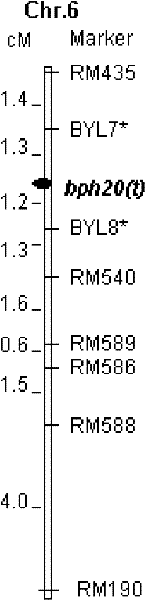
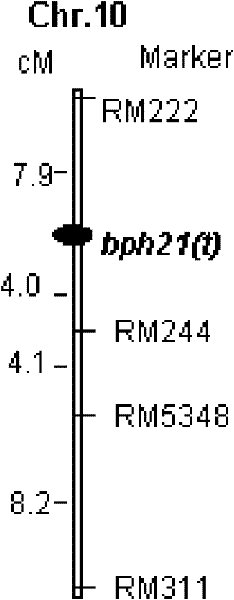
SSR marker BYL8 of brown planthopper resistant genetic locus bph20(t)
A brown planthopper resistance and locus technology, applied in the field of molecular genetics, can solve problems such as changes in resistance stability, and achieve the effects of delaying loss and improving breeding efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0041] Materials and Methods
[0042] 1. Material selection
[0043] After identification of insect resistance, RBPH54 was found to have strong resistance to brown planthopper. Therefore, it was used as a parent and crossed with the susceptible variety TN1, and then backcrossed and selfed after the cross. All generations of plants were identified for insect resistance. (RBPH54 and TN1 were purchased from the Institute of Plant Protection, Guangxi Academy of Agricultural Sciences)
[0044] 2. Identification of insect resistance
[0045] The identification method of brown planthopper resistance refers to the standard seedling plate screening method SSST (IRRI, 1988) used by the International Rice Research Institute, with certain modifications. The soil for raising seedlings is taken from the topsoil of the paddy field. After preliminary treatment, the soil with uniform mud quality is used for raising seedlings. The rice seeds are soaked in water at 25°C for 24 hours, washed and germin...
Embodiment 2
[0080] Example 2 Verification of Molecular Markers
[0081] 1. Materials and methods
[0082] 1.1 Material
[0083] Negative variety: non-resistant gene variety, susceptible variety TN1
[0084] Positive varieties: contain resistance genes, resistant varieties: RBPH54 and ASD7 (purchased from the Institute of Plant Protection, Guangxi Academy of Agricultural Sciences)
[0085] Molecular marker primers: BYL7 and BYL8 and RM222 and RM244 were synthesized by Shanghai Shenggong.
[0086] 1.2 method
[0087] The genomic DNA of rice samples was extracted by CTAB extraction method (the method is the same as that in Example 1). Amplify the sample DNA with primers BYL7 and BYL8 and RM222 and RM244 respectively. The reaction system includes 0.10μM primers, 250μM dNTP, 1×PCR reaction buffer (50mMKCl, 10mM Tris-HCl pH8.3, 1.5mM MgCl 2 ), 100ng DNA template, 1UTaq enzyme. The reaction was carried out in a Tgradient PCR machine. The reaction procedure is: pre-denaturation at 94°C for 5 min, cycling...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com