Nucleic acid detection method
A detection method and nucleic acid technology, applied in the direction of biochemical equipment and methods, microbial measurement/inspection, etc., can solve the problems of multi-variety detection reagent obstacles, and achieve low detection cost, convenient operation, and cost reduction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1)
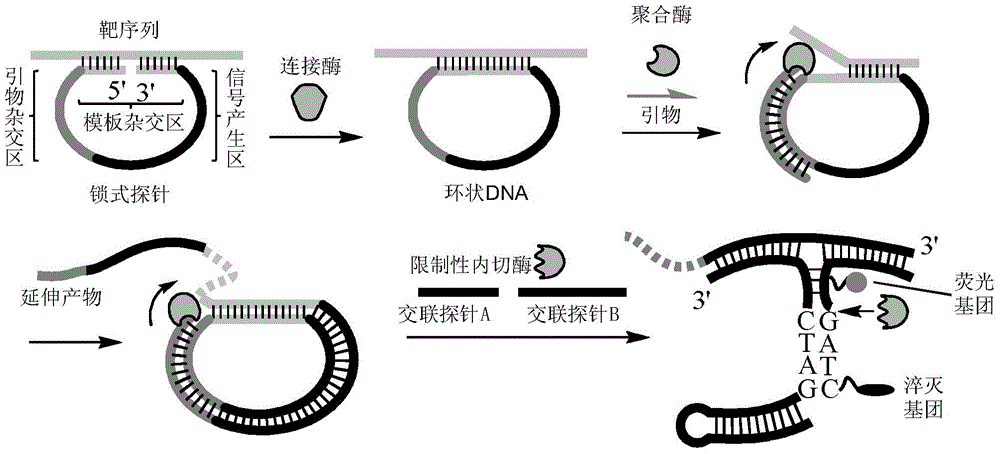
[0050] The nucleic acid detection method of this embodiment comprises the following steps:
[0051] ① Determine the target sequence to be tested. The target sequence for amplification and detection can be any nucleic acid, and the target sequence can be RNA, cDNA, genomic DNA, DNA from pathogenic microorganisms or viruses, or DNA treated with chemical reagents, various enzymes, and physical exposure. The target sequence can exist as single-stranded DNA or RNA, or as dissociated complementary strands.
[0052] The target sequence in this example is a synthetic DNA single strand with a length of 40 nucleotides (see SEQ ID NO 1 in the sequence listing for the DNA sequence 5' to 3'), in which there are 5 nucleotides at the 5' and 3' ends The T base and the target sequence of 30 base nucleotides in the middle can be hybridized with the padlock probe.
[0053] ② Design and synthesize padlock probes according to the target sequence.
[0054] The design principle of padlock probe i...
Embodiment 2)
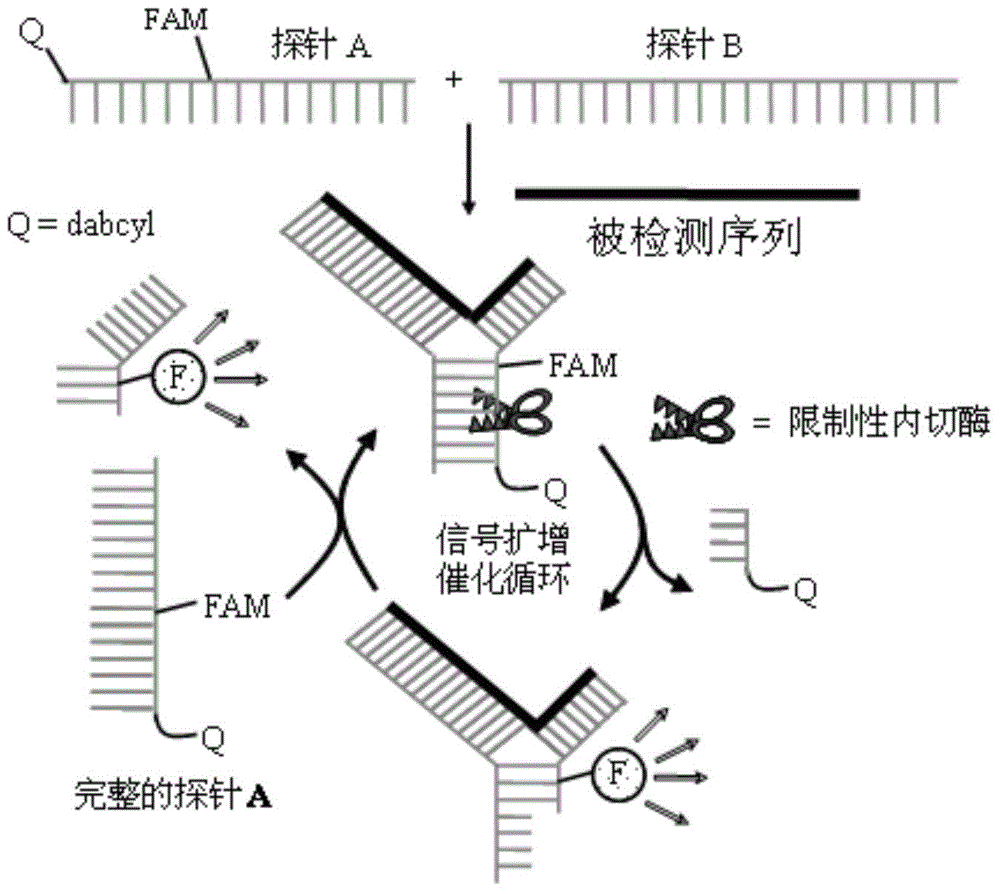
[0073] The nucleic acid detection method of this example is different from Example 1 in that: this example completes the ligation reaction, rolling circle amplification (RCA) reaction and cross-linking probe detection of rolling circle amplification products in one step.
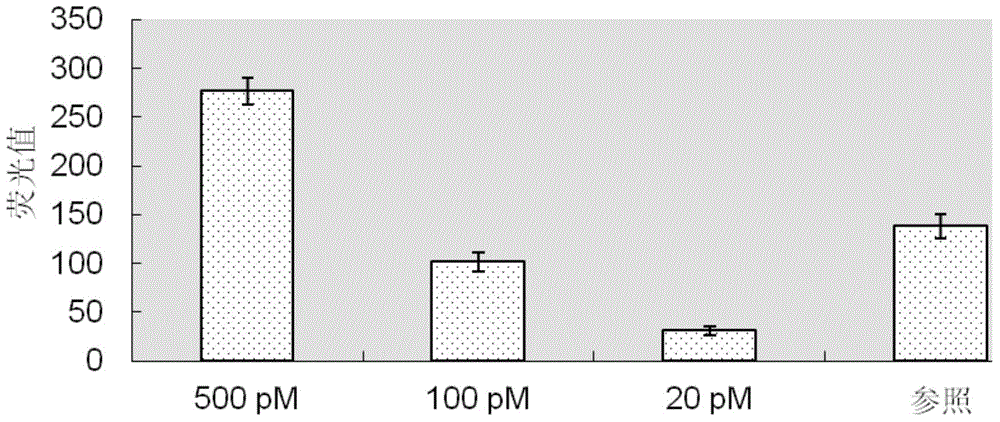
[0074] After completing the determination of the target sequence, the design and synthesis of padlock probes, the preparation of rolling circle amplification primers, and the preparation of cross-linking probes according to steps ① to ④ of Example 1, the padlock probes, rolling circle The mixture of amplification primers, cross-linking probe A, cross-linking probe B, buffer, ligase, polymerase, nuclease and the fragment to be tested is incubated at 20°C to 37°C for 4 to 21 hours and then the fluorescence signal value is monitored As the endpoint value, subtract the initial fluorescence value recorded before incubation without adding nuclease. If the difference before and after is greater than 3 times or more ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com