SSCP (single strand conformation polymorphism) detecting method for animal liver bacterial toxin contamination
A bacterial toxin and animal liver technology, applied in the biological field, can solve the problems of high detection cost, time-consuming and laborious, and inaccurate detection results, and achieve the effects of good repeatability, low detection cost, and easy promotion and application
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
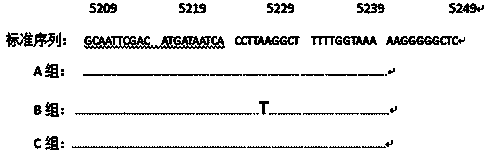
[0035] Example 1: The SSCP detection method of animal liver bacterial toxin contamination, the method comprises liver mitochondrial DNA extraction; in liver mitochondrial DNA, cytochrome tRNA Cys-Tyr The gene fragment at the position 5109-5299 of the gene is amplified; and the point mutation of the gene fragment is analyzed by SSCP to evaluate whether the animal liver is polluted by the bacterial toxin. Three steps. The specific implementation process of the three steps is as follows:
[0036] Step 1, liver mitochondrial DNA extraction:
[0037] First, prepare the reagents in the mitochondrial DNA extraction step, the recipe is as follows:
[0038] (1) SE solution: pH7.8, mixed with 0.25M sucrose, 2.5mM CaCl2, 30mM Tris-HCl and 10mM EDTANa2;
[0039] (2) Solution Ⅰ (TEN), pH 8.0, mixed with 0.15M NaCl, 10mM EDTANa2 and 10mM Tris-HCl;
[0040] (3) Solution II, 1% SDS, containing 0.2N NaOH;
[0041] (4) Solution Ⅲ, 3M Kac, which contains 3M KAc, 5M glacial acetic acid, mix w...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com