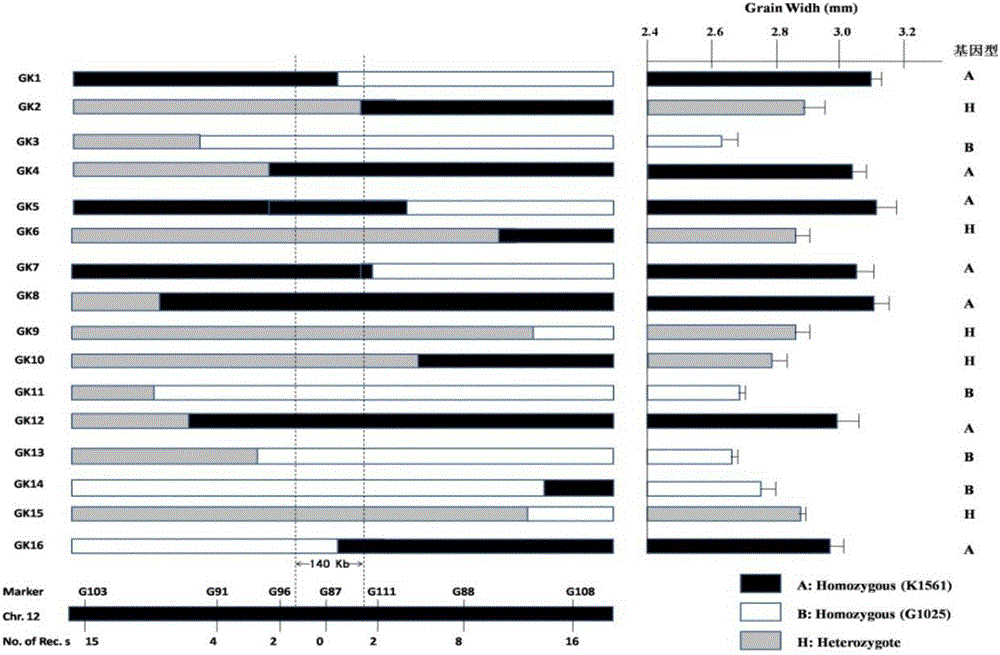
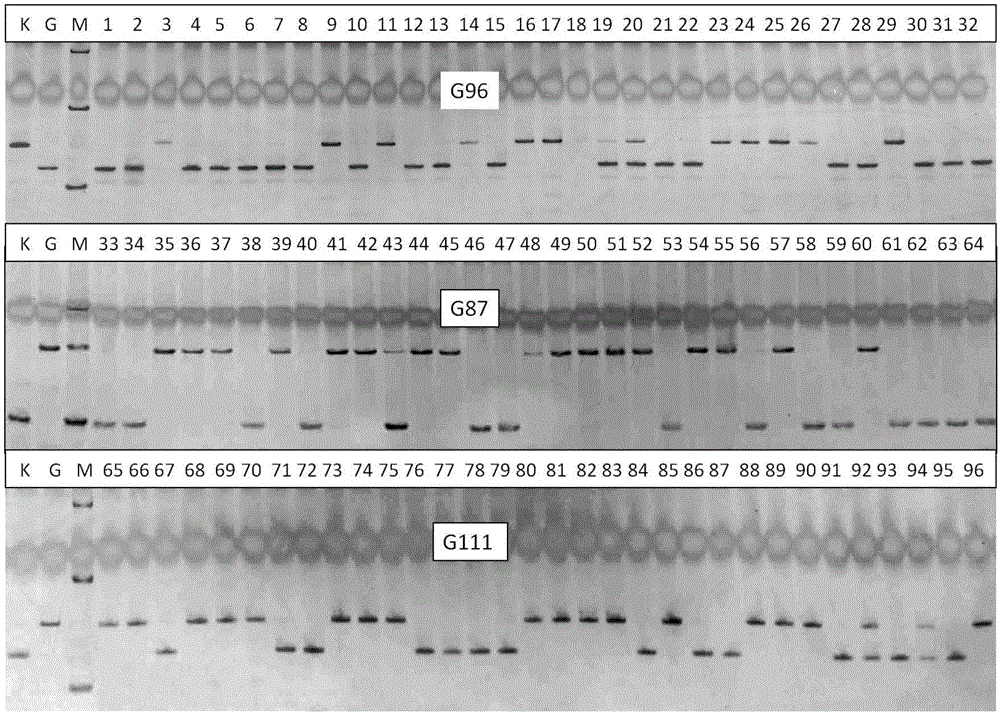
The invention discloses a molecular mark tightly linked with a rice large-grain gene GS12 and application, and belongs to the field of rice high-yield and high-quality breeding and crop molecular genetics. An F2 separation population and a near-isogenic line thereof are obtained by utilizing hybridization of a large-grain variety K1562 and a small-grain variety G1025 through genetic linkage analysis, a large-grain new gene GS12 on a chromosome 12 of rice is finely located, the large-grain new gene GS12 is located between molecular marks G103 and G108, and the selection efficiency of three marks of G96, G87 and G111 in the region are all about 98 percent; the molecular mark tightly linked with the GS12 is utilized for detecting whether the large-grain variety K1561 and derived varieties (lines) thereof contain the GS12 or not. The molecular mark disclosed by the invention is applied to assisted-selection breeding and pyramiding breeding of rice yield and appearance quality, genotype selection can be carried out on low-generation breeding materials in a seedling stage, the breeding efficiency is increased, and the breeding progress is quickened.
Owner:广西壮族自治区农业科学院水稻研究所
Molecular marker of brown planthopper resistance major gene qBph4(t) of paddy rice and application of molecular marker
ActiveCN108165649ANot affectedEasy to identifyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyBrown planthopper
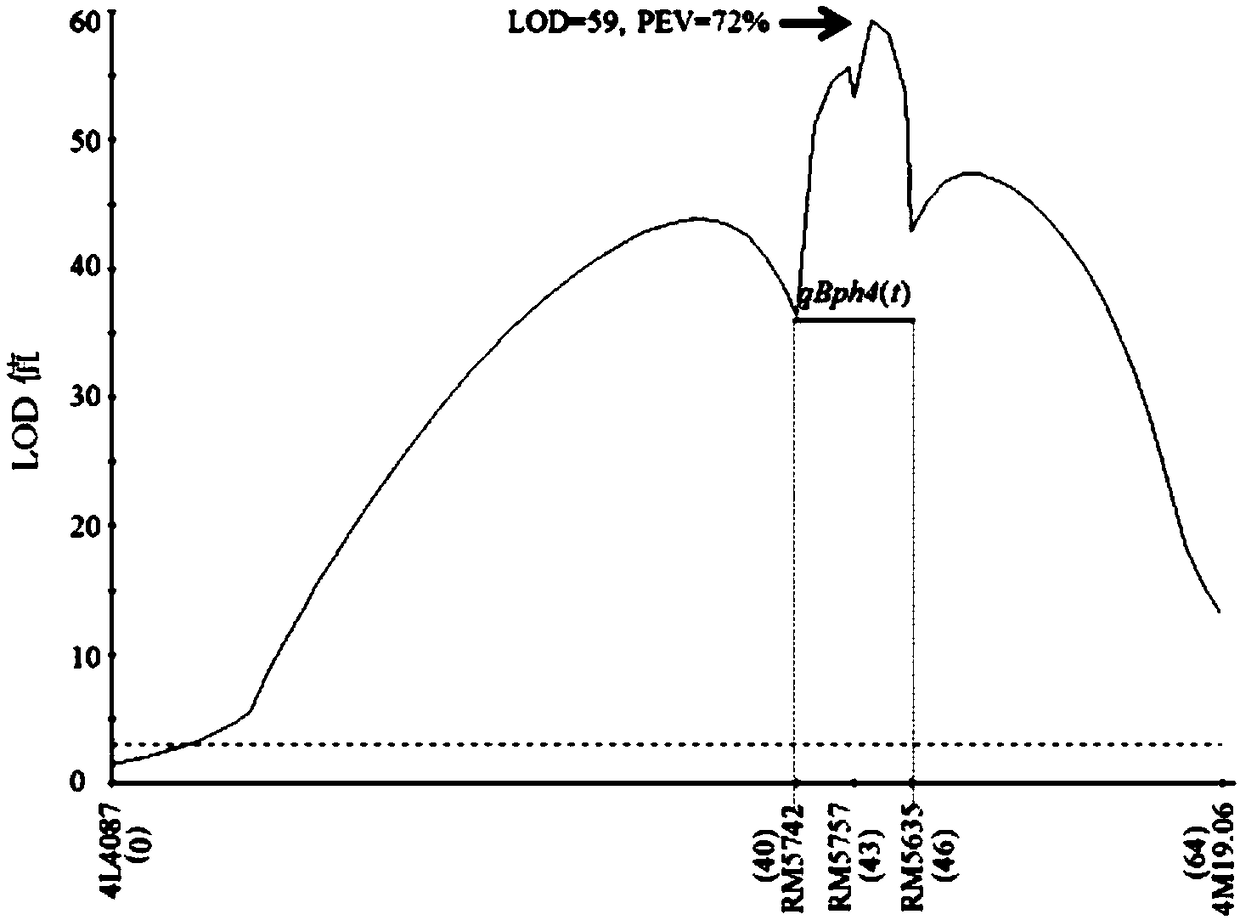
The invention provides a molecular marker of a brown planthopper resistance major gene qBph4(t) of paddy rice and an application of the molecular marker. Genotypes of all single strains of F2 are obtained by hybridization of insect-resistant varieties ARC5984 (male) and 9311 (female) of the paddy rice; genetic linkage analysis is performed according to a brown planthopper resistance level of an F2:3 family at the same time; the resistance major gene qBph4(t) carried by the insect-resistant variety ARC5984 is identified and located in a 6cM interval between molecular markers RM5635 and RM5742;and the resistance major gene qBph4(t) is tightly linked with the molecular marker RM5635. A molecular marker RM5757 is also linked with the gene. The molecular marker can effectively detect whether the insect-resistant variety ARC5984 and derived varieties contain a site of the resistance major gene; the selection efficiency of a brown planthopper resistance plant of the paddy rice is greatly improved; and the brown planthopper resistance variety of the paddy rice containing qBph4(t) is obtained.
Owner:YANGTZE UNIVERSITY
Molecular marker of rice brown planthopper major gene qBph30(t) and application thereof
ActiveCN104328168AQuick filterEasy to identifyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyResistant genes
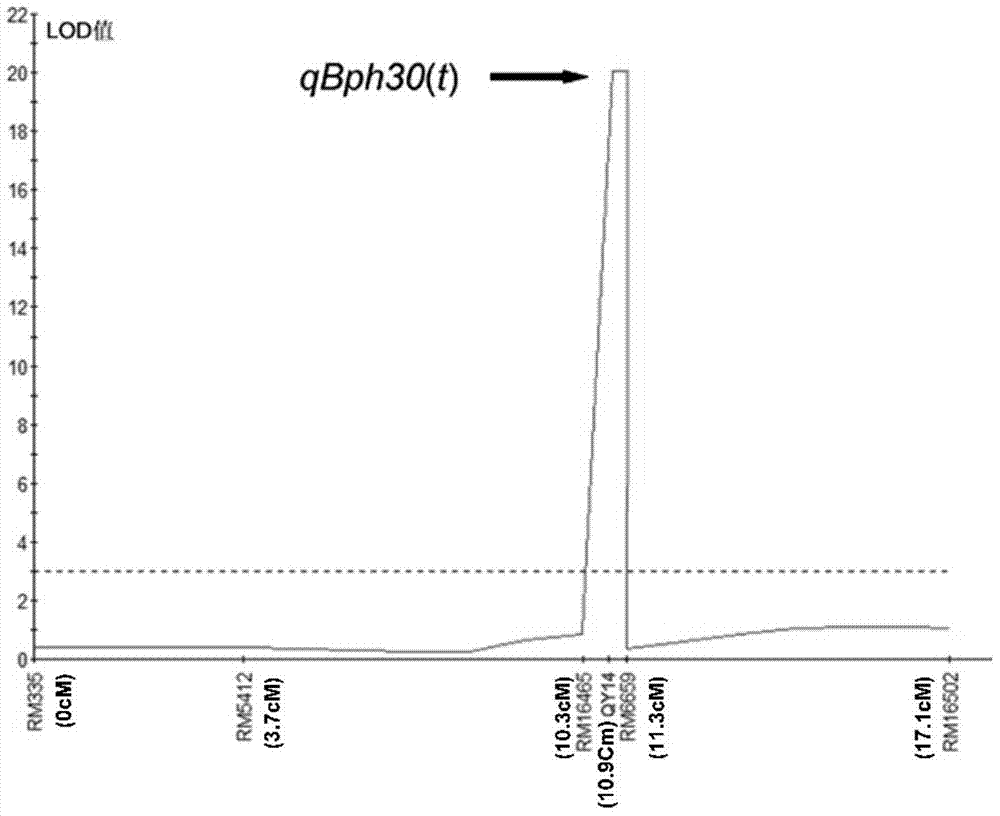
The invention discloses a molecular marker of rice brown planthopper major gene qBph30(t) and an application thereof. In the invention, a close-linkage molecular marker of the resistant gene qBph30(t) in an insect-resistant strain 05BPH16 is obtained through a genotype of each single plant of the second filial generation obtained through hybridization between the rice insect-resistant strain 05BPH16 (male) and mosquito-resistant Qingzhan (female) with genetic linkage analysis with combination of anti-brown planthopper resistance levels in each family in F2:3. The molecular marker can effectively detect whether the resistant major gene exists in the insect-resistant strain 05BPH16 and derived varieties (or strains) or not and can quickly improve selective efficiency of an anti-brown planthopper rice material, thereby obtaining an anti-brown planthopper rice variety containing the qBph30(t) gene.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
New gene Wbph 9 (t) for resisting rice sogatella furcifera, molecular marking method thereof and application
ActiveCN106480066AIncrease resistance levelEfficient identificationPlant peptidesFermentationBiotechnologyAntigen
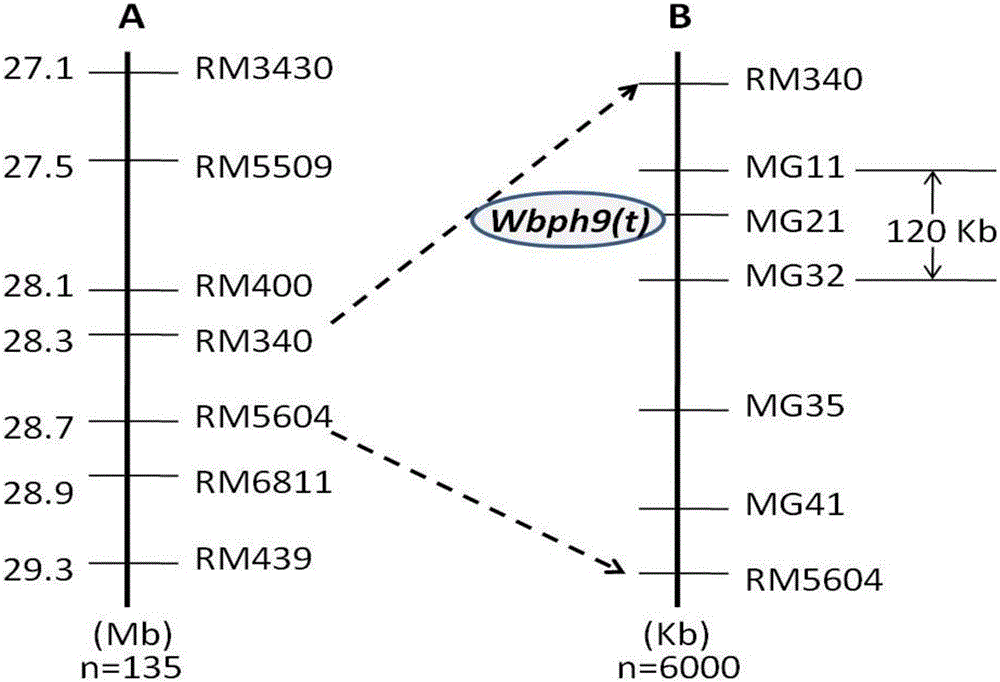
The invention discloses a molecular marking method for tight interlocking of new gene Wbph 9 (t) for resisting rice sogatella furcifera, and application thereof. Through genetic linkage analysis, a variety F41 of the high resistant sogatella furcifera and a variety laurel 1025 of high sensitive sogatella furcifera to obtain F2 which consists of 3 family groups and recombinant inbred line groups; a rice resistant sogatella furcifera gene Wbph 9 (t) on the #6 chromosome of the rice is accurately positioned; the gene is positioned in a 120kb zone between the molecular marker MG11 and MG 32; the selecting efficiency of 1 molecular market MG21 of the zone for the antigen single plant is about 98%; the molecular market tightly interlocked by Wbph 9 (t) is applied to detect if the insect resisting variety K41 and its derivative variety (series) contains the gene; thus new material for resisting sogatella furcifera can be selected. The invention is applied to the molecular marking of the rice sogatella furcifera resistance so as to assist the seed breeding and pyramiding breeding, so as to perform the gene type selection on the low generation of breeding material in seedling period; thus the breeding efficiency is improved, and the breeding progress is accelerated.
Owner:GUANGXI ZHUANG AUTONOMOUS REGION ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com